

Class 9 Science Case Study Questions Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions in Class 9 Science Chapter 14 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving Class 9 Science Case Study Questions Chapter 14 Natural Resources
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Natural Resources Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1:
Oxygen is a very abundant element on our Earth. It is found in the elemental form in the atmosphere to the extent of 21%. It also occurs extensively in the combined form in the Earth’s crust as well as also in the air in the form of carbon dioxide. In the crust, it is found as the oxides of most metals and silicon, and also as carbonate, sulfate, nitrate, and other minerals. It is also an essential component of most biological molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and fats (or lipids).
When we talk of the oxygen cycle, we are mainly referring to the cycle that maintains the levels of oxygen in the atmosphere. Oxygen from the atmosphere is used up in three processes, namely combustion, respiration, and in the formation of oxides of nitrogen. Oxygen is returned to the atmosphere in only one major process, that is, photosynthesis. And this forms the broad outline of the oxygen cycle in nature.
Though we usually think of oxygen as being necessary to live in the process of respiration, it might be of interest to you to learn that some forms of life, especially bacteria, are poisoned by elemental oxygen. In fact, even the process of nitrogen-fixing by bacteria does not take place in the presence of oxygen.
(1) How much oxygen is present in our atmosphere?
Answer: (b) 21 %
(2) Identify the correct statement
- Statement 1 – Oxygen is also an essential component of most biological molecules.
- Statement 2 – Oxygen is returned to the atmosphere through process called photosynthesis
- Statement 3 – Oxygen -cycle maintains the levels of oxygen in the atmosphere.
- Statement 4 – Our atmosphere have 21 % oxygen.
(b) Both 2 & 3
(c) Both 1 & 4
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
(3) Oxygen from the atmosphere is used up in three main processes,
(a) Combustion
(b) Respiration
(c) Formation of oxides of nitrogen
(4) By which process Oxygen is returned to the atmosphere
(a) Respiration
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Photolysis
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) or (c)
(5) Write the molecular formula of oxygen?
Answer: Molecular formula of oxygen is: O2
Case Study 2:
Natural resources are materials or substances that are obtained from the environment and are essential for sustaining life and supporting human activities. They can be classified into two main categories: renewable resources and non-renewable resources. Renewable resources are those that can be replenished or replaced naturally over time, such as sunlight, wind, water, forests, and wildlife. Non-renewable resources, on the other hand, are finite in quantity and cannot be easily replenished. Examples of non-renewable resources include fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, as well as minerals like iron, copper, and gold. It is crucial to manage and utilize natural resources sustainably to ensure their availability for future generations. Conservation and efficient utilization of resources, along with the development of alternative sources, play a significant role in maintaining a balance between human needs and the preservation of the environment.
What are natural resources? a) Materials or substances obtained from the environment b) Artificially created substances c) Human-made objects d) Renewable energy sources Answer: a) Materials or substances obtained from the environment
How are natural resources classified? a) Renewable and non-renewable resources b) Abiotic and biotic resources c) Primary and secondary resources d) Chemical and physical resources Answer: a) Renewable and non-renewable resources
Which type of resource can be replenished or replaced naturally over time? a) Renewable resources b) Non-renewable resources c) Abiotic resources d) Biotic resources Answer: a) Renewable resources
What is an example of a non-renewable resource? a) Sunlight b) Wind c) Coal d) Forests Answer: c) Coal
Why is it important to manage natural resources sustainably? a) To deplete resources for short-term gain b) To ensure their availability for future generations c) To maximize resource extraction d) To disregard environmental preservation Answer: b) To ensure their availability for future generations
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Science Natural Resources Case Study and passage-based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Mcq class 9 social science civics what is democracy why democracy quiz with answers, mcq questions for class 9 with answers for all subjects, class 9 science case study questions chapter 3 atoms and molecules, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Last modified on: 2 years ago
- Reading Time: 4 Minutes
Case Study/Passage Based Questions:
Question 1:
At present the primary nutrient which limits the agricultural yield is nitrogen (N). Some plants are capable to produce more N 2 than they consume. These plants show symbiotic relationship with N 2 -fixing bacteria such as Rhizobium. These bacteria produce root nodules in leguminous plants and convert atmospheric N 2 into nitrogenous compounds. Rhizobium bacteria are gram negative bacteria, which show host specificity and fix N 2 in the presence of a red pigment called leghaemoglobin. It protects nitrogen fixing enzyme nitrogenase from oxygen.
(i) Which of the following statements is incorrect? (A) Leghaemoglobin functions as oxygen scavenger during N 2 -fixation. (B) Enzyme nitrogenase, which is required to fix atmospheric N 2 is active in the presence as well as absence of oxygen. (C) N, P and K are referred to as critical elements for crop plants as they easily become deficient in soil due to higher plant requirement and repeated cultivation. (D) The coordinated activities of the legume and Rhizobium bacteria depend on chemical interactions between the symbiotic partners.
(ii) Read the given statements and select the correct answer. Statement 1: Rhizobium bacteria can also live freely in the soil and cany out N 2 -fixation by themselves. Statement 2: Such Rhizobium bacteria are called free-living N 1 -fixing bacteria. (A) Both statements 1 & 2 are true and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1. (B) Both statements 1 & 2 are true but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement-1 (C) Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false. (D) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
CBSE Expert
Case Study Questions of Chapter 14 Natural Resources PDF Download
Case study Questions on Class 9 Science Chapter 14 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources

In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Natural Resources Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
Oxygen is a very abundant element on our Earth. It is found in the elemental form in the atmosphere to the extent of 21%. It also occurs extensively in the combined form in the Earth’s crust as well as also in the air in the form of carbon dioxide. In the crust, it is found as the oxides of most metals and silicon, and also as carbonate, sulphate, nitrate and other minerals. It is also an essential component of most biological molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids and fats (or lipids).
When we talk of the oxygen-cycle, we are mainly referring to the cycle that maintains the levels of oxygen in the atmosphere. Oxygen from the atmosphere is used up in three processes, namely combustion, respiration and in the formation of oxides of nitrogen. Oxygen is returned to the atmosphere in only one major process, that is, photosynthesis. And this forms the broad outline of the oxygen-cycle in nature.
Though we usually think of oxygen as being necessary to life in the process of respiration, it might be of interest to you to learn that some forms of life, especially bacteria, are poisoned by elemental oxygen. In fact, even the process of nitrogen-fixing by bacteria does not take place in the presence of oxygen.
(1) How much oxygen is present in our atmosphere?
Answer: (b) 21 %
(2) Identify the correct statement
Statement 1 – Oxygen is also an essential component of most biological molecules.
Statement 2 – Oxygen is returned to the atmosphere through process called photosynthesis
Statement 3 – Oxygen -cycle maintains the levels of oxygen in the atmosphere.
Statement 4 – Our atmosphere have 21 % oxygen.
(b) Both 2 & 3
(c) Both 1 & 4
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
(3) Oxygen from the atmosphere is used up in three main processes,
(a) Combustion
(b) Respiration
(c) Formation of oxides of nitrogen
(4) By which process Oxygen is returned to the atmosphere
(a) Respiration
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Photolysis
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) or (c)
(5) Write the molecular formula of oxygen?
Answer: Molecular formula of oxygen is: O2
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Science Natural Resources Case Study and passage-based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
- CBSE Class 10th
CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Answer Key
- JEE Main Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- JEE Advanced Registration
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Animation Courses
- Animation Courses in India
- Animation Courses in Bangalore
- Animation Courses in Mumbai
- Animation Courses in Pune
- Animation Courses in Chennai
- Animation Courses in Hyderabad
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Pune
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Hyderabad
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Design Colleges in India
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET Courses List 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Access premium articles, webinars, resources to make the best decisions for career, course, exams, scholarships, study abroad and much more with
Plan, Prepare & Make the Best Career Choices
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources
Chapter 14: natural resources | ncert science class 9 solutions pdf download.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources : These natural resources class 9 solutions are part of the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science . What do you understand when you hear about natural resources? Have you ever thought about these resources on earth? When you go through class 9 science chapter 14 , you will learn about the natural resources present on the earth. CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources deal with all the important questions mentioned in the chapter. You will get queries based on such concepts in class 9 science chapter 14 question answer . For more understanding of this chapter, you should also check Chapter 14 Natural Resources Class 9 notes, Science. In this article, you will get NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 14.
New: JEE Main 2027: Narayana Scholarship Test Preparation Kit for Class 9
Latest: Important Formulas for Class 9 Science - Chapterwise
Class 9 Science Chapter 14 question answer: When we talk about natural resources, we mean to say that we can use whatever comes from the natural environment, such as water, air, wood, oil, wind energy, natural gas, iron, and coal. Through this article, you can clear your doubts and get a better understanding of the concepts from Chapter 14 Class 9 science . Along with solutions for NCERT class 9 science chapter 14 Natural Resources, you will get NCERT Solutions for other chapters as well.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science: All the exercises and topic-wise NCERT Solutions for Natural Resources Class 9 are mentioned below:
Download PDF
NCERT Exemplar for class 9 science chapter 14 Natural Resources
NCERT solutions for class 9 science chapter 14 Natural Resources: Solved In-Text Question-
Ncert solutions class 9 science natural resources - topic 14.1 the breath of life: air.
Q1. How is our atmosphere different from the atmospheres on Venus and Mars?
Earth's atmosphere is different from the atmosphere on Venus and Mars.
Q 2. How does the atmosphere act as a blanket?
The atmosphere is the thick blanket of air that covers the whole of the Earth. The atmosphere acts as a blanket in the following ways:
(i) It prevents the harmful UV rays from reaching the Earth's surface.
(ii) It helps in maintaining the surface temperature during day and night.
(iii) It protects Earth from celestial objects like asteroids.
Q 3. What causes winds?
The uneven heating of the atmosphere in different regions of the Earth creates some regions of low pressure and some regions of high pressure.
Air from the high-pressure region moves into the area of low pressure. This movement of air from one region to the other creates winds.
Q 4. How are clouds formed?
The heating of the water bodies during the day leads to the evaporation of a large amount of water which then rises up with the hot air.
As the air rises, it expands and cools. This cooling causes the water vapour in the air to condense in the form of tiny droplets around dust particles.
These tiny droplets cluster themselves to form clouds. When these water-drops become heavy, they precipitate and fall down as rain.
In a nutshell, evaporation and condensation are the two main processes involved in the formation of clouds.
Q5. List any three human activities that you think would lead to air pollution.
Three human activities that would lead to air pollution are:
i) Emission of harmful gases and dust particles from vehicles.
ii) Combustion of fossil fuels like coal, petroleum releasing oxides of nitrogen and sulphur.
iii) The smoke released from industries containing harmful gases like sulphur dioxide, oxides of nitrogen.
Natural Resources: NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Solutions
Topic 14.2 Water: A wonderful Liquid
Q1. Why do organisms need water?
Organisms need water for the following activities:
(1) All chemical reaction at the cellular level occurs with water as the solvent.
(2) Water acts as a medium for the transportation of substances in our body.
(3) Terrestrial animals require fresh water for the intake of minerals
(4) Water is required to get rid of waste from the body in the form of sweat and urine.
(5) Water is essential for photosynthesis
CBSE Solutions - NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Question Answer
Topic 14.3 Mineral Riches in the soil
Q1. How is soil formed?
The breaking of rocks near the Earth's surface by various physical, chemical and biological processes over a long period of time leads to the formation of soil.
Factors that help in the formation of soil are:
(i) Sun: Sun heats up rocks during the day causing them to expand. At night these rocks cool down and contract. This unequal expansion and contraction causes cracks in the rocks.
(ii) Water: Water during rainfall after enter these cracks, may freeze and cause the crack to widen. Also, Flowing water wears away rocks over long periods of time breaking it into smaller and smaller particles.
(iii) Wind: Strong winds erode rocks down, which rub with each other.
(iv) Living Organisms: Lichen growing on the surface of the rock, releases certain substances that cause the rock surface to powder down and form a thin layer of soil.
Q2. What is soil erosion?
The removal of the top layer of fertile soil by air, wind, and water is called soil erosion .
Q 3. What are the methods of preventing or reducing soil erosion?
The methods of preventing or reducing soil erosion are:
(i) Afforestation or planting of trees. The roots go deep into the ground and hold the soil thus preventing soil erosion.
(ii) Growth of vegetation. Vegetation ensures that the soil does not get carried away by rainwater or wind.
NCERT Textbook Solutions for class 9 science chapter 14 Natural Resources
Topic 14.5 Ozone Layer
Q1. What are the different states in which water is found during the water cycle?
The different states in which water is found during the water cycle are:
In solid-state as ice/snow.
In a liquid state as rainwater.
In a gaseous state as water vapor in the atmosphere.
Q 2. Name two biologically important compounds that contain both oxygen and nitrogen.
Two biologically important compounds that contain both oxygen and nitrogen are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Q 3. List any three human activities which would lead to an increase in the carbon dioxide content of the air.
Three human activities which would lead to an increase in the carbon dioxide content of air are:
(i) Combustion of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum releases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
(ii) Deforestation leads to an increase in carbon dioxide content in the atmosphere.
(iii) The smoke released from industries contains many harmful gases including carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Q 4. What is the greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is the phenomenon of warming of atmosphere by gases like carbon dioxide and methane.
These gases trap the heat during day time thus keeping the night warm.
Q 5. What are the two forms of oxygen found in the atmosphere?
Two forms of oxygen found in the atmosphere are:
(i) diatomic oxygen O 2
(ii) triatomic Ozone O 3
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources- Solved Exercise Questions
Science Chapter 14 Class 9 Question Answer are explained below in detail for better experience.
Q 1 Why is the atmosphere essential for life?
The atmosphere is very essential for life in the following ways:
(1) It maintains the temperature of Earth and prevents the heat from escaping during the night.
(2) The atmosphere contains nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide which are required for various life processes.
(3) Oxygen in the atmosphere is required for burning, combustion and essential for respiration.
(4) The ozone layer in the stratosphere prevents UV rays from the sun to reach the Earth's surface.
(5) It protects Earth from celestial objects like asteroids and meteors.
Q2. Why is water essential for life?
Water is essential for life for the following reasons:
(3) Terrestrial animals require fresh water for the intake of essential minerals.
(5) Water is essential for photosynthesis by which plants make foo d.
Q3. How are living organisms dependent on the soil? Are organisms that live in water totally independent of soil as a resource?
Soil is a complex mixture, comprising of minerals, organic matter, water, and living organisms. It determines the diversity of life in any area.
Plants need soil for support and also get nutrients to prepare their own food. Herbivore obtains food from these plants. And, a carnivore is directly dependent on the herbivore.
Aquatic animals are also dependent on the soil as a resource. These animals depend on aquatic plants for food, which in turn, requires nutrients from the soil.
Hence, all living organisms directly or indirectly depend on the soil.
Q4. You have seen weather reports on television and in newspapers. How do you think we are able to predict the weather?
The meteorological department predicts the weather. Various instruments are used to collect data like temperature, rainfall, humidity.
Rainfall is measured by a rain gauge. Satellites are used to monitor clouds and predict climate.
Q5. We know that many human activities lead to increasing levels of pollution of the air, water-bodies, and soil. Do you think that isolating these activities to specific and limited areas would help in reducing pollution?
Yes, isolating human activities which leads to increasing levels of pollution of the air, water-bodies, and soil to specific and limited areas would help in reducing pollution.
For example: Having heavy industries outside the main city will drastically decrease the effect of pollution on the population.
Q 6. Write a note on how forests influence the quality of our air, soil and water resources.
(i) Influence of forests on quality of air:
-Forests maintain an oxygen level in the atmosphere. And also reduces the carbon dioxide level.
-Forests maintain the temperature of the environment.
(ii) Influence of forests on quality of soil:
-The roots of the trees bind the soil together thus reducing soil erosion.
-Forests help in maintaining the nutrient cycle.
(iii) Influence of forests on quality of water:
-Forests help in conserving water thus increasing its availability.
-Forests maintain the water cycle in the atmosphere.
Science Class 9 Chapter 14: Important Formulas and Diagrams + eBook link
Did you know that some students perform better on their CBSE exams than others, despite having less time? The fact that they each employ various learning and revision strategies and plans explains this clearly. In addition to the S cience Class 9 Chapter 14 Question Answer , gathering the most important formulas and concepts in one place can help you finish your NCERT science revision faster. Once the ideas are understood, this will enable a quick glance and prompt immediate remembrance.
This helpful ebook was put together by subject matter experts at Careers360 and includes a list of all the critical formulas for NCERT Science Class 9. You can save time and quickly review each important formula with examples that you might encounter on your exams by using this ebook.
Important Topics in Solution of Natural Resources Class 9
The important topics of NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Natural Resources are listed below:
- 14.1 - the Breath of Life: Air
- 14.1.1 - the Role of the Atmosphere in Climate Control
- 14.1.2 - the Movement of Air: Winds
- 14.1.3 - Rain
- 14.1.4 - Air Pollution
- 14.2 - Water: a Wonder Liquid
- 14.2.1 - Water Pollution
- 14.3 - Mineral Riches in the Soil
- 14.4 - Biogeochemical Cycles
- 14.4.1 - the Water-cycle
- 14.4.2 - the Nitrogen-cycle
- 14.4.3 - the Carbon-cycle
- 14.4.3 - (i) the Greenhouse Effect
- 14.4.4 - the Oxygen-cycle
- 14.5 - Ozone Layer
NCERT Solution for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources - Points to Remember
- As you know, water covers 75% of the earth’s surface and is also found underground. These comprise the hydrosphere.
- The air is the mixture of gases that covers the whole of the earth like a blanket, which is called the atmosphere.
- Living things are found where land, air, and water exist.
- Students can refer to the S cience Chapter 14 Class 9 Question Answer to assess themselves on these topics.
- This life-supporting zone of the earth where the atmosphere, the hydrosphere, and therefore the lithosphere interact and make life possible, is known as the biosphere.
- In this NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Solutions, you will study these abiotic components in detail in order to understand their role in sustaining life on earth.
- Quality of life and biodiversity are affected by pollution of the air, water, and soil.
- For saving our natural resources we need to conserve our natural resources and use them in a proper manner.
- Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Question Answer are easy to download and use offline.
Ch 14 Science Class 9 NCERT Solutions : Have you ever thought about how rain is formed? Rain is made up of droplets of water that form from clouds, and rainfall patterns depend on the prevailing wind patterns in an area. In this chapter, you will also study rain, ozone layers, and biogeochemical cycles. If you are having difficulty solving the exercise in the NCERT Textbook, please go through S cience Chapter 14 Class 9 Question Answer provided here.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science: Chapter-wise
Ncert solutions class 9: subject-wise, benefits of ncert solutions for class 9 science chapter 14 natural resources:.
- The Natural Resources Class 9 PDF is very useful from an exam perspective. S cience Class 9 Chapter 14 Question Answer are created by experts, and the language of the solutions is very easy to understand.
- Science Ch 14 Class 9 NCERT Solutions are created as per CBSE guidelines.
- Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 will help you complete your homework and assignments as well.
- If you have any doubts regarding Natural Resources Class 9 Solutions or any other chapter of Class 9 science and maths, you can directly ask our faculty.
- Natural resources class 9th NCERT solutions created by the experienced faculties and experts.
- The Class 9 Science Chapter 14 NCERT Solutions PDF is easy to download and use offline.
- Natural resources Class 9 questions and answers are prepared by subject experts as per the latest CBSE syllabus.
- Class 9 Natural resources NCERT solutions develop a logical approach and methodology towards science.
Also check the NCERT Books and NCERT Syllabus here:
- NCERT Books Class 9 Science
- NCERT Syllabus Class 9 Science
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Syllabus Class 9
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
The advantage of the ncert solutions for class 9 science chapter 14 are given below:
- Natural resources class 9 pdf is very useful from an exam perspective. They are created by experts and the language of the solutions is very easy to understand.
- Solutions for ch 14 science class 9 are created as per CBSE guidelines.
- Solutions for class 9 science chapter 14 will help you to complete your homework and assignment as well.
To score well in the examination, follow the NCERT syllabus and solve the exercise given in the NCERT Book. To practice more problems, students must refer to NCERT Exemplar.
Differences in atmospheric pressure are what create the wind. When there is a difference in atmospheric pressure, air moves from the area of higher pressure to the area of lower pressure, causing winds to blow in various directions and at different speeds.
These are resources that are derived naturally from the environment and without human intervention. Air, sunlight, water, soil, stone, plants, animals, and fossil fuels are typical examples of natural resources.
- Latest Articles
- Popular Articles
Explore Premium
Understand your attachment style and learn how you can reform your relationships, 7 tips to convey your struggles to your loved ones, decision-making: common challenges faced, tips to make good decisions, how stay-at-home parents can care for themselves, teenage relationships: tips to help your teenager deal with a breakup, getting over the pink and blue divide: revising gender roles, artificial rain: concept and techniques, what is lenz’s law in electricity and magnetism and why is it true, cancer treatment: why chemotherapy does not suit all patients, upcoming school exams, national institute of open schooling 12th examination.
Admit Card Date : 28 March,2024 - 22 May,2024
National Institute of Open Schooling 10th examination
Punjab board of secondary education 12th examination.
Exam Date : 05 April,2024 - 27 April,2024
Bihar Board 12th Examination
Admit Card Date : 19 April,2024 - 11 May,2024
Jammu and Kashmir State Board of School Education 10th Examination
Exam Date : 28 April,2024 - 28 April,2024
Popular Questions
A block of mass 0.50 kg is moving with a speed of 2.00 ms -1 on a smooth surface. It strikes another mass of 1.00 kg and then they move together as a single body. The energy loss during the collision is
A person trying to lose weight by burning fat lifts a mass of 10 kg upto a height of 1 m 1000 times. Assume that the potential energy lost each time he lowers the mass is dissipated. How much fat will he use up considering the work done only when the weight is lifted up ? Fat supplies 3.8×10 7 J of energy per kg which is converted to mechanical energy with a 20% efficiency rate. Take g = 9.8 ms −2 :
An athlete in the olympic games covers a distance of 100 m in 10 s. His kinetic energy can be estimated to be in the range
In the reaction,
If we consider that 1/6, in place of 1/12, mass of carbon atom is taken to be the relative atomic mass unit, the mass of one mole of a substance will
With increase of temperature, which of these changes?
Number of atoms in 558.5 gram Fe (at. wt.of Fe = 55.85 g mol -1 ) is
A pulley of radius 2 m is rotated about its axis by a force F = (20t - 5t 2 ) newton (where t is measured in seconds) applied tangentially. If the moment of inertia of the pulley about its axis of rotation is 10 kg m 2 , the number of rotations made by the pulley before its direction of motion if reversed, is
Colleges After 12th
Popular course after 12th.
- DUET (DU JAT)
- BHU UET,BUMAT,
- MAH CET Law
- JEE Advanced
- COMEDK UGET
- JEE Main Paper 2
- AAT (JEE Advanced)
- ISI Admission Test
Explore Career Options (By Industry)
- Construction
- Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Information Technology
Data Administrator
Database professionals use software to store and organise data such as financial information, and customer shipping records. Individuals who opt for a career as data administrators ensure that data is available for users and secured from unauthorised sales. DB administrators may work in various types of industries. It may involve computer systems design, service firms, insurance companies, banks and hospitals.
Bio Medical Engineer
The field of biomedical engineering opens up a universe of expert chances. An Individual in the biomedical engineering career path work in the field of engineering as well as medicine, in order to find out solutions to common problems of the two fields. The biomedical engineering job opportunities are to collaborate with doctors and researchers to develop medical systems, equipment, or devices that can solve clinical problems. Here we will be discussing jobs after biomedical engineering, how to get a job in biomedical engineering, biomedical engineering scope, and salary.
Ethical Hacker
A career as ethical hacker involves various challenges and provides lucrative opportunities in the digital era where every giant business and startup owns its cyberspace on the world wide web. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path try to find the vulnerabilities in the cyber system to get its authority. If he or she succeeds in it then he or she gets its illegal authority. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path then steal information or delete the file that could affect the business, functioning, or services of the organization.
GIS officer work on various GIS software to conduct a study and gather spatial and non-spatial information. GIS experts update the GIS data and maintain it. The databases include aerial or satellite imagery, latitudinal and longitudinal coordinates, and manually digitized images of maps. In a career as GIS expert, one is responsible for creating online and mobile maps.
Data Analyst
The invention of the database has given fresh breath to the people involved in the data analytics career path. Analysis refers to splitting up a whole into its individual components for individual analysis. Data analysis is a method through which raw data are processed and transformed into information that would be beneficial for user strategic thinking.
Data are collected and examined to respond to questions, evaluate hypotheses or contradict theories. It is a tool for analyzing, transforming, modeling, and arranging data with useful knowledge, to assist in decision-making and methods, encompassing various strategies, and is used in different fields of business, research, and social science.
Geothermal Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as geothermal engineers are the professionals involved in the processing of geothermal energy. The responsibilities of geothermal engineers may vary depending on the workplace location. Those who work in fields design facilities to process and distribute geothermal energy. They oversee the functioning of machinery used in the field.
Database Architect
If you are intrigued by the programming world and are interested in developing communications networks then a career as database architect may be a good option for you. Data architect roles and responsibilities include building design models for data communication networks. Wide Area Networks (WANs), local area networks (LANs), and intranets are included in the database networks. It is expected that database architects will have in-depth knowledge of a company's business to develop a network to fulfil the requirements of the organisation. Stay tuned as we look at the larger picture and give you more information on what is db architecture, why you should pursue database architecture, what to expect from such a degree and what your job opportunities will be after graduation. Here, we will be discussing how to become a data architect. Students can visit NIT Trichy , IIT Kharagpur , JMI New Delhi .
Remote Sensing Technician
Individuals who opt for a career as a remote sensing technician possess unique personalities. Remote sensing analysts seem to be rational human beings, they are strong, independent, persistent, sincere, realistic and resourceful. Some of them are analytical as well, which means they are intelligent, introspective and inquisitive.
Remote sensing scientists use remote sensing technology to support scientists in fields such as community planning, flight planning or the management of natural resources. Analysing data collected from aircraft, satellites or ground-based platforms using statistical analysis software, image analysis software or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a significant part of their work. Do you want to learn how to become remote sensing technician? There's no need to be concerned; we've devised a simple remote sensing technician career path for you. Scroll through the pages and read.
Budget Analyst
Budget analysis, in a nutshell, entails thoroughly analyzing the details of a financial budget. The budget analysis aims to better understand and manage revenue. Budget analysts assist in the achievement of financial targets, the preservation of profitability, and the pursuit of long-term growth for a business. Budget analysts generally have a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, economics, or a closely related field. Knowledge of Financial Management is of prime importance in this career.
Underwriter
An underwriter is a person who assesses and evaluates the risk of insurance in his or her field like mortgage, loan, health policy, investment, and so on and so forth. The underwriter career path does involve risks as analysing the risks means finding out if there is a way for the insurance underwriter jobs to recover the money from its clients. If the risk turns out to be too much for the company then in the future it is an underwriter who will be held accountable for it. Therefore, one must carry out his or her job with a lot of attention and diligence.
Finance Executive
Product manager.
A Product Manager is a professional responsible for product planning and marketing. He or she manages the product throughout the Product Life Cycle, gathering and prioritising the product. A product manager job description includes defining the product vision and working closely with team members of other departments to deliver winning products.
Operations Manager
Individuals in the operations manager jobs are responsible for ensuring the efficiency of each department to acquire its optimal goal. They plan the use of resources and distribution of materials. The operations manager's job description includes managing budgets, negotiating contracts, and performing administrative tasks.
Stock Analyst
Individuals who opt for a career as a stock analyst examine the company's investments makes decisions and keep track of financial securities. The nature of such investments will differ from one business to the next. Individuals in the stock analyst career use data mining to forecast a company's profits and revenues, advise clients on whether to buy or sell, participate in seminars, and discussing financial matters with executives and evaluate annual reports.
A Researcher is a professional who is responsible for collecting data and information by reviewing the literature and conducting experiments and surveys. He or she uses various methodological processes to provide accurate data and information that is utilised by academicians and other industry professionals. Here, we will discuss what is a researcher, the researcher's salary, types of researchers.
Welding Engineer
Welding Engineer Job Description: A Welding Engineer work involves managing welding projects and supervising welding teams. He or she is responsible for reviewing welding procedures, processes and documentation. A career as Welding Engineer involves conducting failure analyses and causes on welding issues.
Transportation Planner
A career as Transportation Planner requires technical application of science and technology in engineering, particularly the concepts, equipment and technologies involved in the production of products and services. In fields like land use, infrastructure review, ecological standards and street design, he or she considers issues of health, environment and performance. A Transportation Planner assigns resources for implementing and designing programmes. He or she is responsible for assessing needs, preparing plans and forecasts and compliance with regulations.
Environmental Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as an environmental engineer are construction professionals who utilise the skills and knowledge of biology, soil science, chemistry and the concept of engineering to design and develop projects that serve as solutions to various environmental problems.
Safety Manager
A Safety Manager is a professional responsible for employee’s safety at work. He or she plans, implements and oversees the company’s employee safety. A Safety Manager ensures compliance and adherence to Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) guidelines.
Conservation Architect
A Conservation Architect is a professional responsible for conserving and restoring buildings or monuments having a historic value. He or she applies techniques to document and stabilise the object’s state without any further damage. A Conservation Architect restores the monuments and heritage buildings to bring them back to their original state.
Structural Engineer
A Structural Engineer designs buildings, bridges, and other related structures. He or she analyzes the structures and makes sure the structures are strong enough to be used by the people. A career as a Structural Engineer requires working in the construction process. It comes under the civil engineering discipline. A Structure Engineer creates structural models with the help of computer-aided design software.
Highway Engineer
Highway Engineer Job Description: A Highway Engineer is a civil engineer who specialises in planning and building thousands of miles of roads that support connectivity and allow transportation across the country. He or she ensures that traffic management schemes are effectively planned concerning economic sustainability and successful implementation.
Field Surveyor
Are you searching for a Field Surveyor Job Description? A Field Surveyor is a professional responsible for conducting field surveys for various places or geographical conditions. He or she collects the required data and information as per the instructions given by senior officials.
Orthotist and Prosthetist
Orthotists and Prosthetists are professionals who provide aid to patients with disabilities. They fix them to artificial limbs (prosthetics) and help them to regain stability. There are times when people lose their limbs in an accident. In some other occasions, they are born without a limb or orthopaedic impairment. Orthotists and prosthetists play a crucial role in their lives with fixing them to assistive devices and provide mobility.
Pathologist
A career in pathology in India is filled with several responsibilities as it is a medical branch and affects human lives. The demand for pathologists has been increasing over the past few years as people are getting more aware of different diseases. Not only that, but an increase in population and lifestyle changes have also contributed to the increase in a pathologist’s demand. The pathology careers provide an extremely huge number of opportunities and if you want to be a part of the medical field you can consider being a pathologist. If you want to know more about a career in pathology in India then continue reading this article.
Veterinary Doctor
Speech therapist, gynaecologist.
Gynaecology can be defined as the study of the female body. The job outlook for gynaecology is excellent since there is evergreen demand for one because of their responsibility of dealing with not only women’s health but also fertility and pregnancy issues. Although most women prefer to have a women obstetrician gynaecologist as their doctor, men also explore a career as a gynaecologist and there are ample amounts of male doctors in the field who are gynaecologists and aid women during delivery and childbirth.
Audiologist
The audiologist career involves audiology professionals who are responsible to treat hearing loss and proactively preventing the relevant damage. Individuals who opt for a career as an audiologist use various testing strategies with the aim to determine if someone has a normal sensitivity to sounds or not. After the identification of hearing loss, a hearing doctor is required to determine which sections of the hearing are affected, to what extent they are affected, and where the wound causing the hearing loss is found. As soon as the hearing loss is identified, the patients are provided with recommendations for interventions and rehabilitation such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and appropriate medical referrals. While audiology is a branch of science that studies and researches hearing, balance, and related disorders.
An oncologist is a specialised doctor responsible for providing medical care to patients diagnosed with cancer. He or she uses several therapies to control the cancer and its effect on the human body such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and biopsy. An oncologist designs a treatment plan based on a pathology report after diagnosing the type of cancer and where it is spreading inside the body.
Are you searching for an ‘Anatomist job description’? An Anatomist is a research professional who applies the laws of biological science to determine the ability of bodies of various living organisms including animals and humans to regenerate the damaged or destroyed organs. If you want to know what does an anatomist do, then read the entire article, where we will answer all your questions.
For an individual who opts for a career as an actor, the primary responsibility is to completely speak to the character he or she is playing and to persuade the crowd that the character is genuine by connecting with them and bringing them into the story. This applies to significant roles and littler parts, as all roles join to make an effective creation. Here in this article, we will discuss how to become an actor in India, actor exams, actor salary in India, and actor jobs.
Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats create and direct original routines for themselves, in addition to developing interpretations of existing routines. The work of circus acrobats can be seen in a variety of performance settings, including circus, reality shows, sports events like the Olympics, movies and commercials. Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats must be prepared to face rejections and intermittent periods of work. The creativity of acrobats may extend to other aspects of the performance. For example, acrobats in the circus may work with gym trainers, celebrities or collaborate with other professionals to enhance such performance elements as costume and or maybe at the teaching end of the career.
Video Game Designer
Career as a video game designer is filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. A video game designer is someone who is involved in the process of creating a game from day one. He or she is responsible for fulfilling duties like designing the character of the game, the several levels involved, plot, art and similar other elements. Individuals who opt for a career as a video game designer may also write the codes for the game using different programming languages.
Depending on the video game designer job description and experience they may also have to lead a team and do the early testing of the game in order to suggest changes and find loopholes.
Radio Jockey
Radio Jockey is an exciting, promising career and a great challenge for music lovers. If you are really interested in a career as radio jockey, then it is very important for an RJ to have an automatic, fun, and friendly personality. If you want to get a job done in this field, a strong command of the language and a good voice are always good things. Apart from this, in order to be a good radio jockey, you will also listen to good radio jockeys so that you can understand their style and later make your own by practicing.
A career as radio jockey has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. If you want to know more about a career as radio jockey, and how to become a radio jockey then continue reading the article.
Choreographer
The word “choreography" actually comes from Greek words that mean “dance writing." Individuals who opt for a career as a choreographer create and direct original dances, in addition to developing interpretations of existing dances. A Choreographer dances and utilises his or her creativity in other aspects of dance performance. For example, he or she may work with the music director to select music or collaborate with other famous choreographers to enhance such performance elements as lighting, costume and set design.
Social Media Manager
A career as social media manager involves implementing the company’s or brand’s marketing plan across all social media channels. Social media managers help in building or improving a brand’s or a company’s website traffic, build brand awareness, create and implement marketing and brand strategy. Social media managers are key to important social communication as well.
Photographer
Photography is considered both a science and an art, an artistic means of expression in which the camera replaces the pen. In a career as a photographer, an individual is hired to capture the moments of public and private events, such as press conferences or weddings, or may also work inside a studio, where people go to get their picture clicked. Photography is divided into many streams each generating numerous career opportunities in photography. With the boom in advertising, media, and the fashion industry, photography has emerged as a lucrative and thrilling career option for many Indian youths.
An individual who is pursuing a career as a producer is responsible for managing the business aspects of production. They are involved in each aspect of production from its inception to deception. Famous movie producers review the script, recommend changes and visualise the story.
They are responsible for overseeing the finance involved in the project and distributing the film for broadcasting on various platforms. A career as a producer is quite fulfilling as well as exhaustive in terms of playing different roles in order for a production to be successful. Famous movie producers are responsible for hiring creative and technical personnel on contract basis.
Copy Writer
In a career as a copywriter, one has to consult with the client and understand the brief well. A career as a copywriter has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. Several new mediums of advertising are opening therefore making it a lucrative career choice. Students can pursue various copywriter courses such as Journalism , Advertising , Marketing Management . Here, we have discussed how to become a freelance copywriter, copywriter career path, how to become a copywriter in India, and copywriting career outlook.
In a career as a vlogger, one generally works for himself or herself. However, once an individual has gained viewership there are several brands and companies that approach them for paid collaboration. It is one of those fields where an individual can earn well while following his or her passion.
Ever since internet costs got reduced the viewership for these types of content has increased on a large scale. Therefore, a career as a vlogger has a lot to offer. If you want to know more about the Vlogger eligibility, roles and responsibilities then continue reading the article.
For publishing books, newspapers, magazines and digital material, editorial and commercial strategies are set by publishers. Individuals in publishing career paths make choices about the markets their businesses will reach and the type of content that their audience will be served. Individuals in book publisher careers collaborate with editorial staff, designers, authors, and freelance contributors who develop and manage the creation of content.
Careers in journalism are filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. One cannot afford to miss out on the details. As it is the small details that provide insights into a story. Depending on those insights a journalist goes about writing a news article. A journalism career can be stressful at times but if you are someone who is passionate about it then it is the right choice for you. If you want to know more about the media field and journalist career then continue reading this article.
Individuals in the editor career path is an unsung hero of the news industry who polishes the language of the news stories provided by stringers, reporters, copywriters and content writers and also news agencies. Individuals who opt for a career as an editor make it more persuasive, concise and clear for readers. In this article, we will discuss the details of the editor's career path such as how to become an editor in India, editor salary in India and editor skills and qualities.
Individuals who opt for a career as a reporter may often be at work on national holidays and festivities. He or she pitches various story ideas and covers news stories in risky situations. Students can pursue a BMC (Bachelor of Mass Communication) , B.M.M. (Bachelor of Mass Media) , or MAJMC (MA in Journalism and Mass Communication) to become a reporter. While we sit at home reporters travel to locations to collect information that carries a news value.
Corporate Executive
Are you searching for a Corporate Executive job description? A Corporate Executive role comes with administrative duties. He or she provides support to the leadership of the organisation. A Corporate Executive fulfils the business purpose and ensures its financial stability. In this article, we are going to discuss how to become corporate executive.

