Achieving Successful Business Communication
Introduction.
Communication is a very essential tool for the success of all business types. Success in this perspective can be identified by the achievements of the business which depend on the relationship between the management and the employees. It is also important to maintain high-quality relations with customers for the business to prosper. In addition, communication enables a company to address its market availability in identifying and analyzing its competitive position in the market. It is only through communication that a business can establish its performance from which it can realize and determine new and effective marketing strategies. The business is able to know whether it is a market leader, market challenger or a small market holder.
The most common communication methods on marketing are promotions and advertisement. Business communication can be very difficult at times but with the proper cooperation of models, the process gets simpler. Marketing communication models should consist of the sender, the message to be delivered, the medium through which the message will be delivered, the recipients as well as feedback.
In this essay, I will present the basis of communication, the steps involved in achieving efficient business communication skills as well as some examples. I will also look at some of the factors that are to be put into consideration when choosing a communication method. Finally, I will look at direct marketing as the most effective form of business communication, sales promotion and the use of the media in advertising.

Rationale for communication
With good marketing communication, a company or business is in a position to determine and improve its market share in the business world. Communication helps in evaluating a company’s operations from which it gets views from the public and knows how its products are ranked. The company will be able to employ better tactics in order to increase the market share as well as ensure customer satisfaction. Negative feedback concerning a certain product helps the company in identifying its weak areas in order to improve the quality of its product. All this is aimed at ensuring that the business gets returns as profits.
By working with other businesses, I have learned that the main purpose of communication in business is to inform customers of the existence of certain products or services so that they can buy them. Through marketing, the business is able to persuade its consumers to buy its product, and as a result, it benefits by registering sales increases which ensure maximum profits. Good communication attracts many people to a company’s products who in turn market the product by informing their friends and relatives. A business communication strategy that works best at earning customers’ confidence in the media. From my experience, I have learned that it is always good to appreciate companies and businesses that extra hard to maintain the customers’ satisfaction.
With the highly increasing competition in the business world, it takes communication to provide the necessary information to the consumers to help them compare different products. There is, therefore, the need for companies to do enough research when deciding on strategies to be used in marketing that would create the biggest impact on its clients.
Steps in achieving successful business communication
The first step in achieving successful communication is to identify any barrier in the business. This can be through sharing of ideas to classify challenges that are facing. Such challenges can be obtained by reviewing the daily activities that are carried out. A list of questionnaires may be necessary to give guidance to the review process. Some questions that may be included are: Have the employees been provided with good working conditions? Are they happy with what they are doing? Has the business been able to satisfy all its clients? Is proper information provided to all stakeholders? Is there a good flow of conversations?
While I was working in You – the Spa , one of my areas of concern was employee motivation. I made sure that employees were given incentives not only by paying them fairly but also by allowing them to air their views and trying to help them when faced with difficult situations. In addition, I went to the extent of organizing employees’ come-together parties where we celebrated any specific achievement made; we also had birthday parties for each and every employee. I tried to help them set goals, not only for the Spa but also for their own benefit. My main aim was to make sure that all employees were happy working for my organization because I knew this would be reflected in our customer service.
After reviewing the above issues, then the business has to address these challenges and prioritize those with the most adverse effects to the business. For instance, I once had a case of unsatisfied customers and after handling it, they got contented and left happy. By addressing the challenges faced, not only in businesses but also in other social organizations, the relationship is generally strengthened. It is, therefore, necessary to develop proactive and constructive communication skills in order to tackle these challenges early enough before they turn to the crisis. Once a challenge has been identified, its possible causes should be addressed systematically.
During my work experience, I have learned that communication is more than just giving out messages; it involves speaking, listening, sending and receiving messages. In communication, listening is the key element to make it a success although, without action, the information sent across will be less useful. For business communication to be effective, therefore, listening has to be proficient. When a company is faced with challenges, for instance, it is important to allow those who are aware of the problem to give their ideas concerning the subject. Though it may not always be easy to hold back and let others give their opinion, the practice is necessary for efficient communication in businesses.
After listening to different views on solutions to the problem at hand, a business then moves forward and defines what it intends to accomplish. This is a very critical stage and one has to be proactive in order to achieve success. For instance, one of the suggested solutions may be to improve the business’s relationship with its clients. Strategies to achieve this includes but are not limited to: answering calls in a polite manner, addressing all customers’ concerns, listening and responding to complaints, providing information and thanking customers for their loyalty. This helps in earning consumers’ confidence.
In 2006, I Completed the Incubator Seminar in Front Desk, System Development, and Compensation Plan for Employees, administered by Strategies Advanced Business Education Company from where I learned about the preparation of a communication plan. This is a plan that is prepared after a business defines what it wants to achieve. Things to be included in the plan include: taking employees to seminars that cover topics such as customer care, organizing get-together parties between employers and employees, rewarding employees, holding regular meetings, including major stakeholders in business decision making, and assurance to personal service among others. This plan does not concentrate on solving past problems but on laying down a good foundation that guarantees the future success of the business. A communication plan should take into consideration the availability of resources as well as the objective of the business; whether it is a long time or short time.
Once a communication plan has been prepared, the business now focuses on implementing it effectively. The expected outcome should be kept in mind and the main constituent of the plan reviewed to make sure they are in line with the expected result. The implementation process should involve all business stakeholders but with one member in charge of the process. Once the implementation process is comprehensively in place, the business should reflect on the process to check if it has met the objective of the plan.
The final step towards successful business communication is the evaluation of the results. The business should look back on the initial objectives and compare them with the results achieved to see if the expectations have been met. Once the business is satisfied with the results, it should thank all the parties involved in the process.
Factors to consider when choosing a form of communication
Customers’ needs and demands have changed with time especially with the various products to choose from. The big question today is, with the many competitive products in the market, what will the consumers choose? And how will marketers reach these clients? The media has expanded and new technologies have emerged. For a business to prosper, businessmen should take time to identify and familiarize themselves with customers’ needs. In order to serve clients better; whether old or new ones, businessmen have to first understand them well because different customers have different needs and preferences and they respond differently to different circumstances. Customer service management should be provided in every business organization. Through work and experience, I have realized that all staff members should be provided with sufficient education on customer care provision. Identifying consumers and forming a good relationships with them is the first and key step towards success in any business establishment. This can be achieved through the creation of an atmosphere where the client will feel free to ask for anything. Welcoming and greeting them, calling by their names, showing interest in some events in their lives among others constitute them from moving to other competitors for similar services. For instance, in you-The Spa, I made use of this idea to ensure clients were not kept in the waiting room for more than fifteen minutes, but rather provided with other services such as manicures or quick massages as they waited to be served. This ensures that they don’t feel like their time is being wasted which would otherwise annoy them and may push them away.
Often customers are concerned about the cost as well as the time they spend in obtaining a certain product. Businessmen should therefore adjust these two elements to suit the consumers’ needs as well as their own benefits. For instance, if the goods are made available within the customers’ reach, they will not need to drive far in order to acquire those goods but will buy those within their reach. Today, many products and services have become very competitive which has made some businessmen provide quick delivery methods in order to attract more customers. After identifying and obtaining potential clients, the supplier needs to improve service delivery methods that will ensure that ordered goods are delivered within the shortest time possible. Regular operations should be maintained including opening and closing periods of the business premises, methods of payment and provision of other services such as credit facilities.
External business communication
External business communication involves the use of brochures as well as different forms of advertisement, telephone calls and the use of the internet. The internet has become a very popular mode of communication not only in our social lives but also in business operations. Many businesses are using the internet to carry out their normal operations. This is because the internet is cheap and fast in the delivery of messages. With the changing times, many people are getting access to the internet and becoming more and more dependent on it for their daily activities. In external business communication, the most important thing is the image of the organization that is portrayed to the public. The logo should give a clear representation, the business letterhead should be intended to market self-explanatory and the telephone messages should give a reflection of the professional ability of the business.
Direct marketing
Direct marketing involves one on one approach between the buyer and the seller where marketers meet their targeted customers directly with the products to be sold. It’s a form of direct communication between the producers and the consumers. Direct marketing can be through telephone calls, emails, or the use of catalogs where producers send information on certain products or services directly to potential customers. For this method to be effective, the producer needs to have the contact information of the potential clients such as email addresses, telephone numbers, and mailing addresses. This method is the most cost-effective marketing strategy compared to the other methods but it requires cautious execution.
Direct marketing has been widely used over the years. With the improved technology, businessmen can keep customers’ mailing lists into punched cards and store information on magnetic tapes that are more secure. Computers are also advantageous to businessmen since they reduce the number of documents that have to be stored thus creating more space in the workplace. This way, marketing became easier and potential customers can access any information within seconds.
Businessmen are now keeping stock records and making accounts on computers making direct marketing even easier especially in supplies management. Today, almost every business organization relies partly or wholly on direct marketers to advertise its products and services. However, direct marketing requires more than just advertising. Clear objectives have to be laid down with more emphasis on a good relationship between the business and the customer. With the increased global competition, creativity has to be applied in order to make direct marketing successful.
Other forms of businesses may choose to market their products directly to the final consumer. This is done by the use of sales representatives who personally deliver goods to the doorsteps of customers. This method is best applicable in small companies which are introducing their new products and searching for clients. Through experience, I have realized that this marketing strategy is not only cheap but also efficient. While working in the spa, I designed a plan for launching a personal cosmetic line, Lava Rache and I used direct marketing which turned out to be cost-effective in creating public awareness for these products. It proved to be much cheaper compared to advertising mediums and promotion methods since the sales representatives’ payments depend on the sales made. The company is guaranteed increased sales and the final consumers can as well give their feedback which enables the business to improve the quality of its products where necessary. Direct contact with customers eliminates the costs that would have otherwise been used on discounts or middlemen as payments.
Almost all business organizations use promotion as a way of making their products or services known to the public. Promotion can be done through the media, such as the use of TV, radio, magazines, newspaper, or the internet. A promotion plan should be purposed on increasing sales and creation of the good corporate image. It can also be used to introduce new products.
Most promotion services involve discount offers which will affect the whole chain of transactions from the wholesalers down to final consumers. Since the discounts are offered for only a short period of time, all parties involved in the sales will purchase products in large quantities in order to enjoy the discount. In the end, consumers will get used to those products to the point of buying them even without the discount offer.
As the company becomes exposed, it realizes that it has a social responsibility to the community and all its stakeholders (the shareholders, customers, staff, society, government, etc). Through communication, companies are able to increase their sales which calls for increased profits and consequently, increased shareholders returns. It is the duty of the company to ensure that consumers get high-quality products as well as the provision of good working conditions. All these are best achieved through effective communication.
The most commonly used mode of advertisement by businesses is the media. This is due to its easy accessibility unlike other modes of communication such as newspapers. Effective media communication requires the use of simple language that is easy for the targeted audience to understand. However, the message should be informative enough and it should reflect the business’s mission statement as well. A business’ participation in social activities can be an added advantage in attracting the intended customers. Lastly, sound bites should be obtained from people with authority or holding high positions in the business in order to demonstrate how the business is committed to success.
Sound Bites
Sound bites are brief statements that are obtained from interviews of highly respected people such as politicians and business managers. They clearly state the aim of a business and the nature of certain products. It is therefore the duty of those who are responsible for editing to ensure that they get only the most important points. The points taken are then included in the news broadcast. For sound bites to be effective, the language used should have a clear but brief description that can be easily repeated.
These are impressive propositions that are widely accepted by their own merits. They are usually employed in business advertising to draw people’s attention towards particular features of a certain item. Like sound bites, slogans should give an impression of the benefits of a specific product. They too should be straight and concise, giving an incredible perception about the merchandise and making the consumer feel the need to have that particular product. The first step in designing a persuasive message is to identify the problem then find a fundamental assumption between the interests of both the business and the audience. The last step is to devise a message with a question statement at the end.
A slogan portrays the finest reflection of the product. It is always aimed at making the item appear as the best there is in the market. Examples of such slogans include: ‘Guinness is good for you’, Persil –‘washes whiter’. Some slogans used in water conservation include: ‘conserve water and conserve life’, ‘cut one tree plant two’, ‘rainwater tank, won’t break the bank’. The message in slogans is meant for a specific intention and for a particular audience. A good example of a slogan that has been productive is ‘keep that school girl completion’, Palmolive soap, ‘for survival obey your thirst spirit’. An example of a slogan meant for a specific audience is ‘choosy mother choose Jif peanuts butter’.
The success of any marketing activity in a business depends largely on the way in which the marketing message is sent and received by the targeted customers. Attention and respect are good values for marketers to show their customers in order to succeed in persuading them to buy their products. It is in the best interest of customers that they get all products under one roof to avoid moving from one store to another. Marketers should, therefore, ensure that all their products are easily accessible to customers at all times. The use of proper and polite language is an essential tool for marketers in persuading customers, especially for direct marketers since they interact with the customers instantly.
