
Looking for a free Hamlet PDF? Click below to download Shakespeare’s full Hamlet play in PDF format for free, to read or share.
You can also choose to read both Shakespeare’s Hamlet text and a modern English version of Hamlet online broken down by Act and Scene, or download an ebook version of Hamlet in modern English. Lower down this page is the complete text of Shakespeare’s Hamlet.
Download the complete Hamlet PDF – Shakespeare’s original text
Download a modern English version of Hamlet
Read Hamlet online as either original text or the modern English version
Interested in more than just a Hamlet PDF? We have a whole range of Hamlet resources to chose from:

See All Hamlet Resources
Hamlet | Hamlet summary | Hamlet characters : Claudius , Fortinbras , Horatio , Laertes , Ophelia . Osric , Polonius , Rosencrantz and Guildenstern | Hamlet settings | Hamlet themes | Hamlet in modern English | Hamlet full text | Modern Hamlet ebook | Hamlet for kids ebooks | Hamlet quotes | Hamlet quote translations | Hamlet monologues | Hamlet soliloquies | Hamlet performance history | All about ‘To Be Or Not To Be’
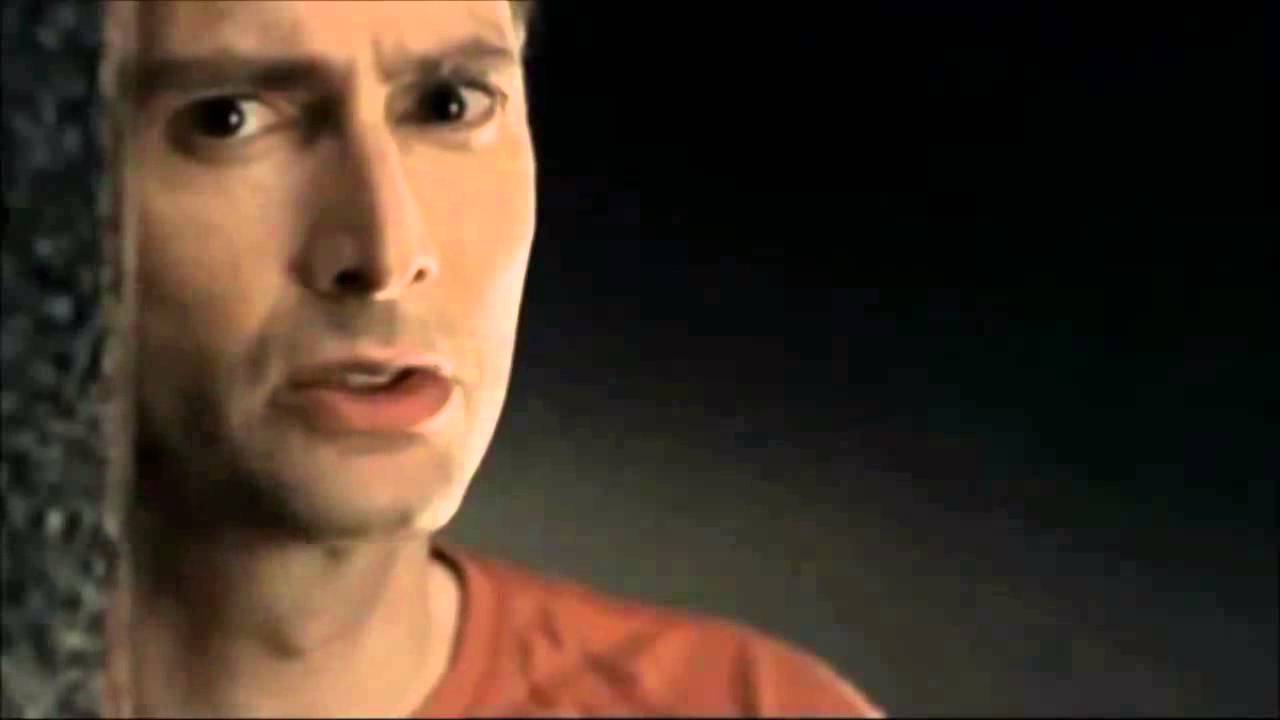

David Tennant speaks Hamlet’s ‘To be or not to be’ soliloquy
Hamlet Full Play
Scene i. elsinore. a platform before the castle..
FRANCISCO at his post. Enter to him BERNARDO BERNARDO Who’s there? FRANCISCO Nay, answer me: stand, and unfold yourself. BERNARDO Long live the king! FRANCISCO Bernardo? BERNARDO He. FRANCISCO You come most carefully upon your hour. BERNARDO ‘Tis now struck twelve; get thee to bed, Francisco. FRANCISCO For this relief much thanks: ’tis bitter cold, And I am sick at heart. BERNARDO Have you had quiet guard? FRANCISCO Not a mouse stirring. BERNARDO Well, good night. If you do meet Horatio and Marcellus, The rivals of my watch, bid them make haste. FRANCISCO I think I hear them. Stand, ho! Who’s there? Enter HORATIO and MARCELLUS HORATIO Friends to this ground. MARCELLUS And liegemen to the Dane. FRANCISCO Give you good night. MARCELLUS O, farewell, honest soldier: Who hath relieved you? FRANCISCO Bernardo has my place. Give you good night. Exit MARCELLUS Holla! Bernardo! BERNARDO Say, What, is Horatio there? HORATIO A piece of him. BERNARDO Welcome, Horatio: welcome, good Marcellus. MARCELLUS What, has this thing appear’d again to-night? BERNARDO I have seen nothing. MARCELLUS Horatio says ’tis but our fantasy, And will not let belief take hold of him Touching this dreaded sight, twice seen of us: Therefore I have entreated him along With us to watch the minutes of this night; That if again this apparition come, He may approve our eyes and speak to it. HORATIO Tush, tush, ’twill not appear. BERNARDO Sit down awhile; And let us once again assail your ears, That are so fortified against our story What we have two nights seen. HORATIO Well, sit we down, And let us hear Bernardo speak of this. BERNARDO Last night of all, When yond same star that’s westward from the pole Had made his course to illume that part of heaven Where now it burns, Marcellus and myself, The bell then beating one,– Enter Ghost MARCELLUS Peace, break thee off; look, where it comes again! BERNARDO In the same figure, like the king that’s dead. MARCELLUS Thou art a scholar; speak to it, Horatio. BERNARDO Looks it not like the king? mark it, Horatio. HORATIO Most like: it harrows me with fear and wonder. BERNARDO It would be spoke to. MARCELLUS Question it, Horatio. HORATIO What art thou that usurp’st this time of night, Together with that fair and warlike form In which the majesty of buried Denmark Did sometimes march? by heaven I charge thee, speak! MARCELLUS It is offended. BERNARDO See, it stalks away! HORATIO Stay! speak, speak! I charge thee, speak! Exit Ghost MARCELLUS ‘Tis gone, and will not answer. BERNARDO How now, Horatio! you tremble and look pale: Is not this something more than fantasy? What think you on’t? HORATIO Before my God, I might not this believe Without the sensible and true avouch Of mine own eyes. MARCELLUS Is it not like the king? HORATIO As thou art to thyself: Such was the very armour he had on When he the ambitious Norway combated; So frown’d he once, when, in an angry parle, He smote the sledded Polacks on the ice. ‘Tis strange. MARCELLUS Thus twice before, and jump at this dead hour, With martial stalk hath he gone by our watch. HORATIO In what particular thought to work I know not; But in the gross and scope of my opinion, This bodes some strange eruption to our state. MARCELLUS Good now, sit down, and tell me, he that knows, Why this same strict and most observant watch So nightly toils the subject of the land, And why such daily cast of brazen cannon, And foreign mart for implements of war; Why such impress of shipwrights, whose sore task Does not divide the Sunday from the week; What might be toward, that this sweaty haste Doth make the night joint-labourer with the day: Who is’t that can inform me? HORATIO That can I; At least, the whisper goes so. Our last king, Whose image even but now appear’d to us, Was, as you know, by Fortinbras of Norway, Thereto prick’d on by a most emulate pride, Dared to the combat; in which our valiant Hamlet– For so this side of our known world esteem’d him– Did slay this Fortinbras; who by a seal’d compact, Well ratified by law and heraldry, Did forfeit, with his life, all those his lands Which he stood seized of, to the conqueror: Against the which, a moiety competent Was gaged by our king; which had return’d To the inheritance of Fortinbras, Had he been vanquisher; as, by the same covenant, And carriage of the article design’d, His fell to Hamlet. Now, sir, young Fortinbras, Of unimproved mettle hot and full, Hath in the skirts of Norway here and there Shark’d up a list of lawless resolutes, For food and diet, to some enterprise That hath a stomach in’t; which is no other– As it doth well appear unto our state– But to recover of us, by strong hand And terms compulsatory, those foresaid lands So by his father lost: and this, I take it, Is the main motive of our preparations, The source of this our watch and the chief head Of this post-haste and romage in the land. BERNARDO I think it be no other but e’en so: Well may it sort that this portentous figure Comes armed through our watch; so like the king That was and is the question of these wars. HORATIO A mote it is to trouble the mind’s eye. In the most high and palmy state of Rome, A little ere the mightiest Julius fell, The graves stood tenantless and the sheeted dead Did squeak and gibber in the Roman streets: As stars with trains of fire and dews of blood, Disasters in the sun; and the moist star Upon whose influence Neptune’s empire stands Was sick almost to doomsday with eclipse: And even the like precurse of fierce events, As harbingers preceding still the fates And prologue to the omen coming on, Have heaven and earth together demonstrated Unto our climatures and countrymen.– But soft, behold! lo, where it comes again! Re-enter Ghost I’ll cross it, though it blast me. Stay, illusion! If thou hast any sound, or use of voice, Speak to me: If there be any good thing to be done, That may to thee do ease and grace to me, Speak to me: Cock crows If thou art privy to thy country’s fate, Which, happily, foreknowing may avoid, O, speak! Or if thou hast uphoarded in thy life Extorted treasure in the womb of earth, For which, they say, you spirits oft walk in death, Speak of it: stay, and speak! Stop it, Marcellus. MARCELLUS Shall I strike at it with my partisan? HORATIO Do, if it will not stand. BERNARDO ‘Tis here! HORATIO ‘Tis here! MARCELLUS ‘Tis gone! Exit Ghost We do it wrong, being so majestical, To offer it the show of violence; For it is, as the air, invulnerable, And our vain blows malicious mockery. BERNARDO It was about to speak, when the cock crew. HORATIO And then it started like a guilty thing Upon a fearful summons. I have heard, The cock, that is the trumpet to the morn, Doth with his lofty and shrill-sounding throat Awake the god of day; and, at his warning, Whether in sea or fire, in earth or air, The extravagant and erring spirit hies To his confine: and of the truth herein This present object made probation. MARCELLUS It faded on the crowing of the cock. Some say that ever ‘gainst that season comes Wherein our Saviour’s birth is celebrated, The bird of dawning singeth all night long: And then, they say, no spirit dares stir abroad; The nights are wholesome; then no planets strike, No fairy takes, nor witch hath power to charm, So hallow’d and so gracious is the time. HORATIO So have I heard and do in part believe it. But, look, the morn, in russet mantle clad, Walks o’er the dew of yon high eastward hill: Break we our watch up; and by my advice, Let us impart what we have seen to-night Unto young Hamlet; for, upon my life, This spirit, dumb to us, will speak to him. Do you consent we shall acquaint him with it, As needful in our loves, fitting our duty? MARCELLUS Let’s do’t, I pray; and I this morning know Where we shall find him most conveniently. Exeunt
SCENE II. A room of state in the castle.
Enter KING CLAUDIUS, QUEEN GERTRUDE, HAMLET, POLONIUS, LAERTES, VOLTIMAND, CORNELIUS, Lords, and Attendants KING CLAUDIUS Though yet of Hamlet our dear brother’s death The memory be green, and that it us befitted To bear our hearts in grief and our whole kingdom To be contracted in one brow of woe, Yet so far hath discretion fought with nature That we with wisest sorrow think on him, Together with remembrance of ourselves. Therefore our sometime sister, now our queen, The imperial jointress to this warlike state, Have we, as ’twere with a defeated joy,– With an auspicious and a dropping eye, With mirth in funeral and with dirge in marriage, In equal scale weighing delight and dole,– Taken to wife: nor have we herein barr’d Your better wisdoms, which have freely gone With this affair along. For all, our thanks. Now follows, that you know, young Fortinbras, Holding a weak supposal of our worth, Or thinking by our late dear brother’s death Our state to be disjoint and out of frame, Colleagued with the dream of his advantage, He hath not fail’d to pester us with message, Importing the surrender of those lands Lost by his father, with all bonds of law, To our most valiant brother. So much for him. Now for ourself and for this time of meeting: Thus much the business is: we have here writ To Norway, uncle of young Fortinbras,– Who, impotent and bed-rid, scarcely hears Of this his nephew’s purpose,–to suppress His further gait herein; in that the levies, The lists and full proportions, are all made Out of his subject: and we here dispatch You, good Cornelius, and you, Voltimand, For bearers of this greeting to old Norway; Giving to you no further personal power To business with the king, more than the scope Of these delated articles allow. Farewell, and let your haste commend your duty. CORNELIUS In that and all things will we show our duty. KING CLAUDIUS We doubt it nothing: heartily farewell. Exeunt VOLTIMAND and CORNELIUS And now, Laertes, what’s the news with you? You told us of some suit; what is’t, Laertes? You cannot speak of reason to the Dane, And loose your voice: what wouldst thou beg, Laertes, That shall not be my offer, not thy asking? The head is not more native to the heart, The hand more instrumental to the mouth, Than is the throne of Denmark to thy father. What wouldst thou have, Laertes? LAERTES My dread lord, Your leave and favour to return to France; From whence though willingly I came to Denmark, To show my duty in your coronation, Yet now, I must confess, that duty done, My thoughts and wishes bend again toward France And bow them to your gracious leave and pardon. KING CLAUDIUS Have you your father’s leave? What says Polonius? LORD POLONIUS He hath, my lord, wrung from me my slow leave By laboursome petition, and at last Upon his will I seal’d my hard consent: I do beseech you, give him leave to go. KING CLAUDIUS Take thy fair hour, Laertes; time be thine, And thy best graces spend it at thy will! But now, my cousin Hamlet, and my son,– HAMLET [Aside] A little more than kin, and less than kind. KING CLAUDIUS How is it that the clouds still hang on you? HAMLET Not so, my lord; I am too much i’ the sun. QUEEN GERTRUDE Good Hamlet, cast thy nighted colour off, And let thine eye look like a friend on Denmark. Do not for ever with thy vailed lids Seek for thy noble father in the dust: Thou know’st ’tis common; all that lives must die, Passing through nature to eternity. HAMLET Ay, madam, it is common. QUEEN GERTRUDE If it be, Why seems it so particular with thee? HAMLET Seems, madam! nay it is; I know not ‘seems.’ ‘Tis not alone my inky cloak, good mother, Nor customary suits of solemn black, Nor windy suspiration of forced breath, No, nor the fruitful river in the eye, Nor the dejected ‘havior of the visage, Together with all forms, moods, shapes of grief, That can denote me truly: these indeed seem, For they are actions that a man might play: But I have that within which passeth show; These but the trappings and the suits of woe. KING CLAUDIUS ‘Tis sweet and commendable in your nature, Hamlet, To give these mourning duties to your father: But, you must know, your father lost a father; That father lost, lost his, and the survivor bound In filial obligation for some term To do obsequious sorrow: but to persever In obstinate condolement is a course Of impious stubbornness; ’tis unmanly grief; It shows a will most incorrect to heaven, A heart unfortified, a mind impatient, An understanding simple and unschool’d: For what we know must be and is as common As any the most vulgar thing to sense, Why should we in our peevish opposition Take it to heart? Fie! ’tis a fault to heaven, A fault against the dead, a fault to nature, To reason most absurd: whose common theme Is death of fathers, and who still hath cried, From the first corse till he that died to-day, ‘This must be so.’ We pray you, throw to earth This unprevailing woe, and think of us As of a father: for let the world take note, You are the most immediate to our throne; And with no less nobility of love Than that which dearest father bears his son, Do I impart toward you. For your intent In going back to school in Wittenberg, It is most retrograde to our desire: And we beseech you, bend you to remain Here, in the cheer and comfort of our eye, Our chiefest courtier, cousin, and our son. QUEEN GERTRUDE Let not thy mother lose her prayers, Hamlet: I pray thee, stay with us; go not to Wittenberg. HAMLET I shall in all my best obey you, madam. KING CLAUDIUS Why, ’tis a loving and a fair reply: Be as ourself in Denmark. Madam, come; This gentle and unforced accord of Hamlet Sits smiling to my heart: in grace whereof, No jocund health that Denmark drinks to-day, But the great cannon to the clouds shall tell, And the king’s rouse the heavens all bruit again, Re-speaking earthly thunder. Come away. Exeunt all but HAMLET HAMLET O, that this too too solid flesh would melt Thaw and resolve itself into a dew! Or that the Everlasting had not fix’d His canon ‘gainst self-slaughter! O God! God! How weary, stale, flat and unprofitable, Seem to me all the uses of this world! Fie on’t! ah fie! ’tis an unweeded garden, That grows to seed; things rank and gross in nature Possess it merely. That it should come to this! But two months dead: nay, not so much, not two: So excellent a king; that was, to this, Hyperion to a satyr; so loving to my mother That he might not beteem the winds of heaven Visit her face too roughly. Heaven and earth! Must I remember? why, she would hang on him, As if increase of appetite had grown By what it fed on: and yet, within a month– Let me not think on’t–Frailty, thy name is woman!– A little month, or ere those shoes were old With which she follow’d my poor father’s body, Like Niobe, all tears:–why she, even she– O, God! a beast, that wants discourse of reason, Would have mourn’d longer–married with my uncle, My father’s brother, but no more like my father Than I to Hercules: within a month: Ere yet the salt of most unrighteous tears Had left the flushing in her galled eyes, She married. O, most wicked speed, to post With such dexterity to incestuous sheets! It is not nor it cannot come to good: But break, my heart; for I must hold my tongue. Enter HORATIO, MARCELLUS, and BERNARDO HORATIO Hail to your lordship! HAMLET I am glad to see you well: Horatio,–or I do forget myself. HORATIO The same, my lord, and your poor servant ever. HAMLET Sir, my good friend; I’ll change that name with you: And what make you from Wittenberg, Horatio? Marcellus? MARCELLUS My good lord– HAMLET I am very glad to see you. Good even, sir. But what, in faith, make you from Wittenberg? HORATIO A truant disposition, good my lord. HAMLET I would not hear your enemy say so, Nor shall you do mine ear that violence, To make it truster of your own report Against yourself: I know you are no truant. But what is your affair in Elsinore? We’ll teach you to drink deep ere you depart. HORATIO My lord, I came to see your father’s funeral. HAMLET I pray thee, do not mock me, fellow-student; I think it was to see my mother’s wedding. HORATIO Indeed, my lord, it follow’d hard upon. HAMLET Thrift, thrift, Horatio! the funeral baked meats Did coldly furnish forth the marriage tables. Would I had met my dearest foe in heaven Or ever I had seen that day, Horatio! My father!–methinks I see my father. HORATIO Where, my lord? HAMLET In my mind’s eye, Horatio. HORATIO I saw him once; he was a goodly king. HAMLET He was a man, take him for all in all, I shall not look upon his like again. HORATIO My lord, I think I saw him yesternight. HAMLET Saw? who? HORATIO My lord, the king your father. HAMLET The king my father! HORATIO Season your admiration for awhile With an attent ear, till I may deliver, Upon the witness of these gentlemen, This marvel to you. HAMLET For God’s love, let me hear. HORATIO Two nights together had these gentlemen, Marcellus and Bernardo, on their watch, In the dead vast and middle of the night, Been thus encounter’d. A figure like your father, Armed at point exactly, cap-a-pe, Appears before them, and with solemn march Goes slow and stately by them: thrice he walk’d By their oppress’d and fear-surprised eyes, Within his truncheon’s length; whilst they, distilled Almost to jelly with the act of fear, Stand dumb and speak not to him. This to me In dreadful secrecy impart they did; And I with them the third night kept the watch; Where, as they had deliver’d, both in time, Form of the thing, each word made true and good, The apparition comes: I knew your father; These hands are not more like. HAMLET But where was this? MARCELLUS My lord, upon the platform where we watch’d. HAMLET Did you not speak to it? HORATIO My lord, I did; But answer made it none: yet once methought It lifted up its head and did address Itself to motion, like as it would speak; But even then the morning cock crew loud, And at the sound it shrunk in haste away, And vanish’d from our sight. HAMLET ‘Tis very strange. HORATIO As I do live, my honour’d lord, ’tis true; And we did think it writ down in our duty To let you know of it. HAMLET Indeed, indeed, sirs, but this troubles me. Hold you the watch to-night? MARCELLUS We do, my lord. HAMLET Arm’d, say you? MARCELLUS Arm’d, my lord. HAMLET From top to toe? MARCELLUS My lord, from head to foot. HAMLET Then saw you not his face? HORATIO O, yes, my lord; he wore his beaver up. HAMLET What, look’d he frowningly? HORATIO A countenance more in sorrow than in anger. HAMLET Pale or red? HORATIO Nay, very pale. HAMLET And fix’d his eyes upon you? HORATIO Most constantly. HAMLET I would I had been there. HORATIO It would have much amazed you. HAMLET Very like, very like. Stay’d it long? HORATIO While one with moderate haste might tell a hundred. MARCELLUS Longer, longer. HORATIO Not when I saw’t. HAMLET His beard was grizzled–no? HORATIO It was, as I have seen it in his life, A sable silver’d. HAMLET I will watch to-night; Perchance ’twill walk again. HORATIO I warrant it will. HAMLET If it assume my noble father’s person, I’ll speak to it, though hell itself should gape And bid me hold my peace. I pray you all, If you have hitherto conceal’d this sight, Let it be tenable in your silence still; And whatsoever else shall hap to-night, Give it an understanding, but no tongue: I will requite your loves. So, fare you well: Upon the platform, ‘twixt eleven and twelve, I’ll visit you. All Our duty to your honour. HAMLET Your loves, as mine to you: farewell. Exeunt all but HAMLET My father’s spirit in arms! all is not well; I doubt some foul play: would the night were come! Till then sit still, my soul: foul deeds will rise, Though all the earth o’erwhelm them, to men’s eyes. Exit
SCENE III. A room in Polonius’ house.
Enter LAERTES and OPHELIA LAERTES My necessaries are embark’d: farewell: And, sister, as the winds give benefit And convoy is assistant, do not sleep, But let me hear from you. OPHELIA Do you doubt that? LAERTES For Hamlet and the trifling of his favour, Hold it a fashion and a toy in blood, A violet in the youth of primy nature, Forward, not permanent, sweet, not lasting, The perfume and suppliance of a minute; No more. OPHELIA No more but so? LAERTES Think it no more; For nature, crescent, does not grow alone In thews and bulk, but, as this temple waxes, The inward service of the mind and soul Grows wide withal. Perhaps he loves you now, And now no soil nor cautel doth besmirch The virtue of his will: but you must fear, His greatness weigh’d, his will is not his own; For he himself is subject to his birth: He may not, as unvalued persons do, Carve for himself; for on his choice depends The safety and health of this whole state; And therefore must his choice be circumscribed Unto the voice and yielding of that body Whereof he is the head. Then if he says he loves you, It fits your wisdom so far to believe it As he in his particular act and place May give his saying deed; which is no further Than the main voice of Denmark goes withal. Then weigh what loss your honour may sustain, If with too credent ear you list his songs, Or lose your heart, or your chaste treasure open To his unmaster’d importunity. Fear it, Ophelia, fear it, my dear sister, And keep you in the rear of your affection, Out of the shot and danger of desire. The chariest maid is prodigal enough, If she unmask her beauty to the moon: Virtue itself ‘scapes not calumnious strokes: The canker galls the infants of the spring, Too oft before their buttons be disclosed, And in the morn and liquid dew of youth Contagious blastments are most imminent. Be wary then; best safety lies in fear: Youth to itself rebels, though none else near. OPHELIA I shall the effect of this good lesson keep, As watchman to my heart. But, good my brother, Do not, as some ungracious pastors do, Show me the steep and thorny way to heaven; Whiles, like a puff’d and reckless libertine, Himself the primrose path of dalliance treads, And recks not his own rede. LAERTES O, fear me not. I stay too long: but here my father comes. Enter POLONIUS A double blessing is a double grace, Occasion smiles upon a second leave. LORD POLONIUS Yet here, Laertes! aboard, aboard, for shame! The wind sits in the shoulder of your sail, And you are stay’d for. There; my blessing with thee! And these few precepts in thy memory See thou character. Give thy thoughts no tongue, Nor any unproportioned thought his act. Be thou familiar, but by no means vulgar. Those friends thou hast, and their adoption tried, Grapple them to thy soul with hoops of steel; But do not dull thy palm with entertainment Of each new-hatch’d, unfledged comrade. Beware Of entrance to a quarrel, but being in, Bear’t that the opposed may beware of thee. Give every man thy ear, but few thy voice; Take each man’s censure, but reserve thy judgment. Costly thy habit as thy purse can buy, But not express’d in fancy; rich, not gaudy; For the apparel oft proclaims the man, And they in France of the best rank and station Are of a most select and generous chief in that. Neither a borrower nor a lender be; For loan oft loses both itself and friend, And borrowing dulls the edge of husbandry. This above all: to thine ownself be true, And it must follow, as the night the day, Thou canst not then be false to any man. Farewell: my blessing season this in thee! LAERTES Most humbly do I take my leave, my lord. LORD POLONIUS The time invites you; go; your servants tend. LAERTES Farewell, Ophelia; and remember well What I have said to you. OPHELIA ‘Tis in my memory lock’d, And you yourself shall keep the key of it. LAERTES Farewell. Exit LORD POLONIUS What is’t, Ophelia, be hath said to you? OPHELIA So please you, something touching the Lord Hamlet. LORD POLONIUS Marry, well bethought: ‘Tis told me, he hath very oft of late Given private time to you; and you yourself Have of your audience been most free and bounteous: If it be so, as so ’tis put on me, And that in way of caution, I must tell you, You do not understand yourself so clearly As it behoves my daughter and your honour. What is between you? give me up the truth. OPHELIA He hath, my lord, of late made many tenders Of his affection to me. LORD POLONIUS Affection! pooh! you speak like a green girl, Unsifted in such perilous circumstance. Do you believe his tenders, as you call them? OPHELIA I do not know, my lord, what I should think. LORD POLONIUS Marry, I’ll teach you: think yourself a baby; That you have ta’en these tenders for true pay, Which are not sterling. Tender yourself more dearly; Or–not to crack the wind of the poor phrase, Running it thus–you’ll tender me a fool. OPHELIA My lord, he hath importuned me with love In honourable fashion. LORD POLONIUS Ay, fashion you may call it; go to, go to. OPHELIA And hath given countenance to his speech, my lord, With almost all the holy vows of heaven. LORD POLONIUS Ay, springes to catch woodcocks. I do know, When the blood burns, how prodigal the soul Lends the tongue vows: these blazes, daughter, Giving more light than heat, extinct in both, Even in their promise, as it is a-making, You must not take for fire. From this time Be somewhat scanter of your maiden presence; Set your entreatments at a higher rate Than a command to parley. For Lord Hamlet, Believe so much in him, that he is young And with a larger tether may he walk Than may be given you: in few, Ophelia, Do not believe his vows; for they are brokers, Not of that dye which their investments show, But mere implorators of unholy suits, Breathing like sanctified and pious bawds, The better to beguile. This is for all: I would not, in plain terms, from this time forth, Have you so slander any moment leisure, As to give words or talk with the Lord Hamlet. Look to’t, I charge you: come your ways. OPHELIA I shall obey, my lord. Exeunt
SCENE IV. The platform.
Enter HAMLET, HORATIO, and MARCELLUS HAMLET The air bites shrewdly; it is very cold. HORATIO It is a nipping and an eager air. HAMLET What hour now? HORATIO I think it lacks of twelve. HAMLET No, it is struck. HORATIO Indeed? I heard it not: then it draws near the season Wherein the spirit held his wont to walk. A flourish of trumpets, and ordnance shot off, within What does this mean, my lord? HAMLET The king doth wake to-night and takes his rouse, Keeps wassail, and the swaggering up-spring reels; And, as he drains his draughts of Rhenish down, The kettle-drum and trumpet thus bray out The triumph of his pledge. HORATIO Is it a custom? HAMLET Ay, marry, is’t: But to my mind, though I am native here And to the manner born, it is a custom More honour’d in the breach than the observance. This heavy-headed revel east and west Makes us traduced and tax’d of other nations: They clepe us drunkards, and with swinish phrase Soil our addition; and indeed it takes From our achievements, though perform’d at height, The pith and marrow of our attribute. So, oft it chances in particular men, That for some vicious mole of nature in them, As, in their birth–wherein they are not guilty, Since nature cannot choose his origin– By the o’ergrowth of some complexion, Oft breaking down the pales and forts of reason, Or by some habit that too much o’er-leavens The form of plausive manners, that these men, Carrying, I say, the stamp of one defect, Being nature’s livery, or fortune’s star,– Their virtues else–be they as pure as grace, As infinite as man may undergo– Shall in the general censure take corruption From that particular fault: the dram of eale Doth all the noble substance of a doubt To his own scandal. HORATIO Look, my lord, it comes! Enter Ghost HAMLET Angels and ministers of grace defend us! Be thou a spirit of health or goblin damn’d, Bring with thee airs from heaven or blasts from hell, Be thy intents wicked or charitable, Thou comest in such a questionable shape That I will speak to thee: I’ll call thee Hamlet, King, father, royal Dane: O, answer me! Let me not burst in ignorance; but tell Why thy canonized bones, hearsed in death, Have burst their cerements; why the sepulchre, Wherein we saw thee quietly inurn’d, Hath oped his ponderous and marble jaws, To cast thee up again. What may this mean, That thou, dead corse, again in complete steel Revisit’st thus the glimpses of the moon, Making night hideous; and we fools of nature So horridly to shake our disposition With thoughts beyond the reaches of our souls? Say, why is this? wherefore? what should we do? Ghost beckons HAMLET HORATIO It beckons you to go away with it, As if it some impartment did desire To you alone. MARCELLUS Look, with what courteous action It waves you to a more removed ground: But do not go with it. HORATIO No, by no means. HAMLET It will not speak; then I will follow it. HORATIO Do not, my lord. HAMLET Why, what should be the fear? I do not set my life in a pin’s fee; And for my soul, what can it do to that, Being a thing immortal as itself? It waves me forth again: I’ll follow it. HORATIO What if it tempt you toward the flood, my lord, Or to the dreadful summit of the cliff That beetles o’er his base into the sea, And there assume some other horrible form, Which might deprive your sovereignty of reason And draw you into madness? think of it: The very place puts toys of desperation, Without more motive, into every brain That looks so many fathoms to the sea And hears it roar beneath. HAMLET It waves me still. Go on; I’ll follow thee. MARCELLUS You shall not go, my lord. HAMLET Hold off your hands. HORATIO Be ruled; you shall not go. HAMLET My fate cries out, And makes each petty artery in this body As hardy as the Nemean lion’s nerve. Still am I call’d. Unhand me, gentlemen. By heaven, I’ll make a ghost of him that lets me! I say, away! Go on; I’ll follow thee. Exeunt Ghost and HAMLET HORATIO He waxes desperate with imagination. MARCELLUS Let’s follow; ’tis not fit thus to obey him. HORATIO Have after. To what issue will this come? MARCELLUS Something is rotten in the state of Denmark. HORATIO Heaven will direct it. MARCELLUS Nay, let’s follow him. Exeunt
SCENE V. Another part of the platform.
