
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download

Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Last modified on: 8 months ago
- Reading Time: 4 Minutes
Case Study Questions:
Question 1:
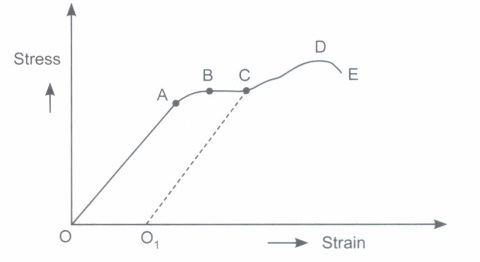
The graph shown below shows qualitatively the relation between the stress and the strain as the deformation gradually increases. Within Hooke’s limit for a certain region stress and strain relation is linear. Beyond that up to a certain value of strain the body is still elastic and if deforming forces are removed the body recovers its original shape.

1. If deforming forces are removed up to which point the curve will be retraced?
(a) upto OA only
(b) upto OB
(d) Never retraced its path
2. In the above question, during loading and unloading the force exerted by the material are conservative up to
(a) OA only
(b) OB only
(c) OC only
(d) OD only
3. During unloading beyond B , say C , the length at zero stress in now equal to
(a) less than original length
(b) greater than original length
(c) original length
(d) can’t be predicted
4. The breaking stress for a wire of unit cross-section is called
(a) yield point
(b) elastic fatigue
(c) tensile strength
(d) Young’s modulus
5. Substances which can be stretched to cause large strains are called
(a) isomers
(b) plastomers
(c) elastomers
(d) polymers
Related Posts
You may also like:, category lists (all posts).
All categories of this website are listed below with number of posts in each category for better navigation. Visitors can click on a particular category to see all posts related to that category.
- Full Form (1)
- Biography of Scientists (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions in Biology (37)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- DPP Biology for NEET (12)
- Blog Posts (35)
- Career Guidance (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths (12)
- Maths Formulas for Class 10 (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths (4)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 10 (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Science (23)
- HOTS for Class 10 Science (17)
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science (10)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Biology Solutions (4)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Chemistry Solutions (5)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Physics Solutions (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science (20)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (15)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Science (4)
- Study Notes for Class 10 Science (17)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Social Science (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science (24)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science (3)
- Topicwise Notes for Class 10 Social Science (4)
- CBSE CLASS 11 (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (11)
- Free Assignments for Class 11 Chemistry (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (8)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship (8)
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Entrepreneurship (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Formulas for Class 11 Maths (6)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths (17)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physical Education (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Physics (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics (12)
- Class 11 Physics Study Notes (5)
- Concept Based Notes for Class 11 Physics (2)
- Conceptual Questions for Class 11 Physics (10)
- Derivations for Class 11 Physics (3)
- Extra Questions for Class 11 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- Numerical Problems for Class 11 Physics (4)
- Physics Formulas for Class 11 (7)
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- CBSE CLASS 12 (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology (13)
- Case Studies for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (5)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (8)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry (16)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 English (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Geography (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 History (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 History (13)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (5)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths (13)
- Maths Formulas for Class 12 (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Problems Based on Class 12 Maths (1)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physics (16)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- Class 12 Physics Conceptual Questions (16)
- Class 12 Physics Discussion Questions (1)
- Class 12 Physics Latest Updates (2)
- Derivations for Class 12 Physics (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Physics (4)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Physics (8)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (18)
- Numerical Problems Based on Class 12 Physics (16)
- Physics Class 12 Viva Questions (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Physics (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Notes for Class 12 Political Science (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Worksheets for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Science (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science (9)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science (26)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths (13)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science (19)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Maths (12)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science (18)
- NCERT Notes for Class 7 Science (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths (5)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science (18)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Science (19)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Social Science (30)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Maths (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths (6)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science (11)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Science (2)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science (4)
- Numerical Problems for Class 8 Science (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 8 Science (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Social Science (27)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science (23)
- CBSE Class 9 English Beehive Notes and Summary (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths (11)
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths (6)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths (12)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Maths (3)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Maths (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 9 (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 9 Science (22)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (11)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Science (1)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Science (15)
- Topic wise MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (2)
- Topicwise Questions and Answers for Class 9 Science (15)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Social Science (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science (19)
- CHEMISTRY (8)
- Chemistry Articles (2)
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) (3)
- Books for CBSE Class 9 (1)
- Books for ICSE Class 10 (3)
- Editable Study Materials (8)
- Exam Special for CBSE Class 10 (3)
- H. C. Verma (Concepts of Physics) (13)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Biology (14)
- Extra Questions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (1)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (5)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Maths (16)
- Important Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (4)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Physics (8)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Maths (7)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Physics (10)
- Topicwise Problems for IIT Foundation Mathematics (4)
- Challenging Physics Problems for JEE Advanced (2)
- Topicwise Problems for JEE Physics (1)
- DPP for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Chemistry (6)
- Chapterwise Questions for JEE Main Physics (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main Physics (8)
- Physics Revision Notes for JEE Main (4)
- JEE Mock Test Physics (1)
- JEE Study Material (1)
- JEE/NEET Physics (6)
- CBSE Syllabus (1)
- Maths Articles (2)
- NCERT Books for Class 12 Physics (1)
- NEET Chemistry (13)
- Important Questions for NEET Physics (17)
- Topicwise DPP for NEET Physics (5)
- Topicwise MCQs for NEET Physics (32)
- NTSE MAT Questions (1)
- Physics (1)
- Alternating Current (1)
- Electrostatics (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (2)
- PowerPoint Presentations (13)
- Previous Years Question Paper (3)
- Products for CBSE Class 10 (15)
- Products for CBSE Class 11 (10)
- Products for CBSE Class 12 (6)
- Products for CBSE Class 6 (2)
- Products for CBSE Class 7 (5)
- Products for CBSE Class 8 (1)
- Products for CBSE Class 9 (3)
- Products for Commerce (3)
- Products for Foundation Courses (2)
- Products for JEE Main & Advanced (10)
- Products for NEET (6)
- Products for ICSE Class 6 (1)
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance (1)
- Topic Wise Study Notes (Physics) (2)
- Topicwise MCQs for Physics (2)
- Uncategorized (138)
Test series for students preparing for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams are available. We also provide test series for School Level Exams. Tests for students studying in CBSE, ICSE or any state board are available here. Just click on the link and start test.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Case Study Questions Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluid
Case study questions class 11 physics chapter 10 mechanical properties of solid.
CBSE Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Mechanical Properties of Solid. Important Case Study Questions for Class 11 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Mechanical Properties of Solid.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Solid
Case study – 1.
The pressure is then defined in a limiting sense as –

Pressure is a scalar quantity. We remind the reader that it is the component of the force normal to the area under consideration. Its dimensions are [ML -1 T -2 ] The SI unit of pressure is N m -2 . It has been named as Pascal (Pa) in honor of the French scientist Blaise Pascal (1623-1662) who carried out pioneering studies on fluid pressure.
The French scientist Blaise Pascal observed that the pressure in a fluid at rest is the same at all points if they are at the same height. Whenever external pressure is applied on any part of a fluid contained in a vessel, it is transmitted undiminished and equally in all directions. This is another form of the Pascal’s law and it has many applications in daily life. A number of devices, such as hydraulic lift and hydraulic brakes, are based on the Pascal’s law.
The pressure of the atmosphere at any point is equal to the weight of a column of air of unit cross-sectional area extending from that point to the top of the atmosphere. At sea level, it is 1.013 × 10 5 Pa (1atm) . Italian scientist Evangelista Torricelli (1608–1647) devised for the first time a method for measuring atmospheric pressure. This device is known as ‘mercury barometer’ the space above the mercury column in the tube which is atmospheric pressure, P a .
Where r is the density of mercury and h is the height of the mercury column in the tube.
1) Mercury barometer is used to measure
a) atmospheric pressure
b) gauge pressure
c) both a and b
d) none of these
2) Pressure is
3) State Pascal’s law.
4) What is atmospheric pressure?
5) Write applications of Pascal’s law
Answer key – 1
3) the pressure in a fluid at rest is the same at all points if they are at the same height. Whenever external pressure is applied on any part of a fluid contained in a vessel, it is transmitted undiminished and equally in all directions.
4) The pressure of the atmosphere at any point is equal to the weight of a column of air of unit cross-sectional area extending from that point to the top of the atmosphere.
5) Following are applications of Pascal’s law
a) Hydraulic lift
b) Hydraulic jack
c) Hydraulic machines
d) Hydraulic brakes
Case Study – 2
Variation of pressure with depth
Thus, the pressure P, at depth below the surface of a liquid open to the atmosphere is greater than atmospheric pressure by an amount rgh. The excess of pressure, P − P a , at depth h is called a gauge pressure at that point. The area of the cylinder is not appearing in the expression of absolute pressure. Thus, the height of the fluid column is important and not cross-sectional or base area or the shape of the container. The liquid pressure is the same at all points at the same horizontal level called as hydrostatic paradox. The flow of the fluid is said to be steady if at any given point, the velocity of each passing fluid particle remains constant in time. This does not mean that the velocity at different points in space is same. The velocity of a particular particle may change as it moves from one point to another. That is, at some other point the particle may have a different velocity, but every other particle which passes the second point behaves exactly as the previous particle that has just passed that point. Each particle follows a smooth path, and the paths of the particles do not cross each other. The path taken by a fluid particle under a steady flow is a streamline. It is defined as a curve whose tangent at any point is in the direction of the fluid velocity at that point. For steady flow equation of continuity hold good and it is a statement of conservation of mass in flow of incompressible fluids. In general
Av = constant
Av gives the volume flux or flow rate and remains constant throughout the pipe of flow. Thus, at narrower portions where the streamlines are closely spaced, velocity increases and it’s vice versa. Steady flow is achieved at low flow speeds. Beyond a limiting value, called critical speed, this flow loses steadiness and becomes turbulent. One sees this when a fast flowing stream encounters rocks, small foamy whirlpool-like regions called white water rapids are formed.
1) The flow of the fluid is said to be steady if at any given point, the velocity of each passing fluid particle
a) Remains constant in time
b) changes continuously
c) continuously increasing
d) None of these
2) According to equation of continuity area is
a) Directly proportional to velocity
b) Inversely proportional to velocity
c) Does not depends upon velocity
3) Give equation of continuity
4) Write a note on Variation of pressure with depth. Give its formula
5) What is hydrostatic paradox?
Answer key – 2
3) For steady flow equation of continuity hold good and it is a statement of conservation of mass in flow of incompressible fluids. In general
Av gives the volume flux or flow rate
Thus, the pressure P, at depth below the surface of a liquid open to the atmosphere is greater than atmospheric pressure by an amount rgh. The excess of pressure, P − P a , at depth h is called a gauge pressure at that point.
5) The liquid pressure is remains the same at all points at the same horizontal level independent on area at base called as hydrostatic paradox.
Case Study – 3
The pressure of the atmosphere at any point is equal to the weight of a column of air of unit cross-sectional area extending from that point to the top of the atmosphere. At sea level, it is 1.013 × 10 5 Pa (1 atm). Italian scientist Evangelista Torricelli (1608–1647) devised for the first time a method for measuring atmospheric pressure.
Where r is the density of mercury and h is the of the mercury column in the tube In the experiment it is found that the mercury column in the barometer has a height of about 76 cm at sea level equivalent to one atmosphere (1 atm). This can also be obtained using the value of r. A common way of stating pressure is in terms of cm or mm of mercury (Hg). A pressure equivalent of 1 mm is called a torr (after Torricelli). 1 torr = 133 Pa. The mm of Hg and torr are used in medicine and physiology. In meteorology, a common unit is the bar and millibar.1 bar = 10 5 Pa. An open tube manometer is a useful instrument for measuring pressure differences.
1) Who gave for the first time a method for measuring atmospheric pressure?
c) Torricelli
d) None of the above
2) 1 torr is equal to
3) What is 1 torr? Where it is used?
4) Which device is used for measurement of pressure difference?
5) What is atmospheric pressure?
Answer key-3
3) A pressure equivalent of 1 mm is called a torr 1torr = 133 Pa.
The mm of Hg and torr are used in medicine and physiology.
4) An open tube manometer is a useful instrument for measuring pressure differences.
5) The pressure of the atmosphere at any point is equal to the weight of a column of air of unit cross-sectional area extending from that point to the top of the atmosphere. At sea level, it is 1.013 × 10 5 Pa (1 atm). 76 cm at sea level equivalent to one atmosphere (1 atm).
Case Study – 4
Whenever external pressure is applied on any part of a fluid contained in a vessel, it is transmitted undiminished and equally in all directions. This is another form of the Pascal’s law and it has many applications in daily life. A number of devices, such as hydraulic lift and hydraulic brakes, are based on the Pascal’s law. In these devices, fluids are used for transmitting pressure.
Fluid flow is a complex phenomenon. Bernoulli’s principle helps in explaining blood flow in artery. The artery may get constricted due to the accumulation of plaque on its inner walls. In order to drive the blood through this constriction a greater demand is placed on the activity of the heart. The speed of the flow of the blood in this region is raised which lowers the pressure inside and the artery may collapse due to the external pressure. The heart exerts further pressure to open this artery and forces the blood through. As the blood rushes through the opening, the internal pressure once again drops due to same reasons leading to a repeat collapse. This may result in heart attack.
Dynamic lift is the force that acts on a body, such as airplane wing, a hydrofoil or a spinning ball, by virtue of its motion through a fluid. In many games such as cricket, tennis, baseball, or golf, we notice that a spinning ball deviates from its parabolic trajectory as it moves through air. This deviation can be partly explained on the basis of Bernoulli’s principle. A ball which is spinning drags air along with it. If the surface is rough more air will be dragged. shows the streamlines of air for a ball which is moving and spinning at the same time. The ball is moving forward and relative to it the air is moving backwards. Therefore, the velocity of air above the ball relative to the ball is larger and below it is smaller .The stream lines, thus, get crowded above and rarified below. This difference in the velocities of air results in the pressure difference between the lower and upper faces and there is a net upward force on the ball. This dynamic lift due to spining is called Magnus effect.
The Venturi-meter is a device to measure the flow speed of incompressible fluid. The principle behind this meter has many applications. The carburetor of automobile has a Venturi channel (nozzle) through which air flows with a high speed. The pressure is then lowered at the narrow neck and the petrol (gasoline) is sucked up in the chamber to provide the correct mixture of air to fuel necessary for combustion. Filter pumps or aspirators, Bunsen burner, atomisers and sprayers used for perfumes or to spray insecticides work on the same principle.
1) The Venturi-meter is a device used to measure the
a) Flow speed of incompressible fluid.
b) Area occupied by fluid.
c) Volume occupied by fluid
2) hydraulic brakes works on principle of
a) Pascal’s law
b) Newton’s law
c) Bernoulli’s principle
3) With the help of Bernoulli’s principle. How heart attack happens?
4) Explain Magnus effect with example of ball with spin in air.
5) What is dynamic lift?
Answer key – 4
3) With the help of Bernoulli’s principle we can explain heart attack phenomenon. The artery may get constricted due to the accumulation of plaque on its inner walls. In order to flow the blood through this constriction a large pressure is exerted on heart. The speed of the flow of the blood in this region is raised which lowers the pressure inside and the artery may collapse due to the external pressure. The heart exerts further pressure to open this artery and forces the blood through. As the blood flows fast trough the opening, the internal pressure once again drops due to same reasons leading to a repeat collapse. This result in heart attack.
4) A ball which is spinning drags air along with it. If the surface is rough more air will be dragged. When ball is moving forward and relative to it the air is moving backwards. Therefore, the velocity of air above the ball relative to the ball is larger and below it is smaller. This difference in the velocities of air results in the pressure difference between the lower and upper faces and there is a net upward force on the ball. This dynamic lift due to spining is called Magnus effect.
5) Dynamic lift is the force that acts on a body due to its motion through a fluid. In many games such as cricket, tennis, we notice that a spinning ball deviates from its parabolic trajectory this is nothing but dynamic lift.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Neet Online Test Pack
12th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் subjects.

