Essay on Financial Management
After reading this essay you will learn about:- 1. Introduction to Financial Management 2. Definition of Financial Management 3. Scope 4. Role in a Business 5. Financial Goals and Objectives 6. Functions.
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Functions of Financial Management

Essay # 1. Introduction to Financial Management:
A business organisation seek to achieve their objectives by obtaining funds from various sources and then investing them in different types of assets, such as plant, buildings, machinery, vehicles etc. Financial management is managing the finances through scientific decision-making.
For making right decisions, financial management needs to understand financial environment within which these decisions operate. Financial management will then be able to analyse these financial information’s to predict likely future results and to plan more carefully their proposed course of action.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Financial management is concerned with the acquisition (investment), financing (arranging funds), and management of assets with some overall goal in mind. Investment decisions begin with a determination of the total amount of assets required by the firm and to determine the money value of the same. Assets that cannot be economically justified, may be reduced, eliminated or replaced.
Financing decisions include decisions regarding mix of financing, type of financing employed, dividend policy and method of acquiring funds i.e., getting a short term loan, or a long term lease arrangement, sale of bonds or stock.
Asset management decisions means managing the assets efficiently after their acquisition.
Success of a firm depends on the ability to raise funds, invest in assets and manage wisely.
Essay # 2. Definition of Financial Management:
Financial management is an internal part of overall management and not a staff function of the organization. It is not only restricted to fund raising process but also covers utilization of funds and monitoring its uses. The finance function is concerned with the process of acquiring an efficient utilization of funds of a business system, in order to maximize the value of the enterprise.
Financial management involves the application of principles of general management to the finance function. These functions influence the operations of other crucial functional areas of the enterprise or firm such as marketing production and personnel. Thus the overall survival of the firm is effected by it financial operations.
“The financial management deals with how the corporation obtains the funds and how it uses them.” —Hoagland
“The financial management refers to the application of skills in the manipulation, use and control of funds.” —Mock, Schultz and Schuckectat
Financial management can also be defined as that part of management, which is related mainly with raising or acquiring the funds for the enterprise or firm in the most economical way, utilizing those funds as profitably as possible, for a given risk level, planning the future investment of those funds and controlling the current performance plus future development by adopting budgeting, cost accounting and financial accounting.
Essay # 3. Scope and Functions of Financial Management :
The main objectives of financial management are to arrange the sufficient funds for meeting short term long term requirements of the enterprise. These finances are procured at minimum cost in order to maximize the profitability.
In view of these factors the financial management scope concentrates on the following areas of finance function.
(i) Estimating the Financial Requirements :
The first job of the finance manager of an enterprise is to estimate short term and long term financial requirements of his business. He will prepare a financial plan for present as well as future for this purpose.
The finance required for procuring fixed assets as well as the working capital needs will have to be ascertained. The estimations should be based on sound financial principles so that funds available with the firm are neither inadequate nor excess.
(ii) Determining the Capital Structure :
After estimating the financial requirements, the finance executives have to decide about the composition of capital. The capital structure refers to the type and proportion of different securities for raising funds. After deciding the quantum of funds needed it should be decided which type of securities should be raised.
The finance executives have to determine the relative proportions of owner’s risk capital and borrowed capital along with short term and long term debt equity ratio.
A decision regarding various sources of funds should be linked with the cost of raising funds. A decision about the kind of securities to be employed and the proportion in which these should be utilized is an important decision which affects the short term and long term financial planning of an enterprise.
(iii) Choice of Sources of Finance :
After preparing a capital structure an appropriate source of finance is chosen. Various sources from which finance may be raised include: shareholders’ debenture holders, banks and other financial institutions and public deposits etc. Finance executive has to evaluate each source or method of finance and select the best source keeping in view the various factors.
The need, purpose, objective, cost involved may be the factors affecting the selection of a suitable source of financing, for instance, if the finances are required for short periods then banks, public deposits and financial institutions may be appropriate, and for long term financial requirements, the share capital and debentures may be useful.
(iv) Investment Decisions :
When the funds have been poured then a decision regarding pattern of investment has to be taken. The funds raised are to be intelligently invested in various assets so as to optimize the returns on investment. The funds will have to be used first for the purchase of fixed assets and then an appropriate part will be retained as working capital.
The utilisation of long term funds requires a proper assessment of different alternatives through capital budgeting and opportunity cost analysis. While spending on various assets, management should be guided by three important principles of safety, liquidity and profitability. A balance should be struck even in these principles for the purpose of optimum returns on investment.
(v) Management of Profits :
The utilisation of surpluses or earnings is also an important factor in financial management. A judicious utilisation of earnings is essential for expansion and diversification plans of the enterprise.
A certain amount out of the total profit may be kept as reserve voluntarily, a portion of surplus may be distributed among the ordinary and preference shareholders, yet another portion may be reinvested. The finance executive must take into consideration the merits and demerits of the alternative scheme of utilizing the funds generated from the enterprise’s own earnings.
(vi) Management of Cash Flow :
Cash flow management is also an important task of finance executive. He has to assess the various cash requirements at different times and then make arrangements for cash needed. Cash may be required to (i) make payments to creditors (ii) for purchase of materials (iii) to meet wage bill (iv) to meet everyday expenses.
The cash management should be such that neither there is shortage of it and nor it is idle. Any shortage of cash will damage the credit worthiness of the firm. The idle cash with the enterprise will mean that it is not properly utilized. In order to know the cash requirements during different periods, the management should arrange for the preparation of cash flow statement in advance.
(vii) Implementation of Financial Controls :
An efficient system of financial management needs the use of various control of devices. Financial control devices generally adopted are (i) Return on Investment (ii) Budgetrary Control (iii) Cost control (iv) Break Even analysis (v) Ratio analysis. The use of various control techniques by the Finance Manager will help him in evaluating the performance in different areas and take corrective action whenever needed.
Essay # 4. Role of Financial Management in a Business:
An effective financial management plays a dynamic role in a modern company’s development.
In earlier days, financial managers were primarily engaged in:
(a) Raising funds, and
(b) Managing the firms cash flow.
But now-a-days with the developments and increasing complexities in the business, responsibility of the financial managers have increased and they are now concerned with the decision-making process involving finance, i.e., capital investment.
