Education Requirements for Engineering Project Managers
Getting started as a engineering project manager.
- What is a Engineering Project Manager
- How to Become
- Certifications
- Tools & Software
- LinkedIn Guide
- Interview Questions
- Work-Life Balance
- Professional Goals
- Engineering Project Manager Resume Examples
- Engineering Project Manager Cover Letter Examples
Start Your Engineering Project Manager Career with Teal
Join our community of 150,000+ members and get tailored career guidance from us at every step

Do You Need a Degree to Become a Engineering Project Manager?
Educational backgrounds of engineering project managers, a snapshot of today's engineering project managers' educational background, evolving trends and the shift in educational preferences, education for aspiring engineering project managers: what matters.
- Project Management Expertise: Gained through specialized certifications or master's programs that focus on project management principles and practices.
- Business and Leadership Skills: Acquired through MBA programs or business-related courses that enhance one's ability to lead teams and manage budgets.
- Technical Proficiency: Maintained by staying abreast of the latest engineering technologies and methodologies, which can be achieved through continuing education and professional development.
Building a Path Forward: Education and Beyond
- Practical Experience: Engaging in engineering projects, even in entry-level roles, to understand the nuances of project lifecycle and team dynamics.
- Continuous Learning: Pursuing ongoing education opportunities, such as workshops, webinars, and industry conferences, to keep skills sharp and up-to-date.
- Networking and Mentorship: Connecting with seasoned Engineering Project Managers and participating in professional organizations to gain insights and support.
The Bottom Line: Diverse Backgrounds, Unified Goals
Most common degrees for engineering project managers, engineering, project management, business administration or management, systems engineering, construction management, popular majors for engineering project managers, engineering management, civil engineering, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, industrial engineering, computer science or information technology, popular minors for engineering project managers, business administration, supply chain management, environmental studies, quality management, why pursue a degree for a engineering project manager career, why pursue a degree for an engineering project manager career, key advantages of a degree in engineering project management, the importance of practical experience, networking opportunities and professional growth, career transition and progression, what can you do with a degree in engineering project management, degree alternatives for a engineering project manager, professional certifications, technical workshops and seminars, online courses and moocs, apprenticeships and on-the-job training, self-directed learning and personal projects, navigating a engineering project manager career without a degree, gain hands-on technical experience, develop project management skills, build a professional network, create a results-oriented portfolio, understand engineering principles, embrace agile and lean methodologies, leverage technology and tools, seek certifications, stay informed about industry developments, highlight transferable skills, education faqs for engineering project manager, do you need to go to college to become a engineering project manager, is it worth it to get a degree for a engineering project manager role, how important is continuous learning for a engineering project manager.
Engineering Project Manager Certifications

More Education for Related Roles
Coordinating dynamic teams, managing resources to deliver projects within timeframes
Driving tech projects from conception to completion, ensuring efficiency and innovation
Orchestrating multiple projects, ensuring alignment with strategic objectives and goals
Leading project execution, ensuring strategic alignment, and driving team performance
Driving tech projects from concept to completion, ensuring efficiency and quality
Driving technical projects from conception to completion, ensuring quality and efficiency

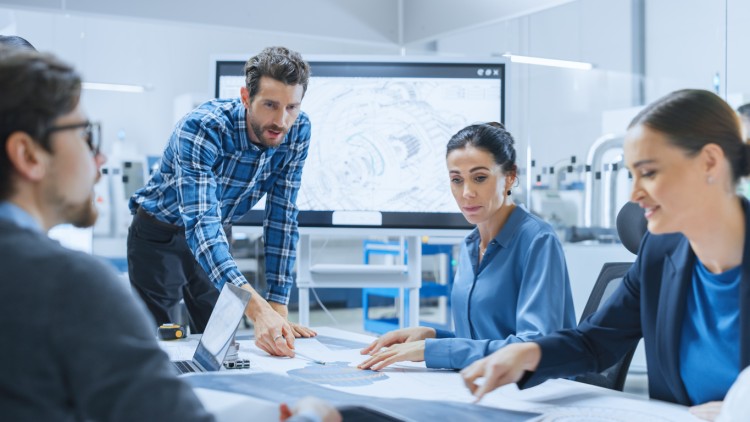
How to Become an Engineering Project Manager
Find schools.
When you click on a sponsoring school or program advertised on our site, or fill out a form to request information from a sponsoring school, we may earn a commission. View our advertising disclosure for more details.
Engineering projects require the coordination of many moving parts, and engineering project managers are the maestro of those moving parts, orchestrating on-time, on-budget, safe, and successful project delivery. They can work on construction projects, engineering projects, or even IT migrations. And while it’s not what you may first think of when considering engineering marvels like the Hoover Dam, proper planning and execution are just as vital as airtight physics and structural analysis, and it can mean the difference between success and failure.
Most engineering project managers have a strong background in engineering fundamentals. Without that background, it’s practically impossible to manage complex engineering projects. Whether they want to work in mechanical, chemical, or civil engineering project management, they have a solid understanding of the mechanics and skillsets that undergird such projects. Furthermore, engineering project management has a role of such extreme importance in engineering projects that it may take a decade or more of education and experience before one is selected to lead a project on their own.
The path is long, and routes to becoming an engineering project manager are many, but we have outlined the most linear and comprehensive route possible below. By following our step-by-step guide, aspiring engineering project managers can keep their options open, go beyond the bare minimum, and aim for success in the top echelons of engineering project management. Read on to get started.
Step-by-Step Guide to Becoming an Engineering Project Manager
Step one: obtain a bachelor’s degree (four years).
After graduating from high school, the first thing an aspiring engineering project manager will need to do is obtain a bachelor’s degree, ideally at a program accredited by the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET). There are not many undergraduate programs that focus specifically on project management, and the few that do generally neglect the engineering side of the equation. Aspiring engineering project managers should use their undergraduate years to build solid engineering fundamentals in the area they wish to eventually do project management, such as civil engineering.
University of North Dakota
As an online option, the University of North Dakota offers a BS in civil engineering. Recognized as a top online engineering program by U.S. News & World Report , its students focus on engineering, design, project management, construction, contract administration, technical support, and research. The university also offers a combined bachelor’s and master’s degree in civil engineering which can be completed in less time.
The program consists of 128 credits and includes classes such as introduction to civil engineering; structural mechanics; civil engineering materials laboratory; soil mechanics; environmental engineering; elementary differential equations; and transportation engineering.
Graduates of the program will have a wide range of job opportunities in engineering design and development, construction management, water resources engineering, geotechnical engineering, structural engineering, site development, transportation engineering, hydraulic engineering, and environmental regulation.
- Location: Grand Forks, ND
- Accreditation: Higher Learning Commission (HLC)
- Expected Time to Completion: 48 to 60 months
- Estimated Tuition: $643.95 per credit
New York University
For an on-campus option, NYU offers a BS in civil engineering. Strongly practice-oriented, with a heavy emphasis on design, the program is modeled off of ABET’s 11 fundamental outcomes to cover the full range of skills and knowledge necessary for modern engineers.
The program consists of 129 credits and includes classes on topics like calculus for engineers; general chemistry for engineers; general physics laboratory; introduction to civil engineering; analysis of determinate structures; structural engineering; geotechnical engineering; construction project management; computing in civil engineering; water resources engineering; engineering mechanics; and fluid mechanics and hydraulics. Electives are available in subjects such as construction project administration, construction scheduling, and cost estimation.
- Location: New York City, NY
- Accreditation: ABET; Middle States Commission on Higher Education
- Expected Time to Completion: 48 months
- Estimated Tuition: $1,683 per credit
Step Two: Establish State Licensure (Timeline Varies)
After you have earned a bachelor’s degree in engineering, you may be eligible to sit for state licensure. Not all states require engineers to be licensed in order to practice, and the requirements vary from state to state, but precise guidelines can be found on the National Council of Examiners for Engineering and Surveying (NCEES) website.
The first step in the licensure process is to pass the fundamentals of engineering (FE) exam. The exam is offered in several subdisciplines, with the civil engineering exam being most relevant for aspiring engineering project managers with a focus on construction engineering. The 110-question exam takes approximately six hours to complete, and a passing score qualifies one as an engineer in training (EIT) or engineering intern (EI). Regardless of the licensure requirements in your state, passing the FE can lead to greater opportunities on your path to becoming an engineering project manager.
Step Three: Obtain a Master’s Degree (9-24 Months)
After you have earned your bachelor’s degree and passed the FE exam, the next step is to obtain a master’s degree. Unlike the undergraduate level, there are plenty of master’s degree programs in engineering project management.
University of California, Berkeley
One such program is available at UC Berkeley, which offers an MS in engineering and project management (EPM). The program seeks to marry solid civil engineering fundamentals with innovative leadership strategies.
Students take classes in topics such as lean construction concepts, supply chain management, advanced project planning, law for engineers, civil systems and the environment, individual research or investigation in selected advanced topics, and technology and sustainability. The program consists of 24 credits and may be completed in nine months or more.
Graduates have a wide range of employment opportunities in the public sector and the private industry, for example in building, engineering consulting, transportation, and industrial construction firms, as well as in private and public owner organizations, both domestically and internationally.
- Location: Berkeley, CA
- Accreditation: Western Association of Schools & Colleges (WASC)
- Expected Time to Completion: 9 months
- Estimated Tuition: California residents ($3,250); non-residents ($6,327)
Northwestern University’s McCormick School of Engineering
Another option is Northwestern University’s McCormick School of Engineering, which offers a master of project management (MPM) degree. Students may choose from five sub-specializations: architecture-engineering-construction (AEC) business management; construction management; real estate development; sustainability; and transport management.
Students take courses such as managerial finance; project scheduling; project funding; project feasibility analysis; cost engineering and control; building construction estimating; principles of project management; real estate development; construction management; intelligent transportation systems; and lean construction. The program may be completed in nine months or more.
Applicants to the program must have an undergraduate degree in engineering or architecture, a minimum grade point average of 3.0, an official transcript from each institution attended, GRE or GMAT scores (waivers available), three letters of recommendation, a current resume or CV, a personal statement, and TOEFL or IELTS test scores for international student applicants whose native language is not English.
Graduates are prepared for leadership roles in the operation, management, and construction of major civil and environmental engineering projects.
- Location: Evanston, IL
- Expected Time to Completion: Part-time (18 to 24 months); full-time (nine to 18 months)
- Estimated Tuition: $5,005 per course
Ohio University
It’s also possible to pursue a master’s degree in a more concrete engineering subdiscipline, such as civil engineering, and look for further project management education and experience later on. As an online option, Ohio University offers a master of science in civil engineering (MSCE) that can be completed in five semesters or more.
Students take classes in communication skills for engineers; construction planning and scheduling; applied civil engineering statistics; advanced steel design; prestressed concrete design; and in situ remediations. The program consists of 60 credits and may be completed entirely online.
To get accepted into the program, applicants must have a bachelor’s degree in civil engineering from an ABET-accredited university with a grade point average of 3.0 or higher.
Graduates will be able to take up roles such as environmental engineers, transportation engineers, structural engineers, construction managers, surveyors, engineering managers, and sustainability engineers.
- Location: Athens, OH
- Expected Time to Completion: five semesters
- Estimated Tuition: In-state ($840 per credit); Out-of-state and international ($859 per credit)
Step Four: Gain Work Experience and Pursue Continuing Education (Timeline Varies)
After earning your master’s degree, it’s time to gain some valuable real-world experience. Engineering project management roles carry a huge amount of responsibility, and it likely will not be possible to lead large projects straight out of school. At this stage of their careers, engineering project managers should focus on gaining all the experience they can, putting their fundamental skills to practice, and building a resume of successful team projects.
Now is also the right time to gain further education in the area of project management, especially if your master’s degree wasn’t specifically geared towards the subject. And even if it was, adding certified education can give you a better chance of landing project management roles with which to cut your teeth.
One such option is a course in project management for engineers and technical professionals, hosted by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). During the three-day course, students learn to discern between projects, programs, and sub-projects; employ integrated case studies to create deliverables; identify techniques and outputs such as critical path, schedule compression, fast-tracking, and resource leveling; and apply project scheduling concepts such as the Activity Gantt Chart, resource-gram, and histogram.
Another option is Coursera’s specialization in engineering project management. Offered in collaboration with the Rice Center for Engineering Leadership, this four-month series covers three areas: initiation and planning; scope, time, and cost management; and risk, quality, teams, and procurement. Students gain a comprehensive understanding of how to manage an engineering project, and those who complete all three areas can simultaneously fulfill all their continuing education requirements for the Project Management Institute’s (PMI) Project Management Professional (PMP) certification (see step six for more information).
Step Five: Become a Professional Engineer (Four Years)
After gaining four years of professional experience, and having passed the FE exam and earned a master’s degree, you are eligible to sit for licensure as a professional engineer (PE).
The PE exam, also hosted by the NCEES, has no specialized test for project management, but it does offer an exam in civil engineering, within which one may specialize in either construction engineering or structural engineering. The 80-question open-book exam takes approximately eight hours to complete. If you earn a passing score, you will be licensed as a professional engineer, which serves as a mark of distinction for an engineering project manager and establishes them as an expert in the technical side of an engineering subdiscipline.
Step Six: Achieve Professional Certification (Timeline Varies)
After you have gained some real-world experience, the next step is to achieve professional certification. Professional certifications specifically dedicated to project management can set you apart and identify you as an expert in this sub-discipline of engineering.
The industry standard for certification is the Project Management Institute (PMI), which offers both the Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) and Project Management Professional (PMP) certifications.
For those looking to manage larger projects and gain more responsibility, the CAPM establishes your understanding of the fundamental knowledge, terminology, and processes of effective process management through a three-hour, 150-question test. Applicants must have either 1,500 hours of project experience or 23 hours of project management education. Those who successfully earn the CAPM must recertify every three years.
For those looking to validate their competence to lead and direct projects and teams, the PMP is the gold standard, with those who hold it earning an average of 25 percent more than non-holders. This is a certification for experienced project managers who have over 4,500 hours of experience directing or leading projects and at least 35 hours of project management education. Applicants must successfully pass the four-hour, 180-question exam for certification. To maintain your PMP, you must earn 60 professional development units (PDUs) every three years.
Helpful Resources for Engineering Project Managers
TThe world of project management is constantly evolving and to keep pace, many engineering project managers choose to join professional societies closely related to their area of specialty. These societies act as a bridge to the larger, global conversation and host conferences, educational resources, and further certifications for engineering project managers, acting as a critical link to the constant learning necessary to be a successful engineering project manager at the top echelons of the industry.
- International Project Management Association (IPMA)
- American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE)
- Project Management Institute (PMI)
- American Academy of Project Management (AAPM)
THANK YOU FOR YOUR INTEREST IN Southern New Hampshire University Online MS - Construction Management

