Oratory Club
Public Speaking Helpline

Poster Vs Oral Presentation: Which Is Best In 2023?
When it comes to presenting information or research, there are two popular options: posters or oral presentations. Choosing between the two can be a tough decision, but fear not! We’re here to help you explore the key differences and find the best fit for your needs. So, let’s dive in and compare the advantages of each approach.
First up, we have posters. These visual displays offer a great way to showcase your work creatively. With posters, you can utilize eye-catching graphics, images, and charts to capture your audience’s attention. Plus, posters allow for easy interaction, as viewers can take their time to study the content at their own pace.
On the other hand, we have oral presentations, which involve speaking in front of an audience to convey your research findings. Oral presentations enable you to engage directly with your peers, expressing your ideas, and answering questions on the spot. They offer a dynamic platform for showcasing your public speaking skills and establishing your expertise.
Now that we’ve introduced both options, let’s delve deeper into the specific merits of each one—poster presentations and oral presentations. By examining the distinct features of these approaches, we can help you make an informed decision that best suits your needs and preferences. So, let’s weigh the pros and cons and find the perfect medium for your next presentation.
When deciding between a poster and an oral presentation, there are several key features to consider.
1. Visual Impact: Posters offer a visual representation of information, while oral presentations allow for direct engagement.
2. Audience Interaction: With posters, viewers can leave comments or ask questions. For oral presentations, immediate feedback is possible.
3. Versatility: Posters can be displayed for extended periods, while oral presentations allow for dynamic delivery.
4. Time Management: Posters can be viewed at any time, while oral presentations have a set duration.
5. Communication Style: Posters rely on visuals, while oral presentations include spoken words and gestures.
Consider these features to determine which format will best suit your needs.

Table of Contents
Key Takeaways: Poster vs Oral Presentation
- Posters are visual displays of information, while oral presentations involve speaking to an audience.
- Posters allow for more creativity in design and visual appeal.
- Oral presentations provide an opportunity for direct interaction and engagement with the audience.
- Posters are often used in conferences or exhibitions, while oral presentations are common in classrooms or professional settings.
- Both formats have their benefits and can be effective in communicating information.
Comparing Poster vs Oral Presentation
In today’s fast-paced world, effective communication is key. Whether it’s presenting research findings, sharing ideas, or conveying information, there are various methods to choose from. Two popular options are posters and oral presentations. In this article, we will explore the differences and similarities between these two formats, to help you make an informed decision on which method is better suited for your needs.
Overview of Posters
Posters are a visual medium for presenting information. They typically consist of a combination of text, images, graphs, and charts. Posters are often used in academic and scientific settings, such as conferences or research symposiums, to showcase research findings or present complex data. They offer a concise and visually appealing way to convey information to a large audience.
Creating a poster involves careful consideration of the layout, design elements, and content. The goal is to effectively communicate the main points of the research or topic in a visually appealing manner. Posters can be displayed on walls or presentation boards, allowing viewers to engage with the information at their own pace.
Overview of Oral Presentations
Oral presentations, on the other hand, involve the delivery of information through spoken words. This format is commonly used in academic, professional, and educational settings. Instead of relying solely on visual aids, oral presentations allow presenters to verbally explain their research or ideas, often supported by slides or visual aids.
An oral presentation typically follows a structured format, with an introduction, body, and conclusion. Presenters are expected to articulate their thoughts clearly, provide engaging explanations, and convey their message effectively. This format allows for direct interaction with the audience through questions, discussions, and feedback.
Key Features Compared
When comparing posters and oral presentations, there are several key features to consider. Let’s explore each of these features in detail and compare the two methods.
Content Delivery
In terms of content delivery, posters and oral presentations offer different approaches. Posters rely heavily on visuals and concise written information to convey the main points. Viewers can read the content at their own pace and spend more time analyzing the information presented. On the other hand, oral presentations focus on verbal communication, allowing presenters to provide more in-depth explanations and engage directly with the audience.
Engagement and Interaction
Posters provide a more self-paced experience for viewers. They can spend as much time as needed to absorb the information, making them suitable for passive engagement. However, posters lack the interactive element that oral presentations offer. Oral presentations allow for real-time interaction, such as question-and-answer sessions or audience feedback, creating a more dynamic and engaging experience.
Presentation Skills
Both posters and oral presentations require distinct presentation skills. Creating an effective poster involves designing an aesthetically appealing layout, using clear and concise language, and organizing information in a logical manner. Oral presentations, on the other hand, require strong public speaking skills, the ability to engage the audience, and effective use of visual aids. Each format requires different skill sets and preparation.
User Experience
The user experience for both posters and oral presentations can vary depending on various factors. For posters, viewers have the flexibility to study the content at their own pace, review specific details, and focus on areas of interest. However, posters may lack the personal touch and direct interaction that oral presentations provide.
In oral presentations, the audience can benefit from real-time explanations, engagement, and the opportunity to ask questions. This format allows for a more dynamic and interactive user experience. However, some audience members may feel overwhelmed by the fast pace or struggle to fully grasp the information presented in the moment.
Pros and Cons
- Visually appealing and engaging.
- Provides a concise overview of research or information.
- Allows viewers to study and analyze content at their own pace.
- Lacks direct interaction and engagement with the audience.
- May require a large amount of space for display.
- Can be challenging to condense complex information into a limited space.
Oral Presentations
- Allows for direct interaction and engagement with the audience.
- Enables presenters to provide in-depth explanations and clarify misunderstandings.
- Creates a dynamic and engaging experience for both presenters and audience members.
- Requires strong public speaking skills and presentation preparation.
- May limit the amount of information that can be covered within a given time frame.
- Relies heavily on the presenter’s ability to convey the message effectively.
Price Comparison
When it comes to cost, posters are generally more affordable compared to oral presentations. Creating a poster requires minimal resources, such as printing costs, design software, and materials for display. On the other hand, oral presentations may involve additional expenses, such as travel costs for attending conferences or professional presentation software.
Comparison Table
Here is a comparison table that highlights the key features of posters and oral presentations:
| Feature | Posters | Oral Presentations | |————————-|—————————————|————————————-| | Content Delivery | Relies on visuals and concise text | Verbal explanations and visual aids | | Engagement and Interaction | Passive engagement for viewers | Real-time interaction with audience | | Presentation Skills | Design and organization | Public speaking and visual aid usage |
Which is Better – Poster vs Oral Presentation
In conclusion, the choice between posters and oral presentations ultimately depends on various factors, such as the nature of the content, audience preferences, and available resources. Both formats have their strengths and limitations, and the decision should be based on the specific goals and circumstances of the presentation.
When choosing between posters and oral presentations, consider the level of audience engagement desired, the complexity of the information being conveyed, and the presentation skills of the presenter. While posters offer a visually appealing and self-paced experience, oral presentations provide real-time interaction and the opportunity for in-depth explanations.
In summary, posters are ideal when conveying concise information visually and when passive engagement is desired. On the other hand, oral presentations are best suited for interactive discussions, in-depth explanations, and audience engagement. Ultimately, the choice between posters and oral presentations should be based on the specific goals and requirements of the presentation.
Three reasons to choose posters:
- Visually engaging and can effectively communicate concise information.
- Allows for self-paced studying and analysis of the content.
- Minimal cost and resource requirements compared to oral presentations.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to presenting information, two common formats are posters and oral presentations. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about these two formats and their differences.
1. Which format is better for presenting information, a poster or an oral presentation?
Both formats have their advantages, and the choice depends on the context and purpose of the presentation. Posters are visually appealing and allow viewers to absorb information at their own pace. They are great for displaying complex data or visuals and can be easily referenced. Oral presentations, on the other hand, allow for direct interaction with the audience and the opportunity to convey information with enthusiasm and charisma. They are more dynamic and can often be more engaging for the audience. Ultimately, it’s important to consider the specific goals of your presentation and choose the format that aligns best with those objectives.
2. What are the main differences between a poster and an oral presentation?
The main difference is the way information is delivered. In a poster, the content is static and can be absorbed visually. Viewers can interpret the information at their own pace and refer back to it when needed. An oral presentation, on the other hand, involves a live performance where the presenter delivers information verbally. This format allows for direct interaction with the audience, the use of visual aids, and the ability to adapt the delivery based on audience reactions. Another difference is the level of preparation required. Posters typically require more time for design and visual arrangement, while oral presentations require more time rehearsing and practicing engaging delivery.
3. Are there any advantages to using a poster instead of an oral presentation?
Yes, there are several advantages to using a poster. Posters are highly visual and can convey complex information in an easily digestible manner. They allow viewers to study the content at their own pace and can be used as reference material even after the presentation. Posters are also ideal for situations where there is limited time for presentations or if the presenter prefers a more hands-off approach. Additionally, posters can be displayed in public areas even after the event, reaching a wider audience and serving as a long-lasting visual representation of the topic.
4. Can an oral presentation be more engaging than a poster?
Yes, an oral presentation can often be more engaging than a poster. Oral presentations allow for direct interaction with the audience, enabling the presenter to capture their attention and convey information using gestures, voice modulation, and visual aids. Presenters can also adapt their delivery based on audience reactions and engage the audience through questions, discussions, or interactive activities. Additionally, the live nature of an oral presentation allows for the presenter’s enthusiasm and passion for the topic to shine through, making it more memorable and impactful for the audience.
5. Can a poster and an oral presentation be used together?
Absolutely! Combining a poster and an oral presentation can be a powerful way to enhance the impact of your message. By creating a visually appealing poster that provides an overview of the topic, you can effectively capture the audience’s attention. Then, during the oral presentation, you can dive deeper into the content, providing additional insights, anecdotes, and engaging the audience in an interactive discussion. This combination allows for the best of both worlds, offering the visual appeal and reference value of a poster, along with the dynamic engagement of an oral presentation.

Poster Presenting Tips : Cal NERDS’ Student Research Poster Presenting Tips
So, to sum it all up, when it comes to presenting information, there are two main options: posters and oral presentations. Posters are like visual aids that can help you explain your ideas with pictures, graphs, and text. On the other hand, oral presentations involve speaking to an audience and sharing your thoughts and information out loud.
Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages. Posters can be a great way to showcase your creativity and make your ideas visual. They allow your audience to take their time and study the information on their own. However, they might not provide enough explanation and can limit your ability to interact with your audience.
Oral presentations, on the other hand, give you a chance to engage with your audience directly. You can use your voice, gestures, and expressions to convey your message. However, they require more preparation and can be nerve-wracking for some people.
In the end, the best method for presenting information depends on your personal style and the situation. If you’re a visual person who likes to express yourself through images and graphs, posters might be your go-to. If you enjoy speaking and connecting with others, oral presentations might be a better fit.
Remember, it’s not about picking a winner between the two, but rather about choosing the method that works best for you and effectively communicates your ideas. So, whether you choose to create a poster or give an oral presentation, embrace the opportunity to share your knowledge and let your creativity shine!
Similar Posts
How to appreciate a presentation.
To appreciate a presentation, actively listen and engage with the content while giving positive feedback and asking thoughtful questions. When you are attentive and involved, it shows the presenter that you value their effort and encourages them to continue delivering high-quality presentations. Providing specific examples of what resonated with you or how you benefited from…
Representation Vs Presentation: Which Is Better For You?
When it comes to expressing ideas, there are two important concepts to consider: representation vs presentation. These terms often pop up in discussions about art, media, and communication. But what exactly do they mean? Well, let’s dive in and explore the difference between representation and presentation in a fun and engaging way! Representation is like…

How to Introduce Group Members in a Presentation Script
In a presentation script, introduce group members by briefly stating their names and roles. In this introduction, we will discuss the best ways to introduce group members in a presentation script, ensuring clarity and engagement with the audience. A well-crafted introduction can set the tone for a successful presentation. When introducing group members, it is…

How to Speak in A Perfect Tone?
To speak in a perfect tone, focus on using clear and confident voice modulation. Here’s how… Speaking with the right tone is essential to effectively communicate your thoughts, emotions, and intentions. It allows you to convey your message with clarity and impact, captivating your audience’s attention. However, achieving a perfect tone requires deliberate practice and…

