How to Create a Research Poster
- Poster Basics
- Design Tips
- Logos & Images

What is a Research Poster?
Posters are widely used in the academic community, and most conferences include poster presentations in their program. Research posters summarize information or research concisely and attractively to help publicize it and generate discussion.
The poster is usually a mixture of a brief text mixed with tables, graphs, pictures, and other presentation formats. At a conference, the researcher stands by the poster display while other participants can come and view the presentation and interact with the author.
What Makes a Good Poster?
- Important information should be readable from about 10 feet away
- Title is short and draws interest
- Word count of about 300 to 800 words
- Text is clear and to the point
- Use of bullets, numbering, and headlines make it easy to read
- Effective use of graphics, color and fonts
- Consistent and clean layout
- Includes acknowledgments, your name and institutional affiliation
A Sample of a Well Designed Poster
View this poster example in a web browser .

Image credit: Poster Session Tips by [email protected], via Penn State
Where do I begin?
Answer these three questions:.
- What is the most important/interesting/astounding finding from my research project?
- How can I visually share my research with conference attendees? Should I use charts, graphs, photos, images?
- What kind of information can I convey during my talk that will complement my poster?
What software can I use to make a poster?
A popular, easy-to-use option. It is part of Microsoft Office package and is available on the library computers in rooms LC337 and LC336. ( Advice for creating a poster with PowerPoint ).
Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, and InDesign
Feature-rich professional software that is good for posters including lots of high-resolution images, but they are more complex and expensive. NYU Faculty, Staff, and Students can access and download the Adobe Creative Suite .
Open Source Alternatives
- OpenOffice is the free alternative to MS Office (Impress is its PowerPoint alternative).
- Inkscape and Gimp are alternatives to Adobe products.
- For charts and diagrams try Gliffy or Lovely Charts .
- A complete list of free graphics software .
A Sample of a Poorly Designed Poster
View this bad poster example in a browser.
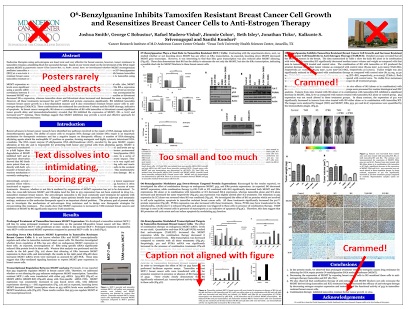
Image Credit: Critique by Better Posters
- Next: Design Tips >>
- Last Updated: Jul 11, 2023 5:09 PM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/posters
Home Blog Design How to Design a Winning Poster Presentation: Quick Guide with Examples & Templates
How to Design a Winning Poster Presentation: Quick Guide with Examples & Templates

How are research posters like High School science fair projects? Quite similar, in fact.
Both are visual representations of a research project shared with peers, colleagues and academic faculty. But there’s a big difference: it’s all in professionalism and attention to detail. You can be sure that the students that thrived in science fairs are now creating fantastic research posters, but what is that extra element most people miss when designing a poster presentation?
This guide will teach tips and tricks for creating poster presentations for conferences, symposia, and more. Learn in-depth poster structure and design techniques to help create academic posters that have a lasting impact.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
- What is a Research Poster?
Why are Poster Presentations important?
Overall dimensions and orientation, separation into columns and sections, scientific, academic, or something else, a handout with supplemental and contact information, cohesiveness, design and readability, storytelling.
- Font Characteristics
- Color Pairing
- Data Visualization Dimensions
- Alignment, Margins, and White Space
Scientific/Academic Conference Poster Presentation
Digital research poster presentations, slidemodel poster presentation templates, how to make a research poster presentation step-by-step, considerations for printing poster presentations, how to present a research poster presentation, final words, what is a research poster .
Research posters are visual overviews of the most relevant information extracted from a research paper or analysis. They are essential communication formats for sharing findings with peers and interested people in the field. Research posters can also effectively present material for other areas besides the sciences and STEM—for example, business and law.
You’ll be creating research posters regularly as an academic researcher, scientist, or grad student. You’ll have to present them at numerous functions and events. For example:
- Conference presentations
- Informational events
- Community centers
The research poster presentation is a comprehensive way to share data, information, and research results. Before the pandemic, the majority of research events were in person. During lockdown and beyond, virtual conferences and summits became the norm. Many researchers now create poster presentations that work in printed and digital formats.

Let’s look at why it’s crucial to spend time creating poster presentations for your research projects, research, analysis, and study papers.

Research posters represent you and your sponsor’s research
Research papers and accompanying poster presentations are potent tools for representation and communication in your field of study. Well-performing poster presentations help scientists, researchers, and analysts grow their careers through grants and sponsorships.
When presenting a poster presentation for a sponsored research project, you’re representing the company that sponsored you. Your professionalism, demeanor, and capacity for creating impactful poster presentations call attention to other interested sponsors, spreading your impact in the field.
Research posters demonstrate expertise and growth
Presenting research posters at conferences, summits, and graduate grading events shows your expertise and knowledge in your field of study. The way your poster presentation looks and delivers, plus your performance while presenting the work, is judged by your viewers regardless of whether it’s an officially judged panel.
Recurring visitors to research conferences and symposia will see you and your poster presentations evolve. Improve your impact by creating a great poster presentation every time by paying attention to detail in the poster design and in your oral presentation. Practice your public speaking skills alongside the design techniques for even more impact.
Poster presentations create and maintain collaborations
Every time you participate in a research poster conference, you create meaningful connections with people in your field, industry or community. Not only do research posters showcase information about current data in different areas, but they also bring people together with similar interests. Countless collaboration projects between different research teams started after discussing poster details during coffee breaks.
An effective research poster template deepens your peer’s understanding of a topic by highlighting research, data, and conclusions. This information can help other researchers and analysts with their work. As a research poster presenter, you’re given the opportunity for both teaching and learning while sharing ideas with peers and colleagues.
Anatomy of a Winning Poster Presentation
Do you want your research poster to perform well? Following the standard layout and adding a few personal touches will help attendees know how to read your poster and get the most out of your information.

The overall size of your research poster ultimately depends on the dimensions of the provided space at the conference or research poster gallery. The poster orientation can be horizontal or vertical, with horizontal being the most common. In general, research posters measure 48 x 36 inches or are an A0 paper size.
A virtual poster can be the same proportions as the printed research poster, but you have more leeway regarding the dimensions. Virtual research posters should fit on a screen with no need to scroll, with 1080p resolution as a standard these days. A horizontal presentation size is ideal for that.
A research poster presentation has a standard layout of 2–5 columns with 2–3 sections each. Typical structures say to separate the content into four sections; 1. A horizontal header 2. Introduction column, 3. Research/Work/Data column, and 4. Conclusion column. Each unit includes topics that relate to your poster’s objective. Here’s a generalized outline for a poster presentation:
- Condensed Abstract
- Objectives/Purpose
- Methodology
- Recommendations
- Implications
- Acknowledgments
- Contact Information
The overview content you include in the units depends on your poster presentations’ theme, topic, industry, or field of research. A scientific or academic poster will include sections like hypothesis, methodology, and materials. A marketing analysis poster will include performance metrics and competitor analysis results.
There’s no way a poster can hold all the information included in your research paper or analysis report. The poster is an overview that invites the audience to want to find out more. That’s where supplement material comes in. Create a printed PDF handout or card with a QR code (created using a QR code generator ). Send the audience to the best online location for reading or downloading the complete paper.
What Makes a Poster Presentation Good and Effective?
For your poster presentation to be effective and well-received, it needs to cover all the bases and be inviting to find out more. Stick to the standard layout suggestions and give it a unique look and feel. We’ve put together some of the most critical research poster-creation tips in the list below. Your poster presentation will perform as long as you check all the boxes.
The information you choose to include in the sections of your poster presentation needs to be cohesive. Train your editing eye and do a few revisions before presenting. The best way to look at it is to think of The Big Picture. Don’t get stuck on the details; your attendees won’t always know the background behind your research topic or why it’s important.
Be cohesive in how you word the titles, the length of the sections, the highlighting of the most important data, and how your oral presentation complements the printed—or virtual—poster.
The most important characteristic of your poster presentation is its readability and clarity. You need a poster presentation with a balanced design that’s easy to read at a distance of 1.5 meters or 4 feet. The font size and spacing must be clear and neat. All the content must suggest a visual flow for the viewer to follow.
That said, you don’t need to be a designer to add something special to your poster presentation. Once you have the standard—and recognized—columns and sections, add your special touch. These can be anything from colorful boxes for the section titles to an interesting but subtle background, images that catch the eye, and charts that inspire a more extended look.
Storytelling is a presenting technique involving writing techniques to make information flow. Firstly, storytelling helps give your poster presentation a great introduction and an impactful conclusion.
Think of storytelling as the invitation to listen or read more, as the glue that connects sections, making them flow from one to another. Storytelling is using stories in the oral presentation, for example, what your lab partner said when you discovered something interesting. If it makes your audience smile and nod, you’ve hit the mark. Storytelling is like giving a research presentation a dose of your personality, and it can help turning your data into opening stories .
Design Tips For Creating an Effective Research Poster Presentation
The section above briefly mentioned how important design is to your poster presentation’s effectiveness. We’ll look deeper into what you need to know when designing a poster presentation.
1. Font Characteristics
The typeface and size you choose are of great importance. Not only does the text need to be readable from two meters away, but it also needs to look and sit well on the poster. Stay away from calligraphic script typefaces, novelty typefaces, or typefaces with uniquely shaped letters.
Stick to the classics like a sans serif Helvetica, Lato, Open Sans, or Verdana. Avoid serif typefaces as they can be difficult to read from far away. Here are some standard text sizes to have on hand.
- Title: 85 pt
- Authors: 65 pt
- Headings: 36 pt
- Body Text: 24 pt
- Captions: 18 pt

If you feel too prone to use serif typefaces, work with a font pairing tool that helps you find a suitable solution – and intend those serif fonts for heading sections only. As a rule, never use more than 3 different typefaces in your design. To make it more dynamic, you can work with the same font using light, bold, and italic weights to put emphasis on the required areas.
2. Color Pairing
Using colors in your poster presentation design is a great way to grab the viewer’s attention. A color’s purpose is to help the viewer follow the data flow in your presentation, not distract. Don’t let the color take more importance than the information on your poster.

Choose one main color for the title and headlines and a similar color for the data visualizations. If you want to use more than one color, don’t create too much contrast between them. Try different tonalities of the same color and keep things balanced visually. Your color palette should have at most one main color and two accent colors.
Black text over a white background is standard practice for printed poster presentations, but for virtual presentations, try a very light gray instead of white and a very dark gray instead of black. Additionally, use variations of light color backgrounds and dark color text. Make sure it’s easy to read from two meters away or on a screen, depending on the context. We recommend ditching full white or full black tone usage as it hurts eyesight in the long term due to its intense contrast difference with the light ambiance.
3. Data Visualization Dimensions
Just like the text, your charts, graphs, and data visualizations must be easy to read and understand. Generally, if a person is interested in your research and has already read some of the text from two meters away, they’ll come closer to look at the charts and graphs.

Fit data visualizations inside columns or let them span over two columns. Remove any unnecessary borders, lines, or labels to make them easier to read at a glance. Use a flat design without shadows or 3D characteristics. The text in legends and captions should stay within the chart size and not overflow into the margins. Use a unified text size of 18px for all your data visualizations.
4. Alignment, Margins, and White Space
Finally, the last design tip for creating an impressive and memorable poster presentation is to be mindful of the layout’s alignment, margins, and white space. Create text boxes to help keep everything aligned. They allow you to resize, adapt, and align the content along a margin or grid.
Take advantage of the white space created by borders and margins between sections. Don’t crowd them with a busy background or unattractive color.

Calculate margins considering a print format. It is a good practice in case the poster presentation ends up becoming in physical format, as you won’t need to downscale your entire design (affecting text readability in the process) to preserve information.
There are different tools that you can use to make a poster presentation. Presenters who are familiar with Microsoft Office prefer to use PowerPoint. You can learn how to make a poster in PowerPoint here.
Poster Presentation Examples
Before you start creating a poster presentation, look at some examples of real research posters. Get inspired and get creative.
Research poster presentations printed and mounted on a board look like the one in the image below. The presenter stands to the side, ready to share the information with visitors as they walk up to the panels.