கணினி பயன்பாடுகள்

கணினி அறிவியல்
வணிகக் கணிதம் மற்றும் புள்ளியியல்.

கணினி தொழில்நுட்பம்

கணக்குப்பதிவியல்

English Subjects

Computer Science

Business Maths and Statistics

Accountancy

Computer Applications

Computer Technology

11th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

9th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

Social Science

சமூக அறிவியல்
6th standard stateboard question papers & study material.

10th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

7th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

8th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

கணிதம் - old

12th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Introductory Micro and Macroeconomics

Business Studies

Indian Society

Physical Education

Bio Technology

Engineering Graphics

Entrepreneurship

Hindi Elective

Home Science

Legal Studies

Political Science

11th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Mathematics

Enterprenership

Applied Mathematics
10th standard cbse subject question paper & study material.

9th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

8th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

7th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

6th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

School Exams

Tamil Nadu State Board Exams

Scholarship Exams

Study Materials , News and Scholarships

Stateboard Tamil Nadu

Free Online Tests

Educational News

Scholarships

Entrance Exams India

Video Materials

11th Standard CBSE
Class 11th Physics - Mechanical Properties of Solids Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023

Class 11th Physics - Mechanical Properties of Solids Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023 Study Materials Sep-09 , 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 11 Physics Subject - Mechanical Properties of Solids, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.

A PHP Error was encountered
Severity: Warning
Message: in_array() expects parameter 2 to be array, null given
Filename: material/details.php
Line Number: 1436
Message: Use of undefined constant EXAM - assumed 'EXAM' (this will throw an Error in a future version of PHP)
Line Number: 1438
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Mechanical properties of solids case study questions with answer key.
Final Semester - June 2015
The atoms in solids are held together by interatomic forces. the average locations of the atoms in a lattice do not change with time and lack mobility. This makes a solid rigid and becomes a cause of elasticity in solids. In some solids such as steel, the atoms are bound together by larger inter-atomic forces than in others. Thus elastic behaviour varies from solid to solid. Even fluids exhibit elasticity. All material bodies get deformed when subjected to a suitable force. The ability of a body to regain its original shape and size is called elasticity. The deforming force per unit area is called stress. The change in dimension divided by the original dimension is called strain. The three kinds of stresses are tensile stress, shearing stress and volumetric stress similarly strains too. According to Hooke's law, within the elastic limit stress is proportional to strain. (i) Which state of matter has volume elasticity? (ii) When we stretch a wire, we have to perform work. Why? What happens to the energy given to the wire in this process? (iii) Define elastic limit. (iv) Define modulus of elastcity on what factors does it depend? (v) Why solids are more elastic and gases are least? (vi) The ratio of radii of two wires of same material is 2 : 1. If these wires are stretched by equal force, find the ratio of stresses Produced in them.
When an elastic body is subjected repeatedly to the action of alternating deforming forces, its behaviour corresponds to that of less elastic bodies due to elastic fatigue. In our daily life, elastic properties are considered while designing a structure of the material. For example, the metallic parts of the machinery are never subjected to a stress beyonds elastic limit otherwise they will get permanently deformed. The thickness of the metallic rope used in the crane in order to lift a given load is decided from the knowledge of elastic limit of the material of the rope and the factor of safety. Similarly the bridges are designed in such a way that they do not bend much or break under the load of heavy traffic, force of strongly blowing wind and its own weight. (i) What does it mean by elastic after effect? (ii) Define elastic fatigue (iii) Why are bridges and girders given I shape? (iv) A hollow shaft is found to be stronger than a solid shaft made of some equal material against twisting. Explain why? (v) Define Poisson's ratio (vi) An elastic wire is cut to half its original length. How would it affect the maximum load that the wire can support? (vii) Why is a spring made of steei, not of copper? (viii) Why are the bridges declared unsafe after long use?
A thin rod of negligible mass and cross-sectional area 4 x 10 -6 m -2 , suspended vertically from one end, has a length of 0.5 m at 100° C, The rod is cooled to 0° C, Young's modulus is 10 11 Nm -2 , Coefficient of linear expansion = 10 - 5 K -1 and g = 10 ms -2 . (i) Determine the decrease in length of the rod on cooling. (ii) What mass must be attached at the lower end of the rod so that the rod is prevented from contracting on cooling? (iii) Determine the total energy stored in the rod. (iv) What is origin of elastic potential energy in a stretched wire? Give its relation with Young's modulus and strain.
*****************************************
- Previous Class 11th Physics - Waves Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
- Next Class 11th Physics - Oscillation Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
Reviews & Comments about Class 11th Physics - Mechanical Properties of Solids Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023

Write your Comment

11th Standard CBSE Physics Videos
CBSE 11th Physics Sample Model Question Paper with Answer Key 2023
11th Standard CBSE Physics Usefull Links

- 10th Standard
Other 11th Standard CBSE Subjects

Other 11th Standard CBSE Physics Study material
Class 11th physics - waves case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 11th physics - oscillation case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 11th physics - kinetic theory case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 11th physics - thermodynamics case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 11th physics - thermal properties of ... click to view, class 11th physics - mechanical properties of ... click to view, class 11th physics - gravitation case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 11th physics - system of particles ... click to view, class 11th physics - work, energy and ... click to view, class 11th physics - motion in a ... click to view, class 11th physics - units and measurements ... click to view, class 11th physics - physical world case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, 11th standard cbse physics annual exam model question 2020 click to view, register & get the solution for class 11th physics - mechanical properties of solids case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.

