Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?

A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
Could boston be the next city to impose congestion pricing, alum has traveled the world to witness total solar eclipses, opening doors: rhonda harrison (eng’98,’04, grs’04), campus reacts and responds to israel-hamas war, reading list: what the pandemic revealed, remembering com’s david anable, cas’ john stone, “intellectual brilliance and brilliant kindness”, one good deed: christine kannler (cas’96, sph’00, camed’00), william fairfield warren society inducts new members, spreading art appreciation, restoring the “black angels” to medical history, in the kitchen with jacques pépin, feedback: readers weigh in on bu’s new president, com’s new expert on misinformation, and what’s really dividing the nation, the gifts of great teaching, sth’s walter fluker honored by roosevelt institute, alum’s debut book is a ramadan story for children, my big idea: covering construction sites with art, former terriers power new professional women’s hockey league, five trailblazing alums to celebrate during women’s history month, alum beata coloyan is boston mayor michelle wu’s “eyes and ears” in boston neighborhoods.
share this!
August 16, 2021
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Bioluminescence first evolved in animals at least 540 million years ago, pushing back previous oldest dated example

Star bars show universe's early galaxies evolved much faster than previously thought

Scientists study lipids cell by cell, making new cancer research possible
2 hours ago

Squids' birthday influences mating: Male spear squids shown to become 'sneakers' or 'consorts' depending on birth date

Study finds rekindling old friendships as scary as making new ones
4 hours ago

How light can vaporize water without the need for heat
5 hours ago

Researchers develop eggshell 'bioplastic' pellet as sustainable alternative to plastic

Previous theory on how electrons move within protein nanocrystals might not apply in every case
6 hours ago

Fruit fly pest meets its evolutionary match in parasitic wasp

World's chocolate supply threatened by devastating virus
Relevant physicsforums posts, studying "useful" vs. "useless" stuff in school, motivating high school physics students with popcorn physics.
Apr 3, 2024
How is Physics taught without Calculus?
Mar 29, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Mar 24, 2024
The changing physics curriculum in 1961
Suggestions for using math puzzles to stimulate my math students.
Mar 21, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you

Training of brain processes makes reading more efficient
Apr 18, 2024

Researchers find lower grades given to students with surnames that come later in alphabetical order
Apr 17, 2024

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024

More than money, family and community bonds prep teens for college success: Study
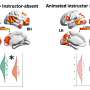
Research reveals significant effects of onscreen instructors during video classes in aiding student learning
Mar 25, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- The Revolution of Yulia Navalnaya
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- What's the Deal With the Bitcoin Halving?
- If You're Dating Right Now , You're Brave: Column
- The AI That Could Heal a Divided Internet
- Fallout Is a Brilliant Model for the Future of Video Game Adaptations
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]

Search form
- Find Stories
- For Journalists
Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework
A Stanford researcher found that students in high-achieving communities who spend too much time on homework experience more stress, physical health problems, a lack of balance and even alienation from society. More than two hours of homework a night may be counterproductive, according to the study.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
• Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
• Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
• Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
Students, read the entire article, then tell us:
Should we get rid of homework? Why, or why not?
Is homework an outdated, ineffective or counterproductive tool for learning? Do you agree with the authors of the paper that homework is harmful and worsens inequalities that exist between students’ home circumstances?
Or do you agree with Mr. Kang that homework still has real educational value?
When you get home after school, how much homework will you do? Do you think the amount is appropriate, too much or too little? Is homework, including the projects and writing assignments you do at home, an important part of your learning experience? Or, in your opinion, is it not a good use of time? Explain.
In these letters to the editor , one reader makes a distinction between elementary school and high school:
Homework’s value is unclear for younger students. But by high school and college, homework is absolutely essential for any student who wishes to excel. There simply isn’t time to digest Dostoyevsky if you only ever read him in class.
What do you think? How much does grade level matter when discussing the value of homework?
Is there a way to make homework more effective?
If you were a teacher, would you assign homework? What kind of assignments would you give and why?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Jeremy Engle joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2018 after spending more than 20 years as a classroom humanities and documentary-making teacher, professional developer and curriculum designer working with students and teachers across the country. More about Jeremy Engle
Are You Down With or Done With Homework?
- Posted January 17, 2012
- By Lory Hough

The debate over how much schoolwork students should be doing at home has flared again, with one side saying it's too much, the other side saying in our competitive world, it's just not enough.
It was a move that doesn't happen very often in American public schools: The principal got rid of homework.
This past September, Stephanie Brant, principal of Gaithersburg Elementary School in Gaithersburg, Md., decided that instead of teachers sending kids home with math worksheets and spelling flash cards, students would instead go home and read. Every day for 30 minutes, more if they had time or the inclination, with parents or on their own.
"I knew this would be a big shift for my community," she says. But she also strongly believed it was a necessary one. Twenty-first-century learners, especially those in elementary school, need to think critically and understand their own learning — not spend night after night doing rote homework drills.
Brant's move may not be common, but she isn't alone in her questioning. The value of doing schoolwork at home has gone in and out of fashion in the United States among educators, policymakers, the media, and, more recently, parents. As far back as the late 1800s, with the rise of the Progressive Era, doctors such as Joseph Mayer Rice began pushing for a limit on what he called "mechanical homework," saying it caused childhood nervous conditions and eyestrain. Around that time, the then-influential Ladies Home Journal began publishing a series of anti-homework articles, stating that five hours of brain work a day was "the most we should ask of our children," and that homework was an intrusion on family life. In response, states like California passed laws abolishing homework for students under a certain age.
But, as is often the case with education, the tide eventually turned. After the Russians launched the Sputnik satellite in 1957, a space race emerged, and, writes Brian Gill in the journal Theory Into Practice, "The homework problem was reconceived as part of a national crisis; the U.S. was losing the Cold War because Russian children were smarter." Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end.
The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier. By the early-1980s, however, the pendulum swung again with the publication of A Nation at Risk , which blamed poor education for a "rising tide of mediocrity." Students needed to work harder, the report said, and one way to do this was more homework.
For the most part, this pro-homework sentiment is still going strong today, in part because of mandatory testing and continued economic concerns about the nation's competitiveness. Many believe that today's students are falling behind their peers in places like Korea and Finland and are paying more attention to Angry Birds than to ancient Babylonia.
But there are also a growing number of Stephanie Brants out there, educators and parents who believe that students are stressed and missing out on valuable family time. Students, they say, particularly younger students who have seen a rise in the amount of take-home work and already put in a six- to nine-hour "work" day, need less, not more homework.
Who is right? Are students not working hard enough or is homework not working for them? Here's where the story gets a little tricky: It depends on whom you ask and what research you're looking at. As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework , points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps." At best, he says, homework shows only an association, not a causal relationship, with academic achievement. In other words, it's hard to tease out how homework is really affecting test scores and grades. Did one teacher give better homework than another? Was one teacher more effective in the classroom? Do certain students test better or just try harder?
"It is difficult to separate where the effect of classroom teaching ends," Vatterott writes, "and the effect of homework begins."
Putting research aside, however, much of the current debate over homework is focused less on how homework affects academic achievement and more on time. Parents in particular have been saying that the amount of time children spend in school, especially with afterschool programs, combined with the amount of homework given — as early as kindergarten — is leaving students with little time to run around, eat dinner with their families, or even get enough sleep.
Certainly, for some parents, homework is a way to stay connected to their children's learning. But for others, homework creates a tug-of-war between parents and children, says Liz Goodenough, M.A.T.'71, creator of a documentary called Where Do the Children Play?
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. "A nag-free activity could engage family time: Ask a parent about his or her own childhood. Interview siblings."

