

Literary Devices & Figures of Speech 101 (+ PDF)
FIGURES OF SPEECH AND OTHER LITERARY TERMS
This post contains hundreds of literary devices, figures of speech and other literary terms.
Are literary devices the same as figures of speech? The simple answer is yes and no. These two terms are similar and different at the same time. Here is a post that explains in detail the differences and similarities between a figure of speech and a literary device.
Figures of Speech or Literary devices refer to the use of language in ways that are unusual or unique.
These expressions are different from the way we ordinarily use language.
A: Ordinary Usage:
I fell asleep at 10:00 pm.
B: Special/Unusual:
Sleep visited me at 10:00 pm.
‘B’ therefore contains a figure of speech. Can you name it? It is called Personification.
Speakers and writers use figures of speech or literary devices to make the ideas they want to put across more striking and effective.
Definitions and Examples of Literary Devices
Now you can go through a collection of some of the most popular literary devices and figures of speech that you will encounter in most Literature tests for high school students.
For each literary device or figure of speech, you will find a brief definition followed by a few examples.
The list also contains examples and illustrations of less-known literary devices and figures of speech in English Literature. By the time you finish reading this post, you will be able to download your free PDF copy for offline use at any time.
Finally, remember that this collection is a mixture of both literary devices and figures of speech. There is more to learn about these two terms in this tutorial.
1. Metaphor
DEFINITION: A metaphor is a figure of speech in which a direct comparison is made between two unlike things without the use of ‘like’ or ‘as’
EXAMPLES 1: Stony eyes. 2. The memory of my blood
3. The necklaces of laughter 4. Beyond the snow of yesterday
5. Days sparkling with ever-new joys
S etting is the place, time or atmosphere within which a story or play occurs.
Example: One major setting of Second Class Citizen, a novel by Buchi Emecheta is Lagos in Nigeria.
P lot refers to the sequence of causes and effects of events in a novel or play.
Top 5 Parts of Narrative Structure
IRONY (VERBAL IRONY) : An irony occurs when there is a difference between what is said and what is meant. Example: 1. My enemies shall continue to prosper.
Definition: A ballad is a poem that tells a story of adventure, of romance, or a hero. It is suitable for singing and usually has stanzas of four lines with a rhyme on the second and fourth lines.
The owl and the cat went to sea
In a beautiful pea-green boat
They took some honey and plenty of money
Wrapped in a five-pound note
The owl looked up to the stars above,
And sang to a small guitar
“O lovely cat! O cat my love
What a beautiful Cat you are
You are You are
What a beautiful Cat you are!”
A satire is a literary work which reveals, ridicules and criticizes bad things in society to reform it for the better.
i. A Man of the People by Chinua Achebe
ii. The Beautiful Ones are Not Yet Born by Ayi Kwei Armah
iii. Animal Farm by George Orwell
iv. Money Galore by Amu Djoleto
v. Anthills of the Savannah by Chinua Achebe
RHYTHM: Rhythm is the musical movement of the lines of poetry found in its metre, stress pattern, punctuation and rhyme.
SONNET: Sonnet poem of fourteen lines usually with a predetermined rhyme scheme of abab, cdcd, efef, and gg. The first eight lines of a Sonnet are called Octave and the last six lines, Sestet . Where the last two lines rhyme, they are called a Couplet.
9. Didactic Literature
DIDACTIC LITERATURE: Didactic Literature refers to any work of art that teaches a moral lesson.
10. Alliteration
ALLITERATION: Alliteration is the repetition of similar initial consonants in a work of art.
i. The cane cracked on the caked khaki.
ii. Stand silent
iii. Bitter bile
iv. Drawn drips
11. Epilogue
EPILOGUE: Epilogue is the final statement (coming at the end) in a work of art.
12. Prologue
PROLOGUE: A prologue is an introductory statement (coming at the beginning) in a work of art. In drama, the prologue is usually played by a CHORUS.
