Breaking News


Petitions of the week
Two cases alleging disability-based discrimination.

This week we highlight cert petitions that ask the Supreme Court to consider, among other things, the viability of certain types of disability-based claims under three federal statutes. One petition involves the Americans with Disabilities Act. Another involves the interaction of the Affordable Care Act and the Rehabilitation Act.
Because an on-the-job arm injury made it harder for her to conduct health inspections for Weld County, Colorado, Laurie Exby-Stolley requested an accommodation in the form of a new position with tasks she could perform. After the county told Exby-Stolley that her proposed arrangement would be unfair to other employees, she resigned. Exby-Stolley then sued the county under the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 for failing to accommodate her injury. Her claim faltered in district court because the jury determined that the county had not terminated her or subjected her to an adverse employment action. The en banc U.S. Court of Appeals for the 10th Circuit reversed on the ground that Exby-Stolley did not need to prove that the county took an adverse action, only that the county failed to accommodate her. Arguing that the U.S. courts of appeals are “nearly evenly divided” on this issue, the county asks for the justices’ review. The case is Board of County Commissioners of Weld County, Colorado v. Exby-Stolley .
CVS Pharmacy Inc. v. Doe involves a class action brought under Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 and Section 1557 of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act. The class members, who are HIV-positive, have health insurance through their employers. Those health plans, in turn, rely on CVS Caremark, a pharmacy benefits manager, to administer their prescription-drug benefits. Under the terms of their benefit plans, the class members can receive in-network prices for their HIV medications by accepting the medications by mail or by picking them up at a CVS pharmacy, but they must pay out-of-network prices at other pharmacies. CVS maintains that this policy applies to all “specialty medications.” Nevertheless, the class members argue that the delivery conditions disproportionately harm plan members with HIV or AIDS, and they demand in-network prices at their chosen pharmacies.
The class members argue that the Rehabilitation Act, which prohibits discrimination on the basis of disability by programs or activities receiving federal funds, allows for disparate-impact claims. Moreover, the ACA, which incorporates the Rehabilitation Act’s enforcement mechanisms, allows them to challenge the terms and conditions of their benefit plans. The district court dismissed the case because the delivery conditions depend on whether the patients receive specialty medications, not whether they are HIV-positive. The U.S. Court of Appeals for the 9th Circuit vacated and remanded for further proceedings on the ground that the benefit plans did not need to uniquely impact people with HIV or AIDS if the plans denied them “medically appropriate dispensing of their medications.” Arguing that the 9th Circuit deepened “a square, widely acknowledged conflict,” CVS asks for the Supreme Court’s review.
These and other petitions of the week are below:
SFR Investments Pool 1, LLC v. M&T Bank 20-908 Issues : (1) Whether the Federal Housing Finance Authority’s structure violates separation of powers and, if so, whether its conservatorship of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac must be set aside; and (2) whether quiet title actions by FHFA, asserting that a state law foreclosure failed to extinguish the agency’s property interests, are contract claims for purposes of 12 U.S.C. § 4617(b)(12) .
Warsaw Orthopedic Inc. v. Sasso 20-1284 Issue : Whether a federal court with exclusive jurisdiction over a claim may abstain in favor of a state court with no jurisdiction over that claim.
AbbVie Inc. v. Federal Trade Commission 20-1293 Issue : Whether the subjective element of the “sham litigation” exception to Noerr-Pennington immunity may be met by an inference from a finding that a challenged lawsuit was objectively baseless, even without evidence that the antitrust defendant actually believed the suit lacked merit or was indifferent to the outcome.
Walker v. Mississippi 20-1306 Issues : (1) Whether the Mississippi Supreme Court failed to adhere to the Supreme Court’s Sixth Amendment jurisprudence requiring counsel in a capital case to conduct a thorough investigation of their client’s background and history, and that purported “tactical” decisions are only reasonable to the extent they are based on such an investigation; and (2) whether Alan Walker was denied the effective assistance of counsel in the preparation and presentation of mitigation at his capital trial.
Board of County Commissioners of Weld County, Colorado v. Exby-Stolley 20-1357 Issue : Whether a plaintiff asserting a failure-to-accommodate claim under the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 must show that the employer’s failure to make the requested accommodation affected the “terms, conditions, [or] privileges of employment”—that is, whether the employee must show that the failure to accommodate amounted to an adverse employment action.
CVS Pharmacy Inc. v. Doe 20-1374 Issues : (1) Whether Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 — and by extension Section 1557 of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, which incorporates the “enforcement mechanisms” of other federal antidiscrimination statutes — provides a disparate-impact cause of action for plaintiffs alleging disability discrimination; and (2) whether, if Section 504 and the ACA create disparate-impact claims, such claims extend to the facially neutral terms and conditions of health insurance plans.
Posted in Cases in the Pipeline
Cases: SFR Investments Pool 1, LLC v. M&T Bank , Warsaw Orthopedic Inc. v. Sasso , AbbVie Inc. v. Federal Trade Commission , Walker v. Mississippi , Board of County Commissioners of Weld County, Colorado v. Exby-Stolley , CVS Pharmacy Inc. v. Doe
Recommended Citation: Andrew Hamm, Two cases alleging disability-based discrimination , SCOTUSblog (Apr. 9, 2021, 1:01 PM), https://www.scotusblog.com/2021/04/two-cases-alleging-disability-based-discrimination/
Privacy Overview

What is the ADA?
- ADA Anniversary
- Learn About the National Network
- Contact Your Region/ADA Center
- ADA National Network Portfolio
- ADA Success Stories
- Projects of the National Network
- Research of the National Network
- Ask ADA Questions
- View ADA Publications & Videos
- Find ADA Training
- Request ADA Training
- Search ADA Web Portal
- Federal Agencies and Resources
- Federal ADA Regulations and Standards
- Architects/Contractors
- People with Disabilities
- State and Local Government
- Emergency Preparedness
- Employment (ADA Title I)
- Facility Access
- General ADA Information
- Hospitality
- Public Accommodations (ADA Title III)
- Service Animals
- State and Local Government (ADA Title II)
- Technology (Accessible)
- Telecommunication (ADA Title IV)
- Transportation
- Region 1 - New England ADA Center
- Region 2 - Northeast ADA Center
- Region 3 - Mid-Atlantic ADA Center
- Region 4 - Southeast ADA Center
- Region 5 - Great Lakes ADA Center
- Region 6 - Southwest ADA Center at ILRU
- Region 7 - Great Plains ADA Center
- Region 8 - Rocky Mountain ADA Center
- Region 9 - Pacific ADA Center
- Region 10 - Northwest ADA Center
- ADA Knowledge Translation Center
- The ADA, Addiction, Recovery and Employment May 6, 2024
- Title III of the ADA and Readily Achievable Barrier Removal May 21, 2024
- Self-Evaluation Part I June 13, 2024
- Self-Evaluation Part II June 14, 2024
- Engaging Kids About Disability Through Animated Cartoons July 16, 2024
You are here
Research brief: experience of discrimination and the ada.
( Printer-friendly PDF version | 264 KB) (Large Print PDF version | 273 KB)

