What is a Marketing Plan & How to Write One [+Examples]
Published: December 27, 2023
For a while now, you've been spearheading your organization's content marketing efforts, and your team's performance has convinced management to adopt the content marketing strategies you’ve suggested.

Now, your boss wants you to write and present a content marketing plan, but you‘ve never done something like that before. You don't even know where to start.
![types of marketing assignment Download Now: Free Marketing Plan Template [Get Your Copy]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/aacfe6c7-71e6-4f49-979f-76099062afa0.png)
Fortunately, we've curated the best content marketing plans to help you write a concrete plan that's rooted in data and produces results. But first, we'll discuss what a marketing plan is and how some of the best marketing plans include strategies that serve their respective businesses.

What is a marketing plan?
A marketing plan is a strategic roadmap that businesses use to organize, execute, and track their marketing strategy over a given period. Marketing plans can include different marketing strategies for various marketing teams across the company, all working toward the same business goals.
The purpose of a marketing plan is to write down strategies in an organized manner. This will help keep you on track and measure the success of your campaigns.
Writing a marketing plan will help you think of each campaign‘s mission, buyer personas, budget, tactics, and deliverables. With all this information in one place, you’ll have an easier time staying on track with a campaign. You'll also discover what works and what doesn't. Thus, measuring the success of your strategy.
Featured Resource: Free Marketing Plan Template

Looking to develop a marketing plan for your business? Click here to download HubSpot's free Marketing Plan Template to get started .
To learn more about how to create your marketing plan, keep reading or jump to the section you’re looking for:
How to Write a Marketing Plan
Types of marketing plans, marketing plan examples, marketing plan faqs, sample marketing plan.

If you're pressed for time or resources, you might not be thinking about a marketing plan. However, a marketing plan is an important part of your business plan.
Marketing Plan vs. Business Plan
A marketing plan is a strategic document that outlines marketing objectives, strategies, and tactics.
A business plan is also a strategic document. But this plan covers all aspects of a company's operations, including finance, operations, and more. It can also help your business decide how to distribute resources and make decisions as your business grows.
I like to think of a marketing plan as a subset of a business plan; it shows how marketing strategies and objectives can support overall business goals.
Keep in mind that there's a difference between a marketing plan and a marketing strategy.

Free Marketing Plan Template
Outline your company's marketing strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
- Pre-Sectioned Template
- Completely Customizable
- Example Prompts
- Professionally Designed
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Marketing Strategy vs. Marketing Plan
A marketing strategy describes how a business will accomplish a particular goal or mission. This includes which campaigns, content, channels, and marketing software they'll use to execute that mission and track its success.
For example, while a greater plan or department might handle social media marketing, you might consider your work on Facebook as an individual marketing strategy.
A marketing plan contains one or more marketing strategies. It's the framework from which all of your marketing strategies are created and helps you connect each strategy back to a larger marketing operation and business goal.
For example, suppose your company is launching a new software product, and it wants customers to sign up. The marketing department needs to develop a marketing plan that'll help introduce this product to the industry and drive the desired signups.
The department decides to launch a blog dedicated to this industry, a new YouTube video series to establish expertise, and an account on Twitter to join the conversation around this subject. All this serves to attract an audience and convert this audience into software users.
To summarize, the business's marketing plan is dedicated to introducing a new software product to the marketplace and driving signups for that product. The business will execute that plan with three marketing strategies : a new industry blog, a YouTube video series, and a Twitter account.
Of course, the business might consider these three things as one giant marketing strategy, each with its specific content strategies. How granular you want your marketing plan to get is up to you. Nonetheless, every marketing plan goes through a particular set of steps in its creation.
Learn what they are below.
- State your business's mission.
- Determine the KPIs for this mission.
- Identify your buyer personas.
- Describe your content initiatives and strategies.
- Clearly define your plan's omissions.
- Define your marketing budget.
- Identify your competition.
- Outline your plan's contributors and their responsibilities.
1. State your business's mission.
Your first step in writing a marketing plan is to state your mission. Although this mission is specific to your marketing department, it should serve your business‘s main mission statement.
From my experience, you want to be specific, but not too specific. You have plenty of space left in this marketing plan to elaborate on how you'll acquire new customers and accomplish this mission.

Need help building your mission statement? Download this guide for examples and templates and write the ideal mission statement.
2. Determine the KPIs for this mission.
Every good marketing plan describes how the department will track its mission‘s progress. To do so, you need to decide on your key performance indicators (KPIs) .
KPIs are individual metrics that measure the various elements of a marketing campaign. These units help you establish short-term goals within your mission and communicate your progress to business leaders.
Let's take our example of a marketing mission from the above step. If part of our mission is “to attract an audience of travelers,” we might track website visits using organic page views. In this case, “organic page views” is one KPI, and we can see our number of page views grow over time.
These KPIs will come into the conversation again in step 4.
3. Identify your buyer personas.
A buyer persona is a description of who you want to attract. This can include age, sex, location, family size, and job title. Each buyer persona should directly reflect your business's current and potential customers. So, all business leaders must agree on your buyer personas.

Create your buyer personas with this free guide and set of buyer persona templates.
4. Describe your content initiatives and strategies.
Here's where you'll include the main points of your marketing and content strategy. Because there's a laundry list of content types and channels available to you today, you must choose wisely and explain how you'll use your content and channels in this section of your marketing plan.
When I write this section , I like to stipulate:
- Which types of content I'll create. These might include blog posts, YouTube videos, infographics, and ebooks.
- How much of it I'll create. I typically describe content volume in daily, weekly, monthly, or even quarterly intervals. It all depends on my workflow and the short-term goals for my content.
- The goals (and KPIs) I'll use to track each type. KPIs can include organic traffic, social media traffic, email traffic, and referral traffic. Your goals should also include which pages you want to drive that traffic to, such as product pages, blog pages, or landing pages.
- The channels on which I'll distribute my content. Popular channels include Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, YouTube, Pinterest, and Instagram.
- Any paid advertising that will take place on these channels.
Build out your marketing plan with this free template.
Fill out this form to access the template., 5. clearly define your plan's omissions..
A marketing plan explains the marketing team's focus. It also explains what the marketing team will not focus on.
If there are other aspects of your business that you aren't serving in this particular plan, include them in this section. These omissions help to justify your mission, buyer personas, KPIs, and content. You can’t please everyone in a single marketing campaign, and if your team isn't on the hook for something, you need to make it known.
In my experience, this section is particularly important for stakeholders to help them understand why certain decisions were made.
6. Define your marketing budget.
Whether it's freelance fees, sponsorships, or a new full-time marketing hire, use these costs to develop a marketing budget and outline each expense in this section of your marketing plan.
You can establish your marketing budget with this kit of 8 free marketing budget templates .
7. Identify your competition.
Part of marketing is knowing whom you're marketing against. Research the key players in your industry and consider profiling each one.
Keep in mind not every competitor will pose the same challenges to your business. For example, while one competitor might be ranking highly on search engines for keywords you want your website to rank for, another competitor might have a heavy footprint on a social network where you plan to launch an account.
Easily track and analyze your competitors with t his collection of ten free competitive analysis templates .
8. Outline your plan's contributors and their responsibilities.
With your marketing plan fully fleshed out, it's time to explain who’s doing what. I don't like to delve too deeply into my employees’ day-to-day projects, but I know which teams and team leaders are in charge of specific content types, channels, KPIs, and more.
Now that you know why you need to build an effective marketing plan, it’s time to get to work. Starting a plan from scratch can be overwhelming if you haven't done it before. That’s why there are many helpful resources that can support your first steps. We’ll share some of the best guides and templates that can help you build effective results-driven plans for your marketing strategies.
Ready to make your own marketing plan? Get started using this free template.
Depending on the company you work with, you might want to create various marketing plans. We compiled different samples to suit your needs:
1. Quarterly or Annual Marketing Plans
These plans highlight the strategies or campaigns you'll take on in a certain period.
Forbes published a marketing plan template that has amassed almost 4 million views. To help you sculpt a marketing roadmap with true vision, their template will teach you how to fill out the 15 key sections of a marketing plan, which are:
- Executive Summary
- Target Customers
- Unique Selling Proposition
- Pricing & Positioning Strategy
- Distribution Plan
- Your Offers
- Marketing Materials
- Promotions Strategy
- Online Marketing Strategy
- Conversion Strategy
- Joint Ventures & Partnerships
- Referral Strategy
- Strategy for Increasing Transaction Prices
- Retention Strategy
- Financial Projections
If you're truly lost on where to start with a marketing plan, I highly recommend using this guide to help you define your target audience, figure out how to reach them, and ensure that audience becomes loyal customers.
2. Social Media Marketing Plan
This type of plan highlights the channels, tactics, and campaigns you intend to accomplish specifically on social media. A specific subtype is a paid marketing plan, which highlights paid strategies, such as native advertising, PPC, or paid social media promotions.
Shane Snow's Marketing Plan for His Book Dream Team is a great example of a social media marketing plan:
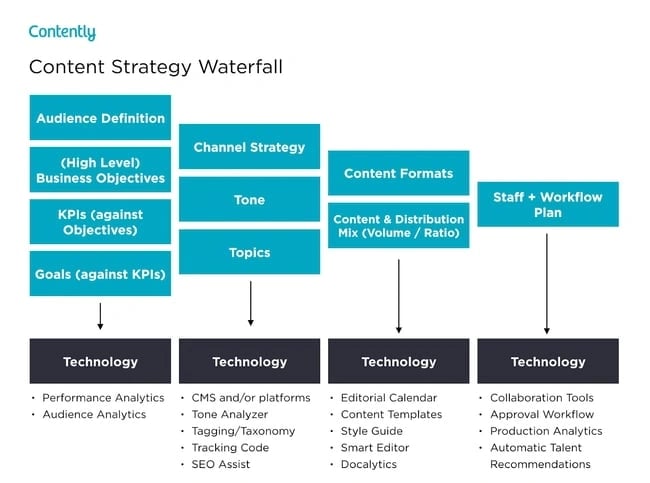
When Shane Snow started promoting his new book, "Dream Team," he knew he had to leverage a data-driven content strategy framework. So, he chose his favorite one: the content strategy waterfall. The content strategy waterfall is defined by Economic Times as a model used to create a system with a linear and sequential approach.
Snow wrote a blog post about how the waterfall‘s content strategy helped him launch his new book successfully. After reading it, you can use his tactics to inform your own marketing plan. More specifically, you’ll learn how he:
- Applied his business objectives to decide which marketing metrics to track.
- Used his ultimate business goal of earning $200,000 in sales or 10,000 purchases to estimate the conversion rate of each stage of his funnel.
- Created buyer personas to figure out which channels his audience would prefer to consume his content.
- Used his average post view on each of his marketing channels to estimate how much content he had to create and how often he had to post on social media.
- Calculated how much earned and paid media could cut down the amount of content he had to create and post.
- Designed his process and workflow, built his team, and assigned members to tasks.
- Analyzed content performance metrics to refine his overall content strategy.
I use Snow's marketing plan to think more creatively about my content promotion and distribution plan. I like that it's linear and builds on the step before it, creating an air-tight strategy that doesn't leave any details out.
![types of marketing assignment → Free Download: Social Media Calendar Template [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/3e56e15d-47bd-46c9-a256-99fde52abfe7.png)
3. Content Marketing Plan
This plan could highlight different strategies, tactics, and campaigns in which you'll use content to promote your business or product.
HubSpot's Comprehensive Guide for Content Marketing Strategy is a strong example of a content marketing plan:

At HubSpot, we‘ve built our marketing team from two business school graduates working from a coffee table to a powerhouse of hundreds of employees. Along the way, we’ve learned countless lessons that shaped our current content marketing strategy. So, we decided to illustrate our insights in a blog post to teach marketers how to develop a successful content marketing strategy, regardless of their team's size.

In this comprehensive guide for modern marketers, you'll learn:
- What exactly content marketing is.
- Why your business needs a content marketing strategy.
- Who should lead your content marketing efforts?
- How to structure your content marketing team based on your company's size.
- How to hire the right people for each role on your team.
- What marketing tools and technology you'll need to succeed.
- What type of content your team should create, and which employees should be responsible for creating them.
- The importance of distributing your content through search engines, social media, email, and paid ads.
- And finally, the recommended metrics each of your teams should measure and report to optimize your content marketing program.
This is a fantastic resource for content teams of any size — whether you're a team of one or 100. It includes how to hire and structure a content marketing team, what marketing tools you'll need, what type of content you should create, and even recommends what metrics to track for analyzing campaigns. If you're aiming to establish or boost your online presence, leveraging tools like HubSpot's drag-and-drop website builder can be extremely beneficial. It helps you create a captivating digital footprint that sets the foundation for your content marketing endeavors.
4. New Product Launch Marketing Plan
This will be a roadmap for the strategies and tactics you‘ll implement to promote a new product. And if you’re searching for an example, look no further than Chief Outsiders' Go-To-Market Plan for a New Product :

After reading this plan, you'll learn how to:
- Validate a product
- Write strategic objectives
- Identify your market
- Compile a competitive landscape
- Create a value proposition for a new product
- Consider sales and service in your marketing plan
If you're looking for a marketing plan for a new product, the Chief Outsiders template is a great place to start. Marketing plans for a new product will be more specific because they target one product versus its entire marketing strategy.
5. Growth Marketing Plan
Growth marketing plans use experimentation and data to drive results, like we see in Venture Harbour’s Growth Marketing Plan Template :
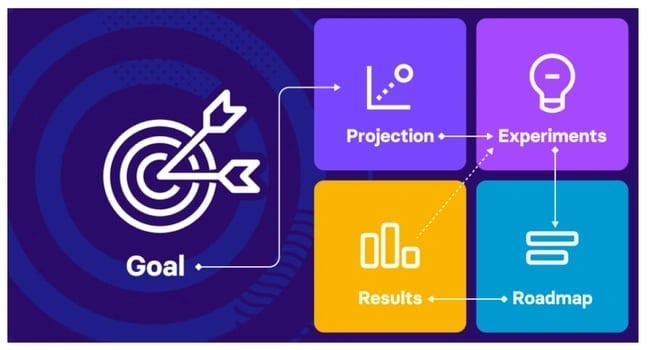
Venture Harbour's growth marketing plan is a data-driven and experiment-led alternative to the more traditional marketing plan. Their template has five steps intended for refinement with every test-measure-learn cycle. The five steps are:
- Experiments

I recommend this plan if you want to experiment with different platforms and campaigns. Experimentation always feels risky and unfamiliar, but this plan creates a framework for accountability and strategy.
- Louisville Tourism
- University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
- Visit Oxnard
- Safe Haven Family Shelter
- Wright County Economic Development
- The Cultural Council of Palm Beach County
- Cabarrus County Convention and Visitors Bureau
- Visit Billings
1. Louisville Tourism

It also divides its target market into growth and seed categories to allow for more focused strategies. For example, the plan recognizes Millennials in Chicago, Atlanta, and Nashville as the core of it's growth market, whereas people in Boston, Austin, and New York represent seed markets where potential growth opportunities exist. Then, the plan outlines objectives and tactics for reaching each market.
Why This Marketing Plan Works
- The plan starts with a letter from the President & CEO of the company, who sets the stage for the plan by providing a high-level preview of the incoming developments for Louisville's tourism industry
- The focus on Louisville as "Bourbon City" effectively leverages its unique cultural and culinary attributes to present a strong brand
- Incorporates a variety of data points from Google Analytics, Arrivalist, and visitor profiles to to define their target audience with a data-informed approach
2. University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign

For example, students who become prospects as freshman and sophomore will receive emails that focus on getting the most out of high school and college prep classes. Once these students become juniors and seniors — thus entering the consideration stage — the emails will focus more on the college application process and other exploratory content.
- The plan incorporates competitive analysis, evaluation surveys, and other research to determine the makeup of its target audience
- The plan lists each marketing program (e.g., direct mail, social media, email etc.) and supplements it with examples on the next page
- Each marketing program has its own objectives, tactics, and KPIs for measuring success
3. Visit Oxnard
This marketing plan by Visit Oxnard, a convention and visitors bureau, is packed with all the information one needs in a marketing plan: target markets, key performance indicators, selling points, personas, marketing tactics by channel, and much more.
It also articulates the organization’s strategic plans for the upcoming fiscal year, especially as it grapples with the aftereffects of the pandemic. Lastly, it has impeccable visual appeal, with color-coded sections and strong branding elements.
- States clear and actionable goals for the coming year
- Includes data and other research that shows how their team made their decisions
- Outlines how the team will measure the success of their plan
4. Safe Haven Family Shelter

This marketing plan by a nonprofit organization is an excellent example to follow if your plan will be presented to internal stakeholders at all levels of your organization. It includes SMART marketing goals , deadlines, action steps, long-term objectives, target audiences, core marketing messages , and metrics.
The plan is detailed, yet scannable. By the end of it, one can walk away with a strong understanding of the organization’s strategic direction for its upcoming marketing efforts.
- Confirms ongoing marketing strategies and objectives while introducing new initiatives
- Uses colors, fonts, and formatting to emphasize key parts of the plan
- Closes with long-term goals, key themes, and other overarching topics to set the stage for the future
5. Wright County Economic Development

Wright County Economic Development’s plan drew our attention because of its simplicity, making it good inspiration for those who’d like to outline their plan in broad strokes without frills or filler.
It includes key information such as marketing partners, goals, initiatives, and costs. The sections are easy to scan and contain plenty of information for those who’d like to dig into the details. Most important, it includes a detailed breakdown of projected costs per marketing initiative — which is critical information to include for upper-level managers and other stakeholders.
- Begins with a quick paragraph stating why the recommended changes are important
- Uses clear graphics and bullet points to emphasize key points
- Includes specific budget data to support decision-making
6. The Cultural Council of Palm Beach County
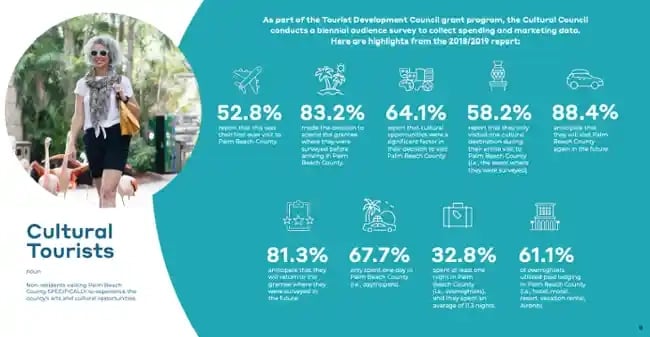
This marketing plan presentation by a cultural council is a great example of how to effectively use data in your plan, address audiences who are new to the industry, and offer extensive detail into specific marketing strategies.
For instance, an entire slide is dedicated to the county’s cultural tourism trends, and at the beginning of the presentation, the organization explains what an arts and culture agency is in the first place.
That’s a critical piece of information to include for those who might not know. If you’re addressing audiences outside your industry, consider defining terms at the beginning, like this organization did.
- Uses quality design and images to support the goals and priorities in the text
- Separate pages for each big idea or new strategy
- Includes sections for awards and accomplishments to show how the marketing plan supports wider business goals
- Defines strategies and tactics for each channel for easy skimming
7. Cabarrus County Convention & Visitors Bureau
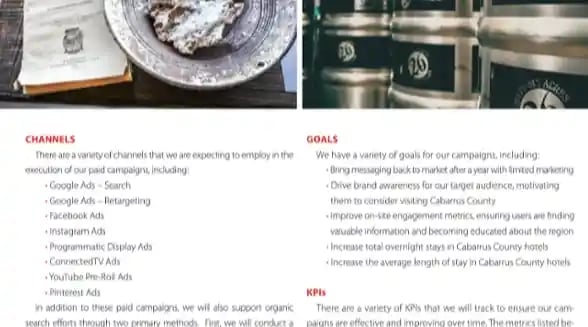
Cabarrus County’s convention and visitors bureau takes a slightly different approach with its marketing plan, formatting it like a magazine for stakeholders to flip through. It offers information on the county’s target audience, channels, goals, KPIs, and public relations strategies and initiatives.
We especially love that the plan includes contact information for the bureau’s staff members, so that it’s easy for stakeholders to contact the appropriate person for a specific query.
- Uses infographics to expand on specific concepts, like how visitors benefit a community
- Highlights the team members responsible for each initiative with a photo to emphasize accountability and community
- Closes with an event calendar for transparency into key dates for events
8. Visit Billings

Visit Billing’s comprehensive marketing plan is like Cabarrus County’s in that it follows a magazine format. With sections for each planned strategy, it offers a wealth of information and depth for internal stakeholders and potential investors.
We especially love its content strategy section, where it details the organization’s prior efforts and current objectives for each content platform.
At the end, it includes strategic goals and budgets — a good move to imitate if your primary audience would not need this information highlighted at the forefront.
- Includes a section on the buyer journey, which offers clarity on the reasoning for marketing plan decisions
- Design includes call-outs for special topics that could impact the marketing audience, such as safety concerns or "staycations"
- Clear headings make it easy to scan this comprehensive report and make note of sections a reader may want to return to for more detail
What is a typical marketing plan?
In my experience, most marketing plans outline the following aspects of a business's marketing:
- Target audience
Each marketing plan should include one or more goals, the path your team will take to meet those goals, and how you plan to measure success.
For example, if I were a tech startup that's launching a new mobile app, my marketing plan would include:
- Target audience or buyer personas for the app
- Outline of how app features meet audience needs
- Competitive analysis
- Goals for conversion funnel and user acquisition
- Marketing strategies and tactics for user acquisition
Featured resource : Free Marketing Plan Template
What should a good marketing plan include?
A good marketing plan will create a clear roadmap for your unique marketing team. This means that the best marketing plan for your business will be distinct to your team and business needs.
That said, most marketing plans will include sections for one or more of the following:
- Clear analysis of the target market
- A detailed description of the product or service
- Strategic marketing mix details (such as product, price, place, promotion)
- Measurable goals with defined timelines
This can help you build the best marketing plan for your business.
A good marketing plan should also include a product or service's unique value proposition, a comprehensive marketing strategy including online and offline channels, and a defined budget.
Featured resource : Value Proposition Templates
What are the most important parts of a marketing plan?
When you‘re planning a road trip, you need a map to help define your route, step-by-step directions, and an estimate of the time it will take to get to your destination. It’s literally how you get there that matters.
Like a road map, a marketing plan is only useful if it helps you get to where you want to go. So, no one part is more than the other.
That said, you can use the list below to make sure that you've added or at least considered each of the following in your marketing plan:
- Marketing goals
- Executive summary
- Target market analysis
- Marketing strategies
What questions should I ask when making a marketing plan?
Questions are a useful tool for when you‘re stuck or want to make sure you’ve included important details.
Try using one or more of these questions as a starting point when you create your marketing plan:
- Who is my target audience?
- What are their needs, motivations, and pain points?
- How does our product or service solve their problems?
- How will I reach and engage them?
- Who are my competitors? Are they direct or indirect competitors?
- What are the unique selling points of my product or service?
- What marketing channels are best for the brand?
- What is our budget and timeline?
- How will I measure the success of marketing efforts?
How much does a marketing plan cost?
Creating a marketing plan is mostly free. But the cost of executing a marketing plan will depend on your specific plan.
Marketing plan costs vary by business, industry, and plan scope. Whether your team handles marketing in-house or hires external consultants can also make a difference. Total costs can range from a few thousand dollars to tens of thousands. This is why most marketing plans will include a budget.
Featured resource : Free Marketing Budget Templates
What is a marketing plan template?
A marketing plan template is a pre-designed structure or framework that helps you outline your marketing plan.
It offers a starting point that you can customize for your specific business needs and goals. For example, our template includes easy-to-edit sections for:
- Business summary
- Business initiatives
- Target market
- Market strategy
- Marketing channels
- Marketing technology
Let’s create a sample plan together, step by step.
Follow along with HubSpot's free Marketing Plan Template .

