Mike Martin
Option exercise and assignment explained w/ visuals.
- Categories: Options Trading
Last updated on February 11th, 2022 , 06:38 am
Buyers of options have the right to exercise their option at or before the option’s expiration. When an option is exercised, the option holder will buy (for exercised calls) or sell (for exercised puts) 100 shares of stock per contract at the option’s strike price.
Conversely, when an option is exercised, a trader who is short the option will be assigned 100 long (for short puts) or short (for short calls) shares per contract.
- Long American style options can exercise their contract at any time.
- Long calls transfer to +100 shares of stock
- Long puts transfer to -100 shares of stock
- Short calls are assigned -100 shares of stock.
- Short puts are assigned +100 shares of stock.
- Options are typically only exercised and thus assigned when extrinsic value is very low.
- Approximately only 7% of options are exercised.
The following sequences summarize exercise and assignment for calls and puts (assuming one option contract ):
Call Buyer Exercises Option ➜ Purchases 100 shares at the call’s strike price.
Call Seller Assigned ➜ Sells/shorts 100 shares at the call’s strike price.
Put Buyer Exercises Option ➜ Sells/shorts 100 shares at the put’s strike price.
Put Seller Assigned ➜ Purchases 100 shares at the put’s strike price.
Let’s look at some specific examples to drill down on this concept.

New to options trading? Learn the essential concepts of options trading with our FREE 160+ page Options Trading for Beginners PDF.

Exercise and Assignment Examples
In the following table, we’ll examine how various options convert to stock positions for the option buyer and seller:

As you can see, exercise and assignment is pretty straightforward: when an option buyer exercises their option, they purchase (calls) or sell (puts) 100 shares of stock at the strike price . A trader who is short the assigned option is obligated to fulfill the opposite position as the option exerciser.
Automatic Exercise at Expiration
Another important thing to know about exercise and assignment is that standard in-the-money equity options are automatically exercised at expiration. So, traders may end up with stock positions by letting their options expire in-the-money.
An in-the-money option is defined as any option with at least $0.01 of intrinsic value at expiration . For example, a standard equity call option with a strike price of 100 would be automatically exercised into 100 shares of stock if the stock price is at $100.01 or higher at expiration.
What if You Don't Have Enough Available Capital?
Even if you don’t have enough capital in your account, you can still be assigned or automatically exercised into a stock position. For example, if you only have $10,000 in your account but you let one 500 call expire in-the-money, you’ll be long 100 shares of a $500 stock, which is a $50,000 position. Clearly, the $10,000 in your account isn’t enough to buy $50,000 worth of stock, even on 4:1 margin.
If you find yourself in a situation like this, your brokerage firm will come knocking almost instantaneously. In fact, your brokerage firm will close the position for you if you don’t close the position quickly enough.
Why Options are Rarely Exercised
At this point, you understand the basics of exercise and assignment. Now, let’s dive a little deeper and discuss what an option buyer forfeits when they exercise their option.
When an option is exercised, the option is converted into long or short shares of stock. However, it’s important to note that the option buyer will lose the extrinsic value of the option when they exercise the option. Because of this, options with lots of extrinsic value remaining are unlikely to be exercised. Conversely, options consisting of all intrinsic value and very little extrinsic value are more likely to be exercised.
The following table demonstrates the losses from exercising an option with various amounts of extrinsic value:
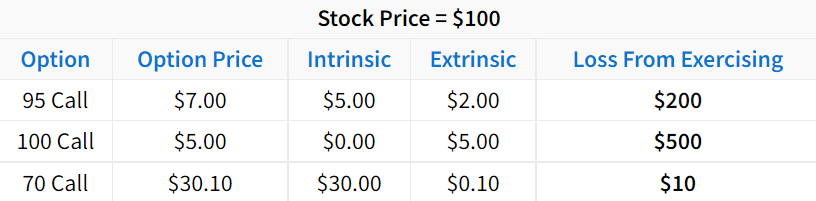
As we can see here, exercising options with lots of extrinsic value is not favorable.
Why? Consider the 95 call trading for $7. Exercising the call would result in an effective purchase price of $102 because shares are bought at $95, but $7 was paid for the right to buy shares at $95.
With an effective purchase price of $102 and the stock trading for $100, exercising the option results in a loss of $2 per share, or $200 on 100 shares.
Even if the 95 call was previously purchased for less than $7, exercising an option with $2 of extrinsic value will always result in a P/L that’s $200 lower (per contract) than the current P/L. F
or example, if the trader initially purchased the 95 call for $2, their P/L with the option at $7 would be $500 per contract. However, if the trader decided to exercise the 95 call with $2 of extrinsic value, their P/L would drop to +$300 because they just gave up $200 by exercising.
7% Of Options Are Exercised
Because of the fact that traders give up money by exercising an option with extrinsic value, most options are not exercised. In fact, according to the Options Clearing Corporation, only 7% of options were exercised in 2017 . Of course, this may not factor in all brokerage firms and customer accounts, but it still demonstrates a low exercise rate from a large sample size of trading accounts.
So, in almost all cases, it’s more beneficial to sell the long option and buy or sell shares instead of exercising. We like to call this approach a “synthetic exercise.”
Congrats! You’ve learned the basics of exercise and assignment. If you’d like to know how the exercise and assignment process actually works, continue to the next section!
Who Gets Assigned When an Option is Exercised?
With thousands of traders long and short options in the market, who actually gets assigned when one of the traders exercises their option?
In this section, we’ll run through the exercise and assignment process for options so you know how the assignment decision occurs.
If a trader is short a single option, how do they get assigned if one of a thousand other traders exercises that option?
The short answer is that the process is random. For example, if there are 5,000 traders who are long a call option and 5,000 traders who are short that call option, an account with the short option will be randomly assigned the exercise notice. The random process ensures that the option assignment system is fair
Visualizing Assignment and Exercise
The following visual describes the general process of exercise and assignment:
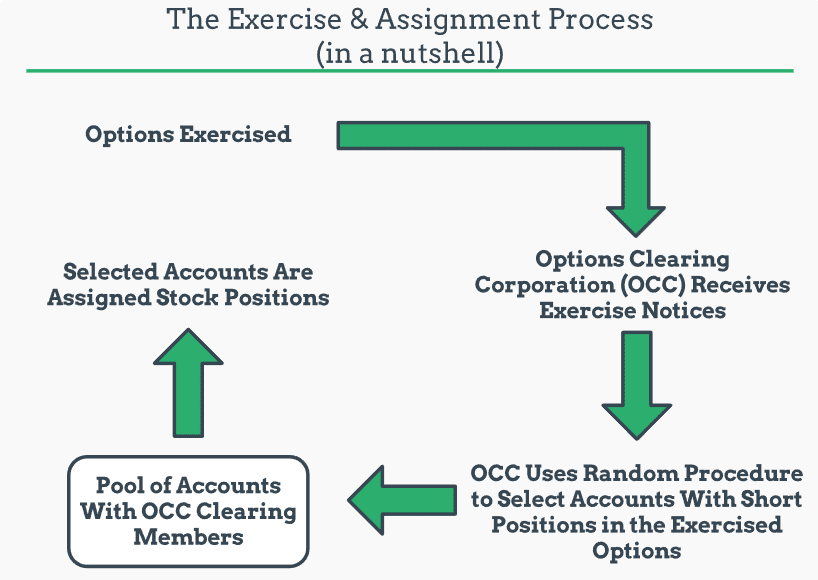
If you’d like, you can read the OCC’s detailed assignment procedure here (warning: it’s intense!).
Now you know how the assignment procedure works. In the final section, we’ll discuss how to quickly gauge the likelihood of early assignment on short options.
Assessing Early Option Assignment Risk
The final piece of understanding exercise and assignment is gauging the risk of early assignment on a short option.
As mentioned early, only 7% of options were exercised in 2017 (according to the OCC). So, being assigned on short options is rare, but it does happen. While a specific probability of getting assigned early can’t be determined, there are scenarios in which assignment is more or less likely.
The following scenarios summarize broad generalizations of early assignment probabilities in various scenarios:

In regards to the dividend scenario, early assignment on in-the-money short calls with less extrinsic value than the dividend is more likely because the dividend payment covers the loss from the extrinsic value when exercising the option.
All in all, the risk of being assigned early on a short option is typically very low for the reasons discussed in this guide. However, it’s likely that you will be assigned on a short option at some point while trading options (unless you don’t sell options!), but at least now you’ll be prepared!
Next Lesson

