- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 6th Standard CBSE all question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 6th Standard CBSE all books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place.

6th Standard CBSE Subjects
6th standard cbse study materials.


Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

Latest CBSE 6th Standard CBSE Study Material Updates
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 1 Class 6 Knowing our Numbers
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Updated for new NCERT Book.
Get NCERT Solutions of Chapter 1 Class 6 Knowing our Numbers with Videos of all questions. All exercise questions and examples are solved with step-by-step answers.
In this chapter, we will
- First revise our concepts of Place Value
- Learn about Indian Number System and International Number System
- Then, we learn how to compare large numbers
- And, add , subtrac t, multiply large numbers
- We study what rounding off is, and how to round off to nearest tens, hundreds, thousands
- We learn about General rule for rounding off , which is used in sum, subtraction and multiplication
- What are Roman Numerals
- Rules for forming Roman Numerals
- List of Roman Numerals for reference
- Roman Numerals for big numbers
Click on an exercise link below to start learning.
Or you can also check the topics from Concept wise, where we have first explained the topic and then ordered the questions from easy to difficult.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Question and Answers
Home » CBSE » Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Question and Answers

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Important Questions – Knowing Our Numbers
Maths is an important subject we study in school. In Class 6, students will learn the basics of the subject, which will be needed in higher classes. The first chapter is about learning numbers. Maths deals with numbers, and students must identify numbers.
Quick Links
In this chapter, students will study larger numbers like thousands, lakhs, etc. They will learn how to express these numbers with the help of commas. The chapter also includes addition and subtraction of larger numbers, how to find the largest among given numbers, etc. This is an easy chapter, but students must practice questions to build their concepts.
Extramarks is a leading company that provides all the important study materials related to CBSE and NCERT. Our experts have made the Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 to help the students in practice. They have collected the questions from the textbook exercises, CBSE sample papers, CBSE past years’ question papers, NCERT Exemplars, and important reference books. They have solved the questions, and experienced professionals have further checked the answers to ensure the best quality of the content.
We provide a wide range of study materials to students, and you can download these after registering on our official website. You will find the CBSE syllabus, CBSE sample papers, CBSE revision notes, CBSE extra questions, CBSE past years’ question papers, NCERT books, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplars, NCERT important questions, vital formulas, and many more.
Get Access to CBSE Class 6 Maths Important Questions with Solutions
Also, get access to CBSE Class 6 Maths Important Questions for other chapters too:
Knowing Our Numbers Class 6 Extra Questions with Solutions
Our experts have made the question series to help students. They have collected the questions from textbook exercises, CBSE sample papers, CBSE past years’ question papers, NCERT Exemplars, and important reference books. They have also solved the questions so that students can follow the answers. Experienced professionals have further checked the solutions to ensure the best quality of the content. Thus, the Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 will help students score better in exams. The important questions are-
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) One lakh = ………….. ten thousand.
(ii) 1 million = ………… hundred thousand.
(iii) 1 crore = ………… ten lakh.
(iv) 1 crore = ………… million.
(v) 1 million = ………… lakh.
(i) 1 lakh = ten ten thousand.
(ii) 1 million = ten hundred thousand.
(iii) 1 crore = ten ten lakh
(iv) 1 crore = ten million
(v) 1 million = ten lakh
Question 2.
(i) 1 metre = ____millimetres.
(ii) 1 centimetre = ____ millimetres.
(iii) 1 kilometre = ____ millimetres.
(iii) 10, 00, 000
Question 3.
(i) 1 gram = ___ milligrams.
(ii) 1 litre = ___ millilitres.
(iii) 1 kilogram = ___ milligrams.
(iii) 10,00,000
Question 4.
Place the commas correctly and write the numerals :
(i) Seventy-three lakh seventy-five thousand three hundred seven.
(ii) Nine crore five lakh forty-one.
(iii) Seven crore fifty-two lakh twenty-one thousand three hundred two.
(iv) Fifty-eight million four hundred twenty- three thousand two hundred two.
(v) Twenty-three lakh thirty thousand ten.
(i) 73,75,307
(ii) 9,05,00,041
(iii) 7,52,21,302
(iv) 5,84,23,202
(v) 23,30,010.
Question 5.
Insert commas in the numbers suitably and write their names according to the Indian System of Numeration:
(i) 87595762
(ii) 8546283
(iii) 99900046
(iv) 98432701
(i) 8,75,95,762 (Eight crore seventy-five lakh ninety-five thousand seven hundred sixty- two)
(ii) 85,46,283 (Eighty-five lakh forty-six thousand two hundred eighty-three)
(iii) 9,99,00,046 (Nine crore ninety-nine lakh forty-six)
(iv) 9,84,32,701 (Nine crores eighty-four lakh thirty-two thousand seven hundred one)
Question 6.
Insert commas in the numbers suitably and write their names according to the International System of Numeration:
(i) 78921092
(ii) 7452283
(iii) 99985102
(iv) 48049831
(i) 78,921,092 (Seventy-eight million nine hundred twenty-one thousand ninety-two)
(ii) 7,452,283 (Seven million four hundred fifty- two thousand two hundred eighty-three)
(iii) 99,985,102 (Ninety-nine million nine hundred eighty-five thousand one hundred two)
(iv) 48,049,831 (Forty-eight million forty-nine thousand eight hundred thirty-one)
Question 7.
A number in which the Sum of all of its factors is equal to twice the number is called a ___ number.
Question 8.
The numbers which have more than just two factors are called ___ numbers.
Question 9.
Two is the only ___ number which is even.
Question 10.
Two numbers having only one as a common factor are called ___ numbers.
Question 11.
The Lowest Common Multiple ( LCM) of two or more given numbers is always the lowest of their common ___.
Question 12.
The Highest Common Factor (HCF) of two or more than two given numbers is also known as the highest of their common ___.
Question 13.
The product of the place values of the two 2’s in 428721 is
(iii) 400000
(iv) 40000000
(iii): Place the values of 2’s in 428721 are 20000 and 20
∴ The required product = 20000 × 2 = 400000
Question 14.
Number 3 × 10000 + 7 × 1000 + 9 × 100 + 0 × 10 + 4 is the same as
(iii) 37904
(iv) 379409
(ii) : 3 × 10000 + 7 × 1000 + 9 × 100 + 0 × 10 + 4
= 30000 + 7000 + 900 + 4 = 37904
Question 15.
If one is added to the greatest 7-digit number, then it will be equal to
(i) 10 thousand
(ii) 1 lakh
(iii) 10 lakh
(iv) One crore
(iv) : The greatest 7-digit number = 99,99,999
Now, 99,99,999 + 1 = 1,00,00,000
Question 16.
The greatest number in which on rounding off to the nearest thousands gives 5000, is
(iv) : (1) Rounding off 5001 to nearest thousands = 5000
(2) Rounding off 5559 to nearest thousands = 6000
(3) Rounding off 5999 to nearest thousands = 6000
(4) Rounding off 5499 to nearest thousands = 5000
And 5499 > 5001
Question 17.
Keeping the place of six in the number 6350947 same, the smallest number which can be obtained by rearranging other digits is
(i) 6975430
(ii) 6043579
(iii) 6034579
(iv) 6034759
(iii) : Tire new number formed = 6034579
Question 18.
The smallest four-digit number having three different digits is
(iv): The smallest 4-digit number with three different digits is 1002.
Question 19.
The number of all the whole numbers between 38 and 68 is
(iii): There are 29 whole numbers between 38 and 68.
Question 20.
The product of the successor and the predecessor of 999 is
(ii) 998000
(iii) 989000
(ii) : Successor of the number 999 = 999 + 1 = 1000
Predecessor of the number 999 = 999 – 1 = 998
Hence, their product = 998 1000 = 998000
Question 21.
Write in expanded form :
(ii) 574021
(iii) 8907010
(i) 74836 is equal to = 7 × 10000 + 4 × 1000 + 8 × 100 + 3 × 10 + 6 × 1
(ii) 574021 is equal to = 5 × 100000 + 7 × 10000 + 4 x 1000 + 0 × 100 + 2 × 10 + 1 × 1
(iii) 8907010 is equal to = 8 × 1000000 + 9 × 100000 + 0 × 10000 + 7 × 1000 + 0 × 100 + 1 × 10 + 0 × 1
Question 22.
A book exhibition was held for 4 days in a school. The number of the tickets sold on the counter on the first, second, third, and the final day was – 1094, 1812, 2050, and 2751. Find the total number of tickets that sold on all four days.
Number of the tickets sold on the first day = 1094
Number of the tickets sold on the second day = 1812
Number of the tickets sold on the third day = 2050
Number of the tickets sold on the final day = 2751
∴Total number of the tickets sold on all of these four days = 1094 + 1812 + 2050 + 2751 = 7,707.
Question 23.
Shekhar is a famous cricket player. He has so far scored a total of 6980 runs in test matches. He wishes to complete 10,000 runs. How many more runs does he need?
Shekhar has so far scored a total of 6980 runs
He wishes to complete a total of 10,000 runs.
Therefore total number of the runs needed by him are = 10,000 – 6980 = 3020 runs
Question 24.
Which of the following given statements is not true?
(i) Both the addition and multiplication are associative for whole numbers.
(ii) Zero is the identity for the multiplication of whole numbers.
(iii) Addition and multiplication are commutative for whole numbers.
(iv) Multiplication is distributive over addition for whole numbers.
(ii): Zero is the identity for the addition of whole numbers.
Question 25.
(i) 0 + 0 = 0
(ii) 0 – 0 = 0
(iii) 0 × 0 = 0
(iv) 0 – 0 = 0
(iv) : 0 + 0 is not defined.
Question 26.
The predecessor of 1 lakh is
(iii) 999999
(iv) 100001
(ii) : 1 lakh = 100000
∴ Predecessor of 100000 = 100000 – 1 = 99999
Question 27.
The successor of 1 million is
(i) Two million
(ii) 1000001
(iii) 100001
(ii) : 1 million = 1000000
∴ Successor of 1000000 = 1000000 + 1 = 1000001
Question 28.
The number of all the even numbers between 58 and 80 is
(i) : Even numbers between the numbers 58 and 80 are 60, 62, 64, 66, 68, 70, 72, 74, 76, 78.
So, these are ten even numbers between 58 and 80.
Question 29.
The Sum of the number of primes numbers between 16 to 80 and between 90 to 100 is
(iii) : Prime numbers between 16 to 80 are – 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73 and 79.
So, there are total 16 prime numbers between 16 to 80.
Also, 97 is the only one prime number between 90 to 100.
So, there is only one prime number between 90 to 100.
∴ Required sum = 16 + 1 = 17
Question 30.
(i) The HCF of the two distinct prime numbers is 1
(ii) The HCF of two coprime numbers is 1
(iii) The HCF of two consecutive even numbers is 2
(iv) The HCF of an even number and an odd number is always even
(iv): The HCF of an even and an odd number is always said to be an odd number.
Question 31.
In an election, the successful candidate was registered 5,77,500 votes, and his nearest rival had secured 3,48,700 votes. By what total margin did the successful candidate win the election?
Number of the votes secured by the successful candidate = 5,77,500
Number of the votes secured by his nearest rival = 3,48,700
Therefore, margin of the votes is necessary to win the election = 5,77,500 – 3,48,700 = 2,28,800
Question 32.
Kirti bookstore sold books worth a total of ₹2,85,891 in the 1st week of June and books worth a total of ₹4,00,768 in the second week of the month. How much was the total sale for the two weeks together? And in which week was the total sale greater and by how much?
Books sold in the first week of the month June are worth ₹2,85,891
