How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.

Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.
Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
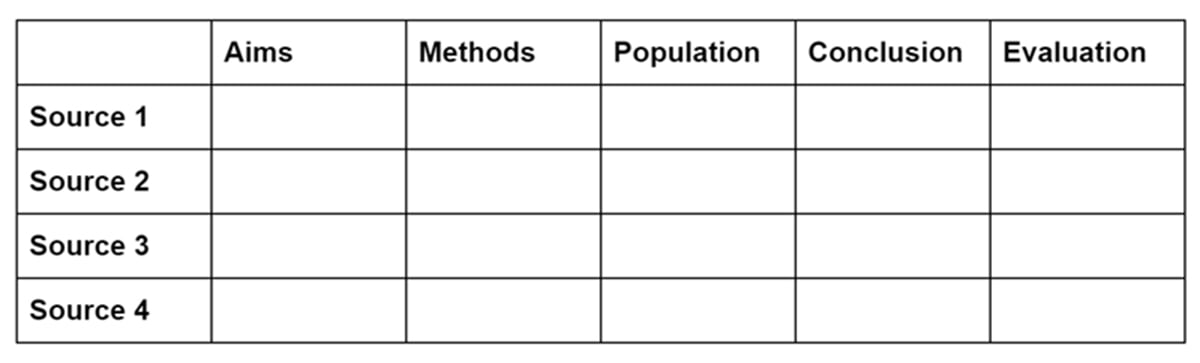
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.
Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
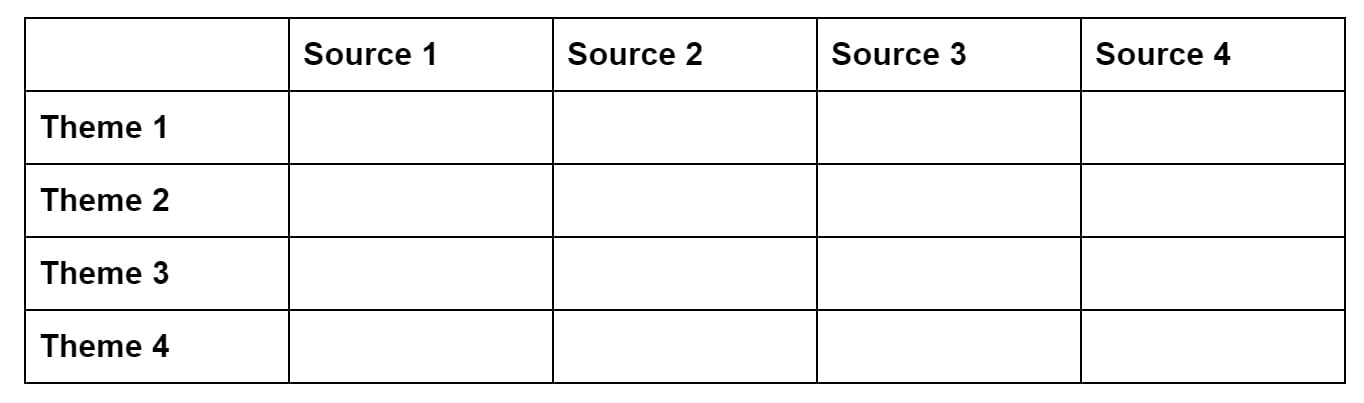
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
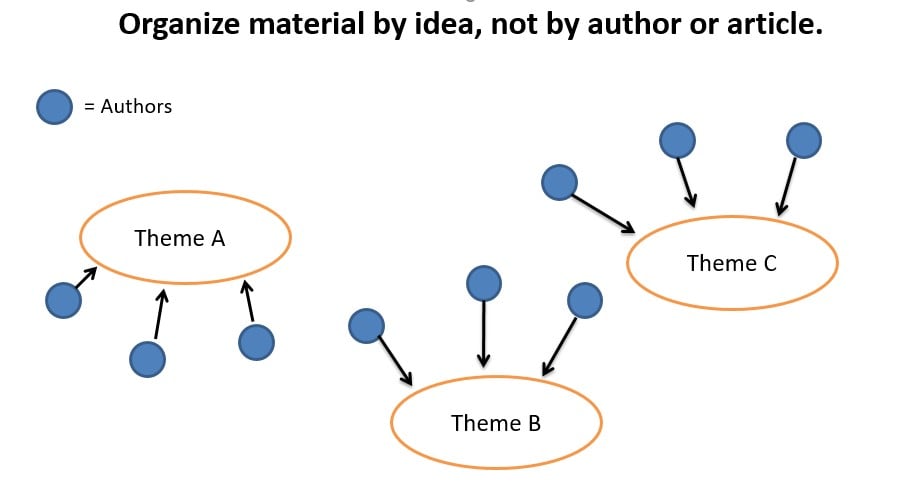
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
- 6. Synthesize
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
- 4. Manage Your References
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
Synthesis Visualization
Synthesis matrix example.
- 7. Write a Literature Review
- Synthesis Worksheet
About Synthesis
Approaches to synthesis.
You can sort the literature in various ways, for example:

How to Begin?
Read your sources carefully and find the main idea(s) of each source
Look for similarities in your sources – which sources are talking about the same main ideas? (for example, sources that discuss the historical background on your topic)
Use the worksheet (above) or synthesis matrix (below) to get organized
This work can be messy. Don't worry if you have to go through a few iterations of the worksheet or matrix as you work on your lit review!
Four Examples of Student Writing
In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D . For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.

Long description of "Four Examples of Student Writing" for web accessibility
- Download a copy of the "Four Examples of Student Writing" chart

Click on the example to view the pdf.

From Jennifer Lim
- << Previous: 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- Next: 7. Write a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 10, 2024 4:46 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
The Sheridan Libraries
- Write a Literature Review
- Sheridan Libraries
- Find This link opens in a new window
- Evaluate This link opens in a new window
Get Organized
- Lit Review Prep Use this template to help you evaluate your sources, create article summaries for an annotated bibliography, and a synthesis matrix for your lit review outline.
Synthesize your Information
Synthesize: combine separate elements to form a whole.
Synthesis Matrix
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other.
After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix or use a citation manager to help you see how they relate to each other and apply to each of your themes or variables.
By arranging your sources by theme or variable, you can see how your sources relate to each other, and can start thinking about how you weave them together to create a narrative.
- Step-by-Step Approach
- Example Matrix from NSCU
- Matrix Template
- << Previous: Summarize
- Next: Integrate >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 10:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/lit-review
Literature Syntheis 101
How To Synthesise The Existing Research (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | August 2023
One of the most common mistakes that students make when writing a literature review is that they err on the side of describing the existing literature rather than providing a critical synthesis of it. In this post, we’ll unpack what exactly synthesis means and show you how to craft a strong literature synthesis using practical examples.
This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp . In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step. If it’s your first time writing a literature review, you definitely want to use this link to get 50% off the course (limited-time offer).
Overview: Literature Synthesis
- What exactly does “synthesis” mean?
- Aspect 1: Agreement
- Aspect 2: Disagreement
- Aspect 3: Key theories
- Aspect 4: Contexts
- Aspect 5: Methodologies
- Bringing it all together
What does “synthesis” actually mean?
As a starting point, let’s quickly define what exactly we mean when we use the term “synthesis” within the context of a literature review.
Simply put, literature synthesis means going beyond just describing what everyone has said and found. Instead, synthesis is about bringing together all the information from various sources to present a cohesive assessment of the current state of knowledge in relation to your study’s research aims and questions .
Put another way, a good synthesis tells the reader exactly where the current research is “at” in terms of the topic you’re interested in – specifically, what’s known , what’s not , and where there’s a need for more research .
So, how do you go about doing this?
Well, there’s no “one right way” when it comes to literature synthesis, but we’ve found that it’s particularly useful to ask yourself five key questions when you’re working on your literature review. Having done so, you can then address them more articulately within your actual write up. So, let’s take a look at each of these questions.

1. Points Of Agreement
The first question that you need to ask yourself is: “Overall, what things seem to be agreed upon by the vast majority of the literature?”
For example, if your research aim is to identify which factors contribute toward job satisfaction, you’ll need to identify which factors are broadly agreed upon and “settled” within the literature. Naturally, there may at times be some lone contrarian that has a radical viewpoint , but, provided that the vast majority of researchers are in agreement, you can put these random outliers to the side. That is, of course, unless your research aims to explore a contrarian viewpoint and there’s a clear justification for doing so.
Identifying what’s broadly agreed upon is an essential starting point for synthesising the literature, because you generally don’t want (or need) to reinvent the wheel or run down a road investigating something that is already well established . So, addressing this question first lays a foundation of “settled” knowledge.
Need a helping hand?
2. Points Of Disagreement
Related to the previous point, but on the other end of the spectrum, is the equally important question: “Where do the disagreements lie?” .
In other words, which things are not well agreed upon by current researchers? It’s important to clarify here that by disagreement, we don’t mean that researchers are (necessarily) fighting over it – just that there are relatively mixed findings within the empirical research , with no firm consensus amongst researchers.
This is a really important question to address as these “disagreements” will often set the stage for the research gap(s). In other words, they provide clues regarding potential opportunities for further research, which your study can then (hopefully) contribute toward filling. If you’re not familiar with the concept of a research gap, be sure to check out our explainer video covering exactly that .

3. Key Theories
The next question you need to ask yourself is: “Which key theories seem to be coming up repeatedly?” .
Within most research spaces, you’ll find that you keep running into a handful of key theories that are referred to over and over again. Apart from identifying these theories, you’ll also need to think about how they’re connected to each other. Specifically, you need to ask yourself:
- Are they all covering the same ground or do they have different focal points or underlying assumptions ?
- Do some of them feed into each other and if so, is there an opportunity to integrate them into a more cohesive theory?
- Do some of them pull in different directions ? If so, why might this be?
- Do all of the theories define the key concepts and variables in the same way, or is there some disconnect? If so, what’s the impact of this ?
Simply put, you’ll need to pay careful attention to the key theories in your research area, as they will need to feature within your theoretical framework , which will form a critical component within your final literature review. This will set the foundation for your entire study, so it’s essential that you be critical in this area of your literature synthesis.
If this sounds a bit fluffy, don’t worry. We deep dive into the theoretical framework (as well as the conceptual framework) and look at practical examples in Literature Review Bootcamp . If you’d like to learn more, take advantage of our limited-time offer to get 60% off the standard price.

4. Contexts
The next question that you need to address in your literature synthesis is an important one, and that is: “Which contexts have (and have not) been covered by the existing research?” .
For example, sticking with our earlier hypothetical topic (factors that impact job satisfaction), you may find that most of the research has focused on white-collar , management-level staff within a primarily Western context, but little has been done on blue-collar workers in an Eastern context. Given the significant socio-cultural differences between these two groups, this is an important observation, as it could present a contextual research gap .
In practical terms, this means that you’ll need to carefully assess the context of each piece of literature that you’re engaging with, especially the empirical research (i.e., studies that have collected and analysed real-world data). Ideally, you should keep notes regarding the context of each study in some sort of catalogue or sheet, so that you can easily make sense of this before you start the writing phase. If you’d like, our free literature catalogue worksheet is a great tool for this task.
5. Methodological Approaches
Last but certainly not least, you need to ask yourself the question: “What types of research methodologies have (and haven’t) been used?”
For example, you might find that most studies have approached the topic using qualitative methods such as interviews and thematic analysis. Alternatively, you might find that most studies have used quantitative methods such as online surveys and statistical analysis.
But why does this matter?
Well, it can run in one of two potential directions . If you find that the vast majority of studies use a specific methodological approach, this could provide you with a firm foundation on which to base your own study’s methodology . In other words, you can use the methodologies of similar studies to inform (and justify) your own study’s research design .
On the other hand, you might argue that the lack of diverse methodological approaches presents a research gap , and therefore your study could contribute toward filling that gap by taking a different approach. For example, taking a qualitative approach to a research area that is typically approached quantitatively. Of course, if you’re going to go against the methodological grain, you’ll need to provide a strong justification for why your proposed approach makes sense. Nevertheless, it is something worth at least considering.
Regardless of which route you opt for, you need to pay careful attention to the methodologies used in the relevant studies and provide at least some discussion about this in your write-up. Again, it’s useful to keep track of this on some sort of spreadsheet or catalogue as you digest each article, so consider grabbing a copy of our free literature catalogue if you don’t have anything in place.

