

COMM 101: Fundamentals of Public Speaking - Valparaiso
- Delivery Skills
- Stage Fright
- Body Language / Non-Verbal Communication
- Listening Skills
- Quotation Resources
- Speech Outline Examples
- Speech Examples
- More Speech Examples
- Presentation Options
- Citation Resources This link opens in a new window
A basic speech outline should include three main sections:
- The Introduction -- This is where you tell them what you're going to tell them.
- The Body -- This is where you tell them.
- The Conclusion -- This is where you tell them what you've told them.
- Speech Outline Formatting Guide The outline for a public speech, according to COMM 101 online textbook The Public Speaking Project , p.p. 8-9.
Use these samples to help prepare your speech outlines and bibliographies:
- Sample Speech Preparation Outline This type of outline is very detailed with all the main points and subpoints written in complete sentences. Your bibliography should be included with this outline.
- Sample Speech Speaking Outline This type of outline is very brief and uses phrases or key words for the main points and subpoints. This outline is used by the speaker during the speech.
- << Previous: Quotation Resources
- Next: Informative Speeches >>
- Last Updated: Sep 22, 2023 4:37 PM
- URL: https://library.ivytech.edu/Valpo_COMM101
- Ask-a-Librarian
- [email protected]
- (219) 464-8514 x 3021
- Library staff | Find people
- Library Guides
- Student Life & Activities
- Testing Services
- B&N Bookstore

How to Write an Effective Speech Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide
- The Speaker Lab
- March 8, 2024
Table of Contents
Mastering the art of speaking starts with crafting a stellar speech outline. A well-structured outline not only clarifies your message but also keeps your audience locked in.
In this article, you’ll learn how to mold outlines for various speech types, weaving in research that resonates and transitions that keep listeners on track. We’ll also show you ways to spotlight crucial points and manage the clock so every second counts. When it’s time for final prep, we’ve got smart tips for fine-tuning your work before stepping into the spotlight.
Understanding the Structure of a Speech Outline
An effective speech outline is like a map for your journey as a speaker, guiding you from start to finish. Think of it as the blueprint that gives shape to your message and ensures you hit all the right notes along the way.
Tailoring Your Outline for Different Speech Types
Different speeches have different goals: some aim to persuade, others inform or celebrate. Each type demands its own structure in an outline. For instance, a persuasive speech might highlight compelling evidence while an informative one focuses on clear explanations. Crafting your outline with precision means adapting it to fit these distinct objectives.
Incorporating Research and Supporting Data
Your credibility hinges on solid research and data that back up your claims. When writing your outline, mark the places where you’ll incorporate certain pieces of research or data. Every stat you choose should serve a purpose in supporting your narrative arc. And remember to balance others’ research with your own unique insights. After all, you want your work to stand out, not sound like someone else’s.
The Role of Transitions in Speech Flow
Slick transitions are what turn choppy ideas into smooth storytelling—think about how bridges connect disparate land masses seamlessly. They’re not just filler; they carry listeners from one thought to another while maintaining momentum.
Incorporate transitions that feel natural yet keep people hooked. To keep things smooth, outline these transitions ahead of time so nothing feels left up to chance during delivery.
Techniques for Emphasizing Key Points in Your Outline
To make certain points pop off the page—and stage—you’ll need strategies beyond bolding text or speaking louder. Use repetition wisely or pause strategically after delivering something significant. Rather than go impromptu, plan out what points you want to emphasize before you hit the stage.
Timing Your Speech Through Your Outline
A watchful eye on timing ensures you don’t overstay—or undercut—your moment under the spotlight. The rhythm set by pacing can be pre-determined through practice runs timed against sections marked clearly in outlines. Practice will help ensure that your grand finale isn’t cut short by surprise.
What Type Of Speaker Are You?
Click below to discover your Speaker Archetype and how to start getting booked and paid to speak!
Depending on the type of speech you’re giving, your speech outline will vary. The key ingredients—introduction, body, and conclusion—are always there, but nuances like tone or message will change with each speaking occasion.
Persuasive Speeches: Convincing With Clarity
When outlining a persuasive speech, arrange your arguments from strong to strongest. The primacy effect works wonders here, so make sure to start off with a strong point. And just when they think they’ve heard it all, hit them with an emotional story that clinches the deal.
You might start by sharing startling statistics about plastic pollution before pivoting to how individuals can make a difference. Back this up with data on successful recycling programs which demonstrate tangible impact, a technique that turns facts into fuel for action.
Informative Speeches: Educating Without Overwhelming
An informative speech shouldn’t feel like drinking from a fire hose of facts and figures. Instead, lay out clear subtopics in your outline and tie them together with succinct explanations—not unlike stepping stones across a stream of knowledge.
If you’re talking about breakthroughs in renewable energy technology, use bullet points to highlight different innovations then expand upon their potential implications one at a time so the audience can follow along without getting lost in technical jargon or complexity.
Ceremonial Speeches: Creating Moments That Matter
In a ceremonial speech you want to capture emotion. Accordingly, your outline should feature personal anecdotes and quotes that resonate on an emotional level. However, make sure to maintain brevity because sometimes less really is more when celebrating milestones or honoring achievements.
Instead of just going through a hero’s whole life story, share the powerful tales of how they stepped up in tough times. This approach hits home for listeners, letting them feel the impact these heroes have had on their communities and sparking an emotional bond.
Incorporating Research in Your Speech Outline
When you’re crafting a speech, the backbone of your credibility lies in solid research and data. But remember, it’s not just about piling on the facts. It’s how you weave them into your narrative that makes listeners sit up and take notice.
Selecting Credible Sources
Finding trustworthy sources is like going on a treasure hunt where not all that glitters is gold. To strike real gold, aim for academic journals or publications known for their rigorous standards. Google Scholar or industry-specific databases are great places to start your search. Be picky. Your audience can tell when you’ve done your homework versus when you’ve settled for less-than-stellar intel.
You want to arm yourself with evidence so compelling that even skeptics start nodding along. A well-chosen statistic from a reputable study does more than decorate your point—it gives it an ironclad suit of armor.
Organizing Information Effectively
Your outline isn’t just a roadmap; think of it as scaffolding that holds up your argument piece by piece. Start strong with an eye-opening factoid to hook your audience right off the bat because first impressions matter—even in speeches.
To keep things digestible, group related ideas together under clear subheadings within your outline. Stick to presenting data that backs up each key idea without wandering down tangential paths. That way, everyone stays on track.
Making Data Relatable
Sure, numbers don’t lie but they can be hard to connect to. If you plan on using stats in your speech, make them meaningful by connecting them to relatable scenarios or outcomes people care about deeply. For instance, if you’re talking health statistics, relate them back to someone’s loved ones or local hospitals. By making the personal connection for your audience, you’ll get their attention.
The trick is using these nuggets strategically throughout your talk, not dumping them all at once but rather placing each one carefully where its impact will be greatest.
Imagine your speech as a road trip. Without smooth roads and clear signs, the journey gets bumpy, and passengers might miss the scenery along the way. That’s where transitions come in. They’re like your speech’s traffic signals guiding listeners from one point to another.
Crafting Seamless Bridges Between Ideas
Transitions are more than just linguistic filler. They’re strategic connectors that carry an audience smoothly through your narrative. Start by using phrases like “on top of this” or “let’s consider,” which help you pivot naturally between points without losing momentum.
To weave these seamlessly into your outline, map out each major turn beforehand to ensure no idea is left stranded on a tangent.
Making Use of Transitional Phrases Wisely
Be cautious: overusing transitional phrases can clutter up your speech faster than rush hour traffic. Striking a balance is key—think about how often you’d want to see signposts on a highway. Enough to keep you confident but not so many that it feels overwhelming.
Pick pivotal moments for transitions when shifting gears from one major topic to another or introducing contrasting information. A little direction at critical junctures keeps everyone onboard and attentive.
Leveraging Pauses as Transition Tools
Sometimes silence speaks louder than words, and pauses are powerful tools for transitioning thoughts. A well-timed pause lets ideas resonate and gives audiences time to digest complex information before moving forward again.
This approach also allows speakers some breathing room themselves—the chance to regroup mentally before diving into their next point with renewed vigor.
Connecting Emotional Threads Throughout Your Speech
Last but not least, don’t forget emotional continuity, that intangible thread pulling heartstrings from start-to-finish. Even if topics shift drastically, maintaining an underlying emotional connection ensures everything flows together cohesively within the larger tapestry of your message.
Techniques for Emphasizing Key Points in Your Speech Outline
When you’re crafting your speech outline, shine a spotlight on what matters most so that your audience doesn’t miss your key points.
Bold and Italicize for Impact
You wouldn’t whisper your punchline in a crowded room. Similarly, why let your main ideas get lost in a sea of text? Use bold or italics to give those lines extra weight. This visual cue signals importance, so when you glance at your notes during delivery, you’ll know to emphasize those main ideas.
Analogies That Stick
A good analogy is like super glue—it makes anything stick. Weave them into your outline and watch as complex concepts become crystal clear. But remember: choose analogies that resonate with your target audience’s experiences or interests. The closer home it hits, the longer it lingers.
The Power of Repetition
If something’s important say it again. And maybe even once more after that—with flair. Repetition can feel redundant on paper, but audiences often need to hear critical messages several times before they take root.
Keep these strategies in mind when you’re ready to dive into your outline. You’ll transform those core ideas into memorable insights before you know it.
Picture this: you’re delivering a speech, and just as you’re about to reach the end, your time’s up. Ouch! Let’s make sure that never happens. Crafting an outline is not only about what to say but also how long to say it.
Finding Balance in Section Lengths
An outline isn’t just bullet points; it’s a roadmap for pacing. When outlining your speech, make sure to decide how much time you’d like to give each of your main points. You might even consider setting specific timers during rehearsals to get a real feel for each part’s duration. Generally speaking, you should allot a fairly equal amount of time for each to keep things balanced.
The Magic of Mini Milestones
To stay on track, a savvy speaker will mark time stamps or “mini milestones” on their outline. These time stamps give the speaker an idea of where should be in their speech by the time, say, 15 minutes has passed. If by checkpoint three you should be 15 minutes deep and instead you’re hitting 20 minutes, it’s time to pick up the pace or trim some fat from earlier sections. This approach helps you stay on track without having to glance at the clock after every sentence.
Utilizing Visual Aids and Multimedia in Your Outline
Pictures speak louder than words, especially when you’re on stage. Think about it: How many times have you sat through a presentation that felt like an eternity of endless bullet points? Now imagine if instead, there was a vibrant image or a short video clip to break up the monotony—it’s game-changing. That’s why integrating visual aids and multimedia into your speech outline isn’t just smart. It’s crucial for keeping your audience locked in.
Choosing Effective Visuals
Selecting the right visuals is not about flooding your slides with random images but finding those that truly amplify your message. Say you’re talking about climate change. In this case, a graph showing rising global temperatures can hit hard and illustrate your chosen statistic clearly. Remember, simplicity reigns supreme; one powerful image will always trump a cluttered collage.
Multimedia Magic
Videos are another ace up your sleeve. They can deliver testimonials more powerfully than quotes or transport viewers to places mere descriptions cannot reach. But be warned—timing is everything. Keep clips short and sweet because no one came to watch a movie—they came to hear you . You might highlight innovations using short video snippets, ensuring these moments serve as compelling punctuations rather than pauses in your narrative.
The Power of Sound
We often forget audio when we think multimedia, yet sound can evoke emotions and set tones subtly yet effectively. Think striking chords for dramatic effect or nature sounds for storytelling depth during environmental talks.
Audiences crave experiences they’ll remember long after they leave their seats. With well-chosen visuals and gripping multimedia elements woven thoughtfully into every section of your speech outline, you’ll give them exactly that.
Rehearsing with Your Speech Outline
When you’re gearing up to take the stage, your speech outline is a great tool to practice with. With a little preparation, you’ll give a performance that feels both natural and engaging.
Familiarizing Yourself with Content
To start off strong, get cozy with your outline’s content. Read through your outline aloud multiple times until the flow of words feels smooth. This will help make sure that when showtime comes around, you can deliver those lines without tripping over tough transitions or complex concepts.
Beyond mere memorization, understanding the heart behind each point allows you to speak from a place of confidence. You know this stuff—you wrote it. Now let’s bring that knowledge front and center in an authentic way.
Mimicking Presentation Conditions
Rehearsing under conditions similar to those expected during the actual presentation pays off big time. Are you going to stand or roam about? Will there be a podium? Think about these details and simulate them during rehearsal because comfort breeds confidence—and we’re all about boosting confidence.
If technology plays its part in your talk, don’t leave them out of rehearsals either. The last thing anyone needs is tech trouble during their talk.
Perfecting Pace Through Practice
Pacing matters big time when speaking. Use timed rehearsals to nail down timing. Adjust speed as needed but remember: clarity trumps velocity every single time.
You want people hanging onto every word, which is hard to do if you’re talking so fast they can barely make out what you’re saying. During rehearsals, find balance between pacing and comprehension; they should go hand-in-hand.
Finalizing Your Speech Outline for Presentation
You’ve poured hours into crafting your speech, shaping each word and idea with precision. Now, it’s time to tighten the nuts and bolts. Finalizing your outline isn’t just about dotting the i’s and crossing the t’s. It’s about making sure your message sticks like a perfectly thrown dart.
Reviewing Your Content for Clarity
Your first task is to strip away any fluff that might cloud your core message. Read through every point in your outline with a critical eye. Think of yourself as an editor on a mission to cut out anything that doesn’t serve a purpose. Ask yourself if you can explain each concept clearly without needing extra words or complex jargon. If not, simplify.
Strengthening Your Argument
The meat of any good presentation lies in its argument, the why behind what you’re saying. Strengthen yours by ensuring every claim has iron-clad backing—a stat here, an expert quote there. Let this be more than just facts tossed at an audience; weave them into stories they’ll remember long after they leave their seats.
Crafting Memorable Takeaways
Audiences may forget details but never how you made them feel—or think. Embed memorable takeaways throughout your outline so when folks step out into fresh air post-talk, they carry bits of wisdom with them.
This could mean distilling complex ideas down to pithy phrases or ending sections with punchy lines that resonate. It’s these golden nuggets people will mine for later reflection.
FAQs on Speech Outlines
How do you write a speech outline.
To craft an outline, jot down your main ideas, arrange them logically, and add supporting points beneath each.
What are the 3 main parts of a speech outline?
An effective speech has three core parts: an engaging introduction, a content-rich body, and a memorable conclusion.
What are the three features of a good speech outline?
A strong outline is clear, concise, and structured in logical sequence to maximize impact on listeners.
What is a working outline for a speech?
A working outline serves as your blueprint while preparing. It’s detailed but flexible enough to adjust as needed.
Crafting a speech outline is like drawing your map before the journey. It starts with structure and flows into customization for different types of talks. Remember, research and evidence are your compass—they guide you to credibility. Transitions act as bridges, connecting one idea to another smoothly. Key points? They’re landmarks so make them shine.
When delivering your speech, keep an eye on the clock and pace yourself so that every word counts.
Multimedia turns a good talk into a great show. Rehearsing polishes that gem of a presentation until it sparkles.
Last up: fine-tuning your speech outline means you step out confident, ready to deliver something memorable because this isn’t just any roadmap—it’s yours.
- Last Updated: March 5, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
- Speech Crafting →
Preparation: How to write a Speech Outline (with Examples)

You have been chosen to give a speech on a particular topic and you reckon that you’re a good speech writer.
However, without a good speech outline, your speech lacks the proper skeleton to put meat on.
A speech outline is to a speech what a blueprint is to an unconstructed building.
So, how do you develop a good speech outline? First, break it down into small steps as this will make it easier for you to prioritize your ideas and organize them in the right order before you add more details to them.
How to Make an Outline for a Speech
Below are steps that will enable you to write an effective speech outline for your presentation.
You should start by asking yourself:
a) What is the big picture?
Before you begin writing your outline, you should take a step back and think about your speech as a whole.

