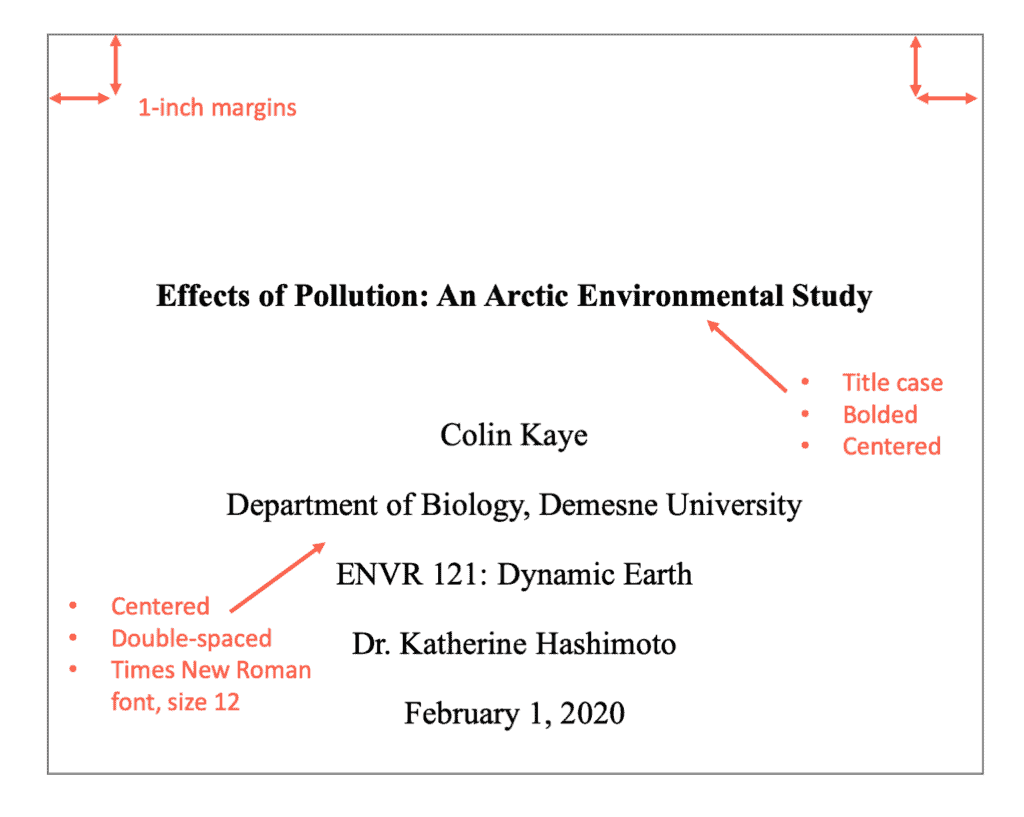
How to Write a Case Study in APA Format
Table of contents
- 1 What Is a Case Study In APA Format?
- 2.1 Sample Of APA Case Study Outline
- 3.1 Title Page in APA for Case Study Project
- 3.2 The Abstract for an APA case study
Whether you study social sciences or life sciences, you’re likely to encounter a case study analysis in your academic journey. These papers demand a lot from students. First, you must have impeccable research and analysis skills. Sample populations, particularly people, can be challenging to analyze. It’s easy to misinterpret data and come up with the wrong conclusions. Additionally, you’ll need to have a knack for writing to present your findings persuasively, backed up by evidence-based arguments that build confidence for your teacher to accept the results of your work. If you need to boost your paper, Papers Owl is here to help you with a wide range of guidelines on how to write a case study in APA.

What Is a Case Study In APA Format?
To make your success, first realize that a case study is detective work. Your research may have an unresolved question or to carry out some testing to validate a hypothesis; in this case, studies are born. Psychology, nursing, and business are common fields this method is applied. In this scientific method, you’ll approach an event, action, individual, etc. And apply a set of circumstances to observe outcomes. Most papers in this field are written in the APA format, which can be a burden for students, especially if they aren’t familiar with this style. If you lack time or motivation for writing, appeal to our professional writers to write a case study in APA format, and we will ensure your paper is perfectly formatted and gets a high grade.
Structure of Case Study Report In APA
First, let’s look at the sections in writing a case study in APA, which shares a few similarities to a typical research paper.
Introduction: Introduce your topic to the reader. Be sure to include the state of current research and where you plan to develop the current state of knowledge. You should include an interesting fact to reinforce your work’s importance and develop an interest in your hypothesis. Finish off with a thesis statement that you’ll focus on your workaround.
Aims: In this section, you answer the questions regarding why you are conducting your research and any questions you’ll explore. Avid case study writer recommends focusing your questions around your thesis. You can develop a triangle with a diagram and drill down your questions in a logical format that matches your paper’s main purpose.
Methods: Writing a case study in APA requires a methods section that details how you conducted your research. Did you conduct any interviews, send out questionnaires, or observe any behaviors? Detail them in this section, and state the environment and circumstances surrounding your data collection.

Results: Now that you’ve identified what you’d planned to accomplish and how you went about it in your APA case study format, it’s time to post the results. Don’t be shy if things don’t go swimmingly. Often in studies, we have unexpected results, which sometimes makes your paper more interesting to read.
Discussion: It’s time for the heart and soul of your paper. After all your research and observation, it is time to have a discourse on the results. The key to how to write a case paper in APA hangs on your ability to interpret the results in a meaningful way. Be sure to focus the discussion on your stated methods and how they pertain to your aims.
Recommendations: Here you want to detail what is to follow your research. Professional case study writers advise stating any knowledge gaps in your work and any unanswered or new questions you had found in the process. Your insights will be useful for others to follow in your footsteps and expand on your analysis.
Sample Of APA Case Study Outline
Example of writing a case study analysis in APA format:

Writing a case study in APA Step By Step
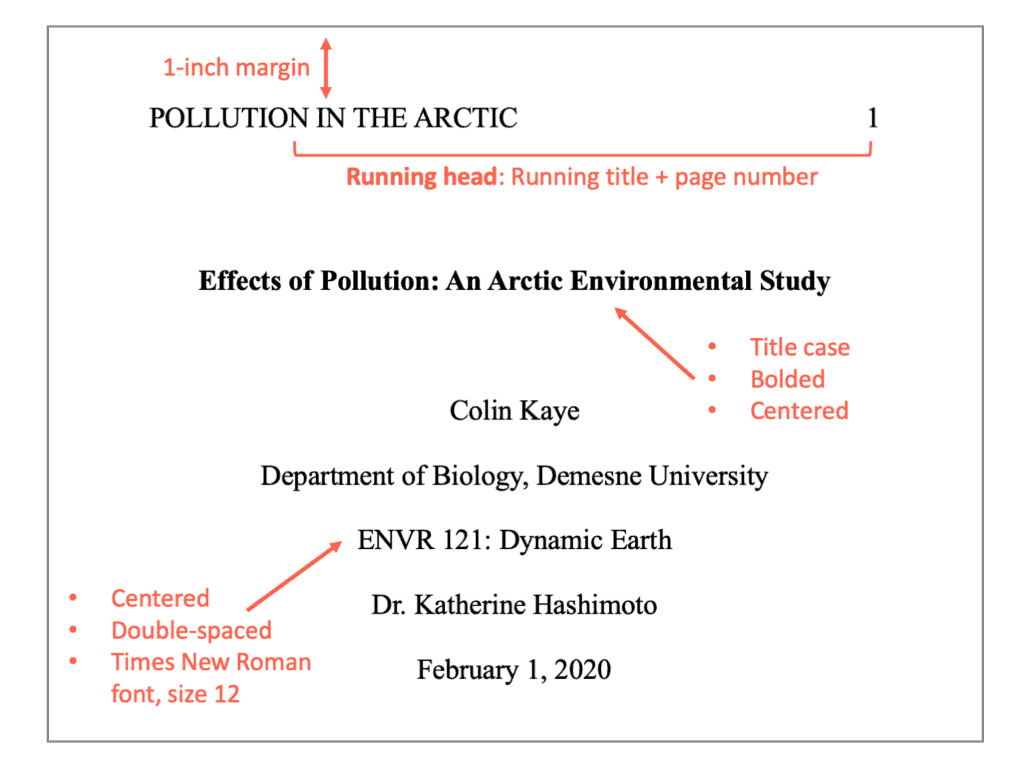
Knowing how to write a case study in APA format is a common question for students. In addition to the typical academic standards, APA has its own requirements that must be adhered to. The first step is to create a heading, known as a running head, that will be present on each page of your paper. The running head includes:
- The page number on the right margin
- A shortened title of your paper in ALL-CAPS no longer than 50 characters to the right
Title Page in APA for Case Study Project
The title of a case study in an APA paper is a requirement. The purpose is to state the name of the work, who the author is, and the institution that sponsored the research. It has the following parts:
- The words “running head” at the top, followed by the actual running head
- The full title of your paper using APA titling no longer than 12 words
- Your name without any designations (Dr/Ph.D./Rev/etc.) and the institution you attend
The Abstract for an APA case study
The abstract of your paper works as a summary to give a brief overview of what it contains. Include the running head at the top; the first line should have the word “abstract” centered. Follow the abstract with 150-250 words summarizing your paper. You may also index some keywords to help find the contents of your work in academic databases. At the end of your summary, indent once, and in italics, indicate keywords related to your work.
Writing an effective college paper requires a lot of planning and formatting to get it done right. Brush up on these guidelines for how to write your paper in APA format . If you need someone to review your work or write any parts of your paper, reach out to our professional writers, who are always willing to lend a hand.
Additionally, with the help of our blog, you can make sure you create a professional PowerPoint presentation that clearly outlines the main points of your paper. If you need help with this, our professional writers can provide guidance.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
How to Write a Case Study Paper in APA Format
Table of contents
The words ‘case study’ sounds intimidating, to say the least. It’s one of those assignments that need thorough research and groundwork before you can get down to writing the paper.
You’ve been asked to write a case study paper in APA format, and you’re wondering where to begin. You are filled with all sorts of questions ranging from what a case study paper consists of, what is the APA format and how you can get started.
Order Now: An Original, Well-Researched Case Study Paper in APA Format
Well, brace yourselves because that’s exactly what this article is about.
10 Elements of a Case Study in APA Format
Most colleges follow MLA or APA citation guidelines. Not following these guidelines would result in getting a low grade. You can also get involved in plagiarism complications , which can cause you to fail your class.
So, let's first begin by learning what is a case study in APA format.
A case study paper is assigned to students to examine a person, place, event, phenomenon, or any other type of analysis to identify, define and showcase key themes and possible solutions that can help in predicting future trends, bring out previously hidden issues that can be analyzed, and understand important research problems with better clarity.
APA is an acronym for American Psychological Association and is an in-text or reference citation format that is used mostly in case studies, literature reviews , method articles, and other advanced academic assignments. The APA format is mostly used for science subjects and niches.
Here are the 10 components of a case study paper in APA format:
1. Abstract paragraph
It's where your hypothesis, predictions, methods, and results come forward. An effective abstract paragraph helps the reader determine if they want to continue reading your paper or not.
Here’s a useful video by Bright Side on writing an abstract.
2. Annotated bibliography
Sources and references that are used in your paper are cited and annotated in the bibliography. Keep in mind to format it in the APA style.
3. Blockquotes
This is a long direct quote that is separated from the regular text. You can use quotes that are 40 words or longer and should be cited accurately.
4. Citation examples
Write an easy-to-read and thorough guide of citation examples and various sources, which will help the reader learn HOW your citations are structured.
5. Et al. usage
It is an abbreviated term for ‘and others' in Latin. This is used to cite multiple authors for one source. These are in-text citations and include the name of only the first author, followed by et al.
6. Footnotes
A way for authors to provide additional information or more insight into an idea that you’ve highlighted in the paper, without distracting the readers from the text. Formatted footnotes should be placed at the bottom of the page.
7. In-text citations
APA in-text citations are supposed to be placed in the content of your paper. The purpose of this is to show the reader who is reading your paper that a specific piece of information found in the content is sourced from somewhere else. These in-text citations are then listed as references in the bibliography or reference page.
8. Page numbers
In an APA formatted paper, page numbers are usually found in 3 places: on every page in the upper right corner, on reference lists, and in-text citations page.
9. Title page
The title page is a very important page and is used in all APA assignments.
The primary role of this page is to present the ‘Title’ or the ‘Topic’ of the paper, which should include elements such as the author’s byline, the name and number of the course, the name of the professor, the institution, or organization that the text was written for, the due date and the page number.
10. Reference page
A reference page and a bibliography can be interchangeable but are preferred to be two separate pages. The reference page includes the list of references and outside sources that were used to craft the information present in the case study paper, whereas a bibliography includes annotations and credited citations.
A 5-Step Process to Write a Case Study in APA Format
Now that we know all the components of a case study paper, it is also important to know how to write a case study paper in APA format using these components.
Here’s how to write a case study in APA format in five steps.
1. Pick your case study topic
Make sure to pick a topic that you’re interested in. This will make your paper more relatable and an interesting read for your audience.
It is also good practice to pick a topic that has enough information and research material available online, so avoid picking a broad or a general topic that has a multitude of information. This can get overwhelming and confusing for you as well as your professors. So instead, narrow down the case study’s topic.
You should have enough ideas about the direction of your case study paper, based on your findings.
2. Study the case
A quality case study is an in-depth, comprehensive project that will require you to put in all your efforts and available researched information. It is not just finding information and discussing it with your peers.
In your case study paper, you need to conduct your own research and share your point of view and other findings and offer possible solutions. You require accurate statistics, relevant examples, and other cited references to be included in your paper to strengthen your case.
From referring to secondary sources of data such as articles and published papers to conducting interviews and gathering primary data, it’s important to include credible sources of information.
3. Write the title page and abstract
Prepare your case study’s title page as well as the abstract paragraph. The title page should include the following:
- Name of the institution;
- Main idea of the investigation.
This page should be in APA format, which means that all the pages used should be numbered accurately, and the title page should be centered in the upper half of the page.
Being a brief summary of the paper, the abstract paragraph is a crucial portion of your case study paper. You need to specify the purpose of the paper, the problems addressed, all the chosen methods to bring results, and possible questions that were raised.
This should be placed on the second page of your case study paper, should not be more than 150-200 words, and needs to be written in a one-block paragraph.
4. Follow the right format
The body of the case study paper should be thorough and should detail the research and findings in an engaging manner.
Since a case study is supposed to provide solutions to an already existing problem, use formal sentences that are structured in a way that your readers can conclude the case study with you.
Formatting your case study paper according to the APA guidelines is a must, as most credible institutions follow this formatting style for their academic write-ups.
The APA guideline recommends:
- Double-space your paper, keeping 1-inch margins on all sides;
- Use 12 pt Times New Roman font;
- Use one-half-inch indentation when starting a new paragraph;
- Should have a running header on each page, as well as section headers.
5. Organize your reference page
Your case study paper requires a reference page that includes all the sources and research material that you’ve used for getting information. These sources should be cited accurately and written in APA style.
Reference page should consist:
- Author’s last name, first name;
- Year of publication (in parenthesis);
- Type the title in italics.
If you use credible sources and neglect to cite them on your reference page, your case study paper might be considered to be plagiarised.
This article on how to write a case study in APA format gives a thorough process of delivering a quality case study paper with the appropriate format. It also aims to provide guidance, important tips, and necessary methods that will help you sail through this writing assignment with ease.
Browse through, learn how to write a case study paper, and get the grades you desire.
Need a helping hand writing the well-researched case study paper? Writers Per Hour is here to help. Our expert writers know how to do a case study paper APA style and plagiarism-free.
Not just writing, but they will take care of the end-to-end process, helping you submit a high-quality paper, written from scratch.
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay

APA Citation Guide (APA 7th Edition): Case Studies
- Advertisements
- Artificial Intelligence
- Audio Materials
- Books, eBooks, Course Packs, Lab Manuals & Pamphlets
- Business Reports from Library Databases
Case Studies
- Class Notes, Class Recordings, Class Lectures and Presentations
- Creative Commons Licensed Works
- Digital Assignments: Citing Your Sources This link opens in a new window
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Games & Objects
- Government Documents
- Images, Infographics, Maps, Charts & Tables
- Indigenous Elders and Knowledge Keepers (Oral Communication)
- Journal Articles
- Legal Resources
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Personal Communications (including interviews, emails, intranet resources)
- Religious & Classical (e.g., Ancient Greek, Roman) Works
- Social Media
- Theses & Dissertations
- Websites (including documents/PDFs posted on websites)
- When Information is Missing
- Works in Another Language / Translations
- Works Quoted in Another Source (Indirect Sources)
- Quoting vs. Paraphrasing
- APA Citation FAQs
- Plagiarism This link opens in a new window
- APA for Faculty This link opens in a new window
- Case Study from a Library Database
- Case Study from a Website
- Case Study from a Book
- << Previous: Business Reports from Library Databases
- Next: Class Notes, Class Recordings, Class Lectures and Presentations >>
- Last Updated: Mar 21, 2024 12:16 PM
- URL: https://library.senecapolytechnic.ca/apa

Thesis Helpers
Find the best tips and advice to improve your writing. Or, have a top expert write your paper.
All You Need To Know About APA Case Study (Top Guide)

Citing a case study in APA is no mean feat for any student, whether in college or university. Most students would opt to have this task completed by expert writers instead of themselves. However, you can know how to cite a case study in APA and write an A+ paper painstakingly.
Well, all the answers you need for this are a few scrolls away. Follow me as we explore how to write a case study in APA like a pro!
Table of Contents
- 1. What Is the APA Citation Case Study?
- 2. Case Study Outline: Structure and Writing Tips
- 3. How To Cite a Case Study in APA: Outline
- 4. General APA Case Study Citation Template
- 5. Case Study Title Page For APA 6 and APA 7
- 5.1. APA 6 Case Study Title Page
- 5.2. APA 7 Case Study Title Page
- 6. APA Case Study Citations
- 7. APA Case Study References
What Is the APA Citation Case Study?
APA is an acronym for the American Psychological Association. It is an in-text and reference list citation format used for case studies, theoretical methodologies, literature reviews, empirical studies, and methodological articles. Its use is most prominent in the science fields.
An APA case study allows readers to understand the types of sources used in a project and their components. The information in the post follows the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association.
It outlines how to properly organize and structure a research paper, explain the grammar guidelines, and cite sources correctly. You will also get the differences between the 6th and 7th editions at the end of this guide.
Case Study Outline: Structure and Writing Tips
A case study is a kind of report, where sections within the essay’s body deal with specific aspects of the case. For instance, your instructor may ask you to focus on particular questions about the issue and organize your writing around those questions.
There are different kinds of case studies, including:
- Historical,
- Problem-oriented,
- Cumulative,
- Critical and
- Illustrative case studies
The type of case study will depend on the topic of discussion. A case structure mainly comprises of the following parts, though this may vary depending on different institutions:
- Cover page: It comprises of the necessary details of the student and class information. These include all authors’ names, institutional affiliation, course number and title, instructor’s name, and due date.
- Table of contents provides an outline of where critical parts of the report can be found and direct the reader accordingly.
- Executive summary: It explains what you will examine in the case study. You will also give an overview of the field you’re researching.
- Introduction: It identifies the focal problem being faced together with background information and the most relevant facts. Any previous studies of the issue come here.
- Case Evaluation: It includes the study’s purpose and the specific questions you are trying to answer. You also have an explanation of why something is working or is not working.
- Proposed solutions: You will give the decision criteria and possible alternatives for solving the problem at hand. They should be realistic ways to decipher what isn’t working or how to improve their current condition.
- Recommendations: Highlight the strategies that you can use to better the situation with explanations on their appropriateness.
- Implementation: It has details on how to execute the recommendations and ensure their success.
- References: Provide citations of sources used in the case study project at any point.
Nonetheless, remember to refer to your assignment instructions to find out what you have to do in the writing process.
How To Cite a Case Study in APA: Outline
The standard in-text citation and reference list formats for a case study require that you have an in-depth understanding of the APA citation style. The APA case study format follows a list of stringent rules which you must abide by to have an A+ paper.
Before embarking on the citation process, ensure that you have the following elements in place:
- The author’s name
- Date of publication
- The title of the case study
- Number of case study
Once the details above are intact, it is now time to curate them into the order recommended for APA citation style. You can request one of our professionally tailored APA format case study example to understand this concept better.
Also, feel free to take any APA style case study paper example below for your motivation:
General APA Case Study Citation Template
- General Style
Author(s). (Year). Title of the case study. The number of the case study. URL. For example, Warbeck, D. (2010). Integrated Management. HBS No. 7-806-122. https://hbsp.oxford.edu/cases/
- Textbook Case Study Format APA
Author(s) or editor(s) of the chapter or case study (Year of the book publication). Title of chapter or case study.
For Example, Jameson, B. (2003). The Role of Online Writing. In J. Ness, Cases in College Students (pp.15-18). HMD Publishing.
- Footnote Structure:
Content Footnote:
1 Student rely on online sites for completing their assignments.
Copyright Attribution:
1 Adapted from “Content Management in the US,” by H. B. Gibbering, 08 June 2005, Harvard Business Review, 3(12), p. 34 ( https://hbr.org/case/hbs_22345 ).
- In-Text Appearance:
First footnote: Branding remains a crucial aspect of digital marketing. 1
Case Study Title Page For APA 6 and APA 7
Here are the differences between the two formats as presented in the screens below. Note, that the title page for APA 7 case study doesn’t require any running head, and the paper title is bold.
APA 6 Case Study Title Page

APA 7 Case Study Title Page

APA Case Study Citations
Apa case study references.
And that is how to reference a case study in APA 6th and 7th edition. Perhaps a sample from one of our professional writing experts can help you. With our online writing help , you can request for an APA style case study paper example and use it as a motivation to get started.
What are you waiting for now?

Make PhD experience your own
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
APA 7th Edition Formatting
A Simple, Step-by-Step Guide + Free Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | June 2023
Formatting your paper in APA 7th edition can feel like a pretty daunting task , and understandably so. In this post, we’ll walk you through the APA 7 requirements, step by step. We’ll also share our free APA template , which you can use to fast-track your writing.
Student vs Professional Papers
First things first, it’s important to clarify that APA 7th edition has slightly different requirements for two different types of papers: student papers and professional papers . In this post, we’ll focus on the requirements for student papers. This will cover pretty much any paper you’ll need to submit as part of a degree program, including a dissertation or thesis (although those can require some small tweaks – more on that later).
Overview: APA 7th Edition Formatting
- APA structure and layout
- General page setup
- The title page
- The abstract
- The main body
- The reference list
- The appendices
- Free APA template
Structure and Layout
Let’s start by looking at the overall structure of a student paper formatted for APA 7th edition, before diving into the details of each section. APA requires that your paper follows a very specific, standardised structure , consisting of the following parts:
The title page : this will include the title of your paper, as well as a subtitle (if required by your university). It will also contain some information about yourself, your department and the course you’re writing the paper for.
The abstract : depending on the length of your paper and the requirements of your university, you may be required to present a brief abstract, summarising the core takeaways from your paper.
The main body : this section is the “heart” of your paper, containing the bulk of your word count. This is where you’ll present your A-grade writing!
The reference list : this section is where you’ll detail all the reference information corresponding to the in-text citations in the main body of your paper (the previous section).
Tables and figures: in the vast majority of cases, universities require that tables and figures are included in the main body of the paper, but if that’s not the case, the alternative is to have a dedicated section for the tables and figures. This is uncommon though, but we’ve mentioned it just in case.
The appendices : depending on the length of your paper and the specific requirements of your university, you may be required to include an appendix or a set of appendices containing supplementary information, such as data sets or evidence of some sort of fieldwork.
These core sections form the standard structure and order of a student paper using APA 7th edition. As we mentioned, not all of these sections are always required (specifically, the abstract, tables and figures section, and the appendix are less common), so be sure to check what your university expects from you before submitting.
Now that we’ve got a big-picture view, let’s look at the specific formatting requirements for each of these sections, step by step.
Generic Page Setup
Before you jump into writing up your paper, you’ll need first set up your document to align with APA 7th edition’s generic page requirements. Alternatively, you download our APA template (which comes fully preformatted) to fast-track your writing.
APA 7th edition requires a 1-inch margin on all sides of your document, for all pages. That said, if you’re writing a dissertation, thesis or any document that will ultimately be bound, your university will likely require a larger left margin to accommodate for binding.
Fonts & sizing
You’ll need to use a specific font and font size consistently throughout your student paper. The approved options for APA 7th edition are as follows:
- Sans serif fonts: 11-point Calibri, 11-point Arial, or 10-point Lucida Sans Unicode
- Serif fonts: 12-point Times New Roman, 11-point Georgia, or normal (10-point) Computer Modern (the default font for LaTeX)
Within figures , you will need to use a sans serif font, typically between 8 and 12 points in size. It’s best to check with your university what their preference is in this regard. For footnotes , you can use whatever the default settings are in your word processor.
In general, all text other than headings needs to be left-aligned and should not be justified . We’ll cover the formatting of headings a little later.
Line spacing
APA 7th edition requires double line spacing throughout the document . There should also be no extra space before and after paragraphs . One exception to this rule is that text within figures or tables can utilise single or 1.5-line spacing. Again, it’s a good idea to check with your university what their specific preference is.
Running header
Last but not least, you’ll need to set up a running header for your document. This should contain the page number and should be positioned in the top right corner of all pages (including the first page). There is no need for footer content unless your university specifically requests it.
With these generic formatting considerations out of the way, let’s dive into the specific requirements for each section of your paper.
The Title Page
The title page is the shop window of your paper; it’s where you make the all-important first impression to your reader. Therefore, it’s really important to make sure your format this exactly as required for APA 7th edition.
Here’s the process you can follow to set up your title page for success.
- Centre-align your curson and create 4 empty lines
- On a new line, type the title of your paper in boldface, using title case
- On a new line, type the subtitle of your paper in boldface, using title case
- Add one blank line, then write your full name on the next line
- On a new line, type your affiliation (your department and university or school name)
- On a new line, type your course code and course name (match the format used by the institution)
- On a new line, type your professor or course instructor’s name
- On a new line, type the due date for your paper
Remember to centre align all of this text and do not use justification . If you’re unsure about how to write using title case, here’s a useful title case converter . To make it all a little more tangible, below is an example of a title page formatted according to APA 7th edition specifications.

