Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More

Business Plan Examples for Students
Ajay Jagtap
- December 29, 2023
26 Min Read

Do you know what’s the most common mistake students and rookie entrepreneurs make while preparing their first business plan?
Of course, it’s the first business plan we’re talking about; there’ll definitely be a few. However, overcomplicating things and failing to consider a business plan example still remains the most common one.
That’s why we decided to come up with a solution. We’ve curated this list of top business plan examples for students to help you get going.
So whether you need a business plan for a college project, start a side hustle, or win a business competition, these examples are just what you need to create business plans that stand out.
Ready to dive in? Let’s start by understanding the key elements of a business plan example:
Key Elements of a Business Plan Example
Business planning is not as complicated of a process as people think it is; they’re just overcomplicating things. (Don’t think so?)
Let’s simplify the key elements that make up a comprehensive business plan; you’ll understand it better that way.
Executive Summary:
Company overview:, market analysis:, products and services:, sales and marketing strategies:, operations plan:, management team:, financial plan:.
That’s pretty much it about the key elements of a business plan example. Next, let’s explore the best business plan examples for students.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI assistant
Get 30% off for Students and educators

Top Business Plan Examples for Students
Now that you already know about the components of a business plan template, let’s review some of the best business plan examples for students.
1. Startup Business Plan Example
Upmetrics’ startup business plan example is the ideal solution for students planning to start up or participate in a business plan competition. This business plan template follows the SBA-approved business planning format used by thousands of successful entrepreneurs.
Whether your startup is about a new-age AI-based application, an online shopping site, or traditional IT consulting—this sample business plan is just what you need.
Unlike any traditional small business plan, this example of a startup business plan is lean and agile in approach, focuses on innovation, and emphasizes market validation.
2. Lean Business Plan Example
Since you’re transitioning from a student to an entrepreneur, you may not have enough time to spend on creating a detailed business plan. That’s where this lean business plan template can help.
It’s a condensed version of a traditional plan summarizing all its sections with a primary focus on covering only the critical aspects of the business.
This template is best for startups or businesses uncertain about business planning and student-turned-entrepreneurs with limited time and resources to prepare a business plan.
3. SBA Business Plan Example
Following an SBA-recommended business plan format is key to securing bank loans and business grants. Since it can be time-consuming to find a template that follows a similar outline as the SBA, this SBA-approved business plan example is the way to get started.
This SBA business plan template has nine primary sections, that include executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization, product description, marketing, funding request, and financial projections.
SBA business plan examples ensure you stay on track and don’t deviate from your funding needs.
4. One-Page Business Plan Example
As you may have already guessed, a one-page business plan is a one-page version of a traditional business plan. Since it’s a condensed version of a business plan, drafting it can be quite easy and quick compared to a lean or traditional plan.
Employees, partners, and vendors often use one-page business plans as a quick overview of your company and banks and investors as a summary of your operations.
While it may not be the ideal choice for entrepreneurs seeking investment or bank loans, students with side hustles and idea-stage startups can consider this option.
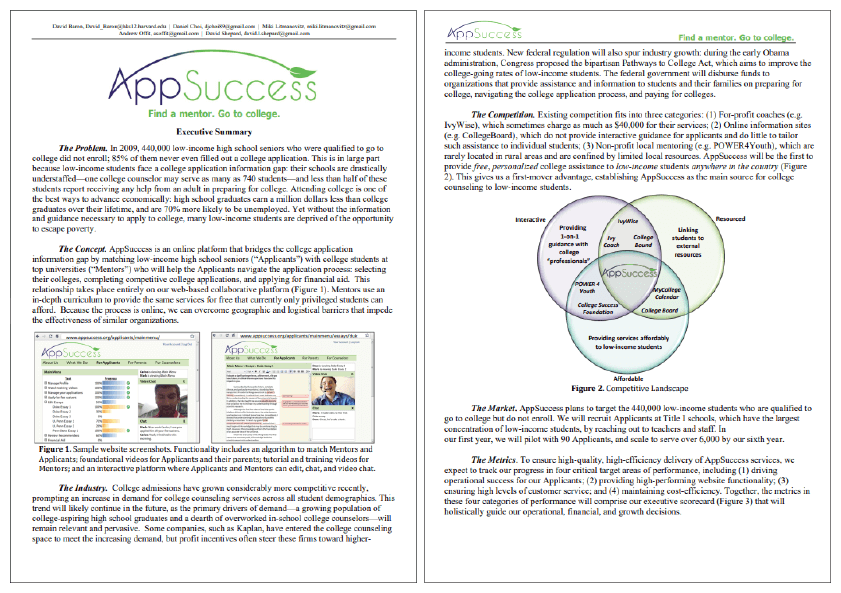
5. HBS Sample Business Plan
Harvard Business School’s new venture competition selected this sample business plan as a finalist in 2011.
This is a business plan of App Success, a collaborative web-based platform that connects low-income high school seniors with college students from top universities; this business will enable them to collaborate on college selection, college applications, and financial aid applications.
This example can be a great reference for those planning to start a mobile or web-based solution.
6. Kean University Sample Business Plan
Kean University organizes a business plan competition every year for its students where students prepare and present business plans to compete, and this is one of the sample business plans the University provides to participants to understand the format.
It’s a business plan of Blue Water Boatworks, Inc., a boat detailing and cleaning company specializing in servicing recreational fiberglass and aluminum watercraft.
This example can be a great reference for those planning to start a business related to housekeeping, cleaning, or maintenance.

7. UVM Sample Business Plan
If you are looking for a strategic business plan for a food business, the University of Vermont’s Fancy Foods Business Plan can be a guiding resource for you.
Despite the fact that it can be a good reference for detailed planning, it was written in 1998, so any statistics and numbers may not seem relevant to today’s market landscape. Make sure you keep that in mind.
You may closely follow this example as a reference if planning to start a food truck, restaurant, or any other business that serves food.
That was the list of best sample business plans for students. However, there’s more to talk about. You now have a business plan example, but what about pitching to investors? Let’s explore free pitch deck examples for students.
Free Pitch Deck Example for Students
Pitching to investors as a first-time founder can be exciting but also overwhelming at times. Worry not; we’ve got a solution—investor pitch templates. We’ve prepared a set of 8 investor pitch templates and examples for students and entrepreneurs to help create winning business pitches.
Whether you need a pitch to find an opportunity, ask for subject matter knowledge, or a problem-solving pitch, these investor pitch examples have got you covered. Download now.
How to write a winning plan for a business plan competition?
Creating a business plan is no different than creating one for a real business. Similar to how entrepreneurs prepare and present business plans to investors, Students in business plan competitions pitch to judges.
In short, the business planning process remains exactly the same. Let’s discuss how you can write a winning plan to help you win a business plan competition.
- Select a compelling business idea : everything starts with a compelling idea. Make sure you have a viable business idea to compete in the competition.
- Refer to winning business plan examples : Once you are sure about your business concept, refer to business plan examples from previous winners and how they planned the sections of their plan.
- Market Research & Industry Analysis : After referring to business plan examples, conduct industry research and market analysis to make your statistical and financial numbers accurate and realistic.
- Understand business model and revenue streams : Since you are preparing a business plan for a company that doesn’t exist, be sure about the business model and how the business will generate profit.
- Use AI business plan generator : Using an AI business plan generator like Upmetrics can be incredibly helpful in speeding up the business planning process. With industry-specific business plan templates and AI assistance to write your plan, you can write the first draft of your plan in literally no time.
- Presentation and visuals : Prepare visuals and graphs to make your business plan visually appealing and numbers digestible. You may not need to prepare these visuals if you use business plan software manually.
- Proofread and edit : Grammatical errors are the last thing judges want to see in a business plan. Make sure you proofread and edit your draft thoroughly before submitting it.
Easy as that, that’s the way to write a perfect business plan that can lead you to victory in any business plan competition on planet Earth. Let’s have a look at a real-life business and financial plan example.

Business and Financial Plan Example for Students
Having learned about business planning for students, let’s quickly discuss a coffee shop sample business plan and financial statements prepared using Upmetrics.
1. Executive Summary
The Cooper’s Cup will be a new cafe in Phoenix, Arizona. The 1,500 square foot café will be located in the newly constructed Market Square Plaza on the northeast corner of 135th Street and Mission Street. The anchor tenant, the Price Chopper grocery store, has already taken occupancy, and the excellent location brings more than 10,000 shoppers weekly.
The Cooper’s Cup, aptly named for the aromatic brown liquid that will fill the cup, fills the void of original cafes in the market and stands out from its corporate peers with its fast food concepts and prompt services. The Cooper’s Cup is the alternative to fast food/commercial/coffee shops and offers a much calmer, civilized gourmet coffee experience.
There are no televisions in the cafe, the background music is subtle, and work from local artists will hang on the walls. The restaurant is well-appointed, with overstuffed leather chairs and sofas in a library-like setting. The cafe is reminiscent of times gone by – yet is cutting edge technologically with WIFI and state-of-the-art espresso machines.
The Cooper’s Cup measures its financial success in terms of increased market share and earnings. This is a tremendous opportunity with a total local market of $54 million! The keys to success will be offering quality gourmet coffees, taking advantage of its small size, and relying on an outstanding barista staff.
To achieve these goals, the cafe will present some of the area’s finest gourmet beans from local distributors. Because of its small size, the restaurant can enjoy larger margins through lower overhead. The cafe will hand-select baristas and offer salaries comparable to the chains. The baristas will be trained to cross-sell and sell higher-margin products.
The primary objectives of the business plan for Cooper’s Cup are below:
- To increase revenues by $36,000 or 5% in Year 2 and $73,000 or 10% by Year 3
- Achieve a profit margin of 5.2% in Year 2 and 6.90% by Year 3
- Be the Cafe of Choice in the Phoenix area and the recipient of the Best Coffeehouse Award.
Guiding Principles
The Cooper’s Cup is committed to values such as excellence, passion, quality, integrity, and leadership, allowing them to navigate challenges and provide for future opportunities. These core beliefs start with their commitment to their products and their employees. Cooper’s Cup rewards excellence and cherishes loyalty. The cafe will work with its employees to build strong businesses and a secure future.
Mission statement
The Cooper’s Cup is committed to its products and employees, which they believe is the recipe for market success.
Key to success
The Cooper’s Cup stands out from the competition. Below are their Keys to Success:
- Great Products : providing exemplary products at market prices – will make customers want to return again and again.
- Hire Quality Baristas : Pay employees rates similar to the larger chains with opportunities for long-term careers and opportunities for advancement with long-term plans to open a second facility.
- Convert Customers to Connoisseurs : Only 40% of the nation’s coffee drinkers consume premium ground and whole bean coffee – this will aid in the continued growth.
Financial Summary
2. Business Overview
The Cooper’s Cup will be a coffee house/cafe located in Phoenix, Arizona. The cozy cafe will be located in the newly completed Market Square Plaza in the Arizona City area. The cafe will serve gourmet coffee, espresso, drip coffee, lattes, and smoothies. The simple pastry offerings may vary with seasonality, but the primary line will be muffins, bread, cookies, scones, and rolls. All pastries will be supplied daily by a local bakery.
The cafe will be owned and operated by Owen Jones, a veteran restaurateur with several years of experience running and managing chain restaurants. The cafe will be open for business Monday – Thursday 7-10, Fridays and Saturdays, 7-11, and closed Sundays.
The Cooper’s Cup will be formed as an S-Corporation owned by Mr. Doe.
Start-Up Summary
The Cooper’s Cup will have seating for 40 patrons. The rent is $2,075 a month, with a three-five-year lease available. The site comprises 1500 square feet of leased space consisting of a dining room, a coffee bar, two restrooms, and a storage room in the back.
This storefront needs to be plumbed and wired appropriately to be used as a restaurant. Painting, new floors, and countertops are also needed. A custom coffee bar needs to be built. With materials bought on sale and volunteer labor, the cost to renovate will be $71,725.
The coffeehouse equipment will consist of two commercial espresso machines, air pots and urns, a commercial blender, a commercial brewer, top-loading coffee bins, barista syrups, cold drink dispenser, frothing equipment, a commercial refrigerator, microwave, and stainless steel prep bar.
The cost of the equipment is $38,275. The furniture will consist of leather couches and chairs (purchased at auction), coffee tables, bookcases, and window treatments. The artwork will come from local artists and be sold on a consignment basis. The books were secured via donations. The total cost to furnish is $14,000. Other startup expenses will be dishes, furniture, rent deposit, and marketing.
Location and Facilities

The new coffeehouse is located in the highly desirable Phoenix, Arizona, area at the northeastern intersection of 135th Street and Mission Street in the Newmarket Square Plaza. The property is situated in an excellent location, with an easy 6-minute drive time to I-435 and 69 Highway.
The property is 95% leased with Price Chopper as the Anchor Tenant. Other tenants include LifeSpring Med Spa, Jane’s Canines (Pet Store & Boarding), Pride Cleaners Kahn Dental, and Swim U.
Price Chopper brings more than 10,000 shoppers per week to the center. The location comprises a population of 9,420 within a one-mile radius, 61,102 within a 2-mile radius, and 149,550 within a 5-mile radius – with a median household income of $120,856. Sprint / Nextel’s corporate office is within 2 miles of the site.
3. Market Analysis
Phoenix, Arizona, is an award-winning place to live and work and is considered the leading business community in the Midwest. National publications and organizations recognize Phoenix for its business environment and livability. Here’s a sampling: 6th Place, America’s Best Places to Live Money, Top 50 Cities to Live and Play, National Geographic Adventure, 3rd Hottest Town in the U.S., Money, Among 20 Best Places to Live & Work Employment Review, One of only 72 Sterling Tree Cities in the U.S., National Arbor Day Foundation, Top 10 best Locations to Raise a Family, Southern Business and Development, 1st Place, Kid Friendly Report Card, Population Connection, 2nd Best City in America to Live Business Development Outlook.
Phoenix is at the core of one of the most dynamic local markets in the U.S. It offers easy access to the Arizona City region’s amenities, and, as part of the Arizona City metropolitan area, it is within the most centrally located major market in the nation. I-35, I-435, I-635, and U.S. Highway 69 all pass through Phoenix, and no point in the city is more than 3.5 miles from a freeway. The city maintains an excellent arterial street network and plans to construct additional lane-miles as the area grows. Three airports serve the region. Arizona City International Airport (MCI) is just 25 interstate highway miles north of Phoenix. Johnson County Executive Airport—the second busiest in Arizona—provides complete services for private business jets and general aviation. New Century AirCenter, just 12 miles southwest of the city, offers available aviation services and accommodates cargo or passenger jets of any size.
Phoenix supplies some of the most highly educated workers in the nation, with 97% of Phoenix adults over age 25 holding at least a high school diploma. Johnson County, where Phoenix is located, ranks first among the country’s 231 counties with populations greater than 250,000. The county ranks sixth in the percentage of adults with at least a bachelor’s degree and 16th with a graduate or professional degree.
The Phoenix area has a population of 175,265, based on the 2010 census. The median household income is $77,881, and the median age is 37.9. (2010 U.S. Census)
Industry Analysis
The U.S. coffee shop industry includes about 20,000 stores with a combined annual revenue of about $10 billion. Major companies include Caribou Coffee, International Coffee & Tea (The Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf), Peet’s Coffee, and Starbucks. The industry is concentrated: the top 50 companies generate more than 70 percent of sales. Coffee shops are part of the specialty eatery industry, including retail outlets specializing in bagels, donuts, frozen yogurt, and ice cream products. (First Research)
Competitive Landscape
Consumer taste and personal income drive demand. The profitability of individual companies depends on the ability to secure prime locations, drive store traffic, and deliver high-quality products. Large companies have advantages in purchasing, finance, and marketing. Small companies can compete effectively by offering specialized products, serving a local market, or providing superior customer service. Specialty eateries, which include coffee shops, are labor-intensive: average annual revenue per worker is about $50,000. Coffee shops compete with convenience stores, gas stations, quick service, fast food restaurants, gourmet food shops, and donut shops. (First Research)
Market Size
The U.S. coffee shop industry includes about 20,000 stores with a combined annual revenue of about $10 billion. Major companies include Caribou Coffee, International Coffee & Tea (The Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf), Pet’s Coffee, and Starbucks. The industry is concentrated: the top 50 companies generate more than 70 percent of sales. (First Research)
Target Market and Segment Strategy
Most adult coffee drinkers said their lifelong habits began during their teenage years. 54% said they began drinking coffee between 13 and 19. Another 22% reported their coffee cravings started between 20 and 24. This means that 76% of adult coffee drinkers began drinking coffee by the time they were 24. So, despite a large amount of marketing and advertising directed at the younger age groups, savvy coffee shop owners will remember to cater some of their offerings to the adult and senior market. (National Coffee Drinking Study).
The Cooper’s Cup will offer a unique experience for coffee enthusiasts by providing a quiet, cozy, yet sophisticated cafe and a sense of refinement and peace in an otherwise hectic and fast-paced world. While other coffee shops cater to convenience with drive-throughs or loud music venues late into the night, the Cooper’s Cup will stand apart from its competitors with its quiet yet soothing ambiance, capturing a truly unique (and much-needed) market niche.
- Unique products (specialized roasts, local ingredients, locally-themed or named drinks, custom drinks by the star barista, etc.)
- Games, puzzles, mind benders, and other activities that encourage customers to linger over their coffee
- Hosting or sponsoring local events (entertainment, readings, book clubs, etc.)
- Using technology to creatively compete in marketing with big chains — services like FourSquare, Yelp, and Google Places can increase visibility in the local market.
- Delivering amazing service from knowledgeable baristas — spend lots of time training staff and utilizing online services like the American Coffee & Barista School.
- Selling coffee-related items (and tracking down any co-marketing opportunities with a local community college or another student-related group in the area)
4. Products and Services
Product/services descriptions.
The Cooper’s Cup’s primary offering is gourmet roasted coffees with mocha, carmelicious, white mocha, candy bar latte, and brewed coffee. Complementing the coffee will be a smoothie line including wild berry, strawberry, peach, mango, and lemonade. Rounding out the simple menu line will be pastries obtained from an outside supplier, freshly made and delivered daily. The pastry offerings may vary with seasonality, but the primary line will be muffins, bread, cookies, scones, and rolls.

