
- October 11, 2023
- Education Advice

Ph.D. vs. Doctorate: What are the Differences?
UOTP Marketing

For those who have a deep-seated attitude, pursuing a doctoral degree can be a tough yet beneficial journey. Currently enrolled in a doctorate program means that a person has already scooched over college admissions, went through high stake tests and exams, and finished all those research papers and long hours spent in university libraries hitting the books. While studying for a doctorate entails asserting oneself to an extensive amount of quality time and money , its significance and purpose usually pave the way to a lucrative end.
After having finished the Master’s Degree , students begin to think about their next step in their academic career. Then, paradoxically, while navigating through academia, they find themselves baffled by the immense terms and terminologies used to label specific degrees. Because the terms “Doctorate” and “Ph.D.” are somehow interlocked and overlap, and because “PhD” is sometimes used inconsistently, it can lead to considerable confusion. Ph.D. vs. Doctorate? You might wonder what their difference is, and why they are important. E xplaining what each of these terms stands for, the difference between them, and why they are valuable, can help you steer yourself down the right path from the outset.
Doctorate Degree vs. Ph.D.

At first glance, it is pretty easy to confuse these two terms. But it is important for everyone to be able to make a distinction between the two. In this article, we will discuss the difference between Ph.D. and Doctorate in detail in order to get rid of any confusion you may have. In the academic world, the terms Doctorate and Ph.D. are currently used interchangeably. Both of them are the top cap of the ladder. However, a doctorate is mostly used as an umbrella term covering many fields ranging from professional degrees, humanities, and scientific disciplines.
A Ph.D. or Doctor of Philosophy, on the other hand, is a subcategory of a doctoral degree, it is much more distinct and clear-cut and is usually narrower in nature encompassing only humanities and scientific fields. In plain English, when someone says they are enrolling on a doctoral degree, it means they are doing a Ph.D. in a specific field. So, technically, in common parlance, there is no difference between the two terms.
But at the other end of the spectrum, one should be careful not to confuse a professional doctoral degree with a Ph.D. The former is more practical and is designed to prepare students to apply existing knowledge to find solutions to real-life problems and has a direct application to a particular profession.
A Ph.D. is theoretical by nature and is more academic and research-focused. it is often fixed on disseminating knowledge by conducting authentic research which means reviewing and identifying gaps in current literature and evaluating the relevance of existing and emerging theories within a particular field.
What Is a Ph.D. Degree and Why Should You Go for It?
Students who acquire a Ph.D. are justly proud — they wear it as a badge of identity in the academic elite. Traditionally, a Ph.D. was associated with teaching, which from Latin licentia docendi meant “license to teach”. However, the concept of Ph.D. has been on shifting sands nowadays and has become a more general term that isn’t necessarily confined to teaching only.
The Value of a PhD

Obtaining a Ph.D. helps you capitalize on the emerging academic opportunities making you more easily identifiable to employers or businesses seeking to fill professional, higher-level job positions. Many of these career options, conversely, are not available to those who do not belong to the Ph.D. club. While pursuing a Ph.D. requires devoting a tremendous effort and time and making significant personal sacrifices pushing the boundaries of knowledge, it’s all in service of the area of study you’re most passionate and zealous about. Ultimately, once you’ve attained your Ph.D., you will have achieved the pinnacle of education— something not too many people have or are able to accomplish.
FREE RESOURCE

A Guide to Choosing and Applying to Ph.D. Programs
Learn everything you need to know about selecting and applying to Ph.D. programs. Learn tips and tricks for a successful application and find your ideal program today!
What Is a Doctorate Degree?
A doctoral or doctorate degree is usually the most advanced degree one can earn in an academic discipline. Many pursue a doctorate degree to increase their professional credibility, be acknowledged as an expert in a specific field, and improve their resume.
A doctorate degree is a graduate-level credential that is usually earned after multiple years of graduate school. Earning a doctoral degree requires a significant level of research and work. In order to get this degree, one has to research a subject thoroughly, conduct new research and analysis, and provide a solution or interpretation into the field. But what types of doctoral degrees are available?
Types of Doctorate Degrees
There are two categories of doctorate degrees: an academic degree and a professional doctorate degree. An academic degree focuses on research, data analysis, and the evaluation of theory. A professional doctorate degree, on the other hand, is considered a terminal degree, which means that one has achieved the most advanced degree in the field. This degree is specifically designed for working professionals who want to grow in their careers.
Professional Doctorate Degrees
A professional doctorate is designed for working professionals who have experience in the field and want to increase their knowledge, improve their credibility, and advance their careers. This degree focuses on applying research to practical issues, coming up with interpretation and solutions, as well as designing effective professional practices within a particular field.
Professional doctoral degrees include:
Doctor of Business Administration (DBA)
The DBA degree is ideal for students who already have a general business background and are interested in delving deeper into the practical and theoretical aspects that underpin business education. More to the point, in DBA you will develop the ability to solve real-life problems, discover the relevant expertise to innovate and uphold complex business issues and so much more. Upon completion, DBA students will possess enhanced leadership and strategic skills as well as the tools to propel their careers in today’s marketplace. The Business Administration industry is keen on finding such graduates with business skills and this is indicated by the immense job positions currently available.
Doctor of Education (Ed.D.)
If you are interested in setting your eyes on creating lifelong learning among your students, making a positive influence in educational culture, contributing to the growing body of research in the education realm , or just enhancing your subject matter expertise, the Doctor of Education program ticks all the boxes. This degree maintains a rigorous approach in academic education that prepares graduates to showcase the skills and expertise to devise solutions in tackling the challenges in contemporary education practice and become transformational leaders in the industry.
Doctor of Computer Science (DCS)
The demand for computer scientists has reached its peak and it is among the most sought-after positions nowadays. With a degree in DCS, you will have the opportunity to design, apply innovative experiments, predict trends and, ultimately, develop a richer understanding and contribute to your area of expertise. After all, who doesn’t want an exciting and financially stable career?
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. we will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours. if there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:.
By clicking the Send me more information button above, I represent that I am 18+ years of age, that I have read and agreed to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy , and agree to receive email marketing and phone calls from UOTP. I understand that my consent is not required to apply for online degree enrollment. To speak with a representative without providing consent, please call +1 (202) 274-2300
- We value your privacy.
Doctor of Medicine (M.D.)
The Doctor of Medicine degree is designed to prepare you for various medical challenges in different settings nationally and internationally. This program will further develop your critical thinking and clinical reasoning skills required for safe, high-quality medical practices. It will also improve your leadership, communication, and teamwork skills for collaborative patient care.
Doctor of Optometry (O.D.)
This professional degree typically requires four years of study. It focuses on basic biological sciences such as anatomy and physiology, microbiology, neuroanatomy, and so on. This doctoral degree will prepare, educate, and train professionals to practice at the highest level of proficiency, professionalism, and integrity.
Doctor of Psychology (PsyD)
The Doctoral of Psychology degree concentrates on the clinical and applied aspects of psychology. This type of doctorate prepares students for professional practice and clinical placement. This degree will be highly beneficial when working directly with patients who need psychology services. In addition, this degree allows doctors of psychology to confidently function as researchers and clinicians.
How to Choose a Ph.D. Program?
Choosing a Ph.D. program can be pretty challenging; it is a big academic decision and investment that requires commitment and perseverance. But how can you pick the right Ph.D. program for you? Well, there are some tips to help you choose the best fit for your goals and preferences:
- Think about the reasons why you want a Ph.D., what you expect to gain from it, and whether it is compatible with your professional goals.
- Consider your research environment.
- Take your time to research, compare, and consider multiple opportunities carefully.
- Pick a subject that interests and motivates you but is also practical.
- Ask your professors and other scholars in the field for advice.
All in all, the terms “Doctorate’’ and “Ph.D.” are in essence the same, which means all Ph.D. students are Doctoral students as well. On the other hand, earning a Ph.D. degree is no joke. If anything, Ph.D. students have the tenacity, patience, persistence, and years of hard work that you can vouch for. Ultimately, deciding what type of doctoral degree you should hop on, depends on your career goals, what you are passionate about and how you are going to achieve it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a doctorate and a ph.d..
In academic contexts, the terms “Doctorate” and “Ph.D.” are often used interchangeably, but there is a distinction. A Doctorate is an umbrella term covering a wide range of fields, including professional degrees, humanities, and scientific disciplines. A Ph.D., or Doctor of Philosophy, is a specific type of doctoral degree, typically focused on research and academic pursuits in the humanities and scientific fields.
Why should I pursue a Ph.D.?
Pursuing a Ph.D. can be a valuable endeavor, as it opens up academic and research opportunities, enhances your expertise in a specific field, and makes you more attractive to employers seeking candidates for high-level positions. It’s a chance to push the boundaries of knowledge and become an expert in your chosen study area.
What are the benefits of a professional doctorate?
Professional doctorate degrees, such as Doctor of Business Administration (DBA) or Doctor of Education (Ed.D.), are designed for working professionals who want to apply research to practical issues in their field. These degrees can enhance your career prospects, leadership skills, and problem-solving abilities within your profession.
How do I choose the right Ph.D. program?
To choose the right Ph.D. program, consider your career goals, research environment, and personal interests. Take your time to research and compare programs, seek advice from professors and experts in your field, and ensure that the program aligns with your professional aspirations.
What are the main differences between academic and professional doctorate degrees?
Academic doctorate degrees focus on research, theory evaluation, and data analysis, often leading to careers in academia or research. Professional doctorate degrees are more practical, designed for working professionals, and concentrate on applying research to real-world problems within a specific field.
Can I earn a Ph.D. in any field?
Ph.D. programs are available in various fields, including humanities, social sciences, natural sciences, engineering, and more. However, the specific availability of Ph.D. programs may vary by field and university.
Is a Ph.D. a challenging journey?
Yes, pursuing a Ph.D. can be a challenging journey that requires dedication, patience, and years of hard work. It involves conducting original research, writing a dissertation, and often teaching or assisting in courses. It’s a significant commitment, but it can be highly rewarding.
What are the potential career opportunities after earning a Ph.D.?
With a Ph.D., you can pursue careers in academia as a professor or researcher, work in research and development roles in various industries, or take on leadership positions in organizations. The specific career path will depend on your field of study and personal interests.
Share it with your friends!
Explore more.

Accounting vs. Finance Degree: Which Major to Choose?

12 Important Bookkeeping Skills You Need for a Successful Career
Recent resources.

What Can You Do with an International Studies Degree [2024]

9 Benefits of Learning a Second Language

Associate’s vs. Bachelor’s: Which One To Choose?

Web Designer vs. Web Developer: What’s the Difference?
INTERESTED IN LEARNING MORE?
Chat with an Admissions Officer Now!