Experience of Discrimination and the ADA
An ada knowledge translation center research brief, sarah parker harris.
Courtney Mullin
Department of Disability and Human Development
University of Illinois at Chicago
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is a civil rights law that creates a legal framework for people with disabilities to address discrimination. Passed in 1990, the ADA represents bipartisan support for disability inclusion in all aspects of public life. Through the ADA, disability is a recognized source of discrimination, similar to “race, color, religion, sex, or national origin” within the Civil Rights Act of 1964. The ADA allows individuals with disabilities to challenge discrimination in the realms of employment, public services, and places of public use. The overarching goal of the ADA is to promote equal opportunity, full participation, independent living, and economic self-sufficiency for all people with disabilities.
ADA and Experiences of Discrimination
Developing a law that prohibits discrimination and creates regulations around access was, and continues to be, an important step in addressing barriers to inclusion. Disability-based discrimination is often related to both prejudices as well as broader social barriers that deny people with disabilities equal opportunities. Some researchers describe the goal of the ADA “…to integrate persons with disabilities into the social mainstream,” (p. 13). 1 The ADA has regulations to address structural barriers (i.e. physical and programmatic issues) and discriminatory practices, in order to impact attitudes towards disability.
Much of the research on discrimination is about causes and frequency of negative attitudes held by people without disabilities. This research brief looks at the experiences of discrimination from the perspective of people with disabilities as a way to better understand the influence of the ADA.
What the Research Says
Discrimination comes in many different forms. Research throughout the last three decades highlights how people with disabilities experience discrimination and negative attitudes. This research brief organizes these ideas as well as how people with disabilities respond to discriminatory experiences. The following section is divided into three areas where there is information from people with disabilities reporting and describing their experiences with discrimination. While people with disabilities experience discrimination in various domains of their public and private lives, these are some topics for which researchers have begun to document the perceptions and experiences of people with disabilities.
Differences in Experiences
The experiences of discrimination amongst people with different disabilities are diverse. Demographic factors have been shown to affect both prevalence and type of discrimination. For example, people whose need for accommodations change at different times, such as people with mental health conditions, are more likely to report workplace discrimination than people with other types of impairments. 2 Another study found that people with physical disabilities experience different attitudes and misperceptions in the workplace when compared to other groups, such as people with learning disabilities. 1 Furthermore, race, gender, and socioeconomic class have also been shown to impact and compound experiences of disability-based discrimination. 3 African Americans, women, and people with low incomes are all more likely to report disability-based discrimination in health care. 3
Social factors such as family, social class, race, and religion also influence how people understand their rights and types of resources available to address inequalities . 1 Timing of a disability onset or diagnosis is also a critical factor, as people have varying kinds of resources at different times in their lives. One study furthers this idea by exploring the relationship between age and disability discrimination through data from the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC), the agency in charge of enforcing the ADA in employment. 4 There is evidence that older workers are more likely to perceive and file complaints regarding employment discrimination. These variances highlight the diversity within the disability community and how people with disabilities experience discrimination in different ways. Recognizing differences in experience is noteworthy as is acknowledging the widespread prevalence of disability-based discrimination.
Employment is one of the most documented and researched areas regarding the ADA and disability-based discrimination. Though prohibited in the ADA, discrimination in the workplace has been a longstanding issue for people with disabilities. Nearly one in ten working adults with disabilities reported experiencing some kind of workplace discrimination within the five years after the passage of the ADA, and almost a third of these respondents permanently exited the workforce. 5
Workplace discrimination is often subtle, however people with disabilities have expressed that negative attitudes towards disability influence their success in employment. 6 One study, which involved sending mock job applications, found that those who disclosed disability (either spinal cord injury or Autism) received 26% fewer expressions of employer interest than applicants that did not include a disability disclosure. 7 Stigmatizing attitudes have been perceived by people with disabilities to negatively impact progress in their careers through not getting hired, being denied promotions, having extended probationary periods, or being treated differently than coworkers without disabilities. 6,7,8,9,10 In a study conducted by the Center for Talent Innovation as described in an article published by the Harvard Business Review , a third of survey respondents with disabilities indicate that they had experienced negative bias in the workplace such as feeling underestimated, insulted, excluded, or had coworkers appear uncomfortable because of their disability. 9 Almost half of these respondents (47%) also report that they would never achieve a leadership role in their company, regardless of their performance or qualifications. 9
Disclosing a disability, or sharing a disability status, is clearly influenced by experiences of discrimination. In one study, less than half of respondents with disabilities (39%) report that they had disclosed to a manager and even fewer had told other colleagues (24%); only 4% of respondents told clients about their disabilities. 11 Reasons for employees with disabilities to hide their disability status include fear of teasing, harassment, potential changes in coworker relationships, being perceived as less capable, and reduced progress in their careers. Not disclosing a disability status has been described as “allowing people with disabilities to be employed ‘without fear of prejudice or discrimination’” (p. 487). 12
Another study found that people with disabilities who do not disclose on a job application, but later disclose their disability status at work, are also met with discriminatory behaviors such as coworker unease, inappropriate questions, and assumptions about their capability. 8 Choosing to disclose a disability status is a delicate situation due to the prevalence of disability discrimination, however there are noted benefits of disclosure for some. For example, one study estimates that employees with disabilities who disclose are more content (65% versus 27%) and less isolated (8% versus 37%) at work than employees who do not disclose. 11
Experiences of employment discrimination are not limited to attitudes, as people with disabilities may face other types of structural barriers. Examples include lack of physical accessibility in the workplace, such as absence of accessible restrooms, inaccessible equipment to perform job tasks, and lack of access to reasonable accommodations. 1 This physical inaccessibility can also impact feelings of isolation. Another study identifies barriers to inclusion in the workplace by interviewing employees with disabilities in large, public-sector organizations. 13 The study reveals that people with disabilities experience both physical and social segregation at work. One of the participants of this study describe how their office places employees with disabilities in “a little corner spot where nobody can see them” (p. 145). 13 The segregated desk location not only physically isolates the participant but also prevents social interactions with colleagues. Access discrimination such as this translates into business concerns as feelings of disability-based discrimination have been shown to significantly reduce job satisfaction. 14
Home and the Community
In addition to work, people with disabilities also experience discrimination in access to housing and the community. Institutionalization is a longstanding issue in the disability community, and often refers to the physical segregation of people with disabilities living and/or spending time in areas that are designated solely for people with disabilities. In a landmark decision as part of Olmstead vs L.C., the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that unjustified segregation violates the ADA. However, there are still many people with disabilities who live and spend time in institutional settings. Researchers explored this topic and found that people with intellectual disabilities who live in institutions report experiences of exclusion and discrimination. 15 These reports include notes of overly restrictive environments, lack of privacy, and difficulty getting involved in the community because of the physical and social segregation as a result living in an institutional setting.
Institutionalization is not the only issue related to community living and experiences of discrimination for people with disabilities. Though not regulated by the ADA, housing is a major issue and source of discrimination for people with disabilities. A study sponsored by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development found that people who are deaf or hard of hearing face significant barriers during the home seeking process, including communicating with housing providers and learning about available units. 16 Additionally, people who use wheelchairs face barriers at several points in the home finding process, including locating accessible units, setting up appointments with providers to be shown units, and getting responses to reasonable modification requests. 16 These issues are made worse by the fact that 14-29% of federally funded housing facilities are estimated to violate federal regulations regarding access. 17
Social and Public Spaces
People with disabilities may experience discrimination when trying to access public spaces. For example, social stigma is another issue faced by people with disabilities. Researchers describe disability stigma, or negative attitudes or misconceptions towards disability, as a relationship between knowledge (ignorance), attitudes (prejudice), and behavior (discrimination). 18 These aspects are well documented in disability-based discrimination. In fact, people with mental health conditions report concerns about being viewed unfavorably based on their disability status, and over half of the respondents said that they have heard offensive statements about mental illness. 19 These factors shape public awareness about the capability of people with disabilities. 20 Many of the mentioned access barriers are rooted in negative attitudes that surround disability.
Another noteworthy example of disability discrimination is access to voting. A research team reviewed information from the U.S. 2012 elections and found that almost a third (30.1%) of voters with disabilities experienced some kind of difficulty in the voting process, which differs greatly from those without disabilities (8.4%). 21 The most common barrier was being able to see the ballot and understanding how to use the voting machines. Voting is a foundational right, and access barriers prohibit the participation of people with disabilities. This exemplifies a sentiment in other literature, that feelings of discrimination faced by people with disabilities can influence identifying as a citizen. 22
Responding to Discrimination
People with disabilities deal with discrimination and stigma in a variety of ways. Some people with disabilities choose to ignore negative attitudes, in order to not perpetually feel upset or the need to consistently react to negative interactions. 1 People with disabilities may not identify negative interactions as discriminatory if they do not have language or words to describe their experiences. 1 In fact, people with disabilities are hesitant to use the ADA or seek litigation due to social factors and describe a “threshold,” or feelings of a “minimum” level, of discrimination that must be reached prior to taking action through the ADA.
While choosing to take legal action is a complex decision, it is a powerful way for people with disabilities to respond to discrimination. Trends in legal filings change over time and are influenced by contextual factors. A review of EEOC case data shows a decrease in allegations from 2001- 2008, prior to the passage of the ADA Amendments Act (ADAAA), which greatly broadened the definition of disability and redefined the intent of the ADA. 23 Since the ADAAA was enacted, there has been a steady increase in allegations regarding disability discrimination. However, many cases are not closed in favor of claimants (i.e. people with disabilities). In fact, a review of EEOC claims from 1992-2011 found only 23.4% of cases are closed with merit, meaning that they affirmed disability discrimination, while 76.6% of cases are closed without merit, meaning in favor of the employer. 23 Additionally, claimants who are perceived as disabled rather than claimants with documented disabilities, are more likely to file charges related to disability discrimination and have cases ruled in their favor. 24 Most discrimination cases are related to job retention or quality of work; the most common allegations of workplace discrimination are discharge and failure to receive reasonable accommodations. 23 Though discrimination in hiring is less common, it is also notable as legal cases regarding hiring are closed in favor of people with disabilities at higher rates than other allegations. 25
The goal of this brief is to present a 'state of the state' of how people with disabilities perceive discrimination in relation to the ADA, the types of issues experienced, and outcomes of these events. People with disabilities face significant discrimination in many areas, including employment and in public and private aspects of life- some of which are covered in this research brief. To date, the majority of research is related to employment and there is limited information related to other areas of private and public life. While disability-based discrimination is a major facet of life for people with disabilities, these experiences are not universal and are influenced by many factors. Responding to discrimination also varies, and people with disabilities must make complex decisions when choosing to invoke legal action such as through the ADA. There is growing public interest in experiences of disability discrimination, and there is a need for more research on experiences of discrimination particularly from the perspective of people with disabilities.
Examples from the ADA National Network
Below are a few examples of how the ADA national network are addressing the issues raised in this brief. For further information on how the ADA Centers can help with issues related to the ADA, please contact the ADA National Network here .
- Giving advocacy tools: A person with vision and hearing disabilities contacted ADA center staff regarding his rights to travel by taxi or public transportation with his service dog. He was very pleased with the explanation he received. After some discussion, the staff person provided the caller with a laminated copy of the explanation, so he could show it to cab drivers where he lives. Having information on hand is helpful to share when traveling with his service dog and helping to advocate for his rights.
- Ensuring parking access: A person reached out to the ADA center to ask a question about accessible street parking regulations, as two spots were added outside of her office that she did not think looked accessible. The technical assistant shared the guidance regarding street accessible parking design and the caller forwarded the information to the city administration. Within 24 hours, the city began to properly mark the spots and the owner of the building moved a bench to align with accessible parking regulations.
- Newsworthy information: Another ADA Center was contacted by a local news station after a wheelchair user reached out to discuss blocking the access aisles in accessible parking spaces. Technical assistants provided information to the news reporter about the purpose of access aisles. A few days later, the reporter followed up with the ADA Center and shared they had received positive comments about the story and how it changed peoples’ attitudes and future actions to help keep access aisles unblocked.
- Engel, D. M., & Munger, F. W. (2003). Rights of inclusion: Law and identity in the life stories of Americans with disabilities. University of Chicago Press.
- Chan, F., McMahon, B. T., Cheing, G., Rosenthal, D. A., & Bezyak, J. (2005). Drivers of workplace discrimination against people with disabilities: The utility of attribution theory. Work, 25(1), 77-88.
- LaVeist, T. A., Rolley, N. C., & Diala, C. (2003). Prevalence and patterns of discrimination among US health care consumers. International Journal of Health Services, 33(2), 331-344.
- Bjelland, M. J., Bruyere, S. M., Von Schrader, S., Houtenville, A. J., Ruiz-Quintanilla, A., & Webber, D. A. (2010). Age and disability employment discrimination: Occupational rehabilitation implications. Journal of occupational rehabilitation, 20(4), 456-471.
- Kennedy, J., & Olney, M. (2001). Job discrimination in the post-ADA era: Estimates from the 1994 and 1995 National Health Interview Surveys. Rehabilitation Counseling Bulletin, 45(1), 24-30.
- Beatty, J. E. (2012). Career barriers experienced by people with chronic illness: A US study. Employee Responsibilities and Rights Journal, 24(2), 91-110.
- Ameri, M., Schur, L., Adya, M., Bentley, F. S., McKay, P., & Kruse, D. (2018). The disability employment puzzle: A field experiment on employer hiring behavior. ILR Review, 71(2), 329-364.
- McKinney, E. L., & Swartz, L. (2019). Employment integration barriers: experiences of people with disabilities. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 1-23.
- Sherbin, L. & Taylor Kennedy, J. (2017, December) The Case for Improving Work for People with Disabilities Goes Way Beyond Compliance. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2017/12/the-case-for-improving-work-for-people-with-disabilities-goes-way-beyond-compliance .
- Vickers, M. H. (2009). Bullying, disability and work: A case study of workplace bullying. Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal, 4(3), 255-272.
- Jain-Link, P. & Taylor Kennedy, J. (2019, June). Why people hide their disabilities at work. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2019/06/why-people-hide-their-disabilities-at-work .
- Goldberg, S. G., Killeen, M. B., & O'Day, B. (2005). The disclosure conundrum: How people with psychiatric disabilities navigate employment. Psychology, Public Policy, and Law, 11(3), 463.
- Robert, P. (2003). Disability oppression in the contemporary U.S. capitalist workplace. Science & Society, 67(2), 136-159.
- Perry, E. L., Hendricks, W., & Broadbent, E. (2000). An exploration of access and treatment discrimination and job satisfaction among college graduates with and without physical disabilities. Human Relations, 53(7), 923-955.
- Jahoda, A., & Markova, I. (2004). Coping with social stigma: People with intellectual disabilities moving from institutions and family home. Journal of intellectual disability research, 48(8), 719-729
- Aranda, C. L. (2015). Targeting Disability Discrimination: Findings and reflections from the national study on housing discrimination against people who are deaf and people who use wheelchairs. Cityscape, 17(3), 103-122.
- Froehlich-Grobe, K., Regan, G., Reese-Smith, J. Y., Heinrich, K. M., & Lee, R. E. (2008). Physical access in urban public housing facilities. Disability and Health Journal, 1(1), 25-29.
- Thornicroft, G., Brohan, E., Kassam, A., & Lewis-Holmes, E. (2008). Reducing stigma and discrimination: Candidate interventions. International journal of mental health systems, 2(1), 3.
- Dickerson, F. B., Sommerville, J., Origoni, A. E., Ringel, N. B., & Parente, F. (2002). Experiences of stigma among outpatients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia bulletin, 28(1), 143-155.
- Hampson, M., Hicks, R., & Watt, B. (2016). Understanding the employment barriers and support needs of people living with psychosis. The Qualitative Report, 21(5), 870-886.
- Schur, L., Adya, M., & Kruse, D. (2013). Disability, voter turnout, and voting difficulties in the 2012 elections. Report to US EAC and RAAV.
- Barton, L. (1993). The struggle for citizenship: the case of disabled people. Disability, Handicap & Society, 8(3), 235-248.
- McMahon, M. C., & McMahon, B. T. (2016). The National EEOC ADA research project: History, available data, and basic findings. Journal of Vocational Rehabilitation, 44(3), 333-342
- Draper, W. R., Reid, C. A., & McMahon, B. T. (2011). Workplace discrimination and the perception of disability. Rehabilitation Counseling Bulletin, 55(1), 29-37.
- McMahon, B. T., Hurley, J. E., West, S. L., Chan, F., Roessler, R., & Rumrill, P. D. (2008). A comparison of EEOC closures involving hiring versus other prevalent discrimination issues under the Americans with Disabilities Act. Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation, 18(2), 106-111.
For More Information, Please Contact:
Sarah Parker Harris ( [email protected] ) and Rob Gould ( [email protected] )
1640 W. Roosevelt Road (MC 626)
Chicago, IL 60608
Phone: (312) 413-1647
Fax: (312) 413-1630
TTY: (312) 413-0453
http://www.ahs.uic.edu/dhd/
SUGGESTED CITATION: Parker Harris, S., Gould, R., and Mullin, C. (2019). ADA research brief: Experiences of discrimination and the ADA (pp. 1-6). Chicago, IL: ADA National Network Knowledge Translation Center.
Language:

1-800-949-4232
Grant Disclaimer
Accessibility
The website was last updated April, 2024
- Default Style
- Green Style
- Orange Style
Case study on the effects of a disability inclusive mindset in a large biotechnology company
Journal of Work-Applied Management
ISSN : 2205-2062
Article publication date: 3 September 2021
Issue publication date: 5 April 2022
Employers increasingly seek a competitive advantage through inclusive hiring practices and recruitment of persons with disabilities. Early research indicates when employers consider individuals for their strengths rather than solely for their needs, the organization prospers. However, details about how companies pursue a disability inclusive workplace and the effect of those efforts are poorly understood.
Design/methodology/approach
An inductive qualitative case study approach was utilized to understand one biotechnology corporation and their approach to recruiting, hiring, and retaining employees with disabilities. Individual and focus group interviews were conducted.
Results suggest that when the company lives its mission around wellness and inclusivity, they benefit from working with and learning from a range of perspectives, furthering their growth. Placing equal emphasis on hiring a diverse workforce and prioritizing supports and wellness practices lead to greater productivity and innovation.
Practical implications
This study illustrates how one company successfully recruits and hires persons with disabilities, resulting in benefits to their financial bottom line and to the organizational culture.
Originality/value
This paper offers insights for other companies intentionally hiring persons with disabilities, providing accommodations in the workplace, and creating an organizational culture where all employees feel valued and supported. These steps have a direct impact on employee engagement, productivity, and retention.
- Diversity initiative
- Inclusivity
- Recruitment
- Employees with disabilities
Ochrach, C. , Thomas, K. , Phillips, B. , Mpofu, N. , Tansey, T. and Castillo, S. (2022), "Case study on the effects of a disability inclusive mindset in a large biotechnology company", Journal of Work-Applied Management , Vol. 14 No. 1, pp. 113-125. https://doi.org/10.1108/JWAM-06-2021-0045
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2021, Chase Ochrach, Kathryn Thomas, Brian Phillips, Ngonidzashe Mpofu, Tim Tansey and Stacie Castillo
Published in Journal of Work-Applied Management . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
Introduction
Employers increasingly recognize the benefits to productivity and organizational culture resulting from hiring persons with disabilities (PWDs) ( Lindsay et al. , 2018 ). Approximately 26% of people in the United States live with one or more of six functional types of disability, including cognitive, hearing, mobility, vision, self-care or independent living-related ( Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2018 ). Representing just over 25% of the US population, PWDs compose a large and valuable pool of current and potential members of the US workforce. However, PWDs continue to face challenges finding gainful employment in the United States, such that PWDs have an unemployment rate more than twice that of people without a disability ( US Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2020 ).
This lack of representation signals a significant problem of missed opportunity, as disability-inclusive hiring practices have been associated with improved productivity at the employee and organizational level ( Tompa et al. , 2021 ). One potential method of increasing rates of employment for PWDs is by increasing companies' awareness of the how much PWDs can contribute to the workforce, particularly in companies that maintain a disability-inclusive mindset ( Lindsay et al. , 2018 ). Companies with a disability-inclusive mindset go beyond maintaining the minimum legal requirement of anti-discrimination laws to create a disability-inclusive culture in all their thinking, policies, and operations. Such companies proactively focus on making the necessary changes needed to identify and remove barriers to full workplace participation for PWDs, including the removal of physical, communication, and attitudinal barriers ( CDC, 2020 ). This kind of mindset is represented by the concept of customized employment, which encourages organizations to customize the relationship between employee and employer based on the individual strengths and needs of both parties ( Inge, 2006 ). Despite several studies demonstrating the benefits of an inclusive culture and workforce at the individual, organizational, and societal level ( Tompa et al. , 2021 ) a specific roadmap for implementing this type of corporate culture remains elusive.
According to Weick's (1979 ) organizational information theory, people in organizations play active roles as creators of their environment through interpretation of information on a systemic level. Specifically, Weick (1979) emphasized the importance a company engaging in ongoing sensemaking, which is the process of rendering meaning from experience and constructing order out of disorder ( Patriotta, 2016 ). Within a company, sensemaking is a reciprocal relationship, such that individuals both create and are influenced by their organizational environment ( Weick, 1979 ). By focusing on communication from both top-down and bottom-up perspectives within a company, sensemaking provides a method of promoting disability-inclusive mindsets through centralized communication and information processing within a company ( Glynn and Watkiss, 2020 ; Weick, 1979 ). Weick conceptualizes sensemaking as central to organizing around a common mission and goal ( Weick, 2005 ). This theory is utilized in the current study by highlighting how a common organizational mission can allow employees across departments to make sense of their role in the company and of the company's role in the community. By engaging in the sensemaking process, leaders of companies can create a disability-inclusive mindset that influences the company culture on all levels to remove barriers and promote inclusive policy and culture for the hiring and retention of PWDs. Weick's theory applies to this case in that the way the organization and its members make sense and meaning of their work through identifying with the organization's inclusive mission and commitment to diversity. Previous studies have applied Weick's theory to various aspects of organization and management ( Tsoukas et al. , 2020 ), including process research ( Langley et al. , 2013 ) and organizational cognition ( Eden and Spender, 1998 ), among others. We extend findings from these and other previous studies to understand how sensemaking as a process furthers mission-based practices centered on diversity and inclusion.
Companies are increasingly moving to appreciate disability inclusion as a valuable contributor to diversity in the workplace ( Gilbride, et al. , 2003 ; Padkapayeva et al. , 2017 ). Research has revealed that companies identify several benefits to employing PWDs, including an expanded hiring pool, positive psychosocial impacts of retention of PWDs on employees with or without disabilities, and increased diversity of the workplace ( CDC, 2020 ; Lindsay et al. , 2018 ). By modifying recruitment and retention strategies, developing disability inclusion mediations, personalizing workplace and workspace modifications for PWDs, and matching the needs and skills of PWDs with the needs of the company, company leadership and human resources (HR) professionals can create disability inclusive mindsets by creating positive social attitudes regarding hiring PWDs ( Gilbride et al. , 2003 ; Padkapayeva et al. , 2017 ).
Research has also suggested that employee job fit, company culture, and previous employer experience with hiring PWDs all increase recruitment and retention of PWDs, which in turn shapes future HR hiring practices and the assumption of inclusive attitudes and perspectives company-wide ( Gilbride et al. , 2003 ). This aligns with findings that companies that reflect on their own practices, learn from their past organizational choices, and adapt to the internal and external environment are more sustainable in the long-term ( Fam et al. , 2017 ; Fergusson et al. , 2020 ). Additionally, HR employees with a higher degree of social awareness can increase the pace at which PWDs are recruited as well as the pace at which exposure-based disability-inclusive mindsets are encouraged in the workplace ( Chan et al. , 2010 ). This is especially important considering the growing centrality of social consciousness in what attracts new employees to work for organizations, underscoring the overall sustainability of that organization ( Brockhaus et al. , 2017 ; Rimanoczy and Pearson, 2010 ). Employing PWDs tends to decrease employer misconceptions, such as the idea that PWDs are not seeking work or are not qualified for company positions ( Bonaccio et al., 2020 ). Employing PWDs has been shown to increase future hiring and retention of job applicants with disabilities resulting in increased integration of workers with disabilities, development of disability-inclusive workplaces, and more sustainable futures for employees and organizations ( Bonaccio et al. , 2020 ; Fergusson et al. , 2020 ). These and other recent studies illustrate the unique benefits to hiring persons with disabilities, yet few offer a specific roadmap for how to actively recruit and hire PWDs and provide individualized accommodations to allow them, and the organization as a whole, to be successful. The current paper attempts to offer tangible suggestions through the illustration of one mid-sized company's successful implementation of a disability-inclusive mission and practices.
This paper is structured as follows. The first section outlines the methods used in this study, which is an inductive case study of one company's approach to hiring and retainment of PWDs. The organization and its specific subdivisions involved in the recruitment, hiring, and retainment of PWDs are described. The results of the study are then outlined, highlighting the company's mission and values, the actual inclusivity practices employed, and the impacts of these practices. The next section of the paper discusses the main findings of the study and connects those findings to existing research on PWDs in the workplace and general organizational culture. In this study, it was found that recruiting, hiring, and supporting PWDs in the workplace resulted in more workplace diversity, a willingness to provide accommodations for all employees, positive corporate climate, and increased productivity. Thus, this paper contributes evidence in support of the positive impacts of initiatives for hiring PWDs on employees, including PWDs, as well as the organization as a whole.
The purpose of this study was to implement an in-depth case study of a biotechnology company that has expressed commitment to inclusive hiring and retainment and a clear recognition of the company-wide benefits of hiring PWDs. We hoped to understand more about the company's mission and values and how these values translate into policy and action that supports hiring, retaining, and supporting all employees, including PWDs. This study was guided by the following questions: (1) What are the overarching attitudes, values, and approaches taken by this company in their efforts to be inclusive and diverse? And, (2) How does this company extend their message of wellbeing and support throughout all levels and departments of the company?
Given the formative nature of this investigation, we used a qualitative case study design that allowed for exploration of events or phenomena from multiple sources, with the purpose of looking into the unique experience of the people's lives and interactions with the environment ( Corbin and Strauss, 2015 ). This inductive qualitative design allowed for an open evaluation of the complexities and considerations involved in recruiting, hiring, supporting and retaining PWDs through in-depth interviews with multiple staff members at different levels within the company ( Maxwell, 1996 ). Interviews and focus groups were utilized to gain an open, in-depth understanding of employees' beliefs and experiences which was essential to informing our qualitative inquiry ( Gill et al. , 2008 ). As this investigation is exploratory in nature and our aim is to place greatest emphasis on the voices of our participants, a qualitative approach was necessary ( Miles and Huberman, 1994 ). The research team involved in data collection and analysis was comprised of six rehabilitation psychology faculty and doctoral students across three universities in the United States. Team members discussed potential biases prior to engaging in data collection and again before completing the analysis to reduce the potential for biases to influence the results.
Organization
The subject of this study is a large biotechnology company centralized in the Midwest. This company has been recognized as a Great Place to Work-Certified™ company, meaning they have been independently evaluated by the third party and recognized for having a positive workplace culture.
Organizational structure
This biotechnology company was described as using a Matrix Organization style where managerial teams spanned different units within the company ( Galbraith, 1971 ). The HR director noted this as key to maintaining priority on employee retention across all units. Part of the company's success in supporting and accommodating their employees was attributed to the division of responsibility within the company. Rather than processing all accommodations requests through a general HR team, their approach involved multiple specialized teams working together to recruit and retain employees. These included teams focused on (1) Recruitment, (2) Wellness, (3) Leaves and Accommodations, (4) Business Partners, and until recently (5) Security, which aligned under another unit in the organization.
The Leaves and Accommodations team has a lead role in processing accommodation requests while also ensuring that all employees and teams are aware of the potential for accommodations and how to use them. As one employee described, “I did not know until I received that initial email that we do have the entire accommodations team. They can reach out if you need anything.” The Business Partners act as the HR representatives across each unit in the company (e.g., the clinical lab). Business Partners were said by the HR director to play a key role in informing the HR team of needs within a particular unit while also ensuring that the company culture, priorities, and values extends to each unit. The Security team, although no longer part of HR, continue to fill several roles in the company, including acting as first responder for physical and mental health needs. These teams do not want the onus to always be on employees but seek to preemptively act in providing support by assessing potential problems within the company's various departments and teams.
Researchers worked with state employment agencies to identify companies with a reputation for inclusive disability hiring. Once identified as a company of interest, the research team worked closely with leadership from the biotechnology company to organize a site visit and to conduct interviews and focus groups. Prior to the site visit, the research team requested access to any written information, forms, or documents relevant to their disability efforts (e.g., company policies). Key personnel were also asked to provide a few written answers regarding the implementation of practices and policies related to their disability initiative. These were reviewed by the research team prior to the site visit in order to allow for better understanding of company activities prior to conducting interviews and focus groups. Researchers met on the day of the site visit to discuss potential biases and strategize how these biases could be minimized. The present study consisted of interviews with the director of human resources (HR) as well as members of the teams responsible for recruiting and for providing accommodations. A focus group was held with four direct-line supervisors and another with seven current employees, some of whom identified as having a disability that significantly impacted their work. All interviews were conducted in person at the company headquarters in the Midwest. Interviews and focus groups were complimented by information obtained through on-site observation, company policies and other written materials, the company website, and a climate survey described in the measures section below. A tour of the facility with an emphasis on any disability-related environmental adjustments, modifications, or supports helped inform data collection and analysis. The interviews and site tour led to the collection of more written policies and procedures that were added to the materials for analysis.
Focus groups and interviews ranged from 20 to 90 min in length. All interviews and focus groups were completed with two members of the research team present, serving to reduce to the possibility of interviewer bias while also enriching the data collection process with multiple perspectives. Audio recordings of all interviews and focus groups were later transcribed for analysis. Approval from the university's Institutional Review Board was also obtained to conduct this study with human subjects, and informed consent was obtained from all participants.
In addition to the on-site observations of the research team, a climate and policy checklist was used to assess the different disability-related aspects of the company during the post-site visit analysis of data. This checklist consisted of 70 disability-related policies or practices that were marked as being present or not present in the company. The semi-structured interviews and focus groups conducted on-site included primarily open-ended questions addressing the recruitment, hiring, integrating, and retaining workers with disabilities. The interviewees were asked to reflect on the company's practices and policies that were intended to create an inclusive environment for workers with disabilities and the results of these efforts.
Data analysis
All data sources were reviewed and coded by two coders before coming to consensus on the major themes and insights. Interview and focus group transcripts were read by each coder initially and data were categorized into practical and mindset themes. Further categories were determined by grouping data into subthemes, including a focus on inclusive practice, supportive climate, emphasis on retainment, and being mission driven. In the event of a disagreement between two coders, a third coder was included to discuss the item until an agreement was reached. Once created, the coding and narrative of the case study were brought to the larger research team for a community-based approach to refining and improving the accuracy of the case study.
This case study focuses on the inclusive hiring and retention practices of a large biotechnology company and the perceived impact of these efforts. In contrast to many other disability diversity case studies, this was not focused on a disability program but rather on capturing a company culture focused on seeking to make disability inclusivity part of all that they do. Results emerged from data collected over several months of 2019 and include analysis across individual and group interviews as well as on-site observation, the climate survey, and written policies (e.g. employee handbook, Autism Workforce guide). Results are broken down into the following categories: (1) Company Mission and Mindset, (2) Disability Inclusive Practices, which include both hiring and retention practices, and (3) Impact of Inclusive Practices. We proceed with a review of each category and their domains.
Company Mission and Mindset
An overarching theme noted throughout the interviews, whether senior management or recent hire to work in the lab, was the sense of the company's value-driven mission. An internal document describing the company Wellness program provided a Vision Statement that captures the ethos of their mission: “We believe our employees are our most valuable resource and through educating and encouraging the health and well-being of our employees, we in turn can achieve a higher level of patient care.” Throughout every interview and every evaluation of the company's organizational documentation and structure, this mission-driven focus emerged. As a member of the Leaves and Accommodations team stated, “We live our mission statement here, whereas other companies have a mission statement. And it's getting everyone on board from top down to have an environment of support.” Multiple members of the management team noted that this sense of mission did not happen by accident or stem from policy alone but was the result of embedding themselves within departments and consistently communicating those core values. Of their role, one manager stated, “We're out there being that kind of culture keeper.”
The first question a lot of companies will ask is, “Are we legally required to do this?” Which is a fine question. It's a valid question because you want to make sure that you're doing everything legally. But I feel like [company's] first question, because we already know we're in legal compliance across the board for Leaves and Accommodations is, “Why not?” and “What can we do?”
I think it starts with that commitment that we want to be an inclusive workforce, but you cannot always anticipate what that is going to mean for the next person who walks through your door. I think if you're coming at it with that yes mindset … You know if you start there, you can usually find a way to make it work.
You're not asking all of your employees to fit one exact requirement, once you're thinking, “What do they need?” and “How do they learn?” … just the mindset of how to help them be successful here, “What does that mean for them?” That's a real shift from, “I'm the boss, and this is how it works here.”
Disability Inclusive Practices
The mission and mindset of the company produced a number of inclusive practices that could be categorized into hiring, retention or some combination of the two.
Inclusive hiring practices
The director of HR spoke to the company's consideration of community in shaping their hiring practices and performance saying, “We look for partnerships with different organizations, both because we want to be a good partner and because of the organization's being really good conduits for people looking for work.” Another manager emphasized the importance they place on partnering with specific government and non-profit agencies aimed at improving the education and employment of diverse members of the local community and organizations in the area.
Speaking to the inclusive mindset that fuels this biotechnology company, an HR manager spoke of how they work with applicants saying, “whether there's a disability or not, our team approaches these interviews with the same level of fairness and equality. And I think that's become just part of the [company's] DNA.” Part of this DNA, or inclusive mindset, was noted to stem from their resources to work with a diverse workforce. The HR manager continued by saying applicants with disabilities “do not even phase our hiring team now because we are so used to the support we get from our Leaves and Accommodation team.”
Inclusive retention practices