Today external factors, like competition, technological change, economic uncertainty, inflation problem etc., create financial managers problem more complicated. He must have flexibility to adopt to the changing external environment for the survival of his firm.
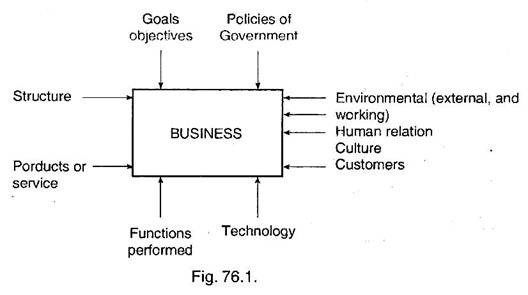
Thus in addition to the job of acquisition, financing and managing the assets, the financial manager is supposed to contribute to the fortunes of the firm and to the optimal growth of the economy as a whole.
He is required to take decisions on:
(i) Investing funds in assets, and
(ii) Obtaining best mix of financing and dividends.
In order to understand the environment in which a finance manager is required to take decision, a sketch indicating business system is given hereunder:
The Financial Management’s main role is therefore to create profit on the capital invested (fixed as well as working capital). Each and every decision related to finance/economy must be optimal. Every business enterprise is set up to earn profit, and no one is interested in taking risk unless he is assured of fair return on the investment. However government organisations have no profit motive but are created to serve the public.
The profit earned by a firm is used for:
(a) Future expansion.
(b) Distributing profit as rewards to owners/shareholders.
Profit earned also serves as an indicator of efficiency and performance of the firm. So as to enable to perform the role of financial management, financial managers must be given proper authority, autonomy, freedom of actions, supporting staff, system for providing necessary information. He should be accountable also for his role.
Essay # 5. Financial Goals and Objectives :
There may be various objectives of a firm, but the goal of a firm is to maximise the wealth of the firm’s owners. Thus we can say that, “the improvement of shareholders value is the one mission that continually guides all corporate decisions and actions” or “the goal of a firm is maximizing the shareholders’ value”. This maximisation of value should be achieved from long term point of view.
The financial goal can be expressed as:
(a) Required profit levels,
(b) Earnings per shares, and
(c) Required rate of return on investment.
For a large firm, where shareholders do not have direct say and the firm is managed by the management, an ordinary shareholder can judge the performance by the market price of the firm’s share. Market price serves as a gauge for business performance, it indicates how well management is doing on behalf of its shareholders.
Management is the agents of the owners or shareholders, and financial management acts for achieving the goal of profit maximization in the shareholders’ best interests.
Social Goals :
While profit maximisation is the primary goal for any business organisation, social responsibility is also important for them. In case of Government organisations and public sector organisations, social responsibility is the primary goal and profit is secondary.
Social responsibility includes service to the people, protecting the consumer, paying fare wages to the employees, upliftment of the weaker sections, welfare facilities like medical education, environment improvement programmes etc.
Financial Objectives :
In making financial decisions, it is important to set out clear objectives.
Following are the basic financial objectives:
(a) Profit maximisation.
(b) Maximisation of shareholders’ owners’ wealth.
(c) Reduction in cost.
(d) Minimising risks.
(e) Sustained increase in the value of firm
(f) Wealth maximisation.
Essay # 6. Functions of Financial Management :
Financial manager is concerned with the following aspects:
1. Identifying the present strengths and weaknesses of the organisation, and the scope for improvement, by conducting the financial analysis.
2. Planning the financial strategies. This involves the consideration of methods and levels of funds raising, profitability and the financing of expansion plan of the organisation.
3. Arranging the funds when required, in the form needed in the most economical way.
4. Conducting financial appraisal of the possible courses of action. The appraisals are needed in respect of possible take overs and mergers, analysis of capital projects, or alternative methods of funding.
5. Advising about capital structure.
6. Consideration of an appropriate level for drawings by dividends to the owners/ shareholders.
7. Ensuring that assets are controlled and used in an efficient manner.
8. Cash management. Preparation of detailed cash budgets and/or forecast funds flow statement so that future problems can be foreseen and remedial measures taken in advance. These take care of both shortage and excess of cash. Finance managers must find ways of raising more funds needed, or investing excess funds for an appropriate length of time.
9. Finance managers are likely to draw attention on other disciplines also, like accounting and budgeting.
In order to enable financial managers to perform above functions satisfactorily, he must have good knowledge of accounting, economics, mathematics, statistics, law especially taxation, financial market etc.
The functions of finance thus involve three major decisions the firm must make:
(a) The investment decisions,
(b) The financing decisions, and
(c) The dividend decisions.
Each of these decisions are taken in relation to the objective of the firm, an optimal combination of these three will maximise the value of the firm to its shareholders. Since the decisions are interrelated, their joint impact on the market price of the firm’s stock must be considered.
(a) Investment Decisions:
This is the most important decision. Capital investment, i.e., allocation of capital to investment proposals is the most important aspect, whose benefits are to be realised in future. As future benefits are not known with certainty, the investment proposals involve risk.
These should, therefore, be evaluated in relation to expected return and risk. Considerable attention is paid to determine the appropriate required rate of return on the investment.
In addition to taking capital investment decisions, finance managers are concerned with the management of current assets efficiently in order to maximise profitability relative to the amount of funds tied up in asset. Investment decisions also include the decisions about mergers and acquisition of another company.
(b) Financing Decisions:
Finance manager is required to determine the best financing mix or capital structure. An optimal financing mix is one in which market price per share could be maximised. Financing decision are taken in relation to the overall valuation of the firm.
Various methods of obtaining short, intermediate, and long term financing are also explored, examined, analysed and a decision is taken. While taking financing decisions, the influence of inflammation on financial markets and on the cost of funds to the firm is also considered.
(c) Dividend Decision:
The dividend decision includes the percentage of earnings paid to stockholders in cash dividends, stock dividends and splits, and the repurchase of stock.
To Meet Funds Requirement of a Firm :
Funds requirement is assessed for different purposes, namely for feasibility study of a project, detailed planning of a project, and for operation and expansion of the business.