Product/Service Sourcing
The Cooper’s Cup has negotiated supplier agreements with several local food-service wholesalers and coffee wholesalers in the Phoenix area that have a reputation for quality and reliability:
- Mean Beans Coffee Roasters
- Phoenix Brewers
- Healthy Harvest Bread Co.
- Mary’s Organics
If one of the abovementioned specialty suppliers cannot meet their needs, the following national suppliers can provide all the food-service products they require. In addition, the following wholesalers will supply the cafe with general restaurant supplies:
- Lawrence Food Products Corp.
- Gerry Food Supply Inc.
Future Products/Services
Young families, which comprise Phoenix’s third largest market share, are often overlooked in the coffee market. Coffeehouses traditionally have not been considered ‘kid’ friendly. To overcome this hurdle, Cooper’s Cup has long-term plans (5 years) to open a 2nd coffee shop: A combination indoor play area/coffee bar. This concept allows parents and caregivers to meet and relax with other adults while the children can enjoy the indoor playground amenities.
Additional future services will include in-store sales for home purchases and an online store.
The website will have the option to purchase a prepaid gift card program – Prepaid gift cards provide immediate cash, reduce credit card transaction charges, and draw new customers to the business.
5. Sales and Marketing Strategies
Swot analysis.
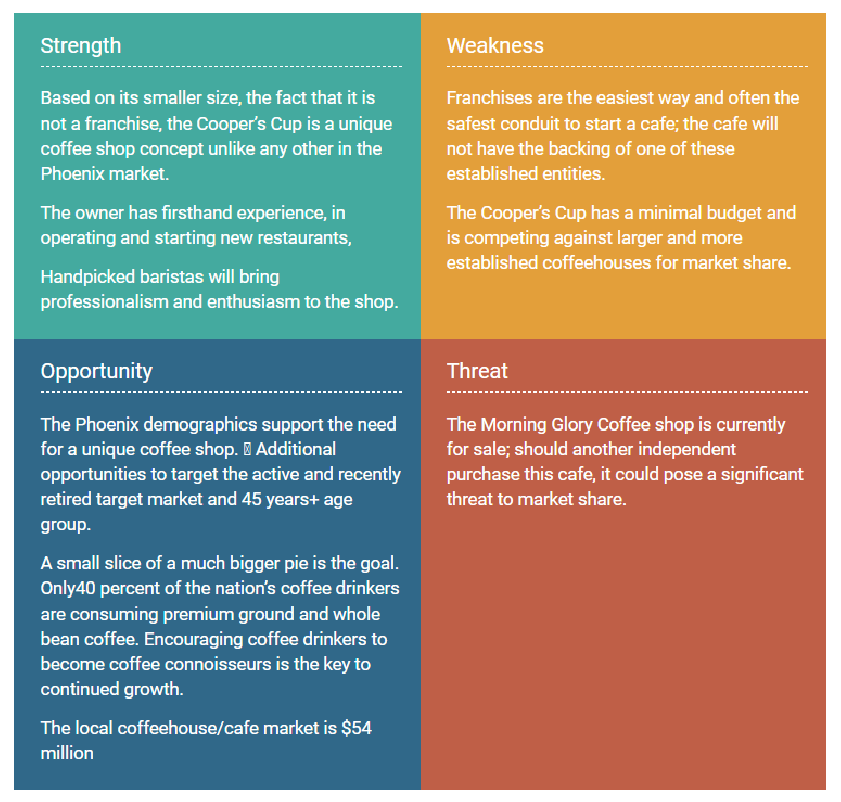
Unique Selling Proposition
The Cooper’s Cup stands out from a crowded sea of coffee chains and franchises. What sets it apart from the competition is primarily its smaller, cozier size combined with premium coffees served by knowledgeable baristas, providing so much energy and enthusiasm for its products.
Market Strategy and Positioning
The Cooper’s Cup utilizes a focus strategy on its Market. By specifically targeting three primary segments, they can cater specifically to their needs.
Senior Market (age 45+)
The Cooper’s Cup will target this Market simply by its well-selected location. Although this demographic group could readily drive downtown, they prefer a local cafe to unwind and relax and historically become some of the most loyal patrons.
Newly Hired Employees
The cafe will attract regular customers (weekly or more) – particularly the newly employed (first job) by providing free WIFI services and providing interesting games in the customer area.
Young Families
The third targeted Market, younger families, often find that coffeehouse is not ‘kid’ friendly. The company has long-term plans to create a combination coffee shop/play area so that parents and caregivers can meet with other adults while the children can enjoy the bounce houses, slides, and indoor playground equipment.
Pricing Strategy
The Cooper’s Cup primarily utilizes competition-based pricing. The cafe does not utilize coupons and discounts (other than opening promotions) because they believe that the most valuable customer demographic of daily coffee consumers is not influenced by discount programs or coupons.
Promotion and Advertising Strategy
- Online Advertising – The Cooper’s Cup will advertise regularly on popular social media sites like Facebook. Compared to traditional print advertising, this is a cost-effective tactic that will allow them to reach prospects in a highly targeted way (e.g., based on criteria such as age, gender, geography, etc.).
- Website – Cooper’s Cup will develop a simple Web site, which will provide basic information about the business, the menu, and links to their presence on the aforementioned social media channels.
- Radio Advertising – During the first six months of operation and the busy holiday shopping season, the business will advertise on local radio stations.
Sales Strategy
The Cooper’s Cup will use the following methods to increase sales revenue (as recommended by Andrew Hetzel on Better Coffee, Better Business):
- The menu will focus on the most profitable products sold. The cafe will always draw customer attention to the best products.
- As warranted, the cafe will raise prices to bolster its brand image. Prices communicate the perceived value of a product, so if set too low, the customers might assume that the beverages are inferior compared to the competition.
- Monitor flavoring inventory – Excess flavoring inventory ties up capital and valuable backroom space for storage. The cafe will utilize 4-6 varieties, including sugar-free offerings.
- Control waste and theft – audit sales and inventory reports to evaluate ingredient waste due to inefficient preparation, returned drinks, and employee consumption. Retail locations can easily waste 20% or more of their daily sales in these three key categories, which is a substantial and unnecessary loss.
- Monitor and evaluate hours of operation.
- Run employee sales contests – The baristas are the salespeople and have great influence over the customer ordering process. All baristas will have some form of sales and customer service training to make each transaction active rather than passive. Sales contests will emphasize high-margin items or cross-selling.
6. Operations Plan
Staffing and training.
An ongoing training and education program will ensure that each staff member learns and implements Cooper’s Cup’s exacting service and operational procedures standards. Staff meetings will reinforce service standards and principles. The Cafe will have detailed work descriptions and training programs for each position, from entry-level employees to the ongoing development of managers and owners. New employees will undergo an extensive training program. This ensures that each guest receives a quality experience from all employees, regardless of how long they have been employed. The Cafe embraces the concept of promoting from within. Excellence in one function typically leads to excellence in another. Regular staff evaluations and training will ensure motivation and address critical issues.
Inventory controls
The founder will be responsible for hiring and training managers who, in turn, will ensure that the day-to-day operations will comply with the standards set by Restaurant policy. Weekly management meetings will provide a forum to review and discuss financial and operational performance. Critical decisions related to purchasing, human resources, marketing, capital expenditures, and customer service will also be addressed.
Purchasing cost controls
Food preparation personnel will follow standardized recipes developed by the founders to control food costs and ensure consistency. The coffee shop will offer an innovative menu with nutritious food and beverages while achieving the most significant margin yield.