Instead, as the authors of The Case Against Homework write, "Homework overload is turning many of us into the types of parents we never wanted to be: nags, bribers, and taskmasters."
Leslie Butchko saw it happen a few years ago when her son started sixth grade in the Santa Monica-Malibu (Calif.) United School District. She remembers him getting two to four hours of homework a night, plus weekend and vacation projects. He was overwhelmed and struggled to finish assignments, especially on nights when he also had an extracurricular activity.
"Ultimately, we felt compelled to have Bobby quit karate — he's a black belt — to allow more time for homework," she says. And then, with all of their attention focused on Bobby's homework, she and her husband started sending their youngest to his room so that Bobby could focus. "One day, my younger son gave us 15-minute coupons as a present for us to use to send him to play in the back room. … It was then that we realized there had to be something wrong with the amount of homework we were facing."
Butchko joined forces with another mother who was having similar struggles and ultimately helped get the homework policy in her district changed, limiting homework on weekends and holidays, setting time guidelines for daily homework, and broadening the definition of homework to include projects and studying for tests. As she told the school board at one meeting when the policy was first being discussed, "In closing, I just want to say that I had more free time at Harvard Law School than my son has in middle school, and that is not in the best interests of our children."
One barrier that Butchko had to overcome initially was convincing many teachers and parents that more homework doesn't necessarily equal rigor.
"Most of the parents that were against the homework policy felt that students need a large quantity of homework to prepare them for the rigorous AP classes in high school and to get them into Harvard," she says.
Stephanie Conklin, Ed.M.'06, sees this at Another Course to College, the Boston pilot school where she teaches math. "When a student is not completing [his or her] homework, parents usually are frustrated by this and agree with me that homework is an important part of their child's learning," she says.
As Timothy Jarman, Ed.M.'10, a ninth-grade English teacher at Eugene Ashley High School in Wilmington, N.C., says, "Parents think it is strange when their children are not assigned a substantial amount of homework."
That's because, writes Vatterott, in her chapter, "The Cult(ure) of Homework," the concept of homework "has become so engrained in U.S. culture that the word homework is part of the common vernacular."
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn.
"Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of time that children will have to do something every night (or several times a week). … This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools — public and private, elementary and secondary."
Brant had to confront this when she cut homework at Gaithersburg Elementary.
"A lot of my parents have this idea that homework is part of life. This is what I had to do when I was young," she says, and so, too, will our kids. "So I had to shift their thinking." She did this slowly, first by asking her teachers last year to really think about what they were sending home. And this year, in addition to forming a parent advisory group around the issue, she also holds events to answer questions.
Still, not everyone is convinced that homework as a given is a bad thing. "Any pursuit of excellence, be it in sports, the arts, or academics, requires hard work. That our culture finds it okay for kids to spend hours a day in a sport but not equal time on academics is part of the problem," wrote one pro-homework parent on the blog for the documentary Race to Nowhere , which looks at the stress American students are under. "Homework has always been an issue for parents and children. It is now and it was 20 years ago. I think when people decide to have children that it is their responsibility to educate them," wrote another.
And part of educating them, some believe, is helping them develop skills they will eventually need in adulthood. "Homework can help students develop study skills that will be of value even after they leave school," reads a publication on the U.S. Department of Education website called Homework Tips for Parents. "It can teach them that learning takes place anywhere, not just in the classroom. … It can foster positive character traits such as independence and responsibility. Homework can teach children how to manage time."
Annie Brown, Ed.M.'01, feels this is particularly critical at less affluent schools like the ones she has worked at in Boston, Cambridge, Mass., and Los Angeles as a literacy coach.
"It feels important that my students do homework because they will ultimately be competing for college placement and jobs with students who have done homework and have developed a work ethic," she says. "Also it will get them ready for independently taking responsibility for their learning, which will need to happen for them to go to college."
The problem with this thinking, writes Vatterott, is that homework becomes a way to practice being a worker.
"Which begs the question," she writes. "Is our job as educators to produce learners or workers?"
Slate magazine editor Emily Bazelon, in a piece about homework, says this makes no sense for younger kids.
"Why should we think that practicing homework in first grade will make you better at doing it in middle school?" she writes. "Doesn't the opposite seem equally plausible: that it's counterproductive to ask children to sit down and work at night before they're developmentally ready because you'll just make them tired and cross?"
Kohn writes in the American School Board Journal that this "premature exposure" to practices like homework (and sit-and-listen lessons and tests) "are clearly a bad match for younger children and of questionable value at any age." He calls it BGUTI: Better Get Used to It. "The logic here is that we have to prepare you for the bad things that are going to be done to you later … by doing them to you now."
According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased on average from about 8 minutes in 1981 to 22 minutes in 2003. A review of research by Duke University Professor Harris Cooper found that for elementary school students, "the average correlation between time spent on homework and achievement … hovered around zero."
So should homework be eliminated? Of course not, say many Ed School graduates who are teaching. Not only would students not have time for essays and long projects, but also teachers would not be able to get all students to grade level or to cover critical material, says Brett Pangburn, Ed.M.'06, a sixth-grade English teacher at Excel Academy Charter School in Boston. Still, he says, homework has to be relevant.
"Kids need to practice the skills being taught in class, especially where, like the kids I teach at Excel, they are behind and need to catch up," he says. "Our results at Excel have demonstrated that kids can catch up and view themselves as in control of their academic futures, but this requires hard work, and homework is a part of it."
Ed School Professor Howard Gardner basically agrees.
"America and Americans lurch between too little homework in many of our schools to an excess of homework in our most competitive environments — Li'l Abner vs. Tiger Mother," he says. "Neither approach makes sense. Homework should build on what happens in class, consolidating skills and helping students to answer new questions."
So how can schools come to a happy medium, a way that allows teachers to cover everything they need while not overwhelming students? Conklin says she often gives online math assignments that act as labs and students have two or three days to complete them, including some in-class time. Students at Pangburn's school have a 50-minute silent period during regular school hours where homework can be started, and where teachers pull individual or small groups of students aside for tutoring, often on that night's homework. Afterschool homework clubs can help.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.) Other schools offer an extended day that allows teachers to cover more material in school, in turn requiring fewer take-home assignments. And for others, like Stephanie Brant's elementary school in Maryland, more reading with a few targeted project assignments has been the answer.
"The routine of reading is so much more important than the routine of homework," she says. "Let's have kids reflect. You can still have the routine and you can still have your workspace, but now it's for reading. I often say to parents, if we can put a man on the moon, we can put a man or woman on Mars and that person is now a second-grader. We don't know what skills that person will need. At the end of the day, we have to feel confident that we're giving them something they can use on Mars."
Read a January 2014 update.
Homework Policy Still Going Strong
Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Commencement Marshal Sarah Fiarman: The Principal of the Matter

Making Math “Almost Fun”
Alum develops curriculum to entice reluctant math learners

Reshaping Teacher Licensure: Lessons from the Pandemic
Olivia Chi, Ed.M.'17, Ph.D.'20, discusses the ongoing efforts to ensure the quality and stability of the teaching workforce

School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: January 23, 2020

Homework is a word that most students dread hearing. After hours upon hours of sitting in class , the last thing we want is more schoolwork over our precious weekends. While it’s known to be a staple of traditional schooling, homework has also become a rather divise topic. Some feel as though homework is a necessary part of school, while others believe that the time could be better invested. Should students have homework? Have a closer look into the arguments on both sides to decide for yourself.

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
Why should students have homework, 1. homework encourages practice.
Many people believe that one of the positive effects of homework is that it encourages the discipline of practice. While it may be time consuming and boring compared to other activities, repetition is needed to get better at skills. Homework helps make concepts more clear, and gives students more opportunities when starting their career .
2. Homework Gets Parents Involved
Homework can be something that gets parents involved in their children’s lives if the environment is a healthy one. A parent helping their child with homework makes them take part in their academic success, and allows for the parent to keep up with what the child is doing in school. It can also be a chance to connect together.
3. Homework Teaches Time Management
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills , forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking. One of the positive effects of homework is that it forces decision making and compromises to be made.
4. Homework Opens A Bridge Of Communication
Homework creates a connection between the student, the teacher, the school, and the parents. It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student.
5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can’t see it in the moment.
6. Homework Reduces Screen Time
Many students in North America spend far too many hours watching TV. If they weren’t in school, these numbers would likely increase even more. Although homework is usually undesired, it encourages better study habits and discourages spending time in front of the TV. Homework can be seen as another extracurricular activity, and many families already invest a lot of time and money in different clubs and lessons to fill up their children’s extra time. Just like extracurricular activities, homework can be fit into one’s schedule.

The Other Side: Why Homework Is Bad
1. homework encourages a sedentary lifestyle.
Should students have homework? Well, that depends on where you stand. There are arguments both for the advantages and the disadvantages of homework.
While classroom time is important, playground time is just as important. If children are given too much homework, they won’t have enough playtime, which can impact their social development and learning. Studies have found that those who get more play get better grades in school , as it can help them pay closer attention in the classroom.
Children are already sitting long hours in the classroom, and homework assignments only add to these hours. Sedentary lifestyles can be dangerous and can cause health problems such as obesity. Homework takes away from time that could be spent investing in physical activity.
2. Homework Isn’t Healthy In Every Home
While many people that think homes are a beneficial environment for children to learn, not all homes provide a healthy environment, and there may be very little investment from parents. Some parents do not provide any kind of support or homework help, and even if they would like to, due to personal barriers, they sometimes cannot. Homework can create friction between children and their parents, which is one of the reasons why homework is bad .
3. Homework Adds To An Already Full-Time Job
School is already a full-time job for students, as they generally spend over 6 hours each day in class. Students also often have extracurricular activities such as sports, music, or art that are just as important as their traditional courses. Adding on extra hours to all of these demands is a lot for children to manage, and prevents students from having extra time to themselves for a variety of creative endeavors. Homework prevents self discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system. This is one of the main disadvantages of homework.
4. Homework Has Not Been Proven To Provide Results
Endless surveys have found that homework creates a negative attitude towards school, and homework has not been found to be linked to a higher level of academic success.
The positive effects of homework have not been backed up enough. While homework may help some students improve in specific subjects, if they have outside help there is no real proof that homework makes for improvements.
It can be a challenge to really enforce the completion of homework, and students can still get decent grades without doing their homework. Extra school time does not necessarily mean better grades — quality must always come before quantity.
Accurate practice when it comes to homework simply isn’t reliable. Homework could even cause opposite effects if misunderstood, especially since the reliance is placed on the student and their parents — one of the major reasons as to why homework is bad. Many students would rather cheat in class to avoid doing their homework at home, and children often just copy off of each other or from what they read on the internet.
5. Homework Assignments Are Overdone
The general agreement is that students should not be given more than 10 minutes a day per grade level. What this means is that a first grader should be given a maximum of 10 minutes of homework, while a second grader receives 20 minutes, etc. Many students are given a lot more homework than the recommended amount, however.
On average, college students spend as much as 3 hours per night on homework . By giving too much homework, it can increase stress levels and lead to burn out. This in turn provides an opposite effect when it comes to academic success.
The pros and cons of homework are both valid, and it seems as though the question of ‘‘should students have homework?’ is not a simple, straightforward one. Parents and teachers often are found to be clashing heads, while the student is left in the middle without much say.
It’s important to understand all the advantages and disadvantages of homework, taking both perspectives into conversation to find a common ground. At the end of the day, everyone’s goal is the success of the student.
Related Articles
Is Homework Valuable or Not? Try Looking at Quality Instead

- Share article
Is there an end in sight to the “homework wars?”
Homework is one those never-ending debates in K-12 circles that re-emerges every few years, bringing with it a new collection of headlines. Usually they bemoan how much homework students have, or highlight districts and even states that have sought to cap or eliminate homework .
Now, a new analysis from the Center for American Progress suggests a more fruitful way of thinking about this problem. Maybe, it suggests, what we should be doing is looking at what students are routinely being asked to do in take-home assignments, how well that homework supports their learning goals (or doesn’t), and make changes from there.
The analysis of nearly 200 pieces of homework concludes that much of what students are asked to do aligns to the Common Core State Standards—a testament to how pervasive the standards are in the U.S. education system, even though many states have tweaked, renamed, or replaced them. However, most of the homework embodied basic, procedural components of the standards, rather than the more difficult skills—such as analyzing or extending their knowledge to new problems.
“We were surprised by the degree of alignment. And we were also surprised by the degree that the homework was rote, and how much some of this stuff felt like Sudoku,” said Ulrich Boser, a senior fellow at CAP. “It made the homework debate make a lot more sense about why parents are frustrated.”
It is also similar to the findings of groups like the Education Trust, which have found that classwork tends to be aligned to state standards, but not all that rigorous.
Collecting Homework Samples
The CAP analysis appears to be one of the first studies to look at homework rigor using a national survey lens. Many studies of homework are based on one school or one district’s assignments, which obviously limits their applicability. Attempts to synthesize all this research have led to some hard-to-parse conclusions. One of the most cited studies concludes there’s some connection for grades 6-12 between homework and test scores, but less so for elementary students, and less of an impact on actual grades.
Another problem is that students’ experiences with homework seem to vary so dramatically: A Brookings Institution report based on survey data from the National Assessment of Educational Progress concluded that, while on average students aren’t overburdened by homework, a subset of students do appear to get hours upon hours.
The CAP analysis, instead, was based on getting a sample of parents from across the country to send in examples of their children’s homework. The researchers used MTurk, a crowdsourcing service offered by Amazon.com to recruit parents. Of the 372 parents who responded, the researchers got a pile of 187 useable assignments. Next, John Smithson, an emeritus researcher at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, had teams grade them on a taxonomy looking at both the content and the “cognitive demand,” or difficulty, of the work. The index fell on a 1 to 10 scale, with a score 4 to 6 range considered as “good” alignment.
The results? On average, math assignments fell within this range, while the ELA ones were slightly weaker, in the 3 to 5 range.
But the real eye-opening graphic is this one, which shows that by far the assignments were mostly low-level.