Books sold in the second week of the month are worth ₹4,00,768
Therefore, the total sale of the books in the two weeks together is
= ₹2,85,891 + ₹4,00,768 = ₹6,86,659
In the 2nd week of the month, the sale of total books was greater.
Therefore, the difference in the sale of books
= ₹4,00,768 – ₹2,85,891 = ₹1,14,877
So, in the second week of June, the total sale of books was more than ₹1,14,877.
Question 33.
Find the difference below between the highest and the lowest numbers that is written using the digits 6, 2, 7, 4, and 3, each only once.
Given digits = 6, 2, 7, 4, 3
Greatest number is = 76432
Least number is = 23467
Therefore, difference = 76432 – 23467 = 52,965
Question 34.
A machine, on average, manufactures 2,825 screws a day. How many screws did it produce in January 2006?
The number of screws that are manufactured in a day = 2,825.
Number of screws that are manufactured in month of January = 31 x 2825 = 87,575
Question 35.
The total distance between the school and the house of a student is 1 km and 875 m. Every day she walks both the ways. Find the total distance she covered in six days.
Distance between the school and her house = 1 km 875 m = (1000 + 875) m = 1875 metre.
Total Distance travelled by the student from school to home and from home to school is = 2 x 1875 = 3750 m
Distance travelled by the student in six days is = 3750 m x 6 – 22500 m = 22 km 500 m.
Therefore, the total distance covered in 6 days = 22 km 500 m.
Question 36.
A merchant had ₹78,592 with her. She placed an order to purchase 40 radio sets at ₹1200 each. How much total money will remain with her after the purchase?
Amount of money present with the merchant = ₹78,592
Total Number of the radio sets = 40
Price of one of the radio set = ₹1200
Therefore, the cost of 40 radio sets = ₹1200 x 40 = ₹48,000
Remaining money left with the merchant = ₹78,592 – ₹48000 = ₹30,592
Hence, the amount of ₹30,592 will remain with her after purchasing the following radio sets.
Question 37.
A vessel has four litres and 500 ml of curd. How many total glasses, each of 25 mL capacity, can be filled?
Quantity of the curd in a vessel = 4 l 500 mL = (4 x 1000 + 500) mL = 4500 mL.
Capacity of 1 glass = 25 mL
Therefore the number of glasses = 4500/25
Question 38.
A student has multiplied the number 7236 by 65 instead of multiplying by 56. Calculate by how much was his answer greater than the right answer?
The student had multiplied the number 7236 by 65 instead of multiplying by 56.
The difference between the two above multiplications is = (65 – 56) x 7236 = 9 x 7236 = 65124
(We don’t have to do both the multiplication)
Hence, the answer that is greater than the correct answer is 65,124.
Question 39.
Estimate each of the following given numbers using the general rule:
(i) 730 + 998
(ii) 796 – 314
(iii) 12,904 + 2,888
(iv) 28,292 – 21,496
Rounding off 730 nearest to hundreds = 700
Rounding off 998 nearest to hundreds = 1,000
∴ 730 + 998 = 700 + 1000 = 1700
Rounding off 796 nearest to hundreds = 800
Rounding off 314 nearest to hundreds = 300
∴ 796 – 314 = 800 – 300 = 500
Rounding off 12,904 nearest to thousands = 13000
Rounding off 2888 nearest to thousands = 3000
∴ 12,904 + 2,888 = 13000 + 3000 = 16000
Rounding off 28,292 nearest to thousands = 28,000
Rounding off 21,496 nearest to thousands = 21,000
∴ 28,292 – 21,496 = 28,000 – 21,000 = 7,000
Question 40.
Estimate the following given products using the general rule:
(i) 578 x 161
(ii)5281 x 3491
(iii) 1291 x 592
(iv) 9250 x 29
(i) 578 x 161 = 600 x 200 = 1,20,000
(ii) 5281 x 3491 = 5000 x 3000 = 1,50,00,000
(iii) 1291 x 592 = 1300 x 600 = 7,80,000
(iv) 9250 x 29 = 9000 x 30 = 2,70,000
Question 41.
Which of the following is not true?
(i) (7 + 8) + 9 = 7 + (8 + 9)
(ii) (7 × 8) × 9 = 7 × (8 × 9)
(iii) 7 + 8 × 9 = (7 + 8) × (7 + 9)
(iv) 7 × (8 + 9) = (7 × 8) + (7 × 9)
(iii) : 7 + 8 × 9 = 7 + 72 = 79,
(7 + 8) × (7 + 9) = 15 × 16 = 240
and 79 ≠ 240
Question 42.
The length of the river ‘Narmada’ is 1290 km. Its length in metres is – _____.
As, 1290 km = (1290 × 1000) m = 1290000 m
Question 43.
The total distance between Srinagar and Leh is 422 km. The same distance in metres is – _____.
As, 422 km= (422 × 1000) m = 422000 m
Question 44.
Writing numbers from the greatest to the smallest is called an arrangement in ___ order.
Question 45.
By reversing the order of the digits of the greatest number made by the five different non-zero digits, we get the new number which is the number of _____ five digits.
By reversing the order of the digits of the greatest number made by the five different non-zero digits, the new number present is the smallest number of these digits.
Question 46.
By adding 1 to the greatest ___ digit number, we get the number ten lakh.
As, greatest six-digit number = 999999
By adding one to 999999, we get 1000000.
Question 47.
The number five crore twenty-three lakh seventy-eight thousand four hundred one can also be written, using the commas, in the Indian System of Numeration as.
5, 23, 78, 401
Question 48.
In the Roman Numeration, the symbol X can be subtracted from – ___, M and C only.
Question 49.
The number 66 in Roman numerals is.
LXVI : 66 = LXVI
Question 50.
The total population of Pune was 2,538,473 in 2001. Rounded off to the nearest thousands, the population was ___.
Question 51.
The smallest whole number is ___.
0 : 0 is the smallest whole number.
Question 52.
The successor of number 106159 is ___.
As, Successor of 106159 is 106159 + 1, i.e., 106160
Question 53.
400 is the predecessor of the number ___.
As, 400 is the predecessor of 400 + 1, i.e., 401
Question 54.
___ is the successor of the largest three digit number.
As, Largest three digit number = 999
And the successor of 999 is 999 + 1, i.e., 1000
Question 55.
If the number 7254*98 is to be divisible by the number 22, then the digit at * is
(iii) : 7254 * 98 is divisible by the number 22 only if it is divisible by both 2 and 11.
Given that the number is even. Therefore it is divisible by the number 2.
7254 * 98 is divisible by 11, only if
(7 + 5 + * + 8) – (2 + 4 + 9) or (20 + *) – 15 or 5 + * is also divisible by 11.
∴ The digit at * place should be filled by 6.
Question 56.
The largest number which will always divide the Sum of any pair of consecutive odd numbers is
(ii)The Sum of any pair of the consecutive odd numbers results in the form of a multiple of 4.
∴ The required largest number is 4.
Question 57.
A number is divisible by five and six. It may not be divisible by
(iv): The Least Common Multiple also known as LCM of 5 and 6 is 30.
And also 30 is divisible by the numbers 10, 15 and 30 but not by the number 60.
Question 58.
The greatest number which will always divide the product of the predecessor and successor of an odd natural number other than 1, is
(ii): As the odd natural numbers other than 1 are – 3, 5, 7, 9 and so on.
Now, we know that the predecessor and successor of 3 are – 2 and 4 respectively, and their product is two × four = 8
Similarly, we know that the predecessor and the successor of 5 are – 4 and 6, respectively, and their product is four × 6 = 24.
Thus, the above shows that the greatest number which always divides the product of the predecessor and the successor of an odd natural number other than 1 is 4.
Question 59.
A person had only ₹ 1000000 with him. He purchased a coloured-T.V. for ₹ 16580, a motorcycle for ₹ 45890 and a flat for ₹ 870000. How much money was left with him?
The total amount a person had was = ₹ 1000000
The total amount he spent on a colour T.V. was = ₹ 16580
The amount he spent on a motorcycle was = ₹ 45890
The amount he spent on a flat was = ₹ 870000
∴ Total amount he spent is = ₹ (16580 + 45890 + 870000) = ₹ 932470
Thus, the total amount left with him = ₹ 1000000 – ₹ 932470 = ₹ 67530
Question 60.
Out of 180000 tablets of Vitamin A, a total of 18734 are distributed among the students in the district. Find the total number of remaining vitamin tablets.
Total tablets of Vitamin A are = 180000
Total number of tablets distributed among the students in the district = 18734
∴ The number of total remaining vitamin tablets = 180000 – 18734 = 161266
Question 61.
Chinmay only had ₹ 610000. He gave a total of ₹ 87500 to Jyoti, ₹ 126380 to Javed and ₹ 350000 to John. How much money was left with him?
Chinmay had a total amount = of ₹ 610000
The total amount he gave to Jyoti = ₹ 87500
The total amount he gave to Javed = ₹ 126380
The total amount he gave to John = ₹ 350009
Total amount given by Chinmay is = ₹ (87500 + 126380 + 350000) = ₹ 563880
Thus, the amount left with him
= ₹ 610000 – ₹ 563880 = ₹ 46120
Benefits of Solving Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Extra Questions
Practise is very important, and it helps students in several ways. Our experts have made the question series to help students in practise. Thus, the questions will help students in several ways, and they will be worthy of their time. The benefits of solving the Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 are as follows-
- The experts have collated the questions from different sources. They have taken help from the textbook exercises, CBSE sample papers, CBSE past years’ question papers, NCERT Exemplars and important reference books. Thus, students don’t have to search for questions in different sources: they will find them in a single pdf. Thus, the Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Important Questions will help them in practise and boost their confidence.
- The experts have not only collected the questions, but they have also provided the solutions. Thus, students can follow the solution if they cannot solve the questions. Also, they can check their answers with the provided explanations. Thus, the Maths Class 6 Chapter 1 Important Questions will help students boost their confidence and improve their exam preparation.
- Many students tend to fear maths because they don’t understand the subject. Their doubts must be cleared, and practice can help boost confidence. They must build the habit of solving questions to build interest in the subject matter. The experts have done a good job of collating the questions for students. They can solve these questions regularly, which will help them improve their knowledge. Thus, the Chapter 1 Class 6 Maths Important Questions will improve their exam preparation.
Extramarks is a leading company that provides all the important study materials related to CBSE and NCERT. We provide the CBSE syllabus, CBSE sample papers, CBSE past years’ question papers, CBSE revision notes, CBSE extra questions, NCERT books, NCERT Exemplars, NCERT solutions, NCERT important questions, vital formulas, and many more. Like the Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 1, you will also find important questions for other chapters. The links to the study materials are given below.
- NCERT books
- Important questions
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE past years’ question papers
- Important formulas
- CBSE extra questions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 Which of the following is the representation of number 74 according to roman numerals?
(b). XXXXXXXIV
(d). DCCXLV
Ans (a). LXXIV
Q.2 What is the greatest 7 digit number formed by using the digits 4 , 9 , 1 and 6? Note that each digit should be used at least once.
(a). 99,99,641
(c). 99,66,441
(d). 11,11,469
Given digits:
9 > 6 > 4 > 1
The greatest 7 digit number using the digits 4, 9, 1 and 6 is 99,99,641.
Q.3 Which one of the following is the estimated product of 47 and 215?
Rounding off 215 to the nearest hundreds, we get 200.
Rounding off 47 to nearest tens, we get 50.
Estimated product
Thus, 10,000 is the estimated product of 47 and 215.
Q.4 Write 645340001 using comma in International System of Numeration.
645,340,001
Q.5 a) How many thousands make a million? b) How many lakhs make a crore?
a) 1000 thousands make 1 million. (? 1 million = 1,000,000 = 1000 thousands) b) 100 lakhs make a crore. (? 1 crore = 1,00,00,000 = 100 lakhs)
Please register to view this section
Cbse important questions for class 6 maths, chapter 2 - whole numbers.