Customer Service
The hospitality business recognizes the client’s support experience is the critical driver to replicate business. The direction will Offer a superior degree of Professionalism by hiring individuals who deliver the ideal attitude to work and teaching them the skills required to accommodate guests. The restaurant will keep high levels of consumer satisfaction with talented, educated, and well-trained workers who understand and implement the fundamentals of fantastic service. Ongoing training will be provided to enable staff to perform their jobs with confidence and ability. Employees are well-spoken, well-versed, and trained to provide friendly, prompt, and professional service to each customer. This practice teaches employees who, by producing an exceptional customer experience, can optimize sales and raise their reimbursement. The team will have the knowledge and service required to create excellent daily service for every customer.
Technology & Software
While the quality of the cuisine and dining experience contributes significantly to a restaurant’s profitability, attention to business and financial details can transform small changes into significant returns. Critical sales, cost of sales, labor, inventory, marketing, and overhead metrics are monitored daily. Trends are evaluated, and constructive actions will be taken where improvement is needed. The management team will have access to the restaurant’s transactions and reports available in its real-time POS (point of sale) and accounting systems. Trends will be evaluated, and corrective action will be implemented as required.
7. Organization Structure
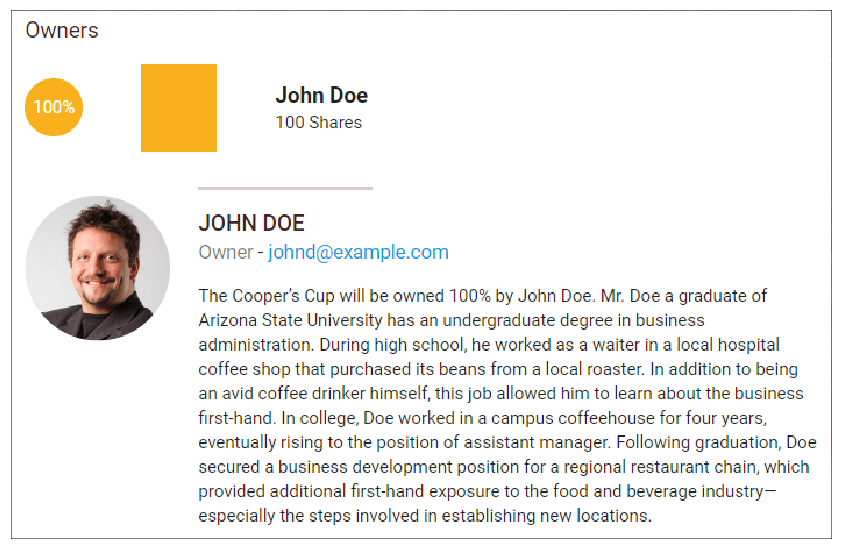
The Cooper’s Cup is formed as an S-Corporation wholly owned by John Doe.
Management Team
The Cooper’s Cup will be owned 100% by John Doe. Mr. Doe, a graduate of Arizona State University, has an undergraduate degree in business administration. During high school, he worked as a waiter in a local hospital coffee shop that purchased its beans from a local roaster. In addition to being an avid coffee drinker, this job allowed him to learn about the business first-hand. In college, Doe worked in a campus coffeehouse for four years, eventually becoming an assistant manager. Following graduation, Doe secured a business development position for a regional restaurant chain, which provided additional first-hand exposure to the food and beverage industry—especially the steps involved in establishing new locations.
Management Team Gaps
The Cooper’s Cup will rely on its POS (Point of Sale) system to generate daily accounting and cost activity reports. Mr. Doe will supply these to an outside bookkeeper for the preparation of annual income taxes.
Personnel Plan
Initially, the cafe will hire 1 manager, 5 baristas, and 2 part-time servers. In Year 2, the cafe plans to hire 1 additional full-time barista.
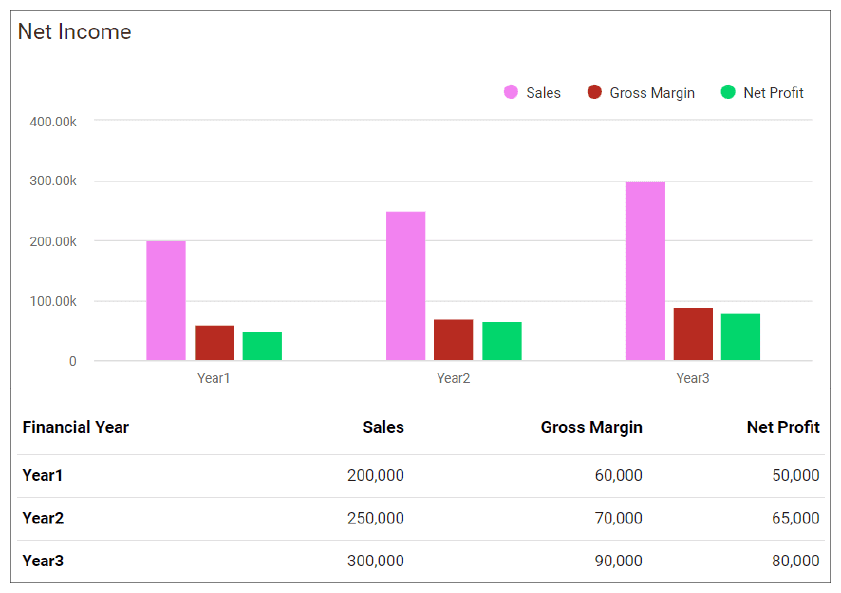
8. Financial Plan
Important assumptions.
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some month’s revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wane in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are cash basis – nonaccrual accounting
- Moderate ramp-up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista’s salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin
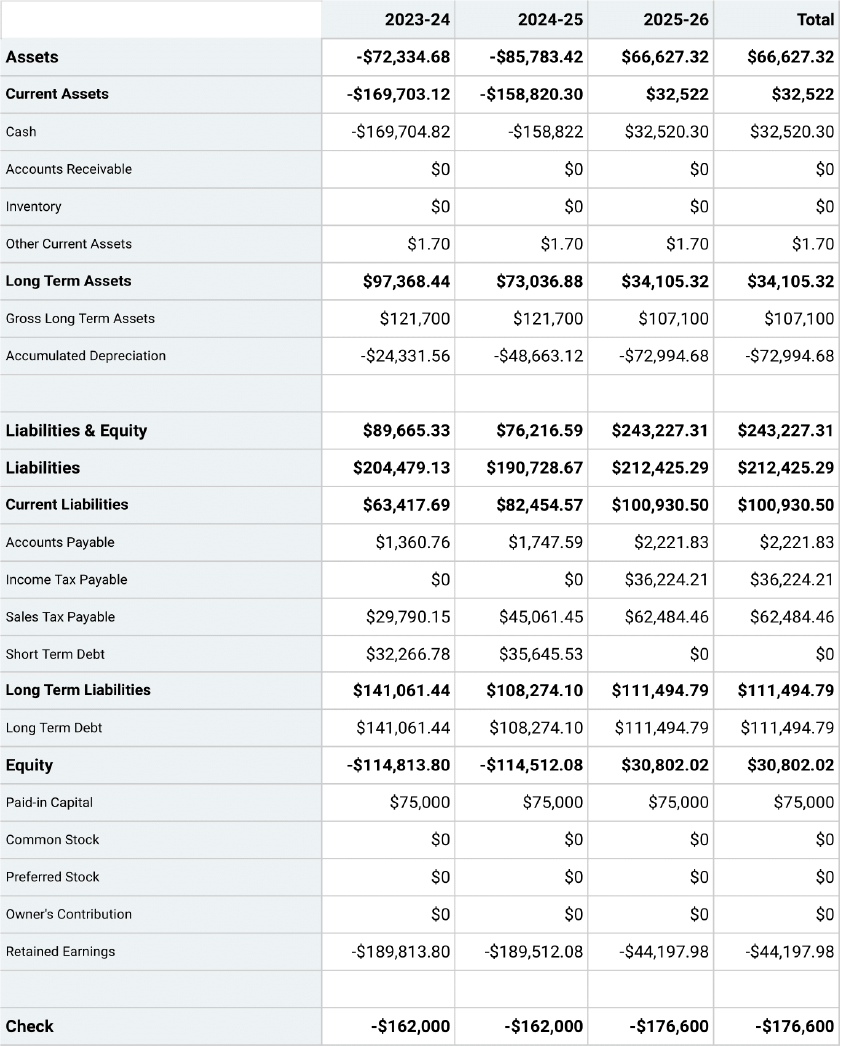
Projected Balance Sheet
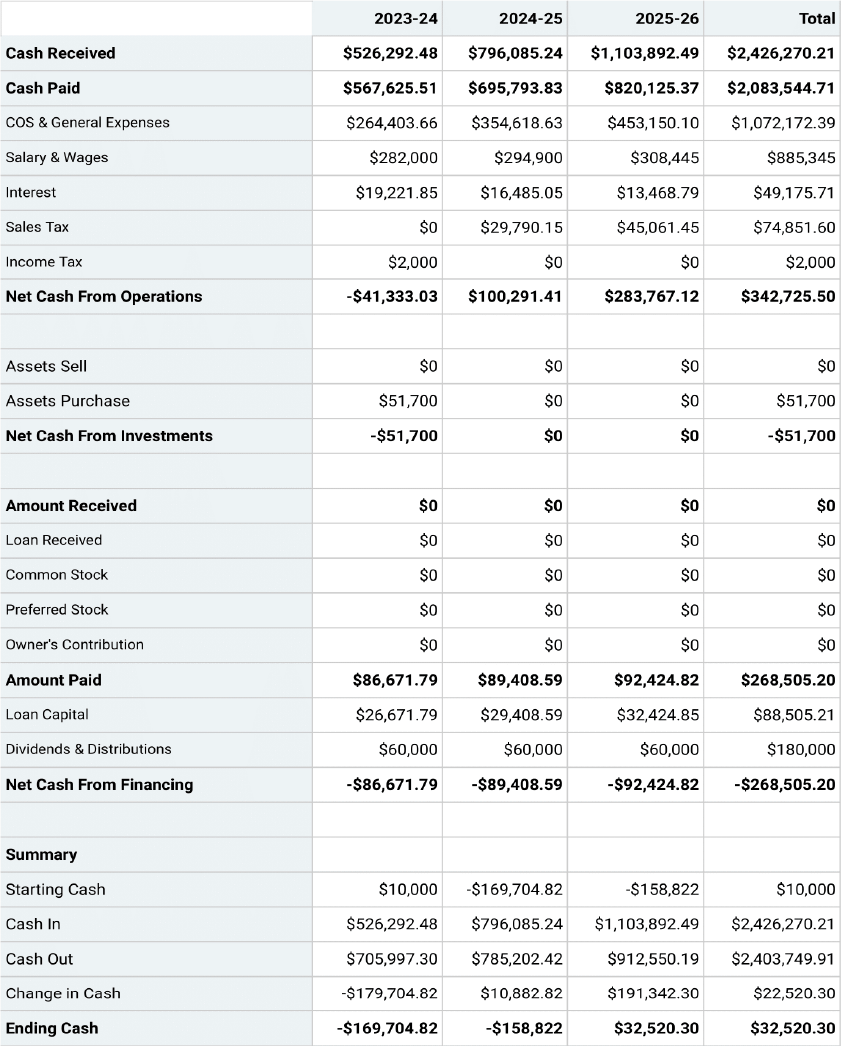
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
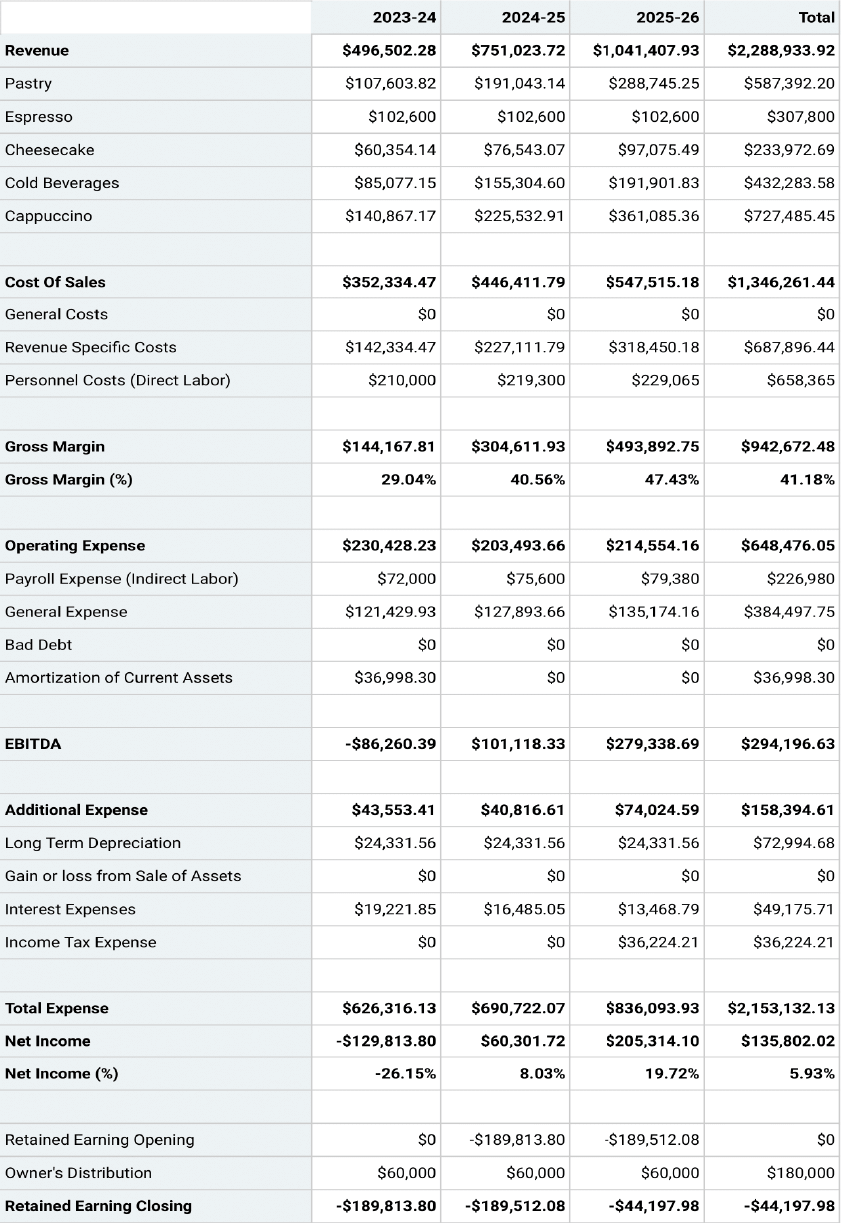
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
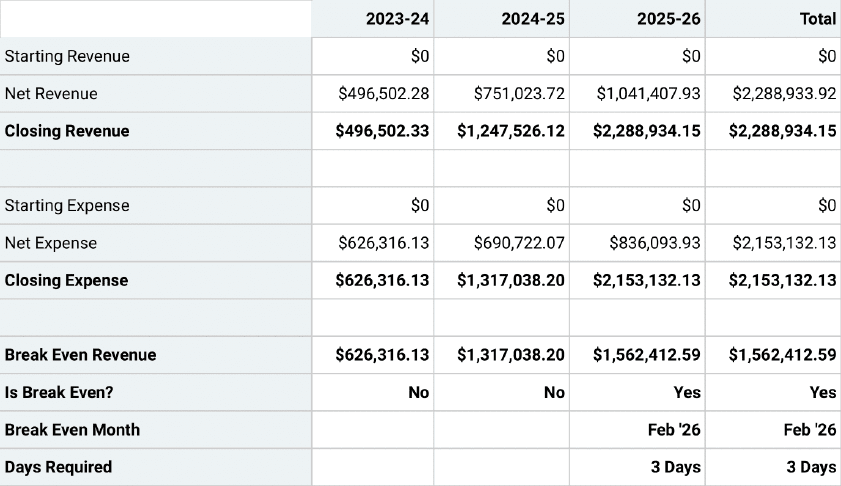
Break Even Analysis
Write Your Business Plan With Upmetrics
Whether you need a business plan to compete in a competition, win investors, or gain a competitive advantage in the market landscape, Upmetrics can help you get started.
Upmetrics is an AI business plan software that comes with AI assistance, financial forecasting features, and 400+ sample business plans so that you can prepare a business plan in no time.
So what are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics and create your business plan in a snap.
Make your plan in half the time & twice the impact with Upmetrics
Fill-in-the-blanks, AI-assistance, and automatic financials make it easy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you write a business plan for a college project.
As mentioned earlier in the article, business planning for a college project or competition is no different than for a real business. You can write your business plan using these step-by-step instructions.
- Select a compelling business idea
- Refer to business plan examples
- Prepare a business plan outline
- Create a company description section
- Conduct market research and industry analysis
- Describe your product and services
- Outline sales and marketing strategies
- Create an operations plan
- Introduce management team
- Prepare financial projections
- Summarize your plan with an executive summary
What is a business plan for students?
A business plan is a necessary business document that highlights its purpose, business goals, product/service offerings, go-to marketing strategies, operations and financial plan, key people involved in the business operations, and other necessary details.
As a student, consider a business plan example as a document that helps you better understand business and industry dynamics and learn how a business operates inside out.
What is a business plan competition for students?
Business plan competitions are competitions mostly organized by universities for students passionate about entrepreneurship and the business world. These competitions offer students a platform to showcase their entrepreneurial skills while also providing opportunities for mentorship and networking.
How can I increase my chances of winning a business plan competition?
There cannot be a straightforward answer to this question, but there’s surely a method that can increase your chances of winning a competition—Using AI-powered business plan software.
Why? An AI tool will make you 10X more productive while writing a business plan and preparing financial forecasts. So you can spend more time researching the market and brainstorming business ideas.
Where can I find more business plan examples for students?
Upmetrics’ library of 400+ business plan examples could be an incredible source for students to find more industry-specific business plan examples. There are examples for almost every small business category, including real estate, retail, entertainment and media, food & beverages, and more.
About the Author

