

Departments
- Applied Physics
- Biomedical Engineering
- Center for Urban Science and Progress
- Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
- Civil and Urban Engineering
- Computer Science and Engineering
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Finance and Risk Engineering
- Mathematics
- Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
- Technology, Culture and Society
- Technology Management and Innovation
Degrees & Programs
- Bachelor of Science
- Master of Science
- Doctor of Philosophy
- Digital Learning
- Certificate Programs
NYU Tandon Bridge
- Undergraduate
- Records & Registration
- Digital Learning Services
- Teaching Innovation
- Explore NYU Tandon
- Year in Review
- Strategic Plan
- Diversity & Inclusion
News & Events
- Social Media
Looking for News or Events ?
Computer Science, M.S.

- Request Information
We offer a highly adaptive M.S. in Computer Science program that lets you shape the degree around your interests. Besides our core curriculum in the fundamentals of computer science, you have a wealth of electives to choose from. You can tailor your degree to your professional goals and interests in areas such as cybersecurity, data science, information visualization, machine learning and AI, graphics, game engineering, responsible computing, algorithms, and web search technology.
Job opportunities in computer science are challenging and diverse, and we expect to see steady demand for highly qualified graduates at all levels. As a graduate, you can explore careers in areas such as applications programming, big data, software engineering, game design and programming, peer-to-peer networks, computer vision and imaging, machine learning and AI, urban computing, and interactive data visualization.
With our M.S. program in Computer Science, you will have significant curriculum flexibility, allowing you to adapt your program to your ambitions and goals as well as to your educational and professional background. You will gain a solid grounding in the fundamentals of computer science, along with access to professional-level courses, and an opportunity to specialize in selected technology areas of your choice.
Admissions Requirements
Admission to this program requires you to have an undergraduate degree in computer science , mathematics , science, or engineering , with a superior undergraduate record from an accredited institution. Applicants with degrees in other fields are considered individually for admission.
Find out more about general Admission Requirements .
- At least 1 year of university-level science.
- A working knowledge of a high-level, general-purpose programming language (preferably C++).
- A basic understanding of computer fundamentals such as computer organization and operation, data structures, and computer architecture.
- Demonstrated ability to communicate in written and spoken English is required for regular status (see below). Foreign students and others for whom English is a second language may be required to undertake preparatory work to improve their language skills.
Students entering with a bachelor’s in computer science or with a bachelor’s in a technical area and a strong minor in computer science should be able to satisfy entrance requirements for the master’s degree program. Generally, entering students are expected to know mathematics through calculus.
Admission with advanced standing is accepted in accordance with the School of Engineering regulations. A maximum of 9 credits may be applied to the M.S. degree from previous graduate work at an acceptable institution.
Students who are lacking the computer science skills needed for the Computer Science Master's Degree are encouraged to enroll into the preparatory Bridge to NYU Tandon program . Pending satisfactory completion, students would be considered for admission towards the master's degree program.
Applicants who satisfy one of the following conditions are not required but encouraged to submit a GRE score:
- M.S. Applicants without a Computer Science or similar background who successfully complete the NYU Tandon Bridge .
- Applicant completes 9 credits under Visiting Student Registration from an approved list of CSE courses and maintains an average grade of B+ or better.
- Applicant has a B.A. or B.S. degree in computer science or computer engineering from NYU, with a GPA of 3.0 or higher.
Preparatory Course
The 100% online NYU Tandon Bridge course prepares students without a Computer Science degree or other substantial programming experience to apply for select NYU Tandon master’s degree programs. In the course, students will learn computer science fundamentals and programming with C++.
Students’ performance in the Bridge will count toward their master’s degree application decisions. The Bridge is a non-credit certificate course, and those who complete the Bridge with a final grade of C or above will earn a Certificate of Completion, and those who earn a B+ or above will receive a Certificate of Completion with Distinction. Note: regardless of performance, successful completion of the Bridge course does not guarantee admission to any academic program.
The NYU Tandon Bridge course is taught by faculty members of the Computer Science department at the NYU Tandon School of Engineering, aided by NYU Tandon Graduate student teaching assistants. Students will participate in interactive online modules, live webinars, assignments, and tests.
Go to: Computer Science Bridge Program
Quick Links
- Graduate Admissions
Program Director

Yi-Jen Chiang
Program admissions chair.
Edward Wong

Andres Zarta
Skip to Content
- News & Events

Request More Information
Enroll in the For-Credit Experience
MS-CS on Coursera
Join the Master of Science in Computer Science (MS-CS) on Coursera, an advanced degree program offered by the University of Colorado Boulder and hosted online through Coursera’s learning platform. Take a broad approach to studying computer science that directly reflects a career in the field. Explore coursework that represents fast-changing developments in fields like AI and robotics, with opportunities to specialize in other job-relevant subjects through interdisciplinary electives in electrical engineering, engineering management, and data science. Admission to this fully accredited program is based on your performance in three preliminary courses, not your academic history.
No application, ever―just start learning and show us you are ready
Simply pass a three-course pathway with a B or better in each course to earn admission. No bachelor’s degree or extensive work experience required.
Courses led by research experts at a top 1% global university
Jumpstart your career with industry-driven courses led by the same award-winning faculty teaching on campus.
No commitment required―enroll now to preview course content
Learn what to expect in the non-credit experience. Upgrade to for-credit at any time for additional benefits & support.
Flexible enrollment options designed to fit your budget and schedule
Enjoy the convenience of targeted courses, short 8-week sessions, and pay-as-you-go tuition.
Access a top-quality degree regardless of your academic background.
Gain acceptance into the program regardless of your educational background or professional experience. Complete a three-course pathway in either algorithms or software architecture on Coursera with at least a B in each course and you will be accepted—even if you do not hold a bachelor’s degree. No transcripts or applications required! Because pathway courses count as part of the required curriculum, you make direct progress on your degree as you work toward admission.
Upgrade your resume with trusted credentials. Graduates of this fully accredited program get the same diploma as our students on campus. The graduate-level coursework is rigorous, and there are no designations saying "online" or "Coursera" on the diploma.
Choose a global university that is ranked among the finest in the world. The Center for World University Rankings (CWUR) placed CU Boulder in the top 1% on its 2021-22 list of global universities, at 68th overall and 38th nationally.
Learn how to get started.
Learn from leading researchers who have critical applied experience.
Advance your career with courses aligned to industry best practices. Learn how to combine theoretical knowledge and technical experience from instructors connected to multinational companies, small businesses, laboratory centers, and applied research projects. You will complete practical, hands-on projects using cloud-based programming environments and Jupyter Notebooks.
The MS-CS on Coursera's broad curriculum directly reflects a career in the field of computer science. You will complete 15 credits of breadth coursework across five full specializations in algorithms, software architecture, machine learning, ethics and computing, and systems. You will also choose 15 credits of elective courses across a variety of topic areas, including human-computer interaction, autonomous systems, data mining, natural language processing, and more – you can even explore courses from other CU degrees on Coursera. This is a non-thesis degree.
Learn more about the value of our curriculum from Dr. Bobby Schnabel describing the Computing, Ethics, and Society specialization in the CU Boulder College of Engineeringand and Applied Sciences newsletter.
See the curriculum.
Preview courses before you commit to the degree.
You can enroll in non-credit versions of the MS-CS curriculum right away. Upgrade and pay tuition at any time during your learning journey and bring your progress with you to the for-credit experience. You must complete additional material and assessments to earn credit; this material is only available after you pay tuition.
Explore the non-credit experience.
- Undergraduate Programs
- Graduate Programs
- Bachelor of Science Post-Baccalaureate
- How It Works
- Student Handbook
- Current Students
Master of Science in Computer Science on Coursera
Quick facts.
- Fully accredited graduate program
- Same diploma as students on campus
- Pay-as-you-go tuition & no hidden fees
- Six 8-week sessions per year
- Weekly office hours with course facilitators
- Ability to earn a certificate on the way to your degree
Enroll in the For-Credit Experience
Apply Visit Give
Departments
- Ann and H.J. Smead Aerospace Engineering Sciences
- Chemical & Biological Engineering
- Civil, Environmental & Architectural Engineering
- Computer Science
- Electrical, Computer & Energy Engineering
- Paul M. Rady Mechanical Engineering
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomedical Engineering
- Creative Technology & Design
- Engineering Education
- Engineering Management
- Engineering Physics
- Integrated Design Engineering
- Environmental Engineering
- Materials Science & Engineering
Affiliates & Partners
- ATLAS Institute
- BOLD Center
- Colorado Mesa University
- Colorado Space Grant Consortium
- Discovery Learning
- Engineering Honors
- Engineering Leadership
- Entrepreneurship
- Herbst Program for Engineering, Ethics & Society
- Integrated Teaching and Learning
- Global Engineering
- Mortenson Center for Global Engineering
- National Center for Women & Information Technology
- Western Colorado University

College of Arts & Sciences
M.S. Program
Admission to the m.s. program.
The M.S. program accepts applications annually to begin study in either the Fall or Spring semester. Information about the application process may be found below or by visiting our FAQ for Prospective Students . Applications are accepted online beginning in mid-July. Visit the Graduate School application page to begin an application.
- Applications for Spring program start : The final submission deadline is October 1 . The admitted students are notified in early November.
- Applications for Fall program start : Priority submission deadline is January 15 , and the final submission deadline: April 1 . The admissions committee begins reviewing applications after the priority deadline. Generally, applications received before March 1 will receive an admission decision by April 1.
Admission Requirements
Successful M.S. applications will hold a B.S. in computer science or a closely-related field or will have significant coursework or professional experience in computer science. A background in computer science topics including data structures and algorithms, hardware and architecture, and computer programming; as well as mathematics including discrete mathematics, probability and statistics, linear algebra, and calculus are expected.
All applicants must meet the requirements specified by the Graduate School in their application FAQ . Additionally, our program requires a TOEFL score of at least 90 or an IELTS score of at least 7.0 to apply.
M.S. Program Requirements and Milestones
The Computer Science M.S. program provides students with two options to deepen their understanding of computer science topics: the coursework option and the thesis option. All M.S. students are initially admitted under the coursework option but may elect the thesis option by selecting an M.S. thesis adviser.
The information below is an overview of these requirements. The official requirements, procedures, and policies are kept in the Graduate Student Handbook .
M.S. Coursework Option
Students electing the M.S. coursework option must complete 30 credits (10 courses) at the graduate level. The coursework includes taking a graduate-level algorithms course as well as a course chosen from the “systems” set detailed on this page.
Students typically complete the M.S. coursework option in two years; the timeline below is based on a typical two-year course of study. Note: Georgetown considers 9 credits (3 courses) to be a full-time course load for enrollment and visa purposes.
M.S. Thesis Option
Students electing the M.S. thesis option must complete 24 credits (8 courses) at the graduate level. The coursework includes a graduate-level algorithms course as well as a course chosen from the “systems” set detailed on this page. In addition, M.S. thesis students must write and defend a master’s thesis containing novel research.
Students typically complete the M.S. thesis option in two years; the timeline below is based on a typical two-year course of study.
Elective Coursework
M.S. students may select as their elective coursework any CS course taught at the graduate level. The department regularly offers courses across multiple disciplines of computer science theory, computer and network security, and data management and processing.
Students may also elect to take up to two external electives as part of their coursework, subject to the approval of the department graduate committee. These external electives may be chosen from graduate-level courses in other departments at Georgetown or may be taken at other D.C. area universities as part of the Consortium of Universities of the Washington Metropolitan Area .

Khoury College of Computer Sciences
Computer science.
Are you a software engineer, software development engineer, related computer science professional, or recent CS graduate looking to make your next career move? Prepare to take on new projects, learn new technologies, hold a leadership role, and help advance the field of computer science in a program known for industry connections and diverse work opportunities.
Experience more. The Master of Science in Computer Science (MSCS) at Northeastern University’s Khoury College of Computer Sciences prepares computer science (CS) professionals in approximately two years to tackle diverse challenges and build the latest technologies. Refine your knowledge and gain expertise in three breadth areas: 1) systems and software, 2) theory and security, and 3) artificial intelligence and data science.
- Prepare for more complex roles, research, or specialized positions with your current company—or take part in experiential co-op and internship opportunities with one of our 700+ partner companies
- Increase your earning potential with a degree from Northeastern, an R1 research institution
- Contribute to the dynamic field of CS with innovative project work across industries
Develop your professional network in Boston
Northeastern’s storied Boston campus, established in 1898, gives you direct access to cutting-edge research and projects in collaboration with other colleges at Northeastern—and other top universities, businesses, governmental agencies, laboratories, and more.
Boston has a rich research and development environment. The city leads in healthcare, education, finance, business, biotechnology, and the life sciences. The combination of internationally recognized institutes and centers in the #5 Best Startup Ecosystem in the World creates exciting opportunities for graduates (Startup Genome, 2021).
Learn More About the Boston Campus
More Details
Unique features.
- Opportunities for paid, full-time co-ops or internships with diverse organizations like Amazon, AWS, Google, Fidelity, Outcomes4Me, Boston Children’s Hospital, Vor Biophamra, and more
- Work with world-leading multinational corporations, creative startups disrupting entire industries, renowned medical institutions developing breakthrough technologies, and governmental organizations working on matters of national security
- Interdisciplinary curriculum incorporates elements of web development, network security, and machine learning
- Faculty with connections to top Boston companies like Action for Boston Community Development, The Jackson Laboratory, Anti-Defamation League, Massachusetts General Hospital, Raytheon, Intel, PwC, Fire Eye, and more
Career Outlook
Positions requiring a master’s in computer science are expected to have a job growth rate of +22%, compared to the average job growth rate of 7–8% (2020–2030, USBLS).
The top employer of graduates of the MSCS program is Amazon. Our graduates also find employment with companies like Google, Meta, Microsoft, F5, Nordstrom, GoDaddy, McKinsey, Zillow, Snowflake, Salesforce, Carfax, and Coinbase.
MSCS program graduates hold positions such as:
- Software development engineer
- Software engineer
- Full-stack developer
Industry-aligned Program
Develop expertise across three breadth areas: systems and software, theory and security, and artificial intelligence and data science. You’ll choose from a range of electives to tailor your program to your interests.
Master’s core courses:
- Programming Design Paradigm
Electives in a range of areas:
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer-Human Interface
- Data Science
- Game Design
- Information Security
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Theory View full curriculum
Testimonials
– amit shesh, professor and director of mscs boston, looking for something different.
A graduate degree or certificate from Northeastern—a top-ranked university—can accelerate your career through rigorous academic coursework and hands-on professional experience in the area of your interest. Apply now—and take your career to the next level.
Program Costs
Paying for the MSCS program We offer a variety of resources, including scholarships and assistantships.
How to Apply Learn more about the application process and requirements.
Requirements
- Online application and application fee
- PDF or scanned copies of unofficial undergraduate transcripts; you can submit official transcripts from colleges/universities attended at the time of admission
- Statement of purpose that should include career goals and expected outcomes and benefits from the program
- Recent professional resumé listing detailed position responsibilities
- Three letters of recommendation
- GPA minimums: 3.0 on a 4.0 scale, 8.0 on a 10.0 scale, or 80 on a 100 scale
- Official TOEFL (100 minimum) or IELTS (7.5 minimum) examination scores (international students only)
- GRE Optional
Questions?: [email protected]
View full application instructions .
Are You an International Student? Find out what additional documents are required to apply.
Global Engagement Learn how our teaching and research benefit from a worldwide network of students, faculty, and industry partners.
Admissions Dates
Applicants must submit the online application and all required admission materials no later than the stated deadlines to be considered for admission. Admissions decisions are made on a rolling basis.
Industry-aligned courses for in-demand careers.
For 100+ years, we’ve designed our programs with one thing in mind—your success. Explore the current program requirements and course descriptions, all designed to meet today’s industry needs and must-have skills.
View curriculum
Your curriculum is designed to give you advanced theoretical knowledge that you can immediately apply to real-world situations. Experiential learning takes place in the form of project work, research opportunities, and paid co-op and internship opportunities.
Work in software development at a top tech firm. Explore the junctions of computer science and bioinformatics, economy, education, language, defense, and more. Think about AI in the context of human-centered computing and apply it to assistive technologies. Research neural networks with the capability to calculate the origins of an epidemic. Make a difference in your work.
Experiential Learning in Boston
Research at Northeastern
Get a roadmap to reach your goals
Your experiential opportunities are closely integrated with both your course curriculum and the advising system. Our career services staff will support you in finding and succeeding in your experiences. A team of academic advisors will also help guide you.
Our Faculty
Northeastern University faculty represents a broad cross-section of professional practices and fields, including finance, education, biomedical science, management, and the U.S. military. They serve as mentors and advisors and collaborate alongside you to solve the most pressing global challenges facing established and emerging markets.