With more and more conferences staying virtual or hybrid, the digital poster presentation is here to stay. Take a look at examples from a poster session at the OHSU School of Medicine .
Use SlideModel templates to help you create a winning poster presentation with PowerPoint and Google Slides. These poster PPT templates will get you off on the right foot. Mix and match tables and data visualizations from other poster slide templates to create your ideal layout according to the standard guidelines.
If you need a quick method to create a presentation deck to talk about your research poster at conferences, check out our Slides AI presentation maker. A tool in which you add the topic, curate the outline, select a design, and let AI do the work for you.
1. One-pager Scientific Poster Template for PowerPoint

A PowerPoint template tailored to make your poster presentations an easy-to-craft process. Meet our One-Pager Scientific Poster Slide Template, entirely editable to your preferences and with ample room to accommodate graphs, data charts, and much more.
Use This Template
2. Eisenhower Matrix Slides Template for PowerPoint

An Eisenhower Matrix is a powerful tool to represent priorities, classifying work according to urgency and importance. Presenters can use this 2×2 matrix in poster presentations to expose the effort required for the research process, as it also helps to communicate strategy planning.
3. OSMG Framework PowerPoint Template

Finally, we recommend presenters check our OSMG Framework PowerPoint template, as it is an ideal tool for representing a business plan: its goals, strategies, and measures for success. Expose complex processes in a simplified manner by adding this template to your poster presentation.
Remember these three words when making your research poster presentation: develop, design, and present. These are the three main actions toward a successful poster presentation.

The section below will take you on a step-by-step journey to create your next poster presentation.
Step 1: Define the purpose and audience of your poster presentation
Before making a poster presentation design, you’ll need to plan first. Here are some questions to answer at this point:
- Are they in your field?
- Do they know about your research topic?
- What can they get from your research?
- Will you print it?
- Is it for a virtual conference?
Step 2: Make an outline
With a clear purpose and strategy, it’s time to collect the most important information from your research paper, analysis, or documentation. Make a content dump and then select the most interesting information. Use the content to draft an outline.
Outlines help formulate the overall structure better than going straight into designing the poster. Mimic the standard poster structure in your outline using section headlines as separators. Go further and separate the content into the columns they’ll be placed in.
Step 3: Write the content
Write or rewrite the content for the sections in your poster presentation. Use the text in your research paper as a base, but summarize it to be more succinct in what you share.
Don’t forget to write a catchy title that presents the problem and your findings in a clear way. Likewise, craft the headlines for the sections in a similar tone as the title, creating consistency in the message. Include subtle transitions between sections to help follow the flow of information in order.
Avoid copying/pasting entire sections of the research paper on which the poster is based. Opt for the storytelling approach, so the delivered message results are interesting for your audience.
Step 4: Put it all together visually
This entire guide on how to design a research poster presentation is the perfect resource to help you with this step. Follow all the tips and guidelines and have an unforgettable poster presentation.
Moving on, here’s how to design a research poster presentation with PowerPoint Templates . Open a new project and size it to the standard 48 x 36 inches. Using the outline, map out the sections on the empty canvas. Add a text box for each title, headline, and body text. Piece by piece, add the content into their corresponding text box.

Transform the text information visually, make bullet points, and place the content in tables and timelines. Make your text visual to avoid chunky text blocks that no one will have time to read. Make sure all text sizes are coherent for all headings, body texts, image captions, etc. Double-check for spacing and text box formatting.
Next, add or create data visualizations, images, or diagrams. Align everything into columns and sections, making sure there’s no overflow. Add captions and legends to the visualizations, and check the color contrast with colleagues and friends. Ask for feedback and progress to the last step.
Step 5: Last touches
Time to check the final touches on your poster presentation design. Here’s a checklist to help finalize your research poster before sending it to printers or the virtual summit rep.
- Check the resolution of all visual elements in your poster design. Zoom to 100 or 200% to see if the images pixelate. Avoid this problem by using vector design elements and high-resolution images.
- Ensure that charts and graphs are easy to read and don’t look crowded.
- Analyze the visual hierarchy. Is there a visual flow through the title, introduction, data, and conclusion?
- Take a step back and check if it’s legible from a distance. Is there enough white space for the content to breathe?
- Does the design look inviting and interesting?
An often neglected topic arises when we need to print our designs for any exhibition purpose. Since A0 is a hard-to-manage format for most printers, these poster presentations result in heftier charges for the user. Instead, you can opt to work your design in two A1 sheets, which also becomes more manageable for transportation. Create seamless borders for the section on which the poster sheets should meet, or work with a white background.
Paper weight options should be over 200 gsm to avoid unwanted damage during the printing process due to heavy ink usage. If possible, laminate your print or stick it to photographic paper – this shall protect your work from spills.
Finally, always run a test print. Gray tints may not be printed as clearly as you see them on screen (this is due to the RGB to CMYK conversion process). Other differences can be appreciated when working with ink jet plotters vs. laser printers. Give yourself enough room to maneuver last-minute design changes.
Presenting a research poster is a big step in the poster presentation cycle. Your poster presentation might or might not be judged by faculty or peers. But knowing what judges look for will help you prepare for the design and oral presentation, regardless of whether you receive a grade for your work or if it’s business related. Likewise, the same principles apply when presenting at an in-person or virtual summit.
The opening statement
Part of presenting a research poster is welcoming the viewer to your small personal area in the sea of poster presentations. You’ll need an opening statement to pitch your research poster and get the viewers’ attention.
Draft a 2 to 3-sentence pitch that covers the most important points:
- What the research is
- Why was it conducted
- What the results say
From that opening statement, you’re ready to continue with the oral presentation for the benefit of your attendees.
The oral presentation
During the oral presentation, share the information on the poster while conversing with the interested public. Practice many times before the event. Structure the oral presentation as conversation points, and use the poster’s visual flow as support. Make eye contact with your audience as you speak, but don’t make them uncomfortable.
Pro Tip: In a conference or summit, if people show up to your poster area after you’ve started presenting it to another group, finish and then address the new visitors.
QA Sessions
When you’ve finished the oral presentation, offer the audience a chance to ask questions. You can tell them before starting the presentation that you’ll be holding a QA session at the end. Doing so will prevent interruptions as you’re speaking.
If presenting to one or two people, be flexible and answer questions as you review all the sections on your poster.
Supplemental Material
If your audience is interested in learning more, you can offer another content type, further imprinting the information in their minds. Some ideas include; printed copies of your research paper, links to a website, a digital experience of your poster, a thesis PDF, or data spreadsheets.
Your audience will want to contact you for further conversations; include contact details in your supplemental material. If you don’t offer anything else, at least have business cards.
Even though conferences have changed, the research poster’s importance hasn’t diminished. Now, instead of simply creating a printed poster presentation, you can also make it for digital platforms. The final output will depend on the conference and its requirements.
This guide covered all the essential information you need to know for creating impactful poster presentations, from design, structure and layout tips to oral presentation techniques to engage your audience better .
Before your next poster session, bookmark and review this guide to help you design a winning poster presentation every time.

Like this article? Please share
Cool Presentation Ideas, Design, Design Inspiration Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Design • January 11th, 2024
How to Use Figma for Presentations
The powerful UI/UX prototyping software can also help us to craft high-end presentation slides. Learn how to use Figma as a presentation software here!

Filed under Design • December 28th, 2023
Multimedia Presentation: Insights & Techniques to Maximize Engagement
Harnessing the power of multimedia presentation is vital for speakers nowadays. Join us to discover how you can utilize these strategies in your work.

