Gender Inequality - Free Essay Examples And Topic Ideas
Gender inequality refers to the unequal treatment or perceptions of individuals based on their gender, manifesting in various areas like the workplace, political representation, and societal norms. Essays on gender inequality could explore historical and contemporary instances, the social and economic implications, and the intersectionality of gender with other forms of discrimination. Furthermore, discussions might cover ongoing efforts to combat gender inequality and promote inclusivity. We’ve gathered an extensive assortment of free essay samples on the topic of Gender Inequality you can find at Papersowl. You can use our samples for inspiration to write your own essay, research paper, or just to explore a new topic for yourself.

Gender Inequality and Feminism
Gender inequality is a concept which has been occurring over a number of years and due to gender differences it fuels up gender inequality, which gave rise to gender socialization. Gender socialization is the process of learning gender roles which emerge from society and nowadays social media, throughout this process men and women learn their roles in society. The most common attribute we ascribe to women is that they can be vulnerable and sensitive, on the other hand, men hear […]
Crime and Social Justice on Gender Inequality
I'm using these five sources to talk about crime and social justice on gender inequality. Gender inequality is more of a social injustice because gender inequality is an unfair practice between men and women being carried out in the society. Within discussing this topic, I talk about racism and sexism. My topic is towards African Americans and women in the workplace. How come African American women or women, in general, are not seen as an equal to men? Cheeks, Maura. […]
The Gender Gap in Political Ambition
The gender gap in political ambition has been a topic extensively researched by political analysts and professors for years. The focus of this essay will be to examine why this gender gap exists and how it directly affects the underrepresentation of women who hold public office in the United States. This essay will explore the ways in which young women are politically socialized and factors in early childhood through high school which affect one’s political motivations. This research also seeks […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
Sexual Harassment in the Work Place and Gender Inequality
Abbas, Sammar. "All Males Are the Same: Exploring Workplace Harassment of Female Employees." Pakistan Journal of Women's Studies, vol. 24, no. 24, 2017, pp. 47-65. EBSCOhost, http://eds.a.ebscohost.com.libproxy.ung.edu/eds/detail/detail?vid=6&sid=735b46f2-7f65-434d-8b37-4967f7b3929f%40sessionmgr4009&bdata=JnNpdGU9ZWRzLWxpdmUmc2NvcGU9c2l0ZQ%3d%3d#db=sih&AN=127020504 Abbas, in "All Males Are the Same: Exploring Workplace Harassment of Female Employees," addresses the issue of workplace sexual harassment towards females, which is common in many countries, specifically the Middle East. The article explores how workplace sexual harassment towards women contributes to the cause of gender inequality. Abbas supports his claim with […]
The Issue of Gender Inequality Within Society
According to the International Labour Organization, “equality in pay has improved in the US since 1979 when women earned about 62% as much as men. In 2010, American women on average earned 81% of what their male counterparts earned. Women’s participation in the U.S. labor force climbed during the 1970s and 1980s, reaching 60 percent in 2000. However, in 2010 this figure has declined to 46.7 percent and is not expected to increase by 2018.” (“Gender Inequality and Women in […]
“Education is the Passport to the Future”
“Education is the passport to the future, for tomorrow belongs to those who prepare for it today” Malcolm X. It can be said that education helps us increase knowledge to actively achieve and meet challenges that can produce changes in which are productive for attaining business innovations, political and economic objectives. In sociological terms education is usually seen as the process of acquiring certain skills or knowledge within an institution designed for that purpose. According (Haralambos & Holborn, 2004), it […]
Gender Inequality in Broadcast Journalism
The news media is one of thea most powerful institution whichs that exerts a tremendous amount of influence on society. Although more women females are entering the male dominated newsroom, women are still underrepresented and excluded in many differentmultiple ways. It is evident that females hold a strong interest in journalism; in fact, sixty- five percent of journalism school graduates are female However, women only represent thirty percent of jobs in journalism. , Tand this gender disparity is evident in […]
Gender Inequality in the Workplace
Gender inequality in the workplace has been an ongoing issue for decades now. Men and women have never been on the same page when it comes to work. Women have always been known to be more of caregivers and men have been given the tougher tasks. Gender stereotypes have always played a major role in assigning women to lower paying and lower status jobs in comparison to men. Discrimination against women can occur in many ways throughout the workplace, such […]
Sappho and Catullus Romantic Rejection
Although Sappho and Catullus lived and worked in different time periods, their ideas on romantic rejection suggest each were victims of unrequited love. Both wrote about their cultural environment of where they lived, their ideas of society, its expectations and inequalities for both women and men as well as their different representations of love. They used their poetry to discuss the gender inequality of their societies and how unfair a society led by men really was in. It dictated the […]
Gender Inequality in the Medical Field
Introduction The medical field is consistently one of the best job fields to enter because of the positive job outlook and high salary. This may not be true for women, however. The large amount of gender discrimination and harassment may be enough to keep women away from the medical field, specifically female doctors. In this day and age there is no reason why women cannot become doctors and they are not lesser than their male peers, especially in the 21st […]
Gender Inequality in Education
Culturally, there is a belief that every individual has the same chance to succeed in society. Even in our constitution, it states that all men are created equal. What is underlying in this belief is that a failure to succeed is the fault of the gender or race of the individual. Inequalities in educational institutions affect students in various ways; providing greater impact on children from lower socio-economic backgrounds and maintaining advantages of those with money, which are then passed […]
Feminism Within the Film Industry
The film industry has had a recurring theme with its woman in film. The theme began as a woman playing a secondary role to males and playing the victim that needs rescuing. The rise of feminism began in the 1950s until the 1970s, at first it was unpopular with the audience and did not make its return until the 1990s. Throughout the years it is shown that woman has become more dominant in their roles as the main matriarch of […]
Gender Inequality in China
"Mao Zedong once said, “women hold up half the sky.” This famous quote has been interpreted by people for nearly one-hundred years. All interpretations tying back to one basic core idea that women hold just as much priority in the world as men do. However, in present-day China, social standards are far from equal between the two genders. Men still earn more money than their female counterparts, the gender ratio of the country is still out of balance, and boys […]
Gender Inequality: Causes and Impacts
Gender Equality is “A state of having same rights, status and opportunities like others, regardless of one’s gender.” Gender inequality is “unequal treatment or perception of an individual based on their gender.” In the United States of America Gender Equality has progressed through the past decades. Due to different Cultural context, countries around the world lack Gender Equality. Gender inequality remains a issue worldwide, mainly in the Middle East and North Africa. Equality of Gender is normalized in the United […]
Gender Inequality Affects Everyone
Gender inequality has never been a new thing in the United States. This cultural phenomenon has deeply rooted in people’s minds and has been affecting their behaviors for a really long time. Gender inequality generally defines as that men and women in some way are not equal. Gender inequality recognizes gender inequality and gender influences an individual’s life experience. These differences stem from the distinctions in biology, psychology, and cultural norms. Some of these differences are based on experience, while […]
Research Paper on Gender Inequality in the Workforce in India
Abstract India demonstrates significant economy growth that contrary to universal norms results in lower female labor force participation. The issue is a deep-rooted problem, which is aggravated by a wide range of factors, the major of which are social norms and insufficient level of training and information on job opportunities. Despite the presence of these constraints, the paper suggests that there is a scope of possible measures, which can be implemented by the government to overcome the problem and mitigate […]
The Gender Wage Gap: Myth or Reality?
Gender inequality has been a persistent issue in the workforce. The gender wage gaps shows the difference between male and female workers’ earnings. In the modern day economy, women are typically paid less than men. The Equal Pay Act was passed in the U.S. on June 10, 1963, it was the beginning of achieving equal economic opportunity for women however, it alone did not solve the issue. In further effort to put an end to the century-old gender wage inequality, […]
Gender Inequality is Still a Huge Issue
Throughout history, men have always been perceived as the dominant gender compared to women. Up until recently, men were the ones going to work while the women stayed home. They did not have hardly any rights, while having to stay home to handle raising the children and keeping up with household chores. Not only that, but women also got constantly abused by their husbands while they got away with it. While in today’s society, things have changed drastically, gender inequality […]
Gender Inequality and Sexual Harassment
Attitudes regarding men’s violence against women shape gender inequality and also the sense of responses to this violence by the victim and others around. This is why we see many violence prevention campaigns media advertisements and social awareness. Attitudes and behaviors shape violence in several domains including culture, gender, institutional response to violence, women’s own responses to victimization and more. Gender role attitudes and their forced upholding play a major role regarding violence towards women [1]. From a young age, […]
Gender Inequality in the United States for Years
Gender inequality has been present in the United States for years. Women have been, and still are, mainly associated with the duties tied to their home. However, the role as the “homemaker” have limitations on women, causing them to experience dissatisfaction in their lives. Women are increasingly pushing against that stereotype, as shown by the increasing number of women, especially married women, that are joining the workforce. This allows women to steer away from being economically dependent on men, and […]
“Gender Inequality: a Greek Life and Legal Implications Study”
Abstract Attending college is supposed to be a time of newfound freedom. This freedom gives incoming students the opportunity to define who they are as a person, and often times the organizations students first join play a vital role in shaping who they are for years to come. When graduates reflect on their college years many say their best memories come from the organizations they joined. At Texas Christian University over half of the student population are in different Greek […]
How Gender Discrimination Effects Children
"It is during their first years that girls and boys learn gendered attitudes and expectations - from parents, caregivers, other family members, and teachers - about how girls and boys/women and men should behave, their social worth and what their role is in society." (e.g. Plan International) Gender inequality is an issue for all of us, but we often don't think about how it affects children. In recent decades, there have been elaborate studies on how sexism and gender stereotyping […]
Gender Inequality in Athletic Sports
Sports are both one of the most idolized and contested activities in our society today. Historically, sports have been used as a display for the public, for both entertainment and social purposes. Sports also provide professional opportunities for athletes and coaches at the highest level of performance. Regardless of the purpose or presentation, sports have created an element in our modern society. While sports have provided opportunities, it has also created underlying effects on social cues in regards to the […]
How to Deal with Gender Inequality in Sports
Looking at today’s fast world, sports has turned out to be a place where individuals can have extraordinary professions in and will likewise have the wages that one can get by owning a business as well, but the posing problem is that it is gender driven. Societal norms have a significant impact on a youth’s life, one of the fields in which it lays impact is sports. The major contributing factor is that since birth, humans observe and learn these […]
An Issue of Gender Inequality in the World
Gender inequality is still an issue in the world. In every five girls, one will not have access to an education. Girls in developing countries are not enrolled in school. Mexico has been dealing with gender inequality for years because women aren’t given the same rights as men. In Mexico, gender stereotypes and discrimination restrict women’s choices. Mexico falls in the bottom half of 144 countries when it comes to gender equality. Women were murdered just because of their gender […]
Gender Inequality and Violence in the United States
Gender inequality in the United States has been an issue since before our time with women and girls making strides since the early 1900’s to gain gender equity. Gender inequality is looked at as a key factor that underpins violence against women, why men produce certain acts of violence over woman and why men are looked at different by society than women, however the topic is complex and requires consideration from different perspectives, including ways to deter the violence. Most […]
Americanah: Gender Pay Gap in Nigeria and North America
In the book Americanah by Chimamanda Adichie, women's earning potentials are vividly shown based on experiences that Ifemelu and her Aunty Uju have in both Nigeria and North America. These earning potentials affect gender roles and expectations in Nigeria and North America because women are expected more to be the house keepers and mothers rather than ever having a job themselves. Nowadays it is much different as the feminist movement continues to grow across the world. This is presented throughout […]
The Roots of Gender Inequality in Developing Countries
In today’s world, gender equality is seen as a crucial need. According to the U.N., “1 in 5 women and girls between the ages of 15-49 have reported experiencing physical or sexual violence by an intimate partner within a 12-month period”. In developed countries, tremendous efforts have been made in order to achieve the goal of gender equality as now in 46 countries, “women now hold more than 30 percent of seats in national parliament in at least one chamber.” […]
An Analysis of the Problem of Gender Inequality
Furthermore, in nations like Yemen, sex variations are seen even in optional school where young men select at a rate 20 rate focuses higher than young ladies. On the off chance that fairness is educated in schools it will change the general public and how individuals think and act bringing about more ladies learning and graduating. As what the speakers have mentioned, gender inequality should be fought by both men and women. It is humans right. Gender inequality has greatly […]
Gender Inequality in Saudi Arabia
Gender inequality has been a major factor for many countries and as every single one of them continue to change and improve for the future, some places have stayed the same over time and are barely coming along and accepting what other areas have already passed on such as having equality not just for men, but for women as well and many of us today don’t realize how some people are not given the freedom to do what we do […]
Related topic
Additional example essays.
- Religion’s Role in Gender Equality
- The Gender Pay Gap and the Equality
- About Gender Discrimination in Sports
- The Oppression And Privilege
- Discrimination in Workplace
- Why Abortion Should be Illegal
- Death Penalty Should be Abolished
- Logical Fallacies in Letter From Birmingham Jail
- How the Roles of Women and Men Were Portrayed in "A Doll's House"
- Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner
- Substance Abuse and Mental Illnesses
- Med school personal statement
How To Write an Essay About Gender Inequality
Understanding gender inequality: the foundation.
To write an essay on gender inequality, it's crucial to start with a clear understanding of what gender inequality entails. It's a broad term that refers to the unequal treatment or perception of individuals based on their gender. Gender inequality manifests in various aspects of life, including but not limited to the workplace, education, politics, and social norms. Begin your essay by defining gender inequality, providing relevant examples from different areas of life, and explaining why it is a significant issue that warrants attention.
Research and Statistics: Building Your Argument
A well-researched essay is a powerful tool. Accumulate data and statistics from credible sources such as academic journals, international organizations (like the UN or WHO), and reputable news outlets. This research should include global perspectives, highlighting how gender inequality varies across different cultures and societies. Use this information to construct a strong argument, supporting your points with evidence. This approach not only adds weight to your essay but also demonstrates a thorough understanding of the topic.
The Historical Perspective: Understanding the Roots
Incorporate a historical perspective to provide depth to your essay. Understanding the historical context of gender inequality helps to explain how and why it persists today. This can include an examination of gender roles throughout history, major movements for gender equality, and significant legal and social changes. A historical lens allows for a comprehensive view of the problem and its evolution over time.
Current Challenges and Debates
Focus on the current state of gender inequality. This section should explore the most pressing issues and debates surrounding gender inequality today. Topics can include the gender pay gap, underrepresentation in leadership positions, societal expectations, and the impact of gender stereotypes. This section can also cover the intersectionality of gender inequality, showing how it intersects with other forms of discrimination like race, class, and sexuality.
Solutions and Actions: Towards a More Equal Future
Every essay should look towards the future. Discuss potential solutions and actions that could be taken to address gender inequality. These can range from policy changes and educational reforms to shifts in cultural attitudes and individual actions. Highlight initiatives already in place that are working towards equality and suggest areas where more work is needed. This section should inspire and suggest practical ways for individuals and societies to contribute to a more gender-equal world.
Conclusion: Summarizing Key Points
Conclude your essay by summarizing the key points discussed. Reiterate the importance of addressing gender inequality and the impact it has on individuals and society as a whole. Your conclusion should leave readers with a clear understanding of the issue, its significance, and a sense of hope or urgency for the future. Remember, a strong conclusion can leave a lasting impression on your readers, motivating them to think more deeply about the subject or even take action.
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Gender Inequality Essay
500+ words essay on gender inequality.
For many years, the dominant gender has been men while women were the minority. It was mostly because men earned the money and women looked after the house and children. Similarly, they didn’t have any rights as well. However, as time passed by, things started changing slowly. Nonetheless, they are far from perfect. Gender inequality remains a serious issue in today’s time. Thus, this gender inequality essay will highlight its impact and how we can fight against it.

About Gender Inequality Essay
Gender inequality refers to the unequal and biased treatment of individuals on the basis of their gender. This inequality happens because of socially constructed gender roles. It happens when an individual of a specific gender is given different or disadvantageous treatment in comparison to a person of the other gender in the same circumstance.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Impact of Gender Inequality
The biggest problem we’re facing is that a lot of people still see gender inequality as a women’s issue. However, by gender, we refer to all genders including male, female, transgender and others.
When we empower all genders especially the marginalized ones, they can lead their lives freely. Moreover, gender inequality results in not letting people speak their minds. Ultimately, it hampers their future and compromises it.
History is proof that fighting gender inequality has resulted in stable and safe societies. Due to gender inequality, we have a gender pay gap. Similarly, it also exposes certain genders to violence and discrimination.
In addition, they also get objectified and receive socioeconomic inequality. All of this ultimately results in severe anxiety, depression and even low self-esteem. Therefore, we must all recognize that gender inequality harms genders of all kinds. We must work collectively to stop these long-lasting consequences and this gender inequality essay will tell you how.
How to Fight Gender Inequality
Gender inequality is an old-age issue that won’t resolve within a few days. Similarly, achieving the goal of equality is also not going to be an easy one. We must start by breaking it down and allow it time to go away.
Firstly, we must focus on eradicating this problem through education. In other words, we must teach our young ones to counter gender stereotypes from their childhood.
Similarly, it is essential to ensure that they hold on to the very same beliefs till they turn old. We must show them how sports are not gender-biased.
Further, we must promote equality in the fields of labour. For instance, some people believe that women cannot do certain jobs like men. However, that is not the case. We can also get celebrities on board to promote and implant the idea of equality in people’s brains.
All in all, humanity needs men and women to continue. Thus, inequality will get us nowhere. To conclude the gender inequality essay, we need to get rid of the old-age traditions and mentality. We must teach everyone, especially the boys all about equality and respect. It requires quite a lot of work but it is possible. We can work together and achieve equal respect and opportunities for all genders alike.
FAQ of Gender Inequality Essay
Question 1: What is gender inequality?
Answer 1: Gender inequality refers to the unequal and biased treatment of individuals on the basis of their gender. This inequality happens because of socially constructed gender roles. It happens when an individual of a specific gender is given different or disadvantageous treatment in comparison to a person of the other gender in the same circumstance.
Question 2: How does gender inequality impact us?
Answer 2: The gender inequality essay tells us that gender inequality impacts us badly. It takes away opportunities from deserving people. Moreover, it results in discriminatory behaviour towards people of a certain gender. Finally, it also puts people of a certain gender in dangerous situations.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


5 Powerful Essays Advocating for Gender Equality
Gender equality – which becomes reality when all genders are treated fairly and allowed equal opportunities – is a complicated human rights issue for every country in the world. Recent statistics are sobering. According to the World Economic Forum, it will take 108 years to achieve gender parity . The biggest gaps are found in political empowerment and economics. Also, there are currently just six countries that give women and men equal legal work rights. Generally, women are only given ¾ of the rights given to men. To learn more about how gender equality is measured, how it affects both women and men, and what can be done, here are five essays making a fair point.
Take a free course on Gender Equality offered by top universities!
“Countries With Less Gender Equity Have More Women In STEM — Huh?” – Adam Mastroianni and Dakota McCoy
This essay from two Harvard PhD candidates (Mastroianni in psychology and McCoy in biology) takes a closer look at a recent study that showed that in countries with lower gender equity, more women are in STEM. The study’s researchers suggested that this is because women are actually especially interested in STEM fields, and because they are given more choice in Western countries, they go with different careers. Mastroianni and McCoy disagree.
They argue the research actually shows that cultural attitudes and discrimination are impacting women’s interests, and that bias and discrimination is present even in countries with better gender equality. The problem may lie in the Gender Gap Index (GGI), which tracks factors like wage disparity and government representation. To learn why there’s more women in STEM from countries with less gender equality, a more nuanced and complex approach is needed.
“Men’s health is better, too, in countries with more gender equality” – Liz Plank
When it comes to discussions about gender equality, it isn’t uncommon for someone in the room to say, “What about the men?” Achieving gender equality has been difficult because of the underlying belief that giving women more rights and freedom somehow takes rights away from men. The reality, however, is that gender equality is good for everyone. In Liz Plank’s essay, which is an adaption from her book For the Love of Men: A Vision for Mindful Masculinity, she explores how in Iceland, the #1 ranked country for gender equality, men live longer. Plank lays out the research for why this is, revealing that men who hold “traditional” ideas about masculinity are more likely to die by suicide and suffer worse health. Anxiety about being the only financial provider plays a big role in this, so in countries where women are allowed education and equal earning power, men don’t shoulder the burden alone.
Liz Plank is an author and award-winning journalist with Vox, where she works as a senior producer and political correspondent. In 2015, Forbes named her one of their “30 Under 30” in the Media category. She’s focused on feminist issues throughout her career.
“China’s #MeToo Moment” – Jiayang Fan
Some of the most visible examples of gender inequality and discrimination comes from “Me Too” stories. Women are coming forward in huge numbers relating how they’ve been harassed and abused by men who have power over them. Most of the time, established systems protect these men from accountability. In this article from Jiayang Fan, a New Yorker staff writer, we get a look at what’s happening in China.
The essay opens with a story from a PhD student inspired by the United States’ Me Too movement to open up about her experience with an academic adviser. Her story led to more accusations against the adviser, and he was eventually dismissed. This is a rare victory, because as Fan says, China employs a more rigid system of patriarchy and hierarchy. There aren’t clear definitions or laws surrounding sexual harassment. Activists are charting unfamiliar territory, which this essay explores.
“Men built this system. No wonder gender equality remains as far off as ever.” – Ellie Mae O’Hagan
Freelance journalist Ellie Mae O’Hagan (whose book The New Normal is scheduled for a May 2020 release) is discouraged that gender equality is so many years away. She argues that it’s because the global system of power at its core is broken. Even when women are in power, which is proportionally rare on a global scale, they deal with a system built by the patriarchy. O’Hagan’s essay lays out ideas for how to fix what’s fundamentally flawed, so gender equality can become a reality.
Ideas include investing in welfare; reducing gender-based violence (which is mostly men committing violence against women); and strengthening trade unions and improving work conditions. With a system that’s not designed to put women down, the world can finally achieve gender equality.
“Invisibility of Race in Gender Pay Gap Discussions” – Bonnie Chu
The gender pay gap has been a pressing issue for many years in the United States, but most discussions miss the factor of race. In this concise essay, Senior Contributor Bonnie Chu examines the reality, writing that within the gender pay gap, there’s other gaps when it comes to black, Native American, and Latina women. Asian-American women, on the other hand, are paid 85 cents for every dollar. This data is extremely important and should be present in discussions about the gender pay gap. It reminds us that when it comes to gender equality, there’s other factors at play, like racism.
Bonnie Chu is a gender equality advocate and a Forbes 30 Under 30 social entrepreneur. She’s the founder and CEO of Lensational, which empowers women through photography, and the Managing Director of The Social Investment Consultancy.
You may also like

15 Great Charities to Donate to in 2024

15 Quotes Exposing Injustice in Society

14 Trusted Charities Helping Civilians in Palestine

The Great Migration: History, Causes and Facts

Social Change 101: Meaning, Examples, Learning Opportunities

Rosa Parks: Biography, Quotes, Impact

Top 20 Issues Women Are Facing Today

Top 20 Issues Children Are Facing Today

15 Root Causes of Climate Change

15 Facts about Rosa Parks

Abolitionist Movement: History, Main Ideas, and Activism Today

The Biggest 15 NGOs in the UK
About the author, emmaline soken-huberty.
Emmaline Soken-Huberty is a freelance writer based in Portland, Oregon. She started to become interested in human rights while attending college, eventually getting a concentration in human rights and humanitarianism. LGBTQ+ rights, women’s rights, and climate change are of special concern to her. In her spare time, she can be found reading or enjoying Oregon’s natural beauty with her husband and dog.

