- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax

How to Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps (+ Template and Examples)
Every successful business has one thing in common, a good and well-executed business plan. A business plan is more than a document, it is a complete guide that outlines the goals your business wants to achieve, including its financial goals . It helps you analyze results, make strategic decisions, show your business operations and growth.
If you want to start a business or already have one and need to pitch it to investors for funding, writing a good business plan improves your chances of attracting financiers. As a startup, if you want to secure loans from financial institutions, part of the requirements involve submitting your business plan.
Writing a business plan does not have to be a complicated or time-consuming process. In this article, you will learn the step-by-step process for writing a successful business plan.
You will also learn what you need a business plan for, tips and strategies for writing a convincing business plan, business plan examples and templates that will save you tons of time, and the alternatives to the traditional business plan.
Let’s get started.
What Do You Need A Business Plan For?
Businesses create business plans for different purposes such as to secure funds, monitor business growth, measure your marketing strategies, and measure your business success.
1. Secure Funds
One of the primary reasons for writing a business plan is to secure funds, either from financial institutions/agencies or investors.
For you to effectively acquire funds, your business plan must contain the key elements of your business plan . For example, your business plan should include your growth plans, goals you want to achieve, and milestones you have recorded.
A business plan can also attract new business partners that are willing to contribute financially and intellectually. If you are writing a business plan to a bank, your project must show your traction , that is, the proof that you can pay back any loan borrowed.
Also, if you are writing to an investor, your plan must contain evidence that you can effectively utilize the funds you want them to invest in your business. Here, you are using your business plan to persuade a group or an individual that your business is a source of a good investment.
2. Monitor Business Growth
A business plan can help you track cash flows in your business. It steers your business to greater heights. A business plan capable of tracking business growth should contain:
- The business goals
- Methods to achieve the goals
- Time-frame for attaining those goals
A good business plan should guide you through every step in achieving your goals. It can also track the allocation of assets to every aspect of the business. You can tell when you are spending more than you should on a project.
You can compare a business plan to a written GPS. It helps you manage your business and hints at the right time to expand your business.
3. Measure Business Success
A business plan can help you measure your business success rate. Some small-scale businesses are thriving better than more prominent companies because of their track record of success.
Right from the onset of your business operation, set goals and work towards them. Write a plan to guide you through your procedures. Use your plan to measure how much you have achieved and how much is left to attain.
You can also weigh your success by monitoring the position of your brand relative to competitors. On the other hand, a business plan can also show you why you have not achieved a goal. It can tell if you have elapsed the time frame you set to attain a goal.
4. Document Your Marketing Strategies
You can use a business plan to document your marketing plans. Every business should have an effective marketing plan.
Competition mandates every business owner to go the extraordinary mile to remain relevant in the market. Your business plan should contain your marketing strategies that work. You can measure the success rate of your marketing plans.
In your business plan, your marketing strategy must answer the questions:
- How do you want to reach your target audience?
- How do you plan to retain your customers?
- What is/are your pricing plans?
- What is your budget for marketing?

How to Write a Business Plan Step-by-Step
1. create your executive summary.
The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans . Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.

Generally, there are nine sections in a business plan, the executive summary should condense essential ideas from the other eight sections.
A good executive summary should do the following:
- A Snapshot of Growth Potential. Briefly inform the reader about your company and why it will be successful)
- Contain your Mission Statement which explains what the main objective or focus of your business is.
- Product Description and Differentiation. Brief description of your products or services and why it is different from other solutions in the market.
- The Team. Basic information about your company’s leadership team and employees
- Business Concept. A solid description of what your business does.
- Target Market. The customers you plan to sell to.
- Marketing Strategy. Your plans on reaching and selling to your customers
- Current Financial State. Brief information about what revenue your business currently generates.
- Projected Financial State. Brief information about what you foresee your business revenue to be in the future.
The executive summary is the make-or-break section of your business plan. If your summary cannot in less than two pages cannot clearly describe how your business will solve a particular problem of your target audience and make a profit, your business plan is set on a faulty foundation.
Avoid using the executive summary to hype your business, instead, focus on helping the reader understand the what and how of your plan.
View the executive summary as an opportunity to introduce your vision for your company. You know your executive summary is powerful when it can answer these key questions:
- Who is your target audience?
- What sector or industry are you in?
- What are your products and services?
- What is the future of your industry?
- Is your company scaleable?
- Who are the owners and leaders of your company? What are their backgrounds and experience levels?
- What is the motivation for starting your company?
- What are the next steps?
Writing the executive summary last although it is the most important section of your business plan is an excellent idea. The reason why is because it is a high-level overview of your business plan. It is the section that determines whether potential investors and lenders will read further or not.
The executive summary can be a stand-alone document that covers everything in your business plan. It is not uncommon for investors to request only the executive summary when evaluating your business. If the information in the executive summary impresses them, they will ask for the complete business plan.
If you are writing your business plan for your planning purposes, you do not need to write the executive summary.
2. Add Your Company Overview
The company overview or description is the next section in your business plan after the executive summary. It describes what your business does.
Adding your company overview can be tricky especially when your business is still in the planning stages. Existing businesses can easily summarize their current operations but may encounter difficulties trying to explain what they plan to become.
Your company overview should contain the following:
- What products and services you will provide
- Geographical markets and locations your company have a presence
- What you need to run your business
- Who your target audience or customers are
- Who will service your customers
- Your company’s purpose, mission, and vision
- Information about your company’s founders
- Who the founders are
- Notable achievements of your company so far
When creating a company overview, you have to focus on three basics: identifying your industry, identifying your customer, and explaining the problem you solve.
If you are stuck when creating your company overview, try to answer some of these questions that pertain to you.
- Who are you targeting? (The answer is not everyone)
- What pain point does your product or service solve for your customers that they will be willing to spend money on resolving?
- How does your product or service overcome that pain point?
- Where is the location of your business?
- What products, equipment, and services do you need to run your business?
- How is your company’s product or service different from your competition in the eyes of your customers?
- How many employees do you need and what skills do you require them to have?
After answering some or all of these questions, you will get more than enough information you need to write your company overview or description section. When writing this section, describe what your company does for your customers.

The company description or overview section contains three elements: mission statement, history, and objectives.
- Mission Statement
The mission statement refers to the reason why your business or company is existing. It goes beyond what you do or sell, it is about the ‘why’. A good mission statement should be emotional and inspirational.
Your mission statement should follow the KISS rule (Keep It Simple, Stupid). For example, Shopify’s mission statement is “Make commerce better for everyone.”
When describing your company’s history, make it simple and avoid the temptation of tying it to a defensive narrative. Write it in the manner you would a profile. Your company’s history should include the following information:
- Founding Date
- Major Milestones
- Location(s)
- Flagship Products or Services
- Number of Employees
- Executive Leadership Roles
When you fill in this information, you use it to write one or two paragraphs about your company’s history.
Business Objectives
Your business objective must be SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.) Failure to clearly identify your business objectives does not inspire confidence and makes it hard for your team members to work towards a common purpose.
3. Perform Market and Competitive Analyses to Proof a Big Enough Business Opportunity
The third step in writing a business plan is the market and competitive analysis section. Every business, no matter the size, needs to perform comprehensive market and competitive analyses before it enters into a market.
Performing market and competitive analyses are critical for the success of your business. It helps you avoid entering the right market with the wrong product, or vice versa. Anyone reading your business plans, especially financiers and financial institutions will want to see proof that there is a big enough business opportunity you are targeting.
This section is where you describe the market and industry you want to operate in and show the big opportunities in the market that your business can leverage to make a profit. If you noticed any unique trends when doing your research, show them in this section.
Market analysis alone is not enough, you have to add competitive analysis to strengthen this section. There are already businesses in the industry or market, how do you plan to take a share of the market from them?
You have to clearly illustrate the competitive landscape in your business plan. Are there areas your competitors are doing well? Are there areas where they are not doing so well? Show it.
Make it clear in this section why you are moving into the industry and what weaknesses are present there that you plan to explain. How are your competitors going to react to your market entry? How do you plan to get customers? Do you plan on taking your competitors' competitors, tap into other sources for customers, or both?
Illustrate the competitive landscape as well. What are your competitors doing well and not so well?
Answering these questions and thoughts will aid your market and competitive analysis of the opportunities in your space. Depending on how sophisticated your industry is, or the expectations of your financiers, you may need to carry out a more comprehensive market and competitive analysis to prove that big business opportunity.
Instead of looking at the market and competitive analyses as one entity, separating them will make the research even more comprehensive.
Market Analysis
Market analysis, boarding speaking, refers to research a business carried out on its industry, market, and competitors. It helps businesses gain a good understanding of their target market and the outlook of their industry. Before starting a company, it is vital to carry out market research to find out if the market is viable.

The market analysis section is a key part of the business plan. It is the section where you identify who your best clients or customers are. You cannot omit this section, without it your business plan is incomplete.
A good market analysis will tell your readers how you fit into the existing market and what makes you stand out. This section requires in-depth research, it will probably be the most time-consuming part of the business plan to write.
- Market Research
To create a compelling market analysis that will win over investors and financial institutions, you have to carry out thorough market research . Your market research should be targeted at your primary target market for your products or services. Here is what you want to find out about your target market.
- Your target market’s needs or pain points
- The existing solutions for their pain points
- Geographic Location
- Demographics
The purpose of carrying out a marketing analysis is to get all the information you need to show that you have a solid and thorough understanding of your target audience.
Only after you have fully understood the people you plan to sell your products or services to, can you evaluate correctly if your target market will be interested in your products or services.
You can easily convince interested parties to invest in your business if you can show them you thoroughly understand the market and show them that there is a market for your products or services.
How to Quantify Your Target Market
One of the goals of your marketing research is to understand who your ideal customers are and their purchasing power. To quantify your target market, you have to determine the following:
- Your Potential Customers: They are the people you plan to target. For example, if you sell accounting software for small businesses , then anyone who runs an enterprise or large business is unlikely to be your customers. Also, individuals who do not have a business will most likely not be interested in your product.
- Total Households: If you are selling household products such as heating and air conditioning systems, determining the number of total households is more important than finding out the total population in the area you want to sell to. The logic is simple, people buy the product but it is the household that uses it.
- Median Income: You need to know the median income of your target market. If you target a market that cannot afford to buy your products and services, your business will not last long.
- Income by Demographics: If your potential customers belong to a certain age group or gender, determining income levels by demographics is necessary. For example, if you sell men's clothes, your target audience is men.
What Does a Good Market Analysis Entail?
Your business does not exist on its own, it can only flourish within an industry and alongside competitors. Market analysis takes into consideration your industry, target market, and competitors. Understanding these three entities will drastically improve your company’s chances of success.

You can view your market analysis as an examination of the market you want to break into and an education on the emerging trends and themes in that market. Good market analyses include the following:
- Industry Description. You find out about the history of your industry, the current and future market size, and who the largest players/companies are in your industry.
- Overview of Target Market. You research your target market and its characteristics. Who are you targeting? Note, it cannot be everyone, it has to be a specific group. You also have to find out all information possible about your customers that can help you understand how and why they make buying decisions.
- Size of Target Market: You need to know the size of your target market, how frequently they buy, and the expected quantity they buy so you do not risk overproducing and having lots of bad inventory. Researching the size of your target market will help you determine if it is big enough for sustained business or not.
- Growth Potential: Before picking a target market, you want to be sure there are lots of potential for future growth. You want to avoid going for an industry that is declining slowly or rapidly with almost zero growth potential.
- Market Share Potential: Does your business stand a good chance of taking a good share of the market?
- Market Pricing and Promotional Strategies: Your market analysis should give you an idea of the price point you can expect to charge for your products and services. Researching your target market will also give you ideas of pricing strategies you can implement to break into the market or to enjoy maximum profits.
- Potential Barriers to Entry: One of the biggest benefits of conducting market analysis is that it shows you every potential barrier to entry your business will likely encounter. It is a good idea to discuss potential barriers to entry such as changing technology. It informs readers of your business plan that you understand the market.
- Research on Competitors: You need to know the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and how you can exploit them for the benefit of your business. Find patterns and trends among your competitors that make them successful, discover what works and what doesn’t, and see what you can do better.
The market analysis section is not just for talking about your target market, industry, and competitors. You also have to explain how your company can fill the hole you have identified in the market.
Here are some questions you can answer that can help you position your product or service in a positive light to your readers.
- Is your product or service of superior quality?
- What additional features do you offer that your competitors do not offer?
- Are you targeting a ‘new’ market?
Basically, your market analysis should include an analysis of what already exists in the market and an explanation of how your company fits into the market.
Competitive Analysis
In the competitive analysis section, y ou have to understand who your direct and indirect competitions are, and how successful they are in the marketplace. It is the section where you assess the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, the advantage(s) they possess in the market and show the unique features or qualities that make you different from your competitors.

Many businesses do market analysis and competitive analysis together. However, to fully understand what the competitive analysis entails, it is essential to separate it from the market analysis.
Competitive analysis for your business can also include analysis on how to overcome barriers to entry in your target market.
The primary goal of conducting a competitive analysis is to distinguish your business from your competitors. A strong competitive analysis is essential if you want to convince potential funding sources to invest in your business. You have to show potential investors and lenders that your business has what it takes to compete in the marketplace successfully.
Competitive analysis will s how you what the strengths of your competition are and what they are doing to maintain that advantage.
When doing your competitive research, you first have to identify your competitor and then get all the information you can about them. The idea of spending time to identify your competitor and learn everything about them may seem daunting but it is well worth it.
Find answers to the following questions after you have identified who your competitors are.
- What are your successful competitors doing?
- Why is what they are doing working?
- Can your business do it better?
- What are the weaknesses of your successful competitors?
- What are they not doing well?
- Can your business turn its weaknesses into strengths?
- How good is your competitors’ customer service?
- Where do your competitors invest in advertising?
- What sales and pricing strategies are they using?
- What marketing strategies are they using?
- What kind of press coverage do they get?
- What are their customers saying about your competitors (both the positive and negative)?
If your competitors have a website, it is a good idea to visit their websites for more competitors’ research. Check their “About Us” page for more information.

If you are presenting your business plan to investors, you need to clearly distinguish yourself from your competitors. Investors can easily tell when you have not properly researched your competitors.
Take time to think about what unique qualities or features set you apart from your competitors. If you do not have any direct competition offering your product to the market, it does not mean you leave out the competitor analysis section blank. Instead research on other companies that are providing a similar product, or whose product is solving the problem your product solves.
The next step is to create a table listing the top competitors you want to include in your business plan. Ensure you list your business as the last and on the right. What you just created is known as the competitor analysis table.
Direct vs Indirect Competition
You cannot know if your product or service will be a fit for your target market if you have not understood your business and the competitive landscape.
There is no market you want to target where you will not encounter competition, even if your product is innovative. Including competitive analysis in your business plan is essential.
If you are entering an established market, you need to explain how you plan to differentiate your products from the available options in the market. Also, include a list of few companies that you view as your direct competitors The competition you face in an established market is your direct competition.
In situations where you are entering a market with no direct competition, it does not mean there is no competition there. Consider your indirect competition that offers substitutes for the products or services you offer.
For example, if you sell an innovative SaaS product, let us say a project management software , a company offering time management software is your indirect competition.
There is an easy way to find out who your indirect competitors are in the absence of no direct competitors. You simply have to research how your potential customers are solving the problems that your product or service seeks to solve. That is your direct competition.
Factors that Differentiate Your Business from the Competition
There are three main factors that any business can use to differentiate itself from its competition. They are cost leadership, product differentiation, and market segmentation.
1. Cost Leadership
A strategy you can impose to maximize your profits and gain an edge over your competitors. It involves offering lower prices than what the majority of your competitors are offering.
A common practice among businesses looking to enter into a market where there are dominant players is to use free trials or pricing to attract as many customers as possible to their offer.
2. Product Differentiation
Your product or service should have a unique selling proposition (USP) that your competitors do not have or do not stress in their marketing.
Part of the marketing strategy should involve making your products unique and different from your competitors. It does not have to be different from your competitors, it can be the addition to a feature or benefit that your competitors do not currently have.
3. Market Segmentation
As a new business seeking to break into an industry, you will gain more success from focusing on a specific niche or target market, and not the whole industry.
If your competitors are focused on a general need or target market, you can differentiate yourself from them by having a small and hyper-targeted audience. For example, if your competitors are selling men’s clothes in their online stores , you can sell hoodies for men.
4. Define Your Business and Management Structure
The next step in your business plan is your business and management structure. It is the section where you describe the legal structure of your business and the team running it.
Your business is only as good as the management team that runs it, while the management team can only strive when there is a proper business and management structure in place.
If your company is a sole proprietor or a limited liability company (LLC), a general or limited partnership, or a C or an S corporation, state it clearly in this section.
Use an organizational chart to show the management structure in your business. Clearly show who is in charge of what area in your company. It is where you show how each key manager or team leader’s unique experience can contribute immensely to the success of your company. You can also opt to add the resumes and CVs of the key players in your company.
The business and management structure section should show who the owner is, and other owners of the businesses (if the business has other owners). For businesses or companies with multiple owners, include the percent ownership of the various owners and clearly show the extent of each others’ involvement in the company.
Investors want to know who is behind the company and the team running it to determine if it has the right management to achieve its set goals.
Management Team
The management team section is where you show that you have the right team in place to successfully execute the business operations and ideas. Take time to create the management structure for your business. Think about all the important roles and responsibilities that you need managers for to grow your business.
Include brief bios of each key team member and ensure you highlight only the relevant information that is needed. If your team members have background industry experience or have held top positions for other companies and achieved success while filling that role, highlight it in this section.

A common mistake that many startups make is assigning C-level titles such as (CMO and CEO) to everyone on their team. It is unrealistic for a small business to have those titles. While it may look good on paper for the ego of your team members, it can prevent investors from investing in your business.
Instead of building an unrealistic management structure that does not fit your business reality, it is best to allow business titles to grow as the business grows. Starting everyone at the top leaves no room for future change or growth, which is bad for productivity.
Your management team does not have to be complete before you start writing your business plan. You can have a complete business plan even when there are managerial positions that are empty and need filling.
If you have management gaps in your team, simply show the gaps and indicate you are searching for the right candidates for the role(s). Investors do not expect you to have a full management team when you are just starting your business.
Key Questions to Answer When Structuring Your Management Team
- Who are the key leaders?
- What experiences, skills, and educational backgrounds do you expect your key leaders to have?
- Do your key leaders have industry experience?
- What positions will they fill and what duties will they perform in those positions?
- What level of authority do the key leaders have and what are their responsibilities?
- What is the salary for the various management positions that will attract the ideal candidates?
Additional Tips for Writing the Management Structure Section
1. Avoid Adding ‘Ghost’ Names to Your Management Team
There is always that temptation to include a ‘ghost’ name to your management team to attract and influence investors to invest in your business. Although the presence of these celebrity management team members may attract the attention of investors, it can cause your business to lose any credibility if you get found out.
Seasoned investors will investigate further the members of your management team before committing fully to your business If they find out that the celebrity name used does not play any actual role in your business, they will not invest and may write you off as dishonest.
2. Focus on Credentials But Pay Extra Attention to the Roles
Investors want to know the experience that your key team members have to determine if they can successfully reach the company’s growth and financial goals.
While it is an excellent boost for your key management team to have the right credentials, you also want to pay extra attention to the roles they will play in your company.
Organizational Chart

Adding an organizational chart in this section of your business plan is not necessary, you can do it in your business plan’s appendix.
If you are exploring funding options, it is not uncommon to get asked for your organizational chart. The function of an organizational chart goes beyond raising money, you can also use it as a useful planning tool for your business.
An organizational chart can help you identify how best to structure your management team for maximum productivity and point you towards key roles you need to fill in the future.
You can use the organizational chart to show your company’s internal management structure such as the roles and responsibilities of your management team, and relationships that exist between them.
5. Describe Your Product and Service Offering
In your business plan, you have to describe what you sell or the service you plan to offer. It is the next step after defining your business and management structure. The products and services section is where you sell the benefits of your business.
Here you have to explain how your product or service will benefit your customers and describe your product lifecycle. It is also the section where you write down your plans for intellectual property like patent filings and copyrighting.
The research and development that you are undertaking for your product or service need to be explained in detail in this section. However, do not get too technical, sell the general idea and its benefits.
If you have any diagrams or intricate designs of your product or service, do not include them in the products and services section. Instead, leave them for the addendum page. Also, if you are leaving out diagrams or designs for the addendum, ensure you add this phrase “For more detail, visit the addendum Page #.”
Your product and service section in your business plan should include the following:
- A detailed explanation that clearly shows how your product or service works.
- The pricing model for your product or service.
- Your business’ sales and distribution strategy.
- The ideal customers that want your product or service.
- The benefits of your products and services.
- Reason(s) why your product or service is a better alternative to what your competitors are currently offering in the market.
- Plans for filling the orders you receive
- If you have current or pending patents, copyrights, and trademarks for your product or service, you can also discuss them in this section.
What to Focus On When Describing the Benefits, Lifecycle, and Production Process of Your Products or Services
In the products and services section, you have to distill the benefits, lifecycle, and production process of your products and services.
When describing the benefits of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Unique features
- Translating the unique features into benefits
- The emotional, psychological, and practical payoffs to attract customers
- Intellectual property rights or any patents
When describing the product life cycle of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Upsells, cross-sells, and down-sells
- Time between purchases
- Plans for research and development.
When describing the production process for your products or services, you need to think about the following:
- The creation of new or existing products and services.
- The sources for the raw materials or components you need for production.
- Assembling the products
- Maintaining quality control
- Supply-chain logistics (receiving the raw materials and delivering the finished products)
- The day-to-day management of the production processes, bookkeeping, and inventory.
Tips for Writing the Products or Services Section of Your Business Plan
1. Avoid Technical Descriptions and Industry Buzzwords
The products and services section of your business plan should clearly describe the products and services that your company provides. However, it is not a section to include technical jargons that anyone outside your industry will not understand.
A good practice is to remove highly detailed or technical descriptions in favor of simple terms. Industry buzzwords are not necessary, if there are simpler terms you can use, then use them. If you plan to use your business plan to source funds, making the product or service section so technical will do you no favors.
2. Describe How Your Products or Services Differ from Your Competitors
When potential investors look at your business plan, they want to know how the products and services you are offering differ from that of your competition. Differentiating your products or services from your competition in a way that makes your solution more attractive is critical.
If you are going the innovative path and there is no market currently for your product or service, you need to describe in this section why the market needs your product or service.
For example, overnight delivery was a niche business that only a few companies were participating in. Federal Express (FedEx) had to show in its business plan that there was a large opportunity for that service and they justified why the market needed that service.
3. Long or Short Products or Services Section
Should your products or services section be short? Does the long products or services section attract more investors?
There are no straightforward answers to these questions. Whether your products or services section should be long or relatively short depends on the nature of your business.
If your business is product-focused, then automatically you need to use more space to describe the details of your products. However, if the product your business sells is a commodity item that relies on competitive pricing or other pricing strategies, you do not have to use up so much space to provide significant details about the product.
Likewise, if you are selling a commodity that is available in numerous outlets, then you do not have to spend time on writing a long products or services section.
The key to the success of your business is most likely the effectiveness of your marketing strategies compared to your competitors. Use more space to address that section.
If you are creating a new product or service that the market does not know about, your products or services section can be lengthy. The reason why is because you need to explain everything about the product or service such as the nature of the product, its use case, and values.
A short products or services section for an innovative product or service will not give the readers enough information to properly evaluate your business.
4. Describe Your Relationships with Vendors or Suppliers
Your business will rely on vendors or suppliers to supply raw materials or the components needed to make your products. In your products and services section, describe your relationships with your vendors and suppliers fully.
Avoid the mistake of relying on only one supplier or vendor. If that supplier or vendor fails to supply or goes out of business, you can easily face supply problems and struggle to meet your demands. Plan to set up multiple vendor or supplier relationships for better business stability.
5. Your Primary Goal Is to Convince Your Readers
The primary goal of your business plan is to convince your readers that your business is viable and to create a guide for your business to follow. It applies to the products and services section.
When drafting this section, think like the reader. See your reader as someone who has no idea about your products and services. You are using the products and services section to provide the needed information to help your reader understand your products and services. As a result, you have to be clear and to the point.
While you want to educate your readers about your products or services, you also do not want to bore them with lots of technical details. Show your products and services and not your fancy choice of words.
Your products and services section should provide the answer to the “what” question for your business. You and your management team may run the business, but it is your products and services that are the lifeblood of the business.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing your Products and Services Section
Answering these questions can help you write your products and services section quickly and in a way that will appeal to your readers.
- Are your products existing on the market or are they still in the development stage?
- What is your timeline for adding new products and services to the market?
- What are the positives that make your products and services different from your competitors?
- Do your products and services have any competitive advantage that your competitors’ products and services do not currently have?
- Do your products or services have any competitive disadvantages that you need to overcome to compete with your competitors? If your answer is yes, state how you plan to overcome them,
- How much does it cost to produce your products or services? How much do you plan to sell it for?
- What is the price for your products and services compared to your competitors? Is pricing an issue?
- What are your operating costs and will it be low enough for you to compete with your competitors and still take home a reasonable profit margin?
- What is your plan for acquiring your products? Are you involved in the production of your products or services?
- Are you the manufacturer and produce all the components you need to create your products? Do you assemble your products by using components supplied by other manufacturers? Do you purchase your products directly from suppliers or wholesalers?
- Do you have a steady supply of products that you need to start your business? (If your business is yet to kick-off)
- How do you plan to distribute your products or services to the market?
You can also hint at the marketing or promotion plans you have for your products or services such as how you plan to build awareness or retain customers. The next section is where you can go fully into details about your business’s marketing and sales plan.
6. Show and Explain Your Marketing and Sales Plan
Providing great products and services is wonderful, but it means nothing if you do not have a marketing and sales plan to inform your customers about them. Your marketing and sales plan is critical to the success of your business.
The sales and marketing section is where you show and offer a detailed explanation of your marketing and sales plan and how you plan to execute it. It covers your pricing plan, proposed advertising and promotion activities, activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success, and the benefits of your products and services.
There are several ways you can approach your marketing and sales strategy. Ideally, your marketing and sales strategy has to fit the unique needs of your business.
In this section, you describe how the plans your business has for attracting and retaining customers, and the exact process for making a sale happen. It is essential to thoroughly describe your complete marketing and sales plans because you are still going to reference this section when you are making financial projections for your business.
Outline Your Business’ Unique Selling Proposition (USP)

The sales and marketing section is where you outline your business’s unique selling proposition (USP). When you are developing your unique selling proposition, think about the strongest reasons why people should buy from you over your competition. That reason(s) is most likely a good fit to serve as your unique selling proposition (USP).
Target Market and Target Audience
Plans on how to get your products or services to your target market and how to get your target audience to buy them go into this section. You also highlight the strengths of your business here, particularly what sets them apart from your competition.

