Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., ai + human expertise – a paradigm shift..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai....
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
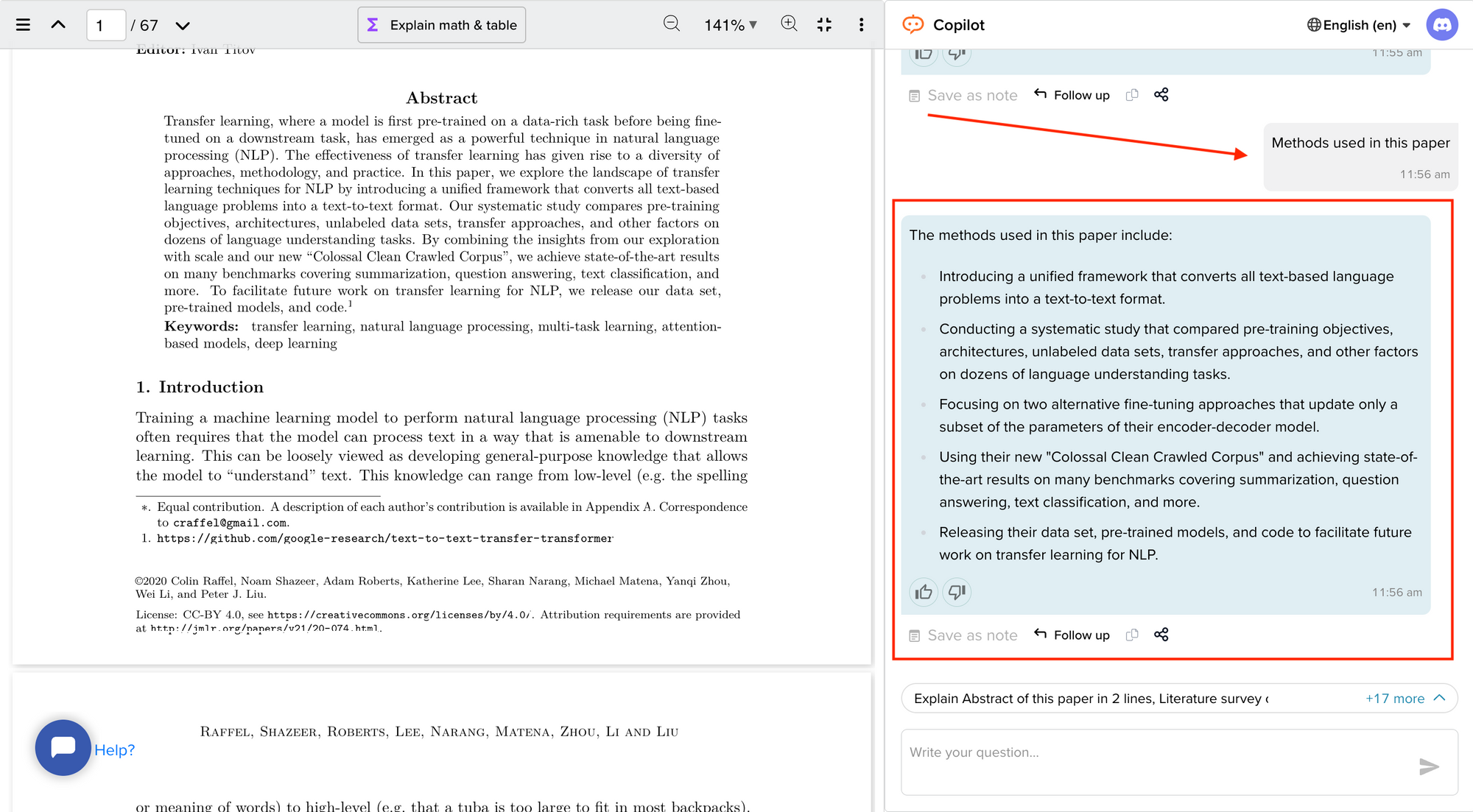
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 1:27 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

How I harnessed media engagement to supercharge my research career
Career Column 09 APR 24

How we landed job interviews for professorships straight out of our PhD programmes
Career Column 08 APR 24

Three ways ChatGPT helps me in my academic writing

How two PhD students overcame the odds to snag tenure-track jobs
Adopt universal standards for study adaptation to boost health, education and social-science research
Correspondence 02 APR 24

Is ChatGPT corrupting peer review? Telltale words hint at AI use
News 10 APR 24

Rwanda 30 years on: understanding the horror of genocide
Editorial 09 APR 24
Junior Group Leader Position at IMBA - Institute of Molecular Biotechnology
The Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) is one of Europe’s leading institutes for basic research in the life sciences. IMBA is located on t...
Austria (AT)
IMBA - Institute of Molecular Biotechnology
Open Rank Faculty, Center for Public Health Genomics
Center for Public Health Genomics & UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center seek 2 tenure-track faculty members in Cancer Precision Medicine/Precision Health.
Charlottesville, Virginia
Center for Public Health Genomics at the University of Virginia
Husbandry Technician I
Memphis, Tennessee
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (St. Jude)
Lead Researcher – Department of Bone Marrow Transplantation & Cellular Therapy
Researcher in the center for in vivo imaging and therapy.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview

Literature Reviews
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain what literature reviews are and offer insights into the form and construction of literature reviews in the humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
Introduction
OK. You’ve got to write a literature review. You dust off a novel and a book of poetry, settle down in your chair, and get ready to issue a “thumbs up” or “thumbs down” as you leaf through the pages. “Literature review” done. Right?
Wrong! The “literature” of a literature review refers to any collection of materials on a topic, not necessarily the great literary texts of the world. “Literature” could be anything from a set of government pamphlets on British colonial methods in Africa to scholarly articles on the treatment of a torn ACL. And a review does not necessarily mean that your reader wants you to give your personal opinion on whether or not you liked these sources.

What is a literature review, then?
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
But how is a literature review different from an academic research paper?
The main focus of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument, and a research paper is likely to contain a literature review as one of its parts. In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Why do we write literature reviews?
Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic. If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a stepping stone. For professionals, they are useful reports that keep them up to date with what is current in the field. For scholars, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the writer in his or her field. Literature reviews also provide a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.
Who writes these things, anyway?
Literature reviews are written occasionally in the humanities, but mostly in the sciences and social sciences; in experiment and lab reports, they constitute a section of the paper. Sometimes a literature review is written as a paper in itself.
Let’s get to it! What should I do before writing the literature review?
If your assignment is not very specific, seek clarification from your instructor:
- Roughly how many sources should you include?
- What types of sources (books, journal articles, websites)?
- Should you summarize, synthesize, or critique your sources by discussing a common theme or issue?
- Should you evaluate your sources?
- Should you provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history?
Find models
Look for other literature reviews in your area of interest or in the discipline and read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or ways to organize your final review. You can simply put the word “review” in your search engine along with your other topic terms to find articles of this type on the Internet or in an electronic database. The bibliography or reference section of sources you’ve already read are also excellent entry points into your own research.
Narrow your topic
There are hundreds or even thousands of articles and books on most areas of study. The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to get a good survey of the material. Your instructor will probably not expect you to read everything that’s out there on the topic, but you’ll make your job easier if you first limit your scope.
Keep in mind that UNC Libraries have research guides and to databases relevant to many fields of study. You can reach out to the subject librarian for a consultation: https://library.unc.edu/support/consultations/ .
And don’t forget to tap into your professor’s (or other professors’) knowledge in the field. Ask your professor questions such as: “If you had to read only one book from the 90’s on topic X, what would it be?” Questions such as this help you to find and determine quickly the most seminal pieces in the field.
Consider whether your sources are current
Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. In the sciences, for instance, treatments for medical problems are constantly changing according to the latest studies. Information even two years old could be obsolete. However, if you are writing a review in the humanities, history, or social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be what is needed, because what is important is how perspectives have changed through the years or within a certain time period. Try sorting through some other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to consider what is currently of interest to scholars in this field and what is not.
Strategies for writing the literature review
Find a focus.
A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the sources themselves as an annotated bibliography would be organized. This means that you will not just simply list your sources and go into detail about each one of them, one at a time. No. As you read widely but selectively in your topic area, consider instead what themes or issues connect your sources together. Do they present one or different solutions? Is there an aspect of the field that is missing? How well do they present the material and do they portray it according to an appropriate theory? Do they reveal a trend in the field? A raging debate? Pick one of these themes to focus the organization of your review.
Convey it to your reader
A literature review may not have a traditional thesis statement (one that makes an argument), but you do need to tell readers what to expect. Try writing a simple statement that lets the reader know what is your main organizing principle. Here are a couple of examples:
The current trend in treatment for congestive heart failure combines surgery and medicine. More and more cultural studies scholars are accepting popular media as a subject worthy of academic consideration.
Consider organization
You’ve got a focus, and you’ve stated it clearly and directly. Now what is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc., that your review needs to include? And in what order should you present them? Develop an organization for your review at both a global and local level:
First, cover the basic categories
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews also must contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper. The following provides a brief description of the content of each:
- Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
- Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
- Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Organizing the body
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario:
You’ve decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you’ve just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale’s portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980’s. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Now consider some typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
- Chronological: If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
- By publication: Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
- By trend: A better way to organize the above sources chronologically is to examine the sources under another trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Under this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
- Thematic: Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a “chronological” and a “thematic” approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.But more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as “evil” in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
- Methodological: A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the “methods” of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed. Once you’ve decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
- Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
- History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
Begin composing
Once you’ve settled on a general pattern of organization, you’re ready to write each section. There are a few guidelines you should follow during the writing stage as well. Here is a sample paragraph from a literature review about sexism and language to illuminate the following discussion:
However, other studies have shown that even gender-neutral antecedents are more likely to produce masculine images than feminine ones (Gastil, 1990). Hamilton (1988) asked students to complete sentences that required them to fill in pronouns that agreed with gender-neutral antecedents such as “writer,” “pedestrian,” and “persons.” The students were asked to describe any image they had when writing the sentence. Hamilton found that people imagined 3.3 men to each woman in the masculine “generic” condition and 1.5 men per woman in the unbiased condition. Thus, while ambient sexism accounted for some of the masculine bias, sexist language amplified the effect. (Source: Erika Falk and Jordan Mills, “Why Sexist Language Affects Persuasion: The Role of Homophily, Intended Audience, and Offense,” Women and Language19:2).
Use evidence
In the example above, the writers refer to several other sources when making their point. A literature review in this sense is just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence to show that what you are saying is valid.
Be selective
Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the review’s focus, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological.
Use quotes sparingly
Falk and Mills do not use any direct quotes. That is because the survey nature of the literature review does not allow for in-depth discussion or detailed quotes from the text. Some short quotes here and there are okay, though, if you want to emphasize a point, or if what the author said just cannot be rewritten in your own words. Notice that Falk and Mills do quote certain terms that were coined by the author, not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. But if you find yourself wanting to put in more quotes, check with your instructor.
Summarize and synthesize
Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each paragraph as well as throughout the review. The authors here recapitulate important features of Hamilton’s study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study’s significance and relating it to their own work.
Keep your own voice
While the literature review presents others’ ideas, your voice (the writer’s) should remain front and center. Notice that Falk and Mills weave references to other sources into their own text, but they still maintain their own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with their own ideas and their own words. The sources support what Falk and Mills are saying.
Use caution when paraphrasing
When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author’s information or opinions accurately and in your own words. In the preceding example, Falk and Mills either directly refer in the text to the author of their source, such as Hamilton, or they provide ample notation in the text when the ideas they are mentioning are not their own, for example, Gastil’s. For more information, please see our handout on plagiarism .
Revise, revise, revise
Draft in hand? Now you’re ready to revise. Spending a lot of time revising is a wise idea, because your main objective is to present the material, not the argument. So check over your review again to make sure it follows the assignment and/or your outline. Then, just as you would for most other academic forms of writing, rewrite or rework the language of your review so that you’ve presented your information in the most concise manner possible. Be sure to use terminology familiar to your audience; get rid of unnecessary jargon or slang. Finally, double check that you’ve documented your sources and formatted the review appropriately for your discipline. For tips on the revising and editing process, see our handout on revising drafts .
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Jones, Robert, Patrick Bizzaro, and Cynthia Selfe. 1997. The Harcourt Brace Guide to Writing in the Disciplines . New York: Harcourt Brace.
Lamb, Sandra E. 1998. How to Write It: A Complete Guide to Everything You’ll Ever Write . Berkeley: Ten Speed Press.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
Troyka, Lynn Quittman, and Doug Hesse. 2016. Simon and Schuster Handbook for Writers , 11th ed. London: Pearson.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
What’s Included: Literature Review Template
This template is structure is based on the tried and trusted best-practice format for formal academic research projects such as dissertations and theses. The literature review template includes the following sections:
- Before you start – essential groundwork to ensure you’re ready
- The introduction section
- The core/body section
- The conclusion /summary
- Extra free resources
Each section is explained in plain, straightforward language , followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover. We’ve also included practical examples and links to more free videos and guides to help you understand exactly what’s required in each section.
The cleanly-formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX.
PS – if you’d like a high-level template for the entire thesis, you can we’ve got that too .
FAQs: Literature Review Template
What format is the template (doc, pdf, ppt, etc.).
The literature review chapter template is provided as a Google Doc. You can download it in MS Word format or make a copy to your Google Drive. You’re also welcome to convert it to whatever format works best for you, such as LaTeX or PDF.
What types of literature reviews can this template be used for?
The template follows the standard format for academic literature reviews, which means it will be suitable for the vast majority of academic research projects (especially those within the sciences), whether they are qualitative or quantitative in terms of design.
Keep in mind that the exact requirements for the literature review chapter will vary between universities and degree programs. These are typically minor, but it’s always a good idea to double-check your university’s requirements before you finalize your structure.
Is this template for an undergrad, Master or PhD-level thesis?
This template can be used for a literature review at any level of study. Doctoral-level projects typically require the literature review to be more extensive/comprehensive, but the structure will typically remain the same.
Can I modify the template to suit my topic/area?
Absolutely. While the template provides a general structure, you should adapt it to fit the specific requirements and focus of your literature review.
What structural style does this literature review template use?
The template assumes a thematic structure (as opposed to a chronological or methodological structure), as this is the most common approach. However, this is only one dimension of the template, so it will still be useful if you are adopting a different structure.
Does this template include the Excel literature catalog?
No, that is a separate template, which you can download for free here . This template is for the write-up of the actual literature review chapter, whereas the catalog is for use during the literature sourcing and sorting phase.
How long should the literature review chapter be?
This depends on your university’s specific requirements, so it’s best to check with them. As a general ballpark, literature reviews for Masters-level projects are usually 2,000 – 3,000 words in length, while Doctoral-level projects can reach multiples of this.
Can I include literature that contradicts my hypothesis?
Yes, it’s important to acknowledge and discuss literature that presents different viewpoints or contradicts your hypothesis. So, don’t shy away from existing research that takes an opposing view to yours.
How do I avoid plagiarism in my literature review?
Always cite your sources correctly and paraphrase ideas in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. You can always check our plagiarism score before submitting your work to help ease your mind.
Do you have an example of a populated template?
We provide a walkthrough of the template and review an example of a high-quality literature research chapter here .
Can I share this literature review template with my friends/colleagues?
Yes, you’re welcome to share this template in its original format (no editing allowed). If you want to post about it on your blog or social media, all we ask is that you reference this page as your source.
Do you have templates for the other dissertation/thesis chapters?
Yes, we do. You can find our full collection of templates here .
Can Grad Coach help me with my literature review?
Yes, you’re welcome to get in touch with us to discuss our private coaching services , where we can help you work through the literature review chapter (and any other chapters).

A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Stellar Literature Review (with Help from AI)

Table of contents

Aren’t all of us mini versions of Sherlock Holmes when browsing data and archives for a research piece? As we go through the process, a comprehensive literature review is an essential toolkit to make your research shine.
A literature review consists of scholarly sources that validate the content. Its primary objective is to offer a concise summary of the research and to let you explore relevant theories and methodologies. Through this review, you can identify gaps in the existing research and bridge them with your contribution.
The real challenge is how to write an excellent literature review. Let’s learn.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is an introduction to your research. It helps you put your perspective to the table, along with a summary of the theme.
What does my literature review communicate?
- Explanation of your research: how the information was collected, the research method, the justification of the chosen data sources, and an overview of the data analysis.
- Framework: the journey from where the concept began and how it is presented.
- Connects the previous and current research:
It presents the broader scope of your research by connecting it to the existing data and debates and underlining how your content fits the prevailing studies.
In an era of information overload, a literature review must be well-structured.
Let’s learn all about the structure and style of a literature review that’ll help you strengthen your research.
Literature review– structure and style
Begin with a question and end it with the solution– the key to structuring a literature review. It resembles an essay’s format, with the first paragraph introducing the readers to the topic and the following explaining the research in-depth.
The conclusion reiterates the question and summarizes the overall insights of your research. There’s no word count restriction. —it depends on the type of research. For example, a dissertation demands lengthy work, whereas a short paper needs a few pages.
In a literature review, maintaining high quality is vital, with a focus on academic writing style. Informal language should be avoided in favor of a more formal tone.
The content avoids contractions, clearly differentiating between previous and current research through the use of past and present tense. Wordtune assists in establishing a formal tone, enhancing your work with pertinent suggestions. This AI-powered tool ensures your writing remains genuine, lucid, and engaging.

The option of refining the tonality offers multiple possibilities for rephrasing a single sentence. Thus, pick the best and keep writing.
Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
Your friendly step-by-step guide to writing a literary review (with help from AI)
Do you find it challenging to begin the literature review? Don’t worry! We’re here to get you started with our step-by-step guide.
1. Narrow down the research scope
Simply begin with the question: What am I answering through my research?
Whether it’s cooking or painting, the real challenge is the prep-up for it rather than performing the task. Once you’re done, it smoothly progresses. Similarly, for your literature review, prepare the groundwork by narrowing down the research scope.
Browse and scoop out relevant data inclining well with your research. While you can’t cover every aspect of your research, pick a topic that isn’t too narrow nor too broad to keep your literature review well-balanced.
2. Hunt relevant literature
The next question: Does this data align with the issue I’m trying to address?
As you review sources of information, hunt out the best ones. Determine which findings help in offering a focused insight on your topic. The best way to pick primary sources is to opt for the ones featured in reliable publications. You can also choose secondary sources from other researchers from a reasonable time frame and a relevant background.
For example, if your research focuses on the Historical Architecture of 18th-century Europe, the first-hand accounts and surveys from the past would hold more weight than the new-age publications.
3. Observe the themes and patterns in sources
Next comes: What is the core viewpoint in most of the research? Has it stayed constant over time, or have the authors differed in their points of view?
Ensure to scoop out the essential aspects of what each source represents. Once you have collected all this information, combine it and add your interpretations at the end. This process is known as synthesis.
Synthesize ideas by combining arguments, findings and forming your new version.
4. Generate an outline
The next question: How can I organize my review effectively? When navigating multiple data sources, you must have noticed a structure throughout the research. Develop an outline to make the process easier. An outline is a skeletal format of the review, helping you connect the information more strategically.
Here are the three different ways to organize an outline– Chronologically, Thematically, or by Methodology.You can develop the outline chronologically, starting from the older sources and leading to the latest pieces. Another way of organizing is to thematically divide the sections and discuss each under the designated sub-heading.
You can even organize it per the research methods used by the respective authors. The choice of outline depends on the subject. For example, in the case of a science paper, you can divide the information into sections like introduction, types of equipment, method, procedure, findings, etc. In contrast, it’s best to present it in divisions based on timelines like Ancient, Middle Ages, Industrial revolutions, etc., for a history paper.
If you’re confused about how to structure the data, work with Wordtune.

With the Generate with AI feature, you can mention your research topic and let Wordtune curate a comprehensive outline for your study.

Having a precise prompt is the key to getting the best results.
5. Start filling!
Your next question must be: Am I ready to compose all the parts of the literature review?
Once you’re ready with the basic outline and relevant sources, start filling in the data. Go for an introductory paragraph first to ensure your readers understand the topic and how you will present it. Ensure you clearly explain the section in the first sentence.
However, if beginning from the first paragraph seems intimidating, don’t worry! Add the main body content to the sub-headings, then jump to the introduction.
Add headings wherever possible to make it more straightforward and guide your readers logically through different sources. Lastly, conclude your study by presenting a key takeaway and summarizing your findings. To make your task easier, work with Wordtune. It helps align your content with the desired tone and refine the structure.
6. Give attention to detail and edit
The last question: Am I satisfied with the language and content written in the literature review? Is it easy to understand?
Once you’re done writing the first draft of a literature review, it’s time to refine it. Take time between writing and reading the draft to ensure a fresh perspective. It makes it easier to spot errors when you disconnect from the content for some time. Start by looking at the document from a bird's eye to ensure the formatting and structure are in order.
After reviewing the content format, you must thoroughly check your work for grammar, spelling, and punctuation. One of the best approaches to editing and proofreading is to use Wordtune . It helps simplify complex sentences, enhance the content quality, and gain prowess over the tonality.
The dos and don’ts of writing a literature review
Writing a stellar literature review requires following a few dos and don'ts. Just like Sherlock Holmes would never overlook a hint, you must pay attention to every minute detail while writing a perfect narrative. To help you write, below are some dos and don'ts to remember.