The 11 biggest hurdles for women’s equality by 2030
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to E-mail
There are only seven years left for the world to fulfil the promises made to girls and women in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, and a new report by UN Women and United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs highlights the biggest challenges remaining for global gender equality.
The 2023 edition of “Progress on the Sustainable Development Goals: The gender snapshot 2023” tracks gender equality across the 17 Sustainable Development Goals and highlights 11 key roadblocks:

1. Lack of women in leadership
With just 27 per cent of parliamentary seats, 36 per cent of local government seats, and 28 per cent of management positions held by women, there is a lack of diverse perspectives in decision-making processes, hindering comprehensive policy formulation.
2. Poverty and lack of economic opportunities
More than 340 million women and girls are projected to live in extreme poverty by 2030. This represents a staggering 8 per cent of the global female population surviving on less than USD 2.15 a day. Social protections, access to decent work, and other support systems are urgently needed to provide a path out of poverty.
3. Workplace discrimination and inequalities
Only 61 per cent of prime working-age women participate in the labour force, compared to 91 per cent of prime working-age men. This affects both economic growth and societal progress. In 2019, for each dollar men earned in labour income, women earned only 51 cents.
4. An imbalance in unpaid care work
On the current trajectory, the gap between the time spent by women and men on unpaid care will narrow slightly, but by 2050, women globally will still be spending 9.5 per cent more time (2.3 more hours per day) on unpaid care work than men. This persistent gap limits women’s participation in education, employment, and other opportunities.
5. Social norms and cultural practices
Harmful practices such as child marriage and female genital mutilation persist. Globally, one in five young women is married before age 18. The prevalence of child marriage highlights the need for attitudinal shifts and the promotion of legal frameworks that safeguard women and girls’ rights.
6. Inadequate access to education and health care
An estimated 110 million girls and young women may remain out of school by 2030. Stalled progress in reducing maternal mortality and expanding educational opportunities call for targeted interventions to meet the 2030 goals.
7. Food insecurity
Nearly 24 per cent of women and girls are expected to experience moderate to severe food insecurity by 2030. Empowering women in food and agricultural systems by enhancing access to land and resources is vital for ensuring food security and economic growth.
8. Violence against women and girls
Each year, 245 million women and girls experience physical and/or sexual violence by an intimate partner. Older women also face higher rates of poverty and violence than older men.
9. Inadequate funding for gender equality initiatives
Only 4 per cent of total bilateral aid is allocated to gender equality and women's empowerment. The additional investment needed for achieving gender equality by 2030 is estimated at USD 360 billion per year.
10. Legal barriers and poorly enforced legislation
At least 28 countries do not have laws granting women equal rights to enter marriage and initiate divorce, and 67 countries lack laws prohibiting direct and indirect discrimination against women. Where legislation does exist to promote gender equality, effective implementation remains a challenge.
11. Lack of access to clean energy and sanitation
An estimated 341 million women and girls are projected to lack electricity by 2030. Universal access could significantly reduce poverty and improve women’s health.
With just seven years remaining to achieve the 2030 targets, concerted efforts and funding are more necessary than ever. Each step forward, no matter how incremental, brings us closer to a future where gender equality is not just a goal, but a reality.
- 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Related content

Op-ed: Improving women’s access to decent jobs

Speech: Gender equality – just, prudent, and essential for everything we all aspire to

Pushing forward for gender equality: CSW68 event showcases strategies for countering pushback and advancing women’s rights around the world
A global story
This piece is part of 19A: The Brookings Gender Equality Series . In this essay series, Brookings scholars, public officials, and other subject-area experts examine the current state of gender equality 100 years after the 19th Amendment was adopted to the U.S. Constitution and propose recommendations to cull the prevalence of gender-based discrimination in the United States and around the world.
The year 2020 will stand out in the history books. It will always be remembered as the year the COVID-19 pandemic gripped the globe and brought death, illness, isolation, and economic hardship. It will also be noted as the year when the death of George Floyd and the words “I can’t breathe” ignited in the United States and many other parts of the world a period of reckoning with racism, inequality, and the unresolved burdens of history.
The history books will also record that 2020 marked 100 years since the ratification of the 19th Amendment in America, intended to guarantee a vote for all women, not denied or abridged on the basis of sex.
This is an important milestone and the continuing movement for gender equality owes much to the history of suffrage and the brave women (and men) who fought for a fairer world. Yet just celebrating what was achieved is not enough when we have so much more to do. Instead, this anniversary should be a galvanizing moment when we better inform ourselves about the past and emerge more determined to achieve a future of gender equality.
Australia’s role in the suffrage movement
In looking back, one thing that should strike us is how international the movement for suffrage was though the era was so much less globalized than our own.
For example, how many Americans know that 25 years before the passing of the 19th Amendment in America, my home of South Australia was one of the first polities in the world to give men and women the same rights to participate in their democracies? South Australia led Australia and became a global leader in legislating universal suffrage and candidate eligibility over 125 years ago.
This extraordinary achievement was not an easy one. There were three unsuccessful attempts to gain equal voting rights for women in South Australia, in the face of relentless opposition. But South Australia’s suffragists—including the Women’s Suffrage League and the Woman’s Christian Temperance Union, as well as remarkable women like Catherine Helen Spence, Mary Lee, and Elizabeth Webb Nicholls—did not get dispirited but instead continued to campaign, persuade, and cajole. They gathered a petition of 11,600 signatures, stuck it together page by page so that it measured around 400 feet in length, and presented it to Parliament.
The Constitutional Amendment (Adult Suffrage) Bill was finally introduced on July 4, 1894, leading to heated debate both within the houses of Parliament, and outside in society and the media. Demonstrating that some things in Parliament never change, campaigner Mary Lee observed as the bill proceeded to committee stage “that those who had the least to say took the longest time to say it.” 1
The Bill finally passed on December 18, 1894, by 31 votes to 14 in front of a large crowd of women.
In 1897, Catherine Helen Spence became the first woman to stand as a political candidate in South Australia.
South Australia’s victory led the way for the rest of the colonies, in the process of coming together to create a federated Australia, to fight for voting rights for women across the entire nation. Women’s suffrage was in effect made a precondition to federation in 1901, with South Australia insisting on retaining the progress that had already been made. 2 South Australian Muriel Matters, and Vida Goldstein—a woman from the Australian state of Victoria—are just two of the many who fought to ensure that when Australia became a nation, the right of women to vote and stand for Parliament was included.
Australia’s remarkable progressiveness was either envied, or feared, by the rest of the world. Sociologists and journalists traveled to Australia to see if the worst fears of the critics of suffrage would be realised.
In 1902, Vida Goldstein was invited to meet President Theodore Roosevelt—the first Australian to ever meet a U.S. president in the White House. With more political rights than any American woman, Goldstein was a fascinating visitor. In fact, President Roosevelt told Goldstein: “I’ve got my eye on you down in Australia.” 3
Goldstein embarked on many other journeys around the world in the name of suffrage, and ran five times for Parliament, emphasising “the necessity of women putting women into Parliament to secure the reforms they required.” 4
Muriel Matters went on to join the suffrage movement in the United Kingdom. In 1908 she became the first woman to speak in the British House of Commons in London—not by invitation, but by chaining herself to the grille that obscured women’s views of proceedings in the Houses of Parliament. After effectively cutting her off the grille, she was dragged out of the gallery by force, still shouting and advocating for votes for women. The U.K. finally adopted women’s suffrage in 1928.
These Australian women, and the many more who tirelessly fought for women’s rights, are still extraordinary by today’s standards, but were all the more remarkable for leading the rest of the world.
A shared history of exclusion
Of course, no history of women’s suffrage is complete without acknowledging those who were excluded. These early movements for gender equality were overwhelmingly the remit of privileged white women. Racially discriminatory exclusivity during the early days of suffrage is a legacy Australia shares with the United States.
South Australian Aboriginal women were given the right to vote under the colonial laws of 1894, but they were often not informed of this right or supported to enroll—and sometimes were actively discouraged from participating.
They were later further discriminated against by direct legal bar by the 1902 Commonwealth Franchise Act, whereby Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people were excluded from voting in federal elections—a right not given until 1962.
Any celebration of women’s suffrage must acknowledge such past injustices front and center. Australia is not alone in the world in grappling with a history of discrimination and exclusion.
The best historical celebrations do not present a triumphalist version of the past or convey a sense that the fight for equality is finished. By reflecting on our full history, these celebrations allow us to come together, find new energy, and be inspired to take the cause forward in a more inclusive way.
The way forward
In the century or more since winning women’s franchise around the world, we have made great strides toward gender equality for women in parliamentary politics. Targets and quotas are working. In Australia, we already have evidence that affirmative action targets change the diversity of governments. Since the Australian Labor Party (ALP) passed its first affirmative action resolution in 1994, the party has seen the number of women in its national parliamentary team skyrocket from around 14% to 50% in recent years.
Instead of trying to “fix” women—whether by training or otherwise—the ALP worked on fixing the structures that prevent women getting preselected, elected, and having fair opportunities to be leaders.
There is also clear evidence of the benefits of having more women in leadership roles. A recent report from Westminster Foundation for Democracy and the Global Institute for Women’s Leadership (GIWL) at King’s College London, shows that where women are able to exercise political leadership, it benefits not just women and girls, but the whole of society.
But even though we know how to get more women into parliament and the positive difference they make, progress toward equality is far too slow. The World Economic Forum tells us that if we keep progressing as we are, the global political empowerment gender gap—measuring the presence of women across Parliament, ministries, and heads of states across the world— will only close in another 95 years . This is simply too long to wait and, unfortunately, not all barriers are diminishing. The level of abuse and threatening language leveled at high-profile women in the public domain and on social media is a more recent but now ubiquitous problem, which is both alarming and unacceptable.
Across the world, we must dismantle the continuing legal and social barriers that prevent women fully participating in economic, political, and community life.
Education continues to be one such barrier in many nations. Nearly two-thirds of the world’s illiterate adults are women. With COVID-19-related school closures happening in developing countries, there is a real risk that progress on girls’ education is lost. When Ebola hit, the evidence shows that the most marginalized girls never made it back to school and rates of child marriage, teen pregnancy. and child labor soared. The Global Partnership for Education, which I chair, is currently hard at work trying to ensure that this history does not repeat.
Ensuring educational equality is a necessary but not sufficient condition for gender equality. In order to change the landscape to remove the barriers that prevent women coming through for leadership—and having their leadership fairly evaluated rather than through the prism of gender—we need a radical shift in structures and away from stereotypes. Good intentions will not be enough to achieve the profound wave of change required. We need hard-headed empirical research about what works. In my life and writings post-politics and through my work at the GIWL, sharing and generating this evidence is front and center of the work I do now.
GIWL work, undertaken in partnership with IPSOS Mori, demonstrates that the public knows more needs to be done. For example, this global polling shows the community thinks it is harder for women to get ahead. Specifically, they say men are less likely than women to need intelligence and hard work to get ahead in their careers.
Other research demonstrates that the myth of the “ideal worker,” one who works excessive hours, is damaging for women’s careers. We also know from research that even in families where each adult works full time, domestic and caring labor is disproportionately done by women. 5
In order to change the landscape to remove the barriers that prevent women coming through for leadership—and having their leadership fairly evaluated rather than through the prism of gender—we need a radical shift in structures and away from stereotypes.
Other more subtle barriers, like unconscious bias and cultural stereotypes, continue to hold women back. We need to start implementing policies that prevent people from being marginalized and stop interpreting overconfidence or charisma as indicative of leadership potential. The evidence shows that it is possible for organizations to adjust their definitions and methods of identifying merit so they can spot, measure, understand, and support different leadership styles.
Taking the lessons learned from our shared history and the lives of the extraordinary women across the world, we know evidence needs to be combined with activism to truly move forward toward a fairer world. We are in a battle for both hearts and minds.
Why this year matters
We are also at an inflection point. Will 2020 will be remembered as the year that a global recession disproportionately destroyed women’s jobs, while women who form the majority of the workforce in health care and social services were at risk of contracting the coronavirus? Will it be remembered as a time of escalating domestic violence and corporations cutting back on their investments in diversity programs?
Or is there a more positive vision of the future that we can seize through concerted advocacy and action? A future where societies re-evaluate which work truly matters and determine to better reward carers. A time when men and women forced into lockdowns re-negotiated how they approach the division of domestic labor. Will the pandemic be viewed as the crisis that, through forcing new ways of virtual working, ultimately led to more balance between employment and family life, and career advancement based on merit and outcomes, not presentism and the old boys’ network?
This history is not yet written. We still have an opportunity to make it happen. Surely the women who led the way 100 years ago can inspire us to seize this moment and create that better, more gender equal future.
- December 7,1894: Welcome home meeting for Catherine Helen Spence at the Café de Paris. [ Register , Dec, 19, 1894 ]
- Clare Wright, You Daughters of Freedom: The Australians Who Won the Vote and Inspired the World , (Text Publishing, 2018).
- Janette M. Bomford, That Dangerous and Persuasive Woman, (Melbourne University Press, 1993)
- Cordelia Fine, Delusions of Gender: The Real Science Behind Sex Differences, (Icon Books, 2010)
This piece is part of 19A: The Brookings Gender Equality Series. Learn more about the series and read published work »
About the Author
Julia gillard, distinguished fellow – global economy and development, center for universal education.
Gillard is a distinguished fellow with the Center for Universal Education at the Brookings Institution. She is the Inaugural Chair of the Global Institute for Women’s Leadership at King’s College London. Gillard also serves as Chair of the Global Partnership for Education, which is dedicated to expanding access to quality education worldwide and is patron of CAMFED, the Campaign for Female Education.
Read full bio
MORE FROM JULIA GILLARD

Advancing women’s leadership around the world
More from the 19a series.

The gender revolution is stalling—What would reinvigorate it?
What’s necessary to reinvigorate the gender revolution and create progress in the areas where the movement toward equality has slowed or stalled—employment, desegregation of fields of study and jobs, and the gender pay gap?

The fate of women’s rights in Afghanistan
John R. Allen and Vanda Felbab-Brown write that as peace negotiations between the Afghan government and the Taliban commence, uncertainty hangs over the fate of Afghan women and their rights.
- Media Relations
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy

Search form
- Find Stories
- For Journalists
Image credit: Getty Images
Stanford scholars examine gender bias and ways to advance equity across society
Stanford scholars have studied the obstacles women face across society – at work, in education, as leaders – and how to reach a more equitable society for everyone.
The overturning of Roe v. Wade has heightened awareness of some of the broader issues the feminist movement and other allies for women’s rights have long championed, particularly advancing gender equality and economic well-being in societies around the globe.
Stanford scholars have studied some of the difficulties of reaching those goals and the many obstacles women face, whether it is at work, in the classroom and education, or as leaders. They have examined how gendered biases are perpetuated, why gender diversity and inclusion are imperative, and what can lead to prejudiced attitudes, assumptions, and adversities ultimately changing.
From the fields of business, social sciences, the humanities, law, education, health, and medicine, here are what Stanford researchers have to say about the evolution of women’s rights and the obstacles to advancing gender equity.
Impacts of overturning Roe v. Wade , and the U.S. Supreme Court
The decision by the U.S Supreme Court to overrule Roe v. Wade in the Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health case will carry many wide-reaching and serious consequences for women, say Stanford professors. By ending the constitutional right to abortion, a protection women have had for nearly 50 years, it will now be up to states to decide what reproductive choices are available for women – regardless of the circumstance.
“No matter the reason a woman seeks to terminate a pregnancy – including because her health is jeopardized, because she was raped, because the fetus has a condition making death likely shortly after birth – a majority of state legislators may usurp that deeply personal decision,” said Stanford law Professor Jane S. Schacter in the wake of the decision.
Here, Stanford professors shed light on the ramifications the reversal will have, as well as research on the divergence between the justices’ positioning versus public opinion, which the Roe v. Wade overruling highlighted.

A constitutional earthquake: Jane Schacter on SCOTUS decision to overturn Roe v. Wade
Stanford law Professor Jane Schacter, an expert on constitutional law and sexuality, discusses the Supreme Court’s decision to end the constitutional right to an abortion.

Using economics to understand the wide-reaching impacts of overturning Roe v. Wade
The greatest burden of abortion restrictions will likely fall onto low-income women and minorities, says Stanford economist Luigi Pistaferri.

Stanford’s Bernadette Meyler on possible SCOTUS decision to overturn Roe v. Wade
Constitutional law scholar Bernadette Meyler discusses the leaked Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization memo and the implications of a possible decision.
The gap between the Supreme Court and most Americans’ views is growing
A new study finds that not only has the court’s majority shifted dramatically rightward in the past two years, its stances are now significantly more conservative than most Americans’.


Protecting reproductive health information after fall of Roe v. Wade
Michelle Mello writes that the overturning of Roe v. Wade – ending federal protection over a woman's right to an abortion – could also expose her personal health data in court.
The pandemic’s effect on women
While the overturning of Roe v. Wade has sent shockwaves across the country, the global pandemic continues to be problematic, particularly among women and people of color. According to Stanford sociologist Shelley Correll , the pandemic alone may set gender equality back a generation as women take on an unfair burden of job losses and child care.
“Feelings of burnout have increased over the last year for both men and women, but more so for women,” Correll said, noting how mental health challenges and the lack of reliable child care continue to be problematic. “My big concern, in terms of gender equality, is that this high level of burnout is going to either drive women out of the paid workforce entirely or cause them to dial back their careers to something that is more manageable.”
Over the coming months, it will be increasingly clear what the ramifications of both the end of Roe v. Wade and the pandemic will have. But what is already apparent is the urgent need to ensure access to health care, child care, and education, Stanford scholars say. Here is some of that research.

It’s time to prioritize humane, thriving work environments
The global pandemic is an opportunity to make fundamental changes to how society approaches work by creating working environments centered around creativity, problem-solving and equity, says Adina Sterling.

The real benefits of paid family leave
Paid family leave is not a “silver bullet” for advancing gender equity in the workplace, Maya Rossin-Slater says, but it is beneficial for family health and well-being outcomes, particularly infant and maternal health and overall financial stability.

Gender equality could be set back by an entire generation, sociologist warns
Coming out of the pandemic is an opportunity to build more equitable workplaces. Otherwise, burnout is likely going to either drive women out of the paid workforce entirely or cause them to dial back their careers, with long-term consequences for gender equality, says Stanford scholar Shelley Correll.

Equity and inclusion key issues in new work-life balance
With work, school and family life all taking place in our homes, the challenges may be greater for women, according to a focus group consisting of corporate and nonprofit leaders convened by Stanford’s VMware Women’s Leadership Innovation Lab.

Stress during pregnancy doubled during pandemic
As the first shelter-in-place orders took hold in California, pregnant women reported substantially elevated depressive symptoms, potentially adversely affecting their health as well as that of their babies.
Feminism and overcoming gender discrimination across history
For feminists, choice over reproductive health symbolized the human right to self-determination , said Estelle Freedman in her seminal book, No Turning Back: The History of Feminism and the Future of Work (Ballantine Books, 2003).
As Freedman explains, “Feminists have increasingly insisted that women’s health and children’s welfare must be central to international reproductive policies. In this way, reproductive choice can help alleviate economic injustice as well as extend human rights to women.”
Freedman, along with other Stanford scholars, has studied the evolution of feminist movements and women’s rights across history and the fight for economic justice and human rights in America and across the globe. Some have also examined these movements’ flaws, including historically overlooking people of color and people with a disability. Here are some of their findings.

How World War I strengthened women’s suffrage
Times of crisis can be catalysts for political change, says Stanford legal scholar Pamela S. Karlan. For women activists in the early 20th century, the catalyst was World War I.
The 19th Amendment is a milestone, not endpoint, for women’s rights in America
As the centennial of the 19th Amendment approaches, the milestone in women’s suffrage must also acknowledge the intersection of gender and racial justice in America, says Stanford scholar Estelle Freedman.

Left out of the vote
As the centennial of the 19th Amendment approaches, Stanford scholar Rabia Belt wants to acknowledge a history often overlooked in discourse about the franchise: people living with disabilities.

Why taking gender out of the equation is so difficult
Even as old stereotypes fade, gender remains “a very sticky category,” says Ashley Martin, assistant professor of organizational behavior.

Power forward
Tara VanDerveer, head coach of the Stanford women’s basketball team, talks about the state of women’s sports on the 50th anniversary of Title IX.
Roadblocks in the workplace
In 2020, women earned 83 cents to every dollar men earned, according to data from the U.S. Census Bureau. While the wage gap has narrowed over time, it still persists. Is it because of discrimination? Occupational differences? Workforce participation?
Scholars at the Stanford Graduate School of Business have tried to answer questions like these, including Stanford labor economist and Professor Emerita Myra Strober, who has dedicated her career to examining sexism across society, including the workplace.
“The American way, if you will, is to reward people who are valuable by paying them more. What’s not fair is rewarding them because you think they’re going to be more valuable before the game even starts. Managers should take people in entry-level positions and try to groom them all to see who turn out to be best,” Strober said in a 2016 interview . Strober suggests companies ought to examine salary disparities, offer paid parental leave and subsidize or offer childcare, and encourage workplace flexibility as ways to diversify and equalize the workplace.
Here is that interview, along with other research from scholars affiliated with the GSB who have examined gender differences and biases in the workplace and in leadership.

Is workplace equality the economy’s hidden engine?
In 1960, 94% of doctors and lawyers were white men. Today that number has fallen to 60%, and the economy has benefited dramatically because of it.

The language of gender bias in performance reviews
How negative stereotypes about men and women creep into a process intended to be meritocratic.

How race influences, amplifies backlash against outspoken women
When women break gender norms, the most negative reactions may come from people of the same race.

Having more power at the bargaining table helps women – but also sparks backlash
A large-scale study of job negotiations finds that women with stronger options were penalized for being too assertive.

How companies can solve the pay equity problem
A labor economist reveals how to close the pay gap.

Solving Silicon Valley’s gender problem
The authors of a survey on women in high tech answer the question: What now?
Making research, education more inclusive
In academic research, particularly the sciences, a gendered perspective has historically been overlooked, says Stanford historian Londa Schiebinger .
Such an oversight has come at a cost: For example, in clinical drug trials, women have been excluded on the grounds of reproductive safety – meaning that when drugs hit market, doses may not be suited for female bodies.
“Integrating sex and gender as variables in research, where relevant, enhances excellence in science and engineering,” said Schiebinger , who is the John L. Hinds Professor in the History of Science in Stanford’s School of Humanities and Sciences. “The operative question is how can we harness the creative power of sex and gender analysis for discovery and innovation? Does considering gender add a valuable dimension to research? Does it take research in new directions?”
Schiebinger has spent her career finding creative ways to make science more inclusive. Here is some of that work, and work by others – including research showing the barriers women have faced as students in K-12 and at the PhD level.

A hidden obstacle for women in academia
A sweeping new study finds that women are penalized for pursuing research perceived to be “feminized” – an implicit bias surprisingly strong in fields associated with women.

Gender diversity is linked to research diversity
Gender diversity in science comes down to more than just who is on the team. The research approaches and types of questions the field addresses also shift – and lead to better science.

Sex and gender analysis improves science, Stanford scholars say
Including a gender and sex analysis in scientific research can open the door to discovery and innovation, according to a study performed by Stanford historian Londa Schiebinger and a group of scholars.

Female researchers pay more attention to sex and gender in medicine
Sex and gender affect how people react to drugs or other therapies, but are often overlooked in research. Stanford researchers find that medical research teams that include women more often account for sex and gender in their work.

Whose history? AI uncovers who gets attention in high school textbooks
Natural language processing reveals huge differences in how Texas history textbooks treat men, women, and people of color.

