Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples

How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
Published on August 30, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation . You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order. Don’t include subjective interpretations of why you found these results or what they mean—any evaluation should be saved for the discussion section .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to write a results section, reporting quantitative research results, reporting qualitative research results, results vs. discussion vs. conclusion, checklist: research results, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about results sections.
When conducting research, it’s important to report the results of your study prior to discussing your interpretations of it. This gives your reader a clear idea of exactly what you found and keeps the data itself separate from your subjective analysis.
Here are a few best practices:
- Your results should always be written in the past tense.
- While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analyzed, it should be written as concisely as possible.
- Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions . Avoid speculative or interpretative words like “appears” or “implies.”
- If you have other results you’d like to include, consider adding them to an appendix or footnotes.
- Always start out with your broadest results first, and then flow into your more granular (but still relevant) ones. Think of it like a shoe store: first discuss the shoes as a whole, then the sneakers, boots, sandals, etc.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

If you conducted quantitative research , you’ll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis .
Your results section should report the results of any statistical tests you used to compare groups or assess relationships between variables . It should also state whether or not each hypothesis was supported.
The most logical way to structure quantitative results is to frame them around your research questions or hypotheses. For each question or hypothesis, share:
- A reminder of the type of analysis you used (e.g., a two-sample t test or simple linear regression ). A more detailed description of your analysis should go in your methodology section.
- A concise summary of each relevant result, both positive and negative. This can include any relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., means and standard deviations ) as well as inferential statistics (e.g., t scores, degrees of freedom , and p values ). Remember, these numbers are often placed in parentheses.
- A brief statement of how each result relates to the question, or whether the hypothesis was supported. You can briefly mention any results that didn’t fit with your expectations and assumptions, but save any speculation on their meaning or consequences for your discussion and conclusion.
A note on tables and figures
In quantitative research, it’s often helpful to include visual elements such as graphs, charts, and tables , but only if they are directly relevant to your results. Give these elements clear, descriptive titles and labels so that your reader can easily understand what is being shown. If you want to include any other visual elements that are more tangential in nature, consider adding a figure and table list .
As a rule of thumb:
- Tables are used to communicate exact values, giving a concise overview of various results
- Graphs and charts are used to visualize trends and relationships, giving an at-a-glance illustration of key findings
Don’t forget to also mention any tables and figures you used within the text of your results section. Summarize or elaborate on specific aspects you think your reader should know about rather than merely restating the same numbers already shown.
A two-sample t test was used to test the hypothesis that higher social distance from environmental problems would reduce the intent to donate to environmental organizations, with donation intention (recorded as a score from 1 to 10) as the outcome variable and social distance (categorized as either a low or high level of social distance) as the predictor variable.Social distance was found to be positively correlated with donation intention, t (98) = 12.19, p < .001, with the donation intention of the high social distance group 0.28 points higher, on average, than the low social distance group (see figure 1). This contradicts the initial hypothesis that social distance would decrease donation intention, and in fact suggests a small effect in the opposite direction.
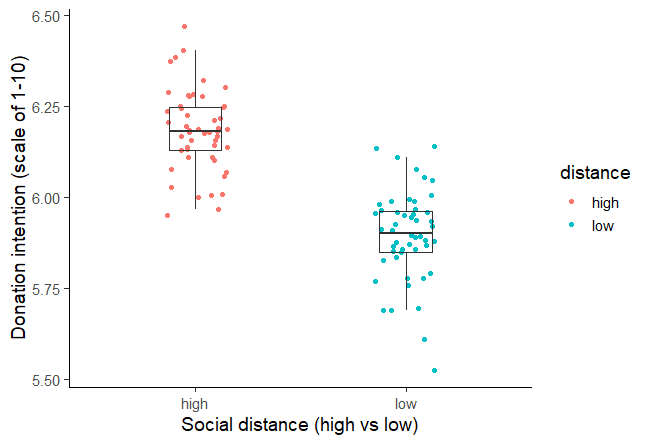
Figure 1: Intention to donate to environmental organizations based on social distance from impact of environmental damage.
In qualitative research , your results might not all be directly related to specific hypotheses. In this case, you can structure your results section around key themes or topics that emerged from your analysis of the data.
For each theme, start with general observations about what the data showed. You can mention:
- Recurring points of agreement or disagreement
- Patterns and trends
- Particularly significant snippets from individual responses
Next, clarify and support these points with direct quotations. Be sure to report any relevant demographic information about participants. Further information (such as full transcripts , if appropriate) can be included in an appendix .
When asked about video games as a form of art, the respondents tended to believe that video games themselves are not an art form, but agreed that creativity is involved in their production. The criteria used to identify artistic video games included design, story, music, and creative teams.One respondent (male, 24) noted a difference in creativity between popular video game genres:
“I think that in role-playing games, there’s more attention to character design, to world design, because the whole story is important and more attention is paid to certain game elements […] so that perhaps you do need bigger teams of creative experts than in an average shooter or something.”
Responses suggest that video game consumers consider some types of games to have more artistic potential than others.
Your results section should objectively report your findings, presenting only brief observations in relation to each question, hypothesis, or theme.
It should not speculate about the meaning of the results or attempt to answer your main research question . Detailed interpretation of your results is more suitable for your discussion section , while synthesis of your results into an overall answer to your main research question is best left for your conclusion .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results.
I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions.
I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics .
I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported or refuted.
I have used tables and figures to illustrate my results where appropriate.
All tables and figures are correctly labelled and referred to in the text.
There is no subjective interpretation or speculation on the meaning of the results.
You've finished writing up your results! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively.
In quantitative research , for each question or hypothesis , state:
- The type of analysis used
- Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics
- Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
In qualitative research , for each question or theme, describe:
- Recurring patterns
- Significant or representative individual responses
- Relevant quotations from the data
Don’t interpret or speculate in the results chapter.
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/results/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, what is your plagiarism score.

- Manuscript Preparation
How to write the results section of a research paper
- 3 minute read
Table of Contents
At its core, a research paper aims to fill a gap in the research on a given topic. As a result, the results section of the paper, which describes the key findings of the study, is often considered the core of the paper. This is the section that gets the most attention from reviewers, peers, students, and any news organization reporting on your findings. Writing a clear, concise, and logical results section is, therefore, one of the most important parts of preparing your manuscript.
Difference between results and discussion
Before delving into how to write the results section, it is important to first understand the difference between the results and discussion sections. The results section needs to detail the findings of the study. The aim of this section is not to draw connections between the different findings or to compare it to previous findings in literature—that is the purview of the discussion section. Unlike the discussion section, which can touch upon the hypothetical, the results section needs to focus on the purely factual. In some cases, it may even be preferable to club these two sections together into a single section. For example, while writing a review article, it can be worthwhile to club these two sections together, as the main results in this case are the conclusions that can be drawn from the literature.
Structure of the results section
Although the main purpose of the results section in a research paper is to report the findings, it is necessary to present an introduction and repeat the research question. This establishes a connection to the previous section of the paper and creates a smooth flow of information.
Next, the results section needs to communicate the findings of your research in a systematic manner. The section needs to be organized such that the primary research question is addressed first, then the secondary research questions. If the research addresses multiple questions, the results section must individually connect with each of the questions. This ensures clarity and minimizes confusion while reading.
Consider representing your results visually. For example, graphs, tables, and other figures can help illustrate the findings of your paper, especially if there is a large amount of data in the results.
Remember, an appealing results section can help peer reviewers better understand the merits of your research, thereby increasing your chances of publication.
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper
- Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions.
- The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is best to avoid overinterpreting the results.
- If the research addresses more than one hypothesis, use sub-sections to describe the results. This prevents confusion and promotes understanding.
- Ensure that negative results are included in this section, even if they do not support the research hypothesis.
- Wherever possible, use illustrations like tables, figures, charts, or other visual representations to showcase the results of your research paper. Mention these illustrations in the text, but do not repeat the information that they convey.
- For statistical data, it is adequate to highlight the tests and explain their results. The initial or raw data should not be mentioned in the results section of a research paper.
The results section of a research paper is usually the most impactful section because it draws the greatest attention. Regardless of the subject of your research paper, a well-written results section is capable of generating interest in your research.