Success does not come easily especially in business where one needs to compete with the growing competitive world. In order to make business communication a success, companies should clearly identify the needs of their customers and develop good relationships between the customers and the employees as well. In the recent future, the direct marketing may replace most of the other conventional ways of advertisement because it is proving to be the most effective and most businessmen and marketers have been using it of late. The success of direct marketing has been greatly contributed by the use of the internet. Direct marketing is way better compared to a conventional advertisement which is very costly considering that the outcome cannot be predicted. The high competition in the markets requires skillful marketers in order to persuade customers to choose their products. It is therefore the duty of business managers to ensure that all their marketers receive the required training on proper marketing strategies in order to ensure maximum sales. It is very clear that marketing is the backbone of a successful business and it should therefore be taken seriously and handled professionally.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, April 28). Achieving Successful Business Communication. https://studycorgi.com/an-effective-business-communication/
"Achieving Successful Business Communication." StudyCorgi , 28 Apr. 2022, studycorgi.com/an-effective-business-communication/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'Achieving Successful Business Communication'. 28 April.
1. StudyCorgi . "Achieving Successful Business Communication." April 28, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/an-effective-business-communication/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Achieving Successful Business Communication." April 28, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/an-effective-business-communication/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "Achieving Successful Business Communication." April 28, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/an-effective-business-communication/.
This paper, “Achieving Successful Business Communication”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: April 28, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1: Effective Business Communication
Venecia Williams
Learning Objectives
- Examine the importance of being a good communicator
- Define the communication process
- Explain 8 essential components of communication
- Discuss the role of ethics in communication
Communication is an activity, skill, and art that incorporates lessons learned across a wide spectrum of human knowledge. Perhaps the most time-honoured form of communication is storytelling. We’ve told each other stories for ages to help make sense of our world, anticipate the future, and certainly to entertain ourselves. The art of storytelling draws on your understanding of yourself, your message, and how you communicate it to an audience that is simultaneously communicating back to you. Your anticipation, reaction, and adaptation to the process will determine how successfully you are able to communicate. You were not born knowing how to write or even how to talk—but in the process of growing up, you have undoubtedly learned how to tell, and how not tell, a story out loud and in writing.
Effective communication takes preparation, practice, and persistence. There are many ways to learn communication skills; the school of experience, or “hard knocks,” is one of them. But in the business environment, a “knock” (or lesson learned) may come at the expense of your credibility through a blown presentation to a client. The classroom environment, with a compilation of information and resources such as a text, can offer you a trial run where you get to try out new ideas and skills before you have to use them to communicate effectively to make a sale or form a new partnership. Listening to yourself, or perhaps the comments of others may help you reflect on new ways to present or perceive, thoughts, ideas and concepts. The net result is your growth; ultimately your ability to communicate in business will improve, opening more doors than you might anticipate.
Importance of Good Communication Skills
Communication is key to your success—in relationships, in the workplace, as a citizen of your country, and across your lifetime. Your ability to communicate comes from experience, and experience can be an effective teacher, but this text and the related business communication course will offer you a wealth of experiences gathered from professional speakers across their lifetimes. You can learn from the lessons they’ve learned and be a more effective communicator right out of the gate.
Business communication can be thought of as a problem-solving activity in which individuals may address the following questions:
- What is the situation?
- What are some possible communication strategies?
- What is the best course of action?
- What is the best way to design the chosen message?
- What is the best way to deliver the message?
In this book, we will examine this problem-solving process and help you learn to apply it in the kinds of situations you are likely to encounter over the course of your career.
Communication Influences Your Thinking about Yourself and Others
We all share a fundamental drive to communicate. Communication can be defined as the process of understanding and sharing meaning (Pearson & Nelson, 2000). You share meaning in what you say and how you say it, both in oral and written forms. If you could not communicate, what would life be like? A series of never-ending frustrations? Not being able to ask for what you need or even to understand the needs of others?
Being unable to communicate might even mean losing a part of yourself, for you communicate your self-concept —your sense of self and awareness of who you are—in many ways. Do you like to write? Do you find it easy to make a phone call to a stranger or to speak to a room full of people? Perhaps someone told you that you don’t speak clearly or your grammar needs improvement. Does that make you more or less likely to want to communicate? For some, it may be a positive challenge, while for others it may be discouraging. But in all cases, your ability to communicate is central to your self-concept.
Take a look at your clothes. What are the brands you are wearing? What do you think they say about you? Do you feel that certain styles of shoes, jewelry, tattoos, music, or even automobiles express who you are? Part of your self-concept may be that you express yourself through texting, or through writing longer documents like essays and research papers, or through the way you speak.
On the other side of the coin, your communications skills help you to understand others—not just their words, but also their tone of voice, their nonverbal gestures, or the format of their written documents provide you with clues about who they are and what their values and priorities may be. Active listening and reading are also part of being a successful communicator.
Communication Influences How You Learn
When you were an infant, you learned to talk over a period of many months. When you got older, you didn’t learn to ride a bike, drive a car, or even text a message on your cell phone in one brief moment. You need to begin the process of improving your speaking and writing with the frame of mind that it will require effort, persistence, and self-correction.
You learn to speak in public by first having conversations, then by answering questions and expressing your opinions in class, and finally by preparing and delivering a “stand-up” speech. Similarly, you learn to write by first learning to read, then by writing and learning to think critically. Your speaking and writing are reflections of your thoughts, experience, and education. Part of that combination is your level of experience listening to other speakers, reading documents and styles of writing, and studying formats similar to what you aim to produce.
As you study business communication, you may receive suggestions for improvement and clarification from speakers and writers more experienced than yourself. Take their suggestions as challenges to improve; don’t give up when your first speech or first draft does not communicate the message you intend. Stick with it until you get it right. Your success in communicating is a skill that applies to almost every field of work, and it makes a difference in your relationships with others.
Remember, luck is simply a combination of preparation and timing. You want to be prepared to communicate well when given the opportunity. Each time you do a good job, your success will bring more success.
Communication Represents You and Your Employer
You want to make a good first impression on your friends and family, instructors, and employer. They all want you to convey a positive image, as it reflects on them. In your career, you will represent your business or company in spoken and written form. Your professionalism and attention to detail will reflect positively on you and set you up for success.
In both oral and written situations, you will benefit from having the ability to communicate clearly. These are skills you will use for the rest of your life. Positive improvements in these skills will have a positive impact on your relationships, your prospects for employment, and your ability to make a difference in the world.
Communication Skills Are Desired by Business and Industry
Oral and written communication proficiencies are consistently ranked in the top ten desirable skills by employer surveys year after year. In fact, high-powered business executives sometimes hire consultants to coach them in sharpening their communication skills. According to the National Association of Colleges and Employers (2018), the following are the top five personal qualities or skills potential employers seek:
- Communication skills (verbal and written)
- Strong work ethic
- Teamwork skills (works well with others, group communication)
- Analytical skills
Knowing this, you can see that one way for you to be successful and increase your promotion potential is to increase your abilities to speak and write effectively. An individual with excellent communication skills is an asset to every organization. No matter what career you plan to pursue, learning to express yourself professionally in speech and in writing will help you get there.
What is Communication?
Many theories have been proposed to describe, predict, and understand the behaviours and phenomena of which communication consists. When it comes to communicating in business, we are often less interested in theory than in making sure our communications generate the desired results. But in order to achieve results, it can be valuable to understand what communication is and how it works. All communication is composed of three parts that make a whole: sharing, understanding, and meaning.
Sharing means doing something together with one or more person(s). In communication, sharing occurs when you convey thoughts, feelings, ideas, or insights to others. You also share with yourself (a process called intrapersonal communication) when you bring ideas to consciousness, ponder how you feel about something, figure out the solution to a problem, or have a classic “Aha!” moment when something becomes clear.
The second keyword is understanding . “To understand is to perceive, to interpret, and to relate our perception and interpretation to what we already know.” (McLean, 2003) Understanding the words and the concepts or objects they refer to is an important part of the communication process.
Finally, meaning is what you share through communication. For example, by looking at the context of a word, and by asking questions, you can discover the shared meaning of the word and better understand the message.
Watch the following video reviewing Types of Communication
- Interpersonal communication is any message exchanged between two or more people.
- Written communication is any message using the written word.
- Verbal, or oral, communication is any message conveyed through speech.
- Nonverbal communication is any message inferred through observation of another person.
Communications Process: Encoding and Decoding
In basic terms, humans communicate through a process of encoding and decoding . The encoder is the person who develops and sends the message. As represented in Figure 1.1 below, the encoder must determine how the message will be received by the audience, and make adjustments so the message is received the way they want it to be received.
Encoding is the process of turning thoughts into communication. The encoder uses a ‘medium’ to send the message — a phone call, email, text message, face-to-face meeting, or other communication tools. The level of conscious thought that goes into encoding messages may vary. The encoder should also take into account any ‘noise’ that might interfere with their message, such as other messages, distractions, or influences.
The audience then ‘decodes’, or interprets, the message for themselves. Decoding is the process of turning communication into thoughts. For example, you may realize you’re hungry and encode the following message to send to your roommate: “I’m hungry. Do you want to get pizza tonight?” As your roommate receives the message, they decode your communication and turn it back into thoughts to make meaning.
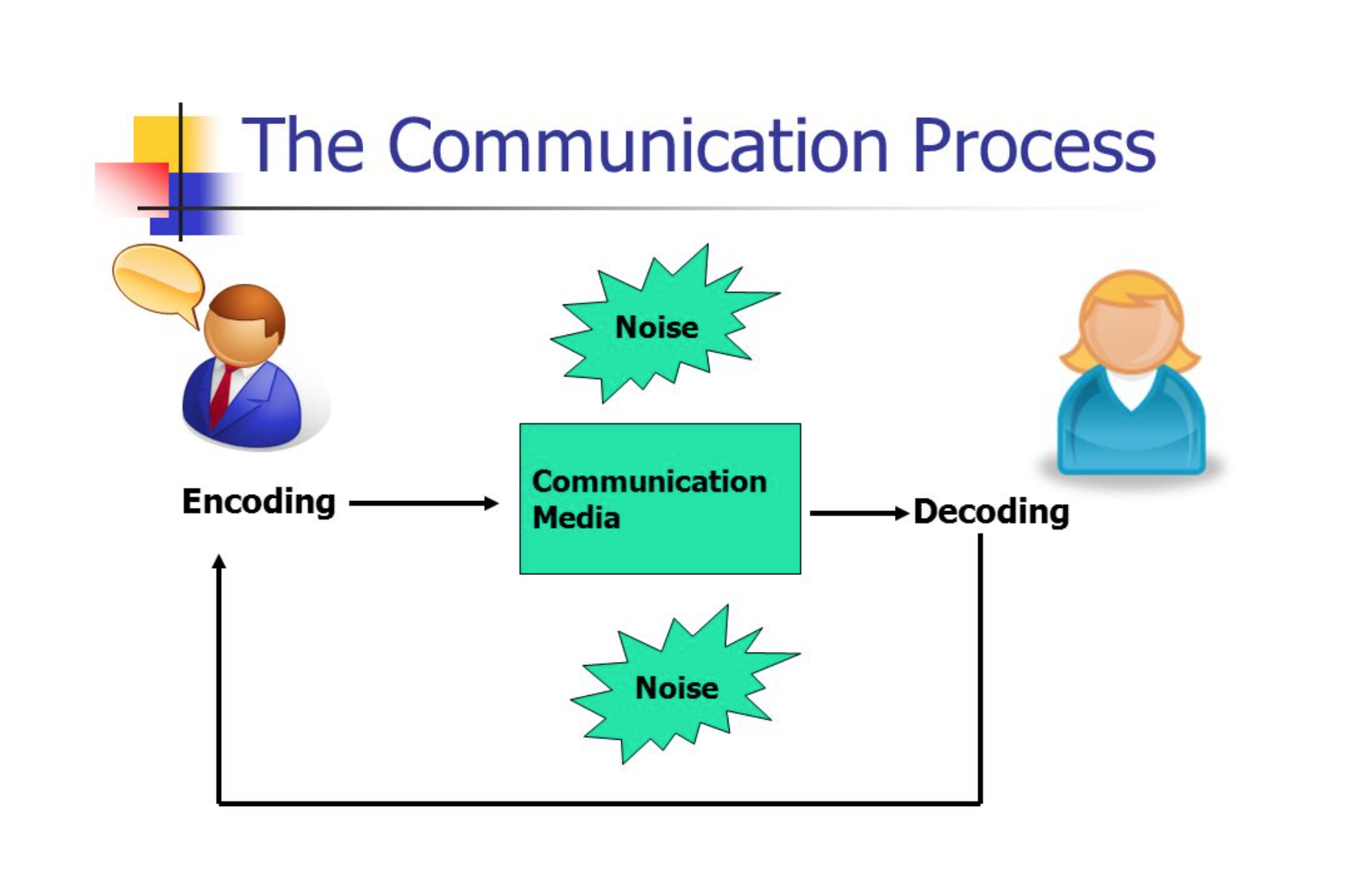
Of course, you don’t just communicate verbally—you have various options, or channels, for communication. Encoded messages are sent through a channel, or a sensory route, on which a message travels to the receiver for decoding. While communication can be sent and received using any sensory route (sight, smell, touch, taste, or sound), most communication occurs through visual (sight) and/or auditory (sound) channels. If your roommate has headphones on and is engrossed in a video game, you may need to get their attention by waving your hands before you can ask them about dinner.