Bringing It All Together
Alright, so we’ve looked at five important questions that you need to ask (and answer) to help you develop a strong synthesis within your literature review. To recap, these are:
- Which things are broadly agreed upon within the current research?
- Which things are the subject of disagreement (or at least, present mixed findings)?
- Which theories seem to be central to your research topic and how do they relate or compare to each other?
- Which contexts have (and haven’t) been covered?
- Which methodological approaches are most common?
Importantly, you’re not just asking yourself these questions for the sake of asking them – they’re not just a reflection exercise. You need to weave your answers to them into your actual literature review when you write it up. How exactly you do this will vary from project to project depending on the structure you opt for, but you’ll still need to address them within your literature review, whichever route you go.
The best approach is to spend some time actually writing out your answers to these questions, as opposed to just thinking about them in your head. Putting your thoughts onto paper really helps you flesh out your thinking . As you do this, don’t just write down the answers – instead, think about what they mean in terms of the research gap you’ll present , as well as the methodological approach you’ll take . Your literature synthesis needs to lay the groundwork for these two things, so it’s essential that you link all of it together in your mind, and of course, on paper.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

excellent , thank you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Jump to navigation

Cochrane Training
Chapter 9: summarizing study characteristics and preparing for synthesis.
Joanne E McKenzie, Sue E Brennan, Rebecca E Ryan, Hilary J Thomson, Renea V Johnston
Key Points:
- Synthesis is a process of bringing together data from a set of included studies with the aim of drawing conclusions about a body of evidence. This will include synthesis of study characteristics and, potentially, statistical synthesis of study findings.
- A general framework for synthesis can be used to guide the process of planning the comparisons, preparing for synthesis, undertaking the synthesis, and interpreting and describing the results.
- Tabulation of study characteristics aids the examination and comparison of PICO elements across studies, facilitates synthesis of these characteristics and grouping of studies for statistical synthesis.
- Tabulation of extracted data from studies allows assessment of the number of studies contributing to a particular meta-analysis, and helps determine what other statistical synthesis methods might be used if meta-analysis is not possible.
Cite this chapter as: McKenzie JE, Brennan SE, Ryan RE, Thomson HJ, Johnston RV. Chapter 9: Summarizing study characteristics and preparing for synthesis. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.4 (updated August 2023). Cochrane, 2023. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook .
9.1 Introduction
Synthesis is a process of bringing together data from a set of included studies with the aim of drawing conclusions about a body of evidence. Most Cochrane Reviews on the effects of interventions will include some type of statistical synthesis. Most commonly this is the statistical combination of results from two or more separate studies (henceforth referred to as meta-analysis) of effect estimates.
An examination of the included studies always precedes statistical synthesis in Cochrane Reviews. For example, examination of the interventions studied is often needed to itemize their content so as to determine which studies can be grouped in a single synthesis. More broadly, synthesis of the PICO (Population, Intervention, Comparator and Outcome) elements of the included studies underpins interpretation of review findings and is an important output of the review in its own right. This synthesis should encompass the characteristics of the interventions and comparators in included studies, the populations and settings in which the interventions were evaluated, the outcomes assessed, and the strengths and weaknesses of the body of evidence.
Chapter 2 defined three types of PICO criteria that may be helpful in understanding decisions that need to be made at different stages in the review:
- The review PICO (planned at the protocol stage) is the PICO on which eligibility of studies is based (what will be included and what excluded from the review).
- The PICO for each synthesis (also planned at the protocol stage) defines the question that the specific synthesis aims to answer, determining how the synthesis will be structured, specifying planned comparisons (including intervention and comparator groups, any grouping of outcome and population subgroups).
- The PICO of the included studies (determined at the review stage) is what was actually investigated in the included studies.
In this chapter, we focus on the PICO for each synthesis and the PICO of the included studies , as the basis for determining which studies can be grouped for statistical synthesis and for synthesizing study characteristics. We describe the preliminary steps undertaken before performing the statistical synthesis. Methods for the statistical synthesis are described in Chapter 10 , Chapter 11 and Chapter 12 .
9.2 A general framework for synthesis
Box 9.2.a A general framework for synthesis that can be applied irrespective of the methods used to synthesize results
Box 9.2.a provides a general framework for synthesis that can be applied irrespective of the methods used to synthesize results. Planning for the synthesis should start at protocol-writing stage, and Chapter 2 and Chapter 3 describe the steps involved in planning the review questions and comparisons between intervention groups. These steps included specifying which characteristics of the interventions, populations, outcomes and study design would be grouped together for synthesis (the PICO for each synthesis: stage 1 in Box 9.2.a ).
This chapter primarily concerns stage 2 of the general framework in Box 9.2.a . After deciding which studies will be included in the review and extracting data, review authors can start implementing their plan, working through steps 2.1 to 2.5 of the framework. This process begins with a detailed examination of the characteristics of each study (step 2.1), and then comparison of characteristics across studies in order to determine which studies are similar enough to be grouped for synthesis (step 2.2). Examination of the type of data available for synthesis follows (step 2.3). These three steps inform decisions about whether any modification to the planned comparisons or outcomes is necessary, or new comparisons are needed (step 2.4). The last step of the framework covered in this chapter involves synthesis of the characteristics of studies contributing to each comparison (step 2.5). The chapter concludes with practical tips for checking data before synthesis (Section 9.4 ).
Steps 2.1, 2.2 and 2.5 involve analysis and synthesis of mainly qualitative information about study characteristics. The process used to undertake these steps is rarely described in reviews, yet can require many subjective decisions about the nature and similarity of the PICO elements of the included studies. The examples described in this section illustrate approaches for making this process more transparent.
9.3 Preliminary steps of a synthesis
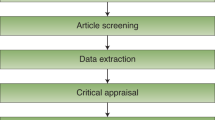
9.3.1 summarize the characteristics of each study (step 2.1).
A starting point for synthesis is to summarize the PICO characteristics of each study (i.e. the PICO of the included studies, see Chapter 3 ) and categorize these PICO elements in the groups (or domains) pre-specified in the protocol (i.e. the PICO for each synthesis). The resulting descriptions are reported in the ‘Characteristics of included studies’ table, and are used in step 2.2 to determine which studies can be grouped for synthesis.
In some reviews, the labels and terminology used in each study are retained when describing the PICO elements of the included studies. This may be sufficient in areas with consistent and widely understood terminology that matches the PICO for each synthesis. However, in most areas, terminology is variable, making it difficult to compare the PICO of each included study to the PICO for each synthesis, or to compare PICO elements across studies. Standardizing the description of PICO elements across studies facilitates these comparisons. This standardization includes applying the labels and terminology used to articulate the PICO for each synthesis ( Chapter 3 ), and structuring the description of PICO elements. The description of interventions can be structured using the Template for Intervention Description and Replication (TIDIeR) checklist, for example (see Chapter 3 and Table 9.3.a ).
Table 9.3.a illustrates the use of pre-specified groups to categorize and label interventions in a review of psychosocial interventions for smoking cessation in pregnancy (Chamberlain et al 2017). The main intervention strategy in each study was categorized into one of six groups: counselling, health education, feedback, incentive-based interventions, social support, and exercise. This categorization determined which studies were eligible for each comparison (e.g. counselling versus usual care; single or multi-component strategy). The extract from the ‘Characteristics of included studies’ table shows the diverse descriptions of interventions in three of the 54 studies for which the main intervention was categorized as ‘counselling’. Other intervention characteristics, such as duration and frequency, were coded in pre-specified categories to standardize description of the intervention intensity and facilitate meta-regression (not shown here).
Table 9.3.a Example of categorizing interventions into pre-defined groups
* The definition also specified eligible modes of delivery, intervention duration and personnel.
While this example focuses on categorizing and describing interventions according to groups pre-specified in the PICO for each synthesis, the same approach applies to other PICO elements.
9.3.2 Determine which studies are similar enough to be grouped within each comparison (step 2.2)
Once the PICO of included studies have been coded using labels and descriptions specified in the PICO for each synthesis, it will be possible to compare PICO elements across studies and determine which studies are similar enough to be grouped within each comparison.
Tabulating study characteristics can help to explore and compare PICO elements across studies, and is particularly important for reviews that are broad in scope, have diversity across one or more PICO elements, or include large numbers of studies. Data about study characteristics can be ordered in many different ways (e.g. by comparison or by specific PICO elements), and tables may include information about one or more PICO elements. Deciding on the best approach will depend on the purpose of the table and the stage of the review. A close examination of study characteristics will require detailed tables; for example, to identify differences in characteristics that were pre-specified as potentially important modifiers of the intervention effects. As the review progresses, this detail may be replaced by standardized description of PICO characteristics (e.g. the coding of counselling interventions presented in Table 9.3.a ).
Table 9.3.b illustrates one approach to tabulating study characteristics to enable comparison and analysis across studies. This table presents a high-level summary of the characteristics that are most important for determining which comparisons can be made. The table was adapted from tables presented in a review of self-management education programmes for osteoarthritis (Kroon et al 2014). The authors presented a structured summary of intervention and comparator groups for each study, and then categorized intervention components thought to be important for enabling patients to manage their own condition. Table 9.3.b shows selected intervention components, the comparator, and outcomes measured in a subset of studies (some details are fictitious). Outcomes have been grouped by the outcome domains ‘Pain’ and ‘Function’ (column ‘Outcome measure’ Table 9.3.b ). These pre-specified outcome domains are the chosen level for the synthesis as specified in the PICO for each synthesis. Authors will need to assess whether the measurement methods or tools used within each study provide an appropriate assessment of the domains ( Chapter 3, Section 3.2.4 ). A next step is to group each measure into the pre-specified time points. In this example, outcomes are grouped into short-term (<6 weeks) and long-term follow-up (≥6 weeks to 12 months) (column ‘Time points (time frame)’ Table 9.3.b ).
Variations on the format shown in Table 9.3.b can be presented within a review to summarize the characteristics of studies contributing to each synthesis, which is important for interpreting findings (step 2.5).
Table 9.3.b Table of study characteristics illustrating similarity of PICO elements across studies
BEH = health-directed behaviour; CON = constructive attitudes and approaches; EMO = emotional well-being; ENG = positive and active engagement in life; MON = self-monitoring and insight; NAV = health service navigation; SKL = skill and technique acquisition. ANCOVA = Analysis of covariance; CI = confidence interval; IQR = interquartile range; MD = mean difference; SD = standard deviation; SE = standard error, NS = non-significant. Pain and function measures: Dutch AIMS-SF = Dutch short form of the Arthritis Impact Measurement Scales; HAQ = Health Assessment Questionnaire; VAS = visual analogue scale; WOMAC = Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index. 1 Ordered by type of comparator; 2 Short-term (denoted ‘immediate’ in the review Kroon et al (2014)) follow-up is defined as <6 weeks, long-term follow-up (denoted ‘intermediate’ in the review) is ≥6 weeks to 12 months; 3 For simplicity, in this example the available data are assumed to be the same for all outcomes within an outcome domain within a study. In practice, this is unlikely and the available data would likely vary by outcome; 4 Indicates that an effect estimate and its standard error may be computed through imputation of missing statistics, methods to convert between statistics (e.g. medians to means) or contact with study authors. *Indicates the selected outcome when there was multiplicity in the outcome domain and time frame.
9.3.3 Determine what data are available for synthesis (step 2.3)
Once the studies that are similar enough to be grouped together within each comparison have been determined, a next step is to examine what data are available for synthesis. Tabulating the measurement tools and time frames as shown in Table 9.3.b allows assessment of the potential for multiplicity (i.e. when multiple outcomes within a study and outcome domain are available for inclusion ( Chapter 3, Section 3.2.4.3 )). In this example, multiplicity arises in two ways. First, from multiple measurement instruments used to measure the same outcome domain within the same time frame (e.g. ‘Short-term Pain’ is measured using the ‘Pain VAS’ and ‘Pain on walking VAS’ scales in study 3). Second, from multiple time points measured within the same time frame (e.g. ‘Short-term Pain’ is measured using ‘Pain VAS’ at both 2 weeks and 1 month in study 6). Pre-specified methods to deal with the multiplicity can then be implemented (see Table 9.3.c for examples of approaches for dealing with multiplicity). In this review, the authors pre-specified a set of decision rules for selecting specific outcomes within the outcome domains. For example, for the outcome domain ‘Pain’, the selected outcome was the highest on the following list: global pain, pain on walking, WOMAC pain subscore, composite pain scores other than WOMAC, pain on activities other than walking, rest pain or pain during the night. The authors further specified that if there were multiple time points at which the outcome was measured within a time frame, they would select the longest time point. The selected outcomes from applying these rules to studies 3 and 6 are indicated by an asterisk in Table 9.3.b .
Table 9.3.b also illustrates an approach to tabulating the extracted data. The available statistics are tabulated in the column labelled ‘Data’, from which an assessment can be made as to whether the study contributes the required data for a meta-analysis (column ‘Effect & SE’) ( Chapter 10 ). For example, of the seven studies comparing health-directed behaviour (BEH) with usual care, six measured ‘Short-term Pain’, four of which contribute required data for meta-analysis. Reordering the table by comparison, outcome and time frame, will more readily show the number of studies that will contribute to a particular meta-analysis, and help determine what other synthesis methods might be used if the data available for meta-analysis are limited.
Table 9.3.c Examples of approaches for selecting one outcome (effect estimate) for inclusion in a synthesis.* Adapted from López-López et al (2018)
9.3.4 Determine if modification to the planned comparisons or outcomes is necessary, or new comparisons are needed (step 2.4)
The previous steps may reveal the need to modify the planned comparisons. Important variations in the intervention may be identified leading to different or modified intervention groups. Few studies or sparse data, or both, may lead to different groupings of interventions, populations or outcomes. Planning contingencies for anticipated scenarios is likely to lead to less post-hoc decision making ( Chapter 2 and Chapter 3 ); however, it is difficult to plan for all scenarios. In the latter circumstance, the rationale for any post-hoc changes should be reported. This approach was adopted in a review examining the effects of portion, package or tableware size for changing selection and consumption of food, alcohol and tobacco (Hollands et al 2015). After preliminary examination of the outcome data, the review authors changed their planned intervention groups. They judged that intervention groups based on ‘size’ and those based on ‘shape’ of the products were not conceptually comparable, and therefore should form separate comparisons. The authors provided a rationale for the change and noted that it was a post-hoc decision.
9.3.5 Synthesize the characteristics of the studies contributing to each comparison (step 2.5)
A final step, and one that is essential for interpreting combined effects, is to synthesize the characteristics of studies contributing to each comparison. This description should integrate information about key PICO characteristics across studies, and identify any potentially important differences in characteristics that were pre-specified as possible effect modifiers. The synthesis of study characteristics is also needed for GRADE assessments, informing judgements about whether the evidence applies directly to the review question (indirectness) and analyses conducted to examine possible explanations for heterogeneity (inconsistency) (see Chapter 14 ).
Tabulating study characteristics is generally preferable to lengthy description in the text, since the structure imposed by a table can make it easier and faster for readers to scan and identify patterns in the information presented. Table 9.3.b illustrates one such approach. Tabulating characteristics of studies that contribute to each comparison can also help to improve the transparency of decisions made around grouping of studies, while also ensuring that studies that do not contribute to the combined effect are accounted for.
9.4 Checking data before synthesis
Before embarking on a synthesis, it is important to be confident that the findings from the individual studies have been collated correctly. Therefore, review authors must compare the magnitude and direction of effects reported by studies with how they are to be presented in the review. This is a reasonably straightforward way for authors to check a number of potential problems, including typographical errors in studies’ reports, accuracy of data collection and manipulation, and data entry into RevMan. For example, the direction of a standardized mean difference may accidentally be wrong in the review. A basic check is to ensure the same qualitative findings (e.g. direction of effect and statistical significance) between the data as presented in the review and the data as available from the original study.
Results in forest plots should agree with data in the original report (point estimate and confidence interval) if the same effect measure and statistical model is used. There are legitimate reasons for differences, however, including: using a different measure of intervention effect; making different choices between change-from-baseline measures, post-intervention measures alone or post-intervention measures adjusted for baseline values; grouping similar intervention groups; or making adjustments for unit-of-analysis errors in the reports of the primary studies.
9.5 Types of synthesis
The focus of this chapter has been describing the steps involved in implementing the planned comparisons between intervention groups (stage 2 of the general framework for synthesis ( Box 9.2.a )). The next step (stage 3) is often performing a statistical synthesis. Meta-analysis of effect estimates, and its extensions have many advantages. There are circumstances under which a meta-analysis is not possible, however, and other statistical synthesis methods might be considered, so as to make best use of the available data. Available summary and synthesis methods, along with the questions they address and examples of associated plots, are described in Table 9.5.a . Chapter 10 and Chapter 11 discuss meta-analysis (of effect estimate) methods, while Chapter 12 focuses on the other statistical synthesis methods, along with approaches to tabulating, visually displaying and providing a structured presentation of the findings. An important part of planning the analysis strategy is building in contingencies to use alternative methods when the desired method cannot be used.
Table 9.5.a Overview of available methods for summary and synthesis
9.6 Chapter information
Authors: Joanne E McKenzie, Sue E Brennan, Rebecca E Ryan, Hilary J Thomson, Renea V Johnston
Acknowledgements: Sections of this chapter build on Chapter 9 of version 5.1 of the Handbook , with editors Jonathan Deeks, Julian Higgins and Douglas Altman. We are grateful to Julian Higgins, James Thomas and Tianjing Li for commenting helpfully on earlier drafts.
Funding: JM is supported by an NHMRC Career Development Fellowship (1143429). SB and RR’s positions are supported by the NHMRC Cochrane Collaboration Funding Program. HT is funded by the UK Medical Research Council (MC_UU_12017-13 and MC_UU_12017-15) and Scottish Government Chief Scientist Office (SPHSU13 and SPHSU15). RJ’s position is supported by the NHMRC Cochrane Collaboration Funding Program and Cabrini Institute.
9.7 References
Chamberlain C, O’Mara-Eves A, Porter J, Coleman T, Perlen SM, Thomas J, McKenzie JE. Psychosocial interventions for supporting women to stop smoking in pregnancy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017; 2 : CD001055.
Hollands GJ, Shemilt I, Marteau TM, Jebb SA, Lewis HB, Wei Y, Higgins JPT, Ogilvie D. Portion, package or tableware size for changing selection and consumption of food, alcohol and tobacco. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015; 9 : CD011045.
Kroon FPB, van der Burg LRA, Buchbinder R, Osborne RH, Johnston RV, Pitt V. Self-management education programmes for osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014; 1 : CD008963.
López-López JA, Page MJ, Lipsey MW, Higgins JPT. Dealing with effect size multiplicity in systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Research Synthesis Methods 2018; 9 : 336–351.
For permission to re-use material from the Handbook (either academic or commercial), please see here for full details.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Published: 08 March 2018
Meta-analysis and the science of research synthesis
- Jessica Gurevitch 1 ,
- Julia Koricheva 2 ,
- Shinichi Nakagawa 3 , 4 &
- Gavin Stewart 5
Nature volume 555 , pages 175–182 ( 2018 ) Cite this article
54k Accesses
871 Citations
730 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Biodiversity
- Outcomes research
Meta-analysis is the quantitative, scientific synthesis of research results. Since the term and modern approaches to research synthesis were first introduced in the 1970s, meta-analysis has had a revolutionary effect in many scientific fields, helping to establish evidence-based practice and to resolve seemingly contradictory research outcomes. At the same time, its implementation has engendered criticism and controversy, in some cases general and others specific to particular disciplines. Here we take the opportunity provided by the recent fortieth anniversary of meta-analysis to reflect on the accomplishments, limitations, recent advances and directions for future developments in the field of research synthesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Eight problems with literature reviews and how to fix them

