NCI LIBRARY
Academic writing skills guide: structuring your assignment.
- Key Features of Academic Writing
- The Writing Process
- Understanding Assignments
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Planning Your Assignments
- Thesis Statements
- Writing Drafts
- Structuring Your Assignment
- How to Deal With Writer's Block
- Using Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Introductions
- Revising & Editing
- Proofreading
- Grammar & Punctuation
- Reporting Verbs
- Signposting, Transitions & Linking Words/Phrases
- Using Lecturers' Feedback
Keep referring back to the question and assignment brief and make sure that your structure matches what you have been asked to do and check to see if you have appropriate and sufficient evidence to support all of your points. Plans can be structured/restructured at any time during the writing process.
Once you have decided on your key point(s), draw a line through any points that no longer seem to fit. This will mean you are eliminating some ideas and potentially letting go of one or two points that you wanted to make. However, this process is all about improving the relevance and coherence of your writing. Writing involves making choices, including the tough choice to sideline ideas that, however promising, do not fit into your main discussion.
Eventually, you will have a structure that is detailed enough for you to start writing. You will know which ideas go into each section and, ideally, each paragraph and in what order. You will also know which evidence for those ideas from your notes you will be using for each section and paragraph.
Once you have a map/framework of the proposed structure, this forms the skeleton of your assignment and if you have invested enough time and effort into researching and brainstorming your ideas beforehand, it should make it easier to flesh it out. Ultimately, you are aiming for a final draft where you can sum up each paragraph in a couple of words as each paragraph focuses on one main point or idea.

Communications from the Library: Please note all communications from the library, concerning renewal of books, overdue books and reservations will be sent to your NCI student email account.
- << Previous: Writing Drafts
- Next: How to Deal With Writer's Block >>
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 10:00 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ncirl.ie/academic_writing_skills
Griffith University
Popular sites
Home > Library > Study and assignment skills > Write assignments > Structure assignments
- Structure assignments
Write assignments
- About the library
- Resources and borrowing
- Study and assignment skills
- Research and publishing
- Visit our libraries
- Study spaces
- Student orientation
- Staff orientation
- Corporate information
- Course resources
- Library guides
- Borrowing and my account
- Interlibrary loan
- Library catalogue help
- Library apps
- Resolve access issues
- Manage your time
- Read effectively
- Think critically
- Make effective notes
- Work in groups
- Prepare for exams
- Assess your skills
- Record and edit video
- Social media
- Effective email communication
- Understand your assessment
- Prepare to search
- Search for information
- Evaluate your sources
- Assignment types
- Write with academic style
- Edit and proofread
- Use feedback
- AGPS Harvard
- Chicago 17 Notes and Bibliography
- Chicago 17 Author-date
- Academic integrity matters
- Manage and plan
- Find and reuse
- Create and capture
- Process and analyse
- Share and archive
- Research metrics
- Researcher profiles
- Before you publish
- Develop a publishing strategy
- Promote your research
- Engage with open research
- Make research open
- Discover open research
- Read and publish agreements
- Academic writing for researchers
- Search and find research literature
- Organise your research literature
- Literature management software
- Systematic-style reviews
- Research repository
- Guide for students
- Staff setup guide
- Add resources
- Structure reading lists
- Request digitisations
- Resources for teaching
- Workshops and eLearning
- Academic skills model
- Support for individual students
- Contact the library
While there are different types of written assignments , most academic writing has a similar structure comprising of:
- Introduction—acts as a roadmap for the reader.
- Body—presents points to support your argument.
- Conclusion—summarises main points discussed.
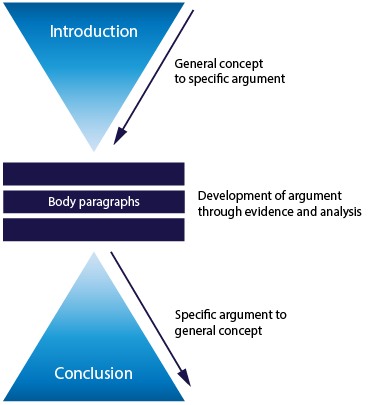
The introduction helps your reader understand where you’re going in your assignment, how you will get there and what they will see along the way.
An introduction should include:
- topic sentence—outline the most important concepts relevant to answering the question
- aim—indicate the focus or purpose of the assignment
- scope—mention any limits of your assignment. What will you emphasise? Will you intentionally leave anything out?
- structure—signal how you will present information in the assignment, and the order the key points will appear
- thesis statement—clearly identify your argument.


Example - Introduction
Online social media network websites allow users to interact with other users creating and sharing content. These social networking websites (SNWs) allow students to create thousands of pieces of content and share it with other users, while educational institutions are using some of these sites and applications to build learning communities with their students. There are several issues related to this increased interaction, namely the ethical use of social media within an educational environment. Two implications of social media will be discussed, focussing on the higher education sector. SNW’s will be defined, and the issues of student privacy related to individual expression and communication in educational forums will be examined. Overall it will be argued that it is imperative for the educational sector, staff and students, to become informed around the privacy issues involved in the use and application of SNWs.
The body consists of paragraphs structured to reflect your critical thinking about the question and the chosen order for presenting your argument.
Each paragraph should include:
- topic sentence—starts each paragraph and expresses the main idea of the paragraph
- evidence and examples—contains explanations to support the key point of the paragraph. Supporting evidence is used to justify, explain or develop your argument.
- concluding sentence—links the main idea of the paragraph back to your argument and to the assignment topic.
The number of paragraphs in your essay will depend upon the length of your essay, and the number of points you wish to argue.

Example - Paragraph
Facebook accounts hold large amounts of personal information of its users and, given the recent data breaches, it is crucial that users understand how to secure personal information. However, research indicates that many users are unaware of how to change the default privacy settings and, therefore, they themselves less secure online (Bones, 2016; Markesh & Pashley 2015). Munoz (2018) contends that at the heart of this dilemma is the fact that private information becomes public once released to a wider social media platform, and consequently, the user loses control over that information. Issues related to this loss include identity theft, cybercrime and inappropriate behaviour such as online stalking and bullying (Gross & Acquisti, 2018). In order to protect and manage online privacy and security, it is important for user to become digitally literate with each social media platform, whether they are being used for personal, professional, or academic reasons.
The conclusion comes at the end of your assignment, summarising the main points discussed.
Importantly, your conclusion should:
- contain no new ideas or information
- briefly list your key points
- relate main points directly back to the question or argument.
You might also make future recommendations, evaluate your argument or forecast patterns of change.

Example - Conclusion
In conclusion this essay has looked at two implications related to the use of social networking websites in the higher education sector. One implication is personal information and online interaction becomes public once it is published online. This implies that staff and students need to become digitally literate in order to interact in an educational setting. Secondly, this essay has raised the challenges of Facebook infrastructure when it comes to implementing social networking into the classroom. Overall, it argues that staff and students need to be aware of the ethical implications of using Facebook in the classroom.
Academic integrity
Understand your academic integrity obligations and responsibilities to act in an honest and ethical manner.
Check out our resources
Ask the library
Common questions.
More answers
We are here to help!
Find us in the libraries or contact us by phone or online.
Request form
(07) 3735 5555
We offer online workshops on researching, referencing, structuring assignments and exam preparation. Come along and improve your skills!
Peer assisted study sessions
Attend a student facilitated group study session.
Griffith mentors study support
Get study support by connecting with a Griffith student mentor.

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that he or she will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove her point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, he or she still has to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and she already knows everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality she or he expects.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Aarhus University logo
AU Studypedia
Assignment structure
The structure of academic assignments often follows a standard outline.
However, depending on the topic of the assignment and the field of study, there may be some variation in the assignment structure. This page provides information about the typical parts of an academic assignment. The page may serve as inspiration on how to put your assignment together, but keep in mind that the structure should be adapted to fit your project, and not the other way around.
Typical content elements
The structure of your assignment depends, among other things, on whether it is a theoretical, empirical or product-oriented assignment. Read more on the page Types of assignments. Moreover, the structure should reflect that your assignment presents one overall argument supported by academic evidence. Read more about assignments as a single argument on the page Argumentation.
Check your academic regulations
The content elements described below are typical parts of an academic assignment, but note that special requirements or recommendations may apply for the structure and content of the assignment you are writing. Therefore, you should always check your academic regulations, and possibly contact your supervisor or teacher at an early stage of the assignment process, so you can incorporate any specific requirements from the start. Be aware that the content elements described below may be called something else in your field of study. Use the terminology traditionally used on your degree programme.
There is often a requirement for major university assignments to include an abstract or a brief summary, either at the beginning or at the end of the assignment. An abstract summarises the assignment’s:
problem and objective
methods
analysis results
conclusion
perspectives
An abstract gives the reader a quick insight into the assignment, so that they can assess whether it is relevant to read.
Note : Not all assignments have to include an abstract. Check your academic regulations or ask your supervisor if you are in doubt. Be aware that the abstract may have to be written in another language than the rest of the assignment.
Introduction
The introduction is where you present the framework of your assignment to your reader and provide an overview of what you want to achieve, and why. This includes a presentation of your topic and the problem you will be looking into, including the relevance of investigating it and how you will go about it.
Edit the introduction continuously in the writing process and write it until the end to make sure that you do not promise more than the assignment provides. Ask yourself whether the conclusion responds to your problem statement, and whether the assignment contains all the aspects you promise in the introduction.
Problem statement/hypothesis
Regardless of whether you formulate it as a problem statement or a hypothesis, the problem addressed in your assignment should stand out clearly. For example, you can write it in italics, highlight it in bold or place it in a separate section with a heading. Read more about how to develop and work with a problem statement on the page Problem statement and hypothesis.
The purpose of the assignment
The overall purpose of the assignment must be stated clearly in the introduction. Stating the purpose means explaining why your assignment is interesting to others and how it contributes to addressing the problem you are investigating. For example, your purpose could be:
Research Overview/Literature Review
At university, you are expected to actively consider pre-existing knowledge about your topic and how it has previously been approached within your field of study. There are several ways to do this depending on the type of assignment and the subject you are studying.
Sometimes you have to present existing research in a separate chapter or section where you discuss the latest research within the field and provide relevant literature reviews. And sometimes, a brief presentation of the most important research will be enough in either the introduction, theory section or elsewhere in the assignment.
Check the academic regulations
Check your academic regulations, or ask your supervisor or teacher about the requirements for including a research overview and pre-existing knowledge in your assignment.
Click here to read more about the conventions for academic work
Note : Not all written assignments have to include an actual research overview. Check your academic regulations or ask your supervisor if you are in doubt.
Philosophy of science
Philosophy of science is a presentation of your approach to what knowledge is and how knowledge is produced. There are different scientific-theoretical schools of thought, with different views on what science is and ought to be.
The schools of thought draw on different ontological understandings (i.e. understandings of how something exists) and different epistemological foundations (i.e. theories of knowledge and assumptions about the world). Examples of scientific-theoretical schools of thought are social constructivism, positivism, phenomenology and hermeneutics.
Explain your scientific-theoretical approach
Your scientific-theoretical approach must be based on philosophy of science literature and must be closely linked to your choices of methods and theories, which you may also elaborate on in this section.
Read more about the use of pre-existing knowledge and independent conclusions on the page Academic standards.
Methods and study design
The chapter on methodology and study design is a prerequisite for the validity of your investigation and analysis. Read more about this on the page about argumentation.
Describe your study design
The methodology section can vary depending on whether your assignment is theoretical, empirical or product-oriented. However, no matter what, it must include a description of how you conduct your study. This is also known as the study design.
The study design refers to the overall framework for data collection and analysis. It should be based on the academic methods you have learned during class, and must be backed by theory of methods.
Explain your choices and trade-offs
Reflecting on and being conscious of the choices that you make is an important part of working academically. Therefore, in the methodology section, you should reflect on your conscious choices and the trade-offs you have had to make (for example due to external circumstances) and how this has affected your study design or your analysis. You can also explain why you have chosen a particular method if there were other obvious alternatives.
The theory section is where you present and account for the theory used in the assignment. Make sure you take an application-oriented approach, i.e. account only for the theory that you actually use to answer your research questions further down in the analysis. Note that the purpose of the theory section is not to report everything you know about a particular field, but to support your study and your analysis as part of your argumentation .
Different ways to integrate theory
You can integrate the theory section in different ways. In some assignments, it makes most sense to have one separate theoretical chapter in which you explain all the theoretical concepts used in your assignment. In other assignments, it may make more sense to briefly present the theory in a separate section and then explain relevant theoretical concepts as they are applied in your analysis. Talk with your supervisor or your teacher about what would be most appropriate in your assignment.
The analysis section of your assignment can take many different forms depending on whether your assignment is theoretical, empirical or product-oriented. The analysis is usually the most comprehensive part of the assignment because this is where you answer your research questions by presenting all your evidence for the overall claim of the assignment.
Read more about argumentation.
Guide your reader through the analysis
Because the analysis is so comprehensive, it is a good idea to use meta-communication to guide the reader through the logic and progress of your assignment. For example, write sub-conclusions to sum up along the way.
Read more about guiding your reader under Academic standards.
Structure of the analysis
In the analysis, the first thing you need to do is present the object, e.g. empirical data or artefacts, that you want to analyse and the tools you want to use for the analysis, e.g. your method, theory or concepts. Then you move on to the actual analysis, where you use the tools to examine the selected object of analysis.
Note that it is difficult to write your analysis section before you have actually performed your analysis because you cannot see patterns, categories, etc. until you have the analysis material in front of you.
Read more about the writing process
In the video below, Master of Arts Rikke Gottfredsen explains what an analysis is (in Danish).
You can structure the analysis using the DAA structure:
Description : Describe the sub-object you are about to analyse (e.g. a quotation or a table).
Analysis : Analyse the sub-object using theories and concepts.
Assessment : Assess what the analysis of the sub-object says about the overall object of analysis.
The DAA structure can be repeated over and over again until all your sub-objects have been analysed.
The discussion part of your assignment is where you criticise and defend your own study, both academically and methodologically. In other words, you have to consider the weaknesses of the assignment while demonstrating that, in spite of these, the assignment is still reliable. This will strengthen the overall argumentation of your assignment.
Discuss your challenges
Encountering challenges during the writing process is quite common, and in some cases, they may serve as input for your discussion section. Note down challenges as they occur, including an explanation of why they occurred. In this way, you will have material for the discussion you are going to write later on.
The conclusion summarises the results of your analysis and reiterates why the assignment is important. It must include clear and well-written answers to the research questions posed in your problem statement, or a confirmation or rejection of the hypothesis tested in your assignment.
Depending on the purpose of your study, which was presented in the introduction, the conclusions may take different forms:
Click here to read more about the characteristics of different purposes of investigation
In addition to answering your research questions, or confirming or rejecting your hypothesis, the conclusion should also summarise the main points and results of the assignment. Moreover, it should include an assessment of your methodology and approach.
The conclusion should never include new material, but should briefly summarise the main points of your study. It can be a good idea to write notes during your writing process that you can use for the conclusion.
Is there a clear link between the introduction and the conclusion?
Once you have finished writing your assignment, try to read the introduction and the conclusion in one go. Then assess whether the promises made in the introduction are being fulfilled in the conclusion, and whether the conclusion answers your research questions/hypothesis.
Perspectives
In some university assignments, you are expected to end the assignment by discussing additional perspectives. The perspectives can be a separate section after the conclusion, they can form part of the conclusion, or they can be integrated into your discussion. Any perspectives should be based on what you have already written in the assignment. In other words, you should not integrate new theory or claims that require new evidence in your perspectives section.
Click here to read about argumentation
Check your academic regulations or talk to your supervisor or teacher if you are uncertain about whether your assignment should contain a perspectives section, and how it should be integrated into the assignment.
Inspiration from assignments by other students
Get a list of thesis titles from your field of study, and draw inspiration from other students’ assignments.
Avoid cheating in your assignment
It is important to follow the rules and guidelines on exam cheating and plagiarism . AU Library guides you on how, so you can easily avoid it.
Writing the Body of an Assignment
Most research in academic English writing tends to focus on aspects of an assignment that are easy for the researcher to analyse. Typically, introductions and conclusions have been considered in much more detail than the main body of an assignment. What comes between the introduction and conclusion (known as the main body ) is often left up to the individual student, and less is known about the typical structures of the main body. On this page, you will find some helpful suggestions and practice activities for developing the body of your assignment, which we hope will 'de-mystify' the process of assignment writing somewhat.
1. What is the structure of the main body of an assignment?
2. Writing the main body of an assignment is a major challenge. Why?
3. Why is it important to be analytical , rather than just descriptive when writing assignments?
- Check out general advice for writing the main body of an assignment
- Download a checklist to help you edit your essays and written work
- Try two practice activities
What is the structure of the main body of an assignment?
The structure of the main body of an assignment is dictated by at least two factors:
a) The title and wording of the assignment (whether it is your own, negotiated with the tutor- or one that has been given to you).
b) The statement of intent that you write in the introduction, based on the title.
Once you have dealt with the above two elements, the main body of the assignment probably then serves to do at least two things:
a) Demonstrate/show your knowledge of the topic, by including relevant evidence;
b) Analyse/evaluate the evidence you have gathered.
The material you use will usually be grouped into broad categories (assignment sections). That is to say, it is strategically organised. Sometimes the broad categories are indicated by sub titles (as in published research). However, in some disciplines, particularly Arts and Humanities and Social Studies undergraduate courses, this is not always desirable or recommended. Scientists and Engineers, on the other hand, will often make their writing more 'user-friendly' by clearly indicating the different sections. Always check with your department to see exactly what the requirements are, and if possible, have a look at some assignments that have been written previously to get a feel for what is required.
back ^
Writing the main body of an assignment is a major challenge. Why?
From the above, writing the main body of an assignment probably sounds remarkably simple! But in fact, it is a major challenge, for a number of reasons:
- It is very easy to wander off the point and to add anecdotal or irrelevant information (one of the biggest causes of examination failure in essay subjects);
Longer assignments can often become shapeless, drifting on with no apparent purpose or aim .
- It is easy to end up by doing something completely different from what you said at the beginning of the assignment. Make sure that you stay 'on track'.
- Too much time is often spent discussing one piece of literature, or one example, and the reader does not get any real sense of academic debate.
- There may be no immediate sense of how one piece of research or writing discussed in an assignment leads on to another. Links between different theories are not always apparent.
The correct items of literature may not be prioritised. Lots of time can be wasted discussing general textbooks instead of primary texts.
It is tempting to 'waffle' in order to 'use up' as many words as you can. This is unwise practice and can also lead to a reduction in marks.
The body of the essay can sometimes become a bit 'mechanical'; following predictable formats can be a reliable and safe, but rather boring way of writing.
Due attention needs to be given to referencing - by no means an easy task.
Use of quotations is often a problem; students often use quotations either because they think it is clever to do so, or because they do not understand the concepts very well. Make sure that your quotations do not simply serve as a decorative ornament, but that you introduce them and comment on them .
It goes without saying that you must always avoid lifting words and phrases from your reading and including them without due acknowledgement ( plagiarism ). Penalties are usually very severe for this kind of practice and you could even end up by failing your assignment.
Analysis vs description: a basic distinction
One of the most important requirements when writing many assignments (depending on the title) is to be analytical, rather than just descriptive. If your assignment title begins with words like these: 'How far do you agree that...?', 'To what extent do you consider that..., or 'Evaluate the success of..., etc, this means that you will need to analyse the topic, as well as describe it . There will obviously be some description: an essay without some descriptive detail would quickly become unreadable! However, the reader will usually be looking for more than description, and if you are looking to cut down on word length, reducing some of the more lengthy descriptions and examples is a useful strategy to adopt.
A key point to remember, then, is that very few assignment titles at university level will require pure description, and most will test your skills of analysis in some capacity. So try to look for the critical point in the essay title.
Unfortunately, it is not very easy to explain exactly what 'being analytical' means. Many tutors say that students need to be more analytical, but saying precisely how to be more analytical (and by implication, more critical) is tricky! The following list is a starting point in helping to build up a picture of what is required in 'analysis'.
- Bringing out the importance of a given aspect of your reading (not just saying again what the writer says).
- Getting the overview/bigger picture , rather than describing an example or case in lots of detail.
- Picking out the key or central aspect of a piece of literature you are reading, rather than describing it from start to finish and 'telling the story'.
- Evaluating (that is, indicating the strengths and weaknesses of) what you are discussing. This is the highest order skill in Bloom's taxonomy of learning (1976), which continues to influence much assessment practice in universities. It requires you to 'stand back' and observe the topic at greater length.
- Comparing different theories to show what they have in common and how they differ (not just saying what the theories are).
- Showing a range of different interpretations of a given fact, detail, opinion or item of literature.
- Adopting the approach that no single theory is the correct one and that there are aspects of all theories that are worth retaining.
- Looking for new questions , as well as answering old ones.
- Avoiding simplistic and passive agreement with the assignment title.
- Adopting a challenging approach to what you read - that is, not just accepting other people's word for it.
- Showing how theories fit in with each other;
- Indicating different schools of thought, and developing your own perspective based on these.
- Recognising the limitations of your own perspective as a writer, and the inevitable impact that your own values and beliefs will have on how you express your opinions
General advice for writing the main body of an assignment
Here is some useful general advice for writing the main body of an assignment.
Plan your work properly before you write . Use brainstorming, mind maps or just a list of points you want to include; whatever works best for you.
Know your audience . Having a good idea of who will be reading your essay or assignment is helpful.
Know what the requirements are . Like any game of skill, in order to write an effective assignment, you have to know what is required. You can't play tennis without knowing the rules of the game. The same is true of writing assignments. The rules of the game are very subtle, of course, and vary from department to department. And unfortunately, even within departments, there may be differences of opinion as to how things should be done. If in doubt, ask your tutor.
Don't expect your tutor to tell you what to say. In some cultures, critical thinking is not strongly encouraged and many assessments are simply a case of reproducing what the lecturer has told you in the lecture. This is not true of the British academic system . In Britain, you are expected to think critically and to react to (as well as simply describe) what you have learned. This is not an easy skill to develop but it usually gets easier over time. You are expected to formulate your own perspective with regard to the material you study. In some ways, it does not really matter so much what you say as how you say it. Whatever your point of view, it needs to be backed up with adequate evidence and material.
Keep the assignment title firmly in mind as you write . Keep looking back at your assignment title in order to remind yourself of what you are supposed to be doing. Keep referring to key words in the title; this is especially useful in examinations, to remind the reader that you are writing relevantly.
Don't 'rewrite' the question in your own words to make it more answerable. In strict terms, you must answer the question set, not the question that you want to answer. Titles will often be worded very specifically and it is your job to rise to the challenge of answering the question. If you rephrase the question and write your own essay, you may fail the assignment or examination.
Keep your essay balanced. Paragraphs should be more or less the same length. Don't write very lengthy paragraphs. If there are two parts to a question, spend about the same time on each (unless of course the marks awarded, or your tutor, indicate differently). The main body should account for at least two thirds of the essay as a whole. If it is less than this, consider shortening the introduction and conclusion and lengthening the main body.
Avoid waffle . Try to write concisely and try to avoid being over-wordy in your style. It is easy to spend 3,000 words saying little or nothing at all. Get your point across as quickly and precisely as you can.
Think about the writing process : Your writing will go through several stages so make sure that you don't agonise too much about your early draft. It is much easier to revise something that is on paper than to revise something that is in your head.
Check your language : If you are worried about your English ask a friend or a writing tutor to help you. Remember, you never get a second chance to make a first impression. Try to get some distance from your work by completing it a few days before submission. Go back to it a day or so before you submit and you will probably be able to adjust aspects of the language.
Use 'hinges' to structure your work: A door has a hinge to help it to open and close. The hinge cannot be seen when you look at the door but without it the door would not function. Similarly, an assignment needs to have hinges (sometimes referred to more commonly as 'signposts' to help the reader through the argument). Another way to think about this is the brake lights of a car. You can't see them when you are driving, but without them, no-one else on the road knows that you are stopping the car. This would be a nightmare for any driver!
Use feedback effectively : Don't just look at your marks when your assignment is returned. Read any comments carefully and act on them . You will not be able to produce a perfect essay first time round.