Kathleen Durant

By enrolling in Northeastern, you’ll gain access to students at 13 campus locations, 300,000+ alumni, and 3,000 employer partners worldwide. Our global university system provides students unique opportunities to think locally and act globally while serving as a platform for scaling ideas, talent, and solutions.
Related Articles

How to Choose a Computer Science Specialization

Northeastern’s MS in Computer Science Curriculum

Is a Master’s in Computer Science Worth the Investment?
- Academics /
Computer Science Master’s Degree Program
Develop advanced technical skills and knowledge to solve real-world challenges.
Online Courses
11 out of 12 total courses
On-Campus Experience
One 3-week summer course
$3,220 per course
Program Overview
The demand for skilled computer scientists is predicted to grow by 21% in the coming years, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. A graduate degree in computer science equips you to stay ahead of the curve and meet the computing challenges of today and tomorrow.
In our rigorous master’s degree program, you’ll focus on advanced computer science theories and applications. Learning from expert faculty from Harvard and industry, you’ll acquire the skills to design, develop, and maintain complex computer and software systems.
Program Benefits
Customizable online curriculum that can be completed part time
Expert instruction from Harvard faculty and industry professionals
Personalized academic and career advising
Real-world capstone experience with industry partners
Entrepreneurial opportunities through Harvard Innovation Labs
Harvard Alumni Association membership upon graduation
Customizable Course Curriculum
Our curriculum is flexible in pace and customizable by design. You can study part time, choosing courses that fit your schedule and align with your professional goals. In the program, you’ll experience the convenience of online learning and the immersive benefits of learning in person.
As you work through the 12-course program, you’ll take core courses in essential computer science topics like data structure, algorithms, and programming languages.
You’ll choose elective courses in topics that interest you most, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, software engineering, or cloud computing.
Learning is hands-on. Classes feature collaborative activities like online discussions and group projects. Through your capstone project, you will have the opportunity to work innovatively and creatively, applying the skills you’ve gained to a real-world challenge.
11 Online Courses
- Primarily asynchronous
- Fall, spring, January session, and summer options
Prepare for your capstone project in a 3-week precapstone course in the summer.
Capstone Project
Collaborate with peers and an industry partner on a project that addresses a real-world challenge.
The path to your degree begins before you apply to the program.
First, you’ll register for and complete 2 required courses, earning at least a B in each. These courses provide a foundation in the principles of computer science, programming languages, and data structures. They are also an investment in your studies, counting toward your degree.
Getting Started
We invite you to explore degree requirements, confirm your initial eligibility, and learn more about our unique “earn your way in” admissions process.
A Faculty of Computer Science Experts
Studying at Harvard Extension School means learning from the world’s best. Our computer science instructors are renowned experts in their field and bring a genuine passion for teaching, with students giving our faculty an average rating of 4.6 out of 5.
Rebecca Nesson
Dean for Academic Programs and Associate Senior Lecturer on Computer Science, Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences
Henry H. Leitner
Senior Lecturer on Computer Science, Harvard University
David J. Malan
Gordon McKay Professor of the Practice of Computer Science, Harvard University
Career Outcomes
Graduates of our Computer Science Master’s Program are well-prepared for careers in computer science, software engineering, software development, systems, or software architecture.
Potential job titles include:
- Computer Scientist
- Software Engineer
- Software Developer
- Systems Architect
- Software Architect
Career Advising and Mentorship
Whatever your career goals, we’re here to support you. Harvard’s Mignone Center for Career Success offers career advising, employment opportunities, Harvard alumni mentor connections, and career fairs like the Harvard Startup Career Fair and the Data Analytics, Science, and Technology Fair held on campus.
Your Harvard University Degree
Upon successful completion of the required curriculum, you will earn the Master of Liberal Arts (ALM) in Extension Studies, Field: Computer Science.
Expand Your Connections: the Harvard Alumni Network
As a graduate, you’ll become a member of the worldwide Harvard Alumni Association (400,000+ members) and Harvard Extension Alumni Association (29,000+ members).
Tuition & Financial Aid
Affordability is core to our mission. When compared to our continuing education peers, it’s a fraction of the cost.
After admission, you may qualify for financial aid . Typically, eligible students receive grant funds to cover a portion of tuition costs each term, in addition to federal financial aid options.
Coffee Chat: All About Technology Programs at HES
Are you interested in learning more about technology graduate degree programs at Harvard Extension School? Attendees joined us for an informational webinar where they had the opportunity to connect with the program director, academic advisor, and alumni.
How long will it take to earn the computer science master’s degree?
Program length is ordinarily anywhere between 2 and 5 years. It depends on your preferred pace and the number of courses you want to take each semester.
For an accelerated journey, we offer year round study, where you can take courses in fall, January, spring, and summer.
While we don’t require you to register for a certain number of courses each semester, you cannot take longer than 5 years to complete the degree.
How do I know if the computer science graduate program is right for me?
Harvard Extension School does not require any specific skills prior to applying, but because this is an advanced degree, it is helpful to have an undergraduate degree in computer science, mathematics, or a related field, as well as some work experience in a technical field. Proficiency in programming languages — Java, Python, C++ — is recommended, and you should possess excellent problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and critical thinking abilities.
How will the computer science graduate program help me improve my career?
A graduate degree in computer science could accelerate your career in several ways — most notably in increased earning potential due to your advanced skills and knowledge. According to recent numbers from Payscale, an individual with a bachelor’s degree in computer science makes an average base salary of $72,000/year. In contrast, a professional with a master’s degree in computer science makes an average base salary of $101,000/year.
Related Programs
- Cybersecurity Master’s Degree Program
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

Program Description
The Master of Science with a Major in Computer Science (MSCS) is a rigorous degree program that includes advanced coursework and research activities on a wide range of computer science subjects such as artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, databases, data science, human-computer interaction, networking, scientific computing, and high-performance computing. MSCS program is intended for the students pursuing professional careers in computing. Students in the MSCS program will learn how to solve real-world problems with advanced computing skills and mathematical knowledge.
The MSCS program serves as both a research program training computer scientists and a professional program training industry practitioners. In order to serve these two audiences, the program provides the following two program models. MSCS students can choose any one of these two models to pursue their MSCS degrees.
MSCS Program Model Options:
- Thesis Model : The thesis model is designed for students who plan to conduct computer science research under the supervision of faculty members in selected areas. It consists of a 6 hours program core, 6 hours thesis (CS 7999), 3 hours research (CS 7998), and 15 hours elective courses. Students choose this model should work with a faculty thesis advisor. Thesis needs to be defended and approved by a thesis committee that consists of at least 3 members.
- Professional Model : The professional model is designed for students who plan to advance their knowledge in computer science and apply their knowledge to industrial applications. It consists of 6 hours program core, and 24 hours elective courses.
The MSCS program features excellent curriculum that blends theoretic foundations of computer science with the state-of-the-art computing technologies. Major areas of study include data science, cyber and network security, high performance computing, and artificial intelligence. The program provides students with opportunities in computer science research, advanced project development, and industrial internship. The MSCS program has a number of premium features, including the integrated use of distance learning technology with intensive faculty-student interactions. Students have a choice of attending class on-campus, remote but “live” at the assigned class time, or remote and viewing the recorded lecture at their convenience. Moreover, the MSCS program is structured with both full-time and part-time study options in order to provide students with maximum flexibility of study. Outstanding students may apply for graduate research assistantships, subject to funding availability.

return to top ↑
Admission, Enrollment, and Graduation Policies
Admission requirements.
The following are requirements beyond the general Admissions requirements.
- Resume/Vita required.
- Two letters of recommendation (Optional- strongly recommended).
- Undergraduate degree from an accredited university.
- 2.75 Minimum GPA for students with an undergraduate degree in a computing discipline, OR a noncomputing discipline. Lower GPA is considered on a case-by-case basis for those who show extraordinary background. Students with an undergraduate degree in a noncomputing discipline may need some foundation courses. If any of the following foundation courses have not been taken in another program, these must be completed at the earliest.
- CS 5000
- CS 5020
- CS 5040
- CS 5070
Streamlined Application Process:
Students who meet the following qualification are eligible for a streamlines application process. To qualify students must:
- Be a current Kennesaw State University student majoring in one of the College of Computing and Software Engineering’s undergraduate programs.
- Have an active petition to graduate in that major
- Have a 3.5 GPA or higher upon graduation and the recommendation of the undergraduate coordinator
- Students who meet these criteria are not required to take the GRE nor submit secondary documentation that includes a resumé or vita, statement of purpose, or letters of recommendation.
Students who wish to apply for admission into a different major may be required to take additional course work. Please contact the program coordinator of that program.
Transfer Credits
A student may transfer a maximum of six semester hours of graduate courses. The transfer of credit for course work completed at another institution will be approved only under the following conditions:
- A minimum grade of “B” was received in the course;
- The content of the course corresponds to that of a course required or permitted in the student’s program at Kennesaw State University;
- The credit to be considered for transfer will not be more than six years old at the time the student enters KSU.
A request for consideration of transfer credit must be submitted to the MSCS program director by the student during the first semester of residence. The request must indicate the specific course(s) for which transfer credit is sought. A copy of the other institution’s transcript and a course description from the catalog must be submitted.
Graduation Requirements
Each candidate must petition to graduate at least one semester prior to completion of program requirements. To complete the petition, students must log into their Owl Express account, click on the “Student Records” tab and select Petition to Graduate. For more information, please view the corresponding section of Academic Policies: 5.0 PROGRAM REQUIREMENTS & GRADUATION .
Program Course Requirements
Required common core (6 credit hours).
- CS 6041:Theory of Computation
- CS 6045:Advanced Algorithms
Program Models (24 Credit Hours)
Thesis model requirements, required courses (9 credit hours).
- CS 7998:Research in Computer Science
- CS 7999:Thesis *
* Repeat for a total of 6 credits
Electives (15 Credit Hours)
Students must complete 15 credit hours, at least 12 credit hours must be from 7000-level or higher. Students may choose to complete one concentration area or a combination of courses listed in Elective Choices below.
Professional Model Requirements
Students must complete 24 credit hours, at least 18 credit hours must be from 7000-level or higher, excluding CS 7998 and CS 7999 . Students may choose to complete one concentration area or a combination of courses listed in Elective Choices below.
Elective Choices
Students may choose to complete one concentration area or any of the following courses:
- Any CS 6000-, 7000-, or 8000-level course
- CSE 7983:Graduate Internship
- DS 7900:Applied Analytics Project Course (One time only)
Artificial Intelligence Concentration
Required courses.
- CS 7267:Machine Learning
- CS 7347:Natural Language Processing
- CS 7375:Artificial Intelligence
Elective Options
Students pursuing this concentration should fill remaining electives with the options below:
- CS 7075:Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
- CS 7253:Graph Algorithms
- CS 7263:Information Retrieval
- CS 7357:Neural Networks and Deep Learning
- CS 7367:Machine Vision
- CS 7990:Special Topics in Computer Science
- CS 7992:Directed Studies (One time only)
Data Science Concentration
- CS 7265:Big Data Analytics
- STAT 8240:Data Mining I
- CS 6025:Operating Systems
- CS 6070:Database Systems
- CS 7050:Data Warehousing and Mining
- CS 7125:Cloud Computing
- CS 7260:Advanced Database Systems
- STAT 7210:Applied Regression Analysis
- STAT 8250:Data Mining II
- MATH 8020:Graph Theory
- MATH 8030:Applied Discrete & Combinatorial Mathematics for Data Analysts
Cyber and Network Security Concentration
- CS 6027:Computer Networks
- CS 7530:Advanced Cryptography
- CS 7540:Network Security
- CS 7535:Software and OS Security
- CS 7537:Digital Forensics
- CS 7545:AI for Security and Privacy
- CS 7550:Internet of Things Security
Program Total (30 Credit Hours)