For feasibility study, only broad estimates are sufficient and are generally obtained from the past experience of the similar works by interpolating the present trends and the condition of the proposed project in comparison to the one whose figures are being adopted. While during detailed planning, estimated requirement is comparatively more realistic, and prepared after going into details more thoroughly.
Here we are discussing the funds requirement for a running business including its long term planning for expansion.
The main function of financial management is to ensure that the firm must have sufficient funds to meet financial obligations when they are needed and to take advantage of investment opportunities. To achieve this objective, a thorough study is conducted about ‘flow of funds’ i.e., statement of funds requirement indicating the amount of fund needed and at what time.
This ‘statement of funds’ is a summary of a firm’s changes in financial position from one period to another. This indicates that how the funds will be used and how it will be financed over specific period of time. This includes the cash as well as non-cash transactions.
Forecast, financial statements are prepared for selected future dates, generally for middle term and long term plans of the firm. Budgets are used for one year, and are prepared only to fulfill the firms’ objectives envisaged in the forecast for that particular year.
These forecast financial statements are based on the sales forecast and future strategies for expanding the business, and includes, forecast income statements, forecast assets, liabilities, shareholders, equity etc.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Financial Management: Objectives, Scope and Functions
- Essay on Financial Management: Top 5 Essays | Branches | Management
- Top 3 Types of Financial Decisions
- Shareholder Value Analysis (SVA) | Firm | Financial Management
We use cookies
Privacy overview.
Financial Management Essay Examples and Topics
Mcdonald’s operation management & supply chain.
- Words: 2479
Apple Strategic Management: Planning and Management Process — Apple Company Essay
- Words: 5021
Strategic Management: The Case of Coca-Cola
Walmart balanced scorecard – a case study.
- Words: 1117
Apple Inc.’s Financial Performance Analysis in 2020
- Words: 1437
Apple Company’s Financial Management
- Words: 1250
Samsung Company’s Financial Performance
- Words: 2498
The Five Forces Analysis of the Low-Cost Airline Industry in Europe
Tesco and sainsbury companies’ capital structure.
- Words: 5810
Relationship Between Average Cost and Marginal Cost
- Words: 1366
Financial Analysis: ADNOC vs. ENOC
- Words: 5008
Morgan and Sunderland’s Management Styles
- Words: 1611
Rule and Principle-Based Accounting: Apple and Samsung
- Words: 1960
The Body Shop: Financial Strategies
Factors that shape the relationship between the buyer and the suppliers.
- Words: 1479
Dove Company’s Pricing Strategy
Apple inc.’s capital projects and funding sources, the ethical issues in financial management, lincoln sports equipment: capital budgeting.
- Words: 5118
Porter Forces Model on Dell Company
- Words: 1142
Carlsen’s Norrkoping Project
- Words: 1889
Walmart Company: Ratios and Analysis
Financial management in medical laboratory.
- Words: 1200
The Sources Available for Funding a New Venture
A strong link between age and salary, financial risks of the walmart customers, tesco: effects of recession on marketing activities, strategic management: movie industry.
- Words: 2090
Accounting and Finance: New Hair Care Product
- Words: 3700
Christine Dior: Financial Strategy
- Words: 2420
Starbucks Corporation’s Balance Sheet Analysis
Babycakes bakery’s budget planning and control.
- Words: 1010
Budgeting and Its Importance in Business
Financial management practices and their impacts.
- Words: 1373
Tesla Inc.’s Financial Performance Assessment
Cost analysis of the mayo clinic contract procurement.
- Words: 1571
Price Elasticity of Demand: Definition
- Words: 1429
Bre-X Minerals Company: Management and Company’s Relationship
- Words: 1108
Starbucks Audit: The Largest Coffeehouse Chain in the World
- Words: 2243
Price of Football Players
- Words: 1125
Apple Inc.’s Financial Performance in 2018-2019
The importance of financial forecasting, intel strategic management.
- Words: 1346
Public Safety Finance: Challenges and Strategies
- Words: 4175
Methods of Business Valuation
- Words: 3142
Financial Performance Appraisal for Etisalat UAE
- Words: 4181
Key Aspects of Buyer and Supplier Relationship
- Words: 1383
Nestlé Group Ratio Analysis Results
- Words: 1503
Financial Management in the Marine Industry
Project finance from the islamic perspective.
- Words: 6989
Hikma Pharmaceuticals: Financial Analysis
- Words: 3165
Enron: The Implications of Accelerated Earnings, Poor Investment Decisions, Too Much Compensation
Mcdonald’s and yum brands, inc.: financial performance, distribution channel in business, decision-making processes in the london olympics 2012.
- Words: 2713
Whole Life Costing vs. Life Cycle Cost in Construction
A2b australia limited’s financial analysis.
- Words: 5380
IBM Inc.’s Financial Performance
- Words: 2261
Amazon and Alibaba: Financial Computation and Analysis
- Words: 1077
Adidas AG: Functional Currency of the Company
Food costs reduction in a food establishment, organisational change at tesco revised.
- Words: 7018
The Meaning and Importance of Credit Rating
Chevron company’s financial management.
- Words: 3725
Emirate Airline: Airline Industry Analysis
- Words: 4588
Budgeting as an Instrument of Internal Control
- Words: 4101
Discussion of Effective Budgetary Control
Factors that affect transportation costs.
- Words: 1492
Managerial Finance and Its Principles
Job aid: financial analyst responsibilities, shopping networks: pricing strategy, j sainsbury plc’s financial management policies.
- Words: 4161
FedEx and UPS: Financial Management
- Words: 3377
Tesco PLC: Increased Audit Risk
- Words: 1374
Successful Business Finance Management’ Factors
- Words: 2530
Waste Management Company’s Financial Management
- Words: 2267
Public Sector Financial Management
- Words: 3151
Strategic financial management
- Words: 1140
Strategies for Efficiency in Business Operations: Economies of Scale
- Words: 1102
Financial Challenges Faced by Startup Organizations in the UAE Due to COVID-19
- Words: 2009
Dough Pizza: A Community-Focused Fast Food Venture in Lynchburg, VA
Financial management in uae healthcare, custom snowboard inc. financial position.
