Curriculum / Math / 7th Grade / Unit 1: Proportional Relationships / Lesson 6

Proportional Relationships
Lesson 6 of 18
Criteria for Success
Tips for teachers, anchor problems, problem set, target task, additional practice.
Represent proportional relationships in graphs.
Common Core Standards
Core standards.
The core standards covered in this lesson
Ratios and Proportional Relationships
7.RP.A.2 — Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities.
7.RP.A.2.A — Decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship, e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table or graphing on a coordinate plane and observing whether the graph is a straight line through the origin.
7.RP.A.2.D — Explain what a point (x, y) on the graph of a proportional relationship means in terms of the situation, with special attention to the points (0, 0) and (1, r) where r is the unit rate.
Foundational Standards
The foundational standards covered in this lesson
6.RP.A.3.A — Make tables of equivalent ratios relating quantities with whole number measurements, find missing values in the tables, and plot the pairs of values on the coordinate plane. Use tables to compare ratios.
The essential concepts students need to demonstrate or understand to achieve the lesson objective
- Graph a proportional relationship in a coordinate plane using a table of values.
- Identify key features of the graph of a proportional relationship: a straight line that passes through the origin.
- Understand the graph of a proportional relationship to represent the set of equivalent ratios of the two quantities, represented as coordinate points.
- Interpret the coordinate point $$(x,y)$$ as it relates to the context of the situation.
Suggestions for teachers to help them teach this lesson
- Lessons 6 and 7 focus on representing proportional relationships in the coordinate plane. Students may need to review concepts and skills around the coordinate plane in order to fully access this lesson.
Lesson Materials
- Graph Paper (2-3 sheets per student)
- Ruler (1 per student)
Unlock features to optimize your prep time, plan engaging lessons, and monitor student progress.
Problems designed to teach key points of the lesson and guiding questions to help draw out student understanding
An amusement park sells tickets that can be used to go on rides and play games. The cost of the tickets is proportional to the number of tickets purchased. The table below shows how many tickets can be purchased for different amounts of money.
Graph the relationship in a coordinate plane. What features do you notice about the graph of a proportional relationship?
Guiding Questions
When Lili’s grandmother uses her rice cooker to make sushi rice, she uses a specific ratio of water to uncooked rice. The graph below shows this relationship.

a. Record the coordinate points from the graph. What do these ordered pairs represent?
b. What is the ratio of water to uncooked rice that Lili’s grandmother uses?
c. If Lili added 6 cups of water to 5 cups of uncooked rice, did she use her grandmother’s ratio? Explain how you know by looking at the graph.
d. What does the point (0, 0) represent in this situation? Why does it make sense that it is included on the graph?
A set of suggested resources or problem types that teachers can turn into a problem set
Give your students more opportunities to practice the skills in this lesson with a downloadable problem set aligned to the daily objective.
A task that represents the peak thinking of the lesson - mastery will indicate whether or not objective was achieved
The graph below shows the relationship between the cost of gasoline and the number of gallons of gasoline purchased at a gas station.

a. Is the cost of gasoline proportional to the amount of gasoline purchased? Explain how you know using the graph.
b. How many gallons of gasoline can you purchase with $15?
c. How much can you expect to pay for 3 gallons of gasoline?
d. What are the coordinates of point P, shown in the graph? Describe what point P means in context of the situation.
Student Response
The following resources include problems and activities aligned to the objective of the lesson that can be used for additional practice or to create your own problem set.
- Include review problems of prior skills such as graphing coordinate points in the coordinate plane, determining and setting up appropriate scale intervals, naming coordinate points in the coordinate plane, distinguishing between points on the $$x$$ -axis and those on the $$y$$ -axis, etc.
- Include problems where students are given a table of values and are asked to represent the relationship in a graph.
- Include problems where students are given a graph of a proportional relationship and must write a table of values to accompany it.
- Include problems where students interpret coordinate points $$(x,y)$$ from both graphs and tables
- Illustrative Mathematics Art Class, Variation 1
Topic A: Representing Proportional Relationships in Tables, Equations, and Graphs
Solve ratio and rate problems using double number lines, tables, and unit rate.
7.RP.A.1 7.RP.A.2
Represent proportional relationships in tables, and define the constant of proportionality.
7.RP.A.2 7.RP.A.2.B
Determine the constant of proportionality in tables, and use it to find missing values.
7.RP.A.2.A 7.RP.A.2.B
Write equations for proportional relationships presented in tables.
7.RP.A.2.B 7.RP.A.2.C
Write equations for proportional relationships from word problems.
7.RP.A.2 7.RP.A.2.C
7.RP.A.2 7.RP.A.2.A 7.RP.A.2.D
Interpret proportional relationships represented in graphs.
7.RP.A.2 7.RP.A.2.D
Create a free account to access thousands of lesson plans.
Already have an account? Sign In
Topic B: Non-Proportional Relationships
Compare proportional and non-proportional relationships.
Determine if relationships are proportional or non-proportional.
Topic C: Connecting Everything Together
Make connections between the four representations of proportional relationships (Part 1).
7.RP.A.2 7.RP.A.2.A 7.RP.A.2.B 7.RP.A.2.C 7.RP.A.2.D
Make connections between the four representations of proportional relationships (Part 2).
Use different strategies to represent and recognize proportional relationships.
Topic D: Solving Ratio & Rate Problems with Fractions
Find the unit rate of ratios involving fractions.
Find the unit rate and use it to solve problems.
7.RP.A.1 7.RP.A.3
Solve ratio and rate problems by setting up a proportion.
Solve ratio and rate problems by setting up a proportion, including part-part-whole problems.
Solve multi-step ratio and rate problems using proportional reasoning, including fractional price increase and decrease, commissions, and fees.
Use proportional reasoning to solve real-world, multi-step problems.