Options Trading for Beginners
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Value in Options Trading Explained

Option Greeks Explained: Delta, Gamma, Theta & Vega
Projectfinance options tutorials.
➥ Bullish Strategies
➥ Bearish Strategies
➥ Neutral Strategies
➥ Vertical Spreads Guide
☆ Options Trading for Beginners ☆
➥ Basics of Calls and Puts
➥ What is a Strike Price?
➥ Option Expiration
➥ Intrinsic and Extrinsic Value
➥ Exercise and Assignment
➥ The Bid-Ask Spread
➥ Volume and Open Interest
➥ Option Chain Explained
➥ Option Greeks 101
➥ Delta Explained
➥ Gamma Explained
➥ Theta Explained
➥ Vega Explained
➥ Implied Volatility Basics
➥ What is the VIX Index?
➥ The Expected Move
➥ Trading VIX Options
➥ Trading VIX Futures
➥ The VIX Term Structure
➥ IV Rank vs. IV Percentile
➥ Option Order Types 101
➥ Stop-Loss Orders On Options Explained
➥ Stop Limit Order in Options: Examples W/ Visuals
➥ Limit Order in Option Trading Explained w/ Visuals
➥ Market Order in Options: Don’t Throw Away Money!
➥ TIF Orders Types Explained: DAY, GTC, GTD, EXT, GTC-EXT, MOC, LOC
Additional Resources
Exercise and Assignment – CME Group
Learn About Exercise and Assignment – CME Group

About the Author
Chris Butler received his Bachelor’s degree in Finance from DePaul University and has nine years of experience in the financial markets.
Chris started the projectfinance YouTube channel in 2016, which has accumulated over 25 million views from investors globally.
Our Authors
Share this post
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Quick Links
Other links.
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
© 2024 projectfinance, All Rights Reserved.
Disclaimer: Neither projectfinance or any of its officers, directors, employees, other personnel, representatives, agents or independent contractors is, in such capacities, a licensed financial adviser, registered investment adviser, registered broker-dealer or FINRA|SIPC|NFA-member firm. projectfinance does not provide investment or financial advice or make investment recommendations. projectfinance is not in the business of transacting trades, nor does projectfinance agree to direct your brokerage accounts or give trading advice tailored to your particular situation. Nothing contained in our content constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, promotion, or endorsement of any particular security, other investment product, transaction or investment. Trading Futures, Options on Futures, and retail off-exchange foreign currency transactions involves substantial risk of loss and is not suitable for all investors. You should carefully consider whether trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances, knowledge, and financial resources. You may lose all or more of your initial investment. Opinions, market data, and recommendations are subject to change at any time. Past Performance is not necessarily indicative of future results.
tastytrade, Inc. (“tastytrade”) has entered into a Marketing Agreement with Project Finance(Marketing Agent”) whereby tastytrade pays compensation to Marketing Agent to recommend tastytrade’ brokerage services. The existence of this Marketing Agreement should not be deemed as an endorsement or recommendation of Marketing Agent by tastytrade and/or any of its affiliated companies. Neither tastytrade nor any of its affiliated companies is responsible for the privacy practices of Marketing Agent or this website. tastytrade does not warrant the accuracy or content of the products or services offered by Marketing Agent or this website. Marketing Agent is independent and is not an affiliate of tastytrade.
Exercising Options
The holder of an american-style option can exercise his right to buy (in the case of a call) or to sell (in the case of a put) the underlying shares of stock. .
They first must direct their brokerage firm to submit an exercise notice to OCC. For an option holder to ensure that they exercise the option on that particular day, the holder must notify his brokerage firm before that day’s cut-off time for accepting exercise instructions.
The brokerage firm notifies OCC that an option holder wishes to exercise an option. OCC then randomly assigns the exercise notice to a clearing member. For an investor, this is generally his brokerage firm chosen at random from a total pool of such firms. The firm must then assign one of its customers who has written (and not covered) that particular option.
Assignment to a customer is either random or on a first-in-first-out basis. This depends on the firm’s method. Ask your brokerage firm which method it uses for assignments.
The holder of an American-style option contract can exercise the option at any time before expiration. Therefore, an option writer may be assigned an exercise notice on a short option position at any time before expiration. If an option writer is short an option that expires in-the-money, they should expect assignment on that contract, though assignment is not guaranteed as some long in-the-money option holders may elect not to exercise in-the-money options. In fact, some option writers are assigned on short contracts when they expire exactly at-the-money or even out-of-the money. This occurrence is usually not predictable.
To avoid assignment on a written option contract on a given day, the position must be closed out before that day's market close. Once assignment is received, an investor has no alternative but to fulfill assignment obligations per the terms of the contract.
There is generally no exercise or assignment activity on options that expire out-of-the-money. Owners usually let them expire with no value. Although this is not always the case as post-market underlying moves may lead to out-of-the-money options being exercised and in-the-money options not being exercised.
READ MORE ON ASSIGNMENT (PDF)
What's the Net?
When an investor exercises a call option, the net price paid for the underlying stock on a per share basis is the sum of the call's strike price plus the premium paid for the call. Likewise, when an investor who has written a call contract is assigned an exercise notice on that call, the net price received on per share basis is the sum of the call's strike price plus the premium received from the call's initial sale.
When an investor exercises a put option, the net price received for the underlying stock on per share basis is the sum of the put's strike price less the premium paid for the put. Likewise, when an investor who has written a put contract is assigned an exercise notice on that put, the net price paid for the underlying stock on per share basis is the sum of the put's strike price less the premium received from the put's initial sale.
Early Exercise/Assignment
For call contracts, owners might exercise early to own the underlying stock to receive a dividend. Check with your brokerage firm on the advisability of early call exercise.
It is extremely important to realize that assignment of exercise notices can occur early, days or weeks in advance of expiration day. Investors should expect this as expiration nears with a call considerably in-the-money and a sizeable dividend payment approaching. Call writers should be aware of dividend dates and the possibility of early assignment.
When puts become deep in-the-money, most professional option traders exercise before expiration. Therefore, investors with short positions in deep in-the-money puts should be prepared for the possibility of early assignment on these contracts.
Volatility is the tendency of the underlying security's market price to fluctuate up or down. It reflects a price change's magnitude. It does not imply a bias toward price movement in one direction or the other. It is a major factor in determining an option's premium.
The higher the volatility of the underlying stock, the higher the premium. This is because there is a greater possibility that the option will move in-the-money. Generally, as the volatility of an underlying stock increases, the premiums of both calls and puts overlying that stock increase and vice versa.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Options and Derivatives
- Strategy & Education
Exercise: Definition and How It Works With Options
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dhir__rajeev_dhir-5bfc262c46e0fb00260a216d.jpeg)
What Is Exercise?
Exercise means to put into effect the right to buy or sell the underlying financial instrument specified in an options contract . In options trading, the holder of an option has the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the option's underlying security at a specified price on or before a specified date in the future.
Key Takeaways
- In options trading, "to exercise" means to put into effect the right to buy or sell the underlying security that is specified in the options contract.
- To exercise an option, you simply advise your broker that you wish to exercise the option in your contract.
- If the holder of a put option exercises the contract, they will sell the underlying security at a stated price within a specific timeframe.
- If the holder of a call option exercises the contract, they will buy the underlying security at a stated price within a specific timeframe.
- Before exercising an option, it is important to consider what type of option you have and whether you can exercise it.
Understanding Exercise
If the owner of an option decides to buy or sell the underlying instrument—instead of allowing the contract to expire worthless or closing out the position —they will be "exercising the option," or making use of the right or privilege that is available in the contract.
An options holder may exercise their right to buy or sell the contract's underlying shares at a specified price—also called the strike price.
- Exercising a put option allows you to sell the underlying security at a stated price within a specific timeframe.
- Exercising a call option allows you to buy the underlying security at a stated price within a specific timeframe.
To exercise an option, you simply advise your broker that you wish to exercise the option in your contract. Your broker will initiate an exercise notice , which informs the seller or writer of the contract that you are exercising the option. The notice is forwarded to the option seller via the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC). The seller is obligated to fulfill the terms of an options contract if the holder exercises the contract.
The decision to exercise an option isn't always a clear-cut one. There are several factors that need to be considered and, more often than not, it's safer to hold or sell the option instead.
The majority of options contracts are not exercised but, instead, are allowed to expire worthless or are closed by opposing positions. For example, the holder of an option can close out a long call or put prior to expiration by selling it, assuming the contract has market value.
If an option expires unexercised, the holder no longer has any of the rights granted in the contract. In addition, the holder loses the premium they paid for the option, along with any commissions and fees related to its purchase.
Things to Consider When Exercising an Option
- What kind of option do you have? This is very important, as contracts have different guidelines. American-style contracts allow you to exercise them before their expiration date. European options may be exercised only after the contract has expired.
- Can you exercise your options? In some cases, such as with employee stock ownership plans (ESOPs), your shares may be vested , meaning that you will need to wait a set amount of time before you exercise the option.
- Will the cost outweigh the benefits? Exercising a contract costs you commission money, so make sure that the exercise price will make you money; otherwise, you'll end up paying more in fees and will lose out on any potential profit.
- Are there taxes involved? You will want to consider any tax implications associated with the type of contract you are exercising. An employee cashing out an ESOP, for example, will have to pay additional tax.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/call-option-4199998-ddd54a71fc9a479f9dda9e5b9943d9c4.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Find a Branch
- Schwab Brokerage 800-435-4000
- Schwab Password Reset 800-780-2755
- Schwab Bank 888-403-9000
- Schwab Intelligent Portfolios® 855-694-5208
- Schwab Trading Services 888-245-6864
- Workplace Retirement Plans 800-724-7526
... More ways to contact Schwab
Chat
- Schwab International
- Schwab Advisor Services™
- Schwab Intelligent Portfolios®
- Schwab Alliance
- Schwab Charitable™
- Retirement Plan Center
- Equity Awards Center®
- Learning Quest® 529
- Mortgage & HELOC
- Charles Schwab Investment Management (CSIM)
- Portfolio Management Services
- Open an Account
The Risks of Options Assignment

