October 2, 2018

Do Violent Video Games Trigger Aggression?
A study tries to find whether slaughtering zombies with a virtual assault weapon translates into misbehavior when a teenager returns to reality
By Melinda Wenner Moyer

Getty Images
Intuitively, it makes sense Splatterhouse and Postal 2 would serve as virtual training sessions for teens, encouraging them to act out in ways that mimic game-related violence. But many studies have failed to find a clear connection between violent game play and belligerent behavior, and the controversy over whether the shoot-‘em-up world transfers to real life has persisted for years. A new study published on October 1 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences tries to resolve the controversy by weighing the findings of two dozen studies on the topic.
The meta-analysis does tie violent video games to a small increase in physical aggression among adolescents and preteens. Yet debate is by no means over. Whereas the analysis was undertaken to help settle the science on the issue, researchers still disagree on the real-world significance of the findings.
This new analysis attempted to navigate through the minefield of conflicting research. Many studies find gaming associated with increases in aggression, but others identify no such link. A small but vocal cadre of researchers have argued much of the work implicating video games has serious flaws in that, among other things, it measures the frequency of aggressive thoughts or language rather than physically aggressive behaviors like hitting or pushing, which have more real-world relevance.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Jay Hull, a social psychologist at Dartmouth College and a co-author on the new paper, has never been convinced by the critiques that have disparaged purported ties between gaming and aggression. “I just kept reading, over and over again, [these] criticisms of the literature and going, ‘that’s just not true,’” he says. So he and his colleagues designed the new meta-analysis to address these criticisms head-on and determine if they had merit.
Hull and colleagues pooled data from 24 studies that had been selected to avoid some of the criticisms leveled at earlier work. They only included research that measured the relationship between violent video game use and overt physical aggression. They also limited their analysis to studies that statistically controlled for several factors that could influence the relationship between gaming and subsequent behavior, such as age and baseline aggressive behavior.
Even with these constraints, their analysis found kids who played violent video games did become more aggressive over time. But the changes in behavior were not big. “According to traditional ways of looking at these numbers, it’s not a large effect—I would say it’s relatively small,” he says. But it’s “statistically reliable—it’s not by chance and not inconsequential.”
Their findings mesh with a 2015 literature review conducted by the American Psychological Association, which concluded violent video games worsen aggressive behavior in older children, adolescents and young adults. Together, Hull’s meta-analysis and the APA report help give clarity to the existing body of research, says Douglas Gentile, a developmental psychologist at Iowa State University who was not involved in conducting the meta-analysis. “Media violence is one risk factor for aggression,” he says. “It's not the biggest, it’s also not the smallest, but it’s worth paying attention to.”
Yet researchers who have been critical of links between games and violence contend Hull’s meta-analysis does not settle the issue. “They don’t find much. They just try to make it sound like they do,” says Christopher Ferguson, a psychologist at Stetson University in Florida, who has published papers questioning the link between violent video games and aggression.
Ferguson argues the degree to which video game use increases aggression in Hull’s analysis—what is known in psychology as the estimated “effect size”—is so small as to be essentially meaningless. After statistically controlling for several other factors, the meta-analysis reported an effect size of 0.08, which suggests that violent video games account for less than one percent of the variation in aggressive behavior among U.S. teens and pre-teens—if, in fact, there is a cause-and effect relationship between game play and hostile actions. It may instead be that the relationship between gaming and aggression is a statistical artifact caused by lingering flaws in study design, Ferguson says.
Johannes Breuer, a psychologist at GESIS–Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences in Germany, agrees, noting that according to “a common rule of thumb in psychological research,” effect sizes below 0.1 are “considered trivial.” He adds meta-analyses are only as valid as the studies included in them, and that work on the issue has been plagued by methodological problems. For one thing, studies vary in terms of the criteria they use to determine if a video game is violent or not. By some measures, the Super Mario Bros. games would be considered violent, but by others not. Studies, too, often rely on subjects self-reporting their own aggressive acts, and they may not do so accurately. “All of this is not to say that the results of this meta-analysis are not valid,” he says. “But things like this need to be kept in mind when interpreting the findings and discussing their meaning.”
Hull says, however, that the effect size his team found still has real-world significance. An analysis of one of his earlier studies, which reported a similar estimated effect size of 0.083, found playing violent video games was linked with almost double the risk that kids would be sent to the school principal’s office for fighting. The study began by taking a group of children who hadn’t been dispatched to the principal in the previous month and then tracked them for a subsequent eight months. It found 4.8 percent of kids who reported only rarely playing violent video games were sent to the principal’s office at least once during that period compared with 9 percent who reported playing violent video games frequently. Hull theorizes violent games help kids become more comfortable with taking risks and engaging in abnormal behavior. “Their sense of right and wrong is being warped,” he notes.
Hull and his colleagues also found evidence ethnicity shapes the relationship between violent video games and aggression. White players seem more susceptible to the games' putative effects on behavior than do Hispanic and Asian players. Hull isn’t sure why, but he suspects the games' varying impact relates to how much kids are influenced by the norms of American culture, which, he says, are rooted in rugged individualism and a warriorlike mentality that may incite video game players to identify with aggressors rather than victims. It might “dampen sympathy toward their virtual victims,” he and his co-authors wrote, “with consequences for their values and behavior outside the game.”
Social scientists will, no doubt, continue to debate the psychological impacts of killing within the confines of interactive games. In a follow-up paper Hull says he plans to tackle the issue of the real-world significance of violent game play, and hopes it adds additional clarity. “It’s a knotty issue,” he notes—and it’s an open question whether research will ever quell the controversy.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Wiley-Blackwell Online Open

Violent video games exposure and aggression: The role of moral disengagement, anger, hostility, and disinhibition
Mengyun yao.
1 Faculty of Psychology, Southwest University, Chongqing China
2 Key Laboratory of Cognition and Personality, Ministry of Education, Southwest University, Chongqing China
Yuhong Zhou
Associated data.
Based on the General Aggression Model (GAM), the current study investigated the interactive effect of personal factors (e.g., sensation‐seeking) and situational factors (e.g., violent video games exposure [VVGE]) on the trait aggressive behavior, and the mediating role of individual difference trait (e.g., moral disengagement, anger, and hostility). We recruited 547 undergraduates (48.45% male) from five Chinese universities. The results showed that VVGE was positively associated with moral disengagement, disinhibition, and the four aggressive traits (physical aggression, verbal aggression, anger, and hostility), which were positively associated with each other. Moral disengagement was positively associated with both the disinhibition and the four aggressive traits. Disinhibition was positively associated with the four aggressive traits as well. When controlled for gender, moral disengagement, anger, and hostility wholly mediated the relationship between VVGE and aggression, but the moderation effect of disinhibition was not significant. These findings support the framework of GAM and indicate that moral disengagement, anger, and hostility may be the factors that increase the risk of a higher level of aggression following repeated exposure to violent video games.
1. INTRODUCTION
Player Unknown's Battlegrounds (PUBG), a shooting game that Chinese players call “chicken dinner”, has recently become popular among young people, quickly overtaking Honor of Kings in terms of popularity. According to the China gaming industry report from January to June 2018, the top two games for sales in the mobile video games market were Action Role Playing Game (29.9%) and Multiplayer Online Battle Arena (MOBA; 17.4%), which accounted for nearly 50% of sales, and the proportion of Shooting Games has also increased significantly. Furthermore, the report showed that 35.9% of the game types were Shooting Games and 17.9% were MOBA in the Chinese client e‐sports game market (China Audio‐video & Digital Publishing Association Game Publishing Committee, 2018 ). Many games of such genres (e.g., PUBG) contain violent content (Teng, Li, & Liu, 2014 ), which explains to a certain extent the universality of violent video games.
Violent video games are those that depict intentional attempts by individuals (nonhuman cartoon characters, real persons, or anything in between) to inflict harm on others (Anderson & Bushman, 2001 ). The effects of violent video games have been a societal concern since the birth of the industry and have attracted much attention from researchers. A large body of research has found that violent video game exposure (VVGE) is associated with increased aggression among individuals at various ages (e.g., Gentile, Bender, & Anderson, 2017 ; Greitemeyer, 2018 ; Krahé, 2014 ; Teng et al., 2019 ; Velez, Greitemeyer, Whitaker, Ewoldsen, & Bushman, 2016 ). Also, some research has examined the pathways in the associations between VVGE and aggression; for instance, mediators such as hostile attribution bias, aggressive norms, and dehumanization (e.g., Anderson, Gentile, & Buckley, 2007 ; Gentile, Li, Khoo, Prot, & Anderson, 2014 ; Greitemeyer & McLatchie, 2011 ; Möller & Krahé, 2009 ), and moderators such as psychoticism, aggressive traits, neuroticism, and conscientiousness (e.g., Markey & Markey, 2010 ; Markey & Scherer, 2009 ). To the best of our knowledge, however, there have been few studies that have examined simultaneously the underlying mechanisms of the link between VVGE and aggression from the perspectives of social cognition (i.e., moral disengagement) and personality trait (i.e., sensation seeking, anger, hostility). Such a comprehensive study could help to develop interventions to reduce the relation between VVGE and aggressive behaviors from a theoretical perspective.
1.1. Violent video games exposure and aggression
Although some recent studies have not found a significant relationship between VVGE and aggression (Ferguson & Kilburn, 2010 ; McCarthy, Coley, Wagner, Zengel, & Basham, 2016 ; Pan, Gao, Shi, Liu, & Li, 2018 ), a relatively solid association has been established in experimental, cross‐sectional, and longitudinal studies in general. For example, most research in this area has found that violent video games increase aggressive thoughts, angry feelings, physiological arousal, and aggressive behaviors, and decrease empathic feelings and helping behaviors (e.g., Anderson et al., 2010 ; Gentile et al., 2017 ; Hasan, Bègue, & Bushman, 2012 ; Verheijen, Burk, Stoltz, Van, & Cillessen, 2018 ). In addition, some research in cognitive neuroscience has provided neuroimaging support for these effects (e.g., Gentile, Swing, Anderson, Rinker, & Thomas, 2016 ; Montag et al., 2012 ), and there are also meta‐analyses that have concluded that violent video games increase aggression (e.g., Bushman, 2016 ; Greitemeyer & Mügge, 2014 ).
How does VVGE affect individual aggression? The General Aggression Model (GAM), a general model to account for aggressive behavior, could answer this question. GAM consists of two major systems: personality development (distal processes) and social encounters (proximate processes). The proximate processes explain individual episodes of aggression using three stages, that is, personal and situational inputs influence internal states (cognition, affect, and arousal), which in turn affect appraisal and decision processes, which in turn influence aggressive and nonaggressive behavioral outcomes. Each cycle of the proximate processes serves as a learning trail that creates aggressive knowledge structures after many repetitions. Distal processes detail how biological and persistent environmental factors influence personality through changes in knowledge structures (aggressive beliefs and attitudes, aggressive perceptual schemata, aggressive expectation schemata, aggressive behavioral scripts, and aggression desensitization) and brain structure and function. The personality, in turn, influences personal and situational factors in a cyclical fashion (Allen, Anderson, & Bushman, 2018 ; Anderson & Bushman, 2002 ; Anderson & Bushman, 2018 ). VVGE has been assumed to be a situational input variable of proximal causal factors and an environmental factor of distal causal factors (Anderson & Bushman, 2018 ), that is, VVGE influences aggression through the two main systems of GAM.
Most violent video games primarily involve physical violence, and many of the multiplayer games also involve verbal violence (Adachi & Willoughby, 2016 ; Lemmens, Valkenburg, & Peter, 2011 ), therefore, we focused on self‐reported forms of physical aggression and verbal aggression in the current study.
1.2. Moral disengagement as a potential mediator
Moral disengagement is a cognitive predisposition that individuals reinterpret their immoral behaviors (Bandura, Barbaranelli, Caprara, & Pastorelli, 1996 ). In general, individuals have their own moral standards that inhibit them from engaging in immoral conduct (Bandura, 1990 ), but these standards can be deactivated selectively through eight moral disengagement mechanisms (Bandura, 1999 ). Thus, an individual's moral disengagement mechanisms may be exerted when they commit aggressive acts.
Previous research has supported the moral disengagement theory that moral disengagement mechanisms can make individuals reconstruct aggression cognitively; thus aggression is more likely to occur (Bandura et al., 1996 ). For instance, numerous cross‐sectional studies have found that moral disengagement is positively associated with various forms of aggressive behavior such as physical aggression, verbal aggression, and bullying (e.g., Bussey, Quinn, & Dobson, 2015 ; Gao, Weng, Zhou, & Yu, 2017 ; Obermann, 2011 ; Rubio‐Garay, Carrasco, & Amor, 2016 ). Also, this correlation was found to be significant in juvenile delinquent samples (Wang, Lei, Yang, Gao, & Zhao, 2016 ; Zapolski, Banks, Lau, & Aalsma, 2018 ). Moreover, longitudinal studies have found that initial moral disengagement can predict later aggression among adolescents (e.g., Barchia & Bussey, 2011 ; Hyde, Shaw, & Moilanen, 2010 ; Paciello, Fida, Tramontano, Lupinetti, & Caprara, 2008 ; Sticca & Perren, 2015 ). In addition, a recent meta‐analysis has reinforced this link (Gini, Pozzoli, & Hymel, 2014 ; Killer, Bussey, Hawes, & Hunt, 2019 ).
Moral disengagement is not only a powerful predictor of aggression but also a product of VVGE. Some longitudinal research has established a stable link between the two, indicating that frequent exposure to violent video games in early sessions can predict higher levels of moral disengagement in later sessions; however, this effect was not found to be significant when the position of these two variables was reversed (Teng, Nie, Pan, Liu, & Guo, 2017 ; Wang, Ryoo, Swearer, Turner, & Goldberg, 2017 ). In addition, some cross‐sectional studies have also found an association between VVGE and higher levels of moral disengagement (Gabbiadini, Andrighetto, & Volpato, 2012 ; Teng, Nie, Guo, & Liu, 2017 ).
As mentioned above, moral disengagement may be a potential mediator in the relationship between VVGE and aggression. Richmond and Wilson ( 2008 ) found that the relationship between violent media exposure frequency and aggression was mediated wholly by moral disengagement. As for violent video games in particular, research has found that dehumanization, one of the moral disengagement mechanisms, mediates the effect of VVGE on aggressive behavior (Greitemeyer & McLatchie, 2011 ). Teng et al. ( 2019 ) further demonstrated through a longitudinal study that moral disengagement mediates the link between VVGE and aggression, especially for early adolescents. However, as the research‐tested adolescents from the ages of 12–19 years, it is unclear whether the results can be generalized to adults.
Our research aimed to further test the role of moral disengagement in the relationship between VVGE and aggression among college students. Based on the literature reviewed above, it is reasonable to expect that moral disengagement would play a mediating role in the relationship. Thus we propose the following hypothesis:
H1 : Moral disengagement will play a mediating role in the relationship between VVGE and aggression.
1.3. Anger and hostility as potential mediators
Anger involves physiological arousal and preparation for aggression, representing the emotional or affective component of behavior, and hostility consists of feelings of ill will and injustice, representing the cognitive component of behavior (Buss & Perry, 1992 ). Research has explored the relationship between VVGE, anger, hostility, aggression, as follows. Anger moderated the relationship between VVGE and aggression (Engelhardt, Bartholow, & Saults, 2011 ; Giumetti & Markey, 2007 ), hostility mediated the relationship between VVGE and aggression (Adachi & Willoughby, 2016 ; Bartholow, Sestir, & Davis, 2005 ; Gentile, Lynch, Linder, & Walsh, 2004 ). But according to GAM, anger, and hostility may also be potential mediators.
According to the short‐term effects (proximal processes) of GAM, violent video gameplay, when combined with a provocation, may increase anger and hostility, thereby increasing the likelihood of subsequent aggressive behavior. The long‐term effects of GAM (distal processes) suggest that repeated exposure to violent video games changes aggressive knowledge structures, and finally contributing to enhanced aggressive personality (Anderson & Bushman, 2002 ; Anderson & Bushman, 2018 ). Rather trait anger and trait hostility are cognition correlated knowledge structures (Anderson & Bushman, 2001 ; Anderson et al., 2010 ). Therefore, according to GAM, anger, and hostility may be potential mediators. Thus, we propose the following hypothesis:
H2 : Anger and Hostility will play a mediating role in the relationship between VVGE and aggression.
1.4. Disinhibition as a potential moderator
Although VVGE has a significant effect on aggression, not all individuals are affected by VVGE in equal measure. Research has found that users with particular characteristics are more susceptible to VVGE effects than others (Exelmans, Custers, & Van den Bulck ( 2015 ); Markey & Markey, 2010 ; Markey & Scherer, 2009 ). According to the GAM, the interactive dynamics of personal and situational (i.e. VVGE) factors, of biological and environmental (i.e. VVGE) factors will influence an individual's aggressive behaviors. Based on this theory, users’ characteristics such as personality traits could moderate the association between VVGE and aggression.
Previous research has found that callous‐unemotional traits, psychoticism, aggressive traits, and empathy could moderate the relationship between VVGE and aggression (Gao et al., 2017 ; Krahé & Möller, 2010 ; Markey & Scherer, 2009 ; Rydell, 2016 ). As another form of personality trait, sensation‐seeking may also serve as a moderator between VVGE and aggression. Sensation seeking is defined by the seeking of varied, novel, complex and intense sensations and experiences, and the willingness to take physical, social, legal and financial risks for the sake of such experiences (Zuckerman, 1994 ). Sensation seeking has been identified as a moderator of the relationship between violent media content and aggression (Slater, Henry, Swaim, & Cardador, 2004 ). However, Bisch and Lee ( 2009 ) found that the interaction effect between violent video games and sensation seeking was not significant. Sensation seeking contains four subscales: thrills and adventure‐seeking; experience seeking; disinhibition; and boredom susceptibility. It may be that particular dimensions are the main factors in the effect of sensation seeking as a moderator.
The disinhibition dimension may be qualitatively different from the other three dimensions (Krcmar & Greene, 1999 ). Disinhibition represents the desire for social and sexual disinhibition as expressed in social drinking, partying, and variety in sexual partners (Zuckerman, 1994 ). It is the reverse of inhibition and describes how people reduce their public self‐awareness, have less concern about the judgment of others, and thus ignore conventional constraints (Lin & Tsai, 2002 ). Research has found that the disinhibition dimension and the experience‐seeking dimension are related to adolescents’ exposure to violent television positively and negatively, respectively (Krcmar & Greene, 1999 ). Additionally, Aluja‐Fabregat ( 2000 ) found a positive relation between disinhibition and exposure to violent films in 8th‐grade boys and girls. Moreover, a recent study that compared gamers (former and ongoing) with non‐gamers found an association between disinhibition and VVGE (Kimmig, Andringa, & Derntl, 2018 ). Consequently, it seems that disinhibition is the main factor in the moderation of the relationship between VVGE and aggression via sensation seeking.
However, although research has identified sensation seeking as a moderator in the relationship between violent media use and aggression, some studies have not found this effect with regard to VVGE. Given the findings cited above, it is reasonable to deduce that the disinhibition dimension may play a different role in the relationship between VVGE and aggression. Thus we propose the following hypothesis:
H3 : Disinhibition will moderate the relationship between violent video games exposure and aggression.
1.5. The present study
The aims of the present study were twofold: first, we aimed to examine the mediating effect of moral disengagement, anger, and hostility in the relationship between VVGE and aggression among college students. Second, we aimed to examine whether disinhibition dimension of sensation seeking plays a role as a moderator between VVGE and aggression. These two questions can address the mechanisms of both mediation (i.e., how does VVGE increase aggression), and moderation (i.e., when and for whom is the effect most potent) of the relationship between VVGE and aggression.
2. METHOD AND MATERIALS
2.1. participants.
The present study used convenient cluster sampling technology to recruit 855 college students from five universities in China as participants, based on the accessibility. We recovered 757 surveys, and among them were 547 valid responses (excluding incomplete surveys and false answers). The final sample included 265 males and 282 females. The participants’ ages ranged from 16 to 26 years ( M = 19.34; standard deviation = 1.01).
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. video game questionnaire.
To measure VVGE, we used the video game questionnaire adapted by Gentile et al. ( 2004 ) from Anderson and Dill ( 2000 ). Participants were asked to list their three favorite video games, including any games played on computers, video game consoles, hand‐held devices, or in video arcades. They were also asked to record the frequency of their play on a 7‐point scale for each game (1 = “rarely”, 7 = “often”). They then rated the extent of the violence of each game's content and graphics on a 7‐point scale (1 = “little or no violence”, 7 = “extremely violent”). The average rating of the video games was used as the overall index of the VVGE. The index was calculated as: ∑[(the content rating + the graphics rating) × (the weekday frequency × 5 + the weekend frequency × 2)] ÷ the number of games. And participants who never played video games were given a VVGE score of one. The higher the score is, the higher the level of VVGE will be. In the present study, Cronbach's α for the scale is 0.83.
2.2.2. Moral disengagement scale (MDS)
The MDS was used to measure moral disengagement (Bandura et al., 1996 ). The Chinese version has been demonstrated to be a reliable and valid measurement (Yang & Wang, 2012 ). The scale includes 32 items divided into eight mechanisms: moral justification, euphemistic language, advantageous comparison, displacement of responsibility, diffusion of responsibility, distorting consequences, attribution of blame, and dehumanization. All items use a 5‐point scale (1 = “strongly disagree”, 5 = “strongly agree”), and higher total scores indicate higher levels of moral disengagement. In the present study, Cronbach's α for the scale is 0.94.
2.2.3. Buss–Perry aggression questionnaire (BPAQ)
The BPAQ consists of 29 items, divided into four dimensions: physical aggression, verbal aggression, anger, and hostility (Buss & Perry, 1992 ). All items use a 5‐point scale (1 = “strongly disagree”, 5 = “strongly agree”). The Chinese version of BPAQ has high validity and reliability (Wang et al., 2016 ). In the present study, Cronbach's α for the scale is 0.91.
The present study used the physical aggression and verbal aggression subscales to assess the trait aggressive behavior, and anger and hostility subscales to access the trait anger and trait hostility. Higher scores indicate higher aggression trait, respectively. In the present study, Cronbach's α for the physical aggression subscale is 0.81, verbal aggression subscale is 0.74, anger subscale is 0.83; hostility subscale is 0.80.
2.2.4. Sensation‐seeking scale (SSS‐V)
The SSS‐V (Zuckerman, Eysenck, & Eysenck, 1978 ) consists of 40 items based on forced choice. Participants choose one statement from two options that best describes them and receive one point for each choice that corresponds to sensation seeking. The Chinese version of the SSS‐V (Wang et al., 2000 ) shows good validity and reliability and has been widely used. In the present study, Cronbach's α for the sensation‐seeking scale is 0.61. The study used the disinhibition subscale to measure disinhibition; higher disinhibition scores represent higher disinhibition tendencies. Cronbach's α for the disinhibition subscale is 0.52, higher disinhibition scores represent higher disinhibition tendencies.
2.3. Procedure and data analysis
The study was approved by the researchers’ University Ethics Committee. Before the investigation, all participants were told that the study was being conducted anonymously and that their information would remain confidential. We then obtained informed consent and participants completed the questionnaires, guided by trained researchers. All the participants were voluntary and they were free to withdraw from the study at any time.
Descriptive statistics, gender differences, correlation analysis, and regression analysis of main variables were conducted using SPSS 22.0. The mediation and moderation analysis was carried out using PROCESS macro (Hayes, 2013 ). The bootstrapping method (Hayes, 2013 ; Preacher & Hayes, 2004 ), which can attain robust standard errors for parameter estimation, was used to test the significance of the mediating effect and moderating effect. We set 5,000 bootstrapping samples and 95% bias‐corrected confidence intervals (CI). Cl containing zero indicated significant effects.
3.1. Preliminary analyses
The study used a self‐report design to collect data, which meant that common method variance may have existed. We used Harman's single‐factor test to test the common method bias. The test showed that there were 36 factors with eigenvalues greater than one, which together explained 65.24% of the total variance, with the largest single factor explaining 14.23% of the variance, which is less than the judgment standards of 40% (Podsakoff, Mackenzie, Lee, & Podsakoff, 2003 ). Therefore, the common method bias was not problematic in this study.
Table Table1 1 shows the correlations between the main variables with gender dummy coded. VVGE was positively associated with moral disengagement, disinhibition, and the four aggressive traits, which were positively correlated with each other. Moral disengagement was positively associated with both the disinhibition and the four aggressive traits. Disinhibition was positively associated with the four aggressive traits. Gender, as a covariate in subsequent analyses, was positively associated with every variable except trait anger.
Correlations and means of study variables
Abbreviation: VVGE, violent video games exposure.
3.2. The mediating effect of moral disengagement, anger, and hostility
To test Hypothesis 1 and Hypothesis 2 that moral disengagement, anger, and hostility would mediate the relationship between VVGE and aggression, we conducted the PROCESS macro Model 4 of SPSS (Hayes, 2013 ) with all data standardized. In the model, VVGE was entered as the predictor, moral disengagement, anger, and hostility as the mediators, aggressive behavior (the composite of physical aggression and verbal aggression) as the outcome variable, and gender was included as a covariate. The mediation effects of moral disengagement (0.03), anger (0.10), and hostility (0.02) were significant (see Table Table2, 2 , Table Table3, 3 , and Figure Figure1). 1 ). Moral disengagement, anger, and hostility accounted for 14.29, 47.62, and 9.52% of the total effect, respectively. When controlling for moral disengagement, anger, and hostility, the direct effect of VVGE on aggression was not significant ( β = 0.06; standard error = 0.03; 95% CI = [−0.001, 0.12]). Moral disengagement, anger, and hostility wholly mediated the relationship between VVGE and aggression with 71.43% of the total effect.
Testing the mediation effect of violent video games exposure on aggression (standardized coefficient)
Abbreviation: CI, confidence interval; VVGE, violent video games exposure.
The direct effect and the mediation effect of moral disengagement, anger, and hostility
Abbreviation: CI, confidence interval; ab, the mediation effect.

