Receptors have two important features:


Specificity
- Temperature.
- This means that a receptor that responds to light will not respond to temperature or pressure.

Generator potentials
- Receptors connect with sensory neurones. When stimulated, the receptor creates a generator potential in the sensory neurone.
- An example where stimulation of the receptor creates a generator potential is in the Pacinian corpuscle.
The Pacinian Corpuscle
The Pacinian corpuscle is a mechanoreceptor found in the skin. Mechanoreceptors respond to changes in pressure to establish a generator potential. The receptor reacts in the following way:
Resting potential
- The Pacinian corpuscle consists of concentric rings of connective tissue that surround a sensory neurone.
- When the corpuscle is not being stimulated it is at resting state.
- At resting state, the charge inside the neurone is more negative than outside (-70mV). This is because there are more Na + ions outside the neurone than inside.
- A difference in charge across the cell membrane is called the potential difference.

Stimulation of the receptor
- When pressure is applied to the Pacinian corpuscle, the rings of connective tissue apply pressure on the sensory neurone.
- The sensory neurone has stretch mediated Na + channels, these channels normally restrict the movement of Na + ions.
- Applied pressure causes the stretch-mediated Na + channels to open.
Generator potential
- Na + ions flood into the sensory neurone through the open Na + channels.
- There are now more Na + ions inside the neurone than outside.
- The charge inside the neurone becomes more positive than outside, so the potential difference has changed.
- The generator potential has been established.