The Abstract
As we mentioned earlier, an abstract is not always required for student papers, but if your university has indicated that they require one, you’ll need to follow a specific format for APA 7th edition. Here’s how you can set it up:
- Start your abstract on a new page
- On the first line, type “Abstract”. This should be boldface and centred
- On a new line, write the abstract. This should be aligned flush left (no indentation) and is typically 150 – 250 words in length.
- On a new line, type “Keywords:”. This should be indented a half inch and italicized
- On the same line, include 3 – 5 relevant keywords. These should all be written in lowercase and should not be italicised. They should be separated by commas and there should be no period after the final keyword.
Here’s an example of an abstract page formatted according to APA 7th edition specifications.

The Main Body
Now we can move on to the important stuff – the body section of your paper. There are quite a few things you need to know about formatting this section for APA 7th edition – let’s unpack it step by step.
Initial set-up
To kick things off, insert a page break and start your main body on a new page . You can then copy and paste the title (and subtitle, if you have one) from your title page onto the first line of your body page.
With your title (and subtitle) in place, you can start your write-up on a new line . This should be left-aligned and the first line of each paragraph should have a half-inch indent . As with the rest of your paper, this section should use double-line spacing.
The first paragraph of your main body does not require a heading as it’s generally assumed that the first paragraph will be introductory in nature. For the rest of the body, you can use headings as you see fit. However, it’s important to understand the specific formatting requirements for APA headings . Here’s a quick overview:
Level 1: Centered, boldface, title case (paragraph text starts on a new line) Level 2: Flush left, boldface, title case (paragraph text starts on a new line) Level 3: Flush left, boldface, italic, title case (paragraph text starts on a new line) Level 4: Indented, boldface, title case, end the heading with a period (paragraph text starts on the same line) Level 5: Indented, boldface, italic, end the heading with a period (paragraph text starts on the same line)
It’s also important to note that headings shouldn’t be labelled with any numbers or letters. For example, “1. Potential Causes”, “2. Consequences”, etc. Instead, you can stick to purely descriptive headings.
Related to this, you should avoid using an excessing number of headings – less is more when it comes to headings. Don’t feel the need to use multiple headings or heading levels, especially for shorter papers. Just keep it simple 🙂

Text styling and punctuation
APA 7th edition has specific requirements with regard to text styling and punctuation. Here are some of the most important requirements you’ll need to follow:
- Use a single space (as opposed to a double space) at the end of each sentence (i.e., after the period)
- Use an Oxford comma when listing out 3 or more items
- Use words to write any number less than 10 , as well as when starting a sentence
- Write out all fractions in text format (e.g., two-thirds, three-quarters, etc.)
- Use numerals for any numbers that represent time , dates , age or money
There are a few important rules to follow in terms of language use when writing your paper using APA format. Most importantly, you’ll need to:
- Use active voice (as opposed to passive voice) as much as possible
- Stick to one verb tense throughout the same and adjacent paragraphs
- Avoid using contractions , colloquial language or excessive jargon
- Use bias-free language – you can learn more about this here
In-text citations
APA 7th edition has a very specific set of requirements regarding how to reference resources within your paper. Here are some of the most important things you need to be aware of:
Author-date system: in-text citations consist of (at a minimum) the lead author’s last name, followed by the date of publication. APA does not use numbers or footnotes to denote citations.
Types of citations: APA allows two types of in-text citations – parenthetical (non-integrative) and narrative (integrative). Parenthetical citations feature the author and date in parentheses (brackets) at the end of the respective sentence. Here’s an example:
APA 7th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen, 2023).
Narrative citations weave the author into the flow of the sentence and only include the date in parentheses at the end of the sentence. Here’s an example:
Jansen states that APA 7th edition is easy for students to grasp if they visit the Grad Coach blog (2023).
Both of these citation formats are acceptable and, in general, it’s a good idea to utilise a mix of both in your writing.
Quotations: when quoting text verbatim from a source, you’ll need to include the page number of the original text in your citation. This number needs to be placed after the date portion of the citation, whether it’s a narrative or parenthetical citation. Here’s an example:
APA 7th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen, 2023, p.45).
Multiple authors: when citing resources that were created by three or more authors, you only need to state the lead author’s last name, followed by “et al.”. Here’s an example:
APA 7th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen et al., 2023).
As we mentioned, APA has an extensive set of requirements regarding how to format and structure in-text citations and references, so please keep in mind that this is not an exhaustive list. If you’d like to learn more, you can visit the referencing section of the APA site here . Below you can find an example of a portion of body content from our free template , which demonstrates the different types of citations.

The Reference List
With your body content taken care of, the next item on the agenda is the reference list. Again, APA has a notably large set of requirements regarding the content and formatting of the reference list. Nevertheless, we’ll cover the basics here to help you get started.
Basic setup
As with all sections, your reference list needs to start on a new page and should be titled “References”. The title should be boldfaced and centred . The reference list should then start on the next line. As with the rest of the document, the reference list should have double line spacing throughout.
The list itself
The reference list should comprise the following:
- All sources cited in the body of your document should feature in the reference list. Make sure that every citation is accounted for in your reference list.
- The references should be ordered alphabetically , according to the lead author’s last name .
- Each entry must include (at a minimum) information regarding the author (s), publication date , the title of the article and the source (e.g., an academic journal).
- All references should be left-aligned and should use a hanging indent – in other words, the second line of any given reference (if it has one) should be indented a half inch.
We have to stress that these are just the basics. APA 7th edition requires that all of your references must be structured and formatted in a very specific way , depending on the type of resource. For example, the content and formatting requirements for a journal article will be significantly different from that of a blog post or magazine article (you can see some examples in our template ).
Simply put, if you plan to draft your reference list manually, it’s important to consult your university’s style guide or the APA manual itself. This leads us to our next point…
In general, it is a terrible idea to try to write up your reference list manually . Given the incredibly high level of detail required, it’s highly likely that you’ll make mistakes if you try to write this section yourself. A much better solution is to use reference management software such as Mendeley or Zotero. Either of these will take care of the formatting and content for you, and they’ll do a much more accurate job of it too. Best of all, they’re both completely free.
If you’re not familiar with any sort of reference management software, be sure to check out our easy-to-follow explainer videos for both Mendeley and Zotero .
The Appendix
Last but not least, we’ve got the appendix (or appendices). The appendix is where you’ll showcase any supporting data for your student paper. This section is not always required , especially for shorter papers, so don’t worry if it sounds unfamiliar. If you’re unsure, check with your university if they require (or even allow) appendices.
If an appendix is required, here’s how you’ll set it up:
- Start the appendix on a new page
- Title the page “Appendix” if there is only one appendix , or “Appendix A”, “Appendix B”, etc. if there are multiple appendices . This title should be boldfaced and centred.
- On a new line, write the title of the appendix . Again, this should be boldfaced and centred.
- On a new line, start your appendix content . As with the body content, the first line of each paragraph should be indented.
An important point to remember is that you need to refer to your appendix within your main body section . This typically means including a line that reads something like “(see Appendix A for more information)”. In other words, your appendix should never be an orphan.
Another important thing to keep in mind is that appendices don’t typically earn marks (at least not directly). To be clear, your appendix can help support the claims you make in your body content (which would have a positive impact on its mark-earning potential), but, in most cases, markers will not award marks to the appendix content itself. If you’re unsure, check with your university what their policy is.

Wrapping Up
In this post, we’ve provided a primer covering the core requirements for student papers using APA 7th edition . To recap, we’ve looked at the following:
One last thing to point out; it might be obvious but it’s important to mention it – if your university has specified anything that contrasts what we’ve discussed here, do follow their guidance . Some universities and/or programmes will have slight variations on the standard APA requirements, and you want to make sure you follow them.

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

APA Style (7th ed.)
- Cite: Why? When?
- Book, eBook, Dissertation
- Article or Report
- Business Sources
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
- In-Text Citation
- Format Your Paper
Format Your Paper
Download and use the editable templates for student papers below: .
- APA 7th ed. Template Document This is an APA format template document in Google Docs. Click on the link -- it will ask for you to make a new copy of the document, which you can save in your own Google Drive with your preferred privacy settings.
- APA 7th ed. Template Document A Microsoft Word document formatted correctly according to APA 7th edition.
- APA 7th ed. Annotated Bibliography template A Microsoft Word document formatted correctly for an annotated bibliography.
Or, view the directions for specific sections below:
Order of sections (section 2.17).
- Title page including Title, Author, University and Department, Class, Instructor, and Date
- Body (including introduction, literature review or background, discussion, and conclusion)
- Appendices (including tables & figures)
Margins & Page Numbers (sections 2.22-2.24)
- 1 inch at top, bottom, and both sides
- Left aligned paragraphs and leave the right edge ragged (not "right justified")
- Indent first line of each paragraph 1/2 inch from left margin
- Use page numbers, including on the title page, 1/2 inch from top and flush with right margin
Text Format (section 2.19)
- Times New Roman, 12 point
- Calibri, 11 point
- Arial, 11 point
- Lucinda Sans Unicode, 10 point
- Georgia, 11 point
- Double-space and align text to the left
- Use active voice
- Don't overuse technical jargon
- No periods after a web address or DOI in the References list.
Tables and Figures In-Text (chapter 7)
- Label tables and figures numerically (ex. Table 1)
- Give each table column a heading and use separating lines only when necessary
- Design the table and figure so that it can be understood on its own, i.e. it does not require reference to the surrounding text to understand it
- Notes go below tables and figures
Title Page (section 2.3)
- Include the title, your name, the class name , and the college's name
- Title should be 12 words or less and summarize the paper's main idea
- No periods or abbreviations
- Do not italicize or underline
- No quotation marks, all capital letters, or bold
- Center horizontally in upper half of the page
Body (section 2.11)
- Align the text to the left with a 1/2-inch left indent on the first line
- Double-space
- As long as there is no Abstract, at the top of the first page, type the title of the paper, centered, in bold , and in Sentence Case Capitalization
- Usually, include sections like these: introduction, literature review or background, discussion, and conclusion -- but the specific organization will depend on the paper type
- Spell out long organization names and add the abbreviation in parenthesis, then just use the abbreviation
- Spell out numbers one through nine and use a number for 10 or more
- Use a number for units of measurement, in tables, to represent statistical or math functions, and dates or times

Headings (section 2.26-2.27)
- Level 1: Center, bold , Title Case
- Level 2: Align left, bold , Title Case
- Level 3: Alight left, bold italics , Title Case
- Level 4: Indented 1/2", bold , Title Case, end with a period. Follow with text.
- Level 5: Indented 1/2", bold italics , Title Case, end with a period. Follow with text.