Basics of Assignment Structure and Format
Some students, particularly those in their freshman years, tend to overthink things and try to go for assignment structures that are unnecessarily complicated, thinking this will help them stand out from their peers and get better grades. It doesn’t have to be that hard.
This guide will give you an overview of basic assignment structure which you can use as a checklist for your assignments. This will help make sure that you haven’t missed any critical sections which are typically expected in assignment papers.
You will have to trust us when we say that your teachers will be really grateful that you’ve stuck to the standard format as it will make their grading process easier.
If you’re pressed for time, you can also head on over to our resources page to download some free assignment paper templates with generic outlines which you can tweak further to suit your needs. However, if you do happen to use any of these, then please ensure to follow our guide on checking document metadata details to avoid being flagged incorrectly for plagiarism.
- Table of Contents
Overview of basic assignment structure
A very common advice is that any written work, which includes assignments, should have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion . This is a form of oversimplification but should you give you general idea of what is expected. In reality, academic writing requires additional subheadings under in the body or main part of your text to convey your ideas in a structured way.
So, here’s a more specific overview of the main structural parts of an assignment.
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Methodology
- Conclusions
We explain each of these in more details in the next sections
What are the essential parts in assignment structure?
The 4 parts of an academic writing work which should be considered essential are Introduction, Body, Conclusion and References . The last one should be obvious to any of our readers, but it’s surprising to see many students overlook the introduction and conclusion sections. Teachers often expect to see a short summary that sets the background and tone for the assignment, and they most definitely want to see what conclusions the student has reached by the end of their paper based on their study and research.

To make it simple, all you need do in the introduction is to give a brief overview of the topic which your paper is about, why this topic is relevant and important. In the conclusions section, you just need to summarize your research process, what you’ve learnt about the topic along the way and any final inferences.
These aren’t sections that you would have to do separate research for – if you’ve done your paper by yourself, you should be able to easily write a conclusion for it in no less than an hour (and we’re being very liberal with that estimation).
This is an easy to way to add in some additional words, which brings you closer to the required word count and reducing the words that you need to write for the other sections too, so why wouldn’t you want to do this, right?
As we have covered in our separate guide on how to manage word count of assignments , the introduction and conclusion sections are almost always included in the word count unless explicitly mentioned otherwise. You should be able to allocate about 200 to 300 words of the word count allowance to each of sections. This would cut down the amount of fresh content you need by about 400 to 600 words right off the bat!
Another critical section to be included in nearly all assignments would be a Table of Contents section. We have a full guide on how to easily make a good table of contents section which your teachers will be grateful to have when they are checking your work!
What are the circumstantial parts in assignment structure?
Moving on to the main part of your assignment, you could have a whole variety of headings and subheadings based on the type of paper that you are writing. Typically,
For thesis and dissertations, an Abstract section is almost always expected. Even if it hasn’t been specifically requested, we would highly recommend including this section for such long format papers because its purpose is to guide the readers with a ‘hook’ and make them more interested in reading your paper.
You can think of this section as a short summary of the main points from each of the broader headings in your paper. You don’t need to have more than 200 words for this section, and it shouldn’t be that hard to write as soon as you are done with your paper since the content that you’ve written should still be fresh in your mind.
The Rationale section is also expected in papers with longer word counts, especially those which are research oriented. In this section, you just need to explain the background of your chosen topic or research problem and why it is relevant and significant. You are expected to justify the need for your research on this topic. Some other research-oriented subsections include Research Aim & Objectives and Research Question , which you may potentially need, especially for long-form writing such as theses and dissertations.
Literature Review is a heading which can be considered as almost essential for most assignments since teachers want to see what external reading you have done on existing academic theory. The reason we have included this in the circumstantial section rather than the essential section above is because there are occasionally some assignments for which teachers explicitly mention not to define or explain academic theory and instead, they expect to see your understanding through direct application to the case.
This type of scenario typically arises when the word count for the assignment is not that high, so a full-blown literature review could be seen as ‘word-padding’ and have a negative impact on your overall grade for that assignment. We go over this issue of word-padding and how you can avoid it in a separate guide on managing word count as mentioned earlier.
A couple of sections that you can include in assignments where you are focusing on a particular industry or company are External Analysis and Internal Analysis respectively. As we cover in our guide on common academic words and what they mean, these are also known as Situational Analysis and Company Analysis , or Macro-analysis and Micro-analysis respectively. For company analysis, SWOT analysis one of the most common tools that are used, while another tool called TOWS is also occasionally used to combine internal and external analysis. Here’s a guide explaining the difference between SWOT and TOWS analysis .
Conceptual Framework is another circumstantial subsection which you may want to add if your research revolves around identifying independent and dependent variables.
For papers which require some research to be done as part of the assignment, you are going to need some sections like Methodology , Findings, Discussion and Analysis .
Within Methodology, you might have other subsections like Data Collection , Sampling Method etc.
What are some additional parts in assignment structure?
A section on Ethical Consent is often expected within the Research Methodology heading if your paper involves primary research gathered from respondents. We have a guide on ethical consent here and you can also check out our resources page to get a free sample ethical consent form which you could use in your papers (but be sure to also check out our guide on how to avoid getting flagged incorrectly for plagiarism so that you do not get wrongly flagged for plagiarism by using this sample form).
For research-oriented assignments, another typical expectation (although it isn’t always the case) is for a Research Timeline which illustrates the research process. This is often presented visually, and we have a separate guide on how to make good Gantt Charts easily using some of our free templates which you can find in our resources section.
Recommendations , and Limitations are also sometimes expected in some assignments, especially those that are long form, such as detailed research work.
If you have a lot of tables and figures in your work, which is usually the case for thesis and dissertations, you should also try to add a list of tables and figures (separate list for each).
Another section that you may wish to include in your assignments, especially if you have too many images or tables within your work, or if these are not to be included in the word count or in the body of the assignment, is the Appendix section. This is just a list of the additional content that is of direct relevance to your research adds to the quality and depth of your assignment. This section is typically not included in the word count allowance. Hence, it is often used to show that you have covered more ground in your research, but could not include it in main body due to word count limitation.

How to plan structure for essay assignments
Unlike standard academic reports, essays typically do not have subheadings but are instead expected to be structured in a logical way such that you transition from one idea to another by interlinking them.
However, we have come across some essay requirements in which the teachers have specifically asked for subheadings that indicate the central theme or idea which is being discussed in each section. If you are going to have subheadings in an essay though, then you should avoid numbering them as you would in other academic papers.
Taking assignment structures from the requirements files
Most teachers expect to see a standard structure in their assignments which helps them identify and assess the key learning outcomes of the module or the assignment. It is often the case that they will leave you some breadcrumbs by spelling out an assignment outline clearly within the requirements file, or in the presentations linked to the coursework, or perhaps during their lectures.
Sometimes, a structure would not have been defined clearly in the assignment requirements file, but there are ways to still get an almost explicit list of necessary headings such as by dissecting the marking guidelines which your tutors typically provide. We cover this in our guide on how to get better grades using a surefire method of drafting an outline which matches what the teachers are expecting.
Other teachers like to spice things up and give you free rein to structure your paper anyway you see it, but with this freedom of choice, you may find yourselves lost if you’re quite new to academic writing. In any of these cases, you can go over the upcoming list of standard sections and subsections that are present in academic papers to cross-check whether you have covered the relevant parts in your papers.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Overview