Before you start writing your marketing and sales plan, you need to have properly defined your target audience and fleshed out your buyer persona. If you do not first understand the individual you are marketing to, your marketing and sales plan will lack any substance and easily fall.
Creating a Smart Marketing and Sales Plan
Marketing your products and services is an investment that requires you to spend money. Like any other investment, you have to generate a good return on investment (ROI) to justify using that marketing and sales plan. Good marketing and sales plans bring in high sales and profits to your company.
Avoid spending money on unproductive marketing channels. Do your research and find out the best marketing and sales plan that works best for your company.
Your marketing and sales plan can be broken into different parts: your positioning statement, pricing, promotion, packaging, advertising, public relations, content marketing, social media, and strategic alliances.
Your Positioning Statement
Your positioning statement is the first part of your marketing and sales plan. It refers to the way you present your company to your customers.
Are you the premium solution, the low-price solution, or are you the intermediary between the two extremes in the market? What do you offer that your competitors do not that can give you leverage in the market?
Before you start writing your positioning statement, you need to spend some time evaluating the current market conditions. Here are some questions that can help you to evaluate the market
- What are the unique features or benefits that you offer that your competitors lack?
- What are your customers’ primary needs and wants?
- Why should a customer choose you over your competition? How do you plan to differentiate yourself from the competition?
- How does your company’s solution compare with other solutions in the market?
After answering these questions, then you can start writing your positioning statement. Your positioning statement does not have to be in-depth or too long.
All you need to explain with your positioning statement are two focus areas. The first is the position of your company within the competitive landscape. The other focus area is the core value proposition that sets your company apart from other alternatives that your ideal customer might consider.
Here is a simple template you can use to develop a positioning statement.
For [description of target market] who [need of target market], [product or service] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [top competition], it [most essential distinguishing feature].
For example, let’s create the positioning statement for fictional accounting software and QuickBooks alternative , TBooks.
“For small business owners who need accounting services, TBooks is an accounting software that helps small businesses handle their small business bookkeeping basics quickly and easily. Unlike Wave, TBooks gives small businesses access to live sessions with top accountants.”
You can edit this positioning statement sample and fill it with your business details.
After writing your positioning statement, the next step is the pricing of your offerings. The overall positioning strategy you set in your positioning statement will often determine how you price your products or services.
Pricing is a powerful tool that sends a strong message to your customers. Failure to get your pricing strategy right can make or mar your business. If you are targeting a low-income audience, setting a premium price can result in low sales.
You can use pricing to communicate your positioning to your customers. For example, if you are offering a product at a premium price, you are sending a message to your customers that the product belongs to the premium category.
Basic Rules to Follow When Pricing Your Offering
Setting a price for your offering involves more than just putting a price tag on it. Deciding on the right pricing for your offering requires following some basic rules. They include covering your costs, primary and secondary profit center pricing, and matching the market rate.
- Covering Your Costs: The price you set for your products or service should be more than it costs you to produce and deliver them. Every business has the same goal, to make a profit. Depending on the strategy you want to use, there are exceptions to this rule. However, the vast majority of businesses follow this rule.
- Primary and Secondary Profit Center Pricing: When a company sets its price above the cost of production, it is making that product its primary profit center. A company can also decide not to make its initial price its primary profit center by selling below or at even with its production cost. It rather depends on the support product or even maintenance that is associated with the initial purchase to make its profit. The initial price thus became its secondary profit center.
- Matching the Market Rate: A good rule to follow when pricing your products or services is to match your pricing with consumer demand and expectations. If you price your products or services beyond the price your customer perceives as the ideal price range, you may end up with no customers. Pricing your products too low below what your customer perceives as the ideal price range may lead to them undervaluing your offering.
Pricing Strategy
Your pricing strategy influences the price of your offering. There are several pricing strategies available for you to choose from when examining the right pricing strategy for your business. They include cost-plus pricing, market-based pricing, value pricing, and more.

- Cost-plus Pricing: This strategy is one of the simplest and oldest pricing strategies. Here you consider the cost of producing a unit of your product and then add a profit to it to arrive at your market price. It is an effective pricing strategy for manufacturers because it helps them cover their initial costs. Another name for the cost-plus pricing strategy is the markup pricing strategy.
- Market-based Pricing: This pricing strategy analyses the market including competitors’ pricing and then sets a price based on what the market is expecting. With this pricing strategy, you can either set your price at the low-end or high-end of the market.
- Value Pricing: This pricing strategy involves setting a price based on the value you are providing to your customer. When adopting a value-based pricing strategy, you have to set a price that your customers are willing to pay. Service-based businesses such as small business insurance providers , luxury goods sellers, and the fashion industry use this pricing strategy.
After carefully sorting out your positioning statement and pricing, the next item to look at is your promotional strategy. Your promotional strategy explains how you plan on communicating with your customers and prospects.
As a business, you must measure all your costs, including the cost of your promotions. You also want to measure how much sales your promotions bring for your business to determine its usefulness. Promotional strategies or programs that do not lead to profit need to be removed.
There are different types of promotional strategies you can adopt for your business, they include advertising, public relations, and content marketing.
Advertising
Your business plan should include your advertising plan which can be found in the marketing and sales plan section. You need to include an overview of your advertising plans such as the areas you plan to spend money on to advertise your business and offers.
Ensure that you make it clear in this section if your business will be advertising online or using the more traditional offline media, or the combination of both online and offline media. You can also include the advertising medium you want to use to raise awareness about your business and offers.
Some common online advertising mediums you can use include social media ads, landing pages, sales pages, SEO, Pay-Per-Click, emails, Google Ads, and others. Some common traditional and offline advertising mediums include word of mouth, radios, direct mail, televisions, flyers, billboards, posters, and others.
A key component of your advertising strategy is how you plan to measure the effectiveness and success of your advertising campaign. There is no point in sticking with an advertising plan or medium that does not produce results for your business in the long run.
Public Relations
A great way to reach your customers is to get the media to cover your business or product. Publicity, especially good ones, should be a part of your marketing and sales plan. In this section, show your plans for getting prominent reviews of your product from reputable publications and sources.
Your business needs that exposure to grow. If public relations is a crucial part of your promotional strategy, provide details about your public relations plan here.
Content Marketing
Content marketing is a popular promotional strategy used by businesses to inform and attract their customers. It is about teaching and educating your prospects on various topics of interest in your niche, it does not just involve informing them about the benefits and features of the products and services you have,

Businesses publish content usually for free where they provide useful information, tips, and advice so that their target market can be made aware of the importance of their products and services. Content marketing strategies seek to nurture prospects into buyers over time by simply providing value.
Your company can create a blog where it will be publishing content for its target market. You will need to use the best website builder such as Wix and Squarespace and the best web hosting services such as Bluehost, Hostinger, and other Bluehost alternatives to create a functional blog or website.
If content marketing is a crucial part of your promotional strategy (as it should be), detail your plans under promotions.
Including high-quality images of the packaging of your product in your business plan is a lovely idea. You can add the images of the packaging of that product in the marketing and sales plan section. If you are not selling a product, then you do not need to include any worry about the physical packaging of your product.
When organizing the packaging section of your business plan, you can answer the following questions to make maximum use of this section.
- Is your choice of packaging consistent with your positioning strategy?
- What key value proposition does your packaging communicate? (It should reflect the key value proposition of your business)
- How does your packaging compare to that of your competitors?
Social Media
Your 21st-century business needs to have a good social media presence. Not having one is leaving out opportunities for growth and reaching out to your prospect.
You do not have to join the thousands of social media platforms out there. What you need to do is join the ones that your customers are active on and be active there.

Businesses use social media to provide information about their products such as promotions, discounts, the benefits of their products, and content on their blogs.
Social media is also a platform for engaging with your customers and getting feedback about your products or services. Make no mistake, more and more of your prospects are using social media channels to find more information about companies.
You need to consider the social media channels you want to prioritize your business (prioritize the ones your customers are active in) and your branding plans in this section.

Strategic Alliances
If your company plans to work closely with other companies as part of your sales and marketing plan, include it in this section. Prove details about those partnerships in your business plan if you have already established them.
Strategic alliances can be beneficial for all parties involved including your company. Working closely with another company in the form of a partnership can provide access to a different target market segment for your company.
The company you are partnering with may also gain access to your target market or simply offer a new product or service (that of your company) to its customers.
Mutually beneficial partnerships can cover the weaknesses of one company with the strength of another. You should consider strategic alliances with companies that sell complimentary products to yours. For example, if you provide printers, you can partner with a company that produces ink since the customers that buy printers from you will also need inks for printing.
Steps Involved in Creating a Marketing and Sales Plan
1. Focus on Your Target Market
Identify who your customers are, the market you want to target. Then determine the best ways to get your products or services to your potential customers.
2. Evaluate Your Competition
One of the goals of having a marketing plan is to distinguish yourself from your competition. You cannot stand out from them without first knowing them in and out.
You can know your competitors by gathering information about their products, pricing, service, and advertising campaigns.
These questions can help you know your competition.
- What makes your competition successful?
- What are their weaknesses?
- What are customers saying about your competition?
3. Consider Your Brand
Customers' perception of your brand has a strong impact on your sales. Your marketing and sales plan should seek to bolster the image of your brand. Before you start marketing your business, think about the message you want to pass across about your business and your products and services.
4. Focus on Benefits
The majority of your customers do not view your product in terms of features, what they want to know is the benefits and solutions your product offers. Think about the problems your product solves and the benefits it delivers, and use it to create the right sales and marketing message.
Your marketing plan should focus on what you want your customer to get instead of what you provide. Identify those benefits in your marketing and sales plan.
5. Focus on Differentiation
Your marketing and sales plan should look for a unique angle they can take that differentiates your business from the competition, even if the products offered are similar. Some good areas of differentiation you can use are your benefits, pricing, and features.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing Your Marketing and Sales Plan
- What is your company’s budget for sales and marketing campaigns?
- What key metrics will you use to determine if your marketing plans are successful?
- What are your alternatives if your initial marketing efforts do not succeed?
- Who are the sales representatives you need to promote your products or services?
- What are the marketing and sales channels you plan to use? How do you plan to get your products in front of your ideal customers?
- Where will you sell your products?
You may want to include samples of marketing materials you plan to use such as print ads, website descriptions, and social media ads. While it is not compulsory to include these samples, it can help you better communicate your marketing and sales plan and objectives.
The purpose of the marketing and sales section is to answer this question “How will you reach your customers?” If you cannot convincingly provide an answer to this question, you need to rework your marketing and sales section.
7. Clearly Show Your Funding Request
If you are writing your business plan to ask for funding from investors or financial institutions, the funding request section is where you will outline your funding requirements. The funding request section should answer the question ‘How much money will your business need in the near future (3 to 5 years)?’
A good funding request section will clearly outline and explain the amount of funding your business needs over the next five years. You need to know the amount of money your business needs to make an accurate funding request.
Also, when writing your funding request, provide details of how the funds will be used over the period. Specify if you want to use the funds to buy raw materials or machinery, pay salaries, pay for advertisements, and cover specific bills such as rent and electricity.
In addition to explaining what you want to use the funds requested for, you need to clearly state the projected return on investment (ROI) . Investors and creditors want to know if your business can generate profit for them if they put funds into it.
Ensure you do not inflate the figures and stay as realistic as possible. Investors and financial institutions you are seeking funds from will do their research before investing money in your business.
If you are not sure of an exact number to request from, you can use some range of numbers as rough estimates. Add a best-case scenario and a work-case scenario to your funding request. Also, include a description of your strategic future financial plans such as selling your business or paying off debts.
Funding Request: Debt or Equity?
When making your funding request, specify the type of funding you want. Do you want debt or equity? Draw out the terms that will be applicable for the funding, and the length of time the funding request will cover.
Case for Equity
If your new business has not yet started generating profits, you are most likely preparing to sell equity in your business to raise capital at the early stage. Equity here refers to ownership. In this case, you are selling a portion of your company to raise capital.
Although this method of raising capital for your business does not put your business in debt, keep in mind that an equity owner may expect to play a key role in company decisions even if he does not hold a major stake in the company.
Most equity sales for startups are usually private transactions . If you are making a funding request by offering equity in exchange for funding, let the investor know that they will be paid a dividend (a share of the company’s profit). Also, let the investor know the process for selling their equity in your business.
Case for Debt
You may decide not to offer equity in exchange for funds, instead, you make a funding request with the promise to pay back the money borrowed at the agreed time frame.
When making a funding request with an agreement to pay back, note that you will have to repay your creditors both the principal amount borrowed and the interest on it. Financial institutions offer this type of funding for businesses.
Large companies combine both equity and debt in their capital structure. When drafting your business plan, decide if you want to offer both or one over the other.
Before you sell equity in exchange for funding in your business, consider if you are willing to accept not being in total control of your business. Also, before you seek loans in your funding request section, ensure that the terms of repayment are favorable.
You should set a clear timeline in your funding request so that potential investors and creditors can know what you are expecting. Some investors and creditors may agree to your funding request and then delay payment for longer than 30 days, meanwhile, your business needs an immediate cash injection to operate efficiently.
Additional Tips for Writing the Funding Request Section of your Business Plan
The funding request section is not necessary for every business, it is only needed by businesses who plan to use their business plan to secure funding.
If you are adding the funding request section to your business plan, provide an itemized summary of how you plan to use the funds requested. Hiring a lawyer, accountant, or other professionals may be necessary for the proper development of this section.
You should also gather and use financial statements that add credibility and support to your funding requests. Ensure that the financial statements you use should include your projected financial data such as projected cash flows, forecast statements, and expenditure budgets.
If you are an existing business, include all historical financial statements such as cash flow statements, balance sheets and income statements .
Provide monthly and quarterly financial statements for a year. If your business has records that date back beyond the one-year mark, add the yearly statements of those years. These documents are for the appendix section of your business plan.
8. Detail Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projections
If you used the funding request section in your business plan, supplement it with a financial plan, metrics, and projections. This section paints a picture of the past performance of your business and then goes ahead to make an informed projection about its future.
The goal of this section is to convince readers that your business is going to be a financial success. It outlines your business plan to generate enough profit to repay the loan (with interest if applicable) and to generate a decent return on investment for investors.
If you have an existing business already in operation, use this section to demonstrate stability through finance. This section should include your cash flow statements, balance sheets, and income statements covering the last three to five years. If your business has some acceptable collateral that you can use to acquire loans, list it in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
Apart from current financial statements, this section should also contain a prospective financial outlook that spans the next five years. Include forecasted income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and capital expenditure budget.
If your business is new and is not yet generating profit, use clear and realistic projections to show the potentials of your business.
When drafting this section, research industry norms and the performance of comparable businesses. Your financial projections should cover at least five years. State the logic behind your financial projections. Remember you can always make adjustments to this section as the variables change.
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section create a baseline which your business can either exceed or fail to reach. If your business fails to reach your projections in this section, you need to understand why it failed.
Investors and loan managers spend a lot of time going through the financial plan, metrics, and projection section compared to other parts of the business plan. Ensure you spend time creating credible financial analyses for your business in this section.
Many entrepreneurs find this section daunting to write. You do not need a business degree to create a solid financial forecast for your business. Business finances, especially for startups, are not as complicated as they seem. There are several online tools and templates that make writing this section so much easier.
Use Graphs and Charts
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section is a great place to use graphs and charts to tell the financial story of your business. Charts and images make it easier to communicate your finances.
Accuracy in this section is key, ensure you carefully analyze your past financial statements properly before making financial projects.
Address the Risk Factors and Show Realistic Financial Projections
Keep your financial plan, metrics, and projection realistic. It is okay to be optimistic in your financial projection, however, you have to justify it.
You should also address the various risk factors associated with your business in this section. Investors want to know the potential risks involved, show them. You should also show your plans for mitigating those risks.
What You Should In The Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection Section of Your Business Plan
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section of your business plan should have monthly sales and revenue forecasts for the first year. It should also include annual projections that cover 3 to 5 years.
A three-year projection is a basic requirement to have in your business plan. However, some investors may request a five-year forecast.
Your business plan should include the following financial statements: sales forecast, personnel plan, income statement, income statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, and an exit strategy.
1. Sales Forecast
Sales forecast refers to your projections about the number of sales your business is going to record over the next few years. It is typically broken into several rows, with each row assigned to a core product or service that your business is offering.
One common mistake people make in their business plan is to break down the sales forecast section into long details. A sales forecast should forecast the high-level details.
For example, if you are forecasting sales for a payroll software provider, you could break down your forecast into target market segments or subscription categories.

Your sales forecast section should also have a corresponding row for each sales row to cover the direct cost or Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). The objective of these rows is to show the expenses that your business incurs in making and delivering your product or service.
Note that your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) should only cover those direct costs incurred when making your products. Other indirect expenses such as insurance, salaries, payroll tax, and rent should not be included.
For example, the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) for a restaurant is the cost of ingredients while for a consulting company it will be the cost of paper and other presentation materials.

2. Personnel Plan
The personnel plan section is where you provide details about the payment plan for your employees. For a small business, you can easily list every position in your company and how much you plan to pay in the personnel plan.
However, for larger businesses, you have to break the personnel plan into functional groups such as sales and marketing.
The personnel plan will also include the cost of an employee beyond salary, commonly referred to as the employee burden. These costs include insurance, payroll taxes , and other essential costs incurred monthly as a result of having employees on your payroll.

3. Income Statement
The income statement section shows if your business is making a profit or taking a loss. Another name for the income statement is the profit and loss (P&L). It takes data from your sales forecast and personnel plan and adds other ongoing expenses you incur while running your business.

Every business plan should have an income statement. It subtracts your business expenses from its earnings to show if your business is generating profit or incurring losses.
The income statement has the following items: sales, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), gross margin, operating expenses, total operating expenses, operating income , total expenses, and net profit.
- Sales refer to the revenue your business generates from selling its products or services. Other names for sales are income or revenue.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) refers to the total cost of selling your products. Other names for COGS are direct costs or cost of sales. Manufacturing businesses use the Costs of Goods Manufactured (COGM) .
- Gross Margin is the figure you get when you subtract your COGS from your sales. In your income statement, you can express it as a percentage of total sales (Gross margin / Sales = Gross Margin Percent).
- Operating Expenses refer to all the expenses you incur from running your business. It exempts the COGS because it stands alone as a core part of your income statement. You also have to exclude taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Your operating expenses include salaries, marketing expenses, research and development (R&D) expenses, and other expenses.
- Total Operating Expenses refers to the sum of all your operating expenses including those exemptions named above under operating expenses.
- Operating Income refers to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is simply known as the acronym EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization). Calculating your operating income is simple, all you need to do is to subtract your COGS and total operating expenses from your sales.
- Total Expenses refer to the sum of your operating expenses and your business’ interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
- Net profit shows whether your business has made a profit or taken a loss during a given timeframe.
4. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the money you have in the bank at any given point. It is often confused with the income statement or the profit and loss statement. They are both different types of financial statements. The income statement calculates your profits and losses while the cash flow statement shows you how much you have in the bank.

5. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement that provides an overview of the financial health of your business. It contains information about the assets and liabilities of your company, and owner’s or shareholders’ equity.
You can get the net worth of your company by subtracting your company’s liabilities from its assets.

6. Exit Strategy
The exit strategy refers to a probable plan for selling your business either to the public in an IPO or to another company. It is the last thing you include in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
You can choose to omit the exit strategy from your business plan if you plan to maintain full ownership of your business and do not plan on seeking angel investment or virtual capitalist (VC) funding.
Investors may want to know what your exit plan is. They invest in your business to get a good return on investment.
Your exit strategy does not have to include long and boring details. Ensure you identify some interested parties who may be interested in buying the company if it becomes a success.