This makes some logical sense when you think about it. Just as with teaching and testing, it is much easier to write homework assignments prioritizing basic arithmetic drills and fill-in-the-blank vocabulary words than ones that get students to “prove” or “generalize” some tenet. (I suspect prepackaged curricula, too, probably lean more toward rote stuff than cognitively demanding exercises.)
Here’s another explanation: Many teachers believe homework should be for practicing known content, not learning something new. This is partially to help close the “homework gap” that surfaces because some students can access parent help or help via technology, while other students can’t. It’s possible that teachers are purposefully giving lower-level work to their students to take home for this reason.
To be sure, Boser said, it’s not that all lower-level work is intrinsically bad: Memorization does have a place in learning. But assignments like color-in-the-blank and word searches are probably just a waste of students’ time. “Homework assignments,” the study says, “should be thought-provoking.”
Study Limitations
The study does come with some significant limitations, so you must use caution in discussing its results. The surveyed population differs from the population at large, overrepresenting mothers over fathers and parents of K-5 students, and underrepresenting black parents. Also, the majority of the assignments the parents sent in came from the elementary grades.
The report makes suggestions on how districts can strategically improve the quality of their homework, rather than deciding to chuck it out altogether.
One is to is to audit homework assignments to make sure they’re actually useful at building some of the more difficult skills. Another is to extend the “curriculum revolution” of the last decade, which has focused more attention on the quality and alignment of textbooks and materials, to homework. A third is to use appropriate technology so students can access out-of-school supports for challenging homework.
A version of this news article first appeared in the Curriculum Matters blog.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update

Is My Kid the Asshole?

Is Homework Helpful or Harmful?
Research suggests homework doesn’t make young kids smarter. but it may widen the achievement gap..

Welcome to Is My Kid the Asshole? , a newsletter from science journalist and author Melinda Wenner Moyer, which you can read more about here . If you like it, please subscribe and/or share this post with someone else who would too.
Hello! I’m excited to be sharing my inaugural Dear Melinda column . This week it’s free for everyone, but next week my Friday column will only go out to paid subscribers , so don’t forget to subscribe. These columns will address a broad range of parenting questions with science.
Right before the pandemic hit, I dug into the science of homework. I had heard from parents that many elementary-aged kids were getting more than the recommended amount — the National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association have long advised that students should get a maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level per night, meaning that first graders should have at most 10 minutes, second graders 20 minutes, and so on — and I wondered: What do we know about how homework affects young kids? Does it help them learn? Does it pose any downsides?
Now that kids are back in school again (and my kids, at least, are once again getting homework), I thought it would be a good time to share what I learned.

First, it’s important to point out that kids didn’t always get homework. In the early 20th century, educators and politicians were adamantly against it. The California state legislature passed a law banning homework for children under the age of 15 in 1901, and in 1930, the American Child Health Association lumped homework in with child labor as the “chief causes of the high death and morbidity rates from tuberculosis and heart disease among adolescents.” Oh my.
Everything changed when the Soviets launched Sputnik in 1957. Worries mounted that American children weren’t as smart as their Russian counterparts. At that point, “homework became an instrument of national defense policy,” explained Carnegie Mellon historian Steven Schlossman and education researcher Brian Gill in a 2011 paper . From 1952 to 1962, the proportion of homework that high schoolers reported doing every night tripled. It dipped again in the anti-establishment ’60s, but in 1983, President Reagan’s National Commission on Excellence in Education lamented that “our once unchallenged pre-eminence in commerce, industry, science, and technological innovation is being overtaken by competitors throughout the world” and called for more homework to help address that concern.
All that is to say: Arguments over homework aren’t new. What’s interesting about this historical back-and-forth, though, is that it has centered almost entirely around homework in high school. At no point did educators and politicians argue that elementary school students should be doing homework. Until very recently.
In 1984, just over 40 percent of American 9-year-olds were doing up to an hour of homework a night. In 2012, that percentage had risen to 57 percent. (These may well be underestimates, too: The numbers are from the National Assessment of Educational Progress tests, which ask students how much homework they had the night before, but teachers often ease up on homework the night before standardized tests.) A 2015 survey of nearly 1,200 parents in Rhode Island revealed that even kindergartners were spending an average of 25 minutes each night on schoolwork.
Pro-homework experts argue that, in addition to helping young kids master lessons, homework is crucial because it teaches self-discipline, responsibility, resilience and conscientiousness. The anti-homework camp, on the other hand, thinks it’s busy work that does more harm than good: “Young children need time outside to move their bodies, free time to recover from the structure and demands placed on them, and quiet time to be alone with their thoughts,” said Emily W. King, a child psychologist in private practice in Raleigh, N.C., and a former school psychologist. Kids also need sleep, and yet surveys show that the more homework kids have, the less sleep they get.
In my house, there’s a four-hour window between the end of the school day and the beginning of the bedtime shuffle. After squeezing in sports, dinner and showers for my kids, there’s barely any time for downtime or imaginative play. The last thing I want to do is sit my kids back down to do more schoolwork.
Plus, overall, the research suggests that homework in elementary school doesn’t do much good.
In middle school and high school, research does generally find a positive association between homework and achievement (though the effects can be hard to tease out; kids who do more homework might fare better because they might come from higher-income families, attend better schools, or are simply more motivated). But that is not the case in elementary school.
In what is by far the most comprehensive analysis of the research on homework, published in 2006, Harris Cooper, a neuroscientist and social psychologist at Duke, and his colleagues found no relationship between the amount of homework elementary school students did and their overall academic achievement. In 2019, according to the National Assessment of Educational Progress, average mathematics test scores were actually lower among fourth graders whose teachers assigned more than 30 minutes of math homework a day.
“There is a misconception that the more homework you give, the more rigorous the education,” said Cathy Vatterott, a professor of education at the University of Missouri at St. Louis and a former middle school teacher and principal.
And yet some experts keep insisting on its value, arguing that homework helps children learn complex tasks and develop resilience. Cooper, the neuroscientist whose study found no relationship between homework and achievement in elementary school, agrees, arguing that homework builds conscientiousness.
I certainly want my kids to develop these skills. But when I hunted for research to support this assertion, all I could find was one 2017 study reporting that German fifth graders who spent more effort on their homework also became more conscientious over the next three years compared to students who put less effort into their homework. When I asked Cooper why, if homework makes elementary school kids more conscientious, this skill isn’t reflected in better academic performance, he told me it’s partly because kids aren’t doing enough homework for it to show an effect.
Even if homework does teach kids to be conscientious, other activities achieve the same goal. “Washing the dishes will teach discipline,” says Barbara Stengel, an education professor emerita at Vanderbilt University’s Peabody College of Education. “Making your bed in the morning will teach discipline.” My son developed resilience playing soccer (especially since his team usually lost); my daughter has learned self-control helping her dad make pancakes.
And too much homework can deprive kids of activities that we know are enriching. Childhood is the one and only period in which we get to enjoy imaginative play and explore diverse interests, yet adults seem hellbent on taking that freedom away and starting the never-ending grind of “real life” ever earlier. It’s cruel — and counterproductive. Studies have shown, for instance, that young kids learn more academic skills when they attend play-based schools rather than more academically oriented schools.
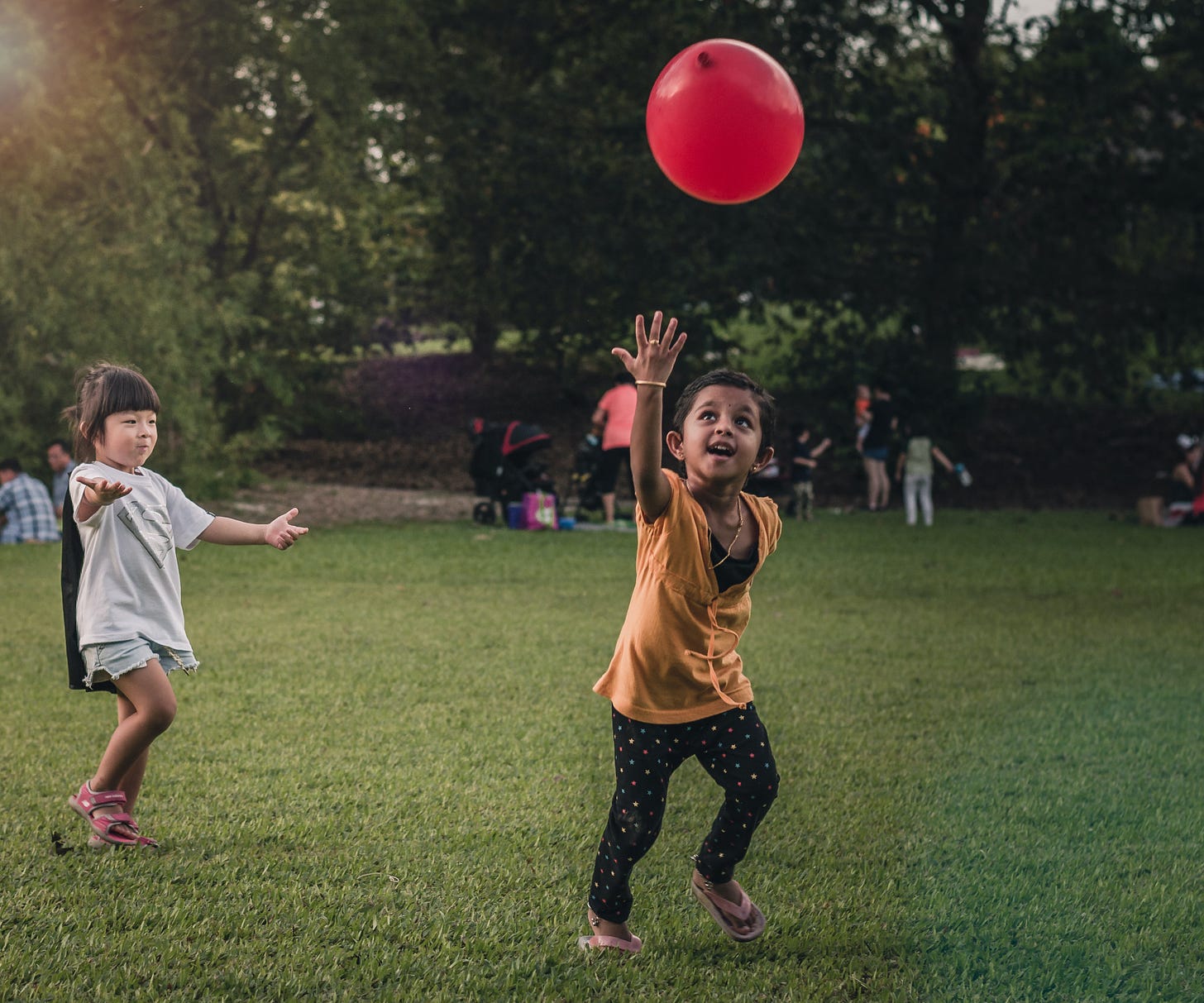