7.RP.A.1 7.RP.A.2 7.RP.A.3
Request a Demo
See all of the features of Fishtank in action and begin the conversation about adoption.
Learn more about Fishtank Learning School Adoption.
Contact Information
School information, what courses are you interested in, are you interested in onboarding professional learning for your teachers and instructional leaders, any other information you would like to provide about your school.

Effective Instruction Made Easy
Access rigorous, relevant, and adaptable math lesson plans for free
- → Resources
- → 7th Grade
- → Slope & Rate of Change
Graphing and Interpreting Graphs of Proportional Relationships Lesson Plan
Get the lesson materials.

Represent Proportional Relationships Graphs & Equations Guided Notes w/ Doodles
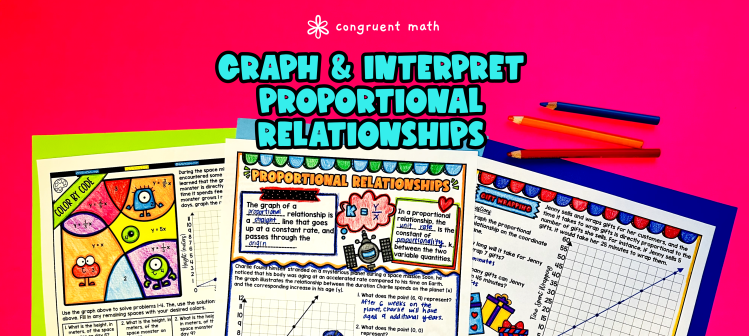
Ever wondered how to teach proportional relationships in an engaging way to your 7th and 8th grade students?
In this lesson plan, students will learn about representing proportional relationships through graphs and equations and explore their real-life applications. Then, they will also practice interpreting graphs of proportional relationships and understanding what the points represent in the context of the problem. Through artistic and interactive guided notes, checks for understanding, practice activities including a doodle & color by number worksheet, and a maze worksheet, students will gain a comprehensive understanding of proportional relationships.
The lesson culminates with a real-life application example that explores how proportional relationships are used in a practical context. Students will learn how to apply their knowledge of proportional relationships to solve real-world problems .
- Standards : CCSS 8.EE.B.5 , CCSS 7.RP.A.2.a , CCSS 7.RP.A.2.b , CCSS 7.RP.A.2.c , CCSS 7.RP.A.2.d
- Topics : Slope & Rate of Change , Ratio & Rates
- Grades : 7th Grade , 8th Grade
- Type : Lesson Plans
Learning Objectives
After this lesson, students will be able to:
Represent proportional relationships using graphs and equations
Interpret graphs and equations of proportional relationships
Calculate the constant of proportionality from a graph or equation
Calculate unit rates from a graph or equation
Explain the meaning of a point on the graph of a proportional relationship in terms of the situation
Explain how graphing proportional relationships is useful in real life
Prerequisites
Before this lesson, students should be familiar with:
H ow to plot points on a coordinate plane
Basic algebraic skills, including operations with decimals and whole numbers
Colored pencils or markers
Guided notes
Key Vocabulary
Proportional relationship
Constant of proportionality
Introduction

As a hook, ask students why understanding proportional relationships is important in real life. You can provide examples such as determining the amount of time it takes to complete a task, or comparing prices at the grocery store. Refer to the last page of the guided notes as well as the FAQs below for more ideas.
Use the first page of the guided notes to introduce the concept of representing proportional relationships with graphs and equations. Walk through the key points such as understanding what each point on the graph represents in terms of the situation, how to calculate the constant of proportionality & unit rate, and how to construct equations based on the constant of proportionality. You can model using the example of Charlie in space, as shown in the guided notes (page 1).
Based on student responses and understanding, reteach any concepts that students need extra help with. Then, have the students move onto the next page of guided notes (page 2) to practice constructing equations, graphing, interpreting graphs of proportional relationships. If your class has a wide range of proficiency levels, you can pull out students for reteaching, while more advanced students can work on the practice exercises independently.
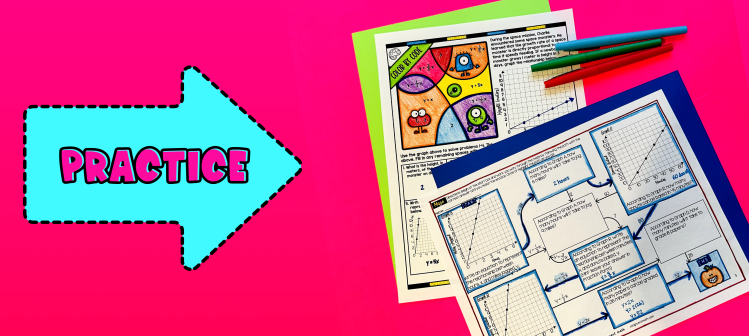
Have students practice graphing proportional relationships, interpreting graphs, and constructing equations using the maze activity (page 3), and color by number activity (page 4). Students will also be asked to solve for constant of proportionality in the practice. Walk around to answer student questions. You can also assign it as homework.
Real-Life Application

Use the last page of the guided notes (page 5) to bring the class back together, and introduce the concept of real-world application of proportional relationships. Explain to students that proportional relationships can be found in various real-life situations. These situations involve two quantities that change together at a constant rate or ratio.
Give examples of real-world scenarios where proportional relationships can be observed, such as:
Distance and Time: Discuss how the distance travelled is directly proportional to the time spent on the road.
Job Wages: Explain how some jobs pay employees based on the number of hours they work. For example, if a person earns $18 per hour, the amount of money they earn is directly proportional to the number of hours they work. As the number of hours worked increases, their earnings also increase.
Recipes: Share how recipes often require proportional measurements of ingredients. For example, if a recipe calls for 2 cups of flour and 1 cup of sugar, the ratio between flour and sugar remains constant even if the total amount of ingredients increases or decreases.