What are the Advantages of Digital Slides?
Digital slides offer numerous advantages, including enhanced accessibility and ease of storage and sharing. They allow for quick access to slides from any location with an internet connection, making them ideal for remote learning or collaborative work. Additionally, digital slides can be stored indefinitely without the risk of physical damage or loss, providing a secure…
Why Is Presenting So Stressful?
Presenting is so stressful because it triggers fear of judgment and the pressure to perform flawlessly in front of an audience. When standing before a group, individuals experience anxiety and the heightened awareness of being evaluated, leading to increased stress levels. Presenting, whether it be a speech, a presentation, or a performance, can be an…
Customize Your Path
Filters Applied
Customize Your Experience.
Utilize the "Customize Your Path" feature to refine the information displayed in myRESEARCHpath based on your role, project inclusions, sponsor or funding, and management center.
Poster and oral presentations
Need assistance with poster presentations?
Get help with poster presentations.
Contact the Research Navigators:
- Email: [email protected]
Poster and oral presentations are typically delivered to academic colleagues at conferences or congresses. Here are some best practices and resources to help develop the content and visuals for a high-impact poster, and plan and practice memorable oral presentations.
The "Related Resources" on this page can be used to tap into Duke’s hub of templates, guides, and services to support researchers developing their presentations.
The Duke Medical Center Library has tips for things to keep in mind before working through the development of a poster presentation, and the Duke University Libraries' Center for Data and Visualization Sciences recorded a talk on preparing effective academic posters .
- Just like with any other publication, the specifications from the conference should be read and understood – there are often size limits or font requirements to keep in mind.
- A good title is critical for posters since presenters get just a few seconds to attract conference goers who are passing by. Make sure the title briefly and memorably portrays the most interesting or central finding of the work.
- Energy should be focused on a solid abstract, as the poster is simply a blown-up visualization of that summary.
- Less is more in poster design. Rather than shrinking fonts to fit the commentary, the commentary should be shrunk to fit the space on the poster, while retaining a readable font and plenty of white space.
The Thompson Writing Program has great general guidance on oral presentations, summarized throughout this page. There are several training opportunities listed in this page's "Related Resources" that can help researchers at all stages to hone their presentation skills.
- Preparing for an oral presentation will take the majority of a researcher's time. The goal of the talk should be fully understood as typically no more than 3-5 key points will be covered in a presentation; the audience and the time allotted should be carefully considered.
- Consideration of “guideposts” for the audience should be given. It is especially important in oral deliveries that information is organized in to meaningful blocks for the audience. Transitions should be emphasized during the presentation.
- Rather than creating a word-for-word speech, researchers should create a plan for each section, idea or point. By reading written points, delivery can be kept fresh.
- To engage audiences, it is a good idea to make strongest points first, and in a memorable way. While background and introduction sections are common in academic presentations, they are often already known to the audience.
The Duke Medical Center Library has tutorials, best practices for general design, and strategies for a high-impact poster presentations. Bass Connections also provides guidance on poster design.
Some important things to keep in mind are:
- Keeping posters simple and focusing on two things: Strong visualizations and small blocks of supporting text. Remember the audience; they will be standing a few feet away. Make sure the content is visible from afar.
- Follow brand guidelines from Duke or Duke School of Medicine . When representing Duke at a conference, it is best practice to align the presentation with institutional standards, including appropriate logos and color schemes.
- Avoid violating copyright protections. Include only images created specifically for this purpose, or use stock photography provided by Duke or other vendors.
- Visualizing data tells the story. The Center for Data and Visualization Sciences has workshops, consultations and other resources to ensure that graphical representations of data are effective.
- Poster presentations can be designed using a variety of software (PowerPoint, Illustrator, Keynote, Inkscape), and templates. When choosing software or templates, consideration should be given to accessibility and understanding by everyone involved in creating the presentation.
- Contact information, citations and acknowledgements: On posters, key articles may be noted or images needing references included. For oral and poster presentations, key contributors should be recognized. Funding sources should also be mentioned on posters and in oral presentations.
- A link or QR code should be included for supplemental materials, citations, movies, etc.
- Before a poster is printed, someone with fresh eyes should review it! Reprinting posters is costly and can take time. There are many options for printing, some on paper and some on fabric, with production times varying. The Medical Center Library has some local options to suggest.
- Practicing in a space that is similar to the actual presentation is a good idea, and doing so within the allotted time. Finishing early to allow good Q&A is also a good idea.
- Family, trusted friends, or colleagues can be great test audiences, and can provide valuable feedback.
- Preparation and practice should be started early and repeated often.
- If it is an important address, researchers may want to videotape a rehearsal run to review and improve performance.
- If a presentation is being digitized, release or permission forms may be needed. Duke has resources available via Scholarworks.
- Once a poster session or oral presentation has been completed, researchers should be sure to add it to their CV or biosketch.
Home Blog Design How to Design a Winning Poster Presentation: Quick Guide with Examples & Templates
How to Design a Winning Poster Presentation: Quick Guide with Examples & Templates

How are research posters like High School science fair projects? Quite similar, in fact.
Both are visual representations of a research project shared with peers, colleagues and academic faculty. But there’s a big difference: it’s all in professionalism and attention to detail. You can be sure that the students that thrived in science fairs are now creating fantastic research posters, but what is that extra element most people miss when designing a poster presentation?
This guide will teach tips and tricks for creating poster presentations for conferences, symposia, and more. Learn in-depth poster structure and design techniques to help create academic posters that have a lasting impact.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
- What is a Research Poster?
Why are Poster Presentations important?
Overall dimensions and orientation, separation into columns and sections, scientific, academic, or something else, a handout with supplemental and contact information, cohesiveness, design and readability, storytelling.
- Font Characteristics
- Color Pairing
- Data Visualization Dimensions
- Alignment, Margins, and White Space
Scientific/Academic Conference Poster Presentation
Digital research poster presentations, slidemodel poster presentation templates, how to make a research poster presentation step-by-step, considerations for printing poster presentations, how to present a research poster presentation, final words, what is a research poster .
Research posters are visual overviews of the most relevant information extracted from a research paper or analysis. They are essential communication formats for sharing findings with peers and interested people in the field. Research posters can also effectively present material for other areas besides the sciences and STEM—for example, business and law.
You’ll be creating research posters regularly as an academic researcher, scientist, or grad student. You’ll have to present them at numerous functions and events. For example:
- Conference presentations
- Informational events
- Community centers
The research poster presentation is a comprehensive way to share data, information, and research results. Before the pandemic, the majority of research events were in person. During lockdown and beyond, virtual conferences and summits became the norm. Many researchers now create poster presentations that work in printed and digital formats.

Let’s look at why it’s crucial to spend time creating poster presentations for your research projects, research, analysis, and study papers.

Research posters represent you and your sponsor’s research
Research papers and accompanying poster presentations are potent tools for representation and communication in your field of study. Well-performing poster presentations help scientists, researchers, and analysts grow their careers through grants and sponsorships.
When presenting a poster presentation for a sponsored research project, you’re representing the company that sponsored you. Your professionalism, demeanor, and capacity for creating impactful poster presentations call attention to other interested sponsors, spreading your impact in the field.
Research posters demonstrate expertise and growth
Presenting research posters at conferences, summits, and graduate grading events shows your expertise and knowledge in your field of study. The way your poster presentation looks and delivers, plus your performance while presenting the work, is judged by your viewers regardless of whether it’s an officially judged panel.
Recurring visitors to research conferences and symposia will see you and your poster presentations evolve. Improve your impact by creating a great poster presentation every time by paying attention to detail in the poster design and in your oral presentation. Practice your public speaking skills alongside the design techniques for even more impact.
Poster presentations create and maintain collaborations
Every time you participate in a research poster conference, you create meaningful connections with people in your field, industry or community. Not only do research posters showcase information about current data in different areas, but they also bring people together with similar interests. Countless collaboration projects between different research teams started after discussing poster details during coffee breaks.
An effective research poster template deepens your peer’s understanding of a topic by highlighting research, data, and conclusions. This information can help other researchers and analysts with their work. As a research poster presenter, you’re given the opportunity for both teaching and learning while sharing ideas with peers and colleagues.
Anatomy of a Winning Poster Presentation
Do you want your research poster to perform well? Following the standard layout and adding a few personal touches will help attendees know how to read your poster and get the most out of your information.

The overall size of your research poster ultimately depends on the dimensions of the provided space at the conference or research poster gallery. The poster orientation can be horizontal or vertical, with horizontal being the most common. In general, research posters measure 48 x 36 inches or are an A0 paper size.
A virtual poster can be the same proportions as the printed research poster, but you have more leeway regarding the dimensions. Virtual research posters should fit on a screen with no need to scroll, with 1080p resolution as a standard these days. A horizontal presentation size is ideal for that.
A research poster presentation has a standard layout of 2–5 columns with 2–3 sections each. Typical structures say to separate the content into four sections; 1. A horizontal header 2. Introduction column, 3. Research/Work/Data column, and 4. Conclusion column. Each unit includes topics that relate to your poster’s objective. Here’s a generalized outline for a poster presentation:
- Condensed Abstract
- Objectives/Purpose
- Methodology
- Recommendations
- Implications
- Acknowledgments
- Contact Information
The overview content you include in the units depends on your poster presentations’ theme, topic, industry, or field of research. A scientific or academic poster will include sections like hypothesis, methodology, and materials. A marketing analysis poster will include performance metrics and competitor analysis results.
There’s no way a poster can hold all the information included in your research paper or analysis report. The poster is an overview that invites the audience to want to find out more. That’s where supplement material comes in. Create a printed PDF handout or card with a QR code (created using a QR code generator ). Send the audience to the best online location for reading or downloading the complete paper.
What Makes a Poster Presentation Good and Effective?
For your poster presentation to be effective and well-received, it needs to cover all the bases and be inviting to find out more. Stick to the standard layout suggestions and give it a unique look and feel. We’ve put together some of the most critical research poster-creation tips in the list below. Your poster presentation will perform as long as you check all the boxes.
The information you choose to include in the sections of your poster presentation needs to be cohesive. Train your editing eye and do a few revisions before presenting. The best way to look at it is to think of The Big Picture. Don’t get stuck on the details; your attendees won’t always know the background behind your research topic or why it’s important.
Be cohesive in how you word the titles, the length of the sections, the highlighting of the most important data, and how your oral presentation complements the printed—or virtual—poster.
The most important characteristic of your poster presentation is its readability and clarity. You need a poster presentation with a balanced design that’s easy to read at a distance of 1.5 meters or 4 feet. The font size and spacing must be clear and neat. All the content must suggest a visual flow for the viewer to follow.
That said, you don’t need to be a designer to add something special to your poster presentation. Once you have the standard—and recognized—columns and sections, add your special touch. These can be anything from colorful boxes for the section titles to an interesting but subtle background, images that catch the eye, and charts that inspire a more extended look.
Storytelling is a presenting technique involving writing techniques to make information flow. Firstly, storytelling helps give your poster presentation a great introduction and an impactful conclusion.
Think of storytelling as the invitation to listen or read more, as the glue that connects sections, making them flow from one to another. Storytelling is using stories in the oral presentation, for example, what your lab partner said when you discovered something interesting. If it makes your audience smile and nod, you’ve hit the mark. Storytelling is like giving a research presentation a dose of your personality, and it can help turning your data into opening stories .
Design Tips For Creating an Effective Research Poster Presentation
The section above briefly mentioned how important design is to your poster presentation’s effectiveness. We’ll look deeper into what you need to know when designing a poster presentation.
1. Font Characteristics
The typeface and size you choose are of great importance. Not only does the text need to be readable from two meters away, but it also needs to look and sit well on the poster. Stay away from calligraphic script typefaces, novelty typefaces, or typefaces with uniquely shaped letters.
Stick to the classics like a sans serif Helvetica, Lato, Open Sans, or Verdana. Avoid serif typefaces as they can be difficult to read from far away. Here are some standard text sizes to have on hand.
- Title: 85 pt
- Authors: 65 pt
- Headings: 36 pt
- Body Text: 24 pt
- Captions: 18 pt

If you feel too prone to use serif typefaces, work with a font pairing tool that helps you find a suitable solution – and intend those serif fonts for heading sections only. As a rule, never use more than 3 different typefaces in your design. To make it more dynamic, you can work with the same font using light, bold, and italic weights to put emphasis on the required areas.
2. Color Pairing
Using colors in your poster presentation design is a great way to grab the viewer’s attention. A color’s purpose is to help the viewer follow the data flow in your presentation, not distract. Don’t let the color take more importance than the information on your poster.