Related Programs
- Architecture & Sustainable Design
- Construction Management
- Engineering Management
- Engineering MBA
- Operations Management
Related FAQS
- 1. How Do I Become a Construction Manager?
- 2. How Do I Become an Engineering Manager?
- 3. Any No GMAT / No GRE Online Engineering Programs?
- 4. Business Analyst vs. Systems Analyst
- 5. Construction Management vs. Engineering Management
Related Articles
Engineering management professors you should know.
Because quality of educators is paramount in the decision-making process for prospective engineering management students, we have compiled this list of professors to know in the field. To be the best, it helps to learn from the best.
Lean Six Sigma Certification Programs
Lean Six Sigma is a blend of two manufacturing concepts focused on minimizing product defects and the wastage of resources. A number of universities offer certification programs in Lean Six Sigma, which can generally be completed in six to 12 weeks.
Online Bachelor’s Degree Programs in Technological Entrepreneurship & Management
Technology and the internet have enabled numerous entrepreneurs to see their ideas come to fruition. It is no surprise that many universities now offer courses and degree programs in technology entrepreneurship.
Online Bachelor’s Degrees in Project Management
An online bachelor’s program in project management generally comprises 120 credit-hours and can be completed in four years. A few courses that students study include estimating and scheduling, project contracting, foundations of project management, international business, and project planning.
Online Bachelor’s Programs in Operations Management
The main goal of operations management is to maximize profits, reduce wastage in production, and ensure that all resources (including labor and materials) are being utilized effectively.

What Does an Engineering Project Manager Do?
Find out what an Engineering Project Manager does, how to get this job, salary information, and what it takes to succeed as an Engineering Project Manager.

The Engineering Project Manager plays an integral role in steering complex projects from conception through to completion, ensuring they are delivered on time, within budget, and to the specified quality standards. This position involves coordinating the efforts of various team members, including engineers, designers, and technicians, to achieve project goals. By serving as the main point of contact for stakeholders and maintaining a clear line of communication, the Engineering Project Manager ensures that all parties are aligned with the project’s objectives and progress. Their expertise not only in technical engineering principles but also in project management methodologies enables them to navigate the challenges of developing innovative solutions while managing resources efficiently. This role demands a blend of technical knowledge, leadership, and strategic planning to successfully bring engineering projects to life.
Engineering Project Manager Job Duties
- Develop project scopes and objectives, involving all relevant stakeholders and ensuring technical feasibility.
- Create and maintain comprehensive project documentation, including project plans, schedules, budgets, and status reports.
- Coordinate internal resources and third parties/vendors for the flawless execution of projects.
- Manage changes to the project scope, project schedule, and project costs using appropriate verification techniques.
- Measure project performance using appropriate systems, tools, and techniques.
- Perform risk management to minimize project risks.
- Establish and maintain relationships with third parties/vendors.
- Oversee the handover of the project to the relevant operational team or department upon completion.
Engineering Project Manager Salary & Outlook
Factors influencing an Engineering Project Manager’s salary include industry sector (e.g., aerospace vs. software), company size, project complexity and budget, years of experience, and specific technical skills related to the projects managed. Leadership abilities and a track record of successful project delivery also significantly impact compensation.
- Median Annual Salary: $120,750 ($58.05/hour)
- Top 10% Annual Salary: $283,500 ($136.3/hour)
The employment of engineering project managers is expected to grow at an average rate over the next decade.
This growth is driven by increasing complexity in engineering projects, the need for specialized management to navigate technological advancements, and the demand for efficient, cost-effective project execution in sectors like construction, technology, and renewable energy, requiring skilled professionals to lead these initiatives.
Engineering Project Manager Job Requirements
Education: An Engineering Project Manager typically holds a Bachelor’s or Master’s Degree in engineering, with majors often in civil, mechanical, electrical, or industrial engineering. Coursework for aspiring managers includes project management, engineering principles, mathematics, and technology applications. Advanced degrees or post-master’s certificates focus on specialized engineering skills, leadership, and complex project management techniques, preparing individuals for higher responsibility roles within engineering projects. Academic backgrounds emphasize analytical skills, problem-solving, and the ability to oversee technical projects from conception to completion.
Experience: Engineering Project Managers typically come from a background rich in hands-on project management experience, often having led multiple complex engineering projects from conception to completion. They possess a deep understanding of technical project requirements, budgeting, and team leadership. Their experience is complemented by on-the-job training and participation in professional development programs, which hone their skills in strategic planning, risk management, and stakeholder communication. Successful candidates have demonstrated a track record of navigating the challenges of engineering projects, showcasing their ability to deliver results within tight deadlines and budgets.
Certifications & Licenses: Certifications and licenses are not universally required for the role of Engineering Project Manager. However, obtaining a Project Management Professional (PMP) certification from the Project Management Institute (PMI) is often beneficial. In some engineering fields, a Professional Engineer (PE) license may enhance credibility and career prospects.
Engineering Project Manager Skills
Risk Management: Engineering Project Managers excel in foreseeing potential project challenges and crafting strategies to counteract them. By thoroughly analyzing project specifications, timelines, and resources, they can predict risks and implement measures to ensure project deliverables are met with minimal disruptions.
Scope Management: Defining, validating, and controlling project boundaries is a critical skill that enables Engineering Project Managers to deliver projects on time, within budget, and according to specifications. Through meticulous planning and execution, they adeptly navigate changes or challenges, ensuring project objectives are achieved with precision.
Cost Estimation: The ability to accurately forecast the financial resources necessary for the completion of engineering projects allows for effective budget allocation and the avoidance of cost overruns. A detailed analysis of project scope, resource needs, potential risks, and market rates is conducted to ensure every financial aspect of the project is carefully planned and accounted for.
Quality Control: Overseeing all phases of design and construction to ensure engineering projects meet specified standards and functionality requirements is a critical responsibility. Coordinating with diverse teams to implement testing protocols, identifying deviations from quality benchmarks, and initiating corrective actions promptly are essential to maintain project integrity and timelines.
Stakeholder Communication: Clear and effective communication with all project stakeholders, from sponsors to team members and clients, is vital for aligning expectations and fostering a collaborative environment. By adeptly conveying technical details, project updates, and potential challenges, an Engineering Project Manager facilitates informed decision-making and maintains project momentum.
Technical Documentation: The creation of clear, comprehensive guides and reports is essential for communicating project specifications, milestones, and technical processes across all team members and stakeholders. This skill ensures the seamless integration of engineering concepts, project timelines, and resource allocations, facilitating streamlined project execution and adherence to quality standards.
Engineering Project Manager Work Environment
Engineering Project Managers often find themselves in a dynamic work environment that blends traditional office settings with on-site project locations. Their workspace is equipped with the latest technology, including project management software and communication tools, ensuring they stay connected with their teams and stakeholders. The nature of their work demands flexibility in work hours, often adjusting to project deadlines which might extend beyond the conventional 9-to-5 schedule.
The dress code varies, leaning towards business casual in the office and safety gear on-site. The culture fosters collaboration and continuous learning, with a strong emphasis on professional development through workshops and seminars. Interaction with team members, clients, and other stakeholders is a daily occurrence, necessitating strong communication skills.
Travel is sometimes required, depending on the project’s location. Despite the fast-paced environment, companies strive to maintain a healthy work-life balance, offering remote work options and flexible schedules. Safety protocols are rigorously followed, especially in on-site settings, to ensure a secure working environment.
Advancement Prospects
Engineering Project Managers can ascend to senior management roles, such as Director of Engineering or VP of Engineering, by demonstrating exceptional leadership and project success. Achieving these positions often requires a track record of delivering complex projects on time and within budget, while also innovating processes and fostering team growth.
To progress, an Engineering Project Manager should focus on strategic project selection, showcasing their ability to handle high-impact projects that align with the company’s long-term goals. Mastery in risk management and decision-making is crucial, as these skills directly contribute to project and organizational success.
Advancement may also lead to opportunities in consultancy or entrepreneurship for those who excel in identifying market needs and leveraging engineering solutions. This path requires a deep understanding of industry trends and customer needs, coupled with the ability to lead cross-functional teams to turn ideas into profitable products or services.
What Does a Director Of Patient Care Services Do?
What does a court assistant do, you may also be interested in..., what does a casino cage cashier do, what does an executive vice president do, 16 clinical specialist skills for your career and resume, what does a postpartum nurse do.