Basic essay structure

Improve your writing
Organise your essays to demonstrate your knowledge, show your research and support your arguments
Essays are usually written in continuous, flowing, paragraphed text and don’t use section headings. This may seem unstructured at first, but good essays are carefully structured.
How your assignment content is structured is your choice. Use the basic pattern below to get started.
Essay structure
An essay consists of three basic parts:, introduction.
The essay itself usually has no section headings. Only the title page, author declaration and reference list are written as headings, along with, for example, appendices. Check any task instructions, and your course or unit handbook, for further details.
Content in assignment introductions can vary widely. In some disciplines you may need to provide a full background and context, whereas other essays may need only a little context, and others may need none.
An introduction to an essay usually has three primary purposes:
- To set the scene
- To tell readers what is important, and why
- To tell the reader what the essay is going to do (signposting)
A standard introduction includes the following five elements:
- A statement that sets out the topic and engages the reader.
- The background and context of the topic.
- Any important definitions, integrated into your text as appropriate.
- An outline of the key points, topic, issues, evidence, ideas, arguments, models, theories, or other information, as appropriate. This may include distinctions or contrasts between different ideas or evidence.
- A final sentence or two which tells the reader your focal points and aims.
You should aim to restrict your introduction to information needed for the topic and only include background and contextual information which helps the reader understand it, or sets the scene for your chosen focal points.
In most essays you will have a considerable range of options for your focus. You will be expected to demonstrate your ability to select the most relevant content to address your focal points.
There are some exceptions. For example, if an assignment brief specifically directs the essay focus or requires you to write broadly about a topic. These are relatively rare or are discipline-specific so you should check your task instructions and discipline and subject area conventions.
Below are examples of an opening statement, a summary of the selected content, and a statement at the end of the introduction which tells the reader what the essay will focus on and how it will be addressed. We've use a fictional essay.
The title of our essay is: 'Cats are better than dogs. Discuss.'
To submit this essay you also would need to add citations as appropriate.
Example of opening statements:
People have shared their lives with cats and dogs for millenia. Which is better depends partly on each animal’s characteristics and partly on the owner’s preferences.
Here is a summary of five specific topics selected for the essay, which would be covered in a little more detail in the introduction:
- In ancient Egypt, cats were treated as sacred and were pampered companions.
- Dogs have for centuries been used for hunting and to guard property. There are many types of working dog, and both dogs and cats are now kept purely as pets.
- They are very different animals, with different care needs, traits and abilities.
- It is a common perception that people are either “cat-lovers” or “dog-lovers”.
- It is a common perception that people tend to have preferences for one, and negative beliefs about and attitudes towards, the other.
Example of closing statements at the end of the introduction:
This essay will examine both cats’ and dogs’ behaviour and abilities, the benefits of keeping them as pets, and whether people’s perceptions of their nature matches current knowledge and understanding.
Main body: paragraphs
The body of the essay should be organised into paragraphs. Each paragraph should deal with a different aspect of the issue, but they should also link in some way to those that precede and follow it. This is not an easy thing to get right, even for experienced writers, partly because there are many ways to successfully structure and use paragraphs. There is no perfect paragraph template.
The theme or topic statement
The first sentence, or sometimes two, tells the reader what the paragraph is going to cover. It may either:
- Begin a new point or topic, or
- Follow on from the previous paragraph, but with a different focus or go into more-specific detail. If this is the case, it should clearly link to the previous paragraph.
The last sentence
It should be clear if the point has come to an end, or if it continues in the next paragraph.
Here is a brief example of flow between two summarised paragraphs which cover the historical perspective:
It is known from hieroglyphs that the Ancient Egyptians believed that cats were sacred. They were also held in high regard, as suggested by their being found mummified and entombed with their owners (Smith, 1969). In addition, cats are portrayed aiding hunters. Therefore, they were both treated as sacred, and were used as intelligent working companions. However, today they are almost entirely owned as pets.
In contrast, dogs have not been regarded as sacred, but they have for centuries been widely used for hunting in Europe. This developed over time and eventually they became domesticated and accepted as pets. Today, they are seen as loyal, loving and protective members of the family, and are widely used as working dogs.
There is never any new information in a conclusion.
The conclusion usually does three things:
- Reminds your readers of what the essay was meant to do.
- Provides an answer, where possible, to the title.
- Reminds your reader how you reached that answer.
The conclusion should usually occupy just one paragraph. It draws together all the key elements of your essay, so you do not need to repeat the fine detail unless you are highlighting something.
A conclusion to our essay about cats and dogs is given below:
Both cats and dogs have been highly-valued for millenia, are affectionate and beneficial to their owners’ wellbeing. However, they are very different animals and each is 'better' than the other regarding care needs and natural traits. Dogs need regular training and exercise but many owners do not train or exercise them enough, resulting in bad behaviour. They also need to be 'boarded' if the owner is away and to have frequent baths to prevent bad odours. In contrast, cats do not need this level of effort and care. Dogs are seen as more intelligent, loyal and attuned to human beings, whereas cats are perceived as aloof and solitary, and as only seeking affection when they want to be fed. However, recent studies have shown that cats are affectionate and loyal and more intelligent than dogs, but it is less obvious and useful. There are, for example, no 'police' or 'assistance' cats, in part because they do not have the kinds of natural instincts which make dogs easy to train. Therefore, which animal is better depends upon personal preference and whether they are required to work. Therefore, although dogs are better as working animals, cats are easier, better pets.
Download our basic essay structure revision sheet
Download this page as a PDF for your essay structure revision notes
Better Essays: Signposting

Paragraphs main body of an assessment


4 Key Points for Effective Assignment Writing

Methodology
By Christina Desouza
Writing an effective assignment is more of an art than a science. It demands critical thinking, thorough research, organized planning, and polished execution. As a professional academic writer with over four years of experience, I've honed these skills and discovered proven strategies for creating standout assignments.
In this article, I will delve into the four key steps of assignment writing, offering detailed advice and actionable tips to help students master this craft.
1. Start With Research
In-depth research is the cornerstone of any high-quality assignment. It allows you to gain a profound understanding of your topic and equip yourself with relevant data, compelling arguments, and unique insights.
Here's how to do it right:
● Diversify Your Sources
Don't limit yourself to the first page of Google results. Make use of academic databases like JSTOR , Google Scholar , PubMed , or your school's online library. These resources house a plethora of scholarly articles, research papers, and academic books that can provide you with valuable information.
● Verify Information
Remember, not all information is created equal. Cross-check facts and data from multiple reliable sources to ensure accuracy. Look for consensus among experts on contentious issues.
● Stay Organized
Keep track of your resources as you go. Tools like Zotero or Mendeley can help you organize your references and generate citations in various formats. This will save you from scrambling to find sources when you're wrapping up your assignment.
1. Prepare Assignment Structure

Creating a well-planned structure for your assignment is akin to drawing a roadmap. It helps you stay on track and ensures that your ideas flow logically. Here's what to consider:
● Develop an Outline
The basic structure of an assignment includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should present the topic and establish the purpose of your assignment. The body should delve into the topic in detail, backed by your research. The conclusion should summarize your findings or arguments without introducing new ideas.
● Use Subheadings
Subheadings make your assignment easier to read and follow. They allow you to break down complex ideas into manageable sections. As a rule of thumb, each paragraph should cover one idea or argument.
● Allocate Word Count
Assignments often come with word limits. Allocate word count for each section of your assignment based on its importance to avoid overwriting or underwriting any part.
1. Start Assignment Writing
Writing your assignment is where your research and planning come to fruition. You now have a robust foundation to build upon, and it's time to craft a compelling narrative.
Here's how to accomplish this:
● Write a Gripping Introduction
Your introduction is the gateway to your assignment. Make it captivating. Start with a hook—a surprising fact, an interesting quote, or a thought-provoking question—to grab your readers' attention. Provide an overview of what your assignment is about and the purpose it serves. A well-crafted introduction sets the tone for the rest of the assignment and motivates your readers to delve deeper into your work.
● Develop a Comprehensive Body
The body of your assignment is where you delve into the details. Develop your arguments, present your data, and discuss your findings. Use clear and concise language. Avoid jargon unless necessary. Each paragraph should cover one idea or argument to maintain readability.
● Craft a Convincing Conclusion
Your conclusion is your final chance to leave an impression on your reader. Summarize your key findings or arguments without introducing new ideas. Reinforce the purpose of your assignment and provide a clear answer to the question or problem you addressed in the introduction. A strong conclusion leaves your readers with a sense of closure and a full understanding of your topic.
● Write Clearly
Use straightforward sentences and avoid jargon. Your goal is to communicate, not to confuse. Tools like Hemingway Editor can help ensure your writing is clear and concise.
● Use Paraphrasingtool.ai
Paraphrasingtool.ai is an AI-powered tool that can enhance your assignment writing. It reformulates your sentences while preserving their meaning. It not only helps you avoid plagiarism but also enhances the readability of your work.
● Cite Your Sources
Citations are a critical part of assignment writing. They acknowledge the work of others you've built upon and demonstrate the depth of your research. Always include in-text citations and a bibliography at the end. This not only maintains academic integrity but also gives your readers resources to delve deeper into the topic if they wish.
1. Review and Proofread The Assignment
Reviewing and proofreading are the final but critical steps in assignment writing. They ensure your assignment is free from errors and that your ideas are coherently presented. Here's how to do it effectively:
● Take a Break
After you finish writing, take a break before you start proofreading. Fresh eyes are more likely to spot mistakes and inconsistencies.
● Read Aloud
Reading your work aloud can help you identify awkward phrasing, run-on sentences, and typos. You're more likely to catch errors when you hear them, as it requires a different type of processing than reading silently.
● Use Proofreading Tools
Digital tools like Grammarly can be your second pair of eyes, helping you spot grammatical errors, typos, and even issues with sentence structure. However, don't rely solely on these tools—make sure to manually review your work as well.
Effective assignment writing is a skill that takes practice to master. It requires meticulous research, organized planning, clear writing, and careful proofreading. The steps and tips outlined in this article are by no means exhaustive, but they provide a solid framework to start from.
Remember, there is always room for improvement. Don't be disheartened by initial challenges. Each assignment is an opportunity to learn, grow, and sharpen your writing skills. So, be persistent, stay curious, and keep refining your craft. With time and practice, you will find yourself writing assignments that are not just excellent, but truly outstanding.

- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more.
Assignments are typically designed to be completed outside of class time and may require independent research, critical thinking, and analysis. They are often graded and used as a significant component of a student’s overall course grade. The instructions for an assignment usually specify the goals, requirements, and deadlines for completion, and students are expected to meet these criteria to earn a good grade.
History of Assignment
The use of assignments as a tool for teaching and learning has been a part of education for centuries. Following is a brief history of the Assignment.
- Ancient Times: Assignments such as writing exercises, recitations, and memorization tasks were used to reinforce learning.
- Medieval Period : Universities began to develop the concept of the assignment, with students completing essays, commentaries, and translations to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of the subject matter.
- 19th Century : With the growth of schools and universities, assignments became more widespread and were used to assess student progress and achievement.
- 20th Century: The rise of distance education and online learning led to the further development of assignments as an integral part of the educational process.
- Present Day: Assignments continue to be used in a variety of educational settings and are seen as an effective way to promote student learning and assess student achievement. The nature and format of assignments continue to evolve in response to changing educational needs and technological innovations.
Types of Assignment
Here are some of the most common types of assignments:
An essay is a piece of writing that presents an argument, analysis, or interpretation of a topic or question. It usually consists of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Essay structure:
- Introduction : introduces the topic and thesis statement
- Body paragraphs : each paragraph presents a different argument or idea, with evidence and analysis to support it
- Conclusion : summarizes the key points and reiterates the thesis statement
Research paper
A research paper involves gathering and analyzing information on a particular topic, and presenting the findings in a well-structured, documented paper. It usually involves conducting original research, collecting data, and presenting it in a clear, organized manner.
Research paper structure:
- Title page : includes the title of the paper, author’s name, date, and institution
- Abstract : summarizes the paper’s main points and conclusions
- Introduction : provides background information on the topic and research question
- Literature review: summarizes previous research on the topic
- Methodology : explains how the research was conducted
- Results : presents the findings of the research
- Discussion : interprets the results and draws conclusions
- Conclusion : summarizes the key findings and implications
A case study involves analyzing a real-life situation, problem or issue, and presenting a solution or recommendations based on the analysis. It often involves extensive research, data analysis, and critical thinking.
Case study structure:
- Introduction : introduces the case study and its purpose
- Background : provides context and background information on the case
- Analysis : examines the key issues and problems in the case
- Solution/recommendations: proposes solutions or recommendations based on the analysis
- Conclusion: Summarize the key points and implications
A lab report is a scientific document that summarizes the results of a laboratory experiment or research project. It typically includes an introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Lab report structure:
- Title page : includes the title of the experiment, author’s name, date, and institution
- Abstract : summarizes the purpose, methodology, and results of the experiment
- Methods : explains how the experiment was conducted
- Results : presents the findings of the experiment
Presentation
A presentation involves delivering information, data or findings to an audience, often with the use of visual aids such as slides, charts, or diagrams. It requires clear communication skills, good organization, and effective use of technology.
Presentation structure:
- Introduction : introduces the topic and purpose of the presentation
- Body : presents the main points, findings, or data, with the help of visual aids
- Conclusion : summarizes the key points and provides a closing statement
Creative Project
A creative project is an assignment that requires students to produce something original, such as a painting, sculpture, video, or creative writing piece. It allows students to demonstrate their creativity and artistic skills.
Creative project structure:
- Introduction : introduces the project and its purpose
- Body : presents the creative work, with explanations or descriptions as needed
- Conclusion : summarizes the key elements and reflects on the creative process.
Examples of Assignments
Following are Examples of Assignment templates samples:
Essay template:
I. Introduction
- Hook: Grab the reader’s attention with a catchy opening sentence.
- Background: Provide some context or background information on the topic.
- Thesis statement: State the main argument or point of your essay.
II. Body paragraphs
- Topic sentence: Introduce the main idea or argument of the paragraph.
- Evidence: Provide evidence or examples to support your point.
- Analysis: Explain how the evidence supports your argument.
- Transition: Use a transition sentence to lead into the next paragraph.
III. Conclusion
- Restate thesis: Summarize your main argument or point.
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your essay.
- Concluding thoughts: End with a final thought or call to action.
Research paper template:
I. Title page
- Title: Give your paper a descriptive title.
- Author: Include your name and institutional affiliation.
- Date: Provide the date the paper was submitted.
II. Abstract
- Background: Summarize the background and purpose of your research.
- Methodology: Describe the methods you used to conduct your research.
- Results: Summarize the main findings of your research.
- Conclusion: Provide a brief summary of the implications and conclusions of your research.
III. Introduction
- Background: Provide some background information on the topic.
- Research question: State your research question or hypothesis.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of your research.
IV. Literature review
- Background: Summarize previous research on the topic.
- Gaps in research: Identify gaps or areas that need further research.
V. Methodology
- Participants: Describe the participants in your study.
- Procedure: Explain the procedure you used to conduct your research.
- Measures: Describe the measures you used to collect data.
VI. Results
- Quantitative results: Summarize the quantitative data you collected.
- Qualitative results: Summarize the qualitative data you collected.
VII. Discussion
- Interpretation: Interpret the results and explain what they mean.
- Implications: Discuss the implications of your research.
- Limitations: Identify any limitations or weaknesses of your research.
VIII. Conclusion
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your paper.
Case study template:
- Background: Provide background information on the case.
- Research question: State the research question or problem you are examining.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the case study.
II. Analysis
- Problem: Identify the main problem or issue in the case.
- Factors: Describe the factors that contributed to the problem.
- Alternative solutions: Describe potential solutions to the problem.
III. Solution/recommendations
- Proposed solution: Describe the solution you are proposing.
- Rationale: Explain why this solution is the best one.
- Implementation: Describe how the solution can be implemented.
IV. Conclusion
- Summary: Summarize the main points of your case study.
Lab report template:
- Title: Give your report a descriptive title.
- Date: Provide the date the report was submitted.
- Background: Summarize the background and purpose of the experiment.
- Methodology: Describe the methods you used to conduct the experiment.
- Results: Summarize the main findings of the experiment.
- Conclusion: Provide a brief summary of the implications and conclusions
- Background: Provide some background information on the experiment.
- Hypothesis: State your hypothesis or research question.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the experiment.
IV. Materials and methods
- Materials: List the materials and equipment used in the experiment.
- Procedure: Describe the procedure you followed to conduct the experiment.
- Data: Present the data you collected in tables or graphs.
- Analysis: Analyze the data and describe the patterns or trends you observed.
VI. Discussion
- Implications: Discuss the implications of your findings.
- Limitations: Identify any limitations or weaknesses of the experiment.
VII. Conclusion
- Restate hypothesis: Summarize your hypothesis or research question.
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your report.
Presentation template:
- Attention grabber: Grab the audience’s attention with a catchy opening.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of your presentation.
- Overview: Provide an overview of what you will cover in your presentation.
II. Main points
- Main point 1: Present the first main point of your presentation.
- Supporting details: Provide supporting details or evidence to support your point.
- Main point 2: Present the second main point of your presentation.
- Main point 3: Present the third main point of your presentation.
- Summary: Summarize the main points of your presentation.
- Call to action: End with a final thought or call to action.
Creative writing template:
- Setting: Describe the setting of your story.
- Characters: Introduce the main characters of your story.
- Rising action: Introduce the conflict or problem in your story.
- Climax: Present the most intense moment of the story.
- Falling action: Resolve the conflict or problem in your story.
- Resolution: Describe how the conflict or problem was resolved.
- Final thoughts: End with a final thought or reflection on the story.
How to Write Assignment
Here is a general guide on how to write an assignment:
- Understand the assignment prompt: Before you begin writing, make sure you understand what the assignment requires. Read the prompt carefully and make note of any specific requirements or guidelines.
- Research and gather information: Depending on the type of assignment, you may need to do research to gather information to support your argument or points. Use credible sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites.
- Organize your ideas : Once you have gathered all the necessary information, organize your ideas into a clear and logical structure. Consider creating an outline or diagram to help you visualize your ideas.
- Write a draft: Begin writing your assignment using your organized ideas and research. Don’t worry too much about grammar or sentence structure at this point; the goal is to get your thoughts down on paper.
- Revise and edit: After you have written a draft, revise and edit your work. Make sure your ideas are presented in a clear and concise manner, and that your sentences and paragraphs flow smoothly.
- Proofread: Finally, proofread your work for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. It’s a good idea to have someone else read over your assignment as well to catch any mistakes you may have missed.
- Submit your assignment : Once you are satisfied with your work, submit your assignment according to the instructions provided by your instructor or professor.
Applications of Assignment
Assignments have many applications across different fields and industries. Here are a few examples:
- Education : Assignments are a common tool used in education to help students learn and demonstrate their knowledge. They can be used to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic, to develop critical thinking skills, and to improve writing and research abilities.
- Business : Assignments can be used in the business world to assess employee skills, to evaluate job performance, and to provide training opportunities. They can also be used to develop business plans, marketing strategies, and financial projections.
- Journalism : Assignments are often used in journalism to produce news articles, features, and investigative reports. Journalists may be assigned to cover a particular event or topic, or to research and write a story on a specific subject.
- Research : Assignments can be used in research to collect and analyze data, to conduct experiments, and to present findings in written or oral form. Researchers may be assigned to conduct research on a specific topic, to write a research paper, or to present their findings at a conference or seminar.
- Government : Assignments can be used in government to develop policy proposals, to conduct research, and to analyze data. Government officials may be assigned to work on a specific project or to conduct research on a particular topic.
- Non-profit organizations: Assignments can be used in non-profit organizations to develop fundraising strategies, to plan events, and to conduct research. Volunteers may be assigned to work on a specific project or to help with a particular task.
Purpose of Assignment
The purpose of an assignment varies depending on the context in which it is given. However, some common purposes of assignments include:
- Assessing learning: Assignments are often used to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic or concept. This allows educators to determine if a student has mastered the material or if they need additional support.
- Developing skills: Assignments can be used to develop a wide range of skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, research, and communication. Assignments that require students to analyze and synthesize information can help to build these skills.
- Encouraging creativity: Assignments can be designed to encourage students to be creative and think outside the box. This can help to foster innovation and original thinking.
- Providing feedback : Assignments provide an opportunity for teachers to provide feedback to students on their progress and performance. Feedback can help students to understand where they need to improve and to develop a growth mindset.
- Meeting learning objectives : Assignments can be designed to help students meet specific learning objectives or outcomes. For example, a writing assignment may be designed to help students improve their writing skills, while a research assignment may be designed to help students develop their research skills.
When to write Assignment
Assignments are typically given by instructors or professors as part of a course or academic program. The timing of when to write an assignment will depend on the specific requirements of the course or program, but in general, assignments should be completed within the timeframe specified by the instructor or program guidelines.
It is important to begin working on assignments as soon as possible to ensure enough time for research, writing, and revisions. Waiting until the last minute can result in rushed work and lower quality output.
It is also important to prioritize assignments based on their due dates and the amount of work required. This will help to manage time effectively and ensure that all assignments are completed on time.
In addition to assignments given by instructors or professors, there may be other situations where writing an assignment is necessary. For example, in the workplace, assignments may be given to complete a specific project or task. In these situations, it is important to establish clear deadlines and expectations to ensure that the assignment is completed on time and to a high standard.
Characteristics of Assignment
Here are some common characteristics of assignments:
- Purpose : Assignments have a specific purpose, such as assessing knowledge or developing skills. They are designed to help students learn and achieve specific learning objectives.
- Requirements: Assignments have specific requirements that must be met, such as a word count, format, or specific content. These requirements are usually provided by the instructor or professor.
- Deadline: Assignments have a specific deadline for completion, which is usually set by the instructor or professor. It is important to meet the deadline to avoid penalties or lower grades.
- Individual or group work: Assignments can be completed individually or as part of a group. Group assignments may require collaboration and communication with other group members.
- Feedback : Assignments provide an opportunity for feedback from the instructor or professor. This feedback can help students to identify areas of improvement and to develop their skills.
- Academic integrity: Assignments require academic integrity, which means that students must submit original work and avoid plagiarism. This includes citing sources properly and following ethical guidelines.
- Learning outcomes : Assignments are designed to help students achieve specific learning outcomes. These outcomes are usually related to the course objectives and may include developing critical thinking skills, writing abilities, or subject-specific knowledge.
Advantages of Assignment
There are several advantages of assignment, including:
- Helps in learning: Assignments help students to reinforce their learning and understanding of a particular topic. By completing assignments, students get to apply the concepts learned in class, which helps them to better understand and retain the information.
- Develops critical thinking skills: Assignments often require students to think critically and analyze information in order to come up with a solution or answer. This helps to develop their critical thinking skills, which are important for success in many areas of life.
- Encourages creativity: Assignments that require students to create something, such as a piece of writing or a project, can encourage creativity and innovation. This can help students to develop new ideas and perspectives, which can be beneficial in many areas of life.
- Builds time-management skills: Assignments often come with deadlines, which can help students to develop time-management skills. Learning how to manage time effectively is an important skill that can help students to succeed in many areas of life.
- Provides feedback: Assignments provide an opportunity for students to receive feedback on their work. This feedback can help students to identify areas where they need to improve and can help them to grow and develop.
Limitations of Assignment
There are also some limitations of assignments that should be considered, including:
- Limited scope: Assignments are often limited in scope, and may not provide a comprehensive understanding of a particular topic. They may only cover a specific aspect of a topic, and may not provide a full picture of the subject matter.
- Lack of engagement: Some assignments may not engage students in the learning process, particularly if they are repetitive or not challenging enough. This can lead to a lack of motivation and interest in the subject matter.
- Time-consuming: Assignments can be time-consuming, particularly if they require a lot of research or writing. This can be a disadvantage for students who have other commitments, such as work or extracurricular activities.
- Unreliable assessment: The assessment of assignments can be subjective and may not always accurately reflect a student’s understanding or abilities. The grading may be influenced by factors such as the instructor’s personal biases or the student’s writing style.
- Lack of feedback : Although assignments can provide feedback, this feedback may not always be detailed or useful. Instructors may not have the time or resources to provide detailed feedback on every assignment, which can limit the value of the feedback that students receive.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
Current students
- Staff intranet
- Find an event
- Academic writing
- Types of academic writing
- Planning your writing
Structuring written work
- Grammar, spelling and vocabulary
- Editing and proofreading
- Evidence, plagiarism and referencing
- Resources and support
Some assignments have a standard format, such as lab reports or case studies, and these will normally be explained in your course materials. For other assignments, you will have to come up with your own structure.
Your structure might be guided by:
- the assignment question. For example, it may list topics or use wording such as ‘compare and contrast’
- the subject matter itself, which may suggest a structure based on chronology, process or location
- your interpretation of the subject matter. For example, problem/solution, argument/counter-argument or sub-topics in order of importance
- the structure of other texts you’ve read in your discipline. Look at how the information is organised and sequenced. Make sure you modify the structure to suit your purpose to avoid plagiarism.
Essays are a very common form of academic writing. Like most of the texts you write at university, all essays have the same basic three-part structure: introduction, main body and conclusion. However, the main body can be structured in many different ways.
To write a good essay:
- know if you’re expected to write an analytical, persuasive or critical essay
- clearly structure your main body and paragraphs
- use appropriate referencing
- use academic language .
Reports generally have the same basic structure as essays, with an introduction, body and conclusion. However, the main body structure can vary widely, as the term ‘report’ is used for many types of texts and purposes in different disciplines.
Find out as much as possible about what type of report is expected.
How to plan your structure
There are many ways to come up with a structure for your work. If you’re not sure how to approach it, try some of the strategies below.
During and after reading your sources, take notes and start thinking about ways to structure the ideas and facts into groups. For example:
- look for similarities, differences, patterns, themes or other ways of grouping and dividing the ideas under headings. This could include advantages, disadvantages, causes, effects, problems, solutions or types of theory
- use coloured highlighters or symbols to tag themes or categories of information in your readings or notes
- cut and paste notes in a document
- physically group your readings or notes into piles.
It’s a good idea to brainstorm a few different ways of structuring your assignment once you have a rough idea of the main issues. Do this in outline form before you start writing – it’s much easier to re-structure an outline than a half-finished essay. For example:
- draw some tree diagrams, mind-maps or flowcharts showing which ideas, facts and references would be included under each heading
- discard ideas that don't fit into your overall purpose, and facts or references that are not useful for what you want to discuss
- if you have a lot of information, such as for a thesis or dissertation, create some tables to show how each theory or reading relates to each heading (this is often called a 'synthesis grid')
- plan the number of paragraphs you need, the topic heading for each one, and dot points for each piece of information and reference needed
- try a few different possible structures until you find the one that works best.
Eventually, you’ll have a plan that is detailed enough for you to start writing. You’ll know which ideas go into each section and, ideally, each paragraph. You will also know where to find evidence for those ideas in your notes and the sources of that evidence.
If you’re having difficulties with the process of planning the structure of your assignment, consider trying a different strategy for grouping and organising your information.
Making the structure clear
Your writing will be clear and logical to read if it’s easy to see the structure and how it fits together. You can achieve this in several ways.
- Use the end of the introduction to show the reader what structure to expect.
- Use headings and sub-headings to clearly mark the sections (if these are acceptable for your discipline and assignment type).
- Use topic sentences at the beginning of each paragraph , to show the reader what the main idea is, and to link back to the introduction and/or headings and sub-headings.
- Show the connections between sentences. The beginning of each sentence should link back to the main idea of the paragraph or a previous sentence.
- Use conjunctions and linking words to show the structure of relationships between ideas. Examples of conjunctions include: however, similarly, in contrast, for this reason, as a result and moreover.
Introductions
Most of the types of texts you write for university need to have an introduction. Its purpose is to clearly tell the reader the topic, purpose and structure of the paper.
As a rough guide, an introduction might be between 10 and 20 percent of the length of the whole paper and has three main parts.
- The most general information, such as background and/or definitions.
- The core of the introduction, where you show the overall topic, purpose, your point of view, hypotheses and/or research questions (depending on what kind of paper it is).
- The most specific information, describing the scope and structure of your paper.
If the main body of your paper follows a predictable template, such as the method, results and discussion stages of a report in the sciences, you generally don’t need to include a guide to the structure in your introduction.
You should write your introduction after you know both your overall point of view (if it is a persuasive paper) and the whole structure of your paper. You should then revise the introduction when you have completed the main body.
Most academic writing is structured into paragraphs. It is helpful to think about each paragraph as a mini essay with a three-part structure:
- topic sentence (also known as introductory sentence)
- body of the paragraph
- concluding sentence (necessary for long paragraphs but otherwise optional).
The topic sentence introduces a general overview of the topic and the purpose of the paragraph. Depending on the length of the paragraph, this may be more than one sentence. The topic sentence answers the question 'what's the paragraph about?'.
The body of the paragraph develops this topic. It may elaborate directly on the topic sentence by giving definitions, classifications, explanations, contrasts, examples and evidence.
The final sentence in many, but not all, paragraphs is the concluding sentence. It does not present new information, but often either summarises or comments on the paragraph content. It can also provide a link, by showing how the paragraph links to the topic sentence of the next paragraph. The concluding sentence often answers the question ‘so what?’, by explaining how this paragraph relates back to the main topic.
You don’t have to write all your paragraphs using this structure. For example, there are paragraphs with no topic sentence, or the topic is mentioned near the end of the paragraph. However, this is a clear and common structure that makes it easy for the reader to follow.
Conclusions
The conclusion is closely related to the introduction and is often described as its ‘mirror image’. This means that if the introduction begins with general information and ends with specific information, the conclusion moves in the opposite direction.
The conclusion usually:
- begins by briefly summarising the main scope or structure of the paper
- confirms the topic that was given in the introduction. This may take the form of the aims of the paper, a thesis statement (point of view) or a research question/hypothesis and its answer/outcome.
- ends with a more general statement about how this topic relates to its context. This may take the form of an evaluation of the importance of the topic, implications for future research or a recommendation about theory or practice.
This material was developed by the the Learning Hub (Academic Language and Learning), which offers workshops, face-to-face consultations and resources to support your learning. Find out more about how they can help you develop your communication, research and study skills .
See our Writing skills handouts .
Related links
- Learning Hub (Academic Language and Learning)
- Learning Hub (Academic Language and Learning) workshops
- Research skills for HDR students
- Reading and note taking
- Critical thinking
- Prepare your thesis
- Website feedback
Your feedback has been sent.
Sorry there was a problem sending your feedback. Please try again
You should only use this form to send feedback about the content on this webpage – we will not respond to other enquiries made through this form. If you have an enquiry or need help with something else such as your enrolment, course etc you can contact the Student Centre.
- Find an expert
- Media contacts

Student links
- How to log in to University systems
- Class timetables
- Our rankings
- Faculties and schools
- Research centres
- Campus locations
- Find a staff member
- Careers at Sydney
- Emergencies and personal safety

- Accessibility

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Types of Assignments
Cristy Bartlett and Kate Derrington

Introduction
As discussed in the previous chapter, assignments are a common method of assessment at university. You may encounter many assignments over your years of study, yet some will look quite different from others. By recognising different types of assignments and understanding the purpose of the task, you can direct your writing skills effectively to meet task requirements. This chapter draws on the skills from the previous chapter, and extends the discussion, showing you where to aim with different types of assignments.
The chapter begins by exploring the popular essay assignment, with its two common categories, analytical and argumentative essays. It then examines assignments requiring case study responses , as often encountered in fields such as health or business. This is followed by a discussion of assignments seeking a report (such as a scientific report) and reflective writing assignments, common in nursing, education and human services. The chapter concludes with an examination of annotated bibliographies and literature reviews. The chapter also has a selection of templates and examples throughout to enhance your understanding and improve the efficacy of your assignment writing skills.
Different Types of Written Assignments
At university, an essay is a common form of assessment. In the previous chapter Writing Assignments we discussed what was meant by showing academic writing in your assignments. It is important that you consider these aspects of structure, tone and language when writing an essay.
Components of an essay
Essays should use formal but reader friendly language and have a clear and logical structure. They must include research from credible academic sources such as peer reviewed journal articles and textbooks. This research should be referenced throughout your essay to support your ideas (See the chapter Working with Information ).

If you have never written an essay before, you may feel unsure about how to start. Breaking your essay into sections and allocating words accordingly will make this process more manageable and will make planning the overall essay structure much easier.
- An essay requires an introduction, body paragraphs and a conclusion.
- Generally, an introduction and conclusion are approximately 10% each of the total word count.
- The remaining words can then be divided into sections and a paragraph allowed for each area of content you need to cover.
- Use your task and criteria sheet to decide what content needs to be in your plan
An effective essay introduction needs to inform your reader by doing four basic things:
Table 15.1 An effective essay
[table “17” not found /]
An effective essay body paragraph needs to:
[table “18” not found /]
An effective essay conclusion needs to:
[table “19” not found /]
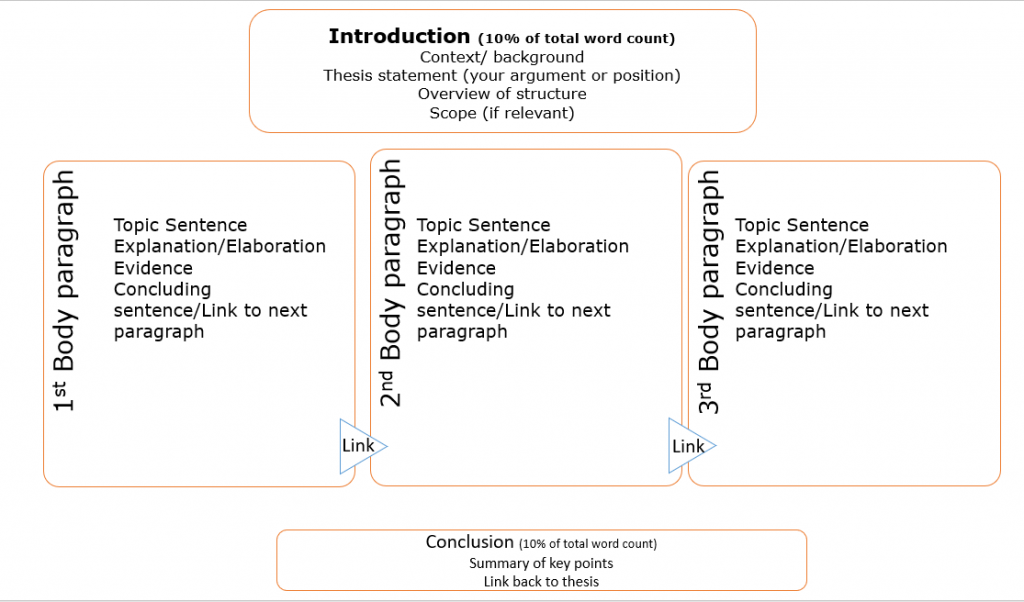
Common types of essays
You may be required to write different types of essays, depending on your study area and topic. Two of the most commonly used essays are analytical and argumentative . The task analysis process discussed in the previous chapter Writing Assignments will help you determine the type of essay required. For example, if your assignment question uses task words such as analyse, examine, discuss, determine or explore, you would be writing an analytical essay . If your assignment question has task words such as argue, evaluate, justify or assess, you would be writing an argumentative essay . Despite the type of essay, your ability to analyse and think critically is important and common across genres.
Analytical essays