The past, present and future of Registered Reports
Raiders of the lost HARK: a reproducible inference framework for big data science
Jennions, M. D ., Lortie, C. J. & Koricheva, J. in The Handbook of Meta-analysis in Ecology and Evolution (eds Koricheva, J . et al.) Ch. 23 , 364–380 (Princeton Univ. Press, 2013)
Article Google Scholar
Roberts, P. D ., Stewart, G. B. & Pullin, A. S. Are review articles a reliable source of evidence to support conservation and environmental management? A comparison with medicine. Biol. Conserv. 132 , 409–423 (2006)
Bastian, H ., Glasziou, P . & Chalmers, I. Seventy-five trials and eleven systematic reviews a day: how will we ever keep up? PLoS Med. 7 , e1000326 (2010)
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Borman, G. D. & Grigg, J. A. in The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-analysis 2nd edn (eds Cooper, H. M . et al.) 497–519 (Russell Sage Foundation, 2009)
Ioannidis, J. P. A. The mass production of redundant, misleading, and conflicted systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Milbank Q. 94 , 485–514 (2016)
Koricheva, J . & Gurevitch, J. Uses and misuses of meta-analysis in plant ecology. J. Ecol. 102 , 828–844 (2014)
Littell, J. H . & Shlonsky, A. Making sense of meta-analysis: a critique of “effectiveness of long-term psychodynamic psychotherapy”. Clin. Soc. Work J. 39 , 340–346 (2011)
Morrissey, M. B. Meta-analysis of magnitudes, differences and variation in evolutionary parameters. J. Evol. Biol. 29 , 1882–1904 (2016)
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Whittaker, R. J. Meta-analyses and mega-mistakes: calling time on meta-analysis of the species richness-productivity relationship. Ecology 91 , 2522–2533 (2010)
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Begley, C. G . & Ellis, L. M. Drug development: Raise standards for preclinical cancer research. Nature 483 , 531–533 (2012); clarification 485 , 41 (2012)
Article CAS ADS PubMed Google Scholar
Hillebrand, H . & Cardinale, B. J. A critique for meta-analyses and the productivity-diversity relationship. Ecology 91 , 2545–2549 (2010)
Moher, D . et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 6 , e1000097 (2009). This paper provides a consensus regarding the reporting requirements for medical meta-analysis and has been highly influential in ensuring good reporting practice and standardizing language in evidence-based medicine, with further guidance for protocols, individual patient data meta-analyses and animal studies.
Moher, D . et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 4 , 1 (2015)
Nakagawa, S . & Santos, E. S. A. Methodological issues and advances in biological meta-analysis. Evol. Ecol. 26 , 1253–1274 (2012)
Nakagawa, S ., Noble, D. W. A ., Senior, A. M. & Lagisz, M. Meta-evaluation of meta-analysis: ten appraisal questions for biologists. BMC Biol. 15 , 18 (2017)
Hedges, L. & Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for Meta-analysis (Academic Press, 1985)
Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw. 36 , 1–48 (2010)
Anzures-Cabrera, J . & Higgins, J. P. T. Graphical displays for meta-analysis: an overview with suggestions for practice. Res. Synth. Methods 1 , 66–80 (2010)
Egger, M ., Davey Smith, G ., Schneider, M. & Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Br. Med. J. 315 , 629–634 (1997)
Article CAS Google Scholar
Duval, S . & Tweedie, R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 56 , 455–463 (2000)
Article CAS MATH PubMed Google Scholar
Leimu, R . & Koricheva, J. Cumulative meta-analysis: a new tool for detection of temporal trends and publication bias in ecology. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 271 , 1961–1966 (2004)
Higgins, J. P. T . & Green, S. (eds) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions : Version 5.1.0 (Wiley, 2011). This large collaborative work provides definitive guidance for the production of systematic reviews in medicine and is of broad interest for methods development outside the medical field.
Lau, J ., Rothstein, H. R . & Stewart, G. B. in The Handbook of Meta-analysis in Ecology and Evolution (eds Koricheva, J . et al.) Ch. 25 , 407–419 (Princeton Univ. Press, 2013)
Lortie, C. J ., Stewart, G ., Rothstein, H. & Lau, J. How to critically read ecological meta-analyses. Res. Synth. Methods 6 , 124–133 (2015)
Murad, M. H . & Montori, V. M. Synthesizing evidence: shifting the focus from individual studies to the body of evidence. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 309 , 2217–2218 (2013)
Rasmussen, S. A ., Chu, S. Y ., Kim, S. Y ., Schmid, C. H . & Lau, J. Maternal obesity and risk of neural tube defects: a meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 198 , 611–619 (2008)
Littell, J. H ., Campbell, M ., Green, S . & Toews, B. Multisystemic therapy for social, emotional, and behavioral problems in youth aged 10–17. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004797.pub4 (2005)
Schmidt, F. L. What do data really mean? Research findings, meta-analysis, and cumulative knowledge in psychology. Am. Psychol. 47 , 1173–1181 (1992)
Button, K. S . et al. Power failure: why small sample size undermines the reliability of neuroscience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 14 , 365–376 (2013); erratum 14 , 451 (2013)
Parker, T. H . et al. Transparency in ecology and evolution: real problems, real solutions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 31 , 711–719 (2016)
Stewart, G. Meta-analysis in applied ecology. Biol. Lett. 6 , 78–81 (2010)
Sutherland, W. J ., Pullin, A. S ., Dolman, P. M . & Knight, T. M. The need for evidence-based conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 19 , 305–308 (2004)
Lowry, E . et al. Biological invasions: a field synopsis, systematic review, and database of the literature. Ecol. Evol. 3 , 182–196 (2013)
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Parmesan, C . & Yohe, G. A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature 421 , 37–42 (2003)
Jennions, M. D ., Lortie, C. J . & Koricheva, J. in The Handbook of Meta-analysis in Ecology and Evolution (eds Koricheva, J . et al.) Ch. 24 , 381–403 (Princeton Univ. Press, 2013)
Balvanera, P . et al. Quantifying the evidence for biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning and services. Ecol. Lett. 9 , 1146–1156 (2006)
Cardinale, B. J . et al. Effects of biodiversity on the functioning of trophic groups and ecosystems. Nature 443 , 989–992 (2006)
Rey Benayas, J. M ., Newton, A. C ., Diaz, A. & Bullock, J. M. Enhancement of biodiversity and ecosystem services by ecological restoration: a meta-analysis. Science 325 , 1121–1124 (2009)
Article ADS PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Leimu, R ., Mutikainen, P. I. A ., Koricheva, J. & Fischer, M. How general are positive relationships between plant population size, fitness and genetic variation? J. Ecol. 94 , 942–952 (2006)
Hillebrand, H. On the generality of the latitudinal diversity gradient. Am. Nat. 163 , 192–211 (2004)
Gurevitch, J. in The Handbook of Meta-analysis in Ecology and Evolution (eds Koricheva, J . et al.) Ch. 19 , 313–320 (Princeton Univ. Press, 2013)
Rustad, L . et al. A meta-analysis of the response of soil respiration, net nitrogen mineralization, and aboveground plant growth to experimental ecosystem warming. Oecologia 126 , 543–562 (2001)
Adams, D. C. Phylogenetic meta-analysis. Evolution 62 , 567–572 (2008)
Hadfield, J. D . & Nakagawa, S. General quantitative genetic methods for comparative biology: phylogenies, taxonomies and multi-trait models for continuous and categorical characters. J. Evol. Biol. 23 , 494–508 (2010)
Lajeunesse, M. J. Meta-analysis and the comparative phylogenetic method. Am. Nat. 174 , 369–381 (2009)
Rosenberg, M. S ., Adams, D. C . & Gurevitch, J. MetaWin: Statistical Software for Meta-Analysis with Resampling Tests Version 1 (Sinauer Associates, 1997)
Wallace, B. C . et al. OpenMEE: intuitive, open-source software for meta-analysis in ecology and evolutionary biology. Methods Ecol. Evol. 8 , 941–947 (2016)
Gurevitch, J ., Morrison, J. A . & Hedges, L. V. The interaction between competition and predation: a meta-analysis of field experiments. Am. Nat. 155 , 435–453 (2000)
Adams, D. C ., Gurevitch, J . & Rosenberg, M. S. Resampling tests for meta-analysis of ecological data. Ecology 78 , 1277–1283 (1997)
Gurevitch, J . & Hedges, L. V. Statistical issues in ecological meta-analyses. Ecology 80 , 1142–1149 (1999)
Schmid, C. H . & Mengersen, K. in The Handbook of Meta-analysis in Ecology and Evolution (eds Koricheva, J . et al.) Ch. 11 , 145–173 (Princeton Univ. Press, 2013)
Eysenck, H. J. Exercise in mega-silliness. Am. Psychol. 33 , 517 (1978)
Simberloff, D. Rejoinder to: Don’t calculate effect sizes; study ecological effects. Ecol. Lett. 9 , 921–922 (2006)
Cadotte, M. W ., Mehrkens, L. R . & Menge, D. N. L. Gauging the impact of meta-analysis on ecology. Evol. Ecol. 26 , 1153–1167 (2012)
Koricheva, J ., Jennions, M. D. & Lau, J. in The Handbook of Meta-analysis in Ecology and Evolution (eds Koricheva, J . et al.) Ch. 15 , 237–254 (Princeton Univ. Press, 2013)
Lau, J ., Ioannidis, J. P. A ., Terrin, N ., Schmid, C. H . & Olkin, I. The case of the misleading funnel plot. Br. Med. J. 333 , 597–600 (2006)
Vetter, D ., Rucker, G. & Storch, I. Meta-analysis: a need for well-defined usage in ecology and conservation biology. Ecosphere 4 , 1–24 (2013)
Mengersen, K ., Jennions, M. D. & Schmid, C. H. in The Handbook of Meta-analysis in Ecology and Evolution (eds Koricheva, J. et al.) Ch. 16 , 255–283 (Princeton Univ. Press, 2013)
Patsopoulos, N. A ., Analatos, A. A. & Ioannidis, J. P. A. Relative citation impact of various study designs in the health sciences. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 293 , 2362–2366 (2005)
Kueffer, C . et al. Fame, glory and neglect in meta-analyses. Trends Ecol. Evol. 26 , 493–494 (2011)
Cohnstaedt, L. W. & Poland, J. Review Articles: The black-market of scientific currency. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 110 , 90 (2017)
Longo, D. L. & Drazen, J. M. Data sharing. N. Engl. J. Med. 374 , 276–277 (2016)
Gauch, H. G. Scientific Method in Practice (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2003)
Science Staff. Dealing with data: introduction. Challenges and opportunities. Science 331 , 692–693 (2011)
Nosek, B. A . et al. Promoting an open research culture. Science 348 , 1422–1425 (2015)
Article CAS ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Stewart, L. A . et al. Preferred reporting items for a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data: the PRISMA-IPD statement. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 313 , 1657–1665 (2015)
Saldanha, I. J . et al. Evaluating Data Abstraction Assistant, a novel software application for data abstraction during systematic reviews: protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Syst. Rev. 5 , 196 (2016)
Tipton, E. & Pustejovsky, J. E. Small-sample adjustments for tests of moderators and model fit using robust variance estimation in meta-regression. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 40 , 604–634 (2015)
Mengersen, K ., MacNeil, M. A . & Caley, M. J. The potential for meta-analysis to support decision analysis in ecology. Res. Synth. Methods 6 , 111–121 (2015)
Ashby, D. Bayesian statistics in medicine: a 25 year review. Stat. Med. 25 , 3589–3631 (2006)
Article MathSciNet PubMed Google Scholar
Senior, A. M . et al. Heterogeneity in ecological and evolutionary meta-analyses: its magnitude and implications. Ecology 97 , 3293–3299 (2016)
McAuley, L ., Pham, B ., Tugwell, P . & Moher, D. Does the inclusion of grey literature influence estimates of intervention effectiveness reported in meta-analyses? Lancet 356 , 1228–1231 (2000)
Koricheva, J ., Gurevitch, J . & Mengersen, K. (eds) The Handbook of Meta-Analysis in Ecology and Evolution (Princeton Univ. Press, 2013) This book provides the first comprehensive guide to undertaking meta-analyses in ecology and evolution and is also relevant to other fields where heterogeneity is expected, incorporating explicit consideration of the different approaches used in different domains.
Lumley, T. Network meta-analysis for indirect treatment comparisons. Stat. Med. 21 , 2313–2324 (2002)
Zarin, W . et al. Characteristics and knowledge synthesis approach for 456 network meta-analyses: a scoping review. BMC Med. 15 , 3 (2017)
Elliott, J. H . et al. Living systematic reviews: an emerging opportunity to narrow the evidence-practice gap. PLoS Med. 11 , e1001603 (2014)
Vandvik, P. O ., Brignardello-Petersen, R . & Guyatt, G. H. Living cumulative network meta-analysis to reduce waste in research: a paradigmatic shift for systematic reviews? BMC Med. 14 , 59 (2016)
Jarvinen, A. A meta-analytic study of the effects of female age on laying date and clutch size in the Great Tit Parus major and the Pied Flycatcher Ficedula hypoleuca . Ibis 133 , 62–67 (1991)
Arnqvist, G. & Wooster, D. Meta-analysis: synthesizing research findings in ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 10 , 236–240 (1995)
Hedges, L. V ., Gurevitch, J . & Curtis, P. S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology 80 , 1150–1156 (1999)
Gurevitch, J ., Curtis, P. S. & Jones, M. H. Meta-analysis in ecology. Adv. Ecol. Res 32 , 199–247 (2001)
Lajeunesse, M. J. phyloMeta: a program for phylogenetic comparative analyses with meta-analysis. Bioinformatics 27 , 2603–2604 (2011)
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Pearson, K. Report on certain enteric fever inoculation statistics. Br. Med. J. 2 , 1243–1246 (1904)
Fisher, R. A. Statistical Methods for Research Workers (Oliver and Boyd, 1925)
Yates, F. & Cochran, W. G. The analysis of groups of experiments. J. Agric. Sci. 28 , 556–580 (1938)
Cochran, W. G. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 10 , 101–129 (1954)
Smith, M. L . & Glass, G. V. Meta-analysis of psychotherapy outcome studies. Am. Psychol. 32 , 752–760 (1977)
Glass, G. V. Meta-analysis at middle age: a personal history. Res. Synth. Methods 6 , 221–231 (2015)
Cooper, H. M ., Hedges, L. V . & Valentine, J. C. (eds) The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-analysis 2nd edn (Russell Sage Foundation, 2009). This book is an important compilation that builds on the ground-breaking first edition to set the standard for best practice in meta-analysis, primarily in the social sciences but with applications to medicine and other fields.
Rosenthal, R. Meta-analytic Procedures for Social Research (Sage, 1991)
Hunter, J. E ., Schmidt, F. L. & Jackson, G. B. Meta-analysis: Cumulating Research Findings Across Studies (Sage, 1982)
Gurevitch, J ., Morrow, L. L ., Wallace, A . & Walsh, J. S. A meta-analysis of competition in field experiments. Am. Nat. 140 , 539–572 (1992). This influential early ecological meta-analysis reports multiple experimental outcomes on a longstanding and controversial topic that introduced a wide range of ecologists to research synthesis methods.
O’Rourke, K. An historical perspective on meta-analysis: dealing quantitatively with varying study results. J. R. Soc. Med. 100 , 579–582 (2007)
Shadish, W. R . & Lecy, J. D. The meta-analytic big bang. Res. Synth. Methods 6 , 246–264 (2015)
Glass, G. V. Primary, secondary, and meta-analysis of research. Educ. Res. 5 , 3–8 (1976)
DerSimonian, R . & Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 7 , 177–188 (1986)
Lipsey, M. W . & Wilson, D. B. The efficacy of psychological, educational, and behavioral treatment. Confirmation from meta-analysis. Am. Psychol. 48 , 1181–1209 (1993)
Chalmers, I. & Altman, D. G. Systematic Reviews (BMJ Publishing Group, 1995)
Moher, D . et al. Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of reporting of meta-analyses. Lancet 354 , 1896–1900 (1999)
Higgins, J. P. & Thompson, S. G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 21 , 1539–1558 (2002)
Download references
Acknowledgements
We dedicate this Review to the memory of Ingram Olkin and William Shadish, founding members of the Society for Research Synthesis Methodology who made tremendous contributions to the development of meta-analysis and research synthesis and to the supervision of generations of students. We thank L. Lagisz for help in preparing the figures. We are grateful to the Center for Open Science and the Laura and John Arnold Foundation for hosting and funding a workshop, which was the origination of this article. S.N. is supported by Australian Research Council Future Fellowship (FT130100268). J.G. acknowledges funding from the US National Science Foundation (ABI 1262402).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Ecology and Evolution, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, 11794-5245, New York, USA
Jessica Gurevitch
School of Biological Sciences, Royal Holloway University of London, Egham, TW20 0EX, Surrey, UK
Julia Koricheva
Evolution and Ecology Research Centre and School of Biological, Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of New South Wales, Sydney, 2052, New South Wales, Australia
Shinichi Nakagawa
Diabetes and Metabolism Division, Garvan Institute of Medical Research, 384 Victoria Street, Darlinghurst, Sydney, 2010, New South Wales, Australia
School of Natural and Environmental Sciences, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, NE1 7RU, UK
Gavin Stewart
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed equally in designing the study and writing the manuscript, and so are listed alphabetically.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Jessica Gurevitch , Julia Koricheva , Shinichi Nakagawa or Gavin Stewart .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Reviewer Information Nature thanks D. Altman, M. Lajeunesse, D. Moher and G. Romero for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

