We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Human Resources 6 Steps to Create a Strategic HR Plan [With Templates]

6 Steps to Create a Strategic HR Plan [With Templates]
Written by: Jessie Strongitharm Aug 25, 2022

The backbone of any successful business is the people and processes behind it — that’s why creating a human resources (HR) plan is key. This strategic document drives your business forward by evaluating where your workforce is at, and comparing it to future needs.
Without an HR plan, organizations can suffer from issues that would have otherwise been avoided. From productivity pitfalls to costly employee turnover, there’s no shortage of risks you can sidestep if you do human resource planning in advance.
Not sure where to start? No worries. I’ve outlined six steps you can take to create an effective HR plan that ensures your organization is well-staffed and well-served. You’ll also find a variety of HR templates that you can customize in just a few clicks — no design expertise required.
Click to jump ahead:
What is human resource planning?
- Assess employees’ current skill levels
- Forecast your labor needs based on available information
- Revisit your organizational design
- Outline how you will manage, motivate and retain talent
- Align your workforce planning with your budget
- Establish KPIs for your human resource planning objectives
Human resource planning is the process of considering the current and future “people needs” of an organization.
This involves evaluating an organization’s workforce structure and protocols to ensure operational goals are met, productivity stays high and future demands for labor and talent can be fulfilled.
The result of this process is the creation of an HR plan, which typically takes the form of a written document sometimes autogenerated using HR software . These documents tend to follow a similar structure to most strategic business plans and are created on an annual basis, by HR managers or company leaders.
Check out the template below for an example.
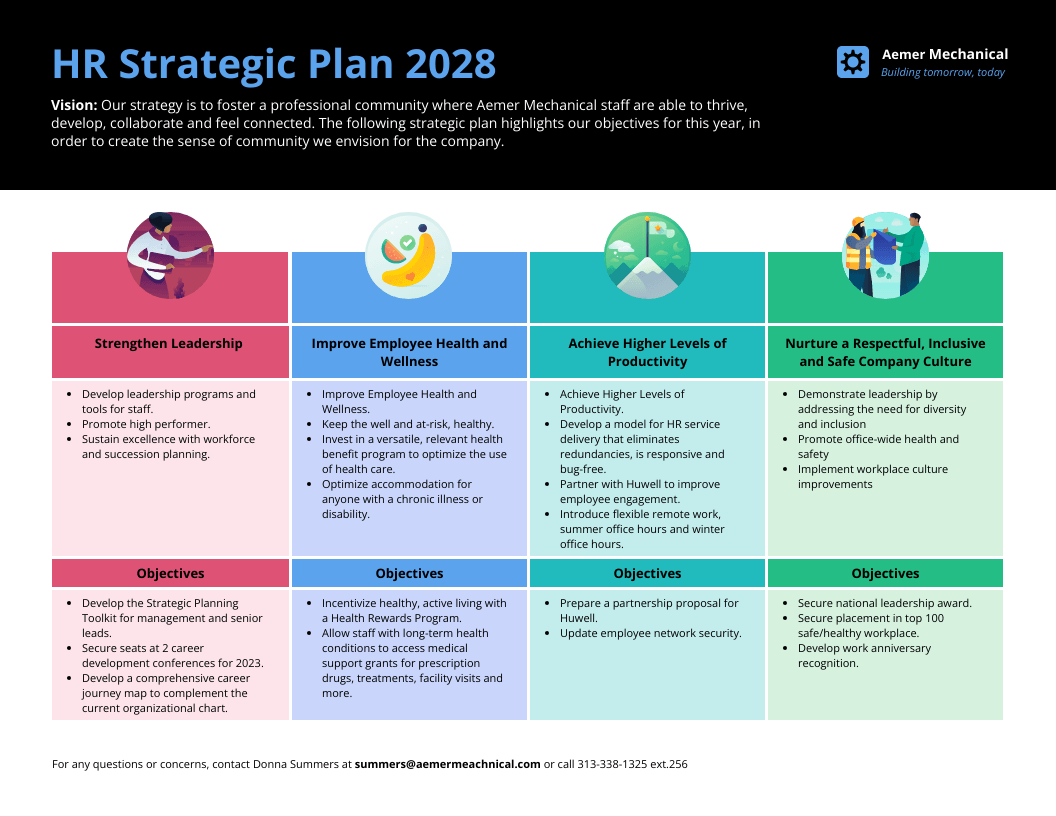
This eye-catching, one-page HR Strategic Plan Template offers a concise summary of your human resource planning efforts, so you can easily share info with colleagues.
Just swap out the text and visual assets for those of your choosing in Venngage’s editor , and you’re off to the races.
6 steps to create a strategic HR plan
Ready to create a strategic plan for the human resources that power your business? Here are six steps to help you succeed at the human resource planning process.
1. Assess current employees’ skill levels
The first step to creating a future-forward HR plan is to assess employees’ current skill sets, and compare them to your operational needs moving forward. This will help you identify gaps and inform any hiring of new employees.
Employees’ skill levels can be assessed by reviewing their work history, hard and soft skills and professional growth over time.
Using a matrix is a great way to understand where the skill gaps in your current workforce exist. Below is an example that describes the skills needed for different marketing roles.
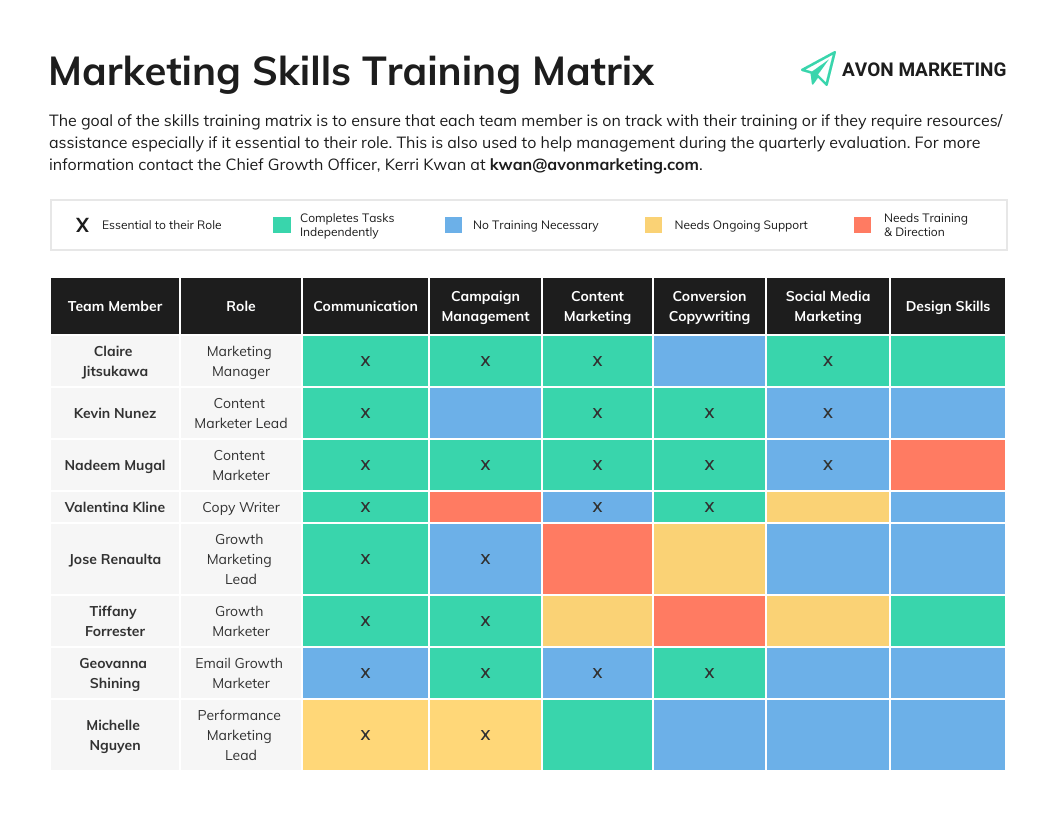
Don’t need it for marketing specifically? No worries — you can fully customize this template by swapping in your own text to examine any human resource gaps.
Another way to assess skills is by giving employees a questionnaire they can fill out. This Employee Competency Assessment Template does just that.

Based on the information collected, you’ll get a sense of what positions best suit each individual, and whether any upskilling or hiring is required.
2. Forecast your labor needs based on available information
Next in your strategic strategic HR management plan, you’ll want to consider the future. This involves accounting for any upcoming changes to your workforce, so operations can continue without error.
When forecasting labor needs, the following should be considered:
- Planned promotions
- Upcoming retirements
- Layoffs
- Personnel transfers
- Extended leaves of absence (i.e. maternity/paternity leave)
Beyond those, it’s a good idea to assess the impact of external conditions on your labor needs during your human resource planning. For example, new technological developments may decrease the amount of employees you require to operate your business.
3. Revisit your organizational design
Organizational design is the process of structuring the way a business operates so it can best achieve its goals. This is hugely important when it comes to your human resource planning process!
With a clear understanding of your organization’s strategic objectives in mind, reviewing your organizational design allows you to understand the staffing requirements you’ll need to succeed at them. This means taking into account your organizational structure and chains of command, as well as how work gets done and the way information flows.
From there, you’ll be able to see which departments need more team members so it can accomplish the organization’s objectives.
An easy way to get started is by using an organizational flow chart.

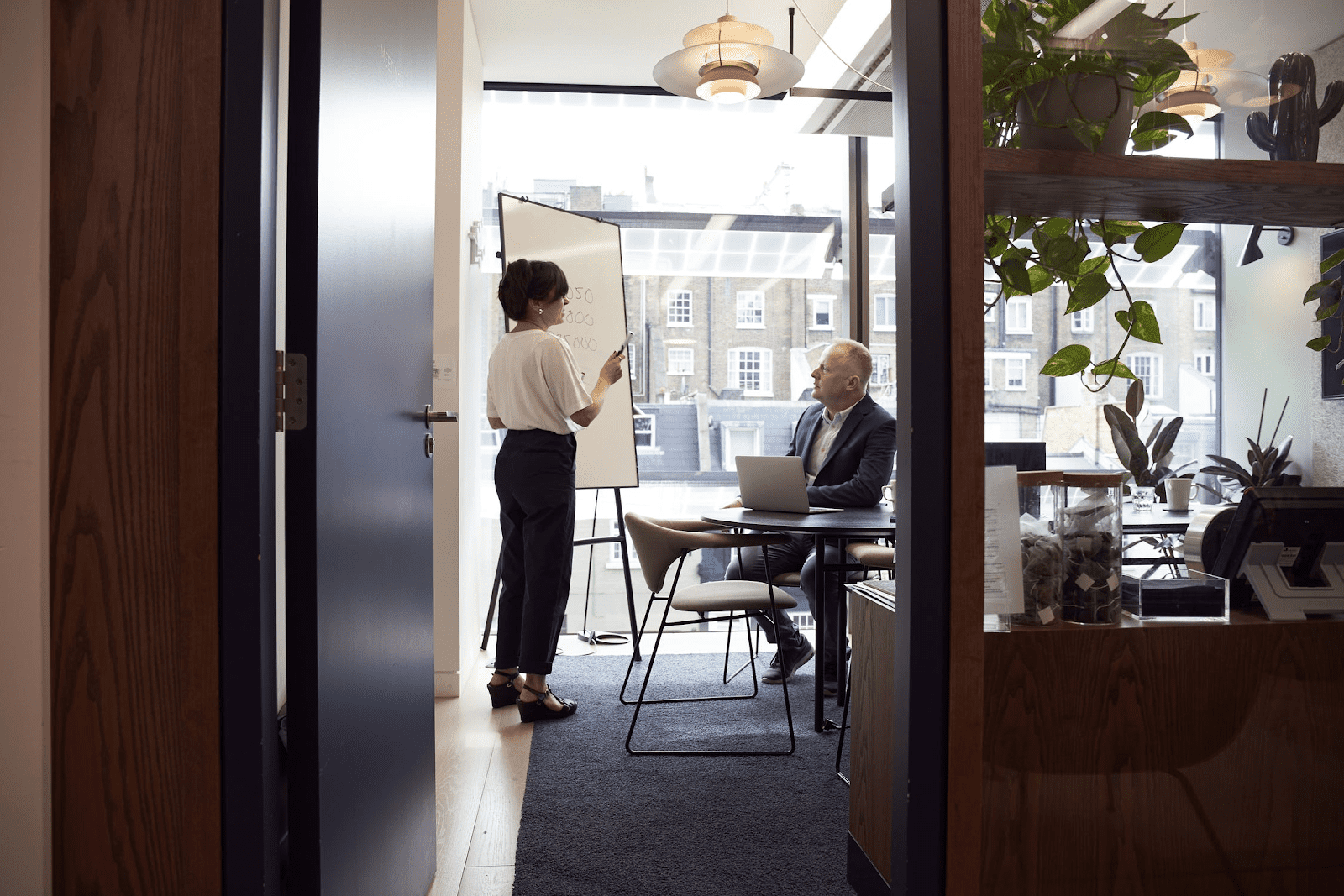
With its color coding and layout, even a new manager can quickly look at this chart to identify the people responsible for leading teams and making decisions.
And if there are any changes, it’s easy to to reflect them in the chart itself. All you need to do is customize the text and visual assets in Venngage’s Chart Maker as desired.
Not quite your style? There’s plenty of other organizational chart templates to choose from.

Here’s an organizational chart that’s perfect for small businesses that have limited employees. One quick look, and you’re good to go.
The bottom line is, no matter how big or small your business may be, you should always revisit your organizational design to optimize your workforce management and business operations.
Related: Types of Organizational Structure [+ Visualization Tips]
4. Outline how you will manage, motivate and retain talent
In this day and age, it’s a known fact that companies must provide more than just a paycheque to attract and retain talent, and encourage growth.
It’s true — studies have shown employees are more engaged in their work when they feel it is meaningful, fulfilling and slightly challenging. So your human resource plan should consider how to inspire such feelings, and what actions you can take to motivate employees to stay. (Hint: a strong HR training and development program is key.)
The talent management infographic template below is a great way to begin.

Using this process chart , you can detail the steps you’ll take to retain the talent you have. Reference it as needed in your human resource planning.
Another great way to keep staff motivated and geared towards their professional growth is by coming up with ideas for employee development . Facilitating a company culture that champions continuous learning guarantees your team will feel supported and challenged in all the right ways.
The two employee development plan templates below will help you do just that.

Though both templates are geared towards healthcare organizations, it’s easy to customize their content in Venngage to promote the continuous learning and development of employees in any industry.
As a result, your employees will be able to reach their full potential, while simultaneously supporting the long-term goals of your organization.
Related: 6 Employee Development Ideas for Efficient Training
5. Align your workforce planning with your budget
Let’s face it, human resources ain’t cheap.
Meaning, if you struggle at organizing and monitoring your HR budget, you’re bound to overspend on your initiatives —and no financially savvy business wants that.
That’s why I recommend including financial information in your HR planning process, so you can reference your budget and expenses as needed. This includes not only hiring and training costs but also the complexities of managing a global payroll for diverse teams.
Ensuring this allows you to stay within range as you work towards achieving your strategic goals for human capital . Plus, you don’t need to use one that contains walls of text and wack-loads numbers. Check out the clean and cheery option below — it’s as easy to fill out as it is to understand.

And if you’re looking to compare a forecasted budget to previous annual spending when strategizing your HR budget, the Budget Comparison Infographic Template below will help.

The bar graph is a great data visualization of annual expenses, organized by category. Just add (or import) any values to Venngage’s editor, swap out the text, and you’re ready to compare with ease.
Related: 10+ Expense Report Templates You Can Edit Easily
6. Establish KPIs for your human resource planning objectives
Measurable results are important when it comes to your HR planning processes, because they indicate whether your strategy is working or not.
Keeping those metrics in mind, your company can make adjustments and improve upon any future plans — AKA strategize for future success in business. That’s why your human resource plan should include info re: the specific key performance indicators (KPI) you’ll be measuring.
KPIs are established to help determine if HR strategies and plans are working. Much like those used for evaluating the performance of marketing or sales plan , KPIs for human resources are measurable results that indicate an organization’s success at achieving predetermined goals.
These may take the form of headcounts, turnover rates, demographic information, time to hire and employee satisfaction scores.
Here’s one employee satisfaction survey you can use to understand your workforce better.
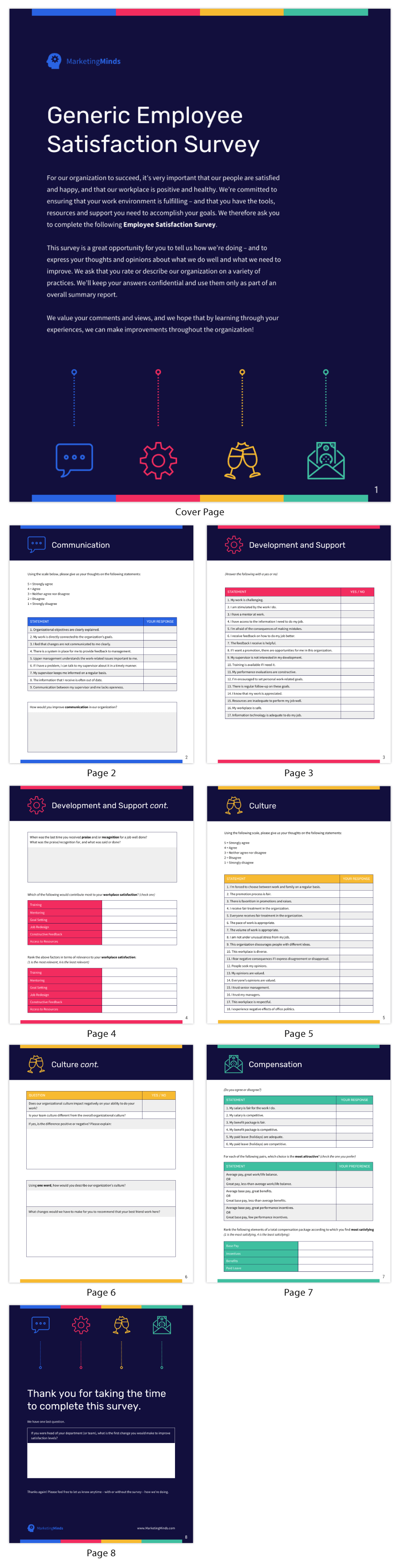
When you’re ready to organize those HR KPIs in a document, the recruiting template below is perfect for keeping tabs at a glance.