Ask students if they can think of any other real-life situations that involve proportional relationships. Encourage them to share their ideas with the class.
Refer to the FAQ section in the resource for more ideas on how to teach real-life applications of proportional relationships.
Additional Self-Checking Digital Practice
If you’re looking for digital practice for Representing Proportional Relationships Graphs & Equations, try my Pixel Art activities in Google Sheets. Every answer is automatically checked, and correct answers unlock parts of a mystery picture. It’s incredibly fun, and a powerful tool for differentiation.
Here are some activities to explore:
Graphs of Proportional Relationships Pixel Art
Constant of Proportionality Pixel Art
Proportional vs. Non-Proportional Relationships Pixel Art
Solving Proportions Pixel Art Google Sheets
Additional Print Practice
A fun, no-prep way to practice Representing Proportional Relationships Graphs & Equations is Doodle Math — they’re a fresh take on color by number or color by code. It includes multiple levels levels of practice, perfect for a review day or sub plan.
Here are some activities to try:
Constant of Proportionality Doodle Math (Winter Themed)
Constant of Proportionality Doodle Math (Thanksgiving Themed)
1. What is a proportional relationship? Open
A proportional relationship is a relationship between two quantities where the ratio of one quantity to the other remains constant. In other words, as one quantity increases or decreases, the other quantity increases or decreases by the same factor.
2. How do you represent a proportional relationship graphically? Open
To represent a proportional relationship graphically, you can plot the ordered pairs on a coordinate plane. Each point on the graph represents a pair of values from the proportional relationship. The graph will show a straight line passing through the origin (0, 0), indicating a constant ratio between the two quantities.
3. How do you write an equation for a proportional relationship? Open
To write an equation for a proportional relationship, you can use the formula y = kx, where y represents one quantity, x represents the other quantity, and k represents the constant of proportionality. The constant of proportionality is the ratio between the two quantities that remains constant.
4. What does a point (x, y) on the graph of a proportional relationship mean in terms of the situation? Open
In terms of the situation, a point (x, y) on the graph of a proportional relationship represents a particular combination of values for the two quantities involved. The x-coordinate represents the input or independent variable, while the y-coordinate represents the output or dependent variable. The point shows how the two quantities are related and how they change together.
5. How do you calculate the constant of proportionality? Open
To calculate the constant of proportionality, you can choose any two corresponding values from the proportional relationship. Divide the y-value by the x-value to find the ratio between the two quantities. The resulting ratio will be the constant of proportionality.
6. What is a unit rate? Open
A unit rate is a rate that compares a quantity to one unit of another quantity. It tells you how much of one quantity is associated with one unit of another quantity. For example, if the constant of proportionality is 3, it means that for every 1 unit increase in the independent variable (x), the dependent variable (y) increases by 3 units.
7. What are some real-life applications of proportional relationships? Open
Proportional relationships can be found in various real-life situations. Some examples include:
The relationship between distance and time in speed measurements.
The relationship between the number of workers and the amount of work completed in a fixed amount of time.
The relationship between the number of items purchased and the total cost at a fixed price per item.

8. How can guided notes and doodles help students understand graphing and equations of proportional relationships? Open
Guided notes and doodles are effective teaching tools that engage students and promote active learning. They provide structured notes and visual representations that support students in understanding and retaining the concepts. By including interactive elements like coloring and problem-solving activities, guided notes and doodles make the learning experience enjoyable and memorable for students. They also serve as valuable references for students to refer back to when practicing or reviewing the topic.
Want more ideas and freebies?
Get my free resource library with digital & print activities—plus tips over email.
Chapter 3, Lesson 6: Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships
- Extra Examples
- Personal Tutor
- Self-Check Quizzes
The resource you requested requires you to enter a username and password below:
Please read our Terms of Use and Privacy Notice before you explore our Web site. To report a technical problem with this Web site, please contact the site producer .

Math Worksheets Land
Math Worksheets For All Ages
- Math Topics
- Grade Levels
Graphing Proportional Relationships Worksheets
How do you graph proportional relationships? Suppose your teacher asks you to graph a proportional relationship between two variables (x and y) with the unit rate of 0.4, which is a change in a single unit of x will cause a change of 0.4 units in y. Let's think about some potential values between x and y. Remember that here we have an independent value x and an independent value y. What that means is that some value of y will be equal to a constant multiplied with the value of x. If we were to express this using an expression, it would be: Y = kx (K equals to any constant number) X, Y = (0, 0), (1, 0.4), (2, 0.8), (3, 1.2), (4, 1.6), (5, 2) If you were to draw a graph of these values, you would know that it is going to make a straight line. It shows that the graph has a proportional relationship. This series of lessons and worksheets will help students learn how to graph and identify graphs of proportional relationships.
Aligned Standard: Grade 8 Expressions and Equations - 8.EE.B.5
- Faster Paces Step-by-Step Lesson - Two boys are riding bikes. Which one moves at a faster pace?
- Guided Lesson - All the problems compare a graph to an equation. So kids find it easier to graph the equation. Yet others find it easier to determine the equation of the graph.
- Guided Lesson Explanation - I like equations and for the answers I put everything into an equation. I will come back and work on this one to have a graph comparison version later this month.
- Independent Practice - It's a big battle royale of graphs versus equations.
- Matching Worksheet -This one is pretty easy because it's matching. I would insist on everyone showing their work.
- Answer Keys - These are for all the unlocked materials above.
Homework Sheets
Compare the graph and the equation without any change.
- Homework 1 - The graph below represents the number of cakes that Eric makes in a day. The equation (right) represents how many cakes Lewis makes in a day. Who makes cakes at a faster rate?
- Homework 2 - When both equations are constant. This makes it very easy to compare.
- Homework 3 - The graph below represents the number of trips made by Truck A over 7 days. The equation below represents the number of trips made by Truck B over 7 days. Who takes more trips over the course of a week?
