Financing | Templates

How To Write an SBA Business Plan [+Free Template]
Published June 13, 2023
Published Jun 13, 2023
REVIEWED BY: Tricia Jones
WRITTEN BY: Andrew Wan
This article is part of a larger series on Business Financing .
- 1. Write the Company Description
- 2. Identify Organization & Management
- 3. Specify the Market Analysis
- 4. Write Descriptions of the Products or Services
- 5. Indicate the Marketing & Sales Strategy
- 6. List Financial Data & Projections
- 7. Write the Financing Request
- 8. Fill In the Appendix & Supplemental Information
- 9. Complete the Executive Summary
- Additional Resources
Bottom Line
If you’re applying for a loan from the Small Business Administration (SBA), there’s a good chance that you’ll need a business plan to get approved. An SBA business plan provides a summary of the various aspects of your business, and we will guide you through the process of creating it, from writing your company description and marketing and sales strategies to completing financial data and projections and your executive summary.
Although there is no standard format, and to help you ensure nothing is overlooked, you can use our SBA business plan template to ensure you cover the most important areas of your company. A well-prepared business plan can improve your chances of getting an SBA loan.
FILE TO DOWNLOAD OR INTEGRATE
SBA Business Plan Template Download

Thank you for downloading!
Step 1: write the company description.
This section should contain information about the purpose of your business. It should include a description of the problem or challenge your product or service aims to solve and what types of individuals or organizations will benefit.
A strong company description should also address the following questions:
- Why does your company exist?
- What problems does your business aim to address?
- What prompted you to start your business?
- What organizations or individuals will benefit from your company’s product or service?
- What makes your company different from others?
- What competitive advantages does your business offer?
- What would a successful product launch look like?
- Does your company have strategic partnerships with other vendors?
Step 2: Identify Organization & Management
Details about the legal and tax structure of your business should be included in this section. It can also be helpful to include an organizational chart of your company. You can include information about each team member’s background and experience and how it is relevant to your company:
- Highlight what business structure you have selected and why. Examples commonly include a sole proprietorship, limited liability company (LLC), partnership, S corporation (S-corp), and C corporation (C-corp)
- Include an organizational chart showing which team members are responsible for the various aspects of your company
- You can include resumes for members of your leadership team highlighting their experience and background
Step 3: Specify the Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your SBA business plan should look at who your competitors will be. Look at what they are doing well, what their weaknesses are, and how your company compares.
The SBA’s market analysis page contains information on how you can approach this. Questions you should also consider addressing should include:
- Who are the major competitors in the market?
- What are competitors doing well and are there areas for improvement?
- How does your company compare to the top competitors?
- How has the product or service evolved over time?
- Are there any trends for supply and demand throughout the year?
- What can your company do to stand apart from the top competitors?
Step 4: Write Descriptions of the Products or Services
In this section, you should detail the product or service offered by your business. You should explain what it does, how it helps your customers, and its expected lifecycle. You can also include things like any expected research and development costs, intellectual property concerns such as patents, what the lifecycle of your product looks like, and what is needed to manufacture or assemble it.
Here are some things to consider as you are working on this section:
- Description of what your product or service does
- How your product or service works
- How your customers will benefit from your product or service
- Illustration of the typical lifecycle
- Any patents or intellectual property you or your competitors have
- Pricing structure
- Plans for research and development
- Discuss plans for handling intellectual property, copyright, and patent filings
Step 5: Indicate the Marketing & Sales Strategy
Details of your marketing and sales strategy will be highly dependent on your business. It’s also something that may evolve and change over time in response to things like the overall economic environment, release of competitor’s products or services, and changes in pricing.
With that being said, here is a list of some items that should be addressed:
- Who is your target audience?
- How will you attract customers?
- How and where will sales be made?
- If applicable, what will the sales process look like?
- Where will you market and advertise your product or service?
- How does your marketing strategy compare to other companies in the industry?
- How much should you spend on marketing?
- What is the expected return on investment for marketing?
- Do you have any data showing the effect of marketing?
Step 6: List Financial Data & Projections
If your business has been running, you should include information about its finances. This should include all streams of revenue and expenses. Data for financial projections should also be included, along with a description of the methodology you used to reach those conclusions.
If available, you should be prepared to provide the following financial documents for at least the last three years to five years:
- Personal and business tax returns
- Balance sheets
- Profit and loss (P&L) statements
- Cash flow statements
- Hard and soft collateral owned by your business
- Business bank statements for the last six to 12 months
Financial projections should include enough data to offer some confidence that your business is viable and will succeed. It’s recommended that you provide monthly projections looking forward at least three years, with annual projections for years four and five.
- Projections for revenue and methodology used in arriving at these figures
- Expected shifts in revenue or expenses as a result of seasonality or other factors affecting supply and demand
- Expected expenses from loan payments, rent, lease payments, marketing and advertising fees, employee salaries, benefits, legal fees, warranty expenses, and more
You can use our SBA loan calculator to help you estimate monthly payments for the funding you’re currently looking for and projections for any additional loans you may need. Monthly payments can fluctuate depending on the terms of your loan. If you’re looking for accurate estimates, you can read our article on SBA loan rates .
Step 7: Write the Financing Request
This section is where you should specify how much funding you need, why you need it, what you’ll use it for, and the impact you expect it will have on your business. It’s also a good idea to indicate when you expect to use the funds over the course of the next three to five years.
Here is a checklist of some important items you should cover:
- How much funding you need and why
- When you will use the funds over the next three to five years
- What you will use the funds for
- The expected impact this will have on your business and how it will help reach your business goals
- The anticipation of any recurring needs for additional funding
- Your strategy for how you expect to pay off the loan
- Any future financial plans for your business
Step 8: Fill In the Appendix & Supplemental Information
This last section of your SBA business plan should include any additional information that may be helpful for lenders. This can include more detailed explanations or clarifications of data from other sections of your business plan.
Here are some examples of documents you can include:
- Business licenses
- Certifications or permits
- Letters of reference
- Photos of products
- Resumes of business owners
- Contractual agreements and other legal documents
Step 9: Complete the Executive Summary
The executive summary, which is the first section in a business plan, should be no more than one to two pages and provide a high-level overview of the items listed below. Since each section above is already detailed, a brief description of those sections will be sufficient:
- Your company’s mission statement
- The background and experience of your leadership team
- The product or service and what purpose it serves
- Your target market for the product or service
- Competitive analysis of other products and services
- Your competitive advantage or why your company will succeed
- Marketing and sales strategy
- Financial projections and funding needs
Depending on the type of SBA loan you’re applying for, certain areas of your business plan may be weighed more heavily than others. You can learn about the SBA loan options you can choose from in our guide on the different types of SBA loans .
Additional Resources for Writing an SBA Business Plan
If you’re looking for additional resources to help you write a business plan, you can consider the options below. Since a business plan is just one of many documents you’ll need, you can also read our guide on how to get an SBA loan if you need help with other areas of the loan process:
- SBA: SBA’s business guide contains information on how you can start a small business. It includes steps on creating a business plan, funding your company, and launching a business.
- SCORE: Through SCORE, you can request to be paired with a mentor and get business-related education. Educational courses come in several formats, including webinars, live events, and online courses.
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): SBDCs provide training and counseling to small business owners. This can help with various aspects of your company such as getting access to working capital, business planning, financial management, and more. You can use the SBA’s tool to find your closest SBDC .
Having a strong SBA business plan can improve your chances of getting approved for an SBA loan. If you’re unsure where to start, you can use our guide and template to cover the most important aspects of your business. You can also see our tips on how to get a small business loan . To get even more ideas on creating a strong business plan, you can also utilize resources through organizations such as SCORE and the SBA itself.
About the Author

Find Andrew On LinkedIn
Andrew Wan is a staff writer at Fit Small Business, specializing in Small Business Finance. He has over a decade of experience in mortgage lending, having held roles as a loan officer, processor, and underwriter. He is experienced with various types of mortgage loans, including Federal Housing Administration government mortgages as a Direct Endorsement (DE) underwriter. Andrew received an M.B.A. from the University of California at Irvine, a Master of Studies in Law from the University of Southern California, and holds a California real estate broker license.
Join Fit Small Business
Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Select the newsletters you’re interested in below.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Successful Business Plan for a Loan

