

Translate this page
Hundreds of scientific articles. written for kids. approved by scientists. free., search or filter, search articles, reading level.
- Elementary school (29)
- Lower high school (245)
- Middle school (183)
- Upper high school (94)
Scientific Topic
- Biodiversity and Conservation (85)
- Biology (69)
- Chemistry (13)
- Energy and Climate (57)
- Food and Agriculture (26)
- Health and Medicine (79)
- Paleoscience (18)
- Physical Science (18)
- Pollution (30)
- Social Science (55)
- Technology (22)
- Water Resources (48)
- All NGSS standards 2-LS4 (2) 3-5-ETS1 (3) 3-LS2 (1) 3-LS3 (2) 3-LS4 (3) 4-ESS3 (3) 4-LS1 (3) 4-PS3 (1) 4-PS4 (1) 5-ESS1 (1) 5-ESS3 (2) 5-PS1 (1) HS-ESS1 (3) HS-ESS2 (19) HS-ESS3 (81) HS-ESS4 (1) HS-ETS1 (12) HS-LS1 (71) HS-LS2 (84) HS-LS3 (27) HS-LS4 (48) HS-PS1 (5) HS-PS2 (2) HS-PS3 (5) HS-PS4 (3) MS-ESS1 (5) MS-ESS2 (14) MS-ESS3 (77) MS-ETS1 (6) MS-LS1 (66) MS-LS2 (74) MS-LS3 (14) MS-LS4 (23) MS-PS1 (3) MS-PS2 (1) MS-PS3 (4) MS-PS4 (3)
- All AP Environmental Science topics 1. The Living World: Ecosystems (68) 2. The Living World: Biodiversity (70) 3. Populations (142) 4. Earth Systems and Resources (30) 5. Land and Water Use (67) 6. Energy Resources and Consumption (18) 7. Atmospheric Pollution (11) 8. Aquatic and Terrestrial Pollution (45) 9. Global Change (97)
- All IB Biology topics 01. Cell biology (2) 02. Molecular biology (38) 03. Genetics (41) 04. Ecology (28) 05. Evolution and biodiversity (32) 06. Human physiology (66) 07. Nucleic acids (5) 08. Metabolism, cell respiration and photosynthesis (9) 09. Plant biology (7) 10. Genetics and evolution (12) 11. Animal physiology (56) A. Neurobiology and behaviour (42) B. Biotechnology and bioinformatics (59) C. Ecology and conservation (6) D. Human physiology (12)
- All Scientific Methods Agricultural yield data (6) Bacterial culture (1) Case study (47) Cell culture (5) Chromatography (2) Climate scenarios (25) Community jury (1) Controlled blinded study (2) Correlational study (1) CRISPR (1) CT (1) Data extrapolation (44) Data reconstruction (19) Data validation (35) DNA sequencing (36) ELISA (6) Experiment (134) Expert committee (1) Field study (40) Fluorescence imaging (11) Gene editing (10) GIS (3) GPS tracking (12) High resolution filming (1) Life cycle assessment (2) Mark-release-recapture (2) Mass spectrometry (11) Meta-analysis (4) Microscopy (22) Observation (47) Onsite study (1) PCR (Polymerase chain reaction) (16) Policy analysis (23) Proxy data (22) Radiocarbon dating (2) Remote sensing (1) Representative sampling (84) Risk analysis (9) Scientific modeling (115) Spectroscopy (1) Survey research (28) Systematic review (20) Tomography scans (2) Tree core sampling (4) X-ray scanner (2)
- All Scientific Figures Bar graph (101) Box and whisker plot (7) Data table (27) Dendrogram (1) Flow chart (4) Histogram (8) Line graph (26) Map (103) Microscopy image (31) Pictograph (85) Pie chart (10) Scatter plot (26) Time series graph (36) Venn diagram (4)
- Research Location Africa (40) Antarctica (2) Asia (34) Australia (15) Europe (74) North America (149) Ocean (38) South America (18) Space (5)
- All Scientist Affiliations Aarhus University (1) Adam Mickiewicz University (1) Aix-Marseille University (1) Amherst College (1) Arizona State University (4) Baylor University (1) Boston University (1) Brown University (1) California Institute of Technology (3) California State University (1) Cardiff University (2) CDC (3) Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles (1) Centre for Communicable Diseases Bangladesh (1) China Agricultural University (1) Chinese Academy of Sciences (1) City University of New York (1) Clemson University (2) Colorado State University (4) Columbia University (1) Complutense University (1) Cornell University (7) CSIRO (1) Duke University (6) Emory University (1) ETH Zurich (2) Five Gyres Institute (1) Forest Research Institute of Baden-Wuerttemberg (1) George Washington University (2) Georgetown University (2) Georgia Institute of Technology (1) Harvard University (10) Hebrew University of Jerusalem (1) Hokkaido University (1) IFPRI (1) Imperial College London (8) Indian Institute of Technology (1) INRS (3) Iowa State University (3) IRSTEA (1) ISAC (1) Johannes Kepler University (2) Johns Hopkins University (4) Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (1) King's College London (1) Kyoto University (1) Lancaster University (2) Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (2) Lehigh University (1) Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (2) Leipzig University (1) London School of Economics (1) LSHTM (5) LSTM (1) Marine Biological Association UK (1) Max Planck Institute (4) McGill University (3) Merrimack College (1) Met Office UK (1) Missouri University of Science and Technology (1) MIT (4) Monash University (1) Murdoch Children's Research Institute (2) Museo Paleontológico Egidio Feruglio (1) Myongji University (1) Nanjing University (1) NASA (6) National Autonomous University of Mexico (1) National Clinical Research Center for Respiratory Diseases (1) National University of Ireland (1) Natural Resources Canada (2) New York University Abu Dhabi (1) NOAA (8) North Carolina State University (1) Northeastern University (2) Norwegian Institute for Nature Research (1) Norwegian University of Science and Technology (1) Oregon State University (1) Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (1) PATH (1) Peking University School of Public Health (1) Pennsylvania State University (4) Pepperdine University (1) Princeton University (2) Purdue University (1) Queen Mary University of London (2) Queensland University of Technology (1) RMIT University (1) Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (1) RPI (1) RTI International (1) Rutgers University (1) San Diego State University (1) Seattle Pacific University (1) Stanford University (8) Stockholm University (2) Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (1) Tampere University (1) Technical University of Denmark (1) Texas A&M University (3) The Francis Crick Institute (1) Trent University (1) Tulane University (2) UC Berkeley (10) UC Davis (4) UC Irvine (1) UC Los Angeles (6) UC Riverside (2) UC San Diego (2) UC Santa Barbara (1) UC Santa Cruz (2) UKCEH (1) United Nations Children’s Fund (1) Universidad Nacional de Colombia (1) Universit of Minnessotta (1) Universität of Osnabrück (1) University of Alaska (1) University of Alberta (1) University of Arizona (1) University of Arkansas (2) University of Auckland (1) University of Bern (1) University of Birmingham (2) University of Bologna (1) University of Bristol (1) University of British Columbia (4) University of Cambridge (3) University of Cape Town (1) University of Central Florida (1) University of Chicago (2) University of Cincinnati (1) University of Connecticut (1) University of Copenhagen (1) University of Dar es Salaam (1) University of East Anglia (1) University of Edinburgh (1) University of Exeter (1) University of Florida (5) University of Georgia (1) University of Groningen (1) University of Hawaii (1) University of Helsinki (2) University of Houston (2) University of Illinois (1) University of Konstanz (1) University of Lausanne (1) University of Leeds (1) University of Liverpool (1) University of London (2) University of Maine (1) University of Manitoba (1) University of Maryland (1) University of Miami (1) University of Michigan (2) University of Minnesota (2) University of Missouri (1) University of Montreal (2) University of Nebraska (1) University of New England Australia (2) University of North Carolina (2) University of Northern Colorado (1) University of Oklahoma (1) University of Otago (1) University of Oviedo (1) University of Oxford (3) University of Patras (1) University of Pennsylvania (2) University of Pittsburgh (1) University of Plymouth (5) University of Potsdam (1) University of Queensland (1) University of Reading (1) University of Rochester (1) University of Sassari (1) University of South Carolina (1) University of South Florida (1) University of Southern California (2) University of Southern Denmark (1) University of Southern Mississippi (1) University of Strathclyde (1) University of Texas (9) University of the Witwatersrand (2) University of Tokyo (1) University of Toulouse (3) University of Tübingen (1) University of Vienna (1) University of Virginia (2) University of Washington (8) University of Western Australia (3) University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee (1) University of York (1) University of Zurich (3) Uppsala University (1) USDA (1) USDA-ARS (2) UT Austin (1) Utah State University (1) Utrecht University (1) Virginia Commonwealth University (1) Virginia Tech (1) Wageningen University (2) Washington University (1) Weill Cornell Medicine (1) West Virginia University (1) Wildlife Conservation Society (1) Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (1) World Bank (1) World Health Organization (1) Yale University (5)
- All Additional Languages Afrikaans (1) Arabic (5) Bengali (1) Bulgarian (37) Burmese (1) Chinese (4) Danish (1) Dutch (3) French (17) German (4) Greek (1) Italian (1) Korean (1) Lao (1) Mongolian (1) Portuguese (2) Russian (2) Spanish (51) Swedish (1)
Articles by Publication Date
Where was the research.

How do bumble bees play?
+ Audio version of article + Links to lessons on bees and animal behavior + Blackboard version of article with bee footage

How can we tell whether we are talking to a computer or a person?
+ Audio version of article + Links to activities about AI and machine learning + Blackboard video version of article

How have the life choices of women in India changed over time?
+ Audio version of article + Links to lessons on demographics and empowering girls + Lesson Idea video

How do animals behave during a solar eclipse?
+ Audio version of article + Get involved: Link to citizen science projects about eclipses + Links to activities about solar eclipses

How do dolphin mothers speak with their babies?
+ Audio version of article + Links to lessons on dolphins and echolocation

What do parenting and brain size have to do with each other?
+ Audio version of article + Two reading levels available + Links to lessons on birds and brains

How does fear speech spread on social media?
+ Audio version of article + Links to lessons on identifying hate speech and misinformation + Link to lessons on how kids can navigate social media

How does the way we think affect our choices about vaccines?
+ Audio version of article + Links to lessons about vaccines and cognitive bias
Popular Articles

Why do measles survivors get sicker?

What can we learn from carbon on Mars?

What can we learn about dinosaur skin using a laser?

How well can a computer think?
Article collections.

Socially Important Scientific Research in 2024 Election Year

Gross and Disgusting Science Articles Collection

8 Research Articles on Women and Girls

High School Intro Biology Collection
Popular lesson ideas.

Data Graphing Activity for 4th-7th Graders

Articles Translated in Multiple Languages

SJK Recommends: The World’s Best STEM Resources. Free.

Ask-A-Scientist Podcast E2: Dr. Allison Master, social psychologist
Learn more about us, funding support by:.