- Associates Degree
- Bachelors Degrees
- Masters Degrees
- Doctoral Degrees
- Faculty & Staff
- Accreditation
- Student Experience
QUICK LINKS
- Admission Requirements
- Military Students
- Financial Aid

- ACADEMIC ADVICE
What’s the Difference Between a Ph.D. and a Doctorate?
- May 1, 2023
Table of Contents
Research (academic), applied (professional), what is a ph.d., is a ph.d. higher than a professional doctorate, doctoral study vs. dissertation, who is it for, what do you learn in each, can a ph.d. be called a doctor, the bottom line.
The terms Ph.D. and Doctorate are often used interchangeably when considering advanced degrees in academia. Both degrees involve rigorous academic study and research, but their focus, duration, and requirements differ. Hence, these significant differences between the two are worth understanding before deciding which path to pursue.
In this article, we will explore the key differences between doctorate vs. Ph.D., including their definitions, the types of programs they are offered in, and the career opportunities they lead to. By the end, you should have a clear understanding of the differences between these two degrees and which one is right for you.
What Is a Doctorate?
A doctorate degree is the highest level of academic degree that can be awarded by a university. It typically requires a minimum of three to five years of advanced study and research beyond a bachelor’s or master’s degree . Doctoral programs are designed to prepare individuals for advanced careers in academia, research, or other professional fields. There are two main types of doctorates: Research (Academic) and Applied (Professional). Let’s talk about each in more detail.
A research doctorate, also known as an academic doctorate, is a type of doctoral degree focused on original research and advancing knowledge in a specific academic field. These programs require students to take advanced coursework in their field and complete original research contributing to the body of knowledge in their study area. The research component is typically the program’s centerpiece, and students are expected to produce a dissertation or thesis that represents a significant contribution to their field of study.
A research doctorate is highly valued in academia, and graduates often pursue careers as professors, researchers, or scholars in their field. While a significant time commitment and dedication are required, they provide individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to make contributions to their field and advance their careers in academia. Examples of research doctorates include the Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.), Doctor of Science (D.Sc.), and Doctor of Education (Ed.D.) , among others.
An applied doctorate, or professional doctorate, is a type of doctoral degree that focuses on applying knowledge and skills in a specific profession or industry. These programs emphasize the practical application of research and theories to solve real-world problems in their field.
The curriculum includes coursework designed to enhance students’ professional skills, including leadership, management, or organizational behavior. An applied doctorate program’s capstone project or dissertation addresses a real-world problem or issue within the student’s profession or industry. The research is conducted in collaboration with professionals in the field.
While applied doctorate programs require a significant time commitment and dedication to a specific profession, they provide individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to become experts in their field and make a great impact. Graduates of such programs are well-prepared to take on leadership roles in their profession. The degree can lead to career advancement and higher salaries.
Examples of applied doctorates include the Doctor of Education (Ed.D.), Doctor of Business Administration (DBA), and Doctor of Psychology (Psy.D.), among others.
Students who have completed advanced studies in a particular academic field and contributed original research to that field are awarded a Ph.D., also known as a Doctor of Philosophy. Ph.D. programs are geared toward developing independent scholars who can conduct original research and advance knowledge in their chosen fields.
The coursework of a Ph.D. program involves advanced studies in the student’s area of interest, coupled with a significant research component. Students must produce a dissertation or thesis that adds to the existing body of knowledge in their field of study.
Ph.D. programs generally require multiple years to complete and lead to opportunities for graduates to work as professors, scholars, or researchers within their field of specialization. While Ph.D. degrees are commonly associated with academic careers, they can also offer advantages for graduates seeking positions in government or industry, as they demonstrate expertise in a specific area and an aptitude for original research.
Comparing a Ph.D. to a professional doctorate is difficult, as both degrees have distinct characteristics and are designed for different purposes.
A Ph.D. is primarily a research-focused degree focused on producing independent scholars who can conduct original research and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field. On the other hand, a professional doctorate focuses on the application of knowledge and skills in a specific profession or industry.
These programs typically emphasize the practical application of research and theories to solve real-world problems in their field. Graduates of professional doctorate programs are well-prepared to take on leadership roles in their profession, and the degree can lead to career advancement and higher salaries.
So, in terms of purpose and focus, Ph.D. and professional doctorate degrees are different. It’s not a matter of one being higher than the other, but rather, it depends on an individual’s career goals and aspirations. Both degrees are considered terminal degrees, meaning they represent the highest level of academic achievement in their respective fields.
Ph.D. vs. Professional Doctorate: Differences
Understanding the differences between a Ph.D. and a professional doctorate can help you make an informed decision about which program is right for you and your career goals. And while both types of degrees require extensive study and research, there are significant differences between the two.
✅ Request information on BAU's programs TODAY!
One of the key differences between a Ph.D. and a professional doctorate is the focus of the doctoral study. Ph.D. programs typically focus on producing independent scholars who can conduct original research and advance knowledge in their chosen field. In contrast, professional doctorate programs emphasize the practical application of research and theories to solve real-world problems in their field.
While both degrees require extensive research, Ph.D. programs often require a significant original contribution to the field in the form of a dissertation, while professional doctorate programs typically require a capstone project or applied research project that demonstrates the student’s ability to apply their knowledge to a real-world problem.
Ph.D. programs are geared toward individuals interested in pursuing an academic career, such as becoming a professor or researcher. These programs prepare students for a life of scholarship and original research.
On the contrary, professional doctorate programs are geared toward professionals already working in a specific profession or industry and wanting to advance their careers through further education. These programs provide students with the knowledge and skills needed to take on leadership roles in their profession or industry.
The content of the curriculum in Ph.D. and professional doctorate programs differs significantly. Ph.D. programs aim to give students extensive knowledge of their field of study and equip them with the skills to conduct original research. On the other hand, professional doctorate programs have a practical focus, with students taking courses that prepare them for leadership positions in their respective professions or industry, including management, ethics, and professional communication.
The title “Doctor” is used to refer to someone who has earned a doctoral degree, whether it is a Ph.D. or a professional doctorate. In academic and professional settings, it is common for individuals with a Ph.D. to be referred to as “Dr.” along with their name, just as someone with a professional doctorate would be.
However, it’s important to note that the title “Doctor” does not necessarily indicate that the person is a medical doctor or a physician. Additionally, it is worth noting that different countries and cultures have different conventions for how the title “Doctor” is used, so it’s always a good idea to check local customs and norms to ensure proper usage.
In conclusion, the decision to pursue a Ph.D. or a professional doctorate ultimately depends on your individual career goals and aspirations. Both degrees are highly respected and can lead to exciting and fulfilling careers.
Remember, the pursuit of advanced education is a challenging but rewarding journey that leads toward new opportunities, personal growth, and the chance to make a positive impact in your field.
Bay Atlantic University
Leave a reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You May Also Like
- 6 minute read
The Ultimate Guide to Standardized Tests in the United States
- January 22, 2021
- 5 minute read
Project Management Methodologies To Know and Use
- March 4, 2022
- 4 minute read
10 Things To Do To Prepare For College
- July 30, 2020
- 8 minute read
How Long You Can Stay in the U.S. on a Student Visa?
- May 17, 2022
- 8 shares 8 0 0
- INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
12 Useful Apps for College Students
- June 3, 2022
Can International Students Work In the USA? Opportunities & How To Find Them
- July 16, 2020
13 Benefits of Going to College
- April 2, 2024
Auditory Learner: Characteristics & Benefits
- 7 minute read
How Much Do Writers Make?
- April 1, 2024
- POLITICAL SCIENCE
What is a Diplomat and What Do They Really Do?
- March 7, 2024
- 7 shares 5 0 2
Request information on BAU's programs TODAY!

- Masters vs PhD – Differences Explained
- Types of Doctorates
The decision of whether or not to pursue a Masters or PhD (or both) after you complete your undergraduate studies is not necessarily a straightforward one. Both are postgraduate degrees but are different in terms of the academic experience and the career paths taken afterwards.
In short, a Masters degree involves a year of study, primarily through taught lectures and a final dissertation research project, whilst a PhD (also referred to as a doctorate degree) is a three-year commitment of independent research on a specific subject.
There’s more to it than that, however – read on for more information.
What Is a Masters Degree?
A Masters degree is the next level of education after the completion of an undergraduate degree, commonly known as a Bachelors.
These degree levels are often referred to in terms of cycles so that a Bachelor’s is a first-cycle degree, a Masters is a second-cycle and finally, a PhD is the third-cycle of higher education (and the highest).
Masters degrees demand an intense period of study, usually centred around a core series of lectures and taught modules, coupled with coursework assignments and exams, followed by the completion of a contained research project usually taking students 3-4 months to complete.
These types of degrees are attractive to recent graduates who want to delve deeper into their specific field of study, gaining some research experience and more specialised knowledge beyond what an undergraduate degree can offer.
Equally, some pursue a Masters degree program in a subject that is only tangentially related to their Bachelors degree, helping them gain a broader depth of knowledge.
These degrees also serve as a significant stepping stone for those already in employment who want to progress their current career development and earn a higher salary. They can also be an excellent method for helping in changing careers completely by learning new skills and subject knowledge.
What Is a PhD Degree?
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is the highest academic degree that can be awarded and is the third and final cycle in the progression of higher education.
A doctoral degree is earned on the basis of producing a significant, independent and novel body of work (a Thesis) that contributes new knowledge to a particular research topic.
These are research degrees that are a significant investment of a candidate’s time, resources and energy and are all but a pre-requisite for anyone considering a career in academia, such as eventually becoming a professor.
There are some exceptions to this, such as those with a medical background who may earn an MD (Doctor of Medicine), which is the equivalent of a PhD.
Doctoral degrees can also have a significant positive impact on career development outside of academia, especially in fields such as engineering, business and finance that have a high demand for highly qualified and capable people.
A graduate student engaged in PhD study is commonly known as a PhD student, PhD candidate or doctoral student.
What are the Benefits of a Masters Degree?
There are several reasons one might consider doing a Masters degree rather than a PhD in their graduate education. These include:
- It takes approximately a third of the time to do compared to a doctorate degree and costs less too.
- It’s a good way to differentiate yourself from those that hold only an undergraduate degree without having to commit to a substantial research degree.
- The end goal is more career-focused as opposed to research-focused. For example, it is practically an ‘easier’ route to changing or progressing your career if that aligns with your professional goals.
What are the Benefits of Doing a PhD?
You may continue on into a doctoral program after a Masters or you may even dive straight in after completing your undergraduate studies. So, what are the advantages of completing this third-cycle?
- You’ll have developed a wealth of transferable skills at graduate school, such as effective communication of complex concepts, multi-tasking time-management and the ability to adapt to and solve unexpected problems.
- A doctorate helps to establish you as an expert within your chosen subject area; your work will hopefully have furthered the knowledge in this.
- It will open up career paths and teaching positions within academia that may otherwise be very difficult to get a hold in (although these career paths will still be very competitive).
- You can add the title ‘Dr’ in front of your name!
Which Degree Is More Impactful: A Masters or a PhD?
On paper, the answer should be clear: A doctorate degree is the highest degree you can earn, so has more impact than a Masters, which in turn has more impact than a Bachelors.
The reality is that the size of the impact (if any) really depends on the subject area and the career path you choose (if the measure of impact is how it positively improves your career prospects, that is).
For someone with aspirations of becoming a professor, a PhD will be of greater value than a Masters alone.
Equally, it’s also possible that someone with a PhD entering a different field or one that doesn’t require a PhD may find that their degree has no bearing on their career or in some cases may even be seen as a ‘negative’ with a concern of the person being ‘over-qualified’ for a position. There are many scenarios in which professional experience would be more valuable to an employer than a doctorate degree.
Check out the links below to our interviews with Prof. Debby Cotton and Dr Nikolay Nikolov to read their experiences of when a going through a PhD program has had a clear benefit (Prof. Cotton) and when it hasn’t been helpful (Dr Nikolov).

Do You Need to Have a Masters to do a PhD?
This really depends on the university, department and sometimes even the project and supervisor.
From a purely application process perspective, some institutions may formally require you to hold a Masters degree relevant to the subject of the PhD project before you can enter their doctoral program.
In another scenario, most universities are unlikely to accept candidates that were awarded below a 2:1 (in the UK) in their undergraduate degree but may consider someone who has ‘made up’ for this with a high-grade Masters.
Lastly, some universities now offer PhD programmes that incorporate an additional year of study in which you would complete a Masters degree before carrying directly on into a PhD project. As you’d expect, even if a university doesn’t formally require you to hold one, a Masters degree can help separate you from other applicants in being accepted on the project.
Check out our detailed guide to doing a PhD without a Master’s .
Why Do a Masters before Your PhD?
Even if you don’t need to have one, it could still be beneficial to begin your postgraduate study by doing a Masters first before you embark on your doctorate journey.
As mentioned previously it’ll help you stand out from applicants that don’t have one, but beyond that, it’ll give you a taster of what research life could be like, especially if you stay at the same university and department for your PhD.
The one-year commitment (in the UK at least) of carrying out a Masters first, and in particular your research project, will help you better understand if this is truly something you want to commit the next three or more years to.
You’ll learn some of the skills of independent research, from performing detailed literature searches to more complex, analytical writing.
At the end of it, you should be in a stronger position to consider your options and decide about whether to continue into a PhD at graduate school.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Masters Degree?
In the UK, a full-time Masters degrees take students one calendar year to complete: The programme of study usually starts in September, the final research project the following April and final project viva around August. Part-time degrees are usually double the time.
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD?
In the UK, most PhD projects take 3-4 years to complete , as reflected by the majority of funded projects offering stipends to cover living expenses of about 3.5 years.
For many reasons, projects may end up taking longer to complete, however. This might be because of difficulties in collecting enough data, or if the project is being done part-time.
Which One is More Expensive to Do?
As you’d expect, as a PhD takes three times as long to complete as a Masters degree, it will cost you more to do as far as university fees are concerned.
Another thing to consider is that many PhD projects come with some level of funding equivalent to a low salary, which may cover the cost of tuition fees and living expenses, whilst it is usually more difficult to obtain funding for Masters study.
Conversely, a Masters graduate may progress into a higher (versus PhD funding) salary sooner whilst a PhD student will endure three years of a comparatively low income.
A Masters vs a PhD: Conclusion
If you’re considering continue further graduate study after your undergraduate degree, the question of doing a Masters vs a PhD is likely to come up. They are both considered an advanced degree, each with their own advantages.
There are benefits to doing either of these graduate programs or even both of them; your decision here can be easier if you have an idea of the career you want to follow or if you know you have a love for research!
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Online Degrees
- Tuition & Financial Aid
- Transferring Credit
- The Franklin Experience
Request Information
We're sorry.
There was an unexpected error with the form (your web browser was unable to retrieve some required data from our servers). This kind of error may occur if you have temporarily lost your internet connection. If you're able to verify that your internet connection is stable and the error persists, the Franklin University Help Desk is available to assist you at [email protected] , 614.947.6682 (local), or 1.866.435.7006 (toll free).
Just a moment while we process your submission.
Popular Posts