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • December 15th, 2023
How to Delete a Text Box in Google Slides
Discover how to delete a text box in Google Slides in just a couple of clicks. Step-by-step guide with images.
Leave a Reply
- Log In Username Enter your ACP Online username. Password Enter the password that accompanies your username. Remember me Forget your username or password ?
- Privacy Policy
- Career Connection
- Member Forums
© Copyright 2024 American College of Physicians, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 190 North Independence Mall West, Philadelphia, PA 19106-1572 800-ACP-1915 (800-227-1915) or 215-351-2600
If you are unable to login, please try clearing your cookies . We apologize for the inconvenience.
Preparing a Poster Presentation
Posters are a legitimate and popular presentation format for research and clinical vignettes. They efficiently communicate concepts and data to an audience using a combination of visuals and text. Most scientific meeting planners take advantage of the popularity and communication efficiency of poster presentations by scheduling more poster than oral presentations. Poster presentations allow the author to meet and speak informally with interested viewers, facilitating a greater exchange of ideas and networking opportunities than with oral presentations. Poster presentations often are the first opportunities for young investigators to present their work at important scientific meetings and preparatory for publication in a peer-reviewed journal.
Poster Production Timeline
In order to be successful, certain prerequisites must be met. First, you must have a desire to be scholastically effective and be willing to put the time into the design and production of the poster. Second, you need organizational skills. Like any other endeavor associated with deadlines, you must be able to deliver the product on time. Posters are associated with more deadlines than oral presentations, due to the necessary interaction with graphic artists, graphic production, and the needs of the meeting itself. Organizational skills are also needed to create a concise and logically structured graphic and text presentation of the research or vignette. In order to help you achieve these goals, this article addresses poster planning, production, and presentation. It may be helpful to create a poster production timeline .
- Determine if your poster will be judged at the scientific meeting. If so, ask for the judging criteria , which will be immensely helpful for you to plan and construct the poster.
- Know the rules . It is your responsibility to know the physical requirements for the poster including acceptable size and how it will be displayed. A 4' × 4' display area cannot accommodate a 6' × 6' poster and a 3' × 3' poster will look insignificant in an 8' × 8' display area. All scientific programs that sponsor a poster session will send you information on the display requirements at the time your poster is accepted for presentation. Review and follow the instructions precisely. However, be warned that not all scientific programs will automatically tell you how the poster will be displayed. Some programs provide a cork/tack-board system that allows you to display your poster by fastening it to a solid display board with stickpins. This gives you the option of displaying your poster as many individual parts (components of the poster, such as abstract, methods, graphics, conclusion, are fastened individually to the display board) or as one piece. Other programs "hang" their posters from a frame by large spring clips. This means that the poster must be created as a single unit and cannot be too heavy for the clips or too light such that it will curl upwards like a window shade. A few programs still use easels to display posters, mandating that the poster be constructed of or placed on a firm backing that can be supported in this way. The point is, find out how the poster will be displayed and engineer a poster that best meets the requirements.
- Determine exactly how the poster will be produced. Will you hire a graphic artist for partial or complete production? Does your institution provide graphic services to your department? Will you need to do this yourself? If payment is required, who will pay for the production? Regardless of who is doing the work and how it will be financed, only you can determine the individual tasks and set the deadlines. Make sure your deadlines include sufficient time to revise the poster if you find mistakes or otherwise need to make changes prior to the scientific meeting. Finally, if you are working with a graphic artist, make your timetable after consultation with him/her so it is realistic and he/she understands your time constraints.
- Compile a list of components that will appear on the poster. There are common elements to all posters, whether they are research presentations or clinical vignettes. At the top center, the poster should display the title, authors, and institutional affiliations. Any necessary acknowledgments can also be placed here. Many scientific programs will insist that the abstract be included on the poster and will specify its location (i.e., upper right corner).
Scientific posters should follow the IMRAD format (Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion) .
- The Introduction presents the background and the purpose of the research. The background information typically consists of a statement summarizing the current knowledge in an area, what knowledge is missing, and how this research project addresses the knowledge gap. A hypothesis can be included in the Introduction.
- The Methods section should specifically address the following areas: research design, research setting, number of patients enrolled in the study, and how they were selected. The Methods section should also include a description of the intervention (if appropriate), a description of the outcome variables and how they were measured, and the method of statistical analysis.
- The Results section includes the quantitative data. This section usually begins with a description of the subjects in the study and a description of those who were not included because they failed to meet the inclusion criteria or dropped out. Include the frequencies of the most important outcome variables. Consider comparisons of the outcome variables between various subgroups within the study (treated vs. untreated, young vs. old, male vs. female, and so forth). Numerical results should include standard deviations or 95% confidence limits and the level of statistical significance should be indicated.
- Finally, in the Discussion section, state concisely what can be concluded from the study and its implications. Make sure that the conclusions are supported by the data presented in the Results and do not present unsubstantiated personal opinion.
Clinical vignette posters generally have three components: Introduction, Case Description, and Discussion. A short Introduction typically describes the context of the case and explains its relevance and importance. When describing the case, follow the basic rules of medical communication by describing in sequence the history, physical examination, investigative studies, and patient's progress and outcome. The main purpose of the discussion is to review why decisions were made and to extract the lesson from the case. Be wary of boasting that your case is the "first" to describe a particular phenomenon, since even the most thorough searches often fail to reveal all instances of similar cases. Keep in mind that the best research and clinical vignette posters are those that make a small number of points (even just one) clearly and succinctly.
As you review your content, make decisions on what can be displayed pictorially. Posters that are mainly text discourage others from visiting and reviewing your work. Make your presentation as visual as possible; not only does it make your poster more appealing, but information can be transmitted more efficiently with a picture, figure, or graph. For example, information on patient demographics could be represented as a pie chart, frequencies of outcomes as bar graphs, and comparisons of means and statistical significance as tables. Clinical vignettes offer an excellent opportunity to display clinical photographs that illustrate important points of pattern recognition.
Finally, find out if you are required to be present during the poster session. Most scientific meetings schedule a period of time for the author to stand by the poster during the session. This enables you to answer questions about your work and, in some situations, is part of the judging process. Find out if and when this is scheduled.
A Few Tips on Poster Appearance:
Avoid clutter.
Limit your poster presentation to a few main ideas. It's better to present a few of your findings well than present all of your findings poorly. Arrange your poster components to read from left to right and top to bottom. Emphasize important points on the poster with lines, frames or boxes, and arrows.
Keep the lettering simple.
Use no more than three different font sizes; the largest for the poster title, second-largest for section titles, and smallest for text. For all lettering, use both upper- and lowercase letters. Words composed of all uppercase letters are difficult to read. The smallest font should be large enough so it is easily read from a distance of 3 to 5 feet (usually, 24-point font).
Keep the colors simple.
Too much color can be distracting, while too little color can be boring and lifeless. Use color mainly to highlight important elements.
You will need to decide how your poster will be constructed. Your budget and available graphic art resources will most likely influence this decision. At one end of the spectrum, you can inexpensively produce a poster with a graphics software package (such as PowerPoint) and a color printer. Your output will be limited to individual components that measure 8" × 11" to 11" × 17". These components will probably need to be mounted on a stiff backing, such as poster board or foam core, to effectively display them. At the other, more expensive end of the spectrum, you can work with the graphic arts department at your institution. They can use sophisticated software programs, such as Quark, to design and create a poster. The electronic version of the poster can be sent by e-mail to a printing or service bureau. Service bureaus produce a variety of visual products including posters, slides, signs, and limited print editions of books. They can print any size poster with all its component parts as a single unit usually within 24 to 48 hours. The cost of this service is difficult to estimate because it is dependent on a number of variables including poster size, use of color, resolution of the print (dpi, or dots per inch), whether it is laminated, or backed with foam core. A moderately priced poster may cost from $500 to $600. The staff in your graphic arts department can help you pick the options that are within your budget.
At the time of production, it is your responsibility to review the first draft, or copy, of the poster. This is your best chance to correct errors and make changes to improve the accuracy and visual attractiveness of the poster. Use the Poster Checklist to aid your review. In addition, have a colleague help you proofread. It's a good idea to have someone unfamiliar with the research or case help you because he or she will quickly identify areas that are confusing or ambiguous. It's a good idea to have someone who is expert in spelling and grammar review the poster as well. As mentioned previously, schedule the proofreading early enough in the process so that you have time to make any corrections or changes prior to the meeting.
As you prepare to travel to the scientific meeting, consider the following tips:
- Arrange for a proper carrying case for your poster. A worthy investment can prevent damage to your poster and your reputation.
- Don't check your poster as luggage. Carry the poster with you at all times. Better your clothes get lost than your poster.
- Come with some basic equipment. Although these items are typically provided at scientific meetings, you may not have quick access to them. Bring with you:
- Push pins, tacks, or stapler
- Know where and when to set up your poster. The room or area reserved for posters is usually noted in the meeting program. Arrive early to set up your poster. This will allow you to adapt to any surprises in the physical layout or unannounced changes in the method of displaying the poster. Additionally, it's easier to put up your poster when there are fewer people competing for space and equipment. Most scientific programs assign a unique identifying number to your poster that corresponds to location of the poster in the display area. Find out what your number is and place your poster in the corresponding spot.
- Know when to "stand-by" your poster. The time will be listed in the meeting program. Arrive on time and stay until the end of scheduled time. Don't wander off; you may miss the judges, your next fellowship director, or your next partner or employer.
- Know when to take your poster down. Meeting rooms turn-over fast. Have a clear understanding when the poster session is over and when the poster must come down. Failure to take the poster down at the appointed time can result in the hotel or convention staff (not so gently) removing it.
- Be prepared to promote yourself. Consider bringing handouts and business cards for those who visit your poster. Use this opportunity to "network" with other professionals who share similar academic interests.
This final section provides examples of what makes a poster effective. As you study the examples, note that they share similar characteristics:
- Organized and easy to follow the flow of information
- Easy to read, using large font size and are not overly dense with text
- Attractive, due to judicious use of colors, use of graphics, and arrangement
Listed below are a number of important poster characteristics and examples illustrating those characteristics:
- Use of a poignant attention getter
- Use of graphics to communicate data
- Well organized poster with easy to follow flow of information
- Overly dense presentation of content
+31 (0)6 5465 1346 | [email protected]
CAUSE AN EFFECT
Blog on science communication
How to design a poster presentation so your research stands out

Giving a poster presentation is not the dream of every scientist, but we help you to make a beautiful and effective poster presentation to take advantage of the networking opportunity!
Your research is important, so why waste everyone’s time with a poster with the main message hidden in bullet points and a design that makes it challenging to decipher text and tables?
Also check out our Poster Design Guidelines
The ultimate guide for good poster presentation design. Use it to create a well-designed poster that stands out and effectively communicates your research. We’ve created this together with conference organizers, scientists and universities. It’s based over a decade of experience with (visual) science communication.

What is the goal of your poster presentation?
A quick reminder: The main goal of a poster presentation is not to share your research results. If that were the case, you could just publish it, email it to colleagues in your field or hand out copies of your paper during conferences. Instead, the goal of standing next to your poster is to have interaction with other researchers in your field , learn from their critical questions, feedback, and suggestions, and make connections for future collaborations.
Your new goal is to present your work clearly and make sure that people stop to talk to you about your work. To achieve this goal, you and your poster need to STAND OUT. If you do it well, presenting your poster is an incredible learning opportunity. In our e-book about designing presentations , we talk a bit more about how to define your goal and message. Think about what your main message is, WHY your message is so important (typically the ‘background’ section) and only then WHAT the evidence is supporting your message (the ‘results’ section).
Write down your research as a story
We do this exercise in our science communication workshops a lot:
Write down your entire research in a single sentence (commas are allowed). Don’t worry if you don’t get it on the first try. In our workshops, we often start out by writing it down in a single paragraph or a one-minute speech and then shorten it until you have a single sentence. Answering the following questions help you get started:
Why are you doing your research? What is your ultimate goal?
e.g. We want to slow down Alzheimer’s disease, find a cure for small-cell carcinoma, find out which cells are responsible for skin cancer. We want to improve patient care in hospitals. We want to understand the environmental causes of obesity. We aim to study the best way to lose weight. We want to develop a new standard for research outcomes. (Just a few examples from our clients)
What is the underlying problem? Sometimes your research goal is more obscure than curing cancer or solving obesity. People will know these are major problems, and you do NOT need to point this out to them. However, you might be solving a problem people don’t know about yet. If that’s the case, you have to explain the problem AND the goal or solution to the problem. e.g. We think there is a better way to diagnose disease X than is currently done because current practice is very costly.
What exactly are you looking at in your research? How are you executing your research?
e.g. you are studying human behavior, performing cell microscopy, literature research in the national archives, interviews in local communities.
e.g. you are using epidemiology, meta-analysis, RCT, In-vitro study, computer modeling, AI, fieldwork, (online) questionnaires.
What makes your research, approach, or team unique?
e.g. We’re doing the first multi-disciplinary research into obesity prevention / We have an international team with over 20 participating countries / We developed a unique new technique or methodology / We combine all available data to date / We have a specific breed of mice that might answer the question better / This is the first time anyone has ever looked at X or used method Y.
This would result in a sentence like this:
To find out how to slow down Alzheimer’s disease, we are using new metabolomic profiling techniques to find pathways to prevent beta-amyloid proteins from forming harmful plaques in the brain.
This can be the new subtitle or large quote of your poster! It’s the main summary of what you’re trying to achieve.

Have a question as your main title
For the main title, you might want to use something even shorter. You can choose to have a question as a main title. This might lure more people to your poster than a statement. What about “Mental health in hospitals: what can health professionals do to ease the pain?”. It’s the perfect start to a conversation. Imagine what the first question would be that you can ask a person approaching you. It does not tell the whole story but makes people curious enough to walk up to your poster to read the answer or have a discussion with you.
Another example:
QUESTION: Will assessing differentiated dysplasia improve risk assessment of leukoplakia better than current WHO standards?
STATEMENT: Adding differentiated dysplasia to classic dysplasia assessment is a stronger prognostic indicator (HR:7.2) for malignant transformation than current WHO standards.
The 5-second science communication rule
In general, you only have a few seconds to grab attention with your poster. People will only stop at your poster if they are drawn in by an interesting title or a stunning design. When they decided to slow down and start reading more, it takes them about 30 seconds to read your poster. This is not reading in a traditional sense, but more skimming the titles. This means that if your titles are words such as Introduction, Methods, Results, Conclusion they will still have no idea what your research is about!
Reading your poster should not be a chore. Test it with some friends or colleagues. Show them your poster for 30 seconds, and ask them what they think is your main message, and what result/word/graph/design piqued their interest.
Poster prep-time!
- Think about what you want to get out of this poster presentation. Do you want to connect with at least 3 senior researchers? Do you want to get feedback on a specific result? Do you want to discuss your methods and ask others how they would do this?
- Prepare what you want to say when someone approaches your poster. Or better yet, what you want to ask them.
- Think about what critical questions people may have about your poster and prepare a short answer. Is your research about dairy and it is funded by the dairy industry? Expect some critical questions. Be grateful you get these questions, it’s what proper scientific discussion is all about!
Do not conform to “standards” imposed by the conference
We know that you often have to adhere to guidelines for your poster presentation. Maybe you have to abide by a standard template from your institution, or have huge logos from every single collaborator (and even pictures of their locations!) on it. We advise that you do NOT give in to these demands without a fight. Remember: these guidelines are not made by science communication experts, but often by the press officer with a desire for a uniform look or by more senior scientists who think design is something achieved by rainbow-colored text effects in Word. You get our frustration…
Of course, it’s good to adhere to the physical format of the poster mount and have large and legible text, but we’ll try to push you out of your comfort zone here a bit. You will not get punished by anyone for using different colors than your institution, use a different font, and use design in a way that makes your research pop. Remember: you can not stand out if your poster looks like all the other boring posters in the room!
TEXT: How to make sure your main message stands out
Don’t structure your presentation like a paper.
Ditch the abstract/introduction/results/conclusion/acknowledgments structure and create your own interesting titles. Instead: write conclusive titles that people can skim. This means that you should make sure that your titles (the largest texts on your poster) tell your story.
Turn headings into conclusions & quotes.
Instead of the vague descriptive title “Costs of diabetes” you can turn it into the main conclusive message: “Total costs of diabetes have increased to $245 billion.” Which one do you prefer?
This means that you do NOT highlight the least interesting words on your paper, but let the MESSAGE stand out. We cringe when we see the words “Background” highlighted in huge bright blue text, and the main message obscured in smaller text.
An example: How to structure your research (based on https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32023777 ).
Which behavioral and nutritional factors are targets for stomach cancer prevention programmes?
A meta-analysis and systematic review of 14 behavioral and nutritional factors in 52,916 studies.
Helicobacter pylori infection, smoking, alcohol, high salt intake were identified as the main factors contributing to stomach cancer.
These results may be utilized for ranking and prioritizing preventable risk factors to implement effective prevention programs.
As you can see, with the new structure, it’s already a short explanation of your entire research! Way to go!
TIP: Does your research show negative results? Shout it from the rooftops! Don’t be disappointed, your research is just as important as anyone else’s. Do not hide it, show it, so other people can learn from it.
DESIGN: Keep it clean and simple
How do you think you will come across if you use different backgrounds, colors and fonts for every slide? Does that really make you look creative and professional? We know it’s tempting, but don’t use every tool PowerPoint has given you to design with. Don’t use gradients, drop-shadows, text effects if you don’t know how to use them.
The design of your poster should support your story, provide structure, and make your presentation more effective. Design can also help distinguish between the main message and supporting information. By using different designs for your main thread and quotes, anecdotes, or examples you make sure people don’t lose sight of your most important messages.
We love to show bad examples, so check out this poster presentation dissection:

Only use bullet points for actual lists
If there is one piece of advice we would love for you to remember from this post: do NOT use bullet points for sentences! It transforms them into weird short sentences and doesn’t make your messages any clearer. Please, only use bullet points for actual lists. Like countries or disease outcomes you are measuring. Disregard your instinct to put bullets before sentences and just write a nice readable paragraph instead. People will love you for it! If you’re feeling creative you can always ask yourself the question of whether there are better ways to visualize your bullet points. Showing the countries you’ve gathered data from in an actual map is MUCH more informative than a list (anybody knows where Kyrgyzstan is located exactly?). We often use https://mapchart.net/world.html for creating maps.
COLOR: When in doubt, start with white and grey, and add a single pop of color.
We’re not going to explain color theory here. And don’t be afraid to use ANY color you want. Just make sure to check whether it has enough contrast with the background to be legible (with the WebAIM contrast checker ). Don’t waste your time on this. When in doubt, choose 1 single color (or shades of the same color) and combine it with black for text and white and light grey for backgrounds, boxes, and borders. Add a single pop of color to create focus where you want the audience to look, e.g. important keywords, arrows, and your main message. We have added some color scheme examples in our Poster Presentation Template (see below).
IMAGES: Only use images that contribute to your message
Text alone can be a bit uninspiring sometimes. We encourage the use of images but make sure they contribute to your message. Either use them to show which topic you are researching (e.g. plane aerodynamics, body fat distribution, or the history of women’s rights), or when they have intrinsic value and show something that you cannot point out in words (e.g. the location of an aorta stent, or the flow of information between low-orbit satellites). Don’t add cute images of people, landscapes, university buildings or flower patterns to spice up your poster. Check out our favorite resources for good free copyright-free images and design tools.
So please don’t use random useless stock photo’s like these in your presentation! #facepalm

GRAPHS: Make sure people can read a graph without having to consult a legend or description.
A graph is better than a table. It’s much easier to understand relationships in your data when presented visually in a graph than as numbers in a table. However, a conclusion drawn from the data, presented as a main conclusion with a single number (e.g. alcohol consumption is 23% higher in France than in Sweden) is better than your run-of-the-mill graph with a vague description of the two axes.
Write graph titles as a conclusion of your result.
Which title do you think is better?
Projected disease prevalence and mortality reduction over 20 years for the population aged 18 to 95 years in nine European countries with lower salt intake.
Lower salt intake reduced the prevalence of stroke in Poland by 13.5%
Don’t use separate legends in your graph (e.g. those boxes on the side of the graph). If possible, put the text/label explaining what a line represents next to the line. This prevents people from having to go back and forth between the graph and legend to understand its message.
- Do not copy your complex research paper title as the title on a poster. Create a short and snappy poster title that draws people in.
- Don’t include any text, graph, or image that does not contribute to your main points. If people can understand your main message without them, leave them out.
- Never apply chart junk in your graphs, remove all unnecessary lines/gradients/grids.
- Don’t use high-contrast boxes with rounded corners: this creates weird arrows between boxes that draw your eye to the area in between text.
- Avoid unclear QR codes, people will have no idea what happens after they scan it and it’s often being used for fraudulent purposes.
- Rewrite the title into an intriguing question or statement, so people know what to talk to you about.
- Your main purpose/unique proposition/interesting result should be the largest text on the poster. You should be able to read it from five meters away.
- Ensure that everything on the poster is self-explanatory. Avoid abbreviations and acronyms.
- Make sure it’s clear from the poster who you are. Highlight one of the authors, or add a (recent, professional) portrait, so people can also find you later if they visited the poster when you were away.
- White. Space. Scientists seem to think that white space is wasted space that needs more text crammed in. The opposite is true. More white space makes your poster seem less daunting, and easier to approach.
- Have a call to action on your poster. Who do you want people to contact, and what would you want to talk about in future communications? Include your Twitter, LinkedIn, email if possible.
- When in doubt about the colors: choose white and light grey and add a single pop of color. It’s the safest bet!
- Avoid jargon. You can get into jargon and details AFTER people have approached you and your poster.
- Use enough contrast between the background and letters so people can actually read it. You can check your contrast at: https://webaim.org/resources/contrastchecker/
Creative ideas for those who are ready to conquer the world with their research:
- Laminate your poster and give people a whiteboard marker to write things on it or highlight sections they think are important. This is not only a nice gimmick that people will remember, but can be good for you as a reminder of the feedback you were given. As an added bonus it gives visitors a chance to interact with each other.
- Bring a prop related to your research to the stand. Do you research fat cells? Bring a pound of lard with you. Do you research tooth health? Bring a plastic jaw with you that people can look at.
Tip: Print on textiles instead of paper. Easier to take with you on a plane without tearing or creasing. However, do this only when you are going to use the poster multiple times, it’s a waste of material otherwise.
To hand out or not to hand out?
A hand-out is a great way to get into depth without cramming every single detail into your poster. But you might just have printed 20 copies and nobody to hand it out to. Also, who reads all the things they collect when they get home? In other words: we do not advise you to bring hand-outs.
As useful as it may seem, we think that making the connection is more important than sharing the details of your research right then and there. So instead, give out your LinkedIn or ResearchGate details or your personal website URL, so you are instantly connected and they will see any new updates you post in their timeline. If they are still interested in the details, you have their contact information to send them your paper when it’s published!

POSTER PRESENTATION – A CASE STUDY
Have you read all our tips but still don’t know how to implement them in your poster? Don’t worry, we will go over a case study of an existing poster presentation.
For this case study, we worked together with Joseph Diab , a PhD candidate in bioanalytical chemistry at The Arctic University of Norway (UiT) doing research into Ulcerative Colitis. He wanted to update his poster for his next poster presentation and volunteered with us to make it better.
The BEFORE poster
The poster he made was a typical poster, not bad at all actually, we’ve seen much, much worse… But there was plenty to improve. Let’s go over the poster to find out what could be improved.

The good thing about the poster was that the main title was written in big text, and he even emphasized the most important words. This is a great way to have it stand out more. He did not fall into the trap of having his paper title as the main title, and put it in smaller text below. He was right to make the conclusion bigger as well.
However, there is room for improvement. When you look at the poster while squinting your eyes, only the main title jumps out at you. There is not much larger text to scan to get a feel for what he’s trying to tell us. We’re also missing the reason he is doing this research. Why is it important to reveal the metabolomic signature? If the urgency is missing, people might walk past your poster.
So, to make his poster better we’ve given Joseph some homework questions about his research. These are his answers:
What do you want to get out of this poster presentation? Joseph: I want to get feedback on how to proceed and validate these finding, and how to unravel the role of microbiota in IBD (Inflammatory bowel disease).
Can you tell me in your own words what the main purpose of your research is? Joseph: IBD is an untreatable nasty disease. The only available treatment just makes the patients go from active inflammation into remission. Most of these patients will develop inflammation again. Moreover, 20-30% of the patients develop very severe outcomes and need surgery, and they might die from complications or from cancer (caused by the treatment failure). In my research, we aim to find a biomarker to predict the outcome from the moments the patient gets the diagnosis.
Why is your research unique? Joseph: This is the first study to determine the full proteomic and transcriptomic profile in treatment-naïve and deep-remission UC patients.
What is the relevance of your results in the real world? Joseph: We are using metabolomics to improve the patient’s stratification in IBD.
We love it when researchers explain something in their own words, it’s so much clearer than when written as a paper! Here are the steps we took to improve his poster:
Step 1: Create an engaging main message.
We’ve rewritten the main message of his poster to include the main goal of his research (to improve IBD treatment) and made it a bit more interesting by adding part of his research results stating that he has found the “first clue”. This is a great way of showing that each research project is just one small step towards final answers, and this can make your audience a bit more curious. Who doesn’t like to figure out clues? This way the title also gives away a part of the results, which makes it easier for people to understand what you’ve accomplished.
Before: Ulcerative Colitis is characterized by altered tryptophan and fatty acid metabolism.
After: Finding biomarkers to improve the personalized treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. Altered tryptophan and fatty acid metabolism provide the first clue.
Step 2: Put the most important messages first.
In Joseph’s poster, like in so many, the conclusion is hidden away at the end of the poster. We’ve moved it up next to the title. In addition, we’ve moved the author affiliations to the bottom of the poster. They were taking up too much prime real estate, and it’s not very relevant for your audience.
Step 3: Create an effective design

We were lucky that Joseph was doing research in a field that is easy to visualize. Ulcerative Colitis is a disease of the large intestines, so we used an illustration of one to enhance the design. This was not just to “make it pretty”, but also to visually show the topic and draw your eye towards the most important message: the conclusion. People recognize an intestine much faster than reading the text.
We stayed away from the boring academic blue. Everybody is using it, which is a good reason to not use it yourself (the easiest way to stand out!). In this case the best choice was to just use the colors from the image. With this bright pink as an accent color, and whites and greys as main colors, you generate a nice cohesive color scheme in a snap!
TIP : If you can find a relevant image for your poster, always use that color in your color scheme! PowerPoint now has an eyedropper tool that enables you to pick any color from an image and use it in texts or boxes.
We wanted to separate the different paragraphs, but not draw too much attention to it by using dark backgrounds, thick borders or lots of contrast, so we used subtle shadow which divides the main sections but does not distract.
Step 4: Emphasize your most important messages
Our advice is to de-emphasize words such as methods and background . However, this might be a bit scary, since it deviates so much from what posters have looked like for years. So we decided to keep it, but use a smaller font size. We used the pink color to emphasize the most important sentences and draw your eyes towards them. If you squint and just read the larger pink text, you should be able to understand the research. We wanted to make it stand out more and make it bigger, but there was not enough space on the poster to increase the font size. An important lesson in working with limitations!
Step 5: Make it engaging and easy to understand for your audience
To make sure the answers to Joseph’s homework were included in the poster, we came up with the “What’s new” section. Just reading this section gives you a very good grasp of the main goal and why the research is unique.
The “How can you help?” section prompts the visitor to have a conversation and invites them to share their ideas about this topic. This is the conversation starter you need for a successful poster presentation.
Step 6: Kill your darlings
There is never enough space on a poster, so we needed to scrap some of the texts and graphs. For each graph, we asked whether it was really necessary to include. Did this graph really contribute to the main message, or could anyone at the conference understand the research perfectly fine without it?
As you can see, we ditched one of the two almost similar multivariate analysis graphs. They showed almost the same thing. We also removed the Venn diagram. It contained some very detailed information that was not essential for the main message and therefore took up too much valuable space.
We also wrote new titles for the graphs in the results section. Instead of a descriptive title (Pathway analysis), we wrote a concluding title (Integrated pathway analysis provides a unique and detailed snapshot of the metabolic changes in the onset of UC.). You want to give away your conclusion from the graph, not have people spend 5 minutes trying to figure it out themselves from looking at the dots.
In the graphs we made the outlying pathways more prominent with the dark blue background, so you can immediately find these pathways without having to read all of them.
Step 7: Background information & call to action
There is always some boring information you have to include, or your supervisors won’t be happy. Logos of your institutions, affiliations, the title of your paper. We put them where they belong: on the bottom of the page in smaller font. Very few people will be interested in this at first glance.
We do want to show who the person is behind the poster, so we kept the headshot of Joseph and added a call to action: Connect with Joseph Diab for more details and a discussion of this paper.
This lowers the threshold for people to connect with Joseph later. After all: he invited them to email him already! Since Joseph is active on Twitter we included his Twitter handle as well as his email address. This is very important. If you want to keep in touch with people who pass by, you have to give them your contact information.
A QR code might sound very hip, but we advise against using it. For starters, it’s not really telling anyone where you will end up. Are you linking to the paper, to Joseph’s personal website, his Twitter account, or his University’s website? People might not even have a smartphone or QR reader. The best thing is to ask people on the spot to connect with you on LinkedIn, Twitter, or send you an email, so you’re sure they will keep in touch.
The result:

Check out Joseph attracting attention with his new poster at the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) 2020 annual congress:
Let us know what you think!
Do you have a question that wasn’t answered in this article? Write to me at [email protected] , or check out our workshop on Poster presentation & Infographic design .
A poster presentation template to not take too seriously
Want to get a head-start on designing your poster? We’ve developed a simple template for your poster to get you ahead of the curve. But don’t take this template too seriously! In fact, we usually advise against using templates, if everybody starts using them, nobody will stand out. It’s your job to make it interesting and fit your needs and limitations.