Multimedia Specialist
A multimedia specialist is a media professional who creates, audio, videos, graphic image files, computer animations for multimedia applications. He or she is responsible for planning, producing, and maintaining websites and applications.
Quality Controller
A quality controller plays a crucial role in an organisation. He or she is responsible for performing quality checks on manufactured products. He or she identifies the defects in a product and rejects the product.
A quality controller records detailed information about products with defects and sends it to the supervisor or plant manager to take necessary actions to improve the production process.
Production Manager
A QA Lead is in charge of the QA Team. The role of QA Lead comes with the responsibility of assessing services and products in order to determine that he or she meets the quality standards. He or she develops, implements and manages test plans.
Process Development Engineer
The Process Development Engineers design, implement, manufacture, mine, and other production systems using technical knowledge and expertise in the industry. They use computer modeling software to test technologies and machinery. An individual who is opting career as Process Development Engineer is responsible for developing cost-effective and efficient processes. They also monitor the production process and ensure it functions smoothly and efficiently.
AWS Solution Architect
An AWS Solution Architect is someone who specializes in developing and implementing cloud computing systems. He or she has a good understanding of the various aspects of cloud computing and can confidently deploy and manage their systems. He or she troubleshoots the issues and evaluates the risk from the third party.
Azure Administrator
An Azure Administrator is a professional responsible for implementing, monitoring, and maintaining Azure Solutions. He or she manages cloud infrastructure service instances and various cloud servers as well as sets up public and private cloud systems.
Computer Programmer
Careers in computer programming primarily refer to the systematic act of writing code and moreover include wider computer science areas. The word 'programmer' or 'coder' has entered into practice with the growing number of newly self-taught tech enthusiasts. Computer programming careers involve the use of designs created by software developers and engineers and transforming them into commands that can be implemented by computers. These commands result in regular usage of social media sites, word-processing applications and browsers.
Information Security Manager
Individuals in the information security manager career path involves in overseeing and controlling all aspects of computer security. The IT security manager job description includes planning and carrying out security measures to protect the business data and information from corruption, theft, unauthorised access, and deliberate attack
ITSM Manager
Automation test engineer.
An Automation Test Engineer job involves executing automated test scripts. He or she identifies the project’s problems and troubleshoots them. The role involves documenting the defect using management tools. He or she works with the application team in order to resolve any issues arising during the testing process.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PACE IIT & Medical, Financial District, Hyd
Enrol in PACE IIT & Medical, Financial District, Hyd for JEE/NEET preparation