1. Create an overview or primary objective.
Our business mission is to provide [service, product, solution] to help [audience] reach their [financial, educational, business related] goals without compromising their [your audience’s valuable asset: free time, mental health, budget, etc.]. We want to improve our social media presence while nurturing our relationships with collaborators and clients.
For example, if I wanted to focus on social media growth, my KPIs might look like this:
We want to achieve a minimum of [followers] with an engagement rate of [X] on [social media platform].
The goal is to achieve an increase of [Y] on recurring clients and new meaningful connections outside the platform by the end of the year.
Use the following categories to create a target audience for your campaign.
- Profession:
- Background:
- Pain points:
- Social media platforms that they use:
- Streaming platforms that they prefer:
For more useful strategies, consider creating a buyer persona in our Make My Persona tool .
Our content pillars will be: [X, Y, Z].
Content pillars should be based on topics your audience needs to know. If your ideal clients are female entrepreneurs, then your content pillars can be: marketing, being a woman in business, remote working, and productivity hacks for entrepreneurs.
Then, determine any omissions.
This marketing plan won’t be focusing on the following areas of improvement: [A, B, C].
5. Define your marketing budget.
Our marketing strategy will use a total of [Y] monthly. This will include anything from freelance collaborations to advertising.
6. Identify your competitors.
I like to work through the following questions to clearly indicate who my competitors are:
- Which platforms do they use the most?
- How does their branding differentiate?
- How do they talk to their audiences?
- What valuable assets do customers talk about? And if they are receiving any negative feedback, what is it about?
7. Outline your plan's contributors and their responsibilities.
Create responsible parties for each portion of the plan.
Marketing will manage the content plan, implementation, and community interaction to reach the KPIs.
- Social media manager: [hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations]
- Content strategist: [hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations]
- Community manager: [hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations]
Sales will follow the line of the marketing work while creating and implementing an outreach strategy.
- Sales strategists: [hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations]
- Sales executives: [hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations]
Customer Service will nurture clients’ relationships to ensure that they have what they want. [Hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations].
Project Managers will track the progress and team communication during the project. [Hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations].
Get started on your marketing plan.
These marketing plans serve as initial resources to get your content marketing plan started. But, to truly deliver what your audience wants and needs, you'll likely need to test some different ideas out, measure their success, and then refine your goals as you go.
Editor's Note: This post was originally published in April 2019, but was updated for comprehensiveness. This article was written by a human, but our team uses AI in our editorial process. Check out our full disclosure t o learn more about how we use AI.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

The Ultimate Guide to Marketing Strategies & How to Improve Your Digital Presence

Diving Deep Into Marketing in Construction (My Takeaways)
![types of marketing assignment 11 Recommendations for Marketers in 2024 [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Marketing%20Recommendations.png)
11 Recommendations for Marketers in 2024 [New Data]
![types of marketing assignment The Top 5 B2C Marketing Trends of 2024 [New HubSpot Blog Data + Expert Insights]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/top%20b2c%20marketing%20trends.png)
The Top 5 B2C Marketing Trends of 2024 [New HubSpot Blog Data + Expert Insights]
![types of marketing assignment 5 Marketing Trends That Might Not Survive in 2024 [HubSpot Research + Expert Insights]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketing%20trends%20that%20might%20not%20survive%202024.png)
5 Marketing Trends That Might Not Survive in 2024 [HubSpot Research + Expert Insights]
Everything You Need to Know About Webinar Marketing

7 Marketing Questions Teams are Asking in 2024 (+Data & Insights)

50 Small Business Marketing Ideas for 2024

How Luxury Brands Market and What You Can Learn

Diving Deep Into Marketing for Dentists (My Takeaways)
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Marketing |
- How to create a winning marketing plan, ...
How to create a winning marketing plan, with 3 examples from world-class teams

A marketing plan helps leaders clearly visualize marketing strategies across channels, so they can ensure every campaign drives pipeline and revenue. In this article you’ll learn eight steps to create a winning marketing plan that brings business-critical goals to life, with examples from word-class teams.
To be successful as a marketer, you have to deliver the pipeline and the revenue.”
In other words—they need a well-crafted marketing plan.
Level up your marketing plan to drive revenue in 2024
Learn how to create the right marketing plan to hit your revenue targets in 2024. Hear best practices from marketing experts, including how to confidently set and hit business goals, socialize marketing plans, and move faster with clearer resourcing.

7 steps to build a comprehensive marketing plan
How do you build the right marketing plan to hit your revenue goals? Follow these eight steps for success:
1. Define your plan
First you need to define each specific component of your plan to ensure stakeholders are aligned on goals, deliverables, resources, and more. Ironing out these details early on ensures your plan supports the right business objectives, and that you have sufficient resources and time to get the job done.
Get started by asking yourself the following questions:
What resources do I need?
What is the vision?
What is the value?
What is the goal?
Who is my audience?
What are my channels?
What is the timeline?
For example, imagine you’re creating an annual marketing plan to improve customer adoption and retention in the next fiscal year. Here’s how you could go through the questions above to ensure you’re ready to move forward with your plan:
I will need support from the content team, web team, and email team to create targeted content for existing customers. One person on each team will need to be dedicated full-time to this initiative. To achieve this, the marketing team will need an additional $100K in budget and one new headcount.
What is the vision?
To create a positive experience for existing customers, address new customer needs, and encourage them to upgrade. We’ll do this by serving them how-to content, new feature updates, information about deals and pricing, and troubleshooting guides.
According to the Sales Benchmark Index (SBI) , CEOs and go-to-market leaders report that more than 60% of their net-new revenue will come from existing customers in 2023. By retaining and building on the customers we have, we can maintain revenue growth over time.
To decrease the customer churn rate from 30% to 10%, and increase upgrades from 20% to 30% in the next fiscal year.
All existing customers.
The main channel will be email. Supporting marketing channels include the website, blog, YouTube, and social media.
The first half of the next fiscal year.
One of the most important things to do as you create your marketing strategy is to identify your target audience . As with all marketing, you need to know who you’re marketing to. If you’re having a hard time determining who exactly your target audience is, try the bullseye targeting framework . The bullseye makes it easy for you to determine who your target audience is by industry, geography, company size, psychographics, demographics, and more.
2. Identify key metrics for success
Now it’s time to define what key marketing metrics you’ll use to measure success. Your key metrics will help you measure and track the performance of your marketing activities. They’ll also help you understand how your efforts tie back to larger business goals.
Once you establish key metrics, use a goal-setting framework—like objectives and key results (OKRs) or SMART goals —to fully flush out your marketing objectives. This ensures your targets are as specific as possible, with no ambiguity about what should be accomplished by when.
Example: If a goal of your marketing plan is to increase email subscriptions and you follow the SMART goal framework (ensuring your objective is specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound) your goal might look like this: Increase email subscription rate from 10% to 20% in H1 .
3. Research your competition
It’s easy to get caught up in your company’s world, but there’s a lot of value in understanding your competitors . Knowing how they market themselves will help you find opportunities to make your company stand out and capture more market share.
Make sure you’re not duplicating your competitors’ efforts. If you discover a competitor has already executed your idea, then it might be time to go back to the drawing board and brainstorm new ways to differentiate yourself. By looking at your competitors, you might be surprised at the type of inspiration and opportunities you’ll find.
To stay ahead of market trends, conduct a SWOT analysis for your marketing plan. A SWOT analysis helps you improve your plan by identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Example: If your competitor launches a social media campaign identical to what you had planned, go back to the drawing board and see how you can build off their campaign. Ask yourself: How can we differentiate our campaign while still getting our message across? What are the weaknesses of their campaign that we can capitalize on? What angles did they not approach?
4. Integrate your marketing efforts
Here’s where the fun comes in. Let’s dive into the different components that go into building a successful marketing plan. You’ll want to make sure your marketing plan includes multiple supporting activities that all add up into a powerful marketing machine. Some marketing plan components include:
Lead generation
Social media
Product marketing
Public relations
Analyst relations
Customer marketing
Search engine optimization (SEO)
Conversational marketing
Knowing where your consumer base spends the most time is significant for nailing this step. You need to have a solid understanding of your target audience before integrating your marketing efforts.
Example: If your target audience is executives that spend a lot of time on LinkedIn, focus your social media strategy around placing branded content on LinkedIn.
5. Differentiate with creative content
Forty-nine percent of marketers say visual images are hugely important to their content strategy. In other words, a clear brand and creative strategy is an essential component to every marketing plan. As you craft your own creative strategy, here are some tips to keep in mind:
Speak to your audience: When defining your creative strategy, think about your audience—what you want them to feel, think, and do when they see your marketing. Will your audience find your creative work relevant? If your audience can’t relate to your creative work, they won’t feel connected to the story you’re trying to tell.
Think outside the box: Find innovative ways to engage your audience, whether through video, animations, or interactive graphics. Know what screens your creative work will live on, whether desktop, mobile, or tablet, and make sure they display beautifully and load quickly across every type of device.
Tie everything back to CTAs: It’s easy to get caught up in the creative process, so it’s important to never lose sight of your ultimate goal: Get your audience to take action. Always find the best way to display strong Calls to Action (CTAs) in your creative work. We live in a visual world—make sure your creative content counts.
Streamline creative production: Once you’ve established a strong creative strategy, the next step is to bring your strategy to life in the production stage. It’s vital to set up a strong framework for your creative production process to eliminate any unnecessary back and forth and potential bottlenecks. Consider establishing creative request forms , streamlining feedback and approval processes, and taking advantage of integrations that might make your designers’ lives easier.
Example: If your brand is fun and approachable, make sure that shows in your creative efforts. Create designs and CTAs that spark joy, offer entertainment, and alleviate the pressure in choosing a partner.
6. Operationalize your marketing plan
Turn your plan into action by making goals, deliverables, and timelines clear for every stakeholder—so teams stay accountable for getting work done. The best way to do this is by centralizing all the details of your marketing plan in one platform , so teams can access the information they need and connect campaign work back to company goals.
With the right work management tool , you can:
Set goals for every marketing activity, and connect campaign work to overarching marketing and business objectives so teams focus on revenue-driving projects.
Centralize deliverables for your entire marketing plan in one project or portfolio .
Mark major milestones and visualize your plan as a timeline, Gantt chart, calendar, list, or Kanban board—without doing any extra work.
Quickly loop in stakeholders with status updates so they’re always up to date on progress. This is extremely important if you have a global team to ensure efforts aren’t being duplicated.
Use automations to seamlessly hand off work between teams, streamlining processes like content creation and reviews.
Create dashboards to report on work and make sure projects are properly staffed , so campaigns stay on track.
With everything housed in one spot, you can easily visualize the status of your entire marketing plan and keep work on track. Building an effective marketing plan is one thing, but how you operationalize it can be your secret to standout marketing.
Example: If your strategy focuses on increasing page views, connect all campaign work to an overarching OKR—like “we will double page views as measured by the amount of organic traffic on our blog.” By making that goal visible to all stakeholders, you help teams prioritize the right work.
See marketing planning in action
With Asana, marketing teams can connect work, standardize processes, and automate workflows—all in one place.

7. Measure performance
Nearly three in four CMOs use revenue growth to measure success, so it’s no surprise that measuring performance is necessary. You established your key metrics in step two, and now it’s time to track and report on them in step eight.
Periodically measure your marketing efforts to find areas of improvement so you can optimize in real-time. There are always lessons to be learned when looking at data. You can discover trends, detect which marketing initiatives performed well, and course-correct what isn’t performing well. And when your plan is complete, you can apply these learnings to your next initiative for improved results.
Example: Say you discover that long-form content is consistently bringing in 400% more page views than short-form content. As a result, you’ll want to focus on producing more long-form content in your next marketing plan.
Marketing plan examples from world-class teams
The best brands in the world bring their marketing plans to life every day. If you’re looking for inspiration, check out these examples from successful marketing teams.
Autodesk grows site traffic 30% three years in a row
When the Autodesk team launched Redshift, it was initially a small business blog. The editorial team executed a successful marketing plan to expand it into a premier owned-media site, making it a destination for stories and videos about the future of making.
The team scaled content production to support seven additional languages. By standardizing their content production workflow and centralizing all content conversations in one place, the editorial team now publishes 2X more content monthly. Read the case study to learn more about how Autodesk runs a well-oiled content machine.
Sony Music boosts creative production capacity by 4X
In recent years the music industry has gone through a pivotal transition—shifting from album sales to a streaming business model. For marketing and creative teams at Sony Music, that meant adopting an “always on” campaign plan.
The team successfully executed this campaign plan by centralizing creative production and approvals in one project. By standardizing processes, the team reduced campaign production time by 75%. Read the case study to learn more about how Sony Music successfully scaled their creative production process.
Trinny London perfects new customer acquisition
In consumer industries, social media is crucial for building a community of people who feel an affinity with the brand—and Trinny London is no exception. As such, it was imperative that Trinny London’s ad spend was targeted to the correct audience. Using a work management tool, Trinny London was able to nail the process of creating, testing, and implementing ads on multiple social channels.
With the help of a centralized tool, Trinny London improved its ad spend and drove more likes and subscriptions on its YouTube page. Read the case study to learn more about how Trinny London capitalized on paid advertising and social media.
Turn your marketing plan into marketing success
A great marketing plan promotes clarity and accountability across teams—so every stakeholder knows what they’re responsible for, by when. Reading this article is the first step to achieving better team alignment, so you can ensure every marketing campaign contributes to your company’s bottom line.
Use a free marketing plan template to get started
Once you’ve created your marketing strategy and are ready to operationalize your marketing plan, get started with one of our marketing templates .
Our marketing templates can help you manage and track every aspect of your marketing plan, from creative requests to approval workflows. Centralize your entire marketing plan in one place, customize the roadmap, assign tasks, and build a timeline or calendar.
Once you’ve operationalized your entire marketing plan with one of our templates, share it with your stakeholders so everyone can work together in the same tool. Your entire team will feel connected to the marketing plan, know what to prioritize, and see how their work contributes to your project objectives . Choose the best marketing template for your team:
Marketing project plan template
Marketing campaign plan template
Product marketing launch template
Editorial calendar template
Agency collaboration template
Creative requests template
Event planning template
GTM strategy template
Still have questions? We have answers.
What is a marketing plan.
A marketing plan is a detailed roadmap that outlines the different strategies your team will use to achieve organizational objectives. Rather than focusing solely on the end goal, a marketing plan maps every step you need to reach your destination—whether that’s driving pipeline for sales, nurturing your existing customer base, or something in-between.
As a marketing leader, you know there’s never a shortage of great campaign and project ideas. A marketing plan gives you a framework to effectively prioritize work that aligns to overarching business goals—and then get that work done. Some elements of marketing plans include:
Current business plan
Mission statement
Business goals
Target customers
Competitive analysis
Current marketing mix
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Marketing budget
What is the purpose of a marketing plan?
The purpose of a marketing plan is to grow your company’s consumer base and strengthen your brand, while aligning with your organization’s mission and vision . The plan should analyze the competitive landscape and industry trends, offer actionable insights to help you gain a competitive advantage, and document each step of your strategy—so you can see how your campaigns work together to drive overarching business goals.
What is the difference between a marketing plan and a marketing strategy?
A marketing plan contains many marketing strategies across different channels. In that way, marketing strategies contribute to your overall marketing plan, working together to reach your company’s overarching business goals.
For example, imagine you’re about to launch a new software product and the goal of your marketing plan is to drive downloads. Your marketing plan could include marketing strategies like creating top-of-funnel blog content and launching a social media campaign.
What are different types of marketing plans?
Depending on what you’re trying to accomplish, what your timeline is, or which facet of marketing you’re driving, you’ll need to create a different type of marketing plan. Some different types of marketing plans include, but aren’t limited to:
General marketing plan: A general marketing plan is typically an annual or quarterly marketing plan that details the overarching marketing strategies for the period. This type of marketing plan outlines marketing goals, the company’s mission, buyer personas, unique selling propositions, and more. A general marketing plan lays the foundation for other, more specific marketing plans that an organization may employ.
Product launch marketing plan: A product launch marketing plan is a step-by-step plan for marketing a new product or expanding into a new market. It helps you build awareness and interest by targeting the right audience, with the right messaging, in the right timeframe—so potential customers are ready to buy your new offering right away. Nailing your product launch marketing plan can reinforce your overall brand and fast-track sales. For a step-by-step framework to organize all the moving pieces of a launch, check out our product marketing launch template .
Paid marketing plan: This plan includes all the paid strategies in your marketing plan, like pay-per-click, paid social media advertising, native advertising, and display advertising. It’s especially important to do audience research prior to launching your paid marketing plan to ensure you’re maximizing ROI. Consult with content strategists to ensure your ads align with your buyer personas so you know you’re showing ads to the right people.
Content marketing plan: A content marketing plan outlines the different content strategies and campaigns you’ll use to promote your product or service. When putting together a content marketing plan, start by identifying your audience. Then use market research tools to get the best insights into what topics your target audience is most interested in.
SEO marketing plan: Your SEO marketing plan should work directly alongside your content marketing plan as you chart content that’s designed to rank in search results. While your content marketing plan should include all types of content, your SEO marketing plan will cover the top-of-funnel content that drives new users to your site. Planning search engine-friendly content is only one step in your SEO marketing plan. You’ll also need to include link-building and technical aspects in order to ensure your site and content are as optimized as possible.
Social media marketing plan: This plan will highlight the marketing strategies you plan to accomplish on social media. Like in any general or digital marketing plan , your social media strategy should identify your ideal customer base and determine how they engage on different social media platforms. From there, you can cater your social media content to your target audience.
Related resources

How Asana uses work management for smoother creative production

Build a marketing operations strategy in 4 steps
How Asana uses work management for more impactful campaigns

