
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

Chapter 9: Microsoft® PowerPoint®
What we’ll cover >>>, presentation software, microsoft powerpoint, slide formatting, slideshow design, transitions, review and distribution.
Presentation software is designed to allow the user to present information in an engaging way with text, pictures, sound, and video. It is a way to communicate ideas in a powerful, organized manner. It utilizes sequences of slides that accompany an audio presentation . The presentation may also be recorded and posted online. The slides are consolidated in virtual files called slide decks. Communication skills are necessary for many careers. Presentation software can help to deliver a message online or in-person to a large audience or small group. The goal is to create a presentation that will leave an impression on the audience, and not distract them from the message you are delivering. The ultimate goal is to create dynamic, interesting presentations that engage your audience.
Presentation software can be part of an integrated suite of tools, or be stand-alone. It can be installed on a computer for full and robust features and integration with other resources; it can be accessed on the web in a light format, and it can be a basic utility tool, like text editing applications. Some programs/suites are payware, such as those used in many workplaces; others are shareware or freeware. Information in this chapter should offer you transferrable skills for use in any word processing application.
Common presentation software programs
- Microsoft PowerPoint : Available across many platforms including mobile devices for ease of use. Integrates well with Microsoft Office.
- Apple Keynote : Included with most Apple devices. Real time collaboration. Use Apple Pencil on your iPad to create diagrams or illustrations that bring your slides to life.
- Google Slides : Integrates with other Google Apps, Q&A feature, Advanced web publishing features.
- Smartphone apps that allow for quick use and editing on-the-go.
- Word processing apps in free/open source office suites.
Since Microsoft® PowerPoint® (MS PowerPoint, PowerPoint) is widely used in business, and we are using Windows, we will focus on this presentation software. There are many similarities across presentation software, so the skills we are learning can be translated to other systems. Some of the tasks in PowerPoint may seem familiar because they were used in other applications. The following Try Me activities are designed to be completed using Microsoft PowerPoint in Office 365 on a PC with Windows 10 or higher.
DEMO EXAMPLE follow-through
Accessing powerpoint.
- In your Computer, use the relevant start menu to open MS PowerPoint (look for little red icon ). On a PC this is a start button on the keyboard, and/or menu on the lower left of the screen. On a Mac, this should be in the top-screen Menu option.
- PowerPoint will open with options to create a blank slideshow, open an existing file, and use templates.
- Observe the various Menu ribbons to learn what they offer.
The User Interface (UI) menus

In PowerPoint, the user interface contains several menu tabs ( tab ), with ‘Ribbons’ ( ribbon ) that display icons (like buttons) with text descriptions of various activities related to a task. On a ribbon, you will often see groups ( group ) of icons for tasks that relate to one another, like the Home ribbon’s Font group, Paragraph group, etc. Some of these icon buttons will do a simple task in one step, while others may open a panel ( panel ) which is a detailed, multi step or tab window of options. Sometimes you may instead see a context dropdown ( dropdown ) menus of options. Shown (in the program’s order) are:
- File : Accesses the program backstage area for various options. Set your preferences for workflow and productivity.
- Home : Basic text functions – formatting, positioning, styles
- Insert : tables, images, shapes, charts, page sections
- Draw : For more effects your can add to a slide, like “circling” an important point.
- Design : Layout of the slides – margins, themes, colors, etc.
- Animations : Transitions and sound.
- Slideshow : For timing and practice.
- Record : For audio recording the slideshow, and for exporting the show to video.
- Review : Spelling, language, tracking, etc.
- View : screen views, rulers, gridlines, windows.
- Additional add -in/specialty tab menus : These are dependent on having MS Word-related add-ins like Acrobat, a reference manager, etc.
- Contextual tab menus : These are contingent on a specific item in the program’s workspace being activated. For instance, clinking on an image, table, or header / footer will activate a context menu/ribbon on the right side of the UI that shows a menu dedicated to actions that can be done specifically for the active item (picture editing).
About Presentations
Presentations are a multi-page slideshow used to present a cohesive set of information/images. They are routinely used to support other documentation, not be the primary report or documentation. This means that a slideshow should focus attention on a few key points with a few bulleted supporting points, not use long paragraphs of text. Use a consistent layout, color palette, image layout/type, and transition style for professionalism.
- Information to be shared should be highlights of main points, which are shared in small amounts that can support a more detailed audio presentation with report and other print handouts. The slideshow highlights, it doesn’t act as the main word-processed document,
- Customary is Title Page, Title and content pages, and Image/Caption pages, with as-needed comparison pages and blank pages with a specific image/content design you need for the show.
- Use rulers and guides to help align your work.
- Presentations can be short to very long, use audio media, and be timed for a specific flow of information.
- Create transition slides for large section transitions.
- Use section and subsection titles to break up information in long shows.
- Use an easy-to-read font/color/style for excellent contrast info reading. Using a good sized-font at every hierarchy level makes the whole slideshow readable, even from the back of a room.
Slideshows are made up of slides with content. Their common MS PowerPoint native (editing) file extension is . ppt x , and their PowerPoint show file extension is .ppsx . They can contain:
- Text paragraphs and lists.
- Images, tables, and clip art.
- Headings, subheadings, captions, and paragraph text.
- Transitions, animations, media, and timed content.
Slideshow Workspace
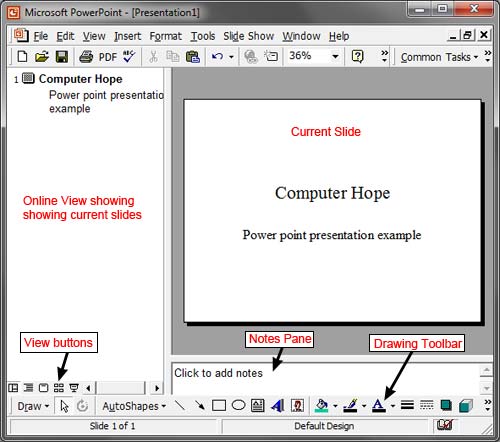
The default workspace for slideshows is a left-hand pane of slide thumbnails, the active slide being edited in the workspace, and a Notes pane below the workspace.
You can navigate through your slides by clicking on the thumbnails, or scrolling down the main workspace.

MedAttrib: author-generated. MS PowerPoint user interface thumbnails, workspace, notes pane.
Views – View Tab
- You can see different views as part of the main interface – lower right-hand side of the user interface, and also from the View tab’s ribbon.
- You can set rulers on or off.
- You can also set guides for aligning text and images.
- You can choose the window view you like to work in, such as normal, outline, slide sorter, notes page, or reading view layouts.
Preferences – File tab
Like MS Word and MS Excel, PowerPoint has a File tab Backstage area which lets you save slides in different formats, prepare them for print, and change the program’s options. You can set your PowerPoint program preferences for slides and program workflow, for smoother productivity, in the ‘backstage’ area of the program.
Same layout as Word, Excel, and Access and allows personalizing, print, save, and publish settings.
Slideshows are saved in the native editing format of PPTX, and when a show is meant to be actually shown when it opens, it is saved as a PPSX (show) format. They can also be saved in PDF format, and individual slides can be saved in image formats.
- You can set a slideshow up for printing out using the Print preview screen. Open the Print Preview screen to see the similar layout to Word and Excel.
- Go into the Info screen to inspect the slideshow for Accessibility and compatibility, and to protect a slideshow.
- Go into the File tab Options section, which you can use the change program settings.

MedAttrib: author-generated. MS PowerPoint user interface screen.
Text placeholder fields
In slideshows, you input text into editable fields (placeholders), with headings, paragraphs, lists, tables, images, etc. Text formatting includes indenting, spacing, and alignment. For instance, the alignment of text can be left, right, centered, or justified alignment; this paragraph is in Left alignment .
These fields also guide the kind of content you might put in them. Gor instance, a slide might have placeholders that state “Click to add title”, “click to add subtitle”. Etc.
Placeholder fields let you add text, and they also offer the option to add other items instead by showing icons that represent a table, an image, a video clip, and more.
Also, when you use a placeholder field for text, the text will routinely be added already in bulleted format. To decrease the level of the text, you need to click tab for an indented second-level of bulleted text. The thing to keep in mind here is that the bulleted text can get smaller quickly, so it is useful to look at your text formatting, make the bulleted text large enough to read, and to make the sub bulleted text, and sub-sub bulleted text, also sized to be readable.
Creating new text
If you don’t yet have text to work on yet when creating a document and setting paragraph formatting to use later as a saved style, consider using Lorem Ipsum, or one of its variants. Fun text fillers can include KittyIpsum, BaconIpsum, or ZombieIpsum. You can find Ipsum generators free online and copy/paste gibberish paragraphs into your document so you can play with some chunks of text. Let’s try some KittyIpsum now!
[Nap all day cat dog hate mouse eat string barf pillow no baths hate everything but kitty poochy. Sleep on keyboard toy mouse squeak roll over. Mesmerizing birds. Poop on grasses licks paws destroy couch intently sniff hand. The dog smells bad gnaw the corn cob.]
Home tab – Clipboard Group
At the very left of the Ribbon is the same clipboard group as we worked on in the Word and Excel chapters, which is a small set of tools you can use in relation to when text, images, and styles have been saved to the clipboard as you work. Clipboard-related activities include copy, cut, paste, and the format painter.
Home tab – Slides group
Every slide can be the same, or a slideshow can use a mix of pre-designed slide formats.
The slide text fields indicate what kind of slideshow page you are working on. A fully designed slideshow might have a title slide, title and contents pages, section header pages, comparison tables, image slides, and/or content (or a picture) with caption slides. You also can choose a blank slide without the editable regions on it fir full flexibility. The Slides group gives you the common slide layouts to choose from.
Home tab – Font Group
“Fonts” refer to the letters (characters) used in text. Font formatting includes resizing, changing the font family, adding bold or emphasis, adjusting spacing between letters, and more. You can right-click on a word or cluster of words for the contextual menu, or use the Home Tab’s font group options. These include font style, size, color, effects like bold / italics / underline, highlighting, and spacing formatting.

MedAttrib: author-generated. MS PowerPoint Fonts panel.
Home tab – Paragraph Group
You can modify your slide text paragraphs/bulleted lines in several ways. You can right-click on a piece of text, and choose “Paragraph” from the contextual menu. You can instead select some text, and use the Home ribbon’s one-touch paragraph group icons. You can also select some text, and choose the Home Tab’s paragraph group panel opener. With any of these, you can do alignment, spacing, indents, lists (bullets and numbers), shading, and borders.
Paragraph panel
The paragraph panel, which you can open from the lower right corner of the Home ribbon’s paragraph group, reveals a panel with several tabs of options: spacing before and after bulleted lines, specific indents, and line spacing.

MedAttrib: author-generated. MS PowerPoint Paragraph panel.
Inserts are basically anything you can insert into a slideshow that supplements your text content. You use the Insert Ribbon to choose what you want to add into a document: pictures, online art, icons, shapes, SmartArt, media, and text-related effects like WordArt.
Options for inserts – Insert tab
Just like Word and Excel, you can modify inserts using a contextual menu designed for the specific insert type: size, color, theme, position, etc. These Tab menu options only appear when you select an inserted item you want to modify.
ACTION: MS PowerPoint Try Me Activity #1
Let’s create a new slideshow, and then learn a few slide formatting tasks.
- Open PowerPoint.
- Open a blank presentation.
- Before you do anything else, save the new file into your Examples / MS_PowerPoint folder as PP _ formatting . pptx .
In the blank slideshow, you should see a single page, It shows placeholder text boxes that PowerPoint uses to help creators guide slide content creation and display. You type into them with your content, and PowerPoint styles the content – per the in-use theme – by hierarchical bulleted lists.
Before adding any text, let’s add more blank slides.
- On the Home ribbon, Slides group, click the New Slides , which gives a dropdown of possible slide layouts.

MedAttrib: author-generated. MS PowerPoint new slides panel.
Since the new slideshow already opens with the Title Slide, lets add a few pages that represent other slide layouts.
- In the New Slide dropdown, choose Title and Content .
- Add another slide using the New Slides icon: Two Content .
- Add another slide using the New Slides icon: Content with Caption .
- SAVE your work: CTRL S / MAC CMD S.
You should have mostly blank 4 slides in your show now – blank except for the placeholder fields.
When using the editable fields, PowerPoint’s default is to offer common heading and subheading styles, text styles, and bulleted hierarchy styles. This design becomes more important when using animations in a show, and how they are prioritized during a finished presentation.
- Go to the first slide. In the first placeholder that reads Click to Add Title, click inside and type First Show .
- In the second placeholder, type By YourName .
- Go to the second slide. In the first field, which reads Click to add title, type Slide Basics .
TIP: Slide Title placeholders. The placeholders that are for adding titles don’t mean that ever slide with one needs the title of the whole slideshow added there. They can also act as titles for a page, or within a section, to help a slideshow’s organization seem more cohesive.
The second placeholder is multi-purpose. You can immediately start typing text in it and use it in that way. However, a semi-transparent set of icons is also in the placeholder, which indicates that you can instead click on one of them to add content that the respective icon represents.