PowerPoint slides
Powerpoint slide for fig. 1, rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Gurevitch, J., Koricheva, J., Nakagawa, S. et al. Meta-analysis and the science of research synthesis. Nature 555 , 175–182 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25753
Download citation
Received : 04 March 2017
Accepted : 12 January 2018
Published : 08 March 2018
Issue Date : 08 March 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25753
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Investigate the relationship between the retraction reasons and the quality of methodology in non-cochrane retracted systematic reviews: a systematic review.
- Azita Shahraki-Mohammadi
- Leila Keikha
- Razieh Zahedi
Systematic Reviews (2024)
Systematic review of the uncertainty of coral reef futures under climate change
- Shannon G. Klein
- Cassandra Roch
- Carlos M. Duarte
Nature Communications (2024)
Meta-analysis reveals weak associations between reef fishes and corals
- Pooventhran Muruga
- Alexandre C. Siqueira
- David R. Bellwood
Nature Ecology & Evolution (2024)
Farming practices to enhance biodiversity across biomes: a systematic review
- Felipe Cozim-Melges
- Raimon Ripoll-Bosch
- Hannah H. E. van Zanten
npj Biodiversity (2024)
Large language models reveal big disparities in current wildfire research
- Zhengyang Lin
- Anping Chen
- Shilong Piao
Communications Earth & Environment (2024)
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

Capstone Form and Style
Evidence-based arguments: synthesis, paraphrasing and synthesis.
Synthesis is important in scholarly writing as it is the combination of ideas on a given topic or subject area. Synthesis is different from summary. Summary consists of a brief description of one idea, piece of text, etc. Synthesis involves combining ideas together.
Summary: Overview of important general information in your own words and sentence structure. Paraphrase: Articulation of a specific passage or idea in your own words and sentence structure. Synthesis: New interpretation of summarized or paraphrased details in your own words and sentence structure.
In the capstone, writers should aim for synthesis in all areas of the document, especially the literature review. Synthesis combines paraphrased information, where the writer presents information from multiple sources. Synthesis demonstrates scholarship; it demonstrates an understanding of the literature and information, as well as the writer’s ability to connect ideas and develop an argument.
Example Paraphrase
From allan and zed (2012, p. 195).
Supervision, one practice in transactional leadership theory, is especially effective for small business owners. Improved retention not only contributes to an efficient workplace, but it promotes local commercial stability and cultural unity. Other management styles informed by transactional theory can also benefit communities.
Sample Paraphrase
Allan and Zed (2012) noted that supervision and other transactional leadership strategies provide advantages for small business owners and their surrounding communities.
This paraphrase DOES:
- include the main idea,
- summarize the key information using fewer words than the original text, and
- include a citation to credit the source.
Synthesis Language
Synthesis is achieved by comparing and contrasting paraphrased information on a given topic. Discussions of the literature should be focused not on study-by-study summaries (see the Creating a Literature Review Outline SMRTguide). Writers should begin by using comparison language (indicated in bold and highlighted text in the examples below) to combine ideas on a given topic:
- Keller (2012) found that X occurred. Likewise, Daal (2013) found that X occurred but also noted that the effects of X differed from those suggested by Keller (2012).
- Schwester (2013) reported results consistent with findings in Hill’s (2011) and Yao’s (2012) studies.
- Although Mehmad (2012) suggested X, O’Donnell (2013) recommended a different approach.
Again, the focus of synthesis is to combine ideas on a given topic and for the writer to use that to review the existing literature or support an overall argument (i.e., in the problem statement, rationale and justification for the method, etc.).
For more information and examples on synthesis, paragraph structure, and the MEAL Plan strategy for writing review additional Form and Style resources:
- SMRTguide on Reverse Outlining and the MEAL Plan
- SMRTguide on Prioritizing Parenthetical Citations
- Reading to Write
- Previous Page: Quoting
- Next Page: MEAL Plan
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Synthesizing Sources

