

Natural Resources PPT | PDF Free Download
Natural Resources PPT | PDF Free To Download: The natural resources may be defined as any material given to us by nature which can be transformed in a way that it becomes more valuable and useful.
Also See: Ecosystem PPT and PDF
Natural Resources PPT | PDF Free To Download

Fig1: Natural Resources
Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources:
There are nine important areas of energy resources and they come into two categories which are as follows:
- Renewable resources
- Non-renewable resources
The energy sources like coal, natural gas, nuclear and oil fall into nonrenewable resources as they are available in a finite quantity. This is because it takes much in furnishing a new supply of these resources. Now, coming to the renewable resources then the energy resources which come under them are geothermal energy, wind energy, solar energy, biomass, and hydro energy. These resources are provided by nature and it doesn’t take much time in their production. The limited sources of energy quickly replaced the important sources of energy which are wind, water, and solar energy.
Also See: General Topics for Presentation
Forest Resources:
Forests are one of the most vital natural resources on this earth. They furnish many environmental services which are essential for life. About 1/3 rd of the earth’s land is covered with forests. The natural forests have been reduced over the years. The major losses occurred in tropical Asia where 1/3 rd of the forest resources have been destroyed.
Commercial uses of a forest: The commercial uses of forest area in the following:
- Domestic and useful products
Also See: Green House PPT
Ecological uses of a forest: The ecological uses of forest are the following:
- Production of oxygen
- Reduces global warming
- Wildlife habitat
- Regulation of hydrological cycle
- Soil conversation
- Pollution moderators
- Production of oxygen: The trees produce oxygen.
- Reduces global warming: The forests absorb the greenhouse gasses like carbon dioxide and reduces global warming.
- Regulation of hydrogen cycle: Forested watersheds acts like giant sponges, absorbs the rainfall slow down the runoff and slowly release the water for recharge of springs. About 50-80% of the moisture in the air comes from forest transpiration which aids in bringing rains.
- Soil conservation: Forests bind the soil particles tightly in their roots and avoid soil erosion.
- Pollution moderators: Forests can absorb many toxic gasses and aids in keeping the air pure.
Water Resources:
Water resources are the water sources that are useful to all living organisms to exist. Water has distinct uses and some of them are as follows:
- Agricultural
- Environmental activities
- Recreational
Also See: Global Warming PPT and PDF
Human beings need fresh water for their requirements and only 2% of the water on the earth is n the form of freshwater bodies and in that also two-third of it is in the form of polar ice caps and glaciers. Day by day the demand of water is increasing and it is expected to increase more in the future. The change in climate also furnishes a major impact on water resources because the climate and hydrological cycles are closely related to each other.
Also See: Water Pollution PPT
Mineral Resources:
Minerals furnish most of the materials which are used to drive machines in industries and vehicles on the roads. The demand for minerals is increasing at a fast rate with the increase in population and also with the increase in their consumption. Types of mineral resources are as below:
- Fuel minerals
- Metallic and non-metallic minerals
Food Resources:
The world generates enough food and products of agriculture which more than sufficient but still many parts of the world is suffering from the lack of food and the main reason for this is the change in climate. The present situation of food resources is defined by few modern driving forces and they are responsible for changing the food production, food markets, and food consumption. They are as below:
- Globalization
- Climate change
- Urbanization
- Prices of energy
In the causes of world food problems has few factors and in them, the decline in the availability of water and overgrazing are the two factors. The decline in the availability of water warns everyone that there will be a lack of water in the agricultural land by 2050. Overgrazing tells about the enhancement in the cattle production which heavily graze the forests or grasslands and this leads to the denude the land area.
Also See: land Pollution PPT
Content of the PPT and PDF for Natural Resources
- What are Natural Resources?
- Value of Natural Resources
- Types of Natural Resources
- Uses of Natural Resources
- Major problems with Natural Resource conservation
- Policy gaps
Here we are giving you Natural Resources PPT with PDF. All you need to do is just click on the download link and get it.
Natural Resources PPT Download
Natural Resources PDF Free Download
It was all about Natural Resources PPT with PDF. If you liked it then please share it or if you want to ask anything then please hit comment button.