MedAttrib: author-generated. MS PowerPoint placeholder content field options.
In this slide, we’ll just add text to see how it works.
Type these lines, pressing your keyboard’s Enter key after each:
- Supporting point
- Third-level point
- Paragraph text
- Place your cursor in from of the line Supporting point, and press Tab.
- Place your cursor in from of the line Third-level point, and press Tab twice.
Observe how PowerPoint “demotes” the bullet levels so that they get smaller. This is a good time to learn that using more than one or two levels of bullets is as far as a viewable presentation should use, although you can also enlarge the size of the text of each bullet.
- Place your cursor in front of the line Paragraph text.
- On the Home ribbon, Paragraph group, click the Bullets icon to ‘turn off’ the bullet on this line. This demonstrate that you do not have to use bullets.
Go to the third slide, which has 3 placeholders. This is a standard comparison slide, which simply describes that you can have two sets of information side-by side. These could be text and graphic, table and graphic, two fields of text, etc.
- In the 1 st placeholder, type Comparison Slide .
- In the 2 nd placeholder (left one), type Item Description .
- In the 3 rd placeholder (right one), click the Online pictures icon , and use the search field that opens to search for (and insert) an image you like.
Go to the fourth slide, which has 3 placeholders. This is a standard content with caption slide, which simply describes that you can have captioned information side-by side with a table, a graphic, etc.
- In the 1 st placeholder, type Text header .
- In the 2 nd placeholder (left one), type Add some text here .
- In the 3 rd placeholder (right one), click the Table icon , and use the dialog box that opens to type 3 in the Number of columns, and 4 in Number of rows.
Now we have a basic slideshow with components we can practice manual font formatting.
Like in Word and Excel, formatting options happen mostly in the Home ribbon, with the Font group and Paragraph group.
Go to the first (Title) slide.
- Select the title text and use the Home ribbon Font group to make the text Bold, and dark blue .
- Select the subtitle text (your name) and use the Home ribbon Font group to make the text italicized .
Go to the second slide. Let’s make the content text larger.
- Select the 1 st bulleted item, and use the Home ribbon Font group to make the text 36 pts .
- Select the 2 nd bulleted item, and use the Home ribbon Font group to make the text 3 2 pts .
- Select the 3 rd bulleted item, and use the Home ribbon Font group to make the text 2 8 pts .
- Select the paragraph text, and use the Home ribbon Font group to make the text 32 pts .
Go to the third slide. Let’s edit the image.
- Click on the image. Like in Word and Excel, an activated image (or other insert) opens a new contextual menu/ribbon. For this image it is a Graphics Format ribbon .
- With your online image active, use the Graphics Format ribbon, Size group, to make the image 6 inches wide.
- Use your cursor to click and drag the image to make it seem more centered, if the resizing moved or altered its centered appearance.
- Click the image, and use the Graphics Format ribbon, Accessibility group , to add accessibility content.
- Click the Alt Text icon , which will open a docked Alt Text panel on the right of your workspace.
- In the Alt Text field, you may already see some text. However, replace it with: “Stock image of a (whatever the image is of).” This tells a screen reader that there is an image and what the image is.
Go to the fourth slide.
- Make the Text Header line bold and a medium-dark gray .
- Use the Home ribbon Font group to make the paragraph text below the Text Header 24 pts in size.
Let’s work on the table. Like in Word and Excel, tables should have a header row, and PowerPoint defaults to adding formatting form one to an inserted table.
- Click in the table’s first cell, which should be in a darker colored row – the header row.
- In the 1 st header cell, type Fave Weekday .
- In the 2 nd header cell, type Fave Activity .
- In the 3 rd header cell, type Saturday F un .
- If you’d like, you can fill in your faves in the table cells below.
Click on the table, and observe that a Table Design ribbon and related layout ribbon to its right appear.
- In the Table Layout ribbon, Table Styles group, choose a different table color and intensity.
- SAVE your work , and close the file. POWERPOINT ACTIVITY #1 FINISHED.

MedAttrib: author-generated. MS PowerPoint example 4-slide show with edits.
Now we’ve had a good introduction to new slides and basic manual font formatting.
Text and paragraph formatting are parts of what happens in a slide. This section is about the overall slideshow itself – how it will present when given as an active animated slideshow, printed out, and consumed by users. Slideshow formatting is characterized by actions that can affect the whole document, and in so doing, add efficiency and steps-saving to general text and paragraph formatting. These include document layout, themes and styles, headers and footers, and some use of sectioning. Much of this will seem familiar from Word and Excel.
Master Slides – View tab
In the View tab Master Views group, you can access a slide master view to show all the potential pages that you can use in a slideshow theme. This is useful, and a good first step to using a theme, so that you can add footer information, make sure your show’s title usage is consistent and correct throughout the show, and make specific style changes to the actual master pages of the show’s theme. You want to minimize having to touch individual slide designs.
The footer section in the slide master lets you add a page number, date, other footer content, and style it so that it appears the same way each time that slide is used.
One thing to not, and this is a reason why the master slides are considered more intermediate in skill; each and every possible style page in the master view needs to be edited for consistency, or else you may insert slides from your modified theme and still see some differences. For instance, if you change the size and content of a slide’s footer in one master view page, you need to make the same change to all the master view slide variations.

MedAttrib: author-generated. MS PowerPoint Slide Master interface.
Setting up slideshows – Design tab
The Design tab allows you to set the physical format of your slideshow, which is a good first starting step in developing a slideshow. This determines how large the slides will be, the orientation of the document, etc. In the Design tab Customize group, the Slide size icon dropdowns lets you choose an existing size or set a custom slide size.

MedAttrib: author-generated. MS PowerPoint themes, and color / font palettes.
Designing documents – Design tab
Themes apply decorative styles to your PowerPoint document (just like in Word and Excel), such as fonts, colors, effect options, paragraph spacing, etc. They can give a slideshow a consistent and attractive appearance and efforts look more professional. In business, they are best used as part of a “package” of documents, such as a slideshow accompanying an annual report with Excel graphs and charts inserted. They can enhance what you want to communicate by adding company branding colors and fonts. You can also:
- Make your slideshow more readable than just black-and-white text
- Tie consistent inserts, like shapes and borders, together with the rest of the document’s “look”
- Use different colors and font styles to punctuate headings from text
- Help your reader respond and/or act in the way you need, and
- Easily update the whole look of your document just by changing the color or font variants
Design: Theming / Design Tips
Like Word and Excel, using themes can be a double-edged sword. While they can add attractiveness to your documents, they can also, if misused, make your work look confusing, be hard to read, and muddy your communication message. Certain types of work should not use themes, like cover letters and resumes, which are routinely expected to be plain and standardized and which the receiver will likely scan into a program for database acquisition.
- Choose theme colors that make sense for the product, service, or idea(s) you are trying to communicate
- Choose theme backgrounds that have good contrast and allow text to be very easy to read
- Choose fonts for readability, based on need for headlines, lots of paragraph texts, easy bulleting, etc.
- Remember that less is more – more colors and font variations in one document can look unprofessional and take away from your message.
- Use themes only when you have full control over your own document – if you have an instructor or employer who does not want them used, then instead focus on using a template of the required styling.
Design: Theme Variants
Theme variants let you change aspects of a theme you select to apply a different core font family to it, or to change the color palette it will work with.
- Fonts : Font families in themes are designed and sized to be readable and hopefully scannable by screen readers for accessibility use. The style will offer a font for titles/subtitles, and another for general text. Available font families come installed with the computer’s operating system, and may also be accessed from the word processing software’s installation or cloud-based accessories.
- Color Palettes : Like fonts, color palettes are included in a style, and can also be changed independently to modify and create a new style. For instance, the overall design style of a theme may work for you, but the color palette assigned to it may not have enough contrast for your audience, or your company may focus on a different rage of core colors.
- Effects : These are subtle styles that can be attached to some inserted items, like image borders, shapes, SmartArt, etc.
Theme Variants
- Page Color : This allows assigning a color to a slide template, with previews of several colors in the theme’s palette.
- Design : The Design tab has a Designer group, with a Design icon that can help you generate additional layout ideas for your show.
ACTION: MS PowerPoint Try Me Activity #2
Let’s work on slideshow design.
Before you start, you should use your file manager utility to make a copy of the PP _ design . pptx file that is in your DataFiles folder, then paste the copy into your Examples / MS_PowerPoint folder.
- If MS PowerPoint isn’t open yet, open PowerPoint.
- Go to the Tile tab Backstage and Open a file, then use the browser dialog panel to find the PP _ design . pptx file that should be in your Examples / MS_ PowerPoint folder, then open the file.
You should have a show with six slides of different layouts. We’ll use this for slide formatting practice. Our goal is look at Master slides, set a theme, and view the slideshow layout.
- Let’s choose a theme. Use the Design ribbon, Themes group, to pick the Facet theme .
- Scroll through the slideshow to see how the theme affects each slide.
- If you see that some text looks off center, you can drag the text box to center it, and also use the Home ribbon’s Paragraph group to change the alignment of the text (like centering).
- Use the Design ribbon, Variants group, to pick a variant color of the Facet theme that you like.
- If you don’t like the selection, click the small arrow at the lower right-hand corner of the Variants group to open a dropdown menu that offers a colors palette , font palette, and effects options.
- Choose a different color palette from the selection.
- Choose the Effects option from the Variants group dropdown, and pick one you like.
In the last activity, we manually changed the font size of some of the bulleted text. Let’s do that here, using the Slide Master view, so that existing slides, and new ones, have larger body text (first three levels of bullets).
- Go to the View ribbon, Master Views group, and click Slide Master . The Slide Master view will show thumbnails at the left of each kind of page the show has built-in, so that you can touch any of them up and have newly created slides follow these Master Page changes. It also provides a Slide Master ribbon, which has the themes and background options, as well as a button to Close Master View.
- From the Thumbnails, choose the top slide , which has the key styles for all bulleted text for the slideshow. Clicking this thumbnail will place an editable version into your workspace.
Notice that there are several placeholders, including three at the bottom that act as footer information.
- In the Slide Master, select the 1 st line of bulleted text, and use the styles toolbar that opens (or the Home tab Font group options) to change the font size to 2 8 pts .
- In the Slide Master, select the 2 nd line of bulleted text, and use the styles toolbar that opens (or the Home tab Font group options) to change the font size to 2 4 pts .
- In the Slide Master, select the 3 rd line of bulleted text, and use the styles toolbar that opens (or the Home tab Font group options) to change the font size to 2 4 pts .
- Close the Slide Master view.
What this does is enlarge the base size of the overall slideshow text. To get more granular changes to every slide, we would need to touch every master slide.
- SAVE your work : CTRL S / MAC CMD S.
- Let’s find out what the slide size is. Use the Design ribbon, Customize group, and choose the Slide Size .
The Slide size defaults to Standard (4:3), with an alternative of (16:9) and of Custom Slide Size. Do not change the size.
TIP: Changing slide size. When slides change to a new size, but any Master Slide changes will revert to the new size’s Master Slide defaults.
- SAVE your work , and close the file. POWERPOINT ACTIVITY #2 FINISHED.
Transitions are one design item that is unique to PowerPoint. Because a slideshow is meant to be active and engaging, and because it may have many slides, one way to keep viewers from having a jolt from immediate slide changes is to program in transitions. A transition might take a couple of or a few seconds, provide a ‘slide separation’ effect, and help keep a show engaging.
Slide transitions – Animations tab
PowerPoint offers a number of build-in animated transition and layout actions. They can be used for an entire slide transition, or a specific in-slide item transition/animation. These give the feel of interaction and movement in presentations and allow creation of complex animated slideshows that can look like Flash Movies..
- Common animation thumbnails appear in the Transitions ribbon.
- The left-most is the Current animation theme.
- Clicking other thumbnails to the right of the Current will change to that of the thumb you choose.
- You can also change the transition speed and sound.
- You can set slide advancement timing so that the presenter stays on a specific schedule.
- A transition can be applied to the current slide, or all slides in the show at one time.
- For a professional and non-jittery feel, you can consider applying the same transition to all the slides.
ACTION: MS PowerPoint Try Me Activity #3
Let’s do some work with transitions, and maybe a simple animation.
Before you start, you should use your file manager utility to make a copy of the PP _ transitions . pptx file that is in your DataFiles folder, then paste the copy into your Examples / MS_PowerPoint folder.
- Open a file, and use the browser dialog panel for the PP _ transitions .docx file that should be in your Examples / MS_ PowerPoint folder, then open it.
You should see six formatted slides. A theme has already been selected, and the Master Page has been updated to have larger base fonts. Our task here is to set slideshow transitions, maybe an animation, and to test the slideshow.
Transitions can be applied one page at a time, or on all slides. We’ll start small then learn more efficient practices.
- Go to the first page of the slide show.
- Activate the slideshow as it currently is. We want to observe how the slideshow works. When you start a slideshow viewing, by default it will begin from the slide you are currently on, unless you tell PowerPoint otherwise.
- Using the Slideshow ribbon, Start Slide Show group, choose the From Beginning icon. You can also use the Status bar’s Slide Show icon. The Function 5 key also starts a slide show.
Okay, now we see the first slide. It is just stuck there. What’s up? The default for moving pages along is to press the keyboard enter button, to click the mouse, or the keyboard Page Down button.
- Press the enter button, and the slide show changes pages. Keep pressing Enter, and the slideshow will progress until you reach the last slide, then it will exit back to the Edit mode.
That was nice. It will be nicer if the pages transition with some kind of effect.
- On the first slide, go to the Transitions ribbon, Transition to this Slide group.
- Click the dropdown to open the dropdown transitions selector. Choose Random Bars from the “Subtle” area.
Look at the thumbnails of the slides. The first slide, which we applied a transition to, has a small star to its left – this indicates there is a transition.
- On the Transitions ribbon, a Preview Icon becomes available at the left. Click it once to preview the transition.
- Now, use the Function5 key (F5) to start the slide show.
The slideshow starts with the transition. You need press Enter to advance the show, and. . . there are no more transitions.
- Use the Escape button to escape the slideshow.
A transition needs to be applied to every slide for every slide to use it. You can set transitions on every slide at one time two ways:
- Select all slides by clicking the first thumbnail, pressing the shift keyboard key, and then selecting the last thumbnail. Once all slides are selected, choose the transition, which will apply to all. Or,
- Use the Transitions ribbon, Timing group, and choose Apply to all.
In our case, make sure you are on the first slide which has the transition, then click the Apply to all. Now all the slides have the star icon.
- Use F5 to run the slideshow, and press Enter to advance the slides. Note that the most pronounced version of the transition happens when the show opens; the remaining pages transition more subtly.
- On the first slide, choose a different transition, such as the more “exciting” Honeycomb.
- On the Transitions ribbon, click the Apply to all, so that the new transition replaces the old one.
- Use F5 to rerun the show.
Can we change the time on a transition? Yes. Make sure you are on the first slide
- Using the Transitions ribbon, Timing group, change the Duration to 1.50.
- Add sound by using the Transitions ribbon, Timing group, and clicking the Sound dropdown. Choose the Chime sound (or another you prefer).
- From the First slide, use the Transitions ribbon and click the Apply to all to add the timing and sound to all the slides.
- Use F5 to rerun the show. The show is more dynamic, and seems to run faster.
Can we use some other method to advance the show besides the Enter button or mouse click? Yes!
Be on the first slide again.
- Using the Transitions ribbon, Timing group, and unclick the On Mouse Click. Put a check in the After checkbox, and adjust the time to read 00.03.
- From the First slide, use the Transitions ribbon and click the Apply to all to add this change.
- Use F5 to run the show. The slides will automatically advance every 3 seconds.
Animations are another design item that is unique to PowerPoint. An animation can be as simple as using a transition-like effect on an item, like fading out a picture. Or it can be used to bring in a list of text one bulleted line at a time. You can create an animated and programmable ‘button’ to advance pages on a slideshow with a click. You would use the Animations tab to add and time animation content so that the show feels like a movie. Animations can be applied to text, to pictures, and to ither inserts like shapes, clipart, WordArt, etc.
You can also open an Animation pane in the Animations tab Advanced Animation group. This pane is necessary because if you have multiple animations in a slideshow, and even on the same page, you will need to tell PowerPoint several things:
- What order to serve the animated items. The standard order is that the first things on a slide animate first – BUT, this can mean the first thing created on the slide, not the first thing in the order you ‘see’ the items.
- The timing of and between animation actions.
- The speed of an animated effect.
- How an animation should start – on a mouse click, on a timed delay, etc.
- How you choose to change the order of animations.
Let’s try an animation.
- First, go to the first slide, and then reset the Advance Slide option back to On Mouse Click, and uncheck the After checkbox. Otherwise, the automatic slide timing will conflict with any animation you create.
- From the First slide, use the Transitions ribbon and click the Apply to all to add this change to all the slides.
- Go to Slide 2, and in delete the contents of the right-hand placeholder, so that you can see the icons to add content.
- Choose the Stock Images, and find some vacation image from another country to import. Once the image imports, it will size itself to the size of the placeholder field.
- Click on the image, then go to the Animations ribbon, Animation group, and choose the Fade animation.
- On the Animations ribbon, Preview group, and click Preview.
- On the Animations ribbon, Timing group, and set the Duration to 1.2, then preview again.
- Go to slide 1, and use F5 to run the show. It should need you to press enter or use a mouse-click to advance the slides.
- Advance to slide 2 and stop. Notice that there is no image.
- Click the mouse or press Enter. The image should fade in.
- Press Enter again to continue advancing the show, or press Escape to escape the show.
- SAVE your work.
Shall we try an animated list of text? Go to Slide 3, which has 4 lines of bulleted text. Let’s determine how we can make each of these line appear one at a time from top to bottom.
- Click on the Slide 3 placeholder with the 4 lines of bulleted text.
- Go to the Animations ribbon, and choose Fly in from the Animation pane.
- Use the Go to the Animations ribbon Preview icon to see the animation. This is how the lines should ideally come in, considering timing, etc.
Look at the Placeholder box’s text, and notice that to the left of each bulleted line, a number appears.