Atomistic Properties of Solids pp 261–289 Cite as
Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Dinker B. Sirdeshmukh 4 ,
- Lalitha Sirdeshmukh 4 &
- K. G. Subhadra 5
- First Online: 01 January 2011
1901 Accesses
1 Citations
Part of the book series: Springer Series in Materials Science ((SSMATERIALS,volume 147))
As we proceed along,we will see that the elastic properties of solids have twofold importance. Firstly,they indicate the mechanical strength of the solid. Secondly,they are very important in understanding the nature of the interatomic forces and in the analysis of lattice vibrations.
- Elastic Property
- Elastic Constant
- Polycrystalline Aggregate
- Crystal Classis
- Isotropic Elastic Medium
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
K.A. Gschneidner,Jr.,Solid State Phys. 16 ,275 (1964)
Article Google Scholar
S.N. Vaidya,G.C. Kennedy,J. Phys. Chem. Solids 31 ,2329 (1970)
Article ADS Google Scholar
S. Bhagavantham, Crystal Symmetry and Physical Properties (Academic Press,New York,1966)
Google Scholar
J.F. Nye, Physical Properties of Crystals (Oxford University Press,London,1957)
MATH Google Scholar
M. Born,K. Huang, Dynamical Theory of Crystal Lattices (Oxford University Press,London,1954)
Y.I. Sirotin,Shaskolskaya, Fundamentals of Crystal Physics (Mir Publishers,Moscow,1982)
H.B. Huntington,Solid State Phys. 7 ,213 (1958)
P.J. Reddy, Crystal Elasticity (Sri Venkateshwara University,Tirupathi,1977)
K.S. Krishnan,S.K. Roy,Proc. Roy. Soc. (London) A210 ,481 (1952)
ADS Google Scholar
R.N. Thurston,H.J. McSkimmin,P. Andreatch Jr.,J. Appl. Phys. 37 ,267 (1966)
J.R. Drabble,R.E. Strathen. Phys. Soc. 92 ,1090 (1967)
S. Haussuhl,P. Preu,Acta Cryst. A34 ,44 (1978)
D.B. Sirdeshmukh,L. Sirdeshmukh,K.G. Subhadra, Alkali Halides – A Handbook of Physical Properties (Springer,Berlin,2001)
W. Voigt,Ann. Phys. (Leipz.) 38 ,573 (1889)
A. Reuss,Z. Angew Math. Phys. 9 ,49 (1929)
R. Hill,Proc. Phys. Soc. (Lond.) A65 ,349 (1952)
H.M. Ledbetter,E.R. Naimon,J. Appl. Phys. 45 ,66 (1974)
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Kakatiya University, Santoshnagar Colony 23A, 500059, Hyderabad, India
Professor Dinker B. Sirdeshmukh & Lalitha Sirdeshmukh
Kakatiya University, Manasarovar Heights- Phase II 832/9, 500009, Secunderabad, India
K. G. Subhadra
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Dinker B. Sirdeshmukh .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Sirdeshmukh, D.B., Sirdeshmukh, L., Subhadra, K.G. (2011). Mechanical Properties of Solids. In: Atomistic Properties of Solids. Springer Series in Materials Science, vol 147. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-19971-4_8
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-19971-4_8
Published : 05 July 2011
Publisher Name : Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN : 978-3-642-19970-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-642-19971-4
eBook Packages : Physics and Astronomy Physics and Astronomy (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Mechanical Properties of Solids
A material is said to be in the solid state if all the atoms of that matter are densely packed together. A solid material has a definite shape and size. In order to change the shape and size of the solid object, an external force needs to be applied. In this chapter, we will learn about the Mechanical Properties of Solids.
- Elasticity and Plasticity
- Applications of Elastic Behaviour of Materials
- Stress and Strain
- Elastic Moduli
- Hooke’s Law and Stress-strain Curve
Customize your course in 30 seconds
- CBSE Class 10th
CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Main Registration
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- GATE 2024 Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Animation Courses
- Animation Courses in India
- Animation Courses in Bangalore
- Animation Courses in Mumbai
- Animation Courses in Pune
- Animation Courses in Chennai
- Animation Courses in Hyderabad
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Pune
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Hyderabad
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Design Colleges in India
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- DDU Entrance Exam
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET PG Admit Card 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Application Form 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET PG Courses 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster

Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Access premium articles, webinars, resources to make the best decisions for career, course, exams, scholarships, study abroad and much more with
Plan, Prepare & Make the Best Career Choices
Mechanical Properties of Solids
Introduction: If all of the atoms in a substance are closely packed together, it is considered to be in the solid-state. The shape and dimensions of solid material are fixed. An external force must be applied to modify the shape and size of the solid item. The Mechanical Properties of Solids will be covered in this chapter.
Latest: JEE Main: high scoring chapters | Past 10 year's papers
Don't Miss: Most scoring concepts for NEET | NEET papers with solutions
New: Aakash iACST Scholarship Test. Up to 90% Scholarship. Register Now
Solids' mechanical properties define properties such as strength and deformation resistance. It represents an object's ability to endure the stress that is applied to it. Elasticity, plasticity, strength, abrasion, hardness, ductility, brittleness, malleability, and toughness are examples of mechanical qualities.
There are some notable properties and the laws governing this chapter 9 of the NCERT textbook for class 11 Physics, Mechanical Properties of Solids. At the end of the chapter, questions are posed to summarise the chapter's overall concepts and topics.
List of topics according to NCERT and JEE Main/NEET syllabus:
- Introduction to Elasticity and Plasticity
- Applications of Elastic Behaviour of Materials
- Stress and Strain
- Elastic Moduli
- Hooke’s Law and Stress-strain Curve.
- Elastic behaviour of solids
- mechanical properties of solids solutions.
Related Topics,
Important concepts discussed in mechanical properties of solids class 11 notes, Solids' mechanical properties determine their numerous qualities, such as their resistance to deformation and their strength. Resistance to deformation refers to an object's ability to resist a change in shape, whereas strength refers to an object's ability to withstand applied force. In NCERT Class 11 Physics, Chapter 9 'Mechanical Properties of Solids' is part of Unit 7 'Properties of Bulk Matter.' It is one of the most essential chapters, In the CBSE Class 11 Physics Examination, Unit 7 has a combined weightage of 20 marks alongside units 8 and 9 which is there in the syllabus. Or one, who want to learn and prepare from physics class 11 mechanical properties of solids notes pdf can refer to all different lectures and free content available.
Resistance of Deformation:
Solids are defined by their size and shape. To modify the size and shape of a solid item, an external force is necessary. If the resistance to deformation is low, an object's shape can be easily modified. The qualities of solids that define their solidity are known as mechanical properties. Plasticity, elasticity, strength, and ductility are some of these characteristics.
Elasticity is described as the property of an object that allows it to restore its original shape and size once a force has been removed. For instance, if we stretch a rubber band to a certain length and then leave it, it will revert to its previous shape.
A Perfectly Elastic Body is described as a body that returns to its original shape and size completely and instantly after the deforming force has been eliminated. Phosphor bronze and quartz fibre, for example.
Plasticity is the property of an object that causes it to change shape when a deforming force is applied and never returns to its previous shape once the deforming force is removed.
Ductility is a quality of an object that allows it to be pulled through thin wires, plates, or sheets. Consider the following scenario: Strength of Gold and Silver:
Strength is defined as the ability to withstand imposed stress without failing.
class 11 physics ch 9 ncert solutions and class 11th physics chapter 9 notes also include,
If a body is distorted as a result of an external force, an internal force is produced at each and every section of the body that attempts to restore the body to its original state. Stress is the name for this internal energy.
Stress = F/A its unit is N/m² or Pascal.
Types of stress:
There are three types of stress:
(a) Longitudinal Stress: Longitudinal Stress occurs when the deforming force of a cylindrical body is applied normally to the area of cross-section. A change in the length of an object occurs when it is subjected to longitudinal stress.
There are two forms of longitudinal stress.-
Tensile force: Tensile stress is defined as an increase in the length of an object as a result of the applied force effect.
Compressional stress occurs when the length of an object decreases as a result of the applied force effect.
(b) Shearing or Tangential Stress: Tangential stress is defined as the restoring force per unit area when the applied force is parallel to the body's cross-sectional area. When applied tangentially, the deforming force causes changes in the shape of the body.
(c) Hydraulic Stress: Hydraulic stress refers to the restoring force that a fluid like water exerts per unit area on a body or item.
Strain is defined as a change in the size and shape of a body caused by the application of a deforming force. Strain is defined as the proportion of a change in shape or size to the initial shape or size. It is nothing more than a number with no dimensions.
There are three different sorts of strains:
Shearing strain is the measurement of the relative displacement on opposite faces of the body caused by shearing stress.
(b) Longitudinal strain : The original length of the body changes as a result of the imposed longitudinal stress. Longitudinal strain is defined as the difference between the current length and the original length
(c) Strain of volume: Hydraulic pressure causes a strain called volume strain. The ratio of change in volume to the initial volume is what it's called. Hooke's Law states that within the elastic limit, strain and stress are proportional to each other.
Stress ∝ Strain
Stress = k * strain
The proportionality constant K, often known as the modulus of elasticity, is used here. Hooke's law is an empirical law that holds true for most materials. Some materials, such as human muscle and rubber, defy Hooke's law.
The curve of Stress and Strain:
A line created by stress and strain is known as the stress-strain curve. A stress-strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain in the ideal case of Hooke's law. It's calculated by progressively adding load to a test coupon and measuring deformation, from which stress and strain may be calculated (see tensile testing). Many properties of a material are revealed by these curves, including Young's modulus, yield strength, and ultimate tensile strength.