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN

ALLEN NEET Coaching
Ace your NEET preparation with ALLEN Online Programs

SAT® | CollegeBoard
Registeration closing on 19th Apr for SAT® | One Test-Many Universities | 90% discount on registrations fee | Free Practice | Multiple Attempts | no penalty for guessing
Everything about Education
Latest updates, Exclusive Content, Webinars and more.
Explore on Careers360
- Board Exams
- Top Schools
- Navodaya Vidyalaya
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 6
NCERT Exemplars
- NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 10 solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Solutions
- NCERT Books for class 6
- NCERT Books for class 7
- NCERT Books for class 8
- NCERT Books for class 9
- NCERT Books for Class 10
- NCERT Books for Class 11
- NCERT Books for Class 12
- NCERT Notes for Class 9
- NCERT Notes for Class 10
- NCERT Notes for Class 11
- NCERT Notes for Class 12
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 6
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 7
- NCERT Syllabus for class 8
- NCERT Syllabus for class 9
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 10
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 11
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 12
- CBSE Date Sheet
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Admit Card
- CBSE Result
- CBSE Result Name and State Wise
- CBSE Passing Marks
CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Board Class 10th
- CBSE Class 10 Date Sheet
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE 10th Exam Pattern
- CBSE Class 10 Answer Key
- CBSE 10th Admit Card
- CBSE 10th Result
- CBSE 10th Toppers
- CBSE Board Class 12th
- CBSE Class 12 Date Sheet
- CBSE Class 12 Admit Card
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Exam Pattern
- CBSE Class 12 Answer Key
- CBSE 12th Result
- CBSE Class 12 Toppers
CISCE Board 10th
- ICSE 10th time table
- ICSE 10th Syllabus
- ICSE 10th exam pattern
- ICSE 10th Question Papers
- ICSE 10th Result
- ICSE 10th Toppers
- ISC 12th Board
- ISC 12th Time Table
- ISC Syllabus
- ISC 12th Question Papers
- ISC 12th Result
- IMO Syllabus
- IMO Sample Papers
- IMO Answer Key
- IEO Syllabus
- IEO Answer Key
- NSO Syllabus
- NSO Sample Papers
- NSO Answer Key
- NMMS Application form
- NMMS Scholarship
- NMMS Eligibility
- NMMS Exam Pattern
- NMMS Admit Card
- NMMS Question Paper
- NMMS Answer Key
- NMMS Syllabus
- NMMS Result
- NTSE Application Form
- NTSE Eligibility Criteria
- NTSE Exam Pattern
- NTSE Admit Card
- NTSE Syllabus
- NTSE Question Papers
- NTSE Answer Key
- NTSE Cutoff
- NTSE Result
Schools By Medium
- Malayalam Medium Schools in India
- Urdu Medium Schools in India
- Telugu Medium Schools in India
- Karnataka Board PUE Schools in India
- Bengali Medium Schools in India
- Marathi Medium Schools in India
By Ownership
- Central Government Schools in India
- Private Schools in India
- Schools in Delhi
- Schools in Lucknow
- Schools in Kolkata
- Schools in Pune
- Schools in Bangalore
- Schools in Chennai
- Schools in Mumbai
- Schools in Hyderabad
- Schools in Gurgaon
- Schools in Ahmedabad
- Schools in Uttar Pradesh
- Schools in Maharashtra
- Schools in Karnataka
- Schools in Haryana
- Schools in Punjab
- Schools in Andhra Pradesh
- Schools in Madhya Pradesh
- Schools in Rajasthan
- Schools in Tamil Nadu
- NVS Admit Card
- Navodaya Result
- Navodaya Exam Date
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission Class 6
- JNVST admit card for class 6
- JNVST class 6 answer key
- JNVST class 6 Result
- JNVST Class 6 Exam Pattern
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission
- JNVST class 9 exam pattern
- JNVST class 9 answer key
- JNVST class 9 Result
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Cetifications
We Appeared in

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources

Chapter 14 Natural Resources Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions
Contact form.
- RS Aggarwal
- ML Aggarwal
- Merchant of Venice
- NCERT Books
- Questions and Answers
- NCERT Notes
- Important Questions
Natural Resources
Ncert solutions for chapter 14 natural resources class 9 science.
Soil is formed by breaking down of rocks at or near the surface of the Earth through various physical, chemical, and biological processes by various factors such as the sun, water, wind, and living organisms.→ Sun: During day time, the rocks are heated up by solar rays. This causes the rocks to expand. During night time, these rocks cool down and contracts, thus the cracks develop in the rock and they break down. → Water: It helps in breaking of rocks in two ways:
Three Human activities are:
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialisation Class 10 History
Related chapters.
- Matter in Our Surroundings
- Is Matter Around Us Pure
- Atoms and Molecules
- Structure of the Atom
- The Fundamental Unit of Life
Related Questions
- NCERT Revision Notes for Chapter 14 Natural Resources Class 9 Science
Report a problem
- Question is incorrect
- Answer is Incorrect
- Spelling Mistakes
- Not explained in detail
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Natural Resources Class 9 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 14 (Free PDF Download)
- Revision Notes

CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 14 - Natural Resources Revision Notes - Free PDF Download
The notes of Natural Resources Class 9 are all about the natural resources of the environment. These are land, air and water. The lithosphere is the solid outermost layer of the earth’s crust. The hydrosphere is the water that is found on the surface of the earth. Also, Class 9 Science Ch 14 notes describes that the atmosphere is the air that covers the earth like a blanket and protects it from harmful radiations. Lastly, the biosphere is the region that has all the biotic and abiotic elements. Therefore, types of natural resources according to Class 9 Science Chapter 14 notes are forest, minerals, animals, air, soil, water and soil. Download the free PDF now.
Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. They can download Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to r evise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 9 Science revision notes for All chapters:

Access Class 9 Science Chapter 14 – Natural resources in 30 Minutes
Natural Resources:
Materials given commonly on earth that can be utilized by living creatures are named to be regular assets. These are the land, the water and the air. The strong peripheral layer of the world's hull is known as the lithosphere. The water that is found on the world's surface, as groundwater, is known as the hydrosphere. The air that covers the entire Earth like a sweeping is known as the air. The district on earth involving both biotic and abiotic segments is called the biosphere.
The Breath Of Life: Air:
Air is a combination of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water fumes. Nitrogen is utilized to create various natural atoms like proteins. Nitrogen is fixed in plants and is moved to creatures through natural way of life. Oxygen is utilized by plants and creatures during the time spent breathing. The burning of non-renewable energy sources likewise requires oxygen. Carbon dioxide is utilized by plants during the time spent photosynthesis. Numerous marine creatures use carbonates broken down in ocean water to make their shells.
The role of the atmosphere in climate control – Atmosphere covers the Earth like a blanket. It prevents the sudden increase of temperature due to sun in the day and also prevents the steady escape of heat from Earth to outer space. The absence of atmosphere on the moon makes the temperature vary from $-{{190}^{\circ }}C$ to ${{110}^{\circ }}C$.
The movement of air: winds - During the day, the air above the land in coastal locations heats up more quickly and rises. As the air rises, a region of low-pressure forms, and air from the sea moves into it. Winds are created by the movement of air from one place to another. The wind would be blowing from the sea to the land during the day. Because soil cools faster than water, the air above the ground cools faster at night.
Rain - During the day, water bodies heat up and evaporate into the atmosphere. The vapour cools as it rises. The vapour condenses into small water droplets, which fall as rain as a result of the precipitation process. The prevailing wind patterns determine rainfall patterns.
Air pollution - Air pollution is the contamination of the air with chemicals, smoke, dust particles, and disease-causing agents. When fossil fuels are burned, distinct nitrogen and sulphur oxides are produced, which dissolve in rain and cause acid rain. The amount of hydrocarbons produced by the combustion of fossil fuels likewise grows. When there are large levels of pollutants present, visibility is reduced. Breathing air contaminated with any of these pollutants on a regular basis raises the risk of allergies, cancer, and heart disease.
Water: A Wonder Liquid:
Water can be found on the surface of the Earth, underground, and as water vapour in the atmosphere. The maximum amount of water available is salty marine water. The majority of the freshwater on the planet is in the form of frozen ice. Water is necessary for plant and animal survival because cellular functions take place in a water media. Dissolved substances are transferred from one portion of the body to another. As a result, in order to survive, organisms must maintain the level of water bodies. The amount of water available determines not just the number of individuals of each species that can survive in a given area, but also the diversity of life there.
Water pollution - Water pollution is defined as the introduction of undesired elements into bodies of water. Fertilizers, pesticides, sewage, chemicals, and detergents are examples of undesirable substances. The amount of dissolved oxygen reduces when the temperature of the water rises owing to pollution. Aquatic creatures get their oxygen from dissolved oxygen. Many aquatic organisms die when the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water is reduced.
Mineral Riches In The Soil:
Another vital natural resource that sustains life is soil. Soil is made up of particles of soil, humus, and living creatures. In between the soil particles, there is also some water in the form of droplets or air. The soil is made up of the sun, water, wind, and living beings. Uneven rock contraction and expansion splits and breaks them down into smaller soil particles. Frozen water lodged in rock fractures and breaks the boulders, turning them into soil. Lichens that grow on the surface of rocks emit chemicals that break down the rocks and turn them into soil. River water breaks down hard rocks into soil particles. Rocks are eroded and sand particles are carried by strong winds.
Humus is a type of soil that contains pieces of decomposed biological creatures. Because it causes the soil to become more porous and allows water and air to permeate deep underground, it is a crucial element in determining the soil structure. The topsoil is the soil's top layer, which contains humus and live creatures in addition to the soil particles.
Soil pollution - Soil contamination is the addition of pollutants that have a negative impact on soil fertility. The usage of fertilisers resulted in the extinction of many beneficial microorganisms and a reduction in soil fertility. Deforestation has resulted in the erosion of the soil's top most productive layer. Soil erosion was also caused by animal overgrazing. Wind and water can also carry fine soil particles away.
Biogeochemical Cycles:
The transfer of matter and energy between the biotic and abiotic components of the biosphere takes place constantly and thus makes the ecosystem dynamic but stable. These transfers take place through various cycles explained below.
Water Cycle:
The entire method wherein water evaporates and falls at the land as rain and later flows again into the ocean thru rivers is called the water cycle. Water is able to dissolve a big variety of substances. As water flows via or over rocks containing soluble minerals a number of them get dissolved withinside the water. Thus, rivers deliver many vitamins from the land to the ocean, and those are utilized by marine organisms. A diagrammatic representation has been shown below.
Nitrogen Cycle:
The nitrogen cycle is the method through which nitrogen is transformed among its diverse chemical forms. This transformation may be finished via each organic and bodily technique. Important techniques withinside the nitrogen cycle encompass fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. Nitrogen makes up to seventy-eight percentage of the earth’s environment.
The percentage of nitrogen withinside the environment is maintained through the nitrogen cycle. Plants and animals can't make use of atmospheric nitrogen quite simply. It must be constant via way of means of a few organisms referred to as nitrogen fixers. Nitrogen-solving microorganisms like Rhizobium stays in symbiotic affiliation withinside the root nodules of sure leguminous plants. These microorganisms convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which is applied quite simply via way of means of plants.
Nitrogen-solving microorganisms alongside unfastened residing microorganisms withinside the soil gain ninety percentage of nitrogen fixation. During lightening, the excessive temperatures and pressures created withinside the air convert nitrogen into oxides of nitrogen. These oxides dissolve in water to offer nitric and nitrous acids and fall on land at the side of rain.
Plants convert those nitrates and nitrites into amino acids. Ammonification is the technique with the aid of which soil microorganisms decompose useless natural dependents and launch ammonia into the soil. Nitrification is the technique with the aid of using which ammonia is transformed into nitrites and nitrates. Denitrification is the technique with the aid of using which nitrates are transformed into atmospheric nitrogen. A diagrammatic representation has been shown below.
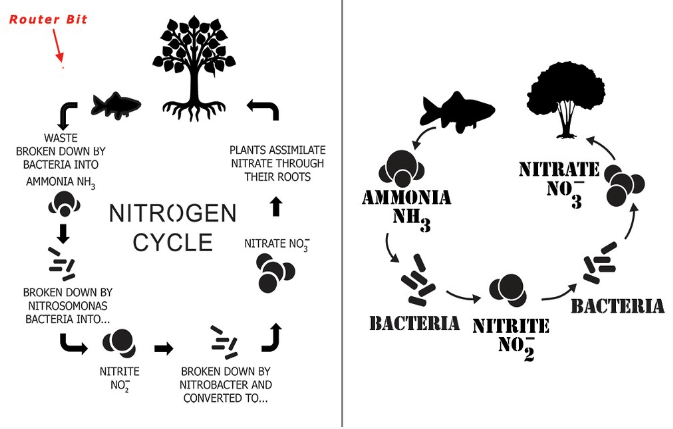
Carbon Cycle:
Carbon takes place withinside the elemental shape as diamonds and graphite. The carbon cycle begins off evolved in plants. Plants use carbon dioxide withinside the ecosystem to synthesize glucose withinside the presence of daylight via means of the procedure of photosynthesis.
Living matters ruin those glucose molecules to supply strength and launch carbon dioxide via respiration. The burning of fuels for numerous wishes like heating, cooking, transportation and commercial strategies provides carbon dioxide to the ecosystem. A diagrammatic representation has been shown below.
Oxygen Cycle:
Oxygen from the environment is used up in 3 processes, particularly combustion, respiratory and withinside the formation of oxides of nitrogen. Oxygen is lower back to the environment in best one predominant procedure this is photosynthesis. A diagrammatic representation has been shown below.
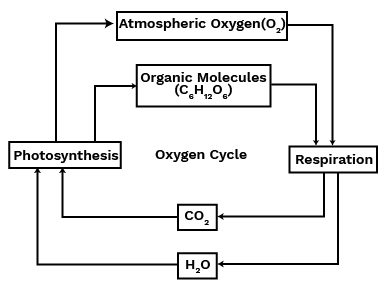
The Greenhouse Effect:
Some gases save you from the break out of warmth from the earth. A boom in the proportion of such gases withinside the environment could cause the common temperatures to boom globally and that is referred to as the inexperienced residence effect. CO 2 is one of the inexperienced residence gases. A boom withinside the CO 2 content material withinside the environment could cause extra warmth to be retained with the aid of using the environment and result in worldwide warming.
Ozone layer:
The ozone layer is found in the stratosphere , one of the layers of the atmosphere. Each molecule of ozone is made from 3 oxygen atoms. It is toxic however it prevents dangerous radiations from accomplishing on the earth’s surface, wherein they'll harm many lifestyles . Chlorofluorocarbon compounds (CFCs) outcomes withinside the depletion of the ozone layer.
Chapter 14 Science Class 9 Notes: A Brief Overview
The main topics included in the natural resource Chapter 14 Class 9 notes are rain, water and its pollution, Greenhouse effect, Biogeochemical cycles, Ozone layer and its depletion. In the following Natural Resources Class 9 Notes, let us gain knowledge about rain and its formation.
As you will see in Class 9th Science Chapter 14 notes, the evaporation and condensation of water are called rain. It is caused by the water cycle.
Class 9 Ch 14 Science notes tell us about the formation of acid rain. Acid rain is produced by the release of various gases such as S0 2 and N0 2 which is released from fuels and vehicles. They dissolve in rain and form sulphuric and nitric acid.
The Class 9 th Natural Resources notes also give us a lesson about water. Water is one of the renewable resources. It is very important for the physiological activities of animals and plants. It is presented in two forms which are surface water and groundwater.
Class 9th Chapter 14 Science Notes: Water Pollution
A change in the biological, chemical and physical properties of water which affects aquatic lives and also makes the water unfit for use or consumption is called water pollution. The main causes of water pollution are:
Removing desirable substances such as oxygen from water.
A water temperature change.
Ch 14 Science Class 9 notes have the details of water pollution explained for you along with proper illustrations.
Notes of Ch 14 Science Class 9: Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse gases like methane, carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxide are present in the atmosphere to stop the heat falling on the Earth and not absorb it. Hence, this keeps it warm and this phenomenon is called the greenhouse effect. That is how Science Class 9 Chapter 14 notes help you to get to know the meaning of the greenhouse effect.
Ozone Layer
The notes of Chapter 14 Class 9 Science tell us that there are three molecules of oxygen that form ozone and hence form a layer in the stratosphere. It also acts as a protective shield and prevents harmful radiations that try to reach the earth. CFCs react with ozone and break ozone which is known as ozone depletion.
Class 9 Ch 14 Science Notes: Biogeochemical Cycles
An interaction between the abiotic and biotic components of biosphere make a system and such flows result in the formation of a cycle which is called a biogeochemical cycle.
Some Of The Cycles Are Mentioned In The Ch 14 Class 9 Science Notes Are:
1. water cycle.
Water-cycle is the process by which water evaporates and as a result, falls on the land as water. The rain flows back to sea with the help of rivers and such a cycle is called the water cycle. The steps included in the water cycle are:
Evaporation
Transpiration
Respiration
Precipitation
2. Nitrogen Cycle
The process by which nitrogen passes from the atmosphere to organisms and soil and returns back into the atmosphere is known as the nitrogen cycle. The processes included in the nitrogen cycle are:
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrification
Ammonification
Denitrification
3. Carbon Cycle
The process in which carbon moves from the atmosphere to earth is called the carbon cycle. The processes involved in the carbon cycle are:
Photosynthesis
Respiration
Decomposition
4. Oxygen Cycle
The process by which oxygen is released in the atmosphere, and carbon dioxide is taken in by the plants from the atmosphere is called the oxygen cycle. Oxygen cycle includes:
Photosynthesis
Why Choose Vedantu?
The language of the materials as prepared by Vedantu is quite easy and student-friendly. The main aim of these notes is that students learn in an effective way. Thus, the quality of the content is particularly focussed upon. Vedantu has experts of the field with years of experience. So you can trust the study material to be completely in alignment with the syllabus as prepared by the board.

FAQs on Natural Resources Class 9 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 14 (Free PDF Download)
1. What are mineral resources? Mention the types.
The natural substances that have chemical and physical properties, as well as the chemical composition, are called mineral resources. Types of it are undiscovered resources, reserves and identified resources.
2. How do forests play a major role in maintaining the water cycle?
Water vapour in the atmosphere directly depends on the transpiration of water present in the leaves. Water stored in a watershed is influenced by forests. Thus, the forest plays an important role in maintaining the water cycle.
3. What are natural resources notes?
CBSE offers notes for chapter 14 of class 9 Science and students can access them through the link-Notes For Class 9 science. The main aim of the notes is to simplify both answers and concepts and so, natural resources are defined as the abundant stock of air, water, soil, minerals, and all living organisms present on the Earth. These resources are useful in supporting life and meeting the needs of people. Specifically, coal, oil, soil, animals, birds, etc. constitute the different natural resources on the planet.
4. What is the greenhouse effect?
Chapter 14 of class 9 in Science is about natural resources. Other concepts like biogeochemical cycles, ozone layer and its depletion, etc. are taught to students in detail. One such concept is the greenhouse effect. CBSE notes define the greenhouse effect as a process through which radiations coming from the sun’s rays are absorbed by the greenhouse gases like CO2 and do not get reflected back into outer space. In short, it is actually the heating of the Earth’s surface. To know more students can refer to the vedantu app also.
5. How does the atmosphere act as a blanket?
This answer is explained with the concept that air is a bad conductor of heat and the atmosphere is full of air. This air contains gases, dust particles, and other things. This prevents the flow of heat in air resulting in a balanced temperature. During the day, the atmosphere prevents the sudden increase in temperature, and at night, it traps the heat by slowing down its escape to maintain an average temperature. The ozone layer also helps in this process.
6. What is the idea conveyed in chapter 14 of class 9 Science?
This chapter covers all the basics and details regarding natural resources. The ideas conveyed in this chapter are purely done to make students aware and understand these resources and their present condition on Earth. Natural resources are very important as they help in maintaining an average temperature, and contain very important gases for sustaining life on Earth. All these ideas are conveyed to the students through this chapter and CBSE notes make it easier for them through its organized structure.
7. How are revision notes for chapter 14 of Science for class 9 students beneficial?
The chapter on Natural resources contains various concepts like the greenhouse effect, biogeochemical cycles, ozone layer, etc. By using notes for learning this chapter, students can save a lot of their time, as every concept is given in crisp details covering each point related to the topic. The language used in the explanation is easy to follow and thus, students can learn the chapter in an efficient way. The material can be trusted as they are created by professional experts. The notes can be downloaded free of cost from the vedantu website (vedantu.com).
STUDY MATERIALS FOR CLASS 9