Related Posts
Biomedical waste management ppt presentation free, monkey and the cap seller story ppt presentation free download, 1210 electrical engineering(eee) seminar topics 2024, 112 iot seminar topics-internet of thing presentation topics 2024.

330 Latest AI (Artificial Intelligence Seminar Topics) 2024

698+ Physics Project Topics For class 12 and Ideas 2024
8 comments already.
Pls explain in detail what is blogger in simple sentences
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

36.1: Introduction to Natural Resource Economics
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 4789

Types of Natural Resources
- Natural resource economics focuses on the supply, demand, and allocation of the Earth’s natural resources.
learning objectives
- Analyze natural resource economics and explain the types of natural resources that exist.
Natural Resource Economics
Natural resource economics focuses on the supply, demand, and allocation of the Earth’s natural resources. It’s goal is to gain a better understanding of the role of natural resources in the economy. Learning about the role of natural resources allows for the development of more sustainable methods to manage resources and make sure that they are maintained for future generations.The goal of natural resource economics is to develop an efficient economy that is sustainable in the long-run.
Importance of the Environment : This diagram illustrates how society and the economy are subsets of the environment. It is not possible for societal and economic systems to exist independently from the environment. For this reason, natural resource economics focuses on understanding the role of natural resources in the economy in order to develop a sufficient and sustainable economy that protects natural resources.
Natural resources are derived from the environment. Some of the resources are essential to survival, while others merely satisfy societal wants. Every man-made product in an economy is composed of natural resources to some degree.
There are numerous ways to classify the types of natural resources, they include the source of origin, the state of development, and the renewability of the resources.
In terms of the source of origin, natural resources can be divided into the following types:
- Biotic: these resources come from living and organic material, such as forests and animals, and include the materials that can be obtained them. Biotic natural resources also include fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum which are formed from organic matter that has decayed.
- Abiotic: these resources come from non-living and non-organic material. Examples of these resources include land, fresh water, air, and heavy metals (gold, iron, copper, silver, etc.).
Natural resources can also be categorized based on their stage of development including:
- Potential resources: these are resources that exist in a region and may be used in the future. For example, if a country has petroleum in sedimentary rocks, it is a potential resource until it is actually drilled out of the rock and put to use.
- Actual resources: these are resources that have been surveyed, their quantity and quality has been determined, and they are currently being used. The development of actual resources is dependent on technology.
- Reserve resources: this is the part of an actual resource that can be developed profitably in the future.
- Stock resources: these are resources that have been surveyed, but cannot be used due a lack of technology. An example of a stock resource is hydrogen.
Natural resources are also classified based on their renewability:
- Renewable natural resources: these are resources that can be replenished. Examples of renewable resources include sunlight, air, and wind. They are available continuously and their quantity is not noticeably affected by human consumption. However, renewable resources do not have a rapid recovery rate and are susceptible to depletion if they are overused.
- Non-renewable natural resources: these resources form extremely slow and do not naturally form in the environment. A resource is considered to be non-renewable when their rate of consumption exceeds the rate of recovery. Examples of non-renewable natural resources are minerals and fossil fuels.
There is constant worldwide debate regarding the allocation of natural resources. The discussions are centered around the issues of increased scarcity (resource depletion) and the exportation of natural resources as a basis for many economies (especially developed nations). The vast majority of natural resources are exhaustible which means they are available in a limited quantity and can be used up if they are not managed correctly. Natural resource economics aims to study resources in order to prevent depletion.
Natural resource utilization is regulated through the use of taxes and permits. The government and individual states determine how resources must be used and they monitor the availability and status of the resources. An example of natural resource protection is the Clean Air Act. The act was designed in 1963 to control air pollution on a national level. Regulations were established to protect the public from airborne contaminants that are hazardous to human health. The act has been revised over the years to continue to protect the quality of the air and health of the public in the United States.
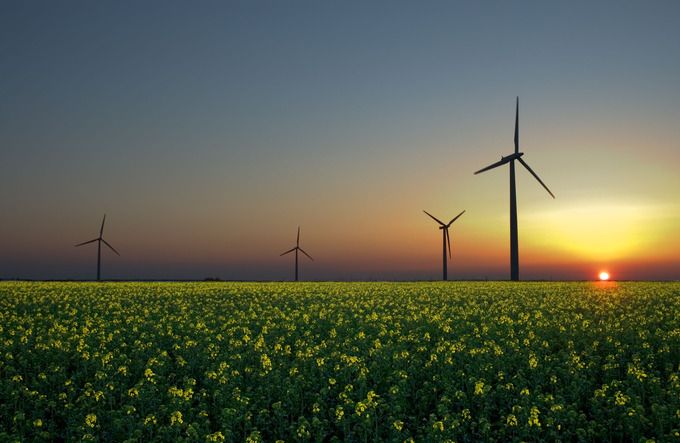