Enter GHOST and HAMLET HAMLET Where wilt thou lead me? speak; I’ll go no further. Ghost Mark me. HAMLET I will. Ghost My hour is almost come, When I to sulphurous and tormenting flames Must render up myself. HAMLET Alas, poor ghost! Ghost Pity me not, but lend thy serious hearing To what I shall unfold. HAMLET Speak; I am bound to hear. Ghost So art thou to revenge, when thou shalt hear. HAMLET What? Ghost I am thy father’s spirit, Doom’d for a certain term to walk the night, And for the day confined to fast in fires, Till the foul crimes done in my days of nature Are burnt and purged away. But that I am forbid To tell the secrets of my prison-house, I could a tale unfold whose lightest word Would harrow up thy soul, freeze thy young blood, Make thy two eyes, like stars, start from their spheres, Thy knotted and combined locks to part And each particular hair to stand on end, Like quills upon the fretful porpentine: But this eternal blazon must not be To ears of flesh and blood. List, list, O, list! If thou didst ever thy dear father love– HAMLET O God! Ghost Revenge his foul and most unnatural murder. HAMLET Murder! Ghost Murder most foul, as in the best it is; But this most foul, strange and unnatural. HAMLET Haste me to know’t, that I, with wings as swift As meditation or the thoughts of love, May sweep to my revenge. Ghost I find thee apt; And duller shouldst thou be than the fat weed That roots itself in ease on Lethe wharf, Wouldst thou not stir in this. Now, Hamlet, hear: ‘Tis given out that, sleeping in my orchard, A serpent stung me; so the whole ear of Denmark Is by a forged process of my death Rankly abused: but know, thou noble youth, The serpent that did sting thy father’s life Now wears his crown. HAMLET O my prophetic soul! My uncle! Ghost Ay, that incestuous, that adulterate beast, With witchcraft of his wit, with traitorous gifts,– O wicked wit and gifts, that have the power So to seduce!–won to his shameful lust The will of my most seeming-virtuous queen: O Hamlet, what a falling-off was there! From me, whose love was of that dignity That it went hand in hand even with the vow I made to her in marriage, and to decline Upon a wretch whose natural gifts were poor To those of mine! But virtue, as it never will be moved, Though lewdness court it in a shape of heaven, So lust, though to a radiant angel link’d, Will sate itself in a celestial bed, And prey on garbage. But, soft! methinks I scent the morning air; Brief let me be. Sleeping within my orchard, My custom always of the afternoon, Upon my secure hour thy uncle stole, With juice of cursed hebenon in a vial, And in the porches of my ears did pour The leperous distilment; whose effect Holds such an enmity with blood of man That swift as quicksilver it courses through The natural gates and alleys of the body, And with a sudden vigour doth posset And curd, like eager droppings into milk, The thin and wholesome blood: so did it mine; And a most instant tetter bark’d about, Most lazar-like, with vile and loathsome crust, All my smooth body. Thus was I, sleeping, by a brother’s hand Of life, of crown, of queen, at once dispatch’d: Cut off even in the blossoms of my sin, Unhousel’d, disappointed, unanel’d, No reckoning made, but sent to my account With all my imperfections on my head: O, horrible! O, horrible! most horrible! If thou hast nature in thee, bear it not; Let not the royal bed of Denmark be A couch for luxury and damned incest. But, howsoever thou pursuest this act, Taint not thy mind, nor let thy soul contrive Against thy mother aught: leave her to heaven And to those thorns that in her bosom lodge, To prick and sting her. Fare thee well at once! The glow-worm shows the matin to be near, And ‘gins to pale his uneffectual fire: Adieu, adieu! Hamlet, remember me. Exit HAMLET O all you host of heaven! O earth! what else? And shall I couple hell? O, fie! Hold, hold, my heart; And you, my sinews, grow not instant old, But bear me stiffly up. Remember thee! Ay, thou poor ghost, while memory holds a seat In this distracted globe. Remember thee! Yea, from the table of my memory I’ll wipe away all trivial fond records, All saws of books, all forms, all pressures past, That youth and observation copied there; And thy commandment all alone shall live Within the book and volume of my brain, Unmix’d with baser matter: yes, by heaven! O most pernicious woman! O villain, villain, smiling, damned villain! My tables,–meet it is I set it down, That one may smile, and smile, and be a villain; At least I’m sure it may be so in Denmark: Writing So, uncle, there you are. Now to my word; It is ‘Adieu, adieu! remember me.’ I have sworn ‘t. MARCELLUS [Within] My lord, my lord,– MARCELLUS [Within] Lord Hamlet,– HORATIO [Within] Heaven secure him! HAMLET So be it! HORATIO [Within] Hillo, ho, ho, my lord! HAMLET Hillo, ho, ho, boy! come, bird, come. Enter HORATIO and MARCELLUS MARCELLUS How is’t, my noble lord? HORATIO What news, my lord? HAMLET O, wonderful! HORATIO Good my lord, tell it. HAMLET No; you’ll reveal it. HORATIO Not I, my lord, by heaven. MARCELLUS Nor I, my lord. HAMLET How say you, then; would heart of man once think it? But you’ll be secret? HORATIO Ay, by heaven, my lord. HAMLET There’s ne’er a villain dwelling in all Denmark But he’s an arrant knave. HORATIO There needs no ghost, my lord, come from the grave To tell us this. HAMLET Why, right; you are i’ the right; And so, without more circumstance at all, I hold it fit that we shake hands and part: You, as your business and desire shall point you; For every man has business and desire, Such as it is; and for mine own poor part, Look you, I’ll go pray. HORATIO These are but wild and whirling words, my lord. HAMLET I’m sorry they offend you, heartily; Yes, ‘faith heartily. HORATIO There’s no offence, my lord. HAMLET Yes, by Saint Patrick, but there is, Horatio, And much offence too. Touching this vision here, It is an honest ghost, that let me tell you: For your desire to know what is between us, O’ermaster ‘t as you may. And now, good friends, As you are friends, scholars and soldiers, Give me one poor request. HORATIO What is’t, my lord? we will. HAMLET Never make known what you have seen to-night. HORATIO My lord, we will not. HAMLET Nay, but swear’t. HORATIO In faith, My lord, not I. MARCELLUS Nor I, my lord, in faith. HAMLET Upon my sword. MARCELLUS We have sworn, my lord, already. HAMLET Indeed, upon my sword, indeed. Ghost [Beneath] Swear. HAMLET Ah, ha, boy! say’st thou so? art thou there, truepenny? Come on–you hear this fellow in the cellarage– Consent to swear. HORATIO Propose the oath, my lord. HAMLET Never to speak of this that you have seen, Swear by my sword. Ghost [Beneath] Swear. HAMLET Hic et ubique? then we’ll shift our ground. Come hither, gentlemen, And lay your hands again upon my sword: Never to speak of this that you have heard, Swear by my sword. Ghost [Beneath] Swear. HAMLET Well said, old mole! canst work i’ the earth so fast? A worthy pioner! Once more remove, good friends. HORATIO O day and night, but this is wondrous strange! HAMLET And therefore as a stranger give it welcome. There are more things in heaven and earth, Horatio, Than are dreamt of in your philosophy. But come; Here, as before, never, so help you mercy, How strange or odd soe’er I bear myself, As I perchance hereafter shall think meet To put an antic disposition on, That you, at such times seeing me, never shall, With arms encumber’d thus, or this headshake, Or by pronouncing of some doubtful phrase, As ‘Well, well, we know,’ or ‘We could, an if we would,’ Or ‘If we list to speak,’ or ‘There be, an if they might,’ Or such ambiguous giving out, to note That you know aught of me: this not to do, So grace and mercy at your most need help you, Swear. Ghost [Beneath] Swear. HAMLET Rest, rest, perturbed spirit! They swear So, gentlemen, With all my love I do commend me to you: And what so poor a man as Hamlet is May do, to express his love and friending to you, God willing, shall not lack. Let us go in together; And still your fingers on your lips, I pray. The time is out of joint: O cursed spite, That ever I was born to set it right! Nay, come, let’s go together. Exeunt
SCENE I. A room in POLONIUS’ house.
Enter POLONIUS and REYNALDO LORD POLONIUS Give him this money and these notes, Reynaldo. REYNALDO I will, my lord. LORD POLONIUS You shall do marvellous wisely, good Reynaldo, Before you visit him, to make inquire Of his behavior. REYNALDO My lord, I did intend it. LORD POLONIUS Marry, well said; very well said. Look you, sir, Inquire me first what Danskers are in Paris; And how, and who, what means, and where they keep, What company, at what expense; and finding By this encompassment and drift of question That they do know my son, come you more nearer Than your particular demands will touch it: Take you, as ’twere, some distant knowledge of him; As thus, ‘I know his father and his friends, And in part him: ‘ do you mark this, Reynaldo? REYNALDO Ay, very well, my lord. LORD POLONIUS ‘And in part him; but’ you may say ‘not well: But, if’t be he I mean, he’s very wild; Addicted so and so:’ and there put on him What forgeries you please; marry, none so rank As may dishonour him; take heed of that; But, sir, such wanton, wild and usual slips As are companions noted and most known To youth and liberty. REYNALDO As gaming, my lord. LORD POLONIUS Ay, or drinking, fencing, swearing, quarrelling, Drabbing: you may go so far. REYNALDO My lord, that would dishonour him. LORD POLONIUS ‘Faith, no; as you may season it in the charge You must not put another scandal on him, That he is open to incontinency; That’s not my meaning: but breathe his faults so quaintly That they may seem the taints of liberty, The flash and outbreak of a fiery mind, A savageness in unreclaimed blood, Of general assault. REYNALDO But, my good lord,– LORD POLONIUS Wherefore should you do this? REYNALDO Ay, my lord, I would know that. LORD POLONIUS Marry, sir, here’s my drift; And I believe, it is a fetch of wit: You laying these slight sullies on my son, As ’twere a thing a little soil’d i’ the working, Mark you, Your party in converse, him you would sound, Having ever seen in the prenominate crimes The youth you breathe of guilty, be assured He closes with you in this consequence; ‘Good sir,’ or so, or ‘friend,’ or ‘gentleman,’ According to the phrase or the addition Of man and country. REYNALDO Very good, my lord. LORD POLONIUS And then, sir, does he this–he does–what was I about to say? By the mass, I was about to say something: where did I leave? REYNALDO At ‘closes in the consequence,’ at ‘friend or so,’ and ‘gentleman.’ LORD POLONIUS At ‘closes in the consequence,’ ay, marry; He closes thus: ‘I know the gentleman; I saw him yesterday, or t’ other day, Or then, or then; with such, or such; and, as you say, There was a’ gaming; there o’ertook in’s rouse; There falling out at tennis:’ or perchance, ‘I saw him enter such a house of sale,’ Videlicet, a brothel, or so forth. See you now; Your bait of falsehood takes this carp of truth: And thus do we of wisdom and of reach, With windlasses and with assays of bias, By indirections find directions out: So by my former lecture and advice, Shall you my son. You have me, have you not? REYNALDO My lord, I have. LORD POLONIUS God be wi’ you; fare you well. REYNALDO Good my lord! LORD POLONIUS Observe his inclination in yourself. REYNALDO I shall, my lord. LORD POLONIUS And let him ply his music. REYNALDO Well, my lord. LORD POLONIUS Farewell! Exit REYNALDO Enter OPHELIA How now, Ophelia! what’s the matter? OPHELIA O, my lord, my lord, I have been so affrighted! LORD POLONIUS With what, i’ the name of God? OPHELIA My lord, as I was sewing in my closet, Lord Hamlet, with his doublet all unbraced; No hat upon his head; his stockings foul’d, Ungarter’d, and down-gyved to his ancle; Pale as his shirt; his knees knocking each other; And with a look so piteous in purport As if he had been loosed out of hell To speak of horrors,–he comes before me. LORD POLONIUS Mad for thy love? OPHELIA My lord, I do not know; But truly, I do fear it. LORD POLONIUS What said he? OPHELIA He took me by the wrist and held me hard; Then goes he to the length of all his arm; And, with his other hand thus o’er his brow, He falls to such perusal of my face As he would draw it. Long stay’d he so; At last, a little shaking of mine arm And thrice his head thus waving up and down, He raised a sigh so piteous and profound As it did seem to shatter all his bulk And end his being: that done, he lets me go: And, with his head over his shoulder turn’d, He seem’d to find his way without his eyes; For out o’ doors he went without their helps, And, to the last, bended their light on me. LORD POLONIUS Come, go with me: I will go seek the king. This is the very ecstasy of love, Whose violent property fordoes itself And leads the will to desperate undertakings As oft as any passion under heaven That does afflict our natures. I am sorry. What, have you given him any hard words of late? OPHELIA No, my good lord, but, as you did command, I did repel his fetters and denied His access to me. LORD POLONIUS That hath made him mad. I am sorry that with better heed and judgment I had not quoted him: I fear’d he did but trifle, And meant to wreck thee; but, beshrew my jealousy! By heaven, it is as proper to our age To cast beyond ourselves in our opinions As it is common for the younger sort To lack discretion. Come, go we to the king: This must be known; which, being kept close, might move More grief to hide than hate to utter love. Exeunt
SCENE II. A room in the castle.
Enter KING CLAUDIUS, QUEEN GERTRUDE, ROSENCRANTZ, GUILDENSTERN, and Attendants KING CLAUDIUS Welcome, dear Rosencrantz and Guildenstern! Moreover that we much did long to see you, The need we have to use you did provoke Our hasty sending. Something have you heard Of Hamlet’s transformation; so call it, Sith nor the exterior nor the inward man Resembles that it was. What it should be, More than his father’s death, that thus hath put him So much from the understanding of himself, I cannot dream of: I entreat you both, That, being of so young days brought up with him, And sith so neighbour’d to his youth and havior, That you vouchsafe your rest here in our court Some little time: so by your companies To draw him on to pleasures, and to gather, So much as from occasion you may glean, Whether aught, to us unknown, afflicts him thus, That, open’d, lies within our remedy. QUEEN GERTRUDE Good gentlemen, he hath much talk’d of you; And sure I am two men there are not living To whom he more adheres. If it will please you To show us so much gentry and good will As to expend your time with us awhile, For the supply and profit of our hope, Your visitation shall receive such thanks As fits a king’s remembrance. ROSENCRANTZ Both your majesties Might, by the sovereign power you have of us, Put your dread pleasures more into command Than to entreaty. GUILDENSTERN But we both obey, And here give up ourselves, in the full bent To lay our service freely at your feet, To be commanded. KING CLAUDIUS Thanks, Rosencrantz and gentle Guildenstern. QUEEN GERTRUDE Thanks, Guildenstern and gentle Rosencrantz: And I beseech you instantly to visit My too much changed son. Go, some of you, And bring these gentlemen where Hamlet is. GUILDENSTERN Heavens make our presence and our practises Pleasant and helpful to him! QUEEN GERTRUDE Ay, amen! Exeunt ROSENCRANTZ, GUILDENSTERN, and some Attendants Enter POLONIUS LORD POLONIUS The ambassadors from Norway, my good lord, Are joyfully return’d. KING CLAUDIUS Thou still hast been the father of good news. LORD POLONIUS Have I, my lord? I assure my good liege, I hold my duty, as I hold my soul, Both to my God and to my gracious king: And I do think, or else this brain of mine Hunts not the trail of policy so sure As it hath used to do, that I have found The very cause of Hamlet’s lunacy. KING CLAUDIUS O, speak of that; that do I long to hear. LORD POLONIUS Give first admittance to the ambassadors; My news shall be the fruit to that great feast. KING CLAUDIUS Thyself do grace to them, and bring them in. Exit POLONIUS He tells me, my dear Gertrude, he hath found The head and source of all your son’s distemper. QUEEN GERTRUDE I doubt it is no other but the main; His father’s death, and our o’erhasty marriage. KING CLAUDIUS Well, we shall sift him. Re-enter POLONIUS, with VOLTIMAND and CORNELIUS Welcome, my good friends! Say, Voltimand, what from our brother Norway? VOLTIMAND Most fair return of greetings and desires. Upon our first, he sent out to suppress His nephew’s levies; which to him appear’d To be a preparation ‘gainst the Polack; But, better look’d into, he truly found It was against your highness: whereat grieved, That so his sickness, age and impotence Was falsely borne in hand, sends out arrests On Fortinbras; which he, in brief, obeys; Receives rebuke from Norway, and in fine Makes vow before his uncle never more To give the assay of arms against your majesty. Whereon old Norway, overcome with joy, Gives him three thousand crowns in annual fee, And his commission to employ those soldiers, So levied as before, against the Polack: With an entreaty, herein further shown, Giving a paper That it might please you to give quiet pass Through your dominions for this enterprise, On such regards of safety and allowance As therein are set down. KING CLAUDIUS It likes us well; And at our more consider’d time well read, Answer, and think upon this business. Meantime we thank you for your well-took labour: Go to your rest; at night we’ll feast together: Most welcome home! Exeunt VOLTIMAND and CORNELIUS LORD POLONIUS This business is well ended. My liege, and madam, to expostulate What majesty should be, what duty is, Why day is day, night night, and time is time, Were nothing but to waste night, day and time. Therefore, since brevity is the soul of wit, And tediousness the limbs and outward flourishes, I will be brief: your noble son is mad: Mad call I it; for, to define true madness, What is’t but to be nothing else but mad? But let that go. QUEEN GERTRUDE More matter, with less art. LORD POLONIUS Madam, I swear I use no art at all. That he is mad, ’tis true: ’tis true ’tis pity; And pity ’tis ’tis true: a foolish figure; But farewell it, for I will use no art. Mad let us grant him, then: and now remains That we find out the cause of this effect, Or rather say, the cause of this defect, For this effect defective comes by cause: Thus it remains, and the remainder thus. Perpend. I have a daughter–have while she is mine– Who, in her duty and obedience, mark, Hath given me this: now gather, and surmise. Reads ‘To the celestial and my soul’s idol, the most beautified Ophelia,’– That’s an ill phrase, a vile phrase; ‘beautified’ is a vile phrase: but you shall hear. Thus: Reads ‘In her excellent white bosom, these, & c.’ QUEEN GERTRUDE Came this from Hamlet to her? LORD POLONIUS Good madam, stay awhile; I will be faithful. Reads ‘Doubt thou the stars are fire; Doubt that the sun doth move; Doubt truth to be a liar; But never doubt I love. ‘O dear Ophelia, I am ill at these numbers; I have not art to reckon my groans: but that I love thee best, O most best, believe it. Adieu. ‘Thine evermore most dear lady, whilst this machine is to him, HAMLET.’ This, in obedience, hath my daughter shown me, And more above, hath his solicitings, As they fell out by time, by means and place, All given to mine ear. KING CLAUDIUS But how hath she Received his love? LORD POLONIUS What do you think of me? KING CLAUDIUS As of a man faithful and honourable. LORD POLONIUS I would fain prove so. But what might you think, When I had seen this hot love on the wing– As I perceived it, I must tell you that, Before my daughter told me–what might you, Or my dear majesty your queen here, think, If I had play’d the desk or table-book, Or given my heart a winking, mute and dumb, Or look’d upon this love with idle sight; What might you think? No, I went round to work, And my young mistress thus I did bespeak: ‘Lord Hamlet is a prince, out of thy star; This must not be:’ and then I precepts gave her, That she should lock herself from his resort, Admit no messengers, receive no tokens. Which done, she took the fruits of my advice; And he, repulsed–a short tale to make– Fell into a sadness, then into a fast, Thence to a watch, thence into a weakness, Thence to a lightness, and, by this declension, Into the madness wherein now he raves, And all we mourn for. KING CLAUDIUS Do you think ’tis this? QUEEN GERTRUDE It may be, very likely. LORD POLONIUS Hath there been such a time–I’d fain know that– That I have positively said ‘Tis so,’ When it proved otherwise? KING CLAUDIUS Not that I know. LORD POLONIUS [Pointing to his head and shoulder] Take this from this, if this be otherwise: If circumstances lead me, I will find Where truth is hid, though it were hid indeed Within the centre. KING CLAUDIUS How may we try it further? LORD POLONIUS You know, sometimes he walks four hours together Here in the lobby. QUEEN GERTRUDE So he does indeed. LORD POLONIUS At such a time I’ll loose my daughter to him: Be you and I behind an arras then; Mark the encounter: if he love her not And be not from his reason fall’n thereon, Let me be no assistant for a state, But keep a farm and carters. KING CLAUDIUS We will try it. QUEEN GERTRUDE But, look, where sadly the poor wretch comes reading. LORD POLONIUS Away, I do beseech you, both away: I’ll board him presently. Exeunt KING CLAUDIUS, QUEEN GERTRUDE, and Attendants Enter HAMLET, reading O, give me leave: How does my good Lord Hamlet? HAMLET Well, God-a-mercy. LORD POLONIUS Do you know me, my lord? HAMLET Excellent well; you are a fishmonger. LORD POLONIUS Not I, my lord. HAMLET Then I would you were so honest a man. LORD POLONIUS Honest, my lord! HAMLET Ay, sir; to be honest, as this world goes, is to be one man picked out of ten thousand. LORD POLONIUS That’s very true, my lord. HAMLET For if the sun breed maggots in a dead dog, being a god kissing carrion,–Have you a daughter? LORD POLONIUS I have, my lord. HAMLET Let her not walk i’ the sun: conception is a blessing: but not as your daughter may conceive. Friend, look to ‘t. LORD POLONIUS [Aside] How say you by that? Still harping on my daughter: yet he knew me not at first; he said I was a fishmonger: he is far gone, far gone: and truly in my youth I suffered much extremity for love; very near this. I’ll speak to him again. What do you read, my lord? HAMLET Words, words, words. LORD POLONIUS What is the matter, my lord? HAMLET Between who? LORD POLONIUS I mean, the matter that you read, my lord. HAMLET Slanders, sir: for the satirical rogue says here that old men have grey beards, that their faces are wrinkled, their eyes purging thick amber and plum-tree gum and that they have a plentiful lack of wit, together with most weak hams: all which, sir, though I most powerfully and potently believe, yet I hold it not honesty to have it thus set down, for yourself, sir, should be old as I am, if like a crab you could go backward. LORD POLONIUS [Aside] Though this be madness, yet there is method in ‘t. Will you walk out of the air, my lord? HAMLET Into my grave. LORD POLONIUS Indeed, that is out o’ the air. Aside How pregnant sometimes his replies are! a happiness that often madness hits on, which reason and sanity could not so prosperously be delivered of. I will leave him, and suddenly contrive the means of meeting between him and my daughter.–My honourable lord, I will most humbly take my leave of you. HAMLET You cannot, sir, take from me any thing that I will more willingly part withal: except my life, except my life, except my life. LORD POLONIUS Fare you well, my lord. HAMLET These tedious old fools! Enter ROSENCRANTZ and GUILDENSTERN LORD POLONIUS You go to seek the Lord Hamlet; there he is. ROSENCRANTZ [To POLONIUS] God save you, sir! Exit POLONIUS GUILDENSTERN My honoured lord! ROSENCRANTZ My most dear lord! HAMLET My excellent good friends! How dost thou, Guildenstern? Ah, Rosencrantz! Good lads, how do ye both? ROSENCRANTZ As the indifferent children of the earth. GUILDENSTERN Happy, in that we are not over-happy; On fortune’s cap we are not the very button. HAMLET Nor the soles of her shoe? ROSENCRANTZ Neither, my lord. HAMLET Then you live about her waist, or in the middle of her favours? GUILDENSTERN ‘Faith, her privates we. HAMLET In the secret parts of fortune? O, most true; she is a strumpet. What’s the news? ROSENCRANTZ None, my lord, but that the world’s grown honest. HAMLET Then is doomsday near: but your news is not true. Let me question more in particular: what have you, my good friends, deserved at the hands of fortune, that she sends you to prison hither? GUILDENSTERN Prison, my lord! HAMLET Denmark’s a prison. ROSENCRANTZ Then is the world one. HAMLET A goodly one; in which there are many confines, wards and dungeons, Denmark being one o’ the worst. ROSENCRANTZ We think not so, my lord. HAMLET Why, then, ’tis none to you; for there is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so: to me it is a prison. ROSENCRANTZ Why then, your ambition makes it one; ’tis too narrow for your mind. HAMLET O God, I could be bounded in a nut shell and count myself a king of infinite space, were it not that I have bad dreams. GUILDENSTERN Which dreams indeed are ambition, for the very substance of the ambitious is merely the shadow of a dream. HAMLET A dream itself is but a shadow. ROSENCRANTZ Truly, and I hold ambition of so airy and light a quality that it is but a shadow’s shadow. HAMLET Then are our beggars bodies, and our monarchs and outstretched heroes the beggars’ shadows. Shall we to the court? for, by my fay, I cannot reason. ROSENCRANTZ We’ll wait upon you. HAMLET No such matter: I will not sort you with the rest of my servants, for, to speak to you like an honest man, I am most dreadfully attended. But, in the beaten way of friendship, what make you at Elsinore? ROSENCRANTZ To visit you, my lord; no other occasion. HAMLET Beggar that I am, I am even poor in thanks; but I thank you: and sure, dear friends, my thanks are too dear a halfpenny. Were you not sent for? Is it your own inclining? Is it a free visitation? Come, deal justly with me: come, come; nay, speak. GUILDENSTERN What should we say, my lord? HAMLET Why, any thing, but to the purpose. You were sent for; and there is a kind of confession in your looks which your modesties have not craft enough to colour: I know the good king and queen have sent for you. ROSENCRANTZ To what end, my lord? HAMLET That you must teach me. But let me conjure you, by the rights of our fellowship, by the consonancy of our youth, by the obligation of our ever-preserved love, and by what more dear a better proposer could charge you withal, be even and direct with me, whether you were sent for, or no? ROSENCRANTZ [Aside to GUILDENSTERN] What say you? HAMLET [Aside] Nay, then, I have an eye of you.–If you love me, hold not off. GUILDENSTERN My lord, we were sent for. HAMLET I will tell you why; so shall my anticipation prevent your discovery, and your secrecy to the king and queen moult no feather. I have of late–but wherefore I know not–lost all my mirth, forgone all custom of exercises; and indeed it goes so heavily with my disposition that this goodly frame, the earth, seems to me a sterile promontory, this most excellent canopy, the air, look you, this brave o’erhanging firmament, this majestical roof fretted with golden fire, why, it appears no other thing to me than a foul and pestilent congregation of vapours. What a piece of work is a man! how noble in reason! how infinite in faculty! in form and moving how express and admirable! in action how like an angel! in apprehension how like a god! the beauty of the world! the paragon of animals! And yet, to me, what is this quintessence of dust? man delights not me: no, nor woman neither, though by your smiling you seem to say so. ROSENCRANTZ My lord, there was no such stuff in my thoughts. HAMLET Why did you laugh then, when I said ‘man delights not me’? ROSENCRANTZ To think, my lord, if you delight not in man, what lenten entertainment the players shall receive from you: we coted them on the way; and hither are they coming, to offer you service. HAMLET He that plays the king shall be welcome; his majesty shall have tribute of me; the adventurous knight shall use his foil and target; the lover shall not sigh gratis; the humourous man shall end his part in peace; the clown shall make those laugh whose lungs are tickled o’ the sere; and the lady shall say her mind freely, or the blank verse shall halt for’t. What players are they? ROSENCRANTZ Even those you were wont to take delight in, the tragedians of the city. HAMLET How chances it they travel? their residence, both in reputation and profit, was better both ways. ROSENCRANTZ I think their inhibition comes by the means of the late innovation. HAMLET Do they hold the same estimation they did when I was in the city? are they so followed? ROSENCRANTZ No, indeed, are they not. HAMLET How comes it? do they grow rusty? ROSENCRANTZ Nay, their endeavour keeps in the wonted pace: but there is, sir, an aery of children, little eyases, that cry out on the top of question, and are most tyrannically clapped for’t: these are now the fashion, and so berattle the common stages–so they call them–that many wearing rapiers are afraid of goose-quills and dare scarce come thither. HAMLET What, are they children? who maintains ’em? how are they escoted? Will they pursue the quality no longer than they can sing? will they not say afterwards, if they should grow themselves to common players–as it is most like, if their means are no better–their writers do them wrong, to make them exclaim against their own succession? ROSENCRANTZ ‘Faith, there has been much to do on both sides; and the nation holds it no sin to tarre them to controversy: there was, for a while, no money bid for argument, unless the poet and the player went to cuffs in the question. HAMLET Is’t possible? GUILDENSTERN O, there has been much throwing about of brains. HAMLET Do the boys carry it away? ROSENCRANTZ Ay, that they do, my lord; Hercules and his load too. HAMLET It is not very strange; for mine uncle is king of Denmark, and those that would make mows at him while my father lived, give twenty, forty, fifty, an hundred ducats a-piece for his picture in little. ‘Sblood, there is something in this more than natural, if philosophy could find it out. Flourish of trumpets within GUILDENSTERN There are the players. HAMLET Gentlemen, you are welcome to Elsinore. Your hands, come then: the appurtenance of welcome is fashion and ceremony: let me comply with you in this garb, lest my extent to the players, which, I tell you, must show fairly outward, should more appear like entertainment than yours. You are welcome: but my uncle-father and aunt-mother are deceived. GUILDENSTERN In what, my dear lord? HAMLET I am but mad north-north-west: when the wind is southerly I know a hawk from a handsaw. Enter POLONIUS LORD POLONIUS Well be with you, gentlemen! HAMLET Hark you, Guildenstern; and you too: at each ear a hearer: that great baby you see there is not yet out of his swaddling-clouts. ROSENCRANTZ Happily he’s the second time come to them; for they say an old man is twice a child. HAMLET I will prophesy he comes to tell me of the players; mark it. You say right, sir: o’ Monday morning; ’twas so indeed. LORD POLONIUS My lord, I have news to tell you. HAMLET My lord, I have news to tell you. When Roscius was an actor in Rome,– LORD POLONIUS The actors are come hither, my lord. HAMLET Buz, buz! LORD POLONIUS Upon mine honour,– HAMLET Then came each actor on his ass,– LORD POLONIUS The best actors in the world, either for tragedy, comedy, history, pastoral, pastoral-comical, historical-pastoral, tragical-historical, tragical- comical-historical-pastoral, scene individable, or poem unlimited: Seneca cannot be too heavy, nor Plautus too light. For the law of writ and the liberty, these are the only men. HAMLET O Jephthah, judge of Israel, what a treasure hadst thou! LORD POLONIUS What a treasure had he, my lord? HAMLET Why, ‘One fair daughter and no more, The which he loved passing well.’ LORD POLONIUS [Aside] Still on my daughter. HAMLET Am I not i’ the right, old Jephthah? LORD POLONIUS If you call me Jephthah, my lord, I have a daughter that I love passing well. HAMLET Nay, that follows not. LORD POLONIUS What follows, then, my lord? HAMLET Why, ‘As by lot, God wot,’ and then, you know, ‘It came to pass, as most like it was,’– the first row of the pious chanson will show you more; for look, where my abridgement comes. Enter four or five Players You are welcome, masters; welcome, all. I am glad to see thee well. Welcome, good friends. O, my old friend! thy face is valenced since I saw thee last: comest thou to beard me in Denmark? What, my young lady and mistress! By’r lady, your ladyship is nearer to heaven than when I saw you last, by the altitude of a chopine. Pray God, your voice, like apiece of uncurrent gold, be not cracked within the ring. Masters, you are all welcome. We’ll e’en to’t like French falconers, fly at any thing we see: we’ll have a speech straight: come, give us a taste of your quality; come, a passionate speech. First Player What speech, my lord? HAMLET I heard thee speak me a speech once, but it was never acted; or, if it was, not above once; for the play, I remember, pleased not the million; ’twas caviare to the general: but it was–as I received it, and others, whose judgments in such matters cried in the top of mine–an excellent play, well digested in the scenes, set down with as much modesty as cunning. I remember, one said there were no sallets in the lines to make the matter savoury, nor no matter in the phrase that might indict the author of affectation; but called it an honest method, as wholesome as sweet, and by very much more handsome than fine. One speech in it I chiefly loved: ’twas Aeneas’ tale to Dido; and thereabout of it especially, where he speaks of Priam’s slaughter: if it live in your memory, begin at this line: let me see, let me see– ‘The rugged Pyrrhus, like the Hyrcanian beast,’– it is not so:–it begins with Pyrrhus:– ‘The rugged Pyrrhus, he whose sable arms, Black as his purpose, did the night resemble When he lay couched in the ominous horse, Hath now this dread and black complexion smear’d With heraldry more dismal; head to foot Now is he total gules; horridly trick’d With blood of fathers, mothers, daughters, sons, Baked and impasted with the parching streets, That lend a tyrannous and damned light To their lord’s murder: roasted in wrath and fire, And thus o’er-sized with coagulate gore, With eyes like carbuncles, the hellish Pyrrhus Old grandsire Priam seeks.’ So, proceed you. LORD POLONIUS ‘Fore God, my lord, well spoken, with good accent and good discretion. First Player ‘Anon he finds him Striking too short at Greeks; his antique sword, Rebellious to his arm, lies where it falls, Repugnant to command: unequal match’d, Pyrrhus at Priam drives; in rage strikes wide; But with the whiff and wind of his fell sword The unnerved father falls. Then senseless Ilium, Seeming to feel this blow, with flaming top Stoops to his base, and with a hideous crash Takes prisoner Pyrrhus’ ear: for, lo! his sword, Which was declining on the milky head Of reverend Priam, seem’d i’ the air to stick: So, as a painted tyrant, Pyrrhus stood, And like a neutral to his will and matter, Did nothing. But, as we often see, against some storm, A silence in the heavens, the rack stand still, The bold winds speechless and the orb below As hush as death, anon the dreadful thunder Doth rend the region, so, after Pyrrhus’ pause, Aroused vengeance sets him new a-work; And never did the Cyclops’ hammers fall On Mars’s armour forged for proof eterne With less remorse than Pyrrhus’ bleeding sword Now falls on Priam. Out, out, thou strumpet, Fortune! All you gods, In general synod ‘take away her power; Break all the spokes and fellies from her wheel, And bowl the round nave down the hill of heaven, As low as to the fiends!’ LORD POLONIUS This is too long. HAMLET It shall to the barber’s, with your beard. Prithee, say on: he’s for a jig or a tale of bawdry, or he sleeps: say on: come to Hecuba. First Player ‘But who, O, who had seen the mobled queen–‘ HAMLET ‘The mobled queen?’ LORD POLONIUS That’s good; ‘mobled queen’ is good. First Player ‘Run barefoot up and down, threatening the flames With bisson rheum; a clout upon that head Where late the diadem stood, and for a robe, About her lank and all o’er-teemed loins, A blanket, in the alarm of fear caught up; Who this had seen, with tongue in venom steep’d, ‘Gainst Fortune’s state would treason have pronounced: But if the gods themselves did see her then When she saw Pyrrhus make malicious sport In mincing with his sword her husband’s limbs, The instant burst of clamour that she made, Unless things mortal move them not at all, Would have made milch the burning eyes of heaven, And passion in the gods.’ LORD POLONIUS Look, whether he has not turned his colour and has tears in’s eyes. Pray you, no more. HAMLET ‘Tis well: I’ll have thee speak out the rest soon. Good my lord, will you see the players well bestowed? Do you hear, let them be well used; for they are the abstract and brief chronicles of the time: after your death you were better have a bad epitaph than their ill report while you live. LORD POLONIUS My lord, I will use them according to their desert. HAMLET God’s bodykins, man, much better: use every man after his desert, and who should ‘scape whipping? Use them after your own honour and dignity: the less they deserve, the more merit is in your bounty. Take them in. LORD POLONIUS Come, sirs. HAMLET Follow him, friends: we’ll hear a play to-morrow. Exit POLONIUS with all the Players but the First Dost thou hear me, old friend; can you play the Murder of Gonzago? First Player Ay, my lord. HAMLET We’ll ha’t to-morrow night. You could, for a need, study a speech of some dozen or sixteen lines, which I would set down and insert in’t, could you not? First Player Ay, my lord. HAMLET Very well. Follow that lord; and look you mock him not. Exit First Player My good friends, I’ll leave you till night: you are welcome to Elsinore. ROSENCRANTZ Good my lord! HAMLET Ay, so, God be wi’ ye; Exeunt ROSENCRANTZ and GUILDENSTERN Now I am alone. O, what a rogue and peasant slave am I! Is it not monstrous that this player here, But in a fiction, in a dream of passion, Could force his soul so to his own conceit That from her working all his visage wann’d, Tears in his eyes, distraction in’s aspect, A broken voice, and his whole function suiting With forms to his conceit? and all for nothing! For Hecuba! What’s Hecuba to him, or he to Hecuba, That he should weep for her? What would he do, Had he the motive and the cue for passion That I have? He would drown the stage with tears And cleave the general ear with horrid speech, Make mad the guilty and appal the free, Confound the ignorant, and amaze indeed The very faculties of eyes and ears. Yet I, A dull and muddy-mettled rascal, peak, Like John-a-dreams, unpregnant of my cause, And can say nothing; no, not for a king, Upon whose property and most dear life A damn’d defeat was made. Am I a coward? Who calls me villain? breaks my pate across? Plucks off my beard, and blows it in my face? Tweaks me by the nose? gives me the lie i’ the throat, As deep as to the lungs? who does me this? Ha! ‘Swounds, I should take it: for it cannot be But I am pigeon-liver’d and lack gall To make oppression bitter, or ere this I should have fatted all the region kites With this slave’s offal: bloody, bawdy villain! Remorseless, treacherous, lecherous, kindless villain! O, vengeance! Why, what an ass am I! This is most brave, That I, the son of a dear father murder’d, Prompted to my revenge by heaven and hell, Must, like a whore, unpack my heart with words, And fall a-cursing, like a very drab, A scullion! Fie upon’t! foh! About, my brain! I have heard That guilty creatures sitting at a play Have by the very cunning of the scene Been struck so to the soul that presently They have proclaim’d their malefactions; For murder, though it have no tongue, will speak With most miraculous organ. I’ll have these players Play something like the murder of my father Before mine uncle: I’ll observe his looks; I’ll tent him to the quick: if he but blench, I know my course. The spirit that I have seen May be the devil: and the devil hath power To assume a pleasing shape; yea, and perhaps Out of my weakness and my melancholy, As he is very potent with such spirits, Abuses me to damn me: I’ll have grounds More relative than this: the play ‘s the thing Wherein I’ll catch the conscience of the king. Exit
SCENE I. A room in the castle.
