Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an expository essay

How to Write an Expository Essay | Structure, Tips & Examples
Published on July 14, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
“Expository” means “intended to explain or describe something.” An expository essay provides a clear, focused explanation of a particular topic, process, or set of ideas. It doesn’t set out to prove a point, just to give a balanced view of its subject matter.
Expository essays are usually short assignments intended to test your composition skills or your understanding of a subject. They tend to involve less research and original arguments than argumentative essays .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When should you write an expository essay, how to approach an expository essay, introducing your essay, writing the body paragraphs, concluding your essay, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about expository essays.
In school and university, you might have to write expository essays as in-class exercises, exam questions, or coursework assignments.
Sometimes it won’t be directly stated that the assignment is an expository essay, but there are certain keywords that imply expository writing is required. Consider the prompts below.
The word “explain” here is the clue: An essay responding to this prompt should provide an explanation of this historical process—not necessarily an original argument about it.
Sometimes you’ll be asked to define a particular term or concept. This means more than just copying down the dictionary definition; you’ll be expected to explore different ideas surrounding the term, as this prompt emphasizes.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An expository essay should take an objective approach: It isn’t about your personal opinions or experiences. Instead, your goal is to provide an informative and balanced explanation of your topic. Avoid using the first or second person (“I” or “you”).
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It’s worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline .
A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Like all essays, an expository essay begins with an introduction . This serves to hook the reader’s interest, briefly introduce your topic, and provide a thesis statement summarizing what you’re going to say about it.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
The body of your essay is where you cover your topic in depth. It often consists of three paragraphs, but may be more for a longer essay. This is where you present the details of the process, idea or topic you’re explaining.
It’s important to make sure each paragraph covers its own clearly defined topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Different topics (all related to the overall subject matter of the essay) should be presented in a logical order, with clear transitions between paragraphs.
Hover over different parts of the example paragraph below to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
The invention of the printing press in 1440 changed this situation dramatically. Johannes Gutenberg, who had worked as a goldsmith, used his knowledge of metals in the design of the press. He made his type from an alloy of lead, tin, and antimony, whose durability allowed for the reliable production of high-quality books. This new technology allowed texts to be reproduced and disseminated on a much larger scale than was previously possible. The Gutenberg Bible appeared in the 1450s, and a large number of printing presses sprang up across the continent in the following decades. Gutenberg’s invention rapidly transformed cultural production in Europe; among other things, it would lead to the Protestant Reformation.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The conclusion of an expository essay serves to summarize the topic under discussion. It should not present any new information or evidence, but should instead focus on reinforcing the points made so far. Essentially, your conclusion is there to round off the essay in an engaging way.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a conclusion works.
The invention of the printing press was important not only in terms of its immediate cultural and economic effects, but also in terms of its major impact on politics and religion across Europe. In the century following the invention of the printing press, the relatively stationary intellectual atmosphere of the Middle Ages gave way to the social upheavals of the Reformation and the Renaissance. A single technological innovation had contributed to the total reshaping of the continent.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An expository essay is a broad form that varies in length according to the scope of the assignment.
Expository essays are often assigned as a writing exercise or as part of an exam, in which case a five-paragraph essay of around 800 words may be appropriate.
You’ll usually be given guidelines regarding length; if you’re not sure, ask.
An expository essay is a common assignment in high-school and university composition classes. It might be assigned as coursework, in class, or as part of an exam.
Sometimes you might not be told explicitly to write an expository essay. Look out for prompts containing keywords like “explain” and “define.” An expository essay is usually the right response to these prompts.
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Expository Essay | Structure, Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 4, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/expository-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Expository Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Modes of Discourse—Exposition, Description, Narration, Argumentation (EDNA)—are common paper assignments you may encounter in your writing classes. Although these genres have been criticized by some composition scholars, the Purdue OWL recognizes the wide spread use of these approaches and students’ need to understand and produce them.
What is an expository essay?
The expository essay is a genre of essay that requires the student to investigate an idea, evaluate evidence, expound on the idea, and set forth an argument concerning that idea in a clear and concise manner. This can be accomplished through comparison and contrast, definition, example, the analysis of cause and effect, etc.
Please note : This genre is commonly assigned as a tool for classroom evaluation and is often found in various exam formats.
The structure of the expository essay is held together by the following.
- A clear, concise, and defined thesis statement that occurs in the first paragraph of the essay.
It is essential that this thesis statement be appropriately narrowed to follow the guidelines set forth in the assignment. If the student does not master this portion of the essay, it will be quite difficult to compose an effective or persuasive essay.
- Clear and logical transitions between the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Transitions are the mortar that holds the foundation of the essay together. Without logical progression of thought, the reader is unable to follow the essay’s argument, and the structure will collapse.
- Body paragraphs that include evidential support.
Each paragraph should be limited to the exposition of one general idea. This will allow for clarity and direction throughout the essay. What is more, such conciseness creates an ease of readability for one’s audience. It is important to note that each paragraph in the body of the essay must have some logical connection to the thesis statement in the opening paragraph.
- Evidential support (whether factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal).
Often times, students are required to write expository essays with little or no preparation; therefore, such essays do not typically allow for a great deal of statistical or factual evidence.
- A bit of creativity!
Though creativity and artfulness are not always associated with essay writing, it is an art form nonetheless. Try not to get stuck on the formulaic nature of expository writing at the expense of writing something interesting. Remember, though you may not be crafting the next great novel, you are attempting to leave a lasting impression on the people evaluating your essay.
- A conclusion that does not simply restate the thesis, but readdresses it in light of the evidence provided.
It is at this point of the essay that students will inevitably begin to struggle. This is the portion of the essay that will leave the most immediate impression on the mind of the reader. Therefore, it must be effective and logical. Do not introduce any new information into the conclusion; rather, synthesize and come to a conclusion concerning the information presented in the body of the essay.
A complete argument
Perhaps it is helpful to think of an essay in terms of a conversation or debate with a classmate. If I were to discuss the cause of the Great Depression and its current effect on those who lived through the tumultuous time, there would be a beginning, middle, and end to the conversation. In fact, if I were to end the exposition in the middle of my second point, questions would arise concerning the current effects on those who lived through the Depression. Therefore, the expository essay must be complete, and logically so, leaving no doubt as to its intent or argument.
The five-paragraph Essay
A common method for writing an expository essay is the five-paragraph approach. This is, however, by no means the only formula for writing such essays. If it sounds straightforward, that is because it is; in fact, the method consists of:
- an introductory paragraph
- three evidentiary body paragraphs
- a conclusion
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Expository Writing: Definition and Examples

Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
What is expository writing, what is an expository paragraph, expository writing examples, how prowritingaid can help you with expository composition.
One of the most common types of writing is expository writing. Whether you’re a student taking an English class or a professional trying to communicate to others in your field, you’ll need to use expository writing in your day-to-day work.
So, what exactly does this term mean?
The short answer is that expository writing refers to any writing designed primarily to explain or instruct.
Read on to learn the definition of expository writing as well as some examples of what this type of writing can look like.
Before we look at examples of expository writing, let’s start with a quick definition of what this term actually means.
Expository Writing Definition
The term expository writing refers to any writing that’s designed to explain something. We use the word expository to describe any passage of writing that’s supposed to present information and help you understand it in an objective way.
Some common examples of expository writing include academic essays, textbooks, instructional guides, and news reports. Good expository writing should be factual, objective, and clear.

To better understand what this term means, think about the difference between a scientific article, a short story, and an advertisement.
The scientific article is considered expository writing because its primary purpose is to explain a particular topic in more detail. It presents data, analyzes what that data means, and focuses on the facts.
On the other hand, the short story isn’t considered expository writing, because its core purpose isn’t to explain or inform—instead, it’s probably trying to entertain you or to take you on a journey. Short stories are narrative writing.
Similarly, an advertisement isn’t expository writing because its core purpose isn’t to explain or inform—instead, it’s trying to persuade you to buy what it’s selling. Advertisements are persuasive writing.
Here’s a quick rundown of what expository essays should and shouldn’t do.
An expository essay should:
Teach the reader about a particular topic
Focus on the facts
Follow a clearly organized structure
Present information and details from credible sources
An expository essay should not:
Try to change the reader’s mind about something
Present the author’s personal opinions
Include made-up narratives or stories
Follow experimental or nonlinear structures

An expository paragraph is exactly what it sounds like—a paragraph of expository writing.
A well-written expository paragraph should follow a specific format to make it as clear and easy to read as possible. Most expository paragraphs do the following things:
Start with a topic sentence, which explains what the paragraph will be about
Then, include 3 – 5 body sentences that provide supporting details for the topic sentence
Finally, wrap things up with a closing sentence that summarizes what the paragraph has said
Writing an expository paragraph is a great way to practice expository writing. That’s because the paragraph follows the same structure as a more complex expository essay, just on a smaller scale.
Most expository essays should follow this format:
Start with an introductory paragraph that includes the thesis statement, which tells the reader the core statement of the essay
Then, include 3 – 5 body paragraphs that provide factual evidence to support the thesis statement
Finally, wrap things up with a concluding paragraph that summarizes what the body paragraphs and thesis statement said
You can see the similarities between the two formats. If you can write a fantastic expository paragraph, you’ll be well-prepared to move on to writing a full expository essay.
Example of Expository Paragraph
Here’s an example of an expository paragraph that follows the structure described above.
The leading cause of death in the United States is heart disease, which can be fatal if it leads to heart attack or cardiac arrest. Heart attacks occur when a blockage in the coronary artery prevents oxygenated blood from reaching the heart. Cardiac arrests occur when the heart stops pumping entirely, which prevents the patient from breathing normally. Both of these problems can be deadly, even in seemingly healthy people who don’t have noticeable risk factors. As a result, heart disease is an important problem that many doctors and scientists are researching.