Strain is the amount of deformation experienced by the body in the direction of force applied, divided by the initial dimensions of the body.
is the change in length and L is the original length of the material.
The strain is a dimensionless quantity as it just defines the relative change in shape.
Elastic Moduli:
The ratio of strain and stress is known as the modulus of elasticity, or Elastic Moduli. It is one of the material's most fundamental features. Young's modulus, Shear modulus, and Bulk modulus are the three forms of elastic moduli.
Young's Rigidity Modulus:
Within the elastic limit, Young's Modulus of Rigidity is defined as the ratio of longitudinal stress to longitudinal strain. Young's Modulus is represented by the letter Y. Metals have high Young Modulus values when compared to other materials.
Y= Normal Stress / Longitudinal Strain
Bulk Modulus of Rigidity:
The ratio of normal stress to volumetric strain within the elastic limit is known as the Bulk Modulus of Rigidity. It is represented by B.
B= Normal Stress / Volumetric Strain
NCERT Notes Subject Wise Link:
- NCERT notes Class 11 Maths
- NCERT notes Class 11 Physics
- NCERT notes Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT notes Class 11 Biology
Importance of Mechanical Properties of Solids class 11:
All applicants preparing for entrance examinations such as JEE and NEET will benefit from the ncert solutions for class 11 physics chapter 9. Mechanical properties of solids notes, are particularly useful for revision when you are short on time and have a lot of material to cover. Every year, they have posted at least two questions from properties of solids and liquids, as has been the case over the past five years. This is one of the most important chapters on the syllabus. So, if you have enough time, tackle solids before fluids because solids introduce us to new concepts such as stress, strain, potential energy, and strain relation. These subjects aren't as important in fluids, but you should start with solids since if you miss a chapter in the middle, you'll end up with a backlog. one must practice all mechanical properties of solids neet questions and furthermore, one should also practice with mechanical properties of solids class 11 questions and answers pdf. Also to prepare the best one must refer to ncert solutions for class 11 physics chapter 9 and class 11 mechanical properties of solids notes combined.
If you have time constraints, then also you should do solids first as it is a small chapter which will not take much time of yours!
NCERT Solutions Subject wise link:
- NCERT solutions for class 11 Physics.
- NCERT solutions for class 11 Chemistry.
- NCERT solutions for class 11 Mathematics.
- NCERT solutions for class 11 Biology.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Subject wise link:
- NCERT exemplar solutions for class 11 Physics.
- NCERT exemplar solutions for class 11 Chemistry.
- NCERT exemplar solutions for class 11 Mathematics.
- NCERT exemplar solutions for class 11 Biology.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
A cylinder's twisting produces pure shear.
It's a substance that can be stretched elastically to huge strain values t.
It is defined as the ratio of the highest load applied to the wire to its original cross-sectional area.
The answer is zero.
This happens when the body is deformed beyond the elastic limit.
Apr 27, 2022 - 12:42 p.m. IST ---STATIC
- Latest Articles
Explore Premium
Artificial rain: concept and techniques, what is lenz’s law in electricity and magnetism and why is it true, cancer treatment: why chemotherapy does not suit all patients, understand your attachment style and learn how you can reform your relationships, 7 tips to convey your struggles to your loved ones, decision-making: common challenges faced, tips to make good decisions, popular questions.
50 mL of 0.2 M ammonia solution is treated with 25 mL of 0.2 M HCl. If pK b of ammonia solution is 4.75, the pH of the mixture will be : Option: 1 3.75 Option: 2 4.75 Option: 3 8.25 Option: 4 9.25
Explore Career Options (By Industry)
- Construction
- Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Information Technology
Data Administrator
Database professionals use software to store and organise data such as financial information, and customer shipping records. Individuals who opt for a career as data administrators ensure that data is available for users and secured from unauthorised sales. DB administrators may work in various types of industries. It may involve computer systems design, service firms, insurance companies, banks and hospitals.
Bio Medical Engineer
The field of biomedical engineering opens up a universe of expert chances. An Individual in the biomedical engineering career path work in the field of engineering as well as medicine, in order to find out solutions to common problems of the two fields. The biomedical engineering job opportunities are to collaborate with doctors and researchers to develop medical systems, equipment, or devices that can solve clinical problems. Here we will be discussing jobs after biomedical engineering, how to get a job in biomedical engineering, biomedical engineering scope, and salary.
Ethical Hacker
A career as ethical hacker involves various challenges and provides lucrative opportunities in the digital era where every giant business and startup owns its cyberspace on the world wide web. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path try to find the vulnerabilities in the cyber system to get its authority. If he or she succeeds in it then he or she gets its illegal authority. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path then steal information or delete the file that could affect the business, functioning, or services of the organization.
GIS officer work on various GIS software to conduct a study and gather spatial and non-spatial information. GIS experts update the GIS data and maintain it. The databases include aerial or satellite imagery, latitudinal and longitudinal coordinates, and manually digitized images of maps. In a career as GIS expert, one is responsible for creating online and mobile maps.
Data Analyst
The invention of the database has given fresh breath to the people involved in the data analytics career path. Analysis refers to splitting up a whole into its individual components for individual analysis. Data analysis is a method through which raw data are processed and transformed into information that would be beneficial for user strategic thinking.
Data are collected and examined to respond to questions, evaluate hypotheses or contradict theories. It is a tool for analyzing, transforming, modeling, and arranging data with useful knowledge, to assist in decision-making and methods, encompassing various strategies, and is used in different fields of business, research, and social science.
Geothermal Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as geothermal engineers are the professionals involved in the processing of geothermal energy. The responsibilities of geothermal engineers may vary depending on the workplace location. Those who work in fields design facilities to process and distribute geothermal energy. They oversee the functioning of machinery used in the field.
Database Architect
If you are intrigued by the programming world and are interested in developing communications networks then a career as database architect may be a good option for you. Data architect roles and responsibilities include building design models for data communication networks. Wide Area Networks (WANs), local area networks (LANs), and intranets are included in the database networks. It is expected that database architects will have in-depth knowledge of a company's business to develop a network to fulfil the requirements of the organisation. Stay tuned as we look at the larger picture and give you more information on what is db architecture, why you should pursue database architecture, what to expect from such a degree and what your job opportunities will be after graduation. Here, we will be discussing how to become a data architect. Students can visit NIT Trichy , IIT Kharagpur , JMI New Delhi .
Remote Sensing Technician
Individuals who opt for a career as a remote sensing technician possess unique personalities. Remote sensing analysts seem to be rational human beings, they are strong, independent, persistent, sincere, realistic and resourceful. Some of them are analytical as well, which means they are intelligent, introspective and inquisitive.
Remote sensing scientists use remote sensing technology to support scientists in fields such as community planning, flight planning or the management of natural resources. Analysing data collected from aircraft, satellites or ground-based platforms using statistical analysis software, image analysis software or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a significant part of their work. Do you want to learn how to become remote sensing technician? There's no need to be concerned; we've devised a simple remote sensing technician career path for you. Scroll through the pages and read.
Budget Analyst
Budget analysis, in a nutshell, entails thoroughly analyzing the details of a financial budget. The budget analysis aims to better understand and manage revenue. Budget analysts assist in the achievement of financial targets, the preservation of profitability, and the pursuit of long-term growth for a business. Budget analysts generally have a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, economics, or a closely related field. Knowledge of Financial Management is of prime importance in this career.
Underwriter
An underwriter is a person who assesses and evaluates the risk of insurance in his or her field like mortgage, loan, health policy, investment, and so on and so forth. The underwriter career path does involve risks as analysing the risks means finding out if there is a way for the insurance underwriter jobs to recover the money from its clients. If the risk turns out to be too much for the company then in the future it is an underwriter who will be held accountable for it. Therefore, one must carry out his or her job with a lot of attention and diligence.
Finance Executive
Product manager.
A Product Manager is a professional responsible for product planning and marketing. He or she manages the product throughout the Product Life Cycle, gathering and prioritising the product. A product manager job description includes defining the product vision and working closely with team members of other departments to deliver winning products.
Operations Manager
Individuals in the operations manager jobs are responsible for ensuring the efficiency of each department to acquire its optimal goal. They plan the use of resources and distribution of materials. The operations manager's job description includes managing budgets, negotiating contracts, and performing administrative tasks.
Stock Analyst
Individuals who opt for a career as a stock analyst examine the company's investments makes decisions and keep track of financial securities. The nature of such investments will differ from one business to the next. Individuals in the stock analyst career use data mining to forecast a company's profits and revenues, advise clients on whether to buy or sell, participate in seminars, and discussing financial matters with executives and evaluate annual reports.
A Researcher is a professional who is responsible for collecting data and information by reviewing the literature and conducting experiments and surveys. He or she uses various methodological processes to provide accurate data and information that is utilised by academicians and other industry professionals. Here, we will discuss what is a researcher, the researcher's salary, types of researchers.
Welding Engineer
Welding Engineer Job Description: A Welding Engineer work involves managing welding projects and supervising welding teams. He or she is responsible for reviewing welding procedures, processes and documentation. A career as Welding Engineer involves conducting failure analyses and causes on welding issues.
Transportation Planner
A career as Transportation Planner requires technical application of science and technology in engineering, particularly the concepts, equipment and technologies involved in the production of products and services. In fields like land use, infrastructure review, ecological standards and street design, he or she considers issues of health, environment and performance. A Transportation Planner assigns resources for implementing and designing programmes. He or she is responsible for assessing needs, preparing plans and forecasts and compliance with regulations.
Environmental Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as an environmental engineer are construction professionals who utilise the skills and knowledge of biology, soil science, chemistry and the concept of engineering to design and develop projects that serve as solutions to various environmental problems.
Safety Manager
A Safety Manager is a professional responsible for employee’s safety at work. He or she plans, implements and oversees the company’s employee safety. A Safety Manager ensures compliance and adherence to Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) guidelines.
Conservation Architect
A Conservation Architect is a professional responsible for conserving and restoring buildings or monuments having a historic value. He or she applies techniques to document and stabilise the object’s state without any further damage. A Conservation Architect restores the monuments and heritage buildings to bring them back to their original state.
Structural Engineer
A Structural Engineer designs buildings, bridges, and other related structures. He or she analyzes the structures and makes sure the structures are strong enough to be used by the people. A career as a Structural Engineer requires working in the construction process. It comes under the civil engineering discipline. A Structure Engineer creates structural models with the help of computer-aided design software.
Highway Engineer
Highway Engineer Job Description: A Highway Engineer is a civil engineer who specialises in planning and building thousands of miles of roads that support connectivity and allow transportation across the country. He or she ensures that traffic management schemes are effectively planned concerning economic sustainability and successful implementation.
Field Surveyor
Are you searching for a Field Surveyor Job Description? A Field Surveyor is a professional responsible for conducting field surveys for various places or geographical conditions. He or she collects the required data and information as per the instructions given by senior officials.
Orthotist and Prosthetist
Orthotists and Prosthetists are professionals who provide aid to patients with disabilities. They fix them to artificial limbs (prosthetics) and help them to regain stability. There are times when people lose their limbs in an accident. In some other occasions, they are born without a limb or orthopaedic impairment. Orthotists and prosthetists play a crucial role in their lives with fixing them to assistive devices and provide mobility.
Pathologist
A career in pathology in India is filled with several responsibilities as it is a medical branch and affects human lives. The demand for pathologists has been increasing over the past few years as people are getting more aware of different diseases. Not only that, but an increase in population and lifestyle changes have also contributed to the increase in a pathologist’s demand. The pathology careers provide an extremely huge number of opportunities and if you want to be a part of the medical field you can consider being a pathologist. If you want to know more about a career in pathology in India then continue reading this article.
Veterinary Doctor
Speech therapist, gynaecologist.
Gynaecology can be defined as the study of the female body. The job outlook for gynaecology is excellent since there is evergreen demand for one because of their responsibility of dealing with not only women’s health but also fertility and pregnancy issues. Although most women prefer to have a women obstetrician gynaecologist as their doctor, men also explore a career as a gynaecologist and there are ample amounts of male doctors in the field who are gynaecologists and aid women during delivery and childbirth.
Audiologist
The audiologist career involves audiology professionals who are responsible to treat hearing loss and proactively preventing the relevant damage. Individuals who opt for a career as an audiologist use various testing strategies with the aim to determine if someone has a normal sensitivity to sounds or not. After the identification of hearing loss, a hearing doctor is required to determine which sections of the hearing are affected, to what extent they are affected, and where the wound causing the hearing loss is found. As soon as the hearing loss is identified, the patients are provided with recommendations for interventions and rehabilitation such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and appropriate medical referrals. While audiology is a branch of science that studies and researches hearing, balance, and related disorders.
An oncologist is a specialised doctor responsible for providing medical care to patients diagnosed with cancer. He or she uses several therapies to control the cancer and its effect on the human body such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and biopsy. An oncologist designs a treatment plan based on a pathology report after diagnosing the type of cancer and where it is spreading inside the body.
Are you searching for an ‘Anatomist job description’? An Anatomist is a research professional who applies the laws of biological science to determine the ability of bodies of various living organisms including animals and humans to regenerate the damaged or destroyed organs. If you want to know what does an anatomist do, then read the entire article, where we will answer all your questions.
For an individual who opts for a career as an actor, the primary responsibility is to completely speak to the character he or she is playing and to persuade the crowd that the character is genuine by connecting with them and bringing them into the story. This applies to significant roles and littler parts, as all roles join to make an effective creation. Here in this article, we will discuss how to become an actor in India, actor exams, actor salary in India, and actor jobs.
Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats create and direct original routines for themselves, in addition to developing interpretations of existing routines. The work of circus acrobats can be seen in a variety of performance settings, including circus, reality shows, sports events like the Olympics, movies and commercials. Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats must be prepared to face rejections and intermittent periods of work. The creativity of acrobats may extend to other aspects of the performance. For example, acrobats in the circus may work with gym trainers, celebrities or collaborate with other professionals to enhance such performance elements as costume and or maybe at the teaching end of the career.
Video Game Designer
Career as a video game designer is filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. A video game designer is someone who is involved in the process of creating a game from day one. He or she is responsible for fulfilling duties like designing the character of the game, the several levels involved, plot, art and similar other elements. Individuals who opt for a career as a video game designer may also write the codes for the game using different programming languages.
Depending on the video game designer job description and experience they may also have to lead a team and do the early testing of the game in order to suggest changes and find loopholes.
Radio Jockey
Radio Jockey is an exciting, promising career and a great challenge for music lovers. If you are really interested in a career as radio jockey, then it is very important for an RJ to have an automatic, fun, and friendly personality. If you want to get a job done in this field, a strong command of the language and a good voice are always good things. Apart from this, in order to be a good radio jockey, you will also listen to good radio jockeys so that you can understand their style and later make your own by practicing.
A career as radio jockey has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. If you want to know more about a career as radio jockey, and how to become a radio jockey then continue reading the article.
Choreographer
The word “choreography" actually comes from Greek words that mean “dance writing." Individuals who opt for a career as a choreographer create and direct original dances, in addition to developing interpretations of existing dances. A Choreographer dances and utilises his or her creativity in other aspects of dance performance. For example, he or she may work with the music director to select music or collaborate with other famous choreographers to enhance such performance elements as lighting, costume and set design.
Social Media Manager
A career as social media manager involves implementing the company’s or brand’s marketing plan across all social media channels. Social media managers help in building or improving a brand’s or a company’s website traffic, build brand awareness, create and implement marketing and brand strategy. Social media managers are key to important social communication as well.
Photographer
Photography is considered both a science and an art, an artistic means of expression in which the camera replaces the pen. In a career as a photographer, an individual is hired to capture the moments of public and private events, such as press conferences or weddings, or may also work inside a studio, where people go to get their picture clicked. Photography is divided into many streams each generating numerous career opportunities in photography. With the boom in advertising, media, and the fashion industry, photography has emerged as a lucrative and thrilling career option for many Indian youths.
An individual who is pursuing a career as a producer is responsible for managing the business aspects of production. They are involved in each aspect of production from its inception to deception. Famous movie producers review the script, recommend changes and visualise the story.
They are responsible for overseeing the finance involved in the project and distributing the film for broadcasting on various platforms. A career as a producer is quite fulfilling as well as exhaustive in terms of playing different roles in order for a production to be successful. Famous movie producers are responsible for hiring creative and technical personnel on contract basis.
Copy Writer
In a career as a copywriter, one has to consult with the client and understand the brief well. A career as a copywriter has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. Several new mediums of advertising are opening therefore making it a lucrative career choice. Students can pursue various copywriter courses such as Journalism , Advertising , Marketing Management . Here, we have discussed how to become a freelance copywriter, copywriter career path, how to become a copywriter in India, and copywriting career outlook.
In a career as a vlogger, one generally works for himself or herself. However, once an individual has gained viewership there are several brands and companies that approach them for paid collaboration. It is one of those fields where an individual can earn well while following his or her passion.
Ever since internet costs got reduced the viewership for these types of content has increased on a large scale. Therefore, a career as a vlogger has a lot to offer. If you want to know more about the Vlogger eligibility, roles and responsibilities then continue reading the article.
For publishing books, newspapers, magazines and digital material, editorial and commercial strategies are set by publishers. Individuals in publishing career paths make choices about the markets their businesses will reach and the type of content that their audience will be served. Individuals in book publisher careers collaborate with editorial staff, designers, authors, and freelance contributors who develop and manage the creation of content.
Careers in journalism are filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. One cannot afford to miss out on the details. As it is the small details that provide insights into a story. Depending on those insights a journalist goes about writing a news article. A journalism career can be stressful at times but if you are someone who is passionate about it then it is the right choice for you. If you want to know more about the media field and journalist career then continue reading this article.
Individuals in the editor career path is an unsung hero of the news industry who polishes the language of the news stories provided by stringers, reporters, copywriters and content writers and also news agencies. Individuals who opt for a career as an editor make it more persuasive, concise and clear for readers. In this article, we will discuss the details of the editor's career path such as how to become an editor in India, editor salary in India and editor skills and qualities.
Individuals who opt for a career as a reporter may often be at work on national holidays and festivities. He or she pitches various story ideas and covers news stories in risky situations. Students can pursue a BMC (Bachelor of Mass Communication) , B.M.M. (Bachelor of Mass Media) , or MAJMC (MA in Journalism and Mass Communication) to become a reporter. While we sit at home reporters travel to locations to collect information that carries a news value.
Corporate Executive
Are you searching for a Corporate Executive job description? A Corporate Executive role comes with administrative duties. He or she provides support to the leadership of the organisation. A Corporate Executive fulfils the business purpose and ensures its financial stability. In this article, we are going to discuss how to become corporate executive.
Multimedia Specialist
A multimedia specialist is a media professional who creates, audio, videos, graphic image files, computer animations for multimedia applications. He or she is responsible for planning, producing, and maintaining websites and applications.
Quality Controller
A quality controller plays a crucial role in an organisation. He or she is responsible for performing quality checks on manufactured products. He or she identifies the defects in a product and rejects the product.
A quality controller records detailed information about products with defects and sends it to the supervisor or plant manager to take necessary actions to improve the production process.
Production Manager
A QA Lead is in charge of the QA Team. The role of QA Lead comes with the responsibility of assessing services and products in order to determine that he or she meets the quality standards. He or she develops, implements and manages test plans.
Process Development Engineer
The Process Development Engineers design, implement, manufacture, mine, and other production systems using technical knowledge and expertise in the industry. They use computer modeling software to test technologies and machinery. An individual who is opting career as Process Development Engineer is responsible for developing cost-effective and efficient processes. They also monitor the production process and ensure it functions smoothly and efficiently.
AWS Solution Architect
An AWS Solution Architect is someone who specializes in developing and implementing cloud computing systems. He or she has a good understanding of the various aspects of cloud computing and can confidently deploy and manage their systems. He or she troubleshoots the issues and evaluates the risk from the third party.
Azure Administrator
An Azure Administrator is a professional responsible for implementing, monitoring, and maintaining Azure Solutions. He or she manages cloud infrastructure service instances and various cloud servers as well as sets up public and private cloud systems.
Computer Programmer
Careers in computer programming primarily refer to the systematic act of writing code and moreover include wider computer science areas. The word 'programmer' or 'coder' has entered into practice with the growing number of newly self-taught tech enthusiasts. Computer programming careers involve the use of designs created by software developers and engineers and transforming them into commands that can be implemented by computers. These commands result in regular usage of social media sites, word-processing applications and browsers.
Information Security Manager
Individuals in the information security manager career path involves in overseeing and controlling all aspects of computer security. The IT security manager job description includes planning and carrying out security measures to protect the business data and information from corruption, theft, unauthorised access, and deliberate attack
ITSM Manager
Automation test engineer.
An Automation Test Engineer job involves executing automated test scripts. He or she identifies the project’s problems and troubleshoots them. The role involves documenting the defect using management tools. He or she works with the application team in order to resolve any issues arising during the testing process.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