These essays usually provide some background description of the relevant theory, situation, problem, case, image, etcetera that is your topic. Being analytical requires you to look carefully at various components or sections of your topic in a methodical and logical way to create understanding.
The purpose of the analytical essay is to demonstrate your ability to examine the topic thoroughly. This requires you to go deeper than description by considering different sides of the situation, comparing and contrasting a variety of theories and the positives and negatives of the topic. Although in an analytical essay your position on the topic may be clear, it is not necessarily a requirement that you explicitly identify this with a thesis statement, as is the case with an argumentative essay. If you are unsure whether you are required to take a position, and provide a thesis statement, it is best to check with your tutor.
Argumentative essays
These essays require you to take a position on the assignment topic. This is expressed through your thesis statement in your introduction. You must then present and develop your arguments throughout the body of your assignment using logically structured paragraphs. Each of these paragraphs needs a topic sentence that relates to the thesis statement. In an argumentative essay, you must reach a conclusion based on the evidence you have presented.
Case Study Responses
Case studies are a common form of assignment in many study areas and students can underperform in this genre for a number of key reasons.
Students typically lose marks for not:
- Relating their answer sufficiently to the case details
- Applying critical thinking
- Writing with clear structure
- Using appropriate or sufficient sources
- Using accurate referencing
When structuring your response to a case study, remember to refer to the case. Structure your paragraphs similarly to an essay paragraph structure but include examples and data from the case as additional evidence to support your points (see Figure 15.5). The colours in the sample paragraph below show the function of each component.
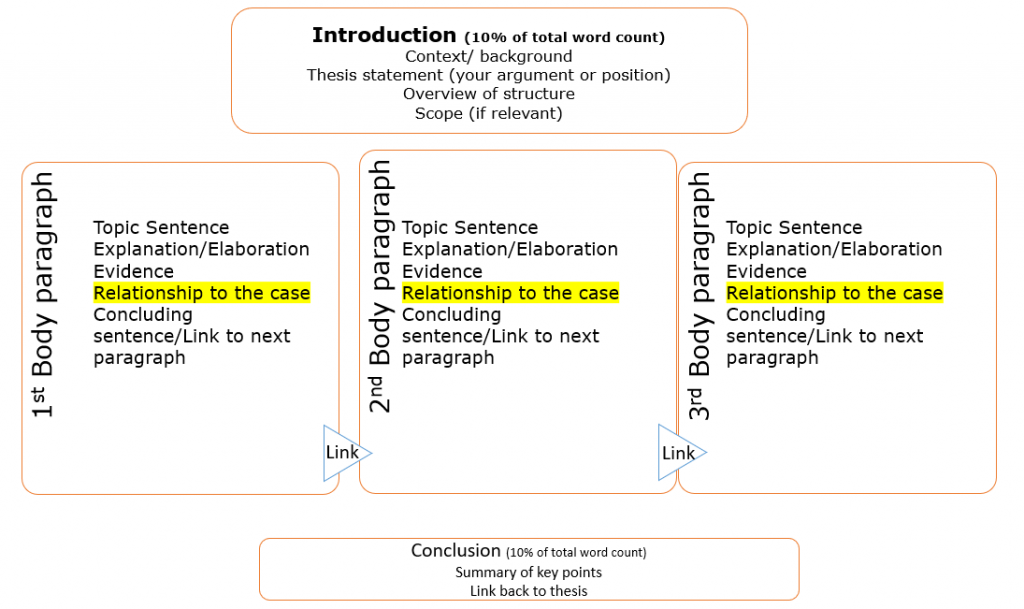
The Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia (NMBA) Code of Conduct and Nursing Standards (2018) play a crucial role in determining the scope of practice for nurses and midwives. A key component discussed in the code is the provision of person-centred care and the formation of therapeutic relationships between nurses and patients (NMBA, 2018). This ensures patient safety and promotes health and wellbeing (NMBA, 2018). The standards also discuss the importance of partnership and shared decision-making in the delivery of care (NMBA, 2018, 4). Boyd and Dare (2014) argue that good communication skills are vital for building therapeutic relationships and trust between patients and care givers. This will help ensure the patient is treated with dignity and respect and improve their overall hospital experience. In the case, the therapeutic relationship with the client has been compromised in several ways. Firstly, the nurse did not conform adequately to the guidelines for seeking informed consent before performing the examination as outlined in principle 2.3 (NMBA, 2018). Although she explained the procedure, she failed to give the patient appropriate choices regarding her health care.
Topic sentence | Explanations using paraphrased evidence including in-text references | Critical thinking (asks the so what? question to demonstrate your student voice). | Relating the theory back to the specifics of the case. The case becomes a source of examples as extra evidence to support the points you are making.
Reports are a common form of assessment at university and are also used widely in many professions. It is a common form of writing in business, government, scientific, and technical occupations.
Reports can take many different structures. A report is normally written to present information in a structured manner, which may include explaining laboratory experiments, technical information, or a business case. Reports may be written for different audiences including clients, your manager, technical staff, or senior leadership within an organisation. The structure of reports can vary, and it is important to consider what format is required. The choice of structure will depend upon professional requirements and the ultimate aims of the report. Consider some of the options in the table below (see Table 15.2).
Table 15.2 Explanations of different types of reports
[table “20” not found /]
Reflective writing

Reflective writing is a popular method of assessment at university. It is used to help you explore feelings, experiences, opinions, events or new information to gain a clearer and deeper understanding of your learning. A reflective writing task requires more than a description or summary. It requires you to analyse a situation, problem or experience, consider what you may have learnt and evaluate how this may impact your thinking and actions in the future. This requires critical thinking, analysis, and usually the application of good quality research, to demonstrate your understanding or learning from a situation. Essentially, reflective practice is the process of looking back on past experiences and engaging with them in a thoughtful way and drawing conclusions to inform future experiences. The reflection skills you develop at university will be vital in the workplace to assist you to use feedback for growth and continuous improvement. There are numerous models of reflective writing and you should refer to your subject guidelines for your expected format. If there is no specific framework, a simple model to help frame your thinking is What? So what? Now what? (Rolfe et al., 2001).
Table 15.3 What? So What? Now What? Explained.
[table “21” not found /]
The Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle
The Gibbs’ Cycle of reflection encourages you to consider your feelings as part of the reflective process. There are six specific steps to work through. Following this model carefully and being clear of the requirements of each stage, will help you focus your thinking and reflect more deeply. This model is popular in Health.
The 4 R’s of reflective thinking
This model (Ryan and Ryan, 2013) was designed specifically for university students engaged in experiential learning. Experiential learning includes any ‘real-world’ activities including practice led activities, placements and internships. Experiential learning, and the use of reflective practice to heighten this learning, is common in Creative Arts, Health and Education.
Annotated Bibliography
What is it.
An annotated bibliography is an alphabetical list of appropriate sources (books, journals or websites) on a topic, accompanied by a brief summary, evaluation and sometimes an explanation or reflection on their usefulness or relevance to your topic. Its purpose is to teach you to research carefully, evaluate sources and systematically organise your notes. An annotated bibliography may be one part of a larger assessment item or a stand-alone assessment piece. Check your task guidelines for the number of sources you are required to annotate and the word limit for each entry.
How do I know what to include?
When choosing sources for your annotated bibliography it is important to determine:
- The topic you are investigating and if there is a specific question to answer
- The type of sources on which you need to focus
- Whether they are reputable and of high quality
What do I say?
Important considerations include:
- Is the work current?
- Is the work relevant to your topic?
- Is the author credible/reliable?
- Is there any author bias?
- The strength and limitations (this may include an evaluation of research methodology).
Literature Reviews
It is easy to get confused by the terminology used for literature reviews. Some tasks may be described as a systematic literature review when actually the requirement is simpler; to review the literature on the topic but do it in a systematic way. There is a distinct difference (see Table 15.4). As a commencing undergraduate student, it is unlikely you would be expected to complete a systematic literature review as this is a complex and more advanced research task. It is important to check with your lecturer or tutor if you are unsure of the requirements.
Table 15.4 Comparison of Literature Reviews
[table “22” not found /]
Generally, you are required to establish the main ideas that have been written on your chosen topic. You may also be expected to identify gaps in the research. A literature review does not summarise and evaluate each resource you find (this is what you would do in an annotated bibliography). You are expected to analyse and synthesise or organise common ideas from multiple texts into key themes which are relevant to your topic (see Figure 15.10). Use a table or a spreadsheet, if you know how, to organise the information you find. Record the full reference details of the sources as this will save you time later when compiling your reference list (see Table 15.5).
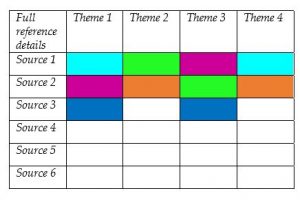
Overall, this chapter has provided an introduction to the types of assignments you can expect to complete at university, as well as outlined some tips and strategies with examples and templates for completing them. First, the chapter investigated essay assignments, including analytical and argumentative essays. It then examined case study assignments, followed by a discussion of the report format. Reflective writing , popular in nursing, education and human services, was also considered. Finally, the chapter briefly addressed annotated bibliographies and literature reviews. The chapter also has a selection of templates and examples throughout to enhance your understanding and improve the efficacy of your assignment writing skills.
- Not all assignments at university are the same. Understanding the requirements of different types of assignments will assist in meeting the criteria more effectively.
- There are many different types of assignments. Most will require an introduction, body paragraphs and a conclusion.
- An essay should have a clear and logical structure and use formal but reader friendly language.
- Breaking your assignment into manageable chunks makes it easier to approach.
- Effective body paragraphs contain a topic sentence.
- A case study structure is similar to an essay, but you must remember to provide examples from the case or scenario to demonstrate your points.
- The type of report you may be required to write will depend on its purpose and audience. A report requires structured writing and uses headings.
- Reflective writing is popular in many disciplines and is used to explore feelings, experiences, opinions or events to discover what learning or understanding has occurred. Reflective writing requires more than description. You need to be analytical, consider what has been learnt and evaluate the impact of this on future actions.
- Annotated bibliographies teach you to research and evaluate sources and systematically organise your notes. They may be part of a larger assignment.
- Literature reviews require you to look across the literature and analyse and synthesise the information you find into themes.
Gibbs, G. (1988). Learning by doing: A guide to teaching and learning methods. Further Education Unit, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford.
Rolfe, G., Freshwater, D., Jasper, M. (2001). Critical reflection in nursing and the helping professions: a user’s guide . Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Ryan, M. & Ryan, M. (2013). Theorising a model for teaching and assessing reflective learning in higher education. Higher Education Research & Development , 32(2), 244-257. doi: 10.1080/07294360.2012.661704
Academic Success Copyright © 2021 by Cristy Bartlett and Kate Derrington is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Get 50% OFF On Your First Order
- how to structure an assignment
A Comprehensive Guide on How to Structure an Assignment

There are several difficulties associated with university life. One of them is composing lengthier assignments and projects that call for more advanced knowledge, collaboration, and analytical skills than you may have encountered in high school. For your assignment to be communicated rationally, convincingly, and with clarity, it must be properly structured. The quality of an assignment carries substantial weight, whether you are a student engaged in an academic endeavor or a professional crafting a business presentation. It exerts a significant influence on the reception and evaluation of your work. The composition of an assignment is not merely a matter of aesthetics; it holds a pivotal role in effectively conveying your ideas and ensuring that your audience comprehends the information you are delivering.
Investing time and effort in organizing your assignment is, in essence, setting the stage for success. However, many students find themselves grappling with the intricacies of assignment structure. Frequently, they embark on the writing process with a blank document, expending a considerable amount of time in an attempt to decipher the appropriate structure, only to find themselves with no tangible progress to showcase.
In order to achieve high grades on your assignments- You must be aware of the essential details regarding how to structure an assignment .
Utilizing these pointers while composing a task. These will assist you in producing quality work. We'll walk you through the process of writing an organized assignment that will wow your readers or evaluators in this blog post. Look at this.
What Exactly Is an Assignment?
An assignment is a piece of academic work that is provided in high school, university, and other institutions. It allows students to learn, practice, and exhibit that they have achieved their educational targets. It also shows the instructor that their students have met the goals they set.
It is the practice of assigning a specific project or piece of labor to someone or sending someone to a certain location to accomplish a job: assigning distinct assignments. Business Reports, Case Study Assignments , Essays, Lab Reports, Research Papers are few of popular categories of assignments.
Overview of the fundamental assignment structure.
A popular piece of advice is that all written work, including assignments, should comprise an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. This is an oversimplification, but it should give you a good indication of what to anticipate. In actuality, extra subheadings inside the body or major section of your work are required to present your thoughts in a systematic manner.
So, here's a more detailed breakdown of the primary structural components of an assignment.
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Methodology
- Conclusions
What are the critical components of assignment structure?
Introduction, Body, Conclusion, and References are the four fundamental elements of an academic writing assignment. The final one should be self-evident to any of our readers, but it's shocking how many students ignore the introduction and conclusion portions. Teachers sometimes want to see a brief summary that establishes the context and tone for the assignment, as well as what conclusions the student has made at the conclusion of their paper centered on their investigation and study.
To put it simply, all you need to accomplish in the beginning is provide a quick synopsis of the topic of the assignment and why it is relevant and significant. In the conclusion part, you simply describe your research method, what you've learned about the issue along the way, and any final conclusions.
These aren't portions that require more research; if you wrote your paper on your own, you should be able to write a conclusion in under an hour.
A Table of Contents part is another important component that should be included in practically all assignments. We offer a complete instruction on how to effortlessly create a decent table of contents part, which your professors will appreciate when they are reviewing your work!
Crucial Advice on how to structure an assignment
1. The first item on our list of recommendations is early research : Even if you don't start writing right away, gathering and digesting the information beforehand can help you focus on the writing you will accomplish.
2. Create an extensive paper trail : Often, while you are in the thick of finalizing your preparations for a project, with deadlines looming and supplies hard to come by, poor note-taking becomes evident. This is due to the fact that when conducting research, it is common to go through and reject items that seem irrelevant, only to realize later—during the writing process—that they actually are.
3. Invest in the Writing Process : Whether it's a research paper, an essay, or any other type of written work, a methodical approach is essential. Begin by brainstorming and writing down ideas as they come to you. This initial phase is critical for releasing your imagination and getting your thoughts flowing. It's absolutely acceptable to not have a thorough comprehension of your issue right away. As a result, start by putting down what you do know.
Writing is frequently a difficult and diverse process that includes phases such as brainstorming, sketching, revising, modifying, and proofing. Attempting to complete all of these steps at once might be difficult.
4. Seek External Feedback : Writing, especially when dealing with complex or specialized topics, can often suffer from logical gaps, confusion, and the risk of misinterpretation. As a writer, your deep familiarity with the subject matter may occasionally hinder your ability to recognize weaknesses in your work. To guarantee the clarity and effectiveness of your writing, it is essential to seek feedback from an external source. Having a second set of eyes, whether from a peer, mentor, or professional editor, can offer priceless perspectives and constructive critiques. These alternative viewpoints can assist you in pinpointing and addressing issues that may elude your initial awareness.
5. Dedicate Time to Revision and Editing : Writing is an iterative process. Once you've completed the initial drafting phase and committed your thoughts to paper, you'll often find that revisions are necessary. This might involve re-reading your work to identify clarity issues, conducting additional research to strengthen your arguments, reorganizing the structure for better flow, and rethinking the way you've presented your ideas.
Revision and editing are not merely about correcting grammar and spelling; they are about refining your content to ensure that it communicates your ideas effectively. It's essential to allocate sufficient time for this phase.
7. Clearly define the structure : Another important tip for ' how to structure an assignment ' is to use paragraphs, subsections, and spatial divisions (layout) to clearly indicate changes in subject matter, focus, and depth. It is occasionally a good idea to write an outline at this point to confirm that your structure makes sense.
8. Finish the introduction last : A great introduction should draw attention to the text's content. It is a promise made to the reader that must be fulfilled. The best introductions will be prepared once you have selected what to convey and how to deliver it. As a result, the greatest technique for writing flawless assignments is to compose the introduction last.
9. Double-check for correctness : Research-based writing is frequently difficult, and it is easy to lose sight of a drafting error. Check your sources and go over your quotations, citations, and evidence thoroughly.
Here are some crucial steps to follow in this regard :
- Scrutinize your sources : Begin by revisiting and cross-referencing the sources you've used in your research. Make sure they are reliable, up-to-date, and relevant to your topic. It's not uncommon for writers to mistakenly reference outdated or unrelated sources, which can undermine the credibility of your work.
- Diligently review quotations : Thoroughly examine the quotations you've incorporated into your writing. Misquoting or misattributing can have serious consequences in academic and professional writing.
10. Proofread thoroughly : This is sometimes overlooked in the rush to meet a deadline, and yet it is typically little faults (typos, punctuation and grammatical issues) that transmit to your reader a feeling of carelessness or incapacity to write. To enhance the quality of your writing and leave a lasting impression on your audience, follow these guidelines:
- Schedule ample time for proofreading : Plan your writing process to include dedicated time for proofreading. Rushing through this step can lead to missed errors and diminish the overall quality of your work.
- A systematic approach : Pay special attention to punctuation, grammar, spelling, and sentence structure. Consider reading your work aloud, as it can help you identify awkward phrasing and grammatical issues.
- Seek external feedback : Fresh eyes can catch errors you might have overlooked, and their feedback can offer valuable insights to enhance the clarity and coherence of your writing.
- Utilize proofreading tools : Take advantage of grammar and spell-checking software. While they are not infallible, they can assist in identifying common mistakes and inconsistencies.
The Bottom Line Good assignment structuring is a skill that may considerably improve your interaction and presentation of ideas. You'll be well on your way to writing well-structured, entertaining, and convincing projects if you follow these steps mentioned in our article ‘how to structure an assignment’ and customize your approach to the unique requirements of your assignment. If you are still unsure about writing your assignment, use AssignmentSanta's assignment writing services . They have extensive experience in their profession. Our professionals hold degrees from prestigious colleges all around the world. They can ensure that your work is completed in accordance with your specifications.
FAQs on how to structure an assignment
What is the structure of an assignment.
An assignment must have a cover page, a content page, an introduction, a body, a conclusion or suggestion, and a reference page.
What are the seven steps to completing a writing assignment?
The seven steps for writing assignments are as follows: Step 1: Examine the Assignment Topic. Step 2: Idea generation and drafting. Step 3: Create Questions for Assignment Writing. Step 4: Conduct research. Step 5: Critical Evaluation and Assignment Writing Preparation. Step 6: Revise. Step 7: Polishing and proofreading.
How should I format the opening page of an assignment?
The objective of the opening page of an assignment is to transmit important information at a first glance, such as your name, your instructor's name, the name of the program, and the due date. As a result, make sure the cover page is tidy, orderly, and free of excessive clutter. The title of the project may also be included on the first page of an assignment.
Eva Johnson
Greetings! My name is Eva Johnson, and I compose literature for a living. I pursued a Doctorate in creative writing after developing a lifetime love of literature, stories, and artistic expression. I became a full-time writing consultant at Assignmentsanta.com thanks to my love for creating original, educational content. Helping students with their academic writing assignments and getting top ratings is enjoyable. Over the years, my devotion has enabled me to publish my writing on numerous other reputable websites and online magazines. I enjoy reading, going on vacation adventures, and trying new foods while I'm not working. I want to read, learn, and experience more as I get older in order to better prepare myself for this ever-changing world.
Related Posts
How to make your assignment stand out with a killer cover page, tips on how to write an assignment, comprehensive guide on how to write introduction for an assignment.
Assignment Santa
Take help from best writing service !!
- literature review
- adhd scholarship canada
- geography essay
- college admission essay
- political essay
- cultural identity essay
- how to write chemistry lab report
- rhetorical analysis essay
- career goals essay
- how to write argumentative essay
- teel structure
- how to write an assignment
- how to make an assignment cover page
- how to write research paper
- thesis statement
- five paragraph essay
- narrative essay
- how many pages is 4000 words
- how to study effectively