13. Romance
ROMANCE: A romance is a work of art filled with intense feelings of excitement, intrigue and suspense.
Example: Don Quixote by Miguel de Cervantes
14. Comic Relief
COMIC RELIEF: Comic relief refers to a point of humour in a tragedy.
15. Conflict
CONFLICT: Conflict in Literature refers to the struggle between opposing forces in a work of art. Conflict is an important ingredient in any piece of good literature.
16. Poetic Justice
POETIC JUSTICE: In Literature, poetic justice occurs when bad or evil is punished and good triumphs (is rewarded).
17. Oxymoron
OXYMORON: Oxymoron refers to the use of two usually opposite terms, close to each other in a brief expression.
i. Most foul, most fair
ii. Pure impiety
iii. Impious purity
iv. Friendly enemy
v. Bittersweet
vi. Harmless lion
vii. Pregnant virgin
33 Examples of Oxymoron in Literature
18. Kinesthetic Imagery
KINESTHETIC IMAGERY: Imagery depicting movement or action.
Example: i. The water crawled feebly into the next hole
ii. She grabbed it with the speed of lightning.
19. Auditory Imagery
AUDITORY IMAGERY: Imagery associated with hearing.
Example: i. They booed us every time we performed
ii. There was a loud silence in the room.
20. Visual Imagery
VISUAL IMAGERY: Imagery appealing to the reader’s or listener’s sense of sight.
21. Tactile Imagery
TACTILE IMAGERY: Tactile imagery is the type of imagery that appeals to our sense of touch .
i. This kind of news can only pierce a man’s heart like a spear.
ii. A loaf of bread can turn into hardwood if not preserved properly.
22. Olfactory Imagery
OLFACTORY IMAGERY: Imagery evoking the reader’s sense of smell.
i. Her beauty filled the room like the fragrance of French lavender.
ii. An offensive stench punched him in the face when he opened the second door.
Top 6 Types of Imagery in Literature
EPIC: An epic is a long narrative poem recounting the great deeds of heroic or supernatural figures from history.
24. Tragic Flaw
TRAGIC FLAW (HARMATIA): The weakness or failing in an otherwise great character which causes their downfall.
25. Reversal
REVERSAL: A reversal in Literature refers to a change in the fortunes of a tragic hero from happiness to sadness.
26. Hyperbole
HYPERBOLE: A hyperbole is an exaggerated statement or an overstatement.
1. At his birth, the earth stood still.
2. Everyone in the country watched the national team play Brazil in the finals.
27. Litotes
LITOTES: Litotes is a literary device in which a point is made in the affirmative by using two negative terms. Another term for Litotes is an understatement
i. It is not uncommon for people to consider facts strange.
ii. I am a member of no unimportant family
28. Euphemism
EUPHEMISM: Euphemism refers to the use of a polite, milder or less direct word or expression to refer to something unpleasant, painful or taboo.
i. Senior citizen FOR Very Old Person
ii. Pass away FOR: Die
29. Synecdoche
SYNECDOCHE: Speaking of a whole by using just a part of it to represent it. (Part to represent a whole). Synecdoche is mostly used with parts of the human body.
Example: i. All hands on deck (Everybody must work).
ii. She has many mouths to feed (many people)
30. Metonymy
METONYMY: Speaking of something by using the name of something closely associated with it. (Usually objects)
i. The crown = The king/queen or monarch
ii. The bottle = Alcoholic beverages
ii. The rod = Punishment or discipline
iv. The law = Police or Justice system
FARCE: A farce in Literature is an extremely funny, hilarious play with elements of absurdity or abnormality
32. Burlesque
BURLESQUE is another term used to describe such farcical plays especially when they are intended to satirize or ridicule other more serious literary works.
33. Revellers
REVELLERS: Revellers in Literature refers to a group of unruly, usually drunk characters engaged in acts of immorality and extreme joy.
34. Alternate Rhyme
ALTERNATE RHYME is a rhyming pattern (scheme) with the first line rhyming with the third, the second with the fourth etc. i.e. abab, cdcd and so on.
Those who live through pain
And have their blood shed
Shall have so much gain
When their victories are read.