Enter KING CLAUDIUS, QUEEN GERTRUDE, POLONIUS, OPHELIA, ROSENCRANTZ, and GUILDENSTERN KING CLAUDIUS And can you, by no drift of circumstance, Get from him why he puts on this confusion, Grating so harshly all his days of quiet With turbulent and dangerous lunacy? ROSENCRANTZ He does confess he feels himself distracted; But from what cause he will by no means speak. GUILDENSTERN Nor do we find him forward to be sounded, But, with a crafty madness, keeps aloof, When we would bring him on to some confession Of his true state. QUEEN GERTRUDE Did he receive you well? ROSENCRANTZ Most like a gentleman. GUILDENSTERN But with much forcing of his disposition. ROSENCRANTZ Niggard of question; but, of our demands, Most free in his reply. QUEEN GERTRUDE Did you assay him? To any pastime? ROSENCRANTZ Madam, it so fell out, that certain players We o’er-raught on the way: of these we told him; And there did seem in him a kind of joy To hear of it: they are about the court, And, as I think, they have already order This night to play before him. LORD POLONIUS ‘Tis most true: And he beseech’d me to entreat your majesties To hear and see the matter. KING CLAUDIUS With all my heart; and it doth much content me To hear him so inclined. Good gentlemen, give him a further edge, And drive his purpose on to these delights. ROSENCRANTZ We shall, my lord. Exeunt ROSENCRANTZ and GUILDENSTERN KING CLAUDIUS Sweet Gertrude, leave us too; For we have closely sent for Hamlet hither, That he, as ’twere by accident, may here Affront Ophelia: Her father and myself, lawful espials, Will so bestow ourselves that, seeing, unseen, We may of their encounter frankly judge, And gather by him, as he is behaved, If ‘t be the affliction of his love or no That thus he suffers for. QUEEN GERTRUDE I shall obey you. And for your part, Ophelia, I do wish That your good beauties be the happy cause Of Hamlet’s wildness: so shall I hope your virtues Will bring him to his wonted way again, To both your honours. OPHELIA Madam, I wish it may. Exit QUEEN GERTRUDE LORD POLONIUS Ophelia, walk you here. Gracious, so please you, We will bestow ourselves. To OPHELIA Read on this book; That show of such an exercise may colour Your loneliness. We are oft to blame in this,– ‘Tis too much proved–that with devotion’s visage And pious action we do sugar o’er The devil himself. KING CLAUDIUS [Aside] O, ’tis too true! How smart a lash that speech doth give my conscience! The harlot’s cheek, beautied with plastering art, Is not more ugly to the thing that helps it Than is my deed to my most painted word: O heavy burthen! LORD POLONIUS I hear him coming: let’s withdraw, my lord. Exeunt KING CLAUDIUS and POLONIUS Enter HAMLET HAMLET To be, or not to be, that is the question, Whether ’tis nobler in the mind to suffer The slings and arrows of outrageous fortune, Or to take arms against a sea of troubles, And by opposing end them? To die: to sleep; No more; and by a sleep to say we end The heart-ache and the thousand natural shocks That flesh is heir to, ’tis a consummation Devoutly to be wish’d. To die, to sleep; To sleep: perchance to dream: ay, there’s the rub; For in that sleep of death what dreams may come When we have shuffled off this mortal coil, Must give us pause: there’s the respect That makes calamity of so long life; For who would bear the whips and scorns of time, The oppressor’s wrong, the proud man’s contumely, The pangs of despised love, the law’s delay, The insolence of office and the spurns That patient merit of the unworthy takes, When he himself might his quietus make With a bare bodkin? who would fardels bear, To grunt and sweat under a weary life, But that the dread of something after death, The undiscover’d country from whose bourn No traveller returns, puzzles the will And makes us rather bear those ills we have Than fly to others that we know not of? Thus conscience does make cowards of us all; And thus the native hue of resolution Is sicklied o’er with the pale cast of thought, And enterprises of great pith and moment With this regard their currents turn awry, And lose the name of action.–Soft you now! The fair Ophelia! Nymph, in thy orisons Be all my sins remember’d. OPHELIA Good my lord, How does your honour for this many a day? HAMLET I humbly thank you; well, well, well. OPHELIA My lord, I have remembrances of yours, That I have longed long to re-deliver; I pray you, now receive them. HAMLET No, not I; I never gave you aught. OPHELIA My honour’d lord, you know right well you did; And, with them, words of so sweet breath composed As made the things more rich: their perfume lost, Take these again; for to the noble mind Rich gifts wax poor when givers prove unkind. There, my lord. HAMLET Ha, ha! are you honest? OPHELIA My lord? HAMLET Are you fair? OPHELIA What means your lordship? HAMLET That if you be honest and fair, your honesty should admit no discourse to your beauty. OPHELIA Could beauty, my lord, have better commerce than with honesty? HAMLET Ay, truly; for the power of beauty will sooner transform honesty from what it is to a bawd than the force of honesty can translate beauty into his likeness: this was sometime a paradox, but now the time gives it proof. I did love you once. OPHELIA Indeed, my lord, you made me believe so. HAMLET You should not have believed me; for virtue cannot so inoculate our old stock but we shall relish of it: I loved you not. OPHELIA I was the more deceived. HAMLET Get thee to a nunnery: why wouldst thou be a breeder of sinners? I am myself indifferent honest; but yet I could accuse me of such things that it were better my mother had not borne me: I am very proud, revengeful, ambitious, with more offences at my beck than I have thoughts to put them in, imagination to give them shape, or time to act them in. What should such fellows as I do crawling between earth and heaven? We are arrant knaves, all; believe none of us. Go thy ways to a nunnery. Where’s your father? OPHELIA At home, my lord. HAMLET Let the doors be shut upon him, that he may play the fool no where but in’s own house. Farewell. OPHELIA O, help him, you sweet heavens! HAMLET If thou dost marry, I’ll give thee this plague for thy dowry: be thou as chaste as ice, as pure as snow, thou shalt not escape calumny. Get thee to a nunnery, go: farewell. Or, if thou wilt needs marry, marry a fool; for wise men know well enough what monsters you make of them. To a nunnery, go, and quickly too. Farewell. OPHELIA O heavenly powers, restore him! HAMLET I have heard of your paintings too, well enough; God has given you one face, and you make yourselves another: you jig, you amble, and you lisp, and nick-name God’s creatures, and make your wantonness your ignorance. Go to, I’ll no more on’t; it hath made me mad. I say, we will have no more marriages: those that are married already, all but one, shall live; the rest shall keep as they are. To a nunnery, go. Exit OPHELIA O, what a noble mind is here o’erthrown! The courtier’s, soldier’s, scholar’s, eye, tongue, sword; The expectancy and rose of the fair state, The glass of fashion and the mould of form, The observed of all observers, quite, quite down! And I, of ladies most deject and wretched, That suck’d the honey of his music vows, Now see that noble and most sovereign reason, Like sweet bells jangled, out of tune and harsh; That unmatch’d form and feature of blown youth Blasted with ecstasy: O, woe is me, To have seen what I have seen, see what I see! Re-enter KING CLAUDIUS and POLONIUS KING CLAUDIUS Love! his affections do not that way tend; Nor what he spake, though it lack’d form a little, Was not like madness. There’s something in his soul, O’er which his melancholy sits on brood; And I do doubt the hatch and the disclose Will be some danger: which for to prevent, I have in quick determination Thus set it down: he shall with speed to England, For the demand of our neglected tribute Haply the seas and countries different With variable objects shall expel This something-settled matter in his heart, Whereon his brains still beating puts him thus From fashion of himself. What think you on’t? LORD POLONIUS It shall do well: but yet do I believe The origin and commencement of his grief Sprung from neglected love. How now, Ophelia! You need not tell us what Lord Hamlet said; We heard it all. My lord, do as you please; But, if you hold it fit, after the play Let his queen mother all alone entreat him To show his grief: let her be round with him; And I’ll be placed, so please you, in the ear Of all their conference. If she find him not, To England send him, or confine him where Your wisdom best shall think. KING CLAUDIUS It shall be so: Madness in great ones must not unwatch’d go. Exeunt
SCENE II. A hall in the castle.
Enter HAMLET and Players HAMLET Speak the speech, I pray you, as I pronounced it to you, trippingly on the tongue: but if you mouth it, as many of your players do, I had as lief the town-crier spoke my lines. Nor do not saw the air too much with your hand, thus, but use all gently; for in the very torrent, tempest, and, as I may say, the whirlwind of passion, you must acquire and beget a temperance that may give it smoothness. O, it offends me to the soul to hear a robustious periwig-pated fellow tear a passion to tatters, to very rags, to split the ears of the groundlings, who for the most part are capable of nothing but inexplicable dumbshows and noise: I would have such a fellow whipped for o’erdoing Termagant; it out-herods Herod: pray you, avoid it. First Player I warrant your honour. HAMLET Be not too tame neither, but let your own discretion be your tutor: suit the action to the word, the word to the action; with this special o’erstep not the modesty of nature: for any thing so overdone is from the purpose of playing, whose end, both at the first and now, was and is, to hold, as ’twere, the mirror up to nature; to show virtue her own feature, scorn her own image, and the very age and body of the time his form and pressure. Now this overdone, or come tardy off, though it make the unskilful laugh, cannot but make the judicious grieve; the censure of the which one must in your allowance o’erweigh a whole theatre of others. O, there be players that I have seen play, and heard others praise, and that highly, not to speak it profanely, that, neither having the accent of Christians nor the gait of Christian, pagan, nor man, have so strutted and bellowed that I have thought some of nature’s journeymen had made men and not made them well, they imitated humanity so abominably. First Player I hope we have reformed that indifferently with us, sir. HAMLET O, reform it altogether. And let those that play your clowns speak no more than is set down for them; for there be of them that will themselves laugh, to set on some quantity of barren spectators to laugh too; though, in the mean time, some necessary question of the play be then to be considered: that’s villanous, and shows a most pitiful ambition in the fool that uses it. Go, make you ready. Exeunt Players Enter POLONIUS, ROSENCRANTZ, and GUILDENSTERN How now, my lord! I will the king hear this piece of work? LORD POLONIUS And the queen too, and that presently. HAMLET Bid the players make haste. Exit POLONIUS Will you two help to hasten them? ROSENCRANTZ We will, my lord. Exeunt ROSENCRANTZ and GUILDENSTERN HAMLET What ho! Horatio! Enter HORATIO HORATIO Here, sweet lord, at your service. HAMLET Horatio, thou art e’en as just a man As e’er my conversation coped withal. HORATIO O, my dear lord,– HAMLET Nay, do not think I flatter; For what advancement may I hope from thee That no revenue hast but thy good spirits, To feed and clothe thee? Why should the poor be flatter’d? No, let the candied tongue lick absurd pomp, And crook the pregnant hinges of the knee Where thrift may follow fawning. Dost thou hear? Since my dear soul was mistress of her choice And could of men distinguish, her election Hath seal’d thee for herself; for thou hast been As one, in suffering all, that suffers nothing, A man that fortune’s buffets and rewards Hast ta’en with equal thanks: and blest are those Whose blood and judgment are so well commingled, That they are not a pipe for fortune’s finger To sound what stop she please. Give me that man That is not passion’s slave, and I will wear him In my heart’s core, ay, in my heart of heart, As I do thee.–Something too much of this.– There is a play to-night before the king; One scene of it comes near the circumstance Which I have told thee of my father’s death: I prithee, when thou seest that act afoot, Even with the very comment of thy soul Observe mine uncle: if his occulted guilt Do not itself unkennel in one speech, It is a damned ghost that we have seen, And my imaginations are as foul As Vulcan’s stithy. Give him heedful note; For I mine eyes will rivet to his face, And after we will both our judgments join In censure of his seeming. HORATIO Well, my lord: If he steal aught the whilst this play is playing, And ‘scape detecting, I will pay the theft. HAMLET They are coming to the play; I must be idle: Get you a place. Danish march. A flourish. Enter KING CLAUDIUS, QUEEN GERTRUDE, POLONIUS, OPHELIA, ROSENCRANTZ, GUILDENSTERN, and others KING CLAUDIUS How fares our cousin Hamlet? HAMLET Excellent, i’ faith; of the chameleon’s dish: I eat the air, promise-crammed: you cannot feed capons so. KING CLAUDIUS I have nothing with this answer, Hamlet; these words are not mine. HAMLET No, nor mine now. To POLONIUS My lord, you played once i’ the university, you say? LORD POLONIUS That did I, my lord; and was accounted a good actor. HAMLET What did you enact? LORD POLONIUS I did enact Julius Caesar: I was killed i’ the Capitol; Brutus killed me. HAMLET It was a brute part of him to kill so capital a calf there. Be the players ready? ROSENCRANTZ Ay, my lord; they stay upon your patience. QUEEN GERTRUDE Come hither, my dear Hamlet, sit by me. HAMLET No, good mother, here’s metal more attractive. LORD POLONIUS [To KING CLAUDIUS] O, ho! do you mark that? HAMLET Lady, shall I lie in your lap? Lying down at OPHELIA’s feet OPHELIA No, my lord. HAMLET I mean, my head upon your lap? OPHELIA Ay, my lord. HAMLET Do you think I meant country matters? OPHELIA I think nothing, my lord. HAMLET That’s a fair thought to lie between maids’ legs. OPHELIA What is, my lord? HAMLET Nothing. OPHELIA You are merry, my lord. HAMLET Who, I? OPHELIA Ay, my lord. HAMLET O God, your only jig-maker. What should a man do but be merry? for, look you, how cheerfully my mother looks, and my father died within these two hours. OPHELIA Nay, ’tis twice two months, my lord. HAMLET So long? Nay then, let the devil wear black, for I’ll have a suit of sables. O heavens! die two months ago, and not forgotten yet? Then there’s hope a great man’s memory may outlive his life half a year: but, by’r lady, he must build churches, then; or else shall he suffer not thinking on, with the hobby-horse, whose epitaph is ‘For, O, for, O, the hobby-horse is forgot.’ Hautboys play. The dumb-show enters Enter a King and a Queen very lovingly; the Queen embracing him, and he her. She kneels, and makes show of protestation unto him. He takes her up, and declines his head upon her neck: lays him down upon a bank of flowers: she, seeing him asleep, leaves him. Anon comes in a fellow, takes off his crown, kisses it, and pours poison in the King’s ears, and exit. The Queen returns; finds the King dead, and makes passionate action. The Poisoner, with some two or three Mutes, comes in again, seeming to lament with her. The dead body is carried away. The Poisoner wooes the Queen with gifts: she seems loath and unwilling awhile, but in the end accepts his love Exeunt OPHELIA What means this, my lord? HAMLET Marry, this is miching mallecho; it means mischief. OPHELIA Belike this show imports the argument of the play. Enter Prologue HAMLET We shall know by this fellow: the players cannot keep counsel; they’ll tell all. OPHELIA Will he tell us what this show meant? HAMLET Ay, or any show that you’ll show him: be not you ashamed to show, he’ll not shame to tell you what it means. OPHELIA You are naught, you are naught: I’ll mark the play. Prologue For us, and for our tragedy, Here stooping to your clemency, We beg your hearing patiently. Exit HAMLET Is this a prologue, or the posy of a ring? OPHELIA ‘Tis brief, my lord. HAMLET As woman’s love. Enter two Players, King and Queen Player King Full thirty times hath Phoebus’ cart gone round Neptune’s salt wash and Tellus’ orbed ground, And thirty dozen moons with borrow’d sheen About the world have times twelve thirties been, Since love our hearts and Hymen did our hands Unite commutual in most sacred bands. Player Queen So many journeys may the sun and moon Make us again count o’er ere love be done! But, woe is me, you are so sick of late, So far from cheer and from your former state, That I distrust you. Yet, though I distrust, Discomfort you, my lord, it nothing must: For women’s fear and love holds quantity; In neither aught, or in extremity. Now, what my love is, proof hath made you know; And as my love is sized, my fear is so: Where love is great, the littlest doubts are fear; Where little fears grow great, great love grows there. Player King ‘Faith, I must leave thee, love, and shortly too; My operant powers their functions leave to do: And thou shalt live in this fair world behind, Honour’d, beloved; and haply one as kind For husband shalt thou– Player Queen O, confound the rest! Such love must needs be treason in my breast: In second husband let me be accurst! None wed the second but who kill’d the first. HAMLET [Aside] Wormwood, wormwood. Player Queen The instances that second marriage move Are base respects of thrift, but none of love: A second time I kill my husband dead, When second husband kisses me in bed. Player King I do believe you think what now you speak; But what we do determine oft we break. Purpose is but the slave to memory, Of violent birth, but poor validity; Which now, like fruit unripe, sticks on the tree; But fall, unshaken, when they mellow be. Most necessary ’tis that we forget To pay ourselves what to ourselves is debt: What to ourselves in passion we propose, The passion ending, doth the purpose lose. The violence of either grief or joy Their own enactures with themselves destroy: Where joy most revels, grief doth most lament; Grief joys, joy grieves, on slender accident. This world is not for aye, nor ’tis not strange That even our loves should with our fortunes change; For ’tis a question left us yet to prove, Whether love lead fortune, or else fortune love. The great man down, you mark his favourite flies; The poor advanced makes friends of enemies. And hitherto doth love on fortune tend; For who not needs shall never lack a friend, And who in want a hollow friend doth try, Directly seasons him his enemy. But, orderly to end where I begun, Our wills and fates do so contrary run That our devices still are overthrown; Our thoughts are ours, their ends none of our own: So think thou wilt no second husband wed; But die thy thoughts when thy first lord is dead. Player Queen Nor earth to me give food, nor heaven light! Sport and repose lock from me day and night! To desperation turn my trust and hope! An anchor’s cheer in prison be my scope! Each opposite that blanks the face of joy Meet what I would have well and it destroy! Both here and hence pursue me lasting strife, If, once a widow, ever I be wife! HAMLET If she should break it now! Player King ‘Tis deeply sworn. Sweet, leave me here awhile; My spirits grow dull, and fain I would beguile The tedious day with sleep. Sleeps Player Queen Sleep rock thy brain, And never come mischance between us twain! Exit HAMLET Madam, how like you this play? QUEEN GERTRUDE The lady protests too much, methinks. HAMLET O, but she’ll keep her word. KING CLAUDIUS Have you heard the argument? Is there no offence in ‘t? HAMLET No, no, they do but jest, poison in jest; no offence i’ the world. KING CLAUDIUS What do you call the play? HAMLET The Mouse-trap. Marry, how? Tropically. This play is the image of a murder done in Vienna: Gonzago is the duke’s name; his wife, Baptista: you shall see anon; ’tis a knavish piece of work: but what o’ that? your majesty and we that have free souls, it touches us not: let the galled jade wince, our withers are unwrung. Enter LUCIANUS This is one Lucianus, nephew to the king. OPHELIA You are as good as a chorus, my lord. HAMLET I could interpret between you and your love, if I could see the puppets dallying. OPHELIA You are keen, my lord, you are keen. HAMLET It would cost you a groaning to take off my edge. OPHELIA Still better, and worse. HAMLET So you must take your husbands. Begin, murderer; pox, leave thy damnable faces, and begin. Come: ‘the croaking raven doth bellow for revenge.’ LUCIANUS Thoughts black, hands apt, drugs fit, and time agreeing; Confederate season, else no creature seeing; Thou mixture rank, of midnight weeds collected, With Hecate’s ban thrice blasted, thrice infected, Thy natural magic and dire property, On wholesome life usurp immediately. Pours the poison into the sleeper’s ears HAMLET He poisons him i’ the garden for’s estate. His name’s Gonzago: the story is extant, and writ in choice Italian: you shall see anon how the murderer gets the love of Gonzago’s wife. OPHELIA The king rises. HAMLET What, frighted with false fire! QUEEN GERTRUDE How fares my lord? LORD POLONIUS Give o’er the play. KING CLAUDIUS Give me some light: away! All Lights, lights, lights! Exeunt all but HAMLET and HORATIO HAMLET Why, let the stricken deer go weep, The hart ungalled play; For some must watch, while some must sleep: So runs the world away. Would not this, sir, and a forest of feathers– if the rest of my fortunes turn Turk with me–with two Provincial roses on my razed shoes, get me a fellowship in a cry of players, sir? HORATIO Half a share. HAMLET A whole one, I. For thou dost know, O Damon dear, This realm dismantled was Of Jove himself; and now reigns here A very, very–pajock. HORATIO You might have rhymed. HAMLET O good Horatio, I’ll take the ghost’s word for a thousand pound. Didst perceive? HORATIO Very well, my lord. HAMLET Upon the talk of the poisoning? HORATIO I did very well note him. HAMLET Ah, ha! Come, some music! come, the recorders! For if the king like not the comedy, Why then, belike, he likes it not, perdy. Come, some music! Re-enter ROSENCRANTZ and GUILDENSTERN GUILDENSTERN Good my lord, vouchsafe me a word with you. HAMLET Sir, a whole history. GUILDENSTERN The king, sir,– HAMLET Ay, sir, what of him? GUILDENSTERN Is in his retirement marvellous distempered. HAMLET With drink, sir? GUILDENSTERN No, my lord, rather with choler. HAMLET Your wisdom should show itself more richer to signify this to his doctor; for, for me to put him to his purgation would perhaps plunge him into far more choler. GUILDENSTERN Good my lord, put your discourse into some frame and start not so wildly from my affair. HAMLET I am tame, sir: pronounce. GUILDENSTERN The queen, your mother, in most great affliction of spirit, hath sent me to you. HAMLET You are welcome. GUILDENSTERN Nay, good my lord, this courtesy is not of the right breed. If it shall please you to make me a wholesome answer, I will do your mother’s commandment: if not, your pardon and my return shall be the end of my business. HAMLET Sir, I cannot. GUILDENSTERN What, my lord? HAMLET Make you a wholesome answer; my wit’s diseased: but, sir, such answer as I can make, you shall command; or, rather, as you say, my mother: therefore no more, but to the matter: my mother, you say,– ROSENCRANTZ Then thus she says; your behavior hath struck her into amazement and admiration. HAMLET O wonderful son, that can so astonish a mother! But is there no sequel at the heels of this mother’s admiration? Impart. ROSENCRANTZ She desires to speak with you in her closet, ere you go to bed. HAMLET We shall obey, were she ten times our mother. Have you any further trade with us? ROSENCRANTZ My lord, you once did love me. HAMLET So I do still, by these pickers and stealers. ROSENCRANTZ Good my lord, what is your cause of distemper? you do, surely, bar the door upon your own liberty, if you deny your griefs to your friend. HAMLET Sir, I lack advancement. ROSENCRANTZ How can that be, when you have the voice of the king himself for your succession in Denmark? HAMLET Ay, but sir, ‘While the grass grows,’–the proverb is something musty. Re-enter Players with recorders O, the recorders! let me see one. To withdraw with you:–why do you go about to recover the wind of me, as if you would drive me into a toil? GUILDENSTERN O, my lord, if my duty be too bold, my love is too unmannerly. HAMLET I do not well understand that. Will you play upon this pipe? GUILDENSTERN My lord, I cannot. HAMLET I pray you. GUILDENSTERN Believe me, I cannot. HAMLET I do beseech you. GUILDENSTERN I know no touch of it, my lord. HAMLET ‘Tis as easy as lying: govern these ventages with your lingers and thumb, give it breath with your mouth, and it will discourse most eloquent music. Look you, these are the stops. GUILDENSTERN But these cannot I command to any utterance of harmony; I have not the skill. HAMLET Why, look you now, how unworthy a thing you make of me! You would play upon me; you would seem to know my stops; you would pluck out the heart of my mystery; you would sound me from my lowest note to the top of my compass: and there is much music, excellent voice, in this little organ; yet cannot you make it speak. ‘Sblood, do you think I am easier to be played on than a pipe? Call me what instrument you will, though you can fret me, yet you cannot play upon me. Enter POLONIUS God bless you, sir! LORD POLONIUS My lord, the queen would speak with you, and presently. HAMLET Do you see yonder cloud that’s almost in shape of a camel? LORD POLONIUS By the mass, and ’tis like a camel, indeed. HAMLET Methinks it is like a weasel. LORD POLONIUS It is backed like a weasel. HAMLET Or like a whale? LORD POLONIUS Very like a whale. HAMLET Then I will come to my mother by and by. They fool me to the top of my bent. I will come by and by. LORD POLONIUS I will say so. HAMLET By and by is easily said. Exit POLONIUS Leave me, friends. Exeunt all but HAMLET Tis now the very witching time of night, When churchyards yawn and hell itself breathes out Contagion to this world: now could I drink hot blood, And do such bitter business as the day Would quake to look on. Soft! now to my mother. O heart, lose not thy nature; let not ever The soul of Nero enter this firm bosom: Let me be cruel, not unnatural: I will speak daggers to her, but use none; My tongue and soul in this be hypocrites; How in my words soever she be shent, To give them seals never, my soul, consent! Exit
SCENE III. A room in the castle.