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
There are many ways you can present information in an expository essay. Here are four of the most popular ways, along with examples of each one.
Problem and Solution Essay
A problem and solution essay presents the reader with a problem and then considers possible solutions to that problem.
Here’s an example passage you might find in a problem and solution essay:
Among the many proposed solutions to rising carbon emissions, one promising possibility is carbon trapping. Scientists are figuring out how to pull carbon emissions out of the atmosphere and trap it in less harmful forms, such as by injecting carbon dioxide underground so it will turn to stone.
Compare and Contrast Essay
This type of essay takes two subjects and compares and contrasts them. It focuses on highlighting the differences and similarities between those two things.
Here’s an example passage of this type of expository writing:
Though country music and R&B music have very different sounds, they also share many similarities. For one thing, both types of music embody a specific cultural identity. For another, both genres trace their roots back to the 1920s, when the Victor Talking Machine Company signed singers from the American South.
Classification Essay
In a classification essay, you describe the categories within a certain group of things.
Here’s an example passage you might find in a classification essay:
There are three ways in which artificial intelligence might become stronger than humans in the future: high speed, high collective intelligence, and high quality. A speed AI would be able to perform calculations and experience the world much faster than humans. A collective intelligence, like a hive mind, would be able to break down a complex task into several parts and pursue them simultaneously. Finally, a quality AI would simply be able to solve more complex problems than humans could.
Process Essay
In a process essay, you give the reader the steps for completing a specific process. This is similar to a how-to guide or an instruction manual.
Here’s an example passage you might find in this type of expository writing:
Caramelize the chopped onions in a frying pan. When the onions have caramelized, mix in the bell peppers, mushrooms, and tomatoes and stir for 4 – 6 minutes or until all the ingredients have softened. If you want to add meat, you can add ground beef and cook for another 4 – 6 minutes. Season with salt and pepper to taste.
Good expository writing should be easy to read. After all, the purpose of exposition is to explain things to your readers, and you won’t be able to accomplish that if they have trouble understanding your writing.
That’s why ProWritingAid can help you write an expository essay. The grammar checker can help you ensure your sentences flow well, you’re not missing any necessary punctuation, and all your words are precise and clear.
Good luck, and happy writing!
Hannah is a speculative fiction writer who loves all things strange and surreal. She holds a BA from Yale University and lives in Colorado. When she’s not busy writing, you can find her painting watercolors, playing her ukulele, or hiking in the Rockies. Follow her work on hannahyang.com or on Twitter at @hannahxyang.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
- How it works
How to Write an Expository Essay
Published by Grace Graffin at August 17th, 2021 , Revised On July 26, 2023
Expository means “to describe or explain something” . It is related to the words ‘exposition’, ‘expound’, and ‘expose’ – to explain or reveal the meaning, to lay open, speak one’s mind.
Whenever there is a need to gather research and describe an idea, a topic , or a process clearly and logically, it is done in the form of an expository essay .
An expository essay requires the writer to take a balanced approach to the subject matter rather than justifying a particular point of view.
Expository essays are assigned to students to evaluate their subject knowledge and composition skills. When compared with argumentative essays , they involve a lot less research.
Definition of Expository Essay
“The expository essay is the type of essay that involves an investigation of an idea or topic, appraises relevant supporting evidence material, and presents an argument in a clear and concise manner. ”
When to Write an Expository Essay
Your school or university could assign an expository essay to you as coursework or as part of an online exam.
However, the guidelines may or may not clearly state that your assignment is an expository essay. If that is the case, then look for keywords like ‘explain’, ‘describe’, ‘define’, etc., to be sure that what has been asked for is an expository essay.
You might even be asked to explain and emphasise a particular concept or term. Writing a simple definition will not be enough because you will be expected to explore the ideas in detail.
Writing an Expository Essay
An expository essay should not be based on your personal experiences and opinions. It rather takes an objective approach. You will be expected to explain the topic in a balanced way without any personal bias.
Make sure to avoid the first and second person (“I” and “You”) when writing an expository essay.
How to Structure an Expository Essay
The structure and format of your expository essay assignment will depend on your school’s guidelines and the topic you are investigating. However, it is always a good idea to develop an outline for your essay before starting to work.
The Five-Paragraph Essay Writing Approach
An expository essay will require you to take the five-paragraph essay approach: an introductory paragraph , a main body paragraph , and a concluding paragraph . This is often referred to as the hamburger style of the essay because, like a hamburger, it contains five main parts: the introduction and conclusion being the bun that encapsulates everything.
Rationale and Thesis Statement
Start your essay with a rationale and thesis, also known as the thesis statement , so your readers know what you set out to achieve in your expository essay assignment. Ensure the thesis statement is narrow enough to follow the guidelines in the assignment brief. If the thesis statement is weak and too broad, you will struggle to produce a flawless expository essay.
The Framework
Construct a framework, so you know what elements will constitute the basis of your essay.
Expository Essay Introduction
Like other essay types , an expository essay begins with an introduction , including a hook, background to the topic, and a thesis statement. Once you have grabbed the readers’ interest, it will be easier to get them to read the remaining essay.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will i need the skill of expository writing after i finish my studies.
It depends on what you are studying for. While you might or might not write any more expository essays after your formal education has ended, the skill will be very useful in certain careers, such as business reports, journalism, and in scientific and technical writing.
How does an expository essay differ from an argumentative essay?
An argumentative essay is usually longer and requires more research. It starts with a claim about something that will need supporting evidence. And both sides of the argument need to be discussed. In an expository essay, there is no requirement to make an original argument and defend/support it.
What is the purpose of expository essays?
This style of essay is necessary when you have to showcase your knowledge on a given subject, or your ability to gather research on one and present your findings.
How long is an expository essay?
There is no fixed length but an expository essay could be part of an exam, in which case it might only be 1,000 words or less. They are usually shorter than argumentative essays . It can depend on the subject under discussion. You will likely be given instructions on the required word count.
Are there different types of expository essay?
There are six different types of expository essay, each with a different purpose.
The six types are:
Process essay – describing a task, a method, how to complete something Cause and effect essay – why something happened and its effects Problem-solution essay – provide analysis of problems and their solutions Compare and contrast essay – describe the similarities and differences between two subjects Definition essay – define the topic in detail and explain the how, what, and why Classification essay – separate the topic’s categories and define them in detail
When you are assigned your essay, you should be able to distinguish which of these approaches you are required to take.
You May Also Like
The paragraphs in the main body of an essay is where you develop the central argument. Here is all you need to know about how to write paragraph for essay.
Here are some tips on writing the main body paragraphs of an essay to help you correctly plan and organize the most critical part of your academic essay.
No sure what are the types of persuasive essay? This article presents the similarities and differences between the most common types of persuasive essays.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

Teacher Habits
Helping Teachers inside the Classroom and Out
How to Write an Expository Essay: Writing Tips & Structure
Have you ever been tasked with writing an expository essay and found yourself struggling to convey information clearly and concisely? Expository essays are a unique form of academic writing, requiring a neutral stance and factual evidence to educate the reader on a specific topic.
In this step-by-step guide on how to write an expository essay, we’ll delve into the intricacies of crafting a compelling expository essay, from brainstorming to polishing the final draft. Prepare to embark on a journey to enhance your writing skills and master the art of expository writing.
Table of Contents
Expository Essay Writing: Key Takeaways
- Expository essays are structured academic writing that analyze a given topic objectively.
- This guide provides a comprehensive approach to crafting an expository essay, from idea generation and research through outlining, drafting, refining and polishing techniques.
- The structure of the essay should include a precise thesis statement with evidence-based body paragraphs and transition words for coherence.
The Essence of Expository Essays
Expository essays are a type of structured academic writing that utilizes factual evidence to analyze or investigate a designated topic. Different from descriptive essays and personal opinion pieces, expository writing focuses on providing the reader with information about a given topic, maintaining a neutral stance. This objective description is crucial in academic settings, where expository essays are often assigned as a means of assessment and featured in various exam formats.
To write a good expository essay, it is important to select an engaging topic and articulate a precise, well-informed thesis statement. Examining expository essay examples can offer valuable insights into constructing a well-organized, informative essay. Remember, creativity and artistry can still be incorporated into expository writing, so don’t let the formulaic nature of such essays discourage you from developing a captivating piece.
Crafting an Effective Expository Essay Outline
An effective expository essay outline is crucial for organizing your thoughts and research, as it serves as the foundation of your essay. The basic structure of an expository essay comprises an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The more comprehensive your outline is, the less time you’ll need to spend on research and writing, ultimately making the writing process more efficient.
There is no specific length for an expository essay; however, it should be sufficient to effectively articulate the thesis statement. Typically, a five-paragraph essay is a common approach, with an introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph. By crafting a detailed outline, you can ensure that each section of your essay supports and builds upon your thesis statement, resulting in a cohesive and well-structured piece.
The Writing Process: Step-by-Step Guide
Now that we’ve covered the fundamentals of expository essays and the importance of outline, let’s dive into the step-by-step guide to writing an expository essay.
This guide will cover idea generation, research, outlining, drafting, refining, and polishing, providing a comprehensive approach to crafting a compelling expository essay, including problem and solution essay techniques.
Generating Ideas and Researching
The first step to write an expository essay is brainstorming potential expository essay topics. Consider the topics discussed in class, anticipate what your teacher might expect, and choose something that genuinely interests you. This will ensure that you are engaged in the writing process and motivated to create a captivating essay. After narrowing down your options, conduct research on each topic to determine if reliable sources are easily accessible and gain a more comprehensive understanding of the subject.
Once you have gathered sufficient information, it’s time to analyze your research and select an expository essay topic that best suits your interests and meets your instructor’s guidelines. Keep in mind that your chosen topic should be able to provide enough factual evidence to support your thesis statement, as this will be the core of your essay. By selecting a strong, engaging topic, you set the foundation for a successful expository essay.
Organizing Thoughts with an Outline
Creating an outline is essential for organizing your thoughts and laying the groundwork for your expository essay. Start by developing a strong thesis statement that outlines the main idea of your essay and provides a well-informed, reasoned response to your research question. Your outline should specify what information will be included in each paragraph, ensuring that each section of your essay supports your thesis statement.
The outline serves as a roadmap, guiding you through the writing process and helping you stay focused on your topic. By organizing your thoughts and research in a logical manner, you’ll find it easier to begin writing and stay on track throughout the development of your expository essay.
Drafting the Essay
With a comprehensive outline in hand, it’s time to start drafting your expository essay. Focus on crafting well-structured body paragraphs that stay on topic and provide factual evidence to support your thesis statement. It’s often beneficial to postpone writing the introduction until after you’ve completed the body paragraphs and conclusion, as this will allow you to develop a more accurate and engaging introduction based on the content of your essay.
As you write, use transition words and sentences to connect ideas, maintain narrative flow, and guide readers through your argument. This will ensure that your essay is coherent and easy to follow, ultimately enhancing the reader’s understanding of your topic.
Refining Your Draft
Once you’ve completed the first draft of your expository essay, it’s time to refine your work. Start by reorganizing content, ensuring that each sentence serves its purpose and enhances the reader’s understanding of your topic. Edit for clarity and coherence, and double-check that your essay remains focused on your thesis statement throughout.
As you review your draft, read the paper as if it’s your first encounter with the topic. This will help you determine if the essay is coherent and if the information provided is relevant to the intended purpose of each section. Remember to abstain from attempting to make a persuasive argument and to utilize opinions as evidence, as this can detract from the objective nature of your expository essay.
Polishing the Essay: Editing and Proofreading
The final step in crafting a compelling expository essay is editing and proofreading. Check for errors in grammar, spelling, and formatting, and ensure that your citations are accurate and adherent to the assigned style guide. Tools like Grammarly can be helpful in detecting errors and phrases that lack clarity, as well as ensuring a uniform tone throughout your essay.
In addition to self-editing, consider having someone else review your work. This can provide a fresh perspective and help identify any remaining inconsistencies or areas that need improvement. With your polished expository essay in hand, you’ll be ready to present your well-researched, informative, and engaging piece to your audience.
Analyzing Expository Essay Examples
Examining expository essay examples can be an invaluable tool in understanding how to create a well-structured, informative essay. By analysing the structure, style, and use of evidence in an expository essay example, you can gain insight into crafting your own compelling piece. Remember, it’s not recommended to directly source information or text from expository essay examples, but they can serve as an inspirational reference for your work.
Take note of how the thesis statement is presented, how the body paragraphs are organized, and how the conclusion effectively summarizes the main points of the essay. By carefully studying expository essay examples, you’ll be better equipped to create your own well-crafted, engaging, and informative piece.
Diving into Expository Essay Types
Expository essays come in various forms, each with its own unique purpose and structure. Understanding the different types of expository essays can aid in selecting a subject and organizing your essay’s overall trajectory and framework. The primary types of expository essays include classification, definition, process, compare-and-contrast, and cause-and-effect essays.
Classification essays identify and organize various subjects within one category, outlining their individual characteristics. A definition essay, on the other hand, provides a clear and concise explanation of a subject matter. A process essay outlines the steps necessary for completing a task, providing the reader with an understanding of the procedure.
Compare-and-contrast essays analyze the differences and similarities between sources cited. Cause-and-effect essays investigate the reasons behind a particular occurrence and the consequences that follow. Familiarizing yourself with these expository essay types will expand your writing capabilities and help you craft a compelling piece.
Structuring Your Expository Essay
To ensure a coherent and engaging expository essay, it’s crucial to understand the expository essay structure, which includes a distinct introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion that support your thesis statement. The introduction should include a precise and succinct thesis statement that outlines the primary focus of your essay, providing the reader with a clear understanding of the topic at hand.
Each body paragraph should contain evidence that supports your thesis statement, ensuring that every section of your essay contributes to the overall argument.
Finally, the conclusion should succinctly summarize the main points and provide a clear and concise statement of the essay’s overarching message. By following this structure, you’ll create a well-organized, informative, and engaging expository essay that effectively communicates your ideas to your audience.
The Role of the Thesis Statement
The thesis statement serves as the foundation of your expository essay, providing a succinct, precise synopsis of the primary point of your essay. A strong, clear, and memorable thesis statement is essential, as it gives the reader a clear understanding of the main focus of your essay and sets the tone for the entire piece. Examples of effective thesis statements include: “The effects of global warming are becoming increasingly evident in our environment,” “The use of technology in the classroom can have both positive and negative effects,” and “The rise of social media has had a profound impact on our society.”
To create a thesis statement, identify your essay topic, conduct research on the topic, and formulate a main idea or argument based on your findings. This statement should be concise and direct, ensuring that your essay remains focused and well-organized throughout the writing process.
Enhancing Your Essay with Transition Words and Sentences
Transition words and sentences play a crucial role in connecting ideas, maintaining narrative flow, and guiding readers through your argument. They serve as the binding element that keeps your essay’s foundation intact, preventing confusion and ensuring that your argument remains coherent and easy to follow. A lack of logical progression of thought can make it difficult for the reader to comprehend your essay’s argument, ultimately compromising its structure.
Examples of transition words and phrases include “however,” “in addition,” “on the other hand,” and “as a result.” By incorporating these transitions into your expository essay, you’ll create a seamless reading experience that effectively communicates your ideas and maintains the reader’s interest throughout the piece.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you start an expository essay.
To start an expository essay, begin with a general statement about your topic that captures the reader’s attention. This should be followed by your thesis or main point of the essay, which can be further supported with three body paragraphs.
Use a formal tone and avoid introducing unnecessary information or summaries.
How do you write an expository essay step by step?
Writing an expository essay can be done step-by-step by organizing your thoughts, researching the topic, formulating a thesis statement, writing an introduction, composing the body paragraphs, and summarizing the essay in the conclusion.
Finally, revise and proofread the essay to ensure its quality.
What is an example of an expository essay?
An example of an expository essay is one that provides readers with a step-by-step guide on how to do something, or a descriptive essay that is loaded with details.
These types of essays seek to explain a particular topic in an informative and logical manner.
What are the 4 parts of the expository essay?
An expository essay is composed of four parts: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
It provides a clear and organized explanation of a specific topic.
What is an expository essay?
An expository essay is an essay that communicates factual information, requiring the student to investigate an idea, evaluate evidence, expound on the idea, and set forth an argument concerning it in a clear and concise manner.
It is important for the student to be able to organize their thoughts and ideas in a logical manner in order to effectively communicate their argument. Splitting the text into paragraphs is a key to better readability. Start a new paragraph whenever you introduce a new idea or change direction in your argument. This will be a success.
In conclusion, crafting a compelling expository essay requires careful planning, research, and organization. By understanding the essence of expository essays, creating an effective outline, following a step-by-step writing process, and analyzing examples, you can develop your writing skills and create an engaging, informative piece.
Familiarize yourself with the different types of expository essays and the importance of structuring your essay to support your thesis statement. Remember to enhance your essay with transition words and sentences, ensuring a smooth, coherent reading experience for your audience. With these tools and techniques in hand, you’re well on your way to mastering the art of expository writing.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Expository Essay
4-minute read
- 29th March 2020
An expository essay explains something. This means investigating an idea, looking at evidence, coming to a conclusion, and explaining your thinking. But how do you write a strong expository essay? Our top tips include:
- Read the essay prompt carefully and using it to guide your research.
- Come up with a thesis statement (i.e., a position that you’ll explain).
- Plan the structure of your essay before you start writing.
- Once you have a first draft, revise and proofread to make sure it is perfect.
For more advice on how this works, check out the guide below.
1. Read Your Essay Prompt
Most expository essay prompts will ask you to do one of the following:
- Define and explain a concept or theory.
- Compare and contrast two ideas.
- Examine a problem and propose a solution.
- Describe a cause and effect relationship.
- Explain a step-by-step process.
- Analyze a broad subject and classify examples into groups.
When you’ve been set an expository assignment, then, check the prompt or question carefully. You can use the phrasing to guide your research. You may also need to select a topic to write about. If so, try to think of something:
- You already know at least something about.
- You find interesting enough to research.
- That fits with the instructions in the essay prompt (e.g., if you’ve been asked to contrast two things, you’ll need a topic that allows for a comparison).
- That is narrow enough to discuss in one essay.
Start by brainstorming topics, then narrow it down to one or two ideas.
2. Come Up with a Thesis Statement
Once you have a topic, you’ll need to do some research and develop a thesis statement. This is the proposition or position that you’ll explain in your essay.
Your thesis statement should be something you can back up with evidence and facts, as well as something that answers the question in your essay prompt. Keep in mind, too, that an expository essay should present a balanced account of the facts available, not personal opinions. For instance, we’ve come up with thesis statements for a few example essay prompts:
When you’ve selected a thesis, make sure you’ve got evidence to back it up! This may mean doing a little more research before you start writing.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
3. Structuring an Expository Essay
The exact length and content of your essay will depend on the topic and prompt. However, most expository essays follow a similar basic structure:
- Introduction – A paragraph where you introduce the essay topic and your thesis statement (i.e., the issue or idea you will explain in the essay).
- Main Body – A series of short paragraphs in which you explain your thesis statement, providing evidence and arguments to support each point.
- Conclusion – A final paragraph where you restate your thesis and how your evidence supports this. Try not to introduce any new information here (if it’s important, it should go in the main body).
- References – If required, include a bibliography of sources you’ve used.
Before you start writing, then, create an essay outline with the structure above in mind and plan what each paragraph will say.
4. Editing and Proofreading
When you have a first draft, take a break and re-read it. Now comes the redrafting ! This is where you go back over your essay and look for areas to improve. Do you provide enough evidence? Is your argument clear? Even a few tweaks may increase your mark, so make sure to redraft at least once!
Finally, make sure to have your essay proofread before you submit it for marking. This will ensure your writing is error free and easy to read, giving you an even better chance of getting the grades you deserve.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write an Expository Essay
Last Updated: December 13, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Tristen Bonacci . Tristen Bonacci is a Licensed English Teacher with more than 20 years of experience. Tristen has taught in both the United States and overseas. She specializes in teaching in a secondary education environment and sharing wisdom with others, no matter the environment. Tristen holds a BA in English Literature from The University of Colorado and an MEd from The University of Phoenix. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 564,689 times.
Expository essays are often assigned in academic settings. In an expository essay, you need to consider an idea, investigate the idea, then explain the idea. Some expository essays may include an argument, while others are purely informative. [1] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source While it may seem overwhelming, writing an expository essay is easy if you take it one step at a time.
Sample Essay Conclusion