How To Become an Engineering Manager

Industry Advice Engineering
Those looking to advance their engineering careers often face a common obstacle. While many advanced positions in engineering aren’t C-suite positions, most attainable advancements are in leadership and management. Since engineering employers don’t require these types of skills in entry-level positions, building a managerial skill set is essential to increasing your professional options long-term.
As new applications for engineering emerge, this growing field needs more leaders capable of managing challenging technical projects and producing successful outcomes. If you’re interested in advancing your career in engineering, here’s everything you need to know about what an engineering manager is, how to become one, and if this career path is worth pursuing.
What Is an Engineering Manager?
First and foremost, an engineering manager oversees an engineering team. Some of their responsibilities include planning, budgeting, training, and completing technical activities involved in the projects they oversee. Engineering managers need technical expertise in engineering to plan and execute projects, but require various leadership skills to effectively manage relationships with internal and external stakeholders.
Engineers works in a wide variety of fields, including, but not limited to:
- Manufacturing/industrial engineering
- Aerospace engineering
- Chemical engineering
- Software engineering
- Biomedical engineering
- Environmental engineering
- Nuclear engineering
- Mechanical engineering
- Civil and industrial engineering
- Agricultural engineering
- Electrical engineering
As a result, managers must develop expertise related to the specific industries and environments in which they work. Having a strong technical background, good communication skills, and a mastery of project management is essential to success as an engineering manager.
For those interested in becoming an engineering manager, the required steps and tentative timeline depend on several factors. Educational background, current job market standards, experience, and industry-specific qualifications all play a major role in how long it will take you to obtain a managerial position in the field. As you explore your options, here are the most important engineering management requirements to keep in mind.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), entry-level positions in engineering management typically require a bachelor’s degree in engineering or a related field. Engineers work with data, equipment, machinery, and materials that are complex and, in some cases, potentially dangerous. Therefore, it’s crucial to have a foundational knowledge and applied skill set specific to engineering.
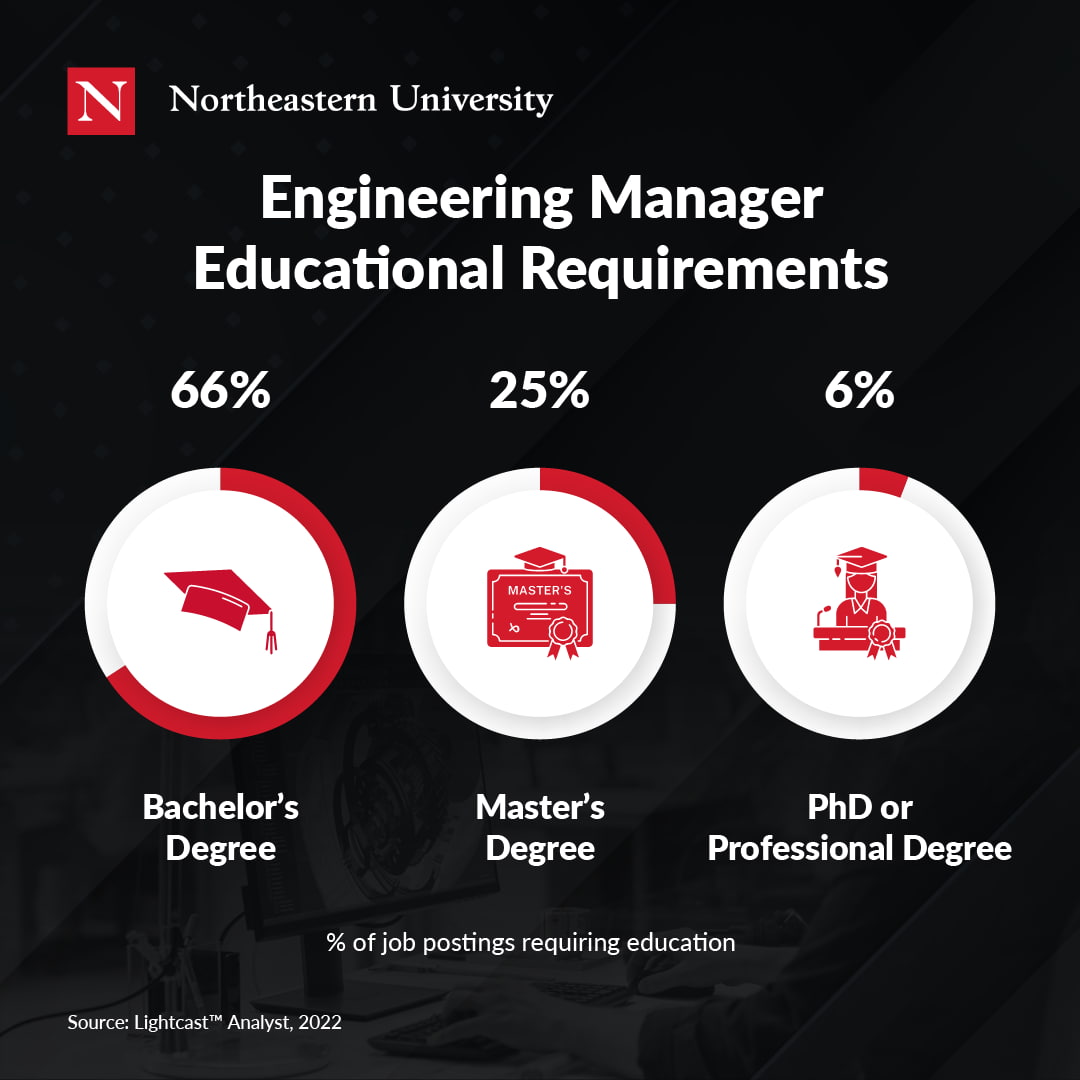
Earning an advanced degree could quicken the process of becoming an engineering manager, but there are other factors to consider before you can apply to job openings. While the best graduate programs incorporate experiential learning, internships, and mentoring from seasoned professionals, experience is an industry-specific requirement.
Background Experience
In general, engineering managers are expected to have five years of experience or more. If you hope to lead a team of engineers, it’s important to understand their day-to-day responsibilities and challenges, which are best observed while on the job. Engineering managers must also analyze problems and develop effective solutions which requires substantial experience working on real-world projects. They are expected to demonstrate proficiency in multiple disciplines, so they often start their career in other related engineering roles, such as a supply chain analyst, operations analyst, and quality assurance technician.
Developing transferable skills can increase your job opportunities and earning potential. According to government data, here are the top skills employers list in engineering manager job postings.

1. Engineering Management
Gaining relevant experience as an engineering manager is, of course, crucial for professionals who want to obtain their first managerial position. Employers want to see evidence that you can supervise operations and teams, make technical and strategic decisions, and carry out successful projects from start to finish. Consider taking on small leadership roles within your current role to show initiative, leadership capabilities, and your potential as a manager.
2. Leadership
Leaders are responsible for motivating teams and delivering positive project outcomes. To accomplish this, you must be comfortable communicating with diverse groups of people, listening to various ideas and concerns, and recognizing the strengths and weaknesses of proposals. Effective leaders are skilled at providing clear direction, letting others act on innovative ideas, and offering training to address skills gaps within the team.
3. Management
General business management skills are beneficial for understanding how to leverage team expertise to achieve specific goals. It’s important to demonstrate good time management, delegation, organization, collaboration, and conflict resolution skills. Management skills don’t have to be developed in managerial roles. Take lead on a project, take on administrative responsibilities, or organize an organization event. All of these show prospective employers that you are management material.
4. Communications
Good communication skills are essential for every job. As an engineering manager, you’ll routinely communicate with technicians, senior managers, supply partners, regulators, clients, and other stakeholders. To succeed, you must be skilled at assessing what’s at stake for each of these parties and managing their expectations. Earning a degree in engineering should aid in developing these skills by conversing with fellow students and faculty members.
5. Planning
Planning is a core part of engineering management. Prospective managers must be skilled at executing company plans to meet various organizational goals. Prioritizing tasks, choosing solutions, and allocating resources are essential aspects of planning that ensure projects and processes are completed on time and on budget. If you’re still an entry-level engineer professional, try to take initiative in the planning process of various projects to add valuable experience to your resumé.
6. Operations
To effectively manage operations, engineering managers must understand the ins and outs of a company’s value chain and how to optimize it. Employers want managers who can evaluate costs, efficiency, and productivity and put measures in place to reduce risks without compromising value. If you’re an engineer that works in operations, including this experience and competency on your resumé could give you a leg up on other managerial applicants.
7. Problem Solving
Engineering is all about using technology to create innovative solutions. Whether it’s developing a consumer product, safer equipment and processes, or more efficient materials, engineering focuses on improvement. As an engineering manager, you’ll need problem-solving skills along with a strong affinity to research, quality testing, and analytical skills.
Qualifications
Obtaining trusted credentials is a great way to stand out to employers. While becoming a Licensed Professional Engineer (PE) is optional, it can increase your career opportunities by communicating your level of industry competency to prospective employers.
The National Society of Professional Engineers oversees licensure, which is often required for government jobs, instructors, managers, and private consultants. Only PEs are authorized to submit engineering plans to public authorities or lead engineering work performed by others. Therefore, this certification is a highly recommended step to becoming an engineering manager.
Is a Career as an Engineering Manager Worth It?
If you’re still deciding whether a career in engineering management is right for you, it’s worth considering the possible value of this career change. Here are three factors you should take into account when choosing an engineering career path.
Engineering management is an advanced role that requires a degree and years of industry experience. Since education is a substantial financial investment, it’s important that a career in engineering management offsets this cost. According to a government report, the median annual compensation for engineering managers is $135,040. Working in bigger enterprises or increasingly specialized roles, however, offers opportunities to earn well above the median as a seasoned manager. This high earning potential can be comforting to those who might worry that advancing their education isn’t worth the investment.

There is plenty of industry growth in the field of engineering. While data shows that engineering manager positions are growing at a rate of 1.7 percent annually, the constant evolution of STEM industries is forcing organizations to hire more technical leaders who are equally proficient at business leadership and operations management. If you’re just entering the field, you can feel confident in the job prospects for graduates in the coming years with this projected growth over the next ten years.

Career Advancement Opportunities
An engineering management career is flexible and can lead to even higher-paying positions. For example, veteran managers often go on to become executives and directors at the highest levels of an organization. This trend isn’t the same across the board, however. Your industry and employer play a major role in both earning and career advancement. Organizations that require more skills, education, and experience typically offer more competitive salaries and larger-scale projects. As a result, more engineering professionals are trying to gain these requirements at an early stage in their career to ensure faster career advancement.
Take the First Step to Becoming an Engineering Manager
An engineering management career has a lot to offer those who love problem solving, combining a range of skills, and inspiring others. Whether you already have engineering experience or you’re looking for an entirely new career path, leadership training can take your job prospects to the next level. Consider enrolling in a master’s degree program, like Northeastern’s Master of Science in Engineering Management program, for a comprehensive education that can equip you with all the skills you need to succeed.
If you’re interested in becoming an engineering manager, check out our Master of Science in Engineering Management program to see how you can achieve your professional goals.
Subscribe below to receive future content from the Graduate Programs Blog.
About shaday stewart, related articles.
11 Data Science Careers Shaping Our Future

How Data Science is Disrupting Supply Chain Management

What Does a Data Scientist Do?
Did you know.
Advanced degree holders earn a salary an average 25% higher than bachelor's degree holders. (Economic Policy Institute, 2021)
Northeastern University Graduate Programs
Explore our 200+ industry-aligned graduate degree and certificate programs.
Most Popular:
Tips for taking online classes: 8 strategies for success, public health careers: what can you do with an mph, 7 international business careers that are in high demand, edd vs. phd in education: what’s the difference, 7 must-have skills for data analysts, in-demand biotechnology careers shaping our future, the benefits of online learning: 8 advantages of online degrees, how to write a statement of purpose for graduate school, the best of our graduate blog—right to your inbox.
Stay up to date on our latest posts and university events. Plus receive relevant career tips and grad school advice.
By providing us with your email, you agree to the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Keep Reading:

The 8 Highest-Paying Master’s Degrees in 2024

Graduate School Application Tips & Advice

How To Get a Job in Emergency Management

Join Us at Northeastern’s Virtual Graduate Open House | March 5–7, 2024
Engineering Manager: Education Requirements, Skills, and Job Outlook
View all blog posts under Articles