The relationship between VVGE, moral disengagement, anger, hostility, and aggressive behavior. VVGE, violent video games exposure
3.3. The moderating effect of disinhibition
To test Hypothesis 3 that disinhibition would moderate the relationship between VVGE and aggression, we conducted the PROCESS macro Model 1 of SPSS with disinhibition as a moderator, VVGE as the predictor, aggressive behavior as the outcome variable, gender as a covariate (Hayes, 2013 ). The results showed that the moderation effect of disinhibition was not significant ( β = −0.04, t = −0.90, 95% CI = [−0.12, 0.04]), see Table Table4 4 .
Testing the moderation effect of violent video games on aggression (standardized coefficient)
4. DISCUSSION
Consistent with H1, our study found that moral disengagement played a mediating role in the relationship between VVGE and aggression, suggesting that college students with high levels of VVGE are more likely to use moral disengagement mechanisms, further resulting in enhanced aggressive behavior trait. This finding is consistent with the research of Teng et al. ( 2019 ), indicating that the mediation effect of moral disengagement can be generalized to adult college students. The result also adds support for the GAM by the indication that VVGE influences an individual's internal state of cognition—specifically, the cognitive predisposition of moral disengagement (Bandura et al., 1996 )—and ultimately an individual's level of aggression (Anderson, & Bushman, 2002 ; Anderson, & Bushman, 2018 ).
Each of the separate links in the mediation model is noteworthy. VVGE was positively associated with moral disengagement, the first stage of the mediation process, and this result is consistent with previous research (e.g., Gabbiadini et al., 2012 ; Greitemeyer & McLatchie, 2011 ). Teng et al. ( 2017 ) explained this result by the use of Bandura's social cognitive theory; that is, VVGE as a contextual variable influences an individual's moral values and cognition, including moral disengagement (Bandura, 2001 ). Moral disengagement was positively associated with aggressive tendencies, the second stage of the mediation process, and this adds support for previous research (e.g., Paciello et al., 2008 ; Wang et al., 2016 ). Bandura's moral disengagement theory proposes that the eight moral disengagement mechanisms can encourage individuals to reconstruct aggression cognitively (e.g., by making the outcome of their behavior appear less harmful; by minimizing their role in the outcome; and by reducing their recognition for the victim), thus aggression is more likely to occur (Bandura et al., 1996 ). Shu, Gino, and Bazerman ( 2011 ) suggest that moral disengagement influences anticipatory guilt reactions, prosocial tendencies, and cognitive and affective reactions; effects that are conducive to immoral or antisocial behavior, such as aggression.
Consistent with H2, our study found that anger and hostility mediated the relationship between VVGE and aggression, suggesting that high level of VVGE is associated with increased anger and hostility in college students, which finally resulted in enhanced aggressive behavior trait. This is in line with the findings from some previous work (Adachi & Willoughby, 2016 ; Bartholow et al., 2005 ; Gentile et al., 2004 ). The result supports the long‐term effects (distal processes) of GAM (Anderson & Bushman, 2002 ; Anderson, & Bushman, 2018 ), that repeated VVGE over longer periods of time leads to elevations in more stable aggressive traits (trait anger, trait hostility), and such traits are part of aggression‐related knowledge structures. Finally, the reinforced knowledge structures contribute to the enhancement of aggressive personality, which further influence individuals’ decision together with situational variables.
With regard to H3, our study found that the moderation role of disinhibition, a dimension of sensation seeking, between VVGE and aggression was not significant. Disinhibition represents stimulation seeking through experiences with other individuals, using substances to feel disinhibited, and living a “hedonistic lifestyle” (Wilson & Scarpa, 2014 ). The characteristics of violent video games provide users with an opportunity for obtaining such experiences above. First, many violent video games are now large online multirole cooperative games, making them a kind of collective activity. Then, violent video games are full of violent and bloody content with immediate reinforcement (Teng et al., 2014 ) whilst a player can be anonymous; characteristics that make playing such games an unrestricted activity. Players of violent video games can do anything they want and perform acts that they cannot do in real life. And in this process, players are in an excited state with increased physiological arousal (Anderson et al., 2010 ); that is, through violent video gameplay, players can feel disinhibited and live a hedonistic lifestyle. These considerations help to explain the strong association between violent video games and disinhibition, but our results suggest that disinhibition is not the main factor in sensation seeking to moderate the relationship between VVGE and aggression. It may be due to the low reliability of sensation seeking scales and the disinhibition subscales. Actually, a few college students said they could not make a decision between some forced choices, because they never experienced some activities on the scale. Besides, some activities are forbidden (such as drugs) and some activities are not suitable to be discussed in public (such as sex) in China. So some items may not adapt to Chinese society situation and should be localized first. Or other materials to measure sensation seeking and inhibition should be considered.
The present study expands previous research by generalizing the mediation effect of moral disengagement to adult college students and exploring trait anger and trait hostility as the mediators in the relationship between VVGE and aggression. The results also add support for the social cognitive theory and the GAM to a certain extent. Reducing exposure to violent video games and the probability of moral standards being deactivated (Teng et al., 2019 ) may be an effective intervention to reduce aggression.
However, the study has several limitations. First, the datasets were collected through cross‐sectional methods, and this limits the inference of causal relationships. Longitudinal research should be conducted in the future. Second, we used self‐report questionnaires to gather the data. Although the common method bias was not problematic, as shown in the preliminary analysis, social desirability bias may exist. Moreover, players with higher levels of moral disengagement or aggression may evaluate the violence level of games lower than their counterparts. Future research could collect data from multiple informants and explore mediation and moderation effects through experimental research. Third, the research methods and sample (using only five universities in southwest China) may have influenced the size of the effects; selecting a more representative sample or improving the research methods may help to increase the size of the effects.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supporting information
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (grant no. 14XSH013, Grant No. 19BSH112), Chongqing Research Program of Basic Research and Frontier Technology (cstc2018jcyjAX0480), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant no. SWU1909226).
Yao M, Zhou Y, Li J, Gao X. Violent video games exposure and aggression: The role of moral disengagement, anger, hostility and disinhibition . Aggr Behav . 2019; 45 :662–670. 10.1002/ab.21860 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Adachi, P. J. C. , & Willoughby, T. (2016). The longitudinal association between competitive video game play and aggression among adolescents and young adults . Child Development , 87 ( 6 ), 1877–1892. 10.1111/cdev.12556 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Allen, J. J. , Anderson, C. A. , & Bushman, B. J. (2018). The general aggression model . Current Opinion in Psychology , 19 , 75–80. 10.1016/j.copsyc.2017.03.034 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aluja‐Fabregat, A. (2000). Personality and curiosity about TV and films violence in adolescents . Personality and Individual Differences , 29 ( 2 ), 379–392. 10.1016/S0191-8869(99)00200-7 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, C. A. , & Bushman, B. J. (2001). Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior, aggressive cognition, aggressive affect, physiological arousal, and prosocial behavior: A meta‐analytic review of the scientific literature . Psychological Science , 12 , 353–359. 10.1111/1467-9280.00366 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, C. A. , & Bushman, B. J. (2002). Human aggression . Annual Review of Psychology , 53 , 27–51. 10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135231 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, C. A. , & Bushman, B. J. (2018). Media violence and the general aggression model . Journal of Social Issues , 74 ( 2 ), 386–413. 10.1111/josi.12275 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, C. A. , & Dill, K. E. (2000). Video games and aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behavior in the laboratory and in life . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 78 , 772–790. 10.1037//0022-3514.78.4.772 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, C. A. , Gentile, D. A. , & Buckley, K. E. (2007). Violent video game effects on children and adolescents: Theory, research, and public policy . Oxford University Press; 10.1111/j.1475-3588.2008.00486_3.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, C. A. , Shibuya, A. , Ihori, N. , Swing, E. L. , Bushman, B. J. , Sakamoto, A. , … Saleem, M. (2010). Violent video game effects on aggression, empathy, and prosocial behavior in eastern and western countries: A meta‐analytic review . Psychological Bulletin , 136 , 151–173. 10.1037/a0018251 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura, A. (1990). Selective activation and disengagement of moral control . Journal of Social Issues , 46 , 27–46. 10.1111/j.1540-4560.1990.tb00270.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura, A. (1999). Moral disengagement in the perpetration of inhumanities . Personality and Social Psychology Review , 3 , 193–209. 10.1207/s15327957pspr0303_3 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura, A. (2001). Social cognitive theory: An agentic perspective . Annual Review of Psychology , 52 , 1–26. 10.1146/annurev.psych.52.1.1 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura, A. , Barbaranelli, C. , Caprara, G. V. , & Pastorelli, C. (1996). Mechanisms of moral disengagement in the exercise of moral agency . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 71 , 364–374. 10.1037//0022-3514.71.2.364 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barchia, K. , & Bussey, K. (2011). Individual and collective social cognitive influences on peer aggression: Exploring the contribution of aggression efficacy, moral disengagement, and collective efficacy . Aggressive Behavior , 37 ( 2 ), 107–120. 10.1002/ab.20375 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bartholow, B. D. , Sestir, M. A. , & Davis, E. B. (2005). Correlates and consequences of exposure to video game violence: Hostile personality, empathy, and aggressive behavior . Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , 31 ( 11 ), 1573–1586. 10.1177/0146167205277205 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bisch, S. J. , & Lee, M. J. (2009). Does violent video game play influence players' aggressive thoughts? An investigation based on sensation seeking tendency. Association for Education in Journalism and Mass Communication . Conference Paper.
- Bushman, B. J. (2016). Violent media and hostile appraisals: A meta‐analytic review . Aggressive Behavior , 42 , 605–613. 10.1002/ab.21655 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Buss, A. H. , & Perry, M. (1992). The aggression questionnaire . Journal of Personality & Social Psychology , 63 , 452–459. 10.1037//0022-3514.63.3.452 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bussey, K. , Quinn, C. , & Dobson, J. (2015). The moderating role of empathic concern and perspective taking on the relationship between moral disengagement and aggression . Merrill‐Palmer Quarterly , 61 , 10–29. 10.13110/merrpalmquar1982.61.1.0010 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- China Audio‐video and Digital Publishing Association Game Publishing Committee . (2018). China Gaming Industry Report . In Chinese.
- Engelhardt, C. R. , Bartholow, B. D. , & Saults, J. S. (2011). Violent and nonviolent video games differentially affect physical aggression for individuals high vs. low in dispositional anger . Aggressive Behavior , 37 ( 6 ), 539–546. 10.1002/ab.20411 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Exelmans, L. , Custers, K. , & Van den Bulck, J. (2015). Violent video games and delinquent behavior in adolescents: A risk factor perspective . Aggressive Behavior , 41 ( 3 ), 267–279. 10.1002/ab.21587 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ferguson, C. J. , & Kilburn, J. (2010). Much ado about nothing: The misestimation and overinterpretation of violent video game effects in Eastern and Western nations: Comment on Anderson et al. (2010) . Psychological Bulletin , 136 , 174–178. 10.1037/a0018566 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gabbiadini, A. , Andrighetto, L. , & Volpato, C. (2012). Brief report: Does exposure to violent video games increase moral disengagement among adolescents? Journal of Adolescence , 35 , 1403–1406. 10.1016/j.adolescence.2012.06.001 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gao, X. , Weng, L. , Zhou, Y. , & Yu, H. (2017). The influence of empathy and morality of violent video game characters on gamers' aggression . Frontiers in Psychology , 8 , 1863 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01863 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gentile, D. A. , Bender, P. K. , & Anderson, C. A. (2017). Violent video game effects on salivary cortisol, arousal, and aggressive thoughts in children . Computers in Human Behavior , 70 , 39–43. 10.1016/j.chb.2016.12.045 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gentile, D. A. , Li, D. , Khoo, A. , Prot, S. , & Anderson, C. A. (2014). Mediators and moderators of long‐term effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior: Practice, thinking, and action . Jama Pediatrics , 168 , 450–457. 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2014.63 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gentile, D. A. , Lynch, P. J. , Linder, J. R. , & Walsh, D. A. (2004). The effects of violent video game habits on adolescent hostility, aggressive behaviors, and school performance . Journal of Adolescence , 27 ( 1 ), 5–22. 10.1016/j.adolescence.2003.10.002 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gentile, D. A. , Swing, E. L. , Anderson, C. A. , Rinker, D. , & Thomas, K. M. (2016). Differential neural recruitment during violent video game play in violent‐and nonviolent‐game players . Psychology of Popular Media Culture , 5 , 39–51. 10.1037/ppm0000009 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gini, G. , Pozzoli, T. , & Hymel, S. (2014). Moral disengagement among children and youth: A meta‐analytic review of links to aggressive behavior . Aggressive Behavior , 40 ( 1 ), 56–68. 10.1002/ab.21502 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giumetti, G. W. , & Markey, P. M. (2007). Violent video games and anger as predictors of aggression . Journal of Research in Personality , 41 ( 6 ), 1234–1243. 10.1016/j.jrp.2007.02.005 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greitemeyer, T. (2018). The spreading impact of playing violent video games on aggression . Computers in Human Behavior , 80 , 216–219. 10.1016/j.chb.2017.11.022 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greitemeyer, T. , & McLatchie, N. (2011). Denying humanness to others: A newly discovered mechanism by which violent video games increase aggressive behavior . Psychological Science , 22 , 659–665. 10.1177/0956797611403320 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greitemeyer, T. , & Mügge, D. O. (2014). Video games do affect social outcomes: A meta‐analytic review of the effects of violent and prosocial video game play . Personality & Social Psychology Bulletin , 40 , 578–589. 10.1177/0146167213520459 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hasan, Y. , Bègue, L. , & Bushman, B. J. (2012). Viewing the world through “blood‐red tinted glasses”: The hostile expectation bias mediates the link between violent video game exposure and aggression . Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 48 , 953–956. 10.1016/j.jesp.2011.12.019 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression‐based approach . New York: Guilford Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hyde, L. W. , Shaw, D. S. , & Moilanen, K. L. (2010). Developmental precursors of moral disengagement and the role of moral disengagement in the development of antisocial behavior . Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology , 38 ( 2 ), 197–209. 10.1007/s10802-009-9358-5 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Killer, B. , Bussey, K. , Hawes, D. , & Hunt, C. (2019). A meta‐analysis of the relationship between moral disengagement and bullying roles in youth . Aggressive Behavior , 45 ( 4 ), 450–462. 10.1002/ab.21833 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kimmig, A. C. S. , Andringa, G. , & Derntl, B. (2018). Potential adverse effects of violent video gaming: Interpersonal‐affective traits are rather impaired than disinhibition in young adults . Frontiers in Psychology , 9 , 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00736. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krahé, B. (2014). Media violence use as a risk factor for aggressive behaviour in adolescence . European Review of Social Psychology , 25 ( 1 ), 71–106. 10.1080/10463283.2014.923177 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krahé, B. , & Möller, I. (2010). Longitudinal effects of media violence on aggression and empathy among German adolescents . Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology , 31 ( 5 ), 401–409. 10.1016/j.appdev.2010.07.003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krcmar, M. , & Greene, K. (1999). Predicting exposure to and uses of television violence . Journal of Communication , 49 , 24–45. 10.1111/j.1460-2466.1999.tb02803.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lemmens, J. S. , Valkenburg, P. M. , & Peter, J. (2011). The effects of pathological gaming on aggressive behavior . Journal of Youth and Adolescence , 40 ( 1 ), 38–47. 10.1007/s10964-010-9558-x [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lin, S. S. J. , & Tsai, C. C. (2002). Sensation seeking and internet dependence of Taiwanese high school adolescents . Computers in Human Behavior , 18 , 411–426. 10.1016/S0747-5632(01)00056-5 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Markey, P. M. , & Markey, C. N. (2010). Vulnerability to violent video games: A review and integration of personality research . Review of General Psychology , 14 ( 2 ), 82–91. 10.1037/a0019000 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Markey, P. M. , & Scherer, K. (2009). An examination of psychoticism and motion capture controls as moderators of the effects of violent video games . Computers in Human Behavior , 25 ( 2 ), 407–411. 10.1016/j.chb.2008.10.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McCarthy, R. J. , Coley, S. L. , Wagner, M. F. , Zengel, B. , & Basham, A. (2016). Does playing video games with violent content temporarily increase aggressive inclinations? A preregistered experimental study . Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 67 , 13–19. 10.1016/j.jesp.2015.10.009 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Möller, I. , & Krahé, B. (2009). Exposure to violent video games and aggression in German adolescents: A longitudinal analysis . Aggressive Behavior , 35 ( 1 ), 75–89. 10.1002/ab.20290 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Montag, C. , Weber, B. , Trautner, P. , Newport, B. , Markett, S. , Walter, N. T. , … Reuter, M. (2012). Does excessive play of violent first‐person‐shooter‐video‐games dampen brain activity in response to emotional stimuli? Biological Psychology , 89 , 107–111. 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2011.09.014 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Obermann, M. L. (2011). Moral disengagement in self‐reported and peer‐nominated school bullying . Aggressive Behavior , 37 ( 2 ), 133–144. 10.1002/ab.20378 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paciello, M. , Fida, R. , Tramontano, C. , Lupinetti, C. , & Caprara, G. V. (2008). Stability and change of moral disengagement and its impact on aggression and violence in late adolescence . Child Development , 79 , 1288–1309. 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2008.01189.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pan, W. , Gao, X. , *Shi, S. , Liu, F. , & Li, C. (2018). Spontaneous brain activity did not show the effect of violent video games on aggression: A resting‐state fMRI study . Frontiers in Psychology , 8 , 2219 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02219 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Podsakoff, P. M. , Mackenzie, S. B. , Lee, J. Y. , & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies . Journal of Applied Psychology , 88 , 879–903. 10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Preacher, K. J. , & Hayes, A. F. (2004). SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models . Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers: A Journal of the Psychonomic Society, Inc , 36 , 717–731. 10.3758/bf03206553 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Richmond, J. , & Wilson, J. C. (2008). Are graphic media violence, aggression and moral disengagement related? Psychiatry Psychology & Law , 15 , 350–357. 10.1080/13218710802199716 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rubio‐Garay, F. , Carrasco, M. A. , & Amor, P. J. (2016). Aggression, anger and hostility: Evaluation of moral disengagement as a mediational process . Scandinavian Journal of Psychology , 57 ( 2 ), 129–135. 10.1111/sjop.12270 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rydell, A. M. (2016). Violent media exposure, aggression and CU traits in adolescence: Testing the selection and socialization hypotheses . Journal of Adolescence , 52 , 95–102. 10.1016/j.adolescence.2016.07.009 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shu, L. L. , Gino, F. , & Bazerman, M. H. (2011). Dishonest deed, clear conscience: When cheating leads to moral disengagement and motivated forgetting . Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , 37 ( 3 ), 330–349. 10.1177/0146167211398138 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Slater, M. D. , Henry, K. L. , Swaim, R. C. , & Cardador, J. M. (2004). Vulnerable teens, vulnerable times: How sensation seeking, alienation, and victimization moderate the violent media content‐aggressiveness relation . Communication Research , 31 , 642–668. 10.1177/0093650204269265 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sticca, F. , & Perren, S. (2015). The chicken and the egg: Longitudinal associations between moral deficiencies and bullying: A parallel process latent growth model . Merrill‐Palmer Quarterly , 61 , 85–100. 10.13110/merrpalmquar1982.61.1.0085 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Teng, Z. , Li, Y. , & Liu, Y. (2014). Online gaming, internet addiction, and aggression in Chinese male students: The mediating role of low self‐control . International Journal of Psychological Studies , 6 ( 2 ), 89 10.5539/ijps.v6n2p89 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Teng, Z. , Nie, Q. , Guo, C. , & Liu, Y. (2017). Violent video game exposure and moral disengagement in early adolescence: The moderating effect of moral identity . Computers in Human Behavior , 77 , 54–62. 10.1016/j.chb.2017.08.031 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Teng, Z. , Nie, Q. , Guo, C. , Zhang, Q. , Liu, Y. , & Bushman, B. J. (2019). A longitudinal study of link between exposure to violent video games and aggression in Chinese adolescents: The mediating role of moral disengagement . Developmental Psychology , 55 ( 1 ), 184–195. 10.1037/dev0000624 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Teng, Z. , Nie, Q. , Pan, Y. , Liu, Y. , & Guo, C. (2017). A cross‐lagged model of the relationship between violent video game exposure and moral disengagement in middle school and high school students . Children and Youth Services Review , 81 , 117–123. 10.1016/j.childyouth.2017.07.029 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Velez, J. A. , Greitemeyer, T. , Whitaker, J. L. , Ewoldsen, D. R. , & Bushman, B. J. (2016). Violent video games and reciprocity: The attenuating effects of cooperative game play on subsequent aggression . Communication Research , 43 ( 4 ), 447–467. 10.1177/0093650214552519 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Verheijen, G. P. , Burk, W. J. , Stoltz, S. E. M. J. , van den Berg, Y. H. M. , & Cillessen, A. H. N. (2018). Friendly fire: Longitudinal effects of exposure to violent video games on aggressive behavior in adolescent friendship dyads . Aggressive Behavior , 44 , 257–267. 10.1002/ab.21748 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, C. , Ryoo, J. H. , Swearer, S. M. , Turner, R. , & Goldberg, T. S. (2017). Longitudinal relationships between bullying and moral disengagement among adolescents . Journal of Youth and Adolescence , 46 ( 6 ), 1304–1317. 10.1007/s10964-016-0577-0 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, W. , Wu, Y. X. , Peng, Z. G. , Lu, S. W. , Yu, L. , Wang, G. P. , … Wang, Y. H. (2000). Test of sensation seeking in a Chinese sample . Personality & Individual Differences , 28 , 169–179. 10.1016/s0191-8869(99)00092-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, X. , Lei, L. , Yang, J. , Gao, L. , & Zhao, F. (2016). Moral disengagement as mediator and moderator of the relation between empathy and aggression among Chinese male juvenile delinquents . Child Psychiatry & Human Development , 48 , 316–326. 10.1007/s10578-016-0643-6 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilson, L. C. , & Scarpa, A. (2014). Aggressive behavior: An alternative model of resting heart rate and sensation seeking . Aggressive Behavior , 40 , 91–98. 10.1002/ab.21504 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang, J. P. , & Wang, X. C. (2012). Effect of moral disengagement on adolescents’ aggressive behavior: Moderated mediating effect . Acta Psychologica Sinica , 44 , 1075–1085. 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.01075 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zapolski, T. C. , Banks, D. E. , Lau, K. S. , & Aalsma, M. C. (2018). Perceived police injustice, moral disengagement, and aggression among juvenile offenders: Utilizing the general strain theory model . Child Psychiatry & Human Development , 49 ( 2 ), 290–297. 10.1007/s10578-017-0750-z [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zuckerman, M. (1994). Behavioral expressions and biosocial bases of sensation seeking . Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zuckerman, M. , Eysenck, S. , & Eysenck, H. J. (1978). Sensation seeking in England and America: Cross‐cultural, age, and sex comparisons . Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology , 46 , 139–149. 10.1037//0022-006x.46.1.139 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 13 March 2018
Does playing violent video games cause aggression? A longitudinal intervention study
- Simone Kühn 1 , 2 ,
- Dimitrij Tycho Kugler 2 ,
- Katharina Schmalen 1 ,
- Markus Weichenberger 1 ,
- Charlotte Witt 1 &
- Jürgen Gallinat 2
Molecular Psychiatry volume 24 , pages 1220–1234 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
547k Accesses
102 Citations
2346 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Neuroscience
It is a widespread concern that violent video games promote aggression, reduce pro-social behaviour, increase impulsivity and interfere with cognition as well as mood in its players. Previous experimental studies have focussed on short-term effects of violent video gameplay on aggression, yet there are reasons to believe that these effects are mostly the result of priming. In contrast, the present study is the first to investigate the effects of long-term violent video gameplay using a large battery of tests spanning questionnaires, behavioural measures of aggression, sexist attitudes, empathy and interpersonal competencies, impulsivity-related constructs (such as sensation seeking, boredom proneness, risk taking, delay discounting), mental health (depressivity, anxiety) as well as executive control functions, before and after 2 months of gameplay. Our participants played the violent video game Grand Theft Auto V, the non-violent video game The Sims 3 or no game at all for 2 months on a daily basis. No significant changes were observed, neither when comparing the group playing a violent video game to a group playing a non-violent game, nor to a passive control group. Also, no effects were observed between baseline and posttest directly after the intervention, nor between baseline and a follow-up assessment 2 months after the intervention period had ended. The present results thus provide strong evidence against the frequently debated negative effects of playing violent video games in adults and will therefore help to communicate a more realistic scientific perspective on the effects of violent video gaming.
Similar content being viewed by others
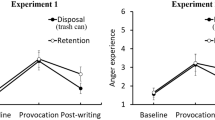
Anger is eliminated with the disposal of a paper written because of provocation
Yuta Kanaya & Nobuyuki Kawai
Microdosing with psilocybin mushrooms: a double-blind placebo-controlled study
Federico Cavanna, Stephanie Muller, … Enzo Tagliazucchi
The process and mechanisms of personality change
Joshua J. Jackson & Amanda J. Wright
The concern that violent video games may promote aggression or reduce empathy in its players is pervasive and given the popularity of these games their psychological impact is an urgent issue for society at large. Contrary to the custom, this topic has also been passionately debated in the scientific literature. One research camp has strongly argued that violent video games increase aggression in its players [ 1 , 2 ], whereas the other camp [ 3 , 4 ] repeatedly concluded that the effects are minimal at best, if not absent. Importantly, it appears that these fundamental inconsistencies cannot be attributed to differences in research methodology since even meta-analyses, with the goal to integrate the results of all prior studies on the topic of aggression caused by video games led to disparate conclusions [ 2 , 3 ]. These meta-analyses had a strong focus on children, and one of them [ 2 ] reported a marginal age effect suggesting that children might be even more susceptible to violent video game effects.
To unravel this topic of research, we designed a randomised controlled trial on adults to draw causal conclusions on the influence of video games on aggression. At present, almost all experimental studies targeting the effects of violent video games on aggression and/or empathy focussed on the effects of short-term video gameplay. In these studies the duration for which participants were instructed to play the games ranged from 4 min to maximally 2 h (mean = 22 min, median = 15 min, when considering all experimental studies reviewed in two of the recent major meta-analyses in the field [ 3 , 5 ]) and most frequently the effects of video gaming have been tested directly after gameplay.
It has been suggested that the effects of studies focussing on consequences of short-term video gameplay (mostly conducted on college student populations) are mainly the result of priming effects, meaning that exposure to violent content increases the accessibility of aggressive thoughts and affect when participants are in the immediate situation [ 6 ]. However, above and beyond this the General Aggression Model (GAM, [ 7 ]) assumes that repeatedly primed thoughts and feelings influence the perception of ongoing events and therewith elicits aggressive behaviour as a long-term effect. We think that priming effects are interesting and worthwhile exploring, but in contrast to the notion of the GAM our reading of the literature is that priming effects are short-lived (suggested to only last for <5 min and may potentially reverse after that time [ 8 ]). Priming effects should therefore only play a role in very close temporal proximity to gameplay. Moreover, there are a multitude of studies on college students that have failed to replicate priming effects [ 9 , 10 , 11 ] and associated predictions of the so-called GAM such as a desensitisation against violent content [ 12 , 13 , 14 ] in adolescents and college students or a decrease of empathy [ 15 ] and pro-social behaviour [ 16 , 17 ] as a result of playing violent video games.
However, in our view the question that society is actually interested in is not: “Are people more aggressive after having played violent video games for a few minutes? And are these people more aggressive minutes after gameplay ended?”, but rather “What are the effects of frequent, habitual violent video game playing? And for how long do these effects persist (not in the range of minutes but rather weeks and months)?” For this reason studies are needed in which participants are trained over longer periods of time, tested after a longer delay after acute playing and tested with broader batteries assessing aggression but also other relevant domains such as empathy as well as mood and cognition. Moreover, long-term follow-up assessments are needed to demonstrate long-term effects of frequent violent video gameplay. To fill this gap, we set out to expose adult participants to two different types of video games for a period of 2 months and investigate changes in measures of various constructs of interest at least one day after the last gaming session and test them once more 2 months after the end of the gameplay intervention. In contrast to the GAM, we hypothesised no increases of aggression or decreases in pro-social behaviour even after long-term exposure to a violent video game due to our reasoning that priming effects of violent video games are short-lived and should therefore not influence measures of aggression if they are not measured directly after acute gaming. In the present study, we assessed potential changes in the following domains: behavioural as well as questionnaire measures of aggression, empathy and interpersonal competencies, impulsivity-related constructs (such as sensation seeking, boredom proneness, risk taking, delay discounting), and depressivity and anxiety as well as executive control functions. As the effects on aggression and pro-social behaviour were the core targets of the present study, we implemented multiple tests for these domains. This broad range of domains with its wide coverage and the longitudinal nature of the study design enabled us to draw more general conclusions regarding the causal effects of violent video games.
Materials and methods
Participants.
Ninety healthy participants (mean age = 28 years, SD = 7.3, range: 18–45, 48 females) were recruited by means of flyers and internet advertisements. The sample consisted of college students as well as of participants from the general community. The advertisement mentioned that we were recruiting for a longitudinal study on video gaming, but did not mention that we would offer an intervention or that we were expecting training effects. Participants were randomly assigned to the three groups ruling out self-selection effects. The sample size was based on estimates from a previous study with a similar design [ 18 ]. After complete description of the study, the participants’ informed written consent was obtained. The local ethics committee of the Charité University Clinic, Germany, approved of the study. We included participants that reported little, preferably no video game usage in the past 6 months (none of the participants ever played the game Grand Theft Auto V (GTA) or Sims 3 in any of its versions before). We excluded participants with psychological or neurological problems. The participants received financial compensation for the testing sessions (200 Euros) and performance-dependent additional payment for two behavioural tasks detailed below, but received no money for the training itself.
Training procedure