Disclaimer: Funders play no role in article selection and writing.
Featured by:

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
How to Write a Research Paper | A Beginner's Guide
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research.
Research papers are similar to academic essays , but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research. Writing a research paper requires you to demonstrate a strong knowledge of your topic, engage with a variety of sources, and make an original contribution to the debate.
This step-by-step guide takes you through the entire writing process, from understanding your assignment to proofreading your final draft.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Understand the assignment, choose a research paper topic, conduct preliminary research, develop a thesis statement, create a research paper outline, write a first draft of the research paper, write the introduction, write a compelling body of text, write the conclusion, the second draft, the revision process, research paper checklist, free lecture slides.
Completing a research paper successfully means accomplishing the specific tasks set out for you. Before you start, make sure you thoroughly understanding the assignment task sheet:
- Read it carefully, looking for anything confusing you might need to clarify with your professor.
- Identify the assignment goal, deadline, length specifications, formatting, and submission method.
- Make a bulleted list of the key points, then go back and cross completed items off as you’re writing.
Carefully consider your timeframe and word limit: be realistic, and plan enough time to research, write, and edit.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
There are many ways to generate an idea for a research paper, from brainstorming with pen and paper to talking it through with a fellow student or professor.
You can try free writing, which involves taking a broad topic and writing continuously for two or three minutes to identify absolutely anything relevant that could be interesting.
You can also gain inspiration from other research. The discussion or recommendations sections of research papers often include ideas for other specific topics that require further examination.
Once you have a broad subject area, narrow it down to choose a topic that interests you, m eets the criteria of your assignment, and i s possible to research. Aim for ideas that are both original and specific:
- A paper following the chronology of World War II would not be original or specific enough.
- A paper on the experience of Danish citizens living close to the German border during World War II would be specific and could be original enough.
Note any discussions that seem important to the topic, and try to find an issue that you can focus your paper around. Use a variety of sources , including journals, books, and reliable websites, to ensure you do not miss anything glaring.
Do not only verify the ideas you have in mind, but look for sources that contradict your point of view.
- Is there anything people seem to overlook in the sources you research?
- Are there any heated debates you can address?
- Do you have a unique take on your topic?
- Have there been some recent developments that build on the extant research?
In this stage, you might find it helpful to formulate some research questions to help guide you. To write research questions, try to finish the following sentence: “I want to know how/what/why…”
A thesis statement is a statement of your central argument — it establishes the purpose and position of your paper. If you started with a research question, the thesis statement should answer it. It should also show what evidence and reasoning you’ll use to support that answer.
The thesis statement should be concise, contentious, and coherent. That means it should briefly summarize your argument in a sentence or two, make a claim that requires further evidence or analysis, and make a coherent point that relates to every part of the paper.
You will probably revise and refine the thesis statement as you do more research, but it can serve as a guide throughout the writing process. Every paragraph should aim to support and develop this central claim.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

A research paper outline is essentially a list of the key topics, arguments, and evidence you want to include, divided into sections with headings so that you know roughly what the paper will look like before you start writing.
A structure outline can help make the writing process much more efficient, so it’s worth dedicating some time to create one.
Your first draft won’t be perfect — you can polish later on. Your priorities at this stage are as follows:
- Maintaining forward momentum — write now, perfect later.
- Paying attention to clear organization and logical ordering of paragraphs and sentences, which will help when you come to the second draft.
- Expressing your ideas as clearly as possible, so you know what you were trying to say when you come back to the text.
You do not need to start by writing the introduction. Begin where it feels most natural for you — some prefer to finish the most difficult sections first, while others choose to start with the easiest part. If you created an outline, use it as a map while you work.
Do not delete large sections of text. If you begin to dislike something you have written or find it doesn’t quite fit, move it to a different document, but don’t lose it completely — you never know if it might come in useful later.
Paragraph structure
Paragraphs are the basic building blocks of research papers. Each one should focus on a single claim or idea that helps to establish the overall argument or purpose of the paper.
Example paragraph
George Orwell’s 1946 essay “Politics and the English Language” has had an enduring impact on thought about the relationship between politics and language. This impact is particularly obvious in light of the various critical review articles that have recently referenced the essay. For example, consider Mark Falcoff’s 2009 article in The National Review Online, “The Perversion of Language; or, Orwell Revisited,” in which he analyzes several common words (“activist,” “civil-rights leader,” “diversity,” and more). Falcoff’s close analysis of the ambiguity built into political language intentionally mirrors Orwell’s own point-by-point analysis of the political language of his day. Even 63 years after its publication, Orwell’s essay is emulated by contemporary thinkers.
Citing sources
It’s also important to keep track of citations at this stage to avoid accidental plagiarism . Each time you use a source, make sure to take note of where the information came from.
You can use our free citation generators to automatically create citations and save your reference list as you go.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
The research paper introduction should address three questions: What, why, and how? After finishing the introduction, the reader should know what the paper is about, why it is worth reading, and how you’ll build your arguments.
What? Be specific about the topic of the paper, introduce the background, and define key terms or concepts.
Why? This is the most important, but also the most difficult, part of the introduction. Try to provide brief answers to the following questions: What new material or insight are you offering? What important issues does your essay help define or answer?
How? To let the reader know what to expect from the rest of the paper, the introduction should include a “map” of what will be discussed, briefly presenting the key elements of the paper in chronological order.
The major struggle faced by most writers is how to organize the information presented in the paper, which is one reason an outline is so useful. However, remember that the outline is only a guide and, when writing, you can be flexible with the order in which the information and arguments are presented.
One way to stay on track is to use your thesis statement and topic sentences . Check:
- topic sentences against the thesis statement;
- topic sentences against each other, for similarities and logical ordering;
- and each sentence against the topic sentence of that paragraph.
Be aware of paragraphs that seem to cover the same things. If two paragraphs discuss something similar, they must approach that topic in different ways. Aim to create smooth transitions between sentences, paragraphs, and sections.
The research paper conclusion is designed to help your reader out of the paper’s argument, giving them a sense of finality.
Trace the course of the paper, emphasizing how it all comes together to prove your thesis statement. Give the paper a sense of finality by making sure the reader understands how you’ve settled the issues raised in the introduction.
You might also discuss the more general consequences of the argument, outline what the paper offers to future students of the topic, and suggest any questions the paper’s argument raises but cannot or does not try to answer.
You should not :
- Offer new arguments or essential information
- Take up any more space than necessary
- Begin with stock phrases that signal you are ending the paper (e.g. “In conclusion”)
There are four main considerations when it comes to the second draft.
- Check how your vision of the paper lines up with the first draft and, more importantly, that your paper still answers the assignment.
- Identify any assumptions that might require (more substantial) justification, keeping your reader’s perspective foremost in mind. Remove these points if you cannot substantiate them further.
- Be open to rearranging your ideas. Check whether any sections feel out of place and whether your ideas could be better organized.
- If you find that old ideas do not fit as well as you anticipated, you should cut them out or condense them. You might also find that new and well-suited ideas occurred to you during the writing of the first draft — now is the time to make them part of the paper.
The goal during the revision and proofreading process is to ensure you have completed all the necessary tasks and that the paper is as well-articulated as possible. You can speed up the proofreading process by using the AI proofreader .
Global concerns
- Confirm that your paper completes every task specified in your assignment sheet.
- Check for logical organization and flow of paragraphs.
- Check paragraphs against the introduction and thesis statement.
Fine-grained details
Check the content of each paragraph, making sure that:
- each sentence helps support the topic sentence.
- no unnecessary or irrelevant information is present.
- all technical terms your audience might not know are identified.
Next, think about sentence structure , grammatical errors, and formatting . Check that you have correctly used transition words and phrases to show the connections between your ideas. Look for typos, cut unnecessary words, and check for consistency in aspects such as heading formatting and spellings .
Finally, you need to make sure your paper is correctly formatted according to the rules of the citation style you are using. For example, you might need to include an MLA heading or create an APA title page .
Scribbr’s professional editors can help with the revision process with our award-winning proofreading services.
Discover our paper editing service
Checklist: Research paper
I have followed all instructions in the assignment sheet.
My introduction presents my topic in an engaging way and provides necessary background information.
My introduction presents a clear, focused research problem and/or thesis statement .
My paper is logically organized using paragraphs and (if relevant) section headings .
Each paragraph is clearly focused on one central idea, expressed in a clear topic sentence .
Each paragraph is relevant to my research problem or thesis statement.
I have used appropriate transitions to clarify the connections between sections, paragraphs, and sentences.
My conclusion provides a concise answer to the research question or emphasizes how the thesis has been supported.
My conclusion shows how my research has contributed to knowledge or understanding of my topic.
My conclusion does not present any new points or information essential to my argument.
I have provided an in-text citation every time I refer to ideas or information from a source.
I have included a reference list at the end of my paper, consistently formatted according to a specific citation style .
I have thoroughly revised my paper and addressed any feedback from my professor or supervisor.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (page numbers, headers, spacing, etc.).
You've written a great paper. Make sure it's perfect with the help of a Scribbr editor!
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
- Writing a Research Paper Conclusion | Step-by-Step Guide
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
More interesting articles
- Academic Paragraph Structure | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Checklist: Writing a Great Research Paper
- How to Create a Structured Research Paper Outline | Example
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- How to Write Topic Sentences | 4 Steps, Examples & Purpose
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Research Paper Damage Control | Managing a Broken Argument
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
What is your plagiarism score?
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Research Paper in High School
What’s covered:, how to pick a compelling research paper topic, how to format your research paper, tips for writing a research paper, do research paper grades impact your college chances.
A research paper can refer to a broad range of expanded essays used to explain your interpretation of a topic. This task is highly likely to be a common assignment in high school , so it’s always better to get a grasp on this sooner than later. Getting comfortable writing research papers does not have to be difficult, and can actually be pretty interesting when you’re genuinely intrigued by what you’re researching.
Regardless of what kind of research paper you are writing, getting started with a topic is the first step, and sometimes the hardest step. Here are some tips to get you started with your paper and get the writing to begin!
Pick A Topic You’re Genuinely Interested In
Nothing comes across as half-baked as much as a topic that is evidently uninteresting, not to the reader, but the writer. You can only get so far with a topic that you yourself are not genuinely happy writing, and this lack of enthusiasm cannot easily be created artificially. Instead, read about things that excite you, such as some specific concepts about the structure of atoms in chemistry. Take what’s interesting to you and dive further with a research paper.
If you need some ideas, check out our post on 52 interesting research paper topics .
The Topic Must Be A Focal Point
Your topic can almost be considered as the skeletal structure of the research paper. But in order to better understand this we need to understand what makes a good topic. Here’s an example of a good topic:
How does the amount of pectin in a vegetable affect its taste and other qualities?
This topic is pretty specific in explaining the goals of the research paper. If I had instead written something more vague such as Factors that affect taste in vegetables , the scope of the research immediately increased to a more herculean task simply because there is more to write about, some of which is overtly unnecessary. This is avoided by specifications in the topic that help guide the writer into a focused path.
By creating this specific topic, we can route back to it during the writing process to check if we’re addressing it often, and if we are then our writing is going fine! Otherwise, we’d have to reevaluate the progression of our paper and what to change. A good topic serves as a blueprint for writing the actual essay because everything you need to find out is in the topic itself, it’s almost like a sort of plan/instruction.
Formatting a research paper is important to not only create a “cleaner” more readable end product, but it also helps streamline the writing process by making it easier to navigate. The following guidelines on formatting are considered a standard for research papers, and can be altered as per the requirements of your specific assignments, just check with your teacher/grader!
Start by using a standard font like Times New Roman or Arial, in 12 or 11 sized font. Also, add one inch margins for the pages, along with some double spacing between lines. These specifications alone get you started on a more professional and cleaner looking research paper.
Paper Citations
If you’re creating a research paper for some sort of publication, or submission, you must use citations to refer to the sources you’ve used for the research of your topic. The APA citation style, something you might be familiar with, is the most popular citation style and it works as follows:
Author Last Name, First Initial, Publication Year, Book/Movie/Source title, Publisher/Organization
This can be applied to any source of media/news such as a book, a video, or even a magazine! Just make sure to use citation as much as possible when using external data and sources for your research, as it could otherwise land you in trouble with unwanted plagiarism.
Structuring The Paper
Structuring your paper is also important, but not complex either. Start by creating an introductory paragraph that’s short and concise, and tells the reader what they’re going to be reading about. Then move onto more contextual information and actual presentation of research. In the case of a paper like this, you could start with stating your hypothesis in regard to what you’re researching, or even state your topic again with more clarification!
As the paper continues you should be bouncing between views that support and go against your claim/hypothesis to maintain a neutral tone. Eventually you will reach a conclusion on whether or not your hypothesis was valid, and from here you can begin to close the paper out with citations and reflections on the research process.
Talk To Your Teacher
Before the process of searching for a good topic, start by talking to your teachers first! You should form close relations with them so they can help guide you with better inspiration and ideas.
Along the process of writing, you’re going to find yourself needing help when you hit walls. Specifically there will be points at which the scope of your research could seem too shallow to create sizable writing off of it, therefore a third person point of view could be useful to help think of workarounds in such situations.
You might be writing a research paper as a part of a submission in your applications to colleges, which is a great way to showcase your skills! Therefore, to really have a good chance to showcase yourself as a quality student, aim for a topic that doesn’t sell yourself short. It would be easier to tackle a topic that is not as intense to research, but the end results would be less worthwhile and could come across as lazy. Focus on something genuinely interesting and challenging so admissions offices know you are a determined and hard-working student!
Don’t Worry About Conclusions
The issue many students have with writing research papers, is that they aren’t satisfied with arriving at conclusions that do not support their original hypothesis. It’s important to remember that not arriving at a specific conclusion that your hypothesis was planning on, is totally fine! The whole point of a research paper is not to be correct, but it’s to showcase the trial and error behind learning and understanding something new.
If your findings clash against your initial hypothesis, all that means is you’ve arrived at a new conclusion that can help form a new hypothesis or claim, with sound reasoning! Getting rid of this mindset that forces you to warp around your hypothesis and claims can actually improve your research writing by a lot!
Colleges won’t ever see the grades for individual assignments, but they do care a bit more about the grades you achieve in your courses. Research papers may play towards your overall course grade based on the kind of class you’re in. Therefore to keep those grades up, you should try your absolute best on your essays and make sure they get high-quality reviews to check them too!
Luckily, CollegeVine’s peer review for essays does exactly that! This great feature allows you to get your essay checked by other users, and hence make a higher-quality essay that boosts your chances of admission into a university.
Want more info on your chances for college admissions? Check out CollegeVine’s admissions calculator, an intuitive tool that takes numerous factors into account as inputs before generating your unique chance of admission into an institute of your selection!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