High-stakes exams can put female students at a disadvantage, Stanford researcher finds
A new study suggests that women are more heavily influenced than men by test anxiety, and points to ways to help close the gender gap.
Essays About Gender Inequality: Top 5 Examples and 8 Helpful Prompts
Essays about gender inequality discuss a timely subject. Discover our guide with examples and prompts to assist you in writing.
Gender inequality is a global issue where one person’s perception and treatment of others depend on predetermined social expectations, leading to discrimination. Children can learn negative stereotypes, live with these biases, and carry them into adulthood. Parents who teach their kids prejudice are one of the reasons for gender inequality that spills into everyone else’s lives.
Organizations like UNICEF actively form partnerships worldwide to stop and promote gender equality . Their efforts include career support, higher quality maternal care, skills development, and more. Your gender inequality essay can help promote gender equality that prevents violence against all genders. In addition, by discussing the topic, more people can better understand the seriousness of the issue. Check out our round-up of the best essay writing apps to get started!
5 Essay Examples
1. gender inequality: sources and consequences by anonymous on edubirdie.com, 2. the issue of gender inequality in the media in america by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 3. gender inequality is a huge issue from past by joshua blake, 4. the problem of gender inequality in the workplace by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 5. gender inequality: are there any positive changes by anonymous on eduzaurus.com, 1. gender inequality: defined, 2. impact of gender inequality, 3. fighting gender inequality, 4. types and causes of gender inequality, 5. gender inequality as a global problem, 6. politics and gender inequality, 7. who are the most affected by gender inequality, 8. gender inequality and family dynamics.
“Humanity requires both men and women to move forward together, and they both are equally important. There are no reasons why women should be seen as the “weaker” sex.”
The author firmly believes that people must control old habits and notions about genders for everyone’s sake. This essay further delves into how culture and history devalue women and prove that men are more powerful as they bring money and do more physical work. The media also assists in making viewers think women are sexual objects, with how most magazines and promotions cater to men’s satisfaction.
The writer understands that gender inequality is impossible to fix immediately. So they recommend parents teach their children to avoid stereotyping. Companies should also ensure equal treatment for both genders when providing job opportunities. They also mention that more influential people will speak about the problem as the unjust treatment continues.
“There is no doubt that every form of media today will have some sort of gender stereotypes and generalizations about male and female roles.”
In this gender inequality essay, the writer explains not only what stereotypes are but also how the media harms the lives of young men and women when these labels are reinforced. This includes the stereotype of being a housewife, the most common stereotype.
The writer describes how the media is at fault for promoting a negative body image. When mainstream channels portray the “perfect” male or female body, and viewers see that they are far from what those ideal types look like, it can lead to physical and mental health problems.
“It is certain that gender inequality is a huge issue from the past to present especially [as it] occurs among women.”
To identify the causes of gender inequality, Blake uses various studies to prove that Hofstede and Schwartz’s framework on the cultural dimension influences the differences between men and women.
A good example is Schwartz’s hierarchy and Hofstede’s power distance, which both refer to unequal power distribution and sources. Some dimensions are very similar and correspond to each other, such as masculinity and mastery, femininity and harmony, autonomy and individualism, conservatism, and collectivism.
“Both genders can have the same education and experience, yet the male gets a higher wage payment compared to female.”
In discussing the topic, the author uses various statistical data to prove that gender inequality in the workplace is still present today but is improving. For example, according to their findings, American men earn one dollar while women earn only 89 cents.
Americans are also against the women who return to work after giving birth and say men shall continue without paternity leave. But ultimately, the writer believes that when there’s gender inequality in a company, they lose the opportunity to keep their best resources.
“Gender inequality can be defined as not giving equal opportunities to people because of their biological sex.”
The essay mentions how TV shows and personalities like Emma Watson , who speak their minds on how the media portrays genders, help shed more light on gender inequality. Therefore, they encourage others to become a part of something revolutionary. However, it also shows little change in gender differences after more people became aware of the situation. The piece also notes how today’s parents are raising their children, allowing them to eliminate gender-based oppression.
8 Prompts for Essays About Gender Inequality

Explain to your readers the main topic and how inequality occurs in modern society. Give an example of gender inequality that is very common and how both sexes react to it. Conclude your essay with recommendations on how these issues can be resolved and avoided.
In reality, gender inequality has negative impacts on everyone. Discuss how this problem takes away opportunities, develops destructive behaviors, and puts people in dangerous situations. Offer real-life examples, surveys, and data to support your claims to make the essay more informative and credible.
Gender inequality has been a prevalent issue since the beginning of time and is still a pressing matter today. Use this prompt to identify and discuss steps governments, organizations, schools, churches, parents, and individuals should take to avoid being gender biased.
Share ways to promote gender equality through simple tasks like sharing household chores between housemates, no matter the gender, calling out sexist jokes, and learning more about the topic.
To make your essay more effective, incorporate convincing and powerful writing. Read our guide on persuasive writing to know more.

Talk about the various types of gender inequality, such as gender discrimination in education, sexual violence, unequal pay and recognition, racism, and ownership inequality. Add their causes and roots.
It’s best if you can interview someone who experiences this imbalance. Let them relay what they felt and why they think it happened. Include other examples to allow your readers to visualize and understand the situations.
Do thorough research and find survey data showing the number of people who are still victims of gender inequality. Look for the best and most reliable source and check how it differs from one location to the other. Discuss your findings and share your opinion on what contributes to this discrimination.
Use this prompt if you want to tackle fundamental problems related to gender inequality. Discuss how women and men are treated in politics and give examples of situations that demonstrate it. The more famous the incidents are, the better. You can also compare if there’s a relevant difference between how female and male politicians lead.
Although all are affected by this bias, who are the most prone to it? Search for applicable data from reputable sources to determine and expound on the number of people involved. Include how these people are influenced and why.
Gender inequality also occurs in wealthy families or nobility, where whoever is in charge of a business or place needs power and the ability to dominate others. Search for countries and cultures that still follow a patriarchal structure. Add your opinion on whether it’s time to modify these structures or its best to keep them as is for traditions’ sake.
If you’re still stuck, maybe this topic is not for you. Check out our general resource of essay writing topics.

Maria Caballero is a freelance writer who has been writing since high school. She believes that to be a writer doesn't only refer to excellent syntax and semantics but also knowing how to weave words together to communicate to any reader effectively.
View all posts
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 06 September 2023
Gender equality: the route to a better world
You have full access to this article via your institution.

The Mosuo people of China include sub-communities in which inheritance passes down either the male or the female line. Credit: TPG/Getty
The fight for global gender equality is nowhere close to being won. Take education: in 87 countries, less than half of women and girls complete secondary schooling, according to 2023 data. Afghanistan’s Taliban continues to ban women and girls from secondary schools and universities . Or take reproductive health: abortion rights have been curtailed in 22 US states since the Supreme Court struck down federal protections, depriving women and girls of autonomy and restricting access to sexual and reproductive health care .
SDG 5, whose stated aim is to “achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls”, is the fifth of the 17 United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, all of which Nature is examining in a series of editorials. SDG 5 includes targets for ending discrimination and violence against women and girls in both public and private spheres, eradicating child marriage and female genital mutilation, ensuring sexual and reproductive rights, achieving equal representation of women in leadership positions and granting equal rights to economic resources. Globally, the goal is not on track to being achieved, and just a handful of countries have hit all the targets.

How the world should oppose the Taliban’s war on women and girls
In July, the UN introduced two new indices (see go.nature.com/3eus9ue ), the Women’s Empowerment Index (WEI) and the Global Gender Parity Index (GGPI). The WEI measures women’s ability and freedoms to make their own choices; the GGPI describes the gap between women and men in areas such as health, education, inclusion and decision making. The indices reveal, depressingly, that even achieving a small gender gap does not automatically translate to high levels of women’s empowerment: 114 countries feature in both indices, but countries that do well on both scores cover fewer than 1% of all girls and women.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made things worse, with women bearing the highest burden of extra unpaid childcare when schools needed to close, and subjected to intensified domestic violence. Although child marriages declined from 21% of all marriages in 2016 to 19% in 2022, the pandemic threatened even this incremental progress, pushing up to 10 million more girls into risk of child marriage over the next decade, in addition to the 100 million girls who were at risk before the pandemic.
Of the 14 indicators for SDG 5, only one or two are close to being met by the 2030 deadline. As of 1 January 2023, women occupied 35.4% of seats in local-government assemblies, an increase from 33.9% in 2020 (the target is gender parity by 2030). In 115 countries for which data were available, around three-quarters, on average, of the necessary laws guaranteeing full and equal access to sexual and reproductive health and rights had been enacted. But the UN estimates that worldwide, only 57% of women who are married or in a union make their own decisions regarding sexual and reproductive health and rights.
Systemic discrimination against girls and women by men, in many contexts, remains a colossal barrier to achieving gender equality. But patriarchy is not some “natural order of things” , argues Ruth Mace, an anthropologist at University College London. Hundreds of women-centred societies exist around the world. As the science writer Angela Saini describes in her latest book, The Patriarchs , these are often not the polar opposite of male-dominated systems, but societies in which men and women share decision making .

After Roe v. Wade: dwindling US abortion access is harming health a year later
One example comes from the Mosuo people in China, who have both ‘matrilineal’ and ‘patrilineal’ communities, with rights such as inheritance passing down either the male or female line. Researchers compared outcomes for inflammation and hypertension in men and women in these communities, and found that women in matrilineal societies, in which they have greater autonomy and control over resources, experienced better health outcomes. The researchers found no significant negative effect of matriliny on health outcomes for men ( A. Z. Reynolds et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117 , 30324–30327; 2020 ).
When it comes to the SDGs, evidence is emerging that a more gender-equal approach to politics and power benefits many goals. In a study published in May, Nobue Amanuma, deputy director of the Integrated Sustainability Centre at the Institute for Global Environmental Strategies in Hayama, Japan, and two of her colleagues tested whether countries with more women legislators, and more younger legislators, are performing better in the SDGs ( N. Amanuma et al. Environ. Res. Lett. 18 , 054018; 2023 ). They found it was so, with the effect more marked for socio-economic goals such as ending poverty and hunger, than for environmental ones such as climate action or preserving life on land. The researchers recommend further qualitative and quantitative studies to better understand the reasons.
The reality that gender equality leads to better outcomes across other SDGs is not factored, however, into most of the goals themselves. Of the 230 unique indicators of the SDGs, 51 explicitly reference women, girls, gender or sex, including the 14 indicators in SDG 5. But there is not enough collaboration between organizations responsible for the different SDGs to ensure that sex and gender are taken into account. The indicator for the sanitation target (SDG 6) does not include data disaggregated by sex or gender ( Nature 620 , 7; 2023 ). Unless we have this knowledge, it will be hard to track improvements in this and other SDGs.
The road to a gender-equal world is long, and women’s power and freedom to make choices is still very constrained. But the evidence from science is getting stronger: distributing power between genders creates the kind of world we all need and want to be living in.
Nature 621 , 8 (2023)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-023-02745-9
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

- Sustainability
- Public health

Nearly half of China’s major cities are sinking — some ‘rapidly’
News 18 APR 24
The world needs a COP for water like the one for climate change
Correspondence 16 APR 24
Don’t dismiss carbon credits that aim to avoid future emissions
Correspondence 02 APR 24

What toilets can reveal about COVID, cancer and other health threats
News Feature 17 APR 24

Smoking bans are coming: what does the evidence say?
News 17 APR 24
It’s time to talk about the hidden human cost of the green transition

Do climate lawsuits lead to action? Researchers assess their impact
News Explainer 16 APR 24

Exclusive: official investigation reveals how superconductivity physicist faked blockbuster results
News 06 APR 24

Is IVF at risk in the US? Scientists fear for the fertility treatment’s future
News 02 APR 24
Postdoctoral Position
We are seeking highly motivated and skilled candidates for postdoctoral fellow positions
Boston, Massachusetts (US)
Boston Children's Hospital (BCH)
Qiushi Chair Professor
Distinguished scholars with notable achievements and extensive international influence.
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Zhejiang University
ZJU 100 Young Professor
Promising young scholars who can independently establish and develop a research direction.
Head of the Thrust of Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Reporting to the Dean of Systems Hub, the Head of ROAS is an executive assuming overall responsibility for the academic, student, human resources...
Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)
Head of Biology, Bio-island
Head of Biology to lead the discovery biology group.
BeiGene Ltd.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

- Previous Article
This paper identifies five key issues that are important for the continued efforts to tackle gender inequality: (i) gender inequality needs to be distinguished from gender gaps. Not all gender gaps necessarily reflect gender inequality as some gender gaps are not driven by the lack of equal rights, responsibilities and opportunities bywomen and girls, and this has important implications on policy designs to address gender inequity. However, the literature has paid little attention to this issue, often using gender inequality and gender gaps interchangeably; (ii) the evolving focus of gender inequality suggests there is still a long way to go to fully address gender inequality. Particularly gender inequality is taking more subtle and implicit forms, though the social and economic benefits from addressing the remaininggender inequality is still likely to be substantial; (iii) addressing gender inequality benefits everyone, not just women. Thus, the entire society should work together, even for each individual’s own interest; (iv) both general policies and targeted gender policies can help address gender inequality.However, as gender inequality becomes more subtle and implicit, targeted gender policies will likely need to play an increasing role, which also makes separating gender inequality from gender gaps all that more important; and (v) addressing gender inequality does not need to start with policies targeted at its root causes, but needs to end with eliminating the root causes. Only then, any remaining gender gaps would only reflect preference and comparative advantage between men and women. The paper concludes by discussing gaps in the literature and policy challenges going forward.
- I. Introduction
Gender gaps have been observed in a broad range of social and economic dimensions and well-documented in the literature. Here gender gaps refer to the observed differences between men and women or between boys and girls in the relevant indicators. For example:
Gender gaps in nutritional intake have been often reported as a result of intra household allocation of resources in South Asia, with also evidence in sub-Sahara Africa ( Pal, 1999 ; World Bank, 2006 ; Hadley and others, 2007 ; Dasgupta, 2016 ; Hafeez and Quintana-Domeque, 2018 ).
In developing countries, while gender gaps in school enrollment have been narrowing rapidly over the recent decades, particularly for preprimary, primary and secondary education, considerable gaps still remain for tertiary education and there are large variations across countries ( Demery and Gaddis, 2009 ; Duflo, 2012 ; Austen and others, 2013 ; Evans and others, 2021 ). Furthermore, significant differences exist in the field of study between male and female students, likely in nearly all countries but with most evidence from advanced economies ( OECD, 2017 ; Cook and others, 2021 ).
Empirical studies, based on subjective self-reporting of unmet healthcare needs, find that women are more likely to report healthcare access related issues (Socías and others, 2016; Daher and others, 2021 ).
Access to formal financial services is generally lower for women than for men. Over time, access to financial services has increased worldwide, but significant gaps remain by gender, and both saving and borrowing services are more accessible to men than to women ( Demirgüç-Kunt and others, 2015 ; Sahay and others, 2020 ).
Differences between male and female labor force participation rates have narrowed, but the gaps remain high in most of the world, with large variations across regions and countries ( Field and others, 2010 ; Alesina and others, 2013 ; Bernhardt and others, 2018 ; Jayachandran, 2021 ). Even when women participate in the labor market, they tend to be overrepresented in certain sectors, often characterized by low status and low pay ( OECD, 2012 ; ILO, 2012 ). Particularly, women are strongly under-represented in corporate managerial positions and political leadership ( Profeta and others, 2014 ; OECD, 2017 ). Even for the same jobs and with similar qualifications, women tend to be paid less ( OECD, 2012 ; OECD, 2017 ; NSF, 2021 ).
Women are subject to more violence at home, in commuting, and at work ( Jayachandran, 2021 ). In addition, legal barriers to women’s rights and opportunities remain pervasive. Women on average have only three-quarters of the legal protections given to men during their working life, ranging from bans on entering some jobs to a lack of equal pay or freedom from sexual harassment ( World Bank, 2021 ).
Many research and policy work often equates gender gaps with gender inequality without clearly defining them. According to UN Women ,
“ Equality between women and men (gender equality) refers to the equal rights, responsibilities and opportunities of women and men and girls and boys. Equality does not mean that women and men will become the same but that women’s and men’s rights, responsibilities and opportunities will not depend on whether they are born male or female. Gender equality implies that the interests, needs and priorities of both women and men are taken into consideration, recognizing the diversity of different groups of women and men. ”
This suggests that not all gender gaps necessarily reflect gender inequality, as defined above. This has important policy implications, that is, policies should focus on eliminating gender inequality, not on achieving an equal gender share or fully closing all gender gaps.
The urgency to address gender inequality stems from its substantial social and economic consequences. First and foremost, gender inequality is a matter of fairness and concerning the wellbeing of women. 1 For example, some gender inequality reflects direct harmful actions against women —such as violence, harassment, and the resulting fear—or restrictions on women’s behaviors, legal or social. More generally, as gender inequality is the result of gender bias and social norms that restrict women’s rights and opportunities, it leads to lower welfare for women. Furthermore, as women account for half of the population, gender inequality means potentially a substantial misallocation of human capital, including both investment in women and utilization of women talent. A growing body of literature shows that reducing gender inequality can help foster better household decision-making, improve firm/institution performance, and generate substantial macroeconomic benefits, through boosting productivity and economic growth, strengthening macroeconomic and financial stability, and lowering income inequality ( Kochhar and others, 2017 ; Sahay and others, 2018 ; Cihák and Sahay, 2020 ; Gonzales and others, 2015 b).
There is clear evidence that gender inequality narrows as countries develop and new technologies, such as labor-saving household appliances, are being developed and widely adopted ( Jayachandran, 2015 ; Tewari and Wang, 2021 ). However, the interrelationships between women empowerment and economic development are probably too weak to be self-sustaining, and because of the social and economic significance of gender inequality, policy actions are needed to speed up the process ( Duflo, 2012 ). For example, around 82 percent of 40-year-old inventors are men, and while this gender gap in innovation is shrinking gradually, at the current rate of convergence, it will take another 118 years to reach gender parity ( Bell and others, 2019 ).
One of the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is to achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls. 2 Many efforts have been taken over the past decades, particularly after the establishment of the SDGs in 2015, to tackle gender inequality. For example, public investment in education has nearly erased the gender gaps in primary and secondary school enrollment; legislative reforms have led to reductions in discrimination; countries have enacted reforms to boost women’s economic opportunities; countries have enacted laws or introduced policies to end child and early marriage, provide paternity and parental leave, reduce the gender wage gap, address violence against women including sexual harassment, and promote women in leadership ( World Bank, 2021 ; OECD, 2014 ; OECD, 2017 ). 3
While globally important progress has been made in some areas (e.g., enrollment in primary and secondary education), substantial gender inequality still remains in many other areas (e.g., enrollment in tertiary education, labor force participation, wages, and leadership positions). Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has disproportionately affected women, further exacerbating pre-existing gender inequality, for example, as women shouldered more burden in taking care of young children when schools were closed ( Albanesi and Kim, 2021 ; Bluedorn and others 2021 ; Fabrizio and others, 2021 ; WEF, 2021 ).
Thus, much work still lies ahead to achieve gender equality, with some forms of gender inequality still existing in nearly all countries and often in relation to the SDGs. As countries seek to step up their efforts to address gender inequality, many questions remain for policymakers. This includes: (i) what are the main forms of gender inequality for countries at different stages of development? (ii) what are the economic benefits from continued efforts to reduce gender inequality, are the benefits diminishing as some gender inequality is being eliminated, and who would benefit from lower gender inequality? (iii) What policies are most effective in addressing gender inequality, what are the tradeoffs of adopting different types of policies, and are some of the policies more about ticking a box rather than making a real difference? And (iv) what are the roles of different types of policies at eliminating gender inequality, given the root causes of gender inequality is often social and cultural?
The literature on the economic impacts of gender inequality and the policies to address gender inequality has been growing rapidly over the recent decades. In addition, many countries have adopted policies to tackle gender inequality for many years, and there is a lot to learn from their experiences. This paper intends to draw on the vast literature—which tends to focus on specific aspects of gender inequality and policies —and the diverse country experiences to provide a holistic view of gender inequality and shed light on some of the key policy questions that can help countries approach gender issues in a more systematic manner. More specifically, the paper identifies five key lessons:
Gender inequality versus gender gaps . Gender inequality differs from gender gaps in important ways, and this has important policy implications. However, the literature often equates gender inequality with gender gaps and use them interchangeably. This paper defines gender gaps as the observed differences between men and women or between boys and girls in the various social and economic indicators, and gender inequality refers to the part of gender gaps that are driven by gender bias and unequal gender rights and opportunities. The rest of the gaps are driven by preference/comparative advantage between men and women. Therefore, policies should be targeted at reducing gender inequality, which does not necessarily mean to fully close all gender gaps.
The evolving focus of gender inequality . Gender inequality extends to nearly every dimension of social and economic activities. The policy focus often varies by country, depending on their circumstances and level of development. There appears to be a shift toward more subtle and implicit forms of gender inequality, as gender reforms deepen, for example, from school enrollment to quality of education and field of study and from labor force participation to distribution of employment across sector s and pay. However, this does not mean that the social and economic impacts of the remaining gender inequality are smaller. In fact, the literature has shown that they could have substantial economic consequences. Furthermore, for countries that are still at the early stage of addressing gender inequality, this suggests that they should learn from the experiences of other countries, and it may be more effective and efficient to tackle different forms of gender inequality simultaneously. For example, countries could consider policy measures to simultaneously address gender inequality in tertiary enrollment and field of study, rather than tackling gender imbalances in field of study only after gender inequality in enrollment is eliminated.
The benefits of reducing gender inequality go beyond women . Gender equality may be seen by some as a zero-sum game, from an economic point of view. Less unpaid work at home and higher labor force participation by women would mean more unpaid work at home and lower labor force participation for men. Better representation at leadership positions by women would mean less for men. It is, however, important to recognize that better gender equality benefits not just women, but it enlarges the economic pie and benefits everyone, through several potential channels: (i) women tend to make better decisions regarding children; (ii) gender-mixed teams are more productive; and (iii) lower gender inequality can bring important macroeconomic benefits to everyone, with stronger economic growth and financial stability, more jobs, and less income inequality.
Policies and their designs matter . Large variations in gender gaps among countries with a similar level of development and in the same region suggest that policy interventions and their designs can make a difference, and this is further illustrated with an econometric analysis of gender laws and regulations and selected gender gaps. In addition, the literature provides strong evidence that a broad range of policy reforms can help reduce gender inequality and ultimately improve social and economic outcomes. However, not all policy interventions work under all circumstances, and policy tradeoffs are often involved. The paper compares general policies and targeted gender policies and discusses some considerations in their designs and implementation.
Policy actions do not have to start with those targeted at the root causes . While gender inequality shows many symptoms, the root causes are typically traced to gender bias and social norms. Ideally, reforms should be directly targeted at the root causes. However, this appears difficult with limited policy options (e.g., educational programs, information campaign, and legal reforms to ensure women’s rights and opportunities), and it takes time to change people’s views and beliefs. Instead, policies have focused on reducing gender inequality in different areas such as education, labor market, and financial access. Not only do these policies have immediate impacts on gender inequality, but they could also help change social norms. While policies may not need to start with the root causes of gender inequality, fully eliminating gender inequality requires eventually addressing the root causes.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section II to VI in turn take on the five key lessons discussed above. Section VII concludes with a discussion on the gaps in the literature and on some considerations in addressing gender inequality going forward.
- II. Gender gaps and gender inequality: definitions and drivers
Gender gaps are defined here as the observed differences between men and women or between boys and girls in the various social and economic indicators. Gender gaps can be considered to consist of two components, one that is caused by unequal rights, responsibilities, and opportunities for women and girls 4 and the other that is driven by women’s preference 5 or comparative advantage between men and women. 6 The former is what is defined in this paper as gender inequality, and the latter is the result of efficient allocation of human capital. For example, for school enrollment in primary and secondary education, it would be expected that most, if not all, of the gender gaps reflect gender inequality. For tertiary education in advanced economies, female enrollment rate is about 25 percent higher than that of male ( Figure 1 ). This gap, however, would not be expected to reflect gender inequality, that is, boys are facing less rights and opportunities. Instead, this likely reflects preference and choices (e.g., girls have comparative advantage in brain-based sectors and the returns to education are higher in such sectors ( Pitt and others, 2012 )). On the other hand, males represent a very small share of employment in registered nurses, some of which may indeed reflect social norms that hinder male’s entry into this profession. 7
Distinguishing between gender gaps and gender inequality has important policy implications. For the part of gender gaps that reflect preference/comparative advantage between men and women, there would be no need for policy intervention as there is no welfare loss from such gaps. For example, in many advanced economies where female tertiary enrollment rate is higher than that of male, there appears no need for policy interventions to further increase male tertiary enrollment rate to close the gap. On the other hand, there is a clear need to address gender inequality as it hurts women’s wellbeing, leads to distortions, and reduces overall social welfare. In many developing economies where female tertiary enrollment rate is lower than that of male due to gender bias, if it is left unaddressed, there would be an underutilization of women’s talent. Recognizing the difficulties often in separating gender inequality from gender gaps, Section V discusses some implications on policy designs.
Better understanding the drivers of gender inequality and gender gaps helps formulate effective policies. Both the theoretical and empirical literature offers evidence on the main drivers of gender gaps and gender inequality, particularly in the context of economic development:
Comparative advantage improves for women as countries develop. Women have a comparative advantage in mentally intensive tasks while men in physical intensive tasks; the process of development entails a growing capital stock and thus reduces the female-male wage gap, which in turn causes female labor force participation to increase ( Galor and Weil, 1996 ). 8 As brain-based sectors grow, if the returns to education are higher in brain-based than in brawn-based occupations, girls’ schooling could overtake that of boys ( Pitt and others, 2012 ). Gender differences in labor productivity as a driver of gender gaps are also supported by empirical evidence ( Qian, 2008 ; Alesina and others, 2013 ; Carranza; 2014 ). This strand of literature highlights the mechanism through which gender gaps narrow as countries develop, by largely reducing the part of gender gaps that reflect preference/comparative advantage between men and women.
Economic development is associated with better physical infrastructure and more advanced technology, making home production more efficient and less labor intensive. Because women perform the lion’s share of household chores, advances in home production technologies mainly free up women’s time and lead to an increase in female labor force participation ( Greenwood and others, 2005 ; Dinkelman, 2011 ; Tewari and Wang, 2021 ). As women performing much home production likely reflects both preference/comparative advantage between men and women and gender bias/social norms, better physical infrastructure and more advanced technology help reduce both components of gender gaps. 9
Gender bias and cultural barriers to women’s rights and opportunities are major drivers of gender gaps ( Jayachandran, 2015 ; Jayachandran, 2021 ; Alesina and others, 2013 ; Bernhardt and others, 2018 ). For example, Fernandez and Fogli (2009) show that whether a female second-generation immigrant in the United States works is strongly influenced by the female employment and fertility norms in her ancestral homeland. One form of barriers is the lack of basic legal rights, preventing women from joining the formal labor market or becoming entrepreneurs in many countries. Women are sometimes legally restricted from heading a household, pursuing a profession, or owning or inheriting assets. Such legal restrictions significantly hamper female labor force participation and pose a drag on female entrepreneurship (World Bank, 2015). Limiting gender bias and cultural barriers helps close gender gaps through reducing gender inequality.
Figure 1 illustrates conceptually the interrelationship between gender gaps, gender inequality, their drivers, and policy interventions to address them:
The root causes of gender inequality are gender bias and social norms that restrict women’s rights and opportunities, which, together with preference /comparative advantage between men and women, are the root drivers of gender gaps.
Gender bias/social norms and preference/comparative advantage between men and women interact with other factors (e.g., development, technological advances, and public policies) in determining gender gaps and gender inequality in different areas such as education, labor market and financial access. In other words, the root causes of gender inequality are gender bias and social norms; gender inequality in different areas are just symptoms of the root causes. This means that while some policies can help reduce gender inequality in some of these areas, fully addressing gender inequality would require the elimination of the root causes, gender bias/social norms.
As discussed above, development, technological advances, and public policies can affect gender bias/social norms and preference/comparative advantage between men and women.
Furthermore, interventions to lower gender inequality in different areas could also in turn alter gender bias/social norms. For example, as women become more educated and more women participate in the labor market, attitude toward women’s education and work may start to shift (see section VI for additional discussions).