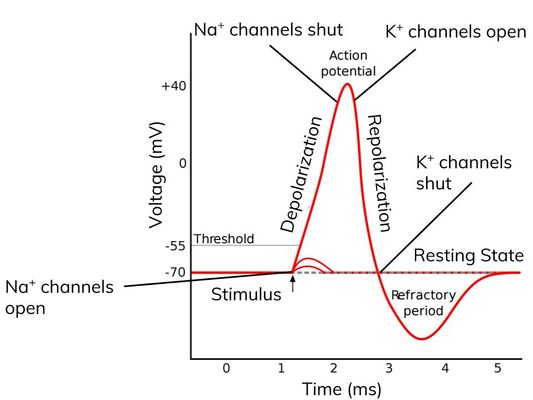
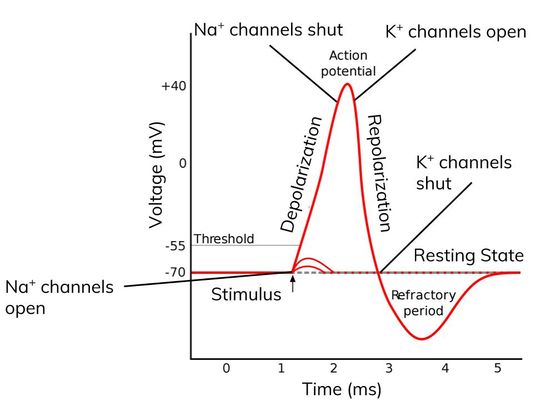
Action potential
- If the generator potential reaches the threshold level (about -50mV) then an action potential is produced in the sensory neurone.
1 Biological Molecules
1.1 Monomers & Polymers
1.1.1 Monomers & Polymers
1.1.2 Condensation & Hydrolysis Reactions
1.2 Carbohydrates
1.2.1 Structure of Carbohydrates
1.2.2 Types of Polysaccharides
1.2.3 End of Topic Test - Monomers, Polymers and Carbs
1.2.4 Exam-Style Question - Carbohydrates
1.2.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Carbohydrates
1.3.1 Triglycerides & Phospholipids
1.3.2 Types of Fatty Acids
1.3.3 Testing for Lipids
1.3.4 Exam-Style Question - Fats
1.3.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Lipids
1.4 Proteins
1.4.1 The Peptide Chain
1.4.2 Investigating Proteins
1.4.3 Primary & Secondary Protein Structure
1.4.4 Tertiary & Quaternary Protein Structure
1.4.5 Enzymes
1.4.6 Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
1.4.7 Enzyme-Controlled Reactions
1.4.8 End of Topic Test - Lipids & Proteins
1.4.9 A-A* (AO3/4) - Enzymes
1.4.10 A-A* (AO3/4) - Proteins
1.5 Nucleic Acids
1.5.1 DNA & RNA
1.5.2 Polynucleotides
1.5.3 DNA Replication
1.5.4 Exam-Style Question - Nucleic Acids
1.5.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Nucleic Acids
1.6.1 Structure of ATP
1.6.2 End of Topic Test - Nucleic Acids & ATP
1.7.1 Structure & Function of Water
1.7.2 A-A* (AO3/4) - Water
1.8 Inorganic Ions
1.8.1 Inorganic Ions
1.8.2 End of Topic Test - Water & Inorganic Ions
2.1 Cell Structure
2.1.1 Introduction to Cells
2.1.2 Eukaryotic Cells & Organelles
2.1.3 Eukaryotic Cells & Organelles 2
2.1.4 Prokaryotes
2.1.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Organelles
2.1.6 Methods of Studying Cells
2.1.7 Microscopes
2.1.8 End of Topic Test - Cell Structure
2.1.9 Exam-Style Question - Cells
2.1.10 A-A* (AO3/4) - Cells
2.2 Mitosis & Cancer
2.2.1 Mitosis
2.2.2 Investigating Mitosis
2.2.3 Cancer
2.2.4 A-A* (AO3/4) - The Cell Cycle
2.3 Transport Across Cell Membrane
2.3.1 Cell Membrane Structure
2.3.2 A-A* (AO3/4) - Membrane Structure
2.3.3 Diffusion
2.3.4 Osmosis
2.3.5 Active Transport
2.3.6 End of Topic Test - Mitosis, Cancer & Transport
2.3.7 Exam-Style Question - Membranes
2.3.8 A-A* (AO3/4) - Membranes & Transport
2.3.9 A-A*- Mitosis, Cancer & Transport
2.4 Cell Recognition & the Immune System
2.4.1 Immune System
2.4.2 The Immune Response
2.4.3 Antibodies
2.4.4 Primary & Secondary Response
2.4.5 Vaccines
2.4.7 Ethical Issues
2.4.8 End of Topic Test - Immune System
2.4.9 Exam-Style Question - Immune System
2.4.10 A-A* (AO3/4) - Immune System
3 Substance Exchange
3.1 Surface Area to Volume Ratio
3.1.1 Size & Surface Area
3.1.2 A-A* (AO3/4) - Cell Size
3.2 Gas Exchange
3.2.1 Single-Celled Organisms
3.2.2 Multicellular Organisms
3.2.3 Control of Water Loss
3.2.4 Human Gas Exchange
3.2.5 Ventilation
3.2.6 Dissection
3.2.7 Measuring Gas Exchange
3.2.8 Lung Disease
3.2.9 Lung Disease Data