35. Secondary Text
SECONDARY TEXT: The part of a play usually written in italics or parentheses and directing the actions of characters or describing the setting.
36. Fiction
FICTION is an imaginary long narrative story. It is also called PROSE or NOVEL.
i. Faceless
ii. The Lord of the Rings
iii. The Great Gatsby
iv. Second Class Citizen
v. Invisible Man
vi. Native Son
37. Autobiography
AUTOBIOGRAPHY: A life story written by the person himself and usually in the first-person narrative voice.
38. Biography
BIOGRAPHY: The life story of a person written by another person.
39. Tragic Hero
TRAGIC HERO: The main character in a tragedy. He is usually a person of a high social status who uses lofty, poetic language but has a human failing (tragic flaw).
40. Syllable
SYLLABLE: A syllable is a linguistic unit on which stress is placed (or not placed) in poetry and other forms of expression.
Example: today (2 syllables) “to” is unstressed and “day” is stressed.
- FOOT: A metrical unit in poetry. It may consist of one stressed and one unstressed syllable, two stressed and one unstressed syllable etc
Example: I vow\ to thee\ my country = 3 feet
- PARODY: An exaggerated imitation, which ridicules another work in a harsh manner.
- PERSONA: The speaking voice in a poem. Usually, the persona is considered as distinct from the poet\writer.
- ROUND CHARACTER: A character who changes and develops as the story progresses. He or she is also called a multi-dimensional character.
- FLAT CHARACTER: A character who does not change or develop much in a story. – a mono-dimensional character. Such a character may also be referred to a stereotype.
- SIMILE: It is comparison between two things or persons that are similar in one point and otherwise dissimilar. It is usually introduced by such words as ‘like’, ‘as’, ‘so’, e.g.
- “A room without books is like a body without a soul”
- “Great men stand like a solitary tower
- “Baaba ran as fast as a horse in the race.
- MIXED METAPHOR/CONFUSED METAPHOR: Two or more different metaphors used in the same sentence with reference to the same subject. e.g. He was fishing for his heart and a long search reached his goal.
- ANTITHESIS: This results when opposites or contrasts are employed in the same sentence usually to emphasize a point.
- Man proposes, God disposes
- Speech is silver but silence is Gold
- They speak like saints and act like devils.
- PARADOX: It is a statement, which seems absurd at first sight and yet proves to be true on second thought. Example
- The child is the father of the man
- Cowards die many times before their death
- The greeter the fool, the better the dancer.
- ANTI-CLIMAX OR BATHOS: It is the opposite of climax consisting in a descent from a higher level to lesser heights, the intensity or importance weakening instead of increasing toward the end e.g. He lost his wife, his child, his household, goods and his dog at one swoop of fate”
- TRANSFERRED EPITHET: An epithet sometimes transferred from its proper words, to another that is closely associated with it. In the sentence the qualifying adjective is transferred from a person to things e.g.
- The ploughman homeward ploughs his weary way
- He lay all night on a sleepless pillow
- PUN OR PARONOMASIA: The use of words of the same sound with different meaning for the sake of humour.
Sample WASSCE English Summary Answers
Nov/Dec WASSCE Registration Fees and Facts
Dreamers often lie
Yes, they lie in bed as they dream
ECHOISM/ONOMATOPOEIA: It is the use of words whose sounds naturally suggest their meaning. e.g.
I bring fresh showers for the thirsty flowers
The arrow whizzed through the air
ALLITERATION/CONSONANCE: It is the repetition of the same initial consonant in several words near one another e.g.
Full fathom five their father lies
After life, fitful fever he sleeps well
Peter piper picked a peck of pickle pepper
INVERSION: It is a change in the natural or usual order of words for the sake of effect or emphasis. Compare the two statements below:
“I will go to Akatsi tomorrow”
To Akatsi tomorrow will I go (inversion)
- SETTING: It refers to the place (location) where an actions and events in the story come. It is the sequence of events in a play or Novel.