Practice Worksheets
The color of the line dot here was requested by many teachers. It shows up well on Smart boards.
- Practice 1 - The equation represents the rate at which Jackson sells books. Who sells more books over 5 hours?
- Practice 2 - The equation represents the rate at which Sarah travels on her scooter. If both Jessie and Sarah were to travel for 7 straight days, who would you predict to travel further?
- Practice 3 - Over a day, who watches more movies?
Math Skill Quizzes
Because of the size of the graph, I can only get two questions on each page.
- Quiz 1 - Who uses strawberries at a faster rate?
- Quiz 2 - Who eats more cookies over the course of a week?
- Quiz 3 - The equation represents the number of greeting cards made by the Kim and the number of sheets used. Who uses fewer sheets?
How to Spot Proportional Relationships on Graphs
When two variables have a proportional relationship, they will exist in a ratio to one another that is constant. This means that when they are visualized on a line graph, first they will form a line that passes through the origin (0, 0). They will exist in some form of the equation y = kx. To translate this for you as x increase, so does y. If the y value decreases, then so does the x value. As a result, they are relentless proportion with one another. Regardless of how big or small their values are, these variables will always be relative to one another.
Get Access to Answers, Tests, and Worksheets
Become a paid member and get:
- Answer keys to everything
- Unlimited access - All Grades
- 64,000 printable Common Core worksheets, quizzes, and tests
- Used by 1000s of teachers!
Worksheets By Email:
Get Our Free Email Now!
We send out a monthly email of all our new free worksheets. Just tell us your email above. We hate spam! We will never sell or rent your email.
Thanks and Don't Forget To Tell Your Friends!
I would appreciate everyone letting me know if you find any errors. I'm getting a little older these days and my eyes are going. Please contact me, to let me know. I'll fix it ASAP.
- Privacy Policy
- Other Education Resource
© MathWorksheetsLand.com, All Rights Reserved
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
EVERYTHING YOU NEED FOR THE YEAR >>> ALL ACCESS
Maneuvering the Middle
Student-Centered Math Lessons
Teaching Proportional Relationships
Some of the links in this post are affiliate links that support the content on this site. Read our disclosure statement for more information.
Proportional relationships are ingrained in our everyday life. While most students pick up on the process to solve fairly quickly, there is so much foundational, conceptual knowledge that we want to acknowledge and emphasize.
Today, let’s examine how proportional relationships go far beyond just solving for a missing number and how to set a foundation for success in Algebra.
THE STANDARDS
7.RP.2 Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities.
- 7.RP.2A Decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship , e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table or graphing on a coordinate plane
- 7.RP.2B Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, diagrams, and verbal descriptions of proportions.
- 7.RP.2C Represent proportional relationships by equations.
- 7.RP.2D Explain what a point (x, y) on the graph of a proportional relationship means in terms of the situation, with special attention to the points (0, 0) and (1, r), where r is the unit rate.
VERTICAL ALIGNMENT
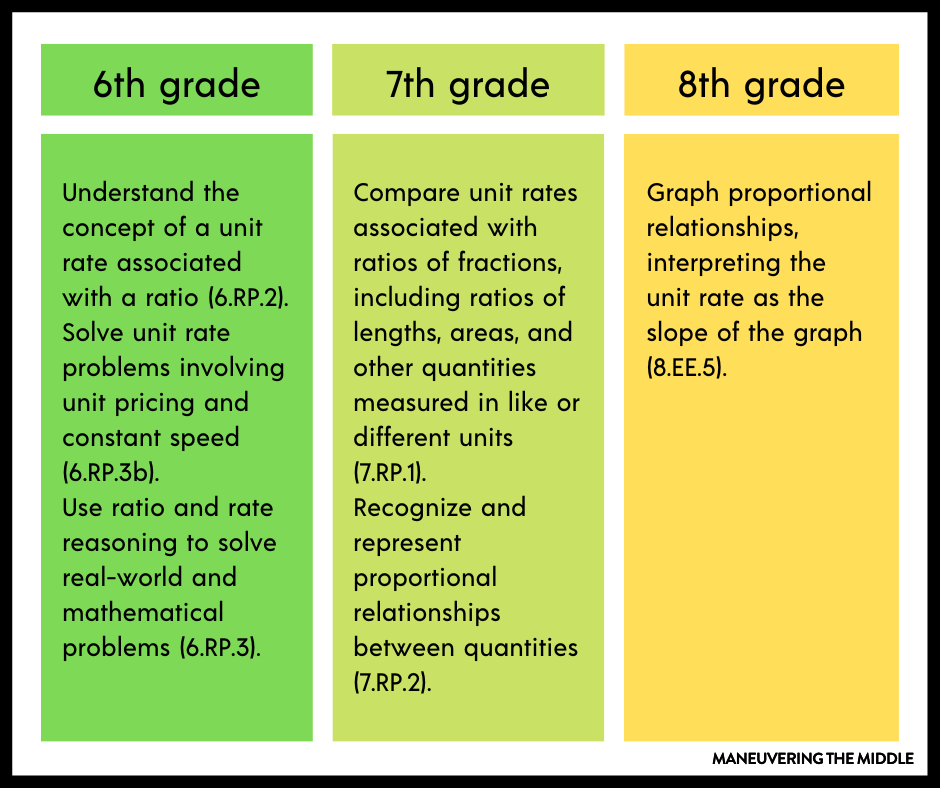
Visual Representations
These standards are heavily weighted with visual representations, including tables, graphs on the coordinate plane, and diagrams. Some students will have been exposed to these multiple representations in 6th grade with standard 6.RP.3 and equivalent ratios . The goal is for students to fluently connect the table, equation, graph, verbal description, and even diagram together. When given one piece of information, students should be able to represent that same information in multiple ways. Students who can do this will have a firm foundation for 8th grade math and Algebra 1.