The emphasis on retaining employees was consistent across all collected information. Multiple HR management spoke of viewing employees as being in long-term careers when hiring on with the company. Employees seem to get the message with one stating, “We heard management talk about wanting to create careers,” in contrast to what the employee described experiencing in other companies as being used for a couple of years. Two methods employed for fostering this career mentality were supporting employees in pursuit of upward movement and facilitating employee engagement within the company. Leadership emphasized providing employees with what they need to be successful, including a change in position or environment when needed. An HR director reported the mutual benefit of this approach by saying, “I am a firm believer that culture and engagement of employees has a very positive effect on revenue, on your total growth as an organization. If we were constantly replacing people, that would be a big time and money sinkhole.” He concluded that recruiting for diversity and then “giving them the tools and the support to really be successful” benefits all.
Inclusive retention practices were often very individually based. One frontline supervisor said, “I do not have any accommodation that's exactly like the other. The [Leaves and Accommodation Team] really tailor to the individual.” A member of the Recruitment team emphasized the importance of getting the employee's perspective when addressing accommodation needs stating, “It might not be something that our team is familiar with, but we get familiar with it really quickly.”
creating a welcoming environment and teaching people what it’s like to work here … The first step is really that inclusive culture of teaching and recognizing that people are coming from different places and at different levels of their readiness in order to actually hit the floor for their job.
Regarding supervisor training, an HR director described the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) and ADA training they provide to supervisors, with the comment that “We do not ask [supervisors] to understand all of the intricacies of it. What we do want them to understand through the training is to be receptive.” Multiple supervisors described the trainings with appreciation for their thoroughness and for the support that was available to them, as captured by the supervisor who stated, “There's [a training] for the inclusive workplace, which is wonderful training.” This supervisor continued, “The fact that they even do that is impressive to me.” It was noted across interviews that providing the trainings in multiple formats (audio-video, written, etc.) was appreciated by supervisors and employees with disabilities alike.
The company was noted for taking a proactive approach to accommodations as part of their retention efforts. One employee shared his experience saying, “Because I identified with a disability through the onboarding process, probably within a week or two from hire, I got an email saying, “Hey, you identified with a disability. Are there any accommodations that we can provide?” Another employee described their supervisor's approach to accommodations after having already been with the company, reporting, “When I started in the lab, I never knew how physical that was. It was actually my supervisor that pulled me aside and said, ‘You know, we have accommodations and we can help you through this.’”
Inclusivity as organizational identity: impact of Inclusive Practices
I would absolutely say that it’s a benefit … By recruiting a diverse population and then giving them the tools and the support to really be successful, that goes a really long way towards engagement and culture, and that certainly has direct impact on the bottom line.
Another manager talked of how providing employee accommodations according to their need improved performance and retention. A front-line supervisor spoke of an employee who was about to be terminated for poor performance. In one of the final meetings before termination, the employee disclosed a hidden disability that had been affecting their work performance. Accommodations were put in place and the employee retained their position through strong performance.
Through working with [PWDs], we've found some of the things that we offer would actually be good to offer to a broader population as well. If we are looking at different ways of learning, different ways of training, for instance, even if somebody has not self-identified as having a disability, we all learn differently … Personally, I think that it gives you a more open mindset, things that I had not considered before.
I think there's an effect on morale … We get a lot of really positive feedback about the diversity of our team. A lot of people who choose to work at [company], I find that a big driver behind their decision to work here is because they have a personal connection to our mission. They feel good about working for a company that offers these accommodations for their colleagues and coworkers. They can see people of different abilities working in different ways towards the same mission.
These positive perceptions often connected directly to job satisfaction and a desire to stay with the company. A front-line supervisor said, “I think it helps us retain the employees who truly want to be here … and helps us keep really talented people.” One employee with a disability stated that she is quick to tell her friends and acquaintances to work at this company. She continued, “If you're looking to improve your life, apply.” More seriously, another employee with a disability described being made fun of at her previous company and how refreshing it was to be able to trust that she would be treated respectfully at this biotechnology company. One of the strongest statements on the retention efforts of the company came from an employee who talked of switching from his partner's health insurance for the first time in years because of the stability he felt in his work. He stated with a tone of pride, “I'm actually going to be taking over the insurance because I feel comfortable here.”
Workplace challenges faced by PWDs result from the intersection of individual needs, societal structures, and employer initiatives, policies, and procedures that influence company culture ( Chan et al. , 2010 ). One way to minimize workplace experiences of discrimination and invalidation for PWDs is for companies to actively value diversity and inclusivity in mission, mindset, and policies through organizational sensemaking. By engaging in ongoing sensemaking, companies can allow for individuals to promote disability-inclusive mindsets by both creating and influencing their organizational environment ( Weick, 1979 ; Glynn and Watkiss, 2020 ). The company at the center of this study specifically organizes their work around the central mission of disability-inclusivity and overarching support and accommodations for all—a common mission through which, as was shared in interviews, employees make meaning of their work. As meaning-making is a human-driven process, this study illuminates how Weick's theory of organizational information can explain the practical implications of organizing a corporate culture around a common goal ( Tsoukas et al. , 2020 ). This approach recognizes PWDs as assets as companies provide them with the supports needed to be successful. Such efforts uplift the individual employee and the company-wide productivity and culture ( Lindsay et al. , 2018 ). This company offers a useful model for other companies looking to implement a disability-inclusive approach that values the contributions of all employees.
Organizational culture as a reciprocal process
Interview participants made it clear that this company values a sense of connectedness and reciprocal respect among team members. Weick (1979) suggests that organizations and those belonging to them experience a reciprocal relationship—that is, individuals both create and are influenced by their organizational environment through the process of sensemaking. This proposition suggests that general organizational attitudes (such as prioritizing inclusivity and diversity in the workplace) must be fed through both top-down and bottom-up pathways. Weick further suggests that the way members of an organization make sense of experiences informs organizational action in a recursive process. This sensemaking process is often equally cognitive and emotional ( Mikkelsen et al. , 2020 ) and can stretch from broad, company-wide search for meaning to the minutiae of even the language used by an organization ( Bakken and Hernes, 2006 ).
Using this framework, the company at the center of this study appears to make opportunistic sense of diversity, seeing PWDs as introducing unique skills, perspectives and talents to the company. This sensemaking process is likely driven both by a recognition of the overall productivity and economic benefits as well as employees' emotional investment in the value of working alongside and learning from diverse team members. The development of an organizational culture and mission is more recursive than linear where both meaning and action influence sensemaking and contribute to the ultimate climate ( Glynn and Watkiss, 2020 ). The company as a whole and the individual employees reciprocally influence each other in terms of company values, productivity, and inclusive culture. This organization clearly benefits from such symbolic interactionism, as interviews with employees and management revealed an unequivocal emphasis placed on supporting and being supported by employees with disabilities.
Dedication to morale and community
Staff and leaders both reported a felt sense of community and a dedication to elevating morale throughout this company. It seems that promoting a sense of connectedness and support fosters positive attitudes, productivity, and customer service for this mid-sized organization. Some researchers suggest that leaders can improve productivity, employee relations, and talent development when they align their actions with valuing a diverse workforce ( Hughes, 2016 ). Thus, fostering acceptance, support, and growth for diverse employees is fundamental to prosperous relationships internally and externally for the organization.
Previous findings suggest that high levels of cohesion among members of a group may predict performance ( Gammage et al. , 2001 ). Additional research suggests when a group agrees on the same organizational goals, they subsequently experience higher rates of group drive, cohesion, and productivity ( Greene, 1989 ). This is apparent in the current case, as interview participants reported feeling the congruence with the company goals of commitment to customer service and valuing and supporting team members.
How to replicate elsewhere
It's deciding as a company, “Are you going to be willing to go that much further for the employee to go above and beyond what the federal government is asking you to do?” But it is completely replicable if you desire that for your company.
I think it starts with that commitment to be an inclusive workforce … But you cannot always anticipate what that is going to mean (The next person who walks through your door, what might they need to be successful?). It is not necessarily something that I think every organization wants to do.
The HR director also encouraged companies to think about their employees in terms of their unique value rather than their ability to fit the model of the organizations' values. Overall, this biotechnology company's employees and administrators seemed optimistic about the possibility of their model, philosophy, and approach to hiring and recruitment to be replicated elsewhere. This approach becomes possible through a stance of curiosity, a willingness to learn, and approaching each potential employee as having a unique skillset and worldview.
Conclusions and implications
Intentionally recruiting, hiring, and retaining PWDs in the workplace increases the diversity of perspectives in the workplace and positively impacts the company bottom line;
Successful outcomes from a company-wide diversity and inclusivity initiative results from both top-down and bottom-up implementational commitment; and
Increasing corporate diversity through this kind of initiative has a positive effect on employee attitudes and engagement and the overall corporate climate.
Americans with Disabilities Act Amendments Act , 42 U.S.C. Ch. 126 § 12101 ( 2008 ).
Bakken , T. and Hernes , T. ( 2006 ), “ Organizing is both a verb and a noun: weick meets Whitehead ”, Organization Studies , Vol. 27 No. 11 , pp. 1599 - 1616 .
Bonaccio , S. , Connelly , C.E. , Gellatly , I.R. , Jetha , A. and Ginis , K.M. ( 2020 ), “ The participation of people with disabilities in the workplace across the employment cycle: employer concerns and research evidence ”, Journal of Business and Psychology , Vol. 35 , pp. 135 - 158 , doi: 10.1007/s10869-018-9602-5 .
Brockhaus , S. , Fawcett , S.E. , Knemeyer , A.M. and Fawcett , A.M. ( 2017 ), “ Motivations for environmental and social consciousness: reevaluating the sustainability-based view ”, Journal of Cleaner Production , Vol. 143 , pp. 933 - 947 .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( 2018 ), “ Disability and health data systems (DHDS) ”, available at : https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/disabilityandhealth/dhds/index.html?CDC_AA_refVal=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cdc.gov%2Fncbddd%2Fdisabilityandhealth%2Fdhds.html ( accessed 1 June 2020 ).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( 2020 ), “ Disability and health inclusion strategies ”, available at : https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/disabilityandhealth/disability-strategies.html ( accessed 5 June 2020 ).
Chan , F. , Strauser , D. , Maher , P. , Lee , E. , Jones , R. and Johnson , E.T. ( 2010 ), “ Demand-side factors related to employment of people with disabilities: a survey of employers in the Midwest region of the United States ”, Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation , Vol. 20 No. 4 , pp. 412 - 419 , doi: 10.1007/s10926-010-9252-6 .
Corbin , J. and Strauss , A. ( 2015 ), Basics of Qualitative Research: Techniques and Procedures for Developing Grounded Theory , 4th ed. , Sage Publications , Newbury Park, CA .
Eden , C. and Spender , J.-C. ( 1998 ), Managerial and Organizational Cognition , Sage , London .
( 2017 ), in Fam , D. , Palmer , J. , Riedy , C. and Mitchell , C. (Eds), Transdisciplinary Research and Practice for Sustainability Outcomes , Routledge , New York, NY .
Fergusson , L. , van der Laan , L. , Shallies , B. and Baird , M. ( 2020 ), “ Work, resilience and sustainable futures: the approach of work-based research to problems and their solutions ”, Journal of Work-Applied Management , Vol. 12 No. 1 , pp. 22 - 41 .
Galbraith , J.R. ( 1971 ), “ Matrix organization designs: how to combine functional and project forms ”, Business Horizons , Vol. 14 No. 1 , pp. 29 - 40 , doi: 10.1016/0007-6813(71)90037-1 .
Gammage , K.L. , Carron , A.V. and Estabrooks , P.A. ( 2001 ), “ Team cohesion and individual productivity: the influence of the norm for productivity and the identifiability of individual effort ”, Small Group Research , Vol. 32 No. 1 , pp. 3 - 18 .
Gilbride , D. , Stensrud , R. , Vandergoot , D. and Golden , K. ( 2003 ), “ Work environments and employers open to hiring and accommodating people with disabilities ”, Rehabilitation Counseling Bulletin , Vol. 46 No. 3 , pp. 130 - 137 , doi: 10.1177/00343552030460030101 .
Gill , P. , Stewart , K. , Treasure , E. and Chadwick , B. ( 2008 ), “ Methods of data collection in qualitative research: interviews and focus groups ”, British Dental Journal , Vol. 204 No. 6 , pp. 291 - 295 .
Glynn , M.A. and Watkiss , L. ( 2020 ), “ Of organizing and sensemaking: from action to meaning and back again in a half‐century of Weick's theorizing ”, Journal of Management Studies , Vol. 57 No. 7 , pp. 1331 - 1354 .
Greene , C.N. ( 1989 ), “ Cohesion and productivity in work groups ”, Small Group Behavior , Vol. 20 No. 1 , pp. 70 - 86 .
Hughes , C. ( 2016 ), “ Using diversity intelligence for an inclusive organization ”, Talent Development , Vol. 70 No. 6 , pp. 76 - 77 .
Inge , K.J. ( 2006 ), “ Customized employment: a growing strategy for facilitating inclusive employment ”, Journal of Vocational Rehabilitation , Vol. 24 No. 3 , pp. 191 - 193 .
Langley , A. , Smallman , C. , Tsoukas , H. and Van de Ven , A. ( 2013 ), “ Process studies of change in organization and management: unveiling temporality, activity, and flow ”, Academy of Management Journal , Vol. 56 , pp. 1 - 13 .
Lindsay , S. , Cagliostro , E. , Albarico , M. , Mortaji , N. and Karon , L. ( 2018 ), “ A systematic review of the benefits of hiring people with disabilities ”, Journal or Occupational Rehabilitation , Vol. 28 , pp. 634 - 655 , doi: 10.1007/s10926-018-9756-z .
Maxwell , J.A. ( 1996 ), Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach , Sage Publications , Thousand Oaks, CA .
Mikkelsen , E.N. , Gray , B. and Petersen , A. ( 2020 ), “ Unconscious processes of organizing: intergroup conflict in mental health care ”, Journal of Management Studies , Vol. 0 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 29 .
Miles , M.B. and Huberman , A.M. ( 1994 ), Qualitative Data Analysis: An Expanded Sourcebook , 2nd ed. , Sage Publications , Thousand Oaks, CA .
Padkapayeva , K. , Posen , A. , Yazdani , A. , Buettgen , A. , Mahood , Q. and Tompa , E. ( 2017 ), “ Workplace accommodations for persons with physical disabilities: evidence synthesis of the peer-reviewed literature ”, Disability and Rehabilitation , Vol. 39 No. 21 , pp. 2134 - 2147 , doi: 10.1080/09638288.2016.1224276 .
Patriotta , G. ( 2016 ), “ What inspires the academy: book reviews and beyond ”, Academy of Management Review , Vol. 41 , pp. 557 - 570 .
Rimanoczy , I. and Pearson , T. ( 2010 ), “ Role of HR in the new world of sustainability ”, Industrial and Commercial Training , Vol. 42 No. 1 , pp. 11 - 17 .
Tompa , E. , Mofidi , A. , Jetha , A. , Lahey , P. and Buettgen , A. ( 2021 ), “ Development and implementation of a framework for estimating the economic benefits of an accessible and inclusive society ”, Equality, Diversity and Inclusion , Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print , doi: 10.1108/EDI-07-2020-0186 .
Tsoukas , H. , Patriotta , G. , Sutcliffe , K.M. and Maitlis , S. ( 2020 ), “ On the way to ithaka [1]: commemorating the 50th anniversary of the publication of Karl E. Weick's the social psychology of organizing ”, Journal of Management Studies , Vol. 57 No. 7 , pp. 1315 - 1330 .
United States Bureau of Labor Statistics ( 2020 ), “ Persons with a disability: labor force characteristics summary – 2019 ”, available at : https://www.bls.gov/news.release/disabl. nr0.htm#:∼:text=(80.7%20percent).-,(See%20table%204.),for%20those% 20without%20a%20disability ( accessed: 24 September 2020 ).
Weick , K. ( 1979 ), The Social Psychology of Organizing , Addison-Wesley Publishing Company , Reading, MA .
Weick , K.E. ( 2005 ), “ The experience of theorizing: sensemaking as topic and resource ”, in Smith , K.G. and Hitt , M.A. (Eds), Great Minds in Management: the Process of Theory Development , Oxford University Press , Oxford , pp. 394 - 413 .
Acknowledgements
Preparation of this manuscript was supported in part by the National Institute on Disability, Independent Living, and Rehabilitation Research through Grant # HHS-2016-ACL-NIDILRR-RT-0138 to Virginia Commonwealth University, Rehabilitation Research and Training Center on Employer Practices. The opinions expressed herein do not necessarily reflect the endorsement or position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Corresponding author
Related articles, we’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
Widespread bias, discrimination directed toward people with disabilities who seek health care
- Feinberg School of Medicine
More than 30 years after the passage of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), people with disabilities report having a difficult time accessing health care and often find that doctors’ offices refuse to accommodate them. Now, a new Northwestern Medicine study of national practices reports that physicians may be choosing to deny care to people with disabilities, and some use discretionary excuses to strategically discharge them from their practice.
Scientists from Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, in collaboration with colleagues from University of Massachusetts and Harvard Medical School, conducted focus groups with physicians drawn from a national database. Physicians who participated in these groups expressed bias toward people with disabilities, and a substantial number of participants reported that they make strategic choices to deny care to people with disabilities, the study found. This includes making statements such as “I am not taking new patients,” “I do not take your insurance,” or telling the patients they need specialized care and therefore, “I am not the doctor for you.”
“Our body of work suggests that physician bias and discriminatory attitudes may contribute to the health disparities that people with disabilities experience,” said corresponding study author Dr. Tara Lagu , director of the Institute for Public Health and Medicine’s Center for Health Services and Outcomes Research at Feinberg and a professor of hospital medicine and medical social sciences. “We need to address the attitudes and behavior that perpetuate the unequal access experienced by our most vulnerable patients.”
Additionally, physicians in the study described a lack of knowledge about how to provide accommodations for people with disabilities, and some expressed adversarial attitudes toward the ADA, saying the legislation “works against physicians.”
“We need to address the attitudes and behavior that perpetuate the unequal access experienced by our most vulnerable patients.”
– Tara Lagu
“The ADA is a key facilitator of autonomy and independence for people with disabilities,” Lagu said. “The physicians’ attitudes toward the ADA were upsetting and disappointing.”
The ADA requires all medical practitioners to provide “full and equal access to their health care services and facilities” for people with disabilities. This includes building accessibility, such as creating spaces that are designed to be user-friendly for everyone, including people who use wheelchairs, canes and mobility scooters; assisting with transferring patients from chair to examining table; and providing sign language interpreters and other accommodations. Prior studies have reported that people with disabilities have difficulty obtaining appointments with physicians and are known to receive less preventive care than their non-disabled counterparts.
“Meaningful improvements in access to high-quality care for people with disabilities will require a multipronged approach and should include changes to medical education, efforts to increase the presence of accessible equipment and changes in our approach to physician reimbursement,” said co-author Carol Haywood , research assistant professor of medical social sciences at Feinberg. “At Northwestern, we are working to lead change through research and also through advocacy and improvement efforts such as the Disability Advocacy Coalition in Medicine, patient safety and quality efforts at Northwestern Memorial Healthcare, and the NM Champion Network Disability Chapter.”
The study was published Oct. 3 in the October issue of the journal Health Affairs.
This study follows work conducted by Lagu in 2012, in which she attempted to make an appointment for a fictional patient who used a wheelchair. Of 256 surveyed practices in the 2012 study, 56 (22%) reported they could not accommodate the patient. Of the rest, more than half planned to transfer the patient using methods considered to be unsafe.
More recently, Lagu and Dr. Lisa Iezzoni , professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, published results of a national survey of physicians: only 56% reported that they welcome patients with disabilities to their practice; 36% said that they know “little or nothing” about the ADA; and only 41% were confident that they could provide similar quality of care to patients with disabilities as they could to those without disability.
Editor’s Picks