- IAMBUS (LIMBIC METRE): One unstressed syllable followed by a stressed one in poetry.
Example: – / – / – / –
- I vow to thee my country
- To you we owe the sea
- THEME: The underlying message in a work of art. Love, hate, materialism, corruption, politics, etc
Example: Chume: Forgive us all
Congregation: Amen
Chume: Forgive us all
(And the, punctuated regularly with Amens)
Yes Father, make you forgive us all. Make you save us from palaver.
Save us from trouble at home. Tell our wives not to give us trouble …..
(The penitent has become placid. She is stretched out flat on the ground)
… Give us money to satisfy our daily necessities. Make you no forget those of
us who dey struggle daily. Those who be clerk today, make them chief clerk tomorrow. Those who are messengers today, make them senior service tomorrow …….
(The Amens grew more and more ecstatic)
Those who are petty trader today, make them big contractor tomorrow. Those who dey sweep street today, give them their own big office tomorrow. It we de walka today, give us our own bicycle tomorrow. I say those who dey walka today, give them their own bicycle tomorrow. Those who have bicycle today, they will ride their own car tomorrow.
(The enthusiasm of the response becomes, at this point quite overpowering) I say those who day push bicycle; give them big car big car tomorrow. Give them big car tomorrow. Give them big car tomorrow, give them big car tomorrow.
One theme of this extract is materialism .
“My people, I have been somewhere
If I turn here, the rain beats me
If I turn there the sun burns me
The firewood of this world
Is for only those who can take heart
That is why not all can gather it ……”
The theme of this extract is suffering
- SOLILOQUY: A character’s speech to himself, which reveals his motives, and state of mind.
- PERSONIFICATION (PROSOPOPEIA): giving human attributes or characteristics to inanimate, lifeless objects or animals or abstract ideas.
- Cruel wishes entered him, departed and entered again
- The sun rose from his bed
- The engine coughed twice
- PASTORAL POETRY: It is about simple, rural life (life in the countryside) especially of shepherds.
Example: “Michael” by William Wordsworth
- SUSPENSE: When a reader is kept in a state of high expectancy, eager to know what will happen next.
Example: In English, my name means hope. In Spanish, it means too many letters. It means sadness, it means waiting. It is like the number nine. A muddy color. It is the Mexican records my father plays on Sunday mornings when his shaving, songs like sobbing.
By delaying the disclosure of the narrator’s name, the writer has used the literary technique known as suspense
- ALLUSION: The reference to issues that re outside the literary work being studied.
Example: A Daniel has come into judgment i.e. Biblical Allusion by Shylock in The MERCHANT OF VENICE by William Shakespeare.
- CLIMAX: The crisis stage in a series of events in a story or play.
- APOSTROPHE: An address to an imaginary person or object as if they were present, usually in poetry.
Example: You my ancestors, come to my aid
- ELEGY: Poetry meant to praise somebody or something.
- DIRGE: A song meant for mourning the dead.
- TRAGEDY: A play in which there occurs a sudden change (reversal) in the hero’s fortunes from happiness to disaster. It ends sadly
Example: Shakespeare’s Hamlet, King Lear, Macbeth and Romeo and Juliet, The Gods Are Not To Blame By Ola Rotimi.
- COMEDY: A play whose characters are usually low or middle class citizens, bringing out their follies and weaknesses in an amusing but educative manner.
Example: Our Husband Has Gone Mad Again by Ola Rotimi And The Trials Of Brother Jero.
- MIME: acting without speech but demonstrating with gesture, bodily movement and facial expression.
- MIMICRY: imitating gestures, speech of others especially in drama.
- ASSONANCE: A type of rhyme pattern in which there is repetition of similar middle vowels.
Example: i. Your name remains in frames of gold
ii. Tall walls fall mightily
- RHYME: sameness of sounds especially in the last syllable of words in line endings of poetry Example: time/clime keep/reap
