Advertisement

10 Big Questions in the U.S. Gun Control Debate
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email
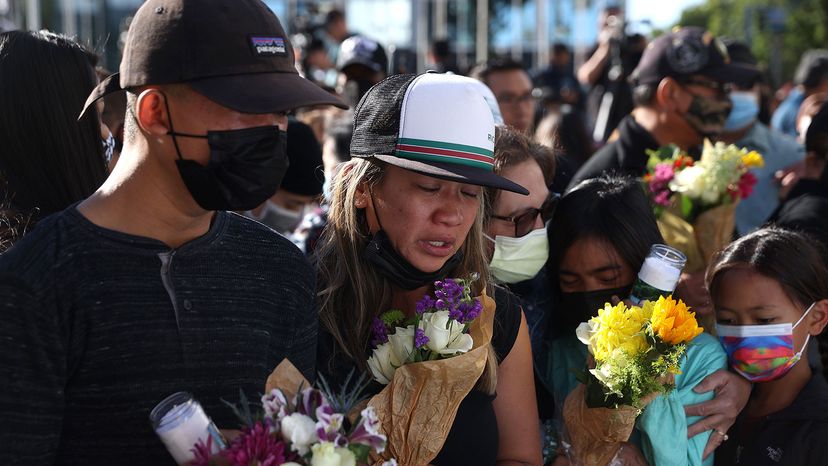

In May 2021, a disgruntled employee at a public transit rail yard in San Jose, California, opened fire on co-workers, firing 39 rounds that killed eight of them and wounding a ninth who later died, before taking his own life in front of law enforcement officers who had rushed to the scene. The mass killer had three 9-millimeter semi-automatic handguns with him and 11 ammunition magazines on his belt. Later, authorities found 12 more firearms and 25,000 rounds of ammunition at the suspect's home [sources: Fernando, Hays and Hauck ; Hanna and Vera ].
The horrific slaughter was yet another shock to a nation that in recent decades has been traumatized again and again by mass shootings, from the killing of 20 elementary school students and six adults by a 20-year-old gunman in Newtown, Connecticut, in 2012, to the massacre of 58 spectators at a country music concert in Las Vegas by a 64-year-old sniper who rained fire down on them from the 32nd floor of a resort hotel [sources: Candiotti and Aarthun ; Hutchinson, et al .].
From 1999 to 2021, more than 2,000 people were killed in mass shootings, according to an analysis by Reuters [source: Canipe and Hartman ]. But mass shootings are just part of the larger pattern of firearm violence. In 2020, despite the pandemic, nearly 20,000 people were killed in homicides and 24,000 died in suicides involving guns [source: Thebault and Rindler ].That unceasing carnage has led many Americans to call for stricter gun laws.
"We need to treat gun violence as a public health issue, " Fred Guttenberg, whose 14-year-old daughter Jaime was killed in a 2018 mass shooting at a high school in Parkland, Florida, explained in a 2021 interview [source: Allen ].
But gun rights advocates say such laws would violate Americans' constitutional right to bear arms. They also argue that citizens need weaponry to defend against criminals. "The only way to stop a bad guy with a gun is with a good guy with a gun, " National Rifle Association executive vice president Wayne LaPierre said in 2012 [source: CBS DC ].
Others even say that gun rights are essential to stave off the possibility of government tyranny.
"The Second Amendment is about maintaining, within the citizenry, the ability to maintain an armed rebellion against the government if that becomes necessary, " Rep. Matt Gaetz, R-Fla., told an audience a political rally in May 2021 [source: Chamberlain ].
So which side is right? That's for you to decide. But to help you make an informed decision, here are answers to 10 big questions in the U.S. gun control debate.
- How Many Guns Are in the U.S.?
- What Does the Second Amendment Say?
- Is the U.S. Gun Homicide Rate Really That High?
- Are There Countries With as Many Guns as the U.S. but With Less Crime?
- Could Technological Advances Make Gun Control Impossible?
- How Often Do Gun Owners Actually Prevent Crimes?
- How Often Are People Killed by Their Own Guns?
- Did the Federal Ban on Assault Weapons Affect Crime?
- Do States With Strict Gun Control Laws Have Less Gun Violence?
- Has American Public Opinion Shifted on Gun Control?
10: How Many Guns Are in the U.S.?
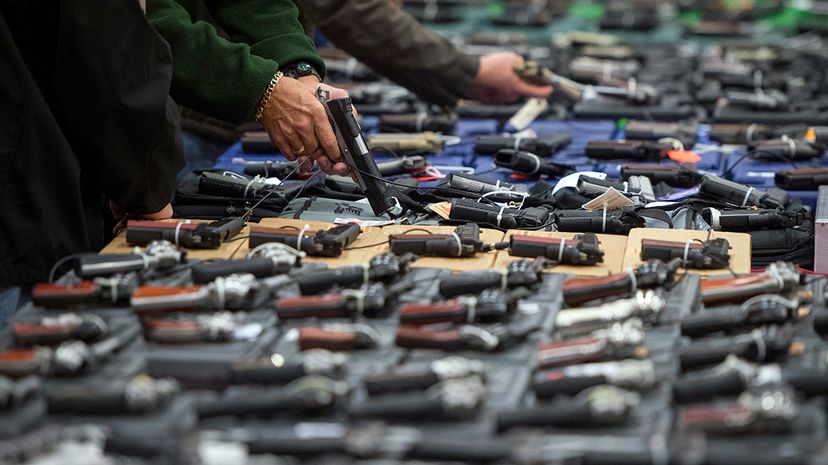

The U.S. has a lot of guns — so many, in fact, that there's more than one firearm for every person who lives in the country. According to the Geneva, Switzerland-based Small Arms Survey, in 2017 there were an estimated 393 million guns in the U.S., including 114 million handguns, 110 million rifles and 86 million shotguns [source: Karp ]. This already huge privately held arsenal is growing at a very fast rate. In 2020 alone, Americans purchased nearly 40 million firearms, according to FBI data [source: McIntyre ].
That may lead you to the mistaken impression that everyone is packing heat. In truth, however, the majority of Americans still are unarmed. A 2020 Gallup Poll found that only 32 percent of Americans personally owned a gun, though 44 percent lived in households in which someone possessed a firearm. Firearm owners were most likely to be male, white, Republicans or politically conservative, live in the South and have a household income of over $100,000. In contrast, only 19 percent of women owned guns, and low percentages of nonwhite Americans, political moderates and liberals, people in the Eastern U.S. and those earning less than $40,000 owned firearms [source: Saad ].
But gun purchases — and gun manufacturing — are both at all-time highs. So, if more guns are being sold, more people must be owning guns, right? Wrong. It appears most of the new gun purchases are by existing gun owners. In fact, a relatively small number of heavily armed people own most of the country's guns. A groundbreaking study published in 2017 by the Russell Sage Foundation found that half of America's gun stock (at the time, approximately 130 million guns) was owned by approximately 14 percent of gun owners [source: Azrael, et al .].
9: What Does the Second Amendment Say?

The Second Amendment to the U.S. Constitution states the following: "A well-regulated militia, being necessary to the security of a free state, the right of the people to keep and bear arms, shall not be infringed." But what that means is the subject of intense debate. Pro-gun partisans argue that the Constitution's framers guaranteed peoples' right to possess and carry just about any sort of firearm. Gun control advocates say it was intended to allow states to maintain the equivalent of today's National Guard units [source: Krouse ].
But as Supreme Court Justice Charles Evans Hughes once noted, "The Constitution is what the judges say it is" [source: Columbia University ]. And so far, probably to both sides' frustration, the courts have never fully defined the Second Amendment and its implications. Instead, the U.S. Supreme Court has issued a series of rulings that mostly have upheld the government's authority to impose restrictions upon weapons.
For example, in the 1937 case U.S. v. Miller , a court upheld a federal statute requiring licensing of sawed-off shotguns, saying that some types of weaponry weren't needed by a militia and thus weren't constitutionally protected. (Gun rights advocates replied that this type of weapon had been used by militia before.) More recently, in the 2008 case District of Columbia v. Heller , the court found that citizens did have a right to possess handguns at home for self-defense. But the justices said the government still could impose other limits — such as banning criminals and those with mental illness from owning guns, regulating gun sales and barring guns from schools and other places [source: Krouse ].
8: Is the U.S. Gun Homicide Rate Really That High?
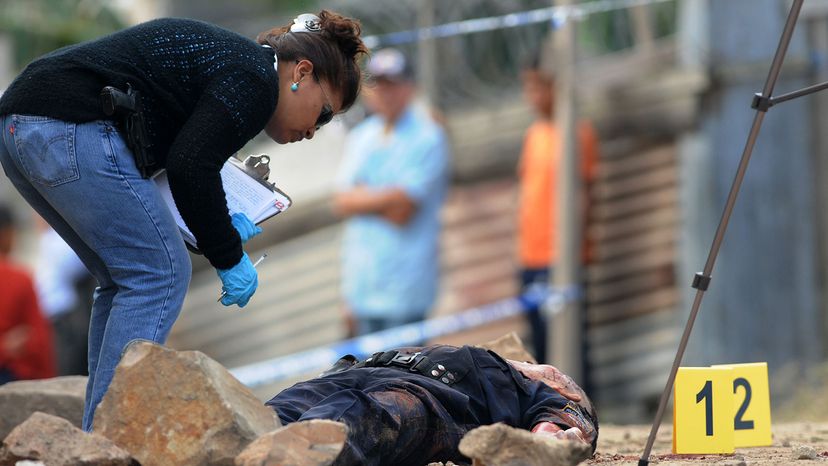

In 2019, guns were used in 13,927 homicides in the U.S. — in nearly 74 percent of murders that year [source: FBI ]. Whether that rate seems high to you depends upon your perspective. According to a global database maintained by the University of Washington's Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, the U.S. ranks 32nd in deaths from gun violence worldwide, with 3.96 killings per 100,000 people [source: Aizenman ].
But many countries in Latin America and the Caribbean had vastly higher rates. El Salvador's gun homicide rate was 36.78 per 100,000 — more than nine times the U.S. rate. Venezuela (33.27), Guatemala (29.06), Colombia (26.36), Brazil (21.93), Bahamas (21.52) and Mexico (16.41) all had proportionately much bigger problems. The Philippines (8.05) and South Africa (5.28) also outdid the U.S., according to the same report.
But those places tend to be developing countries where law and order is weak, or places with political unrest. Compared to other industrialized democracies, the U.S. gun homicide rate is through the roof. The U.K., for example, had just 0.04 gun killings per 100,000 in 2019, and Japan and South Korea had only 0.02. Canada had 0.47. In other words, the U.S. death rate from gun violence was eight times as high as that of Canada and 100 times that of the U.K. [source: Aizenman ].
So here's another question: Would the homicide rate in the U.S. be lower if there were fewer guns available? A comparison with England and Wales suggests that it might be. Those parts of the U.K. actually have higher rates of some violent crimes than the U.S. The English-Welsh assault rate was 925.4 per 100,000 population in 2018, compared to just 246.84 in the U.S., and the robbery rate of 131.227 per 100,000 in 2017 was 33 percent higher than the U.S. rate. But the U.S. has a lot more killing — its homicide rate in 2017 was more than quadruple the English-Welsh homicide rate of 1.2 per 100,000 [source: UNODC ]. As the American Psychological Association concluded in a 2013 report on gun violence, "The use of a gun greatly increases the odds that violence will lead to a fatality."
7: Are There Countries With as Many Guns as the U.S. but With Less Crime?
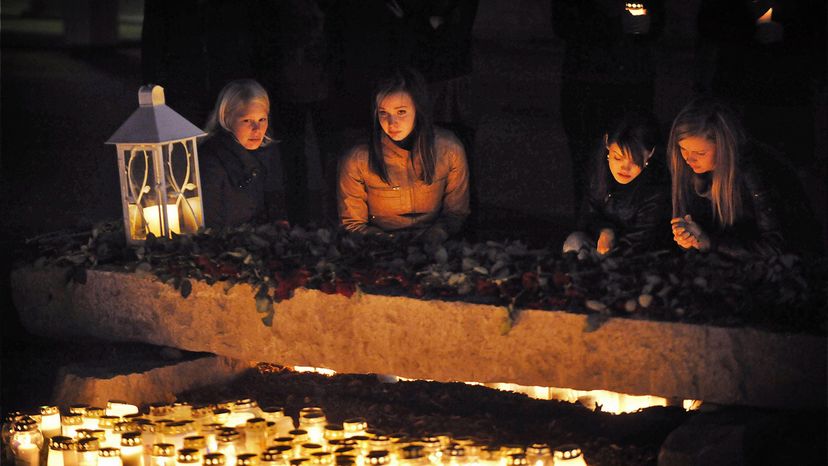

No, because there isn't another country in the world with as many guns as the U.S. The U.S. comprises 4 percent of the world's population, but owns about 40 percent of the world's civilian firearms. The rate of about 121 guns per 100 people is tops in the world, followed by the politically unstable Yemen, at 53 guns per 100 people [source: Small Arms Survey ].
So, let's reframe the question. Are there countries with relatively high gun-ownership rates — and low crime rates? Yes: Finland, which has 32 guns per 100 people, and Canada, which has 34.7 guns per 100 people. (Finland ranks fourth in the world for the rate of private gun ownership.) Finland had just 9 gun homicides in 2016, a rate of 0.20 per 100,000 people. Canada, with 223 gun killings in 2016, had a slightly higher rate of 0.62 per 100,000 [source: Gunpolicy.org ].
But both those countries have stricter gun control laws than the U.S. In Finland, a nation where most use guns for hunting rather than protection, citizens must obtain gun licenses, which must be renewed every five years. They also must state the reason they wish to have a gun — and self-defense is not a valid reason [source: Finnish Police ].
Police deny or revoke permission if an applicant is convicted of a crime — or shows any sort of behavior that authorities think might indicate that he or she wouldn't be safe owning a gun. Large-capacity magazines aren't permitted, and weapons must be stored in locked cabinets and unloaded if taken outside the home [source: Ministry of the Interior ].
But even so, Finland suffered mass shootings at schools in 2007 and 2008, in which gunmen killed 18 people. Since then, Finland has tightened up its gun laws, although it experienced two other mass shootings in 2009 and 2016. Still, Finland's totality of roughly 26 deaths between 2000 and 2019 is a drop in the bucket compared with the thousands of deaths in the U.S. from mass shootings [source: Australian Associated Press ].
6: Could Technological Advances Make Gun Control Impossible?

In recent years, the development of 3D-printing , in which a printer can be used to build a solid object, has the potential to greatly complicate attempts to regulate firearms. The earliest 3D-printed guns were crude single-shot devices. But as Slate writer Ari Schneider reported in 2021 , the technology has come a long way in a short time, and it's now possible to print semi-automatic rifles and pistols that don't have serial numbers or registrations, bypassing background checks. Recently, for example, plans were released for a "100 percent homemade" semi-automatic rifle that is durable enough to shoot thousands of 9 mm rounds. Most of the rifle can be 3D-printed, while the rest can be fabricated from parts available in hardware stores.
3D-printed firearms not only would be easy to make at home, and easy to hide from authorities, but potentially could be far cheaper than weapons manufactured in arms factories and sold by dealers. In just a short time, plans for the 3D-printed rifle were viewed more than 44,000 times on the original website to which the files were uploaded, according to Schneider's article .
Currently, making your own 3D gun is legal under Federal law, which permits the unlicensed manufacturing of firearms, as long as at least some of the parts are metal, according to a February 2021 article in The Trace , an online publication that focuses on gun issues. A few states have moved to clamp down on them, including New Jersey, which requires anyone who wants to use a 3D printer to make a gun to obtain a federal gun-manufacturing license. New Mexico and Virginia are considering similar restrictions.
Law enforcement officials worry about the possibility of violent extremists using 3D printers to fabricate weapons without metal components, which would enable them to be smuggled inside places where guns are prohibited, such as government buildings and airports. So far, though, even plastic guns still would need to use bullets fashioned from metal, which could be spotted [source: Barton and Brownlee ]. Additionally, Design News reported in 2019 on development of a new scanning device with the potential to spot concealed weapons regardless of their composition.
5: How Often Do Gun Owners Actually Prevent Crimes?

People opposed to gun control often have argued that they need firepower to protect themselves against criminals. Take this example from January 2013 when a Georgia woman shot a crowbar-wielding intruder who broke into her home and confronted her and her two young children [source: CBS News ]. A number of armed American citizens have also used their firearms to stop or limit mass killings, including Stephen Willeford, the armed citizen who intervened to confront and pursue a gunman who attacked First Baptist Church of Sutherland Spring, Texas in 2017 [source: CNN ].
Gun control opponents say that a vast number of crimes are prevented by armed citizens, who either shoot an assailant — an event that happened 326 times in 2010, according to a 2012 Wall Street Journal state-by-state analysis of crime statistics — or more often, chase the would-be criminal away by brandishing a weapon [source: Palazzolo and Barry ].
There is some social science to back up that thesis. Perhaps the most often-cited evidence is a 1995 study by Northwestern University School of Law researchers Gary Kleck and Marc Gertz. Based upon a random telephone survey of 5,000 Americans, they concluded that there were between 2.1 and 2.5 million defensive gun uses each year. This works out to about 1 percent use of a gun for defensive purposes [source: Kleck and Gertz ].
But critics questioned whether Kleck's and Gertz's findings were reliable. Harvard public health researcher David Hemenway published a paper refuting this and pointing out that "since only 42 percent of U.S. households own firearms and victims in two-thirds of the occupied households were asleep, the 2.5 million figure requires us to believe burglary victims use their guns in self-defense more than 100 percent of the time" [source: Hemenway ]. Another mid-1990s study, based upon a Justice Department survey of nearly 60,000 households, came up with a much smaller estimate of about 21,500 defensive gun uses annually [source: Committee on Law and Justice ].
Even if the low-end estimates are closer to the truth, this still could mean that tens of thousands of crimes are prevented by gun owners annually. But a 2009 University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine study found that people with a gun were 4.5 times more likely to be shot in an assault than those who were unarmed.
4: How Often Are People Killed by Their Own Guns?

This is the point that gun control proponents often cite to counter arguments that guns deter crime . People who have guns in their households, they argue, actually may be at greater risk of being hurt or killed by a bullet — possibly one fired by an angry spouse or by a child playing with a gun that's been left out and loaded.
Again, there's some social science to support this. A 2003 study published in the journal Injury Prevention found that people in families where someone purchased a gun actually faced an elevated risk of homicide, suicide and accidental death [source: Grassel et al ]. Another study published in 2011 in the American Journal of Public Health found that 43 percent — neatly half — of all homes with guns and kids also had one unlocked firearm.
One big risk is that having a gun within easy reach can escalate an argument or fight into a homicide. A 1992 study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that victims whose family members used a gun in an assault were 12 times more likely to die than when attackers used other weapons such as knives, or their bare hands [source: Saltzman et al ].
However, an article that appeared in the Harvard Journal of Law and Public Policy pointed out that most of the "acquaintance homicides" involved, for instance, drug dealers shooting at each other. "Approximately 90 percent of adult murderers have adult records, with an average adult criminal career ... of six or more years, including four major adult felony arrests," said the authors [source: Kates and Mauser ].
Most Americans who die from gun violence in their own homes actually inflict it upon themselves: More than 47,000 people commit suicide every year in the United States and in 2019, more than half used a firearm [source: ASFP].
3: Did the Federal Ban on Assault Weapons Affect Crime?

In 1994, Congress passed a 10-year ban on the manufacture and sale of new assault weapons, which the law defined as semi-automatic rifles and handguns with certain military-style features — such as folding rifle stocks and threaded barrels for attaching silencers — that didn't have any value to hunters or self-defense. The law also banned magazines with a capacity of more than 10 rounds but exempted weapons manufactured before 1994. The law was allowed to expire in 2004, and how effective it was at preventing crime remains a subject of intense controversy, in part because there wasn't a systematic effort to gather data about its impacts.
A 2004 study by University of Pennsylvania researchers for the Department of Justice found that from 1995 to 2003, gun crimes involving assault weapons that were banned by the law declined in six U.S. cities by between 17 percent and 72 percent. But some of that progress was negated, the researchers found, because even though criminals couldn't buy new assault weapons, they still could easily outfit non-banned weapons with old large-capacity magazines from before the ban, which were plentiful and easily obtained [source: Koper ].
Additionally, manufacturers were able to get around the ban by redesigning weapons and making a few changes to remove the military-style features. The Colt AR-15 that the shooter used to kill moviegoers in the Aurora cinema would have been outlawed under the 1994 ban. Yet he could have used a very similar Colt Match Target rifle that would not have fallen under the ban [source: Plumer ].
After winning election in 2020 on a platform that included gun control, President Joe Biden has pushed Congress to revive the assault weapons ban, and to make high-capacity magazines illegal as well [source: White House ].
2: Do States With Strict Gun Control Laws Have Less Gun Violence?

Critics of gun control often point to places such as the District of Columbia, which has a high rate of gun crimes despite strict gun control laws . But gun control advocates say that states' efforts at gun control are undermined, to a degree, by lax laws in neighboring states. Everytown For Gun Safety , an organization lobbying for stricter gun legislation, points out that nearly 30 percent of guns recovered from crime scenes were first sold in a different state. And a 2009 study by Johns Hopkins University researchers found that cities in states with little regulation of gun dealers had guns passing into criminals' hands at two to four times the rate of cities in states with strict laws [source: ScienceDaily ].
Social scientist Richard Florida, who has analyzed crime and demographic data, has found a strong correlation between lower firearm deaths and tighter gun restrictions, such as bans on assault weapons and requirements for trigger locks and safe storage of guns. He says that gun violence is less likely to occur in states that have gun control laws. Interestingly, he found no correlation between states' unemployment rates or drug use and gun violence, but he did find that states with high poverty, low numbers of college grads and high numbers of working-class jobs also had more gun violence [source: Florida ].
1: Has American Public Opinion Shifted on Gun Control?
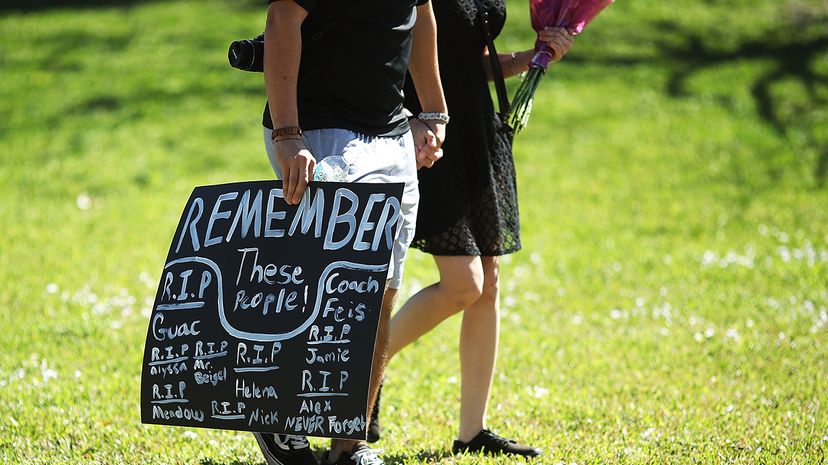
In the early 1990s, Gallup polling showed that 78 percent of Americans favored tighter gun control laws . But that support declined dramatically over the next two decades, and by the mid-to-late 2000s, support dipped to just 44 percent, with nearly as many Americans (43 percent) saying that laws already were strict enough. But in the wake of the Newtown massacre, a December 2012 Gallup poll found a sharp rebound in support, with 58 percent favoring tougher gun statutes, compared to just 34 percent who said they wanted laws to remain the same [source: Saad ]. Since then, support for gun control has fluctuated, often rising in the wake of shootings. Gallup's most recent poll on this issue in November 2020 found that 57 percent of Americans supported stricter gun control [source: Brenan ].
Other recent polls on gun control vary. A Pew Research Center poll released in April 2021 found a narrower majority — 53 percent — supported stricter laws, while a March 2021 Morning Consult-Politico tracking poll found that 64 percent of American voters generally supported more gun control, versus 28 percent who said they were opposed. [sources: Bowden , Pew Research Center ].
But when polls drill down further, they often find that specific gun control measures have even broader support. In the Morning Consult-Politico poll, for example, 83 percent of voters who supported background checks on all weapons purchases and statutes preventing people identified as mentally unstable from owning guns at all. And 76 percent supported banning anyone on a federal watchlist — such as "do not fly" lists — from owning guns, while 73 percent wanted a three-day federal waiting period before a gun could be taken home from a store. Seventy percent backed creation of a national database on gun sales [source: Bowden ].
Similarly, in the Pew poll, Americans strongly backed restrictions on the type of weaponry Americans should be able to buy. Sixty-four percent favored banning magazines that hold more than 10 rounds of ammunition, and 63 percent favored banning assault weapons such as the military-style rifles that often have been used in mass killings [source: Pew Research Center ].
But Gallup data contains another important but often overlooked point. Though the number of Americans who want stricter gun control has gone up and down (and now up again), the overwhelming majority of Americans over the past 20 years have supported laws that restrict firearms. In a Gallup Poll from October 2017, only 4 percent of those polled said they oppose background checks for all gun purchases [source: Brenan ].
However, that same 2017 poll found that a 71 percent were opposed to a ban on handguns for anyone but police or other authorized personnel. Pollsters speculate this could reflect Americans' wish to keep the right of self-defense in the wake of high-profile gun violence .
Gun Control Debate FAQs
How many guns are there in the u.s., what does the u.s. constitution say about gun control, did the federal ban on assault weapons affect crime, what's a semi-automatic gun, is it illegal to not lock up your guns, lots more information.
Author's Note: 10 Big Questions in the U.S. Gun Control Debate
I grew up in western Pennsylvania, where the movie "The Deer Hunter" was set, and where a lot of my neighbors were avid hunters. So the idea of law-abiding people owning guns was never something I questioned. But except for my toy pistols, we didn't have any guns in our home, because my father, who wasn't a hunter, didn't want them around. He'd been a combat medic in the U.S. Army during World War II, and he had a huge, scary scar on his left bicep where a German machine gun bullet hit him on a battlefield in 1945. He'd had to bind up his own arm in a battlefield tourniquet, which enabled him to escape having it amputated. I still have a vivid picture in my mind of what a bullet can do to a person's body. I think that's given me a real-world perspective on the gun issue that a lot of debaters, who tend to get caught up in legal and constitutional abstractions, often seem to lack.
Related Articles
- The Five Most Popular Guns
- Do countries with stricter gun laws really have less crime or fewer homicides?
- What's the difference between a semi-automatic weapon and a machine gun?
- Preventing Suicide While Protecting Gun Rights
- What's a Bump Fire Stock?
- Should We Be Worried About 3D Printable Guns?
- Aizenman, Nurith. "Gun Violence Deaths: How The U.S. Compares With The Rest Of The World. " National Public Radio. March 24, 2021. (May 30, 2021) https://www.npr.org/sections/goatsandsoda/2021/03/24/980838151/gun-violence-deaths-how-the-u-s-compares-to-the-rest-of-the-world
- Allen, Kristine. "Take Note: Fred Guttenberg, Father Of Parkland Shooting Victim, Fights Gun Violence. " WPSU. Feb. 13, 2021. (May 30, 2021) https://radio.wpsu.org/post/take-note-fred-guttenberg-father-parkland-shooting-victim-fights-gun-violence
- American Psychological Association. "Gun Violence: Prediction, Prevention, and Policy." APA.org. 2013. (May 30, 2021) https://www.apa.org/pubs/info/reports/gun-violence-prevention
- ASFP. "Suicide Statistics." (Feb. 15, 2018). https://afsp.org/about-suicide/suicide-statistics/
- Associated Press. "Ban on Assault Rifles Takes Effect in Los Angeles." The New York Times. March 3, 1989. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.nytimes.com/1989/03/03/us/ban-on-assault-rifles-takes-effect-in-los-angeles.html
- Associated Press. "Deadliest Mass Shootings Around The World." Huffingtonpost.com. July 20, 2012. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/07/20/deadliest-mass-shootings_n_1688820.html
- Barrett, Paul. "How Often Do We Use Guns in Self-Defense?" Bloomberg Businessweek. Dec. 27, 2012. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.businessweek.com/articles/2012-12-27/how-often-do-we-use-guns-in-self-defense
- Barron, James. "Nation Reels After Gunman Massacres 20 Children at School in Connecticut." The New York Times. Dec. 14, 2012. (Jan. 26, 2013) http://www.nytimes.com/2012/12/15/nyregion/shooting-reported-at-connecticut-elementary-school.html?hp&_r=0
- Barton, Champe and Brownlee, Chip. "What Are 3D-Printed Guns, and Why Are They Controversial? " The Trace. Feb. 2, 2021. (May 30, 2021) https://www.thetrace.org/2021/02/3d-printer-ghost-gun-legal-liberator-deterrence-dispensed/
- Bass, Frank. "U.S. on Pace for Slowest Decade of Population Growth Since 1930s." Bloomberg.com. Dec. 31, 2012. (Jan. 26, 2013) http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2012-12-31/u-s-on-pace-for-slowest-decade-of-population-growth-since-1930s.html
- Bowden, John. "2 in 3 support stricter gun control laws: poll. " The Hill. April 14, 2021. (May 29, 2021) https://thehill.com/homenews/news/548127-2-in-3-support-stricter-gun-control-laws-poll
- Brenan, Megan. "Support for Stricter U.S. Gun Laws at Lowest Level Since 2016. " Gallup.com. Nov. 16, 2020. (May 30, 2021.) https://news.gallup.com/poll/325004/support-stricter-gun-laws-lowest-level-2016.aspx
- Brenan, Megan. "Support for Stricter Gun Laws Edges Up in U.S." Gallup. Oct. 16, 2017. (Feb. 15, 2018) http://news.gallup.com/poll/220595/support-stricter-gun-laws-edges.aspx
- Brennan, Allison. "Analysis: Fewer U.S. Gun Owners Own More Guns." Cnn.com. July 31, 2012. (Jan. 30, 2012) http://www.cnn.com/2012/07/31/politics/gun-ownership-declining/index.html
- Candiotta, Susan and Aarthun, Sarah. "Police: 20 children among 26 victims of Connecticut school shooting. " CNN. Dec. 15, 2012. (May 29, 2021) https://www.cnn.com/2012/12/14/us/connecticut-school-shooting/index.html
- Canipe, Chris and Hartman, Travis. "A timeline of mass shootings in the U.S." Reuters. April 16, 2021. (May 29, 2021) https://graphics.reuters.com/USA-GUNS/MASS-SHOOTING/nmovardgrpa/
- CBS DC. NRA: " 'Only Way To Stop A Bad Guy With A Gun Is With A Good Guy With A Gun.' " CBS DC. Dec. 21, 2012. (May 30, 2021) https://washington.cbslocal.com/2012/12/21/nra-only-way-to-stop-a-bad-guy-with-a-gun-is-with-a-good-guy-with-a-gun/
- CBS News. "Georgia mother hides children, shoots intruder 5 times during home invasion, police say." Cbsnews.com. Jan. 7, 2013. (Jan. 26, 2013) http://www.cbsnews.com/8301-504083_162-57562397-504083/georgia-mother-hides-children-shoots-intruder-5-times-during-home-invasion-police-say/
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. "Violence-Related Firearm Deaths Among Residents of Metropolitan Areas and Cities --- United States, 2006 -- 2007." Cdc.gov. May 13, 2011. (Jan. 25, 2013) http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6018a1.htm?s_cid=mm6018a1_w
- Chamberlain, Samuel. "Gaetz: Second Amendment about waging 'armed rebellion' if necessary." New York Post. May 27, 2021. (May 30, 2021) https://nypost.com/2021/05/27/gaetz-second-amendment-about-waging-armed-rebellion-if-necessary/
- Civitas Crime. "Comparisons of Crime in OECD Countries." (Jan. 31, 2013) http://www.civitas.org.uk/crime/crime_stats_oecdjan2012.pdf
- CNN. "'Hero' exchanged fire with gunman, then helped chase him down." Nov. 7, 2017 (Feb. 15, 2018) https://www.cnn.com/2017/11/05/us/texas-church-shooting-resident-action/index.html
- Columbia250. "Charles Evans Hughes." C250.columbia.edu. Undated. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://c250.columbia.edu/c250_celebrates/remarkable_columbians/charles_hughes.html
- Committee on Law and Justice. "Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review." National Academies Press. 2004. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=10881&page=103
- Congressional Research Service. "CRS Annotated Constitution: Bearing Arms: Second Amendment." Law.cornell.edu. Undated. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.law.cornell.edu/anncon/html/amdt2_user.html#amdt2_hd2
- Cook, Philip J. and Ludwig, Jens. "Defensive Gun Uses: New Evidence from a National Survey." Journal of Quantitative Criminology. 1998. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://home.uchicago.edu/~ludwigj/papers/JQC-CookLudwig-DefensiveGunUses-1998.pdf
- Cornell University Legal Information Institute. "Second Amendment." Law.cornell.edu. Undated. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.law.cornell.edu/constitution/second_amendment
- Cramer, Clayton J. and Burnett, David. "Tough Targets." Cato.org. 2012. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.cato.org/sites/cato.org/files/pubs/pdf/WP-Tough-Targets.pdf
- Cummings, P. et al. "The association between the purchase of a handgun and homicide or suicide." American Journal of Public Health. June 1997. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1380933/
- FBI. "Expanded Homicide Data Table 8. " FBI. (May 30, 2021) https://ucr.fbi.gov/crime-in-the-u.s/2019/crime-in-the-u.s.-2019/tables/expanded-homicide-data-table-8.xls
- FBI. "2014 Crime in the United States." (Feb. 15, 2018) https://ucr.fbi.gov/crime-in-the-u.s/2014/crime-in-the-u.s.-2014/tables/expanded-homicide-data/expanded_homicide_data_table_1_murder_victims_by_race_ethnicity_and_sex_2014.xls
- Fernando, Christine; Hayes, Christal and Hauck, Grace. "San Jose gunman had cans of gasoline, 22K rounds of ammo at home, officials say: What we know." USA Today. May 28, 2021. (May 29, 2021) https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2021/05/28/san-jose-shooting-samuel-cassidy-questioned-workplace-hatred/7485425002/
- Finnish Police. "Finnish registers for a total of 1.6 million weapons." Poliisi.fi. Aug. 19, 2007. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.poliisi.fi/poliisi/bulletin.nsf/PFBD/9319AD7CAED55862C2257346003A066A?opendocument
- Florida, Richard. "The Geography of Gun Deaths." Theatlantic.com. Jan. 13, 2011. (Jan. 28, 2013) http://www.theatlantic.com/national/archive/2011/01/the-geography-of-gun-deaths/69354/
- Florida, Richard. "Gun Violence in U.S. Cities Compared to the Deadliest Nations in the World." Theatlanticcities.com. Jan. 22, 2013. (Jan. 27 2013) http://www.theatlanticcities.com/politics/2013/01/gun-violence-us-cities-compared-deadliest-nations-world/4412/
- Fox, Kara. "How U.S. gun culture compares with the world in five charts." Feb. 15, 2018. (Feb. 15, 2018) https://www.cnn.com/2017/10/03/americas/us-gun-statistics/index.html
- Gallup. "Guns." Gallup.com. January 2013. (Jan. 26, 2013) http://www.gallup.com/poll/1645/guns.aspx
- General Social Survey. "Have Gun in Home." 2006. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www3.norc.org/GSS+Website/Browse+GSS+Variables/Subject+Index/
- GunPolicy.org. "Finland -- Gun Facts, Figures and the Law." Gunpolicy.org. Undated. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.gunpolicy.org/firearms/region/finland
- GunPolicy.org. "Switzerland -- Gun Facts, Figures and the Law." Gunpolicy.org. Undated. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.gunpolicy.org/firearms/region/switzerland
- Hanna, Jason and Vera, Amir. " Here's what we know about the San Jose rail yard shooting." CNN. May 28, 2021. (May 29, 2021) https://www.cnn.com/2021/05/26/us/san-jose-shooting-what-we-know/index.html
- Hemenway, David. "The Myth of Millions of Annual Self-Defense Gun Uses." Chance. 1997. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.stat.columbia.edu/~gelman/surveys.course/Hemenway1997.pdf
- Hemenway, David. "Risks and Benefits of a Gun in the Home." American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. 2011. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/753058_4
- Hepburn, L. et al. "The US gun stock: results from the 2004 national firearms survey." Injury Prevention. 2007. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://injuryprevention.bmj.com/content/13/1/15.full
- Hutchinson, Bill, etal. "The anatomy of the Las Vegas mass shooting, the deadliest in modern US history." ABC News. Dec. 23, 2018. (May 29, 2021) https://abcnews.go.com/US/anatomy-las-vegas-mass-shooting-deadliest-modern-us/story?id=59797324
- Hoyert, Donna L. and Xu, Jiaquan. "Deaths: Preliminary Data for 2011." Cdc.gov. Oct. 10, 2012. (Jan. 25, 2013) http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr61/nvsr61_06.pdf
- Johnson, Brian R. "Crucial Elements of Police Firearms Training." Looseleaf Law Publications. 2008. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://books.google.com/books?id=mwvu-am3wbcC&pg=PA63&dq=semiautomatic+weapon&hl=en&sa=X&ei=eLsFUfmmC6-C0QHwkoDoDQ&ved=0CGUQ6AEwCQ#v=onepage&q=semiautomatic%20weapon&f=false
- Keng Kuek Ser, Kuang. "Map: Here are countries with the world's highest murder rates." PRI.com. June 27, 2016 (Feb. 15, 2018) https://www.pri.org/stories/2016-06-27/map-here-are-countries-worlds-highest-murder-rates
- Kinard, Jeff and Tucker, Spencer C. "Pistols: An Illustrated History of Their Impact." ABC-CLIO. 2004. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://books.google.com/books?id=ZVnuHX_6bG0C&pg=PA176&dq=invented+the+first+semiautomatic&hl=en&sa=X&ei=j8EFUeG4OKLC0QG4-4C4BQ&ved=0CEAQ6AEwAw#v=onepage&q=%20semiautomatic&f=false
- Kleck, Gary and Gertz, Marc. "Armed Resistance to Crime: The Prevalence and Nature of Self-Defense." Journal of Law and Criminology. 1995. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.saf.org/lawreviews/kleckandgertz1.htm
- Koper, Christopher S. "Updated Assessment of the Federal Assault Weapons Ban: Impacts on Gun Markets and Gun Violence, 1994-2003." U.S. Department of Justice. July 2004. (Jan. 31, 2014) https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/nij/grants/204431.pdf
- Krouse, William J. "Gun Control Legislation." Congressional Research Service. Nov. 14, 2012. (Jan. 26, 2013) http://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/misc/RL32842.pdf
- Limbaugh, Rush. "Limbaugh: The Term "Assault Rifle" Is A "Political Invention." Realclearpolitics.com. Dec. 17, 2012. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.realclearpolitics.com/video/2012/12/17/limbaugh_the_term_assault_rifle_is_a_political_invention.html
- Lindenberger, Michael A. "Ten Years After Columbine, It's Easier to Bear Arms." Time. April 20, 2009. (Jan. 31, 2013) http://www.time.com/time/nation/article/0,8599,1891416,00.html
- Martinez, Michael and Schmidt, Emily. "Gun control advocates march as nation reels from school shootings." Cnn.com. Jan. 26, 2013. (Jan. 26, 2013) http://www.cnn.com/2013/01/26/us/gun-control-rally/index.html
- McIntyre, Douglas A. "Guns in America: Nearly 40 million guns were purchased legally in 2020 and another 4.1 million bought in January. " USA Today. Feb. 10, 2021. (May 30, 2021) https://www.usatoday.com/story/money/2021/02/10/this-is-how-many-guns-were-sold-in-all-50-states/43371461/
- Ministry of the Interior, Finland. "Firearms Act." Finlex.fi. 2003. Jan. 27, 2013. http://www.finlex.fi/en/laki/kaannokset/1998/en19980001.pdf
- Newcomb, Alyssa. "US Gun Homicide Rate Higher Than Other Developed Countries." Abcnews.com. Dec. 18, 2012. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://abcnews.go.com/blogs/headlines/2012/12/us-gun-ownership-homicide-rate-higher-than-other-developed-countries/
- Newstimes.com. "Teacher from Stratford shielded students." Newstimes.com. Dec. 15, 2012. (Jan. 25, 2013) http://www.newstimes.com/local/article/Teacher-from-Stratford-shielded-students-4120759.php
- O'Keefe, Ed. "Lawmakers unveil new assault weapons ban." Washington Post. Jan. 24, 2013. (Jan. 28, 2013) http://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/post-politics/wp/2013/01/24/lawmakers-to-unveil-new-assault-weapons-ban/?hpid=z1
- Palazzolo, Joe and Barry, Rob. "More Killings Called Self-Defense." Wall Street Journal. April 2, 2012. (Jan. 30, 2013) http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303404704577311873214574462.html
- Peterson, Phillip. "The Gun Digest Buyer's Guide to Assault Weapons." Gun Digest Books. 2008. (Jan. 28, 2013) http://books.google.com/books?id=fd9Qc0neMjYC&printsec=frontcover&dq=history+of+assault+rifles&hl=en&sa=X&ei=GuUBUYfBBqS00QHYy4GIDg&ved=0CEkQ6AEwBQ#v=onepage&q=history%20of%20assault%20rifles&f=false
- Pew Research Center. "Amid a Series of Mass Shootings in the U.S., Gun Policy Remains Deeply Divisive. " Pew Research Center. April 20, 2021. (May 29, 2021) https://www.pewresearch.org/politics/2021/04/20/amid-a-series-of-mass-shootings-in-the-u-s-gun-policy-remains-deeply-divisive/
- Raum, Tom and Agiesta, Jennifer. "AP-GfK poll: After Conn. school shooting, nearly 6 in 10 Americans back stricter gun laws." Ap-gfkpoll.com. Jan. 16, 2013. (Jan. 26, 2013) http://ap-gfkpoll.com/uncategorized/our-latest-poll-findings-19
- Saad, Lydia. "Americans Want Stricter Gun Laws, Still Oppose Bans." Gallup. Dec. 12, 2012. (Feb. 15, 2018) http://news.gallup.com/poll/159569/americans-stricter-gun-laws-oppose-bans.aspx
- Saad, Lydia. "What Percentage of Americans Own Guns? " Gallup. Nov. 13, 2020. (May 30, 2021) https://news.gallup.com/poll/264932/percentage-americans-own-guns.aspx
- Saltzman, L.E. et al. "Weapon involvement and injury outcomes in family and intimate assaults." Journal of the American Medical Association. June 10, 1992. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1588718
- Schneider, Ari. "3D-Printed Guns Are Getting More Capable and Accessible. " Slate. Feb. 16, 2021. (May 30, 2021) https://slate.com/technology/2021/02/3d-printed-semi-automatic-rifle-fgc-9.html
- ScienceDaily. "Protection Or Peril? Gun Possession Of Questionable Value In An Assault, Study Finds." Sciencedaily.com. Sept. 30, 2009 (Jan. 27, 2013) https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/09/090930121512.htm
- ScienceDaily. "Regulation And Oversight Of Gun Sales Reduces Trafficking To Criminals, Study Finds." Sciencedaily.com. July 7, 2009. (Jan. 28, 2013) http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/07/090707111749.htm
- Small Arms Survey. "Completing the Count." Smallarmssurvey.org. 2007. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/fileadmin/docs/A-Yearbook/2007/en/full/Small-Arms-Survey-2007-Chapter-02-EN.pdf
- StatisticBrain. "Gun Ownership Statistics and Demographics." Statisticbrain.com. July 20, 2012. (Jan. 30, 2012) http://www.statisticbrain.com/gun-ownership-statistics-demographics/
- Thebault, Reis and Rindler, Danielle. "Shootings never stopped during the pandemic: 2020 was the deadliest gun violence year in decades." Washington Post. March 23, 2021. (May 29, 2021) https://www.washingtonpost.com/nation/2021/03/23/2020-shootings/
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). "DataUNODC. " (May 30, 2021) https://dataunodc.un.org/
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). "UNODC Homicide Statistics." Unodc.org. 2013. (Jan. 27, 2013). http://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/homicide.html
- University of Chicago Press. "An interview with John R. Lott, Jr." Press.uchicago.edu. 1998. (Jan. 26, 2013) http://www.press.uchicago.edu/Misc/Chicago/493636.html
- Washington Post. "Remarks from the NRA press conference on Sandy Hook school shooting, delivered on Dec. 21, 2012 (Transcript)." Washingtonpost.com. Dec. 21, 2012. (Jan. 26, 2013) http://articles.washingtonpost.com/2012-12-21/politics/36018141_1_mayhem-with-minimum-risk-nra-wayne-lapierre
- Weatherby. "New Home Defense Pump Shotgun and Threat Response Rifles." Weatherby.com. Oct. 20, 2009. (Jan. 27, 2013) http://www.weatherby.com/company/pressroom/pressrelease/item/view/44079
- White House. "FACT SHEET: Biden-Harris Administration Announces Initial Actions to Address the Gun Violence Public Health Epidemic. " White House. April 7, 2021. (May 30, 2021) https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2021/04/07/fact-sheet-biden-harris-administration-announces-initial-actions-to-address-the-gun-violence-public-health-epidemic/
- Wiltz, Chris. "Liberty Defense's radar can detect undetectable ghost guns. " Design News. Dec. 26, 2019. (May 30, 2021) https://www.designnews.com/governmentdefense/liberty-defenses-radar-can-detect-undetectable-ghost-guns
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:
Gun Violence in America: The 13 Key Questions (With 13 Concise Answers)
It's not like no one has ever asked them before. There's data everywhere and decades of research. We tracked down the best of it so you don't have to.