Any trader holding a short option position should understand the risks of early assignment. An early assignment occurs when a trader is forced to buy or sell stock when the short option is exercised by the long option holder. Understanding how assignment works can help a trader take steps to reduce their potential losses.
Understanding the basics of assignment
An option gives the owner the right but not the obligation to buy or sell stock at a set price. An assignment forces the short options seller to take action. Here are the main actions that can result from an assignment notice:
- Short call assignment: The option seller must sell shares of the underlying stock at the strike price.
- Short put assignment: The option seller must buy shares of the underlying stock at the strike price.
For traders with long options positions, it's possible to choose to exercise the option, buying or selling according to the contract before it expires. With a long call exercise, shares of the underlying stock are bought at the strike price while a long put exercise results in selling shares of the underlying stock at the strike price.
When a trader might get assigned
There are two components to the price of an option: intrinsic 1 and extrinsic 2 value. In the case of exercising an in-the-money 3 (ITM) long call, a trader would buy the stock at the strike price, which is lower than its prevailing price. In the case of a long put that isn't being used as a hedge for a long stock position, the trader shorts the stock for a price higher than its prevailing price. A trader only captures an ITM option's intrinsic value if they sell the stock (after exercising a long call) or buy the stock (after exercising a long put) immediately upon exercise.
Without taking these actions, a trader takes on the risks associated with holding a long or short stock position. The question of whether a short option might be assigned depends on if there's a perceived benefit to a trader exercising a long option that another trader has short. One way to attempt to gauge if an option could be potentially assigned is to consider the associated dividend. An options seller might be more likely to get assigned on a short call for an upcoming ex-dividend if its time value is less than the dividend. It's more likely to get assigned holding a short put if the time value has mostly decayed or if the put is deep ITM and close to expiration with a wide bid/ask spread on the stock.
It's possible to view this information on the Trade page of the thinkorswim ® trading platform. Review past dividends, the price of the short call, and the price of the put at the call's strike price. While past performance cannot be relied upon to continue, this information can help a trader determine whether assignment is more or less likely.
Reducing the risk associated with assignment
If a trader has a covered call that's ITM and it's assigned, the trader will deliver the long stock out of their account to cover the assignment.
A trader with a call vertical spread 4 where both options are ITM and the ex-dividend date is approaching may want to exercise the long option component before the ex-dividend date to have long stock to deliver against the potential assignment of the short call. The trader could also close the ITM call vertical spread before the ex-dividend date. It might be cheaper to pay the fees to close the trade.
Another scenario is a call vertical spread where the ITM option is short and the out-of-the-money (OTM) option is long. In this case, the trader may consider closing the position or rolling it to a further expiration before the ex-dividend date. This move can possibly help the trader avoid having short stock on the ex-dividend date and being liable for the dividend.
Depending on the situation, a trader long an ITM call might decide it's better to close the trade ahead of the ex-dividend date. On the ex-dividend date, the price of the stock drops by the amount of the dividend. The drop in the stock price offsets what a trader would've earned on the dividend and there would still be fees on top of the price of the put.
Assess the risk
When an option is converted to stock through exercise or assignment, the position's risk profile changes. This change could increase the margin requirements, or subject a trader to a margin call, 5 or both. This can happen at or before expiration during early assignment. The exercise of a long option position can be more likely to trigger a margin call since naked short option trades typically carry substantial margin requirements.
Even with early exercise, a trader can still be assigned on a short option any time prior to the option's expiration.
1 The intrinsic value of an options contract is determined based on whether it's in the money if it were to be exercised immediately. It is a measure of the strike price as compared to the underlying security's market price. For a call option, the strike price should be lower than the underlying's market price to have intrinsic value. For a put option the strike price should be higher than underlying's market price to have intrinsic value.
2 The extrinsic value of an options contract is determined by factors other than the price of the underlying security, such as the dividend rate of the underlying, time remaining on the contract, and the volatility of the underlying. Sometimes it's referred to as the time value or premium value.
3 Describes an option with intrinsic value (not just time value). A call option is in the money (ITM) if the underlying asset's price is above the strike price. A put option is ITM if the underlying asset's price is below the strike price. For calls, it's any strike lower than the price of the underlying asset. For puts, it's any strike that's higher.
4 The simultaneous purchase of one call option and sale of another call option at a different strike price, in the same underlying, in the same expiration month.
5 A margin call is issued when the account value drops below the maintenance requirements on a security or securities due to a drop in the market value of a security or when buying power is exceeded. Margin calls may be met by depositing funds, selling stock, or depositing securities. A broker may forcibly liquidate all or part of the account without prior notice, regardless of intent to satisfy a margin call, in the interests of both parties.
Just getting started with options?
More from charles schwab.