Many educators and psychologists therefore argue that elementary school homework is, for most students, more of a burden than a boon. This can be especially true for disadvantaged kids, who may not have a quiet place in which to do their homework, or who have to look after their siblings, or who don’t have parents (or tutors) available to help with confusing assignments. In these situations, homework can become a major source of stress, a situation in which “all we’re doing is taking family time away, reinforcing failure and causing confusion,” Stengel said.
Some research even suggests that homework worsens the achievement gap, which is as vast now as it was back in 1954.
In a 2011 study , the economist Marte Ronning analyzed data from more than 4,000 Dutch elementary school students, and found that in classes that assigned homework, the test score gap between the highest and lowest-achieving students was larger than it was in classes that did not assign homework.
In another 2011 study of American students, the sociologist Jonathan Daw analyzed how homework shapes individual achievement over time, concluding that homework widens the achievement gap in math, science and reading in secondary school.
A recent study published in American Sociological Review reveals an even more disturbing phenomenon — that disadvantaged kids, who often have the most trouble completing their homework, are also punished for their homework failings more than their wealthier classmates are. The research was conducted before the pandemic by Jessica Calarco, a sociologist at Indiana University. She spent two and a half years studying the third-, fourth- and fifth-grade classes at a public elementary school in a suburb in the Northeast. She conducted in-depth interviews with teachers, administrators, parents and students, observed classes and collected data.
In the classes, the standard punishment for forgotten or incomplete homework was for students to stay in for recess and receive a lower grade. But high-income students, she found, were far less likely to be punished for missing homework than low-income students were.
Calarco attributes this discrepancy in part to teacher incentives. It’s not hard for teachers to discern their students’ economic backgrounds; in fact, it’s part of their job to know what students are dealing with at home. And it’s especially obvious which kids have the wealthiest parents: These are the parents who are most likely to volunteer their time in the classroom and raise money for the school as members of the parent-teacher association. Teachers, Calarco found, treat these children differently. The teachers know it, too, but they don’t feel they have a choice.
“They want to enforce the rules,” she explained, “but at the same time, they worry that if they do enforce those homework rules, they will end up creating conflict with especially the highly involved, privileged parents on whom they are most dependent.”
Calarco speculates that teachers may also subconsciously believe that poorer students needed more strict rules, because they assume the children are not getting that structure from their parents.
One fifth grade student Calarco interviewed for her study was a lower-income student whose mother ran a home day care. When he got home from school each day, he was surrounded by the children his mother cared for, many of whom didn’t leave until 6:30. His mother would try to get him to do his homework anyway, but he would often nod off, get distracted or need to help his ailing grandfather, who also lived with them. By the time she could really sit him down to work on it, it would be 8:30 or 9, and often he wouldn’t get it done. His teacher concluded that “school just isn’t a priority in their house,” and rarely granted him exemptions from the homework rules.
“My sense,” Calarco told me, is that the teachers thought the poorer kids “needed stability and consistency and rules” in a way that higher-income students did not. “And they made those judgments even when — and sometimes because — they knew what those students were facing at home,” she added.
This study is small, of course, based on just one school. But with the other evidence, it makes me wonder: Given that one of our country’s key educational goals is to close the achievement gap, do we really want to be doubling down on an educational tool that seems to do the exact opposite?
There’s a better way forward. Some schools and districts are cutting down on the more rote forms of homework — worksheets and the like — in elementary school. In 2019, 16 percent of American fourth graders reported getting no math homework the night before, compared with only 4 percent in 2015. Instead, many schools are focusing homework assignments on reading, and sometimes that’s all they require.
It’s hard to know how homework amounts will shift now that kids are back in school this year. I hope that they will continue to follow a downward trajectory (and a very unscientific poll I conducted on Twitter yesterday suggests that so far this year, they are), but I worry that some schools will be so focused on catching kids up after last year that they might, instead, start to assign more. This could be an unwelcome burden for students who are already struggling with the transition back to school amid strict Covid-19 protocols.
But maybe, after such a trying year, schools will recognize that the emotional health of their students should be priority — and that homework doesn’t provide much of a benefit. My second grader has had upwards of 40 minutes of homework some nights this fall — one afternoon walking home from the school bus, she burst into tears over how much she had — but I was relieved to hear her teacher tell us during their virtual Curriculum Night earlier this week that if homework causes our kids stress or frustration, we should skip it. We will absolutely do this when it feels warranted — and given what I know from the research, I will not second-guess my decision.
If you’ve enjoyed this post, please subscribe to my newsletter ! Remember, too, that Founding Members will receive a free signed copy of my book, HOW TO RAISE KIDS WHO AREN’T ASSHOLES.

Buy my book!
Ready for more?

ChatGPT for Teachers
Trauma-informed practices in schools, teacher well-being, cultivating diversity, equity, & inclusion, integrating technology in the classroom, social-emotional development, covid-19 resources, invest in resilience: summer toolkit, civics & resilience, all toolkits, degree programs, trauma-informed professional development, teacher licensure & certification, how to become - career information, classroom management, instructional design, lifestyle & self-care, online higher ed teaching, current events, ending the homework debate: expert advice on what works.

After exploring the case against homework as well as the ways homework benefits students , it’s clear that both sides have valid arguments. After examining the evidence, we’ve come up with recommendations for both teachers and parents for homework that contributes to students’ academic growth.
What kind of homework is beneficial?
While some research points to homework increasing test scores, what researchers, parents, teachers, and even students want is homework that deepens content knowledge and thus understanding, critical thinking, and the ability of students to bring those to the classroom.

Homework must focus on quality, not quantity
In the research journal article “When is Homework Worth the Time?”, co-author Robert H. Tai summarizes the analysis of 18,000 tenth-grade transcripts by saying, “The results of this study imply that homework should be purposeful, and that the purpose must be understood by both the teacher and the students.” The authors determined that in order to be worthwhile, homework should meet the following criteria:
- Eliminate specific quantities of homework, such as the common suggestion of 10 minutes per night per grade.
- Instead of length, assignments should focus on making analytical connections.
- Math homework should consist of a small number of different types of exercises instead of large quantities of similiar problems.
- Science assignments should ask students to explore concepts rather than answer prescribed questions.
The study concluded with a call for further research in order to pinpoint the most effective type of homework.
Homework should meet the needs of each student
Another important factor in homework quality has to do with the needs of the recipients. Professor Gerald LeTendre discussed this in Penn State University’s article “Is Homework Bad for Kids?”, saying that young children do not benefit from homework as much as older students, because they lack the awareness and reflection required for good study habits.
Additionally, LeTendre points out that homework must address a child’s “actual academic problem.” In order to discuss these individual academic problems, differentiation, a key term in classroom management, must also be used in out-of-classroom work. LeTendre suggests that homework should be assigned at the individual level and reviewed with the student regularly to ensure its effectiveness.
One differentiation strategy: Flipped classrooms
Of course, differentiated homework leads to questions of fairness and the very real problem of teachers’ time. With increasingly large class sizes, creating individual homework plans for every student could be an insurmountable task. One alternative to such problems is the flipped classroom, where students engage the lecture material outside of the classroom and then classroom time is dedicated to what would have been homework under the traditional setup. Teachers are then free to allow students to work in groups or individually, visiting each group and testing their mastery along the way.
Skills developed through effective homework: Spaced repetition, retrieval practice, desirable difficulties, deliberate practice
Changing the entire functionality of the course isn’t necessary, though, if instructors remember key features of effective homework as identified by the emerging field of Mind, Brain, and Education, says Annie Murphy Paul. In the article “How Can We Make Homework Worthwhile?”, Paul identifies important characteristics such as spaced repetition, retrieval practice, and desirable difficulties.
Spaced repetition
Spaced repetition covers and revisits material over time in ways that traditional homework has not, revisiting material that has been covered in the recent and distant past to reinforce a student’s knowledge base.
Retrieval practice
Retrieval practice can lead to interesting assignments like the role-playing homework described in “How to Create Effective Homework,” in which students adopted a historical persona. Their drive to maintain their character extended into their motivation for completing homework.
Desirable difficulty
Additional and sometimes fun strategies include working with what researchers call “cognitive disfluency” by breaking convention in order to more fully gain the attention of students via changes in fonts or sizes, intentional grammatical errors, and even breaking free of categorically organized homework. A math worksheet that combines division, multiplication, addition, and subtraction problems randomly, for example, garners more attention from the brain than one that focuses on a single skill.
Deliberate practice
Finally, homework must be what Paul calls deliberate practice. Students and teachers must both be fully aware of homework’s purpose and point. This leads to one of the most important points about homework: it is not effective without student buy-in. Both common sense and research show that the only chance a student has to benefit from homework is when the student actually attempts completion — meaning that in addition to being effective, students have to be motivated to complete it. That motivation only comes when students understand how and why homework is important.
Monica Fuglei is a graduate of the University of Nebraska in Omaha and a current adjunct faculty member of Arapahoe Community College in Colorado, where she teaches composition and creative writing.
You may also like to read
- The Homework Debate: How Homework Benefits Students
- The Homework Debate: The Case Against Homework
- Advice on Creating Homework Policies
- Advice on Positive Classroom Management that Works
- Classroom Organization Advice From Expert Stacy Erickson
- Homework in Middle School: Building a Foundation for Study Skills
Categorized as: Tips for Teachers and Classroom Resources
Tagged as: Leadership and Administration , Pros and Cons
- Online & Campus Master's in TESOL and ESL
- Master's in Reading and Literacy Education
- Trauma-Informed Practices in School: Teaching...
- Portals Login
- Office 365 Login
- 2023 – 2024
- 2024 – 2025