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 9 Science Improvement in Food Resources
Case study questions class 9 science chapter 15 improvement in food resources.
CBSE Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Improvement in Food Resources. Important Case Study Questions for Class 9 Exam. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Improvement in Food Resources.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science – Improvement in Food Resources
Different crops require different climatic conditions, temperature and photoperiods for their growth and completion of their life cycle. Photoperiods are related to the duration of sunlight. Growth of plants and flowering are dependent on sunlight. As we all know, plants manufacture their food in sunlight by the process of photosynthesis. There are some crops, which are grown in rainy season, called the kharif season from the month of June to October, and some of the crops are grown in the winter season, called the Rabi season from November to April. Paddy, soyabean, pigeon pea, maize, cotton, green gram and black gram are kharif crops, whereas wheat, gram, peas, mustard, linseed are Rabi crops.
In India there has been a four times increase in the production of food grains from 1952 to 2010 with only 25% increase in the cultivable land area. This increase in production been achieved through the practices involved in farming, we can divide it into three stages. The first is the choice of seeds for planting. The second is the nurturing of the crop plants. The third is the protection of the growing and harvested crops from loss. Thus, the major groups of activities for improving crop yields can be classified as: • Crop variety improvement • Crop production improvement • Crop protection management.
(1) What is kharif season period?
(a) June to July
(b) June to October
(c) June to November
(d) June to December
(2) What is Rabi season period?
(a) November to April
(b) November to March
(c) November to February
(d) November to January
(3) Plants manufacture their food in sunlight by the process called __________
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Photoperiod
(c) Photolysis
(d) None of the above
(4) Enlist the names of Kharif crops.
(5) Enlist the names of Rabi crops.
(4) Kharif crops
Paddy, soyabean, pigeon pea, maize, cotton, green gram and black gram
(5) Rabi crops
Wheat, gram, peas, mustard, linseed are.
Cattle husbandry is done for two purposes— milk and draught labour for agricultural work such as tilling, irrigation and carting. Indian cattle belong to two different species, Bosindicus , cows, and Bosbubalis , buffaloes. Milk-producing females are called milch animals (dairy animals), while the ones used for farm labour are called draught animals.
Milk production dependson the duration of the lactation period, meaning the period of milk production after the birth of a calf. So, milk production can be increased by increasing the lactation period. Exotic or foreign breeds (for example, Jersey, Brown Swiss) are selected for long lactation periods, while local breeds (for example, Red Sindhi, Sahiwal) show excellent resistance to diseases. The two can be cross-bred to get animals with both the desired qualities.
Proper cleaning and shelter facilities for cows and buffaloes are required for humane farming, for the health of the animals and for production of clean milk as well. The food requirements of dairy animals are of two types: (a) maintenance requirement, which is the food required to support the animal to live a healthy life, and (b) milk producing requirement, which is the type of food required during the lactation period.
Cattle suffer from a number of diseases. The diseases, besides causing death, reduce milk production. The external parasites live on the skin and mainly cause skin diseases. The internal parasites like worms, affect stomach and intestine while flukes damage the liver.
(1) Identify the exotic breed of cow
(a) Red Sindhi
(b) Sahiwal
(c) Brown Swiss
(d) All of the above
(2) Identify the correct statements
Statement 1 – Milk production depends on the duration of the lactation period.
Statement 2 – Exotic or foreign breeds are selected for long lactation periods.
Statement 3 – Local breeds show excellent resistance to diseases.
Statement 4 – Animals used for farm labour are called draught animals.
(a) Both 1 & 2
(c) Both 3 & 4
(3) Milk-producing females are termed as
(a) Milch animals
(b) Dairy animals
(c) Draught animals
(d) Both a & b
(4) Enlist any two Indian cattle species.
(5) What are the food requirements of dairy animals?
(4) Indian cattle belong to two different species
- Bosindicus – cows. • Bosbubalis – buffaloes.
(5) The food requirements of dairy animals are of two types
- Maintenance requirement – which is the food required to support the animal to live a healthy life. • Milk producing requirement -which is the type of food required during the lactation period.
Poultry farming is undertaken to raise domestic fowl for egg production and chicken meat. Improved poultry breeds are developed and farmed to produce layers for eggs and broilers for meat. The cross-breeding programmes between Indian (indigenous, for example, Aseel) and foreign (exotic, for example, Leghorn) breeds for variety improvement are focused on to develop new varieties for the following desirable traits— number and quality of chicks; dwarf broiler parent for commercial chick production; summer adaptation capacity/ tolerance to high temperature; low maintenance requirements; reduction in the size of the egg-laying bird with ability to utilise more fibrous cheaper diets formulated using agricultural by-products.
Broiler chickens are fed with vitamin-rich supplementary feed for good growth rate and better feed efficiency. Care is taken to avoid mortality and to maintain feathering and carcass quality. They are produced as broilers and sent to market for meat purposes. For good production of poultry birds, good management practices are important. The housing, nutritional and environmental requirements of broilers are somewhat different from those of egg layers. The daily food requirement for broilers is protein rich with adequate fat. The level of vitamins A and K is kept high in the poultry feeds. Poultry fowl suffer from a number of diseases caused by virus, bacteria, fungi, parasites, as well as from nutritional deficiencies. Appropriate vaccination can prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases and reduce loss of poultry during an outbreak of disease.
(1) Identify the incorrect statements
Statement 1 – Broiler chickens are fed with vitamin-rich supplementary feed for good growth.
Statement 2 – The level of vitamins A and K is kept high in the poultry feeds
Statement 3 – The level of vitamins A and K is kept low in the poultry feeds
Statement 4 – Improved poultry breeds are developed and farmed to produce layers for eggs and broilers for meat.
(2) Poultry breeds which are produce for eggs are termed as _________
(b) Broilers
(c) Indigenous
(3) Poultry breeds which are produce for meat are termed as _________
(4) What are the objectives of cross-breeding programme in Indian and Exotic breed.?
(5) Enlist the name of Indian and Exotic breed.
(4) The cross-breeding programmes between Indian (indigenous, for example, Aseel) and foreign (exotic, for example, Leghorn) breeds for variety improvement are focused on to develop new varieties for the following desirable traits— number and quality of chicks; dwarf broiler parent for commercial chick production; summer adaptation capacity/ tolerance to high temperature; low maintenance requirements; reduction in the size of the egg-laying bird with ability to utilise more fibrous cheaper diets formulated using agricultural by-products.
(5) Indigenous or Indian breed – for example, Aseel
Foreign or Exotic – for example, Leghorn
Honey is widely used and therefore bee keeping for making honey has become an agricultural enterprise. Since bee-keeping needs low investments, farmers use it as an additional income generating activity. In addition to honey, the beehives are a source of wax which is used in various medicinal preparations. The local varieties of bees used for commercial honey production are Apisceranaindica , commonly known as the Indian bee, A. dorsata, the rock bee and A. florae, the little bee. An Italian bee variety, A. mellifera, has also been brought in to increase yield of honey.
The Italian bees have high honey collection capacity. They sting somewhat less. They stay in a given beehive for long periods, and breed very well. For commercial honey production, bee farms or apiaries are established. The value or quality of honey depends upon the pasturage, or the flowers available to the bees for nectar and pollen collection. In addition to adequate quantity of pasturage, the kind of flowers available will determine the taste of the honey.
(1) Which species of bee is commonly known as the Indian bee?
(a) Apisceranaindica
(b) Apisdorsata
(c) Apismellifera
(d) Apis florae
(2) Which species of bee is commonly known as the rock bee?
(3) Which species of bee is commonly known as the little Bee?
(4) Identify the correct statements
Statement 1 – Beehives are a source of wax which is used in various medicinal preparations.
Statement 2 – Apisceranaindica is commonly known as the Indian bee
Statement 3 – Apisdorsata is known as the rock bee
Statement 4 -The quality of honey depends upon the flowers available for nectar and pollen collection.
(b) Both 3 & 4
(5) Enlist the local varieties of bees used for commercial honey production.
(5) The local varieties of bees used for commercial honey production
- Apisceranaindica , commonly known as the Indian bee
- Apisdorsata , the rock bee.
- Apis florae, the little bee.
Fish is a cheap source of animal protein for our food. Fish production includes the finned true fish as well as shellfish such as prawns and molluscs. There are two ways of obtaining fish. One is from natural resources, which is called capture fishing. The other way is by fish farming, which is called culture fishery. The water source of the fish can be either seawater or fresh water, Fishing can thus be done both by capture and culture of fish in marine and freshwater ecosystems
Popular marine fish varieties include pamphlet, mackerel, tuna, sardines, and Bombay duck. Marine fish are caught using many kinds of fishing nets from fishing boats. Some marine fish of high economic value are farmed in seawater. This includes finned fishes like mullets, bhetki, and pearl spots, shellfish such as prawns mussels and oysters as well as seaweed. Oysters are also cultivated for the pearls they make. As marine fish stocks get further depleted, the demand for more fish can only be met by such culture fisheries, a practice called mariculture.
Fresh water resources include canals, ponds, reservoirs and rivers. Brackish water resources, where seawater and fresh water mix together. Most fish production from these resources is through aquaculture.
(1) Fish obtaining from natural resources are termed as _______
(a) Capture fishing
(b) Culture fishing.
(c) Marine fishing.
(d) Freshwater fishing.
(2) Which of the following are marine fish varieties
(a) Pamphlet
(b) Mackerel
(3) Oysters are cultivated for
(a) Perales
(c) Seaweeds
Statement 1 – Fish is a source of animal protein for our food.
Statement 2 – Oysters are also cultivated for the pearls.
Statement 3 – There are two ways of obtaining fish – Natural resources & Fish farming.
Statement 4 – Pamphlet is the popular marine fish varieties.
(5) Enlist the varieties of fishes.
(5) Varieties of fishes are given below,
• Pamphlet • Mackerel • Tuna • Sardines • Bombay duck 0
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
West bengal board class 9 english solution chapter 1 tales of bhola grandpa, rs aggarwal class 8 test paper 5 solutions of playing with numbers, rs aggarwal class 8 test paper 3 solutions of square and square roots, west bengal board class 6 science moulik jougik o misro podartho solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources
Extra questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources with answers is given below. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These questions will be helpful to revise the all topics and concepts. CBSE Class 9 extra questions are the most simple and conceptual questions that are prepared by subject experts for the students to study well for the final exams. By solving these extra questions, students can be very efficient in their exam preparations.
Natural Resources Class 9 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very short answer questions.
1: What is the role of respiration in oxygen cycle? Answer: Oxygen enters in the living world through the process of respiration, i.e., it oxidises the food material (glucose molecule) and produces energy and carbon dioxide.
2: Name the gases which cause greenhouse effect. Answer: Greenhouse effect is caused by carbon dioxide, Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) nitrogen oxide and methane.
3: Name some biologically important organic compounds that contain both oxygen and nitrogen. Answer: Proteins, amino acids and nucleic acids.
4: Name the compound, which is responsible for the depletion of ozone layer in the atmosphere. Answer: Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
5: Which part of solar radiation is absorbed by ozone layer? Answer: Ultraviolet radiation 6: What do you mean by biotic component? Answer: The biotic component means the living organisms, which are present in environment.
7: What do you mean by air pollution? Answer: An increase in the content of harmful or undesirable substances (pollutants) in the air, is called air pollution.
8: Air is also called “breath of life’. Why? Answer: Air is called breath of life because it contains oxygen, which is required by all living organisms for respiration.
9: Which winds bring rain in most parts of India? Answer: The South-West or North-East monsoons.
10: State the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays. Answer: Ultraviolet rays cause cancer and cataract-like diseases to living organisms.
11: Which non-living component of the Earth determine biodiversity of an area? Answer: Water is the determinant of biodiversity of an area.
12: State two factors, which are responsible for polluting water. Answer: Municipal sewage and discharge from industries are responsible for polluting water.
13: What is soil? Answer: Soil is the outermost layer of our Earth, called the crust, which forms the upper surface of land and supports plant growth.
14: What is top soil? How is it responsible for the biodiversity in an area? Answer: It is the topmost layer of the soil that contains humus and living organisms in addition to the soil particles. The quality of top soil is an important factor that decides biodiversity in that area.
15: What are the main substances of biogeochemical cycles? Answer: Its main substances are carbon (C), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) and water 16: Which group of plants contains nitrogen fixing bacteria in their roots? Answer: Leguminous plants such as cereals, pea, bean, etc.
17: Name two organisms, which play vital role in nitrogen fixation.
Answer: The organisms, which play vital role in nitrogen fixation are (i) Rhizobium and blue-green algae, help in fixation of free atmospheric nitrogen. (ii) Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter are nitrifying bacteria, which convert ammonia to nitrite and then nitrite to nitrates. 18: Why step farming is common on hills? Answer: Step farming is common on hills because it slows down the speed of rain water, stops soil erosion and increases water absorption by the soil.
19: Soil formation is done by both biotic and abiotic factors. List the names of these factors by classifying them as biotic and abiotic. Answer: (i) Abiotic factors of soil formation: Sun, water, wind, etc. (ii) Biotic factors of soil formation: herbs, lichens, mosses, microorganisms, etc.
20: Write full form of CFCs. Answer: Chlorofluorocarbons
21: State one use of ozone. Answer: It protects the Earth from harmful radiations like high energy ultraviolet radiations
22: State the role of symbiotic bacteria in nitrogen cycle of nature. Answer: Plants are unable to take atmospheric nitrogen directly. Symbiotic bacteria convert the atmospheric nitrogen into water soluble nitrates, which are easily utilised by plants.
23: Name any one method by which water helps in soil formation. Answer: In physical weathering, water and high temperature cause expansion and contraction of rocks, facilitating their breakdown. As a result forming soil.
24: In which region, the ozone layer is present in the atmosphere? Answer: Ozone layer is present in stratosphere region of the atmosphere.
25: Where the hole in ozone layer have recently detected? Answer: The hole in ozone layer have recently detected over Antarctica.
26: Why the Earth is called as ‘Blue Planet’? Answer: The Earth is called as ‘Blue Planet’ because it is covered with 75% of water.
27: State the process by which carbon enters in the living system. Answer: Respiration is the process by which carbon enters in the living system in the form of carbon dioxide.
28: Name the component of air, which is most essential for living organisms. Answer: Oxygen is the component of air, which is most essential for living organisms.
29: Give two examples where water can be found in the frozen form on the Earth. Answer: Water is found frozen in the ice-caps at two poles and on snow-covered mountains.
30: Why terrestrial life forms require freshwater? Answer: Terrestrial life forms require freshwater because their body cannot tolerate high amount of dissolved salts in saline water.
31: Name two fossil fuels, which are responsible for air pollution. Answer: Coal and petroleum are responsible for air pollution.
32: What do you mean by thermal pollution? Answer: Thermal pollution is increase in temperature of water-bodies due to addition of hot water or hot effluent into it.
33: Give any two effects of soil erosion. Answer: Two effects of soil erosion are (i) Desertification (ii) Reduction in soil futility
34: What is combustion? Answer: Combustion is a process of burning of fossil fuels, to provide energy for various needs like cooking, transportation and industrial processes.
35: Name the process by which oxygen is replenished in nature. Answer: Oxygen is replenished in nature through photosynthesis.
36: What is ozone hole? Answer: Ozone hole is the depletion of ozone gas in ozone layer, as present over Antarctica.
37: Name two freshwater resources, which provide freshwater for human use. Answer: The two freshwater resources, which provide fresh water for human use are: (i) Groundwater (ii) Surface water (ponds, lakes, streams, etc.)
38: What is the direction of air in coastal areas during the day? Answer: During the day, the direction of air current or wind is from sea to land.
39: Which particles form the nuclei for condensation of water vapours in the atmosphere? Answer: Dust and smoke particles.
40: Name the two acids that are present in acid rain. Answer: Two acids present in acid rain are: (i) Nitric acid (ii) Sulphuric acid
Short Answer Type Questions
1: What is lithosphere? Answer: The outer crust of the Earth is called the lithosphere.
2: What is hydrosphere? Answer: The water available on the earth’s surface as well as underground water comprise together as hydrosphere. Water covers 75% of the Earth’s surface.
3: What is atmosphere? Answer: The envelope of air that surrounds the earth is called atmosphere.
4: List the four zones of the atmosphere. Answer: Four zones of atmosphere are:
- Tropospshere
- Stratosphere
- Mesospshere
- Thermospshere
5: What is biosphere?
Answer: This life-supporting zone of the Earth where the atmosphere, the hydrosphere and the lithosphere interact and make life possible, is known as the biosphere. It accommodates several types of living organisms which remain dependent on natural resources. The biosphere ranges between 6km, above sea level and 10kms below sea.
6: How is our atmosphere different from the atmosphere on Venus and Mars?
Answer: Earth’s atmosphere is quite different from the atmosphere present on Venus and Mars. The atmosphere of the earth consists of Nitrogen(79%), Oxygen(20%), small fraction of carbon dioxide and other gases which make it suitable for living. The atmosphere of Venus or Mars has carbon dioxide as the major component (95-97%)
7: How does the atmosphere act as a blanket?
Answer: The atmosphere acts as a blank due to its following functions:
- It plays an important role in temperature control. It maintains the average temperature of the earth fairly constant during the course of whole year.
- It prevents the sudden increase in temperature during the daylight hours.
- During the night, it slows down the escape of heat into outer space.
8: What causes winds?
Answer: Uneven heating of the earth’s surface and water surface causes winds. On heating up the air rises up creating a low pressure region. Air travels from high pressure region to low pressure region forming winds. In addition the rotation of the Earth and the presence of mountain ranges in the paths of the wind also influence to winds.
9: Which gets heated faster land or water? Answer: Land
10: Define air-pollution? Answer: An increase in the content of these harmful substances in air is called air pollution.
11: List any three human activities that you think would lead to air pollution.
Answer: Three human activities leading to air pollution are:
- Rapid urbanization and industrialization.
- Deforestation
- Burning of fuels like coal and petroleum.
- Burning of coal in thermal power plants.
12: Name two diseases caused due to an increased content of pollutants in the air produced due to the burning of fossil fuels. Answer: Bronchitis, asthma, lung cancer.
13: What is smog?
Answer: Smoke + Fog = Smog. The presence of unburnt hydrocarbons in air when mixed with condensed water vapours forms a thick layer called smog. It lowers the visibility during winter season and is an indication of air pollution.
14: How do fossil fuel cause air pollution?
Answer: The fossil fuels like coal and petroleum contain traces of nitrogen and sulphur. When these fuels are burnt, nitrogen and sulphur too are burnt and this produces different oxides of nitrogen and sulphur. These oxides of nitrogen and sulphur are poisonous and can cause respiratory problems. These oxides when mix with rain water give rise to acid water due to formation of nitric and sulphuric acids.
15: What are the effects of acid rain?
Answer: Effects of acid rain are:
- Acidification of soil reduces fertility of soil.
- Destroys aquatic life and pollutes water resources.
- Causes irritation to eyes and skins of human beings and cattle.
- Causes corrosion to buildings, bridges, statues etc.
16: What are biogeochemical cycles? Names two examples.
Answer: Biogeochemical cycles are the cyclic pathways through which chemical substances move through biotic environment (biosphere) and abiotic environment (lithosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere) components of the earth. A few example of biogeochemical cycles are:
- Water Cycle
- Nitrogen Cycle
- Carbon Cycle
- Oxygen cycle
17: In which regions is soil erosion very difficult to revert? Answer: The regions with bare vegetation, mountains and hilly regions, soil erosion is very difficult to reverse.
Long answer Type Questions
1: How are clouds formed?
Answer: Due to various weather phenomena (e.g. uneven heating of land and water bodies on the earth surface), warm and cold convection of air currents generate. Water vapours which are also present in air due to evaporation also rise up. Since air cools down on rising, it leads to condensation of water vapours present in it. Thus vapours condense onto a tiny salt particles called condensation nuclei which form clouds.
Broadly clouds formed are of four types:
- Nimbostratus: (Nimbus means rain). These clouds carry thick precipitation or rains.
- Altostratus: These clouds form a foggy, gray and dull weather look.
- Cirrostratus: these clouds form fluffy cotton like pattern.
- Cirrus: These are high-level clouds seen during fair weather.
2: Meenakshi saw reduction in greenish layer of lichens at the bark of trees at the biology garden of the school. The garden was few metres away from diesel generator placed for electricity backup. She immediately informed the school authorities to check the pollution level of diesel and kerosene used in the generator.
(a) How reduction in Lichens layer is related to pollution? (b) What measures should be taken by school authorities to check the reduction? (c) What qualities are shown by Meenakshi by informing school about the Lichens?
Answer: (a) Lichens are found to be very sensitive to the levels of contaminants like sulphur dioxide in the air. Diesel and Kerosene contain traces of nitrogen and sulphur which for deadly oxides when mixed in air.
(b) School authorities should check the pollution level and quality of fuel used in diesel generator. They should also replace the generator with a better which does not pollute the environment. The generator should be place away from the school premises to avoid inhalation of smoke from it.
(c) She is concerned about air pollution and showed her social responsibility to keep the environment clean and pollution free.
3: Why do organisms need water? OR Why is water essential for life? OR Water is known as ‘A Wonder Liquid’. Justify this statement by giving any two reasons.
Answer: Water is an essential part for living organisms:
- Most of the biochemical processes involve water e.g. photosynthesis takes water as one of the raw material to prepare food.
- The major component of blood is water (plasma) which helps in transportation of food and excretory substances.
- Water is used as part of food as a source of energy.
- Water in sweat cools down the body temperature. Similarly water as transpiration loss in plants controls temperature of the plant as well as it helps in ascent of sap.
- Water is used in many activities like drinking, food preparation, irrigation, power generation and industries.
- Water is an essential medium for aquatic life. Amphibians also need water to carry out reproduction.
- Water is a universal solvent hence it is used in medicines and a many chemical reactions takes place when dissolved in water.
- Water makes up 70% of body weight of human beings and it carries out various metabolic activities in all animals.
4: What is meant by depletion of ozone layer? Mention one important feature of ozone in atmosphere. Identify the factors responsible for the formation of ozone hole.
Answer: The part of atmosphere, at height 320 km above sea level, there is a 5km thick ozone layer. This layer acts as a shield/blanket which absorbs UV radiations from sunlight. Thus it saves biotic life on the earth from the harmful effects UV radiation.
Over Antarctica, there is declining of ozone layer thickness and hole is seen. If depletion of ozone layer dwindles further, it would have severe consequences on the lives of living beings.
Following are the main chemicals responsible for the destruction of ozone layer: 1. chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) 2. halogens (used in fire extinguishers) 3. methane and nitrous oxide
CFCs used as propellants in aeroplanes and coolant in refrigeration are the most damaging, which catalytically destroy ozone and convert it into oxygen.
Value Based Questions
1. It has been made mandatory to install rain water harvesting system and solar water heater in all buildings in urban areas, (i) What is the rationale when rain water already passes into drains? (ii) Why are solar water heaters being installed when electric geezers are available?
Answer: (i) Rain water passed into drain does not enter the ground but is taken out of the urban area and poured into a water body at quite a distance with or without treatment. However, ground water is being withdrawn everywhere for drinking, industrial and irrigation purposes. As a result, the level of ground water is going down and arid conditions are being faced in many areas. In rain water harvesting, rain water from a building is passed directly into ground, dug wells or water pumps. This recharges ground water.
(ii) Installation of solar water heaters is a method of saving electricity which is always in short supply due to rapid urbanisation, Industrialisation and intensive agriculture. Coal/gas based power plants are adding CO 2 to the atmosphere causing global warming. Saving electricity is now an important social responsibility.
2. (i) Sheela saw blue-green algae forming bloom in the village pond, (ii) Fish, which was previously abundant was no-where to be seen. (iii) The pond is giving a stink. Water of the pond is not even fit for cattle. Some of the cattle who were taken to the pond for drinking and bathing have fallen sick, (iv) What explanation will Sheela give for this to the villagers.
Answer: (i) Bloom forming algae occur in a pond only when the quality of pond water has deteriorated due to pollution. Blue-green algae secrete toxins that are harmful to animals and humans,
(ii) Fish must have died due to deficiency of oxygen in pond water. Oxygen deficiency occurs when there is excess of organic matter (organic loading). The aerobic decomposers consume the dissolved oxygen. This is followed by anaerobic decomposition of organic matter. It produces sulphides and other sludge producing substances. Blue-green algae can grow under such circumstances.
(iii) Stink comes from anaerobic breakdown products of organic matter. The toxins released by blue-green algae further deteriorate the quality of water causing sickness and skin rashes in animals and humans.
(iv) Sheela could explain to the villagers that deterioration of pond has been due to excess fertilizers used by them in their fields. Rain wash brought these fertilizers into the pond. There was initial spurt in the growth of plants due to this. The phenomenon is called eutrophication. Excess plant matter slowly caused organic loading of water that reduced its oxygen content, killing the fish and other aquatic animals. So fertilizers should be used very judiciously in the fields.
3. (i) Carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere has reached more than 390 ppm (ii) The Antarctic and arctic waters are becoming acidic causing thinning of animal shells. (iii) Polar ice is melting, (iv) Some low lying islands have submerged in sea.
(a) What are the reasons behind all these changes occurring on earth? (b) Suggest a mechanism to control the same and if possible to reverse the trend.
Answer: (a) The reason for these global changes is faulty recycling of carbon dioxide. More of carbon dioxide is being produced than its consumption in photosynthesis due to
- Excess combustion of fossil fuels in industries, power houses, automobiles, homes and other places,
- Reduced intake of CO 2 by plants due to deforestation,
- Higher amounts of CO 2 entering the atmosphere not only increases its atmospheric concentration but also the concentration of dissolved CO 2 in water, especially in colder seas. This is making colder waters acidic. The acidity is thinning the shells of many marine animals.
- CO 2 is a green house gas which is causing global warming. Rise in global temperature is melting snow over poles. This is raising the level of sea water slowly. It was already submerged some low lying islands.
(b) Suggestions:
- Large scale tree plantation in all vacant areas,
- Reduced felling of forest trees.
- Reducing consumption of fossil fuel by reducing dependence on thermal power plants, increasing efficiency of automobiles and switching over to alternate technologies that do not consume fossil fuels.
4. On a school trip to an industrial estate, students found that the marble used in the office buildings of most factories has lost its shine and become pitted.
(i) What is the reason of marble pitting (ii) Can this factor cause harm to vegetation as well ? (iii) Suggest way to prevent this.
Answer: (i) Pitting and discolouring of marble is due to corrosive action of dry or wet acid rain, comprising sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, emitted during combustion of fossil fuels in industries. The acid reacts with insoluble calcium carbonate of marble and converts it into soluble calcium sulphate and calcium nitrate.
(ii) Yes, Acid rain can also cause harm to vegetation by (a) Direct action of acid over plants causing death of leaves, (b) Solubilisation of essential minerals and their leaching leaving only toxic minerals in the soil.
(c) Use of wet scrubbers to remove acidic gases from the industrial emissions.
- CBSE Notes For Class 9
- Class 9 Science Notes
- Chapter 14: Natural Resources
Natural Resources Class 9 CBSE Notes - Chapter 14
According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been removed from NCERT Class 9 Science textbook .
Introduction to Natural Resources
Earth is the only one on which life exists. The resources of the earth are land, water and air. Other resources include fossil fuels, sunlight, wind, minerals, etc. Biotic factors are referred to as living things in the ecosystem. Air, water and soil form the non-living or abiotic components of the biosphere.
To know more about Natural Resources, visit here .
Air and Air Pollution
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that surrounds a planet. Atmospheric air has 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and 1% of other gases by volume.
Role of atmosphere
The atmosphere keeps the average temperature of Earth steady. It slows down the escape of heat into outer space during the night and prevents a sudden increase in temperature during the day.
Air pollution
- Air pollution is caused by the introduction of pollutants, organic molecules, or other unsafe materials into Earth’s atmosphere
- Causes: Man-made sources include the combustion of fuel, smoke from industries, Burning crackers etc. Natural sources include forest fires, volcanoes, etc.
- E ffects : Respiratory diseases, Global warming, Acid Rain, etc.
To know more about Air pollution, visit here .
Ozone layer
The ozone layer is a thin part of the Earth’s atmosphere, which functions as a shield over the Earth’s stratosphere and absorbs the greatest amount of the Sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The ozone layer comprises high concentrations of ozone (O 3 ) in relation to other parts of the atmosphere.
To know more about the Ozone layer, visit here .
Ozone layer depletion
Ozone layer depletion is the reduction of the amount of ozone in the stratosphere which results in greater UV radiations reaching the Earth’s surface.
To know more about Ozone layer depletion, visit here .
Chlorofluorocarbon ( CFC ) is an organic compound that contains carbon, chlorine and fluorine
Greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon which occurs when the greenhouse gases present in the Earth’s atmosphere trap solar radiation. Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), ozone (O 3 ), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and water vapour (H 2 O) are called greenhouse gases.
To know more about the Greenhouse effect, visit here .
Water: A natural resource
Role of water in everyday life: Water forms two-thirds of our body; it keeps the body’s temperature normal. It is also used for agricultural purposes, Domestic Purposes, Industrial Purposes, etc. Distribution of water on earth: Only 3% of the water on the surface is fresh, and the remaining 97% resides in the ocean.
Water pollution
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies caused by discharging pollutants directly or indirectly into the fresh and clean water bodies without adequate treatment.
The main causes of water pollution are
- Urbanisation.
- Agriculture
- Religious and Social Practices
- Withdrawal of water and drying up of water bodies
To know more causes of water pollution, visit here .
Water cycle
- The water cycle , also known as the hydrologic cycle, is the continuous movement of water from the earth’s surface to the atmosphere and then back to the ground.

