Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

MLA Works Cited Page: Basic Format

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
According to MLA style, you must have a Works Cited page at the end of your research paper. All entries in the Works Cited page must correspond to the works cited in your main text.
Basic rules
- Begin your Works Cited page on a separate page at the end of your research paper. It should have the same one-inch margins and last name, page number header as the rest of your paper.
- Only the title should be centered. The citation entries themselves should be aligned with the left margin.
- Double space all citations, but do not skip spaces between entries.
- Indent the second and subsequent lines of citations by 0.5 inches to create a hanging indent.
- List page numbers of sources efficiently, when needed. If you refer to a journal article that appeared on pages 225 through 250, list the page numbers on your Works Cited page as pp. 225-50 (Note: MLA style dictates that you should omit the first sets of repeated digits. In our example, the digit in the hundreds place is repeated between 2 25 and 2 50, so you omit the 2 from 250 in the citation: pp. 225-50). If the excerpt spans multiple pages, use “pp.” Note that MLA style uses a hyphen in a span of pages.
- If only one page of a print source is used, mark it with the abbreviation “p.” before the page number (e.g., p. 157). If a span of pages is used, mark it with the abbreviation “pp.” before the page number (e.g., pp. 157-68).
- If you're citing an article or a publication that was originally issued in print form but that you retrieved from an online database, you should type the online database name in italics. You do not need to provide subscription information in addition to the database name.
- For online sources, you should include a location to show readers where you found the source. Many scholarly databases use a DOI (digital object identifier). Use a DOI in your citation if you can; otherwise use a URL. Delete “http://” from URLs. The DOI or URL is usually the last element in a citation and should be followed by a period.
- All works cited entries end with a period.
Additional basic rules new to MLA 2021
New to MLA 2021:
- Apps and databases should be cited only when they are containers of the particular works you are citing, such as when they are the platforms of publication of the works in their entirety, and not an intermediary that redirects your access to a source published somewhere else, such as another platform. For example, the Philosophy Books app should be cited as a container when you use one of its many works, since the app contains them in their entirety. However, a PDF article saved to the Dropbox app is published somewhere else, and so the app should not be cited as a container.
- If it is important that your readers know an author’s/person’s pseudonym, stage-name, or various other names, then you should generally cite the better-known form of author’s/person’s name. For example, since the author of Alice's Adventures in Wonderland is better-known by his pseudonym, cite Lewis Carroll opposed to Charles Dodgson (real name).
- For annotated bibliographies , annotations should be appended at the end of a source/entry with one-inch indentations from where the entry begins. Annotations may be written as concise phrases or complete sentences, generally not exceeding one paragraph in length.
Capitalization and punctuation
- Capitalize each word in the titles of articles, books, etc, but do not capitalize articles (the, an), prepositions, or conjunctions unless one is the first word of the title or subtitle: Gone with the Wind, The Art of War, There Is Nothing Left to Lose .
- Use italics (instead of underlining) for titles of larger works (books, magazines) and quotation marks for titles of shorter works (poems, articles)
Listing author names
Entries are listed alphabetically by the author's last name (or, for entire edited collections, editor names). Author names are written with the last name first, then the first name, and then the middle name or middle initial when needed:
Do not list titles (Dr., Sir, Saint, etc.) or degrees (PhD, MA, DDS, etc.) with names. A book listing an author named "John Bigbrain, PhD" appears simply as "Bigbrain, John." Do, however, include suffixes like "Jr." or "II." Putting it all together, a work by Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. would be cited as "King, Martin Luther, Jr." Here the suffix following the first or middle name and a comma.
More than one work by an author
If you have cited more than one work by a particular author, order the entries alphabetically by title, and use three hyphens in place of the author's name for every entry after the first:
Burke, Kenneth. A Grammar of Motives . [...]
---. A Rhetoric of Motives . [...]
When an author or collection editor appears both as the sole author of a text and as the first author of a group, list solo-author entries first:
Heller, Steven, ed. The Education of an E-Designer .
Heller, Steven, and Karen Pomeroy. Design Literacy: Understanding Graphic Design.
Work with no known author
Alphabetize works with no known author by their title; use a shortened version of the title in the parenthetical citations in your paper. In this case, Boring Postcards USA has no known author:
Baudrillard, Jean. Simulacra and Simulations. [...]
Boring Postcards USA [...]
Burke, Kenneth. A Rhetoric of Motives . [...]
Work by an author using a pseudonym or stage-name
New to MLA 9th edition, there are now steps to take for citing works by an author or authors using a pseudonym, stage-name, or different name.
If the person you wish to cite is well-known, cite the better-known form of the name of the author. For example, since Lewis Carroll is not only a pseudonym of Charles Dodgson , but also the better-known form of the author’s name, cite the former name opposed to the latter.
If the real name of the author is less well-known than their pseudonym, cite the author’s pseudonym in square brackets following the citation of their real name: “Christie, Agatha [Mary Westmacott].”
Authors who published various works under many names may be cited under a single form of the author’s name. When the form of the name you wish to cite differs from that which appears on the author’s work, include the latter in square brackets following an italicized published as : “Irving, Washington [ published as Knickerbocker, Diedrich].”.
Another acceptable option, in cases where there are only two forms of the author’s name, is to cite both forms of the author’s names as separate entries along with cross-references in square brackets: “Eliot, George [ see also Evans, Mary Anne].”.
Explore our new content updates to the MLA Handbook Plus platform!
What’s New on MLA Handbook Plus ?
What is mla handbook plus .
MLA Handbook Plus is a new, subscription-based digital product providing online access to the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook. To learn more about MLA Handbook… Read More
What’s New in the Ninth Edition of the MLA Handbook (Spring 2021)
Published in April 2021, the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook works as both a textbook and a reference guide. You can order a copy… Read More
MLA Guide to Digital Literacy , 2nd Edition: An Interview with the Author
by Ellen C. Carillo
Ellen C. Carillo talks to the MLA about the MLA Guide to Digital Literacy , second edition. Read More
Forego versus Forgo
by Erika Suffern
Learn the difference between forego and forgo. Read More
Teaching Resources
A Century of Queer Korean Fiction : An Interview with Samuel Perry
Toward Educational Justice: An Interview with the Editors of Teaching Literature and Writing in Prisons
Henrique Maximiano Coelho Neto’s Sphinx: A Neo-Gothic Novel from Brazil : An Interview with M. Elizabeth Ginway
A Reflection on Disability Studies: Enabling the Humanities on Its Twentieth Anniversary
Teaching Claire de Duras’s Ourika
Teaching Nineteenth-Century Activist Rhetorics Today: An Interview
How and Why to Teach Late-Twentieth-Century Mexicana and Chicana Writers: An Interview
Advice from the Editors
Was and Were with the Subjunctive
Their , There , and They’re : Learn the Difference
Attributive Nouns; or, Why There Is Sometimes No Apostrophe in Terms Such As Teachers Union
Terms for Key Concepts
Laying versus Lying
Getting to the Bottom of Principle and Principal
Does It Really Go without Saying? On Needless Phrases
Ask the MLA
How do i cite a work that has incorrect citation information on its cover sheet.
Some works, especially works contained in databases, may list citation information for the work on a cover sheet or in a footer. If that citation… Read More
How do I cite Twitter now that its name has changed to X?
In 2023 the social media platform Twitter changed its name to X . What does this change mean for citations? When you cite a post published… Read More
How do I cite several e-mails sent on the same day to the same correspondent?
If you are citing several e-mails sent on the same day to the same correspondent, use the subject line of the e-mail to differentiate between… Read More
MLA Style, 9th Edition: Citing a website
- Citing a book
- Citing a newspaper article
- Citing a journal or magazine article
- Citing a website
MLA Core Elements to an entry for a "Works Cited" list
The 9th edition of MLA uses nine core elements to create a works cited entry. Using the information you have, you can create an entry for a source by following the order of the core elements listed below. If a core element does not apply to your source or is missing then proceed to the next core element. Using the core elements correctly requires an understanding of "containers." A source may be part of a larger work or collection (with one or more containers), or it may be a stand alone self-contained work. See the MLA Works Cited: A Quick Guide and use the practice template to better understand this concept.
MLA Optional Elements to an entry for a "Works Cited" list
Optional elements are just what they sound like; they are included at the writer's discretion. They may follow at the end of the entry, or they may follow one of the core elements if there is an element that they clarify. Some optional elements that might be included are: date of original publication, city of publication, the date that you accessed an online source, and other factual items about the source that will assist the reader in locating the item . [MLA Handbook, pages 50-53]
Want to learn more? See Optional Elements: A Primer at the MLA website.
Article from a website, + optional element
Web page + optional element, in-text citations.
Inside your paper, give credit to the works you quote.