Marketing vs. advertising: What’s the difference?
BUS203: Principles of Marketing
Course introduction.
- Time: 31 hours
- College Credit Recommended ($25 Proctor Fee) -->
- Free Certificate
Course Syllabus
First, read the course syllabus. Then, enroll in the course by clicking "Enroll me". Click Unit 1 to read its introduction and learning outcomes. You will then see the learning materials and instructions on how to use them.
Unit 1: The Definition and Principles of Marketing
Many people incorrectly believe that marketing and advertising are the same. In reality, advertising is just one of many tools used in marketing, which is how firms determine which products to offer, how to price those products, and who they should be made available to. We will explore ways marketing departments and independent agencies answer these questions, whether through research, analysis, or trial and error. Once a company identifies its customer and product, marketers must determine the best way to capture the customer's attention. Grabbing the customer's attention may entail undercutting competitors' prices, aggressively marketing with promotions and advertising (like "As Seen on TV" ads), or targeting ideal customers. The strategy a marketing firm chooses for a particular product is vital to the product's success. The idea that "great products sell themselves" is simply not true. By the end of this course, you will be familiar with the art and science of marketing a product.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 6 hours.
Unit 2: Segmenting, Targeting, and Positioning
Philip Kotler, the grand dean of marketing textbooks, has suggested that if marketers can nail their target and position, all other aspects of a marketing campaign will fall into place. Target and position define whom we are trying to reach with our marketing campaign and what message (or position) we will use to connect. The concepts of targeting and positioning are so critical to marketing success that we now dedicate an entire unit to them.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 2 hours.
Unit 3: Customers and Marketing Research
Marketing is all about the customer. But who is the customer? If you are a car manufacturer, you have multiple types of customers. You might have governments and rental agencies that wish to buy fleet vehicles. We call these customers business-to-business (B2B). You would also have dealerships to whom you want to sell your cars; this is also B2B. Then, there are the end-users or dealer's customers. Though the dealer owns the car when it is sold, the manufacturer almost always plays a crucial role in marketing that car. Identifying your target customer can be difficult, but with the proper definitions and the right research, marketers will know their customers better than they know themselves.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 7 hours.
Unit 4: Life Cycles, Offers, Supply Chains, and Pricing
Products do not last forever. New products typically cost more than existing products due to the high costs associated with production and development. Technology products best illustrate this. The fact that initial customers will be early adopters of a new product affects the marketing strategy. As the product grows and matures, the strategy changes; marketers lower the price over time. When a product is in the declining stage, most competitors leave the market, and prices are very low. At each stage, the marketing of the product is different.
When a new product is developed and offered, a company must consider what will create the product's value to the customer, whether the customer is a consumer or another business. Marketers must always ask where a new product will fit in their current lineup and how the new product will serve as an extension of an existing brand. Take the car manufacturer BMW. They make sporty luxury vehicles aimed at the upper-middle and wealthy classes.
Developing an inexpensive, lower-quality vehicle to compete with cars in another class may dilute the brand and hurt sales. However, suppose BMW were to market the vehicle under a different brand. In that case, they could diversify their product portfolio, avoid the risk of diluting the BMW brand and be able to reach new customers all at the same time. Some firms go to great lengths to disassociate their brands from one another, while others embrace a family of brands model. Appropriate decisions vary by industry and strategy. Equally crucial in delivering value to the customer through an offering is how a company sources the goods and services necessary for production and delivers the end product for customers to purchase. This process is known as the supply chain.
Finally, in this unit, we will examine issues in pricing, including the costs of delivering a product, customer and societal perspectives, the impacts of competition, and ultimately the revenues a company may generate.
Unit 5: Distribution and Promotion
Once marketers have identified the right product and determined appropriate pricing, they must decide how to raise awareness and distribute the product effectively. This unit will focus on these decisions. Distribution is a complex process involving taking a product through the manufacturing process, shipping to warehouses, distributing to sellers and customers, and returning products. Marketers must work with supply chain managers to determine the best method to route products. If marketers expect sales to be heavier in the northeast than in the west, additional resources will need to be allocated there to meet demand. There are several strategies for moving a product through various distribution channels. These vary based on anticipated demand, actual demand, and competition. Marketers must have a proactive strategy; they cannot sit on inventory and wait for orders because inventory storage is expensive, and a lack of sales is disruptive.
The final and arguably most vital aspect of marketing is the actual promotion of the product. This can take the form of giveaways, competitions, advertising, sales, and anything else a creative manager can think of. Marketers must consider several aspects. If you employ a sales staff to promote the product, how do you compensate them? If you pay a commission, how much commission will be paid per unit? Will the sales staff be given discretion on price, or do you want to send a consistent message that the price is locked in? If a new company has limited funds for advertising campaigns, might they use public relations tactics to gain free media coverage? These are just a few considerations that marketers must consider. This final unit will provide you with tools to make the best possible promotion decisions.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 5 hours.
Unit 6: Launching a Marketing Campaign
Marketing is not just a matter of internal strategies and customer analysis. There are factors outside of the company that must be considered with any marketing strategy. Though marketers can control how they might respond to customer needs and expectations, they face the often-unpredictable reactions of customers to them. Maintaining customer satisfaction is essential to sustainable success. Marketers need to be sensitive to the regulatory and ethical constraints that may be placed upon them by a wide range of domestic and international industry standards and society's expectations. Companies must also face social forces that challenge their success. For example, marketers must be aware of each region's social and cultural aspects in which they choose to market a product. Even a worldwide brand such as Coca-Cola must adjust its marketing strategy for every region it enters. An awareness of the cultural factors affecting a marketing strategy can make the marketing message much more effective. Often, marketers will address social issues relevant to the lives of their audiences or society with social marketing campaigns. Finally, as a marketing campaign prepares for its launch, all the issues addressed in this and earlier units must come together in a formalized document – the comprehensive marketing plan.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 4 hours.
Unit 7: Social Media Marketing
Social media refers to digital technologies which allow people to interact. The foundation stems from how people talk and behave without a standard set of rules or principles to follow. There can be a shift in social media set by the users, which causes tech developers and marketers to adjust the way they create or produce. Therefore, it is critical to understand social media and stay abreast of the trends and patterns in data. Social media buzz does not necessarily mirror society. The insights found on social media are sometimes a poor reflection of real social life. In this unit, you will understand the trends, content, communication, platforms, and marketing used across social networking sites (SNS). The next sections will guide you in understanding each component.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 3 hours.
Study Guide
This study guide will help you get ready for the final exam. It discusses the key topics in each unit, walks through the learning outcomes, and lists important vocabulary. It is not meant to replace the course materials!
Course Feedback Survey
Please take a few minutes to give us feedback about this course. We appreciate your feedback, whether you completed the whole course or even just a few resources. Your feedback will help us make our courses better, and we use your feedback each time we make updates to our courses.
If you come across any urgent problems, email [email protected].
Certificate Final Exam
Take this exam if you want to earn a free Course Completion Certificate.
To receive a free Course Completion Certificate, you will need to earn a grade of 70% or higher on this final exam. Your grade for the exam will be calculated as soon as you complete it. If you do not pass the exam on your first try, you can take it again as many times as you want, with a 7-day waiting period between each attempt.
Once you pass this final exam, you will be awarded a free Course Completion Certificate .
Saylor Direct Credit
Take this exam if you want to earn college credit for this course . This course is eligible for college credit through Saylor Academy's Saylor Direct Credit Program .
The Saylor Direct Credit Final Exam requires a proctoring fee of $5 . To pass this course and earn a Credly Badge and official transcript , you will need to earn a grade of 70% or higher on the Saylor Direct Credit Final Exam. Your grade for this exam will be calculated as soon as you complete it. If you do not pass the exam on your first try, you can take it again a maximum of 3 times , with a 14-day waiting period between each attempt.
We are partnering with SmarterProctoring to help make the proctoring fee more affordable. We will be recording you, your screen, and the audio in your room during the exam. This is an automated proctoring service, but no decisions are automated; recordings are only viewed by our staff with the purpose of making sure it is you taking the exam and verifying any questions about exam integrity. We understand that there are challenges with learning at home - we won't invalidate your exam just because your child ran into the room!
Requirements:
- Desktop Computer
- Chrome (v74+)
- Webcam + Microphone
- 1mbps+ Internet Connection
Once you pass this final exam, you will be awarded a Credly Badge and can request an official transcript .
Saylor Direct Credit Exam
This exam is part of the Saylor Direct College Credit program. Before attempting this exam, review the Saylor Direct Credit page for complete requirements.
Essential exam information:
- You must take this exam with our automated proctor. If you cannot, please contact us to request an override.
- The automated proctoring session will cost $5 .
- This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam (see allowed resources below).
- You will have two (2) hours to complete this exam.
- You have up to 3 attempts, but you must wait 14 days between consecutive attempts of this exam.
- The passing grade is 70% or higher.
- This exam consists of 54 multiple-choice questions.
Some details about taking your exam:
- Exam questions are distributed across multiple pages.
- Exam questions will have several plausible options; be sure to pick the answer that best satisfies each part of the question.
- Your answers are saved each time you move to another page within the exam.
- You can answer the questions in any order.
- You can go directly to any question by clicking its number in the navigation panel.
- You can flag a question to remind yourself to return to it later.
- You will receive your grade as soon as you submit your answers.
Allowed resources:
Gather these resources before you start your exam.
- Blank paper
What should I do before my exam?
- Gather these before you start your exam:
- A photo I.D. to show before your exam.
- A credit card to pay the automated proctoring fee.
- (optional) Blank paper and pencil.
- (optional) A glass of water.
- Make sure your work area is well-lit and your face is visible.
- We will be recording your screen, so close any extra tabs!
- Disconnect any extra monitors attached to your computer.
- You will have up to two (2) hours to complete your exam. Try to make sure you won't be interrupted during that time!
- You will require at least 1mbps of internet bandwidth. Ask others sharing your connection not to stream during your exam.
- Take a deep breath; you got this!
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
Marketing Strategy: What It Is and How to Create One
A marketing strategy can set your business up for success. Learn why and how to make one for your business.
![types of marketing assignment [Featured image] A women stands in front of a digital whiteboard and leads a marketing strategy meeting with several coworkers.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/2bS9Rd8vBFkIcnziIbAqSY/426ec3a30c1f8dfe120bb9dd8a3c324d/GettyImages-1227481145.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
A marketing strategy is a long-term vision outlining a business’s value proposition to its customers. Rather than describing the concrete actions required in specific advertising campaigns, marketing strategies are a compass used to guide marketing efforts.
While it may be tempting to hash out a marketing plan right away, thinking about the marketing strategy first can improve your product's success and give you a competitive advantage. Learn what marketing strategy is, why it matters, different types, and steps to create your own.
What is a marketing strategy?
A marketing strategy is an overview of how a business or organization will articulate its value proposition to its customers. Generally, a marketing strategy outlines business goals, target market, buyer personas, competitors, and value for customers. It provides a long-term vision for overall marketing efforts, often looking many years ahead.
Advantages of a marketing strategy
Marketing strategies can have a measurable impact on success.
In 2022, CoSchedule surveyed 3,599 marketers and bloggers to identify their most successful marketing practices. They found that marketers who documented their marketing strategy were 331 percent more likely to report success than those who didn’t. Furthermore, marketers who were the most organized were found to be a whopping 674 percent more likely to report success [ 1 ].
Taking the time to create a marketing strategy can benefit your company's brand and bottom line. Watch this video to learn more about how to develop a winning marketing strategy:
Marketing strategy vs. marketing plan
People often use the terms “marketing strategy” and “marketing plan” interchangeably, but in reality, they are two different processes.
A marketing plan describes the concrete actions and marketing tactics undertaken to complete a marketing campaign. Meanwhile, a marketing strategy outlines the big picture of a marketing effort, such as the business's target customers. The strategy describes what the marketing objectives are, while the plan describes how those objectives are going to be achieved.
For example, imagine an e-commerce business that is trying to grow its customer base. They start a referral program to encourage word of mouth but it has little success. If they had created a strategy, they might have realized they needed to tap into new potential customers instead. A digital marketing strategy focused on targeted blog posts and search engine optimization (SEO) would have yielded better results.
Interested in digital marketing? Check out Google Digital Marketing & E-commerce Professional Certificate to gain valuable skills to kickstart a digital marketing career:
Types of marketing strategy
There are many different approaches to marketing – such as social media marketing or content marketing – but strategies for market growth can be found in Ansoff’s matrix . These four strategies are:
Market penetration
Product development
Market development
Diversification
H. Igor Ansoff is a mathematician and business manager who created the matrix to help businesses define their strategies by varying what product is being sold and who the product is being sold to [ 2 ].
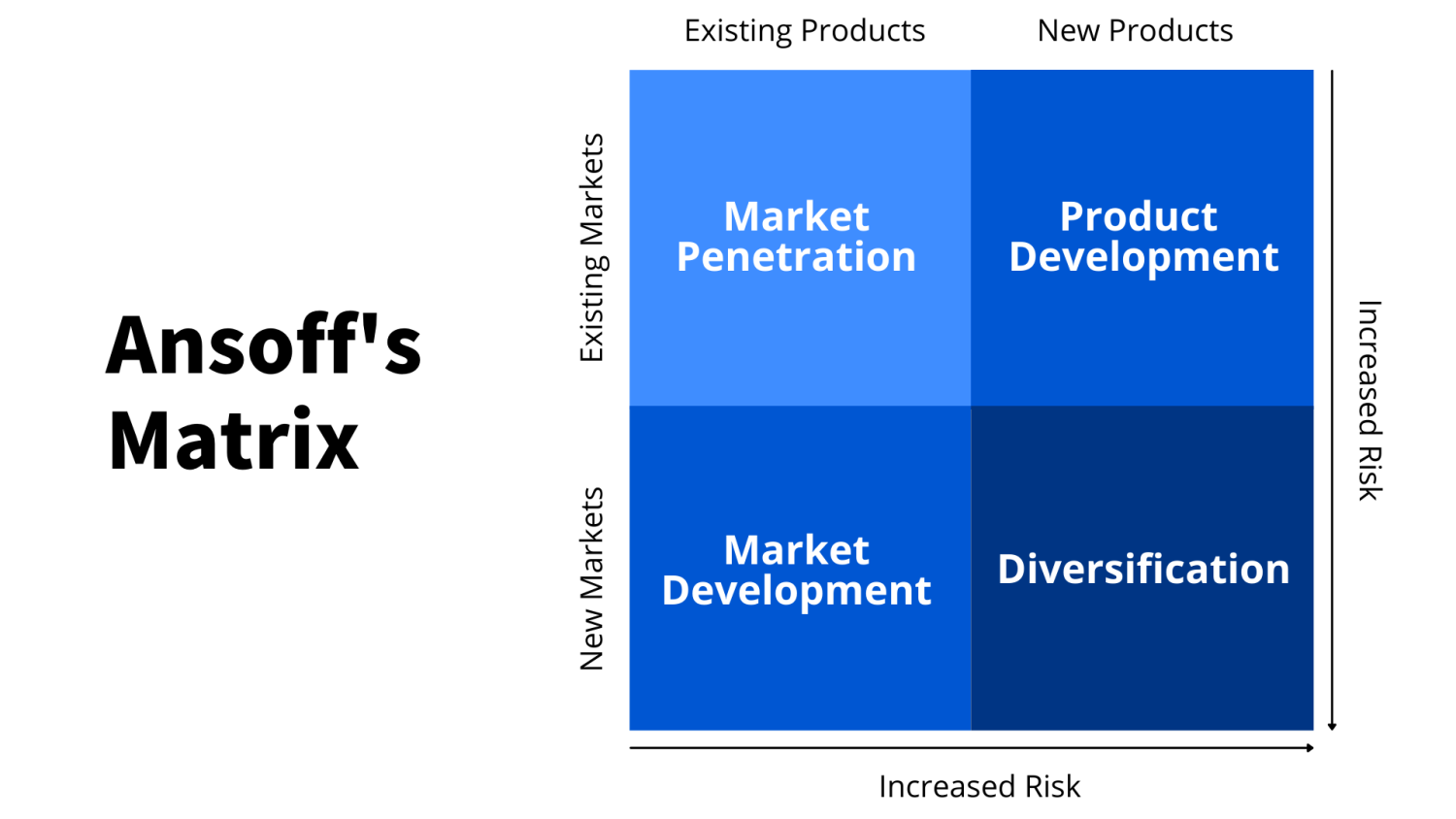
Ansoff’s matrix encourages markets to consider the four Ps , or the “marketing mix":
Product: What is being sold
Place: Where it is being sold
Price: What the product costs
Promotion: How the product is marketed to the target audience
The exact way that a marketer defines the four Ps for their marketing efforts will depend on the growth strategy they are using and the political and economic outlook of their market.
Let’s take a closer look at each strategy from Ansoff’s matrix.
Market penetration strategy
Market penetration strategy is a growth strategy that involves selling existing products to existing markets. It is considered the least risky of all the strategies in Ansoff’s matrix. The strategy is typically considered most beneficial if the market is either growing or the marketer alters its promotional efforts through existing marketing channels [ 2 ].
McDonald's "I'm Lovin' It" campaign
An example of a market penetration strategy can be found in McDonald’s “I’m Lovin’ It” campaign from 2003.
In the early 2000s, McDonald's faced flagging sales and plummeting stock prices. Rather than creating a new product (product development strategy), McDonald's instead focused on attracting existing customers in an existing market with a catchy ad campaign. The result was their wildly successful “I’m Lovin’ it” campaign, which featured a catchy new jingle sung by Justin Timberlake [ 3 ].
“I’m Lovin It” has since become McDonald’s longest-running marketing campaign since its founding in 1940 [ 4 ].
Product development strategy
A product development strategy involves the development of a new product for an already existing market. Typically, it is considered riskier than a market penetration strategy because it requires the creation of a totally new product. In order to be successful, product development strategies typically require innovation and further research into the existing market, including the profiles and needs of the target audience [ 2 ].
Uni Kuru Toga's mechanical pencil for every day writing
An example of a successful (and surprisingly interesting) product development strategy can be seen in the Uni Kuru Toga mechanical pencil.
As odd as it may seem, in the mechanical pencil world the Uni Kuru Toga is something of a star. “[T]he Uni Kuru Toga is the best mechanical pencil for every day writing,” opined the New York Time’s Wirecutter in a 2018 article [ 5 ]. Wired, meanwhile, called it “the ultimate geek tool” [ 6 ].
What makes the pencil so unique? A specially designed internal gear mechanism that rotates the lead so it stays sharp as you write and diamond infused lead that doesn’t easily break under pressure. In effect, as a 2009 commercial for the pencil demonstrated, it was meant for people concerned with even handwriting and durable lead [ 7 ].
While the market for mechanical pencils was already well-established, the Uni Kuru Toga was able to find success through a product development strategy that offered consumers something new and useful.
Market development strategy
A market development strategy takes an existing product into new markets. Much like a product development strategy, a market development strategy is considered riskier than a market penetration strategy because it involves introducing a familiar product into an unfamiliar marketplace. While the product remains the same, the new place it is sold requires possibly new pricing and promotional efforts [ 2 ].
Microsoft's Hololens technology
An example of a market development strategy is when Microsoft introduced its Hololens technology to an additional 29 markets in Europe in November of 2017 [ 8 ]. The augmented reality headset provides a unique user experience that allows professionals to work in a “mixed reality” environment. To promote their efforts, Microsoft released a YouTube video showcasing the unique use cases of the product in the workplace, such as through interactive employee training programs in industrial environments [ 9 ].
Diversification strategy
A diversification strategy involves the development of a new product for a new market. The novelty required of a diversification strategy means that it is also the riskiest of the Ansoff matrix’s four strategies. Diversification strategies require full attention on all of the four Ps – product, price, place, and promotion—but the biggest risks can also lead to the biggest rewards [ 2 ].
Apple's first iPhone
An example of a diversification strategy is when Apple introduced the first iPhone on June 9, 2007 at the MacWorld Expo. At the time, Apple was new to the mobile phone market, but they innovated in the space by adding a music player and web browser to their new touchscreen phone [ 10 ].
“Today Apple is going to reinvent the phone,” CEO Steve Jobs declared before an audience of reporters [ 10 ]. Through much of the presentation, Jobs outlined the phone’s unique value proposition to customers.
It worked. As of June 2022, there were an estimated 1.8 billion active iPhone users [ 11 ].
How to create a marketing strategy
A marketing strategy can set you up for marketing success. As you are creating your own marketing strategy, consider the following steps to help guide your process.
1. Define your business and marketing goals.
The first step in creating an effective marketing strategy is to clarify your business objectives and marketing goals. What are you trying to achieve with your market growth strategy?
The answer to this question will inevitably depend on your particular place in the market and your own comfortability with different risk levels.
Some examples of business and marketing goals include:
Grow customer base
Increase sales
Increase brand awareness
Whatever your objectives, the purpose is simply to consider what you want to actually accomplish by expanding your marketing efforts. These goals will guide the development of your marketing strategy.
2. Conduct market research.
Strategic marketing requires a comprehensive understanding of the marketplace, its economic and political context, and your product or service's place within it.
As you are conducting market research, you'll want to consider these factors:
Competitors, particularly their value proposition and market share
Market size, including the realistic number of customers that would be interested in your products
Market gaps where you can provide value
Possible economic and political realities that could impact the market in the long-term
As you gain a better understanding of the market, you will also better understand how you fit into it and where you can grow in it.
Read more: What Is Competitor Analysis? Definition + Step-by-Step Guide
3. Create a customer profile.
The purpose of every marketing campaign is to connect with potential customers. Your marketing strategy needs to include a comprehensive profile of your target audience.
Consider your target audience in relation to the four P's. Think through the following:
Based on what you know about the market, who is your target audience? What are their key demographics?
What is your product’s value proposition to your customer? (Product)
How much is your target audience willing to pay for your product or service? (Price)
Where does your target audience shop? (Place)
What marketing tactics are most persuasive to your target audience? (Promotion)
As you research and consider these questions, your customer should come more clearly into view, so you can create a strategy with maximum impact.
4. Synthesize and strategize.
Finally, take the goals you have outlined, research you have conducted, and profiles you have created to construct a marketing strategy. The critical question you will want to answer is: how will you align with your target market to meet your overall objectives?
Your answer to this question will be your strategy.
Ultimately, your marketing strategy should cover the following:
Business and marketing objectives
Market overview, including key facts and figures
Competitor research
Customer profile
General statement of strategy highlighting the product’s value proposition to customers
You might consider whether a social media strategy makes sense for your product or service. If so, your strategy could include user-generated content. Go a step further to consider which social media channels fits best with your target audience.
While you may have collected much information as you were conducting research, your marketing strategy doesn’t need to be too long. In fact, a strong marketing strategy can be as short as one page. Remember, this is meant to act as long-term guide for directing specific marketing tactics, not an action plan of how a marketing campaign will be done.
Get market ready
Whether you are seasoned marketing pro or a budding entrepreneur, develop your marketing prowess by building job-ready skills with the Meta Social Media Marketing Professional Certificate .
Article sources
CoSchedule. “ The Marketing Management + Strategy Statistics You Need to Know in 2019 , https://coschedule.com/marketing-statistics.” Accessed February 6, 2023.
Oxford College of Marketing. “ Using the Ansoff Matrix to Develop Marketing Strategy , https://blog.oxfordcollegeofmarketing.com/2016/08/01/using-ansoff-matrix-develop-marketing-strategy/.” Accessed February 6, 2023.
The Take Out. “ TIL McDonald’s ‘I’m Lovin’ It’ jingle was born out of desperation , https://thetakeout.com/history-of-mcdonald-s-i-m-lovin-it-jingle-1846400888.” AccessedFebruary 6, 2023.
Chicago Magazine. “ Five Things You Never Knew About ‘I’m Lovin’ It’ , https://www.chicagomag.com/Chicago-Magazine/November-2014/McDonalds-Im-Lovin-It-Campaign/.” Accessed February 6, 2023.
NYT Wirecutter. “ The Best Mechanical Pencils , https://www.nytimes.com/wirecutter/reviews/best-mechanical-pencils/.” Accessed February 6, 2023.
Wired. “ Kura Toga: The Ultimate Geek Tool , https://www.wired.com/2011/11/kuru-toga-the-ultimate-geek-tool/.” Accessed February 6, 2023.
YouTube (Uni Ball UK). “ Uni Kuru Togat from Mutsibishi Pencil Company , https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=80k7Jl1o8Lc&t=22s.” Accessed February 6, 2023.
Tech Crunch. “ Microsoft expands HoloLens headsets to 29 new markets, now up to 39 , https://techcrunch.com/2017/11/01/microsoft-expands-hololens-headsets-to-29-new-european-markets/.” Accessed February 6, 2023.
YouTube (Microsoft HoloLens). “ Microsoft HoloLens: Mixed Reality in the Modern Workspace , https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EIJM9xNg9xs.” Accessed February 6, 2023.
Computer World. “ Update: Jobs touts iPhone, Apple TV , https://www.computerworld.com/article/2549128/update--jobs-touts-iphone---appletv-.html.” Accessed February 6, 2023.
Earthweb. “ How many people use iPhones in 2022? , https://earthweb.com/how-many-people-use-iphones/.” Accessed February 6, 2023.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.

