An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Family Med Prim Care
- v.4(3); Jul-Sep 2015

Validity, reliability, and generalizability in qualitative research
Lawrence leung.
1 Department of Family Medicine, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada
2 Centre of Studies in Primary Care, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada
In general practice, qualitative research contributes as significantly as quantitative research, in particular regarding psycho-social aspects of patient-care, health services provision, policy setting, and health administrations. In contrast to quantitative research, qualitative research as a whole has been constantly critiqued, if not disparaged, by the lack of consensus for assessing its quality and robustness. This article illustrates with five published studies how qualitative research can impact and reshape the discipline of primary care, spiraling out from clinic-based health screening to community-based disease monitoring, evaluation of out-of-hours triage services to provincial psychiatric care pathways model and finally, national legislation of core measures for children's healthcare insurance. Fundamental concepts of validity, reliability, and generalizability as applicable to qualitative research are then addressed with an update on the current views and controversies.
Nature of Qualitative Research versus Quantitative Research
The essence of qualitative research is to make sense of and recognize patterns among words in order to build up a meaningful picture without compromising its richness and dimensionality. Like quantitative research, the qualitative research aims to seek answers for questions of “how, where, when who and why” with a perspective to build a theory or refute an existing theory. Unlike quantitative research which deals primarily with numerical data and their statistical interpretations under a reductionist, logical and strictly objective paradigm, qualitative research handles nonnumerical information and their phenomenological interpretation, which inextricably tie in with human senses and subjectivity. While human emotions and perspectives from both subjects and researchers are considered undesirable biases confounding results in quantitative research, the same elements are considered essential and inevitable, if not treasurable, in qualitative research as they invariable add extra dimensions and colors to enrich the corpus of findings. However, the issue of subjectivity and contextual ramifications has fueled incessant controversies regarding yardsticks for quality and trustworthiness of qualitative research results for healthcare.
Impact of Qualitative Research upon Primary Care
In many ways, qualitative research contributes significantly, if not more so than quantitative research, to the field of primary care at various levels. Five qualitative studies are chosen to illustrate how various methodologies of qualitative research helped in advancing primary healthcare, from novel monitoring of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) via mobile-health technology,[ 1 ] informed decision for colorectal cancer screening,[ 2 ] triaging out-of-hours GP services,[ 3 ] evaluating care pathways for community psychiatry[ 4 ] and finally prioritization of healthcare initiatives for legislation purposes at national levels.[ 5 ] With the recent advances of information technology and mobile connecting device, self-monitoring and management of chronic diseases via tele-health technology may seem beneficial to both the patient and healthcare provider. Recruiting COPD patients who were given tele-health devices that monitored lung functions, Williams et al. [ 1 ] conducted phone interviews and analyzed their transcripts via a grounded theory approach, identified themes which enabled them to conclude that such mobile-health setup and application helped to engage patients with better adherence to treatment and overall improvement in mood. Such positive findings were in contrast to previous studies, which opined that elderly patients were often challenged by operating computer tablets,[ 6 ] or, conversing with the tele-health software.[ 7 ] To explore the content of recommendations for colorectal cancer screening given out by family physicians, Wackerbarth, et al. [ 2 ] conducted semi-structure interviews with subsequent content analysis and found that most physicians delivered information to enrich patient knowledge with little regard to patients’ true understanding, ideas, and preferences in the matter. These findings suggested room for improvement for family physicians to better engage their patients in recommending preventative care. Faced with various models of out-of-hours triage services for GP consultations, Egbunike et al. [ 3 ] conducted thematic analysis on semi-structured telephone interviews with patients and doctors in various urban, rural and mixed settings. They found that the efficiency of triage services remained a prime concern from both users and providers, among issues of access to doctors and unfulfilled/mismatched expectations from users, which could arouse dissatisfaction and legal implications. In UK, a care pathways model for community psychiatry had been introduced but its benefits were unclear. Khandaker et al. [ 4 ] hence conducted a qualitative study using semi-structure interviews with medical staff and other stakeholders; adopting a grounded-theory approach, major themes emerged which included improved equality of access, more focused logistics, increased work throughput and better accountability for community psychiatry provided under the care pathway model. Finally, at the US national level, Mangione-Smith et al. [ 5 ] employed a modified Delphi method to gather consensus from a panel of nominators which were recognized experts and stakeholders in their disciplines, and identified a core set of quality measures for children's healthcare under the Medicaid and Children's Health Insurance Program. These core measures were made transparent for public opinion and later passed on for full legislation, hence illustrating the impact of qualitative research upon social welfare and policy improvement.
Overall Criteria for Quality in Qualitative Research
Given the diverse genera and forms of qualitative research, there is no consensus for assessing any piece of qualitative research work. Various approaches have been suggested, the two leading schools of thoughts being the school of Dixon-Woods et al. [ 8 ] which emphasizes on methodology, and that of Lincoln et al. [ 9 ] which stresses the rigor of interpretation of results. By identifying commonalities of qualitative research, Dixon-Woods produced a checklist of questions for assessing clarity and appropriateness of the research question; the description and appropriateness for sampling, data collection and data analysis; levels of support and evidence for claims; coherence between data, interpretation and conclusions, and finally level of contribution of the paper. These criteria foster the 10 questions for the Critical Appraisal Skills Program checklist for qualitative studies.[ 10 ] However, these methodology-weighted criteria may not do justice to qualitative studies that differ in epistemological and philosophical paradigms,[ 11 , 12 ] one classic example will be positivistic versus interpretivistic.[ 13 ] Equally, without a robust methodological layout, rigorous interpretation of results advocated by Lincoln et al. [ 9 ] will not be good either. Meyrick[ 14 ] argued from a different angle and proposed fulfillment of the dual core criteria of “transparency” and “systematicity” for good quality qualitative research. In brief, every step of the research logistics (from theory formation, design of study, sampling, data acquisition and analysis to results and conclusions) has to be validated if it is transparent or systematic enough. In this manner, both the research process and results can be assured of high rigor and robustness.[ 14 ] Finally, Kitto et al. [ 15 ] epitomized six criteria for assessing overall quality of qualitative research: (i) Clarification and justification, (ii) procedural rigor, (iii) sample representativeness, (iv) interpretative rigor, (v) reflexive and evaluative rigor and (vi) transferability/generalizability, which also double as evaluative landmarks for manuscript review to the Medical Journal of Australia. Same for quantitative research, quality for qualitative research can be assessed in terms of validity, reliability, and generalizability.