Terms of use
Privacy policy.
Disclaimer: The reference papers provided by Assignment Santa should be used as model papers only. Students are not to copy or submit them as is. These reference papers are strictly intended for research and reference.
A product of Assignmentsanta.com
© 2023 Assignmentsanta.com Media. All rights reserved
How may I help you today?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on February 4, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A good introduction paragraph is an essential part of any academic essay . It sets up your argument and tells the reader what to expect.
The main goals of an introduction are to:
- Catch your reader’s attention.
- Give background on your topic.
- Present your thesis statement —the central point of your essay.
This introduction example is taken from our interactive essay example on the history of Braille.
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: hook your reader, step 2: give background information, step 3: present your thesis statement, step 4: map your essay’s structure, step 5: check and revise, more examples of essay introductions, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Your first sentence sets the tone for the whole essay, so spend some time on writing an effective hook.
Avoid long, dense sentences—start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
The hook should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of the topic you’re writing about and why it’s interesting. Avoid overly broad claims or plain statements of fact.
Examples: Writing a good hook
Take a look at these examples of weak hooks and learn how to improve them.
- Braille was an extremely important invention.
- The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
The first sentence is a dry fact; the second sentence is more interesting, making a bold claim about exactly why the topic is important.
- The internet is defined as “a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities.”
- The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education.
Avoid using a dictionary definition as your hook, especially if it’s an obvious term that everyone knows. The improved example here is still broad, but it gives us a much clearer sense of what the essay will be about.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is a famous book from the nineteenth century.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement.
Instead of just stating a fact that the reader already knows, the improved hook here tells us about the mainstream interpretation of the book, implying that this essay will offer a different interpretation.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Next, give your reader the context they need to understand your topic and argument. Depending on the subject of your essay, this might include:
- Historical, geographical, or social context
- An outline of the debate you’re addressing
- A summary of relevant theories or research about the topic
- Definitions of key terms
The information here should be broad but clearly focused and relevant to your argument. Don’t give too much detail—you can mention points that you will return to later, but save your evidence and interpretation for the main body of the essay.
How much space you need for background depends on your topic and the scope of your essay. In our Braille example, we take a few sentences to introduce the topic and sketch the social context that the essay will address:
Now it’s time to narrow your focus and show exactly what you want to say about the topic. This is your thesis statement —a sentence or two that sums up your overall argument.
This is the most important part of your introduction. A good thesis isn’t just a statement of fact, but a claim that requires evidence and explanation.
The goal is to clearly convey your own position in a debate or your central point about a topic.
Particularly in longer essays, it’s helpful to end the introduction by signposting what will be covered in each part. Keep it concise and give your reader a clear sense of the direction your argument will take.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As you research and write, your argument might change focus or direction as you learn more.
For this reason, it’s often a good idea to wait until later in the writing process before you write the introduction paragraph—it can even be the very last thing you write.
When you’ve finished writing the essay body and conclusion , you should return to the introduction and check that it matches the content of the essay.
It’s especially important to make sure your thesis statement accurately represents what you do in the essay. If your argument has gone in a different direction than planned, tweak your thesis statement to match what you actually say.
To polish your writing, you can use something like a paraphrasing tool .
You can use the checklist below to make sure your introduction does everything it’s supposed to.
Checklist: Essay introduction
My first sentence is engaging and relevant.
I have introduced the topic with necessary background information.
I have defined any important terms.
My thesis statement clearly presents my main point or argument.
Everything in the introduction is relevant to the main body of the essay.
You have a strong introduction - now make sure the rest of your essay is just as good.
- Argumentative
- Literary analysis
This introduction to an argumentative essay sets up the debate about the internet and education, and then clearly states the position the essay will argue for.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
This introduction to a short expository essay leads into the topic (the invention of the printing press) and states the main point the essay will explain (the effect of this invention on European society).
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
This introduction to a literary analysis essay , about Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein , starts by describing a simplistic popular view of the story, and then states how the author will give a more complex analysis of the text’s literary devices.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale. Arguably the first science fiction novel, its plot can be read as a warning about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, and in popular culture representations of the character as a “mad scientist”, Victor Frankenstein represents the callous, arrogant ambition of modern science. However, far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to gradually transform our impression of Frankenstein, portraying him in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
The “hook” is the first sentence of your essay introduction . It should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of why it’s interesting.
To write a good hook, avoid overly broad statements or long, dense sentences. Try to start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 30, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/introduction/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to conclude an essay | interactive example, what is your plagiarism score.
New User? Start here.
4 Basic Tips to Structure an Assignment

Table of Contents
Students in higher academia, typically in universities and colleges, spend more time on writing the main body of an assignment than they do on structuring. The result is that professors are often bogged down by assignments that are rich in details but lack structure and coherence. A well-structured essay helps a student to highlight the main points and present the arguments better.
How To Structure An Assignment?
While there are disciplinary differences regarding the structure to be followed, one can still summarize some important points common to all disciples.
1. All Assignments Should At Least Have 3 Parts:
And those are an introduction, the main body, and a conclusion.
Treat your assignment or your essay like a three-act drama. In the first part, you introduce your reader to the subject matter of the assignment. In the next part, you delve into the main research topic of the assignment and finally, you state your research findings. However, disciplinary requirements should always be kept in mind. Some subjects might call for specialized structures. For instance, science students while writing about their experiments usually follow a three-structure format of a hypothesis, details of an experiment and an inference. A nursing case study should start with a patient’s medical case history, followed by the pathological symptoms, the diagnosis, the treatment received and a post-discharge medical regimen to be followed by the patient. Similarly, a marketing case study should have a brief history of the company followed by a situational analysis, environmental scanning and finally recommendations for the future.
2. The Introduction Is The Most Important Part Of An Assignment:
It’s important to write a convincing introduction in order to retain the attention of the reader. There are usually two ways to write an introduction — a deductive style and an inductive style.
A) Deductive Style:
In a deductive style of writing, a researcher moves from the general to the specific through the process of deduction. It is a ‘top-down’ approach in which a researcher starts with a general introduction and then moves to a specific problem.
“Since there is a lot of traffic congestion in the morning on my way to the office, I must leave my house at least two hours before in order to reach my office at ten o’clock”
B) Inductive Style:
On the other hand, in an inductive style of writing, a researcher moves from the specific to the general. It is a ‘bottom-up’ approach in which specific point(s) add(s) up to some general conclusion. Here is an example, to drive the point home.
“I must leave my house at least two hours before in order to reach my office at ten o’clock. There is a lot of traffic congestion in the morning on my way to the office.”
In the first style, we make a general observation (i.e. heavy traffic congestion) and then use it to deduce early exit from home to reach office on time. But in the second style, we start with a specific piece of information (i.e. my early exit from home) and use it as a supporting statement to make a general observation. Inductive and deductive styles can be followed while writing the introduction of any assignment. A mix of the two is also followed sometimes.
3. State All Your Research Findings In The Main Body Of The Assignment:
This is important from a disciplinary point of view because the purpose of giving an assignment is to observe whether students have understood what has been taught in the class and whether they have the ability to apply it to a specific research problem. Students are required to demonstrate their command over the specific area on which they are writing, here MyAssignmentHelp.com helps students. While there is no particular formula that will work for all disciplines, still there are three things students should always remember while writing an assignment:
a) You should try to stick to the point
b) It is always important to be analytical rather than descriptive
c) You should not write anything that was not promised in the introduction
These are the things you come across very often whenever you read an article on tips to write an essay .
4. Finally Round Up Your Discussion In Your Conclusion:
The student should summarize the principal topics touched upon in the assignment. They should remind the reader(s) about the main arguments and finally state their intervention and where it differs from existing literature on the subject.
It is important to remember that all essays or assignments need not follow all these tips in toto. It is always good to be creative and tweak your writings according to the course requirements or the requirements of the teacher.
The above discussion will, nonetheless, help the students to keep in mind some crucial points that should be common to all well-written assignments across disciplinary boundaries.
Sample Question And Solution Of Basic Tips To Structure An Assignment
Cis5100 assignment 1, question: .
- Define what a Database Management System is.
- Explain why a Database Management System is the appropriate tool for this project.
- Define what a Decision Support System is.
- Explain why a Decision Support System is the appropriate tool for this project.
- From the results of the Decision Support System results discuss the following (keeping in mind the information provided in the preamble on page 2):
Which Mark-up Type would be most appropriate for the business? Why?
What would be the impact on the business profit if the plan to provide a discount to large orders was implemented? Why?
Which Recommended Freight Type would be most appropriate for the business? Why?
Which country would be most appropriate for the business to import from at the moment? Why?
Solution:
- This assignment must be all your own work. It is acceptable to discuss course content with others to improve your understanding and clarify requirements, but solutions to assignment questions must be done on your own.
- You must not copyfrom anyone, including tutors and fellow students, nor allow others to copy your work.
- All Assignments will be checked using collusion monitoring tools to ensure that each assignment is the original work of the submitting student. Assignments that do not adhere to this requirement will be deemed as being the result of collusion or plagiarism. This may lead to severe academic penalties as outlined in USQ Policy Library: Academic Integrity Policy and Procedure. It is your own responsibility to ensure the integrity of your work. Refer to the USQ Policy Library for more details: read more
Writing Assignment Outline: Why Is It Important
An assignment outline is nothing but a plan of what do you wish to include in your paper & The broader elements are broken down in a clear and concise way. Composing an assignment outline has several benefits.
Here’s everything you should know.
- The perfect assignment outline helps students organize their thoughts.
- It helps in finding the most logical order to present academic work.
- In addition to it, an assignment outline helps in connecting one idea to another in a seamless and rational manner.
- It prevents the writer from getting stuck while drafting the final copy.
- The assignment outline categorizes the main points and organizes all paragraphs into an order that creates sense from every aspect.
Now that you know about the essential benefits of composing an assignment outline & doing my assignment service , structure your paper accordingly in order to produce flawless content.
Sure-Fire Tips To Structure An Assignment Flawlessly
Merely knowing about the application and benefits of outlining an assignment isn’t enough. One must also know how to structure an assignment with perfection. Hence, here are the most effective tips to help you outline assignments with perfection. Take note.
- Decide whether you will write the assignment structure by hand or type it.
- Narrow down the topic in case the subject matter appears to be too broad in nature.
- Identify the purpose of your outline and know your intended audience.
- If applicable, then organize your notes, research essay materials, and other components according to the assignment guidelines.
- Now list all supporting ideas and arguments for each major aspect of points to be discussed.
So, put on your thinking cap, focus on each of the aforementioned suggestions, and initiate the task of structuring your assignment like a pro.
How MyAssignmenthelp.Com Can Help Students To Write Their Assignments?
Myassignmenthelp.com is a premier assignment service provider of Australia, the UK, and the US. It has a vast archive of sample assignments on marketing , law , engineering, science and nursing for students’ reference. The professional writers here help out students to structure essays and write assignments with bibliography and proper citations. Students can further buy custom made assignments at reasonable rates.
Most Popular FAQs Searched By Students:
Q.1. how do you structure an assignment.
Ans: Before starting to write your assignment, create a map or a plan to guide you. This will help you make sure that you have not missed out on any of the critical parts of the assignment. In the introduction, give a general orientation for the topic. For every paragraph of the body, start it with the central idea that you are going to talk about. Use linking words to maintain a flow through the different paragraphs as well as keep parity with the thesis statement. In conclusion, take the most important points discussed and end with a suggestion.
Q.2. What Are The Elements Of An Assignment?
Ans: Students must start their assignments with a cover page by using different fonts and graphics to make it look appealing. The cover page must include the student’s details like name, class, subject, etc. After the cover page comes the table of contents. Make sure that you provide the page numbers for easy navigation. The assignment is divided into 3 parts – introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should tell the reader what the assignment is about. The body should contain a logical development of the argument of the paper divided into sub-sections, followed by a justified conclusion.
Q.3. How Do You Write A Perfect Assignment?
Ans: Create a schedule and break the assignment down into manageable chunks. You can also create a basic assignment structure for the points and key arguments. Leave the introduction for the end and start by framing the thesis statement. While structuring your argument, make sure that each point has supporting evidence. As you use sources, add them to your reference list to save time. Summarise your previous arguments and do not introduce new ideas in the conclusion. Edit and proofread your assignment to remove errors and cite all the sources properly.

Hi, my name is Henry Lee. I am 26 and an active tech blogger based in Adelaide. Well, that’s something I do out of passion. To earn a livelihood, I work as a full-time English writing expert at myassignmenthelp.com. I write academic blogs, mainly focused on English and Literature writing. I have 4+ years of experience of guiding students on essays writing on different categories of topics. Apart from this, I love to keep myself updated on the latest happenings in technology. I love new gadgets as much as I love writing. So, when I am not writing, you’ll probably find me indulged in a gaming session or researching about the latest trend in technology.
Related Post

Writing Get your essay and assignment written from scratch by PhD expert
Rewriting: Paraphrase or rewrite your friend's essay with similar meaning at reduced cost
Editing: Proofread your work by experts and improve grade at Lowest cost
Enter phone no. to receive critical updates and urgent messages !
Please upload all relevant files for quick & complete assistance.
Get original papers written according to your instructions and save time for what matters most.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Types of Assignments
Cristy Bartlett and Kate Derrington

Introduction
As discussed in the previous chapter, assignments are a common method of assessment at university. You may encounter many assignments over your years of study, yet some will look quite different from others. By recognising different types of assignments and understanding the purpose of the task, you can direct your writing skills effectively to meet task requirements. This chapter draws on the skills from the previous chapter, and extends the discussion, showing you where to aim with different types of assignments.
The chapter begins by exploring the popular essay assignment, with its two common categories, analytical and argumentative essays. It then examines assignments requiring case study responses , as often encountered in fields such as health or business. This is followed by a discussion of assignments seeking a report (such as a scientific report) and reflective writing assignments, common in nursing, education and human services. The chapter concludes with an examination of annotated bibliographies and literature reviews. The chapter also has a selection of templates and examples throughout to enhance your understanding and improve the efficacy of your assignment writing skills.
Different Types of Written Assignments
At university, an essay is a common form of assessment. In the previous chapter Writing Assignments we discussed what was meant by showing academic writing in your assignments. It is important that you consider these aspects of structure, tone and language when writing an essay.
Components of an essay
Essays should use formal but reader friendly language and have a clear and logical structure. They must include research from credible academic sources such as peer reviewed journal articles and textbooks. This research should be referenced throughout your essay to support your ideas (See the chapter Working with Information ).

