Proposal Template AI
Free proposal templates in word, powerpoint, pdf and more

Action Research Proposal Template: A Comprehensive Guide + Free Template Download + How to Write it
Action research proposal template: a guide for real-world problem solving.
As a researcher dedicated to making a real impact in the world, I understand the importance of developing an action research proposal that goes beyond the standard academic proposal . Action research is a powerful tool for bringing about meaningful change in a specific context, and a well-crafted proposal is essential for ensuring that the research is both rigorous and relevant to the needs of the community or organization being studied. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to creating an action research proposal template, outlining the key components and considerations that set it apart from a traditional research proposal . Whether you are a student, practitioner, or academic, understanding the unique elements of an action research proposal will enable you to approach your research projects with a focus on real-world problem solving and positive change.
Action Research Proposal Template
The Effectiveness of Implementing Technology in a Mathematics Classroom
Background and Introduction:
In this section, provide a brief overview of the research problem and context. Discuss the rationale for conducting the action research and provide a clear statement of the research question or objective.
The incorporation of technology in educational settings has become increasingly prevalent in recent years. However, the effectiveness of using technology in mathematics classrooms is still a subject of debate. This action research aims to investigate the impact of implementing technology on students’ mathematical abilities and engagement in a middle school classroom.
Research Goals and Objectives:
Clearly outline the specific goals and objectives of the action research. What do you hope to achieve through this study? What are the intended outcomes?
The primary goal of this action research is to analyze the impact of technology integration on students’ mathematical performance and attitudes towards the subject. The objectives include assessing changes in students’ test scores, observing their engagement during technology-enhanced lessons, and gathering feedback from both students and teachers about their experiences with technology in the classroom.
Research Methodology:
Detail the research methodology that will be used to conduct the action research. This includes a description of the participants, data collection methods , and data analysis techniques .
The action research will be conducted in a 7th-grade mathematics classroom with a total of 30 students. Data will be collected through pre- and post-assessments, classroom observations, and student and teacher interviews. Quantitative data will be analyzed using statistical methods, while qualitative data will be subjected to thematic analysis to identify recurring patterns and themes.
Action Plan:
Provide a timeline and action plan for implementing the research. How will the data collection and analysis be carried out? What are the key milestones and deadlines?
The action research will be carried out over the course of 10 weeks. Week 1-2 will involve pre-assessments and the introduction of technology integration into the classroom. Weeks 3-8 will focus on implementing technology-enhanced lessons and collecting data through observations and student feedback. Weeks 9-10 will be dedicated to post-assessments and data analysis .
Expected Outcomes and Impact:
Discuss the anticipated outcomes of the action research and the potential impact on the educational setting. How will the findings contribute to the existing knowledge in the field?
It is expected that the findings of this action research will demonstrate the positive impact of technology integration on students’ mathematical performance and engagement. The results will provide valuable insights for educators and policymakers on the effectiveness of using technology in mathematics classrooms, potentially influencing future curriculum and instructional design decisions.
Budget and Resources:
Outline the budget and resources required to conduct the action research. This may include costs for technology equipment, data collection materials, and personnel.
The action research will require funding for the purchase of tablets or laptops for the classroom, as well as printing materials for assessments and consent forms. Additionally, there may be personnel costs for hiring a research assistant to aid in data collection and analysis.
Conclusion:
Summarize the key points of the action research proposal and reiterate the significance of the study . Emphasize the potential benefits of conducting the research and the importance of addressing the research question or objective.
References:
List all of the references cited in the action research proposal using the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA). This section demonstrates the scholarly foundation of the proposed research.
My advice on using the Action Research Proposal Template:
When using this template, be sure to customize it to fit the specific context and goals of your action research. Tailor the examples and language to your own research topic and consider seeking feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the proposal is clear and comprehensive. Pay close attention to the research methodology and action plan, as these sections will guide the implementation and data collection process. Lastly, be diligent in your budget and resource planning to ensure the successful execution of the action research.
Download free Action Research Proposal Template in Word DocX, Powerpoint PPTX, and PDF. We included Action Research Proposal Template examples as well.
Download Free Action Research Proposal Template PDF and Examples Download Free Action Research Proposal Template Word Document
Download Free Action Research Proposal Template Powerpoint
Action Research Proposal Template FAQ
1. what is an action research proposal.
An action research proposal is a document that outlines the plan for an action research project . It includes the background of the issue, the purpose of the research, the research questions , the methodology, and the expected outcomes .
2. What should be included in an action research proposal?
An action research proposal should include an introduction to the research problem, a literature review , the research questions , the methodology, the timeline for the project, the expected outcomes , and a brief discussion of how the research will be implemented and evaluated.
3. How long should an action research proposal be?
An action research proposal should typically be around 5-10 pages long, including all necessary components such as the background, literature review , methodology, and expected outcomes.
4. What is the purpose of an action research proposal?
The purpose of an action research proposal is to outline the plan for conducting an action research project, including the steps to be taken, the goals to be achieved, and the expected impact of the research.
5. Can an action research proposal be modified during the course of the research?
Yes, an action research proposal can be modified as the research progresses and new information becomes available. It is important to be flexible and willing to make changes as needed to ensure the success of the research project.
Related Posts:
- Academic Proposal Template: A Comprehensive Guide +…
- Community Event Proposal Template: A Comprehensive…
- Business Problem Solving Proposal Template: A…
- Community Project Proposal Template: A Comprehensive…
- Change Management Proposal Template: A Comprehensive…
- Change Order Proposal Template: A Comprehensive…
- Research Proposal Template: A Comprehensive Guide +…
- Real Estate Business Proposal Template: A…
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
Published on January 27, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 12, 2024.
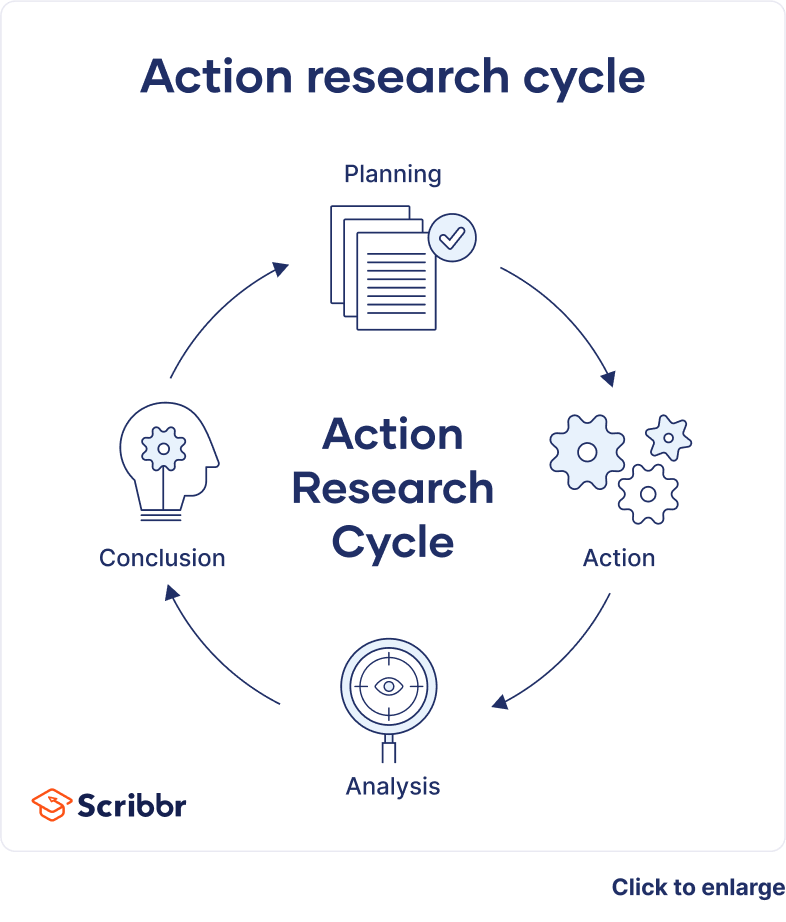
Table of contents
Types of action research, action research models, examples of action research, action research vs. traditional research, advantages and disadvantages of action research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about action research.
There are 2 common types of action research: participatory action research and practical action research.
- Participatory action research emphasizes that participants should be members of the community being studied, empowering those directly affected by outcomes of said research. In this method, participants are effectively co-researchers, with their lived experiences considered formative to the research process.
- Practical action research focuses more on how research is conducted and is designed to address and solve specific issues.
Both types of action research are more focused on increasing the capacity and ability of future practitioners than contributing to a theoretical body of knowledge.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Action research is often reflected in 3 action research models: operational (sometimes called technical), collaboration, and critical reflection.
- Operational (or technical) action research is usually visualized like a spiral following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
- Collaboration action research is more community-based, focused on building a network of similar individuals (e.g., college professors in a given geographic area) and compiling learnings from iterated feedback cycles.
- Critical reflection action research serves to contextualize systemic processes that are already ongoing (e.g., working retroactively to analyze existing school systems by questioning why certain practices were put into place and developed the way they did).
Action research is often used in fields like education because of its iterative and flexible style.
After the information was collected, the students were asked where they thought ramps or other accessibility measures would be best utilized, and the suggestions were sent to school administrators. Example: Practical action research Science teachers at your city’s high school have been witnessing a year-over-year decline in standardized test scores in chemistry. In seeking the source of this issue, they studied how concepts are taught in depth, focusing on the methods, tools, and approaches used by each teacher.
Action research differs sharply from other types of research in that it seeks to produce actionable processes over the course of the research rather than contributing to existing knowledge or drawing conclusions from datasets. In this way, action research is formative , not summative , and is conducted in an ongoing, iterative way.
As such, action research is different in purpose, context, and significance and is a good fit for those seeking to implement systemic change.
Action research comes with advantages and disadvantages.
- Action research is highly adaptable , allowing researchers to mold their analysis to their individual needs and implement practical individual-level changes.
- Action research provides an immediate and actionable path forward for solving entrenched issues, rather than suggesting complicated, longer-term solutions rooted in complex data.
- Done correctly, action research can be very empowering , informing social change and allowing participants to effect that change in ways meaningful to their communities.
Disadvantages
- Due to their flexibility, action research studies are plagued by very limited generalizability and are very difficult to replicate . They are often not considered theoretically rigorous due to the power the researcher holds in drawing conclusions.
- Action research can be complicated to structure in an ethical manner . Participants may feel pressured to participate or to participate in a certain way.
- Action research is at high risk for research biases such as selection bias , social desirability bias , or other types of cognitive biases .
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Action research is conducted in order to solve a particular issue immediately, while case studies are often conducted over a longer period of time and focus more on observing and analyzing a particular ongoing phenomenon.
Action research is focused on solving a problem or informing individual and community-based knowledge in a way that impacts teaching, learning, and other related processes. It is less focused on contributing theoretical input, instead producing actionable input.
Action research is particularly popular with educators as a form of systematic inquiry because it prioritizes reflection and bridges the gap between theory and practice. Educators are able to simultaneously investigate an issue as they solve it, and the method is very iterative and flexible.
A cycle of inquiry is another name for action research . It is usually visualized in a spiral shape following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
George, T. (2024, January 12). What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/action-research/
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2017). Research methods in education (8th edition). Routledge.
Naughton, G. M. (2001). Action research (1st edition). Routledge.
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is an observational study | guide & examples, primary research | definition, types, & examples, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Jevannel's Blog
Learning | Happy Living | Personality Development | Self-Care | Study Tips | Study Essentials | Teaching Tools | Research Tips
#BlogChallenge #blogging #bloggingbranding #GREATGOOGLE #justthoughts #poemporn #poetry #poetryoflove #randomposts bible verse blogging challenge Blogging for Money Blogging for Teaching Bring Gratitute CoVID-19 Dissertation Journey Google Classroom How to Love Research Letting go Oral Care personal notes PhD Student Pinay Teacher poetry Productivity random writing Reading Reflections Research Proposal Research Writing Scholarships Self-Care self care student life studying study tips Teachers Who Blog teaching Teaching Philosophy Teaching Tools travel destinations in the Philippines travel maestra White Teeth writing challenge Yoga Practice