Enter KING CLAUDIUS, ROSENCRANTZ, and GUILDENSTERN KING CLAUDIUS I like him not, nor stands it safe with us To let his madness range. Therefore prepare you; I your commission will forthwith dispatch, And he to England shall along with you: The terms of our estate may not endure Hazard so dangerous as doth hourly grow Out of his lunacies. GUILDENSTERN We will ourselves provide: Most holy and religious fear it is To keep those many many bodies safe That live and feed upon your majesty. ROSENCRANTZ The single and peculiar life is bound, With all the strength and armour of the mind, To keep itself from noyance; but much more That spirit upon whose weal depend and rest The lives of many. The cease of majesty Dies not alone; but, like a gulf, doth draw What’s near it with it: it is a massy wheel, Fix’d on the summit of the highest mount, To whose huge spokes ten thousand lesser things Are mortised and adjoin’d; which, when it falls, Each small annexment, petty consequence, Attends the boisterous ruin. Never alone Did the king sigh, but with a general groan. KING CLAUDIUS Arm you, I pray you, to this speedy voyage; For we will fetters put upon this fear, Which now goes too free-footed. ROSENCRANTZ We will haste us. Exeunt ROSENCRANTZ and GUILDENSTERN Enter POLONIUS LORD POLONIUS My lord, he’s going to his mother’s closet: Behind the arras I’ll convey myself, To hear the process; and warrant she’ll tax him home: And, as you said, and wisely was it said, ‘Tis meet that some more audience than a mother, Since nature makes them partial, should o’erhear The speech, of vantage. Fare you well, my liege: I’ll call upon you ere you go to bed, And tell you what I know. KING CLAUDIUS Thanks, dear my lord. Exit POLONIUS O, my offence is rank it smells to heaven; It hath the primal eldest curse upon’t, A brother’s murder. Pray can I not, Though inclination be as sharp as will: My stronger guilt defeats my strong intent; And, like a man to double business bound, I stand in pause where I shall first begin, And both neglect. What if this cursed hand Were thicker than itself with brother’s blood, Is there not rain enough in the sweet heavens To wash it white as snow? Whereto serves mercy But to confront the visage of offence? And what’s in prayer but this two-fold force, To be forestalled ere we come to fall, Or pardon’d being down? Then I’ll look up; My fault is past. But, O, what form of prayer Can serve my turn? ‘Forgive me my foul murder’? That cannot be; since I am still possess’d Of those effects for which I did the murder, My crown, mine own ambition and my queen. May one be pardon’d and retain the offence? In the corrupted currents of this world Offence’s gilded hand may shove by justice, And oft ’tis seen the wicked prize itself Buys out the law: but ’tis not so above; There is no shuffling, there the action lies In his true nature; and we ourselves compell’d, Even to the teeth and forehead of our faults, To give in evidence. What then? what rests? Try what repentance can: what can it not? Yet what can it when one can not repent? O wretched state! O bosom black as death! O limed soul, that, struggling to be free, Art more engaged! Help, angels! Make assay! Bow, stubborn knees; and, heart with strings of steel, Be soft as sinews of the newborn babe! All may be well. Retires and kneels Enter HAMLET HAMLET Now might I do it pat, now he is praying; And now I’ll do’t. And so he goes to heaven; And so am I revenged. That would be scann’d: A villain kills my father; and for that, I, his sole son, do this same villain send To heaven. O, this is hire and salary, not revenge. He took my father grossly, full of bread; With all his crimes broad blown, as flush as May; And how his audit stands who knows save heaven? But in our circumstance and course of thought, ‘Tis heavy with him: and am I then revenged, To take him in the purging of his soul, When he is fit and season’d for his passage? No! Up, sword; and know thou a more horrid hent: When he is drunk asleep, or in his rage, Or in the incestuous pleasure of his bed; At gaming, swearing, or about some act That has no relish of salvation in’t; Then trip him, that his heels may kick at heaven, And that his soul may be as damn’d and black As hell, whereto it goes. My mother stays: This physic but prolongs thy sickly days. Exit KING CLAUDIUS [Rising] My words fly up, my thoughts remain below: Words without thoughts never to heaven go. Exit
SCENE IV. The Queen’s closet.
Enter QUEEN GERTRUDE and POLONIUS LORD POLONIUS He will come straight. Look you lay home to him: Tell him his pranks have been too broad to bear with, And that your grace hath screen’d and stood between Much heat and him. I’ll sconce me even here. Pray you, be round with him. HAMLET [Within] Mother, mother, mother! QUEEN GERTRUDE I’ll warrant you, Fear me not: withdraw, I hear him coming. POLONIUS hides behind the arras Enter HAMLET HAMLET Now, mother, what’s the matter? QUEEN GERTRUDE Hamlet, thou hast thy father much offended. HAMLET Mother, you have my father much offended. QUEEN GERTRUDE Come, come, you answer with an idle tongue. HAMLET Go, go, you question with a wicked tongue. QUEEN GERTRUDE Why, how now, Hamlet! HAMLET What’s the matter now? QUEEN GERTRUDE Have you forgot me? HAMLET No, by the rood, not so: You are the queen, your husband’s brother’s wife; And–would it were not so!–you are my mother. QUEEN GERTRUDE Nay, then, I’ll set those to you that can speak. HAMLET Come, come, and sit you down; you shall not budge; You go not till I set you up a glass Where you may see the inmost part of you. QUEEN GERTRUDE What wilt thou do? thou wilt not murder me? Help, help, ho! LORD POLONIUS [Behind] What, ho! help, help, help! HAMLET [Drawing] How now! a rat? Dead, for a ducat, dead! Makes a pass through the arras LORD POLONIUS [Behind] O, I am slain! Falls and dies QUEEN GERTRUDE O me, what hast thou done? HAMLET Nay, I know not: Is it the king? QUEEN GERTRUDE O, what a rash and bloody deed is this! HAMLET A bloody deed! almost as bad, good mother, As kill a king, and marry with his brother. QUEEN GERTRUDE As kill a king! HAMLET Ay, lady, ’twas my word. Lifts up the array and discovers POLONIUS Thou wretched, rash, intruding fool, farewell! I took thee for thy better: take thy fortune; Thou find’st to be too busy is some danger. Leave wringing of your hands: peace! sit you down, And let me wring your heart; for so I shall, If it be made of penetrable stuff, If damned custom have not brass’d it so That it is proof and bulwark against sense. QUEEN GERTRUDE What have I done, that thou darest wag thy tongue In noise so rude against me? HAMLET Such an act That blurs the grace and blush of modesty, Calls virtue hypocrite, takes off the rose From the fair forehead of an innocent love And sets a blister there, makes marriage-vows As false as dicers’ oaths: O, such a deed As from the body of contraction plucks The very soul, and sweet religion makes A rhapsody of words: heaven’s face doth glow: Yea, this solidity and compound mass, With tristful visage, as against the doom, Is thought-sick at the act. QUEEN GERTRUDE Ay me, what act, That roars so loud, and thunders in the index? HAMLET Look here, upon this picture, and on this, The counterfeit presentment of two brothers. See, what a grace was seated on this brow; Hyperion’s curls; the front of Jove himself; An eye like Mars, to threaten and command; A station like the herald Mercury New-lighted on a heaven-kissing hill; A combination and a form indeed, Where every god did seem to set his seal, To give the world assurance of a man: This was your husband. Look you now, what follows: Here is your husband; like a mildew’d ear, Blasting his wholesome brother. Have you eyes? Could you on this fair mountain leave to feed, And batten on this moor? Ha! have you eyes? You cannot call it love; for at your age The hey-day in the blood is tame, it’s humble, And waits upon the judgment: and what judgment Would step from this to this? Sense, sure, you have, Else could you not have motion; but sure, that sense Is apoplex’d; for madness would not err, Nor sense to ecstasy was ne’er so thrall’d But it reserved some quantity of choice, To serve in such a difference. What devil was’t That thus hath cozen’d you at hoodman-blind? Eyes without feeling, feeling without sight, Ears without hands or eyes, smelling sans all, Or but a sickly part of one true sense Could not so mope. O shame! where is thy blush? Rebellious hell, If thou canst mutine in a matron’s bones, To flaming youth let virtue be as wax, And melt in her own fire: proclaim no shame When the compulsive ardour gives the charge, Since frost itself as actively doth burn And reason panders will. QUEEN GERTRUDE O Hamlet, speak no more: Thou turn’st mine eyes into my very soul; And there I see such black and grained spots As will not leave their tinct. HAMLET Nay, but to live In the rank sweat of an enseamed bed, Stew’d in corruption, honeying and making love Over the nasty sty,– QUEEN GERTRUDE O, speak to me no more; These words, like daggers, enter in mine ears; No more, sweet Hamlet! HAMLET A murderer and a villain; A slave that is not twentieth part the tithe Of your precedent lord; a vice of kings; A cutpurse of the empire and the rule, That from a shelf the precious diadem stole, And put it in his pocket! QUEEN GERTRUDE No more! HAMLET A king of shreds and patches,– Enter Ghost Save me, and hover o’er me with your wings, You heavenly guards! What would your gracious figure? QUEEN GERTRUDE Alas, he’s mad! HAMLET Do you not come your tardy son to chide, That, lapsed in time and passion, lets go by The important acting of your dread command? O, say! Ghost Do not forget: this visitation Is but to whet thy almost blunted purpose. But, look, amazement on thy mother sits: O, step between her and her fighting soul: Conceit in weakest bodies strongest works: Speak to her, Hamlet. HAMLET How is it with you, lady? QUEEN GERTRUDE Alas, how is’t with you, That you do bend your eye on vacancy And with the incorporal air do hold discourse? Forth at your eyes your spirits wildly peep; And, as the sleeping soldiers in the alarm, Your bedded hair, like life in excrements, Starts up, and stands on end. O gentle son, Upon the heat and flame of thy distemper Sprinkle cool patience. Whereon do you look? HAMLET On him, on him! Look you, how pale he glares! His form and cause conjoin’d, preaching to stones, Would make them capable. Do not look upon me; Lest with this piteous action you convert My stern effects: then what I have to do Will want true colour; tears perchance for blood. QUEEN GERTRUDE To whom do you speak this? HAMLET Do you see nothing there? QUEEN GERTRUDE Nothing at all; yet all that is I see. HAMLET Nor did you nothing hear? QUEEN GERTRUDE No, nothing but ourselves. HAMLET Why, look you there! look, how it steals away! My father, in his habit as he lived! Look, where he goes, even now, out at the portal! Exit Ghost QUEEN GERTRUDE This the very coinage of your brain: This bodiless creation ecstasy Is very cunning in. HAMLET Ecstasy! My pulse, as yours, doth temperately keep time, And makes as healthful music: it is not madness That I have utter’d: bring me to the test, And I the matter will re-word; which madness Would gambol from. Mother, for love of grace, Lay not that mattering unction to your soul, That not your trespass, but my madness speaks: It will but skin and film the ulcerous place, Whilst rank corruption, mining all within, Infects unseen. Confess yourself to heaven; Repent what’s past; avoid what is to come; And do not spread the compost on the weeds, To make them ranker. Forgive me this my virtue; For in the fatness of these pursy times Virtue itself of vice must pardon beg, Yea, curb and woo for leave to do him good. QUEEN GERTRUDE O Hamlet, thou hast cleft my heart in twain. HAMLET O, throw away the worser part of it, And live the purer with the other half. Good night: but go not to mine uncle’s bed; Assume a virtue, if you have it not. That monster, custom, who all sense doth eat, Of habits devil, is angel yet in this, That to the use of actions fair and good He likewise gives a frock or livery, That aptly is put on. Refrain to-night, And that shall lend a kind of easiness To the next abstinence: the next more easy; For use almost can change the stamp of nature, And either [ ] the devil, or throw him out With wondrous potency. Once more, good night: And when you are desirous to be bless’d, I’ll blessing beg of you. For this same lord, Pointing to POLONIUS I do repent: but heaven hath pleased it so, To punish me with this and this with me, That I must be their scourge and minister. I will bestow him, and will answer well The death I gave him. So, again, good night. I must be cruel, only to be kind: Thus bad begins and worse remains behind. One word more, good lady. QUEEN GERTRUDE What shall I do? HAMLET Not this, by no means, that I bid you do: Let the bloat king tempt you again to bed; Pinch wanton on your cheek; call you his mouse; And let him, for a pair of reechy kisses, Or paddling in your neck with his damn’d fingers, Make you to ravel all this matter out, That I essentially am not in madness, But mad in craft. ‘Twere good you let him know; For who, that’s but a queen, fair, sober, wise, Would from a paddock, from a bat, a gib, Such dear concernings hide? who would do so? No, in despite of sense and secrecy, Unpeg the basket on the house’s top. Let the birds fly, and, like the famous ape, To try conclusions, in the basket creep, And break your own neck down. QUEEN GERTRUDE Be thou assured, if words be made of breath, And breath of life, I have no life to breathe What thou hast said to me. HAMLET I must to England; you know that? QUEEN GERTRUDE Alack, I had forgot: ’tis so concluded on. HAMLET There’s letters seal’d: and my two schoolfellows, Whom I will trust as I will adders fang’d, They bear the mandate; they must sweep my way, And marshal me to knavery. Let it work; For ’tis the sport to have the engineer Hoist with his own petard: and ‘t shall go hard But I will delve one yard below their mines, And blow them at the moon: O, ’tis most sweet, When in one line two crafts directly meet. This man shall set me packing: I’ll lug the guts into the neighbour room. Mother, good night. Indeed this counsellor Is now most still, most secret and most grave, Who was in life a foolish prating knave. Come, sir, to draw toward an end with you. Good night, mother. Exeunt severally; HAMLET dragging in POLONIUS
Enter KING CLAUDIUS, QUEEN GERTRUDE, ROSENCRANTZ, and GUILDENSTERN KING CLAUDIUS There’s matter in these sighs, these profound heaves: You must translate: ’tis fit we understand them. Where is your son? QUEEN GERTRUDE Bestow this place on us a little while. Exeunt ROSENCRANTZ and GUILDENSTERN Ah, my good lord, what have I seen to-night! KING CLAUDIUS What, Gertrude? How does Hamlet? QUEEN GERTRUDE Mad as the sea and wind, when both contend Which is the mightier: in his lawless fit, Behind the arras hearing something stir, Whips out his rapier, cries, ‘A rat, a rat!’ And, in this brainish apprehension, kills The unseen good old man. KING CLAUDIUS O heavy deed! It had been so with us, had we been there: His liberty is full of threats to all; To you yourself, to us, to every one. Alas, how shall this bloody deed be answer’d? It will be laid to us, whose providence Should have kept short, restrain’d and out of haunt, This mad young man: but so much was our love, We would not understand what was most fit; But, like the owner of a foul disease, To keep it from divulging, let it feed Even on the pith of Life. Where is he gone? QUEEN GERTRUDE To draw apart the body he hath kill’d: O’er whom his very madness, like some ore Among a mineral of metals base, Shows itself pure; he weeps for what is done. KING CLAUDIUS O Gertrude, come away! The sun no sooner shall the mountains touch, But we will ship him hence: and this vile deed We must, with all our majesty and skill, Both countenance and excuse. Ho, Guildenstern! Re-enter ROSENCRANTZ and GUILDENSTERN Friends both, go join you with some further aid: Hamlet in madness hath Polonius slain, And from his mother’s closet hath he dragg’d him: Go seek him out; speak fair, and bring the body Into the chapel. I pray you, haste in this. Exeunt ROSENCRANTZ and GUILDENSTERN Come, Gertrude, we’ll call up our wisest friends; And let them know, both what we mean to do, And what’s untimely done. O, come away! My soul is full of discord and dismay. Exeunt
SCENE II. Another room in the castle.
Enter HAMLET HAMLET Safely stowed. ROSENCRANTZ: [Within] Hamlet! Lord Hamlet! HAMLET What noise? who calls on Hamlet? O, here they come. Enter ROSENCRANTZ and GUILDENSTERN ROSENCRANTZ What have you done, my lord, with the dead body? HAMLET Compounded it with dust, whereto ’tis kin. ROSENCRANTZ Tell us where ’tis, that we may take it thence And bear it to the chapel. HAMLET Do not believe it. ROSENCRANTZ Believe what? HAMLET That I can keep your counsel and not mine own. Besides, to be demanded of a sponge! what replication should be made by the son of a king? ROSENCRANTZ Take you me for a sponge, my lord? HAMLET Ay, sir, that soaks up the king’s countenance, his rewards, his authorities. But such officers do the king best service in the end: he keeps them, like an ape, in the corner of his jaw; first mouthed, to be last swallowed: when he needs what you have gleaned, it is but squeezing you, and, sponge, you shall be dry again. ROSENCRANTZ I understand you not, my lord. HAMLET I am glad of it: a knavish speech sleeps in a foolish ear. ROSENCRANTZ My lord, you must tell us where the body is, and go with us to the king. HAMLET The body is with the king, but the king is not with the body. The king is a thing– GUILDENSTERN A thing, my lord! HAMLET Of nothing: bring me to him. Hide fox, and all after. Exeunt
SCENE III. Another room in the castle.
Enter KING CLAUDIUS, attended KING CLAUDIUS I have sent to seek him, and to find the body. How dangerous is it that this man goes loose! Yet must not we put the strong law on him: He’s loved of the distracted multitude, Who like not in their judgment, but their eyes; And where tis so, the offender’s scourge is weigh’d, But never the offence. To bear all smooth and even, This sudden sending him away must seem Deliberate pause: diseases desperate grown By desperate appliance are relieved, Or not at all. Enter ROSENCRANTZ How now! what hath befall’n? ROSENCRANTZ Where the dead body is bestow’d, my lord, We cannot get from him. KING CLAUDIUS But where is he? ROSENCRANTZ Without, my lord; guarded, to know your pleasure. KING CLAUDIUS Bring him before us. ROSENCRANTZ Ho, Guildenstern! bring in my lord. Enter HAMLET and GUILDENSTERN KING CLAUDIUS Now, Hamlet, where’s Polonius? HAMLET At supper. KING CLAUDIUS At supper! where? HAMLET Not where he eats, but where he is eaten: a certain convocation of politic worms are e’en at him. Your worm is your only emperor for diet: we fat all creatures else to fat us, and we fat ourselves for maggots: your fat king and your lean beggar is but variable service, two dishes, but to one table: that’s the end. KING CLAUDIUS Alas, alas! HAMLET A man may fish with the worm that hath eat of a king, and eat of the fish that hath fed of that worm. KING CLAUDIUS What dost you mean by this? HAMLET Nothing but to show you how a king may go a progress through the guts of a beggar. KING CLAUDIUS Where is Polonius? HAMLET In heaven; send hither to see: if your messenger find him not there, seek him i’ the other place yourself. But indeed, if you find him not within this month, you shall nose him as you go up the stairs into the lobby. KING CLAUDIUS Go seek him there. To some Attendants HAMLET He will stay till ye come. Exeunt Attendants KING CLAUDIUS Hamlet, this deed, for thine especial safety,– Which we do tender, as we dearly grieve For that which thou hast done,–must send thee hence With fiery quickness: therefore prepare thyself; The bark is ready, and the wind at help, The associates tend, and every thing is bent For England. HAMLET For England! KING CLAUDIUS Ay, Hamlet. HAMLET Good. KING CLAUDIUS So is it, if thou knew’st our purposes. HAMLET I see a cherub that sees them. But, come; for England! Farewell, dear mother. KING CLAUDIUS Thy loving father, Hamlet. HAMLET My mother: father and mother is man and wife; man and wife is one flesh; and so, my mother. Come, for England! Exit KING CLAUDIUS Follow him at foot; tempt him with speed aboard; Delay it not; I’ll have him hence to-night: Away! for every thing is seal’d and done That else leans on the affair: pray you, make haste. Exeunt ROSENCRANTZ and GUILDENSTERN And, England, if my love thou hold’st at aught– As my great power thereof may give thee sense, Since yet thy cicatrice looks raw and red After the Danish sword, and thy free awe Pays homage to us–thou mayst not coldly set Our sovereign process; which imports at full, By letters congruing to that effect, The present death of Hamlet. Do it, England; For like the hectic in my blood he rages, And thou must cure me: till I know ’tis done, Howe’er my haps, my joys were ne’er begun. Exit
SCENE IV. A plain in Denmark.
Enter FORTINBRAS, a Captain, and Soldiers, marching PRINCE FORTINBRAS Go, captain, from me greet the Danish king; Tell him that, by his licence, Fortinbras Craves the conveyance of a promised march Over his kingdom. You know the rendezvous. If that his majesty would aught with us, We shall express our duty in his eye; And let him know so. Captain I will do’t, my lord. PRINCE FORTINBRAS Go softly on. Exeunt FORTINBRAS and Soldiers Enter HAMLET, ROSENCRANTZ, GUILDENSTERN, and others HAMLET Good sir, whose powers are these? Captain They are of Norway, sir. HAMLET How purposed, sir, I pray you? Captain Against some part of Poland. HAMLET Who commands them, sir? Captain The nephews to old Norway, Fortinbras. HAMLET Goes it against the main of Poland, sir, Or for some frontier? Captain Truly to speak, and with no addition, We go to gain a little patch of ground That hath in it no profit but the name. To pay five ducats, five, I would not farm it; Nor will it yield to Norway or the Pole A ranker rate, should it be sold in fee. HAMLET Why, then the Polack never will defend it. Captain Yes, it is already garrison’d. HAMLET Two thousand souls and twenty thousand ducats Will not debate the question of this straw: This is the imposthume of much wealth and peace, That inward breaks, and shows no cause without Why the man dies. I humbly thank you, sir. Captain God be wi’ you, sir. Exit ROSENCRANTZ Wilt please you go, my lord? HAMLET I’ll be with you straight go a little before. Exeunt all except HAMLET How all occasions do inform against me, And spur my dull revenge! What is a man, If his chief good and market of his time Be but to sleep and feed? a beast, no more. Sure, he that made us with such large discourse, Looking before and after, gave us not That capability and god-like reason To fust in us unused. Now, whether it be Bestial oblivion, or some craven scruple Of thinking too precisely on the event, A thought which, quarter’d, hath but one part wisdom And ever three parts coward, I do not know Why yet I live to say ‘This thing’s to do;’ Sith I have cause and will and strength and means To do’t. Examples gross as earth exhort me: Witness this army of such mass and charge Led by a delicate and tender prince, Whose spirit with divine ambition puff’d Makes mouths at the invisible event, Exposing what is mortal and unsure To all that fortune, death and danger dare, Even for an egg-shell. Rightly to be great Is not to stir without great argument, But greatly to find quarrel in a straw When honour’s at the stake. How stand I then, That have a father kill’d, a mother stain’d, Excitements of my reason and my blood, And let all sleep? while, to my shame, I see The imminent death of twenty thousand men, That, for a fantasy and trick of fame, Go to their graves like beds, fight for a plot Whereon the numbers cannot try the cause, Which is not tomb enough and continent To hide the slain? O, from this time forth, My thoughts be bloody, or be nothing worth! Exit
SCENE V. Elsinore. A room in the castle.
Enter QUEEN GERTRUDE, HORATIO, and a Gentleman QUEEN GERTRUDE I will not speak with her. Gentleman She is importunate, indeed distract: Her mood will needs be pitied. QUEEN GERTRUDE What would she have? Gentleman She speaks much of her father; says she hears There’s tricks i’ the world; and hems, and beats her heart; Spurns enviously at straws; speaks things in doubt, That carry but half sense: her speech is nothing, Yet the unshaped use of it doth move The hearers to collection; they aim at it, And botch the words up fit to their own thoughts; Which, as her winks, and nods, and gestures yield them, Indeed would make one think there might be thought, Though nothing sure, yet much unhappily. HORATIO ‘Twere good she were spoken with; for she may strew Dangerous conjectures in ill-breeding minds. QUEEN GERTRUDE Let her come in. Exit HORATIO To my sick soul, as sin’s true nature is, Each toy seems prologue to some great amiss: So full of artless jealousy is guilt, It spills itself in fearing to be spilt. Re-enter HORATIO, with OPHELIA OPHELIA Where is the beauteous majesty of Denmark? QUEEN GERTRUDE How now, Ophelia! OPHELIA [Sings] How should I your true love know From another one? By his cockle hat and staff, And his sandal shoon. QUEEN GERTRUDE Alas, sweet lady, what imports this song? OPHELIA Say you? nay, pray you, mark. Sings He is dead and gone, lady, He is dead and gone; At his head a grass-green turf, At his heels a stone. QUEEN GERTRUDE Nay, but, Ophelia,– OPHELIA Pray you, mark. Sings White his shroud as the mountain snow,– Enter KING CLAUDIUS QUEEN GERTRUDE Alas, look here, my lord. OPHELIA [Sings] Larded with sweet flowers Which bewept to the grave did go With true-love showers. KING CLAUDIUS How do you, pretty lady? OPHELIA Well, God ‘ild you! They say the owl was a baker’s daughter. Lord, we know what we are, but know not what we may be. God be at your table! KING CLAUDIUS Conceit upon her father. OPHELIA Pray you, let’s have no words of this; but when they ask you what it means, say you this: Sings To-morrow is Saint Valentine’s day, All in the morning betime, And I a maid at your window, To be your Valentine. Then up he rose, and donn’d his clothes, And dupp’d the chamber-door; Let in the maid, that out a maid Never departed more. KING CLAUDIUS Pretty Ophelia! OPHELIA Indeed, la, without an oath, I’ll make an end on’t: Sings By Gis and by Saint Charity, Alack, and fie for shame! Young men will do’t, if they come to’t; By cock, they are to blame. Quoth she, before you tumbled me, You promised me to wed. So would I ha’ done, by yonder sun, An thou hadst not come to my bed. KING CLAUDIUS How long hath she been thus? OPHELIA I hope all will be well. We must be patient: but I cannot choose but weep, to think they should lay him i’ the cold ground. My brother shall know of it: and so I thank you for your good counsel. Come, my coach! Good night, ladies; good night, sweet ladies; good night, good night. Exit KING CLAUDIUS Follow her close; give her good watch, I pray you. Exit HORATIO O, this is the poison of deep grief; it springs All from her father’s death. O Gertrude, Gertrude, When sorrows come, they come not single spies But in battalions. First, her father slain: Next, your son gone; and he most violent author Of his own just remove: the people muddied, Thick and unwholesome in their thoughts and whispers, For good Polonius’ death; and we have done but greenly, In hugger-mugger to inter him: poor Ophelia Divided from herself and her fair judgment, Without the which we are pictures, or mere beasts: Last, and as much containing as all these, Her brother is in secret come from France; Feeds on his wonder, keeps himself in clouds, And wants not buzzers to infect his ear With pestilent speeches of his father’s death; Wherein necessity, of matter beggar’d, Will nothing stick our person to arraign In ear and ear. O my dear Gertrude, this, Like to a murdering-piece, in many places Gives me superfluous death. A noise within QUEEN GERTRUDE Alack, what noise is this? KING CLAUDIUS Where are my Switzers? Let them guard the door. Enter another Gentleman What is the matter? Gentleman Save yourself, my lord: The ocean, overpeering of his list, Eats not the flats with more impetuous haste Than young Laertes, in a riotous head, O’erbears your officers. The rabble call him lord; And, as the world were now but to begin, Antiquity forgot, custom not known, The ratifiers and props of every word, They cry ‘Choose we: Laertes shall be king:’ Caps, hands, and tongues, applaud it to the clouds: ‘Laertes shall be king, Laertes king!’ QUEEN GERTRUDE How cheerfully on the false trail they cry! O, this is counter, you false Danish dogs! KING CLAUDIUS The doors are broke. Noise within Enter LAERTES, armed; Danes following LAERTES Where is this king? Sirs, stand you all without. Danes No, let’s come in. LAERTES I pray you, give me leave. Danes We will, we will. They retire without the door LAERTES I thank you: keep the door. O thou vile king, Give me my father! QUEEN GERTRUDE Calmly, good Laertes. LAERTES That drop of blood that’s calm proclaims me bastard, Cries cuckold to my father, brands the harlot Even here, between the chaste unsmirched brow Of my true mother. KING CLAUDIUS What is the cause, Laertes, That thy rebellion looks so giant-like? Let him go, Gertrude; do not fear our person: There’s such divinity doth hedge a king, That treason can but peep to what it would, Acts little of his will. Tell me, Laertes, Why thou art thus incensed. Let him go, Gertrude. Speak, man. LAERTES Where is my father? KING CLAUDIUS Dead. QUEEN GERTRUDE But not by him. KING CLAUDIUS Let him demand his fill. LAERTES How came he dead? I’ll not be juggled with: To hell, allegiance! vows, to the blackest devil! Conscience and grace, to the profoundest pit! I dare damnation. To this point I stand, That both the worlds I give to negligence, Let come what comes; only I’ll be revenged Most thoroughly for my father. KING CLAUDIUS Who shall stay you? LAERTES My will, not all the world: And for my means, I’ll husband them so well, They shall go far with little. KING CLAUDIUS Good Laertes, If you desire to know the certainty Of your dear father’s death, is’t writ in your revenge, That, swoopstake, you will draw both friend and foe, Winner and loser? LAERTES None but his enemies. KING CLAUDIUS Will you know them then? LAERTES To his good friends thus wide I’ll ope my arms; And like the kind life-rendering pelican, Repast them with my blood. KING CLAUDIUS Why, now you speak Like a good child and a true gentleman. That I am guiltless of your father’s death, And am most sensible in grief for it, It shall as level to your judgment pierce As day does to your eye. Danes [Within] Let her come in. LAERTES How now! what noise is that? Re-enter OPHELIA O heat, dry up my brains! tears seven times salt, Burn out the sense and virtue of mine eye! By heaven, thy madness shall be paid by weight, Till our scale turn the beam. O rose of May! Dear maid, kind sister, sweet Ophelia! O heavens! is’t possible, a young maid’s wits Should be as moral as an old man’s life? Nature is fine in love, and where ’tis fine, It sends some precious instance of itself After the thing it loves. OPHELIA [Sings] They bore him barefaced on the bier; Hey non nonny, nonny, hey nonny; And in his grave rain’d many a tear:– Fare you well, my dove! LAERTES Hadst thou thy wits, and didst persuade revenge, It could not move thus. OPHELIA [Sings] You must sing a-down a-down, An you call him a-down-a. O, how the wheel becomes it! It is the false steward, that stole his master’s daughter. LAERTES This nothing’s more than matter. OPHELIA There’s rosemary, that’s for remembrance; pray, love, remember: and there is pansies. that’s for thoughts. LAERTES A document in madness, thoughts and remembrance fitted. OPHELIA There’s fennel for you, and columbines: there’s rue for you; and here’s some for me: we may call it herb-grace o’ Sundays: O you must wear your rue with a difference. There’s a daisy: I would give you some violets, but they withered all when my father died: they say he made a good end,– Sings For bonny sweet Robin is all my joy. LAERTES Thought and affliction, passion, hell itself, She turns to favour and to prettiness. OPHELIA [Sings] And will he not come again? And will he not come again? No, no, he is dead: Go to thy death-bed: He never will come again. His beard was as white as snow, All flaxen was his poll: He is gone, he is gone, And we cast away moan: God ha’ mercy on his soul! And of all Christian souls, I pray God. God be wi’ ye. Exit LAERTES Do you see this, O God? KING CLAUDIUS Laertes, I must commune with your grief, Or you deny me right. Go but apart, Make choice of whom your wisest friends you will. And they shall hear and judge ‘twixt you and me: If by direct or by collateral hand They find us touch’d, we will our kingdom give, Our crown, our life, and all that we can ours, To you in satisfaction; but if not, Be you content to lend your patience to us, And we shall jointly labour with your soul To give it due content. LAERTES Let this be so; His means of death, his obscure funeral– No trophy, sword, nor hatchment o’er his bones, No noble rite nor formal ostentation– Cry to be heard, as ’twere from heaven to earth, That I must call’t in question. KING CLAUDIUS So you shall; And where the offence is let the great axe fall. I pray you, go with me. Exeunt
SCENE VI. Another room in the castle.