Redevelopment of Norris University Center’s East Lawn to begin this summer
‘the night watchman’ named next one book selection, six northwestern faculty named 2024 guggenheim fellows, related stories.

Immigrants are significantly less likely to commit crimes than the U.S.-born
These workers can be pivotal in improving u.s. health equity, guided parent-child discussion can help address subtle racism.
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

Remember Eric Garner? George Floyd?

Lawyers reap big profits lobbying government regulators under the radar

Younger votes still lean toward Biden — but it’s complicated
As part of her research, Tessa Charlesworth challenged the longstanding assumption that implicit biases are so ingrained that they cannot be changed.
Kris Snibbe/Harvard Staff Photographer
Why disability bias is a particularly stubborn problem
Nikki Rojas
Harvard Staff Writer
Researcher says addressing it likely will take some kind of social reckoning
Our most negative societal prejudices can fade, but what sparks that change, and what does it mean when those views haven’t budged in years? Tessa Charlesworth, a postdoc in the Department of Psychology, has dedicated her research in recent years to these questions, and some of her newest analysis has turned up a troubling trend involving implicit biases toward disabilities.
Charlesworth, Ph.D. ’21, who works in the lab of Mahzarin Banaji, has found that those hidden prejudices have hardly changed over a 14-year period and could take more than 200 years to reach neutrality, or zero bias.
“Implicit bias can change. But so far, it’s only changed for some groups,” Charlesworth said. “It changed for sexuality and race bias pretty dramatically. Sexuality biases dropped 64 percent over 14 years, but it hasn’t changed at all for disability, age, or body weight bias. Disability bias over 14 years has only shifted by 3 percent. The disparity between the change in sexuality bias and the stability in disability bias is massive.”
Charlesworth noted that greater shifts are being seen in explicit biases, particularly those about disabilities, which have dropped 37 percent. She said that it is possible, given the long stability in implicit disability bias, that explicit biases could largely disappear before the implicit ones substantially budge.
New data shows that, based on the rate of past movement, it will likely take more than 200 years for implicit disability biases to reach neutrality. Researchers make projections using forecasting techniques similar to those used in predicting stock markets or the weather. By contrast Charlesworth noted that changed attitudes on sexual orientation are already very close to reaching a point where survey respondents do not associate being gay with bad and straight with good.
To track implicit biases, researchers tested how quickly subjects associated different concepts with being good or bad, using a test co-developed by Banaji, Charlesworth’s adviser, the Richard Clarke Cabot Professor of Social Ethics, and a regular co-author. They then relied on data archives from the last 14 years to detect changes. They looked at six different social biases: race, sexuality, skin tone, body weight, age, and disability.
“In and around Cambridge there are so many knobby brick roads with tree roots in the sidewalks that are totally ableist. And yet, for a long time, I just took that for granted and didn’t think it was a problem.” Tessa Charlesworth
Implicit biases, which Charlesworth described as “more automatic and less controlled” than more conscious explicit beliefs, are usually widespread in society and tend to come from personal experiences, upbringing, and the media, she said. Typically the majority of people have positive associations with groups who are dominant or hold power in society, such as those without disabilities or white men. On the other hand, individuals tend to have more negative associations with marginalized groups, including people of color, those with disabilities, or members of the LGBTQ community.
As part of her research, Charlesworth challenged the longstanding assumption that implicit biases are so ingrained that they cannot be changed. She found that was not the case and that implicit bias shifts along with the views of the wider society.
In a Harvard Horizons talk last year, Charlesworth attributed big changes in other implicit attitudes to major social, political, or cultural events, including federal legislation on same-sex marriage, the #MeToo movement, and Black Lives Matter.
“My new research tells us that these are the kinds of social events that are prompting transformation not only in our explicit conscious values, but also in that cognitive monster of implicit bias,” she said. Charlesworth believes it will take a similar movement of national reckoning to spark change in people’s implicit biases about disabilities.
“The amazing thing about Black Lives Matter and previous social movements [is that they] created national conversations that brought that bias to the front of everyone’s mind,” she said. “If you were sitting around at the dinner table, it was hard not to have a conversation about racism in the summer of 2020. I think that changing the conversation and bringing disability bias to the front of the mind for the everyday person will be necessary to change that bias as well.”
Banaji agreed that society needs to change the narrative when it comes to disability.
“Recognizing the truth — that every disability may come with a unique way to know the world that could create innovation, a different way to solve problems,” Banaji said. “When we see somebody in a wheelchair, [let] the first association that pops into our heads be, ‘Wow, I wonder what they know that I don’t know. I wonder what they can teach me that I could never know.’”
Charlesworth says her next move will be to look around the nation to see whether there are localities or regions that are leading change on disability bias. Banaji noted that it could be useful to compare the different investments that city, state, or federal governments make to support the disabled and see whether they correlate with residents’ attitudes.
“There are practices that you can do to start to become even just a little more aware of how implicit bias shows up,” Charlesworth said. “When I first started this research six years ago, I started noticing the number of places that don’t have ramps or the number of places that have really narrow sidewalks. In and around Cambridge there are so many knobby brick roads with tree roots in the sidewalks that are totally ableist. And yet, for a long time, I just took that for granted and didn’t think it was a problem. That’s how implicit bias becomes baked into our environments and can create these associations of who seems to be welcomed or valued.”
Share this article
You might like.
Mother, uncle of two whose deaths at hands of police officers ignited movement talk about turning pain into activism, keeping hope alive

Study exposes how banks sway policy from shadows, by targeting bureaucrats instead of politicians

New IOP poll shows they still plan to show up to vote but are subject to ‘seismic mood swings’ over specific issues
So what exactly makes Taylor Swift so great?
Experts weigh in on pop superstar's cultural and financial impact as her tours and albums continue to break records.

When math is the dream
Dora Woodruff was drawn to beauty of numbers as child. Next up: Ph.D. at MIT.
Three will receive 2024 Harvard Medal
In recognition of their extraordinary service
Disability and Health Stories from People Living with a Disability
- Nickole's Story
- Jerry's Story
- Justin's Story
- Suhana's Story
Real Stories from People living with a Disability
Nickole cheron’s story.