3.2.10 End of Topic Test - Gas Exchange
3.2.11 A-A* (AO3/4) - Gas Exchange
3.3 Digestion & Absorption
3.3.1 Overview of Digestion
3.3.2 Digestion in Mammals
3.3.3 Absorption
3.3.4 End of Topic Test - Substance Exchange & Digestion
3.3.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Substance Ex & Digestion
3.4 Mass Transport
3.4.1 Haemoglobin
3.4.2 Oxygen Transport
3.4.3 The Circulatory System
3.4.4 The Heart
3.4.5 Blood Vessels
3.4.6 Cardiovascular Disease
3.4.7 Heart Dissection
3.4.8 Xylem
3.4.9 Phloem
3.4.10 Investigating Plant Transport
3.4.11 End of Topic Test - Mass Transport
3.4.12 A-A* (AO3/4) - Mass Transport
4 Genetic Information & Variation
4.1 DNA, Genes & Chromosomes
4.1.2 Genes
4.1.3 A-A* (AO3/4) - DNA
4.2 DNA & Protein Synthesis
4.2.1 Protein Synthesis
4.2.2 Transcription & Translation
4.2.3 End of Topic Test - DNA, Genes & Protein Synthesis
4.2.4 Exam-Style Question - Protein Synthesis
4.2.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Coronavirus Translation
4.2.6 A-A* (AO3/4) - Transcription
4.2.7 A-A* (AO3/4) - Translation
4.3 Mutations & Meiosis
4.3.1 Mutations
4.3.2 Meiosis
4.3.3 A-A* (AO3/4) - Meiosis
4.3.4 Meiosis vs Mitosis
4.3.5 End of Topic Test - Mutations, Meiosis
4.3.6 A-A* (AO3/4) - DNA,Genes, CellDiv & ProtSynth
4.4 Genetic Diversity & Adaptation
4.4.1 Genetic Diversity
4.4.2 Natural Selection
4.4.3 A-A* (AO3/4) - Natural Selection
4.4.4 Adaptations
4.4.5 Investigating Natural Selection
4.4.6 End of Topic Test - Genetic Diversity & Adaptation
4.4.7 A-A* (AO3/4) - Genetic Diversity & Adaptation
4.5 Species & Taxonomy
4.5.1 Classification
4.5.2 DNA Technology
4.5.3 A-A* (AO3/4) - Species & Taxonomy
4.6 Biodiversity Within a Community
4.6.1 Biodiversity
4.6.2 Agriculture
4.6.3 End of Topic Test - Species,Taxonomy& Biodiversity
4.6.4 A-A* (AO3/4) - Species,Taxon&Biodiversity
4.7 Investigating Diversity
4.7.1 Genetic Diversity
4.7.2 Quantitative Investigation
5 Energy Transfers (A2 only)
5.1 Photosynthesis
5.1.1 Overview of Photosynthesis
5.1.2 Light-Dependent Reaction
5.1.3 Light-Independent Reaction
5.1.4 A-A* (AO3/4) - Photosynthesis Reactions
5.1.5 Limiting Factors
5.1.6 Photosynthesis Experiments
5.1.7 End of Topic Test - Photosynthesis
5.1.8 A-A* (AO3/4) - Photosynthesis
5.2 Respiration
5.2.1 Overview of Respiration
5.2.2 Anaerobic Respiration
5.2.3 A-A* (AO3/4) - Anaerobic Respiration
5.2.4 Aerobic Respiration
5.2.5 Respiration Experiments
5.2.6 End of Topic Test - Respiration
5.2.7 A-A* (AO3/4) - Respiration
5.3 Energy & Ecosystems
5.3.1 Biomass
5.3.2 Production & Productivity
5.3.3 Agricultural Practices
5.4 Nutrient Cycles
5.4.1 Nitrogen Cycle
5.4.2 Phosphorous Cycle
5.4.3 Fertilisers & Eutrophication
5.4.4 End of Topic Test - Nutrient Cycles
5.4.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Energy,Ecosystems&NutrientCycles
6 Responding to Change (A2 only)
6.1 Nervous Communication
6.1.1 Survival
6.1.2 Plant Responses
6.1.3 Animal Responses
6.1.4 Reflexes
6.1.5 End of Topic Test - Reflexes, Responses & Survival