See examples of how to tell your readers where facts, paraphrases, or quotes in your paper come from at this site from the Purdue OWL: MLA In-text Citations .
- << Previous: Citing a journal or magazine article
- Last Updated: Oct 1, 2023 6:46 PM
- URL: https://libguides.bgsu.edu/MLA
Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- How to format your MLA Works Cited page
MLA Works Cited | 2021 Guidelines & Free Template
Published on June 7, 2021 by Shona McCombes . Revised on March 5, 2024.
In MLA style , the list of Works Cited (also known as a reference list or bibliography) appears at the end of your paper. It gives full details of every source that you cited in an MLA in-text citation .
Like the rest of an MLA format paper, the Works Cited should be left-aligned and double-spaced with 1-inch margins.
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Formatting the works cited page, examples of works cited entries, authors and titles in the works cited list, ordering the list of works cited, frequently asked questions about the works cited.
The Works Cited appears at the end of your paper. The layout is similar to the rest of an MLA format paper :
- Title the page Works Cited, centered and in plain text (no italics, bold, or underline).
- Alphabetize the entries by the author’s last name.
- Use left alignment and double line spacing (no extra space between entries).
- Use a hanging indent on entries that run over onto additional lines.
- Include a header with your last name and the page number in the top right corner.
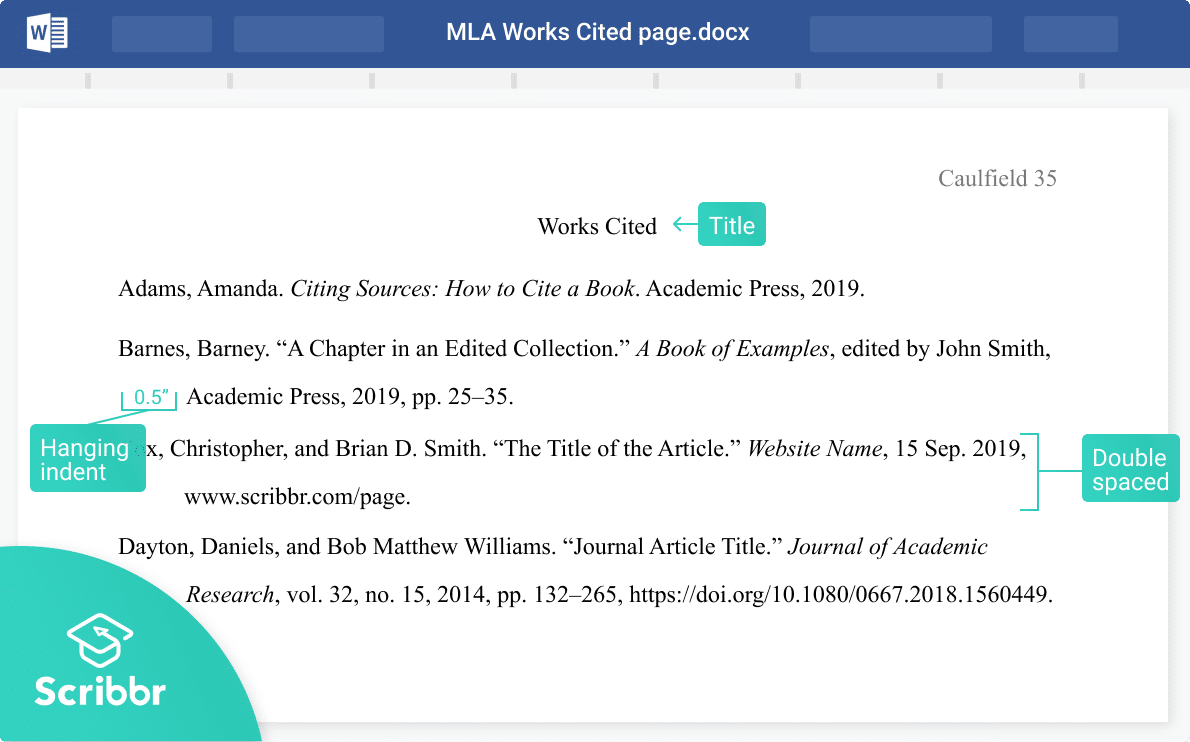
Creating a hanging indent
If an entry is more than one line long, each line after the first must be indented 0.5 inches. This is called a hanging indent, and it helps the reader see where one entry ends and the next begins.
In Microsoft Word, you can create a hanging indent on all entries at once.
- Highlight the whole list and right click to open the Paragraph options.
- Under Indentation > Special , choose Hanging from the drop-down menu.
- Set the indent to 0.5 inches or 1.27cm.
If you’re using Google Docs, the steps are slightly different.
- Highlight the whole list and click on Format > Align and indent > Indentation options .
- Under Special indent , choose Hanging from the dropdown menu.
You can also use our free template to create your Works Cited page in Microsoft Word or Google Docs.
Download Word template Copy Google Docs template
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
MLA provides nine core elements that you can use to build a reference for any source. Mouse over the example below to see how they work.
Author. “Title of the Source.” Title of the Container , Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location.
You only include the elements that are relevant to the type of source you’re citing.
Use the interactive tool to see different versions of an MLA Works Cited entry.
Examples for common source types
The main elements of a book citation are the author, title (italicized), publisher, and year.
- Morrison, Toni. The Bluest Eye . Vintage International, 2007.
If there are other contributors (such as editors or translators), or if you consulted a particular volume or edition of a book, these elements should also be included in the citation.
Book chapter
If a book is a collection of chapters by different authors, you should cite the author and title of the specific work. The container gives details of the book, and the location is the page range on which the chapter appears.
- Andrews, Kehinde. “The Challenge for Black Studies in the Neoliberal University.” Decolonising the University , edited by Gurminder K. Bhambra et al., Pluto Press, 2018, pp. 149–144.
This format also applies to works collected in anthologies (such as poems , plays , or stories ).
Journal article
Journals usually have volume and issue numbers, but no publisher is required. If you accessed the article through a database, this is included as a second container. The DOI provides a stable link to the article.
- Salenius, Sirpa. “Marginalized Identities and Spaces: James Baldwin’s Harlem, New York.” Journal of Black Studies , vol. 48, no. 8, Jul. 2016, pp. 883–902. Sage Journals , https://doi.org/10.1177/0021934716658862.
If there is no DOI, look for a stable URL or permalink instead. Omit the “https://” prefix if using a URL or permalink, but always include it with a DOI.
For websites (including online newspapers and magazines), you usually don’t have to include a publisher. The URL is included, with the “https://” prefix removed. If a web page has no publication date , add an access date instead.
- Coates, Ta-Nehisi. “The Case for Reparations.” The Atlantic , Jun. 2014, www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2014/06/the-case-for-reparations/361631/.
If a web page has no publication date, add an access date instead.
More MLA citation examples
We also have examples for a wide range of other source types.
Play | Poem | Short story | Movie | YouTube video | Newspaper | Interview | Lecture | PowerPoint Image | Song | Podcast | TV show | PDF | TED Talk | Bible | Shakespeare | Constitution
There are a few important formatting rules when writing author names and titles in your Works Cited entries.
Author names
Author names are inverted in the Works Cited list. However, when a second author is listed, their name is not inverted. When a source has three or more authors, only the first author is listed, followed by “ et al. ” (Latin for “and others”). A corporate author may sometimes be listed instead of an individual.
- Smith, John.
- Smith, John, and David Jones.
- Smith, John, et al.
When no author is listed for a source, the Works Cited entry instead begins with the source title. The in-text citation should always match the first element of the Works Cited entry, so in these cases, it begins with the title (shortened if necessary) instead of the author’s last name.
Oxford Classical Dictionary . 4th ed., Oxford UP, 2012.
( Oxford Classical Dictionary )
Source and container titles
The titles of sources and containers are always written in title case (all major words capitalized).
Sources that are part of a larger work (e.g. a chapter in a book, an article in a periodical, a page on a website) are enclosed in quotation marks. The titles of self-contained sources (e.g. a book, a movie, a periodical, a website) are instead italicized. A title in the container position is always italicized.
If a source has no title, provide a description of the source instead. Only the first word of this description is capitalized, and no italics or quotation marks are used.
- Kafka, Franz. “The Metamorphosis.” The Metamorphosis and Other Stories , . . .
- Eliot, George. Middlemarch . . . .
- Mackintosh, Charles Rennie. Chair of stained oak . . . .
Arrange the entries in your Works Cited list alphabetically by the author’s last name. See here for information on formatting annotations in an MLA annotated bibliography.
Multiple sources by the same author(s)
If your Works Cited list includes more than one work by a particular author, arrange these sources alphabetically by title. In place of the author element, write three em dashes for each source listed after the first.
The same applies to works by the same group of authors; replace the author element with three em dashes for subsequent sources.
Note, however, that two sources by “Smith, John, et al.” aren’t necessarily by the exact same authors; the authors represented by “et al.” could be different. Only use the three em dashes if the group of authors is exactly the same in each case; otherwise, repeat the author name and “et al.”
One author in combination with different coauthors
Sometimes, multiple entries will start with the same author, but in combination with different coauthors. Works by the author alone should come first, then works by two authors, and finally works by three or more authors (i.e., entries containing “et al.”).
Within this, sources with two authors are alphabetized by the second author’s last name , while sources using “et al.” are instead alphabetized by the title of the source.
Sources with no author
If there is no author, alphabetize the source based on the title of the work. Ignore articles ( the, a , and an ) for the purposes of alphabetization. If a title begins with a number, alphabetize it as you would if the number was spelled out.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The MLA Works Cited lists every source that you cited in your paper. Each entry contains the author , title , and publication details of the source.
According to MLA format guidelines, the Works Cited page(s) should look like this:
- Running head containing your surname and the page number.
- The title, Works Cited, centered and in plain text.
- List of sources alphabetized by the author’s surname.
- Left-aligned.
- Double-spaced.
- 1-inch margins.
- Hanging indent applied to all entries.
To apply a hanging indent to your reference list or Works Cited list in Word or Google Docs, follow the steps below.
Microsoft Word:
- Under Indentation > Special , choose Hanging from the dropdown menu.
Google Docs:
- Highlight the whole list and click on Format > Align and indent > Indentation options .
- Under Special indent , choose Hanging from the dropdown menu.
When the hanging indent is applied, for each reference, every line except the first is indented. This helps the reader see where one entry ends and the next begins.
A standard MLA Works Cited entry is structured as follows:
Only include information that is available for and relevant to your source.
If a source has two authors, name both authors in your MLA in-text citation and Works Cited entry. If there are three or more authors, name only the first author, followed by et al.
Yes. MLA style uses title case, which means that all principal words (nouns, pronouns , verbs, adjectives , adverbs , and some conjunctions ) are capitalized.
This applies to titles of sources as well as the title of, and subheadings in, your paper. Use MLA capitalization style even when the original source title uses different capitalization .
The fastest and most accurate way to create MLA citations is by using Scribbr’s MLA Citation Generator .
Search by book title, page URL, or journal DOI to automatically generate flawless citations, or cite manually using the simple citation forms.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2024, March 05). MLA Works Cited | 2021 Guidelines & Free Template. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/works-cited/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, a complete guide to mla in-text citations, how to cite a book in mla, how to cite a website in mla, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Please sign in
You need to log in to use the bookmarking feature.