Key Questions to Answer with Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection
Your financial plan, metrics, and projection section helps investors, creditors, or your internal managers to understand what your expenses are, the amount of cash you need, and what it takes to make your company profitable. It also shows what you will be doing with any funding.
You do not need to show actual financial data if you do not have one. Adding forecasts and projections to your financial statements is added proof that your strategy is feasible and shows investors you have planned properly.
Here are some key questions to answer to help you develop this section.
- What is your sales forecast for the next year?
- When will your company achieve a positive cash flow?
- What are the core expenses you need to operate?
- How much money do you need upfront to operate or grow your company?
- How will you use the loans or investments?
9. Add an Appendix to Your Business Plan
Adding an appendix to your business plan is optional. It is a useful place to put any charts, tables, legal notes, definitions, permits, résumés, and other critical information that do not fit into other sections of your business plan.
The appendix section is where you would want to include details of a patent or patent-pending if you have one. You can always add illustrations or images of your products here. It is the last section of your business plan.
When writing your business plan, there are details you cut short or remove to prevent the entire section from becoming too lengthy. There are also details you want to include in the business plan but are not a good fit for any of the previous sections. You can add that additional information to the appendix section.
Businesses also use the appendix section to include supporting documents or other materials specially requested by investors or lenders.
You can include just about any information that supports the assumptions and statements you made in the business plan under the appendix. It is the one place in the business plan where unrelated data and information can coexist amicably.
If your appendix section is lengthy, try organizing it by adding a table of contents at the beginning of the appendix section. It is also advisable to group similar information to make it easier for the reader to access them.
A well-organized appendix section makes it easier to share your information clearly and concisely. Add footnotes throughout the rest of the business plan or make references in the plan to the documents in the appendix.
The appendix section is usually only necessary if you are seeking funding from investors or lenders, or hoping to attract partners.
People reading business plans do not want to spend time going through a heap of backup information, numbers, and charts. Keep these documents or information in the Appendix section in case the reader wants to dig deeper.
Common Items to Include in the Appendix Section of Your Business Plan
The appendix section includes documents that supplement or support the information or claims given in other sections of the business plans. Common items you can include in the appendix section include:
- Additional data about the process of manufacturing or creation
- Additional description of products or services such as product schematics
- Additional financial documents or projections
- Articles of incorporation and status
- Backup for market research or competitive analysis
- Bank statements
- Business registries
- Client testimonials (if your business is already running)
- Copies of insurances
- Credit histories (personal or/and business)
- Deeds and permits
- Equipment leases
- Examples of marketing and advertising collateral
- Industry associations and memberships
- Images of product
- Intellectual property
- Key customer contracts
- Legal documents and other contracts
- Letters of reference
- Links to references
- Market research data
- Organizational charts
- Photographs of potential facilities
- Professional licenses pertaining to your legal structure or type of business
- Purchase orders
- Resumes of the founder(s) and key managers
- State and federal identification numbers or codes
- Trademarks or patents’ registrations
Avoid using the appendix section as a place to dump any document or information you feel like adding. Only add documents or information that you support or increase the credibility of your business plan.
Tips and Strategies for Writing a Convincing Business Plan
To achieve a perfect business plan, you need to consider some key tips and strategies. These tips will raise the efficiency of your business plan above average.
1. Know Your Audience
When writing a business plan, you need to know your audience . Business owners write business plans for different reasons. Your business plan has to be specific. For example, you can write business plans to potential investors, banks, and even fellow board members of the company.
The audience you are writing to determines the structure of the business plan. As a business owner, you have to know your audience. Not everyone will be your audience. Knowing your audience will help you to narrow the scope of your business plan.
Consider what your audience wants to see in your projects, the likely questions they might ask, and what interests them.
- A business plan used to address a company's board members will center on its employment schemes, internal affairs, projects, stakeholders, etc.
- A business plan for financial institutions will talk about the size of your market and the chances for you to pay back any loans you demand.
- A business plan for investors will show proof that you can return the investment capital within a specific time. In addition, it discusses your financial projections, tractions, and market size.
2. Get Inspiration from People
Writing a business plan from scratch as an entrepreneur can be daunting. That is why you need the right inspiration to push you to write one. You can gain inspiration from the successful business plans of other businesses. Look at their business plans, the style they use, the structure of the project, etc.
To make your business plan easier to create, search companies related to your business to get an exact copy of what you need to create an effective business plan. You can also make references while citing examples in your business plans.
When drafting your business plan, get as much help from others as you possibly can. By getting inspiration from people, you can create something better than what they have.
3. Avoid Being Over Optimistic
Many business owners make use of strong adjectives to qualify their content. One of the big mistakes entrepreneurs make when preparing a business plan is promising too much.
The use of superlatives and over-optimistic claims can prepare the audience for more than you can offer. In the end, you disappoint the confidence they have in you.
In most cases, the best option is to be realistic with your claims and statistics. Most of the investors can sense a bit of incompetency from the overuse of superlatives. As a new entrepreneur, do not be tempted to over-promise to get the interests of investors.
The concept of entrepreneurship centers on risks, nothing is certain when you make future analyses. What separates the best is the ability to do careful research and work towards achieving that, not promising more than you can achieve.
To make an excellent first impression as an entrepreneur, replace superlatives with compelling data-driven content. In this way, you are more specific than someone promising a huge ROI from an investment.
4. Keep it Simple and Short
When writing business plans, ensure you keep them simple throughout. Irrespective of the purpose of the business plan, your goal is to convince the audience.
One way to achieve this goal is to make them understand your proposal. Therefore, it would be best if you avoid the use of complex grammar to express yourself. It would be a huge turn-off if the people you want to convince are not familiar with your use of words.
Another thing to note is the length of your business plan. It would be best if you made it as brief as possible.
You hardly see investors or agencies that read through an extremely long document. In that case, if your first few pages can’t convince them, then you have lost it. The more pages you write, the higher the chances of you derailing from the essential contents.
To ensure your business plan has a high conversion rate, you need to dispose of every unnecessary information. For example, if you have a strategy that you are not sure of, it would be best to leave it out of the plan.
5. Make an Outline and Follow Through
A perfect business plan must have touched every part needed to convince the audience. Business owners get easily tempted to concentrate more on their products than on other sections. Doing this can be detrimental to the efficiency of the business plan.
For example, imagine you talking about a product but omitting or providing very little information about the target audience. You will leave your clients confused.
To ensure that your business plan communicates your full business model to readers, you have to input all the necessary information in it. One of the best ways to achieve this is to design a structure and stick to it.
This structure is what guides you throughout the writing. To make your work easier, you can assign an estimated word count or page limit to every section to avoid making it too bulky for easy reading. As a guide, the necessary things your business plan must contain are:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Product or service description
- Target audience
- Market size
- Competition analysis
- Financial projections
Some specific businesses can include some other essential sections, but these are the key sections that must be in every business plan.
6. Ask a Professional to Proofread
When writing a business plan, you must tie all loose ends to get a perfect result. When you are done with writing, call a professional to go through the document for you. You are bound to make mistakes, and the way to correct them is to get external help.
You should get a professional in your field who can relate to every section of your business plan. It would be easier for the professional to notice the inner flaws in the document than an editor with no knowledge of your business.
In addition to getting a professional to proofread, get an editor to proofread and edit your document. The editor will help you identify grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and inappropriate writing styles.
Writing a business plan can be daunting, but you can surmount that obstacle and get the best out of it with these tips.
Business Plan Examples and Templates That’ll Save You Tons of Time
1. hubspot's one-page business plan.

The one-page business plan template by HubSpot is the perfect guide for businesses of any size, irrespective of their business strategy. Although the template is condensed into a page, your final business plan should not be a page long! The template is designed to ask helpful questions that can help you develop your business plan.
Hubspot’s one-page business plan template is divided into nine fields:
- Business opportunity
- Company description
- Industry analysis
- Target market
- Implementation timeline
- Marketing plan
- Financial summary
- Funding required
2. Bplan’s Free Business Plan Template

Bplans' free business plan template is investor-approved. It is a rich template used by prestigious educational institutions such as Babson College and Princeton University to teach entrepreneurs how to create a business plan.
The template has six sections: the executive summary, opportunity, execution, company, financial plan, and appendix. There is a step-by-step guide for writing every little detail in the business plan. Follow the instructions each step of the way and you will create a business plan that impresses investors or lenders easily.
3. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

HubSpot’s downloadable business plan template is a more comprehensive option compared to the one-page business template by HubSpot. This free and downloadable business plan template is designed for entrepreneurs.
The template is a comprehensive guide and checklist for business owners just starting their businesses. It tells you everything you need to fill in each section of the business plan and how to do it.
There are nine sections in this business plan template: an executive summary, company and business description, product and services line, market analysis, marketing plan, sales plan, legal notes, financial considerations, and appendix.
4. Business Plan by My Own Business Institute

My Own Business Institute (MOBI) which is a part of Santa Clara University's Center for Innovation and Entrepreneurship offers a free business plan template. You can either copy the free business template from the link provided above or download it as a Word document.
The comprehensive template consists of a whopping 15 sections.
- The Business Profile
- The Vision and the People
- Home-Based Business and Freelance Business Opportunities
- Organization
- Licenses and Permits
- Business Insurance
- Communication Tools
- Acquisitions
- Location and Leasing
- Accounting and Cash Flow
- Opening and Marketing
- Managing Employees
- Expanding and Handling Problems
There are lots of helpful tips on how to fill each section in the free business plan template by MOBI.
5. Score's Business Plan Template for Startups

Score is an American nonprofit organization that helps entrepreneurs build successful companies. This business plan template for startups by Score is available for free download. The business plan template asks a whooping 150 generic questions that help entrepreneurs from different fields to set up the perfect business plan.
The business plan template for startups contains clear instructions and worksheets, all you have to do is answer the questions and fill the worksheets.
There are nine sections in the business plan template: executive summary, company description, products and services, marketing plan, operational plan, management and organization, startup expenses and capitalization, financial plan, and appendices.
The ‘refining the plan’ resource contains instructions that help you modify your business plan to suit your specific needs, industry, and target audience. After you have completed Score’s business plan template, you can work with a SCORE mentor for expert advice in business planning.
6. Minimalist Architecture Business Plan Template by Venngage

The minimalist architecture business plan template is a simple template by Venngage that you can customize to suit your business needs .
There are five sections in the template: an executive summary, statement of problem, approach and methodology, qualifications, and schedule and benchmark. The business plan template has instructions that guide users on what to fill in each section.
7. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two free business plan templates, filled with practical real-life examples that you can model to create your business plan. Both free business plan templates are written by fictional business owners: Rebecca who owns a consulting firm, and Andrew who owns a toy company.
There are five sections in the two SBA’s free business plan templates.
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Service Line
- Marketing and Sales
8. The $100 Startup's One-Page Business Plan

The one-page business plan by the $100 startup is a simple business plan template for entrepreneurs who do not want to create a long and complicated plan . You can include more details in the appendices for funders who want more information beyond what you can put in the one-page business plan.
There are five sections in the one-page business plan such as overview, ka-ching, hustling, success, and obstacles or challenges or open questions. You can answer all the questions using one or two sentences.
9. PandaDoc’s Free Business Plan Template

The free business plan template by PandaDoc is a comprehensive 15-page document that describes the information you should include in every section.
There are 11 sections in PandaDoc’s free business plan template.
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Products and services
- Operations plan
- Management organization
- Financial plan
- Conclusion / Call to action
- Confidentiality statement
You have to sign up for its 14-day free trial to access the template. You will find different business plan templates on PandaDoc once you sign up (including templates for general businesses and specific businesses such as bakeries, startups, restaurants, salons, hotels, and coffee shops)
PandaDoc allows you to customize its business plan templates to fit the needs of your business. After editing the template, you can send it to interested parties and track opens and views through PandaDoc.
10. Invoiceberry Templates for Word, Open Office, Excel, or PPT

InvoiceBerry is a U.K based online invoicing and tracking platform that offers free business plan templates in .docx, .odt, .xlsx, and .pptx formats for freelancers and small businesses.
Before you can download the free business plan template, it will ask you to give it your email address. After you complete the little task, it will send the download link to your inbox for you to download. It also provides a business plan checklist in .xlsx file format that ensures you add the right information to the business plan.
Alternatives to the Traditional Business Plan
A business plan is very important in mapping out how one expects their business to grow over a set number of years, particularly when they need external investment in their business. However, many investors do not have the time to watch you present your business plan. It is a long and boring read.
Luckily, there are three alternatives to the traditional business plan (the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck). These alternatives are less laborious and easier and quicker to present to investors.
Business Model Canvas (BMC)
The business model canvas is a business tool used to present all the important components of setting up a business, such as customers, route to market, value proposition, and finance in a single sheet. It provides a very focused blueprint that defines your business initially which you can later expand on if needed.

The sheet is divided mainly into company, industry, and consumer models that are interconnected in how they find problems and proffer solutions.
Segments of the Business Model Canvas
The business model canvas was developed by founder Alexander Osterwalder to answer important business questions. It contains nine segments.

- Key Partners: Who will be occupying important executive positions in your business? What do they bring to the table? Will there be a third party involved with the company?
- Key Activities: What important activities will production entail? What activities will be carried out to ensure the smooth running of the company?
- The Product’s Value Propositions: What does your product do? How will it be different from other products?
- Customer Segments: What demography of consumers are you targeting? What are the habits of these consumers? Who are the MVPs of your target consumers?
- Customer Relationships: How will the team support and work with its customer base? How do you intend to build and maintain trust with the customer?
- Key Resources: What type of personnel and tools will be needed? What size of the budget will they need access to?
- Channels: How do you plan to create awareness of your products? How do you intend to transport your product to the customer?
- Cost Structure: What is the estimated cost of production? How much will distribution cost?
- Revenue Streams: For what value are customers willing to pay? How do they prefer to pay for the product? Are there any external revenues attached apart from the main source? How do the revenue streams contribute to the overall revenue?
Lean Canvas
The lean canvas is a problem-oriented alternative to the standard business model canvas. It was proposed by Ash Maurya, creator of Lean Stack as a development of the business model generation. It uses a more problem-focused approach and it majorly targets entrepreneurs and startup businesses.

Lean Canvas uses the same 9 blocks concept as the business model canvas, however, they have been modified slightly to suit the needs and purpose of a small startup. The key partners, key activities, customer relationships, and key resources are replaced by new segments which are:
- Problem: Simple and straightforward number of problems you have identified, ideally three.
- Solution: The solutions to each problem.
- Unfair Advantage: Something you possess that can't be easily bought or replicated.
- Key Metrics: Important numbers that will tell how your business is doing.
Startup Pitch Deck
While the business model canvas compresses into a factual sheet, startup pitch decks expand flamboyantly.
Pitch decks, through slides, convey your business plan, often through graphs and images used to emphasize estimations and observations in your presentation. Entrepreneurs often use pitch decks to fully convince their target audience of their plans before discussing funding arrangements.

Considering the likelihood of it being used in a small time frame, a good startup pitch deck should ideally contain 20 slides or less to have enough time to answer questions from the audience.
Unlike the standard and lean business model canvases, a pitch deck doesn't have a set template on how to present your business plan but there are still important components to it. These components often mirror those of the business model canvas except that they are in slide form and contain more details.

Using Airbnb (one of the most successful start-ups in recent history) for reference, the important components of a good slide are listed below.
- Cover/Introduction Slide: Here, you should include your company's name and mission statement. Your mission statement should be a very catchy tagline. Also, include personal information and contact details to provide an easy link for potential investors.
- Problem Slide: This slide requires you to create a connection with the audience or the investor that you are pitching. For example in their pitch, Airbnb summarized the most important problems it would solve in three brief points – pricing of hotels, disconnection from city culture, and connection problems for local bookings.
- Solution Slide: This slide includes your core value proposition. List simple and direct solutions to the problems you have mentioned
- Customer Analysis: Here you will provide information on the customers you will be offering your service to. The identity of your customers plays an important part in fundraising as well as the long-run viability of the business.
- Market Validation: Use competitive analysis to show numbers that prove the presence of a market for your product, industry behavior in the present and the long run, as well as the percentage of the market you aim to attract. It shows that you understand your competitors and customers and convinces investors of the opportunities presented in the market.
- Business Model: Your business model is the hook of your presentation. It may vary in complexity but it should generally include a pricing system informed by your market analysis. The goal of the slide is to confirm your business model is easy to implement.
- Marketing Strategy: This slide should summarize a few customer acquisition methods that you plan to use to grow the business.
- Competitive Advantage: What this slide will do is provide information on what will set you apart and make you a more attractive option to customers. It could be the possession of technology that is not widely known in the market.
- Team Slide: Here you will give a brief description of your team. Include your key management personnel here and their specific roles in the company. Include their educational background, job history, and skillsets. Also, talk about their accomplishments in their careers so far to build investors' confidence in members of your team.
- Traction Slide: This validates the company’s business model by showing growth through early sales and support. The slide aims to reduce any lingering fears in potential investors by showing realistic periodic milestones and profit margins. It can include current sales, growth, valuable customers, pre-orders, or data from surveys outlining current consumer interest.
- Funding Slide: This slide is popularly referred to as ‘the ask'. Here you will include important details like how much is needed to get your business off the ground and how the funding will be spent to help the company reach its goals.
- Appendix Slides: Your pitch deck appendix should always be included alongside a standard pitch presentation. It consists of additional slides you could not show in the pitch deck but you need to complement your presentation.
It is important to support your calculations with pictorial renditions. Infographics, such as pie charts or bar graphs, will be more effective in presenting the information than just listing numbers. For example, a six-month graph that shows rising profit margins will easily look more impressive than merely writing it.
Lastly, since a pitch deck is primarily used to secure meetings and you may be sharing your pitch with several investors, it is advisable to keep a separate public version that doesn't include financials. Only disclose the one with projections once you have secured a link with an investor.
Advantages of the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck over the Traditional Business Plan
- Time-Saving: Writing a detailed traditional business plan could take weeks or months. On the other hand, all three alternatives can be done in a few days or even one night of brainstorming if you have a comprehensive understanding of your business.
- Easier to Understand: Since the information presented is almost entirely factual, it puts focus on what is most important in running the business. They cut away the excess pages of fillers in a traditional business plan and allow investors to see what is driving the business and what is getting in the way.
- Easy to Update: Businesses typically present their business plans to many potential investors before they secure funding. What this means is that you may regularly have to amend your presentation to update statistics or adjust to audience-specific needs. For a traditional business plan, this could mean rewriting a whole section of your plan. For the three alternatives, updating is much easier because they are not voluminous.
- Guide for a More In-depth Business Plan: All three alternatives have the added benefit of being able to double as a sketch of your business plan if the need to create one arises in the future.
Business Plan FAQ
Business plans are important for any entrepreneur who is looking for a framework to run their company over some time or seeking external support. Although they are essential for new businesses, every company should ideally have a business plan to track their growth from time to time. They can be used by startups seeking investments or loans to convey their business ideas or an employee to convince his boss of the feasibility of starting a new project. They can also be used by companies seeking to recruit high-profile employee targets into key positions or trying to secure partnerships with other firms.
Business plans often vary depending on your target audience, the scope, and the goals for the plan. Startup plans are the most common among the different types of business plans. A start-up plan is used by a new business to present all the necessary information to help get the business up and running. They are usually used by entrepreneurs who are seeking funding from investors or bank loans. The established company alternative to a start-up plan is a feasibility plan. A feasibility plan is often used by an established company looking for new business opportunities. They are used to show the upsides of creating a new product for a consumer base. Because the audience is usually company people, it requires less company analysis. The third type of business plan is the lean business plan. A lean business plan is a brief, straight-to-the-point breakdown of your ideas and analysis for your business. It does not contain details of your proposal and can be written on one page. Finally, you have the what-if plan. As it implies, a what-if plan is a preparation for the worst-case scenario. You must always be prepared for the possibility of your original plan being rejected. A good what-if plan will serve as a good plan B to the original.
A good business plan has 10 key components. They include an executive plan, product analysis, desired customer base, company analysis, industry analysis, marketing strategy, sales strategy, financial projection, funding, and appendix. Executive Plan Your business should begin with your executive plan. An executive plan will provide early insight into what you are planning to achieve with your business. It should include your mission statement and highlight some of the important points which you will explain later. Product Analysis The next component of your business plan is your product analysis. A key part of this section is explaining the type of item or service you are going to offer as well as the market problems your product will solve. Desired Consumer Base Your product analysis should be supplemented with a detailed breakdown of your desired consumer base. Investors are always interested in knowing the economic power of your market as well as potential MVP customers. Company Analysis The next component of your business plan is your company analysis. Here, you explain how you want to run your business. It will include your operational strategy, an insight into the workforce needed to keep the company running, and important executive positions. It will also provide a calculation of expected operational costs. Industry Analysis A good business plan should also contain well laid out industry analysis. It is important to convince potential investors you know the companies you will be competing with, as well as your plans to gain an edge on the competition. Marketing Strategy Your business plan should also include your marketing strategy. This is how you intend to spread awareness of your product. It should include a detailed explanation of the company brand as well as your advertising methods. Sales Strategy Your sales strategy comes after the market strategy. Here you give an overview of your company's pricing strategy and how you aim to maximize profits. You can also explain how your prices will adapt to market behaviors. Financial Projection The financial projection is the next component of your business plan. It explains your company's expected running cost and revenue earned during the tenure of the business plan. Financial projection gives a clear idea of how your company will develop in the future. Funding The next component of your business plan is funding. You have to detail how much external investment you need to get your business idea off the ground here. Appendix The last component of your plan is the appendix. This is where you put licenses, graphs, or key information that does not fit in any of the other components.
The business model canvas is a business management tool used to quickly define your business idea and model. It is often used when investors need you to pitch your business idea during a brief window.
A pitch deck is similar to a business model canvas except that it makes use of slides in its presentation. A pitch is not primarily used to secure funding, rather its main purpose is to entice potential investors by selling a very optimistic outlook on the business.
Business plan competitions help you evaluate the strength of your business plan. By participating in business plan competitions, you are improving your experience. The experience provides you with a degree of validation while practicing important skills. The main motivation for entering into the competitions is often to secure funding by finishing in podium positions. There is also the chance that you may catch the eye of a casual observer outside of the competition. These competitions also provide good networking opportunities. You could meet mentors who will take a keen interest in guiding you in your business journey. You also have the opportunity to meet other entrepreneurs whose ideas can complement yours.
Exlore Further
- 12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
- 13 Sources of Business Finance For Companies & Sole Traders
- 5 Common Types of Business Structures (+ Pros & Cons)
- How to Buy a Business in 8 Steps (+ Due Diligence Checklist)
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Home > Business > Business Startup
How To Write a Business Plan

We are committed to sharing unbiased reviews. Some of the links on our site are from our partners who compensate us. Read our editorial guidelines and advertising disclosure .

Starting a business is a wild ride, and a solid business plan can be the key to keeping you on track. A business plan is essentially a roadmap for your business — outlining your goals, strategies, market analysis and financial projections. Not only will it guide your decision-making, a business plan can help you secure funding with a loan or from investors .
Writing a business plan can seem like a huge task, but taking it one step at a time can break the plan down into manageable milestones. Here is our step-by-step guide on how to write a business plan.
Table of contents
- Write your executive summary
- Do your market research homework
- Set your business goals and objectives
- Plan your business strategy
- Describe your product or service
- Crunch the numbers
- Finalize your business plan

By signing up I agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Step 1: Write your executive summary
Though this will be the first page of your business plan , we recommend you actually write the executive summary last. That’s because an executive summary highlights what’s to come in the business plan but in a more condensed fashion.
An executive summary gives stakeholders who are reading your business plan the key points quickly without having to comb through pages and pages. Be sure to cover each successive point in a concise manner, and include as much data as necessary to support your claims.
You’ll cover other things too, but answer these basic questions in your executive summary:
- Idea: What’s your business concept? What problem does your business solve? What are your business goals?
- Product: What’s your product/service and how is it different?
- Market: Who’s your audience? How will you reach customers?
- Finance: How much will your idea cost? And if you’re seeking funding, how much money do you need? How much do you expect to earn? If you’ve already started, where is your revenue at now?
Step 2: Do your market research homework
The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research . This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to gather this information. Your method may be formal or more casual, just make sure that you’re getting good data back.
This research will help you to understand the needs of your target market and the potential demand for your product or service—essential aspects of starting and growing a successful business.
Step 3: Set your business goals and objectives
Once you’ve completed your market research, you can begin to define your business goals and objectives. What is the problem you want to solve? What’s your vision for the future? Where do you want to be in a year from now?
Use this step to decide what you want to achieve with your business, both in the short and long term. Try to set SMART goals—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound benchmarks—that will help you to stay focused and motivated as you build your business.
Step 4: Plan your business strategy
Your business strategy is how you plan to reach your goals and objectives. This includes details on positioning your product or service, marketing and sales strategies, operational plans, and the organizational structure of your small business.
Make sure to include key roles and responsibilities for each team member if you’re in a business entity with multiple people.
Step 5: Describe your product or service
In this section, get into the nitty-gritty of your product or service. Go into depth regarding the features, benefits, target market, and any patents or proprietary tech you have. Make sure to paint a clear picture of what sets your product apart from the competition—and don’t forget to highlight any customer benefits.
Step 6: Crunch the numbers
Financial analysis is an essential part of your business plan. If you’re already in business that includes your profit and loss statement , cash flow statement and balance sheet .
These financial projections will give investors and lenders an understanding of the financial health of your business and the potential return on investment.
You may want to work with a financial professional to ensure your financial projections are realistic and accurate.
Step 7: Finalize your business plan
Once you’ve completed everything, it's time to finalize your business plan. This involves reviewing and editing your plan to ensure that it is clear, concise, and easy to understand.
You should also have someone else review your plan to get a fresh perspective and identify any areas that may need improvement. You could even work with a free SCORE mentor on your business plan or use a SCORE business plan template for more detailed guidance.
Compare the Top Small-Business Banks
Data effective 1/10/23. At publishing time, rates, fees, and requirements are current but are subject to change. Offers may not be available in all areas.
The takeaway
Writing a business plan is an essential process for any forward-thinking entrepreneur or business owner. A business plan requires a lot of up-front research, planning, and attention to detail, but it’s worthwhile. Creating a comprehensive business plan can help you achieve your business goals and secure the funding you need.
Related content
- 5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business
- How to Get a Business License: What You Need to Know
- What Is a Cash Flow Statement?
Best Small Business Loans
5202 W Douglas Corrigan Way Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Accounting & Payroll
Point of Sale
Payment Processing
Inventory Management
Human Resources
Other Services
Best Inventory Management Software
Best Small Business Accounting Software
Best Payroll Software
Best Mobile Credit Card Readers
Best POS Systems
Best Tax Software
Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime anywhere.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Disclaimer: The information featured in this article is based on our best estimates of pricing, package details, contract stipulations, and service available at the time of writing. All information is subject to change. Pricing will vary based on various factors, including, but not limited to, the customer’s location, package chosen, added features and equipment, the purchaser’s credit score, etc. For the most accurate information, please ask your customer service representative. Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase.
Our mission is to help consumers make informed purchase decisions. While we strive to keep our reviews as unbiased as possible, we do receive affiliate compensation through some of our links. This can affect which services appear on our site and where we rank them. Our affiliate compensation allows us to maintain an ad-free website and provide a free service to our readers. For more information, please see our Privacy Policy Page . |
© Business.org 2023 All Rights Reserved.
Home Blog Business Plan Writer A Comprehensive Guide to Writing Your Business Plan
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing Your Business Plan
Home » A Comprehensive Guide to Writing Your Business Plan
Recent Posts
- Exit Strategy in Business Planning: Understanding Its Importance and Implementation March 6, 2024
- The Future of AI in Business: Advancements, Opportunities, and Challenges March 6, 2024
- EB-5 Visa: Why It Matters and How to Navigate It March 6, 2024
- Hiring a Business Plan Consultant: What You Need to Know March 6, 2024
- Six Secret Benefits You Didn’t Know About Business Plans March 6, 2024
There’s no content to show here yet.
Ready To Get Started?
Our team of business consultants can provide you with one-on-one consulting and strategic advisory to launch or grow your business.
SCHEDULE A CONSULTATION
- Exit Strategy in Business Planning: Understanding Its Importance and Implementation
- The Future of AI in Business: Advancements, Opportunities, and Challenges
- EB-5 Visa: Why It Matters and How to Navigate It
- Hiring a Business Plan Consultant: What You Need to Know
- Six Secret Benefits You Didn’t Know About Business Plans
- Business Plan
- Business Plan Writer
- Client Press