M.S. Degree
Master of science in computer science degree program.
The Master of Science in Computer Science degree prepares students to do meaningful research and to acquire vital skills and insights for solving some of the world’s most complex technological challenges.
- Admission Requirements
In addition to the admission requirements stated above, applicants are expected to demonstrate proficiency at the undergraduate level in four fundamental areas of computer science, and mathematics. The specified UC Davis courses exemplify the material: ♦ Computer Architecture -- ECS 154A (Computer Architecture) ♦ Operating Systems -- ECS 150 (Operating Systems and System Programming) ♦ Programming Languages -- ECS 140A (Programming Languages) ♦ Theoretical Foundations -- ECS 120 (Theory of Computation) or ECS 122A (Algorithm Design and Analysis) ♦ Mathematical Foundations -- ECS 132 (Probability and Statistical Modeling for Computer Science) or MAT 135A (Probability) or STA 131A (Introduction to Probability Theory), and one additional upper-division mathematics course.
These are referred to as the undergraduate proficiency requirements. A grade of B or higher is required for each course used to satisfy these requirements. Students may be admitted with one or more deficiencies in the undergraduate proficiency requirements. It is expected that the student will complete the undergraduate proficiency requirements by the end of their master degree.
- M.S. Plan I and Plan II
The Graduate Program of Computer Science offers two plans for the MS degree with respective capstone requirements. Plan I requires successful completion of a thesis, while Plan II requires successful completion of either a project or a master exam. Students should decide, in consultation with graduate group faculty, which option best suits their individual goals.
All options require 36 units of upper division and graduate coursework. At most 4 of these units may be from upper division courses. The following table summarizes the specific requirements for the thesis, project, and exam options.
Two important notes regarding the above table:
1. Note that while the allowed ECS 299 units may be counted toward the 36 units requirement, ECS 290, 293A, 298, and 299 cannot be counted toward the required graduate courses. A grade of B or better must be obtained in all coursework used to satisfy degree requirements. 2. With respect to the third column (Number of graduate courses required), note that one course of at most 4 units can be a UC Davis upper-division undergraduate course that was completed to satisfy the Undergraduate Proficiency Requirements.
Course Requirements
The courses a student will use in satisfaction of the 36 unit course requirement must be approved by the student’s Thesis Advisor or Project Advisor, or by a Graduate Advisor. A student must have a GPA of 3.0 for the MS degree to be awarded, and a B or better in all coursework used to satisfy the degree requirements. Full-time students must enroll in a minimum of 12 units per quarter. As per UC regulations, students may not enroll in more than 12 units of graduate level courses, nor more than 16 units of combined undergraduate and graduate level courses. The Core Area requirement requires the demonstration of proficiency at the graduate level in three of four specified areas: Architecture, Systems, Theory and Applications.
A student can satisfy the Core Area requirements in one of the following ways:
♦ Completing a Core course in the area with a grade of B or better for Thesis option (Plan I) or Project option (Plan II), and A- or better for Exam option (Plan II) . ♦ By taking a similar graduate course at another institution and earned a grade of B or better for Thesis option (Plan I) or Project option (Plan II) and A- or better for Exam option (Plan II). The student must file a form with the required information and attach the course syllabus and the official transcript indicating the grade received. A Graduate Advisor must review and approve this option. The following list shows the Core classes in each of the four areas: ♦ Architecture Core -- ECS 201A Advanced Computer Architecture; ECS 201C Parallel Architectures; EEC 270 Computer Architecture. ♦ Systems Core -- ECS 240 Programming Languages; ECS 251 Operating Systems; ECS 260 Software Engineering. ♦ Theory Core -- ECS 220 Theory of Computation; ECS 222A Design and Analysis of Algorithms. ♦ Applications Core -- ECS 230 Applied Numerical Linear Algebra; ECS 231 Large-scale Scientific Computation; ECS 234 Computational Functional Genomics; ECS 235A Computer and Information Security; ECS 236 Computer Security Intrusion Detection Based Approach; ECS 252 Computer Networks; ECS 256 Performance Evaluation; ECS 265 Distributed Database Systems; ECS 267 Wide-Area Distributed Information Systems; ECS 268 Scientific Data and Workflow Management; ECS 270 Artificial Intelligence; ECS 271 Machine Learning and Discovery; ECS 272 Information Visualization; ECS 274 Automated Deduction; ECS 275A Advanced Computer Graphics; ECS 276 Advanced Volume Visualization; ECS 277 Advanced Visualization; ECS 278 Computer-Aided Geometric Design; ECS 279 Topics in Character Animation.
- Special Requirements
- Not applicable.
Admissions Committee -- Completed applications are evaluated by the Admissions Committee, with the assistance of other faculty in the Graduate Group. The Admissions Committee consists of six Graduate Group faculty. Based on a review of the entire application, a recommendation is made to accept or decline the applicant’s request for admission. The recommendation is forwarded to the Dean of Graduate Studies for final approval of admission. Notification of admissions decisions will be sent by Graduate Studies. Applications are accepted from September (when the admission system opens) through January 15 for the next Fall-entering class.
Graduate Advisors Committee -- The Graduate Advisors Committee is composed of GGCS faculty members appointed by Graduate Studies. Every student who does not have a Thesis Advisor or Project Advisor will be assigned a Graduate Advisor from the Graduate Advisors Committee. Until a student has a Thesis Advisor or Project Advisor, the assigned Graduate Advisor will monitor the progress of the student and provide guidance on his/her academic program. Each GGCS graduate student is responsible for meeting with his or her Graduate Advisor at least once per quarter.
Thesis Committee -- The student’s Thesis Advisor, in consultation with the student, nominates two additional GGCS faculty members to serve on the Thesis Committee. These nominations are submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies for formal appointment in accordance with Graduate Council policy. The Thesis Advisor serves as Chair of the Thesis Committee. At least two members of this committee must be members of the Academic Senate of the University of California, and a least two members of this committee must be GGCS members. The thesis must be approved by all three members of the Thesis Committee. Project Committee -- The student’s Project Advisor nominates two additional faculty members to serve on the Project Committee. This nomination is submitted to the Graduate Advisors Committee for approval. The responsibility of the Project Committee is to supervise and evaluate the student’s project. A project must be approved by all members of the committee.
Master's Exam Committee -- For students taking the Master’s Exam, the Graduate Advisors Committee, after consultation with the student, nominates three faculty members to serve on the Master’s Exam Committee. The majority of this committee must be GGCS members. The responsibility of this committee is to give the Master’s Exam. The format of the exam is described in Section 8c.
- Advising Structure and Mentoring
A student’s Thesis Advisor or Project Advisor supervises his/her thesis or project, and serves as Chair of the corresponding committee. A student’s Graduate Advisor serves as a resource for information on academic requirements, policies, and procedures in the absence of a Thesis Advisor or Project Advisor. The Graduate Program Coordinator assists students with appointments, requirements, university policies, and in identifying a Thesis Advisor or Project Advisor. The Mentoring Guidelines can be found in the graduate student handbook .
- Advancement to Candidacy
After completing at least one-half the course requirements for the degree, a student must file an application for Advancement to Candidacy. A student must file for candidacy at least one full quarter before completion of all degree requirements and before going on filing fee status. The Candidacy for the Degree of Master form can be found online . A completed form includes a list of courses the student will take to complete degree requirements. Students must have their Thesis Advisor, Project Advisor, or Graduate Advisor sign the candidacy form. If the candidacy is approved, the Office of Graduate Studies will send a copy to the student, his Thesis, Project, or Graduate Advisor, and the Graduate Program Coordinator. If the Office of Graduate Studies determines that a student is not eligible for advancement, the GGCS and the student will be told the reasons for the application’s deferral. Some reasons for deferring an application include a grade point average below 3.0, outstanding “I” grades in required courses, or insufficient units. If changes must be made to the student’s course plan after s/he has advanced to candidacy, a Graduate Advisor must recommend these changes to Graduate Studies.
- Requirements for the Thesis, Project and Master's Examination
Thesis Research for the Master’s thesis is to be carried out under the supervision of a GGCS faculty member of and must represent an original contribution to knowledge in the field. A Master’s thesis is usually based on 6 to 12 units of research carried out under the 299 course number. The thesis should demonstrate the student’s proficiency in research methods and scientific analysis, and a thorough knowledge of the state of the art in the student’s chosen area. A Master’s thesis is a description of an original technical or research contribution of limited scope, or an advanced design study. The thesis research must be conducted while the student is enrolled in the program.
The thesis is submitted to the Thesis Committee at least one month before the student plans to make requested revisions. All Thesis Committee members must approve the thesis and sign the title page before the thesis is submitted to Graduate Studies for final approval. Should the committee determine that the thesis is unacceptable, even with substantial revisions, the program may recommend the student for disqualification from the program to the Dean of Graduate Studies.
The student and Thesis Advisor must meet at least once a quarter with the other two members of the Thesis Committee to discuss progress and any changes in research objectives. The thesis must be filed in a quarter in which the student is registered or on filing fee. Instructions on preparation of the thesis and a schedule of dates for filing the thesis in final form are available from Graduate Studies; the dates are also printed in the UC Davis General Catalog and in the Class Schedule and Registration Guide issued each quarter.
Project A project is carried out under the supervision of the faculty member who serves as Project Advisor. The topic and extent of the project is determined by the faculty member in consultation with the student. A typical project involves the practical solution (implementation) of a software system or an experimental study of a computer hardware/software design.
The Project Committee specifies the project requirements, which may include the delivery of a software prototype system, an interactive demonstration, a written report, and/or an oral presentation of the study. All committee members must approve the project. The Master’s Report Form is then signed by the Thesis Adviser and forwarded to the Office of Graduate Studies. Should the Project Committee determine that the project outcome is unacceptable, the program may recommend the student for disqualification from the program to the Dean of Graduate Studies. Available project topics are listed here .
Master’s Examination The examination is used to ensure that the student has acquired proficient knowledge in core and applied CS areas. The examination may be oral, written, or a combination of both, designated by the Exam Committee, with the objective to strengthen the student’s knowledge in selected core or applied CS areas that can best prepare the student for his/her professional career.
The examination may be taken once the student has completed required courses and advanced to candidacy. However, it is important that the timing of the exam satisfy the regulations as noted in the CCGA handbook (Appendix I, page 36), which indicates that the capstone requirement be completed at or near the end of the coursework for the Master’s degree. A student is allowed to repeat the Master’s Examination only once.
After passing the examination, a copy of the Master’s Report Form (which can be found here ) is signed by a GGCS Graduate Adviser and then forwarded to the Office of Graduate Studies. The deadlines for completing this requirement are listed each quarter in the campus General Catalog (available online or from the Bookstore).
If a student does not pass the exam on the first attempt, the Exam Committee may recommend that the student be reexamined one more time, but only if the Graduate Adviser Committee concurs with the Exam Committee. The examination may not be repeated more than once, and the student is not allowed to retake the exam on a different topic area or in a different category (i.e., switching to Project or Thesis). The Exam Committee provides information concerning the timing and format of a second exam if a student must retake the exam after failing part or the entire first exam. Please note that Graduate Studies requires the Exam Committee’s unanimous vote to pass a student on the exam. A student who does not pass on the second attempt will be recommended for disqualification from further graduate work in the program to the Dean of Graduate Studies.
For either Project or Examination, a candidate must be a registered student or on filing fee status at the time the program submits the form, with the exception of the summer period between the end of the Spring Quarter and the beginning of Fall Quarter. The Graduate Group must file the form with Graduate Studies within one week of the end of the quarter in which the student’s degree will be conferred.
- Normative Time to Degree
♦ Plan I -- It is expected that the student will complete the core area courses within the first 4 quarters of residence. It is expected that the student will complete the MS degree by the end of the seventh (7) quarter of residence, including all course requirements and the approval of the thesis. These deadlines may be extended only by approval of the Graduate Advisors Committee of the Graduate Group.
♦ Plan II -- It is expected that the student will complete the core area courses within the first 4 quarters of residence. It is expected that the student will complete all course work and project/examinations by the end of the 6th quarter of residence. These deadlines may be extended only by approval of the Graduate Advisors Committee of the Graduate Group.
- Sample Schedule (classes may vary and can be taken in different quarters than what is listed) and Sequence of Events
- THESIS ♦ Year 1 -- Fall: ECS 201A, ECS 293A, ECS 390, ECS 299 -- Winter: ECS 240, ECS 252, ECS 299 -- Spring: ECS 222A, ECS 231, ECS 299 ♦ Year 2 -- Fall: ECS 289G, ECS 299; Advance to candidacy -- Winter: ECS 299 -- Spring: ECS 299; Thesis completed PROJECT ♦ Year 1 -- Fall: ECS 201A, ECS 293A, ECS 390, ECS 299 -- Winter: ECS 240, ECS 252, ECS 299 -- Spring: ECS 222A, ECS 231, ECS 299 ♦ Year 2 -- Fall: ECS 289G, ECS 299 -- Winter: ECS 235A, ECS 299; Advance to candidacy -- Spring: ECS 299; Project completed EXAM ♦ Year 1 -- Fall: ECS 201A, ECS 293A, ECS 390, ECS 299 -- Winter: ECS 240, ECS 252, ECS 299 -- Spring: ECS 222A, ECS 231, ECS 299 ♦ Year 2 -- Fall: ECS 289G, ECS 265, ECS 299 -- Winter: ECS 235A, ECS 299; Advance to candidacy -- Spring: ECS 272, ECS 299; Exam completed Note that depending on the added workload, the student may need additional quarters to complete the exam/project/thesis.
- PELP, In Absentia and Filing Fee Status
- Information about PELP (Planned Educational Leave), In Absentia (reduced fees when conducting research out of California), and Filing Fee status can be found in the Graduate Student Guide .
Frequently Asked Master of Science in Computer Science Questions
- How do I get an M.S. in Computer Science?
This varies from student to student but the following list shows the right order of steps and approximate time frame to follow:
Thesis Option Time to Degree: 2 – 3 Years ♦ Complete undergraduate proficiency requirements ♦ Complete 6 graduate courses (includes core courses) ♦ Complete 12 Units of Research (ECS 299) ♦ Additional coursework to total 36 units (this can include up to 4 units of upper division coursework) ♦ Approved thesis Project Option Time to Degree: 2 Years ♦ Complete undergraduate proficiency requirements ♦ Complete 7 graduate courses (includes core courses) ♦ Complete 8 Units of research (ECS 299) ♦ Additional coursework to total 36 units (this can include up to 4 units of upper division coursework) ♦ Successful completion of project Exam Option Time to Degree: 2 Years ♦ Complete undergraduate proficiency requirements ♦ Complete 9 graduate courses (includes core courses) ♦ Additional coursework to total 36 units (this can include up to 4 units of upper division coursework) ♦ Successful completion of comprehensive exams
- What are the core area requirements?
The core area requirements include demonstrated proficiency in three of four areas of computer science at the graduate level: architecture, systems, theory, and applications.
- Can I take courses outside of Computer Science?
Yes, you can take courses outside of computer science. They must be graduate level (2XX) courses, that are 4 units each, related to computer science or your research, if you want them to count towards your degree requirements.
Are there any specific courses outside Computer Science that are recommended for a CS graduate student to take?
Yes, there are several courses that GGCS faculty suggest would be appropriate for CS graduate students:
- ♦ BST 227 - Machine Learning Genomics ♦ CMN 275Y - Computational Social Science
- ♦ DES 178 - Wearable Technologies ♦ EEC 244 - Intro to Neuroengineering ♦ EEC 270 - Computer Architecture ♦ EEC 273 - Networking Architecture & Resource Management ♦ MAE 207 - Engineering Experimentation & Uncertainty Analysis ♦ MAE 228 - Introduction to BioMEMS
- ♦ MAT 258A - Numerical Optimization
- ♦ MAT 258B - Discrete and Mixed-Integer Optimization
♦ STA 208 - Statistical Methods in Machine Learning ♦ STA 220 - Data & Web Technologies for Data Analysis ♦ STA 221 - Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing
NOTE: Please keep in mind the following policies related to coursework counting towards the degree requirements:
- What is the Thesis Option?
A master’s thesis is usually based on 6 to 9 units of laboratory research carried out under the 299 course number. The thesis should demonstrate the student’s proficiency in research methods and scientific analysis, and a thorough knowledge of the state of the art in the student’s chosen area. A master's thesis is a description of an original technical or research contribution of limited scope, or an advanced design project.
- How do I find an advisor to work on my thesis with?
You should have a general idea of the area that you want to do research in, as well as an idea of potential thesis topics. Once you know what area of computer science you want to work in, contact a faculty member in that area and see if they will be willing to advise you. Email tends to be one of the less effective ways to introduce yourself to a faculty member, though sometimes it is the only choice. Better ways of making an introduction are through taking a class with the faculty member, talking with them during office hours, or through seminars and colloquia.
- How do I file a completed thesis?
When your thesis is complete, it must first be approved by a committee of three members. The committee membership must be approved by Graduate Studies, through the Advancement to Candidacy form . The committee members are restricted by the requirements stated in the master’s degree requirements. After the thesis is approved, it must be filed with Graduate Studies. The process can be found on Graduate Studies’ website . The deadlines for filing can be found on Graduate Studies’ calendar .
- What is the Project Option?
A master project is based on laboratory research carried out under the 299 course number, similar to a thesis. The biggest difference between the two is that, unlike the thesis, the faculty member determines what is to be done in a project. A project should demonstrate the student’s proficiency in research methods and scientific analysis, and a thorough knowledge of the state of the art in the student’s chosen area. It tends to be of more limited scope than a thesis, and usually takes less time to complete than a thesis.
- How do I find a project to work on?
Some projects are advertised on this page . Other projects are advertised through the [email protected] listserv. Check your UC Davis email account for potential projects. If you are looking for a different project, faculty members may have other projects available. You should have a general idea of the area that you want to do research in. Once you know what area of computer science you want to work in, contact a faculty member in that area and see if they have any projects available. Email tends to be one of the less effective ways to introduce yourself to a faculty member, though sometimes it is the only choice. Better ways of making an introduction are through taking a class with the faculty member, talking with them during office hours, or through seminars and colloquia.
- What is the Project Committee?
The project committee consists of three members. The chair is the faculty advisor that you are working with. The second and third committee members are usually chosen by both the faculty advisor and student. All committee members need to sign off on a project for a student to graduate.
- How do I file a completed project?
Once you have completed your project, all members of your committee must sign off on the project. There is no need to turn the project into Graduate Studies. However your faculty advisor specifies to submit the project will suffice. After the project is approved, email the graduate student service advisors. Upon notice that the project was completed successfully, the student will be added to the degree conferral list.
- What is the Comprehensive Exam option?
Students who wish to develop breadth at the graduate level in computer science may choose the master examination option. The examination is used to ensure that the student has acquired proficient knowledge in the core areas. The examination may be taken once the student has completed required courses and advanced to candidacy. The possible exams follow the core areas: architecture, systems, theory, and applications. Students pick three of the four core areas that they have taken courses in to be examined in. The examination may be oral, written, or a combination of both, designated by the Exam Committee, with the objective to strengthen the student’s knowledge in selected core or applied CS areas that can best prepare the student for his/her professional career. A student is allowed to repeat the master’s examination only once.
- How do I set up a Comprehensive Exam?
Each quarter current students are sent a survey in which to complete where they can indicate if they wish to take the exams. Once this is confirmed, those students are sent instructions on how to complete the exams.
- How do I submit a completed Comprehensive Exam?
Once the exams are complete, the faculty administering the exams will send the result to the graduate student service advisors. Upon notice that the examination was completed successfully, the student will be added to the degree conferral list.

MASTER OF SCIENCE PROGRAM
The Master of Science (MS) program is intended for people who wish to broaden and deepen their understanding of Computer Science. Columbia University and the New York City environment provide excellent career opportunities in multiple industries.
The program provides a unique opportunity to develop leading-edge in-depth knowledge of specific computer science disciplines. The department currently offers concentration tracks covering eight such disciplines. MS students are encouraged to participate in state-of-the-art research with our research groups and labs.
REQUIREMENTS
- Complete a total of 30 points (Courses must be at the 4000 level or above)
- Maintain at least a 2.7 overall GPA. (No more than 1 D is permitted). The full Academic Standing Policy can be found here .
- Complete the Columbia Engineering Professional Development & Leadership (PDL) requirement (Not applicable to CVN students)
- Satisfy breadth requirements
- Take at least 6 points of technical courses at the 6000 level
- At most up to 3 points of your degree can be Non-CS/Non-track If they are deemed relevant to your track and sufficiently technical in nature. Submit the Non-CS/NonTrack form and the course syllabus to your CS Faculty Advisor for review
TRACK OPTIONS
Choose one of the tracks below, view each track webpage for details on requirements.
Columbia Video Network (CVN) students should also choose from one of the above tracks. For faculty advisement, please contact the assigned track advisors .
Cs ms faculty track advisors.
CS Faculty Advisors will be assigned after you select a track in Mice. If you do not yet have a Mice account but are a CS MS student, please contact [email protected] . Contact your Track Advisor to get special permission for any course not specifically approved on your CS track websites .
DEGREE PROGRESS CHECKLIST
Students should keep an updated copy of their Degree Progress Checklist on hand for any academic progress reviews with their Faculty and/or Admin advisor. This form will also be requested a few weeks before graduation to verify your program requirements are met.
If you are following the old MS track requirements, please refer to the old requirements page
Topics courses.
If you are interested in applying a specialized Topics in Computer Science courses (COMS 4995 or COMS 6998) to your Track electives, please view Topics Courses by Track Approval .
Students may take multiple sections of COMS 4995 and/or COMS 6998, as each topic title will vary by content each semester. If you aren’t sure if a course is the same, please email your MS Faculty Track Advisor.
No approval is required for the course to count as a General Elective.
A list of current and recent Topics Course Descriptions can be found here .
MS IN COMPUTER ENGINEERING
In addition to the Computer Science MS Program, we offer the Computer Engineering MS Program jointly with the Electrical Engineering Department. More information about the program can be found in the Computer Engineering section of the SEAS bulletin and on the Computer Engineering website .
DUAL MS IN JOURNALISM AND COMPUTER SCIENCE
Admitted students will enroll for a total of four semesters. In addition to taking classes already offered at the Journalism and Engineering schools, students will attend a seminar and workshop designed specifically for the dual degree program. The seminar will teach students about the impact of digital techniques on journalism; the emerging role of citizens in the news process; the influence of social media; and the changing business models that will support news gathering. In the workshop, students will use a hands-on approach to delve deeply into information design, focusing on how to build a site, section, or application from concept to development, ensuring the editorial goals are kept uppermost in mind. For more information, please visit the program website .
IMPORTANT AND USEFUL LINKS
- MS TRACK ADVISORS
- MS PROGRAM FAQ
- FIELDWORK/CPT FAQ
- COLUMBIA ENGINEERING RESEARCH OPPORTUNITIES
- COLUMBIA ENGINEERING PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT & LEADERSHIP (PDL) PROGRAM
- COMPUTER SCIENCE ACADEMIC HONESTY POLICY
ADMISSIONS INFORMATION
- SEAS Admissions contact: [email protected]
- CS Admissions contact: [email protected]
Updated 03/25/2024
Find open faculty positions here .