Related: 10+ Customizable HR Report Templates & Examples
How do I make an HR plan?
After you’ve collected the data you need, you’ll want to convey this info in an engaging, professional manner for easy referencing and sharing amongst colleagues. Given this, using Venngage is the best route to go.
Here are the simple steps to help you bring an actionable HR plan to life:
- Outline the information you would like to include in your strategic hr plan
- Pick the human resource planning templates that best suits your needs
- Customize the templates’ text and visual assets so they speak to your organization
- Apply your company’s brand guidelines with a few clicks using Venngage’s automated branding feature, My Brand Kit
- Download and share as desired
Note: sharing is available free-of-charge. However, the option to download your creations and access features like My Brand Kit and Team Collaboration are available with a Business plan .
FAQ about HR plans
How long should an hr plan be .
There are no hard and fast rules when it comes to the length of an HR plan. That being said, if you’re going to share it with colleagues, you probably don’t want to create a 20+ page document. One to five pages should suffice.
Try to be as concise as possible when relaying the facts, and use data visualizations wherever possible to save room.
Do I need an HR contingency plan?
In the same way creating an HR plan is a proactive move that helps your organization account for future needs, it’s a good idea to devise an HR contingency plan. This ensures there’s a back-up plan in place should your initiatives not go as expected.
For example, if you’ve identified that you need five new hires to keep up with consumer demand, but the talent pool is lacking, a contingency plan could house suggestions for restructuring your workforce to mitigate this.
In other words, it’s best-practice to hope for the best, but prepare for the worst.
Is an HR plan different from an employee development plan?
Yes. While an HR plan is a strategic document describing how an organization addresses its personnel-related needs at a high-level, an employee development plan outlines the processes needed to help an individual achieve their professional goals.
Even though the human resource planning process may involve outlining some employee development tactics, it is not unique to each employee as in the case of an employee development plan.
Make your HR planning processes effortless
You don’t need a crystal ball to feel confident about your people moving forward. With a solid HR plan and strategy in place, you’ll prime your workforce — and all business endeavors — to succeed in even the most competitive of markets.
Just remember this: human resources planning, and creating strategic business plans in general, doesn’t have to be exhausting.
With Venngage’s huge selection of professionally-designed templates and easy-to-use editor, all it takes is a few minutes to produce a polished document perfect for all your needs. Sign up for free today !
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2.2 Writing the HRM Plan
Learning objective.
- Describe the steps in the development of an HRM plan.
As addressed in Section 2.1 “Strategic Planning” , the writing of an HRM strategic plan should be based on the strategic plans of the organization and of the department. Once the strategic plan is written, the HR professional can begin work on the HR plan. This is different from the strategic plan in that it is more detailed and more focused on the short term. The six parts described here are addressed in more detail in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” , Chapter 5 “Selection” , Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits” , Chapter 7 “Retention and Motivation” , Chapter 8 “Training and Development” , Chapter 9 “Successful Employee Communication” , Chapter 10 “Managing Employee Performance” , and Chapter 11 “Employee Assessment” .
How Would You Handle This?
Compensation Is a Touchy Subject
As the HR manager, you have access to sensitive data, such as pay information. As you are looking at pay for each employee in the marketing department, you notice that two employees with the same job title and performing the same job are earning different amounts of money. As you dig deeper, you notice the employee who has been with the company for the least amount of time is actually getting paid more than the person with longer tenure. A brief look at the performance evaluations shows they are both star performers. You determine that two different managers hired the employees, and one manager is no longer with the organization. How would you handle this?
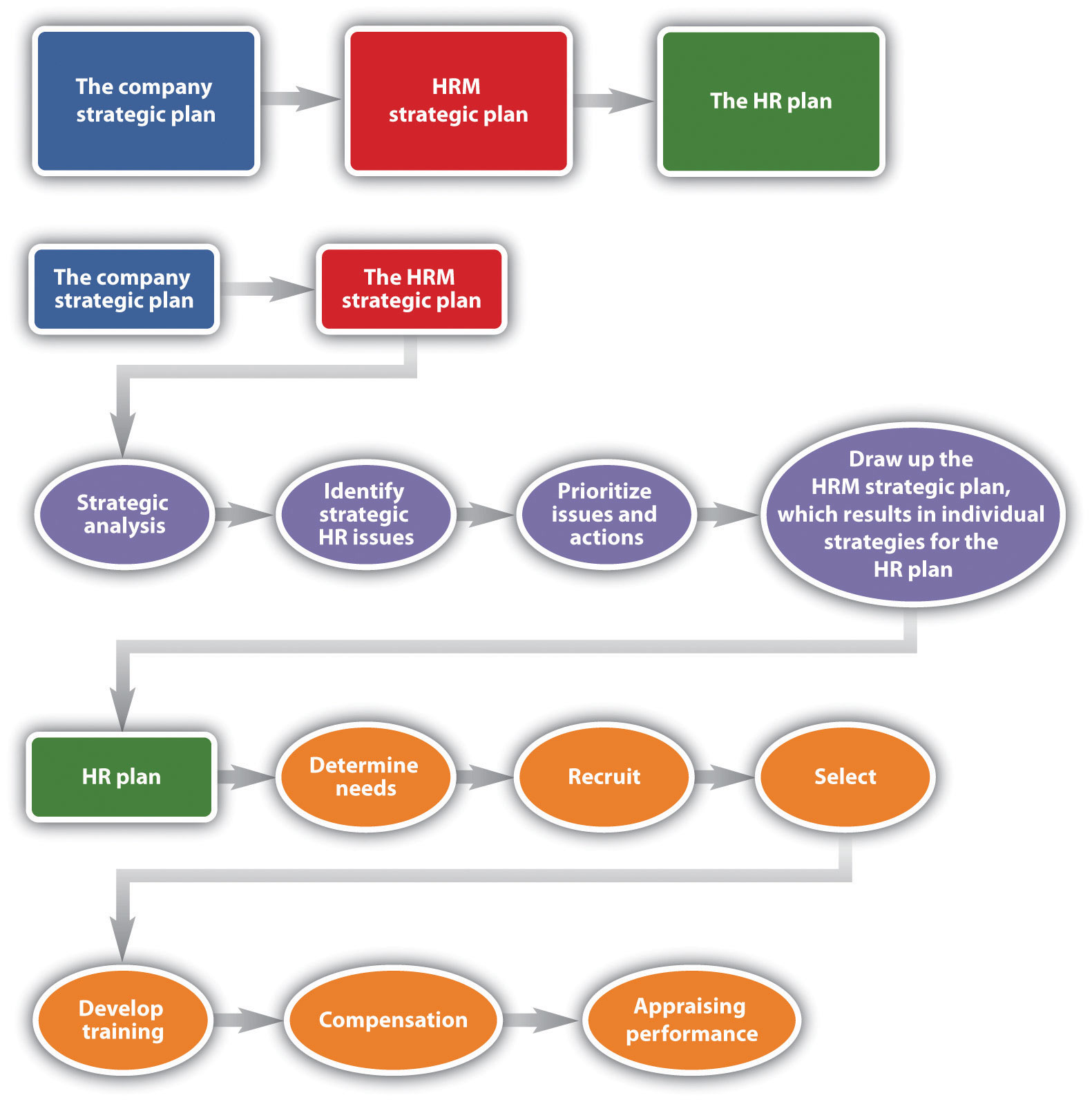
As you can see from this figure, the company strategic plan ties into the HRM strategic plan, and from the HRM strategic plan, the HR plan can be developed.
The six parts of the HRM plan include the following:
- Determine human resource needs. This part is heavily involved with the strategic plan. What growth or decline is expected in the organization? How will this impact your workforce? What is the economic situation? What are your forecasted sales for next year?
- Determine recruiting strategy. Once you have a plan in place, it’s necessary to write down a strategy addressing how you will recruit the right people at the right time.
- Select employees. The selection process consists of the interviewing and hiring process.
- Develop training. Based on the strategic plan, what training needs are arising? Is there new software that everyone must learn? Are there problems in handling conflict? Whatever the training topics are, the HR manager should address plans to offer training in the HRM plan.
- Determine compensation. In this aspect of the HRM plan, the manager must determine pay scales and other compensation such as health care, bonuses, and other perks.
- Appraise performance. Sets of standards need to be developed so you know how to rate the performance of your employees and continue with their development.
Each chapter of this text addresses one area of the HR plan, but the next sections provide some basic knowledge of planning for each area.
Determine Human Resource Needs
The first part of an HR plan will consist of determining how many people are needed. This step involves looking at company operations over the last year and asking a lot of questions:
- Were enough people hired?
- Did you have to scramble to hire people at the last minute?
- What are the skills your current employees possess?
- What skills do your employees need to gain to keep up with technology?
- Who is retiring soon? Do you have someone to replace them?
- What are the sales forecasts? How might this affect your hiring?
These are the questions to answer in this first step of the HR plan process. As you can imagine, this cannot be done alone. Involvement of other departments, managers, and executives should take place to obtain an accurate estimate of staffing needs for now and in the future. We discuss staffing in greater detail in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” .
Many HR managers will prepare an inventory of all current employees, which includes their educational level and abilities. This gives the HR manager the big picture on what current employees can do. It can serve as a tool to develop employees’ skills and abilities, if you know where they are currently in their development. For example, by taking an inventory, you may find out that Richard is going to retire next year, but no one in his department has been identified or trained to take over his role. Keeping the inventory helps you know where gaps might exist and allows you to plan for these gaps. This topic is addressed further in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” .
HR managers will also look closely at all job components and will analyze each job. By doing this analysis, they can get a better picture of what kinds of skills are needed to perform a job successfully. Once the HR manager has performed the needs assessment and knows exactly how many people, and in what positions and time frame they need to be hired, he or she can get to work on recruiting, which is also called a staffing plan . This is addressed further in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” .
Recruitment is an important job of the HR manager. More detail is provided in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” . Knowing how many people to hire, what skills they should possess, and hiring them when the time is right are major challenges in the area of recruiting. Hiring individuals who have not only the skills to do the job but also the attitude, personality, and fit can be the biggest challenge in recruiting. Depending on the type of job you are hiring for, you might place traditional advertisements on the web or use social networking sites as an avenue. Some companies offer bonuses to employees who refer friends. No matter where you decide to recruit, it is important to keep in mind that the recruiting process should be fair and equitable and diversity should be considered. We discuss diversity in greater detail in Chapter 3 “Diversity and Multiculturalism” .
Depending on availability and time, some companies may choose to outsource their recruiting processes. For some types of high-level positions, a head hunter will be used to recruit people nationally and internationally. A head hunter is a person who specializes in matching jobs with people, and they usually work only with high-level positions. Another option is to use an agency that specializes in hiring people for a variety of positions, including temporary and permanent positions. Some companies decide to hire temporary employees because they anticipate only a short-term need, and it can be less expensive to hire someone for only a specified period of time.
No matter how it is done, recruitment is the process of obtaining résumés of people interested in the job. In our next step, we review those résumés, interview, and select the best person for the job.
After you have reviewed résumés for a position, now is the time to work toward selecting the right person for the job. Although we discuss selection in great detail in Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits” , it is worth a discussion here as well. Numerous studies have been done, and while they have various results, the majority of studies say it costs an average of $45,000 to hire a new manager (Herman, 1993). While this may seem exaggerated, consider the following items that contribute to the cost:
- Time to review résumés
- Time to interview candidates
- Interview expenses for candidates
- Possible travel expenses for new hire or recruiter
- Possible relocation expenses for new hire
- Additional bookkeeping, payroll, 401(k), and so forth
- Additional record keeping for government agencies
- Increased unemployment insurance costs
- Costs related to lack of productivity while new employee gets up to speed
Because it is so expensive to hire, it is important to do it right. First, résumés are reviewed and people who closely match the right skills are selected for interviews. Many organizations perform phone interviews first so they can further narrow the field. The HR manager is generally responsible for setting up the interviews and determining the interview schedule for a particular candidate. Usually, the more senior the position is, the longer the interview process takes, even up to eight weeks (Crant, 2009). After the interviews are conducted, there may be reference checks, background checks, or testing that will need to be performed before an offer is made to the new employee. HR managers are generally responsible for this aspect. Once the applicant has met all criteria, the HR manager will offer the selected person the position. At this point, salary, benefits, and vacation time may be negotiated. Compensation is the next step in HR management.
Determine Compensation
What you decide to pay people is much more difficult than it seems. This issue is covered in greater detail in Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits” . Pay systems must be developed that motivate employees and embody fairness to everyone working at the organization. However, organizations cannot offer every benefit and perk because budgets always have constraints. Even governmental agencies need to be concerned with compensation as part of their HR plan. For example, in 2011, Illinois State University gave salary increases of 3 percent to all faculty, despite state budget cuts in other areas. They reasoned that the pay increase was needed because of the competitive nature of hiring and retaining faculty and staff. The university president said, “Our employees have had a very good year and hopefully this is a good shot in the arm that will keep our morale high” (Pawlowski, 2011).
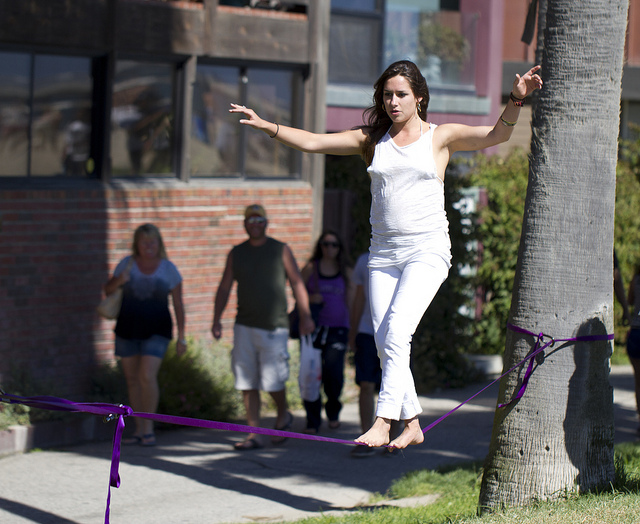
Determination of compensation systems is a balancing act. Compensation should be high enough to motivate current employees and attract new ones but not so high that it breaks the budget.
Nathan Rupert – Venice Beach Tightrope Walker – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
The process in determining the right pay for the right job can have many variables, in addition to keeping morale high. First, as we have already discussed, the organization life cycle can determine the pay strategy for the organization. The supply and demand of those skills in the market, economy, region, or area in which the business is located is a determining factor in compensation strategy. For example, a company operating in Seattle may pay higher for the same job than their division in Missoula, Montana, because the cost of living is higher in Seattle. The HR manager is always researching to ensure the pay is fair and at market value. In Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits” , we get into greater detail about the variety of pay systems, perks, and bonuses that can be offered. For many organizations, training is a perk. Employees can develop their skills while getting paid for it. Training is the next step in the HR planning process.
Develop Training
Once we have planned our staffing, recruited people, selected employees, and then compensated them, we want to make sure our new employees are successful. Training is covered in more detail in Chapter 8. One way we can ensure success is by training our employees in three main areas:
- Company culture. A company culture is the organization’s way of doing things. Every company does things a bit differently, and by understanding the corporate culture, the employee will be set up for success. Usually this type of training is performed at an orientation, when an employee is first hired. Topics might include how to request time off, dress codes, and processes.
- Skills needed for the job. If you work for a retail store, your employees need to know how to use the register. If you have sales staff, they need to have product knowledge to do the job. If your company uses particular software, training is needed in this area.
- Human relations skills. These are non-job-specific skills your employees need not only to do their jobs but also to make them all-around successful employees. Skills needed include communication skills and interviewing potential employees.
Perform a Performance Appraisal
The last thing an HR manager should plan is the performance appraisal. While we discuss performance appraisals in greater detail in Chapter 11 “Employee Assessment” , it is definitely worth a mention here, since it is part of the strategic plan. A performance appraisal is a method by which job performance is measured. The performance appraisal can be called many different things, such as the following:
- Employee appraisal
- Performance review
- Career development review
No matter what the name, these appraisals can be very beneficial in motivating and rewarding employees. The performance evaluation includes metrics on which the employee is measured. These metrics should be based on the job description, both of which the HR manager develops. Various types of rating systems can be used, and it’s usually up to the HR manager to develop these as well as employee evaluation forms. The HR manager also usually ensures that every manager in the organization is trained on how to fill out the evaluation forms, but more importantly, how to discuss job performance with the employee. Then the HR manager tracks the due dates of performance appraisals and sends out e-mails to those managers letting them know it is almost time to write an evaluation.
Human Resource Recall
Have you ever been given a performance evaluation? What was the process and the outcome?
Communication Is Key in Performance Evaluations
(click to see video)
Communication is imperative in any workplace, but especially when giving and receiving a performance evaluation.
Key Takeaways
- Human resource planning is a process that is part of the strategic plan. It involves addressing specific needs within the organization, based on the company’s strategic direction.
- The first step in HR planning is determining current and future human resource needs. In this step, current employees, available employees in the market, and future needs are all analyzed and developed.
- In the second step of the process, once we know how many people we will need to hire, we can begin to determine the best methods for recruiting the people we need. Sometimes an organization will use head hunters to find the best person for the job.
- After the recruiting process is finished, the HR manager will begin the selection process. This involves setting up interviews and selecting the right person for the job. This can be an expensive process, so we always want to hire the right person from the beginning.
- HR managers also need to work through compensation plans, including salary, bonus, and other benefits, such as health care. This aspect is important, since most organizations want to use compensation to attract and retain the best employees.
- The HR manager also develops training programs to ensure the people hired have the tools to be able to do their jobs successfully.
- Of the parts of HR planning, which do you think is most difficult, and why? Which would you enjoy the most, and why?
- Why is it important to plan your staffing before you start to hire people?
- What is the significance of training? Why do we need it in organizations?
Crant, J., “How Long Does an Interview Process Take?” Jobsinminneapolis.com, December 2, 2009, accessed October 28, 2010, http://www.jobsinminneapolis.com/articles/title/How-Long-Does-an-Interview-Process-Take/3500/422 .
Herman, S., Hiring Right: A Practical Guide (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1993), xv.
Pawlowski, S., “Illinois State University to Get Salary Bump,” WJBC Radio, July 11, 2011, accessed July 11, 2011, http://wjbc.com/illinois-state-university-faculty-to-get-salary-bump .
Human Resource Management Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Faculty Resources
Assignments.

The Human Resources Management course includes a series of openly licensed written assignments and discussions aligned to specific learning outcomes and chapters. If you import this course into your learning management system (Blackboard, Canvas, etc.), all of the assignments and discussions (listed in the table, below,) will automatically be loaded into your LMS assignment and discussion-board tools. They can be used as is, modified, combined with your own assignments, or removed altogether.
The assignments in this course align with the following scenario:
You are a college senior who has been selected to participate in a hybrid internship/onboarding program with an elite HR research and advisory firm. Your training consists of a combination of formal education—specifically, enrollment in this Human Resource Management course—and a rotation in support of the principals of the firm. In your rotations, you will synthesize what you’ve learned in the relevant modules to address firm or client issues, conducting additional research as necessary and developing draft deliverables as instructed by the principal consultant. The quality of your deliverables – that is, your ability to convert learning into practical insight – will largely determine whether, at the end of the internship period, you are offered a position with the firm or simply thanked for your participation.
You can view them below or throughout the course.
Rubric for Assignments
There is also a sample rubric to assist you in grading. Instructors may modify these guidelines or use their own.
Discussions
The following discussion assignments will also be preloaded (into the discussion-board tool) in your learning management system if you import the course. They can be used as is, modified, or removed. You can view them below or throughout the course.
Rubric for Discussion Posts
Answer keys for the discussion posts are available to faculty who adopt Waymaker, OHM, or Candela courses with paid support from Lumen Learning. This approach helps us protect the academic integrity of these materials by ensuring they are shared only with authorized and institution-affiliated faculty and staff.
- Assignments. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Pencil Cup. Authored by : IconfactoryTeam. Provided by : Noun Project. Located at : https://thenounproject.com/term/pencil-cup/628840/ . License : CC BY: Attribution