For detailed information and assistance on writing the results of a research paper, refer to Elsevier Author Services.

- Research Process
Writing a good review article

Why is data validation important in research?
You may also like.

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②

The Essentials of Writing to Communicate Research in Medicine

Changing Lines: Sentence Patterns in Academic Writing
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write the Results/Findings Section in Research
What is the research paper Results section and what does it do?
The Results section of a scientific research paper represents the core findings of a study derived from the methods applied to gather and analyze information. It presents these findings in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation from the author, setting up the reader for later interpretation and evaluation in the Discussion section. A major purpose of the Results section is to break down the data into sentences that show its significance to the research question(s).
The Results section appears third in the section sequence in most scientific papers. It follows the presentation of the Methods and Materials and is presented before the Discussion section —although the Results and Discussion are presented together in many journals. This section answers the basic question “What did you find in your research?”
What is included in the Results section?
The Results section should include the findings of your study and ONLY the findings of your study. The findings include:
- Data presented in tables, charts, graphs, and other figures (may be placed into the text or on separate pages at the end of the manuscript)
- A contextual analysis of this data explaining its meaning in sentence form
- All data that corresponds to the central research question(s)
- All secondary findings (secondary outcomes, subgroup analyses, etc.)
If the scope of the study is broad, or if you studied a variety of variables, or if the methodology used yields a wide range of different results, the author should present only those results that are most relevant to the research question stated in the Introduction section .
As a general rule, any information that does not present the direct findings or outcome of the study should be left out of this section. Unless the journal requests that authors combine the Results and Discussion sections, explanations and interpretations should be omitted from the Results.
How are the results organized?
The best way to organize your Results section is “logically.” One logical and clear method of organizing research results is to provide them alongside the research questions—within each research question, present the type of data that addresses that research question.
Let’s look at an example. Your research question is based on a survey among patients who were treated at a hospital and received postoperative care. Let’s say your first research question is:
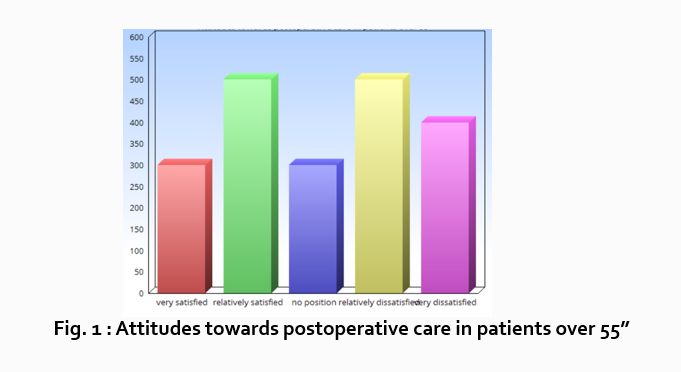
“What do hospital patients over age 55 think about postoperative care?”
This can actually be represented as a heading within your Results section, though it might be presented as a statement rather than a question:
Attitudes towards postoperative care in patients over the age of 55
Now present the results that address this specific research question first. In this case, perhaps a table illustrating data from a survey. Likert items can be included in this example. Tables can also present standard deviations, probabilities, correlation matrices, etc.
Following this, present a content analysis, in words, of one end of the spectrum of the survey or data table. In our example case, start with the POSITIVE survey responses regarding postoperative care, using descriptive phrases. For example:
“Sixty-five percent of patients over 55 responded positively to the question “ Are you satisfied with your hospital’s postoperative care ?” (Fig. 2)
Include other results such as subcategory analyses. The amount of textual description used will depend on how much interpretation of tables and figures is necessary and how many examples the reader needs in order to understand the significance of your research findings.
Next, present a content analysis of another part of the spectrum of the same research question, perhaps the NEGATIVE or NEUTRAL responses to the survey. For instance:
“As Figure 1 shows, 15 out of 60 patients in Group A responded negatively to Question 2.”
After you have assessed the data in one figure and explained it sufficiently, move on to your next research question. For example:
“How does patient satisfaction correspond to in-hospital improvements made to postoperative care?”
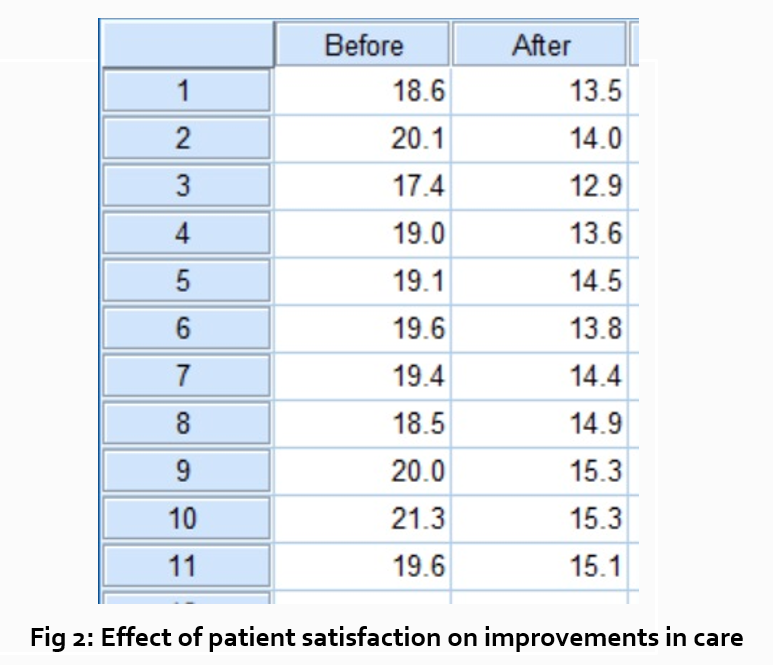
This kind of data may be presented through a figure or set of figures (for instance, a paired T-test table).
Explain the data you present, here in a table, with a concise content analysis:
“The p-value for the comparison between the before and after groups of patients was .03% (Fig. 2), indicating that the greater the dissatisfaction among patients, the more frequent the improvements that were made to postoperative care.”
Let’s examine another example of a Results section from a study on plant tolerance to heavy metal stress . In the Introduction section, the aims of the study are presented as “determining the physiological and morphological responses of Allium cepa L. towards increased cadmium toxicity” and “evaluating its potential to accumulate the metal and its associated environmental consequences.” The Results section presents data showing how these aims are achieved in tables alongside a content analysis, beginning with an overview of the findings:
“Cadmium caused inhibition of root and leave elongation, with increasing effects at higher exposure doses (Fig. 1a-c).”
The figure containing this data is cited in parentheses. Note that this author has combined three graphs into one single figure. Separating the data into separate graphs focusing on specific aspects makes it easier for the reader to assess the findings, and consolidating this information into one figure saves space and makes it easy to locate the most relevant results.
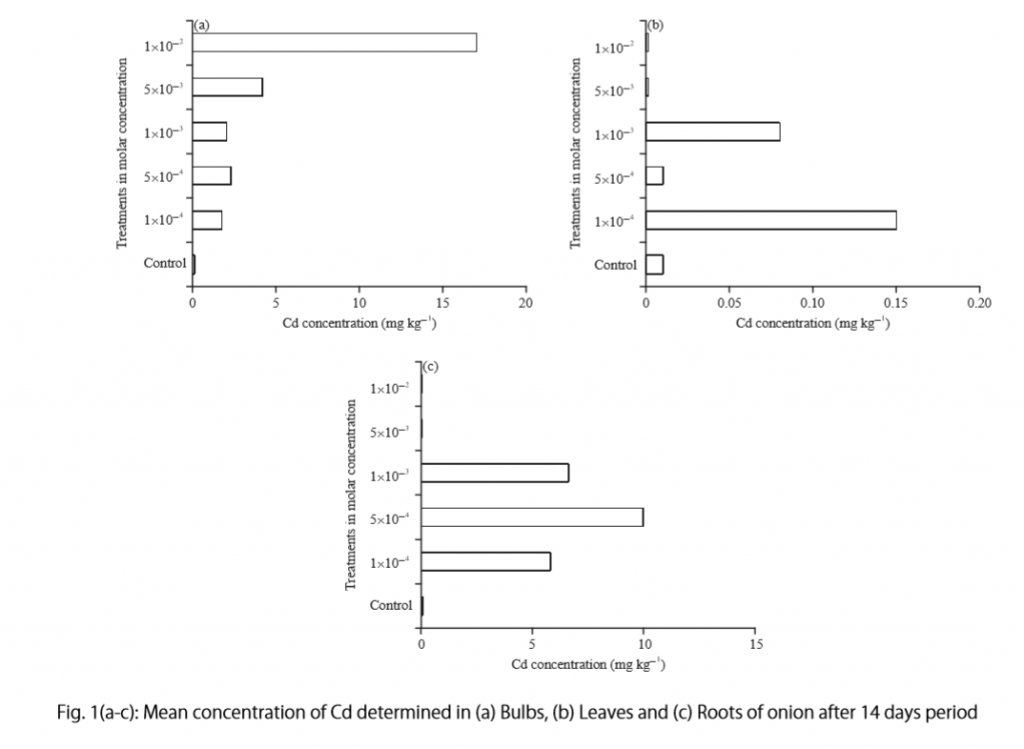
Following this overall summary, the relevant data in the tables is broken down into greater detail in text form in the Results section.