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
When you look for areas where your sources agree or disagree and try to draw broader conclusions about your topic based on what your sources say, you are engaging in synthesis. Writing a research paper usually requires synthesizing the available sources in order to provide new insight or a different perspective into your particular topic (as opposed to simply restating what each individual source says about your research topic).
Note that synthesizing is not the same as summarizing.
- A summary restates the information in one or more sources without providing new insight or reaching new conclusions.
- A synthesis draws on multiple sources to reach a broader conclusion.
There are two types of syntheses: explanatory syntheses and argumentative syntheses . Explanatory syntheses seek to bring sources together to explain a perspective and the reasoning behind it. Argumentative syntheses seek to bring sources together to make an argument. Both types of synthesis involve looking for relationships between sources and drawing conclusions.
In order to successfully synthesize your sources, you might begin by grouping your sources by topic and looking for connections. For example, if you were researching the pros and cons of encouraging healthy eating in children, you would want to separate your sources to find which ones agree with each other and which ones disagree.
After you have a good idea of what your sources are saying, you want to construct your body paragraphs in a way that acknowledges different sources and highlights where you can draw new conclusions.
As you continue synthesizing, here are a few points to remember:
- Don’t force a relationship between sources if there isn’t one. Not all of your sources have to complement one another.
- Do your best to highlight the relationships between sources in very clear ways.
- Don’t ignore any outliers in your research. It’s important to take note of every perspective (even those that disagree with your broader conclusions).
Example Syntheses
Below are two examples of synthesis: one where synthesis is NOT utilized well, and one where it is.
Parents are always trying to find ways to encourage healthy eating in their children. Elena Pearl Ben-Joseph, a doctor and writer for KidsHealth , encourages parents to be role models for their children by not dieting or vocalizing concerns about their body image. The first popular diet began in 1863. William Banting named it the “Banting” diet after himself, and it consisted of eating fruits, vegetables, meat, and dry wine. Despite the fact that dieting has been around for over a hundred and fifty years, parents should not diet because it hinders children’s understanding of healthy eating.
In this sample paragraph, the paragraph begins with one idea then drastically shifts to another. Rather than comparing the sources, the author simply describes their content. This leads the paragraph to veer in an different direction at the end, and it prevents the paragraph from expressing any strong arguments or conclusions.
An example of a stronger synthesis can be found below.
Parents are always trying to find ways to encourage healthy eating in their children. Different scientists and educators have different strategies for promoting a well-rounded diet while still encouraging body positivity in children. David R. Just and Joseph Price suggest in their article “Using Incentives to Encourage Healthy Eating in Children” that children are more likely to eat fruits and vegetables if they are given a reward (855-856). Similarly, Elena Pearl Ben-Joseph, a doctor and writer for Kids Health , encourages parents to be role models for their children. She states that “parents who are always dieting or complaining about their bodies may foster these same negative feelings in their kids. Try to keep a positive approach about food” (Ben-Joseph). Martha J. Nepper and Weiwen Chai support Ben-Joseph’s suggestions in their article “Parents’ Barriers and Strategies to Promote Healthy Eating among School-age Children.” Nepper and Chai note, “Parents felt that patience, consistency, educating themselves on proper nutrition, and having more healthy foods available in the home were important strategies when developing healthy eating habits for their children.” By following some of these ideas, parents can help their children develop healthy eating habits while still maintaining body positivity.
In this example, the author puts different sources in conversation with one another. Rather than simply describing the content of the sources in order, the author uses transitions (like "similarly") and makes the relationship between the sources evident.
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
UMGC Effective Writing Center Write to Synthesize: The Research Essay
Explore more of umgc.
- Writing Resources
In a synthesis, you bring things together. This combination, integration, or merging creates something new--your synthesis. The action of synthesis is basic to our world. Take, for example, what happens when a single oxygen molecule is combined with two hydrogen molecules. Water is created or synthesized. Hard to get more basic than that.
You also use synthesis to make personal decisions. If two instructors are teaching a class you must take, you may synthesize your past experiences with the teachers to choose the best class for you.
Research Essays:
Thesis driven.
In school, when writing a synthesis from your research, your sources may come from the school's library, a textbook, or the Internet. Here are some important points to keep in mind:
First, regardless of where your sources come from or how many you have, what you write should be driven by a thesis that you devise. After reading and studying your sources, you should form a personal point of view, a slant to connect your sources.
Here's a quick example--Let's say you've read three folktales: Goldilocks and the Three Bears, Little Red Riding Hood, and the Pied Piper--and now you must write a synthesis of them. As you study the three sources, you think about links between them and come up with this thesis:
Folktales use fear to teach children lessons.
Then you use this thesis to synthesize your three sources as you support your point of view. You combine elements from the three sources to prove and illustrate this thesis. Your support points could focus on the lessons for children:
- Lesson 1 : Never talk to strangers.
- Lesson 2 : Don't wander from home.
- Lesson 3 : Appearances can deceive us.
This step of outlining your thesis and main points is a crucial one when writing a synthesis. If your goal in writing a research essay is to provide readers a unified perspective based on sources, the unified perspective must be clear before the writing begins.
Once the writing begins, your point of view is then carried through to the paragraph and sentence levels. Let's examine some techniques for achieving the unity that a good synthesis requires. First, here’s an example of an unsuccessful attempt at synthesizing sources:
Many sources agree that capital punishment is not a crime deterrent. [This is the idea around which the sources should be unified. Now comes the sources] According to Judy Pennington in an interview with Helen Prejean, crime rates in New Orleans rise for at least eight weeks following executions (110). Jimmy Dunne notes that crime rates often go up in the first two or three months following an execution. “Death in the Americas” argues that America’s crime rate as a whole has increased drastically since the re-instatement of the death penalty in the 1960s. The article notes that 700 crimes are committed for every 100,000 Americans (2). Helen Prejean cites Ellis in her book to note that in 1980, 500,000 people were behind bars and in 1990 that figure rose to 1.1 million (112).
Sample student paragraph adapted from "Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources." Retrieved 2011 from https://scholarworks.iupui.edu/items/7dda80e7-b0b3-477c-a972-283b48cfdf5c
This paragraph certainly uses a number of sources. However, the sources are presented in a random, grocery list fashion. Besides the main point at the beginning, there is no further attempt to synthesize. The sources seem tossed in, like ingredients in a salad. Let's examine a possible revision of that paragraph and how an adequate synthesis might be achieved:
Major studies suggest that capital punishment fails to deter crime. Helen Prejean, in "Deadman Walking," reviews decades of statistics that indicate capital punishment does little to lower crime. [Key idea from topic sentence—"capital punishment fails to deter crime"— echoed in sentence about source–"capital punishment does little to lower crime." Repetition links source to main idea.] Based on this evidence, Prejean concludes “Executions do not deter crime . . . the U.S. murder rate is no higher in states that do not have the death penalty than those who do” (110). ["Based on this evidence" forces reader to refer back to "statistics" in previous sentence.] Prejean’s point is reiterated from a historical perspective in Dunne's article “Death in the Americas.” [This sentence provides a thought bridge between two sources.] Dunne first points out that, despite the social and economic upheavals from 1930 to 1960, crime rates were unchanged (2). [Linking phrase:"Dunne first points out"] However, after the reinstatement of the death penalty in the 1960s, “crime rates soared” (2). [Linking phase "However, Dunne notes."]
The result is a matrix of connective devices that unifies the sources around a key idea stated at the beginning. Although this matrix seems complex, it is actually built on a simple three-point strategy.
- Stay in charge . You the writer must control the sources, using them to serve your purpose. In good synthesis writing, sources are used to support what you, the writer, have already said in your own words.
- Stay focused . Your main point is not merely stated once and left to wilt. Your main idea is repeated and echoed throughout as a way to link the sources, to weave them together into a strong fabric of meaning.
- Stay strategic . Notice the "source sandwich" strategy at work. First, the author sets up the source with its background and relevance to the point. After the source comes a follows up in his/her own words as a way to bridge or link to the next part. In other words, the writer's own words are used like two slices of bread, with the source in the middle.
Follow these simple principles when using sources in your writing and you will achieve the most important goal of synthesis writing--to create a whole greater than its parts.
Our helpful admissions advisors can help you choose an academic program to fit your career goals, estimate your transfer credits, and develop a plan for your education costs that fits your budget. If you’re a current UMGC student, please visit the Help Center .
Personal Information
Contact information, additional information.
By submitting this form, you acknowledge that you intend to sign this form electronically and that your electronic signature is the equivalent of a handwritten signature, with all the same legal and binding effect. You are giving your express written consent without obligation for UMGC to contact you regarding our educational programs and services using e-mail, phone, or text, including automated technology for calls and/or texts to the mobile number(s) provided. For more details, including how to opt out, read our privacy policy or contact an admissions advisor .
Please wait, your form is being submitted.
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .

Synthesis in Research: Home
What is synthesis?
Synthesizing information is the opposite of analyzing information. When you read an article or book, you have to pull out specific concepts from the larger document in order to understand it. This is analyzing.
When you synthesize information, you take specific concepts and consider them together to understand how they compare/contrast and how they relate to one another. Synthesis involves combining multiple elements to create a whole.
In regard to course assignments, the elements refer to the outside sources you've gathered to support the ideas you want to present. The whole then becomes your conclusion(s) about those sources.