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

MODULE 1: HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING

- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
The Easy Guide to Human Resource Planning with Tools & Templates
Updated on: 23 June 2022
It’s no secret that the key to the continued smooth operation of an organization is its employees – well, the right kind of skillful employees doing their job right. And the way to get that kind of employee working in your organization can only be made possible through proper human resource planning software .
In this post, we have simplified the human resource process for you by breaking it down into four steps and providing you with ready-made templates to immediately execute those tasks.
What is Human Resource Planning
Human resource planning is the process by which organizations assess the current human resources, forecast future requirements or necessities, identify the gaps and come up with a plan to fill them.
Basically, human resource planning, also known as workforce planning and manpower planning, helps you ensure that you have the right number of people with relevant skills in the right kind of job position at the right time.
Importance of human resource planning
Human resource planning plays a major role in making sure that the necessary skills are made available to the organization whenever needed to meet its strategic goals. In addition, there are several more important reasons why human resource planning is crucial to an organization.
- It helps make sure that the existing manpower is being used optimally
- It supports achieving the organization’s strategic goals and objectives by ensuring that the right kind of people are hired to fulfill the demand for labor in a timely manner
- It provides information necessary to carry out other HR functions such as recruitment, selection, promotion, training and development , etc. and define HR policies
- It helps the organization adapt to the changes in the environment caused by competition, technology, government policies, etc. that may result in a need for new employees, new skills, etc.
- It helps identify labor requirements needed to successfully implement expansion and diversification plans
- It also assists with anticipating deficiencies or surpluses in manpower and take the necessary steps to handle the situation
- It helps develop career plans for individual employees and determine the training and development they need
4 Steps in the Human Resource Planning Process
There are 4 broad steps involved in the human resource planning process.
Step 1: Identify the current supply of human resources
The planning process starts by analyzing the current labor pool. Identify the strengths and weaknesses of your organization with regard to the number of employees, their skills, experiences, qualifications, positions, performance levels, age, benefits, salary levels, languages spoken, prior employment, etc.
There are several ways you can go about this step.
- Refer to the past performance reviews
- Gather data from your human resource information system
- Talk to the department heads to get an idea about the employees working under them
- Ask the employees themselves with a questionnaire
- Get employees to do a self-evaluation of themselves with a SWOT analysis
Once you have collected an abundance of information on current employees, transfer them to a skills inventory report . A visual template for a skills inventory that is easier to refer to and understand is given below.
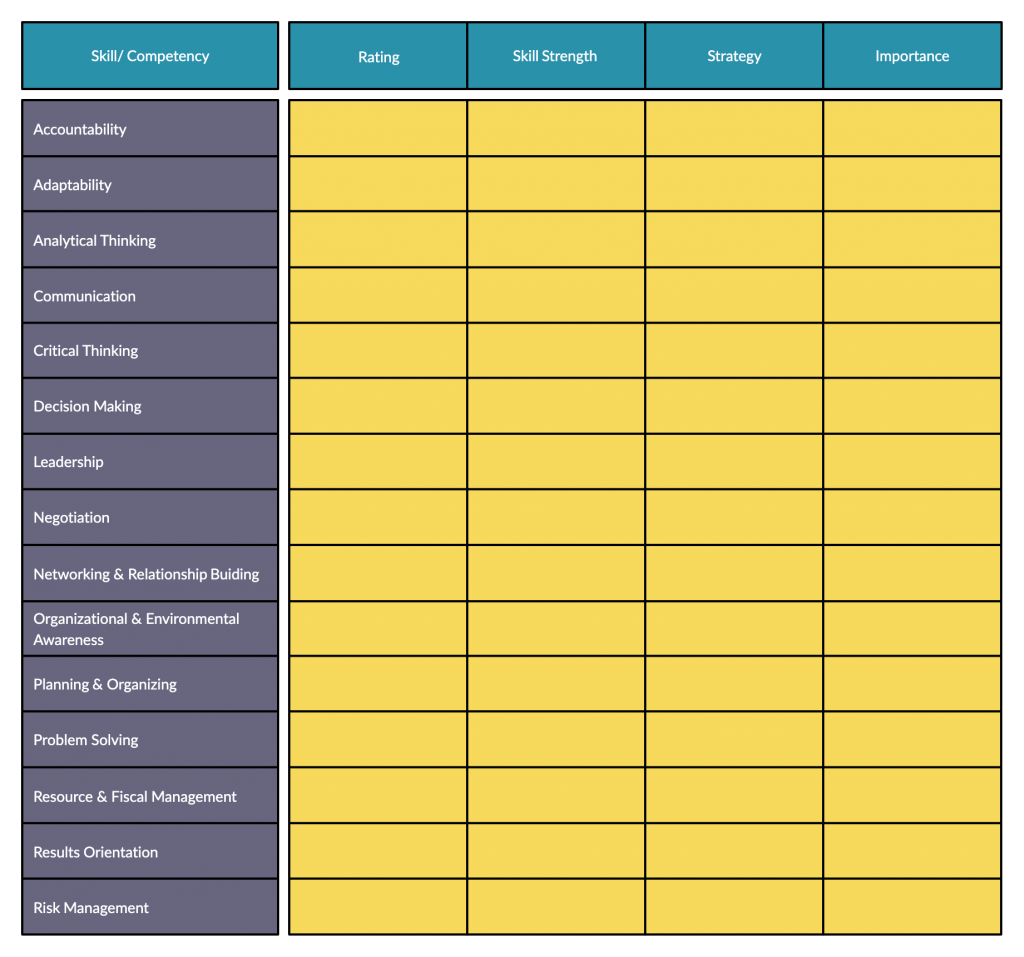
Step 2: Forecast future demand for human resources
This step requires you to understand the future goals of the organization first, as they would have a significant impact on the future human resource demands.
Prior to determining the future needs, you also need to consider factors such as employee turnover rates, market or industry trends, technological advances that will help automate processes, retirements, promotions, layoffs, etc.
Step 3: Analyze the gap between supply and demand for labor
Now that you have clarified what skills are available in your inventory and which you will need for the future, you can clearly see the gaps that exist.
Can the current supply of employees in the organization help fulfill future requirements?
Will you have to offer training and development programs to upgrade the current employees to meet company objectives?
If this is not sufficient, then you will have to recruit new employees with relevant skill sets to match the demand for manpower in the future.
It’s important that you maintain the balance between demand and supply in human resource planning.
Step 4: Develop and implement the plan to meet the gaps
Then comes developing an action plan .
If there’s a deficit of employees, you can spend your efforts on hiring new employees, training existing ones, outsourcing or interdepartmental transfers.
On the other hand, if there’s a surplus of employees, you may need to consider layoff, voluntary retirement schemes, transfers, etc.
Once a plan is devised, it should be integrated with the overall strategy of the organization. And it’s important to monitor the plan and evaluate its effectiveness throughout time.
Human Resource Planning Tools
You can use these tools throughout the different steps of the workforce planning process. They can assist you in analyzing the capability of your current staff, and determine future needs. The templates provided are editable online; simply click on the template to edit it online.
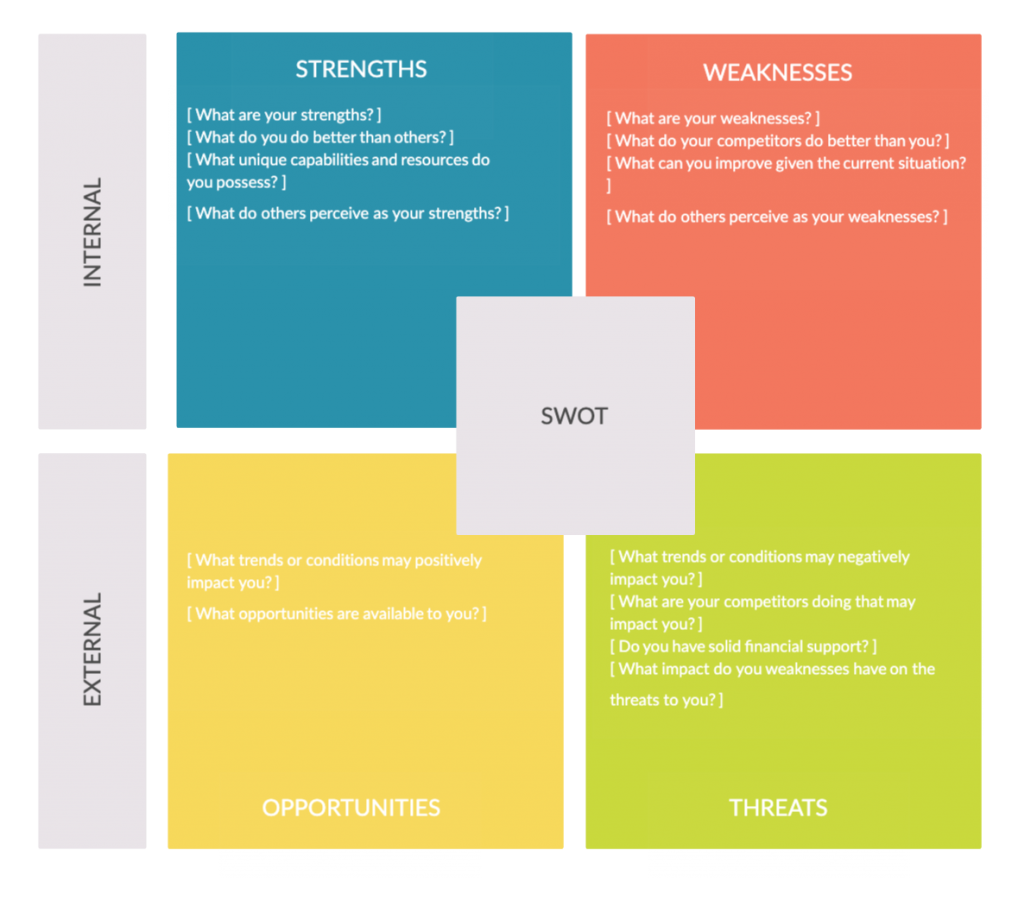
SWOT Analysis
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It can be used as a tool for self-evaluation by individual employees, or as a strategic tool to assess the current state of the organization.
Strengths and weaknesses are the factors that are internal. For example, a strength of your organization could be the presence of skilled employees, but a weakness could be the insufficient numbers of skilled employees.
Opportunities and threats are external factors. For example, the availability of skilled employees in the market could be a great opportunity for you if you are hiring. On the other hand, your competitor poaching your employees with better salaries could pose a threat to you.
The SWOT analysis is one of the most popular tools used during a situation analysis. Some other situation analysis tools you can use with manpower planning are described in our guide to situation analysis .
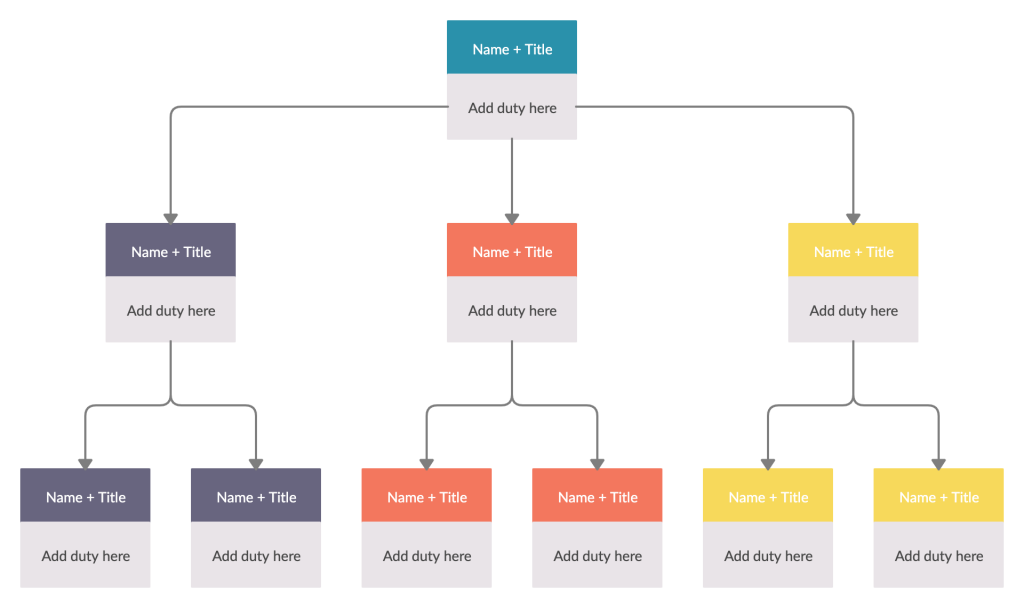
Organizational Chart
An organizational chart is a visual representation of the hierarchy/ structure of an organization. It also highlights reporting relationships between employees, their roles and responsibilities. In human resource planning, it can be used in a number of ways,
- To record information about current employee roles, responsibilities, skills, experiences, etc. You can also add additional information such as their educational qualifications, and demographical data. This will help you quickly identify the right personnel for the job.
- To create a roadmap of the staffing needs. You can mark labor deficiencies and surplusses on your company organizational chart as well.
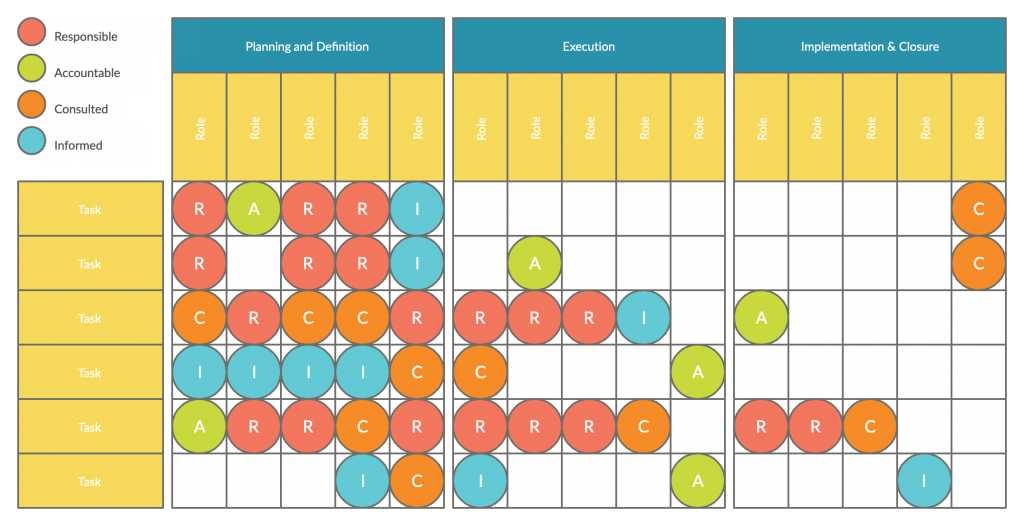
RACI Matrix
This is a chart, project managers use to assign roles and responsibilities to tasks in a project. It highlights who should be responsible, accountable, consulted and informed during a project.
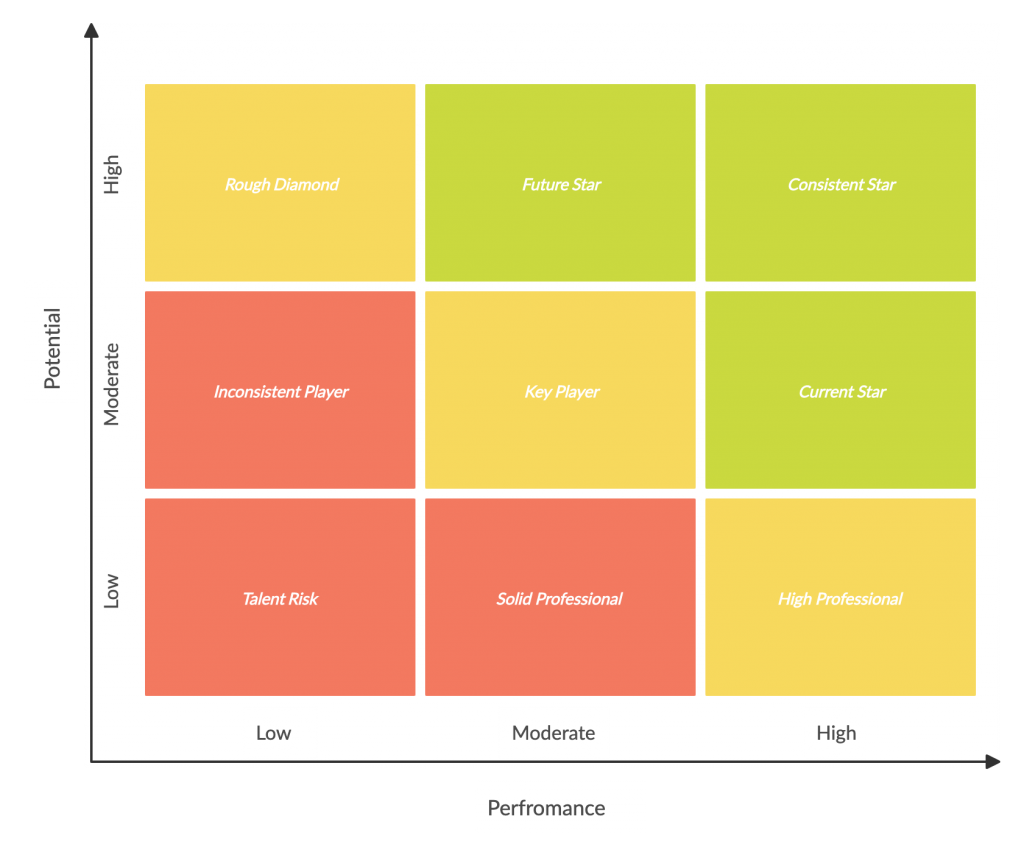
9 Box Grid
The 9 box grid, also known as the performance-potential matrix, is widely used in employee development and succession planning. It helps evaluate your existing employees against their current performance and their future potential performance.
Rating your employees with the help of the 9 box grid helps you identify strong employees and those who are falling behind.
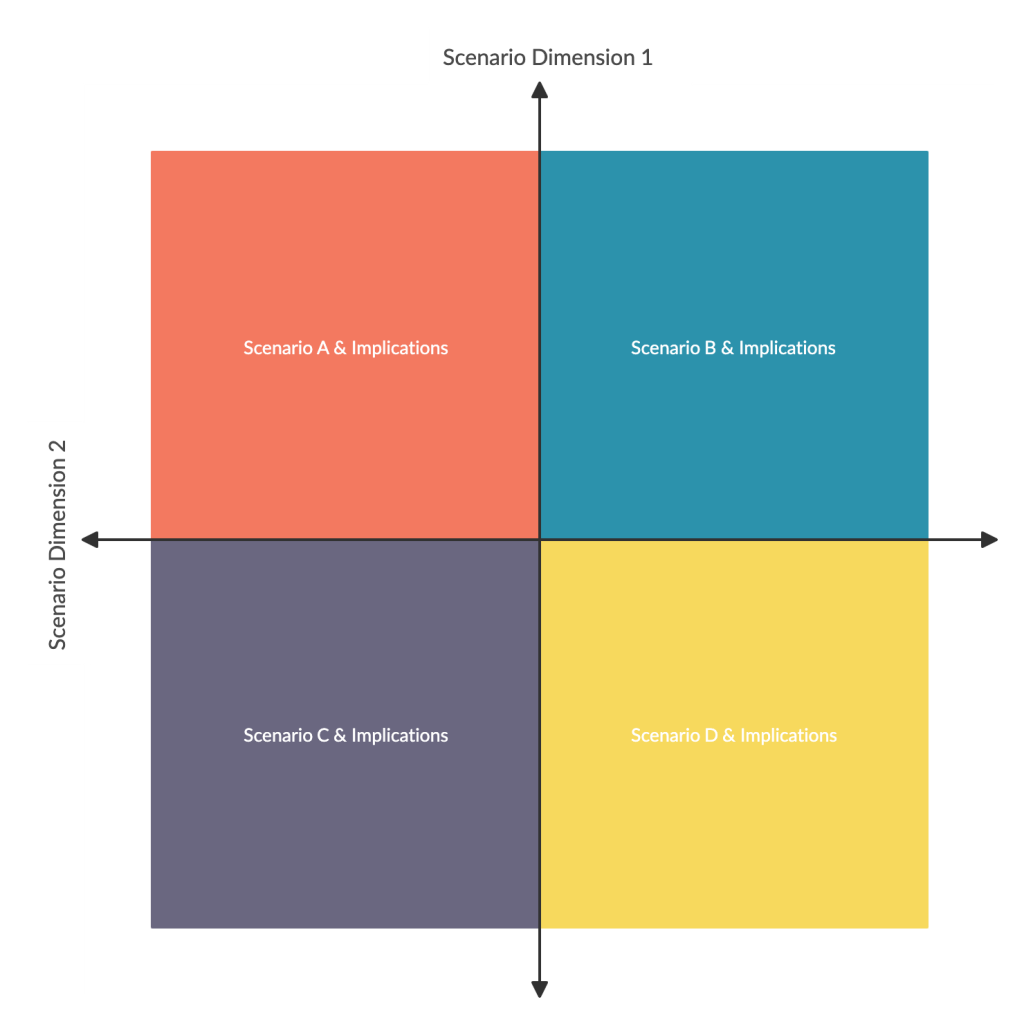
Scenario Planning
There are many scenarios, like technological advancements, natural disasters, political or economic changes that could drastically alter the future direction of your company. Ordinarily, you may not see them coming or plan for them.
By incorporating scenario planning in your strategic planning process, you can identify these different future scenarios, discuss how they will affect your organization and take precautionary measures.
You can incorporate scenario planning with human resource planning by examining scenarios that involve your changing future labor requirements.
Refer to our resource on scenario planning to learn about this tool in more detail.
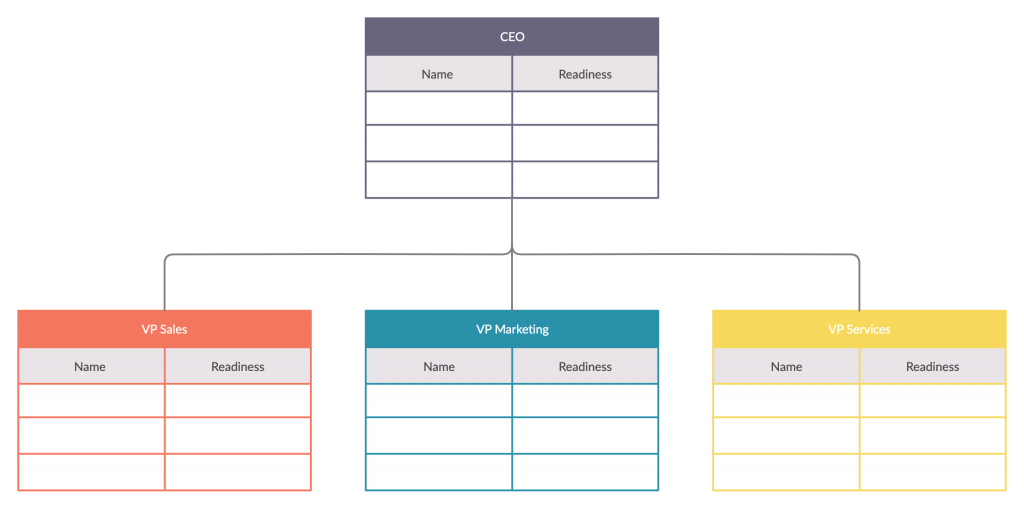
Replacement Chart
This is a diagram that is similar to the organizational chart . It is used to identify potential candidates who can replace an employee who is retiring, transferring, etc. Individual replacement charts can be developed for each significant position in a company along with potential replacements.
Any Tips for Improving Manpower Planning?
In this post, we’ve basically covered everything you need to know about human resource planning , especially if you are a newbie. And we believe the templates provided will help you kickstart your project.
Already an expert in workforce planning? Do share the tips on tools and processes you swear by in the comments section below.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.

More Related Articles

Leave a comment Cancel reply
Please enter an answer in digits: four + 13 =
Download our all-new eBook for tips on 50 powerful Business Diagrams for Strategic Planning.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Human Resource Planning (HRP)
- Understanding HRP
What Is the Goal of Human Resource Planning (HRP)?
- Human Resource Planning FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Business Essentials
Human Resource Planning (HRP) Meaning, Process, and Examples
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
What Is Human Resource Planning (HRP)?
Human resource planning (HRP) is the continuous process of systematic planning to achieve optimum use of an organization's most valuable asset—quality employees. Human resources planning ensures the best fit between employees and jobs while avoiding manpower shortages or surpluses.
There are four key steps to the HRP process. They include analyzing present labor supply, forecasting labor demand, balancing projected labor demand with supply, and supporting organizational goals. HRP is an important investment for any business as it allows companies to remain both productive and profitable.
Key Takeaways
- Human resource planning (HRP) is a strategy used by a company to maintain a steady stream of skilled employees while avoiding employee shortages or surpluses.
- Having a good HRP strategy in place can mean productivity and profitability for a company.
- There are four general steps in the HRP process: identifying the current supply of employees, determining the future of the workforce, balancing between labor supply and demand, and developing plans that support the company's goals.
Michela Buttignol
What Is Human Resource Planning (HRP) Used For?
Human resource planning allows companies to plan ahead so they can maintain a steady supply of skilled employees. The process is used to help companies evaluate their needs and to plan ahead to meet those needs.
Human resource planning needs to be flexible enough to meet short-term staffing challenges while adapting to changing conditions in the business environment over the longer term. HRP starts by assessing and auditing the current capacity of human resources.
Here, identifying a company's skill set and targeting the skills a company needs enables it to strategically reach business goals and be equipped for future challenges. To remain competitive, businesses may need advanced skills or to upskill their employees as the market environment evolves and changes.
To retain employees and remain competitive, HRP often looks at organizational design, employee motivation, succession planning, and increasing return on investment overall.
Challenges of Human Resource Planning (HRP)
The challenges to HRP include forces that are always changing. These include employees getting sick, getting promoted, going on vacation, or leaving for another job. HRP ensures there is the best fit between workers and jobs, avoiding shortages and surpluses in the employee pool.
To help prevent future roadblocks and satisfy their objectives, HR managers have to make plans to do the following:
- Find and attract skilled employees.
- Select, train, and reward the best candidates.
- Cope with absences and deal with conflicts.
- Promote employees or let some of them go.
Investing in HRP is one of the most important decisions a company can make. After all, a company is only as good as its employees, and a high level of employee engagement can be essential for a company's success. If a company has the best employees and the best practices in place, it can mean the difference between sluggishness and productivity, helping to lead a company to profitability.
What Are the Four Steps to Human Resource Planning (HRP)?
There are four general, broad steps involved in the human resource planning process. Each step needs to be taken in sequence in order to arrive at the end goal, which is to develop a strategy that enables the company to successfully find and retain enough qualified employees to meet the company's needs.
Analyzing labor supply
The first step of human resource planning is to identify the company's current human resources supply. In this step, the HR department studies the strength of the organization based on the number of employees, their skills, qualifications, positions, benefits, and performance levels.
Forecasting labor demand
The second step requires the company to outline the future of its workforce. Here, the HR department can consider certain issues like promotions, retirements, layoffs, and transfers—anything that factors into the future needs of a company. The HR department can also look at external conditions impacting labor demand , such as new technology that might increase or decrease the need for workers.
Balancing labor demand with supply
The third step in the HRP process is forecasting the employment demand. HR creates a gap analysis that lays out specific needs to narrow the supply of the company's labor versus future demand. This analysis will often generate a series of questions, such as:
- Should employees learn new skills?
- Does the company need more managers?
- Do all employees play to their strengths in their current roles?
Developing and implementing a plan
The answers to questions from the gap analysis help HR determine how to proceed, which is the final phase of the HRP process. HR must now take practical steps to integrate its plan with the rest of the company. The department needs a budget , the ability to implement the plan, and a collaborative effort with all departments to execute that plan.
Common HR policies put in place after this fourth step may include policies regarding vacation, holidays, sick days, overtime compensation, and termination.
The goal of HR planning is to have the optimal number of staff to make the most money for the company. Because the goals and strategies of a company change over time, human resource planning must adapt accordingly. Additionally, as globalization increases, HR departments will face the need to implement new practices to accommodate government labor regulations that vary from country to country.
The increased use of remote workers by many corporations will also impact human resource planning and will require HR departments to use new methods and tools to recruit, train, and retain workers.
Why Is Human Resource Planning Important?
Human resource planning (HRP) allows a business to better maintain and target the right kind of talent to employ—having the right technical and soft skills to optimize their function within the company. It also allows managers to better train the workforce and help them develop the required skills.
What Is "Hard" vs. "Soft" Human Resource Planning?
Hard HRP evaluates various quantitative metrics to ensure that the right number of the right sort of people are available when needed by the company. Soft HRP focuses more on finding employees with the right corporate culture, motivation, and attitude. Often these are used in tandem.
What Are the Basic Steps in HRP?
HRP begins with an analysis of the available labor pool from which a company can draw. It then evaluates the firm's present and future demand for various types of labor and attempts to match that demand with the supply of job applicants.
Quality employees are a company's most valuable asset. Human resource planning involves the development of strategies to ensure that a business has an adequate supply of employees to meet its needs and can avoid either a surplus or a lack of workers.
There are four general steps in developing such a strategy: first, analyzing the company's current labor supply; second, determining the company's future labor needs; third, balancing the company's labor needs with its supply of employees; and fourth, developing and implementing the HR plan throughout the organization.
A solid HRP strategy can help a company be both productive and profitable.
International Journal of Business and Management Invention. " Human Resource Planning-An Analytical Study ," Page 64.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/kanban.asp-FINAL-1d12162ec5e14cea9d5862bae096895d.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Sling is now Sling by Toast! Learn more
More Features

- Restaurants
- Get Started

Human Resource Planning: Definition, Objectives, And Steps
- Employee Management , Templates & Guides
Human resource planning is an essential part of every successful business. Unfortunately, many managers neglect this vital practice for other, easier tasks because they don’t understand what this type of planning requires.
Other times, managers may not understand how pivotal human resource planning is to their long-term corporate strategy and the ultimate success of their business.
That’s where Sling can help. In this article, we define human resource planning, outline its objectives, and provide a step-by-step guide to implementing this crucial practice in your business.
Table Of Contents
Human Resource Planning Defined
Human resource planning objectives, hrp vs. shrm, hrp and organizational strategy, steps in human resource planning, why human resource planning is important, challenges of human resource planning, scheduling and communication for effective hrp.
Human resource planning (or HRP for short) is the ongoing process of systematically planning ahead to optimize and maximize your business’s most valuable asset — high-quality employees .
When you incorporate HRP into every aspect of your strategy — functional , business , or organizational — you streamline the process of creating the best fit between available jobs and available employees. All while avoiding a shortage or surplus in your workforce.
As simple as that may sound, there’s more to human resource planning than setting up a system and implementing it in your organization.
The objectives of HRP are very specific and can mean the difference between success or stagnation. We’ll discuss those objectives in the next section.