- Words: 3959
Determinants of Wages: Earning Potential Maximization
- Words: 1365
The Walmart Firm’s Funding Strategies for Growth Maximization
Uber: financial performance analysis, the federation employment & guidance service.
- Words: 1511
Interview with a Person in Charge of Financial Management System
Financial performance analysis: edf energy.
- Words: 2987
Gross vs. Taxable Income: What’s the Difference?
Iteos therapeutics: bottom-up valuation.
- Words: 1221
Ford Dealers’ Financial Performance Analysis
Apple inc.: stock price valuation, performance evaluation of an organization: commonwealth bank of australia.
- Words: 1490
Netflix Inc.: Financial Options
The materiality concept in auditing, lawn king: creating a sales forecast.
- Words: 1181
The Relevance of Financial Performance Measures and Targets
- Words: 2576
Almarai Company and Effective Budgeting
- Words: 1764
Chester, Inc. Financial Analysis
- Words: 1482
Negative Effect of Earning Disparity
Lease agreements: option for security devices inc., body shop financial and marketing.
- Words: 1466
The Problem of Approving a Loan Extension
Analysis and viability of ids budget proposal: a strategic approach, selecting a forecasting method for volkswagen ag, reaction to “fundraising” article by gelatt, designing a pay structure for a premier supplier of rubber floor mats.
- Words: 2247
Comcast Corporation’s Financial Management
- Words: 1403
Minimizing Working Capital: Benefits and Challenges
The role of financial planning in business, details of the financial management, common stock and its key characteristics, ethical questions and promotion assignment.
- Words: 1314
Different Purposes of Keeping Financial Records by Business
- Words: 1667
Bluevine: The Loan Repayment Issue
Abc manufacturing: financial management, impairment losses of finances in company, the cash flow-based financial strategy in china, cost management for a bakery business.
- Words: 1164
Financial Management Explained: Scope, Objectives & Importance

In business, financial management is the practice of handling a company’s finances in a way that allows it to be successful and compliant with regulations. That takes both a high-level plan and boots-on-the-ground execution.
What Is Financial Management?
At its core, financial management is the practice of making a business plan and then ensuring all departments stay on track. Solid financial management enables the CFO or VP of finance to provide data that supports creation of a long-range vision, informs decisions on where to invest, and yields insights on how to fund those investments, liquidity, profitability, cash runway and more.
ERP software can help finance teams achieve these goals: A financial management system combines several financial functions, such as accounting, fixed-asset management, revenue recognition and payment processing. By integrating these key components, a financial management system ensures real-time visibility into the financial state of a company while facilitating day-to-day operations, like period-end close processes.
Video: What Is Financial Management?
Objectives of Financial Management
Building on those pillars, financial managers help their companies in a variety of ways, including but not limited to:
- Maximizing profits: Provide insights on, for example, rising costs of raw materials that might trigger an increase in the cost of goods sold.
- Tracking liquidity and cash flow: Ensure the company has enough money on hand to meet its obligations.
- Ensuring compliance: Keep up with state, federal and industry-specific regulations.
- Developing financial scenarios: These are based on the business’ current state and forecasts that assume a wide range of outcomes based on possible market conditions.
- Manage relationships: Dealing effectively with investors and the boards of directors .
Ultimately, it’s about applying effective management principles to the company’s financial structure.
Scope of Financial Management
Financial management encompasses four major areas:
The financial manager projects how much money the company will need in order to maintain positive cash flow, allocate funds to grow or add new products or services and cope with unexpected events, and shares that information with business colleagues.
Planning may be broken down into categories including capital expenses, T&E and workforce and indirect and operational expenses.
The financial manager allocates the company’s available funds to meet costs, such as mortgages or rents, salaries, raw materials, employee T&E and other obligations. Ideally there will be some left to put aside for emergencies and to fund new business opportunities.
Companies generally have a master budget and may have separate sub documents covering, for example, cash flow and operations; budgets may be static or flexible .
Static vs. Flexible Budgeting
Managing and assessing risk.
Line-of-business executives look to their financial managers to assess and provide compensating controls for a variety of risks, including:
Affects the business’ investments as well as, for public companies, reporting and stock performance. May also reflect financial risk particular to the industry, such as a pandemic affecting restaurants or the shift of retail to a direct-to-consumer model .
The effects of, for example, customers not paying their invoices on time and thus the business not having funds to meet obligations, which may adversely affect creditworthiness and valuation, which dictates ability to borrow at favorable rates .
Finance teams must track current cash flow, estimate future cash needs and be prepared to free up working capital as needed.
This is a catch-all category, and one new to some finance teams. It may include, for example, the risk of a cyber-attack and whether to purchase cybersecurity insurance , what disaster recovery and business continuity plans are in place and what crisis management practices are triggered if a senior executive is accused of fraud or misconduct.
The financial manager sets procedures regarding how the finance team will process and distribute financial data, like invoices, payments and reports, with security and accuracy. These written procedures also outline who is responsible for making financial decisions at the company — and who signs off on those decisions.
Companies don’t need to start from scratch; there are policy and procedure templates available for a variety of organization types, such as this one for nonprofits.
Functions of Financial Management
More practically, a financial manager’s activities in the above areas revolve around planning and forecasting and controlling expenditures.
The FP&A function includes issuing P&L statements, analyzing which product lines or services have the highest profit margin or contribute the most to net profitability, maintaining the budget and forecasting the company’s future financial performance and scenario planning.
Managing cash flow is also key. The financial manager must make sure there’s enough cash on hand for day-to-day operations, like paying workers and purchasing raw materials for production. This involves overseeing cash as it flows both in and out of the business, a practice called cash management.
Along with cash management, financial management includes revenue recognition, or reporting the company’s revenue according to standard accounting principles. Balancing accounts receivable turnover ratios is a key part of strategic cash conservation and management. This may sound simple, but it isn’t always: At some companies, customers might pay months after receiving your service. At what point do you consider that money “yours” — and report the good news to investors?
Finally, managing financial controls involves analyzing how the company is performing financially compared with its plans and budgets. Methods for doing this include financial ratio analysis, in which the financial manager compares line items on the company’s financial statements.