Engineers use science and math to solve problems and invent new technologies, products, and structures. Creating software, electronic devices, machinery, and infrastructure all require engineers to design, develop, and test for quality.
Projects that are large in scope generally involve a collection of engineers working together to produce the individual elements that combine to achieve an overall goal. For instance, the space shuttle was the sum of many different elements, including electrical systems, hardware, and aeronautics. For a project to succeed, engineers must work in concert on complicated and interconnected systems.
Engineering managers are often instrumental in projects such as these. Leveraging their leadership and experience, managers guide engineering projects through their many phases to completion — on time and on budget.
Managers for engineering projects use well-developed soft skills to empower and inspire their team members to reach a common goal. Behind every great piece of infrastructure or new tech development is a manager leading a team of devoted engineers.
Those who are interested in becoming an engineering manager need to develop the skills and knowledge base required to lead. Gaining the right combination of experience and education, such as by earning an online Master’s in Engineering Management , can help engineers learn how to oversee the large-scale projects that fuel innovation.
Engineering Manager: Job Description
An engineering manager’s job description often depends on which field of engineering they work in, and there are many.
- Civil engineering pertains to the design and construction of infrastructure such as bridges, railroads, and tunnels.
- Aerospace engineering involves the design, construction, and testing of air- and spacecraft.
- Computer engineering entails the creation of hardware and software.
- Chemical engineering uses the principles of chemistry, math, biology, and physics to design and manufacture chemicals.
- Electrical engineering involves the design, testing, and production of devices and systems that use electricity.
- Industrial engineering focuses on production and service operations and systems in industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and distribution.
Although different in many respects, all of these fields fall under the umbrella of engineering because they use mathematical and scientific principles to address problems and devise solutions.
The day-to-day duties and responsibilities of a civil engineer will vary from those of an aerospace engineer because their projects are so different. But what remains consistent is that every engineering project — regardless of the field — is a series of steps in a process that is intended to accomplish an overall goal.
Engineering Design Process
The engineering design process consists of a series of steps that allows engineers to find a solution for a problem or to meet a particular objective, according to the research and technology organization TWI. That objective could be anything from building a bridge to creating a new piece of software. An engineering manager oversees the process and supports their team as they progress.
TWI breaks down the engineering design process as follows:
- Identify the problem
- Devise solutions with a brainstorming session
- Develop a list of ideas and possible solutions
- List project constraints and criteria
- Identify potential alternative solutions
- Choose an approach
- Create a proposal for the design
- Construct a prototype or model
- Evaluate and test the prototype or model
- Refine the prototype or model
- Based upon improvements, develop a final plan
- Document and communicate results
A manager can apply the engineering design process to virtually any type of project, because it breaks down a complex problem into manageable steps.
Engineering Manager Job Duties and Responsibilities
Engineering managers oversee and support teams of engineers on a given project through the planning, development, and execution stages. They typically work for engineering companies or for corporations that specialize in designing and testing products.
Due to differences among industries and the varying scope of projects, the job description of an engineering manager isn’t universal. However, a core set of duties and responsibilities are widely shared. They include:
- Leading the research and development process for new products and designs
- Determining what resources are needed to complete the project (e.g., staff, equipment)
- Hiring and supervising engineering staff
- Creating a budget proposal
- Checking engineers’ work for accuracy
- Ensuring the team is working efficiently and adhering to the established timeline
- Leading meetings with staff (e.g., weekly stand-up meetings, one-on-one meetings)
- Coordinating with other managers
- Helping engineers run tests and troubleshoot prototypes
- Ensuring that engineers have a safe working environment
- Communicating with stakeholders about the progress of the project
- Evaluating the performance of engineers and aiding their development
- Building technical documentation and project road maps
While no two days are alike for engineering managers, according to the global freelance agency Toptal, their daily workload is generally divided into four main categories:
- Technical: Although engineering managers typically don’t do as much hands-on technical work as the engineers they oversee, they need to serve as a readily available resource that helps their team overcome issues. This may entail resolving a technical issue, such as cleaning up code.
- Managerial: The managerial responsibilities of an engineering manager are similar in many ways to those of managers in any other industry. They’re in charge of training employees, evaluating their work and providing feedback, settling disputes, and serving as a mentor and coach. Additionally, managers are the driving force behind meeting project goals and keeping stakeholders informed about the status of the project.
- Recruiting: Managers need a talented workforce to help them bring a project to fruition. A big part of their job is finding the right people to fill out their team, which means they spend quite a bit of time recruiting. Managers are often responsible for writing job listings and posting them online. They also interview candidates for engineering positions.
- Administrative: Managers are also tasked with performing numerous administrative duties such as sending emails, attending conference calls, organizing and maintaining files, and managing their calendar.
It’s not uncommon for a manager to bounce from troubleshooting code to developing a project timeline to interviewing new engineers in the same week. Managers must be versatile and adaptable.
They also need to be capable of working in a wide variety of settings. Although many engineers work in offices, a manager’s work might require them to be on-site — which could be anywhere from a construction site to a research laboratory. The manufacturing sector is the largest employer of architectural and engineering managers, employing 34% of all managers, according to the most recent data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
How to Become an Engineering Manager
Becoming a successful engineering manager requires both education and experience. Not only do managers need to be one of the most knowledgeable individuals on any given project, but they also need years of experience managing people and projects to be effective.
Engineering Manager Education
Engineering managers need at least a bachelor’s degree in an engineering specialty, along with considerable work experience, to qualify for the position, according to the BLS. Engineers who aspire to be managers can develop their managerial skills by completing a master’s degree in engineering management, technology management, or business administration.
Degree programs for engineering management feature relevant coursework on topics such as industrial and human resource management, quality control, financial management, and accounting, just to name a few. Indeed also notes that degree programs in technology management feature coursework in statistics, project management, quality control, and general management principles.
For those exploring how to become an engineering manager, it’s important to note there isn’t a one-size-fits-all career path. However, an advanced degree can help expand an aspiring manager’s knowledge and develop key managerial competencies. Many engineers interested in managerial careers pursue a Master of Science in Engineering .
Degree programs that include a management specialization usually have the added benefit of offering courses that focus on topics such as portfolio management and organizational behavior. This combination serves to deepen an individual’s understanding of engineering concepts while also developing their leadership skills — both of which are essential at the managerial level.
Engineering Manager Experience
Although a master’s degree will certainly help a candidate stand out to potential employers, engineers typically don’t enter a managerial role without significant work experience. According to Indeed, an engineer can benefit from internships and working on small projects, which help them gain experience and get industry exposure. After that, they can gain further experience on more complex projects where they build designs and/or write complicated code.
According to the BLS, developing the skills and knowledge needed for engineering management takes several years. Engineers usually become team leads before becoming managers. This gives them the chance to gain some experience making big decisions on projects and performing higher-profile tasks.
The path to becoming an engineering manager will be a bit different for everyone, considering the dynamics of each industry. But an advanced degree and considerable on-the-job experience working on complex, high-profile projects can help present a compelling package to employers. Education and experience are the foundational requirements for anyone interested in becoming a great manager.
What Are the Essential Engineering Manager Skills and Qualities?
To succeed, managers must develop a core set of proficiencies that will enable them to lead a team of engineers through the many phases of a complex project. The following are the most in-demand engineering manager skills and qualities, according to Indeed and the BLS:
- Analytical skills for complex problem-solving, checking others’ work, and evaluating information
- Coaching skills for giving constructive feedback to team members in a way that’s clear and helpful
- Well-developed communication and interpersonal skills (written and verbal) for interacting with engineers, project managers, and stakeholders, including communicating complex technical information in a way nonengineers can understand, and giving clear and concise directions or assigning tasks to their team
- Attention to detail for spotting errors — which can cause major complications — in code, documentation, or anything else they review
- Exceptional organizational skills for keeping track of budgets, timelines, and human resources
- Resilience for working well under pressure, which is crucial when solving problems and adapting to new developments at a moment’s notice
In addition to these skills, Indeed provides some best practices for engineering managers to follow to be effective in their position. They include:
- Leading by example so engineers know what’s expected of them, including by holding regular training sessions that target specific skills that will increase their team’s value and productivity
- Setting SMART goals for employees (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-based)
- Keeping lines of communication open and maintaining an open-door policy to be accessible to their employees
- Empowering engineers to identify improvements
- Maintaining technical expertise by actively participating in engineering work when not performing their managerial duties
Developing these key skills and practices can help aspiring managers qualify for numerous opportunities at engineering companies in a variety of industries. Because of the extensive experience and comprehensive skill set required, engineering leadership roles often command competitive salaries.
Engineering Manager Salary and Job Outlook
The median annual salary for architectural and engineering managers was $152,350 in May 2021, according to the BLS, with the highest 10% earning upwards of $208,000. The BLS also breaks down median annual wages by industry. The top five industries by median salary were:
- Scientific research and development services — $187,200
- Management of companies and enterprises — $164,000
- Manufacturing — $151,900
- Architectural, engineering, and related services — $151,900
- Government — $135,150
When it comes to determining an engineering manager’s salary, experience, education, region, industry, and the specific employer all influence how much a manager makes. According to Payscale, the primary ways for an engineering manager to increase their earning potential include changing employers, earning an advanced degree, and expanding their managerial experience by taking on bigger projects and/or managing a larger team.
Payscale also notes the following skills can positively influence salary:
- Strategic planning
- Software development
- Product development
- People management
Job outlook is another area of interest for aspiring engineering managers. According to the BLS, the number of jobs for architectural and engineering managers is projected to grow by 4% between 2020 and 2030, with approximately 14,700 openings expected to be available each year, on average.
Employment growth is also determined by the needs of a specific industry. The BLS expects demand for civil engineers to rise due to the increased need to repair existing infrastructure. Demand for electrical and mechanical engineering services is also expected to increase, as wind turbine farms and other renewable energy sources become increasingly important. Projects in all of these fields require experienced engineering managers to oversee teams and meet objectives.
Become a Leader in an Important Field
Effective management is critical for engineering projects of any size in any industry. Massive endeavors such as spacecraft, electrical power grids, skyscrapers, and nuclear power plants are delivered on time and on budget due to the hard work of engineering managers and their diligent teams of engineers.
Companies and organizations will continue to require the unique talents and skills of engineers to innovate products and create solutions. By extension, managers who know how to run teams and communicate with stakeholders will always be in demand.
As you research how to become an engineering manager, you’ll find there isn’t one standardized process, but some key steps can improve your profile. One of these steps is investing in your education, and the University of California, Riverside’s online Master of Science in Engineering program — with its Engineering Management specialization — offers an ideal path to develop the knowledge base and in-demand skills a manager needs.
In addition to the program’s core coursework, Engineering Management students also take these specialization courses:
- Projects Portfolio Management
- Quality Management
- Engineering Economics
- Engineering Leadership and Organizational Behavior
Designed to meet students’ needs, UCR’s degree program is 100% online with no residency requirement, and can be completed in 13 months. Graduates will be able to apply for the most in-demand engineering jobs as early as next year. Take the first step to becoming a leader in engineering with the University of California, Riverside.
Recommended Reading:
3 Jobs with a Civil Engineering Degree
Pyrotechnic Engineer Salary and Job Outlook
Theme Park Engineering Jobs
Example Sources:
All Together, “What Is Construction Engineering and Project Management?”
Built In, “A Day in the Life of 29 Engineering Managers”
Indeed, “23 Jobs You Can Get With a Master’s Degree in Engineering Management”
Indeed, “Engineering Manager Job Description: Top Duties and Qualifications”
Indeed, “How To Become an Engineering Manager (With Job Overview)”
Indeed, “What Does an Engineering Manager Do? (With Duties and Skills)”
Live Science, “What Is Engineering?”
Owner Team Consultation, “The Importance of Engineering Management”
Payscale, Average Engineering Manager Salary
Toptal, “A Day in the Life of an Engineering Manager”
TWI, “What Is the Engineering Design Process?”
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Architectural and Engineering Managers
Waydev, “A Modern View on an Engineering Manager’s Responsibilities – It’s Harder Than It Looks”
Take charge of your future with an online Master of Science in Engineering
How to Become an Engineering Manager
Engineering managers play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between the technical and managerial aspects of engineering projects. They lead teams, manage resources, and oversee complex engineering initiatives. This article explores the pathway to becoming an engineering manager, delving into the educational requirements, skill development, and career progression associated with this crucial role in the engineering field.
Introduction to the Role of an Engineering Manager
The role of an engineering manager is multifaceted, involving both the technical expertise of an engineer and the strategic acumen of a manager. These professionals are responsible for leading engineering teams, coordinating project activities, and ensuring that technical projects are completed efficiently and effectively. As leaders in the engineering careers sector, engineering managers are instrumental in driving innovation and success within their organizations.
- Industry Importance: In today’s fast-paced technological landscape, engineering managers are essential in various industries, from manufacturing and construction to software development and environmental engineering.
- Role Overview: The primary responsibility of an engineering manager is to oversee engineering projects, manage teams, and collaborate with other departments to align engineering goals with organizational objectives.
Steps to Become an Engineering Manager
Embarking on a career as an engineering manager requires a combination of education, experience, and leadership development.
Step 1: Educational Foundation
- Undergraduate Degree: The foundation for a career in engineering management typically begins with a bachelor’s degree in engineering . This degree provides the technical knowledge essential for understanding the complexities of engineering projects.
- ABET Accreditation: It’s important to ensure that the undergraduate program is an ABET accredited engineering program , which signifies that the curriculum meets high standards of quality and relevance to the industry.
Step 2: Professional Experience
- Engineering Experience: Before stepping into a management role, gaining hands-on experience as an engineer is crucial. This experience allows aspiring managers to develop a deep understanding of engineering processes and challenges.
Step 3: Leadership and Management Skills
- Developing Skills: Aspiring engineering managers should focus on developing key leadership and management skills, including communication, team leadership, project management, and strategic planning.
Step 4: Advanced Education and Certifications
- Further Education: To advance in this career path, many professionals pursue a master’s degree in engineering management . This advanced degree combines engineering principles with business and management skills, preparing individuals for the complexities of engineering leadership roles.
Step 5: Building a Professional Network
- Networking: Building a strong professional network is essential in the field of engineering management. Networking can lead to new opportunities, mentorships, and insights into industry trends.
Special Cases in Engineering Management Career Paths
Engineering management is a diverse field, and certain career paths may require specific steps or qualifications that go beyond the traditional route.
- Industry-Specific Experience: Depending on the industry, some engineering managers may need specialized experience. For instance, those in the aerospace industry might require experience in aerospace engineering projects, while those in software development may need a strong background in software engineering.
- Certifications for Specialized Areas: In addition to a master’s degree in engineering management , certain certifications can be beneficial. For example, certifications in project management, quality management, or specific engineering technologies can enhance an engineering manager’s credentials and expertise.
Why Become an Engineering Manager
Choosing a career as an engineering manager comes with its set of advantages and challenges.
- Impact on Projects: Engineering managers have the opportunity to make significant impacts on projects, driving innovation and efficiency.
- Leadership Opportunities: This role allows professionals to lead teams, mentor junior engineers, and contribute to strategic decision-making.
- Financial Rewards: Engineering managers often command higher salaries compared to non-managerial engineering roles, reflecting their increased responsibilities.
- Increased Responsibilities: The role involves a higher level of responsibility, including managing budgets, timelines, and personnel, which can be challenging.
- Complex Decision-Making: Engineering managers must often make complex decisions that affect the entire project or organization, which can be demanding and stressful.
Despite these challenges, many find the role of an engineering manager to be highly rewarding, combining their passion for engineering with the satisfaction of leadership and management.
Workplaces for Engineering Managers
Engineering managers are integral in a variety of work environments, each offering unique challenges and opportunities.
Corporate Settings
- Engineering Firms: In large engineering firms, managers oversee complex projects, coordinate various teams, and ensure that engineering solutions meet client specifications and standards.
- Manufacturing Companies: Here, engineering managers may focus on improving production processes, overseeing the implementation of new technologies, and maintaining quality control.
Freelance Opportunities
- Consulting Roles: Experienced engineering managers often provide consulting services to businesses, offering expertise in project management, process optimization, and strategic planning.
- Project-Based Work: Freelancing as an engineering manager can involve leading specific projects for different clients, requiring adaptability and a broad skill set.
Government Organizations
- Public Sector Projects: In government roles, engineering managers may work on infrastructure projects, public works, and policy development related to engineering practices.
- Research and Development: Some engineering managers in government agencies are involved in overseeing research projects, often in collaboration with private sector partners.
Other Venues
- Non-Profit Organizations: Engineering managers in non-profits may lead projects that focus on community development, environmental sustainability, or educational initiatives.
- Academia: Some engineering managers transition into academic roles, teaching future engineers and conducting research in engineering management and related fields.
Each of these work environments offers distinct experiences and challenges, providing engineering managers with a wide range of career opportunities.
Salary and Job Outlook for Engineering Managers
As of May 2022, the median annual wage for architectural and engineering managers was $159,920, with an hourly rate of approximately $76.88, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). The salary range for these professionals varies, with the lowest 10 percent earning less than $102,450 and the highest 10 percent earning more than $221,550. The median annual wages in the top industries for these managers were as follows, per the BLS :
- Scientific research and development services: $175,670
- Management of companies and enterprises: $169,140
- Manufacturing: $159,700
- Architectural, engineering, and related services: $157,100
- Government: $141,040.
The job outlook for architectural and engineering managers is promising. Employment in this field is projected to grow 4 percent from 2022 to 2032, about as fast as the average for all occupations, according to the BLS . Approximately 13,600 job openings for architectural and engineering managers are projected each year over the decade. This demand is partly due to the need to replace workers transitioning to different occupations or retiring.
The growth in employment will largely reflect the expansion in industries employing these managers. For instance, the ongoing need for civil engineering services for infrastructure maintenance and renewable energy projects, like wind turbine farms, will likely boost demand for skilled engineering managers.
Career Growth for Engineering Managers
The career trajectory and job growth potential in the field of engineering management are important considerations for anyone planning to pursue this career path.
Career Advancement Opportunities
- Progression Path: Engineering managers typically start their careers as engineers and gradually move up the ladder through experience and further education. The progression can lead to senior management roles, director positions, or even executive-level roles depending on the individual’s skills and aspirations.
- Expanding Skill Set: As they advance in their careers, engineering managers often expand their skill sets to include more strategic planning and business acumen, which can open doors to higher-level opportunities.
Factors Affecting Career Growth
- Technological Advancements: Keeping pace with technological advancements and industry innovations is crucial for career growth in engineering management.
- Professional Networking: Building a strong professional network and staying connected with industry developments can also influence career growth opportunities for engineering managers.
The prospects for career advancement and job growth in engineering management are promising, offering a pathway for continuous professional development and leadership opportunities in the engineering field.
Educational Pathways for Engineering Managers
Pursuing a career in engineering management typically involves a combination of formal education and practical experience. Understanding the educational pathways is crucial for aspiring engineering managers.
Associate Degree
- Role of an Associate Degree: While an associate degree can provide a foundation in engineering principles, it is generally considered a stepping stone rather than a terminal qualification for engineering managers.
Bachelor’s Degree
- Foundational Education: A bachelor’s degree in engineering is essential for starting a career in this field. This degree provides the technical background necessary for understanding engineering concepts and practices.
- ABET Accreditation: Ensuring that the undergraduate program has ABET accreditation is important, as it signifies that the education meets industry standards.
Master’s Degree
- Advanced Qualification: Many engineering managers enhance their qualifications with a master’s degree in engineering management . This advanced degree combines engineering knowledge with business and management skills, preparing individuals for the complexities of managing engineering projects and teams.
Further Studies
- Doctoral Degrees and Certifications: For those interested in the highest levels of leadership or specialized areas of engineering management, doctoral degrees or specific certifications can provide further expertise and recognition.
Each educational level in the field of engineering management equips aspiring professionals with the necessary skills and knowledge for different roles within the industry.
Engineering Manager FAQ
Aspiring engineering managers often have several questions about this career path. Here are some of the most frequently asked questions and their answers:
What Degree Do I Need to Become an Engineering Manager?
- Educational Requirements: The typical educational path starts with a bachelor’s degree in engineering . For higher-level management roles, a master’s degree in engineering management is often preferred or required.
What Do Engineering Managers Do?
- Job Responsibilities: Engineering managers oversee engineering projects from conception to completion. They coordinate teams, manage resources, and liaise between technical staff and upper management. Their role often involves strategic planning, project management, and ensuring that engineering projects meet quality standards.
How Long Does It Take to Become an Engineering Manager?
- Career Path Timeline: The timeline can vary based on individual circumstances. Typically, it involves completing a bachelor’s degree (four years), gaining several years of engineering experience, and then potentially pursuing a master’s degree, which can take an additional two years.
How Much Do Engineering Managers Make?
- Salary Overview: Salaries for engineering managers vary based on experience, industry, and location. Generally, they are among the higher-paid professionals in the engineering field, reflecting their level of responsibility and expertise.
What Skills Do I Need to Be an Engineering Manager?
- Key Skills: Essential skills include strong leadership abilities, effective communication, project management, problem-solving, and a solid foundation in engineering principles. Additionally, engineering managers should have the ability to adapt to changing technologies and industry trends.
Are There Internship Opportunities for Engineering Managers?
- Gaining Experience: While direct internships for engineering management are rare, internships in various engineering disciplines can provide valuable experience. These roles can offer insights into project management and team leadership, which are crucial for an engineering manager’s role.
Embarking on a Career in Engineering Management
Choosing a career as an engineering manager is a decision to take on a role that is both challenging and rewarding. It’s a career that combines the technical depth of engineering with the broad vision of management, creating a unique opportunity to influence the direction and success of engineering projects and teams.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
For those drawn to the field of engineering management, the journey involves a blend of education, practical experience, and continuous professional development. Starting with a solid foundation in engineering through a bachelor’s degree in engineering and progressing through professional experience and potentially a master’s degree in engineering management , aspiring managers can prepare themselves for the multifaceted challenges of this role.
As an engineering manager, the opportunity to lead and innovate within the field of engineering is immense. This role requires a balance of technical knowledge, strategic thinking, and leadership skills, all of which can be developed and honed over time. For those willing to embrace these challenges, the role of an engineering manager can be a fulfilling and impactful career choice.
In a world where engineering and technology continue to drive progress, the role of the engineering manager is more important than ever. This career path offers not only personal and professional growth but also the chance to make a significant contribution to the engineering field and society at large.
Engineering Manager
- Certifications
- Related Topics