Research Basics for Junior and Senior High School Students: Getting Started - Essay Type & Topic
- Getting Started - Essay Type & Topic
- Find & Evaluate Sources
- Write & Edit Your Paper
- Presenting your research
Types of Essays

Narrat ive Essays: Telling a Story In a narrative essay , the writer tells a story about a real-life experience. When writing a narrative essay, writers should try to involve the reader by making the story as vivid as possible.
Descriptive Essays: Painting a Picture A descriptive essay paints a picture with words. A writer might describe a person, p lace, object, or even memory of special significance. The descriptive essay strives to communicate a deeper meaning through the description.
Expository Essays: Just the Facts The expository essay is an informative piece of writing that presents a balanced analysis of a topic. In an expository essay, the writer explains or defines a topic, using facts, statistics, and examples.
Persuasive Essays: Convince Me While like an expository essay in its presentation of facts, the goal of the persuasive essay is to convince the reader to accept the writer’s point of view or recommendation. The writer must build a case using facts and logic, as well as examples, expert opinion, and sound reasoning.
Source: Time4Writing.com, Types of Essays: End the Confusion . https://www.time4writing.com/writing-resources/types-of-essays/
Check it out!
The Research Process

Chosing your topic is research
Step One: Choose a topic
1) Choose a topic of interest as you will be spending a lot of time with it
2) Test your topic against the research: is the topic to broad (overwhelming information) or to narrow (not enough information)
3) Tweek your topic (broaden or narrow as needed)
Before choosing a topic, watch - Picking your topic is research NCSU Libraries
Slides from 7th-12th Grade Research Skills and Writing Workshop

- Next: Find & Evaluate Sources >>
- Last Updated: Feb 20, 2024 2:23 PM
- URL: https://lpl.libguides.com/researchbasics

Junior Research: Home
- Researching
- Finding Sources
- Argumentative
- Audience and Voice
- Web Searching
- Video Resources
What is an Argumentative Paper?
In an argumentative research paper, a student both states the topic they will be exploring and immediately establishes the position they will argue regarding that topic in a thesis statement . This type of paper hopes to persuade its reader to adopt the view presented.
Example : a paper that argues the merits of early exposure to reading for children would be an argumentative essay.
Piedmont College Library
What is an Analytical Paper?
An analytical research paper states the topic that the writer will be exploring, usually in the form of a question, initially taking a neutral stance. The body of the paper will present multifaceted information and, ultimately, the writer will state their conclusion, based on the information that has unfolded throughout the course of the essay. This type of paper hopes to offer a well-supported critical analysis without necessarily persuading the reader to any particular way of thinking.
Example : a paper that explores the use of metaphor in one of Shakespeare's sonnets would be an example of an analytical essay.
Formal Writing
Academic writing has a different tone and style than everyday writing. Here are some of the main characteristics of writing academically.
- First, Second and Third Person : You may have heard about writing in the " third person ". This means you will not be using any personal pronouns such as I, me , we, us, (first person) or you and your (second person). Seen side by side, there is a noticeable contrast in the way first person and third person phrasing sounds:
- First person: I think, I feel, I believe, I am sure, my opinion is, I am quite certain...
- Third person: certainly, undoubtedly, probably, will, likely, may, might, could, possibly...
Unless you are an expert on the topic, it is best to avoid using the first person when writing academically. When you have strong evidence to support your argument, you can successfully use the more confident tone of the third person. The exception to this is reflective writing, which is always written in the first person.
- Contractions : Contracted forms of English; didn’t, isn’t, couldn’t, wouldn't , are not accepted in formal academic writing.
- Slang : Always avoid using slang language (“the kids”, “arvo”, “drunk”).
- Over-complicated language : The more concise and simple the language, the more persuasive it can be. Only the facts should be written and emotional content should be avoided as should flowery language, adjectives and jargon.
University of Notre Dame Library
Synthesizing Information
Log into your Google account if the video will not play.
Synthesis of Research

"Synthesis is defined as combining a number of different parts or ideas to come up with a new idea or theory." [ yourdictionary.com ]
What does it mean to synthesize sources? After you've located a number of great sources for your research project and taken your notes, what's the next step?
An important step between researching and writing (or presenting) is organizing your notes so that you form connections between your sources and your own thoughts and ideas. Synthesizing basically just means "putting things together." Tidewater Community College
Synthesizing is more involved than summarizing information you have located. Instead of just restating the important points from a text, synthesizing involves combining ideas and allowing an evolving understanding of text. Synthesizing is analyzing the research and ideas you have gathered and putting them in your own thoughts to share.
Homework Help : Tutor.com

Tutors available 24/7. Select subject and grade level. En Espanol available 2pm-1am. Provided by NHC Public Library. Use your Student ID number to access program. Always say you are at home when using this program. Get your paper reviewed before you submit it.

Make sure you have your ROI printer code to print out your paper. You will find it in your school email and it will be the same throughout your time at Ashley.
- Copier Use Instructions
Quoting, Paraphrasing and Summarizing
There are three ways of incorporating other people's work into your own research paper.
Quotations, Paraphrasing and Summarizing.
What Are the Differences?
Quotations must be identical to the original, using a narrow segment of the source. They must match the source document word for word and must be attributed to the original author.
Paraphrasing involves putting a passage from source material into your own words. A paraphrase must also be attributed to the original source. Paraphrased material is usually shorter than the original passage, taking a somewhat broader segment of the source and condensing it slightly. At times, your paraphrasing may end up longer than the original passage.
Summarizing involves putting the main idea(s) into your own words, including only the main point(s). Once again, it is necessary to attribute summarized ideas to the original source. Summaries are significantly shorter than the original and take a broad overview of the source material.
All three formats must be cited. See Citations tab for more information.
Purdue Online Writing Lab
Paraphrasing
Seven Important Steps to Paraphrasing
1. Read and reread the entire passage until you understand it.
2. Take Notes : As you are reading, on a sheet of paper jot down any main ideas, key words or specific details.
3. Write it in Your Own Words : Put aside your book or resource, think about what you read, look over your notes and explain what you have read.
4. Compare what you have written with the original passage. Make sure your paraphrase is original, accurate, complete, and objective.
5. If you retain any unique terms or exact phrases from the original source, place quotation marks around them.
6. Transfer your paraphrase to your note card.
7. Cite your source of information.
Adapted from San Jose State University
- Next: Researching >>
- Last Updated: Nov 15, 2022 3:29 PM
- URL: https://ashley.nhcs.libguides.com/juniorresearch

Junior Research Paper: Home
United States History Research Paper
2023 Due Dates

Step 1 : Initial Source Check
Step 2 : Notecards
Step 3 : Bibliography/Thesis
Step 4 : Outline
Step 5 : Initial Draft
Step 6 : Final Paper Submission
Research Skills
- Creating an Annotated Bibliography
- NoodleTools
- American History - Academic Success Corner
- OWL at Purdue MLA Guide
- UW Madison Writing Center
Encyclopedias
- ABC CLIO American Government This link opens in a new window
- ABC CLIO American History This link opens in a new window
- Britannica School This link opens in a new window
- Scholastic Go This link opens in a new window
- Issues & Controversies in American History This link opens in a new window
Other Libraries
- Milwaukee Public Library
Library Books
Gale ebooks.
- Gale eBooks This link opens in a new window
Historical Newspapers
- Historical Newspapers This link opens in a new window
- Newspapers.com Library Edition World Collection This link opens in a new window
- Archive of Wisconsin Newspapers
Magazines, Journals & Current Newspapers
- CQ Researcher This link opens in a new window
- eLibrary This link opens in a new window
- Global Issues In Context This link opens in a new window
- History Reference Center This link opens in a new window
- JSTOR This link opens in a new window
- Opposing Viewpoints In Context This link opens in a new window
- SIRS Knowledge Source This link opens in a new window
Useful Websites
- American Heritage Magazine
- Digital Public Library of America
- Encyclopedia of Milwaukee
- Library of Congress Digital Collections
- Life Magazine
- National Archives Digital Collections
- National Women's History Museum
- National World War II Museum
- World Digital Library
- Last Updated: Sep 19, 2023 9:13 PM
- URL: https://nicolet.libguides.com/JuniorResearchPaper

Introducing PolyPilot:
Our AI-Powered Mentorship Program
How to Publish a Research Paper In High School: 19 Journals and Conferences to Consider

By Alex Yang
Graduate student at Southern Methodist University
9 minute read
So you've been working super hard writing a research paper , and you’ve finally finished. Congrats! It’s a very impressive accolade already, but there’s a way to take it a level further. As we’ve talked about before in our Polygence blog, “ Showcasing your work and sharing it with the world is the intellectual version of ‘pics or it didn’t happen.’ ” Of course, there are lot of different ways to showcase your work , from creating a Youtube video to making a podcast. But one of the most popular ways to showcase your research is to publish your research. Publishing your research can take the great work you’ve already done and add credibility to it, and will make a stronger impression than unpublished research. Further, the process of having your work reviewed by advanced degree researchers can be a valuable experience in itself. You can receive feedback from experts and learn how to improve upon the work you’ve already done.
Before we dive into the various journals and conferences to publish your work, let’s distinguish between the various publishing options that you have as a high schooler, as there are some nuances. Quick disclaimer: this article focuses on journals and conferences as ways to showcase your work. There are also competitions where you can submit your work, and we have written guides on competing in premier competitions like Regeneron STS and competing in Regeneron ISEF .
Publishing Options for High School Students
Peer-reviewed journals.
This is rather self-explanatory, but these journals go through the peer review process, where author(s) submit their work to the journal, and the journal's editors send the work to a group of independent experts (typically grad students or other scientists with advanced degrees) in the same field or discipline. These experts are peer reviewers, who evaluate the work based on a set of predetermined criteria, including the quality of the research, the validity of the methodology, the accuracy of the data, and the originality of the findings. The peer reviewers may suggest revisions or leave comments, but ultimately the editors will decide which suggestions to give to the student.
Once you’ve received suggestions, you have the opportunity to make revisions before submitting your final product back to the journal. The editor then decides whether or not your work is published.

