- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers


How To Write a Research Question

Academic writing and research require a distinct focus and direction. A well-designed research question gives purpose and clarity to your research. In addition, it helps your readers understand the issue you are trying to address and explore.
Every time you want to know more about a subject, you will pose a question. The same idea is used in research as well. You must pose a question in order to effectively address a research problem. That's why the research question is an integral part of the research process. Additionally, it offers the author writing and reading guidelines, be it qualitative research or quantitative research.
In your research paper , you must single out just one issue or problem. The specific issue or claim you wish to address should be included in your thesis statement in order to clarify your main argument.
A good research question must have the following characteristics.

- Should include only one problem in the research question
- Should be able to find the answer using primary data and secondary data sources
- Should be possible to resolve within the given time and other constraints
- Detailed and in-depth results should be achievable
- Should be relevant and realistic.
- It should relate to your chosen area of research
While a larger project, like a thesis, might have several research questions to address, each one should be directed at your main area of study. Of course, you can use different research designs and research methods (qualitative research or quantitative research) to address various research questions. However, they must all be pertinent to the study's objectives.
What is a Research Question?

A research question is an inquiry that the research attempts to answer. It is the heart of the systematic investigation. Research questions are the most important step in any research project. In essence, it initiates the research project and establishes the pace for the specific research A research question is:
- Clear : It provides enough detail that the audience understands its purpose without any additional explanation.
- Focused : It is so specific that it can be addressed within the time constraints of the writing task.
- Succinct: It is written in the shortest possible words.
- Complex : It is not possible to answer it with a "yes" or "no", but requires analysis and synthesis of ideas before somebody can create a solution.
- Argumental : Its potential answers are open for debate rather than accepted facts.
A good research question usually focuses on the research and determines the research design, methodology, and hypothesis. It guides all phases of inquiry, data collection, analysis, and reporting. You should gather valuable information by asking the right questions.
Why are Research Questions so important?
Regardless of whether it is a qualitative research or quantitative research project, research questions provide writers and their audience with a way to navigate the writing and research process. Writers can avoid "all-about" papers by asking straightforward and specific research questions that help them focus on their research and support a specific thesis.
Types of Research Questions

There are two types of research: Qualitative research and Quantitative research . There must be research questions for every type of research. Your research question will be based on the type of research you want to conduct and the type of data collection.
The first step in designing research involves identifying a gap and creating a focused research question.
Below is a list of common research questions that can be used in a dissertation. Keep in mind that these are merely illustrations of typical research questions used in dissertation projects. The real research questions themselves might be more difficult.
Example Research Questions

The following are a few examples of research questions and research problems to help you understand how research questions can be created for a particular research problem.
Steps to Write Research Questions

You can focus on the issue or research gaps you're attempting to solve by using the research questions as a direction.
If you're unsure how to go about writing a good research question, these are the steps to follow in the process:
- Select an interesting topic Always choose a topic that interests you. Because if your curiosity isn’t aroused by a subject, you’ll have a hard time conducting research around it. Alos, it’s better that you pick something that’s neither too narrow or too broad.
- Do preliminary research on the topic Search for relevant literature to gauge what problems have already been tackled by scholars. You can do that conveniently through repositories like Scispace , where you’ll find millions of papers in one place. Once you do find the papers you’re looking for, try our reading assistant, SciSpace Copilot to get simple explanations for the paper . You’ll be able to quickly understand the abstract, find the key takeaways, and the main arguments presented in the paper. This will give you a more contextual understanding of your subject and you’ll have an easier time identifying knowledge gaps in your discipline.
Also: ChatPDF vs. SciSpace Copilot: Unveiling the best tool for your research
- Consider your audience It is essential to understand your audience to develop focused research questions for essays or dissertations. When narrowing down your topic, you can identify aspects that might interest your audience.
- Ask questions Asking questions will give you a deeper understanding of the topic. Evaluate your question through the What, Why, When, How, and other open-ended questions assessment.
- Assess your question Once you have created a research question, assess its effectiveness to determine if it is useful for the purpose. Refine and revise the dissertation research question multiple times.
Additionally, use this list of questions as a guide when formulating your research question.
Are you able to answer a specific research question? After identifying a gap in research, it would be helpful to formulate the research question. And this will allow the research to solve a part of the problem. Is your research question clear and centered on the main topic? It is important that your research question should be specific and related to your central goal. Are you tackling a difficult research question? It is not possible to answer the research question with a simple yes or no. The problem requires in-depth analysis. It is often started with "How" and "Why."
Start your research Once you have completed your dissertation research questions, it is time to review the literature on similar topics to discover different perspectives.
Strong Research Question Samples
Uncertain: How should social networking sites work on the hatred that flows through their platform?
Certain: What should social media sites like Twitter or Facebook do to address the harm they are causing?
This unclear question does not specify the social networking sites that are being used or what harm they might be causing. In addition, this question assumes that the "harm" has been proven and/or accepted. This version is more specific and identifies the sites (Twitter, Facebook), the type and extent of harm (privacy concerns), and who might be suffering from that harm (users). Effective research questions should not be ambiguous or interpreted.
Unfocused: What are the effects of global warming on the environment?
Focused: What are the most important effects of glacial melting in Antarctica on penguins' lives?
This broad research question cannot be addressed in a book, let alone a college-level paper. Focused research targets a specific effect of global heating (glacial melting), an area (Antarctica), or a specific animal (penguins). The writer must also decide which effect will have the greatest impact on the animals affected. If in doubt, narrow down your research question to the most specific possible.
Too Simple: What are the U.S. doctors doing to treat diabetes?
Appropriately complex: Which factors, if any, are most likely to predict a person's risk of developing diabetes?
This simple version can be found online. It is easy to answer with a few facts. The second, more complicated version of this question is divided into two parts. It is thought-provoking and requires extensive investigation as well as evaluation by the author. So, ensure that a quick Google search should not answer your research question.
How to write a strong Research Question?

