Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates

How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Data Analysis in Research: Types & Methods
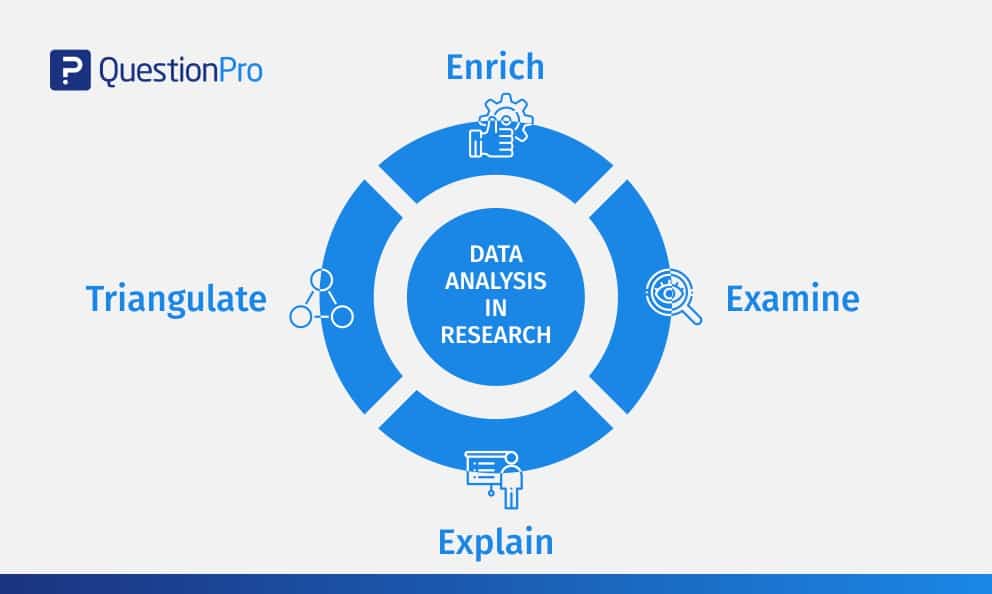
Content Index
Why analyze data in research?
Types of data in research, finding patterns in the qualitative data, methods used for data analysis in qualitative research, preparing data for analysis, methods used for data analysis in quantitative research, considerations in research data analysis, what is data analysis in research.
Definition of research in data analysis: According to LeCompte and Schensul, research data analysis is a process used by researchers to reduce data to a story and interpret it to derive insights. The data analysis process helps reduce a large chunk of data into smaller fragments, which makes sense.
Three essential things occur during the data analysis process — the first is data organization . Summarization and categorization together contribute to becoming the second known method used for data reduction. It helps find patterns and themes in the data for easy identification and linking. The third and last way is data analysis – researchers do it in both top-down and bottom-up fashion.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
On the other hand, Marshall and Rossman describe data analysis as a messy, ambiguous, and time-consuming but creative and fascinating process through which a mass of collected data is brought to order, structure and meaning.
We can say that “the data analysis and data interpretation is a process representing the application of deductive and inductive logic to the research and data analysis.”
Researchers rely heavily on data as they have a story to tell or research problems to solve. It starts with a question, and data is nothing but an answer to that question. But, what if there is no question to ask? Well! It is possible to explore data even without a problem – we call it ‘Data Mining’, which often reveals some interesting patterns within the data that are worth exploring.
Irrelevant to the type of data researchers explore, their mission and audiences’ vision guide them to find the patterns to shape the story they want to tell. One of the essential things expected from researchers while analyzing data is to stay open and remain unbiased toward unexpected patterns, expressions, and results. Remember, sometimes, data analysis tells the most unforeseen yet exciting stories that were not expected when initiating data analysis. Therefore, rely on the data you have at hand and enjoy the journey of exploratory research.
Create a Free Account
Every kind of data has a rare quality of describing things after assigning a specific value to it. For analysis, you need to organize these values, processed and presented in a given context, to make it useful. Data can be in different forms; here are the primary data types.
- Qualitative data: When the data presented has words and descriptions, then we call it qualitative data . Although you can observe this data, it is subjective and harder to analyze data in research, especially for comparison. Example: Quality data represents everything describing taste, experience, texture, or an opinion that is considered quality data. This type of data is usually collected through focus groups, personal qualitative interviews , qualitative observation or using open-ended questions in surveys.
- Quantitative data: Any data expressed in numbers of numerical figures are called quantitative data . This type of data can be distinguished into categories, grouped, measured, calculated, or ranked. Example: questions such as age, rank, cost, length, weight, scores, etc. everything comes under this type of data. You can present such data in graphical format, charts, or apply statistical analysis methods to this data. The (Outcomes Measurement Systems) OMS questionnaires in surveys are a significant source of collecting numeric data.
- Categorical data: It is data presented in groups. However, an item included in the categorical data cannot belong to more than one group. Example: A person responding to a survey by telling his living style, marital status, smoking habit, or drinking habit comes under the categorical data. A chi-square test is a standard method used to analyze this data.
Learn More : Examples of Qualitative Data in Education
Data analysis in qualitative research
Data analysis and qualitative data research work a little differently from the numerical data as the quality data is made up of words, descriptions, images, objects, and sometimes symbols. Getting insight from such complicated information is a complicated process. Hence it is typically used for exploratory research and data analysis .
Although there are several ways to find patterns in the textual information, a word-based method is the most relied and widely used global technique for research and data analysis. Notably, the data analysis process in qualitative research is manual. Here the researchers usually read the available data and find repetitive or commonly used words.
For example, while studying data collected from African countries to understand the most pressing issues people face, researchers might find “food” and “hunger” are the most commonly used words and will highlight them for further analysis.
LEARN ABOUT: Level of Analysis
The keyword context is another widely used word-based technique. In this method, the researcher tries to understand the concept by analyzing the context in which the participants use a particular keyword.
For example , researchers conducting research and data analysis for studying the concept of ‘diabetes’ amongst respondents might analyze the context of when and how the respondent has used or referred to the word ‘diabetes.’
The scrutiny-based technique is also one of the highly recommended text analysis methods used to identify a quality data pattern. Compare and contrast is the widely used method under this technique to differentiate how a specific text is similar or different from each other.
For example: To find out the “importance of resident doctor in a company,” the collected data is divided into people who think it is necessary to hire a resident doctor and those who think it is unnecessary. Compare and contrast is the best method that can be used to analyze the polls having single-answer questions types .
Metaphors can be used to reduce the data pile and find patterns in it so that it becomes easier to connect data with theory.
Variable Partitioning is another technique used to split variables so that researchers can find more coherent descriptions and explanations from the enormous data.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Research Questions and Questionnaires
There are several techniques to analyze the data in qualitative research, but here are some commonly used methods,
- Content Analysis: It is widely accepted and the most frequently employed technique for data analysis in research methodology. It can be used to analyze the documented information from text, images, and sometimes from the physical items. It depends on the research questions to predict when and where to use this method.
- Narrative Analysis: This method is used to analyze content gathered from various sources such as personal interviews, field observation, and surveys . The majority of times, stories, or opinions shared by people are focused on finding answers to the research questions.
- Discourse Analysis: Similar to narrative analysis, discourse analysis is used to analyze the interactions with people. Nevertheless, this particular method considers the social context under which or within which the communication between the researcher and respondent takes place. In addition to that, discourse analysis also focuses on the lifestyle and day-to-day environment while deriving any conclusion.
- Grounded Theory: When you want to explain why a particular phenomenon happened, then using grounded theory for analyzing quality data is the best resort. Grounded theory is applied to study data about the host of similar cases occurring in different settings. When researchers are using this method, they might alter explanations or produce new ones until they arrive at some conclusion.
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
Data analysis in quantitative research
The first stage in research and data analysis is to make it for the analysis so that the nominal data can be converted into something meaningful. Data preparation consists of the below phases.
Phase I: Data Validation
Data validation is done to understand if the collected data sample is per the pre-set standards, or it is a biased data sample again divided into four different stages
- Fraud: To ensure an actual human being records each response to the survey or the questionnaire
- Screening: To make sure each participant or respondent is selected or chosen in compliance with the research criteria
- Procedure: To ensure ethical standards were maintained while collecting the data sample
- Completeness: To ensure that the respondent has answered all the questions in an online survey. Else, the interviewer had asked all the questions devised in the questionnaire.
Phase II: Data Editing
More often, an extensive research data sample comes loaded with errors. Respondents sometimes fill in some fields incorrectly or sometimes skip them accidentally. Data editing is a process wherein the researchers have to confirm that the provided data is free of such errors. They need to conduct necessary checks and outlier checks to edit the raw edit and make it ready for analysis.
Phase III: Data Coding
Out of all three, this is the most critical phase of data preparation associated with grouping and assigning values to the survey responses . If a survey is completed with a 1000 sample size, the researcher will create an age bracket to distinguish the respondents based on their age. Thus, it becomes easier to analyze small data buckets rather than deal with the massive data pile.
LEARN ABOUT: Steps in Qualitative Research
After the data is prepared for analysis, researchers are open to using different research and data analysis methods to derive meaningful insights. For sure, statistical analysis plans are the most favored to analyze numerical data. In statistical analysis, distinguishing between categorical data and numerical data is essential, as categorical data involves distinct categories or labels, while numerical data consists of measurable quantities. The method is again classified into two groups. First, ‘Descriptive Statistics’ used to describe data. Second, ‘Inferential statistics’ that helps in comparing the data .
Descriptive statistics
This method is used to describe the basic features of versatile types of data in research. It presents the data in such a meaningful way that pattern in the data starts making sense. Nevertheless, the descriptive analysis does not go beyond making conclusions. The conclusions are again based on the hypothesis researchers have formulated so far. Here are a few major types of descriptive analysis methods.
Measures of Frequency
- Count, Percent, Frequency
- It is used to denote home often a particular event occurs.
- Researchers use it when they want to showcase how often a response is given.
Measures of Central Tendency
- Mean, Median, Mode
- The method is widely used to demonstrate distribution by various points.
- Researchers use this method when they want to showcase the most commonly or averagely indicated response.
Measures of Dispersion or Variation
- Range, Variance, Standard deviation
- Here the field equals high/low points.
- Variance standard deviation = difference between the observed score and mean
- It is used to identify the spread of scores by stating intervals.
- Researchers use this method to showcase data spread out. It helps them identify the depth until which the data is spread out that it directly affects the mean.
Measures of Position
- Percentile ranks, Quartile ranks
- It relies on standardized scores helping researchers to identify the relationship between different scores.
- It is often used when researchers want to compare scores with the average count.
For quantitative research use of descriptive analysis often give absolute numbers, but the in-depth analysis is never sufficient to demonstrate the rationale behind those numbers. Nevertheless, it is necessary to think of the best method for research and data analysis suiting your survey questionnaire and what story researchers want to tell. For example, the mean is the best way to demonstrate the students’ average scores in schools. It is better to rely on the descriptive statistics when the researchers intend to keep the research or outcome limited to the provided sample without generalizing it. For example, when you want to compare average voting done in two different cities, differential statistics are enough.
Descriptive analysis is also called a ‘univariate analysis’ since it is commonly used to analyze a single variable.
Inferential statistics
Inferential statistics are used to make predictions about a larger population after research and data analysis of the representing population’s collected sample. For example, you can ask some odd 100 audiences at a movie theater if they like the movie they are watching. Researchers then use inferential statistics on the collected sample to reason that about 80-90% of people like the movie.
Here are two significant areas of inferential statistics.
- Estimating parameters: It takes statistics from the sample research data and demonstrates something about the population parameter.
- Hypothesis test: I t’s about sampling research data to answer the survey research questions. For example, researchers might be interested to understand if the new shade of lipstick recently launched is good or not, or if the multivitamin capsules help children to perform better at games.
These are sophisticated analysis methods used to showcase the relationship between different variables instead of describing a single variable. It is often used when researchers want something beyond absolute numbers to understand the relationship between variables.
Here are some of the commonly used methods for data analysis in research.
- Correlation: When researchers are not conducting experimental research or quasi-experimental research wherein the researchers are interested to understand the relationship between two or more variables, they opt for correlational research methods.
- Cross-tabulation: Also called contingency tables, cross-tabulation is used to analyze the relationship between multiple variables. Suppose provided data has age and gender categories presented in rows and columns. A two-dimensional cross-tabulation helps for seamless data analysis and research by showing the number of males and females in each age category.
- Regression analysis: For understanding the strong relationship between two variables, researchers do not look beyond the primary and commonly used regression analysis method, which is also a type of predictive analysis used. In this method, you have an essential factor called the dependent variable. You also have multiple independent variables in regression analysis. You undertake efforts to find out the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable. The values of both independent and dependent variables are assumed as being ascertained in an error-free random manner.
- Frequency tables: The statistical procedure is used for testing the degree to which two or more vary or differ in an experiment. A considerable degree of variation means research findings were significant. In many contexts, ANOVA testing and variance analysis are similar.
- Analysis of variance: The statistical procedure is used for testing the degree to which two or more vary or differ in an experiment. A considerable degree of variation means research findings were significant. In many contexts, ANOVA testing and variance analysis are similar.
- Researchers must have the necessary research skills to analyze and manipulation the data , Getting trained to demonstrate a high standard of research practice. Ideally, researchers must possess more than a basic understanding of the rationale of selecting one statistical method over the other to obtain better data insights.
- Usually, research and data analytics projects differ by scientific discipline; therefore, getting statistical advice at the beginning of analysis helps design a survey questionnaire, select data collection methods, and choose samples.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
- The primary aim of data research and analysis is to derive ultimate insights that are unbiased. Any mistake in or keeping a biased mind to collect data, selecting an analysis method, or choosing audience sample il to draw a biased inference.
- Irrelevant to the sophistication used in research data and analysis is enough to rectify the poorly defined objective outcome measurements. It does not matter if the design is at fault or intentions are not clear, but lack of clarity might mislead readers, so avoid the practice.
- The motive behind data analysis in research is to present accurate and reliable data. As far as possible, avoid statistical errors, and find a way to deal with everyday challenges like outliers, missing data, data altering, data mining , or developing graphical representation.
LEARN MORE: Descriptive Research vs Correlational Research The sheer amount of data generated daily is frightening. Especially when data analysis has taken center stage. in 2018. In last year, the total data supply amounted to 2.8 trillion gigabytes. Hence, it is clear that the enterprises willing to survive in the hypercompetitive world must possess an excellent capability to analyze complex research data, derive actionable insights, and adapt to the new market needs.
LEARN ABOUT: Average Order Value
QuestionPro is an online survey platform that empowers organizations in data analysis and research and provides them a medium to collect data by creating appealing surveys.
MORE LIKE THIS