First, think about the 3 keystones for your presentation or speech, i.e. the audience, your subject matter and of course, you, as the speaker.
Then, write a few notes down about each keystone and how they relate with each other. For instance,
- With regard to your presentation’s subject matter and the audience, what does the audience know about the subject? Do they find the subject interesting or not at all? Is the subject relevant to them?
- What do you as the speaker know about the subject in question? What are the reasons behind your presentation? Do you have any expertise on the matter? What new information will you be sharing with your audience?
A good outline will help you engage with your audience in a way that not only captures their attention but enables them to understand the subject matter.
b) What is your objective?
This refers to the goal of your presentation. Here, you should ask yourself, what do you want your audience to do after your presentation is over?

While the objective for most speakers is for their audience to know something, that may not be enough. The best presentations and speeches are those that move people to act.
If you would prefer to make an impact in such a way, then you should ensure that you are as specific as you can be when deciding on your objective in your speech outline.
c) What is your message?
Your message is what holds your presentation or speech together. This is not to mean that you shouldn’t have different parts in your speech, but it does mean that your speech should have one message that you are trying to put across.

Trying to include several different messages in your speech may confuse your audience, which makes it harder for them to understand the main point you are trying to convey.
To do this, summarize the message of your presentation in one statement. This will not only allow you to understand the message in its entirety but also allow you to explain the message to your audience in a way that is easy to understand.
You can now use the statement you wrote above to help you develop your speech outline. Using the statement to determine whether a certain point supports your main message will ensure that your speech flows and doesn’t include any information not relevant to your subject topic.
d) How is your presentation relevant?
When it comes to a presentation or speech, the audience should always come first. That is why as a speaker, you should always keep your audience in mind when presenting.
If you have already decided on the message you will be conveying to your audience, you should now ask yourself; how is your message relevant to the audience?

If you can’t come up with a reason why your presentation is relevant, then it’s back to the drawing board for you. This could mean that you will be presenting to the wrong audience or you will be giving the wrong presentation.
You can refer back to step (c) then review steps (a) and (b) for clarity.
e) Your speech structure
This is a very important part of your presentation as without it, your speech will have no impact on the audience. Therefore, you should ensure that you include the speech structure in your speech outline.
A structure has 3 basic parts; the introduction, the body and the conclusion. It should be noted though that when working on your speech outline, a common suggestion is to begin with the body before developing both your introduction and conclusion.

Under your speech structure, the introduction is the opening of your speech/presentation. To make a good first impression on your audience, ensure that your introduction is strong.
This doesn’t have to be the usual, “Good morning, my name is YXZ…” Instead, capture your audience’s attention by either telling a story or an interesting fact, recite a quote, ask your audience to recall or imagine something or even ask a rhetorical question!
Related: How to Start a Speech to Engage Your Audience
The body of your presentation represents the bulk of your speech. You should therefore ensure that your main points can be explained in detail and that they have been organized in a logical order that makes your message easy to comprehend.
Similar to your introduction, you should finish on a strong note when it comes to your conclusion. You can do this by linking your conclusion to your introduction, after which you can then echo and summarize your message’s main points.
Different Speech Outline Examples
Below are a few examples of different speech outlines that you can use as a basis to write your own outline. Choosing the right one that works for you may depend on the type of speech you will be giving .
1. Persuasive Speech Outline
Persuasive presentations and speeches usually have a specific purpose in mind; either to urge the audience to take action on something or persuade them to adopt a certain view or opinion of something.

This type of outline allows you, the speaker, to focus on the subject matter point while arguing your case in the most effective and compelling way to your audience.
A persuasive speech outline is made up of these parts:
- An introduction
- The conclusion
- Source Citation
The first three parts are common in most if not all presentations; please refer to step (e) to familiarize yourself with them once more.
A source citation is simply citing the sources for the research and facts that you presented in your speech. Remember you are trying to persuade your audience, so authoritative sources add weight to your argument.
2. Informative Speech Outline
There are different types of informative outlines. These include:
- The informative speech outline
- The informative presentation outline
- The informative essay outline
These outlines are made up of 3 basic parts; the introduction, body and conclusion. For purposes of this article, we will be discussing the informative speech outline.
The central objective of an informative speech is to offer unique, useful and interesting information to your audience. Before choosing your informative speech topic , you should consider your overall objective.

Additionally, there are various types of informative speeches , including:
- Concept - These are used to discuss abstract ideas like ideas and theories.
- Process - These are used when describing broad processes.
- Event - These are used to explain things that may happen, are already happening or those that have happened already.
- Object - These are used when talking about products, places or people.
In addition to this, there are patterns that can be used to organize your speech outline. These will be chosen depending on your speech type.
Types of these patterns include:
- Chronological or sequential - This pattern deals with a sequence of events; which could be useful in demonstration speeches or when discussing historical topics
- Spatial or geographic - Use this pattern when discussing topics that deal with physical spaces
- Logical - This pattern is suitable for a broad topic that has been broken down into sub-topics.
- Advantage-disadvantage - This pattern can be used when you will be examining a range of negative and positive aspects of an event or idea
Furthermore, there are 2 possibilities for preparing a speech outline; the speaking and preparation outline.
The speaking outlines make use of phrases and keywords, which helps keep you focused on the subject matter while the preparation outline is used to help you develop your speech and makes use of full sentences.
3. Demonstrative Speech Outline
A demonstrative speech is an instructional speech that teaches the audience something by demonstrating the process.

Here are the basic steps for a demonstrative speech:
- Ask yourself why you choose this topic and why it is important to the audience
- Provide an overview
- Explain the steps involved in your process
- Talk about variations, other options
- Ensure you allot time for Q&A
- Give a brief summary
For a more in-depth guide on writing demonstrative speeches, click here .
Pro-Tip: Write down the specific purpose of your speech and your topic of discussion as you formulate your generic speech outline.
Conclusion: On Speech Outline Formats
As you become better at writing and delivering speeches, you will soon learn that the different outline formats described above aren’t mutually exclusive. Rather, situations often make it necessary to mix different formats.
What are you waiting for? Go out there and grow your confidence as a speech writer and speaker!
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Student Speech Examples
This section provides examples of student outlines and speeches. Use these to help inform your choices as you begin formatting your informative, persuasive, and/or commemorative speeches.
Fundamentals of Public Speaking Copyright © by Katie Gruber is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
- Speechwriting
How to Write a Speech Outline
Last Updated: January 3, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Emily Listmann is a private tutor in San Carlos, California. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 505,230 times.
A speech outline can increase your confidence and help you keep your place so you sound authoritative and in control. As you write your speech outline, focus on how you'll introduce yourself and your topic, the points you'll cover, and the interests of your audience.
Sample Outline and Writing Help

Crafting Your Introduction

- Keep in mind you may be nervous when you start your speech. Include this in your outline so you won't forget.
- If there's anything about you that relates you to your audience, or to the group that organized the event, you want to include that in your brief greeting as well – especially if you didn't have the benefit of an introduction from someone else.
- For example, you might say "Good afternoon. I'm Sally Sunshine, and I've been a volunteer with the Springfield Animal Society for five years. I'm honored they've invited me to speak here today about the importance of spaying or neutering your pets."

- When choosing your attention-getter, keep your audience in mind. Think about what would grab their attention – not necessarily what you personally find interesting or humorous.
- If you're not sure whether your attention-getter will work, try practicing it in front of friends or family members who are similar in age and interests to the people who will be in the audience when you give your speech.
- For example, if you're giving a speech on spaying and neutering pets to a group of suburban families, you might open with a humorous reference to the Disney movie "101 Dalmatians."

- Briefly explain the importance of the topic or issue you'll be discussing in your speech.
- If your speech is an informative one, explain why the information is important or relevant to your audience.
- For argumentative speeches, explain what might happen if action isn't taken on the issue.
- For example, you might say "Every year, our local animal shelter has to put down 500 unwanted cats and dogs. If all pets were spayed and neutered, it's estimated this number would decrease to under 100."

- If you're giving an argumentative speech, your thesis statement will be a statement of the ultimate point you hope to prove through the information and evidence you lay out in your speech.
- For example, the thesis statement for a speech arguing that all pet owners should spay or neuter their pets might be "Our entire community would benefit if all pets were spayed or neutered."
- The thesis statement for a more informative speech will simply summarize the type of information you're going to provide the audience through your speech.
- For a more scientific speech, your thesis statement will reflect the hypothesis of the scientific study you're presenting in your speech.

- If you're giving a speech for a class in school, your "credibility" may be as simple as the fact that you took the class and researched the topic.
- However, if you have a more personalized interest in the topic of your speech, this is a good time to mention that.
- For an argumentative speech, a personal connection to the subject matter can enhance your credibility. For example, maybe you're giving a speech about local urban housing policy and you became interested in the topic when you learned your family was facing eviction. A personal connection often can mean more to members of your audience than extensive professional experience in the area.

- There's no hard and fast rule, but speeches typically have three main points. You should list them in your introduction in the order you plan to present them in your speech. The order in which you discuss your points depends on the type of speech you're giving.
- For example, your speech on spaying or neutering pets might address the benefits to the pet first, then the benefit to the pet's family, then the benefit to the community at large. This starts small and moves outward.
- For an argumentative speech, you typically want to lead with your strongest argument and work down in order of strength.
- If you're giving an informative speech based on a historical event, you may want to provide your points chronologically. Other informative speeches may be better served by starting with the broadest point and moving to more narrow points.
- Ultimately, you want to order your points in a way that feels natural to you and will enable you to easily transition from one point to another.
Building the Body of Your Speech

- Your first point will be a top-level entry on your outline, typically noted by a Roman numeral.
- Beneath that top-level, you will have a number of sub-points which are comments, statistics, or other evidence supporting that point. Depending on how your outline is formatted, these typically will be letters or bullet points.

- As with the points themselves, with your evidence you typically want to start with the strongest or most important sub-point or piece of evidence and move down. This way, if you start running short on time, you can easily cut the last points without worrying that you're leaving out something important.
- The type of evidence or sub-points you'll want to include will depend on the type of speech you're giving.
- Try to avoid pounding your audience with long series of numbers or statistics – they typically won't retain the information. If you have a significant amount of numerical data or statistics, creating an infographic you can project during your presentation may be more useful.
- Keep in mind that additional personal stories or anecdotes can be particularly effective to get your point across in a speech.
- For example, if your first point in your speech about spaying or neutering pets is that the procedure benefits the pets themselves, you might point out that pets that are spayed or neutered live longer, are at a decreased risk for certain types of cancer, and are generally more healthy than pets who aren't spayed or neutered.

- Avoid over-thinking your transition. It really doesn't need to be incredibly sophisticated. If you can't come up with anything specific, using a simple transitional phrase will work fine.
- For example, you might say "Now that I've discussed how spaying and neutering has a positive effect on your pet's health, I want to move to the effect that spaying and neutering has on your family."
- Some of the most effective transitions turn on a particular word or phrase, such as the word "effect" in the example above.

- When choosing your sub-points or the facts that you want to emphasize in your speech, keep your audience in mind as well as the overall point. Think about what's important to them, or what they potentially would find most surprising or most interesting.
Creating Your Closing

- This transition doesn't need to be fancy – it doesn't even have to be a whole sentence. You can simply say "In conclusion," and then launch into your summary.

- You don't need to go into detail here – you're just reinforcing what you've already told your audience.
- Make sure you don't introduce any new information in your closing summary.
- For example, you might say "As you've seen, spaying or neutering your pet has substantial benefits not only for you and your pet, but also for the community at large."

- If your speech went well, you have fully proven your thesis and demonstrated its importance. This statement should relate back to the summary of your points and present a strong statement.
- Particularly for brief speeches, you can even combine your summary of points with your thesis statement in a single sentence that wraps up your speech.
- For example, you might say "Given the benefits to your pet's health, to your family, and to the overall well-being of your community, it is clear that spaying or neutering pets should be a top priority for all pet owners."