How to Write An Action Research (Proposal)
Action research is a type of research that involves the systematic and reflective study of one’s own practice in order to improve it. It is a practical and collaborative approach to problem-solving that can be used by individuals or groups in various settings. In this guide on How to Write An Action Research , we will outline the steps to writing an action research paper.
Step 1: Select a Problem or Issue
The first step in writing an action research paper is to identify a problem or issue that you would like to address. The problem or issue should be relevant to your area of work or interest and should be specific and measurable. Once you have identified the problem or issue, you can begin to formulate a research question that will guide your inquiry.
Step 2: Review the Literature
The next step is to review the literature on the problem or issue you have identified. This will help you to understand what has been done in the past and what the current state of knowledge is. You should look for both academic and practical sources of information and use them to inform your research question.
Step 3: Develop a Research Plan
The third step is to develop a research plan. This should include a description of the problem or issue, the research question, the data collection methods, and the analysis plan. You should also identify any potential ethical considerations and address them in your plan.
Step 4: Collect Data
The fourth step is to collect data. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as surveys, interviews, observations, and document analysis. The data you collect should be relevant to your research question and should be analyzed using appropriate methods.
Step 5: Analyze the Data
The fifth step is to analyze the data you have collected. This can be done using both quantitative and qualitative methods, depending on the type of data you have collected. The analysis should be guided by your research question and should help you to identify patterns, trends, and relationships in the data.
Step 6: Reflect on the Findings
The sixth step is to reflect on the findings of your analysis. This involves thinking about what the data means in relation to your research question and how it can be used to address the problem or issue you identified at the beginning of the research process.
Step 7: Develop an Action Plan
The final step is to develop an action plan . This should outline the steps you will take to address the problem or issue you identified. The action plan should be based on the findings of your research and should be practical and achievable.
In conclusion, writing an action research paper requires a systematic and reflective approach to problem-solving. It involves identifying a problem or issue, reviewing the literature, developing a research plan, collecting and analyzing data, reflecting on findings, and developing an action plan.
By following these steps on How to Write An Action Research , you can use action research to improve your practice and make a positive impact in your field.
Jevannel is passionate about teaching and learning about anything. She loves to share her words with the world, hoping for readers to get something from her works. She specializes in Science Education and Research and she also writes poetry and many other things.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
One response to “How to Write An Action Research (Proposal)”
[…] We cannot teach what we don’t know yet. Let the students explore. Make them READ. Let them FEEL, and they will enjoy the exciting journey to discover new things, explore various real experiences and develop an understanding of the world through RESEARCH. […]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Sample Action Research Proposal

An action proposal.
Related Papers
Andrew Johnson
This chapter excerpt describes the salient elements and basic process of action research.
Abstract Recent action research books are reviewed. I give attention to books on appreciative inquiry, action science, systems approaches and action learning. Community, health, education and organizational applications are included. Major action research journals are noted.
Margie Comrie
Action Research
In this, the third in a series of two-yearly reviews (see also Dick, 2004, and Dick, 2006), I identify some of the action research literature that has appeared in books and edited collections over approximately the past two years. After an overview of the general action research literature I gather together other relevant literature under the following headings: action learning; community-based participatory research; youth work; educational action research; appreciative inquiry; and action science. I conclude the review with a very brief look at action research journals and special issues, other literature of interest, and an attempt to divine present and emergent trends.
Beata Jałocha
ARIEL MONTECALBO
Action research is a type of research related to one’s professional practice. In the field of education, it can be defined as the process of studying a school, classroom, or teaching-learning situation with the purpose of understanding and improving the quality of actions or instruction. In this sense, it is the ultimate form of teacher reflection. Described in this chapter expert are the basic elements and the steps of action research.
Administrative Science Quarterly
Gerald Susman
Abstract This review of recent action research books covers the period from about mid-2004 to mid-2006, complementing an earlier review (Dick, 2004). After noting some important recent additions to the action research literature, I address the literature on several different applications of action research including education, community, participatory development, and organizations. There are briefer sections on other topics. Action research journals and special issues of other journals are also identified.
Kenneth Zeichner
RELATED PAPERS
Pierre-Marie Bosc
The EMBO Journal
Josué Álvaro
Abdalla Obeidat
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry
Ruben Vardanyan
The Turkish journal of gastroenterology : the official journal of Turkish Society of Gastroenterology
Ulus Akarca
El Profesional de la Informacion
Silvia Salaya Morales
mary bodwell
Carlos Discoli
Voces disidentes contra la misoginia: nuevas perspectivas desde la sociología, la literatura y el arte.
Dolores Vela-García
Annals of Vascular Surgery
Michèle Bertrand
Riskynta ID
Ciência & Saúde Coletiva
Henrique Guerra
Kompleksnoe Ispolʹzovanie Mineralʹnogo syrʹâ/Complex Use of Mineral Resources/Mineraldik Shikisattardy Keshendi Paidalanu
Almat Raskaliyev
Japan Journal of Human Growth and Development Research
Rie Takenaga
Ciência Florestal
Luciano Weber Scheeren
Revista FSA
maria luiza cavalcanti
International Journal of Research
muhammad yaufi
International Journal of Information Technology
Arup Abhinna Acharya
Global Environmental Change
michaela lo
Diagnostic and interventional radiology
Gokce K Atac
Mike Sullivan
Donald Christensen
Lilian Sagio Cezar
Mostafa Rad
The Journal of medical research
Ankita Tandon
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
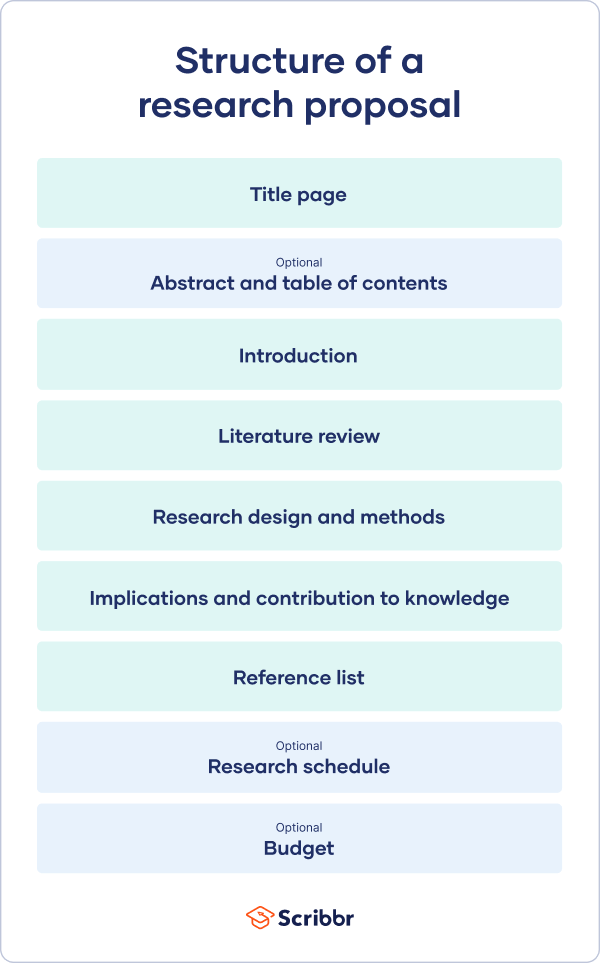
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.

Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide [With Template]
How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide [With Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write A Proposal
Writing a Proposal involves several key steps to effectively communicate your ideas and intentions to a target audience. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each step:
Identify the Purpose and Audience
- Clearly define the purpose of your proposal: What problem are you addressing, what solution are you proposing, or what goal are you aiming to achieve?
- Identify your target audience: Who will be reading your proposal? Consider their background, interests, and any specific requirements they may have.
Conduct Research
- Gather relevant information: Conduct thorough research to support your proposal. This may involve studying existing literature, analyzing data, or conducting surveys/interviews to gather necessary facts and evidence.
- Understand the context: Familiarize yourself with the current situation or problem you’re addressing. Identify any relevant trends, challenges, or opportunities that may impact your proposal.
Develop an Outline
- Create a clear and logical structure: Divide your proposal into sections or headings that will guide your readers through the content.
- Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the problem, its significance, and the proposed solution.
- Background/Context: Offer relevant background information and context to help the readers understand the situation.
- Objectives/Goals: Clearly state the objectives or goals of your proposal.
- Methodology/Approach: Describe the approach or methodology you will use to address the problem.
- Timeline/Schedule: Present a detailed timeline or schedule outlining the key milestones or activities.
- Budget/Resources: Specify the financial and other resources required to implement your proposal.
- Evaluation/Success Metrics: Explain how you will measure the success or effectiveness of your proposal.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points and restate the benefits of your proposal.
Write the Proposal
- Grab attention: Start with a compelling opening statement or a brief story that hooks the reader.
- Clearly state the problem: Clearly define the problem or issue you are addressing and explain its significance.
- Present your proposal: Introduce your proposed solution, project, or idea and explain why it is the best approach.
- State the objectives/goals: Clearly articulate the specific objectives or goals your proposal aims to achieve.
- Provide supporting information: Present evidence, data, or examples to support your claims and justify your proposal.
- Explain the methodology: Describe in detail the approach, methods, or strategies you will use to implement your proposal.
- Address potential concerns: Anticipate and address any potential objections or challenges the readers may have and provide counterarguments or mitigation strategies.
- Recap the main points: Summarize the key points you’ve discussed in the proposal.
- Reinforce the benefits: Emphasize the positive outcomes, benefits, or impact your proposal will have.
- Call to action: Clearly state what action you want the readers to take, such as approving the proposal, providing funding, or collaborating with you.
Review and Revise
- Proofread for clarity and coherence: Check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Ensure a logical flow: Read through your proposal to ensure the ideas are presented in a logical order and are easy to follow.
- Revise and refine: Fine-tune your proposal to make it concise, persuasive, and compelling.
Add Supplementary Materials
- Attach relevant documents: Include any supporting materials that strengthen your proposal, such as research findings, charts, graphs, or testimonials.
- Appendices: Add any additional information that might be useful but not essential to the main body of the proposal.
Formatting and Presentation
- Follow the guidelines: Adhere to any specific formatting guidelines provided by the organization or institution to which you are submitting the proposal.
- Use a professional tone and language: Ensure that your proposal is written in a clear, concise, and professional manner.
- Use headings and subheadings: Organize your proposal with clear headings and subheadings to improve readability.
- Pay attention to design: Use appropriate fonts, font sizes, and formatting styles to make your proposal visually appealing.
- Include a cover page: Create a cover page that includes the title of your proposal, your name or organization, the date, and any other required information.
Seek Feedback
- Share your proposal with trusted colleagues or mentors and ask for their feedback. Consider their suggestions for improvement and incorporate them into your proposal if necessary.
Finalize and Submit
- Make any final revisions based on the feedback received.
- Ensure that all required sections, attachments, and documentation are included.
- Double-check for any formatting, grammar, or spelling errors.
- Submit your proposal within the designated deadline and according to the submission guidelines provided.
Proposal Format
The format of a proposal can vary depending on the specific requirements of the organization or institution you are submitting it to. However, here is a general proposal format that you can follow:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your proposal, your name or organization’s name, the date, and any other relevant information specified by the guidelines.
2. Executive Summary:
- Provide a concise overview of your proposal, highlighting the key points and objectives.
- Summarize the problem, proposed solution, and anticipated benefits.
- Keep it brief and engaging, as this section is often read first and should capture the reader’s attention.
3. Introduction:
- State the problem or issue you are addressing and its significance.
- Provide background information to help the reader understand the context and importance of the problem.
- Clearly state the purpose and objectives of your proposal.
4. Problem Statement:
- Describe the problem in detail, highlighting its impact and consequences.
- Use data, statistics, or examples to support your claims and demonstrate the need for a solution.
5. Proposed Solution or Project Description:
- Explain your proposed solution or project in a clear and detailed manner.
- Describe how your solution addresses the problem and why it is the most effective approach.
- Include information on the methods, strategies, or activities you will undertake to implement your solution.
- Highlight any unique features, innovations, or advantages of your proposal.
6. Methodology:
- Provide a step-by-step explanation of the methodology or approach you will use to implement your proposal.
- Include a timeline or schedule that outlines the key milestones, tasks, and deliverables.
- Clearly describe the resources, personnel, or expertise required for each phase of the project.
7. Evaluation and Success Metrics:
- Explain how you will measure the success or effectiveness of your proposal.
- Identify specific metrics, indicators, or evaluation methods that will be used.
- Describe how you will track progress, gather feedback, and make adjustments as needed.
- Present a detailed budget that outlines the financial resources required for your proposal.
- Include all relevant costs, such as personnel, materials, equipment, and any other expenses.
- Provide a justification for each item in the budget.
9. Conclusion:
- Summarize the main points of your proposal.
- Reiterate the benefits and positive outcomes of implementing your proposal.
- Emphasize the value and impact it will have on the organization or community.
10. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as research findings, charts, graphs, or testimonials.
- Attach any relevant documents that provide further information but are not essential to the main body of the proposal.
Proposal Template
Here’s a basic proposal template that you can use as a starting point for creating your own proposal:
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
I am writing to submit a proposal for [briefly state the purpose of the proposal and its significance]. This proposal outlines a comprehensive solution to address [describe the problem or issue] and presents an actionable plan to achieve the desired objectives.
Thank you for considering this proposal. I believe that implementing this solution will significantly contribute to [organization’s or community’s goals]. I am available to discuss the proposal in more detail at your convenience. Please feel free to contact me at [your email address or phone number].
Yours sincerely,
Note: This template is a starting point and should be customized to meet the specific requirements and guidelines provided by the organization or institution to which you are submitting the proposal.
Proposal Sample
Here’s a sample proposal to give you an idea of how it could be structured and written:
Subject : Proposal for Implementation of Environmental Education Program
I am pleased to submit this proposal for your consideration, outlining a comprehensive plan for the implementation of an Environmental Education Program. This program aims to address the critical need for environmental awareness and education among the community, with the objective of fostering a sense of responsibility and sustainability.
Executive Summary: Our proposed Environmental Education Program is designed to provide engaging and interactive educational opportunities for individuals of all ages. By combining classroom learning, hands-on activities, and community engagement, we aim to create a long-lasting impact on environmental conservation practices and attitudes.
Introduction: The state of our environment is facing significant challenges, including climate change, habitat loss, and pollution. It is essential to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills to understand these issues and take action. This proposal seeks to bridge the gap in environmental education and inspire a sense of environmental stewardship among the community.
Problem Statement: The lack of environmental education programs has resulted in limited awareness and understanding of environmental issues. As a result, individuals are less likely to adopt sustainable practices or actively contribute to conservation efforts. Our program aims to address this gap and empower individuals to become environmentally conscious and responsible citizens.
Proposed Solution or Project Description: Our Environmental Education Program will comprise a range of activities, including workshops, field trips, and community initiatives. We will collaborate with local schools, community centers, and environmental organizations to ensure broad participation and maximum impact. By incorporating interactive learning experiences, such as nature walks, recycling drives, and eco-craft sessions, we aim to make environmental education engaging and enjoyable.
Methodology: Our program will be structured into modules that cover key environmental themes, such as biodiversity, climate change, waste management, and sustainable living. Each module will include a mix of classroom sessions, hands-on activities, and practical field experiences. We will also leverage technology, such as educational apps and online resources, to enhance learning outcomes.
Evaluation and Success Metrics: We will employ a combination of quantitative and qualitative measures to evaluate the effectiveness of the program. Pre- and post-assessments will gauge knowledge gain, while surveys and feedback forms will assess participant satisfaction and behavior change. We will also track the number of community engagement activities and the adoption of sustainable practices as indicators of success.
Budget: Please find attached a detailed budget breakdown for the implementation of the Environmental Education Program. The budget covers personnel costs, materials and supplies, transportation, and outreach expenses. We have ensured cost-effectiveness while maintaining the quality and impact of the program.
Conclusion: By implementing this Environmental Education Program, we have the opportunity to make a significant difference in our community’s environmental consciousness and practices. We are confident that this program will foster a generation of individuals who are passionate about protecting our environment and taking sustainable actions. We look forward to discussing the proposal further and working together to make a positive impact.
Thank you for your time and consideration. Should you have any questions or require additional information, please do not hesitate to contact me at [your email address or phone number].
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?