As we mentioned earlier, human resource planning is about matching the right employees with the right jobs in your business.
You can do this while interviewing prospective employees, or even during the performance review of a long-time team member who is reaching out for more responsibility.
While matching employees to jobs is a big part of human resource planning, the goals of HRP don’t stop there. Other HRP objectives include:
- Adapting to rapid technology changes
- Powering product innovation
- Adjusting to a more globalized economy
- Preparing for generational and cultural shifts
- Anticipating job and skill changes
- Facilitating growth
- Improving business operations
- Mitigating risk
- Preventing talent shortage or surplus
- Complying with local, state, and federal regulations
- Implementing a successful onboarding process
As you can see, HRP is integral to the successful operation of your business and its growth over both the short- and long-term.
Because this process is connected to every aspect of your business , you may feel overwhelmed by the prospect of creating a new HRP strategy.
Don’t let this prevent you from implementing a system that can revolutionize the way your business operates — both now and in the future .
Keep in mind that human resource planning doesn’t have to address all of the objectives on this list from the moment it goes into effect. Start small and expand into different areas once you’ve addressed one or two objectives.
Later on in this article, we discuss a step-by-step method for producing a human resource planning strategy for your business.
But, first, let’s take a moment to discuss one of the most-confused aspects of human resource planning: how it differs from strategic human resource management.

Before we delve into the minutiae of human resources , let’s put the two relevant definitions side-by-side to see how they compare.
Human Resource Planning : HRP is the ongoing process of systematically planning ahead to optimize and maximize your business’s most valuable asset — high-quality employees.
Strategic Human Resource Management : SHRM is a holistic approach to assembling the best team for your business’s growth and success.
At first glance, it may appear that human resource planning is the same thing as strategic human resource management under a different name. They seem so similar because one is actually part of the other.
In this case, HRP is a small part of SHRM. Viewed from a different perspective, SHRM contains and governs HRP.
It’s very much like a set of nesting dolls: the smallest one (HRP) fits nicely into the next largest (SHRM), which, in turn, fits into the next largest, and so on.
For practical purposes, it helps to think about human resource planning as the frontline, boots-on-the-ground application, while strategic human resource management is the guiding principle behind those applications.
In other words, SHRM is the why to HRP’s what.
Another way to think about SHRM and HRP is to view your business as a large, complicated machine.
Human resource planning is one component (a gear, for example) that works with other similar components (e.g., production, logistics, shipping, management, etc.) to keep the machine running.
Strategic human resource management, on the other hand, takes a step back and analyzes the machine itself.
SHRM looks at the performance of each component (each department in your business), how they work together to make everything run smoothly, and what the business as a whole can do to improve.

Let’s return, for a moment, to the example of the nesting dolls mentioned earlier.
We established that human resource planning is the smallest doll and that strategic human resource management is the next largest doll. But what comes after that?
What’s the next largest doll in the series? Organizational strategy.
Organizational strategy , at its most basic, is a plan that specifies how your business will allocate resources to support infrastructure, production, marketing, inventory , and other business activities.
How does this affect human resource planning? Organizational strategy directs strategic human resource management directs human resource planning.
In many ways, the strategy side of your business mirrors the relationship between SHRM and HRP.
Organizational strategy is subdivided into three distinct categories: corporate strategy, business strategy, and functional strategy. Just like SHRM and HRP, each level is a part of the one above it.
Corporate level strategy is the main purpose of your business — it’s the destination toward which your business is moving.
Business level strategy is the bridge between corporate level strategy and much of the “boots-on-the-ground” activity that occurs in functional level strategy.
Functional level strategy is the specific actions and benchmarks you assign to departments and individuals that move your business toward the goals created by your corporate level strategy. They are a direct offshoot of your business level strategies.
With those categories in mind, we start to see the bigger picture of your business. SHRM is a component of your business level strategy, while HRP is a component of your functional level strategy.
Now that you understand the theory behind human resource planning, let’s focus our attention on the practice itself.

1) Analyze Organizational Strategy
Any successful workforce-management program — including human resource planning — is a direct offshoot of your business’s organizational strategy.
Therefore, you should always start your HRP process by analyzing the goals and plans of your organization. With those strategies in mind, you can then move on to crafting a general human resources mission statement.
From there, you can work your way through the various departments in your business to address issues such as:
- Recruitment
- Employee relations
When you have that information written down, you can craft a human resource plan to help your business reach and maintain its goals.
2) Inventory Current Human Resources
After analyzing your organizational strategy, it’s time to take stock of your business’s current human resources.
In the process, it’s beneficial to investigate such variables as:
- Total number of team members you employ
- Who works in what department
- Skills of each employee
- Performance reviews
- Team and individual potential
With that data in hand, you then make sure that your existing workforce is large enough and skilled enough to cover current demands before moving on to the next step in this guide.
3) Forecast The Future Of Your Workforce
Step three is all about planning, prediction, and preparing for the future.
Guided by your organizational strategy and your current employee data, do your best to forecast what the future of your workforce will look like. Be sure to incorporate any goals and plans into your forecast.
Examine variables such as:
- New product offerings
- New services
- A second (or third) location
- Labor costs
- Vendor and supplier relations
- Cost of goods sold
A forecast of this type, coupled with the workforce data from step two, gives you an accurate picture of where your business is right now and where you want it to be five, 10, even 15 years down the road.
4) Estimate Gaps
Armed with the information you’ve produced so far, you can now estimate whether or not there are any gaps in your human resource strategy.
Will you need more employees to get your business from the present to where you want it to be in the future? If so, how many? Will you need fewer employees? If so, how many?
Does your forecast call for a reallocation or redistribution of current team members? If so, how would you go about doing this?
Once you’ve estimated the gaps between your current and future workforce numbers, you can move on to step five, where all the planning and brainstorming comes to fruition.
5) Formulate An Action Plan
Formulating an action plan is where the rubber meets the road, so to speak.
Your action plan should take into account all the analysis that came before it — organizational strategies, current HR inventory, HR forecast, and gaps between present and future — to create a step-by-step system for taking your business from point A to point B.
The action plan will be different for every business. Some businesses may need to begin recruiting and training . Other businesses may need to promote or transition their existing workforce.
Still other businesses may need to develop a retirement program or a redeployment process to deal with surplus employees.
When crafting your plan, start with the theoretical — evolve from X to Y — and then move on to actionable steps that your HR department can take — hire and retain two new team members every year, for example — to transform the theory into reality.
With these steps in mind, you can implement a successful human resource planning system into your business, no matter how many employees you have.
As you go about implementing your business’s HRP, don’t neglect the foundation of all good employer/employee relations: scheduling and communication. We’ll discuss this topic at the end of the article.

6) Integrate With The Rest Of The Company

Now that you’ve got an action plan, your human resource planning efforts will start to yield results.
That said, the integration stage is the most difficult of the entire process, so be ready for some speed bumps.
Without proper preparation — and even with proper preparation, in some cases — both management and frontline employees may show resistance to the proposed changes.
In addition, all departments within your business work together in one way or another (even if it doesn’t at first appear so). This makes the integration phase challenging on many levels.
One of the best ways to integrate human resource planning into the rest of the company is to start with the recruitment , hiring , and training practices in your business.
Once you’ve brought in new, high-potential employees and have begun funneling them into the various departments, you can start to make other changes to accommodate these new hires.
Integrating slowly and pairing the changes with new employees who will further the goals and productivity of each department makes putting your new human resource planning into place much easier.
7) Monitor, Evaluate, And Adjust
The final step in human resource planning is to monitor the new practices, evaluate them for their effectiveness, and adjust as necessary.
In addition to monitoring each department and your business as a whole, it’s also beneficial to zoom in on how any changes made affect the individual employee.
To take the pulse of the front-line worker, include questions about your human resource planning during mid-year reviews and performance appraisals . You can even ask for their opinion when you have them complete an employee self-evaluation .
Monitoring and evaluating in this way will help you get a detailed view of how any new policies, procedures, and practices affect the men and women in the trenches.
Once you have all the information you need, you can then take steps to adjust your human resource planning accordingly.
For that, it’s best to return to the top of this list and start again at step one, incorporating what you learned from the previous run-through.
In essence, then, you can view this list as less of a straight line and more of a circle, with step seven leading directly back into step one. As such, your HRP should be in a constant state of development.

Your business can function without HRP, and, yes, it can be a challenge to get the plans in place, but the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks.
Among other things, HRP can help your business:
- Anticipate workforce needs in a changing market
- Plan for short-term and long-term growth
- Improve operations
- Facilitate staffing changes
- Avoid talent shortage
- Stay ahead of the technology curve
- Remain agile as the market evolves
- Maintain compliance with government laws and regulations
Human capital management is one of the most important parts of your business. HRP helps you maximize that potential.
As beneficial and powerful as human resource planning is, it is not without its drawbacks and challenges.
For one thing, HRP relies on forecasting, which is an imperfect art and is never — and can never be — 100% accurate.
Similarly, you can never account for the ambiguity in the market and the rapid change that could come out of nowhere.
There may be some error when you forecast the future of your workforce. That error will affect the other steps on this list for the good or the bad (depending on how accurate your forecast is).
Realistically, though, that can’t be helped and all you can do is give it your best shot. If you discover errors in your forecasting, you can always return to step one and start the process over with the new information.
Other challenges of the human resource planning process include:
- Resistant workforce
- Inefficient information systems
- Overall cost
- Time and effort
That said, when you are aware of these challenges going in, you can take steps to overcome them right away so that you can get to the benefits sooner.
Scheduling and communication are key components of an effective human resource planning process.
Your team’s schedule is the cornerstone on which you build their work experience. If the schedule doesn’t satisfy all parties — employees and management alike — your business suffers.
Similarly, clear communication with all your employees fosters a strong team and keeps everyone in the loop about employee performance, inventory, standard operating procedures , customer satisfaction , and your business as a whole.
In the 21st century, the best schedules are created and the best communication maintained with help from dedicated software like Sling .
Whether your business has one shift or three, offers flextime or a compressed workweek , or works a 9-to-5 work schedule or a 9/80 work schedule , Sling can help simplify the schedule-creation process.
And with advanced communication features built in, Sling is the only tool you’ll ever need to keep your employees informed about your business and connected with each other.
In fact, we developed the Sling app to streamline communication as well as make scheduling, tracking labor, finding substitutes, assigning tasks, and building employee engagement extremely simple.
There are so many ways Sling can help improve your human resource planning that we don’t have room to talk about them here. So instead of reading about it, why not try it out?
Sign up for a free account and see for yourself how Sling can help you implement the necessary strategies to make your team and your business successful.
For more free resources to help you manage your business better, organize and schedule your team, and track and calculate labor costs, visit GetSling.com today.
See Here For Last Updated Dates: Link
This content is for informational purposes and is not intended as legal, tax, HR, or any other professional advice. Please contact an attorney or other professional for specific advice.
Find the article useful? Share with others:
Related articles
Strategic Human Resource Management: What Is It And Why Is It Important?
Most businesses have some type of human resource management plan — even if it�...

Human Resource Management: What Is It And Why Is It Important?
Regardless of the size of your team, human resource management is crucial for th...