Ideas for Teaching Proportional Relationships
There are tons of great ideas and activities out there, but below are a few of my favorite “tried and true.” They are all easy to incorporate and provide scaffolding for students who struggle in the math classroom.
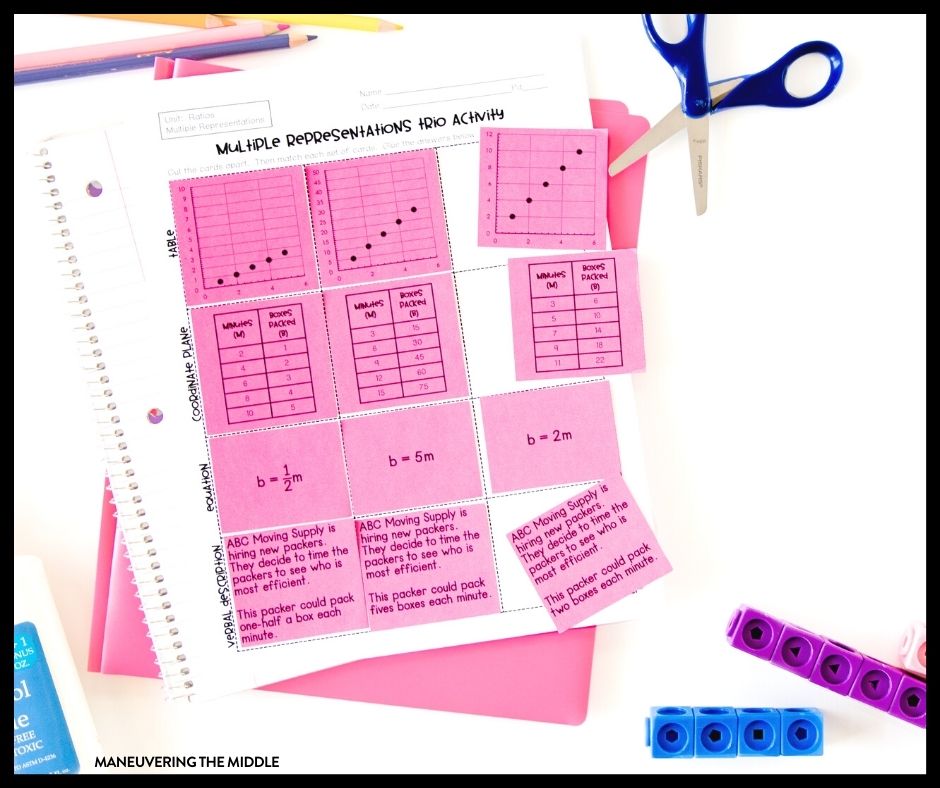
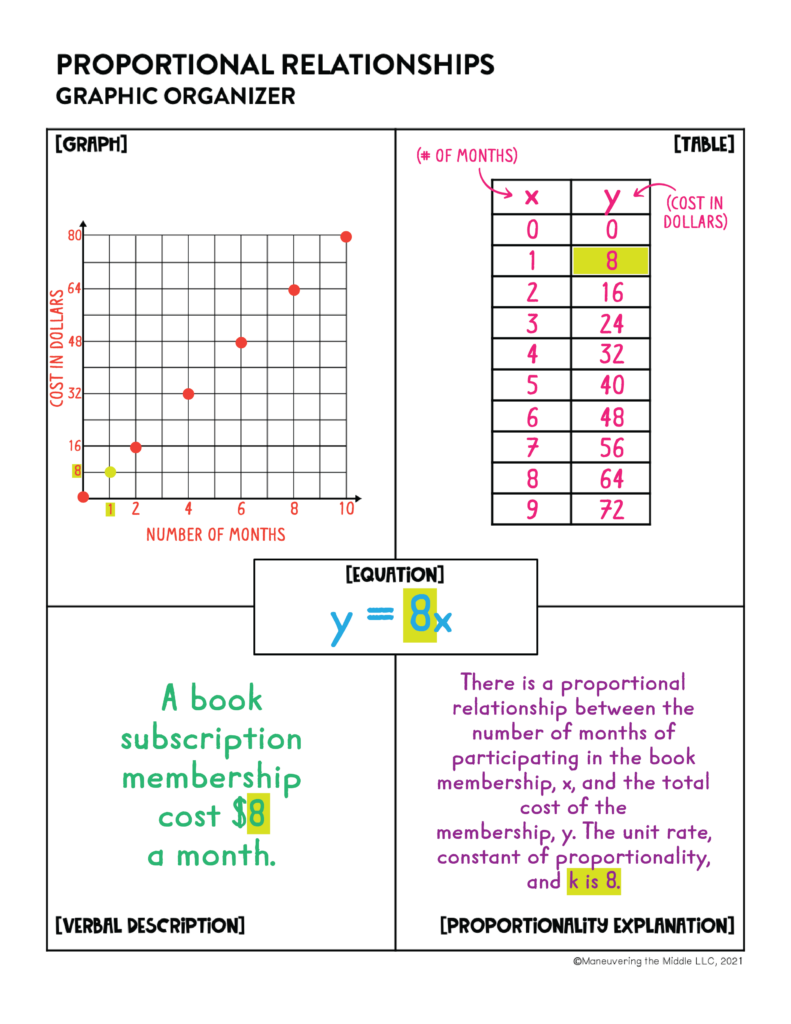
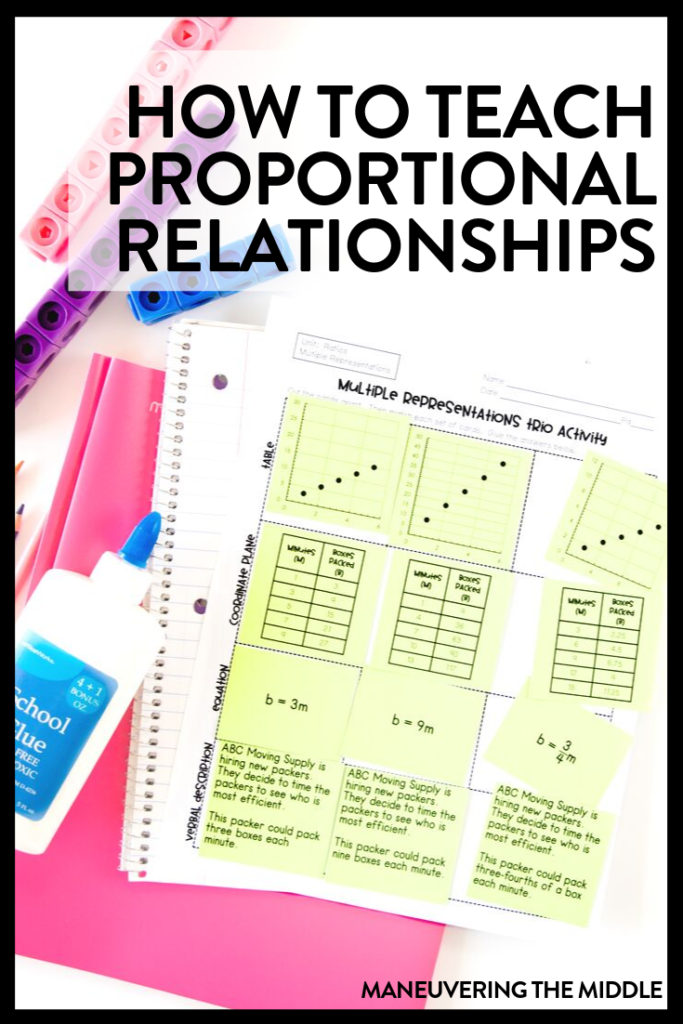
1. Multiple Representations Graphic Organizer
Some students need to see everything together, and that is where this multiple representations graphic organizer comes in handy. It is the perfect size for students to show their work. I really like how the components stay the same, but the given information changes.