6.1.6 Receptors
6.1.7 The Human Retina
6.1.8 Control of Heart Rate
6.1.9 End of Topic Test - Receptors, Retina & Heart Rate
6.2 Nervous Coordination
6.2.1 Neurones
6.2.2 Action Potentials
6.2.3 Speed of Transmission
6.2.4 End of Topic Test - Neurones & Action Potentials
6.2.5 Synapses
6.2.6 Types of Synapse
6.2.7 Medical Application
6.2.8 End of Topic Test - Synapses
6.2.9 A-A* (AO3/4) - Nervous Comm&Coord
6.3 Muscle Contraction
6.3.1 Skeletal Muscle
6.3.2 Sliding Filament Theory
6.3.3 Contraction
6.3.4 Slow & Fast Twitch Fibres
6.3.5 End of Topic Test - Muscles
6.3.6 A-A* (AO3/4) - Muscle Contraction
6.4 Homeostasis
6.4.1 Overview of Homeostasis
6.4.2 Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.3 Controlling Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.4 End of Topic Test - Blood Glucose
6.4.5 Primary & Secondary Messengers
6.4.6 Diabetes Mellitus
6.4.7 Measuring Glucose Concentration
6.4.8 Osmoregulation
6.4.9 Controlling Blood Water Potential
6.4.11 End of Topic Test - Diabetes & Osmoregulation
6.4.12 A-A* (AO3/4) - Homeostasis
7 Genetics & Ecosystems (A2 only)
7.1 Genetics
7.1.1 Key Terms in Genetics
7.1.2 Inheritance
7.1.3 Linkage
7.1.4 Multiple Alleles & Epistasis
7.1.5 Chi-Squared Test
7.1.6 End of Topic Test - Genetics
7.1.7 A-A* (AO3/4) - Genetics
7.2 Populations
7.2.1 Populations
7.2.2 Hardy-Weinberg Principle
7.3 Evolution
7.3.1 Variation
7.3.2 Natural Selection & Evolution
7.3.3 End of Topic Test - Populations & Evolution
7.3.4 Types of Selection
7.3.5 Types of Selection Summary
7.3.6 Overview of Speciation
7.3.7 Causes of Speciation
7.3.8 Diversity
7.3.9 End of Topic Test - Selection & Speciation
7.3.10 A-A* (AO3/4) - Populations & Evolution
7.4 Populations in Ecosystems
7.4.1 Overview of Ecosystems
7.4.2 Niche
7.4.3 Population Size
7.4.4 Investigating Population Size
7.4.5 End of Topic Test - Ecosystems & Population Size
7.4.6 Succession
7.4.7 Conservation
7.4.8 End of Topic Test - Succession & Conservation
7.4.9 A-A* (AO3/4) - Ecosystems
8 The Control of Gene Expression (A2 only)
8.1 Mutation
8.1.1 Mutations
8.1.2 Effects of Mutations
8.1.3 Causes of Mutations
8.2 Gene Expression
8.2.1 Stem Cells
8.2.2 Stem Cells in Disease
8.2.3 End of Topic Test - Mutation & Gene Epression
8.2.4 A-A* (AO3/4) - Mutation & Stem Cells
8.2.5 Regulating Transcription
8.2.6 Epigenetics
8.2.7 Epigenetics & Disease
8.2.8 Regulating Translation
8.2.9 Experimental Data
8.2.10 End of Topic Test - Transcription & Translation
8.2.11 Tumours
8.2.12 Correlations & Causes
8.2.13 Prevention & Treatment
8.2.14 End of Topic Test - Cancer
8.2.15 A-A* (AO3/4) - Gene Expression & Cancer
8.3 Genome Projects
8.3.1 Using Genome Projects
8.4 Gene Technology
8.4.1 Recombinant DNA
8.4.2 Producing Fragments
8.4.3 Amplification
8.4.4 End of Topic Test - Genome Project & Amplification
8.4.5 Using Recombinant DNA
8.4.6 Medical Diagnosis
8.4.7 Genetic Fingerprinting
8.4.8 End of Topic Test - Gene Technologies
8.4.9 A-A* (AO3/4) - Gene Technology
Jump to other topics