The transmission model of communication describes communication as a linear, one-way process in which a sender intentionally transmits a message to a receiver (Ellis & McClintock, 1990). This model focuses on the sender and message within a communication encounter. Although the receiver is included in the model, this role is viewed as more of a target or endpoint rather than part of an ongoing process. You are left to presume that the receiver either successfully receives and understands the message or does not. Think of how a radio message is sent from a person in the radio studio to you listening in your car. The sender is the radio announcer who encodes a verbal message that is transmitted by a radio tower through electromagnetic waves (the channel) and eventually reaches your (the receiver’s) ears via an antenna and speakers in order to be decoded. The radio announcer doesn’t really know if you receive their message or not, but if the equipment is working and the channel is free of static, then there is a good chance that the message was successfully received.
The interaction model of communication describes communication as a process in which participants alternate positions as sender and receiver and generate meaning by sending messages and receiving feedback within physical and psychological contexts (Schramm, 1997). Rather than illustrating communication as a linear, one-way process, the interaction model incorporates feedback, which makes communication a more interactive, two-way process. Feedback includes messages sent in response to other messages. For example, your instructor may respond to a point you raise during class discussion or you may point to the sofa when your roommate asks you where the remote control is. The inclusion of a feedback loop also leads to a more complex understanding of the roles of participants in a communication encounter. Rather than having one sender, one message, and one receiver, this model has two sender-receivers who exchange messages. Each participant alternates roles as sender and receiver in order to keep a communication encounter going. Although this seems like a perceptible and deliberate process, you alternate between the roles of sender and receiver very quickly and often without conscious thought.
The transaction model of communication describes communication as a process in which communicators generate social realities within social, relational, and cultural contexts. In this model, you don’t just communicate to exchange messages; you communicate to create relationships, form intercultural alliances, shape your self-concepts, and engage with others in dialogue to create communities. In short, you don’t communicate about your realities; communication helps to construct your realities (and the realities of others).
The roles of sender and receiver in the transaction model of communication differ significantly from the other models. Instead of labelling participants as senders and receivers, the people in a communication encounter are referred to as communicators. Unlike the interaction model, which suggests that participants alternate positions as sender and receiver, the transaction model suggests that you are simultaneously a sender and a receiver. For example, when meeting a new friend, you send verbal messages about your interests and background, your companion reacts nonverbally. You don’t wait until you are done sending your verbal message to start receiving and decoding the nonverbal messages of your new friend. Instead, you are simultaneously sending your verbal message and receiving your friend’s nonverbal messages. This is an important addition to the model because it allows you to understand how you are able to adapt your communication—for example, adapting a verbal message—in the middle of sending it based on the communication you are simultaneously receiving from your communication partner.
Eight Essential Components of Communication
The communication process can be broken down into a series of eight essential components, each of which serves an integral function in the overall process:
Environment
Interference.
The source imagines, creates, and sends the message. The source encodes the message by choosing just the right order or the best words to convey the intended meaning and presents or sends the information to the audience (receiver). By watching for the audience’s reaction, the source perceives how well they received the message and responds with clarification or supporting information.
“The message is the stimulus or meaning produced by the source for the receiver or audience” (McLean, 2005). The message brings together words to convey meaning but is also about how it’s conveyed — through nonverbal cues, organization, grammar, style, and other elements.
“The channel is the way in which a message or messages travel between source and receiver.” (McLean, 2005). Spoken channels include face-to-face conversations, speeches, phone conversations and voicemail messages, radio, public address systems, and Skype. Written channels include letters, memorandums, purchase orders, invoices, newspaper and magazine articles, blogs, email, text messages, tweets, and so forth.
“The receiver receives the message from the source, analyzing and interpreting the message in ways both intended and unintended by the source” (McLean, 2005).
When you respond to the source, intentionally or unintentionally, you are giving feedback. Feedback is composed of messages the receiver sends back to the source. Verbal or nonverbal, all these feedback signals allow the source to see how well, how accurately (or how poorly and inaccurately) the message was received (Leavitt & Mueller, 1951).
“The environment is the atmosphere, physical and psychological, where you send and receive messages” (McLean, 2005). Surroundings, people, animals, technology, can all influence your communication.
“The context of the communication interaction involves the setting, scene, and expectations of the individuals involved” (McLean, 2005). A professional communication context may involve business suits (environmental cues) that directly or indirectly influence expectations of language and behaviour among the participants.
Interference, also called noise, can come from any source. “Interference is anything that blocks or changes the source’s intended meaning of the message” (McLean, 2005). This can be external or internal/psychological. Noise interferes with normal encoding and decoding of the message carried by the channel between source and receiver.
Your Responsibilities as a Communicator – 4 tips
Whenever you speak or write in a business environment, you have certain responsibilities to your audience, your employer, and your profession. Your audience comes to you with an inherent set of expectations that is your responsibility to fulfill. The specific expectations may change given the context or environment, but two central ideas will remain: be prepared, and be ethical.
Preparation
Being prepared means that you have selected a topic appropriate to your audience, gathered enough information to cover the topic well, put your information into a logical sequence, and considered how best to present it.
Organization
Being organized involves the steps or points that lead your communication to a conclusion. Once you’ve invested time in researching your topic, you will want to narrow your focus to a few key points and consider how you’ll present them. You also need to consider how to link your main points together for your audience so they can follow your message from point to point.
You need to have a clear idea in your mind of what you want to say before you can say it clearly to someone else. It involves considering your audience, as you will want to choose words and phrases they understand and avoid jargon or slang that may be unfamiliar to them. Clarity also involves presentation and appropriate use of technology.
Conciseness
Concise means to be brief and to the point. In most business communications you are expected to ‘get down to business’ right away. Being prepared includes being able to state your points clearly and support them with trustworthy evidence in a relatively straightforward, linear way. Be concise in your choice of words, organization, and even visual aids. Being concise also involves being sensitive to time constraints. Be prepared to be punctual and adhere to deadlines or time limits. Some cultures also have a less strict interpretation of time schedules and punctuality. While it is important to recognize that different cultures have different expectations, the general rule holds true that good business communication does not waste words or time.
Ethics in Communication
Communicating ethically involves being egalitarian, respectful, and trustworthy—overall, practising the “golden rule” of treating your audience the way you would want to be treated. Communication can move communities, influence cultures, and change history. It can motivate people to take a stand, consider an argument, or purchase a product. The degree to which you consider both the common good and fundamental principles you hold to be true when crafting your message directly relates to how your message will affect others.
The Ethical Communicator Is Egalitarian
The word “egalitarian” comes from the root “equal.” To be egalitarian is to believe in basic equality: that all people should share equally in the benefits and burdens of a society. It means that everyone is entitled to the same respect, expectations, access to information, and rewards of participation in a group. To communicate in an egalitarian manner, speak and write in a way that is comprehensible and relevant to all your listeners or readers, not just those who are ‘like you’ in terms of age, gender, race or ethnicity, or other characteristics. In business, an effective communicator seeks to unify the audience by using ideas and language that are appropriate for all the message’s readers or listeners.
The Ethical Communicator Is Respectful
People are influenced by emotions as well as logic. The ethical communicator will be passionate and enthusiastic without being disrespectful. Losing one’s temper and being abusive are generally regarded as showing a lack of professionalism (and could even involve legal consequences for you or your employer). When you disagree strongly with a coworker, feel deeply annoyed with a difficult customer, or find serious fault with a competitor’s product, it is important to express such sentiments respectfully.
The Ethical Communicator Is Trustworthy
Trust is a key component in communication, and this is especially true in business. Your goal as a communicator is to build a healthy relationship with your audience and to do that you must show them how they can trust you and why the information you are about to share with them is believable. Your audience will expect that what you say is the truth as you understand it. This means that you have not intentionally omitted, deleted, or taken information out of context simply to prove your points. They will listen to what you say and how you say it, but also to what you don’t say or do. Being worthy of trust is something you earn with an audience. Many wise people have observed that trust is hard to build but easy to lose.
The “Golden Rule”
When in doubt, remember the “golden rule,” which is to treat others the way you would like to be treated. In all its many forms, the golden rule incorporates human kindness, cooperation, and reciprocity across cultures, languages, backgrounds, ad interests. Regardless of where you travel, with whom you communicate or what your audience is like, remember how you would feel if you were on the receiving end of your communication and act accordingly.
Being a good communicator is essential to becoming a successful business person. Therefore, it is important to learn how to communicate well. The first step in that process is understanding what effective communication means. This will help you to evaluate and improve your communication skills.
End of Chapter Activities
1a. thinking about the content.
What are your key takeaways from this chapter? What is something you have learned or something you would like to add from your experience?
1b. Review Questions
Discussion Questions
- Recall one time you felt offended or insulted in a conversation. What contributed to your perception?
- When someone lost your trust, were they able to earn it back?
- Does the communicator have a responsibility to the audience? Does the audience have a responsibility to the speaker? Why or why not?
1c. Applying chapter concepts to a situation
Communicating with a supervisor
Mako is an international student enrolled in a post-degree program in Vancouver. She has been working at a grocery store for the past three months on Tuesdays, Thursdays and Fridays when she doesn’t have class. Mako enjoys working at the grocery store and gets along well with her colleagues and supervisor. Customers often comment on her professionalism and friendliness and she has noticed that her communication skills have improved.
When she applied for the job and filled out her available hours, she made sure to state that she could only work a maximum of 20 hours per week as an international student. She mentioned it once more during the interview and was told it would not be a problem.
Since then her supervisor has asked her to work overtime in a few instances to accommodate a colleague who was running late. That was not a problem. However, recently her supervisor asked if she could pick up an extra shift for two weeks because one colleague was out sick. Mako is not comfortable working so many hours over her maximum, but she is worried her supervisor might be upset and think she is not a team player.
What should Mako do? How should she communicate her decision to her supervisor?
1d. Summary Writing
Read this article from Salesforce.com on the 10 Must-Have Communication Skills for Business Success . Summarize the article and identify which of these skills you would like to improve.
Content Attribution
This chapter contains content from Communication for Business Professionals – Canadian Edition which was adapted from Business Communication for Success in 2013 by University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing through the eLearning Support Initiative . The 2018 revision continues to be licensed with a Creative Commons license (CC BY-NC-SA) following the precedent of a publisher who has requested that they and the original author not receive attribution.
Ellis, R. and Ann McClintock, You Take My Meaning: Theory into Practice in Human Communication (London: Edward Arnold, 1990), 71.
Leavitt, H., & Mueller, R. (1951). Some effects of feedback on communication. Human Relations, 4 , 401–410.
McLean, S. (2003). The basics of speech communication . Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
McLean, S. (2005). The basics of interpersonal communication (p. 10). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
NACE. (2018). Employers Want to See These Attributes on Students’ Resumes. Retrieved August 26, 2020, from https://www.naceweb.org/talent-acquisition/candidate-selection/employers-want-to-see-these-attributes-on-students-resumes/
Pearson, J. C., & Nelson, P. E. (2000). An introduction to human communication: understanding and sharing . Boston: McGraw Hill.
Schramm, W., The Beginnings of Communication Study in America (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1997).
Video Attribution
This chapter contains the video Types of Communication Interpersonal, Non Verbal, Written Oral Video Lesson Transcript Stud by Zaharul Hafiq from YouTube.com.
Chapter 1: Effective Business Communication by Venecia Williams is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The Science of Strong Business Writing
- Bill Birchard

Lessons from neurobiology
Brain scans are showing us in new detail exactly what entices readers. Scientists can see a group of midbrain neurons—the “reward circuit”—light up as people respond to everything from a simple metaphor to an unexpected story twist. The big takeaway? Whether you’re crafting an email to a colleague or an important report for the board, you can write in a way that delights readers on a primal level, releasing pleasure chemicals in their brains.
Bill Birchard is an author and writing coach who’s worked with many successful businesspeople. He’s drawn on that experience and his review of the scientific literature to identify eight features of satisfying writing: simplicity, specificity, surprise, stirring language, seductiveness, smart ideas, social content, and storytelling. In this article, he shares tips for using those eight S’s to captivate readers and help your message stick.
Strong writing skills are essential for anyone in business. You need them to effectively communicate with colleagues, employees, and bosses and to sell any ideas, products, or services you’re offering.