The violent video game group (5 participants dropped out between pre- and posttest, resulting in a group of n = 25, mean age = 26.6 years, SD = 6.0, 14 females) played the game Grand Theft Auto V on a Playstation 3 console over a period of 8 weeks. The active control group played the non-violent video game Sims 3 on the same console (6 participants dropped out, resulting in a group of n = 24, mean age = 25.8 years, SD = 6.8, 12 females). The passive control group (2 participants dropped out, resulting in a group of n = 28, mean age = 30.9 years, SD = 8.4, 12 females) was not given a gaming console and had no task but underwent the same testing procedure as the two other groups. The passive control group was not aware of the fact that they were part of a control group to prevent self-training attempts. The experimenters testing the participants were blind to group membership, but we were unable to prevent participants from talking about the game during testing, which in some cases lead to an unblinding of experimental condition. Both training groups were instructed to play the game for at least 30 min a day. Participants were only reimbursed for the sessions in which they came to the lab. Our previous research suggests that the perceived fun in gaming was positively associated with training outcome [ 18 ] and we speculated that enforcing training sessions through payment would impair motivation and thus diminish the potential effect of the intervention. Participants underwent a testing session before (baseline) and after the training period of 2 months (posttest 1) as well as a follow-up testing sessions 2 months after the training period (posttest 2).
Grand Theft Auto V (GTA)
GTA is an action-adventure video game situated in a fictional highly violent game world in which players are rewarded for their use of violence as a means to advance in the game. The single-player story follows three criminals and their efforts to commit heists while under pressure from a government agency. The gameplay focuses on an open world (sandbox game) where the player can choose between different behaviours. The game also allows the player to engage in various side activities, such as action-adventure, driving, third-person shooting, occasional role-playing, stealth and racing elements. The open world design lets players freely roam around the fictional world so that gamers could in principle decide not to commit violent acts.
The Sims 3 (Sims)
Sims is a life simulation game and also classified as a sandbox game because it lacks clearly defined goals. The player creates virtual individuals called “Sims”, and customises their appearance, their personalities and places them in a home, directs their moods, satisfies their desires and accompanies them in their daily activities and by becoming part of a social network. It offers opportunities, which the player may choose to pursue or to refuse, similar as GTA but is generally considered as a pro-social and clearly non-violent game.
Assessment battery
To assess aggression and associated constructs we used the following questionnaires: Buss–Perry Aggression Questionnaire [ 19 ], State Hostility Scale [ 20 ], Updated Illinois Rape Myth Acceptance Scale [ 21 , 22 ], Moral Disengagement Scale [ 23 , 24 ], the Rosenzweig Picture Frustration Test [ 25 , 26 ] and a so-called World View Measure [ 27 ]. All of these measures have previously been used in research investigating the effects of violent video gameplay, however, the first two most prominently. Additionally, behavioural measures of aggression were used: a Word Completion Task, a Lexical Decision Task [ 28 ] and the Delay frustration task [ 29 ] (an inter-correlation matrix is depicted in Supplementary Figure 1 1). From these behavioural measures, the first two were previously used in research on the effects of violent video gameplay. To assess variables that have been related to the construct of impulsivity, we used the Brief Sensation Seeking Scale [ 30 ] and the Boredom Propensity Scale [ 31 ] as well as tasks assessing risk taking and delay discounting behaviourally, namely the Balloon Analogue Risk Task [ 32 ] and a Delay-Discounting Task [ 33 ]. To quantify pro-social behaviour, we employed: Interpersonal Reactivity Index [ 34 ] (frequently used in research on the effects of violent video gameplay), Balanced Emotional Empathy Scale [ 35 ], Reading the Mind in the Eyes test [ 36 ], Interpersonal Competence Questionnaire [ 37 ] and Richardson Conflict Response Questionnaire [ 38 ]. To assess depressivity and anxiety, which has previously been associated with intense video game playing [ 39 ], we used Beck Depression Inventory [ 40 ] and State Trait Anxiety Inventory [ 41 ]. To characterise executive control function, we used a Stop Signal Task [ 42 ], a Multi-Source Interference Task [ 43 ] and a Task Switching Task [ 44 ] which have all been previously used to assess effects of video gameplay. More details on all instruments used can be found in the Supplementary Material.
Data analysis
On the basis of the research question whether violent video game playing enhances aggression and reduces empathy, the focus of the present analysis was on time by group interactions. We conducted these interaction analyses separately, comparing the violent video game group against the active control group (GTA vs. Sims) and separately against the passive control group (GTA vs. Controls) that did not receive any intervention and separately for the potential changes during the intervention period (baseline vs. posttest 1) and to test for potential long-term changes (baseline vs. posttest 2). We employed classical frequentist statistics running a repeated-measures ANOVA controlling for the covariates sex and age.
Since we collected 52 separate outcome variables and conduced four different tests with each (GTA vs. Sims, GTA vs. Controls, crossed with baseline vs. posttest 1, baseline vs. posttest 2), we had to conduct 52 × 4 = 208 frequentist statistical tests. Setting the alpha value to 0.05 means that by pure chance about 10.4 analyses should become significant. To account for this multiple testing problem and the associated alpha inflation, we conducted a Bonferroni correction. According to Bonferroni, the critical value for the entire set of n tests is set to an alpha value of 0.05 by taking alpha/ n = 0.00024.
Since the Bonferroni correction has sometimes been criticised as overly conservative, we conducted false discovery rate (FDR) correction [ 45 ]. FDR correction also determines adjusted p -values for each test, however, it controls only for the number of false discoveries in those tests that result in a discovery (namely a significant result).
Moreover, we tested for group differences at the baseline assessment using independent t -tests, since those may hamper the interpretation of significant interactions between group and time that we were primarily interested in.
Since the frequentist framework does not enable to evaluate whether the observed null effect of the hypothesised interaction is indicative of the absence of a relation between violent video gaming and our dependent variables, the amount of evidence in favour of the null hypothesis has been tested using a Bayesian framework. Within the Bayesian framework both the evidence in favour of the null and the alternative hypothesis are directly computed based on the observed data, giving rise to the possibility of comparing the two. We conducted Bayesian repeated-measures ANOVAs comparing the model in favour of the null and the model in favour of the alternative hypothesis resulting in a Bayes factor (BF) using Bayesian Information criteria [ 46 ]. The BF 01 suggests how much more likely the data is to occur under the null hypothesis. All analyses were performed using the JASP software package ( https://jasp-stats.org ).
Sex distribution in the present study did not differ across the groups ( χ 2 p -value > 0.414). However, due to the fact that differences between males and females have been observed in terms of aggression and empathy [ 47 ], we present analyses controlling for sex. Since our random assignment to the three groups did result in significant age differences between groups, with the passive control group being significantly older than the GTA ( t (51) = −2.10, p = 0.041) and the Sims group ( t (50) = −2.38, p = 0.021), we also controlled for age.
The participants in the violent video game group played on average 35 h and the non-violent video game group 32 h spread out across the 8 weeks interval (with no significant group difference p = 0.48).
To test whether participants assigned to the violent GTA game show emotional, cognitive and behavioural changes, we present the results of repeated-measure ANOVA time x group interaction analyses separately for GTA vs. Sims and GTA vs. Controls (Tables 1 – 3 ). Moreover, we split the analyses according to the time domain into effects from baseline assessment to posttest 1 (Table 2 ) and effects from baseline assessment to posttest 2 (Table 3 ) to capture more long-lasting or evolving effects. In addition to the statistical test values, we report partial omega squared ( ω 2 ) as an effect size measure. Next to the classical frequentist statistics, we report the results of a Bayesian statistical approach, namely BF 01 , the likelihood with which the data is to occur under the null hypothesis that there is no significant time × group interaction. In Table 2 , we report the presence of significant group differences at baseline in the right most column.
Since we conducted 208 separate frequentist tests we expected 10.4 significant effects simply by chance when setting the alpha value to 0.05. In fact we found only eight significant time × group interactions (these are marked with an asterisk in Tables 2 and 3 ).
When applying a conservative Bonferroni correction, none of those tests survive the corrected threshold of p < 0.00024. Neither does any test survive the more lenient FDR correction. The arithmetic mean of the frequentist test statistics likewise shows that on average no significant effect was found (bottom rows in Tables 2 and 3 ).
In line with the findings from a frequentist approach, the harmonic mean of the Bayesian factor BF 01 is consistently above one but not very far from one. This likewise suggests that there is very likely no interaction between group × time and therewith no detrimental effects of the violent video game GTA in the domains tested. The evidence in favour of the null hypothesis based on the Bayes factor is not massive, but clearly above 1. Some of the harmonic means are above 1.6 and constitute substantial evidence [ 48 ]. However, the harmonic mean has been criticised as unstable. Owing to the fact that the sum is dominated by occasional small terms in the likelihood, one may underestimate the actual evidence in favour of the null hypothesis [ 49 ].
To test the sensitivity of the present study to detect relevant effects we computed the effect size that we would have been able to detect. The information we used consisted of alpha error probability = 0.05, power = 0.95, our sample size, number of groups and of measurement occasions and correlation between the repeated measures at posttest 1 and posttest 2 (average r = 0.68). According to G*Power [ 50 ], we could detect small effect sizes of f = 0.16 (equals η 2 = 0.025 and r = 0.16) in each separate test. When accounting for the conservative Bonferroni-corrected p -value of 0.00024, still a medium effect size of f = 0.23 (equals η 2 = 0.05 and r = 0.22) would have been detectable. A meta-analysis by Anderson [ 2 ] reported an average effects size of r = 0.18 for experimental studies testing for aggressive behaviour and another by Greitmeyer [ 5 ] reported average effect sizes of r = 0.19, 0.25 and 0.17 for effects of violent games on aggressive behaviour, cognition and affect, all of which should have been detectable at least before multiple test correction.
Within the scope of the present study we tested the potential effects of playing the violent video game GTA V for 2 months against an active control group that played the non-violent, rather pro-social life simulation game The Sims 3 and a passive control group. Participants were tested before and after the long-term intervention and at a follow-up appointment 2 months later. Although we used a comprehensive test battery consisting of questionnaires and computerised behavioural tests assessing aggression, impulsivity-related constructs, mood, anxiety, empathy, interpersonal competencies and executive control functions, we did not find relevant negative effects in response to violent video game playing. In fact, only three tests of the 208 statistical tests performed showed a significant interaction pattern that would be in line with this hypothesis. Since at least ten significant effects would be expected purely by chance, we conclude that there were no detrimental effects of violent video gameplay.
This finding stands in contrast to some experimental studies, in which short-term effects of violent video game exposure have been investigated and where increases in aggressive thoughts and affect as well as decreases in helping behaviour have been observed [ 1 ]. However, these effects of violent video gaming on aggressiveness—if present at all (see above)—seem to be rather short-lived, potentially lasting <15 min [ 8 , 51 ]. In addition, these short-term effects of video gaming are far from consistent as multiple studies fail to demonstrate or replicate them [ 16 , 17 ]. This may in part be due to problems, that are very prominent in this field of research, namely that the outcome measures of aggression and pro-social behaviour, are poorly standardised, do not easily generalise to real-life behaviour and may have lead to selective reporting of the results [ 3 ]. We tried to address these concerns by including a large set of outcome measures that were mostly inspired by previous studies demonstrating effects of short-term violent video gameplay on aggressive behaviour and thoughts, that we report exhaustively.
Since effects observed only for a few minutes after short sessions of video gaming are not representative of what society at large is actually interested in, namely how habitual violent video gameplay affects behaviour on a more long-term basis, studies employing longer training intervals are highly relevant. Two previous studies have employed longer training intervals. In an online study, participants with a broad age range (14–68 years) have been trained in a violent video game for 4 weeks [ 52 ]. In comparison to a passive control group no changes were observed, neither in aggression-related beliefs, nor in aggressive social interactions assessed by means of two questions. In a more recent study, participants played a previous version of GTA for 12 h spread across 3 weeks [ 53 ]. Participants were compared to a passive control group using the Buss–Perry aggression questionnaire, a questionnaire assessing impulsive or reactive aggression, attitude towards violence, and empathy. The authors only report a limited increase in pro-violent attitude. Unfortunately, this study only assessed posttest measures, which precludes the assessment of actual changes caused by the game intervention.
The present study goes beyond these studies by showing that 2 months of violent video gameplay does neither lead to any significant negative effects in a broad assessment battery administered directly after the intervention nor at a follow-up assessment 2 months after the intervention. The fact that we assessed multiple domains, not finding an effect in any of them, makes the present study the most comprehensive in the field. Our battery included self-report instruments on aggression (Buss–Perry aggression questionnaire, State Hostility scale, Illinois Rape Myth Acceptance scale, Moral Disengagement scale, World View Measure and Rosenzweig Picture Frustration test) as well as computer-based tests measuring aggressive behaviour such as the delay frustration task and measuring the availability of aggressive words using the word completion test and a lexical decision task. Moreover, we assessed impulse-related concepts such as sensation seeking, boredom proneness and associated behavioural measures such as the computerised Balloon analogue risk task, and delay discounting. Four scales assessing empathy and interpersonal competence scales, including the reading the mind in the eyes test revealed no effects of violent video gameplay. Neither did we find any effects on depressivity (Becks depression inventory) nor anxiety measured as a state as well as a trait. This is an important point, since several studies reported higher rates of depressivity and anxiety in populations of habitual video gamers [ 54 , 55 ]. Last but not least, our results revealed also no substantial changes in executive control tasks performance, neither in the Stop signal task, the Multi-source interference task or a Task switching task. Previous studies have shown higher performance of habitual action video gamers in executive tasks such as task switching [ 56 , 57 , 58 ] and another study suggests that training with action video games improves task performance that relates to executive functions [ 59 ], however, these associations were not confirmed by a meta-analysis in the field [ 60 ]. The absence of changes in the stop signal task fits well with previous studies that likewise revealed no difference between in habitual action video gamers and controls in terms of action inhibition [ 61 , 62 ]. Although GTA does not qualify as a classical first-person shooter as most of the previously tested action video games, it is classified as an action-adventure game and shares multiple features with those action video games previously related to increases in executive function, including the need for hand–eye coordination and fast reaction times.
Taken together, the findings of the present study show that an extensive game intervention over the course of 2 months did not reveal any specific changes in aggression, empathy, interpersonal competencies, impulsivity-related constructs, depressivity, anxiety or executive control functions; neither in comparison to an active control group that played a non-violent video game nor to a passive control group. We observed no effects when comparing a baseline and a post-training assessment, nor when focussing on more long-term effects between baseline and a follow-up interval 2 months after the participants stopped training. To our knowledge, the present study employed the most comprehensive test battery spanning a multitude of domains in which changes due to violent video games may have been expected. Therefore the present results provide strong evidence against the frequently debated negative effects of playing violent video games. This debate has mostly been informed by studies showing short-term effects of violent video games when tests were administered immediately after a short playtime of a few minutes; effects that may in large be caused by short-lived priming effects that vanish after minutes. The presented results will therefore help to communicate a more realistic scientific perspective of the real-life effects of violent video gaming. However, future research is needed to demonstrate the absence of effects of violent video gameplay in children.
Anderson CA, Bushman BJ. Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior, aggressive cognition, aggressive affect, physiological arousal, and prosocial behavior: a meta-analytic review of the scientific literature. Psychol Sci. 2001;12:353–9.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Anderson CA, Shibuya A, Ihori N, Swing EL, Bushman BJ, Sakamoto A, et al. Violent video game effects on aggression, empathy, and prosocial behavior in eastern and western countries: a meta-analytic review. Psychol Bull. 2010;136:151–73.
Article Google Scholar
Ferguson CJ. Do angry birds make for angry children? A meta-analysis of video game influences on children’s and adolescents’ aggression, mental health, prosocial behavior, and academic performance. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2015;10:646–66.
Ferguson CJ, Kilburn J. Much ado about nothing: the misestimation and overinterpretation of violent video game effects in eastern and western nations: comment on Anderson et al. (2010). Psychol Bull. 2010;136:174–8.
Greitemeyer T, Mugge DO. Video games do affect social outcomes: a meta-analytic review of the effects of violent and prosocial video game play. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 2014;40:578–89.
Anderson CA, Carnagey NL, Eubanks J. Exposure to violent media: The effects of songs with violent lyrics on aggressive thoughts and feelings. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2003;84:960–71.
DeWall CN, Anderson CA, Bushman BJ. The general aggression model: theoretical extensions to violence. Psychol Violence. 2011;1:245–58.
Sestire MA, Bartholow BD. Violent and non-violent video games produce opposing effects on aggressive and prosocial outcomes. J Exp Soc Psychol. 2010;46:934–42.
Kneer J, Elson M, Knapp F. Fight fire with rainbows: The effects of displayed violence, difficulty, and performance in digital games on affect, aggression, and physiological arousal. Comput Hum Behav. 2016;54:142–8.
Kneer J, Glock S, Beskes S, Bente G. Are digital games perceived as fun or danger? Supporting and suppressing different game-related concepts. Cyber Beh Soc N. 2012;15:604–9.
Sauer JD, Drummond A, Nova N. Violent video games: the effects of narrative context and reward structure on in-game and postgame aggression. J Exp Psychol Appl. 2015;21:205–14.
Ballard M, Visser K, Jocoy K. Social context and video game play: impact on cardiovascular and affective responses. Mass Commun Soc. 2012;15:875–98.
Read GL, Ballard M, Emery LJ, Bazzini DG. Examining desensitization using facial electromyography: violent video games, gender, and affective responding. Comput Hum Behav. 2016;62:201–11.
Szycik GR, Mohammadi B, Hake M, Kneer J, Samii A, Munte TF, et al. Excessive users of violent video games do not show emotional desensitization: an fMRI study. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017;11:736–43.
Szycik GR, Mohammadi B, Munte TF, Te Wildt BT. Lack of evidence that neural empathic responses are blunted in excessive users of violent video games: an fMRI study. Front Psychol. 2017;8:174.
Tear MJ, Nielsen M. Failure to demonstrate that playing violent video games diminishes prosocial behavior. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e68382.
Tear MJ, Nielsen M. Video games and prosocial behavior: a study of the effects of non-violent, violent and ultra-violent gameplay. Comput Hum Behav. 2014;41:8–13.
Kühn S, Gleich T, Lorenz RC, Lindenberger U, Gallinat J. Playing super Mario induces structural brain plasticity: gray matter changes resulting from training with a commercial video game. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19:265–71.
Buss AH, Perry M. The aggression questionnaire. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1992;63:452.
Anderson CA, Deuser WE, DeNeve KM. Hot temperatures, hostile affect, hostile cognition, and arousal: Tests of a general model of affective aggression. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 1995;21:434–48.
Payne DL, Lonsway KA, Fitzgerald LF. Rape myth acceptance: exploration of its structure and its measurement using the illinois rape myth acceptance scale. J Res Pers. 1999;33:27–68.
McMahon S, Farmer GL. An updated measure for assessing subtle rape myths. Social Work Res. 2011; 35:71–81.
Detert JR, Trevino LK, Sweitzer VL. Moral disengagement in ethical decision making: a study of antecedents and outcomes. J Appl Psychol. 2008;93:374–91.
Bandura A, Barbaranelli C, Caprara G, Pastorelli C. Mechanisms of moral disengagement in the exercise of moral agency. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1996;71:364–74.
Rosenzweig S. The picture-association method and its application in a study of reactions to frustration. J Pers. 1945;14:23.
Hörmann H, Moog W, Der Rosenzweig P-F. Test für Erwachsene deutsche Bearbeitung. Göttingen: Hogrefe; 1957.
Anderson CA, Dill KE. Video games and aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behavior in the laboratory and in life. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2000;78:772–90.
Przybylski AK, Deci EL, Rigby CS, Ryan RM. Competence-impeding electronic games and players’ aggressive feelings, thoughts, and behaviors. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2014;106:441.
Bitsakou P, Antrop I, Wiersema JR, Sonuga-Barke EJ. Probing the limits of delay intolerance: preliminary young adult data from the Delay Frustration Task (DeFT). J Neurosci Methods. 2006;151:38–44.
Hoyle RH, Stephenson MT, Palmgreen P, Lorch EP, Donohew RL. Reliability and validity of a brief measure of sensation seeking. Pers Individ Dif. 2002;32:401–14.
Farmer R, Sundberg ND. Boredom proneness: the development and correlates of a new scale. J Pers Assess. 1986;50:4–17.
Lejuez CW, Read JP, Kahler CW, Richards JB, Ramsey SE, Stuart GL, et al. Evaluation of a behavioral measure of risk taking: the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART). J Exp Psychol Appl. 2002;8:75–84.
Richards JB, Zhang L, Mitchell SH, de Wit H. Delay or probability discounting in a model of impulsive behavior: effect of alcohol. J Exp Anal Behav. 1999;71:121–43.
Davis MH. A multidimensional approach to individual differences in empathy. JSAS Cat Sel Doc Psychol. 1980;10:85.
Google Scholar
Mehrabian A. Manual for the Balanced Emotional Empathy Scale (BEES). (Available from Albert Mehrabian, 1130 Alta Mesa Road, Monterey, CA, USA 93940); 1996.
Baron-Cohen S, Wheelwright S, Hill J, Raste Y, Plumb I. The “Reading the Mind in the Eyes” Test revised version: A study with normal adults, and adults with Asperger syndrome or high-functioning autism. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2001;42:241–51.
Buhrmester D, Furman W, Reis H, Wittenberg MT. Five domains of interpersonal competence in peer relations. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1988;55:991–1008.
Richardson DR, Green LR, Lago T. The relationship between perspective-taking and non-aggressive responding in the face of an attack. J Pers. 1998;66:235–56.
Maras D, Flament MF, Murray M, Buchholz A, Henderson KA, Obeid N, et al. Screen time is associated with depression and anxiety in Canadian youth. Prev Med. 2015;73:133–8.
Hautzinger M, Bailer M, Worall H, Keller F. Beck-Depressions-Inventar (BDI). Beck-Depressions-Inventar (BDI): Testhandbuch der deutschen Ausgabe. Bern: Huber; 1995.
Spielberger CD, Spielberger CD, Sydeman SJ, Sydeman SJ, Owen AE, Owen AE, et al. Measuring anxiety and anger with the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) and the State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory (STAXI). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers; 1999.
Lorenz RC, Gleich T, Buchert R, Schlagenhauf F, Kuhn S, Gallinat J. Interactions between glutamate, dopamine, and the neuronal signature of response inhibition in the human striatum. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015;36:4031–40.
Bush G, Shin LM. The multi-source interference task: an fMRI task that reliably activates the cingulo-frontal-parietal cognitive/attention network. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:308–13.
King JA, Colla M, Brass M, Heuser I, von Cramon D. Inefficient cognitive control in adult ADHD: evidence from trial-by-trial Stroop test and cued task switching performance. Behav Brain Funct. 2007;3:42.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc. 1995;57:289–300.
Wagenmakers E-J. A practical solution to the pervasive problems of p values. Psychon Bull Rev. 2007;14:779–804.
Hay DF. The gradual emergence of sex differences in aggression: alternative hypotheses. Psychol Med. 2007;37:1527–37.
Jeffreys H. The Theory of Probability. Oxford: Clarendon Press; 1961.
Raftery AE, Newton MA, Satagopan YM, Krivitsky PN. Estimating the integrated likelihood via posterior simulation using the harmonic mean identity. In: Bernardo JM, Bayarri MJ, Berger JO, Dawid AP, Heckerman D, Smith AFM, et al., editors. Bayesian statistics. Oxford: University Press; 2007.
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang A-G, Buchner A. G*Power3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods. 2007;39:175–91.
Barlett C, Branch O, Rodeheffer C, Harris R. How long do the short-term violent video game effects last? Aggress Behav. 2009;35:225–36.
Williams D, Skoric M. Internet fantasy violence: a test of aggression in an online game. Commun Monogr. 2005;72:217–33.
Teng SK, Chong GY, Siew AS, Skoric MM. Grand theft auto IV comes to Singapore: effects of repeated exposure to violent video games on aggression. Cyber Behav Soc Netw. 2011;14:597–602.
van Rooij AJ, Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD, Shorter GW, Schoenmakers TM, Van, de Mheen D. The (co-)occurrence of problematic video gaming, substance use, and psychosocial problems in adolescents. J Behav Addict. 2014;3:157–65.
Brunborg GS, Mentzoni RA, Froyland LR. Is video gaming, or video game addiction, associated with depression, academic achievement, heavy episodic drinking, or conduct problems? J Behav Addict. 2014;3:27–32.
Green CS, Sugarman MA, Medford K, Klobusicky E, Bavelier D. The effect of action video game experience on task switching. Comput Hum Behav. 2012;28:984–94.
Strobach T, Frensch PA, Schubert T. Video game practice optimizes executive control skills in dual-task and task switching situations. Acta Psychol. 2012;140:13–24.
Colzato LS, van Leeuwen PJ, van den Wildenberg WP, Hommel B. DOOM’d to switch: superior cognitive flexibility in players of first person shooter games. Front Psychol. 2010;1:8.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hutchinson CV, Barrett DJK, Nitka A, Raynes K. Action video game training reduces the Simon effect. Psychon B Rev. 2016;23:587–92.
Powers KL, Brooks PJ, Aldrich NJ, Palladino MA, Alfieri L. Effects of video-game play on information processing: a meta-analytic investigation. Psychon Bull Rev. 2013;20:1055–79.
Colzato LS, van den Wildenberg WP, Zmigrod S, Hommel B. Action video gaming and cognitive control: playing first person shooter games is associated with improvement in working memory but not action inhibition. Psychol Res. 2013;77:234–9.
Steenbergen L, Sellaro R, Stock AK, Beste C, Colzato LS. Action video gaming and cognitive control: playing first person shooter games is associated with improved action cascading but not inhibition. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0144364.
Download references
Acknowledgements
SK has been funded by a Heisenberg grant from the German Science Foundation (DFG KU 3322/1-1, SFB 936/C7), the European Union (ERC-2016-StG-Self-Control-677804) and a Fellowship from the Jacobs Foundation (JRF 2016–2018).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Max Planck Institute for Human Development, Center for Lifespan Psychology, Lentzeallee 94, 14195, Berlin, Germany
Simone Kühn, Katharina Schmalen, Markus Weichenberger & Charlotte Witt
Clinic and Policlinic for Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, University Clinic Hamburg-Eppendorf, Martinistraße 52, 20246, Hamburg, Germany
Simone Kühn, Dimitrij Tycho Kugler & Jürgen Gallinat
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Simone Kühn .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary material, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kühn, S., Kugler, D., Schmalen, K. et al. Does playing violent video games cause aggression? A longitudinal intervention study. Mol Psychiatry 24 , 1220–1234 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0031-7
Download citation
Received : 19 August 2017
Revised : 03 January 2018
Accepted : 15 January 2018
Published : 13 March 2018
Issue Date : August 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0031-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
The effect of competitive context in nonviolent video games on aggression: the mediating role of frustration and the moderating role of gender.
- Jinqian Liao
- Yanling Liu
Current Psychology (2024)
Exposure to hate speech deteriorates neurocognitive mechanisms of the ability to understand others’ pain
- Agnieszka Pluta
- Joanna Mazurek
- Michał Bilewicz
Scientific Reports (2023)
The effects of violent video games on reactive-proactive aggression and cyberbullying
- Yunus Emre Dönmez
Current Psychology (2023)
Machen Computerspiele aggressiv?
- Jan Dieris-Hirche
Die Psychotherapie (2023)
Systematic Review of Gaming and Neuropsychological Assessment of Social Cognition
- Elodie Hurel
- Marie Grall-Bronnec
- Gaëlle Challet-Bouju
Neuropsychology Review (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
The evidence that video game violence leads to real-world aggression
A 2018 meta-analysis found that there is a small increase in real-world physical aggression among adolescents and pre-teens who play violent video games. Led by Jay Hull, a social psychologist at Dartmouth College, the study team pooled data from 24 previous studies in an attempt to avoid some of the problems that have made the question of a connection between gaming and aggression controversial.
Many previous studies, according to a story in Scientific American, have been criticized by “a small but vocal cadre of researchers [who] have argued much of the work implicating video games has serious flaws in that, among other things, it measures the frequency of aggressive thoughts or language rather than physically aggressive behaviors like hitting or pushing, which have more real-world relevance.”
Hull and team limited their analysis to studies that “measured the relationship between violent video game use and overt physical aggression,” according to the Scientific American article .
The Dartmouth analysis drew on 24 studies involving more than 17,000 participants and found that “playing violent video games is associated with increases in physical aggression over time in children and teens,” according to a Dartmouth press release describing the study , which was published Oct. 1, 2018, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences .
The studies the Dartmouth team analyzed “tracked physical aggression among users of violent video games for periods ranging from three months to four years. Examples of physical aggression included incidents such as hitting someone or being sent to the school principal’s office for fighting, and were based on reports from children, parents, teachers, and peers,” according to the press release.
The study was almost immediately called in to question. In an editorial in Psychology Today , a pair of professors claim the results of the meta-analysis are not statistically significant. Hull and team wrote in the PNAS paper that, while small, the results are indeed significant. The Psychology Today editorial makes an appeal to a 2017 statement by the American Psychological Association’s media psychology and technology division “cautioning policy makers and news media to stop linking violent games to serious real-world aggression as the data is just not there to support such beliefs.”
It should be noted, however, that the 2017 statement questions the connection between “serious” aggression while the APA Resolution of 2015 , based on a review of its 2005 resolution by its own experts, found that “the link between violent video game exposure and aggressive behavior is one of the most studied and best established. Since the earlier meta-analyses, this link continues to be a reliable finding and shows good multi-method consistency across various representations of both violent video game exposure and aggressive behavior.”
While the effect sizes are small, they’ve been similar across many studies, according to the APA resolution. The problem has been the interpretation of aggression, with some writers claiming an unfounded connection between homicides, mass shootings, and other extremes of violence. The violence the APA resolution documents is more mundane and involves the kind of bullying that, while often having dire long-term consequences, is less immediately dangerous: “insults, threats, hitting, pushing, hair pulling, biting and other forms of verbal and physical aggression.”
Minor and micro-aggressions, though, do have significant health risks, especially for mental health. People of color, LGBTQ people , and women everywhere experience higher levels of depression and anger, as well as stress-related disorders, including heart disease, asthma, obesity, accelerated aging, and premature death. The costs of even minor aggression are laid at the feet of the individuals who suffer, their friends and families, and society at large as the cost of healthcare skyrockets.
Finally, it should be noted that studies looking for a connection between game violence and physical aggression are not looking at the wider context of the way we enculturate children, especially boys. As WSU’s Stacey Hust and Kathleen Rodgers have shown, you don’t have to prove a causative effect to know that immersing kids in games filled with violence and sexist tropes leads to undesirable consequences, particularly the perpetuation of interpersonal violence in intimate relationships.
No wonder, then, that when feminist media critic Anita Saarkesian launched her YouTube series, “ Tropes vs. Women in Video Games ,” she was the target of vitriol and violence. Years later she’d joke about “her first bomb threat,” but that was only after her life had been upended by the boys club that didn’t like “this woman” showing them the “grim evidence of industry-wide sexism.”
Read more about WSU research and study on video games in “ What’s missing in video games .”
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
The relation of violent video games to adolescent aggression: an examination of moderated mediation effect.