MedAttrib : author-generated. MS PowerPoint text slide.
The numbers display the order in which the text will appear. In this case, we do not need to change the order.
- On the Animations ribbon, Timing group, and set the Duration to 1.5 , then preview again. The lines appear more slowly.
- On the Animations ribbon, Timing group, look at the Start field , which shows On Click . There are other options, but we’ll stay with this default.
- Go to Slide 1, then run the slideshow with F5. Use your mouse click or Enter button to advance each slide and animation.
For your own practice, you can try animating the text placeholder contents on slides 4 and 5.
On the final slide, let’s add a large image from your favorite travel place. In this case, you will need to remove the text-only placeholder, and simply import an image in to the page.
- Use the Inserts tab, Images group, Pictures / Online pictures, and search for an image.
- Import the image, and resize it to be about 10 inches wide.
- Use the Picture Format context ribbon to add a predesigned border from the Picture Styles group gallery .
- Click the image, and use the Animations ribbon, Animations group to pick an emphasis animation to apply to the image.
- Use the Animations ribbon, Timing group to change the Duration to 1.25 .
- Run the slideshow from the beginning.
- SAVE your work , and close the file. POWERPOINT ACTIVITY #3 FINISHED.
PowerPoint is about presenting work – in person, as timed online presentations, etc. It is used in meetings, conferences, sales contacts, on websites, in streaming threads, etc. The various illustration, transitions, and animation tools make PowerPoint uniquely capable of having interactive data presentation.
You can also create slide notes, to appear below slides, and/or to be printed out for a separate handout in a meeting.
Output – File tab
Review and distribution of your work is about preparing it for who will be consuming it. Will it stay in a Word document format, be saved as a PDF, printed onto paper, added as website content, populate an add or newspaper article, or be part of a book? Like Word and Excel, a PowerPoint file needs to be:
- Spell checked
- Grammar- and language- reviewed
- Accessibility enabled (alt text, proper use of heading styles, accessibility for screen readers).
- Have versioning considered.
- Have hyperlinks tested.
- Be cited and attributed properly for intellectual honesty.
- Passed for plagiarism and other content integrity needs.
- Presented for readable print viewing.
- Secured for limited/no editing.
- If meant for team collaboration, prepared for making shared/trackable changes, comments, and notes.
Output/distribute work
- You can test and adjust your documents and review your content before it goes live by looking at the File/Print sections Print Preview and settings.
- You can make sure you have added metadata for web/online reference by updating information in the File/Info page.
- Slideshows can be saved in as a slideshow, native slide prepared format, as a template, and in other formats, like images and PDFs.
- You can save files in different formats for distribution in the File backstage areas, like Save As (for current and older versions, RTF, text, and HTML), save as PDF, export, etc.
This should give you a good overview of MS Word skills that you can use in school and as a starter for basic workplace support tasks.
Business Technology Essentials Copyright © 2023 by L.J. Bothell is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Presentation program
Presentation program may refer to any of the following:
1. In general, a presentation is a speech given by one or more speakers in front of an audience covering a new product or idea. For example, Steve Jobs gave a presentation in 2007 to introduce the iPhone .
2. A presentation program is a program that helps create a slideshow that addresses a topic. Presentation programs can be used in businesses and schools for discussing a topic or for teaching. Often, the presenter uses a projector to project the slideshow up on to screen that everyone can see. Below is an example of Microsoft PowerPoint, a commonly used program that creates presentations.
Once created, a person or group of people stand in front of other people and present the presentation . Presentations are shown one slide at a time, to explain the slides topic and then moving to the next slide until all are shown. For example, in a business presentation a co-worker may go through slides that illustrate how well the company is doing, its profits, sales, and other important information.
Examples of presentation programs
Below is a short list of popular presentation programs available today.
- Google Slides
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- iWork Keynote on the Apple
- OpenOffice Impress.
Tips on presentations
- Follow the Guy Kawasaki "10-20-30 rule." Presentations should be no more than 10 slides, last no longer than 20 minutes, and have text no smaller than 30-point font.
- Keep text simple with the "6 by 6 rule," which is six lines of text with six words per line.
- Keep the text sparse and include pictures. There is a reason people say a picture is worth a thousand words.
- Don't read the slides. Your slides should remind you of your talk and allow your audience to see only the important facts.
- Prepare and arrive early to set up so your audience does not have to wait or watch you troubleshoot problems.
- Always look into the audience and not only the slides, keep a steady pace when speaking, and speak loud and clearly so everyone in the room can hear you.
- Do not use bright or flashy colors in an attempt to keep peoples attention. Use pastel colors as the backgrounds with a dark font.
- Enjoy yourself. If you are not having fun or making the slide show entertaining, no one else is going to enjoy your presentation.
Related information
- Creating a presentation slide show online .
- How to create or add a slide in Microsoft PowerPoint.
Business terms , Google Slides , Office , Office 365 , Office Online , OpenOffice , Productivity tools , Projector , Slide deck , Slide show , Software terms
Working with the PowerPoint Interface
In this article, we’ll introduce you to the PowerPoint 2013 interface, which uses the Ribbon from the previous two versions of PowerPoint. You’ll get a closer look at the Ribbon, as well as the Navigation pane and the Status bar. You’ll also learn how to manage your Microsoft account right from a new item above the Ribbon. This module introduces you to the Backstage view, where all of the functions related to your files live. You’ll learn how to save files. Finally, we’ll look at closing files and closing the application.
For instructor-led PowerPoint classes in Los Angeles call us on 888.815.0604.
Understanding the Interface
The PowerPoint interface, including the Ribbon, the Slides tab, the presentation window, the Notes pane, the Comments pane, the Quick Access toolbar, and the Status bar.
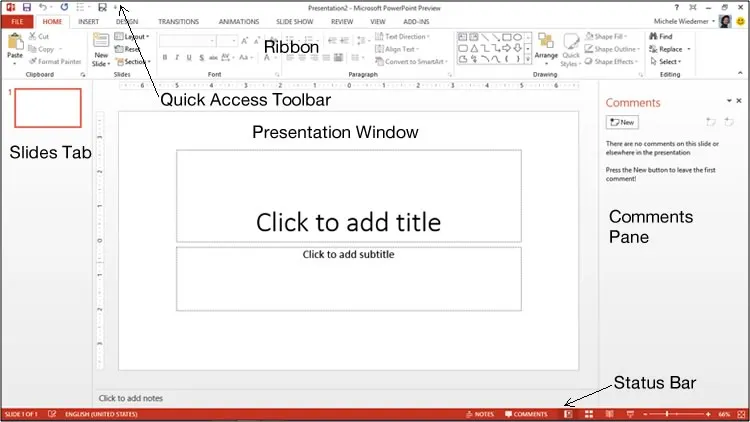
- The Slides tab shows a thumbnail of each slide in the presentation.
- The presentation window is where you can view and edit the entire slide.
- The Status Bar shows the current slide number, as well as the total slides, as well as the language setting for proofing. It also has additional tools for making changes to the view or zoom. If the Notes and Comments pane are not showing, just click on those icons on the Status bar to show them.
- The Notes pane allows you to add speaker notes to the presentation. You can print speaker notes to use when delivering a presentation.
- The Comments pane allows you to add comments to a presentation, especially helpful when working with a team to develop the presentation.
Each Tab in the Ribbon contains many tools for working with your presentation. To display a different set of commands, click the Tab name. Buttons are organized into groups according to their function.
The Quick Access toolbar appears at the top of the PowerPoint window. It provides you with one-click shortcuts to commonly used functions, like save, undo, and redo.
To zoom in or out, use the following procedure.
- Click the minus sign in the Status bar to zoom out. Click the plus sign in the Status bar to zoom in. You can also drag the slider to adjust the zoom.
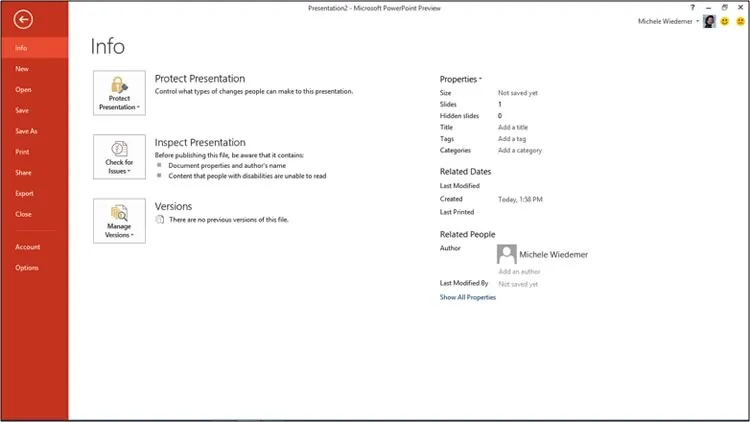
An Introduction to Backstage View
Review the Backstage View, use the following procedure.
- Select the File tab on the Ribbon.

