VCE Study Tips
English Language

Private Tutoring


Only one more step to getting your FREE text response mini-guide!
Simply fill in the form below, and the download will start straight away
English & EAL
The Ultimate Guide to VCE Creative Writing
March 1, 2022

Want insider tips? Sign up here!
Go ahead and tilt your mobile the right way (portrait). the kool kids don't use landscape....
- What Is The Creative Response?
- What Are You Expected To Cover? (Creative Writing Criteria)
- Literary Elements (Characterisation, Themes, Language, Symbolism, Imagery)
- LSG's unique REPLICATE and IMAGINE strategy
- Sample A+ Creative Response
- Writing The Written Explanation
- Resources To Help You Prepare For Your Creative Response
1. What Is The Creative Response?
The Creative Response, which forms part of the ‘Reading and creating texts’ component of the study design, is part of the 1st Area of Study (AoS 1) - meaning that the majority of students will tackle the Creative Response in Term 1. Unlike the analytical text response, in the Creative Response you will be asked to write your own imaginative piece in response to a selected text.
You are expected to read and understand the selected text, analyse its key features, and write a creative piece which demonstrates your comprehension of the text.
2. What Are You Expected To Cover? (Creative Writing Criteria)
The creative writing task assesses your ability to combine features of an existing text with your own original ideas. The key intention here is to demonstrate your understanding of the world of the text. You can achieve this by exploring and applying selected elements from the text, such as context, themes, literary devices like symbols, and/or characters. You should also consider the values embedded within the text - this includes explicit values (which can be seen on the surface of the text) and implied values (values we uncover through analysis of the text’s deeper meaning). Try to reflect these values within your writing.
Your piece will be a creative response, after all, so you should apply the conventions of this style of writing. Firstly, your creative should follow the structure of a beginning, middle, and end. We can also think of this as rising tension, climax, and resolution. Secondly, you should develop an authentic use of language, voice and style to make your writing more engaging and sophisticated. Thirdly, you can use literary devices to build meaning and depth within your piece. As always, your writing should be consistent with the rules of spelling, punctuation, and syntax (that is, written expression) in Standard Australian English.
Part of this assessment is the Written Explanation, which is a chance for you to explain and justify your creative writing choices. Within the Written Explanation, you should reflect on your writing process and analyse your own work. The primary goal here is to explain the links you’ve made to the original text, by considering features like purpose, context, and language.
Ultimately, to put it simply, you are expected to understand the selected text and demonstrate this in your creative piece. If you're looking to quickly increase your creative skills, watch our incredibly popular video below:
3. Literary Elements (Characterisation, Themes, Language, Symbolism, Imagery)
Literary elements are different parts of the creative writing equation that ensure your piece is consistent with the expected features of this type of writing. When selecting which literary elements to include in your piece, remember to consider the original text and ensure that your work, while creative, also demonstrates your ability to replicate some of its elements.
Characterisation
As we know, characters are fictionalised people within the world of a creative text. Almost an entire century ago, the English writer E. M. Forster famously introduced the concept of flat and round characters in his 1927 book, ‘Aspects of the Novel’. According to Forster, flat characters can be defined by a single characteristic; in other words, they are two-dimensional. For example, the characters of The Simpsons could arguably all be defined as flat characters; Homer is characterised as a slob, Flanders is defined by his Christian faith, Lisa is stereotyped as the ‘teacher’s pet’, and Bart is portrayed as rebellious. We can define all of these characters as flat because they are labelled to the audience in these two-dimensional ways.
In contrast to this, round characters have multiple characteristics, which brings them closer to seeming like real, human figures. The personality of these characters extends beyond a single attribute. In Harry Potter , Harry himself is a round character because of how much we learn about him over the course of the series. For example, we find out about Harry’s difficult childhood, his personal challenges, his love interests, and we see his personality grow from book to book.
Whether the characters of your creative are flat or round will depend on their involvement within, and importance to, the storyline of your piece. Generally speaking, however, you should aim for the central character(s) to be round, while any minor characters are likely to be flat. Developing round major characters will ensure that they are realistic and believable. In turn, you’ll be able to better demonstrate your imaginative skills and understanding of the text through these characters.
Themes are the key ideas and issues that are relevant to the storyline of a fictional text. We can identify themes by labelling the main areas of meaning within a text and thinking about the messages that emerge throughout the text. To build your understanding of themes within a particular text and to evaluate the themes of your own creative, consider the following questions:
- What is the text really about, beyond superficial elements like plot and character?
- What is the text saying to its reader?
- What are the core idea(s) or issue(s) within the text?
- What idea(s) or issue(s) do the message(s) of the text correspond with?
To return to our example of The Simpsons , we could say that the themes within this sitcom include love and family, neighbourliness, and social class. From episode to episode, The Simpsons comments on these different issues. For example, Marge and Homer’s relationship, with its domestic setting and marital ups and downs, is a core aspect of the Simpsons household. Likewise, family is a major component of not only the Simpsons themselves, but also the broader Springfield community. The interactions between parents and children is evident on Evergreen Terrace with the Simpsons and the Flanders families, as well as in other settings such as Springfield Elementary School (where even an adult Principal Skinner is seen through his relationship with his elderly mother). These broad areas can be identified as the key thematic concerns of the series because each episode centres around these ideas.
Language refers to the way in which a piece of writing is expressed. We can define this as the ‘style’, or ‘tone’, of a text. The words and phrasing chosen by a writer determine how ideas are communicated. Effective language will be appropriate for the world of the text and contribute to the narrative in a meaningful way. There are a number of ways in which a piece of writing can be articulated and you should consider the nature of your piece and the language of the original text when deciding what type of language is most appropriate for your creative.
Dialogue, on the other hand, is an exchange of conversation between characters. Dialogue is often used to provide context to a text, develop its storyline, or offer direct insight into a character’s thoughts, feelings and personality.
A symbol can be defined as a thing that represents something else. Symbols are typically material objects that hold abstract meaning. For example, in Harry Potter , Harry’s scar is a symbol of his difficult childhood. Because Harry’s scar causes him pain in Voldemort’s presence, it can also be said that the scar is symbolic of the connection forged between Harry and Voldemort when his attempt to kill Harry failed. As this example suggests, symbols are often associated with the text’s themes - in this case, Harry’s scar relates to the themes of childhood and death.
The key with symbolism is to connect a particular theme or idea to a physical object. For example, the theme of grief could be portrayed through a photo of someone who has died. Likewise, the theme of change might be represented by a ticking clock, while a character’s clothing could be a symbol of their wealth or status.
For more literary elements, also known as metalanguage, check out our lists:
Part 1 – Metalanguage Word Bank For Books
Part 2 – Metalanguage Word Bank For Films With Examples
And if that's not enough, you'll also want to check out our How To Write A Killer Creative Study Guide where we unpack these elements in more detail AND analyse imagery, foreshadowing, flash-backs and flash-forwards!
4. LSG's unique REPLICATE and IMAGINE Strategy
If we think about the criteria of creative writing, we’ll see that much of this task involves demonstrating your understanding of the text. For this reason, being able to replicate the world of the text will enable you to showcase your understanding and, in turn, to meet the criteria your teacher will be looking for. Let’s consider how you can strengthen your creative by taking the time to understand the text on a meaningful level and reflect this within your writing.
Step 1: Read
Writing a strong creative piece begins with reading. Reading the text (or watching, in the case of a film) is essential to developing an informed creative response. The more closely you read, the more confidently you’ll be able to engage with the important ideas and textual elements necessary to take your creative from good to great.
While reading the text for the first time, focus on developing your understanding and clarifying any uncertainty. I would recommend taking the time to read a plot summary before beginning on the text - this will allow you to go in with a reasonable idea of what to expect, and also provide a security net to minimise your likelihood of misunderstanding the plot.
While reading the text once is sufficient, you will benefit from reading it twice. A second reading enables you to take the time to annotate key sections of the text and to further your initial understanding. If you choose to read the text a second time, pay extra attention to the themes and inner-workings of the text. This means reading between the lines and starting to form an analytical understanding of what the text is about, beyond surface ideas like plot and character.
Annotating the text (or note-taking, in the case of a film) is an important aspect of any academic reading. The key intention is to ensure your annotation approach is as convenient and accessible as possible. To achieve this, I suggest listing the key themes, allocating a different coloured highlighter to each, and colour-coding sections of the text which you think relate to each specific theme. This will give your annotating process more direction compared to the common approach of simply leaving notes in the margin, which may be time-consuming to read over later.
I would also recommend making the most of coloured tabs - these enable you to immediately see the key sections of the text, rather than flicking through aimlessly. If you can colour-code these tabs according to the same key as your highlighters, you’ll be able to instantly spot which sections correspond with which theme (and trust me, this will come in handy if you decide to replicate these themes in your own creative).
Aside from annotating the text itself, try to ensure that the notes you write are concise - not only will this save you time, but it’ll mean you focus on condensing the key information. In turn, you’ll have less material to sift through later on, giving you the ability to jump straight into planning and drafting your own piece. This video, How to effectively annotate your books for school! and this blog post, How to effectively annotate your texts in VCE will provide you with more helpful strategies to get the most out of annotating.
Step 2: Understand the World of the Text
Regardless of how many times you read the text, your understanding will be strengthened by seeking out resources to help you think about the text on a deeper level. A good starting point for this is to have a look for LSG blog posts and videos that are about your specific text.
Watching or reading interviews with the author of the text is a fantastic way to hear directly about their intention in writing the text - after all, they are the single most authoritative source on the text. The goal here is to understand the author’s intent (something we’ll expand on in Chapter 8: Strengthening Your Creative ) so that you can reflect this within your own writing. Focus on how the author explains certain aspects of their text, as well as any points they make about its context and background.
Additionally, peer discussions and asking questions in class will help you to further develop your understanding of the text and clarify any uncertainty. Seeing the text from another’s perspective will develop your knowledge beyond a superficial understanding of the text and introduce ideas you may not have otherwise considered.
Remember to take notes as you go - these will be useful to reflect on later.
Step 3: Implement Your Understanding
Okay, so you’ve taken the time to read and annotate the text, and you’ve sought out external resources to further develop your comprehension. Now we want to apply this understanding within a creative context. Reflect on what you know about the text. Think closely: What have you learnt about its context, characters, and themes? What elements of the text stand out? The goal here is to draw inspiration from the text and begin to think about which aspects of the text you might like to replicate within your creative piece. Begin to put together a shortlist to keep track of your ideas. The aim here is to develop a picture of the parts of the text you might decide to replicate in your own writing.
Although understanding and replicating the text is important, if we were to only do this, your piece wouldn’t have much creative flair or originality. Here, we’ve taught you the ‘ Replicate ’ component of this strategy . If you’d like additional information about how to elevate this to an A+ standard AND a comprehensive explanation of the ‘ Imagine ’ component, check out our How to Write A Killer Creative study guide !
5. Sample A+ Creative Response
Here's a sample excerpt from a creative piece written by Taylah Russell, LSG tutor and 47 study scorer, in response to the short story 'Waiting' in Cate Kennedy's anthology, Like a House on Fire :
"The clinician presses forcefully into my lower abdomen, refusing to stop and accept my reality. The poor thing, deprived of such hopelessness as I, seems to honestly believe that the longer he agonises over finding something, the more likely it is that some form of life will appear. That those horoscopes in those grimy magazines, written by journalists who’ve probably been fired from their former reputable jobs, may actually hold some validity. I place my hands over my eyes, tentatively pressing against my eyelids, turning my surroundings a dark black and blocking the stream of water that has readied itself to spill when the time comes, when that young boy finally gives up and realises that his degree holds no value in providing me with happiness."
As we can see in this paragraph, the writer is replicating certain themes from the original text, such as grief. Additionally, this piece is written from the perspective of the original protagonist, which means that its characters and context are also directly inspired by Kennedy. Ultimately, by carrying across these text elements of theme, character, and context, the writer is able to clearly demonstrate an extensive knowledge of the text , while also showcasing their creativity. To see more of this creative piece as well as another A+ example, check out the How to Write A Killer Creative study guide !
6. Writing The Written Explanation
For a detailed overview of the Written Explanation, check out our Written Explanation Explained blog post.
7. Resources To Help You Prepare For Your Creative Response
Youtube videos .
We create general creative writing videos where I explain the method behind this task:
We also create videos that outline ways you can set yourself apart in this assessment:
Check out our entire YouTube channel (and don't forget to subscribe for regular new videos!).
Blog Posts
Our awesome team of English high-achievers have written a number of blog posts about creative writing to help you elevate the standard of your work!
5-Step Recipe for Creative Writing
How to achieve A+ in creative writing (Reading and Creating)
"Creative Response to Text" Ideas
Written Explanation - Explained
Reading My 10/10 Marked CREATIVE GAT essay
VCE Creative Response to Runaway by Alice Munro
Study Guide
And if that isn't enough, I'd highly recommend our How To Write A Killer Creative study guide .
In this study guide, we teach you the unique REPLICATE and IMAGINE strategy, a straightforward and methodical approach to creative writing. The study guide also covers our step-by-step method to guide you through every phase of creative writing (no more not knowing where to start!) AND includes excerpts from multiple A+ creative pieces. Find out more and download a free preview here .
Get our FREE VCE English Text Response mini-guide
Now quite sure how to nail your text response essays? Then download our free mini-guide, where we break down the art of writing the perfect text-response essay into three comprehensive steps. Click below to get your own copy today!

Access a FREE sample of our How To Write A Killer Creative study guide
- Learn how to apply key creative frameworks and literary elements to elevate your writing
- Introduces the REPLICATE and IMAGINE strategy , a straightforward and methodical approach to creative writing
- Includes a step-by-step method to guide you through every phase of creative writing
- Explains the Written Explanation component, with multiple annotated A+ examples
- Includes excerpts from multiple A+ creative pieces

We’ve explored creative writing criteria, literary elements and how to replicate the text over on our The Ultimate Guide to VCE Creative Writing blog post . If you need a quick refresher or you’re new to creative writing, I highly recommend checking it out!
Creative Responses in VCE Literature
This was my favourite SAC in Literature; it allows so much creative freedom in creating and recreating a literary work. When else will you be able to depart from the (admittedly rather boring) standard essay structure?!
In your adaptations and transformations SAC (see my blog post about this literature assessment here !), you learnt how the meaning of the text changed as the form changed. Here’s your opportunity to change the meaning of the text, maybe emphasising a particular thematic idea, or perhaps recreating a completely new perspective. Remember – you have almost complete creative licence in this assessment…use it to your advantage!
But don’t forget that the most important part of this task is that you must have a highly convincing connection between the original text and your creative response . There must be a tangible relationship present, through an in-depth understanding of the original text’s features. These features include characterisation (what motivates these characters), setting, context, narrative structure, tone and writing/film style. Establishing a clear nexus between the original text and your creative piece does not mean you need to replicate everything of the text; you can stylistically choose to reject or contrast elements of the original text – as long as these choices are deliberate and unambiguous. Therefore, your creative response must demonstrate that you read your original text closely and perceptively by acknowledging these features of the text.