Gender inequality, gender gaps and their causes
Citation: IMF Working Papers 2022, 232; 10.5089/9798400224843.001.A001
- Download Figure
- Download figure as PowerPoint slide
III. The evolving focus of gender inequality: still a long way to go
Progress on gender equality has continually been made and differs substantially by country, particularly in relation to their stage of development. Consequently, the focus of gender inequality also varies by country and continue to evolve as some gender gaps are closed while others emerge and attract the attention of the public and policymakers. In general, the focus of gender inequality is shifting from gender gaps that are more explicit and visible to the public and policymakers to those that are more subtle and implicit. Given that gender inequality exists in broad areas, this section focuses on education, labor market, financial access, and legal barriers, as examples.
- A. Education
The focus of gender inequality in education appears to be shifting from access to education (e.g., school enrollment) to quality of education and field of study.
For emerging and developing economies as a group, the gender gaps in access to preprimary, primary and secondary education are being closed, though some countries are still lagging behind; however, there are still gaps for tertiary education ( Appendix Figure 1a-1d ). As a result, many emerging and developing economies are still trying to achieve gender equality in access to education, particularly for tertiary education ( Demery and Gaddis, 2009 ; Duflo, 2012 ; Austen and others, 2013 ; Evans and others, 2021 ).
Advanced economies, instead, have been focusing on gender equality in quality of education, including gender distribution by field of study, as they have largely achieved gender equality in access to preprimary, primary and secondary education decades ago and to tertiary education since mid-2000s. For example, across the OECD, boys outperformed girls in mathematics by an average of eight points in 2015 —equivalent to around one-fifth of a year of schooling—and by 5 points in 2018; on the other hand, girls significantly outperform boys in reading in all countries and economies that participated in PISA 2018 ( OECD, 2017 ; OECD, 2019 ).
One area that has received increasing attention is the large differences in field of study between boys and girls, with girls particularly underrepresented in the fields of science and engineering and overrepresented in social science related fields ( Appendix Figure 2 ). The distributions are remarkably similar between more developed economies and the rest of the world, indicating that this is an issue common for all economies ( Appendix Figure 2a shows the global distribution and Appendix Figure 2b shows the distribution for OECD countries during a similar period). For example, college-educated women in the United States have sorted into majors that systematically lower their potential wages relative to men; to what extent women choose a major in anticipation of future family demands, based on individual preferences, under the burden of restrictive social norms, or for any other reason remains an unanswered question ( Sloane and others, 2021 ).
Women appear to be particularly under-represented in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM). In the United State, in 1970, only 9 percent of all doctorates in the science and engineering fields, including social sciences, were awarded to women; by 2018, that share was nearly 47 percent. A closer look indicates that a large part of this is driven by high shares of women in psychology and social sciences. Despite the progress, persistent barriers to women pursuing degrees in STEM fields abound (Cook and others, 20 21).
- B. Labor market
When it comes to the labor market, while efforts are continued to reduce gender inequality in labor force participation, narrow the gender wage gap, and boost the representation of women in political leadership, increasing attention is given to the large gaps in the sectoral distribution of female and male employment, women’s role in innovation, and women’s share in corporate management positions.
The differences between male and female labor force participation rates remain high, although the gaps have been narrowing over the past decades ( Appendix Figure 3a ). The gaps are smaller and also closing more rapidly in advanced economies. The gender gaps in emerging economies, in fact, have widened over the past two decade, and this is almost entirely driven by the declining female labor force participation in China and India. In China, the likely underlying factors include structural changes in the Chinese economy where households can afford to have only one wage earner, reduction in state childcare support, and rising gender-biased hiring practices; in India, the decline may reflect the declining employment in agriculture, safety concerns and the lack of transportation infrastructure for women to join the urban labor force , and the U-shaped relationship between education and labor force participation as education level improves for women ( Li, 2019 ; Zhang and Huang, 2020 ; Gupta and Bhamoriya, 2020 ; Hare, 2016 ). Excluding China and India, the gender gaps in labor force participation rates in emerging economies are still larger than those in developing economies, which partially reflects the large gaps in emerging MENAP countries. Low labor force participation, particularly for women, has been a major policy concern for many advanced economies and some emerging economies, as they face an aging population. As women in these economies tend to be well educated, it would be a considerable waste if they do not fully engage in economic activities.
There are also large gaps in the sectoral distribution of female and male employment, likely reflecting the differences in field of study. In advanced economies, women are less likely to work in the agriculture and industry sectors and more likely to work in the service sector; but there is a shift in the trend around 2018 from the service sector to the industry sector. Emerging and developing economies share broadly similarly trends over the past decade or so: relatively larger shares of women work in the agriculture sector; and women are moving rapidly from the agriculture and industry sectors to the service sector ( Appendix Figure 3b-3d ). In OECD countries, female employment in the service sector accounts for 80 percent of employed women, compared with 60 percent for men. Within this sector, women fill a disproportionately high share of occupations in health and community services, followed by education ( OECD, 2012 ). ILO (2012) finds that women are overrepresented in sectors characterized by low status and low pay.
Gender gaps in occupations within the science and engineering (S&E) field have been a particular concern. In the United States, by 2019 women made up 29 percent of the S&E workers, but female scientists and engineers are more likely to work in non-S&E occupations than in S&E occupations ( Cook and others, 2021 ). In 2019, 70 percent of psychologists were women, but just 14 percent of engineers and 29 percent of the workforce in computer and mathematical sciences were women. Women often start their careers working in the innovation economy, but then leave for various reasons, including the need to provide childcare, the lack of family-leave policies, and poor workplace climate ( Cook and others, 2021 ).
Increasing attention is also paid to women’s role in innovation, widely viewed as a central driver of productivity and economic growth. Gender inequality persists at every state of innovation, from education and training, to the practice of invention, and to the commercialization of those inventions ( Cook, 2019 ; Cook and others, 2021 ). Women hold only 5.5 percent of commercialized patents and represent just 10 percent of US patent inventors and only 15 percent of inventors in the life sciences. This in part reflects women’s underrepresentation in jobs involving development and design ( Hunt and others, 2013 ). In addition, discriminatory practice leads to inequality in patenting outcomes, even without discriminatory laws. Patent applications by women inventors were found to be more likely to be rejected than those of men, and those rejections were less likely to be appealed by the applicant teams. Conditional on being granted, patent applications by women inventors had a smaller fraction of their claims allowed, on average, than did applications by men. Further, those claims allowed had more words added during prosecution, thus reducing their scope and value. The granted patents of women inventors also received fewer citations than those of men and were less likely to be maintained by their assignees ( Cook and Kongcharoen, 2010 ; Jensen and others, 2018 ).
What has received particular attention is the underrepresentation of women in politics and corporate management positions. Representation of women in politics has improved substantially across all economies, with the proportion of seats held by women in national parliaments about doubled over the past two decades, likely due to the high public visibility; the gender gap, however, remains large ( Appendix Figure 4a ). For senior and middle management positions, there has been, however, little progress over the past two decades ( Appendix Figure 4b ). It appears that the success in political leadership has not been trickled down to the corporate world, highlighting the challenges to make changes in less visible areas. Across the 27 EU countries, only 25 percent of business owners with employees are women, and the low share of women had only marginally grown over 2000-2010 in EU27, Canada and United States ( OECD, 2014 ). A number of countries have enacted legislation requiring a set quota of female representation on corporate boards , the effectiveness and efficacy of such policy, however, has been intensely debated ( Kuzmina and Melentyeva, 2021 ; Greene and others, 2020 ; Lleras-Muney and others, 2019 ; Levi and others, 2014 ; Gregory-Smith and others, 2014 ; Strøm and others, 2014 ).
The gender wage gap has declined in most countries where data are available over the past two decades. Significant gap, however, still persist, averaging around 11 percent, and the gap varies substantially across countries ( Appendix Figure 5 ). While a large part of the gender gap in earnings can be explained by women working fewer hours in the labor market than men, women’s work force interruptions, gender differences in occupations and industries, a significant part of the gender pay gap remain unexplained, suggesting that factors such as discrimination and gender differences in psychological attributes and noncognitive skills are also important contributors to the gender pay gap ( OECD, 2017 ; Blau and Kahn, 2017 ). For example, using a personnel dataset from a large Chinese company, Chen and others (2021a) find that the gender wage gap is small in the early stages of careers and becomes increasingly evident when female employees get married and have children. Whereas the short-term peak around childbirth can be explained by women’ reduced working hours, the long-term trend is caused by women’s concentration in lower-level jobs.
- C. Financial access and legal barriers
More attention is gradually drawing to access to credit by female entrepreneurs, as to financial access by females as individuals.
On account ownership at a financial institution/with a mobile-money-service provider, advanced economies have largely closed the gender gap; emerging economies have been making steady progress, with the gap narrowing from 23 percent in 2011 to 7 percent in 2021; little progress, however, has been seen in low-income developing countries over the last decades, with the gap staying at around 27 percent ( Appendix Figure 6a ).
The evidence on whether fintech can help close gender gaps in financial access, particularly in developing and emerging economies, still appears limited. Sahay and others (2020) find that gender gaps are lower on average in digital financial inclusion than in traditional financial inclusion, but there are significant variations across and within geographical regions. Chen and others (2021b) find a large fintech gender gap: while 29 percent of men use fintech products and services, only 21 percent of women do. Various factors contribute to the gender gap in fintech, including financial and digital literacy and socio-culture factors, suggesting that fintech by itself may only have limited impacts in reducing gender inequality in financial access, and policies to address more fundamental drivers of gender inequality are essential ( Khera and others, 2022 ; Chen and others, 2021b ).
On entrepreneurship financing, a significant gender gap still exists, even in advanced economies. Women are less likely than men to report that they can access the financing needed to start a business in all countries except for Mexico and the United States, with an average gap of eight percentage points in OECD countries ( Appendix Figure 6c ).
On legal barriers to gender equality, substantial progress has been made in all country groups, but effective implementation of the enacted laws and regulations remain a challenge in some countries. According to the Women, Business and Law Index, advanced economies have removed almost all the legal barriers to gender equality; significant gaps, however, still exist in emerging and developing economies ( Appendix Figure 6b ). 10 The impact of adopting gender equality legislation, however, would be limited if they are not fully implemented and enforced. For example, there is evidence from Ghana that reforms to inheritance laws led to few positive changes in terms of women’s inheritance ( Gedzi, 2012 ); a positive legal change in Pakistan has not allowed women to claim their entitled inheritances because of factors such as lack of education, patriarchal behaviors, and forced marriages ( Ahmad and others, 2016 ). Furthermore, cultural and economic factors may pose challenges to women exerting their rights, as in the case of reforming gendered land ownership laws in Kenya, Rwanda, and Uganda ( Djurfeldt, 2020 ).
- D. Policy considerations
The literature suggests that there is still a long way to go to achieve gender equality for most economies:
Gender inequality remains large. While advanced economies have largely closed gender gaps in access to education and individual access to financial services, and removed legal barriers to gender equality, gender gaps in leadership positions, labor force participation, and pay remain sizable. Furthermore, more subtle gender gaps still persistent, such as in quality of education including field of study, sectoral distribution of employment, entrepreneurship financing, and innovation. 11 Emerging and developing economies faces additional challenges to achieve equality in access to tertiary education, individual access to financial services, and legal rights.
Closing the remaining gender inequality will likely be more challenging, as countries move to address gender inequality that is more implicit and subtle. This is because such inequality may be less visible to the public and thus may face less social pressures; with the difficulties in distinguishing preference/comparative advantage between men and women from gender bias/cultural barriers for such inequality, effective and efficient policies may be lacking; and addressing such inequality may require changing people’s mindset, which tends to be more difficult.
The social and economic impact of further reducing gender inequality is likely substantial. The more implicit and subtle nature of gender inequality does not necessarily mean less social and economic benefits from removing such forms of inequality. For example, in the case of United States, 94 percent of doctors and lawyers were white men in 1960; by 2010, the fraction was just 62 percent; similar changes in other high-skilled occupations have occurred throughout the U.S. economy during the last 50 years; given that the innate talent for these professions is unlikely to have changed differently across groups, the change in the occupational distribution since 1960 suggests that a substantial pool of innately talented women and black men in 1960 were not pursuing their comparative advantage ; it is estimated that between 20 and 40 percent of growth in aggregate market output per person during the period can be explained by the improved allocation of talent ( Hsieh and others, 2019 ). In a study of PhDs, GDP per capita could be 0.6 to 4.4 percent higher if women and African Americans were able to participate more fully in the innovation economy ( Cook and Yang, 2018 ).
One potential lesson, particular for emerging and developing economies, is that in addressing gender inequality, it may be more effective and efficient for policy designs to consider the whole spectrum of gender inequality, including both the highly visible ones and the more implicit and subtle ones. For example, in closing the gender gap in access to tertiary education, countries should also be mindful about the gender differences in field of study and actively help remove any barriers that may hinder the ability of female students in pursuing STEM fields. Another example would be to pay full attention to both the adoption and the implementation of gender equality laws.
- IV. The benefits of reducing gender inequality go beyond women
The literature has documented broad social and economic benefits from lowering gender inequality, including the increasing emphasis on its macroeconomic effects ( Kolovich and others, 2020 ). Reducing gender inequality affects not only women, but everyone.
First and foremost, women benefit from lower gender inequality. This includes, for example, better career development, higher pay, and less violence, less discrimination and more equal rights, through improvements in human capital development, job opportunities including in leadership positions and as entrepreneurs, access to finance, and legal and regulatory environment.
Second, children benefit from lower gender inequality and women’s empowerment. Women’s choices appear to emphasize child welfare more than those of men, and children seem to be better off when their mothers control relatively more of their family’s resources. For example, Miller (2008) presents evidence on how suffrage rights for American women helped children to benefit from the scientific breakthroughs of the bacteriological revolution, with child mortality declining by 8–15 percent (or 20,000 annual child deaths nationwide), through large increases in local public health spending. Leight and Liu (2020) document that more-educated mothers appear to compensate for differences between their children, investing more in children who exhibit greater noncognitive deficits, while no such effect is found for men. Pitt and others (2003) find that women’s access to credit has a large and statistically significant impact on two of three measures of the child health, but no such effect is found for men.
Third, reducing gender inequality could potentially help increase the productivity of teams and improve the performance of firms and other institutions. This is primarily through the diversity channel, in the sense that mixed-gender teams are more productive and creative and tend to make better decisions ( Rock and Grant, 2016 ; Ozgen, 2021 ). Cook and Kongcharoen (2010) find that all-male and all-female patent teams commercialize their patents less than mixed-gender patent teams, with a similar finding from Østergaard and others (2011 ). Herring (2009) finds that gender diversity is associated with increased sales revenue, more customers, and greater relative profits. A number of studies find that gender quotas at corporate board are associated with improvements in firm performances, though there is still no consensus in the literature ( Strøm and others, 2014 ; Levi and others, 2014 ; Kuzmina and Melentyeva, 2021 ; Owen and Temesvary, 2018 ; Green and others, 2020 ). 12
Fourth, lower gender inequality can bring important macroeconomic benefits to everyone, with stronger economic growth and financial stability, more jobs, and less income inequality ( Kochhar and others, 2017 ; Sahay and others, 2015; Sahay and others, 2018 ; Cihak and Sahay, 2020 ).
Better matching female talent to human capital development and employment, including as corporate and political leaders and entrepreneurs, can substantially boost economic growth and strengthen economic and financial stability. For example, higher female labor force participation can substantially boost economic growth ( Kochhar and others, 2017 ; Kolovich and others, 2020 ). As discussed earlier, between 20 to 40 percent of growth in aggregate market output per person between 1960 and 2010 in the United States can be explained by improved allocation of talent ( Hsieh and others, 2019 ). Innovation is widely viewed as a central driver of productivity growth and output, and gender inequality hinders innovation at every state of the process, particularly as a growing literature is showing better outcomes of more diverse and mixed-gender teams ( Rock and Grant 2016 ; Cook, 2019 ; Cook and others, 2021 ). The literature also finds positive association between financial inclusion and economic growth, and reducing gender inequality in financial access, including through fintech, can thus help increase economic growth, particularly in countries with low levels of financial inclusion (Sahay and others, 2015; Sahay and others, 2020 ). There is also evidence that female leadership, including as financial regulators, is associated with financial and political stability ( Sahay and others, 2018 ; Caprioli, 2005 ).
Reducing gender inequality could also help lower income inequality and, in turn, improve social stability and economic growth ( Gonzales and others, 2015b ). Gender wage gaps directly contribute to income inequality. Conversely, policies to address gender inequality benefit females in low-income households the most, also reducing income inequality. For example, reducing gender gaps in school enrollment means that girls from poor households are more likely to receive education , thereby increasing their lifetime earnings potential ( Demery and Gaddis, 2009 ). In addition, financial inclusion of women is found to have a strong link to lower income inequality; this is because, while financial inclusion benefits everybody, the gains for women are quantitatively larger (Aslan and others, 2017; Cihák and Sahay, 2020 ).
V. Policies and their designs matter: general versus targeted policies
There is strong evidence from the literature that government policies and their designs matter for gender gaps and gender inequality. The key question, however, is how government policies can be designed to achieve gender equality while minimizing their efficiency cost (or maximizing the efficiency benefit).
- A. The role of policies in closing gender gaps
A broad range of government policies and programs can affect gender gaps, such as public investment to improve access to education and healthcare, childcare subsides, paid parental leave, eliminating tax penalties for secondary earners, and laws and regulations to ensure women’s rights and opportunities ( Rim, 2021 ; Ruhm, 1998 ; Dustmann and Schönberg, 2012 ; Heath and Jayachandran, 2018 ; Evans and Yuan, 2022 ; Bick and Fuchs-Schündeln, 2017 ; Olivetti and Petrongolo, 2017 ; Gonzales and others, 2015 a; Hyland and others, 2020 ). For example, Rim (2021) finds that banning gender discrimination in admissions was successful in reducing gender disparity in graduate education. Sometimes, the policy interventions involve tradeoffs between different gender gaps. For example, Ruhm (1998) finds that parental leave is associated with increases in women’s employment, but with reductions in their relative wages at extended durations. Lalive and others (2014) find that, for parental leave, a system that combines cash benefits with job protection dominates other designs in generating time for care immediately after birth while maintaining mothers’ medium-term labor market attachment.
In addition to the large variations in gender gaps by level of development as shown in Section III, gender gaps also vary substantially among countries at a similar level of development and in the same region, for several selected gender gap measures ( Appendix Figure 7 ). Assuming countries in the same region have similar gender social norms, this suggests that government policies potentially play an important role in explaining cross-country variations in gender gaps.
As an illustration, here we estimate the effects of laws and regulations that ensure equal opportunities for women (measured by Women, Business and the Law Index) on five gender gaps (these gaps are selected as they are key measures of women’s economic opportunities, tend to present in many countries, and are widely reported). 13 The estimates are based on a fixed effects specification with a time trend and lagged key independent variable. The model uses per capita GDP in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms to control for level of development, country fixed effects to control for time-invariant factors (e.g., social norms), and a time trend to control for global trends. 14 The results suggest that gender laws and regulations are associated with lower gender gaps in some areas (e.g., account ownership at a financial institution /with a mobile-money-service provider and proportion of seats held by women in national parliaments). The estimates on gender gaps in labor force participation, female share of senor and middle management, and pay are not statistically significant ( Appendix Table 1 ). One likely explanation is that the introduction of gender equality laws and regulations helps raise awareness and can lead to changes that face relatively less barriers (e.g., financial access) or are highly visible by the public (parliament seats). More fundamental changes, however, may take time (e.g., labor force participation, senior and middle management, and pay).
- B. General versus targeted policies
The effects of government policies on gender inequality and economic efficiency would depend on their specific designs and country-specific social and economic structures and conditions, and thus should be assessed on a policy-by-policy basis. There are, however, also commonalities among government policies, and it would be useful to understand their advantages and disadvantages. For example, gender-sensitive government policies can be broadly classified into two groups: general policies that apply to all genders indiscriminately but affect one gender more than the other and targeted policies at a specific gender.
By definition, nearly all macro policies—including fiscal policies, monetary policies, and exchange rate policies as well as macro-financial and macro-structural policies—belong to general policies, as they are primarily intended to boost economic growth and employment and achieve macro and financial stability. This, however, does not necessarily mean that macro policies are gender neutral. In fact, many of these policies have implications on gender gaps and gender inequality, because they affect different segments of the economy differently, and the distributions of female and male population also differ across these segments of the economy. For example, on fiscal policies, family-based income taxation implicitly raises the marginal tax rate for the income of secondary earners—who tend to be women—and contributes to the gender inequality in labor force participation ( Bick and Fuchs-Schündeln, 2017 ); while public education and health spending on average may still favor boys, the benefits from additional spending tend to be captured more by poor girls, as they are more likely to be still lacking access to education and healthcare ( Demery and Gaddis, 2009 ). On financial sector policies, while financial inclusion benefits everyone, the gains for women are quantitatively larger ( Cihák and Sahay, 2020 ). Monetary, exchange rate policies and macro structural policies have also been found to have gender implications. 15
Micro policies refer to government programs that target specific entities such as firms and households, and thus gender-sensitive micro policies can be either general or targeted policies. This includes a variety of programs such as (un)conditional cash transfers, hygiene promotion and water treatment, educational programs on gender equality for students, legal reforms to enhance women’s rights, conditional cash transfers for dropped out girls, reservation of subway cars exclusively for women, and gender quotas on corporate boards or political seats. Many of these programs have been shown to improve outcomes for women or girls ( Hahn and others, 2018 ; Harari, 2019 ; Beaman and others, 2012 ).
In general, targeted gender policies conceptually are less efficient as they exclude males who may be better suited for the opportunities. However, with the presentence of gender inequality (e.g., gender bias and social norms that hinder women’s rights and opportunities), general programs can also be inefficient in the sense that preference may be given to less qualified males. Because gender gaps can be driven by gender inequality or preference/comparative advantage between men and women or most likely both, and empirically it is difficult to separate the two effects, the key challenge for targeted gender policies is how to set the policy target s, as fully closing gender gaps may not be appropriate. Below are a few considerations:
It is not even clear that targeted gender policies are more effective in closing gender gaps. For example, from 267 educational interventions in 54 low- and middle-income countries, general interventions deliver average gains for girls that are comparable to girl-targeted interventions in improving access and learning ( Evans and Yuan, 2022 ). However, the most effective programs may not be the most cost-effective. Due to the lack of cost data, the cost-effectiveness of the programs could not be assessed.
There is evidence that some gender targeted policies may have unintended consequences or lead to inefficiencies. For example, the findings from a program that reserves subway cars exclusively for women in Mexico City suggest that while the program seems to be successful at reducing sexual harassment toward women, it also increases aggression incidents among men ( Aguilar and others, 2021 ). While the policy of setting gender quotas on corporate boards is still intensely debated, some studies find that the policy is associated with negative returns, and the negative effect is less severe for firms with a greater supply of female candidates, and for those that can more easily replace male directors or attract female directors ( Green and others, 2020 ). This appears to indicate that this policy may indeed lead to less qualified women being selected in some circumstances. Furthermore, there is also evidence that the policy has very little discernible impact on women in business beyond its direct effect on the women who made it into boardrooms ( Bertrand and others, 2019 ). This suggests that the policy may be more of ticking a box exercise. Afridi and others (2017) find short-term costs of gender-affirmative action policies for political leadership positions, but that once initial disadvantages recede, women leaders are neither more nor less effective local politicians than men. 16 While this does not mean that these policies should not be pursued, it does raise the need for careful designing such programs, particularly as its long-run or economy-wide impact may be difficult to identify in the studies. 17
For some policies, there is less ambiguity on their efficiency implications. For example, legal reforms to provide equal rights to women, by definition, is addressing gender inequality directly. This may be one potential reason for the rapid progress in removing legal gender barriers. Another example is educational programs on gender inequality, it is in fact more effective to be targeted to both genders , as reducing gender inequality requires the active participation by men as well ( Dhar and others, 2022 ). In some instances, preference/comparative advantage between men and women are expected to play a limited role, such as access to basic education (e.g., preprimary, primary and secondary) and healthcare. In such cases, fully closing the gender gaps would unlikely introduce any major distortions.
General policies tend to introduce less gender-specific distortions, although they can only address gender inequality, often in a more gradual manner. For example, conditional cash transfer programs can help improve school attendance of both boys and girls and benefit girls more than boys because more girls lack access to education in the absence of the programs. However, on the margin, boys are likely still less qualified than girls, even if the programs have helped narrow the gap. With this in mind, general policies may be particularly useful in circumstances where it is difficult to assess to what extent that the gender gaps are due to gender inequality. One potential area is formal labor force participation for which it is unclear how much of the lower labor force participation for women is due to gender inequality and how much is due to preference. In such a case, targeted policies such as wage subsidies for women may not be advisable, while general policies such as childcare subsidies may be more appropriate. 18
In areas where only targeted gender policies may be effective (e.g., in situations where men and women compete with each other), it would make sense to be conservative, by setting the gender quotas low initially and gradually increase them as more evidence becomes available. For example, only targeted gender policies are likely effective in promoting female leadership (e.g., gender quotas on corporate boards), as the number of leadership positions is fixed, and more female leaders mean fewer male leaders. This appears to be the case in some countries that have adopted policies to set gender quotas on corporate boards, through it is unclear if the design is indeed driven by such a consideration. For example, Malaysia’s publicly traded firms must have at least one-woman director on their boards from September 1, 2022; and California requires public companies headquartered in California to have at least one female director by the end of 2019 and at least two (three) female directors on five (six or more) member boards by the end of 2021.
- VI. Policy actions do not have to start with those targeted at the root causes
As discussed in Section II, the root causes of gender inequality are gender bias/social norms that restrict women’s rights and opportunities. Only until the root causes are eliminated, gender equality can be fully achieved; some gender gaps may still remain but are driven by preference /comparative advantage between men and women. Before that, it is unlikely that gender inequality in different areas such as education, labor market, and financial access can be fully removed. With the difficulties in separating gender inequality from efficient allocation, general policies may have difficulties in fully eliminating gender inequality, while targeted gender policies run the risk of either not fully addressing gender inequality or introducing additional gender distortions. With these constraints, how should policies be designed? Should policies only focus on those that are directly targeted at gender inequality (e.g., removing legal barriers) and its root causes (e.g., educational programs and information campaigns)?
This paper argues that addressing gender inequality does not have to solely rely on policies that are targeted at gender inequality and its root causes, and other general and targeted policies can still play a key role in addressing gender inequality, for several reasons:
First, while social norms evolve as countries develop (e.g., higher income, better education, and technological advances), this is often slow, almost by definition. There is evidence that some interventions can help change social norms. This includes educational programs on gender inequality and exposure to (female) role models. For example, an intervention in India that engaged adolescent girls and boys in classroom discussions about gender equality for two years, aiming to reduce their support for societal norms that restrict women ’s and girls’ opportunities, is shown to have persistent effects and leads to shifts in behavior, more so for boys than girls ( Dhar and others, 2022 ). The findings from Bell and others (2019 ) suggest that if girls were as exposed to female inventors as boys are to male inventors in their childhood commuting zones, the current gender gap in innovation would shrink by half. 19 The scope for policies directly targeting gender inequality (e.g., removing legal barriers) also appears limited.
Second, policies to reduce gender inequality in different areas such as education and labor market can be effective, with substantial immediate benefits for women and for the entire society, as discussed throughout the paper and particularly in Section IV. Examples include general policies and targeted gen der policies to improve access to education (e.g., public investment in education and conditional cash transfers for girls) and boost labor force participation (e.g., childcare subsidies and eliminating tax penalties for secondary earners).
Third, policies to address gender inequality in different areas can also indirectly influence gender bias and social norms, the root causes of gender inequality. For example, policies that help narrow the gender inequality in education in turn also help shape gender attitude, as it increases women’s income and bargaining power at home ( Le and Nguyen, 2021 ). Gender quotas in political leadership can help influence adolescent girls’ career aspirations and educational attainment—reflecting primarily a role model effect of female leadership—and reduce gender discrimination in the long-term ( Beaman and others, 2012 ; Pande and Ford, 2012 ). A program to enhance financial inclusion of women—under which rural Indian women received bank accounts, training in account use, and direct deposit of public sector wages into their own (versus husbands ’) accounts— incentivizes women to work and helps liberalize women’s own work-related norms and shift perceptions of community norms ( Field and others, 2021 ).
While addressing gender inequality does not have to start with and solely focus on policies that are targeted at the root causes of gender inequality, it would need to end there, as fully eliminating gender inequality would require addressing the root causes of gender inequality, and policies aiming at reducing gender inequality in different areas can only go so far. Only then, while some gender gaps may still exist, the allocation of human capital would be fully efficient, reflecting preference /comparative advantages between men and women.
- VII. Discussions
This paper identifies five key issues that are particularly important for the continued efforts to tackle gender inequality:
It is critical to clearly define gender inequality and distinguish it from gender gaps. This has important implications on the policy designs to address gender inequity. However, the literature has paid little attention to this issue, often using gender inequality and gender gaps interchangeably. This paper defines gender gaps as the observed differences between men and women or between boys and girls in the various social and economic indicators, and gender inequality refers to the part that is driven by gender bias and unequal gender rights and opportunities. However, empirically estimating the corresponding gender inequality for each gender gap remains a challenge and requires more efforts on data collection and methodological developments.
The focus of gender inequality has been evolving over time. As some gender gaps are closed, other gender gaps are emerging (not necessarily new, but attracting the attentions of the public and policymakers). This suggests that there is still a long way to go to fully addressing gender inequality. Particularly, gender inequality is getting more subtle and implicit, though the social and economic benefits from addressing the remain gender inequality is still likely to be substantial. This highlights the need to apply a gender lens to a broad range of policies and practices to understand their potential implications on gender inequality. Such efforts help develop a comprehensive strategy, instead of a piece-meal approach with which only some gender inequality is addressed at a time.
Addressing gender inequality benefits everyone, not just women. Thus, the entire society should work together, even for each individual’s own interest. Lower gender inequality not only benefits women, but also benefits children—as women trend to emphasize child welfare more than men—and the entire economy through the positive productivity externality from more balanced gender roles, and improved economic growth, financial stability, and income inequality. In addition to further strengthening the empirical evidence in these areas, there is an urgent need for the findings to be incorporated into policy designs and decision-making.
Policies and their designs can help accelerate the decline of gender inequality from economic development and technological advances. Both general policies and targeted gender policies can play a role, and the pros and cons of such policies should be carefully assessed. As gender inequality becomes more subtle and implicit (e.g., in field of study, the distribution of employment across sectors, and mid-level management positions), general policies will typically not work, unlike for school enrollments and labor force participation. Thus, targeted gender policies will need to play a bigger role. More analytical work is needed on what programs work and under what conditions. Also, this means that analytical work geared at separating gender inequality from gender gaps is all that more important.
While fully addressing gender inequality requires the elimination of the root cause s of gender inequality (e.g., gender bias and social norms), this does not mean that policies are not targeted at the root causes of gender inequality do not have a role. In fact, they can still be effective, as they can generate immediate social and economic benefits and indirectly affect gender bias and social norms. Policies directly targeted at the root causes of gender inequality would be generally preferred but appear limited, and research to expand the policy toolkit would be particularly useful.
One general issue in the efforts to address gender inequality is the lack of gender disaggregated data. Great progress has been made. For example, The IMF’s Financial Access Survey (FAS) is a unique source of annual supply-side data on access to and use of basic financial services by gender. The World Development Indicators (WDI) from the World Bank now present many statistics by male and female separately. Missing data, however, are still widespread, particularly in low-income countries. Therefore, continued efforts are still needed to further expand data availability in terms of both coverage and quality.
Another important issue the paper only marginally touches upon is the challenge of turning policy designs into practices. The analysis of Women, Business, and the Law index on several gender gaps suggests that it is not automatic that laws and regulations to promote gender equality will lead to immediate improvements in gender outcomes. Implementation remains a challenge for many countries, particularly developing economies with limited administrative capacity. For example, as reported in Evans and Yuan (2022) , many similar policy interventions have substantially different impacts across countries. Conditional cash transfer in South Africa is the best intervention among the 267 educational interventions in 54 low- and middle-income countries, while conditional cash transfer in the Philippines is one of the ten worst interventions. Thus, the importance of effective implementation cannot be overstated.