In the realm of entrepreneurship, where vision meets execution, a well-crafted business plan serves as the cornerstone of success. Whether you’re launching a startup, seeking funding, or steering an existing business towards growth, a comprehensive business plan provides a roadmap to navigate the complexities of the marketplace and achieve your objectives. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the essential steps and components of writing a business plan that sets you on the path to success.
Understanding the Purpose of a Business Plan
Before delving into the intricacies of crafting a business plan, it’s crucial to understand its purpose and significance. At its core, a business plan is a strategic document that outlines your business idea, objectives, strategies, and action plans. It serves multiple purposes, including:
- Clarifying Your Vision : A business plan helps crystallize your vision for the venture, articulating your goals, values, and aspirations.
- Securing Funding : Whether from investors, lenders, or crowdfunding platforms, a well-developed business plan enhances your credibility and increases your chances of securing funding.
- Guiding Decision-Making : It provides a framework for decision-making, helping you prioritize initiatives, allocate resources, and navigate challenges effectively.
- Attracting Partnerships : A compelling business plan can attract strategic partnerships, collaborations, and alliances essential for growth and expansion.
- Monitoring Progress : It serves as a yardstick against which you can measure your progress, track milestones, and identify areas for improvement.
Key Components of a Business Plan
A comprehensive business plan typically comprises the following key components:
- Executive Summary : A concise overview of your business idea, including your mission statement, product or service offering, target market, competitive advantage, and financial highlights.
- Company Description : An in-depth analysis of your business, including its history, legal structure, ownership, location, and mission statement.
- Market Analysis : A thorough assessment of the industry landscape, target market demographics, trends, competition, and market size.
- Organization and Management : A breakdown of your organizational structure, key personnel, roles, responsibilities, and any relevant partnerships or advisory boards.
- Product or Service Offering : A detailed description of your offerings, including features, benefits, pricing strategy, and intellectual property considerations.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy : A plan for promoting and selling your products or services, encompassing market positioning, branding, distribution channels, sales forecast, and customer acquisition tactics.
- Financial Projections : A comprehensive analysis of your financial outlook, including income statements, balance sheets, cash flow forecasts, break-even analysis, and funding requirements.
- Implementation Plan : A roadmap outlining the steps required to execute your business strategy, including timelines, milestones, resource allocation, and contingency plans.
Steps to Writing Your Business Plan
Now that we’ve outlined the key components, let’s delve into the step-by-step process of writing your business plan:
- Conduct Market Research : Start by conducting thorough market research to gain insights into your industry, target market, competitors, and consumer preferences. Gather data from primary and secondary sources, including industry reports, surveys, and interviews.
- Define Your Business Concept : Clearly articulate your business concept, including your value proposition, target market segment, competitive advantage, and differentiation strategy. Identify the problem you’re solving or the need you’re addressing in the market.
- Set SMART Goals : Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for your business. These goals should align with your vision and mission, guiding your strategic decisions and operational plans.
- Develop Strategies and Tactics : Based on your market analysis and business goals, develop strategic initiatives and tactical plans to achieve your objectives. Outline your marketing strategy, sales approach, operational processes, and financial management protocols in detail.
- Create Financial Projections : Prepare realistic and detailed financial projections for your business, including revenue forecasts, expense budgets, cash flow statements, and profitability analysis. Use conservative estimates and assumptions to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Write and Format Your Plan : Begin writing your business plan, starting with the executive summary and proceeding through each section in a logical sequence. Use clear, concise language, and incorporate visuals such as charts, graphs, and tables to enhance readability.
- Seek Feedback and Revision : Once your business plan is drafted, seek feedback from trusted advisors, mentors, or industry experts. Incorporate their insights and suggestions to refine and improve your plan, ensuring clarity, coherence, and feasibility.
- Finalize and Implement : After incorporating feedback and making necessary revisions, finalize your business plan. Create a polished, professional document that accurately reflects your vision, strategy, and potential for success. Use it as a guiding tool to implement your business strategy and achieve your goals.
Writing a comprehensive business plan is an essential step in launching and growing a successful venture. By carefully outlining your vision, strategy, and execution plan, you provide a roadmap for navigating the challenges and opportunities of entrepreneurship. Whether you’re seeking funding, attracting partners, or guiding your team towards a common goal, a well-crafted business plan serves as a valuable tool for aligning stakeholders, making informed decisions, and driving sustainable growth. So, roll up your sleeves, follow this guide, and embark on your entrepreneurial journey with confidence and clarity. Your business plan is not just a document—it’s a blueprint for success.
Get started today with America’s best rated business plan writing service, Go Business Plans . Join the ranks of thousands of satisfied business owners who trust us with their business planning needs. With our experienced team of business plan writers and consultants, we’ve successfully assisted over 3,000 clients in launching and expanding their businesses. Whether you’re just starting out or seeking growth opportunities, we’re here to guide you every step of the way. Contact us at (855) 840-5451 or fill out our contact form to schedule your free consultation .
- Author Details
- Service Area
- Our Clients
- Frequently Asks Questions
Services Overview

- Business Plan Writers

- Investor Presentation

- Business Plan Consultants

- Bank Business Plan
Immigration

- E2 Visa Business Plan

- EB-5 Visa Business Plan

- L1 Visa Business Plan
Fully Customized Business Plans – No Templates
Schedule free consultation.
Our business plain team is here to help
Shedule Consulation
Our business plan team is here to help
View sample
Check example of our work

- Business Plan Consulting
How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)
- 3 years ago

Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!

What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”
If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand
A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:

When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples
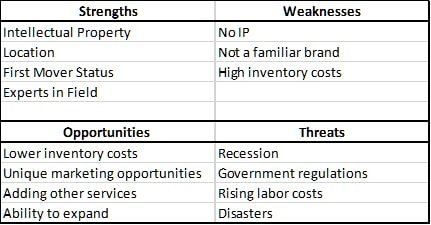
Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:
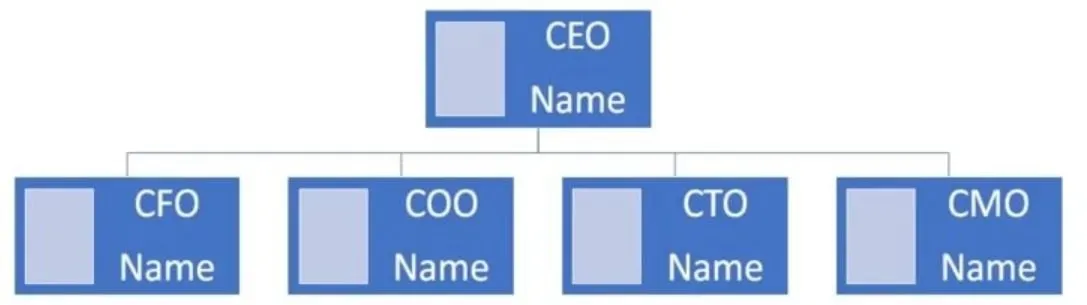
Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.
The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?

Brandon Boushy
Brandon Boushy lives to improve people’s lives by helping them become successful entrepreneurs. His journey started nearly 30 years ago. He consistently excelled at everything he did, but preferred to make the rules rather than follow him. His exploration of self and knowledge has helped him to get an engineering degree, MBA, and countless certifications. When freelancing and rideshare came onto the scene, he recognized the opportunity to play by his own rules. Since 2017, he has helped businesses across all industries achieve more with his research, writing, and marketing strategies. Since 2021, he has been the Lead Writer for UpFlip where he has published over 170 articles on small business success.

Related posts

- September 27, 2023
How to Start a Business: The Ultimate Guide (2024)

- August 3, 2022
Free Business Plan Template (With Examples)

- May 3, 2022
How to Get a Business License (In 3 Steps)
Join the discussion cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
2 thoughts on “How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)”
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
Compare listings
Reset Password
Please enter your username or email address. You will receive a link to create a new password via email.
- The Definitive Guide to Writing a Business Plan

- Startup Culture
- Business Skills
Last Updated: July 25, 2023 By TRUiC Team
This free step-by-step guide to writing a business plan was built just for you, if you aren't really sure what planning a business is all about. To save time, stress and energy we'll walk you through everything you need to know without fluff or heavy brain work.
Instead, we're focusing on the basics. If you're looking to create a super-dense collegiate 40-page plan, then you should probably take a business planning course at the nearest college.
This guide just covers what your average startup needs to dramatically increase chances of follow-through and success. Enjoy!
Note: Business planning software can help you write a professional business plan that will lead you to success.
Step 1) Create A Business Plan Shortcut
For the sake of argument, let’s say you’re the most gifted cat burglar on earth-- a real savvy savant of the steal. Put yourself in the mindset where strategy and planning are time-erasing pleasures, delicious treats that reward you with immense prosperity-- not complex tasks that can be skipped or shelved.
Too many entrepreneurs perceive putting a business plan together as some kind of chore. It's not. When the product or service is something you believe in, it’s as awesome as it is for those cat burglars in the movies, except you're plotting honest work.
Fact : It’s possible to create your initial business plan in less than an hour!
Let’s build a “lean plan” that’s simple to create and helps you identify core assets. You start with a pitch, a single page overview which can become your executive summary later on. It’s your business strategy all on one page that's easy to update as you evolve.
You may be thinking,
“ Wait a minute. If I’m not raising money from investors, why do I need a pitch? ”
Well, after years working with entrepreneurs we've found a pitch is really the ideal format to document your business idea , share it with others, and quickly adjust as you learn more about/analyze how you’re going to build your brand.
Furthermore, once you have your pitch done you can easily convert it into a presentation-ready business plan with massive clarity. To begin, follow the simple outline below or allow tools like LivePlan (what we used for Startup Savant) to walk you through the entire process with examples and video tutorials.
What To Include in Your Pitch
As you tackle your one-pager, mentally channel Twitter and try to keep each section as short/concise as possible-- the size of a solid tweet.
- Mini-Pitch : Typically a refined sentence summarizing your USP (unique selling proposition).
- Market Need : The problem your business solves for your customers.
- Your Solution : How you’re solving the problem through your products and services.
- Primary Competition : The products and services your customers choose today instead of yours.
- Target Market : This is where you detail your ideal client and niche.
- Sales & Marketing : How you plan on marketing.
- Budget & Sales Goals : How much do you project/calculate you’ll sell and how much is it going to cost to make your product or deliver your service? Also, show other key expenses when your business is up and running.
- Milestones : What you’ve achieved so far and your major goals for the next few months and years.
- Team : Why you and your team are the right people to make your company successful.
- Partners & Resources : List primary companies/organizations needed to go the distance.
- Funding Needs : If you need to raise money, how much and where will this capital be going (channels)?
That might seem like a fair amount of work if you’ve never put together a real pitch before, but remember, that’s just one page of content. Another way to look at it is a one page resume for your business.
A Couple Writing Tips
First, you start with the putty. Don’t try to self-edit or curate, just barf everything out on paper as it flows from your brilliant mind. Format each section out and just let it go. That’s putting the basic shape together.
Now you need to let it dry, so walk away for a day (week) or two. After that, begin chipping away and condensing. Cut the fat and keep tightening the ideas until you’re down to one page. Be brutal! Stick to the facts. Numbers are easier, but when you’re tackling words remember the average person these days has a shorter attention span (if not compelled by your ideas) than a goldfish.
Taking Action on This Step
Create a pitch outline from the points mentioned above and refine down to one or two sentences. If you need help, check out LivePlan. It’s a solid tool that walks you through the entire process. Plus, they offer a 50% Discount .
Step 2) What To Include in Your Plan
Now that you have a running outline, it’s time to go deeper into the framework of your platform.
Perhaps you’re thinking the one-page pitch is all you’ll need? That would be like going on a road trip in unfamiliar territory with a map that only shows destinations-- no routes, no roads, no other icons whatsoever. Even if you never plan on showing this to anyone, the process of creating a solid plan optimizes everything about you and your business! Here’s a quick overview of what you need to include in your business plan:
- Cover Page/Pitch
- Executive Summary
- Products & Services
- Target Market
- Marketing & Sales Plan
- Milestones & Metrics
- Company & Management Team
- Financial Plan
If you need extra space for product images, detailed financial forecasts, or general additional info, use the appendix. There are three layers of complexity here. First, your pitch with a very brief summary. Then, your Executive Summary that adds details and context. Then into the finer points of the overall business plan.
Not too shabby, right?
Taking Action on The Step
Please revisit your pitch and find a good way to optimize it just a smidgen. The better your pitch, the better the overall plan.
As you fill in the structure, first focus on providing “mental barf” data you can go through and optimize later. Remember, if you need help, LivePlan will walk you through the entire process with video tutorials and examples.
Step 3) Create a Unique Selling Proposition
When copywriters are given a business idea to optimize, they often begin by defining the USP (unique selling proposition) and mini-pitch. A USP can be just a couple words or an incomplete sentence, while the mini-pitch is usually one or two concise sentences.
Just in case you’re fuzzy on the whole copywriter thing, these folks are paid big bucks to write sales and marketing copy which often includes core slogans.
As an example, here’s what the USP and Pitch for Startup Savant sound like:
USP : " Entrepreneurship Simplified "
Pitch : " Startup Savant is a free website that shows you how to start a business and own your future ." Now let’s get past the “How to Write Your USP 101” stuff and dive straight into three core truths.
USPs & Pitches Evolve
The first thing a copywriter will tell you if you’re struggling with this is to relax. They know sales and branding copy optimizes (matures) over time, especially in the first 2-5 years in business.
If possible, avoid thinking your USP is set in stone, never to be altered. It’s more like a sculpture that the market chips away at. Your pitch evolves as you and your platform do. What matters is whether your USP & Pitch are as refined as they can be based on where you are now.
- USPs can be creative & full of personality, but they also need to make sense.
- Is your pitch wordy and confusing? Hazy or unclear?
- Sometimes you have the right words, they just need to be in an optimized order.
Always be ready to “kill your darlings” as copywriters would say. Meaning, get rid of any and all words,
“ That aren’t necessary for the idea or concept you’re conveying to make perfect sense within the context it’s delivered, and to whom it’s being written to. ”
You can begin with half a page, but systematically chisel down to a core concept like, Entrepreneurship Simplified.
Your Ideal Customers Will Do It For You
Copywriters care what you have to say as a business owner or marketing manager, but they know you’re not the ultimate authority in terms of advertising copy.
They’re writing for buyers. In any and all ways your business can optimize over the years, your customers, clients and users should steer the course as much as possible. Be on the lookout for their valuable signals and indications!
Hop at 20 Questions
Copywriters ask TONS of questions. They’re a bit like copy-detectives in how they search high and low for very precise data from their clients. Never fear giving your users, clients or customers a megaphone with which to bark their concerns.
We all love sharing our opinions, right? Yes we do. Let us. Prompt us. Ask us. Bribe us with incentives and discounts… then listen… carefully. Easily 9 out of 10 entrepreneurs are given the ultimate USPs on silver platters by their customers but fail to recognize when they see, read, or hear them.
- If you’ve been stressing on your USP, relax. If it doesn’t feel perfect right now, or 100% distilled, let it happen naturally.
- Your audience can and will steer the course if you choose to notice their cues. Ask three people you haven’t spoken to before how they feel about your product or service.
- Are there any indications out there waiting to be plucked? Blog or social media comments and reviews are primary starting points. It only takes one solid indicator for the magic “pivots” to cause your business or brand to see huge boosts.
Step 4) Crafting the Executive Summary
In brief, what exactly is an executive summary? An executive summary (ES) is an overview of your business and your vision. It comes first in formal/informal business plans and is ideally 1-2 pages.
The ES introduces your business to your reader. If you don’t nail it, no one’s going to read any further. And if an ES sucks, despite it being professionally crafted, then the business model itself needs work or isn’t worth your time. Every ES should include a brief overview of the following:
- The problem your business addresses.
- Your solution.
- Your target market.
- Why the timing’s right for your brand.
- Financial forecast highlights, along with initial/current customer acquisition costs (CAC) and lifetime customer value (LCV).
If you’re raising money or presenting to investors, you’ll also want to cover:
- Your existing team and partners.
- How much money you’re looking to raise and the type of exit strategies in place.
Ideally your ES should fit on one or two pages and be able to stand alone, apart from your business plan. A common strategy is to send your ES out to investors/family/friends and then the complete plan if more detail is requested.
Remember to try and position your writing for people who don’t know anything about your business before they start reading. Explain things simply so that anyone can understand your opportunity, whether they be an in-tune player, an 8th grader, or a grandma.
- Over the next couple weeks, refresh your ES!
- Who is the first person you’re going to send your ES to that has no real previous knowledge of what your business is? It helps having someone in mind when writing.
- Find one amazing ES to read over and see what you can learn from it. Here and here are two great examples.
Well done, in the next step we’ll help you explain your product or service and how it makes an impact on customers.
Step 5) Understanding Customers
Once upon a time there was this lovely, vibrant and ambitious entrepreneur who decided to sell organic breast enlargement cream. It sold well for a while, but then her numbers plateaued, and eventually began to decline.
She knew her business needed a makeover after years in the trenches. So, she created an automated incentive program, a 25% discount coupon code offer sent with every order in exchange for an anonymous review with a photograph. Just a simple before/after image showing the front of their body from neckline to belly button (to confirm usage).
They started rolling in and here are the gems she unearthed :
- A small portion of her customers were husbands buying a discreet gift for their wives/girlfriends, but most (85%) were transgender folks in transition.
- For the vast majority of her cis-female customers, larger breasts had more to do with enhancing self-esteem/identity and filling out clothes than attracting mates.
- Almost 100% really hammered down on the fact her cream was all-natural, organic and didn’t cause irritation or allergic reactions.
She went back and dusted off her original copy she put together years before.
From: “ A certified organic breast enlargement cream. ”
To something more along the lines of: “ Increase confidence and femininity through an organic non-allergenic breast enlargement cream. ”
When stuck in a rut, and we all get there as entrepreneurs, the quickest and most effective way out is to look at your predicament from different perspectives.
Begin with the fundamental question, “What problem does my product/service solve for customers?” then look deeper and from unique angles. Who are your buyers? They have the answer. And remember, actions speak louder than words.
Oftentimes we rationalize buying things for one reason, but in reality have a more potent ulterior motive. Sure, her customers want larger breasts, that’s what prompt initial sales. But the needs her product solves in their day-to-day lives are more interesting. It actually made her customers feel more confident, happy, and healthy.
Find one deeper way your product or service materializes in everyday life for your customers. Pay close attention to the simple verbiage you and others use to describe it, e.g. “Your earphones really get rid of all the noise on the bus.”
If possible, get hold of one fresh buyer perspective. Who and where are they? That woman in our example had spent years excluding nearly half her customer base in her advertorial copy. Do you use your own product or service? If so, find a way to record yourself explaining it in the most natural language possible. Use a smartphone or leave yourself a voicemail. Then, just listen.
But wait, what if you’re just starting out and don’t have much to draw on in terms of direct customer or user feedback? Glad you asked! In the next section we’re going to talk about competition, which is another valuable source of indicators.
Step 6) Leveraging Competition
What products and/or services are people choosing instead of yours?
Whether you’re new to the market or not, these so-called “competitors” are really the ideal source of optimization for your brand. And it’s not about being better per se. All things equal, it’s more about uniqueness.
Would you rather be a prettier, more flashy brand trying desperately to stand out, or develop intense brand-character that the right people notice? Once you’ve narrowed down your competitors, look at them from new angles to discover what makes you distinctive.
- Can they help you better define your target market/sub-markets?
- How effective are their social media marketing methods and website copy?
- What do you know about their buyers’ needs?
- What do they make “stand out” when shoulder to shoulder with your brand?
A common practice entrepreneurs use in pitch presentations to venture capitalists or investors is the Comparison Matrix.
You’ve seen these a zillion times. In short, list your competitors across the top of the page and your features and benefits along the side, then check the boxes for which company offers each. Don’t forget you can be creative here. You may even already use one of these on your website, or within some other marketing media.
- Could these features and benefits be communicated in different, more compelling ways?
- What real need-based copy is being left out?
- How can you simplify it? An easy way is to reduce the number of competitors, so shoot for less players with more interesting copy.
Got time to put something simple together? In reality what we’re looking for are the things about your competitors that help you stand out.
- Think about your biggest competitor: what do they make obvious about your brand?
- What are you doing with more personality from the perspective of ideal clients or customers?
- Could you take your primary competitor’s copy and make it clearer, or more optimized?
All in all, understanding your competition is an important part of the planning process. This is where you find your true competitive advantage.
For a more in-depth look at how you stand up to the competition, check out LivePlan's Benchmark feature. You can see at-a-glance how you compare to companies just like yours. Tell LivePlan your industry and location, and it shows if/how you're doing better or worse than your competition.
Now let's talk about your unique marketing approach. This will help you stand out and connect with your customers on multiple levels.
Step 7) Create a Marketing Plan
Fred is a brand spanking new entrepreneur with a neat new fitness product he believes is going to make a big splash.
He knows exactly who his ideal customers are and his niche is carved out like a Renaissance marble sculpture. Fred’s also managed to get his hands on $100k in debt-free funding (don’t ask us how, this is hypothetical)…
- His product costs exactly $32 to source, make and package.
- To be competitive, and account for shipping/processing, he’s going live at $55.
- Initial margin is about $13 per sale.
Admittedly, that would be pretty amazing, but that’s because we’re coming from a standpoint of experience. Fred’s just showing up to the 21st-Century party. He’s never built, owned, or managed a business before, let alone an ecommerce platform.
He’s never outsourced a graphic artist or content writer before; never had to choose which analytic dashboard to use; never designed a conversion model or tangled with paid advertising platforms. Let’s say Fred called and begged us to lunch. We accepted. And so there we are, the three amigos with Fred sitting on a huge meal ticket drooling for answers.
“ How Do I Market My Product? ”
Once the table conch gets passed to us, we’re going to hit him hard with massive bombshells:
- Tight responsive funnels can be constructed in a couple months with the right designer, or design agency (website, landing pages, ecommerce setup, branding packages, etc.).
- Initial market testing and adjustment can be bootstrapped.
- There are a variety of intuitive and relatively simple software tools, apps, plugins, add-ons, and cloud-based solutions that range from free to expensive.
- It takes a savvy mix of highly-focused content, social exposure and paid advertising.
- It takes a team.
Question is, what advice would you give Fred? That’s what we’d like you to consider. And it needs to be marketing-based. The money’s there, the production system’s in place, it’s just a matter of reaching his fitness-based audience and selling.
Let’s imagine Fred’s offered you a lifetime, no questions asked, 5% share of his company from now till doomsday. All you have to do is provide valuable direction in these three areas:
- Content : What kind of content should he invest in? Blogs, video, infographics, imagery, etc.
- Social : How to handle social media if he a) doesn’t have the time, b) has no clue what works?
- Paid Advertising : AdWords? Facebook? TV? Magazine ads? How does he get to buyers?
Just let your mind wander, and don’t worry, in the next section we’ll talk about setting milestones for your business.
Step 8) Set Milestones
If there’s one specific part of the entrepreneurial journey that we get really nerdy about, it’s the way people verbally describe their trials and successes. We’re listening intently for clues as to how they set milestones and metrics and then track them.
Let's spend some time pondering the way(s) you’re measuring your journey and how you approach KPIs (key performance indicators) in relation to both your marketing and your competition. Or, if you’re trying to figure out how viable a product idea is, how you’re calculating acceptable setbacks and struggle.
What have you achieved so far and what are your major goals for the next few months or years?
Sure, it’s cliché to talk about tracking milestones in an era of big data, but truth be told too many aspiring entrepreneurs either skip this part until much further down the road when it can’t be ignored anymore, or they only take it seriously in the beginning then fail to stick to the plan.
Avoid Drowning Out Customer Journey!
Of course there are folks who obsess on this part and try to manage a small army of analytic dashboards and amazing software solutions like FreshBooks or Xero.
Once it becomes too much they end up transforming their perspective of the customer journey from something organic into a mesh of math and graphs. Most of their day is spent pouring over dense numbers or marketing data and trying to figure out how to alter this metric or that.
- How many of your milestones are focused entirely on your customers instead of you and your business?
- Instead of views, likes, and shares, what about the amount of service calls you’re getting? How many people are actually reaching out with questions and concerns?
- How well do your metrics allow you to understand each part of their trek from initially discovering your business to making a purchase?
Find ways to do more with less data. It’s always within reach these days, especially when you’re tuned in to your customers!
- Find one way to streamline how you’re dealing with milestones/metrics, or how you intend to.
- Also, look for one single way to be more holistic in your approach to setting goals.
- Find a part of your customer journey/behavior and decide if current metrics help or hinder it.
Need help in this area? LivePlan has a really impressive dashboard to help you set goals and stay accountable over the lifetime of your business. This dramatically increases your chances of success.
Step 9) Refine Aquisition Costs
Without question, failure to clearly know the cost of acquiring customers is a mighty new business demolisher. It’s crushed more entrepreneurial dreams than every economic collapse combined since the creation of fiat currency. To come to grips, or optimize your Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC), begin by figuring out exactly how you’re reaching customers.
Or, if you’re building an initial business plan, how much will it cost to reach buyers on the platforms where they spend their time? Your financials should easily allow you to calculate CAC.
Now, in the simplest terms here’s how:
- Take (estimate) the entire cost of sales and marketing over whatever period of time you’re dealing with, for example when forecasting sales and financials. Make sure to include salaries and any other headcount-related costs.
- Divide that number by the amount of buying customers/clients/users that were acquired within this time.
If you happen to run a purely web-based business, headcount likely doesn’t need to grow as you scale customer acquisition, but it’s a useful metric to include nonetheless.
The second part of this is your Lifetime Customer Value, or LCV, because in most cases 80% of your revenue will come from 20% of overall customers and happen AFTER the initial sale. Never shortchange the follow-through!
If your CAC is too high, it must be able to come down through optimization. If LCV is horrid, then in the long run it’s an unsustainable business model. Or in other words, once CAC exceeds LCV, something needs to change or you’ll have to close shop.
- Begin looking at one stream of cost per lead. So for example, maybe a Google AdWords or Facebook advertising campaign.
- What’s one single way you could get more in touch with a hot-spot within your customers’ buyer experience?
- Let your mind stew a little on the level of ‘touch’ required to increase LCV. How can you up-sell or generate more revenue from each customer long term?
After you make these calculations three or four times, it starts becoming second nature. LivePlan's forecasting handles this pretty well. It walks you through creating expenses that are a certain percentage of sales.
Step 10) Forecast Sales
Smart entrepreneurs start forecasting sales early on.
And while ‘the numbers’ part of business planning can be intimidating, this exercise is definitely a small mountain worth karate chopping down.
Keep in mind that if you get stuck at any point, LivePlan's Forecasting and Budgeting feature is extremely helpful. Whether you're starting a bakery, a subscription software business, or a manufacturing company, LivePlan walks you through the entire forecasting process within a few clicks.
How Detailed Does it Need to Be?
Don’t be too generic and just forecast sales for your entire business. But on the other hand, don’t go nuts and create a forecast for everything you sell if you’ve got a large assortment.
For example, if you’re starting a restaurant you don’t want to create forecasts for each item on the menu.
Instead, focus on broader categories like lunch, dinner, and drinks. Or if you’re starting a clothing brand, forecast key categories like outerwear, casual wear, and so on.
Top-Down or Bottom-up?
In our humble opinion, forecasting “from the top down” can be costly. What that means is figuring out the total size of the market you’re in and trying to capture a small percentage.
For example, in 2015, more than $1.4 billion smartphones were sold worldwide. It’s pretty tempting for a startup to say they’re going to get 1% of that total market. After all, 1% is such a tiny little sliver it’s got to be believable, right?
The problem is this kind of guessing isn’t based on reality. Sure, it looks like it might be credible on the surface, but you have to dig deeper.
- What’s driving those sales?
- How are people finding your new smartphone company?
- Of the people that find out, how many will buy?
Instead of “from the top down,” do a “bottom-up” forecast. Just like the name suggests, bottom-up starts at the bottom and works its way up to a forecast. Start by thinking about how many potential customers you might be able to make contact with.
This could be through advertising, sales calls, or other marketing methods. Of the people you can reach, how many do you think you’ll be able to bring in the door or get onto your website?
And finally, of the people that come in the door, get on the phone, or visit your site, how many will buy?
Here’s an example:
- 10,000 people see my company’s ad online,
- 1,000 people click from the ad to my website,
- 100 people end up making a purchase.
Obviously, these are all nice round numbers, but it should give you an idea of how bottom-up forecasting works. The last step of the bottom-up forecasting method is to think about the average amount that each of those 100 people in our example ends up spending (remember LCV).
On average, do they spend $20? $100? It’s fine to guess here, and the best way to refine your guess is to go out and talk to potential customers. You’ll be surprised how accurate a number you can get with a few simple interviews.
How Far to Forecast
Try forecasting monthly for a year into the future and then just annually for another three to five years.
The further your forecast into the future, the less you’re going to know and the less benefit it’s going to have for your company. After all, the world’s going to change, your business is going to change, and you’ll be updating your forecast to reflect them.
And don’t forget, all forecasts are wrong—that’s fine. Your forecast is just your best guess at what’s going to happen. As you learn more about your business and your customers, you’ll adjust. It’s not set in stone.
- First, remind yourself that ALL forecasts are wrong. Forecasting is more about learning and evolving.
- Without adding too much to your plate, take a look at your monthly sales chart and see what kinds of optimizations forecasting might bring to light. If you aren’t already charting sales, start today or begin planning how.
- Try two easy bottom-up projections with nice round numbers to get the feel for it.
Just remember that sales forecasting doesn’t have to be hard. Anyone can do it and you, as an entrepreneur, are the most qualified to do it for your business. You know your customers and you know your market, so you can forecast your sales.
But if you decide you'd appreciate help, we highly recommend forecasting your sales with LivePlan. LivePlan automatically generates all the charts and graphs you need and automatically includes them in your plan.
Wrapping Up: Formatting Your Plan
The format of your business plan is critical. It goes a long way toward refining and achieving your goals: raising money, setting the strategy for your team and growing your platform. That being the case, let's breeze through seven tips that can help you create, refine, and optimize your brilliant business plan.
1. Always Start with Your Executive Summary
An ES should be written for ideal readers, customers, potential investors or team members, or even just to help you ‘goal-map’ your way to where you need to be. Regardless, nailing the Executive Summary is critical in terms of understanding the potential behind your business idea.
2. End with Supporting Documents
The appendix is composed of key numbers and other details that support your plan. At a minimum, your appendix should include financial forecasts and budgets. Typically, it’s wise to include a Profit & Loss statement, Cash Flow forecast, and a Balance Sheet. With practice and a smidgen of savvy software like LivePlan these pages can take a couple hours or so.
You might also use your appendix to include product diagrams or detailed research findings, depending on your business, your industry, and how deep your business plan needs to go given the reader/purpose.
Quick Recap of the Lineup Pitch Executive Summary Products & Services Target Market Marketing & Sales Plan Milestones & Metrics Company & Management Team Financial Plan & Appendix
3. Keep it Short
Let’s face it: no one has time to read a 40-page business plan. If you’ve nailed your ES, you’ll want to follow up with 8 to 12 additional pages at most in support. Instead of trying to cram everything in using small fonts and tiny margins, focus on trimming down your writing (‘kill your darlings’). Use direct, simple language that gets to the point.
4. Get Visual
As the old adage goes, “ A picture is worth a thousand words. ” This is especially true when you’re formatting a business plan. Use charts and graphs to explain forecasts. Add pictures of your product(s). Again, there are plenty of software solutions that make it easy to do more showing and less telling. That said…
5. Don’t Obsess on Looks
It’s your ideas that matter. A beautiful plan that talks about an ill-conceived business with incomplete financial forecasts is never going to beat a plan that’s formatted poorly but discusses a great, clearly explained vision. Spending days making a beautiful plan isn’t going to make your business ideas better. Instead, focus on polishing the words. Trim extra content you don’t need, and make sure ideas are well-presented.
6. Keep Formatting Simple
- For general formatting use single spacing with an extra space between paragraphs.
- If you’re printing your plan, use a nice serif font like Garamond or Baskerville.
- If your plan will mostly be read on a computer screen, go with a sans serif font like Verdana or Arial.
Why choose different fonts for on-screen versus off-screen? Well, research shows readers have higher comprehension when they read a document with a serif font on paper, and higher comprehension reading with a sans serif font on a screen.
Don’t stress too much about this, though. Choose any one of the four fonts mentioned above and move forward.
- For font size, 10 to 12 point is usually ideal and readable for most people. If you need to reduce the font size to make your plan shorter, then you should be cutting content, not adjusting the font size.
- The same rule goes for margins: use typical one-inch margins to make the plan readable.
Cover pages are always a good idea, too. Use the cover page to show off your logo, tagline, and pitch.
Finally, make sure your plan document flows well and doesn’t have any “widows” or “orphans” when it prints out. A “widow” is when the last line of a paragraph appears alone at the top of a page, and an “orphan” is a single word that gets left behind at the bottom of a paragraph.
7. Get a Second Pair of Eyes
The last piece of advice is to get a second pair of eyes. When you’re the only one working on your plan, you can become blind to common errors. Recruit a friend or family member, or even hire a copy-editing professional to give it that last bit of polish. There’s nothing worse than a plan with grammatical or spelling errors. A second pair of eyes will go a long way toward catching the majority of those potential problems or holes.
- Who’s your second, third, and possibly fourth pair of eyes going to be?
- What’s one part of your business plan you could optimize today?
- What’s one piece of visual content you could add to your appendix?
Exclusive Bonus
If you'd like to try LivePlan yourself, here's an exclusive 50% off LivePlan promo code offered to our readers. You'll have 60 days of risk free planning with their 100% money back guarantee. Enjoy!
Featured Articles

The Top 7 LLC Formation and Incorporation Services

How to Form an LLC

What is an LLC?

Business Plan Development
Masterplans experts will help you create business plans for investor funding, bank/SBA lending and strategic direction
Investor Materials
A professionally designed pitch deck, lean plan, and cash burn overview will assist you in securing Pre-Seed and Seed Round funding
Immigration Business Plans
A USCIS-compliant business plan serves as the foundation for your E-2, L-1A, EB-5 or E-2 visa application
Customized consulting tailored to your startup's unique challenges and goals
Our team-based approach supports your project with personal communication and technical expertise.
Pricing that is competitive and scalable for early-stage business services regardless of industry or stage.
Client testimonials from just a few of the 18,000+ entrepreneurs we've worked with over the last 20 years
Free tools, research, and templates to help with business plans & pitch decks
Writing a Solid Business Plan: Fundamentals and Principles
I’ve worked as a business plan writer since 2006, and it’s been a remarkably fun and fulfilling career for me. I get to see entrepreneurs of all sorts, from all over the world, live out their dreams.
When I’m out and about meeting people in the real world, I don’t dread the question, “What do you do for a living,” like some people do, because I love talking about what I do for a living.
But what I am quite used to is the blank stare that I tend to get, and the follow-up question, “What does that mean?” Other people nod their heads knowingly, especially if they have some experience with business or finance, but once they ask subsequent questions I realize they’re thinking of something completely different. So, I thought it might be helpful to talk about the top questions the Masterplans team gets about business plan writing and what happens when you hire a business plan writer.
What even is a business plan?
The most basic possible question, and what people really mean when they ask me what my job title really means. I love to answer this question, except when I’m trying to explain it to relatives in Greece, or my Spanish-speaking friends! My second- and third-language skills are not strong enough to begin to explain what a business plan is. But, when I try to explain it to them, I break it down into the simplest terms, so maybe that’s the best place to start here. I do this with a series of questions and statements that go like this:
- Have you ever thought about starting your own business? (Inevitably, the answer is yes)
- Well, when you want to start your own business, you will probably need to apply for a loan, or ask an investor for funding. (People nod at this one… I’ve still got their comprehension).
- When you do that, you need to present a document that tells all about the business you’re starting. I write that document.
And bingo, we have a basic level of understanding of what I do. But of course, it’s so much more complicated than that . A traditional business plan is made up of a complete outline of topics and sub-topics that any entrepreneur needs to be able to answer. It’s not always about funding either, even though that’s how I present it to friends. The truth is that every entrepreneur needs a business plan, even if they’re bootstrapping the project out of their own pocket.
In actuality, a business plan is a comprehensive document that explains the details about your business, sets goals and objectives, and guides you going forward. That said, if you are pursuing funding like most entrepreneurs, your document needs to cover a range of required topics.
Let’s take a look at the SBA requirements for the sections that need to be in a business plan:
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Market Analysis
- Organization and Management
- Service or Product line
- Marketing and Sales
- Funding request
- Financial projections
- Appendix (optional)
However, this is an overly broad listing, which doesn’t include many of the sub-sections that are involved. For example, at Masterplans, our Market Analysis covers a variety of sub-sections like Market Segmentation, Market Need, Industry Analysis, Competitive Comparison, and Competitive Edge.
Part of being a good business plan writer means understanding what goes within each section and keeping the content organized into the appropriate area. Some customers have a hard time keeping straight the difference between the "Competitive Comparison" and the "Competitive Edge" sections, but they are quite distinct. Or, it can be tempting to talk about who your customers are in the "Market Analysis" instead of the "Market Segmentation." I’ve even had people mix up marketing tactics with products or services. It takes an experienced hand to keep the content organized.
What is the purpose of a business plan?
A business plan’s highest purpose is to guide entrepreneurs in operating their business on the day-to-day level. It is a foundational document that I think of as the constitution of your business. It tells you everything you need to know about your idea, your goals, your strategy, and the financial picture of a business.
Here at Masterplans, we strongly believe that entrepreneurs need to understand that a business plan is not a one-time use product, like applying for a business loan. Instead, we want our clients to use their business plan all the time, for years into the future, as long as the business exists. It should guide board meetings and management decisions. Your employees should read it so that they understand what your mission is, what steps you need to take to achieve success, and what their role is within your company.
But we admit that there are those one-time, single-serving uses for a business plan that will likely come up for you. You need it to apply for a bank loan. You need it to ask for investment. You need it when applying for a lease on a location. You often need it when applying for certain permits, especially those dealing with compliance issues. And for those of you who are foreign investors seeking a visa , you need it to include in your application packet to USCIS.
Thus, a comprehensive business plan needs to be able to not just guide you in your daily decision-making, but it also needs to answer all the questions that an outside party might ask you when deciding whether to fund your idea or let you lease their space.
Who should write a business plan?
Why, the entrepreneurial team should take the helm in writing a business plan, of course. Did you expect a different answer from a professional business plan writer? At Masterplans, we don’t shy away from delivering honest truth to our clients, because we thrive when they thrive.
The truth is that an entrepreneur who isn’t intimately involved in the writing of their business plan from the start will never fully understand it, and that can hamper them on their path to achieving their goals. It’s imperative that an entrepreneur have a deep understanding of their business plan, or else they won’t be able to follow it!
But, writing a business plan is an intense endeavor that requires a better-than-average command of English writing and style, as well as business theory and financial modeling. Very few people represent the total package, which is why at Masterplans, we work in teams of specialists who together have those skills.
I can write a beautiful market analysis summary, analyze your competitive landscape in-depth, and wrap it all up with an attention-grabbing executive summary, but don’t ask me to explain a complex financial concept like Internal Rate of Return. (I’m being modest; I can tell you all about it, but I’ll leave that to our brilliant financial modelers who understand it in more depth than I do.)
While some entrepreneurs may somehow possess the bare minimum of skills that are required to create a decent business plan, they most certainly don’t have the time. Starting a business involves numerous steps, and entrepreneurs are often pursuing each of those steps while juggling a full-time career and sometimes a family. It’s a lot.
But a key quality shared by the best leaders is knowing when and what to delegate. If you have a dual major in English and Business, and you’ve done this a few times before, then sure, you could probably write a stellar business plan from scratch.
But if you have virtually any other combination of experience, you could benefit greatly from delegating it to a company like ours that can counsel you every step of the way, scheduling out the project into meetings and discrete tasks so that you can be as involved as you should be in the process while still freeing up your time to handle the many other to-dos on your plate. (This benefit still holds true for the dual major, as well!)
Remember, the most important thing is that the business plan actually gets done so that you can use it to start your business, but like any long writing project, it can fall to the wayside when life’s pressures get in the way. Working with a deadline-driven consultancy like ours can help you reach the finish line.
Now that you have a basic introduction to the traditional business plan document, you probably have plenty of questions that go deeper. We’ve done our best to address those with our frequently asked questions about writing business plans .

How to Write a Management Summary for Your Business Plan
Entrepreneurs are often celebrated for their uncanny ability to understand others – their customers, the market, and the ever-evolving global...

Understanding Venture Debt vs Venture Capital
Despite growth in sectors like artificial intelligence, venture capital funding has seen better days. After peaking at $347.5 billion in 2021, there...

Going Beyond Writing: The Multifaceted Role of Business Plan Consultants
Most people think of a professional business plan company primarily as a "business plan writer." However, here at Masterplans, we choose to approach...
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write a Business Plan

Alice Musyoka

Dwight Eisenhower once said, "Plans are worthless, but planning is essential." A business plan is crucial to your company's success.
According to the Small Business Administration (SBA) , 80% of small businesses survive the first year. However, only 50% of businesses survive past the 5-year mark. It gets worse. Only one in three small businesses reach the 10-year mark.
We know the last thing you want to hear when you're starting a new business or expanding your current business is tales of failure, but for many businesses, failure is the reality. And the primary cause of failure is lack of planning.
Businesses fail for different reasons: insufficient financial planning, poor management, inadequate market research, lack of social media presence, and other reasons. All these mistakes are brought on by a lack of planning that can be traced to the company's roots—where the business plan is found.
Before we show you how to write a business plan, we'll start by explaining what a business plan is.
What Is a Business Plan?
Writing your business plan: the eight most crucial sections, tips for writing a business plan, keep it short, polish the business plan to improve its overall look, don't be intimidated when writing a business plan.
It is a document that summarizes the financial and operational objectives of a business. It contains detailed budgets and plans that show how the objectives will be realized. You can think of a business plan as a roadmap to your business’ success. It is a vital tool for anyone starting—or expanding—a business.
Before you create a business plan, it is important to ask yourself the following questions:
- Why am I starting/expanding this business?
- What makes my business different? What is its competitive edge?
- What solution is my company providing?
- Who makes up my company (your management team, key players, and advisors)?
- Who are my customers?
- What must happen for my business to break even?
- How can my business start making profits?
While there are a lot of industry-specific questions you should ask, pay attention to these ones when you're getting started. Be sure to address them in your business plan in a clear, concise, and realistic way.
1. Executive Summary

Here, you briefly explain what your company does and why it will be successful. This is where you include your mission statement, the product or service, and brief information about the company's leadership team, its employees, and its location. If you're asking for financing, include the financial information and the growth plans.
You can write the executive summary first or last as it highlights the points you've made in other sections of your business plan. It is the doorway to your plan. After going through it, the reader may either decide to keep reading or to throw the business plan away. You have to get it right.
2. Company Description
This is where you give detailed information about your company. The company description gives an in-depth overview of your proposed venture.
Write about the problems your business will solve in detail. Be very specific and list the organisations and consumers your business plans to serve. Boast about your business’ strengths.
Does your business have any competitive advantages that will play an important role in making it a success? Are there industry experts on your team? Do you have a perfect location for your business? Include that information here.
3. Market Analysis
You need to have a good understanding of your target market and how it is continually changing. What are successful competitors doing differently? Why is it working? Are you sure there's room for you in this market?
Here is where you answer these questions. You should also use this section to discuss your customers’ needs, where they are, and how you plan to reach them and deliver your products to them.
4. Business Organization and Management
Tell the reader how your business will be structured and who will operate it. Describe the company's legal structure and state whether you plan to incorporate it as an S corporation or C corporation. Explain whether you'll be a sole proprietor or a limited liability company (LLC) and whether you’ll form a limited or a general partnership.
Include an organizational chart that shows who is in charge of what in your company. Explain how each individual's unique experience will play a role in the success of your venture. You can also include the CVs of the key team members.
5. Product or Service Development Plan
Describe the product you're selling or the service you're offering. What is the life cycle of the product? How does it benefit your customers? Share the plans you have for intellectual property—such as patent or copyright filings. If you're still doing research and development for the product or service, explain that in detail.
When describing the product, focus on the customer benefits. Also include details about the suppliers, the costs related to the product or service, and the net revenue expected. You can add pictures and diagrams in this section to help readers visualize.
6. Marketing and Sales Plan

When it comes to marketing, no single approach works permanently. Create a marketing strategy that fits your unique needs. Explain how you will attract and retain customers and how sales will actually happen.
This section is important as you'll refer to it when making financial projections. Be sure to thoroughly describe all your marketing and sales strategies. You should focus on the solution your business is offering and the customers’ buying behaviour. Explain the value that each customer will bring to the business.
7. Financial Plan or Funding Request
At the very least, this section must include a projected profit and loss statement and cash flow tables. You should also explain why you're making those projections. Include the break-even analysis, sales forecast, balance sheet, and business ratios in this section. Convince the reader that your business will be a financial success.
If you're asking for funding, outline your funding requirements. Explain clearly how much funding you will need and what you will use the money for. State whether you want equity or debt, the terms you would like applied, and the time period your request will cover.
8. Appendix
Use this section to provide supporting documents and any other materials you've been asked to provide. Some items that commonly feature in this section are credit histories, letters of reference, product pictures, resumes, patents, permits, licenses, legal documents, and other contracts.
Know Your Audience
When writing a business plan, use language that your audience will understand. For instance, if your company is developing complex software but your prospective investors are not very knowledgeable in IT matters, don't use technical language or acronyms they won't understand.
Most people won't sit down to read your business plan. They will read it as they go through their email or talk on the phone. Be accommodating and explain your product in a simple and direct manner, using terms that can be understood by everyone. If you want to provide the full specifications, include them in the appendix section.
Here are some useful tips:
- Use simple words: instead of "utilize" write "use," instead of "at that point in time" write "then"
- Avoid long, complicated sentences: short sentences are easier to read and digest
- When adding lists, use bullet points: you can flesh them out with short explanations as needed

Business plans are shorter now than they used to be. This could be because they are more common now or because investors have little time to waste wading through documents.
Cover everything you want to convey in 20–30 pages of text. Include another 10 pages for management resumes, monthly projections, and other details. If your business plan is longer than 40 pages, you are not summarizing very well.
You should keep your business plan short for two major reasons. Firstly, investors are busy: no one is going to read a 100-page business plan. Secondly, your business plan is a tool you use to run and grow your business. It is something you'll continue to use and refine over time. If it is too long, you'll have a very hard time revising it.
Besides using the right wording, use text that is simple and inviting. The right images can also help win over investors.
This is what you should do:
- If you have products whose features are difficult to explain in words (or if their appearance is important), include images in the appendix section. Product photos taken by a professional photographer can help investors to understand what you're talking about.
- Only use two fonts for the text. A simple font such as Tahoma, Verdana, or Arial works well for headings. For the body text, use a standard text font like Times New Roman, Book Antigua, or Century.
- Use page breaks to separate charts from text, to separate sections, and to highlight tables.
- Avoid cramming words together and use white space liberally. White space makes your content easily scannable and significantly improves legibility.
- Use a grammar checker like ProWritingAid . The app can also proofread your text and let you know if you're using properly spelled words incorrectly.
Preparing a business plan may seem like a huge undertaking, but it doesn't have to be. No one knows your business like you do—you're the expert. That single reason makes you the best person for the job.
Set aside some time to write your business plan. It's not as challenging as you think.
Want to learn more more great business writing hacks? Download this free book now:

Business Writing Hacks for Flawless Communication
Writing is an essential element of nearly every profession today. whether you are drafting a proposal for a major prospect or collaborating by email, strong communications help colleagues and clients understand your ideas. errors and awkward writing can make you lose credibility., download this guide to learn the techniques professional writers use to write clearly and persuasively..
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Alice Musyoka is a versatile copywriter and content strategist who helps businesses see results from content marketing. Her goal is to make people pause, smile, and read. She's a previous contributor for [Stagetecture](https://stagetecture.com/author/ndanuaj123/). When she's not working, she usually goes for long walks with her son and reconnects with nature. She also loves watching funny movies.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
6 Reasons You Really Need to Write A Business Plan
Published: October 14, 2020
Starting a busine ss can be a daunting task, especially if you’re starting from square one.

It’s easy to feel stuck in the whirlwind of things you’ll need to do, like registering your company, building a team, advertising, the list goes on. Not to mention, a business idea with no foundation can make the process seem incredibly intimidating.
Thankfully, business plans are an antidote for the new business woes that many entrepreneurs feel. Some may shy away from the idea, as they are lengthy documents that require a significant amount of attention and care.
However, there’s a reason why those who take the time to write out a business plan are 16% more likely to be successful than those who don’t. In other words, business plans work.

What is a business plan, and why does it matter?
In brief, a business plan is a roadmap to success. It's a blueprint for entrepreneurs to follow that helps them outline, understand, and cohesively achieve their goals.
Writing a business plan involves defining critical aspects of your business, like brand messaging, conducting market research, and creating pricing strategies — all before starting the company.
A business plan can also increase your confidence. You’ll get a holistic view of your idea and understand whether it's worth pursuing.
So, why not take the time to create a blueprint that will make your job easier? Let’s take a look at six reasons why you should write a business plan before doing anything else.
Six Reasons You Really Need To Write a Business Plan
- Legitimize your business idea.
- Give your business a foundation for success.
- Obtain funding and investments.
- Hire the right people.
- Communicate your needs.
- It makes it easier to sell your business.
1. Legitimize your business idea.
Pursuing business ideas that stem from passions you’ve had for years can be exciting, but that doesn’t necessarily mean it’s a sound venture.
One of the first things a business plan requires you to do is research your target market. You’ll gain a nuanced understanding of industry trends and what your competitors have done, or not, to succeed. You may find that the idea you have when you start is not likely to be successful.
That may feel disheartening, but you can always modify your original idea to better fit market needs. The more you understand about the industry, your future competitors, and your prospective customers, the greater the likelihood of success. If you identify issues early on, you can develop strategies to deal with them rather than troubleshooting as they happen.
It’s better to know sooner rather than later if your business will be successful before investing time and money.
2. Give your business a foundation for success.
Let's say you’re looking to start a clean beauty company. There are thousands of directions you can go in, so just saying, “I’m starting a clean beauty company!” isn’t enough.
You need to know what specific products you want to make, and why you’re deciding to create them. The Pricing and Product Line style="color: #33475b;"> section of a business plan requires you to identify these elements, making it easier to plan for other components of your business strategy.
You’ll also use your initial market research to outline financial projections, goals, objectives, and operational needs. Identifying these factors ahead of time creates a strong foundation, as you’ll be making critical business decisions early on.
You can refer back to the goals you’ve set within your business plan to track your progress over time and prioritize areas that need extra attention.
All in all, every section of your business plan requires you to go in-depth into your future business strategy before even acting on any of those plans. Having a plan at the ready gives your business a solid foundation for growth.
When you start your company, and your product reaches the market, you’ll spend less time troubleshooting and more time focusing on your target audiences and generating revenue.
3. Obtain funding and investments.
Every new business needs capital to get off the ground. Although it would be nice, banks won’t finance loans just because you request one. They want to know what the money is for, where it’s going, and if you’ll eventually be able to pay it back.
If you want investors to be part of your financing plan, they’ll have questions about your business’ pricing strategies and revenue models. Investors can also back out if they feel like their money isn’t put to fair use. They’ll want something to refer back to track your progress over time and understand if you’re meeting the goals you told them you’d meet. They want to know if their investment was worthwhile.
The Financial Considerations section of a business plan will prompt you to estimate costs ahead of time and establish revenue objectives before applying for loans or speaking to investors.
You’ll secure and finalize your strategy in advance to avoid showing up unprepared for meetings with potential investors.
4. Hire the right people.
After you’ve completed your business plan and you have a clear view of your strategies, goals, and financial needs, there may be milestones you need to meet that require skills you don’t yet have. You may need to hire new people to fill in the gaps.
Having a strategic plan to share with prospective partners and employees can prove that they aren’t signing on to a sinking ship.
If your plans are summarized and feasible, they’ll understand why you want them on your team, and why they should agree to work with you.
5. Communicate your needs.
If you don’t understand how your business will run, it’ll be hard to communicate your business’s legitimacy to all involved parties.
Your plan will give you a well-rounded view of how your business will work, and make it easier for you to communicate this to others.
You may have already secured financing from banks and made deals with investors, but a business’ needs are always changing. While your business grows, you’ll likely need more financial support, more partners, or just expand your services and product offers. Using your business plan as a measure of how you’ve met your goals can make it easier to bring people onto your team at all stages of the process.
6. It makes it easier to sell your business.
A buyer won’t want to purchase a business that will run into the ground after signing the papers. They want a successful, established company.
A business plan that details milestones you can prove you’ve already met can be used to show prospective buyers how you’ve generated success within your market. You can use your accomplishments to negotiate higher price points aligned with your business’ value.
A Business Plan Is Essential
Ultimately, having a business plan can increase your confidence in your new venture. You’ll understand what your business needs to succeed, and outline the tactics you’ll use to achieve those goals.
Some people have a lifetime goal of turning their passions into successful business ventures, and a well-crafted business plan can make those dreams come true.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![is writing a business plan hard How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![is writing a business plan hard 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![is writing a business plan hard The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
When Should You Write a Business Plan?

Noah Parsons
11 min. read
Updated April 10, 2024
When’s the right time to write a business plan? My favorite answer is from this proverb:
The best time to plant a tree was 20 years ago. The second best time is now.
Things are changing for business owners at a much faster rate. There’s an increasing level of uncertainty about the future and in order to survive and grow you need to plan now and plan often. The right kind of business planning is something that happens regularly and continues forever.
That’s because business planning is not just about producing a document. Instead, planning is an ongoing, repeating process that helps your business grow healthily. You create a strategy, build budgets, and set goals so that you can measure your progress and make changes when you need to.
Much like the proverb about the tree would imply, planning can be hard to get started. But if you understand the basics of the planning process it can be much easier than you’d think.
- When should you write a business plan?
As I said in the introduction, there’s really no wrong time to write a business plan. Whether you have a new business idea or your business has been up and running for years, putting together a plan is beneficial and necessary .
The real question is, what kind of planning should you do for the stage your business is in? Should a five-year-old business use the same business plan template as a new startup?
The answer is no. Planning isn’t one-size-fits-all. It’s about finding the right size plan for your business stage and needs.
Here are some common times when you should create a plan for your business along with recommendations on the right kind of plan for each specific situation:
When you have a new idea for a business
Figuring out if you can turn an idea into a business can be challenging.
Are your potential customers going to want what you are selling? Will you be able to make a profit? How much money will you need to get off the ground? What do you need to turn your side hustle into a full-time gig? At this stage, the most important thing you can do is write down a quick summary of your business idea using a one-page business plan . This will help you think about who your customers will be and create a rough sketch of what your business numbers look like. You can use a one-page plan to test your assumptions.
Are your customers who you think they are? Will they be willing to pay what you want to charge?
As you gather information, you can quickly revise your plan until you have a business plan and business model that works for turning your idea into a business. This kind of planning will help reduce your risk and get you started the right way, without investing too much time in the planning process.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
When you’re starting a business
If you’ve found product-market fit for your business idea, you’re ready to turn it into a business. You have evidence that your business fills a real need for customers and they’re willing to pay for your solution. This is when a more detailed business plan is useful. You’ll focus on building out revenue forecasts and more detailed expense budgets. This will help you understand what it’s going to take to get your business off the ground and sustain it through the early days. You’ll also expand your business plan to define your target market, detail your marketing and sales strategies, and solidify your operational plans.
When you’re seeking funding
If you need funding to get your business off the ground, you’ll need a thorough business plan with complete financial forecasts . Whether you’re seeking a loan or looking for investors—you’ll need to understand exactly how much money to ask for and how long that money will last as your business grows.
This is where having a cash flow forecast in place pays off. With this forecast, you can predict how much money you’ll need and when you’ll need it. Investors may never ask to see your actual business plan. But, they’ll definitely ask questions that you’ll only be able to answer if you’ve put one together.
They’ll want to know about your target market and market size, details about your competition, your sales and marketing plans, and more. This is all in addition to your financial forecasts. If you’re looking for a loan, many lenders require a business plan as part of the loan application process. Having a polished and impressive plan can even help with the loan process, even though loans are most often made based on the collateral you have rather than the quality of your business idea.
When business conditions are changing
We live in a world of uncertainty. Supply chains get disrupted , the labor market changes, and the price of materials is always shifting. If you think your industry or your market is headed for a significant shift, it’s a good idea to make sure you have a plan in place. This kind of planning focuses on a shift in strategy. Will your marketing and sales strategies change? What expenses will you shift around? How will potential changes in future revenue impact your business and do you have the cash on hand that you need to weather the changes? Planning for change often involves running different financial scenarios and documenting different strategic directions your business may take. Having an initial business plan to base these adjustments on will make the process easier.
When you’re growing your business
Growth should certainly be celebrated, but it often comes with its own significant challenges. For businesses that make and sell products, managing inventory and handling rapidly increasing orders can create a cash crunch. That’s where planning for growth comes in, specifically focused on cash flow . The right kind of planning will help you ensure that you can handle fast growth and give you the time to line up any additional funding you need— before you need it.
When you want to run a healthy business
Most people think of business planning only when they’re starting a business or seeking funding. The reality is that it’s a crucial component of running a business. Just like with personal finance, it’s important to have a budget and revenue goals and then track how things are going on a regular basis. This kind of ongoing planning —where you build a financial forecast and budget and then track your progress as you go—helps you spot problems before they happen and find opportunities for growth that you might have missed. This planning is called growth planning and helps you run your business better.
When you’re buying or selling a business
If you’re buying a business, you’ll want to get a good look at the books before you make a purchase decision. You can use the business’s accounting data and historical performance to create forecasts for future profits and cash. And, if you plan on investing more into the business, you’ll need a plan to know when you’ll be able to recoup your investment. If you’re selling a business, a strong business plan is a valuable sales tool. The business plan explains to prospective buyers how the business works and what the buyer can expect regarding revenue, profits, and cash flow. The more clearly laid out your business operations and performance are for the buyer, the smoother your exit will be.
- Is there a best time to write a business plan?
As an entrepreneur, you have a vision for your business and the drive to turn that vision into a reality. A business plan can certainly help with that. But when is the best time to write one? The answer, like so many things in business, is that it depends.
A recent Harvard Business Review study found that business planning had the most positive impact on businesses when the business plan was written between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business. In fact, planning at this stage increased the chances of success by 8%.
I’ll add a caveat to this study, though. The study did not look at the types of business plans that were written at the different stages of business.
If all of the business plans were in-depth, comprehensive, and detailed, they certainly wouldn’t have as much impact at the idea stage as they have later on in the startup process. Doing detailed planning a bit later in the game makes sense. Detailed planning early on is really a waste of time.
That’s why we recommend a different approach: start with a simple one-page business plan in the beginning, and then expand to a more detailed plan only as you need it.
After you’ve validated your business idea and are in startup mode, a more detailed plan makes sense. You need to explore and understand your operational plan , detailed marketing plan, budgets, and financial forecast.
When you’re fully up and running with a business model that works and a few years of experience under your belt, your planning may simplify again . Planning for established businesses tends to focus mostly on financial management and less on documenting target markets and operations.
This type of flexible and right-sized planning is most likely to have a positive impact throughout the lifecycle of your business. So, instead of waiting for the exact right time to start planning, start with the right kind of planning based on your business stage.
- When can you skip writing a business plan?
There are some situations where writing a business plan may be unnecessary. For example, if you’re starting a very small, simple business that doesn’t require any kind of significant investment, you might be able to get by without a formal plan.
However, even in these cases, it’s still a good idea to take the time to think through your business and write down your goals and strategies. A one-page plan is perfect for these situations and won’t take long to write.
- How long should you spend writing your plan?
The amount of time you should spend writing a business plan depends on several factors—including the size and complexity of your business, and how much detail you need in your plan. On average, it can take anywhere from several weeks to several months to write a comprehensive business plan.
That said, planning doesn’t have to take that long and shouldn’t for most businesses. In fact, a useful one-page plan can be put together in under an hour . You can then add more detail in as little as a day. Then plan to expand your plan as you go, based on what you’ve learned from actually building your business.
Just don’t get too bogged down in the details of planning. The goal of a business plan is to help you focus on what’s important and give you a roadmap for success, not to create a document that will sit on a shelf and collect dust.
So, spend enough time to create a useful plan. Don’t get so caught up in the process that you lose sight of your ultimate goal: building a successful business.
A final word of warning: don’t fall into the trap of letting planning go on for months.
Any time spent planning beyond 3 months is generally a waste of time because your information gets stale. You also miss out on building your business and learning what does and doesn’t work. You’re just stuck in a planning cycle without any results to review and build upon.
- The ideal time to write a business plan is now
Writing a business plan can be a valuable tool for entrepreneurs at any stage of their journey. The key is to write the kind of plan that your business needs for the stage your business is in.
Planning should always start small: What problem are you solving ? Who are you solving it for? Can you make money doing it?
If you can start to answer these questions, you have a business that can work. From there, flesh out the details as needed. If you’re raising money, you’ll need a more detailed plan. If not, focus on a plan that has the details you need to help you achieve your goals.
Whether you write your plan before opening your doors or after you’ve been in business for a while, the important thing is to have a plan that you use to guide your business to success. A good business plan is all about good management—and that’s what all long-lasting businesses need.
If you need additional guidance, check out our roundup of the best free business plan templates .
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
11 Key Components of a Business Plan

How Long Should a Business Plan Be?

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes

5 Min. Read
Business Plan Vs Strategic Plan Vs Operational Plan—Differences Explained
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Updating a Classic: Writing a Great Business Plan
- A business plan can't be a tightly crafted prediction of the future but rather a depiction of how events might unfold and a road map for change.
- The people making the forecasts are more important than the numbers themselves.
- What matters is having all the required ingredients (or a road map for getting them), not the exact form of communication.
- The best money comes from customers, not external investors.
Sean Silverthorne: " How to Write a Great Business Plan " has been one of the most downloaded articles on Harvard Business Publishing since you wrote it in 1997. Why do you think you hit a nerve?
Bill Sahlman: Writing a business plan is a seminal moment in the life of a new venture. Doing so entails committing to paper a vision of the factors that will affect the success or failure of the enterprise. People take the exercise very seriously and get emotionally invested in what they produce.
In that context, the article was written to give insights into how to think about the role of a business plan and its relation to new venture formation. I tried to explain that a business plan can't be a tightly crafted prediction of the future but rather a depiction of how events might unfold and a road map for change. I emphasized the notion that successful entrepreneurs constantly seek the right mixture of people, opportunity, context, and deal. They anticipate what can go wrong, what can go right, and they try to balance risk and reward.
Over the years, I have received many e-mails from folks trying to craft a business plan. They want feedback. Actually, they really want me to say that they are on the right track. I explain that I would need to get to know them and their opportunity much better than what is possible in an e-mail and that the written document is not as important as the people writing it. It's not science—it's art and craft.
Q: In the decade since the original article came out, business conditions have changed. If you were writing this piece today, would you change it much?
A: I don't think the world has changed materially. Successful ventures still have competent people pursuing sensible opportunities, using resources that help, in a favorable context. Yes, the context is very challenging today. But challenges create opportunities.
If gaining access to capital is hard, sometimes that means there will be fewer competitors. This period is almost the antithesis of the Internet bubble when everyone could raise money and start a company regardless of how lamebrained the idea. Also, we have difficult factor markets like energy, but that simply means that there are great opportunities for people with ideas for alternative energy.
Were I rewriting the article today, I might emphasize the importance of controlling your destiny by being conservative about access to capital. Many great ventures in the Internet era (pre-1999) ended up failing because they assumed they would have continued access to cheap capital. Many of those businesses failed, though the underlying idea was sensible. Similarly, we have seen a period when capital markets got ugly, which has a negative effect on all ventures, sensible and nonsensical.
I would also reinforce the idea that entrepreneurship is critical around the world. We are confronted with many crises from health care to the environment to global poverty. Solutions are likely to come from talented private sector and social entrepreneurs.
Q: You wrote in the original article that most business plans "waste too much ink on numbers and devote too little to the information that really matters to intelligent investors." Still true today? What really matters to investors?
A: When there is great uncertainty in the market, investors become quite risk averse. They will only back proven entrepreneurs with truly compelling ideas. People make the numbers, not conversely. So, I still think the people making the forecasts are more important than the numbers themselves.
Q: More and more entrepreneurial ventures are "born global": They seek to address a global market and attract funding from global investors. Should a business plan be tailored in some way for a global audience?
A: We live in a world of democratized access to ideas, human capital, and money. There are fabulous global ventures being started in every corner of the globe. These ventures can raise money locally or globally. They can disperse talent in many countries.
Take a company like Skype. When I visited Skype several years ago, it had 125 employees from 23 countries. The development team was in Estonia, and its headquarters in Europe. Skype had raised seed capital in Europe and in the United States. That's the new model.
Q: On the technology front, software applications such as Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint have added many charting, graphing, and visualizing capabilities. Some business plans are even written as Web pages. Should entrepreneurs avail themselves of these tools for business plans, or do they clutter the message too much?
A: On the first floor of the Rock Center at HBS there is a copy of the original business plan that Arthur Rock wrote for Intel some 40 years ago. It's only a few pages long, but it describes an outstanding team pursuing a new technology. I have seen compelling business plans in the form of a few PowerPoint slides, a couple of scribbled pages, and a brief video. What matters is having all the required ingredients (or a road map for getting them), not the exact form of communication.
Q: If you were to update your "Glossary of Business Plan Terms" and what they really mean ("We seek a value-added investor" really means "We are looking for a passive, dumb-as-rocks investor"), what current terms would you include?
A: The glossary holds today. I think entrepreneurs, investors, and employees need to be suitably skeptical about what they read in business plans. I have read perhaps 5,000 plans and have only seen three companies really meet their plan. That sounds like a pattern to me. If anyone makes a bet based on the company doing exactly as written, he or she will be sadly disappointed.
At the same time, every player has to be somewhat optimistic about the possibility of overcoming inevitable setbacks. I think of ventures as roller coasters, not rocket ships.
Q: Any general advice to entrepreneurs seeking funding in the uncertain capital markets of today?
A: The best money comes from customers, not external investors. I think entrepreneurs need ideas that are so compelling they can get early money from customers. I also believe that great teams with great ideas can continue to access capital on quite attractive terms from outstanding investors. If the short term looks unsettled, that often means that focusing on the long term has a big potential payoff.
- 02 Apr 2024
- What Do You Think?
What's Enough to Make Us Happy?
- 24 Jan 2024
Why Boeing’s Problems with the 737 MAX Began More Than 25 Years Ago
- 23 Apr 2024
- In Practice
Getting to Net Zero: The Climate Standards and Ecosystem the World Needs Now
- 25 Jan 2022
- Research & Ideas
More Proof That Money Can Buy Happiness (or a Life with Less Stress)
- 22 Apr 2024
When Does Impact Investing Make the Biggest Impact?
- Entrepreneurship
- Business Model
- Risk and Uncertainty
- Business Strategy
- Business Plan
- Forecasting and Prediction
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Accessibility Quick Links
- Skip to Online Banking
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Navigation
Are you sure you want to delete this saved card number?
- CIBC Advice Centre
- Smart Business Advice
- The Dos and Don’ts of Writing a Solid Business Plan
Business Plans 201: The dos and don’ts of writing a solid business plan

We get it. That new business or venture that you’ve been dreaming about can be nerve-racking, but it’s possible.
Starting a new business starts with an idea which comes to life with a strong business plan. Your business plan is more than a piece of paper or a writing exercise. It’s a roadmap that will keep you focused and give you a baseline for measuring success and achieving your goals.
It isn’t a fixed or final artifact. Instead, think of it as a living document that you’ll revisit, learn from and adjust as your business grows.
Writing your plan at first may take a lot of effort and it’s normal to go through several drafts. Consult your advisory team as they can support your plan’s development. And your plan will develop as you get new ideas, make new decisions and learn about changing business developments.
Your plan is also key to unlocking funding. Whether you finance your business or solicit investors, either party will want to learn more about your plan before they invest. Effective language is key to communicating your business plan successfully to potential investors.
Follow these guidelines to start writing a solid business plan that communicates your vision and speaks to your audience.
The “dos” for writing a solid business plan
Be professional yet simple.
Writing with a professional tone allows investors to appreciate your vision and understand your short- and long-term goals. At the same time, it’s best to write in a simple manner. Aim for your plan to be understood by a non-expert. Replace jargon with active verbs. You can always get your final draft edited by a professional.
Refer to your business in third person
Writing in third person allows objectivity which can be more convincing and accepted by audiences like banks and investors. Avoid using “we” or “I” throughout your business plan. Writing in first person may come across as too personal. Remember to keep it business, not personal.
Be direct throughout your plan. Avoid ambiguous or vague language. Being direct allows you to be convincing about the steps you’ll take to bring your idea to life.
Supply evidence
Do your research and present data to support your case. Showing statistics about your business, competitors, customers and industry allows investors to get a bigger picture of the survival and growth of your business.
Be realistic
Avoid adding assumptions in your business plan. Instead of over-promising, show solid data backed up by research on how your business can be successful.
Practice makes perfect
Read your business plan out loud. Ask yourself these questions: Does it sound effective? Does it have the tone of confidence? Is it easily understood by your audience? What are the strengths and opportunities to tackle in your plan? Have a friend read your plan and summarize it back to you .
Be optimistic
The language of your business plan should be assertive, yet optimistic. Allow your passion to shine through in your business plan and show your advisor that you’re serious about bringing your vision to life.
The “don’ts ” of writing your business plan
Avoid acronyms and abbreviations.
Use industry specific abbreviations and acronyms only if necessary and if they’re part of your business operations.
Don’t assume the reader knows your industry
Investors and advisors are here to support you. Allow them to understand what industry your business lives in. Provide in-depth knowledge of your industry so they can understand your business functions.
Don’t turn it into an essay
When writing your business plan and conducting industry research, sometimes it’s easy to get sidetracked and turn your plan into an essay. Make sure your business plan has a solid focus and includes all the required information.
Avoid extensive research
Use only credible sources and findings for your research and analysis. It’s a great practice to use government-issued statistics and data. Use this data in your own language for business projections and goals. Simplicity is key.
Don’t be repetitive
Avoid repeating yourself throughout the plan. You can do this by reading your plan out loud and removing duplicate ideas. Include the key points and messages you need to relay.
Don’t forget about it
Be proactive and don’t forget to follow up with your advisor within the right time frame. Communicate with your advisory team and take advantage of your relationships with your investors, business partners and CIBC business advisor.
Updating your business plan on a quarterly basis is a great practice for staying on track of your business growth. Our team is here to support you as you develop your plan and assemble your team.
To create a tailored plan for your business needs and help you achieve your goals, meet with us opens in a new window. . We’re here to help. Talk to a CIBC Business Advisor today by calling 1-866-992-7223 . Opens your phone app.

Written By Lauren Rabindranath
Lauren Rabindranath is a copywriter and communications consultant based in Toronto, Ontario, who works with clients across industries. Working with CIBC Business Banking, Lauren supports content development for online platforms, relating her personal experience as an entrepreneur to CIBC’s tailored services.
Connect with a business banking expert on your schedule or in your community.
Telephone Banking: 1-800-465-2422 Opens your phone app. | Contact us Opens in a new window.
Select your country and language
- English United States English. Opens in a new window.
Please note: Multilanguage sites do not provide full access to all content on CIBC.com. The full CIBC website is available in English and French.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How To Start a Business Plan

3-minute read
- 18th November 2023
The trick to starting any piece of writing is to just jump in and starting to write a business plan is no different! Make some notes on any aspect of your business – any aspect at all. That way, you won’t be staring at a blank page and instead of feeling bewildered, you’ll be feeling great because you’ll have started the process of getting your new business off the ground. And as any entrepreneur will tell you, that’s one good feeling!
Write Something!
The very first step in starting a business plan is to make notes on any ideas you have about any aspect of your business. Once you’ve done that, you can put the kettle on, but not until there’s something, no matter how jumbled, on the page.
Organize Your Notes Into Headings
Now that you have some notes and a coffee (and biscuits – they’re crucial!), see if you can group your various points into similar subject headings. Here are some examples:
· Business name
· Business plan audience
· Management (and staffing structure if you’ll employ staff)
· Products or services
· Start-up funds sources
· Your market
· Competitors
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
· Marketing plan
· Financial projections
What Do You Want Your Business Plan to Achieve?
There are various reasons why you might want to start a business plan. The US government Small Business Administration and the UK government offer great advice on writing a business plan and working out what you want it to achieve. They both also have useful templates that you can download and personalize.
It’s important to think about why you’re going to start writing a business plan , particularly how it’s going to be used. You might just want it as part of your own management tools and as a baseline for monitoring your progress. You’ll also very likely need it to help you raise vital start-up capital. So think carefully about the needs of your audience – as with any piece of writing, it needs to be relevant to your audience.
If you haven’t yet researched your market, competitors, start-up capital requirements, and the likely costs of running your business, now’s the time! If you’re already on it, summarize your findings under the headings you’ve already written. (And put the kettle on again and get the biscuits – you know the drill!)
Make Your Notes Into a Business Plan
Now that you’ve organized your notes and decided on the purpose of your business plan, you can begin to write your plan in more detail. Use a template or make your own (spreadsheet skills come in handy here) and add all your information and projections to it.
Try to strike a balance in your narrative between concise, objective writing and letting your entrepreneurial passion shine through. This is your chance to sell yourself and your vision to the world! But don’t forget that investors or loan providers need to see hard evidence that you know your stuff, have a good understanding of what you’re letting yourself in for, and know exactly what you want from them.
Proofread Your Business Plan
It’s crucial that your business plan is clear and that your writing is error-free. Our knowledge hub has lots of great resources to help you start your business and our experts at Proofed will be happy to edit your business plan for you.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
How to insert a text box in a google doc.
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
How to Write an Online Business Plan in 2024
Written by Vanessa Petersen on July 26, 2023 Blog , Sell Online .
You’ve committed to turning your ecommerce or online business idea into something real. You want your small business to produce revenue and change the course of your life, but what’s your first step in realizing your dream? Developing a plan. If you’re not sure about how to write an online business plan, you’ve come to the right place.
One of the most essential tasks involved in starting any kind of business is to write a business plan. An online business plan won’t look that different from a traditional business plan and will include many of the same elements.
In this post, we’ll show you how to write an online business plan, including all the components and sections. We’ll also walk through how WooCommerce can help you put your plan to action and achieve your business goals.
Why write a business plan?
Starting your own business is a great experience and something that will shape your life, fill you with self-confidence and independence, and inspire other people around you. A new business is also a serious endeavor that will take time, money, sweat, lots of decisions, and a degree of risk.
A traditional business plan template helps you document and keep track of your business goals, challenges, opportunities, and all the steps and processes involved with making your idea work. It will help you conduct thorough market research and set you up for success.
When you write a business plan, it can confirm that you’ve found the best online business to start , or provide clarity about the need to pivot.

It details all the things you will need to do in order to successfully launch and grow your business, and may include revenue projections, timelines for specific goals, concept art for products, and architectural drawings for any brick and mortar aspects of your business.
Business plans help create a structure for your company’s development and keep you grounded in reality, focused, and not distracted by less important matters.
If you have more than one person helping run the business, the business plan also keeps everyone unified around the same set of goals and objectives.
Another reason to write a business plan is for situations where you are presenting your idea to someone else and asking them to invest. In that scenario, your business plan is also a sort of sales document. It makes the argument for why your business idea is so good and well-considered that an investor should want to be a part of it.
But even if you’re self-funding your entire business — which is more common with online businesses — you still want to write the plan for the reasons given earlier.
The benefits of running an online business
Starting an online business or ecommerce store offers many of the same great benefits as any other business, but without as much risk. If you’re thinking of starting a business, here’s why an online one is a great option:
It has low startup costs
Without a storefront, you eliminate so many costs of running a business. With all the bills that come with having property — like rent, parking, furnishings and decor, etc. — there’s a much higher investment required to start a brick-and-mortar-based business. Online businesses still have startup costs, but they are much lower.
It gives you freedom over your schedule
With an online business, you have more freedom to set your own hours, because you don’t always have to be open during the usual times. You can build your business to suit the lifestyle you want. Rearrange your time to get things done in the fastest possible way and take time off when you need it.
You can start small
Once you have a location, it’s yours, and you have to make it work. With an online business, you can start very small, offering just a few products or even just a single service. You can more easily test the waters without making huge commitments with inventory, and other physical investments.
You can more easily pivot
If your online or ecommerce business doesn’t do as well as you expected, it’s easier to pivot and adapt to something new because you haven’t committed so much to making your original idea work. There are many business success stories where the business owner adjusted their idea after gaining some experience, and then it took off. It’s a lot easier to do that when you aren’t tied to a physical location.
But, there’s one thing online businesses have in common with every other type of business: You need a robust business plan to help guide your idea from concept to a successful reality that makes money and fulfills your dreams and goals.
So, let’s get into business planning.

How do I write my own online business plan?
Most formal business plans and business plan templates include seven sections, plus an executive summary. You’ll need to keep in mind who you’re writing your business plan for. If you are taking this to potential investors or will be seeking a business loan, your business plan needs to sell the idea of your business as a great investment opportunity and communicate the skills, expertise, and commitment you personally bring to the table.
Here are the key sections of a traditional business plan format:
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market analysis
- Organization and management
- Service and product line
- Sales and marketing plans
- Financial projections
- Funding request (if working with investors or partners)
Here’s a brief look at each step of creating an online business plan:
Draft an executive summary
In the executive summary, the first section of almost every business plan template, you’ll present your vision and focus on building excitement. If the business plan is a sales document, the executive summary is the lead. It gets the reader engaged and excited to hear more.
Your executive summary should achieve two goals:
- Deliver the basic facts about your business
- Motivate the reader to keep going and get them excited about your idea
What facts should you include? Whatever helps the reader understand your business idea. Describe the industry and niche. Mention the target market. Briefly state the needs or problems your products and services will be solving. Touch on the potential for growth in terms of revenue and customers.
For motivation, describe your mission statement and company values. What will set you apart from the competition? What is your value proposition as a business owner? What makes you different? Again — keep this brief. You’ll elaborate later.
It might be a good move to write all the other sections first, then finish with the executive summary so it will be the most concise and best version of how you describe your business.

Write a company description
Here, you’ll give a brief overview of your company. What are your strengths, skills, and areas of expertise as a business owner that will position you for success? If you have a compelling story behind why you’re starting your business, you can include that too.
Conduct a SWOT analysis
If you’re not sure where to start, consider doing a SWOT analysis , which is a diagram outlining your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
It’s a common part of many business plans and will help paint a realistic picture of what your business can achieve, and what stands in the way. You won’t include all of this in the company description, but your strengths and opportunities may fit here.
Create a mission and vision statement
The company description is also the place to create a mission statement and a vision statement. What’s the difference between these?
The vision is where you’re going, the mission is how you’ll get there. A vision statement paints a picture of a future reality for your customers and perhaps the world at large, as a result of your company’s influence. A mission statement expresses how you will achieve that.
The company description can elaborate on your vision and mission beyond just a single sentence, and later you can fine-tune what you write into a succinct pair of statements. Feeling some writer’s block? See company description templates by industry for some inspiration.
Include any unique attributes
If your company will involve particular attributes such as manufacturing, supply chains, dropshipping, affiliates, coaching or advising, online courses, or other relevant particulars, include that in your company description, too.
State your business location, industry, niche, and other details
Also, state the location of your business, even though it’s online. Name your industry and niche target market again, and describe the nature of your company. For example, is it an ecommerce business, a consulting firm, delivery service, wholesale, or ad-based website? These are just some of many types of online business structures.
You may also want to include whether your business is in any special class of business that might position it for special loan or grant opportunities like women-owned businesses or veteran-owned businesses.
After reading your description, readers should have a good understanding of what your business is about, why it exists, and how it works. Here’s a detailed look at company descriptions , with an example.
Perform a market analysis
A market analysis uses industry research to assess the scope of your business’s target market and describe the current competition in your industry. It can help you estimate the potential for success and prepare for the challenges you may face when you launch your online business or ecommerce shop.
Doing this research, and including it your business plan, can also help you:
- Identify industry trends
- Pinpoint opportunities
- Diminish risks and reduce costs
- Generate new ideas for products and services
- Learn from the failures and shortcomings of your competitors
- Find ways to stand out from your competitors
- Discover new markets
- Refine your marketing plans
Now let’s dig into the elements involved in a thorough market analysis.
Understand your audience
Here, you will explain in detail who your target customers are and why they want or need what you’ll be selling. What problems or needs does your product solve? What will motivate people to buy from you? And why can’t they get it somewhere else just as easily? An ecommerce business competes against other ecommerce businesses as well as brick-and-mortar stores and shopping malls. Stores with omnichannel strategies compete with both. Why would someone choose you?
Share your key customer demographics, psychographics, and interests. Who will you be serving? What drives them?
What are their values? If your product, service, or personal brand will appeal to a customer segment that also shares particular values, that’s a strength, not a weakness, and you can use that to win them over.
Perform customer segmentation
Break down different categories of target customers your business plans to serve. One category could be age. Another might be life situations such as retirees, parents, divorcees, or living with older relatives. You could create a segment of people with particular health conditions, or who live certain lifestyles.

But you can also get way more specific than that. Runners are different from hikers, who are different from bikers, yoga enthusiasts, and gym enthusiasts. Different supplements, philosophies about food, motivations for eating various foods — all of these present near endless possibilities for more narrowly defining your customer segments, all under the broad category of ‘health.’ And you might serve multiple segments.
The more customer segments you know, the more effectively you can market to them. In an online store, good product descriptions call out the various customer segments that product is designed for.
Also, give a sense of the potential size of your target market. How many people need what you’re selling? Show how this market is large enough to justify your business and drive revenue. You might do this by studying revenue reports from other companies in your industry. Or look at specific products related to yours and research their sales and revenue performance.
You may also perform a survey of some kind, or an online quiz, and use that to express the needs your potential customers have that aren’t currently being met.
Perform a competitive analysis
Study your competition. What are they doing well? What areas are they underserving? Where are they underperforming? Make note of what other companies in your industry are struggling with or failing at so that you can deliver something more valuable and gain a competitive advantage.
It could be product quality, customer service, or selection. Maybe their ecommerce store is badly designed and hard to use. Perhaps there’s a huge industry serving the masses, but customers who have more particular tastes or needs aren’t being well-served by the big companies. Those customers might spend more on something that delivers what they really want.
Maybe your key competition has been rocked by scandal. Maybe a company went out of business, was sold, or closed down due to retirement and there’s an opening in the market you want to leverage.
The main point of the competitive analysis is to persuade investors that there’s an underserved market that your business plans to cater to. You must be able to promise something that no one else is currently delivering. Otherwise, why should your business exist? Put them at ease by demonstrating proper market research.
Refer to your SWOT analysis and present any potential threats from the competition here, too.
Outline management and organizational structure
Next, present your management and legal structure. Is your company an LLC, sole proprietorship, S corporation, partnership, or some other arrangement? Who’s in charge of what? If you have different departments, list out the leadership for each one. If relevant, you might even include some information about the expertise of your leaders concerning the areas under their charge and the tasks they’ll be performing.
Remember — if your business plan will be used to persuade investors to help fund your business idea, this sort of information will reassure them that your company has strong and competent leadership.
If there’s a chain of command, use a diagram or other method for laying out who reports to whom.

List your products and services
What are you selling? You’ll touch on this briefly in the earlier sections, but here is where you’ll expand on the details. If you have an array of similar products, such as food flavors or clothing variations, list as many as seem relevant. But focus on the spirit of the business plan — you’re simply communicating what your business is about, not listing every SKU in your projected inventory.
Also, include information about your products such as quality, durability, expirations, patents, and whatever else will give a clear picture of what you’re selling.
For service businesses and memberships that may include multiple packages, bundles, or tiers, describe each of these so your readers get a sense of how you’ll appeal to different types of customers and price points.
Develop a sales and marketing strategy
Having products is great, but how do you intend to sell them? How will people find your business? How will anyone know you exist? And once they know, what will motivate them to buy from you and not from your competition? What is your unique value proposition — the thing that sets you apart from your direct competitors?
You’ll need to develop an initial marketing plan to help promote your business, products, and services to your target customers.
And remember, competition isn’t limited just to other businesses. Sometimes, competition is against the customer’s time, or their budget, or mere indifference — the conflict between doing something and doing nothing. Your SWOT analysis should touch on several of these potential barriers to the success of your online business.
Your marketing plan will obviously change over time, but give your readers and potential investors a sense of how you plan to launch and grow your business.
Discuss media channels you plan to use, such as pay-per-click (PPC) ads , social media , email marketing , affiliate marketing , direct mail, referrals, joint ventures, search engine optimization (SEO), webinars, influencer marketing , and live events. Describe the ones you actually plan to use, and explain the core strategy you’ll begin with and how you will measure success.
Also, include a sense of your marketing budget. If you will have a dedicated marketing team, or actual sales professionals using a particular process or sales script, discuss that as well.
For ecommerce businesses, include a discussion of how you plan to leverage platforms like WooCommerce, which features a host of extensions that can help manage your business , engage customers, save money, and promote growth .
Make financial projections
You’ve made a lot of claims in your business plan, but how will your investors be convinced of your future success? At some point, you have to show them the money.
If this is a brand new business with no income, where will your finances come from for the first year? Give realistic financial projections for anticipated profits and losses, as well as growth expectations for the first five years. Include financial documents if you have them, including profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Include costs of employment, manufacturing, and other investments both one-time and ongoing.
Your financial projections should reference your:
- market analysis
- anticipated sales volume
Investors will feel more confident when they can see your business plan does not rely entirely on just one or two ‘wins.’ For example, if your entire plan hinges on selling on eBay or Amazon , what happens if Amazon suspends your store, changes the terms, or you struggle to get noticed there?
If your plan depends on winning over a few Instagram influencers, what if they don’t come through? It’s really easy to say what you hope will happen. But actually making it happen is another thing. Business success happens more easily when you apply a multi-channel marketing and sales approach.
Your financial projections will feel based in reality, when you can demonstrate some prior successes, either in other businesses you’ve already launched, test audiences, local sales you made, prior experience, or data from other businesses.
Explain your funding request — if applicable
If you intend to ask investors to help fund your business idea, present your request in the final main section of your business plan. If you’ve already secured funding from other sources, include that here as well. An investor will feel better knowing they are not the only one who believes in the potential of your business.
Will your funding request be for a one-time payment, monthly, annually, or at some other interval? How do you plan to repay their investment? Will you allow them to charge interest? How much ROI can you promise them?
How WooCommerce can help
WooCommerce can help you build a scalable online business that supports your business plan. No matter what you’re selling, WooCommerce offers a suite of flexible tools that allows you to customize your store to meet your needs and goals.
Here are just some of the benefits your business will enjoy when you choose to build your store with WooCommerce:
- Sell absolutely anything you can imagine . From physical items and digital downloads to subscriptions, memberships, bookings, courses, and affiliate products, WooCommerce provides everything you need. Want to run a wholesale store? You can do that, too!
- Harness the power of WordPress . Since WooCommerce is a plugin specifically for WordPress, you can take advantage of powerful features like the block editor and blogging capabilities.
- Capture payments securely. Choose from a large number of payment gateways, from popular options like PayPal and Stripe, to more niche processors for specific locations and types of regulated products. And with tools like WooPayments , you can keep customers on-site, capture a variety of currencies, and even accept digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay.
- Customize your shipping options. Offer free shipping, charge based on weight, set fixed prices, or calculate shipping costs based on real-time carrier rates. You can even use extensions like Table Rate Shipping to create complicated shipping rules based on conditions that you set. And with WooCommerce Shipping , you benefit from discounted shipping labels and the ability to print right from your dashboard.
- Connect to your social media channels. Use extensions to sync your store with social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Pinterest. You can even sell on those platforms alongside your store without having to update inventory and information manually.
- Integrate with marketing tools. Quickly connect your store to any number of marketing tools, from email platforms like MailPoet to CRMs like Jetpack CRM . You can also implement a number of marketing strategies, from abandoned cart emails to loyalty programs.
- Keep track of your numbers. Ecommerce accounting is a big part of running an online business. While you can easily view data in your dashboard, you can also sync with tools like QuickBooks to make your accountant’s life a little bit easier.
- Manage inventory. Update your inventory levels manually or connect to tools like Scanventory to sync with your warehouse. Running low or out of stock? Add a wishlist option so customers get an alert as soon as it’s available.
As you can see, WooCommerce is well-equipped to handle any type of online store and support you as you grow. Here are a few more reasons that WooCommerce should be your go-to choice for implementing the ecommerce side of your online business plan:
WooCommerce itself is free! Many extensions for WooCommerce can also be found for free in the WordPress.org plugins library or on the Woo Marketplace . If you need to start your website with a limited budget, but want to build on a platform that can grow to support a thriving, high-traffic store, WooCommerce is an excellent option.
You have full control over your store
Unlike other ecommerce solutions that are tied to the platform’s own web hosting, WooCommerce is designed to be used with WordPress along with any hosting provider of your choice. You are also free to use whatever payment processor you want without any additional fees from WooCommerce. You can also customize your site’s appearance and functionality more extensively than you can with other ecommerce platforms and with less (or no) coding knowledge.
Thousands of free and premium extensions
There are over 800 free and premium extensions for WooCommerce on WooCommerce.com alone and over 1,000 in the WordPress.org plugins library . There are also hundreds of independent developers and agencies that offer premium and custom extensions for WooCommerce so that you can customize your store with the exact features you need.
Excellent support and large community of users
WooCommerce is used by over 3.9 million stores — 23% of all online stores worldwide . The support team is available to answer questions and the documentation library is extensive and thorough. There are also plenty of independent resources for learning how to use WordPress and WooCommerce.
Dedicate time and resources to put your online business plan in action
A successful business plan is one that empowers and guides the business owner to launch their online or ecommerce business, and possibly secure funding. But it only works if you use it.
One advantage of starting an ecommerce store or online business is that you aren’t as locked down by deadlines. With a physical location, once you start paying the rent, you better have your business plan ready to put into action.
But the beauty of being online is that you have more flexibility on the front end. Despite having more wiggle room with your timelines, you still need to keep your momentum going forward. Staying on track with your business projects and goals is one of the keys to reaching profitability sooner and turning your business plan into reality. A few quick tips:
- Schedule your time. Block out hours and specific days to work on your business.
- Treat it like a job, not a hobby. Build on your momentum week after week.
- Always keep learning. Research your industry, competition, target audience, and potential customers. Learn marketing — you can never know too much.
- Try stuff! Take risks, make calls, create campaigns, write content.
Your business plan template should give you a concrete list of tasks and business objectives. Once you write a business plan, then you can implement it.
Frequently asked questions about writing an online business plan
What are the seven steps of a business plan.
The seven key elements of a business plan are the executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization and management, services and products, marketing plan, and financial projections. If you’re making a funding request, that would be an eighth section.
Where can I find business plan templates?
You can find a free business plan template online, for general business plans as well as for specific industries. However, since each business is different and your plan must be authentic and specific to your company — a business plan template can only get you so far.
If you need design inspiration for your own custom business plan template or want to start with a pre-designed template that you can customize, you can purchase one for a relatively low cost through a stock resources site like Envato Market or Creative Market .
Do I need a business plan if I am already running an online business or ecommerce shop?
Business plans aren’t only for people who are launching new businesses. You can create a business plan at any time to help you maintain or change the direction of your store or just to get a better picture of the health of your business. Below are a few different types of business plans that you might want to consider for your established online business:
- Operational business plan. Outlines the structure of your business operations, staffing, and logistics.
- Feasibility plan. Feasibility plans are like mini business plans that cover new business ideas and outline steps for implementation.
- Growth business plan. This plan is for businesses that want to demonstrate opportunities and plans for growth to attract investors.
- Maturing business plan. This plan is for businesses looking to merge with or acquire other companies, significantly expand, or go public.
- Strategic business plan. Any time your business wants to shift strategies regarding products or marketing or any other major changes to your previous business plan, you’ll want to create a new strategic business plan to address your new goals and the steps involved in achieving them.
What software should I use for my online business plan?
Your business plan should include some images, graphs, and graphic elements in the layout, so you’ll want to at least use word processing software to put your business plan together. If you have access to Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Canva, or Adobe Creative Cloud, you’ll have some other options that might lead to a more professional layout.
Here’s a list of free and paid software that can help you put together your online business plan outline:
What do investors want to see in a business plan?
The most important piece of information to show investors in your business plan is potential for profitability. Investors don’t want to throw money at a sinking ship, no matter how cool and exciting the business sounds.
Most investors also want to make sure that they’ll see a decent return on their investment in a relatively short time period — probably around 5-7 years. How much of a return they’ll expect will depend on your industry and what kind of investor they are.
Investors will also want to see that you clearly understand your business, your industry, and that you have concrete, actionable steps for achieving, maintaining, and growing profitability. They’ll want to make sure that the key people on your team also understand your business and the roles they play and they’ll want to see that each person has a good amount of experience in their field and the required skill sets to fulfill their job duties, if not go above and beyond.
Any details you can include that highlight unique aspects of your business will also be important. Any area where you have a competitive edge, are offering a unique or proprietary solution, have established any celebrity endorsements, have the backing of other investors, or have secured special grants will be of special interest to investors.
Create your plan for success
Now that you understand what goes into creating a formal business plan, it’s time to write one! Take the time to think through and consider each aspect of the list included in this article, and you’ll be well on your way to finding success.
And WooCommerce is here to support your business every step of the way, with powerful and flexible tools that help your business grow. Start selling online today !