These are perfect for introducing the various visual representations, but it also can be reused in a clear pocket to use in tutoring or in math intervention . Once students are familiar with the graphic organizer, I would even give students butcher paper and various pieces of information. Then, they would use markers to represent the remaining information. This is a quick informal assessment idea or can even function as partner work for a Friday.
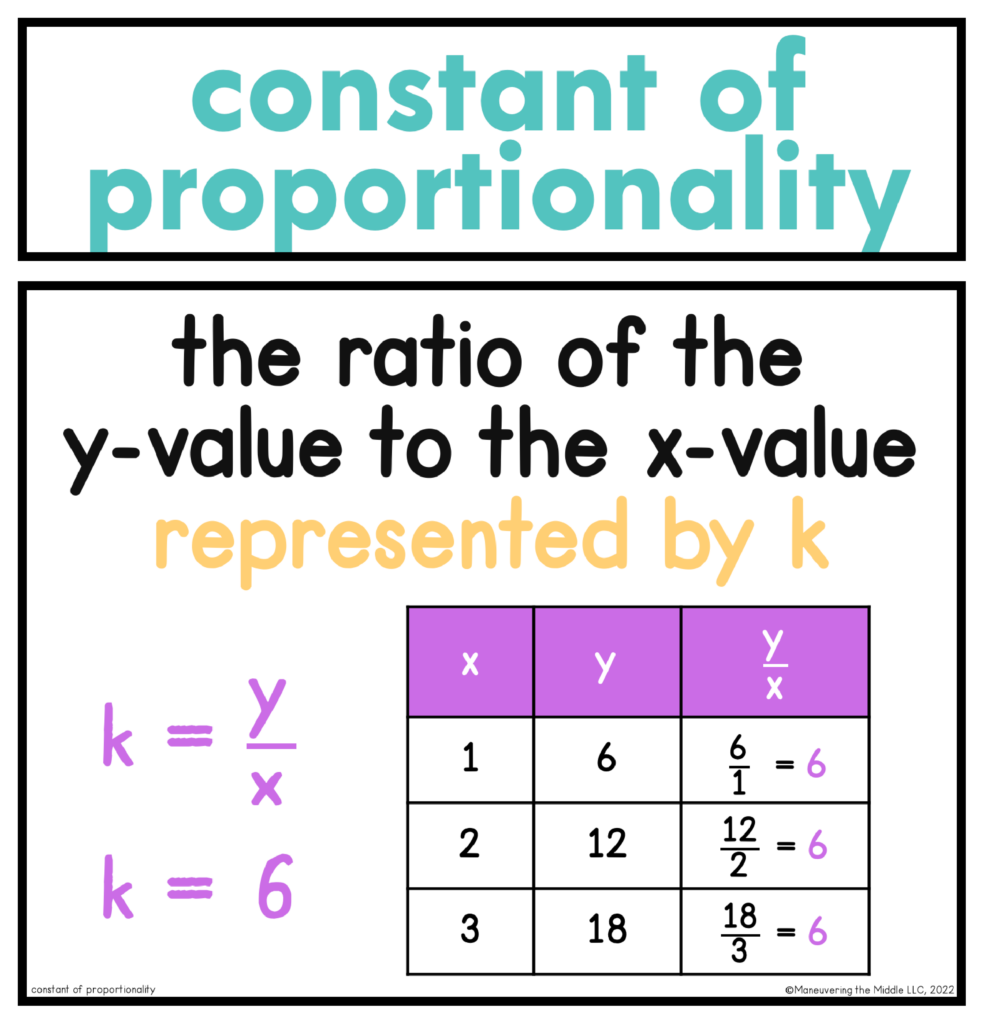
2. Highlight the Unit Rate/Constant of Proportionality
A quick trick to help students see all the connections is to use a highlighter! Model and have students highlight the unit rate/constant of proportionality within the different representations. This is perfect for representing k in the equation and in the table or meeting 7.RP.2D by labeling (1, r) on the graph.