- Bill Birchard is a business author and book-writing coach. His Writing for Impact: 8 Secrets from Science That Will Fire Up Your Reader’s Brain will be published by HarperCollins Leadership in April 2023. His previous books include Merchants of Virtue, Stairway to Earth, Nature’s Keepers, Counting What Counts, and others. For more writing tactics, see his website .
Partner Center
How to Write a Business Essay for Impactful Communication and Analysis

So, you've got a business essay coming up, and you're feeling a mix of excitement and a tad bit overwhelmed, right? Totally get it. Writing a business essay might sound boring, but trust me, it's a skill that's gonna come in handy when you're out there in the real world.
In this article, we're dishing out some awesome tips just for you. Think of it as your secret weapon to tackle those business essays like a pro. We'll keep it real, easy, and super practical – no fancy jargon or complicated theories. Let's dive into the world of business essay writing, where your words can make a big impact. In case you lack time or motivation to finish your assignment, use our business essay writing service to streamline the process.
What Is a Business Essay
Business essays are written pieces that explore and analyze various aspects of business-related topics, often focusing on management, marketing, finance, or entrepreneurship. They provide a platform for students and professionals to articulate their understanding of business concepts, theories, and real-world applications. Typically written in a formal and structured manner, a business essay requires critical thinking, research skills, and the ability to communicate ideas effectively. Whether delving into case studies, discussing industry trends, or evaluating business strategies, the essay aims to provide insights, draw conclusions, and contribute to a deeper understanding of the dynamic world of business.
.webp)
How to Write an Introduction for a Business Essay
A business essay introduction sets the tone for the entire paper and captures the reader's attention. Here are some steps and tips to help you write an effective introduction for a business essay:
- Understand the Purpose of the Introduction
Clearly understand the purpose of your essay. Are you providing an overview of a business concept, analyzing a case study, or arguing a specific point? Tailor your introduction accordingly.
- Start with a Hook
Grab the reader's attention with a compelling hook. This could be a relevant quote, a surprising fact, a rhetorical question, or a thought-provoking statement. The goal is to make the reader want to continue reading.
- Provide Context
After the hook, provide some background or context related to the topic of your essay. Help the reader understand the significance and relevance of the subject matter in the business world.
- Thesis Statement
Clearly state your thesis or the main argument of your essay. This should be a concise and focused statement that outlines what the reader can expect from the rest of the essay. Make sure it is specific and reflects the purpose of your writing.
- Outline the Scope
Briefly outline the main points or areas that your essay will cover. This gives the reader a roadmap of what to expect and helps them understand the structure of your essay.
- Use Clear and Concise Language
Keep your introduction clear and concise. Avoid unnecessary jargon or complex language that might confuse the reader. Aim for clarity and precision.
- Be Relevant
Ensure that every sentence in your introduction is directly related to the topic of your essay. Avoid going off on tangents or providing excessive information that doesn't contribute to the main points.
- Consider the Tone
Choose a tone that is appropriate for your audience and the nature of your essay. Business essays can vary in tone, from formal and academic to more conversational, depending on the context.
Are You a Business Student with a Hectic Schedule?
Try our professional writing service – it can do wonders for your curriculum!
Business Essay Introduction Example
Here’s an example of an introduction for an essay titled “The Rise of E-commerce: Shaping the Future of Retail”:
The retail landscape is undergoing a seismic shift as e-commerce continues to redefine the way consumers shop. In this essay, we explore the profound implications of this digital transformation on traditional retail models and analyze the key strategies businesses are employing to thrive in this dynamic environment. From changing consumer behaviors to the strategic use of technology, the impact of e-commerce on the retail sector is undeniable, prompting businesses to adapt or face the risk of obsolescence.
How to Write a Business Essay
Working on a business essay might seem daunting, but it doesn't have to be. In this guide, we'll break down the process into simple steps to help you navigate through it smoothly. In this next section. We’ll be breaking down the essentials of drawing up a business essay from start to finish. From defining your main argument to structuring your points effectively, let's explore the key strategies that will set you on the path to success.
%20(2).webp)
Analyze the Prompt
Start by carefully reading and understanding the essay prompt. This involves breaking down the question to grasp what it's asking for, identifying the main topics, and recognizing any specific tasks or points to cover. This step helps you set the stage for a focused and relevant essay by ensuring you address all aspects mentioned in the prompt. You can hire a business essay writer to expedite the process if you want.
Think of a Thesis Statement
When writing a business essay, think of the thesis statement as the essay's compass. It should be a concise, strong sentence that lays out your main argument or viewpoint on the topic. Your thesis guides the entire essay, so make sure it's specific, debatable, and gives readers a clear idea of what to expect in your writing.
Create an Outline
We’ve already shared tips on how to write an introduction for a business essay, so let’s move on to the next stages. Organize your thoughts by outlining the main points and structure of your essay. This doesn't have to be too detailed; just a roadmap that helps you see how different ideas connect. An outline ensures a logical flow in your writing and prevents you from going off track. By the way, have you already picked business essay topics ? If not, here’s a list of great ideas you can use!
Provide Topic Background
Before diving into your main points, the business essay writing format implies giving your reader some context about the topic. Briefly introduce the key concepts, relevant facts, or historical background that will help readers understand the importance and relevance of your essay.
Write the Main Body
Start developing your essay by expanding on the main points outlined in your thesis. Each paragraph should focus on a specific idea or argument supported by evidence or examples. Be clear and concise, ensuring a smooth transition between paragraphs. It’s the most difficult part of the assignment, meaning you can use our college essay service to simplify it.
Write a Conclusion
Summarize your key points and conclusively restate your thesis. The conclusion should tie up the loose ends and leave a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid introducing new information but rather reinforce your main argument. For more details about how to write a conclusion for an essay , please refer to our guide.
Add a Bibliography
List all the sources you used in your research. Be meticulous about citing your references properly, following the chosen format (APA, MLA, etc.). This adds credibility to your essay and avoids plagiarism issues.
Edit and Proofread
As you’ve learned how to write a business essay, it’s time to master the art of self-revising. Review your essay for clarity, coherence, and grammatical errors. Editing ensures that your ideas flow smoothly, and proofreading catches any overlooked mistakes. It's a crucial step to polish your essay and present a professional piece of writing. Do you have another assignment on business management ? This guide will help you!
Choose the Writing Format
Reiterate the importance of selecting and adhering to the chosen writing format throughout the essay. Consistency in formatting, citations, and other style elements contributes to the overall professionalism of your work.
Business Essay Example
Business essay examples offer practical assistance to students tackling assignments by showcasing the application of essential writing principles in a real-world context. As a tangible reference, it demonstrates an effective essay structure and how to formulate a clear thesis statement and provide coherent arguments. By examining examples, students can glean insights into research techniques, proper citation practices, and overall essay organization, empowering them to approach their business assignments with increased confidence and proficiency.
Example 1: “The Impact of Technological Advancements on Modern Business Operations”
This essay explores the multifaceted impact of technology on operational efficiency, innovation, customer relations, and global connectivity. From integrating automation and artificial intelligence for streamlined processes to facilitating global expansion through digital platforms, technology emerges as a driving force shaping the success and sustainability of contemporary enterprises. While acknowledging the numerous benefits, the essay also highlights the challenges and ethical considerations inherent in adopting these technologies, emphasizing the need for businesses to navigate these complexities responsibly for long-term growth and competitiveness.
Example 2: “Sustainable Business Practices: A Strategic Imperative for Corporate Success”
This essay explores the pivotal role of sustainable business practices as a strategic imperative for corporate success in the contemporary entrepreneurship scene. Addressing environmental concerns, social consciousness, and economic viability, the essay delves into the multifaceted benefits of adopting sustainable approaches. It discusses how businesses can align profitability with responsible practices, emphasizing environmental stewardship, social impact, and community engagement. The essay underscores the importance of regulatory compliance and risk mitigation in business by examining the economic advantages and innovation opportunities arising from sustainable initiatives.
Final Considerations
Students engage in writing business essays to develop essential skills and knowledge crucial for success in the professional world. These essays serve as a platform for honing critical thinking, analytical, and communication skills, allowing students to articulate and analyze complex business concepts. Through the process of researching, organizing thoughts, and constructing coherent arguments, students gain a deeper understanding of business principles and practices. Business essays also cultivate the ability to synthesize information, evaluate various perspectives, and present well-reasoned conclusions. If you find with task troublesome, you can always tell us, ‘ write my research paper ,’ and one of our wordsmiths will fulfill the assignment quickly.
Writing Business Essays Doesn’t Work for You?
Here’s an alternative – an expert writer with relevant experience and proper skills.
How Many Paragraphs Does a Business Essay Have?
What is the most important part of a business essay, how do you start off a business essay, related articles.
.webp)

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Communication skills in business
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Business essays
- Reading time: 5 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 5 December 2019*
- File format: Text
- Words: 1,394 (approx)
- Number of pages: 6 (approx)
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 1,394 words. Download the full version above.
Communication is very important in people’s lives. People communicate most of the time. Communication is a process of mutual understanding of two or more people. In general it is a mean of connecting people (Cora, 2006) Communication skills are some of the most important skills that you need to succeed in the workplace. We talk to people face to face, and we listen when people talk to us. We write emails and reports, and we read the documents that are sent to us. Communication, therefore, is a process that involves at least two people which is a sender and a receiver. For it to be successful, the receiver must understand the message in the way that the sender intended (Dr. Knna Muthiah, 2012). Thus, communication skill is one of the most important skill in business. This essay aims at stating the significant role of writing and listening and analysing what extent of speaking is the most effective tool for business communication. People often says that “speaking is silver, writing is gold” as stated in David J. Lehner in his article of speaking and writing. Written communication is a mean of communication in which transfer of information from one party to another is done in a written form. There are many example of written communications such as newsletters, memos, books, articles, circulars, reports, posters or even notices. Writing has four stages familiarisation, controlled writing, guided writing and free writing (Badger & White, 1999). Writing is more formal way of communicating compare with speaking. In today’s business world, writing plays a significant role as most of the business contract are finished by writing (J. Flowerdew, 1993). Writing helps to give records, proves and evidence to the person we are communicating because writing is a permanent means of communication. It is very useful if any proof or evidence is needed in communicating. Since they are permanent, written forms of communication also enable recipients to take more time in reviewing the message and providing appropriate feedback. Another advantage of writing is that written messages do not have to be delivered exactly on the spot instead, they can be edited and revised several times before they are sent so that the content can be shaped to maximum effect. Because of these fact, written forms of communication are more suitable to more complex business message that need to includes important information and figures. Therefore, good writing skills will improves inter-organisational efficiency, customer satisfaction and improves organisation image (Bonner, William H., & Lillian H. Chaney, 2003) There are also disadvantages of writing, unlike oral communication people can see face reaction which helps the message sent to be clearer which in written communication the sender could not receive an immediate feedback to his or her message. This may frustrate the sender and may lead to uncertainty in business situation in which immediate response is required. In addition, written communication often take more time to compose. However many organisation realised this situation and offer their employees an online writing course or writing workshop to help them structure their letter or mail efficiently (Murphy, Herta A., & Herbert W. Hildebrandt, 1997). On the other hand, speaking has been playing an important role is business world. People communicate often to do business. Communication is key in building relationship for business. The vast majority of executives still feels that speaking is essential for business purpose, according to a 2009 Forbes Insights survey of more than 750 business professionals. Furthermore, a few respondents said they preferred speaking over technology enabled communicating such as emailing. Speaking “build stronger, more meaningful business relationships,” while allowing better social opportunities to bond with clients and coworkers. It is also easier to read body language and facial expressions and interpret nonverbal communication signals. Respondents overwhelmingly agreed speaking is best for persuasion, leadership, engagement, inspiration, decision-making, accountability, candor, focus and reaching a consensus. Besides that in speaking directly, there is no delay and speakers can get immediate feedback so they can evaluate the level of understanding of their listener. Quick adjustment can be made to change people’s perception or understanding to get a better positive feedbacks. It may help listeners to get better understanding on speaker’s message. Nevertheless. There are also disadvantages towards speaking. While communication via speaking is generally preferable. Email and instant messenger communication can accelerate the discussion for large groups in instances where members can’t interrupt their work schedules to meet. Email is more reliable to do schedule and confirm meetings because people tend to forget, it’s the nature of people’s behavior. Memos are best for longer background pieces that require a deeper level of understanding towards a certain topic. On top of that, speaking did not leave any record so there is no reference available after the conversation to refer as an evidence. Frequently this leads to conflicts and misunderstandings because people cannot remember the message that are sent before or misheard the conversation because of the noise from other speakers. Speakers have to consider the mindset of listeners to be on the same page otherwise the conversation will be ineffective. Speaking should be brief and simple, complicated and complex materials cannot be employ People should be aware of ways speaking and writing complement each other. However speaking and writing are identical in nature. Many studies suggest that speaking is more interesting and clearer to its audience. As Peter Elbow has shown in his article, there are several ways in which writing can be described to reflect stereotyped speech attributes and vice versa. His conclusion is that people should has special awareness of the special relationship between writing and speaking in business (Peter, 1985) People has to know the importance of both method and how to use them. Senders of messages need to adapt to the message and the way communicating to each situation. Both speaking and writing, has various functions in international business communication respectively. To build relationship meeting with each other is more appropriate. Research shows that even with the best products and business practices, you still need strong relationships to succeed in this marketplace. Business is a people activity, people tend to do business with people they know, like, and trust. They prefer to do business with those who they have relationship with. The stronger the relationships with your customers, the greater will be their trust and loyalty in your business (Holz, 2005). The reason of building relationship is to make business through developing relationship with certain people. Talking to each other is a common way of getting to know them. It is a way of people expanding their relationship circle to meet new people like business banquets, celebration or even canteen. Speaking is the most efficient method to know each other and to build trust. Without trust, there can be no cooperation, support and help from others. Whereas, in other context of communication such as reports, emails and letters, writing is important particularly in informal occasion. In fact, the ability to write and present well organised report can effect on the advancement and promotion to greater extent especially for technical hands, managerial personnel and government officials. Speaking is important making negotiation, it is a process between two or more parties. Seeking to discover a common ground and reach an agreement to settle a matter of mutual concern or resolve a conflict. In conclusion, speaking has advantages such as the speed is fast and it can get immediate feedback and modify the ways of speaking to get the message clear. Besides that, listeners can interpret nonverbal message clearer based on the body language used by the speakers. However, speaking is quite short and simple plus there is no record or evidence of the conversation. Listeners, have a great influence to the effect and efficiency of speaking. In contrast, writing is a more formal way of communicating and provides records. It can be send to many people but the speed of interaction is slower compare to speaking and there is no immediate feedback and nonverbal communication. Writers cannot adjust the strategy to influence objectives. In business communication, eventhough in most occasion speaking is being used more than writing, professionals should take suitable methods in communicating. Mix methods of combining writing and speaking is relatively important in certain situations to get a more effective communications considering there are particular occasion, individual, external and internal organisational circumstances and background including social, cultural and ethical barriers.