To know more about the Water cycle, visit here .
Transpiration and Evaporation
Transpiration is the biological process by which water is lost in the form of water vapour from the aerial parts of the plants called stomata. Evaporation is a process by which a liquid or solid is transformed into vapour.
Soil and its formation
Soil is the uppermost layer of the Earth’s crust, formed by the continuous weathering of mountains. Factors causing soil formation are:- Parent material, Time, Climate and Organisms.
Soil composition
Soil is a mixture of organic matter. The basic components of soil are minerals, inorganic matter, water and air. Various types of soil are clay, loam, silt, sand, etc.
The organic constituents, including the dried leaves, twigs, and remains of plants and animals, decompose to form the upper organic layer known as humus. It plays an important role in increasing the fertility of the soil.
Soil pollution
The addition of harmful or toxic chemicals to the soil, which renders it unproductive, is called soil pollution. Fertilizers, insecticides, industrial wastes, accidental oil spills, acid rain, etc., are pollutants and are the main causes of soil pollution.
Soil erosion
Soil erosion is one form of soil degradation. Flowing water, rainwater and the wind are the prime agents which cause soil erosion. This causes loss of topsoil and also reduces crop production potential.
To know more about Soil, visit here .
Bio-geo-chemical cycle
The natural cycle or pathways in which the essential matter is circulated through the biotic and abiotic parts of an ecosystem.
- Biogeochemical = Biological Chemical + Geological Process
To know more about Biogeochemical Cycle, visit here .
Carbon is a chemical element with the symbol C. It is a nonmetallic chemical element found in various forms:
- In Elemental forms- Diamond, graphite
- In Combined form-carbon dioxide, carbonates
- Carbon-containing molecules are proteins, carbohydrates, fats, nucleic acids, vitamins
Carbon cycle
The circulation and transformation of carbon between living things and the environment is called the Carbon Cycle.