PowerPoint displays the Backstage View, open to the Info tab by default. A sample is illustrated below.
Saving Files
To save a presentation that has not been previously saved, use the following procedure.
- Select the Save command in the Backstage View.
- Select the Place where you want to save the presentation.
If you choose your SkyDrive, you can select the Presentations folder. If you choose your Computer, select your Current Folder or one of your Recent Folders . Or in either place, you can choose Browse to select a new location.
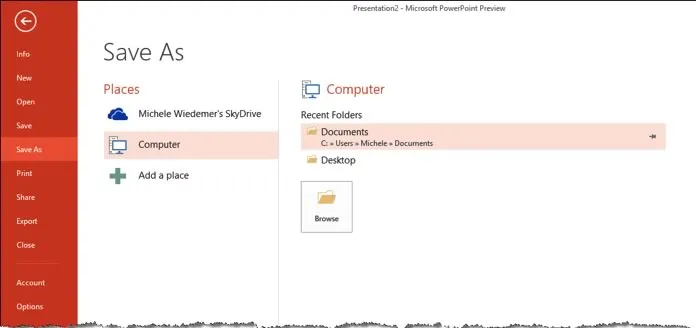
- The Save As dialog opens. Enter a File Name , and if desired, navigate to a new location to store the file. Select Save .
Closing Files vs. Closing PowerPoint
To close a file, use the following procedure.
- Select the File tab from the Ribbon.
- Select Close from The Backstage View.

If you haven’t saved your file, you will see the following message.
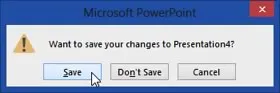
To close the application (if only one presentation is open), use the following procedure.
- Click the X at the top right corner of the window.

Other resources
PowerPoint 2016 Ebook - The Interface
Training videos on PowerPoint 2011 for Mac
Related PowerPoint Lessons
- Starting your first PowerPoint Presentation
- Working with Text in PowerPoint
PowerPoint student reviews
Every year we train thousands of satisfied students...you can read some reviews at the following page -> PowerPoint testimonials .
- Address 915 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 1800. Los Angeles CA 90017
- Phone (888) 815-0604
- Email Show Email
In person v online training
In line with state protocals we have now fully resumed in person or classroom training.

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is PowerPoint: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
What is PowerPoint? This blog provides the essence of PowerPoint, a versatile presentation software by Microsoft. Discover its features, uses, and the art of crafting compelling slideshows. Whether you're a student, professional, or simply curious, explore the power of PowerPoint and learn how to create impactful presentations effortlessly.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals (ERP) MB920
- Microsoft Access Training
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals (CRM) MB910
- Microsoft Word Course
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Marketing MB220

According to Glassdoor , a PowerPoint designer's average salary in the UK is about £37,811 annually. In this blog, you will learn What is PowerPoint, its key features, its benefits, and how to use it, as well as learn some tips for creating effective presentations.
Table of contents
1) What is PowerPoint?
2) Understanding the PowerPoint Interface
3) Key Features of PowerPoint
4) How to use PowerPoint to create a presentation?
5) Benefits of PowerPoint
6) Tips for Creating Effective PowerPoint Presentations
7) Conclusion
What is PowerPoint?
PowerPoint is a versatile and popular presentation software developed by Microsoft (MS). It is a part of the Microsoft Office Suite and offers various features and tools to create visually appealing and engaging presentations. MS PowerPoint allows users to combine text, graphics, multimedia elements, and animations to convey information effectively .
Evolution of PowerPoint

Understanding the PowerPoint Interface
The PowerPoint interface provides a user-friendly environment for creating and editing presentations. Familiarising yourself with its essential components will help you navigate the software efficiently. Here's a breakdown of the MS PowerPoint interface:
1) Ribbon : The Ribbon is located at the top of the MS PowerPoint window and consists of multiple tabs, such as Home, Insert, Design, Transitions, and more.
2) Slides pane : The Slides pane is on the left side of the PowerPoint window. It displays thumbnail images of your presentation slides, allowing you to navigate and rearrange them easily. You can add, delete, duplicate, or hide slides from this pane.
3) Notes pane : The Notes pane is located below the Slides pane. It provides space for adding speaker notes or additional information related to each slide.
4) Slide area : The Slide area occupies the central part of the PowerPoint window. It displays the selected slide, where you can add and arrange content such as text, images, charts, and multimedia elements .
5) Task panes : Task panes are additional panels on the PowerPoint window's right side. They offer various functionalities such as formatting options, slide layouts, animations, etc. Task panes can be opened or closed based on your specific needs.
Understanding the MS PowerPoint interface will help you navigate the software effectively and make the most of its features. Whether you are creating slides, adding content, or applying formatting, having a good grasp of the interface ensures a smooth and productive experience .
Key Features of PowerPoint
When it comes to creating captivating and professional presentations, MS PowerPoint stands out as versatile and feature-rich software. Its array of tools and functionalities enables users to bring their imagination and ideas to life. Moreover, it also helps engage their audience effectively .
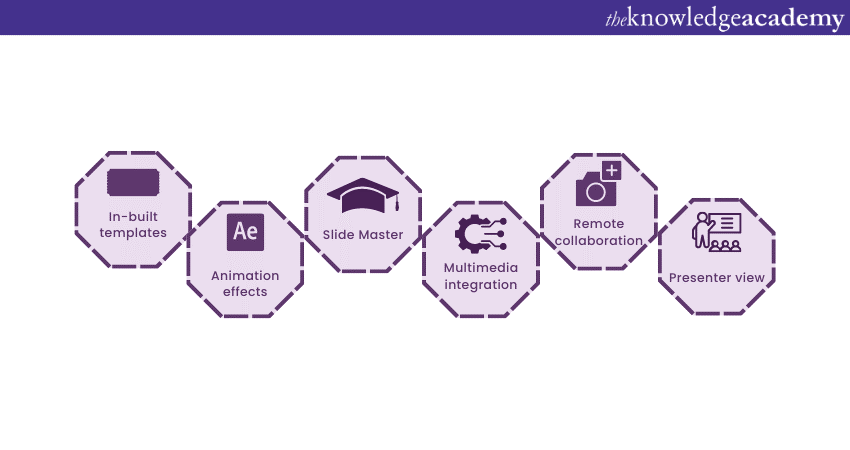
1) Slide Templates : PowerPoint provides a collection of pre-designed templates that make it easy to create visually appealing slides.
2) Slide Master : The Slide Master feature allows users to define the overall layout, font styles, and colour scheme for the entire presentation .
3) Animations and transitions : PowerPoint offers various animation effects and slide transitions to add visual interest and captivate the audience .
4) Multimedia integration : Users can embed images, videos, and audio files directly into their presentations, enhancing the overall impact .
5) Collaboration tools : MS PowerPoint allows multiple users to work on a presentation simultaneously, making it ideal for team projects and remote collaboration .
6) Presenter View : The Presenter View feature gives presenters access to speaker notes, a timer, and a preview of upcoming slides, enabling a seamless presentation experience .
These features collectively contribute to PowerPoint's versatility and make it a powerful tool for developing engaging and impactful presentations.
How to use PowerPoint to create a presentation?
Creating a presentation in PowerPoint is a straightforward process. Whether it's simple animations or explainer videos learning H ow to use PowerPoint is an extremely valuable skill. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to create a presentation:
1) Launch PowerPoint and choose a template or start with a blank slide.
2) Add slides by clicking "New Slide" or using the shortcut key (Ctrl + M).
3) Customise slide content by entering text and inserting visuals.
4) Rearrange slides for a logical flow by dragging them in the slide navigation pane.
5) Apply slide transitions for visual effects in the "Transitions" tab.
6) Add animations to objects in the "Animations" tab.
7) Preview your presentation by clicking "Slide Show".
8) Save your presentation and choose a format (.pptx or .pdf).
9) Share your presentation via email, cloud storage, or collaboration tools.
By following these steps, you can create a well-structured and visually appealing presentation in Microsoft PowerPoint. Remember to keep your content concise, use engaging visuals, and practice your presentation skills to deliver an impactful presentation .
Benefits of PowerPoint
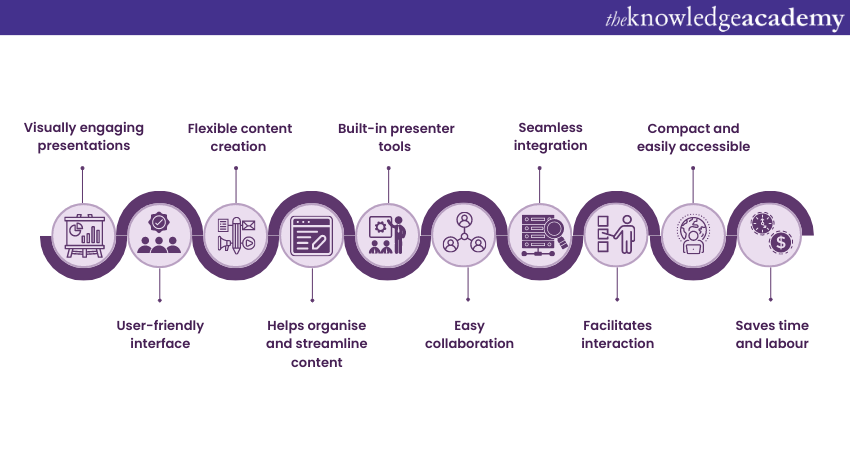
1) Visual appeal : Microsoft PowerPoint allows you to create visually appealing presentations with its wide range of design tools and features. You can use templates, themes, and customisable layouts to make your slides visually engaging and professional .
2) Easy to use : PowerPoint has a user-friendly interface, making it accessible to users of all levels. The intuitive tools and straightforward navigation make it easy to create, edit, and deliver presentations efficiently .
3) Flexibility : PowerPoint provides flexibility in terms of content creation. You can include various types of content, such as text, images, charts, graphs, videos, and audio files, to enhance your message and engage your audience effectively.
4) Organisation and structure : PowerPoint offers features to help you organise and structure your content. You can create multiple slides, use slide masters for consistent formatting, and arrange the sequence of slides to create a logical flow .
5) Presenter tools : PowerPoint includes built-in presenter tools that aid in delivering presentations smoothly. You can use presenter view to see your notes and upcoming slides while your audience sees only the presentation. Additionally, features like slide transitions and animations add visual interest and help you control the flow of information .
6) Collaboration and sharing : PowerPoint allows for easy collaboration and sharing of presentations. Several users can simultaneously work on the same presentation, making it convenient for team projects. You can also share your presentations via email, cloud storage, or online platforms, ensuring easy access for viewers .
7) Integration with other tools : PowerPoint can seamlessly integrate with other Microsoft Office applications, such as Word and Excel. You can import data and charts from Excel or copy and paste content between different Office applications, saving time and effort .
8) Presenter-audience interaction : PowerPoint provides features that facilitate interaction between the presenter and the audience. You can include interactive elements like hyperlinks, buttons, and quizzes to engage your audience and make your presentations more dynamic.
9) Portable and accessible : PowerPoint presentations can be saved in various formats, such as .pptx or .pdf, making them easily accessible on different devices. This portability allows you to deliver presentations on laptops, tablets, or even projectors without compatibility issues .
10) Time and effort savings : PowerPoint simplifies the process of creating presentations, saving you time and effort. The pre-designed templates, slide layouts, and formatting options enable you to create professional-looking presentations efficiently .
Unleash your creativity to deliver captivating presentations that leave a lasting impact with our Microsoft PowerPoint Masterclass – Sign up now!
Tips for Creating Effective PowerPoint Presentations
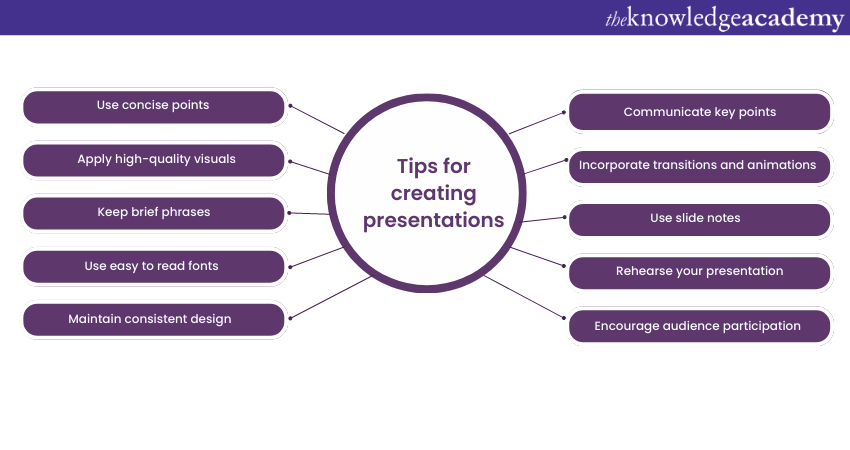
1) Simplicity is key : Keep your slides clean and uncluttered. Use concise bullet points and simple visuals to convey your message effectively .
2) Visuals matter : Incorporate relevant, high-quality visuals such as images, charts, and diagrams to enhance understanding and engagement .
3) Limit text : Avoid overwhelming your audience with excessive text on slides. Use brief phrases or keywords to communicate key points .
4) Choose legible fonts : Opt for clear and readable fonts that are easy to read, even from a distance. Maintain consistency in font styles throughout your presentation .
5) Consistent design : Maintain a consistent design theme, including colours, fonts, and layout, to create a visually appealing and professional presentation.
6) Emphasise important points : Use visual hierarchy techniques, such as font size, colour, and formatting, to draw attention to essential information .
7) Use transitions and animations sparingly : Incorporate slide transitions and animations thoughtfully, focusing on enhancing content and transitions without distracting the audience .
8) S lide notes for guidance : Utilise the slide notes feature to include additional details, explanations, or reminders for a well-prepared and confident presentation.
9) Practice and time yourself : Rehearse your presentation to ensure smooth delivery and stay within the allocated time. Practice helps you refine your content and delivery.
10) Engage the audience : Encourage audience participation through interactive elements, questions, or discussions to foster engagement and make your presentation more memorable.
By implementing these tips, you can create effective MS PowerPoint presentations that capture attention, communicate information clearly, and engage your audience effectively.
Conclusion
We hope this blog has helped you understand What is PowerPoint and how it can help you. It offers powerful features with a user-friendly interface for creating visually appealing presentations. With its tools for organising information, incorporating text and visuals, and delivering impactful content, PowerPoint is a valuable tool for beginners to communicate their ideas effectively .
Master the art of effective communication and productivity and unlock your potential with our comprehensive Microsoft Office Training – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming office applications resources batches & dates.
Thu 16th May 2024
Thu 6th Jun 2024
Thu 4th Jul 2024
Thu 8th Aug 2024
Thu 5th Sep 2024
Thu 10th Oct 2024
Thu 7th Nov 2024
Thu 5th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification

Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Unit 1 Use a Theme Template and Slide Layouts to Create a Presentation
2 Getting to Know PowerPoint
Topics include:, powerpoint 2010, powerpoint help system, the powerpoint window.
PowerPoint 2010 is a complete presentation graphics program that allows you to produce professional looking presentations.
Slides can be created and displayed as a slide show on your computer, video projector, or on the Internet. Information from a PowerPoint presentation can be printed in a handout form or as transparencies.
PowerPoint allows for data to be entered and edited quickly and efficiently. To make changes to the presentation you can edit a slide rather than recreate the presentation. You can also import information from spreadsheets, databases, and word-processing files.
Open PowerPoint by clicking the Start button on the Windows Taskbar, point to Programs, go to Microsoft Office and then click Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2010.
The PowerPoint window contains many elements that are similar to other Microsoft Office programs. These elements include the Office button, Quick Access toolbar, Title bar, Tabs, scroll bars and a Status bar.
Quick access toolbar contains buttons for commonly-used commands.
Title bar indicates the software, the name of the presentation that is open, minimize, maximize, and close buttons.
Tabs contain commands that are pided into related tasks called groups.
Ribbon is the area containing the tabs.
Outline/Slides tab displays the presentation text in the form of an outline. Outline tab is used to organize and develop the content of your presentation. This tab enables you to move slides and text by dragging selected material. Slide tab displays the slides of your presentation as small images. This view allows easy navigation through slides.
Slide pane contains the current slide in your presentation. You can use the vertical scroll bar to view other slides in the presentation.
Notes pane is located below the slide pane and is used to type reference notes. The notes can be printed, then referenced when making the presentation.
View area is located at the right hand bottom of the screen. It contains buttons that allow the ability to switch between PowerPoint views. The first view button allows you to view slides in normal view, the second is called the slide sorter view, the third is called the reader view and the fourth is called the slide show view. This area also contains the zoom feature.
Status bar is located at the bottom of the PowerPoint window, it shows messages and information about the view, such as the slide number and the current theme template used.
Type a topic in the search textbox and click on search. A list of topics that match key words in your topic will display in the Search Results task pane. Click on the topic that interests you.
Presentation Software Copyright © 2013 by bpayne is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
6.2 Designing a Presentation in Microsoft PowerPoint
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Create a new slideshow from a blank presentation
- Create a presentation from a theme or template
- Understand the functions of the Home tab
- Understand the functions of the Design tab
- Understand the functions of the View tab
At WorldCorp, Microsoft PowerPoint presentations are used company-wide for a variety of purposes, such as presenting quarterly sales data or providing training for new sales personnel. As part of the Microsoft 365 suite, PowerPoint has characteristics similar to those of other programs such as Microsoft Word and Microsoft Excel . PowerPoint is divided into various tabs, which appear across a ribbon that helps you organize your actions.
In general, creating a storyboard or outline of a presentation , as outlined in the previous section, is a great starting point, and this is the approach we will use to build My Life in a Snapshot . To get started, this section provides an overview of the PowerPoint program, with a review of several tabs within the ribbon that you will use to develop your first slideshow from scratch. As we start using the primary elements of PowerPoint, you will begin to develop an understanding of how the program works with examples to provide context.
The vast capabilities of PowerPoint enable WorldCorp employees to present complex ideas, facts, and figures in the form of easily digestible visuals. Allowing users to create visual representations of information on the blank canvas slides can allow viewers to interpret, engage with, and expound on what they’re seeing.
Let’s begin by using the blank canvas approach to crafting a presentation.
Getting Started
Open PowerPoint and choose a blank presentation (the first option). You should see a screen that looks like Figure 6.5 , with an arrow highlighting the desired choice. If you want to open an existing presentation, select Open from the left sidebar and search for the file. Another option is to start with a PowerPoint template —a predesigned set of slides that you can use as a starting point for creating a new PowerPoint presentation. Templates include a defined layout and color scheme, and they often include sample text and images that you can replace with your own content. Using template s is a way to save time and ensure consistency in the design of your presentation. Like many organizations, WorldCorp has a preset template that is often used for external communications, such as presentations for clients. However, for the My Life in a Snapshot presentation, you are not restricted to using the template, as this is an internal presentation and is more informal.
In this example, you will start with a blank presentation. After opening this blank document (by double-clicking on Blank Presentation ), you should save it to your computer or to the cloud using a file name that is identifiable to the content of the presentation. As seen in Figure 6.5 , select the Blank Presentation option on the Home screen indicated by the arrow.
In a blank presentation, the initial slide PowerPoint provides is blank except for two placeholders: one for the title and one for the subtitle. When you choose a blank presentation, none of the design elements are defined in advance. The Title Slide layout that is provided by PowerPoint can quickly be altered. Most presentations should have a title. Additionally, the program opens to the Home tab found within the ribbon, as seen in Figure 6.6 . Now, the blank canvas is ready for you to craft My Life in a Snapshot for your team at WorldCorp.
Creating a Presentation with Themes and Templates
Many companies tend to already have a theme developed for use with company presentations. A presentation’s theme refers to the overall design and layout of the slides, including elements such as color scheme, font choices, and graphic elements. Themes are useful because they give you an easy way to create a consistent presentation by using preset fonts and color schemes. If you had chosen a theme instead of a blank presentation, the initial slide would show the same elements, but with the design features of the theme applied. A theme can also include predesigned slide layouts, which can be used to create a cohesive and consistent look throughout the presentation.
Within the New tab, as seen in Figure 6.7 , selecting a theme allows the designer to set the tone and style of the presentation, which can help to engage the audience and convey the message more effectively. Themes can be either built-in or custom-made, depending on the software you are using. PowerPoint offers numerous themes that you can apply and search for in the search window.
Another option that users have is to select a template instead of just a theme. Unlike a theme, a template is a blueprint of a group of slides that can help meet the topic of a presentation. Templates can contain layouts, fonts, colors, and background styles much like a theme. Much like a résumé template in Word, for instance, a template in PowerPoint prompts the user, suggesting sections and topics to include. As an example, a classic conference presentation might have a specific cadence and style. Slides will be arranged to meet the needs of a conference with suggested slides and topics to include. Theme and template options are worth considering and searching for, especially if a theme matches the overall type of presentation you plan to create.
There are benefits to creating a PowerPoint presentation from a theme. First, this approach provides consistency . The program will offer multiple slides with various concepts, all using the same color pattern, style, and texture. A theme allows users to focus on the presentation message without distraction from differing designs, although it does not necessarily guarantee that they will understand the message. Additionally, starting with a theme ensures that all the slides in the presentation will have a professional aesthetic design and layout, making it look polished. Aesthetics is the study of how things look and how we perceive and respond to them. It can also refer to the overall look and feel of something—for example, the aesthetics of a website or a building.
PowerPoint themes often include a multitude of predesigned slide layouts, which can save time and effort in creating your presentation. You can click into the various text boxes or image boxes to provide the required content, copying the desired layouts that work best for you and deleting those that don’t.
Real-World Application
Marketing toolkits.
Most companies now offer their internal stakeholders Marketing Toolkits to use. Marketing Toolkits provide users with the logos, color schemes, outlines, photo depositories, and ideas on what the company is looking for when designing marketing materials. Digital presentation information is almost always included in the toolkit.
With advances in cell phone technology and social media’s growing presence in our lives, companies can now maximize their marketing reach by enlisting their entire workforce into marketing. By providing accessible content for creators and guidelines, any employee can now be a part of promoting their employer.
Not all employees will embrace a Marketing Toolkit. It is only as effective as leadership and the culture of the company allow. See if any companies you know have a Marketing Toolkit online. Does the company toolkit offer guidelines for PowerPoint presentations? Presentations to external stakeholders can be a valuable marketing opportunity.
The themes that PowerPoint provides can be customized to reinforce your company’s image and message by matching the company’s branding and style. The visual design and layout of themes can be chosen to convey the message or tone of the presentation in a more effective way, which can make it more engaging for the audience. These themes can also be easily modified to include different colors, fonts, and graphics, allowing you to personalize the presentation while still maintaining a consistent design.
Themes are helpful, but to learn PowerPoint more deeply, you will also need to learn how to create a presentation from scratch. Start by getting to know the Home tab . The tools found on the Home tab are used to create the general structure of the slideshow, as seen in Figure 6.8 . As an introduction to this group of tools, we will review five key commands, which are circled in the figure: New Slide , Layout tab , the tools in the Font command group, the tools in the Paragraph command group, and Design Ideas .
Using the outline laid out in Figure 6.9 , you can create a slideshow from a blank document to present to the team. From here, you can see how a well-planned presentation of ideas can be created in the form of a PowerPoint slideshow.
Following the outline in Figure 6.9 , the presentation requires five distinct groups of information arranged in numerical order with subtopics. In PowerPoint, you will want to add five slides, each of which will represent one of these groups. To do this, go to the New Slide command group and, with your mouse, select the green button on New Slide four times. (Reminder: PowerPoint provides the first slide by default.) Note that you can change the layout at any time after creating a slide. For this exercise, any layout will do to get started. The default layout provided is fine.
Once complete, there should be five slides listed in the thumbnail pane on the left side of the screen. ( Figure 6.10 shows the first two of five.) You can then use the thumbnail feature to click in and out of individual slides as we develop and edit content that meets the storyboard criteria.
Now that you have created five new slides, you can edit and format them. It’s a good idea to use the same steps to edit and format each. For example, you might create a step called “adding text,” ensuring that every slide that needs text will receive text. The first slide, which is similar to a cover page for the presentation, requires a standard title and subtitle, and these are provided by default.
The next command in the Home tab (see Figure 6.8 ) is Layout tab . When you open the drop-down menu in Layout, you will see that PowerPoint offers nine basic layout options, which are designed to provide variety, balance, and consistency to each presentation design. (One of the options is “blank.” This layout gives you a blank, white canvas to build from, enabling you to design an infinite number of layouts.) For your WorldCorp presentation example, use the default layout Title Slide for the first slide. A title slide is a slide layout that provides space for a title and a subtitle. (Note that you are not using a template here.)
To add your content, click into each text box provided (it says “Click to add title” and “Click to add subtitle”). Start by typing “My Life in a Snapshot” in the first text box. In the second text box, type your name, followed by your title at WorldCorp and your geographic location, as seen in Figure 6.11 .
Next, in the thumbnail panel, select each slide and change the layout for the rest of the slides. Depending on the content of your presentation, it can be helpful to have different layouts on different slides. This presentation will use three different layouts to accommodate different types of information. Follow along by selecting each slide from the thumbnails, then selecting the Home tab, followed by selecting the layout option from the ribbon. You can choose to have information on the slide presented in a different way by changing the slide layout. For example, you could have two groupings of text side by side, as is shown in Figure 6.12 , or have the content on the slide grouped all in one area. Make sure to change the layout setting so it accurately reflects the recommendations found in Figure 6.12 .
Font choice plays a big role in PowerPoint presentations. Each letter, number, or symbol on a slide can be adjusted to a specific design. Using these options allows you to make your text more visually appealing. The process for selecting or changing a font is similar to the way you change a font’s details in Word. In PowerPoint, however, you will often have much less text to manipulate than in a Word file, and the text is usually much larger so an audience can easily view the information from a distance.
When you change font characteristics, be sure to choose what will best meet the audience’s needs. There are a few easy rules of thumb to follow when you create text for a presentation to a large audience. One of them is what’s known as the seven-seven rule —that each slide should have no more than seven lines of text and each line of text should have no more than seven words. This will help prevent you from relying on punctuation or sentence structure to convey your message. When it’s necessary to communicate via paragraphs of text, Word may be a better tool to distribute those types of communication either as handouts along with the presentation or in lieu of the presentation altogether. But, remember, this is only a rule of thumb. It is acceptable to deviate by a few words or lines based on the message and content of the presentation. The point is to keep the slides clear and simple and not to distract from the presenters themselves. Best practices can be a great help in keeping the audience front and center in your mind and staying focused on the purpose of your presentation.
Fill in the required text as displayed in Figure 6.13 . As with changing the layouts, click on each thumbnail, select the required text box, change the font to meet your needs (including the type and color of the font), and adjust the font size as needed. Type the required information (this will be your chance to start explaining who you are to your team), and then make sure to review your work for any errors. Take your time. Word choice can be a challenging task. Make sure that every slide is accounted for. Then, you’re ready to move on to the next step of designing My Life in a Snapshot .
A variety of presentation styles are available, so be sure to take note of the things you like and dislike in the presentations you attend as you develop your own style preferences. Consider the contrast between the text and the background. How easy is it to read the text while listening to a presenter? Does the text work both compressed on a laptop screen (as in a Zoom call) and displayed on a 176-inch projector screen designed for a room full of people? You will notice that the font size and choice are large and easy to read in this project. Later, as you explore the many available options, you are likely to find that the text font needs to match the theme of the presentation.
Next, consider the text. Is this the appropriate content to display? As an example, in Figure 6.14 , you can compare the options for our closing slide choice. Is the use of a graphic image of a question mark the best option, or would a written question, as in the center image, be more effective? In some cases, a combination of pictures and text may work best. There is no perfect answer—PowerPoint gives you many options. But at some point, you will need to make decisions. No matter how creative the formatting of the text, a combination of content may be a better option when deciding what layout and kinds of content to use.
Both the font and the paragraph options have functionality only when a text box has been selected. As with the paragraph options, Office offers a helpful array of choices for line spacing, adding bullets, numbering, aligning text, and adding or removing columns. If the default bullet points or line spacing options provided in the text box layouts are incorrect or missing, this can be a place to add or change the required element. You can make changes within a text box either by selecting the entire text box or by selecting only the location you want to change.
Design Ideas/Designer
The latest option group Microsoft has built into the newest PowerPoint versions is the Design Ideas tab (also called the Designer tab in different versions of PowerPoint). (Refer again to Figure 6.8 .) This is an on/off button that provides advanced slide layouts and “smart” options when turned on. The Design Ideas feature increases the options available to you as the content creator of My Life in a Snapshot —or any presentation you may be called on to create.
Select the first slide in your presentation, which is typically the title slide , and type in the title of the presentation. As the title is added, you can see how quickly a few words can shape an entire slide. Turn on the Design Ideas option in the Home tab . You will notice several options to the right of the screen. These options are often unique to the words and layout you provide. In this step, select an option that fits your personality, and the transformation will occur. An example is provided in the comparison Figure 6.15 from an employee who started not too long ago in WorldCorp’s South Asian Marketing division. The image on the left was the general text the WorldCorp team member typed into the default Title Slide layout. The image on the right is the option they chose that best matched their personality, which was created and offered by the designer in PowerPoint. Keep in mind that the Design Ideas option is available for only one slide at a time.
Because the Design Ideas option was turned on, it reviewed the text within the text boxes and considered several complete design options that could apply. Starting with a very limited bit of information, the Design Ideas option could add multimedia content (3D models, pictures, background themes); alter the text alignment, color, size, and formatting; change the layout; and create an entire theme representing the keywords on the page. It could even add simple animations, such as a snowflake background with snowflakes gently falling. Having these action components is like having an entire production team on call to quickly merge your ideas with existing collaborative content to make exquisite slides.
Instead of using the Design Ideas feature, you may want to design your PowerPoint yourself. The wide range of design options in PowerPoint allows you to change the overall look and feel of your presentation, quickly and easily. By using the built-in template s, color schemes, and slide layouts, you can transform the roughed-out text that you added earlier to polished, professional-looking presentation slides without spending much time and effort on design. (You will learn more about this process in the chapter on Giving Presentations ). Rather than using the Design Ideas feature, which only formats a single slide at a time, the Design tab provides a collection of tools for altering color schemes and layout designs for all of the slides at once. For example, you could change your entire color palette with just a few clicks of the mouse, applying the design to all the slides according to their predefined layout. Additionally, the option to change the slide layout makes it easy to organize the information in a way that is easy for the audience to follow and understand.
In summary, the Design tab in PowerPoint will help to make the process of creating a presentation faster, easier, and more professional-looking, by allowing you to communicate your message in the best possible way for your audience. Building new content for presentations is like building anything else: To do a professional job, you need professional tools, and you need to know how to use them.
Now it’s time to select the design and variation recommended in Figure 6.16 . The first command group on the Design tab focuses on themes. Each theme is unique and modifiable. We have a particular theme we want you to use for the remainder of your slides. Hold down the Control key on your keyboard (Ctrl). With your mouse, select slides 2, 3, 4, and 5 from the thumbnails. Go to the top of the screen and choose the theme circled in Figure 6.16 . The theme will be applied to only the slides you selected. Your uniquely designed title slide will remain. Remember to save your work. You will quickly notice how themes and variations can elevate your design.
For more ideas, you can turn to the Design Ideas pane at the right of the slide area, as shown in Figure 6.16 . (Note that in this figure, the Design Ideas option is called Designer.) For even more ideas, click on See More Design Ideas at the bottom of the pane. This can be accomplished by selecting a particular slide. On the ribbon on the Design tab, the Designer/Design Ideas option will illuminate on the far-right side. Click on the icon and then scroll down, and you can click again on See More Design Ideas. If you have Microsoft 365, your app will be updated as designers add new themes.
The next command group on the Design tab is titled Variants. Variants are essentially modifications you can make within a single theme. These provide a way to add a different overall look. This group initially displays four different color schemes to use with your theme. It lets you change the color combinations, font, or background, or add special effects. For every theme you choose, you can alter the color scheme and font combination (title and regular text). Make sure in your slideshow for My Life in a Snapshot that you have selected both the theme and the corresponding variation of the theme.
Figure 6.17 displays other variant settings that you can customize, including fonts, effects, and background styles. These options can be accessed in the Design tab, within the Variants ribbon, using the down arrow option. Colors, Fonts, Effects, and Background Styles all become options with a multitude of choices.
Selecting the arrow to the right for Colors extends a drop-down list that displays many preset color scheme possibilities, plus a Customize Colors option that allows you to change all of the colors in a scheme. The Font variant lets you pick different fonts for title text and body text. The Effects variant, or Artistic Effects, applies a graphic effect or filter to your slides, such as making them look like a sketch or a painting. Effects can be applied to a single slide or to all slides within the presentation.
The last command group on the Design tab is Customize , which gives options to change the slide size and format the background appearance. You won’t need to use this option for your first presentation, but it is a helpful tool to learn for your future presentations. The slide size command offers two principal choices of aspect ratio , which is the relationship of the slide’s width to its height: standard (compatible with older screen sizes), with an aspect ratio of 4:3, and widescreen (for today’s HD environment), with an aspect ratio of 16:9 ( Figure 6.18 ).
Also found in the Customize group of commands is the Format Background command. Click on it and you will see the menu as shown in Figure 6.19 . This command lets you change the background of a slide by changing the fill to a solid color, gradient fill, pattern fill, and so on. Select fill and then hover over each of the circles to see the available color and background options.
Format Background contains all the options for changing the background: Solid fill, Gradient fill, Picture or texture fill, and Pattern fill. Each option has its own set of elements to adjust. Solid fill is just that—choose a solid color for your background. Gradient fill lets you choose the way the color is spread across the slide, the intensity or transparency of the color, and the shape the background effect follows as it moves across the slide. Finally, you can fill the background with a pattern or a photo.
There are many ways to customize a theme to meet your specific needs. Different color combinations, fonts, effects, and background styles are all elements you can use to customize your presentation. Even small changes may be transformative.
The next tab to review is the View tab. To have a basic understanding of PowerPoint , you will need to know the general purpose of several view options. Within the View ribbon, there are seven command groups. The first three are circled in Figure 6.20 , starting with Presentation Views .
When creating slides, you will typically work with the Normal View , the default view that PowerPoint opens within a new presentation ( Figure 6.21 ). The large window shows the current slide, and the other slides are shown as thumbnails down the left side of the window. The large window gives you plenty of room to focus on developing content and layout for each slide while you can also jump in and out of each slide through the thumbnails.
Outline View shows a list of the slides on the left, highlighting the text rather than the actual slides as pictures. In Outline View, you can scroll through the text of each slide rather than having to jump in and out of individual slides. This can be a great aid when reviewing or organizing text, as seen in Figure 6.22 . (You may have noticed that we changed our title slide to match the theme of the rest of the slides. Now the presentation has a more consistent design.)
Slide Sorter is an option that lays out slides in order, allowing you to move them around with a drag-and-drop of the mouse. This view is useful when you want to add or delete a slide or change their order.
For example, suppose a team member creates a photo album to introduce themselves, with each slide consisting of a single photo. If they select thirty photos, creating an album with thirty slides, Slide Sorter View can help them edit the album by adding or deleting a photo and by arranging the photos in the desired order. In My Life in a Snapshot, with only five slides to edit, this view would be overkill. But with a larger presentation with many more slides, a Slide Sorter View can be a helpful option.
Notes view (or Notes Page ) displays a single slide with the notes below the text or image. These notes are typically designed for the speaker. They may be reminders, citations, or any various notes that the presenter wants to have at their fingertips. This can be handy when a user wants to add or edit a large amount of text. If, for example, they have a lot of text on a slide but are not sure yet which words might be best to highlight for the audience, this area of notes can provide a collection place for content.
The Reading View displays slides one at a time, as they would appear in a slideshow. Utilizing the View option allows you to take any one of the five slides and adjust the size of text boxes and change alignments—all while seeing most of the screen.
The Master Views option group may be a bit advanced for this introductory review, but we will provide a brief example. Within this group, the Slide Master is simply a template of the slide, breaking apart the individual components of the slide layout. This is a time-saving method for creating professional and consistent presentations. You can start with one of the PowerPoint themes or a blank slide, add or change the colors, add borders, change the font, and change or create a layout of your own. You can insert text boxes and object placeholders. When you do this on a master slide, you create a template that unifies the slides in a slideshow. When you have completed a slide that you want to keep as a master slide, select File, Save As, choose a location, and, in file type, choose PowerPoint Template. This is now a Master Slide template that you can use repeatedly.
Handouts Master and Notes Master are specialized viewing modes for specific tasks. The Handouts Master options allow developers to create a template for the PowerPoint printed handout for audience members. Slides can be arranged; titles, dates, and notes can be laid out. Within the Notes Master option group, the view of the slides and printable notes can be arranged as you desire.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/workplace-software-skills/pages/1-chapter-scenario
- Authors: Tammie Bolling, Angela Mitchell, Tanya Scott, Nyrobi Wheeler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Workplace Software and Skills
- Publication date: Nov 29, 2023
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/workplace-software-skills/pages/1-chapter-scenario
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/workplace-software-skills/pages/6-2-designing-a-presentation-in-microsoft-powerpoint
© Jan 3, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Make a “Good” Presentation “Great”
- Guy Kawasaki