...(download the rest of the essay above)
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Communication skills in business . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/business-essays/communication-skills-in-business/> [Accessed 16-03-24].
These Business essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.

Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays
Privacy Overview
How to Use Collaborative Communication at Your Business
Updated: March 11, 2024
Published: June 01, 2023
Knowing how to communicate with workers, managers, and even customers is vital to your business’s success.

This is especially true as the workforce turns virtual, and companies may have workers spread across the globe.
To maintain a productive workforce, train your managers and workers in collaborative communication, which can improve alignment, productivity, and workplace satisfaction.
![communication in business essay Download Now: Complete Guide to Collaborating at Work [Free Guide + Templates]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/7b7e92ee-1d6f-46e1-a984-3c0aa19eb448.png)
Collaborative communication definition
Collaborative communication involves two or more individuals working together, and requires seamless communication (in person or virtually) to discuss ideas and topics. The purpose is to create an environment where everyone in the group can easily share and receive information from one another to complete a task or goal.
It’s best used in scenarios where a group needs ongoing contact to leverage each other’s expertise on a subject.
For example, marketing, product, and sales teams have unique perspectives of the brand, product, and customer experience that make them excellent contributors to the planning of a new brand strategy.
So they open a Slack group to allow open discussions throughout the day to share information about competitor research, market research, relevant news stories, and ideas to guide the brand strategy’s planning and execution.
What makes collaborative communication unique is that it emphasizes sharing knowledge and responsibilities between everyone — without collaboration, the project, task, or goal wouldn’t be reached.
Everyone’s feedback holds weight in decision-making. Other communication methods are just that — a way to send information, but don’t require consistent back and forth to complete a task.
Collaborative communication in business
Collaborative communication can improve a business’s performance and positively impact internal and external stakeholder relationships.
Internal collaborative communication
Internal collaborative communication is when individuals within a company work together and share their opinions, ideas, and expertise to complete a task or reach a common goal.
Adopting collaborative communication methods in your business can enhance your teams’ efficiency, productivity, and creativity. It empowers your people to draw knowledge and experience from one another, so they can make better decisions and provide better outcomes in their daily tasks.
Communicating collaboratively reduces or eliminates roadblocks, and improves motivation and confidence. About three-quarters of employees consider collaboration and teamwork essential.
Plus, it shows workers you care about their success. A 2020 State of Workplace Empathy Report reveals 76% of employees feel an empathetic company can inspire and motivate workers. When done right, it removes hierarchical barriers, enhances work processes, and streamlines distributed/hybrid/remote teams.
Businesses can foster collaborative communication by:
- Hosting virtual brainstorming meetings to give everyone a voice.
- Creating a forum where employees can ask questions about company policies, culture, and initiatives.
- Building a knowledge database or wiki where teams can share information and learn from each other.
- Encourage cross-team meetings and create chat channels to make it easier to reach people across the organization.
External collaborative communication
External collaborative communication is when individuals within a company work with individuals outside of a company to share opinions, insights, and knowledge to complete a task or goal.
For example, an online clothing store may partner with multiple brand ambassadors or influencers to promote its products. So the company builds an online forum where the chosen ambassadors can communicate with the brand and each other about ideas for upcoming launches.
The ambassador’s connection with the brand’s customer base means they’ll have insights into how to reach them effectively.
Another example is a finance company building a tool to help customers track business expenses that enlists the help of current customers. The company provides a free demo account to 20 customers and opens a Slack channel.
In this channel, the company and customers discuss problems and ideas to improve the product design and functionality before its release.
Using current customers means the company will get insights from the people they’re targeting, increasing the odds of attracting more buyers in the future.
Other scenarios in which a business may use external collaborative communication:
- Research projects
- Educational partnerships
- Joint ventures
Collaborative communication skills
Constantly communicating may not come naturally to everyone. To hone in on your collaborative communication skills, try to work on the following skill sets:
Active listening : Hearing what someone is saying while actively participating in the conversation. Active listening involves understanding, paraphrasing, summarizing, asking clarifying questions, and offering suggestions.
Communication etiquette : Knowing how to interact with others to foster positive relationships. This includes understanding the different dialects and tones used in the conversation.
Organized thinking : Organizing your thoughts, ideas, and data — and presenting it in an easily understandable format.
Confidence : Having the courage to stand up for your ideas and beliefs while still considering the thoughts of others.
Empathy : Putting yourself in someone else’s shoes and seeing things from their perspective. Empathy allows for better problem-solving and a deeper understanding of the different perspectives of the group.
Negotiation: Reaching agreements with stakeholders and successfully managing conflict in a respectful, helpful, and productive manner. Negotiations can create a shared understanding between the group and move them closer to the desired outcome.
Team building : Creating a shared vision among stakeholders and an environment of trust that inspires cooperation among team members.
Critical thinking : Analyzing situations and coming up with solutions based on facts and logic. This skill is crucial during important conversations, as it helps everyone stay focused while considering different perspectives.
Creativity : Thinking outside the box and generating innovative ideas that meet the needs of the team. Allow everyone to express their ideas and thoughts during collaborative conversations, so the team can come up with unique solutions.
Relationship building : Building trust and rapport with others, understanding how different people think, and connecting with them in meaningful ways. It also includes handling conflicts peacefully and bringing the group closer together.
Resilience : Handling stress and coming back stronger than before. Resilience allows people to stay focused on their goals while dealing with setbacks.
Leadership : Knowing how to cultivate trust, encourage participation, and ensure everyone stays motivated. A strong leader ensures all aspects of the conversation remain productive, while finding ways to help each person understand the others’ points of view.
Guidelines for collaborative communication
While sharing information is critical in the workplace, there’s a right and wrong way of doing it.
For instance, employees state that 41% of the information they receive isn’t relevant to their role. This means businesses are mass-sending business communications versus segmenting them to those who will find them most useful.
Here’s a look at best practices to make collaborative communication more effective:
- Encourage participation from all team members by asking for input from everyone (be mindful of introverts who prefer to send comments after)
- Set clear expectations and goals, and assign roles for the collaboration (who will be involved and guiding the collaboration)
- Be open and honest about ideas, opinions, and disagreements
- Acknowledge and respect the contributions of each team member
- Encourage active listening and eliminate distractions like notifications and noisy backgrounds (if on video calls)
- Take responsibility for mistakes and focus on solutions
- Provide and accept constructive criticism
- Avoid assumptions and seek clarification when needed
- Exercise empathy for all team members
- Prevent information overload (and sending irrelevant information)
- Accept creative conflict to show teams how to critique in an open and safe environment
Collaborative communication examples
Collaborative communication in the real world is unique to each business. Some use it for internal teams only, while others regularly engage with customers to collect valuable feedback.
Antonella Pisani, CEO of digital marketing and consulting firm Eyeful Media, uses a mix of one-on-one and small group meetings to discuss shared lessons and projects.
Communication tools they use include:
- 15five to facilitate meaningful one-on-ones
- Google Meet for small group meetings
- Slack for real-time and asynchronous conversations
- Asana to track and hold people accountable for deadlines
While collaborative communication is excellent for meetings and project planning, Althea Wiles, CEO of J Althea Creative, a florist education consulting program, uses it in the field. Her team uses voice calls, emails, videos, texts, and social messengers to communicate with each other and their clients.
She also runs a floral design studio, Rose of Sharon Floral Design, where her team collaborates with local florists to maintain an inventory of flowers.
“Someone may get an order for red flowers and not have them in inventory,” says Wiles. “They [can] send out a group text thread to see what others have available. They can then buy a few to fill the order, which allows them to make a better profit and allows others to move some inventory.”
But what about fully remote businesses? David Ellis, founder of SEO agency Teranga Digital Marketing, thrives on using tools like Loom, Slack, and Clickup to reduce meeting overwhelm.
“Working in a remote business with people from nearly six different time zones can get difficult without a foolproof communication and collaboration strategy in place,” says Ellis.
So he introduced the MyCheckins tool for teams to share daily updates each morning, and created three questions everyone must answer:
- What have I accomplished since our last meeting/yesterday (1-3 highlights)?
- What are your priority tasks for the day (1-3 highlights)?
- Is there anything you’d like support with or want to discuss in our meeting today?
“This helps everyone stay on the same page, plus we don’t waste time during our half-hour daily check-in to share updates that can be shared via a simple message.”
Tools for collaborative communication
Having the right tools makes it easier to collaborate with teams, no matter where they are in the building or world. A Gartner Digital Worker Experience Survey shows nearly 80% of workers used collaboration tools in the workplace in 2021.
Here’s a list of commonly used collaboration tools :
- Slack : Communication platform that can facilitate discussions and share files between teams in real time.
- Trello : Project management tool that monitors the progress of projects, assigns tasks to individuals, and tracks deadlines.
- Asana : Task management tool that can assign tasks to team members, set deadlines, and track progress.
- Google Docs : A collaborative document that allows teams to work on the same page.
- Zoom : Video conferencing software for virtual meetings.
- HubSpot's AI Content Assistant Tools : Generate agendas and mission statements to coordinate different teams towards one common goal.
- Google Workspace : Integrated workplace suite that can manage emails, calendars, and collaborative documents.
- Loom : Screen and video recording tool for sharing audio and visual information.
- Hotjar : Website analytics tool that can measure user engagement and send feedback surveys to gather customer insights while they’re using your site or web app.
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, 'ad22bdd9-fd50-4b35-a4f5-7586f5a61a1e', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
What did you think of this article .
Give Feedback

Don't forget to share this post!
Learn strategies for working together in different settings and access to 9 free templates to boost productivity.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

Essay on Effective Business Communication
Students are often asked to write an essay on Effective Business Communication in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Effective Business Communication
What is business communication.
Business communication is how people share information in a company. This can be done in different ways like meetings, emails, or phone calls. Good communication helps a business run smoothly and successfully.
Importance of Effective Communication
Effective communication is very important in business. It helps everyone understand what they need to do. When people communicate well, they can work together better and make the business more successful.
Types of Business Communication
There are two main types of business communication: internal and external. Internal communication is when people inside the business talk to each other. External communication is when the business talks to people outside, like customers or partners.
Improving Business Communication
To improve business communication, it’s important to be clear and concise. This means saying exactly what you mean in a simple way. It’s also important to listen to others and respond to their ideas.
Impact of Effective Communication
When a business communicates effectively, it can solve problems faster, make better decisions, and build stronger relationships. This can lead to more success and growth for the business.
In conclusion, effective communication is key to a successful business. It helps everyone work together and understand what they need to do. By improving communication, a business can become more successful and grow.
250 Words Essay on Effective Business Communication
Business communication is how people share information in a company. It can be between two people, a group, or even between two companies. This sharing can be about plans, ideas, updates, or any other company matters.
Importance of Business Communication
Good business communication is very important. It helps keep everyone in the company on the same page. This means everyone knows what they need to do and what is happening in the company. It also helps build strong relationships between people in the company.