If you have never written an essay before, you may feel unsure about how to start. Breaking your essay into sections and allocating words accordingly will make this process more manageable and will make planning the overall essay structure much easier.
- An essay requires an introduction, body paragraphs and a conclusion.
- Generally, an introduction and conclusion are approximately 10% each of the total word count.
- The remaining words can then be divided into sections and a paragraph allowed for each area of content you need to cover.
- Use your task and criteria sheet to decide what content needs to be in your plan
An effective essay introduction needs to inform your reader by doing four basic things:
Table 20.1 An effective essay
An effective essay body paragraph needs to:
An effective essay conclusion needs to:
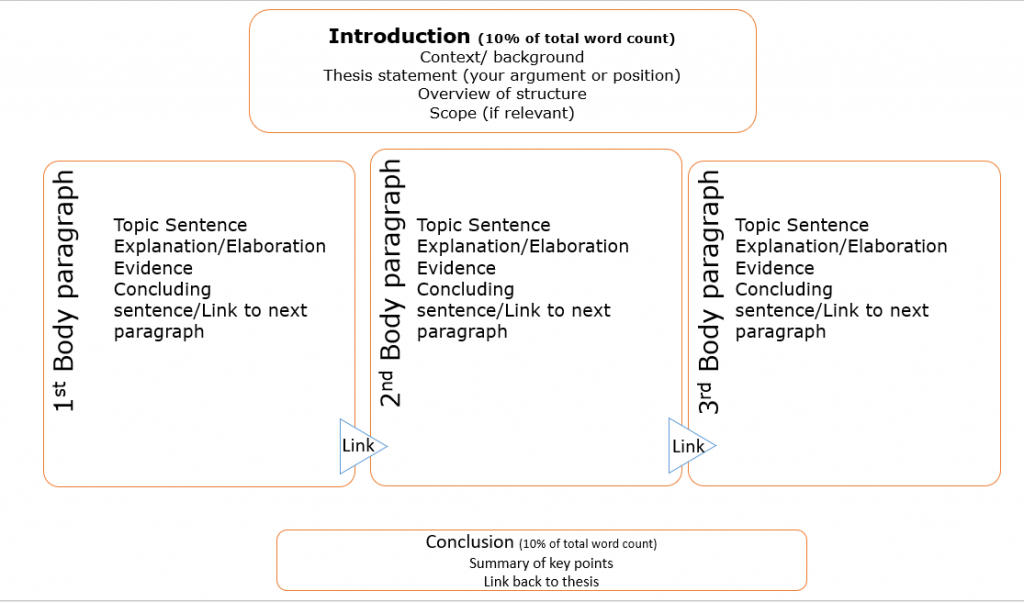
Common types of essays
You may be required to write different types of essays, depending on your study area and topic. Two of the most commonly used essays are analytical and argumentative . The task analysis process discussed in the previous chapter Writing Assignments will help you determine the type of essay required. For example, if your assignment question uses task words such as analyse, examine, discuss, determine or explore, you would be writing an analytical essay . If your assignment question has task words such as argue, evaluate, justify or assess, you would be writing an argumentative essay . Despite the type of essay, your ability to analyse and think critically is important and common across genres.
Analytical essays

These essays usually provide some background description of the relevant theory, situation, problem, case, image, etcetera that is your topic. Being analytical requires you to look carefully at various components or sections of your topic in a methodical and logical way to create understanding.
The purpose of the analytical essay is to demonstrate your ability to examine the topic thoroughly. This requires you to go deeper than description by considering different sides of the situation, comparing and contrasting a variety of theories and the positives and negatives of the topic. Although in an analytical essay your position on the topic may be clear, it is not necessarily a requirement that you explicitly identify this with a thesis statement, as is the case with an argumentative essay. If you are unsure whether you are required to take a position, and provide a thesis statement, it is best to check with your tutor.
Argumentative essays
These essays require you to take a position on the assignment topic. This is expressed through your thesis statement in your introduction. You must then present and develop your arguments throughout the body of your assignment using logically structured paragraphs. Each of these paragraphs needs a topic sentence that relates to the thesis statement. In an argumentative essay, you must reach a conclusion based on the evidence you have presented.
Case Study Responses
Case studies are a common form of assignment in many study areas and students can underperform in this genre for a number of key reasons.
Students typically lose marks for not:
- Relating their answer sufficiently to the case details
- Applying critical thinking
- Writing with clear structure
- Using appropriate or sufficient sources
- Using accurate referencing
When structuring your response to a case study, remember to refer to the case. Structure your paragraphs similarly to an essay paragraph structure but include examples and data from the case as additional evidence to support your points (see Figure 20.5 ). The colours in the sample paragraph below show the function of each component.
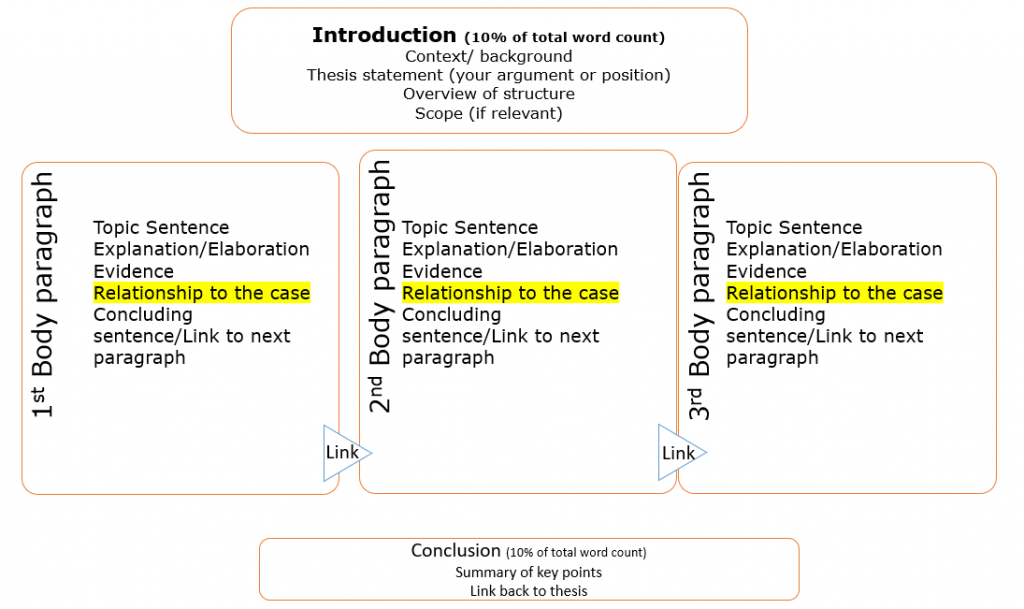
The Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia (NMBA) Code of Conduct and Nursing Standards (2018) play a crucial role in determining the scope of practice for nurses and midwives. A key component discussed in the code is the provision of person-centred care and the formation of therapeutic relationships between nurses and patients (NMBA, 2018). This ensures patient safety and promotes health and wellbeing (NMBA, 2018). The standards also discuss the importance of partnership and shared decision-making in the delivery of care (NMBA, 2018, 4). Boyd and Dare (2014) argue that good communication skills are vital for building therapeutic relationships and trust between patients and care givers. This will help ensure the patient is treated with dignity and respect and improve their overall hospital experience. In the case, the therapeutic relationship with the client has been compromised in several ways. Firstly, the nurse did not conform adequately to the guidelines for seeking informed consent before performing the examination as outlined in principle 2.3 (NMBA, 2018). Although she explained the procedure, she failed to give the patient appropriate choices regarding her health care.
Topic sentence | Explanations using paraphrased evidence including in-text references | Critical thinking (asks the so what? question to demonstrate your student voice). | Relating the theory back to the specifics of the case. The case becomes a source of examples as extra evidence to support the points you are making.
Reports are a common form of assessment at university and are also used widely in many professions. It is a common form of writing in business, government, scientific, and technical occupations.
Reports can take many different structures. A report is normally written to present information in a structured manner, which may include explaining laboratory experiments, technical information, or a business case. Reports may be written for different audiences including clients, your manager, technical staff, or senior leadership within an organisation. The structure of reports can vary, and it is important to consider what format is required. The choice of structure will depend upon professional requirements and the ultimate aims of the report. Consider some of the options in the table below (see Table 20.2 ).
Table 20.2 Explanations of different types of reports
Reflective writing.