Validity in qualitative research means “appropriateness” of the tools, processes, and data. Whether the research question is valid for the desired outcome, the choice of methodology is appropriate for answering the research question, the design is valid for the methodology, the sampling and data analysis is appropriate, and finally the results and conclusions are valid for the sample and context. In assessing validity of qualitative research, the challenge can start from the ontology and epistemology of the issue being studied, e.g. the concept of “individual” is seen differently between humanistic and positive psychologists due to differing philosophical perspectives:[ 16 ] Where humanistic psychologists believe “individual” is a product of existential awareness and social interaction, positive psychologists think the “individual” exists side-by-side with formation of any human being. Set off in different pathways, qualitative research regarding the individual's wellbeing will be concluded with varying validity. Choice of methodology must enable detection of findings/phenomena in the appropriate context for it to be valid, with due regard to culturally and contextually variable. For sampling, procedures and methods must be appropriate for the research paradigm and be distinctive between systematic,[ 17 ] purposeful[ 18 ] or theoretical (adaptive) sampling[ 19 , 20 ] where the systematic sampling has no a priori theory, purposeful sampling often has a certain aim or framework and theoretical sampling is molded by the ongoing process of data collection and theory in evolution. For data extraction and analysis, several methods were adopted to enhance validity, including 1 st tier triangulation (of researchers) and 2 nd tier triangulation (of resources and theories),[ 17 , 21 ] well-documented audit trail of materials and processes,[ 22 , 23 , 24 ] multidimensional analysis as concept- or case-orientated[ 25 , 26 ] and respondent verification.[ 21 , 27 ]
Reliability
In quantitative research, reliability refers to exact replicability of the processes and the results. In qualitative research with diverse paradigms, such definition of reliability is challenging and epistemologically counter-intuitive. Hence, the essence of reliability for qualitative research lies with consistency.[ 24 , 28 ] A margin of variability for results is tolerated in qualitative research provided the methodology and epistemological logistics consistently yield data that are ontologically similar but may differ in richness and ambience within similar dimensions. Silverman[ 29 ] proposed five approaches in enhancing the reliability of process and results: Refutational analysis, constant data comparison, comprehensive data use, inclusive of the deviant case and use of tables. As data were extracted from the original sources, researchers must verify their accuracy in terms of form and context with constant comparison,[ 27 ] either alone or with peers (a form of triangulation).[ 30 ] The scope and analysis of data included should be as comprehensive and inclusive with reference to quantitative aspects if possible.[ 30 ] Adopting the Popperian dictum of falsifiability as essence of truth and science, attempted to refute the qualitative data and analytes should be performed to assess reliability.[ 31 ]
Generalizability
Most qualitative research studies, if not all, are meant to study a specific issue or phenomenon in a certain population or ethnic group, of a focused locality in a particular context, hence generalizability of qualitative research findings is usually not an expected attribute. However, with rising trend of knowledge synthesis from qualitative research via meta-synthesis, meta-narrative or meta-ethnography, evaluation of generalizability becomes pertinent. A pragmatic approach to assessing generalizability for qualitative studies is to adopt same criteria for validity: That is, use of systematic sampling, triangulation and constant comparison, proper audit and documentation, and multi-dimensional theory.[ 17 ] However, some researchers espouse the approach of analytical generalization[ 32 ] where one judges the extent to which the findings in one study can be generalized to another under similar theoretical, and the proximal similarity model, where generalizability of one study to another is judged by similarities between the time, place, people and other social contexts.[ 33 ] Thus said, Zimmer[ 34 ] questioned the suitability of meta-synthesis in view of the basic tenets of grounded theory,[ 35 ] phenomenology[ 36 ] and ethnography.[ 37 ] He concluded that any valid meta-synthesis must retain the other two goals of theory development and higher-level abstraction while in search of generalizability, and must be executed as a third level interpretation using Gadamer's concepts of the hermeneutic circle,[ 38 , 39 ] dialogic process[ 38 ] and fusion of horizons.[ 39 ] Finally, Toye et al. [ 40 ] reported the practicality of using “conceptual clarity” and “interpretative rigor” as intuitive criteria for assessing quality in meta-ethnography, which somehow echoed Rolfe's controversial aesthetic theory of research reports.[ 41 ]
Food for Thought
Despite various measures to enhance or ensure quality of qualitative studies, some researchers opined from a purist ontological and epistemological angle that qualitative research is not a unified, but ipso facto diverse field,[ 8 ] hence any attempt to synthesize or appraise different studies under one system is impossible and conceptually wrong. Barbour argued from a philosophical angle that these special measures or “technical fixes” (like purposive sampling, multiple-coding, triangulation, and respondent validation) can never confer the rigor as conceived.[ 11 ] In extremis, Rolfe et al. opined from the field of nursing research, that any set of formal criteria used to judge the quality of qualitative research are futile and without validity, and suggested that any qualitative report should be judged by the form it is written (aesthetic) and not by the contents (epistemic).[ 41 ] Rolfe's novel view is rebutted by Porter,[ 42 ] who argued via logical premises that two of Rolfe's fundamental statements were flawed: (i) “The content of research report is determined by their forms” may not be a fact, and (ii) that research appraisal being “subject to individual judgment based on insight and experience” will mean those without sufficient experience of performing research will be unable to judge adequately – hence an elitist's principle. From a realism standpoint, Porter then proposes multiple and open approaches for validity in qualitative research that incorporate parallel perspectives[ 43 , 44 ] and diversification of meanings.[ 44 ] Any work of qualitative research, when read by the readers, is always a two-way interactive process, such that validity and quality has to be judged by the receiving end too and not by the researcher end alone.
In summary, the three gold criteria of validity, reliability and generalizability apply in principle to assess quality for both quantitative and qualitative research, what differs will be the nature and type of processes that ontologically and epistemologically distinguish between the two.
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 18, Issue 2
- Issues of validity and reliability in qualitative research
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Helen Noble 1 ,
- Joanna Smith 2
- 1 School of Nursing and Midwifery, Queens's University Belfast , Belfast , UK
- 2 School of Human and Health Sciences, University of Huddersfield , Huddersfield , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Helen Noble School of Nursing and Midwifery, Queens's University Belfast, Medical Biology Centre, 97 Lisburn Rd, Belfast BT9 7BL, UK; helen.noble{at}qub.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2015-102054
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Evaluating the quality of research is essential if findings are to be utilised in practice and incorporated into care delivery. In a previous article we explored ‘bias’ across research designs and outlined strategies to minimise bias. 1 The aim of this article is to further outline rigour, or the integrity in which a study is conducted, and ensure the credibility of findings in relation to qualitative research. Concepts such as reliability, validity and generalisability typically associated with quantitative research and alternative terminology will be compared in relation to their application to qualitative research. In addition, some of the strategies adopted by qualitative researchers to enhance the credibility of their research are outlined.
Are the terms reliability and validity relevant to ensuring credibility in qualitative research?
Although the tests and measures used to establish the validity and reliability of quantitative research cannot be applied to qualitative research, there are ongoing debates about whether terms such as validity, reliability and generalisability are appropriate to evaluate qualitative research. 2–4 In the broadest context these terms are applicable, with validity referring to the integrity and application of the methods undertaken and the precision in which the findings accurately reflect the data, while reliability describes consistency within the employed analytical procedures. 4 However, if qualitative methods are inherently different from quantitative methods in terms of philosophical positions and purpose, then alterative frameworks for establishing rigour are appropriate. 3 Lincoln and Guba 5 offer alternative criteria for demonstrating rigour within qualitative research namely truth value, consistency and neutrality and applicability. Table 1 outlines the differences in terminology and criteria used to evaluate qualitative research.
- View inline
Terminology and criteria used to evaluate the credibility of research findings
What strategies can qualitative researchers adopt to ensure the credibility of the study findings?
Unlike quantitative researchers, who apply statistical methods for establishing validity and reliability of research findings, qualitative researchers aim to design and incorporate methodological strategies to ensure the ‘trustworthiness’ of the findings. Such strategies include:
Accounting for personal biases which may have influenced findings; 6
Acknowledging biases in sampling and ongoing critical reflection of methods to ensure sufficient depth and relevance of data collection and analysis; 3
Meticulous record keeping, demonstrating a clear decision trail and ensuring interpretations of data are consistent and transparent; 3 , 4
Establishing a comparison case/seeking out similarities and differences across accounts to ensure different perspectives are represented; 6 , 7
Including rich and thick verbatim descriptions of participants’ accounts to support findings; 7
Demonstrating clarity in terms of thought processes during data analysis and subsequent interpretations 3 ;
Engaging with other researchers to reduce research bias; 3
Respondent validation: includes inviting participants to comment on the interview transcript and whether the final themes and concepts created adequately reflect the phenomena being investigated; 4
Data triangulation, 3 , 4 whereby different methods and perspectives help produce a more comprehensive set of findings. 8 , 9
Table 2 provides some specific examples of how some of these strategies were utilised to ensure rigour in a study that explored the impact of being a family carer to patients with stage 5 chronic kidney disease managed without dialysis. 10
Strategies for enhancing the credibility of qualitative research
In summary, it is imperative that all qualitative researchers incorporate strategies to enhance the credibility of a study during research design and implementation. Although there is no universally accepted terminology and criteria used to evaluate qualitative research, we have briefly outlined some of the strategies that can enhance the credibility of study findings.
- Sandelowski M
- Lincoln YS ,
- Barrett M ,
- Mayan M , et al
- Greenhalgh T
- Lingard L ,
Twitter Follow Joanna Smith at @josmith175 and Helen Noble at @helnoble
Competing interests None.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review
- Regular Article
- Open access
- Published: 18 September 2021
- Volume 31 , pages 679–689, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Drishti Yadav ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2974-0323 1
72k Accesses
24 Citations
72 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then, references of relevant articles were surveyed to find noteworthy, distinct, and well-defined pointers to good qualitative research. This review presents an investigative assessment of the pivotal features in qualitative research that can permit the readers to pass judgment on its quality and to condemn it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the necessity to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. It also offers some prospects and recommendations to improve the quality of qualitative research. Based on the findings of this review, it is concluded that quality criteria are the aftereffect of socio-institutional procedures and existing paradigmatic conducts. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single and specific set of quality criteria is neither feasible nor anticipated. Since qualitative research is not a cohesive discipline, researchers need to educate and familiarize themselves with applicable norms and decisive factors to evaluate qualitative research from within its theoretical and methodological framework of origin.
Similar content being viewed by others

A worked example of Braun and Clarke’s approach to reflexive thematic analysis
David Byrne

What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research
Patrik Aspers & Ugo Corte
Reporting reliability, convergent and discriminant validity with structural equation modeling: A review and best-practice recommendations
Gordon W. Cheung, Helena D. Cooper-Thomas, … Linda C. Wang
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
“… It is important to regularly dialogue about what makes for good qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 , p. 837)
To decide what represents good qualitative research is highly debatable. There are numerous methods that are contained within qualitative research and that are established on diverse philosophical perspectives. Bryman et al., ( 2008 , p. 262) suggest that “It is widely assumed that whereas quality criteria for quantitative research are well‐known and widely agreed, this is not the case for qualitative research.” Hence, the question “how to evaluate the quality of qualitative research” has been continuously debated. There are many areas of science and technology wherein these debates on the assessment of qualitative research have taken place. Examples include various areas of psychology: general psychology (Madill et al., 2000 ); counseling psychology (Morrow, 2005 ); and clinical psychology (Barker & Pistrang, 2005 ), and other disciplines of social sciences: social policy (Bryman et al., 2008 ); health research (Sparkes, 2001 ); business and management research (Johnson et al., 2006 ); information systems (Klein & Myers, 1999 ); and environmental studies (Reid & Gough, 2000 ). In the literature, these debates are enthused by the impression that the blanket application of criteria for good qualitative research developed around the positivist paradigm is improper. Such debates are based on the wide range of philosophical backgrounds within which qualitative research is conducted (e.g., Sandberg, 2000 ; Schwandt, 1996 ). The existence of methodological diversity led to the formulation of different sets of criteria applicable to qualitative research.