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
Table of Contents
What does a loan business plan include?
What lenders look for in a business plan, business plan for loan examples, resources for writing a business plan.
A comprehensive and well-written business plan can be used to persuade lenders that your business is worth investing in and hopefully, improve your chances of getting approved for a small-business loan . Many lenders will ask that you include a business plan along with other documents as part of your loan application.
When writing a business plan for a loan, you’ll want to highlight your abilities, justify your need for capital and prove your ability to repay the debt.
Here’s everything you need to know to get started.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
A successful business plan for a loan describes your financial goals and how you’ll achieve them. Although business plan components can vary from company to company, there are a few sections that are typically included in most plans.
These sections will help provide lenders with an overview of your business and explain why they should approve you for a loan.
Executive summary
The executive summary is used to spark interest in your business. It may include high-level information about you, your products and services, your management team, employees, business location and financial details. Your mission statement can be added here as well.
To help build a lender’s confidence in your business, you can also include a concise overview of your growth plans in this section.
Company overview
The company overview is an area to describe the strengths of your business. If you didn’t explain what problems your business will solve in the executive summary, do it here.
Highlight any experts on your team and what gives you a competitive advantage. You can also include specific details about your business such as when it was founded, your business entity type and history.
Products and services
Use this section to demonstrate the need for what you’re offering. Describe your products and services and explain how customers will benefit from having them.
Detail any equipment or materials that you need to provide your goods and services — this may be particularly helpful if you’re looking for equipment or inventory financing . You’ll also want to disclose any patents or copyrights in this section.
Market analysis
Here you can demonstrate that you’ve done your homework and showcase your understanding of your industry, current outlook, trends, target market and competitors.
You can add details about your target market that include where you’ll find customers, ways you plan to market to them and how your products and services will be delivered to them.
» MORE: How to write a market analysis for a business plan
Marketing and sales plan
Your marketing and sales plan provides details on how you intend to attract your customers and build a client base. You can also explain the steps involved in the sale and delivery of your product or service.
At a high level, this section should identify your sales goals and how you plan to achieve them — showing a lender how you’re going to make money to repay potential debt.
Operational plan
The operational plan section covers the physical requirements of operating your business on a day-to-day basis. Depending on your type of business, this may include location, facility requirements, equipment, vehicles, inventory needs and supplies. Production goals, timelines, quality control and customer service details may also be included.
Management team
This section illustrates how your business will be organized. You can list the management team, owners, board of directors and consultants with details about their experience and the role they will play at your company. This is also a good place to include an organizational chart .
From this section, a lender should understand why you and your team are qualified to run a business and why they should feel confident lending you money — even if you’re a startup.
Funding request
In this section, you’ll explain the amount of money you’re requesting from the lender and why you need it. You’ll describe how the funds will be used and how you intend to repay the loan.
You may also discuss any funding requirements you anticipate over the next five years and your strategic financial plans for the future.
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
Financial statements
When you’re writing a business plan for a loan, this is one of the most important sections. The goal is to use your financial statements to prove to a lender that your business is stable and will be able to repay any potential debt.
In this section, you’ll want to include three to five years of income statements, cash flow statements and balance sheets. It can also be helpful to include an expense analysis, break-even analysis, capital expenditure budgets, projected income statements and projected cash flow statements. If you have collateral that you could put up to secure a loan, you should list it in this section as well.
If you’re a startup that doesn’t have much historical data to provide, you’ll want to include estimated costs, revenue and any other future projections you may have. Graphs and charts can be useful visual aids here.
In general, the more data you can use to show a lender your financial security, the better.
Finally, if necessary, supporting information and documents can be added in an appendix section. This may include credit histories, resumes, letters of reference, product pictures, licenses, permits, contracts and other legal documents.
Lenders will typically evaluate your loan application based on the five C’s — or characteristics — of credit : character, capacity, capital, conditions and collateral. Although your business plan won't contain everything a lender needs to complete its assessment, the document can highlight your strengths in each of these areas.
A lender will assess your character by reviewing your education, business experience and credit history. This assessment may also be extended to board members and your management team. Highlights of your strengths can be worked into the following sections of your business plan:
Executive summary.
Company overview.
Management team.
Capacity centers on your ability to repay the loan. Lenders will be looking at the revenue you plan to generate, your expenses, cash flow and your loan payment plan. This information can be included in the following sections:
Funding request.
Financial statements.
Capital is the amount of money you have invested in your business. Lenders can use it to judge your financial commitment to the business. You can use any of the following sections to highlight your financial commitment:
Operational plan.
Conditions refers to the purpose and market for your products and services. Lenders will be looking for information such as product demand, competition and industry trends. Information for this can be included in the following sections:
Market analysis.
Products and services.
Marketing and sales plan.
Collateral is an asset pledged to a lender to guarantee the repayment of a loan. This can be equipment, inventory, vehicles or something else of value. Use the following sections to include information on assets:
» MORE: How to get a business loan
Writing a business plan for a loan application can be intimidating, especially when you’re just getting started. It may be helpful to use a business plan template or refer to an existing sample as you’re going through the draft process.
Here are a few examples that you may find useful:
Business Plan Outline — Colorado Small Business Development Center
Business Plan Template — Iowa Small Business Development Center
Writing a Business Plan — Maine Small Business Development Center
Business Plan Workbook — Capital One
Looking for a business loan?
See our overall favorites, or narrow it down by category to find the best options for you.
on Nerdwallet's secure site
U.S. Small Business Administration. The SBA offers a free self-paced course on writing a business plan. The course includes several videos, objectives for you to accomplish, as well as worksheets you can complete.
SCORE. SCORE, a nonprofit organization and resource partner of the SBA, offers free assistance that includes a step-by-step downloadable template to help startups create a business plan, and mentors who can review and refine your plan virtually or in person.
Small Business Development Centers. Similarly, your local SBDC can provide assistance with business planning and finding access to capital. These organizations also have virtual and in-person training courses, as well as opportunities to consult with business experts.
Business plan software. Although many business plan software platforms require a subscription, these tools can be useful if you want a templated approach that can break the process down for you step-by-step. Many of these services include a range of examples and templates, instruction videos and guides, and financial dashboards, among other features. You may also be able to use a free trial before committing to one of these software options.
A loan business plan outlines your business’s objectives, products or services, funding needs and finances. The goal of this document is to convince lenders that they should approve you for a business loan.
Not all lenders will require a business plan, but you’ll likely need one for bank and SBA loans. Even if it isn’t required, however, a lean business plan can be used to bolster your loan application.
Lenders ask for a business plan because they want to know that your business is and will continue to be financially stable. They want to know how you make money, spend money and plan to achieve your financial goals. All of this information allows them to assess whether you’ll be able to repay a loan and decide if they should approve your application.
On a similar note...
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Why Do I Need a Business Plan?
Sections of a business plan, the bottom line.
- Small Business
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
How to secure business financing
Matt Webber is an experienced personal finance writer, researcher, and editor. He has published widely on personal finance, marketing, and the impact of technology on contemporary arts and culture.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/smda1_crop-f0c167dd2b2144f68f352c63d17f7db5.jpg)
A business plan is a document that explains what a company’s objectives are and how it will achieve them. It contains a road map for the company from a marketing, financial, and operational standpoint. Some business plans are more detailed than others, but they are used by all types of businesses, from large, established companies to small startups.
If you are applying for a business loan , your lender may want to see your business plan. Your plan can prove that you understand your market and your business model and that you are realistic about your goals. Even if you don’t need a business plan to apply for a loan, writing one can improve your chances of securing finance.
Key Takeaways
- Many lenders will require you to write a business plan to support your loan application.
- Though every business plan is different, there are a number of sections that appear in every business plan.
- A good business plan will define your company’s strategic priorities for the coming years and explain how you will try to achieve growth.
- Lenders will assess your plan against the “five Cs”: character, capacity, capital, conditions, and collateral.
There are many reasons why all businesses should have a business plan . A business plan can improve the way that your company operates, but a well-written plan is also invaluable for attracting investment.
On an operational level, a well-written business plan has several advantages. A good plan will explain how a company is going to develop over time and will lay out the risks and contingencies that it may encounter along the way.
A business plan can act as a valuable strategic guide, reminding executives of their long-term goals amid the chaos of day-to-day business. It also allows businesses to measure their own success—without a plan, it can be difficult to determine whether a business is moving in the right direction.
A business plan is also valuable when it comes to dealing with external organizations. Indeed, banks and venture capital firms often require a viable business plan before considering whether they’ll provide capital to new businesses.
Even if a business is well-established, lenders may want to see a solid business plan before providing financing. Lenders want to reduce their risk, so they want to see that a business has a serious and realistic plan in place to generate income and repay the loan.
Every business is different, and so is every business plan. Nevertheless, most business plans contain a number of generic sections. Common sections are: executive summary, company overview, products and services, market analysis, marketing and sales plan, operational plan, and management team. If you are applying for a loan, you should also include a funding request and financial statements.
Let’s look at each section in more detail.
Executive Summary
The executive summary is a summary of the information in the rest of your business plan, but it’s also where you can create interest in your business.
You should include basic information about your business, including what you do, where you are based, your products, and how long you’ve been in business. You can also mention what inspired you to start your business, your key successes so far, and your growth plans.
Company Overview
In this section, focus on the core strengths of your business, the problem you want to solve, and how you plan to address it.
Here, you should also mention any key advantages that your business has over your competitors, whether this is operating in a new market or a unique approach to an existing one. You should also include key statistics in this section, such as your annual turnover and number of employees.
Products and Services
In this section, provide some details of what you sell. A lender doesn’t need to know all the technical details of your products but will want to see that they are desirable.
You can also include information on how you make your products, or how you provide your services. This information will be useful to a lender if you are looking for financing to grow your business.
Market Analysis
A market analysis is a core section of your business plan. Here, you need to demonstrate that you understand the market you are operating in, and how you are different from your competitors. If you can find statistics on your market, and particularly on how it is projected to grow over the next few years, put them in this section.
Marketing and Sales Plan
Your marketing and sales plan gives details on what kind of new customers you are looking to attract, and how you are going to connect with them. This section should contain your sales goals and link these to marketing or advertising that you are planning.
If you are looking to expand into a new market, or to reach customers that you haven’t before, you should explain the risks and opportunities of doing so.
Operational Plan
This section explains the basic requirements of running your business on a day-to-day basis. Your exact requirements will vary depending on the type of business you run, but be as specific as possible.
If you need to rent office space, for example, you should include the cost in your operational plan. You should also include the cost of staff, equipment, and any raw materials required to run your business.
Management Team
The management team section is one of the most important sections in your business plan if you are applying for a loan. Your lender will want reassurance that you have a skilled, experienced, competent, and reliable senior management team in place.
Even if you have a small team, you should explain what makes each person qualified for their position. If you have a large team, you should include an organizational chart to explain how your team is structured.
Funding Request
If you are applying for a loan, you should add a funding request. This is where you explain how much money you are looking to borrow, and explain in detail how you are going to use it.
The most important part of the funding-request section is to explain how the loan you are asking for would improve the profitability of your business, and therefore allow you to repay your loan.
Financial Statements
Most lenders will also ask you to provide evidence of your business finances as part of your application. Graphs and charts are often a useful addition to this section, because they allow your lender to understand your finances at a glance.
The overall goal of providing financial statements is to show that your business is profitable and stable. Include three to five years of income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. It can also be useful to provide further analysis, as well as projections of how your business will grow in the coming years.
What Do Lenders Look for in a Business Plan?
Lenders want to see that your business is stable, that you understand the market you are operating in, and that you have realistic plans for growth.
Your lender will base their decision on what are known as the “five Cs.” These are:
- Character : You can stress your good character in your executive summary, company overview, and your management team section.
- Capacity : This is, essentially, your ability to repay the loan. Your lender will look at your growth plans, your funding request, and your financial statements in order to assess this.
- Capital : This is the amount of money you already have in your business. The larger and more established your business is, the more likely you are to be approved for finance, so highlight your capital throughout your business plan.
- Conditions : Conditions refer to market conditions. In your market analysis, you should be able to prove that your business is well-positioned in relation to your target market and competitors.
- Collateral : Depending on your loan, you may be asked to provide collateral , so you should provide information on the assets you own in your operational plan.
How Long Does It Take to Write a Business Plan?
The length of time it takes to write a business plan depends on your business, but you should take your time to ensure it is thorough and correct. A business plan has advantages beyond applying for a loan, providing a strategic focus for your business.
What Should You Avoid When Writing a Business Plan?
The most common mistake that business owners make when writing a business plan is to be unrealistic about their growth potential. Your lender is likely to spot overly optimistic growth projections, so try to keep it reasonable.
Should I Hire Someone to Write a Business Plan for My Business?
You can hire someone to write a business plan for your business, but it can often be better to write it yourself. You are likely to understand your business better than an external consultant.
Writing a business plan can benefit your business, whether you are applying for a loan or not. A good business plan can help you develop strategic priorities and stick to them. It describes how you are going to grow your business, which can be valuable to lenders, who will want to see that you are able to repay a loan that you are applying for.
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Write Your Business Plan .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Fund Your Business .”
Navy Federal Credit Union. “ The 5 Cs of Credit .”
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Term-b-business-plan-70c26342d5374095b3cd7e860d016168.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
How to Write an SBA Business Plan + Template
Noah Parsons
10 min. read
Updated November 21, 2023
Applying for a Small Business Administration loan typically requires a business plan.
Unfortunately, there’s no SBA loan business plan format that guarantees approval. The SBA even states you should “pick a business plan format that works for you.”
While I agree with this sentiment, I’ve found that entrepreneurs who explain how funds will be used and how they will repay the loan tend to be more successful.
Luckily, these details can be covered using our SBA-lender-approved business plan format . I’ll go over that structure in this article, and focus on the sections that the SBA prioritizes, so you can maximize your chances of getting funded .
You can even download a free SBA-lender-approved business plan template to fill out as you read.
Let’s get started.
- Why you need a business plan for SBA loans
SBA loans require good documentation of your business and personal finances. You’ll need to pull together your past tax returns, bank statements, and various application forms depending on the type of SBA loan you apply for.
The bank issuing the loan will also want to know about the future of your business.
They’ll want to see how the loan will be used and if future cash flow projections are realistic and indicate you can afford loan payments.
That’s where writing an SBA business plan comes in.
Not only will your business plan describe your business to the lender, but it will include the financial projections the bank will use to determine if you qualify for the loan .
- What your business plan should include, according to the SBA
Business plans for SBA loans follow a fairly standard structure, but that doesn’t mean you need to follow it exactly.
The SBA even recommends adjusting the plan outline to serve your needs. If a section does not apply to your business, it’s fine just to remove it.
Here’s the successful business plan structure I recommend for SBA loans:
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
1. Executive summary
A great executive summary is a short, simple overview of your business. It should be easy for a loan officer to read and clearly understand what your business does.
When applying for an SBA loan, highlight your:
- Business opportunity
- Financial forecast
- How much money you want to borrow and how it will be used
Remember, an executive summary should be short and to the point. The rest of your business plan will provide additional details.
[Dig deeper: How to write an executive summary ]
2. Company description
Some people call this section “Products and Services.” Either option is fine. The important thing is that you use this section to explain what your business opportunity is.
You need to cover:
- The problem you solve
- Who you’re solving it for
- What your solution is and why it’s better
Be specific and tell the story of your business and your customers. Focus on your strengths and what sets you apart from competitors.
If your company is developing a product, include information on:
- What the product life cycle looks like
- Intellectual property filings
- Current research and development
If these topics don’t apply to your product, that’s fine. Just be sure that the description of what you sell is clear.
3. Market analysis
The market analysis chapter explains who your customers are. It provides an overview of your target market, competition, and industry.
Your target market is essentially a description of your ideal customers. Be sure to include specific demographic information (like age, gender, location, income) and psychographic information (hobbies, purchasing behaviors).
This data should reinforce that your target market needs your solution .
It’s helpful to also include information on the size of your target market . Lenders will want to see evidence of enough potential customers to drive growth.
While your target market information describes your customers, an industry overview discusses the type of business you’re in and its potential for growth.
For example: If you’re starting a fast-casual restaurant, your industry overview might discuss the increased interest in fast-casual dining and how more people are eating in these types of restaurants every year.
Finally, you’ll need to include a competitive analysis . This is a list of current competitors and alternatives, with explanations of why your business is a better option.
Your goal is to show how your business is unique, what opportunities and threats there are, and how you plan to address the competition.
4. Organization and management
Also known as your company overview, this section is where you describe your legal structure, history, and team .
For your SBA loan application, you should focus on describing who is managing the business as clearly as possible.
You may want to include an organizational chart. You should provide detailed resumes for everyone in leadership positions. Each team member’s experience, skills and professional qualifications can mitigate risk in the eyes of a lender .
To show you’re thinking ahead, it’s also helpful to include key positions you plan to fill as you grow.
5. Sales and marketing plan
Your goal in this section is to summarize how you will attract, retain, and sell to your customers.
The marketing strategies and sales methods you describe should always have the customer top of mind, and demonstrate that you know how to connect with them.
To help a loan officer visualize this, you can provide examples of marketing messaging, visuals, and promotions. If you have any research or results to show that your strategy has merit, include those as well.
6. Financial projections
SBA lenders typically require 5 years of financial projections — including profit and loss statements , balance sheets , and cash flow statements .
Be sure to include the SBA loan in your projections in the following areas:
- A liability on your balance sheet.
- Payments on your cash flow.
- Interest expenses on your profit and loss statement.
I’ll dive into specific details of what you should focus on in the “how to improve your chances” section.
Your first year of financial projections should include monthly details. After that, annual summaries are usually sufficient for most SBA lenders. Occasionally, a lender might require 24 months of monthly projections, so check with your bank before submitting your business plan.
If your business is up and running, you must also provide historical financial reports for the past 12-24 months of operations—including income statements and a current balance sheet.
Typically, you will also need to provide reports on your personal finances , including any assets you have, such as a home or car.
Finally, include a section explaining your use of funds—what exactly you plan to use the loan for.
7. Appendix
The appendix is your chance to provide additional documents that support sections of your business plan.
When applying for a loan, these may include:
- Employee resumes
- Licenses and permits
- Patents and other legal documents
- Historical financial statements
- Credit histories
Don’t worry about stuffing your appendix full of additional documentation. Only include information if you believe it will strengthen your approval chances, or if your lender specifically asks for it.
- How to improve your chances of being approved for an SBA loan
Your SBA business plan needs to focus on the loan you are applying for and how that will impact your business financially.
Make sure to include the following information in your financial plan to increase your chances of success with your lender:
Funding request
In your executive summary, document how much money you are asking for. It’s best to put your number where it can be clearly read, instead of trying to bury it deep within your business plan.
Remember, there are limitations to how much you can borrow through SBA-backed loans. Most have a maximum loan amount of $5 million, while SBA Express loans have a maximum loan amount of $350,000.