Planning Your Essay

- If you are writing an expository essay for an assignment, read the assignment guidelines. Ask your instructor if anything seems unclear.

- If you are writing your essay for a class assignment, consider what your instructor will expect you to include in your essay.

- Try listing. List all your ideas for your expository essay. Then look over the list you have made and group similar ideas together. Expand those lists by adding more ideas or by using another prewriting activity. [6] X Research source
- Try freewriting. Write nonstop for about 10 minutes. Write whatever comes to mind and don’t edit yourself. After you finish writing, review what you have written. Highlight or underline the most useful information for your expository essay. Repeat the freewriting exercise using the passages you underlined as a starting point. You can repeat this exercise many times to continue to refine and develop your ideas. [7] X Research source
- Try clustering. Write a brief explanation of the subject of your expository essay on the center of a piece of paper and circle it. Then draw three or more lines extending from the circle. Write a corresponding idea at the end of each of these lines. Continue developing your cluster until you have explored as many connections as you can. [8] X Research source
- Try questioning. On a piece of paper, write out “Who? What? When? Where? Why? How?” Space the questions about two or three lines apart on the paper so that you can write your answers on these lines. Respond to each question in as much detail as you can. [9] X Research source

- Trustworthy internet sources usually include academic institutions like universities or research labs, government websites, and non-profit organizations.

- Identify the author and his or her credentials. Think about what qualifies this person to write about their subject. If the source has no author or the author does not have adequate credentials, then this source may not be trustworthy.
- Check for citations to see if this author has researched the topic well enough. If the author has provided few or no sources, then this source may not be trustworthy.
- Look for bias. Think about whether or not this author has presented an objective, well-reasoned account of the topic. If the author seems to value a particular argument or slant that is not supported or only thinly supported by fact, then this source may not be trustworthy.
- Consider the publication date to see if this source presents the most up to date information on the subject.
- Cross-check some of the information in the source. If you are still concerned about a source, cross-check some of its information against a trustworthy source.

- Show when you have quoted a source word for word by putting it into quotation marks. Include information about the source such as the author’s name, article title or book title, and page number.
- Write down the publishing information of each source. You will need this information for your "References," "Bibliography," or "Works Cited" pages. Format this page according to your instructor's guidelines.

- Make sure your thesis is arguable. Do not state facts or matters of taste. For example, "George Washington was the first president of the United States," is not a good thesis because it states a fact. Likewise, "Die Hard is a great movie," is not a good thesis because it expresses a matter of taste. [16] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
- Make sure your thesis provides enough detail. In other words, avoid just saying that something is "good" or "effective." Instead, say what makes something "good" or "effective. [17] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
Introducing Your Essay

- An engaging hook can take many forms. You could start with an anecdote, an informative and attention-grabbing quote, a bold opinion statement, or anything that will make your readers want to continue with your essay.

- If you are writing about a book, provide the name of the work, the author, and a brief summary of the plot.
- If you are writing about a specific day in history, summarize the day's events. Then, explain how it fits into a broader historical scope.
- If you are writing about a person, name the person and provide a brief biography.
- Keep in mind that your context should lead up to your thesis statement. Explain everything your reader needs to know to understand what your topic is about. Then narrow it down until you reach the topic itself.


Expressing Your Main Points

- A five-paragraph essay should include three body paragraphs. Each body paragraph should discuss a piece of supporting evidence that supports your thesis.
- Even if your essay is longer than five paragraphs, the same principles still apply. Each paragraph should discuss a piece of supporting evidence.

- "Dogs played an active role in Marine Corps missions in the Pacific."
- "The Doberman Pinscher was the official dog of the US Marine Corps during WWII, but all breeds were eligible to train as war dogs."
- "War dogs were even eligible to receive military awards for their service."

- Most of your evidence should be in the form of cited quotes, paraphrases, and summaries from your research.
- Your evidence could also come from interviews, anecdotes, or personal experience.
- Try to provide at least two to three pieces of evidence to support each of your claims.
- For example, if a paragraph starts with, "War dogs were even eligible to receive military awards for their service," the supporting evidence might be a list of dogs who got awards and the awards they were given.

- You could write, "Even though Dobermans were the most common breed used in WWII, they were not the only breed, and were not the only dogs recognized for their help."
Concluding Your Essay

- Note that the second sentence repeats the information provided in your original thesis. It just says it in a new way while also hinting at the information you included in the body of the essay.

- Explain how the topic affects the reader
- Explain how your narrow topic applies to a broader theme or observation
- Call the reader to action or further exploration on the topic
- Present new questions that your essay introduced
Expert Q&A

- If you are unsure about anything as you work on your essay, talk to your instructor or meet with a writing tutor for help. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/expository_essays.html
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/expository-essay/
- ↑ Tristen Bonacci. Licensed English Teacher. Expert Interview. 21 December 2021.
- ↑ http://writing.ku.edu/prewriting-strategies
- ↑ https://grammar.yourdictionary.com/grammar-rules-and-tips/tips-on-writing-an-excellent-expository-essay.html
- ↑ http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/reading-and-researching/notes-from-research
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/thesis-statements/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/thesis-statements/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/using_research/quoting_paraphrasing_and_summarizing/index.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/argument_papers/conclusions.html
About This Article

Before you write an expository essay, take some time to jot down ideas for your essay. Try the clustering method by writing a brief explanation of your subject in a bubble in the center of your page. Then, draw 3 or more lines extending from the circle and jot down idea bubbles that connect to your main theme. Once you have a plan for your expository essay, write out an outline to organize what you’re going to say. Make sure to begin your outline with an engaging introduction sentence. After the introduction sentence, provide some background information and include your thesis statement, which is your main argument. If you’re writing a 5 paragraph essay, you should include 3 body paragraphs after your introduction then a conclusion paragraph that summarizes your main points. However you organize your essay, make sure to include credible sources for important information, like statistics, so your teacher knows that it’s accurate. To learn how to use transitions in your essay, read more from our Writing co-author. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Freida Ghabiliha
Nov 24, 2017
Did this article help you?

Qutaiba Raid
Jan 31, 2018
Maryanne Waqa
Aug 23, 2018
Apr 9, 2018
Nov 25, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How to Write An Expository Paragraph
This guide will tell you how to write an expository paragraph and build your essay writing skills.
An expository paragraph is used to explain or describe something. These paragraphs are part of expository essay writing, making up expository essays and reports. These paragraphs are the building blocks of informative writing projects. Each expository paragraph opens up a central point supporting the project’s thesis statement.
An expository paragraph explains the topic you are discussing in your writing. The primary goal of the paragraph is to educate or inform the reader. This can show the author’s knowledge or expertise on a specific topic. In research papers, these paragraphs typically explain one point in the paper’s structure. They are the primary body paragraphs of expository essay writing projects.
If you need to write an informative research paper, knowing how to write a good expository paragraph is vital. This guide will help you learn how to build this paragraph to support and substantiate your writing. It pairs nicely with our guide for analyzing a paragraph .
Expository Paragraphs in Comparison to Other Writing Types
Step 1: choose your topic, step 2: write a topic sentence, step 3: write introductory sentences, step 4: write the body sentences, step 5: write the concluding sentences, step 6: use expository paragraphs in different types of writing, step 7: prewrite before writing, step 8: create a rough draft, step 9: look for additional expository essay topics, step 10: write your final paragraph, step 11: proofread the work.
Expository writing is one of the four main types of writing . It stands in contrast to narrative, descriptive and persuasive essay paragraphs.
A narrative essay paragraph seeks to tell a personal story or show personal growth. Second, descriptive essay paragraphs describe an item or event using words that pull in the five senses. Third, persuasive essay paragraphs seek to persuade the reader to accept the writer’s point of view on a controversial topic. Finally, expository paragraphs seek to provide information and facts or argue a point. You might also be interested in our list of paragraph writing topics .
How to Write an Expository Paragraph
An expository paragraph has a specific structure. It starts with introductory sentences that include the topic sentence, followed by body sentences, and ends with a conclusion. Interestingly, this follows the basic structure of a five-paragraph essay but replaces the paragraphs with sentences. Check out our guide on the best expository writing topics .
Before you can write an expository paragraph, you must have a topic. This type of paragraph aims to expound on or explain an idea. You will need to find a topic with enough information and research to write a full paragraph. If you are going to write an essay, make sure the topic is sufficient.
To write an expository paragraph, you must first decide your main point. The topic sentence is the basis for all of your prewriting and writing activities. The thesis or topic sentence for the paragraph will tell the reader what they will learn from reading.
This paragraph summarizes the main thoughts that you will explain in the body of the paragraph. If the paragraph argues, you will state your position in the topic sentence. It needs to tell the reader why they should read the paragraph and what they will learn from it.