Jump to a question:
How much gun violence is there in the U.S.?
How many guns are there in the U.S.?
How do mass shootings differ from other types of gun violence?
What gun control laws currently exist?
What could be done to reduce gun violence?
Would fewer guns result in less gun violence?
- Would gun control result in fewer guns?
How often are guns used in self-defense?
Won't criminals kill with other weapons if they don't have guns?
What has worked to reduce gun violence?
Are the White House proposals likely to be effective?
How does the U.S. compare to other countries?
What don't we know yet?
There were 8,583 homicides by firearms in 2011, out of 12,664 homicides total, according to the FBI . This means that more than two-thirds of homicides involve a firearm. 6,220 of those homicides by firearm (72%) are known to have involved a handgun.
It's worth noting that violent crime rates of all types have been steadily decreasing since the early 1990s. No one is quite sure what is causing this decrease, though there are many theories , ranging from tighter gun control laws to more innovative policing and changes in the drug market. Whatever the cause of this decline, America still has a homicide rate of 4.7 murders per 100,000 people, which is one of the highest of all developed countries (see: international comparison).
Gun violence also affects more than its victims. In areas where it is prevalent, just the threat of violence makes neighborhoods poorer. It's very difficult to quantify the total harm caused by gun violence, but by asking many people how much they would pay to avoid this threat -- a technique called contingent valuation -- researchers have estimated a cost to American society of $100 billion dollars .
Guns are also involved in suicides and accidents. 19,392 of 38,264 suicides in 2010 involved a gun (50%), according to the CDC . There were 606 firearm-related accidents in the same year -- about 5% of the number of intentional gun deaths.
There are about 310 million guns in the country . About 40% of households have them, a fraction that has been slowly declining over the last few decades, down from about 50% in the 1960s. Meanwhile, the overall number of guns has increased to about one gun per person, up from one gun for every two persons in the 1960s. This means that gun ownership has gotten much more concentrated among fewer households: if you own one gun, you probably own several. America has the highest rate of gun ownership of any country in the world, by a wide margin (see: international comparison).
( More : A long running poll by Gallup ; the wide-ranging General Social Survey ; a New York Times demographic breakdown by Nate Silver)
The FBI defines a "mass murder" as four or more murders during the same incident. This is an arbitrary number, but a dividing line is useful when asking whether there are differences between mass shootings and other kinds of gun violence. The most comprehensive public list of U.S. mass shootings is the spreadsheet of 62 incidents from 1982-2012, compiled by Mother Jones . Their list shows:
- Mass shootings happen all over the country .
- Killers used a semi-automatic handgun in 75% of incidents, which is about the same percentage as the 72% in overall gun violence.
- Killers used an assault weapon in 40% of incidents. This is much higher than overall assault weapon use in crimes, estimated at less than 2%.
- The guns were obtained legally in 79% of mass shootings.
- Many of the shooters showed signs of mental illness, but in only two cases was there a prior diagnosis.
- There were no cases where an armed civilian fired back.
2012 was the worst year in American history, in terms of total victims. A graph of yearly victims shows a slight upward trend. But the pattern is a lot less clear without the 2012 peak, and because yearly numbers vary so widely, it's likely that there will be many fewer victims next year.
Several criminologists deny that mass shootings are increasing. Although these incidents dominate headlines and conversation, it's important to remember that they account for only a small fraction of gun violence in the United States. For example, the spike of 72 deaths in 2012 includes only 0.8% of all firearm-related homicides in 2011 (the last year for which statistics are available.) Many gun deaths, especially in large cities, never make the news . This means that the most effective gun violence reduction strategies -- in terms of lives saved -- might not target mass shootings at all.
There are two major federal laws that regulate firearm ownership and sales. The National Firearms Act of 1934 restricts civilians from owning automatic weapons, short-barreled shotguns, hand grenades, and other powerful arms. The Gun Control Act of 1968 focuses on commerce. It prohibits mail-order sales of weapons, and requires anyone in the business of selling guns to be federally licensed and keep permanent sales records. It also prohibits knowingly selling a gun to those with prior criminal records, minors, individuals with mental health problems, and a few other categories of people.
The Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act of 1993 requires licensed gun dealers to perform background checks. Background checks are not required for private gun sales (though, as mentioned above, it's still a crime to knowingly sell a gun to someone with a criminal record). To ensure privacy, Section 103(i) of the Act prevents the Federal government from keeping the names submitted for background checks, or using this information to create any sort of registry of gun owners.
From 1994 to 2004, the Federal Assault Weapons Ban prohibited the sale and manufacture of semi-automatic weapons (in which each pull of the trigger fires one shot) with various military features such as large-capacity magazines and pistol grips. It was still legal to keep previously owned weapons. The law expired in 2004 due to a built-in "sunset" clause.
These federal laws set minimum standards, but many states have also passed various types of gun laws. These laws determine which weapons are legal to own, and also set requirements on sales, background checks, storage, open and concealed carrying permits, and sentencing of gun-related crimes.
( More: Gun Laws in the US, State by State , The Guardian , and Gun Control Legislation , Congressional Research Service)
The firearms debate usually revolves around "gun control" -- that is, laws that would make guns harder to buy, carry, or own. But this is not the only way of reducing gun violence. It is possible to address gun use instead of availability. For example, Project Exile moved all gun possession offenses in Richmond, Virginia, to federal courts instead of state courts, where minimum sentences are longer. Policies like these, which concern gun use, are sometimes said to operate on gun "demand," as opposed to gun control laws, which affect "supply."
Similarly, while the idea of new laws gets most of the attention, some projects have focused on enforcing existing laws more effectively, or changing policing strategies the way Boston's Operation Ceasefire did in the 1990s. In fact, launching community-based programs has proven to be one of the most effective strategies for reducing gun violence. (See: What has worked , below.)
There have also been programs based on other principles, such as public safety education and gun buy-back campaigns. The White House proposals (see below ) address both gun access and gun use, and include both new laws and enhanced enforcement of existing laws.
( More: Aiming for Evidence-based Gun Policy , Phillip Cook and Jens Ludwig)
Suppose it were possible to reduce the number of guns in circulation, or make it harder for people to get a gun. Would gun violence go down?
Although countries that offer easier access to guns also have more gun violence , at least among developed nations, this doesn't necessarily mean that more guns cause more deaths . People may own more guns in dangerous places because they want to protect themselves. It's also possible that gun ownership is a deterrent to crime, because criminals must consider the possibility that their intended victim is armed.
Economist John Lott did extensive work on this question in the late 1990s, culminating in his 1998 book More Guns, Less Crime . He studied the effect of right-to-carry laws by examining violent crime rates before and after they were implemented in various states, up until 1992, and concluded that such laws decreased homicides by an average of 8%. Lott's data and methods have been extensively reviewed since then. A massive 2004 report by a 16-member panel of the National Research Council found that there was not enough evidence to say either way whether right-to-carry laws affected violence. In 2010, different researchers re-examined Lott's work, the NRC report, and additional data up through 2006, and reaffirmed that there is no evidence that right-to-carry laws reduce crime.
Meanwhile, other studies have suggested that reduced access to guns would result in less crime. These studies compared homicide rates with gun availability in various states and cities. The most comprehensive estimate is that a 10% reduction in U.S. households with guns would result in a 3% reduction in homicides. Internationally , the effect of reductions in gun ownership might be much larger. This might have to do with the large number of guns already available in the U.S.: Any reduction in gun violence hinges on whether gun control laws would actually make it prohibitively difficult to get a gun.
( More: Gun Rhetoric vs. Gun Facts , Factcheck.org; The Impact of Right to Carry Laws and the NRC Report: Lessons for the Empirical Evaluation of Law and Policy , John J. Donohue III, Abhay Aneja, and Alexandria Zhang)
Does gun control result in fewer guns?
In principle, it's not necessary to keep guns away from everyone , just those who would misuse them. Background checks are promising because a high fraction of future killers already have a criminal record. In one study in Illinois, 71% of those convicted of homicide had a previous arrest, and 42% had a prior felony conviction.
Yet current federal gun regulation (see above) contains an enormous loophole: While businesses that deal in guns are required to keep records and run background checks, guns can be transferred between private citizens without any record. This makes straw purchases easy. In other words, these laws may generally make guns harder to come by, but those who really want them can still obtain them through private sales.
Also, although it's generally illegal to sell guns across state lines, in practice this is very common. There's abundant evidence that under the current system, guns flow easily between legal and illegal markets. Washington, D.C,. banned all handguns in 1976, and Chicago did the same in 1982. In neither case did the percentage of suicides using firearms -- considered a very good proxy for general gun availability -- fall significantly.
Similarly, Illinois had a background check requirement before 1994, so the local gun market was not affected by the passage of the Brady Act, but gun trace data shows that criminals simply switched from smuggling guns from out of state to buying them illegally in state.
( More : Where 50,000 Guns Recovered in Chicago Came From , New York Times )
There are no comprehensive records kept of incidents where guns are used in self-defense, so the only way to know is to ask people. Data from the National Crime Victimization Survey suggest that a gun is used in self-defense about 60,000 to 120,000 times each year . Several other surveys confirm this estimate. By comparison, each year about a million violent crimes involve guns. This means guns are used to commit a crime about 10 times as often as they are used for self-defense.
A few surveys in the early 1990s suggested that there are millions gun self-defense incidents each year, but there are very good reasons to believe that these estimates were improperly calculated and these numbers are way off , more than 10 times too high. If the numbers really were this high, this would imply that pretty much every gunshot wound in America is the result of somebody protecting him or herself.
Even among the more accurate surveys, according to a panel of criminal court judges who reviewed survey respondents' stories, about half the time the gun use was "probably illegal," even assuming the gun itself had been purchased legally.
( More : Gun threats and self-defense gun use , Harvard Injury Control Research Center)
The crux of this question is whether most homicides are planned, or whether killers more often confront their victims with no clear intention. In the second case, adding a gun could result in a fatal shooting that would otherwise have been avoided.
The evidence that weapon does matter goes back decades. In 1968, Franklin Zimring examined cases of knife assaults versus gun assaults in Chicago. The gun attacks were five times more deadly. Moreover, the two sets of attacks were similar in all other dimensions: age, sex, race, whether the victim knew the assailant beforehand, and so forth. A few years later, he repeated his analysis, this time comparing small and large caliber guns. As expected, the victim was much more likely to die from larger caliber guns.
Although it is surely true that a determined killer cannot be stopped by the absence of a gun, this type of evidence indicates that many homicides are unplanned. The outcome depends, at least partially, on the weapon at hand. In that restricted sense, guns do kill people.
( More: Crime is Not the Problem: Lethal Violence in America , by Franklin E. Zimring and Gordon Hawkins)
This is not an easy question to answer, because crime rates can decline for a wide range of reasons . For example, violent crime rates declined sharply all across the country in the mid-1990s, regardless of whether a given area had tightened its gun laws. So based on a naive interpretation of the numbers, any attempt at reducing gun violence in 1995 would have appeared successful by 1998. Then there is the problem of comparing different states or cities: Circumstances differ, and what works in Memphis may fail in Detroit.
Nonetheless, there are some plausible methods for isolating the different factors, using comparison groups or other controls . The most thorough summary is a 2008 meta-analysis where the authors reviewed every prior American gun violence reduction study, examining both the reported effectiveness and the strength of the statistical evidence. Here are some approaches that don't seem to work, at least not by themselves, or in the ways they've been tried so far:
- Stiffer prison sentences for gun crimes.
- Gun buy-backs: In a country with one gun per person, getting a few thousand guns off the street in each city may not mean very much.
- Safe storage laws and public safety campaigns.
We don't really have good enough evidence to evaluate these strategies:
- Background checks, such as the Brady Act requires.
- Bans on specific weapons types, such as the expired 1994 assault weapons ban or the handgun bans in various cities.
These policies do actually seem to reduce gun violence, at least somewhat or in some cases:
- More intensive probation strategies: increased contact with police, probation officers and social workers.
- Changes in policing strategies, such increased patrols in hot spots .
- Programs featuring cooperation between law enforcement, community leaders, and researchers, such as Project Safe Neighborhoods .
There is no obvious solution here, and there's a huge amount we still don't know . But it's possible that combinations of these policies, or variations in a different context, might work better. For example, background checks would probably be more effective if they were also applied to private sales. Also, of course, this list does not include policies that have not yet been tried.
As one group of researchers put it ,
There are no feasible policies that would reduce the rate of gun violence in the United States to that of Western Europe. But we believe there are ways to make a substantial dent in the problem.
( More: The Effectiveness of Policies and Programs That Attempt to Reduce Firearm Violence: A Meta-Analysis , Journalist's Resource. Project Safe Neighborhoods and Violent Crime Trends in US Cities: Assessing Violent Crime Impact , Edmund F. McGarrell, Nicholas Corsaro, Natalie Kroovand Hipple, Timothy S. Bynum)
There is no way to know whether the recent White House proposals will be effective in reducing gun violence. How can there be, when it's so difficult to assess the actual policies that have already been tried, let alone vague plans? But the White House proposals do at least plausibly target several components of the gun violence problem.
Probably the most significant proposal is the idea of requiring background checks for gun sales between private individuals, not just from licensed dealers (with some exceptions, such as transfers within a family). Private sales are currently the main way guns move between legal and illegal owners. However, the White House has yet to specify how a private seller would perform such a check.
There is less evidence for the effectiveness of banning assault weapons and large-capacity magazines. During the 1994-2004 assault weapons ban, the use of assault weapons in crimes fell, but use of large-capacity magazines increased . This is thought to be largely due to the huge number of already-owned LCMs, which were exempt from the ban on manufacturing and sales. If the new law does not address the LCMs already in private hands, it may be decades before it has any real effect.
Removing legal restrictions that prevent the Centers for Disease Control and other agencies from tracking and researching gun violence is also a sensible idea, and follows a long history of calls from scientists (see: what don't we know ).
The U.S. has one of the highest rates of violent crime and homicide, per capita, of any developed country. According to 2008 figures compiled by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, the U.S. homicide rate for 2010 is 5.1 per 100,000 people. Only Estonia's is higher, at 6.3. The next most violent country is Finland, which has a homicide rate of 2.5, half that of the U.S. The remaining 28 developed countries are even lower, with an average of 1.1 homicides per 100,000 people.
But many less developed countries have much higher homicide rates -- for example Columbia (35.9), South Africa (36.8) and Sudan (24.2). This analysis uses the 2012 IMF list of developed countries.
The U.S. also has the highest rate of civilian gun ownership in the world, by far. The best data is from the 2007 Small Arms Survey , which notes:
With less than 5% of the world's population, the United States is home to roughly 35-50 per cent of the world's civilian-owned guns, heavily skewing the global geography of firearms and any relative comparison.
U.S. gun violence has had several decades-long cycles over the past three centuries, but shows a long-term downward trend. Overall homicide rates were similar to Western Europe until the 1850s , but since then violence has declined more slowly in the U.S.
It's tempting to plot the relationship between gun ownership and gun violence across countries, but recent research suggests that gun violence is shaped by "socio-historical and cultural context," which varies regionally, meaning that it's not always possible to make direct comparisons. However, it's still reasonable to compare places with similar histories, and more guns still correlate with more homicides in Western nations. Meanwhile, in developing countries, cities with more guns have more homicides .
( More: Chart: The U.S. has far more gun-related killings than any other developed country , The Washington Post; Facebook post says the U.S. is No. 1 in gun violence. Is it? , Politifact' Gun homicides and gun ownership listed by country , Guardian Data Blog)
A lot! We lack some of the most basic information we need to have a sensible gun policy debate, partially because researchers have been prevented by law from collecting it. The 2004 National Research Council report discussed above identified several key types of missing data : systematic reporting of individual gun incidents and injuries, gun ownership at the local level, and detailed information on the operation of firearms markets. We don't even have reliable data on the number of homicides in each county.
For such sensitive data sets, it would be important to preserve privacy both legally and technically. There have been recent advances in this area, such as anonymous registries . But the Centers for Disease Control, the main U.S. agency that tracks and studies American injuries and death, has been effectively prevented from studying gun violence , due to a law passed by Congress in 1996.
Similarly, anonymized hospital reporting systems are the main ways we know about many other types of injuries, but the Affordable Care Act prevents doctors from gathering information about their patients' gun use . A 2011 law restricts gun violence research at the National Institutes of Health . The legal language prevents these agencies from using any money "to advocate or promote gun control."
This may not technically rule out basic research, but scientists say it has made the issue so sensitive that key funding agencies will not support their work. They point to grant data as evidence of an effective ban. The White House has recently proposed lifting these research restrictions (see above )
( More: NRA Stymies Firearms Research, Scientists Say , The New York Times )
- Newsletters
Site search
- Israel-Hamas war
- 2024 election
- TikTok’s fate
- Supreme Court
- All explainers
- Future Perfect
Filed under:
The biggest questions about gun violence that researchers would still like to see answered
Share this story.
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: The biggest questions about gun violence that researchers would still like to see answered
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/49866299/shutterstock_204546301.0.0.jpg)
There are a few big things we know about gun violence in America: The US has way more guns per capita than any other country. It has far more gun homicides per capita than other wealthy countries. States with more guns have more gun deaths. And people with guns in their homes are more likely to be killed or to kill themselves with guns.
But just as importantly, there’s a lot that researchers still don't know. There’s frustratingly little evidence on what policies work best to reduce gun violence. (Australia saw a drop in homicides and suicides after confiscating everyone’s guns in the 1990s , but that would likely never happen here.) Experts still don’t have a great sense of what impact stricter background checks have, or how the "informal" gun trade operates, or even how people use guns in crimes.
"We have superficial knowledge of most gun violence topics," says Michael Nance, director of the Pediatric Trauma Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. And this ignorance has serious consequences. It’s awfully hard to stop gun violence if we can't even agree on basic facts about how and why it happens.
This ignorance is partly by design. Since the 1990s, Congress has prevented various federal agencies from gathering more detailed data on gun violence. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which has elaborate data gathering and monitoring programs for other public health crises like Ebola or heart disease, has been dissuaded from researching gun violence. The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives can't distribute much of its trace data for research purposes. Obamacare limits doctors' ability to gather data on patients' gun use.
To get a sense of what we’re missing, I surveyed a number of researchers in the field and asked them about the most pressing questions about gun violence that they’d like to see answered. Here's what they said.
We still don’t know some very basic facts about gun violence in America
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/6653635/149080269.jpg)
1) How are guns actually used? Tom Smith of NORC at the University of Chicago pointed out that "studying how guns are actually used in general" was a top research priority — including the question of how many people use guns for defensive purposes.
Other researchers pointed to related questions like: What percentage of gun owners even commit gun crimes? Why do gun accidents occur? Who's involved? Are criminals deterred by guns? These questions are a basic starting point.
2) Can we get better data on the victims of gun violence? Nance also pointed out that our data on the victims of gun violence leaves a lot to be desired. Researchers typically rely on death data ("one of the few known and reliable data points — you can’t hide the bodies," he says). But without more detailed data on who actually owns guns and who is exposed to guns, it can be hard to put these deaths in context.
And it would be good to have more detailed data on gun injuries that don't result in death. Daniel Webster, a professor of health policy and management at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, says, "We still don’t know nearly enough about nonfatal gunshot wounds, including how often they occur." That makes it much harder to get a full picture of gun violence.
3) What state laws, if any, work best to reduce gun violence? Michael Siegel, a professor of public health at Boston University, pointed to these three (broad) topics as the most pressing unanswered questions:
1. What state laws, if any, are effective in reducing rates of firearm violence? 2. Is there a differential impact of state firearm-related laws on homicide rates among white vs. African-American persons? 3. Are higher gun ownership levels related to higher firearm homicide rates because of a causal relationship or because people respond to high homicide rates by purchasing firearms?
There has already been some research on state-level gun control policies. For example, after Connecticut passed a law requiring gun purchasers to first obtain a license, one study found that gun homicides fell by 40 percent . When Missouri repealed a similar law, gun homicides increased by 23 percent . But, in part because they are retrospective and it’s impossible to run controlled experiments, studies like these remain hotly debated.
And there are all sorts of related questions here that (other) researchers would love to know the answers to. Do limits on high-capacity magazines reduce deaths? Do restrictions on alcohol sales make any difference? What about policies that make concealed carry licenses easier to obtain?
To really dig in, researchers would have to study state policies in far more detail. But, says Siegel, that will require need much better data than is currently on offer. He’d like to see more detailed state-level data on household gun ownership, on firearm policies, and on how well (or not) those policies are actually enforced.
4) How do people who commit gun crimes actually get access to their guns? Cathy Barber, who directs the Means Matter Campaign at the Harvard School of Public Health's Injury Control Research Center, listed these as big unanswered questions:
Pretty much every gun starts out as a legal gun. Among the guns that are actually used in crimes, how did they get there? That is, how many are used by their initial legal purchaser and did that person pass a background check? If the gun was not used by the initial purchaser, how did it get to the person who used it in a crime? Straw purchase? Gun trafficking (buying in a state with lax laws and transporting for street sales in state with stricter laws)? Theft? (and what type of theft? Theft from individual homes or from gun shops or what? And if from people’s homes, do these tend to be unsecured guns kept for self-defense purchases – the gun in the bedside table?), etc., etc. I think that both gun rights people and gun control people would be interested in the very specific answers to these questions and figuring out ways that we all could prevent the sort of cross-overs from legal to illegal possession and use.
A couple of other researchers agreed with this line of inquiry. Here’s Nance: "We need to know how weapons move in society to know how to best limit movement in the wrong direction (to those unfit to own)." And here’s Smith: "Understanding the ‘informal' gun market, that is guns that are acquired from others than licenses firearms dealers and therefore without background checks."
5) Is there any way to predict gun suicides? Nearly 21,000 people in the United States use guns to kill themselves each year, accounting for about two-thirds of all gun deaths. "We need to know more about how to predict who will commit suicide using a firearm," says Webster, "and ways to prevent [it]."
Back in 2013, a report from the Institutes of Medicine added some related questions around this topic that needed answering: Does gun ownership affect whether people kill themselves? And what's the best way to restrict firearm access to those with severe mental illnesses?
6) Does media violence have any impact on actual violence? This question came from Brad Bushman, a professor of communication and psychology at Ohio State University:
My research focuses on media violence. We know that youth who see movie characters drink alcohol are more likely to drink alcohol themselves. Similarly, we know that youth who see movie characters smoke cigarettes are more likely to smoke themselves. What about the impact of youth seeing movie characters with guns? Does exposure to movie characters with guns influence youth attitudes and behaviors about guns (e.g., do they think guns are cooler? are they more willing to own or use a gun? do they think guns make males more masculine?)?
7) What do we know about stopping mass shootings? I’ll add one more question to the list, which was considered a pressing research topic in the 2013 Institutes of Medicine report: "What characteristics differentiate mass shootings that were prevented from those that were carried out?"
One big reason current research into US gun violence is so dismal
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/6653641/GettyImages-456691988.jpg)
It’s fair to call gun violence a public health crisis: Some 32,383 Americans were killed by guns in 2013. And for other health crises, like Ebola or heart disease, the CDC usually springs into action, by funding studies and research that look into the best policies to deal with the problem.
But that’s not really the case here. Back in 1996, Congress worked with the National Rifle Association to enact a law banning the CDC from funding any research that would "advocate or promote gun control." Technically, this wasn’t a ban on all gun research (and the CDC wasn’t doing advocacy anyway). But the law seemed vague and menacing enough that the agency shied away from most gun violence research, period.
Funding for gun violence research by the CDC dropped 96 percent between 1996 and 2012. Today, federal agencies spend just $2 million annually on gun violence prevention — compared with, say, $21 million for the study of headaches . And the broader field has withered over that period: Gun studies as a percentage of peer-reviewed research dropped 60 percent since 1996. Today there are only about a dozen researchers in the country whose primary focus is on preventing gun violence.
Private foundations and universities, such as the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, have been partly able to pick up the slack , but private funders can rarely sustain the big, complicated data gathering and monitoring programs that the federal government can conduct. And that’s a problem because, as the researchers above noted, one of the biggest lacunae in gun research is data.
"If you look at other major public health issues, like Zika or Ebola or heart disease, the CDC is really a very authoritative source," says Andrew Rosenberg of the Union of Concerned Scientists. "Privately funded research can be helpful, but there’s no substitute for the CDC. They can do monitoring programs, long-term tracking, the stuff that’s hard to fund with a one-off grant from this or that foundation."
Siegel agrees: "The CDC has a critical role to play, so the first matter that needs to be resolved is restoring the CDC’s ability to conduct firearm-related research."
So will this situation ever change? After the Sandy Hook massacre in 2013, President Obama signed an executive order directing the CDC to start studying "the causes of gun violence." But very little has happened in the years since. The CDC didn’t actually budget. The problem, Rosenberg says, is that so long as that congressional amendment is in place, the CDC is unlikely to move forward.
Lately, there have been some calls to restore research. Republican Rep. Jay Dickey, who spearheaded the original CDC amendment, expressed remorse about the whole thing last year: "I wish we had started the proper research and kept it going all this time. I have regrets. … If we had somehow gotten the research going, we could have somehow found a solution to the gun violence without there being any restrictions on the Second Amendment."
Read more: What no politician wants to admit about gun control
Will you help keep Vox free for all?
At Vox, we believe that clarity is power, and that power shouldn’t only be available to those who can afford to pay. That’s why we keep our work free. Millions rely on Vox’s clear, high-quality journalism to understand the forces shaping today’s world. Support our mission and help keep Vox free for all by making a financial contribution to Vox today.
We accept credit card, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. You can also contribute via
In This Stream
Pulse gay nightclub shooting in orlando: the deadliest in us history.
- One map that puts America's gun violence epidemic in perspective
- The biggest questions that researchers still have about gun violence in America
- Try to scroll through this graphic and you’ll understand America’s gun problem
Next Up In Politics
Sign up for the newsletter today, explained.
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
Thanks for signing up!
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.

How did the cost of food delivery get so high?
Pig kidney transplants are cool. They shouldn’t be necessary.

The voices Oppenheimer left out

Bird flu jumped to cows, then to a human. Who’s next?

Why is there so much lead in American food?