The foundation of all research is the research question. You should therefore spend as much time as necessary to refine your research question based on various data.
You can conduct your research more efficiently and analyze your results better if you have great research questions for your dissertation, research paper , or essay .
The following criteria can help you evaluate the strength and importance of your research question and can be used to determine the strength of your research question:
- Researchable
- It should only cover one issue.
- A subjective judgment should not be included in the question.
- It can be answered with data analysis and research.
- Specific and Practical
- It should not contain a plan of action, policy, or solution.
- It should be clearly defined
- Within research limits
- Complex and Arguable
- It shouldn't be difficult to answer.
- To find the truth, you need in-depth knowledge
- Allows for discussion and deliberation
- Original and Relevant
- It should be in your area of study
- Its results should be measurable
- It should be original
Conclusion - How to write Research Questions?
Research questions provide a clear guideline for research. One research question may be part of a larger project, such as a dissertation. However, each question should only focus on one topic.
Research questions must be answerable, practical, specific, and applicable to your field. The research type that you use to base your research questions on will determine the research topic. You can start by selecting an interesting topic and doing preliminary research. Then, you can begin asking questions, evaluating your questions, and start your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace ResearchGPT . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, read, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on October 26, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
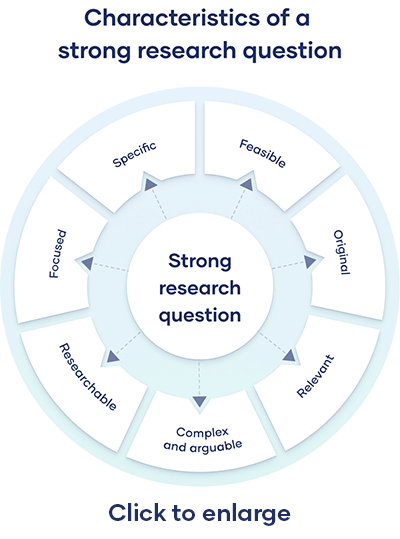
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, using sub-questions to strengthen your main research question, research questions quiz, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
Using your research problem to develop your research question
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
Feasible and specific, complex and arguable, relevant and original.
Chances are that your main research question likely can’t be answered all at once. That’s why sub-questions are important: they allow you to answer your main question in a step-by-step manner.
Good sub-questions should be:
- Less complex than the main question
- Focused only on 1 type of research
- Presented in a logical order
Here are a few examples of descriptive and framing questions:
- Descriptive: According to current government arguments, how should a European bank tax be implemented?
- Descriptive: Which countries have a bank tax/levy on financial transactions?
- Framing: How should a bank tax/levy on financial transactions look at a European level?
Keep in mind that sub-questions are by no means mandatory. They should only be asked if you need the findings to answer your main question. If your main question is simple enough to stand on its own, it’s okay to skip the sub-question part. As a rule of thumb, the more complex your subject, the more sub-questions you’ll need.
Try to limit yourself to 4 or 5 sub-questions, maximum. If you feel you need more than this, it may be indication that your main research question is not sufficiently specific. In this case, it’s is better to revisit your problem statement and try to tighten your main question up.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.

Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-questions/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Nursing Research Nursing Test Bank and Practice Questions (60 Items)

Welcome to your nursing test bank and practice questions for nursing research.
Nursing Research Test Bank
Nursing research has a great significance on the contemporary and future professional nursing practice, thus rendering it an essential component of the educational process. Research is typically not among the traditional responsibilities of an entry-level nurse . Many nurses are involved in either direct patient care or administrative aspects of health care. However, nursing research is a growing field in which individuals within the profession can contribute a variety of skills and experiences to the science of nursing care. Nursing research is critical to the nursing profession and is necessary for continuing advancements that promote optimal nursing care. Test your knowledge about nursing research in this 60-item nursing test bank.
Quiz Guidelines
Before you start, here are some examination guidelines and reminders you must read:
- Practice Exams : Engage with our Practice Exams to hone your skills in a supportive, low-pressure environment. These exams provide immediate feedback and explanations, helping you grasp core concepts, identify improvement areas, and build confidence in your knowledge and abilities.
- You’re given 2 minutes per item.
- For Challenge Exams, click on the “Start Quiz” button to start the quiz.
- Complete the quiz : Ensure that you answer the entire quiz. Only after you’ve answered every item will the score and rationales be shown.
- Learn from the rationales : After each quiz, click on the “View Questions” button to understand the explanation for each answer.
- Free access : Guess what? Our test banks are 100% FREE. Skip the hassle – no sign-ups or registrations here. A sincere promise from Nurseslabs: we have not and won’t ever request your credit card details or personal info for our practice questions. We’re dedicated to keeping this service accessible and cost-free, especially for our amazing students and nurses. So, take the leap and elevate your career hassle-free!
- Share your thoughts : We’d love your feedback, scores, and questions! Please share them in the comments below.
Quizzes included in this guide are:
Recommended Resources
Recommended books and resources for your NCLEX success:
Disclosure: Included below are affiliate links from Amazon at no additional cost from you. We may earn a small commission from your purchase. For more information, check out our privacy policy .
Saunders Comprehensive Review for the NCLEX-RN Saunders Comprehensive Review for the NCLEX-RN Examination is often referred to as the best nursing exam review book ever. More than 5,700 practice questions are available in the text. Detailed test-taking strategies are provided for each question, with hints for analyzing and uncovering the correct answer option.

Strategies for Student Success on the Next Generation NCLEX® (NGN) Test Items Next Generation NCLEX®-style practice questions of all types are illustrated through stand-alone case studies and unfolding case studies. NCSBN Clinical Judgment Measurement Model (NCJMM) is included throughout with case scenarios that integrate the six clinical judgment cognitive skills.