Ajay is a SaaS writer and personal finance blogger who has been active in the space for over three years, writing about startups, business planning, budgeting, credit cards, and other topics related to personal finance. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates
Ready to kickstart your business planning.

– Don’t Miss It

Business Plan Development Guide
(6 reviews)
Lee Swanson, University of Saskatchewan
Copyright Year: 2017
Publisher: OPENPRESS.USASK.CA
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Kevin Heupel, Affiliate Faculty, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 3/4/20
The text does a good job of providing a general outline about writing and developing a written business plan. All of the important steps and components are included. However, the text is light on details, examples, and rationale for each element... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
The text does a good job of providing a general outline about writing and developing a written business plan. All of the important steps and components are included. However, the text is light on details, examples, and rationale for each element of the business plan. Some examples from actual business plans would be helpful.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
For the most part, the content is accurate. The content covers all important aspects of drafting a business plan. I thought the industry analysis could use more information about collecting primary and secondary sources; instead, this information was referenced in the marketing plan section.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
Most of the content relies on cites as far back as 2006; however, when it comes to developing and writing a business plan nothing has changed. Thus, the content is current and there is no concern about it becoming obsolete in the near future.
Clarity rating: 4
The text is clear. There are no difficult terms used and the writing is simple. The text uses a lot of bullet points though, which gets tedious to read for a few pages.
Consistency rating: 5
The text does a good job of maintaining consistency in terms of framework and terminology. The text is organized where it's easy to find the information you want in a quick manner.
Modularity rating: 3
The text has a lot of bullet points and the paragraphs are dense. However, the use of subheading is excellent.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The book is organized as if you're writing a business plan from start to finish, which is helpful as a practical guide.
Interface rating: 5
There are no navigation problems, distortion of images/charts, or any other display features that may distract or confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
The text is free of grammatical errors. The sentence structure is simple with many bullet points, which helps to avoid any grammatical issues.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This book was written by a Canadian professor and provides references to Canadian sources. However, the information in this text can be used for U.S. schools.
This book is very short and provides a good, general overview about the process of creating and writing a business plan. It won't help a reader if he/she is confused about a certain part of the business plan. The reader will have to find another source, such as "Preparing Effective Business Plans" by Bruce Barringer, Ph.D. The book provides links to good resources and a finished business plan that the reader can reference. I would recommend the book for undergraduate courses.
Reviewed by Kenneth Lacho, Professor of Management, The University of New Orleans on 6/19/18
1. Text is relevant to Canada. Not the United States 2. Needs to cover resources available to entrepreneur, e.g., federal government agencies, trade associations, chambers of commerce, economic development agencies. 3. Discuss local economy or... read more
1. Text is relevant to Canada. Not the United States 2. Needs to cover resources available to entrepreneur, e.g., federal government agencies, trade associations, chambers of commerce, economic development agencies. 3. Discuss local economy or economic area relevant to this proposed business. 4. Business model ok as a guide. 5. Suggested mission statement to cover: product/business, target customer, geographical area covered. 6. Need detailed promotion plan, e.g., personal selling, advertising, sales promotion, networking publicity, and social media. 7. How do you find the target market? 8. Chapter 6 too much detail on debt and equity financing. 9. Discuss how to find sources of financing, e.g., angels. 10. Expand coverage of bootstring, crowdfunding. 11. Chapter 4 – good checklist. 12. Chapter 3 - overlaps. 13. Chapter 7 – 3 pages of executive summary – double or single spaced typing. Number all tables, graphs. 14. Some references out-of-date, mostly academic. Bring in trade magazines such as Entrepreneur.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
In my opinion, the content is accurate and error free.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The material is relevant to writing a business plan. I wonder if the Porter, SWOT VRIO, etc. material is too high level for students who may not be seniors or have non-business degrees (e.g., liberal arts). Porter has been around for a while and does have longevity. The author has to be more alert to changes in promotion, e.g., social media and sources of financing, e.g., crowdfunding.
Clarity rating: 3
As noted in No. 9, the tone of the writing is too academic, thus making the material difficult to understand. Paragraphs are too long. Need to define: Porter, TOWS Matrix, VRIO, PESTEL. A student less from a senior or a non-business major would not be familiar with these terms.
Consistency rating: 4
The text is internally consistent. The model approach helps keep the process consistent.
Modularity rating: 4
The process of developing a business plan is divided into blocks which are parts of the business plan. Paragraphs tend to be too long in some spots.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The topics are presented in a logical step-wise flow. The language style is too academic in parts, paragraphs too long. Leaves out the citations. Provides excellent check lists.
There are no display features which confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
The text has no grammatical errors. On the other hand, I found the writing to be too academic in nature. Some paragraphs are too long. The material is more like an academic conference paper or journal submission. Academic citations references are not needed. The material is not exciting to read.
The text is culturally neutral. There are no examples which are inclusive of a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
This book best for a graduate class.
Reviewed by Louis Bruneau, Part Time Faculty, Portland Community College on 6/19/18
The text provides appropriate discussion and illustration of all major concepts and useful references to source and resource materials. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The text provides appropriate discussion and illustration of all major concepts and useful references to source and resource materials.
Contents of the book were accurate, although it could have benefited from editing/proofreading; there was no evidence of bias. As to editing/proofreading, a couple of examples: A. “Figure 1 – Business Plan… “ is shown at the top of the page following the diagram vs. the bottom of the page the diagram is on. (There are other problems with what is placed on each page.) B. First paragraph under heading “Essential Initial Research” there is reference to pages 21 to 30 though page numbering is missing from the book. (Page numbers are used in the Table of Contents.)
The book is current in that business planning has been stable for sometime. The references and resources will age in time, but are limited and look easy to update.
Clarity rating: 5
The book is written in a straightforward way, technical terms that needed explanations got them, jargon was avoided and generally it was an easy read.
The text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 5
The book lends itself to a multi-week course. A chapter could be presented and students could work on that stage of Plan development. It could also be pre-meeting reading for a workshop presentation. Reorganizing the book would be inappropriate.
The topics in the text are presented in a logical, clear fashion.
Generally, the book is free of interface problems. The financial tables in the Sample Plan were turned 90° to maintain legibility. One potential problem was with Figure 6 – Business Model Canvas. The print within the cells was too small to read; the author mitigated the problem by presenting the information, following Figure 6, in the type font of the text.
I found no grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
I require a business plan in a course I teach; for most of the students the assignment is a course project that they do not intend to pursue in real life. I shared the book with five students that intended to develop an actual start-up business; three of them found it helpful while the other two decided not to do that much work on their plans. If I were planning a start-up, I would use/follow the book.
Reviewed by Todd Johnson, Faculty of Business, North Hennepin Community College on 5/21/18
The text is a thorough overview of all elements of a business plan. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The text is a thorough overview of all elements of a business plan.
The content is accurate and seems to lack bias.
Content seems relevant and useful . It does not help an entrepreneur generate ideas, and is very light on crowdfunding and other novel funding source content. It is more traditional. This can be easily updated in future versions, however. "Social Media" appears once in the book, as does "Crowd Funding".
The book is comprehensive, but perhaps not written in the most lucid, accessible prose. I am not sure any college student could pick this up and just read and learn. It would be best used as a "teach along guide" for students to process with an instructor.
The text seems consistent. The author does a nice job of consistently staying on task and using bullets and brevity.
Here I am not so certain. The table of contents is not a good guide for this book. It does make the book look nicely laid out, but there is a lot of complexity within these sections. I read it uncertain that it was well organized. Yes there are many good bits of information, however it is not as if I could spend time on one swathe of text at a time. I would need to go back and forth throughout the text.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 2
Similar to the above. I did not like the flow and organization of this. An editor would help things be in a more logical order.
Interface rating: 2
The interface is just OK. It is not an attractice interface, as it presents text in a very dense manner. The images and charts are hard to follow.
I did not find any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
I a not certain of the origins of Saskatchewan, but I do feel this is a different read. It is more formal and dense than it has to be. This would be a difficult read for my students. I do not feel it is insensitive in any way, or offensive in any way.
I would not adopt this book if given the chance. It is too dense, and not organized very well, even though the information is very good. The density and lack of modularity are barriers to understanding what is obviously very good information.
Reviewed by Mariana Mitova, Lecturer, Bowling Green State University on 2/1/18
Though this textbook has a prescriptive nature, it is quite comprehensive. The author strikes a good balance between presenting concepts in a concise way and providing enough information to explain them. Many every-day examples and live links to... read more
Though this textbook has a prescriptive nature, it is quite comprehensive. The author strikes a good balance between presenting concepts in a concise way and providing enough information to explain them. Many every-day examples and live links to other resources add to the completeness of the textbook.
Content seems accurate.
Since the content is somewhat conceptual, the text will not become obsolete quickly. In addition, the author seems to be updating and editing content often hence the relevance to current developments is on target.
The text is very clear, written in clear and straight-to-the point language.
The organization of content is consistent throughout the entire text.
The textbook is organized by chapters, beginning with overview of the model used and followed by chapters for each concept within the model. Nicely done.
The flow is clear, logical and easy to follow.
Overall, images, links, and text are well organized. Some headlines were misaligned but still easy to follow.
No concerns for grammar.
No concerns for cultural irrelevance.
Reviewed by Darlene Weibye, Cosmetology Instructor, Minnesota State Community and Technical College on 2/1/18
The text is comprehensive and covers the information needed to develop a business plan. The book provides all the means necessary in business planning. read more
The text is comprehensive and covers the information needed to develop a business plan. The book provides all the means necessary in business planning.
The text was accurate, and error-free. I did not find the book to be biased.
The content is up-to-date. I am reviewing the book in 2017, the same year the book was published.
The content was very clear. A business plan sample included operation timelines, start up costs, and all relevant material in starting a business.
The book is very consistent and is well organized.
The book has a table of contents and is broken down into specific chapters. The chapters are not divided into sub topics. I do not feel it is necessary for sub topics because the chapters are brief and to the point.
There is a great flow from chapter to chapter. One topic clearly leads into the next without repeating.
The table of contents has direct links to each chapter. The appearance of the chapters are easy to read and the charts are very beneficial.
Does not appear to have any grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive.
I am incorporating some of the text into the salon business course. Very well written book.
Table of Contents
Introduction
- Chapter 1 – Developing a Business Plan
- Chapter 2 – Essential Initial Research
- Chapter 3 – Business Models
- Chapter 4 – Initial Business Plan Draft
- Chapter 5 – Making the Business Plan Realistic
- Chapter 6 – Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur
- Chapter 7 – Finishing the Business Plan
- Chapter 8 – Business Plan Pitches
References Appendix A – Business Plan Development Checklist and Project Planner Appendix B – Fashion Importers Inc. Business Plan Business Plan Excel Template
Ancillary Material
About the book.
This textbook and its accompanying spreadsheet templates were designed with and for students wanting a practical and easy-to-follow guide for developing a business plan. It follows a unique format that both explains what to do and demonstrates how to do it.
About the Contributors
Dr. Lee Swanson is an Associate Professor of Management and Marketing at the Edwards School of Business at the University of Saskatchewan. His research focuses on entrepreneurship, social entrepreneurship, Aboriginal entrepreneurship, community capacity-building through entrepreneurship, and institutional-stakeholder engagement. Dr. Swanson’s current research is funded through a Social Sciences Humanities Research Council grant and focuses on social and economic capacity building in Northern Saskatchewan and Northern Scandinavia. He is also actively studying Aboriginal community partnerships with resource based companies, entrepreneurship centres at universities, community-based entrepreneurship, and entrepreneurial attitudes and intentions. He teaches upper-year and MBA entrepreneurship classes and conducts seminars on business planning and business development.
Contribute to this Page
See in 90 seconds how LivePlan simplifies
financials for students: Watch
Garretts Bike Shop
Provide real–world business plan examples for your students, inspire confidence in future entrepreneurs and easily create your class syllabus using industry–best business plans., liveplan gives students access to actual business plans so they can practice business planning in and outside of the classroom., it's not just a classroom project. it's your students planning for their futures..

Teach by example
LivePlan's examples of actual business plans show students how they can identify opportunities, meet challenges, and plan their path to profits. Just like real-world entrepreneurs.

No spreadsheets necessary
With all–in–one spreadsheet–free forecasting and pitching tools–students can use LivePlan to build a realistic business plan with accurate projections and compelling pitches. Analyze scenarios. Track progress. Set goals. All in LivePlan.

Works seamlessly with your classroom setup
With LivePlan you can simplify syllabus creation. LivePlan can also be used alongside classroom tools such as Blackboard and Canvas. LivePlan's optional instructional resources can enhance your syllabus with materials that introduce lean planning principles, growth metrics, financial forecasting, and more.
Instructors looking for a great tool to help students develop business plans need to look at Live Plan. The step–by–step process walks students through the entire process from Pitch to Financials. As the Instructor you can also have online access to their plan and provide feedback and comments as the plan develops.

Mike Allen Business Instructor, North Idaho College, Coeur d'Alene, ID
Bring out the best in every student
LivePlan's business plan examples help students turn ideas into top–notch business plans for class projects and startups. The tools, features, and instructional content allow you to focus on bringing out the best in your students for every plan and project.
Before using LivePlan, my students were intimidated by the business planning process. LivePlan breaks it down into manageable steps and takes the mystery out of developing a business plan.

Amy Schulz NACCE Vice President of Education, Membership and Associate Faculty, Feather River College, Quincy, CA
I used LivePlan to develop a business plan for a class project. Turns out, the project became part of a business plan competition where I placed second out of over 200 entries.

Sheila Austin Student
LivePlan provides your students with the tools to

Know the competition
No business operates in a vacuum. LivePlan incorporates real–world industry data, so students can better understand competitors, plan businesses around industry realities, and confidently execute data–driven strategies.

Build business dreams together
From sharing feedback and engaging in discussions, to simultaneously working on different parts of the plan, students can easily collaborate in groups using LivePlan.

Create a plan that fits their needs
Whether small or big, LivePlan can build out the right–sized business plan for your classroom projects. In LivePlan, students can develop a simple lean plan that focuses their ideas, or create a full business plan with all the details and steps necessary to persuade investors, attract partners, and turn their idea into a profitable reality.

With so much happening in the classroom, you need a tool that works with you, not one that makes you do extra work. Used by educators, consultants, entrepreneurs, and students all around the world, LivePlan has been regularly improved and streamlined so it's easy to use.

Develop confidence in their plan and themselves
It's one thing to plan a business. It's another thing to know how to talk about a business plan. Students can develop talking points and practice their pitch in LivePlan so they can discuss their enterprise with confidence and authority.
With LivePlan your students exceed expectations
With LivePlan, students create business plans that:
- Guide them from concept to actionable plan
- Build the confidence necessary to be entrepreneurs
- Combine pitching, forecasting, and collaboration
LivePlan streamlines projects for educators
LivePlan eases project management in the classroom, so instructors can:
- Pinpoint feedback and suggest improvements
- Monitor project progress
- Teach business planning instead of managing multiple apps
Go beyond business plan examples
LivePlan easily integrates into business courses, includes all materials and curriculum to support classroom business projects, and comes with free phone, email, and chat technical support.
The students very much appreciate the guidance the LivePlan program offers. I love the ability to act as a contributor to their plans. The help resources are phenomenal and easy to navigate.

John Shaw Assistant Professor of Management, Davis College of Business – Jacksonville University, Jacksonville, FL
See how LivePlan can upgrade your student's education
Fill out the form below and our LivePlan Partnership Team will be in touch shortly.
Get Your Free LivePlan Account Today
Thanks an educator advocate will be contacting you shortly to set up your free liveplan account..
If you'd like to talk to us before then, please call 1–888–498–6136 Phones are open M–F, 8am–5pm (Pacific time)
Teachers and students love LivePlan
LivePlan really facilitated communication between students who were in a team on the business plan project. Students could comment on sections of their business plan and collaborate on what to change in their plan without having to meet face–to–face.

Amy Valente Assistant Professor of Business, Cayuga Community College, Auburn, New York
LivePlan helped us easily set up the business plan for our startup during our MBA. As soon as the other students saw it, they also wanted LivePlan. The time we saved on planning we could use for operational tasks. It was the ideal solution for us.

The product we produced by using Live Plan was exceptional, far exceeded our expectations, and came out so much better than we could have ever done on our own.

This product is a game-changer. It allows the non–MBA founder to unleash their potential through strategic planning and beautiful design. Highly recommended.

Answers Neuroscience
LivePlan is simply awesome.

Amit Agrawal
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

Business Plans for Kids
Download the Sample Business Plan for Kids
Business Plan for Kids
Teach your students how to write their own business plan and create a successful business.
More Business Planning Resources
The 4 p’s of marketing.
Learn how to market your business with product, pricing, promoting and placement.
How to be a Pro
Tips on making a sales pitch, interviewing for a job, or meeting a potential customer.
Are you Making a Profit?
We’ll help you find out! Use this worksheet to do the math and put your business on the right track.

7 Business Plan Templates for Kids (Free Printables!)
By: Author Amanda L. Grossman
Posted on Last updated: May 7, 2024
Download one of these (mostly) free business plan templates for kids to help your child focus on a business idea.
What do supersoakers, Apple computers, and Nike shoes all have in common?

They all started as a business plan.
A business plan template for kids is great for two reasons:
- Your child can play around with it and get familiar with what's required (even if they never start the business)
- It helps kids focus on just one business idea at a time, and to see if they should move forward with it
No matter which category your own child falls into – just playing with business plans, or they have an actual business idea – I’ve got just the free business plan template for you.
Honestly? I wish my own parents would’ve given me one of these when, as a kid, my childhood friend and I had come up with our first kid business idea: selling bean bags. So, good on you for getting your kids involved with business plans so early in life!
Best Business Plan Templates for Kids
Use one of the business plan templates for kids below with one of these 16 kid business ideas .
OR, help them to use one of their original ideas sending sparks in their brain. You can use these 3 kid business plan examples for help with filling it out.
1. Solid Gold Biz Plan
I’ve been in business for 7 years and I’ve made about every mistake in the book.
Probably one of the biggest? Was that I didn't sit down to write a proper business plan (or, ANY business plan) until I was several years into blogging.
Because of this, I created a free business plan template for kids and teens (on Page 6 of this free printable), so that they practice how to do it right, from the beginning!
What makes my free Solid Gold Biz Plan different is that it starts your child thinking about the problem that they want to solve – because ultimately, that is the purpose of creating a product or a service. To solve a specific problem for people.
It then goes on to ask them simple questions that will focus them in on what it takes to plan out a business idea.
For example, I raise the question of how much it will cost to not only create the product/service but to also deliver it and maintain it. These are sometimes costs forgotten costs when creating a business plan.
2. BizKids’ Guide to Writing a Business Plan
This free business plan guide for kids includes sections for your idea, your marketing (and what makes your product unique), your startup costs, and an area for pricing so that you can make sure you’ll make a profit.

At the end is a one-page summary where your child can write up their answers from the previous pages all in the same place. Great for tacking up on the wall!
3. Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox
Anthony ONeal partnered up with Dave Ramsey to create the Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox , a kid’s entrepreneur kit and small business guide for teens.
In other words, it’s so much more than just a business template for kids!
The entrepreneur kit includes the following:
- Access to the Free Entrepreneur Toolbox app
- Teen Portfolio Book
- DVD of Anthony’s Training Video
- Parent’s Guide Book
- Pack of Thank You Cards
- Deck of Conversation Starter Cards about Starting a Business
- Goal Tracker Poster
Here's my full review of the Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox .
4. Proverbial Home Maker’s Family Business Plan Guide
This is such a fun guide that you can fill out with your child, teen, tween, or even the whole family. It includes family business ideas, a sales ledger, an inventory worksheet, and much more.