Action Research Proposal

Being able to start the processes of research require a researcher to undergo several screening and assessment procedures. Hence, it is not only the execution of how to develop grant proposal , conference proposal examples & samples and other business proposal examples that needed a process guide. Proposals used in the academic and educational fields need one too. One of the initial tasks of a researcher is to come up with an action research proposal. This document should be developed in a strong and effective manner to ensure that the research proposal will be approved.
- 56+ Proposal Examples
- 65+ Free Proposal Examples
As one of the first documents that are necessary to be prepared, it is important for an action research proposal to convince the screening committee that the research proposal can benefit the community and other entities to whom the study is for. Use simple proposal formats when making action research proposals so you can ensure that your target audience can easily understand the content of the document.
Participatory Proposal

Size: 215 KB
Educational Action Research Sample Proposal

Size: 63 KB
Classroom Action Research

Size: 69 KB
How to Create an Outstanding Action Research Proposal
Just like when developing business proposal examples & samples , you have to devote a lot of time and effort when making an action research proposal. This document can make or break the chances of your research to push through. A few ways on how you can make an impressive action research proposal include the following:
1. Ensure that you can present your awareness with the problem at hand. This can make your action research proposal more convincing especially if you can point out the root cause of the problem and how your research proposal can be of help should it be executed. This is also applicable when following the steps on how to prepare a need statement for your grant proposal .
2. List down the precise methods that you will use within the entirety of the research activities. This will allow your action research proposal to look more through and well-prepared.
3. Present current literature and research proposal examples & samples that can serve as one of your research’s foundation. Having significant information and guides related to the research that you would like to immerse in can help the screening committee when it comes to identifying the success potential of your research proposal.
Project Proposal Example

Size: 292 KB
Proposal for Teachers

Size: 175 KB
Dissertation Proposal

Size: 17 KB
Elements of an Effective and Convincing Action Research Proposal
There are different ways on how an action research proposal can be developed and presented. A basic outline that will allow you to showcase the necessary items that should be seen in an action research proposal include these elements:
1. Just like when developing project proposal examples , have an introduction that can present the problem that you would like to provide a solution with. Presenting this at the initial discussion of your action research proposal can convince the screening committee to further look into the content of the paper.
2. Present supporting details that can give an idea on how big the problem is. These items can make the need for your research proposal more necessary. Unlike the processes on how to write a request for proposal , the steps in developing an action research proposal relies more on your own desire to present something necessary and research-worthy to be discussed rather than from a demand coming from a particular entity.
3. Come up with a list of literature review that you can briefly discuss. Having a literature review can solidify your claims that your research is essential to be developed and executed.You may also see how to write a proposal for a project
4. Discuss the entities who are expected to be included in your study.These entities will serve as some of the variables that your research will take into account. Remember that it is not only in service proposal examples where the description of individual or group participation matter.
5. Present the ways and methods on how you plan to execute the research. You can also include a short presentation of your research results assessment.You may also see business proposal letters .
Education Proposal Example

Size: 199 KB
Action Research Proposal Format

Size: 73 KB
Tips When Making an Action Research Proposal
If you already know how to make an event planning service proposal , then you may be interested to broaden your knowledge when it comes to proposal development. If you are one of those who would like to have an understanding with how action research proposals are effectively made, then this discussion is for you. Here are some useful tips that can help you create an action research proposal that has higher chances of getting approved:
1. Be specific with the aspect of the problem that you would like to further study, evaluate or investigate. It is important for you to be precise with what you would like to give focus on so that the entire research activity will be guided accordingly. The same goes with landscaping proposal examples & samples as you have to specify the landscaping activity that will be specifically implemented within a particular area should the proposal be approved.
2. Properly present the initial data that you have collected. The way you organize and showcase the foundation of your action research proposal can affect the impression and perception of the screening committee towards your research proposal.You may also see commercial proposal
3. Use Free Proposal Examples & Samples as your guides. Having references when making an action research proposal can make it easier for you to come up with your own document. This will also help you properly format and put together all the content that you want to present in your action research proposal.You may also see policy proposal examples
Simple Action Research Proposal