Non-Peer-Reviewed Journals
These are just journals that do not undergo a review process. In general, peer-reviewed journals may be seen as more credible and prestigious. However, non-peer-reviewed journals may make it easier and faster to publish your work, which can be helpful if you are pressed for time and applying to colleges soon .
Pre Print Archives
Preprint archives or servers are online repositories where student researchers can upload and share their research papers without undergoing any review process. Preprints allow students to share their findings quickly and get feedback from the scientific community, which can help improve the research while you’re waiting to hear back from journals, which typically have longer timelines and can take up to several months to publish research. Sharing your work in a preprint archive does not prohibit you from, or interfere with submitting the same work to a journal afterwards.
Research Conferences
Prefer to present your research in a presentation or verbal format? Conferences can be a great way to “publish” your research, showcase your public speaking skills, speak directly to your audience, and network with other researchers in your field.
Student-led Journals vs Graduate Student / Professor-led Journals
Some student-led journals may have peer-review, but the actual people peer-reviewing your work may be high school students. Other journals will have graduate students, PhD students, or even faculty reviewing your work. As you can imagine, there are tradeoffs to either option. With an advanced degree student reviewing your work, you can likely expect better and more accurate feedback. Plus, it’s cool to have an expert look over your work! However, this may also mean that the journal is more selective, whereas student-led journals may be easier to publish in. Nonetheless, getting feedback from anyone who’s knowledgeable can be a great way to polish your research and writing.
Strategy for Submitting to Multiple Journals
Ultimately, your paper can only be published in one peer-reviewed journal. Submitting the same paper to multiple peer-reviewed journals at the same time is not allowed, and doing so may impact its publication at any peer-reviewed journal. If your work is not accepted at one journal, however, then you are free to submit that work to your next choice and so on. Therefore, it is best to submit to journals with a strategy in mind. Consider: what journal do I ideally want to be published in? What are some back-ups if I don’t get published in my ideal journal? Preprints, like arXiv and the Research Archive of Rising Scholars, are possible places to submit your work in advance of seeking peer-reviewed publication. These are places to “stake your claim” in a research area and get feedback from the community prior to submitting your paper to its final home in a peer-reviewed journal. You can submit your work to a preprint prior to submitting at a peer-reviewed journal. However, bioRxiv, a reputable preprint server, recommends on their website that a preprint only be posted on one server, so that’s something to keep in mind as well.
Citation and Paper Formats
All of the journals listed below have specific ways that they’d like you to cite your sources, varying from styles like MLA to APA, and it’s important that you double-check the journal’s requirements for citations, titling your paper, writing your abstract, etc. Most journal websites have very detailed guides for how they want you to format your paper, so follow those closely to avoid having to wait to hear back and then resubmit your paper. If you’re looking for more guidance on citations and bibliographies check out our blog post!
19 Journals and Conferences to Publish Your Research as a High Schooler
Now that we’ve distinguished the differences between certain journals and conferences, let’s jump into some of our favorite ones. We’ve divided up our selections based on prestige and reliability, and we’ve made these selections using our experience with helping Polygence students showcase their research .
Most Prestigious Journals
Concord review.
Cost: $70 to Submit and $200 Publication Cost (if accepted)
Deadline: Fixed Deadlines in Feb 1 (Summer Issue), May 1 (Fall), August 1 (Winter), and November 1 (Spring)
Subject area: History / Social Sciences
Type of research: All types of academic articles
The Concord Review is a quarterly journal that publishes exceptional essays written by high school students on historical topics. The journal has been around since 1987 and has a great reputation, with many student winners going to great universities. Further, if your paper is published, your essays will be sent to subscribers and teachers all around the world, which is an incredible achievement.
Papers submitted tend to be around 8,000 words, so there is definitely a lot of writing involved, and the Concord Review themselves say that they are very selective, publishing only about 5% of the essays they receive.
We’ve posted our complete guide on publishing in the Concord Review here.
Journal of Emerging Investigators (JEI)
Deadline: Rolling
Subject area: STEM
Type of research: Original hypothesis-driven scientific research
JEI is an open-access publication that features scientific research papers written by middle and high school students in the fields of biological and physical sciences. The journal includes a comprehensive peer-review process, where graduate students and other professional scientists with advanced degrees will review the manuscripts and provide suggestions to improve both the project and manuscript itself. You can expect to receive feedback in 6-8 weeks.
This should be the go-to option for students that are doing hypothesis-driven, original research or research that involves original analyses of existing data (meta-analysis, analyzing publicly available datasets, etc.). This is not an appropriate fit for students writing literature reviews. Finally, a mentor or parent must submit on behalf of the student.
We’ve had many Polygence students successfully submit to JEI. Check out Hana’s research on invasive species and their effects in drought times.
Very Prestigious Journals
Stem fellowship journal (sfj).
Cost: $400 publication fee
Subject area: All Scientific Disciplines
Type of research: Conference Proceedings, Review Articles, Viewpoint Articles, Original Research
SFJ is a peer-reviewed journal published by Canadian Science Publishing that serves as a platform for scholarly research conducted by high school and university students in the STEM fields. Peer review is conducted by undergraduate, graduate student, and professional reviewers.
Depending on the kind of research article you choose to submit, SFJ provides very specific guidelines on what to include and word limits.
Journal of Student Research (JSR)
Cost: $50 to Submit and $200 Publication Cost (if accepted)
Deadline: Fixed Deadlines in February, May, August, and November
Subject area: All Academic Disciplines
Type of research: Research and review articles, as well as other article types (not peer-reviewed)
The Journal of Student Research (JSR) is an academic journal based in Houston, Texas. It is reviewed by faculty members and accepts research and review articles, as well as other research projects (although those will not undergo the peer-review process).
From our experience, JSR sometimes experiences delays in acceptances and communication during the fall when many students are submitting, so try to submit early if possible and be mindful of deadlines.
Other Great Journal Options
National high school journal of science (nhsjs).
Cost: $250 for publication
Deadline: Rolling
Subject area: All science disciplines
Type of research: Original research, literature review
NHSJS is a journal peer reviewed by high schoolers from around the world, with an advisory board of adult academics. Topics are STEM related, and submission types can vary from original research papers to shorter articles.
Curieux Academic Journal
Cost: $185-215
Subject area: Engineering, Humanities, and Natural Science, Mathematics, and Social Science
Type of research: Including but not limited to research papers, review articles, and humanity/social science pieces.
Curieux Academic Journal is a non-profit run by students and was founded in 2017 to publish outstanding research by high school and middle school students. Curieux publishes one issue per month (twelve per year), so there are many opportunities to get your research published.
The Young Scientists Journal
Deadline: December
Subject area: Sciences
Type of research: Original research, literature review, blog post
The Young Scientists Journal , while a popular option for students previously, has paused submissions to process a backlog. The journal is an international peer-reviewed journal run by students, and creates print issues twice a year.
The journal has also been around for a decade and has a clear track record of producing alumni who go on to work in STEM.
Here’s an example of research submitted by Polygence student Ryan to the journal.
Journal of Research High School (JRHS)
Subject area: Any academic subject including the sciences and humanities
Type of research: Original research and significant literature reviews.
JRHS is an online research journal edited by volunteer professional scientists, researchers, teachers, and professors. JRHS accepts original research and significant literature reviews in Engineering, Humanities, Natural Science, Math, and Social Sciences.
From our experience working with our students to help publish their research, this journal is currently operating with a 15-20 week turnaround time for review. This is a bit on the longer side, so be mindful of this turnaround time if you’re looking to get your work published soon.
Youth Medical Journal
Deadline: March (currently closed)
Subject area: Medical or scientific topics
Type of research: Original research, review article, blog post, magazine article
The Youth Medical Journal is an international, student-run team of 40 students looking to share medical research.
We’ve found that this journal is a good entry point for students new to research papers, but when submissions are busy, in the past they have paused submissions.
Journal of High School Science (JHSS)
Subject area: All topics
Type of research: Original research, literature review, technical notes, opinion pieces
This peer-reviewed STEAM journal publishes quarterly, with advanced degree doctors who sit on the journal’s editorial board. In addition to typical STEM subjects, the journal also accepts manuscripts related to music and theater, which is explicitly stated on their website.
Due to the current large volume of submissions, the review process takes a minimum of 4 weeks from the time of submission.
Whitman Journal of Psychology
Subject area: Psychology
Type of research: Original research, podcasts
The WWJOP is a publication run entirely by students, where research and literature reviews in the field of psychology are recognized. The journal is run out of a high school with a teacher supervisor and student staff.
The WWJOP uniquely also accepts podcast submissions, so if that’s your preferred format for showcasing your work, then this could be the journal for you!
Cost: $180 submission fee
Subject area: Humanities
Type of research: Essay submission
The Schola is a peer-reviewed quarterly journal that showcases essays on various humanities and social sciences topics authored by high school students worldwide. They feature a diverse range of subjects such as philosophy, history, art history, English, economics, public policy, and sociology.
Editors at Schola are academics who teach and do research in the humanities and social sciences
Critical Debates in Humanities, Science and Global Justice
Cost: $10 author fee
Subject area: Ethics and frontiers of science, Biology and ecosystems, Technology and Innovation, Medical research and disease, Peace and civil society, Global citizenship, identity and democracy, Structural violence and society, Psychology, Education, AI, Sociology, Computer Science, Neuroscience, Cultural politics, Politics and Justice, Computer science and math as related to policy, Public policy, Human rights, Language, Identity and Culture, Art and activism
Critical Debates is an international academic journal for critical discourse in humanities, science and contemporary global issues for emerging young scholars
International Youth Neuroscience Association Journal
Subject area: Neuroscience
Type of research: Research papers
Although this student peer-reviewed journal is not currently accepting submissions, we’ve had students recently publish here.
Here’s an example of Nevenka’s research that was published in the November 2022 issue of the journal.
Preprint Archives to Share Your Work In
Subject area: STEM, Quantitative Finance, Economics
arXiv is an open access archive supported by Cornell University, where more than 2 million scholarly articles in a wide variety of topics have been compiled. arXiv articles are not peer-reviewed, so you will not receive any feedback on your work from experts. However, your article does go through a moderation process where your work is classified into a topic area and checked for scholarly value. This process is rather quick however and according to arXiv you can expect your article to be available on the website in about 6 hours.
Although there’s no peer review process, that means the submission standards are not as rigorous and you can get your article posted very quickly, so submitting to arXiv or other preprint archives can be something you do before trying to get published in a journal.
One slight inconvenience of submitting to arXiv is that you must be endorsed by a current arXiv author, which can typically be a mentor or teacher or professor that you have. Here’s an example of a Polygence student submitting their work to arXiv, with Albert’s research on Hamiltonian Cycles.
Subject area: Biology
Type of research: Original research
bioRxiv is a preprint server for biology research, where again the research is not peer-reviewed but undergoes a check to make sure that the material is relevant and appropriate.
bioRxiv has a bit of a longer posting time, taking around 48 hours, but that’s still very quick. bioRxiv also allows for you to submit revised versions of your research if you decide to make changes.
Research Archive of Rising Scholars (RARS)
Subject area: STEM and Humanities
Type of research: Original research, review articles, poems, short stories, scripts
Research Archive of Rising Scholars is Polygence’s own preprint server! We were inspired by arXiv so we created a repository for articles and other creative submissions in STEM and the Humanities.
We launched RARS in 2022 and we’re excited to offer a space for budding scholars as they look to publish their work in journals. Compared to other preprint archives, RARS also accepts a wider range of submission types, including poems, short stories, and scripts.
Conferences to Participate In
Symposium of rising scholars.
Deadline: Twice a year - February and July
Polygence’s very own Symposium of Rising Scholars is a bi-annual academic conference where students present and share their research with their peers and experts. The Symposium also includes a College Admissions Panel and Keynote Speech. In our 8th edition of the Symposium this past March, we had 60 students presenting live, approximately 70 students presenting asynchronously, and over 100 audience members. The keynote speaker was Chang-rae Lee, award-winning novelist and professor at Stanford University.
We’re looking to have our 9th Symposium in Fall of 2023, and you can express your interest now. If you’re interested to see what our Polygence scholars have presented in the past for the Symposium, you can check out their scholar pages here.
Junior Science and Humanities Symposium (JSHS)
Deadline: Typically in November, so for 2024’s competition look to submit in Fall 2023
Subject area: STEM topics
JSHS is a Department of Defense sponsored program and competition that consists of first submitting a written report of your research. If your submission is selected, you’ll be able to participate in the regional symposium, where you can present in oral format or poster format. A select group from the regional symposium will then qualify for the national symposium.
One of the great things about JSHS compared to the journals mentioned above is that you’re allowed to work in teams and you don’t have to be a solo author. This can make the experience more fun for you and your teammates, and allow you to combine your strengths for your submission.
Related Content:
Top 8 Business Journals to Publish Your Research
Why Teens Should Attend the National Student Leadership Conference (NSLC)
How to Brainstorm Your Way to Perfect Research Topic Ideas
Top 20 Most Competitive Summer Programs for High School Students
Want to start a project of your own?
Click below to get matched with one of our expert mentors who can help take your project off the ground!