- Baker Library
- Special Collections
- Fast Answers
- All Services
- Plan Your Visit
- Working Knowledge
- Academic Programs
- Faculty & Research
- Harvard Business Review
- Initiatives
- Map / Directions
Purdue Owl: MLA Formatting & Style Guide
Developed by the Purdue Online Writing Lab. MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Author/Editor (By:)
Contributor, corporate author, related organizations, citation type.
Citation Guide
- A Quick Guide to Resources
Subject Guide

Changes in 9th edition
The 9th edition of the MLA Handbook was published in 2021. In this update, the format for both in-text and Works Cited citations is the same as the 8th edition. The 9th edition also includes this clarification on citing a film/DVD.
A film/DVD: Generally list film directors as key contributors in the Contributor element Blade Runner . 1982. Directed by Ridley Scott, director’s cut, Warner Bros., 1992.
Examples of MLA Style
In-text Citation
Creating a Works Cited Page
With MLA style, you must include a Works Cited page at the end of your paper. A Works Cited page is an alphabetical listing of the resources cited in your paper. Below are some examples of MLA style citations. Note: Some instructors may require access dates for websites or other pieces of information. Please check with your instructor if you have any questions.
- Official MLA Style Center
A Modern Language Association hosted website with information on MLA citation and related resources. The MLA Style Center does not contain the full text of the handbook, although it walks users through the process of creating an entry in the works cited list.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab
Online writing lab with formatting tips and sample papers. The "Cite your source automatically" feature on Purdue Owl pages is part of another website, and not recommended.
- Excelsior Writing Lab
Citation examples, videos, and formatting guides for MLA, APA, and Chicago styles.
- Citing Government Information using MLA
Information on citing government print and electronic resources using MLA citation style. (Courtesy of the University of Nevada-Reno)
- << Previous: Basic APA
- Next: If I Apply >>
- Last Updated: Sep 14, 2023 4:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.pnw.edu/c.php?g=1300509
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!

😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.

🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's MLA Citation Generator?
It's super easy to create MLA style citations with our MLA Citation Generator. Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form.
The generator will produce a formatted MLA citation that can be copied and pasted directly into your document, or saved to MyBib as part of your overall Works Cited page (which can be downloaded fully later!).
MyBib supports the following for MLA style:

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.

Citation Support Guide: MLA Style
- Citing Art & Visual Sources
MLA Style is a style from the Modern Language Association used to format research papers. It is generally used by the humanities, writing, languages, other related subjects. MLA style includes in-text citations, a Works Cited page or reference list, headings, and more.
In-Text Citations
The following examples for in-text citations are from Purdue OWL: MLA In-Text Citations. All citations will ideally have an author and a page number, though there are many examples to follow for different scenarios.
Example 1: Wordsworth stated that Romantic poetry was marked by a "spontaneous overflow of powerful feelings" (263). Example 2: Romantic poetry is characterized by the "spontaneous overflow of powerful feelings" (Wordsworth 263). Example 3: The authors claim that surface reading looks at what is “evident, perceptible, apprehensible in texts” (Best and Marcus 9).
Works Cited (Reference List)
The following examples for reference list citations are from Purdue OWL: MLA Works Cited . While these examples cover popular resources including journal articles, books, and websites, Purdue OWL provides examples on many other types of materials for a number of scenarios (multiple authors, no author, no page number, etc.)
Journal Articles:
Format: Author(s). "Title of Article." Title of Journal , Volume, Issue, Year, pages.
Example: Bagchi, Alaknanda. "Conflicting Nationalisms: The Voice of the Subaltern in Mahasweta Devi's Bashai Tudu ." Tulsa Studies in Women's Literature, vol. 15, no. 1, 1996, pp. 41-50.
Format: Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . City of Publication, Publisher, Publication Date.
Example: Gleick, James. Chaos: Making a New Science . Penguin, 1987.
Format: Author. "Title." Title of container (self contained if book) , Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publication Date, Location (pages, paragraphs and/or URL, DOI or permalink). 2 nd container’s title , Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location, Date of Access (if applicable).
Example: The Purdue OWL Family of Sites . The Writing Lab and OWL at Purdue and Purdue U, 2008, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl. Accessed 23 Apr. 2008.
Note: MLA style also requires that references be listed in alphabetical order by the author's last name and follow specific formatting, including indenting. Please consult the links below for more information.
Paper Format
Your professor may require your entire research paper to be formatted in MLA format. Please consult Purdue OWL's resources on MLA general formatting , as well as a sample of a paper formatted in MLA style . The worksheet to the right of this page can also assist you.
Popular Subjects
The following subjects may use MLA Style:
- Creative Writing
- English Language and Literature
Helpful Resources
MLA Worksheet
- MLA Worksheet This worksheet will help you understand creating documents using MLA format.
Students have many questions about citing sources, and FDU librarians are happy to provide guidance. We can assist by helping you to determine the type of source to be cited, providing a guide to the citation style, and indicating the most relevant section/example. Because citations are often graded, we cannot create or format the citation for you, nor can we correct a list of citations. Please contact the Academic Support Center or the Metro Writing Studio for help creating and formatting citations.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: APA Style >>
- Last Updated: Aug 15, 2023 7:12 AM
- URL: https://library.fdu.edu/citationguide
Metropolitan Library