Composing a literature review demands a holistic research summary, each part exhibiting your understanding and approach. As you write the content, make sure to cover the following points:
- Keep a historical background of the field of research. Highlight the relevant relation between the old studies and your new research.
- Discuss the core issue, question, and debate of your topic.
- Theories lay the foundation of research. While you’re writing a literature review, make sure to add relevant concepts and ideas to support your statements.
- Another critical thing to keep in mind is to define complex terminologies. It helps the readers understand the content with better clarity.
Examples of comprehensive literature reviews
Aren’t good examples the best way to understand a subject? Let’s look into a few examples of literature reviews and analyze what makes them well-written.
1. Critical Thinking and Transferability: A Review of the Literature (Gwendolyn Reece)
An overview of scholarly sources is included in the literature review, which explores critical thinking in American education. The introduction stating the subject’s importance makes it a winning literature review. Following the introduction is a well-defined purpose that highlights the importance of research.
As one keeps reading, there is more clarity on the pros and cons of the research. By dividing information into parts with relevant subheadings, the author breaks a lengthy literature review into manageable chunks, defining the overall structure.
Along with other studies and presented perspectives, the author also expresses her opinion. It is presented with minimal usage of ‘I,’ keeping it person-poised yet general. Toward the conclusion, the author again offers an overview of the study. A summary is further strengthened by presenting suggestions for future research as well.
2. The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review
This literature review is thematically organized on how technology affects language acquisition. The study begins with an introduction to the topic with well-cited sources. It presents the views of different studies to help readers get a sense of different perspectives. After giving these perspectives, the author offers a personalized opinion.
One of the critical aspects that makes this a good literature review is a dedicated paragraph for definitions. It helps readers proceed further with a clear understanding of the crucial terminologies. There’s a comparison of the modern and previous studies and approaches to give an overall picture of the research.
Once the main body is composed, the author integrates recommendations for action-based tips. Thus, the literature review isn’t just summarizing the sources but offering actions relevant to the topics. Finally, the concluding paragraph has a brief overview with key takeaways.
Wordtune: your writing buddy!
A literature review demands the right balance of language and clarity. You must refine the content to achieve a formal tone and clear structure. Do you know what will help you the most? Wordtune !.
The real-time grammar checker leaves no scope for errors and lets you retain precision in writing. This writing companion is all you need for stress-free working and comprehensive literature review development.
Let the narrative begin
A literary review isn't just about summarizing sources; it's about seamlessly bringing your perspective to the table. Always remember to set a narrative for added interest and a brilliant composition. With structure and style being the pillars of a stellar literature review, work with Wordtune to ensure zero compromises on the quality.
Share This Article:

Preparing for Graduate School: 8 Tips to Know
How to Master Concise Writing: 9 Tips to Write Clear and Crisp Content

Title Case vs. Sentence Case: How to Capitalize Your Titles
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
University of Tasmania, Australia
Literature reviews.
- Introduction: who will benefit from this guide?
- Getting started: what is a literature review?
- How to develop a researchable question
- How to find the literature
- How to manage the reading and take notes that make sense
- How to bring it all together: examples, templates, links, guides
Who will benefit from this guide?
This guide is written for undergraduates and postgraduate, course work students who are doing their first literature review.
Higher degree research candidates and academic researchers, please also refer to the Resources for Researchers library guides for more detailed information on writing theses and systematic reviews.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an examination of research in a particular field.
- It gathers, critically analyses, evaluates, and synthesises current research literature in a discipline,
- indicates where there may be strengths, gaps, weaknesses, and agreements in the current research.
It considers:
- what has been done,
- the current thinking,
- research trends,
- principal debates,
- dominant ideas,
- methods used in researching the topic
- gaps and flaws in the research.
http://libguides.lib.msu.edu/c.php?g=96146&p=904793
Different Types of reviews
You may be asked to complete a literature review that is done in a systematic way, that is like a systematic review.
Mostly, the literature review you will be asked to do will be integrative – that is, conclusions are drawn from the literature in order to create something new, such as a new hypothesis to address a question, a solution to a complex problem, a new workplace procedure or training program.
Some elements of what you are asked to do may be like a systematic review, particularly in health fields.
Systematic approach does not mean a systematic review.
A true systematic review is a complex research project:
- conducted in a scientific manner,
- usually with more than one person involved,
- they take a long time to complete
- are generally a project in themselves.
For more information have a look at the Systematic Review library guide .
If you would like to know more about different types of reviews, have a look at the document below:

At the core of a literature review is a synthesis of the research.
While both analysis and synthesis are involved, s ynthesis goes beyond analysis and is a higher order thinking.(Bloom's taxonomy).
Looking at the diagram below, it is evident that synthesis goes well beyond just analysis.

- Analysis asks you to break something down into its parts and compare and contrast with other research findings.
- where they agree and disagree
- the major themes, arguments, ideas in a field
- the questions raised and those yet to be answered.
- This will show the relationships between different aspects of the research findings in the literature.
- It is not a summary, but rather is organised around concepts and themes, where there is a combining of elements to form something new.
Watch this short clip from Utah State University which defines how to go about achieving synthesis.
Synthesis: True or False.
Quick Quiz: check your understanding of synthesis from the video by deciding which of these statements are true or false .
- Next: How to develop a researchable question >>
- Last Updated: Apr 10, 2024 11:56 AM
- URL: https://utas.libguides.com/literaturereviews

- Library Guides
- Literature Reviews
- Writing the Review
Literature Reviews: Writing the Review
Outline of review sections.
Your Literature Review should not be a summary and evaluation of each article, one after the other. Your sources should be integrated together to create a narrative on your topic.
Consider the following ways to organize your review:
- By themes, variables, or issues
- By varying perspectives regarding a topic of controversy
- Chronologically, to show how the topic and research have developed over time
Use an outline to organize your sources and ideas in a logical sequence. Identify main points and subpoints, and consider the flow of your review. Outlines can be revised as your ideas develop. They help guide your readers through your ideas and show the hierarchy of your thoughts. What do your readers need to understand first? Where might certain studies fit most naturally? These are the kinds of questions that an outline can clarify.
An example outline for a Literature Review might look like this:
Introduction
- Background information on the topic & definitions
- Purpose of the literature review
- Scope and limitations of the review (what is included /excluded)
- Historical background
- Overview of the existing research on the topic
- Principle question being asked
- Organization of the literature into categories or themes
- Evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses of each study
- Combining the findings from multiple sources to identify patterns and trends
- Insight into the relationship between your central topic and a larger area of study
- Development of a new research question or hypothesis
- Summary of the key points and findings in the literature
- Discussion of gaps in the existing knowledge
- Implications for future research
Strategies for Writing
Annotated bibliography.
An annotated bibliography collects short descriptions of each source in one place. After you have read each source carefully, set aside some time to write a brief summary. Your summary might be simply informative (e.g. identify the main argument/hypothesis, methods, major findings, and/or conclusions), or it might be evaluative (e.g. state why the source is interesting or useful for your review, or why it is not).
This method is more narrative than the Literature Matrix talked about on the Documenting Your Search page.
Taking the time to write short informative and/or evaluative summaries of your sources while you are researching can help you transition into the drafting stage later on. By making a record of your sources’ contents and your reactions to them, you make it less likely that you will need to go back and re-read many sources while drafting, and you might also start to gain a clearer idea of the overarching shape of your review.
READ EXTANT LIT REVIEWS CLOSELY
As you conduct your research, you will likely read many sources that model the same kind of literature review that you are researching and writing. While your original intent in reading those sources is likely to learn from the studies’ content (e.g. their results and discussion), it will benefit you to re-read these articles rhetorically.
Reading rhetorically means paying attention to how a text is written—how it has been structured, how it presents its claims and analyses, how it employs transitional words and phrases to move from one idea to the next. You might also pay attention to an author’s stylistic choices, like the use of first-person pronouns, active and passive voice, or technical terminology.
See Finding Example Literature Reviews on the Developing a Research Question page for tips on finding reviews relevant to your topic.
MIND-MAPPING
Creating a mind-map is a form of brainstorming that lets you visualize how your ideas function and relate. Draw the diagram freehand or download software that lets you easily manipulate and group text, images, and shapes ( Coggle , FreeMind , MindMaple ).
Write down a central idea, then identify associated concepts, features, or questions around that idea. Make lines attaching various ideas, or arrows to signify directional relationships. Use different shapes, sizes, or colors to indicate commonalities, sequences, or relative importance.

This drafting technique allows you to generate ideas while thinking visually about how they function together. As you follow lines of thought, you can see which ideas can be connected, where certain pathways lead, and what the scope of your project might be. By drawing out a mind-map you may be able to see what elements of your review are underdeveloped and will benefit from more focused attention.
USE VISUALIZATION TOOLS
Attribution.
Thanks to Librarian Jamie Niehof at the University of Michigan for providing permission to reuse and remix this Literature Reviews guide.
Avoiding Bias
Reporting bias.
This occurs when you are summarizing the literature in an unbalanced, inconsistent or distorted way .
Ways to avoid:
- look for literature that supports multiple perspectives, viewpoints or theories
- ask multiple people to review your writing for bias
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 3:50 PM
- URL: https://info.library.okstate.edu/literaturereviews
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- CBE Life Sci Educ
- v.21(3); Fall 2022
Literature Reviews, Theoretical Frameworks, and Conceptual Frameworks: An Introduction for New Biology Education Researchers
Julie a. luft.
† Department of Mathematics, Social Studies, and Science Education, Mary Frances Early College of Education, University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602-7124
Sophia Jeong
‡ Department of Teaching & Learning, College of Education & Human Ecology, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210
Robert Idsardi
§ Department of Biology, Eastern Washington University, Cheney, WA 99004
Grant Gardner
∥ Department of Biology, Middle Tennessee State University, Murfreesboro, TN 37132
Associated Data
To frame their work, biology education researchers need to consider the role of literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks as critical elements of the research and writing process. However, these elements can be confusing for scholars new to education research. This Research Methods article is designed to provide an overview of each of these elements and delineate the purpose of each in the educational research process. We describe what biology education researchers should consider as they conduct literature reviews, identify theoretical frameworks, and construct conceptual frameworks. Clarifying these different components of educational research studies can be helpful to new biology education researchers and the biology education research community at large in situating their work in the broader scholarly literature.
INTRODUCTION
Discipline-based education research (DBER) involves the purposeful and situated study of teaching and learning in specific disciplinary areas ( Singer et al. , 2012 ). Studies in DBER are guided by research questions that reflect disciplines’ priorities and worldviews. Researchers can use quantitative data, qualitative data, or both to answer these research questions through a variety of methodological traditions. Across all methodologies, there are different methods associated with planning and conducting educational research studies that include the use of surveys, interviews, observations, artifacts, or instruments. Ensuring the coherence of these elements to the discipline’s perspective also involves situating the work in the broader scholarly literature. The tools for doing this include literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks. However, the purpose and function of each of these elements is often confusing to new education researchers. The goal of this article is to introduce new biology education researchers to these three important elements important in DBER scholarship and the broader educational literature.
The first element we discuss is a review of research (literature reviews), which highlights the need for a specific research question, study problem, or topic of investigation. Literature reviews situate the relevance of the study within a topic and a field. The process may seem familiar to science researchers entering DBER fields, but new researchers may still struggle in conducting the review. Booth et al. (2016b) highlight some of the challenges novice education researchers face when conducting a review of literature. They point out that novice researchers struggle in deciding how to focus the review, determining the scope of articles needed in the review, and knowing how to be critical of the articles in the review. Overcoming these challenges (and others) can help novice researchers construct a sound literature review that can inform the design of the study and help ensure the work makes a contribution to the field.
The second and third highlighted elements are theoretical and conceptual frameworks. These guide biology education research (BER) studies, and may be less familiar to science researchers. These elements are important in shaping the construction of new knowledge. Theoretical frameworks offer a way to explain and interpret the studied phenomenon, while conceptual frameworks clarify assumptions about the studied phenomenon. Despite the importance of these constructs in educational research, biology educational researchers have noted the limited use of theoretical or conceptual frameworks in published work ( DeHaan, 2011 ; Dirks, 2011 ; Lo et al. , 2019 ). In reviewing articles published in CBE—Life Sciences Education ( LSE ) between 2015 and 2019, we found that fewer than 25% of the research articles had a theoretical or conceptual framework (see the Supplemental Information), and at times there was an inconsistent use of theoretical and conceptual frameworks. Clearly, these frameworks are challenging for published biology education researchers, which suggests the importance of providing some initial guidance to new biology education researchers.
Fortunately, educational researchers have increased their explicit use of these frameworks over time, and this is influencing educational research in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields. For instance, a quick search for theoretical or conceptual frameworks in the abstracts of articles in Educational Research Complete (a common database for educational research) in STEM fields demonstrates a dramatic change over the last 20 years: from only 778 articles published between 2000 and 2010 to 5703 articles published between 2010 and 2020, a more than sevenfold increase. Greater recognition of the importance of these frameworks is contributing to DBER authors being more explicit about such frameworks in their studies.
Collectively, literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks work to guide methodological decisions and the elucidation of important findings. Each offers a different perspective on the problem of study and is an essential element in all forms of educational research. As new researchers seek to learn about these elements, they will find different resources, a variety of perspectives, and many suggestions about the construction and use of these elements. The wide range of available information can overwhelm the new researcher who just wants to learn the distinction between these elements or how to craft them adequately.
Our goal in writing this paper is not to offer specific advice about how to write these sections in scholarly work. Instead, we wanted to introduce these elements to those who are new to BER and who are interested in better distinguishing one from the other. In this paper, we share the purpose of each element in BER scholarship, along with important points on its construction. We also provide references for additional resources that may be beneficial to better understanding each element. Table 1 summarizes the key distinctions among these elements.
Comparison of literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual reviews
This article is written for the new biology education researcher who is just learning about these different elements or for scientists looking to become more involved in BER. It is a result of our own work as science education and biology education researchers, whether as graduate students and postdoctoral scholars or newly hired and established faculty members. This is the article we wish had been available as we started to learn about these elements or discussed them with new educational researchers in biology.
LITERATURE REVIEWS
Purpose of a literature review.
A literature review is foundational to any research study in education or science. In education, a well-conceptualized and well-executed review provides a summary of the research that has already been done on a specific topic and identifies questions that remain to be answered, thus illustrating the current research project’s potential contribution to the field and the reasoning behind the methodological approach selected for the study ( Maxwell, 2012 ). BER is an evolving disciplinary area that is redefining areas of conceptual emphasis as well as orientations toward teaching and learning (e.g., Labov et al. , 2010 ; American Association for the Advancement of Science, 2011 ; Nehm, 2019 ). As a result, building comprehensive, critical, purposeful, and concise literature reviews can be a challenge for new biology education researchers.
Building Literature Reviews
There are different ways to approach and construct a literature review. Booth et al. (2016a) provide an overview that includes, for example, scoping reviews, which are focused only on notable studies and use a basic method of analysis, and integrative reviews, which are the result of exhaustive literature searches across different genres. Underlying each of these different review processes are attention to the s earch process, a ppraisa l of articles, s ynthesis of the literature, and a nalysis: SALSA ( Booth et al. , 2016a ). This useful acronym can help the researcher focus on the process while building a specific type of review.
However, new educational researchers often have questions about literature reviews that are foundational to SALSA or other approaches. Common questions concern determining which literature pertains to the topic of study or the role of the literature review in the design of the study. This section addresses such questions broadly while providing general guidance for writing a narrative literature review that evaluates the most pertinent studies.
The literature review process should begin before the research is conducted. As Boote and Beile (2005 , p. 3) suggested, researchers should be “scholars before researchers.” They point out that having a good working knowledge of the proposed topic helps illuminate avenues of study. Some subject areas have a deep body of work to read and reflect upon, providing a strong foundation for developing the research question(s). For instance, the teaching and learning of evolution is an area of long-standing interest in the BER community, generating many studies (e.g., Perry et al. , 2008 ; Barnes and Brownell, 2016 ) and reviews of research (e.g., Sickel and Friedrichsen, 2013 ; Ziadie and Andrews, 2018 ). Emerging areas of BER include the affective domain, issues of transfer, and metacognition ( Singer et al. , 2012 ). Many studies in these areas are transdisciplinary and not always specific to biology education (e.g., Rodrigo-Peiris et al. , 2018 ; Kolpikova et al. , 2019 ). These newer areas may require reading outside BER; fortunately, summaries of some of these topics can be found in the Current Insights section of the LSE website.
In focusing on a specific problem within a broader research strand, a new researcher will likely need to examine research outside BER. Depending upon the area of study, the expanded reading list might involve a mix of BER, DBER, and educational research studies. Determining the scope of the reading is not always straightforward. A simple way to focus one’s reading is to create a “summary phrase” or “research nugget,” which is a very brief descriptive statement about the study. It should focus on the essence of the study, for example, “first-year nonmajor students’ understanding of evolution,” “metacognitive prompts to enhance learning during biochemistry,” or “instructors’ inquiry-based instructional practices after professional development programming.” This type of phrase should help a new researcher identify two or more areas to review that pertain to the study. Focusing on recent research in the last 5 years is a good first step. Additional studies can be identified by reading relevant works referenced in those articles. It is also important to read seminal studies that are more than 5 years old. Reading a range of studies should give the researcher the necessary command of the subject in order to suggest a research question.
Given that the research question(s) arise from the literature review, the review should also substantiate the selected methodological approach. The review and research question(s) guide the researcher in determining how to collect and analyze data. Often the methodological approach used in a study is selected to contribute knowledge that expands upon what has been published previously about the topic (see Institute of Education Sciences and National Science Foundation, 2013 ). An emerging topic of study may need an exploratory approach that allows for a description of the phenomenon and development of a potential theory. This could, but not necessarily, require a methodological approach that uses interviews, observations, surveys, or other instruments. An extensively studied topic may call for the additional understanding of specific factors or variables; this type of study would be well suited to a verification or a causal research design. These could entail a methodological approach that uses valid and reliable instruments, observations, or interviews to determine an effect in the studied event. In either of these examples, the researcher(s) may use a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods methodological approach.
Even with a good research question, there is still more reading to be done. The complexity and focus of the research question dictates the depth and breadth of the literature to be examined. Questions that connect multiple topics can require broad literature reviews. For instance, a study that explores the impact of a biology faculty learning community on the inquiry instruction of faculty could have the following review areas: learning communities among biology faculty, inquiry instruction among biology faculty, and inquiry instruction among biology faculty as a result of professional learning. Biology education researchers need to consider whether their literature review requires studies from different disciplines within or outside DBER. For the example given, it would be fruitful to look at research focused on learning communities with faculty in STEM fields or in general education fields that result in instructional change. It is important not to be too narrow or too broad when reading. When the conclusions of articles start to sound similar or no new insights are gained, the researcher likely has a good foundation for a literature review. This level of reading should allow the researcher to demonstrate a mastery in understanding the researched topic, explain the suitability of the proposed research approach, and point to the need for the refined research question(s).
The literature review should include the researcher’s evaluation and critique of the selected studies. A researcher may have a large collection of studies, but not all of the studies will follow standards important in the reporting of empirical work in the social sciences. The American Educational Research Association ( Duran et al. , 2006 ), for example, offers a general discussion about standards for such work: an adequate review of research informing the study, the existence of sound and appropriate data collection and analysis methods, and appropriate conclusions that do not overstep or underexplore the analyzed data. The Institute of Education Sciences and National Science Foundation (2013) also offer Common Guidelines for Education Research and Development that can be used to evaluate collected studies.
Because not all journals adhere to such standards, it is important that a researcher review each study to determine the quality of published research, per the guidelines suggested earlier. In some instances, the research may be fatally flawed. Examples of such flaws include data that do not pertain to the question, a lack of discussion about the data collection, poorly constructed instruments, or an inadequate analysis. These types of errors result in studies that are incomplete, error-laden, or inaccurate and should be excluded from the review. Most studies have limitations, and the author(s) often make them explicit. For instance, there may be an instructor effect, recognized bias in the analysis, or issues with the sample population. Limitations are usually addressed by the research team in some way to ensure a sound and acceptable research process. Occasionally, the limitations associated with the study can be significant and not addressed adequately, which leaves a consequential decision in the hands of the researcher. Providing critiques of studies in the literature review process gives the reader confidence that the researcher has carefully examined relevant work in preparation for the study and, ultimately, the manuscript.
A solid literature review clearly anchors the proposed study in the field and connects the research question(s), the methodological approach, and the discussion. Reviewing extant research leads to research questions that will contribute to what is known in the field. By summarizing what is known, the literature review points to what needs to be known, which in turn guides decisions about methodology. Finally, notable findings of the new study are discussed in reference to those described in the literature review.
Within published BER studies, literature reviews can be placed in different locations in an article. When included in the introductory section of the study, the first few paragraphs of the manuscript set the stage, with the literature review following the opening paragraphs. Cooper et al. (2019) illustrate this approach in their study of course-based undergraduate research experiences (CUREs). An introduction discussing the potential of CURES is followed by an analysis of the existing literature relevant to the design of CUREs that allows for novel student discoveries. Within this review, the authors point out contradictory findings among research on novel student discoveries. This clarifies the need for their study, which is described and highlighted through specific research aims.
A literature reviews can also make up a separate section in a paper. For example, the introduction to Todd et al. (2019) illustrates the need for their research topic by highlighting the potential of learning progressions (LPs) and suggesting that LPs may help mitigate learning loss in genetics. At the end of the introduction, the authors state their specific research questions. The review of literature following this opening section comprises two subsections. One focuses on learning loss in general and examines a variety of studies and meta-analyses from the disciplines of medical education, mathematics, and reading. The second section focuses specifically on LPs in genetics and highlights student learning in the midst of LPs. These separate reviews provide insights into the stated research question.
Suggestions and Advice
A well-conceptualized, comprehensive, and critical literature review reveals the understanding of the topic that the researcher brings to the study. Literature reviews should not be so big that there is no clear area of focus; nor should they be so narrow that no real research question arises. The task for a researcher is to craft an efficient literature review that offers a critical analysis of published work, articulates the need for the study, guides the methodological approach to the topic of study, and provides an adequate foundation for the discussion of the findings.
In our own writing of literature reviews, there are often many drafts. An early draft may seem well suited to the study because the need for and approach to the study are well described. However, as the results of the study are analyzed and findings begin to emerge, the existing literature review may be inadequate and need revision. The need for an expanded discussion about the research area can result in the inclusion of new studies that support the explanation of a potential finding. The literature review may also prove to be too broad. Refocusing on a specific area allows for more contemplation of a finding.
It should be noted that there are different types of literature reviews, and many books and articles have been written about the different ways to embark on these types of reviews. Among these different resources, the following may be helpful in considering how to refine the review process for scholarly journals:
- Booth, A., Sutton, A., & Papaioannou, D. (2016a). Systemic approaches to a successful literature review (2nd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. This book addresses different types of literature reviews and offers important suggestions pertaining to defining the scope of the literature review and assessing extant studies.
- Booth, W. C., Colomb, G. G., Williams, J. M., Bizup, J., & Fitzgerald, W. T. (2016b). The craft of research (4th ed.). Chicago: University of Chicago Press. This book can help the novice consider how to make the case for an area of study. While this book is not specifically about literature reviews, it offers suggestions about making the case for your study.
- Galvan, J. L., & Galvan, M. C. (2017). Writing literature reviews: A guide for students of the social and behavioral sciences (7th ed.). Routledge. This book offers guidance on writing different types of literature reviews. For the novice researcher, there are useful suggestions for creating coherent literature reviews.
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORKS
Purpose of theoretical frameworks.
As new education researchers may be less familiar with theoretical frameworks than with literature reviews, this discussion begins with an analogy. Envision a biologist, chemist, and physicist examining together the dramatic effect of a fog tsunami over the ocean. A biologist gazing at this phenomenon may be concerned with the effect of fog on various species. A chemist may be interested in the chemical composition of the fog as water vapor condenses around bits of salt. A physicist may be focused on the refraction of light to make fog appear to be “sitting” above the ocean. While observing the same “objective event,” the scientists are operating under different theoretical frameworks that provide a particular perspective or “lens” for the interpretation of the phenomenon. Each of these scientists brings specialized knowledge, experiences, and values to this phenomenon, and these influence the interpretation of the phenomenon. The scientists’ theoretical frameworks influence how they design and carry out their studies and interpret their data.
Within an educational study, a theoretical framework helps to explain a phenomenon through a particular lens and challenges and extends existing knowledge within the limitations of that lens. Theoretical frameworks are explicitly stated by an educational researcher in the paper’s framework, theory, or relevant literature section. The framework shapes the types of questions asked, guides the method by which data are collected and analyzed, and informs the discussion of the results of the study. It also reveals the researcher’s subjectivities, for example, values, social experience, and viewpoint ( Allen, 2017 ). It is essential that a novice researcher learn to explicitly state a theoretical framework, because all research questions are being asked from the researcher’s implicit or explicit assumptions of a phenomenon of interest ( Schwandt, 2000 ).
Selecting Theoretical Frameworks
Theoretical frameworks are one of the most contemplated elements in our work in educational research. In this section, we share three important considerations for new scholars selecting a theoretical framework.
The first step in identifying a theoretical framework involves reflecting on the phenomenon within the study and the assumptions aligned with the phenomenon. The phenomenon involves the studied event. There are many possibilities, for example, student learning, instructional approach, or group organization. A researcher holds assumptions about how the phenomenon will be effected, influenced, changed, or portrayed. It is ultimately the researcher’s assumption(s) about the phenomenon that aligns with a theoretical framework. An example can help illustrate how a researcher’s reflection on the phenomenon and acknowledgment of assumptions can result in the identification of a theoretical framework.
In our example, a biology education researcher may be interested in exploring how students’ learning of difficult biological concepts can be supported by the interactions of group members. The phenomenon of interest is the interactions among the peers, and the researcher assumes that more knowledgeable students are important in supporting the learning of the group. As a result, the researcher may draw on Vygotsky’s (1978) sociocultural theory of learning and development that is focused on the phenomenon of student learning in a social setting. This theory posits the critical nature of interactions among students and between students and teachers in the process of building knowledge. A researcher drawing upon this framework holds the assumption that learning is a dynamic social process involving questions and explanations among students in the classroom and that more knowledgeable peers play an important part in the process of building conceptual knowledge.
It is important to state at this point that there are many different theoretical frameworks. Some frameworks focus on learning and knowing, while other theoretical frameworks focus on equity, empowerment, or discourse. Some frameworks are well articulated, and others are still being refined. For a new researcher, it can be challenging to find a theoretical framework. Two of the best ways to look for theoretical frameworks is through published works that highlight different frameworks.
When a theoretical framework is selected, it should clearly connect to all parts of the study. The framework should augment the study by adding a perspective that provides greater insights into the phenomenon. It should clearly align with the studies described in the literature review. For instance, a framework focused on learning would correspond to research that reported different learning outcomes for similar studies. The methods for data collection and analysis should also correspond to the framework. For instance, a study about instructional interventions could use a theoretical framework concerned with learning and could collect data about the effect of the intervention on what is learned. When the data are analyzed, the theoretical framework should provide added meaning to the findings, and the findings should align with the theoretical framework.
A study by Jensen and Lawson (2011) provides an example of how a theoretical framework connects different parts of the study. They compared undergraduate biology students in heterogeneous and homogeneous groups over the course of a semester. Jensen and Lawson (2011) assumed that learning involved collaboration and more knowledgeable peers, which made Vygotsky’s (1978) theory a good fit for their study. They predicted that students in heterogeneous groups would experience greater improvement in their reasoning abilities and science achievements with much of the learning guided by the more knowledgeable peers.
In the enactment of the study, they collected data about the instruction in traditional and inquiry-oriented classes, while the students worked in homogeneous or heterogeneous groups. To determine the effect of working in groups, the authors also measured students’ reasoning abilities and achievement. Each data-collection and analysis decision connected to understanding the influence of collaborative work.
Their findings highlighted aspects of Vygotsky’s (1978) theory of learning. One finding, for instance, posited that inquiry instruction, as a whole, resulted in reasoning and achievement gains. This links to Vygotsky (1978) , because inquiry instruction involves interactions among group members. A more nuanced finding was that group composition had a conditional effect. Heterogeneous groups performed better with more traditional and didactic instruction, regardless of the reasoning ability of the group members. Homogeneous groups worked better during interaction-rich activities for students with low reasoning ability. The authors attributed the variation to the different types of helping behaviors of students. High-performing students provided the answers, while students with low reasoning ability had to work collectively through the material. In terms of Vygotsky (1978) , this finding provided new insights into the learning context in which productive interactions can occur for students.
Another consideration in the selection and use of a theoretical framework pertains to its orientation to the study. This can result in the theoretical framework prioritizing individuals, institutions, and/or policies ( Anfara and Mertz, 2014 ). Frameworks that connect to individuals, for instance, could contribute to understanding their actions, learning, or knowledge. Institutional frameworks, on the other hand, offer insights into how institutions, organizations, or groups can influence individuals or materials. Policy theories provide ways to understand how national or local policies can dictate an emphasis on outcomes or instructional design. These different types of frameworks highlight different aspects in an educational setting, which influences the design of the study and the collection of data. In addition, these different frameworks offer a way to make sense of the data. Aligning the data collection and analysis with the framework ensures that a study is coherent and can contribute to the field.
New understandings emerge when different theoretical frameworks are used. For instance, Ebert-May et al. (2015) prioritized the individual level within conceptual change theory (see Posner et al. , 1982 ). In this theory, an individual’s knowledge changes when it no longer fits the phenomenon. Ebert-May et al. (2015) designed a professional development program challenging biology postdoctoral scholars’ existing conceptions of teaching. The authors reported that the biology postdoctoral scholars’ teaching practices became more student-centered as they were challenged to explain their instructional decision making. According to the theory, the biology postdoctoral scholars’ dissatisfaction in their descriptions of teaching and learning initiated change in their knowledge and instruction. These results reveal how conceptual change theory can explain the learning of participants and guide the design of professional development programming.
The communities of practice (CoP) theoretical framework ( Lave, 1988 ; Wenger, 1998 ) prioritizes the institutional level , suggesting that learning occurs when individuals learn from and contribute to the communities in which they reside. Grounded in the assumption of community learning, the literature on CoP suggests that, as individuals interact regularly with the other members of their group, they learn about the rules, roles, and goals of the community ( Allee, 2000 ). A study conducted by Gehrke and Kezar (2017) used the CoP framework to understand organizational change by examining the involvement of individual faculty engaged in a cross-institutional CoP focused on changing the instructional practice of faculty at each institution. In the CoP, faculty members were involved in enhancing instructional materials within their department, which aligned with an overarching goal of instituting instruction that embraced active learning. Not surprisingly, Gehrke and Kezar (2017) revealed that faculty who perceived the community culture as important in their work cultivated institutional change. Furthermore, they found that institutional change was sustained when key leaders served as mentors and provided support for faculty, and as faculty themselves developed into leaders. This study reveals the complexity of individual roles in a COP in order to support institutional instructional change.
It is important to explicitly state the theoretical framework used in a study, but elucidating a theoretical framework can be challenging for a new educational researcher. The literature review can help to identify an applicable theoretical framework. Focal areas of the review or central terms often connect to assumptions and assertions associated with the framework that pertain to the phenomenon of interest. Another way to identify a theoretical framework is self-reflection by the researcher on personal beliefs and understandings about the nature of knowledge the researcher brings to the study ( Lysaght, 2011 ). In stating one’s beliefs and understandings related to the study (e.g., students construct their knowledge, instructional materials support learning), an orientation becomes evident that will suggest a particular theoretical framework. Theoretical frameworks are not arbitrary , but purposefully selected.
With experience, a researcher may find expanded roles for theoretical frameworks. Researchers may revise an existing framework that has limited explanatory power, or they may decide there is a need to develop a new theoretical framework. These frameworks can emerge from a current study or the need to explain a phenomenon in a new way. Researchers may also find that multiple theoretical frameworks are necessary to frame and explore a problem, as different frameworks can provide different insights into a problem.
Finally, it is important to recognize that choosing “x” theoretical framework does not necessarily mean a researcher chooses “y” methodology and so on, nor is there a clear-cut, linear process in selecting a theoretical framework for one’s study. In part, the nonlinear process of identifying a theoretical framework is what makes understanding and using theoretical frameworks challenging. For the novice scholar, contemplating and understanding theoretical frameworks is essential. Fortunately, there are articles and books that can help:
- Creswell, J. W. (2018). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (5th ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. This book provides an overview of theoretical frameworks in general educational research.
- Ding, L. (2019). Theoretical perspectives of quantitative physics education research. Physical Review Physics Education Research , 15 (2), 020101-1–020101-13. This paper illustrates how a DBER field can use theoretical frameworks.
- Nehm, R. (2019). Biology education research: Building integrative frameworks for teaching and learning about living systems. Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Science Education Research , 1 , ar15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43031-019-0017-6 . This paper articulates the need for studies in BER to explicitly state theoretical frameworks and provides examples of potential studies.
- Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice . Sage. This book also provides an overview of theoretical frameworks, but for both research and evaluation.
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORKS
Purpose of a conceptual framework.
A conceptual framework is a description of the way a researcher understands the factors and/or variables that are involved in the study and their relationships to one another. The purpose of a conceptual framework is to articulate the concepts under study using relevant literature ( Rocco and Plakhotnik, 2009 ) and to clarify the presumed relationships among those concepts ( Rocco and Plakhotnik, 2009 ; Anfara and Mertz, 2014 ). Conceptual frameworks are different from theoretical frameworks in both their breadth and grounding in established findings. Whereas a theoretical framework articulates the lens through which a researcher views the work, the conceptual framework is often more mechanistic and malleable.
Conceptual frameworks are broader, encompassing both established theories (i.e., theoretical frameworks) and the researchers’ own emergent ideas. Emergent ideas, for example, may be rooted in informal and/or unpublished observations from experience. These emergent ideas would not be considered a “theory” if they are not yet tested, supported by systematically collected evidence, and peer reviewed. However, they do still play an important role in the way researchers approach their studies. The conceptual framework allows authors to clearly describe their emergent ideas so that connections among ideas in the study and the significance of the study are apparent to readers.
Constructing Conceptual Frameworks
Including a conceptual framework in a research study is important, but researchers often opt to include either a conceptual or a theoretical framework. Either may be adequate, but both provide greater insight into the research approach. For instance, a research team plans to test a novel component of an existing theory. In their study, they describe the existing theoretical framework that informs their work and then present their own conceptual framework. Within this conceptual framework, specific topics portray emergent ideas that are related to the theory. Describing both frameworks allows readers to better understand the researchers’ assumptions, orientations, and understanding of concepts being investigated. For example, Connolly et al. (2018) included a conceptual framework that described how they applied a theoretical framework of social cognitive career theory (SCCT) to their study on teaching programs for doctoral students. In their conceptual framework, the authors described SCCT, explained how it applied to the investigation, and drew upon results from previous studies to justify the proposed connections between the theory and their emergent ideas.
In some cases, authors may be able to sufficiently describe their conceptualization of the phenomenon under study in an introduction alone, without a separate conceptual framework section. However, incomplete descriptions of how the researchers conceptualize the components of the study may limit the significance of the study by making the research less intelligible to readers. This is especially problematic when studying topics in which researchers use the same terms for different constructs or different terms for similar and overlapping constructs (e.g., inquiry, teacher beliefs, pedagogical content knowledge, or active learning). Authors must describe their conceptualization of a construct if the research is to be understandable and useful.
There are some key areas to consider regarding the inclusion of a conceptual framework in a study. To begin with, it is important to recognize that conceptual frameworks are constructed by the researchers conducting the study ( Rocco and Plakhotnik, 2009 ; Maxwell, 2012 ). This is different from theoretical frameworks that are often taken from established literature. Researchers should bring together ideas from the literature, but they may be influenced by their own experiences as a student and/or instructor, the shared experiences of others, or thought experiments as they construct a description, model, or representation of their understanding of the phenomenon under study. This is an exercise in intellectual organization and clarity that often considers what is learned, known, and experienced. The conceptual framework makes these constructs explicitly visible to readers, who may have different understandings of the phenomenon based on their prior knowledge and experience. There is no single method to go about this intellectual work.
Reeves et al. (2016) is an example of an article that proposed a conceptual framework about graduate teaching assistant professional development evaluation and research. The authors used existing literature to create a novel framework that filled a gap in current research and practice related to the training of graduate teaching assistants. This conceptual framework can guide the systematic collection of data by other researchers because the framework describes the relationships among various factors that influence teaching and learning. The Reeves et al. (2016) conceptual framework may be modified as additional data are collected and analyzed by other researchers. This is not uncommon, as conceptual frameworks can serve as catalysts for concerted research efforts that systematically explore a phenomenon (e.g., Reynolds et al. , 2012 ; Brownell and Kloser, 2015 ).
Sabel et al. (2017) used a conceptual framework in their exploration of how scaffolds, an external factor, interact with internal factors to support student learning. Their conceptual framework integrated principles from two theoretical frameworks, self-regulated learning and metacognition, to illustrate how the research team conceptualized students’ use of scaffolds in their learning ( Figure 1 ). Sabel et al. (2017) created this model using their interpretations of these two frameworks in the context of their teaching.