Business Plan Examples
You may be wondering where you can find business plan examples to show your kids or teens.
For starters, you should look right at home. Are you a small business owner?
Then you’ll definitely want my free Take Your Child to Work Day printables – it’s got a section for you to fill in about your own business, which is a perfect business plan example to discuss with your child.
You can also find two business plan examples on the Small Business Administration’s site (scroll down until you see red buttons for Rebecca’s example business plan, and Andrew’s plan).
They’re not entirely kid-friendly but can give lots of ideas for the kind of information and research to put into a business plan.
Business Plan Activity Worksheets
Check out these free PDF Shark Tank worksheets for students . Students or kids can work through coming up with their own business ideas, create an advertisement for it, and a scoring card to judge the business ideas.
You’ll find a free 30-minute Small Business Administration course for young entrepreneurs meant for teens that you can use with your students (or have your child go through).
Hint: In Objective 3, it goes over how to create a business plan.
Are you an educator? Great – you can get a free entrepreneur curriculum for Grades 1 – 12, with lots of worksheets, from the Venture Lab .
Further resources include:
- Teen Business Video Lessons
- EverFI’s Entrepreneurial Expedition
- FEE’s Course on the Entrepreneur’s Role in Creating Value
- Business Plan Note Taker (lots of great prompts to create a business plan with)
Grab 23 more entrepreneur lesson plans here.
I hope you've found some business templates for kid resources that interest you. Below, you'll find other related kid entrepreneurship articles that will help your kids, teens, and students learn about the entrepreneur's career path.
Related Kid Entrepreneurship Resources
- 27 Youth Entrepreneur Awards and Scholarships
- 5 Kid Entrepreneur Kits
- 14 Kid Entrepreneur Books
- 11 Best Business Simulation Games for Kids
- Latest Posts
Amanda L. Grossman
Latest posts by amanda l. grossman ( see all ).
- 19 Unique Kid Piggy Banks (Plus How to Use Them for Money Lessons) - April 3, 2024
- 50 Banking Activities for Kids (Student Financial Literacy) - February 14, 2024
- 14 Christmas Activities for High School Students (they’ll Actually Find Cool) - December 1, 2023
Business Plan Template for Students
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Thinking of starting your own business as a student? We've got you covered! ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Students is the ultimate tool to help you turn your entrepreneurial dreams into reality.
With this template, you can:
- Develop a strategic and detailed plan for your business idea
- Outline your objectives, marketing strategies, and financial projections
- Structure your organizational hierarchy for effective management
- Impress potential investors and stakeholders with a professional and well-thought-out plan
- Stay organized and focused on your goals throughout the entire business development process
Don't let your student status hold you back from achieving your business goals. Get started with ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Students today and pave the way for your future success!
Business Plan Template for Students Benefits
When students use the Business Plan Template, they gain a competitive edge and set themselves up for success by:
- Structuring their business ideas and goals in a comprehensive and organized manner
- Presenting a professional and well-thought-out plan to potential investors or stakeholders
- Creating a clear roadmap for their business, ensuring they stay on track and achieve their objectives
- Developing a solid understanding of key business components like marketing strategies and financial projections
- Gaining valuable experience in business planning and management, setting them up for future entrepreneurial endeavors.
Main Elements of Students Business Plan Template
When it comes to creating a solid business plan, ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Students has got you covered. Here are the main elements you'll find in this template:
- Custom Statuses: Track the progress of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do, ensuring that every step is accounted for and easily manageable.
- Custom Fields: Utilize custom fields such as Reference, Approved, and Section to add important details to your business plan, keeping everything organized and accessible in one place.
- Custom Views: Explore different views like Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide, enabling you to visualize your plan in various formats and dive deep into specific areas of your business plan.
- Collaboration: Collaborate seamlessly with your team by assigning tasks, leaving comments, and attaching files directly within ClickUp, streamlining the entire business planning process.
- Integrations: Integrate with other tools such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and Slack to streamline your workflow and ensure all relevant documents and communication are easily accessible.
With ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Students, you'll have all the tools you need to create a comprehensive, well-structured business plan that will impress potential investors and set you on the path to success.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Students
Creating a business plan as a student can be a daunting task, but with the help of ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you can break it down into manageable steps. Follow these six steps to create a comprehensive business plan that sets you up for success:
1. Define your business idea
Start by clearly defining your business idea. What product or service will you offer? Who is your target audience? What makes your business unique? Use the Docs feature in ClickUp to brainstorm and outline your business concept.
2. Conduct market research
Next, conduct thorough market research to understand your industry, competitors, and target market. Analyze market trends, customer preferences, and potential demand for your product or service. Use the Table view in ClickUp to organize and analyze your research data.
3. Outline your business structure
Determine the legal structure of your business and outline its organizational structure. Will you operate as a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation? Define the roles and responsibilities of key team members and any necessary partnerships. Utilize the Board view in ClickUp to visualize and assign tasks related to your business structure.
4. Develop a marketing strategy
Create a comprehensive marketing strategy to promote your business and attract customers. Identify your unique selling propositions, target marketing channels, and budget for marketing activities. Use the Calendar view in ClickUp to plan and schedule your marketing campaigns.
5. Create a financial plan
Develop a financial plan that includes projected revenue, expenses, and profit margins. Determine your startup costs, pricing strategy, and sales projections. Use custom fields in ClickUp to track and calculate financial data accurately.
6. Set goals and milestones
Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for your business. Break them down into smaller milestones and create a timeline to track your progress. Utilize the Goals feature in ClickUp to set and monitor your business goals.
By following these six steps and utilizing ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you can create a comprehensive and well-structured business plan that will guide you towards success in your entrepreneurial journey.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Students
Students who are aspiring entrepreneurs or learning about business management can use the ClickUp Business Plan Template to develop a comprehensive and structured plan for their business idea.
First, hit "Add Template" to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you'd like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a solid business plan:
- Use the Topics View to organize your plan into different sections such as Executive Summary, Market Analysis, Marketing Strategy, Financial Projections, etc.
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- The Timeline View will allow you to set deadlines and milestones for each section, ensuring you stay on track.
- The Business Plan View will give you an overview of the entire plan, allowing you to see how each section fits together.
- The Getting Started Guide View will provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to use the template effectively.
Customize your business plan further by utilizing the three custom fields: Reference, Approved, and Section. These fields will help you keep track of external resources, approval status, and the specific section each task belongs to.
Monitor and analyze your progress using the various views and custom fields to ensure your business plan is comprehensive and well-structured.
- Business Plan Template for Jollibee
- Business Plan Template for Strategic Planning
- Business Plan Template for Woolworths
- Business Plan Template for Ui Designers
- Business Plan Template for Shoe Retailers
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
- 212 best farm names
How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)
May 24, 2021
Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”

If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video

Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand

A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:
When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples

Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:

Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.

The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?
80% of businesses fail... Learn how not to.
Learn from business failures and successes in 5 min or less. The stories, frameworks, and tactics that will make you a 10x better founder.
Brandon Boushy
Related articles
Recession Proof: 7 Ways to Beat Hard Times
- What happens during recessions
- The definition of recession-proof
- Recession-proof Industries, companies, and jobs
- What to do in a recession
- What to do with your money
- How to protect your money
- How to make money during a recession [/su_note]
What happens in a recession?
- Eight to 12 months , or three quarters of declining demand. (The longest was the Great Recession at 18 months.)
- Unemployment rising to over 5.5%, but potentially as high as 10.8%
- A 4% to 6% decline in year-over-year GDP, which is calculated on a modified income statement.

- People and companies reduce discretionary spending.
- People look for ways to earn extra income.
- Some increase their savings if they have extra income, then savings account balances decrease.
- Companies reduce hiring and then cut jobs when they cannot cut costs any more.
- The stock market declines.
- Banks increase requirements for loans and reduce lending to prevent defaults.
- Total personal income decreases.
- The Federal Reserve normally lowers interest rates, but interest rates, gas, and supply chain issues are responsible for the current decline in GDP.
What is recession-proof?
- Consumer staples like hygiene products
- Discount retailers
- Investments like bonds
- Education[/su_note]
What jobs are recession-proof?
- Teachers : Elementary through high school education doesn't stop because a recession occurs. According to Capital News Service , most recessions create increased demand for higher education because more consumers want to increase their job prospects by investing in their education. 2020 was an exception because people were worried about the transmission of COVID.

- Health Care Professionals : Nurses, doctors, and specialized care providers are also recession-proof careers. This goes for therapists, psychiatrists, and social workers, too.
- Government Employees : Jobs like firefighters, police, first responders, and social workers that work for the government are normally recession-proof jobs because the demand for their services stays the same or increases during a recession.
- Public Service Jobs : People still need garbage pickup, electricity, water, and other essentials to keep their home and community livable so these services make it through a rough patch virtually unscathed.
- Financial Service Providers : Taxes still have to be made, and auto insurance is still required by law. There have been two bank runs in the last hundred years, and the last one saw massive numbers of bailouts. Make sure to go with a conservatively run financial institution, and you should be fine.
What companies are recession-proof?
- Vanguard Total International Stock ETF ( VXUS ): Every country has different economic conditions. International investing can be done at a discount when the dollar is strong. When the dollar weakens again, you can see huge gains in these stocks.
- Vanguard Consumer Staples ETF ( VDC ): These are a mix of Procter & Gamble, Coke, Pepsi, Costco, Walmart, and other companies that people buy from regardless of uncertainty. Economic data show that these companies have built a recession-proof business.
- iShares 0-3 Month Treasury Bond ( SGOV ): Short-term bonds are currently performing better than long-term bonds. The peak levels are at the two-year mark. You can buy them on Treasury Direct if you prefer.
- Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF ( SCHD ): Dividends are like interest paid on stocks, but you can opt for dividend reinvestment to increase your equity. When the prices go back up, you have more stock.
- Health Care Select Sector SPDR Fund ( XLV ): Healthcare spending is a major piece of the economy, regardless of what the rest of the market is doing.
- Vanguard Utilities Index Fund ETF ( VPU ): As we’ve mentioned previously, utilities are recession-proof businesses.
- SPDR Gold MiniShares ( GLDM ): Many people invest in gold to hedge against inflation when they see uncertainty.
- Vanguard S&P 500 ETF ( VOO ): Recessions often occur in different areas at different times, so investing in international stocks might pay off.
What are recession-proof Industries?
- Grocery stores: They sell food, and it’s the absolute last thing in life people can give up.
- Convenience stores: People always need gas to get to their job, and most gas stations have a contract with the gas company where the gas company keeps the gas revenue, and the market keeps the profit from the products in the store.
What to do in a recession?
- Save money as soon as your company is running a profit.
- Create a subscription service; it tends to increase the average revenue per client.
- Pay off debt every month so you can ride out a down market.
- Keep a look out for amazing investment opportunities for your portfolio. Sometimes people sign over their business just to keep from declaring bankruptcy.
- Sell underperforming assets.
- Renegotiate with vendors and landlords.
- Don’t buy anything you don’t need.
- Ask your employees to help. Dan Price almost had to lay off 20% of his company, but his employees opted for pay cuts . Everyone kept their jobs, and he paid them back after they weathered the storm.
- Lower profit margins if necessary. Sometimes lower prices will matter enough to keep customers you would lose otherwise. Remember when everywhere offered $10 pizza? Pizza places used that strategy to protect their stores from closing. Then, after the 2009 recession passed, pizza prices gradually doubled.
- Consider reducing the products and services you offer. Alternatively, add products and services businesses have requested.
What to do with your money in economic downturns

Stock Market
- Purchasing Managers Index : Shows companies are buying materials.
- Durable Goods Orders : Shows demand for industrial products.
- Jobless Claims : Weekly and monthly reports that show how many unemployment claims are being filed. When both weekly and monthly align, it is a good thing. Weekly will show changes first, but monthly will show confirmation that the weekly wasn’t an anomaly.
- Consumer Confidence Index : This shows how confident consumers are. If consumers are confident, the economy will likely trend higher unless unforeseen events occur.
Buy Businesses
- Questions to ask
- Business valuation
- How to buy a business
How to protect your money in an economic downturn

Increase Savings Rate
Decrease unnecessary spending, reduce employees hours, reduce employee pay, how to make money during a recession.

Systemize Your Business
- Automate accounting and bookkeeping.
- Improve your marketing strategy.
- Add a subscription plan.
- Review your services to see which ones lose your money.
Get Rid of Underperforming Assets
- Work vans that are in the shop too often.
- Scrap metal you never took to the recycling yard.
- Equipment you bought thinking you need it, but you never use.
Run Promotions
Develop new skills, keep your morale up.
466 Restaurant Name Ideas You’ll Love (2024)
So you’ve decided to open a restaurant but don’t know what to name it? That’s okay. We have plenty of restaurant name ideas you’ll love.
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"]We’ve grouped our picks for best restaurant names into 17 unique categories to help you choose a restaurant name that works for you. In addition, we’ll discuss how to name a restaurant—and restaurant names to avoid. Check out all of our ideas or click any of the links below to jump straight to the section you need now.
What should I name my restaurant?
32 fancy restaurant names, 20 cute restaurant names, 30 fast food restaurant names, 30 american restaurant names, 30 mexican restaurant name ideas, 30 italian restaurant name ideas, 30 french restaurant names, 22 diner names, 22 fancy café names, 20 buffet restaurant names, 30 bistro names, 30 ‘punny’ restaurant names, 30 beach restaurant names, 30 brunch restaurant names, 30 modern restaurant names, 30 fantasy restaurant names, 20 breakfast restaurant names.
- Did you find cool restaurant names? [/su_note]

Choosing a great restaurant name can be a challenge. We’ve got you covered with some tips to help you find the perfect name for your business.
- Consider a name that reflects the type of cuisine you offer or the overall theme of your restaurant. This gives potential customers a quick idea of what to expect.
- Unique restaurant names help you stand out. If you use a generic name, you might get lost in the crowd.
- Restaurant name ideas should be easy to remember.
- A culinary venture might want to include a reference to its location.
- You’ll want to check if your restaurant name ideas list has trademark availability, then check domain names and social media platforms to see if the good restaurant names are taken.
Remember, the name of your restaurant is a key part of your brand, so take the time to brainstorm and choose a name that resonates with your vision and target audience.
If you want to attract bougie guests to your restaurant, choose a fine dining restaurant name that will impress. First, impress them with your name…then stun them with your impeccable service and first-class cuisine. Here are some fine dining name ideas that will help you make it happen:
1. Aurelian Elegance 2. Orchid Row 3. Éclat Manor 4. Imperium 5. Luxe Lumière 6. Crown on the Plaza 7. Prestige Cellars 8. Riviera Regale 9. Sérénité Soirée 10. Enclave 11. Étoile 12. Maison Tres 13. Café Grandeur 14. Rendezvous 15. Château Chantilly 16. The Emporium
17. Refined Revelry 18. Epicure 19. Illustrious Ivy 20. The New Gourmand 21. Ember 22. Resplendent Ridge 23. Epitome Elegance 24. Luminance 25. Nouveau Table 26. Vista Vérité 27. Apogee Amour 28. In Aura 29. Palatial Palate 30. Panache 31. The Gilded Gastronome 32. Epicurean Elegance
Pro Tip: When it comes to naming a fine dining restaurant, you can go one of two ways: trendy or classic. Select which one you think will draw in your target customer and also be a name you can live with for the life of your restaurant.
Attracting families and kids to your restaurant is easy when its name is adorable. A good restaurant name attracts potential customers to your establishment—just make sure your restaurant’s mission matches the name or else it will be ineffective.
1. Whisker's Whimsy Wagon 2. Sweet Pea Patisserie 3. Sprout ’n’ Sprinkle Spot 4. Bubblegum Bunny Bistro 5. Fairy Floss Café 6. Teddy's Tea Party Tavern 7. Sugar Sprinkle Shack 8. Cotton Candy Cottage 9. Snuggle Bug Bistro 10. Raindrop Ranch Café
11. Kitten's Kitchenette 12. Sunshine & Sprinkles Café 13. Sweetheart Seashore Shack 14. Cupid's Café Corner 15. Sugar Plum Fairy Feasts 16. Little Lamb Luncheon 17. Panda Palate Palace 18. Bunny Hop Bistro 19. Cleopatra's Culinary Haven 20. Galaxy Grub
Pro Tip: You don’t just have to make your name creative, but make it a creative restaurant. The interior should be fun and inviting. Hang local art on the walls and create an atmosphere families will continually come back to.