Among qualitative researchers, the dilemma of governing the measures to assess the quality of research is not a new phenomenon, especially when the virtuous triad of objectivity, reliability, and validity (Spencer et al., 2004 ) are not adequate. Occasionally, the criteria of quantitative research are used to evaluate qualitative research (Cohen & Crabtree, 2008 ; Lather, 2004 ). Indeed, Howe ( 2004 ) claims that the prevailing paradigm in educational research is scientifically based experimental research. Hypotheses and conjectures about the preeminence of quantitative research can weaken the worth and usefulness of qualitative research by neglecting the prominence of harmonizing match for purpose on research paradigm, the epistemological stance of the researcher, and the choice of methodology. Researchers have been reprimanded concerning this in “paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences” (Lincoln & Guba, 2000 ).
In general, qualitative research tends to come from a very different paradigmatic stance and intrinsically demands distinctive and out-of-the-ordinary criteria for evaluating good research and varieties of research contributions that can be made. This review attempts to present a series of evaluative criteria for qualitative researchers, arguing that their choice of criteria needs to be compatible with the unique nature of the research in question (its methodology, aims, and assumptions). This review aims to assist researchers in identifying some of the indispensable features or markers of high-quality qualitative research. In a nutshell, the purpose of this systematic literature review is to analyze the existing knowledge on high-quality qualitative research and to verify the existence of research studies dealing with the critical assessment of qualitative research based on the concept of diverse paradigmatic stances. Contrary to the existing reviews, this review also suggests some critical directions to follow to improve the quality of qualitative research in different epistemological and ontological perspectives. This review is also intended to provide guidelines for the acceleration of future developments and dialogues among qualitative researchers in the context of assessing the qualitative research.
The rest of this review article is structured in the following fashion: Sect. Methods describes the method followed for performing this review. Section Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies provides a comprehensive description of the criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. This section is followed by a summary of the strategies to improve the quality of qualitative research in Sect. Improving Quality: Strategies . Section How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings? provides details on how to assess the quality of the research findings. After that, some of the quality checklists (as tools to evaluate quality) are discussed in Sect. Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality . At last, the review ends with the concluding remarks presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook . Some prospects in qualitative research for enhancing its quality and usefulness in the social and techno-scientific research community are also presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook .
For this review, a comprehensive literature search was performed from many databases using generic search terms such as Qualitative Research , Criteria , etc . The following databases were chosen for the literature search based on the high number of results: IEEE Explore, ScienceDirect, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science. The following keywords (and their combinations using Boolean connectives OR/AND) were adopted for the literature search: qualitative research, criteria, quality, assessment, and validity. The synonyms for these keywords were collected and arranged in a logical structure (see Table 1 ). All publications in journals and conference proceedings later than 1950 till 2021 were considered for the search. Other articles extracted from the references of the papers identified in the electronic search were also included. A large number of publications on qualitative research were retrieved during the initial screening. Hence, to include the searches with the main focus on criteria for good qualitative research, an inclusion criterion was utilized in the search string.
From the selected databases, the search retrieved a total of 765 publications. Then, the duplicate records were removed. After that, based on the title and abstract, the remaining 426 publications were screened for their relevance by using the following inclusion and exclusion criteria (see Table 2 ). Publications focusing on evaluation criteria for good qualitative research were included, whereas those works which delivered theoretical concepts on qualitative research were excluded. Based on the screening and eligibility, 45 research articles were identified that offered explicit criteria for evaluating the quality of qualitative research and were found to be relevant to this review.
Figure 1 illustrates the complete review process in the form of PRISMA flow diagram. PRISMA, i.e., “preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses” is employed in systematic reviews to refine the quality of reporting.
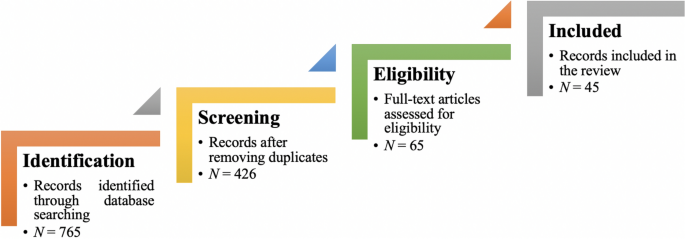
PRISMA flow diagram illustrating the search and inclusion process. N represents the number of records
Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies
Fundamental criteria: general research quality.
Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3 . Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy’s “Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 ). Tracy argues that high-quality qualitative work should formulate criteria focusing on the worthiness, relevance, timeliness, significance, morality, and practicality of the research topic, and the ethical stance of the research itself. Researchers have also suggested a series of questions as guiding principles to assess the quality of a qualitative study (Mays & Pope, 2020 ). Nassaji ( 2020 ) argues that good qualitative research should be robust, well informed, and thoroughly documented.
Qualitative Research: Interpretive Paradigms
All qualitative researchers follow highly abstract principles which bring together beliefs about ontology, epistemology, and methodology. These beliefs govern how the researcher perceives and acts. The net, which encompasses the researcher’s epistemological, ontological, and methodological premises, is referred to as a paradigm, or an interpretive structure, a “Basic set of beliefs that guides action” (Guba, 1990 ). Four major interpretive paradigms structure the qualitative research: positivist and postpositivist, constructivist interpretive, critical (Marxist, emancipatory), and feminist poststructural. The complexity of these four abstract paradigms increases at the level of concrete, specific interpretive communities. Table 5 presents these paradigms and their assumptions, including their criteria for evaluating research, and the typical form that an interpretive or theoretical statement assumes in each paradigm. Moreover, for evaluating qualitative research, quantitative conceptualizations of reliability and validity are proven to be incompatible (Horsburgh, 2003 ). In addition, a series of questions have been put forward in the literature to assist a reviewer (who is proficient in qualitative methods) for meticulous assessment and endorsement of qualitative research (Morse, 2003 ). Hammersley ( 2007 ) also suggests that guiding principles for qualitative research are advantageous, but methodological pluralism should not be simply acknowledged for all qualitative approaches. Seale ( 1999 ) also points out the significance of methodological cognizance in research studies.
Table 5 reflects that criteria for assessing the quality of qualitative research are the aftermath of socio-institutional practices and existing paradigmatic standpoints. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single set of quality criteria is neither possible nor desirable. Hence, the researchers must be reflexive about the criteria they use in the various roles they play within their research community.
Improving Quality: Strategies
Another critical question is “How can the qualitative researchers ensure that the abovementioned quality criteria can be met?” Lincoln and Guba ( 1986 ) delineated several strategies to intensify each criteria of trustworthiness. Other researchers (Merriam & Tisdell, 2016 ; Shenton, 2004 ) also presented such strategies. A brief description of these strategies is shown in Table 6 .
It is worth mentioning that generalizability is also an integral part of qualitative research (Hays & McKibben, 2021 ). In general, the guiding principle pertaining to generalizability speaks about inducing and comprehending knowledge to synthesize interpretive components of an underlying context. Table 7 summarizes the main metasynthesis steps required to ascertain generalizability in qualitative research.
Figure 2 reflects the crucial components of a conceptual framework and their contribution to decisions regarding research design, implementation, and applications of results to future thinking, study, and practice (Johnson et al., 2020 ). The synergy and interrelationship of these components signifies their role to different stances of a qualitative research study.

Essential elements of a conceptual framework
In a nutshell, to assess the rationale of a study, its conceptual framework and research question(s), quality criteria must take account of the following: lucid context for the problem statement in the introduction; well-articulated research problems and questions; precise conceptual framework; distinct research purpose; and clear presentation and investigation of the paradigms. These criteria would expedite the quality of qualitative research.
How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings?
The inclusion of quotes or similar research data enhances the confirmability in the write-up of the findings. The use of expressions (for instance, “80% of all respondents agreed that” or “only one of the interviewees mentioned that”) may also quantify qualitative findings (Stenfors et al., 2020 ). On the other hand, the persuasive reason for “why this may not help in intensifying the research” has also been provided (Monrouxe & Rees, 2020 ). Further, the Discussion and Conclusion sections of an article also prove robust markers of high-quality qualitative research, as elucidated in Table 8 .
Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality
Numerous checklists are available to speed up the assessment of the quality of qualitative research. However, if used uncritically and recklessly concerning the research context, these checklists may be counterproductive. I recommend that such lists and guiding principles may assist in pinpointing the markers of high-quality qualitative research. However, considering enormous variations in the authors’ theoretical and philosophical contexts, I would emphasize that high dependability on such checklists may say little about whether the findings can be applied in your setting. A combination of such checklists might be appropriate for novice researchers. Some of these checklists are listed below:
The most commonly used framework is Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) (Tong et al., 2007 ). This framework is recommended by some journals to be followed by the authors during article submission.
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is another checklist that has been created particularly for medical education (O’Brien et al., 2014 ).
Also, Tracy ( 2010 ) and Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP, 2021 ) offer criteria for qualitative research relevant across methods and approaches.
Further, researchers have also outlined different criteria as hallmarks of high-quality qualitative research. For instance, the “Road Trip Checklist” (Epp & Otnes, 2021 ) provides a quick reference to specific questions to address different elements of high-quality qualitative research.
Conclusions, Future Directions, and Outlook
This work presents a broad review of the criteria for good qualitative research. In addition, this article presents an exploratory analysis of the essential elements in qualitative research that can enable the readers of qualitative work to judge it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. In this review, some of the essential markers that indicate high-quality qualitative research have been highlighted. I scope them narrowly to achieve rigor in qualitative research and note that they do not completely cover the broader considerations necessary for high-quality research. This review points out that a universal and versatile one-size-fits-all guideline for evaluating the quality of qualitative research does not exist. In other words, this review also emphasizes the non-existence of a set of common guidelines among qualitative researchers. In unison, this review reinforces that each qualitative approach should be treated uniquely on account of its own distinctive features for different epistemological and disciplinary positions. Owing to the sensitivity of the worth of qualitative research towards the specific context and the type of paradigmatic stance, researchers should themselves analyze what approaches can be and must be tailored to ensemble the distinct characteristics of the phenomenon under investigation. Although this article does not assert to put forward a magic bullet and to provide a one-stop solution for dealing with dilemmas about how, why, or whether to evaluate the “goodness” of qualitative research, it offers a platform to assist the researchers in improving their qualitative studies. This work provides an assembly of concerns to reflect on, a series of questions to ask, and multiple sets of criteria to look at, when attempting to determine the quality of qualitative research. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the need to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. Bringing together the vital arguments and delineating the requirements that good qualitative research should satisfy, this review strives to equip the researchers as well as reviewers to make well-versed judgment about the worth and significance of the qualitative research under scrutiny. In a nutshell, a comprehensive portrayal of the research process (from the context of research to the research objectives, research questions and design, speculative foundations, and from approaches of collecting data to analyzing the results, to deriving inferences) frequently proliferates the quality of a qualitative research.
Prospects : A Road Ahead for Qualitative Research
Irrefutably, qualitative research is a vivacious and evolving discipline wherein different epistemological and disciplinary positions have their own characteristics and importance. In addition, not surprisingly, owing to the sprouting and varied features of qualitative research, no consensus has been pulled off till date. Researchers have reflected various concerns and proposed several recommendations for editors and reviewers on conducting reviews of critical qualitative research (Levitt et al., 2021 ; McGinley et al., 2021 ). Following are some prospects and a few recommendations put forward towards the maturation of qualitative research and its quality evaluation:
In general, most of the manuscript and grant reviewers are not qualitative experts. Hence, it is more likely that they would prefer to adopt a broad set of criteria. However, researchers and reviewers need to keep in mind that it is inappropriate to utilize the same approaches and conducts among all qualitative research. Therefore, future work needs to focus on educating researchers and reviewers about the criteria to evaluate qualitative research from within the suitable theoretical and methodological context.
There is an urgent need to refurbish and augment critical assessment of some well-known and widely accepted tools (including checklists such as COREQ, SRQR) to interrogate their applicability on different aspects (along with their epistemological ramifications).
Efforts should be made towards creating more space for creativity, experimentation, and a dialogue between the diverse traditions of qualitative research. This would potentially help to avoid the enforcement of one's own set of quality criteria on the work carried out by others.
Moreover, journal reviewers need to be aware of various methodological practices and philosophical debates.
It is pivotal to highlight the expressions and considerations of qualitative researchers and bring them into a more open and transparent dialogue about assessing qualitative research in techno-scientific, academic, sociocultural, and political rooms.
Frequent debates on the use of evaluative criteria are required to solve some potentially resolved issues (including the applicability of a single set of criteria in multi-disciplinary aspects). Such debates would not only benefit the group of qualitative researchers themselves, but primarily assist in augmenting the well-being and vivacity of the entire discipline.
To conclude, I speculate that the criteria, and my perspective, may transfer to other methods, approaches, and contexts. I hope that they spark dialog and debate – about criteria for excellent qualitative research and the underpinnings of the discipline more broadly – and, therefore, help improve the quality of a qualitative study. Further, I anticipate that this review will assist the researchers to contemplate on the quality of their own research, to substantiate research design and help the reviewers to review qualitative research for journals. On a final note, I pinpoint the need to formulate a framework (encompassing the prerequisites of a qualitative study) by the cohesive efforts of qualitative researchers of different disciplines with different theoretic-paradigmatic origins. I believe that tailoring such a framework (of guiding principles) paves the way for qualitative researchers to consolidate the status of qualitative research in the wide-ranging open science debate. Dialogue on this issue across different approaches is crucial for the impending prospects of socio-techno-educational research.
Amin, M. E. K., Nørgaard, L. S., Cavaco, A. M., Witry, M. J., Hillman, L., Cernasev, A., & Desselle, S. P. (2020). Establishing trustworthiness and authenticity in qualitative pharmacy research. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy, 16 (10), 1472–1482.
Article Google Scholar
Barker, C., & Pistrang, N. (2005). Quality criteria under methodological pluralism: Implications for conducting and evaluating research. American Journal of Community Psychology, 35 (3–4), 201–212.
Bryman, A., Becker, S., & Sempik, J. (2008). Quality criteria for quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods research: A view from social policy. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 11 (4), 261–276.
Caelli, K., Ray, L., & Mill, J. (2003). ‘Clear as mud’: Toward greater clarity in generic qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 2 (2), 1–13.
CASP (2021). CASP checklists. Retrieved May 2021 from https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
Cohen, D. J., & Crabtree, B. F. (2008). Evaluative criteria for qualitative research in health care: Controversies and recommendations. The Annals of Family Medicine, 6 (4), 331–339.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2005). Introduction: The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 1–32). Sage Publications Ltd.
Google Scholar
Elliott, R., Fischer, C. T., & Rennie, D. L. (1999). Evolving guidelines for publication of qualitative research studies in psychology and related fields. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38 (3), 215–229.
Epp, A. M., & Otnes, C. C. (2021). High-quality qualitative research: Getting into gear. Journal of Service Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670520961445
Guba, E. G. (1990). The paradigm dialog. In Alternative paradigms conference, mar, 1989, Indiana u, school of education, San Francisco, ca, us . Sage Publications, Inc.
Hammersley, M. (2007). The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research and Method in Education, 30 (3), 287–305.
Haven, T. L., Errington, T. M., Gleditsch, K. S., van Grootel, L., Jacobs, A. M., Kern, F. G., & Mokkink, L. B. (2020). Preregistering qualitative research: A Delphi study. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406920976417.
Hays, D. G., & McKibben, W. B. (2021). Promoting rigorous research: Generalizability and qualitative research. Journal of Counseling and Development, 99 (2), 178–188.
Horsburgh, D. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 12 (2), 307–312.
Howe, K. R. (2004). A critique of experimentalism. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 42–46.
Johnson, J. L., Adkins, D., & Chauvin, S. (2020). A review of the quality indicators of rigor in qualitative research. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 84 (1), 7120.
Johnson, P., Buehring, A., Cassell, C., & Symon, G. (2006). Evaluating qualitative management research: Towards a contingent criteriology. International Journal of Management Reviews, 8 (3), 131–156.
Klein, H. K., & Myers, M. D. (1999). A set of principles for conducting and evaluating interpretive field studies in information systems. MIS Quarterly, 23 (1), 67–93.
Lather, P. (2004). This is your father’s paradigm: Government intrusion and the case of qualitative research in education. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 15–34.
Levitt, H. M., Morrill, Z., Collins, K. M., & Rizo, J. L. (2021). The methodological integrity of critical qualitative research: Principles to support design and research review. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 68 (3), 357.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1986). But is it rigorous? Trustworthiness and authenticity in naturalistic evaluation. New Directions for Program Evaluation, 1986 (30), 73–84.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (2000). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions and emerging confluences. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 163–188). Sage Publications.
Madill, A., Jordan, A., & Shirley, C. (2000). Objectivity and reliability in qualitative analysis: Realist, contextualist and radical constructionist epistemologies. British Journal of Psychology, 91 (1), 1–20.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2020). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Research in Health Care . https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119410867.ch15
McGinley, S., Wei, W., Zhang, L., & Zheng, Y. (2021). The state of qualitative research in hospitality: A 5-year review 2014 to 2019. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 62 (1), 8–20.