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
Junior Paper
Getting it done: balancing your jp with a full course load.

While it may feel like the semester has only just begun, classes are in full swing and, already, junior paper (JP) deadlines are fast approaching. For many majors, the spring semester is where the bulk of the JP work actually takes place. Whether that means writing thousands of words, crunching monstrously large datasets, or debugging hundreds of lines of code, I think we all can agree that a JP draft is better not left to the last minute.
One of the biggest challenges all Princeton students face with independent work, however, is figuring out where they can even find the time to start. With a full course load, weekly assignments, and a myriad of extracurricular obligations, just when exactly is a student to work on their JP? Read on for three tips on how you can fit your JP into a hectic schedule. With the right daily habits, supports, and mindset, you may even find that you enjoy the process more than the final product.
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Looking at Qualitative Research through Junior Papers: An Interview with Albert Lee ‘24

Albert Lee ‘24 is the Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) Chair at Colonial Club, a member of the Students for Prison Education, Abolition, and Reform (SPEAR), and former Senior Writer for The Daily Princetonian.
As a junior, a hot topic for many of my friends lately has been their junior research and senior theses. In brainstorming ideas for this piece, I also thought about the incredible amount of learning that takes place in just a semester. That’s when I got the idea for this paper—to hear from seniors about their recent experiences conducting research for their Junior Papers. So, I reached out to Albert Lee ‘24, a senior majoring in Sociology and pursuing a certificate in Journalism.
Reading Courses: A Guide
As course selection begins, you might find yourself searching endlessly through the Course Offerings webpage, trying to craft the perfect schedule for next semester. You’re probably weighing a number of different factors— the professor, the class topic, the reading list, the different requirements it fulfills— and trying to balance these in the best way possible.There is another possibility here, which you can’t find in the course offerings: reading courses . Not advertised on department websites or listed with course offerings, reading courses are some of Princeton’s hidden academic gems. The University defines a reading course as a specially designed course not normally offered as part of the curriculum that is arranged between a student and a faculty member. These courses count for academic credit, and focus on a topic of the student’s choosing. If you’ve ever dreamed about designing your own course, this is your opportunity.

A manuscript of an Ethiopic Synaxarion in Special Collections
How to use a Reference Room
Most people probably know Trustee Reading Room as that large room with big glass windows on the first floor of Firestone, where you go when you want a really quiet study space. Perhaps you’ve recently studied for midterms or worked on a paper in its sacred silence. Maybe you’ve wondered if there’s more to Trustee than simply providing a quiet atmosphere for study. The answer to that question is: yes, there is. It is the primary reference room of Firestone library– and if you read to the end of this article you will learn how to make the most of this tremendous resource.

Trustee Reading Room in Firestone Library has many reference works
Wright Library: An Under-utilized Resource for Students
When I first walked through the doors of Theodore Sedgwick Wright Library at Princeton Theological Seminary (PTS) on a sweltering September day a few weeks ago, I was struck by three things: the great size of the library, the small number of students there, and its remarkably-strong air conditioning. As I set my things down and cooled off in a quiet study area, I began to work on an assignment for one of my classes. My gratitude for the engineers who designed the building’s cooling system was quickly superseded by my admiration for those who worked together to produce the largest theological library in America and the second largest in the world after the Vatican Library in Rome.
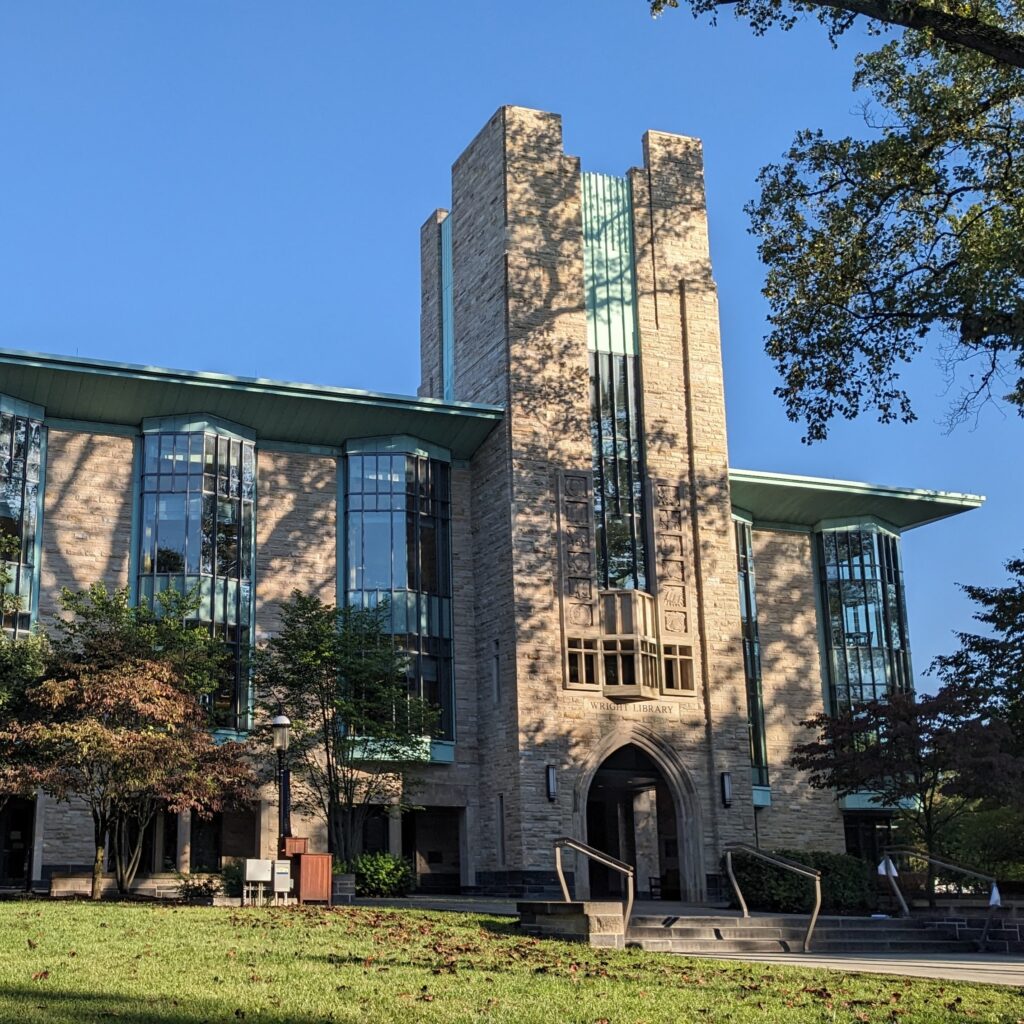

Theodore Sedgwick Wright Library is the main library at Princeton Theological Seminary .
A Figure Speaks a Thousand Words
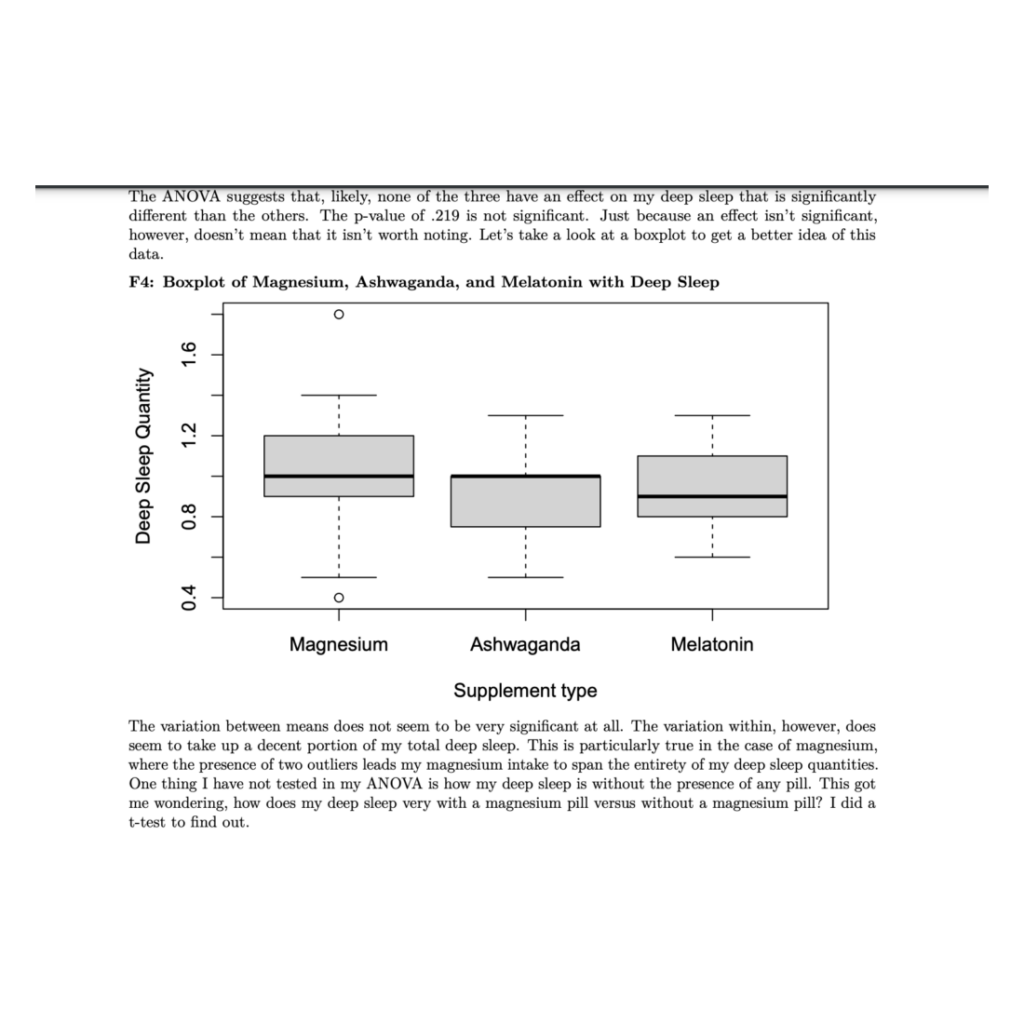
As anyone who has taken one of Princeton’s introductory statistics courses can tell you: informative statistics and figures can and will be incredibly useful in supporting your research. Whether you’re reworking your R1, writing your first JP, or in the final stages of your Senior Thesis, chances are you’ve integrated some useful statistics into your argument. When there are a million different positions that one can take in an argument, statistics appear to be our research’s objective grounding. The data says so, therefore I must be right. Right?
From Law to Coding: Writing my SPIA Quantitative Junior Paper