- 1 Research Institute of Moral Education, College of Psychology, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China
- 2 The Lab of Mental Health and Social Adaptation, Faculty of Psychology, Research Center for Mental Health Education, Southwest University, Chongqing, China
To assess the moderated mediation effect of normative beliefs about aggression and family environment on exposure to violent video games and adolescent aggression, the subjects self-reported their exposure to violent video games, family environment, normative beliefs about aggression, and aggressive behavior. The results showed that there was a significant positive correlation between exposure to violent video games and adolescent aggression; normative beliefs about aggression had a mediation effect on exposure to violent video games and adolescent aggression, while family environment moderated the first part of the mediation process. For individuals with a good family environment, exposure to violent video games had only a direct effect on aggression; however, for those with poor family environment, it had both direct and indirect effects mediated by normative beliefs about aggression. This moderated mediation model includes some notions of General Aggression Model (GAM) and Catalyst Model (CM), which helps shed light on the complex mechanism of violent video games influencing adolescent aggression.
Introduction
Violent video games and aggression.
The relationship between violent video games and adolescent aggression has become a hot issue in psychological research ( Wiegman and Schie, 1998 ; Anderson and Bushman, 2001 ; Anderson et al., 2010 ; Ferguson et al., 2012 ; Greitemeyer, 2014 ; Yang et al., 2014 ; Boxer et al., 2015 ). Based on the General Aggression Model (GAM), Anderson et al. suggested that violent video games constitute an antecedent variable of aggressive behavior, i.e., the degree of exposure to violent video games directly leads to an increase of aggression ( Anderson and Bushman, 2001 ; Bushman and Anderson, 2002 ; Anderson, 2004 ; Anderson et al., 2004 ). Related longitudinal studies ( Anderson et al., 2008 ), meta-analyses ( Anderson et al., 2010 ; Greitemeyer and Mugge, 2014 ), event-related potential studies ( Bailey et al., 2011 ; Liu et al., 2015 ), and trials about juvenile delinquents ( DeLisi et al., 2013 ) showed that exposure to violent video games significantly predicts adolescent aggression.
Although Anderson et al. insisted on using the GAM to explain the effect of violent video games on aggression, other researchers have proposed alternative points of view. For example, a meta-analysis by Sherry (2001) suggested that violent video games have minor influence on adolescent aggression. Meanwhile, Ferguson (2007) proposed that publication bias (or file drawer effect) may have implications in the effect of violent video games on adolescent aggression. Publication bias means that compared with articles with negative results, those presenting positive results (such as statistical significance) are more likely to be published ( Rosenthal and Rosnow, 1991 ). A meta-analysis by Ferguson (2007) found that after publication bias adjustment, the related studies cannot support the hypothesis that violent video games are highly correlated with aggression. Then, Ferguson et al. proposed a Catalyst Model (CM), which is opposite to the GAM. According to this model, genetic predisposition can lead to an aggressive child temperament and aggressive adult personality. Individuals who have an aggressive temperament or an aggressive personality are more likely to produce violent behavior during times of environmental strain. Environmental factors act as catalysts for violent acts for an individual who have a violence-prone personality. This means that although the environment does not cause violent behavior, but it can moderate the causal influence of biology on violence. The CM model suggested that exposure to violent video games is not an antecedent variable of aggressive behavior, but only acts as a catalyst influencing its form ( Ferguson et al., 2008 ). Much of studies ( Ferguson et al., 2009 , 2012 ; Ferguson, 2013 , 2015 ; Furuya-Kanamori and Doi, 2016 ; Huesmann et al., 2017 ) found that adolescent aggression cannot be predicted by the exposure to violent video games, but it is closely related to antisocial personality traits, peer influence, and family violence.
Anderson and his collaborators ( Groves et al., 2014 ; Kepes et al., 2017 ) suggested there were major methodological shortcomings in the studies of Ferguson et al. and redeclared the validity of their own researches. Some researchers supported Anderson et al. and criticized Ferguson’s view ( Gentile, 2015 ; Rothstein and Bushman, 2015 ). However, Markey (2015) held a neutral position that extreme views should not be taken in the relationship between violent video games and aggression.
In fact, the relation of violent video games to aggression is complicated. Besides the controversy between the above two models about whether there is an influence, other studies explored the role of internal factors such as normative belief about aggression and external factors such as family environment in the relationship between violent video games and aggression.
Normative Beliefs About Aggression, Violence Video Games, and Aggression
Normative beliefs about aggression are one of the most important cognitive factors influencing adolescent aggression; they refer to an assessment of aggression acceptability by an individual ( Huesmann and Guerra, 1997 ). They can be divided into two types: general beliefs and retaliatory beliefs. The former means a general view about aggression, while the latter reflects aggressive beliefs in provocative situations. Normative beliefs about aggression reflect the degree acceptance of aggression, which affects the choice of aggressive behavior.
Studies found that normative beliefs about aggression are directly related to aggression. First, self-reported aggression is significantly correlated to normative beliefs about aggression ( Bailey and Ostrov, 2008 ; Li et al., 2015 ). General normative beliefs about aggression can predict young people’s physical, verbal, and indirect aggression ( Lim and Ang, 2009 ); retaliatory normative beliefs about aggression can anticipate adolescent retaliation behavior after 1 year ( Werner and Hill, 2010 ; Krahe and Busching, 2014 ). There is a longitudinal temporal association of normative beliefs about aggression with aggression ( Krahe and Busching, 2014 ). Normative beliefs about aggression are significantly positively related to online aggressive behavior ( Wright and Li, 2013 ), which is the most important determining factor of adolescent cyberbullying ( Kowalski et al., 2014 ). Teenagers with high normative beliefs about aggression are more likely to become bullies and victims of traditional bullying and cyberbullying ( Burton et al., 2013 ). Finally, normative beliefs about aggression can significantly predict the support and reinforcement of bystanders in offline bullying and cyberbullying ( Machackova and Pfetsch, 2016 ).
According to Bandura’s social cognitive theory ( Bandura, 1989 ), violent video games can initiate adolescents’ observational learning. In this situation, not only can they imitate the aggressive behavior of the model but also their understanding and acceptability about aggression may change. Therefore, normative beliefs about aggression can also be a mediator between violent video games and adolescent aggression ( Duan et al., 2014 ; Anderson et al., 2017 ; Huesmann et al., 2017 ). Studies have shown that the mediating role of normative beliefs about aggression is not influenced by factors such as gender, prior aggression, and parental monitoring ( Gentile et al., 2014 ).
Family Environment, Violence Video Games, and Aggression
Family violence, parenting style, and other family factors have major effects on adolescent aggression. On the one hand, family environment can influence directly on aggression by shaping adolescents’ cognition and setting up behavioral models. Many studies have found that family violence and other negative factors are positively related to adolescent aggression ( Ferguson et al., 2009 , 2012 ; Ferguson, 2013 ), while active family environment can reduce the aggressive behavior ( Batanova and Loukas, 2014 ).
On the other hand, family environment can act on adolescent aggression together with other factors, such as exposure to violent video games. Analysis of the interaction between family conflict and media violence (including violence on TV and in video games) to adolescent aggression showed that teenagers living in higher conflict families with more media violence exposure show more aggressive behavior ( Fikkers et al., 2013 ). Parental monitoring is significantly correlated with reduced media violence exposure and a reduction in aggressive behavior 6 months later ( Gentile et al., 2014 ). Parental mediation can moderate the relationship between media violence exposure and normative beliefs about aggression, i.e., for children with less parental mediation, predictability of violent media exposure on normative beliefs about aggression is stronger ( Linder and Werner, 2012 ). Parental mediation is closely linked to decreased aggression caused by violent media ( Nathanson, 1999 ; Rasmussen, 2014 ; Padilla-Walker et al., 2016 ). Further studies have shown that the autonomy-supportive restrictive mediation of parents is related to a reduction in current aggressive behavior by decreasing media violence exposure; conversely, inconsistent restrictive mediation is associated with an increase of current aggressive behavior by enhancing media violence exposure ( Fikkers et al., 2017 ).
The Current Study
Despite GAM and CM hold opposite views on the relationship between violent video games and aggression, both of the two models imply the same idea that aggression cannot be separated from internal and external factors. While emphasizing on negative effects of violent video games on adolescents’ behavior, the GAM uses internal factors to explain the influencing mechanism, including aggressive beliefs, aggressive behavior scripts, and aggressive personality ( Bushman and Anderson, 2002 ; Anderson and Carnagey, 2014 ). Although the CM considers that there is no significant relation between violent video games and aggression, it also acknowledges the role of external factors such as violent video games and family violence. Thus, these two models seem to be contradictory, but in fact, they reveal the mechanism of aggression from different points of view. It will be more helpful to explore the effect of violent video games on aggression from the perspective of combination of internal and external factors.
Although previous studies have investigated the roles of normative beliefs about aggression and family factors in the relationship between violent video games and adolescent aggression separately, the combined effect of these two factors remains unstudied. The purpose of this study was to analyze the combined effect of normative beliefs about aggression and family environment. This can not only confirm the effects of violent video games on adolescent aggression further but also can clarify the influencing mechanism from the integration of GAM and CM to a certain extent. Based on the above, the following three hypotheses were proposed:
Hypothesis 1: There is a significant positive correlation between exposure to violent video games and adolescent aggression.
Hypothesis 2: Normative beliefs about aggression are the mediator of exposure to violent video games and adolescent aggression.
Hypothesis 3: The family environment can moderate the mediation effects of normative beliefs about aggression in exposure to violent video games and adolescent aggression; exposure to violent video games, family environment, normative beliefs about aggression, and aggression constitute a moderated mediation model.
Materials and Methods
Participants.
All subjects gave informed written consent for participation in this investigation, and their parents signed parental written informed consent. The study was reviewed and approved by the Professor Committee of School of Psychology, Nanjing Normal University, which is the committee responsible for providing ethics approvals. A total of 648 Chinese middle school students participated in this study, including 339 boys and 309 girls; 419 students were from cities and towns, and 229 from the countryside. There were 277 and 371 junior and high school students, respectively. Ages ranged from 12 to 19 years, averaging 14.73 ( SD = 1.60).
Video Game Questionnaire (VGQ)
The Video Game Questionnaire ( Anderson and Dill, 2000) required participants to list their favorite five video games and assess their use frequencies, the degree of violent content, and the degree of violent images on a 7-point scale (1, participants seldom play video games, with no violent content or image; 7, participants often play video games with many violent contents and images). Methods for calculating the score of exposure to violent video games: (score of violent content in the game + score of violent images in the game) × use frequency/5. Chen et al. (2012) found that the Chinese version of this questionnaire had high internal consistency reliability and good content validity. The Chinese version was used in this study, and the Cronbach’s α coefficient of the questionnaire was 0.88.
Aggression Questionnaire (AQ)
There were 29 items in AQ ( Buss and Perry, 1992 ), including four dimensions: physical aggression, verbal aggression, anger, and hostility. The scale used 5-point scoring criteria (1, very incongruent with my features; 5, very congruent with my features). Scores for each item were added to obtain the dimension score, and dimension scores were summed to obtain the total score. The Chinese version of AQ had good internal consistency reliability and construct validity ( Ying and Dai, 2008 ). In this study, the Chinese version was used and its Cronbach’s α coefficient was 0.83.
Family Environment Scale (FES)
The FES ( Moos, 1990 ) includes 90 true-false questions and is divided into 10 subscales, including cohesion, expressiveness, conflict, independence, achievement-orientation, intellectual-cultural orientation, active-recreational orientation, moral-religious emphasis, organization, and control. The Chinese version of FES was revised by Fei et al. (1991) and used in this study. Three subscales closely related to aggression were selected, including cohesion, conflict, and moral-religious emphasis, with 27 items in total. The family environment score was the sum of scores of these three subscales (the conflict subscale was first inverted). The Cronbach’s α coefficient of the questionnaire was 0.75.
Normative Beliefs About Aggression Scale (NOBAGS)
There are 20 items in the NOBAGS ( Huesmann and Guerra, 1997 ), which includes retaliation (12 items) and general (8 items) aggression belief. A 4-point Likert scale is used (1, absolutely wrong; 4, absolutely right). The subjects were asked to assess the accuracy of the behavior described in each item. High score means high level of normative beliefs about aggression. The revised Chinese version of NOBAGS consists of two factors: retaliation (nine items) and general (six items) aggression belief. Its internal consistency coefficient and test-retest reliability are 0.81 and 0.79. Confirmative factor analysis showed that this version has good construct validity: χ 2 = 280.09, df = 89, χ 2 / df = 3.15, RMSEA = 0.07, SRMR = 0.04, NFI = 0.95, NNFI = 0.96, and CFI = 0.96 ( Shao and Wang, 2017 ). In this study, the Cronbach’s α coefficient of the Chinese version was 0.88.
Group testing was performed in randomly selected classes of six middle schools. All subjects completed the above four questionnaires.
Data Analysis
IBM SPSS Statistics 22 was used to analysis the correlations among study variables, the mediating effect of normative beliefs about aggression on the relationship between exposure to violent video games and aggression, and the moderating role of family environment in the relationship between exposure to violent video games and normative beliefs about aggression. In order to validate the moderated mediation model, Mplus 7 was also used.
Correlation Analysis Among Study Variables
In this study, self-reported questionnaires were used to collect data, and results might be influenced by common method bias. Therefore, the Harman’s single-factor test was used to assess common method bias before data analysis. The results showed that eigenvalues of 34 unrotated factors were greater than 1, and the amount of variation explained by the first factor was 10.01%, which is much less than 40% of the critical value. Accordingly, common method bias was not significant in this study.
As described in Table 1 , the degree of exposure to violent video games showed significant positive correlations to normative beliefs about aggression and aggression; family environment was negatively correlated to normative beliefs about aggression and aggression; normative beliefs about aggression were significantly and positively related to aggression. The gender difference of exposure to violent video games ( t = 7.93, p < 0.001) and normative beliefs about aggression ( t = 2.74, p < 0.01) were significant, which boys scored significantly higher than girls.
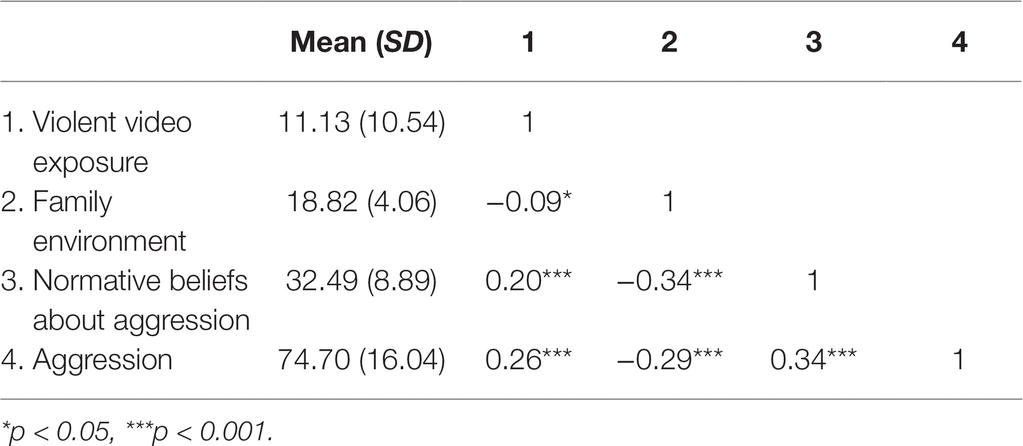
Table 1 . Means, standard deviations, and Pearson correlations among study variables.
Mediating Effect Analysis
To examine the mediation effect of normative beliefs about aggression on the relationship between exposure to violent video games and aggression, gender factor was controlled firstly. Stepwise regression analysis showed that the regression of aggression to violent video games ( c = 0.28, t = 6.96, p < 0.001), the regression of normative beliefs about aggression to violent video games ( a = 0.19, t = 4.69, p < 0.001), and the regression of aggression to violent video games ( c ′ = 0.22, t = 5.69, p < 0.001) and normative beliefs about aggression ( b = 0.31, t = 8.25, p < 0.001) were all significant. Thus, normative beliefs about aggression played a partial mediating role in exposure to violent video games and aggression. The mediation effect value was 0.06, accounting for 21.43% (0.06/0.28) of the total effect.
Moderated Mediation Effect Analysis
After standardizing scores of exposure to violent videogames, normative beliefs about aggression, family environment, and aggression, two interaction terms were calculated, including family environment × exposure to violent video games and family environment × normative beliefs about aggression. Regression analysis was carried out after controlling gender factor ( Table 2 ).
Table 2 . Moderated mediation effect analysis of the relationship between violent video exposure and aggression.
In the first step, a simple moderated model (Model 1) between exposure to violent video games and aggression was established. The result showed that exposure to violent video games had a significant effect on aggression ( c 1 = 0.24, t = 6.13, p < 0.001), while the effect of family environment × exposure to violent video games on aggression was not significant ( c 3 = 0.05, t = −1.31, p = 0.19), indicating that the relationship between exposure to violent video games and aggression was not moderated by family environment.
Next, a moderated model (Model 2) between exposure to violent video games and normative beliefs about aggression was established. The results showed that exposure to violent video games had a significant effect on normative beliefs about aggression ( a 1 = 0.13, t = 3.42, p < 0.001), and the effect of family environment × exposure to violent video games on normative beliefs about aggression was significant ( a 3 = −0.13, t = −3.63, p < 0.01).
In the third step, a moderated mediation model (Model 3) between exposure to violent video games and aggression was established. As shown in Table 2 , the effect of normative beliefs about aggression on aggression was significant ( b 1 = 0.24, t = 6.15, p < 0.001), and the effect of family environment × exposure to violent video games on normative beliefs about aggression was not significant ( b 2 = 0.02, t = 0.40, p = 0.69). Because both a 3 and b 1 were significant, exposure to violent video games, family environment, normative beliefs about aggression, and aggression constituted a moderated mediation model. Normative beliefs about aggression played a mediating role between exposure to violent video games and aggression, while family environment was a moderator between exposure to violent video games and normative beliefs about aggression. Mplus analysis proved that the moderated mediation model had good model fitting (χ 2 / df = 1.54, CFI = 0.99, TLI = 0.98, RMSEA = 0.03, and SRMR = 0.01).
To further analyze the moderating effect of the family environment and exposure to violent video games on normative beliefs about aggression, the family environment was divided into the high and low groups, according to the principle of standard deviation, and a simple slope test was performed ( Figure 1 ). The results found that for individuals with high score of family environment, prediction of exposure to violent video games to normative beliefs about aggression was not significant ( b = 0.08, SE = 0.08, p = 0.37). For individuals with low score of family environment, exposure to violent video games could significantly predict normative beliefs about aggression ( b = 0.34, SE = 0.09, p < 0.001). Based on the overall findings, individuals with high scores of family environment showed a nonsignificant mediating effect of normative beliefs about aggression on the relation of exposure to violent video games and aggression; however, for individuals with low scores of family environment, normative beliefs about aggression played a partial mediating role in the effect of exposure to violent video games on aggression.
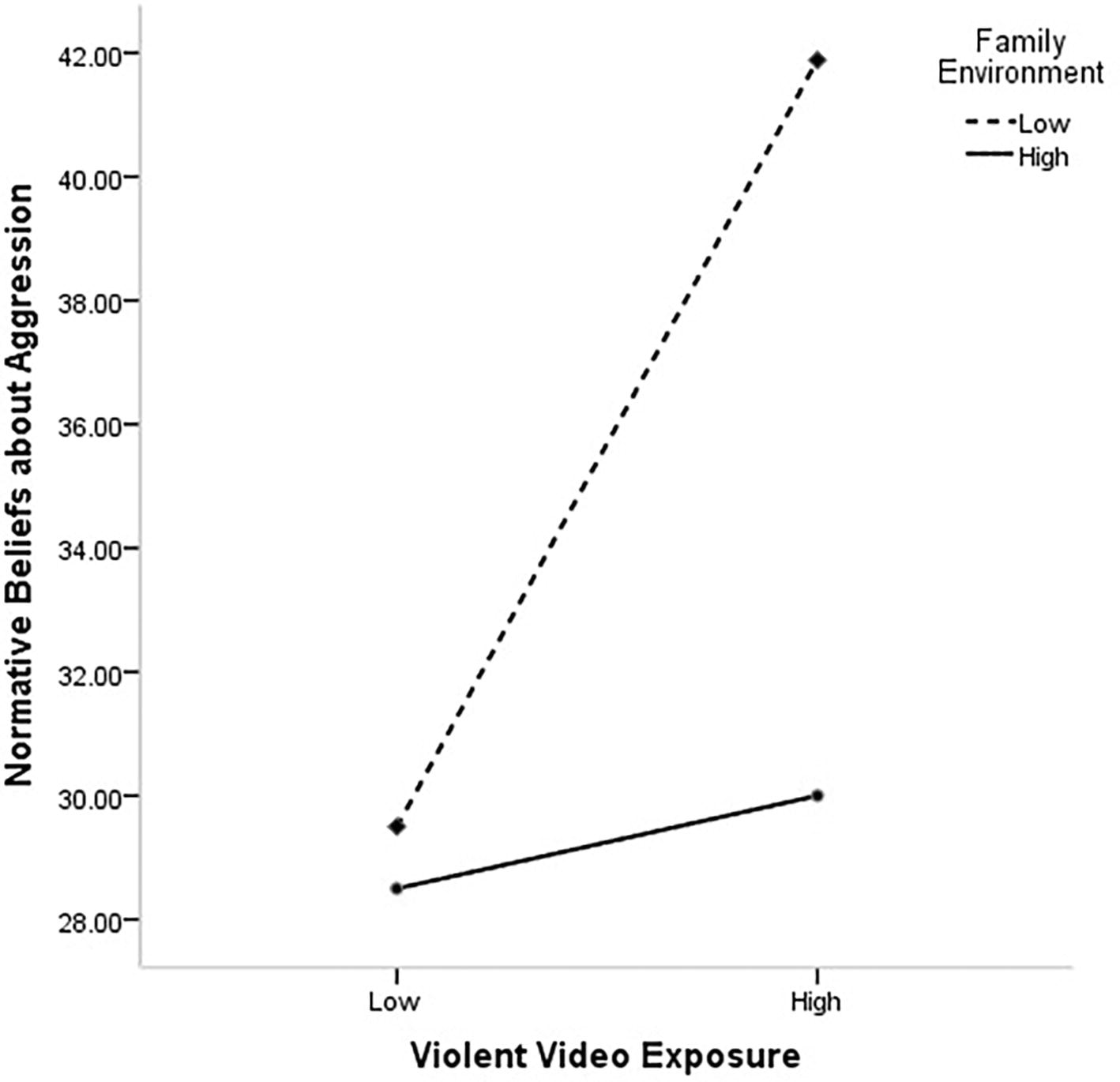
Figure 1 . The moderating effect of the family environment on the relationship between violent video game exposure and normative beliefs about aggression.
Main Findings and Implications
This study found a significantly positive correlation between exposure to violent video games and adolescent aggression, corroborating existing studies ( Anderson, 2004 ; Anderson et al., 2010 ; DeLisi et al., 2013 ; Greitemeyer and Mugge, 2014 ). Anderson et al. (2017) assessed teenagers in Australia, China, Germany, the United States, and other three countries and found that exposure to violent media, including television, movies, and video games, is positively related to adolescent aggression, demonstrating cross-cultural consistency; 8% of variance in aggression could be independently explained by exposure to violent media. In this study, after controlling for gender and family environment, R 2 for exposure to violent video games in predicting adolescent aggression was 0.05, indicating that 5% of variation in adolescent aggression could be explained by exposure to violent media. These consistent findings confirm the effect of exposure to violent video games on adolescent aggression and can be explained by the GAM. According to the GAM ( Bushman and Anderson, 2002 ; Anderson and Carnagey, 2014 ), violent video games can make teenagers acquire, repeat, and reinforce aggression-related knowledge structures, including aggressive beliefs and attitude, aggressive perceptual schemata, aggressive expectation schemata, aggressive behavior scripts, and aggression desensitization. Therefore, aggressive personality is promoted, increasing the possibility of aggressive behavior. The Hypothesis 1 of this study was validated and provided evidence for the GAM.
As shown above, normative beliefs about aggression had a partial mediation effect on the relationship between exposure to violent video games and aggression. Exposure to violent video games, on the one hand, can predict adolescent aggression directly; on the other hand, it had an indirect effect on adolescent aggression via normative beliefs about aggression. According to the above results, when exposure to violent video games changes by 1 standard deviation, adolescent aggression varies by 0.28 standard deviation, with 0.22 standard deviation being a direct effect of exposure to violent video games on adolescent aggression and 0.06 standard deviation representing the effect through normative beliefs about aggression. Too much violence in video games makes it easy for individuals to become accustomed to violence and emotionally apathetic towards the harmful consequences of violence. Moreover, it can make individuals accept the idea that violence is a good way of problem solving, leading to an increase in normative beliefs about aggression; under certain situational cues, it is more likely to become violent or aggressive. This conclusion is supported by other studies ( Gentile et al., 2014 ; Anderson et al., 2017 ; Huesmann et al., 2017 ). Like Hypothesis 1, Hypothesis 2 was validated the GAM.
One of the main findings of this study was the validation of Hypothesis 3: a moderated mediation model was constructed involving exposure to violent video games, family environment, normative beliefs about aggression, and aggression. Family environment moderated the first half of the mediation process of violent video games, normative beliefs about aggression, and aggression. In this study, family environment encompassed three factors, including (1) cohesion reflecting the degree of mutual commitment, assistance, and support among family members; (2) conflict reflecting the extent of anger, aggression, and conflict among family members; and (3) moral-religious emphasis reflecting the degree of emphasis on ethics, religion, and values. Individuals with high scores of family environment often help each other; seldom show anger, attack, and contradiction openly; and pay more attention to morality and values. These positive aspects would help them understand violence in video games from the right perspective, reduce recognition and acceptance of violence or aggression, and diminish the effect of violent video games on normative beliefs about aggression. Hence, exposure to violent video games could not predict normative beliefs about aggression of these individuals. By contrast, individuals with low scores of family environment are less likely to help each other; they often openly show anger, attack, and contradiction and do not pay much attention to morality and values. These negative aspects would not decrease but increase their acceptance of violence and aggression. For these individuals, because of the lack of mitigation mechanisms, exposure to violent video games could predict normative beliefs about aggression significantly.
The moderated mediation model of the relationship between exposure to violent video games and aggression could not only help reveal that exposure to violent video games can affect aggression but also provide an elaboration of the influencing mechanism. According to this model, for individuals with high scores of family environment, exposure to violent video games had only direct effect on aggression. However, for those with low scores of family environment, there was not only a direct effect of exposure to violent video games on aggression but also an indirect effect mediated by normative beliefs about aggression. In short, exposure to violence video games affecting aggression through normative beliefs about aggression is more likely to happen to adolescents with poor family environment than those with good family environment. That is, generation of adolescent aggression is not only related to internal cognitive factors but also to external situations. As Piotrowski and Valkenburg ( Piotrowski and Valkenburg, 2015 ; Valkenburg, 2015 ) pointed out, the effect of violent video games/media on adolescents is a complex interaction of dispositional, developmental, and social factors, and individual differences in susceptibility to these three factors determine the nature and the extent of this influence. The proposed model incorporated some perspectives of GAM and CM: while confirming the effect of exposure to violent video games on aggression occurrence, the combined effect of individual and environmental factors was verified.
Compared with the simple mediation or moderation model, the present moderated mediation model provided deeper insights into the internal mechanism of the effect of violent video games on aggression, providing inspirations for preventing adolescent aggression. First, in view of the close relationship between exposure to violent video games and adolescent aggression, relevant government departments should continue to improve the grading system of video games; meanwhile, parents should appropriately monitor the types of video games used by teenagers as well as the time spent and reduce the degree of exposure to violent video games. Second, by allowing teenagers to objectively distinguish between violence in games and reality, the mediating role of normative beliefs about aggression could inspire people to identify rational ways to solve violence problems and to experience the hurtful consequences of aggression. This would help adolescents change normative beliefs about aggression, establish a correct view of right and wrong, and reduce the occurrence of aggression. Finally, the moderating effect of family environment on the mediation process suggests that more attention should be paid to the important role of family environment. On the one hand, family education is closely related to adolescent aggression. Then, parents should create a good family atmosphere, publicly show anger and aggression as little as possible, and advocate and practice positive moral values. Parents should adopt authoritative styles, abandoning autocratic and indulgent parenting styles ( Casas et al., 2006 ; Sandstrom, 2007 ; Underwood et al., 2009 ; Kawabata et al., 2011 ) to minimize the negative effect of exposure to violent video games. On the other hand, for teenagers with poor family environment, while reducing exposure to violent video games, it is particularly important to change their normative beliefs about aggression, no longer viewing aggression as an alternative way to solve problems.
Limitations
Limitations of the current study should be mentioned. First, only Chinese school students were assessed, in a relatively small number, which could affect sample representativeness. A large sample of teenagers from different countries and in different ages, also including juvenile offenders, would be more accurate in revealing the effect of violent video games on adolescent aggression. Second, this study only focused on violent video games, not involving violent media such as internet and television, daily life events, wars, and other major social events. Indeed, these factors also have important effects on adolescent aggression, and their influencing mechanisms and combined effect are worth investigating further. Third, this study mainly adopted the self-report method. Use of peer, parent, or teacher reports to assess exposure to violent video games and aggression would help improve the effectiveness of the study. Fourth, there might be other mediators, moderating variables and relational models. In addition to normative beliefs about aggression and family environment, individual emotions, personality characteristics, school climate, and companions may play mediating or moderating roles in the relationship between violent video games and aggression. This study developed a moderated mediation model between family environment and normative beliefs about aggression, but the possibility of multiple mediation and mediated moderation models cannot be ruled out.
The current study showed that exposure to violent video games is positively related to adolescent aggression; normative beliefs about aggression have a mediating effect on exposure to violent video games and adolescent aggression, while the family environment regulates the first part of the mediation process. For individuals with good family environment, exposure to violent video games only has a direct effect on aggression; however, for those with poor family environment, there is an indirect effect mediated by normative beliefs about aggression alongside a direct effect. This moderated mediation model incorporates some perspectives of GAM and CM, enriching studies of generative mechanism of adolescent aggression.
Author Contributions
YW and RS conceived the idea of the study. RS analyzed the data. YW and RS interpreted the results and wrote the paper. YW discussed the results and revised the manuscript.
This study was supported by a grant from the National Social Science Foundation of China (14CSH017) to YW.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Anderson, C. A. (2004). An update on the effects of playing violent video games. J. Adolesc. 27, 113–122. doi: 10.1016/j.adolescence.2003.10.009
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Anderson, C. A., and Bushman, B. J. (2001). Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior, aggressive cognition, aggressive affect, physiological arousal, and prosocial behavior: a meta-analytic review of the scientific literature. Psychol. Sci. 12, 353–359. doi: 10.1111/1467-9280.00366
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Anderson, C. A., and Carnagey, N. L. (2014). “The role of theory in the study of media violence: the general aggression model” in Media violence and children. ed. Gentile, D. A. (Westport, CT: Praeger), 103–133.
Google Scholar
Anderson, C. A., Carnagey, N. L., Flanagan, M., Benjamin, A. J., Eubanks, J., and Valentine, J. C. (2004). Violent video games: specific effects of violent content on aggressive thoughts and behavior. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 36, 199–249. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2601(04)36004-1
Anderson, C. A., and Dill, K. E. (2000). Video games and aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behavior in the laboratory and in life. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 78, 772–790. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.78.4.772
Anderson, C. A., Sakamoto, A., Gentile, D. A., Ihori, N., Shibuya, A., Yukawa, S., et al. (2008). Longitudinal effects of violent video games on aggression in Japan and the United States. Pediatrics 122, e1067–e1072. doi: 10.1542/peds.2008-1425
Anderson, C. A., Shibuya, A., Ihori, N., Swing, E. L., Bushman, B. J., Sakamoto, A., et al. (2010). Violent video game effects on aggression, empathy, and prosocial behavior in eastern and western countries: a meta-analytic review. Psychol. Bull. 136, 151–173. doi: 10.1037/a0018251
Anderson, C. A., Suzuki, K., Swing, E. L., Groves, C. L., Gentile, D. A., Prot, S., et al. (2017). Media violence and other aggression risk factors in seven nations. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 43, 986–998. doi: 10.1177/0146167217703064
Bailey, C. A., and Ostrov, J. M. (2008). Differentiating forms and functions of aggression in emerging adults: associations with hostile attribution biases and normative beliefs. J. Youth Adolesc. 37, 713–722. doi: 10.1007/s10964-007-9211-5
Bailey, K., West, R., and Anderson, C. A. (2011). The association between chronic exposure to video game violence and affective picture processing: an ERP study. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 11, 259–276. doi: 10.3758/s13415-011-0029-y
Bandura, A. (1989). “Social cognitive theory” in Annals of child development: Six theories of child development. ed. Vasta, R. (Greenwich, CT: JAI Press), 1–60.
Batanova, M., and Loukas, A. (2014). Unique and interactive effects of empathy, family, and school factors on early adolescents’ aggression. J. Youth Adolesc. 43, 1890–1902. doi: 10.1007/s10964-013-0051-1
Boxer, P., Groves, C. L., and Docherty, M. (2015). Video games do indeed influence children and adolescents’ aggression, prosocial behavior, and academic performance: a clearer reading of Ferguson (2015). Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 10, 671–673. doi: 10.1177/1745691615592239
Burton, K. A., Dan, F., and Wygant, D. B. (2013). The role of peer attachment and normative beliefs about aggression on traditional bullying and cyberbullying. Psychol. Schools 50, 103–115. doi: 10.1002/pits.21663
Bushman, B. J., and Anderson, C. A. (2002). Violent video games and hostile expectations: a test of the general aggression model. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 28, 1679–1686. doi: 10.1177/014616702237649
Buss, A. H., and Perry, M. (1992). The aggression questionnaire. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 63, 452–459. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.63.3.452
Casas, J. F., Weigel, S. M., Crick, N. R., Ostrov, J. M., Woods, K. E., Jansen Yeh, E. A., et al. (2006). Early parenting and children’s relational and physical aggression in the preschool and home contexts. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 27, 209–227. doi: 10.1016/j.appdev.2006.02.003
Chen, H., Liu, Y., and Cui, W. (2012). The relationship between online violent video games and aggressive behavior: the mediating effect of college students’ attitudes towards violence. Chinese J. Special Educ. 8, 79–84.
DeLisi, M., Vaughn, M. G., Gentile, D. A., Anderson, C. A., and Shook, J. (2013). Violent video games, delinquency, and youth violence: new evidence. Youth Violence Juv. J. 11, 132–142. doi: 10.1177/1541204012460874
Duan, D., Zhang, X., Wei, L., Zhou, Y., and Liu, C. (2014). The impact of violent media on aggression: the role of normative belief and empathy. Psychol. Dev. Educ. 30, 185–192.
Fei, L., Shen, Q., Zheng, Y., Zhao, J., Jiang, S., Wang, L., and Wang, X. (1991). Preliminary evaluation of Chinese version of FACES and FES: comparison of normal families and families of schizophrenic patients. Chin. Ment. Health. J. 5, 198–202, 238.
Ferguson, C. J. (2007). Evidence for publication bias in video game violence effects literature: a meta-analytic review. Aggress. Violent Behav. 12, 470–482. doi: 10.1016/j.avb.2007.01.001
Ferguson, C. J. (2013). Adolescents, crime, and the media: A critical analysis. New York, NY: Springer.
Ferguson, C. J. (2015). Do angry birds make for angry children? A meta-analysis of video game influences on children’s and adolescents’ aggression, mental health, prosocial behavior, and academic performance. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 10, 646–666. doi: 10.1177/1745691615592234
Ferguson, C. J., Rueda, S., Cruz, A., Ferguson, D., Fritz, S., and Smith, S. (2008). Violent video games and aggression: causal relationship or byproduct of family violence and intrinsic violence motivation? Crim. Justice Behav. 31, 2231–2237. doi: 10.1002/chin.200028107
Ferguson, C. J., San Miguel, C., Garza, A., and Jerabeck, J. M. (2012). A longitudinal test of video game violence influences on dating and aggression: a 3-year longitudinal study of adolescents. J. Psychiatr. Res. 46, 141–146. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2011.10.014
Ferguson, C. J., San Miguel, C., and Hartley, R. D. (2009). A multivariate analysis of youth violence and aggression: the influence of family, peers, depression, and media violence. J. Pediatr. 155, 904–908. e903. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.06.021
Fikkers, K. M., Piotrowski, J. T., and Valkenburg, P. M. (2017). A matter of style? Exploring the effects of parental mediation styles on early adolescents’ media violence exposure and aggression. Comput. Hum. Behav. 70, 407–415. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2017.01.029
Fikkers, K. M., Piotrowski, J. T., Weeda, W. D., Vossen, H. G. M., and Valkenburg, P. M. (2013). Double dose: high family conflict enhances the effect of media violence exposure on adolescents’ aggression. Societies 3, 280–292. doi: 10.3390/soc3030280
Furuya-Kanamori, L., and Doi, S. A. (2016). Angry birds, angry children, and angry meta-analysts: a reanalysis. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 11, 408–414. doi: 10.1177/1745691616635599
Gentile, D. A. (2015). What is a good skeptic to do? the case for skepticism in the media violence discussion. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 10, 674–676. doi: 10.1177/1745691615592238
Gentile, D. A., Li, D., Khoo, A., Prot, S., and Anderson, C. A. (2014). Mediators and moderators of long-term effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior: practice, thinking, and action. JAMA Pediatr. 168, 450–457. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2014.63
Greitemeyer, T. (2014). Intense acts of violence during video game play make daily life aggression appear innocuous: a new mechanism why violent video games increase aggression. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 50, 52–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2013.09.004
Greitemeyer, T., and Mugge, D. O. (2014). Video games do affect social outcomes: a meta-analytic review of the effects of violent and prosocial video game play. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 40, 578–589. doi: 10.1177/0146167213520459
Groves, C. L., Anderson, C. A., and DeLisi, M. (2014). A response to Ferguson: more red herring. PsycCRITIQUES 59, 9. doi: 10.1037/a0036266
Huesmann, L. R., Dubow, E. F., Boxer, P., Landau, S. F., Gvirsman, S. D., and Shikaki, K. (2017). Children’s exposure to violent political conflict stimulates aggression at peers by increasing emotional distress, aggressive script rehearsal, and normative beliefs favoring aggression. Dev. Psychopathol. 29, 39–50. doi: 10.1017/S0954579416001115
Huesmann, L. R., and Guerra, N. G. (1997). Children’s normative beliefs about aggression and aggressive behavior. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 72, 408–419. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.72.2.408
Kawabata, Y., Alink, L. R. A., Tseng, W. L., Van Ijzendoorn, M. H., and Crick, N. R. (2011). Maternal and paternal parenting styles associated with relational aggression in children and adolescents: a conceptual analysis and meta-analytic review. Dev. Rev. 31, 240–278. doi: 10.1016/j.dr.2011.08.001
Kepes, S., Bushman, B. J., and Anderson, C. A. (2017). Violent video game effects remain a societal concern: reply to Hilgard, Engelhardt, and Rouder (2017). Psychol. Bull. 143, 775–782. doi: 10.1037/bul0000112
Kowalski, R. M., Giumetti, G. W., Schroeder, A. N., and Lattanner, M. R. (2014). Bullying in the digital age: a critical review and meta-analysis of cyberbullying research among youth. Psychol. Bull. 140, 1073–1137. doi: 10.1037/a0035618
Krahe, B., and Busching, R. (2014). Interplay of normative beliefs and behavior in developmental patterns of physical and relational aggression in adolescence: a four-wave longitudinal study. Front. Psychol. 5:1146. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01146
Li, J. B., Nie, Y. G., Boardley, I. D., Dou, K., and Situ, Q. M. (2015). When do normative beliefs about aggression predict aggressive behavior? an application of I3 theory. Aggress. Behav. 41, 544–555. doi: 10.1002/ab.21594
Lim, S. H., and Ang, R. P. (2009). Relationship between boys’ normative beliefs about aggression and their physical, verbal, and indirect aggressive behaviors. Adolescence 44, 635–650.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Linder, J., and Werner, N. E. (2012). Relationally aggressive media exposure and children’s normative beliefs: does parental mediation matter? Fam. Relat. 61, 488–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-3729.2012.00707.x
Liu, Y., Teng, Z., Lan, H., Zhang, X., and Yao, D. (2015). Short-term effects of prosocial video games on aggression: an event-related potential study. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 9:193. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00193
Machackova, H., and Pfetsch, J. (2016). Bystanders’ responses to offline bullying and cyberbullying: the role of empathy and normative beliefs about aggression. Scand. J. Psychol. 57, 169–176. doi: 10.1111/sjop.12277
Markey, P. M. (2015). Finding the middle ground in violent video game research lessons from Ferguson (2015). Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 10, 667–670. doi: 10.1177/1745691615592236
Moos, R. H. (1990). Conceptual and empirical approaches to developing family-based assessment procedures: resolving the case of the Family Environment Scale. Fam. Process 29, 199–208; discussion 209-111. doi: 10.1111/j.1545-5300.1990.00199.x
Nathanson, A. I. (1999). Identifying and explaining the relationship between parental mediation and children’s aggression. Commun. Res. 26, 124–143.
Padilla-Walker, L. M., Coyne, S. M., and Collier, K. M. (2016). Longitudinal relations between parental media monitoring and adolescent aggression, prosocial behavior, and externalizing problems. J. Adolesc. 46, 86–97. doi: 10.1016/j.adolescence.2015.11.002
Piotrowski, J. T., and Valkenburg, P. M. (2015). Finding orchids in a field of dandelions: understanding children’s differential susceptibility to media effects. Am. Behav. Sci. 59, 1776–1789. doi: 10.1177/0002764215596552
Rasmussen, E. E. (2014). Proactive vs. retroactive mediation: effects of mediation’s timing on children’s reactions to popular cartoon violence. Hum. Commun. Res. 40, 396–413. doi: 10.1111/hcre.12030
Rosenthal, R., and Rosnow, R. (1991). Essentials of behavioral research: Methods and data analysis. New York, NY: McGraw Hill.
Rothstein, H. R., and Bushman, B. J. (2015). Methodological and reporting errors in meta-analytic reviews make other meta-analysts angry: a commentary on Ferguson (2015). Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 10, 677–679. doi: 10.1177/1745691615592235
Sandstrom, M. J. (2007). A link between mothers’ disciplinary strategies and children’s relational aggression. Brit. J. Dev. Psychol. 25, 399–407. doi: 10.1348/026151006X158753
Shao, R., and Wang, Y. (2017). Reliability and validity of normative beliefs about aggression scale among middle school students. Chin. J. Clin. Psychol. 25, 1035–1038.
Sherry, J. L. (2001). The effects of violent video games on aggression. Hum. Commun. Res. 27, 409–431. doi: 10.1093/hcr/27.3.409
Underwood, M. K., Beron, K. J., and Rosen, L. H. (2009). Continuity and change in social and physical aggression from middle childhood through early adolescence. Aggress. Behav. 35, 357–375. doi: 10.1002/ab.20313
Valkenburg, P. M. (2015). The limited informativeness of meta-analyses of media effects. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 10, 680–682. doi: 10.1177/1745691615592237
Werner, N. E., and Hill, L. G. (2010). Individual and peer group normative beliefs about relational aggression. Child Dev. 81, 826–836. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01436.x
Wiegman, O., and Schie, E. G. (1998). Video game playing and its relations with aggressive and prosocial behaviour. Brit. J. Soc. Psychol. 37, 367–378. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8309.1998.tb01177.x
Wright, M. F., and Li, Y. (2013). Normative beliefs about aggression and cyber aggression among young adults: a longitudinal investigation. Aggress. Behav. 39, 161–170. doi: 10.1002/ab.21470
Yang, G. S., Huesmann, L. R., and Bushman, B. J. (2014). Effects of playing a violent video game as male versus female avatar on subsequent aggression in male and female players. Aggress. Behav. 40, 537–541. doi: 10.1002/ab.21551
Ying, X., and Dai, C. (2008). Empathy and aggressive behavior of middle school students: the mediating effect of the anger-hostility action. Psychol. Dev. Educ. 24, 73–78.
Keywords: violence video games, aggression, family environment, normative beliefs about aggression, moderated mediation effect
Citation: Shao R and Wang Y (2019) The Relation of Violent Video Games to Adolescent Aggression: An Examination of Moderated Mediation Effect. Front. Psychol . 10:384. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00384
Received: 25 September 2017; Accepted: 07 February 2019; Published: 21 February 2019.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2019 Shao and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yunqiang Wang, [email protected] ; [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Video Games and Violent Behavior Essay (Critical Writing)
Researchers have been conducting research since 1950s to find out if exposing children to media violence leads to subsequent violence as they grow up. Out of 3500 studies, only 18 studies have shown a negative correlation (Cook, 2000). Since children learn about different things in their environment by imitation and observation, it is not easy to keep them away from the influence of the media.
When they watch violence on the media especially where dramatic heroes are involved, they accept that violence is a good way of resolving conflict. Some of the media outlets pass the message that the world is full of violence and justify why individuals should carry weapons to protect themselves and be more aggressive. Media violence insidiously causes the viewers to become insensitive to violence occurring in real life. Frequent playing of video games among children increases their chances of developing violent behavior (Cook, 2000).
Video games use graphic capabilities to show damaged body parts. They personalize the games by using digital images of recognizable personalities depicted as victims in the scenes. Research has shown that there is a high correlation between media violence and violence exhibited by young people.
Below the age of eight years, children are unable to make a distinction between fantasy and reality. To them, the violence they watch on screen is as real as what they witness in their homes and the larger communities. Adolescents are expected to develop abstract thought and social controls from their magical thinking as children. If this important developmental stage of children takes place in an environment that is violent, their minds become distorted .
Since the time video games came into existence, they have been replete with violence intended to inflict pain or cause death on other human beings. From the games that were developed some years ago to the ones that have just been developed, violence is treated as a central component in the games.
The process of determining if a certain video game contains violence is therefore an easy one. Some of the video games that were developed earlier and contained violence include Space Invaders and Wonder Boy. In space Invaders, the player shoots and kills many aliens in successive attacks while in Wonder Boy, violence is depicted when the hero kills monsters that disappear after their death. The hero is subjected to violence when the enemies shoot and throw stones at him.
When he dies, he falls while the enemies or the attackers disappear in a smoke explosion. This is one of the oldest video games that depict a lot of violence. When young people involve themselves in playing such video games, they eventually develop violence as they grow up. They are unable to differentiate between reality and fantasy and to them what happens in the video games should happen in real life (Cook, 2000).
Apart from the early video games that depicted violence, there are also modern video games that are full of violence. The video game Goldeneye 007 is one of the current video games depicting violence. In the game, the bad characters who are killed do not disappear but rather conduct some maneuvers after their death. It is a shooting video game and involves performing different maneuvers depending on where the character has been shot.
Characters shot on their feet move around clutching to their feet while those who are shot around the neck region go down on their knees holding the neck. In these games, there is splashing of blood when a character is shot. When explosives are used in the games, the characters burst into small pieces which are easily recognized. This makes the video games so real to young people who play them.
Kentucky, Paducah, Colorado and Jonesboro are some of the towns which experienced a spate of school shootings. It was discovered that the shooters were students who had developed the habit of playing video games. Dylan Klebold and Eric Harris were two students from Columbine High School who killed 13 people and wounded 23 others before they killed themselves. It was discovered that the two found great enjoyment in playing a bloody video game. Harris developed a customized form of the video with more weapons, two shooters and victims who had no ways of fighting back, features that were characteristic of real shootings .
The other way through which video games encourage violent behavior is the fact that the games contain passive gaming. To play and become the winner requires the player to take the role of the aggressor. As opposed to watching the violence on TV, in these video games the player is the one who commits the acts of violence.
This active involvement in the games has been described as a major way through which the thoughts of the players are altered hence increasing their chances of developing violent behavior. Secondly, instead of punishing violence in the video games, rewards are given to the winners. Some games like sniper and army games increase the level of the players according to the number of people he kills. Frequent watching of these games by young people distorts their thinking by convincing them that engaging in violence is a rewarding affair.
To understand the complex relationship between video games and violence, the General Aggression Model (GAM) was developed. It employs physiological responses, thoughts and feelings to determine how individuals respond to video games depicting aggression. It was identified that violent video games have an impact on the response exhibited by gamers. For instance, individuals who are not naturally violent respond with increased hostility and aggression after they watch violent video games.
The games turn into situational variables responsible for changing the perception of players towards acts of aggression. Apart from the short term effects associated with video games, the games may also contribute towards the development of long-term effects. For instance, watching violent video games may cause the development of aggressive attitudes and beliefs. In addition, players of violent video games may be eventually desensitized to aggressive behaviors .
To find out the relationship between video games and violent behavior, a survey was conducted during this study. In the survey, a group of 10 young men were allowed to play violent video games. They were compared with another group that did not play the video games. The results indicated that the group of young men that played violent video games exhibited high physical and verbal aggression towards their peers and even inanimate things when allowed to interact freely.
On the other hand, the group that did not play the video games did not exhibit such aggression. In addition, when the two groups were asked questions based on hypothetical stories, the answers were different. The answers given by the group that played the video games were in favor of violence while answers from the group that did not play the video games did not favor violence.
Such results are an indication that violent video games encourage young people to become violent. The results of this survey can be interpreted to mean that playing video games actually leads to violent behavior.
Cook, D. (2000). Testimony of the American Academy of Pediatrics on Media Violence. Web.
Kalning, K. (2011). Does Video Violence Make Teens Violent. Web.
Kirby, G., & Goodpaster, J. (2006). Thinking:an interdisciplinary approach to critical and creative thought. New York: Prentice Hall.
Pamf. (2011). The Impact of Video Games on Children. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, August 1). Video Games and Violent Behavior. https://ivypanda.com/essays/video-games-and-violent-behavior-critical-writing/
"Video Games and Violent Behavior." IvyPanda , 1 Aug. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/video-games-and-violent-behavior-critical-writing/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Video Games and Violent Behavior'. 1 August.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Video Games and Violent Behavior." August 1, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/video-games-and-violent-behavior-critical-writing/.
1. IvyPanda . "Video Games and Violent Behavior." August 1, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/video-games-and-violent-behavior-critical-writing/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Video Games and Violent Behavior." August 1, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/video-games-and-violent-behavior-critical-writing/.
- The Relationship between playing Violent Video Games and Children’s Aggressive Behavior - What do the Evidences Show?
- Do Violent Video Games Lead to Aggressive Behavior?
- Violent Video Games and How They Affect Youth Violence
- Do Violent Video Games make People Violent?
- Does Violence in Video Games Affect Youth?
- Do Violent Video Games Contribute to Youth Violence?
- Aliza Razell's "Disappear": Looking Through Gaze and Gender
- Aggression, Violence and Deviance
- Psychology of Aggression and Violence
- Research of Violence in the Media
- Understanding the Social Costs of Narcissism
- The Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy
- Personalistic and Naturalistic Approach in the History of Psychology
- The Personal Conflict Resolution
- Two Stages of Life Development
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
What Research Says About Video Games And Violence In Children
President Trump held a roundtable at the White House Thursday to discuss violent video games and how they relate to school shootings. NPR's Ari Shapiro speaks with Douglas Gentile, psychology professor at Iowa State University, about what research tells us about video games and violence in children.
ARI SHAPIRO, HOST:
President Trump has held a series of White House meetings on gun violence, and the focus of today's was video games. Lawmakers, parent advocates and people from video game companies were invited to talk with the president. The press was not allowed in. Trump has been focused on this subject for a while now. Here's what he said a couple weeks ago.
(SOUNDBITE OF ARCHIVED RECORDING)
PRESIDENT DONALD TRUMP: I'm hearing more and more people say the level of violence on video games is really shaping young people's thoughts.
SHAPIRO: The central question at the heart of this White House meeting is, does playing violent video games turn people into real-life shooters? Douglas Gentile has researched this issue. He's a psychology professor at Iowa State University. Thanks for joining us.
DOUGLAS GENTILE: My pleasure.
SHAPIRO: If you could just begin with the conclusion of your research - if every violent video game disappeared tomorrow, would there be fewer mass shootings?
GENTILE: We don't know the answer to that, but that's because aggression is actually very complicated. It's multi-causal. No one single thing causes it. And when we've had a school shooting, we usually ask the wrong question. We ask, what was the cause? And then we point around at different things such as mental health or violent video games or poverty or whatever. And none of them is it. What is it is when you put them all together. And so would it reduce the risk - yes. How much - we don't know.
SHAPIRO: So if we take a step back from mass shootings and say how much does playing violent video games increase real-life violence and aggression, do we have a clear answer to that?
GENTILE: We have a clear answer when we're talking about aggression. So aggression is any behavior - that could be a verbal behavior, a physical behavior or a relational behavior - that is intended to harm someone else. So if you give someone the cold shoulder, that is aggressive. But that's different from violence, which is only physical and extreme such that if successful, it would cause severe bodily damage or death. And the research on media violence and aggression seems pretty clear - that the more children consume media violence, whether that's in video games, TV or movies, they do become more willing to behave aggressively when provoked.
SHAPIRO: You sort of conflated video games, TV, movies there. In a video game, you're pretending to be the shooter. You're interacting with a virtual world. TV or movies is much more passive. Is there an important distinction there, or is violence violence in media no matter whether it's interactive or passive?
GENTILE: We used to think that video games would have a much larger effect than passive media like TV or movies. But the research has not seemed to bear that out. It seems to be about the same size effect, which is somewhat surprising because they are active, and you are being rewarded for it. But basically what we're coming down to is learning. We can learn from all of these different ways. And it seems we don't learn particularly differently from video games than from TV or movies.
SHAPIRO: Some people have offered a theory that videogames can be catharsis, and expressing violent impulses in a virtual world helps people not express those in the real world. Has that been disproven?
GENTILE: That has been disproven. So how do you memorize a phone number? You repeat it. Does seeing it one more time take it out of your brain? That would be the catharsis idea, right?
SHAPIRO: (Laughter) Right.
GENTILE: But, no, each new time you see it burns it in a little deeper. So in fact, there's no possible way that catharsis can happen, at least not nearly the way people like to talk about it.
SHAPIRO: Do you think the premise of this White House meeting is flawed? I mean, should video games be one focus of this debate over gun violence in America?
GENTILE: I do think it's flawed. I think the problem is that we're seeking a simple solution to a complex problem. And I noticed there are no real aggression researchers at this White House meeting. So we're not even getting the real picture. What we're getting is just a very one-sided and very limited look into only one of the risk factors for aggression.
SHAPIRO: Professor Gentile, thanks very much.
GENTILE: My pleasure.
SHAPIRO: Psychology professor Douglas Gentile of Iowa State University.
Copyright © 2018 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.
- Human Editing
- Free AI Essay Writer
- AI Outline Generator
- AI Paragraph Generator
- Paragraph Expander
- Essay Expander
- Literature Review Generator
- Research Paper Generator
- Thesis Generator
- Paraphrasing tool
- AI Rewording Tool
- AI Sentence Rewriter
- AI Rephraser
- AI Paragraph Rewriter
- Summarizing Tool
- AI Content Shortener
- Plagiarism Checker
- AI Detector
- AI Essay Checker
- Citation Generator
- Reference Finder
- Book Citation Generator
- Legal Citation Generator
- Journal Citation Generator
- Reference Citation Generator
- Scientific Citation Generator
- Source Citation Generator
- Website Citation Generator
- URL Citation Generator
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- AI Writing Guides
- AI Detection Guides
- Citation Guides
- Grammar Guides
- Paraphrasing Guides
- Plagiarism Guides
- Summary Writing Guides
- STEM Guides
- Humanities Guides
- Language Learning Guides
- Coding Guides
- Top Lists and Recommendations
- AI Detectors
- AI Writing Services
- Coding Homework Help
- Citation Generators
- Editing Websites
- Essay Writing Websites
- Language Learning Websites
- Math Solvers
- Paraphrasers
- Plagiarism Checkers
- Reference Finders
- Spell Checkers
- Summarizers
- Tutoring Websites