Choose one main color for the title and headlines and a similar color for the data visualizations. If you want to use more than one color, don’t create too much contrast between them. Try different tonalities of the same color and keep things balanced visually. Your color palette should have at most one main color and two accent colors.
Black text over a white background is standard practice for printed poster presentations, but for virtual presentations, try a very light gray instead of white and a very dark gray instead of black. Additionally, use variations of light color backgrounds and dark color text. Make sure it’s easy to read from two meters away or on a screen, depending on the context. We recommend ditching full white or full black tone usage as it hurts eyesight in the long term due to its intense contrast difference with the light ambiance.
3. Data Visualization Dimensions
Just like the text, your charts, graphs, and data visualizations must be easy to read and understand. Generally, if a person is interested in your research and has already read some of the text from two meters away, they’ll come closer to look at the charts and graphs.

Fit data visualizations inside columns or let them span over two columns. Remove any unnecessary borders, lines, or labels to make them easier to read at a glance. Use a flat design without shadows or 3D characteristics. The text in legends and captions should stay within the chart size and not overflow into the margins. Use a unified text size of 18px for all your data visualizations.
4. Alignment, Margins, and White Space
Finally, the last design tip for creating an impressive and memorable poster presentation is to be mindful of the layout’s alignment, margins, and white space. Create text boxes to help keep everything aligned. They allow you to resize, adapt, and align the content along a margin or grid.
Take advantage of the white space created by borders and margins between sections. Don’t crowd them with a busy background or unattractive color.

Calculate margins considering a print format. It is a good practice in case the poster presentation ends up becoming in physical format, as you won’t need to downscale your entire design (affecting text readability in the process) to preserve information.
There are different tools that you can use to make a poster presentation. Presenters who are familiar with Microsoft Office prefer to use PowerPoint. You can learn how to make a poster in PowerPoint here.
Poster Presentation Examples
Before you start creating a poster presentation, look at some examples of real research posters. Get inspired and get creative.
Research poster presentations printed and mounted on a board look like the one in the image below. The presenter stands to the side, ready to share the information with visitors as they walk up to the panels.

With more and more conferences staying virtual or hybrid, the digital poster presentation is here to stay. Take a look at examples from a poster session at the OHSU School of Medicine .
Use SlideModel templates to help you create a winning poster presentation with PowerPoint and Google Slides. These poster PPT templates will get you off on the right foot. Mix and match tables and data visualizations from other poster slide templates to create your ideal layout according to the standard guidelines.
If you need a quick method to create a presentation deck to talk about your research poster at conferences, check out our Slides AI presentation maker. A tool in which you add the topic, curate the outline, select a design, and let AI do the work for you.
1. One-pager Scientific Poster Template for PowerPoint

A PowerPoint template tailored to make your poster presentations an easy-to-craft process. Meet our One-Pager Scientific Poster Slide Template, entirely editable to your preferences and with ample room to accommodate graphs, data charts, and much more.
Use This Template
2. Eisenhower Matrix Slides Template for PowerPoint

An Eisenhower Matrix is a powerful tool to represent priorities, classifying work according to urgency and importance. Presenters can use this 2×2 matrix in poster presentations to expose the effort required for the research process, as it also helps to communicate strategy planning.
3. OSMG Framework PowerPoint Template

Finally, we recommend presenters check our OSMG Framework PowerPoint template, as it is an ideal tool for representing a business plan: its goals, strategies, and measures for success. Expose complex processes in a simplified manner by adding this template to your poster presentation.
Remember these three words when making your research poster presentation: develop, design, and present. These are the three main actions toward a successful poster presentation.

The section below will take you on a step-by-step journey to create your next poster presentation.
Step 1: Define the purpose and audience of your poster presentation
Before making a poster presentation design, you’ll need to plan first. Here are some questions to answer at this point:
- Are they in your field?
- Do they know about your research topic?
- What can they get from your research?
- Will you print it?
- Is it for a virtual conference?
Step 2: Make an outline
With a clear purpose and strategy, it’s time to collect the most important information from your research paper, analysis, or documentation. Make a content dump and then select the most interesting information. Use the content to draft an outline.
Outlines help formulate the overall structure better than going straight into designing the poster. Mimic the standard poster structure in your outline using section headlines as separators. Go further and separate the content into the columns they’ll be placed in.
Step 3: Write the content
Write or rewrite the content for the sections in your poster presentation. Use the text in your research paper as a base, but summarize it to be more succinct in what you share.
Don’t forget to write a catchy title that presents the problem and your findings in a clear way. Likewise, craft the headlines for the sections in a similar tone as the title, creating consistency in the message. Include subtle transitions between sections to help follow the flow of information in order.
Avoid copying/pasting entire sections of the research paper on which the poster is based. Opt for the storytelling approach, so the delivered message results are interesting for your audience.
Step 4: Put it all together visually
This entire guide on how to design a research poster presentation is the perfect resource to help you with this step. Follow all the tips and guidelines and have an unforgettable poster presentation.
Moving on, here’s how to design a research poster presentation with PowerPoint Templates . Open a new project and size it to the standard 48 x 36 inches. Using the outline, map out the sections on the empty canvas. Add a text box for each title, headline, and body text. Piece by piece, add the content into their corresponding text box.

Transform the text information visually, make bullet points, and place the content in tables and timelines. Make your text visual to avoid chunky text blocks that no one will have time to read. Make sure all text sizes are coherent for all headings, body texts, image captions, etc. Double-check for spacing and text box formatting.
Next, add or create data visualizations, images, or diagrams. Align everything into columns and sections, making sure there’s no overflow. Add captions and legends to the visualizations, and check the color contrast with colleagues and friends. Ask for feedback and progress to the last step.
Step 5: Last touches
Time to check the final touches on your poster presentation design. Here’s a checklist to help finalize your research poster before sending it to printers or the virtual summit rep.
- Check the resolution of all visual elements in your poster design. Zoom to 100 or 200% to see if the images pixelate. Avoid this problem by using vector design elements and high-resolution images.
- Ensure that charts and graphs are easy to read and don’t look crowded.
- Analyze the visual hierarchy. Is there a visual flow through the title, introduction, data, and conclusion?
- Take a step back and check if it’s legible from a distance. Is there enough white space for the content to breathe?
- Does the design look inviting and interesting?
An often neglected topic arises when we need to print our designs for any exhibition purpose. Since A0 is a hard-to-manage format for most printers, these poster presentations result in heftier charges for the user. Instead, you can opt to work your design in two A1 sheets, which also becomes more manageable for transportation. Create seamless borders for the section on which the poster sheets should meet, or work with a white background.
Paper weight options should be over 200 gsm to avoid unwanted damage during the printing process due to heavy ink usage. If possible, laminate your print or stick it to photographic paper – this shall protect your work from spills.
Finally, always run a test print. Gray tints may not be printed as clearly as you see them on screen (this is due to the RGB to CMYK conversion process). Other differences can be appreciated when working with ink jet plotters vs. laser printers. Give yourself enough room to maneuver last-minute design changes.
Presenting a research poster is a big step in the poster presentation cycle. Your poster presentation might or might not be judged by faculty or peers. But knowing what judges look for will help you prepare for the design and oral presentation, regardless of whether you receive a grade for your work or if it’s business related. Likewise, the same principles apply when presenting at an in-person or virtual summit.
The opening statement
Part of presenting a research poster is welcoming the viewer to your small personal area in the sea of poster presentations. You’ll need an opening statement to pitch your research poster and get the viewers’ attention.
Draft a 2 to 3-sentence pitch that covers the most important points:
- What the research is
- Why was it conducted
- What the results say
From that opening statement, you’re ready to continue with the oral presentation for the benefit of your attendees.
The oral presentation
During the oral presentation, share the information on the poster while conversing with the interested public. Practice many times before the event. Structure the oral presentation as conversation points, and use the poster’s visual flow as support. Make eye contact with your audience as you speak, but don’t make them uncomfortable.
Pro Tip: In a conference or summit, if people show up to your poster area after you’ve started presenting it to another group, finish and then address the new visitors.
QA Sessions
When you’ve finished the oral presentation, offer the audience a chance to ask questions. You can tell them before starting the presentation that you’ll be holding a QA session at the end. Doing so will prevent interruptions as you’re speaking.
If presenting to one or two people, be flexible and answer questions as you review all the sections on your poster.
Supplemental Material
If your audience is interested in learning more, you can offer another content type, further imprinting the information in their minds. Some ideas include; printed copies of your research paper, links to a website, a digital experience of your poster, a thesis PDF, or data spreadsheets.
Your audience will want to contact you for further conversations; include contact details in your supplemental material. If you don’t offer anything else, at least have business cards.
Even though conferences have changed, the research poster’s importance hasn’t diminished. Now, instead of simply creating a printed poster presentation, you can also make it for digital platforms. The final output will depend on the conference and its requirements.
This guide covered all the essential information you need to know for creating impactful poster presentations, from design, structure and layout tips to oral presentation techniques to engage your audience better .
Before your next poster session, bookmark and review this guide to help you design a winning poster presentation every time.

Like this article? Please share
Cool Presentation Ideas, Design, Design Inspiration Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Design • January 11th, 2024
How to Use Figma for Presentations
The powerful UI/UX prototyping software can also help us to craft high-end presentation slides. Learn how to use Figma as a presentation software here!

Filed under Design • December 28th, 2023
Multimedia Presentation: Insights & Techniques to Maximize Engagement
Harnessing the power of multimedia presentation is vital for speakers nowadays. Join us to discover how you can utilize these strategies in your work.

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • December 15th, 2023
How to Delete a Text Box in Google Slides
Discover how to delete a text box in Google Slides in just a couple of clicks. Step-by-step guide with images.

Leave a Reply
Preparing Oral and Poster Presentations
- First Online: 02 March 2024
Cite this chapter

- Kimberly M. Rathbun 5
10 Accesses
A poster or oral presentation is a great way to share your research project and get feedback. Designing a poster or preparing an oral presentation should be done within the guidelines set forth by the conference. Traditional posters and oral presentations convey the same information in different formats. When presenting your study, you should know all the details of the project and be able to field any questions from the audience.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Suggested Readings
Barker E, Phillips V. Creating conference posters: structure, form and content. J Perioper Pract. 2021;31(7–8):296–9.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gundogan B, Koshy K, Kurar L, Whitehurst K. How to make an academic poster. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2016;11:69–71.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Naegle KM. Ten simple rules for effective presentation slides. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021;17(12):e1009554.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Emergency Medicine, AU/UGA Medical Partnership, Athens, GA, USA
Kimberly M. Rathbun
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kimberly M. Rathbun .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Emergency Medicine, Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA, USA
Robert P. Olympia
Elizabeth Barrall Werley
Jeffrey S. Lubin
MD Anderson Cancer Center at Cooper, Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, Camden, NJ, USA
Kahyun Yoon-Flannery
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Rathbun, K.M. (2023). Preparing Oral and Poster Presentations. In: Olympia, R.P., Werley, E.B., Lubin, J.S., Yoon-Flannery, K. (eds) An Emergency Physician’s Path. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47873-4_79
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47873-4_79
Published : 02 March 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-47872-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-47873-4
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
21 Poster Presentations
Read time: 8 minutes
This section will outline how to communicate your scientific research in the format of a poster presentation, and provide guidance on designing your poster.
Sections in this chapter
Environment and audience, poster vs. talk, verbal aspect, poster design, virtual posters.