As a business owner, you want your fast food restaurant name to make a lasting impression. We have a great ideas list for you to choose from so you can guarantee you have repeat business time and again.
1. ZapBite Burger Co. 2. Rapid Munch Drive-Thru 3. Swift Savor Express 4. Dash Burger Bistro 5. ZipTaste Tavern 6. SpeedySizzle Grill 7. Snap Chow Hut 8. On the Rise Burgers 9. BlazeBite Fast Fare 10. Zest Meal Spot 11. TurboTaste Drive-Thru 12. Rapid Fuel Bistro 13. Quick Crave Corner 14. Rush Bite Express 15. Dash Munch Depot
16. Speedy Chow Hut 17. Express Burger Joint 18. Swifty Feast Drive-Thru 19. Fast Flash Fare 20. Blaze Bite Express 21. Zoom Burger Stop 22. Snap Chow Shack 23. RushBite Grill 24. Quick Fuel Fast Food 25. RapidRise Diner 26. ZippyMunch Depot 27. Swift Serve Fast Fare 28. Wizard of Oz Grill 29. Apollo's Pizzeria 30. Einstein's Edible Emporium
Pro Tip: What are your unique selling points that would make someone come to your place over other restaurants in the area like McDonald’s? Use your social media channels to get the word out there. The first impression someone has will stay with them forever. Build your brand identity from the very beginning.
American restaurants focus on cooking and serving food like burgers, chicken, and a variety of other options diners associate with Americana. Here are some names that will help your restaurant stand out from the pack:
1. Jazz Junction Diner 2. Great Lakes Galore 3. Southern Spice Station 4. Capital City Eats 5. Big Sky Bistro 6. Redwood Roots Restaurant 7. Everglades Epicure 8. Route 66 Diner 9. Aloha Avenue Café 10. Desert Bloom Bistro 11. Gulf Shores Grille 12. Cascade Café 13. Rocky Roadhouse 14. Magnolia Manor Eats 15. Wild West Whiskers
16. Blue Ridge Bistro 17. Crescent City Cuisine 18. Northern Lights Nosh 19. Grand Canyon Grillhouse 20. Napa Valley Nibbles 21. The Rockies Retreat 22. Sunshine State Supper Club 23. Ozark Oasis Bistro 24. Mount Rushmore Munchies 25. Hudson Valley Hideaway 26. Alamo Alley Café 27. Tundra Trails Tavern 28. Niagara Nosh House 29. Appalachian Attic Eats 30. Bayou Bonfire Bistro

The easy way to name your Mexican restaurant is to simply put whatever name you choose in Spanish. But make sure it actually says what you want it to say so your name lets customers know what to expect when they dine there.
1. Sabor del Sol 2. El Sabroso Cantina 3. Casa de Sazón 4. Delicias de México 5. El Corazón de México 6. La Cocina del Sol 7. Tacos y Tequila 8. Sabores de México 9. El Rincón Picante 10. La Fiesta Mexicana 11. Taquería Tradicional 12. El Ranchito Sabroso 13. Los Sabores Auténticos 14. Comida Mexicana Real 15. Cantina del Sol
16. La Hacienda del Sabor 17. El Sazón Auténtico 18. Las Delicias Mexicanas 19. El Patio Mexicano 20. Sabores y Aromas de México 21. La Cabaña Mexicana 22. El Sabor de Mi Tierra 23. La Cocina Mexicana 24. Auténticos Tamales y Tacos 25. Sazón de la Abuela 26. El Fogón Mexicano 27. Tacos al Pastor y Más 28. La Esquina Mexicana 29. Delicias Caseras de México 30. El Paladar Mexicano
Expert Advice: Your name should evoke a feeling for the potential guest. What do you want your customer to think of when they hear your name? Is it an experience, a food, great service? Make your name something unforgettable.
When selecting an Italian restaurant name, be sure to include words that remind people of Italy and the amazing food they’ve had (or imagined having!) overseas. You can make it fancy or fun. These Italian restaurant names are good for everything from a nice Italian restaurant to pizza and hoagie shops.
1. Bella Cucina 2. Trattoria Romantica 3. La Dolce Vita Ristorante 4. Cucina del Sole 5. Gustoso Italiano 6. Sapori d'Italia 7. Piazza Italia 8. La Cantina della Nonna 9. Al Dente Trattoria 10. Ristorante Buon Gusto 11. La Famiglia Cucina 12. Bella Napoli 13. La Cucina Felice 14. Gusti del Sud 15. La Tavola Trattoria
16. Buona Cucina Italiana 17. Mangia Bene Ristorante 18. Le Delizie Italiane 19. Trattoria del Cuore 20. Osteria del Sole 21. Cucina Amore 22. La Cucina del Gourmet 23. La Pizzeria Rustica 24. Vivace Cucina 25. L'Angolo della Pasta 26. Il Gusto Autentico 27. Delizie D'Italia 28. Il Sapore Italiano 29. La Locanda del Cuoco 30. Trattoria Bella Luna
Pro Tip: Some Italian names can be hard for the average American to pronounce. While it may look nice, make sure the average Joe can pronounce your name or else it will be butchered time and again and your target customer may have a hard time finding you.
Your French restaurant name should include keywords that will show potential customers what your restaurant is all about. Use culinary imagery to inspire them to dine there time and again. Of course you’ll want to make sure you love it as well!
1. Maison de Savoureux 2. L'Éclat Culinaire 3. Le Bistrot de la Coquette 4. L'Étoile Épicurienne 5. Bon Appétit Bistro 6. La Cuisine Charmante 7. Chez L'Artisan 8. Le Délice de Paris 9. Rendezvous Rive Gauch 10. Le Festin Français 11. À Table! 12. L'Auberge du Gourmet 13. Le Petit Plaisir 14. Delice de la Côte 15. La Vie en Rose Brasserie
16. Brasserie Bonheur 17. Le Repaire de Saveurs 18. La Cigogne Gourmande 19. La Provence Gourmande 20. Étoile du Matin 21. Les Délices de la Rivière 22. Belle Assiette 23. Bistro du Soleil 24. Salon Culinaire 25. La Table des Artistes 26. Le Café des Amis 27. Le Bon Vivant 28. Cuisine en Rose 29. L'Escapade Gourmande 30. Trattoria du Midi
Pro Tip: French restaurant name ideas are easy to come up with when you look at how beautiful the language is, both spoken and written. Play with combinations, and you shouldn’t have any trouble coming up with the perfect restaurant name as long as it resonates with your menu and dining experience.
Get those creative juices flowing as you decide on a perfect diner name for your new restaurant. This isn’t just a place to serve food. You’ll be creating delicious dishes and a divine dining experience that will wow your guests, so be sure you have a restaurant name to match.
1. Retro Rocket Diner 2. Tasty Tracks Diner 3. Cosmic Café 4. Flamingo Flavors Diner 5. Blue Moon Bites 6. Starlight Bites 7. Killer Pizza & Sammies Diner 8. Route 66 Eats 9. Atomic Appetites Diner 10. Neon Nights Diner 11. Thunderbird Treatbox
12. Jukebox Jive Diner 13. Bonanza Bites 14. Sock Hop Stop Diner 15. Diner-o-Saurus 16. Rock ’n’ Roll Grub Hub 17. Galaxy Grill 18. Cosmic Cravings Diner 19. Diner Delight Junction 20. Mellow Yellow Diner 21. Retro Rendezvous 22. The Food Truck Diner
Pro Tip: Pick a theme for your diner. Themes are a great way to attract customers and build a strong brand identity. You can even make promotional materials for your new business that feature your theme and make people want to come for a meal!

But here are a few fancy restaurant names for your café that are sure to inspire your culinary venture.
1. Serene Sips Café 2. Château du Café 3. Elysian Espresso 4. Enchanted Eats Emporium 5. La Vie en Rose Café 6. Royal Brew House 7. Gourmet Garden Café 8. Éclatant Elegance 9. Belle Bistro 10. Palais de Pâtisserie 11. Tranquil Tea Terrace
12. Paragon Perks Café 13. Posh Palette Café 14. Elite Elixir Emporium 15. Luxe Lounge Lattes 16. Opulent Oasis Café 17. Café Magnifique 18. Divine Delights Diner 19. Paradiso Patisserie 20. Grandeur Grinds 21. Gourmet Symphony Pastry & Beans 22. Café Gilberto
Pro Tip: Creative restaurant name ideas leave a lasting impression on your branding efforts. Check the availability of the perfect name using online tools.
Consider some of these suggested names for all-you-can-eat restaurant businesses.
1. Worldly Flavors Buffet 2. Culinary Odyssey Buffet 3. Fusion Feast Buffet 4. Melting Pot Buffet 5. Global Gastronomy Buffet 6. Panorama Plate Buffet 7. Eclectic Eats Buffet 8. International Indulgence Buffet 9. Diverse Dining Buffet 10. Ethnic Enclave Buffet
11. Flavor Fusion Buffet 12. Gastronomic Galore Buffet 13. Epicurean Expedition Buffet 14. Heritage Heights Buffet 15. Taste Trek Buffet 16. Crossroads Cuisine Buffet 17. Mosaic Buffet 18. Pan-Continental Buffet 19. Culinary Kaleidoscope Buffet 20. All You Can Eat Oasis Buffet

Consider some of these creative restaurant names for a bistro.
1. Sage & Saffron Bistro 2. Azure Vine Bistro 3. Velvet Petal Bistro 4. Hearthstone Haven Bistro 5. Moonlit Terrace Bistro 6. Willow Whisper Bistro 7. Ember & Elm Bistro 8. Sunflower Serenade Bistro 9. Cobblestone Corner Bistro 10. The Tango Bistro 11. Juniper Junction Bistro 12. Quill & Quinoa Bistro 13. Zephyr Zenith Bistro 14. Rustic Aura Bistro 15. Echoes & Eats Bistro
16. Cobalt Cascade Bistro 17. Alchemy Alley Bistro 18. Luna Lounge Bistro 19. Cedar Crest Bistro 20. Elysian Eats Bistro 21. Tarragon Terrace Bistro 22. Opal Orchid Bistro 23. Citrine Cove Bistro 24. Bistro 360° 25. Marigold Manor Bistro 26. Whispering Woods Bistro 27. Three Serenades Bistro 28. Coral Cascade Bistro 29. Amethyst Arbor Bistro 30. Fireside Flavors Bistro
What are some restaurant names that will make you laugh? We have a few answers below. Restaurant owners who aren’t afraid to include a good pun can benefit from a cute restaurant name that diners won’t soon forget. Here are some restaurant business name ideas that leverage just the right amount of humor and hint at the delicious cuisine you’ll serve.
1. Wok Around the Clock 2. Soy Joy Eatery 3. Stir Crazy Noodle Bar 4. Pho-nomenal Eats 5. Kimchi Krazy 6. Dim Sum Delight 7. Miso Happy Eatery 8. Thai Me Up 9. Wonton Wonder 10. Rice Rice Baby 11. Kung Food Palace 12. Zen Zest Fusion 13. Curry in a Hurry 14. Sushi-licious Spot 15. Tempura Temptations
16. Chop Chop Chopsticks 17. Bao Down Bistro 18. Spice Route Café 19. Noodlegate Kitchen 20. Dumpling Dynasty 21. Ramen Rave 22. Pho Real Bistro 23. Szechuan Sensation 24. Dragon Delish Diner 25. Rollin' Rollin' Sushi 26. Wasabi Wow Café 27. Sesame Street Eats 28. Hoisin Haven 29. Kimchili Kitchen 30. Thai Tanic Treats
A restaurant business on the beach might consider some of these new ideas for a beachy business name:
1. Sandy Toes Café 2. Seaside Bites Shack 3. Wavefront Eats 4. Shoreline Sip Spot 5. Flip Flop Fusion 6. Driftwood Diner 7. Beachcomber's Bistro 8. Saltwater Serenade Café 9. Sunkissed Eateries 10. Seashell Shoreline Snacks 11. Tidepool Treats Tavern 12. Coral Cove Cuisine 13. Seafoam Feasts 14. Boardwalk Bites 15. Coastal Cravings Café
16. Pier Pleasures Restaurant 17. Castaway Cove Café 18. Tiki Tide Tavern 19. Bay Breezes Bistro 20. Lighthouse Lunches 21. Nautical Nosh Nook 22. The Mermaid's Menu 23. Palm Tree Pantry 24. Seagull's Perch Café 25. Shell Seeker's Snack Shack 26. Beach Blanket Bistro 27. Sailors' Supper Spot 28. Sandcastle Café 29. Surfer's Slice Shack 30. Beach Bonfire Bites
Brunch restaurant names are great for attracting those people who can’t decide if they want to get breakfast or lunch.
1. Rise & Dine Café 2. Morning Bliss Bistro 3. Brunchville Bites 4. Sunny Side Up Café 5. Brunch & Munch 6. Daybreak Delights 7. Sunlit Brunchery 8. Early Bird Eats 9. Brunch O'Clock 10. Brunch Barn 11.Midday Munchies Café 12. The Bungalow 13. Sunrise Savory Spot 14. The Brunch Basket 15. Breakfast Boulevard
16. Brunch Bonanza 17. Astrud’s Brunchery 18. Sunbeam Brunch Café 19. Morning Glory Eateries 20. Brunchtime Bliss 21. The Morning Table 22. Brunch Affair Café 23. Bistro Brunchscape 24. Rise & Brunch Café 25. Morning Medley Diner 26. Brunch Oasis 27. Brunch Junction 28. The Brunch Clubhouse 29. Sunlit Spread Café 30. Morning Breeze Bistro

Modern restaurants are defined by their sleek decor and menus that wow diners with innovative options. They increasingly focus on local food and sustainability, too.
1. Urban Palette Eats 2. Metropolis Munchery 3. Modernity Bites 4. Chic & Eats 5. Vibe Valley Eatery 6. Fusion Flux Café 7. Nova Bistro Lounge 8. Trendy Tabletop 9. Echo Eats 10. Zenith Zone Café 11. Savor Sphere 12. Retro Remix Diner 13. Avant Grub 14. Urban Utopia Eats 15. Fusion Foundry
16. Pixel Plate Bistro 17. Pulse Point Eatery 18. Artisan Alley Café 19. The Mod Mix Diner 20. Metro Manifesto 21. Flavor Fusion X 22. Chic & Savory Eats 23. Urban Elegance Eateries 24. Modish 25. The Trend Tavern 26. Urbanite Eatscape 27. Fluxus Bistro 28. ModMotion Café 29. Metro Mingle Bistro 30. Tres Forma Eatery
1. Enchanted Eats Emporium 2. Mystic Morsels Tavern 3. Dragon's Delight Diner 4. Fairyland Feasts 5. Unicorn Utopia Café 6. Sorcerer's Supper Spot 7. Celestial Cuisine Castle 8. Elf & Elemental Eatery 9. Enigma Eats Emporium 10. Phoenix Flame Bistro 11. Mage's Menu Manor 12. Mythical Munchery 13. Mermaid's Galley 14. Fabled Fare Feasts 15. Wizardry & Wonders Diner
16. Griffin's Gourmet Guild 17. Seraphic Supper Spot 18. Fey Feasthouse 19. Astral Aura Eateries 20. Chrono Culinary Cove 21. Arcane Appetites Café 22. Cosmic Creatures Café 23. Elven Enclave Eats 24. Enchanted Grove Grub 25. Dreamer's Dining Den 26. Enigma Elixirs Eatery 27. Wyvern's Wok 28. Faerie Fusions 29. Valkyrie's Vanguard Venue 30. Cosmic Concoctions Castle
1. Rise & Dine Café 2. Morning Glory Griddle 3. Breakfast Boulevard 4. Sunshine Café & Grub 5. Early Riser Eateries 6. Crispy Mornings Café 7. Flapjack Palace 8. Sunny Side Spot 9. Morning Bites Buffet 10. Early Bird Eats
11. The Breakfast Clubhouse 12. Rise ’n’ Shine Café 13. Daybreak Diner Delights 14. Sunrise Serenade Café 15. Crave & Savor Breakfast 16. Golden Morning Griddle 17. Pancake Paradise 18. Morning Morsels Café 19. Fresh Start Eateries 20. A.M. Delights Diner
Did you find some cool restaurant names?
We provided lists of names you might like for your own restaurant. The restaurant’s concept will play a heavy role in how you name your business. A name that will work for a coffee shop won’t work for an elegant restaurant.
Take the time to think about what type of restaurant business you’ll start, then come up with a list of your top names for restaurants. Once you’ve settled on good names of restaurants, check that they are available as a web domain, social media profiles, and as business names.
Did this blog help you think of cool names for your business?
How to Start a $2M/Year Remote Cleaning Business
Have you ever wondered how to start a cleaning company? Cleaning businesses are some of the easiest businesses to start, but some people would prefer to just manage the business, not do the actual cleaning. Here, we explain how to start a remote house cleaning business without needing to do any cleaning yourself.
We talked to Neel Parekh, who started MaidThis in 2013. He built his remote cleaning concept into a company that makes over $166K per month and offers franchises to help small business owners do the same. The best part? He did this while traveling for 5+ years and to over 50 countries.
We’ll share his story about how to start a remote cleaning company, plus tons of great marketing tips and systems advice.
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"]
You’ll learn everything you need to know about starting a remote service business, including:
What is a remote cleaning business?
What businesses can be remote, how to start a remote cleaning business, remote businesses faq.
- Start your own remote business [/su_note]
Get ready to learn how to start a remote cleaning business.
A remote cleaning business is a cleaning company where the owner performs marketing, human resources, and administrative functions of the business from anywhere in the world while outsourcing or hiring local workers to perform the cleaning for customers.
Effectively, you’ll start a cleaning business without cleaning.
Three criteria have to be met for any business to be run remotely:
- The staff have to go to a service location. For example, gyms won’t work, but cleaning companies do.
- The small business should have low overhead. You can’t hold a lot of supplies or inventory.
- Management tasks need to be done remotely.
Neel told us:
[su_quote] This makes service businesses ideal for remote jobs.[/su_quote]
Check out our interview with Neel to learn about remote business success stories.
He has a special offer for UpFlip members to get $6,000 in credit when they start a MaidThis franchise .
Keep reading to get great remote business ideas.
Remote business ideas
Remote businesses normally fall into two categories:
- Online businesses
- Local service businesses
Best online business ideas