Principles of Marketing
(26 reviews)
Copyright Year: 2015
ISBN 13: 9781946135193
Publisher: University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Monisha Gupta, Assistant Professor, Marshall University on 1/2/23
The author of the book has shared that this is an adaptation of a work produced and distributed under a Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-SA). The book has 16 clearly defined chapters, each chapter raises a specific aspect of marketing and... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The author of the book has shared that this is an adaptation of a work produced and distributed under a Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-SA). The book has 16 clearly defined chapters, each chapter raises a specific aspect of marketing and concludes by raising discussion questions and activities. The textbook covers most of the marketing topics that should be included in an introductory course. However, given that the book is dated it is missing some emerging and emergent topics in marketing such as global marketing, data analytics, digital marketing, and the use of social media tools, to name a few. The author has at the outset clarified that the book does not follow the tenets of the 4 Ps of marketing. However, substituting terms such as products or services with terms like “offerings “requires a much deeper understanding of consumer needs, wants, or behavior. This might require a higher level of understanding which might not be in line with the student profile who opts for this course. The author has restructured the traditional 4Ps of the marketing mix and introduces that marketing is composed of four activities centered on customer value: creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging value. Also, the suggested activities created for each chapter are outside the scope of the chapter’s content. For instance, page 24, after Chapter 1 suggests activities such as “ Explain how the marketing goals, strategies, and markets for the nonprofit differ from a for-profit organization” or “Evaluate personal value equation”. These concepts have not been discussed in chapter 1 and are tackled later in the book by the author. These activities might not need more discussion and clarification before students can actively contribute to the solutions. Overall, the book covers most foundation-level content, but the choice of the author’s distinctive terminology might be a concern for students. Moreso, when they progress from this course to advanced levels of marketing and have trouble aligning the core concepts and keywords.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
Not an issue, the content is accurate and provides reference sources.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The OTL textbook is well documented and breaks up the content into smaller and comprehensive blocks of information. If relevance is measured based on the traditional acceptance and present outlook it might fall a little short. The book lacks this by disregarding some key changes in the marketplace such as the pandemic and its impact on consumption cycles, and the emergence of a large service industry. This has reshaped the consumer’s and marketers’ choices of development processes, channel partners, pricing strategies, promotional methodologies, use of social media tools, etc. These aspects need to be addressed in more detail with recent examples for students to appreciate the relevance.
Clarity rating: 5
The author has outlined the content in great detail, making it easy to read and understand the textbook. Easy conversational language and links, for example, appeal to students who can find a great deal on the electronic medium.
Consistency rating: 5
The chapters in the textbook are organized in the same consistent manner in the entire book. This is helpful for the readers and instructors to follow a format.
Modularity rating: 4
The text is easily and readily divided into smaller reading sections that can be assigned. This lends itself to assigning modules by chapters and units within the chapters.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
I have been teaching this course for the past 4 years and have found that explaining what a marketing plan is and then studying the various stages helps the students appreciate the various phases in this process. This textbook has taken a completely different approach by explaining the marketing plan at the end. While the topics are the same the structure impacts the flow and, in my opinion, the ability to hold the student’s interest. I suggest moving Chapter 16 to Chapter 3 followed by Chapter 5.
Interface rating: 3
The textbook was last updated in 2010, making all images, figures, tables, and video clips mildly outdated. The power of audio-visual aids is very powerful, and the quality is becoming better and better. To keep the students engaged the author might like to consider using technology for simulations, video assignments, etc., these can be useful for the students.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
I found no grammatical errors, the content is well-written and easily understandable. The language used is conversational and something the students should find easy to navigate.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
Global and international marketing are the mainstays for today, these aspects have not been addressed in the textbook. It warrants at least a chapter on world cultures, the emergence of MNCs, and geo-demographics relevance. It is important to acknowledge that demographic profiling needs to incorporate cultural diversity. The textbook has all US-based industry examples and consumer responses, ignoring the diverse consumer profile even within the US.
Overall, it is a great attempt to provide such detailed material for the students. Given that it was uploaded in 2010 the book needs to be updated to include more current and global marketing aspects. The textbook was created for an entry-level course in marketing. I enjoy the way the author shares the various career options available for marketing majors. However, the student profile who takes this course includes students who major in finance, and journalism. PR, management, etc. It would be relevant for them to see how these skills are transferable and useful in other work fields. The suggested activities need to be more application based and limited to the content of the preceding chapter. More global and culturally applicable examples need to be included.
Reviewed by Rich Metzger, Adjunct Professor, Massachusetts Bay Community College on 11/24/22
The OTL textbook covers the basic principles necessary to form a marketing foundation. The content should be updated to reflex the Pandemic and Post-Pandemic marketing environment. I felt some topics needed more discussion, and explanation, such... read more
The OTL textbook covers the basic principles necessary to form a marketing foundation. The content should be updated to reflex the Pandemic and Post-Pandemic marketing environment. I felt some topics needed more discussion, and explanation, such as a breakdown by age and characteristics of the population.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
The OTL textbook is relevant and is a good guide to basic marketing principles but could be better. I prefer the OTL textbook to include recent marketing techniques and strategies used in today’s difficult business environment. This ranges from the advent of the non-store or virtual retailing, broken supply chains, damaged distribution channels, inflation, digital marketing, content streaming, and social media, just to mention a few new topics.
I found the OTL textbook easy to read and understand. Good comprehension level and in the use of examples, figures, and images to illustrate or compliment the text.
The OTL textbook’s material is laid out in a logical sequence, culminating with the last chapter dedicated to the Marketing Plan.
Modularity rating: 5
Chapters progress in a logical manner, allowing the reader to digest the material and prepare for the next chapter.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 3
The organization, structure, and flow of the material are fine, but my concern is the lack of an index and a single depository for key terms and chapter highlights.
Interface rating: 4
The images, figures, tables, and video clips need to be revisited for relevancy. The use of these visual aids helps the reader better understand the topics being discussed.
The content is well written, very limited if any grammatical issues. To make the textbook more relevant, consider using socially accepted pronouns, which in turn would elevate the textbook to today’s sociality expectations.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
A chapter on world cultures and the different business nuances and practices (ethics) would be beneficial to a student learning about marketing.
As this is my first experience dealing with OER, I wanted to be fair and open to the possibilities presented by this new resource. For comparison purposes, I used my adopted textbook vs the OTL textbook. My goal is to decide if I could adopt the OTL textbook. Similarly, the adopted textbook and the OTL textbook are for a 100-level course. Both textbooks offer entry-level content, relevant material, easy to read and comprehend, more than enough chapters to fill a semester, Contents, Chapter titles, Learning Objectives, topics, images, figures, examples, video clips, Discussion/Review Questions, Activities, and both textbooks offer a test bank. The OTL textbook has Key Takeaways for each topic presented in a chapter, and the adopted textbook has a section in the back of the textbook titled Chapter Review, which contains Learning Objectives and Key Terms. Differences, the adopted textbook has a price point, an OTL textbook lacks an Index, and the adopted textbook offers PowerPoint Slides, Instructor’s manual, Rubrics, and Case Studies. I was unable to find an Instructor’s Resources section for the OTL textbook, but the OTL textbook provides students with financial relief. I believe I could adopt this textbook with a minimal number of self-adjustments.
Reviewed by Victoria Shaw, Assistant Professor of Marketing, Anderson University on 3/11/22
The book does a good job of highlighting basic marketing principles. However, I do find it lacks the basics of e-commerce (just basic industry terms like SEO), global marketing principles (especially B2C), and using tools like PEST analysis for... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
The book does a good job of highlighting basic marketing principles. However, I do find it lacks the basics of e-commerce (just basic industry terms like SEO), global marketing principles (especially B2C), and using tools like PEST analysis for external assessment. I think the chapters on B2B behavior and Sales while good, may not be the most value-add for the students in class.
No glaring errors at first glance.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
Imagery is very dated. The chapters use the four basic P's, though the latest books tend to introduce up to eight.
Overall, seemed clear and comprehensive. I think the book would have benefitted from multiple, additional visuals to clarify complex topics.
Consistency rating: 4
Seemed consistent across chapters
I liked the way the topics were broken into micro concepts - makes it easy to assign the portions I find most relevant and supplement when needed.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
Structure was logical and sequential.
A bit text heavy at times but errors.
No grammatical errors on first read.
I think the author missed the opportunity to bring marketing to a more global context.
This is a great principles textbook overall. My only complaint is because of some omitted or abbreviated topics, an instructor may have to supplement a bit more in order to ensure the curriculum is up to industry standards. But in a larger class where schedules only allow for selected topics to be covered, this would be a very good start.
Reviewed by Amy Strunk, Lecturer, James Madison University on 11/29/21
Basic marketing concepts are covered with sufficient depth, but newer concepts are missing (like digital marketing). read more
Basic marketing concepts are covered with sufficient depth, but newer concepts are missing (like digital marketing).
Some of the information is dated: for example, most would agree that we are not in the relationship era of marketing, but the textbook states that we are in an undefined era (which would have been true 10 years ago).
The book uses “creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging value” as elements of the marketing mix/strategy rather than the 4 P’s, and actively argues against the 4 P terminology, which is controversial.
The book also uses "offerings" instead of "product". The authors argue for it effectively, but I don't know anyone in the marketing world who uses that term in the real world.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 2
References are dated: - Foursquare (college-age students in 2021 will have no idea what this is) - Some images are out of date (retrieved in 2008) - Mission statements on p. 27 are outdated and reference links are broken. - References to iPod in the time of iPhones
These references will continue to grow stale.
The content is pretty straight forward. Definitions are clear.
The book is consistent in its own frameworks/terminology (stubbornly so).
Modularity rating: 3
Some of the longer sections could benefit from headings and subheadings.
I would recommend that market research come before the "Creating Offerings" section since that process is so integral to product (or "offering") development.
Interface is sufficient.
Some small issues, for example, using the term “Droid” smartphones on page 6—should be Android.
I did not notice any concerted effort to include diverse backgrounds in this text.
Marketing is changing rapidly thanks to technology, and this book is too outdated to address issues like data privacy and hyper-targeting.
Reviewed by Matthew Lunde, Assistant Professor, Pittsburg State University on 6/4/21
the textbooks is very thorough in covering all the topis needed in a principles of marketing class. It even adds a chapter that is not in many other textbooks: "The Marketing Plan." However, my only criticism is that it does not touch on a huge... read more
the textbooks is very thorough in covering all the topis needed in a principles of marketing class. It even adds a chapter that is not in many other textbooks: "The Marketing Plan." However, my only criticism is that it does not touch on a huge topic area nowadays in marketing: sustainability (sustainable marketing and sustainable competitive advantage).
The content is objective, thorough, and accurate. It uses statistics and example businesses and situations effectively to help teach younger college students the fundamentals of marketing.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The content is up-to-date as best as it can be. Whenever any textbook uses statistics, years, numbers, and other figures, it can date the textbook; however, the content is written in a way that it will last for multiple years to come.
Clarity rating: 4
There is some jargon, but the jargon used is needed to help teach the fundamentals of marketing to new students.
It is great how all the terms in the chapters are easy to find and to read because each term is bold.
Yes, the book is broken down into manageable sections for a younger college student to read and interpret effectively and efficiently.
Yes. This textbook is laid out very well. However, one thing I would add in the chapter titles would be "retailing."
Good! Nothing to add here!
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
The book is written well, free of grammatical errors. However, I see "he or she" is used. Nowadays, for inclusivity, the right pronoun to use would be "they."
However, I see "he or she" is used. Nowadays, for inclusivity, the right pronoun to use would be "they."
Reviewed by Felix Flores, Assistant Professor of Marketing, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 4/17/21, updated 5/26/21
The textbook sufficiently covers areas and ideas of subjects and is easy to navigate. I would find it useful to include and discussed an example of an actual marketing plan. read more
The textbook sufficiently covers areas and ideas of subjects and is easy to navigate. I would find it useful to include and discussed an example of an actual marketing plan.
The textbook's content is mostly accurate, error-free, and unbiased.
Some of the links and examples may be dated but contribute to the chapter's main ideas. There are, however, some links that do not work or could be replaced with newer examples. I would recommend reviewing all of the provided links.
The textbook is written in a clear manner.
The textbook is mostly consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
The textbook is easily divisible into smaller reading sections that can be assigned at different points within the course.
The topics are presented in a logical, clear fashion.
Interface rating: 5
The text is free of interface issues or navigation problems.
There may be a small room for improvement in terms of grammar.
I believe the textbook is mostly culturally relevant.
I believe that you can effectively teach a Principles of Marketing class with this textbook, on its own, and especially in combination with other OER textbooks/resources. It will require, however, checking all of the links and updating some examples.
Reviewed by Diane Edmondson, Adjunct Professor, Trine University on 4/16/21
Overall, this textbook covers a majority of the marketing topics that should be covered in a Principles of Marketing class. Since the book is somewhat dated, there is limited coverage on both digital marketing and social media as well as marketing... read more
Overall, this textbook covers a majority of the marketing topics that should be covered in a Principles of Marketing class. Since the book is somewhat dated, there is limited coverage on both digital marketing and social media as well as marketing analytics. These two topic areas have revolutionized the marketing field. However, this marketing textbook contains all of the other key marketing concepts such as the 4 P's of marketing, strategic marketing, target market strategies, consumer and business buying behavior, and how to craft a marketing plan.
Overall, this textbook is accurate and error-free. It does not appear to be biased in any way.
Overall, this textbook is still highly relevant. It is missing some more detailed information related to digital marketing, social media, and marketing analytics as these have drastically changed the marketing field over the past decade; however, the content covered is still relevant to both business-to-business and business-to-consumer markets.
One of the best things about this book is that it is easy to read. The text is written in a way that students should not have a difficult time understanding the concepts being covered. There are multiple examples given for each major topic to help students better understand the material. Terminology is defined to aid understanding.
Overall, a consistent framework is used throughout this textbook. The flow and chapter ordering of the textbook makes natural sense with how it would be taught in the classroom.
The text is made up of 16 chapters; however, each of the chapters is then broken up into multiple subsections. This allows the text to be easily and readily divided into smaller reading sections, based on the desire of the instructor and/or reader.
The chapter layout of this textbook is similar to many other Principles of Marketing textbooks. Topics are presented in a logical and clear manner, which aids readability and understanding.
Overall, the images, charts, tables, and figures were clearly displayed without any distortion. There are a few navigation links that no longer function; however, these are minimal in number.
The Principles of Marketing textbook appears to be free of grammatical errors.
There are a variety of diverse examples throughout the text. None of these should be viewed as culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
Overall, this textbook is well written and covers most of the major marketing topics. The few topics not covered are primarily because these became dominant marketing elements after this textbook was published originally.
Reviewed by Ricardo McCoy, Adjunct Professor, Trine University on 3/3/21
I have been facilitating marketing, analytics, sales, and consumer behavior classes since 2009 and this textbook does a good job of covering all of the marketing mix. Most important, the content is updated and relevant. The layout is... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
I have been facilitating marketing, analytics, sales, and consumer behavior classes since 2009 and this textbook does a good job of covering all of the marketing mix. Most important, the content is updated and relevant. The layout is user-friendly and easy to read.
Based on similar marketing text books I have read, this textbook is accurate and contains content that someone who is unfamiliar with marketing concepts will easily understand. The use of examples throughout the textbook is a good way to help a beginner to marketing understand the subject matter.
I like how this book understands how marketing has changed and explains variables in the environment that is effecting this change. This can be seen in Chapter 1 concerning some of these changes:
Ethic and Social Responsibility Sustainability Service-dominant logic Metrics A Global Environment
It is good to see that the textbook is up-to-date and recognizes that marketing must adapt to these changes. Some of the marketing textbooks I read in the past do not recognize these changes.
Overall, the information throughout the chapters was easy to understand. I like how examples were used throughout each chapter. My only recommendation is to add more illustrations consistently throughout the textbook. Based on my experience, most students like to see illustrations (visualize). I think this helps him or her to understand the subject matter.
Overall, the content throughout the textbook is consistent. However, I notice that some of the chapters have more illustrations than other chapters. I think that using more illustrations (and examples) would make the chapters more user-friendly.
P.S. Links to additional resources would also be a good addition.
The sequence throughout the textbook “flows” from section to section. I like the synergy from chapter to chapter. This helps the student to understand how various factors of marketing work together.
I like how Chapter 1 gives a brief description of marketing while summarizing what will be discussed in the preceding chapters. I also like the “key takeaways” at the end of each chapter. The "review questions" are brief, yet add to what was discussed throughout the chapter. This is good to see.
The overall functionality of the textbook is good. The font size and white space makes the content easy to read. I like the use of color throughout the textbook. For example, the use of green for the “Key Takeaway” and blue for the “Review Questions”.
Although it is difficult to check all the content, I did not see any typos or “wordy” sentences. I like how the content “talks to” rather than “talks at” the student.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This is a difficult question to answer because I did not see anything that was insensitive or offensive. Ideally, the content would continue to embrace diversity and inclusion. This is important because we live in a global economy.
I think that Chapter 5 (“Marketing Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning”) should be followed by Chapter 10 (“Gathering and Using Information: Market Research and Market Intelligence”). Both of these chapters are closely related. To properly perform segmentation and targeting, you must understand analytics / gathering information. I was also looking to see slightly more insights on digital analytics in Chapter 10.
Reviewed by Markus Biegel, Adjunct Faculty, California State University, Dominguez Hills on 8/12/20
I compared it to the McGraw Hill book that I have been using for the past 4 years and the topics (Chapters Topics and Sub-Topics) are pretty identical just in a slightly different order. When looking into how in-depth the book goes, it is not... read more
I compared it to the McGraw Hill book that I have been using for the past 4 years and the topics (Chapters Topics and Sub-Topics) are pretty identical just in a slightly different order. When looking into how in-depth the book goes, it is not quite as comprehensive as the McGraw Hill book. However, it is easy to read.
Marketing always is a bit subjective. I think the book does a great job covering all the important topics as unbiased as possible.
This is a basic marketing course focused on teaching students the fundamentals, the book does a good job at that. Given the current COVID situation, a lot of things have changed in business but not the fundamental theories and practices of the profession. Because of that the relevance of the book is current in my opinion.
The text has a logical flow. There is certainly room for improvement from a formatting standpoint. I think it makes it easier for students to learn key terms and key concepts when they are highlighted on the sidebar (similar as in many mainstream textbooks).
Certainly consistent and comprehensive in all the key terms that this book should cover for Principles of Marketing.
The text is very easy to read. There is good spacing in between the paragraphs and graphics/images help further give the mind a reading break. I also think it is great that links are included to videos, this helps students get a "reading break" which is essential when cramming in a few chapters to study for an exam.
Very well organized text. I just wish the key terms and key concepts were featured separately in an almost duplicate fashion on the side of the main text. I think students are used to using these highlighted areas to study for exams.
Didn't notice any problems with the interface. Could have perhaps used better images here and there but overall does the job.
I am not an English professor and this is my second language but I did not notice any grammatical errors. I am sure there are some, including mistyped words but every book I have used had a few of those.
One of the key concepts in Principles of Marketing is target marketing which certainly can be interpreted as offensive to some people. However, I think the book does a great job at explaining the concept. Again, marketing leans into being somewhat controversial based on the subject matter and business practice.
Can't beat a free book. Seems like a great resource to use for students.
Reviewed by Kirti Celly, Professor, California State University, Dominguez Hills on 8/10/20
Principles begins with a question to spark curiosity for the novice student of marketing. Organized into 16 chapters, it takes a traditional strategic planning, consumer and buyer behavior, research and 4Ps approach that addresses all major areas... read more
Principles begins with a question to spark curiosity for the novice student of marketing. Organized into 16 chapters, it takes a traditional strategic planning, consumer and buyer behavior, research and 4Ps approach that addresses all major areas and ideas in a core marketing class. Given the importance of ethical decision making, it needs to add/bolster content on ethics in marketing and add an index/glossary.
Accurate content with image sources and references. I have not tested all these links.
Since the focus is core content, it is written in a nuts and bolts manner and will stay perennial. Consistent with the conditions of use, the text’s simplicity allows for it to be modified easily.
Written professionally and in simple sentences, this makes for accessible, adequate and easy to understand content. Marketing concepts are defined simply and succinctly throughout.
The key take-aways and review questions after each section of a chapter are supplemented by end of chapter discussion questions and activities throughout. This fits nicely with Bloom’s learning taxonomy.
This is a key feature of this book and one most appreciated by my students.
Another key feature of this book, and one appreciated by my students.
Other than a few formatting and pagination issues, nothing to note. Any links I used worked. For the manner in which I use this book as basic material for my classes, not having an excess of photos and images in the body actually works well. Having URLs for case examples also facilitates easy revision and adaptation for various local and regional teaching and learning contexts.
Simple, easy to read, accessible. I did not notice any grammatical errors.
This is less about this book than about the way in which most business textbooks are written. It is in no way offensive; in fact, its style and variety of examples promotes inclusion and it is adaptable to alternate cultural contexts through a shift in frame to include broader contexts.
Our students appreciate having an accessible zero cost course materials course with adds ons from me, the press, and other OER, and low cost or no cost AV materials and marketing math. Thank you.
Reviewed by Sheryl Spann, Marketing Instructor, Oregon State University on 7/28/20
The textbook begins with the question “What is Marketing?” to assist students new to the field of marketing to understand the real definition of marketing versus their perceived ideas of marketing. This is a great place to start as many students... read more
The textbook begins with the question “What is Marketing?” to assist students new to the field of marketing to understand the real definition of marketing versus their perceived ideas of marketing. This is a great place to start as many students either believe that marketing is strictly sales or do not have a full concept of the many aspects of what encompasses marketing. The text covers most of the key areas of marketing such as consumer behavior, market segmentation and target marketing and the principals relating to product, pricing, placement and promotion. Marketing research, new product development and marketing communications is also covered at a basic level. However, based on my experience in the classroom, a few suggestions are in order. I would add three additional chapters on international marketing, market expansion strategies and ethics and social responsibility. The chapter on professional selling could be removed or covered within chapter one as a portion of the explanation on the aspects of marketing. Lastly, I would add more current marketing articles, one-page cases and small group discussion questions to each chapter. For marketing majors, I would add an appendix at the back of the book discussing the various career opportunities in marketing.
The book content is accurate with terminology and marketing concepts accessible for a university level student. The textbook also cites sources for most of the provided information.
In addition to the textbook content for teaching marketing principals, there are many real-world examples offered to improve student understanding. Although most offer longevity, there is a need to augment current examples with more recent examples including company or product examples representing cultural diversity.
The text is easy to read with a combination of informal and professional language for appropriate student learning and understanding.
The text is internally consistent and provides actual examples of the principals covered as well as review questions to ensure student comprehension. This approach is inline with other “Principals of Marketing” textbooks.
The course material is listed in modular fashion to easily transfer to canvas. However, since “Principals of Marketing” is usually the first marketing course for majors and the only course for this topic for non-majors, I would place the chapter on “Strategic Planning” right before the last chapter on “The Marketing Plan”. As indicated in the “comprehensiveness” section of my comments, I also believe that a few topical chapters such as “International Marketing” should be added to the book to improve its overview of the topic.
In general, the topics are presented and organized in an effective format. The text starts with overarching definitions and concepts and then moves toward providing more details on each topic. I believe that the “Strategic Planning” chapter should be moved to the end of the book before “The Marketing Plan” to ensure that students have the foundation needed to better understand this topic plus use its strategic perspective in the development of a marketing plan.
There did not appear to be any interface issues for this book. All video and web page links also worked well.
The text did not have any grammatical errors.
Although cultural examples were included and relevant, additional cultural diversity elements would improve the book. Also, it is important to include examples that are more current to provide better student discussions of this important marketing topic.
Overall, this textbook is a suitable option for an entry level college course on “Marketing Principals”. Adding chapters on “International Marketing”, “Market Expansion Strategies” and “Ethics & Social Responsibility” as well as updating some of the chapter business examples, case studies and discussion questions would be very helpful plus keep this book “current”. Lastly, including a greater overview of the marketing aspects of cultural diversity plus marketing career options would cause this book to stand out among textbook options for this topic.
Reviewed by Zahra Tohidinia, Assistant Professor, Framingham State University on 6/12/20
The text offers a very good review of key marketing principles and provides a comprehensive introduction to the main concept. I would suggest combining the textbook with relevant current marketing articles and cases. read more
The text offers a very good review of key marketing principles and provides a comprehensive introduction to the main concept. I would suggest combining the textbook with relevant current marketing articles and cases.
The content is accurate and the textbook cites sources for most of the provided information.
The content is relevant to marketing. There are a solid number of examples throughout the book. The content related to digital marketing/social media could be expanded, but overall the content is relevant and robust.
The text is easy to read and provides a good balance of informal and professional language.
The structure of the text is consistent and the book gives example-based explanations of the main concepts. There are review questions at the end of each section as well as discussions and activities at the end of each chapter.
The text is easy to navigate. The book is divided into smaller segments. A hyperlinked (clickable) table of contents makes it really easy to move between different chapters and their corresponding sub-segments.
The topics are presented and organized in an effective format. The text starts with overarching definitions and concepts and then moves toward providing more details on each topic.
The links to the videos that I clicked on worked and each opened a new tab. As mentioned before, the hyperlinks make it very easy to navigate between different sections. In some cases, the image headings were separated from the actual image because of page breaks which can be revised in later editions.
The consumer behavior chapter does a good job with embedding cultural variables into the discussion. This could have been integrated more effectively in the other chapters; especially the chapters involving marketing research and intelligence, as well as market segmentation and positioning
This book covers the main concepts of marketing very effectively. This textbook combined with current articles and relevant cases could serve as a comprehensive set of materials for introductory marketing courses at the undergraduate level.
Reviewed by Christian Gilde, Business Faculty, University of Montana - Western on 1/31/20
The textbook has enough depth and addresses all the major parts of the marketing discourse, such as the environment, marketing strategy, consumer behavior and segmentation, and marketing research, as well as the product, place, price, and... read more
The textbook has enough depth and addresses all the major parts of the marketing discourse, such as the environment, marketing strategy, consumer behavior and segmentation, and marketing research, as well as the product, place, price, and promotion variables.
The explanations, terminology, and concepts in the text are accessible and accurate.
The textbook contains applicable examples of marketing that will help the audience learn and appreciate the marketing realm. Most pieces and examples in the book have longevity. A few applications might need to be updated to make the text more timely.
The text is accessible and will help guide the students through the different dimensions of marketing.
The given text follows a certain presentation canon in terms of marketing terminology, concepts, and applications that can be found in textbooks of similar nature.
Many textbooks in marketing follow a certain modular pattern. This same pattern can be found in this text, with each chapter being split into sections for which particular assignments and experiential learning activities are designed.
As far as the organization and structure of this work are concerned, the marketing text is in line with a good number of other principles texts. The structure, flow, and positioning of the different marketing topics within the individual chapters is logical, with the objectives in the beginning and a re-visitation of the key points and review questions at the end.
The functionality of the text seemed to be working. Web links, images, and figures allow for easy direction-finding.
A few minor grammatical and structural errors can be found in the text.
The cultural illustrations are relevant, to a certain extent. However, it might be useful to update some of these items.
The material in this text is suitable for a basic marketing course. Overall, I would recommend using this text for entry level marketing students.
Reviewed by Kelly Atkins, Associate Professor, East Tennessee State University on 10/21/19
The text contains the expected chapter topics related to Principles of Marketing. In my opinion, there is too much information about Professional Selling (Chapter 13) for the topic of the text. In my opinion, Chapter 11 should include a... read more
The text contains the expected chapter topics related to Principles of Marketing. In my opinion, there is too much information about Professional Selling (Chapter 13) for the topic of the text. In my opinion, Chapter 11 should include a discussion of the basic Communications Model as well as some more modern communications models.
The text content appears to be accurate, error-free and unbiased. In my thorough review, I found nothing to the contrary.
The text contains many relevant, current examples of marketing concepts as well as some images of marketing examples and nice video clips of marketing examples. Some examples in Chapter 2 are from 2006, 2007, 2008 & 2009. These 10+ year old examples are too old to be relevant to students who are only 20 years old. I like the application of marketing concepts to the world of business and to personal branding.
The “voice” of the text is conversational yet professional. The terms used throughout the text seem to be in alignment with other Principles of Marketing textbooks I have used previously.
The text seems to be internally consistent. I saw nothing to indicate otherwise.
The text is organized effectively in most ways, but I have a recommendation. Chapter 3 should be divided into more sections. There are too many learning objectives and key takeaways for section 3.1.
There are significant organization problems in Chapters 4,8 & 13. Each of these chapters is out of order. For example, Chapter 4 is presented in the following sections: 4.4, 4.5, 4.6, 4.7, then 4.1, 4.2, 4.3. The same is true of Chapters 8 & 13.
The way the pages are presented with extra lines on many pages, with figure titles on different pages than the actual figure, or with figure numbers on a different page than the figure itself. See Figures 1.3 and 1.4 in Chapter 1 as examples.
I did not notice any grammar problems in the text (and I typically find lots of grammar problems when I am editing).
In my opinion, he text is culturally sensitive.
• I really like the “key takeaways” and “review questions” at the end of the sections instead of a summary at the end of the chapter. • I would add key terms at the end of each section because the terms and definitions seem to get lost within the chapters. • The “activities” at the end of the chapter are unique and creative. I would use these ideas for my classes.
Reviewed by Donald Chang, Professor, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 4/29/19
The textbook provides basic coverage of main concepts found in most principles of marketing. Overall, the discussion throughout the book tends to be less comprehensive. In some areas, the author glossed over without providing sufficient details.... read more
The textbook provides basic coverage of main concepts found in most principles of marketing. Overall, the discussion throughout the book tends to be less comprehensive. In some areas, the author glossed over without providing sufficient details. To introduce basic concepts, it might be sufficient. For deeper understanding and analysis, it will require additional reading and research by readers. For example, in the very beginning, the author claimed "... about 1950 to 1990, businesses operated in the marketing era" without providing supporting materials to bolster the claim. The discussion also skipped a commonly known period when emphasis on selling was prevalent, skipping from product concept to marketing concepts, while ignoring the discussion on social responsibility in the 80s.
Accuracy is not a major issue for this book. Most contents are explained adequately for concept delivery.
Most basic concepts in marketing, e.g., product life cycle, buying process, pricing strategies, are mostly time free, thus, stay relevant regardless of changes in the marketplace. Examples used are apparently out of date, e.g., iPad. Many of the examples are prior to 2010 so that examples need to be updated to be relevant to today's students. Most basic content is consistent with other textbooks, just on a shallow side.
For marketing, the key strategic decisions are in segmentation, targeting, positioning, and differentiation. It would be probably more appropriate to place strategic planning close to the chapter on segmentation, targeting, and positioning. With so much content in marketing to cover, a standing-alone chapter on professional selling is uncalled for. After all, personal selling is only one of the element of promotion and most companies prefer to train their own sales force, thus very company/product specific, not something could be covered effectively in a principles of marketing textbook. It also incorrectly over-inflates the role of sales in marketing curriculum. Most students, business and non-business, do not see professional selling as their career aspiration either, if they have the choice.
There is an obvious omission in international marketing. The author's claim that global coverage is built in throughout the textbook cannot be observed. Without having a devoted chapter in international marketing, some basic concepts in international management are not presented. The same is for sustainability, ethics, and social responsibility. The author seemed to understand their importance, but not important enough to have their own sections. On the other hand, the author had no issue in having a chapter in professional selling without clear justification for its inclusion. These are obviously the author's own selection bias and personal preferences, not necessarily what students ought to learn from the course.
The writing is good for average college students. It is mostly easy to follow.
The book used "offerings" when referring to products and services consistently throughout the book. Each chapter is presented with discussion questions, activities, key takeaway, review questions with consistent structure and writing style.
The book is organized in a module-like manner, with most materials being free-standing, allowing a section to be borrowed for another marketing course as needed. As the writing is on the succinct side, there is rarely a long writing blocks without division.
While the book is structured well overall, the placement of strategic planning in the very beginning (Chapter 2) is probably off. Students need to know about the subject more before jumping into strategic planning. Other than chapter placement, the overall organization is adequate.
There are no known serious interface issues that are present. Graphs, charts, pictures are clear and easy to see and follow. A few enhancements to market the headings and sub-headings could be added to better break up sections. As examples, "Video Clip" on page 272, 273 could be better presented. The headings are easily overlooked as presented. At times, the reader might not be aware that the topic has shifted to a new one.
The book is grammatical correct overall.
There are no obvious concerns of being culturally insensitive or offensive.
The book is a possible alternative for average high school and college students if the goal is to learn the very fundamental concepts in marketing. For students who look for deeper understanding, this is not the right book for them as much discussion is on the shallow side. The author's own opinions can be found throughout the book without adequate supporting materials. Therefore, it is subject to the author's self selection bias. For marketing major students, I would expect students to learn more than what are presented in this book.
Reviewed by Nicole Lytle, Faculty Lecturer, LaGuardia Community College on 4/24/19
This resources covers all the relevant topics traditionally covered and necessary for an introduction-level course. The material is presented in comprehensive way. read more
This resources covers all the relevant topics traditionally covered and necessary for an introduction-level course. The material is presented in comprehensive way.
I found the text to be accurate, and in line with current marketing practices and pedagogical materials.
The resource is current, but some examples are a bit dated. The instructor using this resource should check all links and examples before assigning.
The resource is clear and easy to understand.
The terminology and framework are consistent with current concepts and expectations of an introductory level course.
The text is well organized; it also lends itself to skipping around and changing the order of the material as the instructor sees fit.
Topics presented are in a logical manner - learning objectives, terms, examples/diagrams, key takeaways, and review questions.
The interface is clear and easy to navigate - clicking images isolates them, which is a good tool for some visual learners.
No grammatical errors were found.
The resources is not culturally offensive, but it also misses the mark for cultural inclusion.
Reviewed by Duane Bernard, Lecturer, Gettysburg College on 3/12/19
The text book covers all of the typical topics for this level of marketing. If there is any criticism it is that some topics are covered very sparsely. For example, the topic of subliminal messaging is given a few sentences. While it is not... read more
The text book covers all of the typical topics for this level of marketing. If there is any criticism it is that some topics are covered very sparsely. For example, the topic of subliminal messaging is given a few sentences. While it is not necessary to cover this in detail, the explanation provided may not be enough for students to understand what it is. I even had a student that commented on the lack of substance in some areas.
I did not come across any areas that were not accurate. It is written well.
The examples are somewhat dated. While it is perfectly fine to present historical examples, the "new" examples need to be updated. In addition, some of the links are broken.
I have not seen any issues with the understandability of the text. I have also not had any negative comments from students.
The text is consistent with its terminology.
The text is easily separated into subunits. I do not use it as a standalone assignment for reading, as I also have many cases and simulations. I have only directly assigned certain sections for homework. This works well.
The book follows the usual formatting and organization of most of these textbooks.
The only issue I have encountered is some broken links that refer to videos. I have not encountered any other issues.
Grammatical errors have not been found.
I have not detect any offensive content. I have not seen a lot that would be inclusive of other backgrounds.
This book is great as a supplement to other course materials such as cases and lecture. I believe its limitation is that it could go into more depth in many sections.
Reviewed by Lori Rumreich, Assistant Professor of Marketing, Marian University on 3/5/19
This book provides comprehensive coverage of marketing principles equivalent to other textbooks. There is very nice coverage of supply chain and logistics beyond many other principles books. The marketing plan section at the end is very useful.... read more
This book provides comprehensive coverage of marketing principles equivalent to other textbooks. There is very nice coverage of supply chain and logistics beyond many other principles books. The marketing plan section at the end is very useful. Overall there is a lot of content to choose from in this text that makes it easy to select what is needed. A searchable pdf in the downloaded format makes it easy to find content.
The content is accurate and unbiased. Some content may be out of date but with the rapid change happening in much of marketing, especially digital/social, that is to be expected.
The rapid pace of change in marketing, especially digital marketing/social media and media in general make it difficult for textbooks to stay up to date. Updates to these sections should be easy to make. The majority of the text is up-to-date and relevant. The use of review questions and key takeaways for sections are very helpful and reinforce learning of each concept.
This text provides practical and real world examples that are interesting and relevant. Writing style is clear and accessible. The use of pictures and the use of color for highlighting tables, charts, special sections, etc. add to the clarity and readability.
There is a consistent style throughout the text. Clear objectives are at the start of each section, key takeaways and review questions are at the end of each section. This creates a very consistent style that is easy to follow and should help with learning.
It would be nice to provide sub units or groups of chapters within a theme or section of marketing but this is not a requirement. Chapters can be easily divided where needed.
I would prefer that market research to be closer to the front of book. Market research is a first step in understanding customer needs, product features, markets, segments, promotion and ad concepts, etc. It seems out of place near the end of the text. Otherwise, the organization is logical and clear.
The searchable pdf version is very easy to navigate and use. The links to videos and other external content are accessible. All content appears clear and free from distortion. Having multiple formats, pdf, kindle, etc., available is a plus for this text.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
The text appears to be culturally relevant. There is good diversity in the photos shown in the text.
Reviewed by Rosemary Prince, Teaching Faculty III, Florida State University on 12/6/18
The concepts covered in Principles of Marketing - 2015 are appropriate for an introductory level course. The discussion of the 4 Ps as creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging provides an interesting perspective. An index and glossary... read more
The concepts covered in Principles of Marketing - 2015 are appropriate for an introductory level course. The discussion of the 4 Ps as creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging provides an interesting perspective. An index and glossary are not included which would be beneficial.
The concepts, definitions and strategies are accurate and unbiased.
The general principles addressed are relevant. Examples should be updated and some links are no longer available. As noted in the learning objectives Social Media keeps changing and the text needs to be updated. Additionally, e-marketing should be expanded given the changes since 2010. The reference information provided with websites resources and examples and framework of the textbook allows for updating with more recent clips, research, templates, etc.
The text is very clear and terminology is easy to understand.
The framework is consistent with the concepts presented in an introductory level marketing text.
The text is presented in units within each chapter that can be separated and or combined with other units for specific learning assignments or extracted to supplement learning.
The topics in the text are presented in logical order for an introductory marketing text. The layout of the textbook including learning objectives, sequencing, terminology, key takeaways, questions and activities is well organized.
Downloading the text as a PDF, the images and charts were clearly visible. The navigation was straightforward and easy. The links to videos were accessible; however, some were no longer available.
Minor grammar errors were noted.
Updating the video examples would provide a more inclusive text.
Reviewed by Melodi Guilbault, Senior University Lecturer, NJIT on 5/21/18
The book covers all content generally covered in a Principles of or Introduction to Marketing course. The issue is that the content is old. The content is based on a text written in 2010. For example, there are only a few short paragraphs on... read more
The book covers all content generally covered in a Principles of or Introduction to Marketing course. The issue is that the content is old. The content is based on a text written in 2010. For example, there are only a few short paragraphs on social media. There is a clear Table of Contents but I did not see an index or glossary.
The content appears to be accurate. I did not note any errors or any bias. But the content is dated.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 1
The content is dated. The content is adapted from a text written in 2010. There have been significant changes since 2010. Although there are a few more recent links most of the links are from before 2010.
The text is easy to read. Students should find the writing easy to follow. Terminology has been clearly explained.
The way the chapters are organized is consistent throughout the text.
The text is easily and readily divisible into smaller reading sections that can be assigned. This is generally done by chapters and units within the chapters.
The topics are presented in the same order as many Principles of or Introduction to Marketing texts.
I could not get any of the videos to open. Other than that I was able to easily navigate through the chapters. The hyperlinks took me to the appropriate text but it would be helpful to have a return button.
The text did not appear to contain any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 2
I did not note any direct effort to be inclusive in the examples provided.
I like the use of the alternative to the 4Ps. I find the 4Ps to be a dated paradigm and it was refreshing to see a different approach.
Reviewed by David C Taylor, Assistant Pofessor, University of Houston on 3/27/18
A very good comprehensive introduction for marketing. Also would serve as a great refresher text for upper-level marketing courses. read more
A very good comprehensive introduction for marketing. Also would serve as a great refresher text for upper-level marketing courses.
The text is very general, but provides accurate descriptions and overviews of concepts and marketing theory.
We could see more on e-marketing or the evolution of social media over traditional advertising. That said, as a primer on the subject of marketing, this is a great tool in lieu of students having to make a purchase.
Clear, easy to read and understand.
Consistency is strong and consistent across chapters.
I don't think molecularity is practical with an general overview text, unless you wanted to utilize some of the chapters as refreshers in broader topic on marketing.
organized consistently and flow is as with other marketing texts
I did not experience any difficulties
No major grammar issues were identified.
Again, a good primer, or refresh for an upper-level marketing course.
Reviewed by Mary Tripp, Business Faculty, St. Paul College on 2/1/18
The textbook covers the material found in the majority of introductory marketing textbooks. The topics covered are appropriate and the scope meets the basic needs of a principles of marketing course. A searchable index would add to the... read more
The textbook covers the material found in the majority of introductory marketing textbooks. The topics covered are appropriate and the scope meets the basic needs of a principles of marketing course. A searchable index would add to the usefulness of this textbook. A table of content exists but unfortunately no subject index or glossary is provided.
Content Accuracy rating: 3
Overall the accuracy of information, based on the publication date, is acceptable. The textbook is listed as published in 2015 on the Open Textbook Library site. However, the internal publication date is 2010. The internal date seems accurate based on the examples and citations used throughout the textbook. The books examples are all about 10 years old. In the world of marketing, that is a problem. The textbook has some grammatical and spelling errors but nothing that would prevent usage.
The textbook is listed as published in 2015 on the Open Textbook Library site. However, the internal publication date is 2010. The internal date seems accurate based on the examples and citations used throughout the textbook. The books examples are all about 10 years old. In the world of marketing, that is a problem. The subjects of pricing, product, and distribution would be easy to update in the text and/or provide supplements in the classroom. However, the promotion related chapters are very out of date in today's tech driven e-marketing and social media marketing world. If this book had been available in 2009 as an open resource, I would have used it. In 2018, it is unlikely that I would use this resource.
The clarity of the book is great. It is written in a straight forward manner that students would easily understand. The minor grammatical and spelling issues do not hinder the reader.
The consistency of the book meets expectations in regards to terminology and framework.
Each chapter has between 3-8 subsections that allows the material to be easily read by students.
The flow of the chapters is a positive element of the textbook. The organization of the book follows the same structure as many of the principles of marketing textbooks. The table of contents could be restructured to group chapters into subunits for greater student comprehension but it is a small detail.
The interface of the book demonstrated no problems other than the links to videos did not work.
The book contained minor grammatical errors but at a level that the average student would not notice.
Cultural Relevance rating: 1
The cultural relevance of the textbook needs attention. There are not many examples/photos that demonstrate a variety of races, ethnicity, or backgrounds.
1. The cover page and the initial first pages are dull and uninspiring. 2. Overall the textbook is visually dull and students would find the lack of visual interest to be a negative. 3. The examples and references are all at least 10 years old. 4. The text contains only three pages on social media. Not nearly sufficient in today's social media driven environment. 5. The textbook lacks examples of nonprofit organization.
Reviewed by Kristin Hagan, Associate Professor, Northern Virginia Community College on 6/20/17
This text includes all of the major learning objectives covered in an introduction to marketing class. The main topics include the definition of marketing, strategic planning, consumer behavior, the 4 Ps, offerings, marketing channels, selling,... read more
This text includes all of the major learning objectives covered in an introduction to marketing class. The main topics include the definition of marketing, strategic planning, consumer behavior, the 4 Ps, offerings, marketing channels, selling, and overview of a marketing plan. The Table of Contents is easy to access; it serves as a helpful search function. The text is missing a glossary of terms; adding one could be beneficial to readers.
Definitions, principles, and concepts presented in the text are correct. In accordance with marketing principles, the facts presented in the text are true to point. The material was presented in an unbiased way and was primarily free of any grammatical errors.
The examples used in the text are up-to-date and relevant. The large number of real world examples given help the reader understand the learning objectives being presented. Revising these examples and other pertinent information in the text would not be an impossible task.
The layout and formatting of the material is clear and concise. The content of the book uses a lot of extended sentences that could be shortened to help the reader better understand the material. The terms and jargon used is relevant and up-to-date.
The text is extremely consistent in its terminology and framework. Its layout is consistent which makes each new chapter and section easily recognizable. Each chapter has review questions and key summery section which reiterates key points and acts as checkpoint for student.
The layout of the text is very modular. Each chapter is broken down into a minimum of three sections which makes the information very learner-friendly. Each section has a defined learning objective and review material at the end of the section.
The text is organized in a logical way where concepts taught at the beginning of the book are built upon later. The information presented flows well throughout the text. The Table of Contents is extremely beneficial and makes key topics easy to locate in the text.
I did not notice that the text featured any interface issues such as navigational problems, unclear images, or other distortions that would confuse the reader. The images and figures presented in the text are clearly visible to the reader. All images and figures can be enlarged if the viewer clicks on the displayed image.
There were few grammatical errors in the text.
This text presents real life examples relevant to mainstream culture and business in America. Depending on the audience, more culturally diverse examples may be more suiting. The text does a fairly good job of using conational business examples however, some of the images of people could be diversified.
The audio clips located throughout the online text are a nice edition that students reading a traditional textbook can not experience.
Reviewed by Oksana Grybovych, Associate professor, University of Northern Iowa on 12/5/16
The text would greatly benefit from a table of contents, glossary, and an index. Otherwise, most content areas are discussed rather thoroughly - even though, as the previous reviewer mentioned, the text is lacking in its application towards... read more
The text would greatly benefit from a table of contents, glossary, and an index. Otherwise, most content areas are discussed rather thoroughly - even though, as the previous reviewer mentioned, the text is lacking in its application towards services and experiences marketing. Speaking of the latter, there is no discussion of marketing experiences as offerings even though this approach is very common these days.
This text seems to target the North American audience, and readers from elsewhere might not readily relate to the examples provided. The authors could also incorporate more examples from a nonprofit sector.
Most chapters are very relevant to the current marketing practices. However, the authors could consider including or expanding more on the subjects of sustainability (e.g. social corporate sustainability) as well as experience marketing.
Key concepts are well defined, but the structure and formatting of the text are somewhat confusing.
The text is structured around the framework that is outlined by the authors in chapter 1.
There are 16 chapters in the text, each of them is broken up into sections. Such structure makes it very manageable for the instructor to use the text in a typical North American semester.
Some of the chapters could be moved around to allow for a better flow of the contents.
The authors could consider moving all references to the end, as well as including a table of contents that the students could navigate (click on the headings), glossary, and an index.
Very few spelling/grammar errors.
It appears that this text is mainly designed for North American white audience, hence is lacking in its cultural relevance.
Overall this is a very good introductory text, I was happy to see the authors incorporate many important topics that are frequently omitted in other texts. At the same time, a few more important topics could be added, the formatting/ structure of the text revised, and more culturally relevant content added.
Reviewed by Chris Blocker, Assistant Professor, Colorado State University on 1/7/16
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond is a very comprehensive text, which addresses the full gamut of topics that an instructor might want to cover. It also offers nice integration of some topics that might normally be neglected, e.g.,... read more
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond is a very comprehensive text, which addresses the full gamut of topics that an instructor might want to cover. It also offers nice integration of some topics that might normally be neglected, e.g., satisfaction metrics, account planning, and other topics.
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond articulates the core principles of marketing with accuracy and precision. There is a tight linkage (typically through use of web links) to established definitions (e.g., AMA) and conceptual frameworks (e.g., Product and Market Entry strategies) that have come to reflect the established body of marketing knowledge.
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond contains relevant and up-to-date themes based upon emerging paradigms (e.g., Service Dominant Logic) that are synthesized across the chapters.
One of the strengths of Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond, which relates to its comprehensiveness, is the clarity offered for all the concepts presented. Key concepts are well-defined and presented in a plain language that is readily accessible to a wide audience.
Although, no unifying framework is offered to connect the chapters, there is an underlying common conceptual core offered within the Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond
Another key strength of Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond is the modularity. Chapters are broken up numerically and into "bite-size" chunks such that instructors would have an easy time assigning aspects of a chapter to modules.
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond follows the common flow of the vast majority of Principles texts by beginning with the organization and high-level strategies, then digging into consumer/buyer behavior, and finally, unpacking the marketing mix.
Navigation is easy for Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond; however, some issues with fonts and size of text within images rendered some distractions
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond is well written and in an accessible style.
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond is not offensive in any way and does offer quite a few diverse examples. However, there is a heavy reliance on North American company examples, such that individuals in other cultures might have difficulty with some.
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond does a really nice job of offering a comprehensive and relevant marketing text that can easily be modularized by instructors. The authors have effectively integrated up-to-date examples that students will find interesting as well as integrated media (e.g., audio clips) and real life profiles (profiling an analytics manager at BNSF) to produce an engaging text.
Reviewed by Marina Jaffey, Instructor & Program Leader Marketing, Camosun College on 10/9/13
This American Principles of Marketing text covers all the key areas & ideas normally included in a first year College/University Introduction to Marketing course. There are 16 chapters in the text and most key topic areas are discussed... read more
This American Principles of Marketing text covers all the key areas & ideas normally included in a first year College/University Introduction to Marketing course. There are 16 chapters in the text and most key topic areas are discussed relatively thoroughly, with the following exceptions: 1. Pricing 2. Retailing and Distribution as it relates to services Rather than structuring the text around the 4Ps or traditional Marketing Mix, the authors follow the premise that marketing is composed of four activities centered on customer value: creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging value. The text does not include a Table of Contents, Contents in Brief, or Glossary and/or Index.
Marketing concepts are defined/explained/discussed accurately. All the examples are American, so not as relevant for Canadian students. Similarly, the Environmental Scan and ethical/legal segments are all based on American trends and laws/business practices. In general, the examples tend to focus on large corporations. More examples from medium/small businesses, as well as not-for-profits, would help to provide a broader perspective for students. Based on the scale below: content is accurate, but has a very American bias.
The content is up-to-date, with the exception of: 1. The three chapters on marketing communications. Marketing communications has been and is continuing to change rapidly, and as a result, it is difficult for text books to remain current. Having said this, I believe that it would be relatively easy to make regular updates to the marketing communications chapters. 2. Although the Distribution chapter is up-to-date, it is lacking in its coverage of distribution as it relates to services, as well as retailing. 3. Perhaps most importantly for Canadian students, is the fact that all the examples and all sections that relate to legislation/business practices in the current text are American. It would be more time consuming to up date the text to reflect the Canadian marketing environment.
Clarity rating: 3
Concepts are explained clearly in the body of the text. Ideas to increase retention are: 1. Include more visuals. The current charts/graphs are small and difficult to read. Many of the figures lack sufficient detail. Visuals serve to summarize concepts at-a-glance and help students to understand/recall a concept. 2. Provide a variety of examples to illustrate concepts. 3. Make better use of formatting to ensure students can see quickly key concepts and definitions on a page, for instance, make better use of headings & subheadings and include key concept definitions in the margins of the page. 4. In addition to the summaries at the end of each section within a chapter, include a final end of chapter summary.
Yes, the text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework. The text presents the marketing mix in terms of four activities or components of marketing: creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging value.
There are 16 chapters in the text which corresponds nicely with a typically 14 week semester. The order of the chapters in the text is as follows: Ch. 1 - What is Marketing? Ch. 2 - Strategic Planning Ch. 3 - Consumer Behaviour Ch. 4 - Business Buying Behaviour Ch. 5 - Market Segmenting, Targeting, & Positioning Ch. 6 - Creating Offerings Ch. 7 - Developing & Managing Offerings Ch. 8 - Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers Ch. 9 - Using Supply Chains to Create Value for Customers Ch. 10 - Gathering and Using Information: Marketing Research & Market Intelligence Ch. 11 - Advertising, IMC, and the Changing Media Landscape Ch. 12 - Public Relations & Sales Promotions Ch. 13 - Professional Selling Ch. 14 - Customer Satisfaction, Loyalty, and Empowerment Ch. 15 - Price Ch. 16 - The Marketing Plan It would be easy and straight forward for an instructor to change the order that these topics are covered in a semester, should he/she wish to do that.
Two changes I recommend are: 1. Put ch. 15 - Price right after ch. 7 - Developing & Managing Offerings. Pricing is a very important marketing concept, and it makes most sense to discuss how to price products/services/offerings right after they are covered in the text. 2. Move ch. 10 - Marketing Research to right after ch. 2 - Strategic Planning. Ch. 2 covers environmental scanning, so it is important for students to learn how to research trends and find information required for planning. Otherwise, the order of the chapters is fine.
Interface rating: 2
I have been working with a print version of the text. A suggestion to make navigation through the print version easier would be to include a Table of Contents, Contents in Brief, and Index/Glossary at the end. Images/charts are small and difficult to read in the print version. Many subheadings sit alone at the bottom of a page. Need to format so that a subheading appears with some or all of the body copy. Also, some chapters begin on the same page that the previous chapter ends. It would be better to start a new chapter on a new page. In several instances, whole pages were simply lists of sources. It is important to cite sources, however it would be better to include these lists of sources at the end of a chapter, rather than in the middle of a chapter.
There are relatively few grammatical or spelling errors. Please see complete list of errors in attached document.
Although the text is not culturally offensive in any way, I believe there could be more examples that reflect a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds. The text mentions that there is a profile of a marketing professional at the beginning of each chapter - this is not the case (no profiles are included). Including profiles of marketing professionals from a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds would be one way of addressing this weaknesses. It would also be appropriate to profile different types of organizations to illustrate marketing concepts/business practices amongst different cultural groups. As mentioned earlier, this is an American text so all examples are American.
Overall this text covers all the key topic areas relevant to a first year college/university overview marketing course. Most topics are covered in an appropriate amount of depth, with a few exceptions including pricing and services marketing. Learning Objectives are included at the start of each segment within a chapter, but not at the start of a chapter. Learning Objectives are all at the lowest two levels of Bloom's Taxonomy - Knowledge (i.e. Describe...) and Comprehension (i.e. Understand...) http://www.coun.uvic.ca/learning/exams/blooms-taxonomy.html The Review Questions and Key Takeaways which appear at the end of each segment within a chapter and the Discussion Questions and Activities at the end of each chapter are generally good and provide students with ways to test understanding and apply relevant concepts. This is an American text, so an instructor would need to provide his/her students with a variety of Canadian examples, as well as Canadian content related to environmental scanning and business practices. All Introduction to Marketing texts offered by publishers provide extensive support materials for instructors and students. I'm not aware of any support materials that come with this text. There are formatting issues which have been mentioned earlier in this review, that would need to be addressed. This review originated in the BC Open Textbook Collection and is licensed under CC BY-ND.
Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: What is Marketing?
- Chapter 2: Strategic Planning
- Chapter 3: Consumer Behavior: How People Make Buying Decisions
- Chapter 4: Business Buying Behavior
- Chapter 5: Market Segmenting, Targeting, and Positioning
- Chapter 6: Creating Offerings
- Chapter 7: Developing and Managing Offerings
- Chapter 8: Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers
- Chapter 9: Using Supply Chains to Create Value for Customers
- Chapter 10: Gathering and Using Information: Marketing Research and Market Intelligence
- Chapter 11: Integrated Marketing Communications and the Changing Media Landscape
- Chapter 12: Public Relations, Social Media, and Sponsorships
- Chapter 13: Professional Selling
- Chapter 14: Customer Satisfaction, Loyalty, and Empowerment
- Chapter 15: Price, the Only Revenue Generator
- Chapter 16: The Marketing Plan
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Principles of Marketing teaches the experience and process of actually doing marketing – not just the vocabulary. It carries five dominant themes throughout in order to expose students to marketing in today's environment:
Service dominant logic — This textbook employs the term "offering" instead of the more traditional First "P" — product. That is because consumers don't sacrifice value when alternating between a product and a service. They are evaluating the entire experience, whether they interact with a product, a service, or a combination. So the fundamental focus is providing value throughout the value chain, whether that value chain encompasses a product, service, or both.
Sustainability — Increasingly, companies are interested in the impact they are having on their local community as well as the overall environment. This is often referred to as the "triple bottom line" of financial, social, and environment performance.
Ethics and social responsibility — Following on the sustainability notion is the broader importance of ethics and social responsibility in creating successful organizations. The authors make consistent references to ethical situations throughout chapter coverage, and end of chapter material in most chapters will encompass ethical situations.
Global coverage — the authors deliberately entitled Chapter 1 "What is Marketing?" Whether it is today's price of gasoline, the current U.S. presidential race, or Midwestern U.S. farming, almost every industry and company needs strong global awareness. And today's marketing professionals must understand the world in which they and their companies operate.
Metrics — Firms today have the potential to gather more information than ever before about their current and potential customers. That information gathering can be costly, but it can also be very revealing. With the potential to capture so much more detail about micro transactions, firms should now be more able to answer "well, what this marketing strategy really worth it?" And "what is the marketing ROI?" And finally, "what is this customer or set of customers worth to us over their lifetime?"
Contribute to this Page