Size: 106 KB
Course Project Action Research Proposal

Size: 25 KB
Do You Want to Have an Attention-Grabbing Action Research Proposal?
When creating an action research proposal, make sure that you are aware of what you are discussing. Workshop Proposal , Accounting Proposal and Concept Proposal Examples & Samples also need to be treated in the same manner. Some action research proposals fail to impress screening committees because of the researcher’s lack of understanding either with regards the problem needed to be faced or the research steps and activities that will be implemented.
Always remember that how you present an action research proposal reflect how you look into the research activity and its potential to be a success. With this, maximize the usage of our downloadable examples so you can develop an action research proposal that can impress your research screening committee.You may also see investment proposal examples
Proposal Maker
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a proposal for a new school recycling program
Compose a proposal for a school field trip to a science museum.
- Visit the University of Nebraska–Lincoln
- Apply to the University of Nebraska–Lincoln
- Give to the University of Nebraska–Lincoln
Search Form
Components of a research proposal.
In general, the proposal components include:
Introduction: Provides reader with a broad overview of problem in context.
Statement of problem: Answers the question, “What research problem are you going to investigate?”
Literature review: Shows how your approach builds on existing research; helps you identify methodological and design issues in studies similar to your own; introduces you to measurement tools others have used effectively; helps you interpret findings; and ties results of your work to those who’ve preceded you.
Research design and methods: Describes how you’ll go about answering your research questions and confirming your hypothesis(es). Lists the hypothesis(es) to be tested, or states research question you’ll ask to seek a solution to your research problem. Include as much detail as possible: measurement instruments and procedures, subjects and sample size.
The research design is what you’ll also need to submit for approval from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) or the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) if your research involves human or animal subjects, respectively.
Timeline: Breaks your project into small, easily doable steps via backwards calendar.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
The goal of a research proposal is twofold: to present and justify the need to study a research problem and to present the practical ways in which the proposed study should be conducted. The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews. They must provide persuasive evidence that a need exists for the proposed study. In addition to providing a rationale, a proposal describes detailed methodology for conducting the research consistent with requirements of the professional or academic field and a statement on anticipated outcomes and benefits derived from the study's completion.
Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005.
How to Approach Writing a Research Proposal
Your professor may assign the task of writing a research proposal for the following reasons:
- Develop your skills in thinking about and designing a comprehensive research study;
- Learn how to conduct a comprehensive review of the literature to determine that the research problem has not been adequately addressed or has been answered ineffectively and, in so doing, become better at locating pertinent scholarship related to your topic;
- Improve your general research and writing skills;
- Practice identifying the logical steps that must be taken to accomplish one's research goals;
- Critically review, examine, and consider the use of different methods for gathering and analyzing data related to the research problem; and,
- Nurture a sense of inquisitiveness within yourself and to help see yourself as an active participant in the process of conducting scholarly research.
A proposal should contain all the key elements involved in designing a completed research study, with sufficient information that allows readers to assess the validity and usefulness of your proposed study. The only elements missing from a research proposal are the findings of the study and your analysis of those findings. Finally, an effective proposal is judged on the quality of your writing and, therefore, it is important that your proposal is coherent, clear, and compelling.
Regardless of the research problem you are investigating and the methodology you choose, all research proposals must address the following questions:
- What do you plan to accomplish? Be clear and succinct in defining the research problem and what it is you are proposing to investigate.
- Why do you want to do the research? In addition to detailing your research design, you also must conduct a thorough review of the literature and provide convincing evidence that it is a topic worthy of in-depth study. A successful research proposal must answer the "So What?" question.
- How are you going to conduct the research? Be sure that what you propose is doable. If you're having difficulty formulating a research problem to propose investigating, go here for strategies in developing a problem to study.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failure to be concise . A research proposal must be focused and not be "all over the map" or diverge into unrelated tangents without a clear sense of purpose.
- Failure to cite landmark works in your literature review . Proposals should be grounded in foundational research that lays a foundation for understanding the development and scope of the the topic and its relevance.
- Failure to delimit the contextual scope of your research [e.g., time, place, people, etc.]. As with any research paper, your proposed study must inform the reader how and in what ways the study will frame the problem.
- Failure to develop a coherent and persuasive argument for the proposed research . This is critical. In many workplace settings, the research proposal is a formal document intended to argue for why a study should be funded.
- Sloppy or imprecise writing, or poor grammar . Although a research proposal does not represent a completed research study, there is still an expectation that it is well-written and follows the style and rules of good academic writing.
- Too much detail on minor issues, but not enough detail on major issues . Your proposal should focus on only a few key research questions in order to support the argument that the research needs to be conducted. Minor issues, even if valid, can be mentioned but they should not dominate the overall narrative.
Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sanford, Keith. Information for Students: Writing a Research Proposal. Baylor University; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences, Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Structure and Writing Style
Beginning the Proposal Process
As with writing most college-level academic papers, research proposals are generally organized the same way throughout most social science disciplines. The text of proposals generally vary in length between ten and thirty-five pages, followed by the list of references. However, before you begin, read the assignment carefully and, if anything seems unclear, ask your professor whether there are any specific requirements for organizing and writing the proposal.
A good place to begin is to ask yourself a series of questions:
- What do I want to study?
- Why is the topic important?
- How is it significant within the subject areas covered in my class?
- What problems will it help solve?
- How does it build upon [and hopefully go beyond] research already conducted on the topic?
- What exactly should I plan to do, and can I get it done in the time available?
In general, a compelling research proposal should document your knowledge of the topic and demonstrate your enthusiasm for conducting the study. Approach it with the intention of leaving your readers feeling like, "Wow, that's an exciting idea and I can’t wait to see how it turns out!"
Most proposals should include the following sections:
I. Introduction
In the real world of higher education, a research proposal is most often written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project or it's the first step in getting approval to write a doctoral dissertation. Even if this is just a course assignment, treat your introduction as the initial pitch of an idea based on a thorough examination of the significance of a research problem. After reading the introduction, your readers should not only have an understanding of what you want to do, but they should also be able to gain a sense of your passion for the topic and to be excited about the study's possible outcomes. Note that most proposals do not include an abstract [summary] before the introduction.
Think about your introduction as a narrative written in two to four paragraphs that succinctly answers the following four questions :
- What is the central research problem?
- What is the topic of study related to that research problem?
- What methods should be used to analyze the research problem?
- Answer the "So What?" question by explaining why this is important research, what is its significance, and why should someone reading the proposal care about the outcomes of the proposed study?
II. Background and Significance
This is where you explain the scope and context of your proposal and describe in detail why it's important. It can be melded into your introduction or you can create a separate section to help with the organization and narrative flow of your proposal. Approach writing this section with the thought that you can’t assume your readers will know as much about the research problem as you do. Note that this section is not an essay going over everything you have learned about the topic; instead, you must choose what is most relevant in explaining the aims of your research.
To that end, while there are no prescribed rules for establishing the significance of your proposed study, you should attempt to address some or all of the following:
- State the research problem and give a more detailed explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction. This is particularly important if the problem is complex or multifaceted .
- Present the rationale of your proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing; be sure to answer the "So What? question [i.e., why should anyone care?].
- Describe the major issues or problems examined by your research. This can be in the form of questions to be addressed. Be sure to note how your proposed study builds on previous assumptions about the research problem.
- Explain the methods you plan to use for conducting your research. Clearly identify the key sources you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Describe the boundaries of your proposed research in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you plan to study, but what aspects of the research problem will be excluded from the study.