Applied Doctorate vs. Ph.D.: What are the Differences?
Making a choice between two similar but different things can be a challenge.
Oh, sure, some things don’t fall under the “do-or-die” category of decision making. With some things, there simply is no wrong choice.
Take a sports car versus an SUV, for example. Either is a great choice, depending on your budget, your lifestyle and your personal preferences.
What about an angus beef burger versus a textured soy protein patty? When it comes to radically opposing food choices, there’s usually a clear-cut winner.
Yet what about the more important things in life … like your career, your future and your doctoral education?
You already know the drill when it comes to deciding if a Ph.D. or doctorate is right for you:
- Investigate each type of degree program.
- Make a list of personal and professional pros and cons for each type of degree.
- Seek the wise counsel of colleagues, academic advisors and professional mentors.
- Make a confident decision about which degree is right for.
But first, let’s define the Ph.D. and the professional doctorate and then look at how they’re different from one another.
What is a Ph.D.?
A Ph.D., or Doctor of Philosophy, is a high-level degree earned after a period of three or more years of graduate-level study, culminating in the creation, submission, presentation and defense of a research dissertation.
The Ph.D. can be awarded in a wide variety of fields, including the sciences, engineering and humanities. The term “philosophy,” according to Wikipedia, “does not refer solely to the field or academic disciple of philosophy, but is used in a broader sense in accordance with its original Greek meaning, which is ‘love of wisdom.’”
For some professions, such as university professor or researcher, the Ph.D. is pretty much de rigueur. Most Ph.D.s are earned as a means of contributing original research findings to an academic community, field of study or professional discipline.
Earning a doctorate is challenging and rewarding, but do you know what to really expect? Download this free guide for tips and insights to help you prepare for success.
What is an applied professional doctorate.
This doctorate is an advanced, high-level degree, too, earned after a period of three or more years of graduate-level study across a wide variety of disciplines. Like the Ph.D. it, too, culminates in the creation, submission, presentation and defense of a research dissertation or similar type of comprehensive final project.
The professional doctorate is also a research-based degree, only it emphasizes looking at existing bodies of knowledge and raising questions for the purposes of solving a problem and applying theories to a real-world setting.
Applied doctorate degrees first became well established in the United Kingdom and Australia and were initially offered in the United States by for-profit colleges and universities. Employer demand for higher skill levels and actionable problem-solving, however, opened up new programs at accredited non-profit institutions.
Different than a theoretical, Ph.D. degree, the professional doctorate is often the best terminal degree for the working professional who’s driven to lead and innovate.
Applied doctoral degree programs offer the opportunity to earn a practical degree that enables both subject mastery and field application.
What is the difference between the Ph.D. and doctorate?
It’s often assumed that a Ph.D. is a teaching-only degree while a professional doctorate is for the corporate player. The truth is, either degree can be valued in an academic or professional setting, depending on the type of institution or organization. Furthermore, either degree could be right for you.
Dr. Christopher Washington, Franklin University’s provost and chief academic officer explains the fundamental difference between the Ph.D. and the applied professional doctorate degree this way:
“With a Ph.D., you generate new theory. With the professional doctorate, you start from a place of practice and what’s going on in the world. You look at existing bodies of knowledge to see what theories have been created. Then you raise questions to determine how to design experiences that test theory to practice. In cultivating these types of practitioner-oriented scholars, there’s potential for a stronger and better relationship between the scholar and the community he or she serves. Such a connection helps us convene people to tackle the hard questions.”
Here we offer a side-by-side comparison of the Ph.D. and the professional doctorate to further demonstrate the differences (and similarities):
As you can see, the differences between the Ph.D. and the applied doctorate are few – and many – most of which are directly related to how earning the degree will impact your career.
Here are a few questions to ask yourself before deciding which degree is right for you :
- Do you want to conduct research or analyze and apply it?
- Do you want to work in an academic or professional setting?
- Do you want to identify problems or lead solutions to them?
Explains Dr. Washington, “If you want to generate new theory and conduct pure science within the pursuit of an academic life, then the Ph.D. is probably more in line with what you’ll need. If, however, you want to advance knowledge within a complex, global practice context while challenging yourself professionally, consider the applied doctorate degree.”

Related Articles

Franklin University 201 S Grant Ave. Columbus , OH 43215
Local: (614) 797-4700 Toll Free: (877) 341-6300 [email protected]
Copyright 2024 Franklin University
Doctoral Degree Programs
Additional information.
- Download the Doctoral Viewbook
Join a world-class community of scholars and education leaders exploring new frontiers in learning and teaching.
Doctoral study at Harvard means full immersion in one of the world's most dynamic and influential intellectual communities. At the Harvard Graduate School of Education, two distinct doctoral programs leverage the extraordinary interdisciplinary strengths of the entire University. The Doctor of Education Leadership (Ed.L.D.) prepares experienced educators for system-level leadership roles in school districts, nonprofit organizations, government agencies, and beyond; and the Doctor of Philosophy in Education (Ph.D.) empowers cutting-edge interdisciplinary research informed by the cognitive sciences, economics, medicine, the humanities, and more.
Doctor of Education Leadership (Ed.L.D.)
The Doctor of Education Leadership (Ed.L.D) is a three-year, practice-based program designed to produce system-level leaders in American pre-K-12 education. The Ed.L.D. curriculum mines the vast intellectual and professional resources of HGSE, the Harvard Business School , and the Harvard Kennedy School , and includes a 10-month residency in the third year.
Doctor of Philosophy in Education (Ph.D.)
The Doctor of Philosophy in Education (Ph.D.) , offered jointly with the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences , provides unrestricted access to faculty and resources at all Harvard graduate and professional schools. This five-year Ph.D. is ideal for conducting groundbreaking interdisciplinary research that directly informs and impacts education practice and policy.
What is a PhD Degree? [2024 Guide]
As you’re taking a look at potential grad school programs, you might be asking yourself, “What is a PhD degree?”

Understanding what a PhD is and what’s involved in earning one can help you decide whether to enroll in this type of doctoral program. You might decide that a PhD is a strategic step for you to take to further your career.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
If you choose to pursue a PhD, you’ll be glad to know that you can also earn this type of degree online through an accredited university.
What Is a PhD Degree?

After earning a bachelors degree and a masters degree, you may be considering taking your education even further.
The next step for you might be a Doctor of Philosophy degree, better known as a PhD. As a terminal degree, a PhD can set you apart as an expert in your field. Earning a doctoral degree is not a small undertaking. The process includes multiple steps and can last for several years.
Components of a Ph.D. degree program often include:
- Advanced courses in your chosen field
- Classes in research methods, data analysis, and scholarly writing
- Examination of current literature and studies related to your field
- Oral or written comprehensive exams
- Original research project—includes writing and defending a major paper about your research
The dissertation, sometimes known as a thesis, is usually the part of a PhD program that takes the longest. During the dissertation process, you’ll work under the supervision of a faculty advisor, often someone whose research interests correlate with yours. You’ll design a research project, carry it out, and write about your findings. This project is meant to contribute new ideas to your field.
A PhD is particularly suitable for students who love school settings and want to pursue academic careers. For instance, professors often have PhDs. It’s also common for scientists and other researchers to hold this type of degree. Outside of academia, a PhD could set you apart as a knowledgeable leader in your field.
Benefits of a PhD Degree

Getting your PhD can be an incredible personal goal worth achieving. Plus, a degree at this level can offer many professional benefits, such as:
- Career advancement . As a person with a PhD, you may be considered an expert in your field. That could help qualify you for a variety of top roles within your line of work.
- Higher earnings . A job promotion or a new employer might offer you a higher salary.
- Networking . You can meet new people and build professional connections as you work toward a PhD.
- Preparation for becoming a professor . Universities typically prefer to hire faculty members who hold PhDs in their area of expertise.
- Research opportunities . Before you can earn your PhD, it’s necessary to complete an original research project called a dissertation. After completing your degree, you may have additional opportunities to contribute research to your field.
If you’re willing to put in the work, then getting your PhD could be worth the effort.
How to Know If a PhD Is Right for Me

Before you sign up for a PhD program, it’s helpful to carefully weigh the decision and make sure it’s the right choice for you. You might ask yourself the following questions:
- Am I willing to commit years to the process ? PhDs take at least 3 years, and most take longer than that.
- Do I want to carry out original research ? This is a research-focused degree, and the purpose is to contribute new ideas or theories to your field.
- Does an academic career interest me ? Many people get PhDs because they want to work in higher education as teachers or researchers. Those who plan to remain as practitioners often consider professional doctorates instead.
It can also be helpful to speak with faculty members and current students to get a feel for what you can expect from PhD studies.
Applying for a Ph.D: Education Requirements

It’s necessary to put in years of study before you can apply for a PhD program. Most students need to hold at least two degrees already. But, in some cases, one may be sufficient.
- Bachelor’s degree . All graduate programs require students to have earned a four-year undergraduate degree before enrolling in advanced studies. Most PhD programs don’t specify that your bachelors degree must be in the same field as your hoped-for doctoral studies, but it can help you move through a graduate-level program with more ease.
- Master’s degree . Colleges often expect students to have earned a master’s degree before applying for PhD studies, but some programs do allow students straight out of bachelor’s degree programs. Doing a master’s degree first can provide strong preparation for the advanced coursework, research, and writing that are required in doctoral programs.
It is often required that the degrees you have be from accredited colleges. It may also be necessary to meet a minimum GPA requirement, such as a score of 3.0 or higher. Some colleges prefer PhD applicants who have graduated from previous programs with honors.
Doctor of Philosophy: Admissions Requirements

Doctoral programs can be quite selective about whom they admit because they’re looking for capable students who can keep up with the demands of the program and contribute valuable new research to the field.
In addition to meeting the education requirements, you’ll also be required to turn in records that demonstrate your academic potential. Here are some common admissions requirements:
- College transcripts and professional resume
- Letters of recommendation from people who know you academically or professionally
- Statement about relevant background, research interests, or professional goals
- Proposal that presents the original research project you’d be interested in doing
- Scores from the GRE or GMAT (not always required)
You might also connect with the department’s faculty members and find someone who would be willing to serve as your academic supervisor for your dissertation. It’s beneficial for this person’s research interests to align with your own.
Some schools have you do this before admission, and others connect admitted students to supervisors later in the enrollment process.
What Does PhD Stand For?

PhD stands for “Doctor of Philosophy.” It doesn’t mean that you’ve studied philosophy at the highest levels. Rather, the word “philosophy” in the name refers back to ancient Greek. It implies that you are someone who loves and seeks wisdom and knowledge.
You can get a PhD in many different subject areas—such as a Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics or a Doctor of Philosophy in Psychology. PhD students explore their chosen field of study in great depth. They also learn how to conduct original research, and they undertake major research projects. By graduation, they are considered experts in their fields.
What Do You Learn in a Doctoral Degree?

In a PhD program, you’ll learn about your chosen area of study, such as biology or sociology. You will also study a niche area within that field in great depth.
Research is a significant topic in any PhD program. Your courses might include topics on:
- Advanced statistics
- Dissertation preparation
- Literature review
- Quantitative and qualitative methods
- Research methodology
These research-focused classes may be tailored to your particular area of study, such as research methodology in the social sciences or advanced statistics in criminal justice research.
What Can You Do with a PhD Degree?