Use of funds
You should also describe how you plan to use the loan and which aspects of the business you want to invest in.
Some SBA loans are designed specifically for expanding export businesses or funding real estate transactions. So, make sure your use of funds description is appropriate for the loan you are applying for.
Cash flow forecast
Be sure to include the loan in your cash flow statements and projections . You want to demonstrate that you’ve planned how you will use and repay the loan.
You need to show:
- When you anticipate receiving the loan.
- How the loan will impact your finances.
- Loan payments for the life of the loan.
Having this prepared won’t just increase the chances of your application being approved—It will make it much easier to manage the loan after you receive funding .
Balance sheet
You’ll also want to put the loan on your projected balance sheet , and show how the loan will get paid down over time.
The money you owe will show up on your balance sheet as a liability, while the cash you receive from the loan will be an asset. Over time, your forecasted balance sheet will show that the loan is getting paid back.
Your lender will want to see that you have forecasted this repayment properly.
Profit & Loss forecast
Your P&L should include the interest expenses for the loan, and show how the interest will impact your profitability in the coming months and years.
- How long does an SBA business plan need to be?
The SBA doesn’t have an official recommended or required business plan length . As a general rule of thumb, you should make your business plan as short and concise as possible.
Your business plan is going to be reviewed by a bank loan officer, and they will be less than excited about the prospect of reading a 50-page business plan.
If possible, keep the written portion of your business plan between 10-15 pages. Your financial forecasts will take up several additional pages.
If you’re struggling to keep it short, try a one-page plan
A great way to start your business plan is with a simple, one-page business plan that provides a brief and compelling overview of your business.
A good one-page plan is easy to read and visually appealing. Once you have your one-page plan, you can expand on the ideas to develop your complete written business plan, and use the one-page plan as your executive summary.
Loan officers will appreciate a concise overview of your business that provides the summary they need before they start looking at your complete business plan and financial plan .
- Resources and tools for writing an SBA business plan
Remember, you can download a free SBA-lender-approved business plan template . It includes detailed instructions to help you write each section, expert guidance and tips, and is formatted as lenders and investors expect.
If you’re looking for a more powerful plan writing tool, one that can also help you create financial forecasts for the use of your loan, I recommend you check out LivePlan .
With LivePlan, you get:
- AI-powered recommendations: Generate and rewrite sections of your plan to be more professional and persuasive.
- Step-by-step instructions: In-app examples, tutorials, and tips to help you write an impressive business plan.
- Automatic financials: Skip the spreadsheets and complex formulas, and quickly create accurate financial forecasts with everything a lender needs.
- A built-in pitch presentation: Print or share your full business plan, one-page pitch, and financial reports—all with a professional and polished look.
Whether you use the template, LivePlan, or try writing a business plan yourself, following the structure and tips from this article will improve your chances of getting an SBA-backed loan.
And for additional SBA-focused resources, check out our guide on how to get an SBA loan .
Create a business plan that maximizes your chances of securing funding
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