Now you are ready to write introductory sentences. How you write the piece may come before the topic sentence or directly after it. These sentences use transition words to move from the paragraph preceding the one you are writing. They also introduce the topic of the paragraph.
If you think of your paragraph like a house, the introductory sentences work as the foundation and the door. They set the stage for the rest of the sentences and give the reader an entry point into your ideas and thoughts.
In these sentences, you should refute counterpoints to your idea, summarize the arguments you will later discuss, and state your problem or issues. It would be best not to suggest that you lack knowledge or use generalizations. It would help if you also did not use a dictionary definition. Finally, do not directly state intentions, such as saying, “In this paragraph, I will discuss. . .”
However, it would be best if you captured the reader’s interest and attention when writing these sentences. For example, you can open with a quotation, surprising fact, anecdote, or statistic, but make it something that will make the reader want to continue reading.
After the introductory sentences, you will have your body sentences. These support the argument in your thesis statement. They may include quotations, paraphrases, and statistics from your research. Every one of the body sentences needs to provide relevant, supportive information. Words that help transition to the following sentence help the paragraph to flow.
Body sentences are the structure of the house you are building with your paragraph. They should be firm and adequately support your topic. They should use examples, statistics, and facts to bring more insight into the topic.
If you use quotes in your body sentences, explain why they are essential to your topic sentence. Use proper citations to credit the original author for quotes and paraphrases in your body sentences.
In an expository paragraph, you can write as many body sentences as possible to explain your point. Each point in an essay outline will usually need one paragraph, so sometimes, these paragraphs can be quite lengthy. However, if you find yourself talking about more than one point, you should break the paragraph into one paragraph per point.
The concluding sentence is the last sentence of the paragraph. It restates the topic sentence and adds closure to the thoughts in the paragraph. It may segway into the next paragraph, but it does not have to do so. The main goal of the concluding sentence is to wrap up what you have said and give your reader a sense of closure.
The conclusion needs to serve as the roof of the house you create in your paragraph. It sums everything up and contains your ideas within the paragraph so that you can move on to the next paragraph.
While the concluding sentence should restate the topic sentence, it should not simply rework the same sentence. It should not contain over-used phrases like “in conclusion” or “to summarize.” It also should not make any absolute claims.
There are several types of expository writing that all use expository paragraphs. Understanding this structure will help you write the following types of essays:
- Process Essays: Process essays are essays that tell how to do something. The body paragraphs of this essay typically explain the process with a step-by-step breakdown. Each paragraph will outline the details of one step.
- Definition Essays: Definition essays will describe and define a subject. To write this type of essay, you will present clear facts about a subject while refuting any common myths. These essays often take on historical events or people and rely on primary sources to define their topics.
- Compare and Contrast Essays: Comparison essays compare and contrast two similar or different items. This type of essay works very well for the five-paragraph essay. The introduction will introduce the two items. The three body paragraphs will focus on their attributes, one paragraph each, and how they are similar and different in the third paragraph. The final paragraph is the conclusion.
- Cause and Effect Essays: A cause and effect essay looks at a cause and its effects, or vice versa. It can analyze how the effects resulted from a particular cause, or it can look at one effect and point out the multiple causes that led to it.
- Classification Essays: Classification essays allow you to write about multiple subjects within one category. You will discuss the unique characteristics of each subject in each of the expository paragraphs in this essay. For example, if you choose to write an expository essay about different breeds of racehorses, your paragraphs could discuss quarter horses, thoroughbreds, and Arabians.
- Problem and Solution Essays: Problem and solution essays use a problem as the central thesis and the solution to that problem as the points in the essay outline. Each point must use expository writing to show that it is a solution, with data and facts to back it up.
As you create your expository paragraph, you want to make sure that you follow the proper writing process. This process starts with prewriting, which involves getting basic ideas down on paper as you brainstorm your topic. Your prewriting may happen when you create your more extensive essay outline, or it may be done when you sit down to write your paragraph.

Once you have your ideas down, you will write a rough draft of your paragraph. This first draft turns your ideas into sentences following the expository paragraph format.
In your rough draft, you may have some grammar or syntax mistakes. These mistakes will get ironed out later in the writing process, so do not stress much about them. However, do try to write as cleanly as possible.
When you write, use the third person voice, and apply proper grammar techniques to your writing. The next few steps will be easier if you choose the proper voice and use good grammar in your rough draft.
If you are looking for expository essay topics to write your paragraphs for your essay, consider your audience. If your instructor gave parameters for your essay topic, start with those. If not, you can use these writing prompts to get your ideas started:
- Write a cause-and-effect essay about a particular historical event, such as a war or significant economic change.
- Write a comparison essay about two pieces of literature.
- Write a descriptive essay about the character of a political or historical figure.
- Give step-by-step directions for how to cook a particular dish.
- Choose a political or ethical problem and use your essay to outline some potential solutions for it.
In addition, you can look to literature, science reviews and studies, news reports, and informative texts to find additional expository essay topic ideas. Look for subject matter with a decent number of resources you can use as sources to write your paragraphs, making the writing task more manageable. Remember, your goal with this type of essay is not to present your opinion but rather to provide information, so you will need the information to write one.
After proofreading your work, you are ready to write your final paragraph. Use the changes you found in your rough draft to draft a final copy that will draw in the reader and clearly explain your points. Format the paragraph according to your teacher’s rules or the publication platform you use.
Now that you have a rough draft of your paragraph, you are ready to proofread it.
You will improve the grammar and syntax during the proofreading process, but you will also make sure the paragraph follows the format. For example, each body sentence needs to support the topic sentence fully, and the transition words help the piece flow. Plan on revising the paragraph at least once to ensure it reads well. For more help with your following essay, read our guide on how to write a lot of words (when you don’t feel like it) .

Nicole Harms has been writing professionally since 2006. She specializes in education content and real estate writing but enjoys a wide gamut of topics. Her goal is to connect with the reader in an engaging, but informative way. Her work has been featured on USA Today, and she ghostwrites for many high-profile companies. As a former teacher, she is passionate about both research and grammar, giving her clients the quality they demand in today's online marketing world.
View all posts
Expository Essay
Complete Guide to Expository Essays: Writing Help and Topics
11 min read
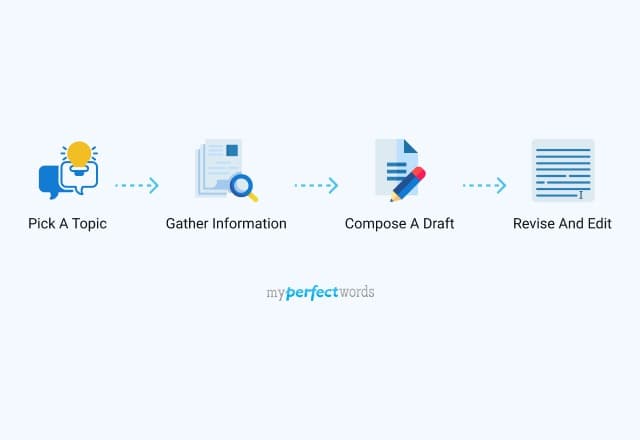
People also read
Interesting Expository Essay Topics For Your Next Paper
How to Write an Expository Essay Outline Like a Pro
Types of Expository Writing - Definition and Examples
Free Expository Essay Examples For Students
Ultimate Guide to Writing an Expository Essay About a Person
Learn to Write an Expository Essay About Yourself
Learn the Basics of Crafting an Expository Essay about a Book
Learn to Write Expository Essay About Mental Health - Examples & Tips
How to Write an Expository Essay about Bullying: A Guide
Expository Essay About Dogs: Steps, Examples & Topics
A Guide to Writing an Expository Essay about Education
Expository Essay About Friendship: A Writing Guide
Discover How to Write Expository Essays About Music – A Step-by-Step Guide
Writing essays can be a real challenge for many students. They often struggle to organize their thoughts and convey them clearly in expository essays.
This struggle leads to essays that lack clarity and fail to captivate the reader’s interest.
But worry not! This guide is your go-to helper. We're going to break down the ins and outs of expository writing using simple steps. Plus, we’ve included some tips and topic ideas, so you can craft essays that are both clear and engaging!
So, keep reading!
- 1. What is an Expository Essay?
- 2. Expository Essay Vs. Argumentative Essay
- 3. Types of Expository Essay
- 4. Structure of an Expository Essay
- 5. How to Write an Expository Essay?
- 6. Expository Essay Example
- 7. Tips for Writing a Good Expository Essay
- 8. Expository Essay Topics
What is an Expository Essay?
An expository essay is a type of essay that seeks to inform, describe, or explain a particular subject or topic.
It's distinct in its approach as it emphasizes presenting facts, analyzing information, and providing a comprehensive understanding without incorporating personal opinions or biases.
Why Write an Expository Essay?
The purpose of writing an expository essay extends beyond academic requirements.
This form of writing nurtures the ability to research deeply, logically organize thoughts, and articulate information coherently.
Developing these skills not only enhances academic performance but also prepares individuals for effectively communicating complex ideas in various real-world scenarios.
Expository Essay Vs. Argumentative Essay
Expository and argumentative essays vary in their purposes and approaches.
Expository essays aim to inform or describe a topic without personal opinions, using a neutral, informative tone.
On the other hand, argumentative essays seek to persuade by presenting a clear viewpoint and supporting it with evidence.
Expository essays follow a simpler structure, providing information, while argumentative essays involve complex structures, presenting and countering arguments. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right essay type for specific writing goals.
Types of Expository Essay
Before we dive into the different types of expository essays, let's check out five common ones:
Descriptive Essays
Descriptive essays aim to create a detailed image or sensory experience in the reader's mind by vividly describing a particular place, object, person, or event.
They use rich language and sensory details to paint a clear picture and evoke emotions, making the reader feel like they're experiencing what's being described.
Process Analysis Essays
In a process analysis essay , the writer breaks down a series of steps needed to achieve a specific task or goal.
They provide a clear, step-by-step guide, making complex tasks easy to understand. For example, they might explain how to bake a cake, fix a bicycle, or perform a scientific experiment.
Compare and Contrast Essays
Compare and contrast essays focus on exploring the similarities and differences between two or more subjects.
They present a balanced view, showing how things are alike and how they're different. Whether it's comparing different cultures, products, historical events, or ideas, these essays aim to offer insights into relationships and contrasts.
Cause and Effect Essays
Cause and effect essays delve into examining the causes that lead to specific effects or the effects that arise from certain causes.
They analyze the relationship between events, explaining why things happen and what outcomes result from those actions or occurrences. They aim to provide a clear understanding of the connections between different elements.
Problem and Solution Essays
Focused on a specific issue, problem and solution essays identify a problem, its causes, and effects, and propose solutions to address and resolve the problem.
They aim to offer practical, effective solutions to real-life issues, providing a roadmap for solving problems or improving situations.
Structure of an Expository Essay
An expository essay typically comprises three main parts: the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Here's what the general structure of an expository essay looks like:
Introduction
The introduction of an expository essay is where the writer presents the topic, provides background information, and ends with a clear thesis statement .
This section aims to grab the reader's attention and set the stage for the discussion that follows.
Body Paragraphs
The body of the essay contains a series of paragraphs that delve deeper into the topic.
Each paragraph should begin with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea or argument.
These paragraphs present evidence, examples, or explanations supporting the thesis statement. Smooth transitions between paragraphs ensure a coherent flow of information.
The conclusion of an expository essay restates the thesis statement using different wording. It summarizes the key points discussed in the body paragraphs.
Finally, it offers a sense of closure, wrapping up the essay's main ideas. It's not just a repetition of earlier information but rather a synthesis of the key points to leave a lasting impression on the reader.
How to Write an Expository Essay?
Writing an expository essay involves a step-by-step process to effectively communicate information. Here's a guide to crafting an expository essay:
Select a Topic
When selecting a topic for an expository essay, it's crucial to choose something that's not only interesting but also suitable for an informative discussion.
Consider the following pointers while choosing an expository essay topic:
- Select a topic that personally interests you.
- Choose a topic that can be explained within the essay's scope
- Choose subjects allowing for an objective, fact-based analysis.
- Consider prevalent issues or areas of curiosity for discussion.
Conduct Research
When researching for your expository essay, explore diverse and credible sources like books, scholarly articles, and reputable websites.
Ensure the information gathered directly relates to your topic and is from reliable sources. Verify the credibility by checking the author's credentials and publication dates.
Consider various perspectives to present a well-rounded view. Organize your findings systematically, keeping detailed notes for citation. This approach helps in crafting a well-informed and supported expository essay.
Create an Outline
Develop a structured outline for your essay. Organize your thoughts, decide on the main points, and arrange them logically.
Here's what the general structure of an expository essay looks like:
This outline template provides a clear structure, allowing for a well-organized and coherent expository essay.
View this in-depth guide on creating an expository essay outline for a structured essay!
Write The Introduction
The introduction of an expository essay plays a pivotal role in engaging the reader and setting the stage for the discussion. Here are the essential components:
- Engaging Hook : Begin your essay with a captivating fact, question, quote, or story related to the topic to captivate the reader's attention and encourage them to continue reading.
- Background Context: Offer essential background information about the topic, providing the necessary context for the reader to understand its relevance and importance.
- Clear Thesis Statement: End the introduction with a clear thesis statement. It should express the main idea or argument of your essay. This statement helps guide the reader, indicating the purpose and direction of your essay.
Compose Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs serve as the essay's core.
Each paragraph starts with a topic sentence introducing the main idea. Back up this idea with evidence or examples to support your point.
Make sure each paragraph smoothly connects to the next for a logical flow of ideas. This structured approach ensures a coherent and well-supported discussion throughout your expository essay.
Write the Conclusion
In the conclusion of your expository essay, recap the main points without introducing new information.
Restate the thesis in different words to reinforce the main argument. Additionally, offer closing thoughts or discuss the broader implications related to the topic. This section serves as a summary, emphasizing the significance of the essay's ideas and their broader relevance.
Revise and Edit
Revision and editing are crucial steps in the essay writing process.
Review the content for coherence and logical flow, ensure the essay structure is smooth and well-organized, and focus on clear, concise language.
Check for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors, verify citations, and seek feedback for improvements. Finally, perform a final proofread to ensure the essay is error-free and polished for submission.
Expository Essay Example
Below is an example illustrating the concept of climate change and its effects, exploring the causes, impacts, and potential solutions.
This essay serves as a basic example of how an expository essay on climate change might be structured, offering insights into its causes, effects, and potential solutions.
Need more examples? Check out these expertly crafted expository essay examples on multiple topics and themes!
Tips for Writing a Good Expository Essay
Here are some tips for writing a good expository essay:
- Ensure the essay has a clear and narrowly defined topic for effective exploration.
- Present facts, statistics, and evidence without incorporating personal opinions or biases.
- Utilize a well-structured format with logical sequencing of ideas and paragraphs.
- Provide detailed and comprehensive explanations to support each point or idea.
- Use diverse and relevant examples to illustrate and reinforce key points.
- Present information in a concise and easily understandable manner, avoiding unnecessary details.
- Use transitional words and phrases for seamless connections between paragraphs and ideas.
- Make sure that all information presented is relevant and sourced from credible, reputable materials.
Expository Essay Topics
Expository essay topics typically revolve around subjects that can be explained, clarified, or described without personal opinions.
They cover a wide array of areas such as science, technology, education, health, social issues, historical events, and more. These topics should allow for in-depth exploration and factual analysis.
Here are some essay topics for students:
Expository Essay Topics for High School Students
- The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers
- Benefits of Exercise and Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Exploring Climate Change: Causes and Effects
- The Importance of Education in Today's Society
- Understanding Cyberbullying and its Impact
- Analyzing a Historical Event: The Civil Rights Movement
- The Advantages and Disadvantages of E-Learning
- Explaining the Process of Photosynthesis
- The Effects of Video Games on Adolescents
- The Role of Leadership in Problem Solving
Expository Essay Topics for University Students
- The Future of Artificial Intelligence and its Ethical Implications
- Analyzing the Impact of Globalization on World Economies
- Climate Change: Policy Interventions and Global Strategies
- The Psychology Behind Procrastination and Ways to Overcome It
- Exploring Renewable Energy Sources and Their Viability
- The Evolution of Social Media and its Societal Impact
- Gender Disparities in the Workplace: Causes and Solutions
- The Effects of Stress on Mental Health in Modern Society
- Analyzing the Influence of Cultural Diversity in Global Business
- Understanding Quantum Mechanics: Principles and Applications
Can’t pick a topic? Have a look at these extensive expository essay topics and get more ideas!
With our steps, tips, and topics, you have all you need to get started on your expository essay.
If you're still encountering challenges in composing your expository essay, our custom essay writing service is here to help.
Our proficient writers specialize in creating well-structured, informative expository essays. With our expert support, you can be sure you’ll receive a top-quality, plagiarism-free essay.
Reach out to our expository essay writing service today to get the help you need. Place your order today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