Wind : Wind is an example of a renewable natural resource. It occurs naturally in the environment and has the ability to replenish itself. It has also been used as a form of energy development through wind turbines.
Basic Economics of Natural Resources
Natural resource economics focuses on the supply, demand, and allocation of the Earth’s natural resources to create a more efficient economy.
- Explain basic natural resource economics
Natural resource economics focuses on the supply, demand, and allocation of the Earth’s natural resources. The main objective of natural resource economics is to gain a better understanding of the role of natural resources in the economy. By studying natural resources, economists learn how to develop more sustainable methods of managing resources to ensure that they are maintained for future generations. Economists study how economic and natural systems interact in order to develop an efficient economy.
As a field of academic research, natural resource economics addresses the connections and interdependence between human economies and natural ecosystems. The focus is how to operate an economy within the ecological constraints of the earth’s natural resources.
Natural Resource Economics : This diagram illustrates that society and the economy are subsets of the environment. It is not possible for social and economic systems to exist independently from the environment. Natural resource economics focuses on the demand, supply, and allocation of natural resources to increase sustainability.
Areas of Study
Economists study the commercial and recreational use and exploitation of resources. Traditionally, natural resource economics focused on fishery, forestry, and mineral models. However, in recent years many more topics have become increasingly important, including air, water, and the global climate. Natural resource economics is studied on an academic level, and the findings are used to shape and direct policy-making for environmental issues.
Examples of areas of study in natural resource economics include:
- welfare theory
- pollution control
- resource exhaustibility
- environmental management
- resource extraction
- non-market valuation
- environmental policy
Additionally, research topics of natural resource economists can include topics such as the environmental impacts of agriculture, transportation and urbanization, land use in poor and industrialized countries, international trade and the environment, and climate change.
Impact of Natural Resource Economics
The findings of natural resource economists are used by governments and organizations to better understand how to efficiently use and sustain natural resources. The findings are used to gain insight into the following environmental areas:
- Extraction: the process of withdrawing resources from nature. Extractive industries are a basis for the primary sector of the economy. The extraction of natural resources substantially increases a country’s wealth. Economists study extraction rates to make sure that resources are not depleted. Also, if resources are extracted too quickly, the sudden inflow of money can cause inflation. Economists seek to maintain a sense of balance within extraction industries.
- Depletion: the using up of natural resources, which is considered to be a global sustainable development issue. Many governments and organizations have become increasingly involved in preserving natural resources. Economists provide data to determine how to balance the needs of societies now and preserve resources for the future.
- Protection: the preservation of natural resources for the future. The findings of economists help governments and organization develop measures of protection to sustain natural resources. Protection policies state the necessary actions internationally, nationally, and individually that must take place to control natural resource depletion that is a result of human activity.
- Management: the use of natural resources taking into account economic, environmental, and social concerns. This process deals with managing natural resources such as land, water, soil, plants, and animals. Particular focus is placed on how the preservation of natural resources impacts the quality of life now and for future generations.
Externalities and Impacts on Resource Allocation
Production and use of resources can have a positive or negative effect on the allocation of the natural resources.
- Examine externalities and how they the impact resource allocation of natural resources.
Resource Allocation
Resource allocation is division of goods for the use of production within the economy. The needs and wants of society as well as industries impact what is produced. Suppliers focus on producing the varieties of goods and services that will yield the greatest satisfaction to consumers. In the long run, externalities directly impact resource allocation. It must be determined whether the production, as well as the process of production, creates more benefits that costs for the producers, consumers, and society as a whole.
Externalities
An externality is a cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur the cost or benefit. In regards to natural resources, production and use of resources can have a positive or negative effect on the allocation of the resources.
External Costs
A negative externality, also called the external cost, imposes a negative effect on a third party to an economic transaction. Many negative externalities impact natural resources negatively because of the environmental consequences of production and use. For example, air pollution from factories and vehicles can cause damage to crops. Likewise, water pollution has a negative impact of plants and animals.