There are many reasons why I chose to major in the Princeton School of Public and International Affairs (SPIA), ranging from the impact that we have through service and the focus on policy and law. One unique feature of SPIA is the ability for concentrators to take more qualitative courses such as SPI333: Law, Institutions, and Public Policy and quantitatively-based courses, such as POL346: Applied Quantitative Analysis . During the Fall of my junior year, I wrote a more qualitative junior paper on risk assessment tools in the pretrial adjudication system and analyzed whether or not they make more biased decisions than do humans (see here to read more about my experience). Headed into my junior spring, I was presented with the choice of writing another qualitative paper or joining a quantitative research lab. Thankfully, I felt confident in my coding abilities due to past courses I had taken which prepared me for this moment (see here to read about how I gained a quantitative background in R as a SPIA major). I chose the lab without hesitation and my spring semester independent research journey began.
Lessons from Junior Independent Work in MAE
In the fall of 2021, I worked in the Computational Turbulent Reacting Flow Laboratory under the guidance of Professor Michael Mueller. In the Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (MAE) department, junior independent research is optional. I enrolled in MAE339: Junior Independent Work in the fall and am currently continuing my research this spring semester. Research was an integral part of my high school experience, and I was excited to start working on independent research in my junior year of college in a different setting. Now, I want to share a few of the lessons I learned from this past semester with you:
Lessons from My First Major Research Essay

As I dive into my second junior paper, I’ve begun to realize how much more serious this paper is than the first one. Gone are the safety rails once provided by Princeton’s History department; instead of a course with concrete deadlines, I am now in the metaphorical Wild West, negotiating with my advisor on a whole bunch of elements: deadlines, research content, framing, among others. Even though it is only February when I write this, the April deadline eyes me ominously. With four classes and an array of extracurricular activities, whatever will I do to survive my second JP? How can I even anticipate the thesis?
At PCUR, we’ve done plenty of reflections on our prior research experiences. The more I think about it, the best thing to do is to reflect on my first JP. In that paper, I explored the attitudes and ideologies of consumption that post-war consumers held, particularly in relation to an acute shortage of nylon stockings . Sifting through dozens of articles in local newspapers, I identified many letters to the editor that female consumers sent in to voice their opinion about how nylons should be distributed, who deserves them, and how the shortage was affecting their everyday lives.
Although I am undoubtedly proud of the final product, there were many things I could improve about it. From the way I kept sources and my reading schedule to my writing method and the final editing process, I could enumerate an endless list. For now, I will highlight two of the biggest takeaways from my first JP, which will be particularly useful given the abbreviated timeline of the second paper.
Journal of Student Research
Journal of Student Research (JSR) is an Academic, Multidisciplinary, and Faculty-reviewed Journal (Houston, Texas) devoted to the Rapid Dissemination of Current Research Published by High School Edition , Undergraduate and Graduate students.
Articles Indexed in Scholarly Databases

The journal seeks articles that are novel, integrative, and accessible to a broad audience, including an array of disciplines. The content of the journal ranges from Applied research to Theoretical research. In general, papers on all topics are welcome to submit. The journal uses an automated process from manuscript submission to publication. Manuscript submission, peer review, and publication are all handled online, and the journal automates all clerical steps during peer review.
Trusted By Student Authors Globally

Focus and Scope
Students strive to be successful at publications, and with JSR, authors aspiring to publish will receive scholarly feedback after the reviews of their submissions are received. This feedback will help authors identify areas of improvement to their submission and help them better understand the process to be successful at publication. Once published, we strive to provide a global platform for our authors to showcase their work.

Faculty-Refereed Review Process
This journal uses a double-blind review, which means that both the reviewer and author identities are concealed from the reviewers, and vice versa, throughout the review process. Authors need to ensure that their manuscripts do not give away their identity to facilitate this. To find out more about the review process, please visit the Author Guidelines page. We invite teachers and faculty interested in reviewing articles for this journal; please visit our Reviewers page for more information.
Open Access Policy
This journal provides access to its published content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge. Learn more about Open Access .
Authors Retain Copyright
Articles published in this journal are under a Creative Commons License , and the authors retain the copyright to their work.
Announcements
Call for papers: volume 13 issue 3.
If you are an undergraduate or graduate student at a college or university aspiring to publish, we are accepting submissions. Submit Your Article Now!
Deadline: 11:59 p.m. May 31, 2024


Junior History Paper Topics
- Finding Topics
- African American
- American Civil War
- Athletes/Sports
- Crime/FBI/Mafia
- Desegregation
- Great Depression
- Immigration
- Muslim American
- Native American
- Prohibition
- Salem Witch Trials
- Vietnam War
- Women's History
NoodleTools
Create note cards and exportable bibliographies (works cited lists) with NoodleTools .
Important: Create your NoodleTools account using the format firstname.lastname as your user name.
Creating a NoodleTools account through the school will give you free access to the full version of NoodleTools with more options than the free version.
After creating an account through our school, you can log in anywhere and keep access to the full version.
To begin, create a new project and select the appropriate Style.
Places to Browse For Ideas
- Digital Public Library of America Primary Source Sets The DPL has over 30 million free to use digital sources including photographs, speeches, documents, artifacts and much more. Browse these primary source sets for ideas.
- National Archives Exhibits Browse the National Archives online exhibits that chronicle major US events through extraordinary primary documents.
- Library of Congress Digital Collections Another great collection of primary documents sorted by topics to inspire research ideas.
- Library of Congress Research Guides
- History.com Topic Browsing Great source of changing subjects such as Presidents, wars, and historical events.
- Crash Course US History Videos Scroll through Crash Course's more than 45 videos on US history subjects.
- US History in Context Browse Topics Page Comprehensive list of topics from Gale US History Database
- America's Historical Newspaper Access to historical newspapers and primary sources.
- PBS Learning Media Browse US History category
- Smithsonian Museum of US History Browse museum's online exhibits
From Our Library: Articles for Junior History Papers

full-text journal and reference articles covering themes, events, individuals and periods in U.S. history from pre-Colonial times to the present
In-depth explorations on issues, includes primary source documents, timelines, biographies, images, historical texts, interviews, and more

- Salem Press Digital version of Salem Press books including Defining Documents series.
Database Off-Site Access
Database Passwords for Off-Campus Access Use this link to access usernames and passwords if you are not on campus and cannot connect to a database directly. You must use your Govs Google account to access this document.
Library Search
- Next: African American >>
- Last Updated: Sep 14, 2023 7:54 PM
- URL: https://research.govsacademy.org/juniorhistory

Hi's Eye
How to write a jrp, lighter side.
2. Set up an automatic reply for your email “Hello friend. As you may know, I am now a junior in high school, so I have no time for things like communication with the outside world. Currently, I am either on a quest for primary sources, in school, sleeping or a combination of the three. If you really need to reach me, don’t. I may return after [your JRP due date] or later, depending on the time needed for recovery. Sincerely, [your name].”
3. Consider completing the process work required by your teacher It will look something like this: You must spend at least 10 hours working on your primary source journal, and the same amount of time on your secondary source journal. No fewer than 100 bibliographical flashcards will be accepted. A weekly updated thesis statement is expected; a daily revised outline is essential; an hourly added source to your Noodlebib account is crucial. (Step 3.5: Re consider completing the process work required by your teacher.)
4. Pick a topic, then another topic, then another topic Your English teacher will tell you that you should be flexible in choosing a specific topic, because throughout the course of writing your paper, you will constantly be tweaking and adjusting your focus. What this really means is that after you take 40 books out of the library, write a 7 page outline and interview at least 5 sources, an unexpected but inevitable outside force will appear and cause you to completely switch your topic. As this will happen no fewer than three times, save yourself the trouble and change your topic thrice immediately.
5. Write your paper (Optional)
6. Switch to size 12 font After writing your 15 perfect pages, make sure that you switch from size 14 to size 12 font. This will free up about two pages, ensuring that you will not be left bored on the night before the paper is due. If you want, you can make up for lost space by inserting a couple of paragraphs on the mating call of the purple cow to check if your teacher is thoroughly reading the paper.
The Student News Site of Westfield High School
- Subscribe Now (1/2 Price)
Comments (1)
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
ikkkey • May 24, 2018 at 12:19 pm
This is a gaming on the web diary and delight is to a great degree interesting about that this blog is made and the name out of this redirection is poker play. Kids reliably need to play this entertainment in the wake of completing their website in contact with homework. that is the reason we ought to give this blog to the youngsters.

The Junior Paper
December 9, 2014, cricket gullickson.
JP (junior paper). Never have these two letters been the source of so much anxiety, stress, and worry.
Coming to Princeton, I knew I would eventually have to face independent work. As a freshman, the very idea of a thesis was terrifying to me. How could I possibly say anything of any importance to anyone in the world, especially when I could barely manage to find my way around campus?
To be honest, the idea working one-on-one with a faculty adviser on independent research was part of the reason I chose to come to Princeton over larger schools of the same caliber, where it would be more difficult (or impossible) to have that kind of opportunity. Yet, when I found the reality of independent work looming over me this year, I was beginning to wonder why I thought this was such a good idea after all.
Typically, Princeton students in the Bachelor of Arts program will write two small independent papers in their junior year. Generally, one of these papers is closely related to the independent research they will focus on for their senior thesis. (Engineering students also have a requirement for a senior thesis or independent project, but typically aren’t required to participate in junior independent work.)
When the year started, I was so scared. I needed to write a short fall JP and also choose an adviser for my spring JP and senior thesis by December 2. Who should my adviser be? What should my topic be? What question should I ask? Where do I even begin? Most of my friends had similar fears. We felt overwhelmed and unprepared and thought we could never do it.
And it has been hard. But it’s completely manageable, and I have found overwhelming support from my department and certificate representatives, potential advisers, former professors, and students in the program. And now, as the semester is nearing an end, I have seen something more important than our complaints and worries over deadlines and meetings. When my friends tell me about their work, I sense their pride in what they have accomplished. When they tell me about their topics for their senior thesis, I sense their excitement in what they’ll be doing. There’s something incredibly fulfilling about saying you have worked on something that no one else has worked on, and about having the ability to focus on what is important to you. I know that I, personally, have had a lot of fun thinking about the evolutionary basis for human moral systems.
JP. Never have two letters been the source of such inspiration, reflection, and excitement.
Related Articles
Printing my thesis, a look into independent research: the politics junior paper, the p in princeton stands for p/d/f.
Stop doing your research essay wrong way!
Writing a research paper: devil in details..
Another task from a professor made you devastated and lost? Of course, because it's something that no one likes to do. Especially a young student who obviously have dozens of other important things to do. What task we are talking about? The monotonous and long, time consuming and confusing one. Yes, it's all about writing a research paper! Why students don't like it? Well, let's see.
First, the job requires a lot of time necessary for searching, reading, comparing, analyzing and then put together. Finding a topic and the data to do a research is just 30% of the task. The major part is to put everything in a proper format. For example, create a suitable and captivating research paper introduction to arouse your professor interest.
Second, it's the efforts to make everything correct and according to requirements. You don't write make a composition with your thoughts and conclusions in chaotic way. You need to make APA research paper to show your knowledge and proficiency. It takes time as well.
Third, it's the amount of workload. Looking for data, then finding the necessary parts, trying to put everything in a proper order and format. Isn't it easier just to have someone doing it for you?
Research essay: 5 steps to success!
Everyone wants to be a great student. Taking major part in college life, getting straight As, being helpful and easy-going. But what if you need help yourself? For instance, with your research essay. How to get it done and not to be exhausted? Here are some tips to help you!
- Calculate you time right. You'll never be able to finish a task overnight, so don't attempt to make a worthy writing when the deadline is tomorrow. Usually the task to write a paper is given long before the actual deadline.
- Choose the topic correctly. You won't be enjoying your work if you don't like the subject. In every task, even the most boring one, there might be something interesting for you. Be creative. Think outside the box. It might be the key to tremendous success!
- Acknowledge that it's time to give in. If you tried and then you failed, there might be other solutions. Like typing in Google "write my paper for me" and be relieved of the burden of the task.
- Divide the whole work into small tasks and steps. Let's face the truth, no one is able to compose the whole essay at one try. Little by little you'll get to the end of the task, but doing it gradually. And keep in mind the advise number 1!
- Rest! Don't stay in front of your PC until your eyes are red, brain not working, coffee not helping. Have a little walk outside, distract yourself from constant work. After that you'll be able to come back to the task with a new wave of energy.
Always check your paper.
No matter what you decide - to make the writing yourself or use professional service to do the task - keep in mind one general rule! Always check the essay to make sure there are no mistakes. There would be a possibility to make edits after you hand the paper to your professor. Look for spelling mistakes, compare the topic and content, check the format.