Home » Blog » Digital Marketing » 10 Ways to Improve Your Digital Marketing Assignment Writing Skills
10 Ways to Improve Your Digital Marketing Assignment Writing Skills

Are you overwhelmed with digital marketing assignments with your poor academic writing skills? If so, read everything you need to know to improve your digital marketing assignment writing skills in the upcoming lines.
In the current century, digitalisation has taken over every aspect of our lives, and its advancement is rapidly increasing, including marketing. Marketing is one of the essential aspects of today’s era, mainly digital marketing.
What is digital marketing? Digital marketing is a crucial component of traditional marketing techniques in which marketers use online-based digital technology containing mobile devices, personal computers, and laptops for running digital marketing campaigns through social media marketing and websites while using the internet.
Also, developing new strategies and digital marketing plans for online marketing and online advertising products.
According to Oxford Reference:
“Using digital technologies such as websites and multimedia, e-mail and digital media including mobile, and wireless, and delivering digital television for promotion, development, and distribution of a brand product and services is called Digital Marketing.”
Ever-Rising Scope of Digital Marketing
Marketing is the most essential part of our society, and no business or brand can be successful without it. As a dynamic and promising career, digital marketing is increasing rapidly. In any case, you have seen ads on the Internet like “ do my chemistry homework ” or something similar, this is an example of marketing in fast-growing niches.
Noble Desktop represents its growing charm:
“The field of digital marketing is projected to grow up to a 10% growth rate from 2021 to 2031, with advancements in artificial intelligence, email marketing and content marketing, virtual and augmented reality for driving more revenue. Digital marketers increase the average wage of a beginner is $51,000 with 0-1 years of experience, $55,000 for 1-3 years, $61,000 for 4-6 years, and $68,000 for 7-9 years.”
All the facts and figures attracted many students to specialising in marketing, and most of them enrolled in digital marketing courses, seeking employment in sales and marketing. Even some of those who come without any prior background in marketing eventually learn the skills and knowledge to make ends meet by working in marketing departments.
But when they encounter assignment writing, they find it hard to manage and seek a detailed guide and some proven tips. Furthermore, they can also get help from assignment writing services to tackle all the assignment writing hurdles.
10 Tips to Improve Your Digital Marketing Assignment Writing Skills
Yes, you can get professional help from Digital Marketing Assignment writers to make your writing process effortless. But before that, you can follow our top 10 ways to improve your digital marketing assignment writing skills to get high scores. So let’s first with the most essential one:
1. Know the Prompt and Instructions
Before you get started, it is essential that you have a complete understanding of the question that is being asked in the assignment. To understand the prompt, read it multiple times and focus on the critical phrases and action words.
Also, look over other instructions that mention the guidelines. If you find something confusing, ask your professor through email or communication for better calcification.
2. Plan Your Digital Marketing Writing Process
Most of the students skip this part and then try to complete the assignment with ambiguous planning till the date of submission. Therefore, it is crucial to make a schedule or a plan by dividing your whole process into small sections.
RMIT University Library represented a writing process planning followed by multiple steps from analysis to submission, shown below.

This section will allow you to address your research question logically. You can also make a Grant chart of sculling assignments by giving these tasks a dedicated time to complete them.
3. Choose Topics Wisely
Topic selection seems like a tiny step in writing a digital marketing assignment, but it is the only step determining the rest of the assignment writing process. Because a wrong topic selection creates difficulties for your assignment completion, this is why students should give their full attention while selecting a topic.
For this purpose, you need to consider the following aspects:
- Your personal interest and expertise
- Fulfil the assignment requirements
- Your instructor’s expectations and suggestions
- Available research sources
- Complete before the due date
Further, here are some digital marketing fields you can consider to choose the topics:
- PPC (Pay Per Click) Advertising
- Social Media Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- Content Marketing
- Affiliate Marketing
- Influencer Marketing
By focusing on these steps, you will be able to select the best topic on which you can write your assignment easily.
4. Brainstorming and Mind Mapping
After selecting a topic, critically think about the topic, gather more and more digital marketing project ideas related to the prompt and then create a mind map. In this step, just sketch your brain, thinking about how your mind relates your ideas with the main topic. For generating a strong mind map, develop three to four main ideas around the subject matter.
Draw lines by connecting each map idea to its supporting details and brainstorm digital marketing assignment ideas, tasks, and questions for each. As a sample, you can see the below mind map example presented by Agus Masrianto in “Model for Improving Firm Digital Marketing Capabilities Based on Adoption Eco-system Readiness and Digital Transformation.”