- You may want to think of a way to bring the entire speech back around to that story you initially told to grab your audience's attention.
- If you have an argumentative or similar speech, your closing lines typically will include a call to action. Give your audience an example of how important the subject of your speech is, and implore them to act on the information you gave them in a specific way.
- When making a call to action, make sure you include specific details, such as where to go, who to contact, and when to act.
- For example, you might say "For the next week, the Springfield Animal Society will be spaying and neutering pets for free at their clinic on 123 Main Street. Call 555-555-5555 to make an appointment for your furry friend today!"

- Particularly if your speech was longer or if you went over the time allotted, be sure to tell them that you appreciate their time.
- As with your initial greeting, including this in your outline ensures you won't forget it in the moment. That doesn't mean you should try to write something verbatim. Rather, you should focus on your thanks being more off-the-cuff and sincere.

- If you want to establish parameters for the questions, be sure to list these in your outline so you can mention them when you announce that you're open for questions.
- Anticipate questions that may be asked dependent on your speech topic. Preemptively answer those questions and include them in your outline.
- You also should note if you only have a specified period of time for questions, or if you're only taking a set number of questions.
Community Q&A
- Outlines can vary in how formal or informal you make them. You could either make it a full script or use shorthand with highlighted main points. Use the outline that works best for you. Thanks Helpful 11 Not Helpful 0
- Use a large font that you can easily read by glancing down. Print your outline and place it on a desk, then stand and look down at the paper. If it's too small or you find yourself leaning over to read it, increase the font size. Thanks Helpful 15 Not Helpful 3
- If you're giving the speech for a class, you may need to turn in an outline of your speech that follows particular content or format requirements. Review your assignment carefully and turn in an outline that follows your instructor's requirements, even if you decide to use a slightly different outline when you give your speech. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/speech-introductions
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/thesis_statement_tips.html
- ↑ https://lewisu.edu/writingcenter/pdf/final-developing-a-speech-outline.pdf
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/speech-evidence
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/publicspeaking/chapter/10-2-keeping-your-speech-moving/
About This Article

The best way to write a speech outline is to write the main points of your greeting and introduction in the first section, including your name and what you’ll be talking about. Then, make a second section with bullet points of all the important details you want to mention in the body of your speech. Make sure to include facts and evidence to back your argument up. Finish your outline with a section that summarizes your points concisely. To learn how to keep your audience's attention throughout your speech, keep reading below! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Ren Solomon
Oct 1, 2018
Did this article help you?

Erick Villegas
Sep 21, 2017
Fernando Patino
Nov 19, 2018
Tristan Doell
Oct 12, 2017
Nov 23, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples
March 17, 2021 - Gini Beqiri
A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything – voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on.
A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing you come across as trustworthy and knowledgeable about the topic you’re discussing.
So, how do you start convincing a group of strangers to share your opinion? And how do you connect with them enough to earn their trust?
Topics for your persuasive speech
We’ve made a list of persuasive speech topics you could use next time you’re asked to give one. The topics are thought-provoking and things which many people have an opinion on.
When using any of our persuasive speech ideas, make sure you have a solid knowledge about the topic you’re speaking about – and make sure you discuss counter arguments too.
Here are a few ideas to get you started:
- All school children should wear a uniform
- Facebook is making people more socially anxious
- It should be illegal to drive over the age of 80
- Lying isn’t always wrong
- The case for organ donation
Read our full list of 75 persuasive speech topics and ideas .

Preparation: Consider your audience
As with any speech, preparation is crucial. Before you put pen to paper, think about what you want to achieve with your speech. This will help organise your thoughts as you realistically can only cover 2-4 main points before your audience get bored .
It’s also useful to think about who your audience are at this point. If they are unlikely to know much about your topic then you’ll need to factor in context of your topic when planning the structure and length of your speech. You should also consider their:
- Cultural or religious backgrounds
- Shared concerns, attitudes and problems
- Shared interests, beliefs and hopes
- Baseline attitude – are they hostile, neutral, or open to change?
The factors above will all determine the approach you take to writing your speech. For example, if your topic is about childhood obesity, you could begin with a story about your own children or a shared concern every parent has. This would suit an audience who are more likely to be parents than young professionals who have only just left college.
Remember the 3 main approaches to persuade others
There are three main approaches used to persuade others:
The ethos approach appeals to the audience’s ethics and morals, such as what is the ‘right thing’ to do for humanity, saving the environment, etc.
Pathos persuasion is when you appeal to the audience’s emotions, such as when you tell a story that makes them the main character in a difficult situation.
The logos approach to giving a persuasive speech is when you appeal to the audience’s logic – ie. your speech is essentially more driven by facts and logic. The benefit of this technique is that your point of view becomes virtually indisputable because you make the audience feel that only your view is the logical one.
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos: 3 Pillars of Public Speaking and Persuasion
Ideas for your persuasive speech outline
1. structure of your persuasive speech.
The opening and closing of speech are the most important. Consider these carefully when thinking about your persuasive speech outline. A strong opening ensures you have the audience’s attention from the start and gives them a positive first impression of you.
You’ll want to start with a strong opening such as an attention grabbing statement, statistic of fact. These are usually dramatic or shocking, such as:
Sadly, in the next 18 minutes when I do our chat, four Americans that are alive will be dead from the food that they eat – Jamie Oliver
Another good way of starting a persuasive speech is to include your audience in the picture you’re trying to paint. By making them part of the story, you’re embedding an emotional connection between them and your speech.
You could do this in a more toned-down way by talking about something you know that your audience has in common with you. It’s also helpful at this point to include your credentials in a persuasive speech to gain your audience’s trust.

Obama would spend hours with his team working on the opening and closing statements of his speech.
2. Stating your argument
You should pick between 2 and 4 themes to discuss during your speech so that you have enough time to explain your viewpoint and convince your audience to the same way of thinking.
It’s important that each of your points transitions seamlessly into the next one so that your speech has a logical flow. Work on your connecting sentences between each of your themes so that your speech is easy to listen to.
Your argument should be backed up by objective research and not purely your subjective opinion. Use examples, analogies, and stories so that the audience can relate more easily to your topic, and therefore are more likely to be persuaded to your point of view.
3. Addressing counter-arguments
Any balanced theory or thought addresses and disputes counter-arguments made against it. By addressing these, you’ll strengthen your persuasive speech by refuting your audience’s objections and you’ll show that you are knowledgeable to other thoughts on the topic.
When describing an opposing point of view, don’t explain it in a bias way – explain it in the same way someone who holds that view would describe it. That way, you won’t irritate members of your audience who disagree with you and you’ll show that you’ve reached your point of view through reasoned judgement. Simply identify any counter-argument and pose explanations against them.
- Complete Guide to Debating
4. Closing your speech
Your closing line of your speech is your last chance to convince your audience about what you’re saying. It’s also most likely to be the sentence they remember most about your entire speech so make sure it’s a good one!
The most effective persuasive speeches end with a call to action . For example, if you’ve been speaking about organ donation, your call to action might be asking the audience to register as donors.
Practice answering AI questions on your speech and get feedback on your performance .
If audience members ask you questions, make sure you listen carefully and respectfully to the full question. Don’t interject in the middle of a question or become defensive.
You should show that you have carefully considered their viewpoint and refute it in an objective way (if you have opposing opinions). Ensure you remain patient, friendly and polite at all times.
Example 1: Persuasive speech outline
This example is from the Kentucky Community and Technical College.
Specific purpose
To persuade my audience to start walking in order to improve their health.
Central idea
Regular walking can improve both your mental and physical health.
Introduction
Let’s be honest, we lead an easy life: automatic dishwashers, riding lawnmowers, T.V. remote controls, automatic garage door openers, power screwdrivers, bread machines, electric pencil sharpeners, etc., etc. etc. We live in a time-saving, energy-saving, convenient society. It’s a wonderful life. Or is it?
Continue reading
Example 2: Persuasive speech
Tips for delivering your persuasive speech
- Practice, practice, and practice some more . Record yourself speaking and listen for any nervous habits you have such as a nervous laugh, excessive use of filler words, or speaking too quickly.
- Show confident body language . Stand with your legs hip width apart with your shoulders centrally aligned. Ground your feet to the floor and place your hands beside your body so that hand gestures come freely. Your audience won’t be convinced about your argument if you don’t sound confident in it. Find out more about confident body language here .
- Don’t memorise your speech word-for-word or read off a script. If you memorise your persuasive speech, you’ll sound less authentic and panic if you lose your place. Similarly, if you read off a script you won’t sound genuine and you won’t be able to connect with the audience by making eye contact . In turn, you’ll come across as less trustworthy and knowledgeable. You could simply remember your key points instead, or learn your opening and closing sentences.
- Remember to use facial expressions when storytelling – they make you more relatable. By sharing a personal story you’ll more likely be speaking your truth which will help you build a connection with the audience too. Facial expressions help bring your story to life and transport the audience into your situation.
- Keep your speech as concise as possible . When practicing the delivery, see if you can edit it to have the same meaning but in a more succinct way. This will keep the audience engaged.
The best persuasive speech ideas are those that spark a level of controversy. However, a public speech is not the time to express an opinion that is considered outside the norm. If in doubt, play it safe and stick to topics that divide opinions about 50-50.
Bear in mind who your audience are and plan your persuasive speech outline accordingly, with researched evidence to support your argument. It’s important to consider counter-arguments to show that you are knowledgeable about the topic as a whole and not bias towards your own line of thought.
- Personal Development
- Sales Training
- Business Training
- Time Management
- Leadership Training
- Book Writing
- Public Speaking
- Live Speaker Training With Brian
- See Brian Speak
- Coaching Programs
- Become a Coach
- Personal Success
- Sales Success
- Business Success
- Leadership Success
How To Write A Speech Outline
Do you have a speech coming up soon, but don’t know where to start when it comes to writing it?
Don’t worry.
The best way to start writing your speech is to first write an outline.
While to some, an outline may seem like an unnecessary extra step — after giving hundreds of speeches in my own career, I can assure you that first creating a speech outline is truly the best way to design a strong presentation that your audience will remember.
Should I Write A Speech Outline?
You might be wondering if you should really bother with a preparation outline. Is a speaking outline worth your time, or can you get through by just keeping your supporting points in mind?
Again, I highly recommend that all speakers create an outline as part of their speechwriting process. This step is an extremely important way to organize your main ideas and all the various elements of your speech in a way that will command your audience’s attention.
Good public speaking teachers will agree that an outline—even if it’s a rough outline—is the easiest way to propel you forward to a final draft of an organized speech that audience members will love.
Here are a few of the biggest benefits of creating an outline before diving straight into your speech.
Gain More Focus
By writing an outline, you’ll be able to center the focus of your speech where it belongs—on your thesis statement and main idea.
Remember, every illustration, example, or piece of information you share in your speech should be relevant to the key message you’re trying to deliver. And by creating an outline, you can ensure that everything relates back to your main point.
Keep Things Organized
Your speech should have an overall organizational pattern so that listeners will be able to follow your thoughts. You want your ideas to be laid out in a logical order that’s easy to track, and for all of the speech elements to correspond.
An outline serves as a structure or foundation for your speech, allowing you to see all of your main points laid out so you can easily rearrange them into an order that makes sense for easy listening.