How to Write an Expository Essay
Sam Benezra
The expository essay is a genre of nonfiction writing in which a writer aims to explain a topic or concept. In this genre of essay writing, the writer is not required to put forward an original argument, but rather aims to educate the reader on a topic. This contrasts with the argumentative and persuasive essay genres, in which the writer takes a clear stance on a controversial topic, with the goal of swaying the reader toward agreeing with their position. An expository essay may cover a controversial topic, but in this genre, the writer will not take a hard stance on the topic, but rather provide a holistic overview of it.
Expository writing aims to be objective and thorough in its analysis. The term “expository” means to explain, describe, or define. In effect, the author should try to present a balanced perspective on the topic at hand. Expository essays most often appear in textbooks, in encyclopedias, in journalistic articles, and in scientific or technical writing.
In academic settings, expository essays are often assigned in high school or university courses to assess students’ understanding of a given topic. An expository essay prompt will typically ask the writer to “explain,” “define,” or “explore,” a given subject.
In this article, we’ll discuss the style, substance, and structure of expository essays.
Style of Expository Writing
In an expository essay, the writer aims to present information as impartially as possible. As a rule, expository essays generally avoid the use of subjective phrasing and vocabulary. They are centered around the presentation of facts and provide less analysis than other forms of writing.
In an argumentative or persuasive essay, writers will typically present facts in conjunction with an analysis. In this context, facts are used as evidence in support of a specific claim or argument, with the intention of leading the reader to a specific conclusion.
In expository writing, facts stand on their own. Any analysis is used toward the purpose of clarifying or explaining the factual information that is presented, not for the purpose of persuading the reader. Expository essays on controversial topics should therefore be dialectical in the sense that they give equal voice to all perspectives on the issue.
Because expository essays strive for this objective tone, they are virtually always written in the third person. The third person enables the writer to remove their subjectivity from the writing as much as possible. In other forms of writing, the writer’s voice may play an important role. In expository writing, the writer should aim to remove their voice as much as possible from the writing, allowing the information presented in the essay to speak for itself.
Process of Writing an Expository Essay
Choose a topic.
The process of writing an essay always begins with choosing a topic to write about. Expository essays generally seek to explain a phenomenon, event, idea, or object. There are a variety of sub-genres of expository writing, including but not limited to:
- Definitional Article: Provides a detailed description of a phenomenon, event, idea or object (for example, an encyclopedia article)
- Journalistic Article: Provides a detailed explanation of a current event or situation (for example, a newspaper article)
- The How-To Article: Describes a process in a series of steps (for example, a recipe)
- The Comparative Essay: Compares and contrasts two or more subjects in an impartial and informative manner
- Analysis of an Issue: Describes an issue and various positions on or solutions for the issue, backed by evidence and data
In all of these sub-genres, the primary purpose of the essay — to inform and educate the reader about the subject of the essay — remains constant.
The research phase is the most important, and often the lengthiest stage in the development of an expository essay. During the research phase, the writer aims to develop a comprehensive understanding of their topic by consulting a variety of sources.
The research process may vary depending on the topic and the type of article. For example, a reporter covering a local crime for a newspaper will likely gather information through interviews of eyewitnesses and the police. They may also include background information about crime in the area by analyzing police records and public databases that provide crime statistics.
In contrast, a graduate student writing an essay on the American economy during World War II would research their topic by reading several books that provide various perspectives on the topic and by analyzing primary sources in research libraries.
A food blogger writing a recipe for peanut butter cookies would consult and experiment with various other recipes in order to develop the best process for making a peanut butter cookie.
In all cases, writers use the research process to develop expertise on the topic of their writing, so that they can then educate their readers.
Organize Information
After completing the research phase, you can start to compile and organize the information you’ve gathered during their research. During this transitional phase, you should start by thinking about how you can present your topic most clearly and logically.
The way information is presented to the reader can vary depending on the writer’s approach. Using our previous example of an essay on the American economy during World War II, the writer may see it fit to present their information chronologically — that is, organized sequentially by time. This approach enables the writer to emphasize changes in the economy at different stages of the war.
Alternatively, the writer could organize their research by categories. In this example, they might organize their paper by different industries in World War II and discuss the features of each industry during this time period in depth.
Both approaches are equally valid, but they provide different perspectives on the topic of the essay. It is important to think broadly about how you want to present your topic and more specifically about key points of emphasis as you organize your research.
Build Outline
After organizing your research in a logical order, you can start to build an outline . A complete outline should contain a draft of your thesis, topic sentences for each body paragraph or section, and evidence organized under each major claim you make throughout the essay. By the time you finish your outline, you should have completely finished gathering and organizing your evidence.
With a complete outline in hand, you can start to write your essay in earnest. With a complete and thorough outline, the essay-writing process should mostly consist of connecting evidence and fleshing out sections of your paper with transitions. It is important that your paper has a natural and logical flow and reads clearly.
Revise/Edit
Once a full draft has been completed, you can start the revision and editing process. In the revision phase, the writer aims to improve the essay by making changes to organization, structure, and word choice. In an expository essay, you should revise with clarity in mind. Often this may mean simplifying sentence structure or word choice or rearranging the structure to flow more logically. Editing refers to the basic process of proofreading the essay and fixing grammatical and spelling errors. Essays will often go through multiple stages of revision and editing before being finalized.
Structure of an Expository Essay
Like other genres of essay writing, expository essays are typically composed of an introduction that includes a thesis statement, body paragraphs featuring supporting details, and a conclusion . Some sub-genres of expository writing may feature variances on this structure. A “How-To” article, for example, may feature a bulleted list of steps in the body rather than traditional supporting paragraphs. However, most expository essays are written in a traditional essay format.
Introduction
The introduction of an expository essay should provide the reader with a general overview of the information that will be presented throughout the essay. The introduction of an expository essay will typically include three key features: a hook or topic sentence, exposition , and a thesis statement .
The hook is the first one or two sentences of an essay. In an expository essay, the hook serves to clearly present the topic of the essay. In some forms of essay writing, there is an emphasis on catching the reader’s interest early on in the essay, hence the phrase “hook”. In persuasive essay writing, for example, the use of an attention-grabbing quote or narrative component early on in an essay can serve to draw the reader into the writer’s perspective, thereby manipulating the reader. In an expository essay, this kind of dramatic flourish is generally unnecessary, and even distracting. Instead, the writer should attempt to introduce the reader as objectively as possible.
After the hook, the writer elaborates on their topic in the exposition , forming the middle of the introduction. In this section, the writer introduces key concepts and characters, which will be analyzed further in the body of the essay.
The thesis statement is typically contained in the last couple sentences of the introduction. In an expository essay, the thesis statement serves to state points of emphasis about the topic of the essay. In this genre of essay writing, the thesis statement does not need to be an arguable claim as it would in an argumentative or persuasive essay. Rather, the thesis statement should serve to bring the reader’s attention to key aspects of the topic that you want to highlight.
The body of an expository essay is composed of separate body paragraphs that individually bring attention to an aspect of the topic. Each of the body paragraphs should present details that support the thesis. Typically, body paragraphs of an expository essay will include the following features: a topic sentence , evidence , and a transition to the next body paragraph.
In the topic sentence of a body paragraph, the writer will always make a general statement that ties back to the thesis or reinforces the thesis statement. Depending on how long the essay is and how it is organized, multiple body paragraphs may discuss the same sub-topic or theme, but they should always serve to introduce an idea or some information that relates to the thesis. Each body paragraph should put forward new information that is necessary to understand the paper’s thesis.
After the topic sentence, the bulk of each body paragraph will be devoted to presenting evidence or information that supports the statement made in the paragraph’s topic sentence.
At the end of each body paragraph, the writer should write a brief transition to the next paragraph, allowing the essay to flow smoothly from one section to the next. The transition should be no longer than a sentence or two.
In the conclusion of an expository essay, the writer should reframe the thesis in light of the information presented throughout the essay. The conclusion should never present any new significant information or evidence. Rather, the writer should use the conclusion to tie together the information presented throughout the essay and to open up a discussion to broader implications.
In Conclusion
In an expository essay, the writer’s main purpose is to inform and educate their audience. In format and structure, expository essays typically resemble other genres of nonfiction essays. However, unlike similar genres like the argumentative or persuasive essay, the expository essay doesn’t aim to advance a position or argument, but rather to present information in as balanced and impartial a manner as possible.