12 Min. Read
10 Reasons You Don’t Qualify for an SBA Disaster Loan

6 Min. Read
What to Do When You Need a Disaster Loan

4 Min. Read
The Different SBA Loan Programs Explained
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Common Scams
- Business Guidance >
How to write a business plan
- Starting Up
A robust business plan is crucial to the success of your new business.
A well-written business plan is important when you’re about to start a business opens in new window .
A business plan is a document that gets to the heart of what your business does, how it works and – most importantly – what makes it different and what will help it succeed.
A good business plan should:
- explain your business objectives opens in new window ;
- be a roadmap that can help you achieve your business objectives;
- highlight potential problems so that you can avoid them impacting on the business;
- identify opportunities and gaps in the market opens in new window ;
- detail shortcomings such as running out of money;
- provide information to help secure a loan or investment opens in new window .
A business plan should be a living document.
Rather than file it away, use it to monitor progress and keep your new business on track.
Starting a business doesn’t come with a set of instructions.
We know that understanding the many different types of financial product in the marketplace can be difficult.
Our Making business finance work for you guide is designed to help you make an informed choice about accessing the right type of finance for you and your business.
Download your free copy
Writing your business plan
This guide will help you research opens in new window and write a good business plan.
It covers presentation and the audience you are writing for, the sections and information to include.
- Business Plan Structure – How to structure and order your business plan, and how long it should be.
- How to approach writing a business plan – Writing for your audience and what your plan should include.
- Business objectives – How to define your business goals over the short, medium and long term.
- Skills and experience – How to detail your experience, and how you’ll tackle any skills gaps opens in new window .
- Target customers – Who your customers are, and what your pricing approach opens in new window is.
- Market and competitors – How to analyse competitors opens in new window and identify market trends.
- Sales and marketing – What promotional activities you’ll use to attract customers opens in new window .
- Operational plans – How to define staffing opens in new window and premises needs opens in new window .
- Financials – What financial information to include, such as breakeven points and margin.
- Appendix – What to put in the appendix at the back of your plan.
1. Business plan structure
It’s important to get the structure right.
Make sure your plan is readable, clear, and easy to understand – and base your content on evidence.
To see a detailed example of a business plan structure, download our free business plan template opens in new window .
- Length – Keep the length to a 15-minute skim read, including only essential information. Put additional detail in the appendix for further reading.
- Executive summary – This appears at the beginning of the Business Plan and should be the last thing you write, summarising everything that is covered in the Business Plan. This includes the business opportunity, customer need, your business proposition and why it will be different in the market.
- Structure – Keep everything simple, using short paragraphs and bullet points, and include relevant graphs and tables, if appropriate. If using statistics, list the source of the information.
- Language – Avoid technical jargon and ‘management speak’, sticking to clear, concise language in plain English. Get a friend to proof read it for spelling errors and to highlight parts that aren’t clear.
Some things are best left out of a good business plan.
Avoid fancy graphics, needless animation and distracting sound effects.
Use readable font sizes – too much small text can make your plan hard going.
2. How to approach writing a business plan
The foundation of any good business plan is research.
You’ll need to find out about your market opens in new window , calculate revenue forecasts opens in new window , and learn about target customers opens in new window .
A good business plan should answer crucial questions about your business.
- Work backwards – Start with your business goals or when you think that your business will start making money, and work back to figure out what you need to do to make your business profitable.
- Be realistic – Make the financials realistic, and look at worse case scenarios so you get a view of what could go wrong and what you would need to do to put things right.
- Be honest – Highlight weaknesses in the market and your business, then detail how you’ll address them and include that in the plan.
- Review the plan – Read the plan from your audience’s perspective, and double-check assumptions. Are they realistic, what could go wrong, and how would you handle a problem that cropped up?
3. Business Objectives
Business objectives opens in new window summarise what your business does and what it offers.
This section should be no longer than a few paragraphs or a single slide, providing a top-level summary of your business.
- Define your business – What does your business do? What services does it provide? opens in new window Who will access it and how much will you charge?
- Be specific – Avoid generic, one-word descriptions such as ‘ hair dressing ’ or ‘plumbing’.For example: Instead of simply writing ‘” Dog grooming opens in new window “, a better description would be: “This is a mobile dog grooming business, delivering grooming services, nutrition and exercise advice to dog owners throughout Hertfordshire. Our fleet of dog spa vans provide tailored treatments using only organic products to your doorstep.”
- Short term objectives – List what your business will achieve in the next year, or its first year of operation.
- Medium – long term objectives – What are the business goals including financial targets in the next one to two years?
Use S.M.A.R.T. objectives to help set your business goals – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Timely – and list both financial and non-financial goals, such as the impact it will have on customers and how your brand will be viewed opens in new window .
For help with setting goals, read our guide on setting business aims and objectives opens in new window .
4. Skills and experience
It’s important to show how your previous experience and skills opens in new window make you qualified to start your business.
A few lines on your experience and skills is useful here.
It’s a good idea to attach your CV as an appendix to the business plan for additional information too.
Remember to
- List relevant experience that directly relates to the new business, along with key skills that will be helpful for your start up.
- List relevant education, courses and transferrable skills such as bookkeeping opens in new window or using Microsoft Office. Explain how they’re relevant.
- Be honest about skills and experience that you lack. Explain how you’ll address this, such as training opens in new window , hiring specialist staff opens in new window or outsourcing elements opens in new window of your business.
5. Target customers
Customers are the heart of any business plan.
It’s essential to show that you understand potential customers and know what they’re looking for from your products and services.
There’s a variety of ways to learn opens in new window about your target customers, including online research, focus groups and surveys.
This information will allow you to choose the right marketing channels opens in new window to offer the ideal product at the right price.
- Include customer demographics – Summarise gender, age and average income or expenditure.
- Location, location, location – If your business is based on footfall, such as a coffee shop opens in new window , or it covers a geographic area such as mobile dog grooming, detail the location of your customers. If it’s an online business opens in new window , your reach might be nationwide, but again show the target demographic, e.g. 18 -30 male and female.
- Addressable market – What is the total size of the customer base opens in new window that would be interested in your business? For example: The addressable market opens in new window for a dog grooming business would be all dog owners in the UK that spend money to groom their pets.
- Target market – Within the addressable market, identify the number of customers your business can target opens in new window . These are customers your business can realistically reach via marketing opens in new window , and is usually constrained by location, pricing and the reach of your marketing activities.
- Customer segmentation – How would you describe large groups of your customers? What are their characteristics? How do they buy products similar to yours? For example: Dog owners who spend lots on grooming and pet services and are willing to pay for luxury treatments could be labelled ‘pampered owners’. By identifying customer groups, you can develop a service that meets their needs (in this case, luxury dog grooming services) at prices they’re willing to pay opens in new window .
- Customer need – Explain in a paragraph the problems faced by the customer, what solution your business will provide, and the benefits of that solution to the customer. For example: Many families living in England have children with gluten intolerance who can’t eat the majority of school snacks, and there are few affordable alternatives available. This business helps parents by offering a range of gluten free, affordable school snacks with packaging that’s fun for kids. This results in happy, healthy children and removes the stress parents feel when packing lunchboxes.
- Set pricing – What will your business charge for products and services opens in new window ? Show how you figured out pricing, examining costs and how much customers are willing to pay. Detail how your pricing stacks up against competitors opens in new window . Is it lower or higher? Why would customers pay more? How can you afford to price it less? Remember being cheaper isn’t always the best way to start a business.
For methods to find out more about your customers, read our guide to market research techniques opens in new window .
6. Market and competitors
Use your business plan to examine the market opens in new window that you’ll be operating in.
Knowing what’s happening in your market, which competitors you need to monitor opens in new window , and their strengths and weaknesses, lets you exploit gaps in the market that will help your business succeed.
This is your chance to show that you really understand your market and ensure your business is able to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
This section should include:
- Market overview – Describe the general market in a few paragraphs, highlighting trends and developments that could be an opportunity. Trends include sales growth opens in new window , new technology, greater efficiencies or new routes to market. Developments may include new regulation or legal requirements opens in new window .
- Market research – Describe briefly the research you’ve carried out, such as surveys, online research, mystery shopping or attending trade shows. Please don’t carry out your research with family and friends – use an unbiased source.
- Competitor overview – Who are the main competitors in your market? Write a short summary for each main competitor. You can include details such as market share, their products, pricing, how many customers that you think that they have, and their marketing activity.
- SWOT analysis – For each competitor and your business, conduct a SWOT analysis opens in new window . This is short for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats.