What Is an Engineering Manager? How to Become One, Salary, Skills.
Engineering managers supervise engineering activities and coordinate key engineering projects. Here’s what to know about an engineering manager’s needed skills, salary and how to become one.

What Is an Engineering Manager?
Engineering managers plan, organize and oversee engineering projects, usually for product creation. They frequently execute strategies to manage overall project requirements, budgets and schedules.
What Do Engineering Managers Do?
Engineering managers guide engineering projects, delegate tasks to engineers and gauge progress to ensure engineering goals are being met.
Engineering Manager Responsibilities
- Initiate and lead engineering projects to create new products or systems.
- Assemble, train and delegate tasks to engineering teams.
- Track project progress and create related reports.
- Propose and implement project schedules, budgets and resources.
- Communicate project needs and metrics to other managers and teams.
Engineering Managers Within a Company
Engineering managers are part of an engineering or IT team and tend to report to a director of engineering within a company.
Importance of Engineering Managers
Engineering managers ensure engineer tasks and project milestones are being met seamlessly and as scheduled. They act as an important mentor for junior engineers and lead for engineering guidelines.
What Skills Are Needed to Be an Engineering Manager?
Qualifications to be an engineering manager.
- Five or more years of experience in engineering, software development, product development or related fields.
- Ability to manage, coordinate and set clear project guidelines for engineering teams.
- Ability to propose project strategies and apply changes where necessary.
- Proficiency in company-specific engineering discipline (for example, electrical engineering, software engineering, etc.).
Engineering Manager Prerequisites
- Bachelor’s degree in computer science, engineering or related field.
Engineering Manager Hard Skills
- Expertise in technical knowledge and company-specific applications.
- Experience in project management and agile methodology software.
- Knowledge of computer programming languages (C, Java, Python, SQL).
- Familiarity with budget management software.
Engineering Manager Soft Skills
- Adaptability.
- Critical thinking.
- Leadership and management.
- Verbal and written communication skills.
Tools and Programs Engineering Managers Use
- Confluence
- Microsoft 365
- Monday.com
How to Become an Engineering Manager
Engineering manager education and experience.
Engineering managers often hold a bachelor’s degree in computer science, engineering or related fields.
Engineering managers will also be expected to obtain five or more years of experience in engineering, development or related roles. Knowledge of project management, leadership and company-specific technical applications are recommended.
Engineering Manager Certificates and Courses
- Agile Crash Course: Agile Project Management; Agile Delivery
- Agile Fundamentals: Including Scrum and Kanban
- Product Development & Systems Engineering
- Understanding Jira for users, managers and admins
Engineering Manager Career Path
After experience in engineering, software development or related management roles, professionals can move into an engineering manager role. From here, professionals may progress into roles like director or engineering and eventually vice president of engineering.
Engineering Manager Salary and Job Outlook
Engineering manager jobs are expected to grow 2 percent by 2031, while software engineering managers will see jobs grow 21 percent by 2028.
The full compensation package for an engineering manager depends on a variety of factors, including but not limited to the candidate’s experience and geographic location. See below for detailed information on the average engineering manager salary.
Expand Your Engineering Manager Career Opportunities
Revamp your professional skill set with Udemy’s online development and engineering courses.
This course include end-to-end practical methods to create Solution Architecture. These concepts can be applied to create solutions for Cloud Platforms, On-Premise Solutions, Hybrid Solutions, etc.
This course will teach you the solution…
Are you ready to take your career to the next level?
Do you want to master Software Architecture and System Design ?
You came to the right place!
In this practical course, you will learn…
Architecting software systems is a skill that is in huge demand, but it is not a readily available skill. To understand why this skill is rare to find, let's go through a few lines from Martin Fowler's blog on architecture.
Careers Related to Engineering Manager
Engineering manager jobs, companies hiring engineering managers, most common skills for engineering manager, related software engineering careers.
- Programs and Courses
- Explore Programs
- Find Courses
- Careers and Relevant NC State Programs
- How to Apply
- Graduate Students
- Non-Degree Studies
- International Students
- Military and Veterans
- Affordability
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid
- Student Resources
- State Authorization
- Professional Licensure
- Student Complaint and Grievance Process
- Faculty and Staff
- Frequently Asked Questions
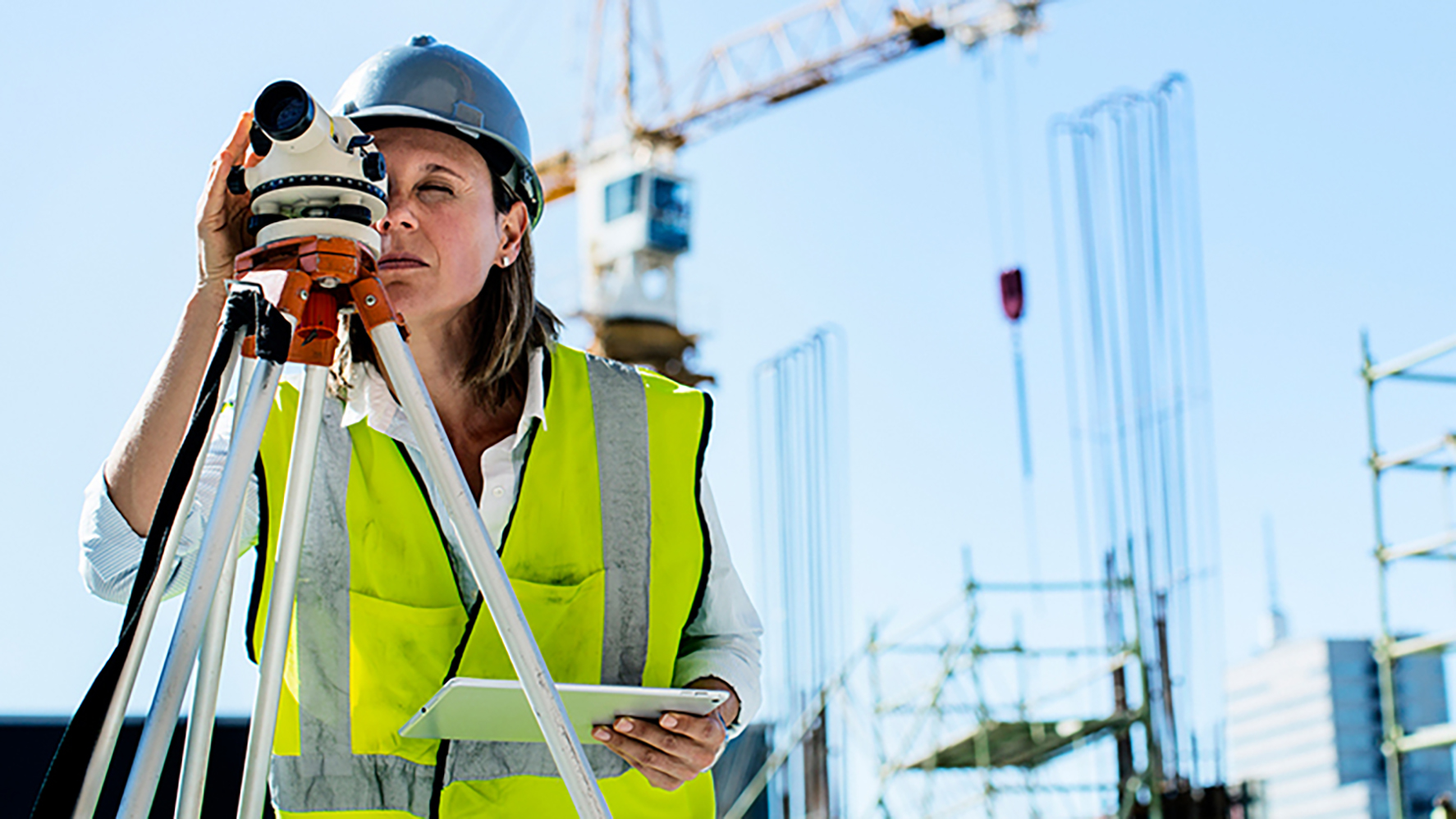