Narragansett High School Library: Junior Research Paper
- Information Literacy
- NoodleTools and Turnitin
- Tech Tools to Try
- Teacher Resources for Virtual Learning
- Copyright Friendly Music and Images
- Art History Project
- Photographers Then and Now
- Photojournalism
- Photojournalism videos
- Ed Psych Booklist
- Digital Access to Children's Books
- Creative Writing Author Project
- Famous Journalists
- Great Expectations
- Junior Research Paper
- Musician Speech
- Persuasive Speech
- Romantic Poets
- Senior Research Paper
- Travel Speech
- Period 2 A/B--Ms. Dully/Senior Paper
- Small Group Presentation--Comets
- Film Aspects
- Chinese Immigration
- Independent Reading
- Left for Dead
- History of Math
- A Changing Community
- Media Center Libguide Scavenger Hunt
- Video Editing Tools
- Big Bio I Experiment
- Environmental Issues
- Exploring Nature
- Genetics Disorder
- Mrs. Uricchio--Planets
- Nuclear Energy Argument Paper
- Personal Climate Story
- Moon/Mars Project
- Pest Project
- Agricultural Practices Awareness
- Wild Rhode Island Explorer
- Bias in News
- Civil Rights Heroes
- Criminal Justice
- CSPAN Project
- Current Events--Immigration
- DBQ Research
- Death Penalty
- Foreign Policy Letter to a Senator
- Get Out the Vote
- Immigration
- Jackson Trials
- Law and Society
- Oral History Project
- Supreme Court Cases
- US History Current Events
- Social Psych Memoirs
- Discrimination Stories
- Gun Control
- Influential Women
- Clinical Disorders--Psychology
- Political Ideology and the Ninja Turtles
- Dorr Rebellion and Voting Rights
- Westward Expansion Podcast
- French Artists
- French Plazas
- Italian Piazzas
- Italian Regions / Italian Cities
- Italian Renaissance
- Make a Change
- Oceania Maps
- Paises del mundo hispanohablante
- Spanish Art Project
- Spanish Plazas
- Travel the World
- Weather to Go
- French Speaking Countries
- CultureGrams Database
- Readers Ink 2023-24
- Readers Ink 2021-22
- February 2020 Selection
- January 2020 Selection
- November 2019 Selection
- 2024 RI Teen Book Award Nominees
- Go to NHS Website This link opens in a new window
- 9th Grade Team Building Activity
Search the Library Collection for Books and Other Materials using the NHS Library Catalog (RICAT/Follett)!
Books to explore.
Some books have been placed on a cart for your perusal. However, there are many more on the library's shelves! Use the library's catalog to search for additional titles.
eBooks to Explore
- Salem Press eBooks Search the following sets here: The Decades, Great Lives from History, Great Events from History, and Great Atheletes.
- Transforming the Screen, 1950-1959 (Gale eBook)
Databases to Explore
- Facts on File (Infobase) Use American History Online, Modern World History Online and Bloom's Literature databases.
- ABC-CLIO Search all four databases at the same time. Your search results will be organized by database. Click on the link to get to your results. **Pop Culture Universe is a great database if your topic is within 1950's popular culture.
- Proquest This link opens in a new window Use the eLibrary database for your research.
- EBSCO Focus your search by using MasterFILE Premier, History Reference Center, Academic Search Elite, and Literary Reference Center.
CRAAPO Test--A Tool for Evaluating Sources
Evaluating Resources: the CRAAPO TEST
Consider the following questions as you evaluate the source and determine its reliability.

Currency : the timeliness of the information
- When was the information published or posted?
- Has the information been revised or updated?
- Is the information current or out-of date for your topic?
- Are the links functional?
Relevance : the importance of the information for your needs
- Does the information relate to your topic or answer your question?
- Who is the intended audience?
- Is the information at an appropriate level (i.e. not too elementary or advanced for your needs)?
- Have you looked at a variety of sources before determining this is one you will use?
- Would you be comfortable using this source for a research paper?
Authority : the source of the information
- Who is the author/publisher/source/sponsor?
- Are the author's credentials or organizational affiliations given?
- What are the author's qualifications to write on the topic?
- Is there contact information, such as a publisher or e-mail address?
- Does the URL reveal anything about the author or source? Examples: (.com (commercial), .edu (educational), .gov (U.S. government), .org (nonprofit organization), .net (network)
Accuracy : the reliability, truthfulness, and correctness of the content
- Where does the information come from?
- Is the information supported by evidence?
- Has the information been reviewed or refereed?
- Can you verify any of the information in another source or from personal knowledge?
- Does the language or tone seem biased and free of emotion?
- Are there spelling, grammar, or other typographical errors?
Purpose : the reason the information exists
- What is the purpose of the information? to inform? teach? sell? entertain? persuade?
- Do the authors/sponsors make their intentions or purpose clear?
- Is the information fact? opinion? Propaganda?
- Does the point of view appear objective and impartial?
- Are there political, ideological, cultural, religious, institutional, or personal biases?
Objectivity : the impartiality of the information
- What institution (company, organization, government, university, etc.) supports this information?
- Does the institution appear to exercise quality control over the information appearing under its name?
- Does the author's affiliation with this particular institution appear to bias the information?
- Is there advertising and does it affect the content and message of the source?
After evaluating this source, do you think you will use it for your paper? Why or why not?
If you are not sure, explain why.
from Meriam Library, California State University, Chico
NHS Database/eBook Passwords
- NHS Database/eBook Passwords 2023-24
Junior Research Paper Topic List

- Facts on File--Modern World History 1950-1959 **Adjust the timeline to search historical events within the decade of the 1950s--change dates to 1950 to 1959
- ABC-CLIO--Pop Culture Universe Events within the decade of the 1950s
- Wikipedia Timeline of 1950s--ONLY FOR IDEAS!!
- ProQuest eLibrary--1950s Popular Culture Research Center
NoodleTools

- Google Slide Deck--How to create citations using NoodleTools Google Slides that show step-by-step how to create citations using NoodleTools.
- Google Slide Deck--Where do I get the information to make a complete and accurate citation?
Turnitin.com
- Turnitin.com Submit papers to your teacher
In order to turn your papers in via this site, you must join the class with your class's ID number.
See your teacher for this ID number and password.
Lateral Reading Technique--A Tool for Evaluating Sources
- << Previous: Huck Finn
- Next: Musician Speech >>
- Last Updated: Apr 12, 2024 10:49 AM
- URL: https://guides.rilinkschools.org/nhsmariners
- Employee Corner
- Skip to Main Content
- Screen Reader Access
- Language English
- Search Search -->

- Vision & Mission
- Thrust Areas
- Achievements
- Former Director Generals
- Administrative Setup
- Call for project proposals
- Junior Research Fellowships [JRF]
- Short Term Studentship [STS]
- Guidelines with Formats
- Adjunct Faculty Scheme
- MD/MS/DM/MCh/MDS Support
- Post Doctoral Research
- ICMR Emeritus Scientist
- Workshop funding support program
- Centre For Advanced Research
- International Travel by Non-ICMR Scientists
- Nurturing Clinical Scientists Scheme
- ICMR Chairs
- List of Approved Projects
- An Overview of International Collaborative Research Projects in Health Research approved by Health Ministry’s Screening Committee (HMSC)
- Consolidated list of International Scientists visited ICMR Hqrs/Divisons
- call for project proposals
- ICMR-DHR International Fellowship Programme for Indian Biomedical Scientists
- ICMR International Fellowship Programme for Biomedical Scientists from Developing Countries*
- Tour Reports of ICMR International Fellowship Programme for Indian Biomedical Scientist
- Online Submission of International Collaborative Projects/HMSC
- Transfer of Biological Material
- International MOUs
- Technology For Collaboration
- Annual Reports
- Annual Accounts
- Downloadable
- Priced Publications
- Courses/Trainings
- Repositories
- MERA-India Newsletter
- Policy Briefs
- Workshops/Conferences/Seminars
- STWs Download
- ICMR Bulletins
- ICMR Headquarters Library Bulletin
- Research Papers
- Hindi Publication
Junior Research Fellowships (JRF)
Forms Required to Fill at Joining and there after
ICMR JRF Examination is the first step in the process of admission to the Ph.D/ Research Programme through council's support. Test for ICMR JRF fellowship are conducted at the 12 centres viz. Bengaluru, Bhopal, Bhubaneshwar, Chandigarh, Chennai, Delhi, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Mumbai, Srinagar and Varanasi once a year. The award of JRF is made on merit basis by holding an entrance examination after issuing a countrywide admission notice. The admission notice is published in leading English Newspapers of India usually during March/April and also on the website. The entrance examination is usually held in the first/second week of July.
ICMR holds a national level examination for determining the eligibility of Indian National candidates for the award of Junior Research Fellowships (JRF) through Indian Council of Medical Research. The award of Junior Research Fellowship to the successful eligible candidates will depend on their finding placement in a medical college / hospital / university / national laboratory / institution of higher learning and research as applicable.
- Two separate merit lists, one comprising the candidates qualifying for life sciences and the second for those candidates qualifying for social sciences, will be made on the basis of their performance in the above test.
- The candidates selected for the JRF programme of ICMR would be permitted to enroll themselves for the Ph.D. programme of any University recognised by the UGC/MCI. However, the JRF programme would not have any connection with the Ph.D. programme. The validity of fellowship awarded to a candidate will be six months.
- Another 100 candidates would be selected for consideration for positions of JRF under various research schemes of ICMR (subject to fulfilling the conditions for appointment under the schemes) for the duration of that scheme. These JRFs would also be permitted to complete Ph.D. while working in the scheme, if enrolled. The validity of result will be two years for placement in ICMR funded projects.
- SC/ST/OBC/Physically handicapped (PH) applicants will be given such special consideration as per policy guidelines. Candidates qualifying for the award of JRF will receive fellowship from ICMR.
Duration and Emoluments
The existing value of the fellowship is at present Rs. 31000/- (Rupees Thirty one thousands only) per month and an annual contingency grant up to Rs. 20,000/- per annum. The local institution shall review the performance of JRF after two years through an appropriate Review Committee constituted by the Head of the institution. The fellow may be awarded SRF after successful assessment by the Review Committee.
- The successful candidates would be notified by post. The list also would be available on the ICMR website.
Joining time
Selected candidates must join their respective course on the prescribed date as indicated in their admission letter. The selection of those who fail to join by the specified date shall automatically stand cancelled.
Procedure for Applying
Before applying, candidates are advised to go through the admission notice published in the advertisement in various Newspapers and the instructions given therein carefully. Fill in the application form according to the instructions given in this prospectus and the admission notice. Incomplete applications will not be considered and no correspondence will be entertained.
Educational Qualification
Post Graduate Degree (M.Sc./MA) in Basic Science or Post Graduate Degree (M.Sc./MA) in Professional Course.
The age limit for admission to the eligibility test is 28 years (upper age limit relaxable upto 5 years in case of candidates belonging to SC/ST, physically handicapped (PH) and female candidates, 3 years in the case of OBC category.
As prescribed by UGC.
Method of Selection
Scheme of test.
The test will consist of one paper of 2 hours duration. The paper will consist of 2 Sections. The Aptitude Section (Section A) will have 50 questions on (i) scientific phenomenon in everyday life; (ii) general knowledge in sciences; and (iii) common statistics. All these questions would be compulsory with each question carrying 1 mark. The subject Specific Section (Section B & C) would pertain to (B) Life Sciences and (C) Social Science. The candidate may attempt questions in either of the two areas. Each area of section B & C would have 100 questions and the candidate may attempt any 75 questions in the predesigned area of Section B or C. Candidates are required to indicate the option for Section B or C in the application form too.
Each question carries one mark. Negative marking @ 0.25 will be made for each of the wrong answer. The questions in both the sections would appear in English only.
The final result will be based on aggregate of 55 % marks obtained in both the sections for General category and OBC and 50% for SC/ST and physically handicapped.
The test will be held in the following streams:
(1) Aptitude test (common for all) (2) Life Sciences (3) Social Sciences. Subjects covered under Life Sciences include microbiology, physiology, molecular biology, genetics, human nutrition, human biology, biotechnology, biochemistry, biophysics, immunology, pharmacology, zoology, environmental sciences, botany, public health veterinary science and bio-informatics. Subjects covered under Social Sciences include psychology, sociology, home sciences, statistics, anthropology, social work and health economics.
Monitoring Mechanism
The fellow shall submit annual reports for 1st year and annual report thereafter as per the prescribed standard proforma. The first annual report should be submitted after 10 months from the date of commencement of the fellowship (through the Guide along with his appraisal) giving complete factual details of the research work done. Subsequent annual reports as per the standard proforma should be submitted through the Guide two months before completion of the fellowship year
English major elected to National Humanities Center Leadership Council
- Leslie King
11 Apr 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Copy address link to clipboard