What are the strengths and weaknesses of your business? How will you address these? What are the future threats that could hurt your business, and where are there potential opportunities?
It’s worth spending some time thinking about the SWOT analysis, and put the SWOT into the main body of the business plan – even the weaknesses!
- Your unique differentiator – What is different about your business compared to the competitors you’ve listed? What weaknesses does your business exploit and how will that attract customers? Explain how and why your business is different in a paragraph.
7. Sales and marketing
How you position your products or services is critical to its success.
This section of a business plan should explain how you’ll reach your customers, how you’ll sell to customers opens in new window and your marketing goals.
- How you’ll reach your customers – What marketing channels opens in new window will you use to reach your customers? Look at where competitors advertise or promote their business. List two or three key channels you can use, and summarise the activity and results you expect these channels to achieve.
- Detail your sales processes – How will you sell your products or services, for example, will you take orders over the internet in a shop opens in new window or provide quotes for your service personally? What are the costs involved in selling? What is the average revenue per sale that you expect?
- What is your key message? – Examples could be great customer service opens in new window , more features or a higher-quality product. How will you communicate that message in your marketing activity?
If you’re starting out in marketing and advertising, you can find advice in our guide on how to advertise your business opens in new window .
8. Operational plans
The operational section concerns how your business will work, what staffing you’ll need opens in new window , where you’ll operate from opens in new window , and the suppliers you’ll use opens in new window .
You’ll need to explain your reasoning behind each one, as well as include details such as salaries and information about your supply chain opens in new window .
- Supply chain – Good suppliers can help your business grow opens in new window , while bad suppliers can create cash flow opens in new window and operational difficulties. Research potential suppliers and shortlist the best opens in new window . What are the risks in using them,? Create a short list of intended suppliers and the relationship you have with them.
- Management – Identify the key roles in your business during start up. How will you recruit to fill the roles? Create a diagram showing the management structure, and list salaries and recruitment costs. Have they made an investment in the business?
- Staffing – What staff do you need opens in new window ? What productivity do you need from staff, such as the number of customers a staff member can serve in an hour? Provide a summary of the roles, and link to details such as salaries, working hours, activity levels opens in new window and hiring costs in the appendix.
- IT, systems and machinery – Explain the IT and infrastructure requirements of your business, such as costs involved in buying machinery and IT platforms. How long would development take and cost? Budget for buying office equipment opens in new window , and include details of information management systems opens in new window , bookkeeping, stock and quality control systems.
- Premises – Where will your business operate from? Explain your reasoning, including any specialist facilities. If you’re running a business such as a shop opens in new window , explain why you’ve selected this location. Costs related to premises can be included in the cash flow forecast.
- Legal and regulatory – If applicable, identify any regulatory authorisations, permissions, or requirements opens in new window that apply to your business, such as planning permission or food safety requirements if opening a restaurant.
- Insurance – What insurance does your business need opens in new window ? Detail who supplies it, what it covers and how much it costs. If you don’t need insurance, explain how you would handle an operational crisis.
- Risks – What could stop your business operating?
9. Financials
Financials underpin your business plan with hard numbers.
If you’re already trading, you’ll be able to use historic revenue data to forecast the profit and loss of your business opens in new window .
If you’re a start up, you’ll need to explain your assumptions and show evidence in your financial forecasts.
Complete a cash flow forecast opens in new window and include it in the appendix.
- Show historic figures – If you’re already trading, show your business activity over the past 6 months in an ‘actual’ cash flow.
- Create a one-year forecast – Show all costs the business needs to start up. Include an explanation of key assumptions such as pricing and the cost of equipment or machinery needed.
- Be realistic about funding – Identify the start up costs needed opens in new window to get your business off the ground. Explain what funding your business will need, what it will be used for, and what type of funding opens in new window you require. Include repayments of any loans opens in new window you are intending to take out.
- Risks and exit strategy – What are the risks to your financial assumptions? How will you manage these risks? If it goes wrong, what is your exit strategy from the market?
For help with working out your launch costs, read our guide on how to calculate business start up costs. opens in new window.
10. Appendix
It’s a good idea to put further detail in the appendix, and refer to it throughout the business plan.
Assumptions explained in detail:
- CV and details about senior managers or business owners
- Market research information, such as survey results
- Insurance opens in new window and regulatory information
- Cash flow forecast opens in new window
Thinking of starting a business? Check out our free online courses in partnership with the Open University on being an entrepreneur.
Our free Learn with Start Up Loans courses opens in new window include:
- Entrepreneurship – from ideas to reality
- First steps in innovation and entrepreneurship opens in new window
- Entrepreneurial behaviour opens in new window
Plus free courses on finance and accounting, project management, and leadership.
Reference to any organisation, business and event on this page does not constitute an endorsement or recommendation from the British Business Bank or its subsidiaries, or the UK Government. Whilst we make reasonable efforts to keep the information on this page up to date, we do not guarantee or warrant (implied or otherwise) that it is current, accurate or complete. The information is intended for general information purposes only and does not take into account your personal situation, nor does it constitute legal, financial, tax or other professional advice. You should always consider whether the information is applicable to your particular circumstances and, where appropriate, seek professional or specialist advice or support.
Feeling Inspired?
You might also like:
- How to buy a small business
- How to decide to take commercial risks as an entrepreneur
- Eight sports-based businesses to start in 2024
Free Startup Business Plan Templates and Examples
By Joe Weller | May 6, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up a variety of the top, professionally designed startup business plan templates, all of which are free to download in PDF, Word, and Excel formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find a one-page startup business plan template , a business plan outline template for startups , a startup business planning template with a timeline , and a sample startup business plan .
Startup Business Plan Template

Download Startup Business Plan Template - Word
Word | Smartsheet
This startup business plan template contains the essential components you need to convey your business idea and strategy to investors and stakeholders, but you can customize this template to fit your needs. The template provides room to include an executive summary, a financial overview, a marketing strategy, details on product or service offerings, and more.
One-Page Startup Business Plan Template
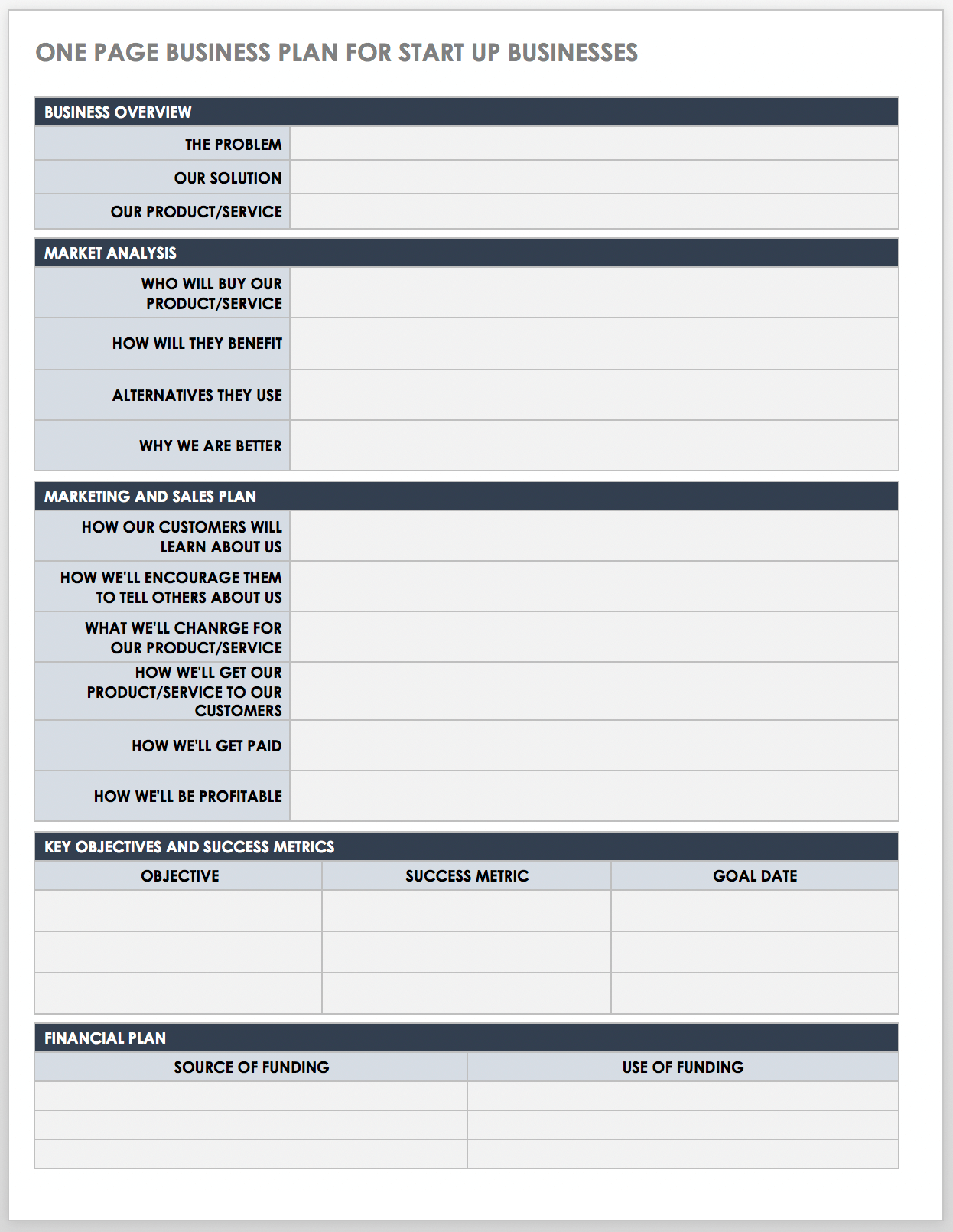
Download One-Page Startup Business Plan Template
Excel | Word | PDF
This one-page business plan is ideal for startup companies that want to document and organize key business concepts. The template offers an easy-to-scan layout that’s ideal for investors and stakeholders. Use this plan to create a high-level view of your business idea and as a reference as you flesh out a more detailed roadmap for your business.
For additional resources, visit " Free One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide ."
Simple Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Template for Startups
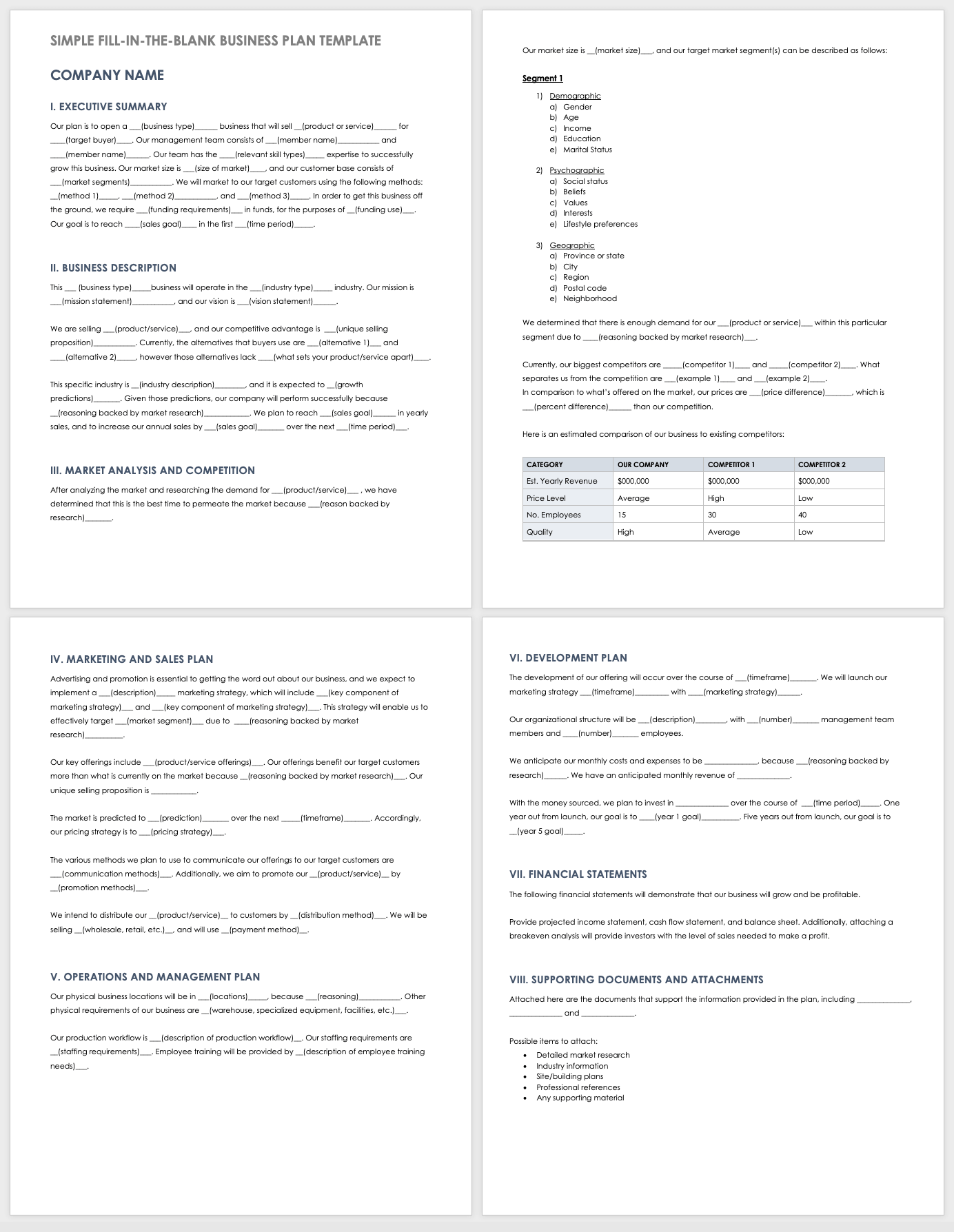
Download Simple Fill-in-the-Blank Business Plan Template for Startups
This comprehensive fill-in-the-blank business plan template is designed to guide entrepreneurs through the process of building a startup business plan. This template comes with a customizable cover page and table of contents, and each section includes sample content that you can modify to fit the needs of your business. For more fill-in business templates, read our "Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates" article.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
This Lean business plan template takes a traditional business plan outline and extracts the most essential elements. Use this template to outline your company and industry overview, convey the problem you are solving, identify customer segments, highlight key performance metrics, and list a timeline of key activities.
Business Plan Outline Template for Startups