What Is a Human Resource Management System (HRMS)?
A human resource management system can help your business get ahead in the game....
Get started today
Schedule faster, communicate better, get things done.
Human Resource Planning: Definition, Importance, Objectives, Process & Prerequisites
In this article we will discuss about human resource planning. Learn about:-
1. Introduction to Human Resource Planning 2. Meaning of Human Resource Planning 3. Definition 4. Need and Importance
5. Objectives 6. Organisation 7. Factors Affecting 8. Human Resource Planning at Different Levels 9. Quantitative and Qualitative Dimensions 10. Prerequisites and Other Details.
- Introduction to Human Resource Planning
- Meaning of Human Resource Planning
- Definition of Human Resource Planning
- Need and Importance of Human Resource Planning
- Objectives of Human Resource Planning
- Organisation of Human Resource Planning
- Factors Affecting Human Resource Planning
- Human Resource Planning at Different Levels
- Quantitative and Qualitative Dimensions of Human Resource Planning
- Prerequisites of Human Resource Planning
- Relationship of Human Resource Planning with Other Personnel Processes
- Cost-Contribution Analysis in Human Resource Planning
- Responsibility of Human Resource Planning
- Integration of Strategic Planning and Human Resource Planning
- Human Resource Planning and Environmental Scanning
- Human Resource Planning – Mapping an Organisation’s Human Capital Architecture
- Edgar Schein’s Human Resource Planning and Development System
- Human Resource Planning – Benefits
- Problems of Human Resource Planning
- Recent Implications of Human Resource Planning
- Recent Trends of Human Resource Planning
Human Resource Planning – Introduction :
Human resources undoubtedly play the most important part in the functioning of an organization. The term ‘resource’ or ‘human resource’ signifies potentials, abilities, capacities, and skills, which can be developed through continuous interaction in an organizational setting.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The interactions, interrelationships, and activities performed all contribute in some way or other to the development of human potential. Organizational productivity, growth of companies, and economic development are to a large extent contingent upon the effective utilization of human capacities.
Hence, it is essential for an organization to take steps for effective utilization of these resources. In the various stages in the growth of an organization, effective planning of human resources plays a key role. Matching the requirements of the job with the individual is important at all stages, including the recruitment procedures, in this endeavour.
When organizations contemplate diversification or expansion, or when employees have to be promoted, human resource planning plays an important role. Further, the organizational plans, goals, and strategies also require effective human resource planning.
Human Resource Planning – Meaning :
E.W. Vetter viewed human resource planning as “a process by which an organisation should move from its current manpower position to its desired manpower position. Through planning, management strives to have the right number and right kind of people at the right places at the right time, doing things which result in both the organisation and the individual receiving maximum long-run benefit.”
According to Leon C. Megginson human resource planning is “an integrated approach to performing the planning aspects of the personnel function in order to have a sufficient supply of adequately developed and motivated people to perform the duties and tasks required to meet organisational objectives and satisfy the individual needs and goals of organisational members.”
Human resource planning may be viewed as foreseeing the human resource requirements of an organisation and the future supply of human resources and- (i) making necessary adjustments between these two and organisational plans; and (ii) foreseeing the possibility of developing the supply of human resources in order to match it with requirements by introducing necessary changes in the functions of human resource management. In this definition, human resource means skill, knowledge, values, ability, commitment, motivation, etc., in addition to the number/of employees.
Human resource planning (HRP) is the first step in the HRM process. HRP is the process by which an organization ensures that it has the right number and kind of people, at the right place, at the right time, capable of effectively and efficiently completing those tasks that will help the organization achieve its overall objectives.
HRP translates the organization’s objectives and plans into the number of workers needed to meet those objectives. The actual HRM process starts with the estimation of the number and kind of people required by the organization for the coming period.
HRP is also known by other names such as ‘Manpower Planning’, ‘Employment Planning’, ‘Labour Planning’, ‘Personnel Planning’, etc. HRP is a sub-system in the total organizational planning. In other words, HRP is derived from the organizational planning just like production planning, sales planning, material planning, etc.
Human Resource Planning – Definition :
The organisation’s objectives and strategies for the future determine future requirement of human resources. It only means that the number and mix of human resources are reaction to the overall organisational strategy. If the intent is to get closer to people possessing requisite qualifications, the organisation should act quickly.
Human Resource Planning or Manpower Planning (HRP) is the process of systematically reviewing HR requirements to ensure that the required number of employees with the required skills is available when they are needed. Getting the right number of qualified people into the right job is the crux of the problem here.
In actual practice, this is not easy. Due to constant changes in labour market conditions, qualified people possessing relevant qualifications are not readily available. The organisation needs to go that extra mile, dig up every source of information and exploit every opportunity that comes its way in order to identify talent.
HRP is simply not a process of matching the supply of people (existing employees and those to be hired or searched for) with openings the organisation expects over a given timeframe. It goes a step further in order to reach out to right kind of people at right time, spending time, resources and energies. Without careful planning, advance thinking and prompt actions, it is next to impossible to get competent and talented people into the organisation.
Human resource planning is the responsibility of both the line and the staff manager. The line manager is responsible for estimating manpower requirements. For this purpose, he provides the necessary information on the basis of the estimates of the operating levels. The staff manager provides the supplementary information in the form of records and estimates.
Human Resource Planning – Need and Importance :
The following points highlight the need and importance of HRP in the organizations:
I. Assessing Future Personnel Needs:
Whether it is surplus labour or labour shortage, it gives a picture of defective planning or absence of planning in an organization. A number of organizations, especially public sector units (PSUs) in India are facing the problem of surplus labour.
It is the result of surplus labour that the companies later on offer schemes like Voluntary Retirement Scheme (VRS) to eliminate surplus staff. Thus, it is better to plan well about employees in advance. Through HRP, one can ensure the employment of proper number and type of personnel.
II. Foundation for Other HRM Functions:
HRP is the first step in all HRM functions. So, HRP provides the essential information needed for the other HRM functions like recruitment, selection, training and development, promotion, etc.
III. Coping with Change:
Changes in the business environment like competition, technology, government guidelines, global market, etc. bring changes in the nature of the job. This means changes in the demand of personnel, content of job, qualification and experience needed. HRP helps the organization in adjusting to new changes.
IV. Investment Perspective:
As a result of change in the mindset of management, investment in human resources is viewed as a better concept in the long run success of the enterprise. Human assets can increase in value as opposed to physical assets. Thus, HRP is considered important for the proper planning of future employees.
V. Expansion and Diversification Plans:
During the expansion and diversification drives, more employees at various levels are needed. Through proper HRP, an organization comes to know about the exact requirement of personnel in future plans.
VI. Employee Turnover:
Every organization suffers from the small turnover of labour, sometime or the other. This is high among young graduates in the private sector. This necessitates again doing manpower planning for further recruiting and hiring.
VII. Conformity with Government Guidelines:
In order to protect the weaker sections of the society, the Indian Government has prescribed some norms for organizations to follow. For example, reservations for SC/ST, BC, physically handicapped, ex-servicemen, etc. in the jobs. While planning for fresh candidates, HR manager takes into consideration all the Government guidelines.
VIII. International Expansion Strategies:
International expansion strategies of an organization depend upon HRP. Under International Human Resource Management (IHRM), HRP becomes more challenging. An organization may want to fill the foreign subsidiary’s key positions from its home country employees or from host-country or from a third country. All this demands very effective HRP.
IX. Having Highly Talented Manpower Inventory:
Due to changing business environment, jobs have become more challenging and there is an increasing need for dynamic and ambitious employees to fill the positions. Efficient HRP is needed for attracting and retaining well qualified, highly skilled and talented employees.
Human Resource Planning – Objectives :
The main objectives of HRP are:
(i) Proper assessment of human resources needs in future.
(ii) Anticipation of deficient or surplus manpower and taking the corrective action.
(iii) To create a highly talented workforce in the organization.
(iv) To protect the weaker sections of the society.
(v) To manage the challenges in the organization due to modernization, restructuring and re-engineering.
(vi) To facilitate the realization of the organization’s objectives by providing right number and types of personnel.
(vii) To reduce the costs associated with personnel by proper planning.
(viii) To determine the future skill requirements of the organization.
(ix) To plan careers for individual employee.
(x) Providing a better view of HR dimensions to top management.
(xi) Determining the training and development needs of employees.
Human Resource Planning – Organisation :
Every line manager is responsible for planning manpower of the respective department and the top management is responsible for the planning of resources for the entire organisation. The personnel department supplies relevant information and data to all the line managers and helps those regarding interdepartmental transfers, promotions, demotions etc. Personnel department also helps in using the techniques and forecasting the manpower.
Personnel department forecasts internal mobility surplus or deficit of human resources for the entire organisation, prepares action plans regarding redeployment, redundancy, employment, development and internal mobility and submits plans to the management at the top which either by its own or by appointing a committee reviews departmental plans and overall plans, make necessary adjustments and finalises the plans. Personnel department in its turn prepares modified plans for the departments based on finalised overall plan and communicates them to respective heads of department.
Personnel department may co-ordinate the control activity of human resource plan and it has to send coordinated reports to the management at the top for actual review, control and monitor the human resource system. The management at the top may appoint a committee consisting of heads of department and external identification of deviations, reasons thereof and steps to be taken to correct the deviations. The committee further helps the management in executing the programmes of corrections.
Human Resource Plan – Factors :
Several factors affect HRP. These factors can be classified into external factors and internal factors.
External Factors :
i. Government Policies – Policies of the government like labour policy, industrial relations policy, policy towards reserving certain jobs for different communities and sons-of the soil, etc. affect the HRP.
ii. Level of Economic Development – Level of economic development determines the level of HRD in the country and thereby the supply of human resources in the future in the country.
iii. Business Environment – External business environmental factors influence the volume and mix of production and thereby the future demand for human resources.
iv. Level of Technology – Level of technology determines the kind of human resources required.
v. International Factors – International factors like the demand for resources and supply of human resources in various countries.
vi. Outsourcing – Availability of outsourcing facilities with required skills and knowledge of people reduces the dependency on HRP and vice-versa.
Internal Factors :
i. Company policies and strategies – Company policies and strategies relating to expansion, diversification, alliances, etc. determines the human resource demand in terms of quality and quantity.
ii. Human resource policies – Human resources policies of the company regarding quality of human resource, compensation level, quality of work-life, etc., influences human resource plan.
iii. Job analysis – Fundamentally, human resource plan is based on job analysis. Job description and job specification determines the kind of employees required.
iv. Time horizons – Companies with stable competitive environment can plan for the long run whereas the firms with unstable competitive environment can plan for only short- term range.
v. Type and quality of information – Any planning process needs qualitative and accurate information. This is more so with human resource plan; strategic, organisational and specific information.
vi. Company’s production operations policy – Company’s policy regarding how much to produce and how much to buy from outside to prepare a final product influence the number and kind of people required.
vii. Trade unions – Influence of trade unions regarding number of working hours per week, recruitment sources, etc., affect the HRP.
Human Resource Planning at Different Levels:
Different institutions make HRP at different levels for their own purposes, of which national level, industry level, unit level, departmental level and job level are important.
i. National level – Generally, government at the centre plan for human resources at the national level. It forecasts the demand for and supply of human resource, for the entire nation.
ii. Sector level – Manpower requirements for a particular sector like agricultural sector, industrial sector or tertiary sector are projected based on the government policy, projected output/operations, etc.
iii. Industry level – Manpower needs of a particular industry like cement, textiles, chemical are predicted taking into account the output/operational level of that particular industry.
iv. Unit level – This covers the estimation of human resource needs of an organisation or company based on its corporate/business plan.
v. Departmental level – This covers the manpower needs of a particular department in a company.
vi. Job level – Manpower needs of a particular job family within department like Mechanical Engineer is forecast at this level.
vii. Information technology – The impact of information technology on business activities, human resource requirement and human resource plan is significant. It requires multi skilled expe rts, preferably less in number.
Human Resource Planning – Quantitative and Qualitative Dimensions :
Human resources have a dual role to play in the economic development of a country. On one hand they are the consumers of the products and services produced by the organizations while on the other hand they are one of the factors of production.
Along with capital and other factors of production, human resources can lead to increase in production and economic development. The rate of growth of human resources is determined by two aspects quantitative and qualitative.
Variables Determining the Quantity of Human Resources:
1. Population Policy:
Some population policies operate by influencing the factors responsible for growth such as fertility, marriage and mortality. These are known as population influencing policies. Another category of policies known as responsive policies are implemented to adjust to observed population trends with the help of programmes like health, nutrition, education, housing, etc. The aim of population policies is to achieve an optimum population for enhancing the country’s development.
2. Population Structure:
The structure or composition of the population is determined by two factors, sex composition and age composition.
(i) Sex Composition:
Sex ratio is the ratio of males to females in the population. It is the basic measure of the sex composition of the population of any area. Higher the number of females, higher will be the population growth rate in future.
(ii) Age Composition:
It is the distribution of population by age groups. Age composition is the result of past trends in fertility and mortality. The supply of labour depends on age composition as economically active population falls in range of 15-65 age groups.
3. Migration:
Net migration is another factor which causes changes in the population. Age and sex composition determine the natural growth in population, but for calculating the overall changes in population it is important to consider net migration also.
Net migration = total immigrants – total emigrants
A positive net migration will lead to a rise in population growth rate while negative net migration will reduce the growth rate of population. Migration can be both interregional and international.
4. Labour Force Participation:
The population of any country consists of workers and non-workers. The workers are the people, usually in age group of 15-65, who participate in economically productive activities by their mental or physical presence.
These include:
i. Employers,
ii. Employees,
iii. Self-employed persons, and
iv. Those engaged in family enterprises without pay.
The others in the population are the non-workers such as students, infants, elderly, beggars, retired people, inmates of jail or mental institutions, unemployed, etc. They do not contribute to any productive economic activity. It is the changes in the working population which affect the growth of human resources. The number of people who are unemployed but available for work also impacts the availability of labour.
Qualitative Aspects of Human Resource Planning:
The quantitative dimensions help to ascertain human resources in numbers while the productive power of human resources is assessed by the qualitative dimensions. For example, there may be hundreds of applicants for 20 vacancies, but out of these only a few may meet the quality standards required for the job.
Factors which determine the quality of human resources are:
1. Education and Training:
The quantity and quality of education and training received by human resources impacts their knowledge and skills. Education and training are important for the upliftment of both individual and society. It can be of two types, formal and informal.
Formal education is imparted through schools and colleges while informal education and training takes place through on-the-job training methods. Formal education stresses the transfer of theoretical knowledge, while informal education emphasizes on practical application of knowledge.
2. Health and Nutrition:
Health and nutrition along with education are vital for Human Resource Development. Health and nutrition impact the quality of life, productivity of labour and the average life expectancy.
Health status is determined by:
(i) Purchasing power of people.
(ii) Public sanitation, climate and availability of medical facilities.
(iii) People’s understanding and knowledge of health, hygiene and nutrition.
3. Equality of Opportunity:
Not all segments of people comprising human resources get equal employment opportunities. There is bound to be some discrimination.
The most common forms of discrimination are:
(i) Social discrimination – Discrimination on basis of gender, religion or social standing.
(ii) Economic discrimination – Discrimination based on financial positions or possession of wealth by the sections of workforce.
(iii) Regional discrimination – These are in form of discrimination between rural and urban population or between people belonging to different regions/ states.
Discrimination affects the quality and productivity of the human resources belonging to different sections of the population. The privileged classes get access to best education, nutrition and health facilities while underprivileged are deprived of their right share in the development process. For the overall, well rounded development of the country’s human resources, effective policies need to be implemented to deal with the problem of discrimination.
Human Resource Planning – Prerequisites :
i. There should be a proper linkage between HR plan and organizational plan.
ii. Top management support is essential.
iii. Proper balance should be kept between the qualitative and quantitative approaches to HRP.
iv. Involvement of operating managers is necessary.
v. Proper alignment between short-term HR plans and long-term HR plans should be there.
vi. HR plan should have in-built flexibility in order to adopt environmental uncertainties.
vii. Time period of HR plan should be appropriate to needs and circumstances of the organization.
Human Resource Planning – Relationship with Other Personnel Processes:
From a systems view, human resource planning is interrelated with many of the organization’s other endeavors in personnel management. The strongest relationship exists between human resource planning and selection. In fact, all selection efforts really are an integral part of the whole human resource planning process.
Organizations that have either stable or increasing human resource needs must go into the external labour market and hire employees even though they generally follow a promotion-from within policy.
In addition, human resource planning is related to both performance appraisal and training and development. Performance appraisals can pinpoint the skills that will be required for employees to move into higher-level positions via promotion, while training and development efforts may then be designed to provide these skills.
To meet organizational goals, human resource planning seeks to ensure that the organization’s demand for individuals at any particular time will be just met by available human resources. This view assumes that “stockpiling” employees at levels greater than needed and being understaffed are both undesirable.
This assumption represents a major difference between planning for human resources and planning for non-human resources. Although it is generally unacceptable to stockpile or build inventories of human resources, organizations may find it necessary or desirable to build up raw materials or finished-goods inventories.
It is unacceptable to hold human resource inventories for three reasons. First, human resources are costly and it may be difficult to justify the expense of excess personnel. There are sounder and more cost-effective options available to personnel planners in business firms. Second, excess people are not engaged in productive work, and are likely to be bored and frustrated by the lack of anything constructive to do.
Such boredom and frustration can create problems because excess people may make unnecessary work for productive people and may even inhibit the firm’s total productive efforts.
Third, since human resources, particularly skilled and professional people, may be in short supply, taking productive workers out of the economy’s labour pool may be considered socially unacceptable.
It is equally undesirable for an organization to operate with too few employees. As with “stockpiled” employees, individuals may feel frustrated, but in this case because of overwork rather than a lack of productive activity. This situation may also be dysfunctional to an organization’s goals.
Consider, for example, a department store during the holiday season with a shortage of sales personnel. In addition to the frustrations experienced by employees, such understaffing may also result in loss of employee efficiency.
Customers may respond to long lines and excessive waiting by taking their business elsewhere, with resultant loss of sales by the organization. Having too many or too few employees may create numerous problems for organizations-problems that can be reduced or eliminated through effective human resource planning.
Human Resource Planning – Cost Contribution Analysis :
Cost-contribution analysis of human resources is most important in HRP with a view to plan for more effective human resource system. The human resource components necessary to maximise employee contribution to the job and the organisation, and minimise the cost, should be determined in advance with the help of human resource accounting techniques.
The optimum human resource system should be planned and determined as the human resources system is the control system in the organisation because it emphasises the human contribution which critically influences the organisational effectiveness. Planning the human resource system includes determining the type of human resource components like creative and innovative skills and abilities, dynamism, leadership qualities, commitment, identification with the organisation, etc., considering the measures to acquire those human resources through recruitment, training and development and adjusting the components.
Similarly, cost of human resource should be streamlined and it should be taken as investment on human resources and not as mere cost. These items include remuneration cost (Pay, allowances, fringe benefits, other indirect costs), recruitment cost (cost of job design, advertising cost, cost for conducting tests, interview, reference checks, medical examination and induction), training costs, etc.
Human Resource Accounting (HRA) envisages capitalisation of all expenses like cost of recruitment, training etc. One of the systems of HRA i.e., replacement cost of human asset is an important tool for the formulation of manpower budget and plan for human resources.
Human Resource Planning – Responsibility :
Human resource planning is the responsibility of the personnel department. In this task, it is aided by the industrial engineering department, the top management and the team of directors of different departments. It is mostly a staffing or personnel function.
The overall responsibility lies with the Board of Directors because, as the manpower planning scheme of Hindustan Lever indicates, “these members are in a position to direct the future course of business, set appropriate goals for the management concerned in the formulation of personnel policies.”
The personnel department’s responsibility is “to recommend relevant personnel policies in respect of manpower planning, devise methods of procedure, and determine the quantitative aspects of manpower planning.”
The responsibilities of the personnel department in regard to manpower planning have been stated by Geisler in the following words:
(i) To assist, counsel and pressurise the operating management to plan and establish objectives;
(ii) To collect and summarise data in total organisation terms and to ensure consistency with long- range objectives and other elements of the total business plan;
(iii) To monitor and measure performance against the plan and keep the top management informed about it; and
(iv) To provide the research necessary for effective manpower and organisational planning.
Integration of Strategic Planning and Human Resource Planning:
Human resource planning like production planning, financial planning and marketing planning, should be a unified, comprehensive and integrated part of the total corporation. Human resource manager provides inputs like key HR areas, HR environmental constraints and internal HR capabilities and HR capability constraints to the corporate strategists. The corporate strategists in turn communicate their needs and constraints to the HR manager. The corporate strategic plan and HR plan thus incorporates both HR and other functional plans.
Corporations formulate plans to fit four time spans:
i. Strategic plans that establish company’s vision, mission and major long-range objectives. The time span for strategic plans is usually considered to be five or more years.
ii. Intermediate – range plans covering about a three year period. These are more specific plans in support of strategic plan.
iii. Operating plans cover about one year. Plans are prepared month by month in sufficient detail for profit, human resources, budget and cost control.
iv. Activity plans are the day-by-day and week-by-week plans. These plans may not be documented presents the link between strategic plan and human resource plan.
Strategic Plan Vis-a-Vis Human Resource Plan- Corporate — Level Plan :
Top management formulates corporate-level plan based on corporate philosophy, policy, vision and mission. The HRM role is to raise the broad and policy issues relating to human resources. The HR issues are related to employment policy, HRD policies, remuneration policies, etc. The HR department prepares HR strategies, objectives and policies consistent with company strategy.
I. Intermediate – Level Plan :
Large-scale and diversified companies organise Strategic Business Units (SBU) for the related activities. SBUs prepare intermediate plans and implement them. HR managers prepare specific plans for acquiring future managers, key personnel and total number of employees in support of company requirements over the next three years.
II. Operation Plan :
Operation plans are prepared at the lowest business profit centre level. These plans are supported by the HR plans relating to recruitment of skilled personnel, developing compensation structure, designing new jobs, developing leadership, improving work-life, etc.
III. Short-Term Activities Plan:
Day-to-day business plans are formulated by the lowest level strategists. Day-to-day HR plans relating to handling employee benefits, grievances, disciplinary cases, accident reports, etc., are formulated by the HR managers.
Human Resource Planning and Environmental Scanning :
Environment influences human resource management as well as business. Environmental scanning helps to know the nature and degree of environmental influence on human resource plan as well as business plan.
Managers have to scan the following environmental factors in particular:
i. Social factors including cultural factors, religious factors, child-care, educational programmes and priorities.
ii. Technological developments including information technology, people soft, automation and robotics.
iii. Economic factors including international, national and regional factors.
iv. Political factors including legal issues, laws and administrative factors.
v. Demographic factors including gender, age and literacy.
vi. Industry growth trends, competitive trends, new products, new processes, services and innovations.
The environmental scanning will help the managers to foresee the possible changes and make the adjustments in order to prevent the possible negative effects and get ready for the positive effects.
In addition to scanning the external environmental factors, organisations like Infosys, Satyam, Volvo and Southwest Airlines scan internal environmental factors. Organisational cultures, employees’ cultures affect the human resource plan as well as other areas of HRM. Organisations conduct cultural audits to know the impact of attitudes, values and activities of employees. As observed by Sears, employee positive attitude has direct and positive impact on customer satisfaction and revenue.
Most of the companies benchmark their standing and progress against each other as environmental scanning and HR planning are aimed at competitive advantage. Benchmarking is identifying the best HR practices like training and compensation in the industry, compare them with those of the firm and take steps to improve the practices to match with those of the best practices in the industry.
Target for benchmarking need not be a competitor, but the best in the industry, or companies in other industries. ‘Human Capital Benchmarking Report’ published by the Saratoga Institute provides information of 900 companies’ practices. Companies can use this source as well as the survey report of ‘Business Today’, published every year in addition to various research reports on pay structure, return on investment per employee, turnover rates, cost per hire, etc.
Human Resource Planning – Mapping an Organisation’s Human Capital Architecture :
The linkage between strategy and HR should focus on the development of core competencies. Some of the MNCs like Sony, Starbucks, Domino’s Pizza and South-West Airlines revolutionised their companies by developing core competencies.
These competencies helped these companies to have leverage by learning faster than others. Core competency is a portfolio of employee skills. Different skills of employees can be grouped based on ‘Strategic value’ they create and their distinctiveness to the organisation.
They are as follows:
i. Core Knowledge Workers:
This group of employees possesses firm-specific skills which are linked to the company’s strategy like R&D skills for pharmaceutical company and teaching skills for university employees. Companies invest in training of these employees, provide them with freedom and autonomy and offer higher salaries.
ii. Traditional Job-Based Employees:
This group of employees possesses skills that are important to the organisation, but are not critical/unique (like accountants, finance, marketing personnel). Companies invest less in developing these employees, but provide short-term financial benefits.
iii. Contract Labour:
This category of employees possesses skills, which are of less strategic value (like clerks, receptionists, drivers, security, etc.). This category of employees is normally hired from external agencies on contact basis. Organisations do not invest in training these employees and the employment relations are transactional.
iv. Alliance/Partners:
This group of employees has unique skills, but not directly related to organisation’s core function like lawyers, auditors and consultants. Companies do not employ them on regular basis, given their tangible link to the strategy but establish long- term alliances and partnerships with them.