Conceptual framework from Sabel et al. (2017) .
A conceptual framework should describe the relationship among components of the investigation ( Anfara and Mertz, 2014 ). These relationships should guide the researcher’s methods of approaching the study ( Miles et al. , 2014 ) and inform both the data to be collected and how those data should be analyzed. Explicitly describing the connections among the ideas allows the researcher to justify the importance of the study and the rigor of the research design. Just as importantly, these frameworks help readers understand why certain components of a system were not explored in the study. This is a challenge in education research, which is rooted in complex environments with many variables that are difficult to control.
For example, Sabel et al. (2017) stated: “Scaffolds, such as enhanced answer keys and reflection questions, can help students and instructors bridge the external and internal factors and support learning” (p. 3). They connected the scaffolds in the study to the three dimensions of metacognition and the eventual transformation of existing ideas into new or revised ideas. Their framework provides a rationale for focusing on how students use two different scaffolds, and not on other factors that may influence a student’s success (self-efficacy, use of active learning, exam format, etc.).
In constructing conceptual frameworks, researchers should address needed areas of study and/or contradictions discovered in literature reviews. By attending to these areas, researchers can strengthen their arguments for the importance of a study. For instance, conceptual frameworks can address how the current study will fill gaps in the research, resolve contradictions in existing literature, or suggest a new area of study. While a literature review describes what is known and not known about the phenomenon, the conceptual framework leverages these gaps in describing the current study ( Maxwell, 2012 ). In the example of Sabel et al. (2017) , the authors indicated there was a gap in the literature regarding how scaffolds engage students in metacognition to promote learning in large classes. Their study helps fill that gap by describing how scaffolds can support students in the three dimensions of metacognition: intelligibility, plausibility, and wide applicability. In another example, Lane (2016) integrated research from science identity, the ethic of care, the sense of belonging, and an expertise model of student success to form a conceptual framework that addressed the critiques of other frameworks. In a more recent example, Sbeglia et al. (2021) illustrated how a conceptual framework influences the methodological choices and inferences in studies by educational researchers.
Sometimes researchers draw upon the conceptual frameworks of other researchers. When a researcher’s conceptual framework closely aligns with an existing framework, the discussion may be brief. For example, Ghee et al. (2016) referred to portions of SCCT as their conceptual framework to explain the significance of their work on students’ self-efficacy and career interests. Because the authors’ conceptualization of this phenomenon aligned with a previously described framework, they briefly mentioned the conceptual framework and provided additional citations that provided more detail for the readers.
Within both the BER and the broader DBER communities, conceptual frameworks have been used to describe different constructs. For example, some researchers have used the term “conceptual framework” to describe students’ conceptual understandings of a biological phenomenon. This is distinct from a researcher’s conceptual framework of the educational phenomenon under investigation, which may also need to be explicitly described in the article. Other studies have presented a research logic model or flowchart of the research design as a conceptual framework. These constructions can be quite valuable in helping readers understand the data-collection and analysis process. However, a model depicting the study design does not serve the same role as a conceptual framework. Researchers need to avoid conflating these constructs by differentiating the researchers’ conceptual framework that guides the study from the research design, when applicable.
Explicitly describing conceptual frameworks is essential in depicting the focus of the study. We have found that being explicit in a conceptual framework means using accepted terminology, referencing prior work, and clearly noting connections between terms. This description can also highlight gaps in the literature or suggest potential contributions to the field of study. A well-elucidated conceptual framework can suggest additional studies that may be warranted. This can also spur other researchers to consider how they would approach the examination of a phenomenon and could result in a revised conceptual framework.
It can be challenging to create conceptual frameworks, but they are important. Below are two resources that could be helpful in constructing and presenting conceptual frameworks in educational research:
- Maxwell, J. A. (2012). Qualitative research design: An interactive approach (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. Chapter 3 in this book describes how to construct conceptual frameworks.
- Ravitch, S. M., & Riggan, M. (2016). Reason & rigor: How conceptual frameworks guide research . Los Angeles, CA: Sage. This book explains how conceptual frameworks guide the research questions, data collection, data analyses, and interpretation of results.
CONCLUDING THOUGHTS
Literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks are all important in DBER and BER. Robust literature reviews reinforce the importance of a study. Theoretical frameworks connect the study to the base of knowledge in educational theory and specify the researcher’s assumptions. Conceptual frameworks allow researchers to explicitly describe their conceptualization of the relationships among the components of the phenomenon under study. Table 1 provides a general overview of these components in order to assist biology education researchers in thinking about these elements.
It is important to emphasize that these different elements are intertwined. When these elements are aligned and complement one another, the study is coherent, and the study findings contribute to knowledge in the field. When literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks are disconnected from one another, the study suffers. The point of the study is lost, suggested findings are unsupported, or important conclusions are invisible to the researcher. In addition, this misalignment may be costly in terms of time and money.
Conducting a literature review, selecting a theoretical framework, and building a conceptual framework are some of the most difficult elements of a research study. It takes time to understand the relevant research, identify a theoretical framework that provides important insights into the study, and formulate a conceptual framework that organizes the finding. In the research process, there is often a constant back and forth among these elements as the study evolves. With an ongoing refinement of the review of literature, clarification of the theoretical framework, and articulation of a conceptual framework, a sound study can emerge that makes a contribution to the field. This is the goal of BER and education research.
Supplementary Material
- Allee, V. (2000). Knowledge networks and communities of learning . OD Practitioner , 32 ( 4 ), 4–13. [ Google Scholar ]
- Allen, M. (2017). The Sage encyclopedia of communication research methods (Vols. 1–4 ). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. 10.4135/9781483381411 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- American Association for the Advancement of Science. (2011). Vision and change in undergraduate biology education: A call to action . Washington, DC. [ Google Scholar ]
- Anfara, V. A., Mertz, N. T. (2014). Setting the stage . In Anfara, V. A., Mertz, N. T. (eds.), Theoretical frameworks in qualitative research (pp. 1–22). Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barnes, M. E., Brownell, S. E. (2016). Practices and perspectives of college instructors on addressing religious beliefs when teaching evolution . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 ( 2 ), ar18. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.15-11-0243 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boote, D. N., Beile, P. (2005). Scholars before researchers: On the centrality of the dissertation literature review in research preparation . Educational Researcher , 34 ( 6 ), 3–15. 10.3102/0013189x034006003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Booth, A., Sutton, A., Papaioannou, D. (2016a). Systemic approaches to a successful literature review (2nd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Booth, W. C., Colomb, G. G., Williams, J. M., Bizup, J., Fitzgerald, W. T. (2016b). The craft of research (4th ed.). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brownell, S. E., Kloser, M. J. (2015). Toward a conceptual framework for measuring the effectiveness of course-based undergraduate research experiences in undergraduate biology . Studies in Higher Education , 40 ( 3 ), 525–544. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2015.1004234 [ Google Scholar ]
- Connolly, M. R., Lee, Y. G., Savoy, J. N. (2018). The effects of doctoral teaching development on early-career STEM scholars’ college teaching self-efficacy . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 17 ( 1 ), ar14. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.17-02-0039 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper, K. M., Blattman, J. N., Hendrix, T., Brownell, S. E. (2019). The impact of broadly relevant novel discoveries on student project ownership in a traditional lab course turned CURE . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 ( 4 ), ar57. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.19-06-0113 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell, J. W. (2018). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (5th ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- DeHaan, R. L. (2011). Education research in the biological sciences: A nine decade review (Paper commissioned by the NAS/NRC Committee on the Status, Contributions, and Future Directions of Discipline Based Education Research) . Washington, DC: National Academies Press. Retrieved May 20, 2022, from www7.nationalacademies.org/bose/DBER_Mee ting2_commissioned_papers_page.html [ Google Scholar ]
- Ding, L. (2019). Theoretical perspectives of quantitative physics education research . Physical Review Physics Education Research , 15 ( 2 ), 020101. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dirks, C. (2011). The current status and future direction of biology education research . Paper presented at: Second Committee Meeting on the Status, Contributions, and Future Directions of Discipline-Based Education Research, 18–19 October (Washington, DC). Retrieved May 20, 2022, from http://sites.nationalacademies.org/DBASSE/BOSE/DBASSE_071087 [ Google Scholar ]
- Duran, R. P., Eisenhart, M. A., Erickson, F. D., Grant, C. A., Green, J. L., Hedges, L. V., Schneider, B. L. (2006). Standards for reporting on empirical social science research in AERA publications: American Educational Research Association . Educational Researcher , 35 ( 6 ), 33–40. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ebert-May, D., Derting, T. L., Henkel, T. P., Middlemis Maher, J., Momsen, J. L., Arnold, B., Passmore, H. A. (2015). Breaking the cycle: Future faculty begin teaching with learner-centered strategies after professional development . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 14 ( 2 ), ar22. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.14-12-0222 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Galvan, J. L., Galvan, M. C. (2017). Writing literature reviews: A guide for students of the social and behavioral sciences (7th ed.). New York, NY: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315229386 [ Google Scholar ]
- Gehrke, S., Kezar, A. (2017). The roles of STEM faculty communities of practice in institutional and departmental reform in higher education . American Educational Research Journal , 54 ( 5 ), 803–833. https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831217706736 [ Google Scholar ]
- Ghee, M., Keels, M., Collins, D., Neal-Spence, C., Baker, E. (2016). Fine-tuning summer research programs to promote underrepresented students’ persistence in the STEM pathway . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 ( 3 ), ar28. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.16-01-0046 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Institute of Education Sciences & National Science Foundation. (2013). Common guidelines for education research and development . Retrieved May 20, 2022, from www.nsf.gov/pubs/2013/nsf13126/nsf13126.pdf
- Jensen, J. L., Lawson, A. (2011). Effects of collaborative group composition and inquiry instruction on reasoning gains and achievement in undergraduate biology . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 10 ( 1 ), 64–73. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.19-05-0098 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kolpikova, E. P., Chen, D. C., Doherty, J. H. (2019). Does the format of preclass reading quizzes matter? An evaluation of traditional and gamified, adaptive preclass reading quizzes . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 ( 4 ), ar52. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.19-05-0098 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Labov, J. B., Reid, A. H., Yamamoto, K. R. (2010). Integrated biology and undergraduate science education: A new biology education for the twenty-first century? CBE—Life Sciences Education , 9 ( 1 ), 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.09-12-0092 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lane, T. B. (2016). Beyond academic and social integration: Understanding the impact of a STEM enrichment program on the retention and degree attainment of underrepresented students . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 ( 3 ), ar39. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.16-01-0070 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lave, J. (1988). Cognition in practice: Mind, mathematics and culture in everyday life . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lo, S. M., Gardner, G. E., Reid, J., Napoleon-Fanis, V., Carroll, P., Smith, E., Sato, B. K. (2019). Prevailing questions and methodologies in biology education research: A longitudinal analysis of research in CBE — Life Sciences Education and at the Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 ( 1 ), ar9. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.18-08-0164 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lysaght, Z. (2011). Epistemological and paradigmatic ecumenism in “Pasteur’s quadrant:” Tales from doctoral research . In Official Conference Proceedings of the Third Asian Conference on Education in Osaka, Japan . Retrieved May 20, 2022, from http://iafor.org/ace2011_offprint/ACE2011_offprint_0254.pdf
- Maxwell, J. A. (2012). Qualitative research design: An interactive approach (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles, M. B., Huberman, A. M., Saldaña, J. (2014). Qualitative data analysis (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nehm, R. (2019). Biology education research: Building integrative frameworks for teaching and learning about living systems . Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Science Education Research , 1 , ar15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43031-019-0017-6 [ Google Scholar ]
- Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice . Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Perry, J., Meir, E., Herron, J. C., Maruca, S., Stal, D. (2008). Evaluating two approaches to helping college students understand evolutionary trees through diagramming tasks . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 7 ( 2 ), 193–201. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.07-01-0007 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Posner, G. J., Strike, K. A., Hewson, P. W., Gertzog, W. A. (1982). Accommodation of a scientific conception: Toward a theory of conceptual change . Science Education , 66 ( 2 ), 211–227. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ravitch, S. M., Riggan, M. (2016). Reason & rigor: How conceptual frameworks guide research . Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Reeves, T. D., Marbach-Ad, G., Miller, K. R., Ridgway, J., Gardner, G. E., Schussler, E. E., Wischusen, E. W. (2016). A conceptual framework for graduate teaching assistant professional development evaluation and research . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 ( 2 ), es2. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.15-10-0225 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reynolds, J. A., Thaiss, C., Katkin, W., Thompson, R. J. Jr. (2012). Writing-to-learn in undergraduate science education: A community-based, conceptually driven approach . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 11 ( 1 ), 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.11-08-0064 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rocco, T. S., Plakhotnik, M. S. (2009). Literature reviews, conceptual frameworks, and theoretical frameworks: Terms, functions, and distinctions . Human Resource Development Review , 8 ( 1 ), 120–130. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534484309332617 [ Google Scholar ]
- Rodrigo-Peiris, T., Xiang, L., Cassone, V. M. (2018). A low-intensity, hybrid design between a “traditional” and a “course-based” research experience yields positive outcomes for science undergraduate freshmen and shows potential for large-scale application . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 17 ( 4 ), ar53. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.17-11-0248 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sabel, J. L., Dauer, J. T., Forbes, C. T. (2017). Introductory biology students’ use of enhanced answer keys and reflection questions to engage in metacognition and enhance understanding . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 16 ( 3 ), ar40. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.16-10-0298 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sbeglia, G. C., Goodridge, J. A., Gordon, L. H., Nehm, R. H. (2021). Are faculty changing? How reform frameworks, sampling intensities, and instrument measures impact inferences about student-centered teaching practices . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 20 ( 3 ), ar39. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.20-11-0259 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwandt, T. A. (2000). Three epistemological stances for qualitative inquiry: Interpretivism, hermeneutics, and social constructionism . In Denzin, N. K., Lincoln, Y. S. (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 189–213). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sickel, A. J., Friedrichsen, P. (2013). Examining the evolution education literature with a focus on teachers: Major findings, goals for teacher preparation, and directions for future research . Evolution: Education and Outreach , 6 ( 1 ), 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1936-6434-6-23 [ Google Scholar ]
- Singer, S. R., Nielsen, N. R., Schweingruber, H. A. (2012). Discipline-based education research: Understanding and improving learning in undergraduate science and engineering . Washington, DC: National Academies Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Todd, A., Romine, W. L., Correa-Menendez, J. (2019). Modeling the transition from a phenotypic to genotypic conceptualization of genetics in a university-level introductory biology context . Research in Science Education , 49 ( 2 ), 569–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-017-9626-2 [ Google Scholar ]
- Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wenger, E. (1998). Communities of practice: Learning as a social system . Systems Thinker , 9 ( 5 ), 2–3. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ziadie, M. A., Andrews, T. C. (2018). Moving evolution education forward: A systematic analysis of literature to identify gaps in collective knowledge for teaching . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 17 ( 1 ), ar11. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.17-08-0190 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Open access
- Published: 15 February 2023
Literature review of stroke assessment for upper-extremity physical function via EEG, EMG, kinematic, and kinetic measurements and their reliability
- Rene M. Maura ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6023-9038 1 ,
- Sebastian Rueda Parra 4 ,
- Richard E. Stevens 2 ,
- Douglas L. Weeks 3 ,
- Eric T. Wolbrecht 1 &
- Joel C. Perry 1
Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation volume 20 , Article number: 21 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
5987 Accesses
15 Citations
Metrics details
Significant clinician training is required to mitigate the subjective nature and achieve useful reliability between measurement occasions and therapists. Previous research supports that robotic instruments can improve quantitative biomechanical assessments of the upper limb, offering reliable and more sensitive measures. Furthermore, combining kinematic and kinetic measurements with electrophysiological measurements offers new insights to unlock targeted impairment-specific therapy. This review presents common methods for analyzing biomechanical and neuromuscular data by describing their validity and reporting their reliability measures.
This paper reviews literature (2000–2021) on sensor-based measures and metrics for upper-limb biomechanical and electrophysiological (neurological) assessment, which have been shown to correlate with clinical test outcomes for motor assessment. The search terms targeted robotic and passive devices developed for movement therapy. Journal and conference papers on stroke assessment metrics were selected using PRISMA guidelines. Intra-class correlation values of some of the metrics are recorded, along with model, type of agreement, and confidence intervals, when reported.
A total of 60 articles are identified. The sensor-based metrics assess various aspects of movement performance, such as smoothness, spasticity, efficiency, planning, efficacy, accuracy, coordination, range of motion, and strength. Additional metrics assess abnormal activation patterns of cortical activity and interconnections between brain regions and muscle groups; aiming to characterize differences between the population who had a stroke and the healthy population.
Range of motion, mean speed, mean distance, normal path length, spectral arc length, number of peaks, and task time metrics have all demonstrated good to excellent reliability, as well as provide a finer resolution compared to discrete clinical assessment tests. EEG power features for multiple frequency bands of interest, specifically the bands relating to slow and fast frequencies comparing affected and non-affected hemispheres, demonstrate good to excellent reliability for populations at various stages of stroke recovery. Further investigation is needed to evaluate the metrics missing reliability information. In the few studies combining biomechanical measures with neuroelectric signals, the multi-domain approaches demonstrated agreement with clinical assessments and provide further information during the relearning phase. Combining the reliable sensor-based metrics in the clinical assessment process will provide a more objective approach, relying less on therapist expertise. This paper suggests future work on analyzing the reliability of metrics to prevent biasedness and selecting the appropriate analysis.
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and disability in developed countries. In the United States, a stroke occurs every 40 s, ranking stroke as the fifth leading cause of death and the first leading cause of disability in the country [ 1 ]. The high prevalence of stroke, coupled with increasing stroke survival rates, puts a growing strain on already limited healthcare resources; the cost of therapy is elevated [ 2 ] and restricted mostly to a clinical setting [ 3 ], leading to 50% of survivors that reach the chronic stage experiencing severe motor disability for upper extremities [ 4 ]. This highlights the need for refined (improved) assessment which can help pair person-specific impairment with appropriately targeted therapeutic strategies.
Rehabilitation typically starts with a battery of standardized tests to assess impairment and function. This initial evaluation serves as a baseline of movement capabilities and usually includes assessment of function during activities of daily living (ADL). Because these clinical assessments rely on trained therapists as raters, the scoring scale is designed to be discrete and, in some cases, bounded. While this improves the reliability of the metric [ 5 ] (i.e., raters more likely to agree), it also reduces the sensitivity of the scale. Furthermore, those assessment scales that are bounded, such as the Fugl-Meyer Assessment (FMA) [ 6 ], Ashworth or Modified Ashworth (MA) Scale [ 7 ], and Barthel Index [ 8 ], suffer from floor/ceiling effects where the limits of the scales become insensitive to the extremes of impairment and function. It is therefore important to develop new clinical assessment methods that are objective, quantifiable, reliable, and sensitive to change over the full range of function and impairment.
Over the last several decades, robotic devices have been designed and studied for administering post-stroke movement therapy. These devices have begun being adopted into clinical rehabilitation practice. More recently, researchers have proposed and studied the use of robotic devices to assess stroke-related impairments as an approach to overcome the limitations of existing clinical measures previously discussed [ 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Robots may be equipped with sensitive measurement devices that can be used to rate the person’s performance in a predefined task. These devices can include measuring kinematic (position/velocity), kinetic (force/torque), and/or neuromuscular (electromyography/electroencephalography) output from the subject during the task. Common sensor-based robotic metrics for post-stroke assessment included speed of response, planning time, movement planning, smoothness, efficiency, range, and efficacy [ 13 , 14 ]. Figure 1 demonstrates an example method for comprehensive assessment of a person who has suffered a stroke with data acquired during robotically administered tests. Furthermore, there is potential for new and more comprehensive knowledge to be gained from a wider array of assessment methods and metrics that combine the benefits of biomechanical (e.g., kinematic and kinetic) and neurological (e.g., electromyographic and electroencephalographic) measures [ 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 ].