Saunders Q & A Review for the NCLEX-RN® Examination This edition contains over 6,000 practice questions with each question containing a test-taking strategy and justifications for correct and incorrect answers to enhance review. Questions are organized according to the most recent NCLEX-RN test blueprint Client Needs and Integrated Processes. Questions are written at higher cognitive levels (applying, analyzing, synthesizing, evaluating, and creating) than those on the test itself.

NCLEX-RN Prep Plus by Kaplan The NCLEX-RN Prep Plus from Kaplan employs expert critical thinking techniques and targeted sample questions. This edition identifies seven types of NGN questions and explains in detail how to approach and answer each type. In addition, it provides 10 critical thinking pathways for analyzing exam questions.

Illustrated Study Guide for the NCLEX-RN® Exam The 10th edition of the Illustrated Study Guide for the NCLEX-RN Exam, 10th Edition. This study guide gives you a robust, visual, less-intimidating way to remember key facts. 2,500 review questions are now included on the Evolve companion website. 25 additional illustrations and mnemonics make the book more appealing than ever.

NCLEX RN Examination Prep Flashcards (2023 Edition) NCLEX RN Exam Review FlashCards Study Guide with Practice Test Questions [Full-Color Cards] from Test Prep Books. These flashcards are ready for use, allowing you to begin studying immediately. Each flash card is color-coded for easy subject identification.

Recommended Links
If you need more information or practice quizzes, please do visit the following links:
An investment in knowledge pays the best interest. Keep up the pace and continue learning with these practice quizzes:
- Nursing Test Bank: Free Practice Questions UPDATED ! Our most comprehenisve and updated nursing test bank that includes over 3,500 practice questions covering a wide range of nursing topics that are absolutely free!
- NCLEX Questions Nursing Test Bank and Review UPDATED! Over 1,000+ comprehensive NCLEX practice questions covering different nursing topics. We’ve made a significant effort to provide you with the most challenging questions along with insightful rationales for each question to reinforce learning.

3 thoughts on “Nursing Research Nursing Test Bank and Practice Questions (60 Items)”
Thanks for the well prepared questions and answers. It will be of a great help for those who look up your contributions.
Hi Zac, we’re having some performance issues with the quizzes so we’re forced to change their settings in the meantime. We are working on a solution and will revert the changes once we’re sure that the problem is resolved. Thanks for the understanding!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply

- Request new password
- Create a new account
Doing Research in the Real World
Student resources, multiple choice quiz.
Take the quiz to test your understanding of the key concepts covered in the chapter. Try testing yourself before you read the chapter to see where your strengths and weaknesses are, then test yourself again once you’ve read the chapter to see how well you’ve understood.
Tip: Click on each link to expand and view the content. Click again to collapse.
PART A: PRINCIPLES AND PLANNING FOR RESEARCH
1. Which of the following should not be a criterion for a good research project?
- Demonstrates the abilities of the researcher
- Is dependent on the completion of other projects
- Demonstrates the integration of different fields of knowledge
- Develops the skills of the researcher
b. Is dependent on the completion of other projects
2. Which form of reasoning is the process of drawing a specific conclusion from a set of premises?
- Objective reasoning
- Positivistic reasoning
- Inductive reasoning
- Deductive reasoning
d: Deductive reasoning
3. Research that seeks to examine the findings of a study by using the same design but a different sample is which of the following?
- An exploratory study
- A replication study
- An empirical study
- Hypothesis testing
b: A replication study
4. A researcher designs an experiment to test how variables interact to influence job-seeking behaviours. The main purpose of the study was:
- Description
- Exploration
- Explanation
d: Explanation
5. Cyber bullying at work is a growing threat to employee job satisfaction. Researchers want to find out why people do this and how they feel about it. The primary purpose of the study is:
c: Exploration
6. A theory:
- Is an accumulated body of knowledge
- Includes inconsequential ideas
- Is independent of research methodology
- Should be viewed uncritically
a: Is an accumulated body of knowledge
7. Which research method is a bottom-up approach to research?
- Deductive method
- Explanatory method
- Inductive method
- Exploratory method
c: Inductive method
8. How much confidence should you place in a single research study?
- You should trust research findings after different researchers have replicated the findings
- You should completely trust a single research study
- Neither a nor b
- Both a and b
a: You should trust research findings after different researchers have replicated the findings
9. A qualitative research problem statement:
- Specifies the research methods to be utilized
- Specifies a research hypothesis
- Expresses a relationship between variables
- Conveys a sense of emerging design
d: Conveys a sense of emerging design
10. Which of the following is a good research question?
- To produce a report on student job searching behaviours
- To identify the relationship between self-efficacy and student job searching behaviours
- Students with higher levels of self-efficacy will demonstrate more active job searching behaviours
- Do students with high levels of self-efficacy demonstrate more active job searching behaviours?
d: Do students with high levels of self-efficacy demonstrate more active job searching behaviours?
11. A review of the literature prior to formulating research questions allows the researcher to :
- Provide an up-to-date understanding of the subject, its significance, and structure
- Guide the development of research questions
- Present the kinds of research methodologies used in previous studies
- All of the above
d: All of the above
12. Sometimes a comprehensive review of the literature prior to data collection is not recommended by:
- Ethnomethodology
- Grounded theory
- Symbolic interactionism
- Feminist theory
b: Grounded theory
13. The feasibility of a research study should be considered in light of:
- Cost and time required to conduct the study
- Access to gatekeepers and respondents
- Potential ethical concerns
14. Research that uses qualitative methods for one phase and quantitative methods for the next phase is known as:
- Action research
- Mixed-method research
- Quantitative research
- Pragmatic research
b: Mixed-method research
15. Research hypotheses are:
- Formulated prior to a review of the literature
- Statements of predicted relationships between variables
- B but not A
- Both A and B
c: B but not A
16. Which research approach is based on the epistemological viewpoint of pragmatism?
- Qualitative research
- Mixed-methods research
c: Mixed-methods research
17. Adopting ethical principles in research means:
- Avoiding harm to participants
- The researcher is anonymous
- Deception is only used when necessary
- Selected informants give their consent
a: Avoiding harm to participants
18. A radical perspective on ethics suggests that:
- Researchers can do anything they want
- The use of checklists of ethical actions is essential
- The powers of Institutional Review Boards should be strengthened
- Ethics should be based on self-reflexivity
d: Ethics should be based on self-reflexivity
19. Ethical problems can arise when researching the Internet because:
- Everyone has access to digital media
- Respondents may fake their identities
- Researchers may fake their identities
- Internet research has to be covert
b: Respondents may fake their identities
20. The Kappa statistic:
- Is a measure of inter-judge validity
- Compares the level of agreement between two judges against what might have been predicted by chance
- Ranges from 0 to +1
- Is acceptable above a score of 0.5
b: Compares the level of agreement between two judges against what might have been predicted by chance
PART B: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
1. Which research paradigm is most concerned about generalizing its findings?
a: Quantitative research
2. A variable that is presumed to cause a change in another variable is called:
- An intervening variable
- A dependent variable
- An independent variable
- A numerical variable
c: An independent variable
3. A study of teaching professionals posits that their performance-related pay increases their motivation which in turn leads to an increase in their job satisfaction. What kind of variable is ‘motivation”’ in this study?
- Extraneous
- Confounding
- Intervening
- Manipulated
c: Intervening
4. Which correlation is the strongest?
5. When interpreting a correlation coefficient expressing the relationship between two variables, it is important not to:
- Assume causality
- Measure the values for X and Y independently
- Choose X and Y values that are normally distributed
- Check the direction of the relationship
a: Assume causality
6. Which of the following can be described as a nominal variable?
- Annual income
- Annual sales
- Geographical location of a firm
d: Geographical location of a firm
7. A positive correlation occurs when:
- Two variables remain constant
- Two variables move in the same direction
- One variable goes up and the other goes down
- Two variables move in opposite directions
b: Two variables move in the same direction
8. The key defining characteristic of experimental research is that:
- The independent variable is manipulated
- Hypotheses are proved
- A positive correlation exists
- Samples are large
a: The independent variable is manipulated
9. Qualitative research is used in all the following circumstances, EXCEPT:
- It is based on a collection of non-numerical data such as words and pictures
- It often uses small samples
- It uses the inductive method
- It is typically used when a great deal is already known about the topic of interest
d: It is typically used when a great deal is already known about the topic of interest
10. In an experiment, the group that does not receive the intervention is called:
- The experimental group
- The participant group
- The control group
- The treatment group
c: The control group
11. Which generally cannot be guaranteed in conducting qualitative studies in the field?
- Keeping participants from physical and emotional harm
- Gaining informed consent
- Assuring anonymity rather than just confidentiality
- Maintaining consent forms
c: Assuring anonymity rather than just confidentiality
12. Which of the following is not ethical practice in research with humans?
- Maintaining participants’ anonymity
- Informing participants that they are free to withdraw at any time
- Requiring participants to continue until the study has been completed
d: Requiring participants to continue until the study has been completed
13. What do we call data that are used for a new study but which were collected by an earlier researcher for a different set of research questions?
- Secondary data
- Field notes
- Qualitative data
- Primary data
a: Secondary data
14. When each member of a population has an equal chance of being selected, this is called:
- A snowball sample
- A stratified sample
- A random probability sample
- A non-random sample
c: A random probability sample
15. Which of the following techniques yields a simple random sample of hospitals?
- Randomly selecting a district and then sampling all hospitals within the district
- Numbering all the elements of a hospital sampling frame and then using a random number generator to pick hospitals from the table
- Listing hospitals by sector and choosing a proportion from within each sector at random
- Choosing volunteer hospitals to participate
b: Numbering all the elements of a hospital sampling frame and then using a random number generator to pick hospitals from the table
16. Which of the following statements are true?
- The larger the sample size, the larger the confidence interval
- The smaller the sample size, the greater the sampling error
- The more categories being measured, the smaller the sample size
- A confidence level of 95 percent is always sufficient
b: The smaller the sample size, the greater the sampling error
17. Which of the following will produce the least sampling error?
- A large sample based on convenience sampling
- A small sample based on random sampling
- A large snowball sample
- A large sample based on random sampling
d: A large sample based on random sampling
18. When people are readily available, volunteer, or are easily recruited to the sample, this is called:
- Snowball sampling
- Convenience sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Random sampling
b: Convenience sampling
19. In qualitative research, sampling that involves selecting diverse cases is referred to as:
- Typical-case sampling
- Critical-case sampling
- Intensity sampling
- Maximum variation sampling
d: Maximum variation sampling
20. A test accurately indicates an employee’s scores on a future criterion (e.g., conscientiousness). What kind of validity is this?
a: Predictive
PART C: DATA COLLECTION METHODS
1. When designing a questionnaire it is important to do each of the following EXCEPT
- Pilot the questionnaire
- Avoid jargon
- Avoid double questions
- Use leading questions
d: Use leading questions
2. One advantage of using a questionnaire is that:
- Probe questions can be asked
- Respondents can be put at ease
- Interview bias can be avoided
- Response rates are always high