There are two main types of business communication: verbal and written. Verbal communication is when people talk face-to-face or on the phone. Written communication is when people write emails, reports, or memos. Both types are important and used often in business.
Keys to Effective Business Communication
To have good business communication, there are a few things you should do. First, be clear and simple. Make sure your message is easy to understand. Second, be respectful. Treat others as you want to be treated. Third, listen well. This shows you value the other person’s ideas and thoughts.
In conclusion, effective business communication is very important. It helps companies run smoothly and builds strong relationships. To be good at it, you need to be clear, respectful, and a good listener.
500 Words Essay on Effective Business Communication
Business communication is the sharing of information between people inside a company to help achieve the company’s goals. It also involves sharing information with people outside the company. This kind of communication can be spoken, written, or even non-verbal (like body language or signs).
Importance of Effective Business Communication
Good business communication is very important. It helps people understand what they need to do and how to do it. It can also help a company do better in the business world.
For example, if a boss can clearly tell their employees what they need to do, the employees can do their jobs better. Or, if a company can clearly tell its customers about its products, the customers will be more likely to buy them.
Key Elements of Effective Business Communication
There are a few key things that can make business communication more effective.
First, the communication needs to be clear. This means that the person sending the message needs to make sure that the person receiving the message can understand it.
Second, the communication needs to be accurate. This means that the information being shared needs to be correct.
Third, the communication needs to be timely. This means that the information needs to be shared at the right time. For example, if a company is having a sale, they need to tell their customers about it before the sale starts, not after it has already ended.
Ways to Improve Business Communication
There are many ways to improve business communication.
One way is to make sure that the person sending the message is clear about what they want to say. They should think about their message before they send it. They should also make sure that their message is easy to understand.
Another way is to make sure that the person receiving the message understands it. They should ask questions if they don’t understand something. They should also make sure that they understand what they are supposed to do after they receive the message.
Finally, a company can use technology to improve their communication. For example, they can use email or video calls to share information. They can also use social media to share information with their customers.
In conclusion, effective business communication is very important. It can help a company do better in the business world. It can also help people do their jobs better. By making sure that their communication is clear, accurate, and timely, a company can make their business communication more effective. They can also use technology to improve their communication.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Effect Of Technology On Communication
- Essay on Effect Of Social Media On Youth
- Essay on Effect Of Social Media On Society
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More From Forbes
How to improve team communication within your business.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Whether your team consists of everyone working in one place, remotely, or a hybrid option, maintaining good, clear communication between everyone is a common struggle among leaders.
Teamwork depends on good communication. As workplace dynamics continue to present communication ... [+] challenges, don’t overlook the importance of using the basics of effective conversation.
Ineffective communication can lower productivity , decrease job satisfaction, and impact stress levels. Poor communication also impacts trust in leadership and peers. So, how can you improve the way people exchange information in your organization and its overall effectiveness? Here are a few examples.
Explain The Reasons Behind Tasks
With the fast pace of day-to-day responsibilities, focusing on accomplishing tasks and initiatives can take precedence. You want to move projects to the next step, cross high priorities off your list and feel good about where you’re headed. Although it may be obvious to you why something needs to get done, it may not be to everyone.
Say you tell the marketing team that the ad campaigns they’ve been working on need a different voice or new direction. You’ve also informed the group that the company will be hiring an outside agency to help. Imagine not talking about the reasons for these changes. Employees on the team are bound to fire up the rumor mill. Even if they don’t talk amongst themselves, wouldn’t they feel uncertain about their skills and futures with the company?
But what if you take the time to explain what new direction you’re looking for and how the agency fits in? Furthermore, you explain how the changes will help the company achieve its goals and how the group can contribute. Suddenly, there are fewer opportunities for rumors to start because there’s less uncertainty behind the changes. The group understands what the business wants to achieve and how all contributors fit into the bigger picture.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024, learn about different communication styles and tools.
Expecting someone to change their communication style is like demanding they change their personality. You’re going to fight a losing battle. Plus, you won’t exactly be building bridges. The only thing you’ll be doing is driving a wedge between you. Perhaps you think it’s a great idea to hold regular brainstorming sessions and meetings on the fly. However, the lack of structure and open forum may be more challenging for employees who need time to prepare.
Personality and communication preferences often go hand in hand. The team’s introverts may need to think through their thoughts alone before presenting them to the group. Expecting them to speak up without preparation does them a disservice. Likewise, you may have a mix of direct and indirect communicators. Managing and engaging with a full range of styles can prevent conversations from stalling.
Using various communication tools can help accommodate diverse preferences and ensure effective communication. For example, utilizing a versatile screen recorder tool, like Zight, can be instrumental in accommodating different communication preferences . By providing the option to record and share information visually, it enhances clarity and comprehension by allowing team members to communicate complex ideas at their own pace and in their preferred format.
Another effective communication tool to consider is Miro. It’s a collaborative online whiteboard that allows team members to brainstorm, visualize ideas, and organize information in real-time.
No matter the communication tool you choose to use for your business, be sure to consider the different communication preferences on your team.
Hold Individual And Group Meetings
Yes, holding team meetings is critical for communication in the workplace. It gets everyone in the same room, lets group members talk about challenges together and efficiently disseminates information. Simultaneously, group discussions can overwhelm some of your team. A team setting may also not be the most appropriate place to discuss sensitive subjects.
In addition, you will have team members who communicate better in a one-to-one dynamic. Holding individual meetings in addition to group get-togethers gives these employees a voice. Regular one-on-ones also let all team members voice concerns and questions they may not want to express to peers. Managers get the chance to provide personalized guidance, especially when it comes to each employee’s career goals.
Individual meetings help develop relationships and build trust. Nonetheless, getting the frequency and duration right might take some experimentation. Research shows holding one-to-ones once a week for 30 minutes can be effective. But so can having individual meetings every two weeks for 45 minutes to an hour. You could also implement a mix of the two. The goal is to create environments where employees are comfortable opening up.
Improving Workplace Communication
The basics of good communication haven’t changed. Even though work arrangements and communication tools might be more multifaceted, productive exchanges start with transparency. Although communication involves exchanging information, effective conversations aren’t just about talking. It’s about understanding the dynamics at play while building relationships and reinforcing psychological safety. Without these factors, communication is simply added noise.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
Organizational Growth and Communication Essay

- Environment
- Information Science
- Social Issues
- Argumentative
- Cause and Effect
- Classification
- Compare and Contrast
- Descriptive
- Exemplification
- Informative
- Controversial
- Exploratory
- What Is an Essay
- Length of an Essay
- Generate Ideas
- Types of Essays
- Structuring an Essay
- Outline For Essay
- Essay Introduction
- Thesis Statement
- Body of an Essay
- Writing a Conclusion
- Essay Writing Tips
- Drafting an Essay
- Revision Process
- Fix a Broken Essay
- Format of an Essay
- Essay Examples
- Essay Checklist
- Essay Writing Service
- Pay for Research Paper
- Write My Research Paper
- Write My Essay
- Custom Essay Writing Service
- Admission Essay Writing Service
- Pay for Essay
- Academic Ghostwriting
- Write My Book Report
- Case Study Writing Service
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Coursework Writing Service
- Lab Report Writing Service
- Do My Assignment
- Buy College Papers
- Capstone Project Writing Service
- Buy Research Paper
- Custom Essays for Sale
Can’t find a perfect paper?
- Free Essay Samples
- Communication
communication in business
Updated 12 May 2022
Subject Communication , HR Management , Management , Workforce
Downloads 43
Category Business , Economics , Sociology
Topic Business Ethics , Business Plan , Business Success , Communication Skills , Organization , Organizational Culture , Organizational Structure , Technology in Business , Workplace
Communication Barriers in the Workplace
Communication is a two-way mechanism, and the inability to do so exposes an entity to a variety of challenges that can stymie a successful and productive communication process. One of the impediments to workplace contact is the physical barrier. The organizational structure can have an impact on the divide between top management and their subordinates, resulting in apprehension and seclusion from contact between the two parties (Jablin & Putnam, 2000).
Language and Cultural Barriers
Language barriers among members of the company can impede interpersonal communication among employees, resulting in misunderstandings and false impressions when expressing their opinions. Cultural barriers can emerge where people from a diverse culture may exhibit issues at work regarding their religion, race, and place of origin. An individual's social status may vary from that of other people, resulting in challenges in the communication process. The ranking of people that is, the high and low-context cultures may impact on the interpretation of information among workers. Gender differences are another barrier, where one gender may have more favors than another thus discomfort of one group from communication with another team that might feel superior.
Organizational Strategies for Effective Communication
Within the organization, there is an embracement of an open organization structure to engage the members and make them feel inclusive. There is, however, entertainment programs that allow all members of the organization to mingle and interact freely. It is a company that encourages diversity training in different languages, especially for the minority cultural group in the firm to involve all its members without them feeling inferior to their workmates (Samovar, Porter, McDaniel & Roy, 2014).
Empowerment and Equal Opportunities
The organization gives clear chances for all members to play a role in the decision making process on the issues that affect them directly. By this, the workers can feel that their opinions and contributions are valued and have a sense of belonging to the firm. There's empowerment of both the female and male employees where there are equal rights and chances for both genders to abolish any barriers between the two (Jablin & Putnam, 2000). The organization values and offers same opportunities to the contribution of every single member irrespective of class and social status, as each person is of great importance in the work environment.
Benefits of Team-Based Communication
A team-based communication method in the workplace concentrates on the collaboration of its group members towards the achievement of universal organizational objectives. It facilitates trust, accountability, and empowerment to all members of the work environment. In teamwork, there is open communication that leads to better decision making and the most appropriate business strategies towards a common interest. Working together gives room for creativity and innovativeness for the growth and development of the company (Jablin & Putnam, 2000).
Transparency and Trust
Union among members in completing their tasks strengthens and brings motivation to achieve the goals of the organization. Team building brings about direct communication among group members; therefore, everyone can stay updated on issues that concern employees' performance in the workplace. It brings about prioritizing, flexibility, efficiency, team spirit, and clarity on work outline. Transparency and open communication channels eliminate fear and difficulty in discussing different matters and giving feedback, and this can enhance the trust among employees and therefore excellent performance.
Strategies for Intercultural Communication
There are various strategies to address intercultural communication in a work environment. In the global world, cross-cultural communication is essential in every organization due to interaction amongst people worldwide. Training and development programs on different cultures through the support of the organization can help promote effective communication. The workforce should be aware of their own culture, willing to learn, curious, listen and observe, and engage in various activities with different cultural groups at regular times. An organization should promote intercultural sensitivity to allow cohesiveness and the enrichment of the organization's cultural identity. Adoption of cross-cultural communication ensures that there is involvement of all workers where the organization concentrates on the employee behavior and not their cultural backgrounds (Samovar et al., 2014). Workshops, work trips, and other activities can help reconcile employees' differences, with their relationships built on respect for each other's way of life.
Jablin, F. M., & Putnam, L. L. (Eds.). (2000). The new handbook of organizational communication: Advances in theory, research, and methods. Sage Publications.
Samovar, L. A., Porter, R. E., McDaniel, E. R., & Roy, C. S. (2014). Intercultural communication: A reader. Cengage Learning.
Deadline is approaching?
Wait no more. Let us write you an essay from scratch
Related Essays
Related topics.
Find Out the Cost of Your Paper
Type your email
By clicking “Submit”, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy policy. Sometimes you will receive account related emails.
A generative AI reset: Rewiring to turn potential into value in 2024
It’s time for a generative AI (gen AI) reset. The initial enthusiasm and flurry of activity in 2023 is giving way to second thoughts and recalibrations as companies realize that capturing gen AI’s enormous potential value is harder than expected .
With 2024 shaping up to be the year for gen AI to prove its value, companies should keep in mind the hard lessons learned with digital and AI transformations: competitive advantage comes from building organizational and technological capabilities to broadly innovate, deploy, and improve solutions at scale—in effect, rewiring the business for distributed digital and AI innovation.
About QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey
QuantumBlack, McKinsey’s AI arm, helps companies transform using the power of technology, technical expertise, and industry experts. With thousands of practitioners at QuantumBlack (data engineers, data scientists, product managers, designers, and software engineers) and McKinsey (industry and domain experts), we are working to solve the world’s most important AI challenges. QuantumBlack Labs is our center of technology development and client innovation, which has been driving cutting-edge advancements and developments in AI through locations across the globe.
Companies looking to score early wins with gen AI should move quickly. But those hoping that gen AI offers a shortcut past the tough—and necessary—organizational surgery are likely to meet with disappointing results. Launching pilots is (relatively) easy; getting pilots to scale and create meaningful value is hard because they require a broad set of changes to the way work actually gets done.