- STANZA: A division of a poem of song.
- CHAPTER: major division of prose.
- PARAGRAPH: A sub-division of chapter.
- FREE VERSE: A poem of irregular and unpredictable line – lengths.
Example: A plea for Mercy by Kwesi Brew.
- BLANK VERSE: Unrhymed five-foot iambic poetry
- HEROIC COUPLETS: Successive five –foot iambic lines rhyming in pairs
- ASIDE: A statement made by an actor on stage but not meant to be heard by the other actors but which may be heard by the audience.
- EPITAPH: An inscription on a tombstone
Example: Your Life Was A blessing To Us
- POLY-SYLLABIC WORD: A word containing only one syllable.
Example: argument, examination.
- MONO-SYLLABIC WORD: A word containing only one syllable.
go, bed, sun
- POINT OF VIEW: The angle from which the narrator sees and narrates events.
- FIRST PERSON NARRATOR: A person who narrates a story in which he takes an active part. He uses the pronoun, “I” a lot. He may be biased and subjective.
- THIRD PERSON (OMNISCIENT) NARRATOR: A narrator who is not part of the story but narrates as an outsider. He uses the third person pronouns – He, She, It, They.
- SECOND PERSON NARRATOR: The narrator who uses the second person pronouns and appears to be addressing the reader directly i.e. “You”.
- EPISODE: An important event or incident in a literary work.
Example: The Outbreak of an epidemic in the Gods Are Not To Blame.
- ORAL LITERATURE: unwritten literature (i) involving the active participation of the performance and the audient (ii) which is communally owned (iii) which tells much about the history and culture of the people (iv) influenced by the environment of the people.
Example: Myth, proverbs, praise songs, dirge, riddles, war songs, folktales, fables.
- PRIMAL MYTH: A piece of oral literature which tells a story about how the world was created.
- DRAMA: A piece of literature meant to be performed. Its key elements include (i) imitation or impersonation (ii) disguise (iii) dance (iv) mime (v) dialogue
Example: The Gods Are Not To Blame, As You Like It, THE TRIALS OF BROTHER JERO, ROMEO AND JULIET, THE MARRIAGE OF ANANSEWA.
- ATTITUDE: The feeling of a writer or one character towards a character. Words used to describe attitude include;
- Positive Attitude: Admiration, like, approval, sympathy
- Negative Attitude: disgust, contempt, disapproval, unsympathetic, dislike
Msimangu opened the book, and read to them first from the book. And Kumalo had not known that his friend had such a voice. For the voice was of gold, and the voice had such love for the words it was reading. The voice shook and beat and trembled, not as the voice of an old man shakes and beats and trembles, or as a leaf shakes and eats and trembles but as a deep bell when it is struck. For it was not only a voice of gold but it was the voice of a man whose heart was golden, reading from a book of golden words.
( Alan Patton – Cry The Beloved Country P 78 )
Kumalo’s attitude towards Msimagu is one of admiration.
- CONTRAST: Presenting two opposing sides of an issues in order to emphasize a point about one side.
- FABLE: A story involving animal characters. Example: The Tortoise and the Birds.
- LANGUAGE OR DICTION: The kind of words and sentence construction (syntax) used in a work of art. It could be: formal or pedantic, archaic or old fashioned, humorous or funny, simple, complex, informal.
- ONOMATOPOEIA: Use of words whose sounds echo their meaning.
Example: i. The bomb boomed
ii. Tooting of horns.
iii. The bells are tolling
iv. Bells are chiming
- ELEMENTS IN THE PLOT OF TRAGEDY: Conflict, reversal, denouement.
- ELEMENTS OF COMEDY: Caricature, humour, wit, parody, absurdity
- NEGRITUDE: Literature, especially poetry meant to celebrate Africa and its black people. Its main proponent is Leopold Sedar Senghor. Example: i) Long long have you held (ii) Black woman (iii) I will pronounce your name, Naett.
- EPITHET: The use of descriptive words especially when added to names, titles etc.
Example: i. Sango, the thunder lion
More Literary Devices and Figures of Speech
Click the NEXT PAGE button below to see a lot more literary devices and figures of speech.
SHARE THIS POST