3. Emphasize Vocabulary
Hopefully, students are familiar with the term “unit rate” and how to find it. Constant of proportionality sounds so cumbersome and challenging. Unit rate is often emphasized when we are talking about unit price (cost per ounce, etc), so I think students have trouble seeing a graph or a table and also using the phrase “unit rate.” Either way, students need to be familiar with the verbiage and understand what a question is asking. Here is a more detailed explanation for why they are the same.
Common Misconceptions
- A relationship is not proportional unless (0,0) is visible in the table or graph
- Dividing x/y to find k
- General confusion about k
- General disconnect between k and proportions
- Proportional relationships only involve positive numbers
- Mixing up x and y on the table, when it is not explicitly stated
Anchor Chart Ideas
Anchor charts are fabulous ways to showcase the content in a visual manner for students to reference. They can easily be created before the lesson or as you are teaching, depending on the content. The visual representations of proportional relationships are perfect for anchor charts.
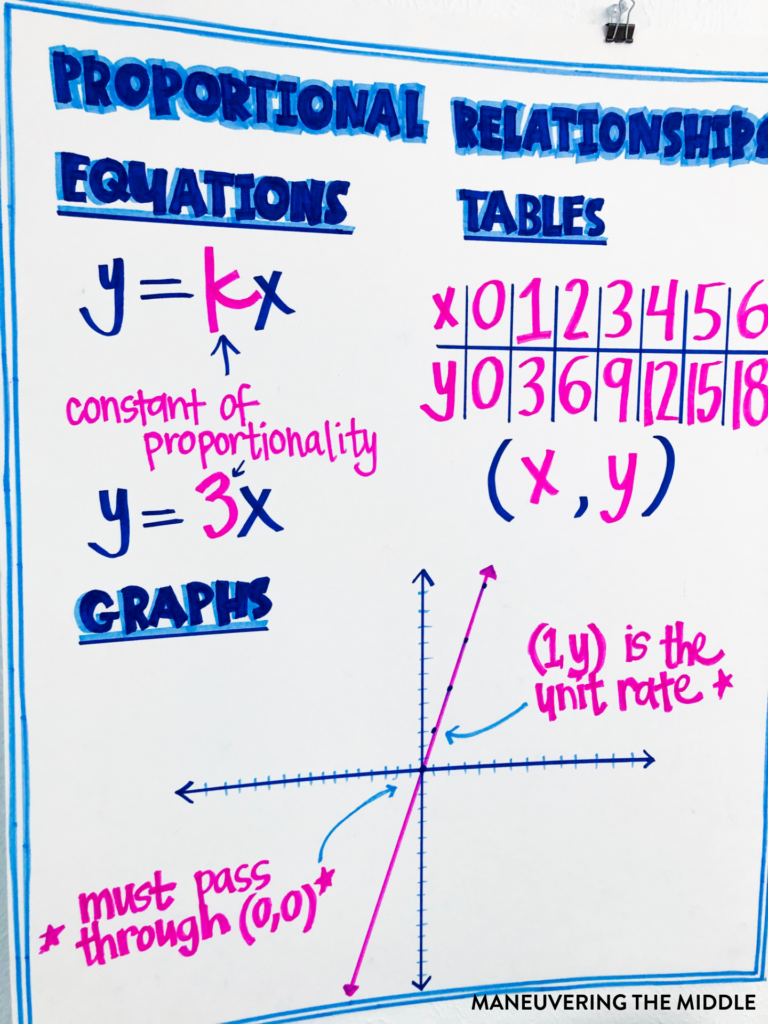
Ideas for Struggling Students
- Practice finding different points in the proportion that aren’t listed on a table.
- Begin with the equation and use and input-output table to create a table.
- Use a four corners graphic organizer.
- Match multiple representations.
- Practice graphing with four quadrants (from 6th grade).
Hopefully, this gives you some ideas for teaching proportions or even insight as to what knowledge your students are coming with. I would love to hear other great activities or ideas you have used! Feel free to share in the comments.
Check out some of our other math concepts posts: percents | ratios | integers
What concept would you like to hear more from us about?

Math Fast Pass
Check out these related products from my shop.

Reader Interactions
September 18, 2017 at 2:16 pm
I would like your permission to the Anchor Chart Ideas image from the following article https://www.maneuveringthemiddle.com/how-to-teach-proportional-relationships/ on my digital notebook that is posted in my online classroom.
I am a teacher at Southwest Career and Technical Academy in Las Vegas, NV.
September 25, 2017 at 1:47 pm
Thanks so much for checking. That is great with me as long as attribution is given to the site. Thanks!
October 22, 2017 at 3:38 pm
This was very helpful in clearing up a misconception I have between ROC and proportionality. Thank you for posting this!!
January 8, 2018 at 4:00 pm
First, thank you for these great resources! In the graphic organizer, what do you have your students write for the “verbal description” and “proportionality description”?
February 3, 2018 at 5:56 pm
Hi! I like to have students write a scenario in the verbal description section and in determine if the relationship is proportional or not in the other.
September 29, 2018 at 4:39 pm
Do you have the activities for this in your TpT store? If so, can you send link?
March 15, 2024 at 10:28 am
Hi, Patty – There are links provided in the blog post about Proportional Relationships!
October 30, 2023 at 3:27 am
Hi, I’m trying to access the proportional relationships graphic organizer. When I click on the link to download it, I am getting a message that says that the resource is not available.
November 7, 2023 at 9:41 am
Hi, Kate! That part of our website can be tricky. I just checked and if you click on the image that says “get your freebie,” (after the first point) it works! If you are still having any trouble, please email us at [email protected] and we will send it over there. Thanks!