Many people earn PhD degrees because they want to teach at the college level. This degree is often required for tenured faculty positions at universities.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics states that most postsecondary teachers earn between $46,690 and $172,130 each year. Research scientists often hold PhDs as well. Examples include medical scientists, biochemists, and physicists.
Additionally, there are some career paths that require a doctorate for licensure. For instance, clinical and counseling psychologists usually need to receive training at the doctoral level before they can practice independently.
Do You Need a Masters to Get a PhD?

Whether you’ll need a masters before you can begin the PhD process will depend on the program you choose.
Many PhD programs require a master’s degree as an admissions requirement. Completing a master’s program can provide a strong research and writing foundation that can help you during this advanced program. Other programs, though, let students enroll with only a bachelors degree.
There might be additional classes required to prepare you for working at the graduate level, so it may take a bit longer to complete your studies. For more information on whether you need a master’s to get a PhD , you can consult the admissions requirements of each program you’re considering.
Can You Get a PhD Online?
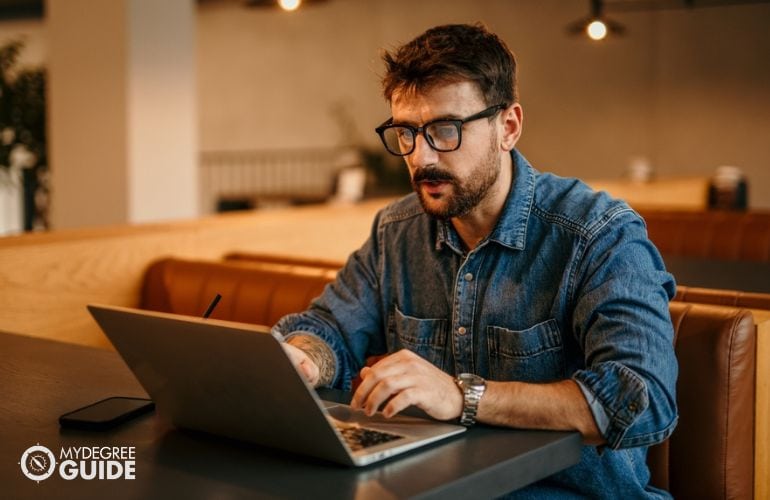

There are many online PhD programs available for aspiring students looking for flexibility. Some PhD programs are offered entirely online. You can take all of your classes online, and you can also receive guidance from your faculty advisor and defend your dissertation from afar.
Other programs are mostly online but require some in-person experiences. You might be asked to come to campus for a week or two of intensive study. Also, you may be asked to show up in person for your dissertation defense. Either way, online PhD studies are often more accessible for working professionals than fully on-campus programs.

How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD?
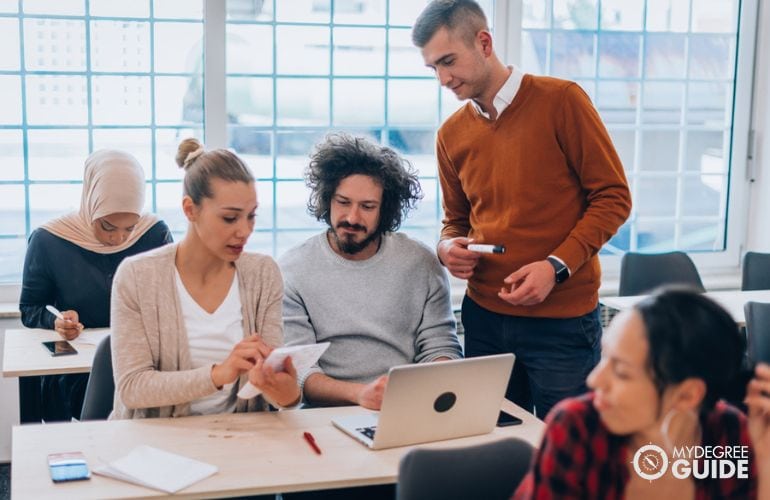

Students often spend 3 to 5 years completing a PhD program. Online programs sometimes include features like year-round classes and short course terms that encourage quick completion.
The shortest PhD programs typically do not involve writing a dissertation. There may be a different final assignment, such as a capstone project, instead. You might be able to finish one of those programs in about 3 years. Not all students finish within 5 years. Some spend around a decade on this massive undertaking. Some PhD programs set an upper limit for completion, such as 7 or 8 years.
Is a PhD a Doctor?
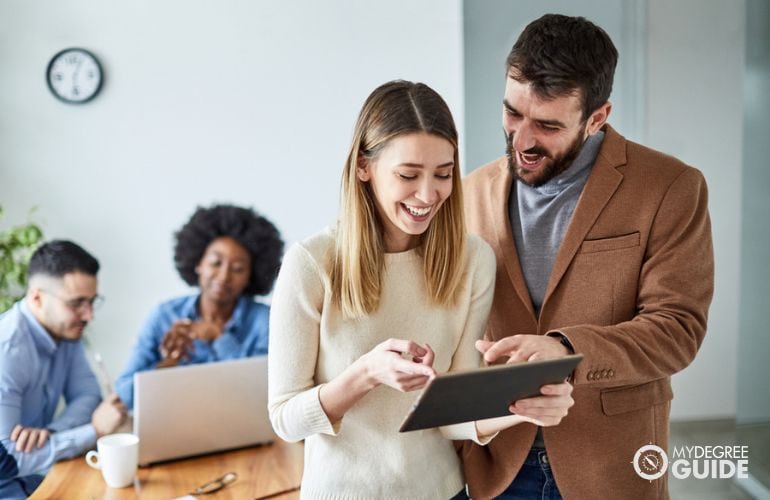

People with PhDs are considered experts in their fields, and the degree includes “Doctor” in its name. For that reason, PhD holders often use the title “Doctor.” A college professor, for example, might go by Dr. Smith.
Even still, there’s a difference between MD vs. PhD. A person who holds a PhD is not a medical doctor. Medical doctors earn a Doctor of Medicine (MD) degree before becoming licensed to practice medicine. In most contexts, though, people refer to professionals with PhDs as “doctors.”
What Jobs Can You Get with a PhD?
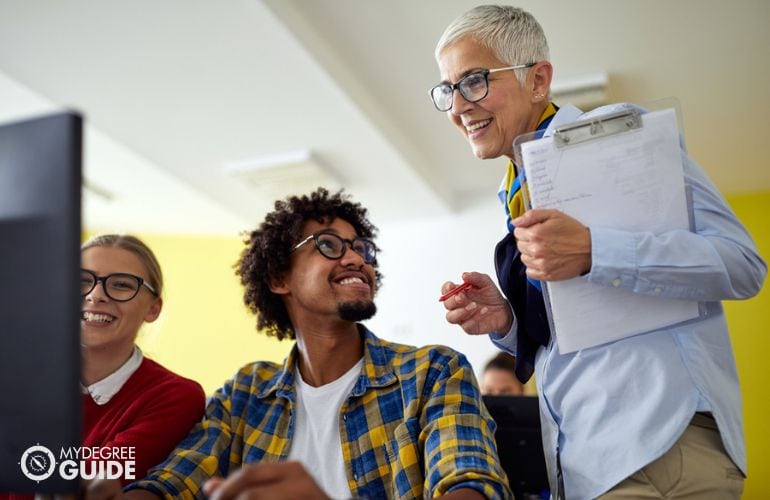

People with doctorate degrees work in both academia and professional practice. Being a college professor is quite popular among people who hold PhDs. The Bureau of Labor Statistics says that a PhD can also be helpful for obtaining jobs in higher education administration, particularly as a dean or a provost.
PhD graduates may work in research as well. Research jobs are available with colleges, government agencies, and private institutions. Researchers are needed in many different fields, including biology, mathematics, computer science, and economics. PhDs also help people rise to the top in their industries, perhaps as chief executives.
How Much Does a PhD Cost?

Some graduate schools charge just $300 to $400 per credit hour. Others may charge $2,000 per credit hour or more.
Per-credit-hour rates between $600 and $1,000 are quite common. It’s helpful to keep in mind that state universities often charge less for in-state residents than nonresidents. Your total number of credit hours may depend on how many years you spend working on your dissertation.
Some universities offer tuition-free PhD programs for qualifying participants. The students may even receive a stipend in exchange for research or teaching assistance. This arrangement is more common for on-campus programs than online ones.
What’s the Difference Between a Doctorate vs. PhD Degrees?
Is a PhD a doctorate degree ? For your terminal degree, you may have the choice between a PhD degree and a professional doctorate. While they are both doctoral degrees, they do have some differences.
Professional doctorates are sometimes a year or two quicker than PhDs, but that’s not always the case.
Is a PhD Worth It?

Yes, a PhD is worth it for many students. For one thing, holding a PhD could be the key to fulfilling your professional dreams.
If you want to be a professor, for instance, there’s a good chance that you’ll be required to have this advanced degree. Even if that’s not your ultimate goal, a PhD could be beneficial. The more education you have, the more your job security usually increases.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, there’s an inverse relationship between education and unemployment. As education increases, unemployment rates decrease.
Getting Your PhD Degree Online

An exciting future as an expert in your field may await. You can earn a PhD to increase your knowledge, prove your capability, and contribute new ideas to your area of study. Getting this degree is an impressive accomplishment, and it may open new doors for your career. For convenience and accessibility, you might take a look at online PhD studies.
Many accredited colleges offer robust online PhD programs. You’ll get to take advanced courses and work with respected professors. An online program can also offer opportunities for completing a thesis or a doctoral project. You could graduate prepared to make a difference in your field.
Why not start exploring your options today?

Get our weekly advice
Keep up-to-date with the latest advice from Abound Grad School.

What Is the Difference Between a Master’s Degree and a Ph.D.?
In the United States, 13.1% of people have a master’s, doctorate, or other advanced degree. Along with the wealth of knowledge and skills you can get from an advanced education, becoming a graduate student is a great way to stand above the remaining 86.9% of Americans as you work toward your career goals.
The most common types of advanced degrees are the master’s degree and the Ph.D. Both are great options for continuing education but still have many differences.
Do you want to learn more about each of these advanced degrees? Keep reading this article for everything you need to know about the difference between a master’s degree and a Ph.D.
Course Structure
When you are getting an advanced degree, it is important to consider the course structure of each program you are interested in. This way, you can find one that helps you learn in the way that makes the most sense to you.
With a master’s degree, you can expect primarily to do coursework throughout the first three semesters. The remaining requirements are composed of a capstone project or thesis that culminates everything you will have learned during your program.
With a Ph.D., you will typically do two years of coursework. After you have completed this work, you will take the remaining years to prepare your dissertation. This requires a lot of research and writing and will allow you to contribute new research to current industry knowledge.
Degree Length
Another significant difference between a master’s degree and a Ph.D. program is the length of time they take to complete. Master’s programs are much shorter and will typically take two years to complete. Some universities even offer accelerated programs that allow you to complete your master’s degree within a single year.
Ph.D.s take much longer to complete—anywhere from 5-6 years! There are a lot of things to cover in any field as you pursue a doctorate. What’s more, the research and writing process of a dissertation can be quite time consuming.
The doctorate degree in the United States is typically inclusive of the curriculum you would receive for a master’s in the same field, with more in-depth study beyond that. Outside of the United States, you will likely have to get a separate master’s degree before you start your Ph.D.
Culmination of Degree
As was mentioned before, the culmination of both master’s degrees and doctorate degrees differ. There are a few main differences between a dissertation and a thesis .
For a master’s degree, you are expected to complete a capstone course or a thesis. This is a paper that is limited to about 40,000 words. The point of a thesis is to allow graduate students to present their research findings and show their aptitude in their field.
The master’s thesis allows you to demonstrate your knowledge about the research area and prove that you can contribute to scholarly work. Once you have completed your thesis, you will go through an extensive editing process before it can be published.
A doctorate degree requires the completion of a dissertation. A dissertation is much longer than a master’s thesis and can be anywhere between 100 to 300 pages long.
Dissertations also typically require an oral defense. You will present your work to a committee and will answer questions about the methodology and interpretation of your dissertation.
To choose the best type of advanced degree for your circumstances, it is also important that you consider the cost of both master’s degrees as well as Ph.D. programs. Comparing degree costs will help you find a degree that you can afford.
Because a Ph.D. takes much longer to complete than a master’s degree, you can expect it to cost a lot more too! That said, many Ph.D. programs provide funding to students. While this funding or stipend is not much, it will often cover the cost of tuition and living expenses.
On the other hand, you are completely responsible for your livelihood while pursuing a master’s degree. That means you’ll have to work hard outside of school, reminding yourself that your future career prospects will likely help you make back what you’ve spent (and then some!).
With a Ph.D., you will take longer to graduate, but you will get a higher return on your investment with an even higher average salary than that of a master’s degree holder.
If you pursue an online graduate degree , you can find much more affordable options for both master’s degrees and doctorate degrees. These also make it much easier to study while you continue to work or pursue other endeavors.
Future Potential
Finally, you need to consider your future potential when it comes to both of these advanced degrees. While money isn’t the only thing that you should consider, you need to know that you will be able to get a reliable job once you graduate with your degree.
With a master’s degree, you will open the door for more job opportunities but not necessarily different career prospects. On the other hand, those with a Ph.D. typically do research for their job, often at a university. This allows you to contribute new data to your field and as well as to become an expert in your industry.
You should also consider your potential salaries with both graduate degrees. Both degrees will advance your career and increase your money-making potential. However, you will almost always be able to make more money when you have a Ph.D.
Becoming a Graduate Student? Learn More About a Master’s Degree and Ph.D.
When you are considering continuing education, there are many different types of degrees to choose from. Both a master’s degree and a Ph.D. are great options to achieve your education and career goals. By learning more about these differences between graduate degrees, you can find the option that works best for your needs.
Do you want help with the advanced degree application process? Abound Grad School can help! Check out our website today to learn more about your education options as a graduate student and to find the best graduate school for you .