Example of instrument for upper extremities bilateral biomechanical and neuromuscular assessment. From this data, a wide variety of measures and metrics for assessment of upper-extremity impairment and function may be reported
- Biomechanical assessment
Many classical methods of assessing impairment or function involve manual and/or instrumented quantification of performance through measures of motion (i.e., kinematic) and force (i.e., kinetic) capabilities. These classical methods rely on the training of the therapist to evaluate the capabilities of the person through keen observation (e.g., FMA [ 6 ] and MA [ 7 ]). The quality of kinematic and kinetic measures can be improved with the use of electronic-based measurements [ 23 ]. Robotic devices equipped with electronic sensors have the potential to improve the objectivity, sensitivity, and reliability of the assessment process by providing a means for more quantitative, precise, and accurate information [ 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ]. Usually, the electronic sensors on a rehabilitation robotic device are used for control purposes [ 29 , 30 , 31 ]. Robotics can also measure movement outputs, such as force or joint velocities, which the clinician may not be able to otherwise measure as accurately (or simultaneously) using existing clinical assessment methods [ 23 ]. With accurate and repeatable measurement of forces and joint velocities, sensor-based assessments have the potential to assess the person’s movement in an objective and quantifiable way. This article reviews validity and reliability of biomechanical metrics in relationship to assessment of motor function for upper extremities.
Electrophysiological features for assessment
Neural signals that originate from the body can be measured using non-invasive methods. Among others, electroencephalograms (EEG) measure cortical electrical activity, and electromyograms (EMG) measure muscle electrical activity. The relative low cost, as well as the noninvasive nature of these technologies make them suitable for studying changes in cortical or muscle activation caused by conditions or injuries of the brain, such as the ones elicited by stroke lesions [ 32 ].
Initially, EMG/EEG were used strictly as clinical diagnostic tools [ 33 , 34 ]. Recent improvements in signal acquisition hardware and computational processing methods have increased their use as viable instruments for understanding and treating neuromuscular diseases and neural conditions [ 32 ]. Features extracted from these signals are being researched to assess their relationship to motor and cognitive deficits [ 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 ] and delayed ischemia [ 34 , 43 ], as well as to identify different uses of the signals that could aid rehabilitation [ 44 ]. Applications of these features in the context of stroke include: (1) commanding robotic prostheses [ 45 , 46 ], exoskeletons [ 21 , 47 , 48 ], and brain-machine interfaces [ 44 , 49 , 50 , 51 ]; and (2) bedside monitoring for sub-acute patients and thrombolytic therapy [ 52 , 53 , 54 ]. Here we review the validity and reliability of metrics derived from electrophysiological signals in relationship to stroke motor assessment for upper extremity.
Reliability of metrics
Robotic or sensor-based assessment tools have not gained widespread clinical acceptance for stroke assessment. Numerous barriers to their clinical adoption remain, including demonstrating their reliability and providing sufficient validation of robotic metrics with respect to currently accepted assessment techniques [ 55 ]. In the assessment of motor function with sensor-based systems, several literature reviews reveal a wide spectrum of sensor-based metrics to use for stroke rehabilitation and demonstrate their validity [ 13 , 42 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 63 , 64 ]. However, in addition to demonstrating validity, new clinical assessments must also demonstrate good or excellent reliability in order to support their adoption in the clinical field. This is achieved by: (1) comparing multiple measurements on the same subject (test–retest reliability), and (2) checking agreement between multiple raters of the same subject (inter-rater reliability). Reliability quantifies an assessment’s ability to deliver scores that are free from measurement error [ 65 ]. Previous literature reviews have presented limited, if any, information on the reliability of the biomechanical robotic metrics. Murphy and Häger [ 66 ], Wang et al. [ 56 ], and Shishov et al. [ 67 ] reviewed reliability, but omitted some important aspects of intra-class correlation methods used in the study (e.g., the model type and/or the confidence interval), which are required when analyzing intra-class correlation methods for reliability [ 68 ]. If the reliability is not properly analyzed and reported, the study runs the risk of having a biased result. Murphy and Häger [ 66 ] also found a lack of studies determining the reliability of metrics in 2015. Since electronic-based assessments require the use of a therapist or an operator to administer the test, an inter-observer reliability test should be investigated to observe the effect of the test administrators on the assessment process. Therefore, both test–retest and inter-observer reliability in biomechanical and electrophysiological metrics are reviewed to provide updated information on the current findings of the metrics’ reliability.
Integrated metrics
Over the past 50 years, numerous examples of integrated metrics have provided valuable insight into the inner workings of human arm function. In the 1970s EMG was combined with kinematic data in patients with spasticity to understand muscle patterns during ballistic arm reach movements [ 69 ], the affects of pharmacological intervention on spastic stretch reflexes during passive vs. voluntary movement [ 70 ], and in the 1990s EMG was combined with kinetic data to understand the effects of abnormal synergy patterns on reach workspace when lifting the arm against gravity [ 71 ]. This work dispelled long-standing theories of muscular weakness and spasticity alone being the major contributors to arm impairment. More recently, quantified aspects of processed EEG and EMG signals are being combined with kinematic data to investigate the compensatory role, and relation to shoulder-related abnormal muscle synergies of the contralesional secondary sensorimotor cortex, in a group of chronic stroke survivors [ 72 ]. These and other works demonstrate convincingly the value of combined metrics and the insights they can uncover that isolated metrics cannot discover alone.
To provide further information on the stroke severity and the relearning process during stroke therapy, researchers are investigating a multi-modal approach using biomechanical and neuromuscular features [ 15 , 16 , 18 , 19 , 21 , 22 ]. Combining both neuromuscular and biomechanical metrics will provide a comprehensive assessment of the person’s movement starting from motor planning to the end of motor execution. Neuromuscular output provides valuable information on the feedforward control and the movement planning phase [ 22 ]. However, neuromuscular signals provides little information on the movement quality that is often investigated with movement function tests or biomechanical output [ 21 ]. Also, using neuromuscular data will provide information to therapist on the neurological status and nervous system reorganization of the person that biomechanical information cannot provide [ 73 ]. The additional information can assist in developing more personalized care for the person with stroke, as well as offer considerable information on the changes that occur at the physiological level.
Paper overview
This paper reviews published sensor-based methods, for biomechanical and neuromuscular assessment of impairment and function after neurological damage, and how the metrics resulting from the assessments, both alone and in combination, may be able to provide further information on the recovery process. Specifically, methods and metrics utilizing digitized kinematic, kinetic, EEG, and EMG data were considered. The “Methods” section explains how the literature review was performed. In “Measures and methods based on biomechanical performance” section, prevailing robotic assessment metrics are identified and categorized including smoothness, resistance, efficiency, accuracy, efficacy, planning, range-of-motion, strength, inter-joint coordination, and intra-joint coordination. In “Measures and methods based on neural activity using EEG/EMG” section, EEG- and EMG-derived measures are discussed by the primary category of analysis performed to obtain them, including frequency power and coherence analyses. The relationship of each method and metric to stroke impairment and/or function is also discussed. Section “Reliability of measures” discusses the reliability of sensor-based metrics and some of the complications in demonstrating the effectiveness of the metrics. Section “Integrated metrics” reviews previous studies on combining biomechanical and neuromuscular data to provide further information on the changes occurring during assessment and training. Finally, Section “Discussions and conclusions” concludes the paper with a discussion on the advantages of combining multi-domain data, which of the metrics from the earlier sections should be considered in future robotic applications, as well as the ones that still require more investigation for either validity and/or reliability.
A literature review was performed following PRISMA guidelines [ 74 ] on biomechanical and neuromuscular assessment in upper-limb stroke rehabilitation. The review was composed of two independent searches on (1) biomechanical robotic devices, and (2) electrophysiological digital signal processing. Figures 2 and 3 show the selection process of the electrophysiological and biomechanical papers, respectively. Each of these searches applied the following steps: In step 1, each researcher searched in Google Scholar for papers between 2000 and 2021 (see Table 1 for search terms and prompts). In step 2, resulting titles and abstracts were screened to remove duplicates, articles in other languages, and articles not related to the literature review. In step 3, researchers read the full texts of articles screened in step 2, papers qualifying for inclusion using the Literature Review Criteria in Table 1 were selected. Finally, in step 4, selected articles from independent review process were read by the other researcher. Uncertainties in determining if a paper should be included/excluded were discussed with the whole research group. Twenty-four papers focus on biomechanical measures (kinematic and kinetic), thirty-three focus on electrophysiological measures (EEG/EMG), and six papers on multimodal approaches combining biomechanical and neuromuscular measures to assess stroke. Three of the six multimodal papers are also reported in the biomechanical section and 3 papers were hand-picked. A total of 60 papers are reviewed and reported.
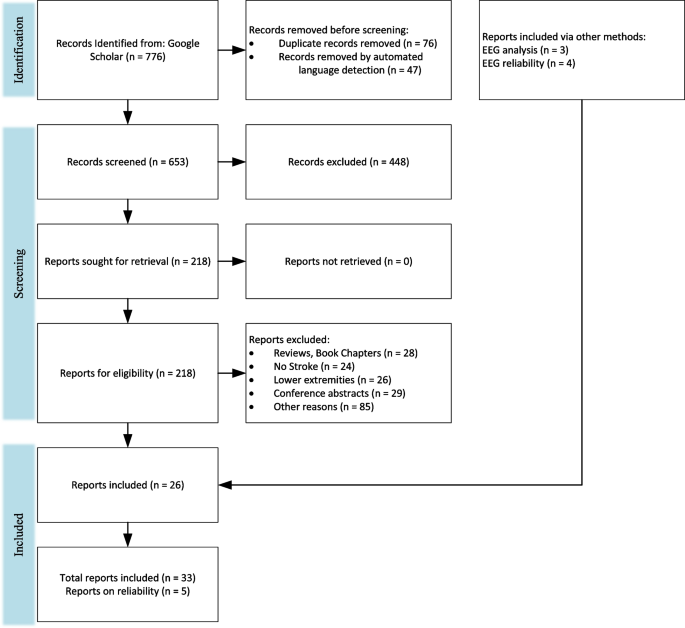
PRISMA flowchart on the selection for electrophysiological papers
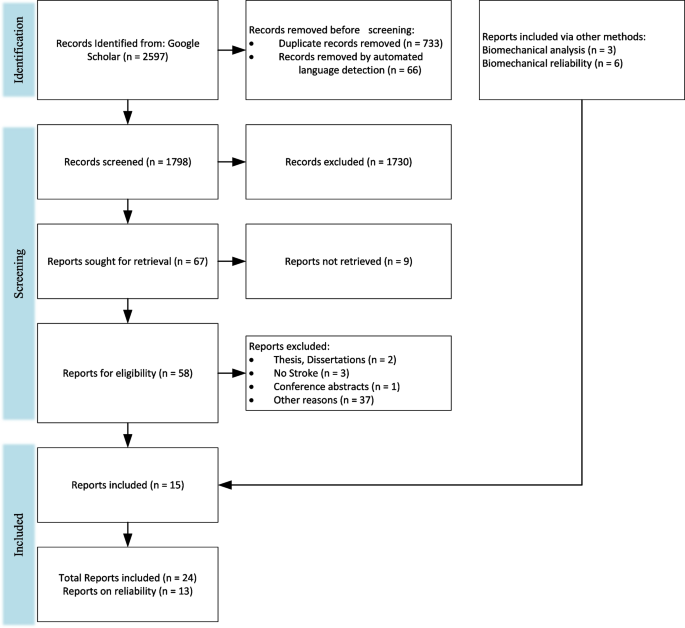
PRISMA flow chart for the selection for biomechanical papers
Measures and methods based on biomechanical performance
This review presents common robotic metrics which have been previously used to assess impairment and function after stroke. Twenty-five biomechanical papers are reviewed, which used both sensor-based and traditional clinical metrics to assess upper-extremity impairment and function. The five common metrics included in the reviewed studies measured the number of velocity peaks (~ 9 studies), path-length ratio (~ 8 studies), the max speed of the arm (~ 7 studies), active range of motion (~ 7 studies), and movement time (~ 7 studies). The metrics are often compared to an established clinical assessment to determine validity of the metric. The sensor-based metrics can be categorized by the aspect in which they evaluate movement quality similar to De Los Reyes-Guzmán et al.: smoothness, efficiency, efficacy, accuracy, coordination, or range of motion [ 14 ]. Resistance, Movement Planning, Coordination, and Strength are included as additional categories since some of the reviewed sensor-based metrics best evaluate those movement aspects. Examples of common evaluation activities and specific metrics that have been computed to quantify movement quality are outlined in Table 2 .
Lack of arm movement smoothness is a key indicator of underlying impairment [ 79 ]. Traditional therapist-administered assessments do not computationally measure smoothness leaving therapists unable to determine the degree to which disruption to movement smoothness is compromising motor function and, therefore, ADL. Most metrics that have been developed to quantify smoothness are based on features of the velocity profile of an arm movement, such as speed [ 80 , 81 ], speed arc length [ 79 ], local minima of velocity [ 10 ], velocity peaks [ 75 , 76 , 81 ], tent [ 80 ], spectral [ 25 ], spectral arc length [ 25 , 81 ], modified spectral arc length [ 79 ], and mean arrest period ratio [ 76 ]. Table 3 summarizes the smoothness metrics and their corresponding equations with equation numbers for reference. The speed metric is expressed as a ratio between the mean speed and the peak speed (Eq. 1). The speed arc length is the temporal length of the velocity profile (Eq. 2). Local minima of velocity and the velocity peaks metrics are measured by counting the number of minimum (Eq. 3) or maximum (Eq. 4) peaks in the velocity profile, respectively. The tent metric is a graphical approach that divides the area under the velocity curve by the area of a single peak velocity curve (Eq. 5). The spectral metric is the summation of the maximal Fourier transformed velocity vector (Eq. 6). The spectral arc-length metric is calculated from the frequency spectrum of the velocity profile by performing a fast Fourier transform operation and then computing the length (Eq. 7). The modified spectral arc length adapts the cutoff frequency according to a given threshold velocity and an upper-bound cutoff frequency (Eq. 8). The modified spectral arc length is then independent of temporal movement scaling. The mean arrest period ratio is the time portion that movement speed exceeds a given percentage of peak speed (Eq. 9).
Another commonly used approach is to analyze the jerk (i.e., the derivative of acceleration) profile. The common ways to assess smoothness using the jerk profile are root mean square jerk, mean rectified jerk, normalized jerk, and the logarithm of dimensionless jerk. The root mean square jerk takes the root-mean-square of the jerk that is then normalized by the movement duration [ 82 ] (Eq. 10). The mean rectified jerk (normalized mean absolute jerk) is the mean of the magnitude jerk normalized or divided by the peak velocity [ 80 , 82 ] (Eq. 11). The normalized jerk (dimensionless-squared jerk) is the square of the jerk times the duration of the movement to the fifth power over the length squared (Eq. 12). It is then integrated over the duration and square rooted. The normalized jerk can be normalized by mean speed, max speed, or mean jerk [ 80 ]. The logarithm of dimensionless jerk (Eq. 13) is the logarithm of normalized jerk defined in Eq. 12 [ 81 ].
It has yet to be determined which smoothness metric is more effective for characterizing recovery of smooth movement. According to Rohrer et al. [ 80 ], the metrics of speed, local minima of velocity, peaks, tent, and mean arrest period ratio showed increases in smoothness for inpatient recovery from stroke, but the mean rectified jerk metric seemed to show a decrease in smoothness as survivors of stroke recovered. Rohrer et al. warned that a low smoothness factor in jerk does not always mean the person is highly impaired. The spectral arc-length metric showed a consistent increase in smoothness as the number of sub-movements decreased [ 25 ], whereas the other metrics showed sudden changes in smoothness. For example, the mean arrest period ratio and the speed metric showed an increase in smoothness with two or more sub-movements, but when two sub-movements started to merge, the smoothness decreased. As a result, the spectral arc-length metric appears to capture change over a wider range of movement conditions in recovery in comparison to other metrics.
The presence of a velocity-dependent hyperactive stretch reflex is referred to as spasticity [ 83 ]. Spasticity results in a lack of smoothness during both passive and active movements and is more pronounced with activities that involve simultaneous shoulder abduction loading and extension of the elbow, wrist, or fingers [ 83 ], which are unfortunately quite common in ADL. A standard approach to assessing spasticity by a therapist involves moving a subject’s passive arm at different velocities and checking for the level of resistance. While this manual approach is subjective, electronic sensors have the potential to assess severity of spasticity in much more objective ways. Centen et al. report a method to assess the spasticity of the elbow using an upper-limb exoskeleton [ 84 ] involving the measurement of peak velocity, final angle, and creep. Sin et al., similarly performed a comparison study between a therapist moving the arm versus a robot moving the arm. An EMG sensor was used to detect the catch and compared with a torque sensor to detect catch angle for the robotic motion [ 85 ]. The robot moving the arm seemed to perform better with the inclusion of either an EMG or a torque sensor than with the therapist moving the arm and the robot simply recording the movement. A related measure that may be correlated with spasticity is the assessment of joint resistance torques during passive movement [ 76 ]. This can provide an assessment of the velocity-dependent resistance to movement that arises following stroke.
Efficiency measures movement fluency in terms of both task completion times and spatial trajectories. In point-to-point reaching, people who have suffered a stroke commonly display inefficient paths in comparison to their healthy side or compared to subjects who are unimpaired [ 10 ]. During the early phases of recovery after stroke, subjects may show slow overall movement speed resulting in longer task times. As recovery progresses, overall speed tends to increase and task times decrease, indicating more effective and efficient motor planning and path execution. Therapists usually observe the person’s efficiency in completing a task and then rate the person’s ability in completing a task in a timely manner. Therefore, both task time (or movement time) [ 10 , 76 , 77 , 86 , 87 ] and mean speed [ 25 , 75 , 77 , 81 , 86 ] are effective ways to assess temporal efficiency. Similar measures used by Wagner et al. include peak-hand velocity and time to peak-hand velocity [ 87 ]. To measure spatial efficiency of movement, both Colombo et al. [ 75 ], Mostafavi [ 77 ], and Germanotta [ 86 ] calculated the movement path length and divided it by the straight-line distance between the start and end points. This is known as the path-length ratio.
Movement planning
Movement planning is associated with feedforward sensorimotor control, elements that occur before the initial phase of movement. A common approach is to use reaction time to assess the duration of the planning phase. In a typical clinical assessment, a therapist can only observe/quantify whether movement can be initiated or not, but has no way to quantify the lag between the signal to initiate movement and initiation of movement. Keller et al., Frisoli et al., and Mostafavi et al. quantified the reaction time to assess movement planning [ 10 , 76 , 77 ] in subjects who have suffered a stroke. Mostafavi assessed movement planning in three additional ways by assessing characteristics of the actual movement: change in direction, movement distance ratio, and maximum speed ratio [ 77 ]. The change in direction is the angular deviation between the initial movement vector and the straight line between the start and end points. The first-movement-distance ratio is the ratio between the distance the hand traveled during the initial movement and the total distance between start and end points. The first-movement-maximum speed ratio is the ratio of the maximum hand speed during the initial phase of the movement divided by the global hand speed for the entire movement task.
Movement efficacy
Movement efficacy measures the person’s ability to achieve the desired task without assistance. While therapists can assess the number of completed repetitions, they have no means to kinetically quantify amount of assistance required to perform a given task. Movement efficacy is quantified by robot sensor systems that can measure: (a) person-generated movement, and/or (b) the amount of work performed by the robot to complete the movement (e.g., when voluntary person-generated movement fails to achieve a target). Hence, movement efficacy can involve both kinematic and kinetic measures. A kinematic metric that can be used to represent movement efficacy is the active movement index, which is calculated by dividing the portion of the distance the person is to complete by the total target distance for the task [ 75 ]. An example metric based on kinetic data is the amount of assistance metric, proposed by Balasubramanian et al. [ 25 ]. It is calculated by estimating the work performed by the robot to assist voluntary movement, and then dividing it by the work performed by the robot as if the person performs the task without assistance from the robot. A similar metric obtained by Germanotta et al. calculates the total work by using the movement’s path length, but Germanotta et al. also calculate the work generated towards the target [ 86 ].
Movement accuracy
Movement accuracy has been characterized by the error in the end-effector trajectory compared to a theoretical trajectory. It measures the person’s ability to follow a prescribed path, whereas movement efficiency assesses the person’s ability to find the most ideal path to reach a target. Colombo et al. measured movement accuracy in people after stroke by calculating the mean-absolute value of the distance, which is the mean absolute value of the distance between each point on the person’s path and the theoretical path [ 75 ]. Figure 4 demonstrates the difference between path-length ratio and mean-absolute value of the distance. The mean-absolute value of the distance computes the error between a desired trajectory and the actual, and the path-length ratio computes the total path length the person’s limb has traveled. Another similar metric is the average inter-quartile range, which quantifies the average “spread” among several trajectories [ 15 ]. Balasubramanian et al. characterized movement accuracy as a measure of the subject’s ability to achieve a target during active reaching. They refer to the metric as movement synergy [ 25 ], and calculate it by finding the distance between the end-effector’s final location and the target location.
Difference between path-length ratio and mean absolute value of the distance. A Path-length ratio. \(d_{ref}\) is the theoretical distance the hand should travel between the start and end point. \(d_{total}\) is the total distance the hand travelled from Start to End. B Mean absolute value of the distance. \(d_{i}\) is the distance between the theoretical path and the actual hand path
Intra-limb coordination
Intra-limb (inter-joint) coordination is a measure of the level of coordination achieved by individual joints of a limb or between multiple joints of the same limb (i.e., joint synergy) when performing a task. Since the upper limb consists of kinematic redundancies, the human arm can achieve a desired outcome in multiple ways. For example, a person might choose to move an atypical joint in order to compensate for a loss of mobility in another joint. Frisoli et al. and Bosecker et al. used the shoulder and elbow angle to find a linear correlation between the two angles in a movement task that required multi-joint movement [ 10 , 78 ]. In terms of clinical assessment, joint angle correlations can illustrate typical or atypical contribution of a joint while performing a multi-joint task.
Inter-limb coordination
Inter-limb coordination refers to a person’s ability to appropriately perform bilateral movements with affected and unaffected arms. Therapists observe the affected limb by often comparing to the unaffected limb during a matching task, such as position matching. Matching can either be accomplished with both limbs moving simultaneously or sequentially, and typically without the use of vision. Dukelow et al. used position matching to obtain measures of inter-limb coordination [ 24 ], including trial-to-trial variability, spatial contraction/expansion, and systematic shifts. Trial-to-trial variability is the standard deviation of the matching hand’s position for each location in the x (distal/proximal), y (anterior/posterior), and both in x and y in the transverse plane. Spatial contraction/expansion is the ratio of the 2D work area of the target hand to the 2D work area of the matching hand during a matching task. Systematic shifts were found by calculating the mean absolute position error between the target and matching hand for each target location.
Semrau et al. analyzed the performance of subjects in their ability to match their unaffected arm with the location of their affected arm [ 88 ]. In the experiment, a robot moved the affected arm to a position and the person then mirrored the position with the unaffected side. The researchers compared the data when the person was able to see the driven limb versus when they were unable to see the driven limb. The initial direction error, path length ratio, response latency, peak speed ratio, and their variabilities were calculated to assess the performance of the person’s ability to perform the task.
Range of motion
Range of motion is a measure of the extent of mobility in one or multiple joints. Traditionally, range of motion can be measured with the use of a goniometer [ 89 ]. The goniometer measures the individual joint range of motion, which takes considerable time. Range of motion can be expressed as a 1-DOF angular measure [ 76 , 89 ], a 2-DOF planar measure (i.e., work area) [ 82 ], or a 3-DOF spatial measure (i.e., workspace) [ 77 ]. Individual joints are commonly measured in joint space, whereas measures of area or volume are typically given in Cartesian space. In performing an assessment of work area or workspace with a robotic device, the measure can be estimated either by: (a) measuring individual joint angles with an exoskeleton device and then using these angles to compute the region swept out by the hand, or (b) directly measuring the hand or fingertips with a Cartesian (end-effector) device. The measurement of individual joint range of motion (ROM) as well as overall workspace have significant clinical importance in assessing both passive (pROM) and active (aROM) range of motion. To measure pROM, the robot drives arm movement while the person remains passive. The pROM is the maximum range of motion the person has with minimal or no pain. For aROM, a robot may place the arm in an initial position/orientation from which the person performs unassisted joint movements to determine the ROM of particular joints [ 76 ], or the area or volume swept by multiple joints. Lin et al. quantified the work area of the elbow and shoulder using potentiometers and derived test–retest reliability [ 89 ]. The potentiometer measurements were then compared to therapist measurements to determine validity.