Florham Library
- Report a Problem
- Library Staff Login

MLA 9th Edition Style Guide
Useful links, available at the wlac library reference desk, citation tools.
- BibMe This is a fully automatic bibliography maker that auto-fills: MLA, APA, Chicago, Turabian
- Citation Builder This is a web-based tool designed to quickly and easily generate citations for sources consulted during the research process.
- KnightCite MLA, APA, Chicago
- Citation Machine APA, MLA, Turabian, Chicago
- Scribbr APA and MLA
Citation Managers
Can't make it to the library? Chat with a librarian any time!
Modern Language Association (MLA) Provides a “universal set of guidelines” for citing sources across all format types and is commonly used iin English Studies, Language and Literature, Literary Criticism, Comparative Literature, and Cultural studies.
Citing sources and creating a Bibliography:
- Gives credit to the author(s)
- Illustrates your ability to locate & evaluate appropriate sources
- Provides evidence for the arguments and conclusions in your paper
- Prevents plagiarism and copyright infringement
- MLA Style Center - Use this site to get help with formatting your paper and citing sources.
- Purdue OWL MLA Format - Use this website for more detail information on how to format your research paper or cite a source.
- In-Text Citation - Consult with this guide to ensure you correctly cite your sources in your paper.
- MLA Tutorial - A simplified guide to MLA style.
- MLA Format: The Basics (Video) - Learn more about the basics of MLA format by watching the very short 3 minutes video.
Print Book with One Author: Author’s Last Name (comma) Author’s First Name (period) Title of Container (Book) (italicized or underlined) (period) Publisher’s Name (comma) Year of Publication (period)
Smith, John. How I Survived High School. Funny Press, 2015.
Ebook with One Author: Author’s Last Name (comma) Author’s First Name (period) Title of Container 1 (Book) (italicized or underlined) (period) Publisher’s Name (comma) Year of Publication (period) Title of Container 2 (Database) (italicized or underlined) (comma) Location (URL) (period)
Smith, John. How I Survived Getting Married. Funniest Press, 2018. eBook Academic Collection , search-ebscohost-com.lasc.idm.oclc.org/login.aspx?direct=true&db=e000xna&AN=102032611fakeurl&site=ehost-live.
In-Text Citation (From Columbia College Guide): In MLA, in-text citations are inserted in the body of your research paper to briefly document the source of your information. Brief in-text citations point the reader to more complete information in the Works Cited list at the end of the paper.
- MLA Paper Template Use this template for your own APA style paper.
- Last Updated: Feb 14, 2024 4:38 PM
- URL: https://libguides.wlac.edu/MLA
Citation Guide
- Citation Home
- MLA Style Guide (9th ed.)
- Core Elements & Containers
- MLA Video Tutorial
In-Text Citation
- Books & eBooks
- Business Sources
- Scholarly Journals
- APA Video Tutorial
- Additional Resources
About MLA Style
- Formatting Your Works Cited Entries
- Formatting Your Research Paper
- MLA Citation Resources
MLA Style is a set of guidelines created by the Modern Language Association for formatting academic manuscripts and citing work created by others. It is used most often to write papers within the humanities and liberal arts . The guidelines dictate how an MLA style paper should be formatted and show writers how to properly construct the two major components involved in citing your sources: the Works Cited list and in-text citations .
MLA Style was updated in 2016 with the publication of the MLA Handbook, 8th edition , (available at both MSJC Libraries) and with the creation of the online MLA Style Center . MLA 8th edition lays out a universal set of core elements that should be included in all citations, regardless of the format of each source . Writers who are accustomed to earlier editions of MLA are encouraged to review the 8th edition handbook or visit the MLA Style Center for further explanation of the changes.
Important Note: Citations created by online databases or citation generators may not be updated to reflect MLA 8th edition changes. Writers will need to check computer generated citations carefully and make necessary corrections.
Works Cited List
Your Works Cited list should begin on a separate page. Entries should appear in alphabetical order and be double-spaced with a hanging indent.
The Works Cited Quick Guide at the online MLA Style Center includes the core elements that should be included in each citation along with a practice template to guide you through building a complete citation.
In addition to the Works Cited page, sources are also cited parenthetically (like this) throughout the body of your paper. In-text citations briefly reference the sources you used at the point they appear in your paper and direct your readers to the full citation in your Works Cited list. A typical example of an in-text citation might include an author's last name and a page number, depending on the source you are citing.
Consult the MLA Handbook or visit Purdue University's Online Writing Lab for help with the basics of in-text citations .
General Formatting and Order of the Works Cited List (MLA 2.7)
- Works Cited list begins on a separate page at the end of your research paper.
- Center the title, Works Cited, at the top of the page.
- Entries are arranged in alphabetical order.
- Entries should be double-spaced between all text.
- Each entry should be indented half an inch on the second and subsequent lines in what is called a hanging indent format. "When the creation of a hanging indent is difficult--in certain digital contexts, for instance--leaving an extra space between entries will serve the same purpose" (MLA 112).
Punctuation (MLA 2.6)
Review the MLA Handbook for specific punctuation details. Generally, punctuation in the Works Cited entries is limited to periods and commas:
- Periods are used after the author, the title and at the end of the information for each container.
- Commas appear within the author's name and between each element of each container.
- Brackets and forward slashes appear under specific circumstances. See MLA 2.6.1 and 2.6.2 for details.
Capitalization (MLA 1.2.1)
Review the MLA Handbook for specific details on proper capitalization. Generally:
- Capitalize the first word, last word, and all principle words of a title, including nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs.
- Do not capitalize articles (a, an, the) unless they are the first word, and other insignificant words in the title.
Titles: Italics vs. Quotation Marks (MLA 25-26)
A title is italicized if the source stands alone, such as a book, journal, magazine or newspaper, database name, or website name.
- The Grapes of Wrath
- New England Journal of Medicine
- Sports Illustrated
- New York Times
- Ebscohost Premier Collection of Databases
Titles of sources that are contained within a larger whole are placed in "quotation marks" . This includes individual essays, stories, plays and poems within a book ; articles within journals, magazines or newspapers ; specific articles, postings, or pages on a website ; individual songs on an album ; single episodes of a television series.
- Epstein, David. "The Damage Done." Sports Illustrated, vol. 113, no.16, 1 Nov. 2010, pp. 42-47. (article within a magazine)
- Despain, Bree. "Community in the Face of Tyranny." The Girl Who Was on Fire: Your Favorite Authors on Suzanne
Collins' Hunger Games Trilogy , edited by Leah Wilson, BenBella Books, 2011, pp. 195-210. (essay within a book)
Online Sources: URLs and DOIs (MLA 2.5.2)
URLs (web addresses) are included at the end of MLA citations to show where online materials are located. These include web pages and websites and sources found in library databases. Articles in journals are often assigned DOIs (digital object identifiers) s ince URLs can change. Follow the guidelines below when citing online sources.
Online database sources:
- DOIs are preferred over URLs in citations. If a DOI is available, cite it instead of a URL. Place doi: in front of it. Example:
Rogers, Wendy, Catriona Mackenzie, and Susan Dodds. "Why Bioethics Needs a Concept of Vulnerability." International Journal of
Feminist Approaches to Bioethics , vol. 5, no. 2, 2012, pp. 11-38. JSTOR , doi:10.2979/intjfemappbio.5.2.11.
- When no DOI is available, the URL should be used. Look for " stable " URLs (also known as as permalinks in some databases) and use those whenever possible. Example:
Feminist Approaches to Bioethics , vol. 5, no. 2, 2012, pp. 11-38. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/10.2979/intjfemappbio.5.2.11.
Web sources:
- Copy and paste the complete URL from your web browser, but leave out http:// or https://
Formatting Your Paper
Formatting in MLA, 8th edition, has not changed from the 7th edition. In general, your research paper should include the following:
- Typed manuscript on letter-sized (8.5x11in.) paper
- Standard font size (e.g., 12 point) in an easily readable typeface (e.g., Times New Roman)
- 1-inch margins on all sides of text (top, bottom, left, right)
- Double-spacing of all text
- A double-spaced Works Cited list beginning on a new page at the end of your manuscript
- Page numbers should be placed in the upper right-hand header, preceded by your last name
- No title page is needed - include information like your name, course number, professor, and date in the upper left-hand corner of the first page. (These should be on separate lines, double-spaced.)
- Title should be centered directly above the text of your paper. (Do not italicize, underline, or place title in quotation marks).
See the section on Formatting a Research Paper at the online MLA Style Center for more information and details on correctly formatting your research paper.
Sample MLA Paper
- The MLA Style Center This site walks you through the details of MLA Style, 8th edition. Examples and templates are provided along with information on properly formatting your papers.
- Purdue OWL - MLA Formatting and Style Guide A helpful guide to the details of MLA Style created by Purdue University Online Writing Lab. Purdue Owl has been updated to reflect 8th edition guidelines.
- << Previous: MLA Style Guide (9th ed.)
- Next: Core Elements & Containers >>
- Last Updated: Feb 22, 2023 11:10 AM
- URL: https://libguides.msjc.edu/citationguide

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
- Writing Lab
- Skip Navigation
- Research and Citation
- MLA Overview and Workshop
- MLA Formatting and Style Guide
- MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics
- MLA Formatting Quotations
- MLA Endnotes and Footnotes
- MLA Works Cited Page: Basic Format
- MLA Works Cited Page: Books
- MLA Works Cited: Periodicals
- MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources
- MLA Works Cited: Other Common Sources
- MLA Additional Resources
- MLA Abbreviations
MLA Sample Works Cited Page
- MLA Sample Paper
- MLA Tables, Figures, and Examples
- MLA PowerPoint Presentation
- MLA Undergraduate Sample Paper
- MLA Classroom Poster
- OWL Mail MLA FAQs
- MLA Mini-posters
- Giving to the OWL
Suggested Resources
- -How to Navigate the New OWL
- -Media File Index
- -OWL Exercises