How do I synthesize information?
Note: These steps offer a guideline, but do what works for you best.
- This is where you really decide if you want to read specific materials
- If you have gathered a substantial amount of literature and reading all of it would prove overwhelming, read the abstracts to get a better idea of the content, then select the materials that would best support your assignment
- Describe and analyze the findings and/or the author's main ideas
- What's the author's message?
- What evidence do they use to support their message?
- What does the author want a reader to understand?
- What is the larger impact of the author's message?
- Compare and contrast the main ideas and other pertinent information you found in each source
- Evaluate the quality and significance of these main ideas
- Interpret the main ideas in the context of your research question or assignment topic
- This is the step where your synthesis of the information will lead to logical conclusions about that information
- These conclusions should speak directly to your research question (i.e. your question should have an answer)
I would like to give credit to Aultman Health Sciences Library. Most of the information used to create this guide is from their English Research libguide .
- Last Updated: Apr 8, 2024 2:29 PM
- URL: https://library.defiance.edu/synthesis
Pilgrim Library :
419-783-2481 , library@ defiance.edu , click the purple "ask us" side tab above.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Dermatol
- v.62(5); Sep-Oct 2017
Summary and Synthesis: How to Present a Research Proposal
Maninder singh setia.
From the MGM Institute of Health Sciences, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Saumya Panda
1 Department of Dermatology, KPC Medical College, Kolkata, West Bengal, India
This concluding module attempts to synthesize the key learning points discussed during the course of the previous ten sets of modules on methodology and biostatistics. The objective of this module is to discuss how to present a model research proposal, based on whatever was discussed in the preceding modules. The lynchpin of a research proposal is the protocol, and the key component of a protocol is the study design. However, one must not neglect the other areas, be it the project summary through which one catches the eyes of the reviewer of the proposal, or the background and the literature review, or the aims and objectives of the study. Two critical areas in the “methods” section that cannot be emphasized more are the sampling strategy and a formal estimation of sample size. Without a legitimate sample size, none of the conclusions based on the statistical analysis would be valid. Finally, the ethical parameters of the study should be well understood by the researchers, and that should get reflected in the proposal.
As we reach the end of an exhaustive module encompassing research methods and biostatistics, we need to summarize and synthesize the key learning points, to demonstrate how one may utilize the different sections of the module to undertake research projects of different kinds. After all, the practical purpose behind publishing such a module is to facilitate the preparation of high quality research proposals and protocols. This concluding part will make an attempt to provide a window to the different sections of the module, underlining the various aspects of design and analysis needed to formulate protocols applicable to different kinds of clinical research in dermatology.
Components of a Research Proposal
The goal of a research proposal is to present and justify the need to study a research problem and to present the practical ways in which the proposed study should be conducted. A research proposal is generally meant to be presented by an investigator to request an agency or a body to support research work in the form of grants. The vast majority of research proposals, in India, however, are not submitted to agency or body for grants, simply because of the paucity of such agencies, bodies, and research grants. Most are academic research proposals, self-financed, and submitted to scientific and ethics committee of an institution. The parts of a proposal include the title page, abstract/project summary, table of contents, introduction, background and review of literature, and the research protocol.
The title page should contain the personal data pertaining to the investigators, and title of the project, which should be concise and comprehensive at the same time. The table of contents, strictly speaking, is not necessary for short proposals. The introduction includes a statement of the problem, purpose, and significance of the research.
The protocol is the document that specifies the research plan. It is the single most important quality control tool for all aspects of a clinical research. It is the instrument where the researcher explains how data will be collected, including the calculation for estimating sample size, and what outcome variables to measure.
A complete clinical research protocol includes the following:
Study design
- Precise definition of the disease or problem
- Completely defined prespecified primary and secondary outcome measures, including how and when these will be assessed
- Clear description of variables
- Well-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Efficacy and safety parameters
- Whenever applicable, stopping guidelines and parameters of interim analyses
- Sample size calculation
- Randomization details
- Plan of statistical analysis
- Detailed description of interventions
- A chronogram of research flow (Gantt chart)
- Informed consent document
- Clinical research form
- Details of budget; and
- References.
(Modified from: Bagatin et al ., 2013).
Project Summary
The project summary is a brief document that consists of an overview, and discusses the intellectual merits, and broader impacts of the research project. Each of these three sections is required to be present and must be clearly defined. The project summary is one of the most important parts of the proposal. It is likely the first thing a reviewer will read, and is the investigators’ best chance to grab their interest, and convince them of the importance, and quality, of their research before they even read the proposal. Though it is the first proposal element in order, many applicants prefer to write the project summary last, after writing the protocol. This allows the writer to better avoid any inconsistencies between the two.
The overview specifies the research goal and it should demonstrate that this goal fits with the principal investigator's long-term research goals. It should specify the proposed research approach and the educational goal of the research project.
The intellectual merits (the contribution your research will make to your field) should specify the current state of knowledge in the field, and where it is headed. It should also clarify what your research will add to the state of knowledge in the field. Furthermore, important to state is what your research will do to enhance or enable other researches in the field. Finally, one should answer why your research is important for the advancement of the field.
The broader impacts (the contribution the research will make to the society) should answer the questions on the benefit to the society at large from the research, and the possible applications of the research, and why the general public would care. It should also clarify how the research can benefit the site of research (medical college or university, etc.) and the funding agency.
Background and Review of Literature
This is an important component of the research protocol. The review should discuss all the relevant literature, the method used in the literature, the lacunae in the literature, and justify the proposed research. We have provided a list of the useful databases in the section on systematic reviews and meta-analysis (Setia, 2017). Some of these are PubMed, Cochrane database, EMBASE, and LILACS.
Provide a critical analysis of the literature
The researcher should not provide a descriptive analysis of literature. For instance, the literature reviews should not be a list of one article followed by the next article. It should be a critical analysis of literature.
A study by XXXX et al . found that the prevalence of psoriasis was 20%. It was a hospital-based study conducted in North India. The prevalence was 35% in males and 12% in females.
Another study by YYYYY et al . found that the prevalence of psoriasis was 14%. The study was conducted in a private clinic in North India. The prevalence was 8% in males and 18% in females.
A third study by ZZZZZ et al . found that the prevalence of psoriasis was 5%. This study was a community-based study. The prevalence was 7% in males and 3% in females.
In this type of review, the researcher has described all the studies. However, it is useful to understand the findings of these three studies and summarize them in researcher's own words.
A possible option can be “ The reported prevalence of psoriasis in the Indian population varied from 5% to 20%. In general, it was higher in hospital-based studies and lower in community-based studies. There was no consistent pattern in the prevalence of psoriasis in males and females. Though some studies found the prevalence to be higher in males, others reported that females had a higher prevalence .”
Discuss the limitations and lacunae of these studies
The researcher should discuss the limitations of the studies. These could be the limitations that the authors have presented in the manuscript or the ones that the researcher has identified. Usually, the current research proposal should try to address the limitations of a previous study.
A study by BBBB et al : “ One of the main limitations of our study was the lack of objective criteria for assessing anemia in patients presenting with psoriasis. We classified the patients based on clinical assessment of pallor .”
The present proposal can mention “ Though previous studies have assessed the association between anemia and psoriasis, they have not used any objective criteria (such as hemoglobin or serum ferritin levels). Furthermore, pallor was evaluated by three clinicians; the authors have not described the agreement between these clinicians .”
In the above example, the authors have stated the limitation of their research in the manuscript. However, in the review of literature, the researcher has added another limitation. It is important to convince the reviewers that the researcher has read and understood the literature. It is also important that some or most of these lacunae should be addressed in the present proposal as far as possible.
Justify the present proposal by review
The researcher should adequately justify the present proposal based on the review of literature. The justification should not only be for the research question, but also the methods, study design, variables of interest, study instruments or measurements, and statistical methods of choice. Sometimes, the justification can be purely statistical. For example, all the previous studies have used cross-sectional data or cross-sectional analysis of longitudinal data in their manuscripts. The present proposal will use methods used for longitudinal data analysis. The researcher should justify the benefit of these methods over the previous statistical methods.
In short, the review should not be a “laundry list” of all the articles. The review should be able to convince the reader that the present research is required and it builds on the existing literature (either as a novel research question, new measurement of the outcome, a better study design, or advanced and appropriate statistical methods).
Kindly try to avoid this justification: “ It has not been done in our center .”
Aims and Objectives
The “aim” of the study is an overarching goal of the study. The objectives are measurable and help the researcher achieve the overall aim.
For example, the overall aim of our study is to assess the long-term health of patients of psoriasis.
The specific objectives are:
- To record the changes in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score in patients with psoriasis over a period of 5 years
- To study the side effects of medications in these patients over a period of 5 years.
It is important to clearly state the objectives, since the research proposal should be designed to achieve these objectives.
For example, the methods should describe the following:
- How will the researcher answer the first objective?
- Where will the researcher recruit the study participants (study site and population)?
- Which patients of psoriasis will be recruited (inclusion and exclusion criteria)?
- What will be the design of the study (cohort, etc.)?
- What are all the variables to be measured to achieve the study outcomes (exposure and outcome variables)?
- How will the researcher measure these variables (clinical evaluation, history, serological examination, etc.)?
- How will the researcher record these data (clinical forms, etc.)?
- How will the researcher analyze the data that have been collected?
- Are there any limitations of these methods? If so, what has the researcher done to minimize the limitations?
All the ten modules on research methodology have to be read and grasped to plan and design any kind of research applicable to one's chosen field. However, some key areas have been outlined below with examples to appreciate the same in an easier manner.
The study setting must be specified. This should include both the geographical location and the population from which the study sample would be recruited.
“The study took place at the antiretroviral therapy clinic of Queen Elizabeth Central Hospital in Blantyre, Malawi, from January 2006 to April 2007. Blantyre is the major commercial city of Malawi, with a population of 1,000,000 and an estimated HIV prevalence of 27% in adults in 2004” (Ndekha et al ., 2009).
This is a perfect example of description of a study setting which underscores the importance of planning it in detail a priori .
Study population, sampling strategy, and sample size
Study population has to be clearly and precisely defined. For example, a study on atopic dermatitis may be conducted upon patients defined according to the UK Working Party's modified diagnostic criteria, or the Hanifin and Rajka's criteria, or some other criteria defined by the investigators. However, it should always be prespecified within the protocol.
Similarly, the eligibility criteria of the participants for the study must be explicit. One truism that is frequently forgotten is that the inclusion and exclusion criteria are mutually exclusive, and one is not the negative image of the other. Eligible cases are included according to a set of inclusion criteria, and this is followed by administration of the exclusion criteria. Thus, in fact, they can never be the negative image of each other.
“Eligible participants were all adults aged 18 or over with HIV who met the eligibility criteria for antiretroviral therapy according to the Malawian national HIV treatment guidelines (WHO clinical stage III or IV or any WHO stage with a CD4 count < 250/mm 3 ) and who were starting treatment with a BMI < 18.5. Exclusion criteria were pregnancy and lactation or participation in another supplementary feeding program” (Ndekha et al ., 2009).
To put in perspective the point we made about inclusion and exclusion criteria, in the above example, “age above 18 years” or “CD4 count >250/mm 3 ” cannot be exclusion criteria, as these have already been excluded.
Sampling strategy has been adequately discussed in the Module 5 of the Methodology series (Setia, 2016). A few points are worth repeating:
- The sampling strategy should never be misrepresented. Example: If you have not done random sampling, no big deal. There are other legitimate sampling strategies available for your study. But once you have mentioned “random sampling” in your protocol, you cannot resort to purposive sampling
- Sometimes, the researcher might want to know the characteristics of a certain problem within a specific population, without caring for generalizability of results. In such a scenario, purposive sampling may be resorted to
- Nonprobability sampling methods such as consecutive consenting sampling or any such convenience sampling are perfectly legitimate and easy to do, particularly in case of dissertations where time and resources are limited.
Sample size is one of the most misunderstood, yet fundamentally important, issues among clinicians and has to be addressed once the study objectives have been set and the design has been finalized. Too small a sample means that there would be a failure to detect change following test intervention. A sample larger than necessary may also result in bad quality data. In either case, there would be ethical problems and wastage of resources. The researcher needs just enough samples to draw accurate inferences, which would be adequately powered (Panda, 2015).
Estimation of sample size has been dealt with adequately in the Module 5 biostatistics series (Hazra et al ., 2016), including the different mathematical derivations and the available software. Sample size determination is a statistical exercise based on the probability of errors in testing of hypothesis, power of the sample, and effect size. Although, relatively speaking, these are simple concepts to grasp, a large number of different study designs and analytical methods lead to a bewilderingly large number of formulae for determining sample size. Thus, the software are really handy and are becoming increasingly popular.
The study design defines the objectives and end points of the study, the type and manner of data collection, and the strategy of data analysis (Panda 2015). The different types of clinical studies have been depicted in Figure 1 . The suitability of various study designs vis-à-vis different types of research questions is summarized in Table 1 .

Types of study (Source: Panda, 2015)
Research questions vis-a-vis study designs

In our previous series of ten modules on methodology, we have discussed all these different kinds of studies and more. Some key issues that require reiteration are given below:
- The control of a case–control study and that of a randomized controlled trial is more different from each other than chalk is from cheese. The former is an observational study, while the latter is an interventional one. Every study with a control group is not a case–control study. For a study to be classified as a case–control study, the study should be an observational study and the participants should be recruited based on their outcome status (Setia, 2016). Apparently, this is not so difficult to understand, yet even now we have publications which confuse between the different kinds of controls (Bhanja et al ., 2015)
- Due to the fact that the outcome and exposure are assessed at the same time point in a cross-sectional study, it is pretty difficult, if not impossible, to derive causal relationships from such a study. At most, one may establish statistical association between exposures and outcomes by calculating the odds ratio. However, these associations must not be confused with causation.
- It is generally said that a cohort design may not be efficient for rare outcomes. However, if the rare outcome is common in some exposures, it may be useful to follow a cohort design. For example, melanoma is a rare condition in India. Hence, if we follow individuals to study the incidence of melanoma, it may not be efficient. However, if we know that, in India, acral lentiginous melanoma is the most commonly reported variant, we should follow a cohort of individuals with acral lentiginous and study the incidence of melanoma in this group (Setia, 2016).
Clinical researchers should also be accustomed with observational designs beyond case–control, cohort, and cross-sectional studies. Sometimes, the unit of analysis has to be a group or aggregate rather than the individual. Consider the following example:
The government introduced the supplementation of salt with iodine for about 20 years. However, not all states have used the same level of iodine in salt. Certain hilly states have used higher quantities compared with other states. Incidentally, you read a report that high iodine levels are associated with psoriasis. You are intrigued to find if introduction of iodine has altered the picture of psoriasis in the country. You feel compelled to design a study to answer this question .
It is obvious that here the unit of study cannot be individuals, but a large population distributed in a certain geographical area. This is the domain of ecologic studies. An allied category of observational studies is named “natural experiments,” where the exposure is not assigned by the investigator (as in an interventional study), but through “natural processes.” These may be through changes in the existing regulations or public policies or, may be, through introduction of new laws (Setia, 2017).
Another category of research questions that cannot be satisfactorily captured by all the quantitative methods described earlier, like social stigma experienced by patients or their families with, say, vitiligo, leprosy, or sexually transmitted infections, are best dealt with by qualitative research. As can be seen by the examples given above, this is a type of research which is very relevant to medical research, yet to which the regular medical researcher has got a very poor exposure, if any. We shall encourage interested researchers to take a look at the 10 th Module of the Methodology series that specifically deals with qualitative research (Setia, 2017).
Clinical studies are experiments that are not conducted in laboratories but in controlled real-life settings on human subjects with some disease. Hence, designing a study involves many pragmatic considerations aside pure methodology. Thus, factors to consider when selecting a study design are objectives of the study, time frame, treatment duration, carryover effects, cost and logistics, patient convenience, statistical considerations, sample size, etc. (Panda, 2015).
Certain truisms regarding study designs should always be remembered: a study design has to be tailored to objectives. The same question may be answered by different designs. The optimum design has to be based on workforce, budgetary allocation, infrastructure, and clinical material that may be commanded by the researchers. Finally, no design is perfect, and there is no design to provide a perfect answer to all research questions relevant to a particular problem (Panda, 2015).
Variables of interest and collection of these variables
Data structure depends on the characteristics of the variables [ Figure 2 ]. A variable refers to a particular character on which a set of data are recorded. Data are thus the values of a variable (Hazra et al ., 2016).