Measures of strength evaluate a person’s ability to generate a force in a direction or a torque about a joint. Strength measurements may involve single or multiple joints. At the individual joint level, strength is typically measured from a predefined position of a person’s arm and/or hand. The person then applies a contraction to produce a torque at the assessed joint [ 76 , 78 ]. Multi-joint strength may also be measured by assessing strength and/or torque in various directions at distal locations along the arm, such as the hand. Lin et al. compared the grip strength obtained from load cells to a clinical method using precise weights, which showed excellent concurrent validity [ 89 ].
Measures and methods based on neural activity using EEG/EMG
Although much information can be captured and analyzed using the kinematic and kinetic measures listed above, their purview is limited. These measures provide insight into the functional outcomes of neurological system performance but provide limited perspective on potential contributing sources of measured impairment [ 90 ]. For a deeper look into the neuromuscular system, measures based on neurological activation are often pursued. As a complement to biomechanical measures, methods based on quantization of neural activity like EEG and EMG have been used to characterize the impact of stroke and its underlying mechanisms of impairments [ 91 , 92 ]. Over the past 20 years, numerous academic research studies have used these measures to explore the effects of stroke, therapeutic interventions, or time on the evolution of abnormal neural activity [ 91 ]. Groups with different levels of neurological health are commonly compared (e.g., chronic/acute/subacute stroke vs. non-impaired, or impairment level) or other specific experimental characteristics (e.g., different rehabilitation paradigms [ 93 , 94 ]). With this evidence, the validity of these metrics has been tested; however, the study of reliability of these metrics is needed to complete the jump from academic to clinical settings.
Extracting biomarkers from non-invasive neural activity requires careful decomposition and processing of raw EEG and EMG recordings [ 32 ]. Various methods have been used, and the results have produced a growing body of evidence for the validity of these biomarkers in providing insight on the current and future state of motor, cognitive, and language skills in people after stroke [ 38 , 95 ]. Some of the biomarkers derived from EEG signals include: power-related band-specific information [ 34 , 35 , 43 , 47 , 53 , 54 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 ], band frequency event-related synchronization and desynchronization (ERS/ERD) [ 22 , 51 , 102 , 103 ], intra-cortical coherence or functional connectivity [ 39 , 59 , 73 , 94 , 104 , 105 , 106 , 107 , 108 , 109 ], corticomuscular coherence (CMC) [ 37 , 110 , 111 , 112 , 113 ], among others [ 114 , 115 ]. Biomarkers extracted from EEG can be used to assess residual functional ability [ 38 , 54 , 73 , 97 , 98 , 99 ], derive prognostic indicators [ 34 , 43 , 104 ], or categorize people into groups (e.g., to better match impairments with therapeutic strategies) [ 39 , 47 , 58 , 116 ].
In the following subsections, valid biomarkers derived mostly from EEG signal features (relationship with motor outcome for a person after stroke) will be discussed and introduced theoretically. Distinctions will be made about the stage after stroke when signals were taken. Findings are reported from 33 studies that have examined the relationship between extracted neural features and motor function for different groups of people after stroke. These records are grouped by quantization methods used including approaches based on measures of frequency spectrum power (n = 9), inter-regional coherence (n = 10 for cortical coherence and n = 9 for CMC), and reliability (n = 5).
Frequency spectrum power
Power measures the amount of activity within a signal that occurs at a specific frequency or range of frequencies. Power can be computed in absolute or relative terms (i.e., with respect to other signals). It is often displayed as a power density spectrum where the magnitudes of signal power can be seen across a range of frequencies. In electro-cognitive research, the representation of power within specific frequency bands has been useful to explain brain activity and to characterize abnormal oscillatory activity due to regional neurological damage [ 32 , 117 ].
Frequency bands in EEG content
Electrical activity in the brain is dominated primarily by frequencies from 0–100 Hz where different frequency bands correspond with different states of activity: Delta (0–4 Hz) is associated with deep sleep, Theta (4–8 Hz) with drowsiness, Alpha (8–13 Hz) with relaxed alertness and important motor activity [ 117 ], and Beta (13–31 Hz) with focused alertness. Gamma waves (> 32 Hz) are also seen in EEG activity; however, their specific relationship to level of alertness or consciousness is still debated [ 32 , 117 ]. Important cognitive tasks have been found to trigger activity in these bands in different ways. Levels of both Alpha and Delta activity have also been shown to be affected by stroke and can therefore be examined as indicators of prognosis or impairment in sub-acute and chronic stroke [ 52 , 100 , 118 ].
Power in acute and sub-acute stroke
For individuals in the early post-stroke (i.e., sub-acute) phase, abnormal power levels can be an indicator of neurological damage [ 98 ]. Attenuation of activity in Alpha and Beta bands have been observed in the first hours after stroke [ 100 ] preceding the appearance of abnormally high Delta activity. Tolonen et al. reported a high correlation between Delta power and regional Cerebral Blood Flow (rCBF). This relationship appears during the sub-acute stroke phase and has been used to predict clinical, cognitive, and functional outcomes [ 119 ]. Delta activity has also been shown to positively correlate with 1-month National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) [ 52 ] and 3-month Rankin scale [ 36 ] assessments.
Based on these findings, several QEEG (Quantitative Electroencephalography) metrics involving ratios of abnormal slow (Delta) and abnormal fast (Alpha and Beta) activity have been developed. The Delta-Alpha Ratio (DAR), Delta-Theta Ratio (DTR), and (Delta + Theta)/(Alpha + Beta) Ratio (DTABR also known as PRI for Power Ratio Index) relate amount of abnormal slow activity with the activity from faster bands and have been shown to provide valuable insight into prognosis of stroke outcome and thrombolytic therapy monitoring [ 98 ]. Increased DAR and DTABR have been repeatedly found to be the QEEG indices that best predict worse outcome for the following: comparing with the Functional Independence Measure and Functional Assessment Measure (FIM-FAM) at 105 days [ 53 ], Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCa) at 90 days [ 54 ], NIHSS at 1 month [ 35 ], modified ranking scale (mRS) at 6 months [ 105 ], NIHSS evolution at multiple times [ 120 ], and NIHSS at 12 months [ 96 ]. DAR was also used to classify people in the acute phase and healthy subjects with an accuracy of 100% [ 58 ].
The ability of basic EEG monitoring to derive useful metrics during the early stage of stroke has made EEG collection desirable for people who have suffered a stroke in intensive care settings. The derived QEEG indices have proven to be helpful to determine Delayed Cerebral Ischemia (DCI), increased DAR [ 43 ], and increased Delta power [ 34 , 118 ]. However, finding the electrode montage with the least number of electrodes that still reveals the necessary information for prognoses is one of the biggest challenges for this particular use of EEG. Comparing DAR from 19 electrodes on the scalp with 4 electrodes on the frontal cortex suggests that DAR from 4 frontal electrodes may be enough to detect early cognitive and functional deficits [ 53 ]. Studies explored the possibility of a single-electrode montage over the Fronto-Parietal area (FP1); the DAR and DTR from this electrode might be a valid predictor of cognitive function after stroke when correlated with the MoCA [ 54 ], relative power in Theta band correlated with mRS and modified Barthel Index (mBI) 30 and 90 days after stroke [ 121 ].
Power in chronic stroke
The role of power-related QEEG indices during chronic stroke and progression of motor functional performance have been examined with respect to rehabilitation therapies, since participants have recovered their motion to a certain degree [ 4 ]. Studies have shown that therapy and functional activity improvements correlate with changes of the shape and delay of event-related desynchronization and synchronization (ERD-ERS) for time–frequency power features when analyzing Alpha and Beta bands on the primary motor cortex for ipsilesional and contralesional hemispheres [ 21 , 22 , 122 ]. Therapies with better outcome tend to have reduced Delta rhythms and increased Alpha rhythms [ 122 ].
Bertolucci [ 47 ] compared starting power spectrum density in different bands for both hemispheres with changes in WMFT and FMA over time. Increased global Alpha and Beta activity was shown to correlate with better WMFT evolution while, increase in contralesional Beta activity was shown to be correlated with FMA evolution. Metrics combining slow and fast activity have also been tested in the chronic stage of stroke, significant negative correlation between DTABR (PRI) at the start of therapy was related to FMA change during robotic therapy [ 99 ]. This finding suggests that DTABR may have promise as prognostic indicators for all stages of stroke.
Brain Symmetry Index (BSI) is a generalized measure of “left to right” (affected to non-affected) power symmetry of mean spectral power per hemisphere. These inter-hemispheric relationships of power have been used as prognostic measures during all stages of stroke. Baseline BSI (during the sub-acute stage) was found to correlate with the FMA at 2 months [ 73 ], mRS at 6 months [ 123 ], and FM-UE predictor when using only theta band BSI for patients in the chronic stage [ 124 ]. BSI can be modified to account for the direction of asymmetry, the directed BSI at Delta and Theta bands proved meaningful to describe evolution from acute to chronic stages of upper limb impairment as measured by FM-UE [ 120 , 125 ]. Table 4 and Table 11 in Appendix 1 communicate power-derived metrics across different stages of stroke documented in this section and their main reported relationships with motor function. Findings are often reported in terms of correlation with clinical tests of motor function.
Brain connectivity (cortical coherence)
Brain connectivity is a measure of interaction and synchronization between distributed networks of the brain and allows for a clearer understanding of brain function. Although cortical damage from ischemic stroke is focal, cortical coherence can explain abnormalities in functionality of remote zones that share functional connections to the stroke-affected zone [ 59 ].
Several estimators of connectivity have been proposed in the literature. Coherency, partial coherence (pCoh) [ 125 ], multiple coherence (mCoh), imaginary part of coherence (iCoh) [ 126 ], Phase Lagged Index (PLI), weighted Phase Lagged Index (wPLI) [ 127 ], and simple ratios of power at certain frequency bands [ 73 ] describe synchronic symmetric activity between ROIs and are referred to as non-directed or functional connectivity [ 128 ]. Estimators based on Granger’s prediction such as partial directed coherence (PDC) [ 129 , 130 , 131 ], or directed transfer Function (DTF) [ 132 , 133 ] and any of their normalizations describe causal relationships between variables and are referred to as directed or effective connectivity [ 134 ]. Connectivity also allows the analysis of brain activity as network topologies, borrowing methods from graph theory [ 32 , 134 ]. Network features such as complexity, linearity, efficiency, clustering, path length, node hubs, and more can be derived from graphs [ 128 ]. Comparisons of these network features among groups with impairment and healthy controls have proven to be interesting tools to understand and characterize motor and functional deficits after stroke [ 108 ].
Studies have used intra- and inter-cortical coherence to expand the clinical understanding of the neural reorganization process [ 59 , 106 , 107 , 108 , 109 ], as a clinical motor and cognitive predictor [ 38 , 94 , 104 , 135 , 136 ], and as a tool to predict the efficacy of rehabilitation therapy [ 94 ]. Table 5 and Table 12 in Appendix 2 briefly summarize the main metrics discussed in this section and their results that are related with motor function assessment. In general, studies have shown that motor deficits in stroke survivors are related to less connectivity to main sensory motor areas [ 38 , 94 , 104 , 137 ], weak interhemispheric sensorimotor connectivity [ 109 , 138 ], less efficient networks [ 106 , 135 ], with less “small world” network patterns [ 108 , 134 ] (small-world networks are optimized to integrate specialized processes in the whole network and are known as an important feature of healthy brain networks).
Survivors of stroke tend to exhibit more modular (i.e., more clustered, less integrated) and less efficient networks than non-impaired controls with the biggest difference occurring in the Beta and Gamma bands [ 106 ]. Modular networks are less “small-world” [ 134 ]; small-world networks are optimized to integrate specialized processes in the whole network and are known as an important feature of healthy brain networks. Such a transition to a less small-world network was observed during the acute stage of stroke (first hours after stroke) and documented to be bilaterally decreased in the Delta band and bilaterally increased in the high Alpha band (also known as Alpha2: 10.5–13 Hz) [ 108 ].
Global connectivity with the ipsilesional primary motor cortex (M1) is the most researched biomarker derived from connectivity and has been studied in longitudinal experiments as a plasticity indicator leading to future outcome improvement [ 38 ], motor and therapy gains [ 94 ], upper limb gains during the sub-acute stage [ 137 ], and as a feature that characterizes stroke survivors’ cognitive deficits [ 104 ]. Pietro [ 38 ] used iCoh to test the weighted node degree (WND), a measure that quantifies the importance of a ROI in the brain, for M1 and reported that Beta-band features are linearly related with motor improvement as measured by FM-UE and Nine-Hole-Peg Test. Beta-band connectivity to ipsilesional M1, as measured by spectral coherence, can be used as a therapy outcome predictor, and more than that, results point heavily toward connectivity between M1 and ipsilesional frontal premotor area (PM) to be the most important variable as a therapy gain predictor; predictions can be further improved by using lesion-related information such as CST or MRI to yield more accurate results [ 94 ]. Comparisons between groups of people with impairment and controls showed significant differences on Alpha connectivity involving ipsilesional M1, this value showed a relation with FMA 3 months for the group with impairment due to stroke [ 104 ].
The relationship between interhemispheric ROI connectivity and motor impairment has been studied. The normalized interhemispheric strength (nIHS) from PDC was used to quantify the coupling between structures in the brain, Beta- and lower Gamma-band features of this quantity in sensorimotor areas exhibited linear relationships with the degree of motor impairment measured by CST [ 136 ]. A similar measure, also derived from PDC used to measure ROI interhemispheric importance named EEG-PDC was used in [ 109 ]; here the results show that Mu-band (10–12 Hz) and Beta-band features could be used to explain results for hand motor function from FM-UE. In another study, Beta debiased weighted phase lag index (dwPLI), correlated with outcome measured by Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) and FM-UE [ 138 ].
Global and local network efficiency for Beta and Gamma bands seem to be significantly decreased in the population who suffered from a stroke compared to healthy controls as reported in [ 106 ]. Newer results, such as the ones pointed out by [ 135 ] found statistically significant relationships between Beta network efficiency, network intradensity derived using a non-parametric method (named Generalized Measure of Association), and functional recovery results given by FM-UE. Global maximal coherence features in the Alpha band have been recently recognized as FM-UE predictors, where coherence was computed using PLI and related to motor outcome by means of linear regression [ 139 ].
Corticomuscular coherence
Corticomuscular coherence (CMC) is a measure of the amount of synchronous activity between signals in the brain (i.e., EEG or MEG) and associated musculature (i.e., EMG) of the body [ 92 ]. Typically measured during voluntary contractions [ 110 ], the presence of coherence demonstrates a direct relationship between cortical rhythms in the efferent motor commands and the discharge of neurons in the motor cortex [ 140 ]. CMC is computed as correlation between EEG and EMG signals at a given frequency. Early CMC research found synchronous (correlated) activity in Beta and low Gamma bands [ 40 , 41 , 42 ]. CMC is strongest in the contralateral motor cortex [ 141 ]. This metric seems to be affected by stroke-related lesions, and thus provides an interesting tool to assess motor recovery [ 111 , 142 , 143 , 144 ]. The level of CMC is lower in the chronic stage of stroke than in healthy subjects [ 112 , 145 ], with chronic stroke survivors showing lower peak CMC frequency [ 146 ], and topographical patterns that are more widespread than in healthy people; highlighting a connection to muscle synergies [ 142 , 147 , 148 ]. CMC has been shown to increase with training [ 37 , 112 , 144 ].
Corticomuscular coherence has been proposed as a tool to: (a) identify the functional contribution of reorganized cortical areas to motor recovery [ 37 , 112 , 141 , 144 , 146 ]; (b) understand functional remapping [ 93 , 142 , 145 ]; and (c) study the mechanisms underlying synergies [ 147 , 148 ]. CMC has shown increased abnormal correlation with deltoid EMG during elbow flexion for people who have motor impairment [ 147 ], and the best muscles to target with rehabilitative interventions [ 148 ]. Changes in CMC have been shown to correlate with motor improvement for different stages of stroke, although follow-up scores based on CMC have not shown statistically significant correlations when compared to clinical metrics [ 37 , 93 ]. Results summarizing CMC on stroke can be found in Table 6 and Table 13 in Appendix 3.
Reliability of measures
Each of the aforementioned measures have the potential to be integrated into robotic devices for upper-limb assessment. However, to improve the clinical acceptability of robotic-assisted assessment, the measurements and derived metrics must meet reliability standards in a clinical setting [ 55 ]. Reliability can be defined as the degree of consistency between measurements or the degree to which a measurement is free of error. A common method to represent the relative reliability of a measurement process is the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) [ 150 ]. Koo and Li suggest a guideline on reporting ICC values for reliability that includes the ICC value, analysis model (one-way random effects, two-way random effects, two-way fixed effects, or two-way mixed effects), the model type per Shrout and Fleiss (individual trials or mean of k trials), model definition (absolute agreement or consistency), and confidence interval [ 68 ]. Koo and Li also provide a flowchart in selecting the appropriate ICC based on the type of reliability and rater information. An ICC value below 0.5 indicates poor reliability, 0.5 to 0.75 moderate reliability, 0.75 to 0.9 good reliability, and above 0.9 excellent reliability. The reviewed papers will be evaluated based on these guidelines. For reporting the ICC, the Shrout and Fleiss convention is used [ 68 ]. The chosen reliability studies are included in the tables if the chosen ICC model, type, definition, and confidence interval are identifiable, and the metrics have previously been used in electronic-based metrics. For studies that report multiple ICC scores due to assessment of test–retest reliability for multiple raters, the lowest ICC reported is included to avoid bias in the reported results.
In the assessment of reliability of data from robotic sensors, common ways to assess reliability are to correlate multiple measurements in a single session (intra-session) and correlate multiple measurements between different sessions (inter-session) measurements (i.e., test–retest reliability) [ 151 ]. Checking for test–retest reliability determines the repeatability of the robotic metric. The repeatability is the ability to reproduce the same measurements under the same conditions. Table 7 shows the test–retest reliability of several robotic metrics. For metrics checking for test–retest reliability, a two-way mixed-effects model with either single or multiple measurements may be used [ 68 ]. Since the same set of sensors will be used to assess subjects, the two-way mixed model is used. The test–retest reliability should be checking for absolute agreement. Checking for absolute agreement (y = x) rather than consistency (y = x + b) determines the reliability without a bias or systematic error. For example, in Fig. 5 , for a two-way random effect with a single measurement checking for agreement gives a score of 0.18. When checking for consistency, the ICC score reaches to 1.00. In other words, the bias has no effect on the ICC score when checking for consistency. Therefore, when performing test–retest reliability, it is important to check for absolute agreement to prevent bias in the test–retest result.
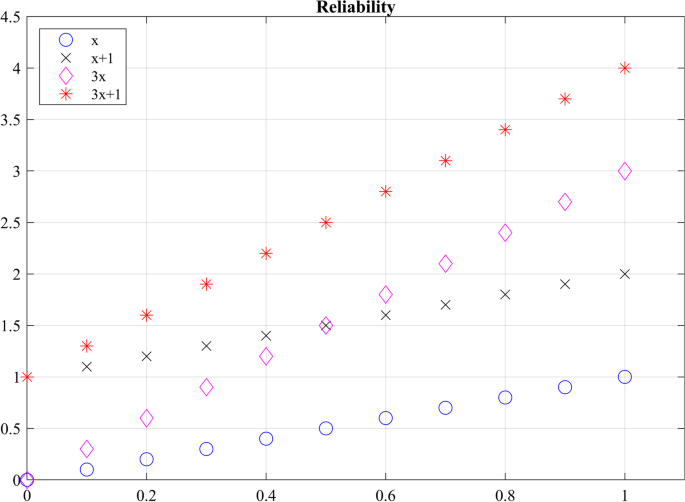
Checking agreement versus consistency among ratings. For y = x, the absolute ICC score is 1 and the consistency ICC score is 1.00. For y = x + 1, the agreement ICC score is 0.18 and the consistency ICC score is 1.00. For y = 3x, the absolute ICC score is 0.32 and the consistency ICC score is 0.60. For y = 3x + 1, the absolute ICC score is 0.13 and the consistency ICC score is 0.60
Not only should a robotic metric demonstrate repeatability, it should also be reproducible when different operators are using the same device. Reproducibility evaluates the change in measurements when conditions have changed. Inter-rater reliability tests have been performed to determine the effect raters have when collecting measurements when two or more raters perform the same experimental protocol [ 68 ]. To prevent a biased result, raters should have no knowledge of the evaluations given by other raters, ensuring that raters’ measurements are independent from one another. Table 8 shows the reproducibility of several robotic biomechanical metrics. All the included studies have used two raters to check for reproducibility. The researchers performed a two-way random effects analysis with either a single measurement or multiple measurements to check for agreement.
Measurement reliability of robotic biomechanical assessment
Of the 24 papers reviewed for biomechanical metrics, 13 papers reported on reliability. 6 papers reported reproducibility and 9 papers reported on repeatability. Overall, the metrics seem to demonstrate good to moderate reliability for both repeatability and reproducibility. However, caution should be exercised in determining which robotic metric is more effective in assessing movement quality based on reliability studies. The quality of measurements is highly dependent on the quality of the robotic device and sensors [ 85 ]. Having a completely transparent robot with a sensitive and accurate sensor will further improve assessment of reliability. Also, the researchers have used different versions of the ICC, as seen in Tables 7 and 8 , which complicates direct comparisons of the metrics.
Reliability of electrophysiological signal features
Of the 33 papers reviewed for electrophysiological metrics, 5 papers reported on reliability. 6 papers reported on repeatability. Convenience of acquiring electrophysiological signals non-invasively is relatively new. Metrics for assessment of upper limb motor impairment in stroke, derived from these signals have shown to be valid in academic settings, but most of these valid metrics have yet to be tested for intra- and inter-session reliability to be used in clinical and rehabilitation settings. Few studies found as a result of our systematic search have looked at test–retest reliability of these metrics. Therefore, we found and manually added records reporting on intra- and inter-session reliability on metrics based on electrophysiological features described in section “Measures and methods based on neural activity using EEG/EMG”, even if reliability was not assessed on people with stroke. Relevant results are illustrated in Table 9 .
Spectral power features of EEG signals have been tested during rest [ 153 , 154 ] and task (cognitive and motor) conditions for different cohorts of subjects [ 102 , 103 ]. Some of the spectral features observed during these experiments are related to timed behavior of oscillatory activity due to cued experiments, such as event-related desynchronization of the Beta band (ERD and Beta rebound) [ 102 ] and topographical patterns of Alpha activity R = 0.9302, p < 0.001 [ 103 ].
Test–retest reliability for rest EEG functional connectivity has been explored for few of the estimators listed in section “Measures and methods based on neural activity using EEG/EMG”: (1) for a cohort of people with Alzheimer by means of the amplitude envelope correlation (AEC), phase lag index (PLI) and weighted phase lag index (wPLI) [ 155 ]; (2) in healthy subjects using iCoh and PLI [ 156 ]; and (3) in infants, by studying differences of inter-session PLI graph metrics such as path length, cluster coefficient, and network “small-worldness” [ 60 ]. Reliability for upper limb CMC has not yet been documented (at least to our knowledge). However, an experiment involving testing reliability of CMC for gait reports low CMC reliability in groups with different ages [ 61 ].
EEG and EMG measurements could be combined with kinematic and kinetic measurements to provide additional information about the severity of impairment and decrease the number of false positives from individual measurements [ 21 ]. This could further be used to explain abnormal relationships between brain activation, muscle activation and movement kinematics, as well as provide insight about subject motor performance during therapy [ 15 ]. The availability of EEG and EMG measures can also enhance aspects of biofeedback given during tests or be used to complement other assessments to provide a more holistic picture of an individual’s neurological function.