- “Results on the bio-accumulation of cadmium were found to be the highest (17.5 mg kgG1) in the bulb, when the concentration of cadmium in the solution was 1×10G2 M and lowest (0.11 mg kgG1) in the leaves when the concentration was 1×10G3 M.”
Captioning and Referencing Tables and Figures
Tables and figures are central components of your Results section and you need to carefully think about the most effective way to use graphs and tables to present your findings . Therefore, it is crucial to know how to write strong figure captions and to refer to them within the text of the Results section.
The most important advice one can give here as well as throughout the paper is to check the requirements and standards of the journal to which you are submitting your work. Every journal has its own design and layout standards, which you can find in the author instructions on the target journal’s website. Perusing a journal’s published articles will also give you an idea of the proper number, size, and complexity of your figures.
Regardless of which format you use, the figures should be placed in the order they are referenced in the Results section and be as clear and easy to understand as possible. If there are multiple variables being considered (within one or more research questions), it can be a good idea to split these up into separate figures. Subsequently, these can be referenced and analyzed under separate headings and paragraphs in the text.
To create a caption, consider the research question being asked and change it into a phrase. For instance, if one question is “Which color did participants choose?”, the caption might be “Color choice by participant group.” Or in our last research paper example, where the question was “What is the concentration of cadmium in different parts of the onion after 14 days?” the caption reads:
“Fig. 1(a-c): Mean concentration of Cd determined in (a) bulbs, (b) leaves, and (c) roots of onions after a 14-day period.”
Steps for Composing the Results Section
Because each study is unique, there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to designing a strategy for structuring and writing the section of a research paper where findings are presented. The content and layout of this section will be determined by the specific area of research, the design of the study and its particular methodologies, and the guidelines of the target journal and its editors. However, the following steps can be used to compose the results of most scientific research studies and are essential for researchers who are new to preparing a manuscript for publication or who need a reminder of how to construct the Results section.
Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study.
- The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches.
- Note length limitations on restrictions on content. For instance, while many journals require the Results and Discussion sections to be separate, others do not—qualitative research papers often include results and interpretations in the same section (“Results and Discussion”).
- Reading the aims and scope in the journal’s “ guide for authors ” section and understanding the interests of its readers will be invaluable in preparing to write the Results section.
Step 2 : Consider your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements and catalogue your results.
- Focus on experimental results and other findings that are especially relevant to your research questions and objectives and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses.
- Catalogue your findings—use subheadings to streamline and clarify your report. This will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Create appendices that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers.
- Decide how you will structure of your results. You might match the order of the research questions and hypotheses to your results, or you could arrange them according to the order presented in the Methods section. A chronological order or even a hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. Consider your audience, evidence, and most importantly, the objectives of your research when choosing a structure for presenting your findings.
Step 3 : Design figures and tables to present and illustrate your data.
- Tables and figures should be numbered according to the order in which they are mentioned in the main text of the paper.
- Information in figures should be relatively self-explanatory (with the aid of captions), and their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for readers to understand the findings without reading all of the text.
- Use tables and figures as a focal point to tell a clear and informative story about your research and avoid repeating information. But remember that while figures clarify and enhance the text, they cannot replace it.
Step 4 : Draft your Results section using the findings and figures you have organized.
- The goal is to communicate this complex information as clearly and precisely as possible; precise and compact phrases and sentences are most effective.
- In the opening paragraph of this section, restate your research questions or aims to focus the reader’s attention to what the results are trying to show. It is also a good idea to summarize key findings at the end of this section to create a logical transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows.
- Try to write in the past tense and the active voice to relay the findings since the research has already been done and the agent is usually clear. This will ensure that your explanations are also clear and logical.
- Make sure that any specialized terminology or abbreviation you have used here has been defined and clarified in the Introduction section .
Step 5 : Review your draft; edit and revise until it reports results exactly as you would like to have them reported to your readers.
- Double-check the accuracy and consistency of all the data, as well as all of the visual elements included.
- Read your draft aloud to catch language errors (grammar, spelling, and mechanics), awkward phrases, and missing transitions.
- Ensure that your results are presented in the best order to focus on objectives and prepare readers for interpretations, valuations, and recommendations in the Discussion section . Look back over the paper’s Introduction and background while anticipating the Discussion and Conclusion sections to ensure that the presentation of your results is consistent and effective.
- Consider seeking additional guidance on your paper. Find additional readers to look over your Results section and see if it can be improved in any way. Peers, professors, or qualified experts can provide valuable insights.
One excellent option is to use a professional English proofreading and editing service such as Wordvice, including our paper editing service . With hundreds of qualified editors from dozens of scientific fields, Wordvice has helped thousands of authors revise their manuscripts and get accepted into their target journals. Read more about the proofreading and editing process before proceeding with getting academic editing services and manuscript editing services for your manuscript.
As the representation of your study’s data output, the Results section presents the core information in your research paper. By writing with clarity and conciseness and by highlighting and explaining the crucial findings of their study, authors increase the impact and effectiveness of their research manuscripts.
For more articles and videos on writing your research manuscript, visit Wordvice’s Resources page.
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Writing a scientific paper.
- Writing a lab report
- INTRODUCTION
Writing a "good" results section
Figures and Captions in Lab Reports
"Results Checklist" from: How to Write a Good Scientific Paper. Chris A. Mack. SPIE. 2018.
Additional tips for results sections.
- LITERATURE CITED
- Bibliography of guides to scientific writing and presenting
- Peer Review
- Presentations
- Lab Report Writing Guides on the Web
This is the core of the paper. Don't start the results sections with methods you left out of the Materials and Methods section. You need to give an overall description of the experiments and present the data you found.
- Factual statements supported by evidence. Short and sweet without excess words
- Present representative data rather than endlessly repetitive data
- Discuss variables only if they had an effect (positive or negative)
- Use meaningful statistics
- Avoid redundancy. If it is in the tables or captions you may not need to repeat it
A short article by Dr. Brett Couch and Dr. Deena Wassenberg, Biology Program, University of Minnesota
- Present the results of the paper, in logical order, using tables and graphs as necessary.
- Explain the results and show how they help to answer the research questions posed in the Introduction. Evidence does not explain itself; the results must be presented and then explained.
- Avoid: presenting results that are never discussed; presenting results in chronological order rather than logical order; ignoring results that do not support the conclusions;
- Number tables and figures separately beginning with 1 (i.e. Table 1, Table 2, Figure 1, etc.).
- Do not attempt to evaluate the results in this section. Report only what you found; hold all discussion of the significance of the results for the Discussion section.
- It is not necessary to describe every step of your statistical analyses. Scientists understand all about null hypotheses, rejection rules, and so forth and do not need to be reminded of them. Just say something like, "Honeybees did not use the flowers in proportion to their availability (X2 = 7.9, p<0.05, d.f.= 4, chi-square test)." Likewise, cite tables and figures without describing in detail how the data were manipulated. Explanations of this sort should appear in a legend or caption written on the same page as the figure or table.
- You must refer in the text to each figure or table you include in your paper.