Event Feedback Software: Top 11 Best in 2024
Apr 9, 2024

Top 10 Free Market Research Tools to Boost Your Business

Best 15 Behavior Analytics Tools to Explore Your User Actions
Apr 8, 2024
Top 7 Concept Testing Tools to Elevate Your Ideas in 2024
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

- RIT Libraries
- Data Analytics Resources
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Electronic Books
- Print Books
- Data Science: Journals
- More Journals, Websites
- Alerts, IDS Express
- Readings on Data
- Sources with Data
- Google Scholar Library Links
- Zotero-Citation Management Tool
- Writing a Literature Review
- ProQuest Research Companion
- Thesis Submission Instructions
- Associations
Writing a Rsearch Proposal
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research. Your paper should include the topic, research question and hypothesis, methods, predictions, and results (if not actual, then projected).
Research Proposal Aims
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
- Introduction
Literature review
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Proposal Format
The proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
Introduction The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.. Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights will your research contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Research design and methods
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions. Write up your projected, if not actual, results.
Contribution to knowledge
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Lastly, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use free APA citation generators like BibGuru. Databases have a citation button you can click on to see your citation. Sometimes you have to re-format it as the citations may have mistakes.
- << Previous: ProQuest Research Companion
- Next: DIR >>
Edit this Guide
Log into Dashboard
Use of RIT resources is reserved for current RIT students, faculty and staff for academic and teaching purposes only. Please contact your librarian with any questions.
Help is Available
Email a Librarian
A librarian is available by e-mail at [email protected]
Meet with a Librarian
Call reference desk voicemail.
A librarian is available by phone at (585) 475-2563 or on Skype at llll
Or, call (585) 475-2563 to leave a voicemail with the reference desk during normal business hours .
Chat with a Librarian
Data analytics resources infoguide url.
https://infoguides.rit.edu/DA
Use the box below to email yourself a link to this guide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
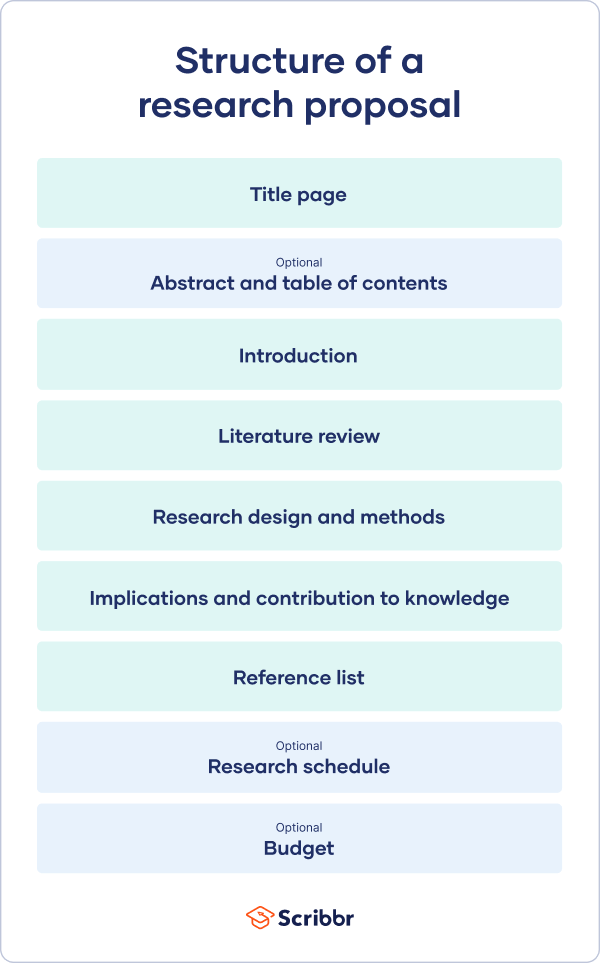
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
How to Create a Data Analysis Plan: A Detailed Guide
by Barche Blaise | Aug 12, 2020 | Writing

If a good research question equates to a story then, a roadmap will be very vita l for good storytelling. We advise every student/researcher to personally write his/her data analysis plan before seeking any advice. In this blog article, we will explore how to create a data analysis plan: the content and structure.
This data analysis plan serves as a roadmap to how data collected will be organised and analysed. It includes the following aspects:
- Clearly states the research objectives and hypothesis
- Identifies the dataset to be used
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Clearly states the research variables
- States statistical test hypotheses and the software for statistical analysis
- Creating shell tables
1. Stating research question(s), objectives and hypotheses:
All research objectives or goals must be clearly stated. They must be Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic and Time-bound (SMART). Hypotheses are theories obtained from personal experience or previous literature and they lay a foundation for the statistical methods that will be applied to extrapolate results to the entire population.
2. The dataset:
The dataset that will be used for statistical analysis must be described and important aspects of the dataset outlined. These include; owner of the dataset, how to get access to the dataset, how the dataset was checked for quality control and in what program is the dataset stored (Excel, Epi Info, SQL, Microsoft access etc.).
3. The inclusion and exclusion criteria :
They guide the aspects of the dataset that will be used for data analysis. These criteria will also guide the choice of variables included in the main analysis.
4. Variables:
Every variable collected in the study should be clearly stated. They should be presented based on the level of measurement (ordinal/nominal or ratio/interval levels), or the role the variable plays in the study (independent/predictors or dependent/outcome variables). The variable types should also be outlined. The variable type in conjunction with the research hypothesis forms the basis for selecting the appropriate statistical tests for inferential statistics. A good data analysis plan should summarize the variables as demonstrated in Figure 1 below.

5. Statistical software
There are tons of software packages for data analysis, some common examples are SPSS, Epi Info, SAS, STATA, Microsoft Excel. Include the version number, year of release and author/manufacturer. Beginners have the tendency to try different software and finally not master any. It is rather good to select one and master it because almost all statistical software have the same performance for basic and the majority of advance analysis needed for a student thesis. This is what we recommend to all our students at CRENC before they begin writing their results section .
6. Selecting the appropriate statistical method to test hypotheses
Depending on the research question, hypothesis and type of variable, several statistical methods can be used to answer the research question appropriately. This aspect of the data analysis plan outlines clearly why each statistical method will be used to test hypotheses. The level of statistical significance (p-value) which is often but not always <0.05 should also be written. Presented in figures 2a and 2b are decision trees for some common statistical tests based on the variable type and research question
A good analysis plan should clearly describe how missing data will be analysed.

7. Creating shell tables
Data analysis involves three levels of analysis; univariable, bivariable and multivariable analysis with increasing order of complexity. Shell tables should be created in anticipation for the results that will be obtained from these different levels of analysis. Read our blog article on how to present tables and figures for more details. Suppose you carry out a study to investigate the prevalence and associated factors of a certain disease “X” in a population, then the shell tables can be represented as in Tables 1, Table 2 and Table 3 below.
Table 1: Example of a shell table from univariate analysis

Table 2: Example of a shell table from bivariate analysis

Table 3: Example of a shell table from multivariate analysis

aOR = adjusted odds ratio
Now that you have learned how to create a data analysis plan, these are the takeaway points. It should clearly state the:
- Research question, objectives, and hypotheses
- Dataset to be used
- Variable types and their role
- Statistical software and statistical methods
- Shell tables for univariate, bivariate and multivariate analysis
Further readings
Creating a Data Analysis Plan: What to Consider When Choosing Statistics for a Study https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4552232/pdf/cjhp-68-311.pdf
Creating an Analysis Plan: https://www.cdc.gov/globalhealth/healthprotection/fetp/training_modules/9/creating-analysis-plan_pw_final_09242013.pdf
Data Analysis Plan: https://www.statisticssolutions.com/dissertation-consulting-services/data-analysis-plan-2/
Photo created by freepik – www.freepik.com

Dr Barche is a physician and holds a Masters in Public Health. He is a senior fellow at CRENC with interests in Data Science and Data Analysis.
Post Navigation
16 comments.
Thanks. Quite informative.
Educative write-up. Thanks.
Easy to understand. Thanks Dr
Very explicit Dr. Thanks
I will always remember how you help me conceptualize and understand data science in a simple way. I can only hope that someday I’ll be in a position to repay you, my dear friend.
Plan d’analyse
This is interesting, Thanks
Very understandable and informative. Thank you..
love the figures.
Nice, and informative
This is so much educative and good for beginners, I would love to recommend that you create and share a video because some people are able to grasp when there is an instructor. Lots of love
Thank you Doctor very helpful.
Educative and clearly written. Thanks
Well said doctor,thank you.But when do you present in tables ,bars,pie chart etc?
Very informative guide!
Submit a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Submit Comment
Receive updates on new courses and blog posts

Never Miss a Thing!
Subscribe to our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates on our webinars, articles and courses.
You have Successfully Subscribed!
What (Exactly) Is A Research Proposal?
A simple explainer with examples + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Whether you’re nearing the end of your degree and your dissertation is on the horizon, or you’re planning to apply for a PhD program, chances are you’ll need to craft a convincing research proposal . If you’re on this page, you’re probably unsure exactly what the research proposal is all about. Well, you’ve come to the right place.
Overview: Research Proposal Basics
- What a research proposal is
- What a research proposal needs to cover
- How to structure your research proposal
- Example /sample proposals
- Proposal writing FAQs
- Key takeaways & additional resources
What is a research proposal?
Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it’s worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face).
The most important word here is “ convince ” – in other words, your research proposal needs to sell your research idea (to whoever is going to approve it). If it doesn’t convince them (of its suitability and manageability), you’ll need to revise and resubmit . This will cost you valuable time, which will either delay the start of your research or eat into its time allowance (which is bad news).

What goes into a research proposal?
A good dissertation or thesis proposal needs to cover the “ what “, “ why ” and” how ” of the proposed study. Let’s look at each of these attributes in a little more detail:
Your proposal needs to clearly articulate your research topic . This needs to be specific and unambiguous . Your research topic should make it clear exactly what you plan to research and in what context. Here’s an example of a well-articulated research topic:
An investigation into the factors which impact female Generation Y consumer’s likelihood to promote a specific makeup brand to their peers: a British context
As you can see, this topic is extremely clear. From this one line we can see exactly:
- What’s being investigated – factors that make people promote or advocate for a brand of a specific makeup brand
- Who it involves – female Gen-Y consumers
- In what context – the United Kingdom
So, make sure that your research proposal provides a detailed explanation of your research topic . If possible, also briefly outline your research aims and objectives , and perhaps even your research questions (although in some cases you’ll only develop these at a later stage). Needless to say, don’t start writing your proposal until you have a clear topic in mind , or you’ll end up waffling and your research proposal will suffer as a result of this.
Need a helping hand?
As we touched on earlier, it’s not good enough to simply propose a research topic – you need to justify why your topic is original . In other words, what makes it unique ? What gap in the current literature does it fill? If it’s simply a rehash of the existing research, it’s probably not going to get approval – it needs to be fresh.
But, originality alone is not enough. Once you’ve ticked that box, you also need to justify why your proposed topic is important . In other words, what value will it add to the world if you achieve your research aims?
As an example, let’s look at the sample research topic we mentioned earlier (factors impacting brand advocacy). In this case, if the research could uncover relevant factors, these findings would be very useful to marketers in the cosmetics industry, and would, therefore, have commercial value . That is a clear justification for the research.
So, when you’re crafting your research proposal, remember that it’s not enough for a topic to simply be unique. It needs to be useful and value-creating – and you need to convey that value in your proposal. If you’re struggling to find a research topic that makes the cut, watch our video covering how to find a research topic .