A successful online business can be created using online business ideas like an:
- Online store: Sell online using dropshipping or Fulfillment by Amazon to make money from people who are online shopping.
- Podcast: Talk about subjects that interest you and earn a living from ads and sponsorships with this online business idea. Learn more about podcasting .
- YouTube creator: Learn how to start an online business by creating YouTube videos .
- Online tutoring business: Start your own online tutoring business or use a tutoring and test prep platform like TutorMe , Skooli , or Wyzant .
- Freelancing: Most freelancers work remotely using platforms like Fiverr and Upwork.
- Online courses: Course creation is a great option for remote businesses because you create the course and can consult from anywhere in the world.
In addition to a remote cleaning business, you might consider other popular remote businesses like eCommerce, human resources, and accounting.
Check out our blog about online businesses for more remote business ideas.
Local service businesses can be remote businesses
You can use Neel’s strategies for service businesses like:
- Cleaning : Neel chose a cleaning business because it is the easiest of the service businesses to apply his techniques. There’s a large pool of qualified employees and lots of places that need cleaning. Plus, everyone has the supplies they need.
- Locksmith: Most of the parts in locks are interchangeable, which means these same strategies could be applied to create a remote locksmith business.
- Painting : A small business painting homes and businesses could be run remotely. You might need AI that pulls up the design documents and calculates the total square feet that need painting, but it can also be calculated using other means.
- Pressure washing : The challenge with pressure washing may be the equipment. You would probably want your remote business to focus on providing referrals to other businesses to remove this challenge.
- HVAC : Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning companies can provide services like preventive maintenance, fan repairs, and filter changes without needing a lot of inventory. You’ll probably want a referral partner for larger fixes, though.
Learn about other service business ideas .

Starting remote businesses is all about creating systems that make it easier for you to run your own business from anywhere in the world. The process of starting a remote cleaning business will include:
- Perform market research.
- Write a business plan.
- Create a website and CRM.
- Set up a payment processor.
- Create your business structure.
- Get remote cleaning business insurance.
- Create cleaning contracts.
- Find cleaners.
- Market your remote business.
[su_quote]I didn’t have a mentor, so I was scared to quit my day job when I hit my freedom number. I cushioned my bank account and wish I had just dove in faster.[/su_quote]
Keep reading for more information about creating a remote business model.
Perform market research
There are plenty of people who have business ideas but never turn them into a profitable business. Your chances of success are much higher if you research what other businesses in the industry do and where there are gaps in the industry.
A remote cleaning business might want to use social media and Google to find locations that have higher population-to-cleaning business ratios.
In our research about the best small-town businesses , we found that locations with more than 416 people per cleaning business tend to be the best places to open a cleaning company.
You also want to understand what marketing strategy, pricing, and services competitors offer. Learn more about market research .
Write a business plan

Every successful business idea needs a business plan. Given we’re talking about a business model that can be run from anywhere in the world, you need to focus on systems.
You’ll want to include the answers to questions like:
What is the cost of starting a remote cleaning business?
Neel told us a remote cleaning business has low startup costs.
[su_quote]I probably spent under $1,000. You just need internet connection, a WordPress website, and a computer. You can grow from there.[/su_quote]
Pro Tip: If you want to grow faster, consider joining a system where a lot of the work is already done for you, like MaidThis Franchise .
What systems do I need for a fully remote business?

You’ll need some systems to run a successful remote business including a(n):
- 24/7 remote call service or VoIP provider (Neel uses DialPad)
- SMS + email automation system (at UpFlip we use MailChimp )
- Online booking system like Launch27 or Booking Koala
- Human resources for your remote business
[su_quote]Basically anything you don’t want to do, or don’t know how to, outsource it.[/su_quote]
You might need translation services if your internet business idea involves providing services in a foreign country or contracting or hiring cleaners whose first language is different than yours.
The best thing about a MaidThis franchise is that they provide aspiring entrepreneurs with everything they need to run a fully remote business.
Create a website and CRM
You’ll need a website and customer relationship management system to operate any remote business. Neel told us:
[su_quote]Just get a $100 WordPress template and then build from there when you first start.[/su_quote]

At a minimum, your remote cleaning business website will need to include:
- Booking page
- Services page (include pricing)
- About us page
- Locations page
Check out the MaidThis website for more information on how they approach each of these.
Website building resources
Some useful resources for building a remote cleaning business website include:
- GoDaddy: Get website hosting, domain names, and email marketing automation through GoDaddy .
- NameCheap: Get domains, email accounts, WordPress hosting, and other services from NameCheap .
- Build a website: Learn how to build a website .
- Creating a brand: Get tips on building a brand .
Your customer relationship management system is a database and interface that helps you easily manage everything going on with your company. Each CRM works slightly differently, but you’ll need a CRM that either includes or connects to your:
- Online booking system
- Call support system
- SMS and email marketing systems
- Payroll and accounting system
- Dispatch system
- Invoicing and payment processing
Many systems include easy integrations with commonly used providers.
CRM resources
- GBG Marketing: Neel and his franchise use a CRM created by GBG Marketing that automates follow-ups and puts booking on autopilot.
- Housecall Pro: Simplify your workflows and grow your business with the easiest-to-use CRM. Get a 14-day trial from Housecall Pro.
- monday.com: One of the most commonly used CRM and project management tools is monday.com . Check out our monday.com review .
- Jobber: This CRM focuses on making service businesses easier to run. It’s fairly intuitive to use. Check out Jobber .
- ClickUp : We use ClickUp at UpFlip. It’s a great system that lets you monitor and control your workflows at a reasonable cost.
- HubSpot: HubSpot is one of the most amazing programs I have ever seen, but the coolest features are complex. Compare HubSpot’s pricing options . I’d suggest starting with the Starter CRM.
Any of these should provide the functionality you need, but each works differently, so check out the demos to decide which you like best.
Set up a payment processor

You’ll need a payment processor to charge your cleaning customers and pay cleaners. Most businesses use Stripe because it is easy to use and integrations are normally built into other software.
Payment processors normally charge a fee based on the value of the transaction PLUS a per-transaction fee. In addition, they may also charge a monthly fee.
You might also consider options like:
- Stax by Fattmerchant
View the table below for a quick overview of the differences between each.
As you can see, there are some details that make it harder to compare payment processors than some other systems, but in most scenarios, Helcim will save you money.
If the vast majority of your payments are in-person Visa payments and your transactions amount to almost exactly $250K or $500K per year, you may be able to save even more with Stax tiered plans.
Pro Tip: One money-saving trick is to make sure that your online business uses technologies to qualify for lower “card-present” fees.
Make your online cleaning business legal
You’ll need to create a business structure, get any business licenses you need, and get a business bank account to run a remote business idea legally. Let’s look at how to accomplish each of these.
Choose a business structure

Small business ideas can make up to $600 before you need to start reporting the income on your taxes. Most business owners start a Limited Liability Company (LLC) and file taxes as an S-Corp.
First, you’ll need to check the USPTO and the Secretary of State website in the location you want to register to make sure the name for your remote business is available. If the name is available, apply for an Employer Identification Number (EIN) and save it somewhere safe.
Then apply for an LLC on your Secretary of State website. We walk you through an example of what the application looks like in this blog .
Next you’ll need to fill out Form 8832 and Form 2553 with the IRS to opt into the S-Corp tax structure, which provides benefits to LLCs like:
- Potentially reduced taxes
- No double taxation
- Wages paid to owners
- Dividends paid with profits
There are plenty of other business structures for online business ideas, but this is one of the best.
Get business licenses and permits for your remote business
You will probably need business licenses in the location(s) where you operate your remote business. This could include tax permits, local business licenses, and other requirements.
Make sure to check with your local authorities or a business law attorney to ensure you comply with all local laws. Each location is different, so you may need someone who has familiarity with multiple locations or specializes in helping unique online businesses.
Don’t forget a business bank account
You’ll need a business bank account to make your remote business easier to manage. In addition, a business bank account protects the limited liability status of a company because it keeps personal and business finances separate.
There are many available business bank accounts, and which one you choose will depend on your small business needs and structure. At the time of writing, I recommend Live Oak Bank because it
- Uses IntraFi Cash Service to provide FDIC insurance up to $10 million
- Was the 2022 leader in SBA loans
- Offers 4.0% interest on its savings accounts
Learn more about opening a business bank account .
Get remote cleaning business insurance

You’ll need small business insurance coverage in case anything goes wrong on the job. You’ll want to consider getting a Business Owners Policy (BOP) that covers:
- General Liability Insurance: Covers liability claims and lawsuits
- Commercial Property Insurance: Protects buildings, inventory, and equipment
- Additional Riders: Covers other business scenarios like shutdowns, errors and omissions (E&O), workers’ compensation, and commercial automobile insurance
Check out Simply Business to get quotes from 16 of America’s best business insurance companies.
Create cleaning contracts
You’ll need to have some contracts prepared before you hire cleaners to work for your remote cleaning business. You’ll need an employment agreement that covers:
- The relationship between your company and the cleaner
- Noncompete terms
Payment structure
- Property damages
Let’s look at each of these in more detail to help you understand how to manage employee or contractor relationships.
Company and cleaner relationship

You’ll want to define whether the cleaners you hire are employees or subcontractors. Many remote businesses will consider all people who work with them as subcontractors, but you have to be careful.
Cristobal Mondragon classified all his employees as independent contractors and that resulted in a hefty fine.
Ultimately, your remote house cleaning business is a digital marketing business that provides cleaners. That means the maids and housekeepers count as independent contractors, but the IRS suggests requesting a ruling for positions you routinely need to fill to verify if the workers are actually employees or subcontractors.
Try out our cleaning business course Want to get all the templates, workflows, and systems that Chris uses to make $5,800 per day? Check out our free cleaning business course !
Noncompete term
A remote cleaning business start-up will probably want noncompete clauses when they hire employees or subcontractors. Remote working may need terms like:
“The subcontractor/employee agrees that all clients are clients of [Company Name]. Performing any work for the clients except through [Company Name] is a violation of the services agreement and will result in the termination of the contract and pursuit of loss income at the rate of $[Amount].”
The paragraph above is just an example. Consult with an attorney or human resource specialist to get a noncompete agreement that is legal in each location where your business operates.

You’ll want to specify how you will pay your cleaning people. Many business owners find that pay-for-performance is the best business model to align unique online business ideas with the employees’ interests. This payment model may mean paying them:
- A percentage of each job
- Incentives for performing certain tasks
[su_quote]I pay my cleaners $25 for each person who provides a review after they cleaned their house. This encourages them to ask for reviews and helps us build faster business growth.[/su_quote]
Property damage
Your virtual business should add terms that protect against items broken or otherwise damaged by your employees. These terms may require subcontractors to carry small business insurance or specify that employees may be responsible for the cost of the replacement up to a certain amount.
Make sure to get legal advice to establish what is legal in the locations you serve.
In addition, you’ll need cleaning contracts for your clients. Many residential home cleaners do not use contracts, but Airbnb cleaners may.
Find cleaners

Neel explained how he finds remote employees:
[su_quote] I’m looking for three main things when hiring people:
- Good reliability
- Good communication
- Good attitude[/su_quote]
He went on to explain that Facebook Marketplace and Craigslist are great places to find employees without spending a lot on hiring. Once you have eligible candidates, Neel told us:
[su_quote]We use an automated five-step recruiting process. That includes:
- Initial screening call that asks questions like do they have business insurance and licenses.
- Then we conduct a second Zoom call to see if they show up and how they interact.
- Send them on a test job.
- Officially onboard.
- Monitor what they do.[/su_quote]
One of the benefits of buying a MaidThis franchise is you get to skip a lot of the mistakes most people experience as they learn how to build a remote cleaning business.
In addition to all the other support and resources, you’ll get access to MaidThis’s detailed standard operating procedures, which are over 1,000 pages long. Find out why in the video below.
Conduct background checks
In-person businesses like cleaning companies rely on customer service from remote teams. You’ll want to make sure every in-person worker has a clean background. That means you’ll need to conduct a background check.
You can consider companies like
- Crtain: Crtain is used by Tesla, Shopify, and Deloitte to get up to 80% faster criminal background checks.
- Checkr: One of the biggest background check companies but sometimes the checks take too long. Issues normally arise when people have criminal backgrounds or have lived in multiple jurisdictions in the last seven years.
UpFlip Cautionary Tale
I have a lot of experience with Checkr background checks because they were run on me for multiple employers. I used to move approximately once per year to go experience new places.
My background checks would ALWAYS take at least a week because they had to check seven jurisdictions. Meanwhile, my significant other’s background checks almost always come back instantaneously.
The other scenario that commonly holds up background checks is criminal charges that don’t necessarily convert easily from one state to another. For instance, Nevada gross misdemeanors are often considered felonies because other states don’t have gross misdemeanors, and they are only available as plea bargains in Nevada.
If you need someone fast, ask screening questions like:
- How many locations have you lived in the last seven years?
- Have you ever been charged with a felony?
These two questions will let you know if screening the applicant will take longer than normal.
Fill out HR paperwork

You’ll need to provide new hire paperwork before managing remote employees in the U.S.
- W-4 Form: This document lets you know how much to deduct for taxes. States that have income tax will also require a state form.
- I-9 Form: This is a proof of identity form that is required to work in the U.S.
- Offer of Employment: This document details exactly what you are offering the new hire.
- Employment Contract: This document details the terms of the employment and goes into more detail than the original offer.
- Emergency Contact Info: You’ll need this document to contact the next of kin if your employee is injured, gets sick, or dies on the job.
- Employee Handbook: Let the employee know what is expected of them, including values, policies, dress codes or uniforms, and other behavior. You need a page for them to sign to document receipt of and agreement with the handbook.
- Payroll and Benefits: Documents like a direct deposit form and any other benefit forms the company offers.
Remote work in other countries may have different requirements. When working remotely, always consult with someone familiar with the laws in the country where the remote team works. Learn more about hiring .
Hiring resources
Some resources that you can use for hiring include:
- Trello: Neel uses Trello to manage the onboarding of remote employees.
- QuickBooks Payroll: Handle your payroll and accounting with QuickBooks .
Market your cleaning business