Remember: Less is more.
A strong presentation is so much more than information pasted onto a series of slides with fancy backgrounds. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others. Here are some unique elements that make a presentation stand out.
- Fonts: Sans Serif fonts such as Helvetica or Arial are preferred for their clean lines, which make them easy to digest at various sizes and distances. Limit the number of font styles to two: one for headings and another for body text, to avoid visual confusion or distractions.
- Colors: Colors can evoke emotions and highlight critical points, but their overuse can lead to a cluttered and confusing presentation. A limited palette of two to three main colors, complemented by a simple background, can help you draw attention to key elements without overwhelming the audience.
- Pictures: Pictures can communicate complex ideas quickly and memorably but choosing the right images is key. Images or pictures should be big (perhaps 20-25% of the page), bold, and have a clear purpose that complements the slide’s text.
- Layout: Don’t overcrowd your slides with too much information. When in doubt, adhere to the principle of simplicity, and aim for a clean and uncluttered layout with plenty of white space around text and images. Think phrases and bullets, not sentences.
As an intern or early career professional, chances are that you’ll be tasked with making or giving a presentation in the near future. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others.
- Guy Kawasaki is the chief evangelist at Canva and was the former chief evangelist at Apple. Guy is the author of 16 books including Think Remarkable : 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a Difference.
Partner Center

Choose the right view for the task in PowerPoint

You can view your PowerPoint file in a variety of ways, depending on the task at hand. Some views are helpful when you're creating your presentation, and some are most helpful for delivering your presentation.
You can find the different PowerPoint view options on the View tab, as shown below.