Negative externality : Air pollution from vehicles is an example of a negative externality. It affects other than those who drive the vehicle and those who sell the gas.
In the case of negative externalities, the marginal private cost of consuming a good is less than the marginal social or public cost. The marginal social benefit should equal the marginal social cost (i.e. production should only be increased when the marginal social benefit exceeds the marginal social cost). When external costs are present, the use of natural resources is inefficient because the social benefit is less than the social cost. In other words, society and the natural resources involved would have been better off if the natural resources had not been used at all.
Developed countries use more natural resources and must enact sustainable development plan for the use of resources. Human needs must be met, but the environment and natural resources must be preserved. Examples of resource depletion include mining, petroleum extraction, fishing, forestry, and agriculture.
External Benefits
Positive externalities, also referred to as external benefits, impose a positive effect on a third party. An example of a positive externality is when crops are pollinated by bees from a neighboring bee farm. In order to achieve the socially optimal equilibrium, the marginal social benefit should equal the marginal social cost (i.e. production should be increased as long as the marginal social benefit exceeds the marginal social cost). Assuming that natural resources are used and also sustained, the external benefits of goods produced by natural resources impacts the majority of the public in a positive way.
- Every man-made product in an economy is composed of natural resources to some degree.
- Natural resources can be classified as potential, actual, reserve, or stock resources based on their stage of development.
- Natural resources are either renewable or non-renewable depending on whether or not they replenish naturally.
- Natural resource utilization is regulated through the use of taxes and permits. The government and individual states determine how resources must be used and they monitor the availability and status of the resources.
- As a field of academic research, natural resource economics addresses the connections and interdependence between human economies and natural ecosystems.
- By studying natural resources, economists learn how to develop more sustainable methods of managing resources to ensure that they are maintained for future generations.
- Natural resource economics is studied on an academic level, and the findings are used to shape and direct policy-making for environmental issues. These issues include resource extraction, depletion, protection, and management.
- Natural resource economics findings impact policies for environmental work including issues such as extraction, depletion, protection, and management.
- An externality is a cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur the cost or benefit.
- A negative externality, also called the external cost, imposes a negative effect on a third party.
- When external costs are present, the market equilibrium use of natural resources is inefficient because the social benefit is less than the social cost. In other words, society would have been better off if fewer natural resources had been used.
- Positive externalities, also referred to as external benefits, imposes a positive effect on a third party.
- Assuming that natural resources are used and also sustained, the external benefits of goods produced by natural resources impacts the majority of the public in a positive way.
- natural resource : Any source of wealth that occurs naturally, especially minerals, fossil fuels, timber, etc.
- Renewable : Sustainable; able to be regrown or renewed; having an ongoing or continuous source of supply; not finite.
- depletion : The consumption of a resource faster than it can be replenished.
- sustainable : Able to be sustained for an indefinite period without damaging the environment, or without depleting a resource.
- externality : An impact, positive or negative, on any party not involved in a given economic transaction or act.
LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
- Curation and Revision. Provided by : Boundless.com. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SPECIFIC ATTRIBUTION
- Boundless. Provided by : Boundless Learning. Located at : www.boundless.com//political-...tion/renewable . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Natural resource economics. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural...urce_economics . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Natural resources. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_resources . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Clean Air Act (United States). Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Clean_A...United_States) . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- depletion. Provided by : Wiktionary. Located at : en.wiktionary.org/wiki/depletion . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- natural resource. Provided by : Wiktionary. Located at : en.wiktionary.org/wiki/natural_resource . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Nested sustainability-v2. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Ne...ability-v2.gif . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Alternative Energies. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Al...e_Energies.jpg . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Natural resource. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_resource . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- sustainable. Provided by : Wiktionary. Located at : en.wiktionary.org/wiki/sustainable . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- externality. Provided by : Wiktionary. Located at : en.wiktionary.org/wiki/externality . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Resource. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Resource . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Externalities. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Externalities . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Resource allocation. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Resource_allocation . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Diesel-smoke. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Diesel-smoke.jpg . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright

Environmental Economics in Theory and Practice pp 216–226 Cite as
Natural Resources: Types, Classification and Scarcity
- Nick Hanley 4 ,
- Jason F. Shogren 5 &
- Ben White 6
413 Accesses
Part of the book series: Macmillan Texts in Economics ((PTE))
The term 'resources' covers a multitude of meanings and it is necessary to be very precise about its use in what follows. We also discuss various measures of resource scarcity, introducing some which will be important in Chapters 9 to 11.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Anderson, F. (1985) Natural Resources in Canada, Toronto: Methuen.
Google Scholar
Anderson, F. and B. Moazzami (1989) 'Resource scarcity re-examined', discussion paper 11-89, Lakehead University, Ontario.
Barnett, H.J. and C. Morse (1963) Scarcity and Growth: The Economics of Natural Resource Scarcity, Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press.
Conrad, J. and C. Clark (1987) Natural Resource Economics: Notes and Problems, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Deadman, D. and R.K. Turner (1988) 'Resource conservation, sustainability and technical change', in R.K. Turner (ed.), Sustainable Environmental Management. London: Belhaven.
Devarjan, S. and A. Fisher (1980) 'Exploration and scarcity', Working Papers in Economic Theory, IP-290, Berkeley: University of California.
Faber, M. and J. Proops (1993) 'Natural resource rents, economic dynamics and structural change', Ecological Economics, 8(1), 17-44.
Article Google Scholar
Fisher, A.C. (1980) Resource and Environmental Economics, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Hall, D. and J. Hall (1984) 'Concepts and measures of natural resource scarcity with a summary of recent trends', Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 11, 363-79.
Hall, D., C. Cleveland and R. Kaufmann (1986) Energy and Resource Quality: the Ecology of the Economic Process, New York: John Wiley.
Harris, D. and B. Skinner (1982) 'The assessment of long-term supplies of minerals', in V.K. Smith and J. Krutilla (eds), Explorations in Natural Resource Economics, Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press.
Hefindahl, O. (1959) Copper Costs and Prices, 1870-1957, Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press.
Johnson, M., F. Bell and J. Bennett (1980) 'Natural resource scarcity: empirical evidence and public policy', Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 7, 256-71.
Norgaard, R. (1975) 'Resource scarcity and new technology in US petroleum development', Natural Resources Journal, 15, 265-82.
Norgaard, R. (1990) 'Economic indicators of resource scarcity: a critical essay', Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 19, 19-25.
Norgaard, R. and R. Howarth (1989) 'The scarcity of resource economies', mimeo, Energy and Resources Programme, University of California, Berkeley.
Skinner, B. (1976) 'A Second Iron Age?', American Scientist, 64, 258-69.
Slade, M. (1982) 'Trends in natural resource commodity prices: an analysis of the time domain', Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 9, 122-37.
Tietenberg, T. (1992) Environmental and Natural Resource Economics, New York: Harper-Collins.
World Resources Institute (1992) World Resources, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Zwartendyk, J. (1973) 'Mineral wealth: how should it be expressed?', Canadian Mining Journal, April, 44-52.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Stirling, UK
Nick Hanley
University of Wyoming, USA
Jason F. Shogren
University of Newcastle upon Tyne, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Copyright information
© 1997 Nick Hanley, Jason F. Shogren and Ben White
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Hanley, N., Shogren, J.F., White, B. (1997). Natural Resources: Types, Classification and Scarcity. In: Environmental Economics in Theory and Practice. Macmillan Texts in Economics. Palgrave, London. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-24851-3_8
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-24851-3_8
Publisher Name : Palgrave, London
Print ISBN : 978-0-333-58236-7
Online ISBN : 978-1-349-24851-3
eBook Packages : Palgrave Economics & Finance Collection Economics and Finance (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Environmental Chemistry
- Natural Resources (Pdf)
Natural Resources
What are natural resources.
Natural resources can be defined as the resources that exist (on the planet) independent of human actions.
These are the resources that are found in the environment and are developed without the intervention of humans. Common examples of natural resources include air, sunlight, water, soil, stone, plants, animals and fossil fuels.
Natural resources are naturally occurring materials that are useful to man or could be useful under conceivable technological, economic or social circumstances or supplies drawn from the earth, supplies such as food, building and clothing materials, fertilizers, metals, water and geothermal power. For a long time, natural resources were the domain of the natural sciences.
Table of Contents
Recommended videos, what are the different types of natural resources, difference between renewable and non-renewable resources.
- The 5 Most Important Natural Resources
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs

Based on the availability are two types of natural resources :
- Renewable: resources that are available in infinite quantity and can be used repeatedly are called renewable resources. Example: Forest, wind, water, etc.
- Non-Renewable: resources that are limited in abundance due to their non-renewable nature and whose availability may run out in the future are called non-renewable resources. Examples include fossil fuels, minerals, etc.
The 5 Most Important Natural Resources are:
- Air: Clean air is important for all the plants, animals and humans to survive on this planet. So, it is necessary to take measures to reduce air pollution.
- Water: 70% of the Earth is covered in water and only 2 % of that is freshwater. Initiative to educate and regulate the use of water should be taken.
- Soil: Soil is composed of various particles and nutrients. It helps plants grow.
- Iron: It is found as mineral silica and is used to build strong weapons, transportation and buildings
- Forests: Forests provide clean air and preserve the ecology of the world. Trees are being cut for housing and construction projects
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What are the key natural resources.
Distribution of the world’s most important natural resources. Other resources include mineral resources such as copper, gold and diamonds, energy resources such as gas, oil, and uranium, as well as agricultural and logging land resources.
What are the uses of natural resources?
Minerals, forest products, water, and soil are just a few of the natural resources that human beings use to produce energy and make use of things. Within a few years or decades, certain natural resources can be replicated. These are referred to as renewable resources.
How do humans depend on natural resources?
Living things need the land’s water, air, and energy, and they live in places with the things they need. For all they do, humans use natural resources.
What are the characteristics of natural resources?
On Earth, it requires sunshine, air, water, land (including all minerals) along with all the plants, crops and animal life which live naturally on or within the characteristics and substances previously identified.
Does recycling save natural resources?
By sustainability, recycling also saves energy and natural resources. We can save natural resources by using materials more than once. Recycling saves trees and water in the case of paper. Growing up to 17 trees saves up to one ton of paper from recycled stock and uses 50 percent less energy.
To learn more download the Natural resources pdf
Natural Resources PDF