- Tables generally should report summary-level data, such as means ± standard deviations, rather than all your raw data. A long list of all your individual observations will mean much less than a few concise, easy-to-read tables or figures that bring out the main findings of your study.
- Only use a figure (graph) when the data lend themselves to a good visual representation. Avoid using figures that show too many variables or trends at once, because they can be hard to understand.
From: https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/imrad-results-discussion
- << Previous: METHODS
- Next: DISCUSSION >>
- Last Updated: Aug 4, 2023 9:33 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/scientificwriting
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 7. The Results
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The results section is where you report the findings of your study based upon the methodology [or methodologies] you applied to gather information. The results section should state the findings of the research arranged in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation. A section describing results should be particularly detailed if your paper includes data generated from your own research.
Annesley, Thomas M. "Show Your Cards: The Results Section and the Poker Game." Clinical Chemistry 56 (July 2010): 1066-1070.

Importance of a Good Results Section
When formulating the results section, it's important to remember that the results of a study do not prove anything . Findings can only confirm or reject the hypothesis underpinning your study. However, the act of articulating the results helps you to understand the problem from within, to break it into pieces, and to view the research problem from various perspectives.
The page length of this section is set by the amount and types of data to be reported . Be concise. Use non-textual elements appropriately, such as figures and tables, to present findings more effectively. In deciding what data to describe in your results section, you must clearly distinguish information that would normally be included in a research paper from any raw data or other content that could be included as an appendix. In general, raw data that has not been summarized should not be included in the main text of your paper unless requested to do so by your professor.
Avoid providing data that is not critical to answering the research question . The background information you described in the introduction section should provide the reader with any additional context or explanation needed to understand the results. A good strategy is to always re-read the background section of your paper after you have written up your results to ensure that the reader has enough context to understand the results [and, later, how you interpreted the results in the discussion section of your paper that follows].
Bavdekar, Sandeep B. and Sneha Chandak. "Results: Unraveling the Findings." Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 63 (September 2015): 44-46; Brett, Paul. "A Genre Analysis of the Results Section of Sociology Articles." English for Specific Speakers 13 (1994): 47-59; Go to English for Specific Purposes on ScienceDirect;Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Results Section. San Francisco Edit; "Reporting Findings." In Making Sense of Social Research Malcolm Williams, editor. (London;: SAGE Publications, 2003) pp. 188-207.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Organization and Approach
For most research papers in the social and behavioral sciences, there are two possible ways of organizing the results . Both approaches are appropriate in how you report your findings, but use only one approach.
- Present a synopsis of the results followed by an explanation of key findings . This approach can be used to highlight important findings. For example, you may have noticed an unusual correlation between two variables during the analysis of your findings. It is appropriate to highlight this finding in the results section. However, speculating as to why this correlation exists and offering a hypothesis about what may be happening belongs in the discussion section of your paper.
- Present a result and then explain it, before presenting the next result then explaining it, and so on, then end with an overall synopsis . This is the preferred approach if you have multiple results of equal significance. It is more common in longer papers because it helps the reader to better understand each finding. In this model, it is helpful to provide a brief conclusion that ties each of the findings together and provides a narrative bridge to the discussion section of the your paper.
NOTE : Just as the literature review should be arranged under conceptual categories rather than systematically describing each source, you should also organize your findings under key themes related to addressing the research problem. This can be done under either format noted above [i.e., a thorough explanation of the key results or a sequential, thematic description and explanation of each finding].
II. Content
In general, the content of your results section should include the following:
- Introductory context for understanding the results by restating the research problem underpinning your study . This is useful in re-orientating the reader's focus back to the research problem after having read a review of the literature and your explanation of the methods used for gathering and analyzing information.
- Inclusion of non-textual elements, such as, figures, charts, photos, maps, tables, etc. to further illustrate key findings, if appropriate . Rather than relying entirely on descriptive text, consider how your findings can be presented visually. This is a helpful way of condensing a lot of data into one place that can then be referred to in the text. Consider referring to appendices if there is a lot of non-textual elements.
- A systematic description of your results, highlighting for the reader observations that are most relevant to the topic under investigation . Not all results that emerge from the methodology used to gather information may be related to answering the " So What? " question. Do not confuse observations with interpretations; observations in this context refers to highlighting important findings you discovered through a process of reviewing prior literature and gathering data.
- The page length of your results section is guided by the amount and types of data to be reported . However, focus on findings that are important and related to addressing the research problem. It is not uncommon to have unanticipated results that are not relevant to answering the research question. This is not to say that you don't acknowledge tangential findings and, in fact, can be referred to as areas for further research in the conclusion of your paper. However, spending time in the results section describing tangential findings clutters your overall results section and distracts the reader.
- A short paragraph that concludes the results section by synthesizing the key findings of the study . Highlight the most important findings you want readers to remember as they transition into the discussion section. This is particularly important if, for example, there are many results to report, the findings are complicated or unanticipated, or they are impactful or actionable in some way [i.e., able to be pursued in a feasible way applied to practice].
NOTE: Always use the past tense when referring to your study's findings. Reference to findings should always be described as having already happened because the method used to gather the information has been completed.
III. Problems to Avoid
When writing the results section, avoid doing the following :
- Discussing or interpreting your results . Save this for the discussion section of your paper, although where appropriate, you should compare or contrast specific results to those found in other studies [e.g., "Similar to the work of Smith [1990], one of the findings of this study is the strong correlation between motivation and academic achievement...."].
- Reporting background information or attempting to explain your findings. This should have been done in your introduction section, but don't panic! Often the results of a study point to the need for additional background information or to explain the topic further, so don't think you did something wrong. Writing up research is rarely a linear process. Always revise your introduction as needed.
- Ignoring negative results . A negative result generally refers to a finding that does not support the underlying assumptions of your study. Do not ignore them. Document these findings and then state in your discussion section why you believe a negative result emerged from your study. Note that negative results, and how you handle them, can give you an opportunity to write a more engaging discussion section, therefore, don't be hesitant to highlight them.
- Including raw data or intermediate calculations . Ask your professor if you need to include any raw data generated by your study, such as transcripts from interviews or data files. If raw data is to be included, place it in an appendix or set of appendices that are referred to in the text.
- Be as factual and concise as possible in reporting your findings . Do not use phrases that are vague or non-specific, such as, "appeared to be greater than other variables..." or "demonstrates promising trends that...." Subjective modifiers should be explained in the discussion section of the paper [i.e., why did one variable appear greater? Or, how does the finding demonstrate a promising trend?].
- Presenting the same data or repeating the same information more than once . If you want to highlight a particular finding, it is appropriate to do so in the results section. However, you should emphasize its significance in relation to addressing the research problem in the discussion section. Do not repeat it in your results section because you can do that in the conclusion of your paper.
- Confusing figures with tables . Be sure to properly label any non-textual elements in your paper. Don't call a chart an illustration or a figure a table. If you are not sure, go here .
Annesley, Thomas M. "Show Your Cards: The Results Section and the Poker Game." Clinical Chemistry 56 (July 2010): 1066-1070; Bavdekar, Sandeep B. and Sneha Chandak. "Results: Unraveling the Findings." Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 63 (September 2015): 44-46; Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Caprette, David R. Writing Research Papers. Experimental Biosciences Resources. Rice University; Hancock, Dawson R. and Bob Algozzine. Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers . 2nd ed. New York: Teachers College Press, 2011; Introduction to Nursing Research: Reporting Research Findings. Nursing Research: Open Access Nursing Research and Review Articles. (January 4, 2012); Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Results Section. San Francisco Edit ; Ng, K. H. and W. C. Peh. "Writing the Results." Singapore Medical Journal 49 (2008): 967-968; Reporting Research Findings. Wilder Research, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Human Services. (February 2009); Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Results. Thesis Writing in the Sciences. Course Syllabus. University of Florida.
Writing Tip
Why Don't I Just Combine the Results Section with the Discussion Section?
It's not unusual to find articles in scholarly social science journals where the author(s) have combined a description of the findings with a discussion about their significance and implications. You could do this. However, if you are inexperienced writing research papers, consider creating two distinct sections for each section in your paper as a way to better organize your thoughts and, by extension, your paper. Think of the results section as the place where you report what your study found; think of the discussion section as the place where you interpret the information and answer the "So What?" question. As you become more skilled writing research papers, you can consider melding the results of your study with a discussion of its implications.