It’s all good and well to have a great topic that’s original and valuable, but you’re not going to convince anyone to approve it without discussing the practicalities – in other words:
- How will you actually undertake your research (i.e., your methodology)?
- Is your research methodology appropriate given your research aims?
- Is your approach manageable given your constraints (time, money, etc.)?
While it’s generally not expected that you’ll have a fully fleshed-out methodology at the proposal stage, you’ll likely still need to provide a high-level overview of your research methodology . Here are some important questions you’ll need to address in your research proposal:
- Will you take a qualitative , quantitative or mixed -method approach?
- What sampling strategy will you adopt?
- How will you collect your data (e.g., interviews, surveys, etc)?
- How will you analyse your data (e.g., descriptive and inferential statistics , content analysis, discourse analysis, etc, .)?
- What potential limitations will your methodology carry?
So, be sure to give some thought to the practicalities of your research and have at least a basic methodological plan before you start writing up your proposal. If this all sounds rather intimidating, the video below provides a good introduction to research methodology and the key choices you’ll need to make.
How To Structure A Research Proposal
Now that we’ve covered the key points that need to be addressed in a proposal, you may be wondering, “ But how is a research proposal structured? “.
While the exact structure and format required for a research proposal differs from university to university, there are four “essential ingredients” that commonly make up the structure of a research proposal:
- A rich introduction and background to the proposed research
- An initial literature review covering the existing research
- An overview of the proposed research methodology
- A discussion regarding the practicalities (project plans, timelines, etc.)
In the video below, we unpack each of these four sections, step by step.
Research Proposal Examples/Samples
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of two successful research proposals (Master’s and PhD-level), as well as our popular free proposal template.
Proposal Writing FAQs
How long should a research proposal be.
This varies tremendously, depending on the university, the field of study (e.g., social sciences vs natural sciences), and the level of the degree (e.g. undergraduate, Masters or PhD) – so it’s always best to check with your university what their specific requirements are before you start planning your proposal.
As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that’s needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very detailed proposal that essentially forms the first three chapters of the dissertation or thesis.
The takeaway – be sure to check with your institution before you start writing.
How do I choose a topic for my research proposal?
Finding a good research topic is a process that involves multiple steps. We cover the topic ideation process in this video post.
How do I write a literature review for my proposal?
While you typically won’t need a comprehensive literature review at the proposal stage, you still need to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the key literature and are able to synthesise it. We explain the literature review process here.
How do I create a timeline and budget for my proposal?
We explain how to craft a project plan/timeline and budget in Research Proposal Bootcamp .
Which referencing format should I use in my research proposal?
The expectations and requirements regarding formatting and referencing vary from institution to institution. Therefore, you’ll need to check this information with your university.
What common proposal writing mistakes do I need to look out for?
We’ve create a video post about some of the most common mistakes students make when writing a proposal – you can access that here . If you’re short on time, here’s a quick summary:
- The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated).
- The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align.
- The research topic is not well justified.
- The study has a weak theoretical foundation.
- The research design is not well articulated well enough.
- Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
- Poor project planning and risk management.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria.
Key Takeaways & Additional Resources
As you write up your research proposal, remember the all-important core purpose: to convince . Your research proposal needs to sell your study in terms of suitability and viability. So, focus on crafting a convincing narrative to ensure a strong proposal.
At the same time, pay close attention to your university’s requirements. While we’ve covered the essentials here, every institution has its own set of expectations and it’s essential that you follow these to maximise your chances of approval.
By the way, we’ve got plenty more resources to help you fast-track your research proposal. Here are some of our most popular resources to get you started:
- Proposal Writing 101 : A Introductory Webinar
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : The Ultimate Online Course
- Template : A basic template to help you craft your proposal
If you’re looking for 1-on-1 support with your research proposal, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the proposal development process (and the entire research journey), step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
51 Comments
I truly enjoyed this video, as it was eye-opening to what I have to do in the preparation of preparing a Research proposal.
I would be interested in getting some coaching.
I real appreciate on your elaboration on how to develop research proposal,the video explains each steps clearly.
Thank you for the video. It really assisted me and my niece. I am a PhD candidate and she is an undergraduate student. It is at times, very difficult to guide a family member but with this video, my job is done.
In view of the above, I welcome more coaching.
Wonderful guidelines, thanks
This is very helpful. Would love to continue even as I prepare for starting my masters next year.
Thanks for the work done, the text was helpful to me
Bundle of thanks to you for the research proposal guide it was really good and useful if it is possible please send me the sample of research proposal
You’re most welcome. We don’t have any research proposals that we can share (the students own the intellectual property), but you might find our research proposal template useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-proposal-template/
Cheruiyot Moses Kipyegon
Thanks alot. It was an eye opener that came timely enough before my imminent proposal defense. Thanks, again
thank you very much your lesson is very interested may God be with you
I am an undergraduate student (First Degree) preparing to write my project,this video and explanation had shed more light to me thanks for your efforts keep it up.
Very useful. I am grateful.
this is a very a good guidance on research proposal, for sure i have learnt something
Wonderful guidelines for writing a research proposal, I am a student of m.phil( education), this guideline is suitable for me. Thanks
You’re welcome 🙂
Thank you, this was so helpful.
A really great and insightful video. It opened my eyes as to how to write a research paper. I would like to receive more guidance for writing my research paper from your esteemed faculty.
Thank you, great insights
Thank you, great insights, thank you so much, feeling edified
Wow thank you, great insights, thanks a lot
Thank you. This is a great insight. I am a student preparing for a PhD program. I am requested to write my Research Proposal as part of what I am required to submit before my unconditional admission. I am grateful having listened to this video which will go a long way in helping me to actually choose a topic of interest and not just any topic as well as to narrow down the topic and be specific about it. I indeed need more of this especially as am trying to choose a topic suitable for a DBA am about embarking on. Thank you once more. The video is indeed helpful.
Have learnt a lot just at the right time. Thank you so much.
thank you very much ,because have learn a lot things concerning research proposal and be blessed u for your time that you providing to help us
Hi. For my MSc medical education research, please evaluate this topic for me: Training Needs Assessment of Faculty in Medical Training Institutions in Kericho and Bomet Counties
I have really learnt a lot based on research proposal and it’s formulation
Thank you. I learn much from the proposal since it is applied
Your effort is much appreciated – you have good articulation.
You have good articulation.
I do applaud your simplified method of explaining the subject matter, which indeed has broaden my understanding of the subject matter. Definitely this would enable me writing a sellable research proposal.
This really helping
Great! I liked your tutoring on how to find a research topic and how to write a research proposal. Precise and concise. Thank you very much. Will certainly share this with my students. Research made simple indeed.
Thank you very much. I an now assist my students effectively.
Thank you very much. I can now assist my students effectively.
I need any research proposal
Thank you for these videos. I will need chapter by chapter assistance in writing my MSc dissertation
Very helpfull
the videos are very good and straight forward
thanks so much for this wonderful presentations, i really enjoyed it to the fullest wish to learn more from you
Thank you very much. I learned a lot from your lecture.
I really enjoy the in-depth knowledge on research proposal you have given. me. You have indeed broaden my understanding and skills. Thank you
interesting session this has equipped me with knowledge as i head for exams in an hour’s time, am sure i get A++
This article was most informative and easy to understand. I now have a good idea of how to write my research proposal.
Thank you very much.
Wow, this literature is very resourceful and interesting to read. I enjoyed it and I intend reading it every now then.
Thank you for the clarity
Thank you. Very helpful.
Thank you very much for this essential piece. I need 1o1 coaching, unfortunately, your service is not available in my country. Anyways, a very important eye-opener. I really enjoyed it. A thumb up to Gradcoach
What is JAM? Please explain.
Thank you so much for these videos. They are extremely helpful! God bless!
very very wonderful…
thank you for the video but i need a written example
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
17 Research Proposal Examples

A research proposal systematically and transparently outlines a proposed research project.
The purpose of a research proposal is to demonstrate a project’s viability and the researcher’s preparedness to conduct an academic study. It serves as a roadmap for the researcher.
The process holds value both externally (for accountability purposes and often as a requirement for a grant application) and intrinsic value (for helping the researcher to clarify the mechanics, purpose, and potential signficance of the study).
Key sections of a research proposal include: the title, abstract, introduction, literature review, research design and methods, timeline, budget, outcomes and implications, references, and appendix. Each is briefly explained below.
Watch my Guide: How to Write a Research Proposal
Get your Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
Research Proposal Sample Structure
Title: The title should present a concise and descriptive statement that clearly conveys the core idea of the research projects. Make it as specific as possible. The reader should immediately be able to grasp the core idea of the intended research project. Often, the title is left too vague and does not help give an understanding of what exactly the study looks at.
Abstract: Abstracts are usually around 250-300 words and provide an overview of what is to follow – including the research problem , objectives, methods, expected outcomes, and significance of the study. Use it as a roadmap and ensure that, if the abstract is the only thing someone reads, they’ll get a good fly-by of what will be discussed in the peice.
Introduction: Introductions are all about contextualization. They often set the background information with a statement of the problem. At the end of the introduction, the reader should understand what the rationale for the study truly is. I like to see the research questions or hypotheses included in the introduction and I like to get a good understanding of what the significance of the research will be. It’s often easiest to write the introduction last
Literature Review: The literature review dives deep into the existing literature on the topic, demosntrating your thorough understanding of the existing literature including themes, strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in the literature. It serves both to demonstrate your knowledge of the field and, to demonstrate how the proposed study will fit alongside the literature on the topic. A good literature review concludes by clearly demonstrating how your research will contribute something new and innovative to the conversation in the literature.
Research Design and Methods: This section needs to clearly demonstrate how the data will be gathered and analyzed in a systematic and academically sound manner. Here, you need to demonstrate that the conclusions of your research will be both valid and reliable. Common points discussed in the research design and methods section include highlighting the research paradigm, methodologies, intended population or sample to be studied, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures . Toward the end of this section, you are encouraged to also address ethical considerations and limitations of the research process , but also to explain why you chose your research design and how you are mitigating the identified risks and limitations.
Timeline: Provide an outline of the anticipated timeline for the study. Break it down into its various stages (including data collection, data analysis, and report writing). The goal of this section is firstly to establish a reasonable breakdown of steps for you to follow and secondly to demonstrate to the assessors that your project is practicable and feasible.
Budget: Estimate the costs associated with the research project and include evidence for your estimations. Typical costs include staffing costs, equipment, travel, and data collection tools. When applying for a scholarship, the budget should demonstrate that you are being responsible with your expensive and that your funding application is reasonable.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: A discussion of the anticipated findings or results of the research, as well as the potential contributions to the existing knowledge, theory, or practice in the field. This section should also address the potential impact of the research on relevant stakeholders and any broader implications for policy or practice.
References: A complete list of all the sources cited in the research proposal, formatted according to the required citation style. This demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the relevant literature and ensures proper attribution of ideas and information.
Appendices (if applicable): Any additional materials, such as questionnaires, interview guides, or consent forms, that provide further information or support for the research proposal. These materials should be included as appendices at the end of the document.
Research Proposal Examples
Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples designed to briefly demonstrate what might be discussed in each section.
1. Education Studies Research Proposals
See some real sample pieces:
- Assessment of the perceptions of teachers towards a new grading system
- Does ICT use in secondary classrooms help or hinder student learning?
- Digital technologies in focus project
- Urban Middle School Teachers’ Experiences of the Implementation of
- Restorative Justice Practices
- Experiences of students of color in service learning
Consider this hypothetical education research proposal:
The Impact of Game-Based Learning on Student Engagement and Academic Performance in Middle School Mathematics
Abstract: The proposed study will explore multiplayer game-based learning techniques in middle school mathematics curricula and their effects on student engagement. The study aims to contribute to the current literature on game-based learning by examining the effects of multiplayer gaming in learning.
Introduction: Digital game-based learning has long been shunned within mathematics education for fears that it may distract students or lower the academic integrity of the classrooms. However, there is emerging evidence that digital games in math have emerging benefits not only for engagement but also academic skill development. Contributing to this discourse, this study seeks to explore the potential benefits of multiplayer digital game-based learning by examining its impact on middle school students’ engagement and academic performance in a mathematics class.
Literature Review: The literature review has identified gaps in the current knowledge, namely, while game-based learning has been extensively explored, the role of multiplayer games in supporting learning has not been studied.
Research Design and Methods: This study will employ a mixed-methods research design based upon action research in the classroom. A quasi-experimental pre-test/post-test control group design will first be used to compare the academic performance and engagement of middle school students exposed to game-based learning techniques with those in a control group receiving instruction without the aid of technology. Students will also be observed and interviewed in regard to the effect of communication and collaboration during gameplay on their learning.
Timeline: The study will take place across the second term of the school year with a pre-test taking place on the first day of the term and the post-test taking place on Wednesday in Week 10.
Budget: The key budgetary requirements will be the technologies required, including the subscription cost for the identified games and computers.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: It is expected that the findings will contribute to the current literature on game-based learning and inform educational practices, providing educators and policymakers with insights into how to better support student achievement in mathematics.
2. Psychology Research Proposals
See some real examples:
- A situational analysis of shared leadership in a self-managing team
- The effect of musical preference on running performance
- Relationship between self-esteem and disordered eating amongst adolescent females
Consider this hypothetical psychology research proposal:
The Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Stress Reduction in College Students
Abstract: This research proposal examines the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction among college students, using a pre-test/post-test experimental design with both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods .
Introduction: College students face heightened stress levels during exam weeks. This can affect both mental health and test performance. This study explores the potential benefits of mindfulness-based interventions such as meditation as a way to mediate stress levels in the weeks leading up to exam time.
Literature Review: Existing research on mindfulness-based meditation has shown the ability for mindfulness to increase metacognition, decrease anxiety levels, and decrease stress. Existing literature has looked at workplace, high school and general college-level applications. This study will contribute to the corpus of literature by exploring the effects of mindfulness directly in the context of exam weeks.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n= 234 ) will be randomly assigned to either an experimental group, receiving 5 days per week of 10-minute mindfulness-based interventions, or a control group, receiving no intervention. Data will be collected through self-report questionnaires, measuring stress levels, semi-structured interviews exploring participants’ experiences, and students’ test scores.
Timeline: The study will begin three weeks before the students’ exam week and conclude after each student’s final exam. Data collection will occur at the beginning (pre-test of self-reported stress levels) and end (post-test) of the three weeks.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: The study aims to provide evidence supporting the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing stress among college students in the lead up to exams, with potential implications for mental health support and stress management programs on college campuses.
3. Sociology Research Proposals
- Understanding emerging social movements: A case study of ‘Jersey in Transition’
- The interaction of health, education and employment in Western China
- Can we preserve lower-income affordable neighbourhoods in the face of rising costs?
Consider this hypothetical sociology research proposal:
The Impact of Social Media Usage on Interpersonal Relationships among Young Adults
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effects of social media usage on interpersonal relationships among young adults, using a longitudinal mixed-methods approach with ongoing semi-structured interviews to collect qualitative data.
Introduction: Social media platforms have become a key medium for the development of interpersonal relationships, particularly for young adults. This study examines the potential positive and negative effects of social media usage on young adults’ relationships and development over time.
Literature Review: A preliminary review of relevant literature has demonstrated that social media usage is central to development of a personal identity and relationships with others with similar subcultural interests. However, it has also been accompanied by data on mental health deline and deteriorating off-screen relationships. The literature is to-date lacking important longitudinal data on these topics.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n = 454 ) will be young adults aged 18-24. Ongoing self-report surveys will assess participants’ social media usage, relationship satisfaction, and communication patterns. A subset of participants will be selected for longitudinal in-depth interviews starting at age 18 and continuing for 5 years.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of five years, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide insights into the complex relationship between social media usage and interpersonal relationships among young adults, potentially informing social policies and mental health support related to social media use.
4. Nursing Research Proposals
- Does Orthopaedic Pre-assessment clinic prepare the patient for admission to hospital?
- Nurses’ perceptions and experiences of providing psychological care to burns patients
- Registered psychiatric nurse’s practice with mentally ill parents and their children
Consider this hypothetical nursing research proposal:
The Influence of Nurse-Patient Communication on Patient Satisfaction and Health Outcomes following Emergency Cesarians
Abstract: This research will examines the impact of effective nurse-patient communication on patient satisfaction and health outcomes for women following c-sections, utilizing a mixed-methods approach with patient surveys and semi-structured interviews.
Introduction: It has long been known that effective communication between nurses and patients is crucial for quality care. However, additional complications arise following emergency c-sections due to the interaction between new mother’s changing roles and recovery from surgery.
Literature Review: A review of the literature demonstrates the importance of nurse-patient communication, its impact on patient satisfaction, and potential links to health outcomes. However, communication between nurses and new mothers is less examined, and the specific experiences of those who have given birth via emergency c-section are to date unexamined.
Research Design and Methods: Participants will be patients in a hospital setting who have recently had an emergency c-section. A self-report survey will assess their satisfaction with nurse-patient communication and perceived health outcomes. A subset of participants will be selected for in-depth interviews to explore their experiences and perceptions of the communication with their nurses.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including rolling recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing within the hospital.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the significance of nurse-patient communication in supporting new mothers who have had an emergency c-section. Recommendations will be presented for supporting nurses and midwives in improving outcomes for new mothers who had complications during birth.