A remote cleaning business will need to use a combination of digital marketing and “boots-on-the-ground” marketing.
Neel loves talking about marketing. He gave us input on how much you should spend to get unique online business ideas to start making money.
How much is the marketing budget for a startup?
To most effectively start a great online business idea, you’ll want to spend 15 to 20% of your desired revenue on a combination of digital and print marketing. Neel told us:
[su_quote]We spend about 5% of revenue on marketing. When you first start, I recommend 15 to 20% of your spending on marketing because once you get a client, it’s pretty easy to keep them.[/su_quote]
As your marketing strategy helps you reach your desired revenue, you can reduce your marketing to maintain revenue and increase profits.
How to offer remote cleaning services

The best business ideas can fall flat if you don’t market them right and find the right clients. You’ll want to use digital marketing skills like:
- Social media
- Search engine optimization
Neel explained how to start a remote house cleaning company and get ahead of the competition fast.
[su_quote]If you answer the call, we close 60% of requests, but if we don’t answer, we only close 16%. So we use a call agency and an automated text messaging system to follow up if we miss the call.[/su_quote]
MaidThis also uses an online booking system to provide potential clients another booking option.
In addition, any time they clean a home, they’ll send postcards to the five houses on either side of it. Neel told us:
[su_quote]If someone in a neighborhood is our client, their neighbors are probably our target audience.[/su_quote]
Neel explained what to include in your calls:
[su_quote]When someone calls, we ask them something like, ‘Do you want weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly cleanings?’ Note we don’t offer them a one-time cleaning.[/su_quote]
Neel also uses automated marketing tools and funnels to help book customers more regularly.
[su_quote] When a client hasn’t requested their home cleaned recently, they’ll send an automated text message. They even have a one-click brownie-sending service (yes, he sends baked goods) to help encourage return customers.[/su_quote]
How to get reviews
Customer reviews are crucial to work remotely. You’ll want to provide great customer service. Then you want to encourage the cleaner to ask for a review because in-person meetings tend to create a better relationship than remote interactions. Neel told us:
[su_quote]Make sure your cleaners ask for reviews because the customer is more likely to review when they ask. We give the cleaners a $25 bonus for every review they get.[/su_quote]
Neel went on to explain:
[su_quote]After each cleaning, we’ll request an automated review that takes about 10 seconds for the customer to review us.[/su_quote]
You can also minimize bad reviews in the business world. Neel shared his secret:
[su_quote]When you get a bad review, call them and offer to send someone over for a complimentary recleaning.[/su_quote]
Useful marketing tools

There are some useful marketing tools that small business owners use to market their companies:
- Canva: Simplify graphic design with Canva . Get access to thousands of templates for website and social media for as low as $4.99 per month.
- SurferSEO: Write blog content faster and rank higher on search engines with SurferSEO .
- MailChimp: Email and SMS marketing automation is one of the keys to success that many small business owners mention. Get started with Mailchimp .
Next we’ll discuss some of the frequently asked questions about remote businesses.
Still considering whether a remote cleaning business is for you? We’ll answer some of the commonly asked questions about companies that work remotely including:
What companies are fully remote?
What is a remote-first company, benefits of remote work for companies, reasons not to allow work from home.

There are plenty of companies that are fully remote, but some of the best small business ideas that you can operate from your own home (or anywhere in the world, like Neel does) include:
- Consulting services: You can be your own boss and advise people on your area of expertise as a business consultant.
- Social media management: Manage other companies’ social media accounts using online communication tools to manage multiple platforms at once.
- Online courses: Online courses can make millions and can approach 90% profits without the need for a physical office.
- Affiliate marketing business: Working as an affiliate marketer is another opportunity to create pieces of content once and let them make you money forever.
- eCommerce business: An eCommerce site that sells print-on-demand products can be a fully remote business.
- Web development: Creating websites or app development is another great remote business.
- Graphic design: Designing digital and print materials for companies doesn’t require being in their physical offices. Just grab a computer and get started.
- Virtual event planning: Start your own business as an event planner. You’ll be working remotely most of the time. When you plan virtual events, it’s 100% remote work.
- Virtual assistant business: A virtual assistant helps business professionals with work that is time-consuming and has to be done but doesn’t create much business value. You can be a virtual assistant with 100% remote work from your own home.
“Remote-first” companies prioritize remote work over in-person jobs. These companies are often similar to fully remote businesses, but they still maintain an office for when people need to get together to achieve their organizational goals.

Whether you run online store ideas or want to start a remote business sanitizing company, there are benefits to remote work for many business owners, companies, and remote employees , including:
- Global talent pool
- Lower costs
- Happier employees
- Freedom to work when and where you want
- Potential efficiency gains
- Lower turnover
- Healthier workforce
- Green initiative compliance
There are also many reasons why you might not want to run a remote business.
There are numerous reasons why companies might not want to allow remote work, including:
- Potential efficiency loss
- Harder to schedule meetings
- Buildings and office furniture are being paid for but not utilized
- Inability to monitor employee behavior
- Difficult to share knowledge
- Harder to build corporate culture
- Lack of control
- Collaboration may suffer
- May cause employee isolation issues
- Difficult to hire efficiently
- Some people work better in person
- Cyber security issues
Where can I learn more about Neel and MaidThis?
You can learn more about Neel and MaidThis on the following sites:
- Neel’s Podcast: The Remote Local
- MaidThis Franchise: Apply to Be a Franchisee
Start your own remote business
We’ve explained how to start a remote cleaning company, shared other online business ideas that can be run remotely, and provided advice from a highly successful business owner about how to start a cleaning business without cleaning.
Now it’s up to you. Will you put in the time and energy it takes to create the systems you need to build a business you can run from anywhere in the world?
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
Become a business owner in less than 90 days
Start your 10-day free trial of the UpFlip Academy and learn how to start your own business from scratch.
Get business advice straight to your Inbox

Download Free Business Plan Examples
Download a free business plan in pdf or word doc format to make writing a plan fast and easy, find your sample plan.
Discover the sample plan that best fits your business. Search our gallery of over 550 sample business plans and find the one that's right for you.
View the Gallery

What You'll Get:
A complete business plan Unlike other blank templates, our business plan examples are complete business plans with all of the text and financial forecasts already filled out. Edit the text to make the plan your own and save hundreds of hours.
A professional business plan template All 550 of our business plans are in the SBA-approved format that’s proven to raise money from lenders and investors.
Instructions and help at every step Get help with clear, simple instructions for each section of the business plan. No business experience necessary.
A Word doc you can edit We don’t just have PDF documents that make editing a challenge. Each plan is available in Word format so you can start editing your business plan example right away.
Key Sections Included in our Example Business Plans:
Executive Summary : A quick overview of your plan and entices investors to read more of your plan.
Company : Describes the ownership and history of your business.
Products and Services : Reviews what you sell and what you’re offering your customers.
Market Analysis : Describes your customers and the size of your target market.
Strategy and Implementation : Provides the details of how you plan on building the business.
Management Team : An overview of the people behind the business and why they’re the right team to make the business a success.
Financial Plan : A complete set of forecasts including a Profit and Loss Statement, Cash Flow Statement, and Balance Sheet.
Looking for a sample business plan PDF? You can download a few PDF examples below:
- Accounting and Bookkeeping Sample Business Plan PDF
- Agriculture Farm Sample Business Plan PDF
- Cleaning Service Sample Business Plan PDF

Need a faster way to write your business plan? LivePlan is the #1 planning tool for over 1 million businesses.

Your download should begin immediately
If your download doesn't begin after 5 seconds, please click here .
View our entire gallery of free downloads
Tweet about it
I just downloaded a free business plan from Bplans.com!#smb #startup
Recommended Articles

Recommended Download

You might also enjoy:

The Small Business Toolkit
Access a free list of must–have resources for new and growing businesses in any industry.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

School Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

School Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their schools.
If you’re unfamiliar with creating a school business plan, you may think creating one will be a time-consuming and frustrating process. For most entrepreneurs it is, but for you, it won’t be since we’re here to help. We have the experience, resources, and knowledge to help you create a great business plan.
In this article, you will learn some background information on why business planning is important. Then, you will learn how to write a school business plan step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a School Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your school as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategies for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a School
If you’re looking to start a school or grow your existing school, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your school to improve your chances of success. Your school business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Schools
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for schools are donations and gifts, tuition, personal savings, credit cards, bank loans, and angel investors. When it comes to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to ensure that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for schools.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a school.
If you want to start a school or expand your current one, you need a business plan. The guide below details the necessary information for how to write each essential component of your school business plan.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the kind of school you are running and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a school that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of schools?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan.
- Give a brief overview of the school industry.
- Discuss the type of school you are operating.
- Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers.
- Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team.
- Offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Overview
In your company overview, you will detail the type of school you are operating.
For example, you might specialize in one of the following types of schools:
- Private K-12 school : this type of school typically charges tuition, and may be affiliated with a religious organization, or specialize in a particular learning method.
- Charter school: this type of school offers primary or secondary education for a tuition, and may receive some public funding, and/or donations. These schools require their students to take state-mandated exams.
- Special subject school: this type of school specializes in teaching a specific subject, such as driving, first-aid, self-defense, fine arts, language, or general tutoring.
- Preschool: this type of school typically serves children who are aged 3 and 4. These schools prepare young children to enter formal education, and are funded by some combination of tuition, donations, and government grants.
In addition to explaining the type of school you will operate, the company overview needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of students served, the number of students accepted into elite formal education institutions, etc.
- Your legal business Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the school industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the school industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your marketing strategy, particularly if your analysis identifies market trends.
The third reason is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your school business plan:
- How big is the school industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential target market for your school? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your school business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: families with elementary-aged children, families with high-school-aged children, families with preschool children.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of school you operate. Clearly, families with high schoolers would respond to different marketing promotions than families with preschoolers, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the potential customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can recognize and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your School Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other schools.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t directly competing with your product or service. This includes public schools, virtual schools, and families who do homeschooling. You need to mention such competition as well.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their business and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as
- What types of students do they serve?
- What type of school are they?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide specialized instruction, either in subject or in method?
- Will you offer courses or services that your competition doesn’t?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a school business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of school that you documented in your company overview. Then, detail the specific products or services you will be offering. For example, will you provide religious-focused K-8 education, college preparatory courses, or single-subject instruction like driving or fine arts?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your plan, you are presenting the courses and/or extracurricular activities you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the site of your school. Document where your company is situated and mention how the site will impact your success. For example, is your school located in a growing neighborhood, in the city center, or will you operate purely online? Discuss how your site might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your school marketing plan is where you will document how you will drive potential customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertise in local papers, radio stations and/or magazines
- Reach out to websites
- Distribute flyers
- Engage in email marketing
- Advertise on social media platforms
- Improve the SEO (search engine optimization) on your website for targeted keywords
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your school, including answering calls, planning and delivering instruction, applying for grants, fundraising, performing administrative tasks, overseeing instructors, handling discipline, scheduling and monitoring extracurricular activities, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to enroll your Xth student, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your school to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your school’s potential to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing schools. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act as mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in running a school or experience with public school administration or who has served on a public school board.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenue and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you enroll 100 or 1,000 students per semester, and/or offer extracurricular activities? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your school, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a lender writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and ensure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
When creating your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a school:
- Cost of equipment and supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Other start-up expenses (if you’re a new business) like legal expenses, permits, computer software, and equipment
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your school location lease or a list of elective courses or extracurricular activities you will offer.
Writing a business plan for your school is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will understand the school industry, your competition, and your customers. You will develop a marketing strategy and will understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful school.
School Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my school business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily write your school business plan.
How Do You Start a School?
Starting a school is easy with these 14 steps:
- Choose the Name for Your School
- Create Your School Business Plan
- Choose the Legal Structure for Your School
- Secure Startup Funding for Your School (If Needed)
- Secure a Location for Your Business
- Register Your School with the IRS
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Get the Required Business Licenses and Permits
- Get Business Insurance for Your School
- Buy or Lease the Right School Equipment
- Develop Your School Business Marketing Materials
- Purchase and Setup the Software Needed to Run Your School
- Open for Business
Learn more about how to start your own school .
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your School business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to learn about Growthink’s business plan writing services .
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Start with a cogent and concise one sentence statement of the business idea. A sentence that is so clear and appealing that the reader can immediately visualise or 'see' the business. You can then go on to describe: The market at which you are aiming. The specific benefits offered by your product or service.
Objectives. The primary objectives of the business plan for Cooper's Cup are below: To increase revenues by $36,000 or 5% in Year 2 and $73,000 or 10% by Year 3. Achieve a profit margin of 5.2% in Year 2 and 6.90% by Year 3. Be the Cafe of Choice in the Phoenix area and the recipient of the Best Coffeehouse Award.
Chapter 1 - Developing a Business Plan. Chapter 2 - Essential Initial Research. Chapter 3 - Business Models. Chapter 4 - Initial Business Plan Draft. Chapter 5 - Making the Business Plan Realistic. Chapter 6 - Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur. Chapter 7 - Finishing the Business Plan.
4. As the class comes back, the teacher writes the words "Business Plan" on the board, and asks the class what they think needs to be included in a business plan. (5 min) 5. From there the teacher will pass out copies of the first part of a transcript from the article How Entrepreneurs Can Create Effective Business Plans. The interview was
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Lean Business Plan Template PDF. This scannable business plan template allows you to easily identify the most important elements of your plan. Use this template to outline key details pertaining to your business and industry, product or service offerings, target customer segments (and channels to reach them), and to identify sources of revenue.
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students is here to guide you every step of the way! With this template, you can: Clearly define your business goals and strategies for success. Create a comprehensive financial plan and projections to attract investors. Identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans.
Create a plan that fits their needs. Whether small or big, LivePlan can build out the right-sized business plan for your classroom projects. In LivePlan, students can develop a simple lean plan that focuses their ideas, or create a full business plan with all the details and steps necessary to persuade investors, attract partners, and turn their idea into a profitable reality.
If you're a university student looking to start your own business venture, using the Business Plan Template in ClickUp can help you get started. Follow these four steps to create a comprehensive business plan: 1. Define your business concept. Begin by clearly defining your business concept.
a business plan is. Now ask why they think it's important for an entrepreneur to write a business plan, and have them work as a class to brainstorm ideas for the components they think would be important to include in one. 2 Explain to students that effective business plans must have these components: • Business description (an explanation
Write the Executive Summary. This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what's in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company. Add a Company Overview. Document the larger company mission and vision.
Download the Sample Business Plan for Kids Business Plan for Kids Teach your students how to write their own business plan and create a successful business. Download the Sample Business Plan for Kids More Business Planning Resources The 4 p's … → read more
Here's my full review of the Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox. 4. Home Sweet Road's My Business Plan. Check out this business plan for kids, which asks kids questions like what makes their idea unique, whether or not their idea is a product or service, and who their customers will be. 5.
Creating a business plan as a student can be a daunting task, but with the help of ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you can break it down into manageable steps. Follow these six steps to create a comprehensive business plan that sets you up for success: 1. Define your business idea. Start by clearly defining your business idea.
8. Write up your financial forecast. This is one of the trickier parts of writing a business plan and requires a good understanding of business finance and accounting. If your business has been trading for a while, you'll want to start off by outlining some historical data, such as sales and gross margin.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
This Business Plan Template from is one of many free downloads available at Bplans.com This template is a simplified business plan outline. It's a good way to get started, but as you know, you can't just type in your details, print it, and turn it in to the bank. Every business is unique, and your business plan should reflect that.
A business plan is a written document that clearly defines the goals of a startup or existing business and outlines specific methods for achieving these goals. An effective business plan acts as the management and financial blueprint for developing and growing your business. Your business plan needs to detail how your business will be ...
For further information, contact the Southeastern MA SBDC office at (508) 673 -9783.". 1. BUSINESS PLAN GUIDE. The following format has been designed to give the business planner a brief list of some of the questions one must address before beginning to write each part of the plan.
A complete business plan Unlike other blank templates, our business plan examples are complete business plans with all of the text and financial forecasts already filled out. Edit the text to make the plan your own and save hundreds of hours. A professional business plan template All 550 of our business plans are in the SBA-approved format that ...
Marketing Plan. Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a school business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of school that you documented in your company overview.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out ...