Reflective writing is a popular method of assessment at university. It is used to help you explore feelings, experiences, opinions, events or new information to gain a clearer and deeper understanding of your learning. A reflective writing task requires more than a description or summary. It requires you to analyse a situation, problem or experience, consider what you may have learnt and evaluate how this may impact your thinking and actions in the future. This requires critical thinking, analysis, and usually the application of good quality research, to demonstrate your understanding or learning from a situation. Essentially, reflective practice is the process of looking back on past experiences and engaging with them in a thoughtful way and drawing conclusions to inform future experiences. The reflection skills you develop at university will be vital in the workplace to assist you to use feedback for growth and continuous improvement. There are numerous models of reflective writing and you should refer to your subject guidelines for your expected format. If there is no specific framework, a simple model to help frame your thinking is What? So what? Now what? (Rolfe et al., 2001).
Table 20.3 What? So What? Now What? Explained.
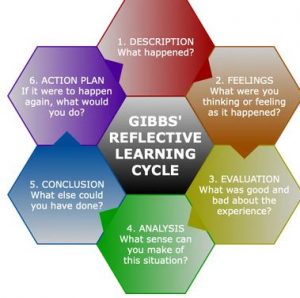
The Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle
The Gibbs’ Cycle of reflection encourages you to consider your feelings as part of the reflective process. There are six specific steps to work through. Following this model carefully and being clear of the requirements of each stage, will help you focus your thinking and reflect more deeply. This model is popular in Health.
The 4 R’s of reflective thinking
This model (Ryan and Ryan, 2013) was designed specifically for university students engaged in experiential learning. Experiential learning includes any ‘real-world’ activities including practice led activities, placements and internships. Experiential learning, and the use of reflective practice to heighten this learning, is common in Creative Arts, Health and Education.
Annotated Bibliography
What is it.
An annotated bibliography is an alphabetical list of appropriate sources (books, journals or websites) on a topic, accompanied by a brief summary, evaluation and sometimes an explanation or reflection on their usefulness or relevance to your topic. Its purpose is to teach you to research carefully, evaluate sources and systematically organise your notes. An annotated bibliography may be one part of a larger assessment item or a stand-alone assessment piece. Check your task guidelines for the number of sources you are required to annotate and the word limit for each entry.
How do I know what to include?
When choosing sources for your annotated bibliography it is important to determine:
- The topic you are investigating and if there is a specific question to answer
- The type of sources on which you need to focus
- Whether they are reputable and of high quality
What do I say?
Important considerations include:
- Is the work current?
- Is the work relevant to your topic?
- Is the author credible/reliable?
- Is there any author bias?
- The strength and limitations (this may include an evaluation of research methodology).
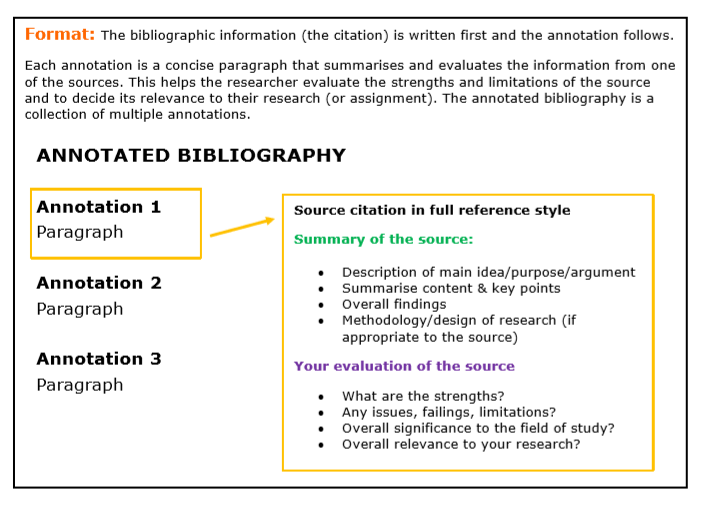
Literature Reviews
It is easy to get confused by the terminology used for literature reviews. Some tasks may be described as a systematic literature review when actually the requirement is simpler; to review the literature on the topic but do it in a systematic way. There is a distinct difference (see Table 20.4 ). As a commencing undergraduate student, it is unlikely you would be expected to complete a systematic literature review as this is a complex and more advanced research task. It is important to check with your lecturer or tutor if you are unsure of the requirements.
Table 20.4 Comparison of Literature Reviews
Generally, you are required to establish the main ideas that have been written on your chosen topic. You may also be expected to identify gaps in the research. A literature review does not summarise and evaluate each resource you find (this is what you would do in an annotated bibliography). You are expected to analyse and synthesise or organise common ideas from multiple texts into key themes which are relevant to your topic (see Figure 20.10 ). Use a table or a spreadsheet, if you know how, to organise the information you find. Record the full reference details of the sources as this will save you time later when compiling your reference list (see Table 20.5 ).
Overall, this chapter has provided an introduction to the types of assignments you can expect to complete at university, as well as outlined some tips and strategies with examples and templates for completing them. First, the chapter investigated essay assignments, including analytical and argumentative essays. It then examined case study assignments, followed by a discussion of the report format. Reflective writing , popular in nursing, education and human services, was also considered. Finally, the chapter briefly addressed annotated bibliographies and literature reviews. The chapter also has a selection of templates and examples throughout to enhance your understanding and improve the efficacy of your assignment writing skills.
- Not all assignments at university are the same. Understanding the requirements of different types of assignments will assist in meeting the criteria more effectively.
- There are many different types of assignments. Most will require an introduction, body paragraphs and a conclusion.
- An essay should have a clear and logical structure and use formal but reader friendly language.
- Breaking your assignment into manageable chunks makes it easier to approach.
- Effective body paragraphs contain a topic sentence.
- A case study structure is similar to an essay, but you must remember to provide examples from the case or scenario to demonstrate your points.
- The type of report you may be required to write will depend on its purpose and audience. A report requires structured writing and uses headings.
- Reflective writing is popular in many disciplines and is used to explore feelings, experiences, opinions or events to discover what learning or understanding has occurred. Reflective writing requires more than description. You need to be analytical, consider what has been learnt and evaluate the impact of this on future actions.
- Annotated bibliographies teach you to research and evaluate sources and systematically organise your notes. They may be part of a larger assignment.
- Literature reviews require you to look across the literature and analyse and synthesise the information you find into themes.
Gibbs, G. (1988). Learning by doing: A guide to teaching and learning methods. Further Education Unit, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford.
Rolfe, G., Freshwater, D., Jasper, M. (2001). Critical reflection in nursing and the helping professions: a user’s guide . Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Ryan, M. & Ryan, M. (2013). Theorising a model for teaching and assessing reflective learning in higher education. Higher Education Research & Development , 32(2), 244-257. doi: 10.1080/07294360.2012.661704
Academic Success Copyright © 2021 by Cristy Bartlett and Kate Derrington is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Assignment writing structure
To write an assignment is not an easy task. If you have already become acquainted with this genre and are eager to start writing, we have gathered for you some useful information, which will be discussed later.
When selecting a topic for an assignment, it should be understood that this genre is not diary entries that you can write for yourself. Essays are written to encourage the reader to act or at least to reflect on this topic. Based on this, it is possible to form an assignment topic that usually contains a question and a problem (for example: “What is more important: oil or cannons?”).
Don’t waste your time! Order your assignment!
Structure of assignment writing
Although the assignment writing structure has a simple form, it has some structural features as well. First of all, they are conditioned by the requirements imposed on this genre. An argument cannot be the author’s phrase: “My grandmother told me about this.” The fact must be officially confirmed. This is quite difficult for a beginner.
First, you need to think about how the structure of assignment writing will look. To do this, just take and sketch out what you will write about. This will be the “skeleton” of your text, in the aftermath, it will grow “flesh.” It is the writing plan that is necessary for each text, and essays especially. Now you understand how to write an assignment structure. You can read more information about how to write an assignment plan .
We can say that the presentation of the essay takes place in three steps.
I. Introduction
The introduction refers to the first paragraph of the text. Writing it is necessary so that the reader is interested in reading the essay to the end. It should be clear about what will be told in the future. However, do not write a lot, a few suggestions will be enough.
II. Main part
In the main part, several points of view on the same issue are considered.
This part of the text can consist of several paragraphs, first comes the thesis — this is the author’s idea, which he is trying to convey to the reader. Then you should write the argument and proof of the previously written thesis. For example, the current situation is from personal or social life, a theory or a proven scientific fact.
There can be two arguments for one thesis because one cannot convince the reader, but simply overload the assignment.
However, the author has the right to add to one thesis an unlimited number of arguments. This will depend on the assignment writing structure and its volume. The main thing is to make the text coherent and logical.
Arguments can be arranged in the sequence:
- Explanation.
- The final statement.
- The conclusion.
III. Final part
In conclusion of the essay, it is necessary to draw the right conclusions for each thesis given in the part of the text. It is how the reader will receive a logical conclusion on the text reading. The author must describe the problem and draw a conclusion.
It turns out that at the beginning of the text, the reader should be interested in the introductory part, and in the end generalize the information presented. This is the basic rule of how to write an assignment structure .
Now we will talk more precisely about each part of the assignment.
The introductory part usually gives general comments on the composition, lists the key concepts, indicate what issues on this topic are going to be considered. Do not forget that the assignment is a short essay; mention only the most basic of its points.
From a well-written introduction, it becomes clear that you understand the topic and intend to answer the questions posed. The plan of the assignment gives an idea of the structure of writing an assignment and its main aspects. In the introduction, you mention the studies conducted and give references to sources. The ideal volume of this part is no more than 10% of the entire work. For example, if the entire composition of 2000 characters, the amount of introduction should not exceed two hundred characters.
At the beginning of the essay, use such stereotyped phrases as “This paper is devoted to …”, “This essay will be considered …» etc. Then you should repeat or slightly modify the wording of the question. For example, the question is: “Consider the latest innovations in the field of computer technology.” Hence, the introduction may sound like this: “This work will analyze the latest developments in the field of computer technology.” Definitions should be clear, not allowing ambiguous interpretation.
In order to make the plan more specific, use phrases of this type:
- “In the beginning, it will be considered …”
- “This report is divided into three parts …”
- “Next, we proceed to the description …”
- “As a result, we will draw conclusions about …”
In the main part, you need to state all the arguments, backed up with illustrations and examples. Based on the logic of the narrative, the text should be divided into paragraphs. Make up the assignment writing structure in such a way that the main part can be smoothly transferred to the conclusion.
In conclusion, you must draw conclusions from all the ideas outlined. Thus, you answer the main question considered in the assignment. If this is provided by the topic, it is necessary to mention the consequences and prospects of the phenomenon under investigation. You can share your views, without forgetting to back them up with arguments.
The components of a good conclusion
- You need not just to sum up, but to finish the work logically. Tell us how the written text is applicable to real life.
- List the most important ideas. Use the theses from the introduction, set them in other words and expressions.
- In conclusion, we need to emphasize the key ideas that were expressed in the main part. If the volume of the composition is large enough, it will be necessary. In conclusion, a short assignment can do without listing the main ideas.
- Use a relevant quote or a spectacular metaphor to encourage the reader to further reflections.
- Forecast the consequences and results of the phenomena described, suggest different solutions to the problem.
What should I refrain from writing an opinion?
It is not necessary to state absolutely new ideas. If it seems to you that you cannot do without them, share them in the main part. Speak confidently, without apologizing or making excuses. Phrases like “At least, I think so” or “Of course, I’m not an expert” are inadmissible.
Do not pay too much attention to minor details. Do not question the arguments given earlier, do not contradict yourself. Most teachers believe the conclusion is the most important part of the assignment. According to its content, one can draw a conclusion about how well you have learned the material and deeply penetrated the essence of the problem. If, after writing the conclusion, you have to correct the rest of the assignment, this will only improve the quality of the text.
In the end, the proportions of the ideal essay should be approximately the following:
- introduction – up to 10% of the total volume of the essay;
- conclusion – no more than 15% of the total volume of the text.
Related assignments:
- Writing Thesis Statements Assignment
- Writing Expectations Assignment
- How to do a 3000 word assignment
- What is an essay assignment and steps to writing
Haven't Found The Paper You Want?
For Only $13.90/page
C Data Types
C operators.
- C Input and Output
- C Control Flow
- C Functions
- C Preprocessors
C File Handling
- C Cheatsheet
C Interview Questions
- C Programming Language Tutorial
- C Language Introduction
- Features of C Programming Language
- C Programming Language Standard
- C Hello World Program
- Compiling a C Program: Behind the Scenes
- Tokens in C
- Keywords in C
C Variables and Constants
- C Variables
- Constants in C
- Const Qualifier in C
- Different ways to declare variable as constant in C
- Scope rules in C
- Internal Linkage and External Linkage in C
- Global Variables in C
- Data Types in C
- Literals in C
- Escape Sequence in C
- Integer Promotions in C
- Character Arithmetic in C
- Type Conversion in C
C Input/Output
- Basic Input and Output in C
- Format Specifiers in C
- printf in C
- Scansets in C
- Formatted and Unformatted Input/Output functions in C with Examples
- Operators in C
- Arithmetic Operators in C
- Unary operators in C
- Relational Operators in C
- Bitwise Operators in C
- C Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators in C
- Increment and Decrement Operators in C
- Conditional or Ternary Operator (?:) in C
- sizeof operator in C
- Operator Precedence and Associativity in C
C Control Statements Decision-Making
- Decision Making in C (if , if..else, Nested if, if-else-if )
- C - if Statement
- C if...else Statement
- C if else if ladder
- Switch Statement in C
- Using Range in switch Case in C
- while loop in C
- do...while Loop in C
- For Versus While
- Continue Statement in C
- Break Statement in C
- goto Statement in C
- User-Defined Function in C
- Parameter Passing Techniques in C
- Function Prototype in C
- How can I return multiple values from a function?
- main Function in C
- Implicit return type int in C
- Callbacks in C
- Nested functions in C
- Variadic functions in C
- _Noreturn function specifier in C
- Predefined Identifier __func__ in C
- C Library math.h Functions
C Arrays & Strings
- Properties of Array in C
- Multidimensional Arrays in C
- Initialization of Multidimensional Array in C
- Pass Array to Functions in C
- How to pass a 2D array as a parameter in C?
- What are the data types for which it is not possible to create an array?
- How to pass an array by value in C ?
- Strings in C
- Array of Strings in C
- What is the difference between single quoted and double quoted declaration of char array?
- C String Functions
- Pointer Arithmetics in C with Examples
- C - Pointer to Pointer (Double Pointer)
- Function Pointer in C
- How to declare a pointer to a function?
- Pointer to an Array | Array Pointer
- Difference between constant pointer, pointers to constant, and constant pointers to constants
- Pointer vs Array in C
- Dangling, Void , Null and Wild Pointers in C
- Near, Far and Huge Pointers in C
- restrict keyword in C
C User-Defined Data Types
C structures.
- dot (.) Operator in C
- Structure Member Alignment, Padding and Data Packing
- Flexible Array Members in a structure in C
- Bit Fields in C
- Difference Between Structure and Union in C
- Anonymous Union and Structure in C
- Enumeration (or enum) in C
C Storage Classes
- Storage Classes in C
- extern Keyword in C
- Static Variables in C
- Initialization of static variables in C
- Static functions in C
- Understanding "volatile" qualifier in C | Set 2 (Examples)
- Understanding "register" keyword in C
C Memory Management
- Memory Layout of C Programs
- Dynamic Memory Allocation in C using malloc(), calloc(), free() and realloc()
- Difference Between malloc() and calloc() with Examples
- What is Memory Leak? How can we avoid?
- Dynamic Array in C
- How to dynamically allocate a 2D array in C?
- Dynamically Growing Array in C
C Preprocessor
- C Preprocessor Directives
- How a Preprocessor works in C?
- Header Files in C
- What’s difference between header files "stdio.h" and "stdlib.h" ?
- How to write your own header file in C?
- Macros and its types in C
- Interesting Facts about Macros and Preprocessors in C
- # and ## Operators in C
- How to print a variable name in C?
- Multiline macros in C
- Variable length arguments for Macros
- Branch prediction macros in GCC
- typedef versus #define in C
- Difference between #define and const in C?
- Basics of File Handling in C
- C fopen() function with Examples
- EOF, getc() and feof() in C
- fgets() and gets() in C language
- fseek() vs rewind() in C
- What is return type of getchar(), fgetc() and getc() ?
- Read/Write Structure From/to a File in C
- C Program to print contents of file
- C program to delete a file
- C Program to merge contents of two files into a third file
- What is the difference between printf, sprintf and fprintf?
- Difference between getc(), getchar(), getch() and getche()
Miscellaneous
- time.h header file in C with Examples
- Input-output system calls in C | Create, Open, Close, Read, Write
- Signals in C language
- Program error signals
- Socket Programming in C
- _Generics Keyword in C
- Multithreading in C
- C Programming Interview Questions (2024)
- Commonly Asked C Programming Interview Questions | Set 1
- Commonly Asked C Programming Interview Questions | Set 2
- Commonly Asked C Programming Interview Questions | Set 3
The structure in C is a user-defined data type that can be used to group items of possibly different types into a single type. The struct keyword is used to define the structure in the C programming language. The items in the structure are called its member and they can be of any valid data type.
C Structure Declaration
We have to declare structure in C before using it in our program. In structure declaration, we specify its member variables along with their datatype. We can use the struct keyword to declare the structure in C using the following syntax:
The above syntax is also called a structure template or structure prototype and no memory is allocated to the structure in the declaration.
C Structure Definition
To use structure in our program, we have to define its instance. We can do that by creating variables of the structure type. We can define structure variables using two methods:
1. Structure Variable Declaration with Structure Template
2. structure variable declaration after structure template, access structure members.
We can access structure members by using the ( . ) dot operator.
In the case where we have a pointer to the structure, we can also use the arrow operator to access the members.
Initialize Structure Members
Structure members cannot be initialized with the declaration. For example, the following C program fails in the compilation.
The reason for the above error is simple. When a datatype is declared, no memory is allocated for it. Memory is allocated only when variables are created.
We can initialize structure members in 3 ways which are as follows:
- Using Assignment Operator.
- Using Initializer List.
- Using Designated Initializer List.
1. Initialization using Assignment Operator
2. initialization using initializer list.
In this type of initialization, the values are assigned in sequential order as they are declared in the structure template.
3. Initialization using Designated Initializer List
Designated Initialization allows structure members to be initialized in any order. This feature has been added in the C99 standard .
The Designated Initialization is only supported in C but not in C++.
Example of Structure in C
The following C program shows how to use structures
typedef for Structures
The typedef keyword is used to define an alias for the already existing datatype. In structures, we have to use the struct keyword along with the structure name to define the variables. Sometimes, this increases the length and complexity of the code. We can use the typedef to define some new shorter name for the structure.
Nested Structures
C language allows us to insert one structure into another as a member. This process is called nesting and such structures are called nested structures . There are two ways in which we can nest one structure into another:
1. Embedded Structure Nesting
In this method, the structure being nested is also declared inside the parent structure.
2. Separate Structure Nesting
In this method, two structures are declared separately and then the member structure is nested inside the parent structure.
One thing to note here is that the declaration of the structure should always be present before its definition as a structure member. For example, the declaration below is invalid as the struct mem is not defined when it is declared inside the parent structure.
Accessing Nested Members
We can access nested Members by using the same ( . ) dot operator two times as shown:
Example of Structure Nesting
Structure pointer in c.
We can define a pointer that points to the structure like any other variable. Such pointers are generally called Structure Pointers . We can access the members of the structure pointed by the structure pointer using the ( -> ) arrow operator.
Example of Structure Pointer
Self-referential structures.
The self-referential structures in C are those structures that contain references to the same type as themselves i.e. they contain a member of the type pointer pointing to the same structure type.
Example of Self-Referential Structures
Such kinds of structures are used in different data structures such as to define the nodes of linked lists, trees, etc.
C Structure Padding and Packing
Technically, the size of the structure in C should be the sum of the sizes of its members. But it may not be true for most cases. The reason for this is Structure Padding.
Structure padding is the concept of adding multiple empty bytes in the structure to naturally align the data members in the memory. It is done to minimize the CPU read cycles to retrieve different data members in the structure.
There are some situations where we need to pack the structure tightly by removing the empty bytes. In such cases, we use Structure Packing. C language provides two ways for structure packing:
- Using #pragma pack(1)
- Using __attribute((packed))__
Example of Structure Padding and Packing
As we can see, the size of the structure is varied when structure packing is performed.
To know more about structure padding and packing, refer to this article – Structure Member Alignment, Padding and Data Packing .
Bit Fields are used to specify the length of the structure members in bits. When we know the maximum length of the member, we can use bit fields to specify the size and reduce memory consumption.
Syntax of Bit Fields
example of bit fields.
As we can see, the size of the structure is reduced when using the bit field to define the max size of the member ‘a’.
Uses of Structure in C
C structures are used for the following:
- The structure can be used to define the custom data types that can be used to create some complex data types such as dates, time, complex numbers, etc. which are not present in the language.
- It can also be used in data organization where a large amount of data can be stored in different fields.
- Structures are used to create data structures such as trees, linked lists, etc.
- They can also be used for returning multiple values from a function.
Limitations of C Structures
In C language, structures provide a method for packing together data of different types. A Structure is a helpful tool to handle a group of logically related data items. However, C structures also have some limitations.
- Higher Memory Consumption: It is due to structure padding.
- No Data Hiding: C Structures do not permit data hiding. Structure members can be accessed by any function, anywhere in the scope of the structure.
- Functions inside Structure: C structures do not permit functions inside the structure so we cannot provide the associated functions.
- Static Members: C Structure cannot have static members inside its body.
- Construction creation in Structure: Structures in C cannot have a constructor inside Structures.
Related Articles
- C Structures vs C++ Structure
Please Login to comment...
- C-Structure & Union
- How to Delete Whatsapp Business Account?
- Discord vs Zoom: Select The Efficienct One for Virtual Meetings?
- Otter AI vs Dragon Speech Recognition: Which is the best AI Transcription Tool?
- Google Messages To Let You Send Multiple Photos
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Stage #3 - Assignment Framework: Take the information gathered in Stage #2 and organise it into the assignment framework chart to finalise your structure. Stage #4 - Assignment Checklist: Go through the Assignment check list to check that you have included everything that is required for each section.
While there are different types of written assignments, most academic writing has a similar structure comprising of: Introduction—acts as a roadmap for the reader. Body—presents points to support your argument. Conclusion—summarises main points discussed. The introduction helps your reader understand where you're going in your ...
The assignment's parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do. Interpreting the assignment. Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Assignment Structure. College writing assignment structure normally consists of 5 sections: A title page will normally include the title of your assignment (ideally catchy and informative), your name, the name of the course, the name of the module, the name of your educational establishment, your educational instructor's name, and the ...
Assignment Writing Template Structure Example Even though each type of written paper requires its own structure and rules to be followed, we have prepared classic structure that will meet requirements most of the time. Firstly, it's required to understand how to write an introduction for an assignment. Introduction / Intro Paragraph
The structure of your assignment depends, among other things, on whether it is a theoretical, empirical or product-oriented assignment. Read more on the page Types of assignments. Moreover, the structure should reflect that your assignment presents one overall argument supported by academic evidence. Read more about assignments as a single ...
Planning your assignment structure Figure 19.3 It is sometimes easier to draft your assignment using the 2-3-1 approach. Image by Sam Karanja used under CC0 licence. When planning and drafting assignments, it is important to consider the structure of your writing. Academic writing should have clear and logical structure and incorporate academic ...
The structure of the main body of an assignment is dictated by at least two factors: a) The title and wording of the assignment (whether it is your own, negotiated with the tutor- or one that has been given to you). b) The statement of intent that you write in the introduction, based on the title. Once you have dealt with the above two elements ...
An assignment is something you'll be asked to produce as part of your course, and is usually assessed. There are many different types of assignment, so make sure ... structure of their work or not! 9 Getting started If you're finding it hard to start writing, break your tasks down into small chunks. Look at your plan and see what
Basics of Assignment Structure and Format. November 1, 2021. Some students, particularly those in their freshman years, tend to overthink things and try to go for assignment structures that are unnecessarily complicated, thinking this will help them stand out from their peers and get better grades. It doesn't have to be that hard.
An essay consists of three basic parts: Introduction. Body. Conclusion. The essay itself usually has no section headings. Only the title page, author declaration and reference list are written as headings, along with, for example, appendices. Check any task instructions, and your course or unit handbook, for further details.
1. Prepare Assignment Structure. Creating a well-planned structure for your assignment is akin to drawing a roadmap. It helps you stay on track and ensures that your ideas flow logically. Here's what to consider: Develop an Outline. The basic structure of an assignment includes an introduction, body, and conclusion.
For students, the most common types of academic writing assignments are listed below. Type of academic text Definition; Essay: A fairly short, self-contained argument, often using sources from a class in response to a question provided by an instructor. ... Pay attention to structure at three levels: the structure of the whole text, paragraph ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more. Assignments are typically designed to be completed outside of class ...
For other assignments, you will have to come up with your own structure. Your structure might be guided by: the assignment question. For example, it may list topics or use wording such as 'compare and contrast' the subject matter itself, which may suggest a structure based on chronology, process or location; your interpretation of the ...
Types of Assignments Cristy Bartlett and Kate Derrington. ... It is important that you consider these aspects of structure, tone and language when writing an essay. Components of an essay. Essays should use formal but reader friendly language and have a clear and logical structure. They must include research from credible academic sources such ...
Overview of the fundamental assignment structure. A popular piece of advice is that all written work, including assignments, should comprise an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. This is an oversimplification, but it should give you a good indication of what to anticipate. In actuality, extra subheadings inside the body or major section of ...
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement, a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas. The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ...
3. State All Your Research Findings In The Main Body Of The Assignment: 4. Finally Round Up Your Discussion In Your Conclusion: Sample Question And Solution Of Basic Tips To Structure An Assignment. CIS5100 Assignment 1. Question: Solution: Writing Assignment Outline: Why Is It Important.
Figure 20.3 Essay structure overview template figure. Image by USQ. Common types of essays. You may be required to write different types of essays, depending on your study area and topic. Two of the most commonly used essays are analytical and argumentative.. The task analysis process discussed in the previous chapter Writing Assignments will help you determine the type of essay required.
In the end, the proportions of the ideal essay should be approximately the following: introduction - up to 10% of the total volume of the essay; conclusion - no more than 15% of the total volume of the text. Assignment writing structure - writing guide. All that you should know about writing assignment Structure of assignment writing.
C Structures. The structure in C is a user-defined data type that can be used to group items of possibly different types into a single type. The struct keyword is used to define the structure in the C programming language. The items in the structure are called its member and they can be of any valid data type.