FREE 6-month trial
Then, enjoy Amazon Prime at half the price – 50% off!
TUN AI – Your Education Assistant
I’m here to help you with scholarships, college search, online classes, financial aid, choosing majors, college admissions and study tips!
TUN Helps Students!
Resource content.
Resources for Students
School Search
Scholarships
Scholarship Search
Start a Scholarship
High School
Copyright, 2024 – TUN, Inc
Student Tools
Free Online Courses
Student Discounts
Back to School
Internships
How to Write an Expository Essay: Outline, & Example
What is an expository essay? This type of writing aims to inform the reader about the subject clearly, concisely, and objectively.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
The keyword here is “ inform ”. You are not trying to persuade your reader to think a certain way or let your own opinions and emotions cloud your work. Just stick to the facts.

Want to learn more? This article by Custom-writing experts will tell you how to write an expository essay step by step! It provides a definition and describes types of expository writing. It also contains tips on choosing a topic and making an outline, ideas for an introduction and conclusion, as well as useful structuring and formatting tips.
- 🔖 Expository Essay Types
- 👣 4-Step Writing Guide
🔗 References
🔖 types of expository writing.
Whenever an essay or article explains complicated details or simplifies a bulk of hard-to-understand information, this type of writing is called expository.
Imagine you are talking to a curious child who keeps asking you “how” and “why” things are such or another. You need to explain everything from scratch, yet making it sound compelling. Small and peculiar details are essential here.
The principal purpose of an expository essay is to elucidate a topic logically and consistently. It is an objective analysis of facts without any reference to the writer’s emotions or opinions.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour

👣 How to Write an Expository Essay Step by Step
🔍 step 1: choose your expository essay topic.
The first step of the writing process implies that you brainstorm, make a list of expository essay ideas, and then choose the topic you like most. Note that your topic shouldn’t be either too broad or too narrow.
Let’s take a look at the expository essay topic examples:
And here are some good expository essay topics that would be a good choice:
- Why does the human body need food and water ?
- What are the different ways to travel long distances?
- General information about audit report.
- Compare the legacy of any two US presidents .
- How can crime be reduced in your local community?
- What is the best way to learn a new language ?
- Establishing successful communication between managers and employees.
- Why do companies use memes as branding strategy ?
- The meaning of the terms diversity and identity .
- Describe how the work climate influence employee performance .
- What emotional appeal is and its role in communication.
- Information’s importance in warfare and commerce .
- Ways to use social media in modern business.
- Basic information and requirements of police detective career .
- What is health information exchange ?
- Characteristics of demonstrative communication.
- The history of the Cow Palace , Daly City.
- Describe the specifics of insurance company business.
- Ways to success in dealing with other people .
- Discuss the significant role of polis in ancient Greece .
- General information about cardiovascular disease .
- What are futuristic fabrics and how are they used in the modern fashion industry?
- Outline the peculiarities and cultural aspects of Indian cuisine .
- Describe the role of waiter in tourism industry .
- Ways to help students with learning disabilities to retain information.
- Four components of information system .
- Code of ethics: definition and its role in decision–making.
- The importance of listening skills .
- Present the similarities and differences between Mesopotamia and Ancient Egyptian culture .
- Give details on climate change in Africa .
- What is emotional intelligence and why is it important?
- Report the main methods to improve student learning .
- Describe the basic components of management practices.
- Contingency theory for effective crisis management.
- Ways of determining the validity of information sources .
- The specifics of coffee culture in different countries.
- Represent the main approaches to managing the team of international managers .
- Describe the peculiarities of popular culture .
- Information about Ferrero company.
- What is a leadership theory and how is it applicable in management?
- Tell about the ways to cite sources for an informative speech .
- The impact of vitamin D on human health.
- Definition and types of plastic surgery .
- How climate changes influence food security .
- Available information about silicon .
- Describe the mediation process and the difficulties usually connected with it.
- What is intelligence and how is it measured?
- Compare the advantages and disadvantages of electric and gas cars .
- General information about mental disorders.
- Outline the most high-risk nutritional practices and their impact on human health.
You might be given a specific topic, or you might have the freedom to choose one. Either way, your starting point is to look at the task you have been set and be sure that your focus remains within its boundaries.
If you do have a choice, then go for a subject that you already have some knowledge of as this will give you a head start at the planning stage. And choose something that interests you—you are probably going to be doing a lot of reading, so that process will be much easier if your curiosity is carrying you forward.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
📑 Step 2: Research and Plan Your Essay
Consider your audience.
It’s always worth clarifying with your teacher who your essay’s intended audience is if it’s not clearly stated in the instructions. Your readership might be limited to your teacher or whoever is assessing your work, so the main goal, in that case, is to convince them that you have a good understanding of the subject and can organize your thoughts in a clear and appropriate way.
Either way, you should be mindful of who you intend to inform as you carry out your research and planning.
Choose Your Sources
You will need to find multiple sources that are relevant and reliable in order to deal with your subject matter accurately and comprehensively. Below is a checklist that might help you choose the right sources for your essay.:
Academic Sources Checklist
Take notes as you read, and cross-check sources. Your goal is to formulate the points you need to deal with the set task and find evidence to support them.
Once you’ve completed this, you will have a clear sense of direction, and if it hasn’t already been assigned, you will be able to compose a thesis statement for your essay that meets the requirements of the task and fits your sources. If you still struggle with the statement, consider trying an expository essay thesis generator to help yourself out.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Now you’re ready to lay down your expository essay outline!
✍️ Step 3: Make Your Expository Essay Outline & Draft
The five-paragraph essay is a classic literary composition and a perfect template for your expository essay format—even if your set task demands something longer.
The outline for a 5-paragraph expository essay is simple:
- Introduction (one paragraph)
- Main body (three paragraphs)
- Conclusion (one paragraph)
Expository Essay Structure: Useful Tips
- Make the introduction of your expository essay short and sweet. Start with a focus statement that will grab your reader’s attention and make them want to read on. Then give an overview of your subject matter and set out the direction that the rest of your essay is going to take. There’s no need to back up your words with evidence at this stage—save the meat and potatoes for the main course.
- Organize the three (or more if necessary) paragraphs of the main body in a logical order. Each of them should deal with a different point and address the focus statement you started with.Begin each paragraph with a clear topic sentence, then support it with your evidence. Each paragraph’s final sentence should lead your reader into the next—just like this one, which says you’re now ready to tie it all up.
- Restate your original focus statement in your expository essay conclusion. his time, include the weight of all the evidence you have provided in the main body. Follow this with a powerful closing statement, and your reader will be on the ropes.
🏁 Step 4: Review Your Expository Essay
Think of your expository essay’s first draft as an uncut diamond—the value is there, but you still have some work to do before it’s ready for the display cabinet at Tiffany and Co.
First, you need to look at the overall content of your essay and ask the questions below.
Expository Essay Checklist: Content
- Does the essay stay focused on the set task throughout?
- Does the introduction give a clear sense of where the rest of the essay is headed?
- Does the main body cover the subject matter in a logical order?
- Is your supporting evidence accurate, relevant, and properly referenced?
- Does the conclusion tie up the essay in a clear, concise, and powerful way?
- Have you stuck to the facts and avoided clouding the essay with your own opinions?
- Will your reader find your essay engaging and enjoyable to read?
- Will your reader be better informed about the subject matter once they have finished the essay?
Be hard on yourself when you go through this process. Step into the shoes of the most critical person you know who loves to highlight your faults. You will come out the other side leaner, meaner, and stronger.
You’re almost there now—just some final polishing required. Your essay is now almost perfect, but proofreading will make it shine. Run it through a spell-checker, then read slowly from the beginning again, asking the questions below.
Expository Essay Checklist: Style
- Is your word choice clear and concise?
- Are there any issues with grammar or spelling?
- Have you been consistent with the use of abbreviations, acronyms, capitalization, etc.?
- Are your quotations and references presented correctly and consistently?
- Is your document formatted correctly and consistently?
Done all that? Congratulations! Your diamond was purchased by Jennifer Lopez, and she plans to show it off on the Oscars red carpet.
The great thing about expository essays is that you only need to concern yourself with the facts. If you follow these four steps, you can’t go wrong. And in addition to your A+ grade, you will also have gained an incredibly useful life skill. The ability to explain a concept to someone in a way that makes them better informed will take you a long way in any environment.
✒️ Expository Essay Example
In this section, you’ll find a free expository essay sample. It focuses on the factors that cause stress in adolescents. Note that the full version of the text is downloadable!
Major Stressors in Teenagers’ Lives
The high dynamics of social interactions is a factor that may cause the fear and anxiety in adolescents who face increased demands and expectations from adults. Being physically developed, teenagers often have a fragile psychological background, and various external drivers, usually related to social adaptation, can be dangerous triggers of stress.
Adolescents are rarely able to entrust their concerns to parents and other adults, which causes isolation, pathological anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. The major stressors in adolescence are social in nature and relate to school relationships, family disagreements, and issues of friendship and love.
✏️ Expository Essay FAQ
In simple terms, an expository essay informs its readers about a subject. It is quite concise, and typically presents a topic with 2-3 subtopics and relevant examples. To make the definition complete, we need to add that you also show your understanding of the topic as you write that paper.
If you are a high school student, we strongly recommend that you start off by creating an outline. You need to highlight a few points in the Body of your essay. Then, create an appropriate introduction. Finally, add a corresponding conclusion.
An expository essay is one of the most typical tasks starting from middle school. Thus, if you are not sure about the essay structure, write an outline first. Then you go step by step: an Introduction, Body, Conclusion. You may write the Body first and add the other two afterward.
An expository essay does not have significant peculiarities in terms of structure. Its outline includes: an Introduction, some Body paragraphs with examples, a Conclusion. Do not choose too many subtopics: such essays are usually just about 5 paragraphs / two pages long.
- Taking Notes from Research Reading:University of Toronto
- Expository Essays // Purdue Writing Lab
- What Is Expository Writing? – ThoughtCo
- Tips on Writing an Excellent Expository Essay – YourDictionary
- 10 Ways Expository Writing Skills: NY Tymes
- Expository Essays: Types, Characteristics & Examples – Study.com
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email
![how to write a body paragraph for an expository essay Short Story Analysis: How to Write It Step by Step [New]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/man-sits-end-trolltunga-before-mountains-284x153.jpg)
Have you ever tried to write a story analysis but ended up being completely confused and lost? Well, the task might be challenging if you don’t know the essential rules for literary analysis creation. But don’t get frustrated! We know how to write a short story analysis, and we are...
![how to write a body paragraph for an expository essay Common Essay Mistakes—Writing Errors to Avoid [Updated]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/avoid-mistakes-ccw-284x153.jpg)
One of the most critical skills that students gain during their college years is assignment writing. Composing impressive essays and research papers can be quite challenging, especially for ESL students. Nonetheless, before learning the art of academic writing, you may make numerous common essay mistakes. Such involuntary errors appear in:...

You’re probably thinking: I’m no Mahatma Gandhi or Steve Jobs—what could I possibly write in my memoir? I don’t even know how to start an autobiography, let alone write the whole thing. But don’t worry: essay writing can be easy, and this autobiography example for students is here to show...
![how to write a body paragraph for an expository essay Why I Want to Be a Teacher Essay: Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/senior-male-professor-writing-blackboard-with-chalk3-284x153.jpg)
Some people know which profession to choose from childhood, while others decide much later in life. However, and whenever you come to it, you may have to elaborate on it in your personal statement or cover letter. This is widely known as “Why I Want to Be a Teacher” essay.
![how to write a body paragraph for an expository essay Friendship Essay: Writing Guide & Topics on Friendship [New]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/smiley-female-friends-fist-bumping-284x153.jpg)
Assigned with an essay about friendship? Congrats! It’s one of the best tasks you could get. Digging through your memories and finding strong arguments for this paper can be an enjoyable experience. I bet you will cope with this task effortlessly as we can help you with the assignment. Just...

When you are assigned an autobiography to write, tens, and even hundreds of questions start buzzing in your head. How to write autobiography essay parts? What to include? How to make your autobiography writing flow? Don’t worry about all this and use the following three simple principles and 15 creative...

“Where is your thesis statement?” asks your teacher in a dramatic tone. “Where is my what?” you want to reply, but instead, you quickly point your finger at a random sentence in your paper, saying, “Here it is…” To avoid this sad situation (which is usually followed by a bad...