Engineering
- 5G Technology Graduate Certificates
- ASIC Design and Verification Graduate Certificates
- Computer Engineering Graduate Certificates
- Electrical Engineering Master's Degrees
- Electrical Engineering Graduate Certificates
- Engineering Management Master's Degrees
- Engineering Management Analytics Graduate Certificates
- Engineering Management Foundations Graduate Certificates
- Forest Biomaterials Master's Degrees
- Materials Informatics Graduate Certificates
Engineering Project Manager
What does a professional in this career do.
An Engineering Project Manager oversees and leads execution of engineering projects, and manages communication and coordination among different types of engineers working on a project. Supervises project schedule, budget, and communications with stakeholders.
Job Outlook
There were 377 Engineering Project Manager job postings in North Carolina in the past year and 10048 in the United States.
In combination with other careers in the Engineering Manager industry, which includes the Engineering Project Manager career, the following graph shows the number of people employed for each year since 2015:
Many new Engineering Project Manager jobs have salaries estimated to be in the following ranges, based on the requirements and responsibilities listed in job postings from the past year.
The average estimated salary in the United States for this career, based on job postings in the past year, is $113,117.
The average estimated salary in North Carolina for this career, based on job postings in the past year, is $106,852.
Percentiles represent the percentage that is lower than the value. For example, 25% of estimated salaries for Engineering Project Manager postings in the United States in the past year were lower than $99,510.
Education and Experience
Posted Engineering Project Manager jobs typically require the following level of education. The numbers below are based on job postings in the United States from the past year. Not all job postings list education requirements.
Posted Engineering Project Manager jobs typically require the following number of years of experience. The numbers below are based on job postings in the United States from the past year. Not all job postings list experience requirements.
Below are listings of the most common general and specialized skills Engineering Project Manager positions expect applicants to have as well as the most common skills that distinguish individuals from their peers. The percentage of job postings that specifically mention each skill is also listed.
Baseline Skills
A skill that is required across a broad range of occupations, including this one.
- Communication (48.09%)
- Leadership (37.19%)
- Management (35.83%)
- Planning (29.43%)
- Coordinating (26.82%)
- Customer Service (25.29%)
- Operations (18.71%)
- Problem Solving (15.69%)
- Scheduling (13.29%)
- Budgeting (12.11%)
Defining Skills
A core skill for this occupation, it occurs frequently in job postings.
- Construction (33.57%)
- Project Management (88.52%)
Necessary Skills
A skill that is requested frequently in this occupation but isn’t specific to it.
- Process Design (9.96%)
- Project Engineering (21.22%)
- Invoicing (15.24%)
- Project Schedules (22.9%)
- Contract Management (3.41%)
- Financial Forecasting (10.21%)
- Change Management (4.12%)
- Mechanical Engineering (10.25%)
- Electrical Construction (14.95%)
- Subcontracting (15.32%)
- Project Implementation (20.61%)
- Procurement (19.74%)
- Construction Management (22.57%)
- Change Orders (21.52%)
- Project Planning (10.73%)
- Capacity Planning (9.15%)
- Project Scoping (9.5%)
- Electrical Engineering (10.59%)
Salary Boosting Skills
A professional who wishes to excel in this career path may consider developing the following highly valued skills. The percentage of job postings that specifically mention each skill is listed.
- Construction (100%)
Alternative Job Titles
Sometimes employers post jobs with Engineering Project Manager skills but a different job title. Some common alternative job titles include:
- Electrical Project Manager
- Engineering Project Lead
- Mechanical Project Manager
- Project Engineering Manager
- Planning Engineer
- Project Engineer
- Civil Project Manager
- Proposal Engineer
- Design Manager
- Transmission Planning Engineer
Similar Occupations
If you are interested in exploring occupations with similar skills, you may want to research the following job titles. Note that we only list occupations that have at least one corresponding NC State Online and Distance Education program.
- Project Manager (General)
- Director of Project Management
- Civil Engineering Manager
Common Employers
Here are the employers that have posted the most Engineering Project Manager jobs in the past year along with how many they have posted.
United States
- GPAC (1400)
- Actalent (284)
- L3Harris Technologies (232)
- CyberCoders (228)
- Lumen Technologies (156)
- Randstad (123)
- Lockheed Martin (73)
- Jacobs Engineering Group (71)
- Power Engineers (68)
- Emerson Electric (66)
North Carolina
- Actalent (31)
- CyberCoders (12)
- Romanoff Group (11)
- Randstad (11)
- Southern Company (7)
- Fountain Electric & Services (5)
- Giles Flythe Engineers (5)
NC State Programs Relevant to this Career
If you are interested in preparing for a career in this field, the following NC State Online and Distance Education programs offer a great place to start!
All wages, job posting statistics, employment trend projections, and information about skill desirability on this page represents historical data and does not guarantee future conditions. Data is provided by and downloaded regularly from Lightcast. For more information about how Lightcast gathers data and what it represents, see Lightcast Data: Basic Overview on Lightcast's Knowledge Base website.

Oct. 24, 2022
What is project management in engineering, engineering management and project management are linked in many ways. learn the key pm methodologies and skills required for engineering pms..

Engineering Project Management Terminology
Engineering Management vs. Project Management
Engineering project management skills, engineering project manager: market outlook and careers.
Request MEML Program Information
Because engineering projects are often so complex, expensive and high-stakes, engineering project management is in high-demand amongst employers and requires a solid grasp of skills not typically covered in an engineer's bachelor's or associate's education. Effective engineering project management is ultimately about influencing people at all levels and ensuring that all the separate work streams are delivered to specification, completed in a timely manner, meet or are below designated budgets, and follow regulatory or legal mandates and requirements. Project management in engineering is typically of interest to engineers who want to develop broader skills to advance their careers by learning the holistic aspects of bringing a product or program to market successfully. A broader perspective, business skills and demonstrated use of soft skills like communications and collaboration can set engineers up for future leadership positions.
The engineering project manager not only understands ‘engineer speak’ and the technical work and context of the engineering teams, he/she is responsible for coordinating and overseeing a cross-functional working group, with representatives from multiple areas, such as finance, market research, technical engineering, IT, manufacturing, and quality assurance. Project managers plan, direct, and coordinate the development and implementation of small and large-scale projects, products or services. These projects have a defined scope, budget and schedule. Project management skills and concepts can be an asset to any engineer, even if you do not want to pursue an engineering project management role.
Engineering project management skills are broadly applicable and in high demand. We saw this during the pandemic when the world changed around us overnight and what had previously been successful no longer worked. Engineering and project management skills helped people to identify new approaches based on the underlying engineering and economic principles.
-- Claudia Zettner , Ph.D, Professor in the Practice, Engineering Project Management
This article will explore the requirements and opportunities for engineering project managers. We will also look at project management terms and methodologies, engineering management vs project management, and the skills required for each.
Return to top
Engineering Project Management Methodologies and Terminology
Engineering project managers use common project management methodologies such as Agile, Scrum, and Waterfall, among others, to complete engineering projects. Implementing the right approach for each project requires companies and engineering managers to be flexible and strategic.
A methodology is an approach or set of processes to organizing your work. In project management, waterfall or predictive and Agile are common methodologies. Some projects are better suited to one or the other. Increasingly, more projects are a hybrid of both predictive and agile. The methodology doesn’t change the work the project delivers, but it does affect the sequence and timing, especially for the project planning phase.
Waterfall, or Predictive Method
The waterfall or predictive method is the traditional approach to project management. It is best suited for projects where the requirements are well understood and the technology is straightforward. A significant effort is spent to create a project plan and define the scope, cost and schedule. The waterfall project management system is used by engineering project managers who have clear processes, designs, and deadlines in place for their projects.
Projects with a large cost of change, like construction projects, are best suited to a waterfall methodology.
Agile Method
Agile is an approach to project management that focuses on incremental deliverables. The project workflow is constantly evaluated and improved based on new information gained during the process. Using the Agile methodology, a team can quickly respond to changes in the scope or direction of the project. Agile can be described as a mindset for delivering value to the customer.
Engineering Example
A mechanical engineering project manager in the electric car industry may use the Agile method of project management when developing ideas for concept cars. This method allows them to work through ideas while managing feedback from the engineering teams who would design the car and the customers who would purchase it.
Scrum Method
Scrum is a type of Agile. Like Agile, Scrum also incorporates continuous improvement into the process to complete a project. Scrum assigns roles on the project team without hierarchy and attempts to keep the workflow simple and transparent. Scrum teams are meant to learn from experience and use set tools and meetings to self-organize. Proponents of Scrum believe it can be applied to any type of organization.
For example, computer engineers have used Scrum to develop software systems, particularly when the methodology incorporates existing engineering practices . The continuous-improvement focus can help teams improve quality, productivity, and estimation accuracy.
PMBOK Method
PMBOK is the overarching book of knowledge for project management and strategies such as Waterfall and Agile fall within PMBOK. Unlike the strategies we covered above, PMBOK is more of a foundation or a reference guide that incorporates project management best practices and principles along with other methods to execute a project.
PMBOK includes five process steps of project management:
- Controlling
Six Sigma Method
Six Sigma identifies and removes the causes of input defects and process waste to improve the quality of the output in an operation. Focused on quality management, this methodology uses empirical and statistical approaches to analysis. Six Sigma was popularized when General Electric embraced it as a business strategy in the mid-1990s; it may be the project management style most often applied to fields outside of engineering.
Six Sigma’s statistical tools are often used by biomedical engineering project managers who are responsible for reducing cost and cycle times as well as product defects in components such as orthopedic joints and other biotechnologies. The process’s value stream mapping and process modeling lead to improved operational efficiency. Its statistical tools identify causes for errors and give engineers an opportunity to develop process improvement strategies before a product is produced.
Lean Method
The Lean project management method is an approach that focuses on maximizing value while minimizing waste. Originally developed in Japan by the Toyota company, the overall goal of the Lean method is to reduce muda, muri, and mura, collectively known as 3M.
- Muda, meaning wastefulness: Reducing work that doesn’t add value improves efficiency
- Muri, meaning irregularity: Adding selective capacity can help level the workload
- Mura, meaning overworked: Minimizing overworking conditions improves morale and productivity
The Lean project management system is used by engineering project managers who want to improve resource efficiency in their processes and projects. Lean tools can be applied in the office as well as the factory.
Engineering management and engineering project management are different roles but leverage many of the same skills and experience. Many engineers will hold both of these roles over their careers.
An engineering manager is responsible for managing groups of engineers, while an engineering project manager leads a cross-functional project team. The project manager’s focus is on the business value that will be delivered by the project. The engineering manager is focused on the professional development of their engineers.
Both the engineering manager and the engineering project manager need education and work experience in engineering. Engineering managers and engineering project managers can come from any engineering field. Engineering managers manage engineers from many different disciplines. Engineering project managers lead projects in every industry.
Engineering project manager roles can happen at many different levels of an organization's hierarchy or reporting structure, whereas engineering managers are typically found between mid-management and executive-levels. For example, project managers for small, short-term projects can be early career individual contributors where the project manager role is an opportunity to lead a team and develop additional leadership skills. As an engineer has success in project management, s/he will be trusted and rewarded with larger and more complex projects. Conversely, project managers for large, mega-projects can be at an executive level in the organization and have a team of hundreds.
So, as an early career employee, you may achieve your first project manager role only a few years after university. The engineering manager role is usually filled by an experienced engineer.
Which Is Right For Me: Engineering Management vs. Project Management?
If you are not sure which path is right for you, it may be helpful to review the MEML@Rice curriculum , which includes a course in Engineering Project Management (EPM) that allows students to earn their PMP Ⓡ project management education/training hours certification test to become a Project Management Professional (PMP Ⓡ ). Although not required, some of the Rice MEML students treat the Rice EPM course like an embedded or "stackable" credential, where they finish the course, sit for the PMP test, and earn the PMP certification. The Rice EPM course is taught by an experienced professor with both a PhD in engineering and certified PMP credentials.
Engineering project managers aim to influence a diverse range of people and teams toward the successful outcome of a project to meet business goals and financial targets. In Industry 4.0 , collaboration and coordination have never been more important, since no one engineer or professional can acquire the full scope of technical expertise required to meet organizational goals as technology rapidly evolves.
The project management discipline is about working strategically, efficiently and effectively. It’s also about delivering change. Industry 4.0 is rapidly changing our world. As engineers, we will not be successful in the future if we keep doing the same things that work today. Project management has concepts and tools that will help us navigate this new world.
Regardless of the PM methodology they ultimately use, engineering project managers need these essential skills:
- Adaptability: To be successful, an engineering project manager must adapt to several different work styles and be flexible to changing timelines and objectives.
- Leadership: Leading a team involves motivating each member to do their best work in a collaborative process to complete the project.
- Organization: Even when using a linear methodology, an engineering project requires organization from the manager. An engineering manager must break the project down into phases, assign tasks to different team members and keep the whole project moving forward.
- Planning: Engineering project managers are responsible for creating a project timeline, estimating work time for each task and each phase, and keeping the project on budget.
- Problem-Solving: Engineering project managers are best positioned on the team to solve problems that arise because they see the whole picture and understand the expected outcomes of the project.
- Communication: Engineering project managers with the ability to clearly communicate can confidently present their concepts and designs to decision-makers in presentations, meetings, and reports, as well as to the various teams they coordinate.
- Influencing Outcomes: Engineering project managers require skills in influencing others, in order to approve or support new proposals, initiatives, and changes.
- Business Acumen: Engineering project managers need to understand how their project creates business value so that they can preserve this value as they manage their projects.
What does a Great Engineering Project Manager Look Like?
Any engineering project manager will have specialized knowledge of project management tools and concepts, as well as engineering work experience.
Here are the 5 qualities of a great, highly-effective Engineering Project Manager:
- Engineering project managers focus on the business value that their project will deliver. It’s about more than cost and schedule. They are fluent in the project economics and understand what drives the value.
- Engineering project managers actively manage their projects and work hard to stay on track. It's not nearly enough to check with your team and update the schedule.
- Engineering project managers think strategically and plan ahead. It is much easier to find solutions to problems in advance when you have the luxury of time and access to experts. When you are reactive, it's too late for many of these solutions.
- Engineering project managers are comfortable with predictive and Agile projects and everything in between. They have a bias for action and don’t need a perfect plan or complete data to get started.
- Engineering project managers foster a learning culture in their project teams. A learning culture leads to improved performance over time but requires self awareness and honest performance assessment.
Engineering PM Market Outlook
In the United States, major engineering projects are underway, including infrastructure upgrades and the energy transition to renewable sources like wind, solar and hydrogen power. Companies need engineering project managers to successfully deliver major projects that are economically sustainable and help achieve net-zero carbon goals. There's also huge demand for engineering project managers in software and data engineering, industrial engineering and supply chain, bioengineering and healthcare, and more.
And globally, as more traditional industries and companies adopt the digital-first practices of leading technology companies, the demand for Agile and Scrum project management continues to grow, needed to help software engineering teams prioritize features/functionality and deliver competitive advantage.
Engineering Project Manager Salary
According to Glassdoor, the average total salary of an engineering project manager is $117,356 , including base pay and additional pay (bonuses and other incentives). Because of the breadth of engineering disciplines, salaries will vary by technical expertise, company size and geography.
How Can I Become an Effective Engineering Project Manager, or Develop More PM Skills as an Engineer?
Even if your title is not engineering project manager, project management tools and concepts will help you be more effective and efficient in work and beyond. The MEML@Rice curriculum is designed to develop well-rounded engineering managers and includes a course in engineering project management that allows students to take the Project Management Professional (PMP) certification test after completion.
If you're considering a MEM or MEML degree program, find one with an engineering project management course that is taught by an engineer with advanced engineering credentials . The engineering project manager may not be an expert in all the technical areas of a project, but s/he can oversee the integration of the financial business case with the engineering, manufacturing, IT and other parts of the project. Engineering project managers can come from almost every engineering background.
Learn More About MEML@Rice
If you’re ready to take the next step to advance your career, fill out the form to connect with a Rice Enrollment Coach.
By submitting your information, you agree that Rice University and others working on its behalf may contact you via phone, email and/or text message. You may opt out at any time.
Project Management Engineer Education Requirements
The educational requirements for a project management engineer typically include a bachelor's degree. According to Bijan Shapoorian , Adjunct Professor at The University of Texas at Arlington, "In most Construction Management programs, Internship courses prepare students for the job market and the industry." He advises students to be flexible and willing to relocate to areas with higher demand for this profession.
While a bachelor's degree is common, a master's degree can also be beneficial. Dr. A. Tye Gardner Ph.D. , Assistant Professor at Weber State University, suggests that "getting a certification in systems engineering will allow students to capitalize on the opportunity" in the field of project management engineering. This can be particularly useful in filling the shortfall in experienced systems engineers.
What education do you need to become a project management engineer?
What degree do you need to be a project management engineer.
The most common degree for project management engineers is bachelor's degree, with 73% of project management engineers earning that degree. The second and third most common degree levels are master's degree degree at 15% and master's degree degree at 9%.
- Bachelor's , 73%
- Master's , 15%
- Associate , 9%
- High School Diploma , 1%
- Other Degrees , 2%
What should I major in to become a project management engineer?
The best college majors for a project management engineer are mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and civil engineering. According to Rutherford Johnson Ph.D. , Lecturer at the University of Minnesota Crookston, "People and companies have seen that many jobs can be done from home or remotely, and the technology exists and is improving to allow that." This trend towards remote work can provide more opportunities for graduates in project management engineering to find work opportunities in various locations.
- Mechanical Engineering , 23%
- Electrical Engineering , 16%
- Civil Engineering , 11%
- Business , 10%
- Other Majors , 40%
Most common colleges for project management engineers
Project management engineers often get their degrees at Purdue University, University of Houston, and Villanova University. Here are the most common colleges for project management engineers in the US based on their resumes.
Best majors for project management engineers
Best colleges for project management engineers.
The best colleges for a project management engineer include Northwestern University, Johns Hopkins University, and Georgia Institute of Technology. These institutions matter for project management engineers as they offer degrees that align with the field's education distribution, with a significant emphasis on Bachelor's and Master's degrees. These colleges were chosen based on metrics such as admissions rate, retention rate, and mean earnings of graduates.