About the Author: Liesbeth Smit
Search for more scicomm tips:, read more about science communication:.

Tool to create your own data visualisation with icons

Increase the visibility of your research project website and reach your target audience

Find inspiration for your design & create a unique style for your research website

Define the goal & pitch for your poster presentation

Our favorite (free) tools to create better designs for science communication

Designing for impact: the lessons I learned from my science communication internship
Become a pro science communicator with our workshops.

IMPACT with science communication
Do you want to have a positive effect on the world? We'll make you think about your goal, audience, and message and ensure you know what it takes to create impact! Also available as a keynote lecture.

Pitch your science to any audience
By understanding your audience and aligning your message to their needs, you can really get your point across. In this workshop you’ll create a short pitch or article to practice just that.

Poster design & graphical abstracts
Create beautiful and effective infographics, posters and graphical abstracts. You will learn the best practices in design to make sure your work gets noticed and is easier to understand.

Science and the media
Do you want to be more confident around journalists or the media? Or do you want to take advantage of the opportunities that social media offer for scientists? We'll get you started!
Contact us to find out what we can do for you!
In English or Dutch
Call Liesbeth: +31 (0)6 5465 1346
Call Stephan: +31 (0)6 245 92 770
Working around the world from the Netherlands Pricing General Terms and Conditions Algemene Voorwaarden Privacy & Cookies
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Palliat Med

Writing Abstracts and Developing Posters for National Meetings
Gordon j. wood.
1 Department of Medicine, Section of Palliative Care and Medical Ethics, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
R. Sean Morrison
2 Department of Geriatrics and Palliative Medicine, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, New York, and the James J. Peters VA, Bronx, New York.
Presenting posters at national meetings can help fellows and junior faculty members develop a national reputation. They often lead to interesting and fruitful networking and collaboration opportunities. They also help with promotion in academic medicine and can reveal new job opportunities. Practically, presenting posters can help justify funding to attend a meeting. Finally, this process can be invaluable in assisting with manuscript preparation. This article provides suggestions and words of wisdom for palliative care fellows and junior faculty members wanting to present a poster at a national meeting describing a case study or original research. It outlines how to pick a topic, decide on collaborators, and choose a meeting for the submission. It also describes how to write the abstract using examples that present a general format as well as writing tips for each section. It then describes how to prepare the poster and do the presentation. Sample poster formats are provided as are talking points to help the reader productively interact with those that visit the poster. Finally, tips are given regarding what to do after the meeting. The article seeks to not only describe the basic steps of this entire process, but also to highlight the hidden curriculum behind the successful abstracts and posters. These tricks of the trade can help the submission stand out and will make sure the reader gets the most out of the hard work that goes into a poster presentation at a national meeting.
Introduction
A track record of successful presentations at national meetings is important for the junior academic palliative medicine clinician. Unfortunately, palliative care fellows report minimal training in how to even start the process by writing the abstract. 1 What follows is a practical, step-by-step guide aimed at the palliative care fellow or junior palliative care faculty member who is hoping to present original research or a case study at a national meeting. We will discuss the rationale for presenting at national meetings, development of the abstract, creation and conduct of the presentation, as well as what to do after the meeting. We will draw on the literature where available 2 – 7 and on our experience where data are lacking. We will focus on the development of posters rather than oral presentations or workshops as these are typically the first and more common experiences for junior faculty and fellows. Finally, in addition to discussing the nuts and bolts of the process, we will also focus on the “hidden curriculum” behind the successful submissions and poster presentations (see Table 1 ).
The Hidden Curriculum: Tips To Get the Most Out of Your Submission

Why Present at National Meetings?
Given that it takes a fair amount of work to put together an abstract and presentation, it is fair to ask what is to be gained from the effort. The standard answer is that presentations at national meetings aid in the dissemination of your findings and help further the field. Although this is certainly true, there are also several practical and personal reasons that should hold at least equal importance to fellows or junior faculty members (see Table 2 ). Perhaps most importantly, presenting at a national meeting helps develop your national reputation. People will begin to know your name and associate it with the topic you are presenting. Additionally, it provides an opportunity to network and collaborate, which can then lead to other projects. Many of us have begun life-long collaborative relationships after connecting with someone at a national meeting. Even if you don't make a personal connection at the meeting, if people begin to associate your name with a topic, they will often reach out to you when they need an expert to sit on a committee, write a paper, or collaborate on a project.
Personal Reasons To Present Abstracts/Posters
Development of a national reputation is important not only in garnering interesting opportunities, but it is also key to career advancement. For fellows, presenting at national meetings can forge connections with future employers and lead to that all-important “first job.” For junior faculty, demonstration of a national reputation is often the main criterion for promotion and presentations at national meetings help establish this reputation. 8 Junior faculty may also make connections that lead to potential job opportunities of which they might not otherwise have been aware.
There are three additional practical reasons to present at a national meeting. First, having something accepted for presentation is often the only way your department will reimburse your trip to the meeting. Second, going through the work of abstract submission and presentation helps tremendously in manuscript preparation. It provides a deadline and forces you to organize your thoughts, analyze your data, and place them in an understandable format. This makes the eventual job of writing the manuscript much less daunting. Third, presenting also allows you to get immediate feedback, which can then make the manuscript stronger before it is submitted. Such feedback often gives the presenter additional ideas for analyses, alternate explanations for findings, and ideas regarding future directions.
Although these personal and practical reasons for presenting are derived from our own experiences, they are concordant with the survey results of 219 presenters at the Society of General Internal Medicine Annual Meeting. 9 This survey also highlighted how posters and oral presentations can meet these needs differently. For example, for these presenters, posters were preferred for getting feedback and criticism and for networking and collaborating. Oral presentations, on the other hand, were preferred for developing a national reputation and sharing important findings most effectively. For all of these reasons, many academic centers have developed highly effective programs for trainees and junior faculty to help encourage submissions 10 , 11 so it is wise to seek out such programs if they exist in your home institution.
Getting Started
Realizing the importance of presenting at national meetings may be the easy part. Actually getting started and putting together a submission is where most fall short. The critical first step is to pick something that interests you. For original research, hopefully your level of interest was a consideration at the beginning of the project, although how anxious you are to work on the submission may be a good barometer for your true investment in the project.
For case studies, make sure the topic, and ideally the case, fuel a passion. Unlike original research, in which mentors and advisors are usually established at study conception, case studies often require you to seek appropriate collaborators when contemplating submission. It is the rare submission that comes from a single author. In choosing collaborators, look for a senior mentor with experience submitting posters and an investment in both you and the topic. There is nothing more disheartening for the junior clinician than having to harass a mentor whose heart is not in the project.
Another critical step is to choose the right meeting for the submission. Although many submissions may be to palliative care meetings (e.g., American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine), there is great benefit to both the field and your career in presenting at other specialty meetings. Presentations at well-recognized nonpalliative care meetings further legitimize the field, increase your national visibility, and lead to interesting and fruitful collaborations. Additionally, these types of presentations may be looked on with more favor by people reviewing your CV who are not intimately familiar with the world of palliative care. Table 1 presents some questions you should discuss with your mentor and ask yourself when choosing a meeting. Some of these questions may have conflicting answers, and you should be thoughtful in weighing what is most important.
Once you have chosen your meeting, go to the meeting's website and review all of the instructions. Check requirements regarding what material can be presented. For example, many meetings will allow you to present data that were already presented at a regional meeting but not data that were previously presented at another national meeting. Most meetings also do not allow you to present data that are already published, although it is generally acceptable to submit your abstract at the same time you submit your paper for publication. If the paper is published before the meeting, make sure to inform the committee—most often you will still be able to present but will be asked to note the publication in your presentation. Regarding the submission, most conferences have very specific instructions and the rules are strict. The applications are generally online with preset fields and word limits. It is helpful to examine review criteria and deadlines for submission, paying particular attention to time zones. Finally, it can be invaluable to read published abstracts from the last meeting and to talk with prior presenters to get a sense of the types of abstracts that are accepted.
The next step is to start writing. The key to success is to leave enough time as there are often unavoidable and unplanned technical issues with the online submission that you will confront. Additionally, you will want to leave time to get input from all of the authors and from people who have not been primarily involved in the project—to make sure that a “naïve” audience understands the message of the abstract. Finally, remember that an abstract/poster does not have to represent all of the data for a study and can just present an interesting piece of the story.
Most submissions require several rewrites. These can become frustrating, but it is important to realize that there is a very specific language for these types of submissions that your mentor should know and that you will learn over time. The most common issue is the need to shorten the abstract to fit the word limit. Strategies to ensure brevity include using the active voice, employing generic rather than trade names for drugs and devices, and avoiding jargon and local lingo. Use no more than two or three abbreviations and always define the abbreviations on first use. Do a spelling/grammar check and also have someone proofread the document before submitting. References are generally not included on abstracts. Most importantly, be concise, write lean, and avoid empty phrases such as “studies show.” A review of 45 abstracts submitted to a national surgical meeting found that concise abstracts were more likely to be accepted, 12 and this small study certainly reflects our experiences as submitters and reviewers.
The Abstract for an Original Research Study
The styles of abstracts for original studies vary. Guidelines exist for manuscript abstracts reporting various types of original research (CONSORT, 13 – 15 IDCRD, 16 PRISMA, 17 QUOROM, and STROBE 18 ) and review of these guidelines can be helpful to provide a format. There are also guidelines that exist for evaluating conference abstracts that may be informative, such as the CORE-14 guidelines for observational studies. 19 In general, a structured abstract style is favored. 20 – 21 In this paper, we will present general styles for each type of abstract that will need to be adapted to the type of study and the rules of the conference. Table 3 outlines the general format for an abstract for original research. Each section contains tips for how to write the section, rather than example text from a study. Therefore, you may find it most helpful to review the figures alongside examples of previously accepted abstracts.
Abstract for an Original Research Study
In any abstract, it is particularly important to focus on the title as it is often the only item people will look at while scanning the meeting program or wandering through the poster session. It should be no more than 10–12 words 2 and should describe what was investigated and how, instead of what was found. It should be engaging, but be cautious with too much use of humor as this can become tiresome and distracting. Below the title, list authors and their affiliations. The remaining sections of the abstract are discussed in the figure.
The Abstract for a Case Study
The abstract for a case study contains many of the same elements as the abstract for original research with a few important differences. Most importantly, you need to use the abstract to highlight the importance of the issue the case raises and convince the reader that both the case and the issue are interesting, novel, and relevant. A general format is provided in Table 4 .
Abstract for a Case Study
Preparing Posters
Once the abstract is prepared, submitted, and, hopefully, accepted, your next job is to prepare the presentation. Whereas a few select abstracts are typically selected for oral presentation (usually 8–10 minutes followed by a short question-and-answer period), the majority of submitted abstracts will be assigned to poster sessions. (Readers interested in advice for oral presentations are referred to reference 22 ). Posters are large (generally approximately 3 × 6 ft) visual representations of your work. Most posters are now one-piece glossy prints from graphics departments or commercial stores, although increasingly academic departments have access to printing facilities that may be less expensive than commercial stores. Additionally, many meetings now partner with on-site printing services, which are convenient and reasonably priced. Generally, the material is prepared on a PowerPoint (or equivalent) slide and this is given to the production facility. The easiest way to prepare your first poster is to ask your institution if it has a preferred or required template. If such a template does not exist, ask for a trusted colleague's slide from an accepted poster. This gives you the format and institutional logos, and you simply need to modify the content. In preparing your poster for printing, review the meeting instructions and try to make your poster as close to the maximum dimensions as possible. Try to complete the poster early to allow for production delays. Consider shipping your poster to the conference or carry it in a protective case and check with the airline regarding luggage requirements. On-site printing eliminates travel hassles but does not allow much time for any problems that may arise.
What goes on the poster?
Both the content and the visual appeal of the poster are important. In fact, one study found that visual appeal was more important than content for knowledge transfer. 23 Although the poster expands the content of your abstract, resist the urge to include too much information. It is helpful to remember the rule of 10s: the average person scans your poster for 10 seconds from 10 feet away. When someone stops, you should be able to introduce your poster in 10 seconds and they should be able to assimilate all of the information and discuss it with you in 10 minutes. 3 Figures 1 and and2 2 show the layouts of posters for a case and for an original study. The general rule is to keep each section as short and simple as possible, which allows for a font large enough (nothing smaller than 24 point 4 ) for easy reading of the title from 10 feet away and the text from 3–5 feet away. Leave blank space and use colors judiciously. Easily read and interpretable figures and simple tables are more visually appealing than text, and they are typically more effective in getting one's message across. It is helpful to get feedback on one's poster before finalizing and printing—ideally from people not familiar with the work to get a true objective view.