Enter HORATIO and a Servant HORATIO What are they that would speak with me? Servant Sailors, sir: they say they have letters for you. HORATIO Let them come in. Exit Servant I do not know from what part of the world I should be greeted, if not from Lord Hamlet. Enter Sailors First Sailor God bless you, sir. HORATIO Let him bless thee too. First Sailor He shall, sir, an’t please him. There’s a letter for you, sir; it comes from the ambassador that was bound for England; if your name be Horatio, as I am let to know it is. HORATIO [Reads] ‘Horatio, when thou shalt have overlooked this, give these fellows some means to the king: they have letters for him. Ere we were two days old at sea, a pirate of very warlike appointment gave us chase. Finding ourselves too slow of sail, we put on a compelled valour, and in the grapple I boarded them: on the instant they got clear of our ship; so I alone became their prisoner. They have dealt with me like thieves of mercy: but they knew what they did; I am to do a good turn for them. Let the king have the letters I have sent; and repair thou to me with as much speed as thou wouldst fly death. I have words to speak in thine ear will make thee dumb; yet are they much too light for the bore of the matter. These good fellows will bring thee where I am. Rosencrantz and Guildenstern hold their course for England: of them I have much to tell thee. Farewell. ‘He that thou knowest thine, HAMLET.’ Come, I will make you way for these your letters; And do’t the speedier, that you may direct me To him from whom you brought them. Exeunt
SCENE VII. Another room in the castle.
Enter KING CLAUDIUS and LAERTES KING CLAUDIUS Now must your conscience my acquaintance seal, And you must put me in your heart for friend, Sith you have heard, and with a knowing ear, That he which hath your noble father slain Pursued my life. LAERTES It well appears: but tell me Why you proceeded not against these feats, So crimeful and so capital in nature, As by your safety, wisdom, all things else, You mainly were stirr’d up. KING CLAUDIUS O, for two special reasons; Which may to you, perhaps, seem much unsinew’d, But yet to me they are strong. The queen his mother Lives almost by his looks; and for myself– My virtue or my plague, be it either which– She’s so conjunctive to my life and soul, That, as the star moves not but in his sphere, I could not but by her. The other motive, Why to a public count I might not go, Is the great love the general gender bear him; Who, dipping all his faults in their affection, Would, like the spring that turneth wood to stone, Convert his gyves to graces; so that my arrows, Too slightly timber’d for so loud a wind, Would have reverted to my bow again, And not where I had aim’d them. LAERTES And so have I a noble father lost; A sister driven into desperate terms, Whose worth, if praises may go back again, Stood challenger on mount of all the age For her perfections: but my revenge will come. KING CLAUDIUS Break not your sleeps for that: you must not think That we are made of stuff so flat and dull That we can let our beard be shook with danger And think it pastime. You shortly shall hear more: I loved your father, and we love ourself; And that, I hope, will teach you to imagine– Enter a Messenger How now! what news? Messenger Letters, my lord, from Hamlet: This to your majesty; this to the queen. KING CLAUDIUS From Hamlet! who brought them? Messenger Sailors, my lord, they say; I saw them not: They were given me by Claudio; he received them Of him that brought them. KING CLAUDIUS Laertes, you shall hear them. Leave us. Exit Messenger Reads ‘High and mighty, You shall know I am set naked on your kingdom. To-morrow shall I beg leave to see your kingly eyes: when I shall, first asking your pardon thereunto, recount the occasion of my sudden and more strange return. ‘HAMLET.’ What should this mean? Are all the rest come back? Or is it some abuse, and no such thing? LAERTES Know you the hand? KING CLAUDIUS ‘Tis Hamlets character. ‘Naked! And in a postscript here, he says ‘alone.’ Can you advise me? LAERTES I’m lost in it, my lord. But let him come; It warms the very sickness in my heart, That I shall live and tell him to his teeth, ‘Thus didest thou.’ KING CLAUDIUS If it be so, Laertes– As how should it be so? how otherwise?– Will you be ruled by me? LAERTES Ay, my lord; So you will not o’errule me to a peace. KING CLAUDIUS To thine own peace. If he be now return’d, As checking at his voyage, and that he means No more to undertake it, I will work him To an exploit, now ripe in my device, Under the which he shall not choose but fall: And for his death no wind of blame shall breathe, But even his mother shall uncharge the practise And call it accident. LAERTES My lord, I will be ruled; The rather, if you could devise it so That I might be the organ. KING CLAUDIUS It falls right. You have been talk’d of since your travel much, And that in Hamlet’s hearing, for a quality Wherein, they say, you shine: your sum of parts Did not together pluck such envy from him As did that one, and that, in my regard, Of the unworthiest siege. LAERTES What part is that, my lord? KING CLAUDIUS A very riband in the cap of youth, Yet needful too; for youth no less becomes The light and careless livery that it wears Than settled age his sables and his weeds, Importing health and graveness. Two months since, Here was a gentleman of Normandy:– I’ve seen myself, and served against, the French, And they can well on horseback: but this gallant Had witchcraft in’t; he grew unto his seat; And to such wondrous doing brought his horse, As he had been incorpsed and demi-natured With the brave beast: so far he topp’d my thought, That I, in forgery of shapes and tricks, Come short of what he did. LAERTES A Norman was’t? KING CLAUDIUS A Norman. LAERTES Upon my life, Lamond. KING CLAUDIUS The very same. LAERTES I know him well: he is the brooch indeed And gem of all the nation. KING CLAUDIUS He made confession of you, And gave you such a masterly report For art and exercise in your defence And for your rapier most especially, That he cried out, ‘twould be a sight indeed, If one could match you: the scrimers of their nation, He swore, had had neither motion, guard, nor eye, If you opposed them. Sir, this report of his Did Hamlet so envenom with his envy That he could nothing do but wish and beg Your sudden coming o’er, to play with him. Now, out of this,– LAERTES What out of this, my lord? KING CLAUDIUS Laertes, was your father dear to you? Or are you like the painting of a sorrow, A face without a heart? LAERTES Why ask you this? KING CLAUDIUS Not that I think you did not love your father; But that I know love is begun by time; And that I see, in passages of proof, Time qualifies the spark and fire of it. There lives within the very flame of love A kind of wick or snuff that will abate it; And nothing is at a like goodness still; For goodness, growing to a plurisy, Dies in his own too much: that we would do We should do when we would; for this ‘would’ changes And hath abatements and delays as many As there are tongues, are hands, are accidents; And then this ‘should’ is like a spendthrift sigh, That hurts by easing. But, to the quick o’ the ulcer:– Hamlet comes back: what would you undertake, To show yourself your father’s son in deed More than in words? LAERTES To cut his throat i’ the church. KING CLAUDIUS No place, indeed, should murder sanctuarize; Revenge should have no bounds. But, good Laertes, Will you do this, keep close within your chamber. Hamlet return’d shall know you are come home: We’ll put on those shall praise your excellence And set a double varnish on the fame The Frenchman gave you, bring you in fine together And wager on your heads: he, being remiss, Most generous and free from all contriving, Will not peruse the foils; so that, with ease, Or with a little shuffling, you may choose A sword unbated, and in a pass of practise Requite him for your father. LAERTES I will do’t: And, for that purpose, I’ll anoint my sword. I bought an unction of a mountebank, So mortal that, but dip a knife in it, Where it draws blood no cataplasm so rare, Collected from all simples that have virtue Under the moon, can save the thing from death That is but scratch’d withal: I’ll touch my point With this contagion, that, if I gall him slightly, It may be death. KING CLAUDIUS Let’s further think of this; Weigh what convenience both of time and means May fit us to our shape: if this should fail, And that our drift look through our bad performance, ‘Twere better not assay’d: therefore this project Should have a back or second, that might hold, If this should blast in proof. Soft! let me see: We’ll make a solemn wager on your cunnings: I ha’t. When in your motion you are hot and dry– As make your bouts more violent to that end– And that he calls for drink, I’ll have prepared him A chalice for the nonce, whereon but sipping, If he by chance escape your venom’d stuck, Our purpose may hold there. Enter QUEEN GERTRUDE How now, sweet queen! QUEEN GERTRUDE One woe doth tread upon another’s heel, So fast they follow; your sister’s drown’d, Laertes. LAERTES Drown’d! O, where? QUEEN GERTRUDE There is a willow grows aslant a brook, That shows his hoar leaves in the glassy stream; There with fantastic garlands did she come Of crow-flowers, nettles, daisies, and long purples That liberal shepherds give a grosser name, But our cold maids do dead men’s fingers call them: There, on the pendent boughs her coronet weeds Clambering to hang, an envious sliver broke; When down her weedy trophies and herself Fell in the weeping brook. Her clothes spread wide; And, mermaid-like, awhile they bore her up: Which time she chanted snatches of old tunes; As one incapable of her own distress, Or like a creature native and indued Unto that element: but long it could not be Till that her garments, heavy with their drink, Pull’d the poor wretch from her melodious lay To muddy death. LAERTES Alas, then, she is drown’d? QUEEN GERTRUDE Drown’d, drown’d. LAERTES Too much of water hast thou, poor Ophelia, And therefore I forbid my tears: but yet It is our trick; nature her custom holds, Let shame say what it will: when these are gone, The woman will be out. Adieu, my lord: I have a speech of fire, that fain would blaze, But that this folly douts it. Exit KING CLAUDIUS Let’s follow, Gertrude: How much I had to do to calm his rage! Now fear I this will give it start again; Therefore let’s follow. Exeunt
SCENE I. A churchyard.
Enter two Clowns, with spades, & c First Clown Is she to be buried in Christian burial that wilfully seeks her own salvation? Second Clown I tell thee she is: and therefore make her grave straight: the crowner hath sat on her, and finds it Christian burial. First Clown How can that be, unless she drowned herself in her own defence? Second Clown Why, ’tis found so. First Clown It must be ‘se offendendo;’ it cannot be else. For here lies the point: if I drown myself wittingly, it argues an act: and an act hath three branches: it is, to act, to do, to perform: argal, she drowned herself wittingly. Second Clown Nay, but hear you, goodman delver,– First Clown Give me leave. Here lies the water; good: here stands the man; good; if the man go to this water, and drown himself, it is, will he, nill he, he goes,–mark you that; but if the water come to him and drown him, he drowns not himself: argal, he that is not guilty of his own death shortens not his own life. Second Clown But is this law? First Clown Ay, marry, is’t; crowner’s quest law. Second Clown Will you ha’ the truth on’t? If this had not been a gentlewoman, she should have been buried out o’ Christian burial. First Clown Why, there thou say’st: and the more pity that great folk should have countenance in this world to drown or hang themselves, more than their even Christian. Come, my spade. There is no ancient gentleman but gardeners, ditchers, and grave-makers: they hold up Adam’s profession. Second Clown Was he a gentleman? First Clown He was the first that ever bore arms. Second Clown Why, he had none. First Clown What, art a heathen? How dost thou understand the Scripture? The Scripture says ‘Adam digged:’ could he dig without arms? I’ll put another question to thee: if thou answerest me not to the purpose, confess thyself– Second Clown Go to. First Clown What is he that builds stronger than either the mason, the shipwright, or the carpenter? Second Clown The gallows-maker; for that frame outlives a thousand tenants. First Clown I like thy wit well, in good faith: the gallows does well; but how does it well? it does well to those that do in: now thou dost ill to say the gallows is built stronger than the church: argal, the gallows may do well to thee. To’t again, come. Second Clown ‘Who builds stronger than a mason, a shipwright, or a carpenter?’ First Clown Ay, tell me that, and unyoke. Second Clown Marry, now I can tell. First Clown To’t. Second Clown Mass, I cannot tell. Enter HAMLET and HORATIO, at a distance First Clown Cudgel thy brains no more about it, for your dull ass will not mend his pace with beating; and, when you are asked this question next, say ‘a grave-maker: ‘the houses that he makes last till doomsday. Go, get thee to Yaughan: fetch me a stoup of liquor. Exit Second Clown He digs and sings In youth, when I did love, did love, Methought it was very sweet, To contract, O, the time, for, ah, my behove, O, methought, there was nothing meet. HAMLET Has this fellow no feeling of his business, that he sings at grave-making? HORATIO Custom hath made it in him a property of easiness. HAMLET ‘Tis e’en so: the hand of little employment hath the daintier sense. First Clown [Sings] But age, with his stealing steps, Hath claw’d me in his clutch, And hath shipped me intil the land, As if I had never been such. Throws up a skull HAMLET That skull had a tongue in it, and could sing once: how the knave jowls it to the ground, as if it were Cain’s jaw-bone, that did the first murder! It might be the pate of a politician, which this ass now o’er-reaches; one that would circumvent God, might it not? HORATIO It might, my lord. HAMLET Or of a courtier; which could say ‘Good morrow, sweet lord! How dost thou, good lord?’ This might be my lord such-a-one, that praised my lord such-a-one’s horse, when he meant to beg it; might it not? HORATIO Ay, my lord. HAMLET Why, e’en so: and now my Lady Worm’s; chapless, and knocked about the mazzard with a sexton’s spade: here’s fine revolution, an we had the trick to see’t. Did these bones cost no more the breeding, but to play at loggats with ’em? mine ache to think on’t. First Clown [Sings] A pick-axe, and a spade, a spade, For and a shrouding sheet: O, a pit of clay for to be made For such a guest is meet. Throws up another skull HAMLET There’s another: why may not that be the skull of a lawyer? Where be his quiddities now, his quillets, his cases, his tenures, and his tricks? why does he suffer this rude knave now to knock him about the sconce with a dirty shovel, and will not tell him of his action of battery? Hum! This fellow might be in’s time a great buyer of land, with his statutes, his recognizances, his fines, his double vouchers, his recoveries: is this the fine of his fines, and the recovery of his recoveries, to have his fine pate full of fine dirt? will his vouchers vouch him no more of his purchases, and double ones too, than the length and breadth of a pair of indentures? The very conveyances of his lands will hardly lie in this box; and must the inheritor himself have no more, ha? HORATIO Not a jot more, my lord. HAMLET Is not parchment made of sheepskins? HORATIO Ay, my lord, and of calf-skins too. HAMLET They are sheep and calves which seek out assurance in that. I will speak to this fellow. Whose grave’s this, sirrah? First Clown Mine, sir. Sings O, a pit of clay for to be made For such a guest is meet. HAMLET I think it be thine, indeed; for thou liest in’t. First Clown You lie out on’t, sir, and therefore it is not yours: for my part, I do not lie in’t, and yet it is mine. HAMLET ‘Thou dost lie in’t, to be in’t and say it is thine: ’tis for the dead, not for the quick; therefore thou liest. First Clown ‘Tis a quick lie, sir; ’twill away gain, from me to you. HAMLET What man dost thou dig it for? First Clown For no man, sir. HAMLET What woman, then? First Clown For none, neither. HAMLET Who is to be buried in’t? First Clown One that was a woman, sir; but, rest her soul, she’s dead. HAMLET How absolute the knave is! we must speak by the card, or equivocation will undo us. By the Lord, Horatio, these three years I have taken a note of it; the age is grown so picked that the toe of the peasant comes so near the heel of the courtier, he gaffs his kibe. How long hast thou been a grave-maker? First Clown Of all the days i’ the year, I came to’t that day that our last king Hamlet overcame Fortinbras. HAMLET How long is that since? First Clown Cannot you tell that? every fool can tell that: it was the very day that young Hamlet was born; he that is mad, and sent into England. HAMLET Ay, marry, why was he sent into England? First Clown Why, because he was mad: he shall recover his wits there; or, if he do not, it’s no great matter there. HAMLET Why? First Clown ‘Twill, a not be seen in him there; there the men are as mad as he. HAMLET How came he mad? First Clown Very strangely, they say. HAMLET How strangely? First Clown Faith, e’en with losing his wits. HAMLET Upon what ground? First Clown Why, here in Denmark: I have been sexton here, man and boy, thirty years. HAMLET How long will a man lie i’ the earth ere he rot? First Clown I’ faith, if he be not rotten before he die–as we have many pocky corses now-a-days, that will scarce hold the laying in–he will last you some eight year or nine year: a tanner will last you nine year. HAMLET Why he more than another? First Clown Why, sir, his hide is so tanned with his trade, that he will keep out water a great while; and your water is a sore decayer of your whoreson dead body. Here’s a skull now; this skull has lain in the earth three and twenty years. HAMLET Whose was it? First Clown A whoreson mad fellow’s it was: whose do you think it was? HAMLET Nay, I know not. First Clown A pestilence on him for a mad rogue! a’ poured a flagon of Rhenish on my head once. This same skull, sir, was Yorick’s skull, the king’s jester. HAMLET This? First Clown E’en that. HAMLET Let me see. Takes the skull Alas, poor Yorick! I knew him, Horatio: a fellow of infinite jest, of most excellent fancy: he hath borne me on his back a thousand times; and now, how abhorred in my imagination it is! my gorge rims at it. Here hung those lips that I have kissed I know not how oft. Where be your gibes now? your gambols? your songs? your flashes of merriment, that were wont to set the table on a roar? Not one now, to mock your own grinning? quite chap-fallen? Now get you to my lady’s chamber, and tell her, let her paint an inch thick, to this favour she must come; make her laugh at that. Prithee, Horatio, tell me one thing. HORATIO What’s that, my lord? HAMLET Dost thou think Alexander looked o’ this fashion i’ the earth? HORATIO E’en so. HAMLET And smelt so? pah! Puts down the skull HORATIO E’en so, my lord. HAMLET To what base uses we may return, Horatio! Why may not imagination trace the noble dust of Alexander, till he find it stopping a bung-hole? HORATIO ‘Twere to consider too curiously, to consider so. HAMLET No, faith, not a jot; but to follow him thither with modesty enough, and likelihood to lead it: as thus: Alexander died, Alexander was buried, Alexander returneth into dust; the dust is earth; of earth we make loam; and why of that loam, whereto he was converted, might they not stop a beer-barrel? Imperious Caesar, dead and turn’d to clay, Might stop a hole to keep the wind away: O, that that earth, which kept the world in awe, Should patch a wall to expel the winter flaw! But soft! but soft! aside: here comes the king. Enter Priest, & c. in procession; the Corpse of OPHELIA, LAERTES and Mourners following; KING CLAUDIUS, QUEEN GERTRUDE, their trains, & c The queen, the courtiers: who is this they follow? And with such maimed rites? This doth betoken The corse they follow did with desperate hand Fordo its own life: ’twas of some estate. Couch we awhile, and mark. Retiring with HORATIO LAERTES What ceremony else? HAMLET That is Laertes, A very noble youth: mark. LAERTES What ceremony else? First Priest Her obsequies have been as far enlarged As we have warrantise: her death was doubtful; And, but that great command o’ersways the order, She should in ground unsanctified have lodged Till the last trumpet: for charitable prayers, Shards, flints and pebbles should be thrown on her; Yet here she is allow’d her virgin crants, Her maiden strewments and the bringing home Of bell and burial. LAERTES Must there no more be done? First Priest No more be done: We should profane the service of the dead To sing a requiem and such rest to her As to peace-parted souls. LAERTES Lay her i’ the earth: And from her fair and unpolluted flesh May violets spring! I tell thee, churlish priest, A ministering angel shall my sister be, When thou liest howling. HAMLET What, the fair Ophelia! QUEEN GERTRUDE Sweets to the sweet: farewell! Scattering flowers I hoped thou shouldst have been my Hamlet’s wife; I thought thy bride-bed to have deck’d, sweet maid, And not have strew’d thy grave. LAERTES O, treble woe Fall ten times treble on that cursed head, Whose wicked deed thy most ingenious sense Deprived thee of! Hold off the earth awhile, Till I have caught her once more in mine arms: Leaps into the grave Now pile your dust upon the quick and dead, Till of this flat a mountain you have made, To o’ertop old Pelion, or the skyish head Of blue Olympus. HAMLET [Advancing] What is he whose grief Bears such an emphasis? whose phrase of sorrow Conjures the wandering stars, and makes them stand Like wonder-wounded hearers? This is I, Hamlet the Dane. Leaps into the grave LAERTES The devil take thy soul! Grappling with him HAMLET Thou pray’st not well. I prithee, take thy fingers from my throat; For, though I am not splenitive and rash, Yet have I something in me dangerous, Which let thy wiseness fear: hold off thy hand. KING CLAUDIUS Pluck them asunder. QUEEN GERTRUDE Hamlet, Hamlet! All Gentlemen,– HORATIO Good my lord, be quiet. The Attendants part them, and they come out of the grave HAMLET Why I will fight with him upon this theme Until my eyelids will no longer wag. QUEEN GERTRUDE O my son, what theme? HAMLET I loved Ophelia: forty thousand brothers Could not, with all their quantity of love, Make up my sum. What wilt thou do for her? KING CLAUDIUS O, he is mad, Laertes. QUEEN GERTRUDE For love of God, forbear him. HAMLET ‘Swounds, show me what thou’lt do: Woo’t weep? woo’t fight? woo’t fast? woo’t tear thyself? Woo’t drink up eisel? eat a crocodile? I’ll do’t. Dost thou come here to whine? To outface me with leaping in her grave? Be buried quick with her, and so will I: And, if thou prate of mountains, let them throw Millions of acres on us, till our ground, Singeing his pate against the burning zone, Make Ossa like a wart! Nay, an thou’lt mouth, I’ll rant as well as thou. QUEEN GERTRUDE This is mere madness: And thus awhile the fit will work on him; Anon, as patient as the female dove, When that her golden couplets are disclosed, His silence will sit drooping. HAMLET Hear you, sir; What is the reason that you use me thus? I loved you ever: but it is no matter; Let Hercules himself do what he may, The cat will mew and dog will have his day. Exit KING CLAUDIUS I pray you, good Horatio, wait upon him. Exit HORATIO To LAERTES Strengthen your patience in our last night’s speech; We’ll put the matter to the present push. Good Gertrude, set some watch over your son. This grave shall have a living monument: An hour of quiet shortly shall we see; Till then, in patience our proceeding be. Exeunt
Enter HAMLET and HORATIO HAMLET So much for this, sir: now shall you see the other; You do remember all the circumstance? HORATIO Remember it, my lord? HAMLET Sir, in my heart there was a kind of fighting, That would not let me sleep: methought I lay Worse than the mutines in the bilboes. Rashly, And praised be rashness for it, let us know, Our indiscretion sometimes serves us well, When our deep plots do pall: and that should teach us There’s a divinity that shapes our ends, Rough-hew them how we will,– HORATIO That is most certain. HAMLET Up from my cabin, My sea-gown scarf’d about me, in the dark Groped I to find out them; had my desire. Finger’d their packet, and in fine withdrew To mine own room again; making so bold, My fears forgetting manners, to unseal Their grand commission; where I found, Horatio,– O royal knavery!–an exact command, Larded with many several sorts of reasons Importing Denmark’s health and England’s too, With, ho! such bugs and goblins in my life, That, on the supervise, no leisure bated, No, not to stay the grinding of the axe, My head should be struck off. HORATIO Is’t possible? HAMLET Here’s the commission: read it at more leisure. But wilt thou hear me how I did proceed? HORATIO I beseech you. HAMLET Being thus be-netted round with villanies,– Ere I could make a prologue to my brains, They had begun the play–I sat me down, Devised a new commission, wrote it fair: I once did hold it, as our statists do, A baseness to write fair and labour’d much How to forget that learning, but, sir, now It did me yeoman’s service: wilt thou know The effect of what I wrote? HORATIO Ay, good my lord. HAMLET An earnest conjuration from the king, As England was his faithful tributary, As love between them like the palm might flourish, As peace should stiff her wheaten garland wear And stand a comma ‘tween their amities, And many such-like ‘As’es of great charge, That, on the view and knowing of these contents, Without debatement further, more or less, He should the bearers put to sudden death, Not shriving-time allow’d. HORATIO How was this seal’d? HAMLET Why, even in that was heaven ordinant. I had my father’s signet in my purse, Which was the model of that Danish seal; Folded the writ up in form of the other, Subscribed it, gave’t the impression, placed it safely, The changeling never known. Now, the next day Was our sea-fight; and what to this was sequent Thou know’st already. HORATIO So Guildenstern and Rosencrantz go to’t. HAMLET Why, man, they did make love to this employment; They are not near my conscience; their defeat Does by their own insinuation grow: ‘Tis dangerous when the baser nature comes Between the pass and fell incensed points Of mighty opposites. HORATIO Why, what a king is this! HAMLET Does it not, think’st thee, stand me now upon– He that hath kill’d my king and whored my mother, Popp’d in between the election and my hopes, Thrown out his angle for my proper life, And with such cozenage–is’t not perfect conscience, To quit him with this arm? and is’t not to be damn’d, To let this canker of our nature come In further evil? HORATIO It must be shortly known to him from England What is the issue of the business there. HAMLET It will be short: the interim is mine; And a man’s life’s no more than to say ‘One.’ But I am very sorry, good Horatio, That to Laertes I forgot myself; For, by the image of my cause, I see The portraiture of his: I’ll court his favours. But, sure, the bravery of his grief did put me Into a towering passion. HORATIO Peace! who comes here? Enter OSRIC OSRIC Your lordship is right welcome back to Denmark. HAMLET I humbly thank you, sir. Dost know this water-fly? HORATIO No, my good lord. HAMLET Thy state is the more gracious; for ’tis a vice to know him. He hath much land, and fertile: let a beast be lord of beasts, and his crib shall stand at the king’s mess: ’tis a chough; but, as I say, spacious in the possession of dirt. OSRIC Sweet lord, if your lordship were at leisure, I should impart a thing to you from his majesty. HAMLET I will receive it, sir, with all diligence of spirit. Put your bonnet to his right use; ’tis for the head. OSRIC I thank your lordship, it is very hot. HAMLET No, believe me, ’tis very cold; the wind is northerly. OSRIC It is indifferent cold, my lord, indeed. HAMLET But yet methinks it is very sultry and hot for my complexion. OSRIC Exceedingly, my lord; it is very sultry,–as ’twere,–I cannot tell how. But, my lord, his majesty bade me signify to you that he has laid a great wager on your head: sir, this is the matter,– HAMLET I beseech you, remember– HAMLET moves him to put on his hat OSRIC Nay, good my lord; for mine ease, in good faith. Sir, here is newly come to court Laertes; believe me, an absolute gentleman, full of most excellent differences, of very soft society and great showing: indeed, to speak feelingly of him, he is the card or calendar of gentry, for you shall find in him the continent of what part a gentleman would see. HAMLET Sir, his definement suffers no perdition in you; though, I know, to divide him inventorially would dizzy the arithmetic of memory, and yet but yaw neither, in respect of his quick sail. But, in the verity of extolment, I take him to be a soul of great article; and his infusion of such dearth and rareness, as, to make true diction of him, his semblable is his mirror; and who else would trace him, his umbrage, nothing more. OSRIC Your lordship speaks most infallibly of him. HAMLET The concernancy, sir? why do we wrap the gentleman in our more rawer breath? OSRIC Sir? HORATIO Is’t not possible to understand in another tongue? You will do’t, sir, really. HAMLET What imports the nomination of this gentleman? OSRIC Of Laertes? HORATIO His purse is empty already; all’s golden words are spent. HAMLET Of him, sir. OSRIC I know you are not ignorant– HAMLET I would you did, sir; yet, in faith, if you did, it would not much approve me. Well, sir? OSRIC You are not ignorant of what excellence Laertes is– HAMLET I dare not confess that, lest I should compare with him in excellence; but, to know a man well, were to know himself. OSRIC I mean, sir, for his weapon; but in the imputation laid on him by them, in his meed he’s unfellowed. HAMLET What’s his weapon? OSRIC Rapier and dagger. HAMLET That’s two of his weapons: but, well. OSRIC The king, sir, hath wagered with him six Barbary horses: against the which he has imponed, as I take it, six French rapiers and poniards, with their assigns, as girdle, hangers, and so: three of the carriages, in faith, are very dear to fancy, very responsive to the hilts, most delicate carriages, and of very liberal conceit. HAMLET What call you the carriages? HORATIO I knew you must be edified by the margent ere you had done. OSRIC The carriages, sir, are the hangers. HAMLET The phrase would be more german to the matter, if we could carry cannon by our sides: I would it might be hangers till then. But, on: six Barbary horses against six French swords, their assigns, and three liberal-conceited carriages; that’s the French bet against the Danish. Why is this ‘imponed,’ as you call it? OSRIC The king, sir, hath laid, that in a dozen passes between yourself and him, he shall not exceed you three hits: he hath laid on twelve for nine; and it would come to immediate trial, if your lordship would vouchsafe the answer. HAMLET How if I answer ‘no’? OSRIC I mean, my lord, the opposition of your person in trial. HAMLET Sir, I will walk here in the hall: if it please his majesty, ’tis the breathing time of day with me; let the foils be brought, the gentleman willing, and the king hold his purpose, I will win for him an I can; if not, I will gain nothing but my shame and the odd hits. OSRIC Shall I re-deliver you e’en so? HAMLET To this effect, sir; after what flourish your nature will. OSRIC I commend my duty to your lordship. HAMLET Yours, yours. Exit OSRIC He does well to commend it himself; there are no tongues else for’s turn. HORATIO This lapwing runs away with the shell on his head. HAMLET He did comply with his dug, before he sucked it. Thus has he–and many more of the same bevy that I know the dressy age dotes on–only got the tune of the time and outward habit of encounter; a kind of yesty collection, which carries them through and through the most fond and winnowed opinions; and do but blow them to their trial, the bubbles are out. Enter a Lord Lord My lord, his majesty commended him to you by young Osric, who brings back to him that you attend him in the hall: he sends to know if your pleasure hold to play with Laertes, or that you will take longer time. HAMLET I am constant to my purpose; they follow the king’s pleasure: if his fitness speaks, mine is ready; now or whensoever, provided I be so able as now. Lord The king and queen and all are coming down. HAMLET In happy time. Lord The queen desires you to use some gentle entertainment to Laertes before you fall to play. HAMLET She well instructs me. Exit Lord HORATIO You will lose this wager, my lord. HAMLET I do not think so: since he went into France, I have been in continual practise: I shall win at the odds. But thou wouldst not think how ill all’s here about my heart: but it is no matter. HORATIO Nay, good my lord,– HAMLET It is but foolery; but it is such a kind of gain-giving, as would perhaps trouble a woman. HORATIO If your mind dislike any thing, obey it: I will forestall their repair hither, and say you are not fit. HAMLET Not a whit, we defy augury: there’s a special providence in the fall of a sparrow. If it be now, ’tis not to come; if it be not to come, it will be now; if it be not now, yet it will come: the readiness is all: since no man has aught of what he leaves, what is’t to leave betimes? Enter KING CLAUDIUS, QUEEN GERTRUDE, LAERTES, Lords, OSRIC, and Attendants with foils, & c KING CLAUDIUS Come, Hamlet, come, and take this hand from me. KING CLAUDIUS puts LAERTES’ hand into HAMLET’s HAMLET Give me your pardon, sir: I’ve done you wrong; But pardon’t, as you are a gentleman. This presence knows, And you must needs have heard, how I am punish’d With sore distraction. What I have done, That might your nature, honour and exception Roughly awake, I here proclaim was madness. Was’t Hamlet wrong’d Laertes? Never Hamlet: If Hamlet from himself be ta’en away, And when he’s not himself does wrong Laertes, Then Hamlet does it not, Hamlet denies it. Who does it, then? His madness: if’t be so, Hamlet is of the faction that is wrong’d; His madness is poor Hamlet’s enemy. Sir, in this audience, Let my disclaiming from a purposed evil Free me so far in your most generous thoughts, That I have shot mine arrow o’er the house, And hurt my brother. LAERTES I am satisfied in nature, Whose motive, in this case, should stir me most To my revenge: but in my terms of honour I stand aloof; and will no reconcilement, Till by some elder masters, of known honour, I have a voice and precedent of peace, To keep my name ungored. But till that time, I do receive your offer’d love like love, And will not wrong it. HAMLET I embrace it freely; And will this brother’s wager frankly play. Give us the foils. Come on. LAERTES Come, one for me. HAMLET I’ll be your foil, Laertes: in mine ignorance Your skill shall, like a star i’ the darkest night, Stick fiery off indeed. LAERTES You mock me, sir. HAMLET No, by this hand. KING CLAUDIUS Give them the foils, young Osric. Cousin Hamlet, You know the wager? HAMLET Very well, my lord Your grace hath laid the odds o’ the weaker side. KING CLAUDIUS I do not fear it; I have seen you both: But since he is better’d, we have therefore odds. LAERTES This is too heavy, let me see another. HAMLET This likes me well. These foils have all a length? They prepare to play OSRIC Ay, my good lord. KING CLAUDIUS Set me the stoops of wine upon that table. If Hamlet give the first or second hit, Or quit in answer of the third exchange, Let all the battlements their ordnance fire: The king shall drink to Hamlet’s better breath; And in the cup an union shall he throw, Richer than that which four successive kings In Denmark’s crown have worn. Give me the cups; And let the kettle to the trumpet speak, The trumpet to the cannoneer without, The cannons to the heavens, the heavens to earth, ‘Now the king dunks to Hamlet.’ Come, begin: And you, the judges, bear a wary eye. HAMLET Come on, sir. LAERTES Come, my lord. They play HAMLET One. LAERTES No. HAMLET Judgment. OSRIC A hit, a very palpable hit. LAERTES Well; again. KING CLAUDIUS Stay; give me drink. Hamlet, this pearl is thine; Here’s to thy health. Trumpets sound, and cannon shot off within Give him the cup. HAMLET I’ll play this bout first; set it by awhile. Come. They play Another hit; what say you? LAERTES A touch, a touch, I do confess. KING CLAUDIUS Our son shall win. QUEEN GERTRUDE He’s fat, and scant of breath. Here, Hamlet, take my napkin, rub thy brows; The queen carouses to thy fortune, Hamlet. HAMLET Good madam! KING CLAUDIUS Gertrude, do not drink. QUEEN GERTRUDE I will, my lord; I pray you, pardon me. KING CLAUDIUS [Aside] It is the poison’d cup: it is too late. HAMLET I dare not drink yet, madam; by and by. QUEEN GERTRUDE Come, let me wipe thy face. LAERTES My lord, I’ll hit him now. KING CLAUDIUS I do not think’t. LAERTES [Aside] And yet ’tis almost ‘gainst my conscience. HAMLET Come, for the third, Laertes: you but dally; I pray you, pass with your best violence; I am afeard you make a wanton of me. LAERTES Say you so? come on. They play OSRIC Nothing, neither way. LAERTES Have at you now! LAERTES wounds HAMLET; then in scuffling, they change rapiers, and HAMLET wounds LAERTES KING CLAUDIUS Part them; they are incensed. HAMLET Nay, come, again. QUEEN GERTRUDE falls OSRIC Look to the queen there, ho! HORATIO They bleed on both sides. How is it, my lord? OSRIC How is’t, Laertes? LAERTES Why, as a woodcock to mine own springe, Osric; I am justly kill’d with mine own treachery. HAMLET How does the queen? KING CLAUDIUS She swounds to see them bleed. QUEEN GERTRUDE No, no, the drink, the drink,–O my dear Hamlet,– The drink, the drink! I am poison’d. Dies HAMLET O villany! Ho! let the door be lock’d: Treachery! Seek it out. LAERTES It is here, Hamlet: Hamlet, thou art slain; No medicine in the world can do thee good; In thee there is not half an hour of life; The treacherous instrument is in thy hand, Unbated and envenom’d: the foul practise Hath turn’d itself on me lo, here I lie, Never to rise again: thy mother’s poison’d: I can no more: the king, the king’s to blame. HAMLET The point!–envenom’d too! Then, venom, to thy work. Stabs KING CLAUDIUS All Treason! treason! KING CLAUDIUS O, yet defend me, friends; I am but hurt. HAMLET Here, thou incestuous, murderous, damned Dane, Drink off this potion. Is thy union here? Follow my mother. KING CLAUDIUS dies LAERTES He is justly served; It is a poison temper’d by himself. Exchange forgiveness with me, noble Hamlet: Mine and my father’s death come not upon thee, Nor thine on me. Dies HAMLET Heaven make thee free of it! I follow thee. I am dead, Horatio. Wretched queen, adieu! You that look pale and tremble at this chance, That are but mutes or audience to this act, Had I but time–as this fell sergeant, death, Is strict in his arrest–O, I could tell you– But let it be. Horatio, I am dead; Thou livest; report me and my cause aright To the unsatisfied. HORATIO Never believe it: I am more an antique Roman than a Dane: Here’s yet some liquor left. HAMLET As thou’rt a man, Give me the cup: let go; by heaven, I’ll have’t. O good Horatio, what a wounded name, Things standing thus unknown, shall live behind me! If thou didst ever hold me in thy heart Absent thee from felicity awhile, And in this harsh world draw thy breath in pain, To tell my story. March afar off, and shot within What warlike noise is this? OSRIC Young Fortinbras, with conquest come from Poland, To the ambassadors of England gives This warlike volley. HAMLET O, I die, Horatio; The potent poison quite o’er-crows my spirit: I cannot live to hear the news from England; But I do prophesy the election lights On Fortinbras: he has my dying voice; So tell him, with the occurrents, more and less, Which have solicited. The rest is silence. Dies HORATIO Now cracks a noble heart. Good night sweet prince: And flights of angels sing thee to thy rest! Why does the drum come hither? March within Enter FORTINBRAS, the English Ambassadors, and others PRINCE FORTINBRAS Where is this sight? HORATIO What is it ye would see? If aught of woe or wonder, cease your search. PRINCE FORTINBRAS This quarry cries on havoc. O proud death, What feast is toward in thine eternal cell, That thou so many princes at a shot So bloodily hast struck? First Ambassador The sight is dismal; And our affairs from England come too late: The ears are senseless that should give us hearing, To tell him his commandment is fulfill’d, That Rosencrantz and Guildenstern are dead: Where should we have our thanks? HORATIO Not from his mouth, Had it the ability of life to thank you: He never gave commandment for their death. But since, so jump upon this bloody question, You from the Polack wars, and you from England, Are here arrived give order that these bodies High on a stage be placed to the view; And let me speak to the yet unknowing world How these things came about: so shall you hear Of carnal, bloody, and unnatural acts, Of accidental judgments, casual slaughters, Of deaths put on by cunning and forced cause, And, in this upshot, purposes mistook Fall’n on the inventors’ reads: all this can I Truly deliver. PRINCE FORTINBRAS Let us haste to hear it, And call the noblest to the audience. For me, with sorrow I embrace my fortune: I have some rights of memory in this kingdom, Which now to claim my vantage doth invite me. HORATIO Of that I shall have also cause to speak, And from his mouth whose voice will draw on more; But let this same be presently perform’d, Even while men’s minds are wild; lest more mischance On plots and errors, happen. PRINCE FORTINBRAS Let four captains Bear Hamlet, like a soldier, to the stage; For he was likely, had he been put on, To have proved most royally: and, for his passage, The soldiers’ music and the rites of war Speak loudly for him. Take up the bodies: such a sight as this Becomes the field, but here shows much amiss. Go, bid the soldiers shoot. A dead march. Exeunt, bearing off the dead bodies; after which a peal of ordnance is shot off
Made it to the bottom? Congratulations! Let us know what you thought of the Hamlet PDF (or indeed of the whole play if you read it!) below in the comments section:
- Pinterest 0
Leave a Reply
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Hamlet Essays Questions and Answers Grade 12 pdf

Hamlet Essays Questions and Answers Grade 12 pdf: There are contextual questions as well as essay questions for The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark .
Table of Contents
Quick FACTS about Hamlet
Who wrote Hamlet?
William Shakespeare
What is the Genre of the Story?
Tragedy; revenge tragedy
Who is the Protagonist?
Prince Hamlet
Explain the major conflict that happens in the story
Hamlet feels a responsibility to avenge his father’s murder by his uncle Claudius, but Claudius is now the king and this complicates matters for Prince Hamlet. Moreover, Hamlet has doubts about whether he can trust his father’s ghost, and whether killing Claudius is the appropriate thing to do.
Explain the rising of the action in the story
The ghost appears to Hamlet and tells Hamlet to avenge his murder; Hamlet pretends to be mad to his hide intentions; Hamlet stages the mousetrap play; Hamlet is reluctant to take the opportunity to kill Claudius while he is praying.
What happens in the climax?
When Hamlet violently stabs Polonius through the arras in Act III, scene iv, he brings himself into unavoidable conflict with the king (Claudius). Another possible climax comes at the end of Act IV, scene iv, when Hamlet resolves to commit himself fully to violent revenge.
What is falling action of a story?
Hamlet is sent to England to be killed; Hamlet returns to Denmark and confronts Laertes at Ophelia’s funeral; the fencing match between Hamlet and Laertes; the deaths of the royal family.
What is the setting (time) for the story?
Elizabethan times . In and around the royal palace in Elsinore, a city in Denmark
Contextual question
In a contextual question, you are given an extract (about 25–30 lines) from the drama. You will then have to answer questions based on the extract. Some answers can be found in the extract. Other questions will test your understanding of other parts of the drama: plot, characters, symbols and themes. Some questions will require that you express your opinion about the drama.
Literary Essay Question
Writing literary essays is a skill requiring preparation, planning and practice. When answering literary essays, you do not re-tell the story. Instead , you need to focus on specific requirements of the set essay question. The number of paragraphs in your literary essay will depend on what the question requires.
Characters in Hamlet
Cl assification of characters according to social status
In Hamlet , the characters’ social standing plays an important role, especially in relation to the Great Chain of Being.
The nobility
This is the noble class, made up of the royal family and the courtiers, whose wealth and position in society were inherited. They had political power and owned most of the land. The nobles in the play include Prince Hamlet, Claudius, Gertrude, King Hamlet and the Fortinbrases.
The commoners
These are people who had no inherited titles or wealth. Most of them had little chance of improving their social status except through their relationships with the nobility. For example, Horatio, Hamlet’s university associates (Guildenstern and Rosencrantz), Polonius and his children, the guards and the grave diggers, all belong to this class.
Some of the commoners are used to provide humour and to comment on the actions of the other characters are doing , e.g. in the graveyard scene.
The clergy in Elizabethan times were given a special role in society. In Hamlet , the priest performs the last rites and burials, as seen during Ophelia’s burial.

Hamlet Essay Question 1
Hamlet’s behaviour throughout the play has unintended consequences. Critically discuss the extent to which you agree with the above statement. Your response should take the form of a well-constructed essay of 400–450 words (2–21⁄2 pages).
How to answer the above essay question: Answer Guide
Candidates might argue that this statement is not entirely true and discuss how Hamlet’s behaviour has either intended or unintended consequences or they might offer a mixed response.
- From the time he learns of his father’s murder, Hamlet is obsessed with the need to avenge his death. This sets him on a course that has many unintended consequences.
- Hamlet intends for his antic disposition to mislead his enemies and to allow him to investigate the Ghost’s accusations. It serves, however, to make Claudius suspicious of him and leads to Rosencrantz and Guildenstern’s spying on him and ultimately their deaths.
- Hamlet’s introspection, self-doubt and anxiety cause him to procrastinate, thus giving Claudius the opportunity to act against him.
- Although Hamlet has the perfect opportunity to kill Claudius while he is at prayer, he decides against it, as he does not want Claudius’s soul to ascend to heaven. His delay gives Claudius time to come up with a plan to kill him. Realising that Hamlet poses a threat to him, Claudius sends Hamlet to England where he will be executed by the English king.
- Hamlet’s boarding of the pirate ship has the unintended consequence of enabling him to return to Denmark and escape execution.
- Hamlet unintentionally kills Polonius when he realises that he is being spied upon in his mother’s room. As a result, Laertes is determined to avenge his father’s death.
- Hamlet’s cruel treatment of Ophelia is a result of his disillusionment with his mother, and women in general. His brutal rejection of her and her father’s death at Hamlet’s hands cause Ophelia to descend into madness and she drowns soon after.
- In order to eliminate the threat that Hamlet poses to him, Claudius poisons Hamlet’s wine at the duel. Gertrude’s death after drinking the poison is a consequence that neither Hamlet nor Claudius could have predicted.
- Fortinbras’s becoming King of Denmark is another unexpected outcome of Hamlet’s commitment to revenge.
- Candidates might argue that much of what Hamlet does is orchestrated and that he has a very clear outcome in mind. They might refer to his deliberate act of feigning madness and his plan to stage a play that mirrors Claudius’s murderous and incestuous actions. Both these acts have the intended outcome of confirming Claudius’s guilt.
Hamlet Essay Question 2
Hamlet is responsible for his own tragic fate. Assess the validity of this statement. Your response should take the form of a well-constructed essay of 400–450 words (2–21⁄2 pages).
- Below is the basis for answering this essay. Use the following as a guideline only. However, also allow for answers that are different, original and show evidence of critical thought and interpretation.
- A range of examples may be used by the candidates to support their arguments.
A mixed response would demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the text.
- Hamlet struggles to reconcile his conscience with the need to avenge his father’s death. His dilemma is that he is prone to philosophic speculation and a desire to make judgements based on reason. He vacillates rather than reacts. While some might construe Hamlet’s behaviour as weak and see him as responsible for his own fate, others might argue that Hamlet’s vacillations are a consequence of his goodness.
- Hamlet has no control over certain events: the murder of his father, Claudius’s ascension to the throne and his marriage to Gertrude.
- Hamlet acknowledges that fate plays a role in the way in which matters unfold: he says that ‘there’s a divinity that shapes our end’. This suggests that, although Hamlet’s flaws may contribute to his downfall, there are elements beyond his control.
- Candidates might argue that Hamlet’s assumed madness is a fatal error of judgement that contributes to the tragic consequences.
- Candidates might argue that Hamlet is solely responsible for his fate because of his self-pitying attitude and his procrastination. The consequent train of events is a result of his failure to act timeously. He ought to have disclosed the presence of the Ghost to Gertrude and then perhaps events might have taken a different turn.
- Candidates who argue that Hamlet has no control over events will focus on issues of fate and/or restrictive circumstances rather than Hamlet’s decisions.
- Fate plays a role when the ship Hamlet travels on is attacked by pirates, resulting in his being saved and returning to Denmark.
- The machinations of Claudius, his collusion with Rosencrantz and Guildenstern, as well as with Polonius and Laertes, make it impossible for Hamlet to be held solely accountable for the tragic unfolding of events.
- When Hamlet does act, he does so impulsively (e.g. the killing of Polonius and his role in the killing of Rosencrantz and Guildenstern). He avoids acting with premeditation. He struggles to react to the Ghost’s request.
Hamlet Essays Questions and Answers Grade 12 pdf Downloads
Download questions and answer guides for Hamlet below:
Questions and Answers
My Courses has a large Questions and Answers repository for the most popular High School and Tertiary Schools subjects. This comes in handy when doing your revision or preparing for exams, tests, research tasks, and assignments.
Ask Us a Question and we will send you the Answer Guide
[super_form id=”33574″]
Website navigation
Hamlet - Entire Play
Download hamlet.
Last updated: Tue, Jun 02, 2020
- PDF Download as PDF
- DOC (for MS Word, Apple Pages, Open Office, etc.) without line numbers Download as DOC (for MS Word, Apple Pages, Open Office, etc.) without line numbers
- DOC (for MS Word, Apple Pages, Open Office, etc.) with line numbers Download as DOC (for MS Word, Apple Pages, Open Office, etc.) with line numbers
- HTML Download as HTML
- TXT Download as TXT
- XML Download as XML
- TEISimple XML (annotated with MorphAdorner for part-of-speech analysis) Download as TEISimple XML (annotated with MorphAdorner for part-of-speech analysis)
Navigate this work
Events before the start of Hamlet set the stage for tragedy. When the king of Denmark, Prince Hamlet’s father, suddenly dies, Hamlet’s mother, Gertrude, marries his uncle Claudius, who becomes the new king.
A spirit who claims to be the ghost of Hamlet’s father describes his murder at the hands of Claudius and demands that Hamlet avenge the killing. When the councilor Polonius learns from his daughter, Ophelia, that Hamlet has visited her in an apparently distracted state, Polonius attributes the prince’s condition to lovesickness, and he sets a trap for Hamlet using Ophelia as bait.
To confirm Claudius’s guilt, Hamlet arranges for a play that mimics the murder; Claudius’s reaction is that of a guilty man. Hamlet, now free to act, mistakenly kills Polonius, thinking he is Claudius. Claudius sends Hamlet away as part of a deadly plot.
After Polonius’s death, Ophelia goes mad and later drowns. Hamlet, who has returned safely to confront the king, agrees to a fencing match with Ophelia’s brother, Laertes, who secretly poisons his own rapier. At the match, Claudius prepares poisoned wine for Hamlet, which Gertrude unknowingly drinks; as she dies, she accuses Claudius, whom Hamlet kills. Then first Laertes and then Hamlet die, both victims of Laertes’ rapier.
Stay connected
Find out what’s on, read our latest stories, and learn how you can get involved.

Essay on Hamlet
William Shakespeare’s ‘Hamlet’ is not just a play; it’s a literary tapestry woven with themes of revenge, madness, morality, and the human condition. This essay aims to delve into the depths of ‘Hamlet’, providing insights for students participating in essay writing competitions.
Set in the kingdom of Denmark, ‘Hamlet’ tells the story of Prince Hamlet’s quest for vengeance against his uncle, Claudius, who has murdered Hamlet’s father, married his mother, and seized the throne. The play is a rich exploration of the complexities of the human psyche, morality, and the consequences of actions.
- Revenge and Justice : Central to the plot is Hamlet’s struggle to avenge his father’s death, a journey that raises questions about justice, morality, and the ethics of revenge.
- Madness : Whether Hamlet’s madness is real or feigned is a topic of much debate, symbolizing the fine line between sanity and insanity in the face of overwhelming grief and rage.
- Life, Death, and the Afterlife : The play frequently contemplates mortality, the fear of death, and the unknowns of the afterlife, epitomized in the famous “To be, or not to be” soliloquy.
- Betrayal and Loyalty : Themes of betrayal, loyalty, and familial duty are prevalent, reflecting the complex interpersonal dynamics of the characters.
Character Analysis
- Hamlet : A complex character, Hamlet is intellectual, melancholic, and philosophical. His internal conflict and contemplative nature drive the play’s narrative.
- Claudius : The antagonist, Claudius’s cunning and deceitful nature contrast starkly with Hamlet’s moral introspection.
- Gertrude and Ophelia : These female characters, often viewed through the lens of the male characters, bring critical perspectives on gender and power dynamics in the play.
Literary Techniques
Shakespeare’s use of soliloquies, symbolism, metaphors, and dramatic irony enriches the play’s narrative, offering a deeper understanding of the characters and themes.
- Soliloquy and Monologue: Shakespeare uses soliloquies and monologues to give the audience insight into the inner thoughts and conflicts of characters, especially Hamlet. The famous “To be or not to be” soliloquy is a prime example.
- Irony: Dramatic irony is a recurring technique in “Hamlet” where the audience knows something that the characters do not, creating tension and suspense. For example, Hamlet’s feigned madness is known to the audience, but not to most characters in the play.
- Foreshadowing: Shakespeare uses foreshadowing to hint at future events and build anticipation. The ghost’s appearance and warnings foreshadow the play’s tragic events.
- Metaphor and Imagery: Rich metaphorical language and vivid imagery enhance the play’s themes and characters. For instance, Hamlet’s comparison of Denmark to an “unweeded garden” reflects the corruption and decay in the kingdom.
- Symbolism: Various symbols, such as the use of poison, mirrors, and the play within a play, are employed to convey deeper meanings and themes in the play.
- Allusion: Shakespeare incorporates allusions to classical mythology, biblical references, and historical events to add layers of meaning and depth to the characters’ speeches and actions.
- Pun and Wordplay: Wordplay, puns, and double meanings are used for humor and to illustrate the characters’ wit and intelligence. Hamlet’s interactions with Polonius and the gravediggers showcase this technique.
- Diction and Language Variation: Shakespeare uses variations in language to distinguish characters and their social status. The nobility often speak in formal verse, while the lower-class characters use prose.
- Rhetorical Devices: Various rhetorical devices like parallelism, antithesis, and repetition are used to emphasize key ideas and create memorable lines.
- Foils: The characters in “Hamlet” are often paired as foils to contrast their personalities and highlight their strengths and weaknesses. Hamlet and Laertes, for example, are foils for each other.
- Structure and Dramatic Devices: The play’s five-act structure, as well as the use of dramatic devices like the play within a play (the “Mousetrap” scene), contribute to the unfolding of the plot and themes.
- Characterization: Shakespeare uses dialogue, actions, and soliloquies to reveal the complexities of his characters, including Hamlet’s internal struggle and Ophelia’s descent into madness.
- Themes and Motifs: Themes like madness, revenge, mortality, and corruption are recurrent motifs throughout the play, and Shakespeare uses literary techniques to explore these themes in depth.
Writing Tips for Students
- Focus on Analysis : Go beyond summarizing the plot. Analyze the characters, themes, and Shakespeare’s language.
- Use Quotations Effectively : Incorporate key quotations to support your analysis, but ensure they are relevant and well-explained.
- Offer Unique Perspectives : Bring your interpretation or perspective to the play, making your essay stand out.
- Contextual Understanding : Understand the historical and cultural context in which Shakespeare wrote ‘Hamlet’.
‘Hamlet’ is a masterpiece that continues to resonate with audiences for its profound exploration of the human experience. In writing an essay on ‘Hamlet’, students have the opportunity to delve into this literary treasure, uncovering the layers of Shakespeare’s artistry, and contributing their voice to the enduring discourse on this classic work.
Essay Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate an essay on the importance of extracurricular activities for student development
Write an essay discussing the role of technology in modern education.
- Utility Menu
Jeffrey R. Wilson
Essays on hamlet.

Written as the author taught Hamlet every semester for a decade, these lightning essays ask big conceptual questions about the play with the urgency of a Shakespeare lover, and answer them with the rigor of a Shakespeare scholar. In doing so, Hamlet becomes a lens for life today, generating insights on everything from xenophobia, American fraternities, and religious fundamentalism to structural misogyny, suicide contagion, and toxic love.
Prioritizing close reading over historical context, these explorations are highly textual and highly theoretical, often philosophical, ethical, social, and political. Readers see King Hamlet as a pre-modern villain, King Claudius as a modern villain, and Prince Hamlet as a post-modern villain. Hamlet’s feigned madness becomes a window into failed insanity defenses in legal trials. He knows he’s being watched in “To be or not to be”: the soliloquy is a satire of philosophy. Horatio emerges as Shakespeare’s authorial avatar for meta-theatrical commentary, Fortinbras as the hero of the play. Fate becomes a viable concept for modern life, and honor a source of tragedy. The metaphor of music in the play makes Ophelia Hamlet’s instrument. Shakespeare, like the modern corporation, stands against sexism, yet perpetuates it unknowingly. We hear his thoughts on single parenting, sending children off to college, and the working class, plus his advice on acting and writing, and his claims to be the next Homer or Virgil. In the context of four centuries of Hamlet hate, we hear how the text draws audiences in, how it became so famous, and why it continues to captivate audiences.
At a time when the humanities are said to be in crisis, these essays are concrete examples of the mind-altering power of literature and literary studies, unravelling the ongoing implications of the English language’s most significant artistic object of the past millennium.
Publications
Why is Hamlet the most famous English artwork of the past millennium? Is it a sexist text? Why does Hamlet speak in prose? Why must he die? Does Hamlet depict revenge, or justice? How did the death of Shakespeare’s son, Hamnet, transform into a story about a son dealing with the death of a father? Did Shakespeare know Aristotle’s theory of tragedy? How did our literary icon, Shakespeare, see his literary icons, Homer and Virgil? Why is there so much comedy in Shakespeare’s greatest tragedy? Why is love a force of evil in the play? Did Shakespeare believe there’s a divinity that shapes our ends? How did he define virtue? What did he think about psychology? politics? philosophy? What was Shakespeare’s image of himself as an author? What can he, arguably the greatest writer of all time, teach us about our own writing? What was his theory of literature? Why do people like Hamlet ? How do the Hamlet haters of today compare to those of yesteryears? Is it dangerous for our children to read a play that’s all about suicide?
These are some of the questions asked in this book, a collection of essays on Shakespeare’s Hamlet stemming from my time teaching the play every semester in my Why Shakespeare? course at Harvard University. During this time, I saw a series of bright young minds from wildly diverse backgrounds find their footing in Hamlet, and it taught me a lot about how Shakespeare’s tragedy works, and why it remains with us in the modern world. Beyond ghosts, revenge, and tragedy, Hamlet is a play about being in college, being in love, gender, misogyny, friendship, theater, philosophy, theology, injustice, loss, comedy, depression, death, self-doubt, mental illness, white privilege, overbearing parents, existential angst, international politics, the classics, the afterlife, and the meaning of it all.
These essays grow from the central paradox of the play: it helps us understand the world we live in, yet we don't really understand the text itself very well. For all the attention given to Hamlet , there’s no consensus on the big questions—how it works, why it grips people so fiercely, what it’s about. These essays pose first-order questions about what happens in Hamlet and why, mobilizing answers for reflections on life, making the essays both highly textual and highly theoretical.
Each semester that I taught the play, I would write a new essay about Hamlet . They were meant to be models for students, the sort of essay that undergrads read and write – more rigorous than the puff pieces in the popular press, but riskier than the scholarship in most academic journals. While I later added scholarly outerwear, these pieces all began just like the essays I was assigning to students – as short close readings with a reader and a text and a desire to determine meaning when faced with a puzzling question or problem.