1. Northwestern University
Evanston, IL • Private
In-State Tuition

2. Johns Hopkins University
Baltimore, MD • Private

3. Georgia Institute of Technology
Atlanta, GA • Private

4. University of Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, PA • Private

5. New York University
New York, NY • Private

6. Stanford University
Stanford, CA • Private

7. University of Michigan - Ann Arbor
Ann Arbor, MI • Private

8. Pennsylvania State University
University Park, PA • Private

9. University of Southern California
Los Angeles, CA • Private

10. Cornell University
Ithaca, NY • Private
20 best online courses for project management engineers
1. Engineering Project Management
Master strategies and tools to more effectively and successfully manage projects.\n\nToday’s professional environment is highly competitive, continuously changing, and difficult to manage. Employees rarely reach positions of leadership without managing one or more projects or a project segment early in their career.\n\nBrought to you by the Rice Center of Engineering Leadership and team behind the engineering management master's program, the goal of this Specialization is to give you the tools...
2. Managing Major Engineering Projects
Accelerate your career by improving your project management skills. This Specialization delivers a rigorous exploration of the best practices for planning and delivering these major engineering projects. You’ll learn about the measures of success, how to resolve challenges of governance and typical financing approaches of these projects.\n\nIf you are an engineer or a project manager and you aspire to get involved with major engineering projects, or you are already working on one, then this...
3. Mastering Construction/Project Management
Mastering Construction-Project Management in less than 10 Hours...
4. Projects Cost Management, Estimating, Budgeting and Control.
Learn how to estimate costs for any project, how to determine budget and how to use Earned Value Management tools. 3 PDU...
5. Construction Cost Estimating and Management
Learn the tools used by construction management professionals to ensure their projects finish under budget...
6. Project Management Essentials
A crash course in the essentials of project management for new project managers...
7. IT Project Budget & Cost Management
Project Management tips to manage a million dollar IT Project budget from start to finish...
8. Project Management - Complete Guide For A+ Project Managers
Complete guide to project management - stakeholders, planning, cost, quality, risks, feasibility, methods & resourcing...
9. Agile Crash Course: Agile Project Management; Agile Delivery
Agile Project Management Basics (Scrum) & Agile Project Management Essentials (Scrum). Plus Agile Certification (Scrum)...
10. Beginning Project Management: Project Management Level One
Project Management: Growing a Successful Career as a Project Manager...
11. Project Management with Primavera P6
Learn practical application of Project Management using Primavera P6 software, version 8.3 or above...
12. Project Management: Simple Software Project Management
Project Management for NEW Project Managers - knowledge, tools, techniques, skills, checklists, guidelines, pitfalls...
13. Construction Project Scheduling
Learn the tools and techniques used by construction management professionals to ensure projects finish on time...
14. Project Management Training
Project Management Certification Training with 4 Full Practice Tests...
15. Project Management: Becoming a Successful Project manager
Project Management...
16. Project Management: Cost & Schedule Monitoring using EVM
Earned Value Management, Project Management, Cost Control & Monitor, Budget, Schedule & Cost Variance, Performance Index...
17. Agile Project Management Bootcamp: Agile Project Management
This Agile Project Management Bootcamp course will allow you to learn the Agile Way! Agile Project Management (Scrum)...
18. Project Management Fundamentals
Practical Project Management worked example using Gantt Charts, PMI, PMP, APM...
19. Project Management Course: Master Project Scope Management
Practical guide to scope development and management - Project Management Certification (PMP, CAPM) Training [Earn 11PDU]...
20. Microsoft Project ADVANCED: Project Management Technics 3PDU
MS PROJECT 2016 ADVANCED Project Management Techniques -incl Enterprise level. HANDS-ON from #1 BESTSELLING INSTRUCTOR...
Top 10 most affordable universities for project management engineers
The most affordable schools for project management engineers are United States Merchant Marine Academy, university of florida, and california state university - long beach.
If the best universities for project management engineers are out of your price range, check out these affordable schools. After factoring in in-state tuition and fees, the average cost of attendance, admissions rate, average net price, and mean earnings after six years, we found that these are the most affordable schools for project management engineers.
1. United States Merchant Marine Academy
Kings Point, NY • Private
Cost of Attendance

2. University of Florida
Gainesville, FL • Private

3. California State University - Long Beach
Long Beach, CA • Private

4. SUNY Farmingdale
Farmingdale, NY • Private

5. California State University - Bakersfield
Bakersfield, CA • Private

6. California State University - Los Angeles

7. University of Puerto Rico - Mayaguez
Mayaguez, PR • Private

8. Florida International University
Miami, FL • Private

9. New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology
Socorro, NM • Private

10. University of South Florida
Tampa, FL • Private
Top 10 hardest universities to get into for project management engineers
The hardest universities for project management engineers to get into are Northwestern University, Johns Hopkins University, and University of Pennsylvania.
Some great schools for project management engineers are hard to get into, but they also set your career up for greater success. The list below shows the most challenging universities to get into for project management engineers based on an institution's admissions rates, average SAT scores accepted, median ACT scores accepted, and mean earnings of students six years after admission.
Admissions Rate
SAT Average
3. University of Pennsylvania
4. stanford university, 5. cornell university, 6. university of southern california.

7. Carnegie Mellon University
Pittsburgh, PA • Private

8. Columbia University in the City of New York

9. Northeastern University
Boston, MA • Private
10. Georgia Institute of Technology
Top 10 easy-to-apply-to universities for project management engineers.
The easiest schools for project management engineers to get into are Texas A&M; University - Kingsville, oregon institute of technology, and oklahoma wesleyan university.
Some schools are much easier to get into. If you want to start your career as a project management engineer without much hassle, check out the list of schools where you will be accepted in no time. We compiled admissions rates, average SAT scores, average ACT scores, and average salary of students six years after graduation to uncover which were the easiest schools to get into for project management engineers.