Types of data and variables (Source: Panda, 2015)
Quantitative data always have a proportional scale among values, and can be either discrete (e.g., number of moles) or continuous (e.g., age). Qualitative data can be either nominal (e.g., blood groups) or ordinal (e.g., Fitzpatrick's phototypes I-VI). Variables can be binary or dichotomous (male/female) or multinomial or polychotomous (homosexual/bisexual/heterosexual) (Panda, 2015).
Changing data scales is possible so that numerical data may become ordinal and ordinal data may become nominal. This may be done when the researcher is not confident about the accuracy of the measuring instrument, is unconcerned about the loss of fine detail, or where group numbers are not large enough to adequately represent a variable of interest. It may also make clinical interpretation easier (Hazra et al ., 2016).
The variables whose effects are observed on other variables are known as independent variables (e.g., risk factors). The latter kind of variables that change as a result of independent variables are known as dependent variables (i.e., outcome). Confounders are those variables that influence the relation between independent and dependent variables (e.g., the clinical effect of sunscreen used as part of a test intervention regimen in melasma). If the researcher fails to control or eliminate the confounder, it will damage the internal validity of an experiment (Panda, 2015).
Biostatistics begins with descriptive statistics that implies summarizing a collection of data from a sample or population. An excellent overview of descriptive statistics has been given in the Module 1 of the Biostatistics series (Hazra et al ., 2016). We would encourage every researcher to embark on designing and collecting data on their own to go through this particular module to have a clear idea on how to proceed further.
Statistical methods
As briefly discussed earlier, the “methods” section should also include a detailed description of statistical methods. It is best to describe the methods for each objective.
For example: Which statistical methods will the researcher use to study the changes in PASI score over time?
It is important to first identify the nature of the outcome – will it be linear or categorical?
- It may be noticed that the PASI is a score and can range from 0 to 72. The researcher can measure the actual score and assess the changes in score. Thus, the researcher will use methods for statistical analysis of continuous data (such as means, standard deviations, t -test, or linear regressions)
- However, the researcher may choose to cut off the PASI score at 60 (of course, there has to be justification!) and call it severe psoriasis. Thus, the researcher will have an outcome variable with two outcomes (Yes: >60 PASI, and No: <60 PASI). Thus, in this case, the researcher will use methods for statistical analysis of categorical data (proportions, Chi-square test, or logistic regression models).
The statistical methods have been described in detail in the Biostatistics section of the series. The reader is encouraged to read all the sections to understand these methods. However, the key points to remember are:
- Identify the nature of the outcome for each objective
- Describe the statistical methods separately for each objective
- Identify the methods to handle confounding and describe them in the statistical methods
- If the researcher is using advanced statistical methods or specific tools, please provide reference to these methods
- Provide the name of the statistical software (including the version) that will be used for data analysis in the present study
- Do not provide a laundry list of all the statistical methods. It just shows that the researcher has not understood the relevance of statistics in the study design.
Multivariate models
In general, multivariate analyses are used in studies and research proposals. These analyses are useful to adjust for confounding (though these are also useful to test for interaction, we shall discuss confounding in this section). For example, we propose to compare two different types of medications in psoriasis. We have used secondary clinical data for this study. The outcome of interest is PASI score. We have collected data on the type of medication, age, sex, and alcohol use. When we compare the PASI score in these two groups, we will use t -test (if linear comparison) or Chi-square test (if PASI is categorized – as described earlier). However, it is possible that age, sex, and alcohol use may also play a role in the clinical progression of psoriasis (which is measured as PASI score). Thus, the researcher would like to account for differences in these variables in the two groups. This can be done using multivariate analytical methods (such as linear regression for continuous variables and logistic regression for categorical dichotomous variables). This is a type of mathematical model in which we include multiple variables: the main explanatory variable (type of drug in this study) and potential confounders (age, sex, and alcohol use in this study). Thus, the outcome (PASI score) after multivariate analyses will be “adjusted” for age, sex, and alcohol use after multivariate analysis. We would like to encourage the readers to consult a statistician for these methods.
TRIVIA: The singular for “data” is “datum,” just as “stratum” is the singular for “strata.” Thus, “ data were analyzed …,” “ data were collected …,” and “ data have been ….”
Clinical Record Forms
We have discussed designing of questionnaires and clinical record forms (CRFs) in detail in two modules. We shall just highlight the most important aspects in this part. The CRF is an important part of the research protocol. The CRF should include all the variables of interest in the study. Thus, it is important to make a list of all parameters of interest before working on the CRF. This can be done by a thorough review of literature and discussion with experts. Once the questionnaire/CRF has been designed, the researcher should pilot it and change according to the feedback from the participants and one's own experience while administering the questionnaire or recording data in the CRF. The CRF should use coded responses (for close-ended questions), this will help in data entry and analysis. If the researcher has developed a scale, the reliability and validity should be tested (methods have been discussed in earlier sections). The CRF can be paper based or computer based (it will depend on the resources).
It is very important to describe the ethics for the present study. It should not be restricted to “ The study will be evaluated by an Institutional Review Committee …” The researcher should demonstrate that s/he has understood the various ethical issues in the present study. The three core principles for ethics are: autonomy (the participants have a right to decide whether to participate in the study or opt out), beneficence/nonmaleficence (the study should not be harmful to participants and the risk–benefit ratio should be adequately understood and described), and justice (all the risks and benefits of the present study should be equally distributed).
The researcher should try to address these issues in the section of “Ethics.” Currently, the National Institutes of Health has proposed the following seven principles of “Ethics in Clinical Research:” social and clinical value, scientific validity, fair subject selection, favorable risk–benefit ratio, independent review, informed consent, and respect for potential and enrolled subjects. The Indian Council of Medical Research has also published guidelines to conduct biomedical research in India. We strongly encourage the readers to be familiar with these guidelines. Furthermore, the researchers should keep themselves updated with changes in these regulations. If it is a clinical trial, the researcher should also be familiar with Schedule Y and Consent form requirements for these types of clinical trials.
Concluding Remarks
This module has been designed as a comprehensive guide for a dermatologist to enable him/her to embark on the exciting journey of designing studies of almost any kind that can be thought to be of relevance to clinical dermatology. There has been a conscious attempt to customize the discussion on design and analysis keeping not only dermatology, but also Indian conditions in mind. However, the module can be of help to any medical doctor embarking on the path to medical research. As contributors, it is our ardent hope that this module might act as a catalyst of good-quality research in the field of dermatology and beyond in India and elsewhere.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Bibliography

Synthesis and Making Connections for Strong Analysis
by acburton | Apr 25, 2024 | Resources for Students , Writing Resources

If Russian Dolls Aren’t For You, Here Are a Few Other Ways to Think About Synthesis
‘Joining the Conversation’: When we perform synthesis in our writing and engage with making connections, we are joining a wider conversation. We are seeing what has already been said about the topic, seeking out what these many perspectives and viewpoints have in common and/or how they differ, and then interpreting these relationships to form our own input to the conversation. We must directly engage with our sources to draw insightful conclusions and share what we think as a result. ‘Building the Bridge’: Synthesis is building the bridge between your sources for the reader. To synthesize or make connections, we must figure out how we get from one source to the other. In other words, we cannot present our sources in isolation (this wouldn’t help create any new meaning). Instead, we need to build the bridge between source A and source B so that our readers can understand what the two, together, suggest about our understanding of a topic. Then, we build a bridge from this new understanding to source C and source D, and so on.
Start Synthesizing
So you want to synthesize information? To start, review the existing literature on your selected topic. When searching for resources, aim to collect a number from various authors, subjects, and settings to broaden your understanding of the material – giving yourself more information to consider in the next stage. Ultimately, you’ll want to find the main idea presented in each source, as well as how the author supports or argues against it, as well as why.
- Compare and Contrast
Compare and contrast the main idea found in each source reviewed. What does each perspective have in common? What are their differences? Begin to consider how these sources ‘fit together’ (or, in other words, build the bridge!). During this stage, you may find that some of your collected resources don’t have as much depth or go into as much detail as you’d like. That’s okay, but you’ll want to consider what effect this might have on your ability to draw a meaningful conclusion once synthesized with other source material.
- Ask, What’s the Significance?
By evaluating the quality and significance of each source, you can begin to consider its relevance within the context of your research or in relation to your topic. How does the relationship of one source to another further your understanding of the topic you are focusing on? What is the larger impact of what is being said or argued?
- Infer the Relationship and Draw Conclusions
By this point, you have gone through the existing literature surrounding your subject and compared/contrasted it, finding the main idea of each, as well as their intended purpose, possible criticisms, strengths, and weaknesses. Finally, you have related these ideas to your own research. Although you may have found that your sources agree or disagree on minor (or major) key details, it is the writer’s job to seek the relationship between these sources, put them in conversation together, and draw meaning through analysis. In some cases, you’ll be asked to offer your own perspective or argumentation. Consider, how might you add to the existing conversation?
Synthesis is all about meaningful connections, it is not summarizing sources side by side. Before you make larger claims about a topic, make sure you build those bridges between the sources you found through research. Nestle them together. Move beyond summary. Then, you can create an interesting and compelling argument. For additional help, make an appointment with the Writing Center!
Works Cited
Kourakos, Evanthia J. “The Matryoshka-Doll Effect.” Medium , Azure’s Whereabouts, 22 Apr. 2016, medium.com/azure-s- whereabouts/the-matryoshka- doll-effect-be9d2760d2e2 .Acces sed 25 Apr. 2024.
“Libguides: English Research: Synthesizing Information.” Synthesizing Information – English Research – LibGuides at Aultman Health Sciences Library , aultman.libguides.com/c.php?g= 545558&p=7711993 . Accessed 25 Apr. 2024.
Should I do a synthesis (i.e. literature review)?
- Questions & Quandaries
- Published: 18 April 2024
Cite this article