Options Expiration: Definitions, a Checklist, & More

Today's Options Market Update

Weekly Trader's Outlook
Related topics.
Options carry a high level of risk and are not suitable for all investors. Certain requirements must be met to trade options through Schwab. Please read the options disclosure document titled Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options before considering any options transaction. Supporting documentation for any claims or statistical information is available upon request.
With long options, investors may lose 100% of funds invested.
Spread trading must be done in a margin account.
Multiple leg options strategies will involve multiple commissions.
Commissions, taxes and transaction costs are not included in this discussion, but can affect final outcome and should be considered. Please contact a tax advisor for the tax implications involved in these strategies.
The information provided here is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered an individualized recommendation or personalized investment advice. The investment strategies mentioned here may not be suitable for everyone. Each investor needs to review an investment strategy for his or her own particular situation before making any investment decision.
Examples provided are for illustrative purposes only and not intended to be reflective of results you can expect to achieve.
Markets Home
Market data home.
Real-time market data
Market Data on Google Analytics Hub
CME DATAMINE:
THE SOURCE FOR HISTORICAL DATA
Services Home
Clearing Advisories
Uncleared margin rules
Insights Home
Subscribe to Research
Get our latest economic research delivered to your email inbox.
The world's most valuable exchange brand
Education Home
Step Into Commodities: Trading Challenge
New to Futures?
This brochure provides an in-depth description of the exercise and assignment process for options on futures that trade on CME Group-designated contract markets:
- Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT)
- Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME)
- Commodity Exchange (COMEX)
- New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX)
Contents include:
- Preliminaries
- Random Assignment
- Pro Rata Assignment
- The Role of the Clearing Member Firm
- Timetables for Option Exercise and Assignment
- Overview of contrary options exercise
Options on Futures
Information about the exercise and assignment process for options on futures on CME Group designated contract markets.
All examples in this report are hypothetical interpretations of situations and are used for explanation purposes only. The views in this report reflect solely those of the author and not necessarily those of CME Group or its affiliated institutions. This report and the information herein should not be considered investment advice or the results of actual market experience.
CME Group is the world’s leading derivatives marketplace. The company is comprised of four Designated Contract Markets (DCMs). Further information on each exchange's rules and product listings can be found by clicking on the links to CME , CBOT , NYMEX and COMEX .
© 2024 CME Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer | Privacy Notice | Cookie Notice | Terms of Use | Data Terms of Use | Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement | Report a Security Concern
- Why Merrill
- Open An Account
- Pricing & Fees
- BofA Preferred Rewards
- Investing & Banking Connected
- Mobile Investing
- Sustainable Investing
- Awards & Accolades
888.637.3343
To find the small business retirement plan that works for you, contact:
Learn more about an advisor's background on FINRA's BrokerCheck
- Merrill Edge ® Self-Directed
- Merrill Guided Investing
- Invest with an Advisor
- Compare All
- General Investing
- Education Accounts
- Mutual Funds
- Fixed Income & Bonds
- Margin Trading
- Order Execution Quality
- Idea Builder
- Merrill Edge MarketPro ®
- Personal Retirement Calculator
- College Cost Calculator
- IRA Selector
- 401(k) Rollover Calculator
- 529 Plan State Tax Calculator
- View All Tools
- New to Investing
- Plan for College
- Tax Planning
- Investing by Life Stages
- Traditional IRA
- Income in Retirement
- Plan for Retirement
- Retirement Tools
- Small Business 401(k)
- Individual 401(k)
- View All Plans
- Get Started Investing
- Investing Basics
- Market & Investing Insights
- Individual Investing Account
- Joint Investing Account
- Custodial Investing Account
- Traditional Inherited IRA
- Roth Inherited IRA
- 529 College Savings Plans
- Custodial UGMA/UTMA Accounts
- Business Investor Account
- lnvesting Costs & Fees
- Pricing & Fees
- Investing & Banking Connected
- Awards & Accolades
- Merrill Edge ® Self-Directed
- Investing with an Advisor
- Compare all
- Fixed Income & Bonds
- Merrill Edge MarketPro ®
- 401(k) Rollover Tool
- View all tools
- Tax Plannning
- Retirement Income Planning
- View all plans
- Market & Investing Insights
- Help When You Want It Find answers to common questions at Merrill Schedule an appointment with Merrill To find the small business retirement plan that works for you, contact: [email protected]

Exercising Options
Submitting exercise or do-not-exercise instructions:.
- All Instructions must be called in and are only applicable to long positions
- Do-Not-Exercise instructions can only be submitted the day of expiration up through market close
- Exercise instructions can be submitted at any time until expiration
- Merrill may take action at any time to close out positions that may not be able to be supported if exercised/assigned. It is extremely important to monitor your open options positions and be aware of your risk exposure.

What's the Net?
Automatic exercise/ assignment, early exercise/assignment, without the jargon, what are options, what are the types of options, what are the greeks, similar articles, options pricing, equity option basics, equity index options.
This material is not intended as a recommendation, offer or solicitation for the purchase or sale of any security or investment strategy. Merrill offers a broad range of brokerage, investment advisory (including financial planning) and other services. Additional information is available in our Client Relationship Summary (PDF) .
I'd Like to
- Create an Emergency Fund
- Create an Investment Strategy
- Open an Account with Merrill
Discover Merrill
- Bank of America Preferred Rewards
- Online Trading
- Awards & Recognition
Representatives are available 24/7
Unlimited $0 Trades
Investing in securities involves risks, and there is always the potential of losing money when you invest in securities.
The performance data contained herein represents past performance which does not guarantee future results. Investment return and principal value will fluctuate so that shares, when redeemed, may be worth more or less than their original cost. Current performance may be lower or higher than the performance quoted. For performance information current to the most recent month end, please contact us.
Net Asset Value (NAV) returns are based on the prior-day closing NAV value at 4 p.m. ET. NAV returns assume the reinvestment of all dividend and capital gain distributions at NAV when paid.
Market price returns are based on the prior-day closing market price, which is the average of the midpoint bid-ask prices at 4 p.m. ET. Market price returns do not represent the returns an investor would receive if shares were traded at other times.
Returns include fees and applicable loads. Since Inception returns are provided for funds with less than 10 years of history and are as of the fund's inception date. 10 year returns are provided for funds with greater than 10 years of history.
Before investing consider carefully the investment objectives, risks, and charges and expenses of the fund, including management fees, other expenses and special risks. This and other information may be found in each fund's prospectus or summary prospectus, if available. Always read the prospectus or summary prospectus carefully before you invest or send money. Prospectuses can be obtained by contacting us.
Expense Ratio – Gross Expense Ratio is the total annual operating expense (before waivers or reimbursements) from the fund's most recent prospectus. You should also review the fund's detailed annual fund operating expenses which are provided in the fund's prospectus.
This material is not intended as a recommendation, offer or solicitation for the purchase or sale of any security or investment strategy. Merrill offers a broad range of brokerage, investment advisory (including financial planning) and other services. Additional information is available in our Client Relationship Summary (Form CRS) (PDF) .
Banking products are provided by Bank of America, N.A. and affiliated banks, Members FDIC and wholly owned subsidiaries of Bank of America Corporation ("BofA Corp.").
Merrill Lynch Life Agency Inc. (MLLA) is a licensed insurance agency and wholly owned subsidiary of BofA Corp.
© 2024 Bank of America Corporation. All rights reserved.
5676695-05112024