Ana -Marcela joins the team as an outreach associate and assistant editor. She values the pursuit of knowledge and is excited to use her research and writing skills to help others fuel their intellectual curiosity. Ana -Marcela is a native Austinite and she earned her Bachelor’s in English Literature from St. Edward’s University. Her favorite author is Gabriel Garcia Marquez. Ana -Marcela spends her free time hiking the greenbelt, cruising the aisles of half price books, or cuddling her cats.

How to Choose a Grad Program as an International Student

How to Network in Graduate School

How to Ace Your Graduate School Interview
What Comes After a Master's Degree?
Know Your Graduate School Options Beyond a Master's
- Choosing a Graduate Program
- Tips & Advice
- Admissions Essays
- Recommendation Letters
- Medical School Admissions
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- Ph.D., Developmental Psychology, Fordham University
- M.A., Developmental Psychology, Fordham University
After receiving your master's degree, there are still more options to study in graduate school, including an additional master's degree, doctorate programs (Ph.D., Ed.D., and others) and certificate programs to consider. These degree and certificate programs all vary in level, time to complete, and more.
Additional Master's Degrees
If you have already earned a master's degree and wish to continue your studies, you might consider a second master's degree. Since master's degrees tend to be specialized degrees, as you grow within your career you may find that a new specialty is required or that two specialties will make you an even more desirable candidate when job hunting. In education, for example, many teachers earn a Master's of Arts in Teaching degree but may return to the classroom to study for a degree in the field in which they are teaching, such as English or mathematics. They may also wish to pursue a degree in organizational leadership, especially if they are looking to grow into an administrative role in the school.
Master's degrees generally take two, sometimes three, years to complete (after earning a bachelor's degree), but pursuing a second degree in a similar discipline might allow you to carry over some credits and complete the program sooner. There are also some accelerated master's programs that can earn you a degree in less than a year; just be prepared for a lot of hard work. All master's programs entail coursework and exams , and, depending on the field, possibly an internship or other applied experience (for example, in some fields of psychology ). Whether a thesis is required to obtain a master's degree depends on the program. Some programs require a written thesis; others offer an option between a thesis and a comprehensive exam . Some programs provide capstone courses, which are usually semester-long courses that provide a comprehensive overview of everything learned within the program and ask students to complete several small thesis statements to demonstrate mastery.
A meaningful way in which master's programs differ from many, but not all, doctoral programs is in the level of financial aid available to students. Most programs do not offer as much assistance to master's students as they do for doctoral students, and so students often pay most if not all of their tuition. Many top institutions even offer full scholarships for doctoral students, but a doctoral program is usually a much more comprehensive and time-consuming educational program, requiring a full-time commitment, versus the possibility of working your full-time job while going for a master's degree.
The value of the master's degree varies by field. In some areas such as business, a master's is the unstated norm and necessary for advancement. Other fields do not require advanced degrees for career advancement. In some cases, a master's degree may hold advantages over a doctoral degree. For example, a master's degree in social work (MSW) may be more cost-effective than a doctoral degree, given the time and funds required to earn the degree and the pay differential. The admission offices at the schools you're applying to can often help you determine which program is best for you.
Ph.D. and Other Doctoral Degrees
A doctoral degree is a more advanced degree and takes more time (often a great deal more time). Depending on the program, a Ph.D. could take four to eight years to complete. Typically, a Ph.D. in North American programs entails two to three years of coursework and a dissertation — an independent research project designed to uncover new knowledge in your field that must be of publishable quality. A dissertation can take a year or more to complete, with most averaging about 18 months. Some fields, like applied psychology, may also require an internship of one year or more.
Most doctorate programs offer various forms of financial aid , from assistantships to scholarships to loans. The availability and types of support vary by discipline (e.g., those in which faculty conduct research sponsored by large grants are more likely to hire students in exchange for tuition) and by the institution. Students in some doctoral programs also earn master's degrees along the way.
Certificate Programs
Certificates can usually be earned in less than a year and are often significantly less expensive than going after additional degrees. If you're wondering what should come after your master's degree and you're not sure if a doctoral program is right for you, this could be the way to go. Certificates range in scope greatly and can allow you to hyperfocus on the areas in which you wish to excel. Some schools even offer certificate programs that are of a masters degree caliber, so you can walk away better prepared for your career and without breaking the bank. Employers who offer tuition assistance may look favorably on a less expensive certificate program as well.
Which Is the Best?
There is no easy answer. It depends on your interests, field, motivation, and career goals. Read more about your field and consult faculty advisers to learn more about which option best fits your career goals. Some final considerations are as follows:
- What types of jobs do a master's degree, doctoral degree, and certificate holders have? Do they differ? How?
- How much will each degree cost? How much will you earn after obtaining each degree? Is the outcome worth the cost? What can you afford?
- How much time do you have to invest in additional schooling?
- Are you interested enough to pursue many years of schooling?
- Will earning a doctoral degree offer a substantial benefit in your employment and advancement opportunities?
Only you know which is the right degree for you. Take your time and ask questions, then carefully weigh what you learn about each, its opportunities, as well as your own needs, interests, and competencies. What comes after a master's degree is up to you.
- A Note About Masters and Doctoral Comprehensive Exams
- Pros and Cons of Earning a Master's Degree Before a PhD
- How to Earn a Doctorate Degree Online
- What Does It Take to Earn a Master's Degree?
- A Doctor of Philosophy or Doctorate
- Business Administration Education and Careers
- Should I Earn a Human Resources Degree?
- Should I Earn a Management Degree?
- Should I Earn an Entrepreneurship Degree?
- Should I Earn an Operations Management Degree?
- Should I Earn a Project Management Degree?
- Should I Earn a Doctorate Degree?
- Should I Earn a Real Estate Degree?
- Types of Nursing Programs and Degrees
- Degree Requirements for Therapists
- Abbreviations and Titles All College Students Should Know
- Tel: +44 (0)23 9431 1545
- WhatsApp: +44 (0)7360 544 612
- Email: [email protected]
- Upcoming events
.png?width=180&height=222&name=UoP_Study%20Online_Stacked%20(1).png)
- Student experience
- Student support services
- Testimonials
- MSc Cyber Security and Digital Forensics
- MSc Data Analytics
- MSc Global Human Resource Management
- MSc Project Management for Construction
- MSc Psychology
- MSc Risk, Crisis and Resilience Management
- Global Professional Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA)
- Teaching team
- Course costs
- Funding options
- What’s the difference between a PhD and a doctorate?
25 Aug 2022
- How you'll learn
In this post, we’ll explore the definitions, differences and similarities of PhDs and doctorates, as well as what a Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA) entails.
After completing a master’s degree and spending time building a career, many professionals consider continuing their education and pursuing a higher level of academic achievement.
Two of the most common options are a PhD or a doctorate, but what is the difference between the two?
Defining a PhD and a doctorate
A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy, is a specific type of doctorate degree that focuses on research in a particular field. It is highly theoretical and involves extensive research to generate new knowledge.
On the other hand, a doctorate degree is an umbrella term for any doctoral-level degree. It can be further categorised into two types: academic and professional.
Academic doctorates, such as a PhD, are focused on research, while professional doctorates, like the Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA) , focus on practical application in professional settings.
Want to know more about the benefits of a DBA? Explore our guide:

Differences between a PhD and a doctorate
While both a PhD and a doctorate are doctoral-level degrees, there are some key differences between the two. One of the main differences is that a PhD is typically an academic degree, while a doctorate can be either academic or professional. Additionally, a PhD is highly theoretical and research-focused, while a professional doctorate is practical and geared toward applying research to specific professional settings.
Similarities between a PhD and a doctorate
Despite their differences, there are also some similarities between a PhD and a doctorate. Both degrees require significant research, critical thinking, and independent study. They are both highly respected and recognised as top-level degrees in their respective fields, and both confer the title of “Doctor” upon completion.
Weighing up your options? Read our guide to the benefits and drawbacks:

Examples of professional doctorates
Examples of professional doctorates include the Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA), Doctorate of Education (EdD), Doctorate of Nursing Practice (DNP), and Doctorate of Psychology (PsyD), among others. These degrees are typically designed for individuals who want to apply research to specific professional settings.
What is a Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA)?
A DBA is a professional doctorate degree that is focused on applying research to real-world business problems. It is typically designed for individuals who are in senior-level or executive positions in private or public sector organisations. A DBA is often seen as a practical alternative to a PhD in business, as it allows professionals to apply research directly to their work .
Benefits of pursuing a Global DBA
Portsmouth Online offers a Global DBA that is online and part-time, making it accessible from anywhere in the world. This course is specifically designed for senior-level professionals who want to become more qualified in the field of business.
The structured modules will help you develop your ability to challenge current thinking and provide authoritative solutions to practical and research problems. Additionally, the applied research in the DBA thesis will allow you to conduct research on a topic that is directly relevant to your organisation.
Choosing between a PhD and a doctorate
Choosing between a PhD and a doctorate depends on your goals and aspirations. If you are interested in academic research and generating new knowledge, a PhD may be the right path for you.
However, if you want to apply research to specific professional settings, a professional doctorate like a DBA may be a better fit. Ultimately, it is important to choose the degree that aligns with your career goals and interests.
Get more guidance on whether a PhD or a doctorate is right for you:

Recent Posts
Your guide to construction law.
Whether you're exploring construction law courses and careers, or are simply curious about what construction law entails and its impact on the ...

What skills does a data analyst need
Whether you’re looking at Data Analyst jobs and want to improve your skillset, or you’re simply intrigued as to the attributes people need to become ...

Types of data analytics
Explore the fundamental concepts of data analytics, including what it is, its pivotal role in business, and the four main types: descriptive, ...