A life experience essay combines the elements of narration, description, and self-reflection. Such a paper has to focus on a single event that had a significant impact on a person’s worldview and values. Writing an essay about life experience prompts students to do the following: evaluate their behavior in specific...

Who has made a significant impact in your life and why? Essay on the topic might be challenging to write. One is usually asked to write such a text as a college admission essay. A topic for this paper can be of your choice or pre-established by the institution. Either...

Are you about to start writing a financial assistance essay? Most probably, you are applying for a scholarship that will provide additional funding for your education or that will help you meet some special research objectives.
![how to write a body paragraph for an expository essay Growing Up Essay: Guide & Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/gardening-concept-with-mother-daughter-284x153.jpg)
What does it mean to grow up? Essays on this topic might be entertaining yet challenging to write. Growing up is usually associated with something new and exciting. It’s a period of everything new and unknown. Now, you’ve been assigned to write a growing up essay. You’re not a kid...
![how to write a body paragraph for an expository essay Murder Essay: Examples, Topics, and Killer Tips [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/man-holding-gun-as-evidence-284x153.jpeg)
Probably, a murder essay is not a fascinating assignment to complete. Talking about people’s deaths or crazy murderers can be depressing. However, all assignments are different, and you are supposed to work on every task hard. So, how are you going to deal with a murder essay? You can make...
How would I cite this site?

Bill, you can find the information about citation here
I really love this, thanks.
Glad you liked the article, Dammy!
Lovely explanation
Thank you, Jamiu!
What is an Expository Essay and How to Write It

You’ve been asked to write an expository essay on a particular topic. You know that an essay is generally a written composition that is usually limited in length and reflects the author’s perspective. However, the “expository” part is a little less clear. Keep reading, and you’ll get enough information to understand what an expository essay is and how to create an effective expository essay that meets the assignment requirements.
Table of Contents
What is an expository essay, what is the purpose of expository writing, when should you write an expository essay, 5 types of expository essays, how to structure an expository essay, how to write an expository essay, key takeaways, frequently asked questions about expository essays.
The expository essay is the appropriate type of essay to write if you need to inform your audience. If your intent is to critically compare, argue, or persuade, you will want to consider a different essay format. To explain it in more detail:
- An expository essay is a type of academic writing that aims to present a balanced and objective analysis of a specific topic.
- Expository essays often employ various techniques to enhance clarity and understanding. These techniques may include definition, comparison and contrast, cause and effect analysis, problem and solution exploration, or descriptive explanations. The writer should also ensure that the essay maintains a neutral and objective tone, avoiding personal biases or emotional language.
- In an expository essay, the writer typically starts with an introduction that presents the topic and provides an overview of what will be discussed in the essay. The body paragraphs then delve into the details, presenting evidence, examples, and relevant information to support the main points. Each paragraph should focus on a specific aspect or subtopic, and the information should be organized logically and coherently.
- Expository essays are commonly assigned in academic settings as they encourage critical thinking, research skills, and the ability to present information in a clear and concise manner.
- The ability to write an expository essay is an essential skill for students and professionals. It promotes critical thinking, objectivity, and clear and concise communication.

The primary goal of expository writing is to explain or clarify a concept, process, or phenomenon using evidence, examples, and logical reasoning. Unlike persuasive or argumentative essays, the purpose of an expository essay is not to convince the reader of a particular viewpoint or opinion, but rather to provide clear and concise information.
The main objectives of expository writing are:
- Informing: Expository writing aims to educate and provide readers with new or valuable information. It seeks to convey facts, details, concepts, or ideas about a topic in a straightforward and concise manner.
- Explaining: Expository writing helps readers grasp complex subjects by breaking them down into simpler terms. It aims to clarify abstract concepts, processes, or phenomena, making them more accessible and understandable.
- Instructing: Expository writing provides step-by-step instructions or guidelines on how to perform a task, accomplish a goal, or understand a process. It offers a clear sequence of actions or explanations to ensure readers can follow and replicate the instructions.
- Presenting an analysis: Expository writing often involves analyzing and evaluating information, data, or evidence related to a particular subject. It may include comparing and contrasting different viewpoints, examining cause-and-effect relationships, or offering an objective evaluation of a situation.
Overall, the purpose of expository writing is to provide readers with accurate, unbiased, and well-organized information about a specific topic. It aims to enhance understanding, broaden knowledge, and facilitate learning by presenting information in a clear, coherent, and logical manner.
An expository essay is a good choice when the goal is to inform, explain, describe, or instruct. You may be assigned an expository essay as part of an in-class exam or coursework assignment. Here are some common situations in which writing an expository essay would be appropriate:
- Academic Assignments: Expository essays are frequently assigned in educational settings. Teachers often use this type of essay to assess students’ understanding of a particular subject or to teach them how to research and present information effectively. They are common in subjects such as English, history, science, social studies, or any discipline that requires a clear explanation or analysis of a topic.
- Instructional or How-to Writing: When you want to provide step-by-step instructions or guidance on how to perform a task, solve a problem, or achieve a specific outcome, an expository essay can be an appropriate format. This type of writing is commonly used in manuals, guidebooks, tutorials, or any instructional material.
- Journalism or News Writing: Expository writing is prevalent in journalism, where the goal is to inform readers about current events, news stories, or investigative reports. Journalists strive to present objective information, provide background details, and explain complex issues clearly to their audience.
- Professional or Technical Writing: In various professional fields, such as business, healthcare, engineering, or law, expository writing is utilized to convey information to colleagues, clients, or the general public. This includes writing reports, memos, manuals, research papers, or any form of communication that requires clear and factual presentation of information.

Expository essays can serve different purposes and present information in various ways. Here are five common types of expository essays:
- Descriptive essay: This type of expository essay focuses on describing a person, place, object, event, or any subject in detail. It aims to create a vivid and sensory-rich portrayal of the topic, using language that appeals to the reader’s senses and emotions.
- Process essay: Also known as a “how-to” essay, a process essay explains a sequence of steps or procedures to accomplish a task or achieve a particular outcome. It provides clear instructions and guidance, breaking down complex processes into manageable and easy-to-follow stages.
- Compare-and-contrast essay: This type of expository essay explores the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. It involves examining various aspects, characteristics, or elements of the subjects and highlighting their similarities, differences, or both.
- Cause-and-effect essay: A cause-and-effect essay explores the reasons (causes) behind an event, situation, or phenomenon, as well as the consequences (effects) that result from it. It aims to analyze and explain the relationship between causes and effects, demonstrating how one factor leads to another.
- Problem-and-solution essay: In this type of expository essay, a specific problem or issue is identified and analyzed, followed by the presentation of potential solutions or strategies to address it. The essay outlines the problem, examines its causes and effects, and proposes practical solutions or recommendations.
It’s important to note that these are not the only types of expository essays, and there can be variations or combinations of these types. Additionally, within each type, the specific approach and structure can vary depending on the requirements of the assignment or the writer’s purpose.
Structuring an expository essay involves organizing your thoughts, ideas, and information in a clear and logical manner. Here is a commonly used structure for an expository essay:
- Begin with an attention-grabbing hook to engage the reader.
- Provide some background information on the topic to set the context.
- Present a clear and concise thesis statement that states the main idea or purpose of the essay.
- Start each paragraph with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main point of the paragraph.
- Support your topic sentence with evidence, facts, examples, or expert opinions that relate to the main point.
- Provide detailed explanations, analysis, or descriptions to clarify and develop your ideas.
- Use transitional words and phrases to ensure smooth flow and coherence between paragraphs and ideas.
- Each paragraph should focus on a specific aspect or subtopic related to the main idea.
- Restate the thesis statement but rephrase it in a way that reinforces the main idea.
- Summarize the main points discussed in the body paragraphs.
- Avoid introducing new information or ideas in the conclusion.
- End with a closing statement that leaves a lasting impression.
Writing an expository essay involves a systematic approach to presenting information in a clear and objective manner. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to write an expository essay:
- Understand the purpose and requirements: Familiarize yourself with the purpose of the essay and any specific guidelines or requirements. Then, determine the topic or subject of your expository essay and gather relevant information and resources.
- Conduct research and gather information: Conduct thorough research on your topic to gather factual information, examples, evidence, or expert opinions.
- Plan and outline: Develop a clear and coherent outline that includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Decide on the main points or subtopics you will cover in each paragraph of your expository essay and arrange your ideas in a logical order that flows well.
- Write the introduction: Be sure to include a clear and concise thesis statement that states the main idea or purpose of your expository essay.
- Write the body paragraphs: Write one paragraph for each main idea, using transitions to ensure a smooth flow throughout.
- Write the conclusion: Restate your thesis statement and summarize the evidence.
- Revise and edit: Review your expository essay for clarity, coherence, and logical flow, and check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. Remember to always maintain an objective tone and focus on presenting information rather than expressing personal opinions.
As you can see, effective expository essays vary widely based on their topic and ultimate purpose. However, they have several important characteristics in common. When you’re writing an expository essay, keep the following tips in mind:
- Use clear, concise, and formal language, avoiding unnecessary jargon or complex terms.
- The thesis statement needs to be clear, concise, and appropriately focused.
- Provide sufficient evidence and examples to support your claims and make your writing more credible.
- Consider the logical flow of your ideas and make sure they are presented in a coherent manner.
- Use appropriate transitions to connect your sentences, paragraphs, and ideas.
- Remember that the specific structure of your expository essay may vary depending on the requirements of your assignment or the complexity of your topic. Adapt the structure as needed while ensuring that your essay is organized and focused on conveying information effectively.
You should consider writing an expository essay when you need to explain, inform, or describe a particular topic or subject to your readers. Expository essays are usually assigned in academic settings, but they can also be used in other contexts, such as writing articles or blog posts. For example, an expository essay would be appropriate for purposes such as explaining the benefits of a healthy lifestyle, describing the process of a scientific experiment, or discussing the impact of technology on society.
Expository essay: The main purpose of an expository essay is to explain, describe, or inform the reader about a particular topic or subject. It should be written in a neutral manner, focusing on presenting facts, explaining concepts, and offering a clear understanding of the topic. Argumentative essay: The primary purpose of an argumentative essay is to present a well-structured argument or position on a specific issue. The writer takes a clear stance on a topic and provides strong arguments, counterarguments, and evidence to support their position. The language used may be more passionate and persuasive to convince the reader.
The length of an expository essay can vary depending on the specific requirements or guidelines provided by your instructor or the purpose of your writing. Expository essays can range from a few hundred words for shorter essays to several thousand words for more in-depth or research-based essays. The number of body paragraphs typically range from three to five, but it can vary based on the complexity of the topic and the amount of information you need to convey.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 10-Point Manuscript Checklist to Ensure High-Quality Journal Submissions
- Confusing Elements of a Research Paper That Trip Up Most Academics
- How to Present Data and Statistics in Your Research Paper: Language Matters
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)
Organization vs. Organisation: Is there a Difference?
Paperpal now supports research paper pdfs: a game-changer for latex users, you may also like, ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , how to make translating academic papers less challenging, self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how..., 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures, 8 most effective ways to increase motivation for....
Political essay topics
Political essay topics: navigating the complex landscape of politics.