Strategic vs. Tactical Financial Management
On a tactical level, financial management procedures govern how you process daily transactions, perform the monthly financial close, compare actual spending to what’s budgeted and ensure you meet auditor and tax requirements.
On a more strategic level, financial management feeds into vital FP&A (financial planning and analysis) and visioning activities, where finance leaders use data to help line-of-business colleagues plan future investments, spot opportunities and build resilient companies.
Importance of Financial Management
Solid financial management provides the foundation for three pillars of sound fiscal governance:
Strategizing
Identifying what needs to happen financially for the company to achieve its short- and long-term goals. Leaders need insights into current performance for scenario planning , for example.
Decision-making
Helping business leaders decide the best way to execute on plans by providing up-to-date financial reports and data on relevant KPIs.
Controlling
Ensuring each department is contributing to the vision and operating within budget and in alignment with strategy.
With effective financial management, all employees know where the company is headed, and they have visibility into progress.
What Are the Three Types of Financial Management?
The functions above can be grouped into three broader types of financial management:
Capital budgeting
Relates to identifying what needs to happen financially for the company to achieve its short- and long-term goals. Where should capital funds be expended to support growth ?
Capital structure
Determine how to pay for operations and/or growth. If interest rates are low, taking on debt might be the best answer. A company might also seek funding from a private equity firm , consider selling assets like real estate or, where applicable, selling equity.
Working capital management
As discussed above, is making sure there’s enough cash on hand for day-to-day operations, like paying workers and purchasing raw materials for production.
#1 Cloud ERP Software
What Is an Example of Financial Management?
We’ve covered some examples of financial management in the “functions” section above. Now, let’s cover how they all work together:
Say the CEO of a toothpaste company wants to introduce a new product: toothbrushes. She’ll call on her team to estimate the cost of producing the toothbrushes and the financial manager to determine where those funds should come from — for example, a bank loan.
The financial manager will acquire those funds and ensure they’re allocated to manufacture toothbrushes in the most cost-effective way possible. Assuming the toothbrushes sell well, the financial manager will gather data to help the management team decide whether to put the profits toward producing more toothbrushes, start a line of mouthwashes, pay a dividend to shareholders or take some other action.
Throughout the process, the financial manager will ensure the company has enough cash on hand to pay the new workers producing the toothbrushes. She’ll also analyze whether the company is spending and generating as much money as she estimated when she budgeted for the project.
NetSuite: Financial Management for Startups and Beyond
At the outset, financial management responsibilities within a startup include making and sticking to a budget that aligns with the business plan, evaluating what to do with profits and making sure your bills get paid and that customers pay you.
Financial management gets more complicated as the company grows and adds finance and accounting contractors or staffers. You must ensure your employees get paid with accurate deductions, properly file taxes and financial statements, and watch for errors and fraud.
This all circles back to our opening discussion of balancing strategic and tactical. By building a plan, you can answer the big questions: Are our goods and services profitable? Can we afford to launch a new product or make that hire? What might the coming 12 to 18 months bring for the business? Solid financial management provides the systems and processes to answer those questions.
Financial management challenges can be daunting for both startups and growing businesses. This is where NetSuite's financial management software comes into play. With its comprehensive, cloud-based solutions, NetSuite ensures that your financial data is accurate, up-to-date, and accessible anytime, anywhere.
From automating complex financial processes to offering real-time visibility into performance, NetSuite is the go-to solution for businesses aiming for seamless integration and efficient financial operations. As your company expands, NetSuite scales with you, ensuring you have the right tools to make informed strategic decisions at every stage. Make the smart choice for your business's financial future with NetSuite.
Financial Management

What is Financial Contingency Plan? A Step-by-Step Guide to Creating One
Creating a financial contingency plan is a wise move for any business. Crises and setbacks can strike suddenly, from natural disasters to economic downturns, technical failures, partner bankruptcies and customer…

Trending Articles

Learn How NetSuite Can Streamline Your Business
NetSuite has packaged the experience gained from tens of thousands of worldwide deployments over two decades into a set of leading practices that pave a clear path to success and are proven to deliver rapid business value. With NetSuite, you go live in a predictable timeframe — smart, stepped implementations begin with sales and span the entire customer lifecycle, so there’s continuity from sales to services to support.
Before you go...
Discover the products that 37,000+ customers depend on to fuel their growth.
Before you go. Talk with our team or check out these resources.
Want to set up a chat later? Let us do the lifting.
NetSuite ERP
Explore what NetSuite ERP can do for you.
Business Guide
Complete Guide to Cloud ERP Implementation
116 Financial Management Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on financial management, ✍️ financial management essay topics for college, 👍 good financial management research topics & essay examples, 🎓 most interesting financial management research titles, 💡 simple financial management essay ideas.
- Coca-Cola Company’s International Financial Management
- Strategic Financial Management: The Link Between Valuation and Financial Decisions
- Amazon Company: Financial Management
- BP and Royal Dutch Shell Companies’ Financial Management
- Financial Operation Exposure Management Principles
- IBM’s Management Accounting & Financial Practices
- Puma SE: Financial Management
- Financial Management Role in Healthcare With the introduction of the Affordable Care Act, electronic health records, and the Medicare billing system, the financial aspect of healthcare requires extra attention.
- Financial Management of Aldar Properties UAE UAE has seen a massive growth in all business sectors and promises more to the investors, but recent financial scam has cast many things under doubts.
- BMW: Global Financial Management and Summary In the case study, the foreign exchange risk management strategy of BMW, discussed in order to identify the effectiveness of the strategies followed by it to get the optimum results.
- Euroland Foods S.A. Strategic Financial Management In the Euroland Foods S.A. company, there are many constraints, among them is capital rationing where the budget for all projects is Euro 120 million.
- Alibaba Corporation’s Financial Management This report offers an examination of Alibaba’s major financial ratios and performance indicators, assessing the firm’s cash flow, liquidity, solvency, and profitability ratios.
- Financial Planning. Money Management Skill Financial literacy can be defined as knowledge about financial planning and management that allows making reasonable choices about money spending and saving.
- Personal Financial Management and Financial Literacy By understanding the basic principles and minor aspects of money management such as the compound interest method, people can avoid bankruptcy and enhance their chances for the side income.