Adventuresome notions of zookeeping, law enforcing, firefighting, doctoring humans or pets, driving a bus, or owning a shop tantalize many 5-year-olds’ minds. Then adulthood sets in, and people often find themselves pursuing passions different from what they imagined during childhood.
But this is not the case with Julie Deacon.
Why it matters
Since her early childhood, the Virginia Tech junior who is majoring in creative writing and minoring in international studies hoped her path would involve writing. That lifelong dream is finding new validation. The National Humanities Center Leadership Council in November accepted Deacon into its membership.
“Julie is a great example of a dedicated student who knows where she wants to go,” said Laura Belmonte, dean of the College of Liberal Arts and Human Sciences, “and with her love of writing and journalism, she is the perfect ambassador for the humanities when it comes to representing Virginia Tech in this highly competitive role on the leadership council.”
The leadership council, housed in the nonprofit National Humanities Center at Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, helps prepare select students with humanities-based leadership skills. These young scholars are from institutions that are center sponsors. Universities nominate them to the council ranks.
Elected students participate in round tables and discussion sessions about the importance of humanistic perspectives in addressing the concerns of contemporary society. They then embark on a semester-long research project, which they will present at a symposium later in the year. After this, they work on other initiatives and career development.
War zone research
Deacon’s focus with her research project involves the extent to which journalism is justifiable in war zones, examining different perspectives on peace coverage and its benefits and detriments.
She will interview journalists and spend time in historical collections.
“In terms of the main focus for the research project, I’ll be able to utilize a lot of past information in archives for firsthand accounts. The American Red Cross archive database has a lot of information on war journalists and peace coverage, as does the National Archives,” she said. “I can use these archives to help build my research project with information from United States wars and worldwide conflicts that involved journalists living on assignment in war zones, and hopefully I’ll be able to get first-hand references from different established journalists. There are so many more resources than I ever thought there would be about such a focused topic.”
Although she is not sure she will pursue this avenue of journalism, she became intrigued with the idea after talking to editor Michael Marshall at the Crozet Gazette, a community newspaper in Virginia where Deacon works as a freelance writer. When she first met him, he mentioned wanting to be a foreign correspondent at the start of his career. Deacon thought that sounded fascinating.
“It’s such an interesting perspective,” she said. “When we think about war, of course our minds naturally go to those directly involved in the fighting, but there are also those who report news and development to the general public. Media and communication are so influenced by how events are reported, where they’re reported, and who’s reporting them. I thought that’d be an interesting topic to dive into, and everything came together to make the role of journalism in war zones the focus of this research project. I’m thankful and excited that the National Humanities Center is giving me the resources to pursue it.”
Early career writing
The realities of a war zone are different from the types of journalism prevalent in Deacon’s writing experience. Currently, she is a digital media intern for the Department of Computer Science at Virginia Tech. Prior to this, when she first started at Virginia Tech, she wrote for the Collegiate Times and then segued to the newspaper in Crozet, Virginia.
Deacon also completed a bridge experience internship with the Center for Excellence in Teaching and Learning at Virginia Tech. A bridge experience offers students an experiential learning opportunity, such as an internship, in exchange for credit toward graduation. For this, Deacon revised and edited content for student access and career development.
After deciding to pursue journalism, she began working for the Crozet Gazette in the summer of 2023 and continues to freelance for the publication.
The latter experience is one she finds fulfilling, delighting in opportunities to interact with a wide variety of people. These include athletes who overcome personal challenges, business owners, and an 85-year-old who was once a member of the Hollywood Foreign Press who reported on the American entertainment industry for predominantly foreign media markets. With the paper’s small team of seven employees, Deacon considers herself fortunate to be able to write alongside these more seasoned writers and that she can continue working for what started as a summer dream job.
“It’s been such a great experience working for a local paper,” she said. “You find out there’s always something to write and talk about, and interesting people to talk to everywhere you go.”
Humanities forward
Deacon finds her peers on the leadership council just as interesting. From Vanderbilt to Yale, there is a vast, diverse group of majors. These include neuroscience, engineering, the arts, and liberal arts, all engaged in propelling the humanities forward. In an age when STEM fields can dominate discussions of education and career prospects, Deacon’s experience at Virginia Tech and her work with the leadership council have made her optimistic about the enduring value of the humanities.
“I completely understand the desire to major in a discipline with guaranteed high pay and job security, but I don’t think those should be the sole reasons to earn your degree in something,” she said. “In my eyes, I think having the opportunity to come to college and choose how you might want to spend your future is an incredibly fortunate thing that we get to do, and it’s important that you focus on what you enjoy and what truly interests you.”
For Deacon, that career is writing. Her journey is one that bridges the divide between STEM and the humanities and speaks to the role of young leaders shaping a more empathetic and understanding world.
Jenny Kincaid Boone
540-314-7207
- College of Liberal Arts and Human Sciences
- Computer Science
- Internships
- Political Science
- Student Organizations
Related Content


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
8 Research Articles on Women and Girls High School Intro Biology Collection Popular Lesson Ideas. Data Graphing Activity for 4th-7th Graders Articles Translated in Multiple Languages SJK Recommends: The World's Best STEM Resources. Free. Ask-A-Scientist Podcast E2: Dr. Allison Master, social psychologist ...
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
Composing a research paper can be a daunting task for first-time writers. In addition to making sure you're using concise language and your thoughts are organized clearly, you need to find a topic that draws the reader in. CollegeVine is here to help you brainstorm creative topics! Below are 100 interesting research paper topics that will ...
The following guidelines on formatting are considered a standard for research papers, and can be altered as per the requirements of your specific assignments, just check with your teacher/grader! Start by using a standard font like Times New Roman or Arial, in 12 or 11 sized font. Also, add one inch margins for the pages, along with some double ...
Narrat ive Essays: Telling a Story In a narrative essay, the writer tells a story about a real-life experience.When writing a narrative essay, writers should try to involve the reader by making the story as vivid as possible. Descriptive Essays: Painting a Picture A descriptive essay paints a picture with words. A writer might describe a person, p lace, object, or even memory of special ...
Purpose. The Columbia Junior Science Journal is a high school research journal seeking original research papers and review articles. We provide high school students with a platform to publish manuscripts in the fields of natural sciences, physical sciences, engineering, and social sciences. Selected CJSJ authors demonstrate the ability to ...
This handbook helps you conduct original research in sociology at the undergraduate level. It covers the steps of independent research, from choosing a topic and a question to analyzing data and writing a paper. It also provides tips on finding data, methods, literature review, and bibliography.
An analytical research paper states the topic that the writer will be exploring, usually in the form of a question, initially taking a neutral stance. The body of the paper will present multifaceted information and, ultimately, the writer will state their conclusion, based on the information that has unfolded throughout the course of the essay.
This research guide will help you get started on the Junior Research Paper. United States History Research Paper. 2023 Due Dates. Step 1: Initial Source Check. Step 2: Notecards. Step 3: Bibliography/Thesis. Step 4: Outline. Step 5: Initial Draft. Step 6: Final Paper Submission . Research Skills.
A paper and abstract describing a student's research are required of all students who wish to enter the TJSHS competition. Students are to select the most appropriate field of research from the following eight categories established by the JSHS: Environmental Science. Biomedical Sciences. Life Sciences. Medicine & Health / Behavioral Sciences.
Junior Research Paper. It's required of all of us. You need to practice doing academic research. It can be intellectually exciting to explore a topic of genuine inquiry. It provides the background for your Senior Project. Use at least 7 sources in your writing, including 2 peer-reviewed articles.
Type of research: Including but not limited to research papers, review articles, and humanity/social science pieces. Curieux Academic Journal is a non-profit run by students and was founded in 2017 to publish outstanding research by high school and middle school students. Curieux publishes one issue per month (twelve per year), so there are ...
Looking at Qualitative Research through Junior Papers: An Interview with Albert Lee '24. Albert Lee '24 is the Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) Chair at Colonial Club, a member of the Students for Prison Education, Abolition, and Reform (SPEAR), and former Senior Writer for The Daily Princetonian. As a junior, a hot topic for many of ...
Journal of Student Research (JSR) is an Academic, Multidisciplinary, and Faculty-reviewed Journal (Houston, Texas) devoted to the Rapid Dissemination of Current Research Published by High School Edition, Undergraduate and Graduate students. Articles Indexed in Scholarly Databases. The journal seeks articles that are novel, integrative, and ...
From Our Library: Articles for Junior History Papers. Study significant periods in American history through a timeline-based interface. Complete editions from hundreds of U.S. newspapers provide primary source content covering eras such as the Revolutionary War, Civil War, World War I, Roaring Twenties, Great Depression, World War II, Civil ...
by Clara Smith During their junior year at WHS, students write a Junior Research Paper. Although teachers do provide students with general information on the proper process to complete the paper, Hi's Eye strongly suggests that students follow the below steps to ensure that they get the most out of the experience. Lighter Side 1....
The Junior Paper. December 9, 2014. Cricket Gullickson. JP (junior paper). Never have these two letters been the source of so much anxiety, stress, and worry. Coming to Princeton, I knew I would eventually have to face independent work. As a freshman, the very idea of a thesis was terrifying to me.
First, the job requires a lot of time necessary for searching, reading, comparing, analyzing and then put together. Finding a topic and the data to do a research is just 30% of the task. The major part is to put everything in a proper format. For example, create a suitable and captivating research paper introduction to arouse your professor ...
Junior Research Paper Topic List. Timelines. Facts on File--Modern World History 1950-1959 **Adjust the timeline to search historical events within the decade of the 1950s--change dates to 1950 to 1959. ABC-CLIO--Pop Culture Universe. Events within the decade of the 1950s.
Definition Junior Researchers. Junior Researcher is a term coined by Eurodoc to refer to people who have been awarded a doctoral degree and are engaged in a temporary and defined period of advanced, not yet fully independent research, either in academia, in the public or in the private sector. Eurodoc believes that there should transparent and ...
A junior from Moraga, California, Van Gilder will be among the presenters at the Imagining Tourists and Tourism conference in Paris in mid-June. During a Winter Term course about the history of New Orleans, Van Gilder wrote a paper on Disneyland's representation of 1920s New Orleans throughout its park history.
Specimen paper for ICMR-JRF (95.0 KB) Revision of rates of emoluments of JRF , SRF and RA (247 KB) FAQs (43 KB) Forms. Forms Required to Fill at Joining and there after ... The award of Junior Research Fellowship to the successful eligible candidates will depend on their finding placement in a medical college / hospital / university / national ...
Putting pen to paper for the humanities, Virginia Tech junior Julie Deacon joins the prestigious National Humanities Center Leadership Council. Delving into the ethical dimensions of journalism in war zones, Deacon's research blends her passion for writing with the enduring relevance of the humanities.