It has been shown that combining EEG, EMG, and kinematic data using a multi-domain approach can produce correlations to traditional clinical assessments, a summary of some of the reviewed studies is presented in Table 10 . Belfatto et al. have assessed people’s ROM for shoulder and elbow flexion, task time, and computed jerk to measure people’s smoothness, while the EMG was used to measure muscle synergies, and EEG detected ERD and a lateralization coefficient [ 21 ]. Comani et al. used task time, path length, normalized jerk, and speed to measure motor performance while observing ERD and ERS during motor training [ 22 ]. Pierella et al. gathered kinematic data from an upper-limb exoskeleton, which assessed the mean tangential velocity, path-length ratio, the number of speed peaks, spectral arc length, the amount of assistance, task time, and percentage of workspace, while observing EEG and EMG activity [ 18 ]. Mazzoleni et al. used the InMotion2 robot system to capture the movement accuracy, movement efficiency, mean speed, and the number of velocity peaks, while measuring brain activity with EEG [ 16 ]. However, further research is necessary to determine the effectiveness of the chosen metrics and methods compared to other more promising methods to assess function. Furthermore, greater consensus in literature is needed to support the clinical use of more reliable metrics. For example, newer algorithms to estimate smoothness such as spectral arc length have been shown to provide greater validity and reliability than the commonly used normalized jerk metric. Despite this evidence, normalized jerk remains a widely accepted measure of movement smoothness.
Discussions and conclusions
In this paper we reviewed studies that used different sensor-acquired biomechanical and electrophysiological signals to derive metrics related to neuromuscular impairment for stroke survivors; such metrics are of interest for robotic therapy and assessment applications. To assess the ability of a given measure to relate with impairment or motor outcome, we looked for metrics where results have been demonstrated to correlate or predict scores from established clinical assessment metrics for impairment and function (validity). Knowing that a metric has some relationship with impairment and function (i.e., that it is valid) is not enough for it to be used in clinical settings if those results are not repeatable (reliable). Thus, we also reviewed the reliability of metrics and related signal features looking for metrics which produce similar results for the same subject during different test sessions and for different raters. With this information, researchers can aim to use metrics that not only seem to be related with stroke, but also can be trusted, with less bias, and with a simpler interpretation. The main conclusions of this review paper are presented as answers to the following research questions.
Which biomechanical-based metrics show promise for valid assessment of function and impairment?
Metrics derived from kinematic (e.g., position & velocity) and kinetic (e.g., force & torque) sensors affixed to robotic and passive mechanical devices have successfully been used to measure biomechanical aspects of upper-extremity function and impairment in people after stroke. The five common metrics included in the reviewed studies measured the number of velocity peaks (~ 9 studies), path-length ratio (~ 8 studies), the maximum speed of the arm (~ 7 studies), active range of motion (~ 7 studies), and movement time (~ 7 studies). The metrics are often compared to an established clinical assessment to determine validity of the metric. According to the review study by Murphy and Häger, the Fugl-Meyer Assessment for Upper Extremity had significant correlation with movement time, movement smoothness, peak velocity, elbow extension, and shoulder flexion [ 66 ]. The movement time and smoothness showed strong correlation with the Action Research Arm Test, whereas speed, path-length ratio, and end-point error showed moderate correlation. Tran et al. reviewed specifically validation of robotic metrics with clinical assessments [ 57 ]. The review found mean speed, number of peak velocities, movement accuracy, and movement duration to be most promising metrics based on validation with clinical assessments. However, the review mentioned that some studies seem to conflict on the correlation between the robotic metric and clinical measures, which could be due to assessment task, subject characteristics, type of intervention, and robotic device. For further information about the validation of sensor-based metrics, please refer to the previously mentioned literature reviews [ 57 , 66 ].
Which biomechanical-based metrics show promise for repeatable assessment?
Repeatable measures, in which measurement taken by a single instrument and/or person produce low variation within a single task, are a critical requirement for assessment of impairment and function. The biomechanical based metrics that show the most promise for repeatability are range of motion, mean speed, mean distance, normal path length, spectral arc length, number of peaks, and task time. Two or more studies used these metrics and demonstrated good and excellent reliability, which implies the metric is robust against measurement noise and/or disturbances. Since the metrics have been used on different measuring instruments, the sensors’ resolution and signal-to-noise ratio appear to have a minimal impact on the reliability. However, more investigation is needed to confirm this robustness. In lieu of more evidence, it is recommended that investigators choose sensors similar or superior in quality to those used in the measuring devices presented in Tables 7 and 8 to achieve the same level of reliability.
What aspects of biomechanical-based metrics lack evidence or require more investigation?
Although many metrics (see previous section) demonstrate good or excellent repeatability across multiple studies, the evidence for reproducibility is limited to single studies. When developing a novel device capable of robotic assistance and assessment, researchers have typically focused their efforts to create a device capable of repeatable and reliable measurements. However, since the person administering the test is using the device to measure the subject’s performance, the reproducibility of the metric must also be considered. The reproducibility of a metric is affected by the ease-of-use of the device; if the device is too complicated to setup and use, there is an increased probability that different operators will observe different measurements. Also, the operator’s instructions to the subject affects the reproducibility, especially in the initial sessions, which may lead to different learning effects, and different assessment results. More studies are needed across multiple sites and operators to determine the reproducibility of the biomechanical metrics reviewed in this paper.
Which neural activity-based metrics (EEG & EMG) show the most promise for reliable assessment?
Electrical neurological signals such as EEG and EMG have successfully been used to understand changes in motor performance and outcome variability across all stages of post-stroke recovery including the first few hours after onset. Experimental results have shown that metrics derived from slow frequency power (delta power, relative delta power, and theta power), and power ratio between slow and fast EEG frequency bands like DAR and DTABR convey useful information both about current and future motor capabilities, as presented in Table 4 and Table 11 in Appendix 1. Multimodal studies using robotic tools for assessment of motor performance have expanded the study of power signal features in people who suffered a stroke in the chronic recovery stage by studying not only rest EEG activity but also task-related activity [ 19 , 21 , 122 ]; ERD-ERS features like amplitude and latency along with biomechanical measures have been shown to correlate with clinical measures of motor performance and to predict a person’s response to movement therapies. EEG power features in general have been found to have good to excellent reliability for test–retest conditions among different populations, across all frequency bands of interest (see Table 9 ).
Functional connectivity (i.e., non-directed connectivity) expands the investigative capacity of EEG measurements, enabling analyzing the brain as a network system by investigating the interactions between regions of interest in the brain while resting or during movement tasks. Inter-hemispheric interactions (interactions between the same ROI in both hemispheres) and global interactions (interactions between the entire brain and an ROI) reported as power or graph indices in Beta and Gamma bands have fruitfully been used to explain motor outcome scores. Although results seem promising, connectivity reliability is still debated with results ranging mostly between moderate to good reliability only for a few connectivity estimators ( PLI, wPLI and iCoh ).
Which neural activity-based metrics (EEG and EMG) lack evidence or require more investigation?
EEG and EMG provide useful non-invasive insight into the human neuromuscular system allowing researchers to make conjectures about its function and structure; however, interpretation of results based on these measures solely must be carefully analyzed within the frame of experimental conditions. Overall, the field needs more studies involving cohorts of stroke survivors to determine the reliability (test–retest) of metrics derived from EEG and EMG signal features that have already shown validity in academic studies.
Metrics calculated from power imbalance between interhemispheric activity like BSI , pwBSI and PRI [ 62 , 73 , 124 ] are a great premise to measure how the brain relies on foreign regions to accomplish tasks related with affected areas. A battery of diverse estimators for connectivity, especially those of effective (directed) connectivity, open the door to investigations into the relationship between abnormal communication of regions of interest and impairment (see Table 5 and Table 12 in Appendix 2). These metrics, although valid have yet to be tested in terms of reliability in clinical use. Reliability for connectivity metrics should specify which estimator was used to derive the metric.
CMC is another exciting neural-activity-based metric lacking sufficient evidence to support its significance. CMC considers and bridges two of the most affected domains for motor execution in neuromuscular system, making it a good candidate for robotic-based therapy and assessment of survivors of stroke [ 147 ]. Although features in the Beta and Gamma bands seem to be related to motor impairment, there is still not agreement about which one is most closely related to motor outcomes. Studies reviewed in this paper considered cortical spatial patterns of maximum coherence, peak frequency shift when compared to healthy controls, latency for peak coherence, among others (see Table 6 and Table 13 in Appendix 3). However, when comparing to motor outcomes, results are not always significant, and test–retest reliability for this metric is yet (to our knowledge) to be documented for the upper extremity (see [ 61 ] for a lower-extremity study).
What standards should be adopted for reporting biomechanical and neural activity-based metrics and their reliability?
For metrics to be accepted as reliable in the clinical field, researchers are asked to follow the guidelines presented in Koo and Li [ 68 ], which provide guidance on which ICC model to use depending on the type of reliability study and what should be reported (e.g., the software they used to compute the ICC and confidence interval). In the papers reviewed, some investigated the learning effects of the assessment task and checked for consistency rather than agreement (see Table 7 ). However, the learning effects should be minimal in a clinical setting between each session, and potential effects should be taken into consideration during protocol design; common practices to minimize the implications of learning effects is to allow practice runs by the patients [ 99 , 122 ] and to remove the first experimental runs [ 81 , 85 ]. By removing this information, signal analysis focuses performance of learned tasks with similar associated behaviors. Therefore, to demonstrate test–retest reliability (i.e., repeatability), the researcher should be checking for absolute agreement. Also, as can be seen in Tables 7 and 8 , there does not seem to be a standard on reporting ICC values. Some researchers report the confidence interval of the ICC value, while others do not. It was also difficult to determine the ICC model used in some of the studies. Therefore, a standard on reporting ICC values is needed to help readers understand the ICC used and prevent bias (see [ 68 ] for suggestive guideline on how to report ICC scores). Also, authors are asked to include the means of each individual session or rater would provide additional information on the variation of the means between the groups. The variation between groups can be shown with Bland–Altman plot, but readers are unable to perform other forms of analysis. To help with this, data from studies should be made publicly available to allow results to be verified and enable further analysis in the future.
When is it advantageous to combine biomechanical and neural activity-based metrics for assessment?
Biomechanical and neural activity provide distinct but complementary information about the neuro-musculoskeletal system, potentially offering a more complete picture of impairment and function after stroke. Metrics derived from kinematic/kinetic information assess motor performance based on motor execution; however, compensatory strategies related to stroke may mask underlying neural deficits (i.e., muscle synergies line up to complete a given task) [ 18 , 21 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 122 ]. Information relevant to these compensatory strategies can be obtained when analyzing electrophysiological activity, as has been done using connectivity [ 59 , 107 ], CMC [ 147 , 148 ] and brain cortical power [ 91 ].
Combining signals from multiple domains, although beneficial in the sense that it would allow a deeper understanding of a subject’s motor ability, is still a subject of exploration. Experimental paradigms play an important role that influences the decision of feature selection; increasing the dimensionality of signals may provide more useful information for analysis, but comes at the expense of experimental costs (e.g., hardware) and time (e.g., subject setup). With all this in mind, merging information from different domains in the hierarchy of the neuro-musculoskeletal system may provide a more comprehensive quantitative profile of a person’s impairment and performance. Examples of robotic multidomain methods such as the ones in [ 18 , 21 ], highlight the importance of this type of assessment for monitoring and understanding the impact of rehabilitation in chronic stroke survivors. In both cases, these methodologies allowed pairing of observed behavioral changes in task execution (i.e., biomechanical data) with corresponding functional recovery, instead of adopted compensation strategies.
What should be the focus of future investigations of biomechanical and/or neural activity-based metrics?
Determining the reliability and validity of sensor-based metrics requires carefully designed experiments. In future investigations, experiments should be conducted that calculate multiple metrics from multiple sensors and device combinations, allowing the effect of sensor type and quality on the measure’s reliability to be quantified. After the conclusion of such experiments, researchers are strongly encouraged to make their anonymized raw data public to allow other researchers to compute different ICCs. Performing comparison studies on the reliability of metrics will produce reliability data to expand Tables 7 , 8 , 9 and improve our ability to compare similar sensor-based metrics. Additional reliability studies should also be performed that include neural features of survivors of stroke, with increased focus on modeling the interactions between these domains (biomechanical and neural activity). It is also important to understand how to successfully combine data from multimodal experiments; many of the studies reviewed in this paper recorded multidimensional data, but performed analysis for each domain separately.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
Activities of daily living
Amplitude envelope correlation
Action research arm test
Active range of motion
Autism spectrum disorder
Box and Blocks test
Brain Symmetry Index
Canonical correlation analysis
Cortico-spinal tract
Delta-alpha ratio
Delayed cerebral ischemia
Direct directed transfer function
Degree of freedom
(Delta + Theta)/(Alpha + Beta)
Directed transfer function
Delta-theta ratio
- Electroencephalography
Electromyography
Event related desynchronization
Event related synchronization
Full frequency directed transfer function
Functional independence measure and functional assessment measure
Fugl-Meyer assessment for upper extremity
Generalized Measure of Association
Generalized partial directed coherence
Intra-class correlations
Imaginary part of coherence
Primary motor cortex
Modified Ashworth
Modified Barthel Index
Multiple coherence
Motricity Index
Montreal Cognitive Assessment
Movement related beta desynchronization
Magnetic resonance imaging
Modified Ranking Scale
Normalized interhemispheric strength
National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale
Non-negative matrix factorization algorithm
Principal component analysis
Partial coherence
Partial directed coherence
Phase lag index, weight phase lag index, debiased weighted phase lag index
Premotor area
Post movement beta rebound
Power Ratio Index
Passive range of motion
Quantitative EEG
Regional cerebral blood flow
Region of interest
Renormalized partial directed coherence
Singular value decomposition
Wolf motor function
Weighted Node Degree Index
Stroke Facts. 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/facts.htm . Accessed 26 Mar 2020.
Ottenbacher KJ, Smith PM, Illig SB, Linn RT, Ostir GV, Granger CV. Trends in length of stay, living setting, functional outcome, and mortality following medical rehabilitation. JAMA. 2004;292(14):1687–95. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.292.14.1687 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Lang CE, MacDonald JR, Gnip C. Counting repetitions: an observational study of outpatient therapy for people with hemiparesis post-stroke. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2007;31(1). https://journals.lww.com/jnpt/Fulltext/2007/03000/Counting_Repetitions__An_Observational_Study_of.4.aspx .
Gresham GE, Phillips TF, Wolf PA, McNamara PM, Kannel WB, Dawber TR. Epidemiologic profile of long-term stroke disability: the Framingham study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1979;60(11):487–91.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Duncan EA, Murray J. The barriers and facilitators to routine outcome measurement by allied health professionals in practice: a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2012;12(1):96.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sullivan KJ, Tilson JK, Cen SY, Rose DK, Hershberg J, Correa A, et al. Fugl-meyer assessment of sensorimotor function after stroke: standardized training procedure for clinical practice and clinical trials. Stroke. 2011;42(2):427–32.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ansari NN, Naghdi S, Arab TK, Jalaie S. The interrater and intrarater reliability of the Modified Ashworth Scale in the assessment of muscle spasticity: limb and muscle group effect. NeuroRehabilitation. 2008;23:231–7.
Wade DT, Collin C. The Barthel ADL Index: a standard measure of physical disability? Int Disabil Stud. 1988;10(2):64–7.
Maggioni S, Melendez-Calderon A, van Asseldonk E, Klamroth-Marganska V, Lünenburger L, Riener R, et al. Robot-aided assessment of lower extremity functions: a review. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2016;13(1):72. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-016-0180-3 .
Frisoli A, Procopio C, Chisari C, Creatini I, Bonfiglio L, Bergamasco M, et al. Positive effects of robotic exoskeleton training of upper limb reaching movements after stroke. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2012;9(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-0003-9-36 .
Groothuis-Oudshoorn CGM, Prange GB, Hermens HJ, Ijzerman MJ, Jannink MJA. Systematic review of the effect of robot-aided therapy on recovery of the hemiparetic arm after stroke. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2006;43(2):171.
Harwin WS, Murgia A, Stokes EK. Assessing the effectiveness of robot facilitated neurorehabilitation for relearning motor skills following a stroke. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2011;49(10):1093–102.
Nordin N, Xie SQ, Wünsche B. Assessment of movement quality in robot- assisted upper limb rehabilitation after stroke: a review. J NeuroEngineering Rehabil. 2014;11:137. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-0003-11-137 .
Article Google Scholar
De Los Reyes-Guzman A, Dimbwadyo-Terrer I, Trincado-Alonso F, Monasterio-Huelin F, Torricelli D, Gil-Agudo A. Quantitative assessment based on kinematic measures of functional impairments during upper extremity movements: a review. Clin Biomech. 2014;29(7):719–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2014.06.013 .
Molteni E, Preatoni E, Cimolin V, Bianchi AM, Galli M, Rodano R. A methodological study for the multifactorial assessment of motor adaptation: integration of kinematic and neural factors. 2010 Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc EMBC’10. 2010;4910–3.
Mazzoleni S, Coscia M, Rossi G, Aliboni S, Posteraro F, Carrozza MC. Effects of an upper limb robot-mediated therapy on paretic upper limb in chronic hemiparetic subjects: a biomechanical and EEG-based approach for functional assessment. 2009 IEEE Int Conf Rehabil Robot ICORR 2009. 2009;92–7.
Úbeda A, Azorín JM, Chavarriaga R, Millán JdR. Classification of upper limb center-out reaching tasks by means of EEG-based continuous decoding techniques. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2017;14(1):1–14.
Pierella C, Pirondini E, Kinany N, Coscia M, Giang C, Miehlbradt J, et al. A multimodal approach to capture post-stroke temporal dynamics of recovery. J Neural Eng. 2020;17(4): 045002.
Steinisch M, Tana MG, Comani S. A post-stroke rehabilitation system integrating robotics, VR and high-resolution EEG imaging. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2013;21(5):849–59. https://doi.org/10.1596/978-1-4648-1002-2_Module14 .
Úbeda A, Hortal E, Iáñez E, Perez-Vidal C, Azorín JM. Assessing movement factors in upper limb kinematics decoding from EEG signals. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(5):1–12.
Belfatto A, Scano A, Chiavenna A, Mastropietro A, Mrakic-Sposta S, Pittaccio S, et al. A multiparameter approach to evaluate post-stroke patients: an application on robotic rehabilitation. Appl Sci. 2018;8(11):2248.
Comani S, Schinaia L, Tamburro G, Velluto L, Sorbi S, Conforto S, et al. Assessing Neuromotor Recovery in a stroke survivor with high resolution EEG, robotics and virtual reality. In: Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). 2015. p. 3925–8.
Kwon HM, Yang IH, Lee WS, Yu ARL, Oh SY, Park KK. Reliability of intraoperative knee range of motion measurements by goniometer compared with robot-assisted arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(3):233–8.
Dukelow SP, Herter TM, Moore KD, Demers MJ, Glasgow JI, Bagg SD, et al. Quantitative assessment of limb position sense following stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2010;24(2):178–87.
Balasubramanian S, Wei R, Herman R, He J. Robot-measured performance metrics in stroke rehabilitation. In: 2009 ICME International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering, CME 2009. 2009.
Otaka E, Otaka Y, Kasuga S, Nishimoto A, Yamazaki K, Kawakami M, et al. Clinical usefulness and validity of robotic measures of reaching movement in hemiparetic stroke patients. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2015;12(1):66.
Singh H, Unger J, Zariffa J, Pakosh M, Jaglal S, Craven BC, et al. Robot-assisted upper extremity rehabilitation for cervical spinal cord injuries: a systematic scoping review. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2018;13(7):704–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/17483107.2018.1425747 .
Molteni F, Gasperini G, Cannaviello G, Guanziroli E. Exoskeleton and end-effector robots for upper and lower limbs rehabilitation: narrative review. PMR. 2018;10(9):174–88.
Jutinico AL, Jaimes JC, Escalante FM, Perez-Ibarra JC, Terra MH, Siqueira AAG. Impedance control for robotic rehabilitation: a robust markovian approach. Front Neurorobot. 2017;11(AUG):1–16.
Google Scholar
Li Z, Huang Z, He W, Su CY. Adaptive impedance control for an upper limb robotic exoskeleton using biological signals. IEEE Trans Ind Electron. 2017;64(2):1664–74.
Marchal-Crespo L, Reinkensmeyer DJ. Review of control strategies for robotic movement training after neurologic injury. J NeuroEngineering Rehabil. 2009;6:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-0003-6-20 .
Cohen MX. Analyzing neural time series data: theory and practice. Cambridge: MIT Press; 2014.
Book Google Scholar
Stafstrom CE, Carmant L. Seizures and epilepsy: an overview. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015;5(6):65–77.
Machado C, Cuspineda E, Valdãs P, Virues T, Liopis F, Bosch J, et al. Assessing acute middle cerebral artery ischemic stroke by quantitative electric tomography. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2004;35(3):116–24.
Finnigan SP, Walsh M, Rose SE, Chalk JB. Quantitative EEG indices of sub-acute ischaemic stroke correlate with clinical outcomes. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007;118(11):2525–31.
Cuspineda E, Machado C, Galán L, Aubert E, Alvarez MA, Llopis F, et al. QEEG prognostic value in acute stroke. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2007;38(3):155–60.
Belardinelli P, Laer L, Ortiz E, Braun C, Gharabaghi A. Plasticity of premotor cortico-muscular coherence in severely impaired stroke patients with hand paralysis. NeuroImage Clin. 2017;14:726–33.
Di PM, Schnider A, Nicolo P, Rizk S, Guggisberg AG. Coherent neural oscillations predict future motor and language improvement after stroke. Brain. 2015;138(10):3048–60.
Chen CC, Lee SH, Wang WJ, Lin YC, Su MC. EEG-based motor network biomarkers for identifying target patients with stroke for upper limb rehabilitation and its construct validity. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(6):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178822 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Conway BA, Halliday DM, Farmer SF, Shahani U, Maas P, Weir AI, et al. Synchronization between motor cortex and spinal motoneuronal pool during the performance of a maintained motor task in man. J Physiol. 1995;489(3):917–24.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Salenius S, Portin K, Kajola M, Salmelin R, Hari R. Cortical control of human motoneuron firing during isometric contraction. J Neurophysiol. 1997;77(6):3401–5.