c: Interview bias can be avoided
3. Which of the following is true of observations?
- It takes less time than interviews
- It is often not possible to determine exactly why people behave as they do
- Covert observation raises fewer ethical concerns than overt
b: It is often not possible to determine exactly why people behave as they do
4. A researcher secretly becomes an active member of a group in order to observe their behaviour. This researcher is acting as:
- An overt participant observer
- A covert non-participant observer
- A covert participant observer
- None of the above
c: A covert participant observer
5. All of the following are advantages of structured observation, EXCEPT:
- Results can be replicated at a different time
- The coding schedule might impose a framework on what is being observed
- Data can be collected that participants may not realize is important
- Data do not have to rely on the recall of participants
b: The coding schedule might impose a framework on what is being observed
6. When conducting an interview, asking questions such as: "What else? or ‘Could you expand on that?’ are all forms of:
- Structured responses
- Category questions
7. Secondary data can include which of the following?
- Government statistics
- Personal diaries
- Organizational records
8. An ordinal scale is:
- The simplest form of measurement
- A scale with an absolute zero point
- A rank-order scale of measurement
- A scale with equal intervals between ranks
c: A rank-order scale of measurement
9. Which term measures the extent to which scores from a test can be used to infer or predict performance in some activity?
- Face validity
- Content reliability
- Criterion-related validity
- Construct validity
c: Criterion-related validity
10. The ‘reliability’of a measure refers to the researcher asking:
- Does it give consistent results?
- Does it measure what it is supposed to measure?
- Can the results be generalized?
- Does it have face reliability?
a: Does it give consistent results?
11. Interviewing is the favoured approach EXCEPT when:
- There is a need for highly personalized data
- It is important to ask supplementary questions
- High numbers of respondents are needed
- Respondents have difficulty with written language
c: High numbers of respondents are needed
12. Validity in interviews is strengthened by the following EXCEPT:
- Building rapport with interviewees
- Multiple questions cover the same theme
- Constructing interview schedules that contain themes drawn from the literature
- Prompting respondents to expand on initial responses
b: Multiple questions cover the same theme
13. Interview questions should:
- Lead the respondent
- Probe sensitive issues
- Be delivered in a neutral tone
- Test the respondents’ powers of memory
c: Be delivered in a neutral tone
14. Active listening skills means:
- Asking as many questions as possible
- Avoiding silences
- Keeping to time
- Attentive listening
d: Attentive listening
15. All the following are strengths of focus groups EXCEPT:
- They allow access to a wide range of participants
- Discussion allows for the validation of ideas and views
- They can generate a collective perspective
- They help maintain confidentiality
d: They help maintain confidentiality
16. Which of the following is not always true about focus groups?
- The ideal size is normally between 6 and 12 participants
- Moderators should introduce themselves to the group
- Participants should come from diverse backgrounds
- The moderator poses preplanned questions
c: Participants should come from diverse backgrounds
17. A disadvantage of using secondary data is that:
- The data may have been collected with reference to research questions that are not those of the researcher
- The researcher may bring more detachment in viewing the data than original researchers could muster
- Data have often been collected by teams of experienced researchers
- Secondary data sets are often available and accessible
a: The data may have been collected with reference to research questions that are not those of the researcher
18. All of the following are sources of secondary data EXCEPT:
- Official statistics
- A television documentary
- The researcher’s research diary
- A company’s annual report
c: The researcher’s research diary
19. Which of the following is not true about visual methods?
- They are not reliant on respondent recall
- The have low resource requirements
- They do not rely on words to capture what is happening
- They can capture what is happening in real time
b: The have low resource requirements
20. Avoiding naïve empiricism in the interpretation of visual data means:
- Understanding the context in which they were produced
- Ensuring that visual images such as photographs are accurately taken
- Only using visual images with other data gathering sources
- Planning the capture of visual data carefully
a: Understanding the context in which they were produced
PART D: ANALYSIS AND REPORT WRITING
1. Which of the following is incorrect when naming a variable in SPSS?
- Must begin with a letter and not a number
- Must end in a full stop
- Cannot exceed 64 characters
- Cannot include symbols such as ?, & and %
b: Must end in a full stop
2. Which of the following is not an SPSS Type variable?
3. A graph that uses vertical bars to represent data is called:
- A bar chart
- A pie chart
- A line graph
- A vertical graph
a: A bar chart
4. The purpose of descriptive statistics is to:
- Summarize the characteristics of a data set
- Draw conclusions from the data
a: Summarize the characteristics of a data set
5. The measure of the extent to which responses vary from the mean is called:
- The normal distribution
- The standard deviation
- The variance
c: The standard deviation
6. To compare the performance of a group at time T1 and then at T2, we would use:
- A chi-squared test
- One-way analysis of variance
- Analysis of variance
- A paired t-test
d: A paired t-test
7. A Type 1 error occurs in a situation where:
- The null hypothesis is accepted when it is in fact true
- The null hypothesis is rejected when it is in fact false
- The null hypothesis is rejected when it is in fact true
- The null hypothesis is accepted when it is in fact false
c: The null hypothesis is rejected when it is in fact true
8. The significance level
- Is set after a statistical test is conducted
- Is always set at 0.05
- Results in a p -value
- Measures the probability of rejecting a true null hypothesis
d: Measures the probability of rejecting a true null hypothesis
9. To predict the value of the dependent variable for a new case based on the knowledge of one or more independent variables, we would use
- Regression analysis
- Correlation analysis
- Kolmogorov-Smirnov test
a: Regression analysis
10. In conducting secondary data analysis, researchers should ask themselves all of the following EXCEPT:
- Who produced the document?
- Is the material genuine?
- How can respondents be re-interviewed?
- Why was the document produced?
c: How can respondents be re-interviewed?
11. Which of the following are not true of reflexivity?
- It recognizes that the researcher is not a neutral observer
- It has mainly been applied to the analysis of qualitative data
- It is part of a post-positivist tradition
- A danger of adopting a reflexive stance is the researcher can become the focus of the study
c: It is part of a post-positivist tradition
12. Validity in qualitative research can be strengthened by all of the following EXCEPT:
- Member checking for accuracy and interpretation
- Transcribing interviews to improve accuracy of data
- Exploring rival explanations
- Analysing negative cases
b: Transcribing interviews to improve accuracy of data
13. Qualitative data analysis programs are useful for each of the following EXCEPT:
- Manipulation of large amounts of data
- Exploring of the data against new dimensions
- Querying of data
- Generating codes
d: Generating codes
14. Which part of a research report contains details of how the research was planned and conducted?
- Introduction
b: Design
15. Which of the following is a form of research typically conducted by managers and other professionals to address issues in their organizations and/or professional practice?
- Basic research
- Professional research
- Predictive research
a: Action research
16. Plagiarism can be avoided by:
- Copying the work of others accurately
- Paraphrasing the author’s text in your own words
- Cut and pasting from the Internet
- Quoting directly without revealing the source
b: Paraphrasing the author’s text in your own words
17. In preparing for a presentation, you should do all of the following EXCEPT:
- Practice the presentation
- Ignore your nerves
- Get to know more about your audience
- Take an advanced look, if possible, at the facilities
b: Ignore your nerves
18. You can create interest in your presentation by:
- Using bullet points
- Reading from notes
- Maximizing the use of animation effects
- Using metaphors
d: Using metaphors
19. In preparing for a viva or similar oral examination, it is best if you have:
- Avoided citing the examiner in your thesis
- Made exaggerated claims on the basis of your data
- Published and referenced your own article(s)
- Tried to memorize your work
c: Published and referenced your own article(s)
20. Grounded theory coding:
- Makes use of a priori concepts from the literature
- Uses open coding, selective coding, then axial coding
- Adopts a deductive stance
- Stops when theoretical saturation has been reached
d: Stops when theoretical saturation has been reached
2.3 Generating Good Research Questions
Learning objectives.
- Describe some techniques for turning research ideas into empirical research questions and use those techniques to generate questions.
- Explain what makes a research question interesting and evaluate research questions in terms of their interestingness.
Generating Empirically Testable Research Questions
Once you have a research idea, you need to use it to generate one or more empirically testable research questions, that is, questions expressed in terms of a single variable or relationship between variables. One way to do this is to look closely at the discussion section in a recent research article on the topic. This is the last major section of the article, in which the researchers summarize their results, interpret them in the context of past research, and suggest directions for future research. These suggestions often take the form of specific research questions, which you can then try to answer with additional research. This can be a good strategy because it is likely that the suggested questions have already been identified as interesting and important by experienced researchers.
But you may also want to generate your own research questions. How can you do this? First, if you have a particular behavior or psychological characteristic in mind, you can simply conceptualize it as a variable and ask how frequent or intense it is. How many words on average do people speak per day? How accurate are our memories of traumatic events? What percentage of people have sought professional help for depression? If the question has never been studied scientifically—which is something that you will learn in your literature review—then it might be interesting and worth pursuing.