Gender Gaps in Education

Gender Gaps in Field of Study

Gender Gaps in Labor Force Participation and Employment by Sector

Gender Gaps in Leadership Positions

Gender Wage Gap in Selected Economies

Gender Gaps in Financial Access and Legal Barriers to Gender Equality

Large Variations in Gender Gaps across Countries
Alternative Specifications on the Effects of Laws and Regulations on Selected Gender Gaps
Afridi Farzana , Vegard Iversen , and M. R. Sharan , 2017 , “ Women Political Leaders, Corruption, and Learning: Evidence from a Large Public Program in India ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change, Volume 66 , Number 1 : 1 – 30 .
- Search Google Scholar
- Export Citation
Aguilar , Arturo , Emilio Gutiérrez , and Paula Soto Villagrá n, 2021 , “ Benefits and Unintended Consequences of Gender Segregation in Public Transportation: Evidence from Mexico City’s Subway System ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 69 , Number 4 : 1379 –1410.
Ahmad , Mahtab , Moazma Batool , and Sophia Dziegielewski , 2016 , “ State of Inheritance Rights: Women in a Rural District in Pakistan ,” Journal of Social Service Research 42 ( 5 ): 622 – 29 .
Albanesi , Stefania , and Jiyeon Kim , 2021 , “ Effects of the COVID-19 Recession on the US Labor Market: Occupation, Family, and Gender ,” The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 35 , No. 3 : 3 - 24 .
Alesina , Alberto , Paola Giuliano , and Nathan Nunn , 2013 , “ On the Origins of Gender Roles: Women and the Plough ,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 128 : 469 – 530 .
Alonso , Cristian , Mariya Brussevich , Era Dabla-Norris , Yuko Kinoshita , and Kalpana Kochhar , 2019 , “ Reducing and Redistributing Unpaid Work: Stronger Policies to Support Gender Equality ,” IMF Working Paper WP/19/225 , International Monetary Fund , Washington DC .
Alonso-Albarran , Virginia , Teresa Curristine , Gemma Preston , Alberto Soler , Nino Tchelishvili , and Sureni Weerathunga , 2021 , “ Gender Budgeting in G20 Countries ,” IMF Working Paper WP/21/269 , International Monetary Fund , Washington DC .
Austen , Siobhan , Monica Costa , Rhonda Sharp , and Diane Elson , 2013 , “ Expenditure Incidence Analysis: A Gender-Responsive Budgeting Tool for Educational Expenditure in Timor-Leste? ” Feminist Economics 19 : 1 – 24 .
Beaman , Lori , Esther Duflo , Rohini Pande , and Petia Topalova , 2012 , “ Female Leadership Raises Aspirations and Educational Attainment for Girls: A Policy Experiment in India ,” Science , 335 ( 6068 ): 582 - 586 .
Becker , Charles , Cecilia Elena Rouse , Mingyu Chen , 2016 , “ Can a Summer Make a Difference? The Impact of the American Economic Association Summer Program on Minority Student Outcomes ,” Economics of Education Review , Volume 53 : 46 - 71 .
Bell , Alex , Raj Chetty , Xavier Jaravel , Neviana Petkova , and John Van Reenen , 2019 , “ Who Becomes an Inventor in America? The Importance of Exposure to Innovation ,” The Quarterly Journal of Economics , 134 ( 2 ): 647 - 713 .
Bergman , Nittai , David Matsa , and Michael Weber , 2022 , “ How Tight Labor Markets Facilitate Broad-Based Employment Growth ”, NBER Working Paper 29651, National Bureau of Economic Research .
Bernhardt , Arielle , Erica Field , Rohini Pande , Natalia Rigol , Simone Schaner , and Charity Troyer-Moore , 2018 , “ Male Social Status and Women’s Work ,” AEA Papers and Proceedings , 108 : 363 - 67 .
Bharadwaj , Prashant , Giacomo De Giorgi , David Hansen , and Christopher A. Neilson , 2016 , “ The Gender Gap in Mathematics: Evidence from Chile ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 65 , Number 1 : 141 – 166 .
Bick , Alexander , and Nicola Fuchs-Schündeln , 2017 , “ Quantifying the Disincentive Effects of Joint Taxation on Married Women’s Labor Supply ,” American Economic Review , 107 ( 5 ): 100 - 104 .
Blau , Francine , and Lawrence Kahn , 2017 , “ The Gender Wage Gap: Extent, Trends, and Explanations ,” Journal of Economic Literature , 55 ( 3 ): 789 - 865 .
Bluedorn , John , Francesca Caselli , Niels-Jakob Hansen , Ippei Shibata , and Marina Tavares , 2021 , “ Gender and Employment in the Covid-19 Recession: Evidence on She-cessions ,” IMF Working Paper WP/21/95 , International Monetary Fund , Washington DC .
Buehren , Niklas , Markus Goldstein , Kenneth Leonard , Joao Montalvao , and Kathryn Vasilaky , 2022 , “ Spillover Effects of Girls’ Empowerment on Brothers’ Competitiveness: Evidence from a Lab-in-the-Field Experiment in Uganda ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 70 , Number 2 : 653 – 670 .
Cabral , Marika , and Marcus Dillender , 2021a , “ Disparities in Health Care and Medical Evaluations by Gender: A Review of Evidence and Mechanisms .” AEA Papers and Proceedings , 111 : 159 - 63 .
Cabral , Marika and Marcus Dillender , 2021 b, “ Gender Differences in Medical Evaluations: Evidence from Randomly Assigned Doctors ,” NBER Working Paper 29541 , National Bureau of Economic Research .
Caprioli , Mary , 2005 , “ Primed for Violence: The Role of Gender Inequality in Predicting Internal Conflict ,” International Studies Quarterly , Vol. 49 , No. 2 : 161 - 178 .
Carranza , Eliana , 2014 , “ Soil Endowments, Female Labor Force Participation, and the Demographic Deficit of Women in India ,” American Economic Journal: Applied Economics , 6 ( 4 ): 197 - 225 .
Chen , Yi , Hong Zhang , and Li-An Zhou , 2021a , “ Motherhood and Gender Wage Differentials within a Chinese Firm ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 70 , Number 1 : 283 –320.
Chen , Sharon , Sebastian Doerr , Jon Frost , Leonardo Gambacorta , and Hyun Song Shin , 2021b , “ The Fintech Gender Gap” , BIS Working Paper No. 931 , Bank for International Settlements (Basel) .
Cihák , Martin and Ratna Sahay , 2020 , “ Finance and Inequality ,” IMF Staff Discussion Note, SDN/20/01 , International Monetary Fund , Washington, DC .
Cook , Lisa , Janet Gerson , and Jennifer Kuan , 2021 , “ Closing the Innovation Gap in Pink and Black ,” NBER Working Paper 29354 , National Bureau of Economic Research .
Cook , Lisa , 2019 , “ The Innovation Gap in Pink and Black ,” in Wisnioski , Hintz , and Stettler Kleine , eds. Does America Need More Innovators? Cambridge, MA : The MIT Press .
Cook , Lisa , and Yanyan Yang , 2018 , “ Missing Women and Minorities: Implications for Innovation and Growth ,” Presentation ( http://www.yanyanyang.com/uploads/5/6/5/2/56523543/aeapinkblack_cookyang.pdf ).
Cook , Lisa , and Chaleampong Kongcharoen , 2010 , “ The Idea Gap in Pink and Black ,” NBER Working Paper 16331 , National Bureau of Economic Research .
Cordoba , Juan , Anni Isojarvi , and Haoran Li , 2021 , “ Equilibrium Unemployment: The Role of Discrimination ,” Finance and Economics Discussion Series 2021-080 . Washington : Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System .
Dhar , Diva , Tarun Jain , and Seema Jayachandran , 2022 , “ Reshaping Adolescents’ Gender Attitudes: Evidence from a School-Based Experiment in India ,” American Economic Review , 112 ( 3 ): 899 - 927 .
Daher , Marilyne , Mahmoud Rifai , Riyad Kherallah , Fatima , Rodriguez , Dhruv Mahtta , Erin Michos , Safi Khan , Laura Petersen , and Salim Virani , 2021 , “ Gender Disparities in Difficulty Accessing Healthcare and Cost-related Medication Non-adherence: The CDC Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) Survey ,” Preventive Medicine , Volume 153 .
Dang , Hai-Anh , Trung Hoang , and Ha Nguyen , 2021 , “ The Long-Run and Gender-Equalizing Impacts of School Access: Evidence from the First Indochina War ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 70 , Number 1 : 453 - 484 .
Dasgupta , Shatanjaya , 2016 , “ Son Preference and Gender Gaps in Child Nutrition: Does the Level of Female Autonomy Matter? ” Review of Development Economics , Volume 20 , Issue 2 : 375 - 386 .
Demery , Lionel , and Isis Gaddis , 2009 , “ Social Spending, Poverty, and Gender Equality in Kenya: A Benefit Incidence Analysis ,” Deutsche Gesellschaft for Technische Zusammenarbeit , Nairobi .
Demirgüç-Kunt , Asli , Leora Klapper , Dorothe Singer , and Peter Van Oudheusden , 2015 , “ The Global Findex Database 2014: Measuring Financial Inclusion around the World ,” Policy Research Working Paper No. WPS 7255 , World Bank , Washington DC .
Dinkelman , Taryn , 2011 , “ The Effects of Rural Electrification on Employment: New Evidence from South Africa ,” American Economic Review , 101 ( 7 ): 3078 - 3108 .
Djurfeldt , Agnes Andersson , 2020 , “ Gendered Land Rights, Legal Reform and Social Norms in the Context of Land Fragmentation—A Review of the Literature for Kenya, Rwanda and Uganda ,” Land Use Policy 90 : 104305 .
Downes , Ronnie , and Scherie Nicol , 2020 , “ Designing and Implementing Gender Budgeting – a Path to Action ,” OECD Journal on Budgeting , Volume 2020 Issue 2 : 67 - 96 .
Duflo , Esther , 2012 , “Women Empowerment and Economic Development”, Journal of Economic Literature , 50 ( 4 ): 1051 – 79 .
Dustmann , Christian , and Uta Schönberg , 2012 , “ Expansions in Maternity Leave Coverage and Children’s Long-Term Outcomes .” American Economic Journal: Applied Economics , 4 ( 3 ): 190 - 224 .
Erten , Bilge , and Martina Metzger , 2019 , “ The Real Exchange Rate, Structural Change, and Female Labor Force Participation ,” World Development , Vol. 117© : 296 - 312 .
Evans , David , Akmal Maryam , and Jakiela Pamela , 2021 , “ Gender Gaps in Education: The Long View ,” IZA Journal of Development and Migration, Sciendo & Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit GmbH (IZA) , vol. 12 ( 1 ): 1 - 27 .
Evans , David , and Fei Yuan , 2022 , “ What We Learn about Girls’ Education from Interventions That Do Not Focus on Girls ,” The World Bank Economic Review , 36 ( 1 ), 2022, 244 – 267 .
Fabrizio , Stefania , Diego Gomes , and Marina Mendes Tavares , 2021 , “ COVID-19 She-Cession: The Employment Penalty of Taking Care of Young Children ,” IMF Working Paper WP/21/58 , International Monetary Fund , Washington DC .
Fernandez , Raquel , and Alessandra Fogli , 2009 , “ Culture: An Empirical Investigation of Beliefs, Work, and Fertility ,” American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics 1 : 146 – 77 .
Field , Erica , Seema Jayachandran , Rohini Pande , 2010 , “ Do Traditional Institutions Constrain Female Entrepreneurship? A Field Experiment on Business Training in India ,” American Economic Review 100 ( 2 ): 125 - 29 .
Field , Erica , Rohini Pande , Natalia Rigol , Simone Schaner , and Charity Troyer Moore , 2021 , “ On Her Own Account: How Strengthening Women’s Financial Control Impacts Labor Supply and Gender Norms .” American Economic Review , 111 ( 7 ): 2342 - 75 .
Galor , Oded , and David Weil , 1996 , “The Gender Gap, Fertility and Growth, American Economic Review, 86 ( 3 ): 374 – 387 .
Gedzi , Victor Selorme , 2012 , “ Women’s Property Relations after Intestate Succession PNDC Law 111 in Ghana ,” Research on Humanities and Social Sciences 2 ( 9 ): 211 – 219 .
Gonzales , Christian , Sonali Jain-Chandra , Kalpana Kochhar , and Monique Newiak , 2015 a, “ Fair Play: More Equal Laws Boost Female Labor Force Participation ,” IMF Staff Discussion Note, SDN/15/02 .
Gonzales , Christian , Sonali Jain-Chandra , Kalpana Kochhar , Monique Newiak , and Tlek Zeinullayev , 2015b , “ Catalyst for Change: Empowering Women and Tackling Income Inequality ,” IMF Staff Discussion Note 15/20 , International Monetary Fund , Washington, DC .
Greene , Daniel , Vincent Intintoli , and Kathleen Kahle , 2020 , “ Do Board Gender Quotas Affect Firm Value? Evidence from California Senate Bill No. 826 ,” Journal of Corporate Finance 60 ( 101526 ).
Greenwood Jeremy , Ananth Seshadri , and Mehmet Yorukoglu , 2005 , “ Engines of Liberation ,” Review of Economic Studies , 72 : 109 – 33 .
Gregory-Smith , Ian , Brian Main , Charles O’Reilly III , 2014 , “ Appointments, Pay and Performance in UK Boardrooms by Gender ,” The Economic Journal . 124 ( 574 ): F109 –F128.
Gupta , Rajesh , and Vaibhav Bhamoriya , 2020 , “ ’Give Me Some Rail’: An Enquiry into Puzzle of Declining Female Labour Force Participation Rate ,” Management and Labour Studies , Volume 46 , issue 1 : 7 - 23 .
Hadley , Craig , David Lindstrom , Fasil Tessema , and Tefara Belachew , 2007 , “ Gender Bias in the Food Insecurity Experience of Ethiopian Adolescents ,” Social Science and Medicine 66 ( 2 ): 427 – 438 .
Hafeez , Naima , and Climent Quintana-Domeque , 2018 , “ Son Preference and Gender-Biased Breastfeeding in Pakistan ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 66 , Number 2 : 179 - 215 .
Hahn , Youjin , Asadul Islam , Kanti Nuzhat , Russell Smyth , and Hee-Seung Yang , 2018 , “ Education, Marriage, and Fertility: Long-Term Evidence from a Female Stipend Program in Bangladesh ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 66 , Number 2 : 383 - 415 .
Harari , Mariaflavia , 2019 , “ Women’s Inheritance Rights and Bargaining Power: Evidence from Kenya ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 68 , Number 1 : 189 - 138 .
Hare , Denise , 2016 , “ What Accounts for the Decline in Labor Force Participation among Married Women in Urban China, 1991–2011? ” China Economic Review , Volume 38© : 251 - 266 .
Heath , Rachal , and Seema Jayachandran , 2018 , “ The Causes and Consequences of Increased Female Education and Labor Force Participation in Developing Countries ,” In: Susan Averett , Laura Argys , and Saul Hoffman (eds), The Oxford handbook of women and the economy, Oxford University Press , New York , page: 395 – 424 .
Herring , Cedric , 2009 , “ Does Diversity Pay?: Race, Gender, and the Business Case for Diversity ,” American Sociological Review , Vol. 74 , No. 2 : 208 - 224 .
Holden , Livia , and Azam Chaudhary , 2013 , “ Daughters’ Inheritance, Legal Pluralism, and Governance in Pakistan ,” Journal of Legal Pluralism and Unofficial Law 45 ( 1 ): 104 –23
Hsieh , Chang-Tai , Erik Hurst , Charles Jones , and Peter Klenow , 2019 , “ The Allocation of Talent and U.S. Economic Growth ,” Econometrica , Vol. 87 , No. 5 : 1439 – 1474 .
Hunt , Jennifer , Jean-Philippe Garant , and Hannah Herman , and David Munroe , 2013 , “ Why Are Women Underrepresented amongst Patentees? ” Research Policy , Elsevier , vol. 42 ( 4 ): 831 - 843 .
Hyland , Marie , Simeon Djankov , and Pinelopi Koujianou Goldberg , 2020 , “ Gendered Laws and Women in the Workforce ,” American Economic Review: Insights , 2 ( 4 ): 475 – 490 .
Hyland , Marie , Simeon Djankov , and Pinelopi Koujianou Goldberg , 2021 , “ Do Gendered Laws Matter for Women’s Economic Empowerment? ” PIIE Working Paper .
International Labour Organization (ILO) , 2012 , “ Employment and Gender Differences in the Informal Economy .” PowerPoint presentation , Geneva .
Jensen , Kyle , Balazs Kovacs , and Olav Sorenson , 2018 , “ Gender Differences in Obtaining and Maintaining Patent Rights ,” Nature Biotechnology 36 : 307 - 309 .
Jayachandran , Seema , 2015 , “ The Roots of Gender Inequality in Developing Countries ,” Annual Review of Economics , Vol. 7 : 63 - 88 .
Jayachandran , Seema , 2021 , “ Social Norms as a Barrier to Women’s Employment in Developing Countries ,” IMF Economic Review , 69 ( 3 ): 576 - 595 .
Khera , Purva , Sumiko Ogawa , Ratna Sahay , and Mahima Vasishth , 2022 , “ Women in Fintech: As Leaders and Users ,” IMF Working Paper WP/22/140 , International Monetary Fund , Washington, DC .
Kim , Jin Ho and Benjamin Williams , 2021 , “ Minimum Wage and Women’s Decision-Making Power within Households: Evidence from Indonesia ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 70 , Number 1 : 359 - 414 .
Kochhar , Kochhar , Sonali Jain-Chandra , and Monique Newiak , 2017 , Women, Work, and Economic Growth: Leveling the Playing Field , International Monetary Fund , Washington, DC .
Kolovich , Lisa , Vivian Malta , Monique Newiak , and David Robinson , 2020 , “ Gender Equality and Macroeconomic Outcomes: Evidence and Policy Implications ,” Oxford Review of Economic Policy , Volume 36 , Number 4 : 743 – 759 .
Kuzmina , Olga , and Valentina Melentyeva , 2021 , “ Gender Diversity in Corporate Boards: Evidence from Quota-Implied Discontinuities ,” ZEW – Centre for European Economic Research Discussion Paper No. 21-023 .
Lalive , Rafael , Analía Schlosser , Andreas Steinhauer , Josef Zweimüller , 2014 , “ Parental Leave and Mothers’ Careers: The Relative Importance of Job Protection and Cash Benefits ,” The Review of Economic Studies , Volume 81 , Issue 1 : 219 – 265 .
Le , Kien , and My Nguyen , 2021 , “ How Education Empowers Women in Developing Countries ,” The B.E. Journal of Economic Analysis & Policy , Vol. 21 , No. 2 : 511 - 536 .
Leight , Jessica and Elaine Liu , 2020 , “ Maternal Education, Parental Investment, and Noncognitive Characteristics in Rural China ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 69 , Number 1 : 213 - 251 .
Levi , Maurice , Kai Li , and Feng Zhang , 2014 , “ Director Genders and Mergers and Acquisitions ,” Journal of Corporate Finance . 28 : 185 – 200 .
Li , Cindy , 2019 , “ Falling Female Labor Force Participation in China and India ,” Pacific Exchang e Blog, Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco ( https://www.frbsf.org/banking/asia-program/pacific-exchange-blog/falling-flpr-china-and-india/ ).
List , John , 2004 , “ The Nature and Extent of Discrimination in the Marketplace: Evidence from the Field ,” The Quarterly Journal of Economics , Vol. 119 , No. 1 : 49 - 89 .
Lleras-Muney , Adriana , Sissel Jensen , Sandra Black , and Marianne Bertrand , 2019 , “ Breaking the Glass Ceiling? The Effect of Board Quotas on Female Labour Market Outcomes in Norway ,” The Review of Economic Studies . 86 ( 1 ): 191 – 239 .
Low , Hamish , and Luigi Pistaferri , 2019 , “ Disability Insurance: Error Rates and Gender Differences ,” NBER Working Paper 26513 , National Bureau of Economic Research .
Maity , Bipasha , 2020 , “ Consumption and Time-Use Effects of India’s Employment Guarantee and Women’s Participation ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 68 , Number 4 : 1185 - 1231 .
Miller , Grant , 2008 , “Women’s Suffrage, Political Responsiveness, and Child Survival in American History”, The Quarterly Journal of Economics , Volume 123 , Issue 3 : 1287 –1327.
NSF , 2021 . \ Women, Minorities, and Persons with Disabilities in Science and Engineering .” Arlington VA : National Science Foundation .