Computer Science at Columbia University
Upcoming events, last day of classes.
Monday 10:00 am
Foundation Models for Robotic Manipulation: Opportunities and Challenges
Wednesday 11:40 am
CSB 451 CS Auditorium
Yunzhu Li, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
Class Day Graduate Ceremony
Sunday 3:00 pm
South Lawn, Morningside Campus
Class Day Undergraduate Ceremony
Monday 11:45 am
In the News
Press mentions, dean boyce's statement on amicus brief filed by president bollinger.
President Bollinger announced that Columbia University along with many other academic institutions (sixteen, including all Ivy League universities) filed an amicus brief in the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of New York challenging the Executive Order regarding immigrants from seven designated countries and refugees. Among other things, the brief asserts that “safety and security concerns can be addressed in a manner that is consistent with the values America has always stood for, including the free flow of ideas and people across borders and the welcoming of immigrants to our universities.”
This recent action provides a moment for us to collectively reflect on our community within Columbia Engineering and the importance of our commitment to maintaining an open and welcoming community for all students, faculty, researchers and administrative staff. As a School of Engineering and Applied Science, we are fortunate to attract students and faculty from diverse backgrounds, from across the country, and from around the world. It is a great benefit to be able to gather engineers and scientists of so many different perspectives and talents – all with a commitment to learning, a focus on pushing the frontiers of knowledge and discovery, and with a passion for translating our work to impact humanity.
I am proud of our community, and wish to take this opportunity to reinforce our collective commitment to maintaining an open and collegial environment. We are fortunate to have the privilege to learn from one another, and to study, work, and live together in such a dynamic and vibrant place as Columbia.
Mary C. Boyce Dean of Engineering Morris A. and Alma Schapiro Professor
{{title}} {{fullname}}
Courses This Semester
- {{title}} ({{dept}} {{prefix}}{{course_num}}-{{section}})
Your browser is unsupported
We recommend using the latest version of IE11, Edge, Chrome, Firefox or Safari.
Computer Science
College of engineering, requirements heading link copy link.

In addition to the Graduate College minimum requirements, students must meet the following program requirements:
- Minimum semester hours required: 36
- Coursework: At least 28 hours (plus thesis hours), 32 hours (plus project hours), 36 hours (for coursework only). 12 hours (for thesis and project options) and 16 hours (for coursework only) must be CS course offerings at the 500 level (excluding CS 590 , CS 595 , CS 596 , CS 597 , CS 598 , and CS 599 ). No more than one special topics course ( CS 594 ) may be counted toward the 500-level CS requirement. At most 8 hours of pre-approved non-CS graduate courses may be counted toward the overall requirement.
- Comprehensive Examination: None
Considering applying for master’s-level study at UIC? Our MS degree booklet provides an introduction to our CS curriculum, students, and alumni.
Options to complete the master's degree Heading link Copy link
Coursework-only option
In the course option, students complete all the credit hours toward the MS only through coursework.
Project option
The project option allows students to demonstrate their learning in the form of a substantive capstone project. The project work must demonstrate a high level of professional skill, but students do not need to formally present or defend their projects.
Thesis option
The thesis option is designed for graduate students with an interest in computer science research. The thesis option is strongly advised for students who may be interested in pursuing a PhD in the future.
MS Students in Their Own Words Heading link Copy link

Lydia Tse ’21 MS in Computer Science
Why did you choose UIC? It’s a great research institution that has an incredible computer science department. UIC is also where my parents met, so it has always had a soft spot in my heart.
What is your academic area of focus within your department? I’ve gravitated toward data-focused classes such as data and text mining, information retrieval, and machine learning.
How is UIC preparing you for your future goals? UIC has provided an environment in which I can thrive through learning and exploring multiple areas of CS. I’m so grateful to be mentored and inspired by so many incredible UIC CS department faculty and peers. Because of their guidance, I’ve been able to explore career paths in CS from teaching to research to industry. If it weren’t for their encouragement and support, I would not be where I am today.
Have you held any internships while at UIC? Synchrony. From there, I landed a full-time job at Nike as a data visualization engineer.
Looking broadly at your field of study, who is the person you admire the most, and why? I’m a huge fan of Dr. Latanya Sweeney. Not only has she blazed so many trails as a top-notch computer scientist, but her work serves as a continual reminder of the responsibility we all share as digital innovators.
What is your favorite thing to do in Chicago? Eating food. There are so many cool restaurants.
Charic Heading link Copy link