SAT® | CollegeBoard
Registeration closing on 19th Apr for SAT® | One Test-Many Universities | 90% discount on registrations fee | Free Practice | Multiple Attempts | no penalty for guessing

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

Resonance Coaching
Enroll in Resonance Coaching for success in JEE/NEET exams

TOEFL ® Registrations 2024
Thinking of Studying Abroad? Think the TOEFL® test. Register now & Save 10% on English Proficiency Tests with Gift Cards

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN
Everything about Education
Latest updates, Exclusive Content, Webinars and more.
Explore on Careers360
- Board Exams
- Navodaya Vidyalaya
- Top Schools
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 6
NCERT Exemplars
- NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 10 solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Solutions
- NCERT Books for class 6
- NCERT Books for class 7
- NCERT Books for class 8
- NCERT Books for class 9
- NCERT Books for Class 10
- NCERT Books for Class 11
- NCERT Books for Class 12
- NCERT Notes for Class 9
- NCERT Notes for Class 10
- NCERT Notes for Class 11
- NCERT Notes for Class 12
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 6
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 7
- NCERT Syllabus for class 8
- NCERT Syllabus for class 9
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 10
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 11
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 12
- CBSE Date Sheet
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Admit Card
- CBSE Result
- CBSE Result Name and State Wise
- CBSE Passing Marks
CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Board Class 10th
- CBSE Class 10 Date Sheet
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE 10th Exam Pattern
- CBSE Class 10 Answer Key
- CBSE 10th Admit Card
- CBSE 10th Result
- CBSE 10th Toppers
- CBSE Board Class 12th
- CBSE Class 12 Date Sheet
- CBSE Class 12 Admit Card
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Exam Pattern
- CBSE Class 12 Answer Key
- CBSE 12th Result
- CBSE Class 12 Toppers
CISCE Board 10th
- ICSE 10th time table
- ICSE 10th Syllabus
- ICSE 10th exam pattern
- ICSE 10th Question Papers
- ICSE 10th Result
- ICSE 10th Toppers
- ISC 12th Board
- ISC 12th Time Table
- ISC Syllabus
- ISC 12th Question Papers
- ISC 12th Result
- IMO Syllabus
- IMO Sample Papers
- IMO Answer Key
- IEO Syllabus
- IEO Answer Key
- NSO Syllabus
- NSO Sample Papers
- NSO Answer Key
- NMMS Application form
- NMMS Scholarship
- NMMS Eligibility
- NMMS Exam Pattern
- NMMS Admit Card
- NMMS Question Paper
- NMMS Answer Key
- NMMS Syllabus
- NMMS Result
- NTSE Application Form
- NTSE Eligibility Criteria
- NTSE Exam Pattern
- NTSE Admit Card
- NTSE Syllabus
- NTSE Question Papers
- NTSE Answer Key
- NTSE Cutoff
- NTSE Result
- NVS Admit Card
- Navodaya Result
- Navodaya Exam Date
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission Class 6
- JNVST admit card for class 6
- JNVST class 6 answer key
- JNVST class 6 Result
- JNVST Class 6 Exam Pattern
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission
- JNVST class 9 exam pattern
- JNVST class 9 answer key
- JNVST class 9 Result
Schools By Medium
- Malayalam Medium Schools in India
- Urdu Medium Schools in India
- Telugu Medium Schools in India
- Karnataka Board PUE Schools in India
- Bengali Medium Schools in India
- Marathi Medium Schools in India
By Ownership
- Central Government Schools in India
- Private Schools in India
- Schools in Delhi
- Schools in Lucknow
- Schools in Kolkata
- Schools in Pune
- Schools in Bangalore
- Schools in Chennai
- Schools in Mumbai
- Schools in Hyderabad
- Schools in Gurgaon
- Schools in Ahmedabad
- Schools in Uttar Pradesh
- Schools in Maharashtra
- Schools in Karnataka
- Schools in Haryana
- Schools in Punjab
- Schools in Andhra Pradesh
- Schools in Madhya Pradesh
- Schools in Rajasthan
- Schools in Tamil Nadu
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Cetifications
We Appeared in
Case Based Questions Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids - NEET MCQ
10 questions mcq test - case based questions test: mechanical properties of solids, attempt all questions sub parts from each question. elasticity vs. plasticity: objects get deformed when pushed, pulled, and twisted. elasticity is the measure of the amount that the object can return to its original shape after these external forces and pressure are removed. the opposite of elasticity is plasticity. when something is stretched, and it stays stretched, the material is said to be plastic. such deformation is said to be plastic deformation. in elastic deformation, atoms of the material are displaced temporarily from their original lattice site. they return back to their original position after the removal of external force. in plastic deformation, atoms of the solid are displaced permanently from their original lattice site. they don’t return back to the original position even after the removal of external load. so, elastic deformation is temporary, whereas plastic deformation is permanent. amount of elastic deformation is very small. but the amount of plastic deformation is quite large. external force required for elastic deformation of solid is quite small. force required for plastic deformation is much higher. total energy absorbed by the material during elastic and plastic deformation region is called modulus of toughness. energy absorbed by the material during elastic deformation is called module of resilience. most materials have an amount of force or pressure for which they deform elastically. if more force or pressure is applied, then they undergo plastic deformation. materials those have a fair amount of plastic deformation before breaking are said to be ductile. materials those can't stretch or bend much without breaking are said to be brittle. copper, aluminium etc. are ductile materials. for this reason those are used for making wires. glass and ceramics are often brittle; they will not bend; they will break. q. which of the following statement is false.
- A. A body is said to be plastic when it deforms due to application of force and return to to its original shape when the deforming force is removed.
- B. External force required for elastic deformation of solid is quite small.
- C. In plastic deformation, atoms of the solid are displaced permanently from their original lattice site
- D. Most materials have an amount of force or pressure for which they deform elastically. If more force or pressure is applied, then they undergo plastic deformation.