Download Business Plan Outline Template for Startups
You can use this business plan outline as a basis to create your own business plan. This template contains all the elements of a traditional business plan, including a title page, a table of contents, and information on what to include in each section. Simplify or expand this outline based on the size and needs of your startup business.
Startup Business Planning Template with Timeline
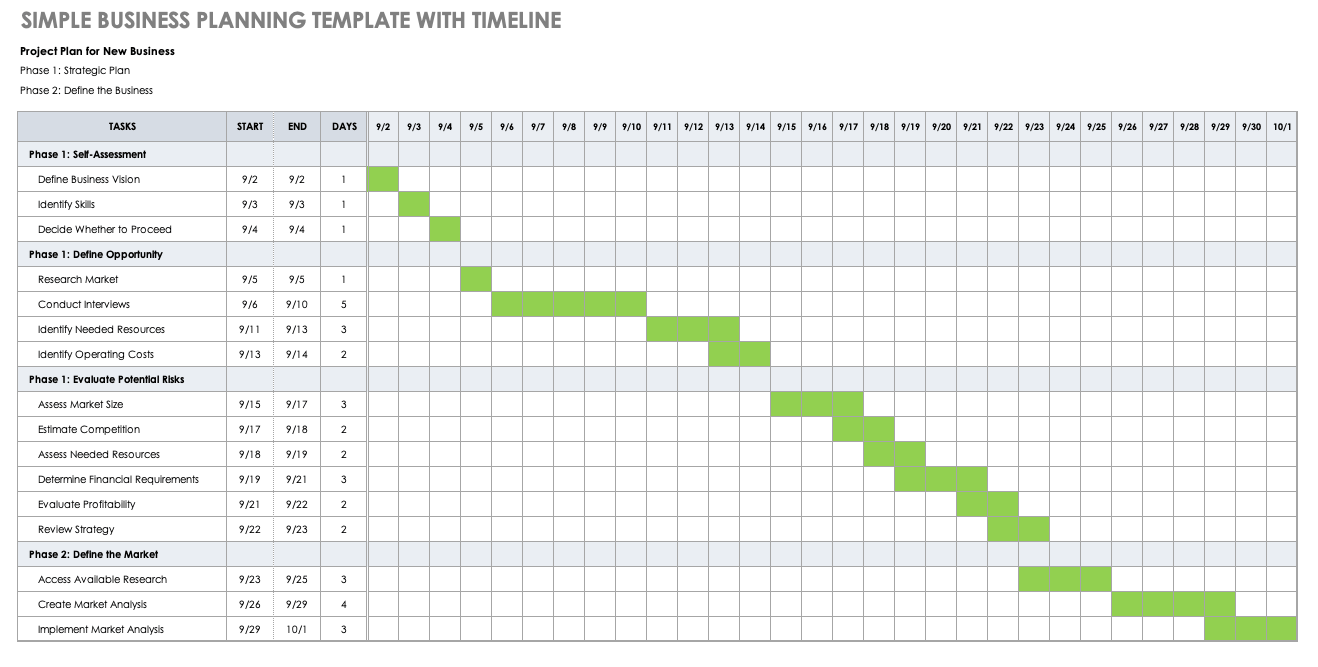
Download Startup Business Planning Template with Timeline
Excel | Smartsheet
As you create your business plan, this business planning template doubles as a schedule and timeline to track the progress of key activities. This template enables you to break down your plan into phases and provides space to include key tasks and dates for each task. For a visual timeline, shade in the cells according to each task’s start and end dates. The timeline ensures that your plan stays on track.
Business Plan Rubric Template for Startups
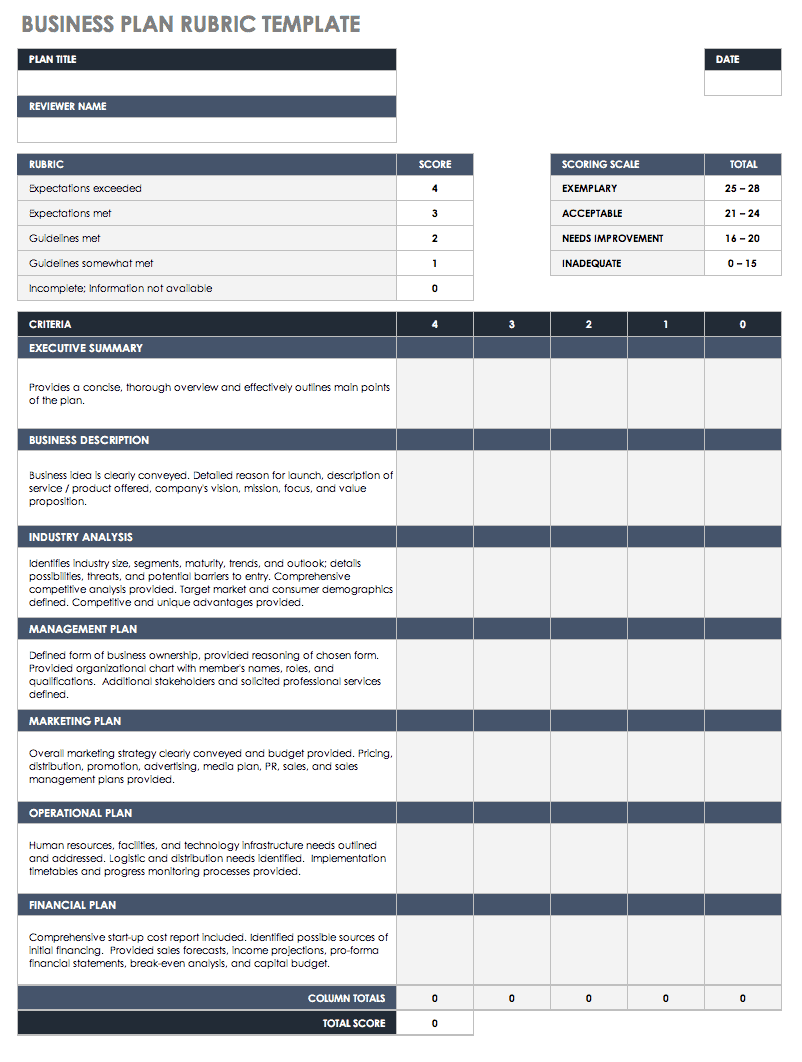
Download Business Plan Rubric Template for Startups
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
If you’re starting a business and want to keep all your ducks in a row, use this rubric to evaluate and score each aspect of your startup business plan. You can tailor this template to the needs of your specific business, and can also highlight areas of your plan that require improvement or expansion. Use this template as a tool to make sure your plan is clear, articulate, and organized. A sharp, insightful, well thought-out plan will definitely get the attention of potential investors and partners.
For additional resources to help support your business planning efforts, check out “Free Startup Plan, Budget, and Cost Templates.”
What’s the Best Business Plan Template for Startups?
The template you choose for your startup business depends on a number of factors, including the size and specific needs of your company. Moreover, as your business grows and your objectives change, you will need to adjust your plan (and possibly your choice of template) accordingly.
Some entrepreneurs find it useful to use a Lean business plan template design in order to jot down a business concept and see if it’s feasible before pursuing it further. Typically one to three pages, a Lean business plan template encourages you to highlight core ideas and strategic activities and remain focused on key points.
Other entrepreneurs prefer a template with a more traditional business plan design, which allows you to go into greater detail and ensure you include every detail. A traditional plan can range from 10 to 100 pages and cover both the high-level and granular particulars of your overall concept, objectives, and strategy.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution, but the following section outlines the minimum that your business plan template should include in order to gain buy-in from potential investors.
What to Include in a Startup Business Plan
Whether you choose to use a template to develop your startup business plan or decide to write one from scratch, you need to include the following elements:
- An overview of your company and the industry in which it operates
- The problem you are solving and the proposed solution
- A description of your product or service offerings, including key features
- The existing alternatives that customers use and your competitive advantage
- The target customer segments and the channels you will use to reach them
- The cost structure and revenue streams associated with your business
- A financial plan, including sales and revenue projections (ideally 3-5 years)
- If applicable, the financial requirements to get your business running, including how you will source and allocate funds
Each of the following sections provides an example of a business plan that you can use for reference as you develop your own.
One-Page Lean Business Plan Example
This Lean business plan example displays a visually appealing and scannable one-page illustration of a business plan. It conveys the key strategies you need to meet your main objectives. Each element of this concise plan provides stakeholders and potential investors with links to resources that support and expand upon the plan’s details, and it can also serve as an investor pitch deck.
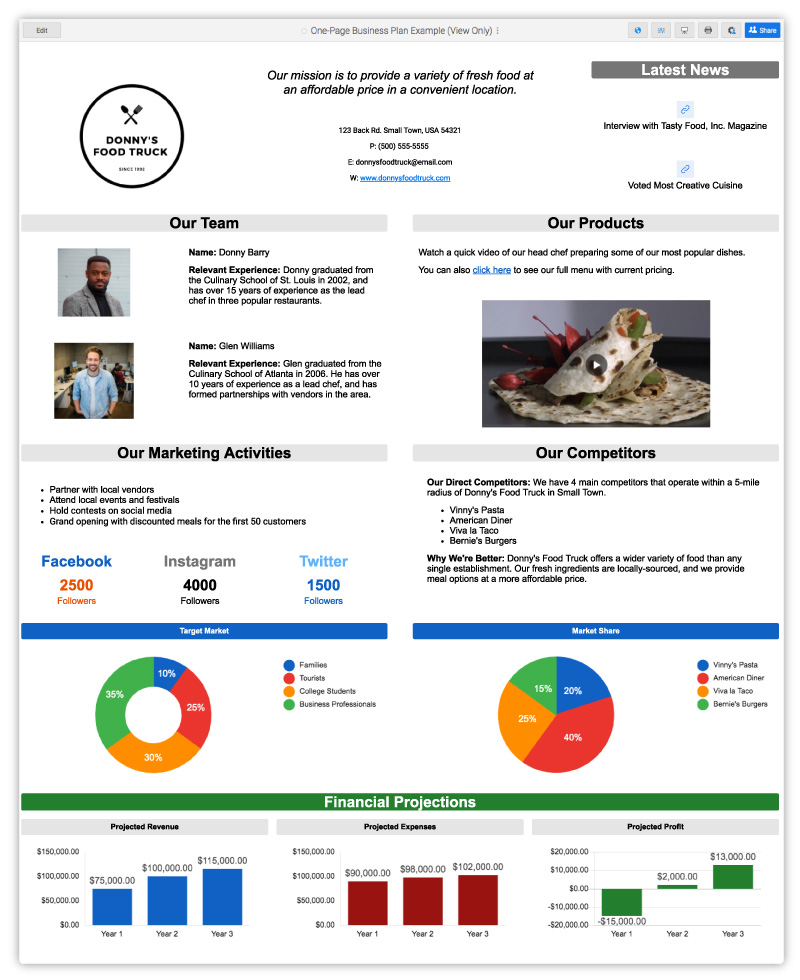
Startup Business Plan Sample
This business plan sample contains all the aspects of a standard business plan. Using a fictional food truck business as the basis for a startup business plan, this sample will give you all the ideas you need to make your plan outstanding.
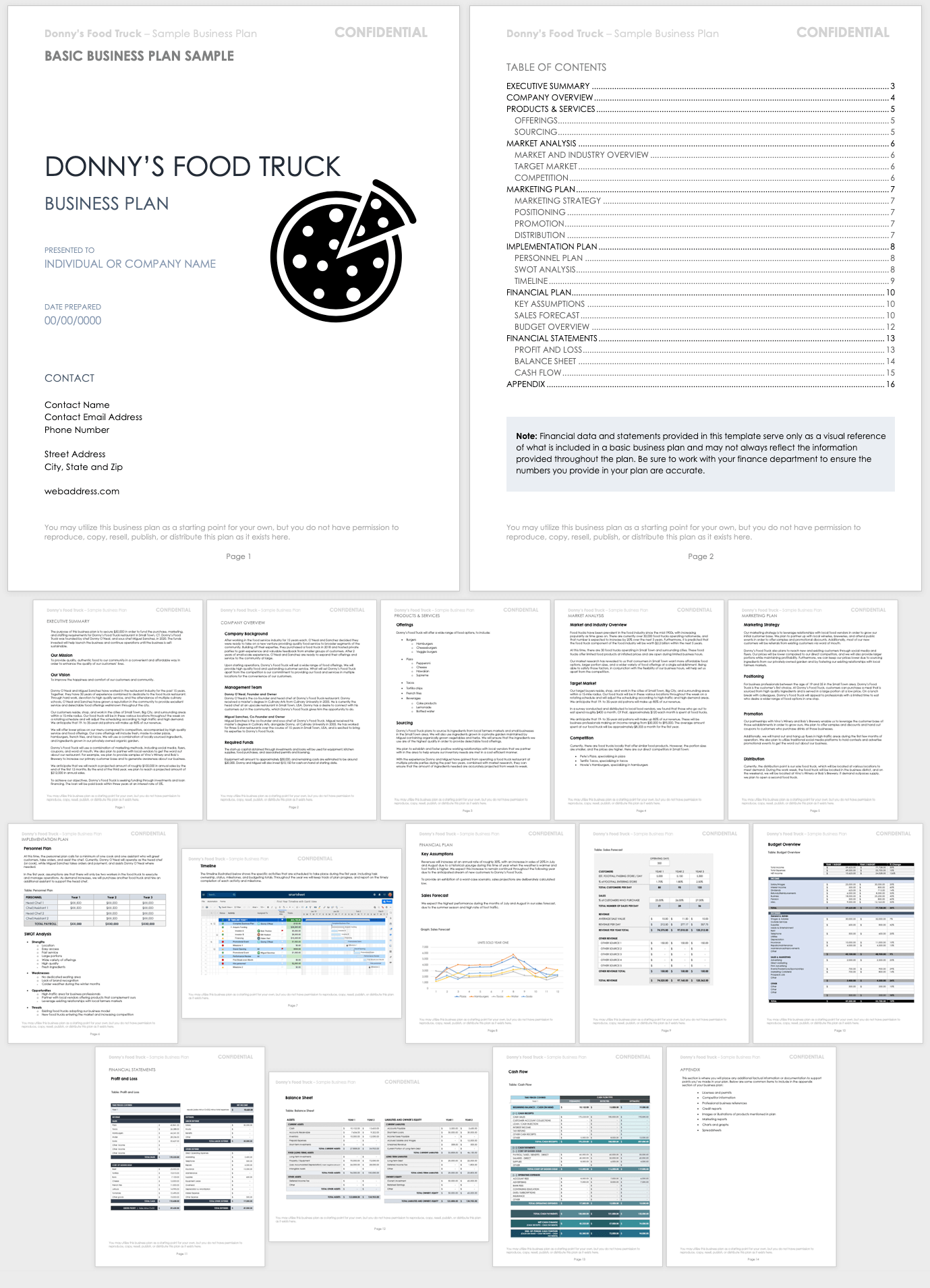
Download Startup Business Plan Sample - PDF
When the time comes that you need more space to lay out your goals and strategies, choose from our variety of free simple business plan templates . You can learn how to write a successful simple business plan here .
Visit this free non-profit business plan template roundup or of you are looking for a business plan template by file type, visit our pages dedicated specifically to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates. Read our articles offering free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options.
Top 10 Tips to Create a Startup Business Plan
Putting together a business plan can be overwhelming and time consuming, especially if you aren’t sure where to begin. Below, we share tips you can use to help simplify the process of developing a startup business plan of your own.
- Use a business plan template, or begin with a business plan outline that provides all the elements of a standard plan to get your ideas down on paper in a structured manner. (You can choose from the selection of templates above.)
- Remove sections from your outline that aren’t relevant or that aren’t necessary to launch and operate your business.
- Compile the data you have gathered on your business and industry, including research on your target market and product or service offerings, details on the competitive landscape, and a financial plan that anticipates the next three to five years. Use that information to fill in the sections of your plan outline.
- Get input and feedback from team members (e.g., finance, marketing, sales) and subject matter experts to ensure that the information you’ve included in the plan is accurate.
- Make certain that the objectives of your plan align with marketing, sales, and financial goals to ensure that all team members are moving in the same direction.
- Although this section of the plan comes first, write the executive summary last to provide an overview of the key points in your business plan.
- Prepare a pitch deck for potential clients, partners, or investors with whom you plan to meet in order to share vital information about your business, including what sets you apart and the direction you are headed.
- Who are the founders and management executives, and what relevant experience do they bring to the table?
- What is the problem you are solving, and how is your solution better than what currently exists?
- What’s the size of the market, and how much market share do you plan to capture?
- What are the trends in your market, and how are you applying them to your business?
- Who are your direct competitors, and what is your competitive advantage?
- What are the key features of your product or service that set it apart from alternative offerings, and what features do you plan to add in the future?
- What are the potential risks associated with your business, and how do you plan to address them?
- How much money do you need to get your business running, and how do you plan to source it?
- With the money you source, how do you plan to use it to scale your business?
- What are the key performance metrics associated with your business, and how will you know when you’re successful?
- Revisit and modify your plan on a regular basis as your goals and strategies evolve.
- Use a work collaboration tool that keeps key information across teams in one place, allows you to track plan progress, and captures updates in real time.
Successfully Implement Your Startup Business Plan with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
- Sample Business Plans
Startup Business Plan