If scientific research has already answered the question of how frequent or intense the behavior or characteristic is, then you should consider turning it into a question about a relationship between that behavior or characteristic and some other variable. One way to do this is to ask yourself the following series of more general questions and write down all the answers you can think of.
- What are some possible causes of the behavior or characteristic?
- What are some possible effects of the behavior or characteristic?
- What types of people might exhibit more or less of the behavior or characteristic?
- What types of situations might elicit more or less of the behavior or characteristic?
In general, each answer you write down can be conceptualized as a second variable, suggesting a question about a relationship. If you were interested in talkativeness, for example, it might occur to you that a possible cause of this psychological characteristic is family size. Is there a relationship between family size and talkativeness? Or it might occur to you that people seem to be more talkative in same-sex groups than mixed-sex groups. Is there a difference in the average level of talkativeness of people in same-sex groups and people in mixed-sex groups? This approach should allow you to generate many different empirically testable questions about almost any behavior or psychological characteristic.
If through this process you generate a question that has never been studied scientifically—which again is something that you will learn in your literature review—then it might be interesting and worth pursuing. But what if you find that it has been studied scientifically? Although novice researchers often want to give up and move on to a new question at this point, this is not necessarily a good strategy. For one thing, the fact that the question has been studied scientifically and the research published suggests that it is of interest to the scientific community. For another, the question can almost certainly be refined so that its answer will still contribute something new to the research literature. Again, asking yourself a series of more general questions about the relationship is a good strategy.
- Are there other ways to define and measure the variables?
- Are there types of people for whom the relationship might be stronger or weaker?
- Are there situations in which the relationship might be stronger or weaker—including situations with practical importance?
For example, research has shown that women and men speak about the same number of words per day—but this was when talkativeness was measured in terms of the number of words spoken per day among university students in the United States and Mexico. We can still ask whether other ways of measuring talkativeness—perhaps the number of different people spoken to each day—produce the same result. Or we can ask whether studying elderly people or people from other cultures produces the same result. Again, this approach should help you generate many different research questions about almost any relationship.
Evaluating Research Questions
Researchers usually generate many more research questions than they ever attempt to answer. This means they must have some way of evaluating the research questions they generate so that they can choose which ones to pursue. In this section, we consider two criteria for evaluating research questions: the interestingness of the question and the feasibility of answering it.
Interestingness
How often do people tie their shoes? Do people feel pain when you punch them in the jaw? Are women more likely to wear makeup than men? Do people prefer vanilla or chocolate ice cream? Although it would be a fairly simple matter to design a study and collect data to answer these questions, you probably would not want to because they are not interesting. We are not talking here about whether a research question is interesting to us personally but whether it is interesting to people more generally and, especially, to the scientific community. But what makes a research question interesting in this sense? Here we look at three factors that affect the interestingness of a research question: the answer is in doubt, the answer fills a gap in the research literature, and the answer has important practical implications.
First, a research question is interesting to the extent that its answer is in doubt. Obviously, questions that have been answered by scientific research are no longer interesting as the subject of new empirical research. But the fact that a question has not been answered by scientific research does not necessarily make it interesting. There has to be some reasonable chance that the answer to the question will be something that we did not already know. But how can you assess this before actually collecting data? One approach is to try to think of reasons to expect different answers to the question—especially ones that seem to conflict with common sense. If you can think of reasons to expect at least two different answers, then the question might be interesting. If you can think of reasons to expect only one answer, then it probably is not. The question of whether women are more talkative than men is interesting because there are reasons to expect both answers. The existence of the stereotype itself suggests the answer could be yes, but the fact that women’s and men’s verbal abilities are fairly similar suggests the answer could be no. The question of whether people feel pain when you punch them in the jaw is not interesting because there is absolutely no reason to think that the answer could be anything other than a resounding yes.
A second important factor to consider when deciding if a research question is interesting is whether answering it will fill a gap in the research literature. Again, this means in part that the question has not already been answered by scientific research. But it also means that the question is in some sense a natural one for people who are familiar with the research literature. For example, the question of whether taking lecture notes by hand can help improve students’ exam performance would be likely to occur to anyone who was familiar with research on note taking and the ineffectiveness of shallow processing on learning.
A final factor to consider when deciding whether a research question is interesting is whether its answer has important practical implications. Again, the question of whether taking notes by hand improves learning has important implications for education, including classroom policies concerning technology use. The question of whether cell phone use impairs driving is interesting because it is relevant to the personal safety of everyone who travels by car and to the debate over whether cell phone use should be restricted by law.
Feasibility
A second important criterion for evaluating research questions is the feasibility of successfully answering them. There are many factors that affect feasibility, including time, money, equipment and materials, technical knowledge and skill, and access to research participants. Clearly, researchers need to take these factors into account so that they do not waste time and effort pursuing research that they cannot complete successfully.
Looking through a sample of professional journals in psychology will reveal many studies that are complicated and difficult to carry out. These include longitudinal designs in which participants are tracked over many years, neuroimaging studies in which participants’ brain activity is measured while they carry out various mental tasks, and complex non-experimental studies involving several variables and complicated statistical analyses. Keep in mind, though, that such research tends to be carried out by teams of highly trained researchers whose work is often supported in part by government and private grants. Also, keep in mind that research does not have to be complicated or difficult to produce interesting and important results. Looking through a sample of professional journals will also reveal studies that are relatively simple and easy to carry out—perhaps involving a convenience sample of university students and a paper-and-pencil task.
A final point here is that it is generally good practice to use methods that have already been used successfully by other researchers. For example, if you want to manipulate people’s moods to make some of them happy, it would be a good idea to use one of the many approaches that have been used successfully by other researchers (e.g., paying them a compliment). This is good not only for the sake of feasibility—the approach is “tried and true”—but also because it provides greater continuity with previous research. This makes it easier to compare your results with those of other researchers and to understand the implications of their research for yours, and vice versa.
Key Takeaways
- Research questions expressed in terms of variables and relationships between variables can be suggested by other researchers or generated by asking a series of more general questions about the behavior or psychological characteristic of interest.
- It is important to evaluate how interesting a research question is before designing a study and collecting data to answer it. Factors that affect interestingness are the extent to which the answer is in doubt, whether it fills a gap in the research literature, and whether it has important practical implications.
- It is also important to evaluate how feasible a research question will be to answer. Factors that affect feasibility include time, money, technical knowledge and skill, and access to special equipment and research participants.
- Practice: Generate three research ideas based on each of the following: informal observations, practical problems, and topics discussed in recent issues of professional journals.
- Practice: Generate an empirical research question about each of the following behaviors or psychological characteristics: long-distance running, getting tattooed, social anxiety, bullying, and memory for early childhood events.
- Practice: Evaluate each of the research questions you generated in Exercise 2 in terms of its interestingness based on the criteria discussed in this section.
- Practice: Find an issue of a journal that publishes short empirical research reports (e.g., Psychological Science , Psychonomic Bulletin and Review , Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin ). Pick three studies, and rate each one in terms of how feasible it would be for you to replicate it with the resources available to you right now. Use the following rating scale: (1) You could replicate it essentially as reported. (2) You could replicate it with some simplifications. (3) You could not replicate it. Explain each rating.