- Southwest Airlines’ Financial Management This paper analyzes the financial and trend ratios of Southwest Airlines, predicts future financial performance, and determines the return on equity.
- Nokia Company’s Financial Analysis and Management Nokia is part of the mobile communications industry which is now one of the most rapidly growing industries in the world. The industry includes multinational companies.
- EasyJet: Financial Management To ensure its survival during lockdowns and travel bans, EasyJet could take every step necessary to reduce costs, conserve cash burn, and enhance liquidity.
- Valero Energy and Chevron Corporations’ Financial Management Valero Energy and Chevron Corporations faced a drastic decline in total revenues in 2020, mainly due to economic upheaval and uncertainty caused by COVID-19.
- Financial Management in Nokia Nokia is part of the mobile communications industry which is now one of the most rapidly growing industries in the world.
- Accounting and Financial Management for Expo 2020 Dubai The use of technology is a fundamental aspect of the organizational development adopted in every aspect of the innovation exhibitions hosted by the association in Dubai.
- Jim’s Auto Body: Financial Management This paper examines the financial management of Jim’s Auto Body. Profitability is among the core elements considered in evaluating financial performance.
- British Airways Group: Financial Management In this report, a critical analysis is made of the financial statements of the British Airways Group for the period February 28, 2008 to March 31, 2009.
- Ramsay Health Care: Financial Management The results of this analysis reveal that Ramsay Health Care is engaging in desirable efforts and strategies that have led to considerable financial gains.
- Financial Management of Marks & Spencer vs. Next Marks and Spencer demonstrates higher profit and liquidity than Next does. However, Next has more capability to pay off its debts judging by its interest cover ratio.
- Project Cost and Finance Management Challenges The cost management functions are complex as projects come with different complexities. Many emerging projects pose different challenges in terms of their characteristics.
- Expo2020 Dubai’s Accounting and Financial Management This paper compares costs and revenues at two levels: state and organizational. Moreover, a comparison with other exhibitions that have been held in the last decade is presented.
- Strategic Financial Management: Diageo plc and SAB Miller plc Both Diageo and SAB Miller have strategic financial management that helps make complex decisions that increase their competitive advantages and eventually increase revenue.
- Public Budgeting Leadership and Financial Management To control the field of public budgeting correctly, one should have ideas about the practical methods of work and the theoretical aspects of this practice.
- JD Sports and Sports Direct Companies Financial Management This paper focuses on the financial analysis of two companies, JD Sports Fashion PLC and Sports Direct International PLC. Both are based in the UK but have a presence in other parts of the world.
- Children’s Programs: Financing and Management This research paper will examine the domains specific to the financial management and planning of children’s programs.
- Financial Management of Healthcare Organizations Healthcare is one of the salient aspects of human beings since it determines their ability to do their daily activities. Sick people cannot perform their roles.
- Financial Management in the Healthcare Industry In this essay, the author focuses on the significance of financial management and the most crucial data for overall management.
- The Neqi Firm’s Financial Management Due to the face mask sales during COVID-19, the Neqi firm, which creates and markets face masks, rose to the top of the list of profitable businesses.
- ABC Manufacturing: Financial Management In this research paper, it is required to evaluate the effectiveness of the financial management of ABC Manufacturing.
- Capital Investment and Financial Management A company’s capital investment is the money it spends on fixed assets like land, machinery, and buildings. Cash, assets, or loans may be used to fund the project.
- Rules of Financial Accounting: Economics and Management It is vital to describe control methods to show how an organization works to stop and curtail dishonest behavior and needless mistakes in its accounting records and data.
- Data Management and Financial Strategies By adopting comprehensive supply chain management, businesses can maximize the three main streams in the supply chain— information flow, product flow, and money flow.
- Possum Inc.’s Multinational Financial Management While Possum Inc. wants to become a multinational corporation, it is expected to know the nature of the local currency of the host currency and its conversion rates.
- Anne Arundel County: Public Finance and Management Analysis of revenue sources is extremely important to understand how the financial health of the county can be improved.
- Financial Management: Growth Financing Growth financing is an important topic of consideration for managers to continue the development of a business.
- Financial Management: Where Does the Money Go It is increasingly possible to hear about the importance of financial literacy in the modern world, which largely boils down to thoughtful money management.
- International Finance and Responsible Financial Management COVID-19 has a variety of ramifications for businesses in the future. Due diligence processes should focus on the target industry and the risks.
- Importance of Financial Management The implementation of non-monetary policies is proven to be useful as governments were able to overcome the financial recession.
- Financial Management During the Recession This paper shall set out to establish whether the recent financial crisis was in any way affected by global financial management or by other economic factors.
- Financial Management and Quality of Healthcare It is important for managers to understand how these facts are used to improve the financial position of the organisation.
- Financial Management: Annual Savings for Retirement The paper will focus on estimating the annual savings that the client needs to make in order to achieve the retirement plan.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act and Financial Management The main concern regarding the Sarbanes-Oxley Act is whether it offers effective frameworks for preventing the falsification of a firm’s financial statements or not.
- Financial Management. Some Important Generalizations The article identifies several financial management approaches and perspectives, which when put in place are likely to hamper financial performance.
- Financial Management Competencies Discussion This article is about financial management: the author considers the most important competencies of a financial manager, liquidity risk, risk, and return scenarios.
- Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA) Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA) provides learning, analysis, and direction to its affiliates on the subjects relating to healthcare finance.
- Financial Management: Evaluation of the New Machine This report evaluates the viability of new trucks that are to be purchased by Southern Suburbs Transport by calculating the net present value.
- Stock Ticker Symbol: Financial Management of the Company The analysis of the company shows that the company has hardships with financial sustainability and adequate management of its assets and liabilities.
- Medical Centers Financial Management Factors that affect the financial performance of these hospitals include the indigent care load, case mix, payer mix, which also includes different levels of self-pay.
- Cyberchamp Inc.’s Ethics and Financial Management This paper aims at discussing the factors to consider while resolving ethical issues and making recommendations for the assistant finance manager in the Cyberchamp Inc. scenario.
- Clayton County Library’s Financial Management Study Limited funding has created financial constraints for Clayton County Library, Georgia. American Libraries experience the greatest threat to their financial stability.