5. Social Work Research Proposals
- Experiences of negotiating employment and caring responsibilities of fathers post-divorce
- Exploring kinship care in the north region of British Columbia
Consider this hypothetical social work research proposal:
The Role of a Family-Centered Intervention in Preventing Homelessness Among At-Risk Youthin a working-class town in Northern England
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effectiveness of a family-centered intervention provided by a local council area in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth. This case study will use a mixed-methods approach with program evaluation data and semi-structured interviews to collect quantitative and qualitative data .
Introduction: Homelessness among youth remains a significant social issue. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in addressing this problem and identify factors that contribute to successful prevention strategies.
Literature Review: A review of the literature has demonstrated several key factors contributing to youth homelessness including lack of parental support, lack of social support, and low levels of family involvement. It also demonstrates the important role of family-centered interventions in addressing this issue. Drawing on current evidence, this study explores the effectiveness of one such intervention in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth in a working-class town in Northern England.
Research Design and Methods: The study will evaluate a new family-centered intervention program targeting at-risk youth and their families. Quantitative data on program outcomes, including housing stability and family functioning, will be collected through program records and evaluation reports. Semi-structured interviews with program staff, participants, and relevant stakeholders will provide qualitative insights into the factors contributing to program success or failure.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Budget: Expenses include access to program evaluation data, interview materials, data analysis software, and any related travel costs for in-person interviews.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in preventing youth homelessness, potentially informing the expansion of or necessary changes to social work practices in Northern England.
Research Proposal Template
Get your Detailed Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
This is a template for a 2500-word research proposal. You may find it difficult to squeeze everything into this wordcount, but it’s a common wordcount for Honors and MA-level dissertations.
Your research proposal is where you really get going with your study. I’d strongly recommend working closely with your teacher in developing a research proposal that’s consistent with the requirements and culture of your institution, as in my experience it varies considerably. The above template is from my own courses that walk students through research proposals in a British School of Education.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
8 thoughts on “17 Research Proposal Examples”
Very excellent research proposals
very helpful
Very helpful
Dear Sir, I need some help to write an educational research proposal. Thank you.

Hi Levi, use the site search bar to ask a question and I’ll likely have a guide already written for your specific question. Thanks for reading!
very good research proposal
Thank you so much sir! ❤️
Very helpful 👌
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Globalstats Academic
Statistic consultant for academic research.

Data Analysis in Quantitative Research Proposal
Definition of data analysis.
Data analysis in quantitative research proposal is one part of the chapter that researchers need in the beginning of writing a research proposal. Whereas in the research, it is an activity after the data from all collected. Activities in data analysis are: grouping data based on variables and types of respondents, tabulating data based on variables from all respondents, presenting data for each variable studied, doing calculations to answer the problem formulation, and doing calculations to test the proposed hypothesis.
Quantitative Data Analysis Techniques
In a research proposal, it must be clear what method of analysis is capable of answering the research hypothesis. Hypothesis is a temporary answer to the research problem. Data analysis techniques in quantitative research commonly use statistics. There are two kinds of statistical data analysis in research. These are descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. Inferential statistics include parametric and non-parametric statistics.
Descriptive statistics
In preparing research proposals, researchers need to explain what is descriptive research. Descriptive statistic is a method to analyze data by describing data without intending to make generalizations. Descriptive statistics only describes the sample data and does not make conclusions that apply to the population. While, conclusion that applies to the population, then the data analysis technique is inferential statistics. In addition descriptive statistics also function to present information in such a way that data generated from research can be utilized by others in need.
Inferential Statistics
When researchers want to generalize broader conclusions in the research proposal, it is necessary to write inferential statistics. Inferential statistics (often also commonly inductive statistics or probability statistics) are statistical techniques used to analyze sample data and the results are applied to populations. It requires a random sampling process.
Inferential research involves statistical probability. Using of probability theory is to approach sample to the population. A conclusion applying to the population has a chance of error and truth level. If the chance of error is 5%, then the truth level is 95%. While the chance of error is 1%, then the truth level is 99%. This opportunity for error and truth is the level of significance. Statistical tables are useful for carrying out tests of the significance of this error. For example, t-test will use table-t. in each table provides significance level of what percentage of the results. For example the correlation analysis found a correlation coefficient of 0.54 and for a significance of 5% it means that a variable relationship of 0.54 can apply to 95 out of 100 samples taken from a population. Inferential statistics is a higher level then descriptive statistics. To that in the research proposal, the flow of conclusions becomes clear. Data Analysis is to make general conclusions (conclusions), make a prediction (prediction), or make an estimate (estimation).

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Data Analytics Proposal Templates with Samples and Examples

Deepika Dhaka
"Without big data analytics, companies are blind and deaf, wandering out onto the web like deer on a freeway." - Geoffrey Moore, American Consultant and Author.
This quote captures the value of data analytics in today's information-rich environment. Data analytics not only provides clarity but also equips businesses with the foresight to thrive in complex markets.
Below are some straightforward stats underscoring the importance of analytics:-
Growth in Data Generation: By 2025, it's estimated that 463 exabytes of data will be generated each day globally.
Demand for Analytics: The global data analytics market is projected to grow from $189.1 billion in 2022 to $332.6 billion by 2027.
Impact on Decision Making: 58% of businesses surveyed reported a significant improvement in decision-making speed with data analytics.
In this rapidly growing data analytics market, your startup needs to strategize smartly to stand out among the top players in the field. With competition intensifying every day, it's important to have a clear and practical approach. In this context, using SlideTeam's services can be a turning point for your company, offering some of the best templates that boost your ability to compete and thrive in the data analytics arena.
The best part is that the 100% customizable nature of the templates provides you with the desired flexibility to edit your presentations. The content-ready slides give you the much-needed structure.
Let’s begin exploring these templates one by one!
Template 1: Data Analytics Solution Deployment Proposal
This PPT Presentation is packed with practical slides for every part of your pitch - from outlining the project context and objectives to detailing your proven process. The template includes sections for showcasing past successes and client testimonials, a clear statement of work, and an overview of the client's investment. This user-friendly tool is your key to crafting compelling proposals that highlight your expertise and resonate with clients, boosting your chances of sealing more deals. Download now!

Download this template
Also, explore this blog with the top 10 Quantitative Research Proposal Examples with Templates and Samples.
Template 2: Project Proposal for Big Data Analytics
This comprehensive template includes everything you need to present a compelling case to potential clients. It starts with a professional cover letter, setting the tone for what's to follow. The core sections cover your unique approach to big data challenges, detailed Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), and investment overview, ensuring transparency and clarity in your offer. The template also includes a section for terms and conditions to safeguard your interests and clients. To help you demonstrate your thorough understanding of the project, it features slides for preliminary requirements and an activity flowchart that represents the project's lifecycle. This template is designed to guide you through every step of proposal preparation, ensuring you leave a lasting impression and increase your chances of success. Download now!

Template 3: Project Context and Objectives for Data Analytics Proposal
Use this PPT Template to provide a clear understanding of the background, the specific needs or problems the client is facing, and the desired outcomes they wish to achieve. This section helps align the analytics project with the client's strategic goals, ensuring that the proposed solution is relevant and tailored to their unique situation. Clearly defining the objectives establishes a roadmap for the project, guides the analytics process, and ensures that every step taken is purposeful and directed towards achieving these goals. It also helps in setting realistic expectations, measuring progress, and evaluating the project's success. Download now!

Explore this blog with Top 10 Statistical Analysis Research Proposal Templates with Samples and Examples .
Template 4: Plan of Action for Data Analytics Proposal
This Plan of Action Template is crucial as it offers a clear roadmap, outlining the specific methodologies and steps to achieve the project's goals. It divides the action plan into 6 weeks and includes activities like analyzing, selecting, implementing, adopting, and scaling. The detail demonstrates your team's competence in building trust with the client and sets clear expectations about the project's scope, timeline, and deliverables. It's essential for tracking progress, evaluating success, and preparing for potential risks, ensuring both parties are aligned and informed throughout the project's lifecycle.
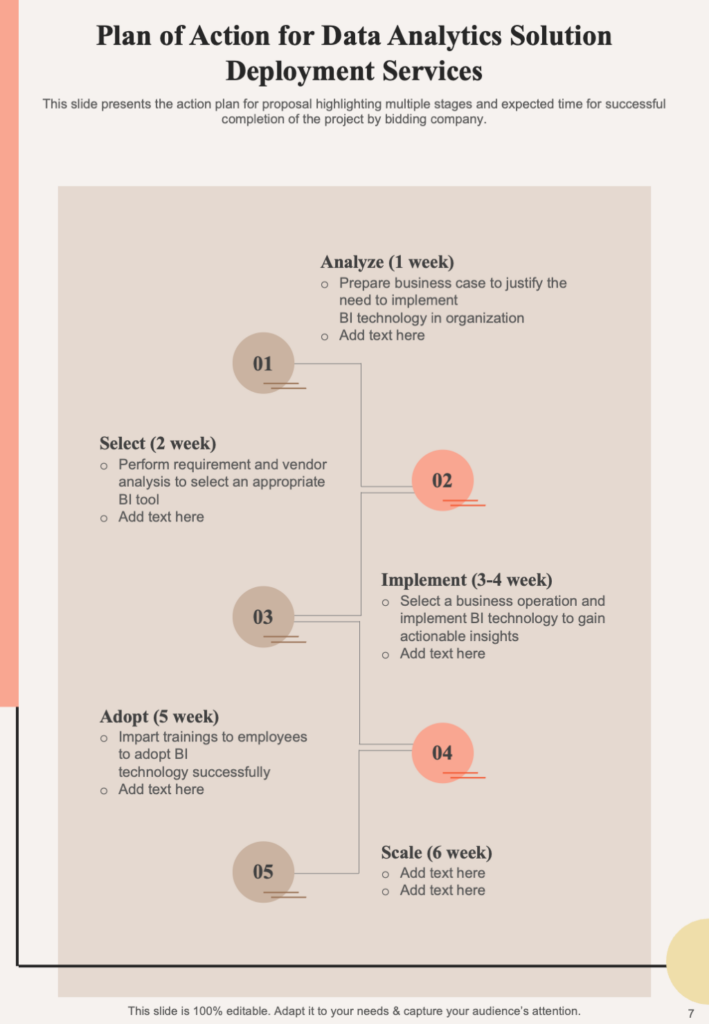
Template 5: Timeframe for Data Analytics Solution Services
This PPT Template showcases the timeframe to provide a clear schedule for the project's key phases, such as requirement analysis, vendor assessment, suite implementation, training, and operational support. This template helps you present realistic expectations for when each stage of the project will be completed and allows for efficient planning and resource allocation. It shows that the project progresses systematically, with each phase building upon the last. This timeline slide demonstrates professionalism and project management skills, building client confidence in your ability to deliver results within a specified period.
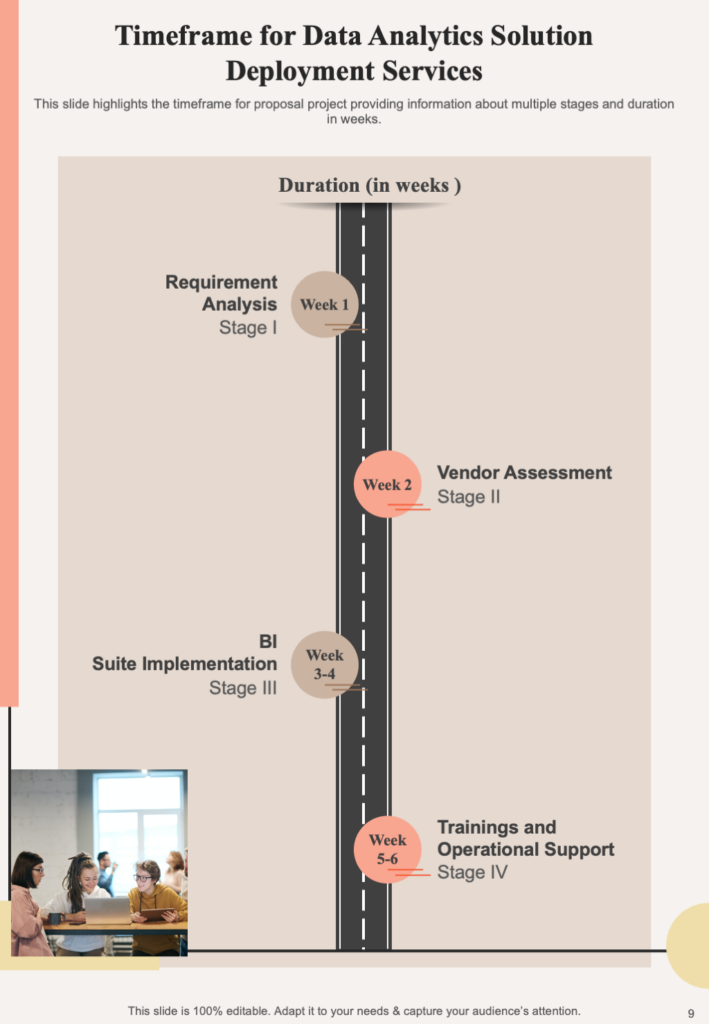
Template 6: Client Testimonial for Data Analytics Proposal
Use this client testimonial slide in your proposal as a strategic move that adds significant value. It is a powerful form of social proof, bolstering the credibility of your services by showcasing your track record of success. Adding this will help build trust with potential clients by presenting real-world evidence of your effectiveness. Client feedback often highlights specific, tangible benefits and outcomes, making your proposal more persuasive and relatable. This PPT slide can set your services apart in a competitive market and allow you to add premium-quality pictures of your clients. Download now to bring authenticity and a human touch to your proposal, reinforcing the value and impact of your services.