Olivetti , Claudia , and Barbara Petrongolo , 2017 , “ The Economic Consequences of Family Policies: Lessons from a Century of Legislation in High-Income Countries ,” Journal of Economic Perspectives , 31 ( 1 ): 205 - 30 .
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) , 2012 , Closing the Gender Gap: Act Now , OECD , Paris .
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) , 2014 , “ Gender Equality: Gender Equality in Entrepreneurship ,” OECD Social and Welfare Statistics database , Paris .
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) , 2017 , “ The Pursuit of Gender Equality: An Uphill Battle ,” OECD , Paris .
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) , 2019 , “ PISA 2018 Results (Volume II): Where All Students Can Succeed ,” OECD , Paris .
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) , 2020 , “ All Hands In? Making Diversity Work for All ,” OECD , Paris .
Østergaard, Christian, Bram Timmermans, and Kari Kristinsson, 2011 , “ Does a Different View Create Something New? The Effect of Employee Diversity on Innovation ,” Research Policy , 40 , 500 – 509 .
Owen , Ann , and Judit Temesvary , 2018 , “ The Performance Effects of Gender Diversity on Bank Boards ,” Journal of Banking and Finance , 90 : 50 - 63 .
Ozgen , Ceren , 2021 , “ The Economics of Diversity: Innovation, Productivity and the Labour Market ,” Journal of Economic Surveys , Volume 35 , Issue 4 : 1168 - 1216 .
Pacheco , Jorge , Francisca Crispi , Tania Alfaro , María Soledad Martínez , and Cristóbal Cuadrado , 2021 , “ Gender Disparities in Access to Care for Time-sensitive Conditions during COVID-19 Pandemic in Chile ,” BMC Public Health , 21 ( 1 ): 1802 .
Pathak , Yuvraj and Karen Macours , 2017 , “ Women’s Political Reservation, Early Childhood Development, and Learning in India ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 65 , Number 4 : 741 - 766 .
Pitt , Mark , Shahidur Khandker , and Jennifer Cartwright , 2006 , “ Empowering Women with Micro Finance: Evidence from Bangladesh ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change 54 ( 4 ): 791 –831.
Pitt , Mark , Shahidur Khandker , Omar Haider Chowdhury , and Daniel Millimet , 2003 , “ Credit Programs for the Poor and the Health Status of Children in Rural Bangladesh ,” International Economic Review , Volume 44 , Issue 1 : 87 - 118 .
Pitt , Mark , Mark Rosenzweig , and Mohammad Nazmul Hassan , 2012 , “ Human Capital Investment and the Gender Division of Labor in a Brawn-Based Economy ,” American Economic Review , 102 ( 7 ): 3531 - 60 .
Profeta , Paola , Livia Amidani Aliberti , Alessandra Casarico , Marilisa D’Amico , and Anna Puccio , 2014 , “ Quotas on Boards: Evidence from the Literature ,” In Women Directors . Palgrave Macmillan , London .
Pal , Sarmistha , 1999 , “ An Analysis of Childhood Malnutrition in Rural India: Role of Gender, Income and Other Household Characteristics ,” World Development 27 ( 7 ): 1151 – 1171 .
Pande , Rohini , and Deanna Ford , 2012 , “ Gender Quotas and Female Leadership ,” World Bank , Washington, DC .
Qian Nancy , 2008 , “ Missing Women and the Price of Tea in China: The Effect of Sex-Specific Earnings on Sex Imbalance ,” Quarterly Journal of Economics , 123 : 1251 – 85 .
Rendall , Michelle , 2017 , “ Brain versus Brawn: The Realization of Women’s Comparative Advantage ,” Working Paper No. 491 , Institute for Empirical Research in Economics , University of Zurich .
Rim , Nayoung , 2021 , “ The Effect of Title IX on Gender Disparity in Graduate Education ,” Journal of Policy Analysis and Management , Vol. 40 , No. 2 : 521 – 552 .
Rock , David , and Heidi Grant , 2016 , “ Why Diverse Teams Are Smarter ,” Harvard Business Review, November 4: https://hbr.org/2016/11/why-diverse-teams-are-smarter , last accessed October 27 , 2021 .
Rubolino , Enrico , 2022 , “ Taxing the Gender Gap: Labor Market Effects of a Payroll Tax Cut for Women in Italy ,” CESifo Working Paper No. 9671 .
Ruhm , Christopher , 1998 , “ The Economic Consequences of Parental Leave Mandates: Lessons from Europe ,” Quarterly Journal of Economics , 113 ( 1 ): 285 – 317 .
Sahay , Ratna , Martin Cihák , and other IMF Staff, 2018 , “ Women in Finance: A Case for Closing Gaps ,” IMF Staff Discussion Note, SDN/18/05 , International Monetary Fund , Washington DC .
Sahay , Ratna , Ulric Eriksson von Allmen , Amina Lahreche , Purva Khera , Sumiko Ogawa , Majid Bazarbash , and Kimberly Beaton , 2020 , “ The Promise of Fintech; Financial Inclusion in the Post COVID-19 Era ,” IMF Working Paper WP/20/09 , International Monetary Fund , Washington DC .
Sloane , Carolyn , Erik Hurst , and Dan Black , 2021 , “ College Majors, Occupations, and the Gender Wage Gap ,” Journal of Economic Perspectives , Volume 35 , Number 4 : 223 – 248 .
Socías , Eugenia , Mieke Koehoorn , and Jean Shoveller , 2015 , “ Gender Inequalities in Access to Health Care among Adults Living in British Columbia, Canada ,” Women’s Health Issues , Volume 26 , Issue 1 : 74 - 79 .
Strøm , Reidar , Bert D’Espallier , and Roy Mersland , 2014 , “ Female Leadership, Performance, and Governance in Microfinance Institutions .” Journal of Banking and Finance 42 : 60 –75.
Tewari , Ishani , and Yabin Wang , 2021 , “ Durable Ownership, Time Allocation, and Female Labor Force Participation: Evidence from China’s “Home Appliances to the Countryside” Rebate ,” Economic Development and Cultural Change , Volume 70 , Number 1 : 87 - 127 .
World Economic Forum (WEF) , 2021 , “ Global Gender Gap Report 2021 ,” World Economic Forum , Geneva .
World Bank , 2006 , “ Repositioning Nutrition as Central to Development: A Strategy for Large Scale Action ,” World Bank , Washington DC .
World Bank , 2021 , Women, Business and the Law 2021 , World Bank , Washington DC .
Xiao , Pengpeng , 2021 , “ Wage and Employment Discrimination by Gender in Labor Market Equilibrium ,” Working Paper 144 , VATT Institute for Economic Research .
Zhang , Eva , and Tianlei Huang , 2020 , “ The Gender Gap in Labor Force Participation Is Widening in China While Narrowing in Other Parts of the World ,” PIIE Charts , Peterson Institute for International Economics ( https://www.piie.com/research/piie-charts/gender-gap-labor-force-participation-widening-china-while-narrowing-other-parts ).
In the rest of the paper, the discussions typically center around gender inequality against women, but the same arguments can be made for gender inequality against men when applicable.
The global commitment to achieving gender equality an d accelerating efforts to end gender inequality is reflected in the 2030 Sustainable Development Goal 5 , which includes nine targets covering discrimination and violence against women, child marriage, unpaid care and domestic work, leadership role, access to reproductive health, rights to economic resources, and technology use to promote women empowerment. In addition, achieving other SDGs could also have important implications for gender equality, for example, under Sustainable Development Goal 4 on quality education .
For example, a number of countries have mandated gender diversity on corporate boards of directors, including Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Iceland, India, Israel, Italy, Kenya, Netherlands, Norway, Pakistan, Portugal, Spain, Quebec of Canada, and California of United States. Malaysia is one recent case and mandates its publicly traded firms to have at least one-woman director on their boards from September 1, 2022.
This includes both taste-based and statistical discrimination; taste-based discrimination refers to less favorable attitudes and prejudice towards women, while statistical discrimination refers to the use of perception or statistics on women as a group in decision-making when information on a specific woman is lacking; for example, firms may make employment and pay decisions, based on average leave days taken and average job turnover rates for women and men; studies have found that statistical discrimination plays an important role in gender gaps , such as in wages and employment ( List, 2004 ; Xiao, 2020; Cordoba and others, 2021 ).
It should be noted that preference here refers to choices made in the absence of gender inequality. This is important as gender inequality and the associated social norms often operate through affecting the willingness of men and women in making certain choices.
For example, the comparative advantage of women often refers to the innate advantage of women in brain versus brawn jobs in the literature.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, around 13 percent of registered nurses in the United States are male in 2021.
The empirical observation of U-shaped female labor force participation over the course of economic development reflects other factors that also influence the decision of women entering the labor market ( Jayachandran, 2021 ). This includes the less need for a second income earner in a household, women’s comparative advantage in rearing children, the need to balance employment with household responsibilities, and social/cultural norms on “suitable” jobs for women, for example, between manufacturing jobs and service sector jobs.
While there is little empirical evidence on to what extent unpaid work is driven by preference and social norms, it is generally recognized that both play a role ( Alonso and others, 2019 ).
The index measures laws and regulations that affect women’s economic opportunities, based on eight indicators structured around women’s interactions with the law as they move through their careers: mobility, workplace, pay, marriage, parenthood, entrepreneurship, assets, and pension. Although it is critical to ensuring women’s economic inclusion, implementation of laws is not currently measured. Instead, Women, Business and the Law identifies legal differences between men and women as one step toward a better understanding of where women’s economic rights may be restricted in practice ( World Bank, 2021 ).
While the paper focuses on education, labor market, financial access and legal barriers, similar patterns are also observed in other areas. For example, in advanced economies, while there are little gender differences in health insurance and the ability to seek healthcare, a growing body of evidence suggests that female patients—relative to male patients—receive less healthcare for similar medical conditions and are more likely to be told by providers that their symptoms are emotionally driven rather than arising from a physical impairment; recent evidence also shows that there are large gender gaps in receiving benefits from social insurance programs that rely on medical evaluations ( Cabral and Dillender, 2021a ). For example, Low and Pistaferri (2019) show that female applicants for Social Security Disability Insurance are 20 percentage points more likely to be rejected than similar male applicants. The gender imbalance in the physician workforce can explain a large part of the gap ( Cabral and Dillender, 2021b ).
The literature of broad diversity (e.g., gender, race, and age) on firm productivity and team performance also yields mixed effects (see OECD (2020) for a review).
The study sample covers all countries between 1990 and 2019, when data are available.
Please see Appendix Table 1 for alternative specifications. Without including a time trend, the estimates are larger, more statistically significant, and have the expected signs for all five gender gaps, including labor force participation. Gonzales and others (2015a) and Hyland and others (2020 ; 2021) do not include a time trend and show similar results. The results from a random effects specification often lie somewhere in between.
See, for example, Bergman and others (2022) on the gender employment implication of the Federal Reserve’s recent move from a strict to an average inflation targeting framework; Erten and Metzger (2019) on currency undervaluation and female labor force participation ; and Kim and Williams (2021) on the effects of the minimum wage on women’s intrahousehold bargaining power.
Beaman and other (2012) , however, find that quota policies for female leadership helps improve adolescent girls’ career aspirations and educational attainment.
For example, the studies typically do not consider the impact of gender quotas on reducing gender bias in the broad society.
One example of targeted policies at gender inequality in employment is a payroll tax cut for female hires, introduced in 2012 in Italy to spur female employment and to stimulate business activity by reducing labor costs. The preferential tax rate is only available in occupations with large gender employment gap and has requirement for length in unemployment, which varies by age, whether in economically disadvantaged areas, and occupation. In addition, the preferential payroll tax scheme is valid for up to 12 months for temporary jobs and 18 months for permanent jobs. Firms can use the payroll tax cut only if overall employment would not decrease with respect to past employment. The complex eligibility criteria highlight the challenges in designing targeted gender policies while limiting their efficiency cost. Rubolino (2022) finds that payroll tax cut generates long-lasting growth in female employment with little effect on net wages and without crowding out male employment. However, the efficiency implication of the reform is not fully analyzed, as it is unclear what would have happened had the tax cut not been gender targeted,
See also Cook and others (2021) and Becker and others (2016) , which show that targeted mentoring programs can have significant and long-lasting effects on inclusion in STEM careers, where income, race, and gender gaps in acquiring education have been due to a lack of mentoring and exposure to science and innovation careers rather than differences in ability.
Table of Contents
- Front Matter
- Tackling Gender Inequality: Definitions, Trends, and Policy Designs
- View raw image
- Download Powerpoint Slide
International Monetary Fund Copyright © 2010-2021. All Rights Reserved.
- [66.249.64.20|81.177.180.204]
- 81.177.180.204
Character limit 500 /500
Gender Inequality Issue and Solutions
Gender inequality is one issue I feel strongly about following its negative impacts on societies. It is the state in which all individuals, regardless of their sex or gender identity, are able to access and enjoy the same opportunities, rights, and resources. Many advancements have been made toward achieving gender equality over the past few decades, but there is still a long way to go. Gender equality is important because it is a human right, essential for economic growth, and helps in ensuring that all genders receive better education, thus making gender inequality an issue.
Gender equality is a key human right that should be enjoyed by everyone. All people – regardless of their gender – should be able to enjoy the same rights and opportunities. I believe that every person, regardless of their sex, deserves equal treatment under the law and deserves an equal opportunity to achieve their dreams. Additionally, gender inequality is an issue since it does not make sense to mistreat someone based on their sex, which they do not have control over; nobody dictated their gender during creation. Gender equality is essential for economic growth in every nation (Smith 13). When women have the same opportunities as men, economies grow faster compared to when only men are favored. Again, the nation cannot reach its full potential if some of its population is held back and oppressed because of their sex.
No gender should be discriminated against because everyone needs education to succeed. All parents wish and support their children to succeed, but on the other hand, chances of finding a job to support the family become limited without education (Smith 11). A lack of education limits women’s opportunities and keeps them in poverty. Women with an education are more likely to have healthier children, earn more money, and be involved in their community development (Smith 5). In many parts of the world, women are still denied education and often trapped in a cycle of poverty and abuse. Many women have lost their lives as a result of depression following the fact that they could not provide for their families (Smith 13). Some of them have also involved themselves in dangerous activities to sustain their families. These women’s deaths are due to struggling to provide for their families due to the lack of education.
Gender equality is a human right that all should enjoy, and nobody deserves mistreatment since no one dictated their gender during their creation. Similarly, gender inequality remains an issue because all genders are needed for economic growth, and nations cannot grow to their potential if part of their population is sabotaged. Conversely, all genders need education for job security to support their families, failure to which they experience depression and get into dangerous activities such as prostitution to raise income.
Smith, Angela. Gender Equality in Changing Times . Springer International Publishing: Imprint: Palgrave Macmillan, 2020.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, December 21). Gender Inequality Issue and Solutions. https://studycorgi.com/gender-inequality-issue-and-solutions/
"Gender Inequality Issue and Solutions." StudyCorgi , 21 Dec. 2022, studycorgi.com/gender-inequality-issue-and-solutions/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'Gender Inequality Issue and Solutions'. 21 December.
1. StudyCorgi . "Gender Inequality Issue and Solutions." December 21, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/gender-inequality-issue-and-solutions/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Gender Inequality Issue and Solutions." December 21, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/gender-inequality-issue-and-solutions/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "Gender Inequality Issue and Solutions." December 21, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/gender-inequality-issue-and-solutions/.
This paper, “Gender Inequality Issue and Solutions”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 11, 2023 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.