Many conferences have poster presentation sessions along with oral presentations. The poster presentation is a format introduced into the American Chemical Society meetings in the 1970s. This format allows more people the opportunity to present their work since many posters can be scheduled for the same time period and in one large room.
The format of a poster presentation allows for a one-on-one and in-depth discussion between the presenter and viewer. For this reason, poster sessions are often combined with social mixers, where people can walk around and browse the posters.
Theoretically, the poster audience is more broad and diverse, since many disciplines present in one large room. For this reason, your poster should be readable or understandable in less than 5 minutes by someone not in your field, who has only general knowledge of the research area. People browse posters and look for something that interests them, and on average spend around 90 seconds viewing a single poster. However, the people who actually attend your poster will likely be those who are interested in your work or work in a similar area.
Attaching business cards and one-page copies of your poster allow viewers to contact you later and get the information without having to take notes.
Table 21.1. Differences between posters and oral presentations (talks)
Posters are mostly non-verbal and visual, so most of this chapter will discuss poster design. However, the verbal aspect of the poster presentation is where many presenters struggle! The most common mistake is for presenters to launch into a detailed overview of the slides, starting at the introduction and working their way through the poster all the way to the acknowledgements. Even a 5-minute overview is too long at a poster! The issue with this approach is that the viewer cannot listen to you and think critically at the same time, and they lose the autonomy of exploring your visuals at their own pace. Follow these tips for a successful poster presentation:
- If someone shows interest in your poster, smile and introduce yourself, then wait.
- If they start to intently view your poster, let them do this silently without interruption.
- If they turn to you, ask if they would like a short overview of your work.
- Start with the key finding, from your conclusion, and state it in a single sentence.
- Then move on to your motivation and methods and details about the results.
- Make sure to pause and make eye contact, which will let viewers ask questions.
- Ask your viewer questions to gauge their interest and background, and encourage discussion
- Point to relevant things on your poster as you present.
There are some aspects of etiquette to giving poster presentations. First of all, you should be at your poster during the specified times. Socializing with friends should be a lower priority, so if your lab members are hanging around your poster you can politely ask them to give you some space. Stay tuned to social cues from your viewer, and let them view the poster silently if they seem to want that. Lastly, consider waiting until after the presentation for drinks.
Format and Size
Posters should be concise, organized, and self-explanatory: the best way to achieve this is to have a central and obvious message. Beyond that, a poster should be easy to view from 1-2 meters away, which means you should limit text to short paragraphs (<20 lines) or bullet points. Remember that you are not writing a full paper! Any text should be in a simple Sans-Serif typeface ( e.g., Arial, Verdana, Calibri) with adequate spacing, and large enough to easily read. Consider using a different font style for the title and headings than the main text. Follow this guide for minimum text sizes:
Title 100 pt (Verdana, bold)
Authors 36 pt (Arial, bold)
Headings 54 pt (Verdana, bold)
Main text 32 pt (Arial)
References 28 point (Arial)
Instead of text, use figures, graphs, and charts to visually communicate of your work. Make sure the text labels and axes are large enough to easily read, following the guide above.
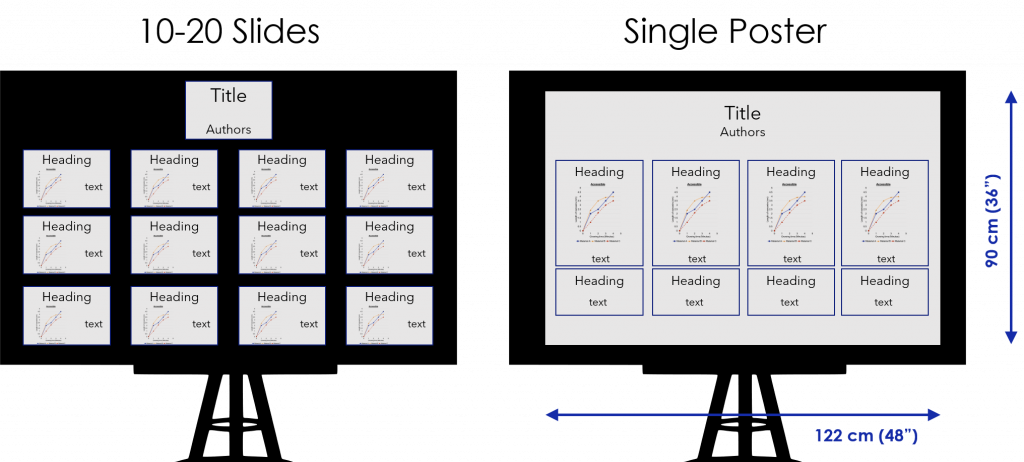
Check the conference website for instructions on the acceptable dimensions for posters. The typically allowed dimensions are 90 cm (36”) high x 122 cm (48”) wide. There are two ways to create your poster (Figure 21.1): 1) print 12-20 regular slides on 8.5″ x 11″ pieces of paper, and arrange them; 2) create a single large poster sheet, either printed on paper or fabric, to fill the whole space.
Posters have all the components of a paper, organized into sections. These sections are not always separate on your poster (see below ‘Layout’), but they should be present in one way or another. See Table 21.2. for a list of sections and their descriptions.
Table 21.2. Poster sections
Sections in your poster are outlined by headings. Instead of using section titles like “Introduction”, use descriptive headings that tell the viewer the key message of the section (Table 21.3).
Table 21.3. Replacing poster headings with descriptive headings
Layout & design.
A thoughtful layout will provide a natural flow that guides people through your poster. It is best to arrange your poster in blocks of columns, so that the audience reads from left to right, top to bottom using “reader’s gravity”. You can number each section block or heading to help the reader to follow the flow of the material.
Posters with symmetric layouts and plenty of ‘white space’ are more visually pleasing, and can also help with flow. Also, place graphics and text to create a symmetrical balance.
Instead of headings like “Introduction”, use descriptive headings to clearly communicate your main points. A lack of headings, plus an asymmetric layout of the material, makes it difficult for the viewer to follow the flow or find a particular section of the poster.
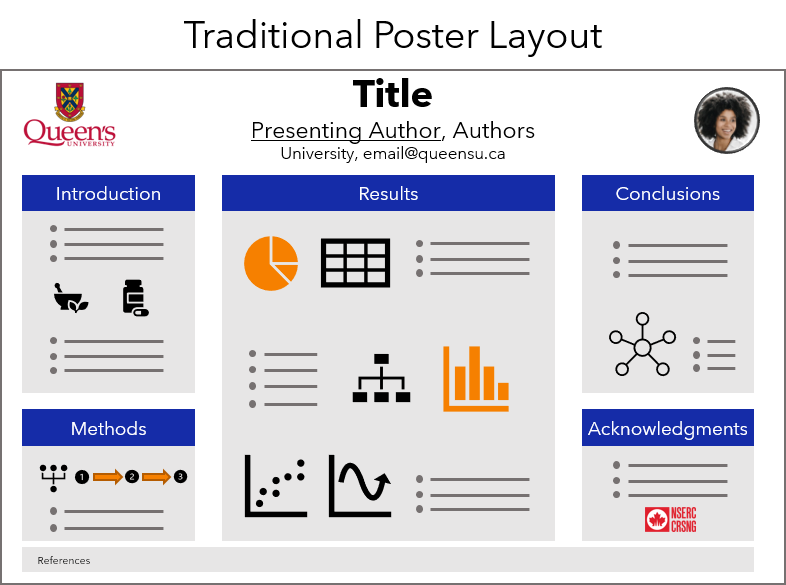
A popular traditional poster format (see Figure 21.2) has a landscape layout and three columns: 1) Introduction and Methods, 25% width; 2) Results arena, 50% Width; 3) Conclusions and Acknowledgements, 25% width. A more modern landscape layout (Figure 21.3) was designed by Mike Morrison , [1] which features a large takeaway sidebar with the key message, and a QR code that links to the paper or a website. This modern poster format also works well in a portrait format (Figure 21.4).

Stick to a theme of 2 or 3 colours, using an accessible colour scheme , and be consistent with the use of colours that have meaning (e.g., in legends). Don’t be afraid to use b right colours to attract attention, but if you overuse them you will wear out readers’ eyes. For the body of your poster, use a light coloured background and dark coloured text. Dark backgrounds with light letters can become tiring to read but are often used for headings.
Don’t start from scratch
There are many poster templates available online! Here are some PowerPoint templates and guides:
BetterPosters.blogspot.com landscape template
BetterPosters.blogspot.com portrait template
BetterPosters.blogspot.com Twitter template
Queen’s Chemistry Landscape Poster Template
Queen’s Chemistry Portrait Poster Template
Online conferences and symposia are becoming more common, including virtual poster sessions. Virtual posters can have animations, videos, and audio narration. These posters can take many formats, but one common format is for the RSC Poster Day on Twitter. They published this guide to creating a version of your poster on Twitter, and how to identify your work using the right hashtag ( e.g., #RSCOrganic, #RSCAnalytical).
Here are some links to the 2020 winners of #RSCPoster Day.
Super excited to share my research on the use of electrochemistry as a tool for drug detection in complex matrices as a #comicsforscience for my first #RSCPoster #RSCAnalytical #RSCPhys #electrochem @DennanyChem @PamelaAllanChem @CarnegieUni @StrathChem @StrathForensics pic.twitter.com/ISzJ55Hbqh — Kelly Brown (@kellybrown_94) March 3, 2020
Excited to share my first #RSCPoster and looking forward to interact with all the #chemtweeps to discuss magnetic photocatalysis 🧲💡 #RSCCat #RSCNano #RSCMat pic.twitter.com/XzwxnIYJyh — Julio Terra, Ph.D. (@_julioterra) March 3, 2020
Here we go again! NEON can deny, oops I mean no-one can deny Hydrogen's BRIGHT future for renewable energy! Here is my fun twist on my LIGHT weight hydrogen storage for mobile fuel cell applications research at @lborouniversity @LboroScience #RSCEnergy #RSCPoster pic.twitter.com/8DzRUHobiA — Lizzie Ashton (@LizzieRAshton) March 3, 2020
- " Critique: The Morrison billboard poster ", Zen Faulkes, April 11, 2019, Better Posters. Accessed 2020-08-31 ↵
Principles of Scientific Communication Copyright © 2020 by Amanda Bongers and Donal Macartney is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
University Library, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign

Research Posters : Oral Presentations
- Elements of a poster
- Step by step
- Visualizations & images
- Illinois logo
- Archiving - Grad Students
- More Resources
- Oral Presentations
- 2024 Undergraduate Research Symposium This link opens in a new window
TIPS FOR ORAL PRESENTATIONS
- How to give a great oral presentation
- Ten Simple Rules for Making Good Oral Presentations
- Top 15 tips to give a good oral presentation
- Designing PowerPoint Slides for a Scientific Presentation
The Speaking Center
The Library offers speaking consultation and practice at the The Speaking Center . Schedule an appointment with us and practice giving your presentation.
CONSIDERING YOUR CONTENT
I have been accepted to present an oral presentation at the Symposium; how do I upload my talk? All oral presentation rooms are equipped with PC laptops (no Apple Mac's) so be sure the format of your presentation is compatible with PCs. In general, we recommend that students save their presentations in two formats: the first being a .PPT (Microsoft PowerPoint) file, and the back-up being a .PDF (Adobe Acrobat) file. Please bring these files on a portable drive (flash drive, etc.) to your oral presentation panel and be sure to show up early to allow enough time to download it to the computer prior to the start of the session.
- Think of, or research, an attention grabber: a story, fact or statistic, or other interesting piece of information that will help draw in the audience right away and frame the talk in a minute or less.
- Focus only on the 3 most important points. Introduce them at the beginning, and repeat them at the very end.
- Have 2-3 specifics/particular points that fall within each of the three categories, and, if possible, also have a brief story or example to illustrate each main point.
- Write out transitions between major points and examples (and practice them) so your speech will flow better. Example: “So far we’ve discussed [x], but on the other end of the spectrum is this other important aspect, [y].”
- Be gender neutral. Even though it may not technically be grammatically correct, today it is acceptable in formal presentations in most contexts to use “they” and “them” instead of she/he, him/her.
- Try, if you can, to incorporate a bit of tasteful humor. It shouldn’t be forced; it needs to fit in with the rest of the speech and feel natural to be funny. Don’t be afraid to improvise during your talk, if you can do so comfortably.
- Have someone else read your speech, or alternately, practice your presentation in front of them – so they can critique the content and delivery.
PRESENTATION DELIVERY
1. Practice and prepare. Practice in front of a mirror. Take a video or audio recording of yourself. Rehearse the presentation in your head when you are unable to rehearse it aloud. With the right amount of practice and preparation, the words will flow more easily on presentation day. Don’t strive for absolute perfection, though: too much rehearsal may make you come across stiff and stifled, not natural.
2. When practicing, pay attention to your voice inflections, including which words and syllables you will emphasize. Be deliberate. Your voice inflections and emphases will affect your audience members’ interpretation, comprehension, and retention of the material.
3. Know how you are going to stand, gesture, and move your body. Practice walking around a bit – moving toward your audience and back towards the screen/lectern, for example. Try to face your audience at all times, and look around the room at individual audience members as much as possible. Make the audience feel like you are directly addressing them. While some movement is fine and can complement your style, be careful not to walk or pace too much; this can be distracting.
4. Wear comfortable professional clothing and comfortable shoes. You will not want to be distracted because you are uncomfortable.
5. Be early. If you are running late, you will be more nervous and have less time to prepare yourself mentally.
6. On the day of the talk, take 10-15 minutes before your presentation to relax, do some deep breathing, and keep your mind off of the presentation for a bit. You want to be relaxed during your presentation.
7. Be confident! Be passionate! Be energetic! You’ve got this. Don’t expect to be perfect, but if you have practiced and you are confident, it will show and make for a great presentation.
- << Previous: More Resources
- Next: 2024 Undergraduate Research Symposium >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 12:09 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.illinois.edu/poster
This page has been archived and is no longer updated
Oral Presentation Structure
Finally, presentations normally include interaction in the form of questions and answers. This is a great opportunity to provide whatever additional information the audience desires. For fear of omitting something important, most speakers try to say too much in their presentations. A better approach is to be selective in the presentation itself and to allow enough time for questions and answers and, of course, to prepare well by anticipating the questions the audience might have.
As a consequence, and even more strongly than papers, presentations can usefully break the chronology typically used for reporting research. Instead of presenting everything that was done in the order in which it was done, a presentation should focus on getting a main message across in theorem-proof fashion — that is, by stating this message early and then presenting evidence to support it. Identifying this main message early in the preparation process is the key to being selective in your presentation. For example, when reporting on materials and methods, include only those details you think will help convince the audience of your main message — usually little, and sometimes nothing at all.
The opening
- The context as such is best replaced by an attention getter , which is a way to both get everyone's attention fast and link the topic with what the audience already knows (this link provides a more audience-specific form of context).
- The object of the document is here best called the preview because it outlines the body of the presentation. Still, the aim of this element is unchanged — namely, preparing the audience for the structure of the body.
- The opening of a presentation can best state the presentation's main message , just before the preview. The main message is the one sentence you want your audience to remember, if they remember only one. It is your main conclusion, perhaps stated in slightly less technical detail than at the end of your presentation.
In other words, include the following five items in your opening: attention getter , need , task , main message , and preview .
Even if you think of your presentation's body as a tree, you will still deliver the body as a sequence in time — unavoidably, one of your main points will come first, one will come second, and so on. Organize your main points and subpoints into a logical sequence, and reveal this sequence and its logic to your audience with transitions between points and between subpoints. As a rule, place your strongest arguments first and last, and place any weaker arguments between these stronger ones.
The closing
After supporting your main message with evidence in the body, wrap up your oral presentation in three steps: a review , a conclusion , and a close . First, review the main points in your body to help the audience remember them and to prepare the audience for your conclusion. Next, conclude by restating your main message (in more detail now that the audience has heard the body) and complementing it with any other interpretations of your findings. Finally, close the presentation by indicating elegantly and unambiguously to your audience that these are your last words.
Starting and ending forcefully
Revealing your presentation's structure.
To be able to give their full attention to content, audience members need structure — in other words, they need a map of some sort (a table of contents, an object of the document, a preview), and they need to know at any time where they are on that map. A written document includes many visual clues to its structure: section headings, blank lines or indentations indicating paragraphs, and so on. In contrast, an oral presentation has few visual clues. Therefore, even when it is well structured, attendees may easily get lost because they do not see this structure. As a speaker, make sure you reveal your presentation's structure to the audience, with a preview , transitions , and a review .
The preview provides the audience with a map. As in a paper, it usefully comes at the end of the opening (not too early, that is) and outlines the body, not the entire presentation. In other words, it needs to include neither the introduction (which has already been delivered) nor the conclusion (which is obvious). In a presentation with slides, it can usefully show the structure of the body on screen. A slide alone is not enough, however: You must also verbally explain the logic of the body. In addition, the preview should be limited to the main points of the presentation; subpoints can be previewed, if needed, at the beginning of each main point.
Transitions are crucial elements for revealing a presentation's structure, yet they are often underestimated. As a speaker, you obviously know when you are moving from one main point of a presentation to another — but for attendees, these shifts are never obvious. Often, attendees are so involved with a presentation's content that they have no mental attention left to guess at its structure. Tell them where you are in the course of a presentation, while linking the points. One way to do so is to wrap up one point then announce the next by creating a need for it: "So, this is the microstructure we observe consistently in the absence of annealing. But how does it change if we anneal the sample at 450°C for an hour or more? That's my next point. Here is . . . "
Similarly, a review of the body plays an important double role. First, while a good body helps attendees understand the evidence, a review helps them remember it. Second, by recapitulating all the evidence, the review effectively prepares attendees for the conclusion. Accordingly, make time for a review: Resist the temptation to try to say too much, so that you are forced to rush — and to sacrifice the review — at the end.
Ideally, your preview, transitions, and review are well integrated into the presentation. As a counterexample, a preview that says, "First, I am going to talk about . . . , then I will say a few words about . . . and finally . . . " is self-centered and mechanical: It does not tell a story. Instead, include your audience (perhaps with a collective we ) and show the logic of your structure in view of your main message.
This page appears in the following eBook
Topic rooms within Scientific Communication

Within this Subject (22)
- Communicating as a Scientist (3)
- Papers (4)
- Correspondence (5)
- Presentations (4)
- Conferences (3)
- Classrooms (3)
Other Topic Rooms
- Gene Inheritance and Transmission
- Gene Expression and Regulation
- Nucleic Acid Structure and Function
- Chromosomes and Cytogenetics
- Evolutionary Genetics
- Population and Quantitative Genetics
- Genes and Disease
- Genetics and Society
- Cell Origins and Metabolism
- Proteins and Gene Expression
- Subcellular Compartments
- Cell Communication
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
© 2014 Nature Education
- Press Room |
- Terms of Use |
- Privacy Notice |

Visual Browse
Poster Presentations
Poster presentations (pdf), considering the audience.
As with any presentation, you should consider who is likely to be listening. In some cases, your audience is going to be people who know a fair bit about your topic or discipline. In other cases, such as a poster session for a family weekend, you are likely to get some people who know the topic, but also many more people who are just curious about the research that is going on. You should plan to adapt based on the person with whom you are interacting. Ask yourself: what does this person likely know and what will they want to know?
Preparing a Pitch
You should plan for having a short (about 2 minutes) summary overview of the project that can give a listener a taste of what you did. You can use that time to answer three big questions:
- What is the topic?
- What did you find? Or What are the results?
- Why is this important?
People will ask follow-up questions if they are interested in learning more or if they are confused about something you said. Think of this pitch as an appetizer: you want to whet someone’s appetite to learn more about your topic, but that small bite may be sufficient for some people.
When thinking about the pitch, keep in mind that you do not need to verbally address every component of the poster in your first remarks. You should, however, be prepared to talk about each component if asked. You should never read directly from the poster to the audience!
Posters with a Partner
If you worked on your project with another person, you should both be prepared to give the basic pitch. You may have parts of the project that each of you is more comfortable talking about in detail, but each of you should know the fundamentals in case you are asked. Then, you can pass off a question to the other person if necessary.
Preparing for Questions
You should anticipate questions from the people who view your poster. One part of your preparation can be brainstorming the likely questions and then practicing answering those questions. If you are presenting your poster at a professional meeting with other people from the discipline, you can expect more technical or content questions than if you are presenting to a more general audience. Some likely general questions you may get are:
- What made you interested in this topic?
- Why was this approach/tool/theory the most appropriate for your project?
- Where do you go from here with this research?
- What was the most interesting/surprising/challenging part of this project?
- How does this project relate to other work you are doing?
Regardless of the question, it’s ok to take a breath and focus before you start to answer. Your response should be focused and succinct as well as appropriate for the audience. If you aren’t sure what someone is asking, ask for clarification!
Ideally, the poster session will give you an opportunity to engage in a dialogue about your work. In fact, that’s one of the main draws of posters as a way to disseminate research findings.
Interacting with Your Poster
You and your poster are a team, working together to present your ideas. Once your poster is mounted, you should position yourself so that you are close to your poster but not blocking it from passersby, especially the title. Additionally:
- You should feel free to move as necessary to show different parts of the poster.
- Gesture to the relevant parts of the poster. You should use your whole hand to point toward something rather than just pointing a finger. Graphs and other data are excellent parts of a poster for gesturing. Avoid turning your back on your audience to gesture. Use the arm closest to the poster to gesture so you are not gesturing across your body or turning.
- Avoid standing with your arms crossed or otherwise looking defensive both while talking and while waiting for an audience. Closed off body language makes you appear less welcoming for someone to approach.
- Don’t forget to smile. Even if you are feeling nervous, you can “fake it ‘til you make it” by adopting a smile and acting confident.
Office / Department Name
Oral Communication Center
Contact Name
Amy Gaffney
Oral Communication Center Director

Help us provide an accessible education, offer innovative resources and programs, and foster intellectual exploration.
Site Search

