116 Air Pollution Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on air pollution, ✍️ air pollution essay topics for college, 🎓 most interesting air pollution research titles, 💡 simple air pollution essay ideas, ❓ research question about air pollution.
- Effects of Air Pollution on Health
- Air Pollution: Effects
- Air Pollution Solutions: How to Improve Air Quality
- Electric Vehicles: Addressing Air Pollution
- Air Pollution in New York City
- Air Pollution: Conducting a Quantitative Study
- Community’s Role in Fighting Air Pollution
- Air Pollution in the UAE and Its Management The following project focuses on investigating the problem of air pollution in the UAE and how it can be managed.
- Environmental Wellness and Problem of Air Pollution Air pollution is one of the main factors affecting the environment. It can be considered as any change in its properties that has a deleterious effect.
- Beijing Looks for Answers to Air Pollution Beijing has undertaken various projects aimed at improving the city’s infrastructure, reducing pollution from coal-fired power plants, and reducing vehicle emissions.
- Environmental Issues: Air Pollution One of the central environmental problems in today’s world is air pollution. With the development of cities, people expand the reach of their technology.
- Air Pollution in South Carolina In South Carolina, one of the most urgent environmental problems is air pollution with ozone and particles, which is hazardous to human health due to deadly diseases likelihood.
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Air Pollution Mobility changes in all types of indoor and outdoor settings have a substantial long-term influence on CO emissions at the national and regional levels.
- The Aerodyne Research Firm: Air Pollution Studies Aerodyne Research is a limited liability company that researches air and air pollution levels, one of the world’s most pressing environmental issues today.
- Electric Vehicles: The Roles in Air Pollution The main purpose of electric vehicles is to eliminate the direct contribution to air pollution through emissions.
- Air Pollution Crisis and Climate Change in China Air pollution is a serious problem in many countries, including China. The main source of air pollutants is fumes from burning fuels in industries or vehicles.
- Methodological Flaws in Studies of Air Pollution and COVID-19 Death Rates The research reviews the considerations related to studying the correlation between ambient air pollution and its effects on the symptoms of COVID-19.
- Air Pollution in the United States Environmental problems affect climatic conditions negatively. In this case, we will discuss air pollution. Air pollution introduces harmful substances into the air.
- Air Pollution Crisis in China and Its Impact on Economy In large industrialized countries such as China, the emission of carbon dioxide has a negative impact on climate conditions, which is hitting the national economy.
- The Effects of Air Pollution The paper addresses air pollution, its causes, significant pollutants, adverse effects of indoor pollutants and air pollution, and air pollution control.
- Outdoor Air Pollution and Uncontrolled Asthma in the San Joaquin Valley, California The study’s purpose was to examine the relationship between air pollution and cases of uncontrolled asthma in the San Joaquin Valley.
- Air Pollution and Its Consequences The paper states that air pollution has been an increasingly major problem affecting the economy, people’s health, and the environment.
- Role of Small Gas-Powered Engines in Air Pollution The purpose of this paper is to discuss the role of small gas-powered engines in air pollution and the associated controversy.
- The Correlation Between Air Pollution and Health The sampled study analyzes and explains how air pollution affect life expectancy and other measures of health.
- Air Pollution Resulting From Small Gas Powered Engines The paper seeks to discuss the effects of small gas-powered engines on air pollution and suggest possible solutions to reduce the levels of air pollution.
- How Air Pollution Impacts Health Air pollution causes a wide range of serious health abnormalities in one’s body. It severely affects the respiratory system, leading to a number of complications.
- The Impact of Air Pollution on Human Health and Well-Being Air pollution causes a wide range of health abnormalities in one’s body. A number of pollutants can cause lung cancer and even some non-lung cancer forms.
- Air Pollution as a Health Risk Factor: Policy Proposal Air pollution is one of the most critical health risk factors. Prolonged exposure to polluted air can result in cancer and respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Providing Solutions for Air Pollution The reasons for air pollution regulations, explaining the concept of averaging time in the U.S. National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS), explaining emission offsets.
- The Alleviation Plans to Air Pollution Throughout the World Air Quality Mitigation Plan is a proposed project which aims at reducing the emissions that affect the air quality by at least fifteen percent.
- Air Pollution: Effects and Regulations This essay analyzes the air pollution effects and regulations based on a simple observation of a smoke coming from a large smokestack.
- Evaluating the Efficacy of Government Spending on Air Pollution Control: A Case Study From Beijing While living in a city often means better conditions and access to goods and services, rapid urban development has been associated with adverse health outcomes due to air pollution.
- Beijing’s Air Pollution Crisis Resolution Beijing’s struggle with poor air quality is far from over. Nevertheless, the government demonstrated its commitment to reducing particulate matter in the atmosphere.
- Clean Air Act: Overall Air Pollution Reducing The problem of environmental pollution and, in particular, the air became especially urgent after the emergence of large industrial enterprises operating on harmful fuel.
- Air Pollution Threats: Parent Education The purpose of this pamphlet is to educate parents on the dangers of air pollution and suggest preventive strategies to keep their children safe.
- Air Pollution Health Risks Information Campaign This paper is dedicated to developing and planning an information campaign about Air Pollution Health Risks in a suburban community with a population of 20,000.
- International Trade and Air Pollution: The Economic Costs of Air Emissions From Waterborne Commerce Vessels in the United States
- Acid Rain Formula and Air Pollution Problem
- Chronic Respiratory Problems: The Link With Air Pollution and Considerations in Medical Care
- Air Pollution and Its Effects on Cancer Risks
- Toxins That Contribute to Air Pollution and Their Effect on Humans
- Adaptive Policy Mechanisms for Transboundary Air Pollution Regulation: Reasons and Recommendations
- Interaction Between Local Air Pollution and Global Warming Policy and Its Policy Implications
- Main Problems for Planet Earth: Air Pollution and Water Pollution
- Addressing Air Pollution Threats With Air Purifiers
- Economic Instruments for Controlling Air Pollution
- Air Pollution and Climate Change in Tanzania
- Demand for Indoor Air Pollution Abatement Interventions
- Protecting China’s Children: Valuing the Health Impacts of Reduced Air Pollution in Chinese Cities
- How Cities Around the World Combat Air Pollution?
- Managing Air Pollution With Urban Transportation
- Controlling Urban Air Pollution Caused by Households: Uncertainty, Prices, and Income
- Measuring Health Benefits From Air Pollution Reduction in Kathmandu Valley
- Air Pollution and ‘Dirty’ Industries: How and Why Does the Composition of Manufacturing Output Change With Economic Development
- Intra-Country Health Inequalities and Air Pollution in Developing Countries
- Air Pollution and Its Effect on Our Health
- Using Clean Coal Technologies to Reduce Air Pollution
- Environment and Happiness: Valuation of Air Pollution in Ten European Countries
- Compliance and Enforcement: Air Pollution Regulation in the U.S. Steel Industry
- State Responsibility for Transboundary Air Pollution in International Law
- Air Pollution: Anthropogenic and Natural Sources, and Conditions in Thailand
- Integrated Air Pollution Management in China: Developing Particulate Matter Control
- Air Pollution and Acute Respiratory Illness: Evidence From Taiwan and Los Angeles
- China’s Air Pollution and Its Effect on COPD Patients
- Air Pollution and Breathing That Kills You
- Educational and Technological Solutions to Air Pollution
- Politics and the True Effects of Air Pollution
- Air Pollution and Energy Loss Due to Construction Activities
- Does Inequality Matter Air Pollution and Health Relationship?
- Air Pollution and Respiratory Ailments Among Children in Urban India: Exploring Causality
- Lung Cancer and CVD Mortality Associated With Ambient Air Pollution
- Environmental Quality and Development: Is There a Kuznets Curve for Air Pollution Emissions?
- Clearing the Air: The Health and Economic Damages of Air Pollution in China
- Reducing Air Pollution Through the Use of Oxygenated Gasoline
- Air Pollution and How It Affects Plants and Animals
- Forest Fires, Air Pollution, and Mortality in Southeast Asia
- Air Pollution and Mortality: Estimating Regional and National Dose-Response Relationships
- Handle With Care: The Local Air Pollution Costs of Coal Storage
- Air Pollution and Infant Health: Lessons From New Jersey
- The Correlation Between Air Pollution and Human Health
- Cost-Effective Control Strategies for Energy-Related Transboundary Air Pollution in Western Europe
- Air Pollution, Children’s Health, and Socio-Economic Status: The Effect of Outdoor Air Quality on Asthma
- The Effects and Costs of Air Pollution on Health Status in Great Britain
- Indoor Air Pollution: Home Is Where the Hazard Is
- Air Pollution and Some of the Diseases and Problems It Causes
- Creating Markets for Air Pollution Control in Europe and the USA
- What Are the Major Sources of Outdoor Air Pollution?
- How Does Air Pollution Lead to Ocean Acidification?
- How Does Air Pollution Affect Biodiversity?
- How Does Urban Sprawl Contribute to Air Pollution?
- Which Gas in the Air Pollution Can Affect Blood Stream Causing to Death?
- How Does Air Pollution Affect Marine Life?
- What Ecosystem Services Are Disrupted by Air Pollution?
- How Does Air Pollution Affect the Lithosphere?
- What Is the Current U.S. Air Pollution Policy?
- What Are the Ways to Reduce Air Pollution and Slow Climate Change?
- How Does Wind Erosion Cause Air Pollution?
- How Does Air Pollution Compromise Human Health?
- What Are Chemicals Typically Found in Air Pollution?
- How Does Air Pollution Affect the Hydrosphere?
- What Are the Natural Sources of Air Pollution?
- How Does Air Pollution Affect Climate Change?
- How Extraction and Combustion of Fossil Fuel Affect Air Pollution?
- How Can Air Pollution and Animal Agriculture Link Together?
- How Do Scientists Studying Air Pollution Affect the Politics and Society?
- What Are the Global Effects of Air Pollution?
- How Does Atmospheric Circulation Affect Air Pollution?
- What Is China Doing About Air Pollution?
- How Does Air Pollution Affect the Carbon Cycle?
- How Could Chemists Be Involved in Addressing Concerns About Air Pollution?
- Do Nuclear Power Plants Cause Air Pollution?
- Are the Most Common Air Pollutants Caused by Chemical Processes?
- How Do Smokers Contribute to Air Pollution?
- What Is the Cost-Effective Means of Controlling Air Pollution?
- What Cardiovascular Diseases Are Caused by Air Pollution?
- Is Air Pollution Mainly a Local Problem or Can It Travel Long Distances?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, October 26). 116 Air Pollution Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/air-pollution-essay-topics/
"116 Air Pollution Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 26 Oct. 2022, studycorgi.com/ideas/air-pollution-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) '116 Air Pollution Essay Topics'. 26 October.
1. StudyCorgi . "116 Air Pollution Essay Topics." October 26, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/air-pollution-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "116 Air Pollution Essay Topics." October 26, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/air-pollution-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "116 Air Pollution Essay Topics." October 26, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/air-pollution-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Air Pollution were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on December 26, 2023 .

Air Pollution Research Paper Topics

This comprehensive guide to air pollution research paper topics is designed to assist students studying environmental science in selecting a suitable topic for their research paper. The guide provides a broad range of topics divided into ten categories, each containing ten unique research topics. Additionally, the guide offers expert advice on how to choose a topic from the multitude of air pollution research paper topics and how to write a compelling research paper on air pollution. The guide also introduces iResearchNet’s writing services, which offer students the opportunity to order a custom air pollution research paper on any topic. The services include a range of features designed to ensure the delivery of high-quality, custom-written papers.
100 Air Pollution Research Paper Topics
Air pollution is a critical environmental issue that affects every living being on the planet. It is a topic that requires in-depth understanding and research. To aid students in their quest for knowledge and to help them in their academic pursuits, we have compiled a comprehensive list of air pollution research paper topics. These topics are categorized into ten different sections, each containing ten unique topics.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Causes of Air Pollution
- The role of industrialization in air pollution.
- The impact of transportation on air pollution.
- The effect of agriculture on air pollution.
- The influence of waste disposal on air pollution.
- The role of deforestation in air pollution.
- The impact of urbanization on air pollution.
- The effect of household activities on air pollution.
- The influence of natural disasters on air pollution.
- The role of power generation in air pollution.
- The impact of mining activities on air pollution.
Effects of Air Pollution
- The impact of air pollution on human health.
- The effect of air pollution on the environment.
- The influence of air pollution on climate change.
- The role of air pollution in biodiversity loss.
- The impact of air pollution on agriculture.
- The effect of air pollution on water bodies.
- The influence of air pollution on the ozone layer.
- The role of air pollution in acid rain.
- The impact of air pollution on urban heat islands.
- The effect of air pollution on mental health.
Air Pollution and Climate Change
- The role of air pollution in global warming.
- The impact of air pollution on weather patterns.
- The influence of air pollution on greenhouse gas emissions.
- The role of air pollution in climate change mitigation.
- The impact of air pollution on climate change adaptation.
- The effect of air pollution on carbon sequestration.
- The influence of air pollution on climate change policies.
- The role of air pollution in climate change communication.
- The impact of air pollution on climate change denial.
- The effect of air pollution on climate change education.
Air Pollution Policies
- The effectiveness of the Clean Air Act in addressing air pollution.
- The impact of the Paris Agreement on air pollution.
- The role of national policies in mitigating air pollution.
- The influence of international cooperation on air pollution.
- The effectiveness of emission standards in addressing air pollution.
- The role of renewable energy policies in mitigating air pollution.
- The impact of transportation policies on air pollution.
- The influence of waste management policies on air pollution.
- The effectiveness of urban planning policies in addressing air pollution.
- The role of education policies in mitigating air pollution.
Air Pollution Solutions
- The role of renewable energy in mitigating air pollution.
- The impact of energy efficiency on air pollution.
- The influence of green building on air pollution.
- The effectiveness of public transportation in addressing air pollution.
- The role of waste management in mitigating air pollution.
- The impact of urban green spaces on air pollution.
- The influence of sustainable agriculture on air pollution.
- The effectiveness of carbon capture and storage in addressing air pollution.
- The role of education in mitigating air pollution.
- The impact of individual actions on air pollution.
Air Pollution and Society
- The social impacts of air pollution.
- The role of media in shaping perceptions of air pollution.
- The influence of air pollution on social inequality.
- The impact of air pollution on social movements.
- The role of community engagement in addressing air pollution.
- The influence of air pollution on public health policies.
- The impact of air pollution on economic development.
- The role of air pollution in urban planning.
- The influence of air pollution on migration patterns.
- The impact of air pollution on cultural practices.
Air Pollution and Health
- The impact of air pollution on respiratory diseases.
- The role of air pollution in cardiovascular diseases.
- The influence of air pollution on allergies.
- The impact of air pollution on mental health.
- The role of air pollution in premature deaths.
- The influence of air pollution on children’s health.
- The impact of air pollution on elderly health.
- The role of air pollution in health inequalities.
- The influence of air pollution on public health interventions.
- The impact of air pollution on health care costs.
Air Pollution and Technology
- The role of technology in monitoring air pollution.
- The impact of technology on reducing air pollution.
- The influence of technology on air pollution modeling.
- The role of technology in air pollution forecasting.
- The impact of technology on air pollution communication.
- The influence of technology on air pollution policies.
- The role of technology in air pollution education.
- The impact of technology on air pollution mitigation.
- The influence of technology on air pollution adaptation.
- The role of technology in air pollution research.
Air Pollution and Economy
- The economic impacts of air pollution.
- The role of air pollution in economic inequality.
- The influence of air pollution on economic development.
- The impact of air pollution on economic policies.
- The role of air pollution in economic planning.
- The influence of air pollution on economic growth.
- The impact of air pollution on economic sustainability.
- The role of air pollution in economic transitions.
- The influence of air pollution on economic resilience.
- The impact of air pollution on economic sectors.
Air Pollution and Ethics
- The ethical implications of air pollution.
- The role of ethics in air pollution policies.
- The influence of ethics on air pollution communication.
- The impact of ethics on air pollution mitigation.
- The role of ethics in air pollution adaptation.
- The influence of ethics on air pollution research.
- The impact of ethics on air pollution education.
- The role of ethics in air pollution decision-making.
- The influence of ethics on air pollution justice.
- The impact of ethics on air pollution futures.
This comprehensive list of topics is designed to inspire and guide students in their quest for knowledge about air pollution. Each topic is a doorway to a vast field of research and understanding. As you embark on your academic journey, remember that the goal is not just to write a research paper but to contribute to the global understanding of air pollution and its impacts. Your research could be the key to solving one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time.
Air Pollution Research Guide
Air pollution is a pressing global issue that poses significant threats to human health and the environment. As students studying environmental science, it is essential to delve into the complexities of air pollution and understand its causes, impacts, and potential solutions. Writing research papers on air pollution topics not only enhances our knowledge but also contributes to the collective effort in combating this environmental challenge. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore a wide range of air pollution research paper topics to inspire and assist you in your academic journey.
The field of environmental science has increasingly focused on air pollution due to its detrimental effects on air quality, climate change, and public health. As the world grapples with the consequences of human activities and industrialization, it becomes crucial to investigate the different dimensions of air pollution and develop innovative approaches to mitigate its impact. Research papers serve as a valuable tool for investigating and disseminating knowledge about air pollution, making them an integral part of environmental science education.
The primary aim of this page is to provide students like you with an extensive array of air pollution research paper topics. By exploring diverse and engaging topics, you can gain a deeper understanding of the various aspects related to air pollution, ranging from its sources and consequences to policy interventions and sustainable solutions. Whether you are just starting your research journey or seeking inspiration for a specific area of interest, this comprehensive list will serve as a valuable resource to guide your exploration and empower you to contribute meaningfully to the field.
Moreover, this page offers expert advice on how to choose the most suitable air pollution research paper topics. With the abundance of available topics, it is important to select a research question that aligns with your interests, academic goals, and the current needs of the field. Our expert tips will help you navigate through the vast landscape of air pollution research and enable you to select a topic that is both relevant and impactful.
In addition to topic selection, we will also provide guidance on how to write an effective air pollution research paper. Writing a research paper requires a systematic approach, from conducting a literature review and collecting data to analyzing findings and presenting a coherent argument. By following our step-by-step instructions and incorporating our writing tips, you can enhance the quality and rigor of your research paper, ensuring that your work makes a valuable contribution to the field of environmental science.
Furthermore, to support your academic journey, we introduce our writing services, offering you the opportunity to order a custom air pollution research paper tailored to your specific requirements. Our team of expert degree-holding writers specializes in environmental science and is equipped with the knowledge and skills to deliver top-quality research papers. With a commitment to in-depth research, customized solutions, and timely delivery, our writing services provide a convenient and reliable option for students seeking assistance in their academic endeavors.
Choosing an Air Topic for Research
Choosing the right air pollution research paper topic is a crucial step in the research process. It sets the foundation for your study and determines the direction of your research. With the vast scope of air pollution issues, it can be challenging to narrow down your focus and select a topic that is both relevant and compelling. In this section, we provide expert advice and 10 valuable tips to help you navigate the process of choosing air pollution research paper topics effectively.
- Identify your research interests : Start by reflecting on your personal interests within the field of air pollution. What aspects of air pollution intrigue you the most? Are you interested in studying the health effects, the impact on ecosystems, policy interventions, or technological solutions? Identifying your research interests will guide you towards topics that resonate with your passion and motivation.
- Consider current issues and debates : Stay informed about the latest developments and ongoing debates in the field of air pollution. Read scientific journals, news articles, and policy reports to understand the pressing issues and emerging trends. By choosing a topic that addresses current concerns, you contribute to the existing knowledge and engage in the relevant conversations.
- Conduct preliminary research : Before finalizing a topic, conduct preliminary research to familiarize yourself with the existing literature and identify research gaps. This will help you refine your research question and ensure that your topic contributes to the existing knowledge base. Look for recent studies, key theories, and seminal works that can provide a solid foundation for your research.
- Define the scope of your study : Determine the scope and boundaries of your research. Are you focusing on a specific geographic region, a particular pollutant, or a certain population group? Clarifying the scope of your study will help you narrow down your topic and ensure that it is manageable within the given time and resources.
- Consider interdisciplinary approaches : Air pollution is a complex issue that requires interdisciplinary perspectives. Consider integrating concepts and methods from various fields such as environmental science, public health, engineering, sociology, and policy studies. This interdisciplinary approach can lead to innovative research and contribute to a holistic understanding of air pollution.
- Engage with stakeholders : Air pollution affects various stakeholders, including communities, policymakers, industry professionals, and advocacy groups. Engaging with these stakeholders can provide valuable insights and enhance the relevance of your research. Consider topics that address the concerns and needs of different stakeholders, ensuring that your research has practical implications and can make a meaningful impact.
- Seek guidance from your professors and mentors : Consult with your professors and mentors who have expertise in the field of air pollution. They can provide valuable guidance, suggest potential research topics, and help you refine your research question. Utilize their knowledge and experience to ensure that your topic aligns with current research trends and academic standards.
- Consider the availability of data : Before finalizing your research topic, consider the availability of data and resources. Ensure that you have access to reliable and relevant data sources that will support your research objectives. Assess the feasibility of data collection and analysis, considering factors such as time constraints, cost, and ethical considerations.
- Aim for a balance between novelty and significance : While it is important to choose a topic that is unique and novel, also consider its significance within the broader field of air pollution research. Balance your desire to explore new avenues with the need for topics that contribute to the existing body of knowledge and have real-world implications.
- Think critically and creatively : Finally, approach the topic selection process with a critical and creative mindset. Think beyond the conventional boundaries and explore unconventional ideas. Consider innovative research methodologies, alternative perspectives, and emerging trends in air pollution research. By thinking critically and creatively, you can identify research topics that are both intellectually stimulating and have the potential for significant contributions.
By following these expert tips, you can navigate the process of choosing air pollution research paper topics with confidence and clarity. Remember that the topic you choose will shape the entire research process, so take the time to select a topic that aligns with your interests, expertise, and aspirations. Now, let’s move on to the next section, where we will provide you with valuable insights on how to write an impactful air pollution research paper.
How to Write an Air Pollution Research Paper
Writing an air pollution research paper requires careful planning, systematic research, and effective organization. In this section, we will guide you through the essential steps and provide you with 10 tips to help you write a well-structured and compelling research paper on air pollution.
- Understand the research question : Start by clearly understanding the research question or objective of your study. Define the specific aspect of air pollution that you intend to investigate and the key research aims. This will provide you with a focused direction and ensure that your paper addresses the core issues related to air pollution.
- Conduct a comprehensive literature review : Before diving into your research, conduct a thorough literature review to familiarize yourself with the existing body of knowledge on air pollution. Identify key theories, concepts, and empirical studies relevant to your topic. The literature review will help you identify research gaps and build a strong theoretical foundation for your study.
- Develop a clear research methodology : Determine the research methodology and data collection techniques that align with your research objectives. Will you conduct experiments, surveys, interviews, or analyze existing datasets? Clearly define your research design, sampling strategy, and data analysis methods to ensure the rigor and validity of your findings.
- Collect and analyze data : If your research involves primary data collection, carefully collect and organize your data using appropriate methods. If you are analyzing secondary data, ensure that the datasets are reliable and relevant to your research objectives. Apply appropriate statistical or qualitative analysis techniques to derive meaningful insights from your data.
- Structure your paper effectively : Organize your research paper using a clear and logical structure. Typically, a research paper includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure smooth transitions between sections and maintain a coherent flow of ideas throughout your paper.
- Write a compelling introduction : Begin your paper with an engaging introduction that provides context and background information on air pollution. Clearly state the research question, explain the significance of your study, and highlight the objectives and expected outcomes. Grab the reader’s attention and set the tone for the rest of the paper.
- Present your findings accurately : In the results section, present your findings in a clear and concise manner. Use appropriate tables, graphs, and figures to present data effectively. Provide relevant statistical measures and interpret the results objectively. Ensure that your findings directly address the research question and support your hypotheses or research objectives.
- Analyze and discuss your results : In the discussion section, analyze and interpret your findings in light of the existing literature. Compare your results with previous studies, identify similarities and differences, and explain any discrepancies. Discuss the implications of your findings and their significance for understanding air pollution and its effects.
- Address limitations and future research : Acknowledge the limitations of your study, such as sample size constraints, data limitations, or potential biases. Suggest avenues for future research to address these limitations and further advance knowledge in the field of air pollution. This demonstrates your critical thinking and opens up opportunities for future research contributions.
- Craft a strong conclusion : Conclude your research paper by summarizing the key findings, emphasizing their significance, and restating the research question and objectives. Discuss the implications of your study for theory, practice, and policy-making in the context of air pollution. Avoid introducing new information in the conclusion and leave the reader with a lasting impression of your research.
By following these tips, you can effectively structure and write an air pollution research paper that contributes to the existing knowledge, addresses key research questions, and provides valuable insights into this critical environmental issue. In the next section, we will introduce you to the writing services offered by iResearchNet, where you can order a custom research paper on any air pollution topic.
Custom Research Paper Writing Services
At iResearchNet, we understand the challenges faced by students in conducting research and writing a high-quality research paper on air pollution. That’s why we offer custom writing services tailored to meet your specific needs. Our team of expert writers, who hold advanced degrees in environmental science, are dedicated to delivering top-notch research papers that showcase your knowledge and understanding of air pollution. When you choose our writing services, you can expect the following:
- Expert degree-holding writers : Our team consists of skilled writers with expertise in environmental science and air pollution research. They have the knowledge and experience to tackle complex topics and deliver well-researched and insightful papers.
- Custom written works : We understand the importance of originality and uniqueness in academic writing. Our writers craft each research paper from scratch, ensuring that it is tailored to your specific requirements and adheres to the highest standards of quality.
- In-depth research : Our writers conduct thorough research using credible sources to gather the most relevant and up-to-date information on air pollution. They critically analyze the literature and integrate it seamlessly into your research paper to support your arguments and strengthen your findings.
- Custom formatting : We are well-versed in various formatting styles, including APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, and Harvard. Our writers will format your research paper according to the specified guidelines, ensuring consistency and professionalism throughout.
- Top quality : Quality is our utmost priority. We strive to deliver research papers that meet the highest academic standards. Our writers pay attention to detail, ensure accurate referencing, and use clear and concise language to convey your ideas effectively.
- Customized solutions : We understand that every research paper is unique. Our writers take a personalized approach, tailoring their writing to your specific research objectives, methodology, and findings. They adapt their writing style and tone to match your requirements and ensure a seamless integration of your ideas.
- Flexible pricing : We offer competitive and flexible pricing options to accommodate your budget. Our pricing is transparent, and there are no hidden fees or additional charges. You can select the pricing plan that suits your needs, whether it’s for a comprehensive research paper or a specific section.
- Short deadlines : We understand that time is of the essence when it comes to academic assignments. Our writers are capable of working under tight deadlines and can deliver your custom research paper within short timeframes, even as little as 3 hours.
- Timely delivery : We are committed to delivering your research paper on time. We understand the importance of meeting deadlines, and our writers work diligently to ensure that your paper is delivered within the agreed-upon timeframe.
- 24/7 support : Our dedicated support team is available 24/7 to assist you with any questions or concerns you may have. Whether you need updates on your order or have inquiries about our services, our friendly support staff is here to provide prompt and helpful assistance.
- Absolute Privacy : We prioritize the privacy and confidentiality of our clients. Your personal information and order details are kept secure and protected. We adhere to strict privacy policies to ensure that your information remains confidential.
- Easy order tracking : Our user-friendly platform allows you to easily track the progress of your order. You can stay updated on the status of your research paper, communicate with your writer, and receive notifications throughout the writing process.
- Money back guarantee : We are confident in the quality of our services and the expertise of our writers. If, for any reason, you are not satisfied with the final product, we offer a money-back guarantee. Your satisfaction is our priority, and we strive to ensure that you are fully content with the research paper you receive.
When you choose iResearchNet, you can be confident in receiving a well-written and thoroughly researched custom air pollution research paper that meets your academic requirements. We value your privacy and guarantee absolute confidentiality throughout the entire process. Our easy order tracking system allows you to stay updated on the progress of your paper, ensuring a seamless experience from start to finish. If, for any reason, you are not satisfied with the final product, we offer a money-back guarantee.
Order Your Custom Air Pollution Research Paper Today!
Are you ready to take the next step in your academic journey and submit a stellar research paper on air pollution? Look no further than iResearchNet. Our team of expert writers and comprehensive writing services are here to support you in your pursuit of academic excellence. With our custom air pollution research paper writing service, you can be confident in receiving a well-researched, high-quality paper tailored to your specific requirements. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to submit a top-notch air pollution research paper that impresses your professors and demonstrates your expertise in the field. Place your order with iResearchNet today and experience the benefits of our custom writing services.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

REVIEW article
Environmental and health impacts of air pollution: a review.

- 1 Delphis S.A., Kifisia, Greece
- 2 Laboratory of Hygiene and Environmental Protection, Faculty of Medicine, Democritus University of Thrace, Alexandroupolis, Greece
- 3 Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois (CHUV), Service de Médicine Interne, Lausanne, Switzerland
- 4 School of Social and Political Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom
One of our era's greatest scourges is air pollution, on account not only of its impact on climate change but also its impact on public and individual health due to increasing morbidity and mortality. There are many pollutants that are major factors in disease in humans. Among them, Particulate Matter (PM), particles of variable but very small diameter, penetrate the respiratory system via inhalation, causing respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, reproductive and central nervous system dysfunctions, and cancer. Despite the fact that ozone in the stratosphere plays a protective role against ultraviolet irradiation, it is harmful when in high concentration at ground level, also affecting the respiratory and cardiovascular system. Furthermore, nitrogen oxide, sulfur dioxide, Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), dioxins, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are all considered air pollutants that are harmful to humans. Carbon monoxide can even provoke direct poisoning when breathed in at high levels. Heavy metals such as lead, when absorbed into the human body, can lead to direct poisoning or chronic intoxication, depending on exposure. Diseases occurring from the aforementioned substances include principally respiratory problems such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), asthma, bronchiolitis, and also lung cancer, cardiovascular events, central nervous system dysfunctions, and cutaneous diseases. Last but not least, climate change resulting from environmental pollution affects the geographical distribution of many infectious diseases, as do natural disasters. The only way to tackle this problem is through public awareness coupled with a multidisciplinary approach by scientific experts; national and international organizations must address the emergence of this threat and propose sustainable solutions.
Approach to the Problem
The interactions between humans and their physical surroundings have been extensively studied, as multiple human activities influence the environment. The environment is a coupling of the biotic (living organisms and microorganisms) and the abiotic (hydrosphere, lithosphere, and atmosphere).
Pollution is defined as the introduction into the environment of substances harmful to humans and other living organisms. Pollutants are harmful solids, liquids, or gases produced in higher than usual concentrations that reduce the quality of our environment.
Human activities have an adverse effect on the environment by polluting the water we drink, the air we breathe, and the soil in which plants grow. Although the industrial revolution was a great success in terms of technology, society, and the provision of multiple services, it also introduced the production of huge quantities of pollutants emitted into the air that are harmful to human health. Without any doubt, the global environmental pollution is considered an international public health issue with multiple facets. Social, economic, and legislative concerns and lifestyle habits are related to this major problem. Clearly, urbanization and industrialization are reaching unprecedented and upsetting proportions worldwide in our era. Anthropogenic air pollution is one of the biggest public health hazards worldwide, given that it accounts for about 9 million deaths per year ( 1 ).
Without a doubt, all of the aforementioned are closely associated with climate change, and in the event of danger, the consequences can be severe for mankind ( 2 ). Climate changes and the effects of global planetary warming seriously affect multiple ecosystems, causing problems such as food safety issues, ice and iceberg melting, animal extinction, and damage to plants ( 3 , 4 ).
Air pollution has various health effects. The health of susceptible and sensitive individuals can be impacted even on low air pollution days. Short-term exposure to air pollutants is closely related to COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, asthma, respiratory disease, and high rates of hospitalization (a measurement of morbidity).
The long-term effects associated with air pollution are chronic asthma, pulmonary insufficiency, cardiovascular diseases, and cardiovascular mortality. According to a Swedish cohort study, diabetes seems to be induced after long-term air pollution exposure ( 5 ). Moreover, air pollution seems to have various malign health effects in early human life, such as respiratory, cardiovascular, mental, and perinatal disorders ( 3 ), leading to infant mortality or chronic disease in adult age ( 6 ).
National reports have mentioned the increased risk of morbidity and mortality ( 1 ). These studies were conducted in many places around the world and show a correlation between daily ranges of particulate matter (PM) concentration and daily mortality. Climate shifts and global planetary warming ( 3 ) could aggravate the situation. Besides, increased hospitalization (an index of morbidity) has been registered among the elderly and susceptible individuals for specific reasons. Fine and ultrafine particulate matter seems to be associated with more serious illnesses ( 6 ), as it can invade the deepest parts of the airways and more easily reach the bloodstream.
Air pollution mainly affects those living in large urban areas, where road emissions contribute the most to the degradation of air quality. There is also a danger of industrial accidents, where the spread of a toxic fog can be fatal to the populations of the surrounding areas. The dispersion of pollutants is determined by many parameters, most notably atmospheric stability and wind ( 6 ).
In developing countries ( 7 ), the problem is more serious due to overpopulation and uncontrolled urbanization along with the development of industrialization. This leads to poor air quality, especially in countries with social disparities and a lack of information on sustainable management of the environment. The use of fuels such as wood fuel or solid fuel for domestic needs due to low incomes exposes people to bad-quality, polluted air at home. It is of note that three billion people around the world are using the above sources of energy for their daily heating and cooking needs ( 8 ). In developing countries, the women of the household seem to carry the highest risk for disease development due to their longer duration exposure to the indoor air pollution ( 8 , 9 ). Due to its fast industrial development and overpopulation, China is one of the Asian countries confronting serious air pollution problems ( 10 , 11 ). The lung cancer mortality observed in China is associated with fine particles ( 12 ). As stated already, long-term exposure is associated with deleterious effects on the cardiovascular system ( 3 , 5 ). However, it is interesting to note that cardiovascular diseases have mostly been observed in developed and high-income countries rather than in the developing low-income countries exposed highly to air pollution ( 13 ). Extreme air pollution is recorded in India, where the air quality reaches hazardous levels. New Delhi is one of the more polluted cities in India. Flights in and out of New Delhi International Airport are often canceled due to the reduced visibility associated with air pollution. Pollution is occurring both in urban and rural areas in India due to the fast industrialization, urbanization, and rise in use of motorcycle transportation. Nevertheless, biomass combustion associated with heating and cooking needs and practices is a major source of household air pollution in India and in Nepal ( 14 , 15 ). There is spatial heterogeneity in India, as areas with diverse climatological conditions and population and education levels generate different indoor air qualities, with higher PM 2.5 observed in North Indian states (557–601 μg/m 3 ) compared to the Southern States (183–214 μg/m 3 ) ( 16 , 17 ). The cold climate of the North Indian areas may be the main reason for this, as longer periods at home and more heating are necessary compared to in the tropical climate of Southern India. Household air pollution in India is associated with major health effects, especially in women and young children, who stay indoors for longer periods. Chronic obstructive respiratory disease (CORD) and lung cancer are mostly observed in women, while acute lower respiratory disease is seen in young children under 5 years of age ( 18 ).
Accumulation of air pollution, especially sulfur dioxide and smoke, reaching 1,500 mg/m3, resulted in an increase in the number of deaths (4,000 deaths) in December 1952 in London and in 1963 in New York City (400 deaths) ( 19 ). An association of pollution with mortality was reported on the basis of monitoring of outdoor pollution in six US metropolitan cities ( 20 ). In every case, it seems that mortality was closely related to the levels of fine, inhalable, and sulfate particles more than with the levels of total particulate pollution, aerosol acidity, sulfur dioxide, or nitrogen dioxide ( 20 ).
Furthermore, extremely high levels of pollution are reported in Mexico City and Rio de Janeiro, followed by Milan, Ankara, Melbourne, Tokyo, and Moscow ( 19 ).
Based on the magnitude of the public health impact, it is certain that different kinds of interventions should be taken into account. Success and effectiveness in controlling air pollution, specifically at the local level, have been reported. Adequate technological means are applied considering the source and the nature of the emission as well as its impact on health and the environment. The importance of point sources and non-point sources of air pollution control is reported by Schwela and Köth-Jahr ( 21 ). Without a doubt, a detailed emission inventory must record all sources in a given area. Beyond considering the above sources and their nature, topography and meteorology should also be considered, as stated previously. Assessment of the control policies and methods is often extrapolated from the local to the regional and then to the global scale. Air pollution may be dispersed and transported from one region to another area located far away. Air pollution management means the reduction to acceptable levels or possible elimination of air pollutants whose presence in the air affects our health or the environmental ecosystem. Private and governmental entities and authorities implement actions to ensure the air quality ( 22 ). Air quality standards and guidelines were adopted for the different pollutants by the WHO and EPA as a tool for the management of air quality ( 1 , 23 ). These standards have to be compared to the emissions inventory standards by causal analysis and dispersion modeling in order to reveal the problematic areas ( 24 ). Inventories are generally based on a combination of direct measurements and emissions modeling ( 24 ).
As an example, we state here the control measures at the source through the use of catalytic converters in cars. These are devices that turn the pollutants and toxic gases produced from combustion engines into less-toxic pollutants by catalysis through redox reactions ( 25 ). In Greece, the use of private cars was restricted by tracking their license plates in order to reduce traffic congestion during rush hour ( 25 ).
Concerning industrial emissions, collectors and closed systems can keep the air pollution to the minimal standards imposed by legislation ( 26 ).
Current strategies to improve air quality require an estimation of the economic value of the benefits gained from proposed programs. These proposed programs by public authorities, and directives are issued with guidelines to be respected.
In Europe, air quality limit values AQLVs (Air Quality Limit Values) are issued for setting off planning claims ( 27 ). In the USA, the NAAQS (National Ambient Air Quality Standards) establish the national air quality limit values ( 27 ). While both standards and directives are based on different mechanisms, significant success has been achieved in the reduction of overall emissions and associated health and environmental effects ( 27 ). The European Directive identifies geographical areas of risk exposure as monitoring/assessment zones to record the emission sources and levels of air pollution ( 27 ), whereas the USA establishes global geographical air quality criteria according to the severity of their air quality problem and records all sources of the pollutants and their precursors ( 27 ).
In this vein, funds have been financing, directly or indirectly, projects related to air quality along with the technical infrastructure to maintain good air quality. These plans focus on an inventory of databases from air quality environmental planning awareness campaigns. Moreover, pollution measures of air emissions may be taken for vehicles, machines, and industries in urban areas.
Technological innovation can only be successful if it is able to meet the needs of society. In this sense, technology must reflect the decision-making practices and procedures of those involved in risk assessment and evaluation and act as a facilitator in providing information and assessments to enable decision makers to make the best decisions possible. Summarizing the aforementioned in order to design an effective air quality control strategy, several aspects must be considered: environmental factors and ambient air quality conditions, engineering factors and air pollutant characteristics, and finally, economic operating costs for technological improvement and administrative and legal costs. Considering the economic factor, competitiveness through neoliberal concepts is offering a solution to environmental problems ( 22 ).
The development of environmental governance, along with technological progress, has initiated the deployment of a dialogue. Environmental politics has created objections and points of opposition between different political parties, scientists, media, and governmental and non-governmental organizations ( 22 ). Radical environmental activism actions and movements have been created ( 22 ). The rise of the new information and communication technologies (ICTs) are many times examined as to whether and in which way they have influenced means of communication and social movements such as activism ( 28 ). Since the 1990s, the term “digital activism” has been used increasingly and in many different disciplines ( 29 ). Nowadays, multiple digital technologies can be used to produce a digital activism outcome on environmental issues. More specifically, devices with online capabilities such as computers or mobile phones are being used as a way to pursue change in political and social affairs ( 30 ).
In the present paper, we focus on the sources of environmental pollution in relation to public health and propose some solutions and interventions that may be of interest to environmental legislators and decision makers.
Sources of Exposure
It is known that the majority of environmental pollutants are emitted through large-scale human activities such as the use of industrial machinery, power-producing stations, combustion engines, and cars. Because these activities are performed at such a large scale, they are by far the major contributors to air pollution, with cars estimated to be responsible for approximately 80% of today's pollution ( 31 ). Some other human activities are also influencing our environment to a lesser extent, such as field cultivation techniques, gas stations, fuel tanks heaters, and cleaning procedures ( 32 ), as well as several natural sources, such as volcanic and soil eruptions and forest fires.
The classification of air pollutants is based mainly on the sources producing pollution. Therefore, it is worth mentioning the four main sources, following the classification system: Major sources, Area sources, Mobile sources, and Natural sources.
Major sources include the emission of pollutants from power stations, refineries, and petrochemicals, the chemical and fertilizer industries, metallurgical and other industrial plants, and, finally, municipal incineration.
Indoor area sources include domestic cleaning activities, dry cleaners, printing shops, and petrol stations.
Mobile sources include automobiles, cars, railways, airways, and other types of vehicles.
Finally, natural sources include, as stated previously, physical disasters ( 33 ) such as forest fire, volcanic erosion, dust storms, and agricultural burning.
However, many classification systems have been proposed. Another type of classification is a grouping according to the recipient of the pollution, as follows:
Air pollution is determined as the presence of pollutants in the air in large quantities for long periods. Air pollutants are dispersed particles, hydrocarbons, CO, CO 2 , NO, NO 2 , SO 3 , etc.
Water pollution is organic and inorganic charge and biological charge ( 10 ) at high levels that affect the water quality ( 34 , 35 ).
Soil pollution occurs through the release of chemicals or the disposal of wastes, such as heavy metals, hydrocarbons, and pesticides.
Air pollution can influence the quality of soil and water bodies by polluting precipitation, falling into water and soil environments ( 34 , 36 ). Notably, the chemistry of the soil can be amended due to acid precipitation by affecting plants, cultures, and water quality ( 37 ). Moreover, movement of heavy metals is favored by soil acidity, and metals are so then moving into the watery environment. It is known that heavy metals such as aluminum are noxious to wildlife and fishes. Soil quality seems to be of importance, as soils with low calcium carbonate levels are at increased jeopardy from acid rain. Over and above rain, snow and particulate matter drip into watery ' bodies ( 36 , 38 ).
Lastly, pollution is classified following type of origin:
Radioactive and nuclear pollution , releasing radioactive and nuclear pollutants into water, air, and soil during nuclear explosions and accidents, from nuclear weapons, and through handling or disposal of radioactive sewage.
Radioactive materials can contaminate surface water bodies and, being noxious to the environment, plants, animals, and humans. It is known that several radioactive substances such as radium and uranium concentrate in the bones and can cause cancers ( 38 , 39 ).
Noise pollution is produced by machines, vehicles, traffic noises, and musical installations that are harmful to our hearing.
The World Health Organization introduced the term DALYs. The DALYs for a disease or health condition is defined as the sum of the Years of Life Lost (YLL) due to premature mortality in the population and the Years Lost due to Disability (YLD) for people living with the health condition or its consequences ( 39 ). In Europe, air pollution is the main cause of disability-adjusted life years lost (DALYs), followed by noise pollution. The potential relationships of noise and air pollution with health have been studied ( 40 ). The study found that DALYs related to noise were more important than those related to air pollution, as the effects of environmental noise on cardiovascular disease were independent of air pollution ( 40 ). Environmental noise should be counted as an independent public health risk ( 40 ).
Environmental pollution occurs when changes in the physical, chemical, or biological constituents of the environment (air masses, temperature, climate, etc.) are produced.
Pollutants harm our environment either by increasing levels above normal or by introducing harmful toxic substances. Primary pollutants are directly produced from the above sources, and secondary pollutants are emitted as by-products of the primary ones. Pollutants can be biodegradable or non-biodegradable and of natural origin or anthropogenic, as stated previously. Moreover, their origin can be a unique source (point-source) or dispersed sources.
Pollutants have differences in physical and chemical properties, explaining the discrepancy in their capacity for producing toxic effects. As an example, we state here that aerosol compounds ( 41 – 43 ) have a greater toxicity than gaseous compounds due to their tiny size (solid or liquid) in the atmosphere; they have a greater penetration capacity. Gaseous compounds are eliminated more easily by our respiratory system ( 41 ). These particles are able to damage lungs and can even enter the bloodstream ( 41 ), leading to the premature deaths of millions of people yearly. Moreover, the aerosol acidity ([H+]) seems to considerably enhance the production of secondary organic aerosols (SOA), but this last aspect is not supported by other scientific teams ( 38 ).
Climate and Pollution
Air pollution and climate change are closely related. Climate is the other side of the same coin that reduces the quality of our Earth ( 44 ). Pollutants such as black carbon, methane, tropospheric ozone, and aerosols affect the amount of incoming sunlight. As a result, the temperature of the Earth is increasing, resulting in the melting of ice, icebergs, and glaciers.
In this vein, climatic changes will affect the incidence and prevalence of both residual and imported infections in Europe. Climate and weather affect the duration, timing, and intensity of outbreaks strongly and change the map of infectious diseases in the globe ( 45 ). Mosquito-transmitted parasitic or viral diseases are extremely climate-sensitive, as warming firstly shortens the pathogen incubation period and secondly shifts the geographic map of the vector. Similarly, water-warming following climate changes leads to a high incidence of waterborne infections. Recently, in Europe, eradicated diseases seem to be emerging due to the migration of population, for example, cholera, poliomyelitis, tick-borne encephalitis, and malaria ( 46 ).
The spread of epidemics is associated with natural climate disasters and storms, which seem to occur more frequently nowadays ( 47 ). Malnutrition and disequilibration of the immune system are also associated with the emerging infections affecting public health ( 48 ).
The Chikungunya virus “took the airplane” from the Indian Ocean to Europe, as outbreaks of the disease were registered in Italy ( 49 ) as well as autochthonous cases in France ( 50 ).
An increase in cryptosporidiosis in the United Kingdom and in the Czech Republic seems to have occurred following flooding ( 36 , 51 ).
As stated previously, aerosols compounds are tiny in size and considerably affect the climate. They are able to dissipate sunlight (the albedo phenomenon) by dispersing a quarter of the sun's rays back to space and have cooled the global temperature over the last 30 years ( 52 ).
Air Pollutants
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports on six major air pollutants, namely particle pollution, ground-level ozone, carbon monoxide, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and lead. Air pollution can have a disastrous effect on all components of the environment, including groundwater, soil, and air. Additionally, it poses a serious threat to living organisms. In this vein, our interest is mainly to focus on these pollutants, as they are related to more extensive and severe problems in human health and environmental impact. Acid rain, global warming, the greenhouse effect, and climate changes have an important ecological impact on air pollution ( 53 ).
Particulate Matter (PM) and Health
Studies have shown a relationship between particulate matter (PM) and adverse health effects, focusing on either short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic) PM exposure.
Particulate matter (PM) is usually formed in the atmosphere as a result of chemical reactions between the different pollutants. The penetration of particles is closely dependent on their size ( 53 ). Particulate Matter (PM) was defined as a term for particles by the United States Environmental Protection Agency ( 54 ). Particulate matter (PM) pollution includes particles with diameters of 10 micrometers (μm) or smaller, called PM 10 , and extremely fine particles with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometers (μm) and smaller.
Particulate matter contains tiny liquid or solid droplets that can be inhaled and cause serious health effects ( 55 ). Particles <10 μm in diameter (PM 10 ) after inhalation can invade the lungs and even reach the bloodstream. Fine particles, PM 2.5 , pose a greater risk to health ( 6 , 56 ) ( Table 1 ).

Table 1 . Penetrability according to particle size.
Multiple epidemiological studies have been performed on the health effects of PM. A positive relation was shown between both short-term and long-term exposures of PM 2.5 and acute nasopharyngitis ( 56 ). In addition, long-term exposure to PM for years was found to be related to cardiovascular diseases and infant mortality.
Those studies depend on PM 2.5 monitors and are restricted in terms of study area or city area due to a lack of spatially resolved daily PM 2.5 concentration data and, in this way, are not representative of the entire population. Following a recent epidemiological study by the Department of Environmental Health at Harvard School of Public Health (Boston, MA) ( 57 ), it was reported that, as PM 2.5 concentrations vary spatially, an exposure error (Berkson error) seems to be produced, and the relative magnitudes of the short- and long-term effects are not yet completely elucidated. The team developed a PM 2.5 exposure model based on remote sensing data for assessing short- and long-term human exposures ( 57 ). This model permits spatial resolution in short-term effects plus the assessment of long-term effects in the whole population.
Moreover, respiratory diseases and affection of the immune system are registered as long-term chronic effects ( 58 ). It is worth noting that people with asthma, pneumonia, diabetes, and respiratory and cardiovascular diseases are especially susceptible and vulnerable to the effects of PM. PM 2.5 , followed by PM 10 , are strongly associated with diverse respiratory system diseases ( 59 ), as their size permits them to pierce interior spaces ( 60 ). The particles produce toxic effects according to their chemical and physical properties. The components of PM 10 and PM 2.5 can be organic (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, dioxins, benzene, 1-3 butadiene) or inorganic (carbon, chlorides, nitrates, sulfates, metals) in nature ( 55 ).
Particulate Matter (PM) is divided into four main categories according to type and size ( 61 ) ( Table 2 ).
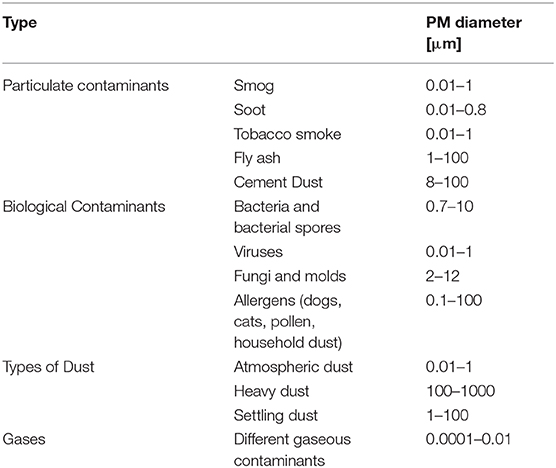
Table 2 . Types and sizes of particulate Matter (PM).
Gas contaminants include PM in aerial masses.
Particulate contaminants include contaminants such as smog, soot, tobacco smoke, oil smoke, fly ash, and cement dust.
Biological Contaminants are microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, mold, and bacterial spores), cat allergens, house dust and allergens, and pollen.
Types of Dust include suspended atmospheric dust, settling dust, and heavy dust.
Finally, another fact is that the half-lives of PM 10 and PM 2.5 particles in the atmosphere is extended due to their tiny dimensions; this permits their long-lasting suspension in the atmosphere and even their transfer and spread to distant destinations where people and the environment may be exposed to the same magnitude of pollution ( 53 ). They are able to change the nutrient balance in watery ecosystems, damage forests and crops, and acidify water bodies.
As stated, PM 2.5 , due to their tiny size, are causing more serious health effects. These aforementioned fine particles are the main cause of the “haze” formation in different metropolitan areas ( 12 , 13 , 61 ).
Ozone Impact in the Atmosphere
Ozone (O 3 ) is a gas formed from oxygen under high voltage electric discharge ( 62 ). It is a strong oxidant, 52% stronger than chlorine. It arises in the stratosphere, but it could also arise following chain reactions of photochemical smog in the troposphere ( 63 ).
Ozone can travel to distant areas from its initial source, moving with air masses ( 64 ). It is surprising that ozone levels over cities are low in contrast to the increased amounts occuring in urban areas, which could become harmful for cultures, forests, and vegetation ( 65 ) as it is reducing carbon assimilation ( 66 ). Ozone reduces growth and yield ( 47 , 48 ) and affects the plant microflora due to its antimicrobial capacity ( 67 , 68 ). In this regard, ozone acts upon other natural ecosystems, with microflora ( 69 , 70 ) and animal species changing their species composition ( 71 ). Ozone increases DNA damage in epidermal keratinocytes and leads to impaired cellular function ( 72 ).
Ground-level ozone (GLO) is generated through a chemical reaction between oxides of nitrogen and VOCs emitted from natural sources and/or following anthropogenic activities.
Ozone uptake usually occurs by inhalation. Ozone affects the upper layers of the skin and the tear ducts ( 73 ). A study of short-term exposure of mice to high levels of ozone showed malondialdehyde formation in the upper skin (epidermis) but also depletion in vitamins C and E. It is likely that ozone levels are not interfering with the skin barrier function and integrity to predispose to skin disease ( 74 ).
Due to the low water-solubility of ozone, inhaled ozone has the capacity to penetrate deeply into the lungs ( 75 ).
Toxic effects induced by ozone are registered in urban areas all over the world, causing biochemical, morphologic, functional, and immunological disorders ( 76 ).
The European project (APHEA2) focuses on the acute effects of ambient ozone concentrations on mortality ( 77 ). Daily ozone concentrations compared to the daily number of deaths were reported from different European cities for a 3-year period. During the warm period of the year, an observed increase in ozone concentration was associated with an increase in the daily number of deaths (0.33%), in the number of respiratory deaths (1.13%), and in the number of cardiovascular deaths (0.45%). No effect was observed during wintertime.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide is produced by fossil fuel when combustion is incomplete. The symptoms of poisoning due to inhaling carbon monoxide include headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, and, finally, loss of consciousness.
The affinity of carbon monoxide to hemoglobin is much greater than that of oxygen. In this vein, serious poisoning may occur in people exposed to high levels of carbon monoxide for a long period of time. Due to the loss of oxygen as a result of the competitive binding of carbon monoxide, hypoxia, ischemia, and cardiovascular disease are observed.
Carbon monoxide affects the greenhouses gases that are tightly connected to global warming and climate. This should lead to an increase in soil and water temperatures, and extreme weather conditions or storms may occur ( 68 ).
However, in laboratory and field experiments, it has been seen to produce increased plant growth ( 78 ).
Nitrogen Oxide (NO 2 )
Nitrogen oxide is a traffic-related pollutant, as it is emitted from automobile motor engines ( 79 , 80 ). It is an irritant of the respiratory system as it penetrates deep in the lung, inducing respiratory diseases, coughing, wheezing, dyspnea, bronchospasm, and even pulmonary edema when inhaled at high levels. It seems that concentrations over 0.2 ppm produce these adverse effects in humans, while concentrations higher than 2.0 ppm affect T-lymphocytes, particularly the CD8+ cells and NK cells that produce our immune response ( 81 ).It is reported that long-term exposure to high levels of nitrogen dioxide can be responsible for chronic lung disease. Long-term exposure to NO 2 can impair the sense of smell ( 81 ).
However, systems other than respiratory ones can be involved, as symptoms such as eye, throat, and nose irritation have been registered ( 81 ).
High levels of nitrogen dioxide are deleterious to crops and vegetation, as they have been observed to reduce crop yield and plant growth efficiency. Moreover, NO 2 can reduce visibility and discolor fabrics ( 81 ).
Sulfur Dioxide (SO 2 )
Sulfur dioxide is a harmful gas that is emitted mainly from fossil fuel consumption or industrial activities. The annual standard for SO 2 is 0.03 ppm ( 82 ). It affects human, animal, and plant life. Susceptible people as those with lung disease, old people, and children, who present a higher risk of damage. The major health problems associated with sulfur dioxide emissions in industrialized areas are respiratory irritation, bronchitis, mucus production, and bronchospasm, as it is a sensory irritant and penetrates deep into the lung converted into bisulfite and interacting with sensory receptors, causing bronchoconstriction. Moreover, skin redness, damage to the eyes (lacrimation and corneal opacity) and mucous membranes, and worsening of pre-existing cardiovascular disease have been observed ( 81 ).
Environmental adverse effects, such as acidification of soil and acid rain, seem to be associated with sulfur dioxide emissions ( 83 ).
Lead is a heavy metal used in different industrial plants and emitted from some petrol motor engines, batteries, radiators, waste incinerators, and waste waters ( 84 ).
Moreover, major sources of lead pollution in the air are metals, ore, and piston-engine aircraft. Lead poisoning is a threat to public health due to its deleterious effects upon humans, animals, and the environment, especially in the developing countries.
Exposure to lead can occur through inhalation, ingestion, and dermal absorption. Trans- placental transport of lead was also reported, as lead passes through the placenta unencumbered ( 85 ). The younger the fetus is, the more harmful the toxic effects. Lead toxicity affects the fetal nervous system; edema or swelling of the brain is observed ( 86 ). Lead, when inhaled, accumulates in the blood, soft tissue, liver, lung, bones, and cardiovascular, nervous, and reproductive systems. Moreover, loss of concentration and memory, as well as muscle and joint pain, were observed in adults ( 85 , 86 ).
Children and newborns ( 87 ) are extremely susceptible even to minimal doses of lead, as it is a neurotoxicant and causes learning disabilities, impairment of memory, hyperactivity, and even mental retardation.
Elevated amounts of lead in the environment are harmful to plants and crop growth. Neurological effects are observed in vertebrates and animals in association with high lead levels ( 88 ).
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons(PAHs)
The distribution of PAHs is ubiquitous in the environment, as the atmosphere is the most important means of their dispersal. They are found in coal and in tar sediments. Moreover, they are generated through incomplete combustion of organic matter as in the cases of forest fires, incineration, and engines ( 89 ). PAH compounds, such as benzopyrene, acenaphthylene, anthracene, and fluoranthene are recognized as toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic substances. They are an important risk factor for lung cancer ( 89 ).
Volatile Organic Compounds(VOCs)
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), such as toluene, benzene, ethylbenzene, and xylene ( 90 ), have been found to be associated with cancer in humans ( 91 ). The use of new products and materials has actually resulted in increased concentrations of VOCs. VOCs pollute indoor air ( 90 ) and may have adverse effects on human health ( 91 ). Short-term and long-term adverse effects on human health are observed. VOCs are responsible for indoor air smells. Short-term exposure is found to cause irritation of eyes, nose, throat, and mucosal membranes, while those of long duration exposure include toxic reactions ( 92 ). Predictable assessment of the toxic effects of complex VOC mixtures is difficult to estimate, as these pollutants can have synergic, antagonistic, or indifferent effects ( 91 , 93 ).
Dioxins originate from industrial processes but also come from natural processes, such as forest fires and volcanic eruptions. They accumulate in foods such as meat and dairy products, fish and shellfish, and especially in the fatty tissue of animals ( 94 ).
Short-period exhibition to high dioxin concentrations may result in dark spots and lesions on the skin ( 94 ). Long-term exposure to dioxins can cause developmental problems, impairment of the immune, endocrine and nervous systems, reproductive infertility, and cancer ( 94 ).
Without any doubt, fossil fuel consumption is responsible for a sizeable part of air contamination. This contamination may be anthropogenic, as in agricultural and industrial processes or transportation, while contamination from natural sources is also possible. Interestingly, it is of note that the air quality standards established through the European Air Quality Directive are somewhat looser than the WHO guidelines, which are stricter ( 95 ).
Effect of Air Pollution on Health
The most common air pollutants are ground-level ozone and Particulates Matter (PM). Air pollution is distinguished into two main types:
Outdoor pollution is the ambient air pollution.
Indoor pollution is the pollution generated by household combustion of fuels.
People exposed to high concentrations of air pollutants experience disease symptoms and states of greater and lesser seriousness. These effects are grouped into short- and long-term effects affecting health.
Susceptible populations that need to be aware of health protection measures include old people, children, and people with diabetes and predisposing heart or lung disease, especially asthma.
As extensively stated previously, according to a recent epidemiological study from Harvard School of Public Health, the relative magnitudes of the short- and long-term effects have not been completely clarified ( 57 ) due to the different epidemiological methodologies and to the exposure errors. New models are proposed for assessing short- and long-term human exposure data more successfully ( 57 ). Thus, in the present section, we report the more common short- and long-term health effects but also general concerns for both types of effects, as these effects are often dependent on environmental conditions, dose, and individual susceptibility.
Short-term effects are temporary and range from simple discomfort, such as irritation of the eyes, nose, skin, throat, wheezing, coughing and chest tightness, and breathing difficulties, to more serious states, such as asthma, pneumonia, bronchitis, and lung and heart problems. Short-term exposure to air pollution can also cause headaches, nausea, and dizziness.
These problems can be aggravated by extended long-term exposure to the pollutants, which is harmful to the neurological, reproductive, and respiratory systems and causes cancer and even, rarely, deaths.
The long-term effects are chronic, lasting for years or the whole life and can even lead to death. Furthermore, the toxicity of several air pollutants may also induce a variety of cancers in the long term ( 96 ).
As stated already, respiratory disorders are closely associated with the inhalation of air pollutants. These pollutants will invade through the airways and will accumulate at the cells. Damage to target cells should be related to the pollutant component involved and its source and dose. Health effects are also closely dependent on country, area, season, and time. An extended exposure duration to the pollutant should incline to long-term health effects in relation also to the above factors.
Particulate Matter (PMs), dust, benzene, and O 3 cause serious damage to the respiratory system ( 97 ). Moreover, there is a supplementary risk in case of existing respiratory disease such as asthma ( 98 ). Long-term effects are more frequent in people with a predisposing disease state. When the trachea is contaminated by pollutants, voice alterations may be remarked after acute exposure. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may be induced following air pollution, increasing morbidity and mortality ( 99 ). Long-term effects from traffic, industrial air pollution, and combustion of fuels are the major factors for COPD risk ( 99 ).
Multiple cardiovascular effects have been observed after exposure to air pollutants ( 100 ). Changes occurred in blood cells after long-term exposure may affect cardiac functionality. Coronary arteriosclerosis was reported following long-term exposure to traffic emissions ( 101 ), while short-term exposure is related to hypertension, stroke, myocardial infracts, and heart insufficiency. Ventricle hypertrophy is reported to occur in humans after long-time exposure to nitrogen oxide (NO 2 ) ( 102 , 103 ).
Neurological effects have been observed in adults and children after extended-term exposure to air pollutants.
Psychological complications, autism, retinopathy, fetal growth, and low birth weight seem to be related to long-term air pollution ( 83 ). The etiologic agent of the neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's and Parkinson's) is not yet known, although it is believed that extended exposure to air pollution seems to be a factor. Specifically, pesticides and metals are cited as etiological factors, together with diet. The mechanisms in the development of neurodegenerative disease include oxidative stress, protein aggregation, inflammation, and mitochondrial impairment in neurons ( 104 ) ( Figure 1 ).
Figure 1 . Impact of air pollutants on the brain.
Brain inflammation was observed in dogs living in a highly polluted area in Mexico for a long period ( 105 ). In human adults, markers of systemic inflammation (IL-6 and fibrinogen) were found to be increased as an immediate response to PNC on the IL-6 level, possibly leading to the production of acute-phase proteins ( 106 ). The progression of atherosclerosis and oxidative stress seem to be the mechanisms involved in the neurological disturbances caused by long-term air pollution. Inflammation comes secondary to the oxidative stress and seems to be involved in the impairment of developmental maturation, affecting multiple organs ( 105 , 107 ). Similarly, other factors seem to be involved in the developmental maturation, which define the vulnerability to long-term air pollution. These include birthweight, maternal smoking, genetic background and socioeconomic environment, as well as education level.
However, diet, starting from breast-feeding, is another determinant factor. Diet is the main source of antioxidants, which play a key role in our protection against air pollutants ( 108 ). Antioxidants are free radical scavengers and limit the interaction of free radicals in the brain ( 108 ). Similarly, genetic background may result in a differential susceptibility toward the oxidative stress pathway ( 60 ). For example, antioxidant supplementation with vitamins C and E appears to modulate the effect of ozone in asthmatic children homozygous for the GSTM1 null allele ( 61 ). Inflammatory cytokines released in the periphery (e.g., respiratory epithelia) upregulate the innate immune Toll-like receptor 2. Such activation and the subsequent events leading to neurodegeneration have recently been observed in lung lavage in mice exposed to ambient Los Angeles (CA, USA) particulate matter ( 61 ). In children, neurodevelopmental morbidities were observed after lead exposure. These children developed aggressive and delinquent behavior, reduced intelligence, learning difficulties, and hyperactivity ( 109 ). No level of lead exposure seems to be “safe,” and the scientific community has asked the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to reduce the current screening guideline of 10 μg/dl ( 109 ).
It is important to state that impact on the immune system, causing dysfunction and neuroinflammation ( 104 ), is related to poor air quality. Yet, increases in serum levels of immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM) and the complement component C3 are observed ( 106 ). Another issue is that antigen presentation is affected by air pollutants, as there is an upregulation of costimulatory molecules such as CD80 and CD86 on macrophages ( 110 ).
As is known, skin is our shield against ultraviolet radiation (UVR) and other pollutants, as it is the most exterior layer of our body. Traffic-related pollutants, such as PAHs, VOCs, oxides, and PM, may cause pigmented spots on our skin ( 111 ). On the one hand, as already stated, when pollutants penetrate through the skin or are inhaled, damage to the organs is observed, as some of these pollutants are mutagenic and carcinogenic, and, specifically, they affect the liver and lung. On the other hand, air pollutants (and those in the troposphere) reduce the adverse effects of ultraviolet radiation UVR in polluted urban areas ( 111 ). Air pollutants absorbed by the human skin may contribute to skin aging, psoriasis, acne, urticaria, eczema, and atopic dermatitis ( 111 ), usually caused by exposure to oxides and photochemical smoke ( 111 ). Exposure to PM and cigarette smoking act as skin-aging agents, causing spots, dyschromia, and wrinkles. Lastly, pollutants have been associated with skin cancer ( 111 ).
Higher morbidity is reported to fetuses and children when exposed to the above dangers. Impairment in fetal growth, low birth weight, and autism have been reported ( 112 ).
Another exterior organ that may be affected is the eye. Contamination usually comes from suspended pollutants and may result in asymptomatic eye outcomes, irritation ( 112 ), retinopathy, or dry eye syndrome ( 113 , 114 ).
Environmental Impact of Air Pollution
Air pollution is harming not only human health but also the environment ( 115 ) in which we live. The most important environmental effects are as follows.
Acid rain is wet (rain, fog, snow) or dry (particulates and gas) precipitation containing toxic amounts of nitric and sulfuric acids. They are able to acidify the water and soil environments, damage trees and plantations, and even damage buildings and outdoor sculptures, constructions, and statues.
Haze is produced when fine particles are dispersed in the air and reduce the transparency of the atmosphere. It is caused by gas emissions in the air coming from industrial facilities, power plants, automobiles, and trucks.
Ozone , as discussed previously, occurs both at ground level and in the upper level (stratosphere) of the Earth's atmosphere. Stratospheric ozone is protecting us from the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. In contrast, ground-level ozone is harmful to human health and is a pollutant. Unfortunately, stratospheric ozone is gradually damaged by ozone-depleting substances (i.e., chemicals, pesticides, and aerosols). If this protecting stratospheric ozone layer is thinned, then UV radiation can reach our Earth, with harmful effects for human life (skin cancer) ( 116 ) and crops ( 117 ). In plants, ozone penetrates through the stomata, inducing them to close, which blocks CO 2 transfer and induces a reduction in photosynthesis ( 118 ).
Global climate change is an important issue that concerns mankind. As is known, the “greenhouse effect” keeps the Earth's temperature stable. Unhappily, anthropogenic activities have destroyed this protecting temperature effect by producing large amounts of greenhouse gases, and global warming is mounting, with harmful effects on human health, animals, forests, wildlife, agriculture, and the water environment. A report states that global warming is adding to the health risks of poor people ( 119 ).
People living in poorly constructed buildings in warm-climate countries are at high risk for heat-related health problems as temperatures mount ( 119 ).
Wildlife is burdened by toxic pollutants coming from the air, soil, or the water ecosystem and, in this way, animals can develop health problems when exposed to high levels of pollutants. Reproductive failure and birth effects have been reported.
Eutrophication is occurring when elevated concentrations of nutrients (especially nitrogen) stimulate the blooming of aquatic algae, which can cause a disequilibration in the diversity of fish and their deaths.
Without a doubt, there is a critical concentration of pollution that an ecosystem can tolerate without being destroyed, which is associated with the ecosystem's capacity to neutralize acidity. The Canada Acid Rain Program established this load at 20 kg/ha/yr ( 120 ).
Hence, air pollution has deleterious effects on both soil and water ( 121 ). Concerning PM as an air pollutant, its impact on crop yield and food productivity has been reported. Its impact on watery bodies is associated with the survival of living organisms and fishes and their productivity potential ( 121 ).
An impairment in photosynthetic rhythm and metabolism is observed in plants exposed to the effects of ozone ( 121 ).
Sulfur and nitrogen oxides are involved in the formation of acid rain and are harmful to plants and marine organisms.
Last but not least, as mentioned above, the toxicity associated with lead and other metals is the main threat to our ecosystems (air, water, and soil) and living creatures ( 121 ).
In 2018, during the first WHO Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health, the WHO's General Director, Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, called air pollution a “silent public health emergency” and “the new tobacco” ( 122 ).
Undoubtedly, children are particularly vulnerable to air pollution, especially during their development. Air pollution has adverse effects on our lives in many different respects.
Diseases associated with air pollution have not only an important economic impact but also a societal impact due to absences from productive work and school.
Despite the difficulty of eradicating the problem of anthropogenic environmental pollution, a successful solution could be envisaged as a tight collaboration of authorities, bodies, and doctors to regularize the situation. Governments should spread sufficient information and educate people and should involve professionals in these issues so as to control the emergence of the problem successfully.
Technologies to reduce air pollution at the source must be established and should be used in all industries and power plants. The Kyoto Protocol of 1997 set as a major target the reduction of GHG emissions to below 5% by 2012 ( 123 ). This was followed by the Copenhagen summit, 2009 ( 124 ), and then the Durban summit of 2011 ( 125 ), where it was decided to keep to the same line of action. The Kyoto protocol and the subsequent ones were ratified by many countries. Among the pioneers who adopted this important protocol for the world's environmental and climate “health” was China ( 3 ). As is known, China is a fast-developing economy and its GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is expected to be very high by 2050, which is defined as the year of dissolution of the protocol for the decrease in gas emissions.
A more recent international agreement of crucial importance for climate change is the Paris Agreement of 2015, issued by the UNFCCC (United Nations Climate Change Committee). This latest agreement was ratified by a plethora of UN (United Nations) countries as well as the countries of the European Union ( 126 ). In this vein, parties should promote actions and measures to enhance numerous aspects around the subject. Boosting education, training, public awareness, and public participation are some of the relevant actions for maximizing the opportunities to achieve the targets and goals on the crucial matter of climate change and environmental pollution ( 126 ). Without any doubt, technological improvements makes our world easier and it seems difficult to reduce the harmful impact caused by gas emissions, we could limit its use by seeking reliable approaches.
Synopsizing, a global prevention policy should be designed in order to combat anthropogenic air pollution as a complement to the correct handling of the adverse health effects associated with air pollution. Sustainable development practices should be applied, together with information coming from research in order to handle the problem effectively.
At this point, international cooperation in terms of research, development, administration policy, monitoring, and politics is vital for effective pollution control. Legislation concerning air pollution must be aligned and updated, and policy makers should propose the design of a powerful tool of environmental and health protection. As a result, the main proposal of this essay is that we should focus on fostering local structures to promote experience and practice and extrapolate these to the international level through developing effective policies for sustainable management of ecosystems.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
IM is employed by the company Delphis S.A.
The remaining authors declare that the present review paper was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
1. WHO. Air Pollution . WHO. Available online at: http://www.who.int/airpollution/en/ (accessed October 5, 2019).
Google Scholar
2. Moores FC. Climate change and air pollution: exploring the synergies and potential for mitigation in industrializing countries. Sustainability . (2009) 1:43–54. doi: 10.3390/su1010043
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
3. USGCRP (2009). Global Climate Change Impacts in the United States. In: Karl TR, Melillo JM, Peterson TC, editors. Climate Change Impacts by Sectors: Ecosystems . New York, NY: United States Global Change Research Program. Cambridge University Press.
4. Marlon JR, Bloodhart B, Ballew MT, Rolfe-Redding J, Roser-Renouf C, Leiserowitz A, et al. (2019). How hope and doubt affect climate change mobilization. Front. Commun. 4:20. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2019.00020
5. Eze IC, Schaffner E, Fischer E, Schikowski T, Adam M, Imboden M, et al. Long- term air pollution exposure and diabetes in a population-based Swiss cohort. Environ Int . (2014) 70:95–105. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2014.05.014
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
6. Kelishadi R, Poursafa P. Air pollution and non-respiratory health hazards for children. Arch Med Sci . (2010) 6:483–95. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2010.14458
7. Manucci PM, Franchini M. Health effects of ambient air pollution in developing countries. Int J Environ Res Public Health . (2017) 14:1048. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14091048
8. Burden of Disease from Ambient and Household Air Pollution . Available online: http://who.int/phe/health_topics/outdoorair/databases/en/ (accessed August 15, 2017).
9. Hashim D, Boffetta P. Occupational and environmental exposures and cancers in developing countries. Ann Glob Health . (2014) 80:393–411. doi: 10.1016/j.aogh.2014.10.002
10. Guo Y, Zeng H, Zheng R, Li S, Pereira G, Liu Q, et al. The burden of lung cancer mortality attributable to fine particles in China. Total Environ Sci . (2017) 579:1460–6. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.147
11. Hou Q, An XQ, Wang Y, Guo JP. An evaluation of resident exposure to respirable particulate matter and health economic loss in Beijing during Beijing 2008 Olympic Games. Sci Total Environ . (2010) 408:4026–32. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.12.030
12. Kan H, Chen R, Tong S. Ambient air pollution, climate change, and population health in China. Environ Int . (2012) 42:10–9. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.03.003
13. Burroughs Peña MS, Rollins A. Environmental exposures and cardiovascular disease: a challenge for health and development in low- and middle-income countries. Cardiol Clin . (2017) 35:71–86. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2016.09.001
14. Kankaria A, Nongkynrih B, Gupta S. Indoor air pollution in india: implications on health and its control. Indian J Comm Med . 39:203–7. doi: 10.4103/0970-0218.143019
15. Parajuli I, Lee H, Shrestha KR. Indoor air quality and ventilation assessment of rural mountainous households of Nepal. Int J Sust Built Env . (2016) 5:301–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsbe.2016.08.003
16. Saud T, Gautam R, Mandal TK, Gadi R, Singh DP, Sharma SK. Emission estimates of organic and elemental carbon from household biomass fuel used over the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP), India. Atmos Environ . (2012) 61:212–20. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.07.030
17. Singh DP, Gadi R, Mandal TK, Saud T, Saxena M, Sharma SK. Emissions estimates of PAH from biomass fuels used in rural sector of Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Atmos Environ . (2013) 68:120–6. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.11.042
18. Dherani M, Pope D, Mascarenhas M, Smith KR, Weber M BN. Indoor air pollution from unprocessed solid fuel use and pneumonia risk in children aged under five years: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bull World Health Organ . (2008) 86:390–4. doi: 10.2471/BLT.07.044529
19. Kassomenos P, Kelessis A, Petrakakis M, Zoumakis N, Christides T, Paschalidou AK. Air Quality assessment in a heavily-polluted urban Mediterranean environment through Air Quality indices. Ecol Indic . (2012) 18:259–68. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.11.021
20. Dockery DW, Pope CA, Xu X, Spengler JD, Ware JH, Fay ME, et al. An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N Engl J Med . (1993) 329:1753–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312093292401
21. Schwela DH, Köth-Jahr I. Leitfaden für die Aufstellung von Luftreinhalteplänen [Guidelines for the Implementation of Clean Air Implementation Plans]. Landesumweltamt des Landes Nordrhein Westfalen. State Environmental Service of the State of North Rhine-Westphalia (1994).
22. Newlands M. Environmental Activism, Environmental Politics, and Representation: The Framing of the British Environmental Activist Movement . Ph.D. thesis. University of East London, United Kingdom (2015).
23. NEPIS (National Service Center for Environmental Publications) US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2017). Available online at: https://www.epa.gov/clean-air-act-overview/air-pollution-current-and-future-challenges (accessed August 15, 2017).
24. NRC (National Research Council). Available online at: https://www.nap.edu/read/10728/chapter/1,2014 (accessed September 17, 2019).
25. Bull A. Traffic Congestion: The Problem and How to Deal With It . Santiago: Nationes Unidas, Cepal (2003).
26. Spiegel J, Maystre LY. Environmental Pollution Control, Part VII - The Environment, Chapter 55, Encyclopedia of Occupational Health and Safety . Available online at: http://www.ilocis.org/documents/chpt55e.htm (accessed September 17, 2019).
27. European Community Reports. Assessment of the Effectiveness of European Air Quality Policies and Measures: Case Study 2; Comparison of the EU and US Air Quality Standards and Planning Requirements. (2004). Available online at: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/archives/cafe/activities/pdf/case_study2.pdf (accessed September 22, 2019).
28. Gibson R, Ward S. Parties in the digital age; a review. J Represent Democracy . (2009) 45:87–100. doi: 10.1080/00344890802710888
29. Kaun A, Uldam J. Digital activism: after the hype. New Media Soc. (2017) 20:2099–106. doi: 10.1177/14614448177319
30. Sivitanides M, Shah V. The era of digital activism. In: 2011 Conference for Information Systems Applied Research(CONISAR) Proceedings Wilmington North Carolina, USA . Available online at: https://www.arifyildirim.com/ilt510/marcos.sivitanides.vivek.shah.pdf (accessed September 22, 2019).
31. Möller L, Schuetzle D, Autrup H. Future research needs associated with the assessment of potential human health risks from exposure to toxic ambient air pollutants. Environ Health Perspect . (1994) 102(Suppl. 4):193–210. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102s4193
32. Jacobson MZ, Jacobson PMZ. Atmospheric Pollution: History, Science, and Regulation. Cambridge University Press (2002). p. 206. doi: 10.1256/wea.243.02
33. Stover RH. Flooding of soil for disease control. In: Mulder D, editor. Chapter 3. Developments in Agricultural and Managed Forest Ecology . Elsevier (1979). p. 19–28. Available online at: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444416926500094 doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-41692-6.50009-4 (accessed July 1, 2019).
34. Maipa V, Alamanos Y, Bezirtzoglou E. Seasonal fluctuation of bacterial indicators in coastal waters. Microb Ecol Health Dis . (2001) 13:143–6. doi: 10.1080/089106001750462687
35. Bezirtzoglou E, Dimitriou D, Panagiou A. Occurrence of Clostridium perfringens in river water by using a new procedure. Anaerobe . (1996) 2:169–73. doi: 10.1006/anae.1996.0022
36. Kjellstrom T, Lodh M, McMichael T, Ranmuthugala G, Shrestha R, Kingsland S. Air and Water Pollution: Burden and Strategies for Control. DCP, Chapter 43. 817–32 p. Available online at: https://www.dcp-3.org/sites/default/files/dcp2/DCP43.pdf (accessed September 17, 2017).
37. Pathak RK, Wang T, Ho KF, Lee SC. Characteristics of summertime PM2.5 organic and elemental carbon in four major Chinese cities: implications of high acidity for water- soluble organic carbon (WSOC). Atmos Environ . (2011) 45:318–25. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.10.021
38. Bonavigo L, Zucchetti M, Mankolli H. Water radioactive pollution and related environmental aspects. J Int Env Appl Sci . (2009) 4:357–63
39. World Health Organization (WHO). Preventing Disease Through Healthy Environments: Towards an Estimate of the Environmental Burden of Disease . 1106 p. Available online at: https://www.who.int/quantifying_ehimpacts/publications/preventingdisease.pdf (accessed September 22, 2019).
40. Stansfeld SA. Noise effects on health in the context of air pollution exposure. Int J Environ Res Public Health . (2015) 12:12735–60. doi: 10.3390/ijerph121012735
41. Ethical Unicorn. Everything You Need To Know About Aerosols & Air Pollution. (2019). Available online at: https://ethicalunicorn.com/2019/04/29/everything-you-need-to-know-about-aerosols-air-pollution/ (accessed October 4, 2019).
42. Colbeck I, Lazaridis M. Aerosols and environmental pollution. Sci Nat . (2009) 97:117–31. doi: 10.1007/s00114-009-0594-x
43. Incecik S, Gertler A, Kassomenos P. Aerosols and air quality. Sci Total Env . (2014) 355, 488–9. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.012
44. D'Amato G, Pawankar R, Vitale C, Maurizia L. Climate change and air pollution: effects on respiratory allergy. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res . (2016) 8:391–5. doi: 10.4168/aair.2016.8.5.391
45. Bezirtzoglou C, Dekas K, Charvalos E. Climate changes, environment and infection: facts, scenarios and growing awareness from the public health community within Europe. Anaerobe . (2011) 17:337–40. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2011.05.016
46. Castelli F, Sulis G. Migration and infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Infect . (2017) 23:283–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2017.03.012
47. Watson JT, Gayer M, Connolly MA. Epidemics after natural disasters. Emerg Infect Dis . (2007) 13:1–5. doi: 10.3201/eid1301.060779
48. Fenn B. Malnutrition in Humanitarian Emergencies . Available online at: https://www.who.int/diseasecontrol_emergencies/publications/idhe_2009_london_malnutrition_fenn.pdf . (accessed August 15, 2017).
49. Lindh E, Argentini C, Remoli ME, Fortuna C, Faggioni G, Benedetti E, et al. The Italian 2017 outbreak Chikungunya virus belongs to an emerging Aedes albopictus –adapted virus cluster introduced from the Indian subcontinent. Open Forum Infect Dis. (2019) 6:ofy321. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofy321
50. Calba C, Guerbois-Galla M, Franke F, Jeannin C, Auzet-Caillaud M, Grard G, Pigaglio L, Decoppet A, et al. Preliminary report of an autochthonous chikungunya outbreak in France, July to September 2017. Eur Surveill . (2017) 22:17-00647. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2017.22.39.17-00647
51. Menne B, Murray V. Floods in the WHO European Region: Health Effects and Their Prevention . Copenhagen: WHO; Weltgesundheits organisation, Regionalbüro für Europa (2013). Available online at: http://www.euro.who.int/data/assets/pdf_file/0020/189020/e96853.pdf (accessed 15 August 2017).
52. Schneider SH. The greenhouse effect: science and policy. Science . (1989) 243:771–81. doi: 10.1126/science.243.4892.771
53. Wilson WE, Suh HH. Fine particles and coarse particles: concentration relationships relevant to epidemiologic studies. J Air Waste Manag Assoc . (1997) 47:1238–49. doi: 10.1080/10473289.1997.10464074
54. US EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) (2018). Available online at: https://www.epa.gov/pm-pollution/particulate-matter-pm-basics (accessed September 22, 2018).
55. Cheung K, Daher N, Kam W, Shafer MM, Ning Z, Schauer JJ, et al. Spatial and temporal variation of chemical composition and mass closure of ambient coarse particulate matter (PM10–2.5) in the Los Angeles area. Atmos Environ . (2011) 45:2651–62. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.02.066
56. Zhang L, Yang Y, Li Y, Qian ZM, Xiao W, Wang X, et al. Short-term and long-term effects of PM2.5 on acute nasopharyngitis in 10 communities of Guangdong, China. Sci Total Env. (2019) 688:136–42. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.470.
57. Kloog I, Ridgway B, Koutrakis P, Coull BA, Schwartz JD. Long- and short-term exposure to PM2.5 and mortality using novel exposure models, Epidemiology . (2013) 24:555–61. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e318294beaa
58. New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services. Current and Forecasted Air Quality in New Hampshire . Environmental Fact Sheet (2019). Available online at: https://www.des.nh.gov/organization/commissioner/pip/factsheets/ard/documents/ard-16.pdf (accessed September 22, 2019).
59. Kappos AD, Bruckmann P, Eikmann T, Englert N, Heinrich U, Höppe P, et al. Health effects of particles in ambient air. Int J Hyg Environ Health . (2004) 207:399–407. doi: 10.1078/1438-4639-00306
60. Boschi N (Ed.). Defining an educational framework for indoor air sciences education. In: Education and Training in Indoor Air Sciences . Luxembourg: Springer Science & Business Media (2012). 245 p.
61. Heal MR, Kumar P, Harrison RM. Particles, air quality, policy and health. Chem Soc Rev . (2012) 41:6606–30. doi: 10.1039/c2cs35076a
62. Bezirtzoglou E, Alexopoulos A. Ozone history and ecosystems: a goliath from impacts to advance industrial benefits and interests, to environmental and therapeutical strategies. In: Ozone Depletion, Chemistry and Impacts. (2009). p. 135–45.
63. Villányi V, Turk B, Franc B, Csintalan Z. Ozone Pollution and its Bioindication. In: Villányi V, editor. Air Pollution . London: Intech Open (2010). doi: 10.5772/10047
64. Massachusetts Department of Public Health. Massachusetts State Health Assessment . Boston, MA (2017). Available online at: https://www.mass.gov/files/documents/2017/11/03/2017%20MA%20SHA%20final%20compressed.pdf (accessed October 30, 2017).
65. Lorenzini G, Saitanis C. Ozone: A Novel Plant “Pathogen.” In: Sanitá di Toppi L, Pawlik-Skowrońska B, editors. Abiotic Stresses in Plant Springer Link (2003). p. 205–29. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-0255-3_8
66. Fares S, Vargas R, Detto M, Goldstein AH, Karlik J, Paoletti E, et al. Tropospheric ozone reduces carbon assimilation in trees: estimates from analysis of continuous flux measurements. Glob Change Biol . (2013) 19:2427–43. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12222
67. Harmens H, Mills G, Hayes F, Jones L, Norris D, Fuhrer J. Air Pollution and Vegetation . ICP Vegetation Annual Report 2006/2007. (2012)
68. Emberson LD, Pleijel H, Ainsworth EA, den Berg M, Ren W, Osborne S, et al. Ozone effects on crops and consideration in crop models. Eur J Agron . (2018) 100:19–34. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2018.06.002
69. Alexopoulos A, Plessas S, Ceciu S, Lazar V, Mantzourani I, Voidarou C, et al. Evaluation of ozone efficacy on the reduction of microbial population of fresh cut lettuce ( Lactuca sativa ) and green bell pepper ( Capsicum annuum ). Food Control . (2013) 30:491–6. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.09.018
70. Alexopoulos A, Plessas S, Kourkoutas Y, Stefanis C, Vavias S, Voidarou C, et al. Experimental effect of ozone upon the microbial flora of commercially produced dairy fermented products. Int J Food Microbiol . (2017) 246:5–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.01.018
71. Maggio A, Fagnano M. Ozone damages to mediterranean crops: physiological responses. Ital J Agron . (2008) 13–20. doi: 10.4081/ija.2008.13
72. McCarthy JT, Pelle E, Dong K, Brahmbhatt K, Yarosh D, Pernodet N. Effects of ozone in normal human epidermal keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol . (2013) 22:360–1. doi: 10.1111/exd.12125
73. WHO. Health Risks of Ozone From Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution . Available online at: http://www.euro.who.int/data/assets/pdf_file/0005/78647/E91843.pdf (accessed August 15, 2019).
74. Thiele JJ, Traber MG, Tsang K, Cross CE, Packer L. In vivo exposure to ozone depletes vitamins C and E and induces lipid peroxidation in epidermal layers of murine skin. Free Radic Biol Med. (1997) 23:365–91. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(96)00617-X
75. Hatch GE, Slade R, Harris LP, McDonnell WF, Devlin RB, Koren HS, et al. Ozone dose and effect in humans and rats. A comparison using oxygen- 18 labeling and bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . (1994) 150:676–83. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.3.8087337
76. Lippmann M. Health effects of ozone. A critical review. JAPCA . (1989) 39:672–95. doi: 10.1080/08940630.1989.10466554
77. Gryparis A, Forsberg B, Katsouyanni K, Analitis A, Touloumi G, Schwartz J, et al. Acute effects of ozone on mortality from the “air pollution and health: a European approach” project. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . (2004) 170:1080–7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200403-333OC
78. Soon W, Baliunas SL, Robinson AB, Robinson ZW. Environmental effects of increased atmospheric carbon dioxide. Climate Res . (1999) 13:149–64 doi: 10.1260/0958305991499694
79. Richmont-Bryant J, Owen RC, Graham S, Snyder M, McDow S, Oakes M, et al. Estimation of on-road NO2 concentrations, NO2/NOX ratios, and related roadway gradients from near-road monitoring data. Air Qual Atm Health . (2017) 10:611–25. doi: 10.1007/s11869-016-0455-7
80. Hesterberg TW, Bunn WB, McClellan RO, Hamade AK, Long CM, Valberg PA. Critical review of the human data on short-term nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) exposures: evidence for NO2 no-effect levels. Crit Rev Toxicol . (2009) 39:743–81. doi: 10.3109/10408440903294945
81. Chen T-M, Gokhale J, Shofer S, Kuschner WG. Outdoor air pollution: nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and carbon monoxide health effects. Am J Med Sci . (2007) 333:249–56. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31803b900f
82. US EPA. Table of Historical SO 2 NAAQS, Sulfur US EPA . Available online at: https://www3.epa.gov/ttn/naaqs/standards/so2/s_so2_history.html (accessed October 5, 2019).
83. WHO Regional Office of Europe (2000). Available online at: https://euro.who.int/_data/assets/pdf_file/0020/123086/AQG2ndEd_7_4Sulfuroxide.pdf
84. Pruss-Ustun A, Fewrell L, Landrigan PJ, Ayuso-Mateos JL. Lead exposure. Comparative Quantification of Health Risks . World Health Organization. p. 1495–1542. Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/cra/chapters/volume2/1495-1542.pdf?ua=1
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
85. Goyer RA. Transplacental transport of lead. Environ Health Perspect . (1990) 89:101–5. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9089101
86. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIH). Lead and Your Health . (2013). 1–4 p. Available online at: https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/materials/lead_and_your_health_508.pdf (accessed September 17, 2019).
87. Farhat A, Mohammadzadeh A, Balali-Mood M, Aghajanpoor-Pasha M, Ravanshad Y. Correlation of blood lead level in mothers and exclusively breastfed infants: a study on infants aged less than six months. Asia Pac J Med Toxicol . (2013) 2:150–2.
88. Assi MA, Hezmee MNM, Haron AW, Sabri MYM, Rajion MA. The detrimental effects of lead on human and animal health. Vet World . (2016) 9:660–71. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2016.660-671
89. Abdel-Shafy HI, Mansour MSM. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt J Pet . (2016) 25:107–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpe.2015.03.011
90. Kumar A, Singh BP, Punia M, Singh D, Kumar K, Jain VK. Assessment of indoor air concentrations of VOCs and their associated health risks in the library of Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int . (2014) 21:2240–8. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-2150-7
91. Molhave L, Clausen G, Berglund B, Ceaurriz J, Kettrup A, Lindvall T, et al. Total Volatile Organic Compounds (TVOC) in Indoor Air Quality Investigations. Indoor Air . 7:225–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0668.1997.00002.x
92. Gibb T. Indoor Air Quality May be Hazardous to Your Health . MSU Extension. Available online at: https://www.canr.msu.edu/news/indoor_air_quality_may_be_hazardous_to_your_health (accessed October 5, 2019).
93. Ebersviller S, Lichtveld K, Sexton KG, Zavala J, Lin Y-H, Jaspers I, et al. Gaseous VOCs rapidly modify particulate matter and its biological effects – Part 1: simple VOCs and model PM. Atmos Chem Phys Discuss . (2012) 12:5065–105. doi: 10.5194/acpd-12-5065-2012
94. WHO (World Health Organization). Dioxins and Their Effects on Human Health. Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dioxins-and-their-effects-on-human-health (accessed October 5, 2019).
95. EEA (European Environmental Agency). Air Quality Standards to the European Union and WHO . Available online at: https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/data-and-maps/figures/air-quality-standards-under-the
96. Nakano T, Otsuki T. [Environmental air pollutants and the risk of cancer]. (Japanese). Gan To Kagaku Ryoho . (2013) 40:1441–5.
97. Kurt OK, Zhang J, Pinkerton KE. Pulmonary health effects of air pollution. Curr Opin Pulm Med . (2016) 22:138–43. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000000248
98. Guarnieri M, Balmes JR. Outdoor air pollution and asthma. Lancet . (2014) 383:1581–92. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60617-6
99. Jiang X-Q, Mei X-D, Feng D. Air pollution and chronic airway diseases: what should people know and do? J Thorac Dis . (2016) 8:E31–40.
100. Bourdrel T, Bind M-A, Béjot Y, Morel O, Argacha J-F. Cardiovascular effects of air pollution. Arch Cardiovasc Dis . (2017) 110:634–42. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2017.05.003
101. Hoffmann B, Moebus S, Möhlenkamp S, Stang A, Lehmann N, Dragano N, et al. Residential exposure to traffic is associated with coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation . (2007) 116:489–496. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.693622
102. Katholi RE, Couri DM. Left ventricular hypertrophy: major risk factor in patients with hypertension: update and practical clinical applications. Int J Hypertens . (2011) 2011:495349. doi: 10.4061/2011/495349
103. Leary PJ, Kaufman JD, Barr RG, Bluemke DA, Curl CL, Hough CL, et al. Traffic- related air pollution and the right ventricle. the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . (2014) 189:1093–100. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201312-2298OC
104. Genc S, Zadeoglulari Z, Fuss SH, Genc K. The adverse effects of air pollution on the nervous system. J Toxicol . (2012) 2012:782462. doi: 10.1155/2012/782462
105. Calderon-Garciduenas L, Azzarelli B, Acuna H, et al. Air pollution and brain damage. Toxicol Pathol. (2002) 30:373–89. doi: 10.1080/01926230252929954
106. Rückerl R, Greven S, Ljungman P, Aalto P, Antoniades C, Bellander T, et al. Air pollution and inflammation (interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, fibrinogen) in myocardial infarction survivors. Environ Health Perspect . (2007) 115:1072–80. doi: 10.1289/ehp.10021
107. Peters A, Veronesi B, Calderón-Garcidueñas L, Gehr P, Chen LC, Geiser M, et al. Translocation and potential neurological effects of fine and ultrafine particles a critical update. Part Fibre Toxicol . (2006) 3:13–8. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-3-13
108. Kelly FJ. Dietary antioxidants and environmental stress. Proc Nutr Soc . (2004) 63:579–85. doi: 10.1079/PNS2004388
109. Bellinger DC. Very low lead exposures and children's neurodevelopment. Curr Opin Pediatr . (2008) 20:172–7. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e3282f4f97b
110. Balbo P, Silvestri M, Rossi GA, Crimi E, Burastero SE. Differential role of CD80 and CD86 on alveolar macrophages in the presentation of allergen to T lymphocytes in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy J Br Soc Allergy Clin Immunol . (2001) 31:625–36. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2001.01068.x
111. Drakaki E, Dessinioti C, Antoniou C. Air pollution and the skin. Front Environ Sci Eng China . (2014) 15:2–8. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2014.00011
112. Weisskopf MG, Kioumourtzoglou M-A, Roberts AL. Air pollution and autism spectrum disorders: causal or confounded? Curr Environ Health Rep . (2015) 2:430–9. doi: 10.1007/s40572-015-0073-9
113. Mo Z, Fu Q, Lyu D, Zhang L, Qin Z, Tang Q, et al. Impacts of air pollution on dry eye disease among residents in Hangzhou, China: a case-crossover study. Environ Pollut . (2019) 246:183–9. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.109
114. Klopfer J. Effects of environmental air pollution on the eye. J Am Optom Assoc . (1989) 60:773–8.
115. Ashfaq A, Sharma P. Environmental effects of air pollution and application of engineered methods to combat the problem. J Indust Pollut Control . (2012) 29.
116. Madronich S, de Gruijl F. Skin cancer and UV radiation. Nature . (1993) 366:23–9. doi: 10.1038/366023a0
117. Teramura A. Effects of UV-B radiation on the growth and yield of crop plants. Physiol Plant . (2006) 58:415–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.1983.tb04203.x
118. Singh E, Tiwari S, Agrawal M. Effects of elevated ozone on photosynthesis and stomatal conductance of two soybean varieties: a case study to assess impacts of one component of predicted global climate change. Plant Biol Stuttg Ger . (2009) 11(Suppl. 1):101–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2009.00263.x
119. Manderson L. How global Warming is Adding to the Health Risks of Poor People . The Conversation. University of the Witwatersrand. Available online at: http://theconversation.com/how-global-warming-is-adding-to-the-health-risks-of-poor-people-109520 (accessed October 5, 2019).
120. Ministers of Energy and Environment. Federal/Provincial/Territorial Ministers of Energy and Environment (Canada), editor. The Canada-Wide Acid Rain Strategy for Post-2000 . Halifax: The Ministers (1999). 11 p.
121. Zuhara S, Isaifan R. The impact of criteria air pollutants on soil and water: a review. (2018) 278–84. doi: 10.30799/jespr.133.18040205
122. WHO. First WHO Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health. (2018). Available online at: https://www.who.int/airpollution/events/conference/en/ (accessed October 6, 2019).
123. What is the Kyoto Protocol? UNFCCC . Available online at: https://unfccc.int/kyoto__protocol (accessed October 6, 2019).
124. CopenhagenClimate Change Conference (UNFCCC) . Available online at: https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/conferences/past-conferences/copenhagen-climate-change-conference-december-2009/copenhagen-climate-change-conference-december-2009 (accessed October 6, 2019).
125. Durban Climate Change Conference,. UNFCCC (2011). Available online at: https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/conferences/past-conferences/copenhagen-climate-change-conference-december-2009/copenhagen-climate-change-conference-december-2009 (accessed October 6, 2019).
126. Paris Climate Change Agreement,. (2016). Available online at: https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement/the-paris-agreement
Keywords: air pollution, environment, health, public health, gas emission, policy
Citation: Manisalidis I, Stavropoulou E, Stavropoulos A and Bezirtzoglou E (2020) Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 8:14. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00014
Received: 17 October 2019; Accepted: 17 January 2020; Published: 20 February 2020.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2020 Manisalidis, Stavropoulou, Stavropoulos and Bezirtzoglou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ioannis Manisalidis, giannismanisal@gmail.com ; Elisavet Stavropoulou, elisabeth.stavropoulou@gmail.com
† These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Public Health
Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review
Ioannis manisalidis.
1 Delphis S.A., Kifisia, Greece
2 Laboratory of Hygiene and Environmental Protection, Faculty of Medicine, Democritus University of Thrace, Alexandroupolis, Greece
Elisavet Stavropoulou
3 Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois (CHUV), Service de Médicine Interne, Lausanne, Switzerland
Agathangelos Stavropoulos
4 School of Social and Political Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom
Eugenia Bezirtzoglou
One of our era's greatest scourges is air pollution, on account not only of its impact on climate change but also its impact on public and individual health due to increasing morbidity and mortality. There are many pollutants that are major factors in disease in humans. Among them, Particulate Matter (PM), particles of variable but very small diameter, penetrate the respiratory system via inhalation, causing respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, reproductive and central nervous system dysfunctions, and cancer. Despite the fact that ozone in the stratosphere plays a protective role against ultraviolet irradiation, it is harmful when in high concentration at ground level, also affecting the respiratory and cardiovascular system. Furthermore, nitrogen oxide, sulfur dioxide, Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), dioxins, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are all considered air pollutants that are harmful to humans. Carbon monoxide can even provoke direct poisoning when breathed in at high levels. Heavy metals such as lead, when absorbed into the human body, can lead to direct poisoning or chronic intoxication, depending on exposure. Diseases occurring from the aforementioned substances include principally respiratory problems such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), asthma, bronchiolitis, and also lung cancer, cardiovascular events, central nervous system dysfunctions, and cutaneous diseases. Last but not least, climate change resulting from environmental pollution affects the geographical distribution of many infectious diseases, as do natural disasters. The only way to tackle this problem is through public awareness coupled with a multidisciplinary approach by scientific experts; national and international organizations must address the emergence of this threat and propose sustainable solutions.
Approach to the Problem
The interactions between humans and their physical surroundings have been extensively studied, as multiple human activities influence the environment. The environment is a coupling of the biotic (living organisms and microorganisms) and the abiotic (hydrosphere, lithosphere, and atmosphere).
Pollution is defined as the introduction into the environment of substances harmful to humans and other living organisms. Pollutants are harmful solids, liquids, or gases produced in higher than usual concentrations that reduce the quality of our environment.
Human activities have an adverse effect on the environment by polluting the water we drink, the air we breathe, and the soil in which plants grow. Although the industrial revolution was a great success in terms of technology, society, and the provision of multiple services, it also introduced the production of huge quantities of pollutants emitted into the air that are harmful to human health. Without any doubt, the global environmental pollution is considered an international public health issue with multiple facets. Social, economic, and legislative concerns and lifestyle habits are related to this major problem. Clearly, urbanization and industrialization are reaching unprecedented and upsetting proportions worldwide in our era. Anthropogenic air pollution is one of the biggest public health hazards worldwide, given that it accounts for about 9 million deaths per year ( 1 ).
Without a doubt, all of the aforementioned are closely associated with climate change, and in the event of danger, the consequences can be severe for mankind ( 2 ). Climate changes and the effects of global planetary warming seriously affect multiple ecosystems, causing problems such as food safety issues, ice and iceberg melting, animal extinction, and damage to plants ( 3 , 4 ).
Air pollution has various health effects. The health of susceptible and sensitive individuals can be impacted even on low air pollution days. Short-term exposure to air pollutants is closely related to COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, asthma, respiratory disease, and high rates of hospitalization (a measurement of morbidity).
The long-term effects associated with air pollution are chronic asthma, pulmonary insufficiency, cardiovascular diseases, and cardiovascular mortality. According to a Swedish cohort study, diabetes seems to be induced after long-term air pollution exposure ( 5 ). Moreover, air pollution seems to have various malign health effects in early human life, such as respiratory, cardiovascular, mental, and perinatal disorders ( 3 ), leading to infant mortality or chronic disease in adult age ( 6 ).
National reports have mentioned the increased risk of morbidity and mortality ( 1 ). These studies were conducted in many places around the world and show a correlation between daily ranges of particulate matter (PM) concentration and daily mortality. Climate shifts and global planetary warming ( 3 ) could aggravate the situation. Besides, increased hospitalization (an index of morbidity) has been registered among the elderly and susceptible individuals for specific reasons. Fine and ultrafine particulate matter seems to be associated with more serious illnesses ( 6 ), as it can invade the deepest parts of the airways and more easily reach the bloodstream.
Air pollution mainly affects those living in large urban areas, where road emissions contribute the most to the degradation of air quality. There is also a danger of industrial accidents, where the spread of a toxic fog can be fatal to the populations of the surrounding areas. The dispersion of pollutants is determined by many parameters, most notably atmospheric stability and wind ( 6 ).
In developing countries ( 7 ), the problem is more serious due to overpopulation and uncontrolled urbanization along with the development of industrialization. This leads to poor air quality, especially in countries with social disparities and a lack of information on sustainable management of the environment. The use of fuels such as wood fuel or solid fuel for domestic needs due to low incomes exposes people to bad-quality, polluted air at home. It is of note that three billion people around the world are using the above sources of energy for their daily heating and cooking needs ( 8 ). In developing countries, the women of the household seem to carry the highest risk for disease development due to their longer duration exposure to the indoor air pollution ( 8 , 9 ). Due to its fast industrial development and overpopulation, China is one of the Asian countries confronting serious air pollution problems ( 10 , 11 ). The lung cancer mortality observed in China is associated with fine particles ( 12 ). As stated already, long-term exposure is associated with deleterious effects on the cardiovascular system ( 3 , 5 ). However, it is interesting to note that cardiovascular diseases have mostly been observed in developed and high-income countries rather than in the developing low-income countries exposed highly to air pollution ( 13 ). Extreme air pollution is recorded in India, where the air quality reaches hazardous levels. New Delhi is one of the more polluted cities in India. Flights in and out of New Delhi International Airport are often canceled due to the reduced visibility associated with air pollution. Pollution is occurring both in urban and rural areas in India due to the fast industrialization, urbanization, and rise in use of motorcycle transportation. Nevertheless, biomass combustion associated with heating and cooking needs and practices is a major source of household air pollution in India and in Nepal ( 14 , 15 ). There is spatial heterogeneity in India, as areas with diverse climatological conditions and population and education levels generate different indoor air qualities, with higher PM 2.5 observed in North Indian states (557–601 μg/m 3 ) compared to the Southern States (183–214 μg/m 3 ) ( 16 , 17 ). The cold climate of the North Indian areas may be the main reason for this, as longer periods at home and more heating are necessary compared to in the tropical climate of Southern India. Household air pollution in India is associated with major health effects, especially in women and young children, who stay indoors for longer periods. Chronic obstructive respiratory disease (CORD) and lung cancer are mostly observed in women, while acute lower respiratory disease is seen in young children under 5 years of age ( 18 ).
Accumulation of air pollution, especially sulfur dioxide and smoke, reaching 1,500 mg/m3, resulted in an increase in the number of deaths (4,000 deaths) in December 1952 in London and in 1963 in New York City (400 deaths) ( 19 ). An association of pollution with mortality was reported on the basis of monitoring of outdoor pollution in six US metropolitan cities ( 20 ). In every case, it seems that mortality was closely related to the levels of fine, inhalable, and sulfate particles more than with the levels of total particulate pollution, aerosol acidity, sulfur dioxide, or nitrogen dioxide ( 20 ).
Furthermore, extremely high levels of pollution are reported in Mexico City and Rio de Janeiro, followed by Milan, Ankara, Melbourne, Tokyo, and Moscow ( 19 ).
Based on the magnitude of the public health impact, it is certain that different kinds of interventions should be taken into account. Success and effectiveness in controlling air pollution, specifically at the local level, have been reported. Adequate technological means are applied considering the source and the nature of the emission as well as its impact on health and the environment. The importance of point sources and non-point sources of air pollution control is reported by Schwela and Köth-Jahr ( 21 ). Without a doubt, a detailed emission inventory must record all sources in a given area. Beyond considering the above sources and their nature, topography and meteorology should also be considered, as stated previously. Assessment of the control policies and methods is often extrapolated from the local to the regional and then to the global scale. Air pollution may be dispersed and transported from one region to another area located far away. Air pollution management means the reduction to acceptable levels or possible elimination of air pollutants whose presence in the air affects our health or the environmental ecosystem. Private and governmental entities and authorities implement actions to ensure the air quality ( 22 ). Air quality standards and guidelines were adopted for the different pollutants by the WHO and EPA as a tool for the management of air quality ( 1 , 23 ). These standards have to be compared to the emissions inventory standards by causal analysis and dispersion modeling in order to reveal the problematic areas ( 24 ). Inventories are generally based on a combination of direct measurements and emissions modeling ( 24 ).
As an example, we state here the control measures at the source through the use of catalytic converters in cars. These are devices that turn the pollutants and toxic gases produced from combustion engines into less-toxic pollutants by catalysis through redox reactions ( 25 ). In Greece, the use of private cars was restricted by tracking their license plates in order to reduce traffic congestion during rush hour ( 25 ).
Concerning industrial emissions, collectors and closed systems can keep the air pollution to the minimal standards imposed by legislation ( 26 ).
Current strategies to improve air quality require an estimation of the economic value of the benefits gained from proposed programs. These proposed programs by public authorities, and directives are issued with guidelines to be respected.
In Europe, air quality limit values AQLVs (Air Quality Limit Values) are issued for setting off planning claims ( 27 ). In the USA, the NAAQS (National Ambient Air Quality Standards) establish the national air quality limit values ( 27 ). While both standards and directives are based on different mechanisms, significant success has been achieved in the reduction of overall emissions and associated health and environmental effects ( 27 ). The European Directive identifies geographical areas of risk exposure as monitoring/assessment zones to record the emission sources and levels of air pollution ( 27 ), whereas the USA establishes global geographical air quality criteria according to the severity of their air quality problem and records all sources of the pollutants and their precursors ( 27 ).
In this vein, funds have been financing, directly or indirectly, projects related to air quality along with the technical infrastructure to maintain good air quality. These plans focus on an inventory of databases from air quality environmental planning awareness campaigns. Moreover, pollution measures of air emissions may be taken for vehicles, machines, and industries in urban areas.
Technological innovation can only be successful if it is able to meet the needs of society. In this sense, technology must reflect the decision-making practices and procedures of those involved in risk assessment and evaluation and act as a facilitator in providing information and assessments to enable decision makers to make the best decisions possible. Summarizing the aforementioned in order to design an effective air quality control strategy, several aspects must be considered: environmental factors and ambient air quality conditions, engineering factors and air pollutant characteristics, and finally, economic operating costs for technological improvement and administrative and legal costs. Considering the economic factor, competitiveness through neoliberal concepts is offering a solution to environmental problems ( 22 ).
The development of environmental governance, along with technological progress, has initiated the deployment of a dialogue. Environmental politics has created objections and points of opposition between different political parties, scientists, media, and governmental and non-governmental organizations ( 22 ). Radical environmental activism actions and movements have been created ( 22 ). The rise of the new information and communication technologies (ICTs) are many times examined as to whether and in which way they have influenced means of communication and social movements such as activism ( 28 ). Since the 1990s, the term “digital activism” has been used increasingly and in many different disciplines ( 29 ). Nowadays, multiple digital technologies can be used to produce a digital activism outcome on environmental issues. More specifically, devices with online capabilities such as computers or mobile phones are being used as a way to pursue change in political and social affairs ( 30 ).
In the present paper, we focus on the sources of environmental pollution in relation to public health and propose some solutions and interventions that may be of interest to environmental legislators and decision makers.
Sources of Exposure
It is known that the majority of environmental pollutants are emitted through large-scale human activities such as the use of industrial machinery, power-producing stations, combustion engines, and cars. Because these activities are performed at such a large scale, they are by far the major contributors to air pollution, with cars estimated to be responsible for approximately 80% of today's pollution ( 31 ). Some other human activities are also influencing our environment to a lesser extent, such as field cultivation techniques, gas stations, fuel tanks heaters, and cleaning procedures ( 32 ), as well as several natural sources, such as volcanic and soil eruptions and forest fires.
The classification of air pollutants is based mainly on the sources producing pollution. Therefore, it is worth mentioning the four main sources, following the classification system: Major sources, Area sources, Mobile sources, and Natural sources.
Major sources include the emission of pollutants from power stations, refineries, and petrochemicals, the chemical and fertilizer industries, metallurgical and other industrial plants, and, finally, municipal incineration.
Indoor area sources include domestic cleaning activities, dry cleaners, printing shops, and petrol stations.
Mobile sources include automobiles, cars, railways, airways, and other types of vehicles.
Finally, natural sources include, as stated previously, physical disasters ( 33 ) such as forest fire, volcanic erosion, dust storms, and agricultural burning.
However, many classification systems have been proposed. Another type of classification is a grouping according to the recipient of the pollution, as follows:
Air pollution is determined as the presence of pollutants in the air in large quantities for long periods. Air pollutants are dispersed particles, hydrocarbons, CO, CO 2 , NO, NO 2 , SO 3 , etc.
Water pollution is organic and inorganic charge and biological charge ( 10 ) at high levels that affect the water quality ( 34 , 35 ).
Soil pollution occurs through the release of chemicals or the disposal of wastes, such as heavy metals, hydrocarbons, and pesticides.
Air pollution can influence the quality of soil and water bodies by polluting precipitation, falling into water and soil environments ( 34 , 36 ). Notably, the chemistry of the soil can be amended due to acid precipitation by affecting plants, cultures, and water quality ( 37 ). Moreover, movement of heavy metals is favored by soil acidity, and metals are so then moving into the watery environment. It is known that heavy metals such as aluminum are noxious to wildlife and fishes. Soil quality seems to be of importance, as soils with low calcium carbonate levels are at increased jeopardy from acid rain. Over and above rain, snow and particulate matter drip into watery ' bodies ( 36 , 38 ).
Lastly, pollution is classified following type of origin:
Radioactive and nuclear pollution , releasing radioactive and nuclear pollutants into water, air, and soil during nuclear explosions and accidents, from nuclear weapons, and through handling or disposal of radioactive sewage.
Radioactive materials can contaminate surface water bodies and, being noxious to the environment, plants, animals, and humans. It is known that several radioactive substances such as radium and uranium concentrate in the bones and can cause cancers ( 38 , 39 ).
Noise pollution is produced by machines, vehicles, traffic noises, and musical installations that are harmful to our hearing.
The World Health Organization introduced the term DALYs. The DALYs for a disease or health condition is defined as the sum of the Years of Life Lost (YLL) due to premature mortality in the population and the Years Lost due to Disability (YLD) for people living with the health condition or its consequences ( 39 ). In Europe, air pollution is the main cause of disability-adjusted life years lost (DALYs), followed by noise pollution. The potential relationships of noise and air pollution with health have been studied ( 40 ). The study found that DALYs related to noise were more important than those related to air pollution, as the effects of environmental noise on cardiovascular disease were independent of air pollution ( 40 ). Environmental noise should be counted as an independent public health risk ( 40 ).
Environmental pollution occurs when changes in the physical, chemical, or biological constituents of the environment (air masses, temperature, climate, etc.) are produced.
Pollutants harm our environment either by increasing levels above normal or by introducing harmful toxic substances. Primary pollutants are directly produced from the above sources, and secondary pollutants are emitted as by-products of the primary ones. Pollutants can be biodegradable or non-biodegradable and of natural origin or anthropogenic, as stated previously. Moreover, their origin can be a unique source (point-source) or dispersed sources.
Pollutants have differences in physical and chemical properties, explaining the discrepancy in their capacity for producing toxic effects. As an example, we state here that aerosol compounds ( 41 – 43 ) have a greater toxicity than gaseous compounds due to their tiny size (solid or liquid) in the atmosphere; they have a greater penetration capacity. Gaseous compounds are eliminated more easily by our respiratory system ( 41 ). These particles are able to damage lungs and can even enter the bloodstream ( 41 ), leading to the premature deaths of millions of people yearly. Moreover, the aerosol acidity ([H+]) seems to considerably enhance the production of secondary organic aerosols (SOA), but this last aspect is not supported by other scientific teams ( 38 ).
Climate and Pollution
Air pollution and climate change are closely related. Climate is the other side of the same coin that reduces the quality of our Earth ( 44 ). Pollutants such as black carbon, methane, tropospheric ozone, and aerosols affect the amount of incoming sunlight. As a result, the temperature of the Earth is increasing, resulting in the melting of ice, icebergs, and glaciers.
In this vein, climatic changes will affect the incidence and prevalence of both residual and imported infections in Europe. Climate and weather affect the duration, timing, and intensity of outbreaks strongly and change the map of infectious diseases in the globe ( 45 ). Mosquito-transmitted parasitic or viral diseases are extremely climate-sensitive, as warming firstly shortens the pathogen incubation period and secondly shifts the geographic map of the vector. Similarly, water-warming following climate changes leads to a high incidence of waterborne infections. Recently, in Europe, eradicated diseases seem to be emerging due to the migration of population, for example, cholera, poliomyelitis, tick-borne encephalitis, and malaria ( 46 ).
The spread of epidemics is associated with natural climate disasters and storms, which seem to occur more frequently nowadays ( 47 ). Malnutrition and disequilibration of the immune system are also associated with the emerging infections affecting public health ( 48 ).
The Chikungunya virus “took the airplane” from the Indian Ocean to Europe, as outbreaks of the disease were registered in Italy ( 49 ) as well as autochthonous cases in France ( 50 ).
An increase in cryptosporidiosis in the United Kingdom and in the Czech Republic seems to have occurred following flooding ( 36 , 51 ).
As stated previously, aerosols compounds are tiny in size and considerably affect the climate. They are able to dissipate sunlight (the albedo phenomenon) by dispersing a quarter of the sun's rays back to space and have cooled the global temperature over the last 30 years ( 52 ).
Air Pollutants
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports on six major air pollutants, namely particle pollution, ground-level ozone, carbon monoxide, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and lead. Air pollution can have a disastrous effect on all components of the environment, including groundwater, soil, and air. Additionally, it poses a serious threat to living organisms. In this vein, our interest is mainly to focus on these pollutants, as they are related to more extensive and severe problems in human health and environmental impact. Acid rain, global warming, the greenhouse effect, and climate changes have an important ecological impact on air pollution ( 53 ).
Particulate Matter (PM) and Health
Studies have shown a relationship between particulate matter (PM) and adverse health effects, focusing on either short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic) PM exposure.
Particulate matter (PM) is usually formed in the atmosphere as a result of chemical reactions between the different pollutants. The penetration of particles is closely dependent on their size ( 53 ). Particulate Matter (PM) was defined as a term for particles by the United States Environmental Protection Agency ( 54 ). Particulate matter (PM) pollution includes particles with diameters of 10 micrometers (μm) or smaller, called PM 10 , and extremely fine particles with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometers (μm) and smaller.
Particulate matter contains tiny liquid or solid droplets that can be inhaled and cause serious health effects ( 55 ). Particles <10 μm in diameter (PM 10 ) after inhalation can invade the lungs and even reach the bloodstream. Fine particles, PM 2.5 , pose a greater risk to health ( 6 , 56 ) ( Table 1 ).
Penetrability according to particle size.
Multiple epidemiological studies have been performed on the health effects of PM. A positive relation was shown between both short-term and long-term exposures of PM 2.5 and acute nasopharyngitis ( 56 ). In addition, long-term exposure to PM for years was found to be related to cardiovascular diseases and infant mortality.
Those studies depend on PM 2.5 monitors and are restricted in terms of study area or city area due to a lack of spatially resolved daily PM 2.5 concentration data and, in this way, are not representative of the entire population. Following a recent epidemiological study by the Department of Environmental Health at Harvard School of Public Health (Boston, MA) ( 57 ), it was reported that, as PM 2.5 concentrations vary spatially, an exposure error (Berkson error) seems to be produced, and the relative magnitudes of the short- and long-term effects are not yet completely elucidated. The team developed a PM 2.5 exposure model based on remote sensing data for assessing short- and long-term human exposures ( 57 ). This model permits spatial resolution in short-term effects plus the assessment of long-term effects in the whole population.
Moreover, respiratory diseases and affection of the immune system are registered as long-term chronic effects ( 58 ). It is worth noting that people with asthma, pneumonia, diabetes, and respiratory and cardiovascular diseases are especially susceptible and vulnerable to the effects of PM. PM 2.5 , followed by PM 10 , are strongly associated with diverse respiratory system diseases ( 59 ), as their size permits them to pierce interior spaces ( 60 ). The particles produce toxic effects according to their chemical and physical properties. The components of PM 10 and PM 2.5 can be organic (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, dioxins, benzene, 1-3 butadiene) or inorganic (carbon, chlorides, nitrates, sulfates, metals) in nature ( 55 ).
Particulate Matter (PM) is divided into four main categories according to type and size ( 61 ) ( Table 2 ).
Types and sizes of particulate Matter (PM).
Gas contaminants include PM in aerial masses.
Particulate contaminants include contaminants such as smog, soot, tobacco smoke, oil smoke, fly ash, and cement dust.
Biological Contaminants are microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, mold, and bacterial spores), cat allergens, house dust and allergens, and pollen.
Types of Dust include suspended atmospheric dust, settling dust, and heavy dust.
Finally, another fact is that the half-lives of PM 10 and PM 2.5 particles in the atmosphere is extended due to their tiny dimensions; this permits their long-lasting suspension in the atmosphere and even their transfer and spread to distant destinations where people and the environment may be exposed to the same magnitude of pollution ( 53 ). They are able to change the nutrient balance in watery ecosystems, damage forests and crops, and acidify water bodies.
As stated, PM 2.5 , due to their tiny size, are causing more serious health effects. These aforementioned fine particles are the main cause of the “haze” formation in different metropolitan areas ( 12 , 13 , 61 ).
Ozone Impact in the Atmosphere
Ozone (O 3 ) is a gas formed from oxygen under high voltage electric discharge ( 62 ). It is a strong oxidant, 52% stronger than chlorine. It arises in the stratosphere, but it could also arise following chain reactions of photochemical smog in the troposphere ( 63 ).
Ozone can travel to distant areas from its initial source, moving with air masses ( 64 ). It is surprising that ozone levels over cities are low in contrast to the increased amounts occuring in urban areas, which could become harmful for cultures, forests, and vegetation ( 65 ) as it is reducing carbon assimilation ( 66 ). Ozone reduces growth and yield ( 47 , 48 ) and affects the plant microflora due to its antimicrobial capacity ( 67 , 68 ). In this regard, ozone acts upon other natural ecosystems, with microflora ( 69 , 70 ) and animal species changing their species composition ( 71 ). Ozone increases DNA damage in epidermal keratinocytes and leads to impaired cellular function ( 72 ).
Ground-level ozone (GLO) is generated through a chemical reaction between oxides of nitrogen and VOCs emitted from natural sources and/or following anthropogenic activities.
Ozone uptake usually occurs by inhalation. Ozone affects the upper layers of the skin and the tear ducts ( 73 ). A study of short-term exposure of mice to high levels of ozone showed malondialdehyde formation in the upper skin (epidermis) but also depletion in vitamins C and E. It is likely that ozone levels are not interfering with the skin barrier function and integrity to predispose to skin disease ( 74 ).
Due to the low water-solubility of ozone, inhaled ozone has the capacity to penetrate deeply into the lungs ( 75 ).
Toxic effects induced by ozone are registered in urban areas all over the world, causing biochemical, morphologic, functional, and immunological disorders ( 76 ).
The European project (APHEA2) focuses on the acute effects of ambient ozone concentrations on mortality ( 77 ). Daily ozone concentrations compared to the daily number of deaths were reported from different European cities for a 3-year period. During the warm period of the year, an observed increase in ozone concentration was associated with an increase in the daily number of deaths (0.33%), in the number of respiratory deaths (1.13%), and in the number of cardiovascular deaths (0.45%). No effect was observed during wintertime.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide is produced by fossil fuel when combustion is incomplete. The symptoms of poisoning due to inhaling carbon monoxide include headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, and, finally, loss of consciousness.
The affinity of carbon monoxide to hemoglobin is much greater than that of oxygen. In this vein, serious poisoning may occur in people exposed to high levels of carbon monoxide for a long period of time. Due to the loss of oxygen as a result of the competitive binding of carbon monoxide, hypoxia, ischemia, and cardiovascular disease are observed.
Carbon monoxide affects the greenhouses gases that are tightly connected to global warming and climate. This should lead to an increase in soil and water temperatures, and extreme weather conditions or storms may occur ( 68 ).
However, in laboratory and field experiments, it has been seen to produce increased plant growth ( 78 ).
Nitrogen Oxide (NO 2 )
Nitrogen oxide is a traffic-related pollutant, as it is emitted from automobile motor engines ( 79 , 80 ). It is an irritant of the respiratory system as it penetrates deep in the lung, inducing respiratory diseases, coughing, wheezing, dyspnea, bronchospasm, and even pulmonary edema when inhaled at high levels. It seems that concentrations over 0.2 ppm produce these adverse effects in humans, while concentrations higher than 2.0 ppm affect T-lymphocytes, particularly the CD8+ cells and NK cells that produce our immune response ( 81 ).It is reported that long-term exposure to high levels of nitrogen dioxide can be responsible for chronic lung disease. Long-term exposure to NO 2 can impair the sense of smell ( 81 ).
However, systems other than respiratory ones can be involved, as symptoms such as eye, throat, and nose irritation have been registered ( 81 ).
High levels of nitrogen dioxide are deleterious to crops and vegetation, as they have been observed to reduce crop yield and plant growth efficiency. Moreover, NO 2 can reduce visibility and discolor fabrics ( 81 ).
Sulfur Dioxide (SO 2 )
Sulfur dioxide is a harmful gas that is emitted mainly from fossil fuel consumption or industrial activities. The annual standard for SO 2 is 0.03 ppm ( 82 ). It affects human, animal, and plant life. Susceptible people as those with lung disease, old people, and children, who present a higher risk of damage. The major health problems associated with sulfur dioxide emissions in industrialized areas are respiratory irritation, bronchitis, mucus production, and bronchospasm, as it is a sensory irritant and penetrates deep into the lung converted into bisulfite and interacting with sensory receptors, causing bronchoconstriction. Moreover, skin redness, damage to the eyes (lacrimation and corneal opacity) and mucous membranes, and worsening of pre-existing cardiovascular disease have been observed ( 81 ).
Environmental adverse effects, such as acidification of soil and acid rain, seem to be associated with sulfur dioxide emissions ( 83 ).
Lead is a heavy metal used in different industrial plants and emitted from some petrol motor engines, batteries, radiators, waste incinerators, and waste waters ( 84 ).
Moreover, major sources of lead pollution in the air are metals, ore, and piston-engine aircraft. Lead poisoning is a threat to public health due to its deleterious effects upon humans, animals, and the environment, especially in the developing countries.
Exposure to lead can occur through inhalation, ingestion, and dermal absorption. Trans- placental transport of lead was also reported, as lead passes through the placenta unencumbered ( 85 ). The younger the fetus is, the more harmful the toxic effects. Lead toxicity affects the fetal nervous system; edema or swelling of the brain is observed ( 86 ). Lead, when inhaled, accumulates in the blood, soft tissue, liver, lung, bones, and cardiovascular, nervous, and reproductive systems. Moreover, loss of concentration and memory, as well as muscle and joint pain, were observed in adults ( 85 , 86 ).
Children and newborns ( 87 ) are extremely susceptible even to minimal doses of lead, as it is a neurotoxicant and causes learning disabilities, impairment of memory, hyperactivity, and even mental retardation.
Elevated amounts of lead in the environment are harmful to plants and crop growth. Neurological effects are observed in vertebrates and animals in association with high lead levels ( 88 ).
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons(PAHs)
The distribution of PAHs is ubiquitous in the environment, as the atmosphere is the most important means of their dispersal. They are found in coal and in tar sediments. Moreover, they are generated through incomplete combustion of organic matter as in the cases of forest fires, incineration, and engines ( 89 ). PAH compounds, such as benzopyrene, acenaphthylene, anthracene, and fluoranthene are recognized as toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic substances. They are an important risk factor for lung cancer ( 89 ).
Volatile Organic Compounds(VOCs)
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), such as toluene, benzene, ethylbenzene, and xylene ( 90 ), have been found to be associated with cancer in humans ( 91 ). The use of new products and materials has actually resulted in increased concentrations of VOCs. VOCs pollute indoor air ( 90 ) and may have adverse effects on human health ( 91 ). Short-term and long-term adverse effects on human health are observed. VOCs are responsible for indoor air smells. Short-term exposure is found to cause irritation of eyes, nose, throat, and mucosal membranes, while those of long duration exposure include toxic reactions ( 92 ). Predictable assessment of the toxic effects of complex VOC mixtures is difficult to estimate, as these pollutants can have synergic, antagonistic, or indifferent effects ( 91 , 93 ).
Dioxins originate from industrial processes but also come from natural processes, such as forest fires and volcanic eruptions. They accumulate in foods such as meat and dairy products, fish and shellfish, and especially in the fatty tissue of animals ( 94 ).
Short-period exhibition to high dioxin concentrations may result in dark spots and lesions on the skin ( 94 ). Long-term exposure to dioxins can cause developmental problems, impairment of the immune, endocrine and nervous systems, reproductive infertility, and cancer ( 94 ).
Without any doubt, fossil fuel consumption is responsible for a sizeable part of air contamination. This contamination may be anthropogenic, as in agricultural and industrial processes or transportation, while contamination from natural sources is also possible. Interestingly, it is of note that the air quality standards established through the European Air Quality Directive are somewhat looser than the WHO guidelines, which are stricter ( 95 ).
Effect of Air Pollution on Health
The most common air pollutants are ground-level ozone and Particulates Matter (PM). Air pollution is distinguished into two main types:
Outdoor pollution is the ambient air pollution.
Indoor pollution is the pollution generated by household combustion of fuels.
People exposed to high concentrations of air pollutants experience disease symptoms and states of greater and lesser seriousness. These effects are grouped into short- and long-term effects affecting health.
Susceptible populations that need to be aware of health protection measures include old people, children, and people with diabetes and predisposing heart or lung disease, especially asthma.
As extensively stated previously, according to a recent epidemiological study from Harvard School of Public Health, the relative magnitudes of the short- and long-term effects have not been completely clarified ( 57 ) due to the different epidemiological methodologies and to the exposure errors. New models are proposed for assessing short- and long-term human exposure data more successfully ( 57 ). Thus, in the present section, we report the more common short- and long-term health effects but also general concerns for both types of effects, as these effects are often dependent on environmental conditions, dose, and individual susceptibility.
Short-term effects are temporary and range from simple discomfort, such as irritation of the eyes, nose, skin, throat, wheezing, coughing and chest tightness, and breathing difficulties, to more serious states, such as asthma, pneumonia, bronchitis, and lung and heart problems. Short-term exposure to air pollution can also cause headaches, nausea, and dizziness.
These problems can be aggravated by extended long-term exposure to the pollutants, which is harmful to the neurological, reproductive, and respiratory systems and causes cancer and even, rarely, deaths.
The long-term effects are chronic, lasting for years or the whole life and can even lead to death. Furthermore, the toxicity of several air pollutants may also induce a variety of cancers in the long term ( 96 ).
As stated already, respiratory disorders are closely associated with the inhalation of air pollutants. These pollutants will invade through the airways and will accumulate at the cells. Damage to target cells should be related to the pollutant component involved and its source and dose. Health effects are also closely dependent on country, area, season, and time. An extended exposure duration to the pollutant should incline to long-term health effects in relation also to the above factors.
Particulate Matter (PMs), dust, benzene, and O 3 cause serious damage to the respiratory system ( 97 ). Moreover, there is a supplementary risk in case of existing respiratory disease such as asthma ( 98 ). Long-term effects are more frequent in people with a predisposing disease state. When the trachea is contaminated by pollutants, voice alterations may be remarked after acute exposure. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may be induced following air pollution, increasing morbidity and mortality ( 99 ). Long-term effects from traffic, industrial air pollution, and combustion of fuels are the major factors for COPD risk ( 99 ).
Multiple cardiovascular effects have been observed after exposure to air pollutants ( 100 ). Changes occurred in blood cells after long-term exposure may affect cardiac functionality. Coronary arteriosclerosis was reported following long-term exposure to traffic emissions ( 101 ), while short-term exposure is related to hypertension, stroke, myocardial infracts, and heart insufficiency. Ventricle hypertrophy is reported to occur in humans after long-time exposure to nitrogen oxide (NO 2 ) ( 102 , 103 ).
Neurological effects have been observed in adults and children after extended-term exposure to air pollutants.
Psychological complications, autism, retinopathy, fetal growth, and low birth weight seem to be related to long-term air pollution ( 83 ). The etiologic agent of the neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's and Parkinson's) is not yet known, although it is believed that extended exposure to air pollution seems to be a factor. Specifically, pesticides and metals are cited as etiological factors, together with diet. The mechanisms in the development of neurodegenerative disease include oxidative stress, protein aggregation, inflammation, and mitochondrial impairment in neurons ( 104 ) ( Figure 1 ).

Impact of air pollutants on the brain.
Brain inflammation was observed in dogs living in a highly polluted area in Mexico for a long period ( 105 ). In human adults, markers of systemic inflammation (IL-6 and fibrinogen) were found to be increased as an immediate response to PNC on the IL-6 level, possibly leading to the production of acute-phase proteins ( 106 ). The progression of atherosclerosis and oxidative stress seem to be the mechanisms involved in the neurological disturbances caused by long-term air pollution. Inflammation comes secondary to the oxidative stress and seems to be involved in the impairment of developmental maturation, affecting multiple organs ( 105 , 107 ). Similarly, other factors seem to be involved in the developmental maturation, which define the vulnerability to long-term air pollution. These include birthweight, maternal smoking, genetic background and socioeconomic environment, as well as education level.
However, diet, starting from breast-feeding, is another determinant factor. Diet is the main source of antioxidants, which play a key role in our protection against air pollutants ( 108 ). Antioxidants are free radical scavengers and limit the interaction of free radicals in the brain ( 108 ). Similarly, genetic background may result in a differential susceptibility toward the oxidative stress pathway ( 60 ). For example, antioxidant supplementation with vitamins C and E appears to modulate the effect of ozone in asthmatic children homozygous for the GSTM1 null allele ( 61 ). Inflammatory cytokines released in the periphery (e.g., respiratory epithelia) upregulate the innate immune Toll-like receptor 2. Such activation and the subsequent events leading to neurodegeneration have recently been observed in lung lavage in mice exposed to ambient Los Angeles (CA, USA) particulate matter ( 61 ). In children, neurodevelopmental morbidities were observed after lead exposure. These children developed aggressive and delinquent behavior, reduced intelligence, learning difficulties, and hyperactivity ( 109 ). No level of lead exposure seems to be “safe,” and the scientific community has asked the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to reduce the current screening guideline of 10 μg/dl ( 109 ).
It is important to state that impact on the immune system, causing dysfunction and neuroinflammation ( 104 ), is related to poor air quality. Yet, increases in serum levels of immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM) and the complement component C3 are observed ( 106 ). Another issue is that antigen presentation is affected by air pollutants, as there is an upregulation of costimulatory molecules such as CD80 and CD86 on macrophages ( 110 ).
As is known, skin is our shield against ultraviolet radiation (UVR) and other pollutants, as it is the most exterior layer of our body. Traffic-related pollutants, such as PAHs, VOCs, oxides, and PM, may cause pigmented spots on our skin ( 111 ). On the one hand, as already stated, when pollutants penetrate through the skin or are inhaled, damage to the organs is observed, as some of these pollutants are mutagenic and carcinogenic, and, specifically, they affect the liver and lung. On the other hand, air pollutants (and those in the troposphere) reduce the adverse effects of ultraviolet radiation UVR in polluted urban areas ( 111 ). Air pollutants absorbed by the human skin may contribute to skin aging, psoriasis, acne, urticaria, eczema, and atopic dermatitis ( 111 ), usually caused by exposure to oxides and photochemical smoke ( 111 ). Exposure to PM and cigarette smoking act as skin-aging agents, causing spots, dyschromia, and wrinkles. Lastly, pollutants have been associated with skin cancer ( 111 ).
Higher morbidity is reported to fetuses and children when exposed to the above dangers. Impairment in fetal growth, low birth weight, and autism have been reported ( 112 ).
Another exterior organ that may be affected is the eye. Contamination usually comes from suspended pollutants and may result in asymptomatic eye outcomes, irritation ( 112 ), retinopathy, or dry eye syndrome ( 113 , 114 ).
Environmental Impact of Air Pollution
Air pollution is harming not only human health but also the environment ( 115 ) in which we live. The most important environmental effects are as follows.
Acid rain is wet (rain, fog, snow) or dry (particulates and gas) precipitation containing toxic amounts of nitric and sulfuric acids. They are able to acidify the water and soil environments, damage trees and plantations, and even damage buildings and outdoor sculptures, constructions, and statues.
Haze is produced when fine particles are dispersed in the air and reduce the transparency of the atmosphere. It is caused by gas emissions in the air coming from industrial facilities, power plants, automobiles, and trucks.
Ozone , as discussed previously, occurs both at ground level and in the upper level (stratosphere) of the Earth's atmosphere. Stratospheric ozone is protecting us from the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. In contrast, ground-level ozone is harmful to human health and is a pollutant. Unfortunately, stratospheric ozone is gradually damaged by ozone-depleting substances (i.e., chemicals, pesticides, and aerosols). If this protecting stratospheric ozone layer is thinned, then UV radiation can reach our Earth, with harmful effects for human life (skin cancer) ( 116 ) and crops ( 117 ). In plants, ozone penetrates through the stomata, inducing them to close, which blocks CO 2 transfer and induces a reduction in photosynthesis ( 118 ).
Global climate change is an important issue that concerns mankind. As is known, the “greenhouse effect” keeps the Earth's temperature stable. Unhappily, anthropogenic activities have destroyed this protecting temperature effect by producing large amounts of greenhouse gases, and global warming is mounting, with harmful effects on human health, animals, forests, wildlife, agriculture, and the water environment. A report states that global warming is adding to the health risks of poor people ( 119 ).
People living in poorly constructed buildings in warm-climate countries are at high risk for heat-related health problems as temperatures mount ( 119 ).
Wildlife is burdened by toxic pollutants coming from the air, soil, or the water ecosystem and, in this way, animals can develop health problems when exposed to high levels of pollutants. Reproductive failure and birth effects have been reported.
Eutrophication is occurring when elevated concentrations of nutrients (especially nitrogen) stimulate the blooming of aquatic algae, which can cause a disequilibration in the diversity of fish and their deaths.
Without a doubt, there is a critical concentration of pollution that an ecosystem can tolerate without being destroyed, which is associated with the ecosystem's capacity to neutralize acidity. The Canada Acid Rain Program established this load at 20 kg/ha/yr ( 120 ).
Hence, air pollution has deleterious effects on both soil and water ( 121 ). Concerning PM as an air pollutant, its impact on crop yield and food productivity has been reported. Its impact on watery bodies is associated with the survival of living organisms and fishes and their productivity potential ( 121 ).
An impairment in photosynthetic rhythm and metabolism is observed in plants exposed to the effects of ozone ( 121 ).
Sulfur and nitrogen oxides are involved in the formation of acid rain and are harmful to plants and marine organisms.
Last but not least, as mentioned above, the toxicity associated with lead and other metals is the main threat to our ecosystems (air, water, and soil) and living creatures ( 121 ).
In 2018, during the first WHO Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health, the WHO's General Director, Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, called air pollution a “silent public health emergency” and “the new tobacco” ( 122 ).
Undoubtedly, children are particularly vulnerable to air pollution, especially during their development. Air pollution has adverse effects on our lives in many different respects.
Diseases associated with air pollution have not only an important economic impact but also a societal impact due to absences from productive work and school.
Despite the difficulty of eradicating the problem of anthropogenic environmental pollution, a successful solution could be envisaged as a tight collaboration of authorities, bodies, and doctors to regularize the situation. Governments should spread sufficient information and educate people and should involve professionals in these issues so as to control the emergence of the problem successfully.
Technologies to reduce air pollution at the source must be established and should be used in all industries and power plants. The Kyoto Protocol of 1997 set as a major target the reduction of GHG emissions to below 5% by 2012 ( 123 ). This was followed by the Copenhagen summit, 2009 ( 124 ), and then the Durban summit of 2011 ( 125 ), where it was decided to keep to the same line of action. The Kyoto protocol and the subsequent ones were ratified by many countries. Among the pioneers who adopted this important protocol for the world's environmental and climate “health” was China ( 3 ). As is known, China is a fast-developing economy and its GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is expected to be very high by 2050, which is defined as the year of dissolution of the protocol for the decrease in gas emissions.
A more recent international agreement of crucial importance for climate change is the Paris Agreement of 2015, issued by the UNFCCC (United Nations Climate Change Committee). This latest agreement was ratified by a plethora of UN (United Nations) countries as well as the countries of the European Union ( 126 ). In this vein, parties should promote actions and measures to enhance numerous aspects around the subject. Boosting education, training, public awareness, and public participation are some of the relevant actions for maximizing the opportunities to achieve the targets and goals on the crucial matter of climate change and environmental pollution ( 126 ). Without any doubt, technological improvements makes our world easier and it seems difficult to reduce the harmful impact caused by gas emissions, we could limit its use by seeking reliable approaches.
Synopsizing, a global prevention policy should be designed in order to combat anthropogenic air pollution as a complement to the correct handling of the adverse health effects associated with air pollution. Sustainable development practices should be applied, together with information coming from research in order to handle the problem effectively.
At this point, international cooperation in terms of research, development, administration policy, monitoring, and politics is vital for effective pollution control. Legislation concerning air pollution must be aligned and updated, and policy makers should propose the design of a powerful tool of environmental and health protection. As a result, the main proposal of this essay is that we should focus on fostering local structures to promote experience and practice and extrapolate these to the international level through developing effective policies for sustainable management of ecosystems.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
IM is employed by the company Delphis S.A. The remaining authors declare that the present review paper was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
- Bibliography
- More Referencing guides Blog Automated transliteration Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Automated transliteration
- Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Referencing guides
Essays on Air Pollution
As you embark on writing an air pollution essay, it's essential to structure your content effectively. Begin with the introductory paragraph, where you provide basic facts, statistics, and definitions to establish context. Depending on the scope of your essay, you may choose to focus on indoor or outdoor pollution. Tailor your introduction to set the tone and direction of your essay.
Delve into the heart of your essay by discussing the problem of air pollution and its sources. Explain why these sources exist and highlight the pollutants involved. Consider various air pollution essay topics, including respiratory issues, child health concerns, ozone layer depletion, and impacts on wildlife and cardiovascular health. From municipal waste management to green energy initiatives, explore potential solutions and effective strategies for mitigating pollution.
In crafting your essay, ensure you present a methodical approach and propose at least one viable solution to address the problem. Draw inspiration from examples of proposal essays, where statistical data and compelling facts enhance the narrative. Your main thesis statement should encapsulate the causes and effects of air pollution.
To add depth to your essay, consider discussing environmental issues in your local area and drawing comparisons to broader ecological challenges. Providing concrete examples and leveraging factual evidence will enrich your argument and make your essay more compelling.
Consider exploring examples of proposal essays on air pollution to gain valuable insights into structuring and presenting your ideas effectively. By incorporating relevant examples, factual information, and a persuasive argument, your essay will resonate with readers and contribute to greater awareness and action on this critical issue.
Hook Examples for Air Pollution Essays
Statistical hook.
Did you know that each year, air pollution causes over 4.2 million premature deaths worldwide? These startling statistics underscore the urgent need to address this global crisis.
Anecdotal Hook
Picture this: A bustling cityscape obscured by a thick haze of smog, where children play wearing masks. This is the stark reality faced by many urban areas grappling with air pollution.
Question Hook
How can we breathe easy when the air we inhale is increasingly toxic? Explore the consequences of air pollution and discover potential solutions to this pressing environmental issue.
Rhetorical Question Hook
Can we afford to ignore the invisible threat that hangs in the air we breathe? Delve into the hidden dangers of air pollution and its far-reaching impact on public health.
Quotation Hook
"The earth does not belong to us: we belong to the earth." — Marlee Matlin. Reflect on this thought-provoking quote as we delve into the environmental implications of air pollution.
Historical Hook
Travel back to the mid-20th century when air quality in major cities like London and Los Angeles was notoriously poor. Explore the historical context of air pollution regulation and its impact.
Definition Hook
What exactly is air pollution, and how does it differ from other environmental issues? Gain a clear understanding of this concept and its multifaceted nature.
Contrast Hook
Contrast the serene beauty of pristine landscapes with images of smog-choked cities. This stark juxtaposition highlights the importance of combating air pollution.
Narrative Hook
Step into the shoes of individuals living in heavily polluted areas and experience their daily struggles. Their stories shed light on the human side of the air pollution crisis.
Shocking Statement Hook
Prepare to be shocked by the surprising sources of indoor air pollution lurking within our homes. The danger may be closer than you think.
Ecological Impacts of Tear Gas
Analysis of the correlation between smog and allergies, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Taming The Traffic Beast: a Solution to Traffic Jams
Air pollution: causes and effects, how does air pollution effect on our health, problem of the air pollution, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
The Move to Reduce Air Pollution to Preserve The Human Population
Air pollution: causes, effects, and solutions, air pollution its causes and damaging effects, air pollution in china, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Human Impacts on The Environment
Cases of air pollution in malaysia, the urgent problem of pollution in modern world, negative impacts of air pollution and steps that the usa is taking to curb this problem, environmental pollution in the transport sector and the benefits of electric cars to our environment, ways you can reduce air pollution from your business , environmental factors and climate influences in california, environmental probelms in pakistan: issues in the big cities, evaluation of the health impact of air pollution in america and china, assessment of the ecological problem arising from air pollutants, analysis of the bronx air pollutants problem and the responsibility of the government, trees against world pollution, informative pollutions, their types, causes, impacts, and solutions, understanding the problem of air pollutants and its impact on temperature, the difficulties in mitigating the effects of climate change in the current world, analysis of the approach to better air quality and reduction of air pollution in the us, review of the documentary "under the dome" and the risks associated with air pollution in china, air filter in thailand, a study on the correlation between changes in air pollution and water sources, the serious problem of air pollution in saudi arabia and the solutions to the environmental issue.
Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere.
Household combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities and forest fires are common sources of air pollution. Pollutants of major public health concern include particulate matter, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide.
Respiratory and heart problems, child health problems, mortality, global warming, acid rain, eutrophication, depletion of the ozone layer, negative effect on wildlife.
Policies and investments that support sustainable land use, cleaner household energy and transport, energy-efficient housing, power generation, industry, and better municipal waste management can effectively reduce key sources of ambient air pollution.
A child born today might not breathe clean air until they are 8. Inhaling air pollution takes away at least 1-2 years of a typical human life. Pollutants that are released into the air, as opposed to land and water pollutants, are the most harmful. Rising levels of air pollution in Beijing has brought a new disease – Beijing cough.
Relevant topics
- Water Pollution
- Fast Fashion
- Ocean Pollution
- Deforestation
- Natural Disasters
- Climate Change
- Global Warming
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Essay on Air Pollution for Students and Children
500+ words essay on air pollution.
Essay on Air Pollution – Earlier the air we breathe in use to be pure and fresh. But, due to increasing industrialization and concentration of poisonous gases in the environment the air is getting more and more toxic day by day. Also, these gases are the cause of many respiratory and other diseases . Moreover, the rapidly increasing human activities like the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation is the major cause of air pollution.

How Air Gets Polluted?
The fossil fuel , firewood, and other things that we burn produce oxides of carbons which got released into the atmosphere. Earlier there happens to be a large number of trees which can easily filter the air we breathe in. But with the increase in demand for land, the people started cutting down of trees which caused deforestation. That ultimately reduced the filtering capacity of the tree.
Moreover, during the last few decades, the numbers of fossil fuel burning vehicle increased rapidly which increased the number of pollutants in the air .
Causes Of Air Pollution
Its causes include burning of fossil fuel and firewood, smoke released from factories , volcanic eruptions, forest fires, bombardment, asteroids, CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons), carbon oxides and many more.
Besides, there are some other air pollutants like industrial waste, agricultural waste, power plants, thermal nuclear plants, etc.
Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is also the cause of air pollution because air pollution produces the gases that greenhouse involves. Besides, it increases the temperature of earth surface so much that the polar caps are melting and most of the UV rays are easily penetrating the surface of the earth.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Effects Of Air Pollution On Health

Moreover, it increases the rate of aging of lungs, decreases lungs function, damage cells in the respiratory system.
Ways To Reduce Air Pollution
Although the level of air pollution has reached a critical point. But, there are still ways by which we can reduce the number of air pollutants from the air.
Reforestation- The quality of air can be improved by planting more and more trees as they clean and filter the air.
Policy for industries- Strict policy for industries related to the filter of gases should be introduced in the countries. So, we can minimize the toxins released from factories.
Use of eco-friendly fuel- We have to adopt the usage of Eco-friendly fuels such as LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas), CNG (Compressed Natural Gas), bio-gas, and other eco-friendly fuels. So, we can reduce the amount of harmful toxic gases.
To sum it up, we can say that the air we breathe is getting more and more polluted day by day. The biggest contribution to the increase in air pollution is of fossil fuels which produce nitric and sulphuric oxides. But, humans have taken this problem seriously and are devotedly working to eradicate the problem that they have created.
Above all, many initiatives like plant trees, use of eco-friendly fuel are promoted worldwide.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [{ “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Mention five effect of air pollution on human health?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “The major risk factor related to human health are asthma, lung cancer, Alzheimer, psychological complications, and autism. Besides, there are other effects of air pollution on a person’s health.”} }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is the effect of air pollution in the environment?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”:”Acid, rain, ozone depletion, greenhouse gases, smog are many other things are the cause of air pollution that affect the environment severely.”} }] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

261 Pollution Essay Topics & Essay Examples
The problem of environmental pollution is one of the main subjects for discussion worldwide. Manufacturing, carbon emissions, plastic, etc., have an adverse impact on air, water, and soil entire the world. That is why it is crucial to understand the problem and develop solutions to mitigate our negative effects on Earth.
In this article, you will find interesting research questions about pollution, ideas for your argumentative and persuasive papers, and essay examples to inspire.
Keep reading!
💡 8 Tips for Writing Essays on Pollution
🏆 best pollution topic ideas & essay examples, 🥇 captivating pollution research topics, 🌩️ shocking pollution essay examples and topic ideas, 🎓 simple & easy topics related to pollution, ✅ most interesting pollution topics to write about, ✍️ pollution essay topics for college, ❓ research questions about pollution.
There is a rising interest in ecological awareness and an overall building desire to move towards sustainable living within society. Thus, a pollution essay requires much more than merely outlining cause and effect occurrences.
Tackling a topic that should be both conscientious and demanding may be a difficult task, but with these few tips below, you can quickly address all pollution essay topics. Here are some ideas on how to make your assigned essay more comfortable to write:
Do your research beforehand. This action will help you start your bibliography, which you should begin by writing down every book and article you hope to use.
Additionally, doing so will help you better understand your subject and be more comfortable writing about it. Readers can always feel when writers are too vague because they want to avoid some aspects of a problem.
Introduce your issue from a historical viewpoint. You should explain the origin of your problem, outlining what changes began affecting the environment and why.
Doing so not only allows engaging your readers but also prevents needlessly confusing them by being evasive about your subject.
If some key terms and processes are not common knowledge, then you should explain them. Topics on pollution have tricky terminology, and you should allow your readers to read your essay while on the same level of knowledge as you.
For example, if you are writing about air pollution, then the terms you use may range from “particulate matter” to “hygroscopicity,” depending on the complexity of your essay’s subject.
The pollution essay thesis statement is a guiding line throughout your writing process. Every sentence you write should relate to your central argument and help advance it forward.
From when you start outlining until you write your conclusion and even when revising your draft, you should always ask yourself whether your writing helps you uphold your thesis.
Use credible sources to support your writing. Book and journal titles, research papers, and even interviews with respected scientists are good examples of what you should include in a bibliography.
You may also use pollution essay quotations to demonstrate scientists’ opinions or statistical numbers. When you reference your facts, your readers trust your writing and accept it as credible and truthful, as well as show a good understanding of the subject.
Give your essay an appropriate heading. Your pollution essay titles should clue your readers in on your argument. Using a “talking” title, which explains your subject at a glance, is a useful way of making your essay stand out among others.
If your subject ties together different issues, then you should think about using subheadings to make your essay more readable.
For example, when writing about nonpoint source pollution, you may need to mention its effects on both ocean and forest environments.
Doing so in different sections of your essay may help you structure your thoughts and bring together your arguments for a well-written conclusion.
Read sample essays written by others to help you understand your subject and essay structure better. Doing so will help you be consistent with your chosen citation style and immerse yourself in your research.
However, do not commit an academic offense by plagiarizing from the work of others.
Need more tips? Want to read an essay example? Visit IvyPanda!
- Water Pollution: Causes, Effects and Possible Solutions This is why clean water is required in all the places to make sure the people and all the living creatures in the planet live a good and healthy life.
- Air and Water Pollution in the Modern World The high number of vehicles in the city has greatly promoted air pollution in the area. Poor sewerage system, high pollution from industries and automobiles are among the major causes of air and water pollutions […]
- Water Pollution: Causes, Effects, and Prevention Farmers should be encouraged to embrace this kind of farming which ensures that the manure used is biodegradable and do not end up accumulating in the water bodies once they are washed off by floods.
- Pollution Caused by Transportation The growth of consignment and travelers’ mobility is associated with the rise of negative impacts of transportation through pollutants. Additionally, the pollutants can be related to fuels’ refining and distribution as well as manufacturing and […]
- How to Protect the Egypt Nile River From Pollution? The secret to the overflowing waters of the Nile is linked to the five months in a year of rain experienced in Ethiopia.
- Garbage Pollution Electronic waste can also be recycled and refurbished.’Reduce’, ‘Reuse’ and ‘Recycle’ are the 3Rs that go a long way in handling the issue of garbage.
- Cultural Pollution:Traditions and Historical Concepts The cultures traditions and historical concepts of the Middle East have over the centuries been characterised as by a distinct sense of variety that stems from a whirlwind of customs and traditions.
- Noise Pollution: Effects, Causes, and Potential Solutions According to the International Program on Chemical Safety, “an adverse effect of noise is defined as a change in the morphology and physiology of organism that results in an impairment of functional capacity, or an […]
- The Impact of Groundwater Pollution on Agriculture and Its Prevention People have to be aware about the impact of their activities on groundwater and be able to improve the conditions, they live under, and this piece of writing will inform each reader about each detail […]
- Ocean Pollution and the Fishing Industry In essence, the activities of over six billion people in the world are threatening the survival and quality of water found in the oceans, lakes and other inland water catchment areas.
- Environmental Pollution: Causes and Solutions The consequences that have risen as a result of neglecting to take care of the environment have now become a reality to the whole of mankind.
- Water Pollution in the Philippines: Metropolitan Manila Area In this brief economic analysis of water pollution in Metro Manila, it is proposed to look at the industrial use of waters and the household use to understand the impact that the population growth and […]
- Environmental Pollution and Its Effect on Health In climate change, due to air pollution, the main force to prevent environmental disasters need to change the approach to the production of substances from fossil fuels.
- Air Travel as a Cause of Severe Pollution Ecologists cite the growth of air travel as one of the factors that are contributing to environmental pollution. Restricting air transport can minimize the amount of noise that airplanes make, therefore improving the quality of […]
- Coca-Cola India and Water Pollution Issues The first difficulty that the representatives of the Coca-Cola Company happened to face due to their campaign in the territory of India was caused by the concerns of the local government.
- Car Air Pollution Further, NO2 can prevent the flow of oxygen in the blood to other parts of the body like the brain. These toxic substances settle in the lungs and disrupt the normal flow of air in […]
- Air Pollution and Its Impact on Human Health Community needs assessment is a systematic process in which the health educator, the nurse and other health care professionals together with the members of the community determine the health problems & needs of the community […]
- Pollution as a Big Problem That Faces the World Pollution is human made, pausing devastating health issues among the community at large, and its management cuts across all spectrums of societies including cultural, political, ethnic, and educational backgrounds Various forms of pollution have contributed […]
- The Ocean Pollution Problem Overview Ocean pollution is the unfavorable upshot due to the entrance of chemicals and particulate substances into the ocean. The land is the key source of ocean pollution in the form of non-point water pollution.
- The Problem of Ocean Pollution in Modern World Wastes such as toxic matter, plastics, and human wastes are some of the major sources of pollution in the ocean. Many people consume fish as food; when marine life is affected by toxic substance in […]
- Environmental Pollution: Causes and Consequences The essay will provide an overview of pollution and proffer solutions to combating pollution for a sustainable environment and health. Preventing pollution lowers the cost to the environment and the economy.
- Nurse Associate’s Role in Air Pollution Prevention This paper analyzes current health promotion strategies in Somerset and the United Kingdom, obstacles to preventative health strategies, health screening programs, the impact of psycho-social, economic, and behavioral factors, epidemiology and genomics, vaccination and immunization […]
- Acid Rain and Ozone Pollution Acid rain and ozone pollution are a form of pollution, which entails the release of gaseous and dust particles in quantities that destroy the integrity of the atmosphere and affect organisms in their respective habitats […]
- The World Oceans Pollution and Overfishing Human beings have taken a lot of time to realize the need for ocean conservation to the extent that the ocean has succumbed to ecological challenges that have affected their lives in a variety of […]
- Hudson River Pollution Concerns Unfortunately, the Industrial Revolution and the subsequent advancement of the local and national economy have turned the River into an object of environmental pollution.
- The Effects of Noise Pollution Noise pollution meaning When speaking about the effects of noise pollution, it is necessary to highlight some fundamentals of the issue.
- Air Pollution Impacts on Weather and Climate Air pollution is rated to be the major cause of discomfort in the living creatures of the world for air is essential for the survival of every living creature.
- Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control Environmental management is dynamic and it is concurrent to the existing management strategies and agenda of the company. Statutes and legislations pertaining to environmental compliance enforce the need to implement environmental management and monitoring of […]
- Air Pollution in Beijing and Its Effects on Society It is worth noting that different regions/countries/cities in the world have different levels of air pollution depending on the intensity/presence of causing agents and the techniques applied in dealing with air pollution.
- Smog, Its Harm and Pollution Reduction Progress Smog can be defined as the mixture of solid and liquid fog and smoke particles that are formed under the impact of high humidity and calm air.
- Cashion Water Quality: Spatial Distribution of Water Pollution Incidents This essay discusses the quality of water as per the report of 2021 obtained from the municipality, the quality issue and the source of pollution, and how the pollution impacts human health and the environment […]
- Environmental Factors and Health Promotion: Indoor and Outdoor Air Pollution This presentation offers some information about the damage of air pollution and presents a health promotion plan with helpful resources and evidence from research.
- Noise and Sound Pollution The noise pollution should be considered by the duration of the sound, the frequency of noise, and whether there is any control to the sound or not.
- Plastic Pollution From a Sociological Standpoint Wagner, as well as Miranda and de Carvalho-Souza, are in favor of increased recycling efforts to prevent more plastic from escaping into the sea.
- Reducing Traffic Noise Pollution in Cairo In conclusion, it seems reasonable to state that the issue of traffic noise pollution is rapidly growing in Egypt’s capital Cairo and increasingly impacts public health.
- Water Pollution: OIL Spills Aspects The effects of the oil spill on a species of ducks called the Harlequin ducks were formulated and the author attempted to trace out the immediate and residual effects of the oil on the birds.
- Technological Applications in Industrial Pollution Prevention I also understand that pollution prevention emerged from the need to protect the environment from degradation and that appropriate regulations require manufacturers to put in place measures to prevent the release of dangerous emissions.
- Pollution and Neglect in America During his stay in Ohio, he is realizing an increase in challenges, which he attributes to neglect by the members of the society.
- Environmental Pollution and Increased Birds Death The increase in the population of different animals may also cause the death of birds. This leads to the extinction of some animals and birds hence massive death.
- Water Pollution and Associated Health Risks The results of plenty of studies indicate the existence of the relation between the contamination of water by hazardous chemicals and the development of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, cancer, asthma, allergies, as well as reproductive […]
- Smog and Air Pollution in Los Angeles The city is often covered with a yellow veil in the sky, so the problem of smog is an actual problem of the state.
- Graveyard Ship Pollution in Kuwait The main legal issue of this case is the collision of two ships that led to the killing of millions of people and the dumping of waste along the sea.
- Environmental Pollution and Human Health The effects of sprawl on health workers are discussed in the article by Pohanka. It is similarly essential to take social justice and fairness into account because the effects of sprawl on population health are […]
- The Ecogeographical Impact of Air Pollution The weakness of the text is that the safety of NPs and their probable toxic effects on human health and the environment are not evaluated.
- Water Pollution as a Crime Against the Environment In particular, water pollution is a widespread crime against the environment, even though it is a severe felony that can result in harm to many people and vast territories.
- Carbon Offsets: Combatting Environmental Pollution I think that using other organizations or projects to offset an entity’s carbon footprint avoids the main goal of any present environmental protection efforts sustainability.
- Environmental Pollution: Waste Landfilling and Open Dumping The solution is simple and practical it is necessary to put efforts into further development of hard industries and stop financing the research of the issue that is useless.
- Air Pollution and Impact of Transportation Emissions of greenhouse gases, air pollution, the release of ballast water, aquatic invasive species, and oil and chemical leaks are only some of the environmental problems that marine transportation continues to cause.
- Pollution and Respiratory Disease in Louisiana The United States of America is an industrial powerhouse, a powerful nation that devoted much of its time to the growth and development of the petrochemical industry.
- Beat Plastic Pollution Essay These tips will help people to reduce the circulation of plastic in their lives. In conclusion, the best method to protect the environment is to minimize the accumulation of plastic waste by recycling, composting, and […]
- Air Pollution and Lung Disease To design a study in order to explore the link between lung disease and air pollution, it would be possible to follow a four-step process started by identifying the level or unit of analysis.
- American Society on Health and Pollution’s Activity The organization is purposed to inspire newly elected leaders to act as examples and lead the way in the promotion of a green economy that is sustainable for all American citizens.
- Environmental Justice: Pollution However, the issue of environmental racism transcends national boundaries and is likely to be repeated in other regions of the world.
- Air Pollution in China: Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics One of the most acute environmental problems in China is air pollution, which the authorities are trying to solve, but still, many people, factories, and active processes of globalization do not allow environmental programs to […]
- CSR Initiatives in Reducing Pollution and Carbon Emissions in GCC The purpose of this paper is to conduct a literature review evaluating the impact of CSR initiatives in reducing pollution and carbon emissions in GCC and the Middle East.
- The Negative Impact of Soil Pollution The picture does not show where the water is coming from, and that is how to determine whether the pollution is from a non-point source.
- Algae Explosion and Nitrogen Pollution in Lakes One of the most problematic aspects of nitrogen pollution as a form of nutrient pollution in lakes is the algae explosion.
- A Pollution Concern in the Anacostia River In addition, the unending sedimentation affected the river’s ecosystem due to the lack of sunshine, especially at the bottom of the river.
- Air Pollution and Child Health Conducting research, leading scholars, and summarizing the results of their efforts allowed the organization to investigate the numerous ways air pollution damages the human body.
- Environmental Protection: Pollution and Fossil Fuels The term used to describe a combination of oil and petroleum-related businesses, fossil fuel has been continuously cited as being dangerous for the planet.
- Importance of Mercury Water Pollution Problem Solutions The severity of the mercury contamination consequences depends on the age of the person exposed to the contamination, the way of contamination, the health condition, and many other factors.
- Issue of Pollution of Everest A policy that can be put in place by Nepal to address the current state of pollution on Everest is limiting the number of climbers to the mountain. The increase in the number of people […]
- The Impact of Atmospheric Pollution on Human Health and the Environment Atmospheric pollution is a set of environmental problems associated with releasing chemicals and accumulating concentrations of natural gases in the air.
- Air Pollution and Vulnerability to Covid-19 In other words, the findings will be used as one of the key arguments for showing that air pollution is detrimental to both individual and societal health.
- Poor Waste Disposal and Pollution in California For instance, the rapid increase in the number of factories and industries in California has led to more waste products in the state.
- Technical Report Pollution in Cities of Trinidad Many people who live in the environment close to the dumping sites are exposed to the daily combustion of the refuse, coupled with the inhalation of the emissions from the combusted material.
- Cultural Pollution in the Middle East The importance of the cultural patriarchal society suffers the whims of the feminist movement that has underscored the cultural values and roles of women.
- Fundamentals of Air Pollution The components of secondary air pollution include ozone and nitrogen oxides. Smog occurs when “car exhausts are exposed to direct sunlight”.
- The Reduction of Agricultural Nutrient Pollution: Possible Solutions The nutrients that are contained in fertilizer or manure may reach water basins and cause a dramatic increase in the populations of phytoplankton and algae.
- The Perspectives of Pollution for International Business Turning to the society’s role in changing the unsustainable system, the most important part of the discussion is usually dedicated to the role-changing possibility in the governmental structure.
- Pollution Problem: Sewage Spills in San Jose Water is a crucial element for all known forms of life to be able to live. Groundwater quality is essential for human consumption and social and economic activities.
- Equipment to Monitor Pollution Emissions In assessing the situation, the vital aspects are: the quality of the decision, the commitment of the subordinates, the knowledge of the leader, the structure of the problem, the probability of subordinates’ commitment, sharing the […]
- Global Plastic Pollution Problem and Its Drivers The primary challenge is the production and use of plastic products, which overwhelm the environment’s capacity to withstand. It cannot be burned because of air contamination, and the process of recycling equally results in plastic […]
- Plastic Pollution and Its Consequences Water in vapor form is also a product of combusted carbon-rich molecules and forms part of the hydrosphere from where it is absorbed into the biosphere.
- Newark Water Crisis: Water Pollution Problem The main problem was rooted in the fact that lead levels in the drinking water were highly elevated, which is dangerous and detrimental to the population’s health.
- Pollution Caused by Plastic Materials However, it is important to note that regardless of the many pleasant and appealing uses of plastics, the numerous health problems and dangers presented to the environment are gruesome.
- Pollution and Illegal Dumping in Chilliwack River Chilliwack River Watershed maintenance is under great pressure because of differing use of resources and activity, high demands for growth and recreation, and impacts to quality of water and riparian habitation from different water-use and […]
- Simply Green Products Firm: Pollution Allegations The natural decomposition is the surety that the company to the environmentalist organizations and the citizens. There is considerable proof that the company has been the primary producer of the packaging materials for the orchards […]
- Atmospheric Pollution Constituents A department dealing with the effects of atmospheric pollutants in the vicinity of an industrial complex has established a data table of measurements of a purity index Y on a scale of 0 to 1000 […]
- Air Pollution: The Problem’ Review Indoor pollution and related conditions are a big burden to the already suffering world according to the reports of the world health organization that it’s the 8th most important risk factor and is perceived to […]
- Law, Property Rights, and Air Pollution In the law of torts, ‘harm’ is considered when there is physical invasion to a person there fore in the case there was no violation of this law as the secretary was not harmed by […]
- Air Pollution in Middle East: Saudi Arabia The rate of air pollution in the world has increased gradually since the advent of the industrial revolution in the early 1800s.
- Global Pollution and Climate Change Both of these works address the topic of Global pollution, Global warming, and Climate change, which are relevant to the current situation in the world.
- Health Science: Pollution and Health The spill was apparently a result of the containing dam wall being weak and the ensuing heavy rains rapidly increased the volume of the contents resulting in breaking of the reservoir.
- Point vs. Non-Point Air Pollution To determine the air pollution source of a large smoke stack, one has to assess the physical characteristics of the smoke; description of the color concentration intensity is it grey or extremely dark?
- Noise Pollution: Best Practicable Means Magistrates’ Court identified Statutory Nuisance in the case and forwarded an abatement order against respondents along with a huge fine for their misconduct that led to noise pollution.
- Public Policy Issue: Particle Pollution in Chicago Metropolitan Area The Chicago metropolitan area has been mentioned quite a number of times in American Lung Association’s State of the Air 2008, an annual report that grades the quality of the air across the different cities […]
- Noise Pollution: Environmental Issue in Lagos, Nigeria The aim of the study would be to understand and evaluate the amount of noise pollution in Lagos, Nigeria and its affects on public health.
- Air Pollution and Health Issues in the US The industry of health care is closely connected to the industrial activities sector, which has the largest impact on the atmosphere through polluting the air, soil, and waters.
- Thames Water Company’s Pollution Issue and Ecocentrism Fines can be treated as a strong solution to this issue even though it is not presupposed by the ethical theory discussed, as they ensure that some funds can be spent on protecting the environment.
- Air Pollution Externalities and Possible Solutions In order to fully integrate public utility, power generation, policy and use of nuclear power in light of the growing concerns on the depletion of natural forms of energy as well as degradation of the […]
- Industrial Pollution in China and USA The pollution of world’s environment with industrial wastes is highly intensified and according to the authors’ opinion the scientific approach is the most significant and useful tool for the purpose of quick resolving of this […]
- Air Pollution and Ecological Perspectives of the Atmosphere The major contributors to CO2, one of the main pollutants in the atmosphere, are the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation.
- Pollution Is a Consistent Demolition of the Earth Pollution means the introduction into the environment of substances or energy that is liable to cause hazards to human health, harm to living resources and ecological systems, damage to structure or interfere with the legitimate […]
- Air Pollution and Its World History From the times of industrial revolution, smoke pollution was a concern and continues to be one with vehicles and industries replacing coal and wood.
- Water Pollution in a Community: Mitigation Plan Though for the fact that planet earth is abundant with water and almost two-thirds of the planet is made up of water still it is viewed that in future years, a shortage of water may […]
- The Influence of Global Warming and Pollution on the Environment This essay is going to address global warming from a psychological point of view with an emphasis on the psychological and social reasons that make it important to tackle this problem which is threatening the […]
- Atmospheric Chemistry – Pollution Ozone, a photochemical pollutant, is formed by the oxidation of explosive organic compounds in the presence of sunlight and oxides of nitrogen in the atmosphere.
- Construction Technology and Air Pollution Hot-list section has new and transferable technology and highlights the features that appeal to construction companies, specifies and designers, owners of the building and end users.
- As China Roars, Pollution Reaches Deadly Extremes The idea is to harness the excess waters of the Yangtze River to replenish the Yellow River which perennially suffers from lack of water and the formation of silt.
- Pollution Control Policy: Glodal Issues Global warming poses a great problem for the global biosphere since it affects the habitat of most of the natural occupants of the global hemisphere.
- Earth’s Atmosphere and Natural Pollution The stratosphere is the next layer of the atmosphere and is from that 7 17 km range to about 30 km above the earth’s surface.
- Atmospheric Pollution and Global Warming Green forests help in soaking the suspended particles in the air and thus clean the air for all of us to breathe.
- Recurrent Pollution of the Tisza River of Hungary The Tisza basin is located almost precisely in the geographical center of Europe and crosses the near-future boundary of the European Union.
- Marine Pollution: Management and International Legislation Marine environment refers to: the physical, chemical, geological and biological components, conditions and factors which interact and determine the productivity of, state, condition and quality of the marine ecosystem, the waters of the seas and […]
- Marine Pollution: Sources, Types, Pathways, and Status By examining sources, types, pathways, and status of water contamination in the context of the World Ocean, it is clear that most marine pollution caused by human actions, especially the mismanagement of plastic debris.
- The Public Perceptions of Air Pollution and Related Policies in London The primary questions for consideration are the public perceptions of air pollution and related policies in London and other cities of the United Kingdom, previous surveys regarding existing policies related to the environment or air […]
- Concerns of Ocean Ecosystem Pollution The range of adverse outcomes for ocean ecosystems can be discussed in volumes; however, the current discussion will focus on trash in the ocean waters, acidification, and the disruption of the marine life cycles.
- Food Distribution and Water Pollution Therefore, food distribution is one of the central reasons for water pollution. According to Greenpeace, one of the ways to improve the ecology of the planet is by creating healthy food markets.
- How China Cuts Its Air Pollution 5, which is the smallest and one of the most harmful polluting particles, were 54 percent lower in the last quarter of 2017 as compared to the same period in 2016, specifically in Beijing.
- Haze Pollution in China One of the outstanding aspects of pollution in the country is that the Chinese are highly desensitized and aware of issues surrounding this matter.
- Pollution and Federal Environmental Policy Pollution continues to influence the flora and the fauna of the United States, as well as people in urban and even rural areas.
- Plastic Pollution and Social Institutions The purpose of this paper is to investigate the political and economic barriers that hamper the efforts to reduce plastic pollution and discuss the ways in how they could be overcome.
- Social Activism Against Plastic Pollution Of the 30 million tons of plastic waste in the United States in 2009, only 7% were sent for recycling, which primarily damages marine life.
- Climate Change: Reducing Industrial Air Pollution One of the most effective measures of air quality in the USA is the Air Quality Index, which estimates air conditions by concentrations of such pollutants as particle solution, nitrogen and sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, […]
- Pollution as a Social Issue and Mass Media’s Role The reason why plastic pollution gained traction only during the 21st century is directly connected to the invention of the Internet and the technological advances in electronics.
- Environmental Ethics. Optimal Pollution: Reality or Myth? The effects of globalization and environmental change have caused the resurgence of environmentalism, yet the necessity to sustain industries and the global economy invalidates the idea of a pollution-free environment.
- Environmental Pollution and Contamination The rains are known to corrode marble and metals, cause respiratory diseases in human beings and increase the acidity of the soil.
- Low Pollution Car Engine The following is a discussion on the introduction of the low pollution car engine and its benefits to the UAE. In addition, pollution and climate change will be a thing of the past.
- Chemistry: Environmental Pollution in Hungary The acidification of water bodies leads to the death of numerous species that are susceptible to the presence of acid. Part of the problem is caused by the fact that Hungary is currently forced to […]
- Environmental Pollution Analysis The author explains that the damaging alterations have become possible due to the use of a large number of pesticides in the area.
- Coal Pollution in China as an Environmental Problem Thesis: Coal pollution in China has been a significant cause of environmental pollution-China being one of the largest coal producers in the world- therefore, necessitating the development of appropriate measures to reduce its severity.
- Air Pollution, Its Constituents and Health Effects The National Ambient Air Quality Standards are the regulations or policies that are adopted by states to ensure the safety of the environment.
- The Deepwater Horizon Oil Platform Pollution The oil spillage in the sea can result to the death of sea animals as well as plants that thrive in the water because of the dangerous chemicals that are contained in the oil.
- Air Pollution in the United Arab Emirates’ Cities In the article called Evaluating the Potential Impact of Global Warming on the UAE Residential Buildings, the author focuses on the negative consequences of global warming on the situation in the United Arab Emirates.
- Advanced Pollution Prevention in the United States In the United States, the overview of the previous legislation shows that the government used to enforce measures that would deal with pollution control which occurred at the final stage of production processes. The Pollution […]
- Climate Change, Air Pollution, Soil Degradation Then followed by outdoor air pollution, soil degradation which can also be called as soil contamination, global overpopulation, drinking water pollution, nuclear waste build-up, disappearing of the water supplies, indoor air pollution, depletion of the […]
- China Shenhua Energy Company: Pollution Reducing Although the Chinese government recognized the issue of pollution and announced a course for liberalization of the economy and a greater emphasis on ecology during the 12th 5-year plan, the transformation from a coal-based energy […]
- Air Pollution in Washington State and Healthy Living of People The problem of air pollution is closely related to the issue of the energy supply of the US. Due to the high level of air pollution in Washington state, there is a growing threat to […]
- Environmental Pollution in the Petroleum Industry At the same time, it threatens nature and creates many long-term issues related to pollution of air, soil, water, the weakening of the ozone layer, and the facilitation of the greenhouse gas effect.
- Air Pollution as a Factor for Renal Cancer Therefore, to prevent renal cancer, it is crucial to examine the primary causes and look for better strategies to curb the issue.
- Podocnemis Lewyana: Habitat Loss, Overfishing and Pollution The second factor is overhunting, which in the case of Magdalena River Turtle leads to the inability of these animals to locate food.
- Pollution in the San Francisco Bay The rivers provide fresh water for domestic use to many civilians, and it is apparent that the authorities have given the power plant the freedom to test the quantity of chemicals in the waste water.
- Indoor Air Pollution: The Silent Killer in Rural India The video “Indoor air pollution: The silent killer” discusses the detrimental impact of indoor air pollution in rural Indian households on people’s health. The problem of indoor air pollution is rather significant, and people should […]
- Air Pollution and China’s Governmental Measures The consequences of air pollution in China are already becoming evident, and not only they are the reason for environmental problems, but also they have a significant influence on the health of Chinese people living […]
- Lake Erie Water Pollution There are worries among the members of the community that the lake could be facing another episode of high toxicity, and they have called for the authorities to investigate the main causes of the pollution […]
- Environmental Pollution and Green Policies Although various scholars are of the view that green technology reduces the level of pollution, adequate research on the use of this form of technology needs to be conducted so as to fully contain environmental […]
- Air Pollution in Beijing and the Decision-Making Bias Severe air pollution in Beijing did not become a subject of worldwide concern and discussion until the 2008 Beijing Olympics, which brought the issue to the attention of the global public due to the immense […]
- “Fort McMurray Fires Cause Air Pollution” by McDiarmid As a rule, the air in Canada is clean and rich in oxygen; however, when the wildfire burst, it affected the ozone layer to a significant degree.
- Air Pollution as the Trigger of the Ecological Catastrophe The key data collection tool is a survey that is targeted at determining the main factors of air pollution, finding out the social opinion regarding the quality of air in different cities, and estimating the […]
- Agricultural Nutrient Pollution and Its Reduction The solutions that have been proposed for the issue are varied: there is the possibility of upgrading farms with the help of better technologies, controlling the use of fertilizers and waste discharge with the help […]
- Water & Air Pollution and Health Issues in Brazil The main environmental effects of pollution include the destruction of marine habitats, water scarcity, and anoxia. The conclusion is informative because the writer includes strategies to alleviate the problem of air and water pollution in […]
- Air Pollution and Respiratory Illnesses in Nigeria The purpose of the article presented was to test the relationship of the respiratory system illness and air pollution in developing countries, especially in Africa.
- Air Pollution Impact on Children’s Health in the US In these parts of the country, the level of air pollution is much higher. Nevertheless, the growing number of vehicles in the United States contributes to air pollution.
- Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Health Effects It emphasizes the fact that air contamination has a negative influence on the health of the representatives of the general public.
- Nebraska Pollution Prevention Project The article is about Nebraska’s Partners in Pollution Prevention program and the benefits it has brought to the state in the reduction of pollution caused by small businesses.
- Storm Water Pollution Prevention Plan All players need to be trained in significant areas of business so as they can handle them with care and beware of the potential they have in causing damage.
- Water Pollution in the US: Causes and Control Although water pollution can hardly be ceased entirely, the current rates of water pollution can be reduced by resorting to the sustainable principle of water use in both the industrial area and the realm of […]
- Economic View on Water and Pollution Some of the water is found in the continents’ rivers, lakes and in the subsurface. This research tries to explain the importance of water especially in an economist’s perspective by explaining the uses of water […]
- Air Pollution in Los Angeles The escalation of congestion in the city has worsened the problem of air pollution because of the volume of unhealthy air emitted in the atmosphere.
- Noise Pollution: Urban Traffic Noise Besides these two, noise also has an effect on the learning of an individual so that it distracts the individual in a way that s/he is not able to learn, as would be the case […]
- Environmental Revolution: Air Pollution in China For instance, a case study of the current pollution levels in China reveals that the country is struggling with the management of hazy weather.
- Pollution & Climate Change as Environmental Risks
- The Knoxville City’s Environmental Pollution
- Aviation’s Environmental Impact and Pollution
- Environmental Behavior and Air Pollution in Ohio
- Water Pollution and Management in the UAE
- Pollution of the Ganges and Its Main Factors
- Pollution Externalities Role in Management Economics
- Marine Pollution and the Anthropogenic Effects Upon It
- The New York City Air Pollution
- Air Pollution Effects on the Health and Environment
- Dealing With Air Pollution
- Environmental Justice and Air Pollution in Canada
- Environment Destruction: Pollution
- Big Coal and the Natural Environment Pollution
- Principles of Air Pollution Control and Analysis
- New York City Air Pollution Problem
- China’s Air Pollution Problem
- Pollution and Human Health
- Business and Pollution Inequality in Poor States
- China’s Air Pollution Is Not Unique
- Water Pollution and Its Challenges
- An Investigation of Green Roofs to Mitigate Air Pollution With Special Reference to Tehran, Iran
- Air Pollution: Human Influence on Environment
- Kuwait’s Desert Pollution
- Water Pollution Sources, Effects and Control
- Issues in Non-Point Source Pollution
- Air Pollution Sources in Houston
- Pollution Prevention in the Industrial Production
- Pollution Caused by Medium-Sized Enterprises and the Means to Prevent It
- Air Pollution: Public Health Impact
- Solutions to the Los Angeles Metropolitan Watershed Pollution Problem
- Economic Impact of Industrial Pollution in China
- Environmental Impacts of Air Pollution
- Pollution in Beijing, China
- Nitrate and Phosphate Pollution of Freshwater Ecosystem: Sources, Impacts and Cost Effective Measurements
- Automobile Pollution in the US
- Chloramine in Drinking Water: When the Threat of Pollution Emerges
- How Mechanical Engineering Used to Prevent and Fix Oil Pollution
- Technologies for Reduction of Automobile Pollution
- “Water and Pollution” Class Game
- How Bad Pollution Is in the Arab World
- Water in Crisis: Public Health Concerns in Africa
- Does Air Pollution in Schools Influence Student Performance?
- Regulation and Management of Haze Pollution in Canada
- Air Pollution Characteristics and Effect
- Impact of Blowing Drums on Air Pollution
- The System for Pollution Offsets
- The Nature of Nonpoint Pollution Control Problem
- Air and Water Pollution
- Health Hazard of Noise Pollution
- Fossil Fuels Subsidies and the Impact of Pollution on Health and Lifetime Earnings
- Causes of Water Pollution and the Present Environmental Solution
- Water Pollution & Diseases (Undeveloped Nations)
- Environmental Pollution in Canada
- The Impact of Industrial Pollution on the Environment
- Water and Water Pollution in Point of Economics’ View
- Air Pollution Sources, Effects and Ways of Minimizing
- Environmental Justice Issues Affecting African Americans: Water Pollution
- Plastic Ocean Pollution on Ocean Life in U.S.
- Air Pollution Effects on the Health in China
- Air Pollution and Health Policy in China
- The Pollution Within: Foreign Substances in the Human Body
- Air Pollution and Its Consequences
- The Problem of Atmospheric Pollution in Modern World
- Four Marketing Practices That Cause Noise Pollution
- Water Pollution and Wind Energy
- Air Pollution by Automobiles
- Air and Water Pollution in Los Angeles
- Tehran Chokes and Blames Severe Pollution on US Sanctions
- Water Pollution Causes and Climate Impacts
- The Case of PBC Pollution in Hudson River
- Preposition 23: Suspension of Air Pollution Control Act
- Climate and Air Pollution
- Urban Pollution – Many Long Years Ago
- Water Pollution Origins and Ways of Resolving
- Can Pollution Rights Trading Effectively Control Environmental Problems?
- Mud Lick Creek Project – Fresh Water Pollution
- A Discussion of Air Pollution & Related Health Implications on the Community
- Car Pollution in Moscow
- What Causes Air Pollution and What Effect Does It Have on People?
- Why Air Pollution Can Harm the Environment Dramatically?
- What Are the Sources of Air Pollution?
- Does Air Pollution Affect Health and Medical Insurance Cost in the Elderly?
- What Are the Causes and Effects of Water Pollution in Lake Huron?
- What Causes Water Pollution and Its Effects?
- What Can the Public Do to Curb Pollution?
- Will COVID-19 Containment and Treatment Measures Drive Shifts in Marine Litter Pollution?
- Does Inequality Matter Air Pollution and Health Relationship?
- Why Environmental Management May Yield No-Regret Pollution Abatement Options?
- How Can Be Organised Curbing Environmental Pollution Through Recycling?
- What Will the Effects Be if We Don’t Stop Plastic Pollution in Our Oceans?
- Does Air Pollution Crowd Out Foreign Direct Investment Inflows?
- Does Off-Farm Employment Contribute to Agriculture-Based Environmental Pollution?
- Does Environmental Pollution Affect Metropolitan Housing Prices?
- Does Financial Instability Increase Environmental Pollution in Pakistan?
- What Are the Leading Factors of Water Pollution Around the World?
- What King of Cost-Effective Control Strategies for Energy-Related Transboundary Air Pollution in Western Europe?
- Which Firms Are More Sensitive to Public Disclosure Schemes for Pollution Control?
- What Are the Kinds of Water Pollution?
- Does Air Pollution Affect Consumption Behavior?
- What Are the Causes and Effects of Water Pollution?
- Does Animal Feeding Operation Pollution Hurt Public Health?
- Does Industry Self-Regulation Reduce Pollution?
- Will Pollution Free Cars Become a Reality of the Near Future?
- Who Pays for Industrial Pollution Abatement?
- Does Trade Promote Environmental Coordination of Pollution in International Rivers?
- Who Suffers From Indoor Air Pollution?
- What Are the Main Ways to Reduce Pollution?
- What Causes Haze Pollution?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 261 Pollution Essay Topics & Essay Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/pollution-essay-examples/
"261 Pollution Essay Topics & Essay Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/pollution-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '261 Pollution Essay Topics & Essay Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "261 Pollution Essay Topics & Essay Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/pollution-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "261 Pollution Essay Topics & Essay Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/pollution-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "261 Pollution Essay Topics & Essay Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/pollution-essay-examples/.
- Noise Pollution Essay Titles
- Air Pollution Research Ideas
- Ocean Pollution Titles
- Global Issues Essay Topics
- Water Pollution Research Topics
- Environmental Protection Titles
- Greenhouse Gases Research Ideas
- Environment Research Topics
- Global Warming Essay Titles
- Climate Change Titles
- Water Issues Research Ideas
- Deforestation Research Ideas
- Hazardous Waste Essay Topics
- Extinction Research Topics
- Environmentalism Essay Topics
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Air pollution.
Air pollution consists of chemicals or particles in the air that can harm the health of humans, animals, and plants. It also damages buildings.
Biology, Ecology, Earth Science, Geography
Loading ...

Air pollution consists of chemicals or particles in the air that can harm the health of humans, animals, and plants. It also damages buildings. Pollutants in the air take many forms. They can be gases , solid particles, or liquid droplets. Sources of Air Pollution Pollution enters the Earth's atmosphere in many different ways. Most air pollution is created by people, taking the form of emissions from factories, cars, planes, or aerosol cans . Second-hand cigarette smoke is also considered air pollution. These man-made sources of pollution are called anthropogenic sources . Some types of air pollution, such as smoke from wildfires or ash from volcanoes , occur naturally. These are called natural sources . Air pollution is most common in large cities where emissions from many different sources are concentrated . Sometimes, mountains or tall buildings prevent air pollution from spreading out. This air pollution often appears as a cloud making the air murky. It is called smog . The word "smog" comes from combining the words "smoke" and " fog ." Large cities in poor and developing nations tend to have more air pollution than cities in developed nations. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) , some of the worlds most polluted cities are Karachi, Pakistan; New Delhi, India; Beijing, China; Lima, Peru; and Cairo, Egypt. However, many developed nations also have air pollution problems. Los Angeles, California, is nicknamed Smog City. Indoor Air Pollution Air pollution is usually thought of as smoke from large factories or exhaust from vehicles. But there are many types of indoor air pollution as well. Heating a house by burning substances such as kerosene , wood, and coal can contaminate the air inside the house. Ash and smoke make breathing difficult, and they can stick to walls, food, and clothing. Naturally-occurring radon gas, a cancer -causing material, can also build up in homes. Radon is released through the surface of the Earth. Inexpensive systems installed by professionals can reduce radon levels. Some construction materials, including insulation , are also dangerous to people's health. In addition, ventilation , or air movement, in homes and rooms can lead to the spread of toxic mold . A single colony of mold may exist in a damp, cool place in a house, such as between walls. The mold's spores enter the air and spread throughout the house. People can become sick from breathing in the spores. Effects On Humans People experience a wide range of health effects from being exposed to air pollution. Effects can be broken down into short-term effects and long-term effects . Short-term effects, which are temporary , include illnesses such as pneumonia or bronchitis . They also include discomfort such as irritation to the nose, throat, eyes, or skin. Air pollution can also cause headaches, dizziness, and nausea . Bad smells made by factories, garbage , or sewer systems are considered air pollution, too. These odors are less serious but still unpleasant . Long-term effects of air pollution can last for years or for an entire lifetime. They can even lead to a person's death. Long-term health effects from air pollution include heart disease , lung cancer, and respiratory diseases such as emphysema . Air pollution can also cause long-term damage to people's nerves , brain, kidneys , liver , and other organs. Some scientists suspect air pollutants cause birth defects . Nearly 2.5 million people die worldwide each year from the effects of outdoor or indoor air pollution. People react differently to different types of air pollution. Young children and older adults, whose immune systems tend to be weaker, are often more sensitive to pollution. Conditions such as asthma , heart disease, and lung disease can be made worse by exposure to air pollution. The length of exposure and amount and type of pollutants are also factors. Effects On The Environment Like people, animals, and plants, entire ecosystems can suffer effects from air pollution. Haze , like smog, is a visible type of air pollution that obscures shapes and colors. Hazy air pollution can even muffle sounds. Air pollution particles eventually fall back to Earth. Air pollution can directly contaminate the surface of bodies of water and soil . This can kill crops or reduce their yield . It can kill young trees and other plants. Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide particles in the air, can create acid rain when they mix with water and oxygen in the atmosphere. These air pollutants come mostly from coal-fired power plants and motor vehicles . When acid rain falls to Earth, it damages plants by changing soil composition ; degrades water quality in rivers, lakes and streams; damages crops; and can cause buildings and monuments to decay . Like humans, animals can suffer health effects from exposure to air pollution. Birth defects, diseases, and lower reproductive rates have all been attributed to air pollution. Global Warming Global warming is an environmental phenomenon caused by natural and anthropogenic air pollution. It refers to rising air and ocean temperatures around the world. This temperature rise is at least partially caused by an increase in the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases trap heat energy in the Earths atmosphere. (Usually, more of Earths heat escapes into space.) Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that has had the biggest effect on global warming. Carbon dioxide is emitted into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels (coal, gasoline , and natural gas ). Humans have come to rely on fossil fuels to power cars and planes, heat homes, and run factories. Doing these things pollutes the air with carbon dioxide. Other greenhouse gases emitted by natural and artificial sources also include methane , nitrous oxide , and fluorinated gases. Methane is a major emission from coal plants and agricultural processes. Nitrous oxide is a common emission from industrial factories, agriculture, and the burning of fossil fuels in cars. Fluorinated gases, such as hydrofluorocarbons , are emitted by industry. Fluorinated gases are often used instead of gases such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). CFCs have been outlawed in many places because they deplete the ozone layer . Worldwide, many countries have taken steps to reduce or limit greenhouse gas emissions to combat global warming. The Kyoto Protocol , first adopted in Kyoto, Japan, in 1997, is an agreement between 183 countries that they will work to reduce their carbon dioxide emissions. The United States has not signed that treaty . Regulation In addition to the international Kyoto Protocol, most developed nations have adopted laws to regulate emissions and reduce air pollution. In the United States, debate is under way about a system called cap and trade to limit emissions. This system would cap, or place a limit, on the amount of pollution a company is allowed. Companies that exceeded their cap would have to pay. Companies that polluted less than their cap could trade or sell their remaining pollution allowance to other companies. Cap and trade would essentially pay companies to limit pollution. In 2006 the World Health Organization issued new Air Quality Guidelines. The WHOs guidelines are tougher than most individual countries existing guidelines. The WHO guidelines aim to reduce air pollution-related deaths by 15 percent a year. Reduction Anybody can take steps to reduce air pollution. Millions of people every day make simple changes in their lives to do this. Taking public transportation instead of driving a car, or riding a bike instead of traveling in carbon dioxide-emitting vehicles are a couple of ways to reduce air pollution. Avoiding aerosol cans, recycling yard trimmings instead of burning them, and not smoking cigarettes are others.
Downwinders The United States conducted tests of nuclear weapons at the Nevada Test Site in southern Nevada in the 1950s. These tests sent invisible radioactive particles into the atmosphere. These air pollution particles traveled with wind currents, eventually falling to Earth, sometimes hundreds of miles away in states including Idaho, Utah, Arizona, and Washington. These areas were considered to be "downwind" from the Nevada Test Site. Decades later, people living in those downwind areascalled "downwinders"began developing cancer at above-normal rates. In 1990, the U.S. government passed the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act. This law entitles some downwinders to payments of $50,000.
Greenhouse Gases There are five major greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere.
- water vapor
- carbon dioxide
- nitrous oxide
London Smog What has come to be known as the London Smog of 1952, or the Great Smog of 1952, was a four-day incident that sickened 100,000 people and caused as many as 12,000 deaths. Very cold weather in December 1952 led residents of London, England, to burn more coal to keep warm. Smoke and other pollutants became trapped by a thick fog that settled over the city. The polluted fog became so thick that people could only see a few meters in front of them.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Illustrators
Educator reviewer, last updated.
March 6, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

Donate to Defend Our Planet
Drilling on public lands, mass wildlife extinctions, worsening climate change—our planet is in crisis. Help us fight back and your gift will be matched $1 for $1.
Air Pollution: Everything You Need to Know
How smog, soot, greenhouse gases, and other top air pollutants are affecting the planet—and your health.

- Share this page block
What is air pollution?
What causes air pollution, effects of air pollution, air pollution in the united states, air pollution and environmental justice, controlling air pollution, how to help reduce air pollution, how to protect your health.
Air pollution refers to the release of pollutants into the air—pollutants that are detrimental to human health and the planet as a whole. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) , each year, indoor and outdoor air pollution is responsible for nearly seven million deaths around the globe. Ninety-nine percent of human beings currently breathe air that exceeds the WHO’s guideline limits for pollutants, with those living in low- and middle-income countries suffering the most. In the United States, the Clean Air Act , established in 1970, authorizes the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to safeguard public health by regulating the emissions of these harmful air pollutants.
“Most air pollution comes from energy use and production,” says John Walke , director of the Clean Air team at NRDC. Driving a car on gasoline, heating a home with oil, running a power plant on fracked gas : In each case, a fossil fuel is burned and harmful chemicals and gases are released into the air.
“We’ve made progress over the last 50 years in improving air quality in the United States, thanks to the Clean Air Act. But climate change will make it harder in the future to meet pollution standards, which are designed to protect health ,” says Walke.
Air pollution is now the world’s fourth-largest risk factor for early death. According to the 2020 State of Global Air report —which summarizes the latest scientific understanding of air pollution around the world—4.5 million deaths were linked to outdoor air pollution exposures in 2019, and another 2.2 million deaths were caused by indoor air pollution. The world’s most populous countries, China and India, continue to bear the highest burdens of disease.
“Despite improvements in reducing global average mortality rates from air pollution, this report also serves as a sobering reminder that the climate crisis threatens to worsen air pollution problems significantly,” explains Vijay Limaye , senior scientist in NRDC’s Science Office. Smog, for instance, is intensified by increased heat, forming when the weather is warmer and there’s more ultraviolet radiation. In addition, climate change increases the production of allergenic air pollutants, including mold (thanks to damp conditions caused by extreme weather and increased flooding) and pollen (due to a longer pollen season). “Climate change–fueled droughts and dry conditions are also setting the stage for dangerous wildfires,” adds Limaye. “ Wildfire smoke can linger for days and pollute the air with particulate matter hundreds of miles downwind.”
The effects of air pollution on the human body vary, depending on the type of pollutant, the length and level of exposure, and other factors, including a person’s individual health risks and the cumulative impacts of multiple pollutants or stressors.
Smog and soot
These are the two most prevalent types of air pollution. Smog (sometimes referred to as ground-level ozone) occurs when emissions from combusting fossil fuels react with sunlight. Soot—a type of particulate matter —is made up of tiny particles of chemicals, soil, smoke, dust, or allergens that are carried in the air. The sources of smog and soot are similar. “Both come from cars and trucks, factories, power plants, incinerators, engines, generally anything that combusts fossil fuels such as coal, gasoline, or natural gas,” Walke says.
Smog can irritate the eyes and throat and also damage the lungs, especially those of children, senior citizens, and people who work or exercise outdoors. It’s even worse for people who have asthma or allergies; these extra pollutants can intensify their symptoms and trigger asthma attacks. The tiniest airborne particles in soot are especially dangerous because they can penetrate the lungs and bloodstream and worsen bronchitis, lead to heart attacks, and even hasten death. In 2020, a report from Harvard’s T.H. Chan School of Public Health showed that COVID-19 mortality rates were higher in areas with more particulate matter pollution than in areas with even slightly less, showing a correlation between the virus’s deadliness and long-term exposure to air pollution.
These findings also illuminate an important environmental justice issue . Because highways and polluting facilities have historically been sited in or next to low-income neighborhoods and communities of color, the negative effects of this pollution have been disproportionately experienced by the people who live in these communities.
Hazardous air pollutants
A number of air pollutants pose severe health risks and can sometimes be fatal, even in small amounts. Almost 200 of them are regulated by law; some of the most common are mercury, lead , dioxins, and benzene. “These are also most often emitted during gas or coal combustion, incineration, or—in the case of benzene—found in gasoline,” Walke says. Benzene, classified as a carcinogen by the EPA, can cause eye, skin, and lung irritation in the short term and blood disorders in the long term. Dioxins, more typically found in food but also present in small amounts in the air, is another carcinogen that can affect the liver in the short term and harm the immune, nervous, and endocrine systems, as well as reproductive functions. Mercury attacks the central nervous system. In large amounts, lead can damage children’s brains and kidneys, and even minimal exposure can affect children’s IQ and ability to learn.
Another category of toxic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), are by-products of traffic exhaust and wildfire smoke. In large amounts, they have been linked to eye and lung irritation, blood and liver issues, and even cancer. In one study , the children of mothers exposed to PAHs during pregnancy showed slower brain-processing speeds and more pronounced symptoms of ADHD.
Greenhouse gases
While these climate pollutants don’t have the direct or immediate impacts on the human body associated with other air pollutants, like smog or hazardous chemicals, they are still harmful to our health. By trapping the earth’s heat in the atmosphere, greenhouse gases lead to warmer temperatures, which in turn lead to the hallmarks of climate change: rising sea levels, more extreme weather, heat-related deaths, and the increased transmission of infectious diseases. In 2021, carbon dioxide accounted for roughly 79 percent of the country’s total greenhouse gas emissions, and methane made up more than 11 percent. “Carbon dioxide comes from combusting fossil fuels, and methane comes from natural and industrial sources, including large amounts that are released during oil and gas drilling,” Walke says. “We emit far larger amounts of carbon dioxide, but methane is significantly more potent, so it’s also very destructive.”
Another class of greenhouse gases, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) , are thousands of times more powerful than carbon dioxide in their ability to trap heat. In October 2016, more than 140 countries signed the Kigali Agreement to reduce the use of these chemicals—which are found in air conditioners and refrigerators—and develop greener alternatives over time. (The United States officially signed onto the Kigali Agreement in 2022.)
Pollen and mold
Mold and allergens from trees, weeds, and grass are also carried in the air, are exacerbated by climate change, and can be hazardous to health. Though they aren’t regulated, they can be considered a form of air pollution. “When homes, schools, or businesses get water damage, mold can grow and produce allergenic airborne pollutants,” says Kim Knowlton, professor of environmental health sciences at Columbia University and a former NRDC scientist. “ Mold exposure can precipitate asthma attacks or an allergic response, and some molds can even produce toxins that would be dangerous for anyone to inhale.”
Pollen allergies are worsening because of climate change . “Lab and field studies are showing that pollen-producing plants—especially ragweed—grow larger and produce more pollen when you increase the amount of carbon dioxide that they grow in,” Knowlton says. “Climate change also extends the pollen production season, and some studies are beginning to suggest that ragweed pollen itself might be becoming a more potent allergen.” If so, more people will suffer runny noses, fevers, itchy eyes, and other symptoms. “And for people with allergies and asthma, pollen peaks can precipitate asthma attacks, which are far more serious and can be life-threatening.”

More than one in three U.S. residents—120 million people—live in counties with unhealthy levels of air pollution, according to the 2023 State of the Air report by the American Lung Association (ALA). Since the annual report was first published, in 2000, its findings have shown how the Clean Air Act has been able to reduce harmful emissions from transportation, power plants, and manufacturing.
Recent findings, however, reflect how climate change–fueled wildfires and extreme heat are adding to the challenges of protecting public health. The latest report—which focuses on ozone, year-round particle pollution, and short-term particle pollution—also finds that people of color are 61 percent more likely than white people to live in a county with a failing grade in at least one of those categories, and three times more likely to live in a county that fails in all three.
In rankings for each of the three pollution categories covered by the ALA report, California cities occupy the top three slots (i.e., were highest in pollution), despite progress that the Golden State has made in reducing air pollution emissions in the past half century. At the other end of the spectrum, these cities consistently rank among the country’s best for air quality: Burlington, Vermont; Honolulu; and Wilmington, North Carolina.
No one wants to live next door to an incinerator, oil refinery, port, toxic waste dump, or other polluting site. Yet millions of people around the world do, and this puts them at a much higher risk for respiratory disease, cardiovascular disease, neurological damage, cancer, and death. In the United States, people of color are 1.5 times more likely than whites to live in areas with poor air quality, according to the ALA.
Historically, racist zoning policies and discriminatory lending practices known as redlining have combined to keep polluting industries and car-choked highways away from white neighborhoods and have turned communities of color—especially low-income and working-class communities of color—into sacrifice zones, where residents are forced to breathe dirty air and suffer the many health problems associated with it. In addition to the increased health risks that come from living in such places, the polluted air can economically harm residents in the form of missed workdays and higher medical costs.
Environmental racism isn't limited to cities and industrial areas. Outdoor laborers, including the estimated three million migrant and seasonal farmworkers in the United States, are among the most vulnerable to air pollution—and they’re also among the least equipped, politically, to pressure employers and lawmakers to affirm their right to breathe clean air.
Recently, cumulative impact mapping , which uses data on environmental conditions and demographics, has been able to show how some communities are overburdened with layers of issues, like high levels of poverty, unemployment, and pollution. Tools like the Environmental Justice Screening Method and the EPA’s EJScreen provide evidence of what many environmental justice communities have been explaining for decades: that we need land use and public health reforms to ensure that vulnerable areas are not overburdened and that the people who need resources the most are receiving them.
In the United States, the Clean Air Act has been a crucial tool for reducing air pollution since its passage in 1970, although fossil fuel interests aided by industry-friendly lawmakers have frequently attempted to weaken its many protections. Ensuring that this bedrock environmental law remains intact and properly enforced will always be key to maintaining and improving our air quality.
But the best, most effective way to control air pollution is to speed up our transition to cleaner fuels and industrial processes. By switching over to renewable energy sources (such as wind and solar power), maximizing fuel efficiency in our vehicles, and replacing more and more of our gasoline-powered cars and trucks with electric versions, we'll be limiting air pollution at its source while also curbing the global warming that heightens so many of its worst health impacts.
And what about the economic costs of controlling air pollution? According to a report on the Clean Air Act commissioned by NRDC, the annual benefits of cleaner air are up to 32 times greater than the cost of clean air regulations. Those benefits include up to 370,000 avoided premature deaths, 189,000 fewer hospital admissions for cardiac and respiratory illnesses, and net economic benefits of up to $3.8 trillion for the U.S. economy every year.
“The less gasoline we burn, the better we’re doing to reduce air pollution and the harmful effects of climate change,” Walke explains. “Make good choices about transportation. When you can, ride a bike, walk, or take public transportation. For driving, choose a car that gets better miles per gallon of gas or buy an electric car .” You can also investigate your power provider options—you may be able to request that your electricity be supplied by wind or solar. Buying your food locally cuts down on the fossil fuels burned in trucking or flying food in from across the world. And most important: “Support leaders who push for clean air and water and responsible steps on climate change,” Walke says.
- “When you see in the news or hear on the weather report that pollution levels are high, it may be useful to limit the time when children go outside or you go for a jog,” Walke says. Generally, ozone levels tend to be lower in the morning.
- If you exercise outside, stay as far as you can from heavily trafficked roads. Then shower and wash your clothes to remove fine particles.
- The air may look clear, but that doesn’t mean it’s pollution free. Utilize tools like the EPA’s air pollution monitor, AirNow , to get the latest conditions. If the air quality is bad, stay inside with the windows closed.
- If you live or work in an area that’s prone to wildfires, stay away from the harmful smoke as much as you’re able. Consider keeping a small stock of masks to wear when conditions are poor. The most ideal masks for smoke particles will be labelled “NIOSH” (which stands for National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) and have either “N95” or “P100” printed on it.
- If you’re using an air conditioner while outdoor pollution conditions are bad, use the recirculating setting to limit the amount of polluted air that gets inside.
This story was originally published on November 1, 2016, and has been updated with new information and links.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
Related Stories

The Particulars of PM 2.5
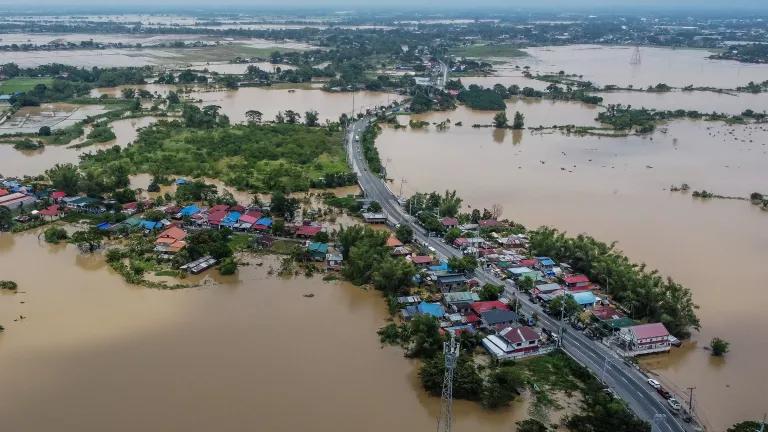

What Are the Effects of Climate Change?
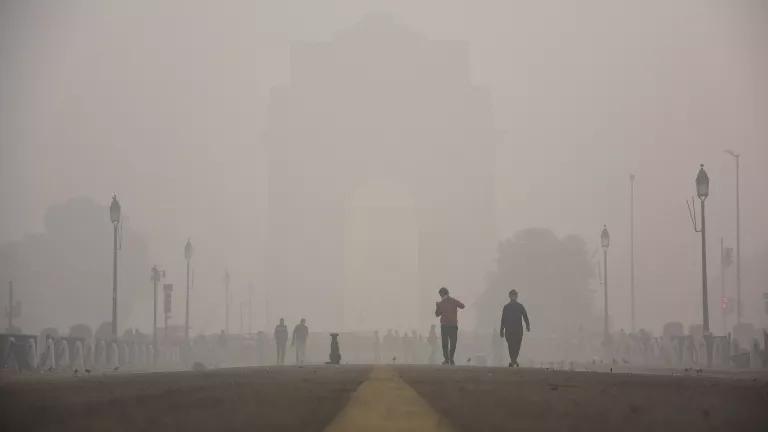

Fossil Fuel Air Pollution Kills One in Five People
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.
Air Pollution - Free Essay Examples And Topic Ideas
Writing an essay on air pollution can be a challenging task. It is a pressing issue that affects the environment, human health, and air quality. To create a well-structured paper, you should follow a clear outline. What’s more, organize your essay into perfectly organized sections. It should consist of an introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. One of the key points here is the statement of the problem, and it is important to make it strong. For example, “Air pollution poses a significant threat due to the release of harmful gases and the presence of dirty smoke particles.” You need to emphasize the importance of taking immediate action to reduce environmental risks and promote clean air for present and future generations. Begin by conducting thorough research on such a phenomenon using reliable and reputable sources. Look for academic journals, scientific publications, government reports, and environmental organizations’ websites. To gain a better understanding of how to structure and develop your paper, you can refer to an air pollution essay example. Analyze how other writers have structured their papers and incorporated studies effectively. It will provide valuable insights on research paper topics and help you organize your thoughts effectively.
While creating informative and argumentative essays about air pollution, it is essential to convey the severity of the issue. Each paragraph should address a specific aspect, presenting evidence and arguments to support the main statement. You can discuss the causes, effects, or solutions related to climate change. The conclusion and introduction for essay on air pollution should provide a concise overview. Do not forget to choose compelling titles which will engage readers. Through thoughts and words, humanity can change the situation and inspire others to take action. An essay on this topic will unite everyone and take steps towards creating a future where pure air is a reality for all!
Air Pollution Causes, Effects & Solutions
Introduction: Pollution is a widespread phenomenon that has been affecting many in the US and around the world for years. Pollutants range from carbon monoxide, mercury, nitrogen dioxide, ozone, and particulate matter. Looking more closely in California, specifically the San Joaquin Valley, the two most dominant pollutants are ozone and particulate matter. Ozone, also known as smog, is an invisible harmful pollutant that causes many health issues. Particulate pollution is a combination of different sized particles that each have different […]
Air Pollution: the Silent Killer
For decades, society has expressed concern for a variety of different types of pollution taking place throughout the globe. One of the most vital types, air pollution, effects every individual on earth as well as our resources. The effects of air pollution create a myriad of problems, specifically an increased chance of health complications. Unclean air affects many of the body's major organs including the lungs, the skin and even the heart. Many individuals are extremely unaware of the havoc […]
Comparison of Smoking Cigarettes and Vaping
The uprise of vaping in comparison to smoking cigarettes is an open-ended debate. It's a tough argument because there isn't enough information to prove whether vaping is a better alternative to smoking or not. Experts are working their hardest to discover an answer on the effects of vaping versus smoking. Many people use vaping as an attempt to stop smoking cigarettes, but the design and attraction to vapes is a possible cause to more people using them. The differences between […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
Indoor and Outdoor Air Pollution
Earth is surrounded by air made up of a mixture of extremely important gases such as oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen. These gases provide humans with oxygen for respiration to occur, and provides carbon dioxide to plants for photosynthesis. It is important for human health that the air we breathe is clean. Due to man-made contributions to the environment and the ecosystem such as deforestation and factories; smog, smoke and other chemical components are put out into the air causing […]

Bing Air Pollution in Beijing
Trade throughout the world has brought people great things for as long as our history books go back, and the trade routes in China date back to long forgotten old goat trails. Today, our world is becoming more and more connected with internet communications and transportation is now faster thanks to globalization. Globalization is when businesses start operating their markets on an international scale, while also developing international factories. Thanks to these technological advances in globalization, small economies across the […]
Public Transportation is the Way to Go
Cities can promote public transportation in many ways. However, many cities fail to do so. They make the postulation that people will utilize public transportation only if they optate to, and it does not require to be promoted. This is far from the truth. Many people may not ken about transportation options in their city, and they may not realize how benign these options can be (Barletta, et al, 2008). There is a postulation by many people that public transportation […]
How to Reduce Air Pollution
The air pollution in Pima County; large quantity is due to internal combustion vehicles, residents have to adopt conservation habits to prevent the state of Arizona from implementing more regulations in the future. Introduction Air pollution is a problem that many cities in the United States are currently dealing with. In the city of Tucson AZ, air pollution is a problem that is being controlled. It has been declared that automobiles are the dominant factor compared to other factors in […]
What is Air Pollution
What if we lived in a world where we had to walk around with oxygen because the air was so bad, breathing it could be deadly to humans? Believe it or not we are heading down that path. Air pollution is slowly affecting our daily lives without people paying any attention. Some people think that it does not exist, often saying that it’s a scam from a certain group of individual or even the government to get their hard earn […]
About Air, Water and Soil Pollution
Air Pollution What health hazards are associated with living indoors? Indoor air pollution can cause big health problems. People who may be exposed to these indoor air pollutants for long periods of time are most at risk to the effects of air pollution. This includes children, adults, and people with long term chronic illnesses. Most indoor air pollution comes from sources that release gases into the air. Things such as air fresheners, and building materials constantly give off air pollution. […]
Air Pollution in Cities
Background: Air pollution is particle matter in the earth’s atmosphere, and it gradually harms humans, animals, plants, and the earth itself. Air pollution arose side to side with the industrial revolution; the rise to modern manufacturing processes. Air pollution is a problem because eventually at this rate the air is being polluted, the sky will be filled with smog and completely black in only a matter of decades. This problem ties in with the needs and wants of society because […]
Air Pollution Scrubber
Introduction Air pollution in urban areas has become an issue affecting human health to a degree unprecedented in human history. The World Health Organization (WHO) recently prioritized the reduction of air pollution, citing: An estimated 4.2 million premature deaths globally are linked to ambient air pollution, mainly from heart disease, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung cancer, and acute respiratory infections in children. Worldwide ambient air pollution accounts for: 29% of all deaths and disease from lung cancer. (World Health […]
Save the Earth from the Plastic Pollution
Pollution is caused by some sort of toxic waste that is thrown into the atmosphere or land nearby. There are many types of pollution, the main are air pollution, plastic pollution, and water pollution, all three are very dangerous to the ecosystem. Pollution is the contamination of the environment in which we live in and it harms nature and living things around it. It is the biggest global killer affecting over 100 million people. That’s more than global diseases like […]
Environmental Air Pollution Monitoring System
Abstract Over the few Decades there is a rapid growth in the transportation facilities. These facilities are meant to serve the humans and make their life easier. Apart from the advantages these facilities also create serious problems to the environment. The first and the foremost is the severe environmental pollution which has caused deterioration of atmosphere, climate change, stratospheric ozone depletion, loss of biodiversity, changes in hydrological systems. Using Arduino technology the concentration of pollutants in the environment at a […]
Air Pollution in Kathmandu
It has already been a year since I left my country. In one way I am so sad that I am ten thousand miles away from my country but on another side, I am a little delighted that finally I am breathing a fresh oxygen away from an infected air of the most polluted city of my country, Kathmandu. Last year my brother was in bed for two weeks due to the viral infection Dozens of roads in the city […]
The Impact of Wildfires on Air Pollution and Human Health
Climate change has many consequences. Some of the most well-known consequences include rising sea levels and increasing temperatures. However, one of the less studied consequences of climate change is the increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires that are occurring due to a drier and warmer climate.8 Therefore, vegetation in those climates lose more water and the amount of dry fuel in the environment will increase. Wildfires that occur due to climate change can also spread faster as climate change has […]
How to Stop Air Pollution in Africa
Pollution is a word that is commonly used around us. We hear it on the way to school, on the news and even while eavesdropping on elderly people just taking a ride on the train. So what exactly does pollution mean? And how did it become a topic that is now widely discussed? What is the solution to this problem we are so accustomed to, but is killing us? It has become increasingly evident that for some that the only […]
Kinds of Pollution: the Future of Environment
Can you stay without light in your life?! Our environment is our light. God created the surroundings in their most beautiful form, but when a shadow got here over this light, our surroundings grew to become darkish and this shadow is us. The environment includes the living and non-living things that an organism interacts with or has an impact on it. Living elements that an organism interacts with are known as biotic elements: animals, plants, etc., abiotic elements are non-living […]
Air Pollution and Health
Air pollution is an evident mater that is only getting worse as time goes on. This is an issue that affects everyone, and it has been proven several times that poor air quality is severely damaging to people's health and wellbeing. There are several things that contribute to air pollution, even things that humans do on a day to day basis. It is imperative that we do all in our power to limit the pollution of our air in order […]
What you Need to Know about Air Pollution
With climate change becoming a major area of concern across the globe, air pollution is a topic that needs to be a closely paid attention to. Globally, cities track and report the air pollution that is produced within their area. To better fix and ideally prevent the air pollution issues in the world, cities are beginning to take steps to improve the air quality that its citizens are breathing daily. Air pollution is a mixture of solid particles and gas […]
Air Pollution and Environmental Quality
Environment refers to the surroundings. These could either be people, houses, factories or anything visible. Policy, on the other hand, is a term used to point out at rules or guidelines set to govern or protect something. In this case, the rules are set to guide the surrounding (Wu 184). Air pollution comes in when a surrounding gets overwhelmed by activities done by people in the name of earning a living (Knox 173). Human activities result in the emission of […]
Air Pollution in Houston
Introduction Houston has been facing an air pollution problem which affects our daily lives. With the establishment of numerous companies and refineries, the smoke and chemicals from them, and the enormous amount of automobile usage contribute to air pollution. The quality of air that Houstonians have been inhaling is detrimental to their health and it consequently places them at risk of suffering from major diseases like asthma, heart disease, and stroke. Although many controls have been considered to reduce air […]
During the Industrial Revolution
During the Industrial Revolution the urbanization of cities and the rise in factories in the US contributed to environmental damage and the health hazards of humans through pollution. This quote, Industries discharged foul, sometimes toxic, solid, liquid, and gaseous wastes into the surrounding air, water, and land (Rosen, 565) tells us how unregulated factories expelled dangerous wastes into the ecosystem without being treated to be harmless. During the Industrial Revolution the lifestyle of Americans in the US changed and population […]
Air Pollution in Vietnam Today
The development of technologies and the demands of human beings are creating severe problems to our planet. Global warming and polluted environment are being reinforced due to the human activities. This is also occurring in my country. Vietnam is developing, so the processes of industrialization are strongly pushed by my government. Tons of gas and industrial waste are emitted to the sky and into the sea. Also, the exploited activities in the forest and ocean are ruining a lot habitats […]
Impact of Air Pollution on Human Health
The quality of the air influences a lot in people lives. Living in an environment free of pollution supposes a better quality of life. In most cases we do not even know the way in which this pollution affects us. According to the World Health Organization website, because air pollution, around 7 million people died (7 million premature death). The growth of our population, the way in which energy is consumed, transportation, the air-conditioned systems, and others cause the emission […]
Managing Air Pollution with Urban Transportation
Abstract: The recent economic expansion along with the population growth experienced in developing countries has had a big impact on the development of large cities like Delhi, India. Accompanied by Delhi's rapid spatial growth over the last 25 years, urban sprawl has been contributing to increased travel. The vehicle fleet projected at current growth rates will result in more than 13 million vehicles in Delhi in 2020. Planning and managing such a rapidly growing transport sector will be a big […]
India’s Air Pollution and Climate Change
The World Health Organization states that around 7 million people die every year from exposure to fine particles in polluted air that penetrate deep into the lungs and cardiovascular systems (Secretariat 2018). Pollution is a worldwide problem. It is defined as the introduction of harmful materials into the environment (National Geographic 1). Materials are a variety of substances known as pollutants and can even be natural. Some of the substances are carbon dioxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO), and carbon monoxide […]
Rise in Air Temperature Worldwide
In order to understand climate change you need to understand the difference between weather and climate. Weather happens over a short period of time while climate happens over a longer period of time.The U.S. government should take aggressive steps to address climate change because it is there responsibility to keep us informed about air pollution,increase in storms,and water issues. High levels of carbon monoxide are being released causing the ozone layer to take in less of the sun's harmful U.V […]
The China Air Pollution
The problem that I will be discussing in this essay is about the pollution in China. The air quality is becoming worse and worse in China each year. Air pollution has been a major issue in China for many years, first record of China having unhealthy and unsafe air quality was back in January of 2005. They are still in the process of reducing the levels of nitrogen dioxide in their air. The water pollution has also been in an […]
Solution to Air Pollution and Environmental Degradation
Introduction In his book, The Ocean of Life, Callum Roberts states, 'Our failure to notice creeping environmental degradation has compromised more than our quality of life.' This is one of many warnings that have been relayed throughout the news, movies, and even children's books, such as Doctor Seuss's The Lorax. These cautionary tales warn us to respect our planet and come together to find solutions. Unfortunately, our ever-growing population, constant consumption of non-renewable resources, poor waste management practices, and over-use […]
Catastrophic Effect of the Pollution in the World
Pollution has a catastrophic effect in the world today and our future. Its caused by the process of making new land, water , air or other parts of the environment that are unsanitary and not able to be used. Simple abiotic factors such as light, sound, and temperature can be considered as a pollutants once they are initiated artificially into an environment. There are three different types of pollution today land, air and water. A pollutant that is most common […]
Additional Example Essays
- Why Should Recycling be Mandatory?
- Plastic Straws Cause and Effect Final Draft
- Recycling Should be Mandatory
- Leadership and the Army Profession
- Why College Should Not Be Free
- Shakespeare's Hamlet Character Analysis
- A Raisin in the Sun Theme
- Why Abortion Should be Illegal
- Death Penalty Should be Abolished
- Professions for Women by Virginia Woolf
- Homeless Veterans
- A psychoanalytical lens to the film Fight Club
Essay About Air Pollution Air pollution is a type of environmental pollution that affects the air and mostly happens because of smoke or other harmful gases, mainly oxides of carbon, sulphur, and nitrogen. It occurs when those gases are introduced into the atmosphere in a way that makes it harmful to humans, animals, and plant. One of the biggest things that cause air pollution are cars, every time you see that smoke that comes from below your car's exhaust pipe, you see air pollution. Air pollution refers to the presence of foreign substances in the air that doesn’t belong there or excessive amounts of certain impurities that wouldn't harm us otherwise. When cars burn gasoline, they emit pollutants. Gasoline fumes escape into the air even when we pump gasoline into our fuel tanks. There are a large number of pollutions that come from cares, the first one is when cars produce carbon monoxide. That happens when the carbon in fuel doesn't burn completely and ruins the air. Second, is when a car's exhaust emits hydrocarbons meaning a toxic compound of hydrogen and carbon. Last, When fuel burns, nitrogen and oxygen react with each other and form nitrogen oxides and that pollutes the air. The air pollution causes a lot of problems like global warming, climate change and it also ruins the environment. An example is that air pollution impacts the process of photosynthesis in many cases, with serious consequences for the purification of the air we breathe. A solution that was invented for air pollution from cars was the Tesla. Tesla is an American automotive and energy company based in California. The main difference between normal cars and Teslas is powering. If gas is the number one fuel for cars around the world, Tesla cars are using electricity as their fuel. This makes a huge impact on the environment pollution as electricity lives no trace whatsoever in the air and the noise is minimal. Aside from air pollution, cities are battling with enormous sound pollution, and if cars become powered by electricity globally, a lot of the environmental problems that I listed will be solved just with this change. Regular vehicles need constant oil checks and if the oil runs out, much of the car won’t function because almost all the parts of the car need some kind of oil. Tesla cars do not need oil at all. Tesla cars work with a powerful battery, which is charged with electricity. This gives juice for the car to run for a certain period of time. This battery is a little similar to the batteries that you can find in your laptop and smartphone, you charge it, it drives for a couple 100 kilometers and then you need to charge it again. Tesla uses lithium-ion batteries in order to power up their supercars. These batteries are extremely powerful. In fact, a battery that you can find in a Tesla car is made out of thousands of lithium-ion cells and weights at least a thousand pound. Tesla cars work with a small motor, which is about the size of a watermelon. This is one of the latest innovations in electronic engineering. It converts electrical energy drawn from the batteries to mechanical power in order to move the vehicle. This is a more efficient technology when compared to the combustion engines that you can find on traditional cars. In other words, people who drive Tesla cars will be able to get a longer range for their charge, which can help them to save money in the long run. In conclusion, I think that Teslas are one of the best solutions for air pollution right now. They don't use gas which helps the environment and decreases the possibilities of global warming which is a very dangerous thing in our world right now. Sure, they aren’t the perfect solution and I'm sure that better solutions will be made in the future or are in the making right now but Tesla is a simple easy solution that is accessible for a lot of people and it makes a big change in our world for the better.
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Air Pollution Essay

Essay on Air Pollution
Environmental changes are caused by the natural or artificial content of harmful pollutants and can cause instability, disturbance, or adverse effects on the ecosystem. Earth and its environment pose a more serious threat due to the increasing pollution of air, water, and soil. Environmental damage is caused by improper resource management or careless human activities. Therefore, any activity that violates the original nature of the environment and leads to degradation is called pollution. We need to understand the origin of these pollutants and find ways to control pollution. This can also be done by raising awareness of the effects of pollutants.
Air pollution is any physical, chemical, or biological change in the air. A certain percentage of the gas is present in the atmosphere. Increasing or decreasing the composition of these gasses is detrimental to survival. This imbalance in gas composition causes an increase in global temperature which is called global warming.
Introduction to air pollution
The Earth and its environment are facing a serious threat by the increasing pollution of the air, water, and soil—the vital life support systems of the Earth. The damage to the environment is caused by improper management of resources or by careless human activity. Hence any activity that violates the original character of nature and leads to its degradation is called pollution. We need to understand the sources of these pollutants and find ways to control pollution. This can be also done by making people aware of the effects of pollutants.
Air with 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, and 1% of all other gasses support life on Earth. Various processes take place to sustain the regular percentage of gasses and their composition in general.
Atmospheric pollution can have natural sources, for example, volcanic eruptions. The gaseous by-products of man-made processes such as energy production, waste incineration, transport, deforestation and agriculture, are the major air pollutants.
Although air is made up of mostly Oxygen and Nitrogen, mankind, through pollution, has increased the levels of many trace gasses, and in some cases, released completely new gasses to the atmosphere.
Air pollution can result in poor air quality, both in cities and in the countryside. Some air pollutants make people sick, causing breathing problems and increasing the likelihood of cancer.
Some air pollutants are harmful to plants, animals, and the ecosystems in which they live. Statues, monuments, and buildings are being corroded by the air pollutants in the form of acid rain. It also damages crops and forests, and makes lakes and streams unsuitable for fish and other plant and animal life.
Air pollution created by man-made resources is also changing the Earth’s atmosphere. It is causing the depletion of the ozone layer and letting in more harmful radiation from the Sun. The greenhouse gasses released into the atmosphere prevents heat from escaping back into space and leads to a rise in global average temperatures. Global warming affects the average sea-level and increases the spread of tropical diseases.
Air pollution occurs when large amounts of gas and tiny particles are released into the air and the ecological balance is disturbed. Each year millions of tons of gasses and particulate matter are emitted into the air.
Primary air pollutants are pollutants, which are directly released into the air. They are called SPM, i.e., Suspended Particulate Matter. For example, smoke, dust, ash, sulfur oxide, nitrogen oxide, and radioactive compounds, etc.
Secondary Pollutants are pollutants, which are formed due to chemical interactions between the atmospheric components and primary pollutants. For example, Smog (i.e. Smoke and fog), ozone, etc.
Major gaseous air pollutants include Carbon Dioxide, Hydrogen Sulfide, Sulfur Dioxide and Nitrogen Oxide, etc.
Natural sources are volcanic eruptions, forest fires, dust storms, etc.
Man-made sources include gasses released from the automobiles, industries, burning of garbage and bricks kilns, etc.
Effects of Air Pollution on Human Health
Air pollution has adverse effects on human health.
Breathing polluted air puts you at higher risk of asthma.
When exposed to ground ozone for 6 to 7 hours, people suffer from respiratory inflammation.
Damages the immune system, endocrine, and reproductive systems.
A high level of air pollution has been associated with higher incidents of heart problems.
The toxic chemicals released into the air are affecting the flora and fauna immensely.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Air Pollution
We can prevent pollution by utilizing raw materials, water energy, and other resources more efficiently. When less harmful substances are substituted for hazardous ones, and when toxic substances are eliminated from the production process, human health can be protected and economic wellbeing can be strengthened.
There are several measures that can be adopted by people to reduce pollution and to save the environment.
Carpooling.
Promotion of public transport.
No smoking zone.
Restricted use of fossil fuels.
Saving energy.
Encouraging organic farming.
The government has put restrictions on the amount of fossil fuels that can be used as well as restrictions on how much carbon dioxide and other pollutants can be emitted. Although the government is attempting to save our environment from these harmful gasses, it is not sufficient. We as a society need to keep the environment clean by controlling the pollution of air.

FAQs on Air Pollution Essay
1. State the Causes of Air Pollution ?
The following are the causes of air pollution.
Vehicular pollution consisting of Carbon Monoxide causes pollution.
Emission of Nitrogen oxide by a large number of supersonic transport airplanes causes deterioration of the Ozone layer and also causes serious damage to the flora and fauna.
The release of Chlorofluorocarbons into the Stratosphere causes depletion of Ozone, which is a serious concern to animals, microscopic, and aquatic organisms.
Burning garbage causes smoke, which pollutes the atmosphere. This smoke contains harmful gases such as Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen oxides.
In India, brick kilns are used for many purposes and coal is used to burn the bricks. They give out huge quantities of Carbon dioxide and particulate matter such as smoke, dust that are very harmful to people working there and the areas surrounding it.
Many cleansing agents release poisonous gases such as Ammonia and Chlorine into the atmosphere.
Radioactive elements emit harmful rays into the air.
Decomposed animals and plants emit Methane and Ammonia gas into the air.
2. What Does Global Warming Mean?
Global warming is the gradual rising average temperature of the Earth's atmosphere due to the concentration of methane in certain toxic gasses such as carbon dioxide. This has a major impact on the world climate. The world is warming. The land and the sea are now warmer than they were at the beginning and temperatures are still rising. This rise in temperature is, in short, global warming. This temperature rise is man-made. The burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere which capture solar heat and raise surface and air temperatures.
3. Name the Alternative Modes of Transport. In What Way Does it Help to Reduce Air Pollution?
Public transport could be an alternative mode of transport. Public transport like trains, buses and trams, can relieve traffic congestion and reduce air pollution from road transport. The use of public transport must be encouraged in order to develop a sustainable transport policy.
4. Mention other means of transportation! How can I help reduce air pollution?
Public transportation can be another mode of transportation. Public transport such as trains, buses and trams can reduce traffic congestion and reduce air pollution from road transport. The use of public transport and to develop sustainable transport policies should be encouraged. While one passenger vehicle has the convenience factor, other modes of transportation reduce travel costs, spend less time, reduce stress, improve health, and reduce energy consumption and parking. Other trips for work include walking/cycling, public transport, hybrid travel and transport.
5. What are the effects of pollution?
Excessive air pollution can increase the risk of heart attack, wheezing, coughing and difficulty breathing, as well as irritation of the eyes, nose and throat. Air pollution can also cause heart problems, asthma, and other lung problems. Due to the emission of greenhouse gases, the composition of the air in the air is disturbed. This causes an increase in global temperature. The damaging ozone layer due to air pollution does not prevent harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun, which cause skin and eye problems in individuals. Air pollution has caused a number of respiratory and heart diseases among people. The incidence of lung cancer has increased in recent decades. Children living in contaminated areas are more likely to develop pneumonia and asthma. Many people die every year due to the direct or indirect effects of air pollution. When burning fossil fuels, harmful gases such as nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides are released into the air. Water droplets combine with these pollutants and become acidic and fall as acid rain, which harms human, animal and plant life.
6. What is the solution to air pollution?
Production of renewable fuels and clean energy. The basic solution to air pollution is to get away from fossil fuels and replace them with other energies such as solar, wind and geothermal. The government limits the amount of fossil fuel that can be used and how much carbon dioxide and other pollutants it can emit. While the government is trying to save our environment from this harmful gas, it is not enough. We as a society need to keep the environment clean by controlling air pollution. To more in detail about air pollution and its causes. To learn more about air pollution and its impact on the environment, visit the Vedantu website.
Air pollution: what are the effects and EU actions to reduce it?
Air quality affects people’s health. Parliament is fighting for stricter rules to regulate pollution.

Poor air quality can cause respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and cancer. But its devastating effects also extend to biodiversity, as it poisons crops and forests, causing significant economic losses.
As part of the zero pollution ambition set out in the EU's European Green Deal , the European Parliament has adopted stricter air quality standards with targets for particulate pollutants.
- Find out what the EU is doing to prevent water pollution

The health cost of air pollution
Air has been polluted for decades by nitrogen dioxide, ozone and particulate matter, with higher concentrations in populated urban areas.
Particulate matter
Particulate matter refers to tiny particles or droplets. Being smaller than a hair, they can pass into the bloodstream through respiration. They can include organic chemicals, dust, soot and metals. Chronic exposure can lead to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases that may be lethal to vulnerable people and can also lead to cancer. In 2020, exposure to particulate matter with a diameter of less than 2.5 microns caused the premature death of at least 238,000 people in the EU, according to the European Environment Agency .

Nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound generated in engines, especially diesel engines. Exposure to it reduces resistance to infection and is associated with an increase in chronic respiratory diseases and premature ageing of the lungs. Nitrogen dioxide pollution caused 49,000 premature deaths in the EU in 2020.
Breathing ozone can irritate the eyes, respiratory tract and mucous membranes. It is particularly dangerous for people suffering from asthma and can be fatal in the case of chronic respiratory and cardiovascular conditions. In 2020, 24,000 people lost their lives prematurely in the EU due to exposure.
Although air pollution remains a problem, abatement policies have improved air quality in Europe over the last three decades. From 2005 to 2020, the number of premature deaths from exposure to particulate matter with a diameter of less than 2.5 microns fell by 45% in the EU.

Loss of biodiversity
According to an analysis by the European Environment agency, 59% of forests and 6% of agricultural land were exposed to harmful levels of ozone in Europe in 2020. Economic losses due to the impact on wheat yields amounted to about €1.4 billion in 35 European countries in 2019. The largest losses were recorded in France, Germany, Poland and Tûrkiye.
- Read more about causes of biodiversity loss
Sources of pollution
More than half of the particulate emissions come from the burning of solid fuels for heating. The residential, commercial and institutional sectors are the main source of particulate pollution in Europe.
Agriculture is also a major polluter, responsible for 94% of ammonia emissions, while road transport is responsible for 37% of nitrogen oxide emissions and agriculture for 19%.
All these emissions have been on a downward trend since 2005, despite the considerable increase in the EU's gross domestic product.
What is the Zero Pollution Action Plan?
The EU's Zero Pollution Plan contributes to the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development . Under the European Green Deal, the EU set the goal of reducing air, water and soil pollution by 2050 to levels that are no longer harmful to health and natural ecosystems and that are within the limits the planet can sustain. It defines a number of objectives to help achieve this goal by 2030:
- cutting premature deaths from air pollution by more than 55%
- reducing EU ecosystems where air pollution threatens biodiversity by 25%
- cutting plastic litter at sea 50% and micro plastics released into the environment by 30%
Stricter limits for several air pollutants
In April 2024, Parliament adopted new rules to improve air quality in the EU . The law sets stricter targets for several pollutants including particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide and ozone to ensure that air quality in the EU is less harmful to human health, natural ecosystems and biodiversity.
EU countries will also need to monitor pollutants that have proved to have a negative impact on health and the environment, such as ultrafine particles, black carbon, mercury and ammonia, where high concentrations are likely to occur.
The Commission should review EU standards by the end of 2030 to align them with the guidelines of the World Health Organization and the latest scientific evidence, if needed. EU countries may request up to 10 years of extra time to reach the air quality targets.
All EU countries should create air quality roadmaps setting out short and long-term measures to meet the new limits for pollutants.
EU countries will have to ensure that citizens may request compensation if their health suffers due to violation of the EU law.
Share this article on:
- Sign up for mail updates
- PDF version
Exposure to air pollution during the first two years of life is associated with worse attention capacity in children
A study highlights the potential impact of traffic-related air pollution (no2) on attentional development.
A growing body of research shows that exposure to air pollution, especially during pregnancy and childhood, may have a negative impact on brain development. Now a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has found that exposure to nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) during the first two years of life is associated with poorer attention capacity in children aged 4 to 8, especially in boys. NO 2 is a pollutant that comes mainly from traffic emissions.
The study, published in Environment International , shows that higher exposure to NO 2 was associated with poorer attentional function in 4- to 6-year-olds, with increased susceptibility to this pollutant observed in the second year of life. This association persisted at an age of 6 to 8 years of age only in boys, with a slightly greater susceptibility period from birth to 2 years of age.
The researchers used data from 1,703 women and their children from the INMA Project birth cohorts in four Spanish regions. Using the home address, the researchers estimated daily residential exposure to NO 2 during pregnancy and the first 6 years of childhood. In parallel, they assessed the attentional function (the ability to choose what to pay attention to and what to ignore) at 4-6 years and 6-8 years, and working memory (the ability to temporarily hold information) at 6-8 years, using validated computerised tests.
Periods of higher susceptibility to air pollution
A previous INMA study reported that exposure to NO 2 during pregnancy and childhood was associated with impaired attentional function in children at 4-5 years of age. The present study found that:
- Higher exposure to NO 2 between 1.3 and 1.6 years of age was associated with higher hit reaction time standard error, an indicator of speed consistency, in the attentional function test at 4-6 years of age.
- Higher exposure to NO 2 between 1.5 and 2.2 years of age was associated with more omission errors.
- Higher exposure to NO 2 between 0.3 and 2.2 years was associated with higher hit reaction time standard error at 6-8 years only in boys.
- No associations were found between higher exposure to NO 2 and working memory in children aged 6 to 8 years.
"These findings underline the potential impact of increased traffic-related air pollution on delayed development of attentional capacity and highlight the importance of further research into the long-term effects of air pollution in older age groups," explains Anne-Claire Binter , last author of the study and postdoctoral researcher at ISGlobal.
As the brain matures
Attentional function is crucial for the development of the brain's executive functions, which manage and control actions, thoughts and emotions to achieve a goal or purpose. "The prefrontal cortex, a part of the brain responsible for executive functions, develops slowly and it is still maturing during pregnancy and childhood," adds Binter. This makes it vulnerable to exposure to air pollution, which has been linked in animal studies to inflammation, oxidative stress, and impaired energy metabolism in the brain.
"In boys, the association between exposure to N0 2 and attentional function may last longer because their brains mature more slowly, which could make them more vulnerable," she points out. To understand this better, future studies should follow people over time to see how age and gender affect the relationship between air pollution and attention span, especially in older age groups.
In conclusion, "this study suggests that early childhood, up to the age of 2, seems to be a relevant period for implementing preventive measures," says Binter. "Even a small effect at the individual level from relatively low levels of exposure, as in this study, can have large consequences at the population level. Exposure to traffic-related air pollution is therefore a determinant of the health of future generations."
- Intelligence
- Child Development
- Learning Disorders
- Air Quality
- Air Pollution
- Environmental Issues
- Air pollution
- Automobile emissions control
- Mercury poisoning
- Early childhood education
- Fossil fuel
- Familiarity increases liking
Story Source:
Materials provided by Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal) . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Kellie L.H.A. Crooijmans, Carmen Iñiguez, Kristina W. Withworth, Marisa Estarlich, Aitana Lertxundi, Ana Fernández-Somoano, Adonina Tardón, Jesús Ibarluzea, Jordi Sunyer, Mònica Guxens, Anne-Claire Binter. Nitrogen dioxide exposure, attentional function, and working memory in children from 4 to 8 years: Periods of susceptibility from pregnancy to childhood . Environment International , 2024; 186: 108604 DOI: 10.1016/j.envint.2024.108604
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Holographic Displays: An Immersive Future
- Harvesting Energy Where River Meets Sea
- Making Diamonds at Ambient Pressure
- Eruption of Mega-Magnetic Star
- Clean Fuel Generation With Simple Twist
- Bioluminescence in Animals 540 Million Years Ago
- Fossil Frogs Share Their Skincare Secrets
- Fussy Eater? Most Parents Play Short Order Cook
- Precise Time Measurement: Superradiant Atoms
- Artificial Cells That Act Like Living Cells
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
share this!
April 23, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
High air pollution in Denmark may impact children's academic performance
by University of Copenhagen
Pollution from traffic, farming and wood stoves may have a negative effect on children's cognitive development, according to a new study published in Environment International on Danish students' performance in the lower secondary school leaving examination.
You probably don't think about it, but in most parts of the country the air we breathe is anything but clean.
In most parts of Denmark air pollution is double the recommended WHO level, with the highest levels found in heavily trafficked cities and southern Denmark, which is affected by polluted air blowing in from the south.
And polluted air can affect our health, previous research has shown. In fact, air pollution is associated with increased risk of respiratory and cardiovascular disease, and in children air pollution can cause asthma and respiratory infections.
Now a new cohort study from the University of Copenhagen shows that air pollution may also affect students' performance in the primary school final examination. The study included 800,000 lower secondary school students.
One of the researchers behind the new study is Associate Professor Youn-Hee Lim from the Department of Public Health, who is an expert on large cohort studies.
"A comparison of children who have been exposed to air pollution below the recommended level with children who have been exposed to air pollution above the safe level shows a significant difference in performance at the primary school examination," Youn-Hee Lim explains.
In fact, children living at the least polluted addresses exceed the children living at addresses with the highest pollution levels by one full grade point for the average of all five subjects in the exam, she explains.
The researchers stress that they are unable to directly prove a causal link and thus conclude with absolute certainty that air pollution leads to lower marks. What they have done is identify a strong association between air pollution and performance at the primary school final examination, and they have accounted for family socioeconomic factors, parent's education, etc., leaving alternative explanations for this associations very unlikely.
"We cannot be certain that there is a causal connection between air pollution and academic performance, but within our epidemiological field of research this type of study is the gold standard and the highest level of certainty one can achieve.
"And our results are supported by other international experimental and epidemiological studies , which show that air pollution can impair children's cognitive development," Professor Zorana Jovanovic Andersen says.
"It is a unique study, as we in Denmark have access to data from school performance records for all students in Denmark, and air pollution data at their address, allowing us to conduct a nationwide study on air pollution and cognitive performance. No one has been able to or done this before."
What the researchers did
The study looked at the type of air pollution known as fine particulate matter , more specifically PM 2.5 pollution.
The researchers examined 800,000 Danish primary school students' grade point average (GPA) in the exit examination linking students' residential exposure to fine particle matter air pollution.
The study showed that children living at the least polluted addresses exceed the children living at addresses with the highest pollution levels by one full grade point for the average of all five subjects in the exam.
To avoid bias, they only compared students within the same school, and then added all the results from the many schools in Denmark together.
Finally, the study considered a series of variables in the model, including socioeconomic background based on the mother's level of education and income, maternal age, mother's country of origin, and parity.
Wood burning, traffic, and agriculture
According to the WHO, the safety level for the so-called PM 2.5 air pollution, which is the one used in this study, is 5 microgram per cubic meter, but most parts of the country show a level of 11 or 12 microgram per cubic meter.
"The pollution recorded in Denmark is mainly a result of what comes from other parts of Europe and local sources in particular wood burning, traffic, and agriculture," Professor Steffen Loft explains.
According to the researchers, the results of the study clearly suggest that air pollution affects children's cognitive development.
"We have used the students' performance at the primary school final examination as a marker for cognitive development, and the connection between air pollution and poorer academic performance suggests that the children's cognitive development has been negatively affected by air pollution , which is really concerning to see at the level of pollution we have in Denmark," Jovanovic Andersen explains.
According to the researchers, this is problematic—for several reasons. First, poorer cognitive development is associated with poorer health in general.
"Second, poorer cognitive development affects the level of education and income in adulthood. In other words, it does not simply affect their health, but their entire life and society as a whole," Jovanovic Andersen concludes.
The researchers stress that structural changes in our way of polluting is necessary for the health of people in Denmark and the rest of Europe.
Journal information: Environment International
Provided by University of Copenhagen
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Artificial intelligence helps scientists engineer plants to fight climate change
21 minutes ago

Ultrasensitive photonic crystal detects single particles down to 50 nanometers

Scientists map soil RNA to fungal genomes to understand forest ecosystems

Researchers show it's possible to teach old magnetic cilia new tricks

Mantle heat may have boosted Earth's crust 3 billion years ago

Study suggests that cells possess a hidden communication system
2 hours ago

Researcher finds that wood frogs evolved rapidly in response to road salts

Imaging technique shows new details of peptide structures

Cows' milk particles used for effective oral delivery of drugs

New research confirms plastic production is directly linked to plastic pollution
3 hours ago
Relevant PhysicsForums posts
Large eruption at ruang volcano, indonesia.
Apr 23, 2024
Unlocking the Secrets of Prof. Verschure's Rosetta Stones
Apr 22, 2024
Tidal friction and global warming
Apr 20, 2024
Iceland warming up again - quakes swarming
Apr 18, 2024
M 4.8 - Whitehouse Station, New Jersey, US
Apr 6, 2024
Major Earthquakes - 7.4 (7.2) Mag and 6.4 Mag near Hualien, Taiwan
Apr 5, 2024
More from Earth Sciences
Related Stories

Air pollution found to impair performance in matriculation exams in mathematical subjects
Feb 8, 2024

Smoggier skies, lower scores? A Brazilian study examines the effects of air pollution on students' cognitive performance
Oct 6, 2021

Polluted air can negatively impact children's test scores, finds study
Nov 16, 2023

Green space around primary schools may improve students' academic performance
Jun 15, 2021

Study reveals air pollution's distracting effect on attention, unveiling underlying neurocognitive mechanisms
Jan 25, 2024

Infants exposed to air pollution are at risk of impaired lung function early in life
Jun 21, 2022
Recommended for you
Modeling broader effects of wildfires in Siberia
8 hours ago

Scientists demonstrate high-resolution lidar sees birth zone of cloud droplets, a first-ever remote observation
4 hours ago
Climate change supercharged a heat dome, intensifying 2021 fire season, study finds
5 hours ago

Airborne observations of Asian monsoon sees ozone-depleting substances lofting into the stratosphere
6 hours ago

Study shows it's not too late to save the West Antarctic Ice Sheet
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Air care: upholding EPA's soot standards crucial for public health, quality of life

In an age when environmental crises plague the world, politicians and industry leaders continue to compromise human lives and environmental health for the sake of short-term economic growth. The U.S. government must properly enforce pollution standards to improve the quality of life for its citizens.
In February, the Biden administration publicly expressed its support for the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) tighter soot pollution standards. Once enforced, these vital measures will improve human health and save thousands of lives.
The soot rule lowers the maximum level of fine particle pollution from the established level set during the Obama administration. To comply with the rule, states and counties must achieve the air quality level outlined in the new standard by 2032 or face penalties.
Shortly after the EPA ruling came out, various state attorney generals filed lawsuits in the interests of their states and manufacturers in those states. They claim the cost of compliance is too great and could jeopardize the infrastructure of additional manufacturing plants, roads and bridges.
These measures may create short-term economic costs for wealthy manufacturers, but they will ultimately benefit the U.S. economy as a whole. According to the EPA , tougher soot pollution standards will generate an estimated $46 billion in net health benefits by 2032.
The World Health Organization estimates that 99% of humans breathe air that exceeds its limits of pollutants. Indoor and outdoor air pollution kills nearly seven million people annually.
Air pollution is experienced predominantly through smog and soot, particulate matter composed of tiny particles that travel in the air. Soot compromises immune systems, depresses lung function, worsens respiratory conditions and hastens death in the most extreme cases.
The American Lung Association’s 2023 State of the Air report indicates that nearly 64 million Americans live in counties where soot pollution reaches unhealthy spikes, and about 19 million people reside in counties where soot exceeds annual limits.
To maintain environmental and economic sustainability, politicians must heed the warnings of agency experts who play a crucial role in safeguarding human health and the environment. The EPA relies on scientific assessments that should not be taken lightly by governments nor the worst of our nation’s polluting industries that continue to selfishly compromise Americans' right to breathe clean air.
The EPA’s stronger standards for harmful soot pollution are not its only actions that have been met with resistance. The EPA came under scrutiny earlier this year with the Supreme Court’s review of the “good neighbor” rule that addresses interstate pollution and restricts smokestack emissions that pollute downwind areas.
Abiding by enforceable anti-pollution standards means industrial facilities must modify their policies and practices and invest in technology that improves the overall quality of air. These actions will curb the trend of premature deaths and other serious conditions that adversely affect employment and deteriorate Americans' quality of life.
As anti-air-pollution standards and rules enter the justice system, the Supreme Court is also weighing whether or not it should overturn the Chevron doctrine . This long-standing doctrine, established in 1984, permits courts to defer to the interpretations of agencies when congressional statutes are ambiguous and legal defenses are sought to uphold environmental policies and regulations.
If the Chevron doctrine is overturned, those who challenge the EPA’s soot ruling will find it easier to derail these critical pollution mitigation efforts as well as regulations from other agencies that address public health, workplace safety, consumer protection and other social and environmental justice issues.
Many of our nation’s communities experience a disproportionate risk of exposure to pollution. Anti-air pollution standards will make a lasting difference in reducing the environmental injustice felt by low-income residents who live in communities close to industrial polluters.
The legal justice system must value our planet and its people over the costs that industries bear to comply with pollution control measures. The government needs to hold corporate polluters accountable for harming American citizens’ health by enforcing pollution laws. Courts have a responsibility to assist citizens experiencing environmental inequities. The interests of American citizens must take precedence over industries’ inadequate attention to environmental justice.
This Earth Day we consider the impact of climate change on human health

The health outcomes of climate change are highlighted this Earth Day. Image: Unsplash/Guillaume de Germain
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Shyam Bishen
Annika green.

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Future of the Environment is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, extreme weather events.
- Earth Day takes place every year on 22 April when we are encouraged to come together to work on solutions to give our planet a healthier future.
- Climate change is one of the biggest challenges to the health of our planet, which also impacts human health worldwide.
- By taking action to mitigate climate change, we can safeguard the well-being of current and future generations and preserve the beauty and diversity of life on Earth.
By 2050, climate change will place immense strain on global healthcare systems, causing 14.5 million deaths and $12.5 trillion in economic losses. This was the warning from the Quantifying the impact of climate change on human health report published in January 2024 by the World Economic Forum in collaboration with Oliver Wyman,
As we celebrate Earth Day , it's essential to reflect on the beauty of our planet and on the challenges it faces, particularly concerning climate change. The environmental effects of climate change are widely discussed, but its impact on human health is significant and often overlooked.
Here, we delve into the profound effects climate change has on our well-being and explore why addressing these issues is crucial for the health of planet Earth and all of its inhabitants. There are five key issues related to climate change that are already impacting human health.
1. Extreme weather events
Climate change intensifies extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, heatwaves, floods and droughts. Forty million people in Africa are living in severe drought conditions and droughts are on the rise in more temperate climes too. Almost 40% of the lower 48 states in the United States and 17% of the European population are facing drought, threatening food and water security.

These extreme weather events can have devastating consequences on human health, leading to injuries, displacement and even loss of life. Increased heatwaves, for example, can exacerbate heat-related illnesses and strain healthcare systems. Heat waves also come with a huge economic toll. It is estimated that $7.1 trillion of productivity could be lost by 2050 as a result of heat waves.
2. Air pollution
The burning of fossil fuels and other human activities contribute to air pollution, which is exacerbated by climate change. Wildfires increasingly are making the news headlines because they cause immense destruction of property and loss of life and livestock, but they also aggravate air pollution. Poor air quality is linked to respiratory diseases, such as asthma, bronchitis and lung cancer. Additionally, pollutants, such as particulate matter and ozone, can worsen cardiovascular health, leading to heart attacks and strokes. Air pollution could lead to 6 to 9 million premature deaths per year by 2060.
The Global Health and Strategic Outlook 2023 highlighted that there will be an estimated shortage of 10 million healthcare workers worldwide by 2030.
The World Economic Forum’s Centre for Health and Healthcare works with governments and businesses to build more resilient, efficient and equitable healthcare systems that embrace new technologies.
Learn more about our impact:
- Global vaccine delivery: Our contribution to COVAX resulted in the delivery of over 1 billion COVID-19 vaccines and our efforts in launching Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, has helped save more than 13 million lives over the past 20 years .
- Davos Alzheimer's Collaborative: Through this collaborative initiative, we are working to accelerate progress in the discovery, testing and delivery of interventions for Alzheimer's – building a cohort of 1 million people living with the disease who provide real-world data to researchers worldwide.
- Mental health policy: In partnership with Deloitte, we developed a comprehensive toolkit to assist lawmakers in crafting effective policies related to technology for mental health .
- Global Coalition for Value in Healthcare: We are fostering a sustainable and equitable healthcare industry by launching innovative healthcare hubs to address ineffective spending on global health . In the Netherlands, for example, it has provided care for more than 3,000 patients with type 1 diabetes and enrolled 69 healthcare providers who supported 50,000 mothers in Sub-Saharan Africa.
- UHC2030 Private Sector Constituency : This collaboration with 30 diverse stakeholders plays a crucial role in advocating for universal health coverage and emphasizing the private sector's potential to contribute to achieving this ambitious goal.
Want to know more about our centre’s impact or get involved? Contact us .
3. Vector-borne diseases
Climate change affects the distribution and behaviour of disease-carrying vectors, such as mosquitoes and ticks. Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns create favourable conditions for the spread of vector-borne diseases, like malaria, dengue fever, Lyme disease and Zika virus, to moderate and previously less affected climate zones, such as Europe and the United States.
These diseases pose significant threats to public health, especially in vulnerable communities with limited access to healthcare. By 2050, an additional 500 million people may be at risk of exposure to vector-borne diseases.
Have you read?
Earth day: what is it, when is it and why is it important, equitable healthcare is the industry's north star. here's how ai can get us there, 4. food and water insecurity.
Changes in climate patterns disrupt agricultural systems, leading to decreased crop yields, food shortages and compromised food safety. In Sub-Saharan Africa, southern Asia and Central America, around 80 million people will be at risk of hunger by 2050.
Moreover, extreme weather events can contaminate water sources, contributing to waterborne diseases, such as cholera and dysentery. Food and water insecurity not only jeopardize physical health but also contribute to malnutrition and widening socio-economic disparities.
5. Mental health impacts
Climate change-induced disasters and environmental degradation can take a toll on mental health too. The loss of homes, livelihoods and communities due to natural disasters can cause psychological distress, anxiety, depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Additionally, the uncertainty and existential threat posed by climate change can lead to eco-anxiety and feelings of helplessness.
If climate change continues to impact human health across these five vectors, it is predicted that the total cumulative healthcare system costs to provide treatment for diseases caused by climate change could reach over $1.1 trillion by 2050 . North and Central America are expected to have to cover nearly half the cost of this because of higher hospitalization and treatment costs in these regions. And, with climate-related disasters disproportionately impacting Asia, it will also have to shoulder a lot of this financial and medical burden
Addressing the health impacts of climate change requires urgent action at individual, community and global levels. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting sustainable agriculture and investing in resilient healthcare infrastructure are crucial steps in mitigating these challenges. Furthermore, prioritizing adaptation strategies and enhancing public health preparedness can help communities withstand and recover from climate-related disasters.
This Earth Day, let's recognize the intrinsic connection between planetary health and human health. By taking decisive action to mitigate climate change and protect our environment, we safeguard the well-being of current and future generations and preserve the beauty and diversity of life on Earth. Together, we can build a healthier, more sustainable future for all.
Healthy and resilient societies
The World Economic Forum has been active in climate action for over a decade, including initiatives such as the Alliance for Clean Air , the Alliance of CEO Climate Leaders and the Forum's work towards nature-positive industry sector transition, amongst others.
These workstreams and activities have focused on climate change mitigation and transition towards net-zero conditions. However, it is recognized that historically, there has been a critical underinvestment in the health implications of climate change, with only 0.5% of multilateral climate funding allocated towards the protection or improvement of human health.
The launch of the Forum’s Climate and Health Initiative at the start of 2023, ahead of the first COP meeting with a dedicated health day, was designed to address this lack of focus on health.
The Initiative’s mission is to help build a healthier and more resilient society to the health impacts of climate change through multistakeholder and cross-sector collaboration and systems transformation. The initiative aims to achieve this through three strategic pillars:
1. Advocacy and visibility
Convene and amplify voices to advance a unified global approach by building a multisector community of thought leaders to deliver a high-impact outreach and engagement campaign.
2. Evidence gathering to catalyze action
Map the research and data on the impact of climate change on health, with a focus on identifying the most critical gaps in understanding and how partners can address these gaps in knowledge.
3. Resilience and preparedness
Identify and accelerate evidence-based approaches to mitigating the health impacts of climate change across sectors. Unlock finances and incentivize climate and health investment.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Health and Healthcare Systems .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Bird flu spread a ‘great concern’, plus other top health stories
Shyam Bishen
April 24, 2024

Scientists have invented a method to break down 'forever chemicals' in our drinking water. Here’s how
Johnny Wood
April 17, 2024

Young people are becoming unhappier, a new report finds

Promoting healthy habit formation is key to improving public health. Here's why
Adrian Gore
April 15, 2024

What's 'biophilic design' and how can it benefit neurodivergent people?
Fatemeh Aminpour, Ilan Katz and Jennifer Skattebol
Why stemming the rise of antibiotic resistance will be an historic achievement
Carel du Marchie Sarvaas
April 11, 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Air Quality Mitigation Plan is a proposed project which aims at reducing the emissions that affect the air quality by at least fifteen percent. Air Pollution: Effects and Regulations. This essay analyzes the air pollution effects and regulations based on a simple observation of a smoke coming from a large smokestack.
The effects of temperature and air pollution on public health are comprehensive and ubiquitous. Therefore, this dissertation deals with the comprehensive topic of climate change and air pollution and their effects on public health. The first chapter examines the effect of temperature on mortality in 148 cities in the U.S.
Car Air Pollution. Further, NO2 can prevent the flow of oxygen in the blood to other parts of the body like the brain. These toxic substances settle in the lungs and disrupt the normal flow of air in […] We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 809 writers online.
Microsoft Word - 5.23.16 Ambient Air Pollution Thesis.docx. Ambient Air Pollution and Lung Cancer Risk in the Women's Health Initiative Observational Study. Shilpa N Gowda. A thesis. submitted in partial fulfillment of the. requirements for the degree of. Master of Public Health. University of Washington. 2016.
100 Air Pollution Research Paper Topics. Air pollution is a critical environmental issue that affects every living being on the planet. It is a topic that requires in-depth understanding and research. To aid students in their quest for knowledge and to help them in their academic pursuits, we have compiled a comprehensive list of air pollution ...
Moreover, air pollution seems to have various malign health effects in early human life, such as respiratory, cardiovascular, mental, and perinatal disorders ( 3 ), leading to infant mortality or chronic disease in adult age ( 6 ). National reports have mentioned the increased risk of morbidity and mortality ( 1 ).
In this thesis we investigate the causal link from short-term air pollution to a series of novel outcome variables. In particular, (1) sleep quality, (2) cough and (3), plans to migrate. Each study is based on China, where poor air quality is widely-understood to be an important social issue, focussing on ne particulate matter (PM
Short-term and long-term adverse effects on human health are observed. VOCs are responsible for indoor air smells. Short-term exposure is found to cause irritation of eyes, nose, throat, and mucosal membranes, while those of long duration exposure include toxic reactions ( 92 ).
Forty studies examined the effects of temperature, three the effects of air pollution, and only one study examined both temperature and air pollution exposures. Due to the small number of studies and limited geographic coverage, and the variation in worker settings, the generalizability of these findings to different populations is limited.
as a spatially representative measure of air pollution and allowing for uncertainty in what is an inherently unknown quantity, when estimating the associated health risks, respectively. For example the majority of air pollution and health studies only consider the health effects of a single pollutant rather than that of overall air quality.
The result highlights the importance of long-range air pollution transport and suggests that emission reductions can improve air quality and have associated health benefits downwind. Therefore, regional cooperation to reduce air pollution transported over long distances may be desirable. Date of publication. December 2018; Keyword
Abstract. Air pollution is an alarming problem, not only in terms of air quality, but also in relation to health issues. Toxic air pollutant concentrations produce harmful impacts on plant health ...
Consult the top 50 dissertations / theses for your research on the topic 'Air pollution.'. Next to every source in the list of references, there is an 'Add to bibliography' button. Press on it, and we will generate automatically the bibliographic reference to the chosen work in the citation style you need: APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago, Vancouver ...
Air Pollution in China. 1 page / 300 words. Air pollution refers to a position of the Earth's atmosphere when harmful or excessive quantities of substances including biological molecules, particulates, and gases are released. As the Chinese economy gained pace, it had a parallel growth for energy consumption as well.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas. Effects Of Air Pollution On Health. The air pollution has many bad effects on the health of people. It is the cause of many skins and respiratory disorder in human beings. Also, it causes heart disease too. Air pollution causes asthma, bronchitis, and many other diseases.
For example, if you are writing about air pollution, then the terms you use may range from "particulate matter" to "hygroscopicity," depending on the complexity of your essay's subject. Tip #4. The pollution essay thesis statement is a guiding line throughout your writing process.
Air pollution consists of chemicals or particles in the air that can harm the health of humans, animals, and plants. It also damages buildings. Pollutants in the air take many forms. They can be gases, solid particles, or liquid droplets. Sources of Air Pollution Pollution enters the Earth's atmosphere in many different ways. Most air pollution is created by people, taking the form of ...
A number of air pollutants pose severe health risks and can sometimes be fatal, even in small amounts. Almost 200 of them are regulated by law; some of the most common are mercury, lead, dioxins ...
33 essay samples found. Writing an essay on air pollution can be a challenging task. It is a pressing issue that affects the environment, human health, and air quality. To create a well-structured paper, you should follow a clear outline. What's more, organize your essay into perfectly organized sections. It should consist of an introduction ...
Fact: Pollution is a problem for modern society. Thesis: Air pollution should be brought under control by legislation and by citizen actions. The first statement is not arguable. Starting with such a statement indicates the paper will simply be a collection of facts gathered, but the student has not done any thinking/analysis of the facts.
Air Pollution and Acid ain Acid rain is now commonly perceived as a major environmental threat but the term is still relatively new and many are confused about its causes. While there are some other commonly cited reasons including natural sources, the main cause of acidity in rain is air pollution, which increases the composition of sulphur oxides and nitrogen oxides and thus lowering the pH ...
Air pollution can result in poor air quality, both in cities and in the countryside. Some air pollutants make people sick, causing breathing problems and increasing the likelihood of cancer. Some air pollutants are harmful to plants, animals, and the ecosystems in which they live. Statues, monuments, and buildings are being corroded by the air ...
Download. 1. Problem Statement: Air pollution is one of the most serious problems in the world. It refers to the contamination of the atmosphere by harmful chemicals or biological materials. It may cause diseases, allergies, and severe health problems in humans and other living organisms and may damage the natural environment.
Technical Contact: Serena Chung, Project Officer. [email protected]; 202-604-9084. Eligibility Contact: Ron Josephson, Eligibility Officer and Science Review Officer. [email protected]; 202-564-7823. Electronic Submissions: [email protected]. If interested in being on the Peer Review Panel, rather than applying, please ...
Parliament is fighting for stricter rules to regulate pollution. Poor air quality can cause respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and cancer. But its devastating effects also extend to biodiversity, as it poisons crops and forests, causing significant economic losses. As part of the zero pollution ambition set out in the EU's ...
0:04. 0:56. Americans are breathing more toxic air now than in the past quarter century, according to a new report from the American Lung Association. The findings released Wednesday show the ...
A growing body of research shows that exposure to air pollution, especially during pregnancy and childhood, may have a negative impact on brain development. Now a study has found that exposure to ...
What the researchers did. The study looked at the type of air pollution known as fine particulate matter, more specifically PM 2.5 pollution.. The researchers examined 800,000 Danish primary ...
According to the EPA, tougher soot pollution standards will generate an estimated $46 billion in net health benefits by 2032. The World Health Organization estimates that 99% of humans breathe air ...
By 2050, climate change will place immense strain on global healthcare systems, causing 14.5 million deaths and $12.5 trillion in economic losses. This was the warning from the Quantifying the impact of climate change on human health report published in January 2024 by the World Economic Forum in collaboration with Oliver Wyman, As we celebrate ...