The Mechanics of Option Trading, Exercise, and Assignment
Options were originally traded in the over-the-counter ( OTC ) market , where the terms of the contract were negotiated. The advantage of the OTC market over the exchanges is that the option contracts can be tailored: strike prices, expiration dates, and the number of shares can be specified to meet the needs of the option buyer. However, transaction costs are greater and liquidity is less.
Option trading really took off when the first listed option exchange — the Chicago Board Options Exchange ( CBOE )— was organized in 1973 to trade standardized contracts, greatly increasing the market and liquidity of options. The CBOE was the original exchange for options, but, by 2003, it has been superseded in size by the electronic International Securities Exchange (ISE), based in New York. Most options sold in Europe are traded through electronic exchanges. Other exchanges for options in the United States include: NYSE Euronext ( NYX ), and the NASDAQtrader.com .
Option exchanges are central to the trading of options:
- they establish the terms of the standardized contracts
- they provide the infrastructure — both hardware and software — to facilitate trading, which is increasingly computerized
- they link together investors, brokers, and dealers on a centralized system, so that traders can from the best bid and ask prices
- they guarantee trades by taking the opposite side of each transaction
- they establish the trading rules and procedures
Options are traded just like stocks — the buyer buys at the ask price and the seller sells at the bid price . The settlement time for option trades is 1 business day ( T+1 ). However, to trade options, an investor must have a brokerage account and be approved for trading options and must also receive a copy of the booklet Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options .
The option holder, unlike the holder of the underlying stock, has no voting rights in the corporation, and is not entitled to any dividends. Brokerage commissions , which are a little higher for options than for stocks, must also be paid to buy or sell options, and for the exercise and assignment of option contracts. Prices are usually quoted with a base price + cost per contract, usually ranging from $5 to $15 minimum charge for up to 10 contracts, with a lower per contract charge, typically $0.50 to $1.50 per contract, for more than 10 contracts. Most brokerages offer lower prices to active traders. Here are some examples of how option prices are quoted:
- $9.99 + $0.75 per contract for online option trades
- $9.99 + $0.75 per contract for online option trades; phone trades are $5 more, and broker-assisted trades are $25 more
- $1.50 per contract with a minimum standard rate of $14.95, with several discounts for active traders
- Sliding commission scale ranging from $6.99 + $0.75 per contract for traders making at least 1500 trades per quarter to $12.99 + $1.25 per contract for investors with less than $50,000 in assets and making fewer than 30 trades per quarter. $19.99 for exercise and assignments.
The Options Clearing Corporation (OCC)
The Options Clearing Corporation ( OCC ) is the counterparty to all option trades. The OCC issues, guarantees, and clears all option trades involving its member firms, including all U.S. option exchanges, and ensures that sales are transacted according to the current rules. The OCC is jointly owned by its member firms — the exchanges that trade options — and issues all listed options, and controls and effects all exercises and assignments. To provide a liquid market, the OCC guarantees all trades by acting as the other party to all purchases and sales of options.
The OCC, like other clearing companies, is the direct participant in every purchase and sale of an option contract. When an option writer or holder sells his contracts to someone else, the OCC serves as an intermediary in the transaction. The option writer sells his contract to the OCC and the option buyer buys it from the OCC.
The OCC publishes, at optionsclearing.com , statistics, news on options, and any notifications about changes in the trading rules, or the adjustment of certain option contracts because of a stock split or that were subjected to unusual circumstances, such as a merger of companies whose stock was the underlying security to the option contracts.
The OCC operates under the jurisdiction of both the Securities and Exchange Commission ( SEC ) and the Commodities Futures Trading Commission ( CFTC ). Under its SEC jurisdiction, OCC clears transactions for put and call options on common stocks and other equity issues, stock indexes, foreign currencies, interest rate composites and single-stock futures . As a registered Derivatives Clearing Organization ( DCO ) under CFTC jurisdiction, the OCC clears and settles transactions in futures and options on futures .
The Exercise of Options by Option Holders and the Assignment to Fulfill the Contract to Option Writers
When an option holder wants to exercise his option, he must notify his broker of the exercise, and if it is the last trading day for the option, the broker must be notified before the exercise cut-off time , which will probably be earlier than on trading days before the last day, and the cut-off time may differ for different option classes or for index options. Although policies differ among brokerages, it is the duty of the option holder to notify his broker to exercise the option before the cut-off time.
When the broker is notified, then the exercise instructions are sent to the OCC, which then assigns the exercise to one of its Clearing Members who are short in the same option series as is being exercised. The Clearing Member will then assign the exercise to one of its customers who is short in the option. The customer is selected by a specific procedure, usually on a first-in, first-out basis, or some other fair procedure approved by the exchanges. Thus, there is no direct connection between an option writer and a buyer.
To ensure contract performance, option writers are required to post margin, the amount depending on how much the option is in the money. If the margin is deemed insufficient, then the option writer will be subjected to a margin call. Option holders don't need to post margin because they will only exercise the option if it is in the money. Options, unlike stocks, cannot be bought on margin.
Because the OCC is always a party to an option transaction, an option writer can close out his position by buying the same contract back, even while the contract buyer retains his position, because the OCC draws from a pool of contracts with no connection to the original contract writer and buyer.
A diagram outlining the exercise and assignment of a call.
Example: No Direct Connection between Investors Who Write Options and those Who Buy Them
John Call-Writer writes an option that legally obligates him to provide 100 shares of Microsoft for the price of $30 until April, 2007. The OCC buys the contract, adding it to the millions of other option contracts in its pool. Sarah Call-Buyer buys a contract that has the same terms that John Call-Writer wrote — in other words, it belongs to the same option series . However, option contracts have no name on them. Sarah buys from the OCC, just as John sold to the OCC, and she just gets a contract giving her the right to buy 100 shares of Microsoft for $30 per share until April, 2007.
Scenario 1 — Exercises of Options are Assigned According to Specific Procedures
In February, the price of Microsoft rises to $35, and Sarah thinks it might go higher in the long run, but since March and April generally are volatile times for most stocks, she decides to exercise her call (sometimes called calling the stock ) to buy Microsoft stock at $30 per share to be able to hold the stock indefinitely. She instructs her broker to exercise her call; her broker forwards the instructions to the OCC, which then assigns the exercise to one of its participating members who provided the call for sale; the participating member, in turn, assigns it to an investor who wrote such a call; in this case, it happened to be John's brother, Sam Call-Writer. John got lucky this time. Sam, unfortunately, either must turn over his appreciated shares of Microsoft, or he'll have to buy them in the open market to provide them. This is the risk that an option writer must take — an option writer never knows when he'll be assigned an exercise when the option is in the money.
Scenario 2 — Closing Out an Option Position by Buying Back the Contract
John Call-Writer decides that Microsoft might climb higher in the coming months, and so decides to close out his short position by buying a call contract with the same terms that he wrote — one that is in the same option series. Sarah, on the other hand, decides to maintain her long position by keeping her call contract until April. This can happen because there are no names on the option contracts. John closes his short position by buying the call back from the OCC at the current market price, which may be higher or lower than what he paid, resulting in either a profit or a loss. Sarah can keep her contract because when she sells or exercises her contract, it will be with the OCC, not with John, and Sarah can be sure that the OCC will fulfill the terms of the contract if she should decide to exercise it later on.
Thus, the OCC allows each investor to act independently of the other .
When the assigned option writer must deliver stock, she can deliver stock already owned, buy it on the market for delivery, or ask her broker to go short on the stock and deliver the borrowed shares. However, finding borrowed shares to short may not always be possible, so this method may not be available.
If the assigned call writer buys the stock in the market for delivery, the writer only needs the cash in his brokerage account to pay for the difference between what the stock cost and the strike price of the call, since the writer will immediately receive cash from the call holder for the strike price. Similarly, if the writer is using margin, then the margin requirements apply only to the difference between the purchase price and the strike price of the option. Full margin requirements, however, apply to shorted stock.
An assigned put writer will need either the cash or the margin to buy the stock at the strike price, even if he intends to sell the stock immediately after the exercise of the put. When the call holder exercises, he can keep the stock or immediately sell it. However, he must have the margin, if he has a margin account, or cash, for a cash account, to pay for the stock, even if he sells it immediately. He can also use the delivered stock to cover a short in the stock. (Note: equity requirements differ because an assigned call writer immediately receives the cash upon delivery of the shares, whereas a put writer or a call holder who purchased the shares may decide to keep the stock.)
Example: Fulfilling a Naked Call Exercise
A call writer receives an exercise notice on 10 call contracts with a strike of $30 per share on XYZ stock on which she is still short. The stock currently trades at $35 per share. She does not own the stock, so, to fulfill her contract, she must buy 1,000 shares of stock in the market for $35,000 then sell it for $30,000, resulting in an immediate loss of $5,000 minus the commissions of the stock purchase and assignment.
Both the exercise and assignment incur brokerage commissions for both holder and assigned writer. Generally, the commission is smaller to sell the option than it is to exercise it. However, there may be no choice if it is the last day of trading before expiration. Although the buying and selling of options is settled in 1 business day after the trade, settlement for an exercise or assignment occurs on the 3 rd business day after the exercise or assignment ( T+3 ), since it involves the purchase of the underlying stock.
Often, a writer will want to cover his short by buying the written option back on the open market. However, once he receives an assignment, then it is too late to cover his short position by closing the position with a purchase. Assignment is usually selected from writers still short at the end of the trading day. A possible assignment can be anticipated if the option is in the money at expiration, the option is trading at a discount, or the underlying stock is about to pay a large dividend.
The OCC automatically exercises any option that is in the money by at least $0.50 ( automatic exercise , Exercise-by-Exception , Ex-by-Ex ), unless notified by the broker not to. A customer may not want to exercise an option that is only slightly in the money if the transaction costs would exceed the net profit from the exercise. In spite of the automatic exercise by the OCC, the option holder should notify his broker by the exercise cut-off time , which may be before the end of the trading day, of an intention to exercise. Exact procedures will depend on the broker.