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Chemistry related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Very good content
superb content
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- All Activities
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Conference of the Parties (COP)
- Events and Meetings
- News Portal
- Media Releases
- Latest Publications
- Publication Series
- Fact Sheets
- Photo Galleries
- WMO Community
- The Secretariat
- Our Mandate
- WMO Members
- Liaison Offices
- Gender Equality
- Partnerships
- Resource Mobilization
- History of IMO and WMO
- Finance and Accountability
- World Meteorological Day
- WMO Building
State of the Global Climate 2023
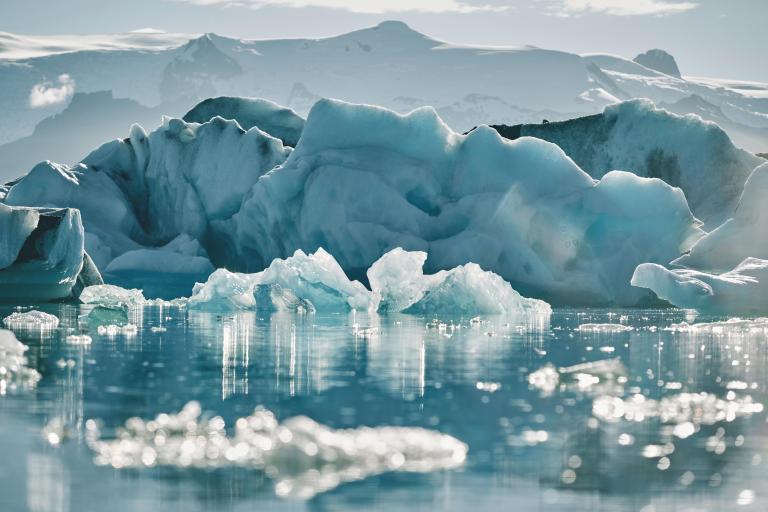

The State of the Global Climate 2023 report shows that records were once again broken, and in some cases smashed, for greenhouse gas levels, surface temperatures, ocean heat and acidification, sea level rise, Antarctic sea ice cover and glacier retreat.
Heatwaves, floods, droughts, wildfires, and rapidly intensifying tropical cyclones caused misery and mayhem, upending everyday life for millions and inflicting many billions of dollars in economic losses.
The WMO report confirmed that 2023 was the warmest year on record, with the global average near-surface temperature at 1.45 °Celsius (with a margin of uncertainty of ± 0.12 °C) above the pre-industrial baseline. It was the warmest ten-year period on record.
Extremes Supplement
Press Release
- State of Global Climate report confirms 2023 as hottest year on record by clear margin
- Records broken for ocean heat, sea level rise, Antarctic sea ice loss and glacier retreat
- Extreme weather undermines socio-economic development
- Renewable energy transition provides hope
- Cost of climate inaction is higher than cost of climate action
Digital resources

State of the Global Climate 2023: Storymap

State of the Climate 2023: User Survey

State of the Climate 2023: Key Climate Indicators
Other editions.