Mima T, Hallett M. Electroencephalographic analysis of cortico-muscular coherence: reference effect, volume conduction and generator mechanism. Clin Neurophysiol. 1999;110(11):1892–9.
Claassen J, Hirsch LJ, Kreiter KT, Du EY, Sander Connolly E, Emerson RG, et al. Quantitative continuous EEG for detecting delayed cerebral ischemia in patients with poor-grade subarachnoid hemorrhage. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004;115(12):2699–710.
Sullivan JL, Bhagat NA, Yozbatiran N, Paranjape R, Losey CG, Grossman RG, et al. Improving robotic stroke rehabilitation by incorporating neural intent detection: preliminary results from a clinical trial. In: 2017 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR). IEEE; 2017. p. 122–7.
Muralidharan A, Chae J, Taylor DM. Extracting attempted hand movements from EEGs in people with complete hand paralysis following stroke. Front Neurosci. 2011. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2011.00039 .
Nam C, Rong W, Li W, Xie Y, Hu X, Zheng Y. The effects of upper-limb training assisted with an electromyography-driven neuromuscular electrical stimulation robotic hand on chronic stroke. Front Neurol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00679 .
Bertolucci F, Lamola G, Fanciullacci C, Artoni F, Panarese A, Micera S, et al. EEG predicts upper limb motor improvement after robotic rehabilitation in chronic stroke patients. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2018;61:e200–1.
Cantillo-Negrete J, Carino-Escobar RI, Carrillo-Mora P, Elias-Vinas D, Gutierrez-Martinez J. Motor imagery-based brain-computer interface coupled to a robotic hand orthosis aimed for neurorehabilitation of stroke patients. J Healthc Eng. 2018;3(2018):1–10.
Bhagat NA, Venkatakrishnan A, Abibullaev B, Artz EJ, Yozbatiran N, Blank AA, et al. Design and optimization of an EEG-based brain machine interface (BMI) to an upper-limb exoskeleton for stroke survivors. Front Neurosci. 2016;10(MAR):122.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Biasiucci A, Leeb R, Iturrate I, Perdikis S, Al-Khodairy A, Corbet T, et al. Brain-actuated functional electrical stimulation elicits lasting arm motor recovery after stroke. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04673-z .
Ang KK, Guan C, Chua KSG, Ang BT, Kuah C, Wang C, et al. Clinical study of neurorehabilitation in stroke using EEG-based motor imagery brain-computer interface with robotic feedback. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol. 2010. pp. 5549–52.
Finnigan SP, Rose SE, Walsh M, Griffin M, Janke AL, Mcmahon KL, et al. Correlation of quantitative EEG in acute ischemic stroke with 30-day NIHSS score: comparison with diffusion and perfusion MRI. Stroke. 2004;35(4):899–903.
Schleiger E, Sheikh N, Rowland T, Wong A, Read S, Finnigan S. Frontal EEG delta / alpha ratio and screening for post-stroke cognitive de fi cits: the power of four electrodes. Int J Psychophysiol. 2014;94(1):19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2014.06.012 .
Aminov A, Rogers JM, Johnstone SJ, Middleton S, Wilson PH. Acute single channel EEG predictors of cognitive function after stroke. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(10): e0185841.
Andresen EM. Criteria for assessing the tools of disability outcomes research. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000. https://doi.org/10.1053/apmr.2000.20619 .
Wang Q, Markopoulos P, Yu B, Chen W, Timmermans A. Interactive wearable systems for upper body rehabilitation: a systematic review. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2017;14(1):1–21.
Tran VD, Dario P, Mazzoleni S. Kinematic measures for upper limb robot-assisted therapy following stroke and correlations with clinical outcome measures: a review. Med Eng Phys. 2018;53:13–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2017.12.005 .
Finnigan S, Wong A, Read S. Defining abnormal slow EEG activity in acute ischaemic stroke: Delta/alpha ratio as an optimal QEEG index. Clin Neurophysiol. 2016;127(2):1452–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2015.07.014 .
Carter AR, Shulman GL, Corbetta M. Why use a connectivity-based approach to study stroke and recovery of function? Neuroimage. 2012;62(4):2271–80.
van der Velde B, Haartsen R, Kemner C. Test-retest reliability of EEG network characteristics in infants. Brain Behav. 2019;9(5):1–10.
Gennaro F, de Bruin ED. A pilot study assessing reliability and age-related differences in corticomuscular and intramuscular coherence in ankle dorsiflexors during walking. Physiol Rep. 2020;8(4):1–12.
Brihmat N, Loubinoux I, Castel-Lacanal E, Marque P, Gasq D. Kinematic parameters obtained with the ArmeoSpring for upper-limb assessment after stroke: a reliability and learning effect study for guiding parameter use. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2020;17(1):130. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-020-00759-2 .
Dewald JPA, Ellis MD, Acosta AM, McPherson JG, Stienen AHA. Implementation of impairment- based neurorehabilitation devices and technologies following brain injury. Neurorehabilitation technology, 2nd edn. 2016. 375–392 p.
Subramanian SK, Yamanaka J, Chilingaryan G, Levin MF. Validity of movement pattern kinematics as measures of arm motor impairment poststroke. Stroke. 2010;41(10):2303–8.
Fayers PM, Machin D. Quality of life: the assessment, analysis and reporting of patient‐reported outcomes . John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated. 2016;3:89-124.
Alt Murphy M, Häger CK. Kinematic analysis of the upper extremity after stroke—how far have we reached and what have we grasped? Phys Ther Rev. 2015;20(3):137–55.
Shishov N, Melzer I, Bar-Haim S. Parameters and measures in assessment of motor learning in neurorehabilitation; a systematic review of the literature. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2017.00082 .
Koo TK, Li MY. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med. 2016;15(2):155–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcm.2016.02.012 .
Angel RW. Electromyographic patterns during ballistic movement of normal and spastic limbs. Brain Res. 1975;99(2):387–92.
McLellan DL. C0-contraction and stretch reflexes in spasticity during treatment with baclofen. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977;40(1):30–8.
Dewald JPA, Pope PS, Given JD, Buchanan TS, Rymer WZ. Abnormal muscle coactivation patterns during isometric torque generation at the elbow and shoulder in hemiparetic subjects. Brain. 1995;118(2):495–510. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/118.2.495 .
Wilkins KB, Yao J, Owen M, Karbasforoushan H, Carmona C, Dewald JPA. Limited capacity for ipsilateral secondary motor areas to support hand function post-stroke. J Physiol. 2020;598(11):2153–67. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP279377 .
Agius Anastasi A, Falzon O, Camilleri K, Vella M, Muscat R. Brain symmetry index in healthy and stroke patients for assessment and prognosis. Stroke Res Treat. 2017;30(2017):1–9.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339: b2700.
Colombo R, Pisano F, Micera S, Mazzone A, Delconte C, Carrozza MC, et al. Assessing mechanisms of recovery during robot-aided neurorehabilitation of the upper limb. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2008;22(1):50–63. https://doi.org/10.1177/1545968307303401 .
Keller U, Schölch S, Albisser U, Rudhe C, Curt A, Riener R, et al. Robot-assisted arm assessments in spinal cord injured patients: a consideration of concept study. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0126948. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126948 .
Mostafavi SM. Computational models for improved diagnosis and prognosis of stroke using robot-based biomarkers. 2016. http://hdl.handle.net/1974/14563 .
Bosecker C, Dipietro L, Volpe B, Krebs HI. Kinematic robot-based evaluation scales and clinical counterparts to measure upper limb motor performance in patients with chronic stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2010;24(1):62–9.
Balasubramanian S, Melendez-Calderon A, Roby-Brami A, Burdet E. On the analysis of movement smoothness. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2015;12(1):112. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-015-0090-9 .
Rohrer B, Fasoli S, Krebs HI, Hughes R, Volpe B, Frontera WR, et al. Movement smoothness changes during stroke recovery. J Neurosci. 2002;22(18):8297–304.
Mobini A, Behzadipour S, Saadat M. Test-retest reliability of Kinect’s measurements for the evaluation of upper body recovery of stroke patients. Biomed Eng Online. 2015;14(1):1–14.
Zariffa J, Myers M, Coahran M, Wang RH. Smallest real differences for robotic measures of upper extremity function after stroke: implications for tracking recovery. J Rehabil Assist Technol Eng. 2018;5:205566831878803. https://doi.org/10.1177/2055668318788036 .
Elovic E, Brashear A. Spasticity : diagnosis and management. New York: Demos Medical; 2011. http://ida.lib.uidaho.edu:2048/login?url=http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=e000xna&AN=352265&site=ehost-live&scope=site .
Centen A, Lowrey CR, Scott SH, Yeh TT, Mochizuki G. KAPS (kinematic assessment of passive stretch): a tool to assess elbow flexor and extensor spasticity after stroke using a robotic exoskeleton. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2017;14(1):1–13.
Sin M, Kim WS, Cho K, Cho S, Paik NJ. Improving the test-retest and inter-rater reliability for stretch reflex measurements using an isokinetic device in stroke patients with mild to moderate elbow spasticity. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2017;2018(39):120–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2018.01.012 .
Germanotta M, Cruciani A, Pecchioli C, Loreti S, Spedicato A, Meotti M, et al. Reliability, validity and discriminant ability of the instrumental indices provided by a novel planar robotic device for upper limb rehabilitation. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2018;15(1):1–14.
Wagner JM, Rhodes JA, Patten C. Reproducibility and minimal detectable change of three-dimensional kinematic analysis of reaching tasks in people with hemiparaesis after stroke. 2008. https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20070255 .
Semrau JA, Herter TM, Scott SH, Dukelow SP. Inter-rater reliability of kinesthetic measurements with the KINARM robotic exoskeleton. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2017;14(1):1–10.
Lin CH, Chou LW, Wei SH, Lieu FK, Chiang SL, Sung WH. Validity and reliability of a novel device for bilateral upper extremity functional measurements. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2014;114(3):315–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2014.02.012 .
Wolf S, Butler A, Alberts J, Kim M. Contemporary linkages between EMG, kinetics and stroke. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2005;15(3):229–39.
Iyer KK. Effective assessments of electroencephalography during stroke recovery : contemporary approaches and considerations. J Neurophysiol. 2017;118(5):2521–5.
Liu J, Sheng Y, Liu H. Corticomuscular coherence and its applications: a review. Front Hum Neurosci. 2019;13(March):1–16.
Pan LLH, Yang WW, Kao CL, Tsai MW, Wei SH, Fregni F, et al. Effects of 8-week sensory electrical stimulation combined with motor training on EEG-EMG coherence and motor function in individuals with stroke. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):1–10.
Wu J, Quinlan EB, Dodakian L, McKenzie A, Kathuria N, Zhou RJ, et al. Connectivity measures are robust biomarkers of cortical function and plasticity after stroke. Brain. 2015;138(8):2359–69.
Mrachacz-Kersting N, Jiang N, Thomas Stevenson AJ, Niazi IK, Kostic V, Pavlovic A, et al. Efficient neuroplasticity induction in chronic stroke patients by an associative brain-computer interface. J Neurophysiol. 2016;115(3):1410–21.
Bentes C, Peralta AR, Viana P, Martins H, Morgado C, Casimiro C, et al. Quantitative EEG and functional outcome following acute ischemic stroke. Clin Neurophysiol. 2018;129(8):1680–7.
Leon-carrion J, Martin-rodriguez JF, Damas-lopez J, Manuel J, Dominguez-morales MR. Delta–alpha ratio correlates with level of recovery after neurorehabilitation in patients with acquired brain injury. Clin Neurophysiol. 2009;120(6):1039–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2009.01.021 .
Finnigan S, van Putten MJAM. EEG in ischaemic stroke: qEEG can uniquely inform (sub-)acute prognoses and clinical management. Clin Neurophysiol. 2013;124(1):10–9.
Trujillo P, Mastropietro A, Scano A, Chiavenna A, Mrakic-Sposta S, Caimmi M, et al. Quantitative EEG for predicting upper limb motor recovery in chronic stroke robot-assisted rehabilitation. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2017;25(7):1058–67.
Jordan K. Emergency EEG and continuous EEG monitoring in acute ischemic stroke. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004;21(5):341–52.
Comani S, Velluto L, Schinaia L, Cerroni G, Serio A, Buzzelli S, et al. Monitoring neuro-motor recovery from stroke with high-resolution EEG, robotics and virtual reality: a proof of concept. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2015;23(6):1106–16.
Espenhahn S, de Berker AO, van Wijk BCM, Rossiter HE, Ward NS. Movement-related beta oscillations show high intra-individual reliability. Neuroimage. 2017;147:175–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.12.025 .
Vázquez-Marrufo M, Galvao-Carmona A, Benítez Lugo ML, Ruíz-Peña JL, Borges Guerra M, Izquierdo AG. Retest reliability of individual alpha ERD topography assessed by human electroencephalography. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(10):1–16.
Dubovik S, Ptak R, Aboulafia T, Magnin C, Gillabert N, Allet L, et al. EEG alpha band synchrony predicts cognitive and motor performance in patients with ischemic stroke. In: Behavioural Neurology. Hindawi Limited; 2013. p. 187–9.
Sheorajpanday RVAA, Nagels G, Weeren AJTMTM, Putten MJAMV, Deyn PPD, van Putten MJAM, et al. Quantitative EEG in ischemic stroke: correlation with functional status after 6 months. Clin Neurophysiol. 2011;122(5):874–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2010.07.028 .
De Vico Fallani F, Astolfi L, Cincotti F, Mattia D, La Rocca D, Maksuti E, et al. Evaluation of the brain network organization from EEG signals: a preliminary evidence in stroke patient. In: Anatomical Record. 2009. p. 2023–31.
Westlake KP, Nagarajan SS. Functional connectivity in relation to motor performance and recovery after stroke. Front Syst Neurosci. 2011;18(5):8.
Caliandro P, Vecchio F, Miraglia F, Reale G, Della Marca G, La Torre G, et al. Small-world characteristics of cortical connectivity changes in acute stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2017;31(1):81–94.
Eldeeb S, Akcakaya M, Sybeldon M, Foldes S, Santarnecchi E, Pascual-Leone A, et al. EEG-based functional connectivity to analyze motor recovery after stroke: a pilot study. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2019;49:419–26.
Myers LJ, O’Malley M. The relationship between human cortico-muscular coherence and rectified EMG. In: International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, NER. IEEE Computer Society; 2003. p. 289–92.
Braun C, Staudt M, Schmitt C, Preissl H, Birbaumer N, Gerloff C. Crossed cortico-spinal motor control after capsular stroke. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25(9):2935–45.
Larsen LH, Zibrandtsen IC, Wienecke T, Kjaer TW, Christensen MS, Nielsen JB, et al. Corticomuscular coherence in the acute and subacute phase after stroke. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;128(11):2217–26.
Ang KK, Chua KSG, Phua KS, Wang C, Chin ZY, Kuah CWK, et al. A randomized controlled trial of EEG-based motor imagery brain-computer interface robotic rehabilitation for stroke. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2015;46(4):310–20.
Liu S, Guo J, Meng J, Wang Z, Yao Y, Yang J, et al. Abnormal EEG complexity and functional connectivity of brain in patients with acute thalamic ischemic stroke. Comput Math Methods Med. 2016;14(2016):1–9.
CAS Google Scholar
Sun R, Wong W, Wang J, Tong RK. Changes in electroencephalography complexity using a brain computer interface-motor observation training in chronic stroke patients : a fuzzy approximate entropy analysis. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017;5(11):444.
Auriat AM, Neva JL, Peters S, Ferris JK, Boyd LA. A review of transcranial magnetic stimulation and multimodal neuroimaging to characterize post-stroke neuroplasticity. Front Neurol. 2015;6:1–20.
Niedermeyer E, Schomer DL, Lopes da Silva FH. Niedermeyer’s electroencephalography: basic principles, clinical applications, and related fields, 6th edn. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.; 2011.
Foreman B, Claasen J. Update in intensive care and emergency medicine. Update in intensive care and emergency medicine. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2012.
Tolonen U, Ahonen A, Kallanranta T, Hokkanen E. Non-invasive external regional measurement of cerebral circulation time changes in supratentorial infarctions using pertechnetate. Stroke. 1981;12(4):437–44.
Saes M, Zandvliet SB, Andringa AS, Daffertshofer A, Twisk JWR, Meskers CGM, et al. Is resting-state EEG longitudinally associated with recovery of clinical neurological impairments early poststroke? A prospective cohort study. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2020;34(5):389–402.
Rogers J, Middleton S, Wilson PH, Johnstone SJ. Predicting functional outcomes after stroke: an observational study of acute single-channel EEG. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2020;27(3):161–72. https://doi.org/10.1080/10749357.2019.1673576 .
Sale P, Infarinato F, Lizio R, Babiloni C. Electroencephalographic markers of robot-aided therapy in stroke patients for the evaluation of upper limb rehabilitation. Rehabil Res. 2015;38(4):294–305.
Sheorajpanday RVA, Nagels G, Weeren AJTM, De Surgeloose D, De Deyn PP, De DPP. Additional value of quantitative EEG in acute anterior circulation syndrome of presumed ischemic origin. Clin Neurophysiol. 2010;121(10):1719–25.
Saes M, Meskers CGM, Daffertshofer A, van Wegen EEH, Kwakkel G. Are early measured resting-state EEG parameters predictive for upper limb motor impairment six months poststroke? Clin Neurophysiol. 2021;132(1):56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2020.09.031 .
Saes M, Meskers CGM, Daffertshofer A, de Munck JC, Kwakkel G, van Wegen EEH. How does upper extremity Fugl-Meyer motor score relate to resting-state EEG in chronic stroke? A power spectral density analysis. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019;130(5):856–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2019.01.007 .
Nolte G, Bai O, Mari Z, Vorbach S, Hallett M. Identifying true brain interaction from EEG data using the imaginary part of coherency. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004;115(10):2292–307.
Stam CJ, Nolte G, Daffertshofer A. Phase lag index: assessment of functional connectivity from multi channel EEG and MEG with diminished bias from common sources. Hum Brain Mapp. 2007;28(11):1178–93.
Bullmore E, Sporns O. Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10(3):186–98.
Baccalá LA, Sameshima K. Partial directed coherence: a new concept in neural structure determination. Biol Cybern. 2001;84(6):463–74.
Baccalá LA, Sameshima K, Takahashi D. Generalized partial directed coherence. Int Conf Digit Signal Process. 2007;3:163–6.
Schelter B, Timmer J, Eichler M. Assessing the strength of directed influences among neural signals using renormalized partial directed coherence. J Neurosci Methods. 2009;179(1):121–30.
Kamiński M, Ding M, Truccolo WA, Bressler SL. Evaluating causal relations in neural systems: Granger causality, directed transfer function and statistical assessment of significance. Biol Cybern. 2001;85(2):145–57.
Korzeniewska A, Mańczak M, Kamiński M, Blinowska KJ, Kasicki S. Determination of information flow direction among brain structures by a modified directed transfer function (dDTF) method. J Neurosci Methods. 2003;125(1–2):195–207.
Fornito A, Bullmore ET, Zalesky A. Fundamentals of brain network analysis. Cambridge: Academic Press; 2016.
Philips GR, Daly JJ, Príncipe JC. Topographical measures of functional connectivity as biomarkers for post-stroke motor recovery. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2017;14(1):67.
Pichiorri F, Petti M, Caschera S, Astolfi L, Cincotti F, Mattia D. An EEG index of sensorimotor interhemispheric coupling after unilateral stroke: clinical and neurophysiological study. Eur J Neurosci. 2018;47(2):158–63.
Hoshino T, Oguchi K, Inoue K, Hoshino A, Hoshiyama M. Relationship between upper limb function and functional neural connectivity among motor related-areas during recovery stage after stroke. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2020;27(1):57–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/10749357.2019.1658429 .
Hordacre B, Goldsworthy MR, Welsby E, Graetz L, Ballinger S, Hillier S. Resting state functional connectivity is associated with motor pathway integrity and upper-limb behavior in chronic stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2020;34(6):547–57.
Riahi N, Vakorin VA, Menon C. Estimating Fugl-Meyer upper extremity motor score from functional-connectivity measures. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2020;28(4):860–8.
Gwin JT, Ferris DP. Beta- and gamma-range human lower limb corticomuscular coherence. Front Hum Neurosci. 2012;11(6):258.
Zheng Y, Peng Y, Xu G, Li L, Wang J. Using corticomuscular coherence to reflect function recovery of paretic upper limb after stroke: a case study. Front Neurol. 2018;10(8):728.
Rossiter HE, Eaves C, Davis E, Boudrias MH, Park CH, Farmer S, et al. Changes in the location of cortico-muscular coherence following stroke. NeuroImage Clin. 2013;2(1):50–5.
Mima T, Toma K, Koshy B, Hallett M. Coherence between cortical and muscular activities after subcortical stroke. Stroke. 2001;32(11):2597–601.
Krauth R, Schwertner J, Vogt S, Lindquist S, Sailer M, Sickert A, et al. Cortico-muscular coherence is reduced acutely post-stroke and increases bilaterally during motor recovery: a pilot study. Front Neurol. 2019;20(10):126.
Bao SC, Wong WW, Leung TW, Tong KY. Low gamma band cortico-muscular coherence inter-hemisphere difference following chronic stroke. In: Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.; 2018. p. 247–50.
von Carlowitz-Ghori K, Bayraktaroglu Z, Hohlefeld FU, Losch F, Curio G, Nikulin VV. Corticomuscular coherence in acute and chronic stroke. Clin Neurophysiol. 2014;125(6):1182–91.
Chen X, Xie P, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Cheng S, Zhang L. Abnormal functional corticomuscular coupling after stroke. NeuroImage Clin. 2018;19:147–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2018.04.004 .
Curado MR, Cossio EG, Broetz D, Agostini M, Cho W, Brasil FL, et al. Residual upper arm motor function primes innervation of paretic forearm muscles in chronic stroke after brain-machine interface (BMI) training. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(10):1–18.
Guo Z, Qian Q, Wong K, Zhu H, Huang Y, Hu X, et al. Altered corticomuscular coherence (CMCoh) pattern in the upper limb during finger movements after stroke. Front Neurol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00410 .
Bruton A, Conway JH, Holgate ST. Reliability: what is it, and how is it measured? Physiotherapy. 2000;86(2):94–9.
Colombo R, Cusmano I, Sterpi I, Mazzone A, Delconte C, Pisano F. Test-retest reliability of robotic assessment measures for the evaluation of upper limb recovery. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2014;22(5):1020–9.
Costa V, Ramírez Ó, Otero A, Muñoz-García D, Uribarri S, Raya R. Validity and reliability of inertial sensors for elbow and wrist range of motion assessment. PeerJ. 2020;8: e9687.
Gasser T, Bächer P, Steinberg H. Test-retest reliability of spectral parameters of the EEG. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1985;60(4):312–9.
Levin AR, Naples AJ, Scheffler AW, Webb SJ, Shic F, Sugar CA, et al. Day-to-day test-retest reliability of EEG profiles in children with autism spectrum disorder and typical development. Front Integr Neurosci. 2020;14:1–12.
Briels CT, Briels CT, Schoonhoven DN, Schoonhoven DN, Stam CJ, De Waal H, et al. Reproducibility of EEG functional connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res Ther. 2020;12(1):1–14.
Marquetand J, Vannoni S, Carboni M, Li Hegner Y, Stier C, Braun C, et al. Reliability of magnetoencephalography and high-density electroencephalography resting-state functional connectivity metrics. Brain Connect. 2019;9(7):539–53.
Lowrey CR, Blazevski B, Marnet J-L, Bretzke H, Dukelow SP, Scott SH. Robotic tests for position sense and movement discrimination in the upper limb reveal that they each are highly reproducible but not correlated in healthy individuals. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2020;17(1):103. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-020-00721-2 .
Simmatis LER, Early S, Moore KD, Appaqaq S, Scott SH. Statistical measures of motor, sensory and cognitive performance across repeated robot-based testing. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2020;17(1):86. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-020-00713-2 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Stephen Goodwin and Aaron I. Feinstein for their contributions to the collection and organization of references on robotic systems, measurements, and metrics.
This work was funded by the National Science Foundation (Award#1532239) and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health & Human Development of the National Institutes of Health (Award#K12HD073945). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Science Foundation nor the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Mechanical Engineering Department, University of Idaho, Moscow, ID, USA
Rene M. Maura, Eric T. Wolbrecht & Joel C. Perry
Engineering and Physics Department, Whitworth University, Spokane, WA, USA
Richard E. Stevens
College of Medicine, Washington State University, Spokane, WA, USA
Douglas L. Weeks
Electrical Engineering Department, University of Idaho, ID, Moscow, USA
Sebastian Rueda Parra
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
RM, and SRP drafted the manuscript and performed the literature search. EW, JP, RS, and DW provided concepts, edited, and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rene M. Maura .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
See Table 11 .
See Table 12 .
See Table 13 .
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Maura, R.M., Rueda Parra, S., Stevens, R.E. et al. Literature review of stroke assessment for upper-extremity physical function via EEG, EMG, kinematic, and kinetic measurements and their reliability. J NeuroEngineering Rehabil 20 , 21 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-023-01142-7
Download citation
Received : 27 May 2021
Accepted : 19 January 2023
Published : 15 February 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-023-01142-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Reliability
- Robot-assisted therapy
- Exoskeleton
- Neurological assessment
- Rehabilitation
- Motor function
Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation
ISSN: 1743-0003
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Life’s Work: An Interview with Hernan Diaz
- Alison Beard