Merriam, S., & Tisdell, E. (2016). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation. San Francisco, US.
Meyer, M., & Dykes, J. (2019). Criteria for rigor in visualization design study. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 26 (1), 87–97.
Monrouxe, L. V., & Rees, C. E. (2020). When I say… quantification in qualitative research. Medical Education, 54 (3), 186–187.
Morrow, S. L. (2005). Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counseling psychology. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52 (2), 250.
Morse, J. M. (2003). A review committee’s guide for evaluating qualitative proposals. Qualitative Health Research, 13 (6), 833–851.
Nassaji, H. (2020). Good qualitative research. Language Teaching Research, 24 (4), 427–431.
O’Brien, B. C., Harris, I. B., Beckman, T. J., Reed, D. A., & Cook, D. A. (2014). Standards for reporting qualitative research: A synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine, 89 (9), 1245–1251.
O’Connor, C., & Joffe, H. (2020). Intercoder reliability in qualitative research: Debates and practical guidelines. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406919899220.
Reid, A., & Gough, S. (2000). Guidelines for reporting and evaluating qualitative research: What are the alternatives? Environmental Education Research, 6 (1), 59–91.
Rocco, T. S. (2010). Criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. Human Resource Development International . https://doi.org/10.1080/13678868.2010.501959
Sandberg, J. (2000). Understanding human competence at work: An interpretative approach. Academy of Management Journal, 43 (1), 9–25.
Schwandt, T. A. (1996). Farewell to criteriology. Qualitative Inquiry, 2 (1), 58–72.
Seale, C. (1999). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 5 (4), 465–478.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 (2), 63–75.
Sparkes, A. C. (2001). Myth 94: Qualitative health researchers will agree about validity. Qualitative Health Research, 11 (4), 538–552.
Spencer, L., Ritchie, J., Lewis, J., & Dillon, L. (2004). Quality in qualitative evaluation: A framework for assessing research evidence.
Stenfors, T., Kajamaa, A., & Bennett, D. (2020). How to assess the quality of qualitative research. The Clinical Teacher, 17 (6), 596–599.
Taylor, E. W., Beck, J., & Ainsworth, E. (2001). Publishing qualitative adult education research: A peer review perspective. Studies in the Education of Adults, 33 (2), 163–179.
Tong, A., Sainsbury, P., & Craig, J. (2007). Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 19 (6), 349–357.
Tracy, S. J. (2010). Qualitative quality: Eight “big-tent” criteria for excellent qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 16 (10), 837–851.
Download references
Open access funding provided by TU Wien (TUW).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Informatics, Technische Universität Wien, 1040, Vienna, Austria
Drishti Yadav
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Drishti Yadav .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Yadav, D. Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 31 , 679–689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Download citation
Accepted : 28 August 2021
Published : 18 September 2021
Issue Date : December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Evaluative criteria
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Internal Validity vs. External Validity in Research
Both help determine how meaningful the results of the study are
Arlin Cuncic, MA, is the author of "Therapy in Focus: What to Expect from CBT for Social Anxiety Disorder" and "7 Weeks to Reduce Anxiety." She has a Master's degree in psychology.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ArlinCuncic_1000-21af8749d2144aa0b0491c29319591c4.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
Verywell / Bailey Mariner
- Internal Validity
- External Validity
Internal validity is a measure of how well a study is conducted (its structure) and how accurately its results reflect the studied group.
External validity relates to how applicable the findings are in the real world. These two concepts help researchers gauge if the results of a research study are trustworthy and meaningful.
Conclusions are warranted
Controls extraneous variables
Eliminates alternative explanations
Focus on accuracy and strong research methods
Findings can be generalized
Outcomes apply to practical situations
Results apply to the world at large
Results can be translated into another context
What Is Internal Validity in Research?
Internal validity is the extent to which a research study establishes a trustworthy cause-and-effect relationship. This type of validity depends largely on the study's procedures and how rigorously it is performed.
Internal validity is important because once established, it makes it possible to eliminate alternative explanations for a finding. If you implement a smoking cessation program, for instance, internal validity ensures that any improvement in the subjects is due to the treatment administered and not something else.
Internal validity is not a "yes or no" concept. Instead, we consider how confident we can be with study findings based on whether the research avoids traps that may make those findings questionable. The less chance there is for "confounding," the higher the internal validity and the more confident we can be.
Confounding refers to uncontrollable variables that come into play and can confuse the outcome of a study, making us unsure of whether we can trust that we have identified the cause-and-effect relationship.
In short, you can only be confident that a study is internally valid if you can rule out alternative explanations for the findings. Three criteria are required to assume cause and effect in a research study:
- The cause preceded the effect in terms of time.
- The cause and effect vary together.
- There are no other likely explanations for the relationship observed.
Factors That Improve Internal Validity
To ensure the internal validity of a study, you want to consider aspects of the research design that will increase the likelihood that you can reject alternative hypotheses. Many factors can improve internal validity in research, including:
- Blinding : Participants—and sometimes researchers—are unaware of what intervention they are receiving (such as using a placebo on some subjects in a medication study) to avoid having this knowledge bias their perceptions and behaviors, thus impacting the study's outcome
- Experimental manipulation : Manipulating an independent variable in a study (for instance, giving smokers a cessation program) instead of just observing an association without conducting any intervention (examining the relationship between exercise and smoking behavior)
- Random selection : Choosing participants at random or in a manner in which they are representative of the population that you wish to study
- Randomization or random assignment : Randomly assigning participants to treatment and control groups, ensuring that there is no systematic bias between the research groups
- Strict study protocol : Following specific procedures during the study so as not to introduce any unintended effects; for example, doing things differently with one group of study participants than you do with another group
Internal Validity Threats
Just as there are many ways to ensure internal validity, there is also a list of potential threats that should be considered when planning a study.
- Attrition : Participants dropping out or leaving a study, which means that the results are based on a biased sample of only the people who did not choose to leave (and possibly who all have something in common, such as higher motivation)
- Confounding : A situation in which changes in an outcome variable can be thought to have resulted from some type of outside variable not measured or manipulated in the study
- Diffusion : This refers to the results of one group transferring to another through the groups interacting and talking with or observing one another; this can also lead to another issue called resentful demoralization, in which a control group tries less hard because they feel resentful over the group that they are in
- Experimenter bias : An experimenter behaving in a different way with different groups in a study, which can impact the results (and is eliminated through blinding)
- Historical events : May influence the outcome of studies that occur over a period of time, such as a change in the political leader or a natural disaster that occurs, influencing how study participants feel and act
- Instrumentation : This involves "priming" participants in a study in certain ways with the measures used, causing them to react in a way that is different than they would have otherwise reacted
- Maturation : The impact of time as a variable in a study; for example, if a study takes place over a period of time in which it is possible that participants naturally change in some way (i.e., they grew older or became tired), it may be impossible to rule out whether effects seen in the study were simply due to the impact of time
- Statistical regression : The natural effect of participants at extreme ends of a measure falling in a certain direction due to the passage of time rather than being a direct effect of an intervention
- Testing : Repeatedly testing participants using the same measures influences outcomes; for example, if you give someone the same test three times, it is likely that they will do better as they learn the test or become used to the testing process, causing them to answer differently
What Is External Validity in Research?
External validity refers to how well the outcome of a research study can be expected to apply to other settings. This is important because, if external validity is established, it means that the findings can be generalizable to similar individuals or populations.
External validity affirmatively answers the question: Do the findings apply to similar people, settings, situations, and time periods?
Population validity and ecological validity are two types of external validity. Population validity refers to whether you can generalize the research outcomes to other populations or groups. Ecological validity refers to whether a study's findings can be generalized to additional situations or settings.
Another term called transferability refers to whether results transfer to situations with similar characteristics. Transferability relates to external validity and refers to a qualitative research design.
Factors That Improve External Validity
If you want to improve the external validity of your study, there are many ways to achieve this goal. Factors that can enhance external validity include:
- Field experiments : Conducting a study outside the laboratory, in a natural setting
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria : Setting criteria as to who can be involved in the research, ensuring that the population being studied is clearly defined
- Psychological realism : Making sure participants experience the events of the study as being real by telling them a "cover story," or a different story about the aim of the study so they don't behave differently than they would in real life based on knowing what to expect or knowing the study's goal
- Replication : Conducting the study again with different samples or in different settings to see if you get the same results; when many studies have been conducted on the same topic, a meta-analysis can also be used to determine if the effect of an independent variable can be replicated, therefore making it more reliable
- Reprocessing or calibration : Using statistical methods to adjust for external validity issues, such as reweighting groups if a study had uneven groups for a particular characteristic (such as age)
External Validity Threats
External validity is threatened when a study does not take into account the interaction of variables in the real world. Threats to external validity include:
- Pre- and post-test effects : When the pre- or post-test is in some way related to the effect seen in the study, such that the cause-and-effect relationship disappears without these added tests
- Sample features : When some feature of the sample used was responsible for the effect (or partially responsible), leading to limited generalizability of the findings
- Selection bias : Also considered a threat to internal validity, selection bias describes differences between groups in a study that may relate to the independent variable—like motivation or willingness to take part in the study, or specific demographics of individuals being more likely to take part in an online survey
- Situational factors : Factors such as the time of day of the study, its location, noise, researcher characteristics, and the number of measures used may affect the generalizability of findings
While rigorous research methods can ensure internal validity, external validity may be limited by these methods.