Preparing oral and poster presentations for conferences
As a PhD student, attending conferences is an exciting part of academic life. Conferences are a chance to share your research findings, learn novel ideas or techniques and travel, whether that is locally, further afield or even internationally. A crucial aspect to conference attending is conveying your research to the wider scientific community, through either a poster or oral presentation.
Preparing your research to present at a conference is a balance. You need to include the same details as you would put in a paper or report, but make it concise to fit reasonably in a poster format, or within a specific talk length, such as 10 minutes. When writing a talk or poster for a specific conference, investigating the style and content of previous years abstracts may help to peg yours at a suitable level. Before you start, check the conference guidelines on oral presentation outlines, poster size, and orientation. Although most conferences allow A0 portrait posters, some are different and it’s advisable to check this before writing.
Preparing your poster
Generally, posters follow a bullet point style divided into four main sections:
- Introduction or Background
- Discussion or Conclusions.
However, there are some other areas of the poster that need attention too.
Firstly, a snappy title is a must. The title must cover the basic outline of the study, yet be intriguing, making the viewer want to read on. The title must be considered during abstract preparation, as whatever you name your abstract will be your poster title. Author names and affiliations sit below the title; the order of this can be important but must be agreed by your research group before poster publication.
The introduction covers the background details of the research involved, using current literature and references. The aims and objectives of the research must be in the introduction, and generally sits well at the end just before the method section to give a sense of flow.
Methods covers obviously what you did to achieve your results. It’s good to be aware of any ethical approval gained for the study, and noting participant numbers, genders and ages, statistical methods used and any chemical in their full unabbreviated names initially, with subsequent references to the ingredients by the standard abbreviations. If the method is tricky to explain, a diagram or photo may help to illustrate, and it is not necessary to repeat the methods in words.
The results section needs to cover all relevant findings. Tables or figures can really help show data, so be imaginative! You’ll need to include statistical p-values to show significances. Finally, the discussion or conclusion section highlights the key findings from your results in punchy language as a ‘take home message’. These need to be clear and concise, covering the exact findings and if possible the relevance of findings to the study and scientific community as a whole.
Oral presentations
For oral presentations the same headings should be followed, with clear simple slides. Keep the number of slides to a minimum to keep the length of the talk on track. A good guideline is around one slide per minute. Set the scene with a clear introduction to the work, indicating the relevance of the study to the general scientific community. Highlight the study aims and objectives, and unlike a poster, you may want to include a hypothesis for further clarity. Diagrams may also help to describe methodology, and helps to keep audience attention as they must listen to you fully to understand the technique.
Results can also be shown on graphs and figures; be careful with tables, as these can appear daunting to the viewer, unless you clearly highlight the numbers or significances of importance to your work. Throughout the results section explain what each experiment or figure means, what is the finding? This will help you lead directly into the conclusions, and you can repeat the key findings already covered in the results, and give a clear take home message to your audience.
And finally...
Whether you’re giving a poster or a talk at a conference, be confident. Who knows your work better than you? This will help you tackle any questions and comments posed, and give you a chance to meet fellow researchers and possible future collaborators. Project your voice, face your audience and above all enjoy yourself!
Dr Caroline Withers
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to prepare and...
How to prepare and deliver an effective oral presentation
- Related content
- Peer review
- Lucia Hartigan , registrar 1 ,
- Fionnuala Mone , fellow in maternal fetal medicine 1 ,
- Mary Higgins , consultant obstetrician 2
- 1 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin, Ireland
- 2 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin; Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Medicine and Medical Sciences, University College Dublin
- luciahartigan{at}hotmail.com
The success of an oral presentation lies in the speaker’s ability to transmit information to the audience. Lucia Hartigan and colleagues describe what they have learnt about delivering an effective scientific oral presentation from their own experiences, and their mistakes
The objective of an oral presentation is to portray large amounts of often complex information in a clear, bite sized fashion. Although some of the success lies in the content, the rest lies in the speaker’s skills in transmitting the information to the audience. 1
Preparation
It is important to be as well prepared as possible. Look at the venue in person, and find out the time allowed for your presentation and for questions, and the size of the audience and their backgrounds, which will allow the presentation to be pitched at the appropriate level.
See what the ambience and temperature are like and check that the format of your presentation is compatible with the available computer. This is particularly important when embedding videos. Before you begin, look at the video on stand-by and make sure the lights are dimmed and the speakers are functioning.
For visual aids, Microsoft PowerPoint or Apple Mac Keynote programmes are usual, although Prezi is increasing in popularity. Save the presentation on a USB stick, with email or cloud storage backup to avoid last minute disasters.
When preparing the presentation, start with an opening slide containing the title of the study, your name, and the date. Begin by addressing and thanking the audience and the organisation that has invited you to speak. Typically, the format includes background, study aims, methodology, results, strengths and weaknesses of the study, and conclusions.
If the study takes a lecturing format, consider including “any questions?” on a slide before you conclude, which will allow the audience to remember the take home messages. Ideally, the audience should remember three of the main points from the presentation. 2
Have a maximum of four short points per slide. If you can display something as a diagram, video, or a graph, use this instead of text and talk around it.
Animation is available in both Microsoft PowerPoint and the Apple Mac Keynote programme, and its use in presentations has been demonstrated to assist in the retention and recall of facts. 3 Do not overuse it, though, as it could make you appear unprofessional. If you show a video or diagram don’t just sit back—use a laser pointer to explain what is happening.
Rehearse your presentation in front of at least one person. Request feedback and amend accordingly. If possible, practise in the venue itself so things will not be unfamiliar on the day. If you appear comfortable, the audience will feel comfortable. Ask colleagues and seniors what questions they would ask and prepare responses to these questions.
It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don’t have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
Try to present slides at the rate of around one slide a minute. If you talk too much, you will lose your audience’s attention. The slides or videos should be an adjunct to your presentation, so do not hide behind them, and be proud of the work you are presenting. You should avoid reading the wording on the slides, but instead talk around the content on them.
Maintain eye contact with the audience and remember to smile and pause after each comment, giving your nerves time to settle. Speak slowly and concisely, highlighting key points.
Do not assume that the audience is completely familiar with the topic you are passionate about, but don’t patronise them either. Use every presentation as an opportunity to teach, even your seniors. The information you are presenting may be new to them, but it is always important to know your audience’s background. You can then ensure you do not patronise world experts.
To maintain the audience’s attention, vary the tone and inflection of your voice. If appropriate, use humour, though you should run any comments or jokes past others beforehand and make sure they are culturally appropriate. Check every now and again that the audience is following and offer them the opportunity to ask questions.
Finishing up is the most important part, as this is when you send your take home message with the audience. Slow down, even though time is important at this stage. Conclude with the three key points from the study and leave the slide up for a further few seconds. Do not ramble on. Give the audience a chance to digest the presentation. Conclude by acknowledging those who assisted you in the study, and thank the audience and organisation. If you are presenting in North America, it is usual practice to conclude with an image of the team. If you wish to show references, insert a text box on the appropriate slide with the primary author, year, and paper, although this is not always required.
Answering questions can often feel like the most daunting part, but don’t look upon this as negative. Assume that the audience has listened and is interested in your research. Listen carefully, and if you are unsure about what someone is saying, ask for the question to be rephrased. Thank the audience member for asking the question and keep responses brief and concise. If you are unsure of the answer you can say that the questioner has raised an interesting point that you will have to investigate further. Have someone in the audience who will write down the questions for you, and remember that this is effectively free peer review.
Be proud of your achievements and try to do justice to the work that you and the rest of your group have done. You deserve to be up on that stage, so show off what you have achieved.
Competing interests: We have read and understood the BMJ Group policy on declaration of interests and declare the following interests: None.
- ↵ Rovira A, Auger C, Naidich TP. How to prepare an oral presentation and a conference. Radiologica 2013 ; 55 (suppl 1): 2 -7S. OpenUrl
- ↵ Bourne PE. Ten simple rules for making good oral presentations. PLos Comput Biol 2007 ; 3 : e77 . OpenUrl PubMed
- ↵ Naqvi SH, Mobasher F, Afzal MA, Umair M, Kohli AN, Bukhari MH. Effectiveness of teaching methods in a medical institute: perceptions of medical students to teaching aids. J Pak Med Assoc 2013 ; 63 : 859 -64. OpenUrl
Oral Presentations: Tips, Significance, Design, Guidelines & Presentation
1) Know your audience
It is always a good idea to structure your talk so that anyone in the audience can understand what you are presenting. A good scientist should be able to present complex, scientific ideas, no matter how technical, in a simple, easy to follow manner. Complexity is not a necessity, it is an annoyance.
Understand your purpose. This way you can get the point of your talk across appropriately and affectively by catering to your specific audience.
2) Be organized
- Whether you are giving a 15 minute talk or a 45 minute talk, make sure you give yourself enough time to deliver all the information you want in a calm manner. Allocate time for questions/answers.
- Be able to summarize your presentation in five minutes.
- Be concise. Use your space wisely. Use illustrations. Check grammar, spelling, and lay out of each slide.
- Keep an outline with you during the presentation; it will help you stay on track.
- Prepare back up slides. These will come in handy if a question comes up about a topic that needs further explanation.
3) Presentation
Practice your talk enough so that you have flow, but no so much that you have the entire talk memorized. Memorizing your talk will bore you and your audience, as it will be monotonous.
4) Be professional
- Know what you are presenting and be ready to answer question during and after the presentation. Do not answer questions vaguely. A knowledgeable scientist is specific and accurate with his/her information.
- Dress up to present with confidence and respect for the audience and the science involved.
- Be enthusiastic. Scientific talks can be boring, as often they are full of technical jargon. Be clear and talk simplistically.
- Make sure the presentation is visually pleasing. Add pertinent graphics and use fewer words.
5) Be aware of technical problems.
Make sure the format you choose for your presentation is compatible with your style of speech. Also, be prepared for technical disasters just before your talk. Be able to give your talk in another format just in case your first choice (ex: PowerPoint presentation) fails to load.
Significance
Oral presentations are an excellent means of communicating basic science or clinical research. Unlike a poster presentation or a written manuscript, the audience during an oral presentation is more attentive as they are focused on the presenter. For the researcher, this is a rare opportunity to shine! In as few as five minutes, the researcher can convey scientific information and give a years worth work some meaning that can be useful to thousands of people. Of course, this also means that in as little as five minutes, the researcher can cause a great deal of confusion by giving a bad presentation.
Just as is the case with written manuscripts and poster presentations, oral presentations must also communicate research to include all aspects of the scientific method. There are, however, no rules as to what order and which format this should be done in. In order to deliver a successful talk, the presenter should be organized, prepared, and enthusiastic about the research being presented.
Design: A General Guideline
Regardless of whether you choose a PowerPoint presentation or transparencies to deliver your talk, here are some general guidelines to keep in mind when designing your presentation.
1) Title (include authors and affiliations)
2) Introduction (Background, Purpose, Hypothesis)
3) Method (A brief introduction to the methodology without too much technical Jargon)
4) Results (Use graphs/charts/table, Provide an extra slide/transparency with a summary of the results, Explain the results)
5) Conclusions/Discussion (Clear explanation of the results, Clinical implications)
6) Future work (Provide information on where the project is headed)
7) Acknowledgment
Presentation
There some people for whom public speaking is as natural as having a conversation with their friends. Conveniently, however, public speaking is an art that can be perfected with enough practice. Here some things to consider before and during the presentation:
- Do not go over the time limit.
- Speak clearly and concisely. Be coherent. Do not ramble, play with the pointer, or move around in circles.
- Dress appropriately.
- Make eye contact.
- Make sure that each slide/transparency is not cluttered with too many points and ideas. Graphs, tables, and charts should be clearly labeled and easy to interpret.
- Practice your talk, but do not memorize a script.
- Be visually and orally interesting.
- Answer questions in a calm, non-condescending manner; do not argue with or interrupt the questioner.
- Be polite and graceful.
- Give a presentation that is focused with one underlying message.

Poster Presentation
At most meetings or conferences, when you present a poster presentation, it means that you will display your poster and be available for viewers to ask questions about your research and how it is represented on your poster. Like an oral presentation delivered with a slideshow, there are many ways to design and present your research on a poster. There are also, however, a few important considerations and conventions to be familiar with.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SATl29FeFw0&feature=youtu.be
Special Instructions for UURAF 2024 Poster Presentations
UURAF 2024 will be a hybrid event consisting of oral, poster, performance, film and exhibit presentations. UURAF is a public event. Do not share confidential information in your abstract or presentation.
For In-person Posters Only
- Create a poster presentation; print and trim final version to a size of 40" x 32" (102 cm x 81 cm); landscape or portrait orientation
- Prepare a short pitch discussing the poster presentation (less than 3 minutes is recommended)
- Share your work with visitors and evaluators
- In-person UURAF Presenter Guide
For Online Posters Only
- Submit presentation materials to online event site by April 8
- Create a poster presentation; save final version as PDF (less than 10MB)
- Create a video discussing their poster presentation (2 to 5 minutes long)
- Upload poster discussion video to YouTube as an unlisted video
- Enable the closed captioning feature to promote accessibility and inclusivity
- Add link for unlisted YouTube video and PDF of poster to the online UURAF event site by April 8
- Participate in asynchronous, online discussions with visitors and evaluators from April 11 - 12
- Virtual UURAF Presenter Guide
Presentation Tips:
- Tips and poster samples
- How to record a PowerPoint presentation
- How to add caption to YouTube videos
- Unlisted video setting
- Attend one of our workshops or peer advising for more assistance
- View example presentations from UURAF 2023
- Intro to UURAF presentation slides
- How to Prepare for an Academic Conference
- 15 Tips for Presenting at a Conference
- Practical Networking Tips
- Request assistance with poster printing fees. Requests are due by March 29 at 11:59 PM. Funding decisions will be made in early April
- Check out our Poster FAQ to learn more about poster presentations and how to prepare them
- Get help from an Undergraduate Research Peer Advisor

- Call us: (517) 884-4384
- Contact Information
- Privacy Statement
- Site Accessibility
- Call MSU: (517) 355-1855
- Visit: msu.edu
- MSU is an affirmative-action, equal-opportunity employer.
- Notice of Nondiscrimination
- Spartans Will.
- © Michigan State University