You’ve got the potential for success. Now’s the time for action.
Got a question about our courses? Complete the form below and a member of our course adviser team will contact you shortly.
Quick links
- Online courses
- Fees and funding
- Application process
- Complaints policy
University links
- MAIN UNIVERSITY WEBSITE
- STUDENT WEBSITE
- VIEW ALL courses
- WhatsApp: +44 (0) 7360 544 612
© 2022 UNIVERSITY OF PORTSMOUTH COOKIES ACCESSIBILITY MODERN SLAVERY PRIVACY WEBSITE TERMS & CONDITIONS
How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?
Earning a Ph.D. from a U.S. grad school typically requires nearly six years, federal statistics show.
How Long It Takes to Get a Ph.D. Degree

Caiaimage | Tom Merton | Getty Images
A Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a "lifelong learner."
Students who have excelled within a specific academic discipline and who have a strong interest in that field may choose to pursue a Ph.D. degree. However, Ph.D. degree-holders urge prospective students to think carefully about whether they truly want or need a doctoral degree, since Ph.D. programs last for multiple years.
According to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a census of recent research doctorate recipients who earned their degree from U.S. institutions, the median amount of time it took individuals who received their doctorates in 2017 to complete their program was 5.8 years. However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey.
Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master's degrees, which means the time spent in grad school is a combination of the time spent pursuing a master's and the years invested in a doctorate. In order to receive a Ph.D. degree, a student must produce and successfully defend an original academic dissertation, which must be approved by a dissertation committtee. Writing and defending a dissertation is so difficult that many Ph.D. students drop out of their Ph.D. programs having done most of the work necessary for degree without completing the dissertation component. These Ph.D. program dropouts often use the phrase " all but dissertation " or the abbreviation "ABD" on their resumes.
According to a comprehensive study of Ph.D. completion rates published by The Council of Graduate Schools in 2008, only 56.6% of people who begin Ph.D. programs earn Ph.D. degrees.
Ian Curtis, a founding partner with H&C Education, an educational and admissions consulting firm, who is pursuing a Ph.D. degree in French at Yale University , says there are several steps involved in the process of obtaining a Ph.D. Students typically need to fulfill course requirements and pass comprehensive exams, Curtis warns. "Once these obligations have been completed, how long it takes you to write your dissertation depends on who you are, how you work, what field you're in and what other responsibilities you have in life," he wrote in an email. Though some Ph.D. students can write a dissertation in a single year, that is rare, and the dissertation writing process may last for several years, Curtis says.
Curtis adds that the level of support a Ph.D. student receives from an academic advisor or faculty mentor can be a key factor in determining the length of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. program. "Before you decide to enroll at a specific program, you’ll want to meet your future advisor," Curtis advises. "Also, reach out to his or her current and former students to get a sense of what he or she is like to work with."
Curtis also notes that if there is a gap between the amount of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. and the amount of time a student's funding lasts, this can slow down the Ph.D. completion process. "Keep in mind that if you run out of funding at some point during your doctorate, you will need to find paid work, and this will leave you even less time to focus on writing your dissertation," he says. "If one of the programs you’re looking at has a record of significantly longer – or shorter – times to competition, this is good information to take into consideration."
He adds that prospective Ph.D. students who already have master's degrees in the field they intend to focus their Ph.D. on should investigate whether the courses they took in their master's program would count toward the requirements of a Ph.D. program. "You’ll want to discuss your particular situation with your program to see whether this will be possible, and how many credits you are likely to receive as the result of your master’s work," he says.
How to Write M.D.-Ph.D. Application Essays
Ilana Kowarski May 15, 2018

Emmanuel C. Nwaodua, who has a Ph.D. degree in geology, says some Ph.D. programs require candidates to publish a paper in a first-rate, peer-reviewed academic journal. "This could extend your stay by a couple of years," he warns.
Pierre Huguet, the CEO and co-founder of H&C Education, says prospective Ph.D. students should be aware that a Ph.D. is designed to prepare a person for a career as a scholar. "Most of the jobs available to Ph.D. students upon graduation are academic in nature and directly related to their fields of study: professor, researcher, etc.," Huguet wrote in an email. "The truth is that more specialization can mean fewer job opportunities. Before starting a Ph.D., students should be sure that they want to pursue a career in academia, or in research. If not, they should make time during the Ph.D. to show recruiters that they’ve traveled beyond their labs and libraries to gain some professional hands-on experience."
Jack Appleman, a business writing instructor, published author and Ph.D. candidate focusing on organizational communication with the University at Albany—SUNY , says Ph.D. programs require a level of commitment and focus that goes beyond what is necessary for a typical corporate job. A program with flexible course requirements that allow a student to customize his or her curriculum based on academic interests and personal obligations is ideal, he says.
Joan Kee, a professor at the University of Michigan with the university's history of art department, says that the length of time required for a Ph.D. varies widely depending on what subject the Ph.D. focuses on. "Ph.D. program length is very discipline and even field-specific; for example, you can and are expected to finish a Ph.D, in economics in under five years, but that would be impossible in art history (or most of the humanities)," she wrote in an email.
Kee adds that humanities Ph.D. programs often require someone to learn a foreign language, and "fields like anthropology and art history require extensive field research." Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame. "Because of this, many if not most Ph.D. students must work to make ends meet, thus further prolonging the time of completion," she says.
Jean Marie Carey, who earned her Ph.D. degree in art history and German from the University of Otago in New Zealand, encourages prospective Ph.D. students to check whether their potential Ph.D. program has published a timeline of how long it takes a Ph.D. student to complete their program. She says it is also prudent to speak with Ph.D. graduates of the school and ask about their experience.
Online Doctoral Programs: What to Expect
Ronald Wellman March 23, 2018

Kristin Redington Bennett, the founder of the Illumii educational consulting firm in North Carolina, encourages Ph.D. hopefuls to think carefully about whether they want to become a scholar. Bennett, who has a Ph.D. in curriculum and assessment and who previously worked as an assistant professor at Wake Forest University , says a Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a "lifelong learner." She says someone contemplating a Ph.D. should ask themselves the following questions "Are you a very curious person... and are you persistent?"
Bennett urges prospective Ph.D. students to visit the campuses of their target graduate programs since a Ph.D. program takes so much time that it is important to find a school that feels comfortable. She adds that aspiring Ph.D. students who prefer a collaborative learning environment should be wary of graduate programs that have a cut-throat and competitive atmosphere, since such students may not thrive in that type of setting.
Alumni of Ph.D. programs note that the process of obtaining a Ph.D. is arduous, regardless of the type of Ph.D. program. "A Ph.D. is a long commitment of your time, energy and financial resources, so it'll be easier on you if you are passionate about research," says Grace Lee, who has a Ph.D. in neuroscience and is the founder and CEO of Mastery Insights, an education and career coaching company, and the host of the Career Revisionist podcast.
"A Ph.D. isn't about rehashing years of knowledge that is already out there, but rather it is about your ability to generate new knowledge. Your intellectual masterpiece (which is your dissertation) takes a lot of time, intellectual creativity and innovation to put together, so you have to be truly passionate about that," Lee says.
Curtis says a prospective Ph.D. student's enthusiasm for academic work, teaching and research are the key criteria they should use to decide whether to obtain a Ph.D. degree. "While the time it takes to complete a doctorate is an understandable concern for many, my personal belief is that time is not the most important factor to consider," he says. "Good Ph.D. programs provide their students with generous stipends, health care and sometimes even subsidized housing."
Erin Skelly, a graduate admissions counselor at the IvyWise admissions consulting firm, says when a Ph.D. students struggles to complete his or her Ph.D. degree, it may have more to do with the student's academic interests or personal circumstances than his or her program.
"The time to complete a Ph.D. can depend on a number of variables, but the specific discipline or school would only account for a year or two's difference," she wrote in an email. "When a student takes significantly longer to complete a Ph.D. (degree), it's usually related to the student's coursework and research – they need to take additional coursework to complete their comprehensive exams; they change the focus of their program or dissertation, requiring extra coursework or research; or their research doesn't yield the results they hoped for, and they need to generate a new theory and conduct more research."
Skelly warns that the average completion time of a Ph.D. program may be misleading in some cases, if the average is skewed based on one or two outliers. She suggests that instead of focusing on the duration of a particular Ph.D. program, prospective students should investigate the program's attritition and graduation rates.
"It is worthwhile to look at the program requirements and the school's proposed timeline for completion, and meet current students to get their input on how realistic these expectations for completion are," Skelly says. "That can give you an honest idea of how long it will really take to complete the program."
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
Tags: graduate schools , education , students
You May Also Like
Find a strong human rights law program.
Anayat Durrani April 18, 2024

Environmental Health in Medical School
Zach Grimmett April 16, 2024

How to Choose a Law Career Path
Gabriel Kuris April 15, 2024

Questions Women MBA Hopefuls Should Ask
Haley Bartel April 12, 2024

Law Schools With the Highest LSATs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 11, 2024

MBA Programs That Lead to Good Jobs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 10, 2024

B-Schools With Racial Diversity
Sarah Wood April 10, 2024

Law Schools That Are Hardest to Get Into
Sarah Wood April 9, 2024

Ask Law School Admissions Officers This
Gabriel Kuris April 9, 2024

Grad School Housing Options
Anayat Durrani April 9, 2024


EdD vs. PhD in Education: What’s the Difference?

Industry Advice Education
If you’re interested in pursuing a doctoral degree in education, one of the first questions you’ll face is: Should I apply for a Doctor of Education (EdD) or a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Education?
The decision between these two culminating degrees can be career-defining as each serves a very different purpose despite being equivalent in level. In order to ensure you choose the path that best aligns with your future goals and career path, it’s important to take the time to first understand the differences in program curriculum and future career opportunities that relate to each degree.
Read on to learn about the defining qualities and key differences of an EdD and a PhD in Education to determine which program is the right fit for you.
EdD vs. PhD in Education
A Doctor of Education (EdD) is a professional degree designed for practitioners pursuing educational leadership roles. A PhD in education , on the other hand, is designed to prepare graduates for research and teaching roles.
“With a PhD, [students are] reviewing the research, seeing a gap in the literature, and generating new knowledge based on a theory or hypothesis,” Joseph McNabb , a professor of practice in Northeastern’s Graduate School of Education , explains. “Conversely, an EdD student starts with a problem of practice and [works to learn] the skills it will take to resolve that complex problem of practice.”

What is an EdD Degree?
An EdD, or Doctor of Education , is a professional doctorate best suited for experienced educators and mid- to senior-level working professionals who want to lead and implement change within their organization.
EdD candidates work in a broad range of fields ranging from K-12 and higher education to nonprofits, government, healthcare, and the military. What each share is a desire to transform their everyday environment and apply the lessons learned through their doctorate to a complex, critical issue facing their workplace.
The EdD is practice-based. Students in an EdD program don’t want to just research their area of interest, but leverage that research in ways that could positively influence their community or organization’s decision-making process.
Learn More: 5 Tips for Choosing Your EdD Concentration
Those who pursue an EdD focus on qualitative, exploratory research. Students collect data and conduct individual interviews, observations, or focus groups to construct hypotheses and develop strategies that can help solve or clarify a specific problem of practice, such as how to support student veterans transitioning to civilian life or how to foster more female leaders in higher education—two dissertation topics recently explored through Northeastern’s EdD program .
Download Our Free Guide to Earning Your EdD
Learn how an EdD can give you the skills to enact organizational change in any industry.
DOWNLOAD NOW
What Can You Do with an EdD Degree?
While an EdD can be applied to a variety of industries and career options—such as K-12, higher education, the nonprofit sector, or civic service—there are several job titles you’ll likely come across within your cohort of classmates. They include:
- Postsecondary Education Administrators: Postsecondary education administrators work in colleges or universities, and typically oversee faculty research, academics, admissions, or student affairs. Some job titles that fall under this category include president, vice president, provost, and dean. The average annual salary for a postsecondary education administrator rings in at $99,940 .
- Elementary and Secondary School Education Administrators: Superintendents, who are the top executives of a school district, fall under this category. They manage academic programs, spending, and the staffing of all educational facilities within their district, and typically earn an average of $106,850 per year .
- Top Executives : In education, a top executive could be a “chief learning officer” or “chief academic officer”—senior-level professionals who drive and develop strategies that help their organization meet critical business goals. Top executives make an average of approximately $100,090 per year .
- Instructional Coordinators : Instructional coordinators create and manage school curricula and other educational materials. They help teachers implement effective classroom learning strategies and measure the effectiveness of what’s being taught and how. The average annual salary for instructional coordinators is roughly $66,490 .