- Terms Used in Financial Management It is important to be aware of some of the general terms the organization uses in its financial management system: a balance sheet, an income statement and the operating cash flow.
- Financial Management and the Secondary Market for Common Stocks This paper will focus on the changes that the secondary market for common stocks in the USA has faced since the 1960s as the reflections of the financial situation in the country.
- Financial Management and Investment Banking This paper will focus on the primary markets, analyze the functions that investment bankers perform in the traditional process for issuing new securities.
- Thai-Lay Fashion Company Ltd.’s Financial Management There are several methods that will help managers make capital investment decisions. These will be discussed here with reference to the Thai-Lay Fashion Company Ltd.
- Carnival Corporation’s Financial Management This paper details an account of the cost behavior of Carnival Corporation Inc. – a large multi-vessel cruise operator.
- A Company’s Value: Financial Management The current paper is aimed to discuss the aspects of financial management of an organization and its stakeholders.
- Financial Ratios: Management and Analysis A high price to earnings ratio suggests that the investors are expecting an enhanced earnings growth in the future as compared to other companies having a lower price to earnings ratio.
- Financial Institutions Management and Sources of Finance Finance is important to any business as it serves different functions which allow the business to run effectively. A company may need additional funds to expand its business operations or expenses.
- Management in Organizations: Financial Issues Creating the environment in which the staff delivers the performance of the finest quality is a necessity for managers in the contemporary business environment.
- Healthcare Organizations Financial Management The suggested paper describes the central components of the healthcare finance and lists phenomena that might impact decision-making regarding particular scenarios.
- Government Budgeting and Financial Management The public budgeting leaders have the responsibility of fulfilling various roles including planning, reforming, and budgeting.
- What Is Financial Management and How to Do It Effectively
- The Role of Financial Management in Elaborating and Implementing Organization’s Strategies
- Effective and Ineffective Financial Management Practices in Health Care
- Innovation in Financial Management: The Impact of Technology
- Building Financial Management Capacity in Fragile and Conflict-Affected States
- Debt Elimination Through Financial Management
- How Financial Management and Corporate Strategy Affect a Firm’s Performance
- Profit vs. Wealth Maximization: A Financial Management Perspective
- Financial Statement and Ratio Analysis: Key Tools to Successful Financial Management
- Hierarchical Clustering Algorithms and Data Security in Financial Management
- Public Financial Management Intervention and Its Impact on Corruption
- Financial Management and Forecasting Using Business Intelligence and Big Data Analytics
- Economic Performance and Corporate Financial Management of Shipping Firms
- Microsoft’s International Financial Management: An Analysis
- Financial Management Practices and Their Impact on Organizational Performance
- Computer Applications for Financial Management
- Antecedent Factors of Financial Management Behavior Among Young Adults
- Financial Management Information Systems and Open Budget Data
- Household Financial Management: The Connection Between Knowledge and Behavior
- Modern System of International Financial Management in Multinational Corporations
- International Financial Management: Exchange Rate Exposure
- Fiscal Decentralization and Public Subnational Financial Management
- Best Practices for Non-Profit Financial Management
- Public Financial Management, Health Financing, and Under-Five Mortality: A Comparative Empirical Analysis
- Entrepreneurial Finance: Fundamentals of Financial Planning and Management for Small Business
- How Technological Evolution in Financial Management Implies a Company’s Success
- Challenges Facing Financial Management in Schools
- Time to Reboot: Rethinking Public Financial Management and Budgeting in Greece
- Financial Management of a Non- vs. For-Profit: Which Is Harder?
- Examining Financial Management in Promoting Sustainable Business Practices & Development
- Banking, Finance, and Financial Management: What’s the Difference
- Improving Public Financial Management in India: Opportunities to Move Forward
- Essential Instruments in the Financial Management of the Companies
- Short-Term Financial and Working Capital Management
- Examining Financial Management Practices in the Context of Smart ICT Use
- Family Financial Management: A Real-World Perspective
- Reforming Public Financial Management Systems in Developing Countries as a Contribution to the Improvement of Governance
- Accounting Use & Abuse in the Australian Public Sector Financial Management Reform Program
- Financial Management Explained: Scope, Objectives, and Importance
- Regional Financial Management Strategies to Improve the Community Welfare
- Financial Management for Public, Health, and Not-for-Profit Organizations
- Technical Efficiency and Financial Management in the Agriculture Industry
- Poor Financial Management Behavior as a Factor Why Students Are Facing Financial Difficulties
- Strengthening Public Financial Management: Exploring Drivers & Effects
- Balancing Long- and Short-Term Financial Management
- Financial Management and Control Procedures for the EU Structural Funds Programs
- The Environment of Public Financial Management: An Economic Perspective
- Introducing Financial Management Information Systems in Developing Countries
- Managing Post-Disaster Reconstruction Finance: International Experience in Public Financial Management
- Lessons From Australian and British Reforms in Results-Oriented Financial Management
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2023, May 7). 116 Financial Management Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/financial-management-essay-topics/
"116 Financial Management Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 7 May 2023, studycorgi.com/ideas/financial-management-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2023) '116 Financial Management Essay Topics'. 7 May.
1. StudyCorgi . "116 Financial Management Essay Topics." May 7, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/financial-management-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "116 Financial Management Essay Topics." May 7, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/financial-management-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2023. "116 Financial Management Essay Topics." May 7, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/financial-management-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Financial Management were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 8, 2024 .
What is financial management?

Checked : Mark A. , Priscilla M.
Latest Update 20 Jan, 2024
Table of content
Introduction
Financial accounting, accounts receivable, investment account, cash account, the importance of good financial management:, what is the corporate financial management, what is corporate financial management, three types of planning, 1. strategic planning:, 2. budget planning:, 3. treasury planning:.
- What is a company's financial management?
But what is meant by financial management?
Receipts must exceed expenses and revenues must exceed expenses. Until then, it's very simple. On the other hand, it is not so simple for management to guarantee the liquidity necessary for its activity. Financial management instruments are invaluable in this regard. We present here the most important instruments. The following tools are the essential bases of financial management and controlling:
Accounting provides management with useful bases for decision-making and helps them control finances. It makes it possible to enter and monitor cash flows and services systematically. The resulting data are used for financial management, planning, and management of the company. Accounting also provides information to external target groups such as donors or the auditors.