Recommended

The Grieved Lands of Africa Quiz: Objective Test Questions and Answers

Caged Bird Questions and Answers (Multiple Choice)

Bat Poem Questions and Answers (D.H. Lawrence)

Solutions to Environmental Pollution Essay Example

Causes of Environmental Pollution Essay Example

Effects of Environmental Pollution Essay Example

30 Examples of Sentences that Omit ‘that’

Reading Comprehension Practice Online

WAEC Poetry Analysis Notes for Senior High Schools

Figures of Speech vs Literary Devices: What’s The Difference?

WAEC Lexis and Structure Part 4: Past Questions and Answers

4 Types of Sentence Structure with Examples (Plus Definition)
4 thoughts on “literary devices & figures of speech 101 (+ pdf)”.
You are doing a great job. Keep the flag flying sir. I’m a literature teacher and I want to know whether my students are to read all the prescribed literature texts or not. Actually, what I’ve been doing is ensure they read texts based on each of the genres both African and Non-African. So I want to know if that works for the poetry or they have to read all of the prescribed poetry. Thanks.
Hi Fatima. Thanks for reaching out. Yes, for the poetry section, students/candidates must study all the 12 prescribed poems. Six for African poetry and another six for non-African poetry. When it comes to prose and drama, only one text should be selected out of the two options in each case. Here is the breakdown. African Drama – one text Non-African Drama – one text African Prose – one text Non-African Prose – one text. So in all, they will be reading four books apart from the twelve poems. Please remember that there is an additional Shakespeare drama text. It is compulsory for the objective test paper. Please let me know if you need any additional information.
You are doing a great job, sir. I’m a new literature teacher in highschool and I have beneficted a great deal from your tentalizing works. We are solidly behind you, and may the almighty Allah continue to bless you with more wisdom.
I’m glad you liked this site, Robert. Thank you.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Get Dependable High School General Arts Textbooks
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