Unlock your full potential with GoStudent tutoring
Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home
Tutors are matched to your specific learning needs
30+ school subjects covered
End of Topic Test - Reflexes, Responses & Survival
The Human Retina
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

The importance of receptors in living organism-A*/A A LEVEL BIOLOGY ESSAY
Subject: Biology
Age range: 16+
Resource type: Unit of work
Last updated
22 June 2020
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

AQA A LEVEL A*/A MODEL BIOLOGY ESSAY
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
This website works best with JavaScript switched on. Please enable JavaScript
- Centre Services
- Associate Extranet
- All About Maths
AS and A-level Biology
- Specification
- Planning resources
- Teaching resources
Assessment resources
- Centre declaration sheets (6)
- Examiner reports (21)
- Mark schemes (26)
- Notes and guidance (2)
- Practice questions (1)
- Question papers (63)
- Paper 1 (32)
- Paper 2 (53)
- Paper 3 (25)
- June 2016 (4)
- June 2017 (10)
- June 2018 (5)
- June 2019 (15)
- June 2022 (25)
- November 2020 (25)
- November 2021 (20)
- Sample set 1 (6)
- A-level (81)
- Applied General (4)
- AS and A-level (1)
- Technical Award (2)
Showing 119 results
Exampro: searchable past paper questions, marks and examiner comments [exampro.co.uk]
Published 12 Dec 2023
Centre declaration sheet 2025
Published 10 Nov 2023 | PDF | 74 KB
Published 10 Nov 2023 | DOC | 520 KB
Centre declaration form: non-exam assessment, fieldwork and live performance 2025
Published 10 Nov 2023 | DOCX | 293 KB
Examiner report (AS): Paper 2 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 143 KB
Question paper (AS): Paper 1 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 1.7 MB
Question paper (AS): Paper 2 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 2 MB
Mark scheme (AS): Paper 1 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 274 KB
Examiner report (AS): Paper 1 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 183 KB
Question paper (A-level): Paper 3 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 983 KB
Question paper (A-level): Paper 2 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 1.2 MB
Mark scheme (AS): Paper 2 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 324 KB
Question paper (A-level): Paper 1 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 1.4 MB
Question paper (Modified A4 18pt) (AS): Paper 2 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 1.5 MB
Question paper (Modified A4 18pt) (AS): Paper 1 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 1 MB
Examiner report (A-level): Paper 3 - June 2022
Question paper (Modified A3 36pt) (AS): Paper 2 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 2.5 MB
Question paper (Modified A3 36pt) (AS): Paper 1 - June 2022
Mark scheme (A-level): Paper 2 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 369 KB
Question paper (Modified A4 18pt) (A-level): Paper 3 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 1.3 MB
A Level Biology
Instant Access to A Level Biology Revision
Sign up now to get access to the entire library of a level biology resources for all exam boards.
Written for
Document information, connected book.
- Related courses
- Unit 1 BIOL1 - Biology and disease
Summary Biology A Level Essay: Receptors
- Institution
- A-Level year 1 and AS Biology
Extended and high scoring essay example for AQA A Level Biology on the question 'The Importance of Receptors in Biology'.
Preview 1 out of 2 pages