The Great Debate: Is Homework Helpful or Harmful?

Is homework helpful? Is it harmful? Does it even matter? These questions have spurred debate in homes and schools worldwide, and they likely will until the end. In this article, we’ll look at some of the main arguments made by both sides of the debate and see where they come from and how they can be countered.
Take note, though—this article will not attempt to sway you toward either side, as that’s not feasible!
The ROI May Not Be Enough
In the end, homework’s pros and cons can only be determined on a case-by-case basis. Students with a strong foundation in math and reading skills will likely see an ROI on their homework efforts. For students struggling with these subjects, however, the negatives may outweigh the positives. But again, what works for one child may not work for another. And finally, there is also a third side to this debate that many parents aren’t aware of—the issue of students’ mental health and stress levels. Before assigning their child any academic work at home, parents should consider all factors.
Homework Interferes With Essential Activities
Homework is often given at the end of a school day and is usually assigned to be completed outside of school. Thus, homework can interfere with family time, extracurricular activities, work, and social life. Moreover, if other tasks must occur (e.g., cooking dinner), doing them first will mean less time for homework later in the evening.
Homework does not adequately prepare students for standardized testing. Standardized testing is based on the curriculum from textbooks and teacher lectures in class; this curriculum was determined by experts who thoroughly studied the material.
Reasons Why Homework Is Good
Homework teaches students to plan, be responsible for their work, and motivate themselves. It also allows children to show what they have learned in the classroom.
It Develops Essential Skills for Success in College and Life
Homework is a chance for your child to develop the skills they need to succeed. It’s not just about learning math facts but also developing skills like patience, problem-solving, and working independently. It can also help kids maintain relationships with their parents at school all day.
Homework doesn’t only give students practice on what they’re learning in class; it helps them stay engaged with their studies by remembering what they learned earlier in the day. Many people think homework is too much work and could lead to burnout, but when done right (in moderation), it can be helpful for kids who are struggling in school.
Homework Serves a Purpose in Teaching Dedication, Time Management, Problem-Solving, Etc.
Homework is beneficial for students to complete, but it’s also essential for teachers to keep in mind that a student’s time should be free of work. The teacher’s job is to ensure the student spends quality time with their family, eats well, and gets enough sleep. Therefore, the teacher must balance productive assignments with doing what’s best for each student.
Reinforces Lessons Taught in the Classroom
Homework is one of the essential parts of a student’s education. It provides students with the practice they need to succeed in the classroom and in future assessments. In addition, homework teaches kids how to set goals and manage their time effectively. Finally, homework allows parents to become more involved in their child’s education by supporting them at home.
Final Thoughts
Homework is beneficial. It is a great way to practice what you have learned in the classroom and helps the teacher gauge your understanding of the material. However, some assignments are not necessary and can be frustrating for students. That’s why at The Tenney School , we only assign homework at the level of what your child has been learning in school and is also aligned with Texas State Standards. If you’re interested in enrolling your child, please reach out!
Contact us today, visit our website , or follow us on Twitter to learn more about our mission and how we’re changing education as we know it!
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
One-to-one private school.
Registration is open for our 2024 school year! Inquire today to get more information on our individualized learning program.
Summer School Registration Open!
Registration is open for our 2024 Summer program! We’re accepting all students in grades 5 – 12!
- Customized Curriculum
- Education Info
- International students
- Learning Environment
- Learning Strategies
- Private School
- Punctuality
- Student Health
- Summer Strategies
- Tenney Subscribers
- Testing Strategies
- Transition Between Schools
- Uncategorized
Would you like to explore a topic?
- LEARNING OUTSIDE OF SCHOOL
Or read some of our popular articles?
Free downloadable english gcse past papers with mark scheme.
- 19 May 2022
How Will GCSE Grade Boundaries Affect My Child’s Results?
- Akshat Biyani
- 13 December 2021
The Best Free Homeschooling Resources UK Parents Need to Start Using Today
- Joseph McCrossan
- 18 February 2022
TEACHING TECHNIQUES
Homework: Useful Teaching Tool or Waste of Time?
- May 18, 2021

- Helpful or harmful?
How is homework helpful?
- Does homework promote learning?
Downsides of homework
- Should students have homework?
- Stress free homework tips
Homework. How can one little word cause so much trouble? Almost all schools require homework , but should they? Let’s take a look at the pros and cons of homework, plus what the research says you should really be doing after school.
As a pupil in the UK, you will without a doubt encounter homework during your school years. Some kids love it, others… not so much! Many parents struggle to make their child complete their homework and to fit it into their family’s busy schedule, and many kids and teens find homework quite boring. But let’s put our feelings about homework to the side, and focus on a more important question – is homework really necessary?

Is homework helpful or harmful?
Well, it depends. There’s loads of debate about homework and whether or not it helps you learn. Researchers have been trying to find the answer to this question since your parents were in school!
It all comes down to the purpose of the homework and the age of the student, as well as their interest in the topic at hand.
For secondary students, homework is useful as a "short and focused intervention .” That means something like a research project that you complete at home. 💻
For primary students, homework can help reinforce skills students are learning in school. It makes sense to practice spelling words at home or working on reading skills , for example.
How does homework promote learning?
One way homework can promote learning is by giving older students a chance to read more content than can be covered in class. For example, a Literature student might read a couple of chapters of a novel at home and then spend the class time discussing its themes with peers. This saves classroom time for the part of learning that’s done with other students.
Research shows that the best homework is closely linked to what you’re learning in the classroom. It should expand your learning and always be something you can complete independently. ✔️
It goes without saying that homework takes time. The more homework you have, the less time you can spend outside or relax.
Homework leaves less time for creative activities that are also very important for brain growth. 🧠
Studies show very little difference in test scores between students who spend lots of time on homework and students who do less homework. For primary school students especially, not many benefits have been found.
So, should students have homework?
In an ideal world, primary students would not have homework. And secondary students would only have short-term homework assignments with a very specific goal, like a book report or a science project.
Since students often do have homework, it shouldn’t take much time - the benefits are the same for a few minutes and a few hours of homework!
Stress-free homework tips
At the end of the day, there may be very little you can do right away about your homework situation. If your teacher assigns it, it must get done – but here are a few tips to make it less stressful:
- It’s a great idea for you to be independent with planning and managing your work time rather than being hounded into starting your homework by your parents. As you get older, it’s up to you to manage yourself – maybe you’d prefer to divide the work up into manageable chunks, for example tackling one subject before dinner and another one after.
- You should have a distraction-free space to work at home. Turn off the television, and keep electronics out of sight to make it easier to stay focused.
- If you’ve had a long school day, it’s a great idea to take some free time after school before starting your homework. You may need a chance to relax and regroup before jumping right into homework.
- If you find yourself struggling with your workload, you should have a chat with your teacher or speak to your parents about it. Homework should closely follow the in-class learning and shouldn’t take more than an hour.
Homework help with GoStudent
If you’re struggling to manage your homework, a GoStudent tutor can help. Our experienced, friendly tutors have a deep understanding of the content they teach, and your tutor can give you the one-on-one support you need to get back on track and be able to finish that homework in no time! 🚀

Popular posts

- By Guy Doza

- By Akshat Biyani

- By Joseph McCrossan
- In LEARNING TRENDS

4 Surprising Disadvantages of Homeschooling
- By Andrea Butler
The 12 Best GCSE Revision Apps to Supercharge Your Revision
More great reads:.