Multigenerational housing is coming back in a big way
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Firearm Ownership, Defensive Gun Usage, and Support for Gun Control: Does Knowledge Matter?
Nathan e. kruis.
1 Department of Criminal Justice, Penn State Altoona, 3000 Ivyside Park, Cypress Building, Room 101E, Altoona, PA 16601 USA
Richard L. Wentling
2 Department of Administration of Justice, Penn State New Kensington, 3550 7th Street Road, Administrative Building Room: 111, New Kensington, PA 15068 USA
Tyler S. Frye
Nicholas j. rowland.
3 Department of Sociology, Penn State Altoona, 3000 Ivyside Park, Smith Building, Room 128H, Altoona, PA 16601 USA
Associated Data
Recent incidents of gun violence have raised questions about public access to “military-style” firearms and the need for more-restrictive forms of gun control. Proponents of more-restrictive forms of gun regulation argue that such measures will help combat the disproportionately high rates of gun crime in the United States. Opponents believe that such measures infringe upon constitutional rights and hinder law-abiding citizens' abilities to adequately defend themselves. This project explores the characteristics of gun owners living in Pennsylvania and public perceptions of three different categories of gun control. Results indicate that most gun owners have received some form of training and take appropriate safety precautions with their firearms. Further, 1 in 4 gun owners reported using their firearm in self-defense at some point in their life. Regarding gun control, most participants favored strategies intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people, such as required background checks for all types of gun purchases, mental health screenings, and mandatory gun education. However, most participants opposed complete firearm bans. Among those who are the least supportive of such polices are those who are the most knowledgeable about gun crime, gun legislation, and gun functioning. Policy implications are discussed within.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s12103-021-09644-7.
Introduction
Gun reform was a key policy issue of the 2020 presidential general election. President Biden and Democratic leaders have advocated for the enactment of “common sense” gun reform efforts, such as assault weapon bans, universal background checks, and increased resources to enforce current gun laws (Lucey, 2021 ). They believe that such reforms will help reduce the disproportionately high rates of gun crime in America. As such, leading Democrats are expected to push to change gun laws in the coming years (Newburger, 2021 ; Phillips, 2021 ). However, while data suggests that many Republicans are generally supportive of gun reform efforts intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people (Cook et al., 2011 ; Oliphant, 2017 ), many Republican leaders view the comprehensive reforms proposed by Democrats as arbitrary, infringing on constitutionally protected rights, and hindering American citizens’ abilities to adequately protect themselves, their families, and their properties. They believe that comprehensive legislation proposed by the Biden administration will only remove guns from the hands of law-abiding citizens and do little to combat gun crime. As such, legislators in many Republican-led jurisdictions have begun passing more-permissive gun policies aimed at limiting the scope of federal (“Democratic” enacted policies) gun control measures at the state level, such as pushing for “Constitutional Carry” laws, “Anti-red flag” legislation and creating “2nd Amendment Sanctuary” cities and states (Balemert, 2021 ; Friend, 2021 ).
The debate is not exclusively political, though. There is also a rift in support for gun control amongst scholars, with some favoring more-restrictive forms of gun control and others favoring less-restrictive forms of gun regulation (Morral et al., 2018 ). The legality and utility of gun regulation has promoted much discussion amongst academics (see Braga et al., 2021 ; Kleck et al., 2016 ; Winkler, 2018 ). Public support for gun control is also mixed and has varied across time, although current estimates suggest that a slight majority favor more-restrictive forms of gun control, but do not favor complete firearm bans (Gallup, 2020 ; Parker et al., 2017 ).
Prior research has attempted to examine correlates of attitudes toward gun polices. Generally, this work has found that those who are the least supportive of more-restrictive forms of gun regulation are those who identify as politically conservative (Kruis et al., 2020 ), whites (Merino, 2018 ), males (O’Brien et al., 2013 ), and gun owners (Merino, 2018 ), as well as those with greater familiarity with firearms (Rosen, 2000 ). A recent article published in the American Journal of Criminal Justice shifted this discussion to the relationship between gun knowledge and support for restrictive forms of gun control (see Kruis et al., 2020 ). In that work, the researchers found an inverse relationship between gun knowledge (i.e., broad “understanding” of gun policies, legislation, and crime) and support for stricter forms of gun control amongst college students. Findings indicated that students who knew more about guns and gun-related matters, reported being less supportive of more-restrictive forms of gun control than students who lacked such knowledge. Unfortunately, methodological limitations (e.g., cross-sectional research design, convenience sampling, student participants, etc.) precluded the authors from drawing firm conclusions about the relationship between gun knowledge and gun functioning. The current project seeks to extend this line of research by exploring the relationship between three types of gun knowledge (i.e., knowledge of gun crime, knowledge of gun legislation, and knowledge of gun functioning) and three different measures of gun control (i.e., general gun control, support for policies that reduce overall gun ownership, support for polices intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people). The current project also extends Kruis et al.’s ( 2020 ) findings related to student gun owners to members of the general public, by exploring the demographic characteristics, training experiences, safety precautions, and defensive gun usage reported by gun owners obtained from a representative sample of Pennsylvania Residents ( N = 522). In achieving these goals, the current study seeks to provide academics and policymakers alike with important information needed to be considered before making gun reforms.
Literature Review
Gun violence.
The United States has disproportionately high rates of gun violence for a developed country (Grinshteyn & Hemenway, 2019 ; Naghavi et al., 2018 ). The U.S. homicide rate is estimated to be about seven times higher than other high-income countries, which researchers suggest is primarily driven by a gun homicide rate that is about 25 times higher (Grinshteyn & Hemenway, 2019 ). In 2019 alone, there were approximately 39,707 firearm-related deaths in the United States, equating to a rate of about 12.1 per 100,000 persons (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC], 2020 )—which is about three times the rate of America’s northern neighbor (i.e., Canada, 4.1 per 100,000; Department of Justice, Government of Canada, n.d.). Among these firearm-related deaths, 23,941 were suicides and 14,414 were homicides (CDC, 2020 ). Guns, particularly handguns, are used to commit many violent crimes and most murders in the United States (National Institute of Justice, 2019 ). In total, guns were used to help commit more than 121,000 violent crimes in 2019 (Federal Bureau of Investigation [FBI], n.d.). According to data collected for the National Crime Victimization Survey (NCVS), guns were used in more than one in three aggravated assaults and about one in five robbery victimizations reported by Americans in 2019, but fewer than 1 in 100 rape and sexual assault victimizations (Bureau of Justice Statistics, 2020 ). In this regard, while guns are used to help commit many crimes, it would be an oversight to ignore that most violent victimizations in the United States do not involve guns (Braga et al., 2021 ). Further, whenever a gun is used during the commission of a violent crime it usually is not fired. In fact, when a gun is used in a crime it is predominately used as an instrument to gain victim compliance. Data suggest that only about one in four victims of nonfatal gun crimes suffer a gunshot wound (Planty & Truman, 2013 ) and overall injury rates for victims of gun crimes tend to be lower than rates for victims of crimes in which other weapons are used (Cook, 1980 ; Cook et al., 2011 ). However, whenever guns are used offenders are more likely to complete the criminal act (Cook et al., 2011 ; Libby & Corzine, 2007 ; Tillyer & Tillyer, 2014 ), and whenever they are fired, victim injuries are more likely to be lethal (Cook, 2018 ; Cook et al., 2011 ).
The Great American Gun Debate
Given high rates of gun crime, many progressives have demanded changes be made to American gun legislation. In a review of the extant literature on firearm instrumentality, Braga et al. ( 2021 ) suggest that there are two sides in the great American gun debate. On the one side of the debate are those who favor more-permissive forms of gun regulation. These advocates tend to conform to the adage endorsed by the National Rifle Association (NRA) “guns don’t kill people, people kill people” (Braga et al., 2021 ; Henigan, 2016 ; Shammas, 2019 ). This group believes that more-restrictive gun control will do little to reduce crime or to save lives (Kleck, 1997 ; Kleck et al., 2016 ; Wolfgang, 1958 ). On the other side of the debate are proponents of more-restrictive forms of gun regulation, or those who believe that “guns do kill people” (Braga et al., 2021 , p. 148). These advocates suggest that reducing firearm availability, especially to who they consider to be dangerous or “at risk” individuals (i.e., felons, the “mentally unstable,” 1 etc.) will help reduce violent gun crimes and suicides, and ultimately, save lives. In Braga et al.’s ( 2021 ) synopsis of propositions introduced by the two sides, the researchers argue that the key distinction between proponents and opponents of stricter forms of gun control relates to the instrumentality of weapons. Specifically, they write “The ‘people kill people’ perspective further suggests that gun control is futile in reducing homicides because determined killers will simply find another way. If guns are not available, assailants will substitute knives, blunt instruments, or other means” (p. 148). Similar sentiments are found within the general public as an increasing number of Americans have purchased firearms, specifically during the Covid-19 pandemic, citing self-defense as a primary driver of ownership (Gallup, 2020 ; Schaeffer, 2021 ). However, proponents of more-restrictive means of gun control assume that even if assailants choose to use other means (i.e., knife, blunt instrument) to carry out their attacks, such attacks will be less fatal (Cook, 1991 ; Cook et al., 2011 ; Henigan, 2016 ). Thus, Braga et al. ( 2021 ) argue that the crux of the debate centers on what researchers refer to “firearm instrumentality,” or whether the presence of firearms makes a criminal event more lethal.
While Braga et al. (2021 ) bring attention to an important point of contention within the debate, their brief synopsis of the two sides in the great debate overlooks arguments pertaining to the perceived ability, or inability, of gun legislation being able to effectively reduce firearm availability, particularly to dangerous and “at risk” people. This issue is a focal point in the debate and a common topic that is an important factor for the general public. Indeed, it is almost commonsensical to believe that if there were no guns, then there would be no gun crime; certainly, proponents of both sides know this to be true. The reality though is that there are a lot of guns. In fact, the United States civilian gun ownership rate is the highest in the world, with estimates suggesting that there are more than 350 million guns owned by Americans (Institute of Medicine & National Research Council, 2013 ). These instruments serve both legitimate (i.e., recreation, hunting, self-defense, etc.) and illegitimate purposes (i.e., criminal activities; Cook et al., 2011 ; Kleck et al., 2016 ). Thus, the real questions in the debate are (1) will strict gun control policies be able to effectively keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” individuals who may want to harm themselves or others? and (2) will restrictive gun control measures prevent law abiding citizens from defending their families, their properties, and their lives?
Opponents of restrictive forms of control believe that more-restrictive gun control policies will do little to disrupt illegal gun markets. They believe that such policies will merely take guns away from law abiding citizens who use firearms for legitimate purposes, including recreation, hunting, and self-defense. Current estimates suggest that there are about 15.2 million hunting license holders in the United States (U.S. Fish & Wildlife Services, 2020 ) and 9.4 million self-described “gun only” deer hunters (Schmidt, 2020 ). The data suggest that a significant portion of Americans use firearms as a source of legal recreation and food acquisition. Data also suggest that a significant number of Americans use guns for self-defense purposes. A 2017 report published by researchers at Pew Charitable trust estimated that approximately 1 in 6 gun owners had used their weapon to defend themselves, their families, or their possessions at some point in their life (Parker et al., 2017 ). While estimates vary greatly, it is speculated that the prevalence of defensive gun usage in the United States ranges from 60,000 to 2.5 million incidents annually (National Research Council, 2013 ), and whenever guns are used in self-defense, the odds of injury to potential victims is significantly reduced (Cook et al., 2011 ; Kleck & Gertz, 1995 ). As such, critics of more-restrictive gun control “argue that gun control laws could increase crime, by disarming prospective victims, reducing their ability to effectively defend themselves, and possibly reducing any deterrent effect that victim gun possession might have on offenders” (Kleck et al., 2016 , p.489).
Opponents of more restrictive measures of gun control turn to research demonstrating that a majority of gun crimes are committed by offenders who illegally obtained the firearm used in the crime (Cook, 2018 ; Roth, 1994 ). Indeed, research suggests that most gun crimes are committed by individuals who are already, under current regulations, legally disqualified from possessing a firearm due to their age, criminal record, or some other characteristic (Cook, 2018 ). However, proponents of more-restrictive gun control use this same research to cite the reality that most firearms used to commit crime originate from a legal manufacturing or distribution supply chain (Cook, 2018 ). Thus, they believe that reducing the number of guns in such markets will ultimately reduce the number of guns available to be used in crimes (Cook et al., 2011 ).
A recent report published by the RAND Corporation found that members of the scholarly community also tend to conform to this “more-restrictive” or “more-permissive” dichotomy (Morral et al., 2018 ). Indeed, there is great disagreement among researchers about the extent to which crime can be reduced through gun control. While research has produced mixed results, evidence from more methodologically sound work has indicated that higher levels of firearm ownership has little, if any, effect on overall violent crime rates (Cook & Ludwig, 2006 ; Cook & Pollack, 2017 ; Cook et al., 2011 ) or suicides (Kleck, 2019a , 2019b ), and that more-restrictive gun control mechanisms are generally ineffective at reducing crime (Kleck & Patterson, 1993 ; Kleck et al., 2016 ; Kleck, 2019b ). 2 However, some research indicates that there may be an association between rates of community gun ownership and homicide rates (Braga et al., 2021 ), suggesting that firearm availability may increase the lethality of violent crimes—although Kleck ( 2021 ) argues that prior work in this area has produced mixed findings, been tautological, and that the data merely demonstrate a positive relationship between gun ownership and the firearm homicide rates (Kleck, 2021 ). There also is evidence suggesting that polices intended to restrict dangerous and/or “at-risk” individuals (i.e., felons, the mentally ill, and “alcoholics”) from accessing firearms may be associated with reductions in crime, suicides, and violence in the community (Andrés & Hempstead, 2011 ; Braga et al., 2021 ; Braga & Cook, 2018 ; Cook et al., 2011 ; Kleck, 2019b ; Kleck et al., 2016 ; Sen & Panjamapirom, 2012 ; Smith & Spiegler, 2020 ; Wright et al., 1999 ). However, there is more research needed in this area before firm conclusions can be drawn.
Types of Gun Control
Cook et al. ( 2011 ) argue that gun-control measures can be “usefully classified into three categories: those that are intended to reduce overall gun ownership; those that are intended to keep guns away from particularly dangerous people; [and] those that are intended to influence choices about how guns are used and to what effect” (p. 259). Mechanisms that are intended to reduce overall gun ownership are those that attempt to keep guns out of the hands of all citizens—law abiding or non-law abiding. Such policies include firearm bans, limited and restrictive licensing, gun buy-back programs, and policies designed to make firearms and ammunition more expensive, and subsequently, less affordable to the average citizen. Although research on public support for such strategies is limited, data suggest that a slight majority of the general public supports banning the manufacturing, possession, and sale of some types of firearms, such as assault rifles, from public use (Gallup, 2020 ), but few support policies banning other types of firearms, such as handguns, from public use (Brenan, 2020 ). 3 Mechanisms that are intended to keep guns away from dangerous or “at-risk” people refer to strategies aimed at keeping guns away from those who are likely to use them for criminal purposes, or to self-harm, such as felons, the untrained, and the mentally ill (Morrall, 2018 ). Measures within this category of gun control include increased screening and monitoring of buyers and dealers in legal gun markets, creating a national firearms database, and outlawing “straw” (i.e., secondary market) purchases. Generally, the public is more supportive of these types of gun control strategies, especially those aimed at barring gun sales to the mentally ill, and those on “no fly” or on law enforcement “watch lists” (Parker et al., 2017 Schaeffer, 2019 ). The third category of “usefully classified” gun control mechanisms are those intended to influence choices about how guns are used and to what effect. This category includes strategies aimed at increasing firearm design regulation (e.g., manufacturing more “smart guns”) and implementing various forms of “focused deterrence” policing strategies, such as “gun oriented patrol tactics” and “hot spots policing” (Cook et al., 2011 , p. 280) Recent research suggests that many members of the general public may have favorable views of smart guns as a safety and crime reduction tool by indicating that they would be inclined to purchase such weapons if they became readily available (Wallace, 2016 ). Controversial, research also indicates mixed public support for “gun oriented” policing tactics, such as stop, question, and frisk polices (Evans & Williams, 2017 ) which is further complicated by the recent surge in firearm purchases (Schaeffer, 2021 ).
Prior Research Assessing Correlates of Support for Gun Control
Trends in public polling tend to inform the direction of gun policies and the overall sentiment of potential voters toward certain restrictions or measures to be introduced. Much of this data is derived from national surveys which are administered through organizations such as Gallup, RAND, and similar organizations via cross-sectional designs. Wozniak ( 2017 ) notes that public opinion toward gun control has remained relatively consistent although support for more restrictive laws concerning the sales of firearms has declined since the 1990s. The most recent data collected by Gallup ( 2020 ) suggest that approximately 57 percent of Americans believe that the laws covering the sale of firearms should be made more strict, which is down more than 20 percentage points since when the organization first started tracking these data in the early 1990s, but up more than 10 percentage points from the start of the 2010s. One aspect that remains relatively high is the support for background checks and limiting access for dangerous or “at-risk” individuals. Barry et al. ( 2019 ) find similar support for the use of universal background checks and limiting access for dangerous or “at-risk” individuals regardless of ownership status to include knowledge and/or safety courses for first-time owners.
Researchers have spent considerable time examining correlates of support for gun control, finding mixed support across demographic groups. Due to this mixed support, an array of proposed gun control measures and policies have faced backlash amid American constituents (see Giffords Law Center for a review of state-specific measures). Generally, though, this work has found that men (Ellison, 1991 ; Kauder, 1993 ; Livingston & Lee, 1992 ; Marciniak & Loftin, 1991 ; Merino, 2018 ; O’Brien et al., 2013 ; Pederson et al., 2015 ; Tyler & Lavrakas, 1983 ), whites (Filindra & Kaplan, 2017 ; McClain, 1983 ; Merino, 2018 ; Secret & Johnson, 1989 ), those who are politically conservative (Filindra & Kaplan, 2017 ; Merino, 2018 ), those who live in rural communities (Brennan et al., 1993 ; Parker et al., 2017 ) and gun owners (Filindra & Kaplan, 2017 ; Merino, 2018 ) are less supportive of more-restrictive forms of gun control than those in reference groups. Additionally, there is evidence suggesting that those who have greater exposure to, and familiarity with firearms (Ellison, 1991 ; Hill et al., 1985 ; Kruis et al., 2020 ; Rosen, 2000 ; Tyler & Lavrakas, 1983 ) favor more-permissive forms of gun control. Recently, Filindra and Kaplan ( 2017 ) found that “drivers of support for gun control” were generally consistent for members of racial minority groups and whites (p. 413). The authors noted that fear, or concern, of crime was generally positively related to support for more-restrictive forms of gun control across racial groups, while political conservativism, being a crime victim, owning a gun, and racial prejudice (i.e., held by Whites and Latinos) were inversely related to support for more-restrictive forms of gun control. Their study, along with earlier work (see Filindra & Kaplan, 2016 ), shed light on a possible relationship between racial resentment and Whites’ and Latinos’ attitudes toward gun control, suggesting that racism, generally, is a correlate of support for less-restrictive forms of gun control among these groups. However, gun ownership among minority and BIPOC communities has continued to rise with the largest increases occurring during the social and civil unrest associated with 2020 (Curcuruto, 2020 ; Parker et al., 2017 ). Crifasi et al. ( 2021 ) extended this line of inquiry and found that minority and BIPOC communities tend to favor less-restrictive gun control measures especially when police or the criminal justice system is involved, but general support for reduced access to firearms remains mixed across group membership.
Other researchers have found that men, generally, are less supportive of more-restrictive forms of gun control (see Ellison, 1991 ; Merino, 2018 ; O’Brien et al., 2013 ; Pederson et al., 2015 ; Tyler & Lavrakas, 1983 ). Some scholars have suggested that guns and pro-gun attitudes serve as a way for men to demonstrate masculinity and to bond with other men. These scholars argue that gun control is perceived as a threat to “male intimacy” and male identity, thus men are more likely to be emersed in gun culture and have favorable views of guns (see Carlson et al., 2018 ). Research has also documented an inverse relationship between educational attainment and support for more-restrictive forms of gun control (Newman & Hartman, 2019 ). Kruis et al. ( 2020 ) recently extended this line of inquiry by examining the relationship between gun knowledge—operationally defined as “one’s understanding of gun legislation, gun policies, and firearm crime”—and support for general gun control using a convenience sample of college students (p. 33). The authors found an inverse relationship between gun knowledge and support for stricter forms of gun control, concluding that students who had greater understanding of gun legislation, gun crime, and gun functioning, were less likely to favor stricter forms of gun control than students with less knowledge in these areas. While informative, this study suffered from a few crucial methodological limitations that preclude the generalizability of the findings. Notably, findings were based on data collected from college students through convenience sampling at three universities. Additionally, the measures of gun control and gun knowledge were broad and prohibited the examination of specific types of gun knowledge and various categories of gun control. Accordingly, the authors called for more work to be done in this area.
Current Study
The goal of the current study was to help contribute to research in this area by exploring public perceptions of various types of gun control mechanisms. In many ways the current study serves as an extension of Kruis et al.’s ( 2020 ) research. Specifically, the methodology employed by Kruis et al. ( 2020 ) were applied to the general public, using a representative sample of Pennsylvania residents ( N = 522) to help answer the following two overarching research questions:
- R1: What are the training experiences, safety precautions, and defensive gun use reported by gun owners in Pennsylvania?
- R2: What is the relationship between firearm knowledge and support for more-restrictive gun control policies?
Regarding our first research question, we were interested in assessing training experiences, safety precautions, and defensive gun usage reported by Pennsylvania gun owners. We were also interested in comparing demographic characteristics, victimization experiences, gun knowledge, and support for different types of gun control between gun owners and non-owners. Our second research question was concerned with testing the generalizability of Kruis et al.’s ( 2020 ) findings from students to members of the general public. Notably, we were interested in expanding upon Kruis et al.’s measures to better explore the relationship between different types of firearm knowledge (i.e., knowledge of gun crime, knowledge of gun policy, and knowledge of gTillyerun functioning) and various categories of gun control (i.e., general gun control, policies aimed at reducing overall gun ownership, and policies aimed at keeping guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people). We hypothesized that increased firearm knowledge would be inversely related to greater support for gun control.
Data for this project came from a larger study aimed at measuring public attitudes toward a variety of social phenomena, including school security measures, campus carry, and perceptions of the police. Specifically, data came from a 64-question original survey created by the authors and administered via the Qualtrics survey platform. The authors used the marketing research team at Qualtrics to locate and recruit a sample of 500+ English speaking residents of Pennsylvania aged 18 or older. Qualtrics maintains active market research panels of more than six million English speaking, non-institutionalized adults capable of giving consent. Participants join a panel through one of three different methods, including a “double opt-in,” direct recruitment by the marketing research team, or voluntary sign up. In exchange for their voluntary participation in surveys, panelists are compensated with small point-based incentives that can be redeemed in various forms, such as Sky Miles or gift cards.
In the Fall of 2020, Qualtrics sent an invitation link to panelists inviting them to participate in the survey. Interested panelists were first screened to determine eligibility. Efforts were made to ensure the representativeness of the sample in terms of race, age, and biological sex. That is, the marketing team was contracted to ensure that participants were screened in a way such that the final sample would be representative of the Pennsylvania general population in terms of race, age, and biological sex. Then, potential participants were shown an informed consent document specifying the goals of the study, potential risks and benefits, and contact information for the principal investigator and institutional review board. Those who consented were then directed to the online survey where they were presented with 64 Likert scale, text entry, and essay-based questions. In total, 680 panelists clicked on the invitation link and participated in the survey in some capacity. Data quality assurance tests revealed that 522 of these cases were valid and complete responses. Thus, all models specified below were based on the 522 cases with complete and valid data. It is important to note at the onset that our data collection strategy represent a convenience sampling approach. That said, comparisons with population estimates revealed that the data collected were generally representative of the Pennsylvania general population in terms of race and sex at the time of data collection, as well as income and geographical location (i.e., rural or urban). However, the median age of the sample (47) was slightly older than that of the general Pennsylvania population (41).
Support for Gun Control
The goal of this study was to assess residents’ support for various categories of gun control. Three different measures were used to capture participants’ disposition toward stricter forms of gun regulation. First, the 9-item measure used in Kruis et al.’s ( 2020 ) original study was used to capture respondents’ disposition toward broad forms of gun control. Items included: (1) “Strict gun legislation will stop future gun-related incidents/mass shootings,” (2) “Guns should not be used for recreational reasons (i.e., hunting, sporting, etc.),” (3) “Gun laws should differentiate between handguns and other guns,” (4) “Military type guns should be banned from public use,” (5) “Mental health screenings should be required to purchase any firearm,” (6) “I think all types of guns should be banned from public use,” (7) “I believe that the Second Amendment needs to be revised to reflect modern times,” (8) “Second Amendment rights allow more guns to be available to the public than necessary,” and (9) “I believe that current gun legislation is appropriate.” Response categories followed a 5-point Likert scale ranging from “Strongly Disagree” (1) to “Strongly Agree” (5). Item #9 was reverse coded and then responses were summed and averaged to create a continuous measure of broad support for gun control with higher numbers indicative of greater support for enhanced firearm regulation (α = 0.832).
To further assess differences in support for distinct types of gun control policies, two measures from Cook et al.’s ( 2011 ) gun control trichotomy were also created and included in analyses. The first measure was intended to capture support for gun control mechanisms aimed at reducing overall firearm ownership. Two items from the survey were used to capture this category of gun control strategies: (1) “Guns should not be used for recreational purposes (i.e., hunting, sporting, etc.)” and (2) “I think all types of guns should be banned from public use.” Responses followed a 5-point Likert scale ranging from “Strongly Disagree” (1) to “Strongly Agree” (5). The two items were combined and averaged to create a scale variable with higher scores reflective of greater support for policies intended to reduce overall firearm ownership (α = 0.797). The second specific type of gun control measured was support for policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous and/or “at-risk” individuals, such as criminals, the untrained, and the mentally ill. Three items for the survey were used to measure participants’ support for this category of gun control policies: (1) “I believe that mandatory gun education will lead to fewer gun related deaths in the U.S.,” (2) “There should be required background checks for all guns purchases,” and (3) “Mental health screenings should be required to purchase any firearm.” Responses followed a 5-point Likert scale ranging from “Strongly Disagree” (1) to “Strongly Agree” (5). The items were combined and averaged to create a scale variable with higher scores reflective of greater support for policies intended to keep guns out of the hands of dangerous and “at risk” people (α = 0.721).
For the purposes of this project, knowledge referred to a participant’s understanding of gun-related phenomena. To capture knowledge, participants were given a “Knowledge Test.” Three different domains of knowledge were assessed: (1) knowledge of gun crime, (2) knowledge of gun policy, and (3) knowledge of gun functioning. Knowledge of gun crime refers to participants' level of understanding of gun-related crime in the United States. Items used to capture this measure included: (1) “Gun related homicides have increased over the last 30 years throughout the U.S.,” (2) “In the last 10 years, most gun related deaths per year in the U.S. have been from suicides,” (3) “A majority of firearms used in criminal offenses were obtained illegally,” (4) “Military-style weapons (for example, “assault rifles”) are used in the majority of gun-related crimes,” (5) “Most firearm owners never commit a gun crime,” and (6) “Most mass shootings in the United states are done with legally obtained firearms.” Knowledge of gun policy refers to participants’ level of understanding of gun-related purchasing and ownership policies. Items used to capture this measure included: (1) “In the U.S., it is illegal to own a fully automatic firearm without a permit,” (2) “When purchasing a firearm from a retail store, a background check is NOT required,” (3) “When purchasing a firearm online from a retail store, one must go through a licensed firearm dealer to acquire it,” (4) “In the U.S., the legal purchasing age of rifles is lower than that of handguns,” (5) “In the U.S., felons cannot legally own a firearm,” and (6) “In the U.S., authorities can legally confiscate guns solely based on an individual’s mental illness.” Knowledge of gun functioning refers to a participant’s level of understanding of how guns work (i.e., gun-related functioning and operational procedures). Items used to capture this measure included: (1) “The “AR” in AR-15 stands for “Assault Rifle 4 ”, (2) “A semi-automatic firearm only fires one round of ammunition per single pull of the trigger,” (3) “The “magazine” is the area of the gun that feeds ammunition into the chamber of the gun,” (4) “An individual must manually engage the hammer on a double-action firearm before the weapon can fire a bullet,” (5) “A bolt-action rifle requires the user to manually cycle every round before the rifle can be fired,” and (6) “All firearms must legally have a safety setting to keep the firearm from firing.” Response categories to all questions included “True,” “False,” and “I Don’t” Know.” Correct answers were coded as a “1” and incorrect answers were coded as a “-1.” Participants were not penalized for selecting “I don’t know” (coded as “0”). Individual items were then combined to create an index measure ranging from − 6 to + 6 with greater scores indicating greater knowledge. See Appendix 1 for specific coding. 5
Experiences
Prior work has shown that experiences with firearms and crime can influence dispositions toward firearms (Ciomek et al., 2020 ; Kleck, 2019a ; Kruis et al., 2020 ). As such, five variables were used to capture participants’ experiences with firearms and crime, including (1) exposure to firearms, (2) perceived firearm familiarity, (3) criminal victimization experience, (4) vicarious criminal victimization experience, and (5) vicarious shooting victimization experience. Exposure was captured using Kruis et al.’s ( 2020 ) 10-item firearm exposure scale (α = 0.955), with items including “I regularly use guns for recreational purposes” and “I am around guns frequently.” Perceived familiarity was captured using Kruis et al.’s ( 2020 ) 3-item perceived familiarity scale (α = 0.872), with items including “I am familiar with current gun legislation in the United States” and “I am familiar with current gun legislation in my state of residence.” Participants were also asked to indicate whether they had ever been the victim of a crime (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”), if someone close to them had ever been the victim of a crime (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”), and if they knew someone who had ever been shot with a firearm (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”).
Training, Safety Precautions, and Gun Use
As the first research question for this project was concerned with examining the characteristics of gun owners, participants were asked to indicate whether they owned a firearm (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”). Those who indicated that they owned a gun were then presented with a series of questions intended to capture their experiences with firearm-related training. Specifically, gun owners were asked if they (1) had taken a formal gun safety course, such as a basic hunter safety education course (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”), (2) received informal gun safety training, through a friend or family member (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”), and/or (3) taken a gun self-defense course (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”). Owners were also asked to report whether or not they took various safety precautions with their firearms, such as using a gun safe or gun lock, keeping their guns unloaded, and/or storing ammunition away from their firearm(s) (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”). Additionally, gun owners were also asked to report if they had ever used their gun to defend themselves 6 (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”).
Demographics
Measures of sex (1 = “male,” 0 = “female”), race (1 = white, 0 = non-white), age (0–max), geographical background (1 = “Urban,” 2 = “Suburban,” and 3 = “Rural”), income (1 = “Less than $10,000” through 12 = “More than $150,000”) and political affiliation (1 = “Republican,” 2 = “Democrat,” and 3 = “Other”) were also captured and included as control variables in the analyses.
Analytic Strategy
Data were analyzed using SPSS version 27. The analysis consisted of 3 main steps. First, all data were cleaned, coded, and preliminary analyses run to assess measures of central tendency and dispersion. Factor analyses (i.e., Principal Component Analysis and Principal Axis Factor Analysis) were used along with reliability estimations to help construct scale variables during the initial data screening process. Support for individual gun control measures were estimated by combining “strongly agree” with “agree” responses and then ranked to help illustrate public support for specific types of gun control strategies. Second, bivariate analyses were conducted to examine differences in mean scores and response categories between gun owners and non-owners. Third, a series of OLS regression models were estimated to explore the relationship between knowledge of gun crime, gun legislation, gun functioning and support for gun control, controlling for relevant “predictors. 7 ” All assumptions of OLS regression were checked prior to constructing the final models reported below. All variables inputted into the regression model had tolerances above 0.1 and Variance Inflation Scores (VIFs) below 10 (Pallant, 2016 ). Normal Quantile–Quantile and Probability-Probability plots indicated the presence of relatively normal distributions, and skewness and kurtosis values for the dependent variables fell within the acceptable range for analyses (− 2.00 and + 2.00, Field, 2016 ).
Descriptive Statistics
Table Table1 1 displays participant demographic information and descriptive statistics. As indicated in Table Table1, 1 , a majority of participants were white (76.4%) and female (50.4%). Participants were fairly evenly distributed in their political affiliation, with about 41 percent identifying as “Democrat,” 37 percent identifying as “Republican,” and 22 percent identifying as “Other.” The mean age of the sample was 49.03 years old. More participants indicated suburban backgrounds (42.1%) than urban (37.2%) and rural (20.7%) backgrounds. In terms of income, the mean score reported was 6.70, suggesting an average household income between $50,000 and $70,000. A little more than a quarter of the sample (27.8%) indicated being a gun owner. Approximately 40 percent of the sample knew a victim of a crime (40.6%) or indicated being the victim of a crime themselves (39.7%). Nearly a third of the sample reported knowing someone who had been shot (32.4%). Regarding gun-related experiences, most participant’s indicated moderate firearm exposure (M = 2.51, SD = 1.25) and a slightly elevated estimate of their perceived familiarity (M = 3.40, SD = 1.00) with current firearm legislation. In terms of actual gun knowledge, participants had more knowledge of gun policy (M = 2.00, SD = 2.16) than gun crime (M = 0.64, SD = 2.08) and gun functioning (M = 0.04, SD = 1.86). In the aggregate, participants expressed moderate support for our general measure of broad gun control policies (M = 3.28, SD = 0.90). However, participants were more supportive of policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people (M = 4.10, SD = 0.88) than they were of policies intended to reduce overall ownership (M = 2.48, SD = 1.31).
Participant demographic information and descriptive statistics (N = 522)
Comparing Owners to Non-Owners
Table Table2 2 displays the results from bivariate analyses (i.e., t-tests and chi-square tests) comparing gun owners (N = 145) to non-owners (N = 377). With the exception of age, gun owners were different from non-owners in all other demographic measures assessed. On average, gun owners were more likely to be male, white, and republican (p ≤ 0.001). They were also more likely to have rural backgrounds ( Χ 2 = 6.315, p ≤ 0.05) and reported higher incomes (t = − 3.481, p ≤ 0.01). Results also show that gun owners were different from non-owners in terms of gun-related experiences, gun knowledge, and support for gun control. Specifically, compared to non-owners, gun owners were more likely to report being the victim of a crime ( Χ 2 = 6.235, p ≤ 0.05) and to know someone who has been shot ( Χ 2 = 5.331, p ≤ 0.05). Owners also reported greater gun exposure (t = − 11.810, p ≤ 0.001) and familiarity (t = − 5.330, p ≤ 0.05) than non-owners. Gun owners were found to have greater knowledge of gun crime (t = − 2.831, p ≤ 0.01), gun policy (t = − 5.317, p ≤ 0.001), and gun functioning (t = − 5.116, p ≤ 0.001) than non-owners, and indicated less support for general gun control mechanisms (t = 5.346, p ≤ 0.001), policies that seek to reduce overall gun ownership (t = 3.318, p ≤ 0.05), and policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people (t = 1.991, p ≤ 0.05).
Comparing gun owners to non-owners (N = 522)
*p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001 (two-tailed tests)
Training, Safety, and Defensive Gun Usage
Our first overarching research question was concerned with examining training experiences, safety precautions taken, and defensive gun usage reported by gun owners. Table Table3 3 displays characteristics of the gun owners in our sample. As indicated in Table Table3, 3 , most owners indicated receiving some form of gun training (89.7%). Nearly three-quarters of the gun owners in our sample reported completing a formal safety training course, such as a basic hunter safety education course (72.4%). A little more than 70 percent indicated receiving informal safety training from a friend or family member, and 42.8 percent reported taking a gun self-defense course. Interestingly, 10.3 percent of all the gun owners in our sample noted that they had not received any form of safety training—formal or informal—nor had they taken a gun self-defense class. In terms of safety precautions taken, most gun owners indicated taking one of measures included in the survey (95.9%). Specifically, 62.1 percent indicated using a gun safe for storage purposes, 39.3 percent reported using gun locks, 50.3 percent expressed that they stored ammunition away from firearms, and 54.4 percent indicated that they kept their guns unloaded. Just six of the 145 gun owners in our sample (4.1%) reported that they did not use any of the safety precautions assessed in our survey. Regarding defensive gun usage, more than a quarter of gun owners (26.9%) reported that they had used a firearm to defend themselves at some point in their life.
Characteristics of gun owners (N = 145)
Our second overarching research question was concerned with assessing public support for gun control. Two different analyses were used to answer this research question. First, descriptive statistics were assessed for individual measures of support for gun control and then ranked by level of support. Table Table4 4 displays the findings from these analyses in order of rank. As noted in Table Table4, 4 , the most publicly supported gun control policy was requiring background checks for all types of gun purchases (86.0%), followed by requiring mental health screenings (79.7%), banning military-style weapons from public use (69.7%), mandating gun education (62.5%), and differentiating laws between handguns and other guns (59.4%). Slightly more than half of the sample also felt that the Second Amendment needed revised “to reflect modern times” (52.7%) and believed that strict gun legislation could stop future gun-related incidents and mass shootings (51.3%). However, most participants did not support completely banning firearms from public use (72.6%) 8 or banning guns for recreational purposes, such as hunting and sport shooting (74.1%).
Support for gun control measures by rank (N = 522)
Second, we estimated a series of OLS regression models to examine variables associated with support for gun control. Table Table5 5 displays results from those analyses. Regarding our general measure of gun control, results indicated that the model fit the data well and explained approximately 31 percent of the variance in general support for gun control ( F = 14.901, p = 0.000, R 2 = 0.312). Nine of the independent variables in that model were found to be statistically significantly related to support for general gun control (p ≤ 0.05). Regarding demographic variables, results showed that compared to Republicans, Democrats (b = 0.589, p ≤ 0.001) indicated more support for gun control. Findings also suggest a marginally significant relationship between identifying as having a “Other” political affiliation (b = 0.176, p ≤ 0.010) and greater support for gun control, compared to identifying as a Republican. Further, results showed that compared to those with rural backgrounds, those with urban backgrounds (b = 0.234, p ≤ 0.05) were more supportive of gun control. Income was also statistically significant (b = 0.045, p ≤ 0.001), with findings suggesting that wealthier individuals were more supportive of gun control. Conversely, gun ownership (b = − 0.234, p ≤ 0.01) was found to be negatively associated with support for increased gun control. In terms of experiences, findings indicated that those who had been the victim of a gun crime (b = 0.188, p ≤ 0.05) and those who perceived having greater familiarity with current gun legislation (b = 0.151, p ≤ 0.001) were more supportive of policies associated with increased gun control. Findings also showed that those who indicated greater firearm exposure (b = − 0.119, p ≤ 0.01) held less support for general gun control mechanisms. Two measures of gun knowledge were also statistically significant in that model. Results showed that knowledge of gun crime (b = − 0.080, p p ≤ 0.001) and knowledge of gun functioning (b = − 0.079, p ≤ 0.001) were inversely related to support for general gun control.
Results from OLS regression analyses predicting support for gun control (N = 522)
a reference category is “Republican”, b reference category is “rural”
† p ≤ .10, * p ≤ .05, ** p ≤ .01, *** p ≤ .001 (two-tailed tests)
The model estimating support for gun control policies intended to reduce overall gun ownership was also statistically significant ( F = 14.992, p = 0.000). The predictors in that model explained approximately 31 percent of the variance in the dependent measure ( R 2 = 0.313). Nine of the independent variables in that model were found to be statistically significant (p ≤ 0.05) and two exhibited a marginally significant association (p ≤ 0.10). Regarding demographic variables, results showed that age (b = − 0.017, p ≤ 0.001) and gun ownership (b = − 0.325, p ≤ 0.01) were negatively associated with the dependent measure, whereas being a Democrat (b = 0.441, p < 0.001), income (b = 0.033, p ≤ 0.05), and having an Urban background (b = 0.560, p ≤ 0.001) were significantly and positively associated with the dependent measure. In terms of experiences, findings indicated that those who had been the victim of a crime (b = 0.208, p ≤ 0.10) were more supportive of policies associated with reducing overall gun ownership. Interestingly, findings also showed that those who indicated greater firearm exposure (b = 0.139, p ≤ 0.05) held more support for such policies, which is opposite the direction for this variable noted in the first model. Knowing a crime victim was found to exhibit a negative, albeit marginally, significant relationship (b = − 0.216, p ≤ 0.10) with support for policies intended to reduce overall ownership. All measures of gun knowledge were statistically significantly related to support for policies aimed at reducing overall gun ownership. Results showed that knowledge of gun crime (b = − 0.110, p ≤ 0.001), knowledge of gun policy (b = − 0.059, p ≤ 0.05), and knowledge of gun functioning (b = − 0.068, p ≤ 0.05) were inversely related to support for policies intended to reduce overall gun ownership.
The last column in Table Table5 5 shows results from the OLS modeling estimating support for gun control policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people. Results indicated that the model fit the data well and explained approximately 14 percent of the variance in gun control mechanisms aimed at keeping guns out of the hands of dangerous people (F = 6.059, p = 0.000, R 2 = 0.142). Six of the independent variables in that model were found to be statistically significant. Regarding demographic variables, results showed that being male (b = − 0.163, p < 0.05) and younger (b = .008, p ≤ 0.01) were negatively related to the dependent measure, whereas income (b = 0.033, p ≤ 0.01) was positively associated with support for policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous individuals. In terms of experiences, findings suggested that greater familiarity with current gun legislation (b = 0.235, p ≤ 0.001) was associated with more support for policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous people, whereas greater exposure was associated with less support (b = − 0.182, p ≤ 0.001). Only one measure of gun knowledge was statistically significant in the model. Results showed that knowledge of gun functioning (b = − 0.077, p ≤ 0.01) was inversely related to support for policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people. 9
This study was concerned with exploring public perceptions of gun control. Specifically, data collected from a representative sample of 522 Pennsylvania residents were used to (1) explore the training experiences, safety practices, and defensive gun usage reported by gun owners, and (2) to examine the correlates of public support for various types of gun control. There are a few findings from analyses that warrant further discussion.
First, there were several notable findings related to training experiences, safety precautions, and defensive gun usage indicated by the gun owners in our sample. Consistent with previous findings, we found that more than 25 percent of the gun owners in our sample had never taken a formal gun safety course, including a basic hunter safety education course (Parker et al., 2017 ; Kruis et al., 2020 ). To expand upon prior work, we also attempted to assess gun training through cultural transmission by asking participants if they had received informal gun training, such as training through a family member or friend. We found that approximately 70 percent of gun owners in our sample had received informal training through a family member or friend. In all, a majority of our sampled gun owners reported receiving some form of gun safety training (i.e., 90 percent). However, collectively, findings revealed that about 10 percent of the gun owners in our sample had received no formal or informal training. This estimate is concerning, given that firearm training courses tend to focus on teaching novice gun handlers how to safely use, transport, and store their firearms, as well as introduce them to relevant gun laws (Rowhani-Rahbar et al., 2018 ). Ill-trained gun owners may be at a greater risk of using their firearms in an unsafe manner or storing them in ways that permit “unauthorized” persons to access and use their weapons, which can result in more firearm-related injuries.
Unfortunately, due to data limitations (i.e., sample size), we were unable to effectively explore the relationship between gun training and safety precautions taken by gun owners. We did find that more than half of the gun owners in our sample reported using gun safes, kept their firearms unloaded at all times, and/or stored ammunition away from firearms in an attempt to prevent others from accessing and/or using their firearms, which helps to prevent accidental discharges. In fact, just six of the 145 gun owners in our sample (4.1%) reported that they took “no safety” precautions, suggesting that most— “trained” and “untrained” gun owners—took some form of gun safety precaution. Supplementary analyses did reveal that two of the six gun owners who indicated they took none of the listed safety precautions also indicated that they had received no formal or informal gun safety training. These data indicate that there was a higher proportion of non-trained gun owners (13.3%) who suggested taking no safety precaution than there were trained gun owners (3.1%). We do want to caution when interpreting these results for two reasons. First, our measures do not capture the “quality” of training received. Second, as noted above, the number of non-trained gun owners and owners who take no-safety precautions was so small that we were unable to conduct any type of meaningful comparison. As such, we encourage future researchers to explore the relationship between gun training and gun safety more thoroughly. We will note, however, that, in synthesizing prior research in this area, scholars at RAND Corporation ( 2020 ) concluded that child access prevention laws, defined as laws that attempt to influence how guns are stored, are effective at reducing unintentional injuries and deaths, as well as suicides, and may be effective at helping to reduce violent crime. Thus, it appears that there may be a relationship between gun storing patterns and rates of firearm-related injuries. As such, if more owners store their weapons properly, then we may see fewer firearm related injuries, suicides, and violent crime.
Another interesting finding emerging from the data was the proportion of defensive gun usage reported by gun owners in our sample. Nearly 27 percent of gun owners in our sample indicated that they had used their gun to defend themselves at some point in their life. This suggests that more than 1 in 4 gun owners in our sample had used their firearm to defend their life, liberty, or property—which, although a slightly higher estimate, mirrors findings reported by the Pew Research Center in 2017 (i.e., 1 in 6 gun owners; see Parker et al., 2017 ). Other research has found that the prevalence of defensive gun usage in the United States ranges from 60,000 to 2.5 million incidents annually (Institute of Medicine & National Research Council, 2013 ). Collectively, these findings indicate that a significant portion of gun owners use—or at least perceive that they use—their firearm(s) for self-defense purposes. As such, any efforts aimed at reforming gun policies in the United States should consider this “utility,” or using firearms as a tool, prior to implementation. While firearms may currently help contribute to a high number of injuries (CDC, 2020 ) and crimes (National Institute of Justice, 2019 ) committed every year in the United States, it is possible that gun control efforts that take guns out of the hands of law-abiding citizens could further exacerbate these numbers by removing a viable protection mechanism from individuals who otherwise may be unable to adequately defend themselves. Prior research has been mixed in findings related to this hypothesis with some work suggested that arming potential victims may be associated with reductions in injuries and loss of property (see Cook et al., 2011 ; Cook, 1991 ; Kleck & Gertz, 1995 ; Southwick, 2000 ) and other research questioning such claims (Hemenway, & Solnick, 2015 ). Similarly, and more broadly, prior research on the effects of gun control related to patterns of gun ownership on patterns of violence and crime have produced mixed results, with some research findings indicating little to no effect (Kleck, 2019a ; Kleck et al., 2016 ; Lott, 2013 ) and others suggesting a positive relationship between gun ownership and gun crime (Billings, 2020 ; Ciomek et al., 2020 ). Accordingly, more research is needed before firm conclusions related to defensive gun usage can be drawn. That said, our data show that gun owners in Pennsylvania may use their weapons in self-defense at a fairly high rate.
Second, there were several interesting findings related to participants’ support for various forms of gun control. In the aggregate, the top three supported gun control measures were: (1) required background checks for all types of gun purchases (86.0%), (2) required mental health screenings for gun purchases (79.7%), and (3) banning military type firearms (i.e., AR or AK platforms) from public use (69.7%). Using prior research (see Cook, 2011 and Kruis et al., 2020 ) we also examined “correlates” of support for gun control measured in three different ways: (1) support for general gun control mechanisms, (2) support for policies aimed at reducing overall gun ownership, and (3) support for policies aimed at keeping firearms away from dangerous people. There were several interesting findings that emerge from those analyses. Notably, most participants seemed to favor polices aimed at keeping guns away from dangerous and “at risk” individuals, such as the untrained, the mentally ill, and justice-involved persons. However, most did not support policies aimed at reducing overall gun ownership (i.e., restricting public gun use and use for recreational purposes)—which is consistent with prior research (Parker et al., 2017 ).
These findings are important to consider in relation to the efficacy of such policies. The dominate research suggests that gun control intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people may be effective at reducing serious violence (Braga & Cook, 2018 ; Kleck et al., 2016 ; RAND, 2020 ), while gun control strategies aimed at reducing community firearm ownership may have little to no effect on overall violent crime rates (Cook & Ludwig, 2006 ; Cook & Pollack, 2017 ; Kleck, 2019b ).
Similarly, several interesting findings emerged in multivariable modeling. Generally, we found that those who are more supportive of gun control were Democrats, those who had Urban backgrounds, those who had less exposure to firearms, and those with larger annual incomes. We also found a significant relationship between specific types of gun knowledge and support for categories of gun control. Participants who had greater knowledge of gun crime and gun functioning were less supportive of general forms of gun control, and those who had greater knowledge of gun functioning were less supportive of restrictive policies. Consistent with findings reported by Kruis et al. ( 2020 ), we found a general inverse relationship between gun knowledge and support for various types of gun control, with a few caveats. We found that those who were more knowledgeable in the areas of gun crime, gun policy, and gun functioning, did not favor more restrictive gun control measures, particularly those aimed at reducing overall gun ownership. However, excluding knowledge of gun functioning, there was no relationship between gun knowledge and support for policies aimed at keeping firearms away from dangerous people, suggesting that both the “knowledgeable” and “non-knowledgeable” are equally likely to support restricted access for potentially dangerous and “at risk” individuals.
Collectively, this research shows that the same gun control strategies with the most public support—and those supported by those with the most gun “knowledge”—are also those with the most empirical support. Similarly, those with the least public support are those that seem to have the least or, at least, questionable empirical support. As such, policymakers may want to direct gun “reform” efforts toward policies intended to keep guns away from persons who are considered to be dangerous or “at risk,” such as felons, the untrained, and those who are mentally ill. At the same time, policymakers need to consider the effects that such actions will have on legal acquisition and take efforts to strengthen law abiding citizens’ abilities to obtain and use firearms legally. For instance, based on the available scholarly literature, we argue that complete firearm bans will likely have little if any positive effect of crime, and our research shows that such policies are largely unsupported by members of the general public. Related, we also suggest that gun control strategies discussed by Cook and Leitzel ( 1996 ) aimed at increasing the price of firearms and ammunition may only prevent law abiding citizens from obtaining weapons and merely increase black market sales or thefts of weapons, which is how most criminals obtain their firearms (Cook, 2018 ; Roth, 1994 ). Thus, better approaches to gun regulation will prevent dangerous and “at risk” people from obtaining firearms, while also protecting law-abiding citizens abilities to access firearms. Unfortunately, as noted by Braga et al. ( 2021 ) the current research provides us with little guidance on how best to achieve this goal. As such, more scholarly work is needed in this area.
Limitations and Directions for Future Research
The most concerning limitation of this study is that it utilized a cross-sectional research design. As such, the temporal relationship between variables remains unknown. Related, data were collected from a sample of Pennsylvania residents and findings are not generalizable beyond those parameters. Additionally, our measures of gun control overlooked an entire category of gun control mechanisms—those that are intended to influence choices about how guns are used and to what effect. Accordingly, we encourage future researchers to use longitudinal research designs, to examine these findings in other populations, and better attempt to capture all categories of gun control mechanisms in instrumentation.
Despite these limitations, this work contributes to the extant literature in several ways. Notably, findings from this study suggest that most gun owners in Pennsylvania have received some form of safety training and take appropriate safety precautions with their firearms. Moreover, findings reveal that many gun owners use guns for self-defense purposes. Regarding gun control, findings reveal that members of the general public tend to be supportive of policies aimed at keeping guns away from dangerous and “at risk” individuals, such as required background checks for all types of gun purchases, mental health screenings, and mandatory gun education. However, members of the general public are not supportive of gun control mechanisms aimed at reducing overall firearm ownership, such as public gun bans. Among those who are the least supportive of such polices are those who are the most knowledgeable about gun crime, gun legislation, and gun functioning.
The long-standing debate of gun rights and ownership tends to center around the concept of “needs” and “wants” in relation to the types of firearms available to the public and the measures used to control the access to these firearms. Much of the empirical literature has produced mixed results when assessing the importance of preventative policies and the associated crimes that can be reduced. This study adds to the growing body of literature seeking more information to adequately inform policymakers regarding gun ownership and public opinions toward restrictive gun laws.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendix 1 Knowledge “Answers”
Knowledge of gun crime.
- Gun related homicides have increased over the last 30 years throughout the U.S. (False, see Gramlich, 2019 ; Gun Violence Archive, 2021 ; and National Institute of Justice, 2019 ).
- In the last 10 years, most gun related deaths per year in the U.S. have been from suicides (True, see Giffords Law Center, 2021a , 2021b , 2021c and Gramlich, 2019 ).
- A majority of firearms used in criminal offenses were obtained illegally (True, see Cook, 2017 , Clark, 2018 , and Fabio et al., 2016 ).
- Military-style weapons (for example, “assault rifles”) are used in the majority of gun-related crimes (False, see Koper et al., 2018 ).
- Most firearm owners never commit a gun crime (True, see Lott, 2016 and Malcom & Swearer, 2018 )
- Most mass shootings in the United States are done with legally obtained firearms (True, see Follman et al., 2021 and Statista Research Department, 2021 )
Knowledge of Gun Policy
- In the U.S., it is illegal to own a fully automatic firearm without a permit. (True, see Giffords Law Center, n.d.)
- When purchasing a firearm from a retail store, a background check is NOT required. (False, see NRA-ILA, n.d. and Yablon, 2020 ).
- When purchasing a firearm online from a retail store, one must go through a licensed firearm dealer to acquire it. (True, see NRA-ILA, n.d. and Yablon, 2020 )
- In the U.S., the legal purchasing age of rifles is lower than that of handguns. (True, see ATF, 2015 ).
- In the U.S., felons cannot legally own a firearm. (True, see Giffords Law Center, 2021 )
- In the U.S., authorities can legally confiscate guns solely based on an individual’s mental illness. (True, see Giffords Law Center, 2021 ).
Knowledge of Gun Functioning
- The “AR” in AR-15 stands for “Assault Rifle.” (False, see National Shooting Sports Foundation, n.d.)
- A semi-automatic firearm only fires one round of ammunition per single pull of the trigger. (True, see Frontline, n.d.)
- The “magazine” is the area of the gun that feeds ammunition into the chamber of the gun. (True, see Wintersteen, 2018 )).
- An individual must manually engage the hammer on a double-action firearm before the weapon can fire a bullet. (False, see Gun News Daily, n.d.)
- A bolt-action rifle requires the user to manually cycle every round before the rifle can be fired. (True, see Huntingsmart, n.d.)
- All firearms must legally have a safety setting to keep the firearm from firing. (False, Giffords Law Center, n.d.)
Declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
1 Research suggests that those who are mentally ill are at a higher odds of committing suicide, especially with a gun, but have relatively low rates of violent crime commission, including firearm violence. In fact, this work suggests that those who are mentally ill are more likely to be the victim of a crime than the perpetrator of a crime. Although, given the extent of under-diagnosis among the mentally ill, the relationship between these variables has been difficult to establish. See Swanson et al. ( 2015 ) and Ramchand and Ayer ( 2021 ).
2 See Kleck ( 2021 ) for a discussion of the quality of research in this area.
3 Research has found that question wording may influence whether people indicate support for a proposed assault weapons ban (Newport, 2019 ). Still, the available data suggest a slight majority of the public supports banning assault weapons.
4 The term “AR” is commonly mistaken to mean “assault rifle” or “automatic rifle” (Palma, 2019 ).
5 At the request of reviewers, we have included informational sources after each question to verify our coding. Efforts were made to include sources with commentary to help readers better understand subject matter. We also tried to incorporate informational sources with a Pennsylvania focus, when available, given that our sample is of Pennsylvania residents.
6 Gun owners were asked, “Have you ever used your gun to defend yourself?”.
7 Here, we refer to “predictor” in the linear manner.
8 As noted in Table Table4, 4 , approximately 27 percent of our sample indicated that they felt all guns should be banned from public use. A reviewer suggested that it would be interesting to explore the relationship between political affiliation and support for public gun bans. Results from chi-square test revealed a statistically significant relationship between political affiliation and support for public gun bans ( Χ 2 = 56.840, p < .001). Specifically, analysis revealed that about 1 in 3 democrats supported such a policy, compared to approximately 1 in 4 Republicans and 1 in 5 individuals who identified as having a “Other” political affiliation.
9 While we are confident that our measures of gun knowledge are valid and reliable measures, at the requests of the reviewers, we also ran a series of supplemental analyses that omitted “questionable” variables within the indices. For instance, we omitted the variables “Gun related homicides have increased over the last 30 years throughout the U.S.” and “A majority of firearms used in criminal offenses were obtained illegally” from knowledge of gun crime. We also omitted “In the U.S., authorities can legally confiscate guns solely based on an individual’s mental illness” from knowledge of gun policy, and “The “AR” in AR-15 stands for “Assault Rifle” from knowledge of gun functioning. Results were similar to the final models reported in the manuscript and are available upon request.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Nathan E. Kruis, Email: ude.usp@231ken .
Richard L. Wentling, Email: ude.usp@gniltnewr .
Tyler S. Frye, Email: ude.usp@4115fst .
Nicholas J. Rowland, Email: ude.usp@21rjn .
- Andrés AR, Hempstead K. Gun control and suicide: The impact of state firearm regulations in the United States, 1995–2004. Health Policy. 2011; 101 (1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2010.10.005. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- ATF. (2015) Does a customer have to be a certain age to buy firearms or ammunition from a licensee? Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.atf.gov/firearms/qa/does-customer-have-be-certain-age-buy-firearms-or-ammunition-licensee
- Balmert, J. (2021). As Biden enters white house, Ohio GOP lawmaker pushes ‘Second Amendment sanctuary state’ . The Enquirer. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.cincinnati.com/story/news/politics/2021/01/29/ohio-gop-second-amendment-sanctuary-state-biden/4274810001/
- Barry CL, Stone EM, Crifasi CK, Vernick JS, Webster DW, McGinty EE. Trends in public opinion on US gun laws: Majorities of gun owners and non-gun owners support a range of measures. Health Affairs. 2019; 38 (10):1727–1734. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2019.00576. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Billings, S. B. (2020). Smoking gun? Linking gun ownership to crime victimization and neighborhood crime. Linking Gun Ownership to Crime Victimization and Neighborhood Crime (April 29, 2020) .
- Braga AA, Cook PJ. The association of firearm caliber with likelihood of death from gunshot injury in criminal assaults. JAMA Network Open. 2018; 1 (3):e180833–e180833. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.0833. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Braga AA, Griffiths E, Sheppard K, Douglas S. Firearm instrumentality: Do guns make violent situations more lethal? Annual Review of Criminology. 2021; 4 :147–164. doi: 10.1146/annurev-criminol-061020-021528. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brenan, M. (2020). Support for stricter U.S. gun laws at lowest level since 2016. Gallup. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://news.gallup.com/poll/325004/support-stricter-gun-laws-lowest-level-2016.aspx
- Brennan PG, Lizotte AJ, McDowall D. Guns, southerness, and gun control. Journal of Quantitative Criminology. 1993; 9 (3):289–307. doi: 10.1007/BF01064463. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bureau of Justice Statistics. (2020). NCVS Victimization Analysis Tool (NVAT). Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.bjs.gov/index.cfm?ty=nvat
- Carlson J, Goss KA, Shapira H, editors. Gun studies: Interdisciplinary approaches to politics, policy, and practice. Routledge; 2018. [ Google Scholar ]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2020). Underlying cause of death 1999–2019 on CDC WONDER online database, Retrieved from https://wonder.cdc.gov/controller/datarequest/D76;jsessionid=8547021C770390B83510480403DA
- Ciomek A, Braga A, Papachristos A. The influence of firearms trafficking on gunshots injuries in a co-offending network. Social Science and Medicine. 2020; 259 :113114. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.113114. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clark, D. (2018). Is most gun crime committed by those who illegally possess guns? Politifact. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.politifact.com/factchecks/2018/mar/12/john-faso/do-illegal-gun-owners-commit-most-gun-crime-rep-fa/
- Cook, P. J. (1980). Reducing injury and death rates in robbery. Policy Analysis , 21–45.
- Cook PJ. The technology of personal violence. Crime and Justice. 1991; 14 :1–71. doi: 10.1086/449183. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook, P.J. (2017). How dangerous people get their guns in America . CBS News: The conversation. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.cbsnews.com/news/gun-sales-how-dangerous-people-get-weapons/
- Cook PJ. Gun markets. Annual Review of Criminology. 2018; 1 :359–377. doi: 10.1146/annurev-criminol-032317-092149. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook PJ, Braga AA, Moore MH. Gun Control. In: Wilson JQ, Petersilia J, editors. Crime and public policy. Oxford University Press; 2011. pp. 257–292. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook PJ, Leitzel JA. Perversity, futility, jeopardy: An economic analysis of the attack on gun control. Law and Contemporary Problems. 1996; 59 :91–118. doi: 10.2307/1192211. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook PJ, Ludwig J. The social costs of gun ownership. Journal of Public Economics. 2006; 90 (1–2):379–391. doi: 10.1016/j.jpubeco.2005.02.003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook PJ, Pollack HA. Reducing access to guns by violent offenders. RSF: the Russell Sage Foundation Journal of the Social Sciences. 2017; 3 (5):2–36. doi: 10.7758/rsf.2017.3.5.01. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Crifasi CK, Ward JA, McGinty EE, Webster DW, Barry CL. Public opinion on gun policy by race and gun ownership status. Preventive Medicine. 2021; 149 :106607. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2021.106607. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Curcuruto, J. (2020). NSSF survey reveals broad demographic appeal for firearm purchases during sales surge of 2020. National Shooting Sports Foundation. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.nssf.org/articles/nssf-survey-reveals-broad-demographic-appeal-for-firearm-purchases-during-sales-surge-of-2020/
- Department of Justice, Government of Canada. (n.d.). Firearms, accidental deaths, suicides and violent crime: An updated review of the literature with special reference to the Canadian situation. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.justice.gc.ca/eng/rp-pr/csj-sjc/jsp-sjp/wd98_4-dt98_4/p3.html#a32
- Ellison CG. Southern culture and firearms ownership. Social Science Quarterly. 1991; 72 (2):267–283. [ Google Scholar ]
- Evans DN, Williams CL. Stop, question, and frisk in New York City: A study of public opinions. Criminal Justice Policy Review. 2017; 28 (7):687–709. doi: 10.1177/0887403415610166. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fabio A, Duell J, Creppage K, O'Donnell K, Laporte R. Gaps continue in firearm surveillance: Evidence from a large US city bureau of police. Social Medicine. 2016; 10 (1):13–21. [ Google Scholar ]
- Federal Bureau of Investigation. (n.d.). Crime data explorer. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://crime-data-explorer.fr.cloud.gov/explorer/national/united-states/crime
- Field, A. (2016). Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics (4th ed). Los Angeles, CA; Sage.
- Filindra A, Kaplan NJ. Racial resentment and whites’ gun policy preferences in contemporary America. Political Behavior. 2016; 38 (2):255–275. doi: 10.1007/s11109-015-9326-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Filindra A, Kaplan NJ. Testing theories of gun policy preferences among Blacks, Latinos, and Whites in America. Social Science Quarterly. 2017; 98 (2):413–428. doi: 10.1111/ssqu.12418. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Follman, M., Aronsen, G., & Pan, D. (2021). US mass shootings, 1982–2021: Data from mother jones’ investigation. MotherJones. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.motherjones.com/politics/2012/12/mass-shootings-mother-jones-full-data/
- Friend, D. (2021). Constitutional carry, 2nd amendment sanctuary, and anti-red flag laws: A look at pro-gun bills in Texas . The Texan. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://thetexan.news/a-look-at-the-pro-gun-bills-filed-in-the-texas-legislature/
- Frontline. (n.d.). Hot guns. PBS. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/shows/guns/more/faq.html
- Gallup. (2020). Guns. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://news.gallup.com/poll/1645/guns.aspx
- Giffords Law Center. (2021a). Statistics. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://giffords.org/lawcenter/gun-violence-statistics/
- Giffords Law Center. (2021b). Mental health reporting in Pennsylvania . Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://giffords.org/lawcenter/state-laws/mental-health-reporting-in-pennsylvania/
- Giffords Law Center. (2021c). Firearm prohibitions in Pennsylvania. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://giffords.org/lawcenter/state-laws/firearm-prohibitions-in-pennsylvania/
- Giffords Law Center. (n.d.) Machine guns and 50 caliber . Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://giffords.org/lawcenter/gun-laws/policy-areas/hardware-ammunition/machine-guns-50-caliber/#footnote_0_5658
- Gramlich, J. (2019). What the data says about gun deaths in the U.S. Pew Research Center. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/08/16/what-the-data-says-about-gun-deaths-in-the-u-s/
- Grinshteyn E, Hemenway D. Violent death rates in the US compared to those of the other high-income countries, 2015. Preventive Medicine. 2019; 123 :20–26. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2019.02.026. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gun News Daily. (n.d.). Single action vs. double action: A guide for beginners. Retrieved from https://gunnewsdaily.com/single-action-vs-double-action/
- Gun Violence Archive. (2021). Past summary ledgers . Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.gunviolencearchive.org/past-tolls
- Hemenway D, Solnick SJ. The epidemiology of self-defense gun use: Evidence from the National Crime Victimization Surveys 2007–2011. Preventive Medicine. 2015; 79 :22–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2015.03.029. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Henigan DA. Guns don’t kill people, people kill people: And other myths about guns and gun control. Beacon Press; 2016. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hill GD, Howell FM, Driver ET. Gender, fear, and protective handgun ownership. Criminology. 1985; 23 (3):541–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-9125.1985.tb00353.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huntingsmart. (n.d.). The firing cycle of a bolt action rifle. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.thecampfirecollective.com/knowledge-base/us/huntingsmart/03/09/
- Institute of Medicine and National Research Council . Priorities for research to reduce the threat of firearm-related violence. National Academies Press; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kauder NB. One-gun-a-month: Measuring public opinion concerning a gun control initiative. Behavioral Sciences and the Law. 1993; 11 (4):353–360. doi: 10.1002/bsl.2370110403. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kleck G. Point blank: Guns and gun violence in America. Aldine de Gruyter; 1997. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kleck, G. (2021). The continuing vitality of flawed research on guns and violence: A comment on Fridel (2020). Justice Quarterly , 1–9.
- Kleck G. Macro-level research on the effect of firearms prevalence on suicide rates: A systematic review and new evidence. Social Science Quarterly. 2019; 100 (3):936–950. doi: 10.1111/ssqu.12602. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kleck G. Regulating guns among young adults. American Journal of Criminal Justice. 2019; 44 (5):689–704. doi: 10.1007/s12103-019-09476-6. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kleck G, Gertz M. Armed resistance to crime: The prevalence and nature of self-defense with a gun. The Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology. 1995; 86 :150–187. doi: 10.2307/1144004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kleck G, Patterson EB. The impact of gun control and gun ownership levels on violence rates. Journal of Quantitative Criminology. 1993; 9 (3):249–287. doi: 10.1007/BF01064462. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kleck G, Kovandzic T, Bellows J. Does gun control reduce violent crime? Criminal Justice Review. 2016; 41 (4):488–513. doi: 10.1177/0734016816670457. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Koper CS, Johnson WD, Nichols JL, Ayers A, Mullins N. Criminal use of assault weapons and high-capacity semiautomatic firearms: An updated examination of local and national sources. Journal of Urban Health. 2018; 95 (3):313–321. doi: 10.1007/s11524-017-0205-7. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kruis NE, Wentling RL, Heirigs MH, Ishoy GA. Assessing the impact of knowledge and location on college students’ perceptions of gun control and campus carry policies: A multisite comparison. American Journal of Criminal Justice. 2020; 45 (1):25–47. doi: 10.1007/s12103-019-09499-z. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Libby NE, Corzine J. Lethal weapons: Effects of firearm types on the outcome of violent encounters. Justice Research and Policy. 2007; 9 (2):113–137. doi: 10.3818/JRP.9.2.2007.113. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Livingston MM, Lee MW. Attitudes toward firearms and reasons for firearm ownership among nonurban youth: Salience of sex and race. Psychological Reports. 1992; 71 (2):576–578. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1992.71.2.576. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lott JR. More guns, less crime: Understanding crime and gun control laws. University of Chicago Press; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lott, J. R. (2016). Concealed carry permit holders across the United States: 2016. Available at SSRN 2814691.
- Lucey, C. (2021). Biden’s gun-policy plans start to take shape . The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.wsj.com/articles/bidens-gun-policy-plans-start-to-take-shape-11613135990
- Malcom, J & Swearer, A. (2018). Here are 8 stubborn facts on gun violence in America . The Heritage Foundation. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.heritage.org/crime-and-justice/commentary/here-are-8-stubborn-facts-gun-violence-america
- Marciniak LM, Loftin C. Measuring protective handgun ownership. Criminology. 1991; 29 (3):531–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-9125.1991.tb01078.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McClain PD. Determinants of black and white attitudes toward gun regulation: A research note. Journal of Criminal Justice. 1983; 11 (1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0047-2352(83)90100-9. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Merino SM. God and guns: Examining religious influences on gun control attitudes in the United States. Religions. 2018; 9 (6):189. doi: 10.3390/rel9060189. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morral, A. R., Schell, T.L., & Tankard, M. (2018). The magnitude and sources of disagreement among gun policy experts. RAND Corporation. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RR2088z1.html . Also available in print form.
- Morrall A. The science of gun policy: A critical synthesis of research evidence on the effects of gun policies in the United States. Rand Health Quarterly. 2018 doi: 10.7249/RR2088. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naghavi M, Marczak LB, Kutz M, Shackelford KA, Arora M, Miller-Petrie M, Tran BX. Global mortality from firearms, 1990–2016. JAMA. 2018; 320 (8):792–814. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.10060. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- National Institute of Justice. (2019). Gun violence in America. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://nij.ojp.gov/topics/articles/gun-violence-america
- National Shooting Sports Foundation. (n.d.). Modern sporting rifle: Introduction. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.nssf.org/msr/
- Newburger, E. (2021). Biden calls for congress to pass stricter gun laws on anniversary of Parkland mass shooting . CNBC. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.cnbc.com/2021/02/14/biden-calls-on-congress-to-reform-gun-laws-on-anniversary-of-parkland-shooting.html
- Newman BJ, Hartman TK. Mass shootings and public support for gun control. British Journal of Political Science. 2019; 49 (4):1527–1553. doi: 10.1017/S0007123417000333. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Newport, F. (2019). Analyzing surveys on banning assault weapons . Gallup. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://news.gallup.com/opinion/polling-matters/268340/analyzing-surveys-banning-assault-weapons.aspx
- NRA-ILA. (n.d.) Background checks for guns . Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.nraila.org/get-the-facts/background-checks-nics/
- O’Brien K, Forrest W, Lynott D, Daly M. Racism, gun ownership, and gun control: Biased attitudes in US whites may influence policy decisions. PLoS ONE. 2013; 8 (10):e77552. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077552. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Oliphant, B.J. (2017). Bipartisan support for some gun proposals, stark partisan divisions on many others. Pew Charitable Trust. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2017/06/23/bipartisan-support-for-some-gun-proposals-stark-partisan-divisions-on-many-others/
- Pallant, J. (2016). SPSS Survival Manual: A Step by Step Guide to Data Analysis Using IBM SPSS, 6th Edn Crows Nest . NSW: Allen &Unwin.
- Palma, B. (2019). Does ‘AR’ in AR-15 Stand for ‘Assault Rifle’? A frequent misconception centers on what the term “AR-15” literally means. Snopes. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.snopes.com/fact-check/meaning-of-ar-in-ar-15-firearm/
- Parker, K., Horowitz, J., Igielnik, R., Oliphant, J.B., & Brown, A. (2017). America’s complex relationship with guns. Pew Charitable Trust. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/2017/06/22/views-on-gun-policy/
- Pederson J, Hall TL, Foster B, Coates JE. Gun ownership and attitudes toward gun control in older adults: Re-examining self-interest theory. American Journal of Social Science Research. 2015; 1 (5):273–281. [ Google Scholar ]
- Phillips, M. (2021). How Biden could tighten gun control without congress. Fox News . Retrieved February 18, 2021, from https://www.foxnews.com/politics/how-could-biden-tighten-gun-control-without-congress-approval
- Planty, M., & Truman, J. L. (2013). Firearm violence, 1993–2011 . Washington, DC: US Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, Bureau of Justice Statistics.
- Ramchand, R. & Ayer, L. (2021). Is mental illness a risk factor for gun violence? RAND. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.rand.org/research/gun-policy/analysis/essays/mental-illness-risk-factor-for-gun-violence.html
- RAND. (2020). What science tells us about the effects of gun policies . Retrieved February 18, 2021, from https://www.rand.org/research/gun-policy/key-findings/what-science-tells-us-about-the-effects-of-gun-policies.html
- Rosen G. Yes and no to gun control. Commentary. 2000; 110 (2):47–53. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roth, J. A. (1994). Firearms and violence . US Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, National Institute of Justice.
- Rowhani-Rahbar A, Lyons VH, Simonetti JA, Azrael D, Miller M. Formal firearm training among adults in the USA: Results of a national survey. Injury Prevention. 2018; 24 (2):161–165. doi: 10.1136/injuryprev-2017-042352. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schaeffer, K. (2019). Share of Americans who favor stricter gun laws has increased since 2017 . Pew Charitable Trust. Retrieved from https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/10/16/share-of-americans-who-favor-stricter-gun-laws-has-increased-since-2017/
- Schaeffer, K. (2021). Key facts about Americans and guns. Pew Charitable Trust. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2021/05/11/key-facts-about-americans-and-guns/
- Schmidt, D. (2020). How many deer hunters in the United States? Deer and Deer Hunting. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.deeranddeerhunting.com/content/blogs/dan-schmidt-deer-blog-whitetail-wisdom/how-many-deer-hunters-in-the-united-states
- Secret PE, Johnson JB. Racial differences in attitudes toward crime control. Journal of Criminal Justice. 1989; 17 (5):361–375. doi: 10.1016/0047-2352(89)90047-0. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sen B, Panjamapirom A. State background checks for gun purchase and firearm deaths: An exploratory study. Preventive Medicine. 2012; 55 (4):346–350. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2012.07.019. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shammas, M. (2019). It’s time to retire the guns don’t kill people—People kill people argument. Guns do kill people. Guns Do Kill People (November 24, 2019) .
- Smith J, Spiegler J. Explaining gun deaths: Gun control, mental illness, and policymaking in the American states. Policy Studies Journal. 2020; 48 (1):235–256. doi: 10.1111/psj.12242. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Southwick L., Jr Self-defense with guns: The consequences. Journal of Criminal Justice. 2000; 28 (5):351–370. doi: 10.1016/S0047-2352(00)00051-9. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Statista Research Department (2021). Mass shootings in the U.S.: Legality of shooter’s weapons, as of May 2021 . Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/476461/mass-shootings-in-the-us-by-legality-of-shooters-weapons/
- Swanson JW, McGinty EE, Fazel S, Mays VM. Mental illness and reduction of gun violence and suicide: Bringing epidemiologic research to policy. Annals of Epidemiology. 2015; 25 (5):366–376. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2014.03.004. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tillyer MS, Tillyer R. Violence in context: A multilevel analysis of victim injury in robbery incidents. Justice Quarterly. 2014; 31 (4):767–791. doi: 10.1080/07418825.2012.696127. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tyler TR, Lavrakas PJ. Support for gun control: The influence of personal, sociotropic, and ideological concerns. Journal of Applied Social Psychology. 1983; 13 (5):392–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1559-1816.1983.tb01747.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Services (2020). National hunting license data. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.fws.gov/wsfrprograms/Subpages/LicenseInfo/Natl%20Hunting%20License%20Report%202020.pdf
- Wallace LN. American preferences for “smart” guns versus traditional weapons: Results from a nationwide survey. Preventive Medicine Reports. 2016; 4 :11–16. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2016.05.005. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Winkler A. Is the second amendment becoming irrelevant. Indian Law Journal. 2018; 93 :253–265. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wintersteen. (2018). 9 Common misused gun terms. Guns and Ammo. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.gunsandammo.com/editorial/9-misused-gun-terms/249625
- Wolfgang ME. Patterns in criminal Homicide. University of Pennsylvania Press; 1958. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wozniak KH. Public opinion about gun control post-Sandy Hook. Criminal Justice Policy Review. 2017; 28 (3):255–278. doi: 10.1177/0887403415577192. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wright MA, Wintemute GJ, Rivara FP. Effectiveness of denial of handgun purchase to persons believed to be at high risk for firearm violence. American Journal of Public Health. 1999; 89 (1):88–90. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.89.1.88. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yablon, A. (2020). Internet gun sales and background checks, explained . The Trace. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.thetrace.org/2016/01/internet-gun-sales-background-checks/