Driscoll, Dana Lynn and Aleksandra Kasztalska. Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
- << Previous: Insiderness
- Next: Using Non-Textual Elements >>
- Last Updated: Apr 3, 2024 10:04 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Endocrinol Metab
- v.17(2); 2019 Apr

The Principles of Biomedical Scientific Writing: Results
Zahra bahadoran.
1 Nutrition and Endocrine Research Center, Research Institute for Endocrine Sciences, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Parvin Mirmiran
2 Department of Clinical Nutrition and Diet Therapy, Faculty of Nutrition Sciences and Food Technology, National Nutrition and Food Technology Research Institute, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Azita Zadeh-Vakili
3 Cellular and Molecular Endocrine Research Center, Research Institute for Endocrine Sciences, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Farhad Hosseinpanah
4 Obesity Research Center, Research Institute for Endocrine Sciences, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Asghar Ghasemi
5 Endocrine Physiology Research Center, Research Institute for Endocrine Sciences, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
The “results section” of a scientific paper provides the results related to all measurements and outcomes that have been posted earlier in the materials and methods section. This section consists of text, figures, and tables presenting detailed data and facts without interpretation and discussion. Results may be presented in chronological order, general to specific order, most to least important order, or may be organized according to the topic/study groups or experiment/measured parameters. The primary content of this section includes the most relevant results that correspond to the central question stated in the introduction section, whether they support the hypothesis or not. Findings related to secondary outcomes and subgroup analyses may be reported in this section. All results should be presented in a clear, concise, and sensible manner. In this review, we discuss the function, content, and organization of the “results section,” as well as the principles and the most common tips for the writing of this section.
The “results section” is the heart of the paper, around which the other sections are organized ( 1 ). Research is about results and the reader comes to the paper to discover the results ( 2 ). In this section, authors contribute to the development of scientific literature by providing novel, hitherto unknown knowledge ( 3 ). In addition to the results, this section contains data and statistical information for supporting or refuting the hypothesis proposed in the introduction ( 4 ).
“Results section” should provide an objective description of the main findings, clearly and concisely, without interpretation ( 5 , 6 ). The authors need to use an interesting combination of text, tables, and figures to answer the study questions and to tell the story without diversions ( 7 ). The systemic assessment of published articles highlights the fact that the literature frequently suffers from selective reporting of results only for certain assessed outcomes, selective reporting of statistical analyses, and confused, ambiguous, incomplete, or misleading presentation of data ( 8 , 9 ).
In this section of our series on the principles of biomedical scientific writing ( 10 , 11 ), we describe the function, content, and organization of the “results section” in a scientific paper (mostly for hypothesis-testing papers) and provide common recommendations that can help authors to write this section more effectively.
2. The Function of the Results Section
The function of the “results section” is to present the main results of experiments described in the materials and methods section ( 12 , 13 ) and to present the supporting data in the form of text, tables, and figures ( 13 ). This section should answer the basic question: “What did the authors find in research?” By providing the results, authors try to elucidate the research data, making it to the point and meaningful ( 13 ).
3. Content of the Results Section
The “results section” includes both results and data that are presented in text, tables, and figures. Results are presented in the text; data (the most important) are presented in figures and tables, with a limited amount presented in the text ( 13 ). Statistically relevant parameters including sample size, P values, and the type of statistics used are also presented in this section ( 13 ).
3.1. Difference Between Data and Results
Data and results are not the same ( 14 ); providing results but no data vs. data but no results should be avoided ( 14 , 15 ). Results are general statements in the main text that summarize or explain what the data (facts and numbers) show ( 13 , 14 ); in other words, results are text descriptions of what is important about data ( 16 ) and give meaning to the data ( 15 ). When reporting data or results, make sure that they are logical ( 2 ). See Box 1 for more differences between results and data.
a The text presented in square brackets is data and the remainder is a result.
3.2. The Appropriate Format for Presenting Data/Results
Depending on how the data best support the findings of the study, the “results section” is structured as text, tables, and figures ( 12 ) and should consist of a dynamic interplay between text and figures/tables; the most important data are usually presented in both formats ( 17 ). The reader should select the mode of presentation in a way that optimizes comprehension of the data; however, as a general rule, if you want to present three or fewer numbers, you should use a sentence; otherwise, you consider a table or a graph ( 18 ).
Selecting the best format for presenting results/data depends on the level of details (exact values or patterns) to present ( 19 ). Tables are useful to present specific information or exact values ( 19 ), and function as reference tools for readers ( 20 ) whereas figures are useful to show comparisons and patterns ( 19 ), functioning as analytic tools ( 20 ).
Tables are meant to summarize large amounts of data, to organize and display data more clearly than words, to compare groups of data, to simplify found information, and to facilitate calculations ( 19 ). A table typically has three or more interrelated columns and three or more interrelated rows; otherwise, presenting the information in the text may be more appropriate ( 19 ).
The functions of figures include: (1) showing the underlying patterns of data that are not presentable in text or tables, (2) displaying data more clearly than they can be done in text or tables, (3) more summarizing a large amount of data than they can be done in text or tables, and (4) improving the understanding and locating the specific information easily and rapidly ( 21 ).
3.3. Results
The primary content of this section includes the most relevant (but not all) results corresponding to the central question posed in the introduction section, whether they support the hypothesis or not ( 12 , 13 ). The secondary findings, e.g., results related to secondary outcomes and subgroup analyses, may also be reported in this section ( 22 ). Results must be presented for both experimental and control groups ( 13 ). Results of each item mentioned in the materials and methods should be given in the results section ( 12 , 15 ).
The text of the “results section” should state and summarize the main results and explain the data presented within tables and/or figures ( 23 ); reiteration of all numbers presented in tables and figures is not recommended ( 22 ); however, readers must be given the main messages derived from a table or figure without having to interpret the data themselves ( 7 ). It means that if there is a large amount of data in a table or figure, restating a key piece of data in the text is acceptable and helps the reader zero in on important data ( 14 ).
3.3.1. Reporting Negative Findings
Authors are highly recommended excluding irrelevant results but not ignoring valid anomalous results that contradict the research hypothesis or do not support the current scientific literature ( 22 ). The Feynman, says “if you are doing an experiment, you should report everything that you think might make it invalid-not only what you think is right about it” ( 24 ). Although reporting null or negative findings is not as straightforward as positive findings, it may lead to reexamining current scientific thinking, and guide scientists towards unabridged science ( 25 ). Reporting negative findings can also prevent the replication of the study and prevent the waste of time and resources ( 25 ). The ignorance of null or negative findings also leads to an overestimation of an effect size or treatment effect in available data ( 9 ).
3.3.2. Referring to Unpublished Results
Referring to unpublished results is not recommend unless there is a strong argument supporting their inclusion ( 14 ); therefore, authors are advised to avoid using the term “data not shown” ( 4 ).
3.3.3. Methods or Interpretation in the Results Section
Generally, the “results section” is not the place for presenting methods and experimental details or interpreting data ( 14 ). When experiments are described in this section, if a result leads to additional experiments, it is better to report the new experimental details in the “results section” ( 14 ). Sometimes authors want to refer to a specific experiment or method in results; in these cases, they should not repeat experimental details, but preferably use a transition phrase to link methods with results ( 14 ). To justify the rationale behind the experiment, using topic sentences/phrases (e.g. in order to determine whether…) provides an overview before giving details ( 12 ); however, in this case, the method statement should not be used as a topic sentence and the main verbs should describe results, not methods (e.g., “ when propranolol was administered during normal ventilation, phospholipids decreased ”; here “ method ” is subordinated in a transition clause and result is the main clause) ( 13 ). Two patterns of sentence structure are recommended for including methods in a result statement: making the method the subject of the sentence or stating the method using a transition phrase or clause and the result in the main clause ( 13 ).
The traditional view of writing the “results section” is just to report data and results without any interpretation; accordingly, the result is not expected to contain statements that need to be referenced (comparisons of findings) ( 13 , 26 ). In another view, some interpretation or brief comparisons that do not fit into the discussion may be included ( 13 , 27 ).