The Pulitzer Prize–winning author reflects on how literature shapes us and more.
In his novel Trust, which won the 2023 Pulitzer Prize, Diaz offered four contrasting perspectives on early-20th-century U.S. capitalism—a treatment that modern-day readers found deeply resonant. The author, who was born in Argentina, raised in Sweden, and now lives in the United States, says he likes to experiment with different voices and “mess with” American mythology. A longtime professor and academic editor, he published his first novel, In the Distance , a Pulitzer finalist, at age 44. Trust was his second.
- Alison Beard is an executive editor at Harvard Business Review and previously worked as a reporter and editor at the Financial Times. A mom of two, she tries—and sometimes succeeds—to apply management best practices to her household. alisonwbeard
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing ...
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis).The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others, "standing on the shoulders of giants", as Newton put it.The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.. Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure ...
Option 1: Chronological (according to date) Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you. ... Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a ...
Example: Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398 ; Systematic review: "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139).
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period. ... British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents ...
WRITING A TARGETED LITERATURE REVIEW a targeted literature review is NOT: ¡ a sophisticated evaluation of the entire literature or literatures related to your topic ¡ a set of thinly connected summaries of important related works haphazardly selected from many subfields a targeted literature review IS: ¡ a carefully curated set of sources from a small number of subfield literatures
The literature review template includes the following sections: Before you start - essential groundwork to ensure you're ready. The introduction section. The core/body section. The conclusion /summary. Extra free resources. Each section is explained in plain, straightforward language, followed by an overview of the key elements that you ...
A literary review isn't just about summarizing sources; it's about seamlessly bringing your perspective to the table. Always remember to set a narrative for added interest and a brilliant composition. With structure and style being the pillars of a stellar literature review, work with Wordtune to ensure zero compromises on the quality.
What is a literature review? A literature review is an examination of research in a particular field. It gathers, critically analyses, evaluates, and synthesises current research literature in a discipline, and . indicates where there may be strengths, gaps, weaknesses, and agreements in the current research. It considers: what has been done,
Literature review is an essential feature of academic research. Fundamentally, knowledge advancement must be built on prior existing work. To push the knowledge frontier, we must know where the frontier is. By reviewing relevant literature, we understand the breadth and depth of the existing body of work and identify gaps to explore.
An example outline for a Literature Review might look like this: Introduction. Background information on the topic & definitions; Purpose of the literature review; Scope and limitations of the review (what is included /excluded) Body. Historical background ; Overview of the existing research on the topic; Principle question being asked
Home; Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews
The second form of literature review, which is the focus of this chapter, constitutes an original and valuable work of research in and of itself (Paré et al., 2015). Rather than providing a base for a researcher's own work, it creates a solid starting point for all members of the community interested in a particular area or topic ( Mulrow ...
A literature review should connect to the study question, guide the study methodology, and be central in the discussion by indicating how the analyzed data advances what is known in the field. ... 2006), for example, offers a general discussion about standards for such work: an adequate review of research informing the study, the existence of ...
Review the most influential work around any topic by area, genre & time. Paper * Patent Grant Clinical-Trial. Web. Expert · Past Year Past 5 Years ALL · LLM Expand Tweak. Web. Try: style transfer · covid vaccine · more | ask questions · text rewriter · review by venue.
This paper suggests future work on analyzing the reliability of metrics to prevent biasedness and selecting the appropriate analysis. ... In step 3, researchers read the full texts of articles screened in step 2, papers qualifying for inclusion using the Literature Review Criteria in Table 1 were selected. Finally, in step 4, selected articles ...
However, there is to our knowledge no available overview of the literature on online group work in health science education. Online group work may cover various forms of group work and online environments. For this scoping review, we chose to define online group work as 'not in-person', meaning group taking place solely online.
The Pulitzer Prize-winning author reflects on how literature shapes us and more. The Pulitzer Prize-winning author reflects on how literature shapes us and more. In his novel Trust, which won ...