Share this:
- 30-day money-back guarantee
- Support teams across the world
- Safe and secure online payments
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Top 10 Business Plan Mistakes When it comes to creating a business plan that attracts investors, these tips will help you get it right the first time.
Every business should have a business plan. Unfortunately, despite the fact that many of the underlying businesses are viable, the vast majority of plans are hardly worth the paper they're printed on. Most "bad" business plans share one or more of the following problems:
1. The plan is poorly written. Spelling, punctuation, grammar and style are all important when it comes to getting your business plan down on paper. Although investors don't expect to be investing in a company run by English majors, they are looking for clues about the underlying business and its leaders when they're perusing a plan. When they see one with spelling, punctuation and grammar errors, they immediately wonder what else is wrong with the business. But since there's no shortage of people looking for capital, they don't wonder for long--they just move on to the next plan.
Before you show your plan to a single investor or banker, go through every line of the plan with a fine-tooth comb. Run your spell check--which should catch spelling and punctuation errors, and have someone you know with strong "English teacher" skills review it for grammar problems.
Style is subtler, but it's equally important. Different entrepreneurs write in different styles. If your style is "confident," "crisp," "clean," "authoritative" or "formal," you'll rarely have problems. If, however, your style is "arrogant," "sloppy," "folksy," "turgid" or "smarmy," you may turn off potential investors, although it's a fact that different styles appeal to different investors. No matter what style you choose for your business plan, be sure it's consistent throughout the plan, and that it fits your intended audience and your business. For instance, I once met a conservative Midwest banker who funded an Indian-Japanese fusion restaurant partly because the plan was--like the restaurant concept--upbeat, trendy and unconventional.
2. The plan presentation is sloppy. Once your writing's perfect, the presentation has to match. Nothing peeves investors more than inconsistent margins, missing page numbers, charts without labels or with incorrect units, tables without headings, technical terminology without definitions or a missing table of contents. Have someone else proofread your plan before you show it to an investor, banker or venture capitalist. Remember that while you'll undoubtedly spend months working on your plan, most investors won't give it more than 10 minutes before they make an initial decision about it. So if they start paging through your plan and can't find the section on "Management," they may decide to move on to the next, more organized plan in the stack.
3. The plan is incomplete. Every business has customers, products and services, operations, marketing and sales, a management team, and competitors. At an absolute minimum, your plan must cover all these areas. A complete plan should also include a discussion of the industry, particularly industry trends, such as if the market is growing or shrinking. Finally, your plan should include detailed financial projections--monthly cash flow and income statements, as well as annual balance sheets--going out at least three years.
4. The plan is too vague. A business plan is not a novel, a poem or a cryptogram. If a reasonably intelligent person with a high school education can't understand your plan, then you need to rewrite it. If you're trying to keep the information vague because your business involves highly confidential material, processes or technologies, then show people your executive summary first (which should never contain any proprietary information). Then, if they're interested in learning more about the business, have them sign noncompete and nondisclosure agreements before showing them the entire plan. [Be forewarned, however: Many venture capitalists and investors will not sign these agreements since they want to minimize their legal fees and have no interest in competing with you in any case.]
5. The plan is too detailed. Do not get bogged down in technical details! This is especially common with technology-based startups. Keep the technical details to a minimum in the main plan--if you want to include them, do so elsewhere, say, in an appendix. One way to do this is to break your plan into three parts: a two- to three-page executive summary, a 10- to 20-page business plan and an appendix that includes as many pages as needed to make it clear that you know what you're doing. This way, anyone reading the plan can get the amount of detail he or she wants.
6. The plan makes unfounded or unrealistic assumptions. By their very nature, business plans are full of assumptions. The most important assumption, of course, is that your business will succeed! The best business plans highlight critical assumptions and provide some sort of rationalization for them. The worst business plans bury assumptions throughout the plan so no one can tell where the assumptions end and the facts begin. Market size, acceptable pricing, customer purchasing behavior, time to commercialization--these all involve assumptions. Wherever possible, make sure you check your assumptions against benchmarks from the same industry, a similar industry or some other acceptable standard. Tie your assumptions to facts.
A simple example of this would be the real estate section of your plan. Every company eventually needs some sort of real estate, whether it's office space, industrial space or retail space. You should research the locations and costs for real estate in your area, and make a careful estimate of how much space you'll actually need before presenting your plan to any investors or lenders.
7. The plan includes inadequate research. Just as it's important to tie your assumptions to facts, it's equally important to make sure your facts are, well, facts. Learn everything you can about your business and your industry--customer purchasing habits, motivations and fears; competitor positioning, size and market share; and overall market trends. You don't want to get bogged down by the facts, but you should have some numbers, charts and statistics to back up any assumptions or projections you make. Well-prepared investors will check your numbers against industry data or third party studies--if your numbers don't jibe with their numbers, your plan probably won't get funded.
8. You claim there's no risk involved in your new venture. Any sensible investor understands there's really no such thing as a "no risk" business. There are always risks. You must understand them before presenting your plan to investors or lenders. Since a business plan is more of a marketing tool than anything else, I'd recommend minimizing the discussion of risks in your plan. If you do mention any risks, be sure to emphasize how you'll minimize or mitigate them. And be well prepared for questions about risks in later discussions with investors.
9. You claim you have no competition. It's absolutely amazing how many potential business owners include this statement in their business plans: "We have no competition."
If that's what you think, you couldn't be further from the truth. Every successful business has competitors, both direct and indirect. You should plan for stiff competition from the beginning. If you can't find any direct competitors today, try to imagine how the marketplace might look once you're successful. Identify ways you can compete, and accentuate your competitive advantages in the business plan.
10. The business plan is really no plan at all. A good business plan presents an overview of the business--now, in the short term, and in the long term. However, it doesn't just describe what the business looks like at each of those stages; it also describes how you'll get from one stage to the next. In other words, the plan provides a "roadmap" for the business, a roadmap that should be as specific as possible. It should contain definite milestones--major targets that have real meaning for your business. For instance, reasonable milestones might be "signing the 100th client" or "producing 10,000 units of product." The business plan should also outline all the major steps you need to complete to reach each milestone.
Smoothing Out the Rough Spots Once you know what mistakes not to make, there are still a few steps you need to take to make your business plan "bulletproof." Be sure you . . .
- Think it through. You might have a great idea, but have you carefully mapped out all the steps you'll need to take to make the business a reality? Think about building your management team, hiring salespeople, setting up operations, getting your first customer, protecting yourself from lawsuits, outmaneuvering your competition, and so on. Think about cash flow and what measures you can take to minimize your expenses and maximize your revenue.
- Do your research. Investigate everything you can about your proposed business before you start writing your business plan--and long before you start the business. You'll also need to continue your research while you write the business plan, since inevitably, things will change as you uncover critical information. And while you're researching, be sure to consult multiple sources since many times the experts will disagree.
- Research your potential customers and competitors. Is your product or service something people really want or need, or is it just "cool"? Study your market. Is it growing or shrinking? Could some sort of disruptive technology or regulatory change alter the market in fundamental ways? Why do you think people will buy your product or service? If you don't have any customers or clients yet, you'll need to convince investors that you have something people really want or need, and more important, that they'll buy it at the price you expect.
- Get feedback. Obtain as much feedback as you can from trusted friends, colleagues, nonprofit organizations, and potential investors or lenders. You'll quickly find that almost everyone thinks they're an expert and they all could do a better job than you. This may be annoying, but it's just part of the feedback process. You'll know when you're done when you've heard the same questions and criticisms again and again and have a good answer to almost everything anyone can throw at you.
- Hire professional help. Find a professional you trust to help guide you through the entire process, fill in knowledge gaps (for instance, if you know marketing but not finance, you should hire a finance expert), provide additional, unbiased feedback, and package your plan in an attractive, professional format.
Writing a business plan is hard work--many people spend a year or more writing their plan. In the early, drafting stages, business plan software can be very helpful. But the hard part is developing a coherent picture of the business that makes sense, is appealing to others and provides a reasonable road map for the future. Your products, services, business model, customers, marketing and sales plan, internal operations, management team and financial projections must all tie together seamlessly. If they don't, you may not ever get your business off the ground.
Andrew Clarke is the CEO of Ground Floor Partners , a business consulting firm that helps early-stage, small and middle-market businesses grow through design and execution of sound business strategies.
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- James Clear Explains Why the 'Two Minute Rule' Is the Key to Long-Term Habit Building
- They Designed One Simple Product With a 'Focus on Human Health' — and Made $40 Million Last Year
- Lock Younger Americans Don't Necessarily Want to Retire in Florida — and the 2 Affordable States at the Top of Their List Might Surprise You
- I Tried Airchat , the Hottest New Social Media App in Silicon Valley — Here's How It Works
- Lock This Side Hustle Is Helping Farmers Earn Up to $60,000 a Year While Connecting Outdoor Lovers With Untouched Wilderness
- Are Franchises in the Clear After the Expanded Joint Employer Rule Was Struck Down? Industry Experts Answer 2 Critical Questions About What's Next.
Most Popular Red Arrow
Passengers are now entitled to a full cash refund for canceled flights, 'significant' delays.
The U.S. Department of Transportation announced new rules for commercial passengers on Wednesday.
Franchising Is Not For Everyone. Explore These Lucrative Alternatives to Expand Your Business.
Not every business can be franchised, nor should it. While franchising can be the right growth vehicle for someone with an established brand and proven concept that's ripe for growth, there are other options available for business owners.
Elon Musk Tells Investors Cheaper Tesla Electric Cars Should Arrive Ahead of Schedule
On an earnings call, Musk told shareholders that Tesla could start producing new, affordable electric cars earlier than expected.
10 Things CIOs are Prioritizing Today to Stay Ahead in 2024
The role of the CIO has become increasingly important as technology continues to shape the business world.
Younger Americans Don't Necessarily Want to Retire in Florida — and the 2 Affordable States at the Top of Their List Might Surprise You
Gen Z and millennials may be decades away from retirement, but some spots are already on their radar.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
Successfully copied link
206-660-6190
Writing a business plan–why is it so hard.
My topics are often the result of recent experiences with clients. This is no exception. I am currently in the midst of writing Business Plans for three of my clients. And I’ve got two more that I will probably be starting soon.
In all cases, we started with the business owner desiring to write the Business Plan. After all, no one knows their business like the owner. Plus, it would minimize my hours. So I provided each owner with my outline of what a Business Plan should include:
Executive Summary (write last)
Market Analysis
Company Description
Organization and Management
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Service or Product Lines
Funding Request (if any)
Risk Mitigation
Financials—Historical and Forecasted
The real heart of a Business Plan is the Market Analysis and how the company will address the opportunity they see in the market. This needs to include the company’s value proposition.
Here is what has happened. In all cases, the business owners had a terrible time and couldn’t even get a good start on writing their Business Plans. Which got me to thinking, why is this so hard? Why is it so hard for anyone to write a Business Plan? I think there are a lot of good reasons.
The Thought Process
When writing a Business Plan, usually we’re trying to grow the business, often substantially. This may mean new products or services, geographic expansion, acquisition or all of the above. This alone is hard to figure out.
But add to that the fact that the business will change with this growth in fundamental ways. The owner’s job will change from being a doer/manager to being a manager/business developer/leader/supervisor. More employees will be needed and some of them will be managers with their own direct reports. The systems of the business, especially the IT infrastructure, will need to be developed to support the growth. Business processes must be developed to maintain quality and consistency. The current organization chart, if there is one, needs to be imagined for a much bigger company. And every slot on the new organization chart needs to be filled in the future. And every future employee’s characteristics need to be imagined and planned for.
In short, the planning task is difficult. Serious, uninterrupted thought must be devoted to the task.
Uninterrupted Time
To devote oneself to this deep thinking and planning, the person writing the Business Plan needs large blocks of uninterrupted time. How often does a business owner have large blocks or uninterrupted time? In the best cases, rarely. In most cases, never.
Business owners are busy supervising staff, making sales, reacting to emergencies and all the rest that comes with running a small to medium-sized business. It is often said that “the urgent drives out the important.” Writing the Business Plan is important but not urgent. But what a business owner deals with every day is often urgent and important.
Perspective
Chances are the business owner has never grown a business before, so this is the first time. Plus, they lack perspective. That is, they are too close to the business to objectively work “on the business” rather than “work in the business.”
It is much like writing or creating an Excel spreadsheet. In both cases, the creator needs someone else to proofread their work. The creator is too close to the work product to review it. In other words, one can never review their own work, at least not very well.
I think it is the same with a Business Plan. The business owner will have many or most of the key ideas about what will be done with the business. But writing the Plan itself is difficult. I find it works better to have the business owner download their thoughts, I ask a bunch of questions, and then I write up the Plan. This Plan is then subject to numerous revisions before being finalized.
Final Thoughts
There are probably other reasons why writing a Business Plan is so difficult for a business owner. We need to keep in mind how important this is. I don’t want to write Business Plans that sit on a shelf. I also don’t write a Plan intended for a lender. I want to write a Business Plan that is going to be executed on by the business owner and their team to achieve their aspirations. The Business Plan should be the template that leads to success.
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
Name (required)
Email (will not be published) (required)
Biden's new student-loan forgiveness plan just began its 30-day public comment period — and anyone can tell the administration what they think of the relief
- The public now has 30 days to comment on Biden's new student-loan forgiveness plan.
- It's the next step in implementing a broader version of debt relief for borrowers.
- The proposals include relief for those with unpaid interest, along with those in repayment for 20 years.

The public has one month to tell President Joe Biden what they think of his new student-loan forgiveness plan .
After announcing details of Biden's second attempt at student-debt relief last week, the Education Department formally published the draft text of the new rules on the Federal Register on Wednesday. The publication of the rules officially kicked off the 30-day public comment, set to end on May 17. Comments can be submitted to the Federal Register here , which the Education Department will then review.
The draft text currently consists of nine rules "that permit separate and distinct types of waivers using the Secretary of Education's longstanding authority under the Higher Education Act," the Education Department said in a Tuesday press release.
Related stories
The rules address distinct types of borrowers that would qualify for relief under this new plan: those whose balances have grown due to unpaid interest, those who would be eligible for relief under certain repayment plans but have not yet enrolled, those who have been in repayment for at least 20 years, and those who have attended programs that left them with too much debt compared to post-graduation earnings.
The Education Department also said a separate rule to address relief for borrowers experiencing financial hardship will be released in the coming months.
"These historic steps reflect President Biden's determination that we cannot allow student debt to leave students worse off than before they went to college," Undersecretary of Education James Kvaal said in a Tuesday statement. "The President directed us to complete these programs as quickly as possible, and we are going to do just that."
The department aims to begin implementing relief as early as this fall. Still, as Business Insider previously reported , legal threats to the relief could imperil the department's timeline. While lawsuits have yet to be formally filed against Biden's administration, Missouri's Attorney General Andrew Bailey wrote on X in response to Biden's relief proposals: "See you in court."
And some experts said a conservative Supreme Court could likely rule like they did with Biden's first debt relief plan, striking it down .
"The administration is certainly still facing a very skeptical Supreme Court," Cary Coglianese, an administrative law professor at the University of Pennsylvania, told BI. "Even though it's a different statute, it's still a skeptical Supreme Court. It's still a pretty big program even though it's a smaller one."
Following the public comment period, the Education Department will review comments and could choose to adjust their proposals based on the feedback they receive. It will then finalize the rule and move toward implementation.
Watch: Why student loans aren't canceled, and what Biden's going to do about it
- Main content
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Biden says the US is rushing weaponry to Ukraine as he signs a $95 billion war aid measure into law
Calling it “a good day for world peace,” President Joe Biden signed into law the $95 billion war aid measure that includes assistance for Ukraine, Israel, Taiwan and other allies, marking an end to the long, painful battle with Republicans in Congress.

The Senate has passed $95 billion in war aid to Ukraine, Israel and Taiwan, sending the legislation to President Joe Biden after months of delays and debate over how involved the United States should be in foreign wars.
President Joe Biden speaks before signing a $95 billion Ukraine aid package that also includes support for Israel, Taiwan, and other allies, in the State Dining Room of the White House, Wednesday, April 24, 2024, in Washington. (AP Photo/Evan Vucci)
- Copy Link copied
President Joe Biden speaks before signing a $95 billion Ukraine aid package that also includes support for Israel, Taiwan, and other allies, in the State Dining Room of the White House, Wednesday, April 24, 2024, in Washington. (AP Photo/Evan Vucci)\
FILE - President Joe Biden speaks about a $95 billion aid package that would help Ukraine in their war against Russia, in the State Dining Room of the White House, Feb. 13, 2024, in Washington. (AP Photo/Evan Vucci)
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Joe Biden said Wednesday that he was immediately rushing badly needed weaponry to Ukraine as he signed into law a $95 billion war aid measure that also included assistance for Israel, Taiwan and other global hot spots.
The announcement marked an end to the long, painful battle with Republicans in Congress over urgently needed assistance for Ukraine, with Biden promising that U.S. weapons shipment would begin making the way into Ukraine “in the next few hours.”
“We rose to the moment, we came together, and we got it done,” Biden said a White House event to announce the bill signing. “Now we need to move fast, and we are.”
But significant damage has been done to the Biden administration’s effort to help Ukraine repel Russia’s invasion during the funding impasse that dates back to August, when the Democratic president made his first emergency spending request for Ukraine. Even with a burst of new weapons and ammunition, it’s unlikely Ukraine will immediately recover after months of setbacks.
Biden immediately approved sending Ukraine $1 billion in military assistance , the first installment from about $61 billion allocated for Ukraine. The package includes air defense capabilities, artillery rounds, armored vehicles and other weapons to shore up Ukrainian forces who have seen morale sink as Russian President Vladimir Putin has racked up win after win.
Meanwhile, Ukraine for the first time has begun using long-range ballistic missiles provided secretly by the United States , bombing a Russian military airfield in Crimea last week and Russian forces in another occupied area overnight, American officials confirmed Wednesday. The U.S. is providing more of the Army Tactical Missile System, known as ATACMS, in the new military package , according to one official who was not authorized to comment and spoke on the condition of anonymity.
Still, longer term, it remains uncertain if Ukraine, after months of losses and massive damage to its infrastructure, can make enough progress to sustain American political support before burning through the latest influx of money.
White House national security adviser Jake Sullivan cautioned that even as new U.S. aid flows into Ukraine, it’s possible that Russia will continue to make tactical gains in the weeks ahead.
“The fact is that it’s going to take some time for us to dig out of the hole that was created by six months of delay,” he said.
Tucked into the measure is a provision that gives TikTok’s Beijing-based parent company, ByteDance , nine months to sell it or face a nationwide prohibition in the United States. The administration and a bipartisan group of lawmakers have called the social media site a growing national security concern, which ByteDance denies.
The bill includes about $26 billion in aid for Israel and about $1 billion in humanitarian relief for Palestinians in Gaza as the Israel-Hamas war continues. Biden said Israel must ensure the humanitarian aid for Palestinians in bill reaches the Hamas-controlled territory “without delay.”
House Speaker Mike Johnson, R-La., delayed the aid package for months as members of his party’s far right wing, including Reps. Marjorie Taylor Greene of Georgia and Thomas Massie of Kentucky, threatened to move to oust him if he allowed a vote to send more assistance to Ukraine. Those threats persist.
Donald Trump, the presumptive Republican presidential nominee, has complained that European allies have not done enough for Ukraine. While the former president stopped short of endorsing the funding package, his tone has shifted in recent days, acknowledging that Ukraine’s survival is important to the United States.
Many European leaders have long been nervous that a second Trump term would mean decreased U.S. support for Ukraine and NATO. The European anxiety was heightened in February when Trump in a campaign speech warned NATO allies that he “would encourage” Russia to “do whatever the hell they want” to countries that don’t meet defense spending goals if he returns to the White House.
It was a key moment in the debate over Ukraine spending. NATO Secretary-General Jens Stoltenberg quickly called out Trump for putting “American and European soldiers at increased risk.” But in reality, the White House maneuvering to win additional funding for Ukraine started months earlier.
Biden, the day after returning from a trip to Tel Aviv following Hamas militants’ Oct. 7 attack on Israel, used a prime-time address to make his pitch for the funding.
At the time, the House was in chaos because the Republican majority had been unable to select a speaker to replace Rep. Kevin McCarthy, R-Calif., who had been ousted weeks earlier at the urging of restive legislators on the right.
Far-right Republicans have adamantly opposed sending more money for Ukraine, with the war appearing to have no end in sight. Biden in August requested more than $20 billion to keep aid flowing into Ukraine, but the money was stripped out of a must-pass spending bill .
By late October, Republicans finally settled on Johnson, a low-profile Louisiana Republican whose thinking on Ukraine was opaque, to serve as the next speaker. Biden during his congratulatory call with Johnson urged him to quickly pass Ukraine aid and began a monthslong, largely behind-the-scenes effort to bring the matter to a vote.
In private conversations with Johnson, Biden and White House officials leaned into the stakes for Europe if Ukraine were to fall to Russia. On explicit orders from Biden, White House officials also avoided directly attacking Johnson over the stalled aid.
Biden praised Johnson and Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell, R-Ky., saying in the end they “stepped up and did the right thing.”
“History will remember this moment,” he said.
At frustrating moments during the negotiations, Biden urged his aides to “just keep talking, keep working,” according to a senior administration official, who insisted on anonymity to discuss internal discussions.
So they did. In a daily meeting convened by White House chief of staff Jeff Zients, the president’s top aides would brainstorm possible ways to better make the case about Ukraine’s dire situation in the absence of aid.
The White House also sought to accommodate Johnson and his various asks. For instance, administration officials at the speaker’s request briefed Reps. Chip Roy, R-Texas, and Ralph Norman, R-S.C., two conservatives who were persistent antagonists of Johnson.
In public, the administration deployed a strategy of downgrading intelligence that demonstrated Russia’s efforts to tighten its ties with U.S. adversaries China, North Korea and Iran to fortify Moscow’s defense industrial complex and get around U.S. and European sanctions.
The $61 billion can help triage Ukrainian forces, but Kyiv will need much more for a fight that could last years, military experts say.
Realistic goals for the months ahead for Ukraine — and its allies — include avoiding the loss of major cities, slowing Russia’s momentum and getting to Kyiv additional weaponry that could help them go on the offensive in 2025, said Bradley Bowman, a defense strategy and policy analyst at the Foundation for the Defense of Democracies in Washington.
“I think Ukrainian success is not guaranteed,” Bowman said, “but Russian success is if we stop supporting Ukraine.”
Biden lamented that the package did not include money to bolster U.S. border security. The White House had proposed including in the package provisions it said would have helped stem the tide of migrants and asylum seekers coming to the U.S. Republicans, however, rejected the proposal at the urging of Trump, who did not want to give Biden the win on an issue that’s been an albatross for the Democratic administration.
Associated Press writers Lolita C. Baldor, Haleluya Hadero, Mary Clare Jalonick and Darlene Superville contributed to this report.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Writing your business plan is about the process and having a blueprint: ... Presentation counts: Reading any long, text-heavy document is hard on the eyes, so format with this in mind. Consider ...
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
Write the Executive Summary. This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what's in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company. Add a Company Overview. Document the larger company mission and vision.
Step 2: Do your market research homework. The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research. This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to ...
Keep it to one or two pages. To make things easier for yourself, write this section last. By then you'll have a stronger understanding of your whole business plan and can more easily pull the ...
A comprehensive business plan typically comprises the following key components: Executive Summary: A concise overview of your business idea, including your mission statement, product or service offering, target market, competitive advantage, and financial highlights. Company Description: An in-depth analysis of your business, including its ...
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
Finally, make sure your plan document flows well and doesn't have any "widows" or "orphans" when it prints out. A "widow" is when the last line of a paragraph appears alone at the top of a page, and an "orphan" is a single word that gets left behind at the bottom of a paragraph. 7. Get a Second Pair of Eyes.
A business plan's highest purpose is to guide entrepreneurs in operating their business on the day-to-day level. It is a foundational document that I think of as the constitution of your business. It tells you everything you need to know about your idea, your goals, your strategy, and the financial picture of a business.
Most people think that writing a business plan has to be hard.I'm here to tell you that it doesn't have to be. In fact, it's possible to write your initial business plan in less than an hour. After all, you're always thinking about your business and the strategies you're going to use to grow, so getting those ideas down on paper shouldn't be hard—it can even be an enjoyable ...
Include the break-even analysis, sales forecast, balance sheet, and business ratios in this section. Convince the reader that your business will be a financial success. If you're asking for funding, outline your funding requirements. Explain clearly how much funding you will need and what you will use the money for.
Six Reasons You Really Need To Write a Business Plan. Legitimize your business idea. Give your business a foundation for success. Obtain funding and investments. Hire the right people. Communicate your needs. It makes it easier to sell your business. 1. Legitimize your business idea.
A recent Harvard Business Review study found that business planning had the most positive impact on businesses when the business plan was written between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business. In fact, planning at this stage increased the chances of success by 8%. I'll add a caveat to this study, though.
Bill Sahlman: Writing a business plan is a seminal moment in the life of a new venture. Doing so entails committing to paper a vision of the factors that will affect the success or failure of the enterprise. People take the exercise very seriously and get emotionally invested in what they produce. In that context, the article was written to ...
Refer to your business in third person. Writing in third person allows objectivity which can be more convincing and accepted by audiences like banks and investors. Avoid using "we" or "I" throughout your business plan. Writing in first person may come across as too personal. Remember to keep it business, not personal.
Make Your Notes Into a Business Plan. Now that you've organized your notes and decided on the purpose of your business plan, you can begin to write your plan in more detail. Use a template or make your own (spreadsheet skills come in handy here) and add all your information and projections to it. Try to strike a balance in your narrative ...
Developing a plan. If you're not sure about how to write an online business plan, you've come to the right place. One of the most essential tasks involved in starting any kind of business is to write a business plan. An online business plan won't look that different from a traditional business plan and will include many of the same elements.
Writing a business plan is hard work--many people spend a year or more writing their plan. In the early, drafting stages, business plan software can be very helpful. But the hard part is ...
Next step: write a business plan. ... Common Mistake #3: Writing Your Business Plan in a Vacuum. It can be hard to project what the future of your business will look like. Plotting out best and ...
Here are a few for your reference: Avoid overcomplicating your language; clarity and conciseness are more important than demonstrating language skills. Do not make unrealistic promises or ...
There are probably other reasons why writing a Business Plan is so difficult for a business owner. We need to keep in mind how important this is. I don't want to write Business Plans that sit on a shelf. I also don't write a Plan intended for a lender. I want to write a Business Plan that is going to be executed on by the business owner and ...
Focus on the importance of your chosen location and anything else that will make your convenience store special. Team and Management. Here, you can define your team's structure. Lay out who will be in charge of in-store operations and who will have input at a more operational business level.
Why you need a Butcher Shop Business Plan. By working through a business plan step by step, you take the time to examine all of the important details and nuances that this business will entail. This exercise also helps you to plan everything from your staff and management team to suppliers and a marketing strategy to help you attract customers.
Many hard-right Republicans remain opposed to this plan, and on Tuesday, Greene won a new ally: Rep. Thomas Massie of Kentucky, who is co-sponsoring the Georgia congresswoman's "motion to vacate ...
The public now has 30 days to comment on Biden's new student-loan forgiveness plan. It's the next step in implementing a broader version of debt relief for borrowers. The proposals include relief ...
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Joe Biden said Wednesday that he was immediately rushing badly needed weaponry to Ukraine as he signed into law a $95 billion war aid measure that also included assistance for Israel, Taiwan and other global hot spots. The announcement marked an end to the long, painful battle with Republicans in Congress over urgently needed assistance for Ukraine, with Biden ...