Internal Validity vs. External Validity
Internal validity and external validity are two research concepts that share a few similarities while also having several differences.

Similarities
One of the similarities between internal validity and external validity is that both factors should be considered when designing a study. This is because both have implications in terms of whether the results of a study have meaning.
Both internal validity and external validity are not "either/or" concepts. Therefore, you always need to decide to what degree a study performs in terms of each type of validity.
Each of these concepts is also typically reported in research articles published in scholarly journals . This is so that other researchers can evaluate the study and make decisions about whether the results are useful and valid.
Differences
The essential difference between internal validity and external validity is that internal validity refers to the structure of a study (and its variables) while external validity refers to the universality of the results. But there are further differences between the two as well.
For instance, internal validity focuses on showing a difference that is due to the independent variable alone. Conversely, external validity results can be translated to the world at large.
Internal validity and external validity aren't mutually exclusive. You can have a study with good internal validity but be overall irrelevant to the real world. You could also conduct a field study that is highly relevant to the real world but doesn't have trustworthy results in terms of knowing what variables caused the outcomes.
Examples of Validity
Perhaps the best way to understand internal validity and external validity is with examples.
Internal Validity Example
An example of a study with good internal validity would be if a researcher hypothesizes that using a particular mindfulness app will reduce negative mood. To test this hypothesis, the researcher randomly assigns a sample of participants to one of two groups: those who will use the app over a defined period and those who engage in a control task.
The researcher ensures that there is no systematic bias in how participants are assigned to the groups. They do this by blinding the research assistants so they don't know which groups the subjects are in during the experiment.
A strict study protocol is also used to outline the procedures of the study. Potential confounding variables are measured along with mood , such as the participants' socioeconomic status, gender, age, and other factors. If participants drop out of the study, their characteristics are examined to make sure there is no systematic bias in terms of who stays in.
External Validity Example
An example of a study with good external validity would be if, in the above example, the participants used the mindfulness app at home rather than in the laboratory. This shows that results appear in a real-world setting.
To further ensure external validity, the researcher clearly defines the population of interest and chooses a representative sample . They might also replicate the study's results using different technological devices.
A Word From Verywell
Setting up an experiment so that it has both sound internal validity and external validity involves being mindful from the start about factors that can influence each aspect of your research.
It's best to spend extra time designing a structurally sound study that has far-reaching implications rather than to quickly rush through the design phase only to discover problems later on. Only when both internal validity and external validity are high can strong conclusions be made about your results.
San Jose State University. Internal and external validity .
Michael RS. Threats to internal & external validity: Y520 strategies for educational inquiry .
Pahus L, Burgel PR, Roche N, Paillasseur JL, Chanez P. Randomized controlled trials of pharmacological treatments to prevent COPD exacerbations: applicability to real-life patients . BMC Pulm Med . 2019;19(1):127. doi:10.1186/s12890-019-0882-y
By Arlin Cuncic, MA Arlin Cuncic, MA, is the author of "Therapy in Focus: What to Expect from CBT for Social Anxiety Disorder" and "7 Weeks to Reduce Anxiety." She has a Master's degree in psychology.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- External Validity | Types, Threats & Examples
External Validity | Types, Threats & Examples
Published on 3 May 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 18 December 2023.
External validity is the extent to which you can generalise the findings of a study to other situations, people, settings, and measures. In other words, can you apply the findings of your study to a broader context?
The aim of scientific research is to produce generalisable knowledge about the real world. Without high external validity, you cannot apply results from the laboratory to other people or the real world.
In qualitative studies , external validity is referred to as transferability.
Table of contents
Types of external validity, trade-off between external and internal validity, threats to external validity and how to counter them, frequently asked questions about external validity.
There are two main types of external validity: population validity and ecological validity.
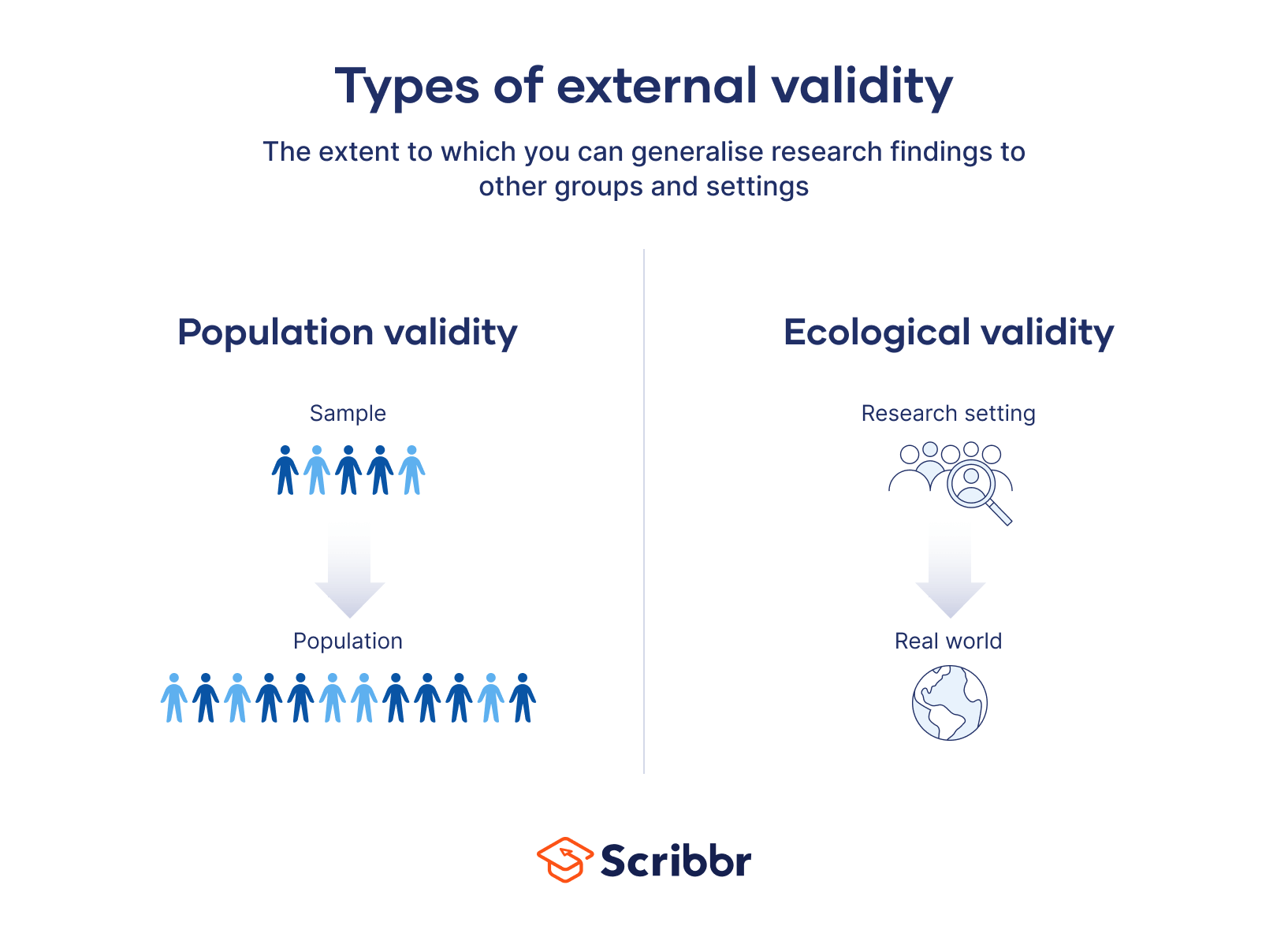
Population validity
Population validity refers to whether you can reasonably generalise the findings from your sample to a larger group of people (the population).
Population validity depends on the choice of population and on the extent to which the study sample mirrors that population. Non-probability sampling methods are often used for convenience. With this type of sampling, the generalisability of results is limited to populations that share similar characteristics with the sample.
You recruit over 200 participants. They are science and engineering students; most of them are British, male, 18–20 years old, and from a high socioeconomic background. In a laboratory setting, you administer a mathematics and science test and then ask them to rate how well they think performed. You find that the average participant believes they are smarter than 66% of their peers.
Here, your sample is not representative of the whole population of students at your university. The findings can only reasonably be generalised to populations that share characteristics with the participants, e.g. university-educated men studying STEM subjects.