HR managers make decisions with regard to whom to employ internally, whom to contract externally and the type of the employment relationship to be maintained. HR manager also considers the cost-benefit approach of internal employment vs. external contract in HRP.
v. Ensuring Fit and Flexibility :
Alignment between strategic planning and programmes, policies and practices of HR is vital and need to achieve two types of fit viz., external fit and internal fit.
A. External Fit:
External fit brings alignment between the business objectives/goals and major HR initiatives/practices. Growth strategy of the company is to be aligned with recruiting people with creative and innovative skills, providing freedom to them and investing on training for developing such skills. Low cost strategy is to be aligned with employing performance/productivity oriented employees.
B. Internal Fit:
Internal fit brings alignment among various HR policies and practices in order to establish configuration that is mutually reinforcing. Efficiency and creativity come from integrated effort of job design, HR Plan, recruitment and selection, training, performance management, compensation and motivation. Therefore, there should be integration among all HR functions. In addition, management should follow either individual approach or team approach for all HR functions.
Successful external and internal strategy and HRM alignment helps the organisation to increase organisational capability and competitive advantage.
vi. Cohort Analysis :
It is an analysis of risk factors of groups in which a group having one or more similar characteristics is closely monitored over time simultaneously with another group. It is one type of clinical study design and should be compared with a cross-sectional study. Cohort studies are largely about the life histories of segments of populations, and the individual people who constitute these segments. This method is used where case study approach is not feasible, creates too many statistical problems, or generally produces unreliable results. This is also called follow up study.
Cohort analysis helps to separate growth metrics from engagement metrics and helps to measure growth and identify growth problems.
Edgar Schein’s Human Resource Planning and Development System:
In his article entitled Increasing Organizational Effectiveness through Better Human Resource Planning and Development, Edgar Schein suggests that the process of HR planning and developing staff must take into account two important sets of needs – the needs of the company, and the needs and desires of the individual employees.
In the new millennium with companies showing less concern about employee career development, it’s useful to pay attention to the idea that when both employee and corporate needs are taken into account, the results, for both parties are much superior to the situation where only one set is considered.
Schein’s approach integrates HR planning and employee development.
This approach contains the following components:
1. Strategic business planning
2. Job/Role planning
3. Manpower planning and Human Resource Inventorying.
In addition staffing processes also form a part of the model
4. Job analysis
5. Recruitment and selection
6. Induction/socialization and initial training
7. Job design and job assignment
8. Development planning
9. Inventorying of development plans
10. Follow-up of development activities
11. Career development processes and a good deal more.
When doing an internal scan for purposes of human resource planning the questions that should be addressed.
When evaluating an organization’s current human resource capabilities for the purposes of human resource planning, the following questions and issues need to be addressed:
1. Are there any key forces affecting the organization’s operations (collective agreements, staffing issues, cultural issues, work/life balance, demographics, technology requirements, budget issues, expectation of clients)?
2. What knowledge, skills, abilities and capabilities does the organization have?
3. What is the company’s current internal environment? What elements support the company’s strategic direction? What elements deter the organization from reaching its goals?
4. How has the organization changed its organizational structure? How is it likely to change in the future?
5. How has the organization changed with respect to the type and amount of work it does and how is it likely to change in the future?
6. How has the organization changed regarding the use of technology and how will it change in the future?
7. How has the company changed with respect to the way people are recruited?
8. What is the public’s (or customers’) perceptions of the quality of the organization’s products, programmes, and/or services? What is being done well? What can be done better?
9. Are current programmes, processes or services contributing to the achievement of specific organizational goals?
When doing an external scan of the environment for purposes of human resources planning (HR planning), we should look for:
In order to do human resource planning, we need to have a sense of both the current external environment, and anticipate things that may happen in the future in the labour market place. We do this via an external scan or environmental scan that can address the following issues and questions.
1. How is the current external environment? What elements of the current environment are relevant to the company? Which are likely to inhibit the company from arriving its goals?
2. What are the company’s specific issues and implications of these issues? What key forces in this environment need to be addressed and which ones are less critical?
3. What is the impact of local trends on the company (demographic, economic, political, intergovernmental, cultural, technology, etc.)?
4. Are there comparable operations that provide a similar service? How might that change? How would that affect the company?
5. Where does the work of the company come from? How might that change and how would it affect the organization?
6. How might the external environment differ in the future? What forces at work might change the external environment? What implications will this have for the organization?
7. What kinds of trends or forces affect similar work in other jurisdictions?
8. What kinds of trends or forces affect the company’s partners/stakeholders and customers?
Human Resource Planning – Benefits :
Human Resource Planning (HRP) anticipates not only the required kind and number of employees but also determines the action plan for all the functions of personnel management.
The major benefits of human resource planning are:
i. It checks the corporate plan of the organisation.
ii. HRP offsets uncertainties and changes to the maximum extent possible and enables the organisation to have right men at right time and in right place.
iii. It provides scope for advancement and development of employees through training, development, etc.
iv. It helps to anticipate the cost of salary enhancement, better benefits, etc.
v. It helps to anticipate the cost of salary, benefits and all the cost of human resources facilitating the formulation of budgets in an organisation.
vi. To foresee the need for redundancy and plan to check it or to provide alternative employment in consultation with trade unions, other organisations and government through remodeling organisational, industrial and economic plans.
vii. To foresee the changes in values, aptitude and attitude of human resources and to change the techniques of interpersonal, management, etc.
viii. To plan for physical facilities, working conditions and the volume of fringe benefits like canteen, schools, hospitals, conveyance, child care centres, quarters, company stores, etc.
ix. It gives an idea of type of tests to be used and interview techniques in selection based on the level of skills, qualifications, intelligence, values, etc., of future human resource.
x. It causes the development of various sources of human resources to meet the organisational needs.
xi. It helps to take steps to improve human resource contributions in the form of increased productivity, sales, turnover, etc.
xii. It facilitates the control of all the functions, operations, contribution and cost of human resources.
Human Resource Planning – Problems:
Though HRP is beneficial to the organisation, employees and trade unions, some problems crop up in the process of HRP.
Important among them are:
1. Resistance by Employers and Employees:
Many employers resist HRP as they think that it increases the cost of manpower as trade unions demand for employees based on the plan, more facilities and benefits including training and development. Further, employers feel that HRP is not necessary as candidates are/will be available as and when required in India due to unemployment situation. Employers’ version may be true about unskilled and clerical staff but it is not true in the case of all other categories as there is shortage for certain categories of human resources.
Trade unions and employees also resist HRP as they view that it increases the workload of employees and prepares programme for securing the human resources mostly from outside. The other reason for their resistance is that HRP aims at controlling the employees through productivity maximisation, etc.
2. Uncertainties:
Uncertainties are quite prominent in human resource practices in India due to absenteeism, seasonal employment, labour turnover, etc. Further, the uncertainties in industrial scene like technological change, marketing conditions also cause uncertainties in human resource management. The uncertainties make the HRP less reliable.
3. Inadequacies of Information System:
Information system regarding human resources has not yet fully developed in Indian industries due to low status given to personnel department and less importance attached to HRP. Further, reliable data and information about the economy, other industries, labour market, trends in human resources, etc., are not available.
Human Resource Planning – Recent Implications :
Most of the organisations, employed human resources without proper HR plans before 1990s. This was more acute in the public sector whose objective was creation of employment opportunities. The absence of human resources planning before 1990s led to the following implications in Indian companies.
(i) Overstaffing – Most of the organisations are found to be overstaffed compared to their counterparts in other countries.
(ii) VRSI Golden-handshake – The absence of human resources planning led to overstaffing. Consequently, most of the organisations announced VRS/Golden-handshake programmes in order to reduce the consequences of overstaffing.
(iii) Delayering and Downsizings Most of the organisations de-layered their organisations and announced downsizing programmes to rectify the consequences of overstaffing.
Human Resource Planning – Recent Trends :
Unfortunately, the human resource planning efforts of organizations have often been inadequate by failing to emphasize the truly systematized approach geared toward meeting overall objectives.
As Lopez and others have observed:
Some organizations have perceived manpower planning primarily in terms of budgeting to control labour costs; others have viewed it as a management development technique; still others see it as a table of back-ups and replacements for current employees; and finally, others have viewed it as a means of establishing a human resource information system and a personnel inventory.
Since each of these approaches is necessarily limited in scope, the state of the art in human resource planning has limped along quite slowly.
Toward More Sophisticated Human Resource Planning:
In recent years, both personnel practitioners and researchers emphasized some of the basic facets of personnel decision making (1) taking systems and contingency approaches, and (2) developing more sophisticated human resource forecasting and planning models. For example, the growth of equal employment opportunity regulations in recent years has increased the awareness of human resource planners of the effects of external changes on personnel systems.
The observations are in order regarding these more sophisticated approaches. First, more complex planning systems have generally been used in larger firms. Large organizations generally must undertake complex human resource planning and can afford the higher costs of such approaches.
Second, although a wide range of human resource models have been developed, some of these models have ignored so many “real life” personnel variables that they have had virtually no practical application. On the positive side, there have been numerous quantitative models that have been very useful to organizations.
There are a number of reasons for the recent increase in the use of more sophisticated human resource planning models. For example, organizations simply have been growing larger and more complex, requiring more sophisticated approaches. This has been especially true in those organizations in which interdependencies have increased.
The invention and development of the computer has made possible the analysis of complex human resource problems that would previously have been so time-consuming as to be cost prohibitive or virtually impossible to deal with by manual computations.
“The manpower mix in organizations had gradually come to focus around highly skilled managerial and technical talent.” Such personnel have at times been in short supply, and more of a lead time has been required for their training and development.
Once an integrated, well-thought-out human resource planning programme has been initiated, managers tend to appreciate its benefits and work together with the firm’s human resource specialists in developing viable programmes-“they are more willing to plan in this area, if only they are shown how to begin,”
Problems with Sophistication in Human Resource Planning:
Despite these reasons for the growth of more sophisticated human resource planning, such approaches face a number of problems:
1. There is an inherent mathematical complexity associated with efforts to model human resource systems.
2. Always there is a lack of certainty surrounding human resource needs in the future, coupled with the existence of an acquisition lead time for meeting those needs. Even if an organization’s human resource planning experts were completely uncertain about the number of operation researchers that would be needed at a point in future, the organization would face no problems if it could at that future time instantaneously obtain any number of such personnel to meet its objectives.
However, lead times are needed to recruit and train new personnel and to train and promote existing employees for new positions or assignments. Acquisition lead times have become more of a problem in recent years because of the needs for highly skilled managerial and professional personnel.
Since this trend is expected to continue in future years, the problem of acquisition lead times creates forecasting difficulties for most organizations.
Finally, human resource plans must be updated more frequently in firms (or in any of their subsystems) in which greater uncertainty exists. As one observer has observed-
“Increasing instability and the greater uncertainties associated with certain job requirements (e.g., research and development or marketing) indicate a requirement for more up-to-date information on emerging needs. This manpower data is increasingly subject to change, and organizational needs dictate timely information with appropriate systems support”.
Related Articles:
- Human Resource Planning Process (with steps)
- Features of Human Resource Planning
- Definition of Human Resource Management
Free HR Project Plan Templates
By Kate Eby | September 22, 2022
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
We’ve rounded up the most comprehensive list of human resources project plan templates for HR managers, HR staffing coordinators, project managers, diversity officers, information specialists (HRISs), and recruiters.
Included on this page, you'll find a sample HR project plan template , an HR project action plan template , an HR staffing plan template , an HR onboarding plan checklist template , and an HR employee training plan template , among others. You’ll also get tips on what to include in your HR project plan.
HR Project Plan Template
Download a Sample HR Project Plan Template for Excel | Google Sheets
Download a Blank HR Project Plan Template for Excel | Google Sheets
Use this visually dynamic HR project plan template to document every detail of your HR project plan. Within the template, you can list and manage tasks, assign them to HR personnel, set priorities and status for each, and track the percentage of task completion for the entire project. The template includes visualizations of your HR project data, including an Overall Task Status pie chart, a horizontal Budget bar chart, and a Pending Items vertical bar chart. This template is available as a blank document or with sample data, and both versions are completely customizable.
For more helpful HR templates and resources, see our article on top Excel templates for human resources .
HR Onboarding Plan Checklist Template
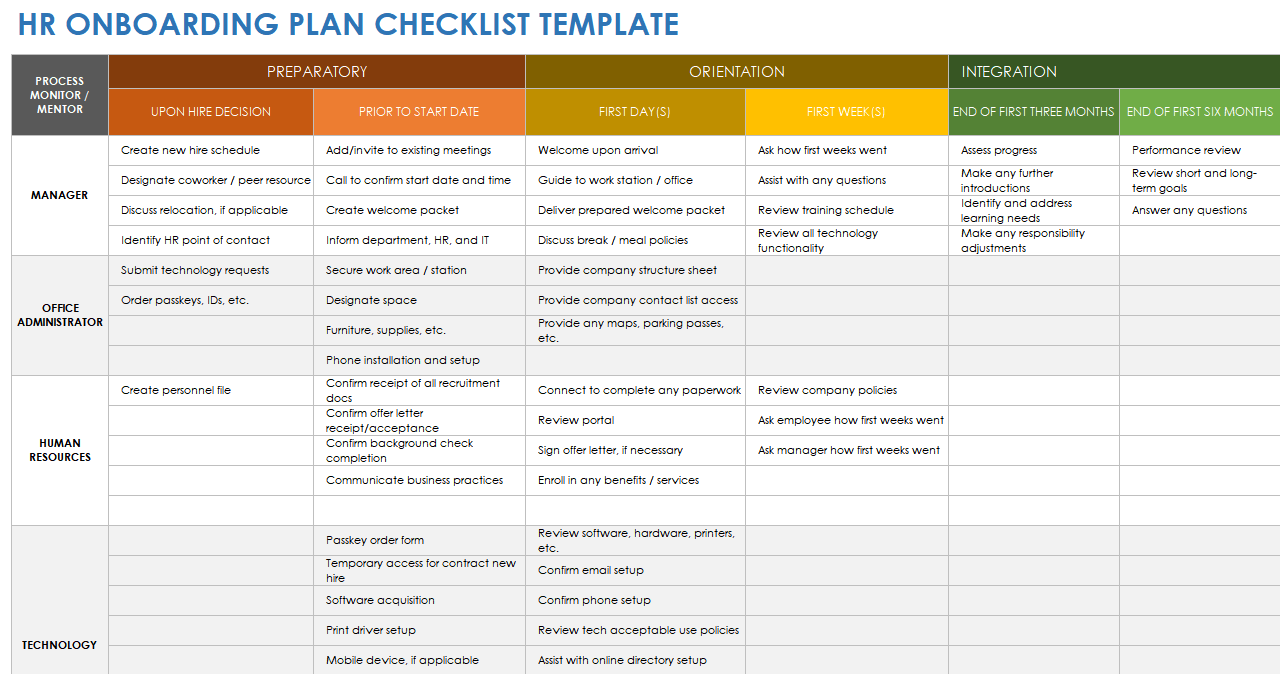
Download an HR Onboarding Plan Checklist Template for Excel | Google Sheets
Use this all-encompassing HR onboarding plan checklist template to ensure that all new hires’ onboarding proceeds successfully and they’re happy they decided to accept your offer. The template includes columns for Preparatory, Orientation, and Integration onboarding tasks, under which you can list each to-do item to make every new hire’s transition to your company as seamless as possible. Use the Process Monitor / Mentor column to assign personnel for each stage in a new employee’s development so that they get up to speed in no time.
For additional project plan tips and resources in Excel format, see our article on top Excel project plan templates .
HR Staffing Plan Template
Download an HR Staffing Plan Template for Excel | Google Sheets
Proactively staff organizational initiatives with this comprehensive HR staffing plan template. Under the template’s Recruiting Source column, list your recruiting source (e.g., Online Recruiting, Vendor Agencies, Campus Recruiting, Job Fairs ), and then itemize the recruiting plan’s budget, hire goal (i.e., number of desired candidates), funding, and status details. The template enables you to assign each staffing-plan item to a team member, and note any lessons learned that could help you with future staffing efforts.
For more details on HR staffing and capacity planning, see our article on human resource planning and forecasts , which includes free templates.
Employee Training Plan Template
Download an Employee Training Plan Template for Excel | Google Sheets
Use this employee training plan template to manage your employees’ career and skills development to ensure that everyone is maturing in their current role and benefitting the organization. Tailor the template to each employee’s skill level or pace, and use it to create training plans for employee development, so that team members increase their capabilities and continue to enrich your workplace.
HR Project Action Plan Template
Download an HR Project Action Plan Template for Excel | Microsoft Word | Google Docs
Whether your HR plan of action is tactical, operational, or strategic, this HR project action plan enables you to state project goals, list required actions, assign each item to a team member, and set a due date for each action-plan item. Whether you need to create a performance improvement plan (PIP) with definitive steps that an employee must take, plan next year’s recruitment efforts, or create some other HR plan of action, this template ensures that all action items are completed and the project is a success.
Check out this article for templates and resources for creating the perfect project plan in Microsoft Word .
HR Strategic Plan Template
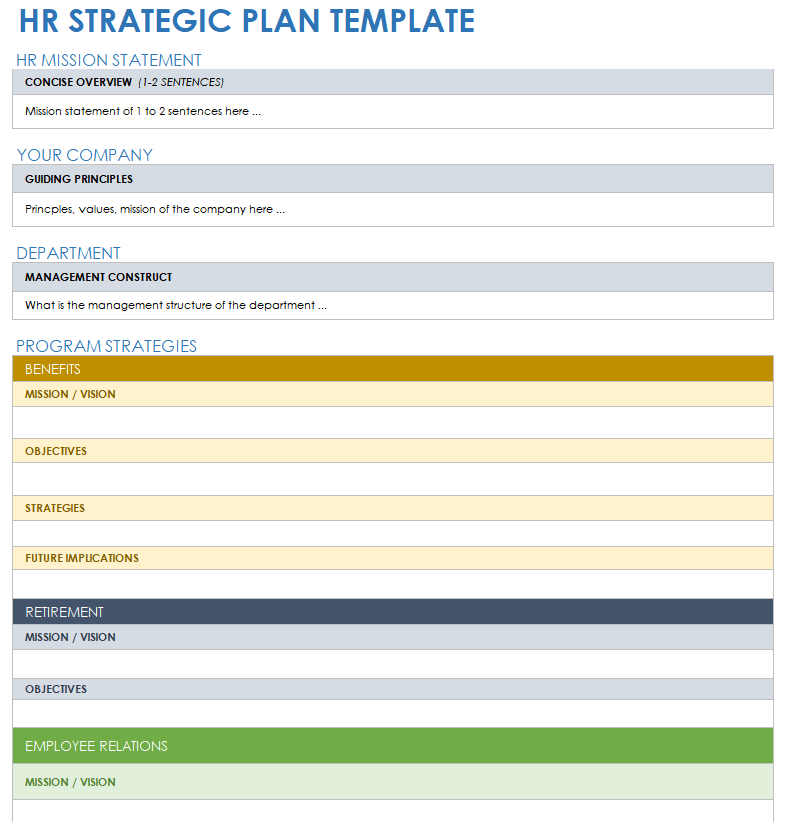
Download an HR Strategic Plan Template for Excel | Microsoft Word | Google Sheets
Keep your HR team members, sponsors, and other stakeholders apprised of your HR plans with this HR strategic planning template. Reiterate your HR mission statement and your company’s guiding principles, and then document the benefits of the HR strategy (mission, objectives, future implications, etc.), the state of employee relations, and the strategic plan’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT). This template helps ensure that any strategy you implement takes all factors into consideration and sets you up for success.
HR Capacity Planning Template
Download an HR Capacity Planning Template for Excel | Google Sheets | Smartsheet
Use this human resources capacity planning template to make sure that you properly allocate resources for a project or as a tool to ensure that you meet staffing requirements for a project to be successfully completed. Ensure timely project delivery by entering all individual task data, start and end dates, and hours required from each resource to complete the project. A pivot table provides a summary of your resource capacity planning data, so any team member or project sponsor can track resource and task status data at a glance.
HR Work Breakdown Structure Template
Download an HR Work Breakdown Structure Template for Microsoft Word | Google Docs
Keep your department apprised of your project plans and strategic developments with this HR work breakdown structure (WBS) template. The template provides a simple, hierarchical outline of the key tasks required for successful project completion. This easily shareable and presentation-friendly template is a great tool for HR teams looking for a simple structure and a visually compelling outline for their project’s planned activities.
HR Transition Plan Template
Download an HR Transition Plan Template for Excel | Google Sheets
Reduce the risk of “brain trust” lost when an employee transitions from one role to another or leaves the company with this HR transition plan template. The template is instrumental in ensuring that you successfully transfer knowledge and training from an employee who is leaving to their backfill. Set to-do tasks, assign sponsors or subject matter experts, and list helpful training the employee should undertake to succeed in their new role.
Get the Most Out of Human Resources Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Human resource planning (HRP) Exploratory Essay
Today, chief executive officers (CEOs) refer to their workforce (or human capital) as their organizations’ chief asset. This statement underpins the importance of the concept of human resource in organizations.
Human resource planning (HRP) enables an organization to better realize its goals by ensuring that it makes efficient and effective use of its human capital.
Today’s workforce is characteristically ambitious and hence, volatile. Rosenberg (n.d.) reiterates that employees switch careers an approximated three times in their working life. Even with this change in the nature of the workforce employer, employee and customer demands and expectations remain the same.
In addition to these, organizations are competing immensely for high quality talent and are at the same time investing heavily in acquiring and retaining it as these is crucial in meeting business objectives and goals.
Thus, HR managers have an additional task, which is HRP that is instrumental in dealing with the element of uncertainty as it pertains to an employee’s future. From an organization’s point of view a translation of HRP is making good use of an employee while he/she is in the organization’s hands.
Yan et al (2009) reiterates that an organization’s workforce (or human capital) is a valuable asset. A robust human capital is a critical success factor in ensuring that the expectations of customers are met, which is the key to positive financial performance.
Realizing such a robust human capital requires a sound and strategic HR policy, which ensures that an organization recruits the best expertise available and makes the best use of it for as long as it can. Forecasting an organization’s current and future financial needs and HRP are core units of such an HR policy.
HRP is according to Dessler (2001, p. 24) the process of “anticipating future demand for staff, allocating different kinds of staff within organisations, and developing systems for calculating human resource requirements based on accurate records and forecasting techniques”. What HRP does is that it facilitates the effective use of an organization’s human capital.
It does this by ensuring that the right personnel are working at the right place and at the right moment. Forecasting an organization’s current and future HR needs involves using either a quantitative approach or a qualitative one.
The quantitative approach to forecasting an organization HR needs involves numerical quantification of employees by use of statistical and mathematical procedures. By grouping the resultant numerical entities into applicable groups it is possible to determine HR excesses, deficits and inconsistencies.
Examples of applicable groups include age, pay, gender, qualifications and performance rating. HR managers co-work with statistical and mathematical experts to ensure that there is accurate quantitative forecasting.
The qualitative approach to forecasting an organization’s HR needs involves consultations with experts. The opinions of the expert drawn from the consultations enlighten the organization on what its HR needs are, specifically, staffing requirements and career development paths to pursue.
The expert bases his/her opinions on evaluations on employee performance and potential for promotion. A comparison of the quantitative and qualitative forecasting approaches reveals that the latter is more popular as it is cost and time saving.
There are a number of factors that HR managers should consider when undertaking HRP. According to Stone (2008) one these factors is women in the workforce. Today’s workforce contains an increasing number of women. An incentive that is greatly contributing to this increase is the use of mother-friendly alternative working arrangements in organizations.
For instance, employers are providing mothers with flexible work arrangements, special parental leaves, job sharing arrangements, childcare facilities within the organization’s premises, telecommuting work arrangements etc. From 1982 to 2005 Australia has seen a rise of 18.7% in the number of females in employment who are between the ages of 18 and 64 years (Australian Bureau of Statistics, 2010).
In addition to this, from 1989 to 2004 Australia has also seen a rise of 6% in the number of working mothers (Australian Bureau of Statistics, 2010). HR managers when doing HRP should be aware of the fact that the number of women in the workforce is on a rise and should therefore put in place mechanisms that attract and retain them.
To illustrate the above point lets take the example of Diane Gibney. Diane returns to work at her former employer’s veterinary clinic after giving birth to her first child. Due to post antenatal commitments she asks her former employer for an alternative working arrangement, namely, flextime which would allow her to work at given times of the day. The employer refuses to offer her such a working arrangement.
Following the employer’s refusal Diane quits her job and with another partner opens their own veterinary clinic. The 14 staff members in Diane’s new clinic are all female. She is sensitive to antenatal commitments and accords her employees flexible working arrangements so that they are able to attend to them. This example underpins the appreciation that employers should give to mother-friendly HR policies.
Another example is that of Caroline Coops. Caroline’s has a strong commitment and a high motivation to work for her current employer. The reason for this is that the employer accommodates flexible working arrangements that particularly enable and empower mothers to attend to their antenatal commitments. Though Caroline is not a mother yet, this provision by her employer has had a profound effect on her.
It gives her piece of mind knowing that when such commitments arise she is able to adjust a working schedule so that she can better attend to her family needs. This example shows that family-friendly HR policies attract women into employment and are instrumental in retaining them in the organization’s workforce.
Employee retention is critical in meeting business objectives as the direct and indirect costs employers incur to employee turnover are phenomenal. Direct costs are those that an employer incurs when replacing the individual who has made the turn over. Indirect costs are those that the employer incurs because of reduced productivity. Attracting high quality talent to an organization is also critical in meeting business objectives.
Flexible working arrangements that are family-friendly enable organizations to attract and retain such talent as shown from the two examples above. In other words, such working arrangements enable employers to combat employee turnover and at the same time attract high quality talent to the organization.
They are a critical business success factors with today’s workforce that contains an increasing number of women and particularly mothers.
According to Stone (2008) another factor for HR managers to consider when doing HRP is globalization. Dessler (2001) describes globalization simply as the venturing of businesses into new international markets. Advances in information technology have been and continue to be instrumental in globalization. Soon the world will be a global village with ecological and socio-political systems that are dependent on each other.
An advantage of globalization is that employers have a bigger market in which they can shop for individuals with the right levels of skill, experience and knowledge.
An outright disadvantage of globalization is that it supports or encourages brain drain. Organizations that are global employers via globalization should manage their multiracial and culturally diverse workforce in such a way that conflicts between employees are at a minimal.
To illustrate that globalization is a factor that HR managers should consider when undertaking HRP we take the example of an American firm which invested in England. The firm bought a textile machinery company near Birmingham. To boost productivity the American manager of the textile machinery company set about on cutting the time lost on tea breaks, which amounted to thirty minutes in a day per employee.
Culturally, having tea in such a manner is not a big issue to Americans but it is to the English. So, by the direction and instruction of the American manager a tea-maker machine was installed in the company. An infuriated workforce went on a riot demanding the removal of the tea-maker machine. The American manager had to comply with the demands of his English workforce.
According to Stone (2008) another factor that HR managers should consider when undertaking HRP is ageing population. The current situation in most economies of the world is a workforce with, first, less people entering it and second, an ageing and near retirement population. This is an impending crisis for employers. Soon, there will be a lack of both skilled and experienced labour.
At the moment, individuals nearing retirement are the ones fuelling a huge portion of workforce growth. This means that when this ageing population retires workforce growth will almost stagnate causing a huge problem to employers.
Additionally, mature age workers tend to be more loyal and productive in comparison to their younger counterparts. It is therefore imperative that HR managers start figuring out how they can retain their organization’s mature workers.
To illustrate that ageing population is a factor that HR managers should consider when undertaking HRP we consider the case of Peter Jordan. Peter Jordan is a business consultant. He is of the opinion that HR managers should redirect their employee retention efforts towards keeping mature workers (Porter, 2008).
Jordan cites this as being crucial in averting or mitigating the effects of an imminent staff and knowledge shortfall that is about to hit in the very near future (Porter, 2008). Jordan additionally points out that there is more justification for this strategy when you consider employee loyalty between the mature and young age workforce (Porter, 2008).
Jordan opines that there is more employee loyalty in mature age workforce than in the young age workforce (Porter, 2008). Craig Perret feels the same way as Jordan’s pointing out that, HR managers should develop policies that encourage the mature age workforce to remain at work (Porter, 2008).
Other factors on top of these three that HR managers should consider when undertaking HRP are employment, organizational structure and culture, outsourcing and technological changes in society. HR managers should take a keen interest on the rate of employment in their countries.
Organizational structure and culture are instrumental in lifting employee morale and commitment to an organization. Technological changes in society can eliminate the need for certain employees in an organization thus bringing in cost cutting benefits. Outsourcing is a means for increasing capacity in organizations so that customer demand is met.
Australian Bureau of Statistics. (2010b). Women’s income . Web.
Dessler, G. (2001). Human Resource Management (8th ed.). Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall Inc.
Porter, L. (2008). Boomers can keep sea change at bay. The Age , p. 23. Web.
Rosenberg McKay, D. (n.d.). How often to people change careers? About.com: Career Planning. Web.
Stone, R. J. (2008). Human Resource Management (6th ed.). Milton, Qld, Australia: Wiley.
Yan, A., Rao, Y., Liao, C. & Gao, C. (2009). Competency identification of sales staff in the agricultural seed industry: Evidence of seed firms in China . Web.
- Effective Employee Retention Strategies
- American School System Overview by Diane Ravitch
- Synesthesia in A Natural History of the Senses by Diane Ackerman
- Managerial Implications of Employee Engagement
- Spotlight on Strategic Human Resource Management
- Building a Restaurant Concept
- Operations Management at JnJ
- Johnson & Johnson Company Human Resource Management Model
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, June 5). Human resource planning (HRP). https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-resource-planning-hrp/
"Human resource planning (HRP)." IvyPanda , 5 June 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/human-resource-planning-hrp/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Human resource planning (HRP)'. 5 June.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Human resource planning (HRP)." June 5, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-resource-planning-hrp/.
1. IvyPanda . "Human resource planning (HRP)." June 5, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-resource-planning-hrp/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Human resource planning (HRP)." June 5, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-resource-planning-hrp/.