Share This Book
- Increase Font Size
Research Tutorial
- Library Research Tutorial
- What Is a Thesis Statement?
- Topic Development
- Improve Your Research Question
- Good and Bad Research Questions
- Video Review
- Sources for Background Reading
- What about Wikipedia?
- Related Terms
- Subject Terms
- Boolean Searching
- Advanced Searching Techniques
- Definition of "Scholarly"
- Subject Guides
- Individual Databases
- Open Access Resources
- Google Scholar
- Library Catalog
- Evaluation of Sources
- Academic Writing
- Writing Resources
- Citing Sources
- Citation Formats
- Citation Resources
- Academic Integrity
- Research on the Job
Characteristics of Good and Bad Research Questions
The figure below gives some examples of good and "not-so-good" research questions.

Transcript of this image
- << Previous: Improve Your Research Question
- Next: Video Review >>
- Last Updated: Nov 9, 2023 10:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.umgc.edu/research-tutorial
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
- Example 2
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures, ethics in science: importance, principles & guidelines , jenni ai review: top features, pricing, and alternatives, 8 most effective ways to increase motivation for....

Starting Your Research Series
- Information Privilege
- About the VPN
- Setting Up & Connecting
- About Get it at UC
- About the Information Cycle
- The Process of Information Creation
- Information Cycle Insights
- Article Types
- Peer Review
Research Question Criteria
- Steps to Develop Your RQ
- Ideas & Inspiration
- From Idea to Library
- Locating Databases
- Selecting Database Subjects
- Exploring Best Bets
- Moving Beyond Best Bets
- Selecting & Using Keywords
- Using Search Strategies
- Crafting a Search String
- Database Organization
- Search Boxes
- Getting More Information
- Finding Similar Results
- Citation Styles
- Finding Citations in Databases
- Creating a Citation
- Citation Management Tools
Sheridan Library, University of Cincinnati Libraries 3:28
Let’s review key criteria from the video. Then you will apply these criteria to sample research questions to determine whether they are strong or weak research questions.
The question, “Should Americans avoid eating fast food daily?” feels like it lacks substance or true debate. If you asked your peers this question, most would likely respond with “Yes, eating fast food every day isn’t good for anyone!”
The question, “What do North American airline companies currently charge for baggage in domestic flights?” also seems weak. Though it will require you to search for information to answer it, your response will not require any deep analysis.
In this question, How can massively multiplayer online games (MMOGs) be banned to avoid future violence? , the questioner seems to suggest that MMOGs are causing violence. However, this may be up for debate.
This second question seems more neutral. What warnings, if any, should massively multiplayer online games (MMOGs) have for users under the age of 13?
If you are interested in, “How has the paparazzi impacted the mental health of California’s elite?”, you would have to also ask yourself if there is sufficient, reliable and credible evidence to answer this question.
For instance, “How might the United States government address the nation’s food insecurity?” is a HUGE question while “ How might non-profits address the food insecurity of men aged 50 and older in Merced?“ is extremely narrow.
“Why does my family love quinoa so much?” might be an interesting question to you, but is it meaningful to anyone else???
However, “ How has the popularity of quinoa impacted the food security of those in Bolivia and Peru?” could interest you AND have relevance to others too.
- << Previous: Developing a Research Question
- Next: Steps to Develop Your RQ >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2024 11:43 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ucmerced.edu/starting-your-research