Charic Farinango Cuervo ’21 MS in Computer Science
Favorite course so far? I really enjoyed CS 415 Computer Vision . We did a project on 3D reconstruction.
What are your plans for after you finish school? I want to stay in AI, maybe data analysis. One option is to stay in the United States via the Optional Practical Training program, but I am required by my Fulbright scholarship to come back to Colombia, so I may work in a private company or university there.
What do you suggest a newcomer to Chicago see or do if they’ve already seen Navy Pier, the Riverwalk, and Skydeck? I like the lakefront, especially in summer. Ride bikes, go to parks, visit museums. I really enjoy that Chicago has different neighborhoods. If you go from one neighborhood to another, you’ll find that they are completely different.
Your primary hobby/outside interest: I like to play guitar and sing. Right now I’m practicing rock music in Spanish from Argentina and Mexico.
The best trip/vacation you’ve ever taken, and why: When I arrived in the United States, the Fulbright program put on an event: a weeklong getaway in Rochester, New York. I got to make friends with Fulbrighters from all over the world and went to Niagara Falls. It was a cool experience.
Contacts Heading link Copy link
If you have further questions about our graduate program, contact us at [email protected] .
You can reach us by phone at (312) 996-5940.
Personalise your experience
Graduate Coursework
Master of Computer Science
- Arrow-right #1 in Australia for Computer Science & Info Systems
- Arrow-right #41 in the world
- Course code: MC-CS
Course overview
Study engineering and it: information session.
Monday 20 May, 6pm-8pm Melbourne Connect
Join us for an in-person information session and Q&A. Connect with our engineering and IT community, and learn more about what graduate study and career opportunities are available to you.
Register now
Computers are changing the world, and our lives. We've been saying that for decades, and we’ll keep saying it, because computing technology just keeps on advancing.
You probably have what a few decades ago would have been called a super-computer sitting in your pocket right now.
The Master of Computer Science will give you a broad base of high-level knowledge to keep up with these advances, with specialist skills in at least one area of knowledge systems, programming languages and distributed computing, information systems, mathematics/statistics, spatial information science or linguistics.
In demand globally
You can use the Master of Computer Science as a pathway to a PhD or to the workforce, where you may meet our alumni working in software design, cybersecurity, information architecture and programming.
If you’re looking for networks to help with internships and job opportunities, or the funds to help you get to Melbourne, we have scholarships and bursaries to get you connected overseas and get you to Melbourne when you can. Find out what you may be eligible for.
Exploring the differences between our IT courses?
Visit our article for more information
Related study areas
- Computer science
- Data and analytics
- Engineering
- Environment
- Information systems
- Information technology and computer science
- Software engineering
Programs and courses
- Future students
- Support uOttawa
- Brightspace
Master of Computer Science
- Degree offered: Master of Computer Science (MCS)
- Registration status options: Full-time; Part-time
- Language of instruction: English
- within two years of full-time study
- For immigration purposes, the summer term (May to August) for this master’s program with Coursework and Project is considered a regularly scheduled break approved by the University. Students should resume full-time studies in September.
- Academic units: Faculty of Engineering , School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science , Ottawa-Carleton Institute for Computer Science (OCICS).
Program Description
Ottawa-Carleton Joint Program
Students who wish to pursue studies in computer science leading to the degree of Master of Computer Science (MCS) or Doctor of Philosophy in Computer Science (PhD) can do so in joint programs offered by the School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS) at the University of Ottawa and the School of Computer Science at Carleton University under the auspices of the Ottawa-Carleton Institute for Computer Science (OCICS). The Institute is responsible for supervising these programs and for providing a framework for interaction between the universities in graduate computer science education. In addition to the faculty members from the two computer science programs, the Institute also has members with computer science expertise from other departments.
The School of Computer Science is a participating unit in the collaborative program in bioinformatics at the master’s level.
Other Programs Offered Within the Same Discipline or in a Related Area
- Master of Computer Science Specialization in Bioinformatics (MCS)
- Doctorate in Philosophy Computer Science (PhD)
Fees and Funding
- Program fees:
The estimated amount for university fees associated with this program are available under the section Finance your studies .
International students enrolled in a French-language program of study may be eligible for a differential tuition fee exemption .
- To learn about possibilities for financing your graduate studies, consult the Awards and financial support section.
- Programs are governed by the general regulations in effect for graduate studies and the regulations in effect at Carleton University.
- In accordance with the University of Ottawa regulation, students have the right to complete their assignments, examinations, research papers, and theses in French or in English. In addition, research activities can be conducted in either English or French or both depending on the language used by the professor and the members of the research group.
- Students may include courses from both universities in their programs, and may select a supervisor from either university, but they should apply to the university with which their supervisor is associated. Their study program is administered by the university at which they are enrolled and is subject to its regulations.
Program Contact Information
Graduate Studies Office, Faculty of Engineering STE 1024 800 King Edward Ave. Ottawa ON Canada K1N 6N5
Tel.: 613-562-5347 Fax.: 613-562-5129 Email: [email protected]
Twitter | Faculty of Engineering Facebook | Faculty of Engineer
For the most accurate and up to date information on application deadlines, language tests and other admission requirements, please visit the specific requirements webpage.
To be eligible, candidates must:
- Have a bachelor of science degree with honours in computer science (or equivalent), with a minimum average of B (70%).
Note: International candidates must check the admission equivalencies for the diploma they received in their country of origin.
- Identify at least one professor who is willing to supervise your research and thesis. We recommend that you contact potential thesis supervisors as soon as possible.
The Accelerated Stream has three additional requirements. Candidates must:
- Complete up to 6 units from the OCICS master’s courses each with 70% (B) or higher grade (taken during their Bachelor’s program in Computer Science or Software Engineering).
- Have an admission average of A- (80%) or higher.
- Have a thesis supervisor.
Language Requirements
Applicants must be able to understand and fluently speak the language of instruction (French or English) in the program to which they are applying. Proof of linguistic proficiency may be required.
Applicants whose first language is neither French nor English must provide proof of proficiency in the language of instruction.
Note: Candidates are responsible for any fees associated with the language tests.
- The admission requirements listed above are minimum requirements and do not guarantee admission to the program.
- Admissions are governed by the general regulations in effect for graduate studies.
Applying to the Co-op Option
In order to apply to the co-op option, you must first be admitted to a program that offers co-op. The co-op option is not available to MCS students in the Accelerated Stream.
Your application must be submitted by the end of the first month of enrollment in your primary program, i.e., by the end of September.
Admission to the co-op option occurs on a competitive basis and is managed by the Co-op Office . Enquiries should be directed to that office.
To be admitted to the co-op option, you must:
- Be enrolled as a full-time student in the master’s in computer science;
- Have a cumulative grade point average of 7.0 or 75%;
- Begin the program in the Fall term;
- Be a Canadian citizen, a permanent resident or an international student (authorization or diplomat)
- Pay the required CO-OP fees.
Qualifying Program
Applicants who lack the required undergraduate preparation may be admitted to a qualifying-year program. The basis for admission to the qualifying year of the master’s program will normally be an honours degree in a related discipline with a B average (70%), provided that the honours program in question includes the equivalent of three years of an honours computer science program. A major degree holder with superior academic standing may be considered for admission to the qualifying year with suitable background preparation.
Master’s with Thesis
Students must meet the following requirements:
Course selection must be approved by the student's academic advisor. A maximum of two three-unit courses at the 4000 level are permitted.
Consult the Ottawa-Carleton Institute for Computer Science for a complete list of courses per category
A student may be permitted to carry out thesis work off campus provided suitable arrangements are made for supervision and experimental work, and prior approval is obtained from the Joint Program Committee.
Students are responsible for ensuring they have met all of the thesis requirements .
Master’s with Thesis, Accelerated Stream
Course selection must be approved by the student's academic advisor. For students in the Accelerated Stream, the two OCICS courses taken as part of their undergraduate degree can be used to satisfy at most two of the above category requirements.
Consult the Ottawa-Carleton Institute for Computer Science for a complete list of courses per category
Master’s with Coursework and Project
Requirements for this program have been modified. Please consult the 2018-2019 calendars for the previous requirements.
To receive this Master’s degree, a student enrolled in the program must successfully complete 30 course units.
Subject to the approval of the graduate coordinator, a student may take up to half of the course units in the program in other disciplines (e.g. electrical engineering, mathematics and physics).
Co-op Option
(Available to students enrolled in the thesis option or the coursework and project option.)
To complete a master’s with coursework and project, you must meet the following requirements :
- Maintain a cumulative grade point average of 7.0 or 75%;
- Obtain a satisfactory grade (P) for each co-op work term: CGI 6001 , CGI 6002 .
- Each work term is graded P/F (pass/fail), based on the employer’s report and on the written report completed by the student. (The report must be 30 pages long, including appendices.) The report is evaluated by the professor in charge of the graduate co-op option in Computer Science.
- The units awarded for co-op terms may not be used to obtain equivalences for other courses. In other words, the co-op units are additional to the minimum requirements of the degree.
Fast-Track from Master’s to PhD
Students enrolled in the master’s program in computer science at the University of Ottawa may be eligible to fast-track directly into the doctoral program without writing a master’s thesis. For additional information, please consult the “Admission Requirements” section of the PhD program.
Note: Students in the Accelerated Stream of the MCS are not eligible for fast-track to the PhD.
Minimum Requirements
The passing grade in all courses is B.
Research Fields & Facilities
Located in the heart of Canada’s capital, a few steps away from Parliament Hill, the University of Ottawa is among Canada’s top 10 research universities.
uOttawa focuses research strengths and efforts in four Strategic Areas of Development in Research (SADRs):
- Canada and the World
- Molecular and Environmental Sciences
With cutting-edge research, our graduate students, researchers and educators strongly influence national and international priorities.
Research at the Faculty of Engineering
Areas of research:
- Chemical and Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
- Mechanical Engineering
For more information, refer to the list of faculty members and their research fields on Uniweb .
CSI 5100 Data Integration (3 units)
Materialized and virtual approaches to integration of heterogeneous and independent data sources. Emphasis on data models, architectures, logic-based techniques for query processing, metadata and consistency management, the role of XML and ontologies in data integration; connections to schema mapping, data exchange, and P2P systems. This course is equivalent to COMP 5306 at Carleton University.
Course Component: Lecture
CSI 5101 Knowledge Representation (3 units)
KR is concerned with representing knowledge and using it in computers. Emphasis on logic-based languages for KR, and automated reasoning techniques and systems; important applications of this traditional area of AI to ontologies and semantic web. This course is equivalent to COMP 5307 at Carleton University.
CSI 5102 Topics in Medical Computing (3 units)
Introductory course on data structures, algorithms, techniques, and software development related to medical computing (in particular spatial modeling). Topics may include: computational geometry algorithms for cancer treatment, medical imaging, spatial data compression algorithms, dynamic programming for DNA analysis. This course is equivalent to COMP 5308 at Carleton University.
CSI 5105 Network Security and Cryptography (3 units)
Advanced methodologies selected from symmetric and public key cryptography, network security protocols and infrastructure, identification, anonymity, privacy technologies, secret-sharing, intrusion detection, firewalls, access control technologies, and defending network attacks. This course is equivalent to COMP 5406 at Carleton University.
Prerequisites: familiarity with basic concepts in networks, network security, and applied cryptography.
CSI 5106 Cryptography (3 units)
Security in encryption algorithms. Encryption and decryption. Entropy, equivocation, and unicity distance. Cryptanalysis and computational complexity. Substitution, transposition, and product ciphers. Symmetric ciphers: block and stream modes. Modular arithmetic. Public key cryptosystems. Factorization methods. Elliptic curve, lattice-based, and homomorphic cryptography. Proofs of security.
CSI 5107 Principle of Intelligent Transportation Systems (3 units)
Fundamental Concepts of ITS. Computer Information and Communication for ITS. The Backbone of ITS Communication, Network Topologies and Configurations. ITS Models and Evaluation Methods. Advanced Transportation Management Systems (ATMS). Advanced Traveler Information Systems (ATIS). Advanced Driver Assistant Systems. Data Stream Management System (DSMS) in the intelligent transportation Systems. Intelligent Traffic Control Algorithms. Traffic Demand Modeling and Analysis. Incident Detection and Collusion Avoidance Algorithms. Smart Mobility and GPS Localization Algorithms. Software Defined Network for ITS. Security & Privacy in ITS
CSI 5108 Introduction to Convex Optimization (3 units)
Mathematics of optimization: linear, nonlinear and convex problems. Convex and affine sets. Convex, quasiconvex and log-convex functions. Operations preserving convexity. Recognizing and formulating convex optimization problems. The Lagrange function, optimality conditions, duality, geometric and saddle-point interpretations. Least-norm, regularized and robust approximations. Statistical estimation, detector design. Adaptive antennas. Geometric problems (networks). Algorithms.
CSI 5110 Principles of Formal Software Development (3 units)
Methodologies in formal software specification, development, and verification. The use of theorem proving, automated deduction, and other related formal methods for software correctness. Applications in program verification and secure computation. This course is equivalent to COMP 5707 at Carleton University.
CSI 5111 Software Quality Engineering (3 units)
Software quality issues. Quality components and metrics. Software process quality. Software reliability engineering. Software design for testability. Requirements capture and validation. Systematic design validation; grey-box approach, test design, implementation and management, case studies in validation and verification of communications software. Object-oriented design and test. Theoretical aspects. This course is equivalent to COMP 5501 at Carleton University.
CSI 5112 Software Engineering (3 units)
Topics of current interest in Software Engineering, such as requirements engineering, precise and advanced modelling, development processes, change management, standards, and emerging types of applications. This course is equivalent to COMP 5207 at Carleton University.
CSI 5113 Foundations Programming Languages (3 units)
Advanced study of programming paradigms from a practical perspective. Paradigms may include functional, imperative, concurrent, distributed, generative, aspect- and object-oriented, and logic programming. Emphasis on underlying principles. Topics may include: types, modules, inheritance, semantics, continuations, abstraction and reflection. This course is equivalent to COMP 5001 at Carleton University.
CSI 5115 Database Analysis and Design (3 units)
The dimensional and multidimensional data models for data warehousing. Data dependencies and decomposition. Structure and use of data definition and manipulation languages. Database economics, engineering, deployment and evolution. Issues in integrity, security, the Internet and distributed databases. Relationships to decision support systems. This course is equivalent to COMP 5503 at Carleton University.
Course Component: Discussion Group, Laboratory, Lecture, Research, Seminar, Work Term, Theory and Laboratory, Tutorial
CSI 5116 Authentication and Software Security (3 units)
Specialized topics in security including advanced authentication techniques, user interface aspects, electronic and digital signatures, security infrastructures and protocols, software vulnerabilities affecting security, non-secure software and hosts, protecting software and digital content. This course is equivalent to COMP 5407 at Carleton University.
CSI 5118 Automated Verification and Validation of Software (3 units)
Topics in formal test derivation methods, test management, high-level, CASE-based verification and validation, data-flow & control-flow measures and metrics for assessing quality of designs and code, regression analysis & testing. This course is equivalent to COMP 5302 at Carleton University.
CSI 5121 Advanced Data Structures (3 units)
Simple methods of data structure design and analysis that lead to efficient data structures for several problems. Topics include randomized binary search trees, persistence, fractional cascading, self-adjusting data structures, van Emde Boas trees, tries, randomized heaps, and lowest common ancestor queries. This course is equivalent to COMP 5408 at Carleton University.
CSI 5122 Software Usability (3 units)
Design principles and metrics for usability. Qualitative and quantitative methods for the evaluation of software system usability: Heuristic evaluation, usability testing, usability inspections and walkthroughs, cognitive walkthroughs, formal usability experimentation. Ethical concerns when performing studies with test users. Economics of usability. Integration of usability engineering into the software engineering lifecycle. This course is equivalent to COMP 5301 at Carleton University.
CSI 5124 Computational Aspects of Geographic Information Systems (3 units)
Computational perspective of geographic information systems (GIS). Data representations and their operations on raster and vector devices: e.g., quadtrees, grid files, digital elevation models, triangular irregular network models. Analysis and design of efficient algorithms for solving GIS problems: visibility queries, point location, facility location. This course is equivalent to COMP 5204 at Carleton University.
CSI 5126 Algorithms in Bioinformatics (3 units)
Fundamental mathematical and algorithmic concepts underlying computational molecular biology; physical and genetic mapping, sequence analysis (including alignment and probabilistic models), genomic rearrangement, phylogenetic inference, computational proteomics and systemics modelling of the whole cell. This course is equivalent to COMP 5108 at Carleton University.
CSI 5127 Applied Computational Geometry (3 units)
Design and analysis of efficient algorithms for solving geometric problems in applied fields such as Geometric Network Design, Geometric Routing and Searching. Geometric spanners, Greedy spanners, Theta-Graphs, Yao-Graphs, Well-Separated Pair Decomposition, Delaunay Triangulations. Introduction to the game of Cops and Robbers. This course is equivalent to COMP 5409 at Carleton University.
CSI 5128 Swarm Intelligence (3 units)
Collective computation, collective action, and principles of self-organization in social agent systems. Algorithms for combinatorial optimization problems, division of labour, task allocation, task switching, and task sequencing with applications in security, routing, wireless and ad hoc networks and distributed manufacturing. This course is equivalent to COMP 5002 at Carleton University.
CSI 5129 Advanced Database Systems (3 units)
In-depth study on developments in database systems shaping the future of information systems, including complex object, object-oriented, object-relational, and semi-structured databases. Data structures, query languages, implementation and applications. This course is equivalent to COMP 5305 at Carleton University.
CSI 5131 Parallel Algorithms and Applications in Data Science (3 units)
Multiprocessor architectures from an application programmer's perspective: programming models, processor clusters, multi-core processors, GPUs, algorithmic paradigms, efficient parallel problem solving, scalability and portability. Projects on high performance computing in Data Science, including data analytics, bioinformatics, simulations. Programming experience on parallel processing equipment. This course is equivalent to COMP 5704 at Carleton University.
CSI 5134 Fault Tolerance (3 units)
Hardware and software techniques for fault tolerance. Topics include modeling and evaluation techniques, error detecting and correcting codes, module and system level fault detection mechanisms, design techniques for fault-tolerant and fail-safe systems, software fault tolerance through recovery blocks, N-version programming, algorithm-based fault tolerance, checkpointing and recovery techniques, and survey of practical fault-tolerant systems. This course is equivalent to COMP 5004 at Carleton University.
CSI 5135 Information Visualization and Visual Analytics (3 units)
Principles, techniques, technology and applications of information visualization for visual data analysis. Topics include human visual perception, cognitive processes, static and dynamic models of image semantics, interaction paradigms, big data visual analysis case studies. This course is equivalent to COMP 5209 at Carleton University.
CSI 5136 Computer Security and Usability (3 units)
Design and evaluation of security and privacy software with particular attention to human factors and how interaction design impacts security. Topics include current approaches to usable security, methodologies for empirical analysis, and design principles for usable security and privacy. This course is equivalent to COMP 5110 at Carleton University.
CSI 5137 Selected Topics in Software Engineering (Category E) (3 units)
Selected topics in Software Engineering (Category E), not covered by other graduate courses. Details will be available from the School at the time of registration. This course is equivalent to COMP 5900 at Carleton University.
CSI 5138 Selected Topics in Theory of Computing (Category T) (3 units)
Selected topics in Theory of Computing (Category T), not covered by other graduate courses. Details will be available from the School at the time of registration. This course is equivalent to COMP 5900 at Carleton University.
CSI 5139 Selected Topics in Computer Applications (Category A) (3 units)
Selected topics in Computer Applications (Category A), not covered by other graduate courses. Details will be available from the School at the time of registration. This course is equivalent to COMP 5900 at Carleton University.
CSI 5140 Selected Topics in Computer Systems (Category S) (3 units)
Selected topics in Computer Systems (Category S), not covered by other graduate courses. Details will be available from the School at the time of registration. This course is equivalent to COMP 5900 at Carleton University.
CSI 5142 Protocols for Mobile and Wireless Networks (3 units)
Link and network layer protocols of wireless networks; applications of wireless networks may be discussed. Topics may include: protocol implementation, mobile IP, resource discovery, wireless LANs/PANs, and Spreadspectrum. Courses CSI 6136 (SYSC 5306), CSI 5142 (COMP 5402) cannot be combined for units. This course is equivalent to COMP 5402 at Carleton University.
Precludes additional credit for SYSC 5306.
CSI 5146 Computer Graphics (3 units)
Principles and advanced techniques in rendering and modelling. Research field overview. Splines, subdivision surfaces and hierarchical surface representations. Physics of light transport, rendering equation and Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function. Classical ray tracing, radiosity, global illumination and modern hybrid methods. Plenoptic function and image-based rendering. This course is equivalent to COMP 5202 at Carleton University.
CSI 5147 Computer Animation (3 units)
Theories and techniques in 3D modeling and animation. Animation principles, categories, and history. Forward and inverse kinematics. Motion capture, editing and retargeting. Flexible bodies. Particle animation. Behavioral animation. Human modeling. Facial animation. Cloth animation and other sub-topics. This course is equivalent to COMP 5201 at Carleton University.
CSI 5148 Wireless Ad Hoc Networking (3 units)
Self-organized, mobile, and hybrid ad hoc networks. Physical, medium access, networks, transport and application layers, and cross-layering issues. Power management. Security in ad hoc networks. Topology control and maintenance. Data communication protocols, routing and broadcasting. Location service for efficient routing. This course is equivalent to COMP 5103 at Carleton University.
CSI 5149 Graphical Models and Applications (3 units)
Bayesian networks, factor graphs, Markov random fields, maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) and maximum likelihood (ML) principles, elimination algorithm, sum-product algorithm, decomposable and non-decomposable models, junction tree algorithm, completely observed models, iterative proportional fitting algorithm, expectation- maximization (EM) algorithm, iterative conditional modes algorithm, variational methods, applications. Courses CSI 5149 (COMP 5007), ELG 5131 (EAGJ 5131) and ELG 7177 (EACJ 5605) cannot be combined for units. This course is equivalent to COMP 5007 at Carleton University.
Permission of the Department is required.
CSI 5151 Virtual Environments (3 units)
Basic concepts. Virtual worlds. Hardware and software support. World modeling. Geometric modeling. Light modeling. Kinematic and dynamic models. Other physical modeling modalities. Multi-sensor data fusion. Anthropomorphic avatars. Animation: modeling languages, scripts, real-time computer architectures. Virtual environment interfaces. Case studies. Courses ELG 5124 (EACJ 5204), CSI 5151 (COMP 5205) cannot be combined for units. This course is equivalent to COMP 5205 at Carleton University.
CSI 5152 Evolving Information Networks (3 units)
Convergence of social and technological networks with WWW. Interplay between information content, entities creating it and technologies supporting it. Structure and analysis of such networks, models abstracting their properties, link analysis, search, mechanism design, power laws, cascading, clustering and connections with work in social sciences. This course is equivalent to COMP 5310 at Carleton University.
CSI 5153 Data Management for Business Intelligence (3 units)
Data management problems and information technology in decision making support in business environments. Topics include advanced data modeling, semantic modeling, multidimensional databases and data warehousing, on-line-analytical processing, elements of data mining, context in data management, data quality assessment, data cleaning, elements of business process modeling. This course emphasizes concepts and techniques rather than specific applications or systems/implementations. This course is equivalent to COMP 5111 at Carleton University.
CSI 5154 Algorithms for Data Science (3 units)
Algorithmic techniques to handle (massive/big) data arising from, for example, social media, mobile devices, sensors, financial transactions. Algorithmic techniques may include locality-sensitive hashing, dimensionality reduction, streaming, clustering, VC-dimension, external memory, core sets, link analysis and recommendation systems. This course is equivalent to COMP 5112 at Carleton University.
CSI 5155 Machine Learning (3 units)
Concepts, techniques, and algorithms in machine learning; representation, regularization and generalization; supervised learning; unsupervised learning; advanced methods such as support vector machines, online algorithms, neural networks, hidden Markov models, and Bayesian networks; curse of dimensionality and large-scale machine learning. Category T in course list. This course is equivalent to COMP 5116 at Carleton University.
Courses CSI 5155 , DTO 5100 , DTO 5101 , ELG 5255 , IAI 5100 , IAI 5101 , MIA 5100 , SYS 5185 cannot be combined for units.
CSI 5161 Principles of Distributed Simulation (3 units)