Why Choose a Traditional Business Plan?
Startups are very different from established businesses. The most obvious reason is that startups don’t have any previous data on how to run their business. This is precisely why a traditional business plan will work for any startup.
There are some vital differences between a traditional business plan and a simple business plan. These differences exist due to several reasons:
- Lack of a definite business model In the early stages, it’s difficult to state the structure of your business model because your business idea and its execution are still in the testing phase. Only after a certain period of trial and error, you would be able to describe your business model.
- No performance history While creating financial projections, an established company examines its credit history, past sales, revenue, expenditure, and growth rate. In contrast, a startup needs to begin with assumptions. You have to predict sales, costs, expenses, growth rate, etc. To increase the accuracy of your predictions, you need to gather reliable factual data to back your predictions.
- Increased risk Startups have an increased risk factor compared to established businesses. This is because startups lack a loyal customer base, an expert team, brand recognition, etc. Devise strategies to overcome the potential risks and challenges that may come your way in the future.
These are the reasons why you need a dedicated business plan for your startup that helps focus on the essential elements while setting up your business.
Before you start writing your business plan, go through the below checkpoints to make sure you are ready for it.
Tips to Create a Business Plan for Your Startup
Writing your first business plan can be overwhelming and confusing. However daunting it may seem, it is still something you can’t avoid.
- Use a startup business plan template: It can be hard to start from scratch, especially when you are unsure of where to begin. A business plan template helps you get started quickly. You can use it to navigate and structure your plan according to your standards
- Tailor your plan: After choosing a template, it is essential to customize it to your business requirements. Remove sections that are irrelevant and create your business plan based on the purpose you need it for. For instance, if you are building a business plan to get funding, the financial section of your business plan needs more emphasis.
- Research thoroughly: Every section of your business plan needs extensive research. Collect data about your market, industry, and competitors. Study their pricing strategies and market trends. Run surveys and talk to your potential customers to understand their needs and problems.
- Compose according to your objectives: It can be easy to lose sight of your objectives and get lost in the process of writing your business plan. To avoid that, make sure that your marketing strategies, operations, and financial goals are aligning with your business objectives.
- Ask for feedback: Once you finish creating a business plan, get your team and various experts to provide your feedback. This helps you revise and make adjustments to your plan before presenting it to an investor or client.
- Be prepared to answer questions: Before you present your startup business plan, it is crucial to prepare yourself to answer any questions related to your plan. It can be because the reader of your business plan may not understand a specific topic or want to test your knowledge. Regardless, keep yourselves informed and ready.
Download a sample startup business plan
Need help writing your business plan from scratch? Here you go; download our free startup business plan pdf to start.
It’s a modern business plan template specifically designed for your house-flipping business. Use the example business plan as a guide for writing your own.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.