Create Smoother Transitions
A speaking outline helps you create smoother transitions between the different parts of your speech.
When you know what’s happening before and after a certain section, it will be easy to accurately deliver transitional statements that make sense in context. Instead of seeming like several disjointed ideas, the parts of your speech will naturally flow into each other.
Save Yourself Time
An outline is an organization tool that will save you time and effort when you get ready to write the final draft of your speech. When you’re working off of an outline to write your draft, you can overcome “blank page syndrome.”
It will be much easier to finish the entire speech because the main points and sub-points are already clearly laid out for you.
Your only job is to finish filling everything in.
Preparing to Write A Speech Outline
Now that you know how helpful even the most basic of speech outlines can be in helping you write the best speech, here’s how to write the best outline for your next public speaking project.
How Long Should A Speech Outline Be?
The length of your speech outline will depend on the length of your speech. Are you giving a quick two-minute talk or a longer thirty-minute presentation? The length of your outline will reflect the length of your final speech.
Another factor that will determine the length of your outline is how much information you actually want to include in the outline. For some speakers, bullet points of your main points might be enough. In other cases, you may feel more comfortable with a full-sentence outline that offers a more comprehensive view of your speech topic.
The length of your outline will also depend on the type of outline you’re using at any given moment.
Types of Outlines
Did you know there are several outline types? Each type of outline is intended for a different stage of the speechwriting process. Here, we’re going to walk through:
- Working outlines
- Full-sentence outlines
- Speaking outlines
Working Outline
Think of your working outline as the bare bones of your speech—the scaffolding you’re using as you just start to build your presentation. To create a working outline, you will need:
- A speech topic
- An idea for the “hook” in your introduction
- A thesis statement
- 3-5 main points (each one should make a primary claim that you support with references)
- A conclusion
Each of your main points will also have sub-points, but we’ll get to those in a later step.
The benefit of a working outline is that it’s easy to move things around. If you think your main points don’t make sense in a certain order—or that one point needs to be scrapped entirely—it’s no problem to make the needed changes. You won’t be deleting any of your prior hard work because you haven’t really done any work yet.
Once you are confident in this “skeleton outline,” you can move on to the next, where you’ll start filling in more detailed information.
Full-sentence outline
As the name implies, your full-sentence outline contains full sentences. No bullet points or scribbled, “talk about x, y, z here.” Instead, research everything you want to include and write out the information in full sentences.
Why is this important? A full-sentence outline helps ensure that you are:
- Including all of the information your audience needs to know
- Organizing the material well
- Staying within any time constraints you’ve been given
Don’t skip this important step as you plan your speech.
Speaking outline
The final type of outline you’ll need is a speaking outline. When it comes to the level of detail, this outline is somewhere in between your working outline and a full-sentence outline.
You’ll include the main parts of your speech—the introduction, main points, and conclusion. But you’ll add a little extra detail about each one, too. This might be a quote that you don’t want to misremember or just a few words to jog your memory of an anecdote to share.
When you actually give your speech, this is the outline you will use. It might seem like it makes more sense to use your detailed full-sentence outline up on stage. However, if you use this outline, it’s all too easy to fall into the trap of reading your speech—which is not what you want to do. You’ll likely sound much more natural if you use your speaking outline.
How to Write A Speech Outline
We’ve covered the types of outlines you’ll work through as you write your speech. Now, let’s talk more about how you’ll come up with the information to add to each outline type.
Pick A Topic
Before you can begin writing an outline, you have to know what you’re going to be speaking about. In some situations, you may have a topic given to you—especially if you are in a public speaking class and must follow the instructor’s requirements. But in many cases, speakers must come up with their own topic for a speech.
Consider your audience and what kind of educational, humorous, or otherwise valuable information they need to hear. Your topic and message should of course be highly relevant to them. If you don’t know your audience well enough to choose a topic, that’s a problem.
Your audience is your first priority. If possible, however, it’s also helpful to choose a topic that appeals to you. What’s something you’re interested in and/or knowledgeable about?
It will be much easier to write a speech on a topic you care about rather than one you don’t. If you can come up with a speech topic that appeals to your audience and is interesting to you, that’s the sweet spot for writing and delivering an unforgettable speech.
Write A Thesis Statement
The next step is to ask yourself two important questions:
- What do you want your audience to take away from your speech?
- How will you communicate this main message?
The key message of your speech can also be called your “thesis statement.”
Essentially, this is your main point—the most important thing you hope to get across.
You’ll most likely actually say your thesis statement verbatim during your speech. It should come at the end of your introduction. Then, you’ll spend the rest of your talk expanding on this statement, sharing more information that will prove the statement is true.
Consider writing your thesis statement right now—before you begin researching or outlining your speech. If you can refer back to this statement as you get to work, it will be much easier to make sure all of the elements correspond with each other throughout your speech.
An example of a good thesis statement might read like this:
- Going for a run every day is good for your health.
- It’s important to start saving for retirement early.
- The COVID-19 pandemic had a negative impact on many small businesses.
The second part of this step is to know how you will communicate your main message . For example, if your key point is that running improves physical health, you might get this across by:
- Citing scientific studies that proved running is good for your health
- Sharing your personal experience of going for a run every day
Your goal is for all of your sub-points and supporting material to reflect and support your main point. At the end of the speech, your audience should be appropriately motivated, educated, or convinced that your thesis statement is true.
Once you have a topic for your presentation and a good thesis statement, you can move on to the bulk of the outline.
The first part of your speech is the introduction, which should include a strong “hook” to grab the attention of your audience. There are endless directions you can go to create this hook. Don’t be afraid to get creative! You might try:
- Telling a joke
- Sharing an anecdote
- Using a prop or visual aid
- Asking a question (rhetorical or otherwise)
These are just a few examples of hooks that can make your audience sit up and take notice.
The rest of your introduction shouldn’t be too long—as a general rule of thumb, you want your introduction to take up about 10% of your entire speech. But there are a few other things you need to say.
Briefly introduce yourself and who you are to communicate why the audience should trust you. Mention why you’re giving this speech.
Explain that you’re going to cover X main points—you can quickly list them—and include your thesis statement.
You could also mention how long your speech will be and say what your audience will take away from it (“At the end of our 15 minutes together today, you’ll understand how to write a resume”).
Then smoothly transition into the body of your speech.
Next, you’ll write the body of your speech. This is the bulk of your presentation. It will include your main points and their sub-points. Here’s how this should look:
Your subpoints might be anecdotes, visual aids, or studies. However you decide to support your main points, make them memorable and engaging. Nobody wants to sit and listen to you recite a dry list of facts.
Remember, the amount of detail you include right now will depend on which outline you’re on. Your first outline, or working outline, doesn’t have to include every last little detail. Your goal is to briefly encapsulate all of the most important elements in your speech.
But beyond that, you don’t need to write down every last detail or example right now. You don’t even have to write full sentences at this point. That will come in your second outline and other future drafts.
Your conclusion should concisely summarize the main points of your speech. You could do this by saying, “To recap as I finish up, today we learned…” and reiterate those primary points.
It’s also good to leave the audience with something to think about and/or discuss. Consider asking them a question that expands on your speech—something they can turn over in their minds the rest of the day.
Or share one final story or quote that will leave them with lasting inspiration. Bonus points if your conclusion circles back around to your introduction or hook.
In other cases, you may want to end with a call to action. Are you promoting something? Make sure your audience knows what it is, how it will benefit them, and where they can find it. Or, your CTA might be as simple as plugging your Twitter handle and asking listeners to follow you.
Finally, don’t forget to say thank you to your audience for taking the time to listen.
Additional Helpful Speechwriting Tips
Your speech outline is important, but it’s not the only thing that goes into preparing to give a presentation. Take a look at these additional tips I recommend to help your speech succeed.
Use Visual Aids
Visual aids are a good way to make sure your audience stays engaged—that they listen closely, and remember what you said. Visual aids serve as an attention-getter for people who may not be listening closely. These aids also ensure that your points are sufficiently supported.
You might choose to incorporate any of the following in your talk:
- A PowerPoint presentation
- A chart or graph
- A whiteboard or blackboard
- A flip chart
- A prop that you hold or interact with
Don’t overdo it. Remember, your speech is the main thing you’re presenting. Any visual aids are just that—aids. They’re a side dish, not the main entrée. Select one primary type of aid for your speech.
If you decide to include visual aids, use your speaking outline to make a note of which items you will incorporate where. You may want to place these items on your working outline. They should definitely be on your full-sentence outline.
Keep Your Audience Engaged
As you write and practice your speech, make sure you’re doing everything you can to keep your audience engaged the entire time. We’ve already talked about including stories and jokes, using visual aids, or asking questions to vary your talk and make it more interesting.
Your body language is another important component of audience engagement. Your posture should be straight yet relaxed, with shoulders back and feet shoulder-width apart. Keep your body open to the audience.
Make eye contact with different people in the audience. Incorporate hand gestures that emphasize certain points or draw attention to your visual aids.
Don’t be afraid to move around whatever space you have. Movement is especially helpful to indicate a clearer transition from one part of your speech to another. And smile! A simple smile goes a long way to help your audience relax.
Practice Your Speech
When you’re done with speechwriting, it’s time to get in front of the mirror and practice. Pay attention to your body language, gestures, and eye contact.
Practice working with any visual aids or props you will be using. It’s also helpful to make a plan B—for instance, what will you do if the projector isn’t working and you can’t use your slides?
Ask a friend or family member if you can rehearse your speech for them. When you’re through, ask them questions about which parts held their attention and which ones didn’t.
You should also use your speaking outline and whatever other notes you’ll be using in your speech itself. Get used to referring to this outline as you go. But remember, don’t read anything verbatim (except maybe a quote). Your speaking outline is simply a guide to remind you where you’re going.
Learn to Speak Like A Leader
There’s a lot of work that goes into writing a speech outline. That’s undeniable. But an outline is the best way to organize and plan your presentation. When your speech outline is ready, it will be a breeze to write and then present your actual speech.
If you’re looking for more help learning how to become a strong public speaker, I recommend my free 5 Minute Speech Formula . This will help you start writing your speech and turn any idea into a powerful message.
« Previous Post Productivity Tips – Be More Productive With Less Effort Next Post » How To Communicate Effectively In Any Situation
About Brian Tracy — Brian is recognized as the top sales training and personal success authority in the world today. He has authored more than 60 books and has produced more than 500 audio and video learning programs on sales, management, business success and personal development, including worldwide bestseller The Psychology of Achievement. Brian's goal is to help you achieve your personal and business goals faster and easier than you ever imagined. You can follow him on Twitter , Facebook , Pinterest , Linkedin and Youtube .
- Most Recent
- The Art of Business Success: A Blueprint for Entrepreneurs
- How to Develop a Habit That Will Last
- How to Write an Author Bio (Examples Included)
- Personal Development Plan Templates for Success
- How to Sell and Become a Master Salesperson
- Free Webinar: How To Write a Book and Become a Published Author
- Free Video Series: 3-Part Sales Mastery Training Series
- Free Assessment: The Confidence Factor
- Free Assessment: Discovering Your Talents
Browse Categories
- Financial Success
Follow Brian & Join the Discussion
- Free Resources
- Best Sellers
- Knowledge Base
- Shipping & Returns
- Privacy Policy
- About Brian
- Brian Recommends
Your Privacy is Guaranteed. We will never give, lease or sell your personal information. Period!
© Copyright 2001-2024 Brian Tracy International. All Rights Reserved.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

13.7: Sample Outline- Persuasive Speech Using Monroe's Motivated Sequence Pattern
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 90292

- Kris Barton & Barbara G. Tucker
- Florida State University & University of Georgia via GALILEO Open Learning Materials
Speech to Actuate:
Sponsoring a Child in Poverty
Specific Purpose:
to actuate my audience to sponsor a child through an agency such as Compassion International.
Introduction (Attention Step)
I. How much is $38? That answer depends on what you make, what you are spending it for, and what you get back for it. (Grabber)
II. $38 per month breaks down to a little more than $1.25 per day, which is probably what you spend on a snack or soda in the break room. For us, it’s not very much. (Rapport)
III. I found out that I can provide better health care, nutrition, and even education for a child in Africa, South America, or Asia for the $38 per month by sponsoring a child through Compassion International. (Credibility)
IV. If I can do it, maybe you can too: (Bridge)
Through a minimal donation each month, you can make the life of a child in the developing world much better.
In the next few minutes I would like to discuss the problem, the work of organizations that offer child sponsorships, how research shows they really do alleviate poverty, and what you can do to change the life of a child. Body
I. The problem is the continued existence and effects of poverty. (Need Step)
A. Poverty is real and rampant in much of the world.
1. According to a 2018 report of the Secretary General of the United Nations, 9.2% of the world lives on less than $1.90 per day.
a. That is 600 million people on the planet.
2. This number is supported by the World Poverty clock of the World Data Lab, which states that 8% of the world’s population lives in extreme poverty.
a. The good news is that this number is one third of what it was in 1990, mostly due to the rising middle class in Asia.
b. The bad news is that 70% of the poor will live in Africa, with Nigeria labeled the “Poverty Capital of the World,” according to the Brookings Institute.
B. Poverty means children do not get adequate health care.
1. One prevalent but avoidable disease is malaria, which takes the lives of 3000 children every day, according to UNICEF.
2. According to the World Health Organization, diarrheal diseases claimed 2.46 million lives in 2012 and is the second leading cause of death of children under 5.
C. Poverty means children do not get adequate nutrition, as stated in a report from UNICEF.
1. Inadequate nutrition leads to stunted growth.
2. Undernutrition contributes to more than one third of all deaths in children under the age of five.
D. Poverty means children are unlikely to reach adult age, according to the CIA World Fact Book quoted on the Infoplease website.
1. Child mortality rate in Africa is 8.04% (percentage dying before age 5), while in North American is .64%
2. Life expectancy in Sub-Saharan Africa is almost 30 years less than in the U.S.
E. Poverty also means children are unlikely to receive education and be trained for profitable work.
1. Nearly a billion people entered the 21st century unable to read a book or sign their names, states the Global Issues website on Poverty Facts.
2. UNESCO, a part of the United Nations, reports that less than a third of adults in Sub-Saharan Africa have completed primary education.
Transition:
Although in all respects poverty is better in 2019 than it has been in the past, poverty is still pervasive and needs to be addressed. Fortunately, some great organizations have been addressing this for many years.
II. Some humanitarian organizations address poverty directly through child sponsorships. (Satisfaction Step)
A. These organizations vary in background but not in purpose. The following information is gleaned from each organization’s websites.
1. Compassion International is faith-based, evangelical.
a. Around since early 1950s, started in Korea.
b. Budget of $887 Million.
c. Serves 1.92 million babies, children, and young adults.
d. Works through local community centers and established churches.
2. World Vision is faith-based, evangelical.
a. Around since the 1950s.
b. Budget of far over $1 Billion.
c. 60% goes to local community programs but more goes to global networks, so that 86% goes to services.
d. World Vision has more extensive services than child sponsorship, such as water purification and disaster relief.
e. Sponsors three million children across six continents
3. Children International is secular.
a. Around since 1936.
b. Budget of $125 Million.
c. 88% of income goes directly to programs and children.
d. Sponsors children in ten countries on four continents
e. Sponsors X across X continents
4. Save the Children is secular, through…
a. One hundred years of history, began in post WWI Europe.
b. Budget of $880 Million.
c. 87% goes to services.
d. Sponsors 134 million children in 120 countries, including 450,000 in U.S.
5. There are other similar organizations, such as ChildFund and PlanUSA.
B. These organizations work directly with local community, on-site organizations.
1. The children are involved in a program, such as after school.
2. The children live with their parents and siblings.
3. The sponsor’s donation goes for medicine, extra healthy, nutritious food, shoes for school, and other items.
4. Sponsors can also help donate for birthdays and holidays to the whole family to buy food or farm animals.
Of course, any time we are donating money to an organization, we want to be sure our money is being effectively and ethnically used.
III. This concern should be addressed in two ways: Is the money really helping, and are the organizations honest? (Continuation of Satisfaction Step)
A. The organizations’ honesty can be investigated.
1. You can check through Charity Navigator.
2. You can check through the Better Business Bureau-Charity.
3. You can check through Charity Watch.
4. You can check through the organizations’ websites.
B. Secondly, is sponsoring a child effective? Yes.
1. According to Bruce Wydick, Professor of Economics at the University of San Francisco, child sponsorship is the fourth most effective strategy for addressing poverty, behind water purification, mosquito nets, and deworming treatments.
2. Dr. Wydick and colleagues’ work has been published in the prestigious Journal of Political Economy from the University of Chicago.
3. He states, “Two researchers and I recently carried out a study (sponsored by the U.S. Agency for International Development) on the long-term impacts of Compassion International’s child sponsorship program. The study, gathering data from over 10,000 individuals in six countries, found substantial impact on adult life outcomes for children who were sponsored through Compassion’s program during the 1980s and ’90s…In adulthood, formerly sponsored children were far more likely to complete secondary school and had a much higher chance of having a white-collar job. They married and had children later in life, were more likely to be church and community leaders, were less likely to live in a home with a dirt floor and more likely to live in a home with electricity.”
To this point I have spoke of global problems and big solutions. Now I want to bring it down to real life with one example.
IV. I’d like to use my sponsored child, Ukwishaka in Rwanda, as an example of how you can. (Visualization Step)
A. I have sponsored her for five years.
B. She is now ten years old.
C. She lives with two siblings and both parents.
D. She writes me, I write her back, and we share photos at least every two months.
E. The organization gives me reports on her project.
F. I hope one day to go visit her.
G. I believe Ukwishaka now knows her life can be more, can be successful.
We have looked at the problem of childhood poverty and how reliable, stable nongovernmental organizations are addressing it through child sponsorships. Where does that leave you?
V. I challenge you to sponsor a child like Ukwishaka. (Action Step)
A. Although I sponsor her through Compassion International, there are other organizations.
B. First, do research.
C. Second, look at your budget and be sure you can do this.
1. You don’t want to start and have to stop.
2. Look for places you “waste” money during the month and could use it this way.
3. Fewer snacks from the break room, fewer movies at the Cineplex, brown bag instead of eating out.
D. Talk to a representative at the organization you like.
E. Discuss it with your family.
F. Take the plunge. If you do.
1. Write your child regularly.
2. Consider helping the family, or getting friends to help with extra gifts.
I. In this speech, we have taken a look at the state of poverty for children on this planet, at organizations that are addressing it through child sponsorships, at the effectiveness of these programs, and what you can do.
II. My goal today was not to get an emotional response, but a realistically compassionate one.
III. You have probably heard this story before but it bears repeating. A little girl was walking with her mother on the beach, and the sand was covered with starfish. The little girl wanted to rescue them and send them back to the ocean and kept throwing them in. “It won’t matter, Honey,” said her mother. “You can’t get all of them back in the ocean.” “But it will matter to the ones that I do throw back,” the little girl answered.
IV. We can’t sponsor every child, but we can one, maybe even two. As Forest Witcraft said, “What will matter in 100 years is that I made a difference in the life of a child.” Will you make a difference?
AGScientific. (2019). Top ten deadly diseases in the world. Retrieved from http://agscientific.com/blog/2016/04/top-10-deadly-diseases/
Compassion International. (2019). Financial integrity: The impact of our compassion. Retrieved from https://www.compassion.com/about/financial.htm
Children’s International. (2019). Accountability. Retrieved from https://www.children.org/learn-more/accountability
Global Issues. (2013, January 7 ). Poverty facts and stats. Retrieved from https://www.globalissues.org/article/26/poverty-facts-and-stat s
Infoplease. (2019). What life expectancy really means. Retrieved form https://www.infoplease.com/world/health-and-social-statistics/life-expectancy-countries-0
Kharas, H., Hamel, K., & Hofer, M. (2018, Dec. 13). Rethinking global poverty reduction in 2019. Retrieved from https://www.brookings.edu/blog/future-development/2018/12/13/rethinking-global-poverty-reduction-in-2019/
Roser, M. (2019). Child and infant mortality rates. Retrieved from https:// ourworldindata.org/child-mortality
Save the Children. (2019). Financial information. Retrieved from https://www.savethechildren.org/us/a...al-information UNICEF.(2008).
Tracking progress on child and maternal nutrition: A survival and development priority. Retrieved from https://www.unicef.org/media/files/Tracking_Progress_on_Child_and_Maternal_Nutrition_EN_110309.pdf UNICEF 2019.
The reality of Malaria. Retrieved from https://www.unicef . org/health/files/health_africamalaria.pdf United Nations. (2019). Poverty eradication. Retrieved from https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/topics/povertyeradication
World Vision. (2019). Financial accountability. Retrieved from https:// www.worldvision.org/about-us/financial-accountability-2 Wydick, B., Glewwe, P., & Rutledge, L. (2013).
Does international child sponsorship work? A six-country study of impacts on adult life outcomes. Journal of Political Economy, 121(2), 393–436. https://doi. org/10.1086/670138 Wydick, B. (2012, Feb.).
Cost-effective compassion. Christianity Today, 56(2), 24-29. Wydick, B. (2013). Want to change the world? Sponsor a child. Christianity Today, 57(5), 20–27.