Chapter 6, Lesson 4: Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships
- Extra Examples
- Personal Tutor
- Self-Check Quizzes
The resource you requested requires you to enter a username and password below:
Please read our Terms of Use and Privacy Notice before you explore our Web site. To report a technical problem with this Web site, please contact the site producer .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Lesson 6 Homework Practice Graphing Proportional Relationships Determine whether each relationship is proportional by graphing on a coordinate plane. Explain your reasoning. 1. Number of Sandwiches 1 5 10 15 20 Cost ($) 3 13.75 25 33.75 40 2. Time (hr) 01235 Number of Gallons 0 600 1200 1800 2400 Find and interpret the constant of ...
Algebra. Algebra questions and answers. NAME DATE PERIOD Lesson 6 Extra Practice Graphing Proportional Relationships 1. Determine whether the relationship shown 2 Determine whether the relationship shown is proportional by graphing on the coordinate proportional hy graphing on the coordinate plane. Explain your reasoning plane.
7.RP.A.2.A — Decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship, e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table or graphing on a coordinate plane and observing whether the graph is a straight line through the origin. 7.RP.A.2.D — Explain what a point (x, y) on the graph of a proportional relationship means in terms of the ...
Graphing proportional relationships. Graph the line that represents a proportional relationship between d and t with the property that an increase of 5 units in t corresponds to an increase of 8 units in d .
A. The point ( 0, 0) shows that any amount of red and blue paint will make the same shade of purple. The point ( 3, 9) shows that 9 liters of red paint are needed for every 3 liters of blue paint. B. The point ( 3, 9) shows that 9 liters of red paint are needed for every 3 liters of blue paint. None of the above. C.
7th grade (Illustrative Mathematics) 8 units · 110 skills. Unit 1 Scale drawings. Unit 2 Introducing proportional relationships. Unit 3 Measuring circles. Unit 4 Proportional relationships and percentages. Unit 5 Rational number arithmetic. Unit 6 Expressions, equations, and inequalities. Unit 7 Angles, triangles, and prisms.
Practice. Have students practice graphing proportional relationships, interpreting graphs, and constructing equations using the maze activity (page 3), and color by number activity (page 4). Students will also be asked to solve for constant of proportionality in the practice. Walk around to answer student questions.
Lesson 6 Reteach Solve Proportional Relationships A proportion is an equation that states that two ratios are equivalent. To determine whether a pair of ratios forms a proportion, use cross products. You can also use cross products to solve proportions. Example 1 Determine whether the pair of ratios −−20 and 24 −−12 form a proportion. 18
Graphing Technology Personal Tutors Other Calculator Keystrokes Meet the Authors About the Cover Scavenger Hunt Recording Sheet Chapter Resources Chapter Readiness Quiz Chapter Test Math in Motion Standardized Test Practice Vocabulary Review Lesson Resources Extra Examples Personal Tutor Self-Check Quizzes
Practice graphing proportional relationships and finding the constant of proportionality with this eighth-grade math worksheet! In this two-page worksheet, students are given several word problems, each of which contains a ratio that defines a proportional relationship between two quantities. Students will use the given ratios to find the ...
Unit 1: Proportional relationships. Learn all about proportional relationships. How are they connected to ratios and rates? What do their graphs look like? What types of word problems can we solve with proportions? Learn all about proportional relationships. How are they connected to ratios and rates? What do their graphs look like?
When two variables have a proportional relationship, they will exist in a ratio to one another that is constant. This means that when they are visualized on a line graph, first they will form a line that passes through the origin (0, 0). They will exist in some form of the equation y = kx. To translate this for you as x increase, so does y.
Lesson 6: Solve Proportional Relationships ... homework_practice_solve_proportional_relationships_answers.pdf: File Size: 524 kb: File Type: pdf: Download File. INTERACTIVE Self-Check Quiz. Reteach Documents: See it again for the first time! reteach_solve_proportional_relationships.pdf:
It's important to note that this sample lesson is the last of a 6-lesson series on "Proportional Relationships," which is part of a 22-lesson unit on Ratios and Proportional Relationships. This sample lesson lays a strong foundation for the work that is to come in the unit, but it is not intended for students to meet
Video transcript. Graph the line that represents a proportional relationship between y and x with a unit rate 0.4. That is, a change of one unit in x corresponds to a change of 0.4 units in y. And they also ask us to figure out what the equation of this line actually is. So let me get my scratch pad out and we could think about it.
Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, diagrams, and verbal descriptions of proportional relationships. 7.RP.A.2d Explain what a point (x, y) on the graph of a proportional relationship means in terms of the situation, with special attention to the points (0, 0) and (1, r) where r is the unit rate.
Lesson 6 Homework Practice Graphing Proportional Relationships Determine whether each relationship is proportional by graphing on a coordinate plane. Explain your reasoning. 1. Number of Sandwiches 1 5 10 15 20 Cost ($) 3 13.75 25 33.75 40 2. Time (hr) 01235 Number of Gallons 0 600 1200 1800 2400 Find and interpret the constant of ...
7.RP.2 Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. 7.RP.2A Decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship, e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table or graphing on a coordinate plane. 7.RP.2B Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, diagrams, and ...
A proportional relationship is one where there is multiplying or dividing between the two numbers. A linear relationship can be a proportional one (for example y=3x is proportional), but usually a linear equation has a proportional component plus some constant number (for example y=3x +4). ( 3 votes) Upvote. Downvote.
Graphing Technology Personal Tutors About the Cover Meet the Authors Other Calculator Keystrokes Scavenger Hunt Recording Sheet Cross-Curricular Projects Chapter Resources Chapter Readiness Quiz Chapter Test Math in Motion Reading in the Content Area Real-World Careers Standardized Test Practice Vocabulary Review Lesson Resources Extra Examples ...
"In Module 1, students build on their Grade 6 experiences with ratios, unit rates, and fraction division to analyze proportional relationships. They decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship, identify constants of proportionality, and represent the relationship by equations. These skills are then applied to real-world problems including scale drawings."