Most Popular
11 days ago
How Educators Can Reinvent Teaching and Learning With AI
10 days ago
Plagiarism vs Copyright
12 days ago
Do Humanities Researchers Read Everything They Cite?
13 days ago
How To Cite A Lecture in MLA
How to cite a source with no author, why teens should not be allowed to play violent video games essay sample, example.

Times when children would spend their entire free time playing with peers in the streets have mostly gone. Modern children and teenagers prefer calmer forms of entertainment, such as watching television, or in a large degree, playing video games. Although video games can contribute to a child’s development, many of them, unfortunately, are extremely violent. Moreover, games propagating murder and violence, such as Mortal Kombat, Outlast, Grand Theft Auto, and so on, are popular and are being advertised everywhere, making teenagers willing to play them; the fact that they are marked by the ESRB (Entertainment Software Rating Board) does not help much. However, considering the nature of such games, they should not be allowed for teens to play.
For the human brain, there is no big difference between a real-life situation, and an imaginary one; this is why we get upset even if we think about something unpleasant. For children and teens, who usually have a rich imagination, everything is even more intense. Virtual experiences for them may feel as real as daily life; this happens due to advanced technologies, making computer graphics look extremely close to reality, and also because players take a first-person role in the killing process (often with the view “from a character’s eyes”). If they would passively watch a violent game, it would make less harm than acting as a character who makes progress through a plot by murdering people and destroying what is in the character’s path. This situation is negative, as a child’s or teen’s brain forms new connections every day—they actually learn and memorize what is going on in their favorite games ( HuffingtonPost ).
Moreover, violent games directly reward violent behavior; many modern games do not simply make make players kill virtual reality characters of other players online, but also grant them with scores (experience) or points for successful acts of violence. These points are usually spent on making a player’s character even more efficient in killing, unlocking new cruel ways of murdering, and so on. Sometimes, players will be even praised directly, verbally; for example, in many online shooters, after conducting a killing, players hear phrases like “Nice shot!” encouraging further violence. This is much worse than watching TV, as TV programs do not offer a reward directly tied to the viewer’s behavior, and do not praise viewers for doing something anti-social ( ITHP ).
According the American Psychological Association, violent video games increase children’s aggression. Dr. Phil McGraw explains, “The number one negative effect is they tend to inappropriately resolve anxiety by externalizing it. So when kids have anxiety, which they do, instead of soothing themselves, calming themselves, talking about it, expressing it to someone, or even expressing it emotionally by crying, they tend to externalize it. They can attack something, they can kick a wall, they can be mean to a dog or a pet.” Additionally, there’s an increased frequency of violent responses from children who play these kinds of video games ( Roanna Cooper ).
Unfortunately, many modern games incorporate violence. Having youth play these video games are dangerous, as teenagers and children usually take a first person role in the killing process, and even get rewarded or praised for doing so. According to numerous studies, this leads to an increase of aggression in them.
John, Laura St. “8 Ways Violent Games Are Bad for Your Kids.” The Huffington Post. TheHuffingtonPost.com, n.d. Web. 09 Apr. 2015.
“The Effects of Violent Video Games. Do They Affect Our Behavior?” ITHP. N.p., n.d. Web. 09 Apr. 2015.
“Children and Violent Video Games.” Dr. Phil.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 09 Apr. 2015.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More from Best Persuasive Essay Examples