Poster for original research.

Poster for case study.
Although it may seem simple enough to prepare a good poster, many fall short. One author reviewed 142 posters at a national meeting and found that 33% were cluttered or sloppy, 22% had fonts that were too small to be easily read, and 38% had research objectives that could not be located in a 1-minute review. 5 Another study of an evaluation tool for case report posters found that the areas most needing improvement were statements of learning objectives, linkages of conclusions to learning objectives, and appropriate amount of words. 24
The Poster Presentation
Posters are presented at “Poster Sessions,” which are designated periods during the meeting when presenters stand by their posters while conference attendees circulate through the room. Refreshments are often served during these sessions and the atmosphere is generally more relaxed and less stressful than during oral presentations. Additionally, the one-on-one contact allows greater opportunity for discussion, feedback, and networking. Awards are often presented to the best posters and ribbons may designate these posters during the session.
The first step to a successful poster presentation is to simply show up. Surveys of conference attendees clearly indicate that it is necessary for the presenter to be with his/her poster for effective communication of the results. 23 This is also your time to grow your reputation, network, and get feedback, so do not miss the opportunity to reap the rewards of your hard work. In preparation, read any specific conference instructions and bring business cards and handouts of the poster or related materials. While standing at your poster, make eye contact with people who approach but allow them to finish reading before beginning a discussion. 4 As noted above, you should be prepared to introduce your poster in 10 seconds then answer questions and discuss as needed. Practicing your introduction and answers to common questions with colleagues before the meeting can be invaluable. Before your presentation, your mentor should also contact important people in the field related to your topic and ask them to come by your poster. You should have a list of these people and know who they are and when they are coming. Standard questions you may ask are included in Table 1 . You should also have prepared questions targeted specifically for each of the people your mentor has contacted. You should then suggest these people as reviewers when you submit your manuscript.
After the Presentation
After the presentation, key steps remain to get the most out of the process. First, ask for feedback so you can make adjustments for the next presentation. Also, think about what parts of the poster you can use for other reasons. It is often helpful to export a graph or figure to use in future presentations. The key is to “double-dip” and use everything to its fullest extent. In addition, to make the maximal use of the networking opportunities you should follow up with anyone who asked for more information or inquired about collaborations. In the excitement of the meeting anything seems possible, but it is easy to lose that momentum when you get home. In one study, only 29% of presenters replied to requests for additional information, and they generally took over 30 days to respond. 25
Finally, and perhaps most importantly, it is critical to write up your work for publication. Although posters are important, publications are the true currency of academia. Unfortunately, the percentage of abstracts that are eventually published is low. 26 When asked why they had yet to publish, respondents in one study 27 cited: lacked time (46%), study still in progress (31%), responsibility for publication belonged to someone else (20%), difficulty with co-authors (17%), and low priority (13%). Factors that have been shown to increase the likelihood of abstract publication include: oral presentation (as opposed to a poster), statistical analysis, number of authors, and university affiliation. 28 – 31 Time to publication is generally about 20 months. 29
Conclusions
Writing abstracts and developing posters for national meetings benefit the field in general and the junior clinician in particular. This process develops critical skills and generates innumerable opportunities. We have presented a stepwise approach based on the literature and our personal experiences. We have also highlighted the hidden curriculum that separates the successful submissions from the rest of the pack. Hopefully, these tools will help palliative care fellows and junior faculty more easily navigate the process and benefit the most from the work they put into their projects.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Morrison is supported by a Mid-Career Investigator Award in Patient Oriented Research from the National Institute on Aging (K24 AG022345). A portion of this work was funded by the National Palliative Care Research Center.
Author Disclosure Statement
No competing financial interests exist.
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Residents & Fellows
- Give to SMHS
The Internal Medicine Current Residents
Poster presentation resources.
Poster presentations are widely used to communicate research findings. A good poster presentation can be an effective way to share the results of your research with your peers in a collegial and nonthreatening atmosphere. Feedback received during a poster session can be invaluable in refining your research and preparing for publication in a peer reviewed journal.
If your abstract has been selected for a poster presentation at a local, regional or national meeting, the research chief resident and program director can offer you guidance to create your poster and prepare for your presentation. You should use our residency poster template for your color scheme and GW logo (you may change the size as you like), and you can use the GW Biomedical Printing office in Ross Hall to create your poster.
Please see our policy on conference reimbursement for information.
- ACP abstract instructions
- SGIM scientific abstract instructions
- SGIM clinical vignette instructions
- Residency Poster Template (you may change size/font, however color and logo should be consistent). Use a sans serif font and be sure to include images, tables or figures and plenty of blank space for easy readability.
Preparing a Poster Presentation - ACP's Guidelines
Poster examples from gw, poster resources.
- The GW SMHS Office of Communications & Marketing offer a complete line of services to assist you with all of your graphic design and photography needs. Newsletters, brochures, posters, the perfect photo, and more! They do it all.
- Download the Official GW Logos to insert in your poster. Choose the format that best suits your software, download, copy and paste.
- Download your copy of "The Face of GW: Graphics Standard Manual" to learn about the approved ways to include GW's institutional brand in printed publications and media.
- The GW Image Bank features photos of GWU and Washington to feed your creative genius.
The following links will take you to banks of Powerpoint scientific poster templates located on other websites. Fill-in the contents, change the layout, fonts and colors according to your design, and submit for printing!. Overall there are over 50 different templates. Please notify the website administrator of any broken links.
- PosterSessions.com
- PosterPresentations.com
- MakeSigns.com
- PostersforResearch.com
- StudentsPosters.com
- Creating Effective Poster Presentations . By George Hess, Kathryn Tosney and Leon Liegel from North Carolina State University.
- Chapter 9: Posters . Briscoe, MH. Preparing Scientific Illustration, Second Edition. (pdf) Excellent resource on the nuts and bolts of preparing a poster, from planning to production.
- How to create a poster that graphically communicates your message . By George R. Hess and Leon H. Liegel. From the department of Biology at The University of Miami.

Creative Services
Case Study: Designing Your Poster

Designing Your Poster
How to design your poster for large format printing.
Academic posters are used for a variety of purposes:
- To advertise your department, university, research group or yourself
- To help start a conversation and raise an interest in your work
- To inform of an issue or persuade
- To make new contacts for collaboration and jobs
A poster is a visual method of presentation and requires a different approach to writing a report or giving a presentation. It allows you to discuss your research and get feedback.
Things to consider before designing your poster
1. objective.
To grab attention and inspire interest. It is important to make it look interesting (if you want it to be read).
There should be a strong central message with your research displayed concisely using well laid out clear text and colourful graphics to attract attention.

2. Audience
Who is your audience?
- General public
How much existing knowledge does your audience have of your research project, methods and terminology? Design your poster accordingly.

- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- Writing a case report...
Writing a case report in 10 steps
- Related content
- Peer review
- Victoria Stokes , foundation year 2 doctor, trauma and orthopaedics, Basildon Hospital ,
- Caroline Fertleman , paediatrics consultant, The Whittington Hospital NHS Trust
- victoria.stokes1{at}nhs.net
Victoria Stokes and Caroline Fertleman explain how to turn an interesting case or unusual presentation into an educational report
It is common practice in medicine that when we come across an interesting case with an unusual presentation or a surprise twist, we must tell the rest of the medical world. This is how we continue our lifelong learning and aid faster diagnosis and treatment for patients.
It usually falls to the junior to write up the case, so here are a few simple tips to get you started.
First steps
Begin by sitting down with your medical team to discuss the interesting aspects of the case and the learning points to highlight. Ideally, a registrar or middle grade will mentor you and give you guidance. Another junior doctor or medical student may also be keen to be involved. Allocate jobs to split the workload, set a deadline and work timeframe, and discuss the order in which the authors will be listed. All listed authors should contribute substantially, with the person doing most of the work put first and the guarantor (usually the most senior team member) at the end.
Getting consent
Gain permission and written consent to write up the case from the patient or parents, if your patient is a child, and keep a copy because you will need it later for submission to journals.
Information gathering
Gather all the information from the medical notes and the hospital’s electronic systems, including copies of blood results and imaging, as medical notes often disappear when the patient is discharged and are notoriously difficult to find again. Remember to anonymise the data according to your local hospital policy.
Write up the case emphasising the interesting points of the presentation, investigations leading to diagnosis, and management of the disease/pathology. Get input on the case from all members of the team, highlighting their involvement. Also include the prognosis of the patient, if known, as the reader will want to know the outcome.
Coming up with a title
Discuss a title with your supervisor and other members of the team, as this provides the focus for your article. The title should be concise and interesting but should also enable people to find it in medical literature search engines. Also think about how you will present your case study—for example, a poster presentation or scientific paper—and consider potential journals or conferences, as you may need to write in a particular style or format.
Background research
Research the disease/pathology that is the focus of your article and write a background paragraph or two, highlighting the relevance of your case report in relation to this. If you are struggling, seek the opinion of a specialist who may know of relevant articles or texts. Another good resource is your hospital library, where staff are often more than happy to help with literature searches.
How your case is different
Move on to explore how the case presented differently to the admitting team. Alternatively, if your report is focused on management, explore the difficulties the team came across and alternative options for treatment.
Finish by explaining why your case report adds to the medical literature and highlight any learning points.
Writing an abstract
The abstract should be no longer than 100-200 words and should highlight all your key points concisely. This can be harder than writing the full article and needs special care as it will be used to judge whether your case is accepted for presentation or publication.
Discuss with your supervisor or team about options for presenting or publishing your case report. At the very least, you should present your article locally within a departmental or team meeting or at a hospital grand round. Well done!
Competing interests: We have read and understood BMJ’s policy on declaration of interests and declare that we have no competing interests.
How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.
Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics

We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
Free Online Case Study Generator
Captivate your clients by highlighting your company's solutions, and get valuable insights to improve your business strategy with Venngage's case study templates.
Create a case study report that looks compelling and converts leads without any design experience. Showcase real success stories and challenges that your products and services helped to solve. Join over 40,000 businesses in using Venngage as a marketing solution.
Design from one of our case study templates
Choose from hundreds of case study templates. see all case study templates, design professional case studies for meetings, and negotiations.

Create your own case studies to share compelling success stories. Showcase products, strategies, and tactics that had made your clients grow. You don't need any design experience! All of our case study template designs are created in-house by professional designers.
You don't need to be a designer to create a professional-looking case study infographic, or in-depth, multi-page reports. Pick from our library of easy-to-edit case study templates.
Get access to high-quality stock photos and choose from over 40,000+ icons and illustrations to use. Venngage also offers a wide variety of chart and data visualization widgets that you can customize.

Want to incorporate your brand's identity? We've got you. My Brand Kit feature lets you upload your company logos, fonts, and colors. Perfect to stand out in your presentation!
Get your team involved when creating case studies. Real-time collaboration allows you to provide feedback and apply changes creating a great design in minutes.
How to create a case study in 5 easy steps:
Showcase your challenges to elevate your brand with ease
Customizable Templates
No design experience? No problem! Our stunning template designs will make your data analysis look great without even trying.

User-Friendly Editor
Easily visualize and present complex case study examples with Venngage editor. Use our Smart features to quickly add or remove shapes, lines, and branches with a single click.

Access Stunning Photography
A case study report is more engaging and impressive when you use Venngage's library of 3 million stock photos. Professional and royalty-free.
Data Visualization
With Venngage's free case study creator, you can add data collected from a Google Sheet or CSV, and the chart automatically populates the data.

24/7 Customer Support
Experiencing issues? Have questions about using a feature or need advice? Our support team is available around the clock.
My Brand Kit
Build your brand through consistency. My Brand Kit lets you incorporate your branding into every asset you design in Venngage.