- Report Copyright Violation
Preview 1 out of 2 pages
- Summarized whole book? Unknown
- Uploaded on September 26, 2020
- Number of pages 2
- Written in 2019/2020
- Type Summary

Book Title: A-Level year 1 and AS Biology
Author(s): CGP Books
- Edition: Unknown
- ISBN: 9781789080254
More summaries for
- Study guide A* A level Biology Notes Section 1 ( Biological Molecules)
- Summary Biology A Level Essay: Shapes
- Summary AQA Nervous impulses and synaptic transmission
- Study Level A/AS Level
- Examinator AQA
- Subject Biology
- Unit Unit 1 BIOL1 - Biology and disease
2 reviews
By: dougieharries • 1 year ago
By: rosaiye • 2 year ago

Reviews received
The benefits of buying summaries with stuvia:.

Guaranteed quality through customer reviews
Stuvia customers have reviewed more than 700,000 summaries. This how you know that you are buying the best documents.

Quick and easy check-out
You can quickly pay through credit card for the summaries. There is no membership needed.

Focus on what matters
Your fellow students write the study notes themselves, which is why the documents are always reliable and up-to-date. This ensures you quickly get to the core!
Frequently asked questions
What do i get when i buy this document.
You get a PDF, available immediately after your purchase. The purchased document is accessible anytime, anywhere and indefinitely through your profile.
Satisfaction guarantee: how does it work?
Our satisfaction guarantee ensures that you always find a study document that suits you well. You fill out a form, and our customer service team takes care of the rest.
Who am I buying these notes from?
Stuvia is a marketplace, so you are not buying this document from us, but from seller charlietrwalker. Stuvia facilitates payment to the seller.
Will I be stuck with a subscription?
No, you only buy these notes for £3.29. You're not tied to anything after your purchase.
Can Stuvia be trusted?
4.6 stars on Google & Trustpilot (+1000 reviews)
98390 documents were sold in the last 30 days
Founded in 2010, the go-to place to buy revision notes and other study material for 14 years now
NEW Create SEO-optimized articles of any YouTube video with our free tool.
Mastering aqa biology essays: strategies for a-level success.
Article created from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X5lGejJiPHY