Gun Control
- Research Starters
- School Shootings
- Video Tutorials & Workshops
Keywords & Search Terms
Use the words or phrases below to search for useful information in the library catalog or databases:
- Assault weapons
- Columbine High School
- Concealed carry
- Firearms and crime
- Firearms law and legislation
- Firearms ownership
- Gun control
- Gun violence
- Sandy Hook Elementary School
- School shootings
- School violence
- Second amendment
- Stand Your Ground
- Youth AND violence
- Virginia Tech
Focus In with Research Question
Gun control is a complex issue that involves crime, legislation, and the Constitution. You could concentrate on one issue and do in-depth research on that, or use several of the questions below to focus more generally on the topic of gun control or gun violence.
- Is gun violence a serious problem in America?
- Does limiting access to guns reduce gun violence?
- What laws exist to control gun ownership?
- How are guns purchased and transferred in America?
- How do other countries regulate gun ownership?
- Should gun rights be controlled by states or by the federal government?
- What are the arguments for regulating gun ownership?
- What are the arguments against regulating gun ownership?
Help! Resources
Find the resources on how to start Writing Your Research Paper
There are MLA Formatting and APA Style Formatting resources to help too!
- << Previous: Books
- Next: School Shootings >>
- Last Updated: Dec 7, 2023 10:36 AM
- URL: https://smc.libguides.com/Guns
Advertisement
Firearm Ownership, Defensive Gun Usage, and Support for Gun Control: Does Knowledge Matter?
- Published: 30 September 2021
- Volume 48 , pages 21–50, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
- Nathan E. Kruis ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2076-314X 1 ,
- Richard L. Wentling 2 ,
- Tyler S. Frye 1 &
- Nicholas J. Rowland 3
14k Accesses
6 Citations
29 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Recent incidents of gun violence have raised questions about public access to “military-style” firearms and the need for more-restrictive forms of gun control. Proponents of more-restrictive forms of gun regulation argue that such measures will help combat the disproportionately high rates of gun crime in the United States. Opponents believe that such measures infringe upon constitutional rights and hinder law-abiding citizens' abilities to adequately defend themselves. This project explores the characteristics of gun owners living in Pennsylvania and public perceptions of three different categories of gun control. Results indicate that most gun owners have received some form of training and take appropriate safety precautions with their firearms. Further, 1 in 4 gun owners reported using their firearm in self-defense at some point in their life. Regarding gun control, most participants favored strategies intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people, such as required background checks for all types of gun purchases, mental health screenings, and mandatory gun education. However, most participants opposed complete firearm bans. Among those who are the least supportive of such polices are those who are the most knowledgeable about gun crime, gun legislation, and gun functioning. Policy implications are discussed within.
Similar content being viewed by others

The Views of Police Officers Toward Gun Legislation and Public Health Policies Driven by Firearm Safety Concerns
Tammy Rinehart Kochel & Scott W. Phillips

Gun Violence Prevention and Mental Health Policy

Gun Buyback Programs in the United States
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Gun reform was a key policy issue of the 2020 presidential general election. President Biden and Democratic leaders have advocated for the enactment of “common sense” gun reform efforts, such as assault weapon bans, universal background checks, and increased resources to enforce current gun laws (Lucey, 2021 ). They believe that such reforms will help reduce the disproportionately high rates of gun crime in America. As such, leading Democrats are expected to push to change gun laws in the coming years (Newburger, 2021 ; Phillips, 2021 ). However, while data suggests that many Republicans are generally supportive of gun reform efforts intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people (Cook et al., 2011 ; Oliphant, 2017 ), many Republican leaders view the comprehensive reforms proposed by Democrats as arbitrary, infringing on constitutionally protected rights, and hindering American citizens’ abilities to adequately protect themselves, their families, and their properties. They believe that comprehensive legislation proposed by the Biden administration will only remove guns from the hands of law-abiding citizens and do little to combat gun crime. As such, legislators in many Republican-led jurisdictions have begun passing more-permissive gun policies aimed at limiting the scope of federal (“Democratic” enacted policies) gun control measures at the state level, such as pushing for “Constitutional Carry” laws, “Anti-red flag” legislation and creating “2nd Amendment Sanctuary” cities and states (Balemert, 2021 ; Friend, 2021 ).
The debate is not exclusively political, though. There is also a rift in support for gun control amongst scholars, with some favoring more-restrictive forms of gun control and others favoring less-restrictive forms of gun regulation (Morral et al., 2018 ). The legality and utility of gun regulation has promoted much discussion amongst academics (see Braga et al., 2021 ; Kleck et al., 2016 ; Winkler, 2018 ). Public support for gun control is also mixed and has varied across time, although current estimates suggest that a slight majority favor more-restrictive forms of gun control, but do not favor complete firearm bans (Gallup, 2020 ; Parker et al., 2017 ).
Prior research has attempted to examine correlates of attitudes toward gun polices. Generally, this work has found that those who are the least supportive of more-restrictive forms of gun regulation are those who identify as politically conservative (Kruis et al., 2020 ), whites (Merino, 2018 ), males (O’Brien et al., 2013 ), and gun owners (Merino, 2018 ), as well as those with greater familiarity with firearms (Rosen, 2000 ). A recent article published in the American Journal of Criminal Justice shifted this discussion to the relationship between gun knowledge and support for restrictive forms of gun control (see Kruis et al., 2020 ). In that work, the researchers found an inverse relationship between gun knowledge (i.e., broad “understanding” of gun policies, legislation, and crime) and support for stricter forms of gun control amongst college students. Findings indicated that students who knew more about guns and gun-related matters, reported being less supportive of more-restrictive forms of gun control than students who lacked such knowledge. Unfortunately, methodological limitations (e.g., cross-sectional research design, convenience sampling, student participants, etc.) precluded the authors from drawing firm conclusions about the relationship between gun knowledge and gun functioning. The current project seeks to extend this line of research by exploring the relationship between three types of gun knowledge (i.e., knowledge of gun crime, knowledge of gun legislation, and knowledge of gun functioning) and three different measures of gun control (i.e., general gun control, support for policies that reduce overall gun ownership, support for polices intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people). The current project also extends Kruis et al.’s ( 2020 ) findings related to student gun owners to members of the general public, by exploring the demographic characteristics, training experiences, safety precautions, and defensive gun usage reported by gun owners obtained from a representative sample of Pennsylvania Residents ( N = 522). In achieving these goals, the current study seeks to provide academics and policymakers alike with important information needed to be considered before making gun reforms.
Literature Review
Gun violence.
The United States has disproportionately high rates of gun violence for a developed country (Grinshteyn & Hemenway, 2019 ; Naghavi et al., 2018 ). The U.S. homicide rate is estimated to be about seven times higher than other high-income countries, which researchers suggest is primarily driven by a gun homicide rate that is about 25 times higher (Grinshteyn & Hemenway, 2019 ). In 2019 alone, there were approximately 39,707 firearm-related deaths in the United States, equating to a rate of about 12.1 per 100,000 persons (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC], 2020 )—which is about three times the rate of America’s northern neighbor (i.e., Canada, 4.1 per 100,000; Department of Justice, Government of Canada, n.d.). Among these firearm-related deaths, 23,941 were suicides and 14,414 were homicides (CDC, 2020 ). Guns, particularly handguns, are used to commit many violent crimes and most murders in the United States (National Institute of Justice, 2019 ). In total, guns were used to help commit more than 121,000 violent crimes in 2019 (Federal Bureau of Investigation [FBI], n.d.). According to data collected for the National Crime Victimization Survey (NCVS), guns were used in more than one in three aggravated assaults and about one in five robbery victimizations reported by Americans in 2019, but fewer than 1 in 100 rape and sexual assault victimizations (Bureau of Justice Statistics, 2020 ). In this regard, while guns are used to help commit many crimes, it would be an oversight to ignore that most violent victimizations in the United States do not involve guns (Braga et al., 2021 ). Further, whenever a gun is used during the commission of a violent crime it usually is not fired. In fact, when a gun is used in a crime it is predominately used as an instrument to gain victim compliance. Data suggest that only about one in four victims of nonfatal gun crimes suffer a gunshot wound (Planty & Truman, 2013 ) and overall injury rates for victims of gun crimes tend to be lower than rates for victims of crimes in which other weapons are used (Cook, 1980 ; Cook et al., 2011 ). However, whenever guns are used offenders are more likely to complete the criminal act (Cook et al., 2011 ; Libby & Corzine, 2007 ; Tillyer & Tillyer, 2014 ), and whenever they are fired, victim injuries are more likely to be lethal (Cook, 2018 ; Cook et al., 2011 ).
The Great American Gun Debate
Given high rates of gun crime, many progressives have demanded changes be made to American gun legislation. In a review of the extant literature on firearm instrumentality, Braga et al. ( 2021 ) suggest that there are two sides in the great American gun debate. On the one side of the debate are those who favor more-permissive forms of gun regulation. These advocates tend to conform to the adage endorsed by the National Rifle Association (NRA) “guns don’t kill people, people kill people” (Braga et al., 2021 ; Henigan, 2016 ; Shammas, 2019 ). This group believes that more-restrictive gun control will do little to reduce crime or to save lives (Kleck, 1997 ; Kleck et al., 2016 ; Wolfgang, 1958 ). On the other side of the debate are proponents of more-restrictive forms of gun regulation, or those who believe that “guns do kill people” (Braga et al., 2021 , p. 148). These advocates suggest that reducing firearm availability, especially to who they consider to be dangerous or “at risk” individuals (i.e., felons, the “mentally unstable,” Footnote 1 etc.) will help reduce violent gun crimes and suicides, and ultimately, save lives. In Braga et al.’s ( 2021 ) synopsis of propositions introduced by the two sides, the researchers argue that the key distinction between proponents and opponents of stricter forms of gun control relates to the instrumentality of weapons. Specifically, they write “The ‘people kill people’ perspective further suggests that gun control is futile in reducing homicides because determined killers will simply find another way. If guns are not available, assailants will substitute knives, blunt instruments, or other means” (p. 148). Similar sentiments are found within the general public as an increasing number of Americans have purchased firearms, specifically during the Covid-19 pandemic, citing self-defense as a primary driver of ownership (Gallup, 2020 ; Schaeffer, 2021 ). However, proponents of more-restrictive means of gun control assume that even if assailants choose to use other means (i.e., knife, blunt instrument) to carry out their attacks, such attacks will be less fatal (Cook, 1991 ; Cook et al., 2011 ; Henigan, 2016 ). Thus, Braga et al. ( 2021 ) argue that the crux of the debate centers on what researchers refer to “firearm instrumentality,” or whether the presence of firearms makes a criminal event more lethal.
While Braga et al. (2021 ) bring attention to an important point of contention within the debate, their brief synopsis of the two sides in the great debate overlooks arguments pertaining to the perceived ability, or inability, of gun legislation being able to effectively reduce firearm availability, particularly to dangerous and “at risk” people. This issue is a focal point in the debate and a common topic that is an important factor for the general public. Indeed, it is almost commonsensical to believe that if there were no guns, then there would be no gun crime; certainly, proponents of both sides know this to be true. The reality though is that there are a lot of guns. In fact, the United States civilian gun ownership rate is the highest in the world, with estimates suggesting that there are more than 350 million guns owned by Americans (Institute of Medicine & National Research Council, 2013 ). These instruments serve both legitimate (i.e., recreation, hunting, self-defense, etc.) and illegitimate purposes (i.e., criminal activities; Cook et al., 2011 ; Kleck et al., 2016 ). Thus, the real questions in the debate are (1) will strict gun control policies be able to effectively keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” individuals who may want to harm themselves or others? and (2) will restrictive gun control measures prevent law abiding citizens from defending their families, their properties, and their lives?
Opponents of restrictive forms of control believe that more-restrictive gun control policies will do little to disrupt illegal gun markets. They believe that such policies will merely take guns away from law abiding citizens who use firearms for legitimate purposes, including recreation, hunting, and self-defense. Current estimates suggest that there are about 15.2 million hunting license holders in the United States (U.S. Fish & Wildlife Services, 2020 ) and 9.4 million self-described “gun only” deer hunters (Schmidt, 2020 ). The data suggest that a significant portion of Americans use firearms as a source of legal recreation and food acquisition. Data also suggest that a significant number of Americans use guns for self-defense purposes. A 2017 report published by researchers at Pew Charitable trust estimated that approximately 1 in 6 gun owners had used their weapon to defend themselves, their families, or their possessions at some point in their life (Parker et al., 2017 ). While estimates vary greatly, it is speculated that the prevalence of defensive gun usage in the United States ranges from 60,000 to 2.5 million incidents annually (National Research Council, 2013 ), and whenever guns are used in self-defense, the odds of injury to potential victims is significantly reduced (Cook et al., 2011 ; Kleck & Gertz, 1995 ). As such, critics of more-restrictive gun control “argue that gun control laws could increase crime, by disarming prospective victims, reducing their ability to effectively defend themselves, and possibly reducing any deterrent effect that victim gun possession might have on offenders” (Kleck et al., 2016 , p.489).
Opponents of more restrictive measures of gun control turn to research demonstrating that a majority of gun crimes are committed by offenders who illegally obtained the firearm used in the crime (Cook, 2018 ; Roth, 1994 ). Indeed, research suggests that most gun crimes are committed by individuals who are already, under current regulations, legally disqualified from possessing a firearm due to their age, criminal record, or some other characteristic (Cook, 2018 ). However, proponents of more-restrictive gun control use this same research to cite the reality that most firearms used to commit crime originate from a legal manufacturing or distribution supply chain (Cook, 2018 ). Thus, they believe that reducing the number of guns in such markets will ultimately reduce the number of guns available to be used in crimes (Cook et al., 2011 ).
A recent report published by the RAND Corporation found that members of the scholarly community also tend to conform to this “more-restrictive” or “more-permissive” dichotomy (Morral et al., 2018 ). Indeed, there is great disagreement among researchers about the extent to which crime can be reduced through gun control. While research has produced mixed results, evidence from more methodologically sound work has indicated that higher levels of firearm ownership has little, if any, effect on overall violent crime rates (Cook & Ludwig, 2006 ; Cook & Pollack, 2017 ; Cook et al., 2011 ) or suicides (Kleck, 2019a , 2019b ), and that more-restrictive gun control mechanisms are generally ineffective at reducing crime (Kleck & Patterson, 1993 ; Kleck et al., 2016 ; Kleck, 2019b ). Footnote 2 However, some research indicates that there may be an association between rates of community gun ownership and homicide rates (Braga et al., 2021 ), suggesting that firearm availability may increase the lethality of violent crimes—although Kleck ( 2021 ) argues that prior work in this area has produced mixed findings, been tautological, and that the data merely demonstrate a positive relationship between gun ownership and the firearm homicide rates (Kleck, 2021 ). There also is evidence suggesting that polices intended to restrict dangerous and/or “at-risk” individuals (i.e., felons, the mentally ill, and “alcoholics”) from accessing firearms may be associated with reductions in crime, suicides, and violence in the community (Andrés & Hempstead, 2011 ; Braga et al., 2021 ; Braga & Cook, 2018 ; Cook et al., 2011 ; Kleck, 2019b ; Kleck et al., 2016 ; Sen & Panjamapirom, 2012 ; Smith & Spiegler, 2020 ; Wright et al., 1999 ). However, there is more research needed in this area before firm conclusions can be drawn.
Types of Gun Control
Cook et al. ( 2011 ) argue that gun-control measures can be “usefully classified into three categories: those that are intended to reduce overall gun ownership; those that are intended to keep guns away from particularly dangerous people; [and] those that are intended to influence choices about how guns are used and to what effect” (p. 259). Mechanisms that are intended to reduce overall gun ownership are those that attempt to keep guns out of the hands of all citizens—law abiding or non-law abiding. Such policies include firearm bans, limited and restrictive licensing, gun buy-back programs, and policies designed to make firearms and ammunition more expensive, and subsequently, less affordable to the average citizen. Although research on public support for such strategies is limited, data suggest that a slight majority of the general public supports banning the manufacturing, possession, and sale of some types of firearms, such as assault rifles, from public use (Gallup, 2020 ), but few support policies banning other types of firearms, such as handguns, from public use (Brenan, 2020 ). Footnote 3 Mechanisms that are intended to keep guns away from dangerous or “at-risk” people refer to strategies aimed at keeping guns away from those who are likely to use them for criminal purposes, or to self-harm, such as felons, the untrained, and the mentally ill (Morrall, 2018 ). Measures within this category of gun control include increased screening and monitoring of buyers and dealers in legal gun markets, creating a national firearms database, and outlawing “straw” (i.e., secondary market) purchases. Generally, the public is more supportive of these types of gun control strategies, especially those aimed at barring gun sales to the mentally ill, and those on “no fly” or on law enforcement “watch lists” (Parker et al., 2017 Schaeffer, 2019 ). The third category of “usefully classified” gun control mechanisms are those intended to influence choices about how guns are used and to what effect. This category includes strategies aimed at increasing firearm design regulation (e.g., manufacturing more “smart guns”) and implementing various forms of “focused deterrence” policing strategies, such as “gun oriented patrol tactics” and “hot spots policing” (Cook et al., 2011 , p. 280) Recent research suggests that many members of the general public may have favorable views of smart guns as a safety and crime reduction tool by indicating that they would be inclined to purchase such weapons if they became readily available (Wallace, 2016 ). Controversial, research also indicates mixed public support for “gun oriented” policing tactics, such as stop, question, and frisk polices (Evans & Williams, 2017 ) which is further complicated by the recent surge in firearm purchases (Schaeffer, 2021 ).
Prior Research Assessing Correlates of Support for Gun Control
Trends in public polling tend to inform the direction of gun policies and the overall sentiment of potential voters toward certain restrictions or measures to be introduced. Much of this data is derived from national surveys which are administered through organizations such as Gallup, RAND, and similar organizations via cross-sectional designs. Wozniak ( 2017 ) notes that public opinion toward gun control has remained relatively consistent although support for more restrictive laws concerning the sales of firearms has declined since the 1990s. The most recent data collected by Gallup ( 2020 ) suggest that approximately 57 percent of Americans believe that the laws covering the sale of firearms should be made more strict, which is down more than 20 percentage points since when the organization first started tracking these data in the early 1990s, but up more than 10 percentage points from the start of the 2010s. One aspect that remains relatively high is the support for background checks and limiting access for dangerous or “at-risk” individuals. Barry et al. ( 2019 ) find similar support for the use of universal background checks and limiting access for dangerous or “at-risk” individuals regardless of ownership status to include knowledge and/or safety courses for first-time owners.
Researchers have spent considerable time examining correlates of support for gun control, finding mixed support across demographic groups. Due to this mixed support, an array of proposed gun control measures and policies have faced backlash amid American constituents (see Giffords Law Center for a review of state-specific measures). Generally, though, this work has found that men (Ellison, 1991 ; Kauder, 1993 ; Livingston & Lee, 1992 ; Marciniak & Loftin, 1991 ; Merino, 2018 ; O’Brien et al., 2013 ; Pederson et al., 2015 ; Tyler & Lavrakas, 1983 ), whites (Filindra & Kaplan, 2017 ; McClain, 1983 ; Merino, 2018 ; Secret & Johnson, 1989 ), those who are politically conservative (Filindra & Kaplan, 2017 ; Merino, 2018 ), those who live in rural communities (Brennan et al., 1993 ; Parker et al., 2017 ) and gun owners (Filindra & Kaplan, 2017 ; Merino, 2018 ) are less supportive of more-restrictive forms of gun control than those in reference groups. Additionally, there is evidence suggesting that those who have greater exposure to, and familiarity with firearms (Ellison, 1991 ; Hill et al., 1985 ; Kruis et al., 2020 ; Rosen, 2000 ; Tyler & Lavrakas, 1983 ) favor more-permissive forms of gun control. Recently, Filindra and Kaplan ( 2017 ) found that “drivers of support for gun control” were generally consistent for members of racial minority groups and whites (p. 413). The authors noted that fear, or concern, of crime was generally positively related to support for more-restrictive forms of gun control across racial groups, while political conservativism, being a crime victim, owning a gun, and racial prejudice (i.e., held by Whites and Latinos) were inversely related to support for more-restrictive forms of gun control. Their study, along with earlier work (see Filindra & Kaplan, 2016 ), shed light on a possible relationship between racial resentment and Whites’ and Latinos’ attitudes toward gun control, suggesting that racism, generally, is a correlate of support for less-restrictive forms of gun control among these groups. However, gun ownership among minority and BIPOC communities has continued to rise with the largest increases occurring during the social and civil unrest associated with 2020 (Curcuruto, 2020 ; Parker et al., 2017 ). Crifasi et al. ( 2021 ) extended this line of inquiry and found that minority and BIPOC communities tend to favor less-restrictive gun control measures especially when police or the criminal justice system is involved, but general support for reduced access to firearms remains mixed across group membership.
Other researchers have found that men, generally, are less supportive of more-restrictive forms of gun control (see Ellison, 1991 ; Merino, 2018 ; O’Brien et al., 2013 ; Pederson et al., 2015 ; Tyler & Lavrakas, 1983 ). Some scholars have suggested that guns and pro-gun attitudes serve as a way for men to demonstrate masculinity and to bond with other men. These scholars argue that gun control is perceived as a threat to “male intimacy” and male identity, thus men are more likely to be emersed in gun culture and have favorable views of guns (see Carlson et al., 2018 ). Research has also documented an inverse relationship between educational attainment and support for more-restrictive forms of gun control (Newman & Hartman, 2019 ). Kruis et al. ( 2020 ) recently extended this line of inquiry by examining the relationship between gun knowledge—operationally defined as “one’s understanding of gun legislation, gun policies, and firearm crime”—and support for general gun control using a convenience sample of college students (p. 33). The authors found an inverse relationship between gun knowledge and support for stricter forms of gun control, concluding that students who had greater understanding of gun legislation, gun crime, and gun functioning, were less likely to favor stricter forms of gun control than students with less knowledge in these areas. While informative, this study suffered from a few crucial methodological limitations that preclude the generalizability of the findings. Notably, findings were based on data collected from college students through convenience sampling at three universities. Additionally, the measures of gun control and gun knowledge were broad and prohibited the examination of specific types of gun knowledge and various categories of gun control. Accordingly, the authors called for more work to be done in this area.
Current Study
The goal of the current study was to help contribute to research in this area by exploring public perceptions of various types of gun control mechanisms. In many ways the current study serves as an extension of Kruis et al.’s ( 2020 ) research. Specifically, the methodology employed by Kruis et al. ( 2020 ) were applied to the general public, using a representative sample of Pennsylvania residents ( N = 522) to help answer the following two overarching research questions:
R1: What are the training experiences, safety precautions, and defensive gun use reported by gun owners in Pennsylvania?
R2: What is the relationship between firearm knowledge and support for more-restrictive gun control policies?
Regarding our first research question, we were interested in assessing training experiences, safety precautions, and defensive gun usage reported by Pennsylvania gun owners. We were also interested in comparing demographic characteristics, victimization experiences, gun knowledge, and support for different types of gun control between gun owners and non-owners. Our second research question was concerned with testing the generalizability of Kruis et al.’s ( 2020 ) findings from students to members of the general public. Notably, we were interested in expanding upon Kruis et al.’s measures to better explore the relationship between different types of firearm knowledge (i.e., knowledge of gun crime, knowledge of gun policy, and knowledge of gTillyerun functioning) and various categories of gun control (i.e., general gun control, policies aimed at reducing overall gun ownership, and policies aimed at keeping guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people). We hypothesized that increased firearm knowledge would be inversely related to greater support for gun control.
Data for this project came from a larger study aimed at measuring public attitudes toward a variety of social phenomena, including school security measures, campus carry, and perceptions of the police. Specifically, data came from a 64-question original survey created by the authors and administered via the Qualtrics survey platform. The authors used the marketing research team at Qualtrics to locate and recruit a sample of 500+ English speaking residents of Pennsylvania aged 18 or older. Qualtrics maintains active market research panels of more than six million English speaking, non-institutionalized adults capable of giving consent. Participants join a panel through one of three different methods, including a “double opt-in,” direct recruitment by the marketing research team, or voluntary sign up. In exchange for their voluntary participation in surveys, panelists are compensated with small point-based incentives that can be redeemed in various forms, such as Sky Miles or gift cards.
In the Fall of 2020, Qualtrics sent an invitation link to panelists inviting them to participate in the survey. Interested panelists were first screened to determine eligibility. Efforts were made to ensure the representativeness of the sample in terms of race, age, and biological sex. That is, the marketing team was contracted to ensure that participants were screened in a way such that the final sample would be representative of the Pennsylvania general population in terms of race, age, and biological sex. Then, potential participants were shown an informed consent document specifying the goals of the study, potential risks and benefits, and contact information for the principal investigator and institutional review board. Those who consented were then directed to the online survey where they were presented with 64 Likert scale, text entry, and essay-based questions. In total, 680 panelists clicked on the invitation link and participated in the survey in some capacity. Data quality assurance tests revealed that 522 of these cases were valid and complete responses. Thus, all models specified below were based on the 522 cases with complete and valid data. It is important to note at the onset that our data collection strategy represent a convenience sampling approach. That said, comparisons with population estimates revealed that the data collected were generally representative of the Pennsylvania general population in terms of race and sex at the time of data collection, as well as income and geographical location (i.e., rural or urban). However, the median age of the sample (47) was slightly older than that of the general Pennsylvania population (41).
Support for Gun Control
The goal of this study was to assess residents’ support for various categories of gun control. Three different measures were used to capture participants’ disposition toward stricter forms of gun regulation. First, the 9-item measure used in Kruis et al.’s ( 2020 ) original study was used to capture respondents’ disposition toward broad forms of gun control. Items included: (1) “Strict gun legislation will stop future gun-related incidents/mass shootings,” (2) “Guns should not be used for recreational reasons (i.e., hunting, sporting, etc.),” (3) “Gun laws should differentiate between handguns and other guns,” (4) “Military type guns should be banned from public use,” (5) “Mental health screenings should be required to purchase any firearm,” (6) “I think all types of guns should be banned from public use,” (7) “I believe that the Second Amendment needs to be revised to reflect modern times,” (8) “Second Amendment rights allow more guns to be available to the public than necessary,” and (9) “I believe that current gun legislation is appropriate.” Response categories followed a 5-point Likert scale ranging from “Strongly Disagree” (1) to “Strongly Agree” (5). Item #9 was reverse coded and then responses were summed and averaged to create a continuous measure of broad support for gun control with higher numbers indicative of greater support for enhanced firearm regulation (α = 0.832).
To further assess differences in support for distinct types of gun control policies, two measures from Cook et al.’s ( 2011 ) gun control trichotomy were also created and included in analyses. The first measure was intended to capture support for gun control mechanisms aimed at reducing overall firearm ownership. Two items from the survey were used to capture this category of gun control strategies: (1) “Guns should not be used for recreational purposes (i.e., hunting, sporting, etc.)” and (2) “I think all types of guns should be banned from public use.” Responses followed a 5-point Likert scale ranging from “Strongly Disagree” (1) to “Strongly Agree” (5). The two items were combined and averaged to create a scale variable with higher scores reflective of greater support for policies intended to reduce overall firearm ownership (α = 0.797). The second specific type of gun control measured was support for policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous and/or “at-risk” individuals, such as criminals, the untrained, and the mentally ill. Three items for the survey were used to measure participants’ support for this category of gun control policies: (1) “I believe that mandatory gun education will lead to fewer gun related deaths in the U.S.,” (2) “There should be required background checks for all guns purchases,” and (3) “Mental health screenings should be required to purchase any firearm.” Responses followed a 5-point Likert scale ranging from “Strongly Disagree” (1) to “Strongly Agree” (5). The items were combined and averaged to create a scale variable with higher scores reflective of greater support for policies intended to keep guns out of the hands of dangerous and “at risk” people (α = 0.721).
For the purposes of this project, knowledge referred to a participant’s understanding of gun-related phenomena. To capture knowledge, participants were given a “Knowledge Test.” Three different domains of knowledge were assessed: (1) knowledge of gun crime, (2) knowledge of gun policy, and (3) knowledge of gun functioning. Knowledge of gun crime refers to participants' level of understanding of gun-related crime in the United States. Items used to capture this measure included: (1) “Gun related homicides have increased over the last 30 years throughout the U.S.,” (2) “In the last 10 years, most gun related deaths per year in the U.S. have been from suicides,” (3) “A majority of firearms used in criminal offenses were obtained illegally,” (4) “Military-style weapons (for example, “assault rifles”) are used in the majority of gun-related crimes,” (5) “Most firearm owners never commit a gun crime,” and (6) “Most mass shootings in the United states are done with legally obtained firearms.” Knowledge of gun policy refers to participants’ level of understanding of gun-related purchasing and ownership policies. Items used to capture this measure included: (1) “In the U.S., it is illegal to own a fully automatic firearm without a permit,” (2) “When purchasing a firearm from a retail store, a background check is NOT required,” (3) “When purchasing a firearm online from a retail store, one must go through a licensed firearm dealer to acquire it,” (4) “In the U.S., the legal purchasing age of rifles is lower than that of handguns,” (5) “In the U.S., felons cannot legally own a firearm,” and (6) “In the U.S., authorities can legally confiscate guns solely based on an individual’s mental illness.” Knowledge of gun functioning refers to a participant’s level of understanding of how guns work (i.e., gun-related functioning and operational procedures). Items used to capture this measure included: (1) “The “AR” in AR-15 stands for “Assault Rifle Footnote 4 ”, (2) “A semi-automatic firearm only fires one round of ammunition per single pull of the trigger,” (3) “The “magazine” is the area of the gun that feeds ammunition into the chamber of the gun,” (4) “An individual must manually engage the hammer on a double-action firearm before the weapon can fire a bullet,” (5) “A bolt-action rifle requires the user to manually cycle every round before the rifle can be fired,” and (6) “All firearms must legally have a safety setting to keep the firearm from firing.” Response categories to all questions included “True,” “False,” and “I Don’t” Know.” Correct answers were coded as a “1” and incorrect answers were coded as a “-1.” Participants were not penalized for selecting “I don’t know” (coded as “0”). Individual items were then combined to create an index measure ranging from − 6 to + 6 with greater scores indicating greater knowledge. See Appendix 1 for specific coding. Footnote 5
Experiences
Prior work has shown that experiences with firearms and crime can influence dispositions toward firearms (Ciomek et al., 2020 ; Kleck, 2019a ; Kruis et al., 2020 ). As such, five variables were used to capture participants’ experiences with firearms and crime, including (1) exposure to firearms, (2) perceived firearm familiarity, (3) criminal victimization experience, (4) vicarious criminal victimization experience, and (5) vicarious shooting victimization experience. Exposure was captured using Kruis et al.’s ( 2020 ) 10-item firearm exposure scale (α = 0.955), with items including “I regularly use guns for recreational purposes” and “I am around guns frequently.” Perceived familiarity was captured using Kruis et al.’s ( 2020 ) 3-item perceived familiarity scale (α = 0.872), with items including “I am familiar with current gun legislation in the United States” and “I am familiar with current gun legislation in my state of residence.” Participants were also asked to indicate whether they had ever been the victim of a crime (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”), if someone close to them had ever been the victim of a crime (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”), and if they knew someone who had ever been shot with a firearm (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”).
Training, Safety Precautions, and Gun Use
As the first research question for this project was concerned with examining the characteristics of gun owners, participants were asked to indicate whether they owned a firearm (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”). Those who indicated that they owned a gun were then presented with a series of questions intended to capture their experiences with firearm-related training. Specifically, gun owners were asked if they (1) had taken a formal gun safety course, such as a basic hunter safety education course (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”), (2) received informal gun safety training, through a friend or family member (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”), and/or (3) taken a gun self-defense course (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”). Owners were also asked to report whether or not they took various safety precautions with their firearms, such as using a gun safe or gun lock, keeping their guns unloaded, and/or storing ammunition away from their firearm(s) (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”). Additionally, gun owners were also asked to report if they had ever used their gun to defend themselves Footnote 6 (1 = “yes” and 0 = “no”).