Customize Venngage's Case Study Templates
- Choose your favorite design from the templates library. We have an extended gallery of layouts you can work on. Just organize your qualitative and quantitative data, add customizable graphs, icons and images, set your brand identity, and start creating a comprehensive case study report.
- Use illustrations, icons and photos: Case studies ought to be visually engaging and inviting. That's why Venngage lets you access 40K+ icons and beautiful illustrations, impressive stock photos, and customizable charts and graphs.
- Create branded content without any design help: Branded case studies help your brand really stand out. They're an excellent form of lead generation and branding building. Showcase your expertise and real-life success stories that will win over your readers.
Collaborate with team members and stakeholders in real-time
- Replace online meetings, email threads, chats, or messages by simply clicking "Share" from the editor to send a private link to your peers.
- Share your designs, so people can work together and make adjustments to achieve the perfect showcase for your strategies.
- Work better together. Provide feedback, share expertise, and have insights for a perfect process mapping design.
Download and share your case study design with a click
- Download your document as a PDF or Interactive PDF (to use hyperlinking).
- To print your document, apply print bleeds in the editor and then download it as a PDF.
- Share your completed design using a share link - no need to download a single thing.
Great features that make your report stand out
- My Brand Kit lets you instantly apply your branding to any template design, saving you hours of time and effort.
- Access Pixabay, Pexels, and other libraries for impressive stock photos from around the world - for free.
- Hundreds of font options and styles to suit your design preferences. You can also request fonts we don't have to maintain your brand look.
How do I sign up for Venngage's case study creator?
To start using Venngage's free case study creator, sign up for free using your email, Facebook or Gmail account. Once you create an account you can choose which template to get started with and start editing in the online editor.
How do I write a case study?
The easiest way to write a case study is to get started with a template. This provides you with a pre-set cover page and table of contents; a variety of page layouts to work with; and a picture of how to organize content, add designs and break up text. A case study is not a technical document that needs to be structured in a specific and formal way. You can get creative but focus on making your content clear and easy to understand.
What's an example of a case study?
Case studies, in business and marketing, are stories of success achieved through a product or service. The product can even be a strategy or framework that was pioneered by an industry thought leader. Many brands publish case studies on their website to share how their clients see tremendous value in using their products. The case study essentially chronicles the entire client journey from having a problem, to finding the solution, and the outcome of that solution.
Try Venngage's Case Study Creator today. Sign up for free!

Get started with our case study templates:
Business case study, content marketing case study, lead generation business case study, social media case study.

Home > Colleges and Departments > WCHP > Physical Therapy > PT Student Works > PT Student Posters > Case Report Posters
Case Report Posters
During the course of two semesters, UNE Doctor of Physical Therapy students who elect the case report track to fulfill the program’s scholarship requirement work with a faculty advisor to gather data about a patient, institution, facility, or other definable unit related to the profession of physical therapy, and create and exhibit a poster following the guidelines, format, and standards for a poster presentation at a professional or scientific meeting.
During distance learning, students instead utilize slide presentations .

The Rehabilitation Of A 75-Year-Old Male Presenting With A Right Hip Flexor Strain Concomitant With Numerous Psychosocial Factors: A Case Report
Jillian Battista, Megan Chapski, Suma Varanasi, Jillian Witwicki, and Tara Paradie
Musculoskeletal disorders, often well understood, are a leading cause of disability worldwide. Concomitant psychosocial factors add a layer of complexity to the physical therapy treatment of musculoskeletal disorders. The purpose of this case report is to highlight the potential impact psychological factors have in the rehabilitation of musculoskeletal disorders, specifically the rehabilitation of a right hip flexor strain.

Development Of A Comprehensive Web-Based Prehabilitation Program For Gastrointestinal Cancer Survivors
Eric Norman, Maryam Nahidian, Amy J. Litterini, and Timothy Fitzgerald
Background: Individuals with frailty who undergo surgical procedures for gastrointestinal cancers are more likely to experience post-surgical complications, have a higher readmission rate, are more likely to be discharged to skilled care, and have an over four-fold risk of mortality. Developing targeted patient education tools and resources may support, and reduce complications for, individuals with frailty undergoing and recovering from major abdominal surgery. Methods: Program development began via the... Read More

Physical Therapy Management Of Low Back Pain In A Young Female With Ankylosing Spondylitis Associated With HLA-B27 Antigen: A Case Report
Jake Adkins
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a form of arthritis characterized by chronic inflammation of the axial skeletal system that causes back pain and loss of mobility with strong potential for slow, eventual spinal fusion. It affects 0.2-0.5% of the United States population and has no known cure, yet greater than 60 genetic components are involved. HLA-B27 is a genetic component highly correlated with AS. Its presence creates inflammatory response at... Read More

Return To Golf In A 71-Year-Old Female After A Mako Robotic-Arm-Assisted Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: A Case Report
Katelyn Austin
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disorder in the elderly. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasties (UKA) have been increasing in prevalence at a rate of 30% each year. Robotic-arm-assisted UKAs increases the accuracy of implant positioning compared to traditional techniques which helps with a quicker recovery. Little literature on UKAs, but total knee arthroplasty (TKA) interventions should focus on knee range of motion (ROM), strengthening, gait training, icing, and... Read More

Physical Therapy Interventions To Increase Independence With Functional Mobility For An Older Individual With Spinal Stenosis: A Case Report
Eleni Bautz
Spinal stenosis includes narrowing of the spinal canal which can affect nerves and other structures that pass through. Symptoms commonly associated with spinal stenosis are pain and paresthesia into the lower extremities. Spinal stenosis is diagnosed through patient history, clinical findings, and/or physical tests. Literature supports the use of physical therapy (PT) for conservative treatment in decreasing signs and symptoms of spinal stenosis The purpose of this case report... Read More

Rehabilitation And Prosthetic Training For An Individual With Bilateral Lower Extremity Amputations Due To Peripheral Vascular Disease: A Case Report
Morgan Bessette
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is a condition in which there is a disruption of blood flow to the extremities. Common causes of PVD include: hypertension (HTN), smoking, cardiac disease and/or diabetes. 12 to 20% of the population greater than 60 years old are affected by PVD. PVD can cause intermittent claudication or critical limb ischemia (CLI) and is therefore the most common cause of lower extremity amputation (LEA). Individuals... Read More

Regaining Independence In Ambulation For A Visually Impaired Patient With Rhabdomyolysis: A Case Report
Brandon Bourgoin
Rhabdomyolysis is a myopathic condition with an acute onset that causes a rapid degradation of muscle tissue. It causes a significantly elevated release of creatine kinase (CK), a muscle enzyme that is a cellular component in healthy muscle tissue, into the blood stream. Common causes include muscle trauma (injury/strenuous activity), drug/alcohol abuse, medications, toxins, infections, and extended periods of immobility. Hallmark signs/symptoms include muscle pain, swelling, weakness, and dark... Read More

Physical Therapy Intervention For An Elderly Patient With Comorbidities Following Surgical Fixation Of A Femoral Neck Fracture: A Case Report
Yu-min Chou
More than 300,000 elderly people over age 65 required hospitalization due to hip fracture in 2016. More than 95% of hip fractures are the result of falls. Strength training programs are suggested for geriatric patients with surgical fixation following hip fracture. Returning to prior level of function and quality of life is the primary goal of rehabilitation for geriatric patients recovering from a hip fracture. Complex comorbidities such as... Read More

Interdisciplinary Administration Of LSVT-BIG By A Physical Therapist And Occupational Therapist On A Patient With Parkinsonism: A Case Report
Shelby Clare
The clinical diagnosis of parkinsonism is “the presence of at least two of the four cardinal signs: resting tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability.” Symptoms often lead to limited functional mobility. Patients who have unilateral bradykinesia with hypokinesia, changes in gait, balance, and decreased quality of life have positively responded to Lee Silverman Voice Technique (LSVT) BIG treatment according to Rehabilitation Research and Practice. LSVT-BIG focuses on increasing movement... Read More

Acute Inpatient Rehabilitation Of A Patient Following A Pontine Stroke With Limited Recorded Medical History: A Case Report
Russell Curl
795,000 strokes occur annually in the United States, or one every 4 seconds. Impairments following a stroke may include deficits in strength, coordination, sensation, and language skills. Expected impairments of pontine strokes include hemiplegia, sensorimotor dysfunction, ataxic hemiparesis, and dysarthria. There is little current research on pontine strokes. The purpose of this case report is to outline the physical therapy plan of care and response to treatment for a... Read More

Functional Mobility Interventions For A Bariatric Patient With Necrotizing Fasciitis: A Case Report
Jakub Cwalinski
Necrotizing Fasciitis is a life threatening soft tissue infection that is characterized by a rapid spreading infection of the subcutaneous tissue. Symptoms include red or purple skin in the affected area, severe pain, fever, and vomiting. Typically, the infection enters the body through a break in the skin such as a cut or burn. Surgical debridement is the mainstay of treatment for necrotizing fasciitis. Intravenous antibiotics are started immediately... Read More
Blood Flow Restriction Therapy And A Comprehensive Home Exercise Program Following An ACL And Meniscal Repair: A Case Report
Kathryn DeMoor
Every year in the United States, up to 60 per 100,000 people sustain an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear. Medial meniscus tears have been reported in roughly 60% of the ACL tear population, while lateral meniscus tears have been reported in approximately 30%. Blood flow restriction therapy (BFRT) has shown improved strength and muscle hypertrophy with low load exercises by occluding blood flow at the proximal thigh. A minimally... Read More

Conservative Management Of A Massive Rotator Cuff Tear And Partial Tear Of The Long Head Of The Biceps: A Case Report
Jessica Diggins
A rotator cuff tear (RCT) is a common injury to the shoulder musculature that increases in prevalence with age. RCT’s can be classified into five categories determined by the muscular involved: Type A: supraspinatus & superior subscapularis; Type B: supraspinatus & entire subscapularis; Type C: supraspinatus, superior subscapularis & infraspinatus; Type D: supraspinatus & infraspinatus tears; Type E: supraspinatus,infraspinatus & teres minor. Massive RCT is classified as >5cm in... Read More

Oncologic And Orthopedic Rehabilitation For A Pancreatic Cancer Survivor Following Total Knee Arthroplasty Revision: A Case Report
Kelsey Dumond and Amy J. Litterini
An estimated 80% of cancer survivors undergoing chemotherapy or radiation to manage their cancer will experience cancer-related fatigue (CRF). The majority of cancer survivors are elderly – a population frequently affected by osteoarthritis (OA). Physical activity is the most recommended and evidence-based non-pharmacologic intervention for CRF. Strong evidence exists for lower-extremity resistance and functional exercise following Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA). Evidence suggests utilization of targeted exercise prior to extensive... Read More

Gait, Strength, And Balance Training For A 43-Year-Old Male Following Acute Right Middle Cerebral Artery Stroke: A Case Report
Victoria Dwyer
A cerebrovascular accident, commonly known as a stroke, is caused by an ischemic or hemorrhagic event affecting arteries that lead to the brain causing them to burst or be occluded. The middle cerebral artery is the most commonly occluded artery involved in a stroke. The four most common risk factors involved in having a stroke are: high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease and pervious strokes. Common impairments associated with... Read More

Treatment Approach For Traumatic Myositis Ossificans Using Ultrasound And Stretch Protocol: A Case Report
Traumatic Myositis Ossificans (MO) can happen at any age, but the highest prevalence occurs in young active males after trauma (60-75% are traumatic). MO can occur from repetitive minor trauma, which is common in horseback riders who develop MO in the adductors and shooters who present with MO in their deltoid. Patients with MO commonly present in the clinic with signs and symptoms of pain, a palpable mass, and... Read More