You can also find the most frequently used views on the task bar at the bottom right of the slide window, as shown below.

Note: To change the default view in PowerPoint, see Change the default view .
Views for creating your presentation
Normal view

Normal view is the editing mode where you’ll work most frequently to create your slides. Below, Normal view displays slide thumbnails on the left, a large window showing the current slide, and a section below the current slide where you can type your speaker notes for that slide.
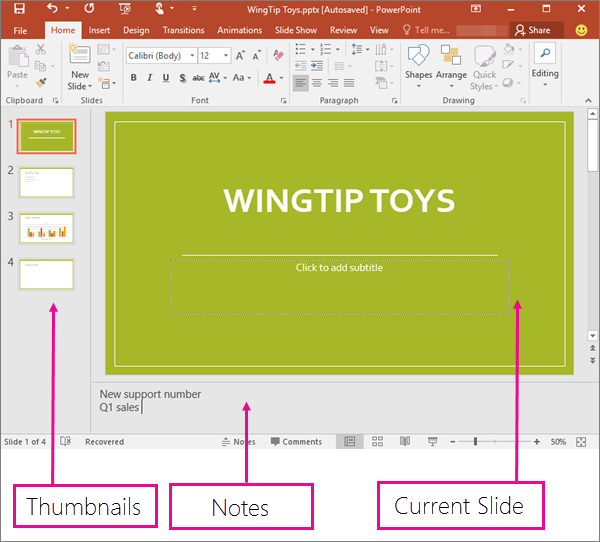
Slide Sorter view

Slide Sorter view (below) displays all the slides in your presentation in horizontally sequenced, thumbnails. Slide show view is helpful if you need to reorganize your slides—you can just click and drag your slides to a new location or add sections to organize your slides into meaningful groups.

For more information about sections, see Organize your PowerPoint slides into sections .
Notes Page view

The Notes pane is located beneath the slide window. You can print your notes or include the notes in a presentation that you send to the audience, or just use them as cues for yourself while you're presenting.

For more information about notes, see Add speaker notes to your slides .
Outline view
You can get to Outline view from the View tab on the ribbon. (In PowerPoint 2013 and later, you can no longer get to Outline view from Normal view. You have to get to it from the View tab.)
Use Outline view to create an outline or story board for your presentation. It displays only the text on your slides, not pictures or other graphical items.
Master views
To get to a master view, on the View tab, in the Master Views group, choose the master view that you want.
Master views include Slide , Handout , and Notes . The key benefit to working in a master view is that you can make universal style changes to every slide, notes page, or handout associated with your presentation.
For more information about working with masters, see:
What is a slide master?
Use multiple slide masters in one presentation
Change, delete, or hide headers and footers on slides, notes, and handouts
Views for delivering and viewing a presentation
Slide show view.

Use Slide Show view to deliver your presentation to your audience. Slide Show view occupies the full computer screen, exactly the way your presentation will look on a big screen when your audience sees it.
Presenter view

Use Presenter view to view your notes while delivering your presentation. In Presenter view, your audience cannot see your notes.
For more information about using Presenter view, see View your speaker notes as you deliver your slide show .
Reading view

Most people reviewing a PowerPoint presentation without a presenter will want to use Reading view. It displays the presentation in a full screen like Slide Show view, and it includes a few simple controls to make it easy to flip through the slides.
The views in PowerPoint that you can use to edit, print, and deliver your presentation are as follows:
Master views: Slide, Handout, and Notes
You can switch between PowerPoint views in two places:
Use the View menu to switch between any of the views

Access the three main views (Normal, Slide Sorter, or Slide Show) on the bottom bar of the PowerPoint window
Views for creating or editing your presentation
Several views in PowerPoint can help you create a professional presentation.
Normal view Normal view is the main editing view, where you write and design your presentations. Normal view has three working areas:
Thumbnail pane
Slides pane

Slide Sorter view Slide Sorter view gives you a view of your slides in thumbnail form. This view makes it easy for you to sort and organize the sequence of your slides as you create your presentation, and then also as you prepare your presentation for printing. You can add sections in Slide Sorter view as well, and sort slides into different categories or sections.
Notes Page view The Notes pane is located under the Slide pane. You can type notes that apply to the current slide. Later, you can print your notes and refer to them when you give your presentation. You can also print notes to give to your audience or include the notes in a presentation that you send to the audience or post on a Web page.
Outline view (Introduced in PowerPoint 2016 for Mac) Outline view displays your presentation as an outline made up of the titles and main text from each slide. Each title appears on the left side of the pane that contains the Outline view, along with a slide icon and slide number. Working in Outline view is particularly handy if you want to make global edits, get an overview of your presentation, change the sequence of bullets or slides, or apply formatting changes.
Master views The master views include Slide, Handout, and Notes view. They are the main slides that store information about the presentation, including background, theme colors, theme fonts, theme effects, placeholder sizes, and positions. The key benefit to working in a master view is that on the slide master, notes master, or handout master, you can make universal style changes to every slide, notes page, or handout associated with your presentation. For more information about working with masters, see Modify a slide master .
Views for delivering your presentation
Slide Show view Use Slide Show view to deliver your presentation to your audience. In this view, your slides occupy the full computer screen.
Presenter view Presenter view helps you manage your slides while you present by tracking how much time has elapsed, which slide is next, and displaying notes that only you can see (while also allowing you to take meeting notes as you present).
Views for preparing and printing your presentation
To help you save paper and ink, you'll want to prepare your print job before you print. PowerPoint provides views and settings to help you specify what you want to print (slides, handouts, or notes pages) and how you want those jobs to print (in color, grayscale, black and white, with frames, and more).
Slide Sorter view Slide Sorter view gives you a view of your slides in thumbnail form. This view makes it easy for you to sort and organize the sequence of your slides as you prepare to print your slides.
Print Preview Print Preview lets you specify settings for what you want to print—handouts, notes pages, and outline, or slides.
Organize your slides into sections
Print your slides and handouts
Start the presentation and see your notes in Presenter view
In PowerPoint for the web, when your file is stored on OneDrive, the default view is Reading view. When your file is stored on OneDrive for work or school or SharePoint in Microsoft 365, the default view is Editing view.
View for creating your presentation
Editing view.
You can get to Editing View from the View tab or from the task bar at the bottom of the slide window.
Editing View is the editing mode where you’ll work most frequently to create your slides. Below, Editing View displays slide thumbnails on the left, a large window showing the current slide, and a Notes pane below the current slide where you can type speaker notes for that slide.
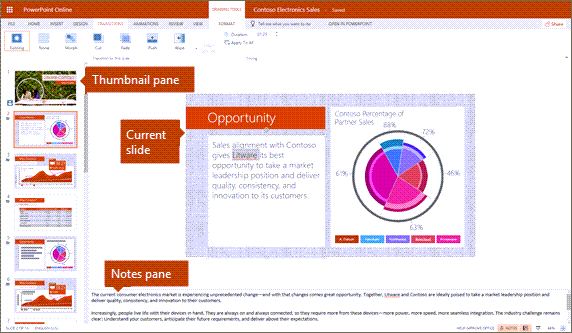
The slide sorter lets you see your slides on the screen in a grid that makes it easy to reorganize them, or organize them into sections, just by dragging and dropping them where you want them.

To add a section right click the first slide of your new section and select Add Section . See Organize your PowerPoint slides into sections for more information.
Views for delivering or viewing a presentation
Use Slide Show view to deliver your presentation to your audience. Slide Show view occupies the full computer screen, exactly the way your presentation looks on a big screen when your audience sees it.
Note: Reading View isn't available for PowerPoint for the web files stored in OneDrive for work or school/SharePoint in Microsoft 365.
Most people reviewing a PowerPoint presentation without a presenter will want to use Reading view. It displays the presentation in a full screen like Slide Show view, and it includes a few simple controls to make it easy to flip through the slides. You can also view speaker notes in Reading View.

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
Cloud Storage
Custom Business Email
Video and voice conferencing
Shared Calendars
Word Processing
Spreadsheets
Presentation Builder
Survey builder
Google Workspace
An integrated suit of secure, cloud-native collaboration and productivity apps powered by Google AI.
Tell impactful stories, with Google Slides
Create, present, and collaborate on online presentations in real-time and from any device.
- For my personal use
- For work or my business
Jeffery Clark
T h i s c h a r t h e l p s b r i d g i n g t h e s t o r y !
E s t i m a t e d b u d g e t
Make beautiful presentations, together
Stay in sync in your slides, with easy sharing and real-time editing. Use comments and assign action items to build your ideas together.
Present slideshows with confidence
With easy-to-use presenter view, speaker notes, and live captions, Slides makes presenting your ideas a breeze. You can even present to Google Meet video calls directly from Slides.
Seamlessly connect to your other Google apps
Slides is thoughtfully connected to other Google apps you love, saving you time. Embed charts from Google Sheets or reply to comments directly from Gmail. You can even search the web and Google Drive for relevant content and images directly from Slides.
Extend collaboration and intelligence to PowerPoint files
Easily edit Microsoft PowerPoint presentations online without converting them, and layer on Slides’ enhanced collaborative and assistive features like comments, action items, and Smart Compose.
Work on fresh content
With Slides, everyone’s working on the latest version of a presentation. And with edits automatically saved in version history, it’s easy to track or undo changes.
Make slides faster, with built-in intelligence
Assistive features like Smart Compose and autocorrect help you build slides faster with fewer errors.
Stay productive, even offline
You can access, create, and edit Slides even without an internet connection, helping you stay productive from anywhere.
Security, compliance, and privacy
Secure by default
We use industry-leading security measures to keep your data safe, including advanced malware protections. Slides is also cloud-native, eliminating the need for local files and minimizing risk to your devices.
Encryption in transit and at rest
All files uploaded to Google Drive or created in Slides are encrypted in transit and at rest.
Compliance to support regulatory requirements
Our products, including Slides, regularly undergo independent verification of their security, privacy, and compliance controls .
Private by design
Slides adheres to the same robust privacy commitments and data protections as the rest of Google Cloud’s enterprise services .
You control your data.
We never use your slides content for ad purposes., we never sell your personal information to third parties., find the plan that’s right for you, google slides is a part of google workspace.
Every plan includes
Collaborate from anywhere, on any device
Access, create, and edit your presentations wherever you are — from any mobile device, tablet, or computer — even when offline.
Get a head start with templates
Choose from a variety of presentations, reports, and other professionally-designed templates to kick things off quickly..
Photo Album
Book Report
Visit the Slides Template Gallery for more.
Ready to get started?

- Interface and Basics
Slide Area in PowerPoint 365 for Windows
Explore the Slide Area, and tricks to make slide editing more productive in PowerPoint 365 for Windows. Also, don't forget the Slide Workspace area which can be a convenient place to store stuff that you might want to use later.
Author: Geetesh Bajaj
Product/Version: PowerPoint 365 for Windows
OS: Microsoft Windows 10 and higher
Date Created: September 6, 2019 Last Updated: September 12, 2023
Learn PowerPoint
Learn how you can select multiple objects in PowerPoint.
The Slide Area The Actual Slide The Slide Workspace The Scroll Bars
The Slide Area
Many new changes have shown up in PowerPoint 365 for Windows and several other versions released in the past. However, one thing that has not changed is PowerPoint's tri-paned interface! So why is the interface called tri-paned? Are there three distinct regions within the PowerPoint 365 interface ? Yes, the Slide Area is one of three principal regions in PowerPoint 365; the other two being the Slides Pane and the Notes Pane .
The Slide area comprises everything within the region highlighted in red , as shown within Figure 1 . This is the area where you work the most, typically through adding and editing slide objects.