Human Resource Management Plan Template [Free Download]
Editorial Team

Download this free Human Resource Management Plan template and use it for your new project. Scroll down to the bottom of the page for the download link.
1 Introduction
Effective human resource management is a critical component of any project. The Human Resource Plan explains how project processes will be used to make the most effective use of the people assigned to the project.
This section of the Human Resource Plan should provide a general description of what the plan includes and explains how the project manager and project team can use the plan to help manage project resources effectively.
The purpose of the Human Resource Plan is to achieve project success by ensuring the appropriate human resources with the necessary skills are acquired, resources are trained if any gaps in skills are identified, team building strategies are clearly defined, and team activities are effectively managed. If used effectively, this plan will serve as a tool to aid in the management of human resource activities throughout the until closure.
This plan includes information regarding the following topics:
- Roles and responsibilities of team members throughout the project
- Project organization charts
- How resources will be acquired
- Timeline for resources/skill sets
- Training required to develop skills
- How performance reviews will be conducted
- Recognition and rewards system
2 Roles and Responsibilities
The roles and responsibilities of team members and stakeholders must be clearly defined in any project. Depending on the organizational structure, project team members may represent many different groups/departments and may have varying degrees of authority and responsibility. In these circumstances, it is common for multiple roles to be assigned to the same position. For this reason, this section is not meant to contain job descriptions, but rather a summary of responsibilities for each role. When listing roles and responsibilities, the following should be included:
- Role – description of the portion of the project for which the member is accountable
- Description – detail of duties and definition of the roles, as they relate to the project
- Responsibility – the work a team member must perform
- Name – the name of the specific individual holding the project role
2.1 Project Team Roles and Responsibilities
Listed below are the roles and responsibilities for the project team:
Senior Project Director
- Plans, directs and oversees the project, and ensures that deliverables and functionality are achieved as defined in the Project Charter, funding documentation, and subsequent project plans
- Maintains accountability for the management of all resources assigned to the project
- Serves as the primary liaison between the project and the Project Sponsor and the Steering Committee
Quality Manager
- Manages both product and process quality activities for the project
- Maintains the requirements management traceability matrix
- Provides insight into project health by reviewing process and product activities for adherence to standards and plans
Technical Lead
- Manages day-to-day activities of technical staff who are engaged in the technical management aspects of the project
- Leads in the technical disciplines of the project, unlike the Senior Project Director and Project Manager who will focus on the overall project management of the project
- Partners with other IT areas to acquire appropriate technical assistance for such areas as enterprise architecture, database, software development, security, testing, configuration management, change management , release management, and other technical areas of the new system
- Provides leadership and support to technical staff that are augmented to the project throughout the project life cycle
- Provides technical support to the Senior Project Director, Project Manager, and to Enterprise Architecture to establish and execute technical policies, processes, and procedures
Implementation Lead
- Manages for the implementation portion of the project
- Provides implementation management leadership through planning, organizing, coordinating, and monitoring implementation activities
- Effectively manages all information technology resources assigned by the project manager
- Interfaces directly with contractors to ensure technical obligations satisfy all objectives and expectations
Application Support Lead
- Oversees and coordinates the change request process for installed software and for ensuring the change requests adhere to specified quality and configuration standards
- Manages application design sessions and walkthroughs, application change management processes and acceptance testing of application changes
- Monitors consultant performance of application support and ensures that the consultant maintains quality control
- Coordinates the testing of the new system
- Works with the Quality Management staff to design test cases and data that will best represent “real-life” scenarios for the system
- Coordinates interface tests with other organizations (county, state, federal) as needed
- Plans, monitors, and evaluates consultant and agency test plans, problem reporting, and resolution process
Configuration Lead
- Supports the Technical Lead by administering the Configuration Management process
- Coordinates the control of all non-product related configuration items
- Manages and coordinates the product related configuration items
- Conducts configuration audits
- Works with Change and Release Management teams for approval to release programs and configuration modifications into the production environment
Operations Lead
- Coordinates and oversees the operations of the new system
- Monitors contractor management of operations and resolution of operations support problems
2.2 Project Stakeholders Roles & Responsibilities
Listed below are the roles and responsibilities for the project stakeholders:
Project Sponsor
- Provides vision, direction, and policy leadership for the project
- Assists in removing barriers and supports change management initiatives
- Participates in the Steering Committee, and provides support to this group as needed
- Has overall authority for the project
- Responsible for ensuring that deliverables and functionality are achieved as defined in the Project Charter and subsequent project plans
Steering Committee
- Acts as the Project stakeholders group
- Ensures that the deliverables and functionality of the project are achieved as defined in the project initiation documents and subsequent project management plans
- Provides high-level project direction, receives project status updates, and addresses and resolves issues, risks, or change requests
Independent Verification and Validation (IV&V)
- Provides independent, technical review and verification of project deliverables, as well as independent testing and auditing of project deliverables against requirements
- Performs deliverable quality assurance and information security control reviews
Department of Finance & Administration Representative
- Provides oversight and approval of funding for state planned IT projects
3 Project Organizational Charts
This section should provide a graphic display of the project tasks and team members. The purpose of this information is to illustrate the reporting structure and responsibilities of team members as they relate to the project tasks.
Tools such as the Responsible/Accountable/Consulted/Informed (RACI) matrix or Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) may be used to aid in communicating roles and responsibilities for the project team. Additionally, organizational or resource breakdown structures may be used to show how responsibilities are assigned by department or by type of resource respectively. The level of detail may vary depending on project complexity.
The graphic below provides a representation of the reporting structure for .
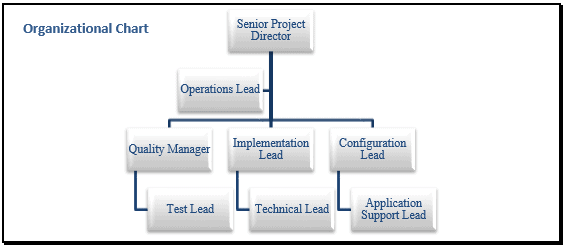
Table 1: Reporting structure
The following RACI chart shows the relationship between project tasks and team members. Any proposed changes to project responsibilities must be reviewed and approved by the Project Manager. Changes will be proposed in accordance with the project’s change control process. As changes are made, all project documents will be updated and redistributed accordingly.
Table 2: RACI chart
R – Responsible for completing the work
A – Accountable for ensuring task completion/sign off
C – Consulted before any decisions are made
I – Informed of when an action/decision has been made
4 Staffing Management
Staffing management relates to all of the reasons staffing is needed, timing of adding and releasing staff as well as training and gap assessment of current staff. This section should contain samples of the following: how human resources will be acquired; the timeline for resource additions and releases; training solutions for any resources with identified skill gaps; how performance reviews will be performed; rewards and recognition systems to be used. It is important to note that, depending on the scope of the project, there may be other circumstances to consider such as government and/or regulatory compliance issues, organizational health and safety, etc.
Day-to-day management of the project staff for is the responsibility of the Senior Project Director and designated functional managers. Performance evaluations, performance issues and recognition, promotions, and disciplinary actions are the responsibility of the state staff respective organizational chain of command.
Staff Acquisition
The Senior Project Director, with support from the Executive Sponsor, will negotiate with functional and department managers to identify and assign resources in accordance with the project organizational structure approved in the project charter. This plan shall also identify various external sourcing mechanisms to hire new project resources. All resources and their anticipated project assignment timeframe must be approved by the appropriate functional/department manager before the resource may begin any project work. The project team must be co-located at the site.
Resource Calendars
The Project will last for {insert timeline}. The chart below provides an estimate of the number of resources required per month for the project.
Figure 1: Resource calendar
Vendor/State Partnering Approach
For the team will implement a model in which the agency project team is expected to work side by side with the vendor to deliver the project. This partnership will facilitate the training & knowledge transfer process to prepare the agency project team to operationalize and own the solution after the solution implementation.
Though vendors are important and are used to implement project products, the State has responsibility for overall review and approval for work produced by vendors. Additionally, knowledge transfer of vendor expertise to State staff is required on all projects throughout the project lifecycle, rather than waiting to transition information at the end of a project.
5 Project Team Training
This section should highlight training needs specific to this project, and should include a high-level project team training plan. If applicable, this section may also include information such as training topics and delivery mechanisms, schedule, cost, expectations, etc.
Staff Training
When new staff joins the project, the Senior Project Director (or delegated project staff) will provide a project orientation. The orientation should include discussions related to the following topics:
- Background of the Project
- Current Status of the Project
- Specific Job Duties and Expectations
- Introduction to the Staff and Consultants
- Overview of the Facility and Infrastructure
- Overview of the Project Processes, including time reporting, attendance, and status meetings
Performance Reviews
The functional manager will review each team member’s assigned work activities at the onset of the project and communicate all expectations of work to be performed. The functional manager will then evaluate each team member throughout the project to evaluate their performance and how effectively they are completing their assigned work. Prior to releasing project resources, the project manager will meet with the appropriate functional manager and provide feedback on employee project performance. The functional managers will then perform a formal performance review on each team member.
Recognition and Rewards
Although the scope of this project does not allow for monetary rewards, there are several planned recognition and reward items for project team members. The Senior Project Director will work with appropriate agency executive staff to identify potential opportunities and tools for creative recognition and rewards.
Suggested Rewards:
- Upon successful completion of the Project, celebration of the success of each team member
- Upon successful completion of the project, any team member who satisfactorily completed all assigned work packages on time will receive a certificate of thanks from the Executive Sponsor
- Team members who successfully complete all of their assigned tasks will have their photo taken for inclusion in the company newsletter
Click here to download Human Resource Management Plan template.
- Project Proposal Template [Free Download]
- Requirements Management Plan Template [Free Download]
- System Design Document Template [Free Download]
- Sample Anti Virus Policy [Free Download]
most recent

Tips & Guides
Instagram polls and everything you need to know.

How to Overcome Challenges of ERP Integration

The Basics of Cryptocurrency Popularity
© 2024 Copyright ProjectPractical.com
- CRM Asignment Help
- MBA Assignment Help
- Statistics Assignment Help
- Market Analysis Assignment Help
- Business Development Assignment Help
- 4p of Marketing Assignment Help
- Pricing Strategy Assignment Help
- CIPD Assignment Help
- SWOT Analysis Assignment Help
- Operations Management Assignment Help
- Corporate Strategy Assignment Help
- Change Management Assignment Help
- Supply Chain Management Assignment Help
- Human Resource Assignment Help
- Management Assignment Help
- Marketing Assignment Help
- Strategy Assignment Help
- Operation Assignment Help
- Marketing Research Assignment Help
- Strategic Marketing Assignment Help
- Project Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Management Assignment Help
- Marketing Management Assignment Help
- Business Assignment Help
- Business Ethics Assignment Help
- Consumer Behavior Assignment Help
- Conflict Management Assignment Help
- Business Statistics Assignment Help
- Managerial Economics Assignment Help
- Project Risk Management Assignment Help
- Nursing Assignment Help
- Clinical Reasoning Cycle
- Nursing Resume Writing
- Medical Assignment Help
- Financial Accounting Assignment Help
- Financial Services Assignment Help
- Finance Planning Assignment Help
- Finance Assignment Help
- Forex Assignment Help
- Behavioral Finance Assignment Help
- Personal Finance Assignment Help
- Capital Budgeting Assignment Help
- Corporate Finance Planning Assignment Help
- Financial Statement Analysis Assignment Help
- Accounting Assignment Help
- Solve My Accounting Paper
- Taxation Assignment Help
- Cost Accounting Assignment Help
- Managerial Accounting Assignment Help
- Business Accounting Assignment Help
- Activity-Based Accounting Assignment Help
- Economics Assignment Help
- Microeconomics Assignment Help
- Econometrics Assignment Help
- IT Management Assignment Help
- Robotics Assignment Help
- Business Intelligence Assignment Help
- Information Technology Assignment Help
- Database Assignment Help
- Data Mining Assignment Help
- Data Structure Assignment Help
- Computer Network Assignment Help
- Operating System Assignment Help
- Data Flow Diagram Assignment Help
- UML Diagram Assignment Help
- Solidworks Assignment Help
- Cookery Assignment Help
- R Studio Assignment Help
- Computer Science Assignment Help
- Law Assignment Help
- Law Assignment Sample
- Criminology Assignment Help
- Taxation Law Assignment Help
- Constitutional Law Assignment Help
- Business Law Assignment Help
- Consumer Law Assignment Help
- Employment Law Assignment Help
- Commercial Law Assignment Help
- Criminal Law Assignment Help
- Environmental Law Assignment Help
- Contract Law Assignment Help
- Company Law Assignment Help
- Corp. Governance Law Assignment Help
- Science Assignment Help
- Physics Assignment Help
- Chemistry Assignment Help
- Sports Science Assignment Help
- Chemical Engineering Assignment Help
- Biology Assignment Help
- Bioinformatics Assignment Help
- Biochemistry Assignment Help
- Biotechnology Assignment Help
- Anthropology Assignment Help
- Paleontology Assignment Help
- Engineering Assignment Help
- Autocad Assignment Help
- Mechanical Assignment Help
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment Help
- Civil Engineering Assignment Help
- Electrical Engineering Assignment Help
- Humanities Assignment Help
- Sociology Assignment Help
- Philosophy Assignment Help
- English Assignment Help
- Geography Assignment Help
- History Assignment Help
- Agroecology Assignment Help
- Psychology Assignment Help
- Social Science Assignment Help
- Public Relations Assignment Help
- Political Science Assignment Help
- Mass Communication Assignment Help
- Auditing Assignment Help
- Dissertation Writing Help
- Sociology Dissertation Help
- Marketing Dissertation Help
- Biology Dissertation Help
- Nursing Dissertation Help
- MATLAB Dissertation Help
- Law Dissertation Help
- Geography Dissertation Help
- English Dissertation Help
- Architecture Dissertation Help
- Doctoral Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Statistics Help
- Academic Dissertation Help
- Cheap Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Help Online
- Dissertation Proofreading Services
- Do My Dissertation
- Business Report Writing
- Programming Assignment Help
- Java Programming Assignment Help
- C Programming Assignment Help
- PHP Assignment Help
- Python Assignment Help
- Perl Assignment Help
- SAS Assignment Help
- Web Designing Assignment Help
- Android App Assignment Help
- JavaScript Assignment Help
- Linux Assignment Help
- Coding Assignment Help
- Mathematics Assignment Help
- Geometry Assignment Help
- Arithmetic Assignment Help
- Trigonometry Assignment Help
- Calculus Assignment Help
- Arts Architecture Assignment Help
- Arts Assignment Help
- Case Study Assignment Help
- History Case Study
- Case Study Writing Services
- Write My Case Study For Me
- Business Law Case Study
- Civil Law Case Study Help
- Marketing Case Study Help
- Nursing Case Study Help
- ZARA Case Study
- Amazon Case Study
- Apple Case Study
- Coursework Assignment Help
- Finance Coursework Help
- Coursework Writing Services
- Marketing Coursework Help
- Maths Coursework Help
- Chemistry Coursework Help
- English Coursework Help
- Do My Coursework
- Custom Coursework Writing Service
- Thesis Writing Help
- Thesis Help Online
- Write my thesis for me
- CDR Writing Services
- CDR Engineers Australia
- CDR Report Writers
- Homework help
- Algebra Homework Help
- Psychology Homework Help
- Statistics Homework Help
- English Homework Help
- CPM homework help
- Do My Homework For Me
- Online Exam Help
- Pay Someone to Do My Homework
- Do My Math Homework
- Macroeconomics Homework Help
- Research Paper Help
- Edit my paper
- Research Paper Writing Service
- Write My Paper For Me
- Buy Term Papers Online
- Buy College Papers
- Paper Writing Services
- Research Proposal Help
- Proofread My Paper
- Report Writing Help
- Story Writing Help
- Grant Writing Help
- CHCDIV001 Assessment Answers
- BSBWOR203 Assessment Answers
- CHC33015 Assessment Answers
- CHCCCS015 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE018 Assessment Answers
- CHCLEG001 Assessment Answers
- CHCPRP001 Assessment Answers
- CHCPRT001 Assessment Answers
- HLTAAP001 Assessment Answers
- HLTINF001 Assessment Answers
- HLTWHS001 Assessment Answers
- SITXCOM005 Assessment Answers
- SITXFSA001 Assessment Answers
- BSBMED301 Assessment Answers
- BSBWOR502 Assessment Answers
- CHCAGE001 Assessment Answers
- CHCCCS011 Assessment Answers
- CHCCOM003 Assessment Answers
- CHCCOM005 Assessment Answers
- CHCDIV002 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE001 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE017 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE023 Assessment Answers
- CHCPRP003 Assessment Answers
- HLTWHS003 Assessment Answers
- SITXWHS001 Assessment Answers
- BSBCMM401 Assessment Answers
- BSBDIV501 Assessment Answers
- BSBSUS401 Assessment Answers
- BSBWOR501 Assessment Answers
- CHCAGE005 Assessment Answers
- CHCDIS002 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE002 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE007 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE025 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE026 Assessment Answers
- CHCLEG003 Assessment Answers
- HLTAID003 Assessment Answers
- SITXHRM002 Assessment Answers
- Elevator Speech
- Maid Of Honor Speech
- Problem Solutions Speech
- Award Presentation Speech
- Tropicana Speech Topics
- Write My Assignment
- Personal Statement Writing
- Narrative Writing help
- Academic Writing Service
- Resume Writing Services
- Assignment Writing Tips
- Writing Assignment for University
- Custom Assignment Writing Service
- Assignment Provider
- Assignment Assistance
- Solve My Assignment
- Pay For Assignment Help
- Assignment Help Online
- HND Assignment Help
- SPSS Assignment Help
- Buy Assignments Online
- Assignment Paper Help
- Assignment Cover Page
- Urgent Assignment Help
- Perdisco Assignment Help
- Make My Assignment
- College Assignment Help
- Get Assignment Help
- Cheap Assignment Help
- Assignment Help Tutors
- TAFE Assignment Help
- Study Help Online
- Do My Assignment
- Do Assignment For Me
- My Assignment Help
- All Assignment Help
- Academic Assignment Help
- Student Assignment Help
- University Assignment Help
- Instant Assignment Help
- Powerpoint Presentation Service
- Last Minute Assignment Help
- World No 1 Assignment Help Company
- Mentorship Assignment Help
- Legit Essay
- Essay Writing Services
- Essay Outline Help
- Descriptive Essay Help
- History Essay Help
- Research Essay Help
- English Essay Writing
- Literature Essay Help
- Essay Writer for Australia
- Online Custom Essay Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Custom Essay Help
- Essay Help Online
- Writing Essay Papers
- Essay Homework Help
- Professional Essay Writer
- Illustration Essay Help
- Scholarship Essay Help
- Need Help Writing Essay
- Plagiarism Free Essays
- Write My Essay
- Response Essay Writing Help
- Essay Editing Service
- Essay Typer
- APA Reference Generator
- Harvard Reference Generator
- Vancouver Reference Generator
- Oscola Referencing Generator
- Deakin Referencing Generator
- Griffith Referencing Tool
- Turabian Citation Generator
- UTS Referencing Generator
- Swinburne Referencing Tool
- AGLC Referencing Generator
- AMA Referencing Generator
- MLA Referencing Generator
- CSE Citation Generator
- ASA Referencing
- Oxford Referencing Generator
- LaTrobe Referencing Tool
- ACS Citation Generator
- APSA Citation Generator
- Central Queensland University
- Holmes Institute
- Monash University
- Torrens University
- Victoria University
- Federation University
- Griffith University
- Deakin University
- Murdoch University
- The University of Sydney
- The London College
- Ulster University
- University of derby
- University of West London
- Bath Spa University
- University of Warwick
- Newcastle University
- Anglia Ruskin University
- University of Northampton
- The University of Manchester
- University of Michigan
- University of Chicago
- University of Pennsylvania
- Cornell University
- Georgia Institute of Technology
- National University
- University of Florida
- University of Minnesota
- Help University
- INTI International University
- Universiti Sains Malaysia
- Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
- University of Malaya
- ERC Institute
- Nanyang Technological University
- Singapore Institute of Management
- Singapore Institute of Technology
- United Kingdom
- Jobs near Deakin University
- Jobs Near CQUniversity
- Jobs Near La Trobe University
- Jobs Near Monash University
- Jobs Near Torrens University
- Jobs Near Cornell University
- Jobs Near National University
- Jobs Near University of Chicago
- Jobs Near University of Florida
- Jobs Near University of Michigan
- Jobs Near Bath Spa University
- Jobs Near Coventry University
- Jobs Near Newcastle University
- Jobs Near University of Bolton
- Jobs Near university of derby
- Search Assignments
- Connect Seniors
- Essay Rewriter
- Knowledge Series
- Conclusion Generator
- GPA Calculator
- Factoring Calculator
- Plagiarism Checker
- Word Page Counter
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Living Calculator
- Quadratic Equation
- Algebra Calculator
- Integral Calculator
- Chemical Balancer
- Equation Solver
- Fraction Calculator
- Slope Calculator
- Fisher Equation
- Summary Generator
- Essay Topic Generator
- Alphabetizer
- Case Converter
- Antiderivative Calculator
- Kinematics Calculator
- Truth Table Generator
- Financial Calculator
- Reflection calculator
- Projectile Motion Calculator
- Paper Checker
- Inverse Function Calculator