May 28 2023
How does outdoor exercises impact our health and well-being? Essay Sample, Example

Should Screen Time Be Limited? Essay Sample, Example

Why Video Games are Good for the Brain. Essay Sample, Example
Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
Essays About Video Games: Top 12 Examples and Prompts
Video games have revolutionized the way we have fun today. If you are writing essays about video games, check out our guide to inspire your writing.
Few can contest the fact that video games have taken over the world. From the basic, almost “primitive” games of the 1970s like Pong to the mind-bending virtual reality games of the 2020s, they have been a source of entertainment for all. Moreover, they have proven quite profitable; countries like Japan and the United States have made tens of billions of dollars solely from the video game market.
Despite their popularity, much has been debated over the potentially harmful side effects that video games may have, particularly on children. One side argues that playing certain video games can lead to people exhibiting violence in the future, while others believe that video games teach players essential life skills. Regardless, they will continue to be a part of our lives for the foreseeable future.
For engaging essays about video games, read the essay examples featured below for inspiration.
1. What electronic games can teach us by Kendall Powell
2. designers are imagining video games without guns by keith stuart, 3. playing video games all summer won’t make you feel worse by nicole wetsman, 4. violent video games bad by andrea newman.
- 5. The health effects of too much gaming by Peter Grinspoon
Writing Prompts For Essays About Video Games
1. video games: good or bad, 2. the benefits of video games, 3. what is your favorite video game, 4. do video games cause people to become violent, 5. video games in your life, 6. video games vs. traditional games, 7. is the video game rating system enough.
“In other studies, researchers found that gamers who trained on Tetris were better at mentally rotating two-dimensional shapes than those who played a control game. Students who played two hours of All You Can E.T., an educational game designed to enhance the executive function of switching between tasks, improved their focus-shifting skills compared with students who played a word search game.”
Powell explains a few possibilities of applying video games to education. As it turns out, certain video games can improve players’ skills, depending on the mechanics. Researchers are inspired by this and hope to take advantage of the competitive, motivational nature of gaming to encourage children to learn. New games are designed to help kids improve their focus, coordination, and resilience, and game designers hope they will succeed.
“Imagine a game where you’re a war reporter seeking to capture the most iconic, representative images in a battle environment: You’d still get the sense of peril that audiences expect from action adventures, but your relationship with the environment would be more profound. It would be Call of Duty from the perspective of a creative participant rather than a violent interloper.”
The graphic nature of some video games is said to make kids violent, so it is only natural that some creators try to change this. Stuart writes that it is possible to maintain the fun that shooter-type games induce without using guns. He gives examples of games where you do not kill your enemy, simply stunning or capturing them instead. He also suggests photography as an alternative to killing in a “shooting” game. Finally, he suggests basing video games around helping others, making friends, and doing more peaceful, creative tasks.
“Any role video games play in skewing well-being that did pop up in the study was too small to have a real-world impact on how people feel, the authors said. People would have to play games for 10 more hours per day than their baseline to notice changes in their well-being, the study found.”
Wetsman counters the widespread belief that video games “destroy your brain.” Research done with a sample of 39,000 players over six weeks has shown that whether one plays video games for long or short periods, their mental health is not impacted much. There are some exceptions; however, there are not enough to conclude that video games are, in fact, harmful.
“Some people believe that the connection between violent games, and real violence is also fairly intuitive. In playing the games kids are likely to become desensitized to gory images;which could make them less disturbing, and perhaps easier to deal with in real life. While video games aren’t about violence their capacity to teach can be a good thing.”
In her essay, Newman writes about the supposed promotion of violence in some video games. However, she believes this violence does not cause people to be more aggressive later. Instead, she believes these games expose children to certain atrocities so they will not be traumatized if they see them in real life. In addition, these games supposedly promote connections and friendships. Finally, Newman believes that these “harmful” can make you a better person.
5. The health effects of too much gaming by Peter Grinspoon
“Gamers need to be educated on how to protect their thumbs, wrists, and elbows, their waistlines, their emotional state, their sleep, and their eyes. Simple education around taking breaks, stretching, eating healthy snacks, and resting and icing your thumb, wrist, or elbow when it starts hurting can address injuries early, before they become significant. For the eyes, gamers can try the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, try to look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds.”
Grinspoon discusses both the benefits and the health risks of gaming. Video games allow people to interact with each other remotely and bond over specific missions or tasks, and some research shows that they have cognitive benefits. However, some gamers may develop vision problems and hand and wrist injuries. Gaming and “staring in front of a screen the whole day” is also associated with obesity. Overall, Grinspoon believes that gaming is best done in moderation.
Looking for more? Check out these essays about hobbies .
Many parents believe that their children’s “bad behavior” is because of video games. Based on your experience and others, decide: are video games good or bad for you? Make sure to read viewpoints from both sides and write an essay based on your position. Would you encourage others to play video games? Discuss these pros and cons for an interesting argumentative essay.
Like anything else, video games have both positive and negative aspects. Explain the good that video games can do for you: the skills they can equip you with, the lessons they can teach, and anything else. Also, include whether you believe their benefits outweigh the disadvantages they may pose.
For your essay, write about your favorite video game and why you chose it. What is its meaning to you, and how has it affected your life? Describe the gameplay mechanics, characters, storyline, and general impact on the gaming community or society. You can write about any game you want, even if you have not played it; just ensure the content is sufficient.
Many claim that playing violent video games can make you violent in the future. Research this phenomenon and conclude whether it is true or not. Is the evidence sufficient? There are many resources on this topic; support your argument by citing credible sources, such as news articles, statistics, and scientific research.
Video games have been a part of almost all our lives. Recall a treasured experience with video games and explain why it is significant. How old were you? Why do you remember it fondly? How did this experience make you feel? Answer these questions in your own words for an exciting essay.

There are stark differences between video and traditional games, such as board games and card games. For an engaging essay, compare and contrast them and write about which is more entertaining, in your opinion. Be creative; this should be based on your own opinions and ideas.
The video game content rating system is used to classify video games based on their appropriateness for specific ages. However, parents complain that they are not strict enough and allow the display of violent content to children. Explore the criteria behind the rating system, decide whether it needs to be changed or not, and give examples to support your argument.
If you are interested in learning more, check out our essay writing tips !
Tip: If writing an essay sounds like a lot of work, simplify it. Write a simple 5 paragraph essay instead.

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts
Follow Polygon online:
- Follow Polygon on Facebook
- Follow Polygon on Youtube
- Follow Polygon on Instagram
Site search
- Dragon’s Dogma 2
- FF7 Rebirth
- Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom
- Baldur’s Gate 3
- PlayStation
- Dungeons & Dragons
- Magic: The Gathering
- Board Games
- All Tabletop
- All Entertainment
- What to Watch
- What to Play
- Buyer’s Guides
- Really Bad Chess
- All Puzzles
Filed under:
- Entertainment
Fallout’s violence and gore are part of its charm
A content warning that shouldn’t turn you away from Fallout’s greatness
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: Fallout’s violence and gore are part of its charm
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/73270677/Fallout_S1_FG_00280518_Still273_3000.0.jpg)
Fans of the Fallout games won’t be shocked to learn that Amazon’s new TV show based on the franchise is gruesomely violent. This is a franchise known for its Bloody Mess perk, and for the VATS system , which lets players target and blow off heads and limbs. But the violence of the Fallout TV series still has the power to shock; viewers can expect multiple severed heads and lopped-off extremities in this post-apocalyptic world where mutated monsters feed on human flesh.
While the gore of Fallout may be uncomfortable to watch, it’s rarely (if ever) gratuitous. Instead, it’s done in the service of world-building. In many cases, it’s played for comedy and surprise, in the style of Sam Peckinpah or Quentin Tarantino films.
The first few minutes of Fallout may give viewers the incorrect impression that the show treats violence only with deadly seriousness. The first episode of the series starts with the nuclear destruction of Los Angeles. It’s a chilling scene, and since young children are involved, it sets a grim tone.
And yes, in later episodes, there are scenes that are difficult to watch. Puppies are incinerated at a research facility. Innocent Vault Dwellers are casually murdered. Body parts are sliced, crushed, and made into human jerky. In the show’s above-ground post-apocalyptic society, extreme violence is presented as a daily occurrence, and that society has the means to address it. Medicines that can instantly heal wounds are as commonplace as off-the-shelf replacement body parts.
Some of the show’s instances of violence are nods to the games. One big shootout plays like a VATS-powered killing spree, in which viewers watch in slo-mo as a bullet rips through multiple poor wastelanders. The show’s creators highlight that bodies are squishy and life is cheap in this world, but that its residents have adapted accordingly. Death and violence don’t seem to bother anyone all that much. Hell, becoming a brainless zombie is treated as something of an inconvenience in Fallout ’s world.
Fallout also delves into body horror. One of the show’s more disturbing creatures, as seen in trailers, is a giant mutant axolotl covered in hundreds of human fingers. Adding an extra layer of grossness, we see one of those creatures vomit up the rotting contents of its massive stomach before it dies. It is extremely unpleasant! We see horrifying examples of human-mutant experiments. Giant mutant cockroaches run rampant, and they burst open with green gooey guts when stomped on.
All of this is to say that violence in the Fallout show is fast, frequent, and unrepentant. But it isn’t dreary or humorless in the way other post-apocalyptic worlds, like The Walking Dead or The Last of Us can be. Instead, it borrows a page from the Mad Max movies. Like the Fallout games, Fallout the TV series isn’t for the queasy. But for fans of black comedy and copious amounts of fake blood, it’s a hoot.
All eight episodes of Fallout season 1 are now streaming on Prime Video.
Your guide to Fallout’s vaults and wastelands
- All the Fallout season 2 news we’ve heard so far
- The Fallout TV series is more like a great sequel to the games than just an adaptation
- Fallout’s first look has a Vault Dweller-Ghoul-Brotherhood showdown
- New Fallout trailer gives us our best look yet at Walton Goggins’ fascinating Ghoul
- Digging through the Fallout TV series’ trailer and everything else we know about the show
- Amazon’s Fallout TV series starts a new plot in the same universe as the games
- Amazon’s Fallout series gives us a look at power armor, ghouls, and a new vault
- Here’s a first look at Amazon’s Fallout TV series
- Everything Fallout has revealed about the NCR
- Every Fallout Easter egg in the Prime Video show
- Fallout fans spent years debating who dropped the bombs — then the show made a call
- Fallout’s glimpse of the Enclave is just the beginning
- The Fallout TV show gives the game’s mascot an origin story that matters
- The Fallout TV show reminds us: Vault-Tec really is that bad
- The Fallout timeline
- Bethesda and Microsoft: A tight relationship over two decades
- Bethesda sues Warner Bros, calls its Westworld game ‘blatant rip-off’ of Fallout Shelter
- A brief history of Bethesda’s many legal tangles
- Fallout: New Vegas endures because of big clunky story swings
- Fallout 76 will be free when the Fallout TV show debuts through Amazon Prime
- I spent 453 hours in Fallout 4 and all I got was this stinkin’ inner peace
- Fallout 76 still has a fan base that’s committed to the core
- How Fallout 76 handles the Brotherhood of Steel
The next level of puzzles.
Take a break from your day by playing a puzzle or two! We’ve got SpellTower, Typeshift, crosswords, and more.
Sign up for the newsletter Patch Notes
A weekly roundup of the best things from Polygon
Just one more thing!
Please check your email to find a confirmation email, and follow the steps to confirm your humanity.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.
Loading comments...
- Tickets & Showtimes
- Trending on RT

- TV & Streaming Shows
- Godzilla & Kong
- 100 Years, 100 Movies
- Best & Popular
Fallout First Reviews: A 'Violent, Fun, Emotional, Epic' Video Game Adaptation, Critics Say
Critics say prime video's new series benefits from strong storytelling, committed performances, and a deft balance of tone, making it one of the best video game adaptations ever..
TAGGED AS: First Reviews , streaming , television , TV
Fallout is the latest video game adaptation to hit the small screen. Created by Geneva Robertson-Dworet and Graham Wagner , and executive produced by Westworld ‘s Jonathan Nolan and Lisa Joy , the eight episode series, inspired by the hit game franchise from Bethesda Softworks drops on Wednesday, April 10 to Amazon Prime Video.
The post-apocalyptic series stars Ella Purnell as Lucy; Aaron Moten as Maximus; and Walton Goggins as The Ghoul. Joining them is an ensemble cast that includes Kyle MacLachlan , Sarita Choudhury , Michael Emerson , Leslie Uggams , Zach Cherry , Moises Arias and Johnny Pemberton , among others.
With nearly three decades of lore under its belt, the video game franchise has drawn a massive fanbase. Needless to say, there’s a lot of hype surrounding the new series. Does it live up to expectations? Here’s what critics are saying about Fallout :
How does it compare to the video games?

Prime Video’s TV adaptation of Fallout does something the games in the legendary franchise never have—put storytelling above all else. — Bernard Boo, Den of Geek
Fallout is the new standard for video game adaptations. This series is violent, fun, emotional, epic, and just plain awesome. — Alex Maidy, JoBlo’s Movie Network
Opting for a new narrative that simply takes place in the Fallout world, the series is a mix of adventure and puzzle-box mystery, with more than enough action scenes to satisfy the RPG faithful. It’s fun, and only occasionally overcomplicated. — Kelly Lawler, USA Today
Fallout takes the ideas of the games and crafts its own story in an already interesting world. Nails the satire, the wackiness, and about everything a fan could want. — Zach Pope, Zach Pope Reviews
Bodies fly, heads explode, and video game logic reigns triumphant. — Niv M. Sultan, Slant Magazine
How is the cast?

(Photo by Prime Video)
All of the performances are great; Purnell is a strong, loveably naive lead, while Moten delivers a fascinatingly, sort-of loathsome turn. Excusing the wonderful pooch that plays CX404, aka Four, Goggins is the runaway MVP, an agent of chilly, smooth-talking chaos somewhere between John Marston and Clarence Boddicker. — Cameron Frew, Dexerto
“I hate it up here,” Lucy mutters early on, and given the horrors to which she’s subjected, nobody could blame her. Yet her quest not only involves no shortage of carnage but also insights into her community and its origins, as well as encounters (some relatively brief) with a strong array of co-stars, including Moisés Arias, Kyle MacLachlan, Sarita Choudhury, Michael Emerson, and Leslie Uggams. — Brian Lowry, CNN
The Ghoul serves as the perfect foil for Lucy and Maximus, with Goggins deploying megatons’ worth of weary charisma in his performance as Fallout’ s resident lone wolf, black hat archetype. — Belen Edwards, Mashable
Emancipation’s Aaron Moten and And Just Like That… standout Sarita Choudhury nail the determined, world-weary drive that propels their characters forward while Justified’ s Walton Goggins gives one of his best performances yet as Cooper Howard, a mutated ghoul of a gunslinger who gives everyone a hard time with biting quips and searing bullet work. — David Opie, Digital Spy
How’s the writing and world-building?

The show’s creators have done such an impeccable job fleshing out the world of Fallout that it feels like the characters are treading stories and quests you’ve experienced yourself in one way or another. — Tanner Dedmon, ComicBook.com
Story-wise, Fallout smartly eschews trying to adapt specific storylines or side-quests from any of the games, but rather concocts a new one set in the rich and familiar landscape. — Brian Lloyd, entertainment.ie
There are plenty of Easter eggs, as you might expect from a video game adaptation, but Fallout manages to make them seem like part of the world, too. It all feels real and believable as pieces of a whole existence that these people have scraped together, which goes a long way toward helping the show’s humor land. Even the Easter eggs feel carefully designed to fit into the world and the lives of the characters, rather than drawing focus away from them or sticking out as a glaring distraction. — Austen Goslin, Polygon
Do the violence and humor work?

It’s strong, it’s goddamn hilarious, and it highlights exactly how to swing for the fences while still knowing where Homebase is. It may be a new series, but Fallout is an instant classic of the streaming age. — Kate Sánchez, But Why Tho? A Geek Community
A bright and funny apocalypse filled with dark punchlines and bursts of ultra-violence, Fallout is among the best video game adaptations ever made. — Matt Purslow, IGN Movies
Finding a tonal balance between the drama and the comedy is a razor’s edge, but Fallout makes it look effortless. As a result, spending time in this hardened world is as fun, engaging, and engrossing as the games. — William Goodman, TheWrap
It’s an equal parts funny and nightmarish show that, like its protagonist, isn’t content to live inside a projection of the past. — Kambole Campbell, Empire Magazine
Crucially, these laugh-out-loud moments of disbelief don’t detract from the harsh reality of this world, which is perhaps even more violent than you might expect, especially for newbies to this franchise. — David Opie, Digital Spy
Any final thoughts?

Fallout is a clever, twisted apocalyptic odyssey that soars as both a video game adaptation and a standalone series. — Lauren Coates, The Spool
For those who have never played the Fallout series, especially those of the time-strapped ilk who can’t just pour hundreds of hours into a game, they should give Prime Video’s Fallout a go. — Howard Waldstein, CBR
Fallout is both totally rad and an absolute blast. — Neil Armstrong, BBC.com
The show’s clearly committed to being the definitive Fallout adaptation, a love letter to fans, no question, while still opening the vault door to welcome in just about everyone else brave enough to step inside. — Jon Negroni, TV Line
There’s really nothing like Fallout on television right now, and that’s ultimately a good thing. — Therese Lacson, Collider
Thumbnail image by Amazon Studios. On an Apple device? Follow Rotten Tomatoes on Apple News .
Related News
25 Most Popular TV Shows Right Now: What to Watch on Streaming
TV Premiere Dates 2024
Fallout : What It Gets Right, and What It Gets Wrong
CinemaCon 2024: Day 3 – Disney Previews Deadpool & Wolverine , Moana 2 , Alien: Romulus , and More
Movie & TV News
Featured on rt.
Weekend Box Office Results: Civil War Earns Highest Opening Weekend for A24
April 15, 2024
30 Most Popular Movies Right Now: What to Watch In Theaters and Streaming
Top Headlines
- 25 Most Popular TV Shows Right Now: What to Watch on Streaming –
- 30 Most Popular Movies Right Now: What to Watch In Theaters and Streaming –
- Nicolas Cage Movies, Ranked by Tomatometer –
- Best Horror Movies of 2024 Ranked – New Scary Movies to Watch –
- Best TV Shows of 2024: Best New Series to Watch Now –
- Best Movies of 2024: Best New Movies to Watch Now –
Fallout Season 1 Review
“War. War never changes.” It’s the ominous line that opens every game in the 26-year-old Fallout RPG series. But while that may ring true for the tone of the eternal nuclear wasteland setting, thankfully the tide has largely turned for TV adaptations of video games. Following in the footsteps of HBO’s The Last of Us and Netflix’s Arcane , Prime Video now has itself an all-time great in Fallout, a confident and accomplished post-apocalypse show that proudly wears its heritage on its sleeve – quite literally, when it comes to its iconic blue-and-yellow Vault-Tec jumpsuits – while simultaneously being a compelling sci-fi drama all of its own.
It’s not hard to see why Amazon went to bat for Fallout. This is a weird, often hyper-violent, sometimes satirical black comedy that sits comfortably next to The Boys . While never quite as puerile or gross as some of Vought’s most extreme moments, Fallout consistently uses the darkness of its irradiated landscape to spin surreal jokes, from a talking brain-in-a-jar to an organ-harvesting robot spouting the honeyed tones of Matt Berry (of What We Do in the Shadows fame).
What's the Best Fallout Game Ever?
Pick a winner.