- If necessary, provide definitions of key concepts, theories, or terms.
III. Literature Review
Connected to the background and significance of your study is a section of your proposal devoted to a more deliberate review and synthesis of prior studies related to the research problem under investigation . The purpose here is to place your project within the larger whole of what is currently being explored, while at the same time, demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methodological approaches they have used, and what is your understanding of their findings and, when stated, their recommendations. Also pay attention to any suggestions for further research.
Since a literature review is information dense, it is crucial that this section is intelligently structured to enable a reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your proposed study in relation to the arguments put forth by other researchers. A good strategy is to break the literature into "conceptual categories" [themes] rather than systematically or chronologically describing groups of materials one at a time. Note that conceptual categories generally reveal themselves after you have read most of the pertinent literature on your topic so adding new categories is an on-going process of discovery as you review more studies. How do you know you've covered the key conceptual categories underlying the research literature? Generally, you can have confidence that all of the significant conceptual categories have been identified if you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations that are being made.
NOTE: Do not shy away from challenging the conclusions made in prior research as a basis for supporting the need for your proposal. Assess what you believe is missing and state how previous research has failed to adequately examine the issue that your study addresses. Highlighting the problematic conclusions strengthens your proposal. For more information on writing literature reviews, GO HERE .
To help frame your proposal's review of prior research, consider the "five C’s" of writing a literature review:
- Cite , so as to keep the primary focus on the literature pertinent to your research problem.
- Compare the various arguments, theories, methodologies, and findings expressed in the literature: what do the authors agree on? Who applies similar approaches to analyzing the research problem?
- Contrast the various arguments, themes, methodologies, approaches, and controversies expressed in the literature: describe what are the major areas of disagreement, controversy, or debate among scholars?
- Critique the literature: Which arguments are more persuasive, and why? Which approaches, findings, and methodologies seem most reliable, valid, or appropriate, and why? Pay attention to the verbs you use to describe what an author says/does [e.g., asserts, demonstrates, argues, etc.].
- Connect the literature to your own area of research and investigation: how does your own work draw upon, depart from, synthesize, or add a new perspective to what has been said in the literature?
IV. Research Design and Methods
This section must be well-written and logically organized because you are not actually doing the research, yet, your reader must have confidence that you have a plan worth pursuing . The reader will never have a study outcome from which to evaluate whether your methodological choices were the correct ones. Thus, the objective here is to convince the reader that your overall research design and proposed methods of analysis will correctly address the problem and that the methods will provide the means to effectively interpret the potential results. Your design and methods should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
Describe the overall research design by building upon and drawing examples from your review of the literature. Consider not only methods that other researchers have used, but methods of data gathering that have not been used but perhaps could be. Be specific about the methodological approaches you plan to undertake to obtain information, the techniques you would use to analyze the data, and the tests of external validity to which you commit yourself [i.e., the trustworthiness by which you can generalize from your study to other people, places, events, and/or periods of time].
When describing the methods you will use, be sure to cover the following:
- Specify the research process you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results obtained in relation to the research problem. Don't just describe what you intend to achieve from applying the methods you choose, but state how you will spend your time while applying these methods [e.g., coding text from interviews to find statements about the need to change school curriculum; running a regression to determine if there is a relationship between campaign advertising on social media sites and election outcomes in Europe ].
- Keep in mind that the methodology is not just a list of tasks; it is a deliberate argument as to why techniques for gathering information add up to the best way to investigate the research problem. This is an important point because the mere listing of tasks to be performed does not demonstrate that, collectively, they effectively address the research problem. Be sure you clearly explain this.
- Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers and pitfalls in carrying out your research design and explain how you plan to address them. No method applied to research in the social and behavioral sciences is perfect, so you need to describe where you believe challenges may exist in obtaining data or accessing information. It's always better to acknowledge this than to have it brought up by your professor!
V. Preliminary Suppositions and Implications
Just because you don't have to actually conduct the study and analyze the results, doesn't mean you can skip talking about the analytical process and potential implications . The purpose of this section is to argue how and in what ways you believe your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the subject area under investigation. Depending on the aims and objectives of your study, describe how the anticipated results will impact future scholarly research, theory, practice, forms of interventions, or policy making. Note that such discussions may have either substantive [a potential new policy], theoretical [a potential new understanding], or methodological [a potential new way of analyzing] significance. When thinking about the potential implications of your study, ask the following questions:
- What might the results mean in regards to challenging the theoretical framework and underlying assumptions that support the study?
- What suggestions for subsequent research could arise from the potential outcomes of the study?
- What will the results mean to practitioners in the natural settings of their workplace, organization, or community?
- Will the results influence programs, methods, and/or forms of intervention?
- How might the results contribute to the solution of social, economic, or other types of problems?
- Will the results influence policy decisions?
- In what way do individuals or groups benefit should your study be pursued?
- What will be improved or changed as a result of the proposed research?
- How will the results of the study be implemented and what innovations or transformative insights could emerge from the process of implementation?
NOTE: This section should not delve into idle speculation, opinion, or be formulated on the basis of unclear evidence . The purpose is to reflect upon gaps or understudied areas of the current literature and describe how your proposed research contributes to a new understanding of the research problem should the study be implemented as designed.
ANOTHER NOTE : This section is also where you describe any potential limitations to your proposed study. While it is impossible to highlight all potential limitations because the study has yet to be conducted, you still must tell the reader where and in what form impediments may arise and how you plan to address them.
VI. Conclusion
The conclusion reiterates the importance or significance of your proposal and provides a brief summary of the entire study . This section should be only one or two paragraphs long, emphasizing why the research problem is worth investigating, why your research study is unique, and how it should advance existing knowledge.
Someone reading this section should come away with an understanding of:
- Why the study should be done;
- The specific purpose of the study and the research questions it attempts to answer;
- The decision for why the research design and methods used where chosen over other options;
- The potential implications emerging from your proposed study of the research problem; and
- A sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship about the research problem.
VII. Citations
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used . In a standard research proposal, this section can take two forms, so consult with your professor about which one is preferred.
- References -- a list of only the sources you actually used in creating your proposal.
- Bibliography -- a list of everything you used in creating your proposal, along with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem.
In either case, this section should testify to the fact that you did enough preparatory work to ensure the project will complement and not just duplicate the efforts of other researchers. It demonstrates to the reader that you have a thorough understanding of prior research on the topic.
Most proposal formats have you start a new page and use the heading "References" or "Bibliography" centered at the top of the page. Cited works should always use a standard format that follows the writing style advised by the discipline of your course [e.g., education=APA; history=Chicago] or that is preferred by your professor. This section normally does not count towards the total page length of your research proposal.
Develop a Research Proposal: Writing the Proposal. Office of Library Information Services. Baltimore County Public Schools; Heath, M. Teresa Pereira and Caroline Tynan. “Crafting a Research Proposal.” The Marketing Review 10 (Summer 2010): 147-168; Jones, Mark. “Writing a Research Proposal.” In MasterClass in Geography Education: Transforming Teaching and Learning . Graham Butt, editor. (New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2015), pp. 113-127; Juni, Muhamad Hanafiah. “Writing a Research Proposal.” International Journal of Public Health and Clinical Sciences 1 (September/October 2014): 229-240; Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005; Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Punch, Keith and Wayne McGowan. "Developing and Writing a Research Proposal." In From Postgraduate to Social Scientist: A Guide to Key Skills . Nigel Gilbert, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), 59-81; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences , Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
- << Previous: Writing a Reflective Paper
- Next: Generative AI and Writing >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.23(2); 2008 Apr