Let’s briefly look at what this has meant for one Pacific region telecommunications company. The company hired a chief data and AI officer with a mandate to “enable the organization to create value with data and AI.” The chief data and AI officer worked with the business to develop the strategic vision and implement the road map for the use cases. After a scan of domains (that is, customer journeys or functions) and use case opportunities across the enterprise, leadership prioritized the home-servicing/maintenance domain to pilot and then scale as part of a larger sequencing of initiatives. They targeted, in particular, the development of a gen AI tool to help dispatchers and service operators better predict the types of calls and parts needed when servicing homes.
Leadership put in place cross-functional product teams with shared objectives and incentives to build the gen AI tool. As part of an effort to upskill the entire enterprise to better work with data and gen AI tools, they also set up a data and AI academy, which the dispatchers and service operators enrolled in as part of their training. To provide the technology and data underpinnings for gen AI, the chief data and AI officer also selected a large language model (LLM) and cloud provider that could meet the needs of the domain as well as serve other parts of the enterprise. The chief data and AI officer also oversaw the implementation of a data architecture so that the clean and reliable data (including service histories and inventory databases) needed to build the gen AI tool could be delivered quickly and responsibly.
Our book Rewired: The McKinsey Guide to Outcompeting in the Age of Digital and AI (Wiley, June 2023) provides a detailed manual on the six capabilities needed to deliver the kind of broad change that harnesses digital and AI technology. In this article, we will explore how to extend each of those capabilities to implement a successful gen AI program at scale. While recognizing that these are still early days and that there is much more to learn, our experience has shown that breaking open the gen AI opportunity requires companies to rewire how they work in the following ways.
Figure out where gen AI copilots can give you a real competitive advantage
The broad excitement around gen AI and its relative ease of use has led to a burst of experimentation across organizations. Most of these initiatives, however, won’t generate a competitive advantage. One bank, for example, bought tens of thousands of GitHub Copilot licenses, but since it didn’t have a clear sense of how to work with the technology, progress was slow. Another unfocused effort we often see is when companies move to incorporate gen AI into their customer service capabilities. Customer service is a commodity capability, not part of the core business, for most companies. While gen AI might help with productivity in such cases, it won’t create a competitive advantage.
To create competitive advantage, companies should first understand the difference between being a “taker” (a user of available tools, often via APIs and subscription services), a “shaper” (an integrator of available models with proprietary data), and a “maker” (a builder of LLMs). For now, the maker approach is too expensive for most companies, so the sweet spot for businesses is implementing a taker model for productivity improvements while building shaper applications for competitive advantage.
Much of gen AI’s near-term value is closely tied to its ability to help people do their current jobs better. In this way, gen AI tools act as copilots that work side by side with an employee, creating an initial block of code that a developer can adapt, for example, or drafting a requisition order for a new part that a maintenance worker in the field can review and submit (see sidebar “Copilot examples across three generative AI archetypes”). This means companies should be focusing on where copilot technology can have the biggest impact on their priority programs.
Copilot examples across three generative AI archetypes
- “Taker” copilots help real estate customers sift through property options and find the most promising one, write code for a developer, and summarize investor transcripts.
- “Shaper” copilots provide recommendations to sales reps for upselling customers by connecting generative AI tools to customer relationship management systems, financial systems, and customer behavior histories; create virtual assistants to personalize treatments for patients; and recommend solutions for maintenance workers based on historical data.
- “Maker” copilots are foundation models that lab scientists at pharmaceutical companies can use to find and test new and better drugs more quickly.
Some industrial companies, for example, have identified maintenance as a critical domain for their business. Reviewing maintenance reports and spending time with workers on the front lines can help determine where a gen AI copilot could make a big difference, such as in identifying issues with equipment failures quickly and early on. A gen AI copilot can also help identify root causes of truck breakdowns and recommend resolutions much more quickly than usual, as well as act as an ongoing source for best practices or standard operating procedures.
The challenge with copilots is figuring out how to generate revenue from increased productivity. In the case of customer service centers, for example, companies can stop recruiting new agents and use attrition to potentially achieve real financial gains. Defining the plans for how to generate revenue from the increased productivity up front, therefore, is crucial to capturing the value.
Upskill the talent you have but be clear about the gen-AI-specific skills you need
By now, most companies have a decent understanding of the technical gen AI skills they need, such as model fine-tuning, vector database administration, prompt engineering, and context engineering. In many cases, these are skills that you can train your existing workforce to develop. Those with existing AI and machine learning (ML) capabilities have a strong head start. Data engineers, for example, can learn multimodal processing and vector database management, MLOps (ML operations) engineers can extend their skills to LLMOps (LLM operations), and data scientists can develop prompt engineering, bias detection, and fine-tuning skills.
A sample of new generative AI skills needed
The following are examples of new skills needed for the successful deployment of generative AI tools:
- data scientist:
- prompt engineering
- in-context learning
- bias detection
- pattern identification
- reinforcement learning from human feedback
- hyperparameter/large language model fine-tuning; transfer learning
- data engineer:
- data wrangling and data warehousing
- data pipeline construction
- multimodal processing
- vector database management
The learning process can take two to three months to get to a decent level of competence because of the complexities in learning what various LLMs can and can’t do and how best to use them. The coders need to gain experience building software, testing, and validating answers, for example. It took one financial-services company three months to train its best data scientists to a high level of competence. While courses and documentation are available—many LLM providers have boot camps for developers—we have found that the most effective way to build capabilities at scale is through apprenticeship, training people to then train others, and building communities of practitioners. Rotating experts through teams to train others, scheduling regular sessions for people to share learnings, and hosting biweekly documentation review sessions are practices that have proven successful in building communities of practitioners (see sidebar “A sample of new generative AI skills needed”).
It’s important to bear in mind that successful gen AI skills are about more than coding proficiency. Our experience in developing our own gen AI platform, Lilli , showed us that the best gen AI technical talent has design skills to uncover where to focus solutions, contextual understanding to ensure the most relevant and high-quality answers are generated, collaboration skills to work well with knowledge experts (to test and validate answers and develop an appropriate curation approach), strong forensic skills to figure out causes of breakdowns (is the issue the data, the interpretation of the user’s intent, the quality of metadata on embeddings, or something else?), and anticipation skills to conceive of and plan for possible outcomes and to put the right kind of tracking into their code. A pure coder who doesn’t intrinsically have these skills may not be as useful a team member.
While current upskilling is largely based on a “learn on the job” approach, we see a rapid market emerging for people who have learned these skills over the past year. That skill growth is moving quickly. GitHub reported that developers were working on gen AI projects “in big numbers,” and that 65,000 public gen AI projects were created on its platform in 2023—a jump of almost 250 percent over the previous year. If your company is just starting its gen AI journey, you could consider hiring two or three senior engineers who have built a gen AI shaper product for their companies. This could greatly accelerate your efforts.
Form a centralized team to establish standards that enable responsible scaling
To ensure that all parts of the business can scale gen AI capabilities, centralizing competencies is a natural first move. The critical focus for this central team will be to develop and put in place protocols and standards to support scale, ensuring that teams can access models while also minimizing risk and containing costs. The team’s work could include, for example, procuring models and prescribing ways to access them, developing standards for data readiness, setting up approved prompt libraries, and allocating resources.
While developing Lilli, our team had its mind on scale when it created an open plug-in architecture and setting standards for how APIs should function and be built. They developed standardized tooling and infrastructure where teams could securely experiment and access a GPT LLM , a gateway with preapproved APIs that teams could access, and a self-serve developer portal. Our goal is that this approach, over time, can help shift “Lilli as a product” (that a handful of teams use to build specific solutions) to “Lilli as a platform” (that teams across the enterprise can access to build other products).
For teams developing gen AI solutions, squad composition will be similar to AI teams but with data engineers and data scientists with gen AI experience and more contributors from risk management, compliance, and legal functions. The general idea of staffing squads with resources that are federated from the different expertise areas will not change, but the skill composition of a gen-AI-intensive squad will.
Set up the technology architecture to scale
Building a gen AI model is often relatively straightforward, but making it fully operational at scale is a different matter entirely. We’ve seen engineers build a basic chatbot in a week, but releasing a stable, accurate, and compliant version that scales can take four months. That’s why, our experience shows, the actual model costs may be less than 10 to 15 percent of the total costs of the solution.
Building for scale doesn’t mean building a new technology architecture. But it does mean focusing on a few core decisions that simplify and speed up processes without breaking the bank. Three such decisions stand out:
- Focus on reusing your technology. Reusing code can increase the development speed of gen AI use cases by 30 to 50 percent. One good approach is simply creating a source for approved tools, code, and components. A financial-services company, for example, created a library of production-grade tools, which had been approved by both the security and legal teams, and made them available in a library for teams to use. More important is taking the time to identify and build those capabilities that are common across the most priority use cases. The same financial-services company, for example, identified three components that could be reused for more than 100 identified use cases. By building those first, they were able to generate a significant portion of the code base for all the identified use cases—essentially giving every application a big head start.
- Focus the architecture on enabling efficient connections between gen AI models and internal systems. For gen AI models to work effectively in the shaper archetype, they need access to a business’s data and applications. Advances in integration and orchestration frameworks have significantly reduced the effort required to make those connections. But laying out what those integrations are and how to enable them is critical to ensure these models work efficiently and to avoid the complexity that creates technical debt (the “tax” a company pays in terms of time and resources needed to redress existing technology issues). Chief information officers and chief technology officers can define reference architectures and integration standards for their organizations. Key elements should include a model hub, which contains trained and approved models that can be provisioned on demand; standard APIs that act as bridges connecting gen AI models to applications or data; and context management and caching, which speed up processing by providing models with relevant information from enterprise data sources.
- Build up your testing and quality assurance capabilities. Our own experience building Lilli taught us to prioritize testing over development. Our team invested in not only developing testing protocols for each stage of development but also aligning the entire team so that, for example, it was clear who specifically needed to sign off on each stage of the process. This slowed down initial development but sped up the overall delivery pace and quality by cutting back on errors and the time needed to fix mistakes.
Ensure data quality and focus on unstructured data to fuel your models
The ability of a business to generate and scale value from gen AI models will depend on how well it takes advantage of its own data. As with technology, targeted upgrades to existing data architecture are needed to maximize the future strategic benefits of gen AI:
- Be targeted in ramping up your data quality and data augmentation efforts. While data quality has always been an important issue, the scale and scope of data that gen AI models can use—especially unstructured data—has made this issue much more consequential. For this reason, it’s critical to get the data foundations right, from clarifying decision rights to defining clear data processes to establishing taxonomies so models can access the data they need. The companies that do this well tie their data quality and augmentation efforts to the specific AI/gen AI application and use case—you don’t need this data foundation to extend to every corner of the enterprise. This could mean, for example, developing a new data repository for all equipment specifications and reported issues to better support maintenance copilot applications.
- Understand what value is locked into your unstructured data. Most organizations have traditionally focused their data efforts on structured data (values that can be organized in tables, such as prices and features). But the real value from LLMs comes from their ability to work with unstructured data (for example, PowerPoint slides, videos, and text). Companies can map out which unstructured data sources are most valuable and establish metadata tagging standards so models can process the data and teams can find what they need (tagging is particularly important to help companies remove data from models as well, if necessary). Be creative in thinking about data opportunities. Some companies, for example, are interviewing senior employees as they retire and feeding that captured institutional knowledge into an LLM to help improve their copilot performance.
- Optimize to lower costs at scale. There is often as much as a tenfold difference between what companies pay for data and what they could be paying if they optimized their data infrastructure and underlying costs. This issue often stems from companies scaling their proofs of concept without optimizing their data approach. Two costs generally stand out. One is storage costs arising from companies uploading terabytes of data into the cloud and wanting that data available 24/7. In practice, companies rarely need more than 10 percent of their data to have that level of availability, and accessing the rest over a 24- or 48-hour period is a much cheaper option. The other costs relate to computation with models that require on-call access to thousands of processors to run. This is especially the case when companies are building their own models (the maker archetype) but also when they are using pretrained models and running them with their own data and use cases (the shaper archetype). Companies could take a close look at how they can optimize computation costs on cloud platforms—for instance, putting some models in a queue to run when processors aren’t being used (such as when Americans go to bed and consumption of computing services like Netflix decreases) is a much cheaper option.
Build trust and reusability to drive adoption and scale
Because many people have concerns about gen AI, the bar on explaining how these tools work is much higher than for most solutions. People who use the tools want to know how they work, not just what they do. So it’s important to invest extra time and money to build trust by ensuring model accuracy and making it easy to check answers.
One insurance company, for example, created a gen AI tool to help manage claims. As part of the tool, it listed all the guardrails that had been put in place, and for each answer provided a link to the sentence or page of the relevant policy documents. The company also used an LLM to generate many variations of the same question to ensure answer consistency. These steps, among others, were critical to helping end users build trust in the tool.
Part of the training for maintenance teams using a gen AI tool should be to help them understand the limitations of models and how best to get the right answers. That includes teaching workers strategies to get to the best answer as fast as possible by starting with broad questions then narrowing them down. This provides the model with more context, and it also helps remove any bias of the people who might think they know the answer already. Having model interfaces that look and feel the same as existing tools also helps users feel less pressured to learn something new each time a new application is introduced.