Produced by Westworld ’s Jonathan Nolan and Lisa Joy, Fallout is set canonically within the world and continuity of the games, but its eight-episode first-season isn't directly connected to anything you may have played. That means no prior experience is necessary in order to jump in with this entirely new cast of characters, starting with Ella Purnell’s Lucy . Raised in Vault 33, one of many fallout shelters built by the Vault-Tec company over 200 years ago , she’s never known life outside its impressively realized steel-and-concrete walls. As such, she’s an embodiment of the can-do spirit of pre-Great War America, which has been preserved for generations in this underground tin can.
In a knowing echo of Fallout 3 ’s opening, Lucy is forced to explore the surface when her father (Kyle MacLachlan) goes missing. Bright and sparky, polite and friendly, she’s totally unequipped for an adventure in the blasted California that awaits outside the vault’s sealed door. The way Purnell is able to project a delightfully naive sense of optimism amongst so much rusted devastation is the source of many early jokes – but more importantly it’s the starting point for an engaging character arc that demands she open her eyes to a world where lies and deceit are everywhere and life is cheap. While Fallout does have well-drawn villains hiding in the shadows, the real antagonist is the wasteland itself and the dog-eat-dog attitudes it forces even our heroes to adopt.
But while Lucy’s outsider (insider?) status makes her the default protagonist, it’s Aaron Moten’s Maximus who proves Fallout’s most compelling lead. Orphaned as a child, he’s found refuge in the Brotherhood of Steel; a faction of military zealots modeled on medieval knights. It’s an organization ill-suited to him – Maximus is an awkward, often cowardly man lacking the bolshy confidence of the Brotherhood’s power-armored warriors, and that clash creates both great humor and drama. It’s through a haphazard lie that he finds his footing in the story, twisting himself into something he’s not, and watching him desperately grapple with that precarious falsehood makes for Fallout’s most fascinating moments . It’s not always easy to root for Maximus – so flawed is his character – but that complexity made him the figure I found myself most invested in.
Lucy and Maximus provide an interesting duality: She’s only ever known the safety of the vault , and he’s only ever known the brutality of the wasteland. But Fallout has another sharp contrast, that of pre- and post-nuclear destruction, explored fantastically through The Ghoul. Played by Walton Goggins, this 250-year-old irradiated mutant is Fallout’s most magnetic presence – a drugged-up lone wanderer with a give-no-shit attitude. Compared to Lucy and Maximus, The Ghoul is the least complex character due to a relatively shallow arc, but he’s no doubt the most enjoyable to watch thanks to Goggins’ all-in performance.
But The Ghoul is just part of who Goggins plays here. Fallout frequently takes trips back in time to before the apocalypse to explore the life of the man The Ghoul used to be. An all-American movie star living a charmed life in retro-futuristic Hollywood, Cooper Howard initially seems the “boring” side of Goggins’ dual role, there simply to establish humanity for a character later totally stripped of it. But this story gradually builds into a truly compelling mystery, providing Goggins a much-needed sense of purpose. This plotline is also where Fallout gets to deliver its source material’s signature satire, with an anti-capitalism message that’s suitably haunting.
What video game RPG should be adapted for TV next?
Cooper’s life could have felt relatively divorced from the main events of Fallout, so different is the visual and narrative fabric of the two, but the past directly connects to the present in a much more interesting way than mere backstory. This design is one of Fallout’s greatest strengths; even what can initially feel like superfluous strands, such as the continuing story of Vault 33 after Lucy has left, turn out to be vital building blocks. Everything is propellant and accelerates towards a killer finale. And while there are a couple of episodes in the second half that slightly falter in terms of balance between storylines and momentum, this is an otherwise superbly structured show.
Every episode tells its own tale from beginning to end – such as Lucy’s run-in with the aforementioned organ harvester, or an encounter with a giant mutant salamander – and while these are clearly smaller parts of a greater whole, they still work as satisfying stories in their own right. In other words, the show is crafted like a chain of RPG quests. It’s a welcome change of pace from the mushy plotting and interchangeable episodes of so many other streaming series; that considered, it’s baffling that all eight episodes are launching simultaneously. If Fallout were a weekly show, we’d have the fun and suspense of discussing it relentlessly between debuts.
One of the greatest challenges Fallout faced was turning the world of the games into a live-action universe. Thanks to a truck-load of Amazon money and talented production designers, though, Nolan, Joy, and showrunners Geneva Robertson-Dworet and Graham Wagner have done an admirable job of it. This is a wonderfully tangible apocalypse, full of colourful oddballs and soundtracked by the 1950s’ best bops. Every space bursts with personality, much of that arriving via the astonishing attention to detail in all the items, weapons, and recognizable iconography. Nuka Cola bottles litter shelves, characters heal themselves with stimpacks, and Vault 33 is inch-for-inch damn near perfect, right down to the emergency override switches. You don’t need to know the games to appreciate the craft behind it, but if you do there’s a lot to love.
By far and away the most enjoyable thing, though, is the Brotherhood of Steel’s T-60 power armour, which is an absolute delight to watch in action. Where you’d expect something ripped from the games in its computer-generated feel as well as its faithful design, instead we get a largely physical prop that feels incredibly present and powerful. And while Fallout isn’t really an all-out action show, when the violence kicks off it’s at its best when the T-60 is involved – that’s when the Bloody Mess perk is activated and the delightfully gloopy gore effects get wheeled out.
Fallout: Complete Playlist

These characters, locations, and situations all feel authentic to Fallout. And yes, while the immaculate, game-accurate production design is partially responsible for this, most of the show’s ultimate success is down to the work of Robertson-Dworet and Wagner and their efforts to make an original story that’s distinctly Fallout. It’s in direct contrast to Paramount+’s dull Halo series , which fails to capture the urgency and spectacle of its source material, despite all the ripped-from-the-games armour designs and FPS action sequences. Fallout’s scripts nail the humor, capture the satire, and understand the subject matter of the series, all without leaning on any pre-existing story. This could have been a live-action replica of game characters and cutscenes you’ve seen before; instead, it’s a fresh and essential story that uses a new medium to enrich the Fallout universe for die-hard fans and rolls out a welcome mat for new audiences.
A bright and funny apocalypse filled with dark punchlines and bursts of ultra-violence, Fallout stands up there with The Last of Us among the best game adaptations ever made. Brilliantly constructed, its three distinct leads travel through cleverly linked storylines that build to a fantastic finale. Along the way, there’s a megaton of treats for long-term fans thanks to immaculate production design and attention to detail, but never at the expense of making this an ideal starting point for the uninitiated. It’s another special effort from Jonathan Nolan and Lisa Joy, and easily earns a big thumbs up.
More Reviews by Matt Purslow
Ign recommends.

The Definitive Voice of Entertainment News
Subscribe for full access to The Hollywood Reporter
site categories
‘fallout’ showrunners on what kind of violence they ruled out in season 1.
Geneva Robertson-Dworet and Graham Wagner talk about the lessons they learned from Jonathan Nolan making their new Prime Video sci-fi action-comedy.
By James Hibberd
James Hibberd
Writer-at-Large
- Share this article on Facebook
- Share this article on Twitter
- Share this article on Flipboard
- Share this article on Email
- Show additional share options
- Share this article on Linkedin
- Share this article on Pinit
- Share this article on Reddit
- Share this article on Tumblr
- Share this article on Whatsapp
- Share this article on Print
- Share this article on Comment

Prime Video’s adaption of the Fallout game franchise is looking like a hit.
Related Stories
Events of the week: 'the sympathizer,' 'fallout' and more, 'the night manager' revived at bbc, amazon with two-season pickup.
The secret to the show’s success seems to be successfully capturing the game franchise’s tricky balance of drama, graphic violence and off-beat humor — something plenty of Western projects have tried and failed to do the in the past (remember Will Smith’s Wild Wild West ?). “I think we’ve seen a lot of big-scoop science fiction television in the last 10 years, and something happened along the way where you can get white-knuckled when you’re spending so much money and it becomes a very serious exercise,” Wagner says. “I feel like this stayed whimsical, stayed fun, and doesn’t take itself too seriously. Hopefully that feels like a new swing in this space and becomes the weirdest version of it. ”
Robertson-Dworet adds, “I love that the games make the apocalypse fun and weird, and I hope that’s something that we properly brought to the screen.”
Below the duo, interviewed last week, take a few questions about the show — such as how Fallout evolved over the course of its development, what kind of violence was considered too extreme, and what lessons they learned from their Westworld veteran director Nolan.
So how did the show creatively evolve from what you were originally thinking to where it ended up?
GENEVA ROBERTSON-DWORET What’s crazy to me is how many things actually remained true throughout these five years. A really fundamental idea Graham and I always thought about was that it’s the mix of comedy and drama that makes Fallout so special. We stayed true to that throughout the process and cared enormously about being very faithful to the mythology.
The scene early on where you have a seemingly tough solider in his weapon-heavy power armor turn into total coward when he was attacked by a bear had me laughing out loud. I had never seen a show build up a hulking armored suit only to completely subvert it.
ROBERTSON-DWORET That’s what’s fun about Fallout , we can either lean into the genre conventions or poke fun at them.
What was the toughest writing challenge when cracking this?
ROBERTSON-DWORET Nailing that tone that we were discussing. We locked in on the idea of three central characters very early. We’re really drawn to a vault dweller ( Ella Purnell ), a member of the Brotherhood of Steel (Aaron Clifton Moten) and a Ghoul ( Walton Goggins ). We were very inspired not just by The Good, the Bad and the Ugly , but by a specific interpretation of The Good, the Bad and the Ugly that Graham has.
WAGNER It’s my interpretation, and I know it’s wrong. But it’s the idea if the same cowboy has been in the Wild West, then the longer you’re out there, that they start as [Clint Eastwood’s hero] Blondie and you end up as [Eli Wallach’s villain] Tuco. That’s sort of our view of Lucy, Max and the Ghoul. Their worldview and ethical compass gets damaged by the amount of time they’ve spent out [in the wasteland].
WAGNER This is more probably for me than Geneva — she’s most used to used to the idea of “anything’s possible.” I’ve learned to artfully cut corners in the half-hour comedy space. I had to turn off the part of my brain that says “you can’t do that” and listen to Jonah and Geneva and swing big at times. That was a big one for me to adjust to.
ROBERTSON-DWORET I spent 10 years writing big studio feature films and the reality of the feature side is, you’re not that involved. When you you create and run a TV show, you’re involved in every step of the process. I was really grateful to Jonah as a mentor to me. The main thing I learned was how much he loves to do things practically. We built an incredible amount for this show. Graham and I always talked about how the power armor will be a [CGI] effect. But no. We built power armor and had dudes walking around in power armor on set, which was amazing. I love the effect and you can totally tell the difference.
WAGNER It was a humbling moment when I asked if I could put on the power armor and the stunt team just politely told me that I’m not physically strong enough.
ROBERTSON-DWORET I didn’t even ask.
You have a lot of fun with graphic violence in the show. I’m curious, what was something you decided not to do? An example where you said, “Let’s draw a line here.”
Walton Goggins is always such a kick. What surprised you most about working with him?
WAGNER It was such a pie-in-the-sky idea. It’s a game we play in the writers room: How would you make this something that you would watch? We’re as cynical of viewers as anybody. And you’re like, “Well, if Walton Goggins is playing a Ghoul, I’d watch that.” Then we wrote it that way. It was a wild ambition, just scheduling alone. This is a guy people want to work with and for good reason. Like every one of our cast members, we’re just so lucky to have them.
What is your favorite iteration of Fallout and your favorite non – Fallout game?
WAGNER The world of the Fallout fandom is like mirroring the world of the games, they’re broken into factions. I want to keep that to myself, because there are elements of all the games in this show. We’re trying to stick to a world in which they all exist.
ROBERTSON-DWORET Gamers have thousands of hours to enjoy each Fallout game. We have eight hours to bring in viewers, introduce them to this world, and tell a story. My interpretation of the Brotherhood slightly evolves over the course of the games. We lean into one interpretation in this season, but it would be lovely to be able to explore some of the other aspects of it in later seasons.
That game also has a new story and new cast each season. Will the show do the same?
Hmm, let me guess: New Vegas for season two?
ROBERTSON-DWORET Well, that would be a big spoiler. Thank you for the idea, though.
I’m certain you don’t need my help!
Fallout is now streaming on Prime Video. Previous: Jonathan Nolan Is Ready to Unleash ‘Fallout’ and Finish ‘Westworld.”
THR Newsletters
Sign up for THR news straight to your inbox every day
More from The Hollywood Reporter
Cbs to re-air billy joel concert special after final minutes cut off, ‘the rookie’ nabs season 7 renewal at abc, cbs greenlights the first black daytime soap opera in 35 years, emmy predictions via the feinberg forecast: scott’s updated projections for 26 categories, ‘suits’ heads to broadcast syndication after streaming conquest, cnn ends gayle king-charles barkley show after limited run.

Fallout's Brutal Fourth Episode Actually Matches The Outrageous Violence Of The Original Games
This article contains spoilers for "Fallout."
Ever since the trailer for Prime Video's "Fallout" series debuted and promised a funny and weird take on the apocalypse, it was obvious that the trademark violence and grim comedy of the video games would be in evidence. Since its 1997 inception, the "Fallout" series has never shied away from depicting the harrowing reality of a post-apocalyptic future, contrasting that against the upbeat American boosterism that characterized the 1950s-era culture from which the series borrows. Now, with its TV debut, co-creators Jonathan Nolan and Lisa Joy have done an excellent job of preserving that amusing yet unsettling tone.
The "Fallout" streaming series is in canon with the video games but tells a wholly original story. What makes the show a success is that it still feels like "Fallout," despite featuring a whole cast of new characters and an original narrative. In other words, the tone of this series is just right, blending dark comedy with pure horror to create a unique take on the post-apocalypse genre that is desperately needed in 2024. "Fallout 3" and "Fallout 4" director and executive producer on the TV show, Todd Howard, spoke to Vanity Fair about maintaining the right balance between humor and horror, saying:
"We had a lot of conversations over the style of humor, the level of violence, the style of violence. Look, 'Fallout' can be very dramatic, and dark, and post-apocalyptic, but you need to weave in a little bit of a wink [...] I think they threaded that needle really well on the TV show."
But if there's one episode where the violence gains the edge, it's surely the fourth episode, which is unrelentingly brutal throughout.
Read more: The 22 Best Cyberpunk Movies Ranked
Comedy And Violence In Fallout
A perfect example of the grim comedy in "Fallout" is the subterranean vault-dwellers. The absurdity of a whole underground society going about their business, as if the world above hasn't been completely scorched and infested with wretched, bloodthirsty creatures literally eating each other, is not only darkly funny but feels like it has parallels to our current moment when major parts of the world are on fire and many of us remain far removed from it. None of this dynamic in the show feels didactic or judgmental, either, just eerily familiar and slightly unsettling in a distinctly "Fallout" way.
This contrast between the humorous and the horrific is bolstered by using that old trick of playing upbeat, wholesome tunes over gratuitously violent sequences. In the very first episode, the inhabitants of Vault 33 are overrun by surface dwellers, who embark on a murderous rampage that's depicted in all its viscera-soaked glory, accompanied by the euphonious sounds of "Some Enchanted Evening." It's certainly a way to kick off the series with a bang, although the bloody sequence still doesn't quite match up to the unrelenting savagery of episode 4.
Entitled "The Ghouls," this chapter sees former Vault 33 resident Lucy MacLean (Ella Purnell) continue her journey through the wasteland as the captive of Walton Goggin's hot Ghoul — and from the outset, things are decidedly grim.
Fallout Episode 4 Is A Bloodbath
Things kick off with a nice little scene in which the Ghoul introduces Lucy to a fellow inhabitant of the wasteland, who's on the verge of turning feral and recalling fond memories of his childhood right at the point Goggins' character delivers a close-range head-shot. Lucy is then forced to cut the meat off the poor guy's back for later consumption by her captor. Lovely stuff. As episode 4 goes on, Lucy attempts to flee the Ghoul, only to be lassoed by the former western star turned irradiated bounty hunter. In the ensuing struggle, she bites off his finger, after which the Ghoul appears to take great pleasure in slowly slicing off one of Lucy's digits. It's all quite graphic, but still not quite as gratuitous as the vault massacre from episode 1. Things get worse from there, however.
After recapturing Lucy, the Ghoul delivers her to a mysterious repurposed grocery store inhabited by a congenial floating robot with a charming English accent who should be immediately recognizable to "Fallout" players. The General Atomics/RobCo model robot is known as Mr. Handy in the games and hosts Ella on her impromptu visit to the gutted grocery store in the TV series. The robot then rummages through a draw of severed fingers and fuses a long-dead digit onto Lucy's bloodied hand. Unfortunately, Mr. Handy then reveals a more sinister side when he states that he's there to remove Lucy's organs, after which the former vault dweller manages to escape to the main room of the grocery store. There, she encounters the real horror of this place.
Fallout Episode 4 Is A Hinge Moment In The Series
Once Lucy finds her way into the main room of the grocery store, she sees various ghouls being held captive by two guards who are whatever the post-apocalyptic equivalent of stoners would be. After forcing the guards to open the various containment chambers, all hell breaks loose, with the feral ghouls tearing their captors to shreds and feasting on their flesh. All of this would be enough gore and violence by itself, but when we're not witnessing all this graphic death in real-time, we're being shown the aftermath of another vault massacre in the episode's B-story, wherein we're taken on what is basically a tour of the various mutilated bodies that adorn the fallen vault's rooms.
Episode 4 seems to be the point at which writer Kieran Fitzgerald was tasked with reminding viewers that the world of "Fallout," darkly funny though it may be, is a truly savage and unforgiving place. While Mr. Handy and his cheerful announcement about harvesting Lucy's organs is amusing, the rest of the violence is just outright graphic. It also recalls the video games themselves, which similarly balanced humor and violence but at times leaned much more into the latter. Anyone who's used the Vault-Tec Assisted Targeting System (V.A.T.S.) in the games and gleefully watched their target's head fulminate in slow motion will know what I mean.
But there's a point the violence, here. Having fought her way out of the organ harvesting factory, by the end of the episode Lucy has transformed from a terrified captive gasping for water into a fully-fledged badass. The violence was a test of the former vault-dweller's mettle, and she came out on top. That helps make the back half of the season a real doozy.
"Fallout" is now streaming on Prime Video.
Read the original article on SlashFilm

Home — Essay Samples — Entertainment — Video Games — Video Games: A Sport or Not
Video Games: a Sport Or not
- Categories: Video Games
About this sample

Words: 689 |
Published: Jan 31, 2024
Words: 689 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, definition and criteria for a sport, video games and their competitive elements, factors that distinguish video games from traditional sports, arguments against video games being considered a sport, counterarguments and rebuttals.
- Physical exertion
- Competitive nature
- Organized structure and rules
- Skill requirement
- Blomberg, R. (2019). Video Games Can Never Be Sport. Huffpost. Retrieved from https://www.huffpost.com/entry/video-games-sport-no_n_5bec5f35e4b0a043787eceeb
- Bromberg, M. (2020). What IS a Sport? And Why Does It Matter? ABC News. Retrieved from https://abcnews.go.com/Entertainment/sport-matter/story?id=67409964
- WHO (2019). WHO | Physical Activity. WHO. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity
- Norris, E. (2021). Esports’ global revenue will break $1 billion in 2020. Medium. Retrieved from https://medium.com/@blakepanzinoesports/esports-global-revenue-will-break-1-billion-in-2020-c8c2f608b368

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Entertainment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
5 pages / 2086 words
2 pages / 831 words
1 pages / 505 words
2 pages / 998 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Video Games
Video games have become an integral part of modern society, with millions of people engaging in gaming activities on a regular basis. The prevalence of video games raises important questions about their impact on individuals, [...]
Can video games make you smarter is a question that has sparked considerable interest and debate in recent years. Video games, once regarded solely as a form of entertainment, have evolved into complex interactive experiences [...]
The notion that video games cause violence has been a topic of debate and concern for many years. However, a wealth of research challenges this belief, suggesting that the relationship between video games and violent behavior is [...]
Video games have become an integral part of modern society, with millions of people across the globe engaging in gaming activities. Despite the widespread popularity of video games, they are often criticized for their negative [...]
Whether or not you are a drum player, drumming on a computer sometimes could be very fun. It is a great way to cut your time when you’re bored or you want to have some fun with your friends. Moreover, those drummers who are [...]
Mobile gaming is quite popular and it started with the first ever mobile game Tetris, this game was launched on the Hagenuk MT – 2000 phone in 1994. Although this was the first ever game it wasn’t as popular as Snake, this was [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Prime Video’s ‘Fallout’ Is an Ultra-Violent and Twistedly Fun Video Game Adaptation: TV Review
By Aramide Tinubu
Aramide Tinubu
- Netflix’s ‘Good Times’ Reboot Is Dated, Humorless and Baffling: TV Review 3 days ago
- Michael Douglas’ ‘Franklin’ Is an Exhausting Account of a Secret Mission During the American Revolution: TV Review 3 days ago
- Prime Video’s ‘Fallout’ Is an Ultra-Violent and Twistedly Fun Video Game Adaptation: TV Review 5 days ago

The big and small screens are stuffed full of post-apocalyptic adventures, yet despite that cluttered landscape, few shows and films stick out to offer something unique for viewers. However, in “ Fallout ” for Prime Video , a thrilling adaptation of the beloved video game series, creators Geneva Robertson-Dworet and Graham Wagner present an off-kilter and fascinating look at humanity in the 23rd century.
Popular on Variety
Video game adaptations have produced a mixed bag. While films, including the recent “Super Mario Bros. Movie” and “Dungeons and Dragons,” saw box office success, others like “Rampage” have not fared so well. On television, there are the successes of HBO’s “The Last of Us” and Netflix’s “The Witcher,” and then there is the less buzzy “Halo” on Paramount+. Here, Wagner and Robertson-Dworet wisely chose to avoid a straight adaptation. Instead, they constructed an original story within the game universe. Moreover, unexpected stylistic choices, including archaic technology, a soundtrack full of hits from Ella Fitzgerald and Bing Crosby and odd mid-20th century dialogue, contrast against disturbingly vicious deaths, making “Fallout” a sensory-fueled feast.
The scope of the series is massive. When the narrative stalls in the sixth episode, recounting Cooper’s life in the months and weeks before the bomb drop, the visuals led by production designer Howard Cummings and art and set direction led by Ann Bartek and Regina Graves keep the audience engaged. Robertson-Dworet and Wagner give their audience intricate looks into various aspects of this universe. From different vaults run by various overseers to the endless deserted sands of California and into the lawless city of Filly, the artisans worked tirelessly to ensure no detail was left unattended.
The first half of “Fallout” is undoubtedly the strongest, as Lucy tries to grapple with the lies she’s been told about the world while barely keeping herself alive. Still, even as the storylines linger too long in less exciting places, viewers are eager to see how the varied mysteries and secrets of the surface and the dwellers will reveal themselves. Bizarre but intensely fun, “Fallout” is like nothing you’ve ever seen; for that reason alone, you won’t be able to turn away.
The eight episodes of “Fallout” premiere on April 11 on Prime Video.
More From Our Brands
From gaming consoles to luggage sets, these are the 15 best walmart spring deals to shop right now, nascar legend tony stewart relists his 415-acre indiana ranch for $22.5 million, caitlin clark drafted no. 1 by wnba’s indiana fever, be tough on dirt but gentle on your body with the best soaps for sensitive skin, crystal kung minkoff leaving real housewives of beverly hills after 3 seasons: ‘it’s very bittersweet’ (watch), verify it's you, please log in.
Review: Why Amazon's 'Fallout' adaptation is so much flippin' fun (the Ghoul helps)