Data are facts and numbers, mostly presented as non-textual elements (usually in tables and figures) where they are easy to read ( 13 , 14 , 28 ). A limited amount of data may also be presented in the text, following a result statement ( 13 ) although too much data in the text make it too long ( Box 1 ) ( 28 ). Data may be in the form of raw data, summarized data, or transformed data ( 13 ); however, it is suggested that raw data (i.e. patients’ records, individual observations) not be presented in results ( 12 ). Note that numerical data are absolute while some data, e.g. microscopic data, are subjective ( 2 ).
3.4.1. Non-Textual Elements
Providing study findings visually, rather than entire textualizing, enables authors to summarize a great deal of data compactly within the text with an appropriate reference; some images convey more than words ( 29 ). The primary purpose of non-textual elements, i.e. tables, graphs, figures, and maps, is to present data such that they can be easily and quickly grasped ( 23 ) while being more informative than when appearing in the text ( 6 ). Tables and figures should be complete/comprehensible, being able to stand alone without the text ( 5 , 12 ).
Non-textual elements should be referred to in the text at the appropriate point ( 5 , 6 , 12 ). Location statements, i.e. statements referring to non-textual elements, may be presented in different patterns (e.g., A. X is shown in table/figure; B. table/figure shows; C. see table/figure; D. as shown in table/figure); pattern B is more and pattern C is less common ( 27 ).

Some general tips about using non-textual elements in the “results section” are reviewed in Box 2 . The most common rules in organizing tables and figures are given in the following. For more information about designing different types of tables/figures/graphs, please refer to additional references ( 7 , 19 , 20 , 30 , 31 ).
3.4.1.1. Tables
The use of tables is an effective way to summarize demographic information and descriptive statistics ( 23 ). Note that tables must have a purpose and be integrated into the text ( 21 ). Tables are most useful to present counts, proportions, and percentages ( 8 ), and are appropriate also for presenting details especially when exact values matter ( 32 ), being are more informative than graphs ( 29 ). However, limited information should be presented in tables; otherwise, most readers find them difficult to read and thus, may ignore them ( 5 , 23 ). Data in tables can be arranged horizontally or vertically; whenever possible, primary comparisons are preferably presented horizontally from left to right ( 19 ).
3.4.1.1.1. Basic Elements of Tables
Tables usually have at least six elements: (1) table number, (2) table title, (3) row headings (stubs), and (4) column headings (boxes), identifying information in rows and columns, (5) data in data field, and (6) horizontal lines (rules). Most also have footnotes, row subheadings, spanner headings (identifying subgroups in column headings), and expanded forms of abbreviations in the table ( 19 , 21 , 31 , 33 ).
The table title should clearly state what appears in it and provide sufficient information on the study, i.e. provide a context helping readers interpret the table information ( 19 ). Some specific details may also be provided including the type and number of subjects or the period of study ( 30 ). For developing the title of a table, one can describe the main cell entries, followed by qualification or more description ( 32 ). The table’s title is presented as a phrase not a full sentence ( 19 ). Authors need to refer to the journal’s style for rules on which words in titles are capitalized.
As a rule, comparing two (or even three) numbers should be side-by-side rather than above and below ( 30 ). Column and row headings help readers find information and they should be included group sizes and measurement units ( 19 ). Tables should be in borderless grids of rows and columns ( 5 , 32 ) with no vertical rule and limited horizontal rules ( 32 ). The first column of a table includes usually a list of variables that are presented in the table; although the first column usually does not need a header, sometimes a simple description of what appears in each row may be provided as the heading of the first column. Units for variables may be placed in parentheses immediately below the row descriptions ( 30 ).
Headings for other columns should also be informative without vague labels, e.g. group A, group B, group C, etc.; instead, a brief description summarizing group characteristics is used ( 30 ). The last column may show P values for comparison between study groups ( 34 ), except for randomized clinical trials, where P values are not needed to compare baseline characteristics of participants ( 7 ). The first letters of lines and column headings in tables should be capitalized.
The fields of tables are points at which columns and rows intersect ( 19 ). Cells of a table are the data field of the table, other than those containing row and column headings ( 21 ). Cells contain information as numerals, text, or symbols ( 19 ). Every cell must contain information; if no information is available, one can use NA in the cell and define it in the footnote as not available or not applicable; alternatively, a dash mark may be inserted ( 19 ). The content of columns need to be aligned ( 19 ); words are usually left aligned, numerals are aligned at decimals, parenthesis, and factors of 10 ( 19 , 21 ).
Table footnotes should be brief, and define abbreviations, provide statistical results, and explain discrepancies in data, e.g., “percentages do not total 100 because of rounding” ( 19 , 30 ). In addition to asterisks usually used to show statistical significance ( 33 ), the following symbols are used, in sequence, for further notes: †, ‡, §, ¶, #, ††, ‡‡ ( 30 ).
3.4.1.1.2. Different Types of Tables
Table of lists, table of baseline or clinical characteristics of subjects, table of comparisons, and table of multivariable results are various types of tables that may be used ( 30 ). The table’s format should be selected according to the purpose of the table ( 30 ). A table of lists just presents a list of items including diagnostic criteria or causes of a disease; it is critical to arrange such tables based on their contents by order (e.g., alphabetical order) or their importance (most to least) ( 30 ). Tables of study participants’ characteristics usually provide a general overview of the essential characteristics of subjects, such as age, sex, race, disease stage, and selected risk factors ( 30 ). The table of comparisons (≥ two groups) provides details for each group and differences between the groups. Tables of multivariable results elaborate results of statistical analyses assessing relationships between predictor (independent) and outcome (dependent) variables, and usually include regression coefficients, standard errors, slopes, partial correlation coefficients, and P values or odds ratio, hazard ratios, and 95% confidence intervals for regression models ( 30 ).
3.4.1.2. Figures
Graphical elements convey the important messages of research ( 20 ). A figure is “any graphical display to present information or data” ( 20 ), and it effectively presents complicated patterns ( 32 ), best used for presenting an important point at a glance or indicating trends or relationships ( 20 ). Like tables, figures should have a purpose and be integrated with the rest of the text ( 21 ).
3.4.1.2.1. Basic Elements of Figures
Most figures that present quantitative information (charts and graphs) have at least seven elements, including figure number, figure caption/legend, data field, vertical scale, horizontal scale, labels, and data (plotting symbols, lines, and so on) ( 21 ). Some figures also have reference lines in the data field to help orient readers and keys that identify data ( 21 ).
Figure caption/legend, usually given below the figure, describes the figure and must reflect the figure entirely, independent of the main text ( 21 , 31 ). For the figure to stand alone, a figure legend needs to be included four parts (a brief title, experimental or statistical information/details, definitions of symbols, line, or bar patterns, and abbreviations) ( 31 ).
Data field is a space in the figure in which data are presented; it is usually bordered on the left by the X-axis (abscissa) and on the bottom by the Y-axis (ordinate) ( 20 , 21 ). Labels identify the variables graphed and the units of measurement ( 21 ). Figure lines should be broad and the labeling text should be large enough to be legible after reduction to a single- or two-column size ( 32 ). Appropriate font size should be used to maintain legibility after fitting figures to publication size ( 31 ).
Scales on each axis should match the data range and be slightly above the highest value ( 20 ). Symbols should be uniform across the figures ( 20 ). The data point symbols should be easily distinguishable; using black and white circles (● - ∘) is the easiest way when two are needed ( 31 ); if more are needed, using up-pointing triangles (▲ - Δ) and squares (■ - □) is suggested ( 31 ). Using symbols, line types, and colors is also effective in differentiating important strata in figures ( 8 ).
3.4.1.2.2. Emphasizing Important Data on Figures
To make figures visually efficient, the subordination of all non-data elements vs. data elements is advised (gridlines should be used as thin as possible and very faint). Directly labeling objects, instead of legends, may keep readers’ attention on the most important parts of the figure ( 8 ). Using different line weights may also be helpful to emphasize the important information/data in figures ( 31 ). The use of color, shading, or 3D perspectives is not suggested unless they serve a specific explanatory function in figure ( 8 ).