Distributed simulation principles and practices. Synchronization protocols: Optimistic vs Conservative, Deadlock detection in conservative simulations, Time warp simulation. Distributed interactive simulation: Data distribution management, Interest management, High Level Architectures (HLA), Run Time Infrastructure (RTI). Distributed web-based simulation. Distributed agent based simulation. Real time applications of distributed simulation. Distributed and collaborative virtual simulations. This course is equivalent to COMP 5606 at Carleton University.
CSI 5163 Algorithm Analysis and Design (3 units)
Topics of current interest in the design and analysis of computer algorithms for graph-theoretical applications; e.g. shortest paths, chromatic number, etc. Lower bounds, upper bounds, and average performance of algorithms. Complexity theory. This course is equivalent to COMP 5703 at Carleton University.
CSI 5164 Computational Geometry (3 units)
Study of design and analysis of algorithms to solve geometric problems; emphasis on applications such as robotics, graphics, and pattern recognition. Topics include: visibility problems, hidden line and surface removal, path planning amidst obstacles, convex hulls, polygon triangulation, point location. This course is equivalent to COMP 5008 at Carleton University.
CSI 5165 Combinatorial Algorithms (3 units)
Design of algorithms for solving problems that are combinatorial in nature, involving exhaustive generation, enumeration, search and optimization. Algorithms for generating basic combinatorial objects (permutations, combinations, subsets) and for solving hard optimization problems (knapsack, maximum clique, minimum set cover). Metaheuristic search, backtracking, branch-and-bound. Computing isomorphism of combinatorial objects (graphs), isomorph-free exhaustive generation. This course is equivalent to COMP 5709 at Carleton University.
CSI 5166 Applications of Combinatorial Optimization (3 units)
Topics in combinatorial optimization with emphasis on applications in Computer Science. Topics include network flows, various routing algorithms, polyhedral combinatorics, and the cutting plane method. This course is equivalent to COMP 5805 at Carleton University.
CSI 5167 Human-Computer Interaction Models, Theories and Frameworks (3 units)
A basis for graduate study in HCI with an emphasis on the application of theory to user interface design. Review of main theories of human behaviour relevant to HCI, including especially Cognitive Dimensions of Notations Framework, Mental Models, Distributed Cognition, and Activity Theory, and their application to design and development of interactive systems. This course is equivalent to COMP 5210 at Carleton University.
CSI 5168 Digital Watermarking (3 units)
Overview of recent advances in watermarking of image, video, audio, and other media. Spatial, spectral, and temporal watermarking algorithms. Perceptual models. Use of cryptography in steganography and watermarking. Robustness, security, imperceptibility, and capacity of watermarking. Content authentication, copy control, intellectual property, digital rights management, and other applications. This course is equivalent to COMP 5309 at Carleton University.
CSI 5169 Wireless Networks and Mobile Computing (3 units)
Computational aspects and applications of design and analysis of mobile and wireless networking. Topics include Physical, Link Layer, Media Access Control, Wireless, Mobile LANs (Local Area Networks), Ad-Hoc, Sensor Networks, Power Consumption optimization, Routing, Searching, Service Discovery, Clustering, Multicasting, Localization, Mobile IP/TCP (Internet Protocol/Transmission Control Protocol), File Systems, Mobility Models, Wireless Applications. Courses CSI 5169 , ELG 6168 cannot be combined for units. This course is equivalent to COMP 5304 at Carleton University.
CSI 5173 Data Networks (3 units)
Mathematical and practical aspects of design and analysis of communication networks. Topics include: basic concepts, layering, delay models, multi-access communication, queuing theory, routing, fault-tolerance, and advanced topics on high-speed networks, ATM, mobile wireless networks, and optical networks. This course is equivalent to COMP 5203 at Carleton University.
CSI 5174 Validation Methods for Distributed Systems (3 units)
Review of formal specification and description techniques for distributed and open systems. Verification techniques. Correctness proofs. Verification of general properties of distributed systems. Analysis and relief strategies. Testing techniques. Test generation strategies. Test architectures. This course is equivalent to COMP 5604 at Carleton University.
CSI 5175 Mobile Commerce Technologies (3 units)
Wireless networks support for m-commerce; m-commerce architectures and applications; mobile payment support systems; business models; mobile devices and their operating systems; mobile content presentation; security issues and solutions; relevant cross layer standards and protocols; case studies. Courses DTI 5175 , CSI 5175 cannot be combined for units. This course is equivalent to COMP 5220 at Carleton University.
CSI 5180 Topics in Artificial Intelligence (3 units)
Selected topics in Artificial Intelligence (A.I.); could include A.I. programming techniques, pattern matching systems, natural language systems, rule-based systems, constraint systems, machine learning systems, and cognitive systems. Applications could include areas in Finance, Medicine, Manufacturing, Smart Cities, Semantic Web, Healthcare, Fraud Detection, Intrusion Detection, Autonomous Vehicles, Opinion mining, Sentiment Analysis or similar areas. Assignments will be both (a) programming-oriented, requiring implementation and/or extensions of prototypes in Lisp and/or Prolog and (b) research-oriented, requiring readings of special topics in current A.I. journals. This course is equivalent to COMP 5100 at Carleton University.
CSI 5183 Evolutionary Computation and Artificial Life (3 units)
Study of algorithms based upon biological theories of evolution, applications to machine learning and optimization problems. Possible topics: Genetic Algorithms, Classifier Systems, and Genetic Programming. Recent work in the fields of Artificial Life (swarm intelligence, distributed agents, behavior-based AI) and of connectionism. This course is equivalent to COMP 5206 at Carleton University.
Precludes additional credit for COMP 4107.
CSI 5185 Statistical and Syntactic Pattern Recognition (3 units)
Topics include a mathematical review, Bayes decision theory, maximum likelihood and Bayesian learning for parametric pattern recognition, non-parametric methods including nearest neighbor and linear discriminants. Syntactic recognition of strings, substrings, subsequences and tree structures. Applications include speech, shape and character recognition. This course is equivalent to COMP 5107 at Carleton University.
CSI 5195 Ethics for Artificial Intelligence (3 units)
Students critically examine topics in applied AI ethics through the lens of contemporary philosophy and applied ethics texts, popular media articles, and technology case studies. Topics may include: bias and fairness; explainability; accountability; privacy; deception; trust/trustworthiness; and metaphors. Methods for applying ethical considerations in technology design are introduced through hands-on design projects. (Category E)
Courses CSI 5195 , DTI 5310 , DTO 5310 , SYS 5295 cannot be combined for units.
CSI 5200 Projects on Selected Topics (3 units)
CSI 5218 Uncertainty Evaluation in Engineering Measurements and Machine Learning (3 units)
Uncertainty, uncertainty propagation, Bayesian inference, sensor fusion, time series, Gaussian processes, integrating scientific/user knowledge into machine learning, neural networks for differential equations, probabilistic deep learning, sequential decision making. Case studies will be drawn from various fields including biomedical, autonomous vehicles, sensors, and signal processing.
The courses CSI 5218 , ELG 5218 cannot be combined for units.
CSI 5308 Principles of Distributed Computing (3 units)
Formal models of distributed environment; theoretical issues in the design of distributed algorithms; message and time complexity; problem solving in distributed settings. Problems discussed may include: coordination and control, information diffusion, leader election, consensus, distributed data operations, computing by mobile entities. This course is equivalent to COMP 5003 at Carleton University.
CSI 5311 Distributed Databases and Transaction Processing (3 units)
Principles involved in the design and implementation of distributed databases and distributed transaction processing systems. Topics include: distributed and multi-database system architectures and models, atomicity, synchronization and distributed concurrency control algorithms, data replication, recovery techniques, and reliability in distributed databases. This course is equivalent to COMP 5101 at Carleton University.
CSI 5312 Distributed Operating Systems (3 units)
Design issues of advanced multiprocessor distributed operating systems: multiprocessor system architectures; process and object models; synchronization and message passing primitives; memory architectures and management; distributed file systems; protection and security; distributed concurrency control; deadlock; recovery; remote tasking; dynamic reconfiguration; performance measurement, modeling, and system tuning. This course is equivalent to COMP 5102 at Carleton University.
CSI 5314 Object-Oriented Software Development (3 units)
Issues in modeling and verifying quality and variability in object-oriented systems. Testable models in model-driven and test-driven approaches. System family engineering. Functional conformance: scenario modeling and verification, design by contract. Conformance to non-functional requirements: goals, forces and tradeoffs, metrics. This course is equivalent to COMP 5104 at Carleton University.
CSI 5340 Introduction to Deep Learning and Reinforcement Learning (3 units)
Fundamental of machine learning; multi-layer perceptron, universal approximation theorem, back-propagation; convolutional networks, recurrent neural networks, variational auto-encoder, generative adversarial networks; components and techniques in deep learning; Markov Decision Process; Bellman equation, policy iteration, value iteration, Monte-Carlo learning, temporal difference methods, Q-learning, SARSA, applications. This course is equivalent to COMP 5340 at Carleton University.
CSI 5341 Learning-based Computer Vision (3 units)
Introduction to learning-based computer vision; statistical learning background; image processing and filtering primer; convolutional neural networks (CNNs), network layers, computer vision data sets and competitions; computer vision problems, in particular, image classification, detection and recognition, semantic segmentation, image generation, multi-view problems and tracking. This course is equivalent to COMP 5341 at Carleton University.
CSI 5342 Ubiquitous Sensing for Smart Cities (3 units)
Sensor and actuator networks. Dedicated and non-dedicated sensing. Vehicular sensing and smart transportation. Software Defined Things. Sensing as a service. Machine and deep learning-based misbehaviour detection. IoT-data analytics ecosystems. Federated Learning. AI-based security solutions. Auction and game theory concepts in ubiquitous sensing. This course is equivalent to COMP 5342 at Carleton University.
CSI 5343 AI-Enabled Communications (3 units)
Wireless networking fundamentals. Device to-device communications. Networking with cognitive radio. Cyber physical systems (CPS). Self-organization. Supervised and unsupervised learning. Reinforcement learning. Deep learning.This course is equivalent to COMP 5343 at Carleton University.
CSI 5344 Geometry Processing (3 units)
The course covers concepts, representations, and algorithms for analyzing and processing 3D geometric datasets. Topics include shape representations (e.g., triangle meshes, points clouds, and implicit functions), and the geometry processing pipeline covering the acquisition (e.g., with laser scanning or depth cameras), reconstruction, manipulation, editing, analysis, and fabrication (3D printing) of geometric models. This course is equivalent to COMP 5115 at Carleton University.
CSI 5345 Internet of Things (IoT) Security (3 units)
The course examines security challenges related to the Internet of Things (IoT), with a focus on consumer IoT devices, software aspects including engineering design, security of communications protocols and wireless access, cryptographic mechanisms, device integration and configuration, and security of IoT applications and platforms. This course is equivalent to COMP 5119 at Carleton University.
CSI 5346 Mining Software Repositories (3 units)
Introduction to the methods and techniques of mining software engineering data. Software repositories and their associated data. Data extraction and mining. Data analysis and interpretation (statistics, metrics, machine learning). Empirical case studies. This course is equivalent to COMP 5117 at Carleton University.
CSI 5347 Trends in Big Data Management (3 units)
Discussion of research papers on hot topics in the area of data management. The list of topics covered in the course generally spans: Data Exploration, Data Cleaning, Data Integration, Data Mining, Data Lake Management, Knowledge Graphs, Graph Processing, Question Answering, Blockchain, Crowdsourcing, Internet of Things, Text Processing, and Training via Weak Supervision. The common characteristic among all these topics is the large scale of data. This course is equivalent to COMP 5118 at Carleton University.
CSI 5350 Machine Learning for Healthcare (3 units)
Principles, techniques, technology and applications of machine learning for medical data such as medical imaging data, genomic data, physiological signals, speech and language. This course is equivalent to COMP 5113 at Carleton University.
CSI 5351 Quantum Communications and Networking (3 units)
Quantum communications and networking; the use of individual photons and teleportation to represent and transmit information. Theoretical (mathematical) principles. Practical aspects (implementation and software simulation) of quantum communications and networking. This course is equivalent to COMP 5114 at Carleton University.
CSI 5352 Internet Measurement and Security (3 units)
Measurement methodologies for understanding complex Internet phenomena and behaviors including: spread of vulnerabilities, remote network topologies, attack patterns, content popularity, Internet censorship, service quality, and adoption of security systems. Tools for efficient measurements, large-scale data analysis, stats, reproducibility of results. Ethical considerations. This course is equivalent to COMP 5500 at Carleton University.
CSI 5380 Systems and Architectures for Electronic Commerce (3 units)
E-commerce system architecture with a focus on relevant design patterns. Web servers, containers, and application frameworks. Web protocols, services, and client technologies. Scaleability through load balancing, clustering, and code optimization. Internationalization, accessibility, and privacy. Data mining and sharing approaches for digital targeted advertising. E-commerce user interface design and evaluation. Current research issues. Hands-on experience with an integrated set of current e-commerce tools. E-commerce development project. Courses EBC 5380, CSI 5380 cannot be combined for units. This course is equivalent to COMP 5405 at Carleton University.
CSI 5386 Natural Language Processing (3 units)
Overview of both rule-based or symbolic methods and statistical methods as approaches to Natural Language Processing (NLP), with more emphasis on the statistical ones. Applications such as information retrieval, text categorization, clustering, and statistical machine translation could be discussed. This course is equivalent to COMP 5505 at Carleton University.
CSI 5387 Data Mining and Concept Learning (3 units)
Concepts and techniques of data mining. Methods for data summarization and data preprocessing. Algorithms for finding frequent patterns and association analysis; classification; cluster analysis and anomaly detection. Model selection, model evaluation and statistical significance testing. Approaches for coping with Big Data. Selected applications of data mining and concept learning. This course is equivalent to COMP 5706 at Carleton University.
Permission of the Department is required. Courses CSI 5387 , DTO 5125, GNG 5125 cannot be combined for units.
CSI 5388 Topics in Machine Learning (3 units)
CSI 5389 Electronic Commerce Technologies (3 units)
Business models and technologies. Search engines. Cryptography. Web services and agents. Secure electronic transactions. Value added e-commerce technologies. Advanced research questions. Courses EBC5389, CSI5389 cannot be combined for units. This course is equivalent to COMP 5401 at Carleton University.
CSI 5390 Learning Systems from Random Environments (3 units)
Computerized adaptive learning for random environments and its applications. Topics include a mathematical review, learning automata which are deterministic/stochastic, with fixed/variable structures, of continuous/discretized design, with ergodic/absorbing properties and of estimator families. This course is equivalent to COMP 5005 at Carleton University.
CSI 5500 Projets en informatique (3 crédits)
Volet : Cours magistral
CSI 5501 Modèles formels de l'information (3 crédits)
CSI 5510 Principles de développement formel de logiciels (3 crédits)
Méthodologies pour la spécification, le développement et la vérification formels de logiciels. Utilisation d'assistants de preuves, de déduction automatisée et d'autres méthodes formelles visant l'exactitude de logiciel. Applications à la vérification de programmes et au calcul sécurisé. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5707 à la Carleton University.
CSI 5511 Génie de la qualité des logiciels (3 crédits)
Critères de la qualité des logiciels. Composantes et métriques de qualité. Qualité du processus de développement des logiciels. Génie de fiabilité des logiciels. Capture et validation d'exigences. Validation systématique de la conception; approche boîte-grise. Conception, implantation et gestion des tests. Étude de cas en validation et vérification des logiciels de communication. Conception orientée objet. Aspects théoriques. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5501 à la Carleton University.
CSI 5526 Algorithmes en bio-informatique (3 crédits)
Assemblage de l'ADN, recherche de gênes, comparaison de chaînes, alignement de séquences, structures grammaticales, structures secondaires et tertiaires. Les récents développements, tels que les puces d'ADN et de protéines. Travail additionnel requis dans le cas des étudiants inscrits sous la cote CSI 5526 .
Permission du Département est requise.
CSI 5537 Thème choisi en génie logiciel (catégorie E) (3 crédits)
Thèmes choisis en génie logiciel (catégorie E), non couverts par d'autres cours de deuxième cycle. Les détails seront disponibles à l'école au moment de l'inscription. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5900 à la Carleton University.
CSI 5538 Thème choisi en théorie de l'informatique (catégorie T) (3 crédits)
Thèmes choisis en théorie de l'informatique (catégorie T), non couverts par d'autres cours de deuxième cycle. Les détails seront disponibles à l'école au moment de l'inscription. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5900 à la Carleton University.
CSI 5539 Thème choisi en application informatique (catégorie A) (3 crédits)
Thèmes choisis en application informatique (catégorie A), non couverts par d'autres cours de deuxième cycle. Les détails seront disponibles à l'école au moment de l'inscription. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5900 à la Carleton University.
CSI 5540 Thème choisi en systèmes informatiques (catégorie S) (3 crédits)
Thèmes choisis en systèmes informatiques (catégorie S), non couverts par d'autres cours de deuxième cycle. Les détails seront disponibles à l'école au moment de l'inscription. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5900 à la Carleton University.
CSI 5555 Apprentissage machine (3 crédits)
Concepts, techniques et algorithmes en apprentissage machine; représentation, régularisation et généralisation; apprentissage supervisé; apprentissage non supervisé; méthodes avancées telles que les machines à vecteur de support, les algorithmes en ligne, les réseaux de neurones; les modèles de Markov cachés et les réseaux bayésiens; le fléau de la dimensionnalité et l'apprentissage machine à grande échelle. Catégorie T dans la liste de cours.
CSI 5561 Sujets en simulation et en optimisation des systèmes (3 crédits)
CSI 5563 Analyse et conception des algorithmes (3 crédits)
CSI 5565 Algorithmes combinatoires (3 crédits)
Conception d'algorithmes pour résoudre des problèmes de nature combinatoire (génération exhaustive, énumération, recherche et optimisation). Algorithmes pour générer des objets combinatoires de base (permutations, combinaisons, sous-ensembles) et pour résoudre des problèmes d'optimisation difficiles (knapsack, clique maximum, couverture minimum). Recherche métaheuristique, retour arrière, branch-and-bound. Calcul de l'isomorphisme des objets combinatoires (graphes), génération exhaustive sans isomorphes. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5709 à l'Université Carleton.
CSI 5571 Télématique : Concepts et logiciels (3 crédits)
CSI 5580 Sujets en intelligence artificielle (3 crédits)
Thèmes choisis en intelligence artificielle (I.A.); pourrait inclure des techniques de programmation en intelligence artificielle, des systèmes d'appariement de formes, des systèmes à langage naturel, des systèmes à base de règles, des systèmes de contraintes, des systèmes d'apprentissage automatique et des systèmes cognitifs. Les applications peuvent couvrir les domaines de la finance, de la médecine, de la fabrication, des villes intelligentes, du Web sémantique, de la détection de fraudes ou d’intrusion, des véhicules autonomes, de l'analyse d’opinion, de l'analyse de sentiments ou d’autres domaines similaires. Les devoirs seront à la fois (a) axés sur la programmation, exigeant l'implémentation et/ou l'extension de prototypes (b) axés sur la recherche, nécessitant des lectures de sujets spéciaux dans des revus d'I.A. contemporaines. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5100 à l'Université Carleton.
CSI 5780 Systèmes et architectures des logiciels pour le commerce électronique (3 crédits)
Architecture du système de commerce électronique et patrons de conception. Serveurs Web, conteneurs et cadres d'application. Protocoles, services, et technologies de client Web. Évolutivité grâce à l'équilibrage de la charge, au clustering et à l'optimisation du code. Internationalisation, accessibilité et confidentialité. Méthodes d'exploration et de partage de données pour la publicité ciblée numérique. Conception et évaluation de l'interface utilisateur pour le commerce électronique. Problèmes de recherche actuels. Expérience pratique avec un ensemble intégré d'outils de commerce électronique actuels. Projet de développement du commerce électronique. Les cours EBC 5380, CSI 5380 ne peuvent pas être combinés pour les unités. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5405 à la Carleton University.
Prerequisite: CSI 5389
CSI 5787 Fouille des données et apprentissage des concepts (3 crédits)
Aspects conceptuels et techniques de l’exploration des données. Méthodes pour l'agrégation et le prétraitement des données. Algorithmes d'extraction de patrons et analyse des règles d'association; partitionnement des données et détection des anomalies. Sélection et évaluation des modèles et tests de signification statistique. Approches pour composer avec les mégadonnées. Choix d'applications en exploration des données et en extraction des concepts.
CSI 5789 Technologies du commerce électronique (3 crédits)
Introduction aux modèles et technologies d'entreprise. Moteurs de recherche. Cryptographie. Services Web et agents. Transactions électroniques sécurisées. Technologies du commerce électronique à valeur ajoutée. Questions de recherche avancées. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5401 à la Carleton University.
Prerequisite: CSI 4110 or equivalent.
CSI 5900 Projets de recherche en informatique / Graduate Projects in Computer Science (3 crédits / 3 units)
Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5902 à la Carleton University. / This course is equivalent to COMP 5902 at Carleton University.
Volet / Course Component: Recherche / Research
CSI 5901 Études dirigées / Directed Studies (3 crédits / 3 units)
A course of independent study under the supervision of a member of the School of Computer Science. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5901 à la Carleton University. / This course is equivalent to COMP 5901 at Carleton University.
CSI 5903 Stage en commerce électronique / Electronic Commerce Work Term (3 crédits / 3 units)
Expérience en milieu de travail. Noté S (satisfaisant) ou NS (non satisfaisant) selon les résultats du rapport écrit et l'évaluation de l'employeur. Préalable : être accepté au programme de certificat en commerce électronique (option technologie) et recevoir la permission du Comité du programme. / Practical experience. Graded S (Satisfactory) / NS (Not satisfactory), to be based on the grades obtained for the written report as well as on the evaluations of the employer.
Volet / Course Component: Cours magistral / Lecture
Permission du Département est requise. / Permission of the Department is required.
CSI 5904 Projet de recherche avancé en commerce électronique / Graduate Project in Electronic Commerce (3 crédits / 3 units)
Projet sur un sujet précis en commerce électronique mené sous la direction d'un professeur. Les cours CSI 5904 , CSI 5903 ne peuvent être combinés pour l'obtention de crédits. / Project on a specific topic in electronic commerce under the supervision of a professor. Courses CSI 5904 , CSI 5903 cannot be combined for units.
Exclusion: CSI 5903 .
CSI 6900 Projets de recherche intensive en informatique / Intensive Graduate Projects in Computer Science (6 crédits / 6 units)
Cours de six crédits s'échelonnant sur une période de deux sessions. L'envergure du projet de recherche exigé dans ce cours est deux fois plus grande que dans le cas de CSI 5900 . Les cours CSI 6900 , CSI 5900 ne peuvent être combinés pour l'obtention de crédits. Cours ouvert uniquement aux étudiants inscrits à la maîtrise sans thèse. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 5903 à la Carleton University. / A two-session course. The project is twice the scope of projects in CSI 5900 . Courses CSI 6900 , CSI 5900 cannot be combined for units. Not to be taken in the thesis option. This course is equivalent to COMP 5903 at Carleton University.
CSI 7131 Advanced Parallel and Systolic Algorithms (3 units)
Continuation of CSI 5131 (COMP 5704). This course is equivalent to COMP 6100 at Carleton University.
CSI 7160 Advanced Topics in the Theory of Computing (3 units)
This course is equivalent to COMP 6601 at Carleton University.
CSI 7161 Advanced Topics in Programming Systems and Languages (3 units)
This course is equivalent to COMP 6603 at Carleton University.
CSI 7162 Advanced Topics in Computer Applications (3 units)
This course is equivalent to COMP 6604 at Carleton University.
CSI 7163 Advanced Topics in Computer Systems (3 units)
This course is equivalent to COMP 6605 at Carleton University.
CSI 7170 Advanced Topics in Distributed Computing (3 units)
This course is equivalent to COMP 6602 at Carleton University.
CSI 7314 Advanced Topics in Object-Oriented Systems (3 units)
Advanced object-oriented software engineering, in particular the issues of reuse and testing. Sample topics include: interaction modeling; class and cluster testing; traceability; design patterns and testing; the C++ standard template library. Students will carry out research. This course is equivalent to COMP 6104 at Carleton University.
CSI 7561 Études avancées en systèmes et langages de programmation (3 crédits)
Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 6603 à la Carleton University.
CSI 7900 Projets de recherche en informatique / Graduate Projects in Computer Science (3 crédits / 3 units)
Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 6902 à la Carleton University. / This course is equivalent to COMP 6902 at Carleton University.
CSI 7901 Études dirigées / Directed Studies (3 crédits / 3 units)
Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 6901 à la Carleton University. / This course is equivalent to COMP 6901 at Carleton University.
CSI 9901 Colloque / Seminar
Volet / Course Component: Séminaire / Seminar
CSI 9902 Colloque / Seminar
CSI 9997 Proposition de thèse de doctorat / Doctoral Thesis Proposal
Within 8 terms following initial registration in the program, a document, generally defining the problem addressed, relating it to the literature, outlining the hypotheses, goals, research methodology, initial results and validation approach, must be submitted to an examination committee and successfully defended. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 6908 à la Carleton University. This course is equivalent to COMP 6908 at Carleton University.
CSI 9998 Examen général de doctorat / Ph.D. Comprehensive
A committee must be assembled and must approve at least 3 topics for written examination: typically, a major and two minor areas. An oral examination occurs if the written exam is passed. Both elements must take place within the first 4 terms following initial registration in the program. The comprehensive examination may be failed, passed conditionally (i.e., with extra course requirements) or passed unconditionally. If failed, this course may be retaken at most one time. Ce cours est équivalent à COMP 6907 à la Carleton University. This course is equivalent to COMP 6907 at Carleton University.
Undergraduate Studies
For more information about undergraduate studies at the University of Ottawa, please refer to your faculty .
Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies
For more information about graduate studies at the University of Ottawa, please refer to your academic unit .
Print Options
Send Page to Printer
Print this page.
Download Page (PDF)
The PDF will include all information unique to this page.
- Faculty of Computer Science & Information Technology
- [email protected]
- +603-79676300