1. Texas A&M University - Kingsville
Kingsville, TX • Private

2. Oregon Institute of Technology
Klamath Falls, OR • Private

3. Oklahoma Wesleyan University
Bartlesville, OK • Private

4. The University of Texas at El Paso
El Paso, TX • Private

5. Pennsylvania State University - Fayette (The Eberly Campus)
Lemont Furnace, PA • Private

6. Notre Dame de Namur University
Belmont, CA • Private

7. The University of Texas Permian Basin
Odessa, TX • Private

8. Saint Martin's University
Lacey, WA • Private

9. University of the Incarnate Word
San Antonio, TX • Private

10. Capitol Technology University
Laurel, MD • Private
Average project management engineer salary by education level
Project management engineers with a Master's degree earn more than those without, at $97,397 annually. With a Bachelor's degree, project management engineers earn a median annual income of $84,079 compared to $67,469 for project management engineers with an Associate degree.
Project Management Engineer Education FAQs
What is the best college for project management engineers, search for project management engineer jobs.
Updated April 5, 2024
Editorial Staff
The Zippia Research Team has spent countless hours reviewing resumes, job postings, and government data to determine what goes into getting a job in each phase of life. Professional writers and data scientists comprise the Zippia Research Team.
- Assistant Project Manager Education Requirements
- Engineer Education Requirements
- Estimator Project Manager Education Requirements
- Management Engineer Education Requirements
- Manager, Project Management Education Requirements
- Manager, Quality Engineer Education Requirements
- Packaging Engineer Education Requirements
- Planning Engineer Education Requirements
- Process Engineer Education Requirements
- Process Improvement Engineer Education Requirements
- Production Engineer Education Requirements
- Project Analyst Education Requirements
- Project Engineer Education Requirements
- Project Engineering Manager Education Requirements
- Project Lead Engineer Education Requirements
- Assistant Project Manager
- Estimator Project Manager
- Management Engineer
- Manager, Project Management
- Manager, Quality Engineer
- Packaging Engineer
- Planning Engineer
- Process Engineer
- Process Improvement Engineer
- Production Engineer
- Project Analyst
- Project Engineer
- Project Engineering Manager
- Project Lead Engineer
- What an Assistant Project Manager Does
- What an Engineer Does
- What an Estimator Project Manager Does
- What a Management Engineer Does
- What a Manager, Project Management Does
- What a Manager, Quality Engineer Does
- What a Packaging Engineer Does
- What a Planning Engineer Does
- What a Process Engineer Does
- What a Process Improvement Engineer Does
- What a Production Engineer Does
- What a Project Analyst Does
- What a Project Engineer Does
- What a Project Engineering Manager Does
- What a Project Lead Engineer Does
- Zippia Careers
- Architecture and Engineering Industry
- Project Management Engineer
- Project Management Engineer Education
Browse architecture and engineering jobs
Engineering Project Manager, Infrastructure Programs & Solutions
Add a favorite.
Don’t have an Apple ID?
- Create one now
- Forgot your Apple ID or password?
Key Qualifications
- Strong influence, persuasion and interpersonal skills.
- Open and concise communication skills.
- Crafting and leading project plans.
- Problem tracking and driving resolutions across teams.
- Committed and results driven
- Critical thinking skills
Description
Education & experience, additional requirements.
- PMP certification a plus but not required.
Pay & Benefits
- At Apple, base pay is one part of our total compensation package and is determined within a range. This provides the opportunity to progress as you grow and develop within a role. The base pay range for this role is between $132,300.00 and $241,500.00, and your base pay will depend on your skills, qualifications, experience, and location. Apple employees also have the opportunity to become an Apple shareholder through participation in Apple’s discretionary employee stock programs. Apple employees are eligible for discretionary restricted stock unit awards, and can purchase Apple stock at a discount if voluntarily participating in Apple’s Employee Stock Purchase Plan. You’ll also receive benefits including: Comprehensive medical and dental coverage, retirement benefits, a range of discounted products and free services, and for formal education related to advancing your career at Apple, reimbursement for certain educational expenses — including tuition. Additionally, this role might be eligible for discretionary bonuses or commission payments as well as relocation. Learn more about Apple Benefits. Note: Apple benefit, compensation and employee stock programs are subject to eligibility requirements and other terms of the applicable plan or program. Apple is an equal opportunity employer that is committed to inclusion and diversity. We take affirmative action to ensure equal opportunity for all applicants without regard to race, color, religion, sex, sexual orientation, gender identity, national origin, disability, Veteran status, or other legally protected characteristics.
Best Global Universities for Engineering in Russia
These are the top universities in Russia for engineering, based on their reputation and research in the field. Read the methodology »
To unlock more data and access tools to help you get into your dream school, sign up for the U.S. News College Compass !
Here are the best global universities for engineering in Russia
Itmo university, tomsk state university, tomsk polytechnic university, lomonosov moscow state university, novosibirsk state university, saint petersburg state university, peter the great st. petersburg polytechnic university, moscow institute of physics & technology, national research nuclear university mephi (moscow engineering physics institute).
See the full rankings
- Clear Filters
- # 307 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 696 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 364 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 587 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 396 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 879 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 632 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 355 in Best Global Universities
- # 809 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 579 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 847 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 652 in Best Global Universities
- # 896 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 679 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 902 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 475 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 915 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 483 in Best Global Universities (tie)

- Life @ NYPA
- Inclusion @ NYPA
- Sustainability @ NYPA
- View All Jobs
- Engineering
- Information Technology
- Commercial Operations
- Human Resources
- Join Our Talent Network
Technical Learning & Development Program Manager (Engineering & Project Management)
White Plains, US
The Technical Learning and Development Program Manager (Engineering and Project Management) is responsible for working with multiple levels of NYPA technical experts to identify and implement technical training programs that support degreed employee technical knowledge development at various levels of the salaried organization. The Program Manager works closely with Talent Development and Strategic Operations to ensure alignment to organizational strategy and objectives, by using a programmatic approach to identifying solutions for skill and knowledge gaps that will enable employee recruitment and retention in the highly competitive utility workplace. NYPA benefits from well-rounded employees that are able to see a path forward for their technical progression in the organization, and this position builds that technical path. Key technical areas such as financial acumen, renewables in the energy sector, and artificial intelligence/machine language are some examples of the technical areas that will be addressed. #LI-AE1
- Responsible for daily management throughout the life cycle of the program.
- Support the stakeholders in planning and development of programs and projects.
- Define the controls, processes, procedures, reporting, etc. to manage the programs.
- Strategize and prioritize resources.
- Monitor progress to ensure that the milestones are being met across the various projects and programs.
- Manage the risks and issues that arise during the program cycle as well as take measures to correct them.
- Manage the program budget and identify internal and external funding sources.
- Coordinate the project(s) and their interdependencies between various projects and programs within departments or business units.
- Strong experience as project or program manager of large and complex projects or programs.
- Advanced knowledge of project and program management methodologies.
- Understanding of the business and strategic goals.
- Able to work with all levels of management internal and external.
- Strong leadership and time management skills.
- Knowledge of budgeting and resource allocations.
- Ability to think strategically, to proactively understand stakeholder needs, and to provide solutions to overcome obstacles.
- Strong written and verbal communication skills with experience delivering engaging, informative, well-organized presentations
- Bachelors degree required
- Minimum 7 years’ experience in Project and/or Program Management
The New York Power Authority is committed to providing fair, competitive, and market-informed compensation. The target salary range for this position is: $108,490.00 - $149,170.00. The salary offered will be determined based on the successful candidates’ relevant experience, knowledge, skills, and abilities.
The New York Power Authority and Canal Corporation believes that diversity, equity, and inclusion drive our success, and we encourage women, people of color, LGBTQIA+ individuals, people with disabilities, members of ethnic minorities, foreign-born residents and veterans to apply. As an equal opportunity employer, NYPA/Canals is committed to building inclusive, innovative work environments with employees who reflect communities across New York and enthusiastically serve them. We proudly celebrate diversity and do not discriminate based on race/color, creed/religion, national origin, citizenship or immigration status, age, disability, military status, gender/sex, sexual orientation, gender identity/expression, pregnancy and related conditions, familial/marital status, domestic violence victim status, predisposing genetic characteristics, arrest/criminal conviction record or any other category protected by law. NYPA/Canals will also provide reasonable accommodations during the hiring process related to candidates’ disabilities, pregnancy-related conditions, religious observances/practices and/or domestic violence concerns. To request an accommodation, please email [email protected] .
New York is Powered by You
We are a team of over 1,900 energy technologists, IT specialists, business experts, hydro engineers, and other professionals leading the energy revolution. With state-of-the-art technology, advanced R&D, and a modernized infrastructure, we provide New Yorkers with low-cost, clean, reliable power — and we are well on the way to becoming the first fully digital utility in the country. At NYPA, you will be empowered to think big, do good, and transform the energy industry.
NYPA on Forbes "Best of" - again!
NYPA is ranked by Forbes as one of America's best midsize employers for 2022 for the fourth consecutive year! Browse today and apply.
Nearest Major Market: White Plains Nearest Secondary Market: New York City Job Segment: Project Manager, Project Engineer, Engineering Manager, Information Technology, IT Manager, Technology, Engineering
©2020 New York Power Authority. The New York Power Authority provides equal employment opportunities to all employees and applicants for employment, in accordance with all applicable federal, state and local laws governing non-discrimination in employment in every location in which the Authority has offices or facilities. The Authority also provides reasonable accommodation to individuals with a disability, in accordance with applicable law. This policy applies to all terms and conditions of employment, including, but not limited to, recruitment, hiring, promotion, termination, layoff, recall, transfer, leaves of absence, compensation and training.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Engineering. A bachelor's or master's degree in engineering is one of the most common starting points for Engineering Project Managers. Specializations such as civil, mechanical, electrical, or industrial engineering provide the technical grounding necessary to understand the intricacies of engineering projects.
Step One: Obtain a Bachelor's Degree (Four Years) After graduating from high school, the first thing an aspiring engineering project manager will need to do is obtain a bachelor's degree, ideally at a program accredited by the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET). There are not many undergraduate programs that focus ...
What level of education is required for Project Engineering Managers? 72% of Project Engineering Managers have a bachelor's degree, 22% major in mechanical engineering. Learn all about Project Engineering Manager educational requirements, degrees, majors, certifications, online courses, and top colleges that will help you advance in a Project Engineering Manager career.
An engineering project manager is a person who directs and assesses the daily operations of an engineering team. When engineers, designers and manufacturers must work together to develop and produce a project, engineering project managers oversee the process. Engineering managers review proposals and supervise much of the budgeting and cost ...
An engineering project manager supervises an engineering project and a team. In contrast, a project engineer is a member of the project team and is more involved in technical aspects. While both share the common goal of completing the project, engineers usually work on specific tasks, and project managers supervise the project's overall progress.
Engineering Project Manager Job Requirements. Education: An Engineering Project Manager typically holds a Bachelor's or Master's Degree in engineering, with majors often in civil, mechanical, electrical, or industrial engineering. Coursework for aspiring managers includes project management, engineering principles, mathematics, and ...
Education. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), entry-level positions in engineering management typically require a bachelor's degree in engineering or a related field. Engineers work with data, equipment, machinery, and materials that are complex and, in some cases, potentially dangerous.
This Project Management for Engineering Professionals Specialization is designed as an introduction to Project Management. ... requirements and purpose for the project. ... These are recognized by PMI for continuing education or can be applied toward the 35 hours of education required for the Project Management Professional (PMP ...
UCR MSE Home / Blog / Engineering Manager: Education Requirements, Skills, and Job Outlook. Engineering Manager: Education Requirements, Skills, and Job Outlook ... But what remains consistent is that every engineering project — regardless of the field — is a series of steps in a process that is intended to accomplish an overall goal.
Step 1: Educational Foundation. Undergraduate Degree: The foundation for a career in engineering management typically begins with a bachelor's degree in engineering. This degree provides the technical knowledge essential for understanding the complexities of engineering projects. ABET Accreditation: It's important to ensure that the ...
Engineering Manager Responsibilities. Initiate and lead engineering projects to create new products or systems. Assemble, train and delegate tasks to engineering teams. Track project progress and create related reports. Propose and implement project schedules, budgets and resources. Communicate project needs and metrics to other managers and teams.
An Engineering Project Manager oversees and leads execution of engineering projects, and manages communication and coordination among different types of engineers working on a project. ... Not all job postings list education requirements. Education Level Percentage; Associate's Degree: 2.56%: Bachelor's Degree: 63.23%: Master's Degree: 14.39% ...
The minimum education requirement to become a project engineer is typically a bachelor's degree with a relevant major. While the industry does not have a standard project engineering degree course, subjects such as mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and civil engineering are popular. The major you choose depends on the type of ...
Here are the 5 qualities of a great, highly-effective Engineering Project Manager: Engineering project managers focus on the business value that their project will deliver. It's about more than cost and schedule. They are fluent in the project economics and understand what drives the value. Engineering project managers actively manage their ...
The educational requirements for a project management engineer are a Bachelor's degree in a field such as Mechanical, Electrical, or Civil Engineering, and a Master's degree in Project Management or a related field. This is supported by a study conducted by Zippia, which showed that 58.6% of project management engineers hold a Bachelor's degree ...
Apply for a Engineering Project Manager, Infrastructure Programs & Solutions job at Apple. ... including wholesale colocation providers in order to understand space and power requirements and effectively administer Apple's data center capacity. The scope of this role will be in both Apple owned data centers and Remote co-locations in ...
Germany. India. Italy. Japan. Netherlands. See the US News rankings for Engineering among the top universities in Russia. Compare the academic programs at the world's best universities.
The Situation Context Framework (SCF), an evolution of the Software Development Context Framework (SDCF), defines the contextual factors to consider when selecting and tailoring a situation-dependent way of working (WoW). The SCF is used to provide context for making decisions about how to organize your WoW to be fit-for-purpose.
The Technical Learning and Development Program Manager (Engineering and Project Management) is responsible for working with multiple levels of NYPA technical experts to identify and implement technical training programs that support degreed employee technical knowledge development at various levels of the salaried organization.
Hi! I'm Katya, a Project Manager with experience in launching diverse projects within Edtech. Skilled in market and needs research, managing cross-functional teams, and project planning. Passionate about education and IT. Currently seeking new job opportunities, so let's connect and collaborate! | Learn more about Katya Galkina's work experience, education, connections & more by visiting ...
15+ years of experience in R&D in ferrous, non-ferrous and special metallurgy industries with 8 years as a Manager of R&D Projects in nickel-based superalloys in Nornikel Group and Aviation Materials Research Institute. Leading downstream projects with $3M- $5M budgets. Managing cross-functional teams of more than 15 people.<br>Fields of professional interest: nickel-based superalloys ...
Position Title :Electrical & Instrumentation Engineering - ManagerAbout the role :About the Role:To manage the Projects Electrical, Instrumentation & Extra low voltage Packages delivery including design and lead the customer interface activities for the various sites (large and small molecule) and various technologies like BioPharma & Chemops technology, Aseptic technology, Solids and ...