This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue (https://owl.english.purdue.edu/). When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice at bottom.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers (7 th ed.) and the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing (3 rd ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Contributors: Tony Russell, Allen Brizee, Elizabeth Angeli, Russell Keck, Joshua M. Paiz, Michelle Campbell, Rodrigo Rodr�guez-Fuentes, Daniel P. Kenzie, Purdue OWL Staff Last Edited: 2013-02-14 10:32:55
This handout provides an example of a Works Cited page in MLA 2009 format.
"Blueprint Lays Out Clear Path for Climate Action." Environmental Defense Fund . Environmental Defense Fund, 8 May 2007. Web. 24 May 2009.
Clinton, Bill. Interview by Andrew C. Revkin. �Clinton on Climate Change.� New York Times . New York Times, May 2007. Web. 25 May 2009.
Dean, Cornelia. "Executive on a Mission: Saving the Planet." New York Times . New York Times, 22 May 2007. Web. 25 May 2009.
Ebert, Roger. "An Inconvenient Truth." Rev. of An Inconvenient Truth , dir. Davis Guggenheim. rogerebert.com . Sun-Times News Group, 2 June 2006. Web. 24 May 2009.
GlobalWarming.org . Cooler Heads Coalition, 2007. Web. 24 May 2009.
Gowdy, John. "Avoiding Self-organized Extinction: Toward a Co-evolutionary Economics of Sustainability." International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology 14.1 (2007): 27-36. Print.
An Inconvenient Truth . Dir. Davis Guggenheim. Perf. Al Gore, Billy West. Paramount, 2006. DVD.
Leroux, Marcel. Global Warming: Myth Or Reality?: The Erring Ways of Climatology . New York: Springer, 2005. Print.
Milken, Michael, Gary Becker, Myron Scholes, and Daniel Kahneman. "On Global Warming and Financial Imbalances." New Perspectives Quarterly 23.4 (2006): 63. Print.
Nordhaus, William D. "After Kyoto: Alternative Mechanisms to Control Global Warming." American Economic Review 96.2 (2006): 31-34. Print.
---. "Global Warming Economics." Science 9 Nov. 2001: 1283-84. Science Online . Web. 24 May 2009.
Shulte, Bret. "Putting a Price on Pollution." Usnews.com . US News & World Rept ., 6 May 2007. Web. 24 May 2009.
Uzawa, Hirofumi. Economic Theory and Global Warming . Cambridge: Cambridge UP, 2003. Print.
The Writing Lab & OWL at Purdue University care about accessiblity and content quality. Contact Jeff Bacha to share your comments and concerns. The OWL at Purdue now conforms to W3C.org -validated and CSS 2.0 standards. Additionally, the site passes the Cynthia Says test for ADA Section 508 compliance .
Copyright �1995-2015 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University . All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use .

MLA Style Guide: Citations & Bibliography
- Get Started Here
- When, Why, & How to Cite
- Formatting Your Paper
- Citations & Bibliography
When Writing Your Bibliography:
- OWL Purdue Sample MLA Paper
Some Helpful Tips:
- Use Works Cited as your header at the top of your page.
- References should be double-spaced.
- Indent all lines after the first line by using a hanging indent. (Ctrl+T in MS Word)
- Use initials for first and middle names, even if the entire name is provided.
- Italicize the journal name and volume number or book title.
- When referring to books, chapters, articles, or Web pages, capitalize only the first letter of the first word of a title and subtitle, the first word after a colon or a dash in the title, and proper nouns.
- Capitalize all major words in journal titles.
- Months are spelled out rather than abbreviated.
- Do not end the citation with a period if it ends in a URL or DOI (digital object identifier).
In-Text (Parenthetical) Citations:
An in-text or parenthetical reference follows a quotation or paraphrase used in the text of your paper and leads the reader to the complete citation in the works cited page.
- Usually, the author and page number are sufficient. (Rosales 15)
- If the author's last name appears at the beginning of the information that needs a citation, just a page number (15) will be sufficient at the end of the information.
- If there is no author, use the first few words of the title ("How to Catfish Noodle")
- For two Authors (Jones and Lee 25) and more than two (Patel et al.)
For more information, see Purdue Owl's page on In-Text Citations:
- MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics
More Helpful Links
- MLA Style Center Direct from the Modern Language Association (MLA), this site offers help on how to do everything MLA. Offers tutorials, tips, and templates.
- MLA Formatting and Style Guide From OWL Purdue University Writing Lab One of the most popular websites regarding citations, bibliographies and plagiarism. Use the search bar on the site to find answers to any obscure question about MLA.
- Norco College Library MLA 9 Style Guide
MLA Citation Guide 9th Edition
General Format: Author(s) Last Name, First Name. Book Title . Edition. City Published. Publisher Name, Year Published. Medium.
Print Articles
General Format: Author(s) Last Name, First name. “Article Title.” Journal Name . Volume Number. Issue Number (Year Published): Pages. Medium.
Online Articles (Database or Web)
General Format: Author(s) Last Name, First name “Article Title.” Journal Name. Volume Number. Issue Number (Year Published): Pages. Date of item or last update of site. Database Name. Medium. Date Accessed.
General Format: Lastname, F. M. (Year, Month Date). Title of page . Site name. URL
What is an Annotated Bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is a list of sources formatted in the manner of a bibliography with a short paragraph after each entry. The paragraph provides a brief summary of the article and its relevancy to the main subject.
When creating an annotated bibliography, consult with your professor about any questions you have. Assignment requirements may vary according to the subject and professor.
- Purdue Owl's Guide to Annotated Bibliographies
- << Previous: Formatting Your Paper
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 9:40 AM
- URL: https://norcocollege.libguides.com/MLAguide

NOTICE: ProQuest e-book platforms will be down for planned maintenance on Saturday, August 12, from 12:00 pm to 3:00 pm CST.
ENG 110 - Petherbridge: MLA Citations
- Scholarly Articles
- MLA Citations
This guide is based on the 8th edition (2016) of the MLA Handbook .
MLA (Modern Language Association) uses the author/page number method for in-text citation . Include in parentheses the author's last name and the appropriate page number after all direct quotations and paraphrased content in your paper: Example: (Pollan 42). For more information, including other methods of incorporating quotes and paraphrased content in your paper, see the "Avoiding Plagiarism" tab and the Recommended Guides section of the "Basics" tab.
For the Works Cited list, MLA requires the use of hanging indents .
Watch these:
Author: Use the full name as given in the source
Author: If one or two authors, give the full names of both
Author: If three or more authors, give the first author and indicate: et al.
Article title: Use " " (not italics or underline)
Journal/Book title: Use italics
URL: omit http:// or https://
URL: Use a DOI if one is available. If not, use a permalink/ persistent/ stable link if one is available.
Samples of Modern Language Association (8th, 2016) Basic Format for the Works Cited list
- Capitalize all significant title and s ubtitle words. - Place of publication is normally not included.
Lastname, Firstname M. and Firstname2 Lastname2. Title of Book: Subtitle of Book .
Publisher, Year of Publication.
Lastname, Firstname M., et al., editors. Title of Book: Subtitle of Book .
Publisher, Year of Publication.
Article in a Periodical
Lastname, Firstname. "Title of Article." Title of Journal,
vol. nn, no. nn, date of issue, pp. nn-nn.
Article in a Periodical, Retrieved from a Library Database
- Give the inclusive page numbers when given.
Lastname, Firstname. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, vol. nn, no. nn, date of issue, pp. nn-nn. Database name, DOIorPersistentURL.
Article in an Online Periodical (not from a library database)
Lastname, Firstname. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, vol. nn, no. nn, date of issue, pp. nn-nn. Website name , URL.
Web Document/Page/Report, Web Video, Web Images
- If citing a whole web site, omit "Title of Work". - The Accessed date (including the word, Accessed) is generally optional, but it is required if there is no publication date . Lastname, Firstname. “Title of Work.” Website name,
Day published Month published Year published,
URL. Accessed Day Month Year.
Citing Digital Content in MLA (7th, 2009)
Taken from Lafayette College's Archives and Special Collections website. You can access it directly here .
Digital Collections Note: MLA no longer requires the use of URLs in MLA citations. For instructors who still wish to require the use of URLs, MLA suggest that the URL appear within angle brackets after the date of access. The URL is given in the samples below.
Magazine Article : Shaw, Diane Windham. “Lafayette and Slavery.” Lafayette Alumni News. Winter 2007. Digital. 13 Jan. 2015. <http://digital.lafayette.edu/collections/magazine/lafalummag- 20070100>.
Newspaper Article : Kelley, Michael. “Damaged Futures. Research Finds Student Athletes are at Greater Risk for Long-Term Health.” The Lafayette. 9 May 2014. Digital. 13 Jan. 2015. <http://digital.lafayette.edu/collections/newspaper/20140509>.
Photograph : “Students Disrupt ROTC Parade on Fisher Field.” 4 May 1969. Historical Photograph Collection. Digital. 13 Jan. 2015. <http://digital.lafayette.edu/collections/historicalphotos/hpc-0269>.
MLA Style Format
Recommended Guides
These are comprehensive citation guides recommended by librarians.
- APA (7th, 2020)
- MLA (8th, 2016)
- Chicago (17th, 2017)
- APA Formatting and Style Guide (7th, 2020)
- MLA Formatting and Style Guide (9th, 2021)
- Chicago Formatting and Style Guide (17th, 2017)
- APA Format and Style Guide (7th, 2020)
- MLA Formatting and Style Guide (9th, 2021)
- Chicago Formatting and Style Guide (17th, 2017)
- << Previous: Websites
- Last Updated: Mar 1, 2024 11:41 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwlax.edu/ENG110-Petherbridge