The Best Maths Games 2022
- By Natalie Lever
- August 16, 2022

Five Top Time Management Skills for Tutors
- By Connie Kulis-Page
- July 1, 2022

How to Become a GoStudent Tutor: Follow These Five Easy Steps
- May 19, 2022
Book a free trial session
Sign up for your free tutoring lesson..
Is Homework Harmful or Helpful

If you are a student your life cannot remain untouched by homework. All educational institutions have teachers assigning homework to students. It is the work that students must finish on their own, outside of their classrooms. Although a homework assignment is aimed at helping students gain better knowledge and understanding of the subject, it often ends up becoming a stressful task for them, leaving many to question – is homework harmful or helpful?
Is Homework Harmful or Helpful: Statistics
Here are some research findings and statistics which are the outcome of some prominent studies and surveys conducted by experts over the decades to find out whether homework is helpful or harmful. Take a look and decide:
- A study conducted by Chinese researchers in 2010, established a connection between disrupted sleep and the overload of homework. It was found that students getting excessive homework on a regular basis ended up having poor routines and unstable schedules.
- In 2015 a Canadian study linked high levels of homework to growing stress and obesity in boys clearly indicating that too much homework can be harmful.
- Recent research done by a Stanford University expert goes on to explain why is homework harmful. The researcher found that more than 56% of students felt that homework was a major cause of stress in their lives. These students were also facing sleep deprivation and a lack of social interactions due to excessive homework. In the same study, homework was found to be counterproductive when given in high volumes on a daily basis. This was resulting in an overall lack of balance in students.
- The harmful effects of homework can be seen on the mental as well as physical health of students.
On the other hand, there are studies that have found data to support homework is helpful and has a positive impact on students in high school.
- According to a study (1987-2003), Prof Harris Cooper from Duke University conducted across several US schools, homework had an overall beneficial effect on the students’ test scores. It also helped improve attitude, especially in students from higher grades. Although even this study points out the complexity of the situation here and stresses the amount of homework to be a major factor in deciding whether homework harmful or helpful
- In yet another ‘is homework harmful or helpful research’ conducted by Prof Ulrich Trautwein and team in 2009 at the University of Tübingen it was found that while excessive homework may stress some students, it might also improve the performance of others making them efficient. Therefore, it is important to find out why is homework helpful for some and not for others.
Why Is Homework Helpful
When trying to find out why and how is homework helpful, here are some reasons to consider:
- Homework helps to improve the student’s overall grades and also enhances the possibility that the student will attend college.
- Homework helps the students to indirectly revise what was taught in the class and even understand the concept better through self-application.
- It lends the teacher an insight into the academic prowess of the students, their capabilities, and also the areas where they might need help.
- It is a great way for the teacher to assess the students on a regular basis without having to give them tests and quizzes which may prove to be more stressful for the students.
- If managed well, homework inculcates good study habits in students and builds their problem-solving skills.
- Parents who help their children with homework get a chance to be involved in their academic life and activities at school.
- Homework presents a chance to delve deeper into certain concepts and improve overall understanding.
- Through homework, students learn the vital skills of time management, prioritization, and organization, that maximize productivity on the whole. ,
Why Is Homework Harmful
If you are wondering why is homework harmful to students, here are some reasons to consider:
- Teachers with the best of intentions can make homework harmful for students when they assign in bulk without realizing the effort the homework demands. Excessive homework gets counterproductive and leaves students panicky, sleepless, and stressed.
- Homework leaves students with no time to spend with their families. Many students do not meet their friends outside of school.
- Students often spend all night on homework, compromising their sleep which in turn negatively impacts their body.
- Those who wonder why is homework harmful must understand that homework leaves no time for students to pursue creative hobbies or sports outside of school. This impacts their personality on the whole.
- If overburdened with homework many students lose the desire to study further and may even quit after school.
Tips To Cope With Homework Without Harming You
You have read about why is homework harmful or helpful, the pros and cons of homework, and even some research inputs. Now here are some tips to cope up with the homework you get so that you gain the most out of it without harming yourself:
- Start early with your assignments. If you truly want to make homework helpful in the long run, you must learn to get organized and manage your time well. The sooner you start your work the more time you will have at hand for other things.
- Always work with a schedule. How is homework harmful if we work with timelines, stay focused, and endeavor to finish as planned? This way homework will only help maximize productivity.
- Finish the most difficult tasks and portions first. Prioritize and manage for best results.
- Take breaks if you find the homework lengthy or hard. It helps.
- Create a system of rewarding yourself when you finish a difficult assignment. This will keep you encouraged.
There is a growing need for teachers to be sensitive to the amount of homework that a child can finish comfortably after school hours. This is vital for the mental and physical health and wellness of the child.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQ
Do i waste time doing my homework.
Whether the time you spend on homework is useful or wasteful depends on how much homework you have, how the teacher responds to incomplete homework, and how much it is interfering with your healthy amount of leisure. While there are many harmful effects of homework when given in excess.
Is homework harmful to my health?
Too much homework can be harmful to your health. If your homework is depriving you of sleep, taking up all your free time, and preventing you from play and exercise, then it can be highly harmful to you in the short and long run.
Can homework be helpful for students?
There is not any definite yes-or-no answer to the question “Is homework harmful or helpful?” Although too much homework can be harmful, if given wisely, it can benefit the students’ academic performance and contribute to their future in higher studies.
Can homework be harmful to students?
Too much homework can be harmful to students and actually jeopardize their health and future. The harmful effects of homework include sleep deprivation, deterioration of physical and mental health, and reduced motivation for learning. It has even been linked to the rising trends in obesity and stress among students.
Alexa Donne is an exceptional online writer who is skilled and passionate about her work. She creates high-quality content that captivates the readers’ attention and ensures you get the best grade in your research papers and essays.
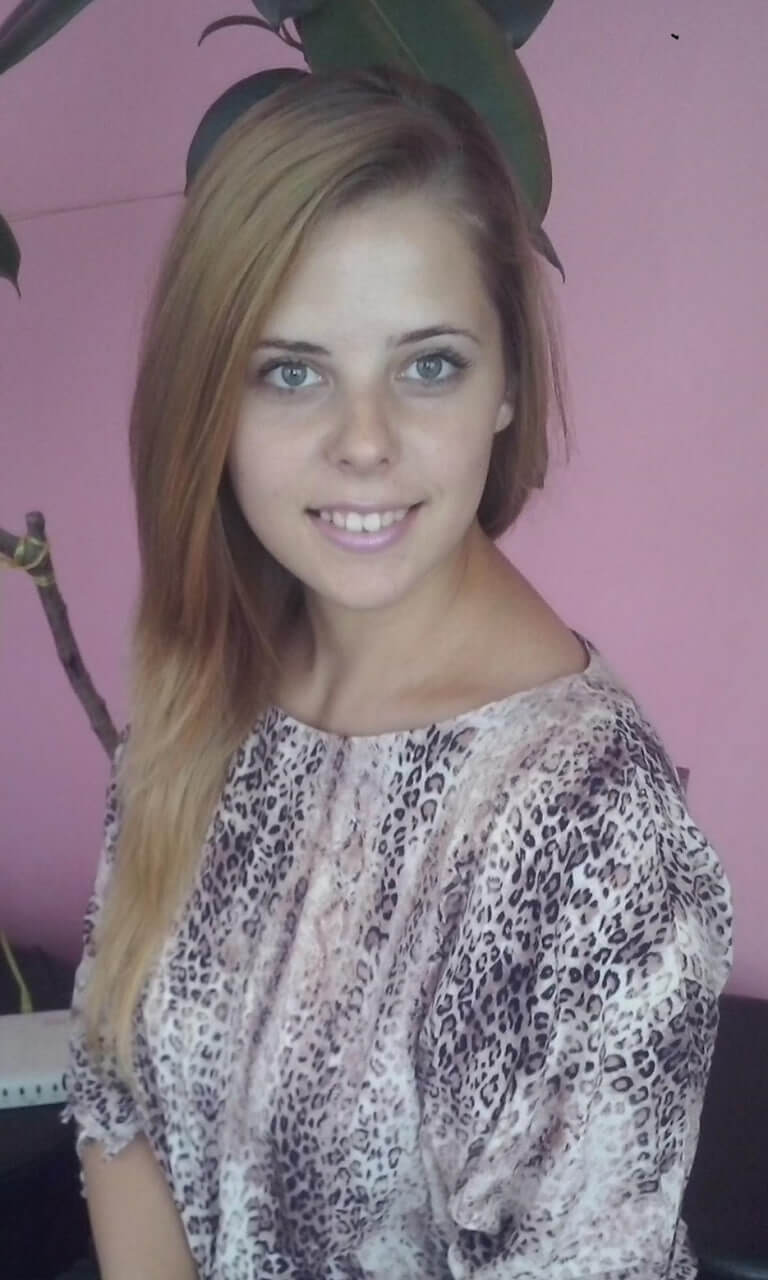

Don't Let Homework Take Over Your Life
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Education and Writing Tips
Is Homework Harmful or Helpful?
The issue of homework has always been one that’s been hotly contested between students and teachers. With homework levels increasing year after year, and the stress levels of students increasing, it’s been suggested that doing away with homework entirely would help students learn better when they’re in school. So, can homework help learning, or is it just busywork?
There are certainly a wide array of benefits to assigning students homework. In a busy classroom, a student may not have the time or the resources to be able to properly understand the concepts they are being taught. When they’re assigned homework that reinforces the ideas from the classroom, the student can work at it at their own pace, and begin to understand the theories they’re being taught.
As well as academic knowledge, homework also helps develop essential skills for later life. Having to do homework means that a student must develop time management, independent working, and research skills. Self reliance can’t easily be taught in a school setting, so homework is the best way of letting students develop it for themselves. However, there are serious downsides to assigning homework. Students with supportive parents will be able to complete their assignments with ease, as they’ll have a suitable environment at home in which to study in, and can call on parents for assistance if and when needed. Not all students are lucky enough to have this arrangement, though, so homework creates a divide between those who do have support and those who don’t. This divide will affect the education of the students who don’t, through no fault of their own.
As well as this, homework can have quite a serious impact on a student’s social and family life. Just as an adult needs a good work/life balance to remain at their best in their job, a student needs time to relax, spend time with their family, and play. If they don’t get this, their performance at school can suffer dramatically. Burnout is a very real danger when it comes to homework.
Homework itself doesn’t appear to be the enemy, but the amount and the intensity of it is. Even teachers with the best intentions at heart can assign too much, causing problems for their students. It seems that the solution is not to abolish homework altogether, but to put limits on how and when it is assigned.
So, is homework harmful or helpful? It can be both, depending on the student’s circumstances, and how much homework is assigned to them. It can help them develop skills that would be difficult to nurture in the school setting, and it can give them the time and space to understand concepts that may have passed them by otherwise. On the other hand, it can have a serious effect on a student’s work/life balance, and can create a divide between the students who get support, and those who don’t. When assigned sparingly and with good reason, a good balance can be maintained and facilitate a student’s learning.
You may also like

How Emerging Technologies Dominate the Education App Industry
Who invented school, how can time tracking help students learn faster.
This blog was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something that helped me. Thanks!
Being a teacher myself, I do know the importance of homework. It adds discipline to the education process.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Is Homework Harmful or Helpful?
- Is Homework Harmful or Helpful? Let Us Shed Some Light!