Speech Outlines for Students

Speech outlines for students? How should you design them, especially younger students like middle school public speaking students ?
Speech textbooks encourage students to write outlines for their speeches. Since audience do not have the advantage of visually seeing the words, a speech’s organization (preview, transitions, signal phrases) is of the utmost importance. An outline allows students to see each point individually.
Creating speech outlines for students can be tricky though. You want to provide an example, but you don’t want to limit their creativity.
Writing outlines with students is an important activity . Looking at a speech line by line aids in transitions, and in creating a balance of material. An outline is also a working document. As students practice their delivery, they can easily add and subtract from an outline. When I taught middle school speech, I found that designing a speech outline with students calmed nerves and gave students a tool for practicing.
Why is it important for students to create a speech outline before delivering their speeches?
Creating a speech outline helps students organize their thoughts, structure their speech, and ensure a clear flow of ideas. It serves as a roadmap for the speech, helping students stay focused and on track. Additionally, outlines help students remember key points and maintain coherence in their delivery.
What are the benefits of starting with speech outlines for students?
Eventually, public speakers move away from the classic outline—a sort of personalized approach takes over a speech outline template. A successful presentation does not mandate a one-size-fits-all-approach.
Still, for new speakers, a sample speech outline that serves as a mentor text helps. Once they focus on a basic speech outline, they can work on eye contact, vocal variety, body language, visual aids—the other components to consider.
So, to begin, an outline is the preferred design. As the teacher, you must decide which speech outline students should use: sentence or topic. Here are pros and cons when deciding between speech outlines for new speakers.

Sentence Outlines
Pros : A sentence outline gives a polished picture of the speech. Speakers can add sentence transitions, which help an audience more than one word transitions. The speech is typically more developed than a speech from a topic outline.
Students can also read over the speech and get an idea of how the speech will sound. From a topic outline, students will need to develop different parts of the speech each time. With a sentence outline, students will hear the speech in their heads, and it may come naturally to them as they deliver the speech.
Cons : Students who dislike writing struggle with this stage. They may enjoy the different pace of a speech class, but they feel that they are writing papers with an additional step (speaking). Finally, speakers can be reluctant to alter a sentence outline. These outlines are longer, and they may leave a portion that needs work because that one portion interferes with the flow of the entire speech.

Topic Outlines
Pros : The short nature of topic outlines is easy to manipulate. During practice, students can add points, practice, and then move or delete what doesn’t work. It is more a working document—moldable.
Topic outlines don’t take long to write. Because they are short, speakers can spend more time practicing the speech than writing the speech.
Cons : Students can write the subjects and not fully think the talking points for the speech. If they practice a topic outline, they may deliver a strong speech. If students do not practice, a speech given from a topic outline is short. A topic sentence does not force students to think completely through a speech. A speaking experience like that can frustrate.
Thesis, Main Points, Transitions: Choosing an Outline
What do I use? At first, I only used sentence outlines. Students were more prepared, and the longer outlines gave them structure. One time (I can’t remember why), I assigned a topic outline. And? As they progressed, the topic outlines turned into sentence outlines. Some students did not write enough information, but for the those who put forth effort, their outlines were their own, very organized and personalized.
Furthermore, to include all the necessary pieces like a main idea, thesis main points, and on, classes benefit from sample outlines. Therefore, I provide students with outline examples for how-to speeches and narrative speeches . Giving examples builds relationships with students and trust because they see my process.
You can always try both versions with classes, and then decide, or allow students to provide input. When deciding what speech outline is best for your circumstances, consider their need for structure and abilities to create different types of outlines.
Now, my classes write sentence outlines until I feel they are capable of a topic outlines. I give students the goal of eventually writing a topic outline, and they are willing to work toward it.
Would public speaking lessons help you? Sign up below, and they’ll be sent your way, for free.
Subscribe to our mailing list to receive updates about new blog posts, freebies, and teaching resources!
Marketing Permissions We will send you emails, but we will never sell your address.
You can change your mind at any time by clicking the unsubscribe link in the footer of any email you receive from us, or by contacting us at [email protected] . We will treat your information with respect. For more information about our privacy practices please visit our website. By clicking below, you agree that we may process your information in accordance with these terms.
We use Mailchimp as our marketing platform. By clicking below to subscribe, you acknowledge that your information will be transferred to Mailchimp for processing. Learn more about Mailchimp’s privacy practices here.

public speaking public speaking activities

23 Informative Speech Outline Student Example
Student Example
Informative Speech Outline
- This is a student example for you to use for your own outline preparation.
- This student’s outline is well developed, coherent, integrates research, follows a strong organizational pattern, and meets all expectations of an outline in a public speaking course.
- Click on the Google Document provided for a sample speech outline.
Public Speaking Copyright © by Dr. Layne Goodman; Amber Green, M.A.; and Various is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Informative Speech
Informative Speech Outline
Informative Speech Outline - Format, Writing Steps, and Examples

People also read
Informative Speech Writing - A Complete Guide
Good Informative Speech Topics & Ideas
Collection of Ideas and ‘How To’ Demonstrative Speech Topics
10+ Informative Speech Examples - Get Inspiration For Any Type
Understanding Different Types of Informative Speeches with Examples
Are you tasked with delivering an informative speech but don’t know how to begin? You're in the right place!
This type of speech aims to inform and educate the audience about a particular topic. It conveys knowledge about that topic in a systematic and logical way, ensuring that the audience gets the intended points comprehensively.
So, how do you prepare for your speech? Here’s the answer: crafting an effective informative speech begins with a well-structured outline.
In this guide, we'll walk you through the process of creating an informative speech outline, step by step. Plus, you’ll get some amazing informative speech outline examples to inspire you.
Let’s get into it!
- 1. What is an Informative Speech Outline?
- 2. How to Write an Informative Speech Outline?
- 3. Informative Speech Outline Examples
What is an Informative Speech Outline?
An informative speech outline is like a roadmap for your presentation. It's a structured plan that helps you organize your thoughts and information in a clear and logical manner.
Here's what an informative speech outline does:
- Organizes Your Ideas: It helps you arrange your thoughts and ideas in a logical order, making it easier for your audience to follow your presentation.
- Ensures Clarity: An outline ensures that your speech is clear and easy to understand. It prevents you from jumping from one point to another without a clear path.
- Saves Time: With a well-structured outline, you'll spend less time searching for what to say next during your speech. It's your cheat sheet.
- Keeps Your Audience Engaged: A well-organized outline keeps your audience engaged and focused on your message. It's the key to a successful presentation.
- Aids Memorization: Having a structured outline can help you remember key points and maintain a confident delivery.
How to Write an Informative Speech Outline?
Writing a helpful speech outline is not so difficult if you know what to do. Here are 4 simple steps to craft a perfect informative outline.
Step 1: Choose an Engaging Topic
Selecting the right topic is the foundation of a compelling, informative speech. Choose unique and novel informative speech topics that can turn into an engaging speech.
Here's how to do it:
- Consider Your Audience: Think about the interests, knowledge, and expectations of your audience. What would they find interesting and relevant?
- Choose Your Expertise: Opt for a topic you're passionate about or knowledgeable in. Your enthusiasm will shine through in your presentation.
- Narrow It Down: Avoid broad subjects. Instead, focus on a specific aspect of the topic to keep your speech manageable and engaging.
With these tips in mind, you can find a great topic for your speech.
Step 2: Conduct Some Research
Now that you have your topic, it's time to gather the necessary information. You need to do thorough research and collect some credible information necessary for the audience to understand your topic.
Moreover, understand the types of informative speeches and always keep the main purpose of your speech in mind. That is, to inform, educate, or teach. This will help you to avoid irrelevant information and stay focused on your goal.
Step 3: Structure Your Information
Now that you have the required information to make a good speech, you need to organize it logically. This is where the outlining comes in!
The basic speech format consists of these essential elements:
Moreover, there are two different ways to write your outline:
- The complete sentence format
- The key points format
In the complete sentence outline , you write full sentences to indicate each point and help you check the organization and content of the speech.
In the key points format, you just note down the key points and phrases that help you remember what you should include in your speech.
Step 4: Review and Revise
Finally, once you've created your initial informative speech outline, you need to review and revise it.
Here's how to go about it:
- Ensure Clarity: Review your outline to ensure that your main points and supporting details are clear and easy to understand.
- Verify Logical Sequence: Double-check the order of your points and transitions. Ensure that the flow of your speech is logical and that your audience can follow it easily.
- Eliminate Redundancy: Remove any redundant or repetitive information. Keep your outline concise and to the point.
- Time Yourself: Estimate how long it will take to deliver your speech. Ensure it fits within the allotted time frame, whether it's a few minutes or an hour.
- Get Feedback: Share your outline with a friend, family member, or colleague and ask for their input. Fresh eyes can provide valuable suggestions for improvement.
Follow these basic steps and write a compelling speech that gives complete knowledge about the topic. Here is a sample outline example that will help you better understand how to craft an informative speech outline.
Informative Speech Outline Format
Informative Speech Outline Examples
Let’s explore a few example outlines to help you visualize an informative speech outline. These examples illustrate the outlines for different topics and subjects.
Mental Health Informative Speech Outline
Stress Informative Speech Outline
Social Media Informative Speech Outline
Informative Speech Outline Template
Informative Speech Outline Sample
To sum it up,
Creating an effective outline is your pathway to delivering an impactful, organized, and engaging speech. Making an outline for your speech ensures that your message shines through with clarity and purpose.
With the help of the steps and examples given above, you will be able to create a well-structured outline for your informative speech. So go ahead and deliver an engaging informative speech with the help of outlines.
Moreover, if you're passionate about public speaking but find speech writing a tedious task, your worries can now take a back seat. At MyPerfectWords.com , we offer a convenient solution.
Our essay writing service is dedicated to providing you with top-notch content, ensuring you get the results you desire.
So, why wait? Buy Speech today and elevate your public speaking game.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Cathy has been been working as an author on our platform for over five years now. She has a Masters degree in mass communication and is well-versed in the art of writing. Cathy is a professional who takes her work seriously and is widely appreciated by clients for her excellent writing skills.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
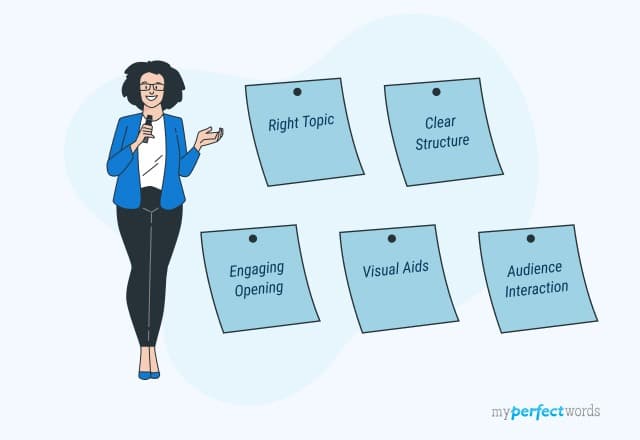
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- Speech examples
- Student Council speeches
Student Council Speeches
By: Susan Dugdale
How to write a winning speech: a template, guidelines, plus example speeches
Student Council Speeches mark the end of an election campaign.
Will yours be successful?
The final answer is in the hands of your fellow students. It's entirely their decision.
However, up until they mark their voting papers 'yes' or 'no' you have the potential to make their choice of candidate for the upcoming year 'you'.
How to write a great student council speech
Use the quick links below to find what you need to write a great student council speech, whether it's the President, Vice-President, Secretary or Treasurer role you're after.