The turn from text to context in recent scholarly books about Hamlet is quizzical since we still don’t have a strong sense of, to quote the title of John Dover Wilson’s 1935 book, What Happens in Hamlet. Is the ghost real? Is Hamlet mad, or just faking? Why does he delay? These are the kinds of questions students love to ask, but they haven’t been – can’t be – answered by reading the play in the context of its sources (recently addressed in Laurie Johnson’s The Tain of Hamlet [2013]), its multiple texts (analyzed by Paul Menzer in The Hamlets [2008] and Zachary Lesser in Hamlet after Q1 [2015]), the Protestant reformation (the focus of Stephen Greenblatt’s Hamlet in Purgatory [2001] and John E. Curran, Jr.’s Hamlet, Protestantism, and the Mourning of Contingency [2006]), Renaissance humanism (see Rhodri Lewis, Hamlet and the Vision of Darkness [2017]), Elizabethan political theory (see Margreta de Grazia, Hamlet without Hamlet [2007]), the play’s reception history (see David Bevington, Murder Most Foul: Hamlet through the Ages [2011]), its appropriation by modern philosophers (covered in Simon Critchley and Jamieson Webster’s The Hamlet Doctrine [2013] and Andrew Cutrofello’s All for Nothing: Hamlet’s Negativity [2014]), or its recent global travels (addressed, for example, in Margaret Latvian’s Hamlet’s Arab Journey [2011] and Dominic Dromgoole’s Hamlet Globe to Globe [2017]).
Considering the context and afterlives of Hamlet is a worthy pursuit. I certainly consulted the above books for my essays, yet the confidence that comes from introducing context obscures the sharp panic we feel when confronting Shakespeare’s text itself. Even as the excellent recent book from Sonya Freeman Loftis, Allison Kellar, and Lisa Ulevich announces Hamlet has entered “an age of textual exhaustion,” there’s an odd tendency to avoid the text of Hamlet —to grasp for something more firm—when writing about it. There is a need to return to the text in a more immediate way to understand how Hamlet operates as a literary work, and how it can help us understand the world in which we live.
That latter goal, yes, clings nostalgically to the notion that literature can help us understand life. Questions about life send us to literature in search of answers. Those of us who love literature learn to ask and answer questions about it as we become professional literary scholars. But often our answers to the questions scholars ask of literature do not connect back up with the questions about life that sent us to literature in the first place—which are often philosophical, ethical, social, and political. Those first-order questions are diluted and avoided in the minutia of much scholarship, left unanswered. Thus, my goal was to pose questions about Hamlet with the urgency of a Shakespeare lover and to answer them with the rigor of a Shakespeare scholar.
In doing so, these essays challenge the conventional relationship between literature and theory. They pursue a kind of criticism where literature is not merely the recipient of philosophical ideas in the service of exegesis. Instead, the creative risks of literature provide exemplars to be theorized outward to help us understand on-going issues in life today. Beyond an occasion for the demonstration of existing theory, literature is a source for the creation of new theory.
Chapter One How Hamlet Works
Whether you love or hate Hamlet , you can acknowledge its massive popularity. So how does Hamlet work? How does it create audience enjoyment? Why is it so appealing, and to whom? Of all the available options, why Hamlet ? This chapter entertains three possible explanations for why the play is so popular in the modern world: the literary answer (as the English language’s best artwork about death—one of the very few universal human experiences in a modern world increasingly marked by cultural differences— Hamlet is timeless); the theatrical answer (with its mixture of tragedy and comedy, the role of Hamlet requires the best actor of each age, and the play’s popularity derives from the celebrity of its stars); and the philosophical answer (the play invites, encourages, facilitates, and sustains philosophical introspection and conversation from people who do not usually do such things, who find themselves doing those things with Hamlet , who sometimes feel embarrassed about doing those things, but who ultimately find the experience of having done them rewarding).
Chapter Two “It Started Like a Guilty Thing”: The Beginning of Hamlet and the Beginning of Modern Politics
King Hamlet is a tyrant and King Claudius a traitor but, because Shakespeare asked us to experience the events in Hamlet from the perspective of the young Prince Hamlet, we are much more inclined to detect and detest King Claudius’s political failings than King Hamlet’s. If so, then Shakespeare’s play Hamlet , so often seen as the birth of modern psychology, might also tell us a little bit about the beginnings of modern politics as well.
Chapter Three Horatio as Author: Storytelling and Stoic Tragedy
This chapter addresses Horatio’s emotionlessness in light of his role as a narrator, using this discussion to think about Shakespeare’s motives for writing tragedy in the wake of his son’s death. By rationalizing pain and suffering as tragedy, both Horatio and Shakespeare were able to avoid the self-destruction entailed in Hamlet’s emotional response to life’s hardships and injustices. Thus, the stoic Horatio, rather than the passionate Hamlet who repeatedly interrupts ‘The Mousetrap’, is the best authorial avatar for a Shakespeare who strategically wrote himself and his own voice out of his works. This argument then expands into a theory of ‘authorial catharsis’ and the suggestion that we can conceive of Shakespeare as a ‘poet of reason’ in contrast to a ‘poet of emotion’.
Chapter Four “To thine own self be true”: What Shakespeare Says about Sending Our Children Off to College
What does “To thine own self be true” actually mean? Be yourself? Don’t change who you are? Follow your own convictions? Don’t lie to yourself? This chapter argues that, if we understand meaning as intent, then “To thine own self be true” means, paradoxically, that “the self” does not exist. Or, more accurately, Shakespeare’s Hamlet implies that “the self” exists only as a rhetorical, philosophical, and psychological construct that we use to make sense of our experiences and actions in the world, not as anything real. If this is so, then this passage may offer us a way of thinking about Shakespeare as not just a playwright but also a moral philosopher, one who did his ethics in drama.
Chapter Five In Defense of Polonius
Your wife dies. You raise two children by yourself. You build a great career to provide for your family. You send your son off to college in another country, though you know he’s not ready. Now the prince wants to marry your daughter—that’s not easy to navigate. Then—get this—while you’re trying to save the queen’s life, the prince murders you. Your death destroys your kids. They die tragically. And what do you get for your efforts? Centuries of Shakespeare scholars dumping on you. If we see Polonius not through the eyes of his enemy, Prince Hamlet—the point of view Shakespeare’s play asks audiences to adopt—but in analogy to the common challenges of twenty-first-century parenting, Polonius is a single father struggling with work-life balance who sadly choses his career over his daughter’s well-being.
Chapter Six Sigma Alpha Elsinore: The Culture of Drunkenness in Shakespeare’s Hamlet
Claudius likes to party—a bit too much. He frequently binge drinks, is arguably an alcoholic, but not an aberration. Hamlet says Denmark is internationally known for heavy drinking. That’s what Shakespeare would have heard in the sixteenth century. By the seventeenth, English writers feared Denmark had taught their nation its drinking habits. Synthesizing criticism on alcoholism as an individual problem in Shakespeare’s texts and times with scholarship on national drinking habits in the early-modern age, this essay asks what the tragedy of alcoholism looks like when located not on the level of the individual, but on the level of a culture, as Shakespeare depicted in Hamlet. One window into these early-modern cultures of drunkenness is sociological studies of American college fraternities, especially the social-learning theories that explain how one person—one culture—teaches another its habits. For Claudius’s alcoholism is both culturally learned and culturally significant. And, as in fraternities, alcoholism in Hamlet is bound up with wealth, privilege, toxic masculinity, and tragedy. Thus, alcohol imagistically reappears in the vial of “cursed hebona,” Ophelia’s liquid death, and the poisoned cup in the final scene—moments that stand out in recent performances and adaptations with alcoholic Claudiuses and Gertrudes.
Chapter Seven Tragic Foundationalism
This chapter puts the modern philosopher Alain Badiou’s theory of foundationalism into dialogue with the early-modern playwright William Shakespeare’s play Hamlet . Doing so allows us to identify a new candidate for Hamlet’s traditionally hard-to-define hamartia – i.e., his “tragic mistake” – but it also allows us to consider the possibility of foundationalism as hamartia. Tragic foundationalism is the notion that fidelity to a single and substantive truth at the expense of an openness to evidence, reason, and change is an acute mistake which can lead to miscalculations of fact and virtue that create conflict and can end up in catastrophic destruction and the downfall of otherwise strong and noble people.
Chapter Eight “As a stranger give it welcome”: Shakespeare’s Advice for First-Year College Students
Encountering a new idea can be like meeting a strange person for the first time. Similarly, we dismiss new ideas before we get to know them. There is an answer to the problem of the human antipathy to strangeness in a somewhat strange place: a single line usually overlooked in William Shakespeare’s play Hamlet . If the ghost is “wondrous strange,” Hamlet says, invoking the ancient ethics of hospitality, “Therefore as a stranger give it welcome.” In this word, strange, and the social conventions attached to it, is both the instinctual, animalistic fear and aggression toward what is new and different (the problem) and a cultivated, humane response in hospitality and curiosity (the solution). Intellectual xenia is the answer to intellectual xenophobia.
Chapter Nine Parallels in Hamlet
Hamlet is more parallely than other texts. Fortinbras, Hamlet, and Laertes have their fathers murdered, then seek revenge. Brothers King Hamlet and King Claudius mirror brothers Old Norway and Old Fortinbras. Hamlet and Ophelia both lose their fathers, go mad, but there’s a method in their madness, and become suicidal. King Hamlet and Polonius are both domineering fathers. Hamlet and Polonius are both scholars, actors, verbose, pedantic, detectives using indirection, spying upon others, “by indirections find directions out." King Hamlet and King Claudius are both kings who are killed. Claudius using Rosencrantz and Guildenstern to spy on Hamlet mirrors Polonius using Reynaldo to spy on Laertes. Reynaldo and Hamlet both pretend to be something other than what they are in order to spy on and detect foes. Young Fortinbras and Prince Hamlet both have their forward momentum “arrest[ed].” Pyrrhus and Hamlet are son seeking revenge but paused a “neutral to his will.” The main plot of Hamlet reappears in the play-within-the-play. The Act I duel between King Hamlet and Old Fortinbras echoes in the Act V duel between Hamlet and Laertes. Claudius and Hamlet are both king killers. Sheesh—why are there so many dang parallels in Hamlet ? Is there some detectable reason why the story of Hamlet would call for the literary device of parallelism?
Chapter Ten Rosencrantz and Guildenstern: Why Hamlet Has Two Childhood Friends, Not Just One
Why have two of Hamlet’s childhood friends rather than just one? Do Rosencrantz and Guildenstern have individuated personalities? First of all, by increasing the number of friends who visit Hamlet, Shakespeare creates an atmosphere of being outnumbered, of multiple enemies encroaching upon Hamlet, of Hamlet feeling that the world is against him. Second, Rosencrantz and Guildenstern are not interchangeable, as commonly thought. Shakespeare gave each an individuated personality. Guildenstern is friendlier with Hamlet, and their friendship collapses, while Rosencrantz is more distant and devious—a frenemy.
Chapter Eleven Shakespeare on the Classics, Shakespeare as a Classic: A Reading of Aeneas’s Tale to Dido
Of all the stories Shakespeare might have chosen, why have Hamlet ask the players to recite Aeneas’ tale to Dido of Pyrrhus’s slaughter of Priam? In this story, which comes not from Homer’s Iliad but from Virgil’s Aeneid and had already been adapted for the Elizabethan stage in Christopher Marlowe’s The Tragedy of Dido, Pyrrhus – more commonly known as Neoptolemus, the son of the famous Greek warrior Achilles – savagely slays Priam, the king of the Trojans and the father of Paris, who killed Pyrrhus’s father, Achilles, who killed Paris’s brother, Hector, who killed Achilles’s comrade, Patroclus. Clearly, the theme of revenge at work in this story would have appealed to Shakespeare as he was writing what would become the greatest revenge tragedy of all time. Moreover, Aeneas’s tale to Dido supplied Shakespeare with all of the connections he sought to make at this crucial point in his play and his career – connections between himself and Marlowe, between the start of Hamlet and the end, between Prince Hamlet and King Claudius, between epic poetry and tragic drama, and between the classical literature Shakespeare was still reading hundreds of years later and his own potential as a classic who might (and would) be read hundreds of years into the future.
Chapter Twelve How Theater Works, according to Hamlet
According to Hamlet, people who are guilty of a crime will, when seeing that crime represented on stage, “proclaim [their] malefactions”—but that simply isn’t how theater works. Guilty people sit though shows that depict their crimes all the time without being prompted to public confession. Why did Shakespeare—a remarkably observant student of theater—write this demonstrably false theory of drama into his protagonist? And why did Shakespeare then write the plot of the play to affirm that obviously inaccurate vision of theater? For Claudius is indeed stirred to confession by the play-within-the-play. Perhaps Hamlet’s theory of people proclaiming malefactions upon seeing their crimes represented onstage is not as outlandish as it first appears. Perhaps four centuries of obsession with Hamlet is the English-speaking world proclaiming its malefactions upon seeing them represented dramatically.
Chapter Thirteen “To be, or not to be”: Shakespeare Against Philosophy
This chapter hazards a new reading of the most famous passage in Western literature: “To be, or not to be” from William Shakespeare’s Hamlet . With this line, Hamlet poses his personal struggle, a question of life and death, as a metaphysical problem, as a question of existence and nothingness. However, “To be, or not to be” is not what it seems to be. It seems to be a representation of tragic angst, yet a consideration of the context of the speech reveals that “To be, or not to be” is actually a satire of philosophy and Shakespeare’s representation of the theatricality of everyday life. In this chapter, a close reading of the context and meaning of this passage leads into an attempt to formulate a Shakespearean image of philosophy.
Chapter Fourteen Contagious Suicide in and Around Hamlet
As in society today, suicide is contagious in Hamlet , at least in the example of Ophelia, the only death by suicide in the play, because she only becomes suicidal after hearing Hamlet talk about his own suicidal thoughts in “To be, or not to be.” Just as there are media guidelines for reporting on suicide, there are better and worse ways of handling Hamlet . Careful suicide coverage can change public misperceptions and reduce suicide contagion. Is the same true for careful literary criticism and classroom discussion of suicide texts? How can teachers and literary critics reduce suicide contagion and increase help-seeking behavior?
Chapter Fifteen Is Hamlet a Sexist Text? Overt Misogyny vs. Unconscious Bias
Students and fans of Shakespeare’s Hamlet persistently ask a question scholars and critics of the play have not yet definitively answered: is it a sexist text? The author of this text has been described as everything from a male chauvinist pig to a trailblazing proto-feminist, but recent work on the science behind discrimination and prejudice offers a new, better vocabulary in the notion of unconscious bias. More pervasive and slippery than explicit bigotry, unconscious bias involves the subtle, often unintentional words and actions which indicate the presence of biases we may not be aware of, ones we may even fight against. The Shakespeare who wrote Hamlet exhibited an unconscious bias against women, I argue, even as he sought to critique the mistreatment of women in a patriarchal society. The evidence for this unconscious bias is not to be found in the misogynistic statements made by the characters in the play. It exists, instead, in the demonstrable preference Shakespeare showed for men over women when deciding where to deploy his literary talents. Thus, Shakespeare's Hamlet is a powerful literary example – one which speaks to, say, the modern corporation – showing that deliberate efforts for egalitarianism do not insulate one from the effects of structural inequalities that both stem from and create unconscious bias.
Chapter Sixteen Style and Purpose in Acting and Writing
Purpose and style are connected in academic writing. To answer the question of style ( How should we write academic papers? ) we must first answer the question of purpose ( Why do we write academic papers? ). We can answer these questions, I suggest, by turning to an unexpected style guide that’s more than 400 years old: the famous passage on “the purpose of playing” in William Shakespeare’s Hamlet . In both acting and writing, a high style often accompanies an expressive purpose attempting to impress an elite audience yet actually alienating intellectual people, while a low style and mimetic purpose effectively engage an intellectual audience.
Chapter Seventeen 13 Ways of Looking at a Ghost
Why doesn’t Gertrude see the Ghost of King Hamlet in Act III, even though Horatio, Bernardo, Francisco, Marcellus, and Prince Hamlet all saw it in Act I? It’s a bit embarrassing that Shakespeare scholars don’t have a widely agreed-upon consensus that explains this really basic question that puzzles a lot of people who read or see Hamlet .
Chapter Eighteen The Tragedy of Love in Hamlet
The word “love” appears 84 times in Shakespeare’s Hamlet . “Father” only appears 73 times, “play” 60, “think” 55, “mother” 46, “mad” 44, “soul” 40, “God" 39, “death” 38, “life” 34, “nothing” 28, “son” 26, “honor” 21, “spirit” 19, “kill” 18, “revenge” 14, and “action” 12. Love isn’t the first theme that comes to mind when we think of Hamlet , but is surprisingly prominent. But love is tragic in Hamlet . The bloody catastrophe at the end of that play is principally driven not by hatred or a longing for revenge, but by love.
Chapter Nineteen Ophelia’s Songs: Moral Agency, Manipulation, and the Metaphor of Music in Hamlet
This chapter reads Ophelia’s songs in Act IV of Shakespeare’s Hamlet in the context of the meaning of music established elsewhere in the play. While the songs are usually seen as a marker of Ophelia’s madness (as a result of the death of her father) or freedom (from the constraints of patriarchy), they come – when read in light of the metaphor of music as manipulation – to symbolize her role as a pawn in Hamlet’s efforts to deceive his family. Thus, music was Shakespeare’s platform for connecting Ophelia’s story to one of the central questions in Hamlet : Do we have control over our own actions (like the musician), or are we controlled by others (like the instrument)?
Chapter Twenty A Quantitative Study of Prose and Verse in Hamlet
Why does Hamlet have so much prose? Did Shakespeare deliberately shift from verse to prose to signal something to his audiences? How would actors have handled the shifts from verse to prose? Would audiences have detected shifts from verse to prose? Is there an overarching principle that governs Shakespeare’s decision to use prose—a coherent principle that says, “If X, then use prose?”
Chapter Twenty-One The Fortunes of Fate in Hamlet : Divine Providence and Social Determinism
In Hamlet , fate is attacked from both sides: “fortune” presents a world of random happenstance, “will” a theory of efficacious human action. On this backdrop, this essay considers—irrespective of what the characters say and believe—what the structure and imagery Shakespeare wrote into Hamlet say about the possibility that some version of fate is at work in the play. I contend the world of Hamlet is governed by neither fate nor fortune, nor even the Christianized version of fate called “providence.” Yet there is a modern, secular, disenchanted form of fate at work in Hamlet—what is sometimes called “social determinism”—which calls into question the freedom of the individual will. As such, Shakespeare’s Hamlet both commented on the transformation of pagan fate into Christian providence that happened in the centuries leading up to the play, and anticipated the further transformation of fate from a theological to a sociological idea, which occurred in the centuries following Hamlet .
Chapter Twenty-Two The Working Class in Hamlet
There’s a lot for working-class folks to hate about Hamlet —not just because it’s old, dusty, difficult to understand, crammed down our throats in school, and filled with frills, tights, and those weird lace neck thingies that are just socially awkward to think about. Peak Renaissance weirdness. Claustrophobicly cloistered inside the castle of Elsinore, quaintly angsty over royal family problems, Hamlet feels like the literary epitome of elitism. “Lawless resolutes” is how the Wittenberg scholar Horatio describes the soldiers who join Fortinbras’s army in exchange “for food.” The Prince Hamlet who has never worked a day in his life denigrates Polonius as a “fishmonger”: quite the insult for a royal advisor to be called a working man. And King Claudius complains of the simplicity of "the distracted multitude.” But, in Hamlet , Shakespeare juxtaposed the nobles’ denigrations of the working class as readily available metaphors for all-things-awful with the rather valuable behavior of working-class characters themselves. When allowed to represent themselves, the working class in Hamlet are characterized as makers of things—of material goods and services like ships, graves, and plays, but also of ethical and political virtues like security, education, justice, and democracy. Meanwhile, Elsinore has a bad case of affluenza, the make-believe disease invented by an American lawyer who argued that his client's social privilege was so great that it created an obliviousness to law. While social elites rot society through the twin corrosives of political corruption and scholarly detachment, the working class keeps the machine running. They build the ships, plays, and graves society needs to function, and monitor the nuts-and-bolts of the ideals—like education and justice—that we aspire to uphold.
Chapter Twenty-Three The Honor Code at Harvard and in Hamlet
Students at Harvard College are asked, when they first join the school and several times during their years there, to affirm their awareness of and commitment to the school’s honor code. But instead of “the foundation of our community” that it is at Harvard, honor is tragic in Hamlet —a source of anxiety, blunder, and catastrophe. As this chapter shows, looking at Hamlet from our place at Harvard can bring us to see what a tangled knot honor can be, and we can start to theorize the difference between heroic and tragic honor.
Chapter Twenty-Four The Meaning of Death in Shakespeare’s Hamlet
By connecting the ways characters live their lives in Hamlet to the ways they die – on-stage or off, poisoned or stabbed, etc. – Shakespeare symbolized hamartia in catastrophe. In advancing this argument, this chapter develops two supporting ideas. First, the dissemination of tragic necessity: Shakespeare distributed the Aristotelian notion of tragic necessity – a causal relationship between a character’s hamartia (fault or error) and the catastrophe at the end of the play – from the protagonist to the other characters, such that, in Hamlet , those who are guilty must die, and those who die are guilty. Second, the spectacularity of death: there exists in Hamlet a positive correlation between the severity of a character’s hamartia (error or flaw) and the “spectacularity” of his or her death – that is, the extent to which it is presented as a visible and visceral spectacle on-stage.
Chapter Twenty-Five Tragic Excess in Hamlet
In Hamlet , Shakespeare paralleled the situations of Hamlet, Laertes, and Fortinbras (the father of each is killed, and each then seeks revenge) to promote the virtue of moderation: Hamlet moves too slowly, Laertes too swiftly – and they both die at the end of the play – but Fortinbras represents a golden mean which marries the slowness of Hamlet with the swiftness of Laertes. As argued in this essay, Shakespeare endorsed the virtue of balance by allowing Fortinbras to be one of the very few survivors of the play. In other words, excess is tragic in Hamlet .
Bibliography
Anand, Manpreet Kaur. An Overview of Hamlet Studies . Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars, 2019.
Anglin, Emily. “‘Something in me dangerous’: Hamlet, Melancholy, and the Early Modern Scholar.” Shakespeare 13.1 (2017): 15-29.
Baker, Christopher. “Hamlet and the Kairos.” Ben Jonson Journal 26.1 (2019): 62-77.
Baker, Naomi. “‘Sore Distraction’: Hamlet, Augustine and Time.” Literature and Theology 32.4 (2018): 381-96.
Belsey, Catherine. “The Question of Hamlet.” The Oxford Handbook of Shakespearean Tragedy, ed. Michael Neill and David Schalkwyk (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2016:
Bevington, David, ed. Twentieth Century Interpretations of Hamlet: A Collection of Critical Essays . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1968.
Bevington, David. Murder Most Foul: Hamlet through the Ages . Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2011.
Bloom, Harold, ed. Modern Critical Interpretations: Hamlet . New York: Chelsea House Publishers, 1986.
Booth, Stephen. “On the Value of Hamlet.” Reinterpretations of Elizabethan Drama. Ed. By Norman Rabkin. New York: Columbia University Press, 1969. 137-76.
Bowers, Fredson. Hamlet as Minister and Scourge and Other Studies in Shakespeare and Milton. Charlottesville, VA: University Press of Virginia, 1989.
Brancher, Dominique. “Universals in the Bush: The Case of Hamlet.” Shakespeare and Space: Theatrical Explorations of the Spatial Paradigm , ed. Ina Habermann and Michelle Witen (New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2016): 143-62.
Bourus, Terri. Young Shakespeare’s Young Hamlet: Print, Piracy, and Performance . New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2014.
Bourus, Terri. Canonizing Q1 Hamlet . Special issue of Critical Survey 31.1-2 (2019).
Burnett, Mark Thornton. ‘Hamlet' and World Cinema . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2019.
Calderwood, James L. To Be and Not to Be: Negation and Metadrama in Hamlet . New York: Columbia, 1983.
Carlson, Marvin. Shattering Hamlet's Mirror: Theatre and Reality . Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 2016.
Cavell, Stanley. “Hamlet’s Burden of Proof.” Disowning Knowledge in Seven Plays of Shakespeare . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003. 179–91.
Chamberlain, Richard. “What's Happiness in Hamlet?” The Renaissance of Emotion: Understanding Affect in Shakespeare and his Contemporaries , ed. Richard Meek and Erin Sullivan (Manchester: Manchester University Press, 2017): 153-74.
Cormack, Bradin. “Paper Justice, Parchment Justice: Shakespeare, Hamlet, and the Life of Legal Documents.” Taking Exception to the Law: Materializing Injustice in Early Modern English Literature , ed. Donald Beecher, Travis Decook, and Andrew Wallace (Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2015): 44-70.
Craig, Leon Harold. Philosophy and the Puzzles of Hamlet: A Study of Shakespeare's Method . London: Bloomsbury, 2014.
Critchley, Simon; Webster, Jamieson. Stay, Illusion!: The Hamlet Doctrine . New York: Pantheon Books, 2013.
Curran, John E., Jr. Hamlet, Protestantism, and the Mourning of Contingency: Not to Be . Aldershot and Burlington, VT: Ashgate, 2006.
Cutrofello, Andrew. All for Nothing: Hamlet's Negativity . Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press, 2014.
Dawson, Anthony B. Hamlet: Shakespeare in Performance . Manchester and New York: Manchester UP, 1995.
Desmet, Christy. “Text, Style, and Author in Hamlet Q1.” Journal of Early Modern Studies 5 (2016): 135-156
Dodsworth, Martin. Hamlet Closely Observed . London: Athlone, 1985.
De Grazia, Margreta. Hamlet without Hamlet . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007.
Dromgoole, Dominic. Hamlet: Globe to Globe : 193,000 Miles, 197 Countries, One Play . Edinburgh: Canongate, 2018.
Dunne, Derek. “Decentring the Law in Hamlet .” Law and Humanities 9.1 (2015): 55-77.
Eliot, T. S. “Hamlet and His Problems.” The Sacred Wood: Essays on Poetry and Criticism . London: Methuen, 1920. 87–94.
Evans, Robert C., ed. Critical Insights: Hamlet . Amenia: Grey House Publishing, 2019.
Farley-Hills, David, ed. Critical Responses to Hamlet, 1600-1900 . 5 vols. New York: AMS Press, 1996.
Foakes, R.A. Hamlet Versus Lear: Cultural Politics and Shakespeare's Art . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1993.
Frank, Arthur W. “‘Who’s There?’: A Vulnerable Reading of Hamlet,” Literaature and Medicine 37.2 (2019): 396-419.
Frye, Roland Mushat. The Renaissance Hamlet: Issues and Responses in 1600 . Princeton: Princeton UP, 1984.
Josipovici, Gabriel. Hamlet: Fold on Fold . New Haven: Yale University Press, 2016.
Kastan, David Scott, ed. Critical Essays on Shakespeare’s Hamlet . New York: G. K. Hall, 1995.
Khan, Amir. “My Kingdom for a Ghost: Counterfactual Thinking and Hamlet.” Shakespeare Quarerly 66.1 (2015): 29-46.
Keener, Joe. “Evolving Hamlet: Brains, Behavior, and the Bard.” Interdisciplinary Literary Studies 14.2 (2012): 150-163
Kott, Jan. “Hamlet of the Mid-Century.” Shakespeare, Our Contemporary . Trans. Boleslaw Taborski. Garden City: Doubleday, 1964.
Lake, Peter. Hamlet’s Choice: Religion and Resistance in Shakespeare's Revenge Tragedies . New Haven: Yale University Press, 2020.
Lerer, Seth. “Hamlet’s Boyhood.” Childhood, Education and the Stage in Early Modern England , ed. Richard Preiss and Deanne Williams (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2017):17-36.
Levy, Eric P. Hamlet and the Rethinking of Man . Madison: Fairleigh Dickinson University Press, 2008.
Lewis, C.S. “Hamlet: The Prince or the Poem?” (1942). Studies in Shakespeare , ed. Peter Alexander (1964): 201-18.
Loftis, Sonya Freeman; Allison Kellar; and Lisa Ulevich, ed. Shakespeare's Hamlet in an Era of Textual Exhaustion . New York, NY: Routledge, 2018.
Luke, Jillian. “What If the Play Were Called Ophelia ? Gender and Genre in Hamlet .” Cambridge Quarterly 49.1 (2020): 1-18.
Gates, Sarah. “Assembling the Ophelia Fragments: Gender, Genre, and Revenge in Hamlet.” Explorations in Renaissance Culture 34.2 (2008): 229-47.
Gottschalk, Paul. The Meanings of Hamlet: Modes of Literary Interpretation Since Bradley . Albequerque: University of New Mexico Press, 1972.
Greenblatt, Stephen. Hamlet in Purgatory . Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press, 2001.
Hunt, Marvin W. Looking for Hamlet . New York and Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan, 2007.
Iyengar, Sujata. "Gertrude/Ophelia: Feminist Intermediality, Ekphrasis, and Tenderness in Hamlet," in Loomba, Rethinking Feminism In Early Modern Studies: Race, Gender, and Sexuality (2016), 165-84.
Iyengar, Sujata; Feracho, Lesley. “Hamlet (RSC, 2016) and Representations of Diasporic Blackness,” Cahiers Élisabéthains 99, no. 1 (2019): 147-60.
Johnson, Laurie. The Tain of Hamlet . Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars, 2013.
Jolly, Margrethe. The First Two Quartos of Hamlet: A New View of the Origins and Relationship of the Texts . Jefferson: McFarland, 2014.
Jones, Ernest. Hamlet and Oedipus . Garden City: Doubleday, 1949.
Keegan, Daniel L. “Indigested in the Scenes: Hamlet's Dramatic Theory and Ours.” PMLA 133.1 (2018): 71-87.
Kinney, Arthur F., ed. Hamlet: Critical Essays . New York: Routledge, 2002.
Kiséry, András. Hamlet's Moment: Drama and Political Knowledge in Early Modern England . Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2016.
Kottman, Paul A. “Why Think About Shakespearean Tragedy Today?” The Cambridge Companion to Shakespearean Tragedy , ed. Claire McEachern (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013): 240-61.
Langis, Unhae. “Virtue, Justice and Moral Action in Shakespeare’s Hamlet .” Literature and Ethics: From the Green Knight to the Dark Knight , ed. Steve Brie and William T. Rossiter (Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars, 2010): 53-74.
Lawrence, Sean. "'As a stranger, bid it welcome': Alterity and Ethics in Hamlet and the New Historicism," European Journal of English Studies 4 (2000): 155-69.
Lesser, Zachary. Hamlet after Q1: An Uncanny History of the Shakespearean Text . Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2015.
Levin, Harry. The Question of Hamlet . New York: Oxford UP, 1959.
Lewis, Rhodri. Hamlet and the Vision of Darkness . Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2017.