Functional School-Based Physical Therapy Management For A Child With Pallister-Killian Syndrome: A Case Report
Cheryl R. Espinosa and Molly Collin
Pallister-Killian Syndrome (PKS) is a rare genetic disorder caused by an additional short arm in chromosome 12. PKS affects multiple systems, which can impact a child’s development. Common clinical manifestations include: hypotonia, visual impairment, hearing loss, coarse facial features, intellectual disability, and congenital heart defects. Improvements in gross motor function have resulted from physical therapy (PT) and rehabilitation involving neurodevelopmental treatment (NDT). Research is limited on the effects of... Read More
Early Mobilization And Functional Mobility Training For A Patient With Triple Vessel Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: A Case Report
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a widely used procedure (200,000 annual cases in the US)1 in individuals with Coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD is a build-up of plaque in the blood vessels that supply the heart, which can result from diabetes, smoking, and a vast number of other conditions. The procedure involves harvesting blood vessels (usually autografts of the patient’s saphenous vein) and surgically attaching them to the... Read More
Physical Therapy Management Of A Patient With Unilateral Headache, Neck, And Shoulder Pain Who Presents With Undiagnosed Mastoiditis: A Case Report
Alexandr Kostenko
Mastoiditis is an infection and inflammation of the mastoid cells. If left untreated, mastoiditis can lead to intracranial complications and ultimately death. Diagnosis is confirmed with imaging such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. Common symptoms include earache, retroauricular pain, headache, mastoid tenderness, hearing loss, and discharge from the ear. Mastoiditis is typically managed with antibiotics, but may require mastoidectomy which is the surgical removal of the mastoid... Read More

Strength And Movement Interventions For A Female Patient With Neck And Upper Back Pain: A Case Report
Ross Kulick

Comprehensive Physical Therapy Management Of Chronic Low Back Pain With Associated Remote Right Hamstring Injury: A Case Report
Emily Larson
Low back pain (LBP) is a health condition associated with back, core, and hip muscle dysfunction as well as reduced lumbar range of motion. Core muscle stabilization, hip abductor strengthening, and lumbar range of motion are all effective techniques for treating patients with chronic LBP. Lumbar muscular imbalance can lead to hamstring injury because of change in the functional load. The purpose of this case report was to review... Read More

Restoring Functional Mobility Following A Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Case Report
Grace Laughlin
An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a dilation of the abdominal aortic artery greater than three centimeters involving all layers of the vessel wall. There are two surgical options for treatment of AAA: open repair and endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR). An endoleak is a complication following EVAR when blood leaks into the aneurysm sac. A type III endoleak occurs when there is a defect between parts of endografts causing... Read More
Tissue Plasminogen Activator Effects On Stroke And Physical Therapy Outcomes In Acute Care: A Case Report
Lindsey Leboeuf
An ischemic stroke occurs when blood flow to an area of the brain is restricted by a blood clot. Symptoms include: Numbness or weakness on one side of the body, facial droop, trouble speaking, and trouble walking. Patients can also display decreased balance, ataxia, flaccidity, spasticity, inattention or neglect, and visual changes. Patients who can identify these symptoms within 3 hours of their onset can be eligible to receive... Read More

Inpatient Rehabilitation For A Cancer Survivor Following A Lumbar Spinal Fusion Secondary To A Pathological Fracture: A Case Report
Nicole Marczak and Amy J. Litterini
Pathologic fractures are considered a skeletal-related event of bone metastasis. Bone metastases indicate a shorter prognosis with the survival rate varying from 6-53 months, depending on the primary type of cancer. Indications for surgery include spinal instability, vertebral collapse with or without neurologic deficit and intolerable pain that is not responsive to conservative treatment. Palliative physical therapy (PT) is provided to the patient and their family to offer education,... Read More
Balance And Strength Interventions For An Individual Post Left Sided MCA CVA: A Case Report
Annie McKenzie
Cerebrovascular accident (CVA), or stroke, is the fifth leading cause of death in the United States (US) with more than 140,000 deaths each year. It is the leading cause of long-term disability in the US, reducing functional mobility in more than half of all stroke survivors ages 65 or older. This condition costs the US approximately 34 billion dollars a year and it is estimated to increase to 108... Read More
Page 1 of 8
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Collections
- Disciplines
Contributors
- Physical Therapy Department
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright

Poster Category: Case Studies
Click on the links below to see the posters and submit feedback. As you scroll, please note the poster number and 1st author's name of your top 3 posters to vote in the new People's Choice Award category.
- View Poster
CS-05 (Best in Case Study)
View Community Engagement posters here>
View Quality Improvement posters here>
View Literature Review posters here>
View Research posters here>
View posters in UT Box here>
Return to the Showcase homepage here>
“R” U ready?: a case study using R to analyze changes in gene expression during evolution
Add to collection, downloadable content.
- Affiliation: School of Medicine, Department of Pharmacology
- Other Affiliation: Clarke University
- Other Affiliation: North Carolina State University
- Other Affiliation: Carroll University
- Other Affiliation: Worcester Polytechnic Institute
- As high-throughput methods become more common, training undergraduates to analyze data must include having them generate informative summaries of large datasets. This flexible case study provides an opportunity for undergraduate students to become familiar with the capabilities of R programming in the context of high-throughput evolutionary data collected using macroarrays. The story line introduces a recent graduate hired at a biotech firm and tasked with analysis and visualization of changes in gene expression from 20,000 generations of the Lenski Lab's Long-Term Evolution Experiment (LTEE). Our main character is not familiar with R and is guided by a coworker to learn about this platform. Initially this involves a step-bystep analysis of the small Iris dataset built into R which includes sepal and petal length of three species of irises. Practice calculating summary statistics and correlations, and making histograms and scatter plots, prepares the protagonist to perform similar analyses with the LTEE dataset. In the LTEE module, students analyze gene expression data from the long-term evolutionary experiments, developing their skills in manipulating and interpreting large scientific datasets through visualizations and statistical analysis. Prerequisite knowledge is basic statistics, the Central Dogma, and basic evolutionary principles. The Iris module provides hands-on experience using R programming to explore and visualize a simple dataset; it can be used independently as an introduction to R for biological data or skipped if students already have some experience with R. Both modules emphasize understanding the utility of R, rather than creation of original code. Pilot testing showed the case study was well-received by students and faculty, who described it as a clear introduction to R and appreciated the value of R for visualizing and analyzing large datasets.
- reproducibility
- Evolutionary Biology
- summary statistics
- data visualization
- data cleaning
- R programming
- High-throughput data analysis
- Case studies
- https://doi.org/10.17615/x4xa-d741
- https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2024.1379910
- In Copyright
- Attribution 4.0 International
- Frontiers in Education
- Frontiers Media SA
This work has no parents.
Select type of work
Master's papers.
Deposit your masters paper, project or other capstone work. Theses will be sent to the CDR automatically via ProQuest and do not need to be deposited.
Scholarly Articles and Book Chapters
Deposit a peer-reviewed article or book chapter. If you would like to deposit a poster, presentation, conference paper or white paper, use the “Scholarly Works” deposit form.
Undergraduate Honors Theses
Deposit your senior honors thesis.
Scholarly Journal, Newsletter or Book
Deposit a complete issue of a scholarly journal, newsletter or book. If you would like to deposit an article or book chapter, use the “Scholarly Articles and Book Chapters” deposit option.
Deposit your dataset. Datasets may be associated with an article or deposited separately.
Deposit your 3D objects, audio, images or video.
Poster, Presentation, Protocol or Paper
Deposit scholarly works such as posters, presentations, research protocols, conference papers or white papers. If you would like to deposit a peer-reviewed article or book chapter, use the “Scholarly Articles and Book Chapters” deposit option.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Abstract. Written for the potentially interested reader. Give an impression of what the paper will be about. No jargon or abbreviation use. Answer the Question "WHAT?". Understandable for specialists and people from all fields. Conclusion/Discussion. Conclude the research or case. Written for the reader who has already read the poster.
Research posters summarize information or research concisely and attractively to help publicize it and generate discussion. The poster is usually a mixture of a brief text mixed with tables, graphs, pictures, and other presentation formats. At a conference, the researcher stands by the poster display while other participants can come and view ...
Skip to start of list. 220 templates. Create a blank Research Poster. Orange and Cream Playful and Illustrative Portrait University Research Poster. Poster by Canva Creative Studio. Green Orange Modern User Persona Landscape Poster. Poster by ruisaxila.
Step 3: Write the content. Write or rewrite the content for the sections in your poster presentation. Use the text in your research paper as a base, but summarize it to be more succinct in what you share. Don't forget to write a catchy title that presents the problem and your findings in a clear way.
Avoid clutter. Limit your poster presentation to a few main ideas. It's better to present a few of your findings well than present all of your findings poorly. Arrange your poster components to read from left to right and top to bottom. Emphasize important points on the poster with lines, frames or boxes, and arrows.
Logos for the trust you are working at, as well as the conference/congress you are attending can be placed on either side of the title. •. Title: this needs to have the largest font size of your entire poster to be eye catching. Keep the title as short as possible - it doesn't need to be a paragraph long [1], [3].
We implemented a mentorship program designed to give trainees feedback on their case report posters at academic meetings. Through this program, our study aim was to 1.) develop and test an evaluation tool to measure the quality of the posters and 2.) identify specific components of the posters most in need of improvement.
Step 2: Put the most important messages first. In Joseph's poster, like in so many, the conclusion is hidden away at the end of the poster. We've moved it up next to the title. In addition, we've moved the author affiliations to the bottom of the poster.
For case studies, make sure the topic, and ideally the case, fuel a passion. Unlike original research, in which mentors and advisors are usually established at study conception, case studies often require you to seek appropriate collaborators when contemplating submission. ... While standing at your poster, make eye contact with people who ...
First Thing First: The Title and Abstract. The title of your abstract is very important. Reflect the content of the paper. Specific and Succinct. Use key words for indexing and for searches. 250 Word Max. Includes the following: The research question or problem. The methods.
Poster Presentation Resources. Poster presentations are widely used to communicate research findings. A good poster presentation can be an effective way to share the results of your research with your peers in a collegial and nonthreatening atmosphere. Feedback received during a poster session can be invaluable in refining your research and ...
Title slide: Start with a title slide that includes the name of the case study, your name and any relevant institutional affiliations. Introduction: Follow with a slide that outlines the problem or situation your case study addresses. Include a hook to engage the audience.
Academic posters are used for a variety of purposes: To advertise your department, university, research group or yourself. To help start a conversation and raise an interest in your work. To inform of an issue or persuade. To make new contacts for collaboration and jobs. A poster is a visual method of presentation and requires a different ...
Posters should be created in portrait format 36" wide and 48" tall in order to fit our poster stanchions. Please print your poster as a single sheet using your university printing services or printing services at a local copy center or print shop. Case Study and Clinical Teaching Posters should include the same elements
14 Case Study Templates. Now that we have explored some of the high level strategies you can use to create a business case study, we will transition to 14 case study design templates you can use with Visme. 1. Fuji Xerox Australia Case Study Template. Customize this template and make it your own!
25,429 templates. Green Minimalist Company Case Study Flyer Portrait. Flyer by Epitomi. Blue and White Clean Corporate Company Case Study. Document by Rongbaaz. Teal Green Grey Professional Gradients Business Case Study and Report Business Presentation. Presentation by Canva Creative Studio. Case Study Doc in Dark Orange Pink Geometric Style.
Writing up. Write up the case emphasising the interesting points of the presentation, investigations leading to diagnosis, and management of the disease/pathology. Get input on the case from all members of the team, highlighting their involvement. Also include the prognosis of the patient, if known, as the reader will want to know the outcome.
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
Arrange the 4 P's of your strategy: your product, price, promotion and place. Choose a design that will mark your audience and look good in your selected place. Make your campaign details the focus of the poster. Add high-quality images of your product or service. Include a relevant call to action.
3. Browse our selection of case study templates and click "create" to get started. 4. Use the drag-and-drop editor, along with royalty-free photos, illustrations, icons and more to customize your design. 5. Download your completed case study design as a PDF or share it using a shareable link. CREATE A CASE STUDY.
Case Report Posters. During the course of two semesters, UNE Doctor of Physical Therapy students who elect the case report track to fulfill the program's scholarship requirement work with a faculty advisor to gather data about a patient, institution, facility, or other definable unit related to the profession of physical therapy, and create ...
Poster Category: Case Studies. Click on the links below to see the posters and submit feedback. As you scroll, please note the poster number and 1st author's name of your top 3 posters to vote in the new People's Choice Award category. Return to the navigation page and vote for the People's Choice Award.
Canva's free poster maker has thousands of templates designed by our team of professional designers. Templates are your shortcut to great design: You'll have a custom poster in minutes. We've got poster templates for every need—from concerts to retail, conferences and quotes. Or design from scratch to create something entirely unique.
This flexible case study provides an opportunity for undergraduate students to become familiar with the capabilities of R programming in the context of high-throughput evolutionary data collected using macroarrays.