Chapter 3 - Playing with Numbers
Chapter 4 - basic geometrical ideas, chapter 5 - understanding elementary shapes, chapter 6 - integers, chapter 7 - fractions, chapter 8 - decimals, chapter 9 - data handling, chapter 10 - mensuration, chapter 11 - algebra, chapter 12 - ratio and proportion, chapter 13 - symmetry, chapter 14 - practical geometry, faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. is class 6 maths chapter 1 easy.
The first chapter of Class 6 Maths provides a few basic ideas related to numbers. They will learn how to express bigger numbers, such as in thousands, lakhs, crores, etc. They will also learn how to use commas to write larger number, add or subtract large numbers, etc. This is an easy chapter because most students have ideas regarding lakhs, crores, or other units of numbers. Thus, students won’t have problems understanding the subject matter if they follow the textbook closely. Students can take help from the Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 prepared by the experts of Extramarks, and they will find a wide variety of questions to solve.
2. How can the question series help students?
Practice is very important for getting better marks in exams. Sometimes, more than the textbook exercises are needed, and students should get help from other sources. The experts of Extramarks have made the question series with help from different sources. They have collated the questions from the textbook exercise, CBSE sample papers, CBSE past years’ question papers, and important reference books. They have solved the questions, and experienced professionals have further checked the answers to ensure the best quality of the content. Thus, the Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 will help students score better in exams. It will also help boost their confidence and incline interest in the subject matter.
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers
Get here the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers and Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Try These Solutions and Practice Tests for revision. It is given here in Hindi and English Medium prepared for academic session 2024-25. According to rationalised syllabus and new books for class 6 Mathematics for CBSE 2024-25, there are only two exercises in chapter 1 Knowing our numbers.
6th Maths Chapter 1 Solutions for CBSE Board
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Try These
- Class 6 Maths Exercise 1.1 in English
- Class 6 Maths Exercise 1.2 in English
6th Maths Chapter 1 Solutions for State Boards
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.2
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.3
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 NCERT Book
- Class 6 Maths Solutions Page
- Class 6 all Subjects Solutions
Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Practice Test 6th Maths Chapter 1 Test 1 6th Maths Chapter 1 Test 2 6th Maths Chapter 1 Test 3 6th Maths Chapter 1 Test 4 6th Maths Chapter 1 Test 5 6th Maths Chapter 1 Test 6
Get class VI Maths Exercise 1.1 and 1.2 at Tiwari Academy in simplified way. 6th Maths Solutions PDF and Video in English and Hindi Medium are prepared in such a way that student can understand it easily. We have updated it for new session based on latest textbooks from NCERT (https://ncert.nic.in/) website. Find the Solutions of Prashnavali 1.1 and 1.2 in Hindi. We are following the latest CBSE Syllabus 2024-25. We work for your help free of cost. Separate links are given to download solutions in PDF file format. In case of any hassle in finding the solutions, please inform us. We will help you at our level best.