Pros and Cons of Homework
Why homework is helpful, why homework is bad, is homework harmful or helpful: debate, general tips for doing homework.
Various authoritative sources like Statistic Brain share an average amount of time students spend on homework per night equals 3 hours. It is unacceptable! The report adds more than 10% of schoolteachers use their authority to assign more than an hour of exercises per single subject. It makes students feel exhausted. So, is homework harmful or helpful? We will try to figure out whether assignments to do at home are useless or beneficial. Would you like to prove why homework is futile? Or do you support the idea of assigning someone to do my homework ? Keep reading to find out some information in favor of or against each side.
Articles about whether homework is harmful or helpful like this should help defend students' points either for or against.
Let's first discuss the pros about homework that benefit students learning out of the classroom. We will cover several factors to show why homework is helpful:
- Review of studied material. When doing exercises at home, a student reviews the material learned in class and additional content provided. It can help get some new insights.
- Better understanding. Doing homework allows students to get a better experience and deepen their knowledge.
- Practice. Usually, such a task bases on information given in class. Students can practice more to improve their skills.
- Improved learning habits and research skills. Doing assignments on one's own helps build learning as well as research skills.
- Reinforces learning. Homework presupposes additional education and research, which contributes to broader knowledge.
- Feedback received. Teachers usually give students feedback on completed work, helping them identify their strong and weak sides.
- Improved time management. When you have some tasks to do during the day, you have to make appropriate plans to cope with all that work.
- Improved academic achievements. Additional research and reviewing of material improves understanding and allows to receive higher grades for tests.
- Excellent problem-solving skills. Indeed, homework is not always that easy. Coping with tons of educational materials and tasks improves one's analytical skills.
- Opportunity to gain new skills. A student can do in-depth research on the topic and find some recent issues of interest.
- Minimum of parental control. When teachers give tasks to do, they usually check them. Thus, parents are relieved of this responsibility.
- More independence & freedom. If students have some material to cover at home, they feel more independent in terms of deadlines and resources to use.
- Ability to set priorities. When students have several tasks with similar deadlines within the same week, they can prioritize them in order of importance.
- Increased responsibility. Students should understand that they are responsible for their learning. Therefore, if you have issues with your studies, you should pay more attention to the process.
- Remote learning. When students cannot attend school or college due to some reasons, studying can be done remotely.
The above points show positive issues. But definitely, it has cons. Here are the facts proving homework can be harmful:
- A statement about academic advantages is an absolute myth. TIMSS proved in their study that 4th-grade kids in regions that set below-average amounts of homework tasks tend to succeed more than their overwhelmed peers. It was tested on math and science assignments. Japan is the country with one of the best academic achievements. They shared no more than 3% of students have more than 3 hours of home tasks per evening. Other countries with excellent academic results do not support heavy loads and lots of homework . Greek students have the worst scores being overloaded with tasks.
- Higher levels of stress are guaranteed! Spending 8 hours or more in an educational institution just to come back home and do more exercises is not the best idea. The mental health of an average child is under threat. Being more emotional and sensitive, a kid quickly gets overwhelmed by the number of homework assignments. Add problems with family, conflicts with friends, first girlfriend or boyfriend – and you will get a formula for a mentally unstable child! Eventually, students lose motivation to do homework .
- School & college homework is irrelevant in 60% of situations. What teachers explain in class and assign to do at home are 2 different things. Each time they post a task distinct from topics covered in the course, a child may face an obstacle while doing homework. They might even think they are not smart enough to cope with it.
- A student may lack interest in specific fields of study. Many students know what they will do in life and their careers since their initial years in the educational institution. Lack of interest makes students succeed in some areas and fail other classes. Such an issue can turn into a real challenge. It is not fair from the beginning, but having to do homework on those subjects one hates is the worst crime!
- The absence of free time is the worst nightmare. Many children share their sufferings about Freddy Krueger and lack of time, and it appears that they fear the last one more! They name overwhelming assignments among primary reasons they do not catch up with various life-important activities.
- There is no objective evidence proving it is helpful. Home assignments are generally considered beneficial. In fact, no reported information or data is proving it is so. Thus, there is no confirmation of positive relation between homework and improved grades.
After weighing all pros & cons, it is possible to answer our question, "Is homework harmful or helpful?". The most popular solution is to achieve a balance in any debate, and this one is not an exception. We gave a hint above. The amount of homework depends on the academic level of every student. The scientists have concluded the best time spent on homework assignments for different age groups are as follows:
- Elementary school – 30-40 minutes;
- Middle school – no more than 90 minutes;
- Junior-high-aged students – no more than 2 hours and a half
Other experts who managed to achieve balance offer a bit different approach. Try multiplying the student's grade by 10 to define the corresponding number of homework minutes per night. It means that a kid from the 6th grade should not be assigned more than an hour of homework tasks per evening. Individual needs and skills matter as well. Sometimes, it just makes sense to learn how to do homework faster . The core outtakes of the article are:
- Keep in mind the primary goal of homework. It helps come up with rote memorization. It also allows getting a more profound knowledge via elaboration and improvement of already existing skills
- Relate the homework assignments to your study goals to gain a better learning experience
- Make it possible to explore several concepts deeper than the rest of the terms
- Give feedback on time. Every student has a right to realize what they did at an acceptable level and what to improve. Quizzes & tests are some of those evaluation tools. Home tasks assist in defining strengths and weaknesses faster
- Ask for online assistance. When you are overloaded with home assignments, it is good to look for homework help websites to avoid stress.
- The participation of parents must be restricted to facilitate the accomplishment of tasks. Parents helping with homework is a common thing these days. But there is no way family members will do the job instead of a kid. Parents who do not enhance learning – leave the kids alone!
- Home assignments should be based on material discussed in class. It should not transform into self-education.
- Students should receive an adequate amount of homework they can cover within the time available daily.
We should face the fact that regardless of all the drawbacks, students are still given a lot of homework. We have prepared some general tips that will help you manage all your tasks faster:
- Start early and leave yourself enough time
- Create a schedule
- Prioritize the assignments
- Do hard tasks first
- Resort to homework help services if you feel you cannot cope with it
- Take breaks
- Try to avoid studying the whole night
- Create a reward system for yourself
The "Is homework harmful or helpful?" question is indeed very debatable. There are many good sides and bad sides too. Hopefully, this article has provided enough information to consider. We believe that there should be a precise balance between studying at school and amount of homework students complete. Every learner should have enough time to pursue their own needs and desires apart from doing assignments at home. In case tasks are overwhelming you, consider asking for professional homework help online. Our services will help you relieve your headaches from writing assignments. Come on, give it a shot, and you'll never regret it!
Each day you return home after school and classes, tired and annoyed. And instead of having a rest, you have to start working on your studies. It is tough to focus on homework when you want to join mates or spend some time on the net. "So how to stay focused to do my homework?" you would ask. We hav...
Have you ever wondered who was that "good man" who invented a bunch of problems for students all over the world who need to do homework? Nothing appears from nowhere, so there are several versions concerning invention of this type of academic activity.The first claim belongs to the group of people w...
Are you a student looking for the best homework planner app? You’ve come to the right place. Whether you face challenges with tests and coursework projects, or simply want to spend meaningful time instead of doing homework assignments, we have a smart solution for you. Online student planners will b...
The great homework help debate, “is homework helpful or harmful” is something that has been going around for decades now. Different stakeholders, including parents, students, and teachers have different views when the question ‘is homework helpful or harmful’ comes around. The advantages and disadvantages of homework are definitely relative.
They primarily depend on the time the students need to put in and the level of difficulty. Also, whether or not teachers should permit parents to help with homework. On the one hand, students feel that it is an unnecessary burden that eats up their time. On the other hand, teachers feel that homework is necessary to reinforce learning. Is homework helpful or harmful will thus, always have two sides to it.

Let us look at is homework helpful or harmful and how you can make doing homework a piece of cake-
Is Homework Helpful or Harmful: Why Homework is Good?
There are a variety of reasons why teachers and educators feel that homework is good for a student’s learning-
Learning reinforcement
This is especially true for younger students. Often students face ‘out of sight, out of mind.’ In the absence of homework, what they learn at school gets lost on the way home. Students, in such a situation, are unable to connect the dots in the next lesson. Homework, thus, acts as a tool to reinforce what is learned at school.
Practice makes perfect
Since the learning speed and capacity of all students is different, why homework is good becomes apparent. Homework encourages the students to practice and re-practice what they learn at school. This way if they have the slightest confusion in any concept, they can rework it and then go back to their teacher with the problem they are facing. This practice helps students master the concepts taught at school and excel academically.
Time management
While lessons in school focus on conceptual clarity, homework aims to help students frame answers to questions in a given time frame. This helps students learn the art of time management. This comes in handy for students during exam time. As they have already spent time answering questions, they are able to finish their exams in the given time and more efficiently.
Art of priority setting
Student life is often a time of confusion and lack of priority setting. Overwhelmed with a number of activities they need to take care of, students are unable to decide the order of doing each one. Doing homework can help students prioritize better as they have to decide which homework to finish first.
Here is a quick guide on how you can get the motivation to pay someone to do my homework .
Is Homework Helpful or Harmful: Why Homework is Bad for You?
If you look at the above section, you may think homework wins the ‘is homework helpful or harmful’ debate. However, there is a flip side to this. This means that there are some disadvantages to homework too. Let us have a look at this flip side of is homework harmful or helpful-
What do you think is homework helpful? Comment below!
Unnecessary stress
According to a survey by Stanford, 56% of students felt that homework was a means of primary stress for them . On the other hand, only 1% of students felt that homework did not cause stress to them. Homework causing stress has many reasons to it. Firstly, students feel the stress of finishing the homework on time. Secondly, they also feel stressed out contemplating the consequences of getting the answers wrong.
Health problems
A direct consequence of stress due to homework comes in the form of health problems. Students who get more homework often suffer from health problems. Headaches, lack of sleep, exhaustion, stomachaches, etc. While these health problems may seem small in the beginning, they can lead to chronic illnesses in the longer run.
Imbalance in life
Spending too much time on homework also prevents students from having an active social life and mingling with friends and peers. Always busy with homework, students are unable to socialize in a healthy manner which leads to difficulty in communication in the later stages of life. Additionally, due to homework, students are unable to take part in extracurricular activities. This stands in the way of their holistic development. Since more career professions now look for all-rounded candidates, such students might get on the back burner.