Quotations (sections 8.26-8.33)
- Include short quotations (40 words or less) in-text with quotation marks
- For quotes more than 40 words, indent the entire quote a half inch from the left margin and double-space it with no quotation marks
- When quoting two or more paragraphs from an original source, indent the first line of each paragraph a half inch from the left margin
- Use ellipsis (...) when omitting sections from a quote and use four periods (....) if omitting the end section of a quote
References (section 2.12)
Begins on a new page following the text of your paper and includes complete citations for the resources you've used in your writing.
- References should be centered and bolded at the top of a new page
- Double-space and use hanging indents (where the first line is on the left margin and the following lines are indented a half inch from the left)
- List authors' last name first followed by the first and middle initials (ex. Skinner, B. F.)
- Alphabetize the list by the first author's last name of of each citation (see sections 9.44-9.49)
- Capitalize only the first word, the first after a colon or em dash, and proper nouns
- Don't capitalize the second word of a hyphenated compound
- No quotation marks around titles of articles
Appendices with Tables, Figures, & Illustrations (section 2.14, and chapter 7)
- Include appendices only to help the reader understand, evaluate, or replicate the study or argument
- Put each appendix on a separate page and align left
- For text, do not indent the first paragraph, but do indent the rest
- If you have only one appendix, label it "Appendix"
- If you have two or more appendices, label them "Appendix A", "Appendix B" and so forth as they appear in the body of your paper
- Label tables and figures numerically (ex. Table 1, or Table B1 and Table B2 if Appendix B has two tables) and describe them within the text of the appendix
- Notes go below tables and figures (see samples on p. 210-226)
Annotated Bibliography
Double-space the entire bibliography. give each entry a hanging indent. in the following annotation, indent the entire paragraph a half inch from the left margin and give the first line of each paragraph a half inch indent. see the template document at the top of this page..
- Check with your professor for the length of the annotation and which elements you should evaluate.
These elements are optional, if your professor or field requires them, but they are not required for student papers:
Abstract (section 2.9).
- Abstract gets its own page
- Center "Abstract" heading and do not indent the first line of the text
- Summarize the main points and purpose of the paper in 150-250 words maximum
- Define abbreviations and acronyms used in the paper
Running Head (section 2.8 )
- Shorten title to 50 characters or less (counting spaces and punctuation) for the running head
- In the top margin, the running head is aligned left, with the page number aligned on the right
- On every page, put (without the brackets): [SHORTENED TITLE OF YOUR PAPER IN ALL CAPS] [page number]
More questions? Check out the authoritative source: APA style blog
- << Previous: In-Text Citation
- Last Updated: Mar 7, 2024 2:29 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uww.edu/apa
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format
APA Format for Students & Researchers
In this guide, students and researchers can learn the basics of creating a properly formatted research paper according to APA guidelines.
It includes information on how to conceptualize, outline, and format the basic structure of your paper, as well as practical tips on spelling, abbreviation, punctuation, and more. The guide concludes with a complete sample paper as well as a final checklist that writers can use to prepare their work for submission.
APA Paper Formatting Basics
- All text should be double-spaced
- Use one-inch margins on all sides
- All paragraphs in the body are indented
- Make sure that the title is centered on the page with your name and school/institution underneath
- Use 12-point font throughout
- All pages should be numbered in the upper right hand corner
- The manual recommends using one space after most punctuation marks
- A shortened version of the title (“running head”) should be placed in the upper left hand corner
Table of Contents
Here’s a quick rundown of the contents of this guide on how to do APA format.
Information related to writing and organizing your paper:
- Paper and essay categories
General paper length
- Margin sizes
- Title pages
- Running Heads
- APA Outline
- APA Abstract
- The body of papers
- APA headings and subheadings
- Use of graphics (tables and figures)
Writing style tips:
Proper tone.
- Reducing bias and labels
- Abbreviation do’s and don’ts
- Punctuation
- Number rules
Citing Your Sources:
- Citing Sources
- In-text Citations
- Reference Page
Proofing Your Paper:
- Final checklist
- Submitting your project
APA Information:
- What is APA
- APA 7 Updates
What you won’t find in this guide: This guide provides information related to the formatting of your paper, as in guidelines related to spacing, margins, word choice, etc. While it provides a general overview of APA references, it does not provide instructions for how to cite in APA format.
For step-by-step instructions for citing books, journals, how to cite a website in APA format, information on an APA format bibliography, and more, refer to these other EasyBib guides:
- APA citation (general reference guide)
- APA In-text citation
- APA article citation
- APA book citation
- APA citation website
Or, you can use our automatic generator. Our APA formatter helps to build your references for you. Yep, you read that correctly.
Writing and Organizing Your APA Paper in an Effective Way
This section of our guide focuses on proper paper length, how to format headings, spacing, and more! This information can be found in Chapter 2 of the official manual (American Psychological Association, 2020, pp. 29-67).
Categories of papers
Before getting into the nitty-gritty details related to APA research paper format, first determine the type of paper you’re about to embark on creating:
Empirical studies
Empirical studies take data from observations and experiments to generate research reports. It is different from other types of studies in that it isn’t based on theories or ideas, but on actual data.
Literature reviews
These papers analyze another individual’s work or a group of works. The purpose is to gather information about a current issue or problem and to communicate where we are today. It sheds light on issues and attempts to fill those gaps with suggestions for future research and methods.
Theoretical articles
These papers are somewhat similar to a literature reviews in that the author collects, examines, and shares information about a current issue or problem, by using others’ research. It is different from literature reviews in that it attempts to explain or solve a problem by coming up with a new theory. This theory is justified with valid evidence.
Methodological articles
These articles showcase new advances, or modifications to an existing practice, in a scientific method or procedure. The author has data or documentation to prove that their new method, or improvement to a method, is valid. Plenty of evidence is included in this type of article. In addition, the author explains the current method being used in addition to their own findings, in order to allow the reader to understand and modify their own current practices.
Case studies
Case studies present information related an individual, group, or larger set of individuals. These subjects are analyzed for a specific reason and the author reports on the method and conclusions from their study. The author may also make suggestions for future research, create possible theories, and/or determine a solution to a problem.
Since APA style format is used often in science fields, the belief is “less is more.” Make sure you’re able to get your points across in a clear and brief way. Be direct, clear, and professional. Try not to add fluff and unnecessary details into your paper or writing. This will keep the paper length shorter and more concise.
Margin sizes in APA Format
When it comes to margins, keep them consistent across the left, right, top, and bottom of the page. All four sides should be the same distance from the edge of the paper. It’s recommended to use at least one-inch margins around each side. It’s acceptable to use larger margins, but the margins should never be smaller than an inch.
Title pages in APA Format
The title page, or APA format cover page, is the first page of a paper or essay. Some teachers and professors do not require a title page, but some do. If you’re not sure if you should include one or not, ask your teacher. Some appreciate the page, which clearly displays the writer’s name and the title of the paper.
The APA format title page for student papers includes six main components:
- the title of the APA format paper
- names of all authors
- institutional affiliation
- course number and title
- instructor’s name
Title pages for professional papers also require a running head; student papers do not.
Some instructors and professional publications also ask for an author’s note. If you’re required or would like to include an author’s note, place it below the institutional affiliation. Examples of information included in an author’s note include an ORCID iD number, a disclosure, and an acknowledgement.
Here are key guidelines to developing your title page:
- The title of the paper should capture the main idea of the essay, but should not contain abbreviations or words that serve no purpose. For example, instead of using the title “A Look at Amphibians From the Past,” title the paper “Amphibians From the Past.” Delete the unnecessary fluff!
- Center the title on the page and place it about 3-4 lines from the top.
- The title should be bolded, in title case, and the same font size as your other page text. Do not underline or italicize the title. Other text on the page should be plain (not bolded , underlined, or italicized ).
- All text on the title page should be double-spaced. The APA format examples paper below displays proper spacing, so go take a look!
- Do not include any titles in the author’s name such as Dr. or Ms. In contrast, for your instructor’s name, use the form they prefer (e.g., Sagar Parekh, PhD; Dr. Minako Asato; Professor Nathan Ian Brown; etc.).
- The institutional affiliation is the school the author attends or the location where the author conducted the research.
In a hurry? Try the EasyBib title page maker to easily create a title page for free.
Sample of an APA format title page for a student paper:
Sample of title page for a professional paper:
Running heads in APA Format
The 7th edition of the American Psychological Association Publication Manual (p. 37) states that running heads are not required for student papers unless requested by the instructor. Student papers still need a page number included in the upper right-hand corner of every page. The 6th edition required a running head for student papers, so be sure to confirm with your instructor which edition you should follow. Of note, this guide follows the 7th edition.
Running heads are required for professional papers (e.g., manuscripts submitted for publication). Read on for instructions on how to create them.
Are you wondering what is a “running head”? It’s basically a page header at the top of every page. To make this process easier, set your word processor to automatically add these components onto each page. You may want to look for “Header” in the features.
A running head/page header includes two pieces:
- the title of the paper
- page numbers.
Insert page numbers justified to the right-hand side of the APA format paper (do not put p. or pg. in front of the page numbers).
For all pages of the paper, including the APA format title page, include the “TITLE OF YOUR PAPER” justified to the left in capital letters (i.e., the running head). If your full title is long (over 50 characters), the running head title should be a shortened version.

Preparing outlines in APA Format
Outlines are extremely beneficial as they help writers stay organized, determine the scope of the research that needs to be included, and establish headings and subheadings.
There isn’t an official or recommended “APA format for outline” structure. It is up to the writer (if they choose to make use of an outline) to determine how to organize it and the characters to include. Some writers use a mix of roman numerals, numbers, and uppercase and lowercase letters.
Even though there isn’t a required or recommended APA format for an outline, we encourage writers to make use of one. Who wouldn’t want to put together a rough outline of their project? We promise you, an outline will help you stay on track.
Here’s our version of how APA format for outlines could look:

Don’t forget, if you’re looking for information on APA citation format and other related topics, check out our other comprehensive guides.
How to form an abstract in APA
An APA format abstract (p. 38) is a summary of a scholarly article or scientific study. Scholarly articles and studies are rather lengthy documents, and abstracts allow readers to first determine if they’d like to read an article in its entirety or not.
You may come across abstracts while researching a topic. Many databases display abstracts in the search results and often display them before showing the full text of an article or scientific study. It is important to create a high quality abstract that accurately communicates the purpose and goal of your paper, as readers will determine if it is worthy to continue reading or not.
Are you wondering if you need to create an abstract for your assignment? Usually, student papers do not require an abstract. Abstracts are not typically seen in class assignments, and are usually only included when submitting a paper for publication. Unless your teacher or professor asked for it, you probably don’t need to have one for your class assignment.
If you’re planning on submitting your paper to a journal for publication, first check the journal’s website to learn about abstract and APA paper format requirements.
Here are some helpful suggestions to create a dynamic abstract:
- Abstracts are found on their own page, directly after the title or cover page.
- Professional papers only (not student papers): Include the running head on the top of the page.
- On the first line of the page, center the word “Abstract” (but do not include quotation marks).
- On the following line, write a summary of the key points of your research. Your abstract summary is a way to introduce readers to your research topic, the questions that will be answered, the process you took, and any findings or conclusions you drew. Use concise, brief, informative language. You only have a few sentences to share the summary of your entire document, so be direct with your wording.
- This summary should not be indented, but should be double-spaced and less than 250 words.
- If applicable, help researchers find your work in databases by listing keywords from your paper after your summary. To do this, indent and type Keywords : in italics. Then list your keywords that stand out in your research. You can also include keyword strings that you think readers will type into the search box.
- Active voice: The subjects reacted to the medication.
- Passive voice: There was a reaction from the subjects taking the medication.
- Instead of evaluating your project in the abstract, simply report what it contains.
- If a large portion of your work includes the extension of someone else’s research, share this in the abstract and include the author’s last name and the year their work was released.
APA format example page:

Here’s an example of an abstract:
Visual design is a critical aspect of any web page or user interface, and its impact on a user’s experience has been studied extensively. Research has shown a positive correlation between a user’s perceived usability and a user’s assessment of visual design. Additionally, perceived web quality, which encompasses visual design, has a positive relationship with both initial and continued consumer purchase intention. However, visual design is often assessed using self-report scale, which are vulnerable to a few pitfalls. Because self-report questionnaires are often reliant on introspection and honesty, it is difficult to confidently rely on self-report questionnaires to make important decisions. This study aims to ensure the validity of a visual design assessment instrument (Visual Aesthetics of Websites Inventory: Short version) by examining its relationship with biometric (variables), like galvanic skin response, pupillometry, and fixation information. Our study looked at participants assessment of a webpage’s visual design, and compared it to their biometric responses while viewing the webpage. Overall, we found that both average fixation duration and pupil dilation differed when participants viewed web pages with lower visual design ratings compared to web pages with a higher visual design rating.
Keywords : usability, visual design, websites, eye tracking, pupillometry, self-report, VisAWI
The body of an APA paper
On the page after the title page (if a student paper) or the abstract (if a professional paper), begin with the body of the paper.
Most papers follow this format:
- At the top of the page, add the page number in the upper right corner of all pages, including the title page.
- On the next line write the title in bold font and center it. Do not underline or italicize it.
- Begin with the introduction and indent the first line of the paragraph. All paragraphs in the body are indented.
Sample body for a student paper:

Most scientific or professional papers have additional sections and guidelines:
- Start with the running head (title + page number). The heading title should be in capital letters. The abstract page should be page 2.
- The introduction presents the problem and premise upon which the research was based. It goes into more detail about this problem than the abstract.
- Begin a new section with the Method and use this word as the subtitle. Bold and center this subtitle. The Method section shows how the study was run and conducted. Be sure to describe the methods through which data was collected.
- Begin a new section with the Results . Bold and center this subtitle. The Results section summarizes your data. Use charts and graphs to display this data.
- Draw conclusions and support how your data led to these conclusions.
- Discuss whether or not your hypothesis was confirmed or not supported by your results.
- Determine the limitations of the study and next steps to improve research for future studies.
Sample body for a professional paper:

Keep in mind, APA citation format is much easier than you think, thanks to EasyBib.com. Try our automatic generator and watch how we create APA citation format references for you in just a few clicks. While you’re at it, take a peek at our other helpful guides, such as our APA reference page guide, to make sure you’re on track with your research papers.
Proper usage of headings & subheadings in APA Format
Headings (p. 47) serve an important purpose in research papers — they organize your paper and make it simple to locate different pieces of information. In addition, headings provide readers with a glimpse to the main idea, or content, they are about to read.
In APA format, there are five levels of headings, each with a different formatting:
- This is the title of your paper
- The title should be centered in the middle of the page
- The title should be bolded
- Use uppercase and lowercase letters where necessary (called title capitalization)
- Place this heading against the left margin
- Use bold letters
- Use uppercase and lowercase letters where necessary
- Place this heading against the left side margin
- End the heading with a period
- Indented in from the left margin
Following general formatting rules, all headings are double spaced and there are no extra lines or spaces between sections.
Here is a visual APA format template for levels of headings:

Use of graphics (tables and figures) in APA Format
If you’re looking to jazz up your project with any charts, tables, drawings, or images, there are certain APA format rules (pp. 195-250) to follow.
First and foremost, the only reason why any graphics should be added is to provide the reader with an easier way to see or read information, rather than typing it all out in the text.
Lots of numbers to discuss? Try organizing your information into a chart or table. Pie charts, bar graphs, coordinate planes, and line graphs are just a few ways to show numerical data, relationships between numbers, and many other types of information.
Instead of typing out long, drawn out descriptions, create a drawing or image. Many visual learners would appreciate the ability to look at an image to make sense of information.
Before you go ahead and place that graphic in your paper, here are a few key guidelines:
- Follow them in the appropriate numerical order in which they appear in the text of your paper. Example : Figure 1, Figure 2, Table 1, Figure 3.
- Example: Figure 1, Figure 2, Table 1, Figure 3
- Only use graphics if they will supplement the material in your text. If they reinstate what you already have in your text, then it is not necessary to include a graphic.
- Include enough wording in the graphic so that the reader is able to understand its meaning, even if it is isolated from the corresponding text. However, do not go overboard with adding a ton of wording in your graphic.
- Left align tables and figures
In our APA format sample paper , you’ll find examples of tables after the references. You may also place tables and figures within the text just after it is mentioned.
Is there anything better than seeing a neatly organized data table? We think not! If you have tons of numbers or data to share, consider creating a table instead of typing out a wordy paragraph. Tables are pretty easy to whip up on Google Docs or Microsoft Word.
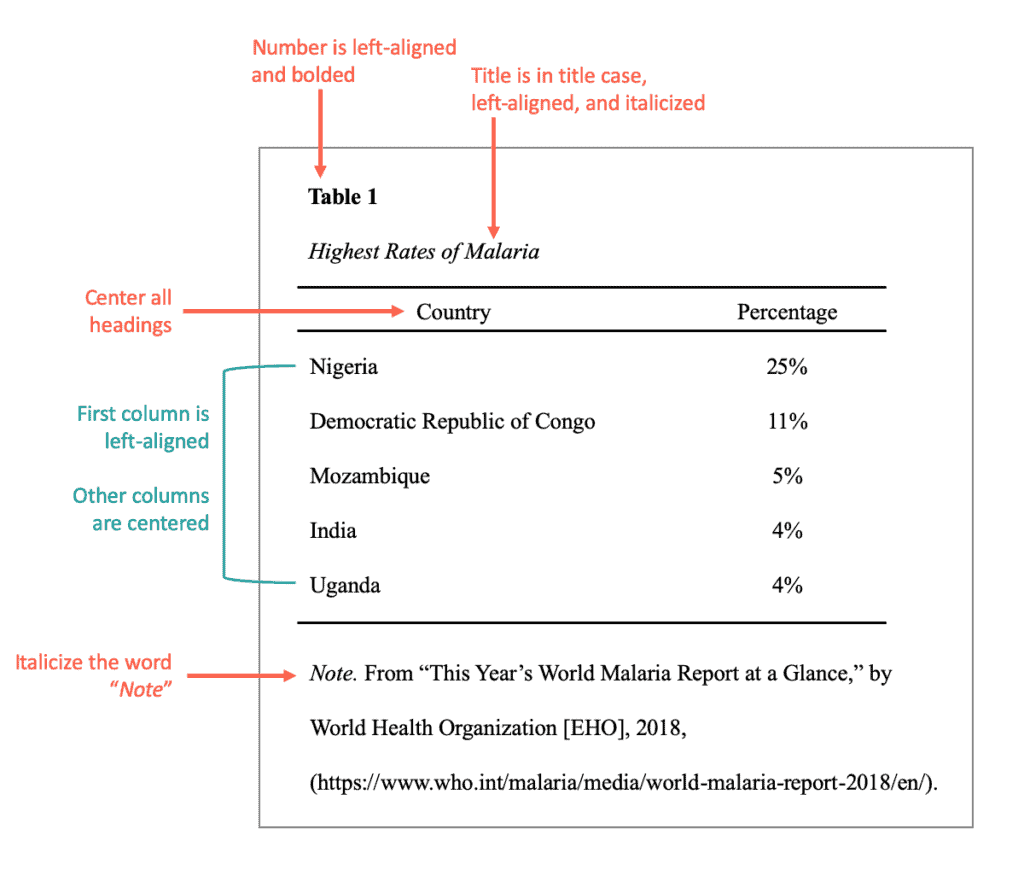
General format of a table should be:
- Table number
- Choose to type out your data OR create a table. As stated above, in APA format, you shouldn’t have the information typed out in your paper and also have a table showing the same exact information. Choose one or the other.
- If you choose to create a table, discuss it very briefly in the text. Say something along the lines of, “Table 1 displays the amount of money used towards fighting Malaria.” Or, “Stomach cancer rates are displayed in Table 4.”
- If you’re submitting your project for a class, place your table close to the text where it’s mentioned. If you’re submitting it to be published in a journal, most publishers prefer tables to be placed in the back. If you’re unsure where to place your tables, ask!
- Include the table number first and at the top. Table 1 is the first table discussed in the paper. Table 2 is the next table mentioned, and so on. This should be in bold.
- Add a title under the number. Create a brief, descriptive title. Capitalize the first letter for each important word. Italicize the title and place it under the table number.
- Only use horizontal lines.
- Limit use of cell shading.
- Keep the font at 12-point size and use single or double spacing. If you use single spacing in one table, make sure all of the others use single spaces as well. Keep it consistent.
- All headings should be centered.
- In the first column (called the stub), center the heading, left-align the information underneath it (indent 0.15 inches if info is more than one line).
- Information in other columns should be centered.
- General . Information about the whole table.
- Specific . Information targeted for a specific column, row, or cell.
- Probability . Explains what certain table symbols mean. For example, asterisks, p values, etc.
Here’s an APA format example of a table:
We know putting together a table is pretty tricky. That’s why we’ve included not one, but a few tables on this page. Scroll down and look at the additional tables in the essay in APA format example found below.
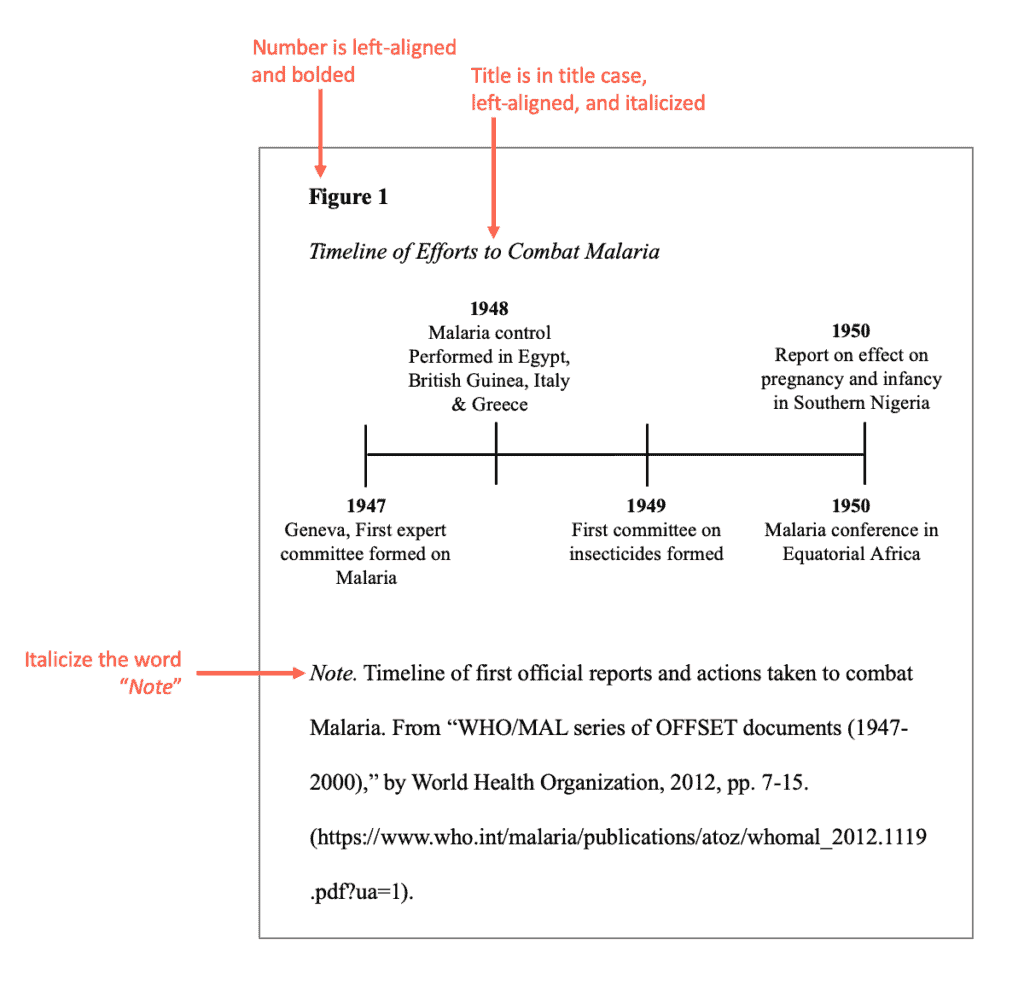
Figures represent information in a visual way. They differ from tables in that they are visually appealing. Sure, tables, like the one above, can be visually appealing, but it’s the color, circles, arrows, boxes, or icons included that make a figure a “figure.”
There are many commonly used figures in papers. Examples APA Format:
- Photographs
- Hierarchy charts
General format of a figure is the same as tables. This means each should include:
- Figure number
Use the same formatting tables use for the number, title, and note.
Here are some pointers to keep in mind when it comes to APA format for figures:
- Only include a figure if it adds value to your paper. If it will truly help with understanding, include it!
- Either include a figure OR write it all out in the text. Do not include the same information twice.
- If a note is added, it should clearly explain the content of the figure. Include any reference information if it’s reproduced or adapted.
APA format sample of a figure:
Photographs:
We live in a world where we have tons of photographs available at our fingertips.
Photographs found through Google Images, social media, stock photos made available from subscription sites, and tons of other various online sources make obtaining photographs a breeze. We can even pull out our cell phones, and in just a few seconds, take pictures with our cameras.
Photographs are simple to find, and because of this, many students enjoy using them in their papers.
If you have a photograph you would like to include in your project, here are some guidelines from the American Psychological Association.
- Create a reference for the photograph. Follow the guidelines under the table and figure sections above.
- Do not use color photos. It is recommended to use black and white. Colors can change depending on the reader’s screen resolution. Using black and white ensures the reader will be able to view the image clearly. The only time it is recommended to use color photos is if you’re writing about color-specific things. For example, if you’re discussing the various shades of leaf coloration, you may want to include a few photographs of colorful leaves.
- If there are sections of the photograph that are not related to your work, it is acceptable to crop them out. Cropping is also beneficial in that it helps the reader focus on the main item you’re discussing.
- If you choose to include an image of a person you know, it would be respectful if you ask their permission before automatically including their photo in your paper. Some schools and universities post research papers online and some people prefer that their photos and information stay off the Internet.
B. Writing Style Tips
Writing a paper for scientific topics is much different than writing for English, literature, and other composition classes. Science papers are much more direct, clear, and concise. This section includes key suggestions, explains how to write in APA format, and includes other tidbits to keep in mind while formulating your research paper.
Verb usage in APA
Research experiments and observations rely on the creation and analysis of data to test hypotheses and come to conclusions. While sharing and explaining the methods and results of studies, science writers often use verbs.
When using verbs in writing, make sure that you continue to use them in the same tense throughout the section you’re writing. Further details are in the publication manual (p. 117).
Here’s an APA format example:
We tested the solution to identify the possible contaminants.
It wouldn’t make sense to add this sentence after the one above:
We tested the solution to identify the possible contaminants. Researchers often test solutions by placing them under a microscope.
Notice that the first sentence is in the past tense while the second sentence is in the present tense. This can be confusing for readers.
For verbs in scientific papers, the APA manual recommends using:
- Past tense or present perfect tense for the explantation of the procedure
- Past tense for the explanation of the results
- Present tense for the explanation of the conclusion and future implications
If this is all a bit much, and you’re simply looking for help with your references, try the EasyBib.com APA format generator . Our APA formatter creates your references in just a few clicks. APA citation format is easier than you think thanks to our innovative, automatic tool.
Even though your writing will not have the same fluff and detail as other forms of writing, it should not be boring or dull to read. The Publication Manual suggests thinking about who will be the main reader of your work and to write in a way that educates them.
How to reduce bias & labels
The American Psychological Association strongly objects to any bias towards gender, racial groups, ages of individuals or subjects, disabilities, and sexual orientation (pp. 131-149). If you’re unsure whether your writing is free of bias and labels or not, have a few individuals read your work to determine if it’s acceptable.
Here are a few guidelines that the American Psychological Association suggests :
- Only include information about an individual’s orientation or characteristic if it is important to the topic or study. Do not include information about individuals or labels if it is not necessary.
- If writing about an individual’s characteristic or orientation, for essay APA format, make sure to put the person first. Instead of saying, “Diabetic patients,” say, “Patients who are diabetic.”
- Instead of using narrow terms such as, “adolescents,” or “the elderly,” try to use broader terms such as, “participants,” and “subjects.”
- “They” or “their” are acceptable gender-neutral pronouns to use.
- Be mindful when using terms that end with “man” or “men” if they involve subjects who are female. For example, instead of using “Firemen,” use the term, “Firefighter.” In general, avoid ambiguity.
- When referring to someone’s racial or ethnic identity, use the census category terms and capitalize the first letter. Also, avoid using the word, “minority,” as it can be interpreted as meaning less than or deficient. Instead, say “people of color” or “underrepresented groups.”
- When describing subjects in APA format, use the words “girls” and “boys” for children who are under the age of 12. The terms, “young woman,” “young man,” “female adolescent,” and “male adolescent” are appropriate for subjects between 13-17 years old; “Men,” and “women,” for those older than 18. Use the term, “older adults.” for individuals who are older. “Elderly,” and “senior,” are not acceptable if used only as nouns. It is acceptable to use these terms if they’re used as adjectives.
Read through our example essay in APA format, found in section D, to see how we’ve reduced bias and labels.
Spelling in APA Format
- In APA formatting, use the same spelling as words found in Merriam-Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary (American English) (p. 161).
- If the word you’re trying to spell is not found in Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary, a second resource is Webster’s Third New International Dictionary .
- If attempting to properly spell words in the psychology field, consult the American Psychological Association’s Dictionary of Psychology
Thanks to helpful tools and features, such as the spell checker, in word processing programs, most of us think we have everything we need right in our document. However, quite a few helpful features are found elsewhere.
Where can you find a full grammar editor? Right here, on EasyBib.com. The EasyBib Plus paper checker scans your paper for spelling, but also for any conjunction , determiner, or adverb out of place. Try it out and unlock the magic of an edited paper.
Abbreviation do’s and don’ts in APA Format
Abbreviations can be tricky. You may be asking yourself, “Do I include periods between the letters?” “Are all letters capitalized?” “Do I need to write out the full name each and every time?” Not to worry, we’re breaking down the publication manual’s abbreviations (p. 172) for you here.
First and foremost, use abbreviations sparingly.
Too many and you’re left with a paper littered with capital letters mashed together. Plus, they don’t lend themselves to smooth and easy reading. Readers need to pause and comprehend the meaning of abbreviations and quite often stumble over them.
- If the abbreviation is used less than three times in the paper, type it out each time. It would be pretty difficult to remember what an abbreviation or acronym stands for if you’re writing a lengthy paper.
- If you decide to sprinkle in abbreviations, it is not necessary to include periods between the letters.
- Example: While it may not affect a patient’s short-term memory (STM), it may affect their ability to comprehend new terms. Patients who experience STM loss while using the medication should discuss it with their doctor.
- Example : AIDS
- The weight in pounds exceeded what we previously thought.
Punctuation in APA Format
One space after most punctuation marks.
The manual recommends using one space after most punctuation marks, including punctuation at the end of a sentence (p. 154). It doesn’t hurt to double check with your teacher or professor to ask their preference since this rule was changed recently (in 2020).
The official APA format book was primarily created to aid individuals with submitting their paper for publication in a professional journal. Many schools adopt certain parts of the handbook and modify sections to match their preference. To see an example of an APA format research paper, with the spacing we believe is most commonly and acceptable to use, scroll down and see section D.
For more information related to the handbook, including frequently asked questions, and more, here’s further reading on the style
It’s often a heated debate among writers whether or not to use an Oxford comma (p. 155), but for this style, always use an Oxford comma. This type of comma is placed before the words AND and OR or in a series of three items.
Example of APA format for commas: The medication caused drowsiness, upset stomach, and fatigue.
Here’s another example: The subjects chose between cold, room temperature, or warm water.
Apostrophes
When writing a possessive singular noun, you should place the apostrophe before the s. For possessive plural nouns, the apostrophe is placed after the s.
- Singular : Linda Morris’s jacket
- Plural : The Morris’ house
Em dashes (long dash) are used to bring focus to a particular point or an aside. There are no spaces after these dashes (p. 157).
Use en dashes (short dash) in compound adjectives. Do not place a space before or after the dash. Here are a few examples:
- custom-built
- 12-year-old
Number rules in APA Format
Science papers often include the use of numbers, usually displayed in data, tables, and experiment information. The golden rule to keep in mind is that numbers less than 10 are written out in text. If the number is more than 10, use numerals.
APA format examples:
- 14 kilograms
- seven individuals
- 83 years old
- Fourth grade
The golden rule for numbers has exceptions.
In APA formatting, use numerals if you are:
- Showing numbers in a table or graph
- 4 divided by 2
- 6-month-olds
Use numbers written out as words if you are:
- Ninety-two percent of teachers feel as though….
- Hundred Years’ War
- One-sixth of the students
Other APA formatting number rules to keep in mind:
- World War II
- Super Bowl LII
- It’s 1980s, not 1980’s!
Additional number rules can be found in the publication manual (p. 178)
Need help with other writing topics? Our plagiarism checker is a great resource for anyone looking for writing help. Say goodbye to an out of place noun , preposition , or adjective, and hello to a fully edited paper.
Overview of APA references
While writing a research paper, it is always important to give credit and cite your sources; this lets you acknowledge others’ ideas and research you’ve used in your own work. Not doing so can be considered plagiarism , possibly leading to a failed grade or loss of a job.
APA style is one of the most commonly used citation styles used to prevent plagiarism. Here’s more on crediting sources . Let’s get this statement out of the way before you become confused: An APA format reference and an APA format citation are two different things! We understand that many teachers and professors use the terms as if they’re synonyms, but according to this specific style, they are two separate things, with different purposes, and styled differently.
A reference displays all of the information about the source — the title, the author’s name, the year it was published, the URL, all of it! References are placed on the final page of a research project.
Here’s an example of a reference:
Wynne-Jones, T. (2015). The emperor of any place . Candlewick Press.
An APA format citation is an APA format in-text citation. These are found within your paper, anytime a quote or paraphrase is included. They usually only include the name of the author and the date the source was published.
Here’s an example of one:
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is even discussed in the book, The Emperor of Any Place . The main character, Evan, finds a mysterious diary on his father’s desk (the same desk his father died on, after suffering from a hypertrophic cardiomyopathy attack). Evan unlocks the truth to his father and grandfather’s past (Wynne-Jones, 2015).
Both of the ways to credit another individual’s work — in the text of a paper and also on the final page — are key to preventing plagiarism. A writer must use both types in a paper. If you cite something in the text, it must have a full reference on the final page of the project. Where there is one, there must be the other!
Now that you understand that, here’s some basic info regarding APA format references (pp. 281-309).
- Each reference is organized, or structured, differently. It all depends on the source type. A book reference is structured one way, an APA journal is structured a different way, a newspaper article is another way. Yes, it’s probably frustrating that not all references are created equal and set up the same way. MLA works cited pages are unique in that every source type is formatted the same way. Unfortunately, this style is quite different.
- Most references follow this general format:
Author’s Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year published). Title of source . URL.
Again, as stated in the above paragraph, you must look up the specific source type you’re using to find out the placement of the title, author’s name, year published, etc.
For more information on APA format for sources and how to reference specific types of sources, use the other guides on EasyBib.com. Here’s another useful site .
Looking for a full visual of a page of references? Scroll down and take a peek at our APA format essay example towards the bottom of this page. You’ll see a list of references and you can gain a sense of how they look.
Bonus: here’s a link to more about the fundamentals related to this particular style. If you want to brush up or catch up on the Modern Language Association’s style, here’s a great resource on how to cite websites in MLA .
In-text APA citation format
Did you find the perfect quote or piece of information to include in your project? Way to go! It’s always a nice feeling when we find that magical piece of data or info to include in our writing. You probably already know that you can’t just copy and paste it into your project, or type it in, without also providing credit to the original author.
Displaying where the original information came from is much easier than you think.Directly next to the quote or information you included, place the author’s name and the year nearby. This allows the reader of your work to see where the information originated.
APA allows for the use of two different forms of in-text citation, parenthetical and narrative Both forms of citation require two elements:
- author’s name
- year of publication
The only difference is the way that this information is presented to the reader.
Parenthetical citations are the more commonly seen form of in-text citations for academic work, in which both required reference elements are presented at the end of the sentence in parentheses. Example:
Harlem had many artists and musicians in the late 1920s (Belafonte, 2008).
Narrative citations allow the author to present one or both of the required reference elements inside of the running sentence, which prevents the text from being too repetitive or burdensome. When only one of the two reference elements is included in the sentence, the other is provided parenthetically. Example:
According to Belafonte (2008), Harlem was full of artists and musicians in the late 1920s.
If there are two authors listed in the source entry, then the parenthetical reference must list them both:
(Smith & Belafonte, 2008)
If there are three or more authors listed in the source entry, then the parenthetical reference can abbreviate with “et al.”, the latin abbreviation for “and others”:
(Smith et al., 2008)
The author’s names are structured differently if there is more than one author. Things will also look different if there isn’t an author at all (which is sometimes the case with website pages). For more information on APA citation format, check out this page on the topic: APA parenthetical citation and APA in-text citation . There is also more information in the official manual in chapter 8.
If it’s MLA in-text and parenthetical citations you’re looking for, we’ve got your covered there too! You might want to also check out his guide on parenthetical citing .
Would you benefit from having a tool that helps you easily generate citations that are in the text? Check out EasyBib Plus!
References page in APA Format
An APA format reference page is easier to create than you probably think. We go into detail on how to create this page on our APA reference page . We also have a guide for how to create an annotated bibliography in APA . But, if you’re simply looking for a brief overview of the reference page, we’ve got you covered here.
Here are some pointers to keep in mind when it comes to the references page in APA format:
- This VIP page has its very own page. Start on a fresh, clean document (p. 303).
- Center and bold the title “References” (do not include quotation marks, underline, or italicize this title).
- Alphabetize and double-space ALL entries.
- Use a readable font, such as Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri, or Lucida (p. 44).
- Every quote or piece of outside information included in the paper should be referenced and have an entry.
- Even though it’s called a “reference page,” it can be longer than one page. If your references flow onto the next page, then that’s a-okay.
- Only include the running head if it is required by your teacher or you’re writing a professional paper.
Sample reference page for a student paper:
Here’s another friendly reminder to use the EasyBib APA format generator (that comes with EasyBib Plus) to quickly and easily develop every single one of your references for you. Try it out! Our APA formatter is easy to use and ready to use 24/7.
Final APA Format Checklist
Prior to submitting your paper, check to make sure you have everything you need and everything in its place:
- Did you credit all of the information and quotes you used in the body of your paper and show a matching full reference at the end of the paper? Remember, you need both! Need more information on how to credit other authors and sources? Check out our other guides, or use the EasyBib APA format generator to credit your sources quickly and easily. EasyBib.com also has more styles than just the one this page focuses on.
- 12-pt. Times New Roman
- 11-pt. Calibri, Arial, Georgia
- 10-pt. Lucida, Sans Unicode, Computer Modern
- If you created an abstract, is it directly after the title page? Some teachers and professors do not require an abstract, so before you go ahead and include it, make sure it’s something he or she is expecting.
- Professional paper — Did you include a running head on every single page of your project?
- Student paper — Did you include page numbers in the upper right-hand corner of all your pages?
- Are all headings, as in section or chapter titles, properly formatted? If you’re not sure, check section number 9.
- Are all tables and figures aligned properly? Did you include notes and other important information directly below the table or figure? Include any information that will help the reader completely understand everything in the table or figure if it were to stand alone.
- Are abbreviations used sparingly? Did you format them properly?
- Is the entire document double spaced?
- Are all numbers formatted properly? Check section 17, which is APA writing format for numbers.
- Did you glance at the sample paper? Is your assignment structured similarly? Are all of the margins uniform?
Submitting Your APA Paper
Congratulations for making it this far! You’ve put a lot of effort into writing your paper and making sure the t’s are crossed and the i’s are dotted. If you’re planning to submit your paper for a school assignment, make sure you review your teacher or professor’s procedures.
If you’re submitting your paper to a journal, you probably need to include a cover letter.
Most cover letters ask you to include:
- The author’s contact information.
- A statement to the editor that the paper is original.
- If a similar paper exists elsewhere, notify the editor in the cover letter.
Once again, review the specific journal’s website for exact specifications for submission.
Okay, so you’re probably thinking you’re ready to hit send or print and submit your assignment. Can we offer one last suggestion? We promise it will only take a minute.
Consider running your paper through our handy dandy paper checker. It’s pretty simple.
Copy and paste or upload your paper into our checker. Within a minute, we’ll provide feedback on your spelling and grammar. If there’s a pronoun , interjection , or verb out of place, we’ll highlight it and offer suggestions for improvement. We’ll even take it a step further and point out any instances of possible plagiarism.
If it sounds too good to be true, then head on over to our innovative tool and give it a whirl. We promise you won’t be disappointed.
What is APA Format?
APA stands for the American Psychological Association . In this guide, you’ll find information related to “What is APA format?” in relation to writing and organizing your paper according to the American Psychological Association’s standards. Information on how to cite sources can be found on our APA citation page. The official American Psychological Association handbook was used as a reference for our guide and we’ve included page numbers from the manual throughout. However, this page is not associated with the association.
You’ll most likely use APA format if your paper is on a scientific topic. Many behavioral and social sciences use this organization’s standards and guidelines.
What are behavioral sciences? Behavioral sciences study human and animal behavior. They can include:
- Cognitive Science
- Neuroscience
What are social sciences? Social sciences focus on one specific aspect of human behavior, specifically social and cultural relationships. Social sciences can include:
- Anthropology
- Political Science
- Human Geography
- Archaeology
- Linguistics
What’s New in the 7th Edition?
This citation style was created by the American Psychological Association. Its rules and guidelines can be found in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . The information provided in the guide above follows the 6th edition (2009) of the manual. The 7th edition was published in 2020 and is the most recent version.
The 7th edition of the Publication Manual is in full color and includes 12 sections (compared to 8 sections in the 6th edition). In general, this new edition differentiates between professional and student papers, includes guidance with accessibility in mind, provides new examples to follow, and has updated guidelines.We’ve selected a few notable updates below, but for a full view of all of the 7th edition changes visit the style’s website linked here .
- Paper title
- Student name
- Affiliation (e.g., school, department, etc.)
- Course number and title
- Course instructor
- 6th edition – Running head: SMARTPHONE EFFECTS ON ADOLESCENT SOCIALIZATION
- 7th edition – SMARTPHONE EFFECTS ON ADOLESCENT SOCIALIZATION
- Pronouns . “They” can be used as a gender-neutral pronoun.
- Bias-free language guidelines . There are updated and new sections on guidelines for this section. New sections address participation in research, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality.
- Spacing after sentences. Add only a single space after end punctuation.
- Tables and figures . The citing format is now streamlined so that both tables and figures should include a name and number above the table/figure, and a note underneath the table/figure.
- 6th ed. – (Ikemoto, Richardson, Murphy, Yoshida 2016)
- 7th ed. – (Ikemoto et al., 2016)
- Citing books. The location of the publisher can be omitted. Also, e-books no longer need to mention the format (e.g., Kindle, etc.)
- Example: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-019-0153-5
- Using URLs. URLs no longer need to be prefaced by the words “Retrieved from.”
New citing information . There is new guidance on citing classroom or intranet resources, and oral traditions or traditional knowledge of indigenous peoples.
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) (2020). American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000