In 2008, a rare winter storm buried Portland, Oregon under more than a foot of snow. The city was gridlocked. Nickole Cheron was stuck in her home for eight days. Many people would consider that an inconvenience. For Nickole, whose muscles are too weak to support her body, those eight days were potentially life-threatening.
Born with spinal muscular atrophy, a genetic disease that progressively weakens the body’s muscles, Nickole is fully reliant on a wheelchair and full-time caregivers for most routine tasks. Being alone for eight days was not an option. So Nickole signed up for “ Ready Now! pdf icon [PDF – 4.8MB] external icon ,” an emergency preparedness training program developed through the Oregon Office of Disability and Health external icon .
“The most important thing I learned from ‘Ready Now!’ was to have a back-up plan in case of an emergency situation ,” she said. “When I heard the snow storm was coming, I emailed all my caregivers to find out who lived close by and would be available. I made sure I had a generator, batteries for my wheelchair, and at least a week’s supply of food, water and prescription medication.”
Nickole said the training was empowering, and reinforced her ability to live independently with a disability. She felt better informed about the potential risks people with disabilities could encounter during a disaster. For example, clinics might close, streets and sidewalks might be impassable, or caregivers might be unable to travel.
Among the tips Nickole learned from Oregon’s “Ready Now!” training are:
- Develop a back-up plan. Inform caregivers, friends, family, neighbors or others who might be able to help during an emergency.
- Stock up on food, water, and any necessary prescription medications, medical supplies or equipment. Have enough to last at least a week.
- Make a list of emergency contact information and keep it handy.
- Keep a charged car battery at home. It can power electric wheelchairs and other motorized medical equipment if there is an electricity outage.
- Learn about alternate transportation and routes.
- Understand the responsibilities and limitations of a “first responder” (for example, members of your local fire department of law enforcement office) during a disaster.
“This training shows people with disabilities that they can do more to triage their situation in a crisis than anyone else can,” she said. “‘Ready Now!’ encourages people with disabilities to take ownership of their own care.”
CDC would like to thank Nikole and the Oregon Office of Disability and Health external icon for sharing this personal story.
Learn about emergency preparedness for people with disabilities »
Jerry’s Story
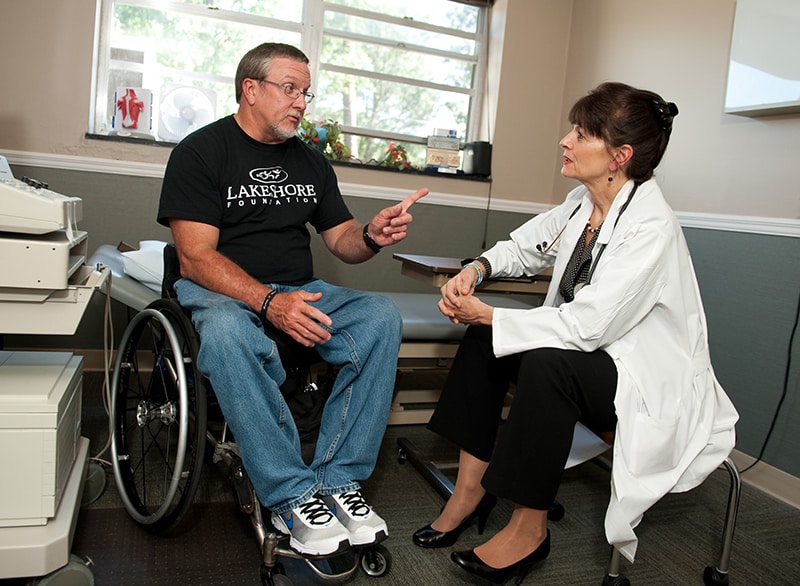
Jerry is a 53 year old father of four children. He’s independent, has a house, raised a family and his adult kids still look to him for support. Jerry recently retired as a computer programmer in 2009, and competes and coaches in several sports. This “healthy, everyday Joe, living a normal life” has even participated in the Boston Marathon. Jerry also has had a disability for over 35 y ears. In 1976 on December 3 (the same day that International Persons with Disabilities Day is recognized) Jerry was hit by a drunk driver. The accident left him as a partial paraplegic.
Jerry’s life is not defined by his disability. He lives life just like anyone else without a disability would live their life. “There’s lots I can do, and there are some things that I can’t do,” said Jerry. “I drive, I invest money. I’m not rich, but I’m not poor. I enjoy being healthy, and being independent.”
As a person with a disability, however, Jerry has experienced many barriers. Recovering from recent rotator cuff surgery, his rehabilitation specialists “couldn’t see past his disability”, administering tests and delivering additional rehabilitation visits that a person without a disability wouldn’t receive. He once was being prepared for surgery when a nurse proclaimed “he doesn’t need an epidural, he’s a paraplegic.” Jerry had to inform the nurse that he was only a partial paraplegic and that he would indeed need an epidural.
Jerry was in line at an Alabama court house to renew his parking permit and also renew his son’s registration. He watched a worker walk down the line and ask people “what do you need?” When she got to Jerry and saw his wheelchair, he was asked “who are you here with?” And Jerry finds it difficult to go to concerts and baseball games with a large family or friends gathering, because rarely are handicap-accessible tickets available for more than two people.
Jerry has seen a lot in over 35 years as someone living with a disability. He’s seen many of the barriers and attitudes towards people with disabilities persist. But he’s also seen many positive changes to get people with disabilities physically active through recreational opportunities such as golf, fishing and even snow-skiing. There are now organizations such as Lakeshore Foundation external icon – where Jerry works part-time coaching youth basketball and track – that provide recreational opportunities.
Jerry states: “I don’t expect the world to revolve around us. I will adapt – just make it so I can adapt.”
Justin’s Story

Justin was first diagnosed with a disability in the form of ADD (attention deficit disorder, now known as ADHD, or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder) at the age of 5 years. The diagnosis resulted in his removal from a regular classroom environment to special education courses. Justin’s parents were informed by Justin’s educators that he probably wouldn’t graduate high school, much less college.
Years later, as a young adult, Justin developed Meniere disease (an inner ear disorder), which affected his hearing and balance. The onset of the disorder left Justin with the scary reality that he could permanently lose his hearing at any time. Justin recalled a former supervisor taking advantage of this knowledge with an inappropriate prank: While speaking in a one-on-one meeting, the sound from the supervisor’s mouth abruptly halted, while his lips continued to move. Justin thought he had gone deaf – until the supervisor started laughing – which Justin could hear. Behaviors like the above took its toll on Justin’s confidence – yet, he knew he could contribute in society.
Spurred in part by adversity, Justin went back to school, earned a business degree, and shortly after, entered the commercial marketing industry. However, despite his education and experience, Justin was still regularly subject to the same stigma. Many of Justin’s work experiences over the course of his career left him feeling ashamed, guilty, offended, and sometimes, even intimidated. Rather than instilling confidence, it left him demoralized – simply because he was differently abled.
In July of 2013, everything changed for Justin. He joined the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention working as a contractor in the Division of Human Development and Disability at the National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities. Justin’s colleagues put an emphasis on making him feel comfortable and respected as a member of a diverse and productive workforce. They welcomed Justin’s diversity, positively contributing to his overall health.
The mission of the Division of Human Development and Disability is to lead public health in preventing disease and promoting equity in health and development of children and adults with or at risk for disabilities. One in two adults with disabilities does not get enough aerobic physical activity 1 , and for Justin, regular physical activity is important to help him combat potentially lethal blood clots due to a genetic blood clotting disorder that he has. Every working hour, Justin walks for a few minutes, stretches, or uses his desk cycle. Justin also participates in walking meetings, which he believes leads to more creative and productive meetings.
Stories such as Justin’s are reminders that employment and health are connected. CDC is proud to support National Disability Employment Awareness Month every October. The awareness month aims to educate about disability employment issues and celebrate the many and varied contributions of America’s workers with disabilities.
Suhana’s Story

Suhana has a sister, Shahrine, who is older by 18 months. While Shahrine’s mother was pregnant with Suhana, their uncle came to town for a visit. During the visit, their uncle was quick to notice that Shahrine did not seem to be talking at an age appropriate level or respond when called upon. Shahrine would also turn up the volume on the television and radio when others could hear it without difficulty. Shahrine’s parents thought that her speech development and behavior were normal for a toddler, but thanks to the uncle expressing his concerns, the family soon took action. A hearing test found that Shahrine was hard of hearing.
Due to Shahrine’s diagnosis, Suhana received a hearing screening at birth and was found to be hard of hearing, as well. Had it not been for the concerns raised by the children’s uncle, not only would Shahrine’s hearing loss have possibly gone on longer without being detected, but Suhana would most likely not have had a hearing screening at birth.
As a result of their early diagnoses, Suhana and Shahrine’s parents were able to gain the knowledge they needed to make sure both of their children could reach their full potential in life. They had access to early services from a team of physicians, speech therapists, counselors, and teachers.
Suhana credits her parents for her own successes, saying that she couldn’t have made it as far as she has without their support and patience. Today, Suhana is employed at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as an epidemiologist with the agency’s Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (EHDI) program. All children who are deaf or hard of hearing receive critical services they need as a result of the EHDI program, which funds the development of data systems and provides technical assistance to help improve screening, diagnosis and early intervention for these infants. When children who are deaf or hard of hearing receive services early, they are more likely to reach their full potential and live a healthy, productive adult life.
CDC is proud to support National Disability Employment Awareness Month every October. The goals of the awareness month are to educate the public about disability employment issues and celebrate the many and varied contributions of America’s workers with disabilities.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vital Signs. [updated 2014 May 6; cited 2014 October 10] Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/vitalsigns/disabilities/
If you would like to share your personal story, please contact us at Contact CDC-INFO
- Policy Makers
- CDC Employees and Reasonable Accommodations (RA)

To receive email updates about this topic, enter your email address:
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
- Armenia response
- Gaza response

- High contrast
- Press centre

Search UNICEF
Case studies on disability and inclusion.
To document UNICEF’s work on disability and inclusion in Europe and Central Asia region, UNICEF Regional Office for Europe and Central Asia has developed a set of five case studies.
UNICEF takes a comprehensive approach to inclusion, working to ensure that all children have access to vital services and opportunities. When UNICEF speaks about “inclusion” this encompasses children with and without disabilities, marginalized and vulnerable children, and children from minority and hard-to-reach groups.
The case studies have a specific focus on children with disabilities and their families. However, many of the highlighted initiatives are designed for broad inclusion and benefit all children. In particular, this case study, covers such topics as: Inclusive Preschool, Assistive Technologies (AT), Early Childhood intervention (ECI), Deinstitutionalisation (DI).
Case studies

Case study 1: “Open source AAC in the ECA Region”
Files available for download (1).

Case study 2: “Inclusive Preschool in Bulgaria”

Case study 3: “Assistive technology in Armenia"

Case study 4: “Early childhood intervention in the ECA region”

Case study 5: “Deinstitutionalization in the ECA region”