100 Literary Devices and Figures of Speech

Writers of poetry and prose use all sorts of devices to add both meaning and texture to their works. This paper collects, defines, and gives examples of a hundred of such devices. It is, for the most part, not original work. Rather it is a quick reference drawn from other sources. Freely available websites such as those noted in the References contain much more detailed definitions and examples. This paper draws heavily on these resources. The purpose of this paper is to make available to writers – and readers – a summary of just a hundred terms in one place. The items in boldface are listed in alphabetical order with definitions in Roman font and examples and further descriptions in Italics.
Related Papers
DaviD chesney
Brihintha Burggee
Daniel Yittrium
Asst.Prof. Ibrahim Talaat Ibrahim Ph.D.
Tracy Jamison Wood
The Polish Journal of Aesthetics
Lorraine Yeung
This paper investigates the emotional import of literary devices deployed in fiction. Reflecting on the often-favored approach in the analytic tradition that locates fictional characters, events, and narratives as sources of readers' emotions, I attempt to broaden the scope of analysis by accounting for how literary devices trigger non-cognitive emotions. I argue that giving more expansive consideration to literary devices by which authors present content facilitates a better understanding of how fiction engages emotion. In doing so, I also explore the somatic dimension of reading fiction.
BUXORO DAVLAT UNIVERSITETI ILMI AXBOROTI
Javid S A B I R Babayev
: The article elaborates joint stylistic devices existing within an example. Figures of speech may be analyzed and found along the sentence from different aspects. It depends on what prism we approach the matter. Several figures of speech might coexist in an example even when we are unaware of their presence in most cases. As we know, a language is composed of different linguistic units which are included in lexicology, grammar, phonetics, onomastics, phraseology, etc. Some language units may jointly emerge in one example. The article reveals that metaphor, dysphemism, antonomasia, as well as antanaclasis, homographs, homophones, pun may coexist in one sentence. Besides, stylistic opportunities of homonyms have been analyzed in the article. Difference between antanaclasis and tongue-twisters has been scrutinized and some obscure details have been determined in the article. Another focus is on the stylistic opportunities of onomastics. The terms of‖pars pro toto‖ and ―totum pro parte‖ are the figures of speech which can be the constituents of onomastics, particularly place names. The article concludes that several figures of speech may easily be found in one example. So it occurs when different views, characteristic features and prisms overlap in one so-called example.
Australian Great War Poetry
Dr Dominic Sheridan
The following supplementary is designed to be a small and quick guide to reading and writing poetry from a purely technical point of view. The artistry we will leave to the poet, but the poetic terms, tools and devices, are all things we should be more aware of when considering poetry critically. Without at least some working knowledge of these things, we will read poetry as though blind, hear poetry as though deaf and create poetry as though dumb. Like any language, if we disregard the grammar, we soon lose structure which will in turn inhibit or destroy meaning.
Acta Linguistica Hafniensia
Peer Bundgaard
Language and Literature
yeshayahu shen
RELATED PAPERS
London 2013, 75th eage conference en exhibition incorporating SPE Europec
Alexander Kitchka
María Ángeles Naval
Impactul antropic asupra calitatii mediului
Liliana Motelica
ABM Proceedings
Herbert Silveira
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
GEETA A/P APPANNAH / MEDIC
Bali Medical Journal
Sofyan Harahap
Revista Arquivos Científicos (IMMES)
Georgianna Santos
Aline Antoneli
Otology Japan
Pierre-Paul Vidal
Computers in Biology and Medicine
Julio Facelli
juana estrada
Rashmi panda
BMC genomics
Lori Schwacke
oladipo dare-abel
OncoTargets and therapy
IJoHVE: Indonesian Journal of Health Vocational Education
Meli mel Diana
Journal of Dairy Science
Joe Hillers
Proceedings of the 3rd annual conference on Systems, programming, and applications: software for humanity
Hoàn Nguyễn
Journal of Hepatology
Juergen MOLL
Journal of Psychology and Theology
Mark Newmeyer
Veterinary Microbiology
Harry W Dickerson
JELIKU (Jurnal Elektronik Ilmu Komputer Udayana)
Afterschool Matters
Barbara Means
Melissa Parker
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Literary Devices & Terms
An acrostic is a piece of writing in which a particular set of letters—typically the first letter of each line, word, or paragraph—spells out a word or phrase with special significance to the text. Acrostics... (read full acrostic explanation with examples) An acrostic is a piece of writing in which a particular set of letters—typically the first letter of each line,... (read more)
An allegory is a work that conveys a hidden meaning—usually moral, spiritual, or political—through the use of symbolic characters and events. The story of "The Tortoise and The Hare" is a well-known allegory with a... (read full allegory explanation with examples) An allegory is a work that conveys a hidden meaning—usually moral, spiritual, or political—through the use of symbolic characters and... (read more)
Alliteration is a figure of speech in which the same sound repeats in a group of words, such as the “b” sound in: “Bob brought the box of bricks to the basement.” The repeating sound... (read full alliteration explanation with examples) Alliteration is a figure of speech in which the same sound repeats in a group of words, such as the... (read more)