These are just a few of the many career opportunities available to EdD graduates.
Learn More: Top Careers with a Doctorate in Education
What is a PhD in Education?
A PhD in Education is a terminal degree best suited for individuals who want to pursue a career in academia or research at the university level.
Students in PhD or doctoral programs take a more theoretical, study-based approach to learning. In most cases, their goal is to master a specific subject or add their unique findings to a body of existing literature. PhD candidates conduct original research in the hopes of driving change in their field or inspiring others to make change based on their work.
A PhD is the degree most popular amongst those who aspire to become a professor or obtain a tenure position. Through these programs, students tend to focus on getting published in well-respected journals, presenting at national conferences, and learning how to teach future educators.
What Can You Do with a PhD in Education?
While some of the above roles can also be earned through a PhD program, the most common job titles for PhD-holders include:
- Postsecondary Teachers: Postsecondary teachers instruct students at a college or university. When they’re not in the classroom, they’re often focused on conducting research, attending conferences, and publishing scholarly papers and books. Postsecondary teachers earn an average $80,840 per year .
- Academic Researcher : Researchers often have the opportunity to create their own centers or institutes, hire staff to help carry out their work, and secure funding for that work. Salaries often vary by subject area, but a general academic researcher typically earns an average $83,971 per year .
EdD or PhD: Which is Better For You?
Once you’ve explored the differences between an EdD and PhD in Education, the most relevant question to consider will be: What’s the next step I want to take in my career, and which degree can help me achieve my professional goals? The answer to this question will determine which degree program you ultimately pursue.
Earning your doctorate can pay off no matter which path you choose. Professionals with a doctoral degree earn an average $98,000 a year —nearly $20,000 more a year than master’s degree holders. Similarly, doctoral degree holders see an unemployment rate of only one percent compared to the national unemployment rate of two percent.
Regardless of which degree you ultimately pursue, there is enormous potential for you to advance your career in the field of education. Evaluating your needs and values will help you understand whether an EdD or PhD in Education is best suited to your personal and professional goals.

This article was originally published in July 2017. It has since been updated for accuracy and relevance.
Subscribe below to receive future content from the Graduate Programs Blog.
About scott w. o'connor, related articles.

What is Learning Analytics & How Can it Be Used?

Reasons To Enroll in a Doctor of Education Program

Why I Chose to Pursue Learning Analytics
Did you know.
The median annual salary for professional degree holders is $97,000. (BLS, 2020)
Doctor of Education
The degree that connects advanced research to real-world problem solving.
Most Popular:
Tips for taking online classes: 8 strategies for success, public health careers: what can you do with an mph, 7 international business careers that are in high demand, 7 must-have skills for data analysts, in-demand biotechnology careers shaping our future, the benefits of online learning: 8 advantages of online degrees, how to write a statement of purpose for graduate school, the best of our graduate blog—right to your inbox.
Stay up to date on our latest posts and university events. Plus receive relevant career tips and grad school advice.
By providing us with your email, you agree to the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Keep Reading:

The 8 Highest-Paying Master’s Degrees in 2024

Graduate School Application Tips & Advice

How To Get a Job in Emergency Management

Join Us at Northeastern’s Virtual Graduate Open House | March 5–7, 2024

- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Parents & Families
- Employers & Partners
Information for
- Request Info
- Academics & Research >
- Graduate Education >
- Graduate Programs >
- Online Programs

Flexible, High-Quality Programs to Advance Your Career
Find an Online Program Corporate Partners Graduate Admissions
Today’s work landscape is constantly evolving, making it challenging to stay a step ahead and successfully differentiate yourself as the “best candidate” for that promotion or new position.
Early and mid-career professionals need to keep their skills and industry knowledge up to date, acumen sharp, and build connections that will help them excel in their field and achieve their career goals. And they need the ability to do it on their own time–while working full time and enjoying home life–without settling for a lower quality education.
Clarkson’s online master’s, certificate and micro-credential programs offer the high-quality and reputable education we’re known for – taught by experienced faculty with decades of teaching and industry experience – in a flexible and easily accessible format.
Because in 2024, it isn’t just about “work-life” balance. It’s about work-life-study balance.

Office of Graduate Admissions Email : [email protected] Phone : 518-631-9831
Request Info Apply Now
Online Graduate Programs
Clarkson University’s fully online degree programs, courses and continuing education options allow you to advance your career through every stage — whether you’re new to the workforce and looking to set yourself up for future opportunities or a seasoned professional looking to land a promotion.
We created our online graduate programs with professionals in mind. As you have unique lives and personal objectives for advancing your education, our online programs offer maximum flexibility so you can earn a reputable degree that fits into your daily life.
You can feel confident knowing you'll leave Clarkson with a valuable set of skills. In 2023, the Princeton Review included us in their "Best Career Services" and "Best Alumni Network" rankings. *And, for students prioritizing high earnings and economic mobility over other factors, Clarkson ranked tenth nationally for universities with less than 10,000 students and more than fifty percent STEM graduates in the New York Times 2023 rankings .
How Online Learning at Clarkson Works
We’re a community of collaborative innovators striving to make an impact through our work — whether in the lab, the boardroom or the field. That mindset remains steadfast no matter where we are: in our online courses, students continue growing their skills alongside other driven, creative individuals while learning from world-renowned faculty.

Fully Online
We currently offer 10+ master’s programs and 13 certificate programs that can be completed fully online. These programs allow you to further your education in a number of areas like engineering, computer science, data science and business.

Course Structure
Our online graduate degree programs combine synchronous and asynchronous learning. Typically, you’ll participate in one live virtual class each week; however, we record the lecture for those unable to attend this time slot. As a result, some students are able to complete their degrees entirely asynchronously.

Part- And Full-Time Study
Most working professionals are interested in part-time study. Our online graduate programs are flexible, so you can take just one course at a time, take on a full-time course schedule, or take time off if needed. Your academic advisor will help you plan out your course schedule and make changes to your degree plan, if needed.
Online Courses and Professional Development
We’re here whenever your skills need a refresh. And, as America’s Corporate Partner University, we collaborate with employers to create fully online professional development programs for their workforce.
Individual Courses
Clarkson offers fully online or paired online courses to currently enrolled undergraduate and graduate students. Check availability for the fall, spring and summer semesters.
Advanced Certificates
Broaden your knowledge base or pivot to an emerging field. For candidates holding a bachelor’s degree, our advanced certificates introduce you to business fundamentals or applications in supply chain management, human resources, data analytics, healthcare management and other areas. And if you decide to move forward with a master’s degree upon completion of the certificate, you can apply those credits towards your degree!
Micro-Credentials
Specialize your engineering and technical knowledge, explore the foundations of leadership or get a glimpse of what it takes to succeed as an entrepreneur. Taught by Clarkson faculty, our micro-credentials are open to alumni and working professionals, as well as current students. Contact the Office of Micro-credentials at [email protected] for more information.
Take the Next Step
Access a Clarkson education at any professional stage, in a format convenient to you.
RIT graduate programs ranked among best in nation by ‘U.S. News & World Report’

Scott Hamilton/RIT
'U.S. News & World Report' ranked RIT’s Saunders College of Business among the best graduate programs in the nation.
Graduate degree programs at Rochester Institute of Technology were named among the best in the nation, according to U.S. News & World Report.
In the U.S. News & World Report Best Graduate Schools 2024 , RIT’s Saunders College of Business tied for 97th as one of the top full-time MBA programs .
New methodologies for ranking full-time MBA programs placed more emphasis on earnings. This ranking factor assessed how each school’s post-graduate salaries across different professions compared with other schools’ post-graduate salaries in those professions.
This change was made to account for the importance of compensation for prospective business school students, the varying vocational interests of students at different schools, and to more fully refine the impact business schools have on their graduates’ starting salaries.
U.S. News is delaying the publication of this year’s best engineering schools due to questions about new ranking indicators pertaining to bibliometric data. Concerns arose about the consideration of affiliated institutions in this area. Results for the best medical schools are also under review.
Typically, US News & World Report ranks annually graduate programs in six fields—business, education, engineering, law, medicine, and nursing to help prospective students make informed decisions. These data-driven rankings have been based on enrollment numbers, job placement rates, faculty statistics, and other indicators.
U.S. News also periodically ranks programs in 12 academic disciplines based on academic reputation. This year, RIT’s computer science MS program in the Golisano College of Computing and Information Sciences tied 70th in the nation.
RIT programs ranked in prior years, based on peer assessment, remain tied:
- 65th for the health care management MS program offered by the College of Health Sciences and Technology;
- 78th for physics ( astrophysical sciences and technology Ph.D. program) offered by the College of Science;
- 188th for the physician assistant MS program offered by the College of Health Sciences and Technology .
- 6th for photography and 23rd among fine arts MFA program, offered in the College of Art and Design ; and
- 119th for the bioinformatics MS program offered by the College of Science.
Peer assessment data regarding the academic quality of programs came from deans, program directors, and senior faculty. U.S. News also surveyed professionals who hire or work with new graduates with degrees from the six disciplines ranked annually.
The complete rankings are available at U.S. News & World Report Best Graduate Schools .
Recommended News
April 19, 2024

Scavenger Hunt for RIT Students planned at Imagine RIT
RIT spices up Imagine RIT with an exciting scavenger hunt exclusively for students. Participants can follow clues to discover selected exhibits, snap selfies with QR codes, and compete for a chance to win one of three $100 Tiger Bucks prizes.

Rochester Institute of Technology breaks ground on new Tiger Stadium
The Democrat and Chronicle speaks to Jacqueline Nicholson, executive director of Intercollegiate Athletics, along with alumni, coaches, and lacrosse players about the excitement of a new home for men's and women's soccer and lacrosse teams.

RIT breaks ground on new soccer, lacrosse stadium
WHAM-TV covers the groundbreaking of the new Tiger Stadium on the RIT campus.