State of the Global Climate 2022

State of the Global Climate 2021
State of the Global Climate 2020

COMMENTS
Uses of Natural Resources. Major problems with Natural Resource conservation. Policy gaps. Reference. Here we are giving you Natural Resources PPT with PDF. All you need to do is just click on the download link and get it. Natural Resources PPT Download. Natural Resources PDF Free Download.
Natural resources are central to human wellbeing. We cannot live without the clean air we breathe, the plants we eat, or the water we drink. We need natural resources to put roofs over our heads and heat our homes. We need them to survive and to thrive. The concept of natural resources refers to naturally occurring living and non-living
Learn about the natural resources of our planet with this interactive and informative PDF presentation. This module covers the topics of air, water and soil, and explains their importance, properties and conservation. This is a part of the Class IX Science curriculum by the Atomic Energy Education Society.
Learn about the types, uses, and conservation of natural resources with this informative and engaging PowerPoint presentation from Madison County Schools. This resource covers topics such as renewable and nonrenewable resources, fossil fuels, water cycle, and recycling. It also includes interactive quizzes and activities to check your understanding.
Natural Resources Unit Overview This unit focuses on natural resources as they relate to sustainable development. It is appropriate for Grades K - 4. It is the goal of the unit to have students increase their ... The case begins with a presentation of the problem and includes important facts and background information. Instructors may add ...
Natural resource economics focuses on the supply, demand, and allocation of the Earth's natural resources. It's goal is to gain a better understanding of the role of natural resources in the economy. Learning about the role of natural resources allows for the development of more sustainable methods to manage resources and make sure that ...
The world has a finite volume of natural resources and a limited ability to produce new resources. Extraction and processing of materials, fuels and food causes 50 per cent of global greenhouse gas emissions and 90 per cent of biodiversity loss and water stress. Our production and consumption are unsustainable, with natural resource use tripling
natural resources.ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Natural resources include renewable and non-renewable sources. Renewable resources are those that regenerate naturally, like air, forests, and solar power. Non-renewable resources like fossil fuels take millions of years to form and are in limited supply.
1980: Ecologist Paul Erlich and economist Julian Simon bet about increased resource scarcity. Erlich picks 5 commodities of his choice: copper, chrome, nickel, tin, and tungsten. Essentially buys $200 of futures from Simon: if prices go up, Simon pays Erlich. If prices go down, Erlich pays Simon. 1990: Erlich sends Simon a check for $576.07.
University of California, San Diego
General training and presentation guidelines: Use good time management to ensure every aspect of your training is completed - but take into account the possible need for translation and ... „Natural resource management‟ is a collective term for the management of natural resources, including wildlife.
powerpoint presentation on natural resources - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. ppt on natural resources
Natural Resources: Types, Classification, Scarcity 217 One obvious distinction between resource types is in terms of their potential for natural growth. Clearly a forest, which may be used as both a material and an energy resource, is different to a deposit of iron ore, in that the former exhibits a natural rate of growth, whilst the latter ...
The 5 Most Important Natural Resources are: Air: Clean air is important for all the plants, animals, humans to survive on this planet. So. it is necessary to take measures to reduce air pollution. Water: 70% of the Earth is covered in water and only 2 % of that is freshwater. Initiative.
Take them on a journey to explore the amazing world of natural resources and discover how we use them. In this instructional slide deck, they will discover the different types of natural resources, from minerals and fossil fuels to water and air. They will also learn about the concept of renewable and nonrenewable resources and how they differ.
Natural resources can be defined as the resources that exist (on the planet) independent of human actions. These are the resources that are found in the environment and are developed without the intervention of humans. Common examples of natural resources include air, sunlight, water, soil, stone, plants, animals and fossil fuels.
much needed conflict resolution framework for disputes that center on natural resources. It can be applied in localized or transboundary conflicts, as well as natural resource disputes that arise in the context of broader peace negotiations. This Guide distills decades of experience in natural resources dispute resolution into an easy-to-access
Management of Natural Resources.ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
The State of the Global Climate 2023 report shows that records were once again broken, and in some cases smashed, for greenhouse gas levels, surface temperatures, ocean heat and acidification, sea level rise, Antarctic sea ice cover and glacier retreat.
Object Moved This document may be found here
Vermont Agency of Natural Resources Julia S. Moore, P.E., Secretary. Agenda • SFY25 ANR Budget Overview • SFY25 ANR Budget - Key Changes - One-Time Investments - Position Changes • On-Going and Significant Initiatives. ... Presentation Template Author: Brackin, Stephanie
EVS UNIT 2 - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document provides an overview of various natural resources including renewable and non-renewable resources, forests, water, minerals, food, and energy. It discusses the importance of conservation and sustainable management of these resources.
Nebraska Department of Natural Resources (NeDNR) Nebraska Department of Natural Resources Preliminary Republican River Basin Forecast for 2024. ... **Values throughout accounting and forecast presentation rounded to nearest 100. Sum of subtotals may not equal totals due to rounding. Final 2021-2022 Accounting Guide Rock Balances, Table 5C.
PRESENTATION Office of State Lands Pursuant to House Rule 14.33, any interested person or any committee member may file with the ... NOTE: Statements may be filed with the House Committee on Natural Resources and Environment via e-mail at [email protected]. Wednesday, March 27, 2024 Committee Room 4 9:00 a.m. INSTRUMENTS TO BE HEARD:
House Environment and Natural Resources Committee . Rhode Island House of Representatives . Re: Support for H7782 - The Clean Heat Standard Act . Dear Chair Bennett and members of the Committee, My name is Dave and I am a resident of Bristol, RI. I'm writing in support of this bill because we need