- the primary purpose of your speech
- a template that includes all the necessary elements of a good Student Council speech
- points to consider carefully before you write
- an example Student Council President speech
- an example Student Council Vice President speech
- an example Student Council Secretary speech
- an example Student Council Treasurer speech
- a printable speech planner and outline to download
- vital tips for rehearsal . These make the difference between looking and sounding polished and bumbling.
- a link to a collection of videoed student council speeches
- how to manage anxiety about speaking in front of others
Understanding your speech purpose
Understanding the nature or purpose of your speech could make all the difference between winning and losing.
Student Council speeches are persuasive speeches . Their ultimate goal is to get you the YES vote.
To help you achieve that use the template, (framework or pattern), below to cover all the essential elements you need to pull together.
In addition, it will structure your speech logically, and effectively, from its opening through to its close.
(I've turned the template into a printable enabling you to plan and outline your speech efficiently and easily. You can download it from the link further down the page.)
Return to Top
Student Council speeches template

- Greeting - Attention Getter - The Hook You'll need an opening statement or rhetorical question to sit your audience up with open ears and minds. For more see: How to write a speech introduction: 12 of the best ways to start.
- Who you are - your name, your place or grade in the school, and maybe, your hobbies or interests, and the clubs or teams you're a member of. For example, Amnesty International, the speech and debate club, cross-country and basketball. And if you've used a campaign slogan work it in. It'll jog people's memories. 'Ah, yes, that person!', they'll think. Being known and familiar gives you a head start.
- What you want - the role you are campaigning for: President, Vice President, Treasurer, Secretary, Historian...
- What you are going to do for the audience - benefits to them in exchange for their vote. (Brief summary -you will expand this in the body of your speech.)
- Credibility - your qualification or expertise establishing your fitness for the role you want. (Brief summary - you will expand this in the body of your speech.)
- Transition leading to...
- Your Main Idea 1 - For example: your goal for the role, what you want to achieve, how you plan to do it, the benefits to your audience - what painful problem(s) will you solve for them, your fitness for the job, transition to...
- Main Idea 2 - Supporting ideas - details and examples - transition to...
- Main Idea 3 - Supporting ideas - details and examples - transition to...
NB. Only include a second and third idea if you have time to expand on them. If not, move through to the conclusion.
- Summary of main points
- Re-statement of what you want - to be elected to the role you're running for
- Re-statement of the benefits to the audience
- Closer, clincher, call for action
Points to consider BEFORE you write your speech

You'll make a better job of completing the printable student council speech template if you take the time to go through the points below.
And then, read the student council speech examples, before you start to write.
Research the role
Think about your audience, what tone or choice of vocabulary is best suited to them.
Avoid trying to impress with either 'big' words or use of slang. Both are traps! Be yourself. Authentic. Real.
Keep your language conversational rather than overly formal and use smaller rather than large sentences.
Try using active rather than passive words. These convey enthusiasm. For examples, see this page on using action verbs . You'll discover how to go from boring bla bla bland to dynamic excitement.
What 'hook' will you use to get them to listen? Humor? Humor is good if it is relevant and inclusive rather than exclusive. (No 'in' jokes!).
Your goal in the role you want
Avoid setting up expectations that you will deliver beyond your capability. :-)
It might be very tempting, but can you really reduce school hours, increase academic standards, introduce a range of exciting new extracurricular activities, as well as have a 'green day' and a movie night every month? Please keep it real!
Your credibility or qualifications
Now is not the time either to be shy or arrogantly big-headed! Let the audience know how right you are for the role you want.
Set yourself apart from other candidates by sharing compelling personal stories or anecdotes that both support your pitch, and show you understand the key issues that matter to your fellow students.
Your school's requirements
If your speech does not meet pre- established criteria in any way you may find it is returned to you edited. It's safer to find out what those criteria are BEFORE writing to avoid having to re-write or worse, being disqualified entirely.
Mockery and personal insults are not clever. They boomerang back on you, letting your audience know you're not to be trusted and neither are you ready for leadership.
Readily acknowledging the skill and expertise of your fellow candidates sincerely in a way that doesn't demean yourself, or them, shows an open mind and maturity.
Aim to have your speech ready BEFORE the deadline.
Give yourself time to prepare thoroughly, including time to review of your opponents' campaigns. That can be very useful for seeing their strengths as well as their weaknesses, which you can then respond to in your own material.
Student Council President speech example
Here's a sample student council speech. I've written it from the perspective of someone running for President.
As you read it, imagine it said aloud. That will help you get the rhythm and flow of language. The speech is between 3 - 4 minutes long, depending on how quickly you speak.
Vote Sophia Clarke for Student Council President

"I’ve got a question for you. I’m not asking you to shout your answer out, or raise your hand. All I’m asking is that you give it room in your mind. Let it sit for a bit, and have a think about it.
My question is – do you believe like I do, that all of us deserve the opportunity to make the best of ourselves? Not second best, 3 rd , or even, highly commended. The BEST.
I’m Sophia Clarke. I’m in the 12 th grade, and I’m running for president. My vision is that each student is enabled to develop the skills and confidence to become the bigger, better version of themselves. The best they can be. Regardless of who they are, and what they need to achieve that.
It’s an audacious goal. Some would say an idealistic, rather than a realistic, one.
However I say it’s awesome. And that you’re intelligent people who realize that reaching any goal starts with taking the first step.
So let me remind you why choosing me, Sophia Clarke, for president, is also choosing a better chance for yourself, and everyone else to grow.
I know you, and I know your needs well. I’ve served on your behalf in multiple roles through my years here; secretary, auditor, public relations officer, and have successfully taken on multiple issues. You’ll know some of those through directly benefiting from them.
It was me who was behind the push to get a regular anti-bullying program running throughout the school. That was two years ago, and now the Teens Against Bullying message underpins what we expect and strive for in our every day dealings with each other.
We know incidents of bullying are far fewer as a result. As our orange tee shirts say we ‘choose kindness, acceptance and inclusion’ for each other, and our selves.
Who has been involved in our mentoring-homework program? Either as a buddy-tutor or as a student getting a helping hand? And who, like me, is passionate about making sure that everybody gets a fair go?
In the past year, under my watch that program has escalated. We have over 50% more tutors across more subject areas and more students taking up the offer of help. That is a fabulous outcome for everybody. Truly win-win.
A tick in the box alongside my name is a tick for the continued growth of those programs. Their value is proven. They allow each of us to grow and experience the strength and confidence that comes from knowing that we can make a positive difference in other people’s lives as well as our own.
When you vote me for President you get my capacity to organize, to liaise, to listen and to speak, working for the benefit of everybody.
A 'yes' for me is a 'yes' for appreciating and celebrating diversity.
A 'yes' for me, Sophia Clarke for President, is 'yes' to a better you.
And together that is a 'yes' to a better life, and a better school, for all of us."
Student Council Vice President speech example
Like the speech above, this one runs to approximately 4 minutes when said aloud. Try it and see.

Nod your head if you've heard of the phrase '2nd fiddle' or '2IC'.
What about 'sidekick'?
Not booting a ball in from a sideline but a trusty partner to whoever it is who has the leading role. Like Robin is for Batman.
Or like, {name of your country's Vice President or Prime Minister} is for {name of country's President or Prime Minister} or {name of your school's Vice Principal} is for {name of your school's Principal}!
Well, that's what I aspire to - to become the trusty, tried and true sidekick to the President on our student council.
My name is Jason Hull. I'm in Grade 12 and proudly standing in front of you today as a candidate for the role of Vice President. Yes, I am asking you to give me something of immense value - your vote.
I know what the issues, here at {name of school} are. As part of my campaign, I've interviewed you, and listened. I promise your ideas will be acted on.
Afterall I've trained for this role, put in the time. You know, I know how to get things done.
Last year I served as Secretary and the year before that I was a representative for the committee - proof that I'm committed to bettering our school environment not just for you, but for everybody!
With your support, I'll be your go-to guy when you want to make sure that your opinions and feedback reach the decision-makers.
One of my main goals as your Vice President is to champion your initiatives: amongst others, that's the library extensions you told me about, the desire for healthier food choices in our cafeteria, and the urgent need to increase and diversify the workforce and out-reach opportunities that so many of you mentioned.
Whether you're passionate about improving our school facilities, or enhancing our community involvement, I'll be there to guide and help you.
In the role of Vice President, I will work alongside the President fulfilling my duties to the best of my ability.
Together, we'll make sure that your concerns, and hopes are not just heard but actively pursued. Not 'I' will make sure, but 'we'.
There is no 'I' in we, and that too, is a prerequisite of the Vice President's position: the capacity to put aside ego and to work productively for the good of all.
Because together, we, the Vice President, the President and the other council members, are stronger and can achieve more.
The Vice President role may be a support act but it's a vital one. To succeed in it, collaboration is key. I promise to work hand in hand not only with the President but also with the entire student council team, our teachers, and our administration on your behalf.
Unity is strength. More than ever, we need to nurture understanding, kindness and respect for each other. Regardless of your grade, interests, or background, I want every one of you to feel valued and heard.
That's a goal many would say is impossible.
However, I say, we need to be the difference we want to see in the world. And to borrow those famous words of Helen Keller's: "Alone we can do so little. Together we can so much."
It would be an honor to be your voice, your eyes and your ears as Vice President.
So, I ask you, will you trust me to have your best interests at heart? Will you enable me to work on your behalf?
And are you willing to give me, Jason Hull, your vote for best sidekick, aka. Vice President?
I'll take those smiles, as a 'Yes'.
Example Student Council speeches for Secretary and Treasurer
Click the link to read an:
- example Student Council speech for the role of Secretary . Plus, an overview of the Secretary's main tasks and responsibilities.
- example Student Council speech for the role of Treasurer . Plus, an overview of the Secretary's main tasks and responsibilities.
(This page was getting far too long to include them both here. ☺)
Get the printable student council speech outline
Click on the image below to open a downloadable printable student council speech planner and outline pdf. (Please note it will open in a new window.)

Your completed outline will provide both the structure and the content you need to efficiently write your speech.
After you've finished writing your speech
Now that you've finished writing, you're ready to begin work on your delivery: how you present the speech to your audience.
The first step in that process is making sure your speech fits comfortably into whatever time you've been allocated.
After that comes rehearsal. The information you need for both steps is below.
Timing and word count
Student Council Speeches are generally brief: around 1-4 minutes long which isn't a lot of time! That's between approximately 150 - 600 words at an average speaking rate of 150 words per minute.
To be safe say your speech out loud as if you were delivering it for real and time it. In some schools going overtime can result in being disqualified.
Going faster to fit everything in
Please do not be tempted to say it faster to get everything you planned said. As a strategy it doesn't work. You'll end up gabbling: speaking far too quickly and people won't be able to understand what you're saying.
Cutting out extra material
If you have got too much material for the time limit, cut it. Choose the least important ideas to let go of first. Then move on to rephrasing to reduce the number of words used to express a point.
When you think it's done, repeat the test. Say it out loud as if you were actually giving it, and time it.
If you're now within the allotted time, you are ready for rehearsal.
For more about word count see: how many words per minute in a speech
How to rehearse your speech

Please, please rehearse your speech ! Do not be tempted to wing it. The more you rehearse the easier it will be to deliver it well.
Remember it is only 1 to 4 minutes long! In that time your goal is to have your audience ready to vote for you.
You can help them make that decision by being confident and prepared. You will show that through:
- your speaking style - natural, sincere, fluent, understandable (clear and able to be heard without straining)
- your body language - relaxed, open gestures, good eye contact and smiling
- your personal grooming or presentation because how you look 'speaks' too. Make sure that your clothing and general grooming supports your speech because, like it or not, you will be judged on both!
Go to: how to rehearse a speech properly .

Videoed Student Council speech examples
How do other people handle a Student Council speech? What's their content and delivery like?
Are they funny? Formal? Too hurried? Confident? Familiar with the audience?
It can help to look at what others have done. Even if it's only to decide their way will not be your way!