You can establish this relationship by:
- Adopting or resisting the same genre as the original text : e.g. an epistolary genre (written in letters) – do letters make an appearance in your text? Is that something you want to highlight? What about writing a monologue or a script if the text is a film or a play?
- Adopting or resisting the author’s writing/language style : does your writer characteristically write plainly or with great descriptive detail? What about irony or humour? Consider the length and style of sentences. Are there frequent uses of symbols or metaphors?
- Adopting or resisting the text’s point of view : do you want to draw readers’ attention to another thematic idea that was not explored in the original text? Will you align with the author’s views and values or will you oppose them? (See my views and values blogpost here!)
- Adopting or resisting the original setting, narrative structure or tone
- Writing through a peripheral character’s perspective : give a voice to a minor character that didn’t have a detailed backstory. Find a gap in the text and create and new perspective.
- Developing a prologue, epilogue or another chapter/scene : what new insight can you add with this addition and extension of the text? It must add something new – otherwise it is a redundant addition.
- Rewriting a key event/scene from another character’s point of view : does this highlight how important narrative perspective is?
- Recontextualising the original text : by putting the same story or characters into a completely different context, for example in the 21st century with technology, how does the meaning change in the narrative?
I chose to write a creative piece from the perspective of an inanimate object that followed the protagonist’s journey throughout the entire film, providing an unexpected point of view of the text. Be original and most importantly, enjoy it!
If you're doing a creative piece - whether for English or Literature - you'll find the following blogs super helpful:
5-Step Recipe for Creative Writing
How To Achieve A+ in Creative Writing (Reading and Creating)
Here’s how to get ahead of this brand new VCE English Unit.
What Is ‘Creating Texts’?
If you’re in Year 12 this year, chances are you will begin studying the Creating Texts Area of Study very soon (if you haven’t started already). This new AoS in the 2024 study design has essentially expanded and replaced the previous study design’s approach to creative writing, now placing a greater focus on the process of creating texts and embracing multiple forms of writing.
Here’s what the study design states the outcome of this unit is:
‘On completion of this unit the student should be able to demonstrate effective writing skills by producing their own texts, designed to respond to a specific context and audience to achieve a stated purpose; and to explain their decisions made through writing processes.’ (VCAA English Study Design, 2024-2027)
So, while before VCAA did not place a heavy focus on this unit, now it is heavily emphasised, being one of the three sections of the English exam. Now, more so than before, you are required to write – even if just a little bit – creatively.
Given that Creating Texts is now reflected in the end-of-year exam, it is very important to nail it. And to do that, you first need to know what this Area of Study is all about.
Framework of Ideas
A big part of this AoS is the Framework of Ideas , which provides students and, perhaps most importantly, schools, with thematic guides to encourage discussion and unique writing. The study design states:
‘ The Framework of Ideas presents four broad ideas through which students can engage with writing’.
Here’s what they are, as directly taken from the study design:
- Writing about country: 'Exploration of place and belonging'
You can also explore ideas of one’s sense of national belonging, the climate crisis, colonisation and decolonisation, and different forms of cultural identities in relation to the land. Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander perspectives can also be addressed.
- Writing about protest: 'Explorations of conflict and contest, what it means to protest, the value of protest, the outcomes of protest, personal stories of protest, struggle and war'
For this framework, you can dive deep into prominent figures who spearheaded social movements through protests, or you can look at protest more broadly and investigate its role and effectiveness within society, the history of protest and its many facets.
- Writing about personal journeys: 'Explorations of ‘life’ or biographical explorations'
Ideas surrounding the importance of storytelling and personal change, and invitations for students to create autobiographical written pieces are also outlined in the study design.
- Writing about play: 'Explorations of experiences and traditions of play and playing in many cultures and through history'
This framework also invites thought into how play intersects with technology, the role of play and make-believe in our daily lives, and even how performance and social media may influence how we view the world today.
NOTE: The study design also offers many other possible ways to explore these ideas, so make sure to check it out and read it carefully. It can be found HERE .
As you can see, the ideas within the frameworks are very broad. This was intentionally done, so that you have ample opportunity to find something within those ideas that engage you. Your school will choose only one of these frameworks, so you are in no way expected to dissect all four – that would be a huge undertaking!
Mentor Texts
There are also four mentor texts for each framework, which range from TED Talks, blog posts, short stories, speeches and argumentative articles, to name a few. Their purpose in the curriculum is to serve as examples of effective writing, as the selected texts show a competent understanding of context, purpose and audience , as well as confident use of textual features such as tone, vocabulary and authorial voice. This is similar to what you might have encountered in Year 11, where you were asked to read and analyse a range of creative texts to then inform your own writing.
When studying your mentor texts, make sure to keep all of this in mind and carefully analyse each text and what is successful about them in relation to your framework. This will make your life much easier when it comes to writing your own.
If you don’t feel very confident in creating texts or think these frameworks are very broad and hard to come up with good ideas for, just remember that you’re not going into this unit completely blind, neither are you expected to write completely from scratch.
Besides your experience last year, your given framework and mentor texts are there to provide a guide to effective writing and introduce you to many different ideas, so make sure to use them to your advantage! Besides, having more freedom in a creative writing task should definitely be viewed as a benefit rather than a hindrance.
Oh No! Does This Mean I Have To Write a Narrative?
No, it doesn’t! If the aforementioned formats of the mentor texts were any indication, this AoS encourages you to embrace the variety of different writing styles.
When before you might have been required to write within a narrative format or asked to ‘fill a gap’ in an already existing short story, now you have the freedom to write in whatever way you want, and it does not need to be a narrative, let alone fictional storytelling.
In the context of the Creating Texts AoS, ‘creative writing’ does not only equate to creating fictional characters, worlds and narratives. Instead, it gives way to the many other forms of writing that show off a writer’s creativity, which is not solely dependent on what is written, but also how and why the text has been written. This links back to the context, purpose and audience idea I talked about before.
The study design also heavily focuses on the process of writing and experimentation and not just the final draft. This AoS is your chance to fully immerse yourself in writing, so you should make sure to brainstorm and try new modes of writing you might not have thought of before. You might end up surprising yourself and coming up with great texts!
So, here’s a non-exhaustive list of writing styles you can choose to tackle:
- Your classic narrative or short story
- Argumentative article
- Transcript of a Podcast episode
- Poetry/Song (just remember you are not allowed to write in these formats for the Exam!)
- Reflective essay
- Biographical texts
You may find that, as you work through the unit, some formats may be more effective than others depending on your framework, chosen audience, chosen tone or even just your personal preference. For example, writing in a blog post format post would be more effective in engaging the particular audience of teens and young adults.
Or, you may choose to convey your ideas with a specific tone in mind. For example, if you want to address your framework in an emotive way you might choose to write a first-person narrative short story. Conversely, if you want to address it in a rational and factual way, you might choose to write an article.
That’s another reason why experimenting and trying new things is so important - so that you can find out what, in your opinion, suits you and the framework best.
What Your SAC Will Look Like
This AoS is worth 60 of the 100 marks allocated for Unit 3, so it is a big deal. However, if you have a look at the study design, those 60 marks are split into three equal parts worth 20 marks each, which means your SAC will consist of three things:
1) ‘A written text constructed in consideration of audience, purpose and context.’ And, of course, your text will also need to be constructed in relation to your chosen framework.
2) ‘A written text constructed in consideration of audience, purpose and context.’ Yep, that’s right. For this SAC you have to create two distinct writing pieces. The assessment task as it is outlined in the study design does not mention whether they need to have completely different formats or audience/purpose/context from one another, so the specifics might be up to your school to decide.
3) ‘A commentary reflecting on writing processes.’ This is the same as a Written Explanation , which you likely have come across before. This is where you write a couple of paragraphs outlining and justifying your choices for each written text you produced, especially in relation to your framework and your audience, purpose and context. Having a successful commentary means you clearly describe the authorial intent in your work, so make sure to be specific and self-analytical in your writing!
What the Exam Will Look Like
The 2024 English exam will be the first exam that follows the new 2024-2027 study design, and the biggest change between now and the previous years is that Section B, which used to ask students to write a Comparative Response to a set of texts they would have studied at school during the year, is now all about Creating Texts . So much so that now Section B is called – you guessed it – ‘Creating texts’.
VCAA has been kind enough to release a sample of this new requirement, which outlines very faithfully what this section will look like in the actual exam. The exam paper consists of a page of general instructions which apply to all students, and then four pages with three pieces of stimulus material each, which relate to each of the four frameworks.
The stimuli consist of one statement, an image, and a section of a poem/story, and the exam paper says you must use ‘at least one’ of them in your writing. (Here’s a quick tip: if the examiners are asking for at least one, use two or more.)
There is also a compulsory title given for each framework, which must be the title of your text.
The instructions in the VCAA sample exam also outline that in Section B ‘you must create one written text ( not including song, poetry or verse)’ , and that ’you must include meaningful connections with ideas drawn from one of the Frameworks of Ideas’ as well as the provided title and the stimulus material. You should choose the framework you have studied in depth at school to write about, and you are also able to refer to your mentor texts, although that is not compulsory in the exam.
Another point is that ‘you must develop your text with a clear purpose, incorporating at least one of the following: to explain, to express, to reflect, to argue.’
You may remember these purposes from the Unit 1 Crafting Texts Area of Study in Year 11. They are pretty much self-explanatory, and chances are that any writing you do will already serve one of these purposes without it being your conscious decision. Also, similar to the stimulus material, try to incorporate two purposes within your piece instead of just one, if possible.
And, as previously was the case as well, Section B is worth one-third of your full exam marks.
You can find the 2024 English sample exam and other very helpful resources such as past exams and exam reports by clicking HERE .
Three Tips to Help You Ace Creating Texts
So, now that we know what Creating Texts is all about, here are three helpful tips to keep in mind as you make your way through this Area of Study:
1) Play to Your Strengths
As you experiment and become familiar with a range of writing styles and formats, you may find that you’ve become really good at writing argumentative essays, or you became more interested in writing short stories, or maybe you remember that in Year 11 you got a high mark for writing a strong reflective essay. Make sure to self-assess and keep in mind what your strengths are in writing, even if they might not be apparent at first glance.
Also remember that, in the exam, you have a very limited amount of time to come up with a unique piece of writing from scratch, so having a text format in mind that you feel really confident and comfortable writing with can provide at least a little bit of guidance and reassurance when you’re writing something new.
2) Choose Formats That Will Help You Show a Deep Understanding of Your Framework
For instance, if you have the ‘writing about play’ framework and you are deeply inspired by an example of how play can help people heal from trauma from one of your mentor texts which happens to be a memoir, you might deem it best to write a short story or a personal fictionalised diary entry which shows you have taken inspiration from that memoir’s central idea, but you are also engaging with the framework’s implications in society.
Of course, this should be judged on a case-by-case basis, but it can be a helpful guide if you feel stuck and unsure of where to start your writing process.
3) Be Flexible
This is especially important for the exam. You don’t want to walk in with a memorised text! Examiners can definitely tell when a student has just route-learned their way into essay writing, and this will undoubtedly be extra noticeable for creative texts, especially when the exam gives you no choice but to integrate their given stimulus material.
This is why becoming used to as many writing formats as possible, alongside consistent planning and brainstorming, are incredibly important skills to develop throughout the year, so that when it comes time to the end-of-year exam you are ready to go regardless of what the examiners throw at you!
The best way to succeed in this Unit, like pretty much all other tasks in English, is to consistently practice your writing and experiment with as many writing styles as you possibly can. Be open to new ways of thinking, not only about the framework you are given, but about the concept of writing itself! Although certainly challenging, the Creating Texts AoS can prove itself to be great fun. So, best of luck in creating texts, and happy writing!
We’ve explored creative writing criteria, literary elements and how to replicate the text over on our The Ultimate Guide to VCE Creative Writing blog post . If you need a quick refresher or you’re new to creative writing, I highly recommend checking it out!
There are two types of people in this world… those who love creative writing, and those who don’t. But no matter which one you are, never fear, your saviour is here (in the form of this simple guide to writing creatively – whether it’s for school, for a writing competition or just for fun)!
What Are the Five Steps?
- Do a brain dump of your ideas!
- Stay true to yourself
- Start small - keep it simple
- Don't be afraid to add "spice"
- Read your writing out loud
STEP 1: Do a brain dump of your ideas!
You’ll often find that your brain is buzzing with possible storylines or scenarios; you’ll feel so overwhelmed trying to pick just one! Or maybe, you’re experiencing “writer’s block”, a mind blank. My tip for this is to set a five-minute timer, get a blank sheet of paper and scribble down everything that comes to your mind! You’ll be surprised at how imaginative your mind can be under pressure! When the timer goes off, take a break and then read through each idea individually before choosing one to develop. This way you’ll be able to clearly see all your thoughts, and maybe even be able to link multiple ideas into a more detailed story !
STEP 2: Stay true to yourself
Creative writing is so different to other text types because it gives you the freedom to choose what you're writing about, and how you're going to do it! So, take advantage of this and write from the heart – don’t try to be someone you’re not. Let your personality shine through your writing. It's usually the stories that have some kind of personal backstory, or are based on a real-life experience that are the most enjoyable to read!
STEP 3: Start small - keep it simple
No one expects you to write a New York Times best seller novel in your first attempt! Even the most talented authors began with a dot point plan or a simple paragraph based on their idea. From my experience, the absolute hardest thing to do is actually get started. Keeping it simple and focusing on getting your ideas down on the page is the easiest way to overcome this hurdle. You can worry about the language and descriptions later, once you have a basic first draft, editing and developing is so much easier!
Want to also know the 11 mistakes high school students tend to make in creative writing? Check out this
STEP 4: Don't be afraid to add "spice"
Now it's time for my favourite part; adding the flavour! This is what will make your writing stand out from the crowd! Take some risks , don’t be afraid to rewrite parts of your piece or use language techniques that are out of your comfort zone!
Here are a few of my favourite features to use when creative writing:
- Flashbacks / Foreshadowing (these are good tools to subtly suggest a character’s backstory and add some mystery – especially if you use third-person language to make it more cryptic)
E.g. As he entered the quadrangle for the first time since the accident, a wave of nostalgia hit Jack… The boy chuckled as the girl ran across the quadrangle to meet him, her cheeks rosy from the frosty air. The pale orange sky was transforming into a deep violet and the new-formed shadows cast dancing silhouettes on the young couple. The boy took the girl’s hand, making a silent promise to himself to protect her smile forever. A promise he would fail to keep…
- Personification (giving inanimate objects some life to spice up your descriptions!)
E.g. Her favourite oak tree stood proudly in the middle of the park, arms outstretched, waving to those that passed by.
- Oxymoron (contradictory words or groups of words)
E.g. Deafening silence, blinding darkness, cold fire
If you want to enhance your language or use different adjectives to what you normally use, https://www.thesaurus.com/ is your best friend! 😉
If you're stuck on how to develop your descriptions and make them more vivid, I suggest relating back to the five senses . Ask yourself, what can the character see? What can they smell? What does the setting they're in sound like?
E.g. He was paralysed in front of the caskets… the cotton wrapped, caterpillar-like bodies, the oppressive silence of the parlour made him feel sick. And the overpowering stench of disinfectant mixed with already-wilting flowers certainly didn’t help.