Is Homework Helpful or Harmful: The Balancing Act
It is definitely true that there are benefits to homework. These advantages make it desirable and do play a significant role in helping students raise their grades. However, as they say, that too much of anything is bad, the same goes for homework too. It is important to note that students and teachers need to strike a balance between a variety of factors for maximum efficiency-
The correct amount
For homework to be genuinely helpful and not become a nightmare for students, it should be of the optimum amount. While there is no standard benchmark as to how much homework is less or more, there are certain parameters that top educators advise. For instance, for a primary school student, the optimum homework should not take more than 20-25 minutes. A middle school student should spend about 45 mins. For a high school student, the amount will depend on the discipline the student opts for, but it should not take more than 1.5- 2 hours.
Consistency
While the amount is one determinant of is homework helpful or harmful, its consistency with classroom learning is also important. This simply means that students should be given homework on the lines of the syllabus done in the class. More often than not teachers complete one topic in class and give away the next one as homework. However, the right approach should be to give practice questions on the first topic itself. Homework on a completely new topic stresses students more than usual and makes them despise it.
How to do your Homework without Stress?
Thanks to the coming together of education and technology, students can have access to instant help when it comes to homework. There are a plethora of homework help edtech platforms that are making life easier for students. Such platforms like TutorBin are a repository of professional tutors who are available to help out students stuck with their homework. They offer a variety of benefits-
- Reduce stress- As students can get some help and guidance from these homework help sites, it reduces their stress. This is especially true when students have very less time in hand and a lot to do.
- Better grades- A study by Stanford illustrates that 33% students are under the pressure of getting good grades which negatively impacts their physical and mental health. These platforms ensure that students receive 100% correct solution with the right methodology. Thus, students are able to achieve better grades and do not feel the burden of homework too much
Key Takeaways
To sum up, the ‘is homework helpful or harmful’ there are a few points one needs to remember-
- Homework has several advantages for students, in short capsules
- Homework reinforces learning and helps the students learn the art of time management and better answer writing
- However, too much homework is bad for a student’s physical and mental health
- It acts as a constant stressor and can even lead to severe headaches, exhaustion and sleeplessness
- It is important to balance the homework to reap the benefits out of it
- Students should receive homework based on which grade they are in and what disciplines they opt for
- Homework should be a practice of what has already been done in class, and not a new topic altogether
- Students have the option of accessing online homework help platforms to seek assistance and reduce their stress and achieve better grades
Do you want to do your homework fast? Check out these interesting tips
If you are ever under the burden of homework and are seeking a burden to bail you out, TutorBin is just a click away. Get homework help from subject matter experts and have the time to develop holistically.
- E- Learning
- Online Learning
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked*
Comment * NEXT
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Hi there! I understand this is somewhat off-topic however I needed to ask. Does managing a well-established website such as yours take a massive amount work? I’m brand new to operating a blog but I do write in my journal every day. I’d like to start a blog so I will be able to share my personal experience and thoughts online.
Please let me know if you have any kind of ideas or tips for brand new aspiring blog owners.
Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It really useful & it helped me out much. I hope to give something back and help others like you aided me.
I really loved reading your blog. I also found your posts very interesting. In fact after reading, I had to go show it to my friend and he enjoyed it as well. So According to my opinion that is a great article about online teaching. Good Job!
You May Also Like

10 Simple Python Projects for Beginners to Build Confidence

From Zero to Hero: Learning Python Through Online Resources

Real-World Java Projects to Enhance Your Portfolio and Skills

Challenges of Doing Calculus Homework & How You Can Overcome It?

Math Homework Help- Guidance to Excel in Math Learning
Online homework help, get homework help.
Get Answer within 15-30 minutes

Check out our free tool Math Problem Solver
About tutorbin, what do we do.
We offer an array of online homework help and other services for our students and tutors to choose from based on their needs and expertise. As an integrated platform for both tutors and students, we provide real time sessions, online assignment and homework help and project work assistance.

Who are we?
TutorBin is an integrated online homework help and tutoring platform serving as a one stop solution for students and online tutors. Students benefit from the experience and domain knowledge of global subject matter experts.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: More People Use Mental Health Benefits When They Hear That Colleagues Use Them Too
- Laura M. Giurge,
- Lauren C. Howe,
- Zsofia Belovai,
- Guusje Lindemann,
- Sharon O’Connor

A study of 2,400 Novartis employees around the world found that simply hearing about others’ struggles can normalize accessing support at work.
Novartis has trained more than 1,000 employees as Mental Health First Aiders to offer peer-to-peer support for their colleagues. While employees were eager for the training, uptake of the program remains low. To understand why, a team of researchers conducted a randomized controlled trial with 2,400 Novartis employees who worked in the UK, Ireland, India, and Malaysia. Employees were shown one of six framings that were designed to overcome two key barriers: privacy concerns and usage concerns. They found that employees who read a story about their colleague using the service were more likely to sign up to learn more about the program, and that emphasizing the anonymity of the program did not seem to have an impact. Their findings suggest that one way to encourage employees to make use of existing mental health resources is by creating a supportive culture that embraces sharing about mental health challenges at work.
“I almost scheduled an appointment about a dozen times. But no, in the end I never went. I just wasn’t sure if my problems were big enough to warrant help and I didn’t want to take up someone else’s time unnecessarily.”
- Laura M. Giurge is an assistant professor at the London School of Economics, and a faculty affiliate at London Business School. Her research focuses on time and boundaries in organizations, workplace well-being, and the future of work. She is also passionate about translating research to the broader public through interactive and creative keynote talks, workshops, and coaching. Follow her on LinkedIn here .
- Lauren C. Howe is an assistant professor in management at the University of Zurich. As head of research at the Center for Leadership in the Future of Work , she focuses on how human aspects, such as mindsets, socioemotional skills, and leadership, play a role in the changing world of work.
- Zsofia Belovai is a behavioral science lead for the organizational performance research practice at MoreThanNow, focusing on exploring how employee welfare can drive KPIs.
- Guusje Lindemann is a senior behavioral scientist at MoreThanNow, in the social impact and organizational performance practices, working on making the workplace better for all.
- Sharon O’Connor is the global employee wellbeing lead at Novartis. She is a founding member of the Wellbeing Executives Council of The Conference Board, and a guest lecturer on the Workplace Wellness postgraduate certificate at Trinity College Dublin.
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Beyond that point, kids don't absorb much useful information, Cooper says. In fact, too much homework can do more harm than good. Researchers have cited drawbacks, including boredom and burnout toward academic material, less time for family and extracurricular activities, lack of sleep and increased stress.
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That's problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
give too much homework, students may be overwhelmed, not complete the homework and ultimately achieve nothing a result. Homework Can Be Beneficial; Yet Nothing Replaces What is Learned in The Classroom . The research mentioned above proved that students did not show considerable gains in achievement after completing homework assignments.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health ...
Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We've known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that "homework had no association with achievement gains" when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7]
The research. The most ... Missouri-St. Louis, supports the "10-minute rule" as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary ...
March 10, 2014 Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework. A Stanford researcher found that students in high-achieving communities who spend too much time on homework experience more stress ...
Calarco, Horn and Chen write, "Research has highlighted inequalities in students' homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students' home lives and in the support ...
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn. "Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of ...
Too much homework may diminish its effectiveness. While research on the optimum amount of time students should spend on homework is limited, there are indications that for high school students, 1½ to 2½ hours per night is optimum. Middle school students appear to benefit from smaller amounts (less than 1 hour per night).
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can't see it in the moment. 6. Homework Reduces Screen Time.
Here's another explanation: Many teachers believe homework should be for practicing known content, not learning something new. This is partially to help close the "homework gap" that ...
In middle school and high school, research does generally find a positive association between homework and achievement (though the effects can be hard to tease out; kids who do more homework might fare better because they might come from higher-income families, attend better schools, or are simply more motivated). But that is not the case in ...
In the third and final part of our series examining whether homework is helpful or harmful to students, we gather expert advice on beneficial homework length and content. ... While some research points to homework increasing test scores, what researchers, parents, teachers, and even students want is homework that deepens content knowledge and ...
Homework is beneficial. It is a great way to practice what you have learned in the classroom and helps the teacher gauge your understanding of the material. However, some assignments are not necessary and can be frustrating for students. That's why at The Tenney School, we only assign homework at the level of what your child has been learning ...
For secondary students, homework is useful as a "short and focused intervention .". That means something like a research project that you complete at home. 💻. For primary students, homework can help reinforce skills students are learning in school. It makes sense to practice spelling words at home or working on reading skills, for example.
When considering the view that homework is harmful, author and speaker Alfie Kohn states that there is no real evidence showing homework to be beneficial to elementary students. In an EdWeek article, he writes that he found no correlation between homework and improved standardized assessment scores. Regarding secondary students, Kohn said that ...
In yet another 'is homework harmful or helpful research' conducted by Prof Ulrich Trautwein and team in 2009 at the University of Tübingen it was found that while excessive homework may stress some students, it might also improve the performance of others making them efficient. Therefore, it is important to find out why is homework helpful ...
Having to do homework means that a student must develop time management, independent working, and research skills. Self reliance can't easily be taught in a school setting, so homework is the best way of letting students develop it for themselves. ... So, is homework harmful or helpful? It can be both, depending on the student's ...
Here are the facts proving homework can be harmful: A statement about academic advantages is an absolute myth. TIMSS proved in their study that 4th-grade kids in regions that set below-average amounts of homework tasks tend to succeed more than their overwhelmed peers. It was tested on math and science assignments.
The great homework help, "is homework helpful or harmful" is something that has been going around for decades now. Different stakeholders, including parents, students and teachers have ...
The great homework help debate, "is homework helpful or harmful" is something that has been going around for decades now. Different stakeholders, including parents, students, and teachers have different views when the question 'is homework helpful or harmful' comes around. The advantages and disadvantages of homework are definitely ...
Yaroslav Danylchenko/Stocksy. Summary. Novartis has trained more than 1,000 employees as Mental Health First Aiders to offer peer-to-peer support for their colleagues. While employees were eager ...