3.4.1.2.3. Different Types of Figures
Two major categories of figures are statistical figures (graphs) and non-statistical figures (clinical images, photographs, diagrams, illustrations, and textual figures) ( 20 ). Graphs are suitable for presenting relationships whereas non-statistical figures are used to confirm findings or provide explanatory information ( 20 ).
In statistical figures, selecting a graphical format (bar graph, line graph, dot plot, and scatterplot) is done according to the type of relationship that authors wish to communicate ( 20 ); for example, line graphs are appropriate for showing trends and bar graphs for magnitudes ( 20 ). Using a graphing format that is easy to interpret is preferred ( 20 ); pie graphs are sparingly used because comparing different angles is complicated with them ( 20 ). Graphs should accurately represent findings; when possible, scales should start at zero, and figure axes should not be altered in order to make data more meaningful ( 20 ).
Non-statistical figures are those that visually present information that does not contain data ( 20 ). Clinical images and photographs [ultrasonograms, computed tomographic scans (CT scans), magnetic resonance images (MRI), images of patients, tissue samples, microscopic findings, and so on] provide absolute proof of findings ( 20 ). Illustrations are used for explaining structures (parts of a cell), mechanisms, and relationships ( 20 ). Diagrams (flowcharts, algorithms, pedigrees, and maps) are useful for displaying complex relations ( 20 ). Textual figures, containing only text, are mostly used for describing steps of a procedure or summarizing guidelines ( 20 ). For photographs, patient information or identifiers should be removed ( 20 ).
3.5. Statistics in the Results Section
Statistics in the “results section” must report data in a way that enables readers to assess the degree of experimental variation and to estimate the variability or precision of the findings ( 22 ). For more details, one can see SAMPL (Statistical Analysis and methods in the Published Literature) guidelines ( 35 ). To report normally distributed data, the mean and estimated variation from mean should be stated ( 13 ). Variability should be reported using standard deviation (SD), which is a descriptive statistic ( 36 ) and reflects the dispersion of individual sample observation of the sample mean ( 37 ). The standard error (SE), an inferential statistic ( 36 ) reflecting the theoretical dispersion of sample means about some population means, characterizes uncertainty about true values of population means ( 37 ). It is useful for assessing the precision of an estimator ( 36 ) and is not an appropriate estimate of the variability in observations ( 37 ). Using “mean (SD or SE)” is preferred to “mean ± SD or SE” because the “±” sign can cause confusion ( 22 ). Increasing sample size decreases SE but not SD ( 36 ). To report data with a skewed distribution, the median and the interquartile range (between 25th and 75th percentiles) should be provided ( 22 ).
To report risk, rates, and ratios, one should use a type of rate (incidence rate, survival rate), ratio (odds ratio, hazards ratio), or risk (absolute risk, relative risk, relative risk reduction) ( 35 ). The measure of precision (95% CI) for estimated risks, rates, and ratios should also be provided ( 35 ). For correlation analysis, the exact values of the correlation coefficient and 95% CI should be reported. Describing correlation using qualitative words (low, moderate, high) without providing a clear definition is not acceptable ( 35 ). Results of regression analysis should include regression coefficients (β) of each explanatory variable, corresponding 95% CI and/or P value and a measure of the “goodness-of-fit” of the model ( 35 ).
3.5.1. Significance Levels
A P value is the probability of consistency between data and the hypothesis being tested ( 38 ). Reporting the exact P values ( P = 0.34 or P = 0.02) rather than the conventional P ( P < 0.05) is recommended for all primary analyses ( 12 , 37 ) as it conveys more information ( 37 ). The use of the term “partially significant” or “marginally significant”, where the P value is almost significant (e.g. P = 0.057) is not acceptable if the significance level is defined as P = 0.05 ( 39 ). Some, however, argue that it is not always necessary to stick to P = 0.05 for the interpretation of results and it is better to report the exact P value and confidence interval for the estimator ( 40 ).
The use of the 95% confidence interval (95% CI) can provide further information compared to P values per se, and prefigures the direction of the effect size (negative or positive), its magnitude, and the degree of precision ( 17 ). A confidence interval characterizes uncertainty about the true value of population parameters ( 37 ). It is essential to provide the sample size (n) and probability values for tests of statistical significance ( 13 ).
Statements about significance must be qualified numerically ( 41 ). In the text, it is suggested that P values be reported as equalities rather than as inequalities in relation to the alpha criterion ( 41 ). In tables and figures, inequalities may be useful for groups of data ( 41 ) where asterisks *, **, and *** are usually used to show statistical significance at 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001 probability levels, respectively ( 33 ).
Although not consistent, P values < 0.001 are reported as P < 0.001; for 0.001 ≤ P values < 0.01, a three-significant digit is recommended, e.g. P = 0.003; for 0.01 ≤ P values < 0.1, a two-significant digit is sufficient (e.g. P = 0.05); for 0.1 ≤ P values ≤ 0.9, a one-significant digit is sufficient (e.g. P = 0.4); and P values > 0.9 are reported as P > 0.9 ( 42 ). For genome-wide association studies, the power of 10 is used for reporting P values, e.g. 6 × 10 -9 ( 42 ). It is generally suggested that zero be used before a decimal point when the value is below one, e.g. 0.37 ( 43 ). According to the American Psychological Association, zero before a decimal point is used for numbers that are below one, but it can also be used for values that may exceed one (e.g. 0.23 cm). Therefore, when statistics cannot be greater than one (e.g. correlations, proportions, and P values), do not use a zero before decimal fraction, e.g. P = .028 not P = 0.028 ( 18 ); this recommendation, however, is not always adopted by everyone. The international standard is P (large italic) although both ‘p’ and ‘P’ are allowed ( 40 ).
4. Organization of the Results Section
There are different ways for organizing the “results section” including ( 1 , 12 , 14 , 22 , 44 ): (1) chronological order, (2) general to specific, (3) most to least important, and (4) grouping results by topic/study groups or experiment/measured parameters. Authors decide which format is more appropriate for the presentation of their data ( 12 ); anyway, results should be presented in a logical manner ( 4 ).
4.1. Different Ways of Organizing the Results Section
4.1.1. chronological order.
The best order for organizing “results section” may be the chronological order ( 22 ). It is considered as the most straightforward approach using subheadings that parallel methods ( 14 ). This order facilitates referring to a method associated with a given result ( 14 ) such that results are presented in the same order as methods ( 15 ).
4.1.2. General to Specific
This format is mostly used in clinical studies involving multiple groups of individuals receiving different treatments ( 14 ). The “results section” usually proceeds from general to more specific findings ( 1 ). Characteristics of the overall study population (sex and age distribution and dropouts) are first given ( 14 ), followed by data and results for each group starting with the control group or the group receiving the standard treatment ( 14 ); finally, the disease group or group receiving the experimental treatment are addressed ( 14 ). As a general rule, secondary results should be given after presenting more important (primary) results, followed by any supporting information ( 22 ). A common order is stating recruitment/response, characteristics of the sample/study participants, findings from the primary analyses, findings from secondary analyses, and any additional or unexpected findings ( 17 ). In other words, the “results section” should be initiated by univariate statistics, followed by bivariate analyses to describe associations between explanatory and outcome variables; finally, it gets through by any multivariate analyses ( 7 ).
4.1.3. Most to Least Important
This format is used in case that the order of presenting results is not critical to their being comprehendible and allows the author to immediately highlight important findings ( 14 ). Results that answer the main question are presented at the beginning of the “results section,” followed by other results in next paragraphs ( 13 ).
4.1.4. Grouping by Topic or Experiment
Comparison of the diagnostic and analytical performance of a number of assays for analytes is an example of using this format ( 14 ).
4.2. Paragraphing of the Results Section
The “results section” may be initiated by two approaches: (1) by giving a general (not detailed) overview of the experiment and (2) by going directly to the results by referring to tables or figures ( 44 ). The first paragraph of this section, along with table 1, describes the characteristics of the study population (number, sex, age, and symptoms) ( 23 ). These data show the comparability of the study groups at baseline and the distribution of potential confounders between groups, as a source of bias that can affect the study findings ( 7 ). It allows the reader to decide whether or not the case and control groups are similar and represent the patient population in their private practice ( 23 ).