Litvin, Margaret. Hamlet's Arab Journey: Shakespeare's Prince and Nasser's Ghost . Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2011.
Loftis, Sonya Freeman, and Lisa Ulevich. “Obsession/Rationality/Agency: Autistic Shakespeare.” Disability, Health, and Happiness in the Shakespearean Body , edited by Sujata Iyengar. Routledge, 2015, pp. 58-75.
Marino, James J. “Ophelia’s Desire.” ELH 84.4 (2017): 817-39.
Massai, Sonia, and Lucy Munro. Hamlet: The State of Play . London: Bloomsbury, 2021.
McGee, Arthur. The Elizabethan Hamlet . New Haven: Yale UP, 1987.
Megna, Paul, Bríd Phillips, and R.S. White, ed. Hamlet and Emotion . New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2019.
Menzer, Paul. The Hamlets: Cues, Qs, and Remembered Texts . Newark: University of Delaware Press, 2008.
Mercer, Peter. Hamlet and the Acting of Revenge . Iowa City: University of Iowa Press, 1987.
Oldham, Thomas A. “Unhouseled, Disappointed, Unaneled”: Catholicism, Transubstantiation, and Hamlet .” Ecumenica 8.1 (Spring 2015): 39-51.
Owen, Ruth J. The Hamlet Zone: Reworking Hamlet for European Cultures . Newcastle-Upon-Tyne: Cambridge Scholars, 2012.
Price, Joeseph G., ed. Hamlet: Critical Essays . New York: Routledge, 1986.
Prosser, Eleanor. Hamlet and Revenge . 2nd ed. Stanford: Stanford UP, 1971.
Rosenberg, Marvin. The Masks of Hamlet . Newark: University of Delaware Press, 1992.
Row-Heyveld, Lindsey. “Antic Dispositions: Mental and Intellectual Disabilities in Early Modern Revenge Tragedy.” Recovering Disability in Early Modern England , ed. Allison P. Hobgood and David Houston Wood. Ohio State University Press, 2013, pp. 73-87.
Shakespeare, William. Hamlet . Ed. Neil Taylor and Ann Thompson. Revised Ed. London: Arden Third Series, 2006.
Shakespeare, William. Hamlet . Ed. Robert S. Miola. New York: Norton, 2010.
Stritmatter, Roger. "Two More Censored Passages from Q2 Hamlet." Cahiers Élisabéthains 91.1 (2016): 88-95.
Thompson, Ann. “Hamlet 3.1: 'To be or not to be’.” The Cambridge Guide to the Worlds of Shakespeare: The World's Shakespeare, 1660-Present, ed. Bruce R. Smith (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2016): 1144-50.
Seibers, Tobin. “Shakespeare Differently Disabled.” The Oxford Handbook of Shakespeare and Embodiement: Gender, Sexuality, and Race , ed. Valerie Traub (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2016): 435-54.
Skinner, Quentin. “Confirmation: The Conjectural Issue.” Forensic Shakespeare (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2014): 226-68.
Slater, Michael. “The Ghost in the Machine: Emotion and Mind–Body Union in Hamlet and Descartes," Criticism 58 (2016).
Thompson, Ann, and Neil Taylor, eds. Hamlet: A Critical Reader . London: Bloomsbury, 2016.
Weiss, Larry. “The Branches of an Act: Shakespeare's Hamlet Explains his Inaction.” Shakespeare 16.2 (2020): 117-27.
Wells, Stanley, ed. Hamlet and Its Afterlife . Special edition of Shakespeare Survey 45 (1992).
Williams, Deanne. “Enter Ofelia playing on a Lute.” Shakespeare and the Performance of Girlhood (New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2014): 73-91
Williamson, Claude C.H., ed. Readings on the Character of Hamlet: Compiled from Over Three Hundred Sources .
White, R.S. Avant-Garde Hamlet: Text, Stage, Screen . Lanham: Fairleigh Dickinson University Press, 2015.
Wiles, David. “Hamlet’s Advice to the Players.” The Players’ Advice to Hamlet: The Rhetorical Acting Method from the Renaissance to the Enlightenment (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2020): 10-38
Wilson, J. Dover. What Happens in Hamlet . 3rd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge UP, 1951.
Zamir, Tzachi, ed. Shakespeare's Hamlet: Philosophical Perspectives . Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2018.
107 Exceptional Hamlet Essay Topics: Questions & Prompts

Every academic paper starts with a captivating idea, and Hamlet research paper or essay shouldn’t be an exception. In the list below, our team has collected unique and inspiring topics for you. You can use them in your writing or develop your own idea according to the format.
Here are some Hamlet essay topics for you:
- Elaborate on the weather in Denmark. How does it reflect the state of affairs and mood in the country? How does it change throughout the play? Start this Hamlet essay by describing the foggy weather in the first scene and gradually provide more examples as evidence.
- Think of irony in Hamlet . How and for what purposes did Shakespeare incorporate it in the play? Provide examples of the lines and situations that can be considered ironic.
- Reflect on Gertrude’s marriages. Why did she marry Claudius? Did they have an affair when King Hamlet was alive? Or did she agree on the new marriage to help the country?
- Compare and contrast Claudius and King Oedipus from Oedipus the King . What character traits do they share? Who is a better politician? Why?
- Explain whether you think Gertrude is on Hamlet’s or Claudius’ side. Did she switch the side by the end of the play? Analyze her conversation with Hamlet and how she later told Claudius that Hamlet was mad. Why did she drink the suspicious (poisoned) wine?
- Analyze the fact that dying Hamlet asked Horatio to spread his story. Will Horatio retell it without changes? Can he tell the truth about what happened at all?
- Examine an approach to violence in Hamlet . Are violence and aggression excessive in the play? How do characters react to it? Comment on how violence is mainly linked to vengeance.
- Consider the Ghost of Old Hamlet and all his appearances in Hamlet . Who saw him? Who do you think can see him? In your Hamlet essay, analyze every scene where he occurred and elaborate on why he did so.
- Talk about the relationship between Gertrude and Old Hamlet. Analyze what we know about their marriage and her reaction to her husband’s death. Did Gertrude see the Ghost in the scene with Hamlet? Could she have pretended that she didn’t?
- If Hamlet had survived, would he have been a good king? Analyze his strengths and weaknesses concerning the matter. Did he prove to be a good leader or politician in the play? Consider that Fortinbras explicitly stated that Hamlet could’ve become a good ruler.
- Elaborate on the way Hamlet killed Polonius in act 3, scene 4. Why did Hamlet act so quickly and calmly when he hesitates to kill his enemy, Claudius? Was this murder intentional? Did Hamlet regret it or freak out about it?
- Explore Hamlet’s mental state. How did grief affect him? His depression and suicidal tendencies are apparent. How do they change throughout the play?
- Compare Hamlet’s attitude towards the only women in the play, Ophelia and Gertrude. Why does he shame both of them for their sexual relationships? Examine his dialogues with his mother and his (ex)girlfriend, where he expresses cruelty. Elaborate on how his mother’s remarriage affected his relationships with the women.
- Examine the madness that Hamlet may or may not obtain. Thanks to his dialogue with Horatio, we know that he fakes his insanity. But could it have changed by the end of the play? What could’ve caused it? Analyze the evidence of his abnormal behavior and whether you can consider it natural, not acted.
- Analyze how Hamlet reflects on suicide. Provide examples from the soliloquies where Hamlet presumably tells the truth about his feelings. He considers suicide as an option, way out of the situation. Why doesn’t he commit it? Or was his death close to suicide?
- Consider whether the Ghost exists or not. A few people have seen him, but may it have been a case of mass hysteria? Hamlet may have gone mad over the death of his father and his mother’s remarriage. What if he imagined his dialogues with deceased King Hamlet? Provide evidence for that opinion or refute it.
- Elaborate on Hamlet’s trust issues. He suspects everyone from the start except for one person. Why does Hamlet trust Horatio? Analyze how the prince never lies during their conversations, even when the truth is a little insane. Why does Horatio believe everything he says?
- Examine friendship in Hamlet . Most of the relationships in the play are based on manipulation and benefit. Who can you see as friends in Hamlet ? Reflect on whether Hamlet values his friendship with Horatio. What can you say about Hamlet’s friends from childhood?
- Analyze the literary period during which Shakespeare came up with Hamlet . What features of the Elizabethan era does he illustrate in the play? Examplify various scenes and dialogues to prove your point.
- Consider prominent theatrical productions of Hamlet . How did they change over the centuries? What does modern theatre do that the Medieval one could not? Did theatrical performances evolve?
- Compare and contrast the original play and Lion King by Disney corporation. What are the key differences that were made in the cartoon? Why did Disney decide to come up with them? Analyze which version do you like more and why.
- Comment on the theme of death and mortality What events and objects made Hamlet obsessed with death? Elaborate on the role that religion plays in his considerations concerning the matter.
- Examine Claudius’ soliloquy . What’s its role in the play? What’s the crucial idea of his speech? Elaborate on the reasons why Claudius, the villain, has a soliloquy in Hamlet .
- Analyze all the symbols of death in the play What symbols from Hamlet refer to mortality? Speculate whether you can call fences, poison, unweeded gardens, flowers, and so on a symbol of death.
- Explore the conflicts of Hamlet . The play combines inner and outer conflicts, which are addressed mainly through Hamlet’s monologues. List the fundamental oppositions and lines that exemplify them.
- Reflect on Hamlet’s relationship with Gertrude Why is he upset with her? How does it affect his actions and opinion about all the women? Does Gertrude love her son?
- Analyze the setting of the play. Does the fact that Hamlet takes place in Denmark play any crucial role? Speculate why Shakespeare may have decided upon this country and support your opinion with evidence.
- Elaborate on Hamlet’s relationship with Ophelia. Does the prince consider her significant? Does he care about her? Compare how he treated Ophelia before and after her death.
- Comment on Hamlet’s religious beliefs Does religion have an impact on the prince’s decisions? Why is Hamlet considered a protestant? Prove your point by providing evidence from the play.
- Reflect on the theme of revenge Why does everyone value revenge in the play? Why do people passionately seek it in the society presented in Hamlet ? Elaborate on what impact it has on the characters’ motivations and decisions.
- Consider the language of Hamlet . Explain that Shakespeare’s play is well-known for its rich language and broad vocabulary. He composed a few characters who pay close attention to the words they say and hear. Why is language crucial for Hamlet?
- Examine Fortinbras. Who is he? Why is he a character foil for Hamlet? Analyze why he succeeded in everything he did and even became the king of Denmark.
- Analyze imagery and descriptions in the play. How does Shakespeare enhance each scene by alternating descriptions of the weather and nature? Provide examples of prominent images presented in the play and elaborate on their purpose.
- Compare Hamlet to Oedipus Rex . What do the characters of the famous plays have in common? Do they have a similar goal? Elaborate on how their character traits affect the endings of the respective plays.
- Explore the deception in Hamlet . What things and events are built on lies? Why and how do characters try to manipulate each other throughout the whole play?
- Elaborate on the imagery of rot and diseases How do unweeded gardens reflect the state of affairs? Explain how ill atmosphere foreshadows and represents problems caused by the actions of the royal court’s members.
- Comment on the role of Rosencrantz and Guildenstern in the play. Speculate whether they are simply comic relief characters or they have another purpose in Hamlet . Why did Shakespeare decide that he needed such characters in the play?
- Analyze Gertrude’s attitude towards Ophelia. Elaborate on the scenes where Gertrude communicates with Ophelia and mentions her. What does the queen think of her and her relationships with Hamlet? How does Gertrude comments on Ophelia’s death?
- Compare Hamlet’s and Horatio’s character traits. In what ways are they different and similar? What Horatio’s qualities Hamlet explicitly admires and lacks?
- Speculate on Shakespeare’s opinion about theatre. Examine a few references to the English stage of the Elizabethan era that the author put in the play in Act 2. How does he comment on the theatre of his own time through Hamlet’s lines of dialogue?
- Explore the relationships between Hamlet and Claudius. Why does Hamlet suspect his uncle from the start? Does Claudius think of Hamlet as dangerous? When does he become highly aware of his nephew’s capabilities?
- Consider the death of Rosencrantz and Guildenstern. When and how did they die? Why does a reader find out about it after the deaths of the royal family members? Speculate on the reasons why it was structured to be so anticlimactic. Why did W. S. Gilbert write a short comic play about them?
- Analyze the reception and comprehension of Hamlet . Why is it one of the most popular Shakespeare’s plays even today? Is it still relevant? Explain why nowadays our understanding of the play differs from the one from the writer’s era.
- Comment on the appearance vs. reality in Hamlet . Why do so many characters pretend to have another personality or obtain character traits that they don’t have? Why does Hamlet see through the pretense?
- Elaborate on Ophelia’s death . Was it a suicide, how gravediggers presumed, or an accident, as Gertrude claimed? Explain in your Hamlet essay the reasons for Ophelia to commit suicide. Did she have a choice?
- Reflect on political corruption. What characters represent corrupted politicians in the play? How do they manipulate public opinion?
- Analyze one movie adaptation of Hamlet . Write about the changes that were made in the film version. What differences from the play did you like? What changes were you surprised to see?
- Examine the political situation in the play. What war did Fortinbras lead? Why? How does it affect Denmark during the play and after it’s the last scene?
- Explore the role of women in Hamlet . The play presents the social norms that were relevant for people of this period. What parts of women’s lives did men explicitly control? Provide examples from the play.
- Compare Laertes and Hamlet . Laertes is known as Hamlet’s character foil. Examine similarities and differences in their character traits.
- Consider the doubt and indecisiveness of Hamlet . Why are such traits uncommon for the genre? What do they say about the prince as a character? Explain how these qualities affect the plot and Hamlet’s thought process.
- Elaborate on the symbolism in the play. Finding symbolism can be challenging as the interpretations differ. Some individuals consider particular objects as symbols, while others don’t. What do you view as examples of symbolism in the play? Why? What role do they play in understanding the story?
- Reflect on the Oedipus complex. Comment on whether Hamlet has it or not. Provide evidence from the play, especially from the scene with Gertrude, to prove your point. How can this idea be approached on the stage? Find examples of theatrical productions where Hamlet and Gertrude had a conversation in her closet.
- Compare and contrast Claudius and Polonius. What character traits do they have in common? Explain how they are not who they are trying to appear. Who is better at lying and manipulating others? Why?
- Examine how revenge affected characters in Hamlet . Three characters wish to avenge their fathers: Laertes, Hamlet, and Fortinbras. How does revenge affect their lives? Who succeeded in getting their revenge?
- Consider the family theme. What role does family play for various characters? Elaborate on how blood ties motivate multiple characters.
- Reflect on Yorick’s role in the play. Who was Yorick? What impact did he have on Hamlet during the prince’s childhood and present time? Elaborate on how Yorick led Hamlet to his last soliloquy.
- Analyze the religious conflict of the play. How did events from Shakespeare’s time affect the theme of religion? Explain how Hamlet presents the conflict between Protestantism and Catholicism through the prince and King Hamlet.
- Comment on the theme of madness. Who went mad in the play? Compare Hamlet’s and Laerte’s insanity to Ophelia’s one. How was her madness different from the other examples?
- Explore Polonius’ character. What was Polonius’ motivation throughout the play? Whom did he manipulate, and why? Explain why he tried to appear a good person and a parent.
- Elaborate on the reasons why Hamlet is the protagonist of the story. What makes him a tragic hero? Why is he considered a good person after every crime he committed and every cruel thing he said to his mother and Ophelia?
- Think of the conflict of good and evil. What imagery is associated with each of them in the play? Does evil spread like a disease?
- Explain how Hamlet differs from other plays of Shakespeare’s time . What new features and connections within the story did the writer present? How did Shakespeare make characters contribute to the plot?
- Analyze the “To be or not to be” speech. It’s one of the most famous lines in history, but what meaning is behind it? Elaborate on the circumstances around the monologue and whether Hamlet is partially lying.
- Reflect on performances of Hamlet. Choose a couple of performances on the stage or in a movie and compare them. Whose version of the character you prefer and why?
- Elaborate on the movie Ophelia (2018). What’s intriguing about a story told from Ophelia’s point of view? Exemplify the differences from the original play and how the change of perspective affected the story.
- Explore Hamlet’s obsession with inaction and action . What stops Hamlet from acting decisively? Exemplify situations from the play when characters act quickly, without any doubt compared to Hamlet’s almost constant hesitance.
- Compare Hamlet and King Lear. What similar character traits have an impact on the respective plays? Can we call the prince and the king victims of the social norms?
- Think of how the play’s themes are relevant nowadays . Which of them remained timeless, relevant for any period? Are any themes become obsolete and useless in today’s world? Elaborate on each theme separately with examples from the play.
- Reflect on Hamlet’s mood swings . Provide examples of how the prince’s mood affects his actions and speech. What can and did influence his mood?
- Examine Polonius’ death. Why was he hiding behind the tapestry during the scene? Was it his idea? How did he die? Elaborate on irony in the way he was murdered. How did it affect the plot?
- Analyze Hamlet as an actor. Is he good at playing a character? Elaborate on his dialogue with the First Player and his opinion about acting.
- Consider the motif of betrayal. Who betrays Hamlet? Explain how the attitude towards this act varies from character to character. How does Hamlet’s betrayal affect Ophelia?
- Explore the connection between honor and revenge . Explain why it’s the principal motivation for such characters as Hamlet, Laertes, and Fortinbras. Comment on scenes where it reveals itself through actions and conversations.
- Elaborate on Hamlet’s death. Was it the only logical conclusion for Hamlet’s psychological and emotional development? Was he satisfied?
- Comment on the genre of the play . Can we call it revenge tragedy without any reservation? How did Shakespeare ruin the genre by Hamlet ?
- Compare Hamlet and the Ghost. What can you say about the language that the characters use? List the lines that state that Hamlet and the Ghost look similar.
- Think of the father-son relationships in the play . Analyze the relationships between Hamlet and King Hamlet and compare them to those of Laertes and Polonius. Which features are common for both of them?
- Elaborate on the name Hamlet . What does it mean? What’s its country of origin? Add a sentence or two about Amleth.
- Consider allusions to historical figures in the play. Why does Hamlet mention Alexander the Great and Julius Caesar in act 5? Why did Shakespeare include allusions at all?
- Examine soliloquies in Hamlet . What’s their role in the play? Provide lines from soliloquies that let us dive into the thoughts and intentions of a character. Does anyone lie during such a speech?
- Compare the two film adaptations of the play. Elaborate on different film techniques and alterations of the plot. Concentrate on one scene in particular and explain what changes were made.
- Explore Hamlet’s nihilism. When does Hamlet start to display features that are inherent to this school of thought? Explain how the prince came to nihilism, what pushed him to this.
- List the most painful moments of Hamlet’s life and elaborate on them. Include events that happened before the first act and within the play. Prove your point with evidence from the prince’s lines.
- Think of what poison represents. What does it refer to? Who dies from poison in the play?
- Consider the play from the public’s perspective. How does Claudius manipulate the public’s opinion? What do people think of the new king and Hamlet?
- Compare and contrast Gertrude and Ophelia. What traits do they have in common? Explain differences and similarities in their affection towards Hamlet. Who controls these women?
- Elaborate on the villain of the story. Who can be considered an antagonist of the play? Why do some people regard Hamlet as a villain?
- Imagine how Hamlet could’ve reacted to modern society. What aspects of the future would he appreciate? What social norms would shock him? Would he be more comfortable in our period?
- Evaluate all the relationships in Hamlet’s life. What’s the most significant one? Why? What relationships changed throughout the play?
- Comment on contradictions in the play. What contradictions does Hamlet face? Is he himself a contradictory character? Provide examples of Hamlet’s contradictions
- Explore the fencing in the last scene of Hamlet . What does it contribute to the story? Does it affect the end of the duel?
- Elaborate on the gravediggers. How did their job affect their attitude towards death? Comment on their humor and whether it’s a coping mechanism. Does it illustrate their perception of life?
- Compare Claudius and King Hamlet. What qualities differentiate them? What do they have in common? Speculate on who was a more talented politician and a better leader.
- Think of comic relief in Hamlet . Comment on how Polonius, Osric, gravediggers, and Hamlet’s dialogues with them enlighten the mood. Was the humor appropriate for revenge tragedies before Shakespeare?
- Consider foreshadowing in the play. What events are foreshadowed early on in Hamlet ? Present lines and features from act 1 that indicate the tragic end.
- Elaborate on justice and truth . How does Shakespeare show attitude towards justice common for this time? Does Hamlet approach fairness differently from the others? Elaborate on how Hamlet both pursue the truth and ignores it.
- Examine the “Get thee to a nunnery, go.” sentence. Why did Hamlet say so to Ophelia? What made the prince think that she was vicious?
- Comment on Hamlet’s cruelty. When does Hamlet become cruel towards other characters? Is he cruel towards himself? Analyze situations where Hamlet talks viciously and whether it’s intentional or not.
- Explore Hamlet’s character . Why is the prince such an unusual figure for revenge tragedies? Explain how Shakespeare created the hero who struggles to act with firmness and constantly reflects on his actions and decisions. Is he easy to understand and relate to?
- Analyze the play within the play. What’s its role in plot development? Why did Hamlet let the play take place? Explain what scene he added and why. Elaborate on the title The Mousetrap .
- Examine the consequences of revenge . What conclusion does Shakespeare provide for the theme of revenge? Explain how does it influence the deaths of Hamlet and Laertes, the absolute victory of Fortinbras.
- Reflect on Hamlet’s hesitance to kill Claudius . Why does he consider murdering his uncle in act 1? What stops him? Illustrate all the occasions when Hamlet could’ve killed Claudius but didn’t, and one time he did. What pushed him in the end?
- Compare Claudius to Laertes. Are there any similarities? How do these characters form an alliance by the end of the play?
- Comment on Gertrude’s guiltiness . Hamlet considers his mother guilty of too many crimes, but was she guilty of anything? Speculate whether she participated in King Hamlet’s murder or had an affair with Claudius before her husband’s death. Was she loyal to Hamlet?
- Elaborate on the “Something is rotten in the state of Denmark …“ line. Who says it? Explain the context of the line, its meaning, and what it foreshadows.
- Examine Polonius’ advice to Laertes. Provide its meaning and reflect on Polonius’ intentions. Why is this speech ironic?
Thanks for checking our list! You can consider some free Hamlet samples or other articles about the play, following the links below.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email
Study Guide Menu
- Summary & Analysis
- Genre & Literary Analysis
- Important Quotes
- Essay Topics
- Essay Samples
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, August 14). 107 Exceptional Hamlet Essay Topics: Questions & Prompts. https://ivypanda.com/lit/hamlet-study-guide/essay-topics/
"107 Exceptional Hamlet Essay Topics: Questions & Prompts." IvyPanda , 14 Aug. 2023, ivypanda.com/lit/hamlet-study-guide/essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2023) '107 Exceptional Hamlet Essay Topics: Questions & Prompts'. 14 August.
IvyPanda . 2023. "107 Exceptional Hamlet Essay Topics: Questions & Prompts." August 14, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/lit/hamlet-study-guide/essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "107 Exceptional Hamlet Essay Topics: Questions & Prompts." August 14, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/lit/hamlet-study-guide/essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "107 Exceptional Hamlet Essay Topics: Questions & Prompts." August 14, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/lit/hamlet-study-guide/essay-topics/.
Home — Essay Samples — Literature — Hamlet — Hamlet Character Analysis
Hamlet Character Analysis
- Categories: Hamlet
About this sample

Words: 612 |
Published: Mar 19, 2024
Words: 612 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, motivations and ambivalence, identity and madness, morality and conscience, impact on the narrative.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Literature

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1267 words
1 pages / 688 words
3 pages / 1533 words
3.5 pages / 1480 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Hamlet
Shakespeare, William. Hamlet. Ed. Ann Thompson and Neil Taylor. London: Arden Shakespeare, 2006. Print.Frye, Northrop. "The Mythos of Autumn." Shakespearean Criticism, edited by Laurie Lanzen Harris, vol. 4, Gale, 1986, pp. [...]
William Shakespeare's play Hamlet is a timeless classic that has captured the hearts of audiences around the world for centuries. The play's protagonist, Hamlet, is a complex and multi-dimensional character, whose significance [...]
In conclusion, Hamlet is a masterpiece of literature and theater, endowed with numerous layers of meaning and exploration. Through our examination of the character of Hamlet, the play's themes and motifs, its symbolism and [...]
Shakespeare's Hamlet is renowned for its complex characters and timeless themes. Among these characters, Hamlet and Laertes stand out as intriguing figures whose parallel journeys ultimately lead to their tragic downfalls. [...]
Critic Northrup Frye has evaluated Hamlet as a play without catharsis, a tragedy in which everything noble and heroic is smothered under ferocious revenge codes, treachery, spying and the consequences of weak actions by broken [...]
Shakespeare’s Hamlet is a play rife with moral dilemmas. Religious codes often clash with desires and instinctual feelings in the minds of the characters, calling into question which courses of action are truly the righteous [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

COMMENTS
Focused on: Reasons for Hamlet's procrastination and its consequences. Characters mentioned: Hamlet, Claudius, Gertrude, Ophelia, Polonius. Role of Women in Twelfth Night and Hamlet by Shakespeare. Genre: Research Paper. Words: 2527. Focused on: Women in Shakespeare's Twelfth Night and Hamlet.
'Although Hamlet sometimes disappoints loved ones, tells lies, and even murders, we are still able to sympathise with him." Discuss this statement in an essay of about 1½ pages, showing clearly whether you believe this to be true. 20 There are many contrasts in the play, Hamlet. For example: there is honesty but also dishonesty, faithfulness and
The word "excessive" is more significant than the word "pride" from the perspective of a theory of tragic excess. In this theory, hamartia is not simply an "error," "mistake," or "flaw.". It is an act or habit of excessively displaying a trait that, if employed moderately, would be perfectly fine.
Hamlet Essay Topics and Outline Examples Essay Title 1: The Tragic Hero in "Hamlet": Analyzing the Complex Character of Prince Hamlet. Thesis Statement: This essay delves into the character of Prince Hamlet in Shakespeare's "Hamlet," examining his tragic flaws, internal conflicts, and the intricate web of relationships that contribute to his downfall, ultimately highlighting his status as a ...
Sample Essay Outlines. PDF Cite. The following paper topics are based on the entire play. Following each topic is a thesis and sample outline. Use these as a starting point for your paper. Topic ...
This document contains a model essay on Shakespeare's 'Hamlet', which has been prescribed for examination in 2017 The essay is designed to fulfil the following aims: It is a revision document. Students should be able to read the essay and revise the key aspects of the relationship discussed in the question.
HAMLET. 2 . The Theme of Madness in Shakespeare's . Hamlet . Although revenge is the most obvious theme in . Hamlet, Shakespeare writes extensively about madness. As the play progresses, the thin line between sanity and madness blurs, leaving readers to wonder if Hamlet is insane. Ophelia has a minor role in the play, but the theme of
Title: Microsoft Word - (9.5) Annotated literature essay - Marzanne - 22Aug 2013.docx Author: marzanne.jansevanren Created Date: 20131016174435Z
The general theme of the play deals with a society that is, or has already gone to pieces. 1. Another theme of the play is that of revenge. Hamlet must avenge his father's death. Revenge is ...
Hamlet's understanding of loyal ambition degrades his introspection, as Fortinbras's determination, "to all that fortune…even for an eggshell" prompts Hamlet's final decision to act a, "carnal, bloody and unnatural" revenge, contrasting his initial indecisive confliction.
Looking for a free Hamlet PDF? Click below to download Shakespeare's full Hamlet play in PDF format for free, to read or share. Browse all Hamlet resources. ... Character summaries, plot outlines, example essays and famous quotes, soliloquies and monologues: All's Well That Ends Well Antony and Cleopatra As You Like It The Comedy of Errors ...
QUESTION 10: HAMLET - ESSAY QUESTION Below is the basis for answering this essay. Use the following as a guideline only. However, also allow for answers that are different, original and show evidence of critical thought and interpretation. A range of examples should be used by the candidates to support their arguments.
wounds Hamlet with the poisoned sword, and then Hamlet wounds Laertes when they accidentally exchange swords. When Laertes reveals the conspiracy, Hamlet wounds the King and forces the poisoned drink upon him. Laertes and Hamlet reconcile, and Laertes dies; Hamlet prevents Horatio from drinking the poison so that he can live to tell the truth.
At the end of each act, there are also act-specific essay questions and a series of enrichment tasks (marking rubrics are provided after the Mini Essay section). In the Mini Essay section, there is also a wide selection of rigorous essay topics, ensuring that students deal with the play in its entirety.
Contextual question. In a contextual question, you are given an extract (about 25-30 lines) from the drama. You will then have to answer questions based on the extract. Some answers can be found in the extract. Other questions will test your understanding of other parts of the drama: plot, characters, symbols and themes.
Everyone Lies: An Analysis of Hamlet. Chunyang Ding IB English HL Ms. Morales 30 March 2014. Ding 2. Shakespeare's masterfully written tragedy, Hamlet, is wrought with tragedy and themes of revenge, but it is equally notable for the deception and lies that the players have towards each other. Throughout the play, characters hatch plans and ...
Toggle Contents Act and scene list. Characters in the Play ; Entire Play Events before the start of Hamlet set the stage for tragedy. When the king of Denmark, Prince Hamlet's father, suddenly dies, Hamlet's mother, Gertrude, marries his uncle Claudius, who becomes the new king.A spirit who claims to be the ghost of Hamlet's father describes his murder at the hands of Claudius and ...
Hamlet. Set in the kingdom of Denmark, 'Hamlet' tells the story of Prince Hamlet's quest for vengeance against his uncle, Claudius, who has murdered Hamlet's father, married his mother, and seized the throne. The play is a rich exploration of the complexities of the human psyche, morality, and the consequences of actions.
QUESTION 10: HAMLET - ESSAY QUESTION • Below is the basis for answering this essay. Use the following as a guideline only. However, also allow for answers that are different, original and show evidence of critical thought and interpretation. • A range of examples should be used by the candidates to support their arguments.
Essays on Hamlet. Written as the author taught Hamlet every semester for a decade, these lightning essays ask big conceptual questions about the play with the urgency of a Shakespeare lover, and answer them with the rigor of a Shakespeare scholar. In doing so, Hamlet becomes a lens for life today, generating insights on everything from ...
107 Exceptional Hamlet Essay Topics: Questions & Prompts. Every academic paper starts with a captivating idea, and Hamlet research paper or essay shouldn't be an exception. In the list below, our team has collected unique and inspiring topics for you. You can use them in your writing or develop your own idea according to the format.
Hamlet is a character driven by conflicting motivations, which adds depth and complexity to his portrayal. From the very beginning of the play, we see Hamlet's ambivalence towards his role as the avenger of his father's murder. While he is initially driven by a sense of duty to his father, he also expresses doubt and uncertainty about his ...