Human Resource Management Functions
Assessment Purpose: The primary purpose of this assessment is to enhance students’ research, analysis and referencing skills.
The secondary purpose is to give students the opportunity to demonstrate their critical thinking and written communication skills.
The third purpose is to demonstrate that you have commenced appropriate research for Assessment 3.
Before starting this assessment, please read the assessment rubric at the end of this document. You should always check the unit website for specific instructions, which may be updated continuously.
Assessment Task: You are required to compile an Annotated bibliography of 5 peer-reviewed journal articles.
Step 1. Select an industry sector. Read the Assessment 3 Essay task and identify which sector you will study for Assessments 2 and 3 (e.g. agriculture; construction; financial services; health care; hospitality; manufacturing; mining; retail; transport).
Step 2. Undertake research of the recent academic literature since 2010. Identify five (5) academic peer reviewed journal articles relevant to the Assessment 3 Essay topic. It is suggested that you align your selected articles with the unit themes from Weeks 3 to 5 (e.g. job design, HR planning, recruitment and selection). It is recommended that you undertake your research via the online ‘search’ of CQUniversity Library. You cannot use articles from your Assessment 1 presentation for Assessment 2.
Step 3. Write 2 paragraphs on each article (400 words) For each journal article, you are to write approximately 400 words in two paragraphs. The first paragraph will summarise the main ideas of the article, identifying the hypothesis, purpose, research methodology and conclusions. The second paragraph will identify how you will use that article in relation to the Assessment 3 Essay.
Step 4. Use an appropriate format Present your Annotated bibliography in a format similar to that provided below. For more information, see the library guide for writing an annotated bibliography.
Topic: Human Resource Management Functions
Annotated Bibliography Introduction: Human Resource Management Functions are broader terms that impactmanagement and performance of any organisation. The HR manager needs to take timely-based and effective recruitment decisions that can help in the achievement of goals. Most of the jurisdictions in organisations that long time in identifying new HR strategies. Change is the necessary aspect of management. The HR manager needs to pool the best resource out of the hundred applicants. This is focused on identification of the Human Resource Management Assignment tools and implementation of new strategies from time to time. To reduce the long-term negative impacts, recruitment, selection training, planning and job-design are important aspects that impact the staffing decisions.
Article 1: Fevre, R. (2012). Social Mobility, Equity and the Politics of Recruitment. Sociology Compass, 6(9), 740-750. Retrieved from: http://unpan1.un.org/intradoc/groups/public/documents/UN/UNPAN021814.pdf
Keywords: Recruitment, Human Resource Management
The purpose of this journal article is to explain how the retention of high-quality professionals is crucial to the success of the organization. The market is extremely competitive. Today, manpower is available with diverse skills. The recruiters need to be more selective. This article is written for the public service audience. The article talks about different recruitment and human resource management strategies. Human Resource Management Assignment manager need to be more careful in the recruitment process. The retention of skilled talent is necessary for the Organization. The HR managers need to develop management strategies impact the staff morale. The highlights of this journal article are external and internal recruitment strategies, on the job training and value-added services to customers (Fevre, 2012). The Human Resource Management Functions and recruitment process can be conducted internally through referrals or promotion or transfer of personnel. The HR managers can advertise the jobs posting through the electronic boards or company newsletters and office memoranda. A commonly observed practice is referrals are word-of-mouth publicity and a lower cost recruiting methodology. The Organization can organize job fairs, and best of the companies can participate. The dozens of candidates are available, all at one place. The recruitment strategy is focused at bringing the job seekers and job givers at one place.
The drawback of this journal article is public service Organizations are more worried about the market share. These organizations operate in a monopolistic environment. The HR managers need to emphasize on the formulation of new strategies that aim at targeting the best experts. The Public-sector organizations need to comprehend the demands and wants of the consumers. Public sector organizations are open to scrutiny. The journal implies attracting the pool of talent for the different opportunities that are available in the market. There must be greater honesty and transparency in HR recruitment practices. A great plethora of opportunities are available in the market. The Human Resource Management Assignment needs to discuss the strategic and tactical role of Human resource implications in the longer run. Although, a commonly observed practice is there are few publicly operating organizations that maintain fairness in the recruitment processes? These organizations are aimed at protecting the individuals from harmful practices. The public service organizations need to maintain the detailed procedures and practices, if necessary to eliminate the discrimination. Cost is one the essential word-of-mouth factor that defines the retention policy of an organization. Another factor is convenience- as it allows the screening of candidates in a shorter span of time.
Article 2: Hoch, J., & Dulebohn, J. (2013). Shared leadership in enterprise resource planning and human resource management system implementation. Human Resource Management Review, 23(1), 114-125. Retrieved from: https://www.ikbooks.com/home/samplechapter?filename=168_Sample-Chapter.pdf
Keywords: Human Resource Planning, Strategic Planning
Human resource planning and strategic planning are the key areas of any Organization. This article refers to adequate source and effective application of human resources. This article is for those organizations who are undertaking an extensive research study. The human resource management functions must be taken to fulfill the mission, vision, and objectives of the Organization. The prime function of any HR in an organization is to hire the right people at the right time. An intermittent re-assessment of all the new developments in the Organization must be reviewed (Hoch &Dulebohn, 2013). The Human resource planning function should aim at effective planning and motivational processes. The Organizations should be able to estimate the number of resources required to run an Organization. Human resource planning is also referred to as- “Manpower planning”. The chief function of human resource department is to carry out the recruitment function at different levels. This can be for different purposes. HR plan operates at a national level, sectoral level, industry level, unit level and departmental level. The main aim of Human Resource Management Assignment is to ensure the demand and supply of manpower at different levels. This can be for serving the educational purposes, industrial developmental purposes or any employment plans made in the organization.
The drawback of this article is the development of concurrent employment plans in any company. The organizations are unable to forecast the need of manpower at different levels. The proportionate distribution of human resources at every level should be decided depending upon significance. The HR planning department must take into account the operational levels of every different department. A specific company is in question when human resource needs are not met with time. A business plan of any company is functional when the objectives defined can evade the unexpected disturbance in the production levels. This specifies lack of talented manpower in the Organization; therefore, appropriate strategies should be adopted. The Human Resource Management Functions should be all-inclusive and cover, marketing plans, financial plans and operational plans of an organization. The HR capabilities must be integrated and unified in an Organization. The organization must be able to fulfil the input needs and serve the desired output to customers. There are environmental constraints in every organization; therefore, a strategic plan must be formulated. The Human resource planning function aims all the employees in an organization to communicate the needs and wants, and constraints felt at different levels. An integration of all the Human resource plans is required at all the levels.
Article 3: Roberts, G. (2002). Employee Performance Appraisal System Participation: A Technique That Works. Public Personnel Management, 31(3), 333-342. Retrieved from: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/93cc/62d7f8a9188c88c509df80b6550f98bc5e7f.pdf
Keywords: Performance Appraisal, Performance Management
This article refers to employee engagement and commitment levels that are made by an employee to an organization. An organization wants a member those feel highly- encouraged and finish the given task on time. This article is for all the low-level and mid-level Organizations who want to study the long-term appraising techniques. The employees should give inner soul to the company’s success. The performance appraisal and performance management are two techniques those are aimed at developing a strong link between the current objectives of employees with the present objective of the Organization. It is similar to mapping your own vision and mission plan with your company’s plan. There must be a co-existence of mutual trust between the employer and employee (Roberts, 2002). The performance appraisal technique measures employee absenteeism from work, the greater engagement with patrons, fewer mistakes and earning higher profits within stipulated period of time. The competitiveness factor among employees can be developed by the utility of the employee engagement technique. The primary objective of a Human Resource Management Functions technique is enhancing the growth and development of individual and Organizations. Performance Management and performance appraisal are two terms which could be used as synonymous to each other. Performance rating methods can be used for foreseeing the performance levels of an employee in an organization.
The critical point in the article is how to review the performance of an employee in an Organization on a concurrent basis. Performance management refers to the successful attainment of objectives in an organization. Performance appraisal function implementation is critical to the success of every organization. The Performance management function is one main component of performance appraisal. To maximize the output and efficiency of groups and employees, the human resource functions must be in place. The performance of various teams existing inorganization is a critical process. The operational performance appraisal system assesses new incomings and plans for the growth and development of employees. In an Organization, where the performance appraisal system has been implemented, more than 60 percent of employees have shown dissatisfaction and did not like receiving. In such a scenario, this process can be thought for complete elimination. The most important aspect is to provide the feedback to the managers and initiate employee participation process. The employees and employers must be able to make the valid decisions. In today’s global competitive world, enhanced output and productivity can be served only when performance appraisal technique is in implementing stage. Managers must take into account all the legal considerations and an effective appraising system must be studied.
Article 4: Lozano, R. (2011). Creativity and Organizational Learning as Means to Foster Sustainability. Sustainable Development, 22(3), 205-216. Retrieved from: https://www.cebma.org/wp-content/uploads/Guide-to-the-after_action_review.pdf
Keywords: Action After Review, Organizational Learning
Organizational learning and development assess the need for intermittent identification of performances and taking lessons from success and failures, from time to time. This article refers to -The Action after Review (AAR) is a human resource management technique that is, conducted at the end of the project or event or a program. This Human Resource Management Assignment article focuses on the domestic and international level companies who are undertaking programs or events and a purposeful study for those who want to review the performance levels. The HR management function of any Organization devises strategies and team learning takes place through objective and mission statement. Action after Review follows a structured approach and identifies the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in a given area of work (Lozano, 2011). Some of the famous companies using Action after Review programs are GE, Motorola, and others. The implementation of Action after Review is a necessary aspect of an Organization as it answers these questions- What are the occurrences in future? What has happened? Whether an employee participation is up to the mark or not? Can the things be improvised in an Organization? The Action after review plan is focused to withstand the resources in an Organization. The management committee needs to propose recommendations.
The critical point in this article is-how to effectively manage one-time projects to long-term events. The management needs to measure the event outcomes, there is always scope for growth and development and good learning prospects. It should be made mandatory for employees to attend the Action after review program. Another critical point is-when Action after review program should be used by the Organizations-just after an event or when a program ends. What functional structure should be adopted by the company practices to provide the maximum advantage to the Organizations? The implementation of Action after review plan is not possible without a moderator. How to define whether informal or spontaneous Action after review plan must be implemented before the event ends or after an event? The formal AAR can be implemented through the help of a facilitator and spontaneous AAR can be directed through team manager. Another critical point in Action after review technique is time barrier. For instance- Informal AAR can be conducted without allotting any time-span. This can be as short as ten minutes and success barriers cannot be measured. A formal AAR can be done within a stipulated time period of one to two hours. Few strategies must be recommended for the successful implementation of informal AAR.
Article 5: Strych, J. (2015). Job Rotation and Employer Learning About Human Capital. SSRN Electronic Journal. Retrieved from:http://ergo-plus.com/wp-content/uploads/Job-Rotation.pdf
Keywords: Job Rotation, Quality Standards
This article reviews the structured exchange of employees between two different departments, within an organization at different time intervals is known as Job Rotation. Enhancement of more work and increase of physical demands, therefore, adds a change in the complete structure of employment. This article is for public sector and private sector an Organization who wants to understand the overall requirements of different rotational jobs. The HR function of any Organization should focus on the development of reliable and methodical job rotations. The advantages of job rotation are focused to share the risk factors present in an organizational environment. The Human Resource Management Assignment function needs to identify the high-risky jobs and address and troubleshoot, whenever possible. When job rotation is implemented within an Organization, it helps in reducing the physical demands associated with a job (Strych, 2015). The job rotation is focused to increase work efficiency and enhance quality standards in different processes. The Job rotation capabilities aim at the elimination of ergonomic problems. The employers must be able to identify the problems as early as possible. Consult management and group leader’s work together to decide on which internal departments are suitable for the job rotation program. Strategically driven job rotation programs give best competitive advantage.
The critical point in this article is the implementation of job rotation program at different units, within a company. The management undergoes through numerous barriers. The crucial aspect is that every department or job is not appropriate for the job rotation program. Some of the problems encountered are- issues with the product quality, employee productivity losses, employees hesitate to rotate because of the difficulties associated with jobs. Restriction of ability is one main reason that inhibits the job rotation process. In industrial organizations, various threats imposed by the union workers, especially for the job compensation rules. The employees are not convinced about the compensation cost that is received. The Human resource management functions find very difficult to implement the job rotation programs. A research study undertaken suggests-employee productivity and product quality suffer with the enactment of job rotation. The company’s culture must be enduring for the successful implementation of frequent job rotation programs. The strategists should draw an effective job design that is, based on job factors- applications utilized, training and development requirements, external and internal forces, frequent opportunities and threats. The productivity gains can become lower without a real-based job rotation program. The employers have greater flexibility levels when adequate training is given to employees on Human Resource Management Functions.
References Fevre, R. (2012). Social Mobility, Equity and the Politics of Recruitment. Sociology Compass, 6(9), 740-750.
Hoch, J., & Dulebohn, J. (2013). Shared leadership in enterprise resource planning and human resource management system implementation. Human Resource Management Review, 23(1), 114-125.
Lozano, R. (2011). Creativity and Organizational Learning as Means to Foster Sustainability. Sustainable Development, 22(3), 205-216.
Roberts, G. (2002). Employee Performance Appraisal System Participation: A Technique That Works. Public Personnel Management, 31(3), 333-342.
Strych, J. (2015). Job Rotation and Employer Learning About Human Capital. SSRN Electronic Journal.
CHECK THE PRICE FOR YOUR PROJECT
Number of pages/words you require, choose your assignment deadline, related samples.
- The Pros and Cons of Globalization on Human Resources Management
- Social interactions assignment and Human development assignment: A Critical Analysis
- Enhancing Organizational Performance through Strategic Human Resource Management
- Overcoming Challenges: Stakeholder Participation in Oman's Renewable Energy Transition
- HRM Considerations for Establishing La Gustocoffee in China: Challenges and Strategies
- (BM562 CW1) HR management and recruitment strategies assignment on designing effective HR policies and guidelines
- HRM ethics assignment on strategies business managers can adopt to ensure fair treatment of their staff
- (SHR011-3) CPD portfolio assignment reflective upon the updated CIPD profession map against the present skills and behaviours
- Human resource management assignment explaining the importance and contribution of human resource
- Human resource assignment focussing on communication marketing of Vaseline
- Human resource management assignment evaluating the influence of organisational culture and organisational changeon British Petroleum
- Human resource management assignment explaining the significance of HR and its duties
- Human resource is involved in recruitment of potential candidates in the organisation, training them to retain them for a definite period of time
- (BMP6026) International HRM assignment on application of International HRM Practices in HSBC Holdings Plc
- (BUSM2022) HRM training assignment on strategies businesses can use to improve staff training programs
- (HRMT11011)Human resource management assignment identifying the HRM issues in Australian workforce
- (HX3W 04)Strategic leadership assignment on the strategic human resources management and its changing landscape in organizations
- Strategic Human Resource Management assignment on Sainsbury's Plc HPM policies
- (BMG935 CRN 13712) Hrm assignment on IHRM policies and practices in the multinational context
- (WELF2010)lifespan development assignment critically analysing Baptist care services Australia
- Employee Retention Assignment Analyzing How Organizations Can Maximize Employee performance
- Employee Satisfaction assignment Plan for Costa Hemel Hempstead
- Human Resource Management assignment focusing on the HR practices of Commonwealth Bank Australia
- (HRMT20024) Human Resource Management Essay: Key Challenges in Attracting and Retaining Workforce in the Education Sector
- (HRMT20024) HRM Essay: Key Challenges in Attracting and Retaining Workforce in Australian Health Sector

Looking for Your Assignment?

FREE PARAPHRASING TOOL

FREE PLAGIARISM CHECKER

FREE ESSAY TYPER TOOL
Other assignment services.
- SCM Assignment Help
- HRM Assignment Help
- Dissertation Assignment Help
- Marketing Analysis Assignment Help
- Corporate Finance Assignment Help

FREE WORD COUNT AND PAGE CALCULATOR

QUESTION BANK
ESCALATION EMAIL
To get answer.
Please Fill the following Details
Thank you !
We have sent you an email with the required document.
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Guidelines and Guidance Library
- Core Practices
- Isolation Precautions Guideline
- Disinfection and Sterilization Guideline
- Environmental Infection Control Guidelines
- Hand Hygiene Guidelines
- Multidrug-resistant Organisms (MDRO) Management Guidelines
- Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections (CAUTI) Prevention Guideline
- Tools and resources
- Evaluating Environmental Cleaning
Infection Control Basics
- Infection control prevents or stops the spread of infections in healthcare settings.
- Healthcare workers can reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections and protect themselves, patients and visitors by following CDC guidelines.
Germs are a part of everyday life. Germs live in our air, soil, water and in and on our bodies. Some germs are helpful, others are harmful.
An infection occurs when germs enter the body, increase in number and the body reacts. Only a small portion of germs can cause infection.
Terms to know
- Sources : places where infectious agents (germs) live (e.g., sinks, surfaces, human skin). Sources are also called reservoirs.
- Susceptible person: someone who is not vaccinated or otherwise immune. For example, a person with a weakened immune system who has a way for the germs to enter the body.
- Transmission: a way germs move to the susceptible person. Germs depend on people, the environment and/or medical equipment to move in healthcare settings. Transmission is also called a pathway.
- Colonization: when someone has germs on or in their body but does not have symptoms of an infection. Colonized people can still transmit the germs they carry.
For an infection to occur, germs must transmit to a person from a source, enter their body, invade tissues, multiply and cause a reaction.
How it works in healthcare settings
Sources can be:.
- People such as patients, healthcare workers and visitors.
- Dry surfaces in patient care areas such as bed rails, medical equipment, countertops and tables).
- Wet surfaces, moist environments and biofilms (collections of microorganisms that stick to each other and surfaces in moist environments, like the insides of pipes).
- Cooling towers, faucets and sinks, and equipment such as ventilators.
- Indwelling medical devices such as catheters and IV lines.
- Dust or decaying debris such as construction dust or wet materials from water leaks.
Transmission can happen through activities such as:
- Physical contact, like when a healthcare provider touches medical equipment that has germs on it and then touches a patient before cleaning their hands.
- Sprays and splashes when an infected person coughs or sneezes. This creates droplets containing the germs, and the droplets land on a person's eyes, nose or mouth.
- Inhalation when infected patients cough or talk, or construction zones kick up dirt and dust containing germs, which another person breathes in.
- Sharps injuries such as when someone is accidentally stuck with a used needle.
A person can become more susceptible to infection when:
- They have underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, cancer or organ transplantation. These can decrease the immune system's ability to fight infection.
- They take medications such as antibiotics, steroids and certain cancer fighting medications. These can decrease the body's ability to fight infection.
- They receive treatments or procedures such as urinary catheters, tubes and surgery, which can provide additional ways for germs to enter the body.
Recommendations
Healthcare providers.
Healthcare providers can perform basic infection prevention measures to prevent infection.
There are 2 tiers of recommended precautions to prevent the spread of infections in healthcare settings:
- Standard Precautions , used for all patient care.
- Transmission-based Precautions , used for patients who may be infected or colonized with certain germs.
There are also transmission- and germ-specific guidelines providers can follow to prevent transmission and healthcare-associated infections from happening.
Learn more about how to protect yourself from infections in healthcare settings.
For healthcare providers and settings
- Project Firstline : infection control education for all frontline healthcare workers.
- Infection prevention, control and response resources for outbreak investigations, the infection control assessment and response (ICAR) tool and more.
- Infection control specifically for surfaces and water management programs in healthcare settings.
- Preventing multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs).
Infection Control
CDC provides information on infection control and clinical safety to help reduce the risk of infections among healthcare workers, patients, and visitors.
For Everyone
Health care providers, public health.

COMMENTS
Here are six steps to help you succeed at the human resource planning process. 1. Assess current employees' skill levels. The first step to creating a future-forward HR plan is to assess employees' current skill sets, and compare them to your operational needs moving forward.
Describe the steps in the development of an HRM plan. As addressed in Section 2.1 "Strategic Planning", the writing of an HRM strategic plan should be based on the strategic plans of the organization and of the department. Once the strategic plan is written, the HR professional can begin work on the HR plan. This is different from the ...
Module Alignment. Assignment: Becoming a Changemaker. Module 1: The Role of Human Resources and Module 2: Human Resources Strategy and Planning. Assignment: Develop a Diversity Allies Program. Module 3: People Analytics & Human Capital Trends and Module 4: Promoting a Diverse Workforce. Assignment: Job Description Research and Development.
Managing Your Human Assets Module 1: Human Resource Planning fModule 1 - p 2 2. DEVELOPING AN HR PLAN 2.1 Forecasting Hiring Needs The daily demands and hectic lifestyle of business owners and managers often has an unfortunate by-product: human resource planning gets placed on the bottom of the list of things to get done.
HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING ASSIGNMENT 1. Linking HR Strategies to a Differentiated Organizational Strategy. Human Resource Policies, provide a framework for organizations in which consistent decisions can be made and about how people are treated with all equity and fairness in an organization ( SpriggHR, 2020).In every organization, there are different HR Policies specific to ensuring that ...
Step 1: Identify the current supply of human resources. The planning process starts by analyzing the current labor pool. Identify the strengths and weaknesses of your organization with regard to the number of employees, their skills, experiences, qualifications, positions, performance levels, age, benefits, salary levels, languages spoken ...
impact areas of human resources (HR) such as recruitment, training, employee. compensation, and performance evaluation (Schwind et al, 2019). The information can. also provide some insight on how well designed (or ill-designed) a job is. Poorly. designed jobs often lead to low productivity, high turnover, resignations, etc. (Schwind et. al, 2019).
The human resource plan relies on identifying deficits or surplus in the company. You'll need to determine if you need to begin recruiting or training, transition, or develop voluntary retirement processes and redeployment in case of a surplus. Include priorities and critical planning issues in your plan.
Human Resource Planning - HRP: Human resource planning, or HRP, is the ongoing, continuous process of systematic planning to achieve optimum use of an organization's most valuable asset — its ...
The actual process of human resource planning involves five general phases. Listed below is a summary of each step to help you navigate the process: 1. Analyze organizational objectives and plans. Success in HR planning relies on its connection to business goals, so you must start with a final purpose in mind.
Human resource planning (HRP) is a part of human resource management (HRM), so discussion of HRP without any overview of HRM is incomplete. For defining HRP it is necessary to define about HRM. 3 Human Resource Management: Human resource management can define as a process of handling and managing people of an organization.
1. Why we love to hate HR 2. Uber finally realizing HR isn't just for recruiting 3. 21 HR jobs of the future Jan. 25 HR Challenges 1. HR Departments get new star power 2. Building work-life boundaries in the WFH era 3. HR's role in building a sustainability strategy Jan. 27 & Feb. 1 Job Analysis and Job Design 1.
Presented by: Binod Ghimire. Concept. • Human resource planning is the process of. forecasting, development, and controlling human. resource in an organization. • According to Stone, "Human ...
Before we delve into the minutiae of human resources, let's put the two relevant definitions side-by-side to see how they compare.. Human Resource Planning: HRP is the ongoing process of systematically planning ahead to optimize and maximize your business's most valuable asset — high-quality employees.. Strategic Human Resource Management: SHRM is a holistic approach to assembling the ...
In this definition, human resource means skill, knowledge, values, ability, commitment, motivation, etc., in addition to the number/of employees. Human resource planning (HRP) is the first step in the HRM process. HRP is the process by which an organization ensures that it has the right number and kind of people, at the right place, at the ...
Use this visually dynamic HR project plan template to document every detail of your HR project plan. Within the template, you can list and manage tasks, assign them to HR personnel, set priorities and status for each, and track the percentage of task completion for the entire project. The template includes visualizations of your HR project data ...
The human resources management plan includes: Roles and Responsibilities of Team Members Throughout the Project. Project Organization Charts. Staffing Management Plan to Include: How resources will be acquired. Timeline for resources/skill sets. Training required to develop skills. How performance reviews will be conducted.
Human resource planning (HRP) enables an organization to better realize its goals by ensuring that it makes efficient and effective use of its human capital. Today's workforce is characteristically ambitious and hence, volatile. Rosenberg (n.d.) reiterates that employees switch careers an approximated three times in their working life.
1 Introduction. Effective human resource management is a critical component of any project. The Human Resource Plan explains how project processes will be used to make the most effective use of the people assigned to the project. This section of the Human Resource Plan should provide a general description of what the plan includes and explains ...
Human resource planning is describe as the existing staffs are the right staff to do the jobs in organisation. Some other points include planning for staff retention, planning for candidate search, training and skills analysis and much more. There are Problem of anticipating manpower by protecting manpower resource in to future, organisation ...
7 Steps to creating an HR strategy. We've outlined 7 key steps based on Deloitte's HR Strategy Framework to help you design an HR strategy: . 1. Consider the market and trends: Analyze the external market and trends that are impacting your industry. 2. Understand the business strategy: Know the business strategy and be clear on the must-win battles for the business, the key value drivers ...
HR practitioners have learned to add value by becoming effective facilitators of senior team strategic planning sessions. Operationally, HR units can ensure their plans and programs support and drive strategic business: Capability Assessment, Capacity Management, SWOT-FS, Importance-Performance Analysis, Benchmarking and Best Practice studies and impact evaluation using Kirkpatrick Level 3 & 4 ...
This is focused on identification of the Human Resource Management Assignment tools and implementation of new strategies from time to time. To reduce the long-term negative impacts, recruitment, selection training, planning and job-design are important aspects that impact the staffing decisions. Article 1: Fevre, R. (2012).
Infection prevention, control and response resources for outbreak investigations, the infection control assessment and response (ICAR) tool and more. Infection control specifically for surfaces and water management programs in healthcare settings. Preventing multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs). Sources. Infection control prevents or stops ...