Published October 31, 2011. Updated May 14, 2020.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Sample Paper
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
We should not use “et al.” in APA reference list entries. If the number of authors in the source is up to and including 20, list all author names and use an ampersand (&) before the final author’s name. If the number of authors is more than 20, list the first 19 authors’ names followed by an ellipsis (but no ampersand), and then add the final author’s name. An example of author names in a reference entry having more than 20 authors is given below:
Author Surname1, F. M., Author Surname2, F. M., Author Surname3, F. M., Author Surname4, F. M., Author Surname5, F. M., Author Surname6, F. M., Author Surname7, F. M., Author Surname8, F. M., Author Surname9, F. M., Author Surname10, F. M., Author Surname11, F. M., Author Surname12, F. M., Author Surname13, F. M., Author Surname14, F. M., Author Surname15, F. M., Author Surname16, F. M., Author Surname17, F. M., Author Surname18, F. M., Author Surname19, F. M., . . . Last Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year).
Alvarez, L. D., Peach, J. L., Rodriguez, J. F., Donald, L., Thomas, M., Aruck, A., Samy, K., Anthony, K., Ajey, M., Rodriguez, K. L., Katherine, K., Vincent, A., Pater, F., Somu, P., Pander, L., Berd, R., Fox, L., Anders, A., Kamala, W., . . . Nicole Jones, K. (2019).
Note that, unlike references with 2 to 20 author names, the symbol “&” is not used here before the last author’s name.
APA 7, released in October 2019, has some new updates. Here is a brief description of the updates made in APA 7.
Different types of papers and best practices are given in detail in Chapter 1.
How to format a student title page is explained in Chapter 2. Examples of a professional paper and a student paper are included.
Chapter 3 provides additional information on qualitative and mixed methods of research.
An update on writing style is included in Chapter 4.
In chapter 5, some best practices for writing with bias-free language are included.
Chapter 6 gives some updates on style elements including using a single space after a period, including a citation with an abbreviation, the treatment of numbers in abstracts, treatment for different types of lists, and the formatting of gene and protein names.
In Chapter 7, additional examples are given for tables and figures for different types of publications.
In Chapter 8, how to format quotations and how to paraphrase text are covered with additional examples. A simplified version of in-text citations is clearly illustrated.
Chapter 9 has many updates: listing all author names up to 20 authors, standardizing DOIs and URLs, and the formatting of an annotated bibliography.
Chapter 10 includes many examples with templates for all reference types. New rules covering the inclusion of the issue number for journals and the omission of publisher location from book references are provided. Explanations of how to cite YouTube videos, power point slides, and TED talks are included.
Chapter 11 includes many legal references for easy understanding.
Chapter 12 provides advice for authors on how to promote their papers.
For more information on some of the changes found in APA 7, check out this EasyBib article .
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

APA 7: Sample Paper
- Paper Sections
- Quote & Paraphrase
- Format in Word
- In-Text Citations
- Reference List
- Sample Paper
Examples of the Different Paper Sections
- Title Page - APA 7 Example
- References Page
- Student Paper - Example in APA Format Includes title page, body, and references.
- Sample Annotated Student Paper in APA Style
- APA 7 Quick Reference Guide
Optional Paper Sections
- Headings - APA 7 Style Guide
- Accessible Use of Colors in APA 7
- Figures - APA 7 The basics of figure setup, including figure components, principles of figure construction, and placement of figures in a paper.
- Tables - APA 7 The basics of table setup, including table components, principles of table construction, and placement of tables in the paper.
- << Previous: Reference List
- Next: FAQs >>