Oxford University Press's Academic Insights for the Thinking World

How do you solve a problem like gender inequality?

Women's Property Rights Under CEDAW
- By José E. Alvarez
- April 19 th 2024
For most women’s rights advocates, the answer is obvious: adopt a human rights framework. At the global level this means using the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), ratified by 189 countries, which requires all states parties to themselves respect gender equality, protect against gender discrimination by others, and fulfill those human rights needs (e.g., right to adequate housing) that stand in the way. Women’s Property Rights Under CEDAW addresses those parts of CEDAW that protect, inter alia , women’s equal rights to access land, financial credit, social benefits, inheritance, and all forms of family property. While CEDAW has been subject to many critiques, my co-authored book defends it against criticisms that it privileges the experiences of Western women, fails to address salient issues (such as violence as discrimination), or marginalizes women’s rights. The book also rejects concerns that the CEDAW Committee’s property jurisprudence advances a “neo-liberal” agenda in favor of commodification, privatization, business deregulation, and economic globalization. The Committee’s outputs demonstrate how the Convention has evolved to incorporate domestic violence and nuanced positions on the male/female “binary,” the public/private divide, and the nature and causes of discrimination, subordination, and marginalization. There is a reason that CEDAW is specifically cited as a justification for progressive new laws around the world as well as in hundreds of national judicial opinions that use the treaty or the Committee’s jurisprudence to interpret existing laws and even national constitutions .
Nonetheless, the limitations that CEDAW shares with other global human rights institutions—from UN bureaucratic and fiscal constraints to a weak “managerial” approach to securing state compliance increasingly manipulated by rights-disrespecting states—encourages those seeking gender justice to seek alternatives or complements. The UN’s Development Agenda —specifically Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 5 to “achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls”—is one of them. Whereas CEDAW relies on a legal binding treaty under which states are obligated to implement at the national level equal rights of women, the SDGs’ 17 pledges are a political, aspirational effort, originating in hortatory General Assembly resolutions. They reflect a results-oriented model for international development for all—and not merely developing states—that set specific policy priorities, help steer action and resources, and use bench-marking backed by data. States’ progress towards achieving gender equality under SDG 5 is measured by nine targets and 14 indicators. This includes, under target 5.1 (to “end all forms of discrimination against all women and girls everywhere”), progress towards achieving indicator 5.1.1 which calls for the adoption of “legal frameworks . . . to promote, enforce, and monitor equality and non-discrimination on the basis of sex.” SDG targets and indicators, subject to periodic review since the SDGs were originally adopted in 2015, are intended to inspire new development thinking. While the SDGs have been criticized for lacking references to human rights, that might be the point.
For governments now caught in bottom-up populist or top-down authoritarian backlashes against human rights, the SDGs offer an appeal not to abstract dignitarian values but to the need to tackle structural obstacles like poverty, hunger, and gender inequality because these hinder economic growth. The SDGs appeal not only to “rule of law” states long accustomed to rights discourse at the domestic and international levels, but to governments—nearly all of them—that want to attract international financial institutions and market actors. They may particularly appeal to governments leery of “Western-centric” human rights or inclined to resist legally binding instruments that impose “sovereignty costs.” To be sure, the SDGs are not value free. Those who praise the SDGs see them as embodying Amartya Sen’s “human capabilities” approach grounded in the need to equalize life’s chances, satisfy basic needs, and level the playing field while paying greatest interest to those with the greatest need. Some may see them as yet the latest attempt to blue-wash the UN’s (and international financial institutions’) “ civilizing mission ,” notwithstanding the pretense of “universal” goals. Feminist critics of SDG 5 may emphasize what SDG targets/indicators fail to measure—namely enjoyment of LGBTQ rights, cyber or economic violence, women’s roles in peace-making and conflict, or the root causes of discrimination and violence against women. Those focusing on property rights might point out that while one SDG 5 indicator seeks data on the proportion of women who have rights to agricultural land, there are no requirements to measure many other kinds of property addressed under CEDAW, such as access to financial services, inheritance, or natural resources. The downside to the nostrum that “what gets measured gets done” is that under the SDGs what is not measured may get ignored.
Notwithstanding the SDGs’ weaknesses as yet another flawed attempt to impose global governance by indicators , advocates for gender equality searching for complements to CEDAW might consider their many other strengths:
(1) The SDGs encourage the collection of gender disaggregated data essential for naming gendered equality gaps and for measuring progress to resolve them.
(2) Many of the indicators (like 5.1.1 above) directly relate to lawyers’ efforts for law reform.
(3) The SDGs’ specificity may be useful for determining whether states are in fact taking “all appropriate measures” to combat discrimination against women as required by CEDAW’s Article 2; they may provide signposts that concretize states’ “due diligence.”
(4) The SDGs supply some useful data not typically demanded under CEDAW (such as, under 5.c.1, the level of governments’ resource allocations devoted to advancing gender equality).
(5) They embrace an integrative approach (suggested by the 54 gender-specific indicators apart from those included in SDG 5) that link gender equality to all the other development goals such as the alleviation of poverty, hunger, and environmental degradation.
(6) They provide more specific rationales for educating governments and the public about why gender equality is necessary to, for example, better address the disproportionate gendered effects of climate change.
(7) By calling attention to the costs of gender inequality to individuals, groups of women, to societies, and to the world—and to the resources needed to redress them—the SDGs demonstrate that advancing gender equality in all its dimensions is not free and that states facing massive sums of debt need help to achieve it.
All of these suggest another formidable benefit: the interconnectivity of the SDGs may enable gender equality activists to bridge silo-ed domains within governments and among international organizations and NGOs. They may help convince those who foolishly think that women’s equality is not their problem.
Featured image by Pawel Czerwinski via Unsplash .
José E. Alvarez is the Herbert and Rose Rubin Professor of International Law at NYU School of Law and the faculty director of its US-Asia Law Institute. He has taught at George Washington, Michigan, and Columbia law schools (where he was the Hamilton Fish Professor of International Law). A former President of the American Society of International Law and co-editor-in-chief of the American Journal of International Law, Professor Alvarez is a member of the Council on Foreign Relations, the Institut de Droit International, and the American Academy of Arts & Sciences
Our Privacy Policy sets out how Oxford University Press handles your personal information, and your rights to object to your personal information being used for marketing to you or being processed as part of our business activities.
We will only use your personal information to register you for OUPblog articles.
Or subscribe to articles in the subject area by email or RSS
Related posts:

Recent Comments
There are currently no comments.
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
Class Notes
Free Class Notes & Study Material
Essay on Gender Inequality
Last Updated on July 3, 2023 By Mrs Shilpi Nagpal
- 2 What is Gender Inequality?
- 3 What are the main causes of Gender Inequality?
- 4 What are the forms of Gender Inequality?
- 5 What are the examples of Gender Inequality?
- 6 What Gender Equality means?
- 7 What are effects of Gender Inequality?
- 8 Where is Gender Inequality most common?
- 9 How to prevent or solve Gender Inequality?
What is Gender Inequality?
Gender inequality refers to the unequal treatment or perceptions of individuals based on their gender. This can take many forms, including unequal access to education, employment, healthcare, and political representation, as well as unequal treatment in the justice system and cultural expectations and stereotypes. Gender inequality is a pervasive issue that affects people of all genders, but it disproportionately affects women and gender minorities.
One of the most significant ways in which gender inequality manifests is in the unequal distribution of power between men and women. This power imbalance is often the result of the unequal distribution of resources, such as education and job opportunities, between men and women. As a result, men are often able to access more resources and opportunities than women, which can lead to women being at a disadvantage in many areas of life.
The unequal distribution of power between men and women can also manifest itself in the form of discrimination and violence against women. In many societies, women are subject to discrimination and violence simply because of their gender. This can take the form of physical violence, such as domestic abuse, or it can be more subtle, such as the discrimination that women face in the workplace.
In addition to discrimination and violence, gender inequality also manifests itself in the form of unequal access to education and job opportunities. In many societies, women are not afforded the same opportunities as men when it comes to education and employment. This can have a significant impact on women’s ability to achieve financial independence and to advance in their careers.
Furthermore, gender inequality can also be seen in the lack of representation of women in leadership positions. In many cases, women are underrepresented in political leadership positions, and this lack of representation can have a significant impact on the policies and decisions that are made on behalf of women.
What are the main causes of Gender Inequality?
There are many factors that contribute to gender inequality, and these can vary depending on the specific context. Some of the main causes include:
- Social and cultural norms and expectations: Many societies have deeply ingrained beliefs and stereotypes about what is considered “appropriate” behavior for men and women. These gender roles can limit the opportunities and choices available to individuals, and can also create unequal power dynamics between men and women.
- Economic factors: Economic inequality is a significant driver of gender inequality. Women are often paid less than men for doing the same work, and they are also less likely to have access to education, training, and other resources that can help them advance in their careers.
- Legal and political factors: In many countries, women are not afforded the same legal rights as men, and they are also underrepresented in political institutions. This can make it more difficult for women to access justice and have their voices heard in the decision-making process.
- Violence and discrimination: Gender-based violence and discrimination are also major contributors to gender inequality. This can include physical, sexual, and emotional abuse, as well as discrimination in education, employment, and other areas.
What are the forms of Gender Inequality?
There are many forms of gender inequality, and these can vary depending on the specific context. Some examples include:
- Economic inequality: This can include unequal pay for the same work, as well as unequal access to education, training, and other resources that can help individuals advance in their careers.
- Unequal representation in political and decision-making institutions: This can include a lack of women in positions of power, such as in government, corporate boards, and other institutions where decisions are made.
- Violence and discrimination: This can include physical, sexual, and emotional abuse, as well as discrimination in education, employment, and other areas.
- Limited access to healthcare and reproductive rights: This can include unequal access to healthcare services, as well as restrictions on reproductive rights, such as the right to access contraception and safe abortion services.
- Stereotypes and gender roles: This can include limiting beliefs about what is considered “appropriate” behavior for men and women, which can limit the opportunities and choices available to individuals and create unequal power dynamics between men and women.
What are the examples of Gender Inequality?
- Unequal pay for the same work: In many countries, women are paid less than men for doing the same job. This can be a result of discrimination, but it can also be due to other factors, such as women being more likely to work in lower-paying industries or to take time off work to care for children or other family members.
- Unequal representation in political and decision-making institutions: In many countries, women are underrepresented in political institutions and other decision-making bodies. This can make it more difficult for women to have their voices heard and to influence the policies and decisions that affect their lives.
- Violence and discrimination: Gender-based violence and discrimination are widespread issues that affect people of all genders. This can include physical, sexual, and emotional abuse, as well as discrimination in education, employment, and other areas.
- Limited access to healthcare and reproductive rights: In some countries, women and other gender minorities may have limited access to healthcare services, including reproductive health services. This can be due to a lack of access to facilities, cost, or legal restrictions on certain services.
- Stereotypes and gender roles: Many societies have deeply ingrained beliefs and stereotypes about what is considered “appropriate” behavior for men and women. These gender roles can limit the opportunities and choices available to individuals, and can also create unequal power dynamics between men and women.
What Gender Equality means?
What are effects of gender inequality.
- Economic inequality and poverty: Gender inequality can limit women’s access to education, training, and other resources that can help them advance in their careers. This can lead to lower wages and a higher risk of poverty, particularly for women who are also marginalized due to factors such as race, sexual orientation, or disability.
- Health disparities: Gender inequality can also lead to health disparities, as women and gender minorities may have limited access to healthcare services, including reproductive health services. This can lead to higher rates of preventable illnesses and injuries, as well as other negative health outcomes.
- Violence and discrimination: Gender-based violence and discrimination are also major consequences of gender inequality. This can include physical, sexual, and emotional abuse, as well as discrimination in education, employment, and other areas.
- Inequality in political representation and decision-making: Gender inequality can also lead to unequal representation in political institutions and other decision-making bodies. This can make it more difficult for women and gender minorities to have their voices heard and to influence the policies and decisions that affect their lives.
Where is Gender Inequality most common?
How to prevent or solve gender inequality.
Preventing gender inequality requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying causes and the specific ways in which it manifests. Some potential strategies for preventing gender inequality include:
- Promoting gender equality in education: Ensuring that girls and boys have equal access to education and training can help to prevent gender inequality. This can include providing girls with the same opportunities as boys to attend school, as well as addressing gender stereotypes and biases in the education system.
- Supporting women’s economic empowerment: Providing women with equal access to economic opportunities, such as education and training, as well as supportive policies and infrastructure, can help to prevent gender inequality. This can include initiatives such as promoting women’s entrepreneurship and leadership, as well as policies that support women’s participation in the labor market, such as paid parental leave and affordable childcare.
- Addressing violence and discrimination: Addressing violence and discrimination against women and gender minorities is essential for preventing gender inequality. This can include efforts to prevent violence, such as through education and awareness-raising, as well as providing support and services to survivors. It can also involve addressing discrimination in education, employment, and other areas.
- Promoting gender equality in political and decision-making institutions: Ensuring that women and gender minorities have equal representation in political and decision-making institutions is crucial for preventing gender inequality. This can include initiatives to increase women’s political participation, such as quota systems, as well as addressing the barriers that can prevent women from participating in the political process.
Overall, gender inequality is a pervasive issue that affects individuals and societies around the world. It is the result of the unequal distribution of power, resources, and opportunities between men and women, and it manifests itself in a variety of ways, including discrimination, violence, and the lack of representation in leadership positions. To address this issue, it is necessary to take action to promote gender equality and to ensure that women have the same opportunities as men to achieve their full potential.
About Mrs Shilpi Nagpal
Author of this website, Mrs. Shilpi Nagpal is MSc (Hons, Chemistry) and BSc (Hons, Chemistry) from Delhi University, B.Ed. (I. P. University) and has many years of experience in teaching. She has started this educational website with the mindset of spreading free education to everyone. In addition to this website, author also has a Youtube channel, here is the link Class Notes Youtube Channel
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Social Inequality — Gender Inequality
Essays on Gender Inequality
Gender inequality essay topics and outline examples, essay title 1: unveiling gender inequality: root causes, impact, and paths to equality.
Thesis Statement: This essay delves into the multifaceted issue of gender inequality, examining its underlying causes, its pervasive impact on society, and the strategies and movements aimed at achieving gender equality and justice.
- Introduction
- Understanding Gender Inequality: Social Constructs, Stereotypes, and Bias
- Economic Disparities: Gender Wage Gap, Occupational Segregation, and Glass Ceilings
- Education and Empowerment: Gender Disparities in Access and Opportunities
- Violence Against Women: Domestic Violence, Harassment, and Human Rights Violations
- Global Perspectives: Gender Inequality in Different Cultural and Geographical Contexts
- The Role of Advocacy: Movements, Legislation, and Progress Towards Equality
- Conclusion: The Ongoing Struggle for Gender Equality
Essay Title 2: Intersectionality and Gender Inequality: Examining the Overlapping Forms of Discrimination
Thesis Statement: This essay explores the concept of intersectionality within the context of gender inequality, analyzing how overlapping factors such as race, class, sexuality, and disability intersect with gender to create unique experiences of discrimination and privilege.
- Intersectionality Defined: Interplay of Identity, Power, and Discrimination
- Race and Gender: The Experiences of Women of Color
- Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty, Wealth, and Economic Disparities
- Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity: LGBTQ+ Issues and Discrimination
- Disability and Gender: Challenges Faced by Disabled Women
- Intersectionality in Action: Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
- Empowerment and Solidarity: Intersectional Feminism and Social Change
- Conclusion: Embracing Intersectionality in the Fight Against Gender Inequality
Essay Title 3: Breaking the Glass Ceiling: Women's Leadership and Gender Equality in the Corporate World
Thesis Statement: This essay focuses on women's leadership in the corporate world, examining the challenges and barriers they face in reaching leadership positions, the importance of diversity in leadership, and the potential for change in the business sphere.
- The Gender Leadership Gap: Statistics and Trends in Corporate Leadership
- Barriers to Women's Advancement: Stereotypes, Bias, and Family-Work Balance
- The Business Case for Gender Diversity: Benefits to Companies and Economies
- Women Breaking Barriers: Success Stories and Female Role Models in Business
- Initiatives for Change: Corporate Policies, Mentorship Programs, and Gender Parity Goals
- The Future of Women in Leadership: Prospects for Gender Equality in the Corporate World
- Conclusion: Advancing Women's Leadership for a More Inclusive Future
Sexism in Chase and Sanborn Advertising
Gender inequality in the great gatsby, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Gender Hierarchies, Stereotypes, and The Fight for Equality
The problem of gender inequality in the workplace, the issue of gender inequality in the media in america, the national organization for women struggling with gender inequality going on in the workplace, schools, and home, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Gender Inequality and Women in The Workplace
Gender inequality: causes and solutions, the influence of social norms on gender inequality, the effects of gender inequality on society and the economy, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
The Issue of Gender Equality in Workplace
Gender inequality in the film industry, sexism and gender inequality in the workplace in the us, the experience of gender inequality in the awakening, a novel by kate chopin, the impact of gender on income inequality, the necessity of feminism in a patriarchal society: death of a salesman, sociological perspectives of sexual orientation and inequality, systemic discrimination against women firefighters, the effect of a double glass ceiling on minority women, the problem of gender inequality in sports, gender equality as a matter of social justice, impact of experience and education on womens wages, the role of social stratification in inequality within the education system, the problem of a lack of female leaders, why gender equality is still not achieved, it wasn't hysteria; it was institutionalized sexism, gender equality and its effect on advertisement and fashion photography, the issue of gender equality: a review of literature, jo goodwin parker's discussion of poverty and feminization, social injustice issue: transgenders and restrooms, relevant topics.
- Gender Equality
- Gender Wage Gap
- Gun Control
- Pro Choice (Abortion)
- Women's Rights
- Freedom of Speech
- Assisted Suicide
- Women's Suffrage
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Essay on Gender Issues
Students are often asked to write an essay on Gender Issues in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Gender Issues
Understanding gender issues.
Gender issues refer to social problems and debates related to the rights and roles of different genders. These issues often arise from societal norms and stereotypes.
Common Gender Issues
Some common gender issues include gender discrimination, gender pay gap, and gender-based violence. These problems persist in many societies, limiting opportunities for certain genders.
Addressing Gender Issues
To address gender issues, we need to promote gender equality, respect, and tolerance. Education plays a crucial role in this, helping to challenge stereotypes and promote understanding.
250 Words Essay on Gender Issues
Introduction.
Gender issues refer to the social and cultural constructs surrounding the roles, behaviors, activities, and attributes that society considers appropriate for men and women. They encompass a broad spectrum of concerns, including gender inequality, stereotypes, and the impact of societal norms on individuals’ lives.
Gender Inequality
Despite significant strides towards equality, gender inequality remains a pervasive issue worldwide. It manifests in various sectors such as education, employment, and politics. Women often face wage gaps, limited opportunities for advancement, and underrepresentation in decision-making positions. This disparity not only undermines women’s rights but also hampers economic development and societal progress.
Gender Stereotypes
Gender stereotypes, deeply rooted in societal norms and cultural traditions, contribute significantly to gender issues. They shape expectations and attitudes about what men and women can or cannot do, often limiting individuals’ potential and freedom to express their identities. Challenging these stereotypes is crucial to fostering a society that values diversity and individuality.
Implications and Solutions
Gender issues have profound implications for individuals and societies, affecting mental health, self-esteem, and societal harmony. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach that includes education, policy changes, and societal transformation. Encouraging open dialogue, promoting gender-sensitive education, and implementing laws that ensure equal opportunities are fundamental steps towards a more gender-balanced society.
In conclusion, gender issues remain a significant challenge. However, through collective efforts, we can challenge the status quo, dismantle harmful stereotypes, and strive for a society where everyone, regardless of their gender, can thrive and contribute effectively.
500 Words Essay on Gender Issues
Gender issues have been a significant area of concern in society for many years. These issues are not just about the biological differences between males and females, but also about the social constructs that define masculinity and femininity. They affect all aspects of life, including social, economic, political, and cultural spheres.
One of the most prominent gender issues is inequality. Despite significant strides towards equality, disparities persist in various domains. For instance, the gender wage gap remains a global issue, with women often earning less than men for the same work. This inequality extends to leadership roles, where women are underrepresented, particularly in politics and corporate boardrooms.
Stereotypes play a significant role in perpetuating gender issues. Societal expectations and norms often confine individuals to specific roles and behaviors based on their gender. For example, women are often expected to be nurturing and emotional, while men are expected to be strong and unemotional. These stereotypes can limit individual growth and potential, leading to a lack of diversity and innovation in society.
Gender and Education
Education is another area where gender issues are prevalent. Despite the global push for girls’ education, many societies still prioritize boys’ education, leading to high illiteracy rates among women, particularly in developing countries. Moreover, educational curricula often reinforce gender stereotypes, thereby perpetuating gender norms and roles.
Gender-Based Violence
Gender-based violence is a pervasive and critical issue. This form of violence, which disproportionately affects women and girls, includes physical, sexual, and psychological harm. It is often rooted in power imbalances and can occur in various settings, including homes, schools, workplaces, and public spaces.
Gender and Intersectionality
Intersectionality, a concept introduced by Kimberlé Crenshaw, highlights how gender issues are intertwined with other forms of discrimination, such as race, class, and sexual orientation. This intersectionality means that individuals can face multiple, overlapping forms of discrimination, making it crucial to address gender issues in a holistic manner.
Addressing gender issues requires a comprehensive approach that challenges societal norms, promotes gender equality, and advocates for policies that protect individuals from gender-based discrimination and violence. It is crucial to educate society about the harmful effects of gender stereotypes and the importance of gender equality for social development. By doing so, we can create a society where everyone, regardless of their gender, can achieve their full potential.
In conclusion, gender issues are complex and multifaceted, affecting all aspects of life. Understanding and addressing these issues is essential for creating a more equitable and inclusive society.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Right to Freedom
- Essay on Importance of Freedom
- Essay on Focus
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
The Language of Gender Identity
More from our inbox:, power over principle in the g.o.p., upgrading our electric grid, shakespeare’s insights, still relevant today.