Have an account?
Suggestions for you See more

Scientific Method
10.4k plays, 6th - 8th , universal declaration of human rights, 7th - 10th , english literacy, professional development , java method, university .

Research questions and hypothesis
10 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
Which are 2 research question forms?
Main questions and hypothesis
Central question and subquestions
Super question and subquestions
Main question and objective
It is a specific goal for the research
Research question
Central question
Predictions that involve variables and statistical tests.
Central and subquestions
What is a central question?
It narrows the focus of the study but leave open the questioning
It defines what the research study hopes to learn.
A broad question that asks for an exploration of the central phenomenon or concept in a study.
A prediction the researcher makes about the expected relationships among variables
To write a good quantitative research question and hypotheses it is important...
Not to relate one or more independent variables to one or more dependent variables
To focus on a single phenomenon or concept.
Relate one or more independent variables to one or more dependent variables.
No, this is not the answerxD
Type of QUALITATIVE central question
Ethnography
Alternative hyphotesis
Nondirectional
Null, alternative, and non-directional are forms of...
Research questions
Central questions
Read the next definition: “The investigator makes a prediction (higher, more change) about something basing this prediction on studies”. To what type of Hypothesis forms does this definition belong to?
Alternative or directional
Subquestions
In the model for descriptive questions and hypotheses. Which are the two different types of question?
Alternative or directional, Null
Ethnography and subquestions
Descriptive and inferential
Central question and Non-directional
Choose the correct descriptive question.
What do you conclude about the topic?
What would happened if you go?
What are the student's achievement levels (or grades) in science classes?
What is the problem?
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
research questions. They lay the foundation for the research study. sub-questions. Therefore, they determine the research design or plan of the research. Through __________, you can precisely determine the type of data and the method of collecting, analyzing and presenting data. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1. The type of research focused on finding a solution to an immediate practical problem is termed as: A. Basic research B. Applied research C. Explanatory research D. Descriptive research, 2. The principles of ethics in nursing research include: A. Beneficence B. Respect for human dignity C. Justice D.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
There are two types of research: Qualitative research and Quantitative research. There must be research questions for every type of research. Your research question will be based on the type of research you want to conduct and the type of data collection. The first step in designing research involves identifying a gap and creating a focused ...
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
Research questions should not be answerable with a simple "yes" or "no" or by easily-found facts. They should, instead, require both research and analysis on the part of the writer. They often begin with "How" or "Why.". Begin your research. After you've come up with a question, think about the possible paths your research ...
These exams offer a rigorous question set to assess your understanding, prepare you for actual examinations, and benchmark your performance. You're given 2 minutes per item. For Challenge Exams, click on the "Start Quiz" button to start the quiz. Complete the quiz: Ensure that you answer the entire quiz.
Multiple Choice Quiz. Take the quiz to test your understanding of the key concepts covered in the chapter. Try testing yourself before you read the chapter to see where your strengths and weaknesses are, then test yourself again once you've read the chapter to see how well you've understood. Tip: Click on each link to expand and view the ...
A second important criterion for evaluating research questions is the feasibility of successfully answering them. There are many factors that affect feasibility, including time, money, equipment and materials, technical knowledge and skill, and access to research participants. Clearly, researchers need to take these factors into account so that ...
Good Research Questions. Bad Research Questions. Have no simple answer - are open-ended and consider cause/effect. Have simple or easy answers - can be answered with one word, a number, or a list. Are "researchable" - can be answered with accessible research, facts, and data. Cannot be answered -- there is no answer, or the information to ...
Choose a broad topic, such as "learner support" or "social media influence" for your study. Select topics of interest to make research more enjoyable and stay motivated. Preliminary research. The goal is to refine and focus your research question. The following strategies can help: Skim various scholarly articles.
Then you will apply these criteria to sample research questions to determine whether they are strong or weak research questions. #1 Create a research question that is not easily answered or over-simplified. It has substance, requiring explanation and analysis. You don't want it answered with a simple yes or no.
Mixed-methods studies. Mixed-methods studies typically require a set of both quantitative and qualitative research questions. Separate questions are appropriate when the mixed-methods study focuses on the significance and differences in quantitative and qualitative methods and not on the study's integrative component (Tashakkori & Teddlie, 2010).
Summary. Research question begins with an idea which is then transformed into a research question. A research question: clear, focused, and concise statement that conveys the objectives of the research and its potential findings. Should be expressed in a simple, straight-forward language.
Begin the research and writing process using the following tips: Research your question: Now that you have a research question, you can begin exploring possible answers to it. Your research question allows you to begin researching in a clear direction. Create a thesis statement: Once you have a clear understanding of your research question and ...
1 pt. area of concern when there is a gap in knowledge that requires a solution; defined by what you do not. know or understand about your practical problem. practical problem. research problem. pure research. 3. Multiple Choice. 30 seconds.
1 pt. Which are 2 research question forms? Main questions and hypothesis. Central question and subquestions. Super question and subquestions. Main question and objective. 2. Multiple Choice. 20 seconds.