Any option that is sold on the last trading day before expiration would likely be bought by a market maker. Because a market maker's transaction costs are lower than for retail customers, a market maker may exercise an option even if it is only a few cents in the money. Thus, any option writer who does not want to be assigned should close out his position before expiration day if there is any chance that it will be in the money even by a few pennies.
Early Exercise
Sometimes, an option will be exercised before its expiration day — called early exercise , or premature exercise . Because options have a time value in addition to intrinsic value, most options are not exercised early. However, there is nothing to prevent someone from exercising an option, even if it is not profitable to do so, and sometimes it does occur, which is why anyone who is short an option should expect the possibility of being assigned early.
When an option is trading below parity (below its intrinsic value), then arbitrageurs can take advantage of the discount to profit from the difference, because their transaction costs are very low. An option with a high intrinsic value will have little time value, and so, because of the difference between supply and demand in the market at any given moment, the option could be trading for less than its true worth. An arbitrageur will almost certainly take advantage of the price discrepancy for an instant profit. Anyone who is short an option with a high intrinsic value should expect a good possibility of being assigned an exercise.
Example: Early Exercise by Arbitrageurs Profiting from an Option Discount
XYZ stock is currently at $40 per share. Calls on the stock with a strike of $30 are selling for $9.80. This is a difference of $0.20 per share, enough of a difference for an arbitrageur, whose transaction costs are typically much lower than for a retail customer, to profit immediately by selling short the stock at $40 per share, then covering his short by exercising the call for a net of $0.20 per share minus the arbitrageur's small transaction costs.
Option discounts will only occur when the time value of the option is small, because either it is deep in the money or the option will soon expire.
Option Discounts Arising from an Imminent Dividend Payment on the Underlying Stock
When a large dividend is paid by the underlying stock, its price drops on the ex-dividend date, resulting in a lower value for the calls. The stock price may remain lower after the payment, because the dividend payment lowers the book value of the company. This causes many call holders to either exercise early to collect the dividend, or to sell the call before the drop in stock price. When many call holders sell at the same time, it causes the call to sell at a discount to the underlying, thereby creating opportunities for arbitrageurs to profit from the price difference. However, there is some risk that the transaction will lose money, because the dividend payment and drop in stock price may not equal the premium paid for the call, even if the dividend is more than the time value of the call.
Example: Arbitrage Profit/Loss Scenario for a Dividend-Paying Stock
XYZ stock is currently trading at $40 per share and will pay a dividend of $1 the next day. A call with a $30 strike is selling for $10.20, the $0.20 being the time value of the premium. So an arbitrageur decides to buy the call and exercise it to collect the dividend. Since the dividend is $1, but the time value is only $0.20, this could lead to a profit of $0.80 per share, but on the ex-dividend date, the stock drops to $39. Adding the $1 dividend to the share price yields $40, which is still less than buying the stock for $30 + $10.20 for the call. It might be profitable if the stock does not drop as much on the ex-date or it recovers after the ex-date sufficiently to make it profitable. But this is a risk for the arbitrageur, and this transaction is, thus, known as risk arbitrage , because the profit is not guaranteed.
2019 Statistics for the Fate of Options
Data Source: https://www.optionseducation.org/referencelibrary/faq/options-exercise
All option writers who didn't close out their position earlier by buying an offsetting contract made the maximum profit — the premium — on those contracts that expired. Option writers have lost at least something when the option is exercised, because the option holder wouldn't exercise it unless it was in the money. The more the exercised option was in the money, the greater the loss is for the assigned option writer and the greater the profits for the option holder. A closed out transaction could be at a profit or a loss for both holders and writers of options, but closing out a transaction is usually done either to maximize profits or to minimize losses, based on expected changes in the price of the underlying security until expiration.
Expiration Process and Risks
Expiration, exercise, assignment, and associated risks.
This article contains some basic facts about the options expiration process and the risks associated with options exercise, assignment, and expiration. Please note that the information provided below is not exhaustive and that additional risks beyond those discussed below may exist. You should fully understand the risks of trading options before you trade. For more information, please read the Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options . If you have any questions about the exercise or expiration process, please contact Customer Support.
Expiration Day
Automatic exercise of in-the-money options.
The Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) will automatically exercise any expiring options that close $0.01 in-the-money or more on Expiration Day. In-the-money is defined as the stock’s official OCC closing price being $0.01 HIGHER than the Strike Price for call options or $0.01 LOWER than the Strike Price for put options. You may also choose not to exercise in-the-money options that would otherwise be automatically exercised by entering do-not-exercise instructions through the E*TRADE platform before 4:30 PM CT / 5:30 PM ET on the Expiration Date. Any instructions submitted to E*TRADE by telephone are processed on a best-efforts basis. If you fail to provide sufficient time for an E*TRADE broker to assist, your expiring options may still be exercised.
Exercise of Out-of-the-Money Options
The OCC will not automatically exercise expiring options that close in-the-money by less than $0.01 or which are out-of-the-money. These options may still be exercised, but you are required to enter an exercise request through the E*TRADE platform before 4:30 PM CT / 5:30 PM ET on the Expiration Date to exercise these options. Any requests submitted to E*TRADE by telephone are processed on a best-efforts basis. If you fail to provide sufficient time for an E*TRADE broker to assist, your expiring options may not be exercised.
Short Out-of-the-Money Options May be Assigned
The holder of a long options position may choose to exercise the options contracts even if they finish out-of-the-money. In some cases, exercising out-of-the-money options may be economically beneficial due to stock price changes in the extended hours session. If you are short options which appear out-of-the-money, there is no guarantee that you will NOT be assigned those contracts.
Short In-the-Money Options May Not Automatically be Assigned
The holder of a long options position may choose to NOT exercise the options even if they finish in-the-money. In some cases, it may be economically beneficial not to exercise an in-the-money option due to stock price changes in the extended hours session. If you are short options which appear in-the-money, there is no guarantee that you will be assigned those contracts.
Exercises, Assignments and Your Account Equity
You should review your positions prior to expiration to determine whether you have adequate equity in your account to carry the underlying position prior to exercising options. You should also determine whether you have adequate equity in the account if a short options position is assigned to your account. It may make sense to close positions in expiring options prior to the market close to avoid the risks if you do not have adequate capital in your account, or if you do not want to bear the risks associated with a long or short stock position. Also, you should consider the possibility that you may be assigned on a short option position even if the option is out-of-the-money.
E*TRADE May Buy or Sell in Your Account to Manage Expiration Risk
E*TRADE reserves the right to liquidate or cover expiring option positions which would result in undue risk and/or margin deficit related to exercise or assignment.
Accounts with insufficient equity on hand prior to exercise or assignment are subject to unwarranted risk of adverse price change in the underlying security upon delivery. To protect against the excessive risk of an adverse movement in the underlying security, E*TRADE may intervene to mitigate the risk on your behalf. Such intervention may include closing out existing positions, buying, or selling stock against expected exercises or assignments, or entering “Do Not Exercise” instructions for positions expiring in-the-money. Any losses incurred from actions taken to mitigate risk are the sole responsibility of the account holder.
E*TRADE initiates expiration-related liquidations two hours prior to the market close but does reserve the right to begin the process sooner or later if conditions warrant any alteration. If E*TRADE deems it necessary to take action in your account to mitigate risk potential exercise/assignment risk, you will be responsible for any market losses and will be charged broker assist fees.
E*TRADE is under no obligation to manage such risks and we expect each customer to actively manage and mitigate the potential risks involved with expiring option positions. Failure by a customer to effectively manage the risk of expiring positions may also result in the account being restricted from opening new positions to limit any further increase in exposure.
Spreads and Expiration Risk
Spread positions can have unique expiration risks associated with them. An expiring spread where the long leg of the spread is in-the-money by less than $0.01 and the short leg of the spread is in-the-money more than $0.01 may require special attention on your part to manage the expiration risks. You are responsible for managing this risk and all other risks associated with any unhedged spread legs that expire in-the-money. If you do not want to exercise an expiring in-the-money leg of a spread, you must enter do-not-exercise instructions through the E*TRADE platform before 4:30 PM CT / 5:30 PM ET on the Expiration Date. Any instructions submitted to E*TRADE by telephone are processed on a best-efforts basis. If you fail to provide sufficient time for an E*TRADE broker to assist, your expiring in-the-money leg of a spread may still be exercised.
The Assignment Process
E*TRADE processes the assignments made by OCC to customers with short options positions on a random basis. E*TRADE will process assignments and exercises in your account on the first eligible day following expiration.
Managing Risks Following Expiration
You may need to review your account and manage any positions that generate margin charges, and the risk resulting from exercises or assignments on the trading day following expiration. You are responsible for any positions created in your account as a result of the expiration process. If you do not take appropriate action, you may receive a margin call or E*TRADE may liquidate positions in your account.
Early Exercise of Options
If you wish to exercise an option contract prior to the last business day before expiration (“Expiration Day” typically Friday but note below)** you must enter an exercise request through the E*TRADE platform by 4:30 PM CT / 5:30 PM ET on the Expiration Day. Failure to do so will result in the contracts not being exercised on that business day. This is especially critical if you intend to exercise call options on the business day prior to an ex-dividend date to own stock and be eligible to receive the dividend. Any requests submitted to E*TRADE by telephone are processed on a best-efforts basis. If you fail to provide sufficient time for an E*TRADE broker to assist, your contacts may not be exercised on that business day.
Halted Securities
Options on halted securities may not be automatically exercised or assigned regardless of whether they are in-the-money. Holders of long option positions in halted securities may need to make an independent determination of the value of the option deliverable in deciding whether to exercise or not. Holders wishing to exercise an option on a halted security will need to notify E*TRADE with their instructions to exercise before 3:30 PM CT / 4:30 PM ET (subject to holiday schedules) on the expiration day. Please also note that E*TRADE may impose higher margin rates on these securities, and may ensure availability of funds sufficient to sustain hard-to-borrow fees before honoring exercise instructions if the exercise would result in a short underlying position.
** Expiration Day typically occurs Friday, or Thursday if that is the last trading day of the week.
Certain securities may also have Monday and Wednesday Expiration Dates.