It is an integral part of the operating accounts and documents all the processes in concrete figures. It calculates the overall result of the company from the income statement. In addition, it informs managers of the current financial situation in the balance sheet and the company's development in the income statement.
Accounts receivable are part of financial accounting. It records all the commercial operations associated with customers, in particular receivables and credits, deliveries, and other services.
The investment account provides the main decision bases for investments. It takes into account all the data that can be calculated and thus helps to assess the risks associated with the planned investments, their profitability, and their amortization.
The cash account compares revenue and expenses. Companies can thus ensure that they always have sufficient financial means to pay their invoices on time.
For businesses, sound financial planning is the key to success. It allows an organization to start its commercial activities and to continue. The content of financial management is particularly important for SMEs and start-ups. Their objective must be to use the available resources effectively and efficiently. It is up to management to know the tools that help it in financial management. The management of a company must control the company's financial flows and the company's associated processes to guarantee liquidity.
But financial management is not limited to tedious obligations and controlling activities. Ideally, it allows management to steer its strategy with precision, to make the necessary changes in due time, and to mobilize employees for the common cause.
Money is the lifeblood of any business. Only by having capital is it possible to buy everything you need to start a company and make the right investments for its growth. For this reason, it is necessary to plan and manage the incoming and outgoing cash flows better. Let's see what corporate financial management is and why it is important.
Planning the resources available and any future investments is the first step in getting a company off the ground. To achieve your business objectives, you need to put all the strategic tools necessary to face the market , and, among these, there is financial management. A company does not operate isolated from the context in which it finds itself: to each of its actions correspond market reactions, which are not always positive. For this reason, money management must be carefully planned to be able to face any moments of crisis and support long-term business development.
Financial management is responsible for making decisions on income and expenses and collecting and payment methods. Machinery, patents, plants, raw materials, human resources: everything has a cost. It is not necessary to be a high finance expert to understand that money is the basis for every company's survival. To keep a business going, you need to know exactly what the available money is used for and constantly monitor the flows.
Whether it's production, human resource management, or marketing, every business function consumes or produces money. Therefore, financial management is not an isolated discipline in its own right, but concerns all company activities and allows the entrepreneur to understand what has the greatest impact on liquidity movements.
Proper corporate financial management should include at least four stages:
- forecast of financial needs;
- finding the necessary resources;
- achieving the balance between collected and employed means and their coordination;
- Control phase.
Depending on the time frame in which you want to operate, corporate financial management can have different objectives and methods. We can identify three different types of planning:
Operates in the medium to long term, over a time ranging from three to five years on average. Strategic corporate financial planning has to do with particular projects or events in corporate life and often takes the form of a "business plan," which outlines and evaluates commercial choices, investments, and sources of financing, as well as financial sustainability and convenience of the "Business plan" itself.
Operates in the short term, generally within one year. With financial budget planning, the company's economic budget is transformed into a plan that quantifies its income and expenses, checking that the net flow remains active and sustainable with respect to the company's needs and banking positions. In this context, the determining factor is time: the company must demonstrate its profitability over the year, while the financial budget must be drawn up every month.
Here we work in the very short term, or in a period of three or four months. The treasury's financial planning analyzes the reality taking into account the firm's fixed costs, the due dates towards customers, and the due dates towards suppliers. Subsequently, it tries to predict the company's liquidity in the very short term, which can vary from a few days to a few months, and it is a programming that must be constantly revised.
The cash flows (inflows and outflows) may depend on operational decisions (such as the purchase of raw materials) or strategic (such as the decision to change obsolete machinery). But it is essential to have the tools to understand how and how any decision impacts the company's financial situation.

We Will Write an Essay for You Quickly
What is a company's financial management?
The concept of finance is so broad that a post like today is certainly not enough to be able to summarize it. In fact, when we talk about finance, we can refer to private finance, which includes the finance of a natural person, companies, and others in search of the necessary financial activities to meet their own sustainability and development requirements. Or, we can refer to the concept of public finance, which instead concerns the revenue and disbursements of the state, such as central, regional government, and semi-public financial issues.
Financial management is an integral part of global management. As a rule, when it comes to financial management, we speak of a branch of activity that deals with the company's financial managers' numerous aspects and oriented tasks. The term financial management has been defined by authors (Howard and Upton), financial management is an "application of general management," using principles in financial decision-making. For others like Weston Brigham, financial management is an area of financial decision making, which seeks to harmonize individual motivations and business objectives. Still, for others (Joseph Massie), financial management is the operational activity of a company. It aims to obtain and effectively use the funds necessary for efficient management of financial resources, with consequent explanation in operations of various natures.
Beyond the definitions provided by the doctrine, and trying to get to the right mix, financial management mainly deals with the management of funds belonging to or attributable to a company. In simple words, the financial management practiced by commercial enterprises is the set of activities that are aimed at managing the financial requirement and its coverage by applying a series of short, medium, and long term.
Looking for a Skilled Essay Writer?

- West Valley College; Saratoga, CA
No reviews yet, be the first to write your comment
Write your review
Thanks for review.
It will be published after moderation
Latest News

What happens in the brain when learning?
10 min read
20 Jan, 2024

How Relativism Promotes Pluralism and Tolerance

Everything you need to know about short-term memory
This website uses cookies to provide you with the most relevant information. Please accept cookies for better performance.
- Annotated Bibliography
- Coursework Writing
- Book Reports
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Capstone Project
- Excel Homework
- Article Writing
- Article Critique
- Blog Article
- Scholarship Essay
- Marketing Plan
- White Paper
- Research Proposal
- Dissertation
- Thesis Proposal
- Proofreading
- IB Extended Essay
- Grant Proposal
- Write My Interview Essay
- Questions-Answers
- Literature Review
- Literary Analysis
- Business Plan
- Research Paper
- Discussion Board Post
- Response Reaction Paper
- Letter Writer
- Questionnaire
- Book Review
- Interview Essay
- Affiliate Program
- Write My Outline
- Rewriting Service
- Problem Solving Essay
- How It Works
- --> --> --> --> --> -->