To know more about Carbon Cycle, visit here .
Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle is the recycling and reusing of nitrogen in different forms to meet the demands of various environmental activities.

To know more about Nitrogen Cycle, visit here .
Oxygen Cycle
It is a biological process which helps maintain the oxygen level.
Photosynthesis is a biological process used by plants to prepare their food with the help of sunlight and energy.

To know more about Oxygen Cycle, visit here .
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 9 Science Notes Chapter 14: Natural Resources
What are the consequences of cfc emissions.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) and halons destroy the earth’s protective ozone layer, which shields the earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV-B) rays generated from the sun.
What are the steps in the ‘Hydrologic cycle’?
The Hydrologic cycle is the water cycle, and it consists of three major processes: evaporation, condensation and precipitation.
What are the uses of humus?
Humus allows water and oxygen to reach and feed plant roots. By allowing excess water to drain, organic material prevents vital nutrients from leaching out of the soil.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Case Study 1: Oxygen is a very abundant element on our Earth. It is found in the elemental form in the atmosphere to the extent of 21%. It also occurs extensively in the combined form in the Earth's ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Natural Resources. CASE 1. Nitrogen gas makes up 78% of our atmosphere and nitrogen is also a part of many molecules essential to life like proteins, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and some vitamins. Nitrogen is found in other biologically important compounds such as alkaloids and urea too.
Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1: At present the primary nutrient which limits the agricultural yield is nitrogen (N). Some plants are capable to produce more N 2 than they consume. These plants show symbiotic relationship with N 2 -fixing bacteria such as Rhizobium. These bacteria produce root nodules in leguminous plants and ...
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: Oxygen is a very abundant element on our Earth. It is found in the elemental form in the atmosphere to the extent of 21%. It also occurs extensively in the combined form in the Earth's ...
Topics and Sub Topics in Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources: Natural Resources. The Breath of Life: Air. Water: A Wonder Liquid. Mineral Riches in the Soil. Biogeochemical Cycles. Ozone Layer. These solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science. Here we have given Class 9 NCERT Science Textbook Solutions for Chapter 14 ...
Practice Tests. Timed Tests. Select the number of questions for the test: Select the number of questions for the test: TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources chapter. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving skills with expert advice.
NCERT Solutions describe the answer in an understandable way to reach all level of students. NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources comes under Unit 4 and can fetch you 6 marks easily. This chapter includes topics like. The breath of life: Air (5 questions) Water: A wonder liquid (3 questions)
The Class 9 Science Chapter 14 NCERT Solutions PDF is easy to download and use offline. Natural resources Class 9 questions and answers are prepared by subject experts as per the latest CBSE syllabus. Class 9 Natural resources NCERT solutions develop a logical approach and methodology towards science.
The following are the important topics that are discussed in chapter 14, natural resources for class 9 students. Introduction to natural resources. Introduction to air. Introduction to air pollution. Ozone layer and its depletion. Water: A Wonder Liquid. Water pollution. Mineral Riches in the Soil. Biogeochemical Cycles: Carbon cycle and ...
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 14 Natural Resources. CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 14 helps students to clear their doubts and to score good marks in the board exam. All the questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework.
Through these NCERT Solutions, students should not waste time and adopt a strategy that helps them operate and learn at maximum efficiency. Chapter 14 Natural Resources NCERT Questions and Answers help in building a great foundation of concepts and make easy for the students to understand basics.It will set a good foundation for your future goals and improve learning habits.
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 14 Natural Resources Class 9 Science Book Solutions. 1. How is our atmosphere different from the atmospheres on Venus and Mars ? Answer. Earth's atmosphere is a mixture of nitrogen (79%), oxygen (20%), and a small fraction of carbon dioxide, water vapours and other gases. This makes the existence of life possible on ...
The important questions of Natural Resources Class 9 will help the students to understand the topics covered in this chapter in-depth and prepare for their examination in an orderly manner. Class 9 Science Ch 14 extra questions or important questions are written in a simple and easy-to-understand language by the subject-matter experts at Vedantu. To get a fair idea about the subject, students ...
CBSE Class 9 Science Notes Chapter 14 Natural Resources. Facts that Matter. Life exists on earth due to its ambient temperature, water, food and energy from the sun. Lithosphere: The outer crust of the earth is called the lithosphere. Hydrosphere: Sum of all water bodies is called hydrosphere. Atmosphere: Air that covers the earth is called the ...
Revision notes for class 9 chapter 14 natural resources is given here. Revision is one of the most important parts of the study. Revising the chapter will help the students to recollect the concepts what they have learned so far. Educational experts advise students to revise the topics before a night of exam so that they can develop a ...
Therefore, types of natural resources according to Class 9 Science Chapter 14 notes are forest, minerals, animals, air, soil, water and soil. Download the free PDF now. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. They can download Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Improvement in Food Resources. CASE 1. Different crops require different climatic conditions, temperature and photoperiods for their growth and completion of their life cycle. Photoperiods are related to the duration of sunlight. Growth of plants and flowering are dependent on sunlight.
2: Name the gases which cause greenhouse effect. Answer: Greenhouse effect is caused by carbon dioxide, Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) nitrogen oxide and methane. 3: Name some biologically important organic compounds that contain both oxygen and nitrogen. Answer: Proteins, amino acids and nucleic acids.
water, and food. The resources available on the Earth and the energy from the Sun are necessary to meet the basic requirements of all life-forms on the Earth. What are these resources on the Earth? These are the land, the water and the air. The outer crust of the Earth is called the lithosphere. Water covers 75% of the Earth's surface.
1-MARK QUESTIONS. Question.1 Name the three processes in which oxygen is used. Answer. Combustion, respiration and in the formation of oxides of nitrogen. Question.2 Name two natural resources available on the earth. [SAII -2014] Answer. Water and air. More Resources for CBSE Class 9.
Answer: The minerals in the soil depend upon the rocks from which the soil is formed. So, the rocks are the major source of minerals in the soil. Question 14. Name the two gases given out during the burning of fossil fuels which dissolve in rain to form acid rain. Answer: Sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen.
Water: A natural resource. Role of water in everyday life: Water forms two-thirds of our body; it keeps the body's temperature normal. It is also used for agricultural purposes, Domestic Purposes, Industrial Purposes, etc. Distribution of water on earth: Only 3% of the water on the surface is fresh, and the remaining 97% resides in the ocean.