Attempt All Questions sub parts from each question. Elasticity vs. plasticity: Objects get deformed when pushed, pulled, and twisted. Elasticity is the measure of the amount that the object can return to its original shape after these external forces and pressure are removed. The opposite of elasticity is plasticity. When something is stretched, and it stays stretched, the material is said to be plastic. Such deformation is said to be plastic deformation. In elastic deformation, atoms of the material are displaced temporarily from their original lattice site. They return back to their original position after the removal of external force. In plastic deformation, atoms of the solid are displaced permanently from their original lattice site. They don’t return back to the original position even after the removal of external load. So, elastic deformation is temporary, whereas plastic deformation is permanent. Amount of elastic deformation is very small. But the amount of plastic deformation is quite large. External force required for elastic deformation of solid is quite small. Force required for plastic deformation is much higher. Total energy absorbed by the material during elastic and plastic deformation region is called modulus of toughness. Energy absorbed by the material during elastic deformation is called module of resilience. Most materials have an amount of force or pressure for which they deform elastically. If more force or pressure is applied, then they undergo plastic deformation. Materials those have a fair amount of plastic deformation before breaking are said to be ductile. Materials those can't stretch or bend much without breaking are said to be brittle. Copper, aluminium etc. are ductile materials. For this reason those are used for making wires. Glass and ceramics are often brittle; they will not bend; they will break. Q. Aluminium is a ............... materials.
- D. Both (b) and (c)
Attempt All Questions sub parts from each question. Elasticity vs. plasticity: Objects get deformed when pushed, pulled, and twisted. Elasticity is the measure of the amount that the object can return to its original shape after these external forces and pressure are removed. The opposite of elasticity is plasticity. When something is stretched, and it stays stretched, the material is said to be plastic. Such deformation is said to be plastic deformation. In elastic deformation, atoms of the material are displaced temporarily from their original lattice site. They return back to their original position after the removal of external force. In plastic deformation, atoms of the solid are displaced permanently from their original lattice site. They don’t return back to the original position even after the removal of external load. So, elastic deformation is temporary, whereas plastic deformation is permanent. Amount of elastic deformation is very small. But the amount of plastic deformation is quite large. External force required for elastic deformation of solid is quite small. Force required for plastic deformation is much higher. Total energy absorbed by the material during elastic and plastic deformation region is called modulus of toughness. Energy absorbed by the material during elastic deformation is called module of resilience. Most materials have an amount of force or pressure for which they deform elastically. If more force or pressure is applied, then they undergo plastic deformation. Materials those have a fair amount of plastic deformation before breaking are said to be ductile. Materials those can't stretch or bend much without breaking are said to be brittle. Copper, aluminium etc. are ductile materials. For this reason those are used for making wires. Glass and ceramics are often brittle; they will not bend; they will break. Q. Which of the following 4 stress-strain graphs represent a ductile material and a brittle material?
A is for a brittle material, B is for a ductile material
A is for a brittle material, D is for a ductile material
A is for a brittle material, C is for a ductile material
C is for a brittle material, A is for a ductile material
A typical stress–strain curve for a brittle material is linear. Hence graph A is for brittle material. Graph C is for a ductile material
Attempt All Questions sub parts from each question.
Elasticity vs. plasticity: Objects get deformed when pushed, pulled, and twisted. Elasticity is the measure of the amount that the object can return to its original shape after these external forces and pressure are removed. The opposite of elasticity is plasticity. When something is stretched, and it stays stretched, the material is said to be plastic. Such deformation is said to be plastic deformation. In elastic deformation, atoms of the material are displaced temporarily from their original lattice site. They return back to their original position after the removal of external force. In plastic deformation, atoms of the solid are displaced permanently from their original lattice site. They don’t return back to the original position even after the removal of external load. So, elastic deformation is temporary, whereas plastic deformation is permanent. Amount of elastic deformation is very small. But the amount of plastic deformation is quite large. External force required for elastic deformation of solid is quite small. Force required for plastic deformation is much higher. Total energy absorbed by the material during elastic and plastic deformation region is called modulus of toughness. Energy absorbed by the material during elastic deformation is called module of resilience. Most materials have an amount of force or pressure for which they deform elastically. If more force or pressure is applied, then they undergo plastic deformation. Materials those have a fair amount of plastic deformation before breaking are said to be ductile. Materials those can't stretch or bend much without breaking are said to be brittle. Copper, aluminium etc. are ductile materials. For this reason those are used for making wires. Glass and ceramics are often brittle; they will not bend; they will break.
Q. Hooks law is applicable for
- A. Plastic materials
- B. Elastic materials
- C. Both (a) and (b)
- D. Brittle materials
Q. Ceramic is a ............... material
- D. Both (a) and (c)
Sagging of a bridge A bridge is designed such that it can withstand the load of the flowing traffic, the force of winds and its own weight. Let us consider the case of a beam loaded at the centre and supported near its ends as shown in Figure. A beam of length l, breadth b, and depth d when loaded at the centre by a load W sags by an amount given by
From the equation, we see that to reduce the bending for a given load, one should use a material with a large Young’s modulus Y. For a given material, increasing the depth d rather than the breadth b is more effective in reducing the bending, since δ is proportional to d –3 and to b –1 (of course the length l of the span should be as small as possible).
Amongst bridge materials steel has the highest and most favorable strength qualities, and it is therefore suitable for the most daring bridges with the longest spans. Normal building steel has compressive and tensile strengths of 370 N/sq mm, about ten times the compressive strength of a medium concrete and a hundred times its tensile strength. A special merit of steel is its ductility due to which it deforms considerably before it breaks, because it begins to yield above a certain stress level.
Q. To reduce bending of a beam
- A. For a given length and material depth should be greater than breadth
- B. For a given length and material breadth should be greater than depth
- C. For a given length and material depth should be equal to breadth
- D. Breadth and depth has no effect
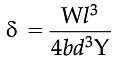
From the equation, we see that to reduce the bending for a given load, one should increase the depth d rather than the breadth b since δ is proportional to d –3 and to b –1 .
Q. Why ductility is the special merit of steel?
- A. Ductility allows structures to bend and deform to some extent without rupturing.
- B. Ductility offers the structure a high rigidity
- C. Ductility prevents the structure to sag while overloaded
- D. Ductility offers less corrosion
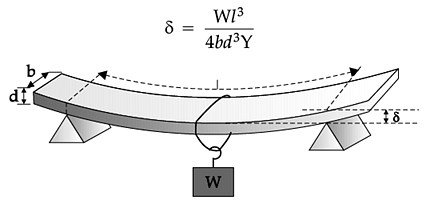
Q. Compressive strength of normal building steel is about ................ times of the compressive strength of medium concrete.
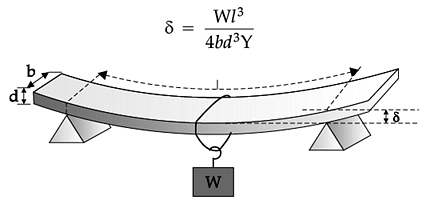
Q. A bar of length l, breadth b, and depth d, supported at two ends when loaded at the centre by a load W sags by an amount given by
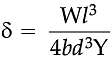
Q. What is the special merit of steel over concrete is its
- A. Malleability
- B. Brittleness
- C. Conductivity
- D. Ductility
Top Courses for NEET

Related Content
How to prepare for neet.

Important Questions for Case Based Questions Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids
Case based questions test: mechanical properties of solids mcqs with answers, online tests for case based questions test: mechanical properties of solids, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
- Physics Important Questions
- Class 11 Physics
- Chapter 8: Mechanical Properties Solids
Important Questions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 - Mechanical Properties of Solids
The Important Questions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids are provided below. Physics is one of the most important subjects in Class 11, as the concepts of this standard are included in the board examination. Mechanical Properties of Solids is one of the scoring sections of the Physics subject. Students must study hard so that they can solve any type of question asked from this chapter in the exam. It will also increase their scores in Physics papers`.
Important Questions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 – Mechanical Properties of Solids

Stay tuned with BYJU’S and learn interesting topics like current electricity , thermodynamics, laws of motion, and many more with the help of interactive and engaging video lessons.
Also, Access CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Papers
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- DK Goel Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 Notes PDF (Handwritten & Short Notes)
The Mechanical Properties Of Solids is one of the important chapters of the Class 11th Physics. Students can easily cover the chapter with the help of the Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 notes. In the notes, all the concepts and topics are explained in a creative and precise manner.
The Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 notes are considered to be important study material throughout the preparation. As it helps students to understand the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids in many different ways. One of the important ways is by practising questions given in the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids notes. By practising many questions students can increase their overall score in the examination by performing too well in the examination.
Mechanical Properties Of Solids Notes PDF
The Class 11 Physics notes is a written explanation for every passage or concepts included in the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids. These Mechanical Properties Of Solids notes are available in the Portable Document Format. The PDF of the Class 11 Physics Notes can be easily downloaded without any difficulty. With the help of the downloaded revision notes, Class 11 students can pay attention to the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids to be able to perform well in the board examinations as well as in the competition exam.
How to Download the Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 Notes?
To refer to the Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 notes, students can look through the given steps. Those important steps are:
- Open the Selfstudys website.
- Click the navigation bar, a drop down menu will appear.
- Select NCERT Books & Solutions from the given list.
- Click NCERT Notes from the given list.
- A new page will appear, select Class 11th from the list of classes.
- Select Physics from the list of subjects.
- Again a new page will appear, select the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids to be able to download the revision Notes.
Features of the Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 Notes
Features are considered to be an important or noticeable part of the Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 notes. Those important features are:
- Explanations are Provided: In the Mechanical Properties Of Solids notes, explanations are provided to each and every topic as well as definitions. According to the explanations, students can understand the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids in a fine way.
- Different Types of Questions are Included: Inside the Class 11 Mechanical Properties Of Solids notes, different types of questions are included. Those questions are: example questions, objective type questions, very short type answers, short type questions, long type questions, numerical problems, etc.
- Simple Language: These Class 11 Physics notes are created by subject matter experts in a very easy and simple language. It is formed in an easy language so that Class 11 students can understand each topic and question of the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids.
- Colourful Content are Given: Content included in the Class 11 Mechanical Properties Of Solids notes are in a colourful manner. This colourful content can attract many Class 11 students to cover the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids in a proper way.
- Hints and Solutions are Provided: To tackle the questions given in Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 Notes, students can refer to the Hints and Solutions given in the PDF file of Class 11 Revision Notes of Mechanical Properties Of Solids. With the help of hints and solutions, students can not only tackle the questions but can develop a good understanding in the overall chapter.
Advantages of the Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 Notes
Completing the chapter with the help of Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 notes can provide good results to students. This is one of the important advantage of Class 11 Physics notes, other than this are:
- Helps to Memorise Topics: With the help of Class 11 Physics notes, students can easily memorise topics discussed in the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids.
- Summary is Given: After covering all topics of the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids, a brief summary is given. Through the summary, students can get an idea about the important topics and definitions.
- A Quick Revision Can Be Done: With the help of Class 11 Physics notes, students can have a quick revision of the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids. Through the last minute revision, students can identify the weak points for the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids.
- All Topics are Covered: In the Mechanical Properties Of Solids notes, all the topics and concepts are covered in an elaborate manner. Understanding the topics and concepts in a detailed way can help students to increase their comprehensive skills.
- Increases the Accuracy Level: Routine exercise of questions from the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids can help students to increase their accuracy level. Accuracy level mainly helps Class 11 students to increase their quality in giving answers for the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids.
When Is The Right Time To Go Through Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 Notes?
After having a brief knowledge about the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids, students can look through the Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 notes. With the help of notes, students can recall all topics and concepts of Mechanical Properties Of Solids in a better way.
Although, generally, it is advised to all the students to use the revision notes on a weekly basis to recall the previous learnings. Along with this, using the Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 notes at the time of exam preparation helps a lot so, using the Class 11 Physics Notes during exam preparation can be the right time.
Tips for Students to Cover the Chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids Using Notes
It is a must that Class 11 students should follow some strategic tips to understand Mechanical Properties Of Solids. By understanding topics, students can score well in the questions related to the Mechanical Properties Of Solids. Below, we have mentioned some strategic tips, students can use -
- Look Through the Chapter: First tip is to look through all the topics included in the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids. Students can get a brief idea about all the topics and concepts of the Class 11th Physics chapter using Notes or Syllabus.
- Complete the Concepts: After getting some idea about the chapter and its topics, students can complete all the topics and concepts with the help of Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 notes. However, notes are only ideal to recall the previou learning so, with the help of Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 notes students can only revise the complete concepts of the Class 11 Physics chapter.
- Practising Questions: To understand topics of the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids, students need to practise questions in a fine way. Different kinds of questions are included in the Mechanical Properties Of Solids notes. Those questions given to practise are: objective questions, short type questions, very short type questions, short type questions, etc.
- Note Down the Mistakes: While practising Mechanical Properties Of Solids questions from the given notes, students are advised to note down all the mistakes. By noting down the mistakes, students can easily improvise their preparation level for the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids.
- Correction of Mistakes: Correcting the errors are equally important as solving questions from the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids. It can aid students to solve all their doubts regarding the chapter Mechanical Properties Of Solids.
- Take Frequent Breaks: It is very necessary for Class 11 students to take frequent breaks while preparing for Mechanical Properties Of Solids. Frequent breaks can help students to focus and grab more information from the revision notes of Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11.
- Proper Revision: Try to do proper revision of all the concepts and topics you have studied so far. Irregular revision can put you in devastating situations while recalling all the topics you have studied so far in Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 notes.
- Sleep Well and Eat Healthy: Taking care of yourself is very important during study and when you are trying to revise the topics like Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 using notes then you must pay attention to the quality sleep and healthy diet so that your brain can efficiently manage all the topics you have studied so far.
Why is it Important for Class 11 Students to Refer to the Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 Notes?
It is necessary for Class 11 students to refer to the Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 notes as it can aid to progress in the chapter. It is also important to refer as it provides many important contents from concepts to important formulas and derivation. Necessary information included in the Class 11 Physics notes are: definitions, concepts, topics, questions, etc.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Mechanical Properties of Solids