STEP 5: Read your writing out loud
It can be awkward at first, but have some fun with it! Put on an accent, pretend you're a narrator, and read your writing. It really helps you to gauge the flow of the piece , and also identify things you might need to change. Or even better, read your writing to a friend or family member - ask them how they feel and what their initial thoughts are after hearing your piece .
Either way, reflection is one of the best ways to improve your writing and get it to the next level.
That’s all there is to it folks! Follow this simple recipe and you’ll be cooking up a creative-writing storm! Good luck! 😊
Want more tips on how you can achieve an A+ in creative writing? Read this blog post.
- What is a Written Explanation?
- Creative Response-Based Written Explanations
- Oral Presentation-Based Written Explanations
1. What is a Written Explanation?
Written Explanation (also known as Statement of Intention, SOE, and various other names throughout different schools) is a short introductory piece to your essay. The Written Explanation is intended to explore the reasons behind why you made particular writing decisions. This is done via FLAPC:
F orm, L anguage, A udience, P urpose, C ontext
2. Creative Response-Based Written Explanations
The following is taken from the VCAA study design for Creative Response-Based Written Explanations:
'a written explanation of creative decisions and how these demonstrate understanding of the text.'
Most assessors are quite lenient with how you want to approach the Written Explanation – there is no rigid structure that you need to abide by. As we will discuss below, this allows you to consider which aspects of form, language, audience, purpose and context you wish to include. Each of the points should establish why you have written your piece. They are considered as part of your SAC and thus, are marked accordingly. They are not examinable during the English exam.
There are traditionally three forms of writing accepted in assessments: expository, creative or persuasive essay.
‘I chose to write in an expository style, employing conventions of format and style of a traditional essay. This allows me to express my ideas in a logical order while adopting a sophisticated tone.’
When writing, you choose particular words and phrases to illustrate your ideas. Think about what type of language have you used and why. Perhaps your piece is formal or informal, sophisticated or simple, or from a first or third person perspective. All these factors are important in shaping your Context piece. Also consider language techniques you may have incorporated such as repetition, rhetorical questions, metaphors, symbolism and more.
‘I have chosen to write from a first person perspective to shed light on the inner workings of Gardiner from The Lieutenant .'
You must select a targeted audience for your essay. Your choice can be adults to young children, or even to your future self. Make sure your target audience is suitable for your essay – select a group that would realistically be interested in your work.
‘My piece is to be published in an anthology for those who have had difficulty assimilating into a new group or culture. As they have familiarity with the concepts I discuss, I intend for readers to depart with a greater understanding and appreciation of the ideas in my written piece.’
The purpose section is where you discuss the message you would like to send to your audience. Here you discuss your contention or arguments; whether you completely agree, disagree or a bit of both in regards to your prompt.
‘The purpose of this essay is to demonstrate that there can be different outcomes from encountering conflict: firstly, that conflicts can change many people through growth in understanding or a sense of self-development and secondly, that there are times when people remain unaffected by conflict and thus, unchanged.’
Since your essay is based on your studied text, you should provide a brief discussion of the basic ideas behind the Context . You can do this prior to your Purpose section since it is a good lead-in.
‘In this essay, I explored the idea that ‘Conflict inevitably changes people’; a concept heavily explored in The Lieutenant . Every person encounters conflict. It drives individuals to challenge themselves, and deal with new experiences.'
Different schools will set different word limits for Written Explanations. These can range from 300 – 350 words based on the VCAA study design. With such a small word limit, be succinct and choose wisely what you will discuss in order to score the maximum marks allocated to Written Explanations.
3. Oral Presentation-Based Written Explanations
The VCAA study design requests students write:
'a written statement of intention to accompany the student’s own oral presentation, articulating the intention of decisions made in the planning process, and how these demonstrate understanding of argument and persuasive language.'
Using the topic, 'Why we need to stop crying "cultural appropriation" when cultural exchange is far more important ', let's see how this can be done with FLAPC with some examples below (if you need help selecting a topic, check out our 2020 Oral Presentation topics to get those brain juices flowing ):
‘I chose to adopt the conventions of a persuasive speech, where I use a structure of presenting my main ideas by rebutting arguments made by the opposition. Throughout my speech, I embed persuasive tactics in an effort to firstly, encourage engagement from the audience and secondly, sway them to readily accept my point of view.
‘Since I am an Asian-Australian, I have purposefully forgone the opportunity to adopt a persona and instead, have chosen to write from a first person perspective as I can uniquely shed light on my own experiences towards cultural exchange and how that has directly impacted me. My speech heavily focuses on delivering tangible examples, such as anecdotes and social media usage, as I aim to heighten the topic’s relevancy and relatability for my audience. Moreover, as my focus is to reinforce positive attitudes towards cultural exchange, I have adopted a light-hearted approach with humour through the first portion of my speech, then moving into an urgent tone towards the end to highlight the importance of this issue.'
'I have opted to target young Australian adults since we are the generation of the future, and have a major role to play in positively shaping the Australian society’s views and attitudes towards cultural exchange.
'I aim to convince my audience that it is too easy to cry 'cultural appropriation' by being overly sensitive, and instead, we need to consider the benefits of cultural exchange. Cultural exchange itself, has shaped the world as we know it today – it has an important role in globalisation, understanding foreign cultures and the development of Australian society.'
'Australia is known to be one of the most multicultural countries in the world. However, recent media has drawn attention to cries of 'cultural appropriation' towards Indigenous Australians and other cultures, claiming that we fail to appreciate and respect cultural values when we take others' culture for our own (whether it be fashion, music, food or otherwise).'
Sample FLAPC compiled and rearranged for flow and fluency:
Australia is known to be one of the most multicultural countries in the world. However, recent media has drawn attention to cries of 'cultural appropriation' towards Indigenous Australians and other cultures, claiming that we fail to appreciate and respect cultural values when we take others' culture for our own (whether it be fashion, music, food or otherwise). I aim to convince my audience that it is too easy to cry 'cultural appropriation' by being overly sensitive, and instead, we need to consider the benefits of cultural exchange. Cultural exchange itself, has shaped the world as we know it today – it has an important role in globalisation, understanding foreign cultures and the development of Australian society. I chose to adopt the conventions of a persuasive speech, where I use a structure of presenting my main ideas by rebutting arguments made by the opposition. Throughout my speech, I embed persuasive tactics in an effort to firstly, encourage engagement from the audience and secondly, sway them to readily accept my point of view. Since I am an Asian-Australian, I have purposefully forgone the opportunity to adopt a persona and instead, have chosen to write from a first person perspective as I can uniquely shed light on my own experiences towards cultural exchange and how that has directly impacted me. This also has an additional persuasive effect as I invite my audience to relate to my opinions through their own similar experiences as young Australian adults. I have opted to target this audience since we are the generation of the future, and have a major role to play in positively shaping the Australian society’s views and attitudes towards cultural exchange. My speech heavily focuses on delivering tangible examples, such as anecdotes and social media usage, as I aim to heighten the topic’s relevance and relatability for my audience. Moreover, as my focus is to reinforce positive attitudes towards cultural exchange, I have adopted a light-hearted approach with humour through the first portion of my speech, then moving into an urgent tone towards the end to highlight the importance of this issue.
Download a PDF version of this blog for printing or offline use
Need more help with your Creative Response? Check out How To Achieve A+ in Creative Writing (Reading and Creating)!
See how Lisa achieved full marks in her SAC in her Advice for A+ Oral Presentations guide.
Runaway is usually studied in the Australian curriculum under Area of Study 1 - Creative Response. For a detailed guide on Creative Response, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Creative Writing .
The biggest challenge of the creative writing SAC in VCE is figuring out how to balance your own ideas and style with that of the text you’re studying. The assessment requires you to incorporate elements of a text into your writing without copying the original narrative. In this case, Runaway by Alice Munro (2004) is a short story collection that explores themes of marriage, loss, mother/daughter relationships, womanhood and more. To be able to emulate Munro’s writing style within your original piece, it’s important to analyse the most frequent devices she incorporates into her work. By focusing specifically on the three stories ‘Chance’, ‘Soon’ and ‘Silence’, we can understand how Munro writes and how to embed that into a Creative Response.
If you would like more information on the themes in Runaway , you can refer to this blog post.
- Literary Devices
Literary devices can be defined as the techniques that an author uses in writing to convey meaning and their ideas within their work. These devices construct the story and emphasise key themes , which are particularly important to note when studying a text in VCE English. There are many devices that you may already be familiar with - metaphors, similes and repetition are commonly used in a variety of types of writing. For example, repetition of a certain word or phrase within a text highlights that it has significance and is reinforcing a particular idea or theme. By identifying which literary devices an author prefers to include in their novel, you can gain an understanding of their style and have a practical method for emulating it within a Creative Response. Below is a breakdown of some of the techniques woven by Munro throughout ‘Chance’, ‘Soon’ and ‘Silence.’
Embedded Narrative
An embedded narrative is like a story within a story, often with the intention of lending symbolic significance to the narrative. In ‘Chance’, Munro includes many references to Greek mythology, embedding a story within the broader narrative. The myths she has chosen are similar to events in Juliet’s life, creating an intentional comparison.
For instance, Juliet’s affection for Eric prompts her to visit his home where she meets Christa and Ailo, two women Eric has had a relationship with. Upon meeting them, Juliet is reminded of ‘Briseis and Chryseis’, who were ‘playmates’ of a Greek king. Munro’s use of this embedded narrative within Juliet’s story reveals how Juliet feels jealous of the two women and sees them as incapable of having a serious relationship with Eric. To echo this in a Creative Response, you might want to include either a myth, folktale or historical event that relates to your narrative and the characters within it.
Time Progression/Regression
Time progression/regression refers to jumping back and forwards in time within a story to give context to certain characters or events. For example, the narrative moves back and forth in ‘Silence’ to slowly reveal the before and after of Juliet and Penelope’s estrangement. This helps to inform the reader of Penelope’s motives for no longer speaking to Juliet, and how Juliet deals with the pain of losing a relationship with her daughter. Any movement through time is typically shown through section breaks in the writing, as it alerts the reader that one scene has ended and a new one has begun. These moments might interrupt the chronological narrative, or you might choose to jump backwards and forwards consistently, although this can make your piece more complicated.
Epistolary Elements
‘Epistolary’ is defined as literary work ‘in the form of letters’. Munro weaves elements of this within Runaway, including letters within several of the stories. The letters help to convey the narrative through one character’s perspective, providing insight into their motivations and perspectives. This is particularly effective when the story is written in the third person, as a letter is usually in the first person, allowing for characters to be understood on a deeper level.
In ‘Soon’, Juliet’s letter to Eric demonstrates their intimacy as a couple. Munro has constructed the letter so that it contains very mundane details about Juliet’s time with Sara, instead of just the exciting or alarming news she might have to share. The personal nature of the letter conveys just how close Eric and Juliet are, and how different her relationship with him is from that with Sara. Epistolary elements can be easily included as a small section of a Creative Response as correspondence between two of your characters.
Finally, Munro often uses italics to emphasise certain words or phrases that are particularly important. Italics can also convey the tone of a character, as they might draw attention to some words spoken in excitement or anger. For example, when Juliet meets Joan at the church in ‘Silence’, Joan’s dialogue often has italics to highlight when she is making passive-aggressive remarks about Juliet’s relationship with Penelope. Munro is demonstrating that Joan has been influenced by Penelope in her opinion of Juliet, as she clearly dislikes her and speaks in a condescending manner towards her. You might decide to implement italics only in dialogue, or to use it in other parts of your response, to highlight an important moment within the plot.
Tips for Emulating Munro’s Style
While emulating the style of an author is an important component of a Creative Response, coming up with your own ideas is equally important! To find an idea that you are invested in, think about the parts of Runaway that really spoke to you and that you would like to explore more; this could be a broad theme or a specific character. It is easier to write about something you are interested in than something you feel obligated to write about. Come up with potential responses that you are excited to write, and then plan accordingly by asking “How can I incorporate parts of Munro’s style into this piece?”
To plan out your piece, start by creating a simple plot structure to guide your writing. If it helps, this can include a 3-act structure consisting of a set-up, conflict, and resolution; or you might prefer to do a simple dot point plan instead. When considering what literary devices you would like to include, pick at least one literary technique, and work on making it fit with your idea. Focus on incorporating that one as best as you can before you move on to another one. You might want to pick a second technique that is more subtle, like italics, and start applying that in your second or third draft.
It’s getting closer to the Literature exam and you’re probably starting to get more serious about avoiding dropping too many SAC marks! Depending on which order your school does Literature SACs in, you may be currently facing the often feared ‘Creative Response’. Whether you feel beyond excited to finally bring some creative flair to Literature, or you’re totally scared at the thought of creating something new, I wanted to use this blog post to help you achieve at least ten of the marks in this section. That is through the reflective commentary, which you can totally score full marks on if you put in the effort.
The VCAA Literature Study Design determines that students must submit ‘a reflective commentary establishing connections with the original text’. This aspect of the assessment counts for 10 of the 60 marks available for the Creative Response outcome. The study design further denotes that students must
‘reflect critically upon their own responses as they relate to the text, and discuss the purpose context of their creations’.
This allows your schools and teachers to direct in a relatively broad way on how you should form your reflective commentary, and may mean your friends at other schools write theirs in a very different way. In this blog post I will leave you with a suggestion of how I best believe a reflective commentary could be structured to include all important aspects, as well as tips on how to include all of what the study design asks. As I said, these are ten marks that can easily be snatched with just a little bit of hard work and attention to detail, so why not snatch them?
To induce the things needed to be included in the reflective commentary, we can look to the key knowledge and key skills points outlined in the study design:
Key knowledge:
- the point of view, context and form of the original text,
- the ways the central ideas of the original text are represented,
- the features of the original text including ideas, images characters and situations, and the language in which these are expressed,
- techniques used to create, recreate or adapt a text and how they represent particular concerns or attitudes.
Key skills:
- identify elements of construction, context, point of view and form particular to the text, and apply understanding of these in a creative response
- choose stylistically appropriate features including characterisation, setting, narrative, tone and style
- critically reflect on how language choices and literary features from the original text are used in the adaptation
What you’re really trying to do in your reflective commentary is prove to your teacher that you are hitting all these key knowledge and key skills points. As you write, ensure you are discussing how the author uses point of view, context, form, elements of construction and stylistic features in their text. It is than imperative that you describe how you have similarly used such device in your creative response. Ensure that you also discuss how you are involving the ideas and themes of the text in your creative piece, and how you are discussing them further, or exploring them in greater depth. Obviously only talk about those that are relevant to your creative response!
Sample reflective commentary
Having scored a 10/10 in my own reflective commentary, I will provide a structure that can be used to ensure you are including everything you need. I discussed my own reactions to the original text, and described how I wanted to rouse similar reactions in the reader of my creative response.
In your reflective commentary, it can be easier to put everything under subheadings. These are the ones that I used:
-Characterisation
-Literary features (here I chose 7 particular literary features used in my text and discussed how I emulated them)
Under each of these paragraphs, I analysed how the author used such features to create and convey meaning, and discussed how I, in my own piece, drew on her use of them and expanded on her ideas. Here is an example of my ‘Purpose’ paragraph, which will hopefully give you an idea on how you might write your own commentary! My text was Cate Kennedy’s Dark Roots , in particular the short story ‘What Thou and I Did, Till we Loved’.
In my piece, I ultimately attempted to lead the reader to a place of discomfort, faced with a situation that they wish never to be faced with. When I first read What Thou and I Did, Till we Loved (Dark Roots, Cate Kennedy), I simply wished never to be in Rebecca’s position, as I was sobered by the sadness of her demise as she watched her lover fade away. I sought to elicit the same response from the reader, as I aimed to convey the deterioration that both lovers suffer, as well as the loss of communication between them. I also attempted to allow the reader to question the humanity in keep people alive by machines and drugs, and whether it is fair to force people to live an unnatural life. I have sought to explore this even further than What Thou and I Did, Till we Loved bringing in the question of euthanasia and whether we have a right to die as Kyle begs of Max to “kill me” at the end of the piece, and Max concedes that “[he] would if [he] could”. The themes of my piece seeks to explore are the ways of coping with grief, guilt at causing the illness of a loved one, a life with a lack of substance, and the loss of communication due to illness.
Hopefully you’re feeling better about how you might go about completing your creative response, and getting that 10/10 on your reflective commentary!
The Erratics is usually studied in the Australian curriculum as a Text Response. For a detailed guide on Text Response, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response .
Within the intimate Albertan landscape of her memoir, The Erratics , author Vicki Laveau-Harvie guides her readers through the inhospitable terrain that marked her family environment. Laveau-Harvie’s memoir is complex, showcasing the complicated dynamics that arise within her dysfunctional family. Understanding the ideas and values that underpin these family tensions is crucial to scoring well in The Erratics , which is why this blog will break down the key themes and quotes to help you analyse the memoir.
Family & Trauma
Truth & perspective, choice & agency.
Family lies at the heart of The Erratics . Both sisters spent their childhoods navigating the hostile familial setting fostered by their mother’s turbulent behaviour, resulting in a profound trauma that manifests itself in their present lives. The ways in which they manage this trauma, whilst reestablishing a connection with their family, is a core aspect of Laveau-Harvie’s memoir.
‘We’ve been disowned and disinherited…When something bad happens to them, we’ll know soon enough and we’ll deal with it together. I don’t realise at the time, but when I say that, I imply care. I imply there may be something to salvage. I misspeak. But I’m flying there anyhow. So is my sister. Blood calls to blood. What can I tell you?’ (p. 17)
From the outset, Laveau-Harvie asserts the underlying tension of her memoir. Having established her mother to be as ‘mad as a meat-axe’ in the first chapter, the reader may find Laveau-Harvie’s decision to return to Canada bizarre, to say the least. However, for Vicki the choice makes sense, having promised her sister that she will return to support her when ‘something bad happens’.
Laveau-Harvie suggests that people cannot completely separate themselves from their blood relations, and that most importantly, a moral obligation to one’s family and self-preservation are not mutually exclusive. Rather, she suggests that there exists a ‘precarious balance’ between these commitments and that one’s family cannot be ignored in times of need, because, ultimately, ‘blood calls to blood’.
‘...everybody knows a family Christmas will always go badly, that even the most extremely lowered family expectations will not be met. Magazines publish the same articles…year after year, on why we harbour these wildly unrealistic expectations of family unity.’ (p. 54)
Laveau-Harvie challenges the ‘wildly unrealistic expectations’ of familial culture depicted in countless generations of Canadian magazines. She uses the imagery of a ‘family Christmas…go[ing] badly’ to dismantle the idea of a traditionally wholesome festive season, suggesting that such compassion is inaccessible in the presence of her mother’s ‘mercurial’ personality.
Additionally, Laveau-Harvie’s insistence that ‘everybody knows a family Christmas will always go badly’ is immediately juxtaposed by the gracious dinner she shares with her friends. Laveau-Harvie appreciates how they ‘light up their properties in such joyous fashion’ relative to the ‘Hotel California’ her parents reside in. Thus, Laveau-Harvie invites her readers to reflect upon the value she places on this fulfilment of familial duty; how all it takes is an act of selfless humanity to restore (to some extent) the vision that ‘family unity’ is not ‘unrealistic’, but rather, completely possible.
'...the giant Douglas fir…It has prospered, cutting off the view of the Rockies…even though it should have never flourished…The tree is full of tiny birds, red-breasted nuthatches who live in it year-round…' (p. 42)
Laveau-Harvie uses the Douglas fir as a symbol of survival, emblematic of the extraordinary circumstances under which she was able to 'flourish'. Laveau-Harvie recounts her numerous travels throughout the memoir – Canada, Australia and Hong Kong – her decision to 'opt for geography' acting as a means of self-preservation, placing distance between herself and her family (in particular, her mother). It is made clear from the prologue that the Okotoks Erratic foothills, also called the Rockies, are a motif for the indomitable presence of the mother ( see here for more on setting in The Erratics ) from which Laveau-Harvie escapes.
Hence when the Douglas fir is described to have '[cut] off the view of the Rockies' it conveys Laveau-Harvie’s success in physically removing herself from the hostile family setting she was trapped in. However, note that Laveau-Harvie’s geographical location does not relieve her of her trauma – she openly explains how she 'walk[s] like an invalid through life'. Regardless of this, Laveau-Harvie 'prosper[s]…even though [she] should have never flourished', parenting kind and compassionate children ('tiny birds') of her own despite the immeasurable anguish she endured during her own childhood. Thus, Laveau-Harvie demonstrates the capacity to break a vicious cycle of trauma created by her mother, instead using her own 'principle of pre-emptive karma' to limit passing on her grief.
A reflection of a specific six-year period of her life, Laveau-Harvie uses her memoir to explore the multifaceted nature of truth, how a shared experience can give rise to varying perspectives and responses. An intimate piece of storytelling in its own right, The Erratics is a platform from which Laveau-Harvie urges the reader to discover their own truth, whilst cherishing a balanced view of reality
'This is not untrue. My sister feels differently. She has her truth and I have mine but she isn’t the one doing the talking right now.' (p. 12)
Consistently throughout The Erratics , Laveau-Harvie emphasises the differences between the sisters, and the varying extents to which their past trauma has affected and damaged them. She suggests that despite a shared upbringing, with the same malignant presence of their mother, one’s perspective is unique to the individual. It also raises discussion about the truth the reader is presented in the memoir. As the author, Laveau-Harvie guides her readership through events as they pertain to her memory - the subjectivity of her memoir is something Laveau-Harvie openly admits to her readers.
Regardless, there are clear distinctions between how the sisters respond to their trauma. The sister struggles to 'negate a past that haunts her', feeling 'the blows of the past continuously in her present'. Conversely, Laveau-Harvie’s past 'is not merely faded…it’s not there', with many of her memories repressed to help her survive her anguish. Thus, Laveau-Harvie affirms how one’s response to trauma is dependent on the individual, how one’s truth is often adapted to their needs in order to survive.
'The aurora borealis are fading. Well, he says, show’s over. Gotta see a man about a dog. You should move on too. You’ll have more scope now, for the good stuff. He waves his arm. Wider view, he says. Farther reach. But only for the good stuff.' (p. 217)
Bookending her memoir with the geological construction and spiritual origins of the Okotoks Erratic foothills, Laveau-Harvie ultimately uses her memoir as a reflective process that helps her find 'closure' towards her mother’s legacy. Initially conveying her mother’s menace through the 'danger' of the Rockies, Laveau-Harvie’s connection with the Albertan landscape helps her see hope within the 'landscape of uncommon beauty'. Her mother’s life 'tainted' by mental illness, Laveau-Harvie comes to an understanding that her behaviour, much like the harshness of the Canadian winter, was 'nothing personal'. Thus, upon her mother’s death, Laveau-Harvie crafts an intimate interaction between her mother and Napi the Trickster, closing her memoir with the hopeful wish that her mother now lives a life with 'wider view…farther reach…but only for the good stuff'. Hence, in a final act of forgiveness, Laveau-Harvie honours the life of her mother, whose potential was tarnished by mental illness.
'My sister says her suburb is working-class; she also tells me that she considers herself working-class…I try to make her see that we have sprung desperately from a violently aspirational upper-middle-class background, and that I see that as part of the greater malaise we live with.' (p. 186)
Laveau-Harvie continues to emphasise the differences between her and her sister, with one focus being how their values have developed in response to their trauma. There is a clear difference between the sisters when they discuss their definitions of ‘working-class’; the sister argues that she and her suburb are working-class, defined by 'having a job'. Contrastingly, Laveau-Harvie 'tr[ies] to make her see that [they] have sprung…from a violently aspirational upper-middle-class background', and expresses some concern towards her societal status being 'part of the greater malaise [they] live with'.
The sister chooses to identify as 'working-class', thereby highlighting how her parent’s obsession with the accumulation of material wealth has influenced her perception of class and privilege. Amassing an 'impressive wall of properties', the sister parallels her father’s 'pride…at the sight of watching his wife spend big'. On the other hand, Laveau-Harvie openly acknowledges her family’s privilege but instead perceives it as a 'malaise' and chooses to separate herself from any degree of avarice. Thus, the reader is invited to reflect upon the differences between the sisters’ perspectives, how the sister may still be in thrall to her parent’s values, whereas Laveau-Harvie’s sense of self is inextricably linked to the natural landscape over material possessions.
Many characters that feature in Laveau-Harvie’s memoir are elderly, and experience a unique set of challenges that only comes with the ageing process. The mother and the father, for example, both endure deteriorating health conditions that compromise their independence and autonomy. As such, Laveau-Harvie offers an interesting insight into what it’s like to observe and deal with ageing parents who struggle to accept the limits of their age.
'My father is looking far away, back in a moment when life was excitement and danger and possibilities…’ (p. 91)
Laveau-Harvie’s father often finds himself reminiscing over his past, reflecting on war-time memories or the wealth he accumulated from his work in the oil industry. Although, Laveau-Harvie does suggest to her readers that these stories become more exaggerated each time they are told, highlighting the difficulty the father has in coping with his ageing body. Laveau-Harvie illustrates how the ageing process inevitably incurs a loss of independence and autonomy, and uses the characterisation of her father to emphasise the challenge of reconciling with this isolating experience.
By 'looking far away, back in a moment when life was excitement and danger and possibilities', Vicki’s father uses his memories to retain the feeling that 'he’s twenty and bullet-proof'. Reminiscing over his act of heroism during the war, the father commends himself for the 'precise calculations' that enabled him and his copilot to perform a 'remarkable manoeuvre'. Thus Laveau-Harvue uses this hyperbolic description of her father’s story to reveal how elderly people must often depend upon their past memories to maintain a sense of autonomy in the present.
Laveau-Harvie suggests that elderly individuals such as her father must 'confront the real' in accepting that the ageing process will physically hinder their independence, leaving them to feel rejected by their own bodies. Hence, Laveau-Harvie exposes her readers to how the ageing process can be an inherently challenging experience for elderly individuals to accept.
'It happens, they say. With older people They come to, and a whole married life of disappointment and bitterness slips out, like an organ escaping an incision, like a balloon filled with acid. It bursts on impact, burning holes in their spouses’ clothing and leaving little round scars on their flesh that never heal completely.' (p. 19)
There are many marriages and long-term relationships mentioned throughout the memoir: the mother and the father, the aunt and the uncle and the sister and her partner. Even Laveau-Harvie herself is divorced from 'the father of [her] children'. Laveau-Harvie acknowledges the difficulty in maintaining these types of relationships; how they are often marked by histories that invariably include events that are never resolved or forgiven. Laveau-Harvie explores this notion through her use of metaphor, likening the 'bitterness' of unresolved conflict to 'a balloon filled with acid…burst[ing] on impact'. Here, she asserts the importance of forgiveness in a long-term relationship, affirming its capacity to maintain and restore compassion, love and empathy.
Moreover, Laveau-Harvie suggests that in the absence of forgiveness, marital conflicts are left to foster 'disappointment and bitterness' that is released when people enter elderly life. Laveau-Harvie conveys how the 'burning holes' in a long-term relationship can compromise its stability, leaving 'little round scars…that never heal completely' - thereby reinforcing the feelings of isolation and despondency endured by The Erratic ’s elderly characters. Thus, Laveau-Harvie reinforces the value of forgiveness, how a willingness to empathise with a partner, especially early in a relationship, can minimise the 'bitterness' experienced when one ages.
'We’re like the king and the queen, my uncle says, every time we see any of them, whenever they visit. Like the king and the queen. They smile at the fullness of their life: love and problems, success and loss, pride and a hefty measure of grief. A well-worn life fully lived, perspectives widening with each new baby, blossoming like one of those paper flower buds that unfold into unexpected beauty when you plunge them into water. ' (p. 86)
With Laveau-Harvie’s parents at the forefront of the memoir, it seemingly appears that she depicts only a grim image of old age. Whilst she does offer these insights, Laveau-Harvie also portrays the emotionally rich and satisfying life lived by her ageing aunt and uncle. 'Smil[ing] at the fullness of their life', the aunt and the uncle 'peer endearingly' over their extended family. Their 'perspectives widening with each new baby', Laveau-Harvie also uses the virtuous imagery of her aunt and uncle to emphasise the value of an emotionally rich elderly life.
Metaphorically referred to as 'the king and the queen', Laveau-Harvie uses the connotations of royalty imbued in this metaphor to emphasise the richness of a life spent in a nurturing family environment, where widening perspectives help ageing individuals find a 'fullness' in their life despite the 'hefty measure of grief' endured. Thus, Laveau-Harvie juxtaposes her aunt and uncle’s willingness to engage with family against her parent’s 'disown[ment] and disinherit[ment]' of their daughters.
Throughout their lives, the sisters have suffered immeasurable trauma at the hands of their parent’s decisions. Yet, despite this, the two daughters demonstrate that they possess a strength of character capable of making the most difficult of decisions. Laveau-Harvie explores the significance of employing one’s agency in reconnecting with, and restoring, familial relationships.
'It means always try to do the decent thing, the rational thing, the selfless thing, the boring thing, because then you won’t have to beat yourself up with guilt until your early stress-induced death…Do nothing you know you will live to regret.' (p. 80)
'Tattoo[ed]' 'on the corner of [her] soul', the philosophy to live without regret is permanently engrained as part of Laveau-Harvie’s character, a testament to the integrity she holds that allows her to make the difficult decision to return to Canada and reconcile with her trauma. Laveau-Harvie fully understands the challenges, and even dangers, she would be facing upon her return. Despite having been disinherited two decades prior, and entirely aware of her mother’s volatility, Laveau-Harvie ultimately chooses to use her agency and confront, reconcile and heal from her past.
Interestingly, Laveau-Harvie’s sister also exhibits similar behaviour. When her mother is hospitalised, the sister also returns to Alberta; she takes upon herself several responsibilities involving the cleaning and organising of her parent’s house (which ultimately risks her life as she triggers an angioedema attack). This therefore invites the reader to reflect upon the sister’s willingness to do 'the selfless thing[s]' necessary to help her family; and perhaps suggests that to live with no regrets is a philosophy shared by two sisters 'petrified by grief'.
'I reminded her that Dad went along with my mother in disinheriting us, removing any right we had to help him in his old age; that, most hurtfully of all, he believed everything she told him about us, even though he now holds other views. It is as a result of his own inability to act that he now barely has a connection with us and has none whatsoever with his grandchildren.' (p. 187)
When the reader is first introduced to the father, they are met with the imagery of a frail old man suffering from a starvation diet enforced by his cruel and narcissistic wife. However, as the memoir progresses, Laveau-Harvie limits the reader’s sympathy towards her father, who she instead affirms is a victim of his own design. Laveau-Harvie holds her father accountable for the passiveness that perpetuated the mother’s unpredictable behaviour. Illustrating how her father 'went along with [the] mother in disinheriting' herself and her sister, Laveau-Harvie challenges the extent to which her father’s intervention could have mitigated the devastating 'swathe of misery' cast by the mother. Therefore, Laveau-Harvie asserts the power of one’s voice, suggesting that had her father employed his agency then perhaps the extent of his daughters’ trauma could have been minimised.
'There are the dangers and difficulties you summon up the courage to deal with physically, every day, in the lab or the forest, and then there are the blows that fall from the air, unseen, unpredictable, but nonetheless brutal and crippling. Confronting the real makes you a person of substance; fending off the invisible light that always blindsides you makes you Chicken Little, hoping to absorb a little warmth from the lights on the tree.' (p. 65)
'Confronting the real', Laveau-Harvie demonstrates that to begin the healing process and reconcile with the past, one must make the difficult choice to 'summon up the courage to deal with…the blow that fall from the air'. Upon her return to Canada, Laveau-Harvie faces the 'unseen' and 'unpredictable' challenges her mother has imposed. She deals with the web of lies spun by her mother, the bureaucracy of the hospital workers and her starved father’s declining health. However, despite the overwhelming trauma of her past and the challenge of being reunited with her parents, Laveau-Harvie ultimately chooses to use her agency and 'confront the real', enduring the 'brutal and crippling' blows along the way.
Want to dive deeper into this text? Check out our blog post on Understanding the Symbolic Nature of Setting in The Erratics.
Last updated 20/10/19
Planning is an essential part of any successful text response essay. It helps you ensure that you’re answering the prompt, utilising enough quotes and writing the most unique and perceptive analysis possible! The hard part of this is that you only have about FIVE MINUTES to plan each essay in the Year 12 English exam… (more info on the best way to tackle that challenge in this video !)
So, I developed the FIVE TYPES of essay prompts to help students streamline their planning process and maximise every minute of their SACs and exams.
By identifying the type of prompt you’re being challenged with immediately, a number of parameters or guidelines are already set in place. For a specific type of prompt, you have specific criteria to meet – for example, in a metalanguage-based prompt , you immediately know that any evidence you brainstorm in your planning stage should be based around the literary techniques used in your given text.
If you’d like the full picture on our best FREE advice on Text Response, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response here .
1. Theme-Based Prompt
‘Ambition in the play Macbeth leads to success.’ Discuss. ( Macbeth )
When you’re presented with a theme-based prompt, you can automatically shift your brainstorming and planning towards the themes mentioned in the prompt along with any others that you can link to the core theme in some way.
In regard to this Macbeth prompt, for example, you could explore the different ways the theme of ambition is presented in the text. Additionally, the themes of guilt and power are intimately related to ambition in the text, so you can use those other ideas to aid your brainstorming and get you a step ahead of the rest of the state come exam day.
2. Character-Based Prompt
‘Frankenstein’s hubris is what punishes him.’ Discuss. ( Frankenstein )
These prompts are pretty easy to spot – if you see a character’s name in the prompt, there you have it; you have a character-based prompt on your hands.
Once you know this, you can assume that each example you brainstorm has to be relevant to the specific character named in the prompt in some way. Also, you can explore how the actions of characters don’t occur in isolation – they’re almost always interrelated. Remember, however, that the actions of characters are always connected to the themes and ideas the author is trying to convey.
This type of prompt also grants you some freedoms that other types don’t give. For example, unlike a Theme-based prompt, a character-based prompt means that it’s perfectly fine to write about characters in the topic sentences of your body paragraphs.
3. How-Based Prompt
‘How does Grenville showcase Rooke’s inner conflict in The Lieutenant ?’ ( The Lieutenant )
Unlike other prompts, the ‘How’ positions you to focus more on the author’s writing intentions. This can be achieved by discussing metalanguage – language that describes language (read my blog post about it here ). These prompts tell you immediately that you need to be thinking about the literary techniques explored in the text and explain how they affect the narrative.
Rather than using specific techniques to frame your specific arguments, it’s best to use them as evidence to support arguments that attack the main themes/ideas mentioned in the prompt.

4. Metalanguage or Film-Technique-Based Prompt
‘Hitchcock’s use of film techniques offers an unnerving viewing experience’. Discuss. ( Rear Window )
This type of prompt is very similar to How-based prompts, specifically in the fact that the discussion of literary techniques is essential.
For this type of prompt specifically, however, the actual techniques used can form more of a basis for your arguments, unlike in How-based prompts .
5. Quote-Based Prompt
“Out, damned spot!” How does Shakespeare explore the burden of a guilty conscience in Macbeth ? ( Macbeth )
Countless students ask me every year, “What do I do when there’s a quote in the prompt?!” My reply to these questions is actually fairly straightforward!
There are two main things that you should do when presented with this type of prompt. Firstly, contextualise the quote in your essay and try to use it in your analysis in some way. Secondly, interpret the themes and issues addressed in the quote and implement these into your discussion. The best place to do both of these is in a body paragraph – it weaves in seamlessly and allows for a good amount of analysis, among other reasons!
When faced with unknown prompts in a SAC or your exam, it's reassuring to have a formulaic breakdown of the prompt so that your brain immediately starts categorising the prompt - which of the 5 types of prompts does this one in front of me fall into? To learn more about brainstorming, planning, essay structures for Text Response, read our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response .
1. Summary 2. Themes 3. Symbols and Analysis 4. Quotes 5. Sample Essay Topics 6. Essay Topic Breakdown
Alice Munro is a Canadian Nobel-Prize-winning author of short stories , and Runaway , first published in 2004, is a collection of eight such stories (though kind of actually only six, because three of them are sequential). These stories examine the lives of Canadian women throughout the last century, but not all of them are necessarily realistic to what daily life actually looks like. Rather, Munro uses borderline-supernatural events (which some critics say feel staged or contrived) to shed light on the tensions and challenge s of gender in modern life.
This can mean that some of the stories are quite hard to follow; they go through all these twists and turns, and the lines between stories start blurring after a while. Let’s go through each in a bit more detail before jumping into our analysis.
2. Story-by-Story Characters and Summary
The titular story is about a woman Carla , her husband Clark , their goat Flora , and their elderly neighbour Sylvia Jamieson . There are many runaways in the story: Carla ran away from her middle-class home to marry Clark, Flora the goat literally runs away, a scandalous lie about Sylvia’s late husband gets a bit out of hand, and now Sylvia is helping Carla run away once again, this time from Clark. Few of these runaways are really very successful: this story is really interrogating why and how.
Chance/Soon/Silence
The next three stories are sequential, and revolve around Juliet , a well-educated classicist who is working as a teacher in the first story, ‘Chance’ - it is set in 1965 and she is 21. In this story, she meets her lover Eric Porteous on a train, then finds him again six months later. Eric is sleeping around with a few women in light of his wife’s declining health and eventual passing, but by ‘Soon’ he and Juliet have settled down and had a baby together - Penelope .
‘Soon’ focuses more on the relationship between Juliet and her parents, in particular her mother Sara . Juliet feels a bit out of place now at home, and feels guilty about not being more present for Sara. In turn, ‘Silence’ depicts her own daughter running away from her. Juliet returns to her studies and only hears about Penelope’s life through a chance encounter with a friend who reveals that Penelope is now a mother herself.
The next story is about Grace , an older woman revising the family home of her husband Maury Travers . Their marriage never had a lot of passion in it really - Grace was always more interested in Maury’s family - but both of them were just doing what was expected of them. The contrast comes from Maury’s brother Neil , a doctor who accompanies Grace on a hospital trip when she cuts her foot. This trip becomes longer and more sensual, feeling adulterous even though very little actually transpires between them - the story raises questions around what counts as cheating, and what marriages should entail.
‘Trespasses’ is slightly deliberately disorienting from the start (which is actually the end of the story). We go on a flashback in the middle to learn about a father, Harry , and his daughter Lauren . One day when moving house, Lauren finds a cardboard box - Harry explains that it contains the ashes of a dead baby who he and his wife Eileen (Lauren’s mother) had had before Lauren. This leads to Lauren questioning if she was adopted, which is further complicated by Delphine , a worker at a hotel who seems to think Lauren is her biological daughter. The ending (which was teased at the beginning) is the evening of confrontation between the four characters where the truth is finally revealed.
Conversely, ‘Tricks’ has a more linear plot to follow. Robin is a carer for her asthmatic sister Joanne , but she’s taken to watching Shakespeare plays in the next town once a year. One year, she meets a European clockmaker Danilo who plans to meet her next year when she is back in town - but this doesn’t go to plan at all. It’s only 40 years later that Robin finds out Danilo had a twin brother, which is why the plan had gone downhill.
The last story in the collection is arguably the most complex, and it’s broken into 5 parts to reflect that complexity. It follows Nancy as she ages from a fresh high school graduate to an old woman by the end of the sequence, including her marriage to the town doctor Wilf . Importantly, the stories also cover her friendship with Tessa , who has the supernatural powers mentioned in the title. However, by the third story, Tessa has been abandoned in a mental hospital and she has lost her powers. Throughout the stories, we also see Ollie , Wilf’s cousin (or a figment of Nancy’s imagination according to this analysis), who seems to be responsible for Tessa’s demise.
Let’s start tracing some of the common themes between the stories.
A key theme explored throughout many of the stories is marriage and domesticity . There’s a strong sense that it’s an underwhelming experience : it doesn’t live up to expectations and it particularly dampens the lives of the women involved. Nancy’s marriage to Wilf in ‘Powers’ only happens because she feels guilty - 'I could hardly [turn him down] without landing us both in…embarrassment' - but, as a result, she loses her fun, intellectual streak as he tells her to put down her book, 'give Dante a rest'. A similar fate befalls Juliet, who gives up her study in the process of becoming married.
Marriage is also sometimes explored as a deliberate choice , even if it might have unintended consequences - for example, Carla’s marriage to Clark is described as a life that she 'chose'. This interpretation is more unclear though, and is contradicted in other stories like Passion, where Grace’s marriage is described as 'acquiescence ', acceptance without protest. It’s even contradicted to some extent in the same story: Munro compares Carla’s marriage to a 'captive' situation, where she might’ve chosen to enter the marriage, but after that has little say in how it goes.
This sounds a bit trite, but the title is a key theme as well - just not necessarily in the physical sense . Consider all of these different definitions and how they pop up in the stories. In ‘Runaway’, Carla and the goat run away, but also the lie Carla tells Clark about Leon, a runaway lie that taints his relationship with Sylvia completely. Some runaways are described as accidents - 'she – Flora – slipped through' - while others are much more deliberate. The question here is how much control we actually have over our own lives . Not a lot, it would seem.
The other side of runaway/s is to think about who the victim in each runaway is. Does somebody run away because they are 'in a bad situation, the way it happens', a victim of circumstance , or do they run away because they feel guilty , or because they’re abandoning someone else, the true victim of being left behind? Carla does seem like more of a victim of circumstance with good reason to run away, but think about Nancy leaving Tessa behind in ‘Powers’: ‘“I’ll write to you”, she said…she never did.’
This question about who the real victim is might be the hardest to answer for ‘Silence’. Juliet’s daughter abandons her, but it’s not like there’s a strong history of positive mother-daughter relationships in their family: Juliet wasn’t able to give Sara what she needed ( 'she had not protected Sara') and in turn isn’t able to quite give Penelope what she needs either (Penelope having a 'hunger for the things that were not available to her in her home '). At the same time, Penelope’s abandonment does feel quite callous and inexplicable , even if Juliet feels like it’s what she deserves; Munro suggests at the end of the story that a reunion would be an 'undeserved blessing[]'. The intertextuality with Aethiopica reveals Juliet’s good intentions, her similarity to the 'great-hearted queen of Ethiopia', but it doesn’t quite give us the satisfaction of a neat resolution either.
Ethics and Morality
Finally, Munro’s stories also raise questions around morality . Besides what we’ve already covered - adultery, runaways - there are further questions raised around parenthood , particularly in ‘Trespasses’. Harry seems to share a bit too much information with his child, who really doesn’t need to know about the dead baby just yet. Lauren is 'not short of information', and it’s worth questioning where that boundary should be for a child of her age.
But not all ethical questions have simple answers : as in ‘Tricks’ they can sometimes just have 'outrageous', cruel punchlines that don’t reveal themselves for decades. Munro doesn’t necessarily have all the answers on this one. She brings up complex moral situations but does not pass judgment on any.
4. Symbols & Analysis
Greek elements.
Throughout the stories, Munro brings in a few elements of Greek mythology or literature . The intertextuality in ‘Silence’ is one example, drawing on the classical text Aethiopica , but there are a few more scattered throughout the stories: the constellations of Orion and Cassiopeia in ‘Chance’ and an oracle-like figure in Tessa, a main character in ‘Powers’. All of these elements have some significance:
- Cassiopeia is known for her arrogance and vanity, which parallels with the way Juliet detaches herself from her life ('she had made herself into a rather superior, invulnerable observer' - despite her very real vulnerabilities)
- Orion is known for his forbidden romance with the virgin goddess Artemis, which parallels with Eric’s romance with Juliet (Juliet being relatively inexperienced with men herself, with all of her experiences being 'fantasy')
- Oracles in mythology are like mouthpieces of the gods who can prophesy about the future. They were often women, so oracles were unusually influential in their male-dominated societies. The question is whether this parallels with Tessa at all: even though she has these supernatural powers, are there other forms of power she might lack instead?
In general, intertextuality is a way to enrich a text by drawing parallels and linking characters to existing stories or archetypes. Here, Munro uses classical texts to add dimension to her characters in a way that is almost-but-not-quite commentary. Pre-existing Greek myths are a way for us to see what’s really going on .
(Rail)Roads and Transit
The other symbol that comes up a few times in the stories is roads or railroads - basically places where runaways might happen . ‘Chance’ is set in the middle of a train journey, ‘Tricks’ involves a couple of train journeys, ‘Runaway’ maps the roads leading in and out of Carla’s home, and almost all of ‘Passion’ takes place on the road. If we broaden ‘places where runaways might happen’ to include planes as well, then we can add ‘Powers’ and ‘Silence’ to the list.
All of these spaces are what might be called liminal - they’re ‘in-between’ spaces with an air of suspense about what can happen. It’s probably most prominent in ‘Passion’, where Grace describes the events of that road trip as a 'passage” in her life, both physically and metaphorically. In general though, they’re the settings where the wildest and most significant events tend to happen.
- 'She—Flora—slipped through.'
- 'She (referring to Carla) chose this life with Clark.'
- 'She is just in a bad situation, the way it happens.'
- 'She saw him as the architect of the life ahead of them, herself as the captive, her submission both proper and exquisite.'
- 'She might be free.' - this is the second last line in the story. Note the ambiguity here (and through all these quotes, to be honest) about which ‘she’ is being referred to (Carla, Flora or even Sylvia)
- 'Juliet was twenty-one years old and already the possessor of a B.A. and an M.A. in classics.'
- 'The problem was that she was a girl. If she got married—which might happen…—she would waste all her hard work.'
- 'She had made herself into a rather superior, invulnerable observer.'
- '…the two of them (referring to Sara and Juliet) intertwined. And then abruptly, Juliet hadn’t wanted any more of it.'
- 'But she had not protected Sara. When Sara had said, soon I’ll see Juliet , Juliet had found no reply. Could it not have been managed?…She had put everything away.'
- Penelope supposedly had a 'hunger for the things that were not available to her in her home.'
- 'Penelope does not have a use for me.'
- 'She hopes as people who know better hope for undeserved blessings, spontaneous remissions, things of that sort.'
- Grace, watching a movie with Maury, felt 'rage…because that was what girls were supposed to be like. That’s what men - people, everybody - thought they should be like. Beautiful, treasured, spoiled, selfish, pea-brained. That was what a girl should be, to be fallen in love with.'
- 'It was not in her nature, of course, to be so openly dumbfounded, so worshipful, as he was.'
- 'Describing this passage, this change in her life, later on, Grace might say - she did say - that it was as if a gate had clanged shut behind her. But at the time there was no clang - acquiescence simply rippled through her.'
- Lauren 'had been brought up to believe that children and adults could be on equal terms with each other.'
- 'How could she be sure that they had not got her as a replacement? If there was one big thing she hadn’t known about, why could there not be another?'
- 'Forgive us our trespasses' - note the ambiguity of ‘trespasses’ (does it mean sins as in the prayer, or overstepping boundaries, or both?)
- 'Some of the best-looking, best-turned-out women in town are those who did not marry.'
- 'A means to an end, those tricks are supposed to be.'
- 'I couldn’t stand for the poor man (referring to Wilf) to have had two girls turn him down’
- 'I used to have a feeling something really unusual would occur in my life, and it would be important to have recorded everything. Was that just a feeling?'
- 'She could be upset to see you leave without her. So I’ll give you an opportunity just to slip away.'
- 'He has nearly forgotten that he ever believed in her powers, he is now only anxious for her and for himself, that their counterfeit should work well.'
Having great quotes is one thing, but you also want to make sure you know How To Embed Quotes in Your Essay Like a Boss !
6. Sample Essay Topics
- What does Runaway teach us about romance?
- Carla, Grace and Tessa are more similar than different in terms of their relationships with the men in their lives. Do you agree?
- How does Munro contrast younger and older women in Runaway ?
- What does the setting contribute to the overall effect of Runaway ?
- 'Forgive us our trespasses.' What types of boundaries are created and overstepped in Runaway ?
7. Essay Topic Breakdown
Whenever you get a new essay topic, you can use LSG’s THINK and EXECUTE strategy , a technique to help you write better VCE essays. This essay topic breakdown will give you a brief glimpse on the THINK part of the strategy. If you’re unfamiliar with this strategy, then check it out in How To Write A Killer Text Response .
Within the THINK strategy, we have 3 steps, or ABC. These ABC components are:
Step 1: A nalyse
Step 2: B rainstorm
Step 3: C reate a Plan
‘Forgive us our trespasses.’ What types of boundaries are created and overstepped in Runaway ?
Step 1: Analyse
This quote is from ‘Trespasses’ and captures the double meaning of the word as both overstepping physical boundaries and sinning in the moral or religious sense . It’s likely we’ll want to talk about both interpretations - physically trespassing but also encroaching on boundaries in immoral ways. Note that the prompt also includes the action words ‘created’ and ‘overstepped’, meaning that there’ll be a pretty diverse range of examples that we’ll need to use to answer this prompt comprehensively.
Step 2: Brainstorm
Let’s start with physical boundaries : Carla’s marriage and the fences on her property and the US-Canada border in ‘Powers’ come to mind. Then, we’ve got non-physical boundaries: emotionally as in ‘Chance’ and ethically as in ‘Trespasses’. This is where we start getting into whether these boundaries are created or overstepped .
Clark creates boundaries for Carla and her attempts to break free from them are unsuccessful. The border in ‘Powers’ is more of an excuse for Nancy to neglect Tessa, a boundary she creates and never makes the effort to overstep. Finally, the ethical boundaries in ‘Trespasses’ are overstepped from the get-go. How can we synthesise these ideas into one essay?
Step 3: Create a Plan
I think the trick with questions like this is not to just allocate different types of boundaries and/or different action words to each paragraph. Try to think of creative ways to string these ideas together that also build towards a bigger picture or overall contention about the text as a whole. This example plan explores physical and emotional boundaries but makes a bigger argument that they are often associated with regret in Munro’s stories.
Paragraph 1 : Physical boundaries are both the most intentional and the most difficult to overstep.
- Carla’s farmstead is isolated and bordered by roads; her marriage to Clark and her life on this farmstead is likened to a 'captive' situation, with Clark being the 'architect' of it all
- Munro ends Runaway on a pessimistic note about Carla’s ability to leave this boundary: 'She might be free'
- International borders also constitute physical barriers, and these are used by Nancy in ‘Powers’ to avoid responsibility; because this is an active decision (‘“I’ll write to you”, she said…she never did.’), it’s a barrier that never really gets broken. Similar to Penelope in ‘Silence’
Paragraph 2 : Munro’s stories, however, focus more on emotional boundaries , and the way these are applied varies greatly. This variation underscores their complexity .
- Emotional boundaries when created can prevent intimacy: Juliet 'ma[kes] herself into a rather superior, invulnerable observer' so as to avoid commitment. These boundaries come back to bite when she has a daughter
- Conversely, they cause a great deal of harm when overstepped: for example, ‘Trespasses’ sees 'crazy and dangerous' adults toy with the life of a child, constantly assuming that she 'can take it' when in fact this is not the case
Paragraph 3 : Regardless, Munro’s characters often come to regret the boundaries they erect or overstep.
- Carla’s ambivalence about her marriage is tinged with regret either way: when she’s there, she wants to escape, and when she escapes, she questions if she has 'anything left in [her]'
- Juliet reflects on the boundaries she puts up between herself and Penelope and realises that 'spontaneous remissions' between them are undeserved and impossible
- In ‘Powers’, Nancy struggles with the guilt of abandoning Tessa: many years later, she still wants to 'open [the past] up' and understand her motives. However, it is too late, and the boundaries are already there
- Munro does not suggest that boundaries are inherently good or bad, but her stories show how they can be sources of regret when treated improperly
Runaway is usually studied in the Australian curriculum under Area of Study 1 - Creative Response. Check out Audrey's blog on how to approach Runaway as a Creative Response for more.
For a detailed guide on Creative Response as a whole, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Creative Writing .
This blog was updated on 21/10/2020.
2. Background
4. Chapter 1 Plot and Analysis
7. Sample Essay Topics
8. Essay Topic Breakdown
The Secret River is usually studied in the Australian curriculum under Area of Study 1 - Text Response. For a detailed guide on Text Response, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response .
The Secret River is a historical novel telling the story of William Thornhill, a poor Englishman from the early 19th century who was deported and transported to New South Wales, Australia in 1806 for theft. This novel tells the story of Australia's founding and the moral choices made when Europeans colonised land that was already inhabited by Aboriginal people.
During 18th century to mid 19th century, 162,000 men and women were transported to Australia, with majority from England. These people, known as ‘convicts’, had committed crimes such as larceny and robbery – acts which were considered severe offenses and demanded heavy sentences. In order to deal with the overwhelming masses of criminals, the government exported crowds of convicts to Australia to serve their term as labourers. The reason driving the deportation included an attempt to decrease poverty and crime in England while concurrently developing the British colony in Australia.
Many of the fleets from England were destined for New South Wales, Australia. Those on the fleets included the criminals, marines, and their families. Living in a penal colony, the criminals were employed depending on their various skills: farmer, boatman, servant etc. The settlers were award a ‘ticket of leave’ if they presented good behaviour during labour. This meant that settlers would become emancipists, where they were set free from the government’s sentence and could begin a life for themselves by making their own living. This suited the government’s goal for a successful and thriving colony since it would only be possible if people were to work for themselves, and not under the terrain of the government.
Although Australia was chiefly populated with Indigenous Australians, the first century of colonisation saw a drastic decline in their population. This was due to a clash of desire for the land; the native’s innate protection of their land and the white settlers struggle to declare their right to an area already inhibited by natives – possibly for 40,000 years. The two cultures failed to ever create a peace agreement or compensation and as a result, the frontier was often marked with blood. Overtime, a successful of the British colony meant that white settlement overpowered any possibility of the natives retaining their land. The Secret River’s exploration of this powerful change in Australia’s history is a poignant reflection of the past, and demands attention to the sensitive issue of Australian and native relationship that is still present today.
Set during the early 19th century. Located in London, Sydney and on the Hawkesbury.
Chapter 1: Strangers
The Alexander , a transport ship for convicts has reached New South Wales, Australia after a travelling across the world for majority of the year. William Thornhill, an Englishman convicted to sentence his ‘natural life in the Year of Our Lord eighteen hundred and six’ [pg 3] will serve as a labourer.
During his first night in New South Wales, where their homes are ‘only a flap of bark, a screen of sticks and mud,’ Thornhill digested the new land with its ‘rich dank smells…restless water…no Pole star’; an environment vastly differentiated from England. The unfamiliar situation is overwhelming as ‘he had not cried, not for thirty years….but now his throat was thickening.’ In his despair, Thornhill describes how being sentenced to New South Wales could potentially be worse than dying itself.
Initially, Thornhill believed his tears are clouding his vision since the ‘darkness moved in front of him’ [pg 5]. However, he then realised that a human, ‘as black as the air itself’ stood before him. The unusual appearance of this human struck Thornhill since ‘his skin swallowed the light…[and] eyes were set so deeply into the skull.’ Although clothed, Thornhill ironically felt ‘skinless’ against the other who was completely naked and holding a spear. Thornhill repeatedly demanded that the man ‘be off’, for fear of his family and himself being attacked. Despite his shouting, this only impelled the man to move closer to the point where they almost touched. The ‘black man’ [pg 6] reproduced ‘be off’ in Thornhill’s exact tone. While Thornhill’s fear of this strange human is prominent, he grappled the strength to exert a bold, intrepid veneer, as ‘he was not about to surrender to any naked black man’. When he glanced back to his wife and children however, the man promptly disappeared, leaving only the darkness behind. Thornhill returned to his hut where he laid back down to rest yet ‘every muscle was tensed…the cold moment of finding that unforgiving thing in his flesh.’
Environmental / Landscape conflict
For Thornhill, who has spent a lifetime in England, the confrontation of a new environment evokes a powerful sense of unfamiliarity. The unknown land presents him with various intrapersonal conflicts, one of which is the difference between England and Australian stars. While the physical distance of this new land from Thornhill’s home is demonstrated by the lack of a ‘Pole Star, a friend to guide him on the Thames, [and] no Bear that he had known all his life,’ [pg 4] the unrecognisable stars above Australia only depict a ‘blaze, unreadable, [and] indifferent.’ His conflict demonstrates his physical and emotional distance from Thames, a place he grown up surrounded by compared to Australia, where learning begins from the very basics, as shown when he absorbs the natural landscape around him. The night described as ‘huge and damp, flowing in and bringing with it the sounds of its own life’ [pg 3] highlights how the Australian land is unique, possessing qualities of existence.
Thornhill’s sense of negligence in the vast forest that continues ‘mile after mile’ is illustrated through the imagery of the ‘trees [which] stood tall over him,’ depicting that nature is a powerful and dominant force over the Europeans. While the trees render him insignificant, it also demonstrates his alienation from the environment. The ‘Alexander,’ a common traditional English name, represents an intrusion of the Europeans onto the Australian land, further highlighting the idea that they do not belong on this island.
The Australian land is depicted to be harsh and unforgiving, as highlighted through the imagery of ‘dirt chill...sharp stab...alien stars' [pg 4] This conflict with the brutal landscape, along with the unknown leaves Thornhill apprehensive of what is to come. His feeling that he was ‘nothing more than a flea on the side of some enormous quiet creature’ [pg 4] depicts the Australian land almost like a monster. Additionally, the words ‘restless’ draw to the idea that the land is at discomfort or uneasy to have new inhabitants.
Racial/Cultural conflict
The conflict between two cultures is shown through the initial encounter between Thornhill and an Indigenous Australian. Without any conversation, the tension between the two is clear, merely through their actions in each other’s prescence. Thornhill notes the Aboriginal male’s tattoos, yet regards them as ‘scars’ since he is unaware to their culture. Even before this man, Thornhill is still infused with a sense of nakedness because of his unfamiliarity. His feeling that ‘every muscle was tensed…the cold moment of finding that unforgiving thing in his flesh’ highlights the tension of his first encounter of an Australian Aboriginal while it also foreshadows a suffering and anguish for his time ahead.
If you'd like to see the all Chapter plots, their analysis, along with important quotes, then have a look at our The Secret River Study Guide .
Conflict with land quotes
“Now it had fetched up at the end of the earth.” [pg 3]
“…this prison whose bars were ten thousand miles of water.” [pg 3]
“foreign darkness” [pg 3]
“…soughing of the forest, mile after mile.” [pg 3]
“He was nothing more than a flea on the side of some enormous quiet creature.” [pg 4]
Thornhill’s inner conflict quotes
“He had not cried, not for thirty years, not since he was a hungry child to young to know that crying did not fill your belly.” [pg 4]
“But every muscle was tensed, anticipating the shock in his neck or his belly, his hand going to the place, the cold moment of finding that unforgiving thing in his flesh.” [pg 6]
Racism quotes
“It took a moment to understand that the stirring was a human, as black as the air itself.” [pg 5]
“Clothed as he was, Thornhill felt skinless as a maggot.” [pg 5]
“This was a kind of madness, as if a dog were to bark in English.” [pg 6]
“He was not about to surrender them to any naked black man.” [pg 6]
Sample Essay Topics
1. William Thornhill is more worthy of our respect than our reprehension. Do you agree?
2. How does Kate Grenville explore hierarchy?
3. How does The Secret River’s symbolism enhance its exploration of alienation?
4. “Fear could slip unnoticed into anger, as if they were one and the same.” The Thornhills’ anger is valid. To what extent do you agree?
Now it's your turn! Give these essay topics a go. For more sample essay topics, head over to our The Secret River Study Guide to practice writing essays using the analysis you've learnt in this blog!
- Essay Topic Breakdown
Whenever you get a new essay topic, you can use LSG’s THINK and EXECUTE strategy , a technique to help you write better VCE essays. This essay topic breakdown will focus on the THINK part of the strategy. If you’re unfamiliar with this strategy, then check it out in How To Write A Killer Text Response .
Theme-Based essay prompt: T he Secret River depicts many layers of conflict, within but also between its key characters. Discuss
The key term of this prompt is conflict , but I think it’s also important to analyse how it’s discussed—as something that exists in layers , and something that can happen both within and between characters. This seems to hint at the idea that conflict can be internal—that is a single character can feel conflicted about something—as well as external—that is two or more characters can have some kind of dispute. This prompt will require us to think about all these different types of conflict.
Let’s start with the most internal layer—conflicts with the self. In terms of key characters, consider William but also Sal: what debates do they have with themselves, or what do they say or do that shows they feel conflicted or unsure about something?
Then, let’s broaden that out to interpersonal conflicts between characters. How do William and Sal, for example, come into conflict with their neighbours—both their white neighbours and their Aboriginal neighbours? How do they come into conflict with each other, even?
Maybe it’s worth separating the racial conflict into another category—conflicts between groups of characters, rather than individual characters. If we make this distinction, we need to be prepared to back it up—in what ways is this conflict of a different nature?
Step 3: Create a plan
I think we can pretty justifiably separate out our layers of conflict into those categories: interpersonal, interpersonal and interracial. This gives us three neat(-ish) paragraphs and a clear, affirmative contention: yes, there are many layers of conflict, and those are the three layers.
P1: At its most intimate layer, conflict is internal—the moral dilemmas of William and Sal are particularly strong examples.
P2: Conflict can also be interpersonal—we can see this between William and Dan, or William and his neighbours, or between William and Sal even. It’s up to you which way you cut this paragraph.
P3: However, perhaps the central conflict that the novel is built around is interracial conflict between white colonisers and the Aboriginal people whose land they occupied. To extend the prompt a little, we can talk about conflict not just between characters or people, but also between value systems. For example, the way colonisers saw land and property were fundamentally incompatible with how Aboriginal people saw it—this is another type of conflict.
In this sense, we’re largely agreeing with the prompt, backing up the distinction between interpersonal and interracial conflict, and finding a way to extend on it a little towards the end. We can build this into the contention as well: there are many layers of conflict, but they occur not just between characters. They can also exist between the broad cultural values of entire groups of people as well.
If you find this essay breakdown helpful, then you might want to check out our The Secret River Study Guide where we cover 5 A+ sample essays (written by a 50 study scorer!) with EVERY essay annotated and broken down on HOW and WHY these essays achieved A+ so you reach your English goals! Let's get started.
The Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response
How To Write A Killer Text Response Study Guide
How to embed quotes in your essay like a boss
How to turn your Text Response essays from average to A+
5 Tips for a mic drop worthy essay conclusion
Updated on 11/12/2020
Nine Days by Toni Jordan is currently studied in VCE English under Area of Study 1 - Text Response. For a detailed guide on Text Response, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response .
- Main Characters
- Themes, Ideas and Values
- Essay Topics
1. Summary
Jordan’s novel traces the tumultuous lives of the Westaway family and their neighbours through four generations as they struggle through World War II (1939-45), the postwar period of the late 1940s and 50s, the 1990s and the early 2000s. Composed of nine chapters and subsequently nine unique perspectives of life, their family home in Rowena Parade, Richmond, becomes the focal point for Jordan’s exploration of femininity, masculinity, family and Australian society.
2. Main Characters
Kip westaway.
'Mr. Husting always says first impressions count' (p. 5)
'Mr. Husting holds his other hand out flat and instead of an apple there’s a shilling.' (p. 6)
'I own the lanes, mostly. I know the web of them, every lane in Richmond.' (p. 21)
'When they put me in the grave, I know what it’ll say on the stone, if I get a stone, if they don’t bury me like a stray cat at the tip' (p. 29)
'I didn’t say goodbye to Dad! On account of a book' (p. 158)
'This photo won’t be out of my sight from now on. You’ve given me my sister back, Alec.' (p. 260)
Francis Westaway
'THE SHADOW CANNOT BE DEFEATED!' (p. 145)
'The toughest gang in Richmond! And they want me, Francis Westaway!' (p. 155)
'I see a purple jewel hanging on a gold chain. It’s a beaut, the prettiest thing I’ve ever seen…There’s no way I’m sharing this. It’s mine.' (p. 174)
'Do you understand how sensitive a reputation is? It’s up to me to be respectable. I’m the eldest. It’s my responsibility.' (p. 200)
Connie Westaway
'Ma sitting with her dress lifted up to her face, Connie on her knees beside her, holding her arms, cooing soft like Ma is a baby.' (Kip, p. 35)
'We women do what’s expected. You [men] can do almost anything you care to think of.' (p. 280)
'It seems that all my life I’ve had nothing I’ve desired and I’ve given up having desire at all. Now I know what it feels like to want and I will give anything to have it' (p. 285)
'I thought we’d have more time than this. We’ve only just made it.' (p. 290)
Jean Westaway
'Those moments, when [Kip] reminds me of Tom. I have to leave the room. The fury rises up my legs and up my body like a scream and it’s all I can do not to let it out.' (p. 212)
'We all die alone' (p. 212)
'This is not how I imagined it to be. Children. Mothering.' (p. 212)
'And for things like this, for girls like Connie and saving her future, there is a respectable woman who runs a business in Victoria Street' (pp. 221-222)
'I’d never of done it with boys but Connie, she was different.' (p. 239)
'we’re respectable people.' (p. 218)
Tom Westaway
‘Kipper’s old man…dropped off the tram in Swan Street somewhat worse for a whiskey or three and hit his head. Blam, splashed his brains all over the road. A sad end.’ (Pike, p. 24)
‘As a girl I had plenty of suitors, but none like Tom. Best behaviour in front of my father, children all brought up in the church by him.’ (p. 212)
Stanzi Westaway
‘The parcel is for Stanzi: inside is an old-fashioned coin, dull silver, with a king’s head on one side. It has a silver chain threaded through a hole in the middle. Stanzi looks like she’s about to cry.’ (Alec, p. 254)
‘She doesn’t mean to be hurtful. She is worries for me, that’s all…if she really thought I was in terrible trouble, she would be gentler.’ (Charlotte about Stanzi, p. 126)
‘the oblivious insouciance of the entitled’ (p. 51)
Charlotte Westaway
‘I say the question over and over: should I keep the baby?’ (p. 142)
‘The herbs are evidence of an understanding of our place in the universe…an acknowledgement of the delicate balance in our bodies…’ (p. 116)
‘There was only one place I could go: my sister’s’ (p. 124)
‘They contain all the hopes of the human spirit, all the refusal to quit, to keep believing people can feel better’ (p. 116)
Alec Westaway
‘Yet here I am. Away from home in a world of strangers. Alone. Forgotten.’ (p. 241)
‘This waiting for my life to start, it’s driving me mental.’ (p. 244)
‘I don’t sketch. Instead I concentrate on the scene the scene in front of me so I can remember it later.’ (p. 251)
Libby Westaway
‘All the things I remember, everything about my life, our family, my childhood: it’s all real because Libby knows it too.’ (Alec, p. 273)
Jack Husting
‘I can see both sides.’ (p. 80)
‘Just let me kiss you, Connie. I’d die a happy man.’ (p. 284)
Ava and Sylvester Husting
‘If we have to send boys to fight…it’s layabout boys with no responsibilities, the Kip Westaways of the world, who ought to be going.’ (Ava, p. 102)
‘That shilling. Our little secret. Gentlemen’s honour.’ (Sylvester, p. 8)
Annabel Crouch
‘You’re a good girl, Annabel.’ (Mr. Crouch, p. 177)
‘I’d like to compliment their dresses, but I don’t know what to say.’ (p. 190)
‘He is killing himself, I know that. I won’t have him for much longer.’ (Annabel, p. 207)
‘No mother, no brothers. Working your youth away, looking after an old man.’ (p. 179)
3. Themes, Ideas and Values
‘Family house, family suburb, family man’ (Charlotte about Kip, p. 140)
‘Stuck here…looking after your old man. You should have a family of your own by now.’ (Mr. crouch to Annabel, pp. 178-179)
The theme of family is a recurring one that develops over time. Jordan’s inclusion of other families such as the Crouches, the Churches, the McCarthys and the Stewarts stands in contrast to the Westaways. The juxtaposition of family life in this way allows the reader to see how such factors like wealth, class and reputation can affect the family dynamic especially within the war period. The idea of family is strained by the pressures of war because with many families' sons and husbands away it left the other family members to adopt other roles - not only physically, but the conventional emotional roles of traditional families of the time are redistributed, specifically within the Westaway household. Jordan postulates that the role family plays in providing emotional/physical support is of far greater importance than the necessity to abide by society's idea of what family should look like.
Women and Reproductive Rights
‘I tell her about shame and the way it’s always the women who wear it. I spare her nothing. I say loose women and no morals and I say bastard and I say slut.’ (Jean, p. 220)
‘You don’t have to have it, you know.’ (Stanzi, p. 132)
‘Your body, your choice…That’s what our feminist foremothers fought for’ (p. 134)
‘What if he wanted to know his child, doesn’t he have the right?’ (pp. 133-134)
Jordan highlights the controversial issues of premarital sex, abortion and the rights of women within the mid 20th and early 21st century. Indeed, it is this theme of women that becomes inextricably linked with the effect of a damaged reputation. When Connie falls pregnant, Jean implores that she has an abortion, in secret of course, in order to preserve her and her family’s reputation within the small community. The issue of abortion is later revisited when Charlotte becomes pregnant in the 1990s, where the contrast between the time periods becomes evident; while unplanned pregnancy is greatly stigmatised in the 1940s, the 1990s offers Charlotte a far wider array of options. It is through Jordan’s depiction of the two cases – Connie’s horrific backyard abortion, and Charlotte’s adjustment to parenthood – that she suggests the perceptions and attitudes towards morality, reputation and women have shifted over time, emphasising the importance of reproductive rights in the development of women.
Masculinity
‘I remember coming home from school once, crying. I would have been around six or seven. I was picked last for some team. That was me, the kid without a father.’ (Alec, p. 262)
‘”Westaway,” Cooper says. “Get in. For once in your life, do not be a pussy.”’ (p. 267)
Within the parameters of her text, Jordan articulates how men conform or reject masculine tropes in an effort to fit into society. Toughness, bulling and unsavory activity are presented as the characteristics of a man through such depictions of Mac and his gang. In its connection to the war period, the novel partly focuses on the notion that in order to be classified as a man he must first go through struggle and hardship as presented in the group of strangers taunting Jack, ultimately bullying him into certain ideals of masculinity which prove toxic and consequential - Jack dies as a result. It is Jordan who advocates for a balanced personality of both ‘masculine’ and 'feminine’ characteristics as suggested in the character development of Kip; evolving, learning and devising a true meaning of what it means to be a man outside of its conventional brutality.
Attitudes Towards Asia
‘She is with a customer or sweeping the floor with a broom made from free-range straw that died of natural causes or singing Kumbaya to the wheatgrass so it is karmically aligned.’ (Stanzi, p. 50)
‘The fear of the Nips coming made him a better man.’ (Annabel, p. 178)
‘always wanted to go to India [to study yoga] at a proper ashram.’ (pp. 132-133)
‘She makes her eyes go big and round like some manga puppy’ (p. 264)
Through both overt and subtle language, Jordan makes reference to the attitudes towards Asia which were prevalent at the time, specifically within the war period that saw many Australians ‘[fearing] the nip’. The derogative slang used for the Japanese represents a lack of understanding and fear (the bombing of Darwin and attack on Sydney left many feeling particularly vulnerable to the Japanese). Exacerbated by the fact that Japanese culture was not widely understood and was often misrepresented, the Japanese were stereotyped as brutal and inhuman. Over the course of the novel, attitudes towards Asia dramatically shift especially within the early 1990s of Stanzi and Charlotte's generation. The philosophical ideas of the east are often referenced by characters like Charlotte as she draws on them to make sense of her own complex life. The novel sees another shift in ideology represented through Alec as his generation's perception turns to a more commercial view. Asian culture has earned a place in mainstream media and western life without such gruesome and violent connotations as were previously held during the time of World War II.
By the way, to download a PDF version of this blog for printing or offline use, click here !
4. Literary Devices
- Throughout her perspective driven text, Jordan makes many references to classic novels which help create a literary context for the narrative and lend themselves to the evolution of the characters throughout the course of the text.
- Alexandre Dumas’ The Three Musketeers – Kip’s characteristic trait of heroism when he sees the gang waiting for him and says ‘on-bloody-guard, d’Artagnan’ (p. 22)
- Charles Dickens’ Great Expectations and Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn – both coming-of-age stories about young men struggling within a tough world, only getting by on their wits and strength.
- Brontë sisters' Jane Eyre and Wuthering Heights – their reference is used in discerning a customer’s knowledge on the texts, but reveals only a surface level understanding due to the novels carrying a certain cultural value.
- Jonathan Swift’s Gulliver’s Travels – referenced by Jack Husting in relation to his adventures in the country. Its use pertains to how Jack feels out of place in his home town after leaving a boy and returning a grown man.
- A historical novel that plays with ideas of placing invented characters into a reconstructed world of the past.
- Uses elements of both realism and impressionism to create the text.
Realist Elements:
- A strong focus on everyday life within a particular society with reference to real historical detail.
- Incorporates a logical and strong foundation of context that can be easily digested and believed by the reader.
- Can use an omniscient narrator (all-knowing).
Impressionist Elements:
- Each chapter offers detail and presents a vivid interpretation of specific events.
- Sensory experiences are emphasised by the use of descriptive and poetic language.
- The linear flow of the narrative is disrupted by its construction in a non-chronological order, thereby forcing the reader to piece the whole narrative together at the end.
- Varied depending on the character’s perspective and time of perspective.
- Language is used to historicise each chapter through use of slang, colloquialisms, formal and proper English.
- The novel revolves around the Westaway’s family home in Rowena Parade, Richmond over the course of four generations.
- Rather than them move or the location change it evolves, paralleling the growth and evolution undergone by each of the Westaway family members.
- Inspired by a photograph in the collection of Argus war photos held at the State Library of Victoria, Jordan uses this image capturing a private and intimate moment to establish the premise for each of the book's chapters.
- Titled Nine Days and composed of nine unique perspectives on life at a given time, Jordan offers insight into the emotional livelihood of each narrator and attaches both intimate and historical significance to their stories.
5. Essay Topics
- Toni Jordan’s Nine Days describes a world in which life in the 1930s and 40s was much harder than life in the 21st century. Do you agree?
- In Nine Days , older Kip’s point of view is very unrealistic. To what extent do you agree?
- Toni Jordan’s Nine Days shows us people can choose whether they end up happy or not. Discuss.
- The mood by the end of Nine Days is ultimately uplifting and positive. Do you agree?
- There is more tragedy in Nine Days than there is joy. To what extent do you agree?
- Nine Days , by Toni Jordan, shows the best and worst of Australian culture. Discuss
- Jordan suggests that appreciation of family is integral to personal happiness. Discuss.
- 'Your body, your choice.' What do the different experiences of Connie and Charlotte reveal about changing societal attitudes towards women?
- There are many characters who are largely hidden figures within the text. What significance is produced by including and excluding different perspectives?
6. Essay Topic Breakdown
Whenever you get a new essay topic, you can use LSG’s THINK and EXECUTE strategy - a technique to help you write better VCE essays. This essay topic breakdown will focus on the THINK part of the strategy. If you’re unfamiliar with this strategy, then check it out in How To Write A Killer Text Response because it’ll dramatically enhance how much you can take away from the following essays and more importantly, your ability to apply this strategy in your own writing.
Within the THINK strategy, we have 3 steps, or ABC. These ABC components are: Step 1: A nalyse Step 2: B rainstorm Step 3: C reate a Plan
THINK How-based prompt: How does Nine Days explore the relationship between the past and the present ?
This is a ‘how’ essay prompt, so in our planning, we need to identify the ways in which the author accomplishes their task. When analysing your question it is important to know what the question is asking of you, so make sure you highlight the keywords and understand their meaning by themselves and in the context of the question. For example, this question is not just asking about the past and present, but rather the connection between the two - so if you discussed the past and the present separately you wouldn’t be answering the question.
Brainstorming is different for everyone, but what works for me is focusing on the key idea, which here would be the relationship between the past and the present, and listing my thoughts out. Not all the ideas will be as equally relevant/good, but I like to have things written down to then improve or simply not use in favour of other ideas.
Past → Present: Westaway family home, the house changes as the family grows Past → Present: Connie’s tragic abortion compared to Charlotte’s options in the 1990s, women’s rights evolving over time Past → Present: Melbourne becoming more multicultural, Alec’s chapter reveals how Melbourne has changed compared to chapters set in earlier times Past → Present: Kip teaching Alec to cherish those in front of us after seeing Connie’s picture Past → Present: Second World War contrast to 9/11 and war in Afghanistan
Now that I have all my ideas listed out I choose my strongest three to flesh out. There are different things that make an idea strong, but the things I consider are: - Do I have enough evidence to support this idea? - Is the idea substantial enough to turn into a whole paragraph? - Do I have an author’s views and values statement? - Can I include context or metalanguage into this idea?
Using the questions above, I decided to use the following ideas: - Westaway family home, the house changes as the family grows (symbolism) - Kip teaching Alec to cherish those in front of them (focus on characterisation) - Melbourne becoming more multicultural (can talk about historical context)
Contention: Through the use of setting and characterisation, Jordan’s Nine Days reveals how the past and present are interconnected. P1: Westaway home embodying the familial connection P2: The past is not completely separate from the present, it teaches us lessons that are pertinent to contemporary life (Alec) P3: Melbourne becoming more multicultural
If you found this helpful, then you might want to check out our A Killer Text Guide: Nine Days ebook which has an A+ sample essay in response to this prompt, complete with annotations on HOW and WHY the essay achieved A+! The study guide also includes 4 more essay topic breakdowns and sample A+ essays, detailed analysis AND a comprehensive explanation of LSG’s unique BBT strategy to elevate your writing!
Hey everyone! This is Part 2 in a series of videos I will release on VCE Study Guides. The content goes through the sample VCAA Chickens Range Free article which you can find here . Feel free to analyse it yourself, then check out how I’ve analysed the article!
I’m super excited to share with you my first ever online tutorial course for VCE English/EAL students on How to achieve A+ for Language Analysis !!!
I created this course for a few reasons:
Language Analysis is often the key weakness for VCE English/EAL students, after my workshops, students always wish we had spent even more time on Language Analysis, many of you have come to me seeking private tuition however since I am fully booked out, I wanted to still offer you a chance to gain access to my ‘breakthrough’ method of tutoring Language Analysis,I am absolutely confident in my unique and straightforward way of teaching Language Analysis which has lead to my students securing exceptional A graded SAC and exam scores!
Are you a student who:
struggles to identify language techniques?
finds it difficult to identify which tones are adopted in articles?
has no idea explaining HOW the author persuades?
finds it difficult to structure your language analysis essay?
becomes even more unsure when comparing 2 or 3 articles?
feels like your teacher at school never explained language analysis properly?
prefers learning when it’s enjoyable and easy to understand?
wants to stand out from other students across the cohort?
wants to know the secrets of 45+ English high achievers?
wants to know what examiners are looking for?
sees room for improvement whether you’re an average student or a pro?
wants to get a head start and maximise your potential in VCE?
This is what you will accomplish by the end of the course:
Be able to successfully identify language techniques in articles and images
Be able to successfully identify tones adopted in articles and images
Be able to analyse a single article or image
Be able to analyse 2 or more articles and/or images
Be able to apply your new skills coherently and clearly in essay writing
You will be able to accurately describe HOW an author uses language to persuade
You will be able to plan and write a language analysis essay structure (single article/image)
You will be able to plan and write a language analysis essay structure (2 or more articles/images)
You will understand common pitfalls and how to avoid these in language analysis
Be confident when approaching your SACs and exam
Know exactly what examiners are looking for and how to ‘WOW’ them
Know how to distinguish yourself from other students
Have unlimited help in course forum from myself and other VCE students
You will become a better VCE English language analysis student!
To find out more, you can check out the full details of the course here !
See you in the course!
Get exclusive weekly advice from Lisa, only available via email.
Power-up your learning with free essay topics, downloadable word banks, and updates on the latest VCE strategies.
latest articles
Check out our latest thought leadership on enterprise innovation., vce english unit 3, area of study 2: creating texts - what is it.

Breaking Down Themes & Key Quotes in The Erratics by Vicki Laveau-Harvie

Developing Interpretations SAC Guide: Interpreting Alias Grace
Keep in touch
Have questions? Get in touch with us here - we usually reply in 24 business hours.
Unfortunately, we won't be able to answer any emails here requesting personal help with your study or homework here!

Copyright © Lisa's Study Guides. All Rights Reserved. The VCAA does not endorse and is not affiliated with Lisa's Study Guides or vcestudyguides.com. The VCAA provides the only official, up to date versions of VCAA publications and information about courses including the VCE. VCE® is a registered trademark of the VCAA.
03 9028 5603 Call us: Monday to Friday between 3pm - 6pm or leave us a message and we'll call you back! Address: Level 2 Little Collins St Melbourne 3000 VIC
VCE ENGLISH: Write a Text Response Introduction
One of the most important pieces of knowledge to any Year 12 English student is how to write a text response essay. Commonly seen as the easiest essay, the method of structuring a text response is often overly simplified, or simply not understood by students! The introduction to an essay is the very first thing your examiner/teacher will read, and is therefore very important to helping you immediately stand out and differentiate yourself from the crowd.
Firstly, your introduction is important because it is a key aspect to fulfilling the criterion of appropriate structure. Be clear and concise: it is always better to be clear than to use lots of big words which are not appropriate for the situation.
An introduction can be divided into three steps:
- Firstly, briefly set up context . This might include the type of text (e.g. play, novel, short stories, poem collection etc.), very basic historical context (time period, subject matter), and any very important information which is the basis to the essay. Definitely do not spend more than one sentence doing so, as the most important part of the essay is to show your own opinion/knowledge of the given text, not just summarising what it is about.
- Explicitly outline your contention . Your contention must be clearly addressing all aspects of the topic you are given, and it also needs to demonstrate that you can think independently (if you are aiming for top grades), even uniquely. Your angle on the topic is the single most important aspect to the essay.
- Finally, briefly signpost the upcoming arguments in your essay. These are the points, or mini-contentions, forming the basis of each body paragraph. You should aim for at least 3 body paragraphs, up to 5 if you are ambitious. These mini-contentions must each relate both to the overall contention, and thus to the topic, which will add a feeling of cohesion and continuity to the essay
Overall, there is no need to write more than three or four or so sentences! If you write these sentences well, however, you will immediately create a positive impression of the essay, crucial to gaining the reader's attention.
If you loved this article, you will LOVE all of our other articles, such as: Effective Study Techniques , The ATAR and The Importance of Practice .
About Learnmate
Learnmate is a trusted Australian community platform that connects students who want 1:1 or small group study support, with tutors who are looking to share their knowledge and earn an income. From primary school to high school subjects — from science and maths to niche subjects like visual communication — Learnmate can help you improve academic performance or boost confidence, at your pace with the tutor that you choose.
We pride ourselves in offering a reliable and positive experience for both our students and tutors. Every tutor that joins the platform is vetted to meet a level of academic excellence, teaching qualification or relevant experience. All tutors are provided the opportunity to complete professional training.
Students and parents can easily find and screen for tutors based on their location, their subject results or skill level, and whether they provide in-person or online sessions. Learnmate is proud to provide tutors in Melbourne , Sydney , Geelong , Brisbane , Hobart , Canberra , Perth & Adelaide , and other locations.
Learnmate also has tutors for all curriculums: HSC , IB , QCE , BSSS, SACE , TASC, WACE , VCE and UMAT
Go online and let Learnmate help you get ahead. Start your search today.
"> "> share this post.
Article Author
Find online & in-person tutors near you, recent posts.

VCE SACs: Maximising Your Scores and Understanding Their Impact
Mastering VCE SACs: A Comprehensive Guide As part of the Victorian Certificate of Education (VCE), School Assessed Coursework (SACs) are...
March 26, 2024

Understanding Liquidity Analysis in VCE Accounting: Part One
In the latter part of the VCE Accounting course, students focus extensively on evaluating the financial performance of businesses. An...
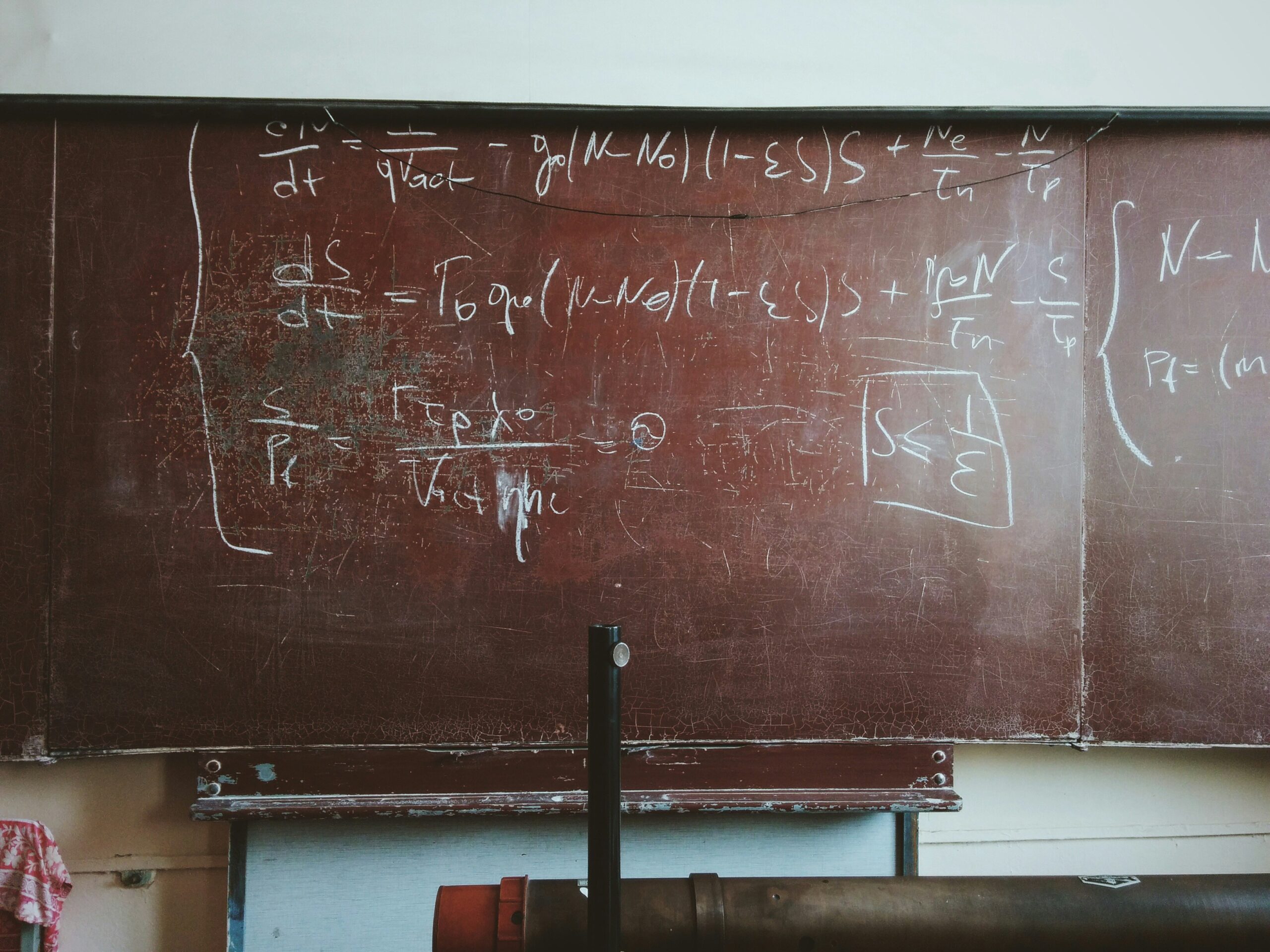
Understanding Composite Functions in VCE Maths Methods: A Guide to Understanding and Applying Them
Hi there! My name is Daniela and I am a VCE Math Methods and Biology tutor on Learnmate. I graduated...
March 13, 2024


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The good news is, all of that learning is now funnelled into VCE’s Text Response, one of the three parts of the VCE English study design. Text Response, officially known as ‘Reading and Responding’ in the study design, is the first Area of study (AoS 1) - meaning that the majority of students will tackle the Text Response SAC in Term 1.
Section A – Your Analytical Interpretation of a Text. The first text response within your VCE English examination will require you to pick a text in which you have studied thoroughly in Unit 3 and write your own analytical interpretation of the text. The exam will provide two essay questions for each text and you will choose one to respond to.
How to write a great text response essay for VCE English? Here I share the template structure that I used that help me achieve a raw 50 and a Premier's award...
Tip #4: Don’t Quote Everything in Your Essay. It’s normal to feel overwhelmed by the amount of text that you are presented with in an article, as well the short amount of time you have to analyse it. As surprising as it may sound, to write a good VCE argument analysis you do not need to analyse everything. Instead, it is about how you pick ...
An expert summary on Essay Structure for VCE English 1&2. Covers everything you need to know to write top essays and ace your SAC's and exams!Sign up for ton...
An essay introduction should contain four main elements: The title and author of the text. A clear contention. Body paragraph signposting. Metalanguage or vocabulary specific to each text and prompt. A contention is an argument, usually articulated in a single sentence, that responds directly to the essay prompt.
Your piece will be a creative response, after all, so you should apply the conventions of this style of writing. Firstly, your creative should follow the structure of a beginning, middle, and end. We can also think of this as rising tension, climax, and resolution. Secondly, you should develop an authentic use of language, voice and style to ...
Tip #1: Create a table of themes and motifs. Create a table of themes and motifs within the studied text, combining overarching ideas and quote combinations. This ‘ TEE table ‘ will allow you to group your ideas and establish pockets of knowledge that will come in handy when approaching an essay question.
VCE ENGLISH: Write a Text Response Introduction. One of the most important pieces of knowledge to any Year 12 English student is how to write a text response essay. Commonly seen as the easiest essay, the method of structuring a text response is often overly simplified, or simply not understood by students! The introduction to an essay is the ...