FYS: Curiosity & Creativity (Romack)
- Finding Research Articles
- WorldCat: For finding books, articles, media
- Search Tips
- Citation and Plagiarism
- SIFT: Information Evaluation
- Anatomy of an Article
Additional Resources
GENERAL RESOURCE:
- Modern Language Association Answers frequently asked questions, including ones about how to cite recent information formats such as tweets and e-books. Additional resources are at https://style.mla.org/
FORMATTING / STYLE:
- Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL): General Formatting Guidelines for headers, first pages, and other format details within MLA style.
IN-TEXT CITATIONS:
- Purdue OWL: In-text Citations Explains the basics of citing within your text. Includes examples for multiple authors and different types of sources.
- Purdue OWL: Formatting Quotations Guidelines for formatting short and long quotations within your text.
WORKS CITED:
- Purdue OWL: Works Cited Page Basic Format Explains basic formatting rules for your works cited page. Then, once you are ready to create a works cited entry for a source, use the menu on the left of the screen to select the right type of source (Books, Periodicals, Electronic Sources, Other Common Sources). This menu also includes helpful information about creating tables, PowerPoint presentations, and more.
MLA Style Manuals
There are two different manuals for MLA Style Citations: the Handbook and the Style Manual. The Handbook was revised in 2021; copies of both the new 2021 9th edition and the older 2016 8th edition are listed below.
Plagiarism Explanation in <3 Minutes
Key Elements of a Citation
There are certain pieces of information that you should note as you are doing your research. In various types of citations, these elements will be important to recognize and take note of:
- Author's full name (and whether or not there are multiple authors).
- Full precise title of book, journal article, dissertation, etc.
- If resource is book, dissertation, or AV item, place of publication . name of publisher , and date of publication .
- If resource is an article from a journal or newspaper, you need to note not only the author and title of the article but also the precise title of the journal/newspaper in which the article was published, the volume and/or issue number, the date of the publication , and the pagination of the article.
- If the resource is digital, note if it has been assigned a " D.O.I. " = Digital Object Identification (number).
- If you found the article as the result of a search on an online database, note the name of the database NOT the name of the vendor (EBSCO, ProQuest, Gale, Web of Science, etc. are vendors, NOT databases names).
Direct Quotes, Summaries & Paraphrases
- Direct Quotations
- Common Knowledge
YOU SHOULD CITE WHEN:
- Referring to a source and stating someone else's opinions, thoughts, ideas, or research
- Using an image or media file that you did not create

WHEN REFERRING TO A SOURCE, YOU HAVE THREE OPTIONS FOR USING IT:

- Directly Quoting
- Summarizing
- Paraphrase
"Which option you should choose depends on how much of a source you are using, how you are using it, and what kind of paper you are writing, since different fields use sources in different ways." Grounds for Argument. When to Quote, Paraphrase, or Summarize a Source . Used under CC BY NC SA
Image: Random quote by Gabriel Jones . Used under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
YOU DO NOT NEED TO CITE:
- Your thoughts and your interpretations
- Common knowledge
WHAT IS A DIRECT QUOTATION:
" Must be identical to the original, using a narrow segment of the source. They must match the source document word for word and must be attributed to the original author." Purdue University Online Writing Lab. (2012). Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing
- If summarizing or paraphrasing cannot capture the essence or meaning of the text
- To retain a specific or unique phrasing used by the source's author
- If you are analyzing the text itself (often in English or language classes)
BE ADVISED:
Most of the time when you cite a source, you want to summarize or paraphrase. Direct quotations should be used sparingly when the situation meets the criteria above. When you do use direct quotations:
- Do not take the quote out of context. The author's meaning should not change.
- Be sure to integrate multiple sources within your text. You don't want to have a paper or a passage that seems to have come only from one source, with little original text from you.
- Use transitions to make sure your quote adds to your paper without interrupting its flow.
HOW TO CITE A DIRECT QUOTATION:
- Place quotation marks around the entire word-for-word passage, whether it's a phrase or a sentence.
- Attribute with an in-text citation ; most citation styles request that you provide a page or paragraph number when directly citing.
- If your quotation is longer, check with your citation style guide to see if additional formatting is necessary (block quotations, for example).
- When and How Much to Quote From the Harvard Guide to Using Sources
WHAT IS A SUMMARY:
" Involves putting the main idea(s) into your own words, including only the main point(s).... Summaries are significantly shorter than the original and take a broad overview of the source material." Purdue University Online Writing Lab. (2012). Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing
"Similar to paraphrasing, summarizing involves using your own words and writing style to express another author's ideas. Unlike the paraphrase, which presents important details, the summary presents only the most important ideas of the passage." University of Houston-Victoria Student Success Center (n.d.). Decide when to Quote, Paraphrase & Summarize.
- To provide necessary background information for your audience
- When broad, concise information will suffice
HOW TO CITE A SUMMARY:
- Attribute with an in-text citation ; some citation styles request that you provide a page or paragragh number whenever available.
- You should not be using any word-for-word quotations or language unique to the source, so you do NOT need quotation marks around your summary.
- When and How to Summarize From the Harvard Guide to Using Sources
WHAT IS A PARAPHRASE:
"A paraphrase is a detailed restatement in your own words of a written or sometimes spoken source material. Apart from the changes in organization, wording, and sentence structure, the paraphrase should be nearly identical in meaning to the original passage. It should also be near the same length as the original passage and present the details of the original." University of Houston-Victoria Student Success Center (n.d.). Decide when to Quote, Paraphrase & Summarize.
Paraphrasing is "your own rendition of essential information and ideas expressed by someone else, presented in a new form." Purdue University Online Writing Lab. (2012). Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing

- "When the wording is less important than the meaning of the source" University of Houston-Victoria Student Success Center (n.d.). Decide when to Quote, Paraphrase & Summarize.
- If a summary would not provide enough specific details
HOW TO CITE A PARAPHRASE:
- When paraphrasing, you must change both the sentence structure and language of the original text. Therefore, since you will be changing the text, you do NOT need quotation marks around your paraphrase.
- Purdue OWL: Paraphrasing Includes 6 steps to effective paraphrasing and examples.
- When and How to Paraphrase From the Harvard Guide to Using Sources
COMMON KNOWLEDGE:
It doesn't necessarily mean that most people would know it offhand. And sometimes it's a judgment call because what seems like common knowledge to one person isn't to another. H ere are good rules of thumb:
- If you can find the same information in multiple places, stated in relatively the same way, it's common knowledge ( Generally, it is said that you should find the information three to five sources)
- If most people are aware of this fact, or if it's general reference, it's common knowledge
CAUTION: Opinions and unique terminology/phrasing do not qualify as common knowledge.

Tips for Avoiding Plagiarism
READ THE SOURCE IN ITS ENTIRETY
- It's easy to take something out of context if you only read a portion of it! If you read the entire source, you should have a better feel of the author's meaning.
TAKE DETAILED NOTES AS YOU READ
- Anytime you note something word-for-word, immediately place it in quotation marks. Also note what page or section you found it on.
- On each page, make sure you note the original source and the date you accessed the source. This will make citation much easier, especially if you are working with multiple sources or doing research over a long stretch of time.
- Try not to mix your own thoughts and commentary with excerpts from your source. Keep them on separate pages, draw two columns on your page, or switch your pen color.
- If you find it difficult to take notes with electronic sources - or if you find yourself drawn to the copy-paste method - print out your sources and deal with them in print form.
RETURN TO YOUR NOTES LATER
- In order to do this, you must not procrastinate on your projects. If you don't have sufficient time, you won't do your best work, and it may lead you to make poor decisions when including your sources. Remember, if you get caught plagiarizing, the situation or your intentions won't be an excuse. Build in time to synthesize and properly work in your sources.
- Make sure the source is fresh in your mind, but not right in front of you. If you see the original text, you are more likely to want to use their terms and sentence structure.
- Check your writing against the original. Remember, you should have changed the sentence structure and the language but the meaning of the source should still be the same. Any language that is unique to the source should be placed in quotation marks or removed. You may find it necessary to do several edits.
CONSULT WITH THE EXPERTS
- If you need a second opinion, ask! Ask a librarian, a classmate, the Writing Center, or your professor.
- << Previous: Search Tips
- Next: SIFT: Information Evaluation >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 7:35 AM
- URL: https://libguides.butler.edu/c.php?g=1393526

QUICK LINKS
Library Hours Study Rooms My Library Account Library Website

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Note: The MLA considers the term "e-book" to refer to publications formatted specifically for reading with an e-book reader device (e.g., a Kindle) or a corresponding web application.These e-books will not have URLs or DOIs. If you are citing book content from an ordinary webpage with a URL, use the "A Page on a Web Site" format above.
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice. ... MLA Formatting and Style Guide Overview of how to create MLA in-text citations and reference lists In-Text Citations. Resources on using in-text citations in MLA style ...
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA website citation includes the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the website (in italics), the publication date, and the URL (without "https://"). If the author is unknown, start with the title of the page instead. If the publication date is unknown, or if the content is ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
MLA Style Center, the only authorized Web site on MLA style, provides free resources on research, writing, and documentation.
1. Author. Begin with the author's last name, followed by a comma, and then the remainder of the author's name as it was listed in the work. This element should end with a period. If the remainder of the author's name ended with a period, do not follow it with another period. [MLA Handbook, pages 21-25] 2.
Like the rest of an MLA format paper, the Works Cited should be left-aligned and double-spaced with 1-inch margins. You can use our free MLA Citation Generator to create and manage your Works Cited list. Choose your source type and enter the URL, DOI or title to get started. Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Developed by the Purdue Online Writing Lab. MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Basic MLA - Citation Guide - Library Guides at Purdue University Northwest. MLA. Changes in 9th edition. The 9th edition of the MLA Handbook was published in 2021. In this update, the format for both in-text and Works Cited citations is the same as the 8th edition. The 9th edition also includes this clarification on citing a film/DVD.
Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form. The generator will produce a formatted MLA ...
Example: The Purdue OWL Family of Sites. The Writing Lab and OWL at Purdue and Purdue U, 2008, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl. Accessed 23 Apr. 2008. Note: MLA style also requires that references be listed in alphabetical order by the author's last name and follow specific formatting, including indenting.
MLA Style Center - Use this site to get help with formatting your paper and citing sources.; Purdue OWL MLA Format - Use this website for more detail information on how to format your research paper or cite a source.; In-Text Citation - Consult with this guide to ensure you correctly cite your sources in your paper.; MLA Tutorial - A simplified guide to MLA style.
The guidelines dictate how an MLA style paper should be formatted and show writers how to properly construct the two major components involved in citing your sources: the Works Cited list and in-text citations. MLA Style was updated in 2016 with the publication of the MLA Handbook, 8th edition, (available at both MSJC Libraries) and with the ...
Summary: MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers (7 th ed.) and the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing (3 rd ed.), offers examples for the general format ...
General Guidelines. Type your paper on a computer and print it out on standard, white 8.5 x 11-inch paper. Double-space the text of your paper, and use a legible font (e.g. Times New Roman). Whatever font you choose, MLA recommends that the regular and italics type styles contrast enough that they are recognizable one from another.
MLA Formatting and Style Guide From OWL Purdue University Writing Lab One of the most popular websites regarding citations, bibliographies and plagiarism. Use the search bar on the site to find answers to any obscure question about MLA.
This vidcast introduces the viewers to the basics of MLA style documentation, focusing on the list of works cited. For more information on this, please see t...
The preparation of papers and manuscripts in MLA style is covered in chapter four of the MLA Handbook, and chapter four of the MLA Style Manual. Below are some basic guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style. General Guidelines. Type your paper on a computer and print it out on standard, white 8.5 x 11-inch paper.
MLA (8th, 2016) Chicago (17th, 2017) Online Writing Lab (OWL) at Purdue University (guides developed by Purdue graduate students) APA Formatting and Style Guide (7th, 2020) MLA Formatting and Style Guide (9th, 2021) Chicago Formatting and Style Guide (17th, 2017) EasyBib Writer Center Guides to Formatting (guides developed by Chegg)
Purdue OWL: Works Cited Page Basic Format Explains basic formatting rules for your works cited page. Then, once you are ready to create a works cited entry for a source, use the menu on the left of the screen to select the right type of source (Books, Periodicals, Electronic Sources, Other Common Sources).