- QUICK LINKS
Court Cases That Shaped Disability Services in Education
Court cases and summaries.
by Brian Rose, JD (Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey)
1. Southeastern Community College v. Davis, 442 U.S. 397 (U.S. Supreme Court, 1979)
Summary: The nursing school rejected the application of student who had a hearing impairment. The school believed that the student would be unable to satisfy the clinical requirements of program. The school was unwilling to allow the student to waive out of the clinical components of program or to assign an aid that would help her to communicate in a clinical setting. The Supreme Court determined that Section 504 did not require the College of Nursing to admit student. The Court's rationale was that 504 did not prohibit institutions from establishing physical qualifications for admission to the clinical program and that the accommodations requested by student amounted to "affirmative action" that was not required under 504. The Court defined "otherwise qualified" as person who can meet all of the program requirements in spite of "handicap".
Key Points: Technical standards are permissible; the ruling begins to define "otherwise qualified"; it sets forth an analysis to determine what accommodations are reasonable (required) and what accommodations would impact the essential elements of a program (not required).
2. Pushkin v. Regents of the University of Colorado (10th Cir. 1981)
Summary : Pushkin was an M.D. with multiple sclerosis applying for a medical residency at the University of Colorado Psychiatry unit. He was denied admission. Those in the interview committee justified their decision to deny him admission, stating that (a) they were concerned how patients would react to Dr. Pushkin; (b) they felt Dr. Pushkin had not come to terms with his disability, and that this would affect his ability to treat patients; (c) Dr. Pushkin would not be able to handle the stress on the job on account of his condition; (d) and that Dr. Pushkin would require too much medical care to be able to satisfy the requirements of the job. The members of the admission1s committee gleaned all this from a 45-minute interview. Dr. Pushkin's therapist offered testimony stating his belief that Dr., Pushkin would be able to handle the stress of the job. Dr. Pushkin offered information on how he would handle his need for on-going medical treatment. The 10th Circuit found that the residency program had discriminated against Dr. Pushkin.
Key Points : Pushkin makes clear that there must be an individualized inquiry into the circumstances of each individual and that broad stereotypes of the limitations of individuals with various disabilities are not properly the basis of a decision that someone is not "otherwise qualified". Typical applications in higher education involve students in clinical placements or teacher education programs. Pushkin teaches that we may not stereotype students with disabilities when deciding whether they are otherwise qualified for such programs, but rather consider how each individual student can or cannot meet program requirements.
3. Wynne v. Tufts University School of Medicine, 976 F.2d 791, 932 F.2d 19 (1st Cir. 1992 and 1991 (en banc)
Summary : Wynne was a medical school student with a learning disability appealing his academic dismissal on the basis that Tufts had not properly accommodated his disability. Most critically, Wynne had wanted Tufts to refrain from using multiple-choice exams when testing him. Tufts refused this accommodation request. Initially the 1st Circuit was unwilling to accept Tufts's explanation as to why it would only use multiple-choice tests. The Court indicated that, while some deference was owed to an institution making academic judgments, such institutions nevertheless have a duty to seek out reasonable means of accommodating students with disabilities. The Court further indicated that to conscientiously carry out this duty, institutions should show that relevant officials considered reasonable means of accommodating a student, considered their feasibility and effect on the program, and came to a justifiable conclusion that providing such accommodations would result in lowering academic standards or substantially modifying the program in question. When the matter came back to the Court a second time, the Court accepted Tufts explanation that critical thinking skills were taught by use of multiple choice exams and therefore allowed the dismissal of Wynne to stand.
Key Points : Wynne tells us what thought process an institution should go through before refusing to provide an accommodation on the basis that doing so would lower academic standards and /or substantially modify a program of study. In essence, an institution should show that (a) officials with relevant duties and experiences considered the accommodation request; (b) that they meaningfully considered the impact on the program and the availability of alternatives; and (c) that they reached a rational conclusion that accommodations could not be offered. Wynne Clarifies "otherwise qualified" to mean "can complete program requirements with or without reasonable accommodation".
4. Ohio Civil Rights Commission v. Case Western Reserve University, 666 N.E.2d 1376 (Ohio Sup Ct. 1996)
Summary : A blind applicant to the CWRU Medical School was denied admission and filed suit under state disability law that used the same statutory language as the Section 504 regulations. The Court majority relied heavily upon an Association of American Medical College technical standard that medical school candidates must have an ability to "observe" in finding for the university on the basis that the student was not otherwise qualified. The majority opinion identified various tasks that the student would be unable to do such as insert an IV or directly observe an x-ray and make independent judgments. The majority ignored experiences of a blind medical school graduate (Hartman) who had attended the Temple University Medical School as not "probative". Dissenting opinion seemed to believe that reasonable accommodation existed given the experiences of Hartman at Temple.
Key Points : The fundamental question is how far one has to go to accommodate someone before the accommodation becomes "unreasonable". Both majority and dissenting opinions handle this issue poorly in our view. Hartman's experience at Temple was important, but not for reasons cited by the dissenters. Temple found it necessary to provide constant one-on-one assistance to Hartman, to exempt him from certain requirements and to do so at cost of help to other students. This amounts to a substantial change in the way in which the program is taught and the provision of personal aids that go above and beyond what relevant law requires. In that respect, if Temple's handling of Hartman is the only way that a student can complete the requirements, it is not reasonable to require this of an institution. The facts show what an example of "undue burden" might be. The decision also stands for the proposition that a school can require that its graduates be able to perform a full range of functions (i.e. to be generalists) and need not make an accommodation that exempts a student from certain pieces of a program that s/he cannot complete. For example, an arts school can require all graduates to complete "dance" even though they will not all necessarily have to dance to pursue their desired careers and even though students with mobility impairments may not be able to complete the requirement.
5. Guckenberger v. Boston University, 974 F. Supp. 106 (D. Mass. 1997)
Summary : A class action suit by students with learning disabilities was brought against Boston University alleging discrimination principally because BU would no longer approve course substitutions for a foreign language requirement for students with LD. Using analysis in Wynne, the court ultimately determined that, if BU could establish by such a "deliberative process" that allowing a substitute for a foreign language requirement would either lower academic standards or substantially alter the program of study, it could refuse to permit course substitutions for students with LD.
Key Points : The existence or merits of LD as a diagnosis were never called into question by BU or the court. Course substitutions are not per se required as an accommodation if the university can justify unwillingness to offer substitution through deliberative process outlined in Wynne.
6. Anderson v. University of Wisconsin, No. 87-2335. (7th Cir. 1988)
Summary : Anderson was an alcoholic law student who failed his first semester and was readmitted on 2 other occasions to try and complete his first year of law studies. Each time he was unable to complete his studies due to the return of difficulties related to alcoholism, including harassing behavior. When the law school denied Anderson readmission for a 4th time, he brought suit alleging discrimination and seeking reinstatement. The court refused to reinstate Anderson finding that the record had not established that he had overcome his alcoholism sufficiently to assume that he would be able to appropriate engage in the study of law.
Key Points : Individual inquiry is required, but when that inquiry shows that a student is unable to meet program requirements, schools may refuse to admit / readmit the student. Students who left the university due to behavioral problems associated with a disability can be required to demonstrate that they have been able to function without behavioral difficulties for a period of time before being readmitted.
7. Frank v. State of New York, 972 F. Supp. 130, (N.D.NY 1997)
Summary : Frank is one of a handful of federal court decisions where the court refused to accept into evidence medical testimony about "Multiple Chemical Sensitivity" (MCS), finding that such testimony did not meet federal evidentiary standards for reliability. Frank was an employment case, not a higher education case.
Key Points : DS offices sometimes tie themselves in knots trying to accommodate MCS. This case establishes that it is appropriate to call into question documentation of MCS and to refuse to provide accommodations on the basis that no disability has been established. MCS should be distinguished from cases where students have strong reactions to specifically identified allergens.
8. Sutton v. United Airlines Inc., No. 97-1943, (U.S. Sup Ct. 1999)
Summary : The plaintiffs were twins who both had poor vision when uncorrected by glasses. United Airlines refused to hire them as pilots given their poor uncorrected vision. The plaintiffs sued alleging discrimination on the basis of disability. The Supreme Court determined that plaintiffs did not have a "disability" and therefore were not entitled to invoke the protections of the ADA. The decision focused upon the definition of "disability" in the ADA. The Court determined that when assessing whether someone has a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits a major life activity, mitigating measures (eyeglasses in this instance) must be considered. Given that plaintiffs' corrected vision (i.e. vision wearing glasses) was relatively normal, the Court determined that they were not substantially limited in seeing.
Key Points : Sutton invalidated guidance previously provided in ADA regulations that stated that mitigating measures should not be considered when assessing whether someone has a disability. A typical application in higher education might be that students with ADD who take Ritalin could be determined not to be substantially limited in learning and thus not entitled to accommodations, if, when on Ritalin, they function at, better than or near to "normal". Sutton possibly leaves open the question as to whether someone can be required to take their meds before they are eligible to be considered for accommodations.
9. PGA Tour Inc. v. Casey Martin, No.00-24 (U.S. Sup. Ct. 2001)
Summary : A professional golfer with a mobility impairment sought the right to use a cart in PGA competitions as an accommodation to a mobility impairment. The court determined that it would not fundamentally alter the game of golf to allow Martin to use a cart in PGA competitions.
Key Points : ADA does not require institutions to provide accommodations that would "fundamentally" alter a program of study. Decided under Title III of the ADA, Martin nonetheless gives public and private higher education institutions a perspective on what the current Supreme Court might regard to be a "fundamental alteration". Specifically, the court wrote that a fundamental alteration is something that either changes such an essential aspect of the "game" that it makes it a different game, or something that not only accommodates the person with a disability, but gives him / her an advantage over others and thereby fundamentally alters the character of the competition. It is not yet clear whether Martin portends a broad or narrow view of what might be a fundamental alteration in higher education.
Starbucks discrimination lawsuit awarded white employee $25 million: Legal experts weigh in
Shannon Phillips received $25.6 million in damages after a six-day trial.
A federal jury this week found that Starbucks discriminated against a white manager who was fired amid an uproar over the company's treatment of Black customers at a store in Philadelphia five years ago.
The ex-manager, Shannon Phillips, received $25.6 million in damages after a six-day trial, Phillips' attorneys previously told ABC News.
The resolution of a lawsuit against one of the nation's largest employers drew attention to the standard for proving discrimination as well as the federal protection against bias afforded to all racial groups, regardless of whether they've faced historical marginalization, experts told ABC News.
The jury appears to have been persuaded in part by the argument that Phillips was fired as part of a public relations effort undertaken by Starbucks in response to racial justice backlash, which may carry implications for how corporations act in such circumstances, experts added.
Starbucks did not immediately respond to ABC News' request for comment. In court documents , the company rejected allegations of discrimination, saying that it disciplined Phillips for "legitimate, nondiscriminatory, non-retaliatory reasons."
MORE: Starbucks ordered to pay over $25 million to white former manager who claimed racial discrimination
Here's what to know about the Starbucks discrimination case and its implications, according to legal experts:
Why did the jury find that race played a role in the firing of the Starbucks employee?
In 2018, two Black men -- Donte Robinson and Rashon Nelson -- were arrested at a Philadelphia-area Starbucks store after an employee called 911 and accused them of trespassing because they had not made a purchase.
The two men later reached a private settlement with Starbucks and the City of Philadelphia, which agreed to pay each of the men $1 and establish a $200,000 fund for young entrepreneurs.
Phillips, a then-regional director who had worked at the company for nearly 13 years, was terminated less than a month after the incident.
In an initial lawsuit filed by Phillips in 2019, she said she was not at the store that day nor involved in the lead-up to the arrests, alleging instead that her race played a "determinative role" in her termination.
A key piece of evidence in the case centered on testimony from a Black district manager who said he thought race had played a role in Starbucks' decision to fire Phillips and allow him to remain with the company, Phillips' attorney previously told ABC News.
MORE: Target faces criticism from artists involved with Pride month products over response to boycott: ‘Quick to fold’
Legal experts concurred with that assessment, saying that the plaintiff's ability to point to disparate treatment of a relevant employee was critical to the jury's finding of discrimination.
"My understanding is that in these cases what you have to have is a comparative," Rick Rossein, a professor of employee discrimination law at the City University of New York Law School, told ABC News. "Here you have a Starbucks manager giving that type of testimony."
In court documents, Starbucks contested this account of its actions, saying instead that it disciplined Phillips based on poor performance. Phillips "appeared overwhelmed, frozen and lacked awareness of how critical the situation was for Starbucks and its partners," the company claimed .
Related Stories

What witnesses said about Trump, classified docs
- Apr 24, 4:58 PM

Secret Service prepares for Trump in contempt
- Apr 23, 4:16 PM

OJ Simpson dies at 76
- Apr 11, 6:32 PM
Phillips appeared to further persuade the jury with her explanation for the alleged mistreatment, describing her firing as part of the company's effort to minimize the public relations fallout from the arrests, the experts added.
"Evidence points to Starbucks taking action against an employee in order to address public opinion as opposed to really addressing the question of who was involved in making that decision," Risa Lieberwitz, a professor of labor and employment law at the Cornell University School of Industrial and Labor Relations, told ABC News.
Is it unusual for workplace discrimination cases to be brought on behalf of white people?
Phillips’ case is unusual because the majority of cases alleging a violation of federal discrimination law on the basis of race involve non-white people, legal experts told ABC News.
Legal precedent that reaches as high as the Supreme Court affirms that the measure at issue, Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, protects white workers who experience discrimination, they added.
"Anti-discrimination law that deals with race discrimination applies to any allegation of race discrimination whether it would be against a white employee, a Black employee or another racial group," Lieberwitz said.
While discrimination lawsuits on behalf of white individuals are uncommon, white plaintiffs have proven more likely to succeed than non-white ones when federal judges adjudicate their racial discrimination claims, said Wendy Greene, a professor of anti-discrimination law at Drexel University Law School and the director of the Center for Law, Policy and Social Action.
MORE: 'Thrown in their faces': Bud Light salespeople say boycott is hurting commission
"The surprise for many people, however, is that federal civil rights laws initially designed to address the longstanding, systemic racial segregation, exclusion and discrimination endured by individuals identifying as non-white are seemingly more effective at redressing racial discrimination against individuals who identify as white," Greene told ABC News.
What are the implications of the finding that Starbucks discriminated in this case?
The decision in this case could heighten scrutiny of large companies in their treatment of workers who belong to groups protected against discrimination as well as complicate efforts to discipline workers charged with improving a company's performance on racial justice issues, experts said.
"We're in the era where people are looking very carefully at decision-making by major corporations," Rosstein said.
Greene, meanwhile, said that the decision could make it more difficult for companies to supervise workers involved in the implementation of racial justice initiatives, since companies could be accused of racial discrimination if they discipline such employees.
MORE: With anti-drag laws on the rise, drag queens reclaim the art as form of protest
Management must balance the need to create a work environment free of racial discrimination with a simultaneous commitment to "ensure workplaces are free of racial exclusion and subordination, which are often couched as acts of racial discrimination against white employees in favor of non-white people," Greene said.
The large award for damages in the Starbucks case could "discourage employers from disciplining or terminating employees they believe are not effectively handling complaints of discrimination," she added.
Related Topics

Your recycled plastic bags may end up here
- Apr 23, 9:48 PM

Airlines must give refunds for canceled flights
- Apr 24, 11:06 AM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events