Mechanical Properties of Solids Class 11 Notes
In this article, students will get to learn and fetch mechanical properties of solids class 11 notes. We are going to discuss the properties that solids have such as elastic behaviour of solids, stress and strain, stress-strain curve, Hooke’s law and elastic moduli.
What are the Mechanical Properties of Solids?
Mechanical properties of solids elaborates the characteristics such as the resistance to deformation and their strength. Strength is the ability of an object to withstand the applied stress, to what extent can it bear the stress. Resistance to deformation is how resistant any object is to the change of shape. If the resistance to deformation is less, the object can easily change its shape and vice versa.
Therefore, some of the mechanical properties of solids include:
Elasticity: When we stretch an object, it changes its shape and when we leave, it regains its shape. Or we can say it is the property to regain the original shape once the external force is removed. Example: Spring
Plasticity: When an object changes its shape and never comes back to its original shape even when external force is removed. It is the property of permanent deformation. Example: Plastic materials.
Ductility: When an object can be pulled in thin sheets, wires or plates, it has the ductile properties. It is the property of being drawn into thin wires/sheets/plates. Example: Gold or Silver
Strength: The ability to withstand applied stress without failure. Many categories of objects have higher strength than others.
There are various other properties but in this chapter of class 11 Physics mechanical properties of solids, we will mainly focus on the elasticity of solids.
Stress and Different Types of Stress
It is the restoring force that develops on an object in the opposite direction; it is measured per unit area. For example, when a rubber ball is applied by an external force with our hands to compress it, at the same time the ball develops an opposite force that restrains it; however, both the forces are equal in magnitude. This restoring force developed by the object or ball is called stress.
Stress = Force/Area
The S.I. unit of Stress is N/m square or Pascal (Pa)
Different Types of Stress are
Longitudinal Stress: Longitude means lengthwise; therefore, it can be defined as the restoring force per unit area when the force applied is normal to the cross-sectional area of the cylindrical body. There is change in the length of the object taking place. Example, when a cylindrical rubber object is tied with a heavy object, there will be longitudinal stress acting upon and the change in the length of the object takes place.
Longitudinal stress is divided into two sub-categories:
Tensile stress: In the above example, it can be said that tensile stress develops when force is applied to stretch the cylinder.
Compressive stress: When force is applied to compress the object.
Tangential or Shearing Stress
It is the restoring force per unit area when the force applied is parallel to the cross-sectional area of the body. There is a relative displacement occurring between the opposite faces of the body.
Hydraulic Stress
It is the restoring force per unit area when the force is applied by a fluid like water on the body or object. Suppose, a ball made of rubber (which can be compressed) is dipped inside a river or sea, there is a force acting on the ball from all directions due to the pressure of the water. It results in the minor contraction of the ball. It is an example of hydraulic stress that you can include in the notes of mechanical properties of solids.
Strain and different Kinds of Strain
It is a measure of the deformation that can represent the displacement between particles in the body relative to a reference length.
Strain is dimensionless quantity. If a rubber object is stretched from both the sides, the change in length represents the strain.
Different Types of Strain are
Longitudinal Strain: It is the change in length to the original length of the body due to the applied longitudinal stress. It is a change in length divided by the original length.
Shearing Strain: It is the measure of the relative displacement of the opposite faces of the body due to the shearing stress. Shearing strain can be represented by tan Θ.
Volume Strain: It is the ratio of change in volume to the original volume as a result of the hydraulic stress. It is the change in volume divided by the initial or original volume.
Hooke’s Law
It is named after the scientist Robert Hooke. Hooke’s Law states that stress developed is directly proportional to the strain produced in an object, within elastic limit (if the object is elastic material). An object that can come back to the original shape is its elasticity. Therefore, hooke’s law applies to elastic objects. It doesn’t apply to the plasticity property of solids.
It can be, therefore, represented as Stress = k * Strain
Where k is the modulus of elasticity
Stress-Strain Curve
A curve drawn between stress and strain is called the stress-strain curve. When stress and stress are drawn along the y-axis and x-axis respectively, a linear graph is formed in the ideal situation of Hooke’s law. However, when actual experiments are drawn, a curve is formed known as the stress-strain curve as shown below.
Solid is one of the four crucial conditions of issue (the others being fluid, gas, and plasma). The atoms in a strong are firmly pressed together and contain minimal measure of active energy. A strong is portrayed by primary inflexibility and protection from a power applied to the surface. Not at all like a fluid, a strong article doesn't stream to assume the state of its holder, nor does it extend to fill the whole accessible volume like a gas. The particles in a strong are bound to one another, either in a customary mathematical cross-section (glasslike solids, which incorporate metals and standard ice), or unpredictably (an indistinct strong, for example, normal window glass). Solids can't be compacted with little strain through gases can be compacted with little tension in light of the fact that the particles in a gas are inexactly pressed.
The part of physical science that arranges with solids is called strong state physical science and is the fundamental part of dense matter physical science (which likewise incorporates fluids). Materials science is essentially worried about the physical and substance properties of solids. Strong state science is particularly worried about the combination of novel materials, just as the study of recognizable proof and substance arrangement.
Microscopic Description
The particles, atoms or particles that make up solids might be set up in a methodical rehashing design, or sporadically. Materials whose constituents are organised in a standard example are known as gems. Now and again, the customary request can proceed solidly over an enormous scope, for instance precious stones, where every jewel is a solitary gem. Strong items that are sufficiently huge to see and deal with are seldom made out of a solitary precious stone, however rather are made of countless single gems, known as crystallites, whose size can shift from a couple of nanometers to a few metres. Such materials are called polycrystalline. Practically all normal metals, and numerous ceramics, are polycrystalline.
In different materials, there is no long-range request in the place of the molecules. These solids are known as shapeless solids; models incorporate polystyrene and glass.
Regardless of whether a strong is glasslike or indistinct relies upon the material in question, and the conditions wherein it was shaped. Solids that are shaped by lethargic cooling will quite often be translucent, while solids that are frozen quickly are bound to be undefined. In like manner, the particular precious stone design embraced by a translucent strong relies upon the material in question and on how it was shaped.
While numerous normal items, for example, an ice solid shape or a coin, are artificially indistinguishable all through, numerous other normal materials include various substances stuffed together. For instance, an average stone is a total of a few unique minerals and mineraloids, with no particular substance piece. Wood is a characteristic natural material consisting essentially of cellulose filaments inserted in a network of natural lignin. In materials science, composites of beyond what one constituent material can be intended to have wanted properties.
Classes of Solids
The powers between the molecules in a strong can take an assortment of structures. For instance, a gem of sodium chloride (normal salt) is composed of ionic sodium and chlorine, which are held together by ionic bonds. In diamond or silicon, the iotas share electrons and structure covalent bonds. In metals, electrons are partaken in metallic bonding. Some solids, especially most natural mixtures, are held along with van der Waals powers coming about because of the polarisation of the electric charge cloud on every atom. The dissimilarities between the sorts of strong outcome from the contrasts between their holding.
The apex of New York's Chrysler Building, the world's tallest steel-upheld block building, is clad with treated steel.
Metals commonly are solid, thick, and great conduits of both power and hotness. The heft of the components in the intermittent table, those to one side of a corner to corner line attracted from boron to polonium, are metals. Combinations of at least two components in which the significant part is a metal are known as composites.
Individuals have been involving metals for an assortment of purposes since ancient occasions. The strength and dependability of metals has prompted their boundless use in development of structures and different designs, just as in many vehicles, numerous apparatuses and devices, pipes, street signs and railroad tracks. Iron and aluminium are the two most generally utilised primary metals. They are likewise the most bountiful metals in the Earth's covering. Iron is most generally utilised as a combination, steel, which contains up to 2.1% carbon, making it a lot harder than unadulterated iron.
Since metals are great conveyors of power, they are important in electrical apparatuses and for conveying an electric flow over significant distances with little energy misfortune or dissemination. Accordingly, electrical power matrices depend on metal links to convey power. Home electrical frameworks, for instance, are set up with copper for its great leading properties and simple machinability. The high warm conductivity of most metals additionally makes them helpful for burner cooking tools.
The investigation of metallic components and their compounds makes up a critical piece of the fields of strong state science, physical science, materials science and designing.
Metallic solids are held together by a high thickness of shared, delocalized electrons, known as "metallic holding". In a metal, particles promptly lose their peripheral ("valence") electrons, shaping positive particles. The free electrons are spread over the whole string, which is held together solidly by electrostatic cooperations between the particles and the electron cloud. The enormous number of free electrons provides metals with their high upsides of electrical and warm conductivity. The free electrons additionally forestall transmission of noticeable light, making metals hazy, sparkly and glistening.
Further developed models of metal properties consider the impact of the positive particle centres on the delocalised electrons. As most metals have translucent design, those particles are generally organised into an occasional cross section . Numerically, the capability of the particle centres can be treated by different models, the least difficult being the almost free electron model.
Minerals are normally happening solids framed through different land processes under high tensions. To be named a genuine mineral, a substance should have a precious stone construction with uniform actual properties all through. Minerals range in organisation from unadulterated components and basic salts to extremely complex silicates with a huge number of known structures. Interestingly, a stone example is an arbitrary total of minerals or potentially mineraloids, and has no particular substance organisation. By far most of the stones of the Earth's covering comprise of quartz (glasslike SiO 2 ), feldspar, mica, chlorite, kaolin, calcite, epidote, olivine, augite, hornblende, magnetite, hematite, limonite and a couple of different minerals. A few minerals, similar to quartz, mica or feldspar are normal, while others have been found in a couple of areas around the world. The biggest gathering of minerals by a long shot is the silicates (most shakes are ≥95% silicates), which are made to a great extent out of silicon and oxygen, with the expansion of particles of aluminium, magnesium, iron, calcium and different metals.
Si3N4 clay bearing parts
Clay solids are made out of inorganic mixtures, normally oxides of substance components. They are synthetically inactive, and frequently are fit for enduring compound disintegration that happens in an acidic or scathing climate. Earthenware production for the most part can endure high temperatures going from 1000 to 1600 °C (1800 to 3000 °F). Special cases incorporate non-oxide inorganic materials, like nitrides, borides and carbides.
Conventional artistic unrefined substances incorporate earth minerals, for example, kaolinite, later materials incorporate aluminium oxide (alumina). The cutting edge ceramic materials, which are named progressed earthenware production, incorporate silicon carbide and tungsten carbide. Both are esteemed for their scraped area opposition, and henceforth observe use in such applications as the wear plates of devastating hardware in mining activities.
Most clay materials, like alumina and its mixtures, are framed from fine powders, yielding a fine grained polycrystalline microstructure that is loaded up with light-dispersing focuses similar to the frequency of noticeable light. In this manner, they are for the most part hazy materials, rather than straightforward materials. Ongoing nanoscale (for example sol-gel) innovation has, notwithstanding, made conceivable the creation of polycrystalline straightforward ceramics, for example, straightforward alumina and alumina compounds for such applications as high-power lasers. Progressed earthenware production is likewise utilised in the medication, electrical and hardware enterprises.
Earthenware designing is the science and innovation of making strong state artistic materials, parts and gadgets. This is done either by the activity of hotness, or, at lower temperatures, utilising precipitation responses from compound arrangements. The term incorporates the decontamination of natural substances, the review and creation of the synthetic mixtures concerned, their development into parts, and the investigation of their design, synthesis and properties.
Precisely talking, clay materials are fragile, hard, solid in pressure and feeble in shearing and strain. Weak materials might display critical elasticity by supporting a static burden. Durability demonstrates how much energy a material can ingest before mechanical disappointment, while break strength (signified KIc ) depicts the capacity of a material with inborn microstructural defects to oppose crack by means of break development and proliferation. Assuming a material has an enormous worth of break strength, the essential standards of crack mechanics propose that it will probably go through malleable crack. Weak break is exceptionally normal for generally artistic and glass-ceramic materials that regularly display low (and conflicting) upsides of KIc.
For an illustration of uses of ceramics, the outrageous hardness of zirconia is used in the production of blade sharp edges, just as other modern cutting devices. Ceramics, for example, alumina, boron carbide and silicon carbide have been utilised in tactical armour carriers to repulse enormous type rifle shoot. Silicon nitride parts are utilised in clay metal rollers, where their high hardness makes them wear safe. As a general rule, earthenware production is synthetically safe and can be utilised in wet conditions where steel orientation would be helpless to oxidation (or rust).
As one more illustration of artistic applications, in the mid 1980s, Toyota investigated the creation of an adiabatic clay motor with a working temperature north of 6000 °F (3300 °C). Artistic motors don't need a cooling framework and subsequently permit a significant weight decrease and along these lines more prominent eco-friendliness. In a regular metallic motor, a large part of the energy let out of the fuel should be dispersed as waste hotness to forestall an emergency of the metallic parts. Work is additionally being done in creating artistic parts for gas turbine motors. Turbine motors made with ceramics could work all the more productively, giving aeroplanes more prominent reach and payload for a limited measure of fuel. Such motors are not underway, notwithstanding, in light of the fact that the assembling of clay parts in the adequate accuracy and toughness is troublesome and expensive. Handling strategies regularly bring about a wide conveyance of minute blemishes that often assume an inconvenient part in the sintering system, bringing about the multiplication of breaks, and extreme mechanical disappointment.