How to prepare a Research Proposal
Health research, medical education and clinical practice form the three pillars of modern day medical practice. As one authority rightly put it: ‘Health research is not a luxury, but an essential need that no nation can afford to ignore’. Health research can and should be pursued by a broad range of people. Even if they do not conduct research themselves, they need to grasp the principles of the scientific method to understand the value and limitations of science and to be able to assess and evaluate results of research before applying them. This review paper aims to highlight the essential concepts to the students and beginning researchers and sensitize and motivate the readers to access the vast literature available on research methodologies.
Most students and beginning researchers do not fully understand what a research proposal means, nor do they understand its importance. 1 A research proposal is a detailed description of a proposed study designed to investigate a given problem. 2
A research proposal is intended to convince others that you have a worthwhile research project and that you have the competence and the work-plan to complete it. Broadly the research proposal must address the following questions regardless of your research area and the methodology you choose: What you plan to accomplish, why do you want to do it and how are you going to do it. 1 The aim of this article is to highlight the essential concepts and not to provide extensive details about this topic.
The elements of a research proposal are highlighted below:
1. Title: It should be concise and descriptive. It must be informative and catchy. An effective title not only prick’s the readers interest, but also predisposes him/her favorably towards the proposal. Often titles are stated in terms of a functional relationship, because such titles clearly indicate the independent and dependent variables. 1 The title may need to be revised after completion of writing of the protocol to reflect more closely the sense of the study. 3
2. Abstract: It is a brief summary of approximately 300 words. It should include the main research question, the rationale for the study, the hypothesis (if any) and the method. Descriptions of the method may include the design, procedures, the sample and any instruments that will be used. 1 It should stand on its own, and not refer the reader to points in the project description. 3
3. Introduction: The introduction provides the readers with the background information. Its purpose is to establish a framework for the research, so that readers can understand how it relates to other research. 4 It should answer the question of why the research needs to be done and what will be its relevance. It puts the proposal in context. 3
The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1
The importance of the statement of the research problem 5 : The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology, work plan and budget etc). It is an integral part of selecting a research topic. It will guide and put into sharper focus the research design being considered for solving the problem. It allows the investigator to describe the problem systematically, to reflect on its importance, its priority in the country and region and to point out why the proposed research on the problem should be undertaken. It also facilitates peer review of the research proposal by the funding agencies.
Then it is necessary to provide the context and set the stage for the research question in such a way as to show its necessity and importance. 1 This step is necessary for the investigators to familiarize themselves with existing knowledge about the research problem and to find out whether or not others have investigated the same or similar problems. This step is accomplished by a thorough and critical review of the literature and by personal communication with experts. 5 It helps further understanding of the problem proposed for research and may lead to refining the statement of the problem, to identify the study variables and conceptualize their relationships, and in formulation and selection of a research hypothesis. 5 It ensures that you are not "re-inventing the wheel" and demonstrates your understanding of the research problem. It gives due credit to those who have laid the groundwork for your proposed research. 1 In a proposal, the literature review is generally brief and to the point. The literature selected should be pertinent and relevant. 6
Against this background, you then present the rationale of the proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing.
4. Objectives: Research objectives are the goals to be achieved by conducting the research. 5 They may be stated as ‘general’ and ‘specific’.
The general objective of the research is what is to be accomplished by the research project, for example, to determine whether or not a new vaccine should be incorporated in a public health program.
The specific objectives relate to the specific research questions the investigator wants to answer through the proposed study and may be presented as primary and secondary objectives, for example, primary: To determine the degree of protection that is attributable to the new vaccine in a study population by comparing the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups. 5 Secondary: To study the cost-effectiveness of this programme.
Young investigators are advised to resist the temptation to put too many objectives or over-ambitious objectives that cannot be adequately achieved by the implementation of the protocol. 3
5. Variables: During the planning stage, it is necessary to identify the key variables of the study and their method of measurement and unit of measurement must be clearly indicated. Four types of variables are important in research 5 :
a. Independent variables: variables that are manipulated or treated in a study in order to see what effect differences in them will have on those variables proposed as being dependent on them. The different synonyms for the term ‘independent variable’ which are used in literature are: cause, input, predisposing factor, risk factor, determinant, antecedent, characteristic and attribute.
b. Dependent variables: variables in which changes are results of the level or amount of the independent variable or variables.
Synonyms: effect, outcome, consequence, result, condition, disease.
c. Confounding or intervening variables: variables that should be studied because they may influence or ‘mix’ the effect of the independent variables. For instance, in a study of the effect of measles (independent variable) on child mortality (dependent variable), the nutritional status of the child may play an intervening (confounding) role.
d. Background variables: variables that are so often of relevance in investigations of groups or populations that they should be considered for possible inclusion in the study. For example sex, age, ethnic origin, education, marital status, social status etc.
The objective of research is usually to determine the effect of changes in one or more independent variables on one or more dependent variables. For example, a study may ask "Will alcohol intake (independent variable) have an effect on development of gastric ulcer (dependent variable)?"
Certain variables may not be easy to identify. The characteristics that define these variables must be clearly identified for the purpose of the study.
6. Questions and/ or hypotheses: If you as a researcher know enough to make prediction concerning what you are studying, then the hypothesis may be formulated. A hypothesis can be defined as a tentative prediction or explanation of the relationship between two or more variables. In other words, the hypothesis translates the problem statement into a precise, unambiguous prediction of expected outcomes. Hypotheses are not meant to be haphazard guesses, but should reflect the depth of knowledge, imagination and experience of the investigator. 5 In the process of formulating the hypotheses, all variables relevant to the study must be identified. For example: "Health education involving active participation by mothers will produce more positive changes in child feeding than health education based on lectures". Here the independent variable is types of health education and the dependent variable is changes in child feeding.
A research question poses a relationship between two or more variables but phrases the relationship as a question; a hypothesis represents a declarative statement of the relations between two or more variables. 7
For exploratory or phenomenological research, you may not have any hypothesis (please do not confuse the hypothesis with the statistical null hypothesis). 1 Questions are relevant to normative or census type research (How many of them are there? Is there a relationship between them?). Deciding whether to use questions or hypotheses depends on factors such as the purpose of the study, the nature of the design and methodology, and the audience of the research (at times even the outlook and preference of the committee members, particularly the Chair). 6
7. Methodology: The method section is very important because it tells your research Committee how you plan to tackle your research problem. The guiding principle for writing the Methods section is that it should contain sufficient information for the reader to determine whether the methodology is sound. Some even argue that a good proposal should contain sufficient details for another qualified researcher to implement the study. 1 Indicate the methodological steps you will take to answer every question or to test every hypothesis illustrated in the Questions/hypotheses section. 6 It is vital that you consult a biostatistician during the planning stage of your study, 8 to resolve the methodological issues before submitting the proposal.
This section should include:
Research design: The selection of the research strategy is the core of research design and is probably the single most important decision the investigator has to make. The choice of the strategy, whether descriptive, analytical, experimental, operational or a combination of these depend on a number of considerations, 5 but this choice must be explained in relation to the study objectives. 3
Research subjects or participants: Depending on the type of your study, the following questions should be answered 3 , 5
- - What are the criteria for inclusion or selection?
- - What are the criteria for exclusion?
- - What is the sampling procedure you will use so as to ensure representativeness and reliability of the sample and to minimize sampling errors? The key reason for being concerned with sampling is the issue of validity-both internal and external of the study results. 9
- - Will there be use of controls in your study? Controls or comparison groups are used in scientific research in order to increase the validity of the conclusions. Control groups are necessary in all analytical epidemiological studies, in experimental studies of drug trials, in research on effects of intervention programmes and disease control measures and in many other investigations. Some descriptive studies (studies of existing data, surveys) may not require control groups.
- - What are the criteria for discontinuation?
Sample size: The proposal should provide information and justification (basis on which the sample size is calculated) about sample size in the methodology section. 3 A larger sample size than needed to test the research hypothesis increases the cost and duration of the study and will be unethical if it exposes human subjects to any potential unnecessary risk without additional benefit. A smaller sample size than needed can also be unethical as it exposes human subjects to risk with no benefit to scientific knowledge. Calculation of sample size has been made easy by computer software programmes, but the principles underlying the estimation should be well understood.
Interventions: If an intervention is introduced, a description must be given of the drugs or devices (proprietary names, manufacturer, chemical composition, dose, frequency of administration) if they are already commercially available. If they are in phases of experimentation or are already commercially available but used for other indications, information must be provided on available pre-clinical investigations in animals and/or results of studies already conducted in humans (in such cases, approval of the drug regulatory agency in the country is needed before the study). 3
Ethical issues 3 : Ethical considerations apply to all types of health research. Before the proposal is submitted to the Ethics Committee for approval, two important documents mentioned below (where appropriate) must be appended to the proposal. In additions, there is another vital issue of Conflict of Interest, wherein the researchers should furnish a statement regarding the same.
The Informed consent form (informed decision-making): A consent form, where appropriate, must be developed and attached to the proposal. It should be written in the prospective subjects’ mother tongue and in simple language which can be easily understood by the subject. The use of medical terminology should be avoided as far as possible. Special care is needed when subjects are illiterate. It should explain why the study is being done and why the subject has been asked to participate. It should describe, in sequence, what will happen in the course of the study, giving enough detail for the subject to gain a clear idea of what to expect. It should clarify whether or not the study procedures offer any benefits to the subject or to others, and explain the nature, likelihood and treatment of anticipated discomfort or adverse effects, including psychological and social risks, if any. Where relevant, a comparison with risks posed by standard drugs or treatment must be included. If the risks are unknown or a comparative risk cannot be given it should be so stated. It should indicate that the subject has the right to withdraw from the study at any time without, in any way, affecting his/her further medical care. It should assure the participant of confidentiality of the findings.
Ethics checklist: The proposal must describe the measures that will be undertaken to ensure that the proposed research is carried out in accordance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki on Ethical Principles for Medical research involving Human Subjects. 10 It must answer the following questions:
- • Is the research design adequate to provide answers to the research question? It is unethical to expose subjects to research that will have no value.
- • Is the method of selection of research subjects justified? The use of vulnerable subjects as research participants needs special justification. Vulnerable subjects include those in prison, minors and persons with mental disability. In international research it is important to mention that the population in which the study is conducted will benefit from any potential outcome of the research and the research is not being conducted solely for the benefit of some other population. Justification is needed for any inducement, financial or otherwise, for the participants to be enrolled in the study.
- • Are the interventions justified, in terms of risk/benefit ratio? Risks are not limited to physical harm. Psychological and social risks must also be considered.
- • For observations made, have measures been taken to ensure confidentiality?