Master of Computer Science (Applied Computing) ( Mixed Mode )

The purpose of Master of Computer Science (Applied Computing) programme is to provide advanced training and knowledge in the field of Computer Science. Our program offers a profound and in-depth education in several core areas of computer science. The program guides each individual student in taking a meaningful path through the variety of course offers and designing a profile that matches both personal inclinations and prospective career opportunities.
Career Opportunity
- Computer and Information Scientist
- Computer/Multimedia Programmer/Developer
- Software Engineer
- Computer Systems Analyst
- Database Administrator
- Network and Computer Systems
- Administrator/Analyst
- Multimedia Producer/Developer
- Academician/Researcher
Course Structure
ELECTIVE COURSES Choose 2 of these elective courses ( 6 Credits Hour)
( Note : Not all courses will be offered every semester; the actual courses offered will depend on the availability of staff and the number of registered students).
Entry Requirement
- A bachelor’s degree with Honours or a equivalent in Computer Science/Information Technology/related field from a recognized university with a CGPA of 3.0 and above/equivalent, OR
- A bachelor's degree in Computer Science/Information Technology/related field from a recognized university with a CGPA in the range of 2.50 – 2.99/equivalent can be considered provided the fulfilment of the University requirements.
International applicants are required to:
- have at least IELTS Band 6.0 (Academic) or TOEFL score of 550 (paper based) / 213 (computer based) / 80 (internet based) / PTE minimum 57 scoreif their first degree from a university whose English language is not the medium of instruction, OR
- pass an English Proficiency test approved by the university
Intake Schedule
- International
Dr. Asmiza Abdul Sani Programme Coordinator +603 7967 6438 [email protected]
Mrs. Rohani Mohamed Arifin Administrative Assistance +603 7967 6380 [email protected]
Last Update: 15/06/2023
- Apply to UVU
Master of Computer Science
About program.
UVU's Master of Computer Science (MCS) program equips students with diverse skills necessary for tackling complex challenges across various industries, from fighter jets and e-commerce to medical software and video games. Unlike the broad foundation offered at the undergraduate level, the MCS program delves deeper, preparing students to handle large-scale projects and embrace leadership roles in the high-tech workforce. With a curriculum that balances rigorous theoretical knowledge with practical, industry-relevant skills, this program aligns with UVU's commitment to fostering lifelong learners and leaders poised to contribute significantly to a globally interdependent community.
Apply now

Enrollment Deadlines
Application deadline, program begins, fall semester, admission requirements.
To be considered for admission, make sure you have:
- A bachelor’s degree in computer science or a closely related field.
- An overall grade point average of 3.0 or higher.
- CS 2300 Discrete Structures I
- CS 2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures
- CS 2810 Computer Organization and Architecture
- CS 3060 Operating Systems Theory
- MATH 1210 Calculus I
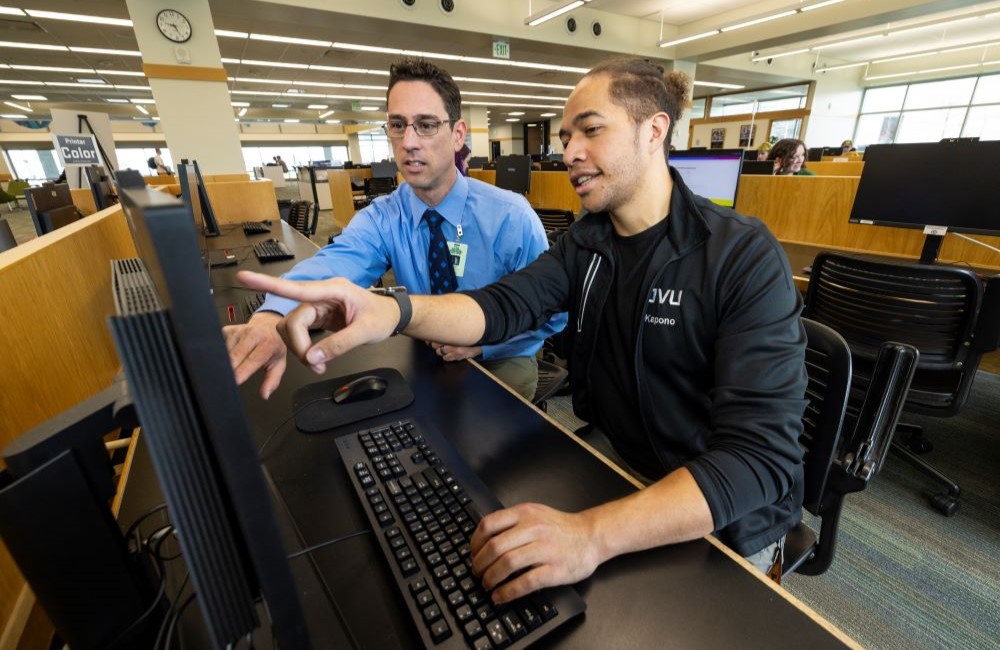

Admission Process
During the application process, you will also:
- Complete the online application, which includes an online statement of purpose.
- Provide two letters of recommendation with name and email.
- Send all official university transcripts.
- Pay the application fee.

You're Applying Right?
Get started today:, utah valley university.
Jump to navigation
- UTCS Direct
New Virtual Master’s Program in AI Breaks Traditional Learning Methods
Submitted by Anonymous on Tue, 02/20/2024 - 10:00am
by Cassandra Ozuna
The newly introduced Online Master's in Artificial Intelligence (MSAI) program at the University of Texas at Austin is strategically designed to meet the dynamic needs of the AI sector while placing a strong emphasis on ethical considerations. Throughout the program, students are immersed in challenging coursework, including a compulsory "Ethics in AI" course that underscores the importance of responsible AI utilization, incorporating assignments featuring AI tools such as ChatGPT. Boasting a flexible schedule and top-notch instructional videos, the program caters to a diverse student body worldwide, nurturing an active community via platforms like Slack and Discord. As UT's fastest-growing online master's offering, the MSAI not only imparts essential AI skills but also primes students for the swiftly expanding job market. This is particularly significant given projections indicating a staggering 97 million new AI-related positions within the next two years, underscoring the program's dedication to global knowledge dissemination.
Read the full article authored by Melanie Faz at The Daily Texan
- Undergraduate Office
- Graduate Office
- Office of External Affairs
- Mission Statement
- Emergency Information
- Site Policies
- Web Accessibility Policy
- Web Privacy Policy
- Graduate Catalog >
- Norm Asbjornson College of Engineering >
- Gianforte School of Computing >
M.S. In Cybersecurity
Montana State University's Gianforte School of Computing offers an MS in Cybersecurity. The MS in Cybersecurity requires a minimum of 30 post-baccalaureate credits and is designed for students who have earned a baccalaureate degree in Computer Science (CS) or a related program. Students may pursue the Master's degree under a thesis option or a courses-only option.
The MS in Cybersecurity is aligned with the requirements necessary to pursue the National Security Agency (NSA) Centers of Academic Excellence (CAE) Cyber Defense Education (CDE) certification. Two tracks (CDE-Masters) are currently being offered which will be validated as Technical Program of Studies (PoS) by CAE.
The courses listed below (for both tracks) are designed with outcomes that match Knowledge Units (KUs) necessary to meet certification criteria. A KU is a grouping of topics that needs to be covered by either a single or multiple courses in the PoS. In some cases, a single course may cover multiple KUs. CAE-CDE certification requires that students cover 22 KUs, and both programs are specifically designed to meet this criterion. For specific information regarding the mapping of KUs to courses, please contact Dr. Clemente Izurieta ([email protected]).
Thesis Master's candidates must present and defend their thesis in a public departmental seminar. The number of credits listed at the 500 level or higher (including thesis credits) on the program of study must total at least 21.
Required courses include:
- CSCI 532, Algorithms, 3 credits
- CSCI 538, Computability, 3 credits
- CSCI 590 (Master's Thesis option only), 10 credits
MS in Cybersecurity Program Requirements - ThesisTrack - 30 credits
Students on the thesis track must complete a Program of Study of at least 30 credits which includes at least 20 credits of coursework and 10 credits of thesis. The Program of Study is to be filled out during a student's first semester of graduate school in consultation with his or her advisor.
Note: To enter the program, a student will need to have earned a computer science or closely related bachelor's degree and have the equivalent knowledge of MSU's CSCI 112 (Programming in C) and CSCI 460 (Operating Systems) courses.
Required Courses (that MSU currently offers)
- CSCI 476, Computer Security, 3 credits
- CSCI 466, Computer Networks, 3 credits
- CSCI 521, Distributed System Implementation, 3 credits
- CSCI 540, Advanced Database Systems, 3 credits
- ESOF 422, Advanced Software Engineering, 3 credits
- CSCI 590, Thesis, 10 credits. The Thesis must be aligned with a cybersecurity topic and the student must make an academic contribution that advances the body of knowledge in the domain. CSCI 590 counts for 7 KUs.
MS in Cybersecurity Program Requirements - Courses-Only Track - 30 credits
Students on the courses-only track must complete a Program of Study of at least 30 credits. The Program of Study is to be filled out during a student's first semester of graduate school in consultation with his or her advisor.
Note: To enter the program, a student will need to have earned a computer engineering, electrical engineering or closely related bachelor's degree and have the equivalent knowledge of MSU's CSCI 112 (Programming in C) and CSCI 460 (Operating Systems) courses.
- CSCI 550, Advanced Data Mining, 3 credits
- 6 credits of elective courses at the discretion of the student in collaboration with an advisor.
Montana State University
P.O. Box 172220
Bozeman, MT 59717-2220
Telephone: (406) 994-6650
Fax: (406) 994-1972
Email: [email protected]
Location: 101 Montana Hall
Antoni Campeau
Print Options
Send Page to Printer
Print this page.
Download Page (PDF)
The PDF will include all information unique to this page.
Full Catalog
A PDF of the entire 2023-2024 catalog.