Template 7: Statement of Work for Data ANalytics Proposal
Including a Statement of Work (SoW) in a Proposal is crucial as it provides a clear outline of the project's scope, deliverables, and the specific services offered. Use this PowerPoint Template to establish critical terms and conditions, including payment terms, cancellation policies, and payment terms, ensuring both parties understand their responsibilities and obligations. This clarity fosters accountability, aids in risk management, and enhances trust between the service provider and the client. Download now!
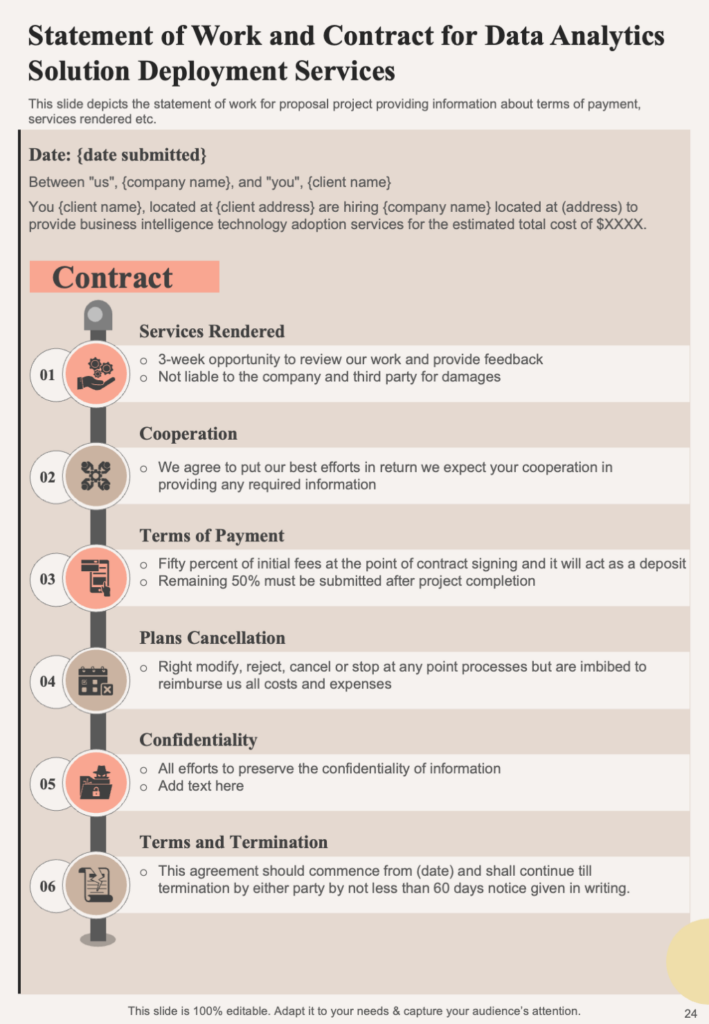
Template 8: Cover Letter for Data Analytics Proposal
This cover letter template is essential as it creates a strong first impression, setting the tone for the entire proposal. It personalizes the approach, directly addressing the potential client, and highlights key aspects of your proposal, drawing attention to what sets you apart. This content-ready slide clarifies the proposal's intent and purpose and plays a crucial role in building the reader's interest and engagement from the outset, increasing the likelihood of your proposal being seriously considered.
Template 9: Project Proposal for Big Data Analytics Services
This PowerPoint Template is crafted to showcase your services with impact and elegance. Tailored for flexibility, it allows you to detail your approach, expertise, and distinct solutions, ensuring your proposal captures attention. Ideal for securing client interest, it emphasizes the strategic benefits of your big data analytics services. The included slide outlines your methodology for executing data science projects, covering essential stages like Analysis, Requirements Development, Model Development, Testing and Evaluation, and Delivery. Get it now!

Template 10: Activity Flowchart for Big Data Analytics Proposal
Incorporate this Activity Flowchart to provide a clear visual representation of the project's stages, including data collection, preparation, modeling, model testing, and production. It demonstrates your systematic approach and methodology, enhancing the clarity and effectiveness of communication with clients. This visual aid not only sets precise expectations about the project’s scope but also aids in project management, ensuring the team and client are aligned on the project's progression and milestones. Get it now!
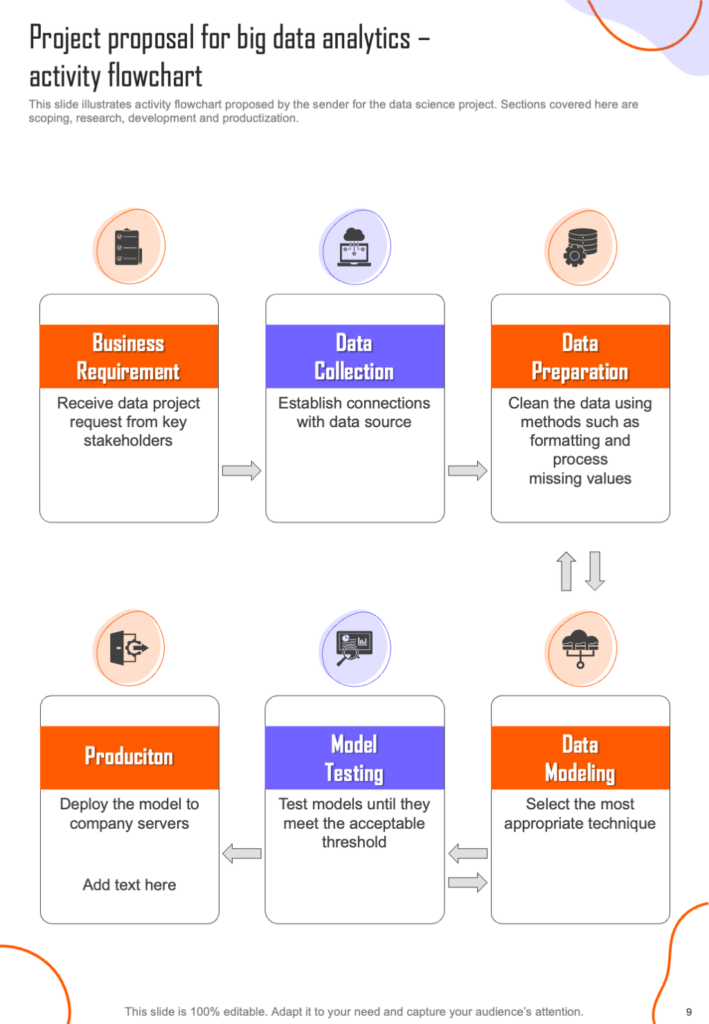
In conclusion, when pitching a Data Analytics Proposal, your presentation's clarity, professionalism, and persuasiveness can make a significant difference. SlideTeam's templates are designed to enhance these aspects of your proposal, offering a range of customizable slides catering to typical data analytics project elements. From showcasing project plans and methodologies to presenting complex data insights in a visually appealing manner, these templates are your go-to tool for creating a compelling narrative.
Download now to get started!
Related posts:
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
- [Updated 2023] How to Design The Perfect Product Launch Presentation [Best Templates Included]
- 99% of the Pitches Fail! Find Out What Makes Any Startup a Success
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Templates to Devise a Data Governance Framework for Your Company

Top 10 Data Privacy Templates to Achieve Your Compliance Goals

Top 10 Templates to Present Qualitative and Quantitative Data Analysis in Research Proposal