For higher population validity, your sample would need to include people with different characteristics (e.g., women, nonbinary people, and students from different fields, countries, and socioeconomic backgrounds).
Samples like this one, from Western, educated, industrialised, rich, and democratic (WEIRD) countries, are used in an estimated 96% of psychology studies , even though they represent only 12% of the world’s population. As outliers in terms of visual perception, moral reasoning, and categorisation (among many other topics), WEIRD samples limit broad population validity in the social sciences.
Ecological validity
Ecological validity refers to whether you can reasonably generalise the findings of a study to other situations and settings in the ‘real world’.
In a laboratory setting, you set up a simple computer-based task to measure reaction times. Participants are told to imagine themselves driving around the racetrack and double-click the mouse whenever they see an orange cat on the screen. For one round, participants listen to a podcast. In the other round, they do not need to listen to anything.
In the example above, it is difficult to generalise the findings to real-life driving conditions. A computer-based task using a mouse does not resemble real-life driving conditions with a steering wheel. Additionally, a static image of an orange cat may not represent common real-life hurdles when driving.
To improve ecological validity in a lab setting, you could use an immersive driving simulator with a steering wheel and foot pedal instead of a computer and mouse. This increases psychological realism by more closely mirroring the experience of driving in the real world.
Alternatively, for higher ecological validity, you could conduct the experiment using a real driving course.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Internal validity is the extent to which you can be confident that the causal relationship established in your experiment cannot be explained by other factors.
There is an inherent trade-off between external and internal validity ; the more applicable you make your study to a broader context, the less you can control extraneous factors in your study.
Threats to external validity are important to recognise and counter in a research design for a robust study.
Participants are given a pretest and a post-test measuring how often they experienced anxiety in the past week. During the study, all participants are given an individual mindfulness training and asked to practise mindfulness daily for 15 minutes in the morning.
How to counter threats to external validity
There are several ways to counter threats to external validity:
- Replications counter almost all threats by enhancing generalisability to other settings, populations and conditions.
- Field experiments counter testing and situation effects by using natural contexts.
- Probability sampling counters selection bias by making sure everyone in a population has an equal chance of being selected for a study sample.
- Recalibration or reprocessing also counters selection bias using algorithms to correct weighting of factors (e.g., age) within study samples.
The external validity of a study is the extent to which you can generalise your findings to different groups of people, situations, and measures.
The two types of external validity are population validity (whether you can generalise to other groups of people) and ecological validity (whether you can generalise to other situations and settings).
There are seven threats to external validity : selection bias , history, experimenter effect, Hawthorne effect , testing effect, aptitude-treatment, and situation effect.
Attrition bias can skew your sample so that your final sample differs significantly from your original sample. Your sample is biased because some groups from your population are underrepresented.
With a biased final sample, you may not be able to generalise your findings to the original population that you sampled from, so your external validity is compromised.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, December 18). External Validity | Types, Threats & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 25 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/external-validity-explained/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, the 4 types of validity | types, definitions & examples, internal validity | definition, threats & examples, reliability vs validity in research | differences, types & examples.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Research Tools and Apps
External Validity: Types, Research Methods & Examples

External validity is one of the main goals of researchers who want to find reliable cause-and-effect relationships in qualitative research.
When research has this validity, the results can be used with other people in different situations or places. Because without this validity, analysis can’t be generalized, and researchers can’t apply the results of studies to the real world. So, psychology research needs to be conducted outside a lab setting.
Still, sometimes they prefer to research how variables cause each other instead of being able to generalize the results.
In this article, we’ll talk about what external validity means, its types, and its research design methods.
LEARN ABOUT: Theoretical Research
What is external validity?
External validity describes how effectively the findings of an experiment may be generalized to different people, places, or times. Most scientific investigations do not intend to obtain outcomes that only apply to the few persons who participated in the study.
Instead, researchers want to be able to take the results of an experiment and use them with a larger group of people. It is a big part of what inferential statistics try to do.
For example, if you’re looking at a new drug or educational program, you don’t want to know that it works for only a few people. You want to use those results outside the experiment and beyond those participating. It is called “generalizability,” the essential part of this validity.
Types of external validity
Generally, there are three main types of this validity. We’ll discuss each one below and give examples to help you understand.
Population validity
Population validity is a kind of external validity that looks at how well the study’s results applied to a larger group of people. In this case, “population” refers to the group of people about whom a researcher is trying to conclude. On the other hand, a sample is a particular group of people who participate in the research.
If the results from the sample can apply to a larger group of people, then the study is valid for a large population.
Example: low population validity
You want to test the theory about how exercise and sleep are linked. You think that adults will sleep better when they do physical activities regularly. Your target group is adults in the United States, but your sample comprises about 300 college students.
Even though they are all adults, it might be hard to ensure the population validity in this case because the sampling model of students only represents some adults in the US.
So, your study has a limited amount of population validity, and you can only apply the results to some of the population.
Ecological validity
Ecological validity is another type of external validity that shows how well the research results can be used in different situations. In simple terms, ecological validity is about whether or not your results can be used in the real world.
So, if a study has a lot of ecological validity, the results can be used in the real world. On the other hand, low validity means that the results can’t be used outside the experiment.
Example: low ecological validity
The Milgram Experiment is a classic example of low ecological validity.
Stanley Milgram studied authority in the 1960s. He randomly chose participants and directed them to employ higher and higher voltage shocks to penalize wrong-answering actors. The study showed great obedience to authorities despite fake shock and victim behaviors.
The results of this study are revolutionary for the field of social psychology. However, it is often criticized because it has little ecological validity. Milgram’s set-up was not like real-life situations.
In the experiment, he set up a situation where the participants couldn’t avoid obeying the rules. But the reality of the issue can be very different.
Temporal validity
When figuring out external validity, time is just as important as the number of people involved and confusing factors.
The concept of temporal validity refers to how findings evolve. Particularly, this form of validity refers to how well the research results can be extended to another period.
High temporal validity means that research results can be used correctly in different times and places and that factors will be important in the future.
Imagine that you’re a psychologist, and you’re studying how people act the same.
You found out that social pressure from the majority group has a big effect on the choices of the minority. Because of this, people act similarly. Even though famous psychologist Solomon Asch did this research in the 1950s, the results can still be used in the real world today.
This study, therefore, has temporal validity even after nearly a century.
Research methods of external validity
There are a lot of methods you can do to improve the external validity of your research. Some things that can improve are given below:
Field experiments
Field experiments are like conducting research outside rather than in a controlled environment like a laboratory.
Criteria for inclusion and exclusion
Establishing criteria for who can participate in the research and ensuring that the group being examined is properly identified
Realism in psychology
If you want the participants to believe that the events that take place throughout the study are true, you should provide them with a cover story regarding the purpose of the research. So that they don’t behave any differently than they would in real life based on the fact.
Replication
Doing the study again with different samples or in a different place to see if you get the same results. When many studies have been done on the same topic, a meta-analysis can be used to see if the effect of an independent variable can be repeated to make it more reliable.
Reprocessing
It is like using statistical methods to fix problems with external validity, like reweighting groups if they were different in a certain way, such as age.
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
As stated in the article, the ability to replicate the results of an experiment is a key component of its external validity. Using the sampling methods the external validity can be improved in the research.
Researchers compare the results to other relevant data to determine the external validity. They can also do the research with more people from the target population. It’s hard to figure out external validity in research, but it’s important to use the results in the future.
The QuestionPro research suite is an enterprise-level research tool that can help you with your research process and surveys.
We at QuestionPro provide tools for data collection, such as our survey software, and a library of insights for any lengthy study. If you’re interested in seeing a demo or learning more, visit the Insight Hub.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

In-App Feedback Tools: How to Collect, Uses & 14 Best Tools
Mar 29, 2024
11 Best Customer Journey Analytics Software in 2024

17 Best VOC Software for Customer Experience in 2024
Mar 28, 2024

CEM Software: What it is, 7 Best CEM Software in 2024
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Internal vs. External Validity | Understanding Differences & Threats
Internal vs. External Validity | Understanding Differences & Threats
Published on May 15, 2019 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Internal and external validity are two ways of testing cause-and-effect relationships.
The validity of a study is largely determined by the experimental design . To ensure the validity of the tools or tests you use, you also have to consider measurement validity .
Table of contents
Trade-off between internal and external validity, threats to internal validity, threats to external validity, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about internal and external validity.
Better internal validity often comes at the expense of external validity (and vice versa ). The type of study you choose reflects the priorities of your research.
A solution to this trade-off is to conduct the research first in a controlled (artificial) environment to establish the existence of a causal relationship, followed by a field experiment to analyze if the results hold in the real world.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

There are eight factors that can threaten the internal validity of your research. They are explained below using the following example:
There are three main factors that might threaten the external validity of our study example.
There are various other threats to external validity that can apply to different kinds of experiments.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
I nternal validity is the degree of confidence that the causal relationship you are testing is not influenced by other factors or variables .