5. Conduct Extensive Research
Conduct extensive keyword research on your specific topic to cover every query relevant to the subject matter. While doing research, collect both types of data:
- Primary information
- Secondary information
Your primary data is first-hand data for better evaluation that comes from your self-observation. On the other hand, utilise secondary sources of information, which include internet search engines, library books, encyclopaedias and databases.
6. Follow a Global Assignment Structure
While writing any type of assignment, from essay to case study, there is a general digital marketing assignment structure that is standard to compose an effective academic paper. It includes three main sections:
- Introduction
- Main body paragraph
Conclusion
Begin with a captivating introduction by stating your personal statement, continue it with a detailed explanation in the main body paragraph, and finally, conclude your assignment on digital marketing by summarising all the key points and emphasising the importance of your topic and its application.
7. Add Reference and Citations
If you want to make your work more authentic and trustworthy in front of your reader, then add references and citations. It is one of the best tips that enhance the worth of your assignment. There are different types of citation styles that are mostly used by institutes, such as:
- Vancouver
- Chicago
- Harvard
But in cases where your professor is guiding you to follow a specific referencing style, then make sure to follow the instructions.
8. Filtered Your Digital Marketing Assignment
After completing the writing process, do not submit it for revision multiple times. Filtered your assignment first against minor mistakes you skipped while drafting your work. In this step, look over the following:
- Grammatical flaws
- Punctuation
- Capitalisation
- Typos errors
- Spelling mistakes
After removing all the above mistakes, you create a refined form of your digital marketing assignment to impress your professor.
9. Check Plagiarism
Plagiarism is the most serious offence that can result in various serious consequences. To overcome all the barriers to stand out from the rest of the class, you must cross-check your content against plagiarism. Checking plagiarism is not a task to handle manually. But for this purpose, you can use a plagiarism checker or a detector.
Submit your document by uploading it from your computer, or you can also copy and paste content. Go to get a percentage of unique and plagiarism content with just one click. You will get plagiarism reports in just a few seconds. If work is caught as plagiarised somewhere, remove it and create plagiarism-free content.
10. Ask For Feedback
Our last tip that makes a big impact is to look for a third eye for a bird’s eye view of your assignment. For this purpose, ask for feedback from your class fellows or any other expert.
If you want to check your work from a professional in digital marketing, make an impressive email to deliver your message with a humble request and ask for honest feedback. This is the best way to improve your mistakes and learn from your flaws.
Digital marketing assignment writing is a most technical process because, with the advances of digital marketing, its theory concepts and technologies become more advanced, giving a tough time to most students. Students face many difficulties in understanding its prompts and composing a good piece of paper because of a lack of good academic writing skills.
If you are one of them and struggling with your assignment on digital marketing, follow the above ways to improve your digital marketing writing assignment skills. But if it still makes you upset, then avail yourself of beneficial assignment writing help from a suitable firm.
About the Author
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Subscribe to receive our latest articles
Enter your email address:
Delivered by FeedBurner

- Advertising
- Artificial Intelligence
- B2B marketing
- Content marketing
- Digital Marketing
- Facebook Marketing
- Home business
- Instagram marketing
- Lead generation
- LinkedIn Marketing
- Online Gaming
- Pinterest Marketing
- Social Media
- Twitter Marketing
- Uncategorized
- Website Marketing
Recent Posts
- 4 Ways to Get Instagram followers and Enjoy Instagram Follower Growth
- The Impact of Google Reviews on Small Business Success
- How to Cultivate a Successful E-commerce Business
- Your Laptop Buying Checklist: 5 Factors You Can’t Afford to Ignore
- 7 SEO Strategies That Will Skyrocket Your eCommerce Sales

Recent Comments
- Mim Majed on Top 6 Social Media Tips For Maximum Marketing Impact
- haneena nasri on How To Handle a Negative Comment On Social Media
- baweja on Top 7 Facebook Tools For Ads
- NA7 WhatsApp on 5 Types of Facebook Ads and How to Use Them Effectively
- college Brawl on 5 Types of Facebook Ads and How to Use Them Effectively
Privacy Overview
Pin it on pinterest.
- Sun. Mar 31st, 2024
Business Mens Edition
Keeping Businesses Informed
6 Top Tips To Write Marketing Assignments Like A Pro
The key to writing a practical marketing assignment is to use your strengths. Here we discuss the tips for writing marketing assignments like a pro.
If you have spent many hours developing your marketing profile, you know what makes a marketer successful.
Your marketing communications plan should have a framework and processes in place to avoid getting lost in the middle and missing meaningful communication opportunities.
You also need to establish clear, measurable objectives and metrics and how and when you will achieve those objectives.
- The success of your marketing thesis may depend on how you can deliver the efforts considerably.
- The project summary gives you a list of the tasks and their status. This should contain questions to write a marketing assignment that is tailored specifically for a professional marketing company.
- By creating this checklist, you’ll be sure that you get the correct answers to all your questions and that you have sufficient answers to complete your role in managing marketing effectively.
When writing a Marketing Assignment as a Professional, your primary objectives should be to
- Write a professional profile.
- Describe the project, team, and its goals.
- Describe your desired outcomes.
- Cover two types of marketing you need to define while writing a marketing assignment, online and offline.
Follow these tips for your perfect assignment to get the best results
1. Online marketing can be used for various types of social media marketing

- It consists of a few key steps: Log on to a website. Find out who your prospects are. List your services. Make an offer. Communicate offers to potential customers via email, phone, or any other communication.
- Use email marketing as your primary means of marketing, but make sure that your offers are engaging.
2. Reliability and quick turnaround of the transactions

Online marketing is the process of engaging potential buyers in one large, centralized form to get feedback, suggestions, or questions.
- The focus is on getting customers to make a decision. In the case of online shopping, one’s decision affects other people’s actions, which may affect other customers’ decisions.
3. Write the outline to the client or business owner

- business goals.
- how to create value.
- marketer persona or persona profile.
- and business process.
4. You should create an online form

5. Your content should be catchy and attractive

6. Find quotes and examples for your marketing assignment and feel free to use them

- Marketing is about what products and services are offered, the perceived success of those products and services, and the opportunity cost of the lack thereof.
- If your writing is going well and you are using good writing techniques, you may be prepared to submit the assignment. If you are unsure, it would be recommended to consult a professional and get your writing back on track by asking for marketing assignment help .
You can always follow the above guidelines to write your marketing assignment like a pro and avoid common assignment writing mistakes , but if you still face any obstacles, you can search online for help, because investing in your writing skills can pay off and you may make money online as a student with content writing .
Author Profile

Latest entries

Blogger and Educator by Passion | Contributor to many Business Blogs in the United Kingdom | Fascinated to Write Blogs in News & Education I have completed a journalism summer course at the London School of Journalism and manage various blogs.
Related Post
How can a local seo audit help businesses, top 5 business branding tips on a budget, 5 ideas to make your fashion brand stand out from the rest, 5 ways to advertise a happy hour at your bar, 3 expert tips for industrial equipment for business, how to make international calls.
- Success Stories
They Ask, You Answer Mastery
A coaching & training program that drives unmatched sales & marketing results.
Sales Performance Mastery
Improve the competencies and close rates of your sales organization.
Website Mastery
Web design, development & training for your team.
HubSpot Mastery
Everything you need to get the most from HubSpot.
AI Enablement Mastery
Unlock the power of AI in all aspects of your revenue operations.
More Services
- Paid Search & Social
- Request a Speaker
- Join the Community
Learning Center
Free resources to help you improve the way you market, sell and grow your business.
- Podcast Episodes
- Tools & Assessments
Quick Links
- What is They Ask, You Answer
- Free Sales & Marketing Assessment
- Certifications
- The Endless Customers Podcast
- Meet the Team
- Certified Coaches
Free Assessment: How does your sales & marketing measure up?
Free Assessment:

By Liz Murphy
Oct 14, 2019
Join 40,000+ sales and marketing pros who receive our weekly newsletter.
Get the most relevant, actionable digital sales and marketing insights you need to make smarter decisions faster... all in under five minutes.
How to create a digital marketing strategy (+ examples)

How to create a digital marketing strategy
- Digital marketing strategy assessment.
- Align your company on a new way of doing business.
- Create content that drives revenue.
- Create the seven types of marketing and sales videos guaranteed to generate results.
- Integrate content into your sales process through 'assignment selling.'
- Evaluate your company website against the seven 'perfect inbound website' principles.
- Report regularly on content wins to your team.
- Understand what companies that see the most digital marketing success all have in common.
Who is this article for?
- You're a new digital marketer who has been tasked with creating a digital marketing strategy (usually content or inbound marketing-based) for the first time, and you don't know where to start, OR
- You're a seasoned marketing leader who knows something needs to change. Your current strategy isn't bringing in the results leadership and sales want to see, and you're looking for a proven approach that will increase traffic, leads, and sales.
Important note: Whether you call it digital marketing, content marketing, or inbound marketing, you're in the right place.
What will this article teach you?
You know what really grinds my gears? Articles that promise to teach you how to do something big, but then ends up being fluffy search engine-bait that isn't detailed enough for you to take action in any sort of meaningful way.
So, my promise to you is that I won't do that.
In fact, based on the principles of They Ask, You Answer , here is exactly what you'll know how to do by the end of this article:
- How to assess your current digital marketing strategy.
- How to gain buy-in from sales and leadership and get everyone excited about participating in your strategy, since a lack thereof is the #1 killer of digital marketing success.
- How to create a content strategy that targets the topics that are guaranteed to not only increase website traffic, but also generate more qualified leads that, ultimately, translate into more sales.
- Why video is critical to your digital marketing success, and how to create a video strategy around the top marketing and sales video types that get results.
- How to integrate your content into the sales process as part of your digital marketing strategy — we call this "assignment selling."
- The seven essential ways you need to update your company website so it becomes your top sales team member.
- How to showcase and highlight wins, as a part of your digital marketing strategy.
🔎 Related: What is They Ask, You Answer?
What this article is not
If you're looking for a simple, turnkey digital marketing strategy here, you're not going to find it. Don't worry, I'm going to give you everything you need to create an effective digital marketing strategy for your company, outlined in detail, step-by-step.
But you're going to have to do some heavy-lifting. Because, if you want to crush your most aggressive sales and marketing goals, you can't approach the creation of your digital marketing strategy with any degree with passivity.
So, this is your last warning that this article is not for the faint of heart.
It's dense. It's meaty. It's my attempt to give you everything you need to absolutely kill it in 2020, because I believe all marketers deserve a chance to be the hero at their company.
Ready? Let's do this. 🔥
1. Assess the effectiveness your current digital marketing strategy ( 100% optional step )
It's virtually impossible to determine what (if anything) should change with your digital marketing strategy if you don't know where you stand right now. That's what this step is all about.
As a digital sales and marketing company that's spent the past 10 years helping hundreds of companies from around the world (from all industries, B2B and B2C), we've seen what works and what doesn't, up close and personal.
So, earlier this year, we released our totally free Digital Sales and Marketing Scorecard :
This scorecard quite literally scores your current digital marketing strategy by evaluating the six components of your business that are proven to have the most impact on your success:
- How well your company is aligned around your approach to digital marketing.
- The scope of your content strategy , based on data we've collected over 10 years of what topics drive the most revenue.
- Your current marketing technology stack — because if you don't have the right tech to measure the ROI of your digital marketing, you'll never be able to prove the efficacy of your strategy.
- How much your sales team is (or isn't) involved in your efforts — time and again, we've seen digital marketing strategies soar (or crash and burn), based on sales engagement in the process.
- Your use of video as part of your digital marketing strategy. (Video is proven to shorten the sales cycle and build trust faster than any other type of content.)
- Finally, we help you assess your company website for the six core features of what we call the Perfect Inbound Website .
In addition to receiving a numerical score, we'll tell you how well you stack up against other world-class companies who have seen remarkable digital sales and marketing results, and provide you with the exact Inbound Success Playbooks you need to focus on first, based on where you are currently.
( Fun fact: All of our Inbound Success Playbooks are ungated and do not require an email address to access them.)
Because I hate fake-outs, here is an important note about our Digital Sales and Marketing Scorecard
Yes, you need to provide your email address in order to see your Digital Sales and Marketing Scorecard results.
However, while I am highlighting the scorecard as the first step to creating your strategy, it is 100% optional to complete it. Not filling out the scorecard will in no way prevent you from completing any of the steps that follow for creating your digital marketing strategy .
I actually considered writing this article without including this step. But, ultimately, I felt like I was going out of my way to exclude it, since it can be a powerful evaluation tool for companies, should they choose to take advantage of it.
So, just know that I am only including the scorecard for genuinely "pure of heart" reasons. (And everything else I will link to below as an additional resource is completely ungated and ready for your use.)
2. Get sales and leadership buy-in for your digital marketing strategy
I've been kicking around the digital marketing world for almost six years — in the good ol' days, I had to walk uphill (both ways) in the snow if I needed to smash the publish button on an article.
But while a lot has changed since I defected from publishing to join the marketing industry, there are two things that haven't:
- Marketing is often viewed by sales and leadership as an expense , rather than a profit center; and that's only become even more true, with the rise of content and inbound marketing — which feels like homework with very little payoff.
- Unfortunately, #1 is, more often than not, the kiss of death for marketers. Because if you don't have buy-in from sales and leadership, your digital marketing strategy will fail , plain and simple. Or, at the very least, you'll never be able to realize the full growth potential of your traffic, leads, and sales, were your whole team bought in on what you're doing.
That's why earning the buy-in of your sales and leadership teams is a critical initial step in achieving success with your digital marketing strategy.
In short, you need to initiate a cultural revolution within your own company.
Facilitate an inbound culture workshop to create alignment and build excitement
Creating a company culture wherein your sales, leadership, subject matter experts, and so forth are all on-board with your digital marketing strategy isn't something you can accomplish with an email or a short announcement at an all hands meeting.
Moreover, if you've already been dabbling with inbound or content marketing, you can't expect to get your sales reps, subject matter experts, or anyone else at your company excited about creating content without bringing everyone to discover the why behind becoming the most trusted voice in your space, and how you're going to do it.
So, in this step, you will bring everyone together for something we call an Inbound Culture Workshop .
Why do we recommend an Inbound Culture Workshop? And what should you cover in your own Inbound Culture Workshop?
In this video interview, I MPACT Director of Inbound Strategy and Video Training Zach Basner answers both of those questions in detail:
(If you're short on time, here's a handy-dandy "Cliff's Notes" version of this conversation .)
This is a workshop we facilitate for companies as an unbiased third party — which can sometimes be a smart move — but there are also distinct advantages to facilitating the workshop on your own, as the digital marketing owner or leader at your company.
🔎 Related: What should be covered in an Inbound Culture Workshop?
It doesn't matter how you choose to facilitate your workshop, so long as you have one. Trust me when I say making this a priority will determine how successful you are going forward through the rest of this process.
3. Create a content strategy laser-focused around topics guaranteed to drive revenue
OK, now it's time to get down to business. The goal of the content you create for your digital marketing strategy is simple — to establish your company as the most trusted voice in your space by answering all of the questions of your potential buyers as honestly and transparently as possible .
So, if you have a topic that doesn't do exactly that, you need to cut it from your editorial content calendar. It's useless fluff.
What should you be creating content about?
As IMPACT's content director, I know more than anyone how much of a struggle it can be to build editorial content calendars for a digital marketing strategy.
How do you know what content you should be creating?
And which content topics should be prioritized over others?
We've found that there are five very specific topic categories of buyer questions that are proven across all industries (B2B and B2C) to move the revenue needle for companies.
We call these topics The Big 5 , and they are:
- Pricing and cost ( How to create a perfect cost article )
- Comparisons ( Comparison article best practices )
- Problems ( How to create a perfect problems article )
- Reviews ( How to write about your competitors on your website )
- "Best of" ( "Best of" article example )
Why these topics? We, as consumers, are obsessed with finding answers to the questions that fall into those five categories, more than any other.
Think about the last few purchases you've made as a consumer, large and small.
You likely researched your potential purchase online first because you want to know how much something will cost before you buy it. You want to compare your options before making a decision. You don't want to be surprised with problems down the road, so you research them in advance. You want to know what other people think about an item or service you're considering, so you know you're making a good choice. And, finally, you want to know what's really the "best" product, service, strategy, and so forth.
I'll be honest with you — some of these topics are going to make you feel downright uncomfortable. You don't want to talk about pricing. You don't want to breathe a word about your competitors. And you certainly don't want to talk about potential problems with your products.
But if you don't, you won't be controlling the conversation — someone else will be, and that "someone" will likely be your competitor.
More than that, you will see the results you want with this content strategy. So, trust me when I say your discomfort is a good thing. Or, if you don't trust me, trust these companies who embraced The Big 5 and saw huge returns from it.
And yes, The Big 5 can fit into your pillar content strategy easily.
🔎 Related: The ultimate blogging tips guide for digital marketing teams
Priority and pacing for your content
If you're just starting out with a content-based digital marketing strategy, we recommend that you do the following:
- Make a list of the products and/or services that have the most influence over your bottom line. Focus your content efforts on these first.
- For those products and/or services, brainstorm topics with your team that fall under The Big 5. (Sales should be involved.)
- Next, focus your content creation efforts on topics that are toward the bottom of the funnel, such as cost topics.
- Plan to produce between two and three pieces of content at minimum per week.
Honestly, even if you've been doing content or inbound marketing for awhile, I'd recommend you follow some version of that process I just outlined. You'll likely have some content gaps you'll need to fill in, and those should be prioritized by your most important products and services.
🔎 Related: Free content calendar template (+ getting started tips)
4. Create marketing and sales videos that are proven to get results
Research shows that video is the most trusted resource for consumers at each stage in the buying process. Not only that, our buyers are spending a vast majority of their time online watching videos. Bottom line, video is powerful .
Video will build trust and captivate your audience more than any other type of content. Not only that, the strategic use of video during your sales process will compel people to take action and shorten your sales cycle:

How much of your website is currently video-based?
We’d wager the answer is probably somewhere between 0 and 10%.
The good news is that your competitors are likely in the same boat. That means there is no better time than right now to fully embrace video as a sales initiative through visual selling. In fact, the mindset we teach all our clients at IMPACT — which consistently yields the greatest results (traffic, leads, and sales) — is:
We are all media companies, whether we like it or not.
When done correctly, video will be a powerful addition to your toolbox, proven to not only establish trust more quickly with your buyers but also shorten your sales cycle.
Here are the 7 types of videos you need to be creating
The Selling 7 are seven types of sales and marketing videos that — like The Big 5 — have proven time and again to move the revenue needle for B2B and B2C companies.
80% videos are those that answer the most common questions all your prospects ask about your products and services — and probably proactively answer a few they haven’t thought of.
🔎 Related: How to make amazing 80% videos (+ examples)
Employee bio videos
These are short videos where your team speaks directly to the camera and introduces themselves, which allows your prospects to see, hear, and know your team before they even meet.
🔎 Related: How to make amazing employee bio videos (+ examples)
Product and service page videos
These videos significantly reduce the burden placed on your buyers to take the time to understand how your product/service will help them, while also breaking through the “noise” of all the words on your site.
🔎 Related: Example of a service page video
Landing page videos
Every landing page with a form on it needs a video that builds trust by addressing any questions or doubts someone might have — “Should I complete this form? Are they going to be spamming me after I fill it out?”
🔎 Related: 3 examples of great landing page videos that convert
“Bad fit” videos
When you’re honest about who you shouldn’t work with (and explain why), you not only become dramatically more attractive to your good-fit prospects, you show you’re transparent and trustworthy.
🔎 Related: Why you need to talk about who you're not right for (+ examples)
Customer journey videos
In this video, your customer will share the problem they were looking to address, the journey they took to fix that problem (with your company), and where they are today because of that journey.
🔎 Related: Examples of customer journey videos
“Claims we make” Videos
How many claims do you make that your competitors also make? For example, “Our people are the best.” Back up those claims by showing them with video, because words are not enough.
🔎 Related: 6 examples of "claims we make" videos we love
5. Integrate your content into the sales process with 'assignment selling'
Assignment selling is the act of purposefully sharing written, video, and audio content that is educational about your products and/or service with the express goal of addressing any pressing concerns and questions your prospects may have.
That way your prospects are much, much, much more prepared for any sales appointments they have with your team. And the conversations become much more focused around their specific challenges and goals, and how you can hep them, rather than wasting time answering the questions every single prospect has, regardless of their situation.
🔎 Related: How to implement assignment selling (+ examples)
6. Evaluate your website for the 7 key elements of the 'Perfect Inbound Website'
What works and what doesn't on company websites is always changing as trends, aesthetic preferences, and technology are constantly evolving.
We've found, however, there are seven fundamental elements that, when executed correctly, transform a company's website from a static digital billboard to its #1 sales rep . And they are:
- Homepage design and messaging
- Self-selection and configuration tools
- Obsess over honest education
- Premium education
- Textual and visual content mix
- Social proof
To be honest, evaluating and updating your website so it is the Perfect Inbound Website is a complex and comprehensive process unto itself.
So, to help you, we've created this comprehensive (ungated) playbook about building the Perfect Inbound Website .
It reviews each of the above items in detail, including what you should be looking for, how to evaluate your current site for those items, and the strategic steps you need to take to get your website where it needs to be.
7. Recognize content wins in visible ways to the rest of the company on a regular basis
One of the best ways to keep your team motivated and excited about participating in creating written and visual content for your digital marketing strategy is to spotlight what we call "content wins" with your company on a regular basis.
For example, at IMPACT, we have a weekly, company-wide "all hands" meeting. During that meeting, IMPACT Head of Editorial Content Ramona Sukhraj and I have a dedicated time in the agenda to share:
- The top five new articles (by views) from the previous week. We include their photo and the title of the article on their slide.
- A closed deal highlight, where we walk through all of the content a contact (or contacts) consumed before their deal closed. (A recent deal from a few weeks back featured a contact who consumed 250+ pieces of content!)
- How much influenced revenue can be attributed to our pillar content strategy . (We're at $850,000+ and climbing.)
That way we're making team members feel valued and proud of the work they're creating, and we're constantly reinforcing the value of our strategy by tying those efforts directly to bottom-line gains.
How you implement this at your company will likely look different, based on what opportunities you have at your disposal. That said, you should consider this step and indispensable part of your digital marketing strategy, as recognition of your colleagues will keep the spark of excitement for your digital marketing strategy alive .
Finally, here is what companies that see the most digital marketing success all have in common
Whew — that was a lot, wasn't it?
Still, you can't expect big results from your digital marketing strategy if you aren't willing to put in the effort. But before I send you on your way to digital sales and marketing glory, I want to leave you with some insight that will inspire you going into 2020.
Over the past 10 years, in working with hundreds of companies around the world, we’ve discovered there are seven characteristics companies that see the most success with their digital marketing strategies all share.
They understand that buyer expectations have changed
They know the “old school ways” of advertising no longer work. Now, potential buyers turn to the internet for every single question they want answered.
They are the absolute best teachers in their space
All employees embrace a mindset of: “I want to be viewed as the best teacher and most trusted resource in our industry. I want people, when they have a problem, to think of our company.”
They create the content that drives traffic, leads, and sales
They understand buyers are obsessed with finding answers online to questions about pricing, problems, comparisons, reviews, and “best of” lists, when making a purchasing decision. (These are The Big 5 we talked about earlier.)
They have a dedicated content manager
They get that unless someone is the designated “owner” of their inbound and content efforts, those efforts will be deprioritized and nothing will get done.
They understand the power of video
They understand video is a win for both sales and marketing — it builds trust with your audience faster and more effectively than any other type of content, and it shortens the sales cycle.
They've invested in the right technology
They know if they can’t generate revenue with inbound, it’s not worth the investment. But they also know they need to right technology in order to prove the financial ROI of their efforts. (We're a big fan of HubSpot for driving digital success in this arena.)
They've built the 'Perfect Inbound Website'
They have a fast, data-driven website with a clear homepage design, compelling messaging, self-selection tools, premium education content, textual and visual content, and social proof.
Now, it's your turn to write your own digital marketing success story .
Related Articles
Boost your seo: is your agency holding you back [endless customers podcast s.1 ep. 15].
Organic Social Media Marketing: Grow Your Audience Without Ads
'The Big 5': Best Business Blog Topics to Drive Traffic and Sales (+ examples)
'Business is Booming — So Why Should I Invest in Marketing?' (+ Video)
20 Value Proposition Examples that Every Marketer Can Learn From in 2024
How to talk about price on your website (+ examples).
5 Examples of Companies with Great Multi-Brand Websites
Website conversions in 2024 — stop, start, keep.
10 Marketing Objective Examples To Guide and Focus Your Strategy
4 Questions for Defining a Winning Value Proposition in 2024
How is impact different from other agencies, video marketing: what your 2024 business video strategy must include.
Create Better Website Videos by Avoiding These 3 Mistakes
4 ways to recession-proof your website in 2024, 4 brand positioning techniques to drive your marketing strategy, is content marketing dead in 2024, how should my marketing budget change with ai, sales vs marketing in 2024: what’s the difference, what should a 2024 content marketing strategy include, hubspot pricing: your guide to everything hubspot costs.
Why Trust Is the True Currency for All Business
10 marketing kpis you should be tracking.
How To Become a Better Business Coach
Do You Need a New Website? Maybe Not
How to create a content map to solve your marketing guesswork.
Join the 40,000+ sales and marketing pros who receive our weekly insights, tips, and best practices.
Thanks, stay tuned for our upcoming edition..
Resources: Discussions and Assignments
Module 9 assignment: marketing plan, part 2, student instructions.
Complete the following information about the organization and products and/or services you will focus on as you develop a complete marketing plan throughout the course. You may need to do research to get answers to the questions below. The subject for this assignment should be the organization and products and/or services you identified for the Marketing Plan, Part 1 Assignment.
Marketing Information and Research
Research question.
Describe an important question you need to answer or a problem you are trying to solve in order to help the organization meet its goals and objectives.
Information Needed
Describe the information your organization needs to make effective decisions about how to answer this question or solve this problem.
Research Recommendations
What research do you recommend in order to provide the information you need? What research method(s) would you use to get the information you need? Will it involve secondary data and research? Primary research such as interviews, focus groups and surveys? Why do you recommend this research approach?
Customer Decision-Making Profile
Identifying the Customer and Problem
Describe a primary decision maker in your target segment: who they are, what they like, how they make buying decisions. Describe the primary problem(s) your organization, product or service will help them solve.
Factors Influencing Customer Decisions
Provide a brief profile of your target segment using at least three of the following categories:
- Geographic characteristics: e.g., location, region, population size or climate.
- Personal and demographic characteristics: e.g., age, gender, family size, family life stage, income, personality.
- Social and Psychological characteristics: e.g., culture, social class, lifestyle, motivation, attitudes, reference groups, beliefs.
- Situational characteristics: e.g., buying situation, level of involvement, market offerings, frequency of use, brand loyalty.
- B2B/organizational buying considerations: e.g., individual factors, organizational factors, business environment factors, types of complexity
Reaching the Customer
Based on this profile, identify 2-3 marketing strategies or tactics you believe would be effective at reaching this target segment, and briefly explain why they are a good fit.
Positioning and Differentiation
Positioning and differentiation explain what you want to be known for in the market, and how you are different from competitors. Respond to the following questions.
Competitive Advantages
List the competitive advantages of the product, service or organization you’re focusing on: the things that make it different from competitors in positive ways.
Market Niche and Positioning Strategy
Describe the market niche you want to fill, along with the positioning strategy you recommend using. Why do you think this is the right approach?
Positioning Statement
Develop a positioning statement using this formula: “To [target audience], [product/service/organization name] is the only [category or frame of reference] that [points of differentiation/benefits delivered] because [reasons to believe].
Repositioning Considerations
Do you recommend a repositioning that improves on what the organization has been using up to this point? Why or why not?
Brand Description
What is the “brand” you are trying to build? What do people think about this brand today, and how do they experience it?
Brand Promise
What is the brand promise for this brand? If one hasn’t been defined yet, create one. If you believe the brand promise needs improvement, please suggest how you would refine it. Why is your recommended brand promise a good fit?
Brand Voice and Personality
Describe your brand voice and personality using the is/is never template:
- [Brand] is:
- [Brand] is never:
Brand Positioning and Strategy
Make a recommendation about brand positioning and/or branding strategy to help build the brand and contribute to align it with what your target segment wants. How will this contribute to the success of your product, service or organization?
Sample Grading Rubric
Total points possible for Marketing Information and Research Assignment: 60 pts.
Branding Grading Rubric
Total points possible for Branding Assignment: 40 pts.
Total points possible for Marketing Plan, Part 2 Assignment (Marketing Information and Research, and Branding combined): 100 pts.
- Assignment: Marketing Plan, Part 2. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution

Marketing Plan Exercise
MARKETING PLAN PROJECT—PART I
During this course, you will develop a marketing plan as part of a semester-long project. The marketing plan that you develop will build throughout the course over nine chapters of this textbook.
The purpose of Part I of this marketing plan project is twofold:
- To become familiar with the Marketing Plan Template
- To select a company or product for which you will be building the marketing plan throughout the semester
Instructions:
- Download the Marketing Plan Template and SAVE THIS DOCUMENT where you can easily access it again, because you will be completing additional sections of the plan throughout the course.
- Select a company or product which will form the basis of your marketing plan. When selecting a company, please be sure to select a company or product that will (a) be of interest to you throughout the course and (b) have sufficient information available about the company on the internet for you to conduct research and make informed decisions in your marketing plan.
- When selecting a company, please be sure NOT to choose a company that is so huge that it serves many diverse markets. For example, General Electric produces electrical and electronic equipment, aircraft engines, medical electronics; it also provides financial services and more. Procter & Gamble also has diverse product lines, including beauty, grooming, health care, fabric and home care, and feminine and family care. In the “real world,” you would not prepare a single marketing plan for the entire company; instead, each division and/or product line would develop its own marketing plan. Therefore, if you want to use a large company, select a brand or product line for the purpose of your marketing plan.
- On the Marketing Plan Template, add your name and course number to the header.
- Complete the Company Profile Information on the Marketing Plan Template for the company you have selected.
- Save the template with a new name using this naming convention: Course_First/LastName/Project Title. Example, MKTG101_JohnSmith_Marketing Plan.
- Submit this document to your instructor as directed.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Dr. Maria Gomez Albrecht, Dr. Mark Green, Linda Hoffman
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Marketing
- Publication date: Jan 25, 2023
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-marketing-plan-exercise
© Jan 9, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
11 Types of Advertising Explained with Examples
Chances are you have one of the best products or services, but what’s the use if nobody knows about it and it’s not generating the sales you were aiming for? That’s exactly where advertising comes into play. Whether it’s a creative slogan, catchy jingle, or an innovative bus ad, advertising examples are everywhere; they come in all kinds, shapes, and sizes.
Also, did you know that an average human is exposed to almost 6000-10,000 ads per day?
Nonetheless, with so much competition and noise, how can you create a winning ad campaign for your business?
Fret not; we at Marketingtutor.net have curated a list of some of the top-notch types of advertising campaigns that can take your business to a whole brand new level.
Let’s find out!
Table of Contents
What Is Advertising?
Advertising is more like a form of marketing communication, it’s one of the crucial elements of the organization’s marketing strategy. Businesses across the globe use advertising to spread the word about their services and products through several channels.
What’s more, today’s fast-paced tech world has changed the landscape of advertising, with broadcast and print serving as conventional formats, whereas digital format serves as the contemporary option.
Also, with advancements in tech, companies have the ability to gain a new customer base and track the performance of their ad campaigns.
11 Different Types of Advertising
Before you let your imagination fly and think of catchy jingles or clever slogans, you need to consider what kind of ad campaign you would like to run for your business.
By no means are we saying creativity doesn’t matter; IT DOES, but targeting your audience and choosing the right platform is what matters the most in achieving the company’s strategic goals?
Here’s a list of some of the types of advertising with examples that you can choose and pick wisely!
Television Advertising
Are you seeking an extensive reach that can cater to a large market? Television advertising can be the answer to your business needs. That’s because it has the edge of sound, movement, color, and sound to persuade buyers to buy the product.
Albeit it’s costly, if you are looking at the bigger picture, more customer base, extensive reach, it’s completely worth it.
Companies can market their services and products through 20, 40, and 60 seconds television commercials. Nevertheless, the cost of the ad depends on other several factors, including:
- Length of the ad.
- The number of networks.
- Geographic reach.
- Time of the day.
- Frequency of airing
Example – Wendy’s Where is the Beef
It is perhaps one of the most iconic and catchy taglines of the 1980s; Burger King and McDonald’s were ruling the fast-food market because they were promoting the size of their burgers by naming them “Whopper” and “Big Mac.” Wendy had to come up with something more novel and catchy to grab the public’s attention.
Wendy’s clever slogan TV commercial,“Where is the Beef” had a lasting impact on fast food advertising. Never before had a fast-food burger joint gained such cultural clout; even today, people utter the catchphrase when seeking more substance.
Radio Advertising
If your target audience listens to a particular radio station, radio advertising can come in very handy to reach your target market and gain new customers.
The target audience can hear radio ads while running day-to-day errands (doing household chores, driving, etc.), radio also enables the repetition of ads just like TV commercials that, in turn, help organizations get more recognition and customer base.
Example – Sprite Radio Ad
When it comes to an ad that is short, loud, crisp, and sweet, Sprite tops the list. With this ad campaign, the company was able to target its audience without having to say much.
Yes, the slurping sound effect gave all the feel to its audience.
Print Advertising
Print advertising refers to the advertisements that we often see in magazines, flyers, newspapers, etc. Businesses can advertise their services and products in the local newspaper, whether within separate classified sections or either throughout the paper, to reach a target audience within the geographic region.
Example – Ecovia: Stop the Violence
Several companies came forward to create awareness about car accidents. However, none was successful in achieving a massive social media awareness the way Ecovia did with its “Stop the Violence” print ad campaign.
The company preferred using body illustrations to speak to the target audience, trying to convince them, “don’t drink and drive.”
Social Media Advertising
How to keep up with today’s digital-driven world? We are living in a golden era, where social media can either make or break your business. Businesses worldwide use social media ads to promote their services and products.
With social media ads, companies have the ability to target a specific customer base, age group, etc. Also, the companies have two options; they can either pay platforms for displaying their ads or opt for an organic method.
Example – Sephora
It is a multinational beauty retailer famous among women of all age groups.
Since videos are one of the vital components that exhibits a high-engagement rate, so Sephora came up with a stunning video ad campaign to reach its target audience. The campaign performed well than the previous campaigns with 32% higher return and 41% increase in click-through rate.
Paid Search Advertising
It is a type of online advertising that is usually known as PPC (pay-per-click). Businesses that prefer using paid search advertising only pay a fee when people click on their advertisements. They compete for specific keywords, usually connected to their industry, as well as the visibility of their ads on the search engine.
Example – Converse “DOMAINATION”
Converse – a global footwear brand, teamed up with one of the marketing agencies , Anomoly, to create an innovative and novel way to communicate with its teenage audience.
Instead of selling their products directly to the targeted audience, the company employed Google AdWords to connect with the audience by being relevant and encouraging conversations.
Their strategy was to come up with such terms that their potential customers used to search. This way, the global brand was able to fetch the attention of its target audience in a fun and creative way.
Outside Advertising
Outside advertising is also called out-of-home ads because it’s the advertisement that people see outside their homes. For instance, the ads we see on the billboards , transit vehicles, inside subway cars, and on the side of the bus.
Companies usually use outdoor ads to grab the attention of a large population within a geographic location. All in all, businesses prefer using bold images and fewer words so the advertisement can be easily understood.
Example – McDonald’s Clock Billboard
Nothing can beat this fast-food chain, whether it’s about coming up with creative slogans or outdoor ads billboards. Yes, the famous fast-food multinational company stands out with its clock billboard that reminds you they are open 24/7.
Mobile Advertising
Mobile ads have become one of the most important tools for marketing because of the explosion of social media. Also, mobile ads can easily reach the users/target audience via mobile device with internet access, such as a tablet or smartphone.
Users can see the mobile ads through different channels, including web pages, within mobile apps, or social media. For instance, if someone is playing a video game on the mobile, chances are they will encounter ads for similar games in between rounds of playing game.
Example – Snapchat Ad & Filter: Lucky Charms
Lucky Charms wanted to do something out of the box for St. Patrick’s Day. They planned to team up with Snapchat to create an innovative and gamified filter for the promotion of their unicorn-based cereal.
The campaign was so successful that over 12 million Snapchat users used the filter, giving Lucky Charms a tremendous engagement rate on the site and a branding boost.
Direct Mail Advertising
It is a type of print advertising in which adverts are usually mailed to the target audience. Catalogs, flyers, newsletters, and brochures are some examples of direct mail ads.
This strategy allows businesses to identify more targeted demographic than any other type of print ads formats because advertisements are delivered through a direct mailing list.
Example – Nestle Kit Kat Chunky
Who doesn’t like receiving a free chocolate bar voucher in the mail? Well, that’s what Nestle did to promote its product, Kit Kat Chunky.
They encouraged the users to claim their Kit Kat from the local corner shop, with a personalized note, “ we are sorry we couldn’t deliver your parcel ” card claiming that the product wouldn’t fit in the mailbox owing to its chunkiness.
Thus, the company was able to see the surge in the purchase by customizing each leaflet and exciting people’s taste buds.
Display Advertising
Display advertising is a strategy that promotes a product or service through visuals, i.e., images and videos on web pages, social media platforms, and various display networks. Display advertising encourages its target audience to click on the ad and redirect to the advertiser’s website to complete the direction action (purchase). Remarketing and retargeting are a few methods used in display advertising. For example, when a user visits a website, he might accept the browser cookies that grant permission to that site to track his journey. If the visitor does not make a purchase, the advertiser (brand) may target him on another website by placing ads of products and services to influence his purchase decision.
Product Placement Advertising
In product placement ads, companies have to pay to have their services or products inserted in media content, such as movies or television shows. Although the content doesn’t directly promote the product, it is still accessible to the target audience.
This strategy helps businesses reach an even targeted audience more privately.
Example – Reese’s Pieces in E.T (Extra-Terrestrial)
Reese’s are the chocolate miniatures of the Hershey Company that were featured in one of the most iconic films of 1982, the Extra-Terrestrial (E.T).
Did you know that this product placement ad led to a surge in sales by a whopping 300%?
Public Service Advertising
Public service advertising promotes a cause in the general public’s best interest. It is also known as a public service announcement (PSA) or a community service announcement (CSA). These ads are broadcast on television, radio, and newspapers to reach the masses.
The primary aim of the PSAs is to aware the audience about a specific issue and alter their attitude.
This type of advertising is more often used by government agencies and non-profitable organizations to educate consumers about specific issues, i.e., health and safety.
The Takeaway
Choosing what type of advertising you need to run for your business is indeed an overwhelming endeavor as it can make or break your brand name.
Every advertising campaign has its own perks; you need to determine what you are aiming to achieve, only then will you be on your way to mastering the ad area.
About The Author
shaharYar Ahmad Ranjhaa

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.2: Types of Marketing Information
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 16487
Illuminating the Marketing Picture
There are three primary types of marketing information marketers use to gain insights that will contribute to wise marketing choices: internal data , competitive intelligence, and marketing research .
Internal Data
Internal data consists of the information companies collect about their customers and prospective customers, typically as part of their internal operations. Marketing departments, for example, maintain information about the interest and leads they generate from prospective customers and how they are interacting with these contacts. They may capture information used for segmentation and targeting purposes, such as geographic location, gender, age, buying behaviors, and communication preferences. Information about Web site visitors, traffic, and other customer engagement activities can be another useful type of internal data. Additionally, sales teams capture and maintain information about who is buying the product, where buyers are located, buying patterns, and behaviors. Sales and marketing teams may also maintain information about customer references, success stories, and how prospective customers are progressing toward becoming new clients.
Other parts of the organization capture also capture and maintain data that may be useful as marketing information. Accounting and billing departments track information about customers such as how much they spend with the organization, when they buy, and other payment details. Product managers and customer support organizations maintain information about customers implementing or using products, problems or issues they run into, and satisfaction levels with the company and products.
Historically, it was standard for each department to maintain these data in their own systems rather than in a common system or database that all parts of the organization could access. This presented challenges for marketers, who had a difficult time gaining access to complete, up-to-date internal data, since the information would need to be pulled out of the various systems and put into usable formats before they could conduct any sort of analysis.
Increasingly, organizations capture and maintain internal data by using information systems and databases shared across multiple departments. A database is a set of structured data accessible via a computer, and the data can be organized so that it’s available for a variety of different uses, such as marketing or financial analysis. Shared information systems may include large enterprise systems designed to support business processes and functions, customer support systems, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems, among others.
“Database marketing,” also known as marketing analytics, takes internal data several steps further. Large databases collect massive amounts of data from a variety of sources: customer demographic and profile data linked to in-store and online purchasing history, Web site search terms, page views, social media posts, and other data. In a process called data mining, computer algorithms search for patterns in the data and generate recommendations and insights about how to increase sales.
With access to accurate, up-to-date internal data, marketers gain a better understanding of who the organization is serving and how it is performing relative to its goals for sales, customer satisfaction, and other priorities. Marketers rely on internal data to manage communications and interaction with customers and prospects, as they track the series of interactions that take place when a prospective customer is making a purchase decision. They may also use internal data to identify patterns that make someone more likely to become a customer, and behaviors that contribute to any given customer type having a higher or lower total lifetime value.
To illustrate the power of internal data, consider this example from Trident Marketing, a company that conducts marketing and sales activities for other businesses like home security firm ADT, satellite media company DirectTV, and Travel Resorts of America. It used marketing analytics to generate insights based on internal data from its customer-service call centers, order systems, CRM systems, search engine results, and external credit-bureau data about customers. The resulting recommendations were powerful and provided specific guidance about the following:
When to call a consumer, which product to pitch, and which salesperson is best suited to close the sale. Plus, sophisticated analytic models can also predict which consumers are likely to cancel services within twelve months—a metric that goes straight to the bottom line because the company must compensate its customers for consumer churn. [1]
Using this information, the company was able to apply sales and marketing techniques to increase sales, profitability, and customer retention on behalf of its clients. In fact, revenue increased nearly 1000 percent over four years. [2]
Competitive Intelligence
Competitive intelligence is marketing information that helps marketers and other members of an organization better understand their competitors and competitive market dynamics. Common types of competitive intelligence include the following:
- Product information: Who is making products that compete with your offerings? What features or capabilities make these products attractive to prospective customers? How do these features compare to yours? How are products packaged and offered to customers?
- Market share and penetration: Which companies in your competitive market sell the most products to your target market, and how much do they sell? Which organizations are considered the market leaders? How is market share evolving over time?
- Pricing strategy: What do competitors charge for their products? What pricing structure and strategies do they use? What special pricing or discounting do they offer? How does this affect your pricing and position relative to competitors?
- Competitive positioning and messaging: What are competitors saying about themselves? What are they saying to current and prospective clients or other stakeholders about your organization or products? How effective are their messages at generating interest in competitor products or diminishing interest in yours? What keywords are competitors dominating in search engines?
- Win/loss analysis: What proportion of new sales are you winning or losing? Why are people selecting your product over competitors’? Why are they selecting a competitor’s offering instead of yours?
Companies tend to guard sensitive information closely, such as detailed information about product cost, pricing structure, and market share. In fact, there are market analysts who specialize in competitive intelligence because it can be so difficult to obtain. However, anyone in a marketing role should maintain a general level of awareness about competitors and what’s happening in their market, and there are fairly easy ways to do this. Marketers can learn a lot directly from competitors, such as reading their Web sites, following them on social media, and monitoring press releases and other published content to understand what they are communicating to the market and to prospective customers. Information can also come from industry-focused newsletters, blogs, social media conversations, reports, conferences, and other forums that discuss new developments and key players in a product category or market.
When marketing activities are associated with a higher-priced sale and a complex decision process, sales and marketing organizations may conduct some type of win/loss analysis after a purchasing decision is made. A win/loss analysis captures information from individuals involved in a sale to understand the key factors influencing the final purchasing decision. It can help marketers better understand how to improve the marketing mix—product, price, promotion, placement—in order to improve sales performance in comparison with competitors.
All of these activities can provide useful insights about how customers view the choices available to them, as well as how competitors view and compete in the market. As with internal data, a better understanding of these factors helps marketers improve the marketing mix to compete more effectively and become a preferred choice for customers.
Marketing Research
Marketing research is a systematic process for identifying marketing opportunities and solving marketing problems, using customer insights derived from the collection and analysis of marketing information. Marketing research identifies the problem to be solved or the opportunity to be explored, as well as the information required to address research questions. It also involves processes for collecting the information, analyzing it, identifying insights, and reporting findings and recommendations to those who will take action based on the results. [3]
Marketing research may cover a full spectrum of topics related to customers, products, and market dynamics, and it can use a variety of research methods (which will be discussed later in this module). In general, marketing research requires some additional information beyond what marketers have at their fingertips (like, say, internal data). Sometimes it is necessary to collect new primary data directly from target audiences, such as current or prospective customers. In other situations, marketing research uses secondary data captured previously by another organization. Marketing research may incorporate internal data and/or competitive intelligence in order to provide a more complete answer to a marketing problem or question.
Common subjects for marketing research include:
- Environmental factors and how they affect consumer behavior. These include factors such as the health of the economy, the legal environment, market trends and other social factors, technology and its influence, and cultural factors that make doing business different in one region or country compared to others.
- Customer attitudes, behaviors, and perceptions . Marketing research can be essential in understanding customer needs, how their needs are or aren’t being met by the market, views about various products and companies, satisfaction levels, preferences for product features and pricing, the consumer decision-making process, and factors that influence it.
- Product research. Product research explores where opportunities and gaps exist for improving existing products or introducing new ones, concept testing, sizing the market for a product, market penetration, prioritizing product features and preferences, testing product effectiveness and customer receptivity, user testing, pricing strategies, product naming and branding, and gauging how to position a product relative to competitors.
- Marketing, advertising, and promotion research. This area of research seeks to improve the effectiveness and reach of marketing activities such as market segmentation, messaging and communications, advertising and media testing, events and sponsorships, packaging and display testing.
- Corporate research. Corporate research investigates corporate reputation and opportunities for strengthening an organization’s position in the market through brand building, research and development, mergers and acquisitions, strategic partnerships, corporate planning and profitability.
Marketing research is usually a wise investment when it’s undertaken to inform decisions involving a significant shift in direction, whether that shift is associated with a product, brand, message, tone, corporate image or other area linked to a major change and related investment. Marketing research projects may be large or small in terms of time, scope, cost, and resources involved. With a simple project, it could take an in-house marketer just a few hours to formulate research questions and analyze a data set from internal or secondary data sources, with no external costs. Complex marketing research projects may take longer than a year to complete and cost hundreds of thousands of dollars paid to research firms that specialize in particular markets or types of research.
As organizations grow, they may employ a marketing research director to oversee and coordinate research activities to ensure that they are getting accurate data and useful results. Smaller organizations without this internal capacity may hire a marketing research company or consultant to conduct the project, lead data collection, provide analysis, and advise on the best methods for interpreting and acting on research findings.
American retail giant Target employed extensive marketing research to help it figure out how to rebuild its brand after a sales slump. The slump was triggered by an unsuccessful repositioning move as a “bargain brand” during the economic downturn of 2008 and a highly publicized data breach in 2013 that left many customers distrustful of the company. Company leadership used marketing research to identify opportunities to reinvigorate the Target brand and win new audiences.

Target Shopper. Authored by : Wm. Mag.. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/jojomelons/2041121410/ . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
A strategy unveiled in 2015 targets young Hispanic moms as a new and growing demographic the company wants to win over, in addition to suburban “soccer moms” who have been the company’s mainstay segment. Targeted advertising (no pun intended), product development, and the in-store experience are all being tested and refined to appeal to this segment. [4]
In 2019, Target created commercials targeting college students living in dorms, further expanding their targeted segments:
You can view the transcript for “Make the most out of a small space” here (opens in new window) .
- www.chiefmarketer.com/big-data-marketing-analytics-can-help-sales/ ↵
- www.fuzzyl.com/wp-content/uploads/49415_TridentMarketingIncreases_Case-Study_PRF2_May18_12-2.pdf ↵
- www.ama.org/AboutAMA/Pages/Definition-of-Marketing.aspx ↵
- www.washingtonpost.com/news/business/wp/2015/03/04/targets-new-strategy-we-need-more-than-just-minivan-moms/ ↵
Marketing91
Marketing Environment – Definition, Types, Importance and Examples
March 11, 2020 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Marketing
Various environmental factors affect the way a business is operated. These environmental factors can be divided into two broad categories, such as the internal environment and the external environment. A business is required to adapt to these marketing environments to stay profitable and ahead in the competition . In this article, you will learn about different types of marketing environments and various components of the marketing environment.
Table of Contents
The marketing environment can be defined as a combination of both internal environmental factors and external environmental factors. These marketing environments surround a business and influence the operations of the business.
What is the marketing environment?
A marketing environment is a combination of internal and external environmental forces and factors that influences the business operation of a business and its ability to serve its customers. It is essential to know both internal as well as external environmental factors. Therefore, enterprises keep checking on them to do their business without any legal trouble and to generate maximum profit.
The internal marketing environment consists of factors like material, machines, workers, money, etc. All of these components are necessary to run a business successfully. For example, if the raw material is not available on time and in sufficient quantity, then the work of production will become slow, and the company will not be able to fulfill the demand of the product in the market .
On the other hand, the external marketing environment can be divided into two categories, such as macro external marketing environment and micro external marketing environment. The microenvironment is closely related to the business and constitutes all external business activities such as distribution and promotion of products of the company.
The macro-environmental components affect all the companies serving in a single industry similarly. For example, changes in the laws and rules related to production or doing business will apply to all companies likely. In the next section, you will learn about all the internal as well as external components of an organization.
Components of the marketing environment