5 Best Data Lake Templates for AWS and Azure Cloud Platform
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

Research Methods and Design
Module 6: data sources and proposal, how to write a research proposal.
At the end of this subject, the main product you should have to show for it is a research proposal. A research proposal helps your colleagues and supervisors evaluate you proposed research, assess the appropriateness of you methods, and identify problems ahead of time, sot hey can be fixed.
This pathway will provide you with the understanding needed for writing up your research proposal. It will explain the components of a research proposal, and provide you with a template for writing it up.
- Understand the components of a research proposal
- Understand the process of writing up a research proposal
- Become familiar with the format and template of a UOW research proposal
Research proposal template
At the university of Wollongong, in the Faculty of Law, Humanities and the Arts, there are some expectations with regards to research proposals. Prospective Honours/Masters by Research/PhD students are required to complete a research proposal and submit this with the formal application form and relevant documents. The proposal should be no more than 3,000 words in length (excluding references). The numbers in parentheses indicate an estimate of the portion that should be devoted to each section. This does not suggest that all sections should be this portion exactly, but it should provide guidance as to the relative priorities of the proposal. The proposal should contain the following elements.
- Suggested research title
- Introduction (15%) – The introduction should situate the question(s) you are addressing. Why is the question important? How will answering it advance knowledge in international studies? What is the broader social/political/geopolitical context that frames your question? What are the broader issues that the research is trying to explain? (Be sure your research question(s) are clearly stated in this section)
- Literature review (25%) – The literature review should demonstrate that your research question is anchored in and contributes to a body of literature(s). You should demonstrate awareness of key research in the relevant fields and provide an analytical summary of current knowledge. This section should also describe and justify the general theoretical approach/framework applied in your proposed research.
- Research design (10%) – This section should describe your approach to researching the proposed problem. The research design (descriptive, comparative, case study, narrative, etc.) should be described and justified as appropriate to address the research problem you have identified.
- Methods and Data (20%) – This section should indicate the data sources needed to answer the research question and the general methodological approach taken. Items to address include: key propositions or hypotheses; concepts; independent and dependent variable(s); indicators; cross-section or longitudinal approach; unit of analysis; sampling; validity and reliability; etc. (Please note: not all of these topics apply for all projects so please address what is relevant to your work.) For students doing theory based projects please indicate what data sources you will utilise and your general method.
- Proposed analyses (20%) – This section should describe how you intend to analyse the data to address your research question(s). Is the project qualitative, quantitative or a mixed methods approach? Please identify the techniques you will use to analyse the data. Note: qualitative methods typically require coding AND analysis of data. Both stages should be described in this section
- Proposed timeframe for the study (10%) – Outline a timetable for completion of the project (6 months for honours, 2 years for full-time Masters students, 3 years for PhD).
Components of a research proposal
A research proposal begins with a title page. The title is centered in the upper half of the page, with each important word capitalized. The title should clearly and concisely (in about 12 words or fewer) communicate the primary variables and research questions. This sometimes requires a main title followed by a subtitle that elaborates on the main title, in which case the main title and subtitle are separated by a colon. Here are some titles from recent issues of professional international studies journals:
- Benefits of global partnerships to facilitate access to medicines in developing countries: a multi-country analysis of patients and patient outcomes in GIPAP
- Grounding the European public sphere: looking beyond the mass media to digitally mediated issue publics
- “Smartness” without vision: the Moroccan regime in the face of acquiescent elites and weak social mobilization
Introduction
The introduction begins on the second page of the proposal. The heading at the top of this page is the full title of the manuscript, with each important word capitalized as on the title page. The introduction usually includes three distinct subsections, although these are typically not identified by separate headings. The opening introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting, the literature review discusses relevant previous research, and the closing restates the research question and comments on the method used to answer it.
Tip: write the introduction last. It makes sense to start writing the introduction first, but in fact, after your proposal is written, you will often find that the introduction is easier to write. You will then have a better understanding of what background is relevant to the reader, and what needs to be emphasised.
The opening , which is usually a paragraph or two in length, introduces the research question and explains what is interesting about it, and who it is interesting/important to. To capture the reader’s attention, researcher Daryl Bem [1] recommends starting with general observations about the topic under study, expressed in ordinary language (not technical jargon)—observations that are about people and their behaviour (not about researchers or their research). After capturing the reader’s attention, the opening should go on to introduce the research question and explain why it is interesting. Will the answer fill a gap in the literature? Will it provide a test of an important theory? Does it have practical implications? Giving readers a clear sense of what the research is about and why they should care about it will motivate them to continue reading the literature review—and will help them make sense of it.
A condensed literature review : Immediately after the opening comes a condensed literature review, which describes relevant previous research on the topic in a condensed way. It should NOT be simply a list of past studies. Instead, it constitutes a kind of argument for why the research question is worth addressing. By the end of the literature review, readers should be convinced that the research question makes sense and that the present study is a logical next step in the ongoing research process. It is not your full literature review at this stage, but just a sample of the main tenants of your argument, which lead to the way you plan to address your research questions. The closing of the introduction — typically the final paragraph or two — usually includes two important elements. The first is a clear statement of the main research question or hypothesis. This statement tends to be more formal and precise than in the opening and is often expressed in terms of operational definitions of the key variables. The second is a brief overview of the method and some comment on its appropriateness.
Literature review
The purpose of the literature review is to develop an argument for the method you chose to use in our research, and why this method is suitable for addressing your research question. The argument has to be based on scholarly academic sources. The literature review is also meant to give the reader a summary of the current knowledge on your topic: how can you group the various authors under consideration? What assumptions do they share? Do they agree about the implications of their work? Do they prioritize things the same and/or correctly? what gaps are there in those views? Like any effective argument, the literature review must have some kind of structure. For example, it might begin by describing a phenomenon in a general way along with several studies that demonstrate it, then describing two or more competing theories of the phenomenon, and finally presenting a hypothesis to test one or more of the theories. Or it might describe one phenomenon, then describe another phenomenon that seems inconsistent with the first one, then propose a theory that resolves the inconsistency, and finally present a hypothesis to test that theory. In applied research, it might describe a phenomenon or theory, then describe how that phenomenon or theory applies to some important real-world situation, and finally suggest a way to test whether it does, in fact, apply to that situation. Looking at the literature review in this way emphasizes a few things:
- It is extremely important to start with an outline of the main points that you want to make, organised in the order that you want to make them. The basic structure of your argument, then, should be apparent from the outline itself.
- It is important to emphasise the structure of your argument in your writing. One way to do this is to begin the literature review by summarising your argument even before you begin to make it. “This proposal describes two apparently contradictory phenomena, present a new theory that has the potential to resolve the apparent contradiction, and finally present a novel hypothesis to test the theory.” Another way is to open each paragraph with a sentence that summarises the main point of the paragraph and links it to the preceding points. These opening sentences provide the “transitions” that many beginning researchers have difficulty with. Instead of beginning a paragraph by jumping into a description of a previous study, such as “Williams (2004) found that…,” it is better to start by indicating something about why you are describing this particular study. Here are some simple examples:
Another example of this phenomenon comes from the work of Williams (2004). Williams (2004) offers one explanation of this phenomenon. An alternative perspective has been provided by Williams (2004). We used a method based on the one used by Williams (2004).
- Remember that your goal is to construct an argument for why your research question is interesting and worth addressing—not necessarily why your favourite answer to it is correct. In other words, your literature review must be balanced. If you want to emphasise the generality of a phenomenon, then of course you should discuss various studies that have demonstrated it. However, if there are other studies that have failed to demonstrate it, you should discuss them too. Or if you are proposing a new theory, then of course you should discuss findings that are consistent with that theory. However, if there are other findings that are inconsistent with it, again, you should discuss them too. It is acceptable to argue that the balance of the research supports the existence of a phenomenon or is consistent with a theory (and that is usually the best that researchers in psychology can hope for), but it is not acceptable to ignore contradictory evidence. Besides, a large part of what makes a research question interesting is uncertainty about its answer.
Research design
In this section, you need to not only describe your research design, but also explain how that design is beneficial for answering your research questions. Does it provide breadth? depth? objectivity? The research design can usually be justified with previous research which has used a similar design, or, in contrast, by showing that there is little research in the area using such design, and a need for it.
Methods and data
The methods and data section is where you describe how you conducted your data collection. An important principle for writing a method section is that it should be clear and detailed enough that other researchers could replicate the study by following your “recipe.” This means that it must describe all the important elements of the study—basic demographic characteristics of the participants, how they were recruited, whether they were randomly assigned, how the variables were manipulated or measured, how counterbalancing was accomplished, and so on. At the same time, it should avoid irrelevant details such as the fact that the study was conducted in Classroom 37B of the Industrial Technology Building or that the questionnaire was double-sided and completed using pencils. The method section begins immediately after the introduction ends with the heading “Methods”. Immediately after this is the subheading “Participants,” which indicates how many participants you intend to involve (if any), and how they will be recruited.
Reflection activity: research proposal
Share the answers to the following questions with the group in the discussion forum.
- What aspect of the research proposal task do you currently find the most challenging and why?
- ↑ Bem, D. J. (2003). Writing the empirical journal article. In J. M. Darley, M. P. Zanna, & H. R. Roediger III (Eds.), The compleat academic: A practical guide for the beginning social scientist (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.

Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
- MEDICAL ASSISSTANT
- Abdominal Key
- Anesthesia Key
- Basicmedical Key
- Otolaryngology & Ophthalmology
- Musculoskeletal Key
- Obstetric, Gynecology and Pediatric
- Oncology & Hematology
- Plastic Surgery & Dermatology
- Clinical Dentistry
- Radiology Key
- Thoracic Key
- Veterinary Medicine
- Gold Membership
The Research Proposal: Analysing Data
Introduction This chapter is linked to the analysing data section of the web program. As well as describing how you intend collecting the data for your research study in your research proposal, you need to state how you will analyse the data. The problem is that ‘raw’ data on their own are meaningless, so before we can use the data, they need to be organised and interpreted – in other words, analysed (Botti & Endacott 2005). If you have data from a quantitative research study, they will normally be in a numerical form; in order to use these data, you need to use statistics to analyse them. For many people, the term statistics can immediately make them panic, even mentally switch off, but in fact dealing with statistics can be fun! We all use statistics every day without thinking of it as statistics. The statistics we typically use most frequently are ‘averages’ and ‘percentages’ – as in the average age of the footballers playing for Manchester City is …, or the percentage of girls who go to university to take a nursing degree is …,and so on. So statistics are nothing to fret about, as you will discover as you work through this chapter. Totally different from the analysis of data obtained from a quantitative research study is the analysis of data obtained from a qualitative research study. Here the data may be numerical, but they mainly comprise words, or sometimes non-verbal and non-numerical data such as drawings. In many ways, qualitative research data are harder to analyse because, unlike with quantitative research data which convert readily to statistics – and there are many different tests/computer programs to analyse the statistics for you – qualitative data analysis is less direct and possibly a little nebulous, as you will see. Although there are certain processes that we can use to help us analyse our qualitative data, the fact is that qualitative data are more open to interpretation than are quantitative data. Therefore, we shall start by looking at, and discussing, how we can analyse data from quantitative research studies. Quantitative data analysis First, a brief resume of the types of data collection from chapter 8. When we are undertaking quantitative research, data collection involves the production of numerical data to address the research objectives, questions and/or hypotheses. During this process, the variables in the study are measured using a variety of techniques, including: observation; interview; questionnaire; scales; physiological measurements. Data analysis What do we mean by data analysis? Well, data analysis is a process we use in order to reduce, organise and give meaning to the data we have collected by using the data collection tools discussed in chapter 8. Within quantitative research, the analysis of data involves the use of: descriptive and exploratory procedures to describe the study variables and the sample; statistical techniques in order to test any proposed relationships; techniques that will help us to make predictions; techniques that will allow us to examine cause and effect. It is worth pointing out at that, unlike in the past, when dealing with statistics we no longer need to do calculations ourselves. Computers can perform most analyses. The choice of technique that is used in any research study is determined mainly by: the research objectives, questions or hypotheses; the research design; the research instruments and how/what they can measure. So, without further ado, let us start by looking at how we can undertake and analyse quantitative research, with a brief introduction to statistics. Introduction to statistics Always treat statistics with caution as well as respect, for as the British prime minister Benjamin Disraeli (1804–1881) once famously (or infamously) said: ‘There are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies and statistics.’ In this section we are going to take a general look at what we mean by statistics and statistical data. So, let us start with some definitions: Data We talk about data in statistics. Data (singular ‘datum’) are things known or assumed as a basis for inference, or, to put it more simply, ‘Pieces of information that are collected during a study’ (Burns & Grove 2005: 733). Statistics Statistics are concerned with the systematic collection of numerical data and their interpretation. Burns & Grove (2005: 752) refer to a statistic as simply ‘a numerical value obtained from a sample that is used to estimate the parameters of a population’ . The word’statistics’ can be used to refer to: numerical facts, such as the number of people living in a particular town; the study of ways of collecting and interpreting these facts. It can be argued that figures are not facts in themselves. It is only when they are interpreted that they become relevant to discussions and decisions. So statistics are there to inform our discussions – they are a means to an end, not an end in themselves. Sample You may recall from chapter 7 that a sample is a group of people, events, behaviours or other elements you need to have in order to conduct your research study. Population A population is what we call the group of individuals or elements that meets the sampling criteria (a sample being representative of that population). So, if we were interested in looking at the number of childhood cancers diagnosed in 2006 in the United Kingdom (i.e. our ‘population’), we might not be able to survey the entire population of children with cancer in that year living in the UK, and so we would look at a sample taken from all the children with cancer in 2006 living in the UK (see chapter 7 for the criteria we need to apply to our sample). Parameter Parameter has, like many English words, several meanings. According to the Concise Oxford Dictionary (1991) it can be defined as: a quantity constant in the case considered but varying in different cases; a measurable (or quantifiable) characteristic or feature; a constant element or factor, particularly serving as a limit or boundary. You may be wondering at this point what this means in terms of research. Well, to simplify matters, let us look at the definition given by Burns & Grove (2005 : 745): ‘a measure or numerical value of a population’ – in other words, the numbers found in any given population. Statistics can be divided into two types: Descriptive statistics Description ‘involves identifying and understanding the nature and attributes of nursing phenomena and sometimes the relationships among these phenomena’ (Burns & Grove 2005: 733). According to Sim & Wright (2000), descriptive statistics have two functions: 1. organising, summarising and presenting numerical data; 2. describing the distribution (i.e. the structure of the data collected) which will help with the analysis of inferential statistics, which are much more complex (Botti & Endacott 2005). Descriptive statistics include the presentation of data in tables and diagrams, as well as the calculation of percentages, averages, measures of dispersion (the variation or variability within the statistics) and correlation (the degree of relationship between two variables), in order to show the relevant features of the data and reduce them to manageable proportions. In other words, descriptive statistics involve the summary of the statistics in such a way that the researcher can organise the data in these statistics and give them meaning and insight. Inductive/inferential statistics Inductive or inferential statistics involve methods of inferring properties of a population on the basis of known results from a sample that is representative of the population. To infer is to deduce or conclude from facts and reasoning (Shorter Oxford English Dictionary 2007), and inference is the use of inductive reasoning to move from a specific case to a general truth (and hence is also known as inductive reasoning). The Shorter Oxford English Dictionary gives one meaning of inductive as ‘leading on to’, and according to Burns & Grove (2005: 739), in relation to statistics, inductive reasoning is ‘reasoning from the specific to the general in which particular instances are observed and then combined into a larger whole – or general statement’. Thus, with these types of statistics, statistics are used to infer results from the specific study of a sample to a general statement about the larger population. So, inferential statistics are statistics that are designed to allow an inference to be made from a sample statistic to a population parameter. They are commonly used to test hypotheses (see chapter 5) that consist of similarities and differences in subsets of the sample under study. These methods are based directly on probability theory. Probability theory ‘addresses relative rather than absolute causality. Thus, from a probability perspective, a cause will not produce a specific effect each time that particular cause occurs, but the probability value indicates how frequently the effect might occur with the cause’ (Burns & Grove 2005: 747); in other words, given a certain situation, behaviour or event, how often that situation, behaviour or event might cause a particular result. So much for the general background to statistics; now we can start to look at some actual simple statistics. To begin with, you need to know that symbols are used in statistics to simplify their presentation. Some of the more common ones are given below. Symbols used in statistics As a form of shorthand, we use symbols instead of words: μ (lower-case Greek letter mu) = the mean χ (lower-case Greek letter chi) = each of the individual operations Σ (capital Greek letter sigma) = the operation of summing all the values of χ. n = number of observations σ (lower-case Greek letter sigma) = standard deviation (also symbolised by ‘s’). x = mean value s 2 = variance SS = sum of squared errors When you come to the statistical equations, you can refer to this list for the meanings of the symbols. Now, to boost your confidence and to demonstrate that statistics can be quite simple (and perhaps a little fun) it is time to look at some simple and common statistical calculations, which are regularly used in statistics – and to some extent in our everyday lives, although you may not be aware that you are using them. Average ‘Average’ is a measure of central tendency and of location. It summarises a group of figures and smoothes out any abnormalities. It also provides a mental picture of the distribution that it represents. In addition, it can provide knowledge about the whole distribution. The word is often used loosely in everyday conversation; however, used in this way, it can conceal important facts. There is more than one kind of average, so we shall consider these next, commencing with the type that we use most often when we talk about the ‘average’. Arithmetic mean ‘Arithmetic mean’ is the type of average to which most people refer when they use the word ‘average’, and it can be defined as the sum of the items divided by the number of these items. So, arithmetic mean = ‘the total value of items’ % the ‘total number of items’ or in symbols: Where Σ = the sum of χ (value of items) and n = number of items. The actual mathematical equation is For example, if we were to look at the ages of child branch student nurses, a group of 21 students, in their first year the university, we might find that there are: 11 aged 18 years 5 aged 19 2 aged 20 1 aged 25 1 aged 33 1 aged 51 According to our equation, to get the arithmetic mean of the group’ s age, we add all the ages together (= 442) and divide that by 21. This gives us an average of 21 years (or 21.047619 if you used a calculator). So we can see that the average age of this group of students on commencement at the university is 21 years. But can we now say that the age of child branch students on commencing university everywhere is 21 years? Hopefully, your answer is no. After what you have read in chapter 7 and 8, as well as in the web program, you should have realised that the group (our sample) is far too small for us to be able to generalise to child branch students everywhere else (the population). To Do Using the method and equation above, work out the arithmetic mean average age of your friends. You should also have noticed that, even in our small sample, our average of 21 years conceals a very important fact: the great majority of these students are aged 18–20 years when they commence university; there are just three students in the group who are aged 21 years or over. Therefore, the average does not give an accurate idea of the group’s age range, let alone allowing us to generalise. Always bear in mind the words of Thomas Carlyle (1840: 9) ‘A witty statesman said, you might prove anything by figures.’ However, we do have a couple of calculations that we can do with these figures that can give us a more realistic average. The first of these is the median. Median The median, another type of average, is the value of the middle item of a distribution which is set out in order. i.e. n plus 1 divided by 2, where n is the number of items. Now we can return to the ages of the cohort of 21 child branch student nurses when they commence at the university, namely: 11 aged 18 years 5 aged 19 2 aged 20 1 aged 25 1 aged 33 1 aged 51 To Do Use the formula above for median calculations, and work out the median of the group. Remember that the middle point of the ages of the group when laid out in a line from youngest to oldest is the median Did you get the same answer? You can see that the mid-point is the age at rank order number 11, which in this case is 18 years (as there are ten ages before that one and ten after it). If we look at the formula , then the mid-point is 21+1 divided by 2, or i.e. in this case the eleventh age in the row, which is 18. To Do Now do the same calculation with the ages of your friends. Is it different from your arithmetic mean average? It may be if you have friends of many different ages. In our example, does the median age give a more accurate idea of the group as a whole than the arithmetic mean average does? I think you would agree that the answer has to be yes, because 18 years is closer to the age of the great majority of the group. However, it still does not identify the anomaly that is the ages of the older students. So, we have yet another type of average to look at – the mode. Mode The mode is the numerical value of a score that occurs with the greatest frequency in a distribution. However, it does not necessarily indicate the centre of the set of data (Burns & Grove 2005). To Do Using the ages of our group of child branch students, work out the modal age of the group and see if you get the answer that we do. Again, use the ages to work out the mode (remember that the mode is the number that occurs most often): 11 aged 18 years 5 aged 19 2 aged 20 1 aged 25 1 aged 33 1 aged 51 In this case, 18 years of age occurs more frequently than any other age in our group; therefore the mode of the group is 18 years. In this case, the mode is the same as the median (but both are different from the mean), but this is not always the case. Consequently, you need to look closely at any statistics, because they are not always what they seem to be. To Do Again, using the ages of your friends, work out the mode of their ages. How does it compare with the other two ‘averages’? Finally, let us look at range. Range The range is an everyday method of describing the dispersion (spread) of data. It can be defined as the highest value in a distribution less the lowest. Let us look again at our group of child branch student nurses. The range of ages is 18–51 years. Therefore, the range of ages is 51 – 18 years = 33 years. If you combine this with a modal age of 18, what does this tell you about the general age of student nurses in the child branch? Answer: with a modal age of 18, although there is a range of 33 years (from 18 to 51 years), whilst most of the student nurses are young, there are some older ones (and even one of 51 years), but most of the child branch student nurses are at the younger end of the age range. To Do Finally, work out the range of ages of your group of friends. Now you can reflect on your friends, their ages and whether you have friends mainly of the same age as you or friends whose ages are very wide-ranging. Does this say anything about you and your criteria for friendship? So, you can see that statistics are not just a string of numbers and lots of calculations, but are a starting point for debate and discussion. Reflection on averages Often range is given along with mean, median or mode. Why? Answer: the advantage of giving range and one of the averages is that you get a much better idea of the group’s ages as in the example of the child branch student nurses. It also overcomes the problem of how we demonstrate that there are some major anomalies in our group, which are virtually ignored by the various averages. (The ‘anomalies’ in our example are the students who are much older than most of the group.) So, we can say that the group of child branch student nurses has a: mean of 21 years median of 18 years mode of 18 years range of 18–51 years and we now have a clearer picture of the group in terms of their ages. Standard deviation We just have one more important simple statistic to discuss: standard deviation. Standard deviation is a simple measure of the variability or dispersion (distribution) of a set of data. Basically, it measures the spread of the data about the mean value. A low standard deviation is an indication that all the individual data points are very close to the same value (i.e. the mean – see above), while a high standard deviation is an indication that the data are spread over a wide range of values. There is a formula to help us to work out standard deviation: The same symbol you were introduced to earlier are relevant to this formula. So this formula (in words) is ‘Standard deviation (σ) equals the square root (√) of the sum of (Σ) the mean value minus the mean squared ([χ–μ] 2 ), divided by the number of observations (n). For an example of how we calculate a standard deviation, let us look at the group of students (our population) we used above in our discussion of averages. We want to find the standard deviation of: 18 18 18 18 18 18 18 18 18 18 18 19 19 19 19 19 20 20 25 33 51 years First, we have to work out the arithmetic mean. We have already done this and obtained a mean of 21. Now we need to subtract that from each of the ages and square the result. So, for example, 18 – 21 = –3, and squared = 9 (minus numbers squared = positive numbers). Score Deviation Squared deviation χ χ − μ (χ − μ) 2 18 −3 9 18 −3 9 18 −3 9 18 −3 9 18 −3 9 18 −3 9 18 −3 9 18 −3 9 18 −3 9 18 −3 9 18 −3 9 19 −2 4 19 −2 4 19 −2 4 19 −2 4 19 −2 4 20 −1 2 20 −1 2 25 4 16 33 12 144 51 12 900 Next we have to add up these results. (This is where a calculator comes in handy, and even more so for the next two parts of the equation.) The total of the squared deviations is 1,183, which we now divide by the number of subjects (21), or 1,183 ÷ 21 = 56.34. Now find the square root of 56.34, which is 7.505997601918082 (rounded = 7.5). This is the standard deviation, but what do we do with it? The 7.5 score that we have for this group of students is used to give us an idea of the spread of the data that we have regarding the age of the age range. So if the mean is 21, first we have to see how many of the students fall within one standard deviation (i.e. 7.5) of the mean. In other words, how many students fall within the range of 13.5 – 28.5 (7.5 either side of 21). Well, 18 out of 21 fall between 13.5 and 21, whilst one falls within the range between 21 and 28.5. That means that 19 out of 21 (90%) of the student nurses fall within one standard deviation of the mean. Next we look at how many fall between 6 and 13.5 and between 28.5 and 36 (i.e. within the second standard deviation). The answer is that none falls between 6 and 13.5, and one falls between 28.5 and 36 (5%). Finally, three standard deviations would be ages between 0 and 6 and between 36 and 43.5 – the answer is none. The only remaining student falls between 43.5 and 51, which is four standard deviations. So, given these results, it is clear that, although the group is very homogeneous as regards their ages, there are two students who cause the spread of data to be extensive. According to Hinton (1995: 15–16), in many cases ‘most of the scores (about two-thirds – about 66.7%) will lie within one standard deviation less than, and one standard deviation greater than, the mean’. Our group does not quite fit that finding, with 90% being within one standard deviation, however, there is a special reason for this, and that is that our population is unique in that student nurses, particularly child branch students, are generally starting out in the world afterleaving school, and so they will generally be around the same age. A word of caution – the formula works for a population. If, however,we wanted to calculate the standard deviation of a sample, the formula is slightly different, namely: However, the rest of the calculation is as described above, but with the final stage of the calculation using the denominator n – 1 rather than just n. Summary This concludes our brief look at statistics. All the statistics you will encounter are variants of these. Some of them may be more complicated, but, like the examples given above, all are attempting to make sense of numerical data. Finally, a reminder to be wary of statistics when they are presented to you: ‘He uses statistics as a drunken man uses a lamp post – for support rather than illumination’ (attributed to Andrew Lang, 1844–1912) . Data analysis Let us commence our look at data analysis by looking at a hypothetical research study. There are different ways of approaching our research question/ hypothesis, and the way we put together our research question will determine the type of methodology, data collection method, statistics, analysis and presentation we shall use to approach our research problem. Examples of research questions Are females more likely to be nurses than males? Is the proportion of males who are nurses the same as the proportion of females? Is there a relationship between gender and becoming a nurse? In these examples, you can see that there are three ways to approach the research problem, which is concerned with the relationship between males and females in nursing, but the way in which the problem is expressed as a question will determine your methodology. Another research problem with variables Hypothesis
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Related posts:
- The Research Proposal:Research Design
- The Research Proposal: Current Research Issues in Healthcare
- Philosophical Assumptions
- The Research Proposal: Developing the Research Question
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Comments are closed for this page.

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
How to write a research proposal?
Department of Anaesthesiology, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Devika Rani Duggappa
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or ‘blueprint’ for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project should flow smoothly. Even today, many of the proposals at post-graduate evaluation committees and application proposals for funding are substandard. A search was conducted with keywords such as research proposal, writing proposal and qualitative using search engines, namely, PubMed and Google Scholar, and an attempt has been made to provide broad guidelines for writing a scientifically appropriate research proposal.
INTRODUCTION
A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[ 1 ] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under ‘Research methodology II’ section [ Table 1 ] in this issue of IJA) and to request for grants. However, there are very few universally accepted guidelines for preparation of a good quality research proposal. A search was performed with keywords such as research proposal, funding, qualitative and writing proposals using search engines, namely, PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus.
Five ‘C’s while writing a literature review

BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[ 2 ] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the credibility, achievability, practicality and reproducibility (repeatability) of the research design.[ 3 ] Four categories of audience with different expectations may be present in the evaluation committees, namely academic colleagues, policy-makers, practitioners and lay audiences who evaluate the research proposal. Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; ‘be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for crystal clarity and plan before you write’. A researcher must be balanced, with a realistic understanding of what can be achieved. Being persuasive implies that researcher must be able to convince other researchers, research funding agencies, educational institutions and supervisors that the research is worth getting approval. The aim of the researcher should be clearly stated in simple language that describes the research in a way that non-specialists can comprehend, without use of jargons. The proposal must not only demonstrate that it is based on an intelligent understanding of the existing literature but also show that the writer has thought about the time needed to conduct each stage of the research.[ 4 , 5 ]
CONTENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution.
In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators, (iii) institutional affiliation (degree of the investigator and the name of institution where the study will be performed), details of contact such as phone numbers, E-mail id's and lines for signatures of investigators.
The main contents of the proposal may be presented under the following headings: (i) introduction, (ii) review of literature, (iii) aims and objectives, (iv) research design and methods, (v) ethical considerations, (vi) budget, (vii) appendices and (viii) citations.[ 4 ]
Introduction
It is also sometimes termed as ‘need for study’ or ‘abstract’. Introduction is an initial pitch of an idea; it sets the scene and puts the research in context.[ 6 ] The introduction should be designed to create interest in the reader about the topic and proposal. It should convey to the reader, what you want to do, what necessitates the study and your passion for the topic.[ 7 ] Some questions that can be used to assess the significance of the study are: (i) Who has an interest in the domain of inquiry? (ii) What do we already know about the topic? (iii) What has not been answered adequately in previous research and practice? (iv) How will this research add to knowledge, practice and policy in this area? Some of the evaluation committees, expect the last two questions, elaborated under a separate heading of ‘background and significance’.[ 8 ] Introduction should also contain the hypothesis behind the research design. If hypothesis cannot be constructed, the line of inquiry to be used in the research must be indicated.
Review of literature
It refers to all sources of scientific evidence pertaining to the topic in interest. In the present era of digitalisation and easy accessibility, there is an enormous amount of relevant data available, making it a challenge for the researcher to include all of it in his/her review.[ 9 ] It is crucial to structure this section intelligently so that the reader can grasp the argument related to your study in relation to that of other researchers, while still demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. It is preferable to summarise each article in a paragraph, highlighting the details pertinent to the topic of interest. The progression of review can move from the more general to the more focused studies, or a historical progression can be used to develop the story, without making it exhaustive.[ 1 ] Literature should include supporting data, disagreements and controversies. Five ‘C's may be kept in mind while writing a literature review[ 10 ] [ Table 1 ].
Aims and objectives
The research purpose (or goal or aim) gives a broad indication of what the researcher wishes to achieve in the research. The hypothesis to be tested can be the aim of the study. The objectives related to parameters or tools used to achieve the aim are generally categorised as primary and secondary objectives.
Research design and method
The objective here is to convince the reader that the overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem and to impress upon the reader that the methodology/sources chosen are appropriate for the specific topic. It should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
In this section, the methods and sources used to conduct the research must be discussed, including specific references to sites, databases, key texts or authors that will be indispensable to the project. There should be specific mention about the methodological approaches to be undertaken to gather information, about the techniques to be used to analyse it and about the tests of external validity to which researcher is committed.[ 10 , 11 ]
The components of this section include the following:[ 4 ]
Population and sample
Population refers to all the elements (individuals, objects or substances) that meet certain criteria for inclusion in a given universe,[ 12 ] and sample refers to subset of population which meets the inclusion criteria for enrolment into the study. The inclusion and exclusion criteria should be clearly defined. The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article “Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples” published in this issue of IJA.
Data collection
The researcher is expected to give a detailed account of the methodology adopted for collection of data, which include the time frame required for the research. The methodology should be tested for its validity and ensure that, in pursuit of achieving the results, the participant's life is not jeopardised. The author should anticipate and acknowledge any potential barrier and pitfall in carrying out the research design and explain plans to address them, thereby avoiding lacunae due to incomplete data collection. If the researcher is planning to acquire data through interviews or questionnaires, copy of the questions used for the same should be attached as an annexure with the proposal.
Rigor (soundness of the research)
This addresses the strength of the research with respect to its neutrality, consistency and applicability. Rigor must be reflected throughout the proposal.
It refers to the robustness of a research method against bias. The author should convey the measures taken to avoid bias, viz. blinding and randomisation, in an elaborate way, thus ensuring that the result obtained from the adopted method is purely as chance and not influenced by other confounding variables.
Consistency
Consistency considers whether the findings will be consistent if the inquiry was replicated with the same participants and in a similar context. This can be achieved by adopting standard and universally accepted methods and scales.
Applicability
Applicability refers to the degree to which the findings can be applied to different contexts and groups.[ 13 ]
Data analysis
This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated. Author should also mention the names of statistician and suitable software which will be used in due course of data analysis and their contribution to data analysis and sample calculation.[ 9 ]
Ethical considerations
Medical research introduces special moral and ethical problems that are not usually encountered by other researchers during data collection, and hence, the researcher should take special care in ensuring that ethical standards are met. Ethical considerations refer to the protection of the participants' rights (right to self-determination, right to privacy, right to autonomy and confidentiality, right to fair treatment and right to protection from discomfort and harm), obtaining informed consent and the institutional review process (ethical approval). The researcher needs to provide adequate information on each of these aspects.
Informed consent needs to be obtained from the participants (details discussed in further chapters), as well as the research site and the relevant authorities.
When the researcher prepares a research budget, he/she should predict and cost all aspects of the research and then add an additional allowance for unpredictable disasters, delays and rising costs. All items in the budget should be justified.
Appendices are documents that support the proposal and application. The appendices will be specific for each proposal but documents that are usually required include informed consent form, supporting documents, questionnaires, measurement tools and patient information of the study in layman's language.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. Although the words ‘references and bibliography’ are different, they are used interchangeably. It refers to all references cited in the research proposal.
Successful, qualitative research proposals should communicate the researcher's knowledge of the field and method and convey the emergent nature of the qualitative design. The proposal should follow a discernible logic from the introduction to presentation of the appendices.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
- Online Degree Explore Bachelor’s & Master’s degrees
- MasterTrack™ Earn credit towards a Master’s degree
- University Certificates Advance your career with graduate-level learning
- Top Courses
- Join for Free
What Is Data Analysis? (With Examples)
Learn what data analysis is and the types and processes to help your business or organization run more efficiently. Explore four types of data analysis with examples.
![research proposal data analysis example [Featured image] A female data analyst takes notes on her laptop at a standing desk in a modern office space](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/3L2GDaRbbIs97ppJL0d497/6d98dca6f3b8854d1fd697a7f0130f8c/What_is_data_analysis.png?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
Data analysis is the practice of working with data to glean useful information, which can then be used to make informed decisions.
"It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly, one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts," Sherlock Holmes proclaims in Sir Arthur Conan Doyle's A Scandal in Bohemia .
This idea lies at the root of data analysis. When we can extract meaning from data, it empowers us to make better decisions. And we’re living in a time when we have more data than ever at our fingertips.
Companies are wisening up to the benefits of leveraging data. Data analysis can help a bank personalize customer interactions, a health care system predict future health needs, or an entertainment company create the next big streaming hit.
The World Economic Forum Future of Jobs Report 2020 listed data analysts and scientists as the top emerging jobs, followed immediately by AI and machine learning specialists and big data specialists [ 1 ]. In this article, you'll learn more about the data analysis process and different types of data analysis, as well as recommended courses to help you get started in this exciting field.
Data analysis process
As the data available to companies continues to grow both in amount and complexity, so too does the need for an effective and efficient process by which to harness the value of that data. The data analysis process typically moves through several iterative phases. Let’s take a closer look at each.
Identify the business question you’d like to answer. What problem is the company trying to solve? What do you need to measure, and how will you measure it?
Collect the raw data sets needed to help you answer the identified question. Data collection might come from internal sources, like a company’s client relationship management (CRM) software, or from secondary sources, like government records or social media application programming interfaces (APIs).
Clean the data to prepare it for analysis. This often involves purging duplicate and anomalous data, reconciling inconsistencies, standardizing data structure and format, and dealing with white spaces and other syntax errors.
Analyze the data. By manipulating the data using various data analysis techniques and tools, you can find trends, correlations, outliers, and variations that tell a story. During this stage, you might use data mining to discover patterns within databases or data visualization software to help transform data into an easy-to-understand graphical format.
Interpret the results of your analysis to see how well the data answered your original question. What recommendations can you make based on the data? What are the limitations of your conclusions?
Watch this video to hear how Kevin, Director of Data Analytics at Google, defines data analysis.
Types of data analysis (with examples)
Data can be used to answer questions and support decisions in many different ways. Identifying the best way to analyze your data can help you familiarize yourself with the four types of data analysis commonly used in the field.
In this section, we’ll take a look at each of these data analysis methods, along with an example of how each might be applied in the real world.
Descriptive analysis
Descriptive analysis tells us what happened. This type of analysis helps describe or summarize quantitative data by presenting statistics. For example, descriptive statistical analysis could show the sales distribution across a group of employees and the average sales figure per employee.
Descriptive analysis answers the question, “What happened?”
Diagnostic analysis
If the descriptive analysis determines the “what,” diagnostic analysis determines the “why.” Let’s say a descriptive analysis shows an unusual influx of patients in a hospital. Drilling into the data further might reveal that many of these patients shared symptoms of a particular virus. This diagnostic analysis can help you determine that an infectious agent—the “why”—led to the influx of patients.
Diagnostic analysis answers the question, “Why did it happen?”
Predictive analysis
So far, we’ve looked at types of analysis that examine and draw conclusions about the past. Predictive analytics uses data to form projections about the future. Using predictive analysis, you might notice that a given product has had its best sales during September and October each year, leading you to predict a similar high point during the upcoming year.
Predictive analysis answers the question, “What might happen in the future?”
Prescriptive analysis
Prescriptive analysis takes all the insights gathered from the first three types of analysis and uses them to form recommendations for how a company should act. Using our previous example, this type of analysis might suggest a market plan to build on the success of the high sales months and harness new growth opportunities in the slower months.
Prescriptive analysis answers the question, “What should we do about it?”
This last type is where the concept of data-driven decision-making comes into play.
What is data-driven decision-making (DDDM)?
Data-driven decision-making, sometimes abbreviated to DDDM, can be defined as the process of making strategic business decisions based on facts, data, and metrics instead of intuition, emotion, or observation.
This might sound obvious, but in practice, not all organizations are as data-driven as they could be. According to the global management consulting firm McKinsey Global Institute, data-driven companies are better at acquiring new customers, maintaining customer loyalty, and achieving above-average profitability [ 2 ].
Get started with Coursera.
If you’re interested in a career in the high-growth field of data analytics, you can begin building job-ready skills with the Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate . Prepare yourself for an entry-level job as you learn from Google employees—no experience or degree is required. Once you finish, you can apply directly to employers, including Google.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Where is data analytics used .
Just about any business or organization can use data analytics to help inform their decisions and boost their performance. Some of the most successful companies across a range of industries—from Amazon and Netflix and Starbucks—integrate data into their business plans to improve their overall business performance.
What are the top skills of a data analyst?
Data analysis makes use of a range of analysis tools and technologies. Some of the top skills for data analysts include SQL, data visualization, statistical programming languages (like R and Python), machine learning, and spreadsheets.
Do data analysts need to be good at math?
Data analytics tends to be less math-intensive than data science. While you probably won’t need to master any advanced mathematics, a foundation in basic math and statistical analysis can help set you up for success.
Article sources
World Economic Forum. " The Future of Jobs Report 2020 , https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Future_of_Jobs_2020.pdf." Accessed April 1, 2024.
McKinsey & Company. " Five facts: How customer analytics boosts corporate performance , https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/marketing-and-sales/our-insights/five-facts-how-customer-analytics-boosts-corporate-performance." Accessed April 1, 2024.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.

COMMENTS
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
analysis plan: example. • The primary endpoint is free testosterone level, measured at baseline and after the diet intervention (6 mo). • We expect the distribution of free T levels to be skewed and will log-transform the data for analysis. Values below the detectable limit for the assay will be imputed with one-half the limit.
Template 3 - Project Context and Objectives of Research Data Analysis Proposal. Click Here to Download. This slide simplifies the process of impressing your clients. It explains your project's context and objectives, leaving a lasting impact on your audience. Project Context: We provide a clear and concise space for explaining the background ...
A Sample Quantitative Research Proposal Written in the APA 6th Style [Note: This sample proposal is based on a composite of past proposals, simulated information and references, and material I've included for illustration purposes - it is based roughly on a ... guide the analysis of data. First, it is hypothesized that perceptions of life ...
Definition of research in data analysis: According to LeCompte and Schensul, research data analysis is a process used by researchers to reduce data to a story and interpret it to derive insights. The data analysis process helps reduce a large chunk of data into smaller fragments, which makes sense. Three essential things occur during the data ...
The curated collection of the Top 10 Statistical Analysis Research Proposal Templates offers a valuable resource for researchers and scholars. These templates, real-world samples, and examples provide a solid foundation for crafting compelling research proposals. By harnessing these tools, researchers can streamline proposal creation, ensuring ...
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it's important, and how you will conduct your research. Your paper should include the topic, research question and hypothesis, methods, predictions, and results (if not actual, then projected). ... Demonstrate that you have carefully considered the data, tools, and procedures ...
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level project, and one for a PhD-level ...
QDA Method #1: Qualitative Content Analysis. Content analysis is possibly the most common and straightforward QDA method. At the simplest level, content analysis is used to evaluate patterns within a piece of content (for example, words, phrases or images) or across multiple pieces of content or sources of communication. For example, a collection of newspaper articles or political speeches.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
A good data analysis plan should summarize the variables as demonstrated in Figure 1 below. Figure 1. Presentation of variables in a data analysis plan. 5. Statistical software. There are tons of software packages for data analysis, some common examples are SPSS, Epi Info, SAS, STATA, Microsoft Excel.
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
The first step in a data analysis plan is to describe the data collected in the study. This can be done using figures to give a visual presentation of the data and statistics to generate numeric descriptions of the data. Selection of an appropriate figure to represent a particular set of data depends on the measurement level of the variable.
Research Proposal Examples. Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples designed to briefly demonstrate what might be discussed in each section. ... - Outline the data analysis techniques (e.g., statistical analysis, thematic analysis) - Outline your validity and ...
Include any additional supporting materials, such as survey questionnaires, interview guides, or data analysis plans. Research Proposal Format. The format of a research proposal may vary depending on the specific requirements of the institution or funding agency. However, the following is a commonly used format for a research proposal: 1. Title ...
Definition of Data Analysis. Data analysis in quantitative research proposal is one part of the chapter that researchers need in the beginning of writing a research proposal. Whereas in the research, it is an activity after the data from all collected. Activities in data analysis are: grouping data based on variables and types of respondents ...
Template 4: Plan of Action for Data Analytics Proposal. This Plan of Action Template is crucial as it offers a clear roadmap, outlining the specific methodologies and steps to achieve the project's goals. It divides the action plan into 6 weeks and includes activities like analyzing, selecting, implementing, adopting, and scaling.
A research proposal is generally meant to be presented by an investigator to request an agency or a body to support research work in the form of grants. ... The present proposal will use methods used for longitudinal data analysis. The researcher should justify the benefit of these methods over the previous statistical methods ...
Become familiar with the format and template of a UOW research proposal Research proposal template. At the university of Wollongong, in the Faculty of Law, Humanities and the Arts, there are some expectations with regards to research proposals. Prospective Honours/Masters by Research/PhD students are required to complete a research proposal and ...
The Research Proposal: Analysing Data. Introduction. This chapter is linked to the analysing data section of the web program. As well as describing how you intend collecting the data for your research study in your research proposal, you need to state how you will analyse the data. The problem is that 'raw' data on their own are meaningless ...
A data analysis plan is a roadmap for how you're going to organize and analyze your survey data—and it should help you achieve three objectives that relate to the goal you set before you started your survey: Answer your top research questions. Use more specific survey questions to understand those answers. Segment survey respondents to ...
The investigator specifies the maximum discrepancy between the sample and population proportion of ± 5%. To determine the sample size, the investigator would use the formula. n = (z/p)2π(1-π), n = the required sample size. p = the desired maximum discrepancy (i.e. ± 5%) π = the population proportion.
Data analysis . This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated.
Explore four types of data analysis with examples. Data analysis is the practice of working with data to glean useful information, which can then be used to make informed decisions. "It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly, one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts," Sherlock ...