Demographics
Measures of sex (1 = “male,” 0 = “female”), race (1 = white, 0 = non-white), age (0–max), geographical background (1 = “Urban,” 2 = “Suburban,” and 3 = “Rural”), income (1 = “Less than $10,000” through 12 = “More than $150,000”) and political affiliation (1 = “Republican,” 2 = “Democrat,” and 3 = “Other”) were also captured and included as control variables in the analyses.
Analytic Strategy
Data were analyzed using SPSS version 27. The analysis consisted of 3 main steps. First, all data were cleaned, coded, and preliminary analyses run to assess measures of central tendency and dispersion. Factor analyses (i.e., Principal Component Analysis and Principal Axis Factor Analysis) were used along with reliability estimations to help construct scale variables during the initial data screening process. Support for individual gun control measures were estimated by combining “strongly agree” with “agree” responses and then ranked to help illustrate public support for specific types of gun control strategies. Second, bivariate analyses were conducted to examine differences in mean scores and response categories between gun owners and non-owners. Third, a series of OLS regression models were estimated to explore the relationship between knowledge of gun crime, gun legislation, gun functioning and support for gun control, controlling for relevant “predictors. Footnote 7 ” All assumptions of OLS regression were checked prior to constructing the final models reported below. All variables inputted into the regression model had tolerances above 0.1 and Variance Inflation Scores (VIFs) below 10 (Pallant, 2016 ). Normal Quantile–Quantile and Probability-Probability plots indicated the presence of relatively normal distributions, and skewness and kurtosis values for the dependent variables fell within the acceptable range for analyses (− 2.00 and + 2.00, Field, 2016 ).
Descriptive Statistics
Table 1 displays participant demographic information and descriptive statistics. As indicated in Table 1 , a majority of participants were white (76.4%) and female (50.4%). Participants were fairly evenly distributed in their political affiliation, with about 41 percent identifying as “Democrat,” 37 percent identifying as “Republican,” and 22 percent identifying as “Other.” The mean age of the sample was 49.03 years old. More participants indicated suburban backgrounds (42.1%) than urban (37.2%) and rural (20.7%) backgrounds. In terms of income, the mean score reported was 6.70, suggesting an average household income between $50,000 and $70,000. A little more than a quarter of the sample (27.8%) indicated being a gun owner. Approximately 40 percent of the sample knew a victim of a crime (40.6%) or indicated being the victim of a crime themselves (39.7%). Nearly a third of the sample reported knowing someone who had been shot (32.4%). Regarding gun-related experiences, most participant’s indicated moderate firearm exposure (M = 2.51, SD = 1.25) and a slightly elevated estimate of their perceived familiarity (M = 3.40, SD = 1.00) with current firearm legislation. In terms of actual gun knowledge, participants had more knowledge of gun policy (M = 2.00, SD = 2.16) than gun crime (M = 0.64, SD = 2.08) and gun functioning (M = 0.04, SD = 1.86). In the aggregate, participants expressed moderate support for our general measure of broad gun control policies (M = 3.28, SD = 0.90). However, participants were more supportive of policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people (M = 4.10, SD = 0.88) than they were of policies intended to reduce overall ownership (M = 2.48, SD = 1.31).
Comparing Owners to Non-Owners
Table 2 displays the results from bivariate analyses (i.e., t-tests and chi-square tests) comparing gun owners (N = 145) to non-owners (N = 377). With the exception of age, gun owners were different from non-owners in all other demographic measures assessed. On average, gun owners were more likely to be male, white, and republican (p ≤ 0.001). They were also more likely to have rural backgrounds ( Χ 2 = 6.315, p ≤ 0.05) and reported higher incomes (t = − 3.481, p ≤ 0.01). Results also show that gun owners were different from non-owners in terms of gun-related experiences, gun knowledge, and support for gun control. Specifically, compared to non-owners, gun owners were more likely to report being the victim of a crime ( Χ 2 = 6.235, p ≤ 0.05) and to know someone who has been shot ( Χ 2 = 5.331, p ≤ 0.05). Owners also reported greater gun exposure (t = − 11.810, p ≤ 0.001) and familiarity (t = − 5.330, p ≤ 0.05) than non-owners. Gun owners were found to have greater knowledge of gun crime (t = − 2.831, p ≤ 0.01), gun policy (t = − 5.317, p ≤ 0.001), and gun functioning (t = − 5.116, p ≤ 0.001) than non-owners, and indicated less support for general gun control mechanisms (t = 5.346, p ≤ 0.001), policies that seek to reduce overall gun ownership (t = 3.318, p ≤ 0.05), and policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people (t = 1.991, p ≤ 0.05).
Training, Safety, and Defensive Gun Usage
Our first overarching research question was concerned with examining training experiences, safety precautions taken, and defensive gun usage reported by gun owners. Table 3 displays characteristics of the gun owners in our sample. As indicated in Table 3 , most owners indicated receiving some form of gun training (89.7%). Nearly three-quarters of the gun owners in our sample reported completing a formal safety training course, such as a basic hunter safety education course (72.4%). A little more than 70 percent indicated receiving informal safety training from a friend or family member, and 42.8 percent reported taking a gun self-defense course. Interestingly, 10.3 percent of all the gun owners in our sample noted that they had not received any form of safety training—formal or informal—nor had they taken a gun self-defense class. In terms of safety precautions taken, most gun owners indicated taking one of measures included in the survey (95.9%). Specifically, 62.1 percent indicated using a gun safe for storage purposes, 39.3 percent reported using gun locks, 50.3 percent expressed that they stored ammunition away from firearms, and 54.4 percent indicated that they kept their guns unloaded. Just six of the 145 gun owners in our sample (4.1%) reported that they did not use any of the safety precautions assessed in our survey. Regarding defensive gun usage, more than a quarter of gun owners (26.9%) reported that they had used a firearm to defend themselves at some point in their life.
Our second overarching research question was concerned with assessing public support for gun control. Two different analyses were used to answer this research question. First, descriptive statistics were assessed for individual measures of support for gun control and then ranked by level of support. Table 4 displays the findings from these analyses in order of rank. As noted in Table 4 , the most publicly supported gun control policy was requiring background checks for all types of gun purchases (86.0%), followed by requiring mental health screenings (79.7%), banning military-style weapons from public use (69.7%), mandating gun education (62.5%), and differentiating laws between handguns and other guns (59.4%). Slightly more than half of the sample also felt that the Second Amendment needed revised “to reflect modern times” (52.7%) and believed that strict gun legislation could stop future gun-related incidents and mass shootings (51.3%). However, most participants did not support completely banning firearms from public use (72.6%) Footnote 8 or banning guns for recreational purposes, such as hunting and sport shooting (74.1%).
Second, we estimated a series of OLS regression models to examine variables associated with support for gun control. Table 5 displays results from those analyses. Regarding our general measure of gun control, results indicated that the model fit the data well and explained approximately 31 percent of the variance in general support for gun control ( F = 14.901, p = 0.000, R 2 = 0.312). Nine of the independent variables in that model were found to be statistically significantly related to support for general gun control (p ≤ 0.05). Regarding demographic variables, results showed that compared to Republicans, Democrats (b = 0.589, p ≤ 0.001) indicated more support for gun control. Findings also suggest a marginally significant relationship between identifying as having a “Other” political affiliation (b = 0.176, p ≤ 0.010) and greater support for gun control, compared to identifying as a Republican. Further, results showed that compared to those with rural backgrounds, those with urban backgrounds (b = 0.234, p ≤ 0.05) were more supportive of gun control. Income was also statistically significant (b = 0.045, p ≤ 0.001), with findings suggesting that wealthier individuals were more supportive of gun control. Conversely, gun ownership (b = − 0.234, p ≤ 0.01) was found to be negatively associated with support for increased gun control. In terms of experiences, findings indicated that those who had been the victim of a gun crime (b = 0.188, p ≤ 0.05) and those who perceived having greater familiarity with current gun legislation (b = 0.151, p ≤ 0.001) were more supportive of policies associated with increased gun control. Findings also showed that those who indicated greater firearm exposure (b = − 0.119, p ≤ 0.01) held less support for general gun control mechanisms. Two measures of gun knowledge were also statistically significant in that model. Results showed that knowledge of gun crime (b = − 0.080, p p ≤ 0.001) and knowledge of gun functioning (b = − 0.079, p ≤ 0.001) were inversely related to support for general gun control.
The model estimating support for gun control policies intended to reduce overall gun ownership was also statistically significant ( F = 14.992, p = 0.000). The predictors in that model explained approximately 31 percent of the variance in the dependent measure ( R 2 = 0.313). Nine of the independent variables in that model were found to be statistically significant (p ≤ 0.05) and two exhibited a marginally significant association (p ≤ 0.10). Regarding demographic variables, results showed that age (b = − 0.017, p ≤ 0.001) and gun ownership (b = − 0.325, p ≤ 0.01) were negatively associated with the dependent measure, whereas being a Democrat (b = 0.441, p < 0.001), income (b = 0.033, p ≤ 0.05), and having an Urban background (b = 0.560, p ≤ 0.001) were significantly and positively associated with the dependent measure. In terms of experiences, findings indicated that those who had been the victim of a crime (b = 0.208, p ≤ 0.10) were more supportive of policies associated with reducing overall gun ownership. Interestingly, findings also showed that those who indicated greater firearm exposure (b = 0.139, p ≤ 0.05) held more support for such policies, which is opposite the direction for this variable noted in the first model. Knowing a crime victim was found to exhibit a negative, albeit marginally, significant relationship (b = − 0.216, p ≤ 0.10) with support for policies intended to reduce overall ownership. All measures of gun knowledge were statistically significantly related to support for policies aimed at reducing overall gun ownership. Results showed that knowledge of gun crime (b = − 0.110, p ≤ 0.001), knowledge of gun policy (b = − 0.059, p ≤ 0.05), and knowledge of gun functioning (b = − 0.068, p ≤ 0.05) were inversely related to support for policies intended to reduce overall gun ownership.
The last column in Table 5 shows results from the OLS modeling estimating support for gun control policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people. Results indicated that the model fit the data well and explained approximately 14 percent of the variance in gun control mechanisms aimed at keeping guns out of the hands of dangerous people (F = 6.059, p = 0.000, R 2 = 0.142). Six of the independent variables in that model were found to be statistically significant. Regarding demographic variables, results showed that being male (b = − 0.163, p < 0.05) and younger (b = .008, p ≤ 0.01) were negatively related to the dependent measure, whereas income (b = 0.033, p ≤ 0.01) was positively associated with support for policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous individuals. In terms of experiences, findings suggested that greater familiarity with current gun legislation (b = 0.235, p ≤ 0.001) was associated with more support for policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous people, whereas greater exposure was associated with less support (b = − 0.182, p ≤ 0.001). Only one measure of gun knowledge was statistically significant in the model. Results showed that knowledge of gun functioning (b = − 0.077, p ≤ 0.01) was inversely related to support for policies intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people. Footnote 9
This study was concerned with exploring public perceptions of gun control. Specifically, data collected from a representative sample of 522 Pennsylvania residents were used to (1) explore the training experiences, safety practices, and defensive gun usage reported by gun owners, and (2) to examine the correlates of public support for various types of gun control. There are a few findings from analyses that warrant further discussion.
First, there were several notable findings related to training experiences, safety precautions, and defensive gun usage indicated by the gun owners in our sample. Consistent with previous findings, we found that more than 25 percent of the gun owners in our sample had never taken a formal gun safety course, including a basic hunter safety education course (Parker et al., 2017 ; Kruis et al., 2020 ). To expand upon prior work, we also attempted to assess gun training through cultural transmission by asking participants if they had received informal gun training, such as training through a family member or friend. We found that approximately 70 percent of gun owners in our sample had received informal training through a family member or friend. In all, a majority of our sampled gun owners reported receiving some form of gun safety training (i.e., 90 percent). However, collectively, findings revealed that about 10 percent of the gun owners in our sample had received no formal or informal training. This estimate is concerning, given that firearm training courses tend to focus on teaching novice gun handlers how to safely use, transport, and store their firearms, as well as introduce them to relevant gun laws (Rowhani-Rahbar et al., 2018 ). Ill-trained gun owners may be at a greater risk of using their firearms in an unsafe manner or storing them in ways that permit “unauthorized” persons to access and use their weapons, which can result in more firearm-related injuries.
Unfortunately, due to data limitations (i.e., sample size), we were unable to effectively explore the relationship between gun training and safety precautions taken by gun owners. We did find that more than half of the gun owners in our sample reported using gun safes, kept their firearms unloaded at all times, and/or stored ammunition away from firearms in an attempt to prevent others from accessing and/or using their firearms, which helps to prevent accidental discharges. In fact, just six of the 145 gun owners in our sample (4.1%) reported that they took “no safety” precautions, suggesting that most— “trained” and “untrained” gun owners—took some form of gun safety precaution. Supplementary analyses did reveal that two of the six gun owners who indicated they took none of the listed safety precautions also indicated that they had received no formal or informal gun safety training. These data indicate that there was a higher proportion of non-trained gun owners (13.3%) who suggested taking no safety precaution than there were trained gun owners (3.1%). We do want to caution when interpreting these results for two reasons. First, our measures do not capture the “quality” of training received. Second, as noted above, the number of non-trained gun owners and owners who take no-safety precautions was so small that we were unable to conduct any type of meaningful comparison. As such, we encourage future researchers to explore the relationship between gun training and gun safety more thoroughly. We will note, however, that, in synthesizing prior research in this area, scholars at RAND Corporation ( 2020 ) concluded that child access prevention laws, defined as laws that attempt to influence how guns are stored, are effective at reducing unintentional injuries and deaths, as well as suicides, and may be effective at helping to reduce violent crime. Thus, it appears that there may be a relationship between gun storing patterns and rates of firearm-related injuries. As such, if more owners store their weapons properly, then we may see fewer firearm related injuries, suicides, and violent crime.
Another interesting finding emerging from the data was the proportion of defensive gun usage reported by gun owners in our sample. Nearly 27 percent of gun owners in our sample indicated that they had used their gun to defend themselves at some point in their life. This suggests that more than 1 in 4 gun owners in our sample had used their firearm to defend their life, liberty, or property—which, although a slightly higher estimate, mirrors findings reported by the Pew Research Center in 2017 (i.e., 1 in 6 gun owners; see Parker et al., 2017 ). Other research has found that the prevalence of defensive gun usage in the United States ranges from 60,000 to 2.5 million incidents annually (Institute of Medicine & National Research Council, 2013 ). Collectively, these findings indicate that a significant portion of gun owners use—or at least perceive that they use—their firearm(s) for self-defense purposes. As such, any efforts aimed at reforming gun policies in the United States should consider this “utility,” or using firearms as a tool, prior to implementation. While firearms may currently help contribute to a high number of injuries (CDC, 2020 ) and crimes (National Institute of Justice, 2019 ) committed every year in the United States, it is possible that gun control efforts that take guns out of the hands of law-abiding citizens could further exacerbate these numbers by removing a viable protection mechanism from individuals who otherwise may be unable to adequately defend themselves. Prior research has been mixed in findings related to this hypothesis with some work suggested that arming potential victims may be associated with reductions in injuries and loss of property (see Cook et al., 2011 ; Cook, 1991 ; Kleck & Gertz, 1995 ; Southwick, 2000 ) and other research questioning such claims (Hemenway, & Solnick, 2015 ). Similarly, and more broadly, prior research on the effects of gun control related to patterns of gun ownership on patterns of violence and crime have produced mixed results, with some research findings indicating little to no effect (Kleck, 2019a ; Kleck et al., 2016 ; Lott, 2013 ) and others suggesting a positive relationship between gun ownership and gun crime (Billings, 2020 ; Ciomek et al., 2020 ). Accordingly, more research is needed before firm conclusions related to defensive gun usage can be drawn. That said, our data show that gun owners in Pennsylvania may use their weapons in self-defense at a fairly high rate.
Second, there were several interesting findings related to participants’ support for various forms of gun control. In the aggregate, the top three supported gun control measures were: (1) required background checks for all types of gun purchases (86.0%), (2) required mental health screenings for gun purchases (79.7%), and (3) banning military type firearms (i.e., AR or AK platforms) from public use (69.7%). Using prior research (see Cook, 2011 and Kruis et al., 2020 ) we also examined “correlates” of support for gun control measured in three different ways: (1) support for general gun control mechanisms, (2) support for policies aimed at reducing overall gun ownership, and (3) support for policies aimed at keeping firearms away from dangerous people. There were several interesting findings that emerge from those analyses. Notably, most participants seemed to favor polices aimed at keeping guns away from dangerous and “at risk” individuals, such as the untrained, the mentally ill, and justice-involved persons. However, most did not support policies aimed at reducing overall gun ownership (i.e., restricting public gun use and use for recreational purposes)—which is consistent with prior research (Parker et al., 2017 ).
These findings are important to consider in relation to the efficacy of such policies. The dominate research suggests that gun control intended to keep guns away from dangerous and “at risk” people may be effective at reducing serious violence (Braga & Cook, 2018 ; Kleck et al., 2016 ; RAND, 2020 ), while gun control strategies aimed at reducing community firearm ownership may have little to no effect on overall violent crime rates (Cook & Ludwig, 2006 ; Cook & Pollack, 2017 ; Kleck, 2019b ).
Similarly, several interesting findings emerged in multivariable modeling. Generally, we found that those who are more supportive of gun control were Democrats, those who had Urban backgrounds, those who had less exposure to firearms, and those with larger annual incomes. We also found a significant relationship between specific types of gun knowledge and support for categories of gun control. Participants who had greater knowledge of gun crime and gun functioning were less supportive of general forms of gun control, and those who had greater knowledge of gun functioning were less supportive of restrictive policies. Consistent with findings reported by Kruis et al. ( 2020 ), we found a general inverse relationship between gun knowledge and support for various types of gun control, with a few caveats. We found that those who were more knowledgeable in the areas of gun crime, gun policy, and gun functioning, did not favor more restrictive gun control measures, particularly those aimed at reducing overall gun ownership. However, excluding knowledge of gun functioning, there was no relationship between gun knowledge and support for policies aimed at keeping firearms away from dangerous people, suggesting that both the “knowledgeable” and “non-knowledgeable” are equally likely to support restricted access for potentially dangerous and “at risk” individuals.
Collectively, this research shows that the same gun control strategies with the most public support—and those supported by those with the most gun “knowledge”—are also those with the most empirical support. Similarly, those with the least public support are those that seem to have the least or, at least, questionable empirical support. As such, policymakers may want to direct gun “reform” efforts toward policies intended to keep guns away from persons who are considered to be dangerous or “at risk,” such as felons, the untrained, and those who are mentally ill. At the same time, policymakers need to consider the effects that such actions will have on legal acquisition and take efforts to strengthen law abiding citizens’ abilities to obtain and use firearms legally. For instance, based on the available scholarly literature, we argue that complete firearm bans will likely have little if any positive effect of crime, and our research shows that such policies are largely unsupported by members of the general public. Related, we also suggest that gun control strategies discussed by Cook and Leitzel ( 1996 ) aimed at increasing the price of firearms and ammunition may only prevent law abiding citizens from obtaining weapons and merely increase black market sales or thefts of weapons, which is how most criminals obtain their firearms (Cook, 2018 ; Roth, 1994 ). Thus, better approaches to gun regulation will prevent dangerous and “at risk” people from obtaining firearms, while also protecting law-abiding citizens abilities to access firearms. Unfortunately, as noted by Braga et al. ( 2021 ) the current research provides us with little guidance on how best to achieve this goal. As such, more scholarly work is needed in this area.
Limitations and Directions for Future Research
The most concerning limitation of this study is that it utilized a cross-sectional research design. As such, the temporal relationship between variables remains unknown. Related, data were collected from a sample of Pennsylvania residents and findings are not generalizable beyond those parameters. Additionally, our measures of gun control overlooked an entire category of gun control mechanisms—those that are intended to influence choices about how guns are used and to what effect. Accordingly, we encourage future researchers to use longitudinal research designs, to examine these findings in other populations, and better attempt to capture all categories of gun control mechanisms in instrumentation.
Despite these limitations, this work contributes to the extant literature in several ways. Notably, findings from this study suggest that most gun owners in Pennsylvania have received some form of safety training and take appropriate safety precautions with their firearms. Moreover, findings reveal that many gun owners use guns for self-defense purposes. Regarding gun control, findings reveal that members of the general public tend to be supportive of policies aimed at keeping guns away from dangerous and “at risk” individuals, such as required background checks for all types of gun purchases, mental health screenings, and mandatory gun education. However, members of the general public are not supportive of gun control mechanisms aimed at reducing overall firearm ownership, such as public gun bans. Among those who are the least supportive of such polices are those who are the most knowledgeable about gun crime, gun legislation, and gun functioning.
The long-standing debate of gun rights and ownership tends to center around the concept of “needs” and “wants” in relation to the types of firearms available to the public and the measures used to control the access to these firearms. Much of the empirical literature has produced mixed results when assessing the importance of preventative policies and the associated crimes that can be reduced. This study adds to the growing body of literature seeking more information to adequately inform policymakers regarding gun ownership and public opinions toward restrictive gun laws.
Research suggests that those who are mentally ill are at a higher odds of committing suicide, especially with a gun, but have relatively low rates of violent crime commission, including firearm violence. In fact, this work suggests that those who are mentally ill are more likely to be the victim of a crime than the perpetrator of a crime. Although, given the extent of under-diagnosis among the mentally ill, the relationship between these variables has been difficult to establish. See Swanson et al. ( 2015 ) and Ramchand and Ayer ( 2021 ).
See Kleck ( 2021 ) for a discussion of the quality of research in this area.
Research has found that question wording may influence whether people indicate support for a proposed assault weapons ban (Newport, 2019 ). Still, the available data suggest a slight majority of the public supports banning assault weapons.
The term “AR” is commonly mistaken to mean “assault rifle” or “automatic rifle” (Palma, 2019 ).
At the request of reviewers, we have included informational sources after each question to verify our coding. Efforts were made to include sources with commentary to help readers better understand subject matter. We also tried to incorporate informational sources with a Pennsylvania focus, when available, given that our sample is of Pennsylvania residents.
Gun owners were asked, “Have you ever used your gun to defend yourself?”.
Here, we refer to “predictor” in the linear manner.
As noted in Table 4 , approximately 27 percent of our sample indicated that they felt all guns should be banned from public use. A reviewer suggested that it would be interesting to explore the relationship between political affiliation and support for public gun bans. Results from chi-square test revealed a statistically significant relationship between political affiliation and support for public gun bans ( Χ 2 = 56.840, p < .001). Specifically, analysis revealed that about 1 in 3 democrats supported such a policy, compared to approximately 1 in 4 Republicans and 1 in 5 individuals who identified as having a “Other” political affiliation.
While we are confident that our measures of gun knowledge are valid and reliable measures, at the requests of the reviewers, we also ran a series of supplemental analyses that omitted “questionable” variables within the indices. For instance, we omitted the variables “Gun related homicides have increased over the last 30 years throughout the U.S.” and “A majority of firearms used in criminal offenses were obtained illegally” from knowledge of gun crime. We also omitted “In the U.S., authorities can legally confiscate guns solely based on an individual’s mental illness” from knowledge of gun policy, and “The “AR” in AR-15 stands for “Assault Rifle” from knowledge of gun functioning. Results were similar to the final models reported in the manuscript and are available upon request.
Andrés, A. R., & Hempstead, K. (2011). Gun control and suicide: The impact of state firearm regulations in the United States, 1995–2004. Health Policy, 101 (1), 95–103.
Article Google Scholar
ATF. (2015) Does a customer have to be a certain age to buy firearms or ammunition from a licensee? Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.atf.gov/firearms/qa/does-customer-have-be-certain-age-buy-firearms-or-ammunition-licensee
Balmert, J. (2021). As Biden enters white house, Ohio GOP lawmaker pushes ‘Second Amendment sanctuary state’ . The Enquirer. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.cincinnati.com/story/news/politics/2021/01/29/ohio-gop-second-amendment-sanctuary-state-biden/4274810001/
Barry, C. L., Stone, E. M., Crifasi, C. K., Vernick, J. S., Webster, D. W., & McGinty, E. E. (2019). Trends in public opinion on US gun laws: Majorities of gun owners and non-gun owners support a range of measures. Health Affairs, 38 (10), 1727–1734.
Billings, S. B. (2020). Smoking gun? Linking gun ownership to crime victimization and neighborhood crime. Linking Gun Ownership to Crime Victimization and Neighborhood Crime (April 29, 2020) .
Braga, A. A., & Cook, P. J. (2018). The association of firearm caliber with likelihood of death from gunshot injury in criminal assaults. JAMA Network Open, 1 (3), e180833–e180833.
Braga, A. A., Griffiths, E., Sheppard, K., & Douglas, S. (2021). Firearm instrumentality: Do guns make violent situations more lethal? Annual Review of Criminology, 4 , 147–164.
Brenan, M. (2020). Support for stricter U.S. gun laws at lowest level since 2016. Gallup. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://news.gallup.com/poll/325004/support-stricter-gun-laws-lowest-level-2016.aspx
Brennan, P. G., Lizotte, A. J., & McDowall, D. (1993). Guns, southerness, and gun control. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 9 (3), 289–307.
Bureau of Justice Statistics. (2020). NCVS Victimization Analysis Tool (NVAT). Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.bjs.gov/index.cfm?ty=nvat
Carlson, J., Goss, K. A., & Shapira, H. (Eds.). (2018). Gun studies: Interdisciplinary approaches to politics, policy, and practice . Routledge.
Google Scholar
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2020). Underlying cause of death 1999–2019 on CDC WONDER online database, Retrieved from https://wonder.cdc.gov/controller/datarequest/D76;jsessionid=8547021C770390B83510480403DA
Ciomek, A., Braga, A., & Papachristos, A. (2020). The influence of firearms trafficking on gunshots injuries in a co-offending network. Social Science and Medicine, 259 , 113114.
Clark, D. (2018). Is most gun crime committed by those who illegally possess guns? Politifact. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.politifact.com/factchecks/2018/mar/12/john-faso/do-illegal-gun-owners-commit-most-gun-crime-rep-fa/
Cook, P. J. (1980). Reducing injury and death rates in robbery. Policy Analysis , 21–45.
Cook, P. J. (1991). The technology of personal violence. Crime and Justice, 14 , 1–71.
Cook, P.J. (2017). How dangerous people get their guns in America . CBS News: The conversation. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.cbsnews.com/news/gun-sales-how-dangerous-people-get-weapons/
Cook, P. J. (2018). Gun markets. Annual Review of Criminology, 1 , 359–377.
Cook, P. J., Braga, A. A., & Moore, M. H. (2011). Gun Control. In J. Q. Wilson & J. Petersilia (Eds.), Crime and public policy (pp. 257–292). Oxford University Press.
Cook, P. J., & Leitzel, J. A. (1996). Perversity, futility, jeopardy: An economic analysis of the attack on gun control. Law and Contemporary Problems, 59 , 91–118.
Cook, P. J., & Ludwig, J. (2006). The social costs of gun ownership. Journal of Public Economics, 90 (1–2), 379–391.
Cook, P. J., & Pollack, H. A. (2017). Reducing access to guns by violent offenders. RSF: the Russell Sage Foundation Journal of the Social Sciences, 3 (5), 2–36.
Crifasi, C. K., Ward, J. A., McGinty, E. E., Webster, D. W., & Barry, C. L. (2021). Public opinion on gun policy by race and gun ownership status. Preventive Medicine, 149 , 106607.
Curcuruto, J. (2020). NSSF survey reveals broad demographic appeal for firearm purchases during sales surge of 2020. National Shooting Sports Foundation. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.nssf.org/articles/nssf-survey-reveals-broad-demographic-appeal-for-firearm-purchases-during-sales-surge-of-2020/
Department of Justice, Government of Canada. (n.d.). Firearms, accidental deaths, suicides and violent crime: An updated review of the literature with special reference to the Canadian situation. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.justice.gc.ca/eng/rp-pr/csj-sjc/jsp-sjp/wd98_4-dt98_4/p3.html#a32
Ellison, C. G. (1991). Southern culture and firearms ownership. Social Science Quarterly, 72 (2), 267–283.
Evans, D. N., & Williams, C. L. (2017). Stop, question, and frisk in New York City: A study of public opinions. Criminal Justice Policy Review, 28 (7), 687–709.
Fabio, A., Duell, J., Creppage, K., O’Donnell, K., & Laporte, R. (2016). Gaps continue in firearm surveillance: Evidence from a large US city bureau of police. Social Medicine, 10 (1), 13–21.
Federal Bureau of Investigation. (n.d.). Crime data explorer. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://crime-data-explorer.fr.cloud.gov/explorer/national/united-states/crime
Field, A. (2016). Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics (4th ed). Los Angeles, CA; Sage.
Filindra, A., & Kaplan, N. J. (2016). Racial resentment and whites’ gun policy preferences in contemporary America. Political Behavior, 38 (2), 255–275.
Filindra, A., & Kaplan, N. J. (2017). Testing theories of gun policy preferences among Blacks, Latinos, and Whites in America. Social Science Quarterly, 98 (2), 413–428.
Follman, M., Aronsen, G., & Pan, D. (2021). US mass shootings, 1982–2021: Data from mother jones’ investigation. MotherJones. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.motherjones.com/politics/2012/12/mass-shootings-mother-jones-full-data/
Friend, D. (2021). Constitutional carry, 2nd amendment sanctuary, and anti-red flag laws: A look at pro-gun bills in Texas . The Texan. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://thetexan.news/a-look-at-the-pro-gun-bills-filed-in-the-texas-legislature/
Frontline. (n.d.). Hot guns. PBS. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/shows/guns/more/faq.html
Gallup. (2020). Guns. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://news.gallup.com/poll/1645/guns.aspx
Giffords Law Center. (2021a). Statistics. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://giffords.org/lawcenter/gun-violence-statistics/
Giffords Law Center. (2021b). Mental health reporting in Pennsylvania . Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://giffords.org/lawcenter/state-laws/mental-health-reporting-in-pennsylvania/
Giffords Law Center. (2021c). Firearm prohibitions in Pennsylvania. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://giffords.org/lawcenter/state-laws/firearm-prohibitions-in-pennsylvania/
Giffords Law Center. (n.d.) Machine guns and 50 caliber . Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://giffords.org/lawcenter/gun-laws/policy-areas/hardware-ammunition/machine-guns-50-caliber/#footnote_0_5658
Gramlich, J. (2019). What the data says about gun deaths in the U.S. Pew Research Center. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/08/16/what-the-data-says-about-gun-deaths-in-the-u-s/
Grinshteyn, E., & Hemenway, D. (2019). Violent death rates in the US compared to those of the other high-income countries, 2015. Preventive Medicine, 123 , 20–26.
Gun News Daily. (n.d.). Single action vs. double action: A guide for beginners. Retrieved from https://gunnewsdaily.com/single-action-vs-double-action/
Gun Violence Archive. (2021). Past summary ledgers . Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.gunviolencearchive.org/past-tolls
Hemenway, D., & Solnick, S. J. (2015). The epidemiology of self-defense gun use: Evidence from the National Crime Victimization Surveys 2007–2011. Preventive Medicine, 79 , 22–27.
Henigan, D. A. (2016). Guns don’t kill people, people kill people: And other myths about guns and gun control . Beacon Press.
Hill, G. D., Howell, F. M., & Driver, E. T. (1985). Gender, fear, and protective handgun ownership. Criminology, 23 (3), 541–552.
Huntingsmart. (n.d.). The firing cycle of a bolt action rifle. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.thecampfirecollective.com/knowledge-base/us/huntingsmart/03/09/
Institute of Medicine and National Research Council. (2013). Priorities for research to reduce the threat of firearm-related violence . National Academies Press.
Kauder, N. B. (1993). One-gun-a-month: Measuring public opinion concerning a gun control initiative. Behavioral Sciences and the Law, 11 (4), 353–360.
Kleck, G. (1997). Point blank: Guns and gun violence in America . Aldine de Gruyter.
Kleck, G. (2021). The continuing vitality of flawed research on guns and violence: A comment on Fridel (2020). Justice Quarterly , 1–9.
Kleck, G. (2019a). Macro-level research on the effect of firearms prevalence on suicide rates: A systematic review and new evidence. Social Science Quarterly, 100 (3), 936–950.
Kleck, G. (2019b). Regulating guns among young adults. American Journal of Criminal Justice, 44 (5), 689–704.
Kleck, G., & Gertz, M. (1995). Armed resistance to crime: The prevalence and nature of self-defense with a gun. The Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology, 86 , 150–187.
Kleck, G., & Patterson, E. B. (1993). The impact of gun control and gun ownership levels on violence rates. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 9 (3), 249–287.
Kleck, G., Kovandzic, T., & Bellows, J. (2016). Does gun control reduce violent crime? Criminal Justice Review, 41 (4), 488–513.
Koper, C. S., Johnson, W. D., Nichols, J. L., Ayers, A., & Mullins, N. (2018). Criminal use of assault weapons and high-capacity semiautomatic firearms: An updated examination of local and national sources. Journal of Urban Health, 95 (3), 313–321.
Kruis, N. E., Wentling, R. L., Heirigs, M. H., & Ishoy, G. A. (2020). Assessing the impact of knowledge and location on college students’ perceptions of gun control and campus carry policies: A multisite comparison. American Journal of Criminal Justice, 45 (1), 25–47.
Libby, N. E., & Corzine, J. (2007). Lethal weapons: Effects of firearm types on the outcome of violent encounters. Justice Research and Policy, 9 (2), 113–137.
Livingston, M. M., & Lee, M. W. (1992). Attitudes toward firearms and reasons for firearm ownership among nonurban youth: Salience of sex and race. Psychological Reports, 71 (2), 576–578.
Lott, J. R. (2013). More guns, less crime: Understanding crime and gun control laws . University of Chicago Press.
Lott, J. R. (2016). Concealed carry permit holders across the United States: 2016. Available at SSRN 2814691.
Lucey, C. (2021). Biden’s gun-policy plans start to take shape . The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.wsj.com/articles/bidens-gun-policy-plans-start-to-take-shape-11613135990
Malcom, J & Swearer, A. (2018). Here are 8 stubborn facts on gun violence in America . The Heritage Foundation. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.heritage.org/crime-and-justice/commentary/here-are-8-stubborn-facts-gun-violence-america
Marciniak, L. M., & Loftin, C. (1991). Measuring protective handgun ownership. Criminology, 29 (3), 531–540.
McClain, P. D. (1983). Determinants of black and white attitudes toward gun regulation: A research note. Journal of Criminal Justice, 11 (1), 77–81.
Merino, S. M. (2018). God and guns: Examining religious influences on gun control attitudes in the United States. Religions, 9 (6), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/rel9060189
Morral, A. R., Schell, T.L., & Tankard, M. (2018). The magnitude and sources of disagreement among gun policy experts. RAND Corporation. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RR2088z1.html . Also available in print form.
Morrall, A. (2018). The science of gun policy: A critical synthesis of research evidence on the effects of gun policies in the United States. Rand Health Quarterly . https://doi.org/10.7249/RR2088
Naghavi, M., Marczak, L. B., Kutz, M., Shackelford, K. A., Arora, M., Miller-Petrie, M., & Tran, B. X. (2018). Global mortality from firearms, 1990–2016. JAMA, 320 (8), 792–814.
National Institute of Justice. (2019). Gun violence in America. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://nij.ojp.gov/topics/articles/gun-violence-america
National Shooting Sports Foundation. (n.d.). Modern sporting rifle: Introduction. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.nssf.org/msr/
Newburger, E. (2021). Biden calls for congress to pass stricter gun laws on anniversary of Parkland mass shooting . CNBC. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.cnbc.com/2021/02/14/biden-calls-on-congress-to-reform-gun-laws-on-anniversary-of-parkland-shooting.html
Newman, B. J., & Hartman, T. K. (2019). Mass shootings and public support for gun control. British Journal of Political Science, 49 (4), 1527–1553.
Newport, F. (2019). Analyzing surveys on banning assault weapons . Gallup. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://news.gallup.com/opinion/polling-matters/268340/analyzing-surveys-banning-assault-weapons.aspx
NRA-ILA. (n.d.) Background checks for guns . Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.nraila.org/get-the-facts/background-checks-nics/
O’Brien, K., Forrest, W., Lynott, D., & Daly, M. (2013). Racism, gun ownership, and gun control: Biased attitudes in US whites may influence policy decisions. PLoS ONE, 8 (10), e77552. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077552
Oliphant, B.J. (2017). Bipartisan support for some gun proposals, stark partisan divisions on many others. Pew Charitable Trust. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2017/06/23/bipartisan-support-for-some-gun-proposals-stark-partisan-divisions-on-many-others/
Pallant, J. (2016). SPSS Survival Manual: A Step by Step Guide to Data Analysis Using IBM SPSS, 6th Edn Crows Nest . NSW: Allen &Unwin.
Palma, B. (2019). Does ‘AR’ in AR-15 Stand for ‘Assault Rifle’? A frequent misconception centers on what the term “AR-15” literally means. Snopes. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.snopes.com/fact-check/meaning-of-ar-in-ar-15-firearm/
Parker, K., Horowitz, J., Igielnik, R., Oliphant, J.B., & Brown, A. (2017). America’s complex relationship with guns. Pew Charitable Trust. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/2017/06/22/views-on-gun-policy/
Pederson, J., Hall, T. L., Foster, B., & Coates, J. E. (2015). Gun ownership and attitudes toward gun control in older adults: Re-examining self-interest theory. American Journal of Social Science Research, 1 (5), 273–281.
Phillips, M. (2021). How Biden could tighten gun control without congress. Fox News . Retrieved February 18, 2021, from https://www.foxnews.com/politics/how-could-biden-tighten-gun-control-without-congress-approval
Planty, M., & Truman, J. L. (2013). Firearm violence, 1993–2011 . Washington, DC: US Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, Bureau of Justice Statistics.
Ramchand, R. & Ayer, L. (2021). Is mental illness a risk factor for gun violence? RAND. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.rand.org/research/gun-policy/analysis/essays/mental-illness-risk-factor-for-gun-violence.html
RAND. (2020). What science tells us about the effects of gun policies . Retrieved February 18, 2021, from https://www.rand.org/research/gun-policy/key-findings/what-science-tells-us-about-the-effects-of-gun-policies.html
Rosen, G. (2000). Yes and no to gun control. Commentary, 110 (2), 47–53.
Roth, J. A. (1994). Firearms and violence . US Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, National Institute of Justice.
Rowhani-Rahbar, A., Lyons, V. H., Simonetti, J. A., Azrael, D., & Miller, M. (2018). Formal firearm training among adults in the USA: Results of a national survey. Injury Prevention, 24 (2), 161–165.
Schaeffer, K. (2019). Share of Americans who favor stricter gun laws has increased since 2017 . Pew Charitable Trust. Retrieved from https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/10/16/share-of-americans-who-favor-stricter-gun-laws-has-increased-since-2017/
Schaeffer, K. (2021). Key facts about Americans and guns. Pew Charitable Trust. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2021/05/11/key-facts-about-americans-and-guns/
Schmidt, D. (2020). How many deer hunters in the United States? Deer and Deer Hunting. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.deeranddeerhunting.com/content/blogs/dan-schmidt-deer-blog-whitetail-wisdom/how-many-deer-hunters-in-the-united-states
Secret, P. E., & Johnson, J. B. (1989). Racial differences in attitudes toward crime control. Journal of Criminal Justice, 17 (5), 361–375.
Sen, B., & Panjamapirom, A. (2012). State background checks for gun purchase and firearm deaths: An exploratory study. Preventive Medicine, 55 (4), 346–350.
Shammas, M. (2019). It’s time to retire the guns don’t kill people—People kill people argument. Guns do kill people. Guns Do Kill People (November 24, 2019) .
Smith, J., & Spiegler, J. (2020). Explaining gun deaths: Gun control, mental illness, and policymaking in the American states. Policy Studies Journal, 48 (1), 235–256.
Southwick, L., Jr. (2000). Self-defense with guns: The consequences. Journal of Criminal Justice, 28 (5), 351–370.
Statista Research Department (2021). Mass shootings in the U.S.: Legality of shooter’s weapons, as of May 2021 . Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/476461/mass-shootings-in-the-us-by-legality-of-shooters-weapons/
Swanson, J. W., McGinty, E. E., Fazel, S., & Mays, V. M. (2015). Mental illness and reduction of gun violence and suicide: Bringing epidemiologic research to policy. Annals of Epidemiology, 25 (5), 366–376.
Tillyer, M. S., & Tillyer, R. (2014). Violence in context: A multilevel analysis of victim injury in robbery incidents. Justice Quarterly, 31 (4), 767–791.
Tyler, T. R., & Lavrakas, P. J. (1983). Support for gun control: The influence of personal, sociotropic, and ideological concerns. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 13 (5), 392–405.
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Services (2020). National hunting license data. Retrieved February 15, 2021, from https://www.fws.gov/wsfrprograms/Subpages/LicenseInfo/Natl%20Hunting%20License%20Report%202020.pdf
Wallace, L. N. (2016). American preferences for “smart” guns versus traditional weapons: Results from a nationwide survey. Preventive Medicine Reports, 4 , 11–16.
Winkler, A. (2018). Is the second amendment becoming irrelevant. Indian Law Journal, 93 , 253–265.
Wintersteen. (2018). 9 Common misused gun terms. Guns and Ammo. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.gunsandammo.com/editorial/9-misused-gun-terms/249625
Wolfgang, M. E. (1958). Patterns in criminal Homicide . University of Pennsylvania Press.
Book Google Scholar
Wozniak, K. H. (2017). Public opinion about gun control post-Sandy Hook. Criminal Justice Policy Review, 28 (3), 255–278.
Wright, M. A., Wintemute, G. J., & Rivara, F. P. (1999). Effectiveness of denial of handgun purchase to persons believed to be at high risk for firearm violence. American Journal of Public Health, 89 (1), 88–90.
Yablon, A. (2020). Internet gun sales and background checks, explained . The Trace. Retrieved July 25, 2021, from https://www.thetrace.org/2016/01/internet-gun-sales-background-checks/
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Criminal Justice, Penn State Altoona, 3000 Ivyside Park, Cypress Building, Room 101E, Altoona, PA, 16601, USA
Nathan E. Kruis & Tyler S. Frye
Department of Administration of Justice, Penn State New Kensington, 3550 7th Street Road, Administrative Building Room: 111, New Kensington, PA, 15068, USA
Richard L. Wentling
Department of Sociology, Penn State Altoona, 3000 Ivyside Park, Smith Building, Room 128H, Altoona, PA, 16601, USA
Nicholas J. Rowland
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nathan E. Kruis .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 45.8 kb)
Appendix 1 knowledge “answers”, knowledge of gun crime.
Gun related homicides have increased over the last 30 years throughout the U.S. (False, see Gramlich, 2019 ; Gun Violence Archive, 2021 ; and National Institute of Justice, 2019 ).
In the last 10 years, most gun related deaths per year in the U.S. have been from suicides (True, see Giffords Law Center, 2021a , 2021b , 2021c and Gramlich, 2019 ).
A majority of firearms used in criminal offenses were obtained illegally (True, see Cook, 2017 , Clark, 2018 , and Fabio et al., 2016 ).
Military-style weapons (for example, “assault rifles”) are used in the majority of gun-related crimes (False, see Koper et al., 2018 ).
Most firearm owners never commit a gun crime (True, see Lott, 2016 and Malcom & Swearer, 2018 )
Most mass shootings in the United States are done with legally obtained firearms (True, see Follman et al., 2021 and Statista Research Department, 2021 )
Knowledge of Gun Policy
In the U.S., it is illegal to own a fully automatic firearm without a permit. (True, see Giffords Law Center, n.d.)
When purchasing a firearm from a retail store, a background check is NOT required. (False, see NRA-ILA, n.d. and Yablon, 2020 ).
When purchasing a firearm online from a retail store, one must go through a licensed firearm dealer to acquire it. (True, see NRA-ILA, n.d. and Yablon, 2020 )
In the U.S., the legal purchasing age of rifles is lower than that of handguns. (True, see ATF, 2015 ).
In the U.S., felons cannot legally own a firearm. (True, see Giffords Law Center, 2021 )
In the U.S., authorities can legally confiscate guns solely based on an individual’s mental illness. (True, see Giffords Law Center, 2021 ).
Knowledge of Gun Functioning
The “AR” in AR-15 stands for “Assault Rifle.” (False, see National Shooting Sports Foundation, n.d.)
A semi-automatic firearm only fires one round of ammunition per single pull of the trigger. (True, see Frontline, n.d.)
The “magazine” is the area of the gun that feeds ammunition into the chamber of the gun. (True, see Wintersteen, 2018 )).
An individual must manually engage the hammer on a double-action firearm before the weapon can fire a bullet. (False, see Gun News Daily, n.d.)
A bolt-action rifle requires the user to manually cycle every round before the rifle can be fired. (True, see Huntingsmart, n.d.)
All firearms must legally have a safety setting to keep the firearm from firing. (False, Giffords Law Center, n.d.)
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kruis, N.E., Wentling, R.L., Frye, T.S. et al. Firearm Ownership, Defensive Gun Usage, and Support for Gun Control: Does Knowledge Matter?. Am J Crim Just 48 , 21–50 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12103-021-09644-7
Download citation
Received : 09 March 2021
Accepted : 02 September 2021
Published : 30 September 2021
Issue Date : February 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12103-021-09644-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Gun control
- Defensive gun usage
- Perceptions of firearms
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