When life gives you giant radioactive cockroaches, you say, "Okey dokey!"
At least you do if you're Lucy (Ella Purnell), the eternally optimistic protagonist of Amazon Prime's "Fallout" ( streaming Wednesday , 9 EDT/6 PDT, ★★★ out of four). The crux of the adaptation of the popular post-apocalyptic video game series is the contrast of Lucy's peppy step with the backdrop of a desolate, violent and dirty world, 200 years after nuclear Armageddon. Silly against serious. Americana against anarchy. A future stuck in the past.
This retro-futuristic style comes to life in vivid Technicolor in the series, which feels like the video game come to life in the best way possible, full of exaggerated costumes, cartoonish violence and very big guns. But there's a strong story underneath all those 1950s outfits and two-headed cows. "Fallout" is very aware that its roots are fun, but not mindless. And while there is plenty of room in the zeitgeist for sober and emotional game adaptations (HBO's "The Last of Us") and also for the juvenile ("The Super Mario Bros. Movie"), "Fallout" finds a unique and lively place in the middle.
Where to find it: 'Fallout' is coming to Prime earlier than expected: Release date, time, cast, how to watch
"Fallout" starts with Lucy, a plucky young citizen of Vault 33, a clean and safe fallout bunker occupied by the decedents of those rich enough to afford a spot back in the 1950s when the U.S. and the Soviet Union nuked each other into oblivion. The world of the vault is full of '50s kitsch and can-do spirit; Lucy believes she was born to "save America." But when raiders from the lawless surface break into the bunker and kidnap Lucy's father (Kyle MacLachlan), she decides to brave the nuclear wasteland to save him.
There's also Maximus (Aaron Moten), a lowly grub in the psuedo-religious "Brotherhood of Steel" military who wants to be a "knight" and drive a mechanized power suit (think of a more buff Iron Man). And most enigmatic of all is the Ghoul (the always delightful Walton Goggins), a mutated, deformed being who's lately buried alive. The three eventually connect as Maximus and the Ghoul pursue a mysterious doctor (Michael Emerson) whom Lucy happens to run into. The Ghoul wants a bounty, Maximus wants to impress his superiors and Lucy might be able to get her dad back with the doctor's help. That's if they aren't killed by irradiated bears along the way.
The series, explained: Amazon's 'Fallout' TV show is a video game adaptation that's a 'chaotic' morality tale
Unfortunately, Maximus' character arc and storyline is by far the weakest aspect of the series. Neither the scripts nor Moten give the character depth or understandable motivation. Even the intentionally ill-defined Ghoul comes off as a more self-assured character. And worse, it's in the complex, jargon-y "Brotherhood of Steel" that the sci-fi gobbledygook starts to sound like white noise, even if you love hard sci-fi.
Still, two out of three strong leads ain't bad, and Purnell – with her anime eyes – and Goggins with his mischievous grin are more than enough to carry "Fallout" across the wasteland. Series creators Geneva Robertson-Dworet ("Captain Marvel") and Graham Wagner ("Silicon Valley") are loyal to the game's spirit, yet wisely avoid common video game adaptation clichés, like an overreliance on "first-person" perspective and a too-literal recreation of the original story. Opting for an new narrative that simply takes place in the "Fallout" world, the series is a mix of adventure and puzzle-box mystery, with more than enough action scenes to satisfy the RPG faithful. It's fun, and only occasionally overcomplicated.
And if the violence is quite frequent and exquisitely graphic? Hey, it all gels in a fictional world where Goggins doesn't have a nose.
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.
How One Family Lost $900,000 in a Timeshare Scam
A mexican drug cartel is targeting seniors and their timeshares..
This transcript was created using speech recognition software. While it has been reviewed by human transcribers, it may contain errors. Please review the episode audio before quoting from this transcript and email [email protected] with any questions.
Hello, James.
Hey. How’s it going?
Yeah. I’m not having much luck. So the problem is funding. And all of my money is in Mexico, all of it.
From “The New York Times,” I’m Katrin Bennhold. This is “The Daily.” A massive scam targeting elderly Americans who own timeshare properties has resulted in hundreds of millions of dollars sent to Mexico.
Once you move forward and make your payment, if anything were to happen, he will directly pay you the full amount of what you’re entitled to, including the gains. He will pay you the full amount.
You’ve got all my money. It’s been sent. I sold a freaking house.
Listen to this. I sold a house that I grew up in so that I could come up with funds to send to Mexico.
I don’t even have anything from the sale, nothing.
My colleague Maria Abi-Habib on one victim who lost everything and the people on the other side of the phone.
That’s it. That’s it. There’s nothing —
You know what? That’s what has been said every freaking time. Every time, just pay this. That releases the funds.
But that’s why we won’t allow it to happen again. This is the last time, James.
It’s Friday, April 12.
Maria, you’ve been looking into this scam that’s targeting Americans. Where did your investigation start?
So several weeks ago, I received a phone call from a lawyer based in St. Petersburg, Florida, who had been contacted by a family who was very concerned that the father, this man named James, was in the middle of being scammed. He’d sent hundreds of thousands dollars to Mexico. And he was considering sending another $157,000 when his daughter decided to call up this law firm and try to get her father to stop, stop sending money to Mexico.
So I called him a few weeks ago as I was trying to understand what was going on.
Hi, James. How are you?
Good. Thank you.
He’s asked that his last name be withheld for privacy concerns because he’s quite embarrassed about the story that I’m about to tell you.
You’re retired now, but what were you doing for work? And if your wife was working, what was her job?
I was with the Highway Patrol.
James is a retired state trooper from California. And his wife Nikki is a former school nurse.
She was born in ‘51. So 71-ish.
Two. She’s just reminded me, 72.
And they’re both in their early 70s. And they own this timeshare that is in Lake Tahoe, California. And they bought it in the 1990s for about $8,000.
And for someone who did not grow up vacationing in a timeshare, remind me how exactly timeshares work.
Timeshares are essentially vacation properties. And they tend to be beach resorts. And multiple people can buy into this property. The ownership is a shared ownership. And this gives you the right to use the timeshare for one to two weeks out of every year.
And so James and Nikki used their timeshare every other year with their daughters. But as they hit retirement age and their daughters are growing up and starting their own families, they’re just not really using it that much anymore. And timeshares require the owners to pay off yearly maintenance fees. And so they’re starting to think about maybe letting go of their timeshare and selling it.
Then one day, in late 2022, James gets a phone call from a company that is purporting to be based out of Atlanta, Georgia called Worry Free Vacations.
Worry Free Vacations?
That sounds enticing.
Yeah. And they start off with a simple question, which is, do you want to buy a timeshare? And James says, I already have a timeshare. And then they say, great. Well, what about selling the timeshare? Do you want to sell? There’s this Mexican businessman, and he’s interested in your timeshare. And he’s willing to buy it for about $20,000.
So we figured, well, what the heck? If we can make a few bucks on it, we’ll go for it.
And James jumps at the opportunity.
And did he do anything to try and verify that this was real?
Yeah. So remember, James is former law enforcement. And he feels very confident in his abilities to sniff out untrustworthy people. So he goes online, and he googles this Mexican businessman and sees that, yeah, he is a real person.
He’s a very well-respected individual in Mexico, very well off. And —
And this makes James feel at ease, that he’s selling to a legitimate person, that Worry Free Vacations are who they claim to be and that he’s going to double his money overnight, essentially.
And what happens next?
Well, a couple of weeks after he makes the agreement with the buyer, he’s told that he needs to send a couple thousand dollars to facilitate the purchase.
What does that mean, facilitate?
[MUSIC PLAYING]
I can’t remember specifically whether it was supposed to be cross-border registration —
So he’s being told that there are these fees that are paid directly to the Mexican government.
Or SPID or some other fee that was Mexican government required or not.
A lot of these fees are the same types of fees that you would pay in the United States for a real estate transaction. So he begins wiring money to an account in Mexico.
After that —
— a few days later, we get a notification. Well, everything went well, except that we have to pay an additional fee.
Every time that he sends one fee, he’s being told that he’s got to send another fee right afterwards.
Does he get suspicious at any point?
His wife is suspicious. After the first couple of payments, she starts saying, this does not feel right.
But James is the former law enforcement officer, right? And he’s the one that basically handles the family finances. And he’s confident that all of this is going to work out because he’s being told that the buyer of the timeshare will reimburse James for all of these fees once the sale goes through.
Michael from the Worry Free Vacations was constantly reassuring me the money’s in that account. Check with the commercial escrow account. It’s there. It’s just these fees have to be paid, and you’re being reimbursed for all of this.
They’re sending James documents that show all of the reimbursements that he’s owed and how much money he’s going to get. And this just makes him feel like all of this is kosher.
We have this commercial escrow company that was involved out of New York. So there was an air of legitimacy that I was comfortable with.
Maybe OK, these guys just need one more fee and everything is going to finally be cleared.
But about a year in, James starts to get suspicious. He begins asking questions because he wants his money.
And every time I asked, hey, is there a way I can get a partial release of these funds, there was always no, these funds have to be paid from your account before they’re released.
But Worry Free Vacations, they pivot. And they tell him that, listen, there are all these complications. It’s going to be really hard to get your money out from this transaction.
I could pay about $30,000 and change to reinvest the $313,000 into an environmentally-conscious development in Loreto, Mexico.
Instead, we’ve got this other investment opportunity in Mexico.
And I’m sure you know where that is, over on the East Coast of Baja.
And that is going to make you a huge return, even more money than you had thought that you were going to make, much more than the $20,000.
I’m supposed to have 54 million pesos in a Mexican bank account.
So this is now no longer just about his timeshare. They are now partners in a real estate investment.
Right. And there’s this whole new round of fees and fines associated with that.
So how many payments would you say?
Quite a few. Couple dozen at least, maybe more.
When was your last payment?
It would have been 17 January.
Uh-huh. And what was that for?
Good question.
And all along, he believed it was necessary to pay these costs just to get the money that he’s owed.
The amount of money that I’ve sent to Mexico is just freaking exorbitant. And I mean, it is approaching $900,000 or more.
And at this point, he’s sent about $900,000 to Mexico over about a year and a half.
Nearly $1 million.
That was almost all the money that he and his wife had saved for their retirement.
It also included money from the sale of James’s childhood home and money that he had borrowed from his daughter and son-in-law, about $150,000 from them.
It’s awful. So they were completely cleaned out by these guys.
Yeah. And this is when his daughter asks a law firm to look into this, which is the point in the story when I meet James. And when we start talking, it was clear to me that he just did not know what to think, even after losing this much money.
So this started in 2022. When did it end?
We’re still in it.
And he’s still talking to the scammers.
And as a matter of fact, presently, there was a request for $157,000 and change to clear up this whole thing. It would clear the entire issue out. Now —
And James is even considering putting a second mortgage on his house to send that money that he’d been promised would finally clear all this up — one final payment of $157,000.
It really sounds like he’s still wanted to believe that this was somehow legit.
Yeah. It was pretty clear to me that he was being scammed. But I didn’t definitively know what was going on, so I asked him if he could start recording his phone calls with the scammers.
Would you be so kind as to do me a favor?
Would you be willing to give them a call and record them?
[LAUGHS]: I’ll let you in on a little secret. I’ve been recording them.
And it turns out he already had been.
Worry Free Vacations.
So he shared the recordings of these calls that he’d had with these scammers over the last year or so. And it was just remarkable. It gave me huge insight into how the scam worked and the way that it sounded over the phone.
Is this is Michael in? I think he’s trying to call me. I couldn’t get through pick up.
Yes, I believe he did try to call you, sir. Give me a second. I think he’s only going to be in for a couple of minutes. One second.
There are two main takeaways for me listening to these calls.
Good afternoon. Michael McCarthy.
Michael, I missed your call. I was trying to pick up.
Yeah, don’t worry. Yeah, I figured something was wrong with your phone. Everything OK?
The first is that these scammers had really gotten to know James so well, and they really made James believe that Worry Free was a company that was working for him.
That’s why we need to hurry up and get this money over to you. Because hey, I’m losing my mind too. I’m not even here to convince you, James. I’m not — I’m your broker, and —
One of the things they continuously say is, trust me.
Look, I’m doing everything I can in my power and will on my end. So James, just look — like I told you from the get-go, I’m going to resolve this. And we are doing it. I just need you to focus on the goal.
They would refocus the conversation on what James needed to do to get his money back.
Look, if you make your payment as a security deposit, right away they will release the funds to you. With these —
And the other thing —
I’ve been having so much trouble trying to reach you, and I have not been successful.
— is that the scammers had created this elaborate cast of characters.
Why don’t you answer my calls?
And some of them were really aggressive. James shared a recording of this one man who claimed to be an agent for the Mexican government. And he basically started yelling at James.
I don’t care if your wife is at the hospital. To be honest with you, I don’t give a damn! But you know where I do give a damn? It’s your money, and my name is written all over it! Do you understand?
And he even threatened James. If James didn’t pay off these fines, then he would lose all the money that he’d sent to Mexico already.
You could get the best lawyer you want. You could get whoever you want. And this is not a threat. This is facts. But anyways, who am I to convince you, right?
Well, thank you for the information. And — are you still there? Hello?
Wow. So these scammers were basically doing a good cop, bad cop routine to stop James from walking away and to squeeze every last penny out of him.
If you provide me your email, contact information, I will certainly be happy to forward all of the wire transfer information from my bank account to you so that you can see where those funds went.
Yeah, that would be great. I have your email.
James asks me, a reporter who’s based in Mexico, who speaks the language, if I could help him figure out where his money had gone to.
Thank you very much. I really appreciate your assistance.
I’m just doing my job. Thanks again, and we’ll talk soon.
And the only way that I could figure that out was to understand who was on the other side of the phone.
We’ll be right back.
So Maria, who was on the other side of that phone line?
So by the time that I’d met James, I’d already gotten a tip from US law enforcement agencies that they were seeing a new trend. Mexican drug cartels were getting involved in the timeshare scam industry.
Drug cartels?
Yeah. And not just any drug cartel. This is one of the most notorious, violent, bloody drug cartels that exists in Mexico and Latin America, the Jalisco New Generation cartel. And when I looked at James’s bank records, guess what? All the money that he was sending was going to various bank accounts that were all located in Jalisco state in Mexico.
Wow. So why would the drug cartels get into the timeshare scamming business?
It is a huge business. The FBI told me that it’s about $300 million in profits over the last five years.
But the thing is is that the potential for it to actually be multitudes more is huge. Because the FBI estimates that most of the scams are actually not even reported. In fact, only about 20 percent are. So that means the total timeshare scam business could actually be much larger than the $300 million that they have knowledge of over the last five years.
But wait. I thought the drug business was a pretty lucrative business in itself. So why get into the scamming of elderly people for their properties in Lake Tahoe?
Well, you have to remember that these drug cartels, they’re not just doing one thing. They’re doing multiple things. They’re essentially conglomerates. Because it’s really expensive to run a cartel. You need to pay off officials, both Mexican and American. You need to maintain basically an army in order to secure your routes up to the United States, ports of entry into Mexico from Colombia. And any big business, you need to diversify your income to make sure that you keep the money flowing. Because you never know when one business is going to be shut down by authorities or taken over by your rivals.
We’ve reported that they’re now in the avocado business and the construction business. And timeshare fraud is basically no different than any of those. So we’re seeing that the cartels have their fingers in many pies, the legitimate and the illegitimate economy here in Mexico.
It’s kind of fascinating to think of these drug cartels as like sprawling diversified business empires. But when did the cartels first get into the scamming business?
So Jalisco New Generation started about 15 years ago.
And when they started to consolidate their empire in Jalisco state, they found that there were all these scam timeshare call centers all over the state that were being run by various players, and that this was a huge, huge moneymaker. Because essentially, all you have to do is call up retired senior citizens in the US and Canada. It doesn’t take that much money to run that kind of a scheme. There’s no product you’re making.
So essentially, they conducted a hostile takeover of these call centers. They went in. They kicked down doors and dragged out the people who were managing these call centers by their hair and threatened to kill them unless they gave up the call centers or started handing over a cut of what they made. And slowly, slowly Jalisco New Generation cartel took over the entire timeshare fraud industry.
Interesting. Were you able to find any of these call centers?
So these call centers are pretty hard to find. They look like any other storefront. But I was able to visit two that were located in an upscale neighborhood in Guadalajara, which is the capital of Jalisco state. And it was just really perturbing because it was just so normal. Two villas about a mile away from each other outside. Outside of one villa, parents were walking by, holding their children’s hands as they did drop off at school.
It was right next to a park where people taking their morning exercise or their dogs for a walk. There was no real sign that the cartel was doing business there. But a few months before, Mexican law enforcement had found the bodies of eight young people who had used to work at one of these call centers and said that the Jalisco cartel had killed them.
Wow. What happened?
So I wasn’t able to talk directly to any of the victims’ families. They’re just too scared. But in general, this is usually how it starts.
The cartel seeks out English speakers to work for their call centers. Sometimes they don’t even tell them what exactly they are doing. They would tell the recruits that the job was adjacent to the hotel industry.
You have to remember, Jalisco is a huge, huge tourism magnet for Americans and Canadians and others. And the cartel would get their call lists from bribing hotel employees to give them the names of people who stayed at these hotels and also at the timeshare resorts. And the people who would work at the call centers are provided the names and a manual of what you need to do when you call, like a loose script of how to try to suck as much money as you can out of these people up North in Canada and the States.
So we don’t know for sure what exactly happened with the eight young Mexicans who were killed last year. But through an intermediary, one sibling told us that when their family member knew what their job actually was, they became extremely uncomfortable and tried to leave the call center and find another job maybe.
But the Jalisco New Generation cartel is known for being extremely brutal. They chop off heads, and they’ll put them on the gates of a playground, for instance. So that everybody in the neighborhood knows what went down. And in this case, it’s possible that they wanted to send a warning that there’s no defection from their timeshare call centers.
So basically making a very scary example of these guys, in case anyone else is thinking about quitting one of the call centers.
Exactly. And one man, who runs an organization who advocates for missing people and actually organizes search parties to comb the forests of Jalisco state looking for the missing, says that he knows of about 30 people who have disappeared from the call centers in Jalisco state since 2017. So while Americans and Canadians might be losing much of their life savings, in Mexico, this is actually deadly.
Are the authorities doing anything about this?
Not really, other than the fact that these two call centers were shut down. The authorities haven’t arrested others. They’re not putting pressure on Mexican banks, for instance, to look into these payments coming from senior citizens in the US or Canada. And you have to remember that people are really afraid. But you also have to remember that in Mexico things are not that clear. There is a lot of corruption and government collusion with organized crime and cartels.
And the tourism industry, it is huge in Mexico and particularly in Jalisco state. This is a multi-billion dollar industry. They don’t want Americans or Canadians or Europeans who are coming to Jalisco for its beautiful beaches and its mountains to hear about these stories regarding the cartels being involved in the tourism industry and think, I’m not going to send my family there for that beach vacation. It’s just simply too dangerous.
So everybody has an incentive to have the scam continue, whether because they’re too afraid and don’t want to speak out or because they’re in on it.
So in a way, local authorities have an interest in sweeping it under the carpet in order to just maintain this idea of a tourist destination.
Exactly. I mean, the spokeswoman for the prosecutor’s office was very responsive to me until I told her what I wanted to ask her questions about. And then she just simply never answered any of my texts or phone calls.
So Maria, based on everything you know, all the information you have, would you say that you’re confident that the cartels were the ones who scammed James?
Yes, 100 percent. Everything I’ve seen points in that direction.
What did James say when you told him this?
So it took him quite a while to really allow himself to believe it. On the advice of his lawyers, he stopped picking up the phone calls. And about a week ago, they stopped after the scammers kept trying to call him.
But you said he was in it for over a year. Why do you think it took him so long?
Can you tell me, after all of that had been presented to you, why do you think you weren’t willing to be entirely convinced?
Well, I actually asked him that question.
That’s a very good question. Why wasn’t I able to pick up on that right away? And I think in the back of my mind, I’m finding out that I’m a little more stubborn than I thought I was.
And for him, it was pretty complicated.
And I think that I didn’t want to believe that I had fallen for this. I didn’t feel I was that foolish and stupid when it came to this. You know? I guess I didn’t want to believe that I could be fooled.
To come to terms with the fact that he had lost so much money was to come to terms with the fact that he wasn’t the person that he thought that he was, that he wasn’t this kind of clever former law enforcement officer who was used to fighting the bad guys and winning.
I’m disappointed in myself. There’s a huge level of anger towards the perpetrators. And all of those things wrapped into one. And part of that, I think, contributes to not wanting to actually believe that I was wrong.
Hmm. Yeah, I hear you. I’m sorry. I can hear the pain in your voice.
[LAUGHS]: Yeah.
Some of it’s based on shame, right? That he lost all this money, everything that he’s worked for, and the fact that this was all supposed to be money that his children and his grandchildren were going to inherit. And now it’s gone.
And have you told your daughter that you think you’ve come to terms with the fact that this might have been a scam?
Oh, she’s been involved. Yeah. They know.
My daughter does.
I’m sorry. This is a tough time.
So I’ve got to make some sort of arrangement to compensate them for this on top of our regular debt. So yeah. It’s been a swell experience, all of it brought on by my — evidently, my stubbornness to believe that I couldn’t possibly be a victim.
How’s your wife doing throughout this whole process, with this new knowledge?
She’s not real happy, obviously, at all. I hear a lot of “I told you so.” And at this point, I’ve got no defense. She’s absolutely right. There’s no question about it.
Do you worry this is going to affect your marriage?
Yes, there has been an effect.
And do you think that at this point there’s any way for James and his family to get some kind of justice or at least find some kind of closure?
Ay. Justice? Unlikely.
At this point, I’m not necessarily expecting much in the way of restitution.
And as for closure, it’s a little bit too soon to tell. In a way, James has gone through several stages of acceptance for what happened. There’s fear. There’s shame. There’s resignation. And now he’s talking to me partly because he feels like it’s a public service, that he needs to be vocal so that other people don’t go through what he’s gone through and fall for the scam. And I think it also helps him feel a little bit empowered in a situation for over the last year and a half he was at the mercy of these people who were calling him multiple times a week.
I want to try to get as much information to as many of these official organizations as possible. I have a streak of anger through me now that I’ve developed to the point where I’m not going to let this go.
Well, Maria, thank you.
Thank you for having me.
Here’s what else you need to know today. OJ Simpson, the football star who was accused and later acquitted of murdering his former wife and her friend, died of cancer at his home in Las Vegas, his family said Thursday. He was 76.
Today’s episode was produced by Astha Chaturvedi and Will Reid, with help from Clare Toeniskoetter and Lindsay Garrison. It was edited by Brendan Klinkenberg and Michael Benoist, contains original music by Marion Lozano, Rowan Niemisto, Dan Powell, Pat McCusker, and Will Reid, and was engineered by Chris Wood. Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly.
[THEME MUSIC]
That’s it for “The Daily.” I’m Katrin Bennhold. See you on Monday.

- April 15, 2024 • 24:07 Iran’s Unprecedented Attack on Israel
- April 14, 2024 • 46:17 The Sunday Read: ‘What I Saw Working at The National Enquirer During Donald Trump’s Rise’
- April 12, 2024 • 34:23 How One Family Lost $900,000 in a Timeshare Scam
- April 11, 2024 • 28:39 The Staggering Success of Trump’s Trial Delay Tactics
- April 10, 2024 • 22:49 Trump’s Abortion Dilemma
- April 9, 2024 • 30:48 How Tesla Planted the Seeds for Its Own Potential Downfall
- April 8, 2024 • 30:28 The Eclipse Chaser
- April 7, 2024 The Sunday Read: ‘What Deathbed Visions Teach Us About Living’
- April 5, 2024 • 29:11 An Engineering Experiment to Cool the Earth
- April 4, 2024 • 32:37 Israel’s Deadly Airstrike on the World Central Kitchen
- April 3, 2024 • 27:42 The Accidental Tax Cutter in Chief
- April 2, 2024 • 29:32 Kids Are Missing School at an Alarming Rate
Hosted by Katrin Bennhold
Produced by Asthaa Chaturvedi and Will Reid
With Clare Toeniskoetter and Lynsea Garrison
Edited by Brendan Klinkenberg and Michael Benoist
Original music by Marion Lozano , Rowan Niemisto , Dan Powell , Pat McCusker and Will Reid
Engineered by Chris Wood
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music
Warning: this episode contains descriptions of violence.
A massive scam targeting older Americans who own timeshare properties has resulted in hundreds of millions of dollars sent to Mexico.
Maria Abi-Habib, an investigative correspondent for The Times, tells the story of a victim who lost everything, and of the criminal group making the scam calls — Jalisco New Generation, one of Mexico’s most violent cartels.
On today’s episode

Maria Abi-Habib , an investigative correspondent for The New York Times based in Mexico City.

Background reading
How a brutal Mexican drug cartel came to target seniors and their timeshares .
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Katrin Bennhold is the Berlin bureau chief. A former Nieman fellow at Harvard University, she previously reported from London and Paris, covering a range of topics from the rise of populism to gender. More about Katrin Bennhold
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Some blame violent video games for school shootings, increases in bullying, and violence towards women, arguing that the games desensitize players to violence, reward players for simulating violence, and teach children that violence is an acceptable way to resolve conflicts, while others argue that a majority of the research on the topic is deeply flawed and that no causal relationship has ...
The meta-analysis does tie violent video games to a small increase in physical aggression among adolescents and preteens. Yet debate is by no means over. Whereas the analysis was undertaken to ...
Their research article "Violent Video Game Effects on Aggression, Empathy, and Prosocial Behavior in Eastern and Western Countries: A Meta-Analytic Review" demonstrates that the period spent on playing video games is a leading factor in aggressive behavior (Sandra et al. 2017). They use the meta-analytic procedures as their primary approach.
Violent video games have an impact on the player's aggression (Anderson et al., 2010; Greitemeyer & Mügge, 2014), but—as the present study shows—they also increase aggression in the player's social network. In particular, participants who do not play violent video games reported to be more aggressive the more their friends play violent ...
The violence and aggression that stains the youth of today, as a result of these video games, is unquestionably a cancer that ought to be uprooted or at least contained by parents, school leaders, governments […] We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 809 writers online.
Violent video games are those that depict intentional attempts by individuals (nonhuman cartoon characters, real persons, or anything in between) to inflict harm on others (Anderson & Bushman, 2001). The effects of violent video games have been a societal concern since the birth of the industry and have attracted much attention from researchers.
It is a widespread concern that violent video games promote aggression, reduce pro-social behaviour, increase impulsivity and interfere with cognition as well as mood in its players. Previous ...
The case that violent video game play increases aggressive behavior has been made most forcefully by Anderson et al. (6; see also refs.7 and 8).Specifically, these authors undertook a comprehensive metaanalysis of the literature on the impact of violent video game play on six categories of aggressive response: cognition, affect, arousal, empathy/sensitization to violence, overt aggressive ...
The Dartmouth analysis drew on 24 studies involving more than 17,000 participants and found that "playing violent video games is associated with increases in physical aggression over time in children and teens," according to a Dartmouth press release describing the study, which was published Oct. 1, 2018, in the Proceedings of the National ...
In the first step, a simple moderated model (Model 1) between exposure to violent video games and aggression was established. The result showed that exposure to violent video games had a significant effect on aggression (c 1 = 0.24, t = 6.13, p < 0.001), while the effect of family environment × exposure to violent video games on aggression was not significant (c 3 = 0.05, t = −1.31, p = 0. ...
Negative Effects Article 1: "Violent Video Game Effects on Aggression, Empathy, and Prosocial Behavior in Eastern and Western Countries: A Meta-Analytic Review" This is a scholarly article published by the American Psychological Association and written by Craig Anderson and seven other reputable researchers in the psychology field.
An Enduring Debate on 'Do Video Games Cause Violence'. 2 pages / 1073 words. Introduction This essay is written in the hopes to challenge the reader's idea of video games and how they affect us as a society and mentally. Video games have exploded in popularity over the years and are only becoming a more common hobby.
Violence in Video Games Essay. There is a common opinion that violent video games and aggressive behavior are connected. However, some researchers and public authorities challenge this opinion and argue that there is no relationship between violence and cruel video games (Przybylski and Netta 16). The dispute exists as there is evidence that ...
Video Games and Violent Behavior Essay (Critical Writing) Researchers have been conducting research since 1950s to find out if exposing children to media violence leads to subsequent violence as they grow up. Out of 3500 studies, only 18 studies have shown a negative correlation (Cook, 2000). Since children learn about different things in their ...
Introduction. The relationship between video games and violence has been a contentious issue for several decades, with some arguing that video games contribute to aggressive behavior and real-world violence. However, a growing body of research challenges this perspective, suggesting that video games do not cause violence.
The global video game industry was worth contributing $159.3 billion in 2020, a 9.3% increase of 9.3% from 2019. Violent video games have been blamed for school shootings, increases in bullying, and violence towards women. Critics argue that these games desensitize players to violence, reward players for simulating violence, and teach children ...
ARI SHAPIRO, HOST: President Trump has held a series of White House meetings on gun violence, and the focus of today's was video games. Lawmakers, parent advocates and people from video game ...
Video Games Don't Cause Violence: Dispelling The Myth. The notion that video games cause violence has been a topic of debate and concern for many years. However, a wealth of research challenges this belief, suggesting that the relationship between video games and violent behavior is far more complex than commonly portrayed. This essay explores ...
Long Essay on Violence in Video Games is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10. The internet is filled with articles about the side effects of playing online, multiplayer games. Online gaming and video games started to have fun online and have now grown to become a community. There are many types of research about the pros and cons of ...
According the American Psychological Association, violent video games increase children's aggression. Dr. Phil McGraw explains, "The number one negative effect is they tend to inappropriately resolve anxiety by externalizing it. So when kids have anxiety, which they do, instead of soothing themselves, calming themselves, talking about it ...
5. . The health effects of too much gaming by Peter Grinspoon. "Gamers need to be educated on how to protect their thumbs, wrists, and elbows, their waistlines, their emotional state, their sleep, and their eyes.
Amazon Prime Video's new Fallout TV show is bloody and gory, but its extreme graphic violence is intentional — and funny. Just like the games.
Prime Video's TV adaptation of Fallout does something the games in the legendary franchise never have—put storytelling above all else. — Bernard Boo, Den of Geek Fallout is the new standard for video game adaptations. This series is violent, fun, emotional, epic, and just plain awesome. — Alex Maidy, JoBlo's Movie Network Opting for a new narrative that simply takes place in the ...
A bright and funny apocalypse filled with dark punchlines and bursts of ultra-violence, Fallout is among the best video game adaptations ever made.
This is an adaptation of a violent video game. Violence is certainly part of the game and the mythology of what this world is. But we want it to exist in another world. It's very intentionally ...
The violence was a test of the former vault-dweller's mettle, and she came out on top. That helps make the back half of the season a real doozy. "Fallout" is now streaming on Prime Video.
Get a tailor-made essay on 'Why Violent Video Games Shouldn't Be Banned'? Get original essay. Definition and Criteria for a Sport. Before determining whether video games are a sport, it's essential to define what qualifies as a sport. A sport is an activity involving physical exertion, skill, and competition with an organized structure and rules.
A standout in the world of video game adaptation, Prime Video's "Fallout" is a violent but intriguing look into the beloved post-apocalyptic universe.
The crux of the adaptation of the popular post-apocalyptic video game series is the contrast of Lucy's peppy step with the backdrop of a desolate, violent and dirty world, 200 years after nuclear ...
Warning: this episode contains descriptions of violence. A massive scam targeting older Americans who own timeshare properties has resulted in hundreds of millions of dollars sent to Mexico.