- H. Carrie Chen 1 ,
- Ayelet Kuper 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Jennifer Cleland 5 &
- Patricia O’Sullivan 6
257 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This column is intended to address the kinds of knotty problems and dilemmas with which many scholars grapple in studying health professions education. In this article, the authors address the question of whether one should conduct a literature review or knowledge synthesis, considering the why, when, and how, as well as its potential pitfalls. The goal is to guide supervisors and students who are considering whether to embark on a literature review in education research.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Two junior colleagues come to you to ask your advice about carrying out a literature review on a particular topic. “Should they?” immediately pops into your mind, followed closely by, if yes, then what kind of literature review is appropriate? Our experience is that colleagues often come to suggest a literature review to “kick start” their research (in fact, some academic programs require them as part of degree requirements), without a full understanding of the work involved, the different types of literature review, and what type of literature review might be most suitable for their research question. In this Questions and Quandaries, we address the question of literature reviews in education research, considering the why, when, and how, as well as potential pitfalls.
First, what is meant by literature review? The term literature review has been used to refer to both a review of the literature and a knowledge synthesis (Maggio et al., 2018 ; Siddaway et al., 2019 ). For our purposes, we employ the term as commonly used to refer to a knowledge synthesis , which is a formal comprehensive review of the existing body of literature on a topic. It is a research approach that critically integrates and synthesizes available evidence from multiple studies to provide insight and allow the drawing of conclusions. It is an example of Boyer’s scholarship of integration (Boyer, 1990 ). In contrast, a review of the literature is a relatively casual and expedient method for attaining a general overview of the state of knowledge on a given topic to make the argument that a new study is needed. In this interpretation, a literature review serves as a key starting point for anyone conducting research by identifying gaps in the literature, informing the study question, and situating one’s study in the field.
Whether a formal knowledge synthesis should be done depends on if a review is needed and what the rationale is for the review. The first question to consider is whether a literature review already exists. If no, is there enough literature published on the topic to warrant a review? If yes, does the previous review need updating? How long has it been since the last review and has the literature expanded so much or are there important new studies that need integrating to justify an updated review? Or were there flaws in the previous review that one intends to address with a new review? Or does one intend to address a different question than the focus of the previous review?
If the knowledge synthesis is to be done, it should be driven by a research question. What is the research question? Can it be answered by a review? What is the purpose of the synthesis? There are two main purposes for knowledge synthesis– knowledge support and decision support. Knowledge support summarizes the evidence while decision support takes additional analytical steps to allow for decision-making in particular contexts (Mays et al., 2005 ).
If the purpose is to provide knowledge support, then the question is how or what will the knowledge synthesis add to the literature? Will it establish the state of knowledge in an area, identify gaps in the literature/knowledge base, and/or map opportunities for future research? Cornett et al., performed a scoping review of the literature on professional identity, focusing on how professional identity is described, why the studies where done, and what constructs of identity were used. Their findings advanced understanding of the state of knowledge by indicating that professional identity studies were driven primarily by the desire to examine the impact of political, social and healthcare reforms and advances, and that the various constructs of professional identity across the literature could be categorized into five themes (Cornett et al., 2023 ).
If, on the other hand, the purpose of the knowledge synthesis is to provide decision support, for whom will the synthesis be relevant and how will it improve practice? Will the synthesis result in tools such as guidelines or recommendations for practitioners and policymakers? An example of a knowledge synthesis for decision support is a systematic review conducted by Spencer and colleagues to examine the validity evidence for use of the Ottawa Surgical Competency Operating Room Evaluation (OSCORE) assessment tool. The authors summarized their findings with recommendations for educational practice– namely supporting the use of the OSCORE for in-the-moment entrustment decisions by frontline supervisors in surgical fields but cautioning about the limited evidence for support of its use in summative promotions decisions or non-surgical contexts (Spencer et al., 2022 ).
If a knowledge synthesis is indeed appropriate, its methodology should be informed by its research question and purpose. We do not have the space to discuss the various types of knowledge synthesis except to say that several types have been described in the literature. The five most common types in health professions education are narrative reviews, systematic reviews, umbrella reviews (meta-syntheses), scoping reviews, and realist reviews (Maggio et al., 2018 ). These represent different epistemologies, serve different review purposes, use different methods, and result in different review outcomes (Gordon, 2016 ).
Each type of review lends itself best to answering a certain type of research question. For instance, narrative reviews generally describe what is known about a topic without necessarily answering a specific empirical question (Maggio et al., 2018 ). A recent example of a narrative review focused on schoolwide wellbeing programs, describing what is known about the key characteristics and mediating factors that influence student support and identifying critical tensions around confidentiality that could make or break programs (Tan et al., 2023 ). Umbrella reviews, on the other hand, synthesize evidence from multiple reviews or meta-analyses and can illuminate agreement, inconsistencies, or evolution of evidence on a topic. For example, an umbrella review on problem-based learning highlighted the shift in research focus over time from does it work, to how does it work, to how does it work in different contexts, and pointed to directions for new research (Hung et al., 2019 ).
Practical questions for those considering a literature review include whether one has the time required and an appropriate team to conduct a high-quality knowledge synthesis. Regardless of the type of knowledge synthesis and use of quantitative or qualitative methods, all require rigorous and clear methods that allow for reproducibility. This can take time, up to 12–18 months. A high-quality knowledge synthesis also requires a team whose members have expertise not only in the content matter, but also in knowledge synthesis methodology and in literature searches (i.e. a librarian). A team with multiple reviewers with a variety of perspectives can also help manage the volume of large reviews, minimize potential biases, and strengthen the critical analysis.
Finally, a pitfall one should be careful to avoid is merely summarizing everything in the literature without critical evaluation and integration of the information. A knowledge synthesis that merely bean counts or presents a collection of unconnected information that has not been reflected upon or critically analyzed does not truly advance knowledge or decision-making. Rather, it leads us back to our original question of whether it should have been done in the first place.
Boyer, E. L. (1990). Scholarship reconsidered: Priorities of the professoriate (pp. 18–21). Princeton University Press.
Cornett, M., Palermo, C., & Ash, S. (2023). Professional identity research in the health professions—a scoping review. Advances in Health Sciences Education , 28 (2), 589–642.
Article Google Scholar
Gordon, M. (2016). Are we talking the same paradigm? Considering methodological choices in health education systematic review. Medical Teacher , 38 (7), 746–750.
Hung, W., Dolmans, D. H. J. M., & van Merrienboer, J. J. G. (2019). A review to identify key perspectives in PBL meta-analyses and reviews: Trends, gaps and future research directions. Advances in Health Sciences Education , 24 , 943–957.
Maggio, L. A., Thomas, A., & Durning, S. J. (2018). Knowledge synthesis. In T. Swanwick, K. Forrest, & B. C. O’Brien (Eds.), Understanding Medical Education: Evidence, theory, and practice (pp. 457–469). Wiley.
Mays, N., Pope, C., & Popay, J. (2005). Systematically reviewing qualitative and quantitative evidence to inform management and policy-making in the health field. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy , 10 (1_suppl), 6–20.
Siddaway, A. P., Wood, A. M., & Hedges, L. V. (2019). How to do a systematic review: A best practice guide for conducting and reporting narrative reviews, meta-analyses, and meta-syntheses. Annual Review of Psychology , 70 , 747–770.
Spencer, M., Sherbino, J., & Hatala, R. (2022). Examining the validity argument for the Ottawa Surgical Competency operating room evaluation (OSCORE): A systematic review and narrative synthesis. Advances in Health Sciences Education , 27 , 659–689.
Tan, E., Frambach, J., Driessen, E., & Cleland, J. (2023). Opening the black box of school-wide student wellbeing programmes: A critical narrative review informed by activity theory. Advances in Health Sciences Education . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-023-10261-8 . Epub ahead of print 02 July 2023.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Georgetown University School of Medicine, Washington, DC, USA
H. Carrie Chen
Wilson Centre for Research in Education, University Health Network, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Ayelet Kuper
Division of General Internal Medicine, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center, Toronto, Canada
Department of Medicine, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
Jennifer Cleland
University of California San Francisco School of Medicine, San Francisco, CA, USA
Patricia O’Sullivan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to H. Carrie Chen .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Chen, H.C., Kuper, A., Cleland, J. et al. Should I do a synthesis (i.e. literature review)?. Adv in Health Sci Educ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-024-10335-1
Download citation
Published : 18 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-024-10335-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Help | Advanced Search
Astrophysics > High Energy Astrophysical Phenomena
Title: population synthesis of galactic pulsars with machine learning.
Abstract: This thesis work represents the first efforts to combine population synthesis studies of the Galactic isolated neutron stars with deep-learning techniques with the aim of better understanding neutron-star birth properties and evolution. In particular, we develop a flexible population-synthesis framework to model the dynamical and magneto-rotational evolution of neutron stars, their emission in radio and their detection with radio telescopes. We first study the feasibility of using deep neural networks to infer the dynamical properties at birth and then explore a simulation-based inference approach to predict the birth magnetic-field and spin-period distributions and the late-time magnetic-field decay for the observed radio pulsar population. Our results for the birth magneto-rotational properties agree with the findings of previous works while we constrain the late-time evolution of the magnetic field in neutron stars for the first time. Moreover, this thesis also studies possible scenarios to explain the puzzling nature of recently discovered periodic radio sources with very long periods of the order of thousands of seconds. In particular, by assuming a neutron-star origin, we study the spin-period evolution of a newborn neutron star interacting with a supernova fallback disk and find that the combination of strong, magnetar-like magnetic fields and moderate accretion rates can lead to very large spin periods on timescales of ten thousands of years. Moreover, we perform population synthesis studies to assess the possibility for these sources to be either neutron stars or magnetic white dwarfs emitting coherently through magnetic dipolar losses. These discoveries have opened up a new perspective on the neutron-star population and have started to question our current understanding of how coherent radio emission is produced in pulsar magnetospheres.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- INSPIRE HEP
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

COMMENTS
On This Page: Step 1 Organize your sources. Step 2 Outline your structure. Step 3 Write paragraphs with topic sentences. Step 4 Revise, edit and proofread. When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you've read - you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and ...
Use the worksheet (above) or synthesis matrix (below) to get organized. This work can be messy. Don't worry if you have to go through a few iterations of the worksheet or matrix as you work on your lit review! The Four Examples of Student Writing come from a synthesis exercise created by Candice Benjes-Small.
Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix. Published on July 4, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan.Revised on May 31, 2023. Synthesizing sources involves combining the work of other scholars to provide new insights. It's a way of integrating sources that helps situate your work in relation to existing research.. Synthesizing sources involves more than just summarizing.
Meta-Study: What is it? "Meta-study is a research approach involving analysis of the theory, methods, and findings of qualitative research and the synthesis of these insights into new ways of thinking about phenomenon" [, p.1]. Data type: Three analytic components are undertaken prior to synthesis. Data includes qualitative findings (meta ...
When asked to synthesize sources and research, many writers start to summarize individual sources. However, this is not the same as synthesis. In a summary, you share the key points from an individual source and then move on and summarize another source. In synthesis, you need to combine the information from those multiple sources and add your ...
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other. After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix or use a citation manager to help you see how they relate to each other and apply to each of your themes or variables. By arranging your sources by theme or ...
In this post, we'll unpack what exactly synthesis means and show you how to craft a strong literature synthesis using practical examples. This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp. In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step.
Box 9.2.a provides a general framework for synthesis that can be applied irrespective of the methods used to synthesize results. Planning for the synthesis should start at protocol-writing stage, and Chapter 2 and Chapter 3 describe the steps involved in planning the review questions and comparisons between intervention groups. These steps included specifying which characteristics of the ...
Meta-analysis is the quantitative, scientific synthesis of research results. Since the term and modern approaches to research synthesis were first introduced in the 1970s, meta-analysis has had a ...
Local synthesis occurs at the paragraph level when writers connect individual pieces of evidence from multiple sources to support a paragraph's main idea and advance a paper's thesis statement. A common example in academic writing is a scholarly paragraph that includes a main idea, evidence from multiple sources, and analysis of those ...
Synthesis is achieved by comparing and contrasting paraphrased information on a given topic. Discussions of the literature should be focused not on study-by-study summaries (see the Creating a Literature Review Outline SMRTguide). Writers should begin by using comparison language (indicated in bold and highlighted text in the examples below) to combine ideas on a given topic:
4. Restructure your notes by concept. Now, each of those concepts gets its own two-column notes page. This time, the authors will go on the left-hand column and you will transfer the notes from step two specific to that concept on the right side. Think of it as if you were cutting apart your article notes, categorizing them by concept and ...
Argumentative syntheses seek to bring sources together to make an argument. Both types of synthesis involve looking for relationships between sources and drawing conclusions. In order to successfully synthesize your sources, you might begin by grouping your sources by topic and looking for connections. For example, if you were researching the ...
This step of outlining your thesis and main points is a crucial one when writing a synthesis. If your goal in writing a research essay is to provide readers a unified perspective based on sources, the unified perspective must be clear before the writing begins. Once the writing begins, your point of view is then carried through to the paragraph ...
The synthesis matrix is a chart that allows a researcher to sort and categorize the different arguments presented on an issue. Across the top of the chart are the spaces to record sources, and along the side of the chart are the spaces to record the main points of argument on the topic at hand. As you examine your first source, you will work ...
The originators of meta-narrative synthesis, critical interpretive synthesis and meta-study all articulate what might be termed a 'subjective idealist' approach to knowledge. Paterson et al state that meta-study shies away from creating 'grand theories' within the health or social sciences and assume that no single objective reality will be ...
Synthesis is a form of analysis related to comparison and contrast, classification and division. On a basic level, synthesis involves bringing together two or more sources, looking for themes in each. In synthesis, you search for the links between various materials in order to make your point. Most advanced academic writing relies heavily on ...
The writing process for composing a good synthesis essay requires curiosity, research, and original thought to argue a certain point or explore an idea. Synthesis essay writing involves a great deal of intellectual work, but knowing how to compose a compelling written discussion of a topic can give you an edge in many fields, from the social sciences to engineering.
The project summary is a brief document that consists of an overview, and discusses the intellectual merits, and broader impacts of the research project. Each of these three sections is required to be present and must be clearly defined. The project summary is one of the most important parts of the proposal.
A synthesis paper is a written discussion that incorporates support from multiple sources to examine a variety of viewpoints related to a thesis. It is commonly used in various types of assignments such as analysis papers, research papers, argument papers, and business reports. To write an effective synthesis essay, it is crucial to establish a clear purpose, carefully select and evaluate ...
Synthesis "present new ideas based on interpretations of other evidence or arguments" (Writing Center) Audio: So, we like to think of thesis and synthesis as connected, as interlocking. That's why they are both in this webinar today. We define the thesis at the Writing Center as a brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose.
1. Introduction. Research or scientific synthesis is the integration and assessment of knowledge and research findings pertinent to a particular issue with the aim of increasing the generality and applicability of, and access to, those findings (Hampton & Parker 2011, Magliocca et al., 2014, Baron et al. 2017).Synthesis of existing research and case studies can also generate new knowledge.
Chapter 5 (Synthesis and interpretation of findings) covers the following topics: definition of discussion; importance of a good discussion; general rules of discussion; content of discussion ...
Each time we dig into a source, we're searching for the nuances of that source's ideas - their thesis or argument, their purpose, criticisms, weaknesses, etc. one doll after another. When we dig deeper and continue to open up the source, we're bound to unearth something new, down to the finest detail.
This column is intended to address the kinds of knotty problems and dilemmas with which many scholars grapple in studying health professions education. In this article, the authors address the question of whether one should conduct a literature review or knowledge synthesis, considering the why, when, and how, as well as its potential pitfalls. The goal is to guide supervisors and students who ...
This thesis work represents the first efforts to combine population synthesis studies of the Galactic isolated neutron stars with deep-learning techniques with the aim of better understanding neutron-star birth properties and evolution. In particular, we develop a flexible population-synthesis framework to model the dynamical and magneto-rotational evolution of neutron stars, their emission in ...