Program Chairs
Kevin Duh, Helena Gomez, Steven Bethard
- Custom Social Profile Link
NAACL 2024 presentation modes, acceptance types, and participation experiences
Oral-poster and short-long equality.
At NAACL 2024, we are striving to set all main conference papers on equal ground. So whether you submitted a long paper or a short paper, whether you decide to attend the event in-person or virtually, and whether you are assigned an oral presentation or a poster presentation, you are allowed the same 13 minute video recording on the virtual site. Similarly, we have not taken any actual or perceived measures of paper quality into account when making oral vs. poster presentation decisions, so there is no prestige associated with getting to present in an oral vs. a poster format.
Main Conference vs Findings
There are two main differences between NAACL main conference papers and NAACL findings papers. The first is acceptance rate: main conference papers have a lower acceptance rate than findings papers. The second is registration: main conference papers will not be published unless at least one author pays full registration fees for the conference, while findings papers will be published even if no author registers for the conference.
To increase the visibility of NAACL Findings papers, authors who choose to attend the conference will be offered a poster presentation (either in-person or virtual, depending on how they attend). We hope this opportunity to showcase their work encourages more Findings authors to attend NAACL 2024!
In-Person vs Virtual Attendance
At NAACL 2024, we are trying to improve both the in-person and virtual experiences. For this, we are implementing the following two actions:
- A pre-conference virtual poster session that will be held on Thursday, June 13, 2024, avoiding conflicts with the conference’s in-person sessions. We are still finalizing the schedule, but the virtual event will include different sessions to accommodate various time zones. We hope this move will encourage all attendees, both virtual and in-person, to join the virtual poster session!
- Oral presentations will be in-person to avoid Zoom fatigue for in-person attendees. (Oral presentations will still be live-streamed for all virtual attendees.) We hope this move will encourage more in-person engagement with oral presenters!
In-person attendees can expect access to:
- Live keynotes, plenaries, and panels
- More than 100 live oral presentations
- More than 400 live poster presentations
- More than 200 virtual poster presentations (at the pre-conference event)
- Recorded presentations for all papers (on the virtual conference site)
Virtual attendees can expect access to:
- Live-streamed keynotes, plenaries, and panels
- More than 100 live-streamed oral presentations
We hope to see you all in Mexico City, in-person or virtually!

- Oral Poster Symposia Moderators & Discussants
- Oral Poster Symposia Presenters
Presentation Guidelines: Oral Poster Symposia Moderators and Discussants
There are 10-12 posters in each Oral Poster Symposium, with two moderators and two discussants. The moderators may structure the session as they prefer. A suggested program includes three-minute presentations by each poster presenter, then 30 minutes of general poster viewing, followed by a focused discussion among clusters of four poster presenters.
The three-minute introductory presentations provide an overview of each author’s work. These brief presentations, with a maximum of three slides, should focus on the rationale for the study and how the results provide new insights and/or mechanisms. Attendees can then view all the posters and interact directly with the author for about 30 minutes.
Before the meeting, the moderators will group the posters into logical clusters, typically with four posters per group. After the general viewing period, presenters will discuss the posters in each group. Moderators also ask each presenter to come prepared with at least one question for each of the other presenters in the group. They encourage co-authors and mentors to participate actively in the discussion—those interactions are what make a poster symposium more informative and engaging than a platform session.
Oral Poster Symposium co-moderators should confer about six weeks prior to the meeting to confirm their presentation format, group the posters in a logical manner, and communicate with the abstract presenters. All participants should familiarize themselves with the abstracts in the symposia. An Oral Poster Symposium discussant helps fuel the discussion by asking relevant questions from the audience, with the goal of increasing audience participation and engagement.
Presentation Guidelines: Oral Poster Symposia Presenters
Overview: Please read the guidelines for Oral Poster Symposia moderators and discussants to get an overview of the format’s structure and rationale.
Set-Up: Each poster board is numbered sequentially in your session. Locate your assigned poster board and mount your poster within the time noted on these instructions. Pushpins will be provided in the area.
Take-Down: Please disassemble your posted materials at the end of the session. Any materials left on the poster board at the end of the session will be removed and discarded. PAS will not be responsible for posters left at the end of session.
Poster Board Dimension: Surface of the board: 4 feet high and 8 feet wide (1.22 metres and 2.44 metres) . Note: poster must fit on the board but does not have to be the same size as the board.
Header: Prepare a headline that identifies your research to be mounted at the top of the poster board. Lettering should be 1½” (3.81 cm) high or more. Include authors and their affiliations under the header. Disclosure information should be visibly notated on poster presentation immediately following the poster title and authors.
Organization: The key is to achieve clarity and simplicity. Do not overload or overcrowd the poster. Use a coherent sequence (top to bottom or left to right) to guide the viewer through the poster. Use figures, tables, graphs and photographs when appropriate; keep text brief. It may be helpful to have materials pre-mounted on mounting boards. All materials should be legible from a distance.
Typography: Avoid using abbreviations, acronyms and jargon. Font should be consistent throughout.
Completion: Ask yourself the following questions about your poster:
➊ What do I want the viewer to remember?
➋ Is the message clear?
➌ Do important points stand out?
➍ Is there a balance between words/illustrations?
➎ Is the pathway through the poster clear?
➏ Is the poster understandable without oral explanation?
New for PAS 2020: Maximize the impact of your research by recording a three-minute audio explanation of your poster presentation using PosterCast , a free smartphone app. More information on PosterCast . Note that even though the posters in Oral Poster Symposia have, by definition, an oral component, we encourage presenters to also make a PosterCast recording to further extend the reach of their work.
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- Office Directory
- Add or Edit Profile
- Financial Management Practices
- Development and Alumni Relations
- Benefits and Services
- Employee Appreciation Programs
- The Five Functions of DEI
- Communication
- Recruitment
- DEI Dashboard
- 2020 Report
- 2019 Report
- Student Ambassadors
- Education Library
- Education Technology Services
- Graduate Studies
- Courses and Workshops
- Video Production Guidelines
- Promotional Posting Guidelines
- Research and Development
- Records and Reporting
- Dean's Advisory Board
- Service, Leadership, and Outreach
- Student Success
- Diversity Plan
- 100th Anniversary Book
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Targeted Engagements
- Global Gateway for Teachers
- Overseas Short-Term Study Experiences
- External Grant Opportunities
- Our Global Reach
- Faculty and Student Int'l Engagement
- IU Global Gateways
- Indiana Global Education Outreach
- Int'l Partnerships
- Visiting Int'l Scholars
- Int'l Student Ambassadors
- Academic Programs
- International Journals
- News & Events
- Int'l Student Resources
- CAEP Annual Reporting Measures
- CAEP Accreditation Visit Call for Third-Party Comments
- SoE Data Dashboards (Faculty)
- Licensure Requirements
- Employment Outcomes
- Employer Evaluations
- Student Teaching Survey Reports
- Attrition & Completion Rates
- Graduate Survey Results
- Indiana Teachers of the Year
- Emergency Action Plan
- SoE Emergency Information
- School Violence
- Report Facility Issue
- Direct Admit Scholars
- TEP Application Guidelines
- Accessible Virtual Tour
- Field Trips
- Non-School of Education Scholarships
- Graduate Student Funding
- Student Emergency Fund
- Campus Financial Aid Resources
- INSPIRE Living-Learning Center
- All Programs
- License Additions
- Master's Programs
- Doctoral Programs FAQ
- Specialist Programs
- Certificate Programs
- Doctoral Minors
- Licensure Programs
- Transition to Teaching
- New Zealand
- Northern Ireland
- Navajo Nation Program
- Urban Program
- IU Bloomington Students
- Guest Campus Students
- Partner Campus Students
- Student Spotlights
- Teacher Spotlights
- Cost & Financial Aid
- Online Learning
- Tuition and Fees
- Registration
- Block Enrollment Course Information
- Student Teaching Registration Information
- Program Sheets
- Forms & Publications
- Credit Overload Request
- Four Year Plan
- Academic Calendar
- Undergraduate Bulletin
- Background Check
- Early Field Experiences
- Student Teaching Forms
- Preparation
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Student Organizations
- Counseling and Student Services
- Dean's List
- Report Your Concerns
- Scholarships
- Career Coaching
- Student Teaching Fair
- Health and Human Services Career Day
- Explore Possibilities
- Get Experience
- Stay Connected
- Professional Distinction
- Educator Wellbeing Distinction
- Workshops and Training
- Recruiting Policies
- Classroom Presentations
- Graduation Deadlines
- Leave Policy
- Online Students
- Graduation Application
- Guidelines for Multi-Article Dissertations
- G901 Permission Request
- Qualifying Examinations
- 2022 Scholars
- 2021 Scholars
- 2020 Scholars
- 2023 Scholars
- Program-Specific Information
- International Student Ambassadors
- Student Affiliates in School Psychology
- Dissertation & Thesis Announcements
- Approved Core Inquiry Courses
- Holmes Scholars Program
- Initial Licensure
- License Renewal
- Licensing Outside Indiana
- Knowledge Base
- Graduate Bulletin
- Teaching with Technology Lab
- Support Services
- Volunteering Opportunities
- Faculty Directory
- Counseling and Educational Psychology
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Chair's Welcome
- IST Conference
- Faculty Bookshelf
- Faculty Meetings
- Policies and Procedures
- Instructional Consulting
- In Memoriam
- Office of Research and Development
- 2023 Highlights
- Research Centers
- Funded Research
- Research Findings
- Translation to Practice
- Equity in Action
- Overview and Project Timeline
- Analysis in Progress
- Presentations
- Accomplishments
- Teacher Study Group
- "Creative Paths to Peace" Grant
- Proffitt Internal Grant Competition
- Proffitt Summer Faculty Fellowship Program
- Tilaar Faculty Support Fund
- Cost-Share and Matching Funds on External Grant Proposals
- Current Visiting Scholars
- Become a Visiting Scholar
- Visiting Scholar Policies
- COVID-19 Entry Updates
- Flexible Workspace
- Faculty & Staff Giving Campaign
- Donor Spotlights
- Get Involved
- Submit a Nomination
- Alumni Magazine
- Alumni Board of Directors
- Counseling and Wellness Clinic
- Learning and Developmental Evaluation Clinic
- Current Cohort
- Past Cohorts
- Nominate a Teacher
- How to Apply
- Armstrong Teacher Panel Archive
- Current Jacobs Educators
- Past Winners
- Advisory Board
- Teachers' Examples
- Research-to-Practice Briefs
- Speaker Series
- Baxter Online STEM Student Challenges
- Educating for Environmental Change (EfEC)
- Dual Language Immersion (DLI)
- Global Learning for Pre-Service Teachers Workshops
- Global Literacy Invitation Project
- Global STEAM
- In-Service Teachers Workshops
- Principals’ Academy on Internationalizing K-12 Schools
- School of Education Curriculum Internationalization
- Medical Research Education Project
- Project LIFT
- Saturday Art School
- Past Lesson Plans
- Partners in Education (PIE)
- Maker Mobile
- Past Mentors
- Apply to Be a Mentor
- HOPE Training Modules
- HOPE for Cadets
- AAC in Action
- Celebration of Excellence
- C&I Graduate Research Symposium
- Invited Sessions
- Visiting Bloomington
- Science Education Research Symposium
- Convocation
- Diggs Symposium
- Virtual Events
- Advisory Committee
- Education Law Resources
School of Education
Special education symposium highlights student work.
By Catherine Winkler
Friday, April 19, 2024