Politics affects almost every element of our life. From economic policies to international relations ideas, politics is a fascinating subject for study and discussion. Political essay topics are essential for studying, evaluating, and debating these broad issues. These essays allow writers to explore political institutions, ideologies, and issues, offering arguments, insights, and critiques that help us comprehend political processes.
Purpose and definition of an expository essay
Before discussing the many political essay topics available to writers and scholars, we first define an expository essay. Expository essays explain, inform, or describe a topic clearly, concisely, and logically. Expository essays present facts and clarify the topic, unlike persuasive essays. Political essays may explain political theories, analyze policy consequences, or examine the origins and outcomes of a political movement.
Understanding expository essays: delving into the essence and objectives
Expository essays underpin the academic study of many areas, including politics. A common task in these essays is to explore various political topics to write about. Expository essays inform, explain, or describe things in a clear, concise, and logical manner, unlike persuasive or argumentative essays. This purpose requires presenting facts, data, and explanations without taking sides or trying to persuade.
An expository essay's foundation is facts. The writer's primary purpose is to inform the reader by deconstructing politics essay topics like political theories, assessing policy effects, or studying political movements. These essays help explain complex topics by giving facts objectively. The clarity and neutrality allow readers to establish their own opinions based on the information and explanations.
The structure of expository essays in political science
Expository essays, especially when delving into politics essay topics, must be well-organized to convey information and aid comprehension. A good political science essay has an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each part is crucial to the essay's success.
- Introduction : The essay on politics begins with an introductory paragraph. It introduces the topic and essential points. The opening of political science essays may offer background on the theories, policies, or movements being discussed. A concise thesis statement that outlines the essay's primary points is essential to the start.
- Body paragraphs : Each body paragraph examines a specific aspect of the topic in detail. In political essays, a paragraph may evaluate a theory, debate policy consequences, or chronicle a political movement. Each paragraph should start with a topic sentence that introduces the central concept for clarity and coherence. Provide proof, facts, and extensive explanations in supporting sentences. Examples, case studies, and trustworthy citations strengthen the analysis.
- Conclusion : The conclusion summarizes the body paragraphs and supports the political essay argument. The conclusion of political science articles may discuss the findings' broader implications or suggest future research. Notably, the conclusion should conclude the article without adding additional material.
Political science explanatory essays simplify complex issues with their format. This requirement helps writers think clearly, and readers understand politics essay complexity.
Writing tips for crafting an effective political expository essay
The following tips will help you explore political themes and write an intriguing and intellectually stimulating essay. Remember, a well-written political essay can add new viewpoints to political science discussions.
- Choose your topic wisely : Choose an attractive, research-worthy topic. Make it relevant to political discussions.
- Research thoroughly : Before writing, do extensive research. Academic journals, respected news sites, and political analyst books are reliable. It helps provide accurate and complete information.
- Create a clear thesis statement : Your thesis statement should summarize your essay's central topic. It keeps your article on track and focused.
- Use facts and evidence : Prove your points with evidence. It can include statistics, historical examples, or expert quotes. Remember to enlighten and explain, not persuade.
- Stay objective and neutral : Expository writings should be unbiased. Avoid personal opinions and present multiple viewpoints.
- Incorporate examples and case studies : Examples and case studies clarify your points and are practical applications of political theory.
- Write clearly and concisely : Don't use jargon or complicated language. Easy-to-understand essays are more effective.
- Cite your sources : Proper citation of sources is essential in academic writing. It credits the original authors and lends credence to your writing.
- Revise and edit : Remember to value revision and editing. Proofread your arguments for grammar, coherence, and consistency. It makes essays more persuasive and readable.
- Reflect on contemporary implications : Connect your topic to current events or political discussions. Your essay must be relevant to today's politics.
- Seek feedback : Before finishing your essay, receive comments from your peers, instructors, or mentors. Their observations and suggestions can be helpful.
The role of essay writing services in crafting compelling political essays
Essay writing is both a problem and an opportunity in the dynamic and complex realm of political discourse. Whether you're writing about globalization, democracy vs. authoritarianism, or other political essay topics, it takes time, effort, and knowledge to write a convincing argument. Essay writing services reviews help students, academics, and everyone interested in politics find reliable assistance in crafting their essays.
These services can help you structure essays, make coherent and appealing arguments, and understand research and citation best practices. Essay writing services like speedypaper.com or essaymarket.net may help you write political essays that match academic requirements and add to the debate on your issue while managing several tasks or tight constraints. You may improve your studying, writing, and political arguments by using the help of experienced writers.
Choosing intriguing and meaningful political essay topics is essential. A comprehensive list of 105 political essay topics covering a wide range of subjects and opinions is provided to help:
- The impact of globalization on national sovereignty
- Democracy vs. authoritarianism: a comparative analysis
- The role of social media in modern political campaign strategy
- Climate change politics and policy responses
- The evolution of feminist political movements
- Electoral systems around the world: a comparative study
- The politics of immigration and border control
- Political corruption: causes, effects, and solutions
- The influence of political ideology on education policy
- The United Nations and global governance
- The rise of populist movements in the 21st century
- The impact of economic sanctions as a political tool
- Nationalism in the contemporary world
- The role of technology in espionage and surveillance
- Privacy rights versus national security concerns
- The politics of healthcare reform
- The effects of colonialism on modern-day political structures
- Political implications of artificial intelligence and automation
- The future of the European Union
- The relationship between politics and religion
- Gun control laws: a comparative analysis
- The politics of disaster response and preparedness
- Political dynasties and their influence on democracy
- The role of international organizations in conflict resolution
- The impact of trade policies on international relations
- Voter suppression and electoral fairness
- The politics of language and identity
- Environmental justice and policy making
- The influence of lobbyists and special interest groups on policy
- Cyber warfare and international security
- Political satire as a form of political critique
- The role of ethics in politics
- Political implications of the global refugee crisis
- The intersection of race and politics in America
- Gender equality in political representation
- The politics of space exploration and colonization
- Political aspects of the global pandemic response
- The influence of historical treaties on modern-day international relations
- The role of youth in political activism
- Media censorship and freedom of speech in politics
- The economics of climate change policies
- The impact of political decisions on scientific research
- The politics of animal rights and welfare
- The role of the judiciary in shaping political landscapes
- Political memoirs as a source of historical insight
- The politics of food security and agriculture
- The relationship between economic inequality and political instability
- The influence of cultural diplomacy on international relations
- The politics of water resources and management
- The role of indigenous peoples in political movements
- Political consequences of the digital divide
- The impact of celebrity endorsements on political campaign
- The politics of urban planning and development
- The role of propaganda in shaping political opinions
- Political implications of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology
- The challenge of maintaining privacy in the digital age
- The politics of aging populations and social security
- The impact of international sporting events on national identity
- Political strategies for combating terrorism
- Political movement analysis of art and culture
- The politics of education reform
- The influence of military power on global politics
- Political challenges of renewable energy adoption
- The role of non-governmental organizations in political advocacy
- The politics of historical memory and reconciliation
- The impact of transportation policies on urban development
- Political aspects of global health initiatives
- The role of political cartoons in societal critique
- The impact of voter ID laws on electoral participation
- The politics of minimum wage laws
- The role of whistleblowers in political transparency
- Political debates around net neutrality
- The influence of political scandals on public trust
- The politics of drug legalization and decriminalization
- The role of the media in shaping political discourse analysis
- Political aspects of genetic engineering and biotechnology
- The impact of international trade agreements on local economies
- The politics of public transportation system
- Political discourse analysis in artificial intelligence ethics
- The influence of outer space treaties on international relations
- The politics of disaster risk reduction and management
- The role of student movements in political change
- Political implications of the sharing economy
- The politics of pension reforms
- The influence of social movements on legislative change
- The role of political parties in democratic governance
- Political challenges of internet governance
- The impact of demographic shifts on the political landscape
- The politics of cultural heritage preservation
- Political debates around euthanasia and assisted suicide
- The influence of international law on state sovereignty
- The politics of nuclear disarmament
- The role of public opinion in policymaking
- Political aspects of water scarcity and management
- The impact of digital media on political mobilization
- The politics of energy security and policy
- The role of diplomacy in preventing international conflicts
- Political challenges of managing global commons
- The influence of economic policies on political stability
- The politics of scientific innovation and regulation
- The impact of social welfare policies on poverty reduction
- The politics of land use and zoning regulations
- The role of local governments in environmental protection
- Political debates around capital punishment
- The influence of international migration on national identities
These political essay topics offer several perspectives for inquiry, analysis, and conversation. This list can help students, researchers, and those interested in politics become familiar with the complex realm of politics through writing.
Contemporary political topics are those that address current issues and debates shaping the political landscape. These topics often focus on recent events, emerging trends, and pressing challenges facing societies at local, national, and global levels.
Navigating political essay topics requires staying informed about current events, understanding diverse perspectives, and critically analyzing complex issues. Consider topics that are of personal interest, align with your expertise, or have significant societal implications. Engage with reputable sources and be prepared to explore multiple viewpoints.
Start with thorough research to understand your chosen topic's background and implications. Develop a clear thesis statement and support it with evidence and examples. Remain objective, anticipate counterarguments, and craft a well-structured essay for clarity and persuasion.
Related articles

How to Choose a Writing Service?

How to Pay Someone to Take Your Online Class and not Get Caught

Quetext Plagiarism Checker

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It's worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline. A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
The five-paragraph Essay. A common method for writing an expository essay is the five-paragraph approach. This is, however, by no means the only formula for writing such essays. If it sounds straightforward, that is because it is; in fact, the method consists of: an introductory paragraph; three evidentiary body paragraphs; a conclusion; Resources
Suppose you use the five-paragraph model for your expository essay. In that case, the five parts of the paper are the introduction, body paragraph 1, body paragraph 2, body paragraph 3, and the conclusion. What is a good expository essay topic? Picking the right topic depends on what type of expository essay you are writing. Expository essays ...
How to Write a Strong Body Paragraph for an Essay. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 2 min read. From magazines to academic essays, you can find body paragraphs across many forms of writing. Learn more about how to write engaging body paragraphs that support the central idea of your writing project. From magazines to ...
Finally, wrap things up with a concluding paragraph that summarizes what the body paragraphs and thesis statement said. You can see the similarities between the two formats. If you can write a fantastic expository paragraph, you'll be well-prepared to move on to writing a full expository essay. Example of Expository Paragraph. Here's an ...
The Five-Paragraph Essay Writing Approach. An expository essay will require you to take the five-paragraph essay approach: an introductory paragraph, a main body paragraph, and a concluding paragraph. This is often referred to as the hamburger style of the essay because, like a hamburger, it contains five main parts: the introduction and ...
Writing an expository essay can be done step-by-step by organizing your thoughts, researching the topic, formulating a thesis statement, writing an introduction, composing the body paragraphs, and summarizing the essay in the conclusion. Finally, revise and proofread the essay to ensure its quality.
The main types of expository essays are: 1. Cause and effect essay: This essay type requires the writer to explain why something occurred and what happened as a result. 2. Compare and contrast essay: For a comparison essay, the writer takes two subjects or ideas and analyzes their similarities and differences. 3.
1. Read Your Essay Prompt. Most expository essay prompts will ask you to do one of the following: Define and explain a concept or theory. Compare and contrast two ideas. Examine a problem and propose a solution. Describe a cause and effect relationship. Explain a step-by-step process.
2. Body paragraph. After understanding how to start an expository essay the next step is to construct substantial body paragraphs. Each body paragraph in an expository essay consists of a topic sentence, its explanation, and a transition statement. A single idea should be introduced in each paragraph.
An essay is a piece of writing made up of a number of paragraphs. Each paragraph has a specifi c role in an essay. In a fi ve-paragraph essay, the fi rst paragraph is an introduction; the second, third, and fourth paragraphs form the body of the essay; and the fi fth paragraph is a conclusion (see diagram on page 4).
A five-paragraph essay should include three body paragraphs. Each body paragraph should discuss a piece of supporting evidence that supports your thesis. ... Once you have a plan for your expository essay, write out an outline to organize what you're going to say. Make sure to begin your outline with an engaging introduction sentence.
In the body section of your essay, you make arguments, explain ideas, and give evidence. This video will show you how to write a strong paragraph in just 3 s...
Step 1: Choose Your Topic. Before you can write an expository paragraph, you must have a topic. This type of paragraph aims to expound on or explain an idea. You will need to find a topic with enough information and research to write a full paragraph. If you are going to write an essay, make sure the topic is sufficient.
Here are some tips for writing a good expository essay: Ensure the essay has a clear and narrowly defined topic for effective exploration. Present facts, statistics, and evidence without incorporating personal opinions or biases. Utilize a well-structured format with logical sequencing of ideas and paragraphs.
This lesson discusses what personal expository essay writing is and explains how to outline and build the body paragraphs. It focuses on the three main types...
To write an effective expository essay, research needs to be conducted on the topic to find credible sources. Then, the findings should be presented along with their own analysis to explain the research and the connections between the sources. Every essay will have three parts: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion.
Typically, body paragraphs of an expository essay will include the following features: a topic sentence, evidence, and a transition to the next body paragraph. In the topic sentence of a body paragraph, the writer will always make a general statement that ties back to the thesis or reinforces the thesis statement.
Expository Essay Structure: Useful Tips. Make the introduction of your expository essay short and sweet. Start with a focus statement that will grab your reader's attention and make them want to read on. Then give an overview of your subject matter and set out the direction that the rest of your essay is going to take.
Expository essay: The main purpose of an expository essay is to explain, describe, or inform the reader about a particular topic or subject. It should be written in a neutral manner, focusing on presenting facts, explaining concepts, and offering a clear understanding of the topic. Argumentative essay: The primary purpose of an argumentative ...
An Expository Essay has 5 sections: Introductory paragraph First body paragraph Second body paragraph Third body paragraph Concluding paragraph. ALL Good Writing must Contain Development: Give information that will make your essay interesting and fun to read. Anecdotes: little short stories that create a picture in our minds when we read your ...
The number of paragraphs may vary depending on your assignment requirements and topic complexity. A standard 5-paragraph argumentative essay has three body paragraphs: two are for arguments that support your thesis, and one is for a rebuttal (counterarguments your opponents have on the issue). When writing, remember the following aspects:
The structure of expository essays in political science. Expository essays, especially when delving into politics essay topics, must be well-organized to convey information and aid comprehension. A good political science essay has an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each part is crucial to the essay's success.