These NCERT Solutions are based on latest CBSE – NCERT Textbooks for the CBSE exams 2024-25. Download NCERT Solutions in PDF format to use it offline or use as it is online without downloading.
In 6 Maths Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers, we will study about comparing the number (smaller or greater), selecting the smallest or greatest numbers, order of numbers (ascending or descending).
Ascending order: Ascending order means arrangement from the smallest to the greatest. Descending order: Descending order means arrangement from the greatest to the smallest.
Concepts of Place values, face values and questions based on the numbers as follow: Starting from the greatest 6-digit number, write the previous five numbers in descending order. Starting from the smallest 8-digit number, write the next five numbers in ascending order. The Indian System of Numeration: In our Indian System of Numeration, Commas are used to mark thousands, lakhs and crores. We use ones, tens, hundreds, thousands and then lakhs and crores. The first comma comes after hundreds place and marks thousands. The second comma comes two digits later. It comes after ten thousands place and marks lakh. The third comma comes after another two digits. It comes after ten lakh place and marks crore.

Important Questions on 6 Maths Chapter 1
Fill in the blank: 1 lakh = _______________ ten thousand.
Fill in the blank: 1 lakh = 10 ten thousand
Place commas correctly and write the numerals: Seventy-three lakh seventy-five thousand three hundred seven.
Insert commas suitable and write the names according to indian system of numeration: 87595762.
8,75,95,762 Eight crore seventy-five lakh ninety-five thousand seven hundred sixty-two.
Estimate each of the following using general rule: 730 + 998
730 round off to 700 998 round off to 1000 Estimated sum 1700
Estimate the following product using general rule: 578 x 161
578 x 161 578 round off to 600 161 round off to 200 The estimated product = 600 x 200 = 1,20,000
We are here to help you. For educational help any time you can leave a message, we will call you with in 24 hours. Our prime motive is to help the students without any delay free of cost. NCERT Books and their solutions are given in offline as well as online mode.
How many exercises, questions, and examples are there in chapter 1 of class 6th Maths?
There are 2 exercises in chapter 1 (Knowing our Numbers) of class 6th Maths. In the first exercise (Ex 1.1), there are 4 questions. Questions 1 and 2, each having five parts, and questions 3 and 4, each having four parts. In the second exercise (Ex 1.2), there are 12 word problem questions. So, there are in all 16 questions in chapter 1 (Knowing our Numbers) of class 6th Maths. There are 6 examples in chapter 1 (Knowing our Numbers), which are good for exams point of view.
What are the main topics to study in chapter 1 of class 6th Maths?
In chapter 1 of class 6th Maths, students will study:
- 1. Comparing Numbers.
- 2. How many numbers can you make?
- 3. Shifting digits.
- 4. Introducing 10,000.
- 5. Revisiting place value.
- 6. Introducing 1, 00,000.
- 7. Larger numbers.
- 8. An aid in reading and writing large numbers.
- 9. Use of commas.
- 10. Large Numbers in Practice.
Is chapter 1 of class 6th Maths difficult?
Chapter 1 of class 6th Maths is neither too easy nor too difficult. It lies in the middle of easy and difficult because some parts of this chapter are easy, and some are difficult. However, the difficulty level of any chapter varies from student to student. So, Chapter 1 of class 6th Maths is easy or not depends on students also. Some students find it complicated, some find it simple, and some find it in the middle of simple and difficult.
How much time, students need to do chapter 1 of class 6th Maths?
Students need a maximum of 5-6 days to do chapter 1 of class 6th Maths if they give at least 1-2 hours per day to this chapter. This time is an approximate time. This time can vary because no students have the same working speed, efficiency, capability, etc.
Chapter 2: Whole Numbers »
Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1: Knowing our Numbers - Exercise 1.1
- NCERT Solutions


NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 (Ex 1.1)
NCERT Maths Book Class 6 Chapter 1 - Knowing your Numbers is an ideal study material for students to comprehensively understand the dynamics of mathematics. Students can download NCERT solution PDF for the latest CBSE NCERT Books for Class 6 Maths online from Vedantu that come with step by step techniques to solve problems. The NCERT Class 6 Maths PDF is designed with compliance to the latest CBSE curriculum. Download NCERT Solutions PDF for exam preparation via their mock tests. Subjects like Science, Maths, English,Hindi will become easy to study if you have access to NCERT Solution for Class 6 Science, Maths solutions and solutions of other subjects.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1-Knowing Our Numbers
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) $1$Lakh in terms of ten thousand?
Ans: $1$ lakh is $10$ ten thousand
(b) $1$ Million in terms of hundred thousand
Ans: $1$ million is $10$ hundred thousand
(c) $1$ crore in terms of ten lakh
Ans: $1$ crore is $10$ ten lakh
(d) $1$ million in terms of lakh
Ans: $1$ million is $10$ lakh
2. Place commas correctly and write the numerals:
(a) Seventy three lakh seventy five thousand three hundred seven.
Ans: Seventy-three lakh seventy-five thousand three hundred seven in numerals is written as shown
$73,75,307$
(b) Nine crore five lakh forty one.
Ans: Nine crore five lakh forty-one in numerals is written as shown
$9,05,00,041$
(c) Seven crore fifty two lakh twenty one thousand three hundred two.
Ans: Seven crore fifty-two lakh twenty-one thousand three hundred two in numerals is written as shown
$7,52,21,302$
(d) Fifty eight million four hundred twenty three thousand two hundred two.
Ans: Fifty-eight million four hundred twenty-three thousand two hundred two in numerals is written as shown
$58,423,202$
(e) Twenty three lakh thirty thousand ten.
Ans: Twenty-three lakh thirty thousand ten in numerals is written as shown
$23,30,010$
3. Insert commas suitably and write the names according to Indian system of numeration:
(a) $87595762$
Ans: Commas and names according to Indian system of numeration is given as shown
$8,75,95,762\to $Eight crore seventy-five lakh ninety-five thousand seven hundred sixty-two
(b) $8546283$
$85,46,283\to $Eighty-five lakh forty-six thousand two hundred eighty-three
(c) $99900046$
$9,99,00,046\to $Nine crore ninety-nine lakh forty-six
(d) $98432701$
$9,84,32,701\to $Nine crore eighty-four lakh thirty-two thousand seven hundred one
4. Insert commas suitably and write the names according to International system of numeration:
(a) $78921092$
Ans: Commas and names according to International system of numeration is given as shown:
$78,921,092\to $seventy-eight million nine hundred twenty-one thousand ninety-two
(b) $7452283$
$7,452,283\to $seven million four hundred fifty-two thousand two hundred eighty-three
(c) $99985102$
$99,985,102\to $Ninety-nine million nine hundred eighty five thousand one hundred two
(d) $48049831$
$48,049,831\to $Forty-eight million forty-nine thousand eight hundred thirty-one
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 - Exercise 1.1
The NCERT Solution for Class 6 Maths eases understanding by providing a step-by-step guide to the problems in Exercise 1.1. It allows students to understand large numbers thoroughly, which has further implications outside conventional mathematics.
The NCERT books online comprise every problem in the exercise, such as converting from international method to the Indian method or vice versa.
Here is a list of the problems included in the first exercise of Class 6 Maths Chapter 1
NCERT Maths Class 6 Exercise 1.1 Question 1
The first question is a simple Fill in the Blanks that asks students to convert numbers from the numeration method to another. The cue to the conversion will be given with the usage of varying naming systems.
For instance, 1 Lakh = ___ ten thousand.
This question segment will help students test their assessment skills of different numerical methods as well as their understanding of the same. The NCERT books PDF can be used by students to solve the problems.
NCERT Maths Class 6 Exercise 1.1 Question 2
This question assesses students’ understanding of large numbers by numerical names. It poses large numbers in words and asks students to write the numeric version of it by placing the commas. The commas should be per the Indian numeric system. For instance, nine crores five lakh forty one should be written as 9, 05, 00, 041 as the name is in the Indian system. Students can refer to the NCERT Books download for solutions.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Exercise 1.1 Question 3
This question poses numbers without any comma splicing and asks students to put commas according to the Indian system of numeration. It also asks students to write number names as per the Indian system.
For instance, 99900046 as per given instructions should be rewritten as 9,99,00,046 and named as Nine crore ninety-nine lakh forty-six.
In case students cannot understand the method, they can look up in the NCERT books PDF for a thorough understanding of the step-by-step guide.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Exercise 1.1 Question 4
Regarding this question, students need to put commas and rewrite the numbers according to the International numeric system. They also need to write the names of the numbers in compliance with such an International method. For example, 48049831 needs to be rewritten as 48, 049, 831, and the name for it should be Forty-eight million forty-nine thousand eight hundred and thirty-one. Students can take the help of the Class 6th Maths NCERT Solutions for a better grip on how to solve the same.
These are the types of questions that students will come across in exercise 1.1 of the CBSE NCERT Class 6 Maths textbook. Students can also look for solutions to other exercises in the PDF provided by Vedantu.
NCERT Maths Book Class 6 Chapter 1 Knowing your Numbers – An Overview
The NCERT Class 6 Maths solution from Vedantu allows students to develop a keen analytical sense, reasoning power, and problem-solving ability. It also leaves room for culturing creative and critical thinking in young minds.
The NCERT Solution for Class 6 Maths is devised in a fashion that will hone their mathematical skills and prepare them for future endeavors. In the case of the chapter in discussion - it is the introductory chapter of Class 6.
NCERT Maths Book Class 6 Chapter 1 Solutions deals with the basic mathematical component of large numbers. In this chapter, students will learn about large numbers up to 1 Crore. This chapter begins with methods of numeration used internationally as well as in India.
It will also have information regarding Roman numerals and the estimation of large numbers. It will allow students to comprehend large numbers and name them according to international and Indian methods.
Our solutions offer shortcut techniques for easier understanding. The procedures used in CBSE 6th Class Maths Textbook Solutions are the standard method used across all CBSE schools.
The solution covers every chapter included in the CBSE Class 6 Maths textbook. These include:
Chapter 1 – Knowing Our Numbers
Chapter 2 – Whole Numbers
Chapter 3 – Playing with Numbers
Chapter 4 – Basic Geometrical Ideas
Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes
Chapter 6 – Integers
Chapter 7 – Fractions
Chapter 8 – Decimals
Chapter 9 – Data Handling
Chapter 10 – Mensuration
Chapter 11 – Algebra
Chapter 12 – Ratio and Proportion
Chapter 13 – Symmetry
Chapter 14 – Practical Geometry
Vedantu: Your Go-to Study Partner
Vedantu provides a vast assortment of study materials in an easy and comprehensive manner for all subjects. Students can avail of the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths and other subjects in PDF format from the Vedantu website for free.
Students can have hassle-free access to these solutions from anywhere on the go. They do not have to register with Vedantu to utilize the study materials.
Along with free access, students can also download these PDF solutions on cell phones to read them offline.
These solutions are crafted as per the syllabus prescribed by CBSE so students can avail of the latest study materials quickly and easily.
So, download your NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths and other subjects now to ace your upcoming examinations.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1: Knowing our Numbers - Exercise 1.1
1. What is asked in the exercise questions of Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers Exercise 1.1?
In the first question of the Class 6 Maths textbook Chapter 1 Ex 1.1., students are asked to fill in the blanks based on their knowledge of the number conversion from one Numeration method to another. In the second question, students are asked to write the corresponding numerical value of the numbers written with words along with commas at the right place. The third question is given without comma splicing and students are asked to put commas as per the Indian System of Numeration. As per the fourth questions, students are asked to rewrite the numbers according to their International Numeric System.
2. Where can I find exercise-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Mathematics Chapter 1?
Students can find exercise-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 on Vedantu, a premier e-learning solution. These solutions are designed as per the NCERT guidelines and exam pattern. Students can find the free downloadable PDFs of Exercise 1.1 and other exercises of Class 6 Maths Chapter 1. These materials are prepared by subject matter experts at Vedantu and help score well in the paper.
3. What does Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers of Class 6 Maths deal with?
Knowing Our Numbers, the first chapter of Class 6 NCERT Mathematics textbook, teaches students how to compare two or more numbers. It also makes students aware of both the system of numeration (Indian and International). It teaches them how to read numbers and use commas as per these systems. Knowing Our Numbers is an interesting chapter that makes students capable of reading and writing large numbers correctly.
4. How to express numbers in the Indian System of Numeration?
As per the Indian System of Numeration, the figures like tens, hundreds, thousands, lakhs and crores are used. Commas are used to mark thousands, lakhs and crores. The first comma is used after hundred’s place, the second comma comes after the fifth digit from right, third comes after the seventh digit and so on. For example- 6, 09, 20, 563 which will be read as Six Crores Nine Lakhs Twenty Thousand Five Hundred and Sixty-three.
5. Where can I avail myself of the Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1?
The solutions are easily available on the Vedantu site. You can follow these steps to avail them:
Click on this link
The webpage with Vedantu’s solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 will open.
To download this, click on the Download PDF button and you can view the solutions offline.
6. How many problems are there in each exercise of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1?
Each exercise of Chapter 1 of NCERT Class 6 has its own different set of exercises spanning across different topics related to the content taught in the chapters. For the solutions of these exercises, one can easily access them from Solutions of the NCERT Mathematics textbook of Class 6 Chapter 1 and download the PDF version without any cost. The solutions provided by Vedantu are free of cost and are also available on the Vedantu Mobile app.
7. Is NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 easy?
The First Chapter is a bit enjoyable if you understand the methods as it starts off with the basics. But as you progress, things may get perplexing because there are various ways to answer a question or problem. The chapters of Class 6 are basic but vast, and it's easy to become lost in all the formulas and derivations. However, with enough practice, you will be able to ace every exam with flying colours.
8. What do prime numbers mean?
There are two factors in a prime number – themselves and 1. When dividing a prime number, no remainder is obtained. 17 is a prime number. 1 and 17 are the only possible factors. Because it has just one factor (1), 1 isn't considered a prime number. There are a total of 25 prime numbers from 1 to 100. It is important to have a basic knowledge about prime numbers as well as the other different types of numbers.
9. What concepts do Chapter 1 of NCERT Class 6 Maths emphasise on?
Introduction and Comparing Numbers are the two primary sub-topics. Students will study a variety of number-related features, such as how to compare numbers, how to write numbers with commas, how to construct multiple numbers from a set of digits, how to find the biggest and smallest numbers, and so on. Students will also learn how to use commas and read and write big figures.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6
Cbse study materials for class 6, cbse study materials.

- Lakhmir Singh
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 6 – 10, 12 for Maths, Science, SST
Cbse case study questions for maths, science, social science.
CBSE Case Study Questions: Case Study Questions for all Class 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 11 and 12 by Experienced Teachers. We Net Ex. Arranged here Important Case Based Questions for CBSE Board – Maths, Science, Social Science, English.
One must keep in mind to not discover the answers straight forwardly within the given entry but moreover think effectively to determine the answer. Case based questions are either MCQs or Attestation Reason Questions, so for endeavoring such questions you must take after the run the show of end. Case studies capture a range of perspectives, as opposed to the single view of an individual you get with a survey response or interview. This gives the opportunity to gain a greater understanding of the subject in hand and reduces the potential for any bias, by diluting the agenda of a particular individual.

- Case Study Questions Class 6 Science
- Case Study Questions Class 7 Science
- Case Study Questions Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science Case Study Question
- Case Study Question for Class 10 Basic Maths
- Case Study Question for Class 10 Maths Standard
- Case Study Question for Class 10 Science
- Case Study Question for Class 10 Social Science
- Case Study Question for Class 10 Computer
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Question
- Class 11 Physics Case Study Question
- Class 11 Chemistry Case Study Question
- CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Case study Questions & Answers
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Case study Questions & Answers
- CBSE Class 12 History Case study Questions & Answers
- CBSE Class 12 Economics Case study Questions & Answers
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Case study Questions & Answers
- CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Case study Questions & Answers
- Case Study Question for Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Physics Case Study Question
Due to a little test, the case ponder can conduct an in-depth investigation. – Case ponders make openings for a wealthy surrender of information, and the profundity of investigation can in turn bring tall levels of legitimacy (i.e. giving an exact and comprehensive degree of what the think about is trusting to degree).
There is no maths question
Hein to. Konsa class ka need hein
where is socail case based question ?????
social science class vii
Social science class 7
Class 7 Maths case study besed questions
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Worksheet for class 2 maths, counting by 2’s worksheet for class 2 as per nep pattern, the first war of independence 1857 class 10 icse complete notes pdf, west bengal board class 9 bengali ei tar porichay solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Knowing Your Numbers
NCERT Solutions for class 6 maths chapter 1 exercise 1.1 Knowing Your Numbers will help students explore topics like place value, number system, larger numbers, use of commas, Indian and International System of numeration . The NCERT solutions class 6 maths chapter 1 exercise 1.1 has 4 simple problems in different formats.
With the help of this exercise, students will understand how commas are used to mark thousands and millions. It comes after every three digits from the right. The first comma marks thousands and the next comma marks millions in the International System of Numeration. This exercise will also help students understand the difference between the systems. Class 6 maths NCERT solutions chapter 1 exercise 1.1 Knowing Your Numbers is available for free pdf download that can be accessed below.
☛ Download NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1
Exercise 1.1 Class 6 Chapter 1 Download PDF

More Exercises in Class 6 Maths Chapter 1
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.2
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.3
NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Tips
NCERT solutions class 6 maths chapter 1 exercise 1.1 Knowing Your Numbers is a simple exercise that will help students understand how to arrange numbers in ascending and descending order . It will also help students revisit the concept of place value. The questions in this exercise come in different formats like filling in the blanks and placing the commas.
NCERT solutions class 6 maths chapter 1 exercise 1.1 is a fairly easy exercise with questions of the same difficulty level. Students need to constantly revise the concepts and go through all the solved examples.
Download Cuemath NCERT Solutions PDF for free and start learning!
- Bihar Board
SRM University
Ap inter results.
- AP Board Results 2024
- UP Board Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- MP Board Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 - Real Numbers (Published by CBSE)
Cbse class 10 maths cased study question bank for chapter 1 - real numbers is available here. this question bank is very useful to prepare for the class 10 maths exam 2021-2022..

The Central Board of Secondary Education has introduced the case study questions in class 10 exam pattern 2021-2022. The CBSE Class 10 questions papers of Board Exam 2022 will have questions based on case study. Therefore, students should get familiarised with these questions to do well in their board exam.
We have provided here case study questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 - Real Numbers. These questions have been published by the CBSE board itself. Students must solve all these questions at the same time they finish with the chapter - Real numbers.
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 - Real Numbers
To enhance the reading skills of grade X students, the school nominates you and two of your friends to set up a class library. There are two sections- section A and section B of grade X. There are 32 students in section A and 36 students in section B.

1. What is the minimum number of books you will acquire for the class library, so that they can be distributed equally among students of Section A or Section B?
Answer: c) 288
2. If the product of two positive integers is equal to the product of their HCF and LCM is true then, the HCF (32 , 36) is
Answer: b) 4
3. 36 can be expressed as a product of its primes as
a) 2 2 × 3 2
b) 2 1 × 3 3
c) 2 3 × 3 1
d) 2 0 × 3 0
Answer: a) 2 2 × 3 2
4. 7 × 11 × 13 × 15 + 15 is a
a) Prime number
b) Composite number
c) Neither prime nor composite
d) None of the above
Answer: b) Composite number
5. If p and q are positive integers such that p = ab 2 and q= a 2 b, where a , b are prime numbers, then the LCM (p, q) is
Answer: b) a 2 b 2
CASE STUDY 2:
A seminar is being conducted by an Educational Organisation, where the participants will be educators of different subjects. The number of participants in Hindi, English and Mathematics are 60, 84 and 108 respectively.

1. In each room the same number of participants are to be seated and all of them being in the same subject, hence maximum number participants that can accommodated in each room are
Answer: b) 12
2. What is the minimum number of rooms required during the event?
Answer: d) 21
3. The LCM of 60, 84 and 108 is
Answer: a) 3780
4. The product of HCF and LCM of 60,84 and 108 is
Answer: d) 45360
5. 108 can be expressed as a product of its primes as
a) 2 3 × 3 2
b) 2 3 × 3 3
c) 2 2 × 3 2
d) 2 2 × 3 3
Answer: d) 2 2 × 3 3
CASE STUDY 3:
A Mathematics Exhibition is being conducted in your School and one of your friends is making a model of a factor tree. He has some difficulty and asks for your help in completing a quiz for the audience.
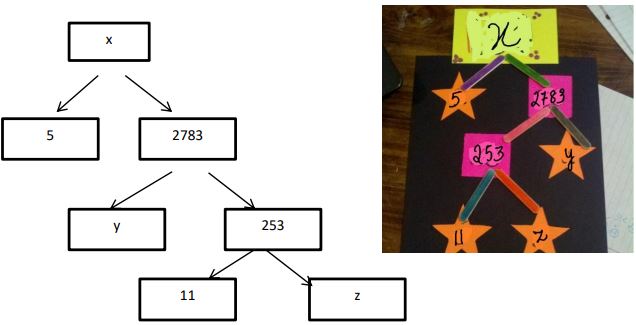
Observe the following factor tree and answer the following:
1. What will be the value of x?
Answer: b) 13915
2. What will be the value of y?
Answer: c) 11
3. What will be the value of z?
Answer: b) 23
4. According to Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic 13915 is a
a) Composite number
b) Prime number
d) Even number
Answer: a) Composite number
5. The prime factorisation of 13915 is
a) 5 × 11 3 × 13 2
b) 5 × 11 3 × 23 2
c) 5 × 11 2 × 23
d) 5 × 11 2 × 13 2
Answer: c) 5 × 11 2 × 23
Also Check:
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths - All Chapters
Tips to Solve Case Study Based Questions Accurately
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- Rajasthan Anganwadi Vacancy 2024
- MP Board 5th, 8th Result 2024
- UP Board 10th 12th Result 2024
- 2nd PUC Karnataka Result 2024
- 2nd PUC Result 2024 Karnataka When, Where, and How
- 2nd PUC Toppers List 2024
- karresults.nic.in Karnataka 2nd PUC Results 2024
- TN SET Application Form 2024
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 10
Latest Education News
viral brain teaser find the odd socks in the bunch within 19 seconds
[Official] AP Inter Results 2024 Manabadi Date and Time Announced: BIEAP 1st, 2nd Year Results Today at 11 AM, Stay Updated
Who Won Yesterday IPL Match: MI vs RCB, Match 25, Check All Details and Latest Points Table
All Can See Camel But Only 1% Of Genius Can Find The Horse Hidden In The Picture. 33 Seconds Left!
Who Won Yesterday IPL Match: RR vs GT, Match 24, Check All Details and Latest Points Table
[Current] Orange Cap and Purple Cap Holders in IPL 2024
[Today] IPL 2024 Points Table: Team Rankings and Net Run Rate
List of Fastest 50 in T20 International Cricket
IPL Points Table 2024: आईपीएल 2024 अपडेटेड पॉइंट टेबल यहां देखें, राजस्थान को मिली पहली हार
Fastest 50 in IPL History (2008 - 2024)
Fastest 50s In IPL History: आईपीएल इतिहास के सबसे तेज़ अर्द्धशतक की पूरी लिस्ट यहां पढ़े
Lok Sabha Election 2024 के पहले फेज के 10 सबसे अमीर उम्मीदवारों की लिस्ट यहां देखें
Purple Cap in IPL 2024: इन पांच गेंदबाजों में है पर्पल कैप की रेस, कौन निकलेगा सबसे आगे?
IPL Orange Cap 2024: दिलचस्प हो गयी है ऑरेंज कैप की रेस, ये युवा बल्लेबाज रेस में है शामिल
Genius IQ Test: Find the value of the word “MATH” in 10 seconds!
Picture Puzzle IQ Test: Only 1% With Keen Vision Can Spot A Chocolate Ice Cream In 12 Seconds!
AP Inter Results 2024 Live: BIEAP Manabadi Intermediate (1st, 2nd Year) Results to Release on April 12 at 11 AM; Check Official Notice Online
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Only 1% With Eagle Vision Can Spot A White Sock In 12 Seconds!
TS Inter Results 2024 Date and Time: Manabadi TSBIE 1st and 2nd Year Telangana Results on April 25? Know Latest Updates
AP Inter 1st Year Results 2024: Manabadi 1st Year Result Date And Time at bie.ap.gov.in
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 6
- NCERT 6 Maths
- Chapter 1: Knowing Our Numbers
- Exercise 1.1
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers Exercise 1.1
The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers Exercise 1.1 has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise. Counting things or objects that we see in our day-to-day life has become easier by knowing numbers. For example, we can count the number of students in a class and represent them in numbers without any effort. Students can improve their abilities to solve problems by referring to the PDF of the NCERT Solutions of Class 6 Maths Exercise 1.1 of Chapter 1 from the answers provided underneath.
- Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers
- Chapter 2 Whole Numbers
- Chapter 3 Playing with Numbers
- Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas
- Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Chapter 6 Integers
- Chapter 7 Fractions
- Chapter 8 Decimals
- Chapter 9 Data Handling
- Chapter 10 Mensuration
- Chapter 11 Algebra
- Chapter 12 Ratio and Proportion
- Chapter 13 Introduction to Symmetry
- Chapter 14 Practical Geometry
- Exercise 1.1 Chapter 1 Knowing our Numbers
- Exercise 1.2 Chapter 1 Knowing our Numbers
- Exercise 1.3 Chapter 1 Knowing our Numbers
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Chapter 1: Knowing Our Numbers Exercise 1.1
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) 1 lakh = ………….. ten thousand.
(b) 1 million = ………… hundred thousand.
(c) 1 crore = ………… ten lakh.
(d) 1 crore = ………… million.
(e) 1 million = ………… lakh.
(a) 1 lakh = 10 ten thousand
(b) 1 million = 10 hundred thousand
= 10,00,000
(c) 1 crore = 10 ten lakh
= 1,00,00,000
(d) 1 crore = 10 million
(e) 1 million = 10 lakh
= 1,000,000
2. Place commas correctly and write the numerals:
(a) Seventy-three lakh seventy-five thousand three hundred seven.
(b) Nine crore five lakh forty-one.
(c) Seven crore fifty-two lakh twenty-one thousand three hundred two.
(d) Fifty-eight million four hundred twenty-three thousand two hundred two.
(e) Twenty-three lakh thirty thousand ten.
(a) The numeral of seventy-three lakh seventy-five thousand three hundred seven is 73,75,307
(b) The numeral of nine crore five lakh forty-one is 9,05,00,041
(c) The numeral of seven crore fifty-two lakh twenty-one thousand three hundred two is 7,52,21,302
(d) The numeral of fifty-eight million four hundred twenty-three thousand two hundred two is 5,84,23,202
(e) The numeral of twenty-three lakh thirty thousand ten is 23,30,010
3. Insert commas suitably and write the names according to Indian System of Numeration:
(a) 87595762 (b) 8546283 (c) 99900046 (d) 98432701
(a) 87595762 – Eight crore seventy-five lakh ninety-five thousand seven hundred sixty-two
(b) 8546283 – Eighty-five lakh forty-six thousand two hundred eighty-three
(c) 99900046 – Nine crore ninety-nine lakh forty-six
(d) 98432701 – Nine crore eighty-four lakh thirty-two thousand seven hundred one
4. Insert commas suitably and write the names according to International System of Numeration:
(a) 78921092 (b) 7452283 (c) 99985102 (d) 48049831
(a) 78921092 – Seventy-eight million nine hundred twenty-one thousand ninety-two
(b) 7452283 – Seven million four hundred fifty-two thousand two hundred eighty-three
(c) 99985102 – Ninety-nine million nine hundred eighty-five thousand one hundred two
(d) 48049831 – Forty-eight million forty-nine thousand eight hundred thirty-one
Access Other Exercise Solutions of Class 6 Maths Chapter 1: Knowing Our Numbers
Exercise 1.2 Solutions
Exercise 1.3 Solutions
Also, explore –
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1
NCERT Solutions for Class 6
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
It is so good.
it was help full for me
Thank you so much 🥰💗
It is very helpful
It is so GOOD
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions of Chapter 1 Real Numbers
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions in Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 1 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Real Numbers
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 9 Maths Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Real Numbers Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: A Mathematics Exhibition is being conducted in your school and one of your friends is making a model of a factor tree. He has some difficulty and asks for your help in completing a quiz for the audience.

Observe the following factor tree and answer the following:
1. What will be the value of x?
Answer: b) 13915
2. What will be the value of y?
Answer: c) 11
3. What will be the value of z?
Answer: b) 23
4. According to the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic 13915 is a
a) Composite number
b) Prime number
c) Neither prime nor composite
d) Even number
Answer: a) Composite number
5. The prime factorization of 13915 is
a) 5 × 11 3 × 13 2
b) 5 × 11 3 × 23 2
c) 5 × 11 2 × 23
d) 5 × 11 2 × 13 2
Answer: c) 5 × 112 × 23
Case Study 2: Srikanth has made a project on real numbers, where he finely explained the applicability of exponential laws and divisibility conditions on real numbers. He also included some assessment questions at the end of his project as listed below. Answer them.
(i) For what value of n, 4 n ends in 0?
(a) 10 (b) when n is even (c) when n is odd (d) no value of n
Answer: (d) no value of n3
(ii) If a is a positive rational number and n is a positive integer greater than 1, then for what value of n, an is a rational number?
(a) when n is any even integer (b) when n is any odd integer (c) for all n > 1 (d) only when n=0
Answer: (c) for all n > 1
(iii) If x and y are two odd positive integers, then which of the following is true?
(a) x 2 +y 2 is even (b) x 2 +y 2 is not divisible by 4 (c) x 2 +y 2 is odd (d) both (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) both (a) and (b)
(iv) The statement ‘One of every three consecutive positive integers is divisible by 3’ is
(a) always true (b) always false (c) sometimes true (d) None of these
Answer:(a) always true
(v) If n is any odd integer, then n 2 – 1 is divisible by
(a) 22 (b) 55 (c) 88 (d) 8
Answer: (d) 8
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 1 Real Numbers with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Maths Real Numbers Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Mcq questions of class 9 social science history chapter 4 forest society and colonialism with answers, mcq questions of class 9 social science geography chapter 6 population with answers, class 9 civics case study questions chapter 4 working of institutions, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

COMMENTS
Knowing Our Numbers Case Study Questions. Case Study Question 1: The population of Delhi in 2017 was 19072564 and it increased to 25704625 in 2021. (i) Write the population of 2021 in words. (a) two crore fifty seven lakh four thousand six hundred twenty five. (b) twenty five lakh seventy thousand six hundred twenty five.
Learning APP for Students. CBSE 6th Standard CBSE all question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 6th Standard CBSE all books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions.
Knowing Our Numbers Class 6 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type. Question 1. Write the smallest three digit number whose value does not change on reversing its digits. The required number is 101. Question 2. Write the greatest three digit number which does not change on reversing its digits. The required number is 999.
Updated for new NCERT Book. Get NCERT Solutions of Chapter 1 Class 6 Knowing our Numbers with Videos of all questions. All exercise questions and examples are solved with step-by-step answers. In this chapter, we will. First revise our concepts of Place Value. Learn about Indian Number System and International Number System.
Study Important Questions for Class 6 Mathematics Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers. Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark) 1. Write the numeration for 80956124 in the Indian system. Ans: The numeration for 80956124 in the Indian system is, 8, 09, 56, 124. Eight crore nine lakh fifty-six thousand one hundred twenty-four.
5. Find the difference between the greatest and the least 5-digit number that can be written using the digits 6, 2, 7, 4, and 3 each only once. Solutions: Digits given are 6, 2, 7, 4, 3. Greatest 5-digit number = 76432. Least 5-digit number = 23467. Difference between the two numbers = 76432 - 23467 = 52965.
Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Important Questions - Knowing Our Numbers. Maths is an important subject we study in school. In Class 6, students will learn the basics of the subject, which will be needed in higher classes. The first chapter is about learning numbers. Maths deals with numbers, and students must identify numbers.
Important Topics under NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1. Chapter 1 of the class 6 maths syllabus is on 'Knowing Our Numbers'. This is a very important chapter in class 6 that develops a student's number sense. This crucial chapter in the class 6 maths syllabus is divided into 5 major sections or topics.
NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 ... In the case where the number of digits is the same, the number with the larger leftmost digit is considered to be the greater number. We put commas after 3 digits in the Indian system. These commas are put after 3,5,7, thus separating the thousand, lakh, and crore. However, in the International System, we put ...
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1. These NCERT Solutions are based on latest CBSE - NCERT Textbooks for the CBSE exams 2024-25. Download NCERT Solutions in PDF format to use it offline or use as it is online without downloading. In 6 Maths Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers, we will study about comparing the number (smaller or ...
Introduction Ascending and Descending Order and Shifting Digits Larger Numbers and Estimates BODMAS Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 6 Maths Notes Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers. A number is a mathematical value used to count and measure different objects. With the help of the numbers, we all are able to add, subtract, divide and multiply.
NCERT Maths Book Class 6 Chapter 1 - Knowing your Numbers is an ideal study material for students to comprehensively understand the dynamics of mathematics. Students can download NCERT solution PDF for the latest CBSE NCERT Books for Class 6 Maths online from Vedantu that come with step by step techniques to solve problems. The NCERT Class 6 Maths PDF is designed with compliance to the latest ...
CBSE Case Study Questions for Maths, Science, Social Science for Class Class 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 11 and 12 by Experienced Subject Teachers. 100% FREE Exercise & Practice for CBSE, NCERT and ICSE Book Solutions
In Chapter 1 Knowing our numbers, we discuss about Comparing Numbers Worksheet, Large Numbers In Practice, Using Brackets and Roman Numerals Chart. You can find the other. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers. Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.2; Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.3
The NCERT solutions class 6 maths chapter 1 exercise 1.1 has 4 simple problems in different formats. With the help of this exercise, students will understand how commas are used to mark thousands and millions. It comes after every three digits from the right. The first comma marks thousands and the next comma marks millions in the International ...
CBSE Class 10 Maths Cased Study Question Bank for Chapter 1 - Real Numbers is available here. This question bank is very useful to prepare for the Class 10 Maths Exam 2021-2022. By Gurmeet Kaur
Solutions: (a) The numeral of seventy-three lakh seventy-five thousand three hundred seven is 73,75,307. (b) The numeral of nine crore five lakh forty-one is 9,05,00,041. (c) The numeral of seven crore fifty-two lakh twenty-one thousand three hundred two is 7,52,21,302. (d) The numeral of fifty-eight million four hundred twenty-three thousand ...
5. The prime factorization of 13915 is. a) 5 × 11 3 × 13 2. b) 5 × 11 3 × 23 2. c) 5 × 11 2 × 23. d) 5 × 11 2 × 13 2. Show Answer. Case Study 2: Srikanth has made a project on real numbers, where he finely explained the applicability of exponential laws and divisibility conditions on real numbers. He also included some assessment ...