Expiration, exercise, and assignment
Unlike stocks, options have set expiration , exercise , and assignment dates.
Each option contract has a set expiration date. This date significantly impacts the value of the option contract because it limits the time you can buy, sell, or exercise the option contract. Once an option contract expires, it will stop trading and either be exercised or expire worthless.
The following are a few important things to keep in mind as the expiration date of an option contract approaches:
- We’ll attempt to exercise any option you own that is $0.01 or more in-the-money, as long as your investment account has the required buying power, such as for a call option, or the necessary underlying shares to sell, such as for a put option. Keep in mind that managing your options positions, including taking proactive steps to mitigate risk, is ultimately your responsibility.
- If you don’t have enough buying power or underlying shares to exercise your option, we may attempt to sell the contract in the market for you within the last 30 minutes before the market closes on the options' expiration date.
- Robinhood’s risk checks are designed to close positions based on the position’s value, the implied risk, and your current account portfolio and value, among other things.
Moneyness of an option
In-the-money, at-the-money, and out-of-the-money refer to the position of the underlying security’s price relative to the strike price of the option. They’re also sometimes referred to as the moneyness of an option.
To learn more, check out Options trading from the pros .
If your option is in-the-money at the market’s close, Robinhood will attempt to exercise it for you at expiration unless:
- You don’t have sufficient buying power.
- The exercise would result in a short stock position.
- You’ve asked Robinhood to submit a Do Not Exercise (DNE) request on your behalf. Keep in mind, the cut-off time for submitting a DNE request is 5 PM ET.
Once your contract expires, it’ll move to your expired contracts in your account History .
After-hours price movements can change the in-the-money or out-the-money status of an options contract.
If for any reason we can't sell your contract, and you don’t have the necessary buying power or shares to exercise it, we may attempt to submit a DNE request to the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), and your contract should expire worthless.
To determine if an option position is “at risk of being in-the-money,” Robinhood will calculate an estimated upper and lower bound for the underlying security’s close price on the expiration date. If your option’s strike price falls within these parameters, we may place an order to close your position.
If your option is in-the-money, Robinhood will typically exercise it for you at expiration automatically. However, you can also exercise your options contract early in the app:
- Navigate to the options position detail screen
- Select Exercise
You’ll then be guided through steps to exercise your contract.
Before expiration day, an early exercise request will be submitted immediately if it’s placed during regular market hours (9 AM-4 PM ET) and trading days. Contact us before 5 PM ET if you’d like to cancel an exercise request.
Early exercise requests submitted after 4 PM ET will be queued for the next trading day. You can cancel a pending exercise request until 11:59 PM ET.
On expiration day, you won’t be able to submit an early exercise request in the app or on the web after 4 PM ET. Contact us to request an exercise request after 4 PM ET. We’ll try to accommodate exercise requests until 5 PM ET on a best-effort basis.
How to confirm
After you exercise an option, you’ll get an in-app confirmation that your option was exercised and that the associated shares are pending. You’ll also get an email and an in-app notification before the next trading day confirming that your option was exercised or assigned (after we receive confirmation from the OCC).
How to submit a DNE
If your option is out-of-the-money, Robinhood will take no action and the contract will typically expire. If you’d like to submit a DNE request, you must contact us before 5 PM on the expiration date .
When you are assigned, you have the obligation to fulfill the terms of the contract. When you sell-to-open an options contract, you can be assigned at any point prior to expiration (regardless of the underlying share price).
Depending on the collateral held for a short contract, a few different things can occur. For more details, check out Navigating exercise & assignment .
Check out Advanced options strategies (Level 3) to learn more about calls, puts, and multi-leg options strategies.
Unassigned anticipated assignment
On rare occasions, the in-the-money short option of a spread won’t get assigned. This happens when the counterparty files a DNE request for their in-the-money option, or a post-market movement shifts the option from in-the-money to out-of-the-money (and the contract holder decides not to exercise). In this scenario, you’ll likely be long or short the stock the following trading day, potentially resulting in an account deficit or margin call.
All resulting short stock positions must be covered the following trading day.
The scenario listed above could result in a gain or loss that’s greater than theoretical max gain or loss on the position.
Early assignment
If you’re trading a multi-leg options strategy and are assigned a short position before expiration, keep the following in mind, such as any account deficits or margin calls .
Decreased buying power
Early assignment may result in decreased buying power. This is because the positions you hold are used to calculate your buying power, and at the time you’re assigned, you may not have the shares (for call spreads) or the buying power (for put spreads) needed to cover the deficit in your account. If you have an account deficit, you can’t open new positions until the deficit is resolved.
Account deficits
Early assignment may also result in an account deficit if it causes you to use more buying power than you have available. When you have an account deficit, there are a few potential actions that you can take, including exercising your long contract or buying/selling shares. If you have an account deficit and choose to exercise your long contract to increase your buying power, you will not be able to open new positions while your exercise is pending. But you should be able to open new positions once your exercise has been processed if exercising your long contract is sufficient to cover your account deficit.
Margin calls
Early assignment may also result in margin call if it causes your account value to fall below your margin maintenance requirement. When you have a margin call, there are a few potential actions that you can take: exercising your long contract, buying/selling shares by placing orders, or depositing enough funds to cover the margin call. If you have a margin call and choose to exercise your long contract to decrease your margin deficiency, your margin call may persist while your exercise is pending or, further, if the exercise was not sufficient enough to cover your margin deficit. If exercising your long contract is sufficient to cover your margin deficiency, any margin calls should be satisfied once your exercise is processed.
Early assignment and exercise
Keep in mind that we can’t process an early assignment before the end of the trading day and, so we can’t exercise the long leg until the next trading day (at the earliest). That’s because the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) doesn’t notify us of your assignment until after the market closes (when they process assignments). While funds and shares that result from exercises are made available immediately during market hours, positions exercised after market hours are queued and credited to your account the next trading day.
Pending shares
If an option is exercised before expiration.
A few things can happen if your option is exercised early (also known as an early-exercise), depending on the time of day.
If the early exercise occurs during market hours (9 AM-4 PM ET), the associated shares will show in your account immediately, and will no longer show as a pending exercise in your account.
If the early exercise occurs after 4 PM ET, it’ll be queued for the next trading day, and the associated shares will remain pending until the exercise has cleared.
Some underlying assets (like exchange-traded products) are eligible for late-close options trading until 4:15 PM ET. Check out Options trading hours for details.
If a long option exercised or assigned at expiration
Once your contract has been exercised or assigned, we’ll hold the associated shares or cash collateral until we receive confirmation from the OCC that all aspects of the exercise or assignment have cleared. This process typically takes 1 business day. Once completed, the pending state of the exercise or assignment will be removed and your account will be updated accordingly.
Finding your trade details
- Select Account (person icon) → in the app, Menu (3 bars)
- Select History
- Select the option you’re looking for (e.g. XYZ $1,200 Call Oct. 21 Exercise)
Options dividend risk
Dividend risk is the risk that you’ll get assigned on a short call position (either as part of a covered call or spread) the trading day before the underlying security’s ex-dividend date. If this happens and you don’t own 100 shares of the stock, you’ll open the ex-date with a short stock position and actually be responsible for paying that dividend yourself. You can potentially avoid this by closing any position that includes a short call option at any time before the end of regular market hours on the trading day before the ex-date.
Robinhood may take action in your brokerage account to close any positions that have dividend risk the trading day before an ex-dividend date. Generally, we’ll only take action if the dividend that would be owed upon assignment represents a large portion of your total account value, which we’ll try to do on a best-effort basis.
Options dividend example
Let’s say, XYZ is going to pay a dividend as follows:
- Ex-date: October 1
- Record date: October 3
- Pay date: October 31
If you’re short, or you’ve sold an option call contract for XYZ that’s expiring on or after October 1, you’re at risk of an assignment.
For example, if you get assigned on September 30, you’d have a short position of 100 shares that were exercised by the counterparty (a person who bought and exercised the call option) when the market opens on October 1. If this occurs, you’ll have to deliver the underlying shares and pay the counterparty the dividend that is associated with these shares.
In this example, you’d owe a dividend of $100, which is $1 x 100 shares. We’d automatically deduct the dividend amount from your account, even if it causes you to have a negative balance.
You can avoid this dividend risk by closing your option before the market closes on any trading day before the ex-dividend date.
The day before the ex-dividend, we’ll try to prevent you from selling to open new short call options that are likely to be assigned that same night if the underlying symbol ex-dividend date occurs on the next trading day. This is only temporary, and you can open new short call positions on or after the ex-dividend date.
Disclosures
Any hypothetical examples are provided for illustrative purposes only. Actual results will vary.
Content is provided for educational purposes only, doesn't constitute tax or investment advice, and isn't a recommendation for any security or trading strategy. All investments involve risk, including the possible loss of capital. Past performance doesn't guarantee future results.
If multiple options positions or strategies are established in the same underlying symbol, Robinhood Financial may deem it necessary to pair or re-pair the separately established options positions or strategies together as part of its risk management process.
Robinhood Financial doesn't guarantee favorable investment outcomes. The past performance of a security or financial product doesn't guarantee future results or returns.
Customers should consider their investment objectives and risks carefully before investing in options. Because of the importance of tax considerations to all options transactions, the customer considering options should consult their tax advisor as to how taxes affect the outcome of each options strategy.
Margin trading involves interest charges and risks, including the potential to lose more than deposited or the need to deposit additional collateral in a falling market. Before using margin, customers must determine whether this type of trading strategy is right for them given their specific investment objectives, experience, risk tolerance, and financial situation. For more information, review Robinhood Financial’s Margin Disclosure Statement , Margin Agreement and FINRA Investor Information . These disclosures have information on Robinhood Financial’s lending policies, interest charges, and the risks associated with margin accounts.