Best Online Computer Science Programs of 2024
More on our picks, oregon state university ecampus.
Vault Verified
Why we chose it: Oregon State University offers a reputable online computer science degree as well as the option to fast-track your education with a post-baccalaureate option that earns a degree in half the time. OSU is institutionally accredited by the Northwest Commission on Colleges and Universities (NWCCU). Students attending the university’s Ecampus can choose from two programs: applied computer science or cybersecurity, with an honors degree available.
- Cybersecurity degree option
- Fast-track post-bacc option
- 89% acceptance rate
- 180 credits required for bachelor’s
- Price rises to $561 per credit hour for post-baccalaureate degree
- 65% graduation rate
Arizona State University
Why we chose it: Students at Arizona State University Online can choose a bachelor’s in computer science, earning the same degree as students who attend the school on campus. ASU (including its online program) is a large public university accredited by the Higher Learning Commission (HLC).
- ABET-accredited program
- Same course content as on-campus courses
- 70% acceptance rate
- Credits hours are pricey
- Minimum test scores required for admission
- Transfer students need a 3.0 GPA or better
University of Florida
Why we chose it: Students at the University of Florida Online can combine a liberal arts foundation with computer science skills when they enroll in the B.S. in computer science program. This medium-sized public school, which is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges (SACSCOC), offers a very low average cost ($4,500) and high average earnings compared to the median.
- 72% graduation rate
- Low in-state tuition
- High average earnings compared to median
- Test scores required for admission
- 66% admissions rate
- Higher tuition for out-of-state students
Florida International University
Why we chose it: Students at Florida International University, a large public institution based in Miami, have the option to earn an online B.A. in computer science. This is an online CS degree with a twist: students can add skills in other fields, such as business or health. This may make you more marketable and open the door to solving technology programs in other fields. A B.A. or B.S. in information technology and a B.S. in computer engineering are a few of the other fully-online options at FIU. FIU’s computer science undergraduate programs are accredited by ABET.
- B.A. in computer science is less math-and-science-heavy than a B.S.
- Affordable tuition for in-state students
- ABET accredited
- Costly for out-of-state students
- A B.A. degree won’t be the right fit for some students
- 67% graduation rate
Georgia Tech
Why we chose it: For students looking for an affordable, graduate-level computer science degree, the Online Master of Science in Computer Science (OMSCS) from Georgia Institute of Technology may be worth exploring. This program offers an M.S. via a massive open online course (MOOC) format, which provides asynchronous instruction for just $180 per credit hour. You can take up to six years to graduate.
- Affordable graduate-level degree
- Self-paced instruction
- Federal aid eligible
- 16% acceptance rate
- Not all students are seeking a graduate degree
- MOOC format may not be suitable for some students
University of North Dakota
- ABET-accredited
- Access to on-campus computing labs
- Select courses offer synchronous lectures
- 52% graduation rate
- Asynchronous format may be challenging for some students
University of Colorado Boulder
Why we chose it: If you already have a bachelor’s degree but want to go back to school for computer science, the University of Colorado Boulder offers a post-baccalaureate option. There’s also a master’s in computer science degree option with no bachelor’s required. UC Boulder offers working adults flexibility, free tutoring, outstanding student support and accelerated degree options.
- Post-bacc and master’s options
- Robust student support services
- Test scores not required for admission
- May not be a fit for first-time students
- No traditional bachelor’s option for computer science
Why we chose it: An online computer science degree from Auburn University is ideal for transfer students or someone seeking a second degree. As a large public university based in Auburn, Alabama, the school offers flexible education from an ABET-accredited program.
- Fully online
- Requires 60 credit hours to graduate
- Test scores recommended for admission
- More suitable for transfer students
University of Missouri – St. Louis
Why we chose it: Students at the University of Missouri–St. Louis have several options for earning an online computer science degree, including a B.S. in computer science, B.S. in computing technology and a B.S. in cybersecurity with an emphasis in computer science. You can also earn online certificates in computer programming, cybersecurity, mobile apps and computing. All online computer science programs at this mid-sized public university are STEM-designated, and the school is recognized by the Department of Homeland Security and National Security Administration for excellence in cybersecurity education.
- Multiple degree options
- STEM-designated programs
- DHS/NSA-recognized programs
- 59% graduation rate
- 57% acceptance rate
- Average earnings post-graduation
Regis University
Why we chose it: Regis University is a medium-sized private school based in Denver, Colorado, and accredited by the Higher Learning Commission (HLC). Its undergraduate computer science program is accredited by ABET (formerly the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, Inc.) and can be completed entirely online. Motivated students have the option to earn their bachelor’s and master’s simultaneously with Regis’s FastForward program.
- 100% online program
- Can earn master’s simultaneously
- On the expensive side
- 58% graduation rate
- Low faculty diversity
How to Choose an Online Computer Science Program
Choosing the right online computer science program will depend on your reasons for choosing an online CS degree. Are you focused on flexibility, price or prestige? Narrow down your options for online computer science programs by considering the following factors:
- Accreditation: The school you choose must be an accredited institution. Regionally accredited schools are a good choice, and ABET accreditation for a computer science program is a reputable marker of quality.
- Cost: Look at the overall tuition you’ll need to pay, and consider whether speeding up your progress (such as with an accelerated program) will save you money. If you’re looking for an online degree completion program, check whether your current credits will transfer.
- Reputation: A university’s reputation doesn’t guarantee the sort of education you’ll receive, but it could open doors to post-graduate employment.
- Outcomes: Regarding employment, check out how graduates fare on the job market, what their average salary is and what kinds of employers hire them.
- Student support: Another factor that can determine your success at an online university is the level of student support you’ll receive. Look for schools that offer tutoring and student services as well as career coaching and support.
How To Apply
Applying to an online computer science program is much like applying to any other online college: You’ll provide your personal information, academic history, letters of reference and other documents. And you may need to pay an application fee. When you’ve chosen a school that seems to meet your needs, you can apply online using the following steps.
- Submit the correct application: You may need to use a specific application type depending on the number of transferable credits you have. Some schools require you to apply using an application specific to the online program, while others accept both the Common App and direct application. Check carefully that you’re using the right application for the program you’re interested in and your previous college credits (if any).
- Transcript: Typically, you’ll need to provide information about your prior academic history, whether that’s your official high school transcript, your previous bachelor’s degree, or something else. The school will specify during the application process what documentation is required.
- Test scores: If your application requires standardized test scores or college placement information, you may need to arrange to have these sent to the school directly from the testing service. This is more likely if you’ve graduated from high school within the past few years.
- Essay: Some applicants may be required to submit an essay for admission. Take the time to craft a personalized essay according to the application prompt and submit it in the proper format.
- Track your application: You may be able to complete your application in stages, saving it and resuming your work later. After you’ve submitted your application, paid any necessary application fees, and uploaded your documents, track your application progress to make sure you don’t miss any requests for more documentation from the school.
Should You Enroll in a Computer Science Program?
A computer science degree can lay the foundation for your career and help uplevel your salary. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) , the average annual salary for computer science and information technology professionals was $100,530 as of May 2022, more than double the median annual salary of $46,310.
But incomes are never guaranteed, and you’ll need to weigh the price of your education against your future earnings prospects as well as the opportunity cost of spending two years or more studying for a new degree. As you consider whether enrolling in an online computer science program is worth it, keep in mind the following factors.
Career Opportunities
The number of open roles in computer science is expected to outpace many other fields, with an average of 377,500 openings projected each year, according to the BLS. Completing an online computer science degree can open the door to new jobs and even whole new careers, including programming, software development, data analysis and cybersecurity.
Income Potential
According to data from the U.S. Department of Education , graduates of our top 10 online computer science programs earn an average of $50,876 to $96,375 annually in the years after completing their degree.
Online Convenience
If your question isn’t whether you should get a computer science degree, but whether to complete it online, consider how important convenience and flexibility are to you. If you’re a busy working adult with family or volunteer commitments, online classes might best fit your schedule. Online schools also allow you to skip the hassle of meeting on campus, so you won’t need to worry about commuting, parking or paying for room and board.
Cost is often another factor when deciding what degree to earn and where to earn it. While not every choice on our list has a discounted price tag, you’ll often find that online colleges offer a more affordable path to a degree compared to traditional residential schools.
How To Pay for Your Degree
If you want to get your CS degree online, you have a few options for paying for it. Filling out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) can help you and your university determine whether you’re eligible for federal student loans, grants or other types of aid. Some universities may require you to complete a CSS Profile, which helps determine whether you’re eligible for non-federal student aid.
- Financial aid: This includes federal Direct Loans, which may be subsidized or unsubsidized by the federal government. These loans must be repaid after you graduate. PLUS loans are federal loans for graduate or professional students or parents of students. Federal grants, such as Pell grants, do not need to be repaid. Federal work-study provides employment which helps students pay for school.
- Scholarships: Scholarships may be given by the school, a department within the school, or an outside organization to help you pay for tuition. They don’t need to be repaid but they can be taxable in some instances.
- Employer funding: Many employers offer tuition assistance to employees to help pay for college, although the amount and timeline may depend on whether you’re full-time or part-time and how long you’ve been with the company, among other factors.
- Tuition assistance: Military members may be able to use Tuition Assistance to pay for college while on duty, up to $4,500 per year depending on the branch.
Accreditation for Online Computer Science Degrees
A university’s accreditation shows it complies with certain quality standards as determined by the accrediting agency. Choosing an accredited online school helps you ensure that you’re paying for high-quality instruction, not a diploma mill, and it’s also a requirement to receive federal financial aid.
For online computer science degrees, the program’s accreditation can be important too. Many CS programs are accredited by ABET, which evaluates the course content, assessments, student outcomes and several other factors. A CS program that is ABET-accredited has demonstrated that it meets these standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are online computer science degrees worth it.
Online computer science degrees, just like any other CS degree, can help you find a new job and earn a good salary. The only difference is that you’ve completed your education remotely instead of attending classes on campus. According to the U.S. Department of Education , the median salary for computer and IT jobs tops six figures and more than 680,000 jobs in this field are expected to be added by 2031. So an online computer science degree could be a valuable investment in your career.
Is It Better to Learn Computer Science Online or In Person?
The best learning format for computer science will depend on your preferences as a student. If you prefer to study at your own pace, need more flexibility and have the discipline to manage your time and assignments from home, online school could be a good fit. On the other hand, if face time with your professor and classmates is a higher priority and you depend on the routine of traveling to class, you may find an on-campus degree to be a better option.
What Are Some High-Paying Jobs I Can Get With A Computer Science Degree?
With a bachelor’s degree, the average salary for computer network architects is $126,900. For database administrators, it’s $112,120, and for information security analysts, it’s $112,00. You can see more median salaries for this industry by checking the BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook .
Article Sources
At Newsweek Vault, our team of dedicated writers and editors are not just experts in their respective fields but also committed to delivering content that meets the highest standards of journalistic integrity. We analyze primary sources, including peer-reviewed studies, authoritative government sites and insights from leading industry professionals and ensure that every piece of information is researched, fact-checked and presented with accuracy and relevance.
- Occupational Outlook Handbook . U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Accessed on March 31, 2024.
- Compare Schools and Fields of Study . U.S. Department of Education. Accessed on March 31, 2024.
- Computer Science Education Week: Explore In-Demand IT Jobs . U.S. Department of Labor Blog. Accessed on March 31, 2024.
The post Best Online Computer Science Programs of 2024 first appeared on Newsweek Vault .

Tepper School of Business

An MBA Designed for The Intelligent Future
Explore Program Formats
The business landscape is changing, and you can co-create its future.
Tepper’s stem-designated mba program delivers the analytical and leadership skills you’ll need to lead where human intelligence unleashes the power of data, and interdisciplinary teamwork drives innovation..
- MBA Curriculum
- MBA Programs
- MBA Admissions
Request Information
Start your application, a top-ranked mba program, #16 business school, u.s. news & world report, #2 online mba.
See More Rankings
MBA Formats
- September-May
- Varied schedule
- Summer internship
Online Hybrid
- Flexible online courses
- Several immersive Access Weekends each year
Accelerated
- For individuals with undergrad business coursework experience
- Same Full-Time MBA or Online Hybrid MBA degree. Faster.
- Full-Time Accelerated: 16 months with internship; 12 months without internship
- Online Hybrid Accelerated: 24 months
No class profile available
Teamwork Is Our Engine
You will never find a “one-size-fits-all” program at tepper. here, you will see smart students contribute diverse outlooks and skillsets to form a surprisingly close-knit community . together, you’ll collaborate to solve tough business challenges using data and creativity., with a powerful combination of advanced analytics and personalized leadership coaching , the tepper mba gives you a formidable advantage over the competition..

Chart Your Path to a Tepper MBA
Follow 7 steps to progress toward admission ... and earn an application fee waiver.
Full-Time Path
Online Hybrid Path

Are You a "Right Fit" Candidate?
The admit.me index (ami) — a free, automated profile review for mba candidates — gives you a candidate profile score, details of what affected your score, and recommends opportunities to strengthen your candidacy., the score is not expressly indicative of your likelihood of being admitted into the tepper mba program and we encourage you to contact our admissions team to discuss your results..

Conversations About Life at Tepper
On the student-led humans of tepper podcast, students, alumni, and faculty discuss their tepper experiences..
Browse Podcast Episodes

Life at Tepper

Entrepreneurship

- Tepper 2023
- Course List
- Academic Calendar
- Privacy Policy
- Statement of Assurance
- Tepper Information Center
- Journalists & Media
- Tepper Gear Store

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Overview. In the Stanford Computer Science Master's degree, you will complete coursework covering the fundamental aspects of computer science and deepen your expertise in at least one specialized area of study. If you want to pursue the degree on a part-time basis, so as not to interrupt your career, you can enroll in as few as one course per ...
The 100% online NYU Tandon Bridge course prepares students without a Computer Science degree or other substantial programming experience to apply for select NYU Tandon master's degree programs. In the course, students will learn computer science fundamentals and programming with C++. Learn More about Bridge.
The MS-CS on Coursera's broad curriculum directly reflects a career in the field of computer science. You will complete 15 credits of breadth coursework across five full specializations in algorithms, software architecture, machine learning, ethics and computing, and systems. You will also choose 15 credits of elective courses across a variety ...
You'll learn advanced concepts in computer science topics, such as software design, computer language theory, programming, and computer architecture. While your exact coursework will vary by the program you choose, you can expect to study key concepts, including: Software development. Computer systems. Data structures. Algorithms and computation.
The MS program in computer science prepares students to undertake fundamental and applied research in computing. The program welcomes motivated and dedicated students to work with world-class faculty on projects across the field of computing and augmented intelligence. Students may choose a thesis or nonthesis option as their culminating event.
Vanderbilt University's MS in computer science program from the electrical engineering and computer science department offers both thesis and non-thesis degree options. The thesis option is research-heavy and requires students to write and defend a research thesis. The non-thesis option is coursework-only.
The Computer Science M.S. program provides students with two options to deepen their understanding of computer science topics: the coursework option and the thesis option. All M.S. students are initially admitted under the coursework option but may elect the thesis option by selecting an M.S. thesis adviser. The information below is an overview ...
Programs. We offer three program options for Computer Science that can be earned completely online; an online Master of Science in Computer Science or earn a Post-Master's Computer Science Certificate via online, hybrid, or on-site courses. Master's Degree Admissions and Program Requirements Post-Master's Certificate Admissions and ...
The Master of Science in Computer Science is a course offered by Northeastern's Boston Campus. Learn more and register today. ... Positions requiring a master's in computer science are expected to have a job growth rate of +22%, compared to the average job growth rate of 7-8% (2020-2030, USBLS).
Computer Science Master's Degree Program. Develop advanced technical skills and knowledge to solve real-world challenges. Online Courses. 11 out of 12 total courses. On-Campus Experience. One 3-week summer course. Tuition. $3,220 per course. Get Info.
The Master of Science with a Major in Computer Science (MSCS) is a rigorous degree program that includes advanced coursework and research activities on a wide range of computer science subjects such as artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, databases, data science, human-computer interaction, networking, scientific computing, and high ...
As a nondegree-seeking graduate student, you can take master's-level computer science courses without being admitted to the program. This provides you the opportunity to establish a high graduate GPA, try out courses, meet the English proficiency requirement or earn a professional certification credential.
Tuition rates for master's in computer science online programs vary significantly among schools. Tuition for our ranked programs—which include both public and private colleges—ranges from ...
The Master of Science in Computer Science degree prepares students to do meaningful research and to acquire vital skills and insights for solving some of the world's most complex technological challenges. ... Yes, you can take courses outside of computer science. They must be graduate level (2XX) courses, that are 4 units each, related to ...
The Master of Science (MS) program is intended for people who wish to broaden and deepen their understanding of Computer Science. Columbia University and the New York City environment provide excellent career opportunities in multiple industries. ... If you are interested in applying a specialized Topics in Computer Science courses (COMS 4995 ...
Requirements for a CS master's degree. In the United States, the common requirements for completing a master's degree in computer science include completing a set number of course credits (anywhere from 30 to 60 credits, depending on the program), producing a thesis or capstone project, and fulfilling other factors around timeliness and ...
Use the link at left to download our MS program overview in PDF. In addition to the Graduate College minimum requirements, students must meet the following program requirements: Coursework: At least 28 hours (plus thesis hours), 32 hours (plus project hours), 36 hours (for coursework only). 12 hours (for thesis and project options) and 16 hours ...
The M.S. degree program requires all students to complete 30 credits according to the following degree requirements. Students must: complete one of the degree-required options/concentrations (accounts for 6 credit units). Research option (requires the approval of a supervising professor): Students must enroll in CUS 795 and CUS 796 Master's ...
In demand globally. You can use the Master of Computer Science as a pathway to a PhD or to the workforce, where you may meet our alumni working in software design, cybersecurity, information architecture and programming. If you're looking for networks to help with internships and job opportunities, or the funds to help you get to Melbourne ...
The Master of Computer Science is a postgraduate coursework degree. You will complete core, foundation and specialist units, and have the opportunity to undertake a specialisation. You will also complete a professional capstone or research project. You will complete: 4 x foundation subjects; 3 x computing professional core subjects
Master advanced computer science concepts in the following areas: algorithms design and analysis, database systems, software engineering, and systems. Students can complete a thesis or opt for additional coursework. Students who choose the thesis option will have the opportunity to conduct research with AUM faculty.
Compulsory Courses:1. 9 course units in computer science (CSI) at the graduate level, including: 9 Units. 3 course units in Software Engineering (Category E)2. 3 course units in the Theory of Computing (Category T)2. 3 course units in Computer Applications (Category A) or in Computer Systems (Category S)2.
A bachelor's degree with Honours or a equivalent in Computer Science/Information Technology/related field from a recognized university with a CGPA of 3.0 and above/equivalent, OR A bachelor's degree in Computer Science/Information Technology/related field from a recognized university with a CGPA in the range of 2.50 - 2.99/equivalent can be considered provided the fulfilment of the ...
UVU's Master of Computer Science (MCS) program equips students with diverse skills necessary for tackling complex challenges across various industries, from fighter jets and e-commerce to medical software and video games. Unlike the broad foundation offered at the undergraduate level, the MCS program delves deeper, preparing students to handle ...
The newly introduced Online Master's in Artificial Intelligence (MSAI) program at the University of Texas at Austin is strategically designed to meet the dynamic needs of the AI sector while placing a strong emphasis on ethical considerations. Throughout the program, students are immersed in challenging coursework, including a compulsory "Ethics in AI" course that underscores
Montana State University's Gianforte School of Computing offers an MS in Cybersecurity. The MS in Cybersecurity requires a minimum of 30 post-baccalaureate credits and is designed for students who have earned a baccalaureate degree in Computer Science (CS) or a related program. Students may pursue the Master's degree under a thesis option or a courses-only option.
Why we chose it: Students at Florida International University, a large public institution based in Miami, have the option to earn an online B.A. in computer science. This is an online CS degree ...
If you're looking to get started as a computer scientist, explore a bachelor's or master's degree in computer science offered on Coursera. ... Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals. Coursera Footer.
The Master of Science in Business Analytics program requires 30 credits (10 courses): 18 credits of core courses, 9 credits of electives, and a required 3-credit applied capstone course. The program follows the 8-week module format and courses are offered in the evening to accommodate working professionals.
Tepper MBA The business landscape is changing, and you can co-create its future. Tepper's STEM-designated MBA program delivers the analytical and leadership skills you'll need to lead where human intelligence unleashes the power of data, and interdisciplinary teamwork drives innovation.