Getting to scale means that businesses will need to stop building one-off solutions that are hard to use for other similar use cases. One global energy and materials company, for example, has established ease of reuse as a key requirement for all gen AI models, and has found in early iterations that 50 to 60 percent of its components can be reused. This means setting standards for developing gen AI assets (for example, prompts and context) that can be easily reused for other cases.
While many of the risk issues relating to gen AI are evolutions of discussions that were already brewing—for instance, data privacy, security, bias risk, job displacement, and intellectual property protection—gen AI has greatly expanded that risk landscape. Just 21 percent of companies reporting AI adoption say they have established policies governing employees’ use of gen AI technologies.
Similarly, a set of tests for AI/gen AI solutions should be established to demonstrate that data privacy, debiasing, and intellectual property protection are respected. Some organizations, in fact, are proposing to release models accompanied with documentation that details their performance characteristics. Documenting your decisions and rationales can be particularly helpful in conversations with regulators.
In some ways, this article is premature—so much is changing that we’ll likely have a profoundly different understanding of gen AI and its capabilities in a year’s time. But the core truths of finding value and driving change will still apply. How well companies have learned those lessons may largely determine how successful they’ll be in capturing that value.

The authors wish to thank Michael Chui, Juan Couto, Ben Ellencweig, Josh Gartner, Bryce Hall, Holger Harreis, Phil Hudelson, Suzana Iacob, Sid Kamath, Neerav Kingsland, Kitti Lakner, Robert Levin, Matej Macak, Lapo Mori, Alex Peluffo, Aldo Rosales, Erik Roth, Abdul Wahab Shaikh, and Stephen Xu for their contributions to this article.
This article was edited by Barr Seitz, an editorial director in the New York office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier

Rewired to outcompete

Meet Lilli, our generative AI tool that’s a researcher, a time saver, and an inspiration
Intercultural Communication in Business Essay
Introduction, developing effective communication, adapting to the local community’s culture.
This paper seeks to analyze a video case study from a film clip that shows a scene in which an expatriate developer from the United States is trying to get approval from Arab officials to establish a hospital. The developer comes with an American cultural mindset, where decision-making concerning changes is influenced by linear thinking and time schedules. On the other hand, the Arab official’s decision-making is influenced by different values. Therefore, change leaders must operate within the social and cultural rules in a specific context to develop effective communication and adapt to the local community’s culture.
The importance for change leaders to understand the social and cultural values when conducting business abroad cannot be underemphasized. Leaders of American organizations establishing businesses in foreign countries must have the knowledge and expertise to develop an organizational culture to promote a competitive advantage and foster change. The culture plays a vital role in an organization’s success, especially when conducting business overseas. According to Society for Human Resource Management (2018), “organizational leaders and Human Resource (HR) professionals should understand the national cultural values in the countries in which the organization operates to ensure that management and HR practices are appropriate and will be effective in operations in those countries” (p. 5). If the American developer could understand the reason Arab officials did not give their approval, they could reason with each other and come to an agreement.
The goal of an organizational leader when merging with a foreign business is to be fully engaged and have the means to foster change on a global scale. Cultural differences need to be considered when implementing an organizational culture in a foreign country. Top Leaders and HR representatives within organizations must be able to respond to various communication styles encountered by foreign counterparts effectively. Open communication lines are critical in initiating organizational changes and developing lasting relationships with foreign business leaders. However, positive communication cannot be established between representatives of two different cultures if they do not understand and value the social and cultural rules of each other and the differences between them, like the American developer and Arab officials in the case under discussion.
Organizations consider numerous factors when expanding their business to a foreign country. Two of the main reasons for global expansion are increasing customers and gaining market exposure. An organizational leader needs to fully understand the country’s social and cultural values when merging and conducting business. According to Abner (2015), “the cultural differences can determine whether the business is successful or not” (p. 1). Leaders need to research and analyze the values of the local communities. Leaders must know what products and services are needed by the consumers of foreign countries. Additionally, an important cultural factor to consider when conducting business overseas is the language differences encountered and how leaders plan to overcome those barriers. Having prior knowledge of cultural differences will save time when pursuing business abroad.
Every country worldwide has its own specific social and cultural norms, especially when conducting business. American organizational leaders must be able to adapt to other countries’ cultural norms. Numerous American organizations are venturing to European nations to establish businesses. Thus, they need to be aware of specific cultural and social norms. For instance, Uzialko (2018) reports that “in Italy, business is often personal, and relationship-driven, so expect to spend a significant amount of time getting to know your Italian business partners and developing a relationship with them” (p. 5). Many American organizational leaders are driven to make deals quickly, but some countries prefer developing relationships before conducting business. Thereby, the American developer in the case could have had more chances of gaining officials’ approval if the developer had been more sensitive to the local traditions.
Overall, developing effective communication and adapting to the local community’s culture are the primary reasons organizational leaders must consider the social and cultural rules in specific contexts. The video case demonstrates that the American developer and the Arab officials cannot agree since different values influence their decision-making. For an organization to be successful in the global market, leaders must conduct extensive research and fully understand the cultural and social values of the foreign country. If organization leaders do so, their companies have higher chances of establishing positive business relationships with foreign partners. However, if they fail to meet their partners’ expectations concerning other countries’ cultural and social norms, any chance of establishing a business overseas may be diminished.
Abner, B. (2015). 4 considerations before taking your business international. The Business Journals. Web.
Society for Human Resource Management. (2018). Understanding and developing organizational culture. Web.
Uzialko, A., C. (2022). 17 International business customs that could make or break a deal. Business News Daily. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 20). Intercultural Communication in Business. https://ivypanda.com/essays/intercultural-communication-in-business/
"Intercultural Communication in Business." IvyPanda , 20 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/intercultural-communication-in-business/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Intercultural Communication in Business'. 20 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Intercultural Communication in Business." October 20, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/intercultural-communication-in-business/.
1. IvyPanda . "Intercultural Communication in Business." October 20, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/intercultural-communication-in-business/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Intercultural Communication in Business." October 20, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/intercultural-communication-in-business/.
- Risk Management in a Real Estate Developer Company: Evergrande Group
- Intercultural Communication Perspectives
- Adapting Business to the New Consumer
- Diverse Contexts and Intercultural Communication at Work
- Adapting New Social, Economic and Technological Changes in Business
- Intercultural Communication Barriers
- Challenges of Effective Intercultural Communication
- Interpersonal and Intercultural Communication at the Workplace
- Challenges of Adapting to Another Culture
- Intercultural Communication Led by UNESCO
- Crisis Management & Communication During COVID-19
- Leadership Communication and Management
- Effective Communication at the Workplace
- The Subway Firm's Quality Assurance Department
- Communication Challenges Facing the Company: Business Letter

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Business communication can be very difficult at times but with the proper cooperation of models, the process gets simpler. Marketing communication models should consist of the sender, the message to be delivered, the medium through which the message will be delivered, the recipients as well as feedback. In this essay, I will present the basis ...
Introduction. Communication is important in people's lives, as it is a mean of exchanging information from one person to another (Kushal, n.d, pp 1). In business, communication is necessary, as it plays a role in negotiation between an entrepreneur and the customer, and between the distributor and the entrepreneurs, among others.
Summary. Transformational leaders are exceptional communicators. In this piece, the author outlines four communication strategies to help motivate and inspire your team: 1) Use short words to talk ...
Usage of virtual communication tools in business communication and negotiation - a factor of increased efficiency. TEM Journal, 3 (2), 167-174. This essay, "Importance of Communication in Business" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database. You can use it for research and reference purposes to write your own paper.
Abstract and Figures. Communication, as a management function is the process of creating, communicating and interpreting ideas, facts, opinions and feelings about work performance, organisational ...
Before writing a business communication essay, you need to understand perfectly what this term stands for. Business communication is an exchange of information, opinions, and ideas. This process can occur between people within one company or outside it. It can be intentional or unintentional, verbal or nonverbal, internal and external.
Business executives rate the ability of business communication skills as among the personal factors necessary in gaining a job. As stated by Hynes (2005)" effective business communication is the key to planning, leading, organizing, and controlling the resources of the organizations to achieve objectives" (Conrad & Newberry, 2011, p112).
Effective communication is the process of exchanging ideas, thoughts, opinions, knowledge, and data so that the message is received and understood with clarity and purpose. When we communicate effectively, both the sender and receiver feel satisfied. Communication occurs in many forms, including verbal and non-verbal, written, visual, and ...
Effective communication takes preparation, practice, and persistence. There are many ways to learn communication skills; the school of experience, or "hard knocks," is one of them. But in the business environment, a "knock" (or lesson learned) may come at the expense of your credibility through a blown presentation to a client.
This page of the essay has 477 words. Download the full version above. Communication is the key to success in any business. Whether you are trying to sell a product , answer a query or complaint or convince your colleagues to adopt a certain course of action , good communication often means the difference between success and failure. Moreover ...
Read more on Business communication or related topics Business writing and Neuroscience. Bill Birchard is a business author and book-writing coach. His Writing for Impact: 8 ...
Using effective communication skills can benefit a business and its employees in a variety of ways, including: 1. Building better teams. Effective communication builds a positive atmosphere where teams can flourish. When communication is positive and encouraging, team members become stronger and work better together.
Introduction. Business communication is abound in today's society. The ability to communicate has always had its advantages, with its rich history, and traditions, modern business communication is valued as a modern day concept. Business executives rate the ability of business communication skills as among the personal factors necessary in ...
Communication is at the core of most international business operations. Organizations are created, managed, lead, and dissolved through communication, which plays a major role in the exchange of knowledge, the development and maintenance of relationships, the negotiation of deals, and the establishment and preservation of partnerships.
These essays serve as a platform for honing critical thinking, analytical, and communication skills, allowing students to articulate and analyze complex business concepts. Through the process of researching, organizing thoughts, and constructing coherent arguments, students gain a deeper understanding of business principles and practices.
Communication is a process of mutual understanding of two or more people. In general it is a mean of connecting people (Cora, 2006) Communication skills are some of the most important skills that you need to succeed in the workplace. We talk to people face to face, and we listen when people talk to us. We write emails and reports, and we read ...
Businesses can foster collaborative communication by: Hosting virtual brainstorming meetings to give everyone a voice. Creating a forum where employees can ask questions about company policies, culture, and initiatives. Building a knowledge database or wiki where teams can share information and learn from each other.
Taylor, S. (2005). Communication for Business: A Practical Approach. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education Ltd. This essay, "Ensuring an Effective Business Communication" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database. You can use it for research and reference purposes to write your own paper.
Business Communication Essay example. Business communication needs to become interpersonal again. No matter how we believe our human forms came into existence, we were built to need personal contact and function best with face-to-face communication. As children, we desired comfort from touch, a hug from our mothers.
500 Words Essay on Effective Business Communication What is Business Communication? Business communication is the sharing of information between people inside a company to help achieve the company's goals. It also involves sharing information with people outside the company. This kind of communication can be spoken, written, or even non ...
Communication barriers: What they are and how to eliminate them. Let's examine each of the major barriers to effective communication—what they are, what they look like in practice, and ways to overcome them. 1 Language barriers. Language barriers involve miscommunications related to vernacular differences or translation difficulties.
Hold Individual And Group Meetings. Yes, holding team meetings is critical for communication in the workplace. It gets everyone in the same room, lets group members talk about challenges together ...
Organizational Growth and Communication Essay In order for healthcare organizations to effectively convey their planned expansion goals to stakeholders, it is imperative that they possess strong communication skills. The ability to communicate growth plans clearly and concisely is crucial for any healthcare business's success. It is essential for leaders to recognize the significance of ...
Currently, there is a particular trend in business communication such that communication is moving from the old types of face-to-face meetings to the utilization of modern technologies such as conferencing. The main point to note here is that effective communication forms part of the backbone of business operations.
Business Communication Essay example. Decent Essays. 1794 Words. 8 Pages. Open Document. Business communication needs to become interpersonal again. No matter how we believe our human forms came into existence, we were built to need personal contact and function best with face-to-face communication. As children, we desired comfort from touch, a ...
Communication is a two-way mechanism, and the inability to do so exposes an entity to a variety of challenges that can stymie a successful and productive communication process. One of the impediments to workplace contact is the physical barrier. The organizational structure can have an impact on the divide between top management and their ...
The ability of a business to generate and scale value from gen AI models will depend on how well it takes advantage of its own data. As with technology, targeted upgrades to existing data architecture are needed to maximize the future strategic benefits of gen AI: Be targeted in ramping up your data quality and data augmentation efforts.
An organizational leader needs to fully understand the country's social and cultural values when merging and conducting business. According to Abner (2015), "the cultural differences can determine whether the business is successful or not" (p. 1). Leaders need to research and analyze the values of the local communities.