Click the link to access a collection ten videoed student council campaign speeches from the 2018 student council executive board candidates for Malvern Preparatory School, Malvern, Pennsylvania, USA.
At the foot of the article you'll find links to the videos of the school's 2015, 2016 and 2017 student council campaign speeches.
A word of warning
Ps. panic not.

If you find yourself getting anxious over the thought of delivering your speech, please check this page for help.
- How to deal with acute public speaking anxiety: 14 ways that will help

speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Elevator Speech [Outline + 13 Examples]

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.
Capturing your background, skills, and objectives into a short and clever elevator speech can be difficult. How do you know what to keep and what to leave out? How do you make an impression in such a short time?
Standing out with your elevator speech doesn’t have to be complicated. With a little practice, you’ll gain confidence in introducing yourself at a job interview, career fair, and, of course, on an elevator ride! Here’s a quick guide to help you craft the perfect pitch along with several elevator speech examples.
In this article:
Tips for Creating a Good Elevator Speech
A sample elevator speech outline, checklist for fine-tuning, elevator speech examples.

The elements that make up a great elevator speech outline are pretty straightforward. You need to describe who you are, what you do, and what your goal is. While the elevator speech template stays the same whether you’re speaking with a potential employer or a sales prospect, you might add other elements to match your unique situation.
Here are a few tips for crafting your personal elevator pitch:
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
- Keep it 30 to 60 seconds long.
- Use persuasive speech to spark your listener’s interest.
- Showcase your qualifications or skills.
- For a sales pitch, try starting with an open-ended question.
- Describe who you help and what problem you aim to help them solve.
- Be ready to customize your speech to fit your target audience.
Whether you’re a business owner preparing for a networking event or a job seeker attending a job fair, you can benefit from perfecting a succinct and effective elevator pitch. A go-to elevator speech comes in handy when you’re introducing yourself to new people in general. Have a business card on hand and ready to deliver as well.
Your elevator speech can also provide the right content for social media bios or a resume objective statement. This statement represents your personal brand, so keep it consistent across all social media channels.
Be sure to practice your elevator statement over and over so that you’re able to deliver it naturally, even in a moment’s notice. If you’re stumped for ideas, draw from the elevator speech examples listed below.
This model suggestion plan assists you to avoid creating a sales pitch. It must be from your mouth and supporting body language gestures, and about your skills and abilities. Use each idea to write one short powerful sentence.
The 10 speech topics I will explicate right now in the next paragraphs are primers to write a carefully planned and prepared presentation that grabs attention and says a lot in a few words.
Remember: tweak till it fits your personality and decisive nature.
ABOUT YOU 1. Smile to your counterpart, and open with a statement or question that grabs attention: a hook that prompt your listener to ask questions. 2. Tell who you are: describe you and your company. 3. Tell what you do and show enthusiasm.
WHAT DO YOU OFFER 4. Tell what problems have solved or contributions you have made. 5. Offer a vivid example. 6. Tell why you are interested in your listener.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS 7. Tell what very special service, product or solutions you can offer him or her. 8. What are the advantages of working with you? In what do you differ from competative companies?
HOW DO YOU DO IT 9. Give a concrete example or tell a short story, show your uniqueness and provide illustrations on how you work.
CALL FOR ACTION 10. What is the most wanted response? Do you want a business card, a referral or an corporate appointment for a presentation after your elevator speech ?
OTHER BUSINESS QUESTIONS
These are other points, questions and business subjects you could ask:
- Who is your target?
- How large is your market volume?
- How do you make profits?
- What are the background, major milestones and achievements of your team?
- Who are your competitors, how do they solve a problem? What is your strength and advantage compared to them? What is your Unique Selling Proposition?
- Are there special patents or technology? Do you have a special approach in client management? And so on.
STEP 1: First write down all that comes up in your mind.
STEP 2: Then cut the jargon and details. Make strong short and powerful sentences. Eliminate unnecessary words.
STEP 3: Connect phrases to each other. Your elevator speech address has to flow natural and smoothly. Do not rush, keep eye contact all the time and work steady to the grande finale: the call to action.
STEP 4: Memorize key points and practice out loud – test it with a close relative in the safe environment of your home.
STEP 5: Have you really answered the key question of your listener: What’s In It For Me?
STEP 6: Create different versions for different business situations of your elevator speech. Note them on professional business cards:
Perfect your own elevator presentation by learning from others. Here are a few effective elevator pitch examples to help you craft your own:
1. Job Seeker Elevator Pitch Example
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JH0Thez9gvA
You run into all kinds of people at the elevator, even a hiring manager. This sample elevator speech is a good example for those looking for a job interview. It shows how you can highlight your skills and experience even when you’re caught off guard. Notice how she also has a business card ready?
“I’m excited to hear back because the position helps me to use my brand management and social media skills…”
2. Recent Graduate Great Elevator Pitch
This is an excellent example for those who recently graduated with a bachelor degree in business. Notice that she states exactly what she’s looking for – an internship or job opportunity. In just 41 seconds, she states her experience, skills, and some good details about her personality that make her the perfect job candidate.
“I hope to incorporate my business knowledge into consumer trend analysis and strengthening relationships among consumers…”
3. College Student Personal Elevator Speech
This college freshman opens with her interest in the company. She states her major and reflects on high school experiences, also sharing relevant awards she has won for her skills.
“I’ve gotten awards for my leadership skills and I’m very involved with my college…”
4. Personal Brand Elevator Pitch Template
This college graduate pitches his personal brand through stating the skills he acquired in his education, the type of job he is looking for, and why he wants to work in that type of job. He offers a good mix of talking about his own experience while also focusing on how he’ll help clients. He ends his speech with the call to action of directing his audience to his website.
“I strive to lead a team on various projects one day.”
5. Personal Brand Pitch with a Personal Touch
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m_paOrg5Zpg
Video pitches are becoming increasingly popular for those looking to connect with brands online. This college student’s personal brand sales pitch stands out because it opens and closes with inspirational music. She explains her personal promise and future plans to receive her master degree.
“I promise to always bring positivity to the table and to remain hard working and dedicated no matter what the task.”
6. Business Plan Effective Elevator Speech
This example is perfect for a small business owner looking to pitch a product. The speaker opens with a compelling situation that appeals to his target market, offers his solution and details the features and benefits, announces his promise, and states his objective – all in 51 seconds.
“Don’t let frost bite your buns. Get the hot seat!”
7. Small Business Elevator Speech Sample
Opening with an interesting fact of how much Americans spend on fishing each year, the speaker follows up with an open-ended question to immediately grab audience attention from her target market. This is a great example of a sales pitch to investors, as the speaker outlines her plan for marketing her product and making their ROI (Return on Investment).
“Our goal is to revolutionize the economics of fishing in favor of the customer.”
8. Financial Advisor Elevator Speech
Ron Coleman explains who he is as a financial advisor, who he works for, and what exactly he helps his clients do. Additionally, he explains the type of people who benefit from his services.
“I’m confident that if given the opportunity I can provide you with the service and the coverage you need in order to protect your business, you, and your family from a variety of different risks.”
9. The Career Fair Elevator Pitch
This funny elevator speech example is the perfect model for a job seeker attending a job fair. The speaker highlights the importance of expressing interest in the company by acknowledging their work and asking a related open-ended question. Of course, lead with your own experience and skills that are relevant to the company representative whom you’re speaking with.
“I read on your website that you are the only company that has increased efficiency by employing mannequins. Can you tell me a bit more about that process?”
10. Good Elevator Speech for Speed Networking
This example from a holistic marketing mentor shows how you can sum up who you are, what you do, and the people you can help in one quick and savvy sentence.
“I help wellness professionals find additional revenue streams so that they can help more people and live a life of ease and grace.”
11. Extreme Sale Pitch Example with Iron Man Jericho Missile Test Scene
Sure, you might not ever get the opportunity to pitch a missile system, but you can take away a lot from Robert Downey Jr.’s confidence as Iron Man. Notice how he opens with a thought-provoking question, offers his guarantee, and humbly ends with a bonus.
“That’s how Dad did it, that’s how America did it, and it’s worked out pretty well so far.”
12. Don Draper’s Funny but Effective Sales Pitch
This funny elevator speech example shows the importance of using a tagline for your personal brand.
“From a basket of kisses she picks one. It makes her unique. It colors her kiss. And her kiss, well, it colors her man. Mark your man.”
13. Real Estate Elevator Speech Example
This is the perfect elevator pitch example for real estate agents. Stacy talks about what she specializes in and highlights her experience in the real estate industry.
“If you know of someone who is looking for a real estate agent in the metropolitan Kansas City, Missouri area that is professional, knowledgeable, and technologically savvy, that’s me!”
Best Man Speech Outline [Examples + Template]
Father of the Bride Speech [With Outlines and Examples]
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
Ohio State faculty adviser: Student protest arrests show start of 'A wave of repression'

Two Ohio State University students were arrested Tuesday and charged with misdemeanor criminal trespassing during an on-campus demonstration.
Ohio State University police officers arrested the students at Meiling Hall, a classroom and administrative building near the Wexner Medical Center, according to police reports. About 60 individuals had gathered to protest the Hamas-Israel war in Gaza and fossil fuel divestment.
The Dispatch is not naming the students, as they have not been charged with a felony. One student, a sociology major, is a member of Ohio Youth for Climate Justice, and the other is a journalism major and a member of OSU's Students for Justice in Palestine chapter.
Police said the students "failed to leave the area and failed to stop disrupting" an event being held in the building's lobby.
I am no longer a proud Buckeye. Ohio State president using dog whistle to muzzle free speech
A video posted by student organizers shows a group of protesters gathered on the steps outside Meiling Hall wearing pro-Palestine shirts and chanting "Free Palestine." In the video, an OSU police officer walks down the steps, points at a student, turns back to give a thumbs up to other officers before three officers walked the individual up the steps and into custody.
Another video showed about a dozen police officers and university officials blocking the building's entrance and pushing a student after officers pulled the student inside the building's safety vestibule.
What happened at Tuesday's protest at Ohio State?
Isabella Guinigundo — an Ohio State fourth-year student and communications director of Ohio Youth for Climate Justice, a statewide organization that advocates for environmental justice — said the protest was organized by several groups. It was meant to be Ohio Youth for Climate Justice's last event of the semester.
Guinigundo said students initially gathered at Mirror Lake and were met by Office of Student Life employees and OSU police officers, who warned them that there would be "no tolerance for amplified noise" because it was Reading Day, a day on the academic calendar before exams begin for students to study. They were also told they could only chant outdoors, she said.
Guinigundo said the students chose not to use the megaphones and loud speakers they brought to comply with the rules. The group eventually marched to Meiling Hall, where the OSU Wexner Medical Center Board of Trustees' Quality and Professional Affairs committee was meeting.
The group held its own "People's Board Meeting" outside the building, Guinigundo said. At some point, she said police officers told the group it could be heard from inside the building's lobby. One was arrested shortly after the warning.
Ben Johnson, a university spokesman, said the students received "multiple warnings" before their arrest that they were being too loud. The two students who were arrested were individuals who "continued at the same volume" after being warned, he said.
"Well established university policy prohibits disrupting the university’s mission, administrative functions and campus-life activities. This includes demonstrations that disrupt classroom and administrative buildings," Johnson said.
Disruptive noise, according to the university's space rules, includes, but is not limited to: amplified sound, other loud noise that is audible more than 50 feet from the source of the sound and/or noise occurring during the restricted hours above.
Guinigundo said most protesters took a step back from the doors to regroup when police arrested another student.
Johnson said it was "only when warnings weren't heeded" that students were arrested.
"Ohio State has an unwavering commitment to freedom of speech and took this action in alignment with our space use rules to provide for the orderly conduct of university business," Johnson said.
Ohio State students, faculty say police 'wanted to make an example'
Sumaya Hamadmad, an Ohio State research scientist, attended the protest as a member of the Faculty and Staff for Justice in Palestine group. She said students complied with all rules given by university officials. They were so quiet at times, she said, she could barely hear what was being said to the group.
"You could hear more noise on a regular school day," she said. "This was meant to intimidate students."
Guinigundo agreed.
"OSUPD wanted to make an example out of our organizations," she said.
Pranav Jani, faculty adviser for Students for Justice in Palestine and an associate professor of English at Ohio State, said he believes "Ohio State has been laying the groundwork for these arrests for a long time."
"A wave of repression is starting, and we can expect it to get worse," he said.
Jani said Ohio State has suspended a student group, charged individual students under the university's code of conduct for nonviolent protests and "has basically accused students of inciting violence and hate." He said he's been in meetings with administrators and students for weeks, "and while private sympathies are expressed, actions and arrests speak louder than words."
Hamadmad said she is worried that universities calling police officers on their own students, like what is happening with student protesters at Columbia University , is setting dangerous precedent.
"Ohio State, like universities around the country, has failed to protect or even show basic empathy for their Palestinian and pro-Palestinian students and faculty, which include Muslim, Arab, Jewish, Christian and many others," Jani said. "It’s a damn shame."
Ohio State president said university will 'continue to prioritize safety'
The arrests come a day after Ohio State President Ted Carter said in an end-of-the-semester email that he respects students' right to freedom of speech, but "will not compromise" on matters of safety.
Ohio State will "continue to prioritize safety," Carter said in the email, including having university police officers and trained staff on-site for demonstrations, and enforcing space rules that prohibit "intentional disruptions of university events, classes, exams or programming, including commencement."
OSU's spring commencement is May 5 at Ohio Stadium.
Johnson said he is "cautiously optimistic that people will by and large be respectful" at protests as the semester draws to a close.
Guinigundo said protesters appreciate the support they've received, but she hopes people remember the reason they are protesting in the first place.
"Our hearts should be with Gaza," she said.
Sheridan Hendrix is a higher education reporter for The Columbus Dispatch. Sign up for Extra Credit, her education newsletter, here .
@sheridan120
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Unpacking the truth of antisemitism on college campuses