Options University 10: Spreads – Exercise and Assignment
Video summary (1 and a half minutes).
The closing price of the stock on expiry establishes which options finish in the money and subject to exercise or assignment or those that finish out of the money, and worthless. Because option spreads involve both buying and selling of options, if the entire spread finishes out of the money, it either expires worthless, with nothing exercised or assigned. If a spread finishes completely in the money, it expires at its max value, with the options exercised and assigned, canceling each other out, and profits or losses determined. However, if only part of a spread is in the money, the position runs the risk of being assigned or auto-exercised and a resulting stock position may occur. Therefore many investors close spreads before expiry, if only part of the spread is in the money, or if the stock is close enough to the spread that that may occur.
COMPLEMENTARY READING
- Glossary of Options Trading Terms
- 6 Option Spreads Explained (Videos)
Stay in the loop
Be the first to hear product announcements and get daily market content from The Orbit.

- Transfer Webull to E*Trade
- Regulation T Extension Fee
- Etrade Futures Margin
- Schwab Guardian Account
- American Funds Transfer Fee

- Privacy Policy
- Terms Of Service
IRA-Reviews.com provides reviews of services based on our personal opinions. We may be compensated by the businesses we review. The content presented on IRA-Reviews.com does not constitute investment advice and should not be used as the basis for any investment decision. Copyright 2011-2024 IRA-Reviews.com. All rights are reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn about options exercise and options assignment before taking a position, not afterward. This guide can help you navigate the dynamics of options expiration. So your trading account has gotten options approval, and you recently made that first trade—say, a long call in XYZ with a strike price of $105. Then expiration day approaches and ...
Assignment occurs when the buyer exercises an options contract on or before expiration, and the seller must fulfill the obligation by either buying or selling the underlying security at the exercise price. As a seller of options, you can be assigned at any time prior to expiration regardless of the underlying share price—meaning you might ...
The exercise and assignment process is automated and the seller, who is selected at random from the available pool of investors holding the short options positions, is informed when the ...
Another important thing to know about exercise and assignment is that standard in-the-money equity options are automatically exercised at expiration. So, traders may end up with stock positions by letting their options expire in-the-money. An in-the-money option is defined as any option with at least $0.01 of intrinsic value at expiration.
An option assignment represents the seller's obligation to fulfill the terms of the contract by either selling or buying the underlying security at the exercise price. This obligation is triggered when the buyer of an option contract exercises their right to buy or sell the underlying security. To ensure fairness in the distribution of American ...
A call option is the right to buy the underlying future at the strike price. The process for activating that "right", is called "exercising the right" or simply to "exercise" the option. For a call option, that activity is also referred to as "calling the underlying" away from the option seller. Options buyers (either put or ...
Assignment. The holder of an American-style option contract can exercise the option at any time before expiration. Therefore, an option writer may be assigned an exercise notice on a short option position at any time before expiration. If an option writer is short an option that expires in-the-money, they should expect assignment on that ...
Exercise means to put into effect the right specified in a contract. In options trading, the option holder has the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying instrument at a ...
When an option is converted to stock through exercise or assignment, the position's risk profile changes. This change could increase the margin requirements, or subject a trader to a margin call, 5 or both. This can happen at or before expiration during early assignment. The exercise of a long option position can be more likely to trigger a ...
Brochure describing exercise and assignment process for options trades on CME Group exchanges: Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT), Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), Commodity Exchange (COMEX), and New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX). Includes an overview of the contrary options exercise process.
Trading, rolling, assignment, or exercise of any portion of the strategy will result in a new maximum loss, gain and breakeven calculation, which will be materially different from the calculation when the strategy remains intact with all of the contemplated legs or positions. This is applicable to all options strategies inclusive of long ...
Money › Options The Mechanics of Option Trading, Exercise, and Assignment. Options were originally traded in the over-the-counter (OTC) market, where the terms of the contract were negotiated.The advantage of the OTC market over the exchanges is that the option contracts can be tailored: strike prices, expiration dates, and the number of shares can be specified to meet the needs of the ...
What are option exercise and assignment? Exercise. As the holder of a long option contract, you have the right but not the obligation to buy (in the case of a call option) or sell (in the case of a put option) the underlying instrument (stock, index, ETF, or other asset) at the strike price purchased.
Options exercise is the process of converting an options contract into the underlying shares of stock. Exercising an options contract is irrevocable as exercise begins the process of assignment by the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC). Options contract buyers may exercise the contract anytime before expiration with American-style contracts.
Expiration, Exercise, Assignment, and Associated Risks. This article contains some basic facts about the options expiration process and the risks associated with options exercise, assignment, and expiration. Please note that the information provided below is not exhaustive and that additional risks beyond those discussed below may exist.
Option assignment occurs when the owner of an option exercises their right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specific price on or before expiration. When a call option is assigned, the owner buys shares at the strike price. For example, if XYZ stock is trading for $45 and you sold one XYZ 50 Put, the put buyer has the right to sell 100 ...
Early assignment/exercise - For a variety of reasons the holder of an option may want to exercise the contract early, before expiry. This is typically done when the option is at or close to 100 deltas and in the money.
Early assignment and exercise. Keep in mind that we can't process an early assignment before the end of the trading day and, so we can't exercise the long leg until the next trading day (at the earliest). That's because the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) doesn't notify us of your assignment until after the market closes (when they ...
talk about exercise and assignment, and then position management examples, focus on calls there, buying calls and the covered call, if the stock moves in various ways, what can you do, what are you looking at as far as managing those positions. Options are not set-it-and-forget-it type of investments, you
Video Summary (1 and a half minutes) The closing price of the stock on expiry establishes which options finish in the money and subject to exercise or assignment or those that finish out of the money, and worthless. Because option spreads involve both buying and selling of options, if the entire spread finishes out of the money, it either ...
In both cases, some brokers will charge fees. Nowadays, however, not all that many brokers still charge assignments and exercise fees. This is part of an overall movement toward low-cost or no-cost discount brokers. One big exception is TradeStation, who charges $14.95 for both options exercise and assignment. Ultimately, you may want to choose ...
Puts are at greater risk of early assignment as time value becomes negligible. In the case of puts, the game changes. When you exercise a put, you're selling stock and receivingcash. So it can be tempting to get cash now as opposed to getting cash later. However, once againyou must factor time value into the equation.
When you are long options, you have control over whether those options are exercised (until expiration when any long options position that is in-the-money by $0.01 or more will automatically be exercised). Assignment relates to when you are short options. Having sold options contracts you may have an obligation to sell (short Call) or buy ...