For clinical trials, the number of patients completing the protocol in each treatment/study group, the number of patients lost to follow-up, and the number and reasons for excluded/withdrawn subjects should be given. Commenting on whether baseline characteristics of study groups are statistically similar or different is also important ( 1 ). For further information, authors can consult reporting guidelines for the main study types available at http://www.equator-network.org.
The number of the middle paragraphs depends on the number of research questions/hypotheses and the types of statistical analyses; each hypothesis or specific analysis typically devotes at least a paragraph to itself ( 1 ). Figure legends, description of the methods and results for control groups should not be given at the beginning of paragraphs, as they do not narrate the story ( 28 ). However, sometimes, it is needed that results of the control group are presented first (e.g. for establishing the stability of baseline) ( 13 ).
5. Emphasizing Important Results
Since not all results are equally important, the reader must be able to distinguish important results and authors have to emphasize important information and de-emphasize less important information ( 13 ). There are various techniques for emphasizing important information, including condensing or omitting less important information, subordinating less important information, placing important results at the power position, and labeling, stating, and repeating important information ( 13 ).
For condensing or omitting less important information, you should be careful not to duplicate/repeat data in tables and figures or repeat them in the text ( 4 , 6 , 12 ); one or two values from tables/figures can be repeated in the text for emphasis ( 13 ).
For subordinating less important information, one should not use table titles, figure legends or methods statement as a topic sentence in the text ( 13 , 22 ). Instead, after stating the first result relevant to the table/figure, you can cite it in parenthesis ( 13 ). Since a result states a message and creates an expectation, it is a more powerful topic sentence than a figure legend or table title ( 13 ). Sometimes, control results can be subordinated by incorporating them into experimental results ( 13 ).
To highlight more important results (those that help answer questions), authors can put these results at the beginning of paragraphs, the strongest power position ( 12 , 22 , 28 ), followed by supporting details and control results ( 28 ).
Moreover, key findings may receive more attention by using a signal (e.g. we found or we observed) at the beginning of the sentence ( 13 ).
6. Other Considerations
6.1. length and paragraphing.
To see the forest for the tree, the “results section” should be as brief and uncluttered as possible ( 13 ), which can be accomplished by having a well-organized “materials and methods” section ( 3 ) and avoiding unnecessary repetition ( 13 ); for example, similar results for several variables can be reported together. The “results section” of an original manuscript usually includes 2 - 3 pages (~1000 words) with a 1.5 line spacing, font size 11 (including tables and figures) ( 45 ), and 4 - 9 paragraphs (each 130 words) on average ( 45 ); a paragraph should be devoted to one or more closely related figures ( 4 ).
Presenting additional results/data as supplementary materials is a suggestion for keeping the “results section” brief ( 17 ). In addition to save the text space, supplementary materials improve the presentation and facilitate communications among scientists ( 46 , 47 ). According to Springer, supplementary materials can be used for presenting data that are not needed to support the major conclusions but are still interesting. However, keep in mind that the unregulated use of supplementary materials is harmful to science ( 47 ). Supplementary materials should be referred to at the appropriate points in the main text.
For referring to results obtained in hypothesis testing studies, using past tenses is recommended ( 4 , 12 - 14 ); non-textual elements should be referred using present tenses, e.g. “as seen in table 1 …” or “table 1 shows …” in descriptive studies, results are reported in the present tense ( 13 ).
6.3. Word Choice
Although adverbs/adjectives are commonly used to highlight the importance of results, it is recommended altogether avoiding the use of such qualitative/emotive words in the “results section” ( 7 , 13 ). Some believe that qualitative words should not be used because they may imply an interpretation of findings ( 17 ). In biomedical publications, the terms ‘significant, significance, and significantly’ (followed by P values) are used to show statistical relationships and should not be used for other purposes for which, other terms such as substantial, considerable, or noteworthy can be used ( 14 ). See Box 3 for appropriate word choice for the “results section.”
In the “results section,” to make a comparison between the results, i.e. stating the similarity/equivalence or difference/non-equivalence, using appropriate signals is recommended ( 27 ). To show a similarity, a signal to the reader may be used such as “like”, “alike”, “similar to”, and “the same as”; to show differences, the following signals can be used: “but”, “while”, “however”, “in contrast”, “more likely than”, and “less likely than” ( 27 ).
6.4. Reporting Numbers
Numbers play an important role in scientific communication and there are some golden rules for reporting numbers in a scientific paper ( 43 , 48 ). Significant figures (significant digits) should reflect the degree of precision of the original measurement ( 12 ). The number of digits reported for a quantity should be consistent with scientific relevance ( 37 ); for example, a resolution to 0.001 units is necessary for pH but a resolution of < 1 mm Hg is unimportant for blood pressure ( 37 ). Avoid using “about” or “approximately” to qualify a measurement or calculation ( 12 ). The use of percentage for sample sizes of < 20 and decimal for sample sizes of < 100 is not recommended ( 43 ).
The numbers should be spelled out at the beginning of a sentence or when they are less than 10, e.g., twelve students improved… ( 43 ). In a sentence, the authors should be consistent where they use numbers as numerals or spelled-out ( 43 ). Before a unit of a measure, time, dates, and points, numbers should be used as numerals, e.g. 12 cm; 1 h 34 min; at 12:30 A.M., and on a 7-point scale ( 18 ).
A space between the numeral and the unit should be considered, except in the case of %. Because the terms “billion,” “trillion,” and “quadrillion” imply different numbers in Europe and the USA, they should not be used ( 48 ). To express ranges in text, the terms “to” or “through” are preferred to dashes; in tables, the use of dashes or hyphens is recommended ( 48 ).
7. Conclusions
The “results section” of a biomedical manuscript should clearly present findings of the study using an effective combination of results and data. Some dos and don’ts of writing the “results section” are provided in Box 4 . Authors should try to find the best format using a dynamic interplay between text and figures/tables. Results can be organized in different ways including chronological order or most to least important; however, results should be presented in a manner that makes sense.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Ms. Niloofar Shiva for critical editing of English grammar and syntax of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interests: It is not declared by the authors.
Funding/Support: Research Institute for Endocrine Sciences supported the study.
How to Write an Effective Results Section
Affiliation.
- 1 Rothman Orthopaedics Institute, Philadelphia, PA.
- PMID: 31145152
- DOI: 10.1097/BSD.0000000000000845
Developing a well-written research paper is an important step in completing a scientific study. This paper is where the principle investigator and co-authors report the purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions of the study. A key element of writing a research paper is to clearly and objectively report the study's findings in the Results section. The Results section is where the authors inform the readers about the findings from the statistical analysis of the data collected to operationalize the study hypothesis, optimally adding novel information to the collective knowledge on the subject matter. By utilizing clear, concise, and well-organized writing techniques and visual aids in the reporting of the data, the author is able to construct a case for the research question at hand even without interpreting the data.
- Data Analysis
- Peer Review, Research*
- Publishing*
- Sample Size

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Checklist: Research results 0 / 7. I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results. I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions. I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported ...
Research results refer to the findings and conclusions derived from a systematic investigation or study conducted to answer a specific question or hypothesis. These results are typically presented in a written report or paper and can include various forms of data such as numerical data, qualitative data, statistics, charts, graphs, and visual aids.
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper. Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions. The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is ...
Step 1: Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study. The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will ...
The results section of a research paper tells the reader what you found, while the discussion section tells the reader what your findings mean. The results section should present the facts in an academic and unbiased manner, avoiding any attempt at analyzing or interpreting the data. Think of the results section as setting the stage for the ...
Present the results of the paper, in logical order, using tables and graphs as necessary. Explain the results and show how they help to answer the research questions posed in the Introduction. Evidence does not explain itself; the results must be presented and then explained. Avoid: presenting results that are never discussed; presenting ...
Wilder Research, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Human Services. (February 2009); Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Results. Thesis Writing in the Sciences. Course Syllabus. University of Florida.
The “results section” is the heart of the paper, around which the other sections are organized . Research is about results and the reader comes to the paper to discover the results . In this section, authors contribute to the development of scientific literature by providing novel, hitherto unknown knowledge .
Developing a well-written research paper is an important step in completing a scientific study. This paper is where the principle investigator and co-authors report the purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions of the study. A key element of writing a research paper is to clearly and objectively report the study's findings in the Results section.