To the Editor:
Re “ The Problem With Saying ‘Sex Assigned at Birth, ’” by Alex Byrne and Carole K. Hooven (Opinion guest essay, nytimes.com, April 3):
Mr. Byrne and Ms. Hooven argue that use of “assigned sex” terminology “creates doubt about a biological fact when there shouldn’t be any.” But sex characteristics are not “a biological fact”; they are rather a series of facts — anatomical, hormonal and genetic — that are not always in alignment.
The term “sex assignment” derives from the medical literature of the 1940s and 1950s, in which physicians grappled with what was then called “hermaphroditism” and is now called “intersex” or “D.S.D.,” for disorders or differences of sex development.
To conclude that the words “assigned at birth” are needless is to deny the complexity of biological sex and to erase both the history of intersex conditions and the embodied reality of the people who are born and live with them.
Barbara M. Chubak New York The writer is an associate professor of urology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
Transgender people like me do not exist as a topic of rational debate, something to be tossed around in discourse; we are people, and our lives exist far beyond your philosophizing. Articles like this are not only unnecessary, but they are also harmful, patronizing and dehumanizing.
The phrase “sex assigned at birth” is causing no one any harm, and it is not meant to replace “sex.” We are not advocating the end of “male” and “female.”
“Sex assigned at birth” is simply meant to convey the following notion: This individual was born as one sex, but their current body and/or lived experiences may contradict that. It allows trans people the very medical clarity this article claims to strive for. If I, a trans man far into his medical transition, were to walk into a doctor’s office and claim to simply be “female,” utter confusion could follow.
But we should not have to defend ourselves under the guise of rational discourse. We have bigger issues. In Texas, my parents would be possibly liable for child abuse for allowing me to transition as a teenager — so stop treating us as if we do not know what we are talking about.
When people tell you the language that makes them the most comfortable, you use it and move on. You may believe sex to be black and white, as it may be the most convenient reality for you to live in, but for many of us, our bodies are the gray areas.
Max Greenhill New York
I fully agree with this essay: Biological sex is accurately recorded at birth; it is not arbitrarily “assigned.”
The reason activists are pushing the sex-assigned-at-birth terminology is not simply that they want more empathy and inclusiveness for trans persons, but that they want the public to believe that one’s birth sex was, as the authors say, an educated guess at best. If the public accepts that idea, they will be more agreeable to the idea that one’s misassigned sex needs to be corrected later when the individual is old enough to determine their “true, authentic self.”
Most adults don’t care what gender someone declares, but biological sex is a scientific fact. The range of “genders” now being proclaimed is making the whole concept of gender meaningless. Every behavior, feeling, mood, attribute, sexual orientation or social statement does not constitute a gender.
Mark Godburn Norfolk, Conn.
The problem is not that we are confusing the male/female binary; the problem is that the human gender story is bigger than a simple binary, and our language does not reflect that, but it should.
Intersex people exist and have always existed. People whose gender expression doesn’t match their biological presentation exist and have always existed. The authors are correct that language is powerful, but in this case they have the power dynamic exactly backward.
When we adhere to strict binary language, we are asking gender-abundant people to amputate whole parts of themselves. We need to allow people to flourish in the language that fits them.
As my 9-year-old recently explained to my 6-year-old, “You don’t really know what gender a baby is when it’s born, because you know their parts, but you don’t know their heart.”
Meghan Lin St. Paul, Minn.
Thank you, thank you, thank you for publishing this guest essay by Alex Byrne and Carole K. Hooven. In a society inundated with well-meaning absurdities such as “sex assigned at birth” and “pregnant people,” this message desperately needs to be broadcast, received and acted upon.
Mark Featherstone Alameda, Calif.
Re “ Sununu Says Trump ‘Contributed’ to Insurrection, but Still Has His Support ” (news article, nytimes.com, April 14):
Gov. Chris Sununu of New Hampshire now says he will support Donald Trump for president, even as he concedes that Mr. Trump “absolutely contributed” to an attempted insurrection on Jan. 6. Like many of his fellow Republicans, Mr. Sununu has chosen power over principle.
Ethics don’t flash on and off like neon lights. Integrity cannot be situational. And character isn’t a chameleon that shifts to secure political advantage. History will record all the elected officials who embraced Mr. Trump’s mendacity while looking away from the democratic principles they swore an oath to uphold.
Welcome to the club, Governor Sununu.
Maryellen Donnellan Falls Church, Va.
Re “ The U.S. Urgently Needs a Bigger Grid. Scientists Have a Faster Solution ” (Business, April 10):
The nation’s current power lines that were built in the 1950s and 1960s have a 50-year life expectancy, meaning that they have surpassed their intended life span. As the U.S. evaluates how to meet new electric demand, the materials in the grid must not just be replaced, but also efficiently planned and upgraded.
To lower energy costs and improve reliable access to electricity, we should use new technologies that allow more power to be transported across the same size transmission towers that are currently in use. Further, the same amount of power could be transported across smaller, low-impact towers, which could reduce siting and permitting obstacles — thus saving time and money.
Significant transmission capacity is required to meet rising demands on the electrical system, withstand frequent extreme weather events and balance a changing resource mix. Deploying improved technologies in constructing a nationwide transmission grid is key to meeting these needs — because America needs a modern grid now more than ever.
Christina Hayes Washington The writer is the executive director of Americans for a Clean Energy Grid.
With “ O.J. and the Monster Jealousy ” (column, April 14) and “ Trump’s Insatiable Bloodlust ” (column, April 7), Maureen Dowd evokes two of Shakespeare’s greatest characters — Othello and Macbeth — to demonstrate that the playwright’s insights remain as perceptive and significant today as they were more than 400 years ago.
As his friend and fellow dramatist Ben Jonson wrote of Shakespeare, “He was not of an age but for all time!”
Brad Bradford Upper Arlington, Ohio
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Gender pay gap in U.S. hasn’t changed much in two decades
The gender gap in pay has remained relatively stable in the United States over the past 20 years or so. In 2022, women earned an average of 82% of what men earned, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of median hourly earnings of both full- and part-time workers. These results are similar to where the pay gap stood in 2002, when women earned 80% as much as men.
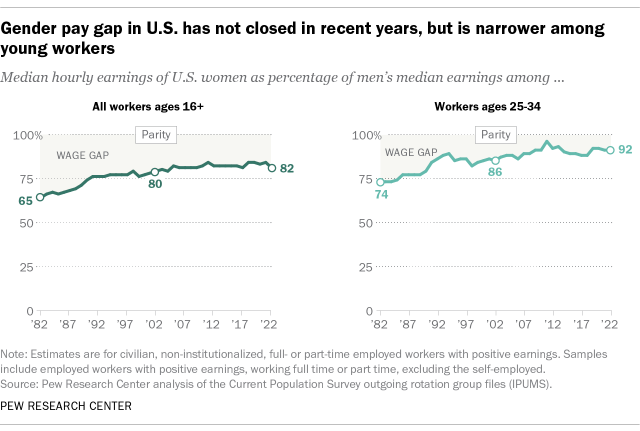
As has long been the case, the wage gap is smaller for workers ages 25 to 34 than for all workers 16 and older. In 2022, women ages 25 to 34 earned an average of 92 cents for every dollar earned by a man in the same age group – an 8-cent gap. By comparison, the gender pay gap among workers of all ages that year was 18 cents.
While the gender pay gap has not changed much in the last two decades, it has narrowed considerably when looking at the longer term, both among all workers ages 16 and older and among those ages 25 to 34. The estimated 18-cent gender pay gap among all workers in 2022 was down from 35 cents in 1982. And the 8-cent gap among workers ages 25 to 34 in 2022 was down from a 26-cent gap four decades earlier.
The gender pay gap measures the difference in median hourly earnings between men and women who work full or part time in the United States. Pew Research Center’s estimate of the pay gap is based on an analysis of Current Population Survey (CPS) monthly outgoing rotation group files ( IPUMS ) from January 1982 to December 2022, combined to create annual files. To understand how we calculate the gender pay gap, read our 2013 post, “How Pew Research Center measured the gender pay gap.”
The COVID-19 outbreak affected data collection efforts by the U.S. government in its surveys, especially in 2020 and 2021, limiting in-person data collection and affecting response rates. It is possible that some measures of economic outcomes and how they vary across demographic groups are affected by these changes in data collection.
In addition to findings about the gender wage gap, this analysis includes information from a Pew Research Center survey about the perceived reasons for the pay gap, as well as the pressures and career goals of U.S. men and women. The survey was conducted among 5,098 adults and includes a subset of questions asked only for 2,048 adults who are employed part time or full time, from Oct. 10-16, 2022. Everyone who took part is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used in this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology .
The U.S. Census Bureau has also analyzed the gender pay gap, though its analysis looks only at full-time workers (as opposed to full- and part-time workers). In 2021, full-time, year-round working women earned 84% of what their male counterparts earned, on average, according to the Census Bureau’s most recent analysis.
Much of the gender pay gap has been explained by measurable factors such as educational attainment, occupational segregation and work experience. The narrowing of the gap over the long term is attributable in large part to gains women have made in each of these dimensions.
Related: The Enduring Grip of the Gender Pay Gap
Even though women have increased their presence in higher-paying jobs traditionally dominated by men, such as professional and managerial positions, women as a whole continue to be overrepresented in lower-paying occupations relative to their share of the workforce. This may contribute to gender differences in pay.
Other factors that are difficult to measure, including gender discrimination, may also contribute to the ongoing wage discrepancy.
Perceived reasons for the gender wage gap
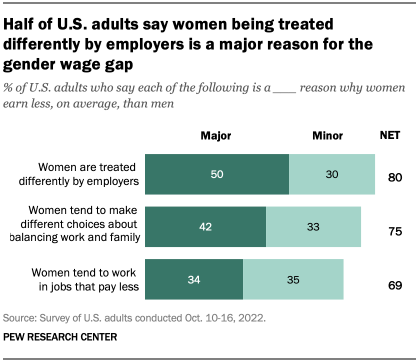
When asked about the factors that may play a role in the gender wage gap, half of U.S. adults point to women being treated differently by employers as a major reason, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in October 2022. Smaller shares point to women making different choices about how to balance work and family (42%) and working in jobs that pay less (34%).
There are some notable differences between men and women in views of what’s behind the gender wage gap. Women are much more likely than men (61% vs. 37%) to say a major reason for the gap is that employers treat women differently. And while 45% of women say a major factor is that women make different choices about how to balance work and family, men are slightly less likely to hold that view (40% say this).
Parents with children younger than 18 in the household are more likely than those who don’t have young kids at home (48% vs. 40%) to say a major reason for the pay gap is the choices that women make about how to balance family and work. On this question, differences by parental status are evident among both men and women.
Views about reasons for the gender wage gap also differ by party. About two-thirds of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents (68%) say a major factor behind wage differences is that employers treat women differently, but far fewer Republicans and Republican leaners (30%) say the same. Conversely, Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say women’s choices about how to balance family and work (50% vs. 36%) and their tendency to work in jobs that pay less (39% vs. 30%) are major reasons why women earn less than men.
Democratic and Republican women are more likely than their male counterparts in the same party to say a major reason for the gender wage gap is that employers treat women differently. About three-quarters of Democratic women (76%) say this, compared with 59% of Democratic men. And while 43% of Republican women say unequal treatment by employers is a major reason for the gender wage gap, just 18% of GOP men share that view.
Pressures facing working women and men
Family caregiving responsibilities bring different pressures for working women and men, and research has shown that being a mother can reduce women’s earnings , while fatherhood can increase men’s earnings .
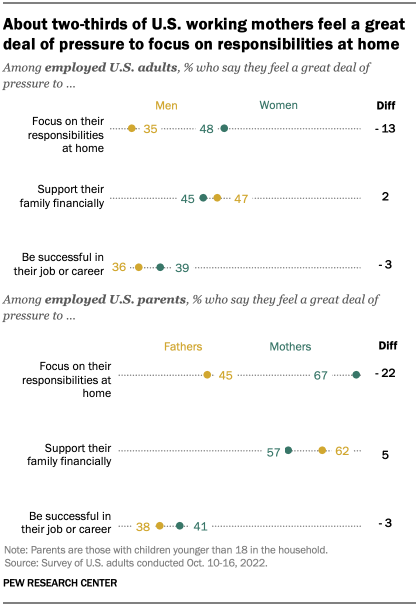
Employed women and men are about equally likely to say they feel a great deal of pressure to support their family financially and to be successful in their jobs and careers, according to the Center’s October survey. But women, and particularly working mothers, are more likely than men to say they feel a great deal of pressure to focus on responsibilities at home.
About half of employed women (48%) report feeling a great deal of pressure to focus on their responsibilities at home, compared with 35% of employed men. Among working mothers with children younger than 18 in the household, two-thirds (67%) say the same, compared with 45% of working dads.
When it comes to supporting their family financially, similar shares of working moms and dads (57% vs. 62%) report they feel a great deal of pressure, but this is driven mainly by the large share of unmarried working mothers who say they feel a great deal of pressure in this regard (77%). Among those who are married, working dads are far more likely than working moms (60% vs. 43%) to say they feel a great deal of pressure to support their family financially. (There were not enough unmarried working fathers in the sample to analyze separately.)
About four-in-ten working parents say they feel a great deal of pressure to be successful at their job or career. These findings don’t differ by gender.
Gender differences in job roles, aspirations
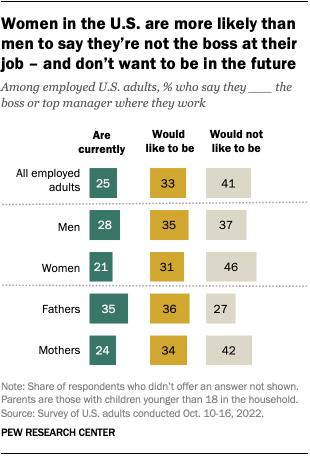
Overall, a quarter of employed U.S. adults say they are currently the boss or one of the top managers where they work, according to the Center’s survey. Another 33% say they are not currently the boss but would like to be in the future, while 41% are not and do not aspire to be the boss or one of the top managers.
Men are more likely than women to be a boss or a top manager where they work (28% vs. 21%). This is especially the case among employed fathers, 35% of whom say they are the boss or one of the top managers where they work. (The varying attitudes between fathers and men without children at least partly reflect differences in marital status and educational attainment between the two groups.)
In addition to being less likely than men to say they are currently the boss or a top manager at work, women are also more likely to say they wouldn’t want to be in this type of position in the future. More than four-in-ten employed women (46%) say this, compared with 37% of men. Similar shares of men (35%) and women (31%) say they are not currently the boss but would like to be one day. These patterns are similar among parents.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published on March 22, 2019. Anna Brown and former Pew Research Center writer/editor Amanda Barroso contributed to an earlier version of this analysis. Here are the questions used in this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology .
What is the gender wage gap in your metropolitan area? Find out with our pay gap calculator
- Gender & Work
- Gender Equality & Discrimination
- Gender Pay Gap
- Gender Roles

Women have gained ground in the nation’s highest-paying occupations, but still lag behind men
Diversity, equity and inclusion in the workplace, the enduring grip of the gender pay gap, more than twice as many americans support than oppose the #metoo movement, women now outnumber men in the u.s. college-educated labor force, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
Gender, Age and Racial Inequality Issues Essay
Modern world tends to break stereotypes, leaving arrogant and superior attitude behind, constantly raising questions of all types of equality on all levels. Women work at the same positions and in the same spheres as men do. There are no restrictions on colored people to public areas access as it was less than a century ago. Still there are some acute issues dealing with racial, gender and age inequality that strike unexpectedly bringing up the questions not yet solved.
Shockingly, but even today in the developed countries female employees earn less than men. In The U.S., the average of 2010 shows that women earn only 78 cents of every dollar of men’s salary (The White House, n.d., para. 1). Different restrictions are applied in the connection to the issue or raising children. The priority in case of the vacant position in the company is given to a male candidate rather than to a female candidate, because she is more likely to leave the job because she will have kids or will need maternity leave.
Only a few companies provide major support and acceptable conditions for childcare while mother works. Despite a significant progress of developed European countries in that sphere, the childcare in the U.S. is considered more of a woman matter (Harvard Summer School, 2014, para. 9), thus a mother ends up having two jobs: first, the one where she earns money, second, taking care of the household and kids.
The issue of age discrimination is a great problem of the modern world too. It is basically raised when the person seeks for a job. Age discrimination hits both people under twenty-five, because they might be considered too young to do the job, and people over forty, because they might be overqualified or less likely to be involved into training process for the position. The situation of people over fifty and sixty, in this case, seems to be entirely hopeless. There is also a tendency to formation of age-based hierarchy within co-workers team. As Snowdon notes “In general terms, people in their 40s were viewed as having the highest status, while on average people aged over 70 were given a higher status than those in their 20s” (Snowdon, 2012, para. 11).
Racial inequality is majorly expressed while the everyday attitude, when people reject to take a taxi driven by a person of an “inappropriate” race or nationality or to rent a house to a family for the same reasons. The formation of in-town and in-state clusters where the people of other race, nationality, and origin are strongly not welcomed, where inappropriate conditions for “strangers” are created can also be considered as a form of racial inequality.
The rate of annual income within the United States also provides a demonstration of a difference in well-being and thus the inequality between white and non-white families (Gordon, 2014, para. 5). The percentage of homeowners is also significantly higher among white families, comparing to non-white. The median value of primary residence of white families also exceeds the median value of primary residence of non-white families.
Despite the modern level of development and broad proclamation of humanistic ideas, there still exist some issues of gender, age, and racial inequality. This statement refers not only to the situation of developing and underdeveloped countries that struggle social problems, solved in Europe and the United States a long time ago. The problems of inequality hit Europe and the U.S., as well. The rate is, of course significantly lower, but the problem, nevertheless, exists and has to be solved as it brings up the issues of humiliation and discrimination within society.
Gordon, C. (2014). Racial Inequality . Web.
Harvard Summer School. (2104). Gender Inequality and Women in the Workplace. Web.
Snowdon, G. (2012). Young and older people experience age discrimination at work . Web.
The White House. (n.d.). Did You Know That Women Are Still Paid Less Than Men? Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 4). Gender, Age and Racial Inequality Issues. https://ivypanda.com/essays/gender-age-and-racial-inequality-issues/
"Gender, Age and Racial Inequality Issues." IvyPanda , 4 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/gender-age-and-racial-inequality-issues/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Gender, Age and Racial Inequality Issues'. 4 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Gender, Age and Racial Inequality Issues." March 4, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/gender-age-and-racial-inequality-issues/.
1. IvyPanda . "Gender, Age and Racial Inequality Issues." March 4, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/gender-age-and-racial-inequality-issues/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Gender, Age and Racial Inequality Issues." March 4, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/gender-age-and-racial-inequality-issues/.
- The Perspectives of White and Non-White Communities
- Non-White Experience: Stereotyping and Discrimination
- Khayatt on Non-White Women's Problems in Canada
- Impact of Free Childcare on Parents Willingness to Go Back to Work or College
- Inequality Among White and Non-White Students
- Childcare From a Licensed Center Is Better Than a Babysitter
- Extensive Childcare Costs in Garfield Park Community
- Childcare Issues in the United States Navy
- Is Childcare an Issue in the Navy’s Retention?
- Childcare in Society Setting
- Equality and Globalization: Changing Gender Expectations
- Gender Equality and Globalization' Issues
- A Disadvantaged Start Hurts Boys More Than Girls
- Gender Discrimination in Russian Workplaces
- Misogyny and Homophobia as Oppression Tools

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An Issue of Gender Inequality in the World Words: 510 Pages: 2 7186. Gender inequality is still an issue in the world. In every five girls, one will not have access to an education. Girls in developing countries are not enrolled in school. Mexico has been dealing with gender inequality for years because women aren't given the same rights as men.
Answer 2: The gender inequality essay tells us that gender inequality impacts us badly. It takes away opportunities from deserving people. Moreover, it results in discriminatory behaviour towards people of a certain gender. Finally, it also puts people of a certain gender in dangerous situations. Share with friends.
After an early unsuccessful attempt, Rwanda invested seriously in gender budgeting beginning in 2011. 23 24 The budget is focused on closing gaps and strengthening women's roles in key sectors ...
A new global analysis of progress on gender equality and women's rights shows women and girls remain disproportionately affected by the socioeconomic fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic, struggling with disproportionately high job and livelihood losses, education disruptions and increased burdens of unpaid care work. Women's health services, poorly funded even before the pandemic, faced ...
This essay will examine some of the causes that affect the gap in the treatment of men and women, and its ramifications, particularly regarding developing countries. Gender Inequality: The Role of Media. The media plays a major role in gender socialization because of the ways it chooses to portray women.
Activists are charting unfamiliar territory, which this essay explores. "Men built this system. No wonder gender equality remains as far off as ever.". - Ellie Mae O'Hagan. Freelance journalist Ellie Mae O'Hagan (whose book The New Normal is scheduled for a May 2020 release) is discouraged that gender equality is so many years away.
8. Violence against women and girls. Each year, 245 million women and girls experience physical and/or sexual violence by an intimate partner. Older women also face higher rates of poverty and violence than older men. 9. Inadequate funding for gender equality initiatives.
This piece is part of 19A: The Brookings Gender Equality Series.In this essay series, Brookings scholars, public officials, and other subject-area experts examine the current state of gender ...
Taking a global look at gender inequality, Diva Dhar, Senior Programme Officer, Gender Data and Evidence, at the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, writes on one of the most glaring manifestations of inequality between men and women: the gap in unpaid care work, which she argues must be better analysed and researched.
Gender Inequality as a Global Issue Essay. Gender inequality is a global issue where men and women enjoy different levels of representation in various spheres of life. Generally predisposed against females, multiple factors conspire to limit their opportunities for education and employment, as well as, in more extreme cases, lead to violence.
According to Oxfam (2011, p 1), quoting UN (2005, pp 2), gender inequality that has resulted in the discrimination of women through denial of basic human rights is a leading cause of poverty in the world today. Oxfam (2011, p 2) adds that majority of women in the world have little or no control on matters of sexuality, reproduction and marital ...
July 19, 2022 Stanford scholars examine gender bias and ways to advance equity across society. Stanford scholars have studied the obstacles women face across society - at work, in education, as ...
8 Prompts for Essays About Gender Inequality. 1. Gender Inequality: Defined. Gender inequality essays can open space for important conversations. Explain to your readers the main topic and how inequality occurs in modern society. Give an example of gender inequality that is very common and how both sexes react to it.
The fight for global gender equality is nowhere close to being won. Take education: in 87 countries, less than half of women and girls complete secondary schooling, according to 2023 data.
The Gender Gap Is Taking Us to Unexpected Places. Mr. Edsall contributes a weekly column from Washington, D.C., on politics, demographics and inequality. In one of the most revealing studies in ...
A final area of focus in attaining gender equality is women's economic and political empowerment. Though women comprise more than 50% of the world's population, they only own 1% of the world's wealth. Throughout the world, women and girls perform long hours of unpaid domestic work. In some places, women still lack rights to own land or to ...
This paper identifies five key issues that are important for the continued efforts to tackle gender inequality: (i) gender inequality needs to be distinguished from gender gaps. Not all gender gaps necessarily reflect gender inequality as some gender gaps are not driven by the lack of equal rights, responsibilities and opportunities bywomen and girls, and this has important implications on ...
Topics: Gender, Gender Inequality, Gender Issues, Inequality Words: 467 Pages: 2. Gender inequality is one issue I feel strongly about following its negative impacts on societies. It is the state in which all individuals, regardless of their sex or gender identity, are able to access and enjoy the same opportunities, rights, and resources.
For most women's rights advocates, the answer is obvious: adopt a human rights framework. At the global level this means using the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), ratified by 189 countries, which requires all states parties to themselves respect gender equality, protect against gender discrimination by others, and fulfill those human rights ...
Gender inequality is a pervasive issue that affects people of all genders, but it disproportionately affects women and gender minorities. One of the most significant ways in which gender inequality manifests is in the unequal distribution of power between men and women. This power imbalance is often the result of the unequal distribution of ...
Gender Inequality Essay Topics and Outline Examples Essay Title 1: Unveiling Gender Inequality: Root Causes, Impact, and Paths to Equality. Thesis Statement: This essay delves into the multifaceted issue of gender inequality, examining its underlying causes, its pervasive impact on society, and the strategies and movements aimed at achieving gender equality and justice.
Check our 100% free gender inequality essay, research paper examples. Find inspiration and ideas Best topics Daily updates. ... This paper examines the gender issues of equality and representation in the K-12 education system and gives out the major findings based on the observed trends from the structured study of literature in the area.
500 Words Essay on Gender Issues ... One of the most prominent gender issues is inequality. Despite significant strides towards equality, disparities persist in various domains. For instance, the gender wage gap remains a global issue, with women often earning less than men for the same work. This inequality extends to leadership roles, where ...
Re "The Problem With Saying 'Sex Assigned at Birth,'" by Alex Byrne and Carole K. Hooven (Opinion guest essay, nytimes.com, April 3): Mr. Byrne and Ms. Hooven argue that use of "assigned ...
The gender gap in pay has remained relatively stable in the United States over the past 20 years or so. In 2022, women earned an average of 82% of what men earned, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of median hourly earnings of both full- and part-time workers. These results are similar to where the pay gap stood in 2002, when women earned 80% as much as men.
While it is widely assumed that poor countries will suffer more from climate change, and that climate change will exacerbate inequalities within countries, systematic and large-scale evidence on this issue has been limited. In this systematic literature review, we examine and synthesize the evidence from the literature. Drawing from 127 individual papers, we find robust evidence that climate ...
Gender, Age and Racial Inequality Issues Essay. Modern world tends to break stereotypes, leaving arrogant and superior attitude behind, constantly raising questions of all types of equality on all levels. Women work at the same positions and in the same spheres as men do. There are no restrictions on colored people to public areas access as it ...