Last month, students from the special education program came together in a research symposium that showcased their important work.
Coordinated by Professor Derek Nord and doctoral students Nell Krahnke and Ikfina Maufuriyah, the annual event included poster sessions and oral presentations from several students. A graduate of the doctoral program, Luke Sun, provided the keynote address, while researchers from the Indiana Institute on Disability and Community were also able to present more on their work.
“The seminar gives students and faculty a chance to see what everyone is working on. For students, it's a chance to get feedback from faculty. Since part of doctoral work is presenting at conferences, the seminar is a very laid back and low-key way to experience what a poster session or oral presentation at a conference might look like. For faculty, they get to see what students they don't know very well are working on,” Krahnke said, adding, “For the organizers, it counts as a service toward our portfolio, which is a plus. But it's also a chance to get a slightly more in depth idea of how planning events works. It means using slightly different skills than we might be using in our day to day work, but time management and juggling multiple different pieces of a project are both a major aspect of it. Those are skills that are really applicable to our research and teaching work as well.”
Start your life-changing journey
Additional links and resources.
- From the Dean
- Annual Report
- International Engagement
- Accreditation
- Measures of Success
- Emergency Preparedness
- Departments
- Instructor Resources
- Undergraduate
- Community of Teachers
- Research Initiatives
- Funding Opportunities
- Visiting International Scholars
- Undergraduate Portal
- Graduate Portal
- Academic Resources
- Career Connections
- Research Help
- Maker Education
- Youth Programs
- Award Programs
- CHG Counseling Services
- Staff Council
- Visit the School
- Alumni Spotlights
- Distinguished Alumni Award
Indiana University Bloomington School of Education
SOE Knowledge Base
SOE Intranet (Legacy)

Wysocki Research Group
Wysocki Lab at ASMS 2024
Wysocki group will attend the 72nd ASMS 2024 in Anaheim, CA, June 2-6, 2024.
Welcome to stop by and see our oral and poster presentation if you are attending ASMS in person!
- Kristie L Baker ; Anusha Kumar; Aniruddha Sahasrabuddhe; Hossein Ashrafian; Thomas J. Magliery; Vicki H. Wysocki, Characterizing a Surface Salt Bridge in the Four-Helix Bundle Rop by Surface-Induced Activation and Variable Temperature Electrospray Ionization. (TOB pm: Ion Mobility: Structure Determination & Applications, Jun.4 th 2:30-2:50 PST)
- Andrew J Arslanian ; Vicki H. Wysocki, Source-induced Quaternary Structural Changes Revealed by Surface-induced Dissociation and Top-down Electron Capture Dissociation. (WOC pm: Fundamentals: Ion Activation and Dissociation, Jun.5 th 2:50-3:10 PST)
- Evan N Whitford ; Philip C. Lacey; Elijah Day; Steffen Lindert; Vicki H. Wysocki, Covalent Labeling to Probe a Protein with an Intrinsically Disordered Domain. (WP 206 Covalent Labeling and Chemical Crosslinking I)
- Zhixin Xu ; Chen Du; Eduardo Olmedillas; Regina M. Edgington; Sophie R. Harvey; Erica Ollmann Saphire; Vicki H. Wysocki, Determination of Glycoform Masses of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Variants by Electron Capture Charge Reduction Mass Spectrometry. (WP 321 Glycoproteins I )
- William J Moeller ; Mark P Foster; Vicki H Wysocki, Variable Temperature Electrospray Measurement of Enthalpy and Entropy of Tryptophan Binding to Ring Shaped Protein TRAP. (ThP 525 Instrumentation: New Developments in Ionization and Sampling)
- Martha Ortega Zepeda ; Yu-Fu Lin; Dalton T Snyder; Vicki H Wysocki, Analysis of Gas Phase Protein Complex Unfolding in Positive and Negative nESI. (MP475 Ion Mobility: Applications I)
- Yuan Gao ; Jamison Law; Venkat Gopalan; Vicki H. Wysocki, Use of native mass spectrometry to characterize the binding of substrate and inhibitors to Salmonella FraB deglycase, a drug target. (MP 697 Proteins: Complexes/Non-covalent Interactions)
- Zihao Qi ; Charles E. Bell; Vicki H. Wysocki, Investigating the DNA binding behaviors and inhibition for human Rad52-DNA binding domain by native mass spectrometry and surface-induced dissociation. (MP 699 Proteins: Complexes/Non-covalent Interactions)
- Philip Lacey ; Chengliang Wang; Jianbin Ruan; Vicki H Wysocki, Heterogeneous Non-Canonical Inflammasome Oligomerization Probed by Narrow Quadrupole Selections and Electron Capture Charge Reduction. (MP 716 Proteins: Complexes/Non-covalent Interactions )
- Carla V.T. O’Neale ; Sophie R. Harvey; Vicki H. Wysocki; Kevin L. Schey, Studies of Aquaporin-0 Lipid Binding in the Bovine Lens via Native Mass Spectrometry. (WP 647 Proteins: General and Membrane)
- Qianyi Wang ; Qianjie Wang; Zihao Qi; William Moeller; Shaolei Lu; Xiaowen Liu; Chiung-Kuei Huang; Vicki Wysocki; Liangliang Sun, Developing Advanced Capillary Zone Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry Techniques for Multi-Level Proteomics of Complex Biological Samples. (ThP 750 Proteomics: Intact Proteins and Top Down Analysis II)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Comparison: Poster vs Oral Presentation. When deciding between a poster and an oral presentation, there are several key features to consider. 1. Visual Impact: Posters offer a visual representation of information, while oral presentations allow for direct engagement. 2.
Whether presenting a poster, giving an oral presentation, or taking part in a virtual event, researchers should practice their presentation. Practicing in a space that is similar to the actual presentation is a good idea, and doing so within the allotted time. Finishing early to allow good Q&A is also a good idea.
Step 3: Write the content. Write or rewrite the content for the sections in your poster presentation. Use the text in your research paper as a base, but summarize it to be more succinct in what you share. Don't forget to write a catchy title that presents the problem and your findings in a clear way.
Posters & Oral Presentations. Good scientific research involves a sound methodology and a novel idea that can be tested simply and repeatedly to give valid, trustworthy results. However, even the most clinically significant research is useless if it is not communicated successfully. Scientific ideas are novel, sometimes simple in theory, but ...
Poster Presentation Everything you include in your presentation should help convey the message. Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words! If you find that you have too much text on your slides or poster, try to replace it with a graphical schematic and make sure to cite the source of these images. This is often preferred to chunky blocks ...
English Communication for Scientists, Unit 5.1. Poster presentations may not seem as prestigious as oral presentations, but they are a great opportunity to interact with other scientists in your ...
Designing a poster or preparing an oral presentation should be done within the guidelines set forth by the conference. Traditional posters and oral presentations convey the same information in different formats. When presenting your study, you should know all the details of the project and be able to field any questions from the audience.
Many conferences have poster presentation sessions along with oral presentations. The poster presentation is a format introduced into the American Chemical Society meetings in the 1970s. This format allows more people the opportunity to present their work since many posters can be scheduled for the same time period and in one large room.
5. Be early. If you are running late, you will be more nervous and have less time to prepare yourself mentally. 6. On the day of the talk, take 10-15 minutes before your presentation to relax, do some deep breathing, and keep your mind off of the presentation for a bit. You want to be relaxed during your presentation. 7.
Oral presentations at a conference or internal seminar differ from scientific papers: they are more localized in space and time; they impose a sequence and rhythm to the audience; and they ...
Gesture to the relevant parts of the poster. You should use your whole hand to point toward something rather than just pointing a finger. Graphs and other data are excellent parts of a poster for gesturing. Avoid turning your back on your audience to gesture. Use the arm closest to the poster to gesture so you are not gesturing across your body ...
In an oral session, speakers present their work one-by-one in a series of short lectures (usually no more than 30 minutes, and potentially as little as 10 minutes). Each speaker presents, takes questions for a few minutes, and is followed by the next one. These presentations are usually in a room with a seated audience, in a lecture-style format.
Oral presentations. For oral presentations the same headings should be followed, with clear simple slides. Keep the number of slides to a minimum to keep the length of the talk on track. A good guideline is around one slide per minute. Set the scene with a clear introduction to the work, indicating the relevance of the study to the general ...
Delivery. It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don't have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
an oral presentation, you can tell a story and lead your listeners along particular paths of reasoning and thought. With posters, your audience is free to key in on specific points that they may be particularly interested in, and they will have more time to do this. ORAL PRESENTATIONS . I. Time. Oral presentations will be . 2. 5. minutes. long.
Oral presentations are an excellent means of communicating basic science or clinical research. Unlike a poster presentation or a written manuscript, the audience during an oral presentation is more ... some meaning that can be useful to thousands of people. Of course, this also means that in as little as ...
For In-person Posters Only. Create a poster presentation; print and trim final version to a size of 40" x 32" (102 cm x 81 cm); landscape or portrait orientation. Prepare a short pitch discussing the poster presentation (less than 3 minutes is recommended) Share your work with visitors and evaluators. In-person UURAF Presenter Guide.
At the right conference, and with some planning and effort, poster presentations can be a fruitful experience. They can be a great introduction to the conference world, help build confidence and can lead to connections or invitations to other Universities to present your work. Current PhD candidate Toni Brown, presenting her work at Society for ...
Oral-Poster and Short-Long Equality At NAACL 2024, we are striving to set all main conference papers on equal ground. So whether you submitted a long paper or a short paper, whether you decide to attend the event in-person or virtually, and whether you are assigned an oral presentation or a poster presentation, you are allowed the same 13 ...
Oral and Poster Presentations. ... research is hampered by the lack of a universal definition or theoretical framework. Aim. ... Training was held in March 2018, and leaflets and posters were displayed for the 3-month period. An embedded experimental mixed-methods design was used, with data collected via SystmONE questionnaires, surveys and ...
Presentation Guidelines: Oral Poster Symposia Moderators and Discussants. There are 10-12 posters in each Oral Poster Symposium, with two moderators and two discussants. The moderators may structure the session as they prefer. A suggested program includes three-minute presentations by each poster presenter, then 30 minutes of general poster ...
Then the same kind of talk at a secondary conference. Then a oral presentation at a parallel session in big confernence in your field, followed by oral/parallel/small. Poster in my opinion comes after all of this. Not sure what you mean by workshop, and tutorial. If you are the one leading the workshop, giving the tutorial, it's a big thing.
Generally, oral presentations are regarded as "of higher status" than posters, thus fitting in as oral presentation might be more competitive. Share. Improve this answer. Follow answered Aug 20, 2018 at 12:19. Scientist Scientist. 9,214 5 5 gold badges 34 34 silver badges 66 66 bronze badges. Add a ...
Add headers if necessary to clarify the structure of your poster, and add everything else that is needed, such as literature, acknowledgements. Ensure that author name(s) and affiliation are on the poster. 7) Review, revise, optimize. Ask your co-authors and/or colleagues to comment on a draft version of your poster.
Last month, students from the special education program came together in a research symposium that showcased their important work.. Coordinated by Professor Derek Nord and doctoral students Nell Krahnke and Ikfina Maufuriyah, the annual event included poster sessions and oral presentations from several students. A graduate of the doctoral program, Luke Sun, provided the keynote address, while ...
CAMBRIDGE, Mass.--(BUSINESS WIRE)-- ReNAgade Therapeutics, a company unlocking the limitless potential for RNA medicines, today announced an oral and poster presentation highlighting preclinical data supporting its comprehensive RNA technology platform at the American Society of Gene & Cell Therapy (ASGCT) 27 th Annual Meeting being held May 7-11, 2024, in Baltimore, Maryland.
Ring Therapeutics, a life sciences company founded by Flagship Pioneering to revolutionize genetic medicines with its commensal virome platform, today announced an oral presentation and two poster presentations at the 27th Annual American Society of Gene & Cell Therapy (ASGCT) Conference, to be held in Baltimore, Maryland from May 7 - 11, 2024.
Wysocki group will attend the 72nd ASMS 2024 in Anaheim, CA, June 2-6, 2024. Welcome to stop by and see our oral and poster presentation if you are attending ASMS in person! Oral. Kristie L Baker; Anusha Kumar; Aniruddha Sahasrabuddhe; Hossein Ashrafian; Thomas J. Magliery; Vicki H. Wysocki, Characterizing a Surface Salt Bridge in the Four ...
Oral presentation to discuss CRISPR-associated gene editing inactivating herpes virus; Two poster presentations highlight the potential of EBT-104 for the treatment of HSV-1 Keratitis ...