Odette Yousef
Colleges have become a flashpoint in discussions about rising antisemitism. But some on those campuses say the alarm from politicians and groups distorts reality and their motives should be examined.
(SOUNDBITE OF ARCHIVED RECORDING)
UNIDENTIFIED PROTESTORS #1: (Chanting) No peace on stolen land.
AILSA CHANG, HOST:
Those are the sounds of some of the latest campus protests that have broken out across the U.S. over Israel's war in Gaza.
SCOTT DETROW, HOST:
That includes the University of Texas and Austin, where protesters directed their message at the governor.
UNIDENTIFIED PROTESTORS #2: (Chanting) Hey, Greg Abbott. You will see...
UNIDENTIFIED PROTESTOR #1: (Chanting) Palestine will be free.
UNIDENTIFIED PROTESTORS #2: (Chanting) ...Palestine will be free.
CHANG: At least a dozen campuses have seen protests since last week. Many students and professors want their school administrators to call for a cease-fire. Now, these protests largely have been peaceful, and among the protesters are some Jewish students. One of them at the University of Southern California told CBS News this.
UNIDENTIFIED STUDENT: As an Israeli Jewish person, I feel that it is absolutely crucial for me to stand with Muslim friends and peers, especially when they are being accused of antisemitism simply for criticizing my government.
CHANG: But some protests have prompted in-person class cancellations and arrests. Early this morning, police arrested more than 100 pro-Palestinian protesters outside Emerson College in Boston. And some students and alumni are worried about antisemitism. Former Columbia student Elise Mordos spoke to NPR earlier this week.
ELISE MORDOS: Jewish people deserve to be treated just like everybody else. We're a minority group, and we deserve to be treated equally and fairly.
DETROW: Leaders at the highest level of government are responding. Here's President Biden earlier this week.
PRESIDENT JOE BIDEN: I condemn antisemitic protests. That's why I've set up a program to deal with that. I also condemn those who don't understand what's going on with the Palestinians.
CHANG: Yesterday House Speaker Mike Johnson visited Columbia University and spoke afterwards on Fox News.
MIKE JOHNSON: We have to call this madness out for what it is. It was chaos on that campus. I mean, we were looking out to a sea of students' faces with rage. So many of them don't even know what the heck they're talking about.
DETROW: The Israel government has called the protesters terrorists on social media. Republican Congressmen have called for the National Guard to be brought in. Yet many, especially those on the campuses, say that these outside voices are not helping.
CHANG: All right, we're going to bring in now NPR's Lisa Hagen and extremism correspondent Odette Yousef to try to disentangle some of this for us. And, Odette, I want to start with you. Can you just help us get a handle on this current moment? Like, when we hear about this concerning rise in antisemitism on campuses, what is that looking like right now?
ODETTE YOUSEF, BYLINE: So Ailsa, speaking with people on college campuses, what we're hearing is a spectrum of activity that could be considered antisemitic. And in general, those have fallen into three categories. First, there's been speech - targeted hate speech, protest slogans that may make some Jewish students feel unsafe, even speech that endorses the violence of Hamas. This can be very unnerving. But in the U.S., it is protected by the First Amendment. The second category is more along the lines of discrimination and civil rights violations - so students being excluded from activities or groups, you know, perhaps even feeling targeted by faculty because of their religion or identity. And then there's a third category, which is violence and physical intimidation. And that's where extremism researchers pay very close attention.
CHANG: All right, so tell us more about that category.
YOUSEF: So here, I really think about two things. First is hate crimes and incidents, but I also think about conspiracy theories. And we're going to get to those in a bit, but let's start with hate crime data first. So we won't see 2024 hate crime data from the FBI until next year. So instead, you know, many people have been looking to outside organizations, especially the Anti-Defamation League, for numbers. The problem is that the ADL changed its methodology after October 7. After that conflict began, the ADL started to include specific speech expressions in its audit of antisemitism, including certain anti-Zionist phrases and phrases that express support for Hamas. And for extremism researchers, you know, this is not traditional.
CHANG: Interesting.
YOUSEF: I spoke with Brian Levin of the Center for the Study of Hate and Extremism at Cal State San Bernardino about this.
BRIAN LEVIN: Creating this kind of category casts more heat than light. So let's stick to things where we already have well-established, yearslong acceptance and vetting of more acceptable things of looking at.
YOUSEF: You know, Levin points out, Ailsa, that this kind of new methodology could potentially dragnet Jewish voices who are proud of their religion and heritage but who oppose Israel's war in Gaza in its count of antisemitism. But regardless, you know, Levin's own data have also shown that antisemitism has been reaching a record level nationally.
CHANG: And you said, Odette, that there's this other component that you look at here, which is conspiracy theories. Can you just explain more about what those conspiracy theories are?
YOUSEF: Yeah. So antisemitic conspiracy theories are like the portal to hate-driven violence against all kinds of people, you know, including Black people and immigrants. In recent years, Ailsa, several major mass violence events in the U.S. have been motivated by belief in the great replacement. And that is a conspiracy theory that baselessly claims that powerful Jews are diluting the white Christian American population. The neo-Nazi rally in 2017 in Charlottesville is one example.
CHANG: Right.
YOUSEF: So it's surprising to hear figures like former President Trump and even Democratic Senator John Fetterman compare mostly peaceful campus protesters of today to those neo-Nazis. Amy Spitalnick is the CEO of the Jewish Council for Public Affairs. Previously, she helped spearhead a successful lawsuit against the organizers of the Charlottesville rally.
AMY SPITALNICK: This was an attempted mass murder that was planned meticulously for months and months in advance by avowed neo-Nazis who had shrines to Hitler. This doesn't mean that there aren't very real antisemites on the left who have done awful things on college campuses in the last 6 1/2 months. But to compare the complexity of what we're seeing at Columbia or on other college campuses to what happened in Charlottesville is deeply wrong.
YOUSEF: And something worth highlighting, Ailsa, about the campus protests today is that all the attention on them is providing an opportunity for another deeply antisemitic conspiracy theory to circulate.
CHANG: Let's talk about that. I want to turn to Lisa for that. Tell us more about what that antisemitic conspiracy theory is.
LISA HAGEN, BYLINE: So to answer that, here's a clip from Senator Ted Cruz from his podcast this week.
TED CRUZ: Cultural Marxism has taken over our college campuses. It has become the dominant ideology.
HAGEN: That phrase, cultural Marxism, goes back to the 1960s. It was used to describe what some on the right saw as a threatening academic movement to destroy traditional Western values. They mischaracterized the work of a small group of intellectuals, many of whom were Jews who had fled from Nazi Germany. So this was a really complicated academic discourse that got flattened by right-wing political strategists into a familiar and false trope about a cabal of Jews destroying traditional values.
CHANG: So what's the impact of this idea of cultural Marxism on that academic discourse?
HAGEN: So this phrase is used by the same partisan figures who oppose diversity and inclusion efforts or teaching about the role of race in American history. And going back to Amy Spitalnick, she has her disagreements with some of the approaches and language used in today's campus protests. And she says Jews are rightfully concerned about antisemitism. But she also has serious concerns about characterizing campus protesters as broadly motivated by antisemitism or violence.
SPITALNICK: And so when loud voices are trying to exploit concerns around antisemitism to advance this broader reactionary, extremist agenda, we need to understand what's happening there. And I'm not sure that the vast majority of people actually see how this is a deliberate effort.
HAGEN: It's an effort she says she's seen crafted intentionally to tear apart Jewish communities and their coalitions with other marginalized people. And Spitalnick says none of that is going to make anyone safer.
CHANG: That was NPR's Lisa Hagen and Odette Yousef. Thank you both so much.
YOUSEF: Thank you.
HAGEN: Thanks.
Copyright © 2024 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The outline for a public speech, according to COMM 101 online textbook The Public Speaking Project, p.p. 8-9. Use these samples to help prepare your speech outlines and bibliographies: Sample Speech Preparation Outline
When outlining your speech, make sure to decide how much time you'd like to give each of your main points. You might even consider setting specific timers during rehearsals to get a real feel for each part's duration. Generally speaking, you should allot a fairly equal amount of time for each to keep things balanced.
how to outline a speech: the 4 essentials steps involved in writing an outline - detailed sequential help, with examples, covering: 1. choosing a topic, 2. audience analysis, 3. choosing the best organizational pattern to fit your speech purpose, 4. what to put in each part of your speech: introduction, body and conclusion. a printable speech ...
It lets the audience know that the speech is about to end. Like the introduction, the conclusion can be broken into two parts: the review and the final statement. A. Review: During the first part of the conclusion, the speaker restates the topic of the speech and each main point. B. Final Statement: The speech ends with a strong final statement.
Reason 3 ( Provide one reason as to why listeners should act or think the way your thesis suggests.) Example 1 - Support for the reason given above. Example 2 - Support for the reason given above. The most important part of a persuasive speech is the conclusion, second to the introduction and thesis statement.
Before you begin writing your outline, you should take a step back and think about your speech as a whole. First, think about the 3 keystones for your presentation or speech, i.e. the audience, your subject matter and of course, you, as the speaker. Then, write a few notes down about each keystone and how they relate with each other.
Student Speech Examples. This section provides examples of student outlines and speeches. Use these to help inform your choices as you begin formatting your informative, persuasive, and/or commemorative speeches. Previous: A Note about Reflection. Next: Outline and Visual Aid Examples.
1. State your first point. The outline of the body of your speech will begin with the first point you intend to make in your speech. Write out a smooth transition from your introduction into the body of your speech. Your first point will be a top-level entry on your outline, typically noted by a Roman numeral.
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples. A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything - voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on. A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing ...
Speech Outline Definition. When trying to present information, whether to persuade or inform, creating an outline can assist in constructing and executing an effective speech. Through the use of ...
To create a working outline, you will need: A speech topic. An idea for the "hook" in your introduction. A thesis statement. 3-5 main points (each one should make a primary claim that you support with references) A conclusion. Each of your main points will also have sub-points, but we'll get to those in a later step.
An Informative Speech focus on educating an audience through the use of facts and evidence to establish credibility. It can include definitions, explanations, descriptions, visual images, demonstrations. It should focus on speaking about objects, events, processes, concepts, and examples. An informative speech does not attempt to persuade and ...
This page titled 13.7: Sample Outline- Persuasive Speech Using Monroe's Motivated Sequence Pattern is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Kris Barton & Barbara G. Tucker (GALILEO Open Learning Materials) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a ...
How to Speech: 4 Key steps to doing what you are talking about. Example: Step One: Clean the chicken of any unwanted feathers and giblets. Step Two: Spice the chicken and add stuffings. Step Three: Set oven to 425 degrees Fahrenheit. Step Four: Place chicken in the oven and cook for an hour.
3.3 Explanatory Speech. 3.4 Demonstration Speech. 4 Informative Speech Outline Templates. 5 Checklist for Your Informative Speech. 5.1 Eye Contact. 5.2 Tone of Your Voice. 5.3 Expressive Hand and Body Gestures. 6 Informative Speech Samples. 7 Tips for Your Informative Speech from a Professional.
Writing outlines with students is an important activity. Looking at a speech line by line aids in transitions, and in creating a balance of material. An outline is also a working document. As students practice their delivery, they can easily add and subtract from an outline. When I taught middle school speech, I found that designing a speech ...
Speech 101 - Narrative Speech Outline . General Purpose: To share a personal experience and the insight or lesson gained. Specific Purpose: After hearing my speech, my audience will understand the importance of expressing their gratitude to the people they love. Thesis: It's important to show your gratitude and love to your friends,
In this video how to write a speech in 5-minutes. Plus, I give speech examples. We also take a look at opening remarks, speech structure, storytelling, and c...
Informative Speech Outline. This is a student example for you to use for your own outline preparation. This student's outline is well developed, coherent, integrates research, follows a strong organizational pattern, and meets all expectations of an outline in a public speaking course. Click on the Google Document provided for a sample speech ...
Step 1: open the speech with a greeting and introduction. As a matter of courtesy, it is a good thing to open the speech with a greeting. Follow this by introducing yourself. Take time also to thank those who have attended that event as well as its organizers. Lastly, thank the person who asked you to arise and speak.
2. Body. The body section allows you to provide details of the particular topic of your speech. Section 1. Write the main idea of the section. Provide supporting details, examples, and evidence to support the idea. Smoothly transition to the next main point of your speech. Section 2.
Student Council President speech example Here's a sample student council speech. I've written it from the perspective of someone running for President. As you read it, imagine it said aloud. That will help you get the rhythm and flow of language. The speech is between 3 - 4 minutes long, depending on how quickly you speak.
STEP 3: Connect phrases to each other. Your elevator speech address has to flow natural and smoothly. Do not rush, keep eye contact all the time and work steady to the grande finale: the call to action. STEP 4: Memorize key points and practice out loud - test it with a close relative in the safe environment of your home.
Ohio State students, faculty say police 'wanted to make an example' Sumaya Hamadmad, an Ohio State research scientist, attended the protest as a member of the Faculty and Staff for Justice in ...
After reports of harassment by demonstrators, some Jewish students said they felt unsafe. Others said they felt safe, while condemning antisemitism. By Luis Ferré-Sadurní, Colbi Edmonds and ...
Jewish students from across Columbia University told their stories about their encounters with anti-Israel protesters, Jonathan A. Greenblatt writes.
First, there's been speech - targeted hate speech, protest slogans that may make some Jewish students feel unsafe, even speech that endorses the violence of Hamas. This can be very unnerving.
In my book, Sustainable.Resilient. Free.: The Future of Public Higher Education, I attempt to make the argument that higher education, particularly public higher education, is an example of infrastructure, a necessity for the fulfillment of the promise made by the country's founders in the Declaration of Independence regarding life, liberty. and the pursuit of happiness.
Since the Oct. 7 Hamas attacks on Israel, administrators at Columbia had tried to calibrate their approaches to the demonstrations, balancing free-speech rights with the security of Jewish students.
Some Jewish students and others have said they appreciated the response, while some left-leaning faculty members, students, free speech advocates and others have said it was too harsh.