There are broadly two components of the marketing environment, such as the internal environment and external environment. Different types of parts of the marketing environment are categorized under these two broad categories.
The internal environment of a business can be controlled, but there is very little control of a business in the external marketing environment. Let us learn about both components one by one.
1. Internal environment
The internal environment is formed of all the internal factors and forces of an organization. The internal environment of an organization is within the control of the marketer, and he can change or modify the environment as per the demand in the market and requirement of the business.
The following are the five factors that form the internal environment of an organization. These factors are also referred to as five Ms of a business.
All the components of the internal environment are as important as that of the components of an external environment. However, the internal environment factors are changed according to the change in the external marketing components. For example, an organization is required to upgrade its technology if new technology in the market is introduced.
The internal environment of an organization also includes the marketing department, the sales department, the human resource department, and the manufacturing department.
2. External Marketing environment
The external marketing environment consists of all the external marketing factors that exist outside the organization, and the marketer has little or no control over the external marketing environment factors.
The external marketing environment can be divided into two categories, such as microenvironment and the macro environment .
Let us learn about both macro and micro environments one by one.
A. Microenvironment
The microenvironment of a business consists of all the factors and forces that are directly associated with the company. The micro components of the external environment are also known as task environments.
The following are the various components of the micro external environment.
1. Suppliers
Suppliers are an essential part of every organization. Suppliers supplies material and all other types of resources required for the production of products. A company can run its business successfully only if its suppliers supply material of good quality and on time.
2. Market intermediaries
Market intermediaries are the intermediary parties that help a business to distribute its products in the market. The market intermediaries can be wholesalers, retailers, and distributors. All of these market intermediaries are an essential part of the business as they are the face of the company in the market and represent the products of the company in the market.
3. Partners
Business partners are the business entities that conduct business with the organization. For example, advertising agencies, banking and insurance companies , market research organization s, brokers, and transportation companies, etc. A company is required to partner with several other companies to run a successful business.
4. Customers
Customers are the most crucial component of the business. Customers are the target audience of the product, and the preference of customers influences all the marketing and business efforts of a company.
The public is people other than the target audience of the organization. The public plays a vital role in the success of the business as it can build or destroy the image of a company in the market. The public has the power to influence the purchasing decision of the target audience. Especially in the times of the internet, the ability to control the public has increased as they can share their views about your products and services on the internet freely.
6. Competitors
The last but not least component of the microenvironment is the competitors of a business. The competitors are the other businesses that sell similar products as your products or are part of the same strategic group in the industry.
B. Macro Environment
Macro components of a marketing environment consist of all external forces and factors that impact the whole industry rather than just changing an organization directly. Therefore, the macro marketing environment is also referred to as a large environment.
The following are the six components of the macro environment. Let us learn about them one by one.
1. Technological environment
Technology is one of the elements that have great potential to influence the business of an organization. It is dynamic, as it changes rapidly. Technology provides several threats and opportunities to the business environment .
The technological environment consists of research and development in technology, innovation, inducement of technology, and technical alternatives, etc.
2. Demographic environment
The demographic environment component of the macro marketing environment consists of people that form a market. The population of the demographic environment can be characterized based on various factors such as age, gender, density, size, location, race, and occupation, etc.
The demographic environment is a crucial component for business as the company design and builds its products based on the characteristics of the demographic environment.
3. Social-cultural environment
The social-cultural component of a macro environment is formed using values, lifestyle, culture , beliefs, and prejudices of the target audience of a business. The social-cultural environment varies from one region to another region.
People living in one area might prefer a different type of product than the preference of the product of the people of any other region. Businesses are required to have in-depth knowledge of the social-cultural environment to design a product or service that is preferred by most people.
4. Economic environment
The economic environment component is a type of component that influences all industries. The economic environment affects the purchasing power and spending patterns of the buyers.
The following are the different factors that form an economic environment.
- Interest Rates.
- Gross Domestic Products (GDP).
- Gross National Product (GNP).
- Income distribution.
- Government funding.
- Other significant economic variables.
5. Political-legal environment:
The political-legal environment consists of laws and policies of a country. In addition to rules and procedures, the political-legal environment also includes agencies and pressure groups . All of these political entities impact the working capacity of the industry in society.
6. Physical environment:
The last component of the macro environment is the physical environment in which an organization exists. The following are the components of the physical environment.
- Climate condition
- Environmental change.
- Availability of the raw material.
- Natural resources like water.
Examples of the marketing environment
Examples of the internal marketing environment.
The best example of an internal marketing environment is the office culture of the organization. Your office culture consists of the values, beliefs, and attitudes of your employees . All of these factors determine how the employees of your organization will behave. For example, in an organization where employees are encouraged to perform in a team and support the members of the group are more likely to perform better than the organization where employees compete with one another.
Moreover, employees are likely to perform better in a positive internal marketing environment rather than an environment where employees are nagged continuously and pressured to perform well. Google is one of the best companies that provide a positive and very healthy internal environment to its employees. Because of this, Google is now one of the leading companies in the industry.
Examples of the external marketing environment

The external marketing environment of an organization is formed of micro and macro environment. The microenvironment consists of suppliers, market intermediaries, partners, customers, public, and competitors, etc. for example, suppliers of an organization alter the business environment of an organization to a certain extent. If suppliers supply good quality material and supply that material on time, then the organization can produce the right quality products and can fulfill the demand in the market efficiently.
Another vital component of the micro marketing environment is the market intermediaries. The market intermediaries of your business play an essential role in the success of your business. They are the face of your company. They interact with your customers daily and understand your customers and also your product. Let us take the example of a retailer. A retailer sells products from different companies in the market. It is in the hands of a retailer to decide whether to promote your product or not.
The sales of your products will significantly depend on the people who represent you in the market. Therefore, it is necessary to provide proper incentives to your representatives and provide a good margin to them on your products so that they promote your products to their customers rather than promoting the products of your competitors.
On the other hand, a macro marketing environment does not affect an organization directly but affects the whole industry. An organization is required to perform its business operations according to the macro-environment factors. The examples of the macro-environment are demographic environment, social-cultural environment, economic environment, political-legal environment, physical environment, and technological environment, etc.
The business operations of an organization are controlled by the laws and policies decided by the government. In addition to this, the technological environment influences the business environment more than any other macro-environment factor. A business is required to upgrade the technology that it uses for business operations from time to time in order to stay ahead in the competition.
The technological environment has both advantages and disadvantages for an organization as an organization is always required to think of innovation to compete with its competitors. On the other hand, it is also costly for an organization to update its technology regularly.
Importance of marketing environment

The marketing environment holds great importance when it comes to conducting business successfully. Businesses of all sizes, whether small or large or required to do their business within the marketing environment.
The existence of the company, its profits, and its losses largely depends on the internal as well as the external environment around it. Therefore, it becomes essential for a marketer to understand and study the marketing environment thoroughly to generate profits and stay in business for a more extended period.
Let us understand why the understanding and knowledge of the marketing environment is necessary to run a successful business.
1. To learn about your competitors:
A business needs to learn about its competitors to stay ahead in the competition. Different companies fight for a single opportunity in a niche market using different strategies .
A deeper understanding of the marketing environment helps a marketer to learn about the business strategies and plans of their competitors. Having this knowledge helps the marketers to understand the policy of their competitors and plan their business strategies accordingly.
2. To learn about your customers:
Customers are an essential part of a business. All the business activities of a company are focused on serving its customers better. Therefore, a company gives great importance to learn about their customers and their changing preferences to serve them better and to have a long relationship with them. The marketing environment helps the marketer to understand the customers and their preferences.
For example, when there is a slowdown in the economy and inflation is on the surge. At such times, people either prefer to spend less or cease their spending to save money.
Therefore, people look for goods and services at lower prices. Consequently, a company must either introduce new products with lower prices or sell their products at discounted prices so that they can still make sales when there is an economic slowdown.
3. Necessary for future planning
A business is required to plan to meet the demand of the market and produce as per the latest trends in the market. It is essential to learn about the internal and external environment to plan efficiently.
4. To make most out of the latest trends
Trends change rapidly, and the change is rapid in fashion and other similar industries. Companies that are part of such industries are required to keep a check on the changing trends. To do this, they learn about every aspect of the marketing environment so that they can prepare a foolproof plan for the future.
5. To learn about all the threats and opportunities related to business
Understanding the marketing environment is necessary to learn about the risks and opportunities associated with the company. The marketer can take advantage of being a first-mover if they know the opportunities related to the business. Moreover, a business must learn about the threat associated with the company to take precautions to stay safe.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Marketing
Related posts:
- Competitive Environment – Definition, Types, Factors and Examples
- What is Macro Environment? Definition, Factors, & Examples
- Importance of Marketing Environment
- Political Environment: Meaning, Examples & PEST (ELI) Analysis
- What is Micro Environment in Business? Definition & Factors
- What is Internal Environment? Definition and Key Factors
- Individual Marketing and its Impact on Today’s Business Environment
- 5 sales myth which have to be ignored in today’s sales environment
- Features of Business Environment – Meaning and 10 Important Features
- Outdoor Advertising – Definition, Importance, Types and Examples
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
It was the best fact owsome
Marketing sales for good and services.
best article i’ve read in a long time.
Clearly explained thank you
BEST ARTICLE
omg it’s full with knowledge. thank you very much
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Types of Assignments
Cristy Bartlett and Kate Derrington

Introduction
As discussed in the previous chapter, assignments are a common method of assessment at university. You may encounter many assignments over your years of study, yet some will look quite different from others. By recognising different types of assignments and understanding the purpose of the task, you can direct your writing skills effectively to meet task requirements. This chapter draws on the skills from the previous chapter, and extends the discussion, showing you where to aim with different types of assignments.
The chapter begins by exploring the popular essay assignment, with its two common categories, analytical and argumentative essays. It then examines assignments requiring case study responses , as often encountered in fields such as health or business. This is followed by a discussion of assignments seeking a report (such as a scientific report) and reflective writing assignments, common in nursing, education and human services. The chapter concludes with an examination of annotated bibliographies and literature reviews. The chapter also has a selection of templates and examples throughout to enhance your understanding and improve the efficacy of your assignment writing skills.
Different Types of Written Assignments
At university, an essay is a common form of assessment. In the previous chapter Writing Assignments we discussed what was meant by showing academic writing in your assignments. It is important that you consider these aspects of structure, tone and language when writing an essay.
Components of an essay
Essays should use formal but reader friendly language and have a clear and logical structure. They must include research from credible academic sources such as peer reviewed journal articles and textbooks. This research should be referenced throughout your essay to support your ideas (See the chapter Working with Information ).

If you have never written an essay before, you may feel unsure about how to start. Breaking your essay into sections and allocating words accordingly will make this process more manageable and will make planning the overall essay structure much easier.
- An essay requires an introduction, body paragraphs and a conclusion.
- Generally, an introduction and conclusion are approximately 10% each of the total word count.
- The remaining words can then be divided into sections and a paragraph allowed for each area of content you need to cover.
- Use your task and criteria sheet to decide what content needs to be in your plan
An effective essay introduction needs to inform your reader by doing four basic things:
Table 20.1 An effective essay
An effective essay body paragraph needs to:
An effective essay conclusion needs to:
Common types of essays
You may be required to write different types of essays, depending on your study area and topic. Two of the most commonly used essays are analytical and argumentative . The task analysis process discussed in the previous chapter Writing Assignments will help you determine the type of essay required. For example, if your assignment question uses task words such as analyse, examine, discuss, determine or explore, you would be writing an analytical essay . If your assignment question has task words such as argue, evaluate, justify or assess, you would be writing an argumentative essay . Despite the type of essay, your ability to analyse and think critically is important and common across genres.
Analytical essays

These essays usually provide some background description of the relevant theory, situation, problem, case, image, etcetera that is your topic. Being analytical requires you to look carefully at various components or sections of your topic in a methodical and logical way to create understanding.
The purpose of the analytical essay is to demonstrate your ability to examine the topic thoroughly. This requires you to go deeper than description by considering different sides of the situation, comparing and contrasting a variety of theories and the positives and negatives of the topic. Although in an analytical essay your position on the topic may be clear, it is not necessarily a requirement that you explicitly identify this with a thesis statement, as is the case with an argumentative essay. If you are unsure whether you are required to take a position, and provide a thesis statement, it is best to check with your tutor.
Argumentative essays
These essays require you to take a position on the assignment topic. This is expressed through your thesis statement in your introduction. You must then present and develop your arguments throughout the body of your assignment using logically structured paragraphs. Each of these paragraphs needs a topic sentence that relates to the thesis statement. In an argumentative essay, you must reach a conclusion based on the evidence you have presented.
Case Study Responses
Case studies are a common form of assignment in many study areas and students can underperform in this genre for a number of key reasons.
Students typically lose marks for not:
- Relating their answer sufficiently to the case details
- Applying critical thinking
- Writing with clear structure
- Using appropriate or sufficient sources
- Using accurate referencing
When structuring your response to a case study, remember to refer to the case. Structure your paragraphs similarly to an essay paragraph structure but include examples and data from the case as additional evidence to support your points (see Figure 20.5 ). The colours in the sample paragraph below show the function of each component.
The Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia (NMBA) Code of Conduct and Nursing Standards (2018) play a crucial role in determining the scope of practice for nurses and midwives. A key component discussed in the code is the provision of person-centred care and the formation of therapeutic relationships between nurses and patients (NMBA, 2018). This ensures patient safety and promotes health and wellbeing (NMBA, 2018). The standards also discuss the importance of partnership and shared decision-making in the delivery of care (NMBA, 2018, 4). Boyd and Dare (2014) argue that good communication skills are vital for building therapeutic relationships and trust between patients and care givers. This will help ensure the patient is treated with dignity and respect and improve their overall hospital experience. In the case, the therapeutic relationship with the client has been compromised in several ways. Firstly, the nurse did not conform adequately to the guidelines for seeking informed consent before performing the examination as outlined in principle 2.3 (NMBA, 2018). Although she explained the procedure, she failed to give the patient appropriate choices regarding her health care.
Topic sentence | Explanations using paraphrased evidence including in-text references | Critical thinking (asks the so what? question to demonstrate your student voice). | Relating the theory back to the specifics of the case. The case becomes a source of examples as extra evidence to support the points you are making.
Reports are a common form of assessment at university and are also used widely in many professions. It is a common form of writing in business, government, scientific, and technical occupations.
Reports can take many different structures. A report is normally written to present information in a structured manner, which may include explaining laboratory experiments, technical information, or a business case. Reports may be written for different audiences including clients, your manager, technical staff, or senior leadership within an organisation. The structure of reports can vary, and it is important to consider what format is required. The choice of structure will depend upon professional requirements and the ultimate aims of the report. Consider some of the options in the table below (see Table 20.2 ).
Table 20.2 Explanations of different types of reports
Reflective writing.

Reflective writing is a popular method of assessment at university. It is used to help you explore feelings, experiences, opinions, events or new information to gain a clearer and deeper understanding of your learning. A reflective writing task requires more than a description or summary. It requires you to analyse a situation, problem or experience, consider what you may have learnt and evaluate how this may impact your thinking and actions in the future. This requires critical thinking, analysis, and usually the application of good quality research, to demonstrate your understanding or learning from a situation. Essentially, reflective practice is the process of looking back on past experiences and engaging with them in a thoughtful way and drawing conclusions to inform future experiences. The reflection skills you develop at university will be vital in the workplace to assist you to use feedback for growth and continuous improvement. There are numerous models of reflective writing and you should refer to your subject guidelines for your expected format. If there is no specific framework, a simple model to help frame your thinking is What? So what? Now what? (Rolfe et al., 2001).
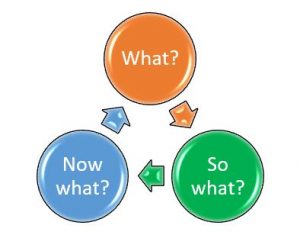
Table 20.3 What? So What? Now What? Explained.
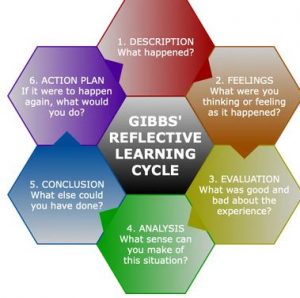
The Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle
The Gibbs’ Cycle of reflection encourages you to consider your feelings as part of the reflective process. There are six specific steps to work through. Following this model carefully and being clear of the requirements of each stage, will help you focus your thinking and reflect more deeply. This model is popular in Health.
The 4 R’s of reflective thinking
This model (Ryan and Ryan, 2013) was designed specifically for university students engaged in experiential learning. Experiential learning includes any ‘real-world’ activities including practice led activities, placements and internships. Experiential learning, and the use of reflective practice to heighten this learning, is common in Creative Arts, Health and Education.
Annotated Bibliography
What is it.
An annotated bibliography is an alphabetical list of appropriate sources (books, journals or websites) on a topic, accompanied by a brief summary, evaluation and sometimes an explanation or reflection on their usefulness or relevance to your topic. Its purpose is to teach you to research carefully, evaluate sources and systematically organise your notes. An annotated bibliography may be one part of a larger assessment item or a stand-alone assessment piece. Check your task guidelines for the number of sources you are required to annotate and the word limit for each entry.
How do I know what to include?
When choosing sources for your annotated bibliography it is important to determine:
- The topic you are investigating and if there is a specific question to answer
- The type of sources on which you need to focus
- Whether they are reputable and of high quality
What do I say?
Important considerations include:
- Is the work current?
- Is the work relevant to your topic?
- Is the author credible/reliable?
- Is there any author bias?
- The strength and limitations (this may include an evaluation of research methodology).
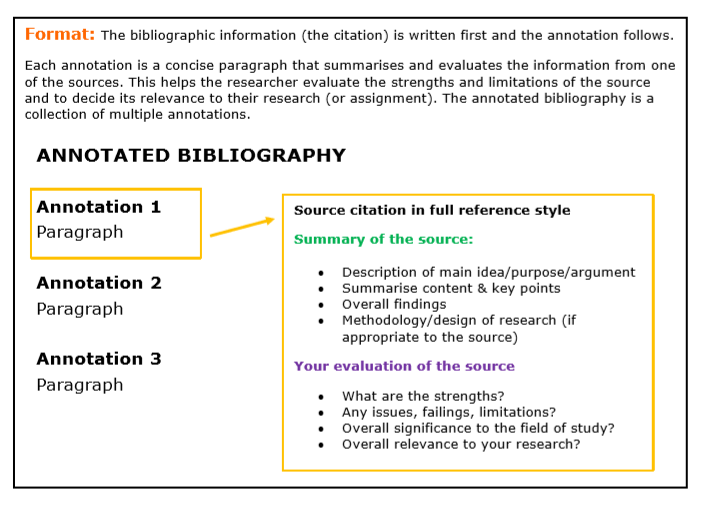
Literature Reviews
It is easy to get confused by the terminology used for literature reviews. Some tasks may be described as a systematic literature review when actually the requirement is simpler; to review the literature on the topic but do it in a systematic way. There is a distinct difference (see Table 20.4 ). As a commencing undergraduate student, it is unlikely you would be expected to complete a systematic literature review as this is a complex and more advanced research task. It is important to check with your lecturer or tutor if you are unsure of the requirements.
Table 20.4 Comparison of Literature Reviews
Generally, you are required to establish the main ideas that have been written on your chosen topic. You may also be expected to identify gaps in the research. A literature review does not summarise and evaluate each resource you find (this is what you would do in an annotated bibliography). You are expected to analyse and synthesise or organise common ideas from multiple texts into key themes which are relevant to your topic (see Figure 20.10 ). Use a table or a spreadsheet, if you know how, to organise the information you find. Record the full reference details of the sources as this will save you time later when compiling your reference list (see Table 20.5 ).
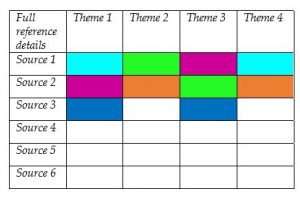
Overall, this chapter has provided an introduction to the types of assignments you can expect to complete at university, as well as outlined some tips and strategies with examples and templates for completing them. First, the chapter investigated essay assignments, including analytical and argumentative essays. It then examined case study assignments, followed by a discussion of the report format. Reflective writing , popular in nursing, education and human services, was also considered. Finally, the chapter briefly addressed annotated bibliographies and literature reviews. The chapter also has a selection of templates and examples throughout to enhance your understanding and improve the efficacy of your assignment writing skills.
- Not all assignments at university are the same. Understanding the requirements of different types of assignments will assist in meeting the criteria more effectively.
- There are many different types of assignments. Most will require an introduction, body paragraphs and a conclusion.
- An essay should have a clear and logical structure and use formal but reader friendly language.
- Breaking your assignment into manageable chunks makes it easier to approach.
- Effective body paragraphs contain a topic sentence.
- A case study structure is similar to an essay, but you must remember to provide examples from the case or scenario to demonstrate your points.
- The type of report you may be required to write will depend on its purpose and audience. A report requires structured writing and uses headings.
- Reflective writing is popular in many disciplines and is used to explore feelings, experiences, opinions or events to discover what learning or understanding has occurred. Reflective writing requires more than description. You need to be analytical, consider what has been learnt and evaluate the impact of this on future actions.
- Annotated bibliographies teach you to research and evaluate sources and systematically organise your notes. They may be part of a larger assignment.
- Literature reviews require you to look across the literature and analyse and synthesise the information you find into themes.
Gibbs, G. (1988). Learning by doing: A guide to teaching and learning methods. Further Education Unit, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford.
Rolfe, G., Freshwater, D., Jasper, M. (2001). Critical reflection in nursing and the helping professions: a user’s guide . Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Ryan, M. & Ryan, M. (2013). Theorising a model for teaching and assessing reflective learning in higher education. Higher Education Research & Development , 32(2), 244-257. doi: 10.1080/07294360.2012.661704
Academic Success Copyright © 2021 by Cristy Bartlett and Kate Derrington is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

COMMENTS
Example. Places like Times Square in New York are examples of outbound marketing reaching its peak, both in terms of the space used to get the message across and the budget needed to broadcast it. Some of what you can see in the picture below is outbound marketing through billboards. 5. Content marketing.
Marketing Plan vs. Business Plan. A marketing plan is a strategic document that outlines marketing objectives, strategies, and tactics. A business plan is also a strategic document. But this plan covers all aspects of a company's operations, including finance, operations, and more. It can also help your business decide how to distribute ...
1. Inbound marketing. Inbound marketing is a strategy used to bring potential customers to you instead of sharing a message out. This is a long-term strategy that involves many different types of digital marketing tactics to encourage a potential customer to move further down the marketing funnel.
Gathering real life examples to use throughout your assignment is essential for a number of reasons: 1 - Expands your knowledge. 2 - Provides insights into what other organisations are doing ...
You need to have a solid understanding of your target audience before integrating your marketing efforts. Example: If your target audience is executives that spend a lot of time on LinkedIn, focus your social media strategy around placing branded content on LinkedIn. 5. Differentiate with creative content.
Unit 1: The Definition and Principles of Marketing. Many people incorrectly believe that marketing and advertising are the same. In reality, advertising is just one of many tools used in marketing, which is how firms determine which products to offer, how to price those products, and who they should be made available to.
4: Marketing Strategy. Expand/collapse global location. 4.23: Assignment- Marketing Plan, Part I. Page ID. Lumen Learning. Lumen Learning. Student Instructions: Complete the following information about the organization and products and/or services you will focus on as you develop a complete marketing plan throughout the course.
A marketing strategy is an overview of how a business or organization will articulate its value proposition to its customers. Generally, a marketing strategy outlines business goals, target market, buyer personas, competitors, and value for customers. It provides a long-term vision for overall marketing efforts, often looking many years ahead.
Principles of Marketing teaches the experience and process of actually doing marketing - not just the vocabulary. ... video assignments, etc., these can be useful for the students. ... It would also be appropriate to profile different types of organizations to illustrate marketing concepts/business practices amongst different cultural groups ...
7. Add Reference and Citations. If you want to make your work more authentic and trustworthy in front of your reader, then add references and citations. It is one of the best tips that enhance the worth of your assignment. There are different types of citation styles that are mostly used by institutes, such as: APA.
The bottom line is that target marketing is a more efficient, effective, and affordable way to reach customers and generate business. It's simply a subset of the total market. Keep in mind that the target market isn't the same as the target audience. The target audience is narrower in that it refers to the group of consumers you expect to ...
The subject for this assignment should be the organization and products and/or services you identified for the Marketing Plan, Parts 1 and 2 Assignments. When you submit this assignment, you should submit it as a complete marketing plan, including all your work from Marketing Plan Assignments, Parts 1 and 2. All elements of your marketing plan ...
When writing a Marketing Assignment as a Professional, your primary objectives should be to. Write a professional profile. Describe the project, team, and its goals. Describe your desired outcomes. Cover two types of marketing you need to define while writing a marketing assignment, online and offline.
In simple terms, digital marketing relates to promotion and advertisement of certain ideas and services via electronic means. While it's mostly related to Internet technologies, digital marketing also covers mobile phones, digital street banners, online intellectual property protection, and anything where electronic platforms are used.
Create content that drives revenue. Create the seven types of marketing and sales videos guaranteed to generate results. Integrate content into your sales process through 'assignment selling.'. Evaluate your company website against the seven 'perfect inbound website' principles. Report regularly on content wins to your team.
The subject for this assignment should be the organization and products and/or services you identified for the Marketing Plan, Part 1 Assignment. ... organizational factors, business environment factors, types of complexity; Reaching the Customer. Based on this profile, identify 2-3 marketing strategies or tactics you believe would be effective ...
The subject for this assignment should be the organization and products and/or services you identified for the Marketing Plan, Part 1 Assignment. ... organizational factors, business environment factors, types of complexity; Reaching the Customer. Based on this profile, identify 2-3 marketing strategies or tactics you believe would be effective ...
Marketing Plan Exercise. During this course, you will develop a marketing plan as part of a semester-long project. The marketing plan that you develop will build throughout the course over nine chapters of this textbook. The purpose of Part I of this marketing plan project is twofold: Download the Marketing Plan Template and SAVE THIS DOCUMENT ...
Radio Advertising. If your target audience listens to a particular radio station, radio advertising can come in very handy to reach your target market and gain new customers. The target audience can hear radio ads while running day-to-day errands (doing household chores, driving, etc.), radio also enables the repetition of ads just like TV commercials that, in turn, help organizations get more ...
Without going into details about the methods, it's another typical third-person case study designed to build trust. 6. Video marketing case study: L'Oréal and YouTube. In this case study, various members of L'Oréal's global marketing team break down exactly how they used YouTube ads to launch a new product.
Marketing research may cover a full spectrum of topics related to customers, products, and market dynamics, and it can use a variety of research methods (which will be discussed later in this module). In general, marketing research requires some additional information beyond what marketers have at their fingertips (like, say, internal data).
1. Internal environment. The internal environment is formed of all the internal factors and forces of an organization. The internal environment of an organization is within the control of the marketer, and he can change or modify the environment as per the demand in the market and requirement of the business.
Types of Assignments Cristy Bartlett and Kate Derrington. Figure 20.1 By recognising different types of assignments and understanding the purpose of the task, you can direct your writing skills effectively to meet task requirements. Image by Armin Rimoldi used under CC0 licence. Introduction. As discussed in the previous chapter, assignments are a common method of assessment at university.