External validity is the extent to which your results can be generalized to other contexts.
The validity of your experiment depends on your experimental design .
There are eight threats to internal validity : history, maturation, instrumentation, testing, selection bias , regression to the mean, social interaction and attrition .
The two types of external validity are population validity (whether you can generalize to other groups of people) and ecological validity (whether you can generalize to other situations and settings).
There are seven threats to external validity : selection bias , history, experimenter effect, Hawthorne effect , testing effect, aptitude-treatment and situation effect.
Experimental design means planning a set of procedures to investigate a relationship between variables . To design a controlled experiment, you need:
- A testable hypothesis
- At least one independent variable that can be precisely manipulated
- At least one dependent variable that can be precisely measured
When designing the experiment, you decide:
- How you will manipulate the variable(s)
- How you will control for any potential confounding variables
- How many subjects or samples will be included in the study
- How subjects will be assigned to treatment levels
Experimental design is essential to the internal and external validity of your experiment.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2023, June 22). Internal vs. External Validity | Understanding Differences & Threats. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/internal-vs-external-validity/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, internal validity in research | definition, threats, & examples, external validity | definition, types, threats & examples, sampling methods | types, techniques & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
Neag School of Education
Educational Research Basics by Del Siegle
External validity.
Note to EPSY 5601 Students: An understanding of the difference between population and ecological validity is sufficient. Mastery of the sub categories for each is not necessary for this course.
External Validity (Generalizability) –to whom can the results of the study be applied–
There are two types of study validity: internal (more applicable with experimental research) and external. This section covers external validity.
External validity involves the extent to which the results of a study can be generalized (applied) beyond the sample. In other words, can you apply what you found in your study to other people (population validity) or settings (ecological validity). A study of fifth graders in a rural school that found one method of teaching spelling was superior to another may not be applicable with third graders (population) in an urban school (ecological).
Threats to External Validity
Population Validity the extent to which the results of a study can be generalized from the specific sample that was studied to a larger group of subjects
- the extent to which one can generalize from the study sample to a defined population– If the sample is drawn from an accessible population, rather than the target population, generalizing the research results from the accessible population to the target population is risky. 2. the extent to which personological variables interact with treatment effects– If the study is an experiment, it may be possible that different results might be found with students at different grades (a personological variable).
Ecological Validity the extent to which the results of an experiment can be generalized from the set of environmental conditions created by the researcher to other environmental conditions (settings and conditions).
- Explicit description of the experimental treatment (not sufficiently described for others to replicate) If the researcher fails to adequately describe how he or she conducted a study, it is difficult to determine whether the results are applicable to other settings.
- Multiple-treatment interference (catalyst effect) If a researcher were to apply several treatments, it is difficult to determine how well each of the treatments would work individually. It might be that only the combination of the treatments is effective.
- Hawthorne effect (attention causes differences) Subjects perform differently because they know they are being studied. “…External validity of the experiment is jeopardized because the findings might not generalize to a situation in which researchers or others who were involved in the research are not present” (Gall, Borg, & Gall, 1996, p. 475)
- Novelty and disruption effect (anything different makes a difference) A treatment may work because it is novel and the subjects respond to the uniqueness, rather than the actual treatment. The opposite may also occur, the treatment may not work because it is unique, but given time for the subjects to adjust to it, it might have worked.
- Experimenter effect (it only works with this experimenter) The treatment might have worked because of the person implementing it. Given a different person, the treatment might not work at all.
- Pretest sensitization (pretest sets the stage) A treatment might only work if a pretest is given. Because they have taken a pretest, the subjects may be more sensitive to the treatment. Had they not taken a pretest, the treatment would not have worked.
- Posttest sensitization (posttest helps treatment “fall into place”) The posttest can become a learning experience. “For example, the posttest might cause certain ideas presented during the treatment to ‘fall into place’ ” (p. 477). If the subjects had not taken a posttest, the treatment would not have worked.
- Interaction of history and treatment effec t (…to everything there is a time…) Not only should researchers be cautious about generalizing to other population, caution should be taken to generalize to a different time period. As time passes, the conditions under which treatments work change.
- Measurement of the dependent variable (maybe only works with M/C tests) A treatment may only be evident with certain types of measurements. A teaching method may produce superior results when its effectiveness is tested with an essay test, but show no differences when the effectiveness is measured with a multiple choice test.
- Interaction of time of measurement and treatment effect (it takes a while for the treatment to kick in) It may be that the treatment effect does not occur until several weeks after the end of the treatment. In this situation, a posttest at the end of the treatment would show no impact, but a posttest a month later might show an impact.
Bracht, G. H., & Glass, G. V. (1968). The external validity of experiments. American Education Research Journal, 5, 437-474. Gall, M. D., Borg, W. R., & Gall, J. P. (1996). Educational research: An introduction. White Plains, NY: Longman.
Del Siegle, Ph.D. Neag School of Education – University of Connecticut [email protected] www.delsiegle.com

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In assessing validity of qualitative research, the challenge can start from the ontology and epistemology of the issue being studied, e.g. the concept of "individual" is seen differently between humanistic and positive psychologists due to differing philosophical perspectives: Where humanistic psychologists believe "individual" is a ...
The aim of scientific research is to produce generalizable knowledge about the real world. Without high external validity, you cannot apply results from the laboratory to other people or the real world. These results will suffer from research biases like undercoverage bias. In qualitative studies, external validity is referred to as ...
Creswell and Millers' work advances the debate on validity in qualitative research in several ways. It elegantly unites different worldviews or paradigms within qualitative research with key perspectives by which the validity of qualitative research can be assessed: that of the researcher, the respondent, and the external reader.
Some researchers prefer to adopt the same criteria of internal and external validity in qualitative research. Examples are the works of Aubin-Auger et al. (2008), Ergene, Yazici and Delice (2016), and Miles and Huberman (1984). However, this does not seem to be the standard. On the contrary, several authors prefer to propose and adopt different
Although the tests and measures used to establish the validity and reliability of quantitative research cannot be applied to qualitative research, there are ongoing debates about whether terms such as validity, reliability and generalisability are appropriate to evaluate qualitative research.2-4 In the broadest context these terms are applicable, with validity referring to the integrity and ...
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then ...
design, and moves the responsibility for incorporating and maintaining reliability and validity from external reviewers' judgements to the investigators themselves. Finally, we make a plea for a return to terminology for ensuring rigor that is used by mainstream science. Keywords: reliability; validity; verification; qualitative research
To enhance the validity of qualitative research, researchers recommend the use of validity checklists (Creswell & Miller, 2000; Maxwell, 1996; Lincoln & Guba, 1985; Whittemore, Chase, & Mandle, 2001). A validity checklist assists the researcher in establishing techniques that will be used for the duration of the research to strengthen validity ...
Differences. The essential difference between internal validity and external validity is that internal validity refers to the structure of a study (and its variables) while external validity refers to the universality of the results. But there are further differences between the two as well. For instance, internal validity focuses on showing a ...
Validity in Qualitative 2. Feedback: "Soliciting feedback from others is an extremely useful strategy for identifying validity threats, your own biases and assumptions, and flaws in your logic or methods" (Maxwell, 1996, p. 94). Member Checks: "systematically soliciting feedback about one's data and conclusions from the people you are ...
The aim of scientific research is to produce generalisable knowledge about the real world. Without high external validity, you cannot apply results from the laboratory to other people or the real world. In qualitative studies, external validity is referred to as transferability.
The criterion of validity and reliability in qualitative research can be achieved by presenting evaluations related to concepts in the context of trustworthiness such as credibility, accuracy of ...
However, a major concern regarding qualitative research is the great variety of epistemic, philosophical, and ontological aspects involved. 13,14,18 Recent evidence suggests that some structured ways of dealing with the diverse quality dimensions of qualitative research, such as internal and external validity, reliability, objectivity ...
External validity is the validity of applying the conclusions of a scientific study outside the context of that study. In other words, it is the extent to which the results of a study can generalize or transport to other situations, people, stimuli, and times. ... Qualitative research. Within the qualitative research paradigm, external validity ...
External validity is one of the main goals of researchers who want to find reliable cause-and-effect relationships in qualitative research. When research has this validity, the results can be used with other people in different situations or places. Because without this validity, analysis can't be generalized, and researchers can't apply ...
Internal and external validity are two ways of testing cause-and-effect relationships. Internal validity refers to the degree of confidence that the causal relationship being tested is trustworthy and not influenced by other factors or variables. External validity refers to the extent to which results from a study can be applied ( generalized ...
In a similar fashion to transferability serving in place of external validity, qualitative research discusses the credibility of the findings to understand a study's internal validity. In qualitative research, credibility refers to the confidence that the data and its analysis are valid and reliable. As Patton (1999) observed, the credibility ...
External Validity. (Generalizability) -to whom can the results of the study be applied-. There are two types of study validity: internal (more applicable with experimental research) and external. This section covers external validity. External validity involves the extent to which the results of a study can be generalized (applied) beyond ...