The Slide area includes three elements, as marked in Figure 1 , above:
A. The actual slide
B. The Slide Workspace (the blank area surrounding the slide)
C. The scrollbars that let you navigate between slides (or the same slide when you zoom the view to a larger percentage)
We discuss each of these individual interface elements next.
The Actual Slide
This is the actual slide where you can add slide objects such as text, pictures, charts, etc. When you use Slide Show view to display your PowerPoint presentation, you only get to see objects that are placed within this area.
You normally click on a text placeholder and type some text to replace the dummy text in the placeholder, as shown in Figure 2 . You can also do so much more such as inserting shapes, pictures, charts, or other slide objects.

PowerPoint provides three extra interface features that help in placing the elements properly on the slide. These are part of the slide area but you'll not be able to see them until they are activated.
Horizontal and vertical rulers appear at the top and to the left of the slide. Learn more about Rulers in PowerPoint .
A grid of evenly spaced dots appears directly on the slide and helps you position slide objects. Learn more about Gridlines in PowerPoint .
A pair of horizontal and vertical lines intersecting at the middle of the slide. You can also add more guides as required. Learn more about Guides in PowerPoint .
The Slide Workspace
This is the grey area behind the slide. All objects you place here can be edited and animated, although they won't show up in Slide Show view.
This makes the Workspace a convenient place to store stuff that you might want to use later. You can also store slide objects in the Workspace so that they animate from this Workspace into the actual Slide! Also, any sound objects you place in the Workspace play because sound objects are only heard and not seen!
Figure 3 shows a slide that has objects within the actual Slide and in the extended Slide Workspace.

The Scroll Bars
There are two scroll bars:
- The vertical scroll bar, placed towards the right of the slide (shown highlighted red within Figure 4 ) is always visible. The vertical scroll bar can be used to navigate from one slide to the other. To move forward and backward from one slide to the other, click one of the double-headed arrows at the bottom of the vertical scroll bar, as referred in Figure 4 . You can also drag the handle box in the vertical scroll bar and move up or down to navigate several slides at a time.
- The horizontal slide bar (shown highlighted blue within Figure 4 ), shows up when you zoom your slide to a larger view, or if your Slide Workspace contains objects.

01 05 06 - Interface Overview: Slide Area in PowerPoint (Glossary Page)
Slide Area in PowerPoint 365 for Mac Slide Area in PowerPoint 2019 for Windows Slide Area in PowerPoint 2016 for Windows Slide Area in PowerPoint 2016 for Mac Slide Area in PowerPoint 2013 for Windows Slide Area in PowerPoint 2011 for Mac Slide Area in PowerPoint 2010 for Windows Slide Area in PowerPoint 2007 for Windows Slide Area in PowerPoint for the Web
You May Also Like: How to Pitch and Win People Round | Diya - Deepam PowerPoint Templates
Popular Posts

PowerPoint Keyboard Shortcuts and Sequences: PowerPoint 2016, 2013, 2011, 2010, 2007 and 2003 for Windows PowerPoint 2016 and 2011 for Mac PowerPoint Online for Windows and Mac
Have your ever used keyboard shortcuts and sequences in PowerPoint? Or are you a complete keyboard aficionado? Do you want to learn about some new shortcuts? Or do you want to know if your favorite keyboard shortcuts are documented?
Go and get a copy of our PowerPoint Keyboard Shortcuts and Sequences ebook.
Microsoft and the Office logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Home | PowerPoint | Photoshop | PowerPoint Templates | PowerPoint Tutorials | Blog | Notes | Ezine | Media Kit | Feedback | Site Map | About Us | Contact Us Link to Us | Privacy | Testimonials PowerPoint Backgrounds | Christian PowerPoint Backgrounds | Business PowerPoint Presentation Templates
Plagiarism will be detected by Copyscape
- Member Home
- Subscriptions
- Add a New Credit Card
- Change Email
- Change Password

An Introduction to Google Workspace
Oct 31, 2023 | Administrative Professionals , Technology
With over two billion active users , Google Workspace has certainly made a name for itself. Formerly known as G Suite, the cloud-based productivity and collaboration solution is used by more than six million businesses, with more hopping on board every day.

Is yours one of them?
Being asked to learn new technology or software is always stressful. Transitioning from what you’ve always used to something you’ve never worked with before can be tough — but without change , where would we be?
Whether your office is making the switch to Google Workspace or you just want to add it to your skillset, here’s what you need to know.
What is Google Workspace?
Google Workspace is a collaboration and productivity suite, similar to Microsoft 365, that allows you to create and share documents, spreadsheets, and presentations, manage your email, and attend virtual meetings. It’s browser-based, which means everything is done directly from your web browser.
Some of Google Workspace’s main features include:
- Google Drive (cloud-storage)
- Google Docs (word processing app)
- Google Sheets (spreadsheets)
- Google Slides (slideshows and presentations)
- Google Meet (video conferencing)
- Google Calendar
- Google Keep (note-taking app)
The good news is that if you’re already a Gmail user, you already have access to all these apps. All that’s left is to learn how to use them!
Getting Started With Google Workspace
If you have a Gmail account, just open Gmail in a browser window, sign in, and navigate to the Google Apps button on the top righthand side of your screen. (If you don’t have a Gmail account, it’s free to create one !) Once you click the apps button, it will display all your available apps, as well as a link to the Workspace Marketplace where you can browse for new ones.
Most of the apps are incredibly user-friendly, but if you need help getting started, Google has you covered with tons of guides that include cheat sheets, best practices, and more.
- Start with the Guides for New Users . This page walks you through everything from the initial switch to what to do on the first day, the first week, and beyond.
- Next, explore the Google Workspace Learning Center which also includes comprehensive onboarding guides, productivity tips, hybrid workplace tips, business tutorials, and direct links to product help centers.
- Finally, identify a personal or work project where you can begin using the Google apps. This will help you learn the apps and get comfortable with how they work.
The Innovative Admin ™ never stops learning, growing, or exploring – especially when it comes to technology! Even if you’re not using Google Workspace at the office now, you might be in the future. By learning how to use and leverage the various apps in the productivity and collaboration suite now, you can set yourself up for future success!
© 2023 Julie Perrine International, LLC
HOW TO USE THIS ARTICLE IN YOUR NEWSLETTER OR WEBSITE
Want to use this article in your newsletter, ezine or website? You can — just as long as you include this complete blurb with it:
Julie Perrine, CAP-OM, is the founder and CEO of All Things Admin, providing training, mentoring and resources for administrative professionals worldwide. Julie applies her administrative expertise and passion for lifelong learning to serving as an enthusiastic mentor, speaker and author who educates admins around the world on how to be more effective every day. Learn more about Julie’s books — The Innovative Admin : Unleash the Power of Innovation in Your Administrative Career and The Organized Admin : Leverage Your Unique Organizing Style to Create Systems, Reduce Overwhelm, and Increase Productivity, and Become a Procedures Pro : The Admin’s Guide to Developing Effective Office Systems and Procedures.

Check Out Julie’s Books!


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
LibreOffice Impress, one of the most popular free and open-source presentation programs. In computing, a presentation program (also called presentation software) is a software package used to display information in the form of a slide show.It has three major functions: an editor that allows text to be inserted and formatted; a method for inserting and manipulating graphic images and media clips
Open Office. The Menu bar, at the top of the program window, lists commands to create, format, and edit presentations. The menu options include File, Edit, View, and Insert. The Tool bar is an array of buttons for quick access to commonly used commands and tools you'll need when you make a presentation.
The default workspace for slideshows is a left-hand pane of slide thumbnails, the active slide being edited in the workspace, and a Notes pane below the workspace. You can navigate through your slides by clicking on the thumbnails, or scrolling down the main workspace. MedAttrib: author-generated. MS PowerPoint user interface thumbnails ...
A presentation program's work environment is the interface. It includes options and commands that enable you to create an effective presentation. The work environments for different presentation programs, such as Microsoft PowerPoint, OpenOffice Impress, Prezi, and Apple Keynote, vary slightly, although the basic elements remain the same.
normal. The ________ is the main workspace and displays the current slide. slide pane. Which of the following views would you use to simultaneously display multiple slides and easily change the order of the slides, or to delete one or more slides? slide sorter. The opening slide in a presentation uses the ________ layout. title slide.
A presentation program is a program that helps create a slideshow that addresses a topic. Presentation programs can be used in businesses and schools for discussing a topic or for teaching. Often, the presenter uses a projector to project the slideshow up on to screen that everyone can see. Below is an example of Microsoft PowerPoint, a ...
For instructor-led PowerPoint classes in Los Angelescall us on 888.815.0604. Understanding the Interface. The PowerPoint interface, including the Ribbon, the Slides tab, the presentation window, the Notes pane, the Comments pane, the Quick Access toolbar, and the Status bar. The Slides tab shows a thumbnail of each slide in the presentation.
PowerPoint is a versatile and popular presentation software developed by Microsoft (MS). It is a part of the Microsoft Office Suite and offers various features and tools to create visually appealing and engaging presentations. MS PowerPoint allows users to combine text, graphics, multimedia elements, and animations to convey information ...
Google Slides is a presentation tool that allows you to make both online and offline presentations. Google first offered a presentation program for Google Docs in 2007. Google's free presentation software has been named Google Slides since 2012. The basic Google Slides is free. And Google's premium office software, Google Workspace (formerly G ...
Title bar indicates the software, the name of the presentation that is open, minimize, maximize, and close buttons. Tabs contain commands that are pided into related tasks called groups. Ribbon is the area containing the tabs. Outline/Slides tab displays the presentation text in the form of an outline. Outline tab is used to organize and ...
The main workspace of a presentation program where you can view and edit slides is called the slide pane. The slide pane is part of the interface that includes several components such as the title bar, ribbon interface, and other tools like the Quick Access toolbar.
Select the first slide in your presentation, which is typically the title slide, and type in the title of the presentation. As the title is added, you can see how quickly a few words can shape an entire slide. Turn on the Design Ideas option in the Home tab. You will notice several options to the right of the screen.
When in doubt, adhere to the principle of simplicity, and aim for a clean and uncluttered layout with plenty of white space around text and images. Think phrases and bullets, not sentences. As an ...
Slide Sorter view. You can get to Slide Sorter view from the task bar at the bottom of the slide window, or from the View tab on the ribbon. Slide Sorter view (below) displays all the slides in your presentation in horizontally sequenced, thumbnails. Slide show view is helpful if you need to reorganize your slides—you can just click and drag ...
Present slideshows with confidence. With easy-to-use presenter view, speaker notes, and live captions, Slides makes presenting your ideas a breeze. You can even present to Google Meet video calls ...
E. Slide Area. Displays the active slide. To learn more, visit our Slide Area in PowerPoint page.. F. Task Pane. The Task Pane contains more options and appears when you choose an option in one of the Ribbon tabs. For example, if you click the Format Background button within the Design tab of the Ribbon, the Format Background Task Pane opens (refer to Figure 1, shown earlier on this page).
Microsoft PowerPoint is a presentation program used to create slideshows composed of ... Software version numbers were altered again to create parity across the suite - every program was called version 7.0 meaning all but Word missed out versions. ... Publisher for Windows 95 and Project 95 had some 16-bit components even though their main ...
A group of slides is called a ________. Question options: deck. Which of the following is the default PowerPoint workspace view? normal. The ________ is the main workspace and displays the current slide. slide pane. Which of the following views would you use to simultaneously display multiple slides and easily change the order of the slides, or ...
The Slide area comprises everything within the region highlighted in red, as shown within Figure 1. This is the area where you work the most, typically through adding and editing slide objects. Figure 1: Slide area within PowerPoint 365 interface for Windows. The Slide area includes three elements, as marked in Figure 1, above:
Figure 1: Main window of Impress; oval indicates the Hide/Show markers Tip You can remove the Slides pane or Tasks pane from view by clicking the X in the upper right corner. You can also show or hide these panes using View > Slide Pane or View > Tasks Pane. You can also hide these panes in order to maximize the Workspace area by clicking the Hide/Show marker in the middle of the vertical
A) Have phrases begin with active voice. B) Use short phrases instead of complete sentences. C) Use parallel construction with your bullets. D) Follow the 6 x 6 guideline of no more than six words per line and six lines per slide. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like slide, deck, normal and more.
Answer: A) Array of buttons for quick access to commonly used commands and tools: Tool bar. That's what most people will use most of the time, to quickly perform the most common tasks. B) List of commands to create, format and edit presentations: Menu Bar. When the features listed in the tool bar aren't enough, we go to the Menu system, which ...
Google Workspace is a collaboration and productivity suite, similar to Microsoft 365, that allows you to create and share documents, spreadsheets, and presentations, manage your email, and attend virtual meetings. It's browser-based, which means everything is done directly from your web browser. Some of Google Workspace's main features include:
Question options: 9. The ________ file format preserves structure and most text formatting when transferring documents between applications or platforms. .rtf. A ________ divides presentation content into meaningful groups of slides. section. ______ is a visual representation of data or knowledge. an infographic.