Research setting 5 : The research setting includes all the pertinent facets of the study, such as the population to be studied (sampling frame), the place and time of study.
Study instruments 3 , 5 : Instruments are the tools by which the data are collected. For validated questionnaires/interview schedules, reference to published work should be given and the instrument appended to the proposal. For new a questionnaire which is being designed specifically for your study the details about preparing, precoding and pretesting of questionnaire should be furnished and the document appended to the proposal. Descriptions of other methods of observations like medical examination, laboratory tests and screening procedures is necessary- for established procedures, reference of published work cited but for new or modified procedure, an adequate description is necessary with justification for the same.
Collection of data: A short description of the protocol of data collection. For example, in a study on blood pressure measurement: time of participant arrival, rest for 5p. 10 minutes, which apparatus (standard calibrated) to be used, in which room to take measurement, measurement in sitting or lying down position, how many measurements, measurement in which arm first (whether this is going to be randomized), details of cuff and its placement, who will take the measurement. This minimizes the possibility of confusion, delays and errors.
Data analysis: The description should include the design of the analysis form, plans for processing and coding the data and the choice of the statistical method to be applied to each data. What will be the procedures for accounting for missing, unused or spurious data?
Monitoring, supervision and quality control: Detailed statement about the all logistical issues to satisfy the requirements of Good Clinical Practices (GCP), protocol procedures, responsibilities of each member of the research team, training of study investigators, steps taken to assure quality control (laboratory procedures, equipment calibration etc)
Gantt chart: A Gantt chart is an overview of tasks/proposed activities and a time frame for the same. You put weeks, days or months at one side, and the tasks at the other. You draw fat lines to indicate the period the task will be performed to give a timeline for your research study (take help of tutorial on youtube). 11
Significance of the study: Indicate how your research will refine, revise or extend existing knowledge in the area under investigation. How will it benefit the concerned stakeholders? What could be the larger implications of your research study?
Dissemination of the study results: How do you propose to share the findings of your study with professional peers, practitioners, participants and the funding agency?
Budget: A proposal budget with item wise/activity wise breakdown and justification for the same. Indicate how will the study be financed.
References: The proposal should end with relevant references on the subject. For web based search include the date of access for the cited website, for example: add the sentence "accessed on June 10, 2008".
Appendixes: Include the appropriate appendixes in the proposal. For example: Interview protocols, sample of informed consent forms, cover letters sent to appropriate stakeholders, official letters for permission to conduct research. Regarding original scales or questionnaires, if the instrument is copyrighted then permission in writing to reproduce the instrument from the copyright holder or proof of purchase of the instrument must be submitted.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Digg
Latest Earthquakes | Chat Share Social Media
Using structured decision making to assess management alternatives to inform the 2024 update of the Minnesota Invasive Carp Action Plan
This report summarizes the results of a structured decision making process started by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources to develop and evaluate various invasive carp management strategies to inform a 2024 update of the Minnesota Invasive Carp Action Plan. The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources invited State, Federal, Tribal, and nongovernmental organization partners to participate in online and in-person workshops to elicit concerns and perform an expert-based assessment of potential invasive carp management strategies to address those concerns. The participatory group divided into two subgroups: the values team and the technical team. The values team specified 12 management objectives that captured the major interest group concerns. The technical and values teams developed 18 different invasive carp management strategies to compare. The technical team then scored each strategy in terms of how well it met each management objective. The values team weighted the management objectives to assess where tradeoffs might need to be made. The results of this process captured the wide range of partner concerns and technical opinions using a transparent, repeatable, and rigorous method. The analyses suggest that tradeoffs between management efficacy and cost are likely. Furthermore, considerable uncertainty exists among the technical experts regarding which strategy is likely to be most effective or cost-efficient. Followup analyses were done to assess how resolving uncertainty among experts could affect decision making and guide future monitoring efforts.
Citation Information
Related content, max post van der burg, phd, chief - spatial and ecological analytics branch, mike colvin, phd, research ecologist.
Southeast Asia Research Group
2024 Summer Conference
1-3 july | hong kong.
Save the date! Our summer conference will be hosted by the Southeast Asia Research Centre at the City University of Hong Kong from July 1 to July 3, 2024 .
Call for Paper/Panel Proposals
Mid-/Advanced-Career Thematic Sessions at the SEAREG Conference provide more established scholars of Southeast Asia the opportunity to present their research and gain valuable feedback from the SEAREG community.
Thematic Sessions will feature two or three working papers that are substantively connected to one another, as well as a discussant. Sessions will be conducted in an APSA-style format of fifteen minute paper presentations followed by 10 minutes of discussant comments before opening to questions from the audience.
Examples of Thematic Sessions in the past include “Challenges of Political Inclusion: Examining Minority Representation, State Policies, and Religious Organizations in Democratic and Authoritarian Regimes,” “The Dynamics of Public Participation in Vietnam,” “Exploring Subnational Democratic Variations in Indonesia: Insights from Electoral Democracy, Neighbourhood Leaders, and Ideological Diversity,” “Politics and Development in Southeast Asia,” and “Unpacking Causal Relationships: Exploring the Role of Colonial Narratives, Bureaucratic Selection, and Mosques in Shaping Societal Outcomes.”
All paper or panel proposals for Thematic Sessions should fit within SEAREG's broad mission: to provide a forum for presenting and discussing the best new research by social scientists working on Southeast Asia .
Because the purpose of the SEAREG Thematic Sessions is to engage with more established scholars, lead authors for the working papers should be at least three years beyond their PhD . Although co-authored papers will be considered, all presenters and discussants named in the proposal should be at least three years post-PhD completion.
To apply, please submit the following via this link to a Google Form:
For a paper submission (we will determine your panel assignment if accepted): •Title and abstracts of the paper (2,500 max characters) •Names and affiliations of author(s) (indicate the presenter)
For a panel submission: •Thematic session abstract of 200 words •Title and abstracts of the two or three papers (2,500 max characters) •Names and affiliations of presenters and discussant for the session
We strongly encourage all sessions to attend to and recognize the diversity of our scholarly community when submitting their proposals.
The application deadline is June 1, 2024 . The review of proposals will begin immediately following the deadline.
For any questions, please email Nico Ravanilla ( [email protected] ).
Thank you, and we look forward to seeing many of you at our Summer Conference!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
Action Research Proposal Template: A Guide for Real-World Problem Solving. As a researcher dedicated to making a real impact in the world, I understand the importance of developing an action research proposal that goes beyond the standard academic proposal.Action research is a powerful tool for bringing about meaningful change in a specific context, and a well-crafted proposal is essential for ...
All content in this area was uploaded by Mercedita Penarijo Dampog on May 16, 2021 . ... ACTION RESEARCH PROPOSAL TEMPLATE. LEAD PROPONENT . DAMPOG, MERCEDITA, P. MEMBER . BALADAD, NELIA, DL.
Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. It was first coined as a term in 1944 by MIT professor Kurt Lewin.A highly interactive method, action research is often used in the social ...
Action research (AR) is a methodical process of self-inquiry accomplished by practitioners to unravel work-related problems. This paper analyzed the action research reports (ARRs) in terms of ...
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Step 1: Select a Problem or Issue. The first step in writing an action research paper is to identify a problem or issue that you would like to address. The problem or issue should be relevant to your area of work or interest and should be specific and measurable. Once you have identified the problem or issue, you can begin to formulate a ...
1. Research Proposal Format Example. Following is a general outline of the material that should be included in your project proposal. I. Title Page II. Introduction and Literature Review (Chapters 2 and 3) A. Identification of specific problem area (e.g., what is it, why it is important). B. Prevalence, scope of problem.
Action Research Proposal Rubric (EDCC 551 Action Research in Educational Settings) Candidate:_____Instructor:_____Date:_____ DUE: Exemplary - 3 Proficient - 2 Does Not Meet ... Content, Topics Addressed Summary of topics provides excellent, thorough background to research question; analyzes and
Andrew Johnson. Action research is a type of research related to one's professional practice. In the field of education, it can be defined as the process of studying a school, classroom, or teaching-learning situation with the purpose of understanding and improving the quality of actions or instruction.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
We walk you through two successful research proposals (Master's PhD-level), as well as our free research proposal. Download PDF or Word. About Us; Services. 1-On-1 Coaching. Topic Ideation; ... All content copyright Grad Coach 2024 · The Grad Coach logo is a registered trade mark: UK00003956375 · Tutors' Association ID: 55870609
1. Title Page: Include the title of your proposal, your name or organization's name, the date, and any other relevant information specified by the guidelines. 2. Executive Summary: Provide a concise overview of your proposal, highlighting the key points and objectives.
1. Just like when developing project proposal examples, have an introduction that can present the problem that you would like to provide a solution with. Presenting this at the initial discussion of your action research proposal can convince the screening committee to further look into the content of the paper. 2.
In general, the proposal components include: Introduction: Provides reader with a broad overview of problem in context. Statement of problem: Answers the question, "What research problem are you going to investigate?" Literature review: Shows how your approach builds on existing research; helps you identify methodological and design issues in studies similar to your own; introduces you to ...
The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews.
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer. [ 2] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about ...
ACTION RESEARCH Session 6.1 Perparing the Action Research Proposal 6 2 You may also mention any data or current research in the area of your topic and highlight the gap that you plan to address in the Action Research. 3 It is also here that you cite any theory, related studies, DepEd policies, or laws that would strengthen your claims about the intervention or treatment that you
Description of EDCC 551 Action Research Course EDCC 551: Action Research in Educational Settings (3 credits) Course Description: This course is designed to give an overview of action research, particularly action research that is conducted within educational settings. Emphasis is placed upon gaining an understanding of the
It puts the proposal in context. 3. The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1. The importance of the statement of the research problem 5: The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology ...
An Action Research Proposal. December 2016. Chapter: 1. Authors: Norlita B. Nemenzo. Department of Education of the Philippines. References (5) Content uploaded by Norlita B. Nemenzo. Author content.
An action research proposal is a document written to explain the problems faced in a particular field such as education or medicine and the actions that can be taken to solve those problems. Take an example of an action research proposal about the reading strategies in primary school.
1 Action Research Proposal: Research Procedures Jenna Hassett American College of Education RES5153 Dr. Audra Pickett March 10, 2023. 2 Research Procedures In recent years, the field of education has agreed that teaching content is no longer the priority for students, but rather they should be mastering skills that can be applied to different ...
With this solicitation, NIJ seeks research partnership proposals that meet the needs and missions of local justice and service provider entities — including police, corrections, courts, victim services, forensic science service providers, and community safety and adult and juvenile justice entities — and the communities they serve. These partnerships should apply a data-driven, problem ...
This bipartisan tax package, which passed the House by a vote of 357-70, would revive proven pro-growth policies like restoring full and immediate research and development expensing and 100% bonus ...
This report summarizes the results of a structured decision making process started by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources to develop and evaluate various invasive carp management strategies to inform a 2024 update of the Minnesota Invasive Carp Action Plan. The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources invited State, Federal, Tribal, and nongovernmental organization partners to participa
Call for Paper/Panel Proposals. Mid-/Advanced-Career Thematic Sessions at the SEAREG Conference provide more established scholars of Southeast Asia the opportunity to present their research and gain valuable feedback from the SEAREG community.. Thematic Sessions will feature two or three working papers that are substantively connected to one another, as well as a discussant.
Central Intelligence Agency Director William Burns presented a new proposal to help advance a deal between Israel and Hamas to end the six-month war in Gaza and release remaining hostages.