- MJC Library & Learning Center
- Research Guides
Guns in America
- Gun Issues Research
Pro Con Arguments
Start learning about your topic, create research questions to focus your topic, find books in the mjc library catalog, find articles in library databases, find web resources, cite your sources, key search words.
Use the words below to search for useful information in books and articles .
- gun control
- gun violence
- Second Amendment
- assault weapons
- school shootings
Background Reading:
It's important to begin your research learning something about your subject; in fact, you won't be able to create a focused, manageable thesis unless you already know something about your topic.
This step is important so that you will:
- Begin building your core knowledge about your topic
- Be able to put your topic in context
- Create research questions that drive your search for information
- Create a list of search terms that will help you find relevant information
- Know if the information you’re finding is relevant and useful
If you're working from off campus , you'll need to sign in if you aren't already logged into your MJC email or Canvas. If you are prompted to sign in, use the same credentials you use with email and Canvas.
All of these resources are free for MJC students, faculty, & staff.
- Issues and Controversies: Gun Control June 2022 article giving opposing answers to the question "Should the United States Adopt Stronger Gun Control Laws?"
- CQ Researcher: Gun Violence: have efforts to control firearms reached a turning point? Comprehensive overview article from 2018
- Gale eBooks: Gun Control A collection of overview articles from a variety of specialized encyclopedias
- Gale eBooks: Gun Safety A collection of overview articles from a variety of specialized encyclopedias
- America's Gun Wars: A Cultural History of Gun Control in the United States This eBook from 2019 examines the controversies surrounding gun control in the U.S., which, it asserts, are about whether to prioritize the traditional values of rugged independence or newer values of communitarian interdependence.
- Gun Legislation The library's collection of eBooks on U.S. legislation on guns.
The issues surrounding gun violence, gun safety, and gun legislation are complex. You could concentrate on one issue and do in-depth research on that, or use several of the questions below to focus more generally on the topic of guns.
- Is gun violence a serious problem in America?
- Does limiting access to guns reduce gun violence?
- What laws exist to control gun ownership?
- How are guns purchased and transferred in America?
- How do other countries regulate gun ownership?
- Should gun rights be controlled by states or by the federal government?
- What are the arguments for regulating gun ownership?
- What are the arguments against regulating gun ownership?
Why Use Books:
Use books to read broad overviews and detailed discussions of your topic. You can also use books to find primary sources , which are often published together in collections.
Where Do I Find Books?
You'll use the library catalog to search for books, ebooks, articles, and more.
What if MJC Doesn't Have What I Need?
If you need materials (books, articles, recordings, videos, etc.) that you cannot find in the library catalog , use our interlibrary loan service .
All of these resources are free for MJC students, faculty, & staff.
- Gale Databases This link opens in a new window Search over 35 databases simultaneously that cover almost any topic you need to research at MJC. Gale databases include articles previously published in journals, magazines, newspapers, books, and other media outlets.
- EBSCOhost Databases This link opens in a new window Search 22 databases simultaneously that cover almost any topic you need to research at MJC. EBSCO databases include articles previously published in journals, magazines, newspapers, books, and other media outlets.
- Access World News This link opens in a new window Search the full text of editions of record for local, regional, and national U.S. newspapers as well as full-text content of key international sources. Your source for The Modesto Bee for local and regional news from January 1989 to the present. more... less... Watch this short video to learn how to find The Modesto Bee .
- Kanopy This link opens in a new window A video streaming database containing thousands documentary films suitable for research. Use the search terms guns, gun violence, or gun control for films on both sides of the issue.
- Films on Demand This link opens in a new window Thousands of credible streaming documentaries and clips. Search guns, gun safety, gun violence, gun control more... less... Instructions for embedding Films on Demand into Canvas .
Search Google Scholar:

Browse Featured Web Sites:
- Everytown for Gun Safety "The largest gun violence prevention organization in America"
- National Rifle Association "While widely recognized today as a major political force and as America's foremost defender of Second Amendment rights, the NRA has, since its inception, been the premier firearms education organization in the world."
- Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives "A unique law enforcement agency in the United States Department of Justice that protects our communities from violent criminals, criminal organizations, the illegal use and trafficking of firearms, the illegal use and storage of explosives, acts of arson and bombings, acts of terrorism, and the illegal diversion of alcohol and tobacco products"
Your instructor should tell you which citation style they want you to use. Click on the appropriate link below to learn how to format your paper and cite your sources according to a particular style.
- Chicago Style
- ASA & Other Citation Styles
- Last Updated: Feb 26, 2024 2:56 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mjc.edu/guns
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 and CC BY-NC 4.0 Licenses .
168 Gun Control Topics & Research Questions
In this gun control topics compilation, we offer a polarizing discourse surrounding firearms regulations. Gun control is a complex and contentious issue encompassing discussions about individual rights, public safety, and the role of government in citizen welfare. These gun control essay topics will show diverse perspectives on gun control policies.
🤔 TOP 7 Gun Control Topics
🏆 best gun control topics, ✅ pro gun control essay topics, ❌ against gun control essay topics, 👍 gun control essay examples, 🎓 interesting gun control research questions, 💡 simple gun control essay topics, ❓ more gun violence titles.
- Gun Control Rebuttal in the United States
- Effects of Gun Control Measures in the United States
- A Court Case That Influenced Federal Decision on Gun Control
- The Effects of Gun Control on Crimes
- Gun Control Laws in the United States
- The Issue of Gun Control in the US
- Analysis and Criticism of the US Gun Control Laws
- The Problem of Gun Control in Watertown Watertown has experienced many cases of shootings and robbery with violence. The gun control is a significant problem in Watertown and should be addressed by all means possible.
- Gun Control, Self-Defense, and Beneficence to All The annotated bibliography meets all the criteria and helps to reveal the topic of gun control in the USA from different angles.
- Gun Control in the United States The guns are indispensable from the perspective of self-defense that is the stumbling block of firearm ownership in the United States.
- US Gun Policy: Article Credibility and Usefulness The article draws a parallel between the United States and other leading developed economies to paint a clear image of the high number of gun owners in the United States.
- The United States Needs Stricter Gun Control Laws To ensure the safety of citizens, it is necessary to impose stricter laws related to gun control in the United States.
- Gun Control Legislation Should Be Revised The paper states that it is necessary to revise the legislation on arms control. Changes must be made to ensure the good of all US citizens.
- Gun Control Laws Introduced by Executive Branch The executive branch has introduced various laws that guide the citizens. One of the policies involves gun control and has led to endless debates in the country.
- Discussion Board Post: Gun Control Gun control represents a critical set of laws and regulations regarding the control over the civilian population’s proper use, prevention, or restriction of firearms.
- What Can be Done About Gun Control in the US? There are many measures that the US government can imply to overcome the gun problem in the country but there is a high chance they will face public outrage by doing so.
- The Gun Control in the United States The essay discusses the current situation with gun control in the United States and possible measures to improve it.
- The Debate on Gun Control. Law Control While some individuals believe that there is a need for stricter laws, others argue that bearing a legal firearm is a fundamental human right that must be protected.
- The Situation of Gun Control The purpose of this paper is to discuss the issue associated with firearms regulation and examine the situation of gun control in different countries.
- Gun Control Laws Analysis The availability of guns is not the reason for the rise of violence and aggression. People use it for protecting themselves, relaxation.
- Gun Control and Legalization in the USA While some individuals consider the issue of gun control to be a crime, others consider it a rights issue, in addition to being political issue, safety, and racial issue.
- Strengthening Background Checks: The Need to Enhance Firearm Purchase Screening.
- Assault Weapons Ban: Curbing High-Capacity Firearms Proliferation.
- Red Flag Laws: How to Prevent Access to Firearms for Individuals at Risk.
- Closing Gun Show and Online Loopholes: Tightening Sales Regulations.
- Can Mandatory Waiting Periods Reduce Impulsive Firearm Purchases?
- Licensing and Registration as ways to Promote Accountability in Gun Ownership.
- Gun Buyback Programs: How to Encourage Voluntary Firearm Surrender?
- Do Safe Storage Laws Prevent Unauthorized Access to Firearms?
- Gun Control and Domestic Violence Prevention.
- How Strict Should Be Mental Health Evaluations to Ensure Responsible Firearm Ownership?
- Firearm Trafficking and Straw Purchases: Combating Illicit Trade.
- Youth Access to Firearms: Implementing Age Restrictions.
- Gun Control and Suicide Prevention.
- The Role of Gun Control in School Safety Measures.
- Gun Control and Reducing Police Shootings.
- Law Enforcement and Gun Control: Perspectives from the Field.
- International Models of Effective Gun Control Policies.
- Gun Control and Reducing Accidental Firearm Deaths.
- Economic Implications of Gun Violence: Healthcare Costs and Productivity Loss.
- Building Consensus: Finding Common Ground in the Gun Control Debate.
- Individual Liberties and Gun Ownership as a Part of Second Amendment.
- The Efficacy of Gun Control Measures in Reducing Crime Rates.
- Assessing Gun-Free Zones Impact on Public Safety.
- The Role of Firearms Ownership in Self-Defense and Personal Security.
- Firearms as a Deterrent: Examining the Potential of Armed Citizens.
- The Slippery Slope Argument: How Gun Control Can Lead to Further Restrictions.
- Law-Abiding Citizens and the Burden of Stricter Gun Control Laws.
- The Policy Should Target Criminals, Not Law-Abiding Gun Owners.
- Gun Control and the Challenge of Enforcing Regulations.
- Defending Against Tyranny: The Historical Context of the Second Amendment.
- The Cultural Significance of Guns in American Society.
- Concealed Carry Laws: Empowering Citizens for Personal Protection.
- What Are the Root Causes of Gun Violence?
- The Realities of Criminal Access to Firearms.
- Gun Control and its Potential Impact on Minority Communities.
- Law Enforcement Response Time: The Need for Immediate Self-Defense.
- The Role of Gun Ownership in Deterring Home Invasions.
- Major Lessons of International Gun Control Policies.
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Gun-Free Zone Policies.
- Balancing Public Safety with Individual Autonomy: The Ethical Debate.
- Argument of Origin: Gun Control An individual carries many different emotional and physical responses to sociological and economical stress and these stresses can be affected by violence and probable chance of violence.
- The Position of Major Political Parties on Gun Control Gun politics and gun control has been one of the most controversial issues in the United States of America politics.
- The Gun Control Controversy in the Constitutional Context Gun control is a controversial subject. Some argue that U.S. citizens do not need firearms today in the way they did at the time of the country’s founding.
- Gun Control and Safe Firearm Ownership The problem of gun ownership and control in the United States of America has been a controversial issue for many decades.
- Emma Gonzalez Calling for Gun Control Legislation Emma Gonzalez advocates for the enactment of particular laws that will regulate gun sales properly, especially the policies related to effective wellness and background checkups.
- No Gun Control: Dropping Ineffective Measures Gun control has become one of the most debated issues in American society, creating two irreconcilable groups for and against heightened firearm regulation.
- Gun Control Issues and Solution in the US The US is the only developed country with the highest cases of gun violence. Gun ownership is protected by the Constitution. Many states have enacted gun control rules.
- Gun Control Laws in the USA It is important to analyze the essays’ epistemology and to examine the used sources to focus on the discussion of such essay topics as the necessity of gun control laws.
- Gun Control History and Relevant Cases in the US The mass killing of 20 children in Newton, Connecticut and the killing of 9 worshipers at a church in Charleston, California prompted gun-control advocates to reawaken the debate.
- US Gun Control: Losing Freedom or Safeguarding? Gun control has long been among the chief sources of debate in the US. This polarizing topic presents a powerful political tool and extensively used by Democrats and Republicans.
- Problem of the Gun Control Laws Many people die yearly due to handgun linked incidents. The number of casualties who die from gun related accidents, in the country, is much higher compared to other bordering countries.
- Gun Control and Anti-Violence Programs in the USA The USA is known for its high levels of violent crime. The issue of gun control is brought up every time a school shooting or a violent robbery happens.
- US Gun Control Measures and Crime Rates Reduction Gun control is an essential step that will ensure people account for several security aspects as is evident in this discussion.
- American Gun Control Laws: Reasons to Implement Gun control laws can be a necessary precaution that can reduce the risk of homicide. Yet, policy-makers should develop the most optimal strategies for implementing this policy.
- Gun Control in the United States Gun control has become a popular, controversial term, especially in America that covers a broad range of obligations regarding firearms.
- Gun Control: New Restriction Laws New restricting laws to regulate the situation with gun violence can be discussed as effective legitimate steps because they respond to the public’s vision of the problem.
- Gun Control: US Domestic Policy The paper reveals that the relationship between gun ownership and violence in the US is misleading, the government does not have a right to control gun ownership.
- Gun Control and School Shootings The adoption of stricter gun control laws can be useful for reducing the risk of shootings in various educational organizations.
- The Debate Over Gun Control The debate surrounding gun control has two differing sides: the pro-gun control and anti-gun control. This paper focuses on evaluating the two opinions in the gun control debate.
- Why Gun Control Laws Should be Scrapped With all the facts available, we can confidently debunk statements that gun control can indeed reduce crime rates because there is no evidence to prove that claim.
- Political Sciences: Gun Control in the United States This paper underlines the reasons why gun control should be tightened across the United States, because allowing increased access to guns means increased damage to society.
- The Constitution and Gun Control
- Gun Control and Its Effects on Children
- Violence Policy Center Gun Control
- The Dichotomy Over Civilian Gun Control
- Gun Control Laws Should Not Be Regulated for Unnecessary Reasons
- The Current Loose Regulation of Gun Control Laws
- Gun Control and the State of Utah
- Federalists and Early American Gun Control
- Regulating the American Gun Control
- The National Rifle Association on Gun Control
- Liberals Love Gun Control
- Gun Control and the Issue of Violence Among Kids
- America Needs Criminal Control, Not Gun Control
- The Reasoning Behind Gun Control Laws
- Gun Control Firearms Firearm Crime
- Gun Control Pros and Cons in the United States
- The History, Politics, Stakeholders, and Legislation of Gun Control Laws
- Gun Control Laws Hurt the People
- The Need for Strict Gun Control in the United States
- The Gun Control and Ownership Battle in the United States
- The Stricter Gun Control Laws in the United States and Its Efficiency
- The Truth Behind the Demand for More Gun Control
- America Should Have Stricter Gun Control
- Gun Control Crime Rate Police
- The First Federal Gun Control Law
- Arguing Against New Jersey Gun Control Laws
- The Truth About Mass Shootings and Gun Control
- Gun Control Laws Take Guns Away From Law-Abiding Citizens
- American Federalism and Gun Control
- Louisiana Needs Gun Control Laws
- The Three Arguments and Myths of Gun Control
- Gun Control Laws Are Not Strict Enough for Society
- Public Gun Control and the United States
- The Desperate Need for Gun Control
- Gun Control and the Crime Rate
- The Great Gun Control Debate
- Youth and Gun Control
- Opposing Gun Control With the Right to Bear Arms
- Gun Control and the Rights of the Second Amendment
- Gun Control, Good Idea or Bad Idea
- Gun Control and the Federal Government
- Laws, Loopholes, and Gun Control
- Gun Control Has Many Effects in the USA
- Gun Control Should Not Be the Issue in Canada
- The Government and Gun Control
- Gun Control Laws Will Not Reduce Crime
- The Risks and Threats of Carrying Handguns in Society and the Importance of Gun Control
- Gun Control Will Not Reduce Crime
- The Issue and Debate of Gun Control
- Gun Control and the Issue of Owning Firearms
- Too Many Homicides, Too Little Gun Control
- Gun Control and Linkage Mechanisms
- Updating Gun Control Laws
- The Ineffective Gun Control Laws
- The Second Amendment Versus the Idea of Gun Control
- Gun Control Firearms and Freedom
- The Reasons Why Being Pro-gun Control Is Effective in Achieving Peace
- The Argument for Stricter Gun Control Laws
- Gun Control Restricting Rights or Protecting People
- The Pros and Cons of Gun Control in the United States
- Is Gun Control Likely To Reduce Violent Killings?
- What Are the Gun Control Rates in Australia?
- Why Do Experience and Culture Matter in the Gun Control Debate?
- What Are the Early American Origins of Gun Control?
- What Are the Effects and Consequences of Gun Control?
- Are Americans Shifting in the View on Gun Control?
- What Are the Alternative Approaches to the Gun Control Debate?
- Why the Movement for Gun Control in America Is Missing?
- What Is the State Gun Control Advocacy Tactics and Resources?
- Is Gun Control Really About People Control?
- What Is the Attitude Measurement and the Gun Control Paradox?
- How To Use the Issue Crawler to Map Gun Control Issue-networks?
- How To Explain Variation in Gun Control Policy Advocacy Tactics Among Local Organizations?
- What Is Media Influence on Attitudes Toward Guns and Gun Control?
- What Is the Factual Foundation for Certain Key Assumptions of Gun Control?
- Why Media Polls on Gun Control Are Often Unreliable?
- What Are Police Beliefs and Attitudes About Gun Control?
- How Does the News Media Cover Gun Control?
- What Are the Effects of State and Federal Gun Control Laws on School Shootings?
- What Is the Impact of Gun Control Legislation on Suicide?
- Does Gun Control Reduce Crime or Does Crime Increase Gun Control?
- What Are the Effects of Political Culture on Gun Control and Legislation?
- What Are the Effects of Cueing and Framing on Youth Attitudes Towards Gun Control?
- Why Do People Support Gun Control?
- What Is the Blockchain Solution to Gun Control?
- What Is the Ideology of Gun Ownership and Gun Control in the United States?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, March 1). 168 Gun Control Topics & Research Questions. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/gun-control-essay-topics/
"168 Gun Control Topics & Research Questions." StudyCorgi , 1 Mar. 2022, studycorgi.com/ideas/gun-control-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) '168 Gun Control Topics & Research Questions'. 1 March.
1. StudyCorgi . "168 Gun Control Topics & Research Questions." March 1, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/gun-control-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "168 Gun Control Topics & Research Questions." March 1, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/gun-control-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "168 Gun Control Topics & Research Questions." March 1, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/gun-control-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Gun Control were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 21, 2024 .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 10 December 2019
The psychology of guns: risk, fear, and motivated reasoning
- Joseph M. Pierre 1
Palgrave Communications volume 5 , Article number: 159 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
250k Accesses
25 Citations
411 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Politics and international relations
- Social policy
The gun debate in America is often framed as a stand-off between two immutable positions with little potential to move ahead with meaningful legislative reform. Attempts to resolve this impasse have been thwarted by thinking about gun ownership attitudes as based on rational choice economics instead of considering the broader socio-cultural meanings of guns. In this essay, an additional psychological perspective is offered that highlights how concerns about victimization and mass shootings within a shared culture of fear can drive cognitive bias and motivated reasoning on both sides of the gun debate. Despite common fears, differences in attitudes and feelings about guns themselves manifest in variable degrees of support for or opposition to gun control legislation that are often exaggerated within caricatured depictions of polarization. A psychological perspective suggests that consensus on gun legislation reform can be achieved through understanding differences and diversity on both sides of the debate, working within a common middle ground, and more research to resolve ambiguities about how best to minimize fear while maximizing personal and public safety.
Discounting risk
Do guns kill people or do people kill people? Answers to that riddle draw a bright line between two sides of a caricatured debate about guns in polarized America. One side believes that guns are a menace to public safety, while the other believes that they are an essential tool of self-preservation. One side cannot fathom why more gun control legislation has not been passed in the wake of a disturbing rise in mass shootings in the US and eyes Australia’s 1996 sweeping gun reform and New Zealand’s more recent restrictions with envy. The other, backed by the Constitutional right to bear arms and the powerful lobby of the National Rifle Association (NRA), fears the slippery slope of legislative change and refuses to yield an inch while threatening, “I’ll give you my gun when you pry it from my cold, dead hands”. With the nation at an impasse, meaningful federal gun legislation aimed at reducing firearm violence remains elusive.
Despite the 1996 Dickey Amendment’s restriction of federal funding for research on gun violence by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (Rostron, 2018 ), more than 30 years of public health research supports thinking of guns as statistically more of a personal hazard than a benefit. Case-control studies have repeatedly found that gun ownership is associated with an increased risk of gun-related homicide or suicide occurring in the home (Kellermann and Reay, 1986 ; Kellermann et al., 1993 ; Cummings and Koepsell, 1998 ; Wiebe, 2003 ; Dahlberg et al., 2004 ; Hemenway, 2011 ; Anglemeyer et al., 2014 ). For homicides, the association is largely driven by gun-related violence committed by family members and other acquaintances, not strangers (Kellermann et al., 1993 , 1998 ; Wiebe, 2003 ).
If having a gun increases the risk of gun-related violent death in the home, why do people choose to own guns? To date, the prevailing answer from the public health literature has been seemingly based on a knowledge deficit model that assumes that gun owners are unaware of risks and that repeated warnings about “overwhelming evidence” of “the health risk of a gun in the home [being] greater than the benefit” (Hemenway, 2011 ) should therefore decrease gun ownership and increase support for gun legislation reform. And yet, the rate of US households with guns has held steady for two decades (Smith and Son, 2015 ) with owners amassing an increasing number of guns such that the total civilian stock has risen to some 265 million firearms (Azrael et al., 2017 ). This disparity suggests that the knowledge deficit model is inadequate to explain or modify gun ownership.
In contrast to the premise that people weigh the risks and benefits of their behavior based on “rational choice economics” (Kahan and Braman, 2003 ), nearly 50 years of psychology and behavioral economics research has instead painted a picture of human decision-making as a less than rational process based on cognitive short-cuts (“availability heuristics”) and other error-prone cognitive biases (Tversky and Kahneman, 1974 ; Kunda, 1990 ; Haselton and Nettle, 2006 ; Hibert, 2012 ). As a result, “consequentialist” approaches to promoting healthier choices are often ineffective. Following this perspective, recent public health efforts have moved beyond educational campaigns to apply an understanding of the psychology of risky behavior to strike a balance between regulation and behavioral “nudges” aimed at reducing harmful practices like smoking, unhealthy eating, texting while driving, and vaccine refusal (Atchley et al., 2011 ; Hansen et al., 2016 ; Matjasko et al., 2016 ; Pluviano et al., 2017 ).
A similar public health approach aimed at reducing gun violence should take into account how gun owners discount the risks of ownership according to cognitive biases and motivated reasoning. For example, cognitive dissonance may lead those who already own guns to turn a blind eye to research findings about the dangers of ownership. Optimism bias, the general tendency of individuals to overestimate good outcomes and underestimate bad outcomes, can likewise make it easy to disregard dangers by externalizing them to others. The risk of suicide can therefore be dismissed out of hand based on the rationale that “it will never happen to me,” while the risk of homicide can be discounted based on demographic factors. Kleck and Gertz ( 1998 ) noted that membership in street gangs and drug dealing might be important confounds of risk in case control studies, just as unsafe storage practices such as keeping a firearm loaded and unlocked may be another (Kellerman et al., 1993 ). Other studies have found that the homicide risk associated with guns in the home is greater for women compared to men and for non-whites compared to whites (Wiebe, 2003 ). Consequently, white men—by far the largest demographic that owns guns—might be especially likely to think of themselves as immune to the risks of gun ownership and, through confirmation bias, cherry-pick the data to support pre-existing intuitions and fuel motivated disbelief about guns. These testable hypotheses warrant examination in future research aimed at understanding the psychology of gun ownership and crafting public health approaches to curbing gun violence.
Still, while the role of cognitive biases should be integrated into a psychological understanding of attitudes towards gun ownership, cognitive biases are universal liabilities that fall short of explaining why some people might “employ” them as a part of motivated reasoning to support ownership or to oppose gun reform. To understand the underlying motivation that drives cognitive bias, a deeper analysis of why people own guns is required. In the introductory essay to this journal’s series on “What Guns Mean,” Metzl ( 2019 ) noted that public health efforts to reduce firearm ownership have failed to “address beliefs about guns among people who own them”. In a follow-up piece, Galea and Abdalla ( 2019 ) likewise suggested that the gun debate is complicated by the fact that “knowledge and values do not align” and that “these values create an impasse, one where knowing is not enough” (Galea and Abdalla, 2019 ). Indeed, these and other authors (Kahan and Braman, 2003 ; Braman and Kahan, 2006 ; Pierre, 2015 ; Kalesan et al., 2016 ) have enumerated myriad beliefs and values, related to the different “symbolic lives” and “social meanings” of firearms both within and outside of “gun culture” that drive polarized attitudes towards gun ownership in the US. This essay attempts to further explore the meaning of guns from a psychological perspective.
Fear and gun ownership
Modern psychological understanding of human decision-making has moved beyond availability heuristics and cognitive biases to integrate the role of emotion and affect. Several related models including the “risk-as-feelings hypothesis” (Loewenstein et al., 2001 ), the “affect heuristic” (Slovic et al., 2007 ); and the “appraisal-tendency framework” (Lerner et al., 2015 ) illustrate how emotions can hijack rational-decision-making processes to the point of being the dominant influence on risk assessments. Research has shown that “perceived risk judgments”—estimates of the likelihood that something bad will happen—are especially hampered by emotion (Pachur et al., 2012 ) and that different types of affect can bias such judgments in different ways (Lerner et al., 2015 ). For example, fear can in particular bias assessments away from rational analysis to overestimate risks, as well as to perceive negative events as unpredictable (Lerner et al., 2015 ).
Although gun ownership is associated with positive feelings about firearms within “gun culture” (Pierre, 2015 ; Kalesan et al., 2016 ; Metzl, 2019 ), most research comparing gun owners to non-gun owners suggests that ownership is rooted in fear. While long guns have historically been owned primarily for hunting and other recreational purposes, US surveys dating back to the 1990s have revealed that the most frequent reason for gun ownership and more specifically handgun ownership is self-protection (Cook and Ludwig, 1997 ; Azrael et al., 2017 ; Pew Research Center, 2017 ). Research has likewise shown that the decision to obtain a firearm is largely motivated by past victimization and/or fears of future victimization (Kleck et al., 2011 ; Hauser and Kleck, 2013 ).
A few studies have reported that handgun ownership is associated with past victimization, perceived risk of crime, and perceived ineffectiveness of police protection within low-income communities where these concerns may be congruent with real risks (Vacha and McLaughlin, 2000 , 2004 ). However, gun ownership tends to be lower in urban settings and in low-income families where there might be higher rates of violence and crime (Vacha and McLaughlin, 2000 ). Instead, the largest demographic of gun owners in the US are white men living in rural communities who are earning more than $100K/year (Azrael et al., 2017 ). Mencken and Froese ( 2019 ) likewise reported that gun owners tend to have higher incomes and greater ratings of life happiness than non-owners. These findings suggest a mismatch between subjective fear and objective reality.
Stroebe and colleagues ( 2017 ) reported that the specific perceived risk of victimization and more “diffuse” fears that the world is a dangerous place are both independent predictors of handgun ownership, with perceived risk of assault associated with having been or knowing a victim of violent crime and belief in a dangerous world associated with political conservatism. These findings hint at the likelihood that perceived risk of victimization can be based on vicarious sources with a potential for bias, whether through actual known acquaintances or watching the nightly news, conducting a Google search or scanning one’s social media feed, or reading “The Armed Citizen” column in the NRA newsletter The American Rifleman . It also suggests that a general fear of crime, independent of actual or even perceived individual risk, may be a powerful motivator for gun ownership for some that might track with race and political ideology.
Several authors have drawn a connection between gun ownership and racial tensions by examining the cultural symbolism and socio-political meaning of guns. Bhatia ( 2019 ) detailed how the NRA’s “disinformation campaign reliant on fearmongering” is constructed around a narrative of “fear and identity politics” that exploits current xenophobic sentiments related to immigrants. Metzl ( 2019 ) noted that during the 1960s, conservatives were uncharacteristically in favor of gun control when armed resistance was promoted by Malcolm X, the Black Panther Party, and others involved in the Black Power Movement. Today, Metzl argues, “mainstream society reflexively codes white men carrying weapons in public as patriots, while marking armed black men as threats or criminals.” In support of this view, a 2013 study found that having a gun in the home was significantly associated with racism against black people as measured by the Symbolic Racism Scale, noting that “for each 1 point increase in symbolic racism, there was a 50% greater odds of having a gun in the home and a 28% increase in the odds of supporting permits to carry concealed handguns” (O’Brien et al., 2013 ). Hypothesizing that guns are a symbol of hegemonic masculinity that serves to “shore up white male privilege in society,” Stroud ( 2012 ) interviewed a non-random sample of 20 predominantly white men in Texas who had licenses for concealed handgun carry. The men described how guns help to fulfill their identities as protectors of their families, while characterizing imagined dangers with rhetoric suggesting specific fears about black criminals. These findings suggest that gun ownership among white men may be related to a collective identity as “good guys” protecting themselves against “bad guys” who are people of color, a premise echoed in the lay press with headlines like, “Why Are White Men Stockpiling Guns?” (Smith, 2018 ), “Report: White Men Stockpile Guns Because They’re Afraid of Black People” (Harriott, 2018 ), and “Gun Rights Are About Keeping White Men on Top” (Wuertenberg, 2018 ).
Connecting the dots, the available evidence therefore suggests that for many gun owners, fears about victimization can result in confirmation, myside, and optimism biases that not only discount the risks of ownership, but also elevate the salience of perceived benefit, however remote, as it does when one buys a lottery ticket (Rogers and Webley, 2001 ). Indeed, among gun owners there is widespread belief that having a gun makes one safer, supported by published claims that where there are “more guns”, there is “less crime” (Lott, 1998 , 1999 ) as well as statistics and anecdotes about successful defensive gun use (DGU) (Kleck and Gertz, 1995 , 1998 ; Tark and Kleck, 2004 ; Cramer and Burnett, 2012 ). Suffice it to say that there have been numerous debates about how to best interpret this body of evidence, with critics claiming that “more guns, less crime” is a myth (Ayres and Donohue, 2003 ; Moyer, 2017 ) that has been “discredited” (Wintemute, 2008 ) and that the incidence of DGU has been grossly overestimated and pales in comparison to the risk of being threatened or harmed by a gun in the home (Hemenway, 1997 , 2011 ; Cook and Ludwig, 1998 ; Azrael and Hemenway, 2000 ; Hemenway et al., 2000 ). Attempts at objective analysis have concluded that surveys to date have defined and measured DGU inconsistently with unclear numbers of false positives and false negatives (Smith, 1997 ; McDowall et al., 2000 ; National Research Council, 2005 ; RAND, 2018 ), that the causal effects of DGU on reducing injury are “inconclusive” (RAND, 2018 ), and that “neither side seems to be willing to give ground or see their opponent’s point of view” (Smith, 1997 ). With the scientific debate about DGU mirrored in the lay press (Defilippis and Hughes, 2015 ; Kleck, 2015 ; Doherty, 2015 ), a rational assessment of whether guns make owners safer is hampered by a lack of “settled science”. With no apparent consensus, motivated reasoning can pave the way to the nullification of opposing arguments in favor of personal opinions and ideological stances.
For gun owners, even if it is acknowledged that on average successful DGU is much less likely than a homicide or suicide in the home, not having a gun at all translates to zero chance of self-preservation, which are intolerable odds. The bottom line is that when gun owners believe that owning a gun will make them feel safer, little else may matter. Curiously however, there is conflicting evidence that gun ownership actually decreases fears of victimization (Hauser and Kleck, 2013 ; Dowd-Arrow et al., 2019 ). That gun ownership may not mitigate such fears could help to account for why some individuals go on to acquire multiple guns beyond their initial purchase with US gun owners possessing an average of 5 firearms and 8% of owners having 10 or more (Azrael et al., 2017 ).
Gun owner diversity
A psychological model of the polarized gun debate in America would ideally compare those for or against gun control legislation. However, research to date has instead focused mainly on differences between gun owners and non-gun owners, which has several limitations. For example, of the nearly 70% of Americans who do not own a gun, 36% report that they can see themselves owning one in the future (Pew Research Center, 2017 ) with 11.5% of all gun owners in 2015 having newly acquired one in the previous 5 years (Wertz et al., 2018 ). Gun ownership and non-ownership are therefore dynamic states that may not reflect static ideology. Personal accounts such as Willis’ ( 2010 ) article, “I Was Anti-gun, Until I Got Stalked,” illustrate this point well.
With existing research heavily reliant on comparing gun owners to non-gun owners, a psychological model of gun attitudes in the US will have limited utility if it relies solely on gun owner stereotypes based on their most frequent demographic characteristics. On the contrary, Hauser and Kleck ( 2013 ) have argued that “a more complete understanding of the relationship between fear of crime and gun ownership at the individual level is crucial”. Just so, looking more closely at the diversity of gun owners can reveal important details beyond the kinds of stereotypes that are often used to frame political debates.
Foremost, it must be recognized that not all gun owners are conservative white men with racist attitudes. Over the past several decades, women have comprised 9–14% of US gun owners with the “gender gap” narrowing due to decreasing male ownership (Smith and Son, 2015 ). A 2017 Pew Survey reported that 22% of women in the US own a gun and that female gun owners are just as likely as men to belong to the NRA (Pew Research Center, 2017 ). Although the 36% rate of gun ownership among US whites is the highest for any racial demographic, 25% of blacks and 15% of Hispanics report owning guns with these racial groups being significantly more concerned than whites about gun violence in their communities and the US as a whole (Pew Research Center, 2017 ). Providing a striking counterpoint to Stroud’s ( 2012 ) interviews of white gun owners in Texas, Craven ( 2017 ) interviewed 11 black gun owners across the country who offered diverse views on guns and the question of whether owning them makes them feel safer, including if confronted by police during a traffic stop. Kelly ( 2019 ) has similarly offered a self-portrait as a female “left-wing anarchist” against the stereotype of guns owners as “Republicans, racist libertarians, and other generally Constitution-obsessed weirdos”. She reminds us that, “there is also a long history of armed community self-defense among the radical left that is often glossed over or forgotten entirely in favor of the Fox News-friendly narrative that all liberals hate guns… when the cops and other fascists see that they’re not the only ones packing, the balance of power shifts, and they tend to reconsider their tactics”.
Although Mencken and Froese ( 2019 ) concluded that “white men in economic distress find comfort in guns as a means to reestablish a sense of individual power and moral certitude,” their study results actually demonstrated that gun owners fall into distinguishable groups based on different levels of “moral and emotional empowerment” imparted by guns. For example, those with low levels of gun empowerment were more likely to be female and to own long guns for recreational purposes such as hunting and collecting. Other research has shown that the motivations to own a gun, and the degree to which gun ownership is related to fear and the desire for self-protection, also varies according to the type of gun (Stroebe et al., 2017 ). Owning guns, owning specific types of guns (e.g. handguns, long guns, and so-called “military style” semi-automatic rifles like AR-15s), carrying a gun in public, and keeping a loaded gun on one’s nightstand all have different psychological implications. A 2015 study reported that new gun owners were younger and more likely to identify as liberal than long-standing gun owners (Wertz et al., 2018 ). Although Kalesan et al. ( 2016 ) found that gun ownership is more likely among those living within a “gun culture” where ownership is prevalent, encouraged, and part of social life, it would therefore be a mistake to characterize gun culture as a monolith.
It would also be a mistake to equate gun ownership with opposition to gun legislation reform or vice-versa. Although some evidence supports a strong association (Wolpert and Gimpel, 1998 ), more recent studies suggest important exceptions to the rule. While only about 30% of the US population owns a gun, over 70% believes that most citizens should be able to legally own them (Pew Research Center, 2017 ). Women tend to be more likely than men to support gun control, even when they are gun owners themselves (Kahan and Braman, 2003 ; Mencken and Froese, 2019 ). Older (age 70–79) Americans likewise have some of the highest rates of gun ownership, but also the highest rates of support for gun control (Pederson et al., 2015 ). In Mencken and Froese’s study ( 2019 ), most gun owners reporting lower levels of gun empowerment favored bans on semi-automatic weapons and high-capacity magazines and opposed arming teachers in schools. Kahan and Braman ( 2003 ) theorized that attitudes towards gun control are best understood according to a “cultural theory of risk”. In their study sample, those with “hierarchical” and “individualist” cultural orientations were more likely than those with “egalitarian” views to oppose gun control and these perspectives were more predictive than other variables including political affiliation and fear of crime.
In fact, both gun owners and non-owners report high degrees of support for universal background checks; laws mandating safe gun storage in households with children; and “red flag” laws restricting access to firearms for those hospitalized for mental illness or those otherwise at risk of harming themselves or others, those convicted of certain crimes including public display of a gun in a threatening manner, those subject to temporary domestic violence restraining orders, and those on “no-fly” or other watch lists (Pew Research Center, 2017 ; Barry et al., 2018 ). According to a 2015 survey, the majority of the US public also opposes carrying firearms in public spaces with most gun owners opposing public carry in schools, college campuses, places of worship, bars, and sports stadiums (Wolfson et al., 2017 ). Despite broad public support for gun legislation reform however, it is important to recognize that the threat of gun restrictions is an important driver of gun acquisition (Wallace, 2015 ; Aisch and Keller, 2016 ). As a result, proposals to restrict gun ownership boosted gun sales considerably under the Obama administration (Depetris-Chauvin, 2015 ), whereas gun companies like Remington and United Sporting Companies have since filed for bankruptcy under the Trump administration.
A shared culture of fear
Developing a psychological understanding of attitudes towards guns and gun control legislation in the US that accounts for underlying emotions, motivated reasoning, and individual variation must avoid the easy trap of pathologizing gun owners and dismissing their fears as irrational. Instead, it should consider the likelihood that motivated reasoning underlies opinion on both sides of the gun debate, with good reason to conclude that fear is a prominent source of both “pro-gun” and “anti-gun” attitudes. Although the research on fear and gun ownership summarized above implies that non-gun owners are unconcerned about victimization, a closer look at individual study data reveals both small between-group differences and significant within-group heterogeneity. For example, Stroebe et al.’s ( 2017 ) findings that gun owners had greater mean ratings of belief in a dangerous world, perceived risk of victimization, and the perceived effectiveness of owning a gun for self-defense were based on inter-group differences of <1 point on a 7-point Likert scale. Fear of victimization is therefore a universal fear for gun owners and non-gun owners alike, with important differences in both quantitative and qualitative aspects of those fears. Kahan and Braham ( 2003 ) noted that the gun debate is not so much a debate about the personal risks of gun ownership, as it is a one about which of two potential fears is most salient—that of “firearm casualties in a world with insufficient gun control or that of personal defenselessness in a world with excessive control”.
Although this “shared fear” hypothesis has not been thoroughly tested in existing research, there is general support for it based on evidence that fear is an especially potent influence on risk assessment and decision-making when considering low-frequency catastrophic events (Chanel et al., 2009 ). In addition, biased risk assessments have been linked to individual feelings about a specific activity. Whereas many activities in the real world have both high risk and high benefit, positive attitudes about an activity are associated with biased judgments of low risk and high benefit while negative attitudes are associated with biased judgments of high risk and low benefit (Slovic et al., 2007 ). These findings match those of the gun debate, whereby catastrophic events like mass shootings can result in “probability neglect,” over-estimating the likelihood of risk (Sunstein, 2003 ; Sunstein and Zeckhauser, 2011 ) with polarized differences regarding guns as a root cause and gun control as a viable solution. For those that have positive feelings about guns and their perceived benefit, the risk of gun ownership is minimized as discussed above. However, based on findings from psychological research on fear (Loewenstein et al., 2001 ; Slovic et al., 2007 ), the reverse is also likely to be true—those with negative feelings about guns who perceive little benefit to ownership may tend to over-estimate risks. Consistent with this dichotomy, both calls for legislative gun reform, as well as gun purchases increase in the wake of mass shootings (Wallace, 2015 ; Wozniak, 2017 ), with differences primarily predicted by the relative self-serving attributional biases of gun ownership and non-ownership alike (Joslyn and Haider-Markel, 2017 ).
Psychological research has shown that fear is associated with loss of control, with risks that are unfamiliar and uncontrollable perceived as disproportionately dangerous (Lerner et al., 2015 ; Sunstein, 2003 ). Although mass shootings have increased in recent years, they remain extremely rare events and represent a miniscule proportion of overall gun violence. And yet, as acts of terrorism, they occur in places like schools that are otherwise thought of as a suburban “safe spaces,” unlike inner cities where violence is more mundane, and are often given sensationalist coverage in the media. A 2019 Harris Poll found that 79% of Americans endorse stress as a result of the possibility of a mass shooting, with about a third reporting that they “cannot go anywhere without worrying about being a victim” (American Psychological Association, 2019 ). While some evidence suggests that gun owners may be more concerned about mass shootings than non-gun owners (Dowd-Arrow et al., 2019 ), this is again a quantitative difference as with fear of victimization more generally. There is little doubt that parental fears about children being victims of gun violence were particularly heightened in the wake of Columbine (Altheide, 2019 ) and it is likely that subsequent school shootings at Virginia Tech, Sandy Hook Elementary, and Stoneman Douglas High have been especially impactful in the minds of those calling for increasing restrictions on gun ownership. For those privileged to be accustomed to community safety who are less worried about home invasion and have faith in the police to provide protection, fantasizing about “gun free zones” may reflect a desire to recreate safe spaces in the wake of mass shootings that invoke feelings of loss of control.
Altheide ( 2019 ) has argued that mass shootings in the US post-Columbine have been embedding within a larger cultural narrative of terrorism, with “expanded social control and policies that helped legitimate the war on terror”. Sunstein and Zeckhauser ( 2011 ) have similarly noted that following terrorist attacks, the public tends to demand responses from government, favoring precautionary measures that are “not justified by any plausible analysis of expected utility” and over-estimating potential benefits. However, such responses may not only be ineffective, but potentially damaging. For example, although collective anxieties in the wake of the 9/11 terrorist attacks resulted in the rapid implementation of new screening procedures for boarding airplanes, it has been argued that the “theater” of response may have done well to decrease fear without any evidence of actual effectiveness in reducing danger (Graham, 2019 ) while perhaps even increasing overall mortality by avoiding air travel in favor of driving (Sunstein, 2003 ; Sunstein and Zeckhauser, 2011 ).
As with the literature on DGU, the available evidence supporting the effectiveness of specific gun laws in reducing gun violence is less than definitive (Koper et al., 2004 ; Hahn et al., 2005 ; Lee et al., 2017 ; Webster and Wintemute, 2015 ), leaving the utility of gun reform legislation open to debate and motivated reasoning. Several authors have argued that even if proposed gun control measures are unlikely to deter mass shooters, “doing something is better than nothing” (Fox and DeLateur, 2014 ) and that ineffective counter-terrorism responses are worthwhile if they reduce public fear (Sunstein and Zeckhauser, 2011 ). Crucially however, this perspective fails to consider the impact of gun control legislation on the fears of those who value guns for self-protection. For them, removing guns from law-abiding “good guys” while doing nothing to deter access to the “bad guys” who commit crimes is illogical anathema. Gun owners and gun advocates likewise reject the concept of “safe spaces” and regard the notion of “gun free zones” as a liability that invites rather than prevents acts of terrorism. In other words, gun control proposals designed to decrease fear have the opposite of their intended effect on those who view guns as symbols of personal safety, increasing rather than decreasing their fears independently of any actual effects on gun violence. Such policies are therefore non-starters, and will remain non-starters, for the sizeable proportion of Americans who regard guns as essential for self-preservation.
In 2006, Braman and Kahan noted that “the Great American Gun Debate… has convulsed the national polity for the better part of four decades without producing results satisfactory to either side” and argued that consequentialist arguments about public health risks based on cost–benefit analysis are trumped by the cultural meanings of guns to the point of being “politically inert” (Braman and Kahan, 2006 ). More than a decade later, that argument is iterated in this series on “What Guns Mean”. In this essay, it is further argued that persisting debates about the effectiveness of DGU and gun control legislation are at their heart trumped by shared concerns about personal safety, victimization, and mass shootings within a larger culture of fear, with polarized opinions about how to best mitigate those fears that are determined by the symbolic, cultural, and personal meanings of guns and gun ownership.
Coming full circle to the riddle, “Do guns kill people or do people kill people?”, a psychologically informed perspective rejects the question as a false dichotomy that can be resolved by the statement, “people kill people… with guns”. It likewise suggests a way forward by acknowledging both common fears and individual differences beyond the limited, binary caricature of the gun debate that is mired in endless arguments over disputed facts. For meaningful legislative change to occur, the debate must be steered away from its portrayal as two immutable sides caught between not doing anything on the one hand and enacting sweeping bans or repealing the 2nd Amendment on the other. In reality, public attitudes towards gun control are more nuanced than that, with support or opposition to specific gun control proposals predicted by distinct psychological and cultural factors (Wozniak, 2017 ) such that achieving consensus may prove less elusive than is generally assumed. Accordingly, gun reform proposals should focus on “low hanging fruit” where there is broad support such as requiring and enforcing universal background checks, enacting “red flag” laws balanced by guaranteeing gun ownership rights to law-abiding citizens, and implementing public safety campaigns that promote safe firearm handling and storage. Finally, the Dickey Amendment should be repealed so that research can inform public health interventions aimed at reducing gun violence and so that individuals can replace motivated reasoning with evidence-based decision-making about personal gun ownership and guns in society.
Aisch G, Keller J (2016). What happens after calls for new gun restrictions? Sales go up. New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2015/12/10/us/gun-sales-terrorism-obama-restrictions.html . Accessed 19 Nov 2019.
Altheide DL (2019) The Columbine shootings and the discourse of fear. Am Behav Sci 52:1354–1370
Article Google Scholar
American Psychological Association (2019). One-third of US adults say fear of mass shootings prevents them from going to certain places or events. Press release, 15 August 2019. https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/2019/08/fear-mass-shooting . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Anglemeyer A, Horvath T, Rutherford G (2014) The accessibility of firearms and risk for suicide and homicide victimization among household members: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Int Med 160:101–110
Google Scholar
Atchley P, Atwood S, Boulton A (2011) The choice to text and drive in younger drivers: behavior may shape attitude. Accid Anal Prev 43:134–142
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ayres I, Donohue III JJ (2003) Shooting down the more guns, less crime hypothesis. Stanf Law Rev 55:1193–1312
Azrael D, Hemenway D (2000) ‘In the safety of your own home’: results from a national survey on gun use at home. Soc Sci Med 50:285–291
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Azrael D, Hepburn L, Hemenway D, Miller M (2017) The stock and flow of U.S. firearms: results from the 2015 National Firearms Survey. Russell Sage Found J Soc Sci 3:38–57
Barry CL, Webster DW, Stone E, Crifasi CK, Vernick JS, McGinty EE (2018) Public support for gun violence prevention policies among gun owners and non-gun owners in 2017. Am J Public Health 108:878–881
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bhatia R (2019). Guns, lies, and fear: exposing the NRA’s messaging playbook. Center for American Progress. https://www.americanprogress.org/issues/guns-crime/reports/2019/04/24/468951/guns-lies-fear/ . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Braman D, Kahan DM (2006) Overcoming the fear of guns, the fear of gun control, and the fear of cultural politics: constructing a better gun debate. Emory Law J 55:569–607
Cook PJ, Ludwig J (1997). Guns in America: National survey on private ownership and use of firearms. National Institute of Justice. https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles/165476.pdf . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Chanel O, Chichilnisky G(2009) The influence of fear in decisions: Experimental evidence. J Risk Uncertain 39(3):271–298
Article MATH Google Scholar
Cook PJ, Ludwig J (1998) Defensive gun use: new evidence from a national survey. J Quant Criminol 14:111–131
Cramer CE, Burnett D (2012). Tough targets: when criminals face armed resistance from citizens. Cato Institute https://object.cato.org/sites/cato.org/files/pubs/pdf/WP-Tough-Targets.pdf . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Craven J (2017). Why black people own guns. Huffington Post. https://www.huffpost.com/entry/black-gun-ownership_n_5a33fc38e4b040881bea2f37 . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Cummings P, Koepsell TD (1998) Does owning a firearm increase or decrease the risk of death? JAMA 280:471–473
Dahlberg LL, Ikeda RM, Kresnow M (2004) Guns in the home and risk of a violent death in the home: findings from a national study. Am J Epidemiol 160:929–936
Defilippis E, Hughes D (2015). The myth behind defensive gun ownership: guns are more likely to do harm than good. Politico. https://www.politico.com/magazine/story/2015/01/defensive-gun-ownership-myth-114262 . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Depetris-Chauvin E (2015) Fear of Obama: an empirical study of the demand for guns and the U.S. 2008 presidential election. J Pub Econ 130:66–79
Doherty B (2015). How to count the defensive use of guns: neither survey calls nor media and police reports capture the importance of private gun ownership. Reason. https://reason.com/2015/03/09/how-to-count-the-defensive-use-of-guns/ . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Dowd-Arrow B, Hill TD, Burdette AM (2019) Gun ownership and fear. SSM Pop Health 8:100463
Fox JA, DeLateur MJ (2014) Mass shootings in America: moving beyond Newtown. Homicide Stud 18:125–145
Galea S, Abdalla SM (2019) The public’s health and the social meaning of guns. Palgrave Comm 5:111
Graham DA. The TSA doesn’t work—and never has. The Atlantic. https://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2015/06/the-tsa-doesnt-work-and-maybe-it-doesnt-matter/394673/ . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Hahn RA, Bilukha O, Crosby A, Fullilove MT, Liberman A, Moscicki E, Synder S, Tuma F, Briss PA, Task Force on Community Preventive Services (2005) Firearms laws and the reduction of violence: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med 28:40–71
Hansen PG, Skov LR, Skov KL (2016) Making healthy choices easier: regulation versus nudging. Annu Rev Public Health 37:237–51
Harriott M (2018). Report: white men stockpile guns because they’re afraid of black people. The Root. https://www.theroot.com/report-white-men-stockpile-guns-because-they-re-afraid-1823779218 . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Haselton MG, Nettle D (2006) The paranoid optimist: an integrative evolutionary model of cognitive biases. Pers Soc Psychol Rev 10:47–66
Hauser W, Kleck G (2013) Guns and fear: a one-way street? Crime Delinquency 59:271–291
Hemenway (1997) Survey research and self-defense gun use: an explanation of extreme overestimates. J Crim Law Criminol 87:1430–1445
Hemenway D, Azrael D, Miller M (2000) Gun use in the United States: results from two national surveys. Inj Prev 6:263–267
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hemenway D (2011) Risks and benefits of a gun in the home. Am J Lifestyle Med 5:502–511
Hibert M (2012) Toward a synthesis of cognitive biases: how noisy information processing can bias human decision making. Psychol Bull 138:211–237
Joslyn MR, Haider-Markel DP (2017) Gun ownership and self-serving attributions for mass shooting tragedies. Soc Sci Quart 98:429–442
Kahan DM, Braman D (2003) More statistics, less persuasion: a cultural theory of gun-risk perceptions. Univ Penn Law Rev 151:1291–1327
Kalesan B, Villarreal MD, Keyes KM, Galea S (2016) Gun ownership and social gun culture. Inj Prev 22:216–220
Kellermann AL, Reay DT (1986) Protection or peril? An analysis of fire-arm related deaths in the home. N Engl J Med 314:1557–1560
Kellermann AL, Rivara FP, Rushforth NB, Banton JG, Reay DT, Francisco JT, Locci A, Prodzinski J, Hackman BB, Somes G (1993) Gun ownership as a risk factor for homicide in the home. N Engl J Med 329:1084–1091
Kellerman AL, Somes G, Rivara F, Lee R, Banton J (1998) Injuries and deaths due to firearms in the home. J Trauma Inj Infect Crit Care 45:263–267
Kelly K (2019) I’m a left-wing anarchist. Guns aren’t just for right-wingero. Vox. https://www.vox.com/first-person/2019/7/1/18744204/guns-gun-control-anarchism . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Kleck G (2015) Defensive gun use is not a myth: why my critics still have it wrong. Politico. https://www.politico.com/magazine/story/2015/02/defensive-gun-ownership-gary-kleck-response-115082 . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Kleck G, Kovandzic T, Saber M, Hauser W (2011) The effect of perceived risk and victimization on plans to purchase a gun for self-protection. J Crim Justice 39:312–319
Kleck G, Gertz M (1995) Armed resistance to crime: the prevalence and nature of self-defense with a gun. J Crim Law Criminol 86:150–187
Kleck G, Gertz M (1998) Carrying guns for protection: results from the national self-defense survey. J Res Crime Delinquency 35:193–224
Koper CS, Woods DJ, Roth JA (2004) An updated assessment of the federal assault weapons ban: impacts on gun markets and gun violence, 1994–2003. https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/nij/grants/204431.pdf . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Kunda Z (1990) The case for motivated reasoning. Psychol Bull 108:480–498
Lee LK, Fleegler EW, Farrell C, Avakame E, Srinivasan S, Hemenway D, Monuteaux MC (2017) Firearm laws and firearm homicides: a systematic review. JAMA Int Med 177:106–119
Lerner JS, Li Y, Valdesolo P, Kassam KS (2015) Emotion and decision making. Ann Rev Psychol 66:799–823
Loewenstein GF, Weber EU, Hsee CK, Welch N (2001) Risk as feelings. Psychol Bull 127:267–286
Lott JR (1998) More guns, less crime. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Lott JR (1999) More guns, less crime: a response to Ayres and Donohue. Yale Law & Economics Research paper no. 247 https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=248328 . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Matjasko JL, Cawley JH, Baker-Goering M, Yokum DV (2016) Applying behavioral economics to public health policy: illustrative examples and promising directions. Am J Prev Med 50:S13–S19
McDowall D, Loftin C, Presser S (2000) Measuring civilian defensive firearm use: a methodological experiment. J Quant Criminol 16:1–19
Mencken FC, Froese P (2019) Gun culture in action. Soc Prob 66:3–27
Metzl J (2019) What guns mean: the symbolic lives of firearms. Palgrave Comm 5:35
Article ADS Google Scholar
Moyer MW (2017). More guns do not stop more crimes, evidence shows. Sci Am https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/more-guns-do-not-stop-more-crimes-evidence-shows/ . Accessed 19 Nov 2019.
National Research Council (2005) Firearms and violence: a critical review. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
O’Brien K, Forrest W, Lynott D, Daly M (2013) Racism, gun ownership and gun control: Biased attitudes in US whites may influence policy decisions. PLoS ONE 8(10):e77552
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Pachur T, Hertwig R, Steinmann F (2012) How do people judge risks: availability heuristic, affect heuristic, or both? J Exp Psychol Appl 18:314–330
Pederson J, Hall TL, Foster B, Coates JE (2015) Gun ownership and attitudes toward gun control in older adults: reexamining self interest theory. Am J Soc Sci Res 1:273–281
Pew Research Center (2017) America’s complex relationship with guns. https://www.pewsocialtrends.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2017/06/Guns-Report-FOR-WEBSITE-PDF-6-21.pdf . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Pierre JM (2015) The psychology of guns. Psych Unseen. https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/psych-unseen/201510/the-psychology-guns . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Pluviano S, Watt C, Della Salla S (2017) Misinformation lingers in memory: failure of three pro-vaccination strategies. PLoS ONE 23(7):e0811640
RAND (2018) The challenges of defining and measuring defensive gun use. https://www.rand.org/research/gun-policy/analysis/essays/defensive-gun-use.html . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Rogers P, Webley P (2001) “It could be us!”: cognitive and social psychological factors in UK National Lottery play. Appl Psychol Int Rev 50:181–199
Rostron A (2018) The Dickey Amendment on federal funding for research on gun violence: a legal discussion. Am J Public Health 108:865–867
Slovic P, Finucane ML, Peters E, MacGregor DG (2007) The affect heuristic. Eur J Oper Res 177:1333–1352
Smith TW (1997) A call for a truce in the DGU war. J Crim Law Criminol 87:1462–1469
Smith JA (2018) Why are white men stockpiling guns? Sci Am Blogs. https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/observations/why-are-white-men-stockpiling-guns/ . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Smith TW, Son J (2015). General social survey final report: Trends in gun ownership in the United States, 1972–2014. http://www.norc.org/PDFs/GSS%20Reports/GSS_Trends%20in%20Gun%20Ownership_US_1972-2014.pdf . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Stroebe W, Leander NP, Kruglanski AW (2017) Is it a dangerous world out there? The motivational biases of American gun ownership. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 43:1071–1085
Stroud A (2012) Good guys with guns: hegemonic masculinity and concealed handguns. Gend Soc 26:216–238
Sunstein CR (2003) Terrorism and probability neglect. J Risk Uncertain 26:121–136
Sunstein CR, Zeckhauser R (2011) Overreaction to fearsome risks. Environ Resour Econ 48:435–449
Tark J, Kleck G (2004) Resisting crime: the effects of victim action on the outcomes of crimes. Criminol 42:861–909
Tversky A, Kahneman D (1974) Judgment under uncertainty: heuristics and biases. Science 185:1124–1131
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Vacha EF, McLaughlin TF (2000) The impact of poverty, fear of crime, and crime victimization on keeping firearms for protection and unsafe gun-storage practices” A review and analysis with policy recommendations. Urban Educ 35:496–510
Vacha EF, McLaughlin TF (2004) Risky firearms behavior in low-income families of elementary school children: the impact of poverty, fear of crime, and crime victimization on keeping and storing firearms. J Fam Violence 19:175–184
Wallace LN (2015) Responding to violence with guns: mass shootings and gun acquisition. Soc Sci J 52:156–167
Webster DW, Wintemute GJ (2015) Effects of policies designed to keep firearms from high-risk individuals. Ann Rev Public Health 36:21–37
Wertz J, Azrael D, Hemenway D, Sorenson S, Miller M (2018) Differences between new and long-standing US gun owners: results from a National Survey. Am J Public Health 108:871–877
Wiebe DJ (2003) Homicide and suicide risks associated with firearms in the home: a national case-control study. Ann Emerg Med 47:771–782
Willis J (2010). I was anti-gun, until I got stalked. Salon. https://www.salon.com/2010/10/21/buying_gun_protect_from_stalker/ . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Wintemute GJ (2008) Guns, fear, the constitution, and the public’s health. N. Engl J Med 358:1421–1424
Wolfson JA, Teret SP, Azrael D, Miller M (2017) US public opinion on carrying firearms in public places. Am J Public Health 107:929–937
Wolpert RM, Gimpel JG (1998) Self-interest, symbolic politics, and public attitudes toward gun control. Polit Behav 20:241–262
Wozniak KH (2017) Public opinion about gun control post-Sandy Hook. Crim Just Pol Rev 28:255–278
Wuertenberg N (2018). Gun rights are about keeping white men on top. Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/made-by-history/wp/2018/03/09/gun-rights-are-about-keeping-white-men-on-top . Accessed 19 Nov 2019
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Department of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences, Los Angeles, USA
Joseph M. Pierre
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Joseph M. Pierre .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Pierre, J.M. The psychology of guns: risk, fear, and motivated reasoning. Palgrave Commun 5 , 159 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-019-0373-z
Download citation
Received : 30 July 2019
Accepted : 27 November 2019
Published : 10 December 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-019-0373-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Packing heat: on the affective incorporation of firearms.
- Jussi A. Saarinen
Topoi (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
Public Health
Research shows policies that may help prevent mass shootings — and some that don't.

Nell Greenfieldboyce

Demonstrators attend a candlelight vigil Wednesday in Fairfax, Va., for the victims of the Uvalde and Buffalo mass shootings. Allison Bailey/Reuters Connect hide caption
Demonstrators attend a candlelight vigil Wednesday in Fairfax, Va., for the victims of the Uvalde and Buffalo mass shootings.
Every mass shooting in the U.S. raises calls for better policies to prevent such tragedies. There's evidence suggesting that certain kinds of laws may reduce deaths from mass shootings, say scientists who study the field — but those policy options are not the ones usually discussed in the wake of these events.
The body of research scientists have to draw from is limited, notes Michael Anestis , executive director of the New Jersey Gun Violence Research Center at Rutgers University. "Mass shooting research is a very small portion of gun violence research," he says.
That's because mass shootings account for less than 1% of the roughly 40,000 people killed by guns each year in this country, Anestis explains. "They're horrific, they are all too common, and yet, it's just the very tip of the iceberg, right?"
Those researchers who do study gun violence tend to focus on the kinds of violence, like suicide , associated with the most deaths, he says. But, he adds, the entire field of gun violence research has long been neglected and hardly funded.

How The CDC's Reluctance To Use The 'F-Word' — Firearms — Hinders Suicide Prevention
"There is money out there, but it is really far below where it should be given the amount of injury and death and economic costs associated with gun violence," says Anestis. "It's just disproportionally underfunded."
Two approaches worked better than others
Still, some studies have findings about what might prevent mass shootings.
One such study took advantage of the fact that in the U.S., gun laws vary from state to state. "That is, honestly, less than ideal from a public safety standpoint, but it does provide researchers with opportunities," says Daniel Webster , co-director of the Johns Hopkins Center for Gun Violence Solutions.
He and some colleagues recently analyzed more than 30 years of data on shootings in the U.S. that involved four or more victims. They compared states to try to tease out the effect of various gun laws. "I have to acknowledge that this is a really hard and, frankly, inexact science," says Webster.
Despite those limitations, he says, "We did find two policies that had significant protective effects in lowering rates of fatal mass shootings."
One was a requirement that a gun purchaser go through a licensing process. "A licensing process requires someone to, you know, directly apply and engage with law enforcement, sometimes there's safety training and other requirements," says Webster.
Another approach that seemed to reduce deaths from mass shootings was state bans on buying large-capacity magazines or ammunition-feeding devices for semi-automatic weapons.
That makes intuitive sense, says Webster, because these items allow a shooter to fire many bullets in a short amount of time without interruption. If a shooter has to stop and reload, victims could escape or fight back.
There's another study of mass shootings showing that this kind of law seemed to have a protective effect. David Hemenway , director of the Harvard Injury Control Research Center, worked with colleagues to examine the effect of banning large-capacity magazines on almost three decades of mass shootings in different states.
"The states which had bans did much better in terms of having fewer mass shootings, and the mass shootings that occurred were much less lethal in terms of the number of people dying," says Hemenway.
What about background checks or having police at schools?
In the wake of a mass shooting, people often argue for the need for comprehensive background checks, says Webster. He supports that policy but says his research doesn't show that it's linked to a reduction in this particular kind of deadly event.
An additional common refrain after a mass shooting, he says, is a call for policies that make it easier for people to carry guns so they can defend themselves. "Well, guess what, the data do not bear that out at all," says Webster. "If anything, it shows higher rates of fatal mass shootings in response to weaker regulations for concealed carry by civilians."
And while school systems might try to respond to the threat of mass shootings by having police officers on site or having students go through drills, "as far as I know, there's not strong research about any of those things," says Hemenway.
Keeping guns away from young people, whether through safe storage of firearms in a home or age restrictions on purchasing, would be expected to have a protective effect, says Webster, based on data showing that "the peak ages for violent offending with firearms is roughly 18 to 21."
The public health risks associated with young people drinking alcohol inspired a ban on drinking under the age of 21, he says. But the shooter in Uvalde was able to legally buy semi-automatic rifles just after his 18th birthday.
It seems plausible that age restrictions might make it harder for young adults to access weapons capable of creating a mass shooting, says Anestis, but "do we have large data-based resources to evaluate those policies? No, we don't."
One emerging policy option that has some preliminary evidence behind it is allowing police officers to temporarily take guns away from people who seem to pose an imminent danger. A study in California that looked at how this process got used over a two-year period in that state found 21 occasions when it was done in response to threats of a mass shooting — several of which involved schools.
It's not possible to know if taking away those guns actually prevented mass shootings, but researchers say it's still important data given the general dearth of information and limited funding for research. One study in 2017 found that guns killed about as many people each year as sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection, but funding for gun violence research was about 0.7% of that for sepsis.
"There's so many things to study in the gun area, and we've had not nearly enough studies for 25 years," says Hemenway. "Once you scratch the surface right now about what is known, we know so little."
- gun research
- mass shootings
- gun violence
- Share full article
Gun Control, Explained
A quick guide to the debate over gun legislation in the United States.

By The New York Times
As the number of mass shootings in America continues to rise , gun control — a term used to describe a wide range of restrictions and measures aimed at controlling the use of firearms — remains at the center of heated discussions among proponents and opponents of stricter gun laws.
To help understand the debate and its political and social implications, we addressed some key questions on the subject.
Is gun control effective?
Throughout the world, mass shootings have frequently been met with a common response: Officials impose new restrictions on gun ownership. Mass shootings become rarer. Homicides and suicides tend to decrease, too.
After a British gunman killed 16 people in 1987, the country banned semiautomatic weapons like the ones he had used. It did the same with most handguns after a school shooting in 1996. It now has one of the lowest gun-related death rates in the developed world.
In Australia, a 1996 massacre prompted mandatory gun buybacks in which, by some estimates , as many as one million firearms were then melted into slag. The rate of mass shootings plummeted .
Only the United States, whose rate and severity of mass shootings is without parallel outside conflict zones, has so consistently refused to respond to those events with tightened gun laws .
Several theories to explain the number of shootings in the United States — like its unusually violent societal, class and racial divides, or its shortcomings in providing mental health care — have been debunked by research. But one variable remains: the astronomical number of guns in the country.
America’s gun homicide rate was 33 per one million people in 2009, far exceeding the average among developed countries. In Canada and Britain, it was 5 per million and 0.7 per million, respectively, which also corresponds with differences in gun ownership. Americans sometimes see this as an expression of its deeper problems with crime, a notion ingrained, in part, by a series of films portraying urban gang violence in the early 1990s. But the United States is not actually more prone to crime than other developed countries, according to a landmark 1999 study by Franklin E. Zimring and Gordon Hawkins of the University of California, Berkeley. Rather, they found, in data that has since been repeatedly confirmed , that American crime is simply more lethal. A New Yorker is just as likely to be robbed as a Londoner, for instance, but the New Yorker is 54 times more likely to be killed in the process. They concluded that the discrepancy, like so many other anomalies of American violence, came down to guns. More gun ownership corresponds with more gun murders across virtually every axis: among developed countries , among American states , among American towns and cities and when controlling for crime rates. And gun control legislation tends to reduce gun murders, according to a recent analysis of 130 studies from 10 countries. This suggests that the guns themselves cause the violence. — Max Fisher and Josh Keller, Why Does the U.S. Have So Many Mass Shootings? Research Is Clear: Guns.
Every mass shooting is, in some sense, a fringe event, driven by one-off factors like the ideology or personal circumstances of the assailant. The risk is impossible to fully erase.
Still, the record is confirmed by reams of studies that have analyzed the effects of policies like Britain’s and Australia’s: When countries tighten gun control laws, it leads to fewer guns in private citizens’ hands, which leads to less gun violence.
What gun control measures exist at the federal level?
Much of current federal gun control legislation is a baseline, governing who can buy, sell and use certain classes of firearms, with states left free to enact additional restrictions.
Dealers must be licensed, and run background checks to ensure their buyers are not “prohibited persons,” including felons or people with a history of domestic violence — though private sellers at gun shows or online marketplaces are not required to run background checks. Federal law also highly restricts the sale of certain firearms, such as fully automatic rifles.
The most recent federal legislation , a bipartisan effort passed last year after a gunman killed 19 children and two teachers at an elementary school in Uvalde, Texas, expanded background checks for buyers under 21 and closed what is known as the boyfriend loophole. It also strengthened existing bans on gun trafficking and straw purchasing.
— Aishvarya Kavi
Advertisement
What are gun buyback programs and do they work?
Gun buyback programs are short-term initiatives that provide incentives, such as money or gift cards, to convince people to surrender firearms to law enforcement, typically with no questions asked. These events are often held by governments or private groups at police stations, houses of worship and community centers. Guns that are collected are either destroyed or stored.
Most programs strive to take guns off the streets, provide a safe place for firearm disposal and stir cultural changes in a community, according to Gun by Gun , a nonprofit dedicated to preventing gun violence.
The first formal gun buyback program was held in Baltimore in 1974 after three police officers were shot and killed, according to the authors of the book “Why We Are Losing the War on Gun Violence in the United States.” The initiative collected more than 13,000 firearms, but failed to reduce gun violence in the city. Hundreds of other buyback programs have since unfolded across the United States.
In 1999, President Bill Clinton announced the nation’s first federal gun buyback program . The $15 million program provided grants of up to $500,000 to police departments to buy and destroy firearms. Two years later, the Senate defeated efforts to extend financing for the program after the Bush administration called for it to end.
Despite the popularity of gun buyback programs among certain anti-violence and anti-gun advocates, there is little data to suggest that they work. A study by the National Bureau of Economic Research , a private nonprofit, found that buyback programs adopted in U.S. cities were ineffective in deterring gun crime, firearm-related homicides or firearm-related suicides. . Evidence showed that cities set the sale price of a firearm too low to considerably reduce the supply of weapons; most who participated in such initiatives came from low-crime areas and firearms that were typically collected were either older or not in good working order.
Dr. Brendan Campbell, a pediatric surgeon at Connecticut Children’s Medical Center and an author of one chapter in “Why We Are Losing the War on Gun Violence in the United States,” said that buyback programs should collect significantly more firearms than they currently do in order to be more effective.
Dr. Campbell said they should also offer higher prices for handguns and assault rifles. “Those are the ones that are most likely to be used in crime,” and by people attempting suicide, he said. “If you just give $100 for whatever gun, that’s when you’ll end up with all these old, rusted guns that are a low risk of causing harm in the community.”
Mandatory buyback programs have been enacted elsewhere around the world. After a mass shooting in 1996, Australia put in place a nationwide buyback program , collecting somewhere between one in five and one in three privately held guns. The initiative mostly targeted semiautomatic rifles and many shotguns that, under new laws, were no longer permitted. New Zealand banned military-style semiautomatic weapons, assault rifles and some gun parts and began its own large-scale buyback program in 2019, after a terrorist attack on mosques in Christchurch. The authorities said that more than 56,000 prohibited firearms had been collected from about 32,000 people through the initiative.
Where does the U.S. public stand on the issue?
Expanded background checks for guns purchased routinely receive more than 80 or 90 percent support in polling.
Nationally, a majority of Americans have supported stricter gun laws for decades. A Gallup poll conducted in June found that 55 percent of participants were in favor of a ban on the manufacture, possession and sale of semiautomatic guns. A majority of respondents also supported other measures, including raising the legal age at which people can purchase certain firearms, and enacting a 30-day waiting period for gun sales.
But the jumps in demand for gun control that occur after mass shootings also tend to revert to the partisan mean as time passes. Gallup poll data shows that the percentage of participants who supported stricter gun laws receded to 57 percent in October from 66 percent in June, which was just weeks after mass shootings in Uvalde, Texas, and Buffalo. A PDK poll conducted after the shooting at Robb Elementary School in Uvalde found that 72 percent of Republicans supported arming teachers, in contrast with 24 percent of Democrats.
What do opponents of gun control argue?
Opponents of gun control, including most Republican members of Congress, argue that proposals to limit access to firearms infringe on the right of citizens to bear arms enshrined in the Second Amendment to the Constitution. And they contend that mass shootings are not the result of easily accessible guns, but of criminals and mentally ill people bent on waging violence.
— Annie Karni
Why is it so hard to push for legislation?
Polling suggests that Americans broadly support gun control measures, yet legislation is often stymied in Washington, and Republicans rarely seem to pay a political price for their opposition.
The calculation behind Republicans’ steadfast stonewalling of any new gun regulations — even in the face of the kind unthinkable massacres like in Uvalde, Texas — is a fairly simple one for Senator Kevin Cramer of North Dakota. Asked what the reaction would be from voters back home if he were to support any significant form of gun control, the first-term Republican had a straightforward answer: “Most would probably throw me out of office,” he said. His response helps explain why Republicans have resisted proposals such as the one for universal background checks for gun buyers, despite remarkably broad support from the public for such plans — support that can reach up to 90 percent nationwide in some cases. Republicans like Mr. Cramer understand that they would receive little political reward for joining the push for laws to limit access to guns, including assault-style weapons. But they know for certain that they would be pounded — and most likely left facing a primary opponent who could cost them their job — for voting for gun safety laws or even voicing support for them. Most Republicans in the Senate represent deeply conservative states where gun ownership is treated as a sacred privilege enshrined in the Constitution, a privilege not to be infringed upon no matter how much blood is spilled in classrooms and school hallways around the country. Though the National Rifle Association has recently been diminished by scandal and financial turmoil , Democrats say that the organization still has a strong hold on Republicans through its financial contributions and support, hardening the party’s resistance to any new gun laws. — Carl Hulse, “ Why Republicans Won’t Budge on Guns .”
Yet while the power of the gun lobby, the outsize influence of rural states in the Senate and single-voter issues offer some explanation, there is another possibility: voters.
When voters in four Democratic-leaning states got the opportunity to enact expanded gun or ammunition background checks into law, the overwhelming support suggested by national surveys was nowhere to be found. For Democrats, the story is both unsettling and familiar. Progressives have long been emboldened by national survey results that show overwhelming support for their policy priorities, only to find they don’t necessarily translate to Washington legislation and to popularity on Election Day or beyond. President Biden’s major policy initiatives are popular , for example, yet voters say he has not accomplished much and his approval ratings have sunk into the low 40s. The apparent progressive political majority in the polls might just be illusory. Public support for new gun restrictions tends to rise in the wake of mass shootings. There is already evidence that public support for stricter gun laws has surged again in the aftermath of the killings in Buffalo and Uvalde, Texas. While the public’s support for new restrictions tends to subside thereafter, these shootings or another could still produce a lasting shift in public opinion. But the poor results for background checks suggest that public opinion may not be the unequivocal ally of gun control that the polling makes it seem. — Nate Cohn, “ Voters Say They Want Gun Control. Their Votes Say Something Different. ”
Firearm Researcher Surveys
Expert Surveys: Firearm Researchers
Expert Survey 1: Gun in Home & Suicide
Expert Survey 2: Relative Number of Self-defense & Criminal Gun Uses
Expert Survey 3: Concealed Carry Laws & Crime
Expert Survey 4: Gun in Home & Female Homicide Victimization
Expert Survey 5: Safe Storage of Firearm in Home & Suicide
Expert Survey 6: Eddie Eagle Gun Safety Program & Gun Accidents
Expert Survey 7: Does a Gun Make a Home Safer?
Expert Survey 8: Strong Gun Laws & Homicide
Expert Survey 9: Background Checks & Gun Access
Expert Survey 10: Gun on Person Outside Home & Risk of Being Killed
Expert Survey 11: Guns Used in Crime & States’/Nations’ Gun Laws
Expert Survey 12: Guns, Robbery and Burglary
Expert Survey 13: Gun Proliferation, Permissive Gun Policies, & Public Health
Expert Survey 14: Citizens Carrying Firearms & Public Safety
Expert Survey 15: Interpersonal Violent Acts with a Gun by Individuals with Mental Illness
Expert Survey 16: Gun Buyback and Reduction in Violent Deaths (Australia)
Expert Survey 17: Licensed Handgun Purchases and Firearm Violence
Expert Survey 18: Annual Self-Defense Gun Uses
Expert Survey 19: Contagion of Gun Carrying
Expert Survey 20: Improvements in Medical Care
Expert Survey 21: Guns in Community and Safety Perceptions
Every month firearms researchers are asked four questions, in the following format. First, responders are asked to give their level of agreement with a statement: (a) strongly disagree, (b) disagree, (c) neither agree nor disagree, (d) agree, or (e) strongly agree (or “I don’t know”). Respondents are then asked to rate the quality of the scientific evidence about this issue/statement. Then they are asked their level of familiarity with the issue/statement, and finally their area of research (e.g., public health/medicine; sociology/criminology; public policy).
The surveys are conducted on Qualtrics.
Expert firearms researchers were defined as those individuals that 1) publish in peer-reviewed journals and 2) publish specifically about firearms in the public health, public policy, sociology, or criminology literature. Expert researchers were defined as first authors on at least 1 peer-reviewed journal article from 2011 to the present (February 2014). It was felt that including all authors would overweight the public health/medicine area of research since articles there tend to have more authors.
Papers were identified through keyword searches using databases including Web of Science, Sociological Abstracts, Criminal Justice Abstracts and MEDLINE. Authors included scientists from criminology, public health and social science.
In March 2014, a total of 1180 citations were reviewed. The following categories of citations were removed:
- Book reviews
- Case studies
- Articles without a clear author
Certain journal categories were also excluded:
- Law journals – not peer-reviewed
- Forensic journals – it became too subjective to ascertain which forensic articles were relevant (e.g., studies of bullet types in certain crimes)
Certain topics were deemed to be irrelevant based on keywords. These included:
- History articles – e.g., “military history” or “civil war”
- Engineering and manufacturing articles
- Medical treatment articles – e.g., “treatment,” “management,” “procedures”
- Psychology and psychiatry of gun users and victims – e.g., “resilience”
- Different types of guns including nail, air, mole or electron guns
A total of 468 citations were included. Duplicate entries were removed and 358 distinct first authors were found. Of these, a total of 287 working email addresses were found and included in this survey study.
News from the School

Bethany Kotlar, PhD '24, studies how children fare when they're born to incarcerated mothers

Soccer, truffles, and exclamation points: Dean Baccarelli shares his story

Health care transformation in Africa highlighted at conference

COVID, four years in
Hot Topics: Gun Control
Places to start, let's do the numbers, some activist groups, current news.
- School, Youth, and Gang Violence
- Gun Legislation, Controls, and Rights
- Mass Shootings
- Extending Your Research
What's the Issue?
G un control is a much discussed topic in American politics, education and society, and when new mass shootings occur the discussion begins with renewed vigor. Research topics could include looking at mass shootings causes and aftermath, youth and school gun violence, exploring arguments and statistics on both sides of the issue, examining the issue in domestic terror and border control, and researching and comparing the history of gun use and controls in America and other countries.
Librarian, Head of Research & Instruction

- Gun Policy Pew Research Center
- Gun Policy in America Rand
- Gun Violence CQ Researcher Report, August 2022
- U.S. Gun Policy: Global Comparisons Council on Foreign Relations, 2022

- Firearm Mortality Centers for Disease Control
- Firearms in the US - Statistics and facts Statista Dossier
- Guns: In-Depth Gallup
- Key Facts about Americans and Guns Pew Research Center
- Mass Shootings in 2023 Gun Violence Archive
- Violent crime statistics in the US Statista Dossier
- Brady Campaign to Prevent Gun Violence
- Center for Gun Violence Solutions
- Gun Owners of America
- National Association for Gun Rights
- National Rifle Association
- States United to Prevent Gun Violence
- Violence Policy Center
- ABC News: Gun Control
- Huffington Post: Gun Control
- NPR: Gun Control
- PBS News Hour: Gun Control
- US News & World Reports: Gun Control and Gun Rights
Newspaper Databases
- Ethnic NewsWatch
- Global Newsstream This link opens in a new window
- Nexis Uni National and international news
Selected Books
- Next: School, Youth, and Gang Violence >>
- Last Updated: Dec 22, 2023 12:24 PM
- URL: https://libguides.library.umaine.edu/guncontrol
5729 Fogler Library · University of Maine · Orono, ME 04469-5729 | (207) 581-1673
Read our research on: Abortion | Podcasts | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
Gun control and the media, spikes in attention and shifts in conversation.
In the four months since the Newtown, Connecticut shootings, the tone of the conversation about gun control on Twitter has shifted sharply several times in apparent response to ongoing events, according to a Pew Research Center analysis of nearly 21 million tweets from December 18 through April 21.

In that period, the Twitter sentiment overall was almost balanced between those supporting stronger gun control measures (42% of the conversation) and those opposed (38%), according to the report. That is in contrast to the first three days after the December 14 attack when an earlier Pew Research report found that pro-gun control voices dominated their opponents 64% to 21%. But what stands out even more is the fluid nature of the debate on Twitter. In 10 of the 18 weeks studied, assertions favoring tougher regulations outnumbered those opposing; in seven of those weeks, the sentiment against a new law was more prominent. In one of those weeks, the mix was exactly even.
The findings also suggest that while pro-gun control forces dominated in the emotional and painful hours immediately following the attack, over time the conversation shifted to reflect the nation’s more divided view of gun control that has become evident in recent years. At the same time, one of the biggest shifts in Twitter opinion occurred the week of the April 17 Senate vote, when sentiment favoring tougher gun laws outstripped expressions of opposition by 3-1.

One key player opposing tighter gun laws-the National Rifle Association-faced more criticism than support on Twitter. In the four months studied, 58% of the assertions related to the NRA expressed opposition to the group compared with 42% that backed the organization.
Overall, the study found that 60% of the Twitter conversation about guns from December 18-April 21 focused on the legislative debate with another 9% focused on the NRA. Straight news accounts of events made up 26% of the conversation.
This examination of the coverage and conversation surrounding the gun debate also found that President Barack Obama was a key newsmaker and driver of the narrative, with spikes in social and mainstream media attention correlating closely with some of his actions and remarks on behalf of tighter gun control. And an analysis of 20 key terms used in the coverage of the gun issue reveals that two of them -“Newtown” and “gun control”-were clearly the most prominent in the media.
These findings are part of a study by the Pew Research Center that examined the coverage and conversation about gun policy from December 10, 2012-April 21, 2013. That included an examination of nearly 21 million relevant Twitter posts, 20 key gun debate-related phrases in 24 major U.S. newspapers and on 2,090 news programs on cable and broadcast television. In addition, Pew Research analyzed public searches for terms related to the gun debate on Google, using Boolean search techniques. ( See methodology )
The Twitter Conversation
From the day of the Newtown massacre to the defeat of the legislation, the tone of conversation on Twitter shifted a number of times as one side or the other intensified its social presence. The first major shift occurred quickly after the attack as the outpouring of initial support eroded during the week of December 18-23, when 30% of the conversation called for more gun control and 35% opposed it. After two weeks in which tighter gun law supporters once again outnumbered their opponents, another change occurred. From January 7-20, opposition to new gun laws gained prominence with 49% of the conversation compared with 35% that supported new gun legislation. Two events that perhaps rallied anti-gun control voices in that period were the launch of former Congresswoman Gabrielle Giffords’ gun control campaign on January 8 and President Obama’s release of his gun proposals on January 16.
One such tweet in that period asked Second Amendment supporters to join a “Take Control of Gun Control Week” campaign on Facebook. And the NRA itself was busy tweeting that week, noting in one post that “Since the Federal ‘Assault Weapons’ Ban expired in 2004, murder and overall violent-crime rates have fallen.”
The next major shift in sentiment occurred in early February (4-10), when what had been evenly-split sentiment turned strongly in favor of gun control (47% to 35%). That dynamic lasted until the week of March 11-17, when gun control opponents edged ahead of supporters (44% to 41%). That coincided with a time when the legislative process around a new gun law heated up in the Senate.
After sentiments opposing tougher gun laws outnumbered those of supporters in four of the next five weeks, the pendulum swung yet again. During the week of the April 17 Senate vote (April 15-21), supporters of tougher gun control once again dominated the conversation (65% to 21). That 65%-21% margin almost mirrors exactly the sentiments in the first three days after the tragedy, with 64% of the assertions favoring tougher laws and 21% opposing.
The week of the vote also saw a major spike in the volume of the Twitter conversation, with more than two million relevant posts, roughly double of what it had been each of the previous two weeks.
A number of the most frequently retweeted posts at that time were highly critical of the Senate vote. “There should be a background check before the NRA is allowed to buy a senator,” declared one. “Congratulations, felons! The Senate has upheld your right to buy guns without a background check. Send your donations to @NRA ,” read another. A tweet from Obama urged followers to retweet the message, “I am one of the 92% of Americans who support background checks for gun sales.”
While the debate sentiment frequently shifted on Twitter, recent public opinion surveys have found broader public opinion moving away from gun control in recent months. An Associated Press poll released last week found the share of Americans favoring stricter gun laws dropping from 58% to 49% since January. Similarly, a USA Today poll conducted April 18-21 reported 49% of Americans favored a new gun control law while 45% opposed it, a shift from the 61% who supported stricter gun laws back in February. Pew Research will be updating its own trend on this question in the coming weeks, but just reported a related finding that 47% of Americans had a negative view of the Senate’s rejection of new legislation with 39% offering a positive opinion .
Two Terms Dominate the Gun Conversation
One central finding across a number of media outlets is that two terms-“Newtown” and “gun control”-were the most prominent ways the media had of characterizing or discussing the issue.
A Lexis search of 24 newspapers from December 10-April 21 found that “gun control” appeared in 7,245 stories-more than the terms “National Rifle Association” (3,178) “second amendment” (2,047) and “gun rights” (1,421) combined. “Newtown” was second the most frequent term, appearing in 6,175 stories.

In assessing television news coverage on cable and broadcast, Pew Research found that 866 shows out of 2,090 mentioned the term “gun control” barely edging out the term “Newtown,” which appeared on 864 shows. “Gun control” was the leading term on cable news (656 programs out of 1,425) and No. 2 on network broadcast news at 210 shows out of 665. “Newtown” ranked second on cable (605 shows) and first on broadcast at 259.

The Google Trends data reveal the same basic pattern in public searches for key phrases related to the gun debate. “Newtown” represented the most-searched term and was so in every week but one. After that, “gun control” was searched most frequently.
The dominance of these terms highlights the continuing evocation of “Newtown,” the site of the tragedy, as a central catalyst and factor in the ongoing gun control debate. It also suggests that the phrase “gun control,” whether accurately or not, has become a kind of neutral way to reference the ongoing legislative effort in the press narrative and discussion.
Barack Obama as the Central Player
By many different measures, President Obama-who campaigned extensively for tougher gun control laws-was a key driver of the news and conversation on the topic. Overall, Obama’s name was tied to more gun-related search terms than any other individual or Congress in general.
There were several notable spikes in attention that followed a presidential action. One was his December 19 announcement of a Gun Violence Task Force headed by Vice President Joseph Biden. The other was his unveiling of gun control proposals on January 16, which came one day after the NRA released an ad calling him an “elitist hypocrite” because his daughters had Secret Service protection at school.
On Twitter, the biggest week for volume (more than three million relevant posts) was December 18-23, followed by January 14-20 at 2.3 million relevant posts. Obama’s actions on January 16 also corresponded with the biggest week for people searching for the term “gun control” and “Obama gun” on Google. More broadly, the term “Obama gun” was searched almost twice as frequently on Google as the terms “gun Congress” and “gun bill” over the four months studied.

In newspaper stories, these two weeks also showed spikes in volume, according to our search term analysis. The term “gun control” appeared in 861 stories, the week of December 17-23, a high water mark. After that came 741 mentions of that term from January 14-20. The term “gun control” also appeared in the most television news programs the week of December 17-23 (90).
Over the four months studied, only two terms, “gun control” (7,245) and “Newtown” (6,175) appeared in more newspaper stories that included the words “Obama” and “gun” (4,592).
And in all the television news analyzed over four months, “Obama” and “gun” were found to be mentioned in close proximity on more programs (623) than any of the gun related terms other than “Newtown” (864) and “gun control” (866). The National Rifle Association trailed close behind, at 601 programs.

Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
Report Materials
Table of contents, key findings about the online news landscape in america, among u.s. latinos, the internet now rivals television as a source for news, americans’ online news use is closing in on tv news use, 10 facts about the changing digital news landscape, long-form reading shows signs of life in our mobile news world, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

How Asking Gun Control Questions Differently Dramatically Changes the Results: Comparing NPR/PBS versus the Crime Prevention Research Center
Jul 10, 2023 | Original Research , Survey
A survey in May for NPR/PBS NewsHour by Marist had the headline: “ Most Americans say curbing gun violence is more important than gun rights .” The Survey from May 15th through the 18th claimed: “ 6 in 10 say controlling gun violence is more important than protecting gun rights .” The survey asked: “Do you think it is more important to: Protect Gun Rights or Control Gun Violence.” The survey received massive news attention, extensive coverage on public radio and television affiliates nationwide, and other mainstream media such as USA Today and The Hill . The headlines in these other outlets echoed the headlines provided by public radio and television.
But here is the problem, despite gun control advocates being labeled as supporting “safety” and wanting to “reduce violence,” that is something that people on both sides of the debate believe. The way the NPR/PBS framed the question, it isn’t surprising that people respond as they do. SImilarly, you want to ask the question so that only gun ownership is associated with reducing violence?
To try to make the survey more balanced, we reworded the question to ask:
“Which of the following methods do you think is more effective in reducing violent crime?: Enacting stricter gun laws or Allowing people to protect themselves with guns.”
There was another difference in our surveys. The NPR/PBS NewsHour survey by Marist talked to 1,166 registered voters, but our survey looked at a more selective 1,000 likely general election voters with a 95% confidence interval of 3.1%. While the NPR/PBS survey found a large statistically significant gap, with many more people favoring reducing violence than protecting gun rights, our survey showed a statistical tie between the two methods of reducing violent crime.
We re-examined two other questions in the NPR/PBS NewsHour by Marist.
They asked whether people approve of Stand Your Ground laws. Their question read: “Some states have enacted legislation known as ‘stand your ground laws.’ Under those laws, people who are in a public place and believe that their life or safety is in danger are allowed to kill or injure the person who they think is threatening them. Do you approve or disapprove of those laws?”
One critical problem with their question is the phrase: “are allowed to kill or injure the person who they think is threatening them.” That is incorrect. People aren’t allowed to kill or injure someone they think is threatening them. There is a “reasonable person” standard where a reasonable person who believed they were at serious risk of death or injury would be allowed to use force proportional to the harm without retreating as far as possible. That is quite a difference. The NPR/PBS NewsHour survey incorrectly makes it look like a person has much discretion to arbitrarily shot someone and can use much more force than is proportional.
While the NPR/PBS NewsHour survey shows that people support Stand Your Ground laws by 58%-to-40%, they have underestimated support. We instead asked: “Some states have enacted legislation known as ‘stand your ground laws.’ Under these laws, a person who is in a public place and is in a situation where a ‘reasonable person’ would believe that they are at serious risk of death or injury is allowed to use necessary force that is proportional to the harm they face without having to retreat as far as possible. Do you approve or disapprove of these laws?”
With that question, we found that the gap increased from the 18 percentage points that NPR/PBS obtained to the 43 percentage point margin we found. The 66%-to-23% margin in our survey showed that all demographic groups supported Stand Your Ground laws, with even Democrats supporting it by 52%-to-35% and liberals by 54%-to-39%.
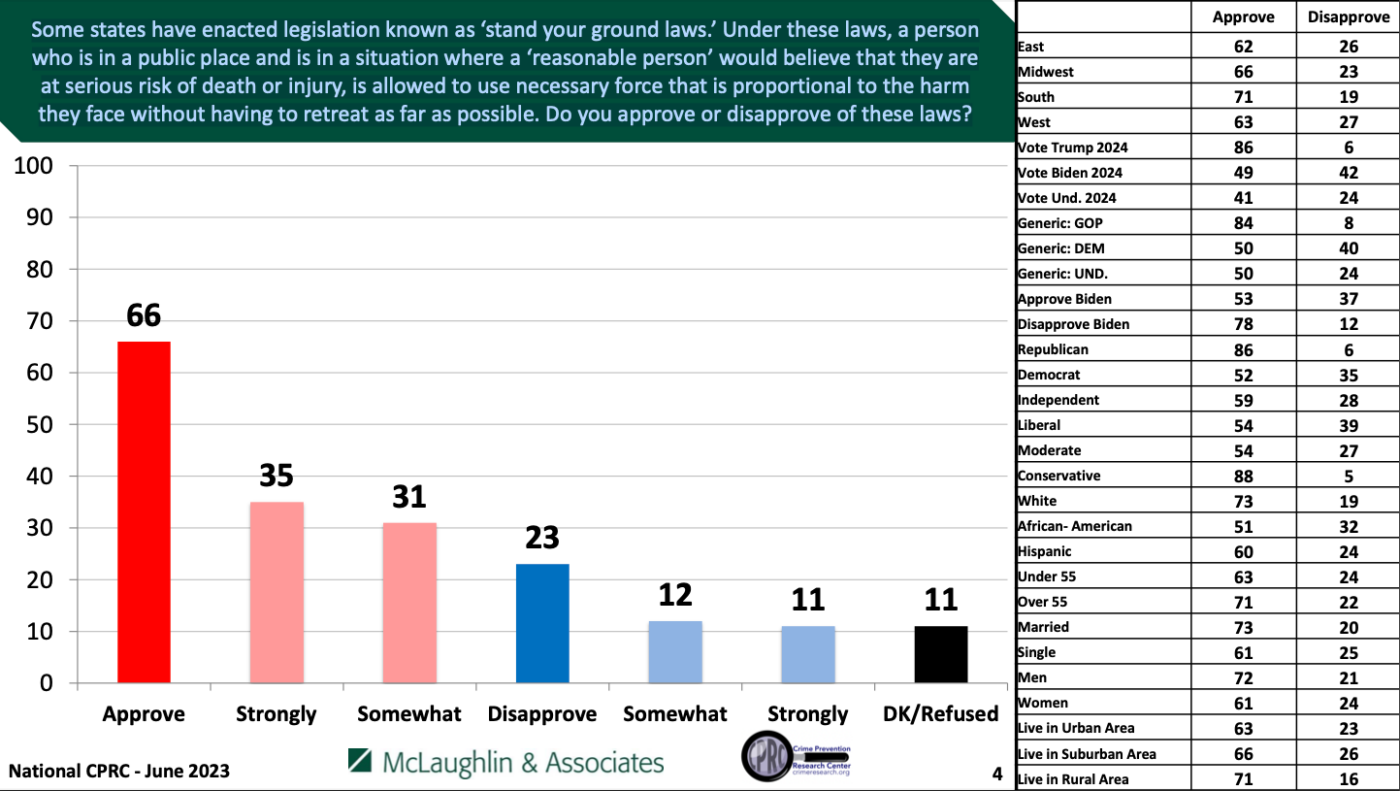
Finally, we redid the NPR/PBS survey question on mass shootings. They asked: “When you hear about a mass shooting in the U.S., is your first reaction: More people need to carry a gun or This country needs stricter gun laws.” And they found that people supported stricter laws by a 62%-to-35% margin. We slightly changed the question: “To allow people to protect themselves with guns or To enact stricter gun laws.”
While we still found that more people supported stricter gun laws, our margin was much smaller. Their gap was 27 percentage points, but ours was just 10 (41%-to-51%), with the standard divided response between Republicans/Democrats, liberals/conservatives, and urban/rural. While our results show a much smaller margin, it is still statistically significant.
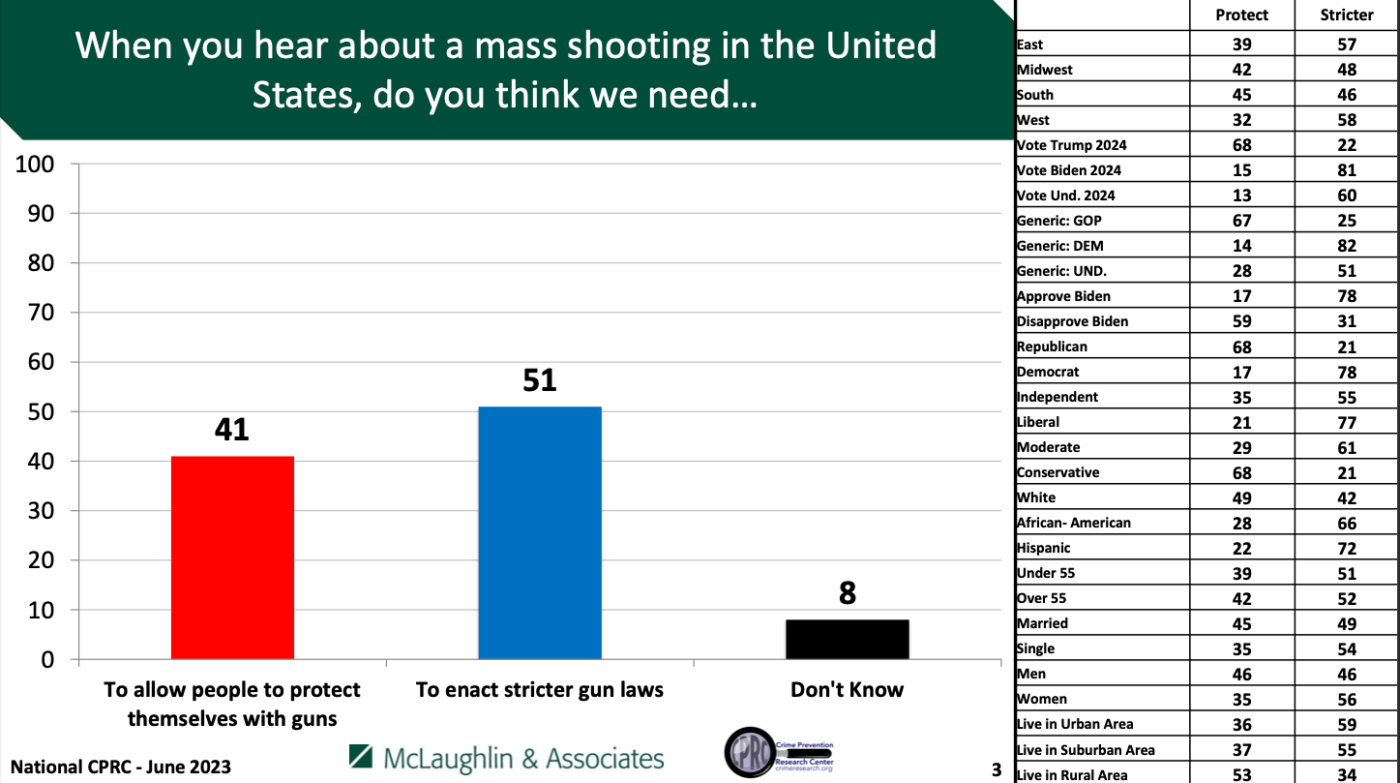
Share this:
Search by Topic
Recent posts, new economist/yougov poll puts guns as tied with civil rights for the 6th most important among usa adults, cprc in the news: reason, the college fix, the tennessee conservative, bearing arms (4), and more, while relatively few democrats, liberals, and the high income people are very concerned about crime, blacks, women, and conservatives are most concerned.
- On Armed American Radio: To Discuss John’s Debate on the Second Amendment at the University of Wisconsin – Madison
- Guy Rivera, who Murdered NYPD Officer Jonathan Diller and Almost Murdered His Partner, was Arrested 21 Times, but Apparently was Only Sentenced Twice
- Amicus Brief
- Assault Weapon Ban
- background checks
- Bail Reform
- Campus carry
- Concealed Handgun Permit Report
- Concealed Handgun Permits
- Constitutional Carry
- Coronavirus
- Criminal Justice System
- Defensive Gun Use
- Democrats supporting the 2nd Amendment
- Early Release of Criminals Parole/Bail
- False Reporting of Crimes
- Gang violence and mass shootings
- Government Corruption
- gun control
- Gun Control Advocates
- Gun Control Laws
- Gun Control Myths
- Gun Free Zones
- Gun law court cases
- gun show regulations
- Guns to fight totalitarianism
- Historical uses of guns
- Illegal Aliens
- Investigative News Piece
- James Craig
- judicial confirmations
- Law Enforcement
- Legislation
- Letters That We Submitted
- Mass Public Killings non-shootings
- mass public shooters supporting gun control
- Mass Public Shootings
- Media Coverage
- Michael Bloomberg
- More Guns, Less Crime
- Original Research
- Political violence
- Prosecutors
- Public Health
- Racist Arguments by Control Advocates
- Red Flag Laws
- Response to Critics
- Second Amendment
- Semi-auto gun ban
- Social Media Censorship
- Stand Your Ground
- technology and crime
- Use of our work in legal cases
- Victim's Rights
- weaponizing government

by johnrlott | Apr 2, 2024 | Survey
Asking whether "guns" are an important issue for Americans is not particularly useful as both those concerned about the right to self-defense and gun control advocates may both answer yes. While a new Economist/YouGov poll (p. 36) from March 24-26, 2024 has guns and...

by johnrlott | Apr 1, 2024 | Media Coverage
Concealed handgun permit holders are “extremely law-abiding” and make up an insignificant portion of violations, John Lott told The Fix via email. The Crime Prevention Research Center president said permit holders are convicted of firearms violations at...
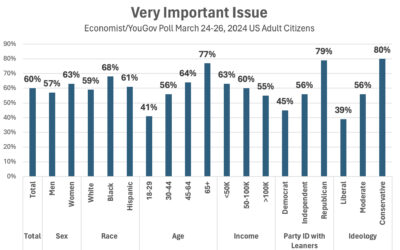
by johnrlott | Mar 31, 2024 | Featured
A new Economist/YouGov poll confirms what we have seen before in surveys: high income people as well as liberals and Democrats are the least concerned about crime, though other surveys also show that those with a graduate school education are also the least concerned....
Press Release
Fraunhofer at the hannover messe 2024, solutions for efficient and trustworthy artificial intelligence.
Research News / April 02, 2024
There is a high demand for AI solutions in industrial applications. These solutions need to be efficient, trustworthy and secure in order to be used in series production or quality control, for example. However, the new possibilities opened up by generative AI also raise questions. Can users rely on what a chatbot says? How can vulnerabilities in an AI model be detected early on during development? At the Hannover Messe 2024, the Fraunhofer Institute for Intelligent Analysis and Information Systems IAIS and the institutes of the Fraunhofer Big Data and Artificial Intelligence Alliance will be presenting two exhibits and several use cases centering on trustworthy AI solutions.

AI offers a wealth of potential for industrial manufacturing, spanning fields such as automation, quality checks, and process optimization. “We are currently receiving a lot of inquiries from companies that have developed AI prototypes and want to put them into series production. To make the scale-up a success, these AI solutions have to be tested systematically so it is also possible to identify vulnerabilities that did not become apparent in the prototype,” explains Dr. Maximilian Poretschkin, Head of AI Assurance and Certification at Fraunhofer IAIS.
Industry attendees at the Hannover Messe 2024 (April 22–26, 2024) can visit the Fraunhofer booth (Booth B24, Hall 2) and explore various exhibits and concrete use cases to learn more about applications and solutions for trustworthy AI and how to incorporate them securely and reliably into their business processes.
Exhibit 1: AI Reliability for Production: Assessment tools for systematic testing of AI models
One such application is a testing tool for AI models used in production or in mechanical and plant engineering. The tool can be used to systematically pinpoint vulnerabilities in AI systems as a way to ensure that they are reliable and robust. “Our methodology is based on specifying the AI system’s scope of application detail. Specifically, we parametrize the space of possible inputs that the AI-system processes and give it a semantic structure. The AI testing tools that we have developed in the KI.NRW flagship project "ZERTIFIZIERTE KI", among others, can then be used to detect weaknesses in AI-systems,” Poretschkin explains.
Fraunhofer and other partners involved in the research project are working to develop assessment methods concerning the quality of AI systems: The AI assessment catalog provides companies with a practically tested guide that enables them to make their AI systems efficient and trustworthy. A recent white paper also addresses the question of how AI applications developed with generative AI and foundation models can be assessed and made secure.
Exhibit 2: “Who’s deciding here?!”: What can artificial intelligence decide — and what decisions can it not yet make?
The collective exhibit titled “Who’s deciding here?!”, which the Fraunhofer BIG DATA AI Alliance will be presenting at the Hannover Messe 2024, is also all about trustworthy AI. The exhibit ties in with the topic of freedom, the theme set by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) for its Science Year in 2024. How do technologies like artificial intelligence influence our freedom to make decisions? How trustworthy are the AI systems that will likely be used increasingly in applications involving sensitive data, such as credit checks?
The exhibit is designed as an interactive game inviting attendees to reflect on everyday uses of AI. Which decisions can we — and do we want to — leave to AI algorithms, and which decisions would be better made ourselves? Major topics here include object recognition in autonomous driving, the risk of discrimination by AI, and identifying fake news. Sebastian Schmidt, a data scientist working on trustworthy AI at Fraunhofer IAIS, explains: “The game lets everyone experience where AI can be a helpful assistant and where it’s better for humans to participate in the decision. The goal is always to arrive at the right decision without taking decision-making authority and independence away from humans.” This year, the interactive exhibit will also be touring on the MS Wissenschaft ship.
Use cases for professional applications
The institutes of the Fraunhofer BIG DATA AI Alliance will also be presenting several real-life applications from various fields. All use cases present the same question: How can AI technology be used safely and securely?
Safe driving: Uncertainty Wrapper
Handling uncertainty reliably is a crucial factor in the use of AI predictions in many fields of application. The Uncertainty Wrapper developed by the Fraunhofer Institute for Experimental Software Engineering IESE checks how certain or uncertain the AI’s output is. Examples include object recognition involving street signs.
Identifying fake news: DisCo
Fake news is spreading like wildfire on social media. Forensic text analysis techniques developed by the Fraunhofer Institute for Secure Information Technology SIT are used to process texts for journalists, highlighting passages that could use a closer look.
Large AI language models for companies: OpenGPT-X
In the OpenGPT-X consortium project funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK), experts from research organizations and the business sector are training large AI language models with as many as 24 European languages under the leadership of Fraunhofer IAIS and IIS. The plan is to make these models available to companies on an open-source basis in the future so they can develop applications based on generative AI and optimize processes.
Trustworthiness of sensitive production data: DigiWeld
This AI solution from the Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA enables machine and plant manufacturers to utilise the benefits of artificial intelligence without having to collect sensitive production data from their customers.
Ethical principles and human-centered AI: the ADA Lovelace Center
At the ADA Lovelace Center for Analytics, Data and Applications by Fraunhofer IIS, researchers are working on human-centred and ethical issues. In particular, a social and behavioural science approach is used to explain why people accept AI (or not) and what consequences its use has for the individual.
AI research for German technological sovereignty
Through all these solutions, the Fraunhofer researchers are making an important contribution to unlocking the potential of AI in the real world. “The current development of generative AI is a prime example of the huge potential and the many challenges surrounding this forward-looking technology in terms of security, transparency, and privacy. Many of the technologies and solutions we see today originate outside Europe. The research done by the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft is helping to maintain and grow the technological sovereignty and independence of German companies,” says Dr. Sonja Holl-Supra, Managing Director of the Fraunhofer BIG DATA AI Alliance, which comprises over 30 Fraunhofer institutes and brings together Fraunhofer’s expertise across the field of AI.
The AI Act recently adopted by the European Parliament also provides for AI assessments. Assessment tools developed for this purpose can help implement this requirement.
Attendees can visit the joint Fraunhofer booth (Booth B24, Hall 2) at the Hannover Messe 2024 (April 22–26, 2024) to explore the exhibit centering on the reliability of AI in production, the interactive game “Who’s deciding here?!” and Fraunhofer’s solutions for trustworthy AI.
- Research News April 2024 - Solutions for efficient and trustworthy artificial intelligence [ PDF 0.23 MB ]
- Fraunhofer Institute for Intelligent Analysis and Information Systems IAIS (iais.fraunhofer.de)
- Digital Press Kit for the Hannover Messe 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The report identifies key questions in 10 dimensions of gun violence: 1) Firearm suicide. 2) Community-based gun violence. 3) Intimate partner violence. 4) Shootings by law enforcement. 5) Mass shootings. 6) Unintentional shootings. 7) Impacts of lawful gun ownership. 8) Gun access during high-risk periods.
Other recent polls on gun control vary. A Pew Research Center poll released in April 2021 found a narrower majority — 53 percent — supported stricter laws, while a March 2021 Morning Consult-Politico tracking poll found that 64 percent of American voters generally supported more gun control, versus 28 percent who said they were opposed.
Mass shootings happen all over the country. Killers used a semi-automatic handgun in 75% of incidents, which is about the same percentage as the 72% in overall gun violence. Killers used an ...
There has already been some research on state-level gun control policies. For example, after Connecticut passed a law requiring gun purchasers to first obtain a license, one study found that gun ...
The CDC initiated a gun-violence research program in the 1980s, but in 1996, influenced by the pro-gun National Rifle Association, Congress adopted the Dickey Amendment, which banned the use of government research funding to advocate for gun control, and cut the CDC budget by $2.6 million, which happened to be the budget of the gun-violence ...
Opponents of more restrictive measures of gun control turn to research demonstrating that a majority of gun crimes are committed by offenders ... and firearm crime"—and support for general gun control using a convenience sample of college students (p. 33). The authors found an inverse relationship between gun knowledge and support for ...
For example, gun buyback programs may raise awareness of guns and gun violence in a community but have not been shown to reduce mortality (Makarios & Pratt, 2012). Such data can inform policy. President Obama's January 2013 executive orders about gun violence include directing the CDC to research the causes and prevention of gun violence.
Focus In with Research Question. Gun control is a complex issue that involves crime, legislation, and the Constitution. You could concentrate on one issue and do in-depth research on that, or use several of the questions below to focus more generally on the topic of gun control or gun violence. Is gun violence a serious problem in America?
Recent incidents of gun violence have raised questions about public access to "military-style" firearms and the need for more-restrictive forms of gun control. Proponents of more-restrictive forms of gun regulation argue that such measures will help combat the disproportionately high rates of gun crime in the United States. Opponents believe that such measures infringe upon constitutional ...
This eBook from 2019 examines the controversies surrounding gun control in the U.S., which, it asserts, are about whether to prioritize the traditional values of rugged independence or newer values of communitarian interdependence. Gun Legislation. The library's collection of eBooks on U.S. legislation on guns.
168 Gun Control Topics & Research Questions. In this gun control topics compilation, we offer a polarizing discourse surrounding firearms regulations. Gun control is a complex and contentious issue encompassing discussions about individual rights, public safety, and the role of government in citizen welfare.
Evaluating. individuals' attitudes about gun control is a valuable way to change policy and to enact. legislation that might make neighborhoods and the country a safer place. After studying the data. and completing the interviews, there is no universal response people have after losing a loved one to gun violence.
For example, of the nearly 70% of Americans who do not own a gun, 36% report that they can see themselves owning one in the future (Pew Research Center, 2017) with 11.5% of all gun owners in 2015 ...
One study in 2017 found that guns killed about as many people each year as sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection, but funding for gun violence research was about 0.7% of that for sepsis.
Much of current federal gun control legislation is a baseline, governing who can buy, sell and use certain classes of firearms, with states left free to enact additional restrictions.. Dealers ...
Harvard Injury Control Research Center ... Every month firearms researchers are asked four questions, in the following format. First, responders are asked to give their level of agreement with a statement: (a) strongly disagree, (b) disagree, (c) neither agree nor disagree, (d) agree, or (e) strongly agree (or "I don't know ...
5 Questions: A Constitutional Expert Discusses Gun Control. As the country mourned 49 deaths in the worst mass shooting in U.S. history and wondered what could have been done to prevent the tragedy, Democrats and Republicans introduced gun-safety measures in the Senate. Opponents, led by the National Rifle Association, cite the second amendment ...
G un control is a much discussed topic in American politics, education and society, and when new mass shootings occur the discussion begins with renewed vigor. Research topics could include looking at mass shootings causes and aftermath, youth and school gun violence, exploring arguments and statistics on both sides of the issue, examining the ...
And an analysis of 20 key terms used in the coverage of the gun issue reveals that two of them -"Newtown" and "gun control"-were clearly the most prominent in the media. These findings are part of a study by the Pew Research Center that examined the coverage and conversation about gun policy from December 10, 2012-April 21, 2013.
Research questions for gun control may include inquiries into the effectiveness of different gun control policies, the impact of gun violence on public health, and the relationship between gun ownership and crime rates. 1. How does gun control impact crime rates? Research suggests that stricter gun control measures can lead to lower rates of ...
A survey in May for NPR/PBS NewsHour by Marist had the headline: "Most Americans say curbing gun violence is more important than gun rights."The Survey from May 15th through the 18th claimed: "6 in 10 say controlling gun violence is more important than protecting gun rights."The survey asked: "Do you think it is more important to: Protect Gun Rights or Control Gun Violence."
Solutions for efficient and trustworthy artificial intelligence. There is a high demand for AI solutions in industrial applications. These solutions need to be efficient, trustworthy and secure in order to be used in series production or quality control, for example. However, the new possibilities opened up by generative AI also raise questions.