APA Formatting and Style (7th ed.) for Student Papers
- What's New in the 7th ed.?
- Principles of Plagiarism: An Overview
- Basic Paper Formatting
- Basic Paper Elements
- Punctuation, Capitalization, Abbreviations, Apostrophes, Numbers, Plurals
- Tables and Figures
- Reference Page Format
- Periodicals (Journals, Magazines, Newspapers)
- Books and Reference Works
- Webpage on a Website
- Discussion Post
- Company Information & SWOT Analyses
- Dissertations or Theses
- ChatGPT and other AI Large Language Models
- Online Images
- Online Video
- Computer Software and Mobile Apps
- Missing Information
- Two Authors
- Three or More Authors
- Group Authors
- Missing Author
- Chat GPT and other AI Large Language Models
- Secondary Sources
- Block Quotations
- Fillable Template and Sample Paper
- Government Documents and Legal Materials
- APA Style 7th ed. Tutorials
- Additional APA 7th Resources
- Grammarly - your writing assistant
- Writing Center - Writing Skills This link opens in a new window
- Brainfuse Online Tutoring
APA 7th ed. Fillable Word Template and Sample Paper
- APA 7th ed. Template Download this Word document, fill out the title page and get writing!
- Sample Paper APA 7th ed. Our APA sample paper shows you how to format the main parts of a basic research paper.
- APA 7th Sample Papers from Purdue Owl
- << Previous: Block Quotations
- Next: Government Documents and Legal Materials >>
- Last Updated: Feb 16, 2024 2:28 PM
- URL: https://national.libguides.com/apa_7th
Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- APA Style 7th edition
- APA headings and subheadings
APA Headings and Subheadings | With Sample Paper
Published on November 7, 2020 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on October 24, 2022.
Headings and subheadings provide structure to a document. They signal what each section is about and allow for easy navigation of the document.
APA headings have five possible levels. Each heading level is formatted differently.
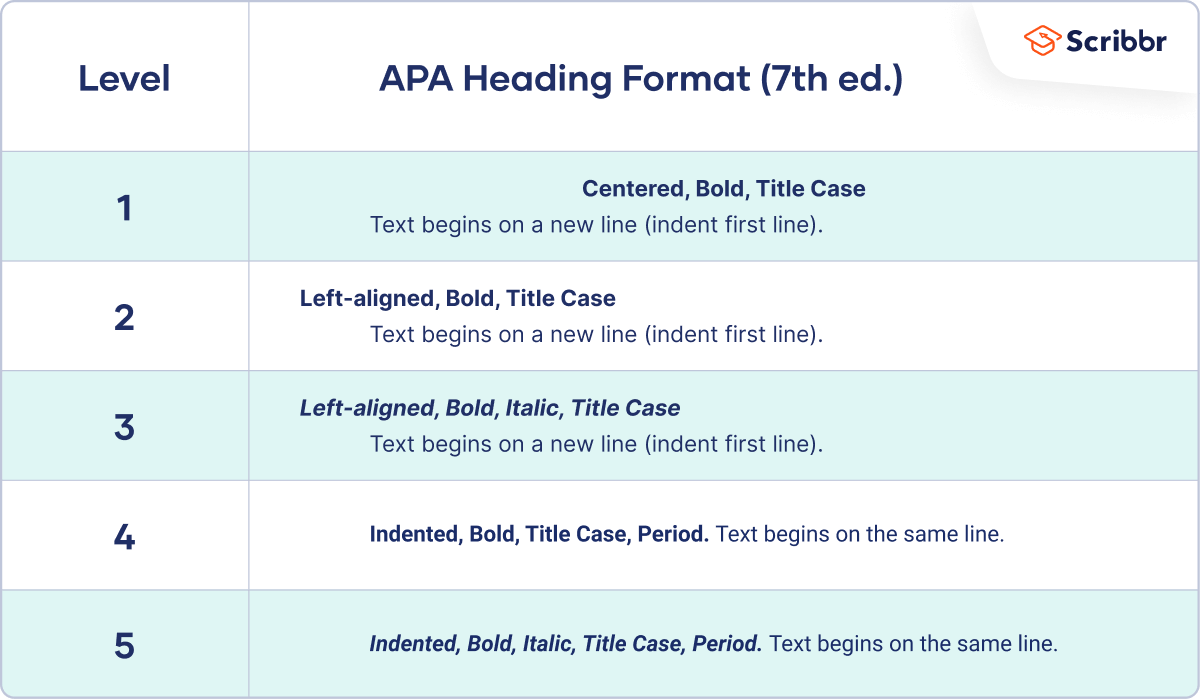
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Additional guidelines for apa headings, how many heading levels should you use, when to use which apa heading level, section labels vs headings, sample paper with apa headings, using heading styles in word or google docs.
As well as the heading styles, there are some other guidelines to keep in mind:
- Double-space all text, including the headings.
- Use the same font for headings and body text (e.g., Times New Roman 12pt.).
- Don’t label headings with numbers or letters.
- Don’t add extra “enters” above or below headings.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Depending on the length and complexity of your paper, you may not use all five heading levels. In fact, shorter student papers may have no headings at all.
It’s also perfectly fine for some sections in your paper to go as deep as five levels, where others use only heading level 1.
Heading level 1 is used for main sections like “ Methods ”, “ Results ”, and “ Discussion ”. There is no “ Introduction ” heading at the beginning of your paper because the first paragraphs are understood to be introductory.
Heading level 2 is used for subsections under level 1. For example, under “Methods” (level 1) you may have subsections for “Sampling Method” and “Data Analysis” (level 2). This continues all the way down to heading level 5.
Always use at least two subheadings or none at all. If there is just one subheading, the top-level heading is sufficient.
In addition to regular headings, APA works with “section labels” for specific parts of the paper. They’re similar to headings but are formatted differently. Section labels are placed on a separate line at the top of a new page in bold and centered.
Use section labels for the following sections in an APA formatted paper :
- Author note
- Paper title
- Reference page
Are your APA in-text citations flawless?
The AI-powered APA Citation Checker points out every error, tells you exactly what’s wrong, and explains how to fix it. Say goodbye to losing marks on your assignment!
Get started!

Instead of formatting every heading individually, you can use the “Styles” feature in Word or Google Docs. This allows you to save the styling and apply it with just a click.
The first time you use APA Style, you need to update the default heading styles to reflect the APA heading guidelines. Click here for the instructions for Microsoft Word and Google Docs .
An added benefit of using the “Styles” feature is that you can automatically generate a table of contents .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2022, October 24). APA Headings and Subheadings | With Sample Paper. Scribbr. Retrieved March 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-style/apa-headings/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, apa title page (7th edition) | template for students & professionals, creating an apa style table of contents, apa format for academic papers and essays, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

APA 7th Edition Referencing Guide1
- What is APA?
In-text citations
- Reference list
- Chapter in an edited book
- Journal articles & Databases
- Works with multiple authors
- Webpages & online
- General images faqs
- Audiovisual media
- Personal communication
- Study material
- New Zealand legislation
- Other resources
- Tricky health resources
- Health books
- Health journals
- Health web resources
- Systematic reviews
- Point-of-care resources
- Visual health resources
- Tricky health FAQs
- APA for publication
Referencing legal cases
Guidelines for referencing legal cases:
- Include the names of the parties involved in the case—e.g., Smith v Jones
- Give the date of the case in square brackets—e.g., [2017]
- Provide the New Zealand Law Report (NZLR) or court case number.
- When referencing a case from the Courts of New Zealand website, include a retrieval date as the information is held publicly for 28 days only.
For example:
Reference list entries
Crown v Thompson [2013] NZLR 617.
Milner v R [2014] NZCA 366. Retrieved August 1, 2014, from https://www.courtsofnz.govt.nz/from/decisions/judgments
Use the name of the case in italics and give the date in square brackets. For example:
- Last Updated: Mar 20, 2024 8:19 AM
- URL: https://libguides.wintec.ac.nz/APA7

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
General format for citing case studies: Author(s). (Year). Title of case study. Number of case study. URL. Examples: Harvard Business School Case Study Smith, S. (2003). ... (Examples courtesy of APA Style Guidelines & Examples - NAIT Library.) Textbook Case Study Author(s) or editor(s) of the chapter or entry or case study. (Year of book).
The Abstract for an APA case study. The abstract of your paper works as a summary to give a brief overview of what it contains. Include the running head at the top; the first line should have the word "abstract" centered. Follow the abstract with 150-250 words summarizing your paper.
Author/Authors. Rules for handling works by a single author or multiple authors that apply to all APA-style references in your reference list, regardless of the type of work (book, article, electronic resource, etc.)
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
Throughout your paper, you need to apply the following APA format guidelines: Set page margins to 1 inch on all sides. Double-space all text, including headings. Indent the first line of every paragraph 0.5 inches. Use an accessible font (e.g., Times New Roman 12pt., Arial 11pt., or Georgia 11pt.).
This should be placed on the second page of your case study paper, should not be more than 150-200 words, and needs to be written in a one-block paragraph. 4. Follow the right format. The body of the case study paper should be thorough and should detail the research and findings in an engaging manner.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here. Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader
Reference List Citation: Last Name of Case Study/Chapter Author, Author's First Initial. (Publication Year of Book). Title of case study or chapter.
APA Case Study References. Provide initials and surnames for up to seven authors in a reference. If eight or more authors exist, use three spaced ellipsis points after the sixth author, followed by the last author name (no ampersand). Write surnames and initials for up to 20 authors in a reference.
Therefore, it's really important to make sure your format this exactly as required for APA 7th edition. Here's the process you can follow to set up your title page for success. Centre-align your curson and create 4 empty lines. On a new line, type the title of your paper in boldface, using title case.
When citing a case study, the format in MLA and APA is similar to that of a report, and in Chicago style, it is similar to that of a book. ... The templates and examples below will demonstrate how to cite a case study in MLA, APA, and Chicago styles. MLA 9. Structure: Author Last Name, Author First Name.
These sample papers demonstrate APA Style formatting standards for different student paper types. Students may write the same types of papers as professional authors (e.g., quantitative studies, literature reviews) or other types of papers for course assignments (e.g., reaction or response papers, discussion posts), dissertations, and theses.
Format. 1. Centered, Boldface, Title Case Heading Text begins ... but a few of the most important and general instructions are described below. Consult chapter 5 of the APA Publication Manual (7 th ... between groups of people, focus on the qualities that are relevant to the situation at hand. For example, in a study of sex chromosome-linked ...
Body (section 2.11) Align the text to the left with a 1/2-inch left indent on the first line; Double-space; As long as there is no Abstract, at the top of the first page, type the title of the paper, centered, in bold, and in Sentence Case Capitalization; Usually, include sections like these: introduction, literature review or background, discussion, and conclusion -- but the specific ...
APA 7, released in October 2019, has some new updates. Here is a brief description of the updates made in APA 7. Different types of papers and best practices are given in detail in Chapter 1. How to format a student title page is explained in Chapter 2. Examples of a professional paper and a student paper are included.
Optional Paper Sections. Headings - APA 7 Style Guide. Accessible Use of Colors in APA 7. Figures - APA 7. The basics of figure setup, including figure components, principles of figure construction, and placement of figures in a paper. Tables - APA 7.
On the first line of the page, write the section label "References" (in bold and centered). On the second line, start listing your references in alphabetical order. Apply these formatting guidelines to the APA reference page: Double spacing (within and between references) Hanging indent of ½ inch.
APA 7th ed. Fillable Word Template and Sample Paper. APA 7th ed. Template Download this Word document, fill out the title page and get writing! Sample Paper APA 7th ed. Our APA sample paper shows you how to format the main parts of a basic research paper. APA 7th Sample Papers from Purdue Owl ...
papers (a change from APA 6). Page numbers begin on the first page and follow on every subsequent page without interruption. No other information (e.g., authors' last names) is required. Note: your instructor may ask for a running head or your last name before the page number. You can look at the APA professional sample paper for guidelines on ...
Headings and subheadings provide structure to a document. They signal what each section. is about and allow for easy navigation of the document. APA headings have five possible levels. Each heading level is formatted differently. Note: Title case simply means that you should capitalize the first word, words with four or more letters, and all ...
Guidelines for referencing legal cases: Include the names of the parties involved in the case—e.g., Smith v Jones. Give the date of the case in square brackets—e.g., [2017] Provide the New Zealand Law Report (NZLR) or court case number. When referencing a case from the Courts of New Zealand website, include a retrieval date as the ...
There are five levels of heading in APA Style. Level 1 is the highest or main level of heading, Level 2 is a subheading of Level 1, Level 3 is a subheading of Level 2, and so on through Levels 4 and 5. The number of headings to use in a paper depends on the length and complexity of the work. If only one level of heading is needed, use Level 1.
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the student title page. Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize major words of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired.