- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

Present Your Data Like a Pro
- Joel Schwartzberg

Demystify the numbers. Your audience will thank you.
While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn’t guarantee a good presentation. It’s all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by sharing too many details at once. The only data points you should share are those that significantly support your point — and ideally, one point per chart. To avoid the debacle of sheepishly translating hard-to-see numbers and labels, rehearse your presentation with colleagues sitting as far away as the actual audience would. While you’ve been working with the same chart for weeks or months, your audience will be exposed to it for mere seconds. Give them the best chance of comprehending your data by using simple, clear, and complete language to identify X and Y axes, pie pieces, bars, and other diagrammatic elements. Try to avoid abbreviations that aren’t obvious, and don’t assume labeled components on one slide will be remembered on subsequent slides. Every valuable chart or pie graph has an “Aha!” zone — a number or range of data that reveals something crucial to your point. Make sure you visually highlight the “Aha!” zone, reinforcing the moment by explaining it to your audience.
With so many ways to spin and distort information these days, a presentation needs to do more than simply share great ideas — it needs to support those ideas with credible data. That’s true whether you’re an executive pitching new business clients, a vendor selling her services, or a CEO making a case for change.
- JS Joel Schwartzberg oversees executive communications for a major national nonprofit, is a professional presentation coach, and is the author of Get to the Point! Sharpen Your Message and Make Your Words Matter and The Language of Leadership: How to Engage and Inspire Your Team . You can find him on LinkedIn and X. TheJoelTruth
Partner Center
Home Blog Design Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)
Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)
In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey. Different types of visualizations serve distinct purposes. Whether you’re dealing with how to develop a report or simply trying to communicate complex information, how you present data influences how well your audience understands and engages with it. This extensive guide leads you through the different ways of data presentation.
Table of Contents
What is a Data Presentation?
What should a data presentation include, line graphs, treemap chart, scatter plot, how to choose a data presentation type, recommended data presentation templates, common mistakes done in data presentation.
A data presentation is a slide deck that aims to disclose quantitative information to an audience through the use of visual formats and narrative techniques derived from data analysis, making complex data understandable and actionable. This process requires a series of tools, such as charts, graphs, tables, infographics, dashboards, and so on, supported by concise textual explanations to improve understanding and boost retention rate.
Data presentations require us to cull data in a format that allows the presenter to highlight trends, patterns, and insights so that the audience can act upon the shared information. In a few words, the goal of data presentations is to enable viewers to grasp complicated concepts or trends quickly, facilitating informed decision-making or deeper analysis.
Data presentations go beyond the mere usage of graphical elements. Seasoned presenters encompass visuals with the art of storytelling with data, so the speech skillfully connects the points through a narrative that resonates with the audience. Depending on the purpose – inspire, persuade, inform, support decision-making processes, etc. – is the data presentation format that is better suited to help us in this journey.
To nail your upcoming data presentation, ensure to count with the following elements:
- Clear Objectives: Understand the intent of your presentation before selecting the graphical layout and metaphors to make content easier to grasp.
- Engaging introduction: Use a powerful hook from the get-go. For instance, you can ask a big question or present a problem that your data will answer. Take a look at our guide on how to start a presentation for tips & insights.
- Structured Narrative: Your data presentation must tell a coherent story. This means a beginning where you present the context, a middle section in which you present the data, and an ending that uses a call-to-action. Check our guide on presentation structure for further information.
- Visual Elements: These are the charts, graphs, and other elements of visual communication we ought to use to present data. This article will cover one by one the different types of data representation methods we can use, and provide further guidance on choosing between them.
- Insights and Analysis: This is not just showcasing a graph and letting people get an idea about it. A proper data presentation includes the interpretation of that data, the reason why it’s included, and why it matters to your research.
- Conclusion & CTA: Ending your presentation with a call to action is necessary. Whether you intend to wow your audience into acquiring your services, inspire them to change the world, or whatever the purpose of your presentation, there must be a stage in which you convey all that you shared and show the path to staying in touch. Plan ahead whether you want to use a thank-you slide, a video presentation, or which method is apt and tailored to the kind of presentation you deliver.
- Q&A Session: After your speech is concluded, allocate 3-5 minutes for the audience to raise any questions about the information you disclosed. This is an extra chance to establish your authority on the topic. Check our guide on questions and answer sessions in presentations here.
Bar charts are a graphical representation of data using rectangular bars to show quantities or frequencies in an established category. They make it easy for readers to spot patterns or trends. Bar charts can be horizontal or vertical, although the vertical format is commonly known as a column chart. They display categorical, discrete, or continuous variables grouped in class intervals [1] . They include an axis and a set of labeled bars horizontally or vertically. These bars represent the frequencies of variable values or the values themselves. Numbers on the y-axis of a vertical bar chart or the x-axis of a horizontal bar chart are called the scale.
Real-Life Application of Bar Charts
Let’s say a sales manager is presenting sales to their audience. Using a bar chart, he follows these steps.
Step 1: Selecting Data
The first step is to identify the specific data you will present to your audience.
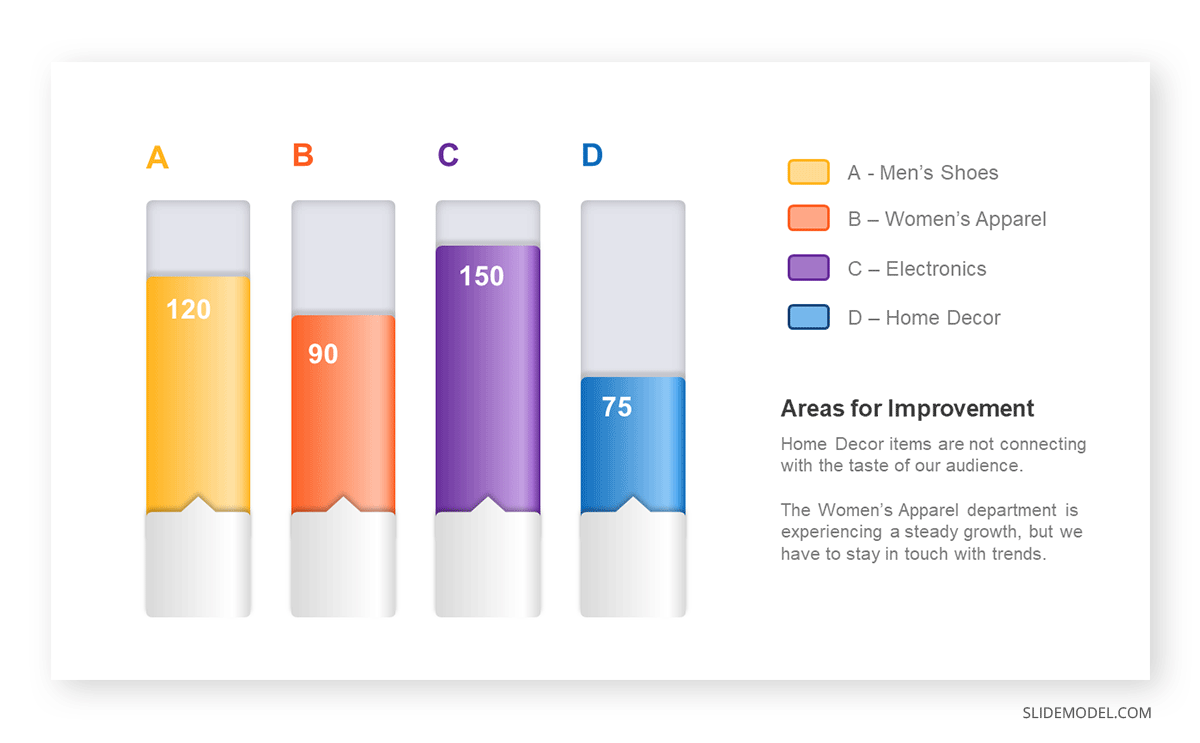
The sales manager has highlighted these products for the presentation.
- Product A: Men’s Shoes
- Product B: Women’s Apparel
- Product C: Electronics
- Product D: Home Decor
Step 2: Choosing Orientation
Opt for a vertical layout for simplicity. Vertical bar charts help compare different categories in case there are not too many categories [1] . They can also help show different trends. A vertical bar chart is used where each bar represents one of the four chosen products. After plotting the data, it is seen that the height of each bar directly represents the sales performance of the respective product.
It is visible that the tallest bar (Electronics – Product C) is showing the highest sales. However, the shorter bars (Women’s Apparel – Product B and Home Decor – Product D) need attention. It indicates areas that require further analysis or strategies for improvement.
Step 3: Colorful Insights
Different colors are used to differentiate each product. It is essential to show a color-coded chart where the audience can distinguish between products.
- Men’s Shoes (Product A): Yellow
- Women’s Apparel (Product B): Orange
- Electronics (Product C): Violet
- Home Decor (Product D): Blue
Bar charts are straightforward and easily understandable for presenting data. They are versatile when comparing products or any categorical data [2] . Bar charts adapt seamlessly to retail scenarios. Despite that, bar charts have a few shortcomings. They cannot illustrate data trends over time. Besides, overloading the chart with numerous products can lead to visual clutter, diminishing its effectiveness.
For more information, check our collection of bar chart templates for PowerPoint .
Line graphs help illustrate data trends, progressions, or fluctuations by connecting a series of data points called ‘markers’ with straight line segments. This provides a straightforward representation of how values change [5] . Their versatility makes them invaluable for scenarios requiring a visual understanding of continuous data. In addition, line graphs are also useful for comparing multiple datasets over the same timeline. Using multiple line graphs allows us to compare more than one data set. They simplify complex information so the audience can quickly grasp the ups and downs of values. From tracking stock prices to analyzing experimental results, you can use line graphs to show how data changes over a continuous timeline. They show trends with simplicity and clarity.
Real-life Application of Line Graphs
To understand line graphs thoroughly, we will use a real case. Imagine you’re a financial analyst presenting a tech company’s monthly sales for a licensed product over the past year. Investors want insights into sales behavior by month, how market trends may have influenced sales performance and reception to the new pricing strategy. To present data via a line graph, you will complete these steps.
First, you need to gather the data. In this case, your data will be the sales numbers. For example:
- January: $45,000
- February: $55,000
- March: $45,000
- April: $60,000
- May: $ 70,000
- June: $65,000
- July: $62,000
- August: $68,000
- September: $81,000
- October: $76,000
- November: $87,000
- December: $91,000
After choosing the data, the next step is to select the orientation. Like bar charts, you can use vertical or horizontal line graphs. However, we want to keep this simple, so we will keep the timeline (x-axis) horizontal while the sales numbers (y-axis) vertical.
Step 3: Connecting Trends
After adding the data to your preferred software, you will plot a line graph. In the graph, each month’s sales are represented by data points connected by a line.
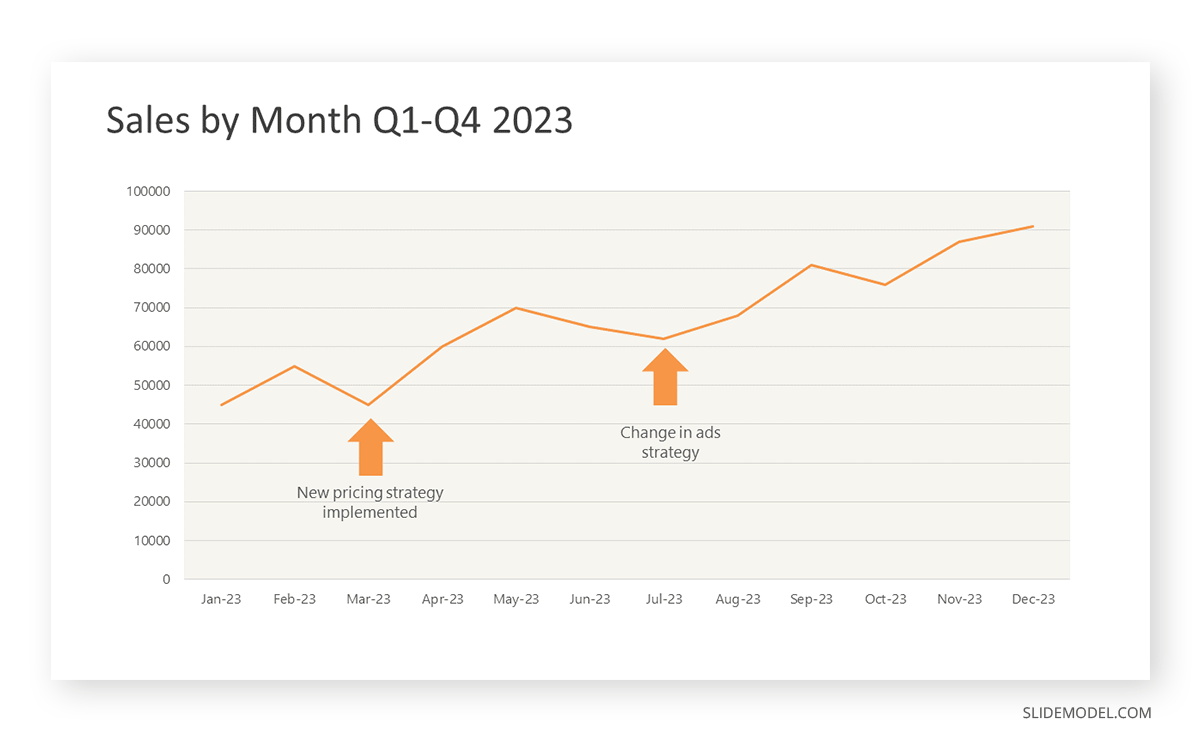
Step 4: Adding Clarity with Color
If there are multiple lines, you can also add colors to highlight each one, making it easier to follow.
Line graphs excel at visually presenting trends over time. These presentation aids identify patterns, like upward or downward trends. However, too many data points can clutter the graph, making it harder to interpret. Line graphs work best with continuous data but are not suitable for categories.
For more information, check our collection of line chart templates for PowerPoint .
A data dashboard is a visual tool for analyzing information. Different graphs, charts, and tables are consolidated in a layout to showcase the information required to achieve one or more objectives. Dashboards help quickly see Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). You don’t make new visuals in the dashboard; instead, you use it to display visuals you’ve already made in worksheets [3] .
Keeping the number of visuals on a dashboard to three or four is recommended. Adding too many can make it hard to see the main points [4]. Dashboards can be used for business analytics to analyze sales, revenue, and marketing metrics at a time. They are also used in the manufacturing industry, as they allow users to grasp the entire production scenario at the moment while tracking the core KPIs for each line.
Real-Life Application of a Dashboard
Consider a project manager presenting a software development project’s progress to a tech company’s leadership team. He follows the following steps.
Step 1: Defining Key Metrics
To effectively communicate the project’s status, identify key metrics such as completion status, budget, and bug resolution rates. Then, choose measurable metrics aligned with project objectives.
Step 2: Choosing Visualization Widgets
After finalizing the data, presentation aids that align with each metric are selected. For this project, the project manager chooses a progress bar for the completion status and uses bar charts for budget allocation. Likewise, he implements line charts for bug resolution rates.
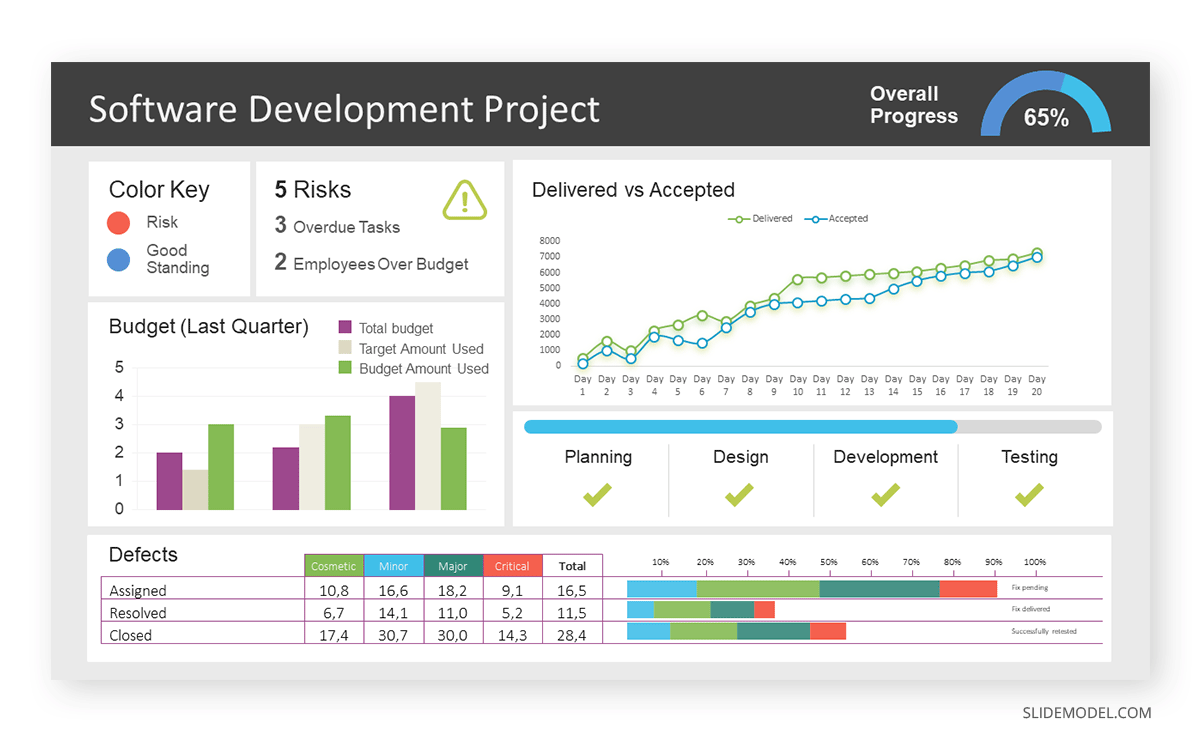
Step 3: Dashboard Layout
Key metrics are prominently placed in the dashboard for easy visibility, and the manager ensures that it appears clean and organized.
Dashboards provide a comprehensive view of key project metrics. Users can interact with data, customize views, and drill down for detailed analysis. However, creating an effective dashboard requires careful planning to avoid clutter. Besides, dashboards rely on the availability and accuracy of underlying data sources.
For more information, check our article on how to design a dashboard presentation , and discover our collection of dashboard PowerPoint templates .
Treemap charts represent hierarchical data structured in a series of nested rectangles [6] . As each branch of the ‘tree’ is given a rectangle, smaller tiles can be seen representing sub-branches, meaning elements on a lower hierarchical level than the parent rectangle. Each one of those rectangular nodes is built by representing an area proportional to the specified data dimension.
Treemaps are useful for visualizing large datasets in compact space. It is easy to identify patterns, such as which categories are dominant. Common applications of the treemap chart are seen in the IT industry, such as resource allocation, disk space management, website analytics, etc. Also, they can be used in multiple industries like healthcare data analysis, market share across different product categories, or even in finance to visualize portfolios.
Real-Life Application of a Treemap Chart
Let’s consider a financial scenario where a financial team wants to represent the budget allocation of a company. There is a hierarchy in the process, so it is helpful to use a treemap chart. In the chart, the top-level rectangle could represent the total budget, and it would be subdivided into smaller rectangles, each denoting a specific department. Further subdivisions within these smaller rectangles might represent individual projects or cost categories.
Step 1: Define Your Data Hierarchy
While presenting data on the budget allocation, start by outlining the hierarchical structure. The sequence will be like the overall budget at the top, followed by departments, projects within each department, and finally, individual cost categories for each project.
- Top-level rectangle: Total Budget
- Second-level rectangles: Departments (Engineering, Marketing, Sales)
- Third-level rectangles: Projects within each department
- Fourth-level rectangles: Cost categories for each project (Personnel, Marketing Expenses, Equipment)
Step 2: Choose a Suitable Tool
It’s time to select a data visualization tool supporting Treemaps. Popular choices include Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, PowerPoint, or even coding with libraries like D3.js. It is vital to ensure that the chosen tool provides customization options for colors, labels, and hierarchical structures.
Here, the team uses PowerPoint for this guide because of its user-friendly interface and robust Treemap capabilities.
Step 3: Make a Treemap Chart with PowerPoint
After opening the PowerPoint presentation, they chose “SmartArt” to form the chart. The SmartArt Graphic window has a “Hierarchy” category on the left. Here, you will see multiple options. You can choose any layout that resembles a Treemap. The “Table Hierarchy” or “Organization Chart” options can be adapted. The team selects the Table Hierarchy as it looks close to a Treemap.
Step 5: Input Your Data
After that, a new window will open with a basic structure. They add the data one by one by clicking on the text boxes. They start with the top-level rectangle, representing the total budget.
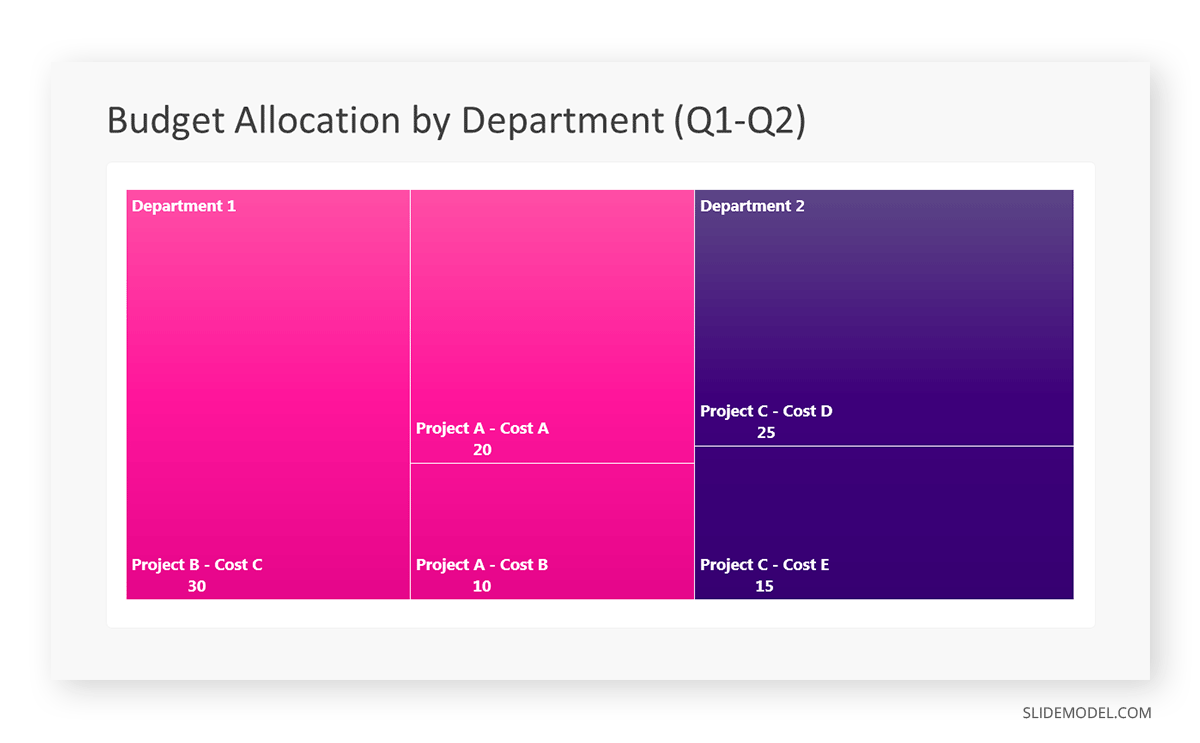
Step 6: Customize the Treemap
By clicking on each shape, they customize its color, size, and label. At the same time, they can adjust the font size, style, and color of labels by using the options in the “Format” tab in PowerPoint. Using different colors for each level enhances the visual difference.
Treemaps excel at illustrating hierarchical structures. These charts make it easy to understand relationships and dependencies. They efficiently use space, compactly displaying a large amount of data, reducing the need for excessive scrolling or navigation. Additionally, using colors enhances the understanding of data by representing different variables or categories.
In some cases, treemaps might become complex, especially with deep hierarchies. It becomes challenging for some users to interpret the chart. At the same time, displaying detailed information within each rectangle might be constrained by space. It potentially limits the amount of data that can be shown clearly. Without proper labeling and color coding, there’s a risk of misinterpretation.
A heatmap is a data visualization tool that uses color coding to represent values across a two-dimensional surface. In these, colors replace numbers to indicate the magnitude of each cell. This color-shaded matrix display is valuable for summarizing and understanding data sets with a glance [7] . The intensity of the color corresponds to the value it represents, making it easy to identify patterns, trends, and variations in the data.
As a tool, heatmaps help businesses analyze website interactions, revealing user behavior patterns and preferences to enhance overall user experience. In addition, companies use heatmaps to assess content engagement, identifying popular sections and areas of improvement for more effective communication. They excel at highlighting patterns and trends in large datasets, making it easy to identify areas of interest.
We can implement heatmaps to express multiple data types, such as numerical values, percentages, or even categorical data. Heatmaps help us easily spot areas with lots of activity, making them helpful in figuring out clusters [8] . When making these maps, it is important to pick colors carefully. The colors need to show the differences between groups or levels of something. And it is good to use colors that people with colorblindness can easily see.
Check our detailed guide on how to create a heatmap here. Also discover our collection of heatmap PowerPoint templates .
Pie charts are circular statistical graphics divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a proportionate part of the whole, making it easy to visualize the contribution of each component to the total.
The size of the pie charts is influenced by the value of data points within each pie. The total of all data points in a pie determines its size. The pie with the highest data points appears as the largest, whereas the others are proportionally smaller. However, you can present all pies of the same size if proportional representation is not required [9] . Sometimes, pie charts are difficult to read, or additional information is required. A variation of this tool can be used instead, known as the donut chart , which has the same structure but a blank center, creating a ring shape. Presenters can add extra information, and the ring shape helps to declutter the graph.
Pie charts are used in business to show percentage distribution, compare relative sizes of categories, or present straightforward data sets where visualizing ratios is essential.
Real-Life Application of Pie Charts
Consider a scenario where you want to represent the distribution of the data. Each slice of the pie chart would represent a different category, and the size of each slice would indicate the percentage of the total portion allocated to that category.
Step 1: Define Your Data Structure
Imagine you are presenting the distribution of a project budget among different expense categories.
- Column A: Expense Categories (Personnel, Equipment, Marketing, Miscellaneous)
- Column B: Budget Amounts ($40,000, $30,000, $20,000, $10,000) Column B represents the values of your categories in Column A.
Step 2: Insert a Pie Chart
Using any of the accessible tools, you can create a pie chart. The most convenient tools for forming a pie chart in a presentation are presentation tools such as PowerPoint or Google Slides. You will notice that the pie chart assigns each expense category a percentage of the total budget by dividing it by the total budget.
For instance:
- Personnel: $40,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 40%
- Equipment: $30,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 30%
- Marketing: $20,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 20%
- Miscellaneous: $10,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 10%
You can make a chart out of this or just pull out the pie chart from the data.
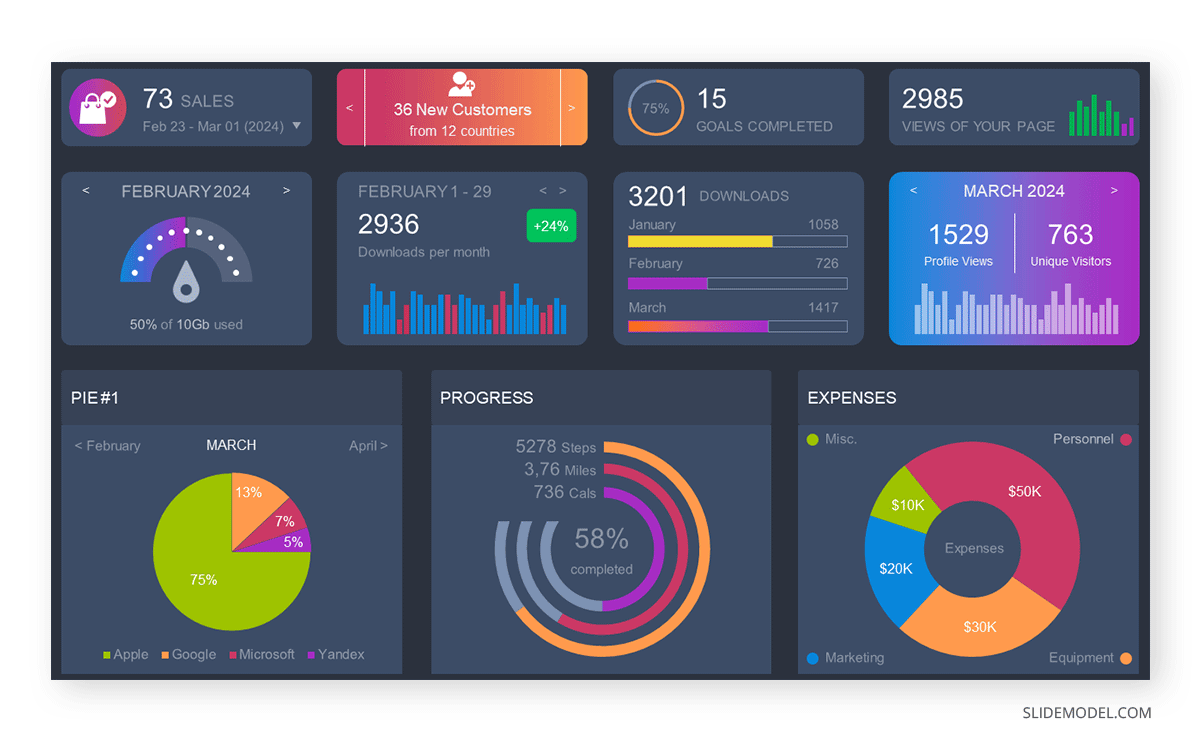
3D pie charts and 3D donut charts are quite popular among the audience. They stand out as visual elements in any presentation slide, so let’s take a look at how our pie chart example would look in 3D pie chart format.
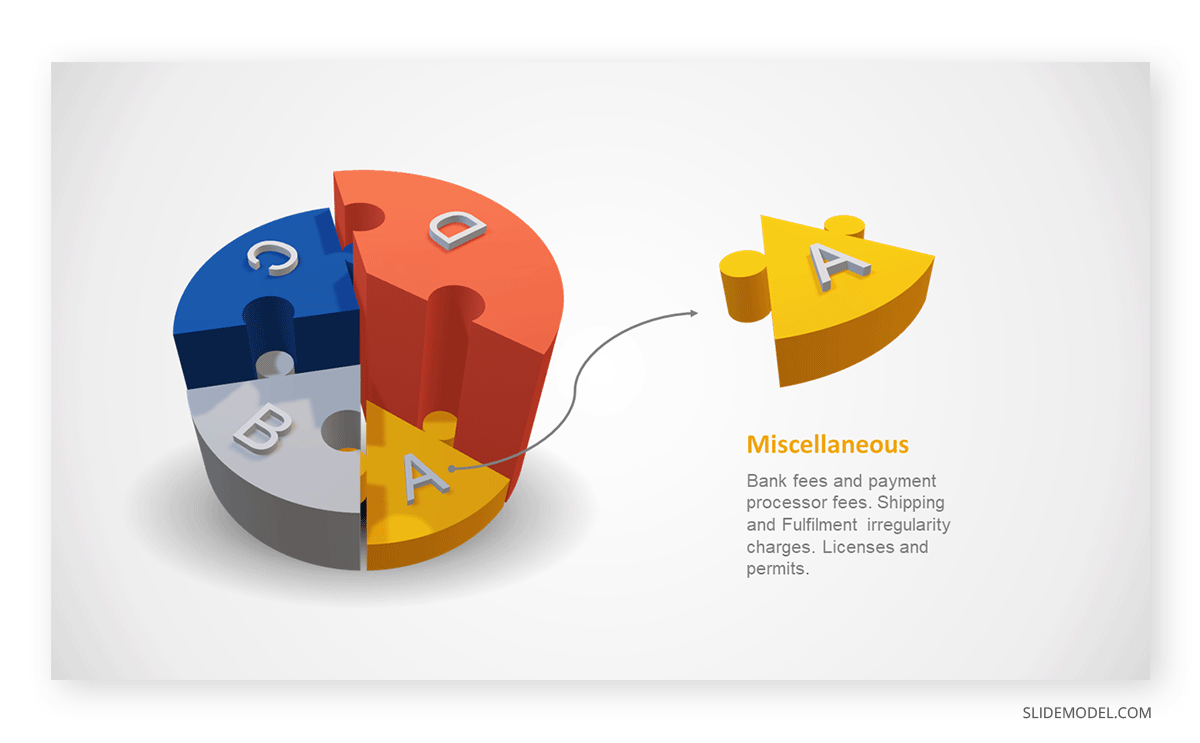
Step 03: Results Interpretation
The pie chart visually illustrates the distribution of the project budget among different expense categories. Personnel constitutes the largest portion at 40%, followed by equipment at 30%, marketing at 20%, and miscellaneous at 10%. This breakdown provides a clear overview of where the project funds are allocated, which helps in informed decision-making and resource management. It is evident that personnel are a significant investment, emphasizing their importance in the overall project budget.
Pie charts provide a straightforward way to represent proportions and percentages. They are easy to understand, even for individuals with limited data analysis experience. These charts work well for small datasets with a limited number of categories.
However, a pie chart can become cluttered and less effective in situations with many categories. Accurate interpretation may be challenging, especially when dealing with slight differences in slice sizes. In addition, these charts are static and do not effectively convey trends over time.
For more information, check our collection of pie chart templates for PowerPoint .
Histograms present the distribution of numerical variables. Unlike a bar chart that records each unique response separately, histograms organize numeric responses into bins and show the frequency of reactions within each bin [10] . The x-axis of a histogram shows the range of values for a numeric variable. At the same time, the y-axis indicates the relative frequencies (percentage of the total counts) for that range of values.
Whenever you want to understand the distribution of your data, check which values are more common, or identify outliers, histograms are your go-to. Think of them as a spotlight on the story your data is telling. A histogram can provide a quick and insightful overview if you’re curious about exam scores, sales figures, or any numerical data distribution.
Real-Life Application of a Histogram
In the histogram data analysis presentation example, imagine an instructor analyzing a class’s grades to identify the most common score range. A histogram could effectively display the distribution. It will show whether most students scored in the average range or if there are significant outliers.
Step 1: Gather Data
He begins by gathering the data. The scores of each student in class are gathered to analyze exam scores.
After arranging the scores in ascending order, bin ranges are set.
Step 2: Define Bins
Bins are like categories that group similar values. Think of them as buckets that organize your data. The presenter decides how wide each bin should be based on the range of the values. For instance, the instructor sets the bin ranges based on score intervals: 60-69, 70-79, 80-89, and 90-100.
Step 3: Count Frequency
Now, he counts how many data points fall into each bin. This step is crucial because it tells you how often specific ranges of values occur. The result is the frequency distribution, showing the occurrences of each group.
Here, the instructor counts the number of students in each category.
- 60-69: 1 student (Kate)
- 70-79: 4 students (David, Emma, Grace, Jack)
- 80-89: 7 students (Alice, Bob, Frank, Isabel, Liam, Mia, Noah)
- 90-100: 3 students (Clara, Henry, Olivia)
Step 4: Create the Histogram
It’s time to turn the data into a visual representation. Draw a bar for each bin on a graph. The width of the bar should correspond to the range of the bin, and the height should correspond to the frequency. To make your histogram understandable, label the X and Y axes.
In this case, the X-axis should represent the bins (e.g., test score ranges), and the Y-axis represents the frequency.
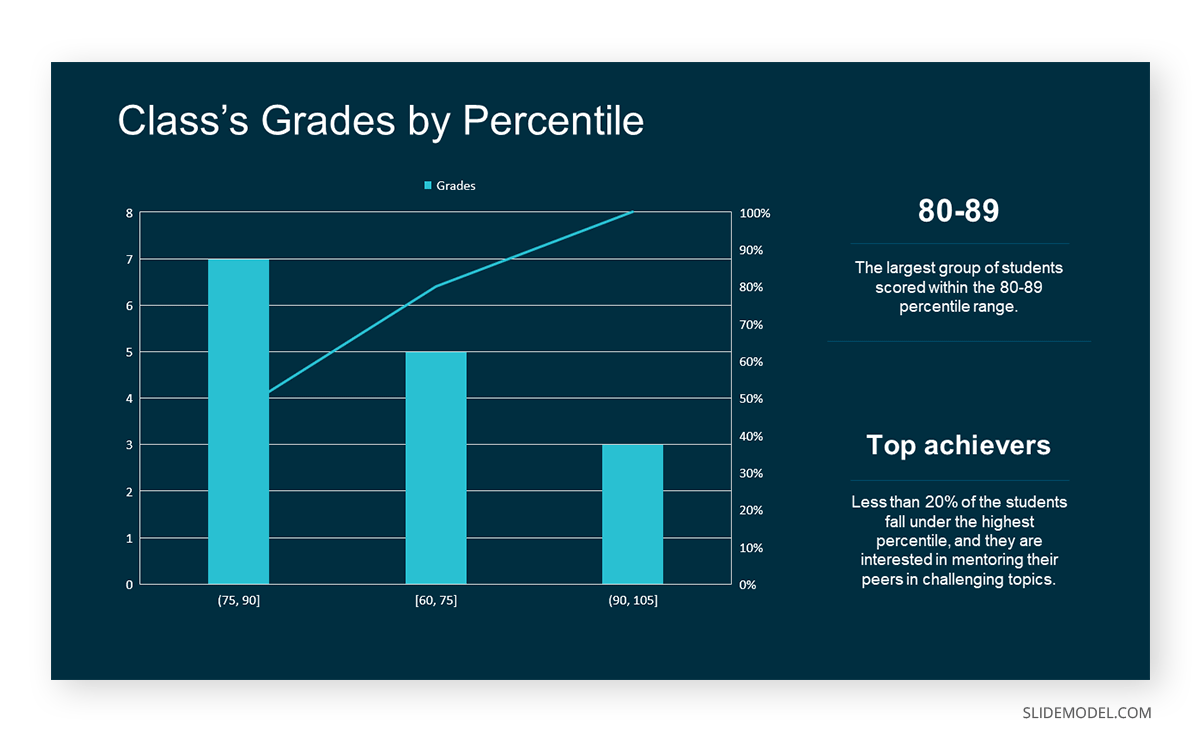
The histogram of the class grades reveals insightful patterns in the distribution. Most students, with seven students, fall within the 80-89 score range. The histogram provides a clear visualization of the class’s performance. It showcases a concentration of grades in the upper-middle range with few outliers at both ends. This analysis helps in understanding the overall academic standing of the class. It also identifies the areas for potential improvement or recognition.
Thus, histograms provide a clear visual representation of data distribution. They are easy to interpret, even for those without a statistical background. They apply to various types of data, including continuous and discrete variables. One weak point is that histograms do not capture detailed patterns in students’ data, with seven compared to other visualization methods.
A scatter plot is a graphical representation of the relationship between two variables. It consists of individual data points on a two-dimensional plane. This plane plots one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. Each point represents a unique observation. It visualizes patterns, trends, or correlations between the two variables.
Scatter plots are also effective in revealing the strength and direction of relationships. They identify outliers and assess the overall distribution of data points. The points’ dispersion and clustering reflect the relationship’s nature, whether it is positive, negative, or lacks a discernible pattern. In business, scatter plots assess relationships between variables such as marketing cost and sales revenue. They help present data correlations and decision-making.
Real-Life Application of Scatter Plot
A group of scientists is conducting a study on the relationship between daily hours of screen time and sleep quality. After reviewing the data, they managed to create this table to help them build a scatter plot graph:
In the provided example, the x-axis represents Daily Hours of Screen Time, and the y-axis represents the Sleep Quality Rating.
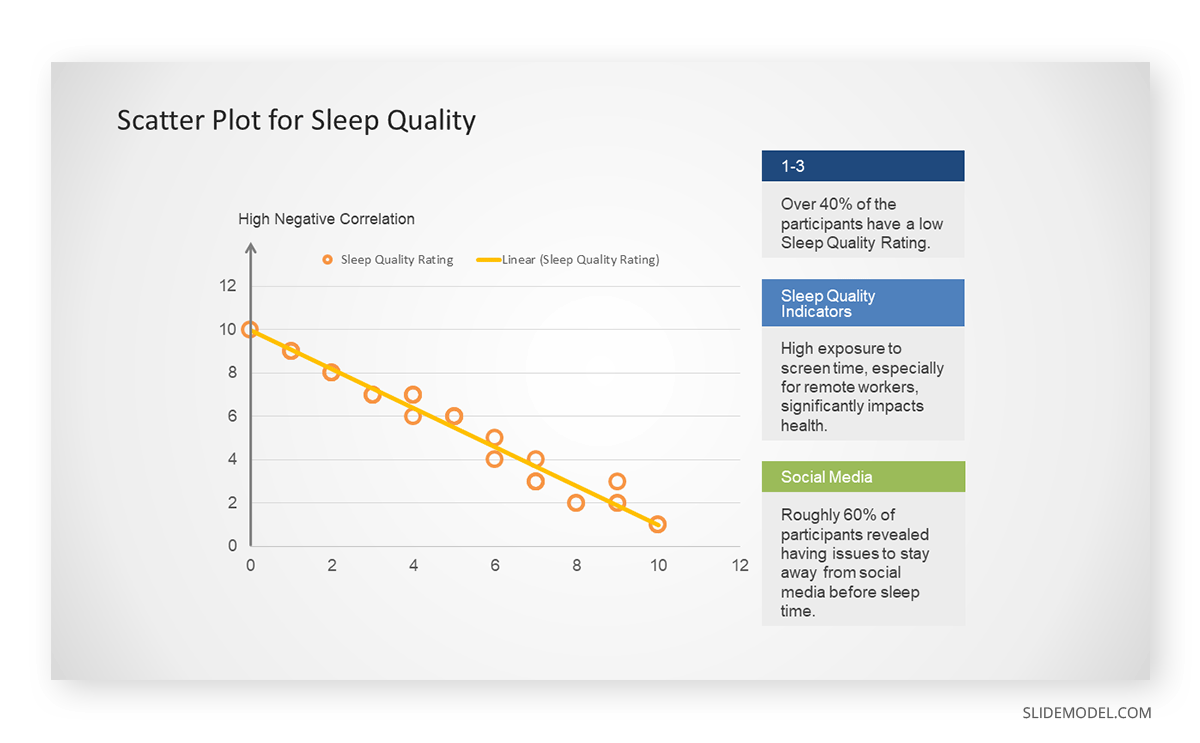
The scientists observe a negative correlation between the amount of screen time and the quality of sleep. This is consistent with their hypothesis that blue light, especially before bedtime, has a significant impact on sleep quality and metabolic processes.
There are a few things to remember when using a scatter plot. Even when a scatter diagram indicates a relationship, it doesn’t mean one variable affects the other. A third factor can influence both variables. The more the plot resembles a straight line, the stronger the relationship is perceived [11] . If it suggests no ties, the observed pattern might be due to random fluctuations in data. When the scatter diagram depicts no correlation, whether the data might be stratified is worth considering.
Choosing the appropriate data presentation type is crucial when making a presentation . Understanding the nature of your data and the message you intend to convey will guide this selection process. For instance, when showcasing quantitative relationships, scatter plots become instrumental in revealing correlations between variables. If the focus is on emphasizing parts of a whole, pie charts offer a concise display of proportions. Histograms, on the other hand, prove valuable for illustrating distributions and frequency patterns.
Bar charts provide a clear visual comparison of different categories. Likewise, line charts excel in showcasing trends over time, while tables are ideal for detailed data examination. Starting a presentation on data presentation types involves evaluating the specific information you want to communicate and selecting the format that aligns with your message. This ensures clarity and resonance with your audience from the beginning of your presentation.
1. Fact Sheet Dashboard for Data Presentation

Convey all the data you need to present in this one-pager format, an ideal solution tailored for users looking for presentation aids. Global maps, donut chats, column graphs, and text neatly arranged in a clean layout presented in light and dark themes.
Use This Template
2. 3D Column Chart Infographic PPT Template
Represent column charts in a highly visual 3D format with this PPT template. A creative way to present data, this template is entirely editable, and we can craft either a one-page infographic or a series of slides explaining what we intend to disclose point by point.
3. Data Circles Infographic PowerPoint Template
An alternative to the pie chart and donut chart diagrams, this template features a series of curved shapes with bubble callouts as ways of presenting data. Expand the information for each arch in the text placeholder areas.
4. Colorful Metrics Dashboard for Data Presentation
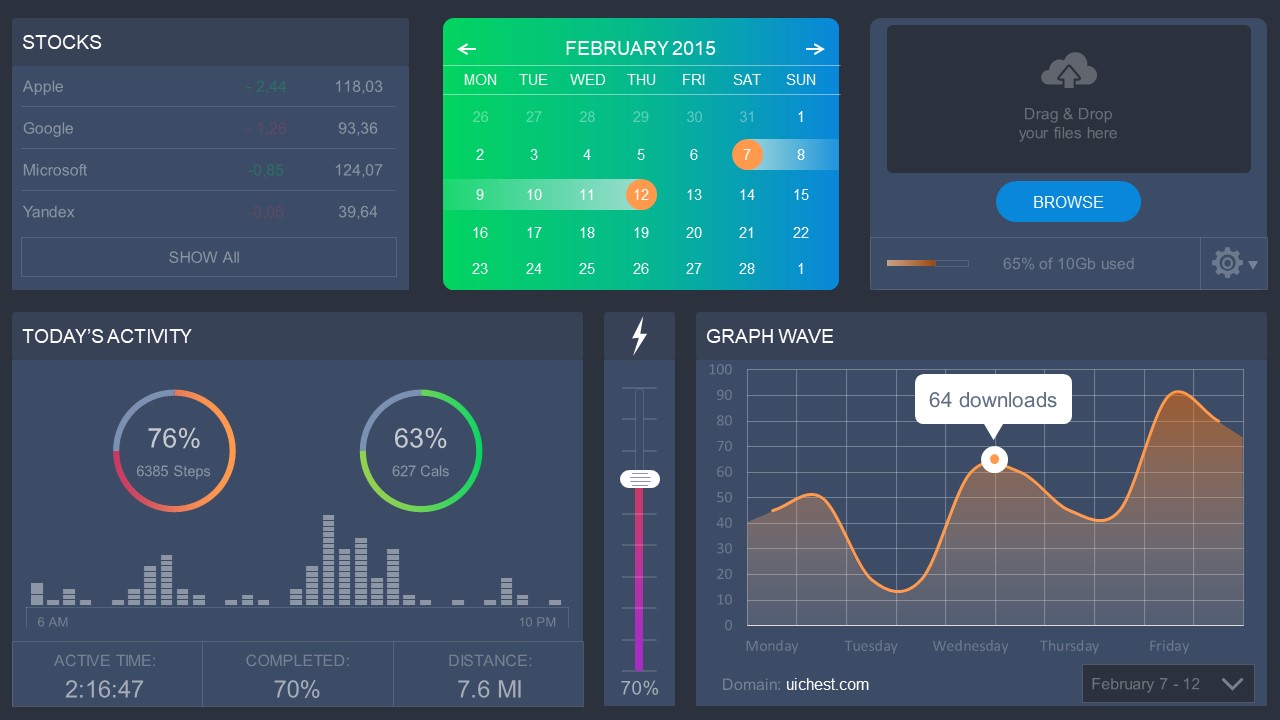
This versatile dashboard template helps us in the presentation of the data by offering several graphs and methods to convert numbers into graphics. Implement it for e-commerce projects, financial projections, project development, and more.
5. Animated Data Presentation Tools for PowerPoint & Google Slides
A slide deck filled with most of the tools mentioned in this article, from bar charts, column charts, treemap graphs, pie charts, histogram, etc. Animated effects make each slide look dynamic when sharing data with stakeholders.
6. Statistics Waffle Charts PPT Template for Data Presentations
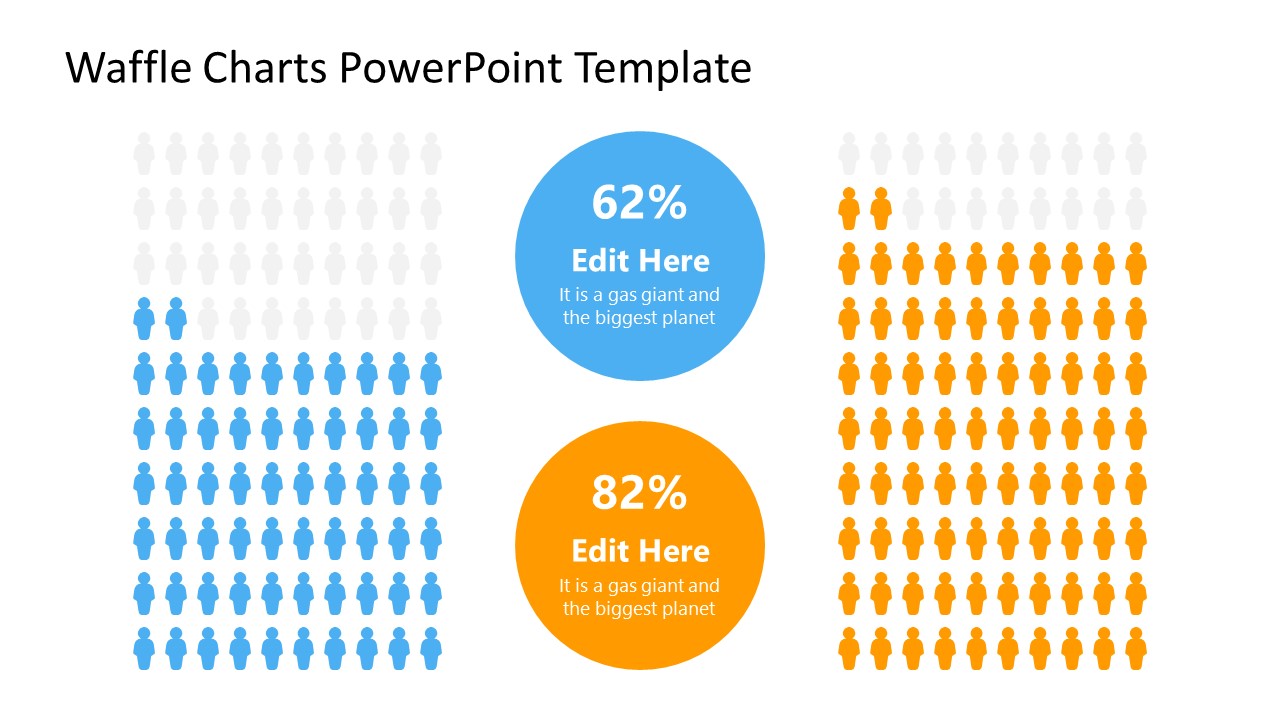
This PPT template helps us how to present data beyond the typical pie chart representation. It is widely used for demographics, so it’s a great fit for marketing teams, data science professionals, HR personnel, and more.
7. Data Presentation Dashboard Template for Google Slides
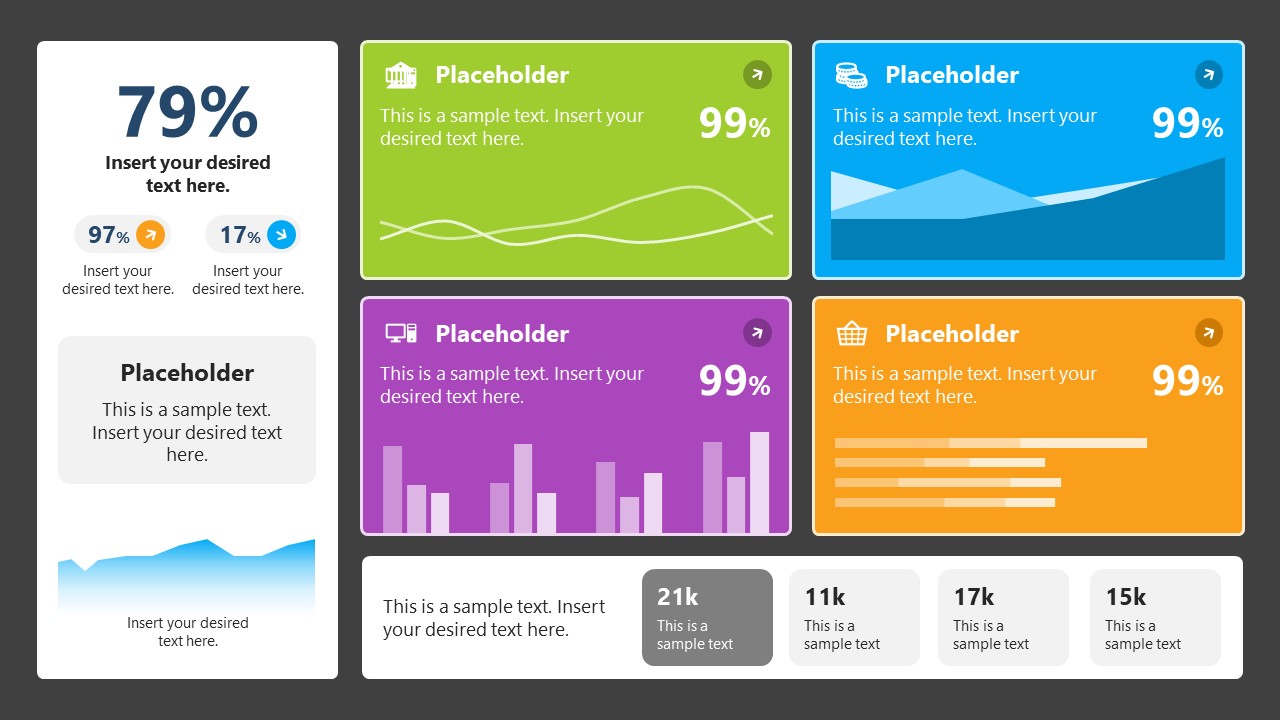
A compendium of tools in dashboard format featuring line graphs, bar charts, column charts, and neatly arranged placeholder text areas.
8. Weather Dashboard for Data Presentation
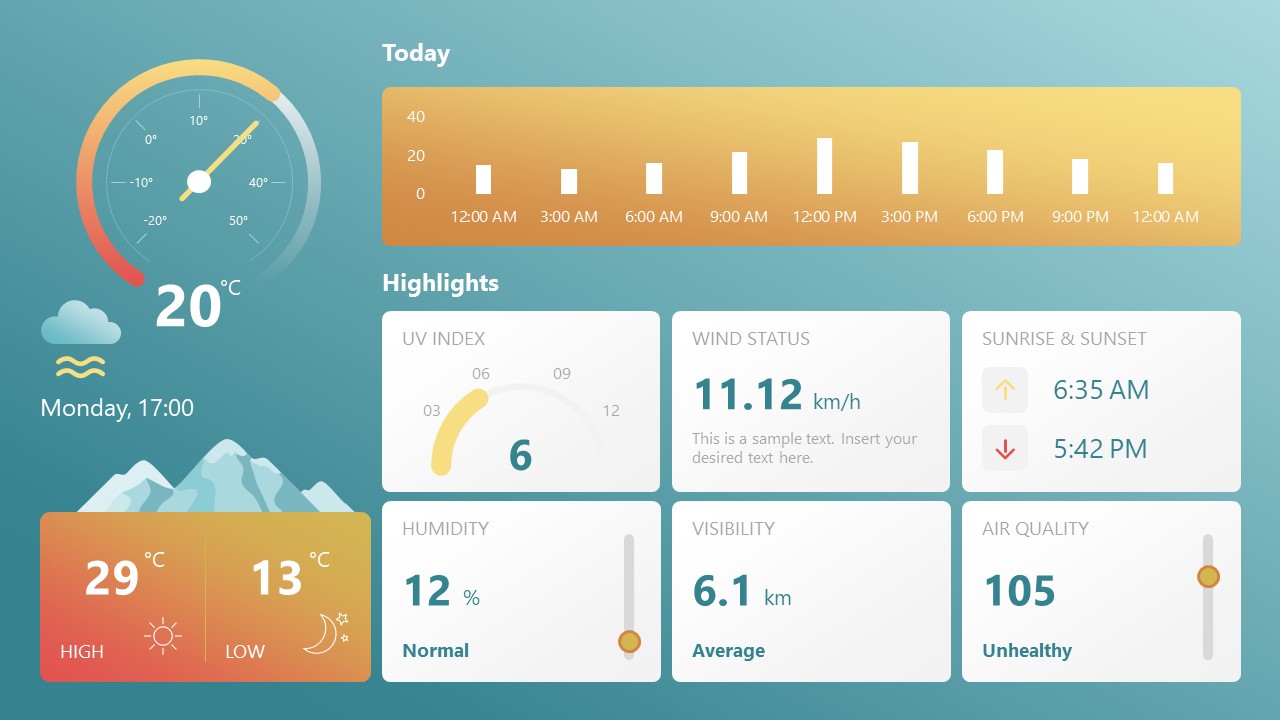
Share weather data for agricultural presentation topics, environmental studies, or any kind of presentation that requires a highly visual layout for weather forecasting on a single day. Two color themes are available.
9. Social Media Marketing Dashboard Data Presentation Template
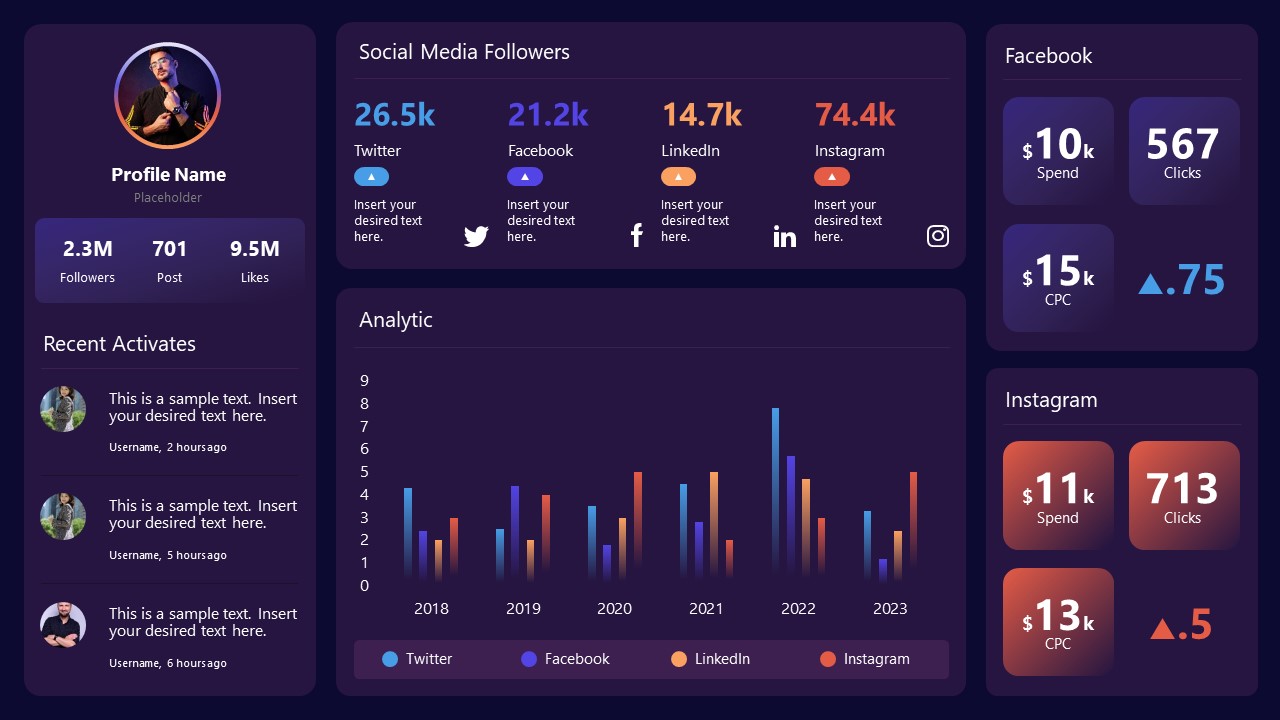
Intended for marketing professionals, this dashboard template for data presentation is a tool for presenting data analytics from social media channels. Two slide layouts featuring line graphs and column charts.
10. Project Management Summary Dashboard Template
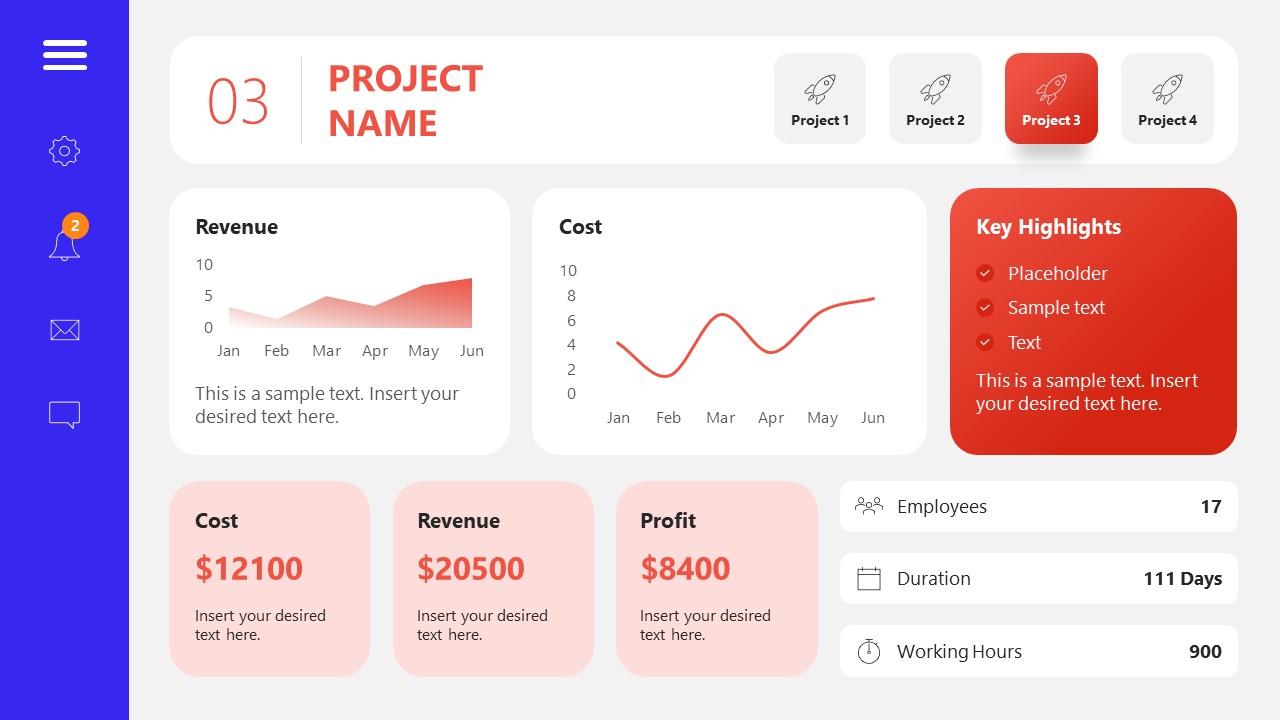
A tool crafted for project managers to deliver highly visual reports on a project’s completion, the profits it delivered for the company, and expenses/time required to execute it. 4 different color layouts are available.
11. Profit & Loss Dashboard for PowerPoint and Google Slides
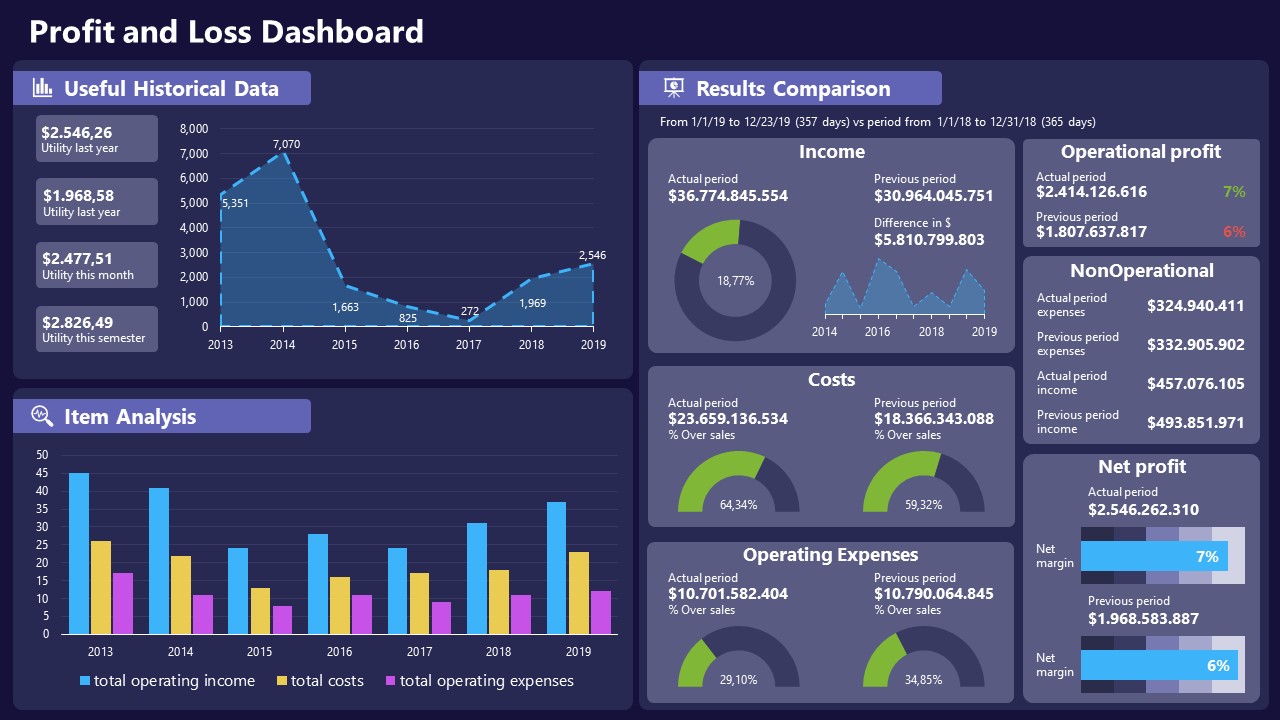
A must-have for finance professionals. This typical profit & loss dashboard includes progress bars, donut charts, column charts, line graphs, and everything that’s required to deliver a comprehensive report about a company’s financial situation.
Overwhelming visuals
One of the mistakes related to using data-presenting methods is including too much data or using overly complex visualizations. They can confuse the audience and dilute the key message.
Inappropriate chart types
Choosing the wrong type of chart for the data at hand can lead to misinterpretation. For example, using a pie chart for data that doesn’t represent parts of a whole is not right.
Lack of context
Failing to provide context or sufficient labeling can make it challenging for the audience to understand the significance of the presented data.
Inconsistency in design
Using inconsistent design elements and color schemes across different visualizations can create confusion and visual disarray.
Failure to provide details
Simply presenting raw data without offering clear insights or takeaways can leave the audience without a meaningful conclusion.
Lack of focus
Not having a clear focus on the key message or main takeaway can result in a presentation that lacks a central theme.
Visual accessibility issues
Overlooking the visual accessibility of charts and graphs can exclude certain audience members who may have difficulty interpreting visual information.
In order to avoid these mistakes in data presentation, presenters can benefit from using presentation templates . These templates provide a structured framework. They ensure consistency, clarity, and an aesthetically pleasing design, enhancing data communication’s overall impact.
Understanding and choosing data presentation types are pivotal in effective communication. Each method serves a unique purpose, so selecting the appropriate one depends on the nature of the data and the message to be conveyed. The diverse array of presentation types offers versatility in visually representing information, from bar charts showing values to pie charts illustrating proportions.
Using the proper method enhances clarity, engages the audience, and ensures that data sets are not just presented but comprehensively understood. By appreciating the strengths and limitations of different presentation types, communicators can tailor their approach to convey information accurately, developing a deeper connection between data and audience understanding.
[1] Government of Canada, S.C. (2021) 5 Data Visualization 5.2 Bar Chart , 5.2 Bar chart . https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/edu/power-pouvoir/ch9/bargraph-diagrammeabarres/5214818-eng.htm
[2] Kosslyn, S.M., 1989. Understanding charts and graphs. Applied cognitive psychology, 3(3), pp.185-225. https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA183409.pdf
[3] Creating a Dashboard . https://it.tufts.edu/book/export/html/1870
[4] https://www.goldenwestcollege.edu/research/data-and-more/data-dashboards/index.html
[5] https://www.mit.edu/course/21/21.guide/grf-line.htm
[6] Jadeja, M. and Shah, K., 2015, January. Tree-Map: A Visualization Tool for Large Data. In GSB@ SIGIR (pp. 9-13). https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1393/gsb15proceedings.pdf#page=15
[7] Heat Maps and Quilt Plots. https://www.publichealth.columbia.edu/research/population-health-methods/heat-maps-and-quilt-plots
[8] EIU QGIS WORKSHOP. https://www.eiu.edu/qgisworkshop/heatmaps.php
[9] About Pie Charts. https://www.mit.edu/~mbarker/formula1/f1help/11-ch-c8.htm
[10] Histograms. https://sites.utexas.edu/sos/guided/descriptive/numericaldd/descriptiven2/histogram/ [11] https://asq.org/quality-resources/scatter-diagram

Like this article? Please share
Data Analysis, Data Science, Data Visualization Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!
Filed under Presentation Ideas • January 6th, 2024
All About Using Harvey Balls
Among the many tools in the arsenal of the modern presenter, Harvey Balls have a special place. In this article we will tell you all about using Harvey Balls.

Filed under Business • December 8th, 2023
How to Design a Dashboard Presentation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Take a step further in your professional presentation skills by learning what a dashboard presentation is and how to properly design one in PowerPoint. A detailed step-by-step guide is here!
Leave a Reply
A Step-by-Step Guide to the Data Analysis Process
Like any scientific discipline, data analysis follows a rigorous step-by-step process. Each stage requires different skills and know-how. To get meaningful insights, though, it’s important to understand the process as a whole. An underlying framework is invaluable for producing results that stand up to scrutiny.
In this post, we’ll explore the main steps in the data analysis process. This will cover how to define your goal, collect data, and carry out an analysis. Where applicable, we’ll also use examples and highlight a few tools to make the journey easier. When you’re done, you’ll have a much better understanding of the basics. This will help you tweak the process to fit your own needs.
Here are the steps we’ll take you through:
- Defining the question
- Collecting the data
- Cleaning the data
- Analyzing the data
- Sharing your results
- Embracing failure
On popular request, we’ve also developed a video based on this article. Scroll further along this article to watch that.
Ready? Let’s get started with step one.
1. Step one: Defining the question
The first step in any data analysis process is to define your objective. In data analytics jargon, this is sometimes called the ‘problem statement’.
Defining your objective means coming up with a hypothesis and figuring how to test it. Start by asking: What business problem am I trying to solve? While this might sound straightforward, it can be trickier than it seems. For instance, your organization’s senior management might pose an issue, such as: “Why are we losing customers?” It’s possible, though, that this doesn’t get to the core of the problem. A data analyst’s job is to understand the business and its goals in enough depth that they can frame the problem the right way.
Let’s say you work for a fictional company called TopNotch Learning. TopNotch creates custom training software for its clients. While it is excellent at securing new clients, it has much lower repeat business. As such, your question might not be, “Why are we losing customers?” but, “Which factors are negatively impacting the customer experience?” or better yet: “How can we boost customer retention while minimizing costs?”
Now you’ve defined a problem, you need to determine which sources of data will best help you solve it. This is where your business acumen comes in again. For instance, perhaps you’ve noticed that the sales process for new clients is very slick, but that the production team is inefficient. Knowing this, you could hypothesize that the sales process wins lots of new clients, but the subsequent customer experience is lacking. Could this be why customers don’t come back? Which sources of data will help you answer this question?
Tools to help define your objective
Defining your objective is mostly about soft skills, business knowledge, and lateral thinking. But you’ll also need to keep track of business metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). Monthly reports can allow you to track problem points in the business. Some KPI dashboards come with a fee, like Databox and DashThis . However, you’ll also find open-source software like Grafana , Freeboard , and Dashbuilder . These are great for producing simple dashboards, both at the beginning and the end of the data analysis process.
2. Step two: Collecting the data
Once you’ve established your objective, you’ll need to create a strategy for collecting and aggregating the appropriate data. A key part of this is determining which data you need. This might be quantitative (numeric) data, e.g. sales figures, or qualitative (descriptive) data, such as customer reviews. All data fit into one of three categories: first-party, second-party, and third-party data. Let’s explore each one.
What is first-party data?
First-party data are data that you, or your company, have directly collected from customers. It might come in the form of transactional tracking data or information from your company’s customer relationship management (CRM) system. Whatever its source, first-party data is usually structured and organized in a clear, defined way. Other sources of first-party data might include customer satisfaction surveys, focus groups, interviews, or direct observation.
What is second-party data?
To enrich your analysis, you might want to secure a secondary data source. Second-party data is the first-party data of other organizations. This might be available directly from the company or through a private marketplace. The main benefit of second-party data is that they are usually structured, and although they will be less relevant than first-party data, they also tend to be quite reliable. Examples of second-party data include website, app or social media activity, like online purchase histories, or shipping data.
What is third-party data?
Third-party data is data that has been collected and aggregated from numerous sources by a third-party organization. Often (though not always) third-party data contains a vast amount of unstructured data points (big data). Many organizations collect big data to create industry reports or to conduct market research. The research and advisory firm Gartner is a good real-world example of an organization that collects big data and sells it on to other companies. Open data repositories and government portals are also sources of third-party data .
Tools to help you collect data
Once you’ve devised a data strategy (i.e. you’ve identified which data you need, and how best to go about collecting them) there are many tools you can use to help you. One thing you’ll need, regardless of industry or area of expertise, is a data management platform (DMP). A DMP is a piece of software that allows you to identify and aggregate data from numerous sources, before manipulating them, segmenting them, and so on. There are many DMPs available. Some well-known enterprise DMPs include Salesforce DMP , SAS , and the data integration platform, Xplenty . If you want to play around, you can also try some open-source platforms like Pimcore or D:Swarm .
Want to learn more about what data analytics is and the process a data analyst follows? We cover this topic (and more) in our free introductory short course for beginners. Check out tutorial one: An introduction to data analytics .
3. Step three: Cleaning the data
Once you’ve collected your data, the next step is to get it ready for analysis. This means cleaning, or ‘scrubbing’ it, and is crucial in making sure that you’re working with high-quality data . Key data cleaning tasks include:
- Removing major errors, duplicates, and outliers —all of which are inevitable problems when aggregating data from numerous sources.
- Removing unwanted data points —extracting irrelevant observations that have no bearing on your intended analysis.
- Bringing structure to your data —general ‘housekeeping’, i.e. fixing typos or layout issues, which will help you map and manipulate your data more easily.
- Filling in major gaps —as you’re tidying up, you might notice that important data are missing. Once you’ve identified gaps, you can go about filling them.
A good data analyst will spend around 70-90% of their time cleaning their data. This might sound excessive. But focusing on the wrong data points (or analyzing erroneous data) will severely impact your results. It might even send you back to square one…so don’t rush it! You’ll find a step-by-step guide to data cleaning here . You may be interested in this introductory tutorial to data cleaning, hosted by Dr. Humera Noor Minhas.
Carrying out an exploratory analysis
Another thing many data analysts do (alongside cleaning data) is to carry out an exploratory analysis. This helps identify initial trends and characteristics, and can even refine your hypothesis. Let’s use our fictional learning company as an example again. Carrying out an exploratory analysis, perhaps you notice a correlation between how much TopNotch Learning’s clients pay and how quickly they move on to new suppliers. This might suggest that a low-quality customer experience (the assumption in your initial hypothesis) is actually less of an issue than cost. You might, therefore, take this into account.
Tools to help you clean your data
Cleaning datasets manually—especially large ones—can be daunting. Luckily, there are many tools available to streamline the process. Open-source tools, such as OpenRefine , are excellent for basic data cleaning, as well as high-level exploration. However, free tools offer limited functionality for very large datasets. Python libraries (e.g. Pandas) and some R packages are better suited for heavy data scrubbing. You will, of course, need to be familiar with the languages. Alternatively, enterprise tools are also available. For example, Data Ladder , which is one of the highest-rated data-matching tools in the industry. There are many more. Why not see which free data cleaning tools you can find to play around with?
4. Step four: Analyzing the data
Finally, you’ve cleaned your data. Now comes the fun bit—analyzing it! The type of data analysis you carry out largely depends on what your goal is. But there are many techniques available. Univariate or bivariate analysis, time-series analysis, and regression analysis are just a few you might have heard of. More important than the different types, though, is how you apply them. This depends on what insights you’re hoping to gain. Broadly speaking, all types of data analysis fit into one of the following four categories.
Descriptive analysis
Descriptive analysis identifies what has already happened . It is a common first step that companies carry out before proceeding with deeper explorations. As an example, let’s refer back to our fictional learning provider once more. TopNotch Learning might use descriptive analytics to analyze course completion rates for their customers. Or they might identify how many users access their products during a particular period. Perhaps they’ll use it to measure sales figures over the last five years. While the company might not draw firm conclusions from any of these insights, summarizing and describing the data will help them to determine how to proceed.
Learn more: What is descriptive analytics?
Diagnostic analysis
Diagnostic analytics focuses on understanding why something has happened . It is literally the diagnosis of a problem, just as a doctor uses a patient’s symptoms to diagnose a disease. Remember TopNotch Learning’s business problem? ‘Which factors are negatively impacting the customer experience?’ A diagnostic analysis would help answer this. For instance, it could help the company draw correlations between the issue (struggling to gain repeat business) and factors that might be causing it (e.g. project costs, speed of delivery, customer sector, etc.) Let’s imagine that, using diagnostic analytics, TopNotch realizes its clients in the retail sector are departing at a faster rate than other clients. This might suggest that they’re losing customers because they lack expertise in this sector. And that’s a useful insight!
Predictive analysis
Predictive analysis allows you to identify future trends based on historical data . In business, predictive analysis is commonly used to forecast future growth, for example. But it doesn’t stop there. Predictive analysis has grown increasingly sophisticated in recent years. The speedy evolution of machine learning allows organizations to make surprisingly accurate forecasts. Take the insurance industry. Insurance providers commonly use past data to predict which customer groups are more likely to get into accidents. As a result, they’ll hike up customer insurance premiums for those groups. Likewise, the retail industry often uses transaction data to predict where future trends lie, or to determine seasonal buying habits to inform their strategies. These are just a few simple examples, but the untapped potential of predictive analysis is pretty compelling.
Prescriptive analysis
Prescriptive analysis allows you to make recommendations for the future. This is the final step in the analytics part of the process. It’s also the most complex. This is because it incorporates aspects of all the other analyses we’ve described. A great example of prescriptive analytics is the algorithms that guide Google’s self-driving cars. Every second, these algorithms make countless decisions based on past and present data, ensuring a smooth, safe ride. Prescriptive analytics also helps companies decide on new products or areas of business to invest in.
Learn more: What are the different types of data analysis?
5. Step five: Sharing your results
You’ve finished carrying out your analyses. You have your insights. The final step of the data analytics process is to share these insights with the wider world (or at least with your organization’s stakeholders!) This is more complex than simply sharing the raw results of your work—it involves interpreting the outcomes, and presenting them in a manner that’s digestible for all types of audiences. Since you’ll often present information to decision-makers, it’s very important that the insights you present are 100% clear and unambiguous. For this reason, data analysts commonly use reports, dashboards, and interactive visualizations to support their findings.
How you interpret and present results will often influence the direction of a business. Depending on what you share, your organization might decide to restructure, to launch a high-risk product, or even to close an entire division. That’s why it’s very important to provide all the evidence that you’ve gathered, and not to cherry-pick data. Ensuring that you cover everything in a clear, concise way will prove that your conclusions are scientifically sound and based on the facts. On the flip side, it’s important to highlight any gaps in the data or to flag any insights that might be open to interpretation. Honest communication is the most important part of the process. It will help the business, while also helping you to excel at your job!
Tools for interpreting and sharing your findings
There are tons of data visualization tools available, suited to different experience levels. Popular tools requiring little or no coding skills include Google Charts , Tableau , Datawrapper , and Infogram . If you’re familiar with Python and R, there are also many data visualization libraries and packages available. For instance, check out the Python libraries Plotly , Seaborn , and Matplotlib . Whichever data visualization tools you use, make sure you polish up your presentation skills, too. Remember: Visualization is great, but communication is key!
You can learn more about storytelling with data in this free, hands-on tutorial . We show you how to craft a compelling narrative for a real dataset, resulting in a presentation to share with key stakeholders. This is an excellent insight into what it’s really like to work as a data analyst!
6. Step six: Embrace your failures
The last ‘step’ in the data analytics process is to embrace your failures. The path we’ve described above is more of an iterative process than a one-way street. Data analytics is inherently messy, and the process you follow will be different for every project. For instance, while cleaning data, you might spot patterns that spark a whole new set of questions. This could send you back to step one (to redefine your objective). Equally, an exploratory analysis might highlight a set of data points you’d never considered using before. Or maybe you find that the results of your core analyses are misleading or erroneous. This might be caused by mistakes in the data, or human error earlier in the process.
While these pitfalls can feel like failures, don’t be disheartened if they happen. Data analysis is inherently chaotic, and mistakes occur. What’s important is to hone your ability to spot and rectify errors. If data analytics was straightforward, it might be easier, but it certainly wouldn’t be as interesting. Use the steps we’ve outlined as a framework, stay open-minded, and be creative. If you lose your way, you can refer back to the process to keep yourself on track.
In this post, we’ve covered the main steps of the data analytics process. These core steps can be amended, re-ordered and re-used as you deem fit, but they underpin every data analyst’s work:
- Define the question —What business problem are you trying to solve? Frame it as a question to help you focus on finding a clear answer.
- Collect data —Create a strategy for collecting data. Which data sources are most likely to help you solve your business problem?
- Clean the data —Explore, scrub, tidy, de-dupe, and structure your data as needed. Do whatever you have to! But don’t rush…take your time!
- Analyze the data —Carry out various analyses to obtain insights. Focus on the four types of data analysis: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive.
- Share your results —How best can you share your insights and recommendations? A combination of visualization tools and communication is key.
- Embrace your mistakes —Mistakes happen. Learn from them. This is what transforms a good data analyst into a great one.
What next? From here, we strongly encourage you to explore the topic on your own. Get creative with the steps in the data analysis process, and see what tools you can find. As long as you stick to the core principles we’ve described, you can create a tailored technique that works for you.
To learn more, check out our free, 5-day data analytics short course . You might also be interested in the following:
- These are the top 9 data analytics tools
- 10 great places to find free datasets for your next project
- How to build a data analytics portfolio
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Data Analysis – Process, Methods and Types
Data Analysis – Process, Methods and Types
Table of Contents

Data Analysis
Definition:
Data analysis refers to the process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, drawing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. It involves applying various statistical and computational techniques to interpret and derive insights from large datasets. The ultimate aim of data analysis is to convert raw data into actionable insights that can inform business decisions, scientific research, and other endeavors.
Data Analysis Process
The following are step-by-step guides to the data analysis process:
Define the Problem
The first step in data analysis is to clearly define the problem or question that needs to be answered. This involves identifying the purpose of the analysis, the data required, and the intended outcome.
Collect the Data
The next step is to collect the relevant data from various sources. This may involve collecting data from surveys, databases, or other sources. It is important to ensure that the data collected is accurate, complete, and relevant to the problem being analyzed.
Clean and Organize the Data
Once the data has been collected, it needs to be cleaned and organized. This involves removing any errors or inconsistencies in the data, filling in missing values, and ensuring that the data is in a format that can be easily analyzed.
Analyze the Data
The next step is to analyze the data using various statistical and analytical techniques. This may involve identifying patterns in the data, conducting statistical tests, or using machine learning algorithms to identify trends and insights.
Interpret the Results
After analyzing the data, the next step is to interpret the results. This involves drawing conclusions based on the analysis and identifying any significant findings or trends.
Communicate the Findings
Once the results have been interpreted, they need to be communicated to stakeholders. This may involve creating reports, visualizations, or presentations to effectively communicate the findings and recommendations.
Take Action
The final step in the data analysis process is to take action based on the findings. This may involve implementing new policies or procedures, making strategic decisions, or taking other actions based on the insights gained from the analysis.
Types of Data Analysis
Types of Data Analysis are as follows:
Descriptive Analysis
This type of analysis involves summarizing and describing the main characteristics of a dataset, such as the mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and range.
Inferential Analysis
This type of analysis involves making inferences about a population based on a sample. Inferential analysis can help determine whether a certain relationship or pattern observed in a sample is likely to be present in the entire population.
Diagnostic Analysis
This type of analysis involves identifying and diagnosing problems or issues within a dataset. Diagnostic analysis can help identify outliers, errors, missing data, or other anomalies in the dataset.
Predictive Analysis
This type of analysis involves using statistical models and algorithms to predict future outcomes or trends based on historical data. Predictive analysis can help businesses and organizations make informed decisions about the future.
Prescriptive Analysis
This type of analysis involves recommending a course of action based on the results of previous analyses. Prescriptive analysis can help organizations make data-driven decisions about how to optimize their operations, products, or services.
Exploratory Analysis
This type of analysis involves exploring the relationships and patterns within a dataset to identify new insights and trends. Exploratory analysis is often used in the early stages of research or data analysis to generate hypotheses and identify areas for further investigation.
Data Analysis Methods
Data Analysis Methods are as follows:
Statistical Analysis
This method involves the use of mathematical models and statistical tools to analyze and interpret data. It includes measures of central tendency, correlation analysis, regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and more.
Machine Learning
This method involves the use of algorithms to identify patterns and relationships in data. It includes supervised and unsupervised learning, classification, clustering, and predictive modeling.
Data Mining
This method involves using statistical and machine learning techniques to extract information and insights from large and complex datasets.
Text Analysis
This method involves using natural language processing (NLP) techniques to analyze and interpret text data. It includes sentiment analysis, topic modeling, and entity recognition.
Network Analysis
This method involves analyzing the relationships and connections between entities in a network, such as social networks or computer networks. It includes social network analysis and graph theory.
Time Series Analysis
This method involves analyzing data collected over time to identify patterns and trends. It includes forecasting, decomposition, and smoothing techniques.
Spatial Analysis
This method involves analyzing geographic data to identify spatial patterns and relationships. It includes spatial statistics, spatial regression, and geospatial data visualization.
Data Visualization
This method involves using graphs, charts, and other visual representations to help communicate the findings of the analysis. It includes scatter plots, bar charts, heat maps, and interactive dashboards.
Qualitative Analysis
This method involves analyzing non-numeric data such as interviews, observations, and open-ended survey responses. It includes thematic analysis, content analysis, and grounded theory.
Multi-criteria Decision Analysis
This method involves analyzing multiple criteria and objectives to support decision-making. It includes techniques such as the analytical hierarchy process, TOPSIS, and ELECTRE.
Data Analysis Tools
There are various data analysis tools available that can help with different aspects of data analysis. Below is a list of some commonly used data analysis tools:
- Microsoft Excel: A widely used spreadsheet program that allows for data organization, analysis, and visualization.
- SQL : A programming language used to manage and manipulate relational databases.
- R : An open-source programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphics.
- Python : A general-purpose programming language that is widely used in data analysis and machine learning.
- Tableau : A data visualization software that allows for interactive and dynamic visualizations of data.
- SAS : A statistical analysis software used for data management, analysis, and reporting.
- SPSS : A statistical analysis software used for data analysis, reporting, and modeling.
- Matlab : A numerical computing software that is widely used in scientific research and engineering.
- RapidMiner : A data science platform that offers a wide range of data analysis and machine learning tools.
Applications of Data Analysis
Data analysis has numerous applications across various fields. Below are some examples of how data analysis is used in different fields:
- Business : Data analysis is used to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and financial performance. This includes customer segmentation, sales forecasting, and market research.
- Healthcare : Data analysis is used to identify patterns and trends in patient data, improve patient outcomes, and optimize healthcare operations. This includes clinical decision support, disease surveillance, and healthcare cost analysis.
- Education : Data analysis is used to measure student performance, evaluate teaching effectiveness, and improve educational programs. This includes assessment analytics, learning analytics, and program evaluation.
- Finance : Data analysis is used to monitor and evaluate financial performance, identify risks, and make investment decisions. This includes risk management, portfolio optimization, and fraud detection.
- Government : Data analysis is used to inform policy-making, improve public services, and enhance public safety. This includes crime analysis, disaster response planning, and social welfare program evaluation.
- Sports : Data analysis is used to gain insights into athlete performance, improve team strategy, and enhance fan engagement. This includes player evaluation, scouting analysis, and game strategy optimization.
- Marketing : Data analysis is used to measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, understand customer behavior, and develop targeted marketing strategies. This includes customer segmentation, marketing attribution analysis, and social media analytics.
- Environmental science : Data analysis is used to monitor and evaluate environmental conditions, assess the impact of human activities on the environment, and develop environmental policies. This includes climate modeling, ecological forecasting, and pollution monitoring.
When to Use Data Analysis
Data analysis is useful when you need to extract meaningful insights and information from large and complex datasets. It is a crucial step in the decision-making process, as it helps you understand the underlying patterns and relationships within the data, and identify potential areas for improvement or opportunities for growth.
Here are some specific scenarios where data analysis can be particularly helpful:
- Problem-solving : When you encounter a problem or challenge, data analysis can help you identify the root cause and develop effective solutions.
- Optimization : Data analysis can help you optimize processes, products, or services to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance.
- Prediction: Data analysis can help you make predictions about future trends or outcomes, which can inform strategic planning and decision-making.
- Performance evaluation : Data analysis can help you evaluate the performance of a process, product, or service to identify areas for improvement and potential opportunities for growth.
- Risk assessment : Data analysis can help you assess and mitigate risks, whether it is financial, operational, or related to safety.
- Market research : Data analysis can help you understand customer behavior and preferences, identify market trends, and develop effective marketing strategies.
- Quality control: Data analysis can help you ensure product quality and customer satisfaction by identifying and addressing quality issues.
Purpose of Data Analysis
The primary purposes of data analysis can be summarized as follows:
- To gain insights: Data analysis allows you to identify patterns and trends in data, which can provide valuable insights into the underlying factors that influence a particular phenomenon or process.
- To inform decision-making: Data analysis can help you make informed decisions based on the information that is available. By analyzing data, you can identify potential risks, opportunities, and solutions to problems.
- To improve performance: Data analysis can help you optimize processes, products, or services by identifying areas for improvement and potential opportunities for growth.
- To measure progress: Data analysis can help you measure progress towards a specific goal or objective, allowing you to track performance over time and adjust your strategies accordingly.
- To identify new opportunities: Data analysis can help you identify new opportunities for growth and innovation by identifying patterns and trends that may not have been visible before.
Examples of Data Analysis
Some Examples of Data Analysis are as follows:
- Social Media Monitoring: Companies use data analysis to monitor social media activity in real-time to understand their brand reputation, identify potential customer issues, and track competitors. By analyzing social media data, businesses can make informed decisions on product development, marketing strategies, and customer service.
- Financial Trading: Financial traders use data analysis to make real-time decisions about buying and selling stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments. By analyzing real-time market data, traders can identify trends and patterns that help them make informed investment decisions.
- Traffic Monitoring : Cities use data analysis to monitor traffic patterns and make real-time decisions about traffic management. By analyzing data from traffic cameras, sensors, and other sources, cities can identify congestion hotspots and make changes to improve traffic flow.
- Healthcare Monitoring: Healthcare providers use data analysis to monitor patient health in real-time. By analyzing data from wearable devices, electronic health records, and other sources, healthcare providers can identify potential health issues and provide timely interventions.
- Online Advertising: Online advertisers use data analysis to make real-time decisions about advertising campaigns. By analyzing data on user behavior and ad performance, advertisers can make adjustments to their campaigns to improve their effectiveness.
- Sports Analysis : Sports teams use data analysis to make real-time decisions about strategy and player performance. By analyzing data on player movement, ball position, and other variables, coaches can make informed decisions about substitutions, game strategy, and training regimens.
- Energy Management : Energy companies use data analysis to monitor energy consumption in real-time. By analyzing data on energy usage patterns, companies can identify opportunities to reduce energy consumption and improve efficiency.
Characteristics of Data Analysis
Characteristics of Data Analysis are as follows:
- Objective : Data analysis should be objective and based on empirical evidence, rather than subjective assumptions or opinions.
- Systematic : Data analysis should follow a systematic approach, using established methods and procedures for collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data.
- Accurate : Data analysis should produce accurate results, free from errors and bias. Data should be validated and verified to ensure its quality.
- Relevant : Data analysis should be relevant to the research question or problem being addressed. It should focus on the data that is most useful for answering the research question or solving the problem.
- Comprehensive : Data analysis should be comprehensive and consider all relevant factors that may affect the research question or problem.
- Timely : Data analysis should be conducted in a timely manner, so that the results are available when they are needed.
- Reproducible : Data analysis should be reproducible, meaning that other researchers should be able to replicate the analysis using the same data and methods.
- Communicable : Data analysis should be communicated clearly and effectively to stakeholders and other interested parties. The results should be presented in a way that is understandable and useful for decision-making.
Advantages of Data Analysis
Advantages of Data Analysis are as follows:
- Better decision-making: Data analysis helps in making informed decisions based on facts and evidence, rather than intuition or guesswork.
- Improved efficiency: Data analysis can identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks in business processes, allowing organizations to optimize their operations and reduce costs.
- Increased accuracy: Data analysis helps to reduce errors and bias, providing more accurate and reliable information.
- Better customer service: Data analysis can help organizations understand their customers better, allowing them to provide better customer service and improve customer satisfaction.
- Competitive advantage: Data analysis can provide organizations with insights into their competitors, allowing them to identify areas where they can gain a competitive advantage.
- Identification of trends and patterns : Data analysis can identify trends and patterns in data that may not be immediately apparent, helping organizations to make predictions and plan for the future.
- Improved risk management : Data analysis can help organizations identify potential risks and take proactive steps to mitigate them.
- Innovation: Data analysis can inspire innovation and new ideas by revealing new opportunities or previously unknown correlations in data.
Limitations of Data Analysis
- Data quality: The quality of data can impact the accuracy and reliability of analysis results. If data is incomplete, inconsistent, or outdated, the analysis may not provide meaningful insights.
- Limited scope: Data analysis is limited by the scope of the data available. If data is incomplete or does not capture all relevant factors, the analysis may not provide a complete picture.
- Human error : Data analysis is often conducted by humans, and errors can occur in data collection, cleaning, and analysis.
- Cost : Data analysis can be expensive, requiring specialized tools, software, and expertise.
- Time-consuming : Data analysis can be time-consuming, especially when working with large datasets or conducting complex analyses.
- Overreliance on data: Data analysis should be complemented with human intuition and expertise. Overreliance on data can lead to a lack of creativity and innovation.
- Privacy concerns: Data analysis can raise privacy concerns if personal or sensitive information is used without proper consent or security measures.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Cluster Analysis – Types, Methods and Examples

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Discriminant Analysis – Methods, Types and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free

Data Analysis and Presentation Skills: the PwC Approach Specialization
Make Smarter Business Decisions With Data Analysis. Understand data, apply data analytics tools and create effective business intelligence presentations
Taught in English
Some content may not be translated

Instructor: Alex Mannella
Financial aid available
157,084 already enrolled
Specialization - 5 course series
(9,833 reviews)
Skills you'll gain
- Data Analysis
- Microsoft Excel
- Data Visualization
- Presentation
Details to know

Add to your LinkedIn profile
See how employees at top companies are mastering in-demand skills

Advance your subject-matter expertise
- Learn in-demand skills from university and industry experts
- Master a subject or tool with hands-on projects
- Develop a deep understanding of key concepts
- Earn a career certificate from PwC

Earn a career certificate
Add this credential to your LinkedIn profile, resume, or CV
Share it on social media and in your performance review

If you are a PwC Employee, gain access to the PwC Specialization and Courses for free using the instructions on Vantage.
This Specialization will help you get practical with data analysis, turning business intelligence into real-world outcomes. We'll explore how a combination of better understanding, filtering, and application of data can help you solve problems faster - leading to smarter and more effective decision-making. You’ll learn how to use Microsoft Excel, PowerPoint, and other common data analysis and communication tools, and perhaps most importantly, we'll help you to present data to others in a way that gets them engaged in your story and motivated to act.
Please note: If you'd like to audit the courses in this Specialization, you'll need to enroll in each course separately and then you will see the audit option.
This specialization was created by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP with an address at 300 Madison Avenue, New York, New York, 10017.
Applied Learning Project
This specialization will include a project at the end of each module and a capstone project at the end of the specialization. Each project will provide you the chance to apply the skills of that lesson. In the first module you'll plan an analysis approach, in the second and third modules you will analyze sets of data using the Excel skills you learn. In the fourth module you will prepare a business presentation.
In the final Capstone Project, you'll apply the skills you’ve learned by working through a mock client business problem. You'll analyze a set of data, looking for the business insights. Then you'll create and visualize your findings, before recording a video to present your recommendations to the client.
Data-driven Decision Making
What you'll learn.
Welcome to Data-driven Decision Making. In this course, you'll get an introduction to Data Analytics and its role in business decisions. You'll learn why data is important and how it has evolved. You'll be introduced to “Big Data” and how it is used. You'll also be introduced to a framework for conducting Data Analysis and what tools and techniques are commonly used. Finally, you'll have a chance to put your knowledge to work in a simulated business setting.
This course was created by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP with an address at 300 Madison Avenue, New York, New York, 10017.
Problem Solving with Excel
This course explores Excel as a tool for solving business problems. In this course you will learn the basic functions of excel through guided demonstration. Each week you will build on your excel skills and be provided an opportunity to practice what you’ve learned. Finally, you will have a chance to put your knowledge to work in a final project. Please note, the content in this course was developed using a Windows version of Excel 2013.
Data Visualization with Advanced Excel
In this course, you will get hands-on instruction of advanced Excel 2013 functions. You’ll learn to use PowerPivot to build databases and data models. We’ll show you how to perform different types of scenario and simulation analysis and you’ll have an opportunity to practice these skills by leveraging some of Excel's built in tools including, solver, data tables, scenario manager and goal seek. In the second half of the course, will cover how to visualize data, tell a story and explore data by reviewing core principles of data visualization and dashboarding. You’ll use Excel to build complex graphs and Power View reports and then start to combine them into dynamic dashboards.
Note: Learners will need PowerPivot to complete some of the exercises. Please use MS Excel 2013 version. If you have other MS Excel versions or a MAC you might not be able to complete all assignments. This course was created by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP with an address at 300 Madison Avenue, New York, New York, 10017.
Effective Business Presentations with Powerpoint
This course is all about presenting the story of the data, using PowerPoint. You'll learn how to structure a presentation, to include insights and supporting data. You'll also learn some design principles for effective visuals and slides. You'll gain skills for client-facing communication - including public speaking, executive presence and compelling storytelling. Finally, you'll be given a client profile, a business problem, and a set of basic Excel charts, which you'll need to turn into a presentation - which you'll deliver with iterative peer feedback.
Data Analysis and Presentation Skills: the PwC Approach Final Project
In this Capstone Project, you'll bring together all the new skills and insights you've learned through the four courses. You'll be given a 'mock' client problem and a data set. You'll need to analyze the data to gain business insights, research the client's domain area, and create recommendations. You'll then need to visualize the data in a client-facing presentation. You'll bring it all together in a recorded video presentation.

With offices in 157 countries and more than 208,000 people, PwC is among the leading professional services networks in the world. Our purpose is to build trust in society and solve important problems. We help organisations and individuals create the value they’re looking for, by delivering quality in assurance, tax and advisory services.
Why people choose Coursera for their career

New to Business Essentials? Start here.

Open new doors with Coursera Plus
Unlimited access to 7,000+ world-class courses, hands-on projects, and job-ready certificate programs - all included in your subscription
Advance your career with an online degree
Earn a degree from world-class universities - 100% online
Join over 3,400 global companies that choose Coursera for Business
Upskill your employees to excel in the digital economy
Frequently asked questions
How long does it take to complete the specialization.
Exactly how long it takes will vary, depending on your schedule. Most learners complete the Specialization in five to six months.
What background knowledge is necessary?
You don't need any background knowledge. We've designed this Specialization for learners who are new to the field of data and analytics.
Do I need to take the courses in a specific order?
We recommend you take them in the order they appear on Coursera. Each course builds on the knowledge you learned in the last one.
Will I earn university credit for completing the Specialization?
Coursera courses and certificates don't carry university credit, though some universities may choose to accept Specialization Certificates for credit. You should check with your institution to find out more.
What will I be able to do upon completing the Specialization?
You'll be able to use the data and analytics framework to develop a plan to solve a business problem. You'll be able to use Excel to analyze data using formulas and present a series of visualizations with a summary recommendation to solve the business problem. You'll also be able to take data and create a dynamic data dashboard in Excel that accepts inputs and refreshes with new data. Finally, you'll be able to develop and deliver a presentation using PowerPoint and the results of your data analysis - so you can share your point of view on how to solve the business problem.
How do I audit the Specialization?
If you'd like to audit the courses in this Specialization, you'll need to enroll in each course separately and then you will see the audit option.
What tools do I need for this Specialization?
In the "Data Visualization and Advance Excel" course learners will need PowerPivot to complete some of the exercises. Please use MS Excel 2013 version. If you have other MS Excel versions or a MAC you might not be able to complete all assignments.
Is this course really 100% online? Do I need to attend any classes in person?
This course is completely online, so there’s no need to show up to a classroom in person. You can access your lectures, readings and assignments anytime and anywhere via the web or your mobile device.
What is the refund policy?
If you subscribed, you get a 7-day free trial during which you can cancel at no penalty. After that, we don’t give refunds, but you can cancel your subscription at any time. See our full refund policy Opens in a new tab .
Can I just enroll in a single course?
Yes! To get started, click the course card that interests you and enroll. You can enroll and complete the course to earn a shareable certificate, or you can audit it to view the course materials for free. When you subscribe to a course that is part of a Specialization, you’re automatically subscribed to the full Specialization. Visit your learner dashboard to track your progress.
Is financial aid available?
Yes. In select learning programs, you can apply for financial aid or a scholarship if you can’t afford the enrollment fee. If fin aid or scholarship is available for your learning program selection, you’ll find a link to apply on the description page.
Can I take the course for free?
When you enroll in the course, you get access to all of the courses in the Specialization, and you earn a certificate when you complete the work. If you only want to read and view the course content, you can audit the course for free. If you cannot afford the fee, you can apply for financial aid Opens in a new tab .

More questions

- Certifications

Data Analysis 101: How to Make Your Presentations Practical and Effective
- December 27, 2022
- 53 Comments
Understanding Importance of Data Analysis
The results of data analysis can give business the vital insights they need to turn in to successful and profitable ventures. It could be the difference between a successful business operation and a business operation that is in trouble.
Data analysis, though one of the most in-demand job roles globally, doesn’t require a degree in statistics or mathematics to do well, and employers from a wide variety of industries are very keen to recruit data analysts.
Businesses hire data analysts in the field of finance, marketing, administration, HR, IT and procurement, to name just a few. Understand the big picture and provide answers. By engaging in data analysis, you can actually delve deep and discover hidden truths that most business people would never be able to do.
What skills you should master to be a data analyst?
While Data Analyst roles are on the rise, there are certain skills that are vital for anyone who wants to become a data analyst . Before the job, a candidate needs to have either a degree in statistics, business or computer science or a related subject, or work experience in these areas.
If you’re interested in becoming a data analyst, you’ll need to know:
- Programming and algorithms
- Data Visualization
- Open-source and cloud technologies
- No coding experience is required.
How much is a data analyst worth? Data analysts earn an average salary of £32,403 per annum, according to jobs site Glassdoor. This pays for a salary, with benefits such as medical insurance and paid leave included in the starting salary. If you think you have the right skills, there are plenty of roles on offer.
What data analysis entails
Data analysis is an analytical process which involves recording and tabulating (recording and entering, entering and tabulating) the quantities of a product, such as numbers of units produced, costs of materials and expenses.
While data analyst can take different forms, for example in databases, in other structures such as spreadsheets, numbers are the main means of data entry. This involves entering and entering the required data in a data analysis system such as Excel.
For example, although a database doesn’t require a data analyst, it can still benefit from data analysis techniques such as binomial testing, ANOVA and Fisher’s exact tests. Where is the data analysis courses in IT? Given the ever-increasing reliance on technology in business, data analysis courses are vital skills.
What are the types of data analysis methods?
- Cluster analysis
The act of grouping a specific set of data in a manner that those elements are more similar to one another than to those in other groups – hence the term ‘cluster.’ Since there is no special target variable while doing clustering, the method is often used to find hidden patterns in the data. The approach is purposely used to offer additional context to a particular trend or dataset.
- Cohort analysis
This type of data analysis method uses historical data to examine and compare a determined segment of users’ behavior, which can then be grouped with others with similar characteristics. By using this data analysis methodology, it’s possible to gain a wealth of insight into consumer needs or a firm understanding of a broader target group.
A dependent variable is an element of a complex system that is assumed to have a single cause, but it’s affected by multiple factors, thus giving researchers an indication as to how a complex system function.
- Regression analysis
The regression analysis is used to predict how the value of a dependent variable changes when one or more independent variables change, stay the same or the dependent variable is not moved. Regression is a sophisticated statistical method that includes mathematical functions that are typically called “segmentation,” “distribution,” and “intercept” functions.
Regression is a type of regression analysis that only contains linear and quadratic functions. You can change the types of factors (or the independent variables) that are selected in regression analysis (it’s typically called “nonlinear regression analysis”) by changing the order in which the models are constructed.To begin, let’s explain how regression analysis works.
Examples in business world
The Oracle Corporation is one of the first multinational companies to adopt this type of analysis method, based on which the company was able to develop predictive modelling systems for marketing purposes.
In a more specific sense, a Regression analysis is a popular type of data analysis used for analyzing the likelihood that a random variable will move up or down a range of parameters in response to a change in a specific control variable.
Companies who use this type of analysis are looking for trends and patterned performance over time. For example, how a company may respond to a rising cost of labor and its effect on its business bottom line, a weather-related issue like an earthquake, a new advertising campaign, or even a surge in customer demand in some areas.
What are basic pointers to consider while presenting data
Recognize that presentation matters.
Too often, analysts make the mistake of presenting information in order to show an abstracted version of it. For instance, say a B2B company has 4 ways to improve their sales funnel:
- More Visually Engaging
- More Easily Transacted
- More Cost Effective
Then, “informative” would mean that a B2B company needs to optimize their sales funnel to each of these to be more “convenient, faster, easier, more visually engaging, or most cost effective.” Sure, it would be nice if they all improved – they would all provide a competitive advantage in some way. But that’s not what the data tells us.
Don’t scare people with numbers
When you’re presenting data, show as many as possible, in as many charts as possible. Then, try to talk through the implications of the data, rather than overwhelming people with an overwhelming amount of data.
Why? Research suggests that when a number is presented in a visual, people become more likely to process it and learn from it. I recommend using video, text, graphs, and pictures to represent your numbers. This creates a more visually appealing data set. The number of followers on Twitter is visually appealing. The number of followers on Facebook is visually appealing. But nobody looks at their Twitter followers. If you don’t know what your numbers mean, how will your audience? That doesn’t mean numbers aren’t important.
Maximize the data pixel ratio
The more data you show to a critical stakeholder, the more likely they are to get lost and distracted from what you’re actually trying to communicate. This is especially important in the case of people in the sales and marketing function.
Do you have a sales person out in the field who is trying to close a deal? It would be a shame if that person got lost in your Excel analytics and lost out on the sale. This problem also occurs on the web.
Consider how web visitors respond to large, colorful charts and graphs. If we’re talking about visualizations that depict web performance, a visual might be helpful. But how often do we see this done? Research shows that people respond better to web-based data in a simplified, less complex format.
Save 3-D for the movies
There are great stories in the universe. This is an oversimplification, but if you look at history, humans only understand stories. We are great storytellers. We develop, through trial and error, our own intuition about the “right” way to tell stories.
One of the most powerful and effective ways to present data is to go beyond the visual to the audible, that is, to tell stories in a way that people can relate to. Everything you hear about computers being a series of numbers is wrong. We visualize numbers in a precise, quantitative way. But the numbers are not a collection of isolated events. To understand them, we need to understand the broader context.
Friends don’t let friends use pie charts
Businesses and analysts have done this since pie charts first appeared on Microsoft Excel sheets. When presenting data, break down your pie chart into its component segments.
As opposed to an equal-sized circle for the average earnings for all the employees, share a pie chart where the percentages for each individual segment are different, with a link to the corresponding chart.
Pair with explanatory text, show their correlation, and make your choice based on your audience, not on whether you want to scare or “educate” them. The majority of audiences will see the same image, regardless of whether it’s presented in a bar chart, bar chart, line chart, or something else.
Choose the appropriate chart
Does the data make logical sense? Check your assumptions against the data. Are the graphs charting only part of the story? Include other variables in the graphs. Avoid using axis labels to mislead. Never rely on axes to infer, “logical” conclusions. Trust your eyes: you know what information your brain can process.
Think of numbers like music — they are pleasing, but not overwhelming. Save 3D for the movies. When everyone is enjoying 4K, 8K, and beyond, it’s hard to envision your audience without the new stuff. I remember the first time I got to see HDTV. At home, I sat behind a chair and kept turning around to watch the TV. But at the theatre, I didn’t need a chair. All I had to do was look up, and see the giant screen, the contrast, and the detail.
Don’t mix chart types for no reason
Excel chart s with colored areas help people focus. Arrows give us scale. Assume your audience doesn’t understand what you’re saying, even if they do. Nobody wants to open a recipe book to learn how to cook soup. Instead, we start with a recipe.
Use a formula to communicate your analysis with as few words as possible. Keep it simple. Resist the urge to over-complicate your presentation. A word cloud is not a word cloud. A bar chart is not a bar chart. If you use a word cloud to illustrate a chart, consider replacing a few words with a gif. A bar chart doesn’t need clouds. And a bar chart doesn’t need clouds. If there’s one thing that’s sure to confuse your audience, it’s bar charts.
Use color with intention
Use color with intention. It’s not about pretty. When it comes to presenting data clearly, “informative” is more important than “beautiful.”
However, visualizations like maps, axes, or snapshots can help visual communication to avoid this pitfall. If you are going to show a few locations on a map, make sure each location has a voice and uses a distinct color. Avoid repeating colors from the map or bottom bar in all the visuals. Be consistent with how you present the data . A pie chart is not very interesting if all it shows is a bunch of varying sizes of the pie.
Data analysis in the workplace, and how it will impact the future of business
Business leaders are taking note of the importance of data analysis skills in their organisation, as it can make an enormous impact on business.
Larger organisations such as Google, Amazon and Facebook employ huge teams of analysts to create their data and statistics. We are already seeing the rise of the next generation of big data analysts – those who can write code that analyses and visualizes the data and report back information to a company to help it improve efficiency and increase revenue.
The increasing need for high-level understanding of data analysis has already led to the role of data analyst becoming available at university level. It is no longer a mandatory business qualification but one that can enhance your CV.
By understanding the importance of each variable, you can improve your business by managing your time and creating more effective systems and processes for running your business. The focus shifts from just providing services to providing value to your customers, creating a better, more intuitive experience for them so they can work with your company for the long-term.
Adopting these small steps will allow you to be more effective in your business and go from being an employee to an entrepreneur.
Share This Post:
53 thoughts on “data analysis 101: how to make your presentations practical and effective”.
Buy Zyvox Online – Special offer: Save up to $498 – buy antibiotics online and get discount for all purchased!
Thanks again for the post.Thanks Again. Cool.
Thanks for great information. What trips can you recommend in 2024? Astro tourism, eco diving, home swapping, train stations are the new food destinations,sports tourism, coolcationing, gig tripping, private group travel?
Enjoyed every bit of your article.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
Really appreciate you sharing this post. Want more.
I am so grateful for your blog. Really Great.
Hey, thanks for the blog post.
Great, thanks for sharing this blog.Thanks Again. Will read on…
Thanks for sharing, this is a fantastic blog.Thanks Again. Great.
Thanks for sharing, this is a fantastic article.Really thank you! Fantastic.
Major thankies for the article post.Thanks Again. Will read on…
Hey, thanks for the blog post. Cool.
A round of applause for your blog post.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
Appreciate you sharing, great article post. Great.
wow, awesome blog.Much thanks again. Cool.
Say, you got a nice blog.Really thank you! Cool.
Enjoyed every bit of your blog article.Much thanks again. Want more.
A round of applause for your blog post.Much thanks again. Cool.
I’m not sure where you’re getting your info, but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more. Thanks for wonderful info I was looking for this info for my mission.
Im thankful for the blog post.Much thanks again.
A big thank you for your article.Really thank you!
I truly appreciate this article post.Really looking forward to read more. Really Cool.
I really enjoy the article post.Much thanks again.
wow, awesome blog.Thanks Again. Will read on…
Awesome blog post.Much thanks again. Much obliged.
Im thankful for the blog.Much thanks again. Want more.
Thanks a lot for the post.Much thanks again. Want more.
I really liked your article.Really thank you! Really Cool.
A round of applause for your post.Thanks Again. Much obliged.
Say, you got a nice article.Really thank you! Fantastic.
I value the blog article. Really Cool.
A round of applause for your blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
Really appreciate you sharing this blog article. Really Cool.
Really informative article. Really Great.
Fantastic article post.Really looking forward to read more. Really Great.
I really liked your post.Much thanks again. Much obliged.
Beneficial document helps make frequent advance, appreciate it write about, this pile-up connected with expertise is usually to hold finding out, focus is usually the beginning of money.
I really liked your blog article.Much thanks again. Really Great.
I really liked your article post.Really thank you! Fantastic.
Great, thanks for sharing this blog.Thanks Again. Awesome.
Enjoyed every bit of your blog article. Cool.
I really enjoy the blog. Want more.
Im grateful for the blog.Thanks Again. Awesome.
Very neat blog.Thanks Again. Cool.
Muchos Gracias for your blog article.
Im grateful for the post.Really looking forward to read more. Keep writing.
Great, thanks for sharing this post.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
Thank you ever so for you article post.Really looking forward to read more. Will read on…
Great article post.Much thanks again. Great.
I really like and appreciate your blog post.Thanks Again. Awesome.
Really appreciate you sharing this blog. Really Cool.
Greetings! Incredibly helpful suggestions within this short article! It’s the very little adjustments that make the greatest modifications. Quite a few many thanks for sharing!
Awesome blog.Really looking forward to read more. Much obliged.
Add a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Get A 5X Raise In Salary
Reset Password
Insert/edit link.
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content
Table of Contents
What is data analysis, why is data analysis important, what is the data analysis process, data analysis methods, applications of data analysis, top data analysis techniques to analyze data, what is the importance of data analysis in research, future trends in data analysis, choose the right program, what is data analysis: a comprehensive guide.

In the contemporary business landscape, gaining a competitive edge is imperative, given the challenges such as rapidly evolving markets, economic unpredictability, fluctuating political environments, capricious consumer sentiments, and even global health crises. These challenges have reduced the room for error in business operations. For companies striving not only to survive but also to thrive in this demanding environment, the key lies in embracing the concept of data analysis . This involves strategically accumulating valuable, actionable information, which is leveraged to enhance decision-making processes.
If you're interested in forging a career in data analysis and wish to discover the top data analysis courses in 2024, we invite you to explore our informative video. It will provide insights into the opportunities to develop your expertise in this crucial field.
Data analysis inspects, cleans, transforms, and models data to extract insights and support decision-making. As a data analyst , your role involves dissecting vast datasets, unearthing hidden patterns, and translating numbers into actionable information.
Data analysis plays a pivotal role in today's data-driven world. It helps organizations harness the power of data, enabling them to make decisions, optimize processes, and gain a competitive edge. By turning raw data into meaningful insights, data analysis empowers businesses to identify opportunities, mitigate risks, and enhance their overall performance.
1. Informed Decision-Making
Data analysis is the compass that guides decision-makers through a sea of information. It enables organizations to base their choices on concrete evidence rather than intuition or guesswork. In business, this means making decisions more likely to lead to success, whether choosing the right marketing strategy, optimizing supply chains, or launching new products. By analyzing data, decision-makers can assess various options' potential risks and rewards, leading to better choices.
2. Improved Understanding
Data analysis provides a deeper understanding of processes, behaviors, and trends. It allows organizations to gain insights into customer preferences, market dynamics, and operational efficiency .
3. Competitive Advantage
Organizations can identify opportunities and threats by analyzing market trends, consumer behavior , and competitor performance. They can pivot their strategies to respond effectively, staying one step ahead of the competition. This ability to adapt and innovate based on data insights can lead to a significant competitive advantage.
Become a Data Science & Business Analytics Professional
- 11.5 M Expected New Jobs For Data Science And Analytics
- 28% Annual Job Growth By 2026
- $46K-$100K Average Annual Salary
Post Graduate Program in Data Analytics
- Post Graduate Program certificate and Alumni Association membership
- Exclusive hackathons and Ask me Anything sessions by IBM
Data Analyst
- Industry-recognized Data Analyst Master’s certificate from Simplilearn
- Dedicated live sessions by faculty of industry experts
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Felix Chong
Project manage , codethink.
After completing this course, I landed a new job & a salary hike of 30%. I now work with Zuhlke Group as a Project Manager.
Gayathri Ramesh
Associate data engineer , publicis sapient.
The course was well structured and curated. The live classes were extremely helpful. They made learning more productive and interactive. The program helped me change my domain from a data analyst to an Associate Data Engineer.
4. Risk Mitigation
Data analysis is a valuable tool for risk assessment and management. Organizations can assess potential issues and take preventive measures by analyzing historical data. For instance, data analysis detects fraudulent activities in the finance industry by identifying unusual transaction patterns. This not only helps minimize financial losses but also safeguards the reputation and trust of customers.
5. Efficient Resource Allocation
Data analysis helps organizations optimize resource allocation. Whether it's allocating budgets, human resources, or manufacturing capacities, data-driven insights can ensure that resources are utilized efficiently. For example, data analysis can help hospitals allocate staff and resources to the areas with the highest patient demand, ensuring that patient care remains efficient and effective.
6. Continuous Improvement
Data analysis is a catalyst for continuous improvement. It allows organizations to monitor performance metrics, track progress, and identify areas for enhancement. This iterative process of analyzing data, implementing changes, and analyzing again leads to ongoing refinement and excellence in processes and products.
The data analysis process is a structured sequence of steps that lead from raw data to actionable insights. Here are the answers to what is data analysis:
- Data Collection: Gather relevant data from various sources, ensuring data quality and integrity.
- Data Cleaning: Identify and rectify errors, missing values, and inconsistencies in the dataset. Clean data is crucial for accurate analysis.
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): Conduct preliminary analysis to understand the data's characteristics, distributions, and relationships. Visualization techniques are often used here.
- Data Transformation: Prepare the data for analysis by encoding categorical variables, scaling features, and handling outliers, if necessary.
- Model Building: Depending on the objectives, apply appropriate data analysis methods, such as regression, clustering, or deep learning.
- Model Evaluation: Depending on the problem type, assess the models' performance using metrics like Mean Absolute Error, Root Mean Squared Error , or others.
- Interpretation and Visualization: Translate the model's results into actionable insights. Visualizations, tables, and summary statistics help in conveying findings effectively.
- Deployment: Implement the insights into real-world solutions or strategies, ensuring that the data-driven recommendations are implemented.
1. Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a powerful method for understanding the relationship between a dependent and one or more independent variables. It is applied in economics, finance, and social sciences. By fitting a regression model, you can make predictions, analyze cause-and-effect relationships, and uncover trends within your data.
2. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis encompasses a broad range of techniques for summarizing and interpreting data. It involves descriptive statistics (mean, median, standard deviation), inferential statistics (hypothesis testing, confidence intervals), and multivariate analysis. Statistical methods help make inferences about populations from sample data, draw conclusions, and assess the significance of results.
3. Cohort Analysis
Cohort analysis focuses on understanding the behavior of specific groups or cohorts over time. It can reveal patterns, retention rates, and customer lifetime value, helping businesses tailor their strategies.
4. Content Analysis
It is a qualitative data analysis method used to study the content of textual, visual, or multimedia data. Social sciences, journalism, and marketing often employ it to analyze themes, sentiments, or patterns within documents or media. Content analysis can help researchers gain insights from large volumes of unstructured data.
5. Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is a technique for uncovering underlying latent factors that explain the variance in observed variables. It is commonly used in psychology and the social sciences to reduce the dimensionality of data and identify underlying constructs. Factor analysis can simplify complex datasets, making them easier to interpret and analyze.
6. Monte Carlo Method
This method is a simulation technique that uses random sampling to solve complex problems and make probabilistic predictions. Monte Carlo simulations allow analysts to model uncertainty and risk, making it a valuable tool for decision-making.
7. Text Analysis
Also known as text mining , this method involves extracting insights from textual data. It analyzes large volumes of text, such as social media posts, customer reviews, or documents. Text analysis can uncover sentiment, topics, and trends, enabling organizations to understand public opinion, customer feedback, and emerging issues.
8. Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis deals with data collected at regular intervals over time. It is essential for forecasting, trend analysis, and understanding temporal patterns. Time series methods include moving averages, exponential smoothing, and autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models. They are widely used in finance for stock price prediction, meteorology for weather forecasting, and economics for economic modeling.
9. Descriptive Analysis
Descriptive analysis involves summarizing and describing the main features of a dataset. It focuses on organizing and presenting the data in a meaningful way, often using measures such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation. It provides an overview of the data and helps identify patterns or trends.
10. Inferential Analysis
Inferential analysis aims to make inferences or predictions about a larger population based on sample data. It involves applying statistical techniques such as hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis. It helps generalize findings from a sample to a larger population.
11. Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
EDA focuses on exploring and understanding the data without preconceived hypotheses. It involves visualizations, summary statistics, and data profiling techniques to uncover patterns, relationships, and interesting features. It helps generate hypotheses for further analysis.
12. Diagnostic Analysis
Diagnostic analysis aims to understand the cause-and-effect relationships within the data. It investigates the factors or variables that contribute to specific outcomes or behaviors. Techniques such as regression analysis, ANOVA (Analysis of Variance), or correlation analysis are commonly used in diagnostic analysis.
13. Predictive Analysis
Predictive analysis involves using historical data to make predictions or forecasts about future outcomes. It utilizes statistical modeling techniques, machine learning algorithms, and time series analysis to identify patterns and build predictive models. It is often used for forecasting sales, predicting customer behavior, or estimating risk.
14. Prescriptive Analysis
Prescriptive analysis goes beyond predictive analysis by recommending actions or decisions based on the predictions. It combines historical data, optimization algorithms, and business rules to provide actionable insights and optimize outcomes. It helps in decision-making and resource allocation.
Our Data Analyst Master's Program will help you learn analytics tools and techniques to become a Data Analyst expert! It's the pefect course for you to jumpstart your career. Enroll now!
Data analysis is a versatile and indispensable tool that finds applications across various industries and domains. Its ability to extract actionable insights from data has made it a fundamental component of decision-making and problem-solving. Let's explore some of the key applications of data analysis:
1. Business and Marketing
- Market Research: Data analysis helps businesses understand market trends, consumer preferences, and competitive landscapes. It aids in identifying opportunities for product development, pricing strategies, and market expansion.
- Sales Forecasting: Data analysis models can predict future sales based on historical data, seasonality, and external factors. This helps businesses optimize inventory management and resource allocation.
2. Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Disease Diagnosis: Data analysis is vital in medical diagnostics, from interpreting medical images (e.g., MRI, X-rays) to analyzing patient records. Machine learning models can assist in early disease detection.
- Drug Discovery: Pharmaceutical companies use data analysis to identify potential drug candidates, predict their efficacy, and optimize clinical trials.
- Genomics and Personalized Medicine: Genomic data analysis enables personalized treatment plans by identifying genetic markers that influence disease susceptibility and response to therapies.
- Risk Management: Financial institutions use data analysis to assess credit risk, detect fraudulent activities, and model market risks.
- Algorithmic Trading: Data analysis is integral to developing trading algorithms that analyze market data and execute trades automatically based on predefined strategies.
- Fraud Detection: Credit card companies and banks employ data analysis to identify unusual transaction patterns and detect fraudulent activities in real time.
4. Manufacturing and Supply Chain
- Quality Control: Data analysis monitors and controls product quality on manufacturing lines. It helps detect defects and ensure consistency in production processes.
- Inventory Optimization: By analyzing demand patterns and supply chain data, businesses can optimize inventory levels, reduce carrying costs, and ensure timely deliveries.
5. Social Sciences and Academia
- Social Research: Researchers in social sciences analyze survey data, interviews, and textual data to study human behavior, attitudes, and trends. It helps in policy development and understanding societal issues.
- Academic Research: Data analysis is crucial to scientific physics, biology, and environmental science research. It assists in interpreting experimental results and drawing conclusions.
6. Internet and Technology
- Search Engines: Google uses complex data analysis algorithms to retrieve and rank search results based on user behavior and relevance.
- Recommendation Systems: Services like Netflix and Amazon leverage data analysis to recommend content and products to users based on their past preferences and behaviors.
7. Environmental Science
- Climate Modeling: Data analysis is essential in climate science. It analyzes temperature, precipitation, and other environmental data. It helps in understanding climate patterns and predicting future trends.
- Environmental Monitoring: Remote sensing data analysis monitors ecological changes, including deforestation, water quality, and air pollution.
1. Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics provide a snapshot of a dataset's central tendencies and variability. These techniques help summarize and understand the data's basic characteristics.
2. Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics involve making predictions or inferences based on a sample of data. Techniques include hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis. These methods are crucial for drawing conclusions from data and assessing the significance of findings.
3. Regression Analysis
It explores the relationship between one or more independent variables and a dependent variable. It is widely used for prediction and understanding causal links. Linear, logistic, and multiple regression are common in various fields.
4. Clustering Analysis
It is an unsupervised learning method that groups similar data points. K-means clustering and hierarchical clustering are examples. This technique is used for customer segmentation, anomaly detection, and pattern recognition.
5. Classification Analysis
Classification analysis assigns data points to predefined categories or classes. It's often used in applications like spam email detection, image recognition, and sentiment analysis. Popular algorithms include decision trees, support vector machines, and neural networks.
6. Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis deals with data collected over time, making it suitable for forecasting and trend analysis. Techniques like moving averages, autoregressive integrated moving averages (ARIMA), and exponential smoothing are applied in fields like finance, economics, and weather forecasting.
7. Text Analysis (Natural Language Processing - NLP)
Text analysis techniques, part of NLP , enable extracting insights from textual data. These methods include sentiment analysis, topic modeling, and named entity recognition. Text analysis is widely used for analyzing customer reviews, social media content, and news articles.
8. Principal Component Analysis
It is a dimensionality reduction technique that simplifies complex datasets while retaining important information. It transforms correlated variables into a set of linearly uncorrelated variables, making it easier to analyze and visualize high-dimensional data.
9. Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection identifies unusual patterns or outliers in data. It's critical in fraud detection, network security, and quality control. Techniques like statistical methods, clustering-based approaches, and machine learning algorithms are employed for anomaly detection.
10. Data Mining
Data mining involves the automated discovery of patterns, associations, and relationships within large datasets. Techniques like association rule mining, frequent pattern analysis, and decision tree mining extract valuable knowledge from data.
11. Machine Learning and Deep Learning
ML and deep learning algorithms are applied for predictive modeling, classification, and regression tasks. Techniques like random forests, support vector machines, and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have revolutionized various industries, including healthcare, finance, and image recognition.
12. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Analysis
GIS analysis combines geographical data with spatial analysis techniques to solve location-based problems. It's widely used in urban planning, environmental management, and disaster response.
- Uncovering Patterns and Trends: Data analysis allows researchers to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. By examining these patterns, researchers can better understand the phenomena under investigation. For example, in epidemiological research, data analysis can reveal the trends and patterns of disease outbreaks, helping public health officials take proactive measures.
- Testing Hypotheses: Research often involves formulating hypotheses and testing them. Data analysis provides the means to evaluate hypotheses rigorously. Through statistical tests and inferential analysis, researchers can determine whether the observed patterns in the data are statistically significant or simply due to chance.
- Making Informed Conclusions: Data analysis helps researchers draw meaningful and evidence-based conclusions from their research findings. It provides a quantitative basis for making claims and recommendations. In academic research, these conclusions form the basis for scholarly publications and contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field.
- Enhancing Data Quality: Data analysis includes data cleaning and validation processes that improve the quality and reliability of the dataset. Identifying and addressing errors, missing values, and outliers ensures that the research results accurately reflect the phenomena being studied.
- Supporting Decision-Making: In applied research, data analysis assists decision-makers in various sectors, such as business, government, and healthcare. Policy decisions, marketing strategies, and resource allocations are often based on research findings.
- Identifying Outliers and Anomalies: Outliers and anomalies in data can hold valuable information or indicate errors. Data analysis techniques can help identify these exceptional cases, whether medical diagnoses, financial fraud detection, or product quality control.
- Revealing Insights: Research data often contain hidden insights that are not immediately apparent. Data analysis techniques, such as clustering or text analysis, can uncover these insights. For example, social media data sentiment analysis can reveal public sentiment and trends on various topics in social sciences.
- Forecasting and Prediction: Data analysis allows for the development of predictive models. Researchers can use historical data to build models forecasting future trends or outcomes. This is valuable in fields like finance for stock price predictions, meteorology for weather forecasting, and epidemiology for disease spread projections.
- Optimizing Resources: Research often involves resource allocation. Data analysis helps researchers and organizations optimize resource use by identifying areas where improvements can be made, or costs can be reduced.
- Continuous Improvement: Data analysis supports the iterative nature of research. Researchers can analyze data, draw conclusions, and refine their hypotheses or research designs based on their findings. This cycle of analysis and refinement leads to continuous improvement in research methods and understanding.
Data analysis is an ever-evolving field driven by technological advancements. The future of data analysis promises exciting developments that will reshape how data is collected, processed, and utilized. Here are some of the key trends of data analysis:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are expected to play a central role in data analysis. These technologies can automate complex data processing tasks, identify patterns at scale, and make highly accurate predictions. AI-driven analytics tools will become more accessible, enabling organizations to harness the power of ML without requiring extensive expertise.
2. Augmented Analytics
Augmented analytics combines AI and natural language processing (NLP) to assist data analysts in finding insights. These tools can automatically generate narratives, suggest visualizations, and highlight important trends within data. They enhance the speed and efficiency of data analysis, making it more accessible to a broader audience.
3. Data Privacy and Ethical Considerations
As data collection becomes more pervasive, privacy concerns and ethical considerations will gain prominence. Future data analysis trends will prioritize responsible data handling, transparency, and compliance with regulations like GDPR . Differential privacy techniques and data anonymization will be crucial in balancing data utility with privacy protection.
4. Real-time and Streaming Data Analysis
The demand for real-time insights will drive the adoption of real-time and streaming data analysis. Organizations will leverage technologies like Apache Kafka and Apache Flink to process and analyze data as it is generated. This trend is essential for fraud detection, IoT analytics, and monitoring systems.
5. Quantum Computing
It can potentially revolutionize data analysis by solving complex problems exponentially faster than classical computers. Although quantum computing is in its infancy, its impact on optimization, cryptography , and simulations will be significant once practical quantum computers become available.
6. Edge Analytics
With the proliferation of edge devices in the Internet of Things (IoT), data analysis is moving closer to the data source. Edge analytics allows for real-time processing and decision-making at the network's edge, reducing latency and bandwidth requirements.
7. Explainable AI (XAI)
Interpretable and explainable AI models will become crucial, especially in applications where trust and transparency are paramount. XAI techniques aim to make AI decisions more understandable and accountable, which is critical in healthcare and finance.
8. Data Democratization
The future of data analysis will see more democratization of data access and analysis tools. Non-technical users will have easier access to data and analytics through intuitive interfaces and self-service BI tools , reducing the reliance on data specialists.
9. Advanced Data Visualization
Data visualization tools will continue to evolve, offering more interactivity, 3D visualization, and augmented reality (AR) capabilities. Advanced visualizations will help users explore data in new and immersive ways.
10. Ethnographic Data Analysis
Ethnographic data analysis will gain importance as organizations seek to understand human behavior, cultural dynamics, and social trends. This qualitative data analysis approach and quantitative methods will provide a holistic understanding of complex issues.
11. Data Analytics Ethics and Bias Mitigation
Ethical considerations in data analysis will remain a key trend. Efforts to identify and mitigate bias in algorithms and models will become standard practice, ensuring fair and equitable outcomes.
Our Data Analytics courses have been meticulously crafted to equip you with the necessary skills and knowledge to thrive in this swiftly expanding industry. Our instructors will lead you through immersive, hands-on projects, real-world simulations, and illuminating case studies, ensuring you gain the practical expertise necessary for success. Through our courses, you will acquire the ability to dissect data, craft enlightening reports, and make data-driven choices that have the potential to steer businesses toward prosperity.
Having addressed the question of what is data analysis, if you're considering a career in data analytics, it's advisable to begin by researching the prerequisites for becoming a data analyst. You may also want to explore the Post Graduate Program in Data Analytics offered in collaboration with Purdue University. This program offers a practical learning experience through real-world case studies and projects aligned with industry needs. It provides comprehensive exposure to the essential technologies and skills currently employed in the field of data analytics.
Program Name Data Analyst Post Graduate Program In Data Analytics Data Analytics Bootcamp Geo All Geos All Geos US University Simplilearn Purdue Caltech Course Duration 11 Months 8 Months 6 Months Coding Experience Required No Basic No Skills You Will Learn 10+ skills including Python, MySQL, Tableau, NumPy and more Data Analytics, Statistical Analysis using Excel, Data Analysis Python and R, and more Data Visualization with Tableau, Linear and Logistic Regression, Data Manipulation and more Additional Benefits Applied Learning via Capstone and 20+ industry-relevant Data Analytics projects Purdue Alumni Association Membership Free IIMJobs Pro-Membership of 6 months Access to Integrated Practical Labs Caltech CTME Circle Membership Cost $$ $$$$ $$$$ Explore Program Explore Program Explore Program
1. What is the difference between data analysis and data science?
Data analysis primarily involves extracting meaningful insights from existing data using statistical techniques and visualization tools. Whereas, data science encompasses a broader spectrum, incorporating data analysis as a subset while involving machine learning, deep learning, and predictive modeling to build data-driven solutions and algorithms.
2. What are the common mistakes to avoid in data analysis?
Common mistakes to avoid in data analysis include neglecting data quality issues, failing to define clear objectives, overcomplicating visualizations, not considering algorithmic biases, and disregarding the importance of proper data preprocessing and cleaning. Additionally, avoiding making unwarranted assumptions and misinterpreting correlation as causation in your analysis is crucial.
Data Science & Business Analytics Courses Duration and Fees
Data Science & Business Analytics programs typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Learn from Industry Experts with free Masterclasses
Data science & business analytics.
How Can You Master the Art of Data Analysis: Uncover the Path to Career Advancement
Develop Your Career in Data Analytics with Purdue University Professional Certificate
Career Masterclass: How to Get Qualified for a Data Analytics Career
Recommended Reads
Big Data Career Guide: A Comprehensive Playbook to Becoming a Big Data Engineer
Why Python Is Essential for Data Analysis and Data Science?
The Best Spotify Data Analysis Project You Need to Know
The Rise of the Data-Driven Professional: 6 Non-Data Roles That Need Data Analytics Skills
Exploratory Data Analysis [EDA]: Techniques, Best Practices and Popular Applications
All the Ins and Outs of Exploratory Data Analysis
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.

Skills for Learning : Research Skills
Data analysis is an ongoing process that should occur throughout your research project. Suitable data-analysis methods must be selected when you write your research proposal. The nature of your data (i.e. quantitative or qualitative) will be influenced by your research design and purpose. The data will also influence the analysis methods selected.
We run interactive workshops to help you develop skills related to doing research, such as data analysis, writing literature reviews and preparing for dissertations. Find out more on the Skills for Learning Workshops page.
We have online academic skills modules within MyBeckett for all levels of university study. These modules will help your academic development and support your success at LBU. You can work through the modules at your own pace, revisiting them as required. Find out more from our FAQ What academic skills modules are available?
Quantitative data analysis
Broadly speaking, 'statistics' refers to methods, tools and techniques used to collect, organise and interpret data. The goal of statistics is to gain understanding from data. Therefore, you need to know how to:
- Produce data – for example, by handing out a questionnaire or doing an experiment.
- Organise, summarise, present and analyse data.
- Draw valid conclusions from findings.
There are a number of statistical methods you can use to analyse data. Choosing an appropriate statistical method should follow naturally, however, from your research design. Therefore, you should think about data analysis at the early stages of your study design. You may need to consult a statistician for help with this.
Tips for working with statistical data
- Plan so that the data you get has a good chance of successfully tackling the research problem. This will involve reading literature on your subject, as well as on what makes a good study.
- To reach useful conclusions, you need to reduce uncertainties or 'noise'. Thus, you will need a sufficiently large data sample. A large sample will improve precision. However, this must be balanced against the 'costs' (time and money) of collection.
- Consider the logistics. Will there be problems in obtaining sufficient high-quality data? Think about accuracy, trustworthiness and completeness.
- Statistics are based on random samples. Consider whether your sample will be suited to this sort of analysis. Might there be biases to think about?
- How will you deal with missing values (any data that is not recorded for some reason)? These can result from gaps in a record or whole records being missed out.
- When analysing data, start by looking at each variable separately. Conduct initial/exploratory data analysis using graphical displays. Do this before looking at variables in conjunction or anything more complicated. This process can help locate errors in the data and also gives you a 'feel' for the data.
- Look out for patterns of 'missingness'. They are likely to alert you if there’s a problem. If the 'missingness' is not random, then it will have an impact on the results.
- Be vigilant and think through what you are doing at all times. Think critically. Statistics are not just mathematical tricks that a computer sorts out. Rather, analysing statistical data is a process that the human mind must interpret!
Top tips! Try inventing or generating the sort of data you might get and see if you can analyse it. Make sure that your process works before gathering actual data. Think what the output of an analytic procedure will look like before doing it for real.
(Note: it is actually difficult to generate realistic data. There are fraud-detection methods in place to identify data that has been fabricated. So, remember to get rid of your practice data before analysing the real stuff!)
Statistical software packages
Software packages can be used to analyse and present data. The most widely used ones are SPSS and NVivo.
SPSS is a statistical-analysis and data-management package for quantitative data analysis. Click on ‘ How do I install SPSS? ’ to learn how to download SPSS to your personal device. SPSS can perform a wide variety of statistical procedures. Some examples are:
- Data management (i.e. creating subsets of data or transforming data).
- Summarising, describing or presenting data (i.e. mean, median and frequency).
- Looking at the distribution of data (i.e. standard deviation).
- Comparing groups for significant differences using parametric (i.e. t-test) and non-parametric (i.e. Chi-square) tests.
- Identifying significant relationships between variables (i.e. correlation).
NVivo can be used for qualitative data analysis. It is suitable for use with a wide range of methodologies. Click on ‘ How do I access NVivo ’ to learn how to download NVivo to your personal device. NVivo supports grounded theory, survey data, case studies, focus groups, phenomenology, field research and action research.
- Process data such as interview transcripts, literature or media extracts, and historical documents.
- Code data on screen and explore all coding and documents interactively.
- Rearrange, restructure, extend and edit text, coding and coding relationships.
- Search imported text for words, phrases or patterns, and automatically code the results.
Qualitative data analysis
Miles and Huberman (1994) point out that there are diverse approaches to qualitative research and analysis. They suggest, however, that it is possible to identify 'a fairly classic set of analytic moves arranged in sequence'. This involves:
- Affixing codes to a set of field notes drawn from observation or interviews.
- Noting reflections or other remarks in the margins.
- Sorting/sifting through these materials to identify: a) similar phrases, relationships between variables, patterns and themes and b) distinct differences between subgroups and common sequences.
- Isolating these patterns/processes and commonalties/differences. Then, taking them out to the field in the next wave of data collection.
- Highlighting generalisations and relating them to your original research themes.
- Taking the generalisations and analysing them in relation to theoretical perspectives.
(Miles and Huberman, 1994.)
Patterns and generalisations are usually arrived at through a process of analytic induction (see above points 5 and 6). Qualitative analysis rarely involves statistical analysis of relationships between variables. Qualitative analysis aims to gain in-depth understanding of concepts, opinions or experiences.
Presenting information
There are a number of different ways of presenting and communicating information. The particular format you use is dependent upon the type of data generated from the methods you have employed.
Here are some appropriate ways of presenting information for different types of data:
Bar charts: These may be useful for comparing relative sizes. However, they tend to use a large amount of ink to display a relatively small amount of information. Consider a simple line chart as an alternative.
Pie charts: These have the benefit of indicating that the data must add up to 100%. However, they make it difficult for viewers to distinguish relative sizes, especially if two slices have a difference of less than 10%.
Other examples of presenting data in graphical form include line charts and scatter plots .
Qualitative data is more likely to be presented in text form. For example, using quotations from interviews or field diaries.
- Plan ahead, thinking carefully about how you will analyse and present your data.
- Think through possible restrictions to resources you may encounter and plan accordingly.
- Find out about the different IT packages available for analysing your data and select the most appropriate.
- If necessary, allow time to attend an introductory course on a particular computer package. You can book SPSS and NVivo workshops via MyHub .
- Code your data appropriately, assigning conceptual or numerical codes as suitable.
- Organise your data so it can be analysed and presented easily.
- Choose the most suitable way of presenting your information, according to the type of data collected. This will allow your information to be understood and interpreted better.
Primary, secondary and tertiary sources
Information sources are sometimes categorised as primary, secondary or tertiary sources depending on whether or not they are ‘original’ materials or data. For some research projects, you may need to use primary sources as well as secondary or tertiary sources. However the distinction between primary and secondary sources is not always clear and depends on the context. For example, a newspaper article might usually be categorised as a secondary source. But it could also be regarded as a primary source if it were an article giving a first-hand account of a historical event written close to the time it occurred.
- Primary sources
- Secondary sources
- Tertiary sources
- Grey literature
Primary sources are original sources of information that provide first-hand accounts of what is being experienced or researched. They enable you to get as close to the actual event or research as possible. They are useful for getting the most contemporary information about a topic.
Examples include diary entries, newspaper articles, census data, journal articles with original reports of research, letters, email or other correspondence, original manuscripts and archives, interviews, research data and reports, statistics, autobiographies, exhibitions, films, and artists' writings.
Some information will be available on an Open Access basis, freely accessible online. However, many academic sources are paywalled, and you may need to login as a Leeds Beckett student to access them. Where Leeds Beckett does not have access to a source, you can use our Request It! Service .
Secondary sources interpret, evaluate or analyse primary sources. They're useful for providing background information on a topic, or for looking back at an event from a current perspective. The majority of your literature searching will probably be done to find secondary sources on your topic.
Examples include journal articles which review or interpret original findings, popular magazine articles commenting on more serious research, textbooks and biographies.
The term tertiary sources isn't used a great deal. There's overlap between what might be considered a secondary source and a tertiary source. One definition is that a tertiary source brings together secondary sources.
Examples include almanacs, fact books, bibliographies, dictionaries and encyclopaedias, directories, indexes and abstracts. They can be useful for introductory information or an overview of a topic in the early stages of research.
Depending on your subject of study, grey literature may be another source you need to use. Grey literature includes technical or research reports, theses and dissertations, conference papers, government documents, white papers, and so on.
Artificial intelligence tools
Before using any generative artificial intelligence or paraphrasing tools in your assessments, you should check if this is permitted on your course.
If their use is permitted on your course, you must acknowledge any use of generative artificial intelligence tools such as ChatGPT or paraphrasing tools (e.g., Grammarly, Quillbot, etc.), even if you have only used them to generate ideas for your assessments or for proofreading.
- Academic Integrity Module in MyBeckett
- Assignment Calculator
- Building on Feedback
- Disability Advice
- Essay X-ray tool
- International Students' Academic Introduction
- Manchester Academic Phrasebank
- Quote, Unquote
- Skills and Subject Suppor t
- Turnitin Grammar Checker
{{You can add more boxes below for links specific to this page [this note will not appear on user pages] }}
- Research Methods Checklist
- Sampling Checklist
Skills for Learning FAQs

0113 812 1000
- University Disclaimer
- Accessibility
A Guide To The Methods, Benefits & Problems of The Interpretation of Data

Table of Contents
1) What Is Data Interpretation?
2) How To Interpret Data?
3) Why Data Interpretation Is Important?
4) Data Interpretation Skills
5) Data Analysis & Interpretation Problems
6) Data Interpretation Techniques & Methods
7) The Use of Dashboards For Data Interpretation
8) Business Data Interpretation Examples
Data analysis and interpretation have now taken center stage with the advent of the digital age… and the sheer amount of data can be frightening. In fact, a Digital Universe study found that the total data supply in 2012 was 2.8 trillion gigabytes! Based on that amount of data alone, it is clear the calling card of any successful enterprise in today’s global world will be the ability to analyze complex data, produce actionable insights, and adapt to new market needs… all at the speed of thought.
Business dashboards are the digital age tools for big data. Capable of displaying key performance indicators (KPIs) for both quantitative and qualitative data analyses, they are ideal for making the fast-paced and data-driven market decisions that push today’s industry leaders to sustainable success. Through the art of streamlined visual communication, data dashboards permit businesses to engage in real-time and informed decision-making and are key instruments in data interpretation. First of all, let’s find a definition to understand what lies behind this practice.
What Is Data Interpretation?
Data interpretation refers to the process of using diverse analytical methods to review data and arrive at relevant conclusions. The interpretation of data helps researchers to categorize, manipulate, and summarize the information in order to answer critical questions.
The importance of data interpretation is evident, and this is why it needs to be done properly. Data is very likely to arrive from multiple sources and has a tendency to enter the analysis process with haphazard ordering. Data analysis tends to be extremely subjective. That is to say, the nature and goal of interpretation will vary from business to business, likely correlating to the type of data being analyzed. While there are several types of processes that are implemented based on the nature of individual data, the two broadest and most common categories are “quantitative and qualitative analysis.”
Yet, before any serious data interpretation inquiry can begin, it should be understood that visual presentations of data findings are irrelevant unless a sound decision is made regarding measurement scales. Before any serious data analysis can begin, the measurement scale must be decided for the data as this will have a long-term impact on data interpretation ROI. The varying scales include:
- Nominal Scale: non-numeric categories that cannot be ranked or compared quantitatively. Variables are exclusive and exhaustive.
- Ordinal Scale: exclusive categories that are exclusive and exhaustive but with a logical order. Quality ratings and agreement ratings are examples of ordinal scales (i.e., good, very good, fair, etc., OR agree, strongly agree, disagree, etc.).
- Interval: a measurement scale where data is grouped into categories with orderly and equal distances between the categories. There is always an arbitrary zero point.
- Ratio: contains features of all three.
For a more in-depth review of scales of measurement, read our article on data analysis questions . Once measurement scales have been selected, it is time to select which of the two broad interpretation processes will best suit your data needs. Let’s take a closer look at those specific methods and possible data interpretation problems.
How To Interpret Data? Top Methods & Techniques

When interpreting data, an analyst must try to discern the differences between correlation, causation, and coincidences, as well as many other biases – but he also has to consider all the factors involved that may have led to a result. There are various data interpretation types and methods one can use to achieve this.
The interpretation of data is designed to help people make sense of numerical data that has been collected, analyzed, and presented. Having a baseline method for interpreting data will provide your analyst teams with a structure and consistent foundation. Indeed, if several departments have different approaches to interpreting the same data while sharing the same goals, some mismatched objectives can result. Disparate methods will lead to duplicated efforts, inconsistent solutions, wasted energy, and inevitably – time and money. In this part, we will look at the two main methods of interpretation of data: qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Qualitative Data Interpretation
Qualitative data analysis can be summed up in one word – categorical. With this type of analysis, data is not described through numerical values or patterns but through the use of descriptive context (i.e., text). Typically, narrative data is gathered by employing a wide variety of person-to-person techniques. These techniques include:
- Observations: detailing behavioral patterns that occur within an observation group. These patterns could be the amount of time spent in an activity, the type of activity, and the method of communication employed.
- Focus groups: Group people and ask them relevant questions to generate a collaborative discussion about a research topic.
- Secondary Research: much like how patterns of behavior can be observed, various types of documentation resources can be coded and divided based on the type of material they contain.
- Interviews: one of the best collection methods for narrative data. Inquiry responses can be grouped by theme, topic, or category. The interview approach allows for highly focused data segmentation.
A key difference between qualitative and quantitative analysis is clearly noticeable in the interpretation stage. The first one is widely open to interpretation and must be “coded” so as to facilitate the grouping and labeling of data into identifiable themes. As person-to-person data collection techniques can often result in disputes pertaining to proper analysis, qualitative data analysis is often summarized through three basic principles: notice things, collect things, and think about things.
After qualitative data has been collected through transcripts, questionnaires, audio and video recordings, or the researcher’s notes, it is time to interpret it. For that purpose, there are some common methods used by researchers and analysts.
- Content analysis : As its name suggests, this is a research method used to identify frequencies and recurring words, subjects, and concepts in image, video, or audio content. It transforms qualitative information into quantitative data to help discover trends and conclusions that will later support important research or business decisions. This method is often used by marketers to understand brand sentiment from the mouths of customers themselves. Through that, they can extract valuable information to improve their products and services. It is recommended to use content analytics tools for this method as manually performing it is very time-consuming and can lead to human error or subjectivity issues. Having a clear goal in mind before diving into it is another great practice for avoiding getting lost in the fog.
- Thematic analysis: This method focuses on analyzing qualitative data, such as interview transcripts, survey questions, and others, to identify common patterns and separate the data into different groups according to found similarities or themes. For example, imagine you want to analyze what customers think about your restaurant. For this purpose, you do a thematic analysis on 1000 reviews and find common themes such as “fresh food”, “cold food”, “small portions”, “friendly staff”, etc. With those recurring themes in hand, you can extract conclusions about what could be improved or enhanced based on your customer’s experiences. Since this technique is more exploratory, be open to changing your research questions or goals as you go.
- Narrative analysis: A bit more specific and complicated than the two previous methods, it is used to analyze stories and discover their meaning. These stories can be extracted from testimonials, case studies, and interviews, as these formats give people more space to tell their experiences. Given that collecting this kind of data is harder and more time-consuming, sample sizes for narrative analysis are usually smaller, which makes it harder to reproduce its findings. However, it is still a valuable technique for understanding customers' preferences and mindsets.
- Discourse analysis : This method is used to draw the meaning of any type of visual, written, or symbolic language in relation to a social, political, cultural, or historical context. It is used to understand how context can affect how language is carried out and understood. For example, if you are doing research on power dynamics, using discourse analysis to analyze a conversation between a janitor and a CEO and draw conclusions about their responses based on the context and your research questions is a great use case for this technique. That said, like all methods in this section, discourse analytics is time-consuming as the data needs to be analyzed until no new insights emerge.
- Grounded theory analysis : The grounded theory approach aims to create or discover a new theory by carefully testing and evaluating the data available. Unlike all other qualitative approaches on this list, grounded theory helps extract conclusions and hypotheses from the data instead of going into the analysis with a defined hypothesis. This method is very popular amongst researchers, analysts, and marketers as the results are completely data-backed, providing a factual explanation of any scenario. It is often used when researching a completely new topic or with little knowledge as this space to start from the ground up.
Quantitative Data Interpretation
If quantitative data interpretation could be summed up in one word (and it really can’t), that word would be “numerical.” There are few certainties when it comes to data analysis, but you can be sure that if the research you are engaging in has no numbers involved, it is not quantitative research, as this analysis refers to a set of processes by which numerical data is analyzed. More often than not, it involves the use of statistical modeling such as standard deviation, mean, and median. Let’s quickly review the most common statistical terms:
- Mean: A mean represents a numerical average for a set of responses. When dealing with a data set (or multiple data sets), a mean will represent the central value of a specific set of numbers. It is the sum of the values divided by the number of values within the data set. Other terms that can be used to describe the concept are arithmetic mean, average, and mathematical expectation.
- Standard deviation: This is another statistical term commonly used in quantitative analysis. Standard deviation reveals the distribution of the responses around the mean. It describes the degree of consistency within the responses; together with the mean, it provides insight into data sets.
- Frequency distribution: This is a measurement gauging the rate of a response appearance within a data set. When using a survey, for example, frequency distribution, it can determine the number of times a specific ordinal scale response appears (i.e., agree, strongly agree, disagree, etc.). Frequency distribution is extremely keen in determining the degree of consensus among data points.
Typically, quantitative data is measured by visually presenting correlation tests between two or more variables of significance. Different processes can be used together or separately, and comparisons can be made to ultimately arrive at a conclusion. Other signature interpretation processes of quantitative data include:
- Regression analysis: Essentially, it uses historical data to understand the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. Knowing which variables are related and how they developed in the past allows you to anticipate possible outcomes and make better decisions going forward. For example, if you want to predict your sales for next month, you can use regression to understand what factors will affect them, such as products on sale and the launch of a new campaign, among many others.
- Cohort analysis: This method identifies groups of users who share common characteristics during a particular time period. In a business scenario, cohort analysis is commonly used to understand customer behaviors. For example, a cohort could be all users who have signed up for a free trial on a given day. An analysis would be carried out to see how these users behave, what actions they carry out, and how their behavior differs from other user groups.
- Predictive analysis: As its name suggests, the predictive method aims to predict future developments by analyzing historical and current data. Powered by technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, predictive analytics practices enable businesses to identify patterns or potential issues and plan informed strategies in advance.
- Prescriptive analysis: Also powered by predictions, the prescriptive method uses techniques such as graph analysis, complex event processing, and neural networks, among others, to try to unravel the effect that future decisions will have in order to adjust them before they are actually made. This helps businesses to develop responsive, practical business strategies.
- Conjoint analysis: Typically applied to survey analysis, the conjoint approach is used to analyze how individuals value different attributes of a product or service. This helps researchers and businesses to define pricing, product features, packaging, and many other attributes. A common use is menu-based conjoint analysis, in which individuals are given a “menu” of options from which they can build their ideal concept or product. Through this, analysts can understand which attributes they would pick above others and drive conclusions.
- Cluster analysis: Last but not least, the cluster is a method used to group objects into categories. Since there is no target variable when using cluster analysis, it is a useful method to find hidden trends and patterns in the data. In a business context, clustering is used for audience segmentation to create targeted experiences. In market research, it is often used to identify age groups, geographical information, and earnings, among others.
Now that we have seen how to interpret data, let's move on and ask ourselves some questions: What are some of the benefits of data interpretation? Why do all industries engage in data research and analysis? These are basic questions, but they often don’t receive adequate attention.
Your Chance: Want to test a powerful data analysis software? Use our 14-days free trial & start extracting insights from your data!
Why Data Interpretation Is Important

The purpose of collection and interpretation is to acquire useful and usable information and to make the most informed decisions possible. From businesses to newlyweds researching their first home, data collection and interpretation provide limitless benefits for a wide range of institutions and individuals.
Data analysis and interpretation, regardless of the method and qualitative/quantitative status, may include the following characteristics:
- Data identification and explanation
- Comparing and contrasting data
- Identification of data outliers
- Future predictions
Data analysis and interpretation, in the end, help improve processes and identify problems. It is difficult to grow and make dependable improvements without, at the very least, minimal data collection and interpretation. What is the keyword? Dependable. Vague ideas regarding performance enhancement exist within all institutions and industries. Yet, without proper research and analysis, an idea is likely to remain in a stagnant state forever (i.e., minimal growth). So… what are a few of the business benefits of digital age data analysis and interpretation? Let’s take a look!
1) Informed decision-making: A decision is only as good as the knowledge that formed it. Informed data decision-making can potentially set industry leaders apart from the rest of the market pack. Studies have shown that companies in the top third of their industries are, on average, 5% more productive and 6% more profitable when implementing informed data decision-making processes. Most decisive actions will arise only after a problem has been identified or a goal defined. Data analysis should include identification, thesis development, and data collection, followed by data communication.
If institutions only follow that simple order, one that we should all be familiar with from grade school science fairs, then they will be able to solve issues as they emerge in real-time. Informed decision-making has a tendency to be cyclical. This means there is really no end, and eventually, new questions and conditions arise within the process that need to be studied further. The monitoring of data results will inevitably return the process to the start with new data and sights.
2) Anticipating needs with trends identification: data insights provide knowledge, and knowledge is power. The insights obtained from market and consumer data analyses have the ability to set trends for peers within similar market segments. A perfect example of how data analytics can impact trend prediction is evidenced in the music identification application Shazam . The application allows users to upload an audio clip of a song they like but can’t seem to identify. Users make 15 million song identifications a day. With this data, Shazam has been instrumental in predicting future popular artists.
When industry trends are identified, they can then serve a greater industry purpose. For example, the insights from Shazam’s monitoring benefits not only Shazam in understanding how to meet consumer needs but also grant music executives and record label companies an insight into the pop-culture scene of the day. Data gathering and interpretation processes can allow for industry-wide climate prediction and result in greater revenue streams across the market. For this reason, all institutions should follow the basic data cycle of collection, interpretation, decision-making, and monitoring.
3) Cost efficiency: Proper implementation of analytics processes can provide businesses with profound cost advantages within their industries. A recent data study performed by Deloitte vividly demonstrates this in finding that data analysis ROI is driven by efficient cost reductions. Often, this benefit is overlooked because making money is typically viewed as “sexier” than saving money. Yet, sound data analyses have the ability to alert management to cost-reduction opportunities without any significant exertion of effort on the part of human capital.
A great example of the potential for cost efficiency through data analysis is Intel. Prior to 2012, Intel would conduct over 19,000 manufacturing function tests on their chips before they could be deemed acceptable for release. To cut costs and reduce test time, Intel implemented predictive data analyses. By using historical and current data, Intel now avoids testing each chip 19,000 times by focusing on specific and individual chip tests. After its implementation in 2012, Intel saved over $3 million in manufacturing costs. Cost reduction may not be as “sexy” as data profit, but as Intel proves, it is a benefit of data analysis that should not be neglected.
4) Clear foresight: companies that collect and analyze their data gain better knowledge about themselves, their processes, and their performance. They can identify performance challenges when they arise and take action to overcome them. Data interpretation through visual representations lets them process their findings faster and make better-informed decisions on the company's future.
Key Data Interpretation Skills You Should Have
Just like any other process, data interpretation and analysis require researchers or analysts to have some key skills to be able to perform successfully. It is not enough just to apply some methods and tools to the data; the person who is managing it needs to be objective and have a data-driven mind, among other skills.
It is a common misconception to think that the required skills are mostly number-related. While data interpretation is heavily analytically driven, it also requires communication and narrative skills, as the results of the analysis need to be presented in a way that is easy to understand for all types of audiences.
Luckily, with the rise of self-service tools and AI-driven technologies, data interpretation is no longer segregated for analysts only. However, the topic still remains a big challenge for businesses that make big investments in data and tools to support it, as the interpretation skills required are still lacking. It is worthless to put massive amounts of money into extracting information if you are not going to be able to interpret what that information is telling you. For that reason, below we list the top 5 data interpretation skills your employees or researchers should have to extract the maximum potential from the data.
- Data Literacy: The first and most important skill to have is data literacy. This means having the ability to understand, work, and communicate with data. It involves knowing the types of data sources, methods, and ethical implications of using them. In research, this skill is often a given. However, in a business context, there might be many employees who are not comfortable with data. The issue is the interpretation of data can not be solely responsible for the data team, as it is not sustainable in the long run. Experts advise business leaders to carefully assess the literacy level across their workforce and implement training instances to ensure everyone can interpret their data.
- Data Tools: The data interpretation and analysis process involves using various tools to collect, clean, store, and analyze the data. The complexity of the tools varies depending on the type of data and the analysis goals. Going from simple ones like Excel to more complex ones like databases, such as SQL, or programming languages, such as R or Python. It also involves visual analytics tools to bring the data to life through the use of graphs and charts. Managing these tools is a fundamental skill as they make the process faster and more efficient. As mentioned before, most modern solutions are now self-service, enabling less technical users to use them without problem.
- Critical Thinking: Another very important skill is to have critical thinking. Data hides a range of conclusions, trends, and patterns that must be discovered. It is not just about comparing numbers; it is about putting a story together based on multiple factors that will lead to a conclusion. Therefore, having the ability to look further from what is right in front of you is an invaluable skill for data interpretation.
- Data Ethics: In the information age, being aware of the legal and ethical responsibilities that come with the use of data is of utmost importance. In short, data ethics involves respecting the privacy and confidentiality of data subjects, as well as ensuring accuracy and transparency for data usage. It requires the analyzer or researcher to be completely objective with its interpretation to avoid any biases or discrimination. Many countries have already implemented regulations regarding the use of data, including the GDPR or the ACM Code Of Ethics. Awareness of these regulations and responsibilities is a fundamental skill that anyone working in data interpretation should have.
- Domain Knowledge: Another skill that is considered important when interpreting data is to have domain knowledge. As mentioned before, data hides valuable insights that need to be uncovered. To do so, the analyst needs to know about the industry or domain from which the information is coming and use that knowledge to explore it and put it into a broader context. This is especially valuable in a business context, where most departments are now analyzing data independently with the help of a live dashboard instead of relying on the IT department, which can often overlook some aspects due to a lack of expertise in the topic.
Common Data Analysis And Interpretation Problems

The oft-repeated mantra of those who fear data advancements in the digital age is “big data equals big trouble.” While that statement is not accurate, it is safe to say that certain data interpretation problems or “pitfalls” exist and can occur when analyzing data, especially at the speed of thought. Let’s identify some of the most common data misinterpretation risks and shed some light on how they can be avoided:
1) Correlation mistaken for causation: our first misinterpretation of data refers to the tendency of data analysts to mix the cause of a phenomenon with correlation. It is the assumption that because two actions occurred together, one caused the other. This is inaccurate, as actions can occur together, absent a cause-and-effect relationship.
- Digital age example: assuming that increased revenue results from increased social media followers… there might be a definitive correlation between the two, especially with today’s multi-channel purchasing experiences. But that does not mean an increase in followers is the direct cause of increased revenue. There could be both a common cause and an indirect causality.
- Remedy: attempt to eliminate the variable you believe to be causing the phenomenon.
2) Confirmation bias: our second problem is data interpretation bias. It occurs when you have a theory or hypothesis in mind but are intent on only discovering data patterns that support it while rejecting those that do not.
- Digital age example: your boss asks you to analyze the success of a recent multi-platform social media marketing campaign. While analyzing the potential data variables from the campaign (one that you ran and believe performed well), you see that the share rate for Facebook posts was great, while the share rate for Twitter Tweets was not. Using only Facebook posts to prove your hypothesis that the campaign was successful would be a perfect manifestation of confirmation bias.
- Remedy: as this pitfall is often based on subjective desires, one remedy would be to analyze data with a team of objective individuals. If this is not possible, another solution is to resist the urge to make a conclusion before data exploration has been completed. Remember to always try to disprove a hypothesis, not prove it.
3) Irrelevant data: the third data misinterpretation pitfall is especially important in the digital age. As large data is no longer centrally stored and as it continues to be analyzed at the speed of thought, it is inevitable that analysts will focus on data that is irrelevant to the problem they are trying to correct.
- Digital age example: in attempting to gauge the success of an email lead generation campaign, you notice that the number of homepage views directly resulting from the campaign increased, but the number of monthly newsletter subscribers did not. Based on the number of homepage views, you decide the campaign was a success when really it generated zero leads.
- Remedy: proactively and clearly frame any data analysis variables and KPIs prior to engaging in a data review. If the metric you use to measure the success of a lead generation campaign is newsletter subscribers, there is no need to review the number of homepage visits. Be sure to focus on the data variable that answers your question or solves your problem and not on irrelevant data.
4) Truncating an Axes: When creating a graph to start interpreting the results of your analysis, it is important to keep the axes truthful and avoid generating misleading visualizations. Starting the axes in a value that doesn’t portray the actual truth about the data can lead to false conclusions.
- Digital age example: In the image below, we can see a graph from Fox News in which the Y-axes start at 34%, making it seem that the difference between 35% and 39.6% is way higher than it actually is. This could lead to a misinterpretation of the tax rate changes.
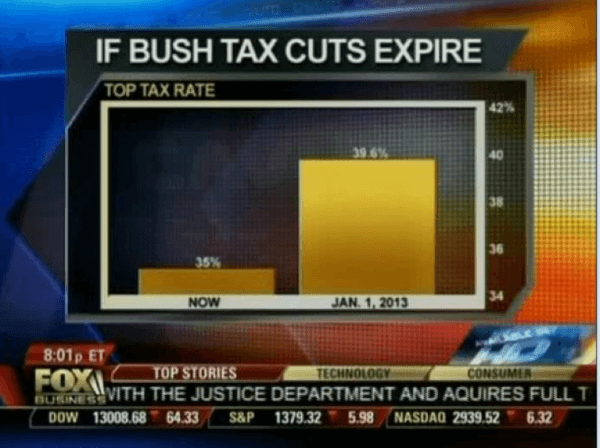
* Source : www.venngage.com *
- Remedy: Be careful with how your data is visualized. Be respectful and realistic with axes to avoid misinterpretation of your data. See below how the Fox News chart looks when using the correct axis values. This chart was created with datapine's modern online data visualization tool.
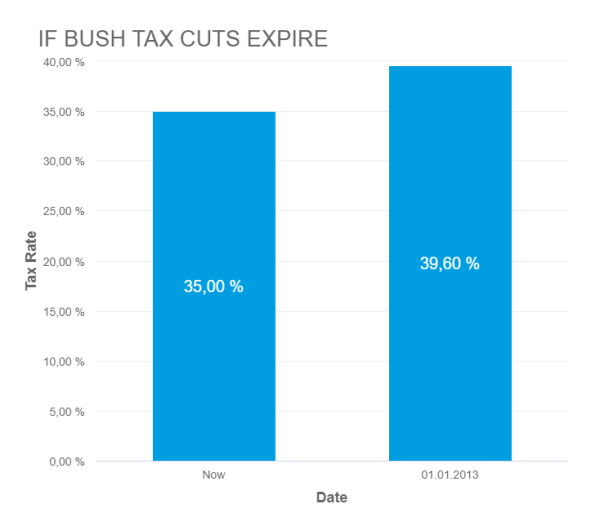
5) (Small) sample size: Another common problem is using a small sample size. Logically, the bigger the sample size, the more accurate and reliable the results. However, this also depends on the size of the effect of the study. For example, the sample size in a survey about the quality of education will not be the same as for one about people doing outdoor sports in a specific area.
- Digital age example: Imagine you ask 30 people a question, and 29 answer “yes,” resulting in 95% of the total. Now imagine you ask the same question to 1000, and 950 of them answer “yes,” which is again 95%. While these percentages might look the same, they certainly do not mean the same thing, as a 30-person sample size is not a significant number to establish a truthful conclusion.
- Remedy: Researchers say that in order to determine the correct sample size to get truthful and meaningful results, it is necessary to define a margin of error that will represent the maximum amount they want the results to deviate from the statistical mean. Paired with this, they need to define a confidence level that should be between 90 and 99%. With these two values in hand, researchers can calculate an accurate sample size for their studies.
6) Reliability, subjectivity, and generalizability : When performing qualitative analysis, researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations when interpreting the data. In some cases, this type of research can be considered unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that might or might not affect the results. This is paired with the fact that the researcher has a primary role in the interpretation process, meaning he or she decides what is relevant and what is not, and as we know, interpretations can be very subjective.
Generalizability is also an issue that researchers face when dealing with qualitative analysis. As mentioned in the point about having a small sample size, it is difficult to draw conclusions that are 100% representative because the results might be biased or unrepresentative of a wider population.
While these factors are mostly present in qualitative research, they can also affect the quantitative analysis. For example, when choosing which KPIs to portray and how to portray them, analysts can also be biased and represent them in a way that benefits their analysis.
- Digital age example: Biased questions in a survey are a great example of reliability and subjectivity issues. Imagine you are sending a survey to your clients to see how satisfied they are with your customer service with this question: “How amazing was your experience with our customer service team?”. Here, we can see that this question clearly influences the response of the individual by putting the word “amazing” on it.
- Remedy: A solution to avoid these issues is to keep your research honest and neutral. Keep the wording of the questions as objective as possible. For example: “On a scale of 1-10, how satisfied were you with our customer service team?”. This does not lead the respondent to any specific answer, meaning the results of your survey will be reliable.
Data Interpretation Best Practices & Tips
Data analysis and interpretation are critical to developing sound conclusions and making better-informed decisions. As we have seen with this article, there is an art and science to the interpretation of data. To help you with this purpose, we will list a few relevant techniques, methods, and tricks you can implement for a successful data management process.
As mentioned at the beginning of this post, the first step to interpreting data in a successful way is to identify the type of analysis you will perform and apply the methods respectively. Clearly differentiate between qualitative (observe, document, and interview notice, collect and think about things) and quantitative analysis (you lead research with a lot of numerical data to be analyzed through various statistical methods).
1) Ask the right data interpretation questions
The first data interpretation technique is to define a clear baseline for your work. This can be done by answering some critical questions that will serve as a useful guideline to start. Some of them include: what are the goals and objectives of my analysis? What type of data interpretation method will I use? Who will use this data in the future? And most importantly, what general question am I trying to answer?
Once all this information has been defined, you will be ready for the next step: collecting your data.
2) Collect and assimilate your data
Now that a clear baseline has been established, it is time to collect the information you will use. Always remember that your methods for data collection will vary depending on what type of analysis method you use, which can be qualitative or quantitative. Based on that, relying on professional online data analysis tools to facilitate the process is a great practice in this regard, as manually collecting and assessing raw data is not only very time-consuming and expensive but is also at risk of errors and subjectivity.
Once your data is collected, you need to carefully assess it to understand if the quality is appropriate to be used during a study. This means, is the sample size big enough? Were the procedures used to collect the data implemented correctly? Is the date range from the data correct? If coming from an external source, is it a trusted and objective one?
With all the needed information in hand, you are ready to start the interpretation process, but first, you need to visualize your data.
3) Use the right data visualization type
Data visualizations such as business graphs , charts, and tables are fundamental to successfully interpreting data. This is because data visualization via interactive charts and graphs makes the information more understandable and accessible. As you might be aware, there are different types of visualizations you can use, but not all of them are suitable for any analysis purpose. Using the wrong graph can lead to misinterpretation of your data, so it’s very important to carefully pick the right visual for it. Let’s look at some use cases of common data visualizations.
- Bar chart: One of the most used chart types, the bar chart uses rectangular bars to show the relationship between 2 or more variables. There are different types of bar charts for different interpretations, including the horizontal bar chart, column bar chart, and stacked bar chart.
- Line chart: Most commonly used to show trends, acceleration or decelerations, and volatility, the line chart aims to show how data changes over a period of time, for example, sales over a year. A few tips to keep this chart ready for interpretation are not using many variables that can overcrowd the graph and keeping your axis scale close to the highest data point to avoid making the information hard to read.
- Pie chart: Although it doesn’t do a lot in terms of analysis due to its uncomplex nature, pie charts are widely used to show the proportional composition of a variable. Visually speaking, showing a percentage in a bar chart is way more complicated than showing it in a pie chart. However, this also depends on the number of variables you are comparing. If your pie chart needs to be divided into 10 portions, then it is better to use a bar chart instead.
- Tables: While they are not a specific type of chart, tables are widely used when interpreting data. Tables are especially useful when you want to portray data in its raw format. They give you the freedom to easily look up or compare individual values while also displaying grand totals.
With the use of data visualizations becoming more and more critical for businesses’ analytical success, many tools have emerged to help users visualize their data in a cohesive and interactive way. One of the most popular ones is the use of BI dashboards . These visual tools provide a centralized view of various graphs and charts that paint a bigger picture of a topic. We will discuss the power of dashboards for an efficient data interpretation practice in the next portion of this post. If you want to learn more about different types of graphs and charts , take a look at our complete guide on the topic.
4) Start interpreting
After the tedious preparation part, you can start extracting conclusions from your data. As mentioned many times throughout the post, the way you decide to interpret the data will solely depend on the methods you initially decided to use. If you had initial research questions or hypotheses, then you should look for ways to prove their validity. If you are going into the data with no defined hypothesis, then start looking for relationships and patterns that will allow you to extract valuable conclusions from the information.
During the process of interpretation, stay curious and creative, dig into the data, and determine if there are any other critical questions that should be asked. If any new questions arise, you need to assess if you have the necessary information to answer them. Being able to identify if you need to dedicate more time and resources to the research is a very important step. No matter if you are studying customer behaviors or a new cancer treatment, the findings from your analysis may dictate important decisions in the future. Therefore, taking the time to really assess the information is key. For that purpose, data interpretation software proves to be very useful.
5) Keep your interpretation objective
As mentioned above, objectivity is one of the most important data interpretation skills but also one of the hardest. Being the person closest to the investigation, it is easy to become subjective when looking for answers in the data. A good way to stay objective is to show the information related to the study to other people, for example, research partners or even the people who will use your findings once they are done. This can help avoid confirmation bias and any reliability issues with your interpretation.
Remember, using a visualization tool such as a modern dashboard will make the interpretation process way easier and more efficient as the data can be navigated and manipulated in an easy and organized way. And not just that, using a dashboard tool to present your findings to a specific audience will make the information easier to understand and the presentation way more engaging thanks to the visual nature of these tools.
6) Mark your findings and draw conclusions
Findings are the observations you extracted from your data. They are the facts that will help you drive deeper conclusions about your research. For example, findings can be trends and patterns you found during your interpretation process. To put your findings into perspective, you can compare them with other resources that use similar methods and use them as benchmarks.
Reflect on your own thinking and reasoning and be aware of the many pitfalls data analysis and interpretation carry—correlation versus causation, subjective bias, false information, inaccurate data, etc. Once you are comfortable with interpreting the data, you will be ready to develop conclusions, see if your initial questions were answered, and suggest recommendations based on them.
Interpretation of Data: The Use of Dashboards Bridging The Gap
As we have seen, quantitative and qualitative methods are distinct types of data interpretation and analysis. Both offer a varying degree of return on investment (ROI) regarding data investigation, testing, and decision-making. But how do you mix the two and prevent a data disconnect? The answer is professional data dashboards.
For a few years now, dashboards have become invaluable tools to visualize and interpret data. These tools offer a centralized and interactive view of data and provide the perfect environment for exploration and extracting valuable conclusions. They bridge the quantitative and qualitative information gap by unifying all the data in one place with the help of stunning visuals.
Not only that, but these powerful tools offer a large list of benefits, and we will discuss some of them below.
1) Connecting and blending data. With today’s pace of innovation, it is no longer feasible (nor desirable) to have bulk data centrally located. As businesses continue to globalize and borders continue to dissolve, it will become increasingly important for businesses to possess the capability to run diverse data analyses absent the limitations of location. Data dashboards decentralize data without compromising on the necessary speed of thought while blending both quantitative and qualitative data. Whether you want to measure customer trends or organizational performance, you now have the capability to do both without the need for a singular selection.
2) Mobile Data. Related to the notion of “connected and blended data” is that of mobile data. In today’s digital world, employees are spending less time at their desks and simultaneously increasing production. This is made possible because mobile solutions for analytical tools are no longer standalone. Today, mobile analysis applications seamlessly integrate with everyday business tools. In turn, both quantitative and qualitative data are now available on-demand where they’re needed, when they’re needed, and how they’re needed via interactive online dashboards .
3) Visualization. Data dashboards merge the data gap between qualitative and quantitative data interpretation methods through the science of visualization. Dashboard solutions come “out of the box” and are well-equipped to create easy-to-understand data demonstrations. Modern online data visualization tools provide a variety of color and filter patterns, encourage user interaction, and are engineered to help enhance future trend predictability. All of these visual characteristics make for an easy transition among data methods – you only need to find the right types of data visualization to tell your data story the best way possible.
4) Collaboration. Whether in a business environment or a research project, collaboration is key in data interpretation and analysis. Dashboards are online tools that can be easily shared through a password-protected URL or automated email. Through them, users can collaborate and communicate through the data in an efficient way. Eliminating the need for infinite files with lost updates. Tools such as datapine offer real-time updates, meaning your dashboards will update on their own as soon as new information is available.
Examples Of Data Interpretation In Business
To give you an idea of how a dashboard can fulfill the need to bridge quantitative and qualitative analysis and help in understanding how to interpret data in research thanks to visualization, below, we will discuss three valuable examples to put their value into perspective.
1. Customer Satisfaction Dashboard
This market research dashboard brings together both qualitative and quantitative data that are knowledgeably analyzed and visualized in a meaningful way that everyone can understand, thus empowering any viewer to interpret it. Let’s explore it below.
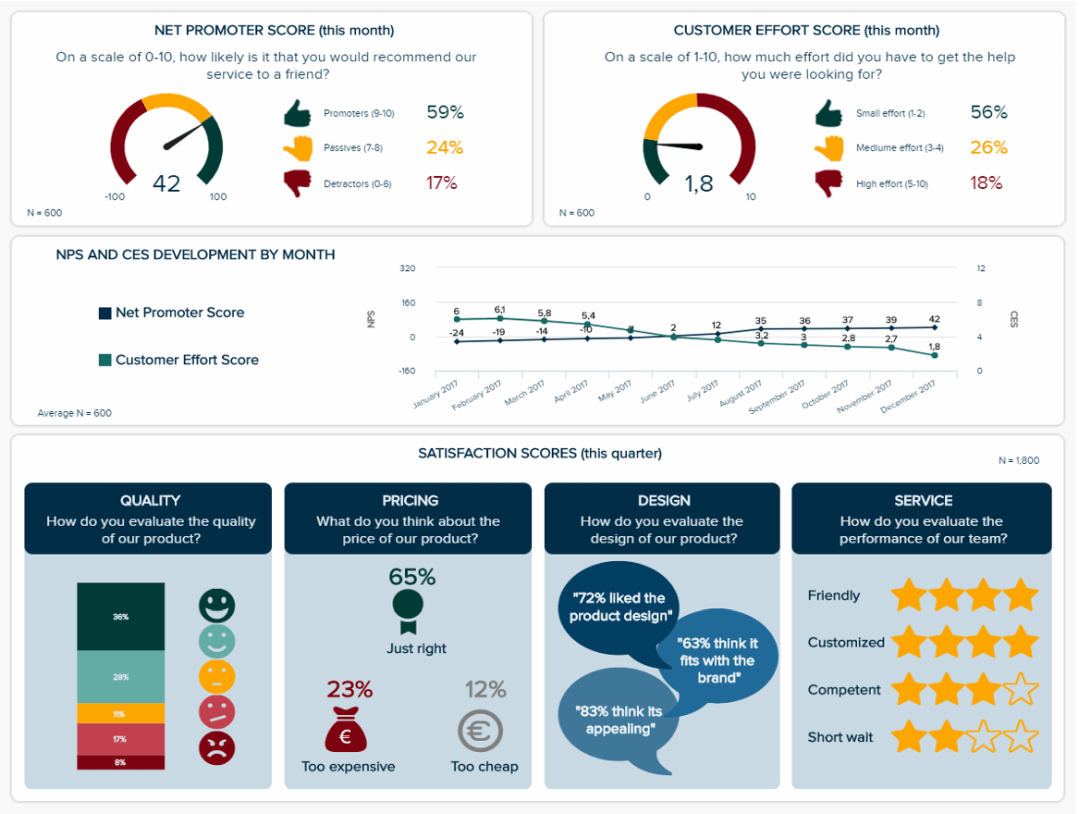
**click to enlarge**
The value of this template lies in its highly visual nature. As mentioned earlier, visuals make the interpretation process way easier and more efficient. Having critical pieces of data represented with colorful and interactive icons and graphs makes it possible to uncover insights at a glance. For example, the colors green, yellow, and red on the charts for the NPS and the customer effort score allow us to conclude that most respondents are satisfied with this brand with a short glance. A further dive into the line chart below can help us dive deeper into this conclusion, as we can see both metrics developed positively in the past 6 months.
The bottom part of the template provides visually stunning representations of different satisfaction scores for quality, pricing, design, and service. By looking at these, we can conclude that, overall, customers are satisfied with this company in most areas.
2. Brand Analysis Dashboard
Next, in our list of data interpretation examples, we have a template that shows the answers to a survey on awareness for Brand D. The sample size is listed on top to get a perspective of the data, which is represented using interactive charts and graphs.
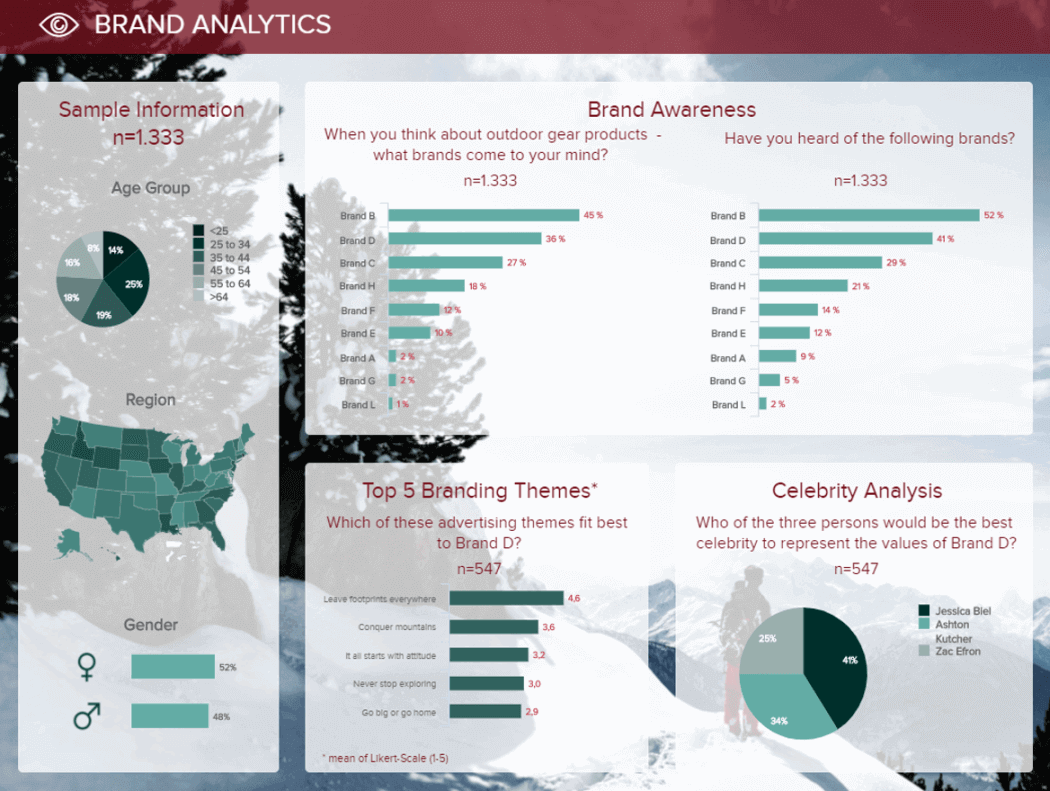
When interpreting information, context is key to understanding it correctly. For that reason, the dashboard starts by offering insights into the demographics of the surveyed audience. In general, we can see ages and gender are diverse. Therefore, we can conclude these brands are not targeting customers from a specified demographic, an important aspect to put the surveyed answers into perspective.
Looking at the awareness portion, we can see that brand B is the most popular one, with brand D coming second on both questions. This means brand D is not doing wrong, but there is still room for improvement compared to brand B. To see where brand D could improve, the researcher could go into the bottom part of the dashboard and consult the answers for branding themes and celebrity analysis. These are important as they give clear insight into what people and messages the audience associates with brand D. This is an opportunity to exploit these topics in different ways and achieve growth and success.
3. Product Innovation Dashboard
Our third and last dashboard example shows the answers to a survey on product innovation for a technology company. Just like the previous templates, the interactive and visual nature of the dashboard makes it the perfect tool to interpret data efficiently and effectively.
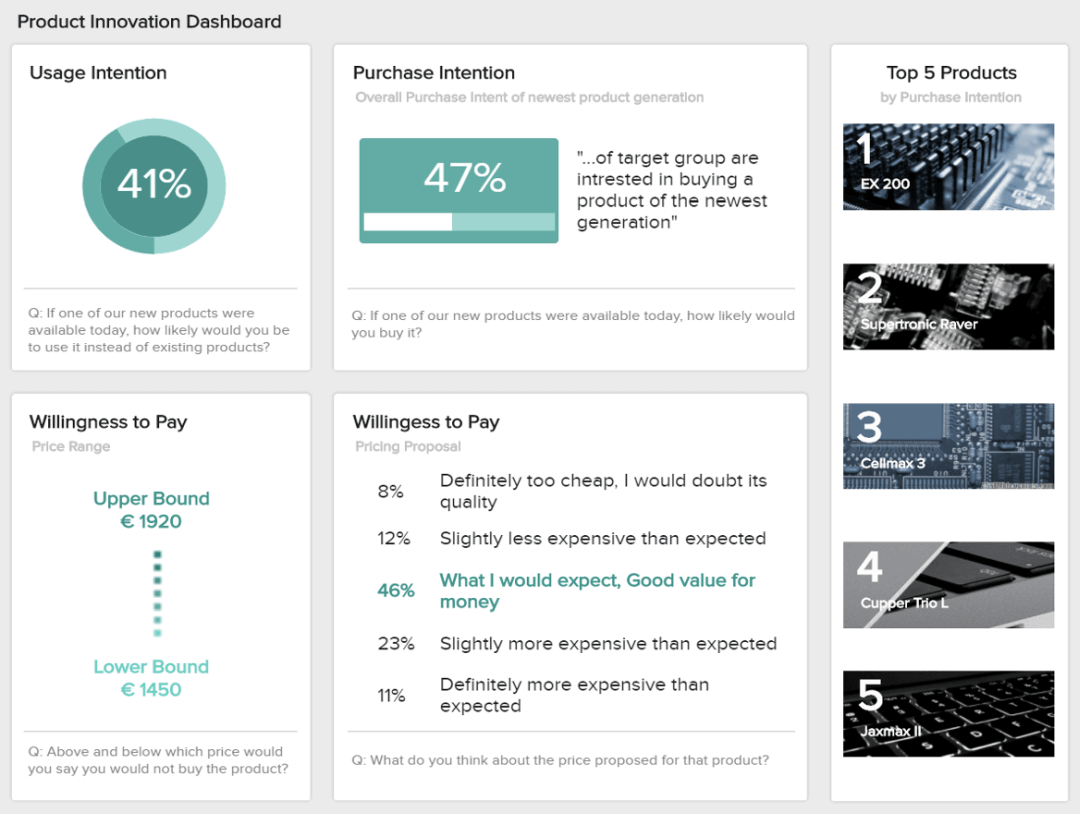
Starting from right to left, we first get a list of the top 5 products by purchase intention. This information lets us understand if the product being evaluated resembles what the audience already intends to purchase. It is a great starting point to see how customers would respond to the new product. This information can be complemented with other key metrics displayed in the dashboard. For example, the usage and purchase intention track how the market would receive the product and if they would purchase it, respectively. Interpreting these values as positive or negative will depend on the company and its expectations regarding the survey.
Complementing these metrics, we have the willingness to pay. Arguably, one of the most important metrics to define pricing strategies. Here, we can see that most respondents think the suggested price is a good value for money. Therefore, we can interpret that the product would sell for that price.
To see more data analysis and interpretation examples for different industries and functions, visit our library of business dashboards .
To Conclude…
As we reach the end of this insightful post about data interpretation and analysis, we hope you have a clear understanding of the topic. We've covered the definition and given some examples and methods to perform a successful interpretation process.
The importance of data interpretation is undeniable. Dashboards not only bridge the information gap between traditional data interpretation methods and technology, but they can help remedy and prevent the major pitfalls of the process. As a digital age solution, they combine the best of the past and the present to allow for informed decision-making with maximum data interpretation ROI.
To start visualizing your insights in a meaningful and actionable way, test our online reporting software for free with our 14-day trial !
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Data Visualization
10 Data Presentation Examples For Strategic Communication
By Krystle Wong , Sep 28, 2023

Knowing how to present data is like having a superpower.
Data presentation today is no longer just about numbers on a screen; it’s storytelling with a purpose. It’s about captivating your audience, making complex stuff look simple and inspiring action.
To help turn your data into stories that stick, influence decisions and make an impact, check out Venngage’s free chart maker or follow me on a tour into the world of data storytelling along with data presentation templates that work across different fields, from business boardrooms to the classroom and beyond. Keep scrolling to learn more!
Click to jump ahead:
10 Essential data presentation examples + methods you should know
What should be included in a data presentation, what are some common mistakes to avoid when presenting data, faqs on data presentation examples, transform your message with impactful data storytelling.
Data presentation is a vital skill in today’s information-driven world. Whether you’re in business, academia, or simply want to convey information effectively, knowing the different ways of presenting data is crucial. For impactful data storytelling, consider these essential data presentation methods:
1. Bar graph
Ideal for comparing data across categories or showing trends over time.
Bar graphs, also known as bar charts are workhorses of data presentation. They’re like the Swiss Army knives of visualization methods because they can be used to compare data in different categories or display data changes over time.
In a bar chart, categories are displayed on the x-axis and the corresponding values are represented by the height of the bars on the y-axis.
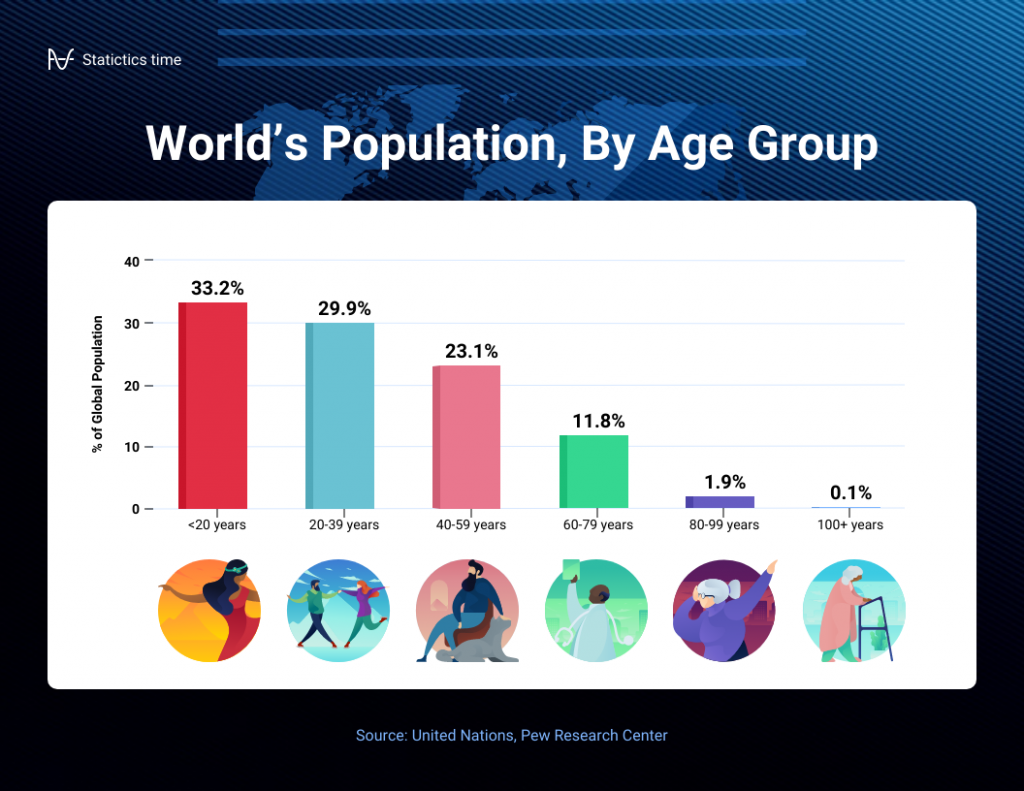
It’s a straightforward and effective way to showcase raw data, making it a staple in business reports, academic presentations and beyond.
Make sure your bar charts are concise with easy-to-read labels. Whether your bars go up or sideways, keep it simple by not overloading with too many categories.
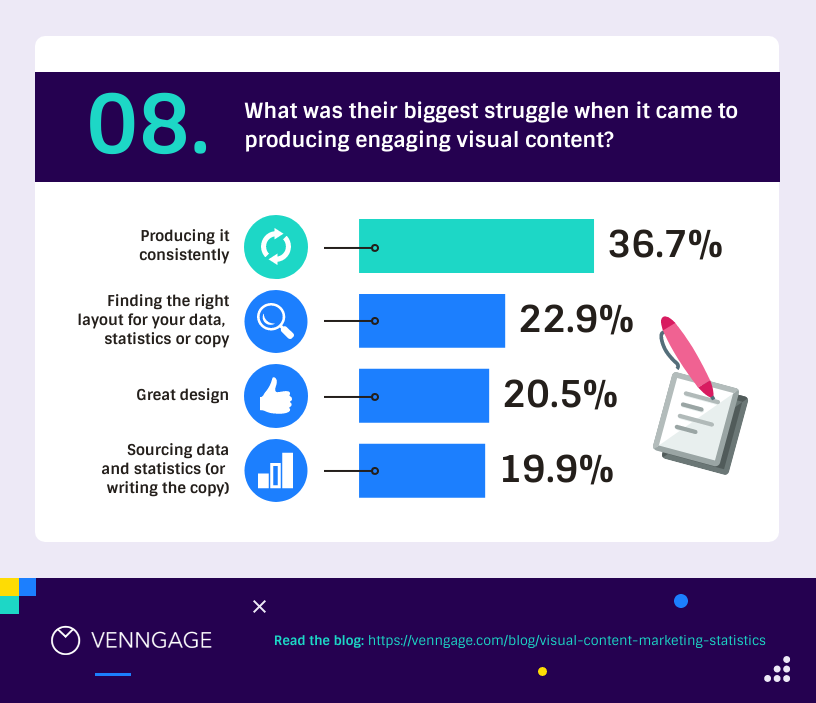
2. Line graph
Great for displaying trends and variations in data points over time or continuous variables.
Line charts or line graphs are your go-to when you want to visualize trends and variations in data sets over time.
One of the best quantitative data presentation examples, they work exceptionally well for showing continuous data, such as sales projections over the last couple of years or supply and demand fluctuations.
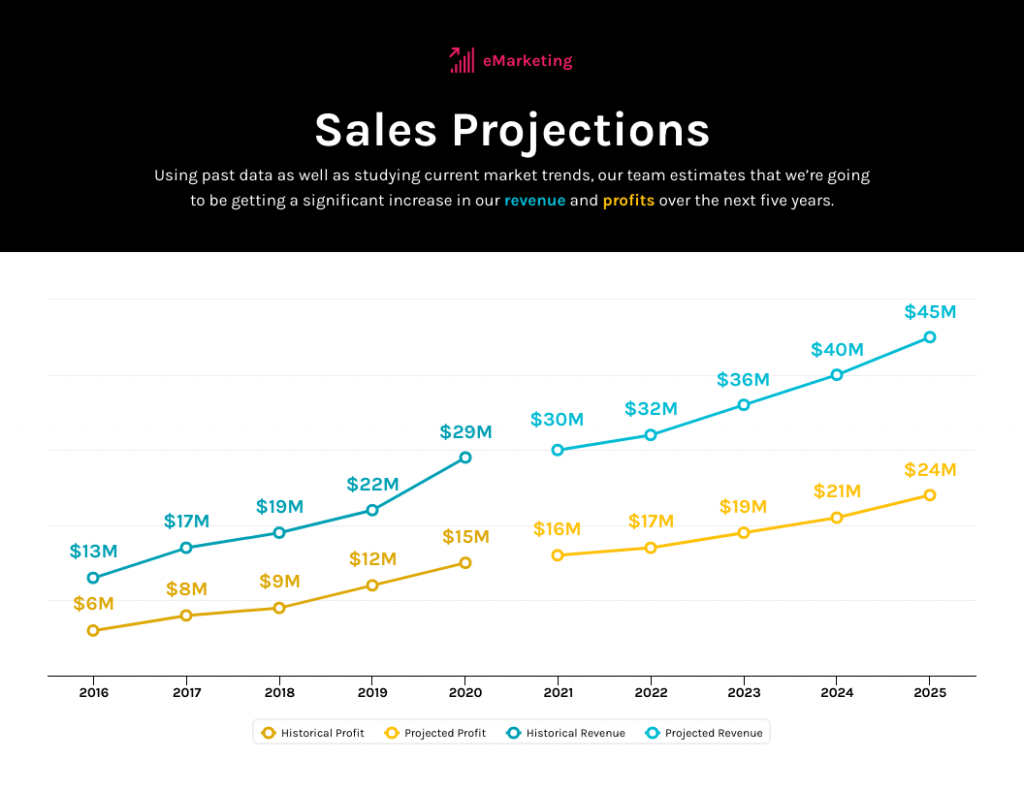
The x-axis represents time or a continuous variable and the y-axis represents the data values. By connecting the data points with lines, you can easily spot trends and fluctuations.
A tip when presenting data with line charts is to minimize the lines and not make it too crowded. Highlight the big changes, put on some labels and give it a catchy title.
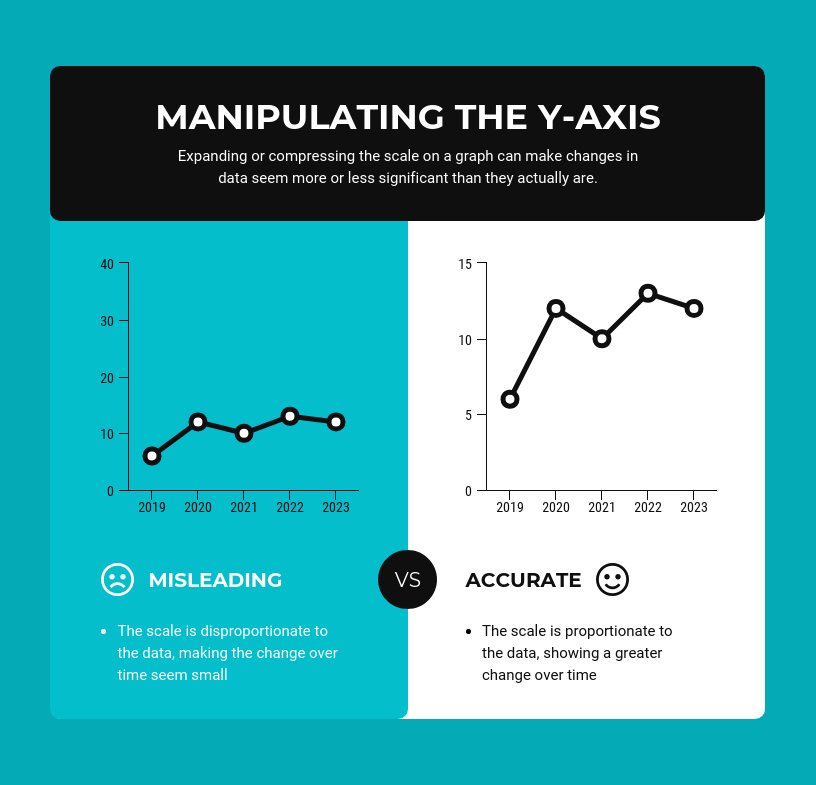
3. Pie chart
Useful for illustrating parts of a whole, such as percentages or proportions.
Pie charts are perfect for showing how a whole is divided into parts. They’re commonly used to represent percentages or proportions and are great for presenting survey results that involve demographic data.
Each “slice” of the pie represents a portion of the whole and the size of each slice corresponds to its share of the total.
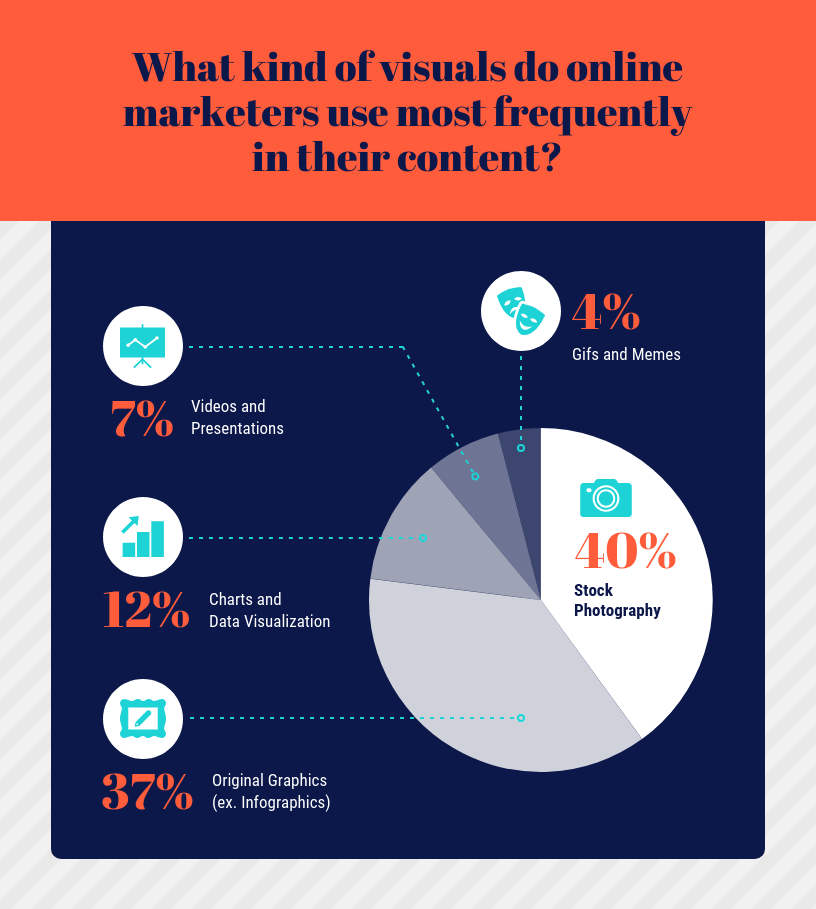
While pie charts are handy for illustrating simple distributions, they can become confusing when dealing with too many categories or when the differences in proportions are subtle.
Don’t get too carried away with slices — label those slices with percentages or values so people know what’s what and consider using a legend for more categories.
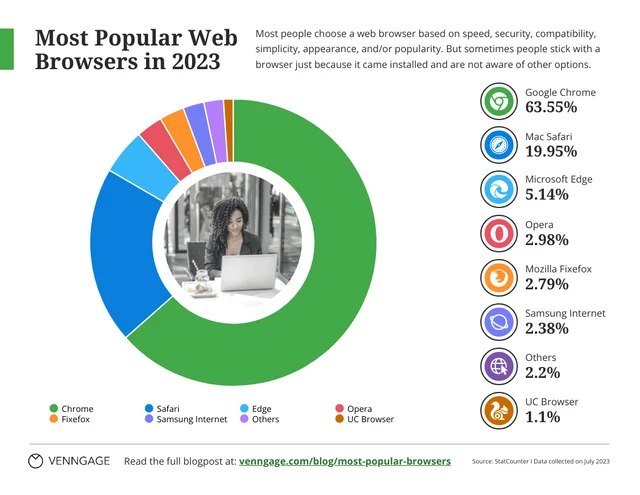
4. Scatter plot
Effective for showing the relationship between two variables and identifying correlations.
Scatter plots are all about exploring relationships between two variables. They’re great for uncovering correlations, trends or patterns in data.
In a scatter plot, every data point appears as a dot on the chart, with one variable marked on the horizontal x-axis and the other on the vertical y-axis.
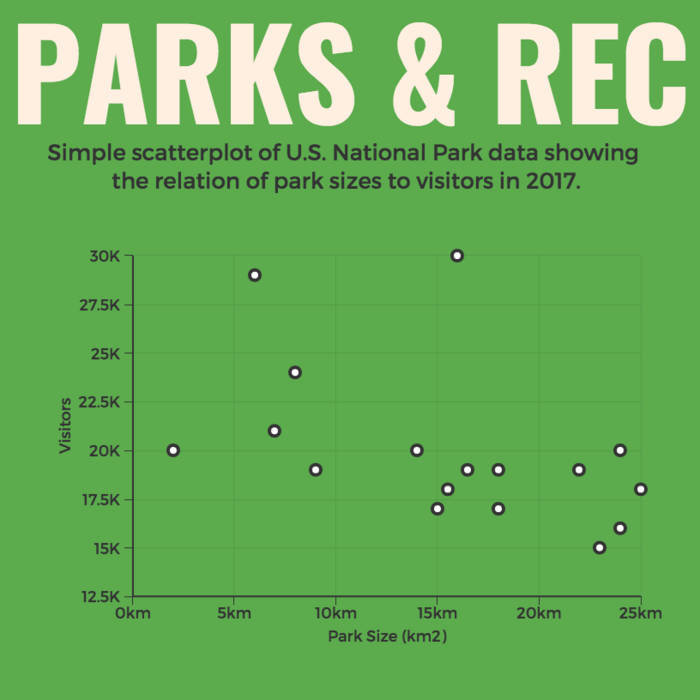
By examining the scatter of points, you can discern the nature of the relationship between the variables, whether it’s positive, negative or no correlation at all.
If you’re using scatter plots to reveal relationships between two variables, be sure to add trendlines or regression analysis when appropriate to clarify patterns. Label data points selectively or provide tooltips for detailed information.
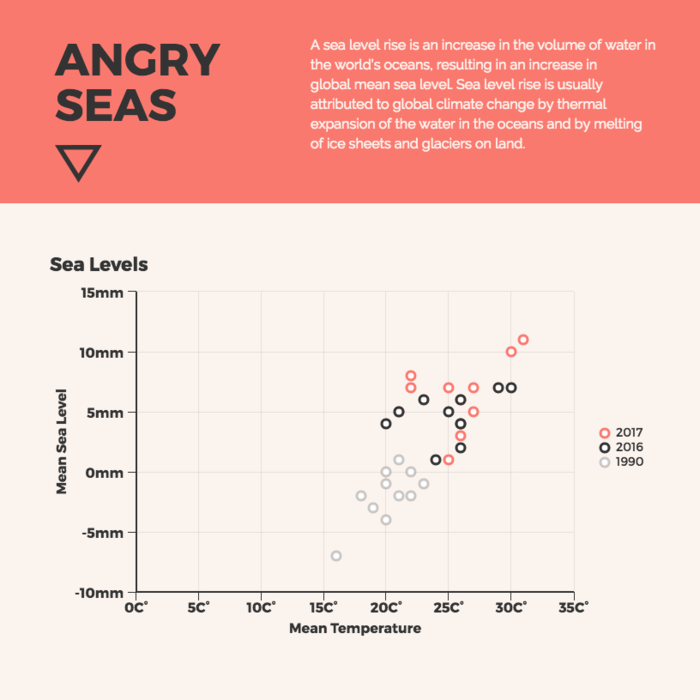
5. Histogram
Best for visualizing the distribution and frequency of a single variable.
Histograms are your choice when you want to understand the distribution and frequency of a single variable.
They divide the data into “bins” or intervals and the height of each bar represents the frequency or count of data points falling into that interval.
Histograms are excellent for helping to identify trends in data distributions, such as peaks, gaps or skewness.
Here’s something to take note of — ensure that your histogram bins are appropriately sized to capture meaningful data patterns. Using clear axis labels and titles can also help explain the distribution of the data effectively.
6. Stacked bar chart
Useful for showing how different components contribute to a whole over multiple categories.
Stacked bar charts are a handy choice when you want to illustrate how different components contribute to a whole across multiple categories.
Each bar represents a category and the bars are divided into segments to show the contribution of various components within each category.
This method is ideal for highlighting both the individual and collective significance of each component, making it a valuable tool for comparative analysis.
Stacked bar charts are like data sandwiches—label each layer so people know what’s what. Keep the order logical and don’t forget the paintbrush for snazzy colors. Here’s a data analysis presentation example on writers’ productivity using stacked bar charts:
7. Area chart
Similar to line charts but with the area below the lines filled, making them suitable for showing cumulative data.
Area charts are close cousins of line charts but come with a twist.
Imagine plotting the sales of a product over several months. In an area chart, the space between the line and the x-axis is filled, providing a visual representation of the cumulative total.
This makes it easy to see how values stack up over time, making area charts a valuable tool for tracking trends in data.
For area charts, use them to visualize cumulative data and trends, but avoid overcrowding the chart. Add labels, especially at significant points and make sure the area under the lines is filled with a visually appealing color gradient.
8. Tabular presentation
Presenting data in rows and columns, often used for precise data values and comparisons.
Tabular data presentation is all about clarity and precision. Think of it as presenting numerical data in a structured grid, with rows and columns clearly displaying individual data points.
A table is invaluable for showcasing detailed data, facilitating comparisons and presenting numerical information that needs to be exact. They’re commonly used in reports, spreadsheets and academic papers.
When presenting tabular data, organize it neatly with clear headers and appropriate column widths. Highlight important data points or patterns using shading or font formatting for better readability.
9. Textual data
Utilizing written or descriptive content to explain or complement data, such as annotations or explanatory text.
Textual data presentation may not involve charts or graphs, but it’s one of the most used qualitative data presentation examples.
It involves using written content to provide context, explanations or annotations alongside data visuals. Think of it as the narrative that guides your audience through the data.
Well-crafted textual data can make complex information more accessible and help your audience understand the significance of the numbers and visuals.
Textual data is your chance to tell a story. Break down complex information into bullet points or short paragraphs and use headings to guide the reader’s attention.
10. Pictogram
Using simple icons or images to represent data is especially useful for conveying information in a visually intuitive manner.
Pictograms are all about harnessing the power of images to convey data in an easy-to-understand way.
Instead of using numbers or complex graphs, you use simple icons or images to represent data points.
For instance, you could use a thumbs up emoji to illustrate customer satisfaction levels, where each face represents a different level of satisfaction.

Pictograms are great for conveying data visually, so choose symbols that are easy to interpret and relevant to the data. Use consistent scaling and a legend to explain the symbols’ meanings, ensuring clarity in your presentation.
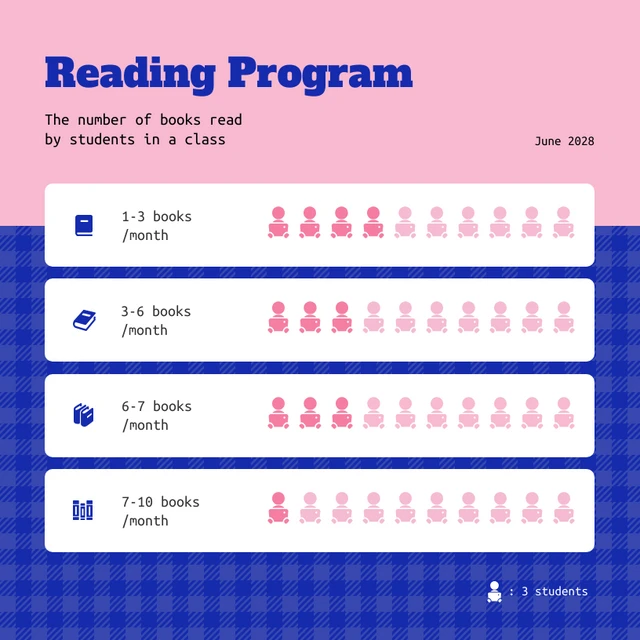
Looking for more data presentation ideas? Use the Venngage graph maker or browse through our gallery of chart templates to pick a template and get started!
A comprehensive data presentation should include several key elements to effectively convey information and insights to your audience. Here’s a list of what should be included in a data presentation:
1. Title and objective
- Begin with a clear and informative title that sets the context for your presentation.
- State the primary objective or purpose of the presentation to provide a clear focus.

2. Key data points
- Present the most essential data points or findings that align with your objective.
- Use charts, graphical presentations or visuals to illustrate these key points for better comprehension.
3. Context and significance
- Provide a brief overview of the context in which the data was collected and why it’s significant.
- Explain how the data relates to the larger picture or the problem you’re addressing.
4. Key takeaways
- Summarize the main insights or conclusions that can be drawn from the data.
- Highlight the key takeaways that the audience should remember.
5. Visuals and charts
- Use clear and appropriate visual aids to complement the data.
- Ensure that visuals are easy to understand and support your narrative.
6. Implications or actions
- Discuss the practical implications of the data or any recommended actions.
- If applicable, outline next steps or decisions that should be taken based on the data.
7. Q&A and discussion
- Allocate time for questions and open discussion to engage the audience.
- Address queries and provide additional insights or context as needed.
Presenting data is a crucial skill in various professional fields, from business to academia and beyond. To ensure your data presentations hit the mark, here are some common mistakes that you should steer clear of:
Overloading with data
Presenting too much data at once can overwhelm your audience. Focus on the key points and relevant information to keep the presentation concise and focused. Here are some free data visualization tools you can use to convey data in an engaging and impactful way.
Assuming everyone’s on the same page
It’s easy to assume that your audience understands as much about the topic as you do. But this can lead to either dumbing things down too much or diving into a bunch of jargon that leaves folks scratching their heads. Take a beat to figure out where your audience is coming from and tailor your presentation accordingly.
Misleading visuals
Using misleading visuals, such as distorted scales or inappropriate chart types can distort the data’s meaning. Pick the right data infographics and understandable charts to ensure that your visual representations accurately reflect the data.
Not providing context
Data without context is like a puzzle piece with no picture on it. Without proper context, data may be meaningless or misinterpreted. Explain the background, methodology and significance of the data.
Not citing sources properly
Neglecting to cite sources and provide citations for your data can erode its credibility. Always attribute data to its source and utilize reliable sources for your presentation.
Not telling a story
Avoid simply presenting numbers. If your presentation lacks a clear, engaging story that takes your audience on a journey from the beginning (setting the scene) through the middle (data analysis) to the end (the big insights and recommendations), you’re likely to lose their interest.
Infographics are great for storytelling because they mix cool visuals with short and sweet text to explain complicated stuff in a fun and easy way. Create one with Venngage’s free infographic maker to create a memorable story that your audience will remember.
Ignoring data quality
Presenting data without first checking its quality and accuracy can lead to misinformation. Validate and clean your data before presenting it.
Simplify your visuals
Fancy charts might look cool, but if they confuse people, what’s the point? Go for the simplest visual that gets your message across. Having a dilemma between presenting data with infographics v.s data design? This article on the difference between data design and infographics might help you out.
Missing the emotional connection
Data isn’t just about numbers; it’s about people and real-life situations. Don’t forget to sprinkle in some human touch, whether it’s through relatable stories, examples or showing how the data impacts real lives.
Skipping the actionable insights
At the end of the day, your audience wants to know what they should do with all the data. If you don’t wrap up with clear, actionable insights or recommendations, you’re leaving them hanging. Always finish up with practical takeaways and the next steps.
Can you provide some data presentation examples for business reports?
Business reports often benefit from data presentation through bar charts showing sales trends over time, pie charts displaying market share,or tables presenting financial performance metrics like revenue and profit margins.
What are some creative data presentation examples for academic presentations?
Creative data presentation ideas for academic presentations include using statistical infographics to illustrate research findings and statistical data, incorporating storytelling techniques to engage the audience or utilizing heat maps to visualize data patterns.
What are the key considerations when choosing the right data presentation format?
When choosing a chart format , consider factors like data complexity, audience expertise and the message you want to convey. Options include charts (e.g., bar, line, pie), tables, heat maps, data visualization infographics and interactive dashboards.
Knowing the type of data visualization that best serves your data is just half the battle. Here are some best practices for data visualization to make sure that the final output is optimized.
How can I choose the right data presentation method for my data?
To select the right data presentation method, start by defining your presentation’s purpose and audience. Then, match your data type (e.g., quantitative, qualitative) with suitable visualization techniques (e.g., histograms, word clouds) and choose an appropriate presentation format (e.g., slide deck, report, live demo).
For more presentation ideas , check out this guide on how to make a good presentation or use a presentation software to simplify the process.
How can I make my data presentations more engaging and informative?
To enhance data presentations, use compelling narratives, relatable examples and fun data infographics that simplify complex data. Encourage audience interaction, offer actionable insights and incorporate storytelling elements to engage and inform effectively.
The opening of your presentation holds immense power in setting the stage for your audience. To design a presentation and convey your data in an engaging and informative, try out Venngage’s free presentation maker to pick the right presentation design for your audience and topic.
What is the difference between data visualization and data presentation?
Data presentation typically involves conveying data reports and insights to an audience, often using visuals like charts and graphs. Data visualization , on the other hand, focuses on creating those visual representations of data to facilitate understanding and analysis.
Now that you’ve learned a thing or two about how to use these methods of data presentation to tell a compelling data story , it’s time to take these strategies and make them your own.
But here’s the deal: these aren’t just one-size-fits-all solutions. Remember that each example we’ve uncovered here is not a rigid template but a source of inspiration. It’s all about making your audience go, “Wow, I get it now!”
Think of your data presentations as your canvas – it’s where you paint your story, convey meaningful insights and make real change happen.
So, go forth, present your data with confidence and purpose and watch as your strategic influence grows, one compelling presentation at a time.

Research Techniques for Computer Science, Information Systems and Cybersecurity pp 115–138 Cite as
Data Collection, Presentation and Analysis
- Uche M. Mbanaso 4 ,
- Lucienne Abrahams 5 &
- Kennedy Chinedu Okafor 6
- First Online: 25 May 2023
432 Accesses
This chapter covers the topics of data collection, data presentation and data analysis. It gives attention to data collection for studies based on experiments, on data derived from existing published or unpublished data sets, on observation, on simulation and digital twins, on surveys, on interviews and on focus group discussions. One of the interesting features of this chapter is the section dealing with using measurement scales in quantitative research, including nominal scales, ordinal scales, interval scales and ratio scales. It explains key facets of qualitative research including ethical clearance requirements. The chapter discusses the importance of data visualization as key to effective presentation of data, including tabular forms, graphical forms and visual charts such as those generated by Atlas.ti analytical software.
- Computer science data
- Cybersecurity data analysis
- Cybersecurity experiments
- Information systems data collection
- Information systems visualization
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Bibliography
Abdullah, M. F., & Ahmad, K. (2013). The mapping process of unstructured data to structured data. Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Research and Innovation in Information Systems (ICRIIS) , Malaysia , 151–155. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRIIS.2013.6716700
Adnan, K., & Akbar, R. (2019). An analytical study of information extraction from unstructured and multidimensional big data. Journal of Big Data, 6 , 91. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-019-0254-8
Article Google Scholar
Alsheref, F. K., & Fattoh, I. E. (2020). Medical text annotation tool based on IBM Watson Platform. Proceedings of the 2020 6th international conference on advanced computing and communication systems (ICACCS) , India , 1312–1316. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCS48705.2020.9074309
Cinque, M., Cotroneo, D., Della Corte, R., & Pecchia, A. (2014). What logs should you look at when an application fails? Insights from an industrial case study. Proceedings of the 2014 44th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks , USA , 690–695. https://doi.org/10.1109/DSN.2014.69
Gideon, L. (Ed.). (2012). Handbook of survey methodology for the social sciences . Springer.
Google Scholar
Leedy, P., & Ormrod, J. (2015). Practical research planning and design (12th ed.). Pearson Education.
Madaan, A., Wang, X., Hall, W., & Tiropanis, T. (2018). Observing data in IoT worlds: What and how to observe? In Living in the Internet of Things: Cybersecurity of the IoT – 2018 (pp. 1–7). https://doi.org/10.1049/cp.2018.0032
Chapter Google Scholar
Mahajan, P., & Naik, C. (2019). Development of integrated IoT and machine learning based data collection and analysis system for the effective prediction of agricultural residue/biomass availability to regenerate clean energy. Proceedings of the 2019 9th International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Technology – Signal and Information Processing (ICETET-SIP-19) , India , 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICETET-SIP-1946815.2019.9092156 .
Mahmud, M. S., Huang, J. Z., Salloum, S., Emara, T. Z., & Sadatdiynov, K. (2020). A survey of data partitioning and sampling methods to support big data analysis. Big Data Mining and Analytics, 3 (2), 85–101. https://doi.org/10.26599/BDMA.2019.9020015
Miswar, S., & Kurniawan, N. B. (2018). A systematic literature review on survey data collection system. Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information Technology Systems and Innovation (ICITSI) , Indonesia , 177–181. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICITSI.2018.8696036
Mosina, C. (2020). Understanding the diffusion of the internet: Redesigning the global diffusion of the internet framework (Research report, Master of Arts in ICT Policy and Regulation). LINK Centre, University of the Witwatersrand. https://hdl.handle.net/10539/30723
Nkamisa, S. (2021). Investigating the integration of drone management systems to create an enabling remote piloted aircraft regulatory environment in South Africa (Research report, Master of Arts in ICT Policy and Regulation). LINK Centre, University of the Witwatersrand. https://hdl.handle.net/10539/33883
QuestionPro. (2020). Survey research: Definition, examples and methods . https://www.questionpro.com/article/survey-research.html
Rajanikanth, J. & Kanth, T. V. R. (2017). An explorative data analysis on Bangalore City Weather with hybrid data mining techniques using R. Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Current Trends in Computer, Electrical, Electronics and Communication (CTCEEC) , India , 1121-1125. https://doi/10.1109/CTCEEC.2017.8455008
Rao, R. (2003). From unstructured data to actionable intelligence. IT Professional, 5 , 29–35. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/3426648_From_Unstructured_Data_to_Actionable_Intelligence
Schulze, P. (2009). Design of the research instrument. In P. Schulze (Ed.), Balancing exploitation and exploration: Organizational antecedents and performance effects of innovation strategies (pp. 116–141). Gabler. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-8349-8397-8_6
Usanov, A. (2015). Assessing cybersecurity: A meta-analysis of threats, trends and responses to cyber attacks . The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319677972_Assessing_Cyber_Security_A_Meta-analysis_of_Threats_Trends_and_Responses_to_Cyber_Attacks
Van de Kaa, G., De Vries, H. J., van Heck, E., & van den Ende, J. (2007). The emergence of standards: A meta-analysis. Proceedings of the 2007 40th Annual Hawaii International Conference on Systems Science (HICSS’07) , USA , 173a–173a. https://doi.org/10.1109/HICSS.2007.529
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Cybersecurity Studies, Nasarawa State University, Keffi, Nigeria
Uche M. Mbanaso
LINK Centre, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
Lucienne Abrahams
Department of Mechatronics Engineering, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Nigeria
Kennedy Chinedu Okafor
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Mbanaso, U.M., Abrahams, L., Okafor, K.C. (2023). Data Collection, Presentation and Analysis. In: Research Techniques for Computer Science, Information Systems and Cybersecurity. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30031-8_7
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30031-8_7
Published : 25 May 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-30030-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-30031-8
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- Dissertation writing
- Topic formulation
- Concept note writing
- Research Proposal
- Introduction writing
- Literature Review
- Research Methodology
- Research instruments formulation
- Data collection
- Statistical analysis
- Data presentation and analysis writing
- Conclusions and recommendations
- Journal Article Writing
- Assignment writing
- Turnitin Plagiarism checks and reducing
- DEFENSE COACHING
- WRITING WORKSHOPS
- WRITING TUTORIALS AND COACHING
- WRITING CONSULTATION
- EDITING AND PROOFREADING
- PRINTING AND BINDING
- ADVICE AND MORE
What comes to your mind when you read or hear the words DATA PRESENTATION AND ANALYSIS?
What comes to your mind may include;
- Response rate
- Demographic analysis
DEFINITION: The data presentation and analysis chapter presents and analyses data collected from a research. Some of the major issues discussed in this section include the response rate, the demographic profile of the respondents and the main research findings which are discussed as per objective. Findings can either be presented orally (viva) or as a written document (project/ dissertation / thesis) (Robindos Research Consultancy, 2020).
- At Robindos Research Consultancy we assist our clients to present and analyse their data.
Data presentation and analysis chapter structure!!!
There is no fixed structure writing the data presentation and analysis chapter and usually universities and supervisors provide their preferred structure. However, the common structure at Robindos Research Consultancy is as follows;
- Introduction
- Background information of respondents
- The other discussions should be in line with you research objectives (may be under sub headings related to your objectives)
- Chapter summary
How to present research data?
The result section of an original research paper provides answer to this question “What was found?” The amount of findings generated in a typical research project is often much more than what can accommodate in one article. So, the first thing the author needs to do is to make a selection of what is worth presenting. Having decided that, he/she will need to convey the message effectively using a mixture of text, tables and graphics. The level of details required depends a great deal on the target audience of the paper.
Some general rules of data presentation!!!
- Always use past tense in describing results
- The main core of the result section consists of text, tables and graphics
- Text provides narration and interpretation of the data presented
- Leave the process of data collection to the methods section
- Simple data with few categories is better presented in text form
- Tables are useful in summarising large amounts of data systemically and graphics should be used to highlight evidence and trends in the data presented
- The content of the data presented must match the research questions and objectives of the study in order to give meaning to the data presented
- Keep the data and its statistical analyses as simple as possible to give the readers maximal clarity
Text, tables or graphics?
These complement each other in providing clear reporting of research findings. Do not repeat the same instrument in more than one structure. Select the best method to convey the message.
Text : Data, which often are numbers and figures, are better presented in tables and graphics, while the interpretation are better stated in text. By doing so, we do not need to repeat the values the text (which will be illustrated in tables or graphics), and we can interpret the data for the readers. However, if there are too few variables, the data can be easily described in a simple sentence including its interpretation. For example, the majority of diabetic patients enrolled in the study were male (80%) compared to female (20%). Using qualitative words to attract the readers’ attention is not helpful. Such words like “remarkably” decreased, “extremely” different and “obviously” higher are redundant. The exact values in the data will show just how remarkable, how extreme and how obvious the findings are. Avoid redundant words. Do not repeat the result within the text, tables and figures. Well-constructed tables and graphics should be self-explanatory, thus detailed explanation in the text is not required. Only important points and results need to be highlighted in the text.
Tables: Tables are useful to highlight precise numerical values; proportions or trends are better illustrated with charts or graphics. Tables summarise large amounts of related data clearly and allow comparison to be made among groups of variables. Generally, well-constructed tables should be self-explanatory with four main parts: title, columns, rows and footnotes.
- Title;Keep it brief and relate clearly the content of the table. Words in the title should represent and summarise variables used in the columns and rows rather than repeating the columns and rows’ titles.
- Columns and rows; Columns are vertically listed data, and rows are horizontally listed data. Similar data ought to be presented in columns. Often these are dependant variables and allow clearer comparison among groups. A table with too many dependent variables would become too wide for a page. There are two alternatives to this problem. We can list the dependant variables in the first left column and independent variables across the top. However, doing so should not compromise clarity of the message we want to get across. The second alternative is to cut down unnecessary columns, which, can be replaced by footnotes explaining their definition.
- Footnotes; These add clarity to the data presented. They are listed at the bottom of tables. Their use is to define unconventional abbreviation, symbols, statistical analysis and acknowledgement (if the table is adapted from a published table).
Graphics: Graphics are particularly good for demonstrating a trend in the data that would not be apparent in tables. It provides visual emphasis and avoids lengthy text description. However, presenting numerical data in the form of graphs will lose details of its precise values which tables are able to provide. The authors have to decide the best structure of getting the intended message across. Is it for data precision or emphasis on a particular trend and pattern? Likewise, if the data is easily described in text, than text will be the preferred method, as it is more costly to print graphics than text.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
TheJoelTruth. While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn't guarantee a good presentation. It's all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by ...
A method of data analysis that is the umbrella term for engineering metrics and insights for additional value, direction, and context. By using exploratory statistical evaluation, data mining aims to identify dependencies, relations, patterns, and trends to generate advanced knowledge.
Written by Coursera Staff • Updated on Nov 20, 2023. Data analysis is the practice of working with data to glean useful information, which can then be used to make informed decisions. "It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts," Sherlock ...
Step 1: Define Your Data Hierarchy. While presenting data on the budget allocation, start by outlining the hierarchical structure. The sequence will be like the overall budget at the top, followed by departments, projects within each department, and finally, individual cost categories for each project. Example:
Data Visualization and Presentation. Data visualization is a vital skill, especially when presenting your findings to non-technical stakeholders. Using data visualization tools you can share your insights with stakeholders and other target audiences. The statistical analysis needs to be easy to understand and easier to apply while making data-driven decisions.
1. Step one: Defining the question. The first step in any data analysis process is to define your objective. In data analytics jargon, this is sometimes called the 'problem statement'. Defining your objective means coming up with a hypothesis and figuring how to test it.
Data analytics is a multidisciplinary field that employs a wide range of analysis techniques, including math, statistics, and computer science, to draw insights from data sets. Data analytics is a broad term that includes everything from simply analyzing data to theorizing ways of collecting data and creating the frameworks needed to store it.
Data Analysis. Definition: Data analysis refers to the process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, drawing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. It involves applying various statistical and computational techniques to interpret and derive insights from large datasets.
Each project will provide you the chance to apply the skills of that lesson. In the first module you'll plan an analysis approach, in the second and third modules you will analyze sets of data using the Excel skills you learn. In the fourth module you will prepare a business presentation. In the final Capstone Project, you'll apply the skills ...
A data analysis presentation is a common format for sharing your insights, but it can also be challenging and time-consuming to prepare and deliver. ... Explain how your data analysis answers your ...
Data analysis is an analytical process which involves recording and tabulating (recording and entering, entering and tabulating) the quantities of a product, such as numbers of units produced, costs of materials and expenses. While data analyst can take different forms, for example in databases, in other structures such as spreadsheets, numbers ...
This method of displaying data uses diagrams and images. It is the most visual type for presenting data and provides a quick glance at statistical data. There are four basic types of diagrams, including: Pictograms: This diagram uses images to represent data. For example, to show the number of books sold in the first release week, you may draw ...
Data analysis is a catalyst for continuous improvement. It allows organizations to monitor performance metrics, track progress, and identify areas for enhancement. This iterative process of analyzing data, implementing changes, and analyzing again leads to ongoing refinement and excellence in processes and products.
Key Objectives of Data Presentation. Here are some key objectives to think about when presenting financial analysis: Visual communication. Audience and context. Charts, graphs, and images. Focus on important points. Design principles. Storytelling. Persuasiveness.
Overview. Data analysis is an ongoing process that should occur throughout your research project. Suitable data-analysis methods must be selected when you write your research proposal. The nature of your data (i.e. quantitative or qualitative) will be influenced by your research design and purpose. The data will also influence the analysis ...
data analysis, the process of systematically collecting, cleaning, transforming, describing, modeling, and interpreting data, generally employing statistical techniques. Data analysis is an important part of both scientific research and business, where demand has grown in recent years for data-driven decision making.Data analysis techniques are used to gain useful insights from datasets, which ...
2. Brand Analysis Dashboard. Next, in our list of data interpretation examples, we have a template that shows the answers to a survey on awareness for Brand D. The sample size is listed on top to get a perspective of the data, which is represented using interactive charts and graphs. **click to enlarge**.
analysis to use on a set of data and the relevant forms of pictorial presentation or data display. The decision is based on the scale of measurement of the data. These scales are nominal, ordinal and numerical. Nominal scale A nominal scale is where: the data can be classified into a non-numerical or named categories, and
Data analysis is the process of developing answers to questions through the examination and interpretation of data. The basic steps in the analytic process consist of identifying issues, determining the availability of suitable data, deciding on which methods are appropriate for answering the questions of interest, applying the methods and ...
8. Tabular presentation. Presenting data in rows and columns, often used for precise data values and comparisons. Tabular data presentation is all about clarity and precision. Think of it as presenting numerical data in a structured grid, with rows and columns clearly displaying individual data points.
Abstract. This chapter covers the topics of data collection, data presentation and data analysis. It gives attention to data collection for studies based on experiments, on data derived from existing published or unpublished data sets, on observation, on simulation and digital twins, on surveys, on interviews and on focus group discussions.
DEFINITION: The data presentation and analysis chapter presents and analyses data collected from a research. Some of the major issues discussed in this section include the response rate, the demographic profile of the respondents and the main research findings which are discussed as per objective. Findings can either be presented orally (viva ...