FAQs on Mechanical Properties of Solids
1. How Do We Find Notes of Mechanical Properties of Solids for Class 11?
Students can get well-explained notes for mechanical properties of solids for class 11 Physics through online platforms. Most trusted educational platforms are available on the internet for aspirants where they can understand all topics in the easiest manner. All the topics are covered well with simple examples which can be seen in day-to-day lives.
2. What are the Mechanical Properties of Solids Class 11?
The various properties exhibited by a solid object that include elasticity, plasticity, ductility and strength are the mechanical properties of solids class 11 Physics subject.
3. What is biofortification?
At the point when a material acts flexibly and shows a direct connection among anxiety, it is called straightly versatile material. For this situation, stress is straightforwardly corresponding to strain OR you can say that "for little deformity, stress is straightforwardly relative to strain". Accordingly, in straightforward terms, Hooke's law expresses that the strain in a strong is relative to the applied pressure inside the flexible furthest reaches of that strong. Understudies can allude to Chapter 9 of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics while responding to the reading material inquiries to find out about the ideas. Both section savvy and exercise insightful arrangements are accessible which can be utilised by the understudies dependent on their requirements.
4. What is Strain and explain its types?
(i) Longitudinal strain: If the disfiguring power creates an adjustment of length alone, the strain delivered in the body is called longitudinal strain or malleable strain.
(ii) Volumetric strain: If the disfiguring power creates an adjustment of volume alone, the strain delivered in the body is called volumetric strain.
(iii) Shear strain: The point slant made in the body due digressive pressure communicated is called shear strain. It is given as:
The greatest pressure to which the body can recapture its unique status on the evacuation of the distorting power is called versatile cutoff.
5. What is the stress-strain curve?
Stress-strain bends are helpful to comprehend the rigidity of a given material.
The bend from O to An is straight. In this district, Hooke's Proportional breaking point law complies.
In the district from A to 6 anxiety is not. corresponding. In any case, the body recovers its unique aspect, when the heap is taken out.
Point B in the bend is yield point or versatile cutoff and the comparing pressure is known as the yield strength of the material.
The bend past B shows the district of plastic distortion.
Point D on the bend shows the rigidity of the material. Past this point, extra strain prompts a crack in the given material.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Solids Case Study Questions: Question 1: The graph shown below shows qualitatively the relation between the stress and the strain as the deformation gradually increases. Within Hooke's limit for a certain region stress and strain relation is linear. Beyond that up to a … Continue reading Case Study Questions for ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Solid Case Study - 1. The property of a body, by virtue of which it tends to regain its original size and shape when the applied force is removed, is known as elasticity and the deformation caused is known as elastic deformation. However, if you apply force to a lump of putty ...
Case Study. (i) All three states of matter (i.e., solid, liquids and gases) have volume elasticity. (ii) When we stretch a wire, the work has been done against interatomic forces. This work is stored in the wire in the form of elastic potential energy. (iii) Elastic limit is the upper limit of deforming force upto which, if deforming force is ...
4) The pressure of the atmosphere at any point is equal to the weight of a column of air of unit cross-sectional area extending from that point to the top of the atmosphere. 5) Following are applications of Pascal's law. a) Hydraulic lift. b) Hydraulic jack. c) Hydraulic machines.
Mechanical Properties of Solids 8.1 Introduction As we proceed along, we will see that the elastic properties of solids have twofold importance. Firstly, they indicate the mechanical strength of the solid. Secondly, they are very important in understanding the nature of the interatomic forces and in the analysis of lattice vibrations.
Mechanical Properties of Solids. We now turn to discuss the properties of solids, especially of monatomic solids, alloys, and simple compounds. ... of aggregates of very small crystals that are themselves fairly simple; commonly, they have variable composition. The study of solids goes under various names: crystallography, solid state physics ...
Select amount. $10. $20. $30. $40. Other. UP Class 11 Physics 2 units · 6 skills. Unit 1 Units and Measurement. Unit 2 Mechanical properties of solids.
Unit 13: Mechanical properties of solids. About this unit. Whether you want to build a small house or a big bungalow, a small bridge or a giant sea link, understanding the elastic properties of materials is the key. In this unit, we will explore some of these elastic properties and look at some engineering applications.
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 11 Physics Subject - Mechanical Properties of Solids, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
8.1 Introduction. As we proceed along,we will see that the elastic properties of solids have twofold importance. Firstly,they indicate the mechanical strength of the solid. Secondly,they are very important in understanding the nature of the interatomic forces and in the analysis of lattice vibrations. When an elastic solid is stressed,it ...
not? Answers to such questions begin with the study of how relatively simple kinds of loads or forces act to deform different solids bodies. In this chapter, we shall study the 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Stress and strain 8.3 Hooke's law 8.4 Stress-strain curve 8.5 Elastic moduli 8.6 Applications of elastic behaviour of materials Summary Points to ...
Mechanical Properties of Solids. A material is said to be in the solid state if all the atoms of that matter are densely packed together. A solid material has a definite shape and size. In order to change the shape and size of the solid object, an external force needs to be applied. In this chapter, we will learn about the Mechanical Properties ...
Mechanical properties of solids notes, are particularly useful for revision when you are short on time and have a lot of material to cover. Every year, they have posted at least two questions from properties of solids and liquids, as has been the case over the past five years. This is one of the most important chapters on the syllabus.
Ans: Stretching of coil spring is determined by shear modulus as when a coil spring is stretched, neither its length nor its volume or its shape changes. 2. The spherical ball contracts in volume by 0.1% when subjected to a uniform normal pressure of 100 atmosphere. Calculate the bulk modulus of material of the ball.
Chapter 9 -Mechanical Properties Of Solids 1. Introduction A rigid body refers to a hard solid object having a definite shape and size. However, in reality, bodies can be stretched, compressed and bent. Even the strongest rigid steel bar can be deformed when a sufficiently large external force is applied on it.
The notes of mechanical properties of solids class 11 are available on Vedantu in PDF format and students can download it for free. Mechanical properties of Solids come under Unit VII- Properties of Bulk Matter. This entire unit is very important from an examination point of view and carries a total weightage of 20 marks.
Solid mechanics (also known as mechanics of solids) is the branch of continuum mechanics that studies the behavior of solid materials, especially their motion and deformation under the action of forces, temperature changes, phase changes, and other external or internal agents.. Solid mechanics is fundamental for civil, aerospace, nuclear, biomedical and mechanical engineering, for geology, and ...
The Case Based Questions Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids questions and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus.The Case Based Questions Test: Mechanical Properties of Solids MCQs are made for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Case ...
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Solids are important resources that help students understand the topics and prepare well for the exam. It is very important to make notes while studying each topic thoroughly. It is important to solve the questions from the textbook and get well-versed in the topics.
Mechanical Properties of Solids is one of the scoring sections of the Physics subject. Students must study hard so that they can solve any type of question asked from this chapter in the exam. It will also increase their scores in Physics papers`. Important Questions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 - Mechanical Properties of Solids
To refer to the Mechanical Properties Of Solids Class 11 notes, students can look through the given steps. Those important steps are: Open the Selfstudys website. Click the navigation bar, a drop down menu will appear. Select NCERT Books & Solutions from the given list. Click NCERT Notes from the given list.
As a result, some of the mechanical properties of solids are as follows: Elasticity: When we stretch an object, it changes shape, and when we release it, it returns to its original shape. Or, to put it another way, it is the ability to return to its previous shape once an external force is eliminated. Spring is an example.
Mechanical properties of solids elaborates the characteristics such as the resistance to deformation and their strength. Strength is the ability of an object to withstand the applied stress, to what extent can it bear the stress. Resistance to deformation is how resistant any object is to the change of shape. If the resistance to deformation is ...
The preparation of cement-based supplementary cementitious materials is an important method for the efficient use of iron tailings and the reduction in CO2 emissions. The aim of this study is to improve the reactivity of iron tailings by mixing them with steel slag, slag, and fly ash through orthogonal tests to solve the problem that iron tailings cannot be utilised on a large scale. The ...
Safe and efficient recycling of industrially generated machined chips is a high-priority technological issue. In this study, the effect of SiC particles (SiCp) on the microstructure and mechanical properties of SiCp/AZ91D composites is systematically analyzed, and the reinforcement mechanism of SiCp on composites is investigated. Different contents of SiCp/AZ91D composites are fabricated by ...
The paper considers an approach to studying the influence of elastic properties of aerospace structures on their relative motion during separation. Based on the assumptions characteristic of the process under study, a model is developed that allows for a visual mechanical interpretation: the total motion is decomposed during separation into a portable motion (rotational and translational in ...