RIT and URMC partner to study microplastic’s impact on the environment and human health
WROC-TV talks to Christy Tyler, professor in the Thomas H. Gosnell School of Life Sciences, about how climate change will impact microplastics.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Hispanic enrollment reaches new high at four-year colleges in the U.S., but affordability remains an obstacle
Hispanic enrollment at postsecondary institutions in the United States has seen an exponential increase over the last few decades, rising from 1.5 million in 2000 to a new high of 3.8 million in 2019 – partly reflecting the group’s rapid growth as a share of the overall U.S. population.
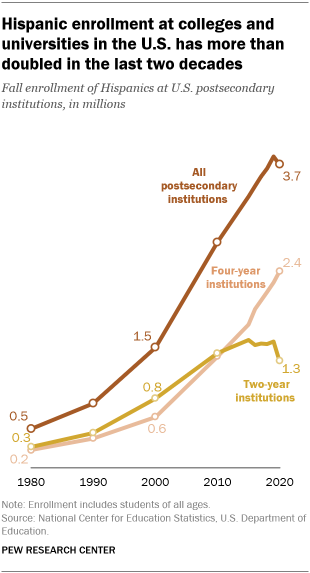
However, the COVID-19 pandemic brought a decline in postsecondary enrollment among Hispanics and most other racial and ethnic groups. In fall 2020, there were 640,000 fewer students – including nearly 100,000 fewer Hispanics – enrolled at U.S. colleges and universities than in the previous year, according to the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES).
The decline for Hispanics, and other racial and ethnic groups, in 2020 was driven by a drop in enrollment at two-year institutions. Hispanic enrollment at two-year colleges declined by about 230,000, or 15%, from 2019 to 2020. It appears that this trend continued into fall 2021, as there was a decline in the number of higher education institutions where Hispanics make up at least 25% of students – known as Hispanic-Serving Institutions – from 569 in fall 2020 to 559 in fall 2021 . (NCES has not yet released postsecondary enrollment data for fall 2021.)
Hispanic enrollment at four-year institutions, by contrast, continued to rise even during the first year of the pandemic, increasing by about 140,000 students, or 6%, from 2019 to 2020. Hispanic enrollment at such institutions has increased every year for decades. Between 2000 and 2020, the number of Latinos enrolled at four-year institutions jumped from 620,000 to 2.4 million, a 287% increase. By comparison, overall student enrollment at four-year institutions in the U.S. grew by 50% during this time.
This Pew Research Center analysis about Hispanics and college enrollment relies on data from sources including the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) and the Census Bureau’s 2021 Current Population Survey Annual Social and Economic Supplement (IPUMS).
To explore the factors contributing to the gap among racial and ethnic groups in college completion, we surveyed 9,676 U.S. adults between Oct. 18-24, 2021. Everyone who took part is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the survey questions used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology .
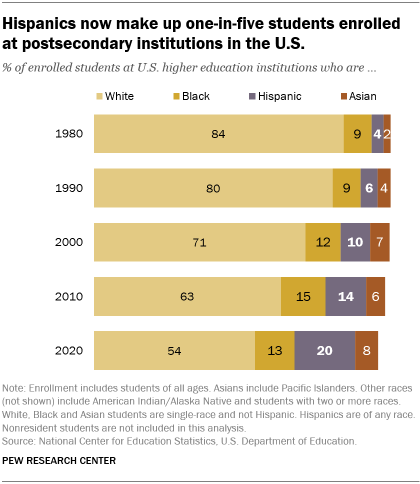
Latinos make up a growing share of all students enrolled at postsecondary institutions. In 1980, there were about 470,000 Latinos enrolled at degree-granting postsecondary institutions, accounting for 4% of all students. By 2000, Latino enrollment had increased to 1.5 million, or 10% of all students. And by 2020, 3.7 million Latinos were enrolled, accounting for a fifth of all postsecondary students.
Asian enrollment at postsecondary institutions has also grown sharply in recent decades, though not as quickly as Hispanic enrollment. The Asian share of postsecondary students nearly quadrupled from 2% in 1980 to 8% in 2020. The share of postsecondary students who are Black increased far more slowly, from 9% in 1980 to 13% in 2020, while White students saw a considerable decrease in their share of enrollment, from 84% to 54%.
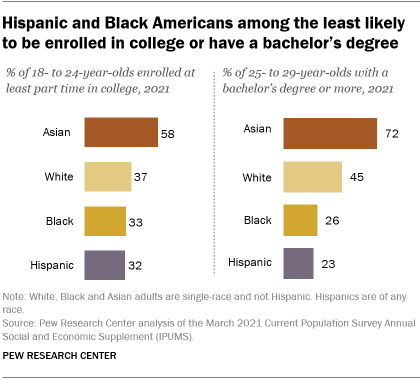
Despite growing enrollment, relatively small shares of young Hispanics are enrolled in college or have obtained a bachelor’s degree. In 2021, about three-in-ten Latinos ages 18 to 24 (32%) were enrolled at least part time in college, a similar share to Black Americans (33%) and a lower share than among White (37%) and Asian (58%) adults of the same age, according to a Pew Research Center analysis of Current Population Survey data. Among Latinos, some 35% of young women 18 to 24 were enrolled at least part time in college in 2021, compared with 28% of men of the same age group.
In 2021, about a quarter of Latinos ages 25 to 29 (23%) had earned a bachelor’s degree, up from 14% in 2010. A similar share of Black Americans in this age group (26%) had obtained a bachelor’s degree, while 45% of White Americans and 72% of Asian Americans ages 25 to 29 had done so. Hispanic women ages 25 to 29 were more likely than Hispanic men in the same age range to have a college degree (27% vs. 20%) – a pattern also seen among other racial and ethnic groups.
Overall, a 62% majority of U.S. adults ages 25 and older do not have a bachelor’s degree, including about eight-in-ten Hispanics (79%).
Financial constraints a major reason why Hispanics do not finish a four-year degree
Financial considerations are a key reason why Americans overall do not complete a four-year degree, and this is particularly true for Hispanics, according to an October 2021 Pew Research Center survey .
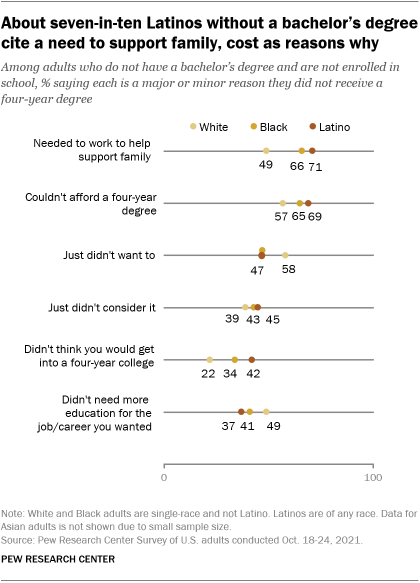
Among Latinos who do not have a bachelor’s degree and are not enrolled in school, about seven-in-ten Latinos (71%) say a major or minor reason why is that they need to work to help support family, while 69% say they couldn’t afford a four-year degree.
Affordability restrictions may include the overall cost of college, lack of reliable transportation or a desire to not take on debt. Hispanics are more likely than other students to avoid taking on debt and more likely to report difficulties paying back student loans .
Personal factors also play a role in college completion. Close to half of Hispanics who have not obtained a four-year degree (47%) say they just did not want to pursue one. There is a notable difference by gender, with 54% of Hispanic men and 40% of Hispanic women citing this as a reason for not finishing college.
Other factors play a role, too. Among Latinos without a bachelor’s degree, about four-in-ten (42%) say they did not think they would get into a four-year college – a significantly higher share than among White Americans (22%). In addition, 37% of Latinos without a bachelor’s degree say they did not think they needed a four-year degree for the job or career they wanted. This is similar to the share of Black Americans who say the same, (41%) but lower than the share of White Americans (49%).
Note: Here are the survey questions used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology .
- Affirmative Action
- Higher Education
- Hispanics/Latinos & Education

Striking findings from 2023
Private, selective colleges are most likely to use race, ethnicity as a factor in admissions decisions, americans and affirmative action: how the public sees the consideration of race in college admissions, hiring, asian americans hold mixed views around affirmative action, more americans disapprove than approve of colleges considering race, ethnicity in admissions decisions, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A doctorate degree is a graduate-level credential that is usually earned after multiple years of graduate school. Earning a doctoral degree requires a significant level of research and work. In order to get this degree, one has to research a subject thoroughly, conduct new research and analysis, and provide a solution or interpretation into the ...
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: philosophiae doctor or doctor philosophiae) is the most common degree at the highest academic level, awarded following a course of study and research. The degree is abbreviated PhD and sometimes, especially in the U.S., as Ph.D. It is derived from the Latin Philosophiae Doctor, pronounced as three separate letters (/ p iː eɪ tʃ ˈ d iː ...
A doctoral degree is a graduate-level credential typically granted after multiple years of graduate school, with the time-to-degree varying depending on the type of doctoral program, experts say ...
While a Ph.D. and a doctorate award "Doctor" titles, a Ph.D. tends to be an academic degree while a doctorate is usually a professional degree. Ph.D.s often focus on extensive research and may lead to job titles such as research scientist, historian, philosopher, professor or engineer. Because a doctorate typically provides students with ...
The two most common types of graduate degrees are master's and doctoral degrees: A master's is a 1-2 year degree that can prepare you for a multitude of careers. A PhD, or doctoral degree, takes 3-7 years to complete (depending on the country) and prepares you for a career in academic research. A master's is also the necessary first ...
Doctorate degrees are designed for current or aspiring working professionals who want to become industry leaders. These programs also enable students to increase their knowledge and credibility. PhD programs attract students who want to expand their knowledge of research methodologies and theories. These learners also frequently pursue academic ...
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. This is one of the highest level academic degrees that can be awarded. PhD is an abbreviation of the Latin term (Ph)ilosophiae (D)octor. Traditionally the term 'philosophy' does not refer to the subject but its original Greek meaning which roughly translates to 'lover of wisdom'.
The Ph.D. is the most common research doctorate. Although the title stands for "doctor of philosophy," students can earn Ph.D.s in a wide range of subjects, including science and technology. In contrast, applied research doctorates often relate to specific fields, such as education, music, or social work. The main difference between the two is ...
A Doctor of Philosophy, often known as a PhD, is a terminal degree —or the highest possible academic degree you can earn in a subject. While PhD programs (or doctorate programs) are often structured to take between four and five years, some graduate students may take longer as they balance the responsibilities of coursework, original research ...
A Ph.D. is primarily a research-focused degree focused on producing independent scholars who can conduct original research and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field. On the other hand, a professional doctorate focuses on the application of knowledge and skills in a specific profession or industry.
Doctorate, or doctoral, is an umbrella term for many degrees — PhD among them — at the height of the academic ladder. Doctorate degrees fall under two categories, and here is where the confusion often lies. The first category, Research (also referred to as Academic) includes, among others: Doctor of Philosophy (PhD)**.
A PhD is a Doctor of Philosophy. In answer to the question, "Is a PhD a doctor," the answer is yes. Both a PhD and a professional doctorate like an EdD earn you the title of "doctor.". But there are differences between the types of doctoral degrees. Learn more about a PhD vs. a professional doctorate below.
A Masters degree is the next level of education after the completion of an undergraduate degree, commonly known as a Bachelors. These degree levels are often referred to in terms of cycles so that a Bachelor's is a first-cycle degree, a Masters is a second-cycle and finally, a PhD is the third-cycle of higher education (and the highest).
A PhD is a terminal academic degree students typically pursue when they're interested in an academic or research career. A PhD is the highest possible academic degree a student can obtain. PhD stands for "Doctor of Philosophy," which refers to the immense knowledge a student gains when earning the degree. While you can actually get a PhD in ...
Many people believe that the DPhil and PhD are different degrees. This is not true. 'DPhil' is an abbreviation of 'Doctor of Philosophy'. Essentially, 'DPhil' and 'PhD' are two different ways of referring to the same doctoral degree. 'DPhil' is traditionally a British term and so only a few universities (most notably, the ...
A Ph.D., or Doctor of Philosophy, is a high-level degree earned after a period of three or more years of graduate-level study, culminating in the creation, submission, presentation and defense of a research dissertation. The Ph.D. can be awarded in a wide variety of fields, including the sciences, engineering and humanities.
The Doctor of Education Leadership (Ed.L.D) is a three-year, practice-based program designed to produce system-level leaders in American pre-K-12 education. The Ed.L.D. curriculum mines the vast intellectual and professional resources of HGSE, the Harvard Business School, and the Harvard Kennedy School, and includes a 10-month residency in the ...
People with PhDs are considered experts in their fields, and the degree includes "Doctor" in its name. For that reason, PhD holders often use the title "Doctor.". A college professor, for example, might go by Dr. Smith. Even still, there's a difference between MD vs. PhD. A person who holds a PhD is not a medical doctor.
Culmination of Degree. As was mentioned before, the culmination of both master's degrees and doctorate degrees differ. There are a few main differences between a dissertation and a thesis. For a master's degree, you are expected to complete a capstone course or a thesis. This is a paper that is limited to about 40,000 words.
Other fields do not require advanced degrees for career advancement. In some cases, a master's degree may hold advantages over a doctoral degree. For example, a master's degree in social work (MSW) may be more cost-effective than a doctoral degree, given the time and funds required to earn the degree and the pay differential.
A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy, is a specific type of doctorate degree that focuses on research in a particular field. It is highly theoretical and involves extensive research to generate new knowledge. On the other hand, a doctorate degree is an umbrella term for any doctoral-level degree.
Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame ...
A Doctor of Education (EdD) is a professional degree designed for practitioners pursuing educational leadership roles. A PhD in education, on the other hand, is designed to prepare graduates for research and teaching roles. "With a PhD, [students are] reviewing the research, seeing a gap in the literature, and generating new knowledge based ...
Mason has 14 graduate programs in the top 50 in U.S. News rankings. April 10, 2024 / By. Sarah Holland. George Mason's nursing doctorate program is 1st among public universities in U.S. News and World Report graduate program rankings; the law school is top three in the Washington, Maryland and Virginia region.
A Ph.D. from National University costs $26,520, while the same degree from Kennesaw State University costs a minimum of $18,384. However, the tuition rates for Ph.D. programs vary significantly ...
Online Graduate Programs. Clarkson University's fully online degree programs, courses and continuing education options allow you to advance your career through every stage — whether you're new to the workforce and looking to set yourself up for future opportunities or a seasoned professional looking to land a promotion.
Graduate degree programs at Rochester Institute of Technology were named among the best in the nation, according to U.S. News & World Report.. In the U.S. News & World Report Best Graduate Schools 2024, RIT's Saunders College of Business tied for 97th as one of the top full-time MBA programs.. New methodologies for ranking full-time MBA programs placed more emphasis on earnings.
Overall, Latinos accounted for 8% of professional degree holders in the U.S. in 2021. Another 250,000 Latinos with advanced degrees, or 10%, had a doctoral degree, such as a Ph.D. or Ed.D. Among all Americans, 72% of those with a graduate degree have a master's degree as their highest level of education, while 17% have a professional degree ...
Hispanic enrollment at postsecondary institutions in the United States has seen an exponential increase over the last few decades, rising from 1.5 million in 2000 to a new high of 3.8 million in 2019 - partly reflecting the group's rapid growth as a share of the overall U.S. population.. However, the COVID-19 pandemic brought a decline in postsecondary enrollment among Hispanics and most ...
The annual ranking of MEDCoE's graduate health programs include: - The U.S. Army Graduate Program in Anesthesia Nursing ranked second out of 131 Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist and Doctor ...