In conclusion, a business plan is an extremely handy device to get the best out of your efforts if you use it the right way. Planning your business involves consideration of several aspects that make up your business like the type of your industry, the stage of your business, the number of competitors, market size, etc.
Nonetheless, business planning always acts as a plus while tackling the challenges your business will face. It provides you with a proper structure to deal with your business problems head-on.
So, are you thinking of starting your own business? Then go ahead and start planning!
After getting started with Upmetrics , you can copy this startup business plan template into your business plan, modify the required information, and download your startup business plan pdf or doc file. It’s the fastest and easiest way to start writing a business plan for your new startup.
Related Articles On Business Plan Writing
- How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
- Deciding the Ideal Length of Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Your Business Plan
- Browse Through 400+ Free Business Plan Examples
- How to Design a Detailed Table of Contents for Your Business Plan
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

Original text

Do you want to increase the odds that your business startup will be a success? Download this step-by-step business plan template to lay the groundwork for your new business.
Writing a business plan allows you to carefully think through every step of starting your company so you can better prepare and handle any challenges. While a thorough business plan is essential in the financing process, it's helpful even if you don’t need outside financing.
Creating a business plan can:
- Help you discover any weaknesses in your business idea so you can address them before you open for business
- Identify business opportunities you may not have considered and plan how to take advantage of them
- Analyze the market and competition to strengthen your idea
- Give you a chance to plan strategies for dealing with potential challenges so they don’t derail your startup
- Convince potential partners, customers, and key employees that you’re serious about your idea and persuade them to work with you
- Force you to calculate when your business will make a profit and how much money you need to reach that point so that you can be prepared with adequate startup capital
- Determine your target market and how to reach them
A detailed, step-by-step plan gives you a blueprint you can refer to during the startup process and helps you maintain momentum.
What this business plan template includes
Writing a business plan for a startup can sometimes seem overwhelming. To make the process easier and more manageable, this template will guide you step-by-step. The template includes easy-to-follow instructions for completing each business plan section, questions to help you think through each aspect, and corresponding fillable worksheet/s for critical sections.
After you complete the 11 worksheets, you will have a working business plan for your startup to show your SCORE mentor .
Business plan sections covered in this template:
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Products and Services
- Marketing Plan
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organization
- Startup Expenses and Capitalization
- Financial Plan
The Appendices include documents that supplement information in the body of the plan. These might be contracts, leases, purchase orders, intellectual property, key managers’ resumes, market research data or anything that supports assumptions or statements made in the plan.
The last section of the template, “Refining Your Plan,” explains ways to modify your plan for specific purposes, such as getting a bank loan, or for specific industries, such as retail or manufacturing.
Complete the Business Plan Template for a Startup Business to create a working business plan for your startup.
Then, contact a SCORE mentor to review and refine your plan online or in person.
Quick Start Business Plan The aim of this module is to give you the tools, direction and ideas you need to build a business plan. If you're starting a business then a business plan is essential, because it forces you to think through your ideas and options.
10 Business Planning Tips for Starting a Business In this webinar, you'll learn 10 business planning tips to help you start your entrepreneurial journey on the right path.
Business Plan 101: Sales & Marketing The sales and marketing section of your business plan describes how you intend to sell your product. Learn what you should include in this section.
Copyright © 2024 SCORE Association, SCORE.org
Funded, in part, through a Cooperative Agreement with the U.S. Small Business Administration. All opinions, and/or recommendations expressed herein are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the SBA.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Completing your Start Up Loan application. Download our free template to help you organise your thoughts and develop your plans. You wouldn't build a house without a detailed blueprint of your plans, a set of tools and a clear idea of the costs. We feel the same way about building a business. That's why we require our applicants to provide ...
This section is the most important for most businesses, as it can make or break a lender's confidence and willingness to extend credit. Always include the following documents in the financial ...
Your Start Up Loan: Describe how you will use your Start Up Loan and how it will help you achieve these objectives: This question is designed to help us understand why you need a Start Up Loan and how it will help you move your business forward. 2. Your skills and experience
Step 7: Write the Financing Request. This section is where you should specify how much funding you need, why you need it, what you'll use it for, and the impact you expect it will have on your business. It's also a good idea to indicate when you expect to use the funds over the course of the next three to five years.
Character. A lender will assess your character by reviewing your education, business experience and credit history. This assessment may also be extended to board members and your management team ...
An SBA business plan template is the document you must hand into the bank or credit union when requesting a loan for a start-up business. The US Small Business Administration (SBA), a government agency that backs small businesses, provides guidance and other assistance. As such, this document is crucial to convincing them and loan agencies that ...
Here are a few business plan examples that you may find helpful: Sample business plan outline; Small business plan template; Comprehensive business plan writing; Business Plan Workbook for Loan Applications; Start preparing your business plan. Finally, you understand the importance and key elements of drafting a business plan for securing a ...
Business plan template for a startup (from SCORE) Business plan template for traditional businesses (from the SBA) Business plan template for retail or eCommerce (from Shopify; requires email address) Resources For Writing A Business Plan For A Loan. These tools and resources can help you create a solid business plan for a loan.
Common sections are: executive summary, company overview, products and services, market analysis, marketing and sales plan, operational plan, and management team. If you are applying for a loan ...
In 2020, SBA's flagship 7(a) loan program approved more than 42,000 loans totalling $22 billion.Yet, SBA loans are notoriously difficult to obtain for small businesses: less than 15% of SBA loan applications were granted by big banks. If you're applying for a SBA loan, you will need a solid business plan template for your loan application.. In this article we go through, step-by-step, all ...
Loan officers will appreciate a concise overview of your business that provides the summary they need before they start looking at your complete business plan and financial plan. Resources and tools for writing an SBA business plan. Remember, you can download a free SBA-lender-approved business plan template. It includes detailed instructions ...
1. Cover Page and Table of Contents. Your business plan for a loan application is a professional document, so be sure it looks professional. The cover page should contain the name of your business and your contact information. If you have a logo, it should go on the cover.
Show historic figures - If you're already trading, show your business activity over the past 6 months in an 'actual' cash flow. Create a one-year forecast - Show all costs the business needs to start up. Include an explanation of key assumptions such as pricing and the cost of equipment or machinery needed.
Here are the core components of a successful business plan for funding. 1. An Executive Summary. The executive summary should cover the essential information about your business: what it does, who it serves, and what you're looking for from the people who read it.
Download Annual Business Budget Template. Excel | Smartsheet. As a startup becomes established, this template can be used to create a budget showing totals on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis. You can create a projected 12-month budget as well as compare financial data to the previous year's performance.
Download Startup Business Plan Template - Word. Word | Smartsheet. This startup business plan template contains the essential components you need to convey your business idea and strategy to investors and stakeholders, but you can customize this template to fit your needs. The template provides room to include an executive summary, a financial ...
A business plan template is a guide that consists of an outline of all the required sections of a perfect business plan. It also includes step-by-step instructions on how to write each section of the business plan. A good business plan usually consists of an executive summary, business overview, market analysis, operations plan, and so on.
The last section of the template, "Refining Your Plan," explains ways to modify your plan for specific purposes, such as getting a bank loan, or for specific industries, such as retail or manufacturing. Complete the Business Plan Template for a Startup Business to create a working business plan for your startup.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Jane Haskins practiced law for 20 years, representing small businesses in startup, dissolution, business transactions and litigation. She has written hundreds of articles on legal, intellectual ...
301 Moved Permanently. openresty