Introduction
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on how to excel in AQA Biology A-Level essays, a component that accounts for a significant portion of your final grade. Preparing for these essays can seem daunting, but with the right approach and understanding, you can significantly enhance your performance and boost your overall grade.
The Importance of the AQA Biology Essay
The AQA A-Level Biology essay, particularly in Paper 3, is worth almost 10% of the total grade, making it a critical area for scoring high marks. Through detailed analysis of past essay titles across different specifications, we identify common themes and patterns to help students prepare effectively. While predictions of exact essay titles are not possible, focusing on recurring themes can guide your revision strategy.
Disclaimer on Essay Predictions
It's crucial to note that while this guide offers insights into potential essay titles based on past patterns, these are not predictions. Relying solely on these suggestions without a broader study could be misleading. The aim is to use these titles as a basis for practice and revision.
Key Essay Titles to Consider
Let's delve into three challenging essay titles that could enhance your revision efforts:
The Importance of Responses to Internal and External Environments in Organisms : This essay title focuses on how organisms adjust to changes in their environments, requiring a deep understanding of homeostasis, osmoregulation, and blood glucose control. For example, discussing the role of insulin in lowering blood glucose levels illustrates the complexity of internal environment responses.
The Importance of Energy Transfers Between and Within Organisms : Here, the focus shifts to energy transfer processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, and food chains. Students should emphasize the efficiency of energy transfers and the significance of energy loss at different trophic levels, applying A-Level concepts to demonstrate understanding beyond GCSE knowledge.
The Importance of the Control of Processes in Organisms : This title invites discussion on regulatory mechanisms within organisms, such as the role of spindle fibers in mitosis, transcription factors in gene expression, and ADH in osmoregulation. Highlighting the importance of these control processes is crucial to scoring high marks.
Strategies for Essay Success
- Understand the Mark Scheme : Familiarize yourself with the AQA mark scheme and examiner reports to grasp what distinguishes a high-scoring essay from a mediocre one.
- Practice with Purpose : Regularly practice writing essays on these themes, focusing on structuring your arguments coherently and including relevant A-Level content.
- Revise Broadly : While these essay titles are valuable for focused revision, ensure you cover the entire AQA Biology specification to prepare for any curveballs in the exam.
Essay Boot Camp
For students seeking additional support, consider enrolling in an essay boot camp course. These courses offer detailed guidance on essay writing skills, topic mastery, and techniques to maximize marks.
Mastering the AQA Biology essay requires a strategic approach to revision, an understanding of key themes, and practice. By focusing on the areas highlighted in this guide, you can approach your A-Level Biology exam with confidence, ready to tackle essays that showcase your knowledge and analytical skills.
For more detailed insights into each essay title and further resources, including the essay boot camp, check out the video linked below.
Watch the full video here
Ready to automate your customer support with AI?
Join over 150+ businesses, websites and startups automating their customer support with a custom trained GPT chatbot.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Biology is detailed and comprehensive A-level content, uses appropriate terminology, and is very well written and always clearly explained. No significant errors or irrelevant material. For top marks in the band, the answer shows evidence of reading beyond specification requirements. 16-20. Relational.
AQA Education (AQA) is a registered charity (number 1073334) and a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (number 3644723). Our registered address is AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX. Biology essay titles This document contains the essay titles and mark schemes used in AQA A-level Biology examinations since 2007.
The levels scheme states that more than two A-level topics need to be addressed to get higher than 10 marks. A minimum of four topics is required to get higher than 15 marks. A topic area is a numbered sub-section in the specification. For example, for the 2017 'diffusion' essay, gas exchange (3.3.2) was a topic area.
44 essay titles and indiciative mark schemes for AQA A level biology Paper 3 25 mark essay question. contents essay mark schemes general guidance. Skip to document. University; High School. Books; Discovery. ... Receptors convert stimuli into electrical impulses in nerve cells [25] Q14. Inorganic ions include those of sodium, phosphorus and ...
AQA A Level Biology - 25 Mark Essays. 23 terms. biotig. Preview. The importance of shapes fitting together in cells and organisms. 5 terms. Laurencr5. Preview. Biology topic 1A-Biological molecules.
The importance of ions in biology. Click the card to flip 👆. 1.) Na+ ions in cotransport of glucose. - importance: Na+ ion concentration gradient is what drives the movement of glucose into cell - utilising energy efficiently. 2.) Na+ ions in osmoregulation. - Loop of Henle - maintains Na+ ion gradient. - importance: ensures water can leave ...
Pacinian corpuscles are a type of receptor found deep in the skin. They are present in the skin of fingers, soles of the feet as well as in joints, tendons and ligaments. They respond to changes in pressure. When these receptors are stimulated by pressure on the skin it leads to the establishment of a generator potential.
Stimulation of the receptor. When pressure is applied to the Pacinian corpuscle, the rings of connective tissue apply pressure on the sensory neurone. The sensory neurone has stretch mediated Na + channels, these channels normally restrict the movement of Na + ions. Applied pressure causes the stretch-mediated Na + channels to open.
The levels mark scheme for the essay contains a number of words and statements that are open to different interpretations. This commentary defines the meanings of these words and statements in the context of marking the essay. Many words and statements are used in the AQA Biology A-Level - Receptors MS PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
The importance of receptors in living organism-A*/A A LEVEL BIOLOGY ESSAY. Subject: Biology. Age range: 16+. Resource type: Unit of work. File previews. docx, 8.03 KB. AQA A LEVEL A*/A MODEL BIOLOGY ESSAY. Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
The importance of shapes fitting together in cells and organisms. 1) Enzyme properties and digestion. 2) Protein structure. 3) Plasma membrane structure and cell transport. 4) Antigens, antibodies, B cells & T cells. 5) Vaccines. 6) Structure of DNA. 7) DNA Replication (not PCR) 8) Transcription & translation.
Question paper (A-level): Paper 1 - June 2022 Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 1.4 MB Question paper (Modified A4 18pt) (AS): Paper 2 - June 2022
A-level Biology focuses on providing students, tutors and teachers with detailed revision materials for A-Level Biology. Over 22,000 learners have used our materials to pass their exams. Need a tutor? Check out our partner, Spires.
that essays fall into being the 11-15 level, followed by the 16-20 level and the 6-10 level. The 21-25 level is the next most common mark band for essays, highlighting that it is relatively rare that an essay meets the requirements to achieve a mark over 20 on the A-level biology essay.
Paper 3 for AQA A-level biology contains the 25 mark essay (almost 10% of your A-level grade). Follow along as I plan 3 titles that haven't come up in nearl...
Carbon dioxide may affect organisms directly or indirectly. Describe and explain these effects. The causes of disease in humans. 25 mark essay titles and points that can be used for them :) AQA BIOL5 Essay Titles Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.
se The Immune Response in living organisms prevents any harmful pathogens from invading precious organisms within the body. Receptors are involved in detection of harmful substances and initiate a response in a according manner. T cells are one of the major components of the immune system and rely on receptors to carry out their functions. Their roles include directly killing infected host ...
Mammalian Sensory Receptors. A cell that responds to a stimulus is called a receptor cell. Receptor cells are transducers - they convert energy from one form (such as light, heat or sound) into energy in an electrical impulse within a sensory neurone. Each receptor will only respond to a specific stimulus. Receptors of the body act as ...
Action potentials. There are channel proteins in the axon membrane that allow sodium ions or potassium ions to pass through; When an action potential is stimulated (eg. by a receptor cell) in a neurone, the following steps occur:; Sodium ion channels in the axon membrane open; Sodium ions pass into the axon down the electrochemical gradient (there is a greater concentration of sodium ions ...
Biology Essay Plans. The importance of nitrogen containing substances in biological systems (25 marks) DNA: Has nitrogen containing bases- base pairing In eukaryotes, found in nucleus as histone associated chromosomes Stores genetic information and allows genetic continuity through generations Replicated semi conservatively using DNA helicase and DNA polymerase to form 2 identical molecules ...
Summary Biology A Level Essay: Receptors. Module. Unit 1 BIOL1 - Biology and disease. Institution. AQA. Book. A-Level year 1 and AS Biology. Extended and high scoring essay example for AQA A Level Biology on the question 'The Importance of Receptors in Biology'. Preview 1 out of 2 pages.
AQA A level Biology Essay. The importance of responses to changes in the internal and external environment of an organism. Click the card to flip 👆. Control of heart rate (changes in pH and pressure) Control of blood glucose (glucagon and insulin) Osmoregulation (water potential changes) Action potentials/ pacinian corpuscles (stimulus)
The AQA A-Level Biology essay, particularly in Paper 3, is worth almost 10% of the total grade, making it a critical area for scoring high marks. Through detailed analysis of past essay titles across different specifications, we identify common themes and patterns to help students prepare effectively. While predictions of exact essay titles are ...
Sensory Receptor Cells. A cell that responds to a stimulus is called a receptor cell. Receptor cells are transducers - they convert energy in one form (such as light, heat or sound) into energy in an electrical impulse within a sensory neurone. Receptor cells are often found in sense organs (eg. light receptor cells are found in the eye)
The Human Retina. The eye is a sense organ containing receptors sensitive to light intensity and colour. Receptors are groups of specialised cells that can generate an electrical impulse in a sensory neurone. The eye contains two types of receptor cell: Rod cells which are sensitive to light intensity.