- Case Studies
The following three case studies illustrate common problem types that ACDL has worked on for people with disabilities in New South Wales. All case studies have been de-identified.
CASE STUDY 1 – Assistance Animals
Maria has diabetes, depression, anxiety, agoraphobia and chronic back pain. Two years ago, her GP recommended that she get an assistance dog to assist with her disabilities. Maria has trained her dog to be a diabetic alert dog, so he can let her know if her blood sugar is crashing, and she also finds that her dog greatly assists her with her other disabilities via companionship, increased physical movement and general comfort.
Maria bought an apartment in a strata complex last year, and notified the strata manager that she had an assistance dog. The strata manager said it shouldn’t be a problem but she would need to submit an application to the body corporate. She did so prior to moving in and provided supporting documents from her doctor highlighting how the dog alleviated her disabilities. She also provided information on the level of training the dog had been given. However, the Strata manager said she could not keep the dog as she had not provided sufficient information about his accreditation, and therefore Maria had to be apart from her dog for some months.
After obtaining documents and consider Maria’s matter, ACDL wrote a letter to the Strata manager on Maria’s behalf, explaining that her dog satisfies the requirements disability discrimination legislation as the dog is trained to alleviate her disability and trained to an appropriate standard in a public place, and that Maria would be bringing her dog onto the property as at that date. Maria was then able to bring her dog onto the property with confidence.
CASE STUDY 2 – Education
Omar is a 13 year old student in Year 7 at a public school. He has autism, ADHD, ODD and anxiety, and has a behavioural management plan in place. Due to his disabilities, he often acts out in a silly or joking manner, including swearing, and he often lashes out physically when distressed, which is why his behavioural management plan focuses on ways to calm him down. The school follows a strict discipline policy for anything that is seen as misbehaviour: any student who swears or engages in any physical altercation of any level is automatically suspended for 2 days, and progressively longer suspensions occur for each new breach of behaviour.
Omar experienced increasingly long suspensions throughout year 7 for minor incidents of physical altercation with other students as a result of bullying, firstly for 2 days, then 4 days, then 5 days, culminating in a 20 day suspension for appearing to threaten a teacher. The teacher and other students interpreted this as clowning around rather than a genuine threat and the situation was quickly defused. The incident was not even mentioned by his teacher to his parents until the suspension occurred some days later. His mother repeatedly requested that the discipline and suspension policy be amended to take into account Omar’s tendency to act out inappropriately, and institute alternative forms of discipline in accordance with his behavioural management plan, such as detention or similar. The School did not do so, and after the last long suspension, Omar was again found to be misbehaving and was threatened with expulsion.
ACDL wrote a letter of advice to Omar’s mother on the prospects of success of a claim of disability discrimination, noting that there was a strong case of indirect discrimination in the School’s treatment of Omar’s in relation to the discipline policy, in that he could not comply with the discipline policy because of his disabilities, and the School had failed to make reasonable adjustments which would accommodate his disabilities despite repeated requests. ACDL explained the process and options for making a discrimination complaint, as well as providing referrals for assistance with challenging the procedural decision to expel him on other grounds. Omar’s mother said that she found the advice very helpful and allowed her to consider all her options clearly.
CASE STUDY 3 – Employment
Danielle was diagnosed with Hepatitis C. She worked at an accounting firm and did not tell them about it when she got the job. She was worried about what they would think and she did not think that her diagnosis would affect the way she did her job.
One day, she told a close workmate. When she came to work the next day, she found that her workmate had told other people. After lunch, there was a note on her desk calling her a ‘druggie’.
Danielle was really upset. After a few days, she decided to ask for a meeting with her employer to tell her what had happened. Danielle’s employer seemed shocked to hear about the behaviour of the others but was worried that if he said something it might cause conflict within the team. He said he would say something to the other employees, but kept putting off actually doing so.
Danielle approached ACDL for advice. ACDL told her that she might have a complaint of disability discrimination or harassment under the law, but Danielle did not want to make a complaint at this point in time. ACDL wrote a letter detailing the requirements under disability discrimination law and asking the employer to resolve the matter swiftly.
Upon receiving the letter, Danielle’s employer called an urgent staff meeting to discuss the importance of a safe work place and the policy on harassment and discrimination. Danielle’s complaint was then dealt with in accordance with the workplace grievance policy and the situation was resolved.
Some helpful resources:
- Legal Resources
- COVID-19 Specific Resources
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Law Reform and Submissions
Australian Centre for Disability Law
We promote and protect the human and legal rights of people with disability and their supporters through legal advocacy. We do this by providing free legal advice and representing people with disability discrimination cases.
Through our work we proactively aim for recognition and respect of human and legal rights, remove barriers, eliminate discrimination, empower people with disability, and increase provision of access to justice.
Useful Links
Hours & info.
Our advice line is open Mondays, Wednesdays between 9.30am – 12.30pm and Thursdays 1.30pm – 4.30 pm
Voice: 1800 800 708 or (02) 7229 0061 Fax: (02) 8088 6069
Email: [email protected] or [email protected] (for non-legal advice)
Postal: PO Box 989 Strawberry Hills NSW 2012
How can we help?
- Share this page via email
- Share this page via Facebook
- Share this page via Twitter
- Share this page via Instagram
- Visit our YouTube profile
Disability Discrimination Case Study – The Equality Act 2010
BY ADISH FARKHAD, EMPLOYER LAW

Taken from: NRAS magazine, Autumn 2012
The following is a real case which Adish dealt with…
Joe suffers from left hip early osteoarthritis with femoroacetabular impingement. He believes that this condition amounts to a disability within the meaning of the Equality Act 2010. Joe is currently employed as a Personal Trainer at “All About Health” gymnasium (his “Employer”) and has worked with them for the past 10 years. Joe was diagnosed with hip early osteoarthritis with femoroacetabular impingement 3 years ago. He feels that he has been treated less favourably by his Employer because of his disability, contrary to the Equality Act 2010. Joe has, on several occasions, made his Employer aware that he is suffering from a disability for which he requires reasonable adjustments to his working practices. Joe has requested the following adjustments: 1. regular breaks from his shifts so that he can rest to ease the pain in his hip; 2. a reduction in his hours but not so much of a reduction that would prevent him from earning a living. He wants to work 27 hours per week; 3. an adjustment to the shift pattern for Personal Trainers to allow him to work Mondays and Tuesday which are his busiest days (so that he can continue to look after his key clients); and 4. that his Employer waives its unreasonable request that Joe works every weekend (the quietest times) as part of his working hours as Joe wants to be treated in the same way as his non-disabled colleagues who only have to work one weekend per month. Employee Booklets
Whilst Joe’s Employer has been on notice of his disability for over 3 years; it has persistently failed to make any adjustments to accommodate his disability. Joe’s manager regularly picks on him for demonstrating his hip pain in the way that he sometimes walks around the gym. His manager’s view is that Joe’s physical impairment does not create a positive image for the gymnasium and its Personal Trainers. The subjecting of Joe to disability discrimination has meant that Joe has been prevented from working the reduced hours he requested and this has had a detrimental effect on his current health which has exacerbated the effects of his disability. Two months ago, Joe raised a formal grievance as he felt that he had no alternative but to do so in circumstances where all of his previous concerns raised verbally had been ignored. Joe’s Employer did not uphold his grievance and denied all liability for discrimination. Joe’s Employer did, however, agree to reduce his hours to 20 hours per week (with no flexibility or adjustment to enable him to work in excess of that should the need arise), requesting that he works at the quietest times every weekend and preventing him from working at the busiest times on Mondays and Tuesdays. He has also been allowed to take a 10-minute break when he feels in pain on the condition that he authorises the break with his manager so that his manager is aware of his whereabouts. Joe’s Employer wishes to vary Joe’s terms and conditions of employment to reflect his new working hours (20 hours per week) and days of work to include working every weekend. Joe was told that he would face “proceedings” if he does not accept the proposed varied terms. Joe considers that his Employer has failed to give any good reason for not agreeing to make the adjustments he requested and that the proposed adjustments that it is willing to make are unreasonable in the circumstances. Joe is aware that new staff are being recruited or being asked to cover Mondays and Tuesdays (his Employer has the maximum number of Personal Trainers already because it is allowing employees without a disability to work on a Monday and Tuesday instead of him). Joe went to see a solicitor for legal advice to see if he had any potential employment claims against his Employer. He was advised that the Equality Act 2010 requires employers to make reasonable adjustments for employees who have a disability. Also, that employees with a disability should not be treated less favourably because of a disability. In Joe’s case, his employer did not provide any business reasons as to why it could not allow Joe to work 27 hours per week and on a Monday and/or Tuesday. Joe’s Employer had not sought a medical opinion from an Occupational Health Therapist about his disability and what recommended adjustments could be made. In all the circumstances, therefore, Joe’s Employer had failed to make reasonable adjustments. In addition to this, Joe’s Employer subjected him to less favourable treatment by insisting he works at the quietest times every weekend (when his colleagues who did not suffer from a disability did not have to work every weekend) and by insisting that he seeks his manager’s approval before taking breaks, in circumstances when it knew Joe had been bullied by him and that it would not always be possible to obtain such authority. In addition to a claim for disability discrimination, Joe could also claim victimisation under the Equality Act 2010 because he was subjected to further less favourable treatment because he made a complaint (by raising his grievance) about disability discrimination, as his Employer threatened that he would face ‘proceedings’ if he does not accept the proposed variation to his terms and conditions of employment. Joe was advised that if he were to pursue a claim in the Employment Tribunal for disability discrimination, he would be entitled to compensation for his injury to feelings, his future loss of income (if he were to resign and leave the gymnasium) and possibly the personal injury he had suffered due to his condition becoming worse as a result of his Employer’s failure to accommodate his disability. It was also explained to Joe that the Employment Tribunal would make a recommendation about reasonable adjustments for his continued employment (if he did not leave). At the interview with his solicitor, Joe was concerned about the costs involved in pursuing an Employment Tribunal claim. However, when his solicitor discussed the matter with him, it became clear that he had Legal Expenses Insurance which would fund legal assistance. Joe was very surprised he had not realised he had such cover in his Home and Contents Policy. Joe’s solicitor assisted him to apply to his insurers for funding and then issued an Employment Tribunal claim on his behalf. Employer Law The Equality Act 2010 is the law which bans unfair treatment and helps achieve equal opportunities in the workplace and in wider society. For further information and to download publications visit: www.homeoffice.gov.uk/equalities/equality-act
Privacy Overview

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Two cases alleging disability-based discrimination. By Andrew Hamm. on Apr 9, 2021 at 1:01 pm. This week we highlight cert petitions that ask the Supreme Court to consider, among other things, the viability of certain types of disability-based claims under three federal statutes. One petition involves the Americans with Disabilities Act.
Premier Rehab Keller, PLLC (2022)—The Court holds that a person suing for disability discrimination under the Affordable Care Act or Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 cannot recover damages for emotional distress. U.S. Supreme Court cases describe the government's intolerance of disability discrimination.
December 2021: Carl is an inmate in a correctional centre. east. Use of goods lift denied to man with cerebral palsy. August 2021: River loves to read. east. School boy with disability banned from out of school care. February 2021: Emil is a school-aged boy and was diagnosed with ADHD. east. Signature affected by Multiple Sclerosis.
After this liability finding, the case will now proceed to damages and injunctive relief. United Airlines, Inc.: filed June 2009, lower court dismissed and 7th Cir. reversed on 9/7/12 - The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Seventh Circuit reversed the dismissal of a disability discrimination lawsuit filed by the Commission against United Airlines ...
Selected List of Press Releases Announcing Litigation Filings and Resolutions in Recent Race Harassment Cases. Selected List of Pending And Resolved Cases Involving Farmworkers from 1999 to the Present. Significant Disability Discrimination Litigation Filed or Resolved: July 2013-July 24, 2014.
A federal jury recently delivered a eye-popping $125,150,000 verdict in a disability discrimination case against Walmart. The case, EEOC v. Wal-Mart Stores East, E.D. Wis., No. 1:17-cv-00070 (E.D ...
This research brief looks at the experiences of discrimination from the perspective of people with disabilities as a way to better understand the influence of the ADA. HIGHLIGHTS OF FINDINGS. The majority of research on people with disabilities' experiences with discrimination is related to employment. Disability-based discrimination is both ...
The decision in Barrow v Kellogg Brown & Root (UK) Ltd [2021] is notable for the size of the award made by the tribunal: £2,567,831.97, which is the second largest disability discrimination award ever. The outcome is a salutary reminder of a tribunal's ability to make a substantial award in favour of claimants.
In contrast to many other disability diversity case studies, this was not focused on a disability program but rather on capturing a company culture focused on seeking to make disability inclusivity part of all that they do. ... One way to minimize workplace experiences of discrimination and invalidation for PWDs is for companies to actively ...
This study follows work conducted by Lagu in 2012, in which she attempted to make an appointment for a fictional patient who used a wheelchair. Of 256 surveyed practices in the 2012 study, 56 (22%) reported they could not accommodate the patient. Of the rest, more than half planned to transfer the patient using methods considered to be unsafe.
Charlesworth, Ph.D. '21, who works in the lab of Mahzarin Banaji, has found that those hidden prejudices have hardly changed over a 14-year period and could take more than 200 years to reach neutrality, or zero bias. "Implicit bias can change. But so far, it's only changed for some groups," Charlesworth said. "It changed for sexuality ...
case study for workplace disability advocacy in that they create a very necessary, yet isolated safe space where those with varying disabilities can work. While working internally to assist in the empow-erment and local employment rates of people with disabilities, their work can help to understand disability advocacy in a larger context.
Jerry's life is not defined by his disability. He lives life just like anyone else without a disability would live their life. "There's lots I can do, and there are some things that I can't do," said Jerry. "I drive, I invest money. I'm not rich, but I'm not poor.
The case studies in this article provide real-world examples of employers found to be in violation of EEOC regulations. It includes snapshots of violations and guidance for how those employers could've prevented EEOC issues. By examining these case studies, employers can learn from the mistakes of others in similar industries and avoid EEOC ...
Fact Sheet: Disability Discrimination. Title I of the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 prohibits private employers, state and local governments, employment agencies and labor unions from discriminating against qualified individuals with disabilities in job application procedures, hiring, firing, advancement, compensation, job training ...
Disability Discrimination Case Studies: Real-Life Workplace Experiences. Navigating the complexities of disability discrimination laws within the workplace can be daunting. The extent of an employer's obligation to accommodate can vary significantly based on individual circumstances. Often, these laws intersect with regulations governing family ...
The case studies have a specific focus on children with disabilities and their families. However, many of the highlighted initiatives are designed for broad inclusion and benefit all children. In particular, this case study, covers such topics as: Inclusive Preschool, Assistive Technologies (AT), Early Childhood intervention (ECI ...
5. Guckenberger v. Boston University, 974 F. Supp. 106 (D. Mass. 1997) Summary: A class action suit by students with learning disabilities was brought against Boston University alleging discrimination principally because BU would no longer approve course substitutions for a foreign language requirement for students with LD.Using analysis in Wynne, the court ultimately determined that, if BU ...
The decision in this case could heighten scrutiny of large companies in their treatment of workers who belong to groups protected against discrimination as well as complicate efforts to discipline ...
In 2023, Ian Clifford, a former employee of IBM, won a disability discrimination case against the company. The case centered on IBM's decision to terminate Clifford's employment after he was diagnosed with a mental health condition. Clifford had been employed by IBM for over 20 years when he was diagnosed with depression in 2017. He […]
The following three case studies illustrate common problem types that ACDL has worked on for people with disabilities in New South Wales. All case studies have been de-identified. ... ACDL wrote a letter of advice to Omar's mother on the prospects of success of a claim of disability discrimination, noting that there was a strong case of ...
Disability Discrimination Case Study - The Equality Act 2010. BY ADISH FARKHAD, EMPLOYER LAW. Taken from: NRAS magazine, Autumn 2012. The following is a real case which Adish dealt with…. Joe suffers from left hip early osteoarthritis with femoroacetabular impingement. He believes that this condition amounts to a disability within the ...
Developing a disability equality scheme in a secondary school helps staff and students address discrimination across all strands. In developing its disability equality scheme, Framwellgate (secondary) School in Durham set up a disability equality group drawn from pupils, governors, parents, as well as teaching, support and administrative staff.