In literature, an allusion is an unexplained reference to someone or something outside of the text. Writers commonly allude to other literary works, famous individuals, historical events, or philosophical ideas, and they do so in... (read full allusion explanation with examples) In literature, an allusion is an unexplained reference to someone or something outside of the text. Writers commonly allude to... (read more)
An anachronism is a person or a thing placed in the wrong time period. For instance, if a novel set in Medieval England featured a trip to a movie-theater, that would be an anachronism. Although... (read full anachronism explanation with examples) An anachronism is a person or a thing placed in the wrong time period. For instance, if a novel set... (read more)
Anadiplosis is a figure of speech in which a word or group of words located at the end of one clause or sentence is repeated at or near the beginning of the following clause or... (read full anadiplosis explanation with examples) Anadiplosis is a figure of speech in which a word or group of words located at the end of one... (read more)
An analogy is a comparison that aims to explain a thing or idea by likening it to something else. For example, a career coach might say, "Being the successful boss or CEO of a company... (read full analogy explanation with examples) An analogy is a comparison that aims to explain a thing or idea by likening it to something else. For... (read more)
An anapest is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which two unstressed syllables are followed by a stressed syllable. The word "understand" is an anapest, with the unstressed syllables of "un" and "der" followed... (read full anapest explanation with examples) An anapest is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which two unstressed syllables are followed by a stressed syllable.... (read more)
Anaphora is a figure of speech in which words repeat at the beginning of successive clauses, phrases, or sentences. For example, Martin Luther King's famous "I Have a Dream" speech contains anaphora: "So let freedom... (read full anaphora explanation with examples) Anaphora is a figure of speech in which words repeat at the beginning of successive clauses, phrases, or sentences. For... (read more)
An antagonist is usually a character who opposes the protagonist (or main character) of a story, but the antagonist can also be a group of characters, institution, or force against which the protagonist must contend.... (read full antagonist explanation with examples) An antagonist is usually a character who opposes the protagonist (or main character) of a story, but the antagonist can... (read more)
Antanaclasis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated within a sentence, but the word or phrase means something different each time it appears. A famous example of antanaclasis is... (read full antanaclasis explanation with examples) Antanaclasis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated within a sentence, but the word... (read more)
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human characteristics, emotions, and behaviors to animals or other non-human things (including objects, plants, and supernatural beings). Some famous examples of anthropomorphism include Winnie the Pooh, the Little Engine that Could, and Simba from... (read full anthropomorphism explanation with examples) Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human characteristics, emotions, and behaviors to animals or other non-human things (including objects, plants, and supernatural beings). Some famous... (read more)
Antimetabole is a figure of speech in which a phrase is repeated, but with the order of words reversed. John F. Kennedy's words, "Ask not what your country can do for you, ask what you... (read full antimetabole explanation with examples) Antimetabole is a figure of speech in which a phrase is repeated, but with the order of words reversed. John... (read more)
Antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, usually within parallel grammatical structures. For instance, Neil Armstrong used antithesis when he stepped onto the surface of the moon in 1969... (read full antithesis explanation with examples) Antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, usually within parallel grammatical structures. For instance,... (read more)
An aphorism is a saying that concisely expresses a moral principle or an observation about the world, presenting it as a general or universal truth. The Rolling Stones are responsible for penning one of the... (read full aphorism explanation with examples) An aphorism is a saying that concisely expresses a moral principle or an observation about the world, presenting it as... (read more)
Aphorismus is a type of figure of speech that calls into question the way a word is used. Aphorismus is used not to question the meaning of a word, but whether it is actually appropriate... (read full aphorismus explanation with examples) Aphorismus is a type of figure of speech that calls into question the way a word is used. Aphorismus is... (read more)
Aporia is a rhetorical device in which a speaker expresses uncertainty or doubt—often pretended uncertainty or doubt—about something, usually as a way of proving a point. An example of aporia is the famous Elizabeth Barrett... (read full aporia explanation with examples) Aporia is a rhetorical device in which a speaker expresses uncertainty or doubt—often pretended uncertainty or doubt—about something, usually as... (read more)
Apostrophe is a figure of speech in which a speaker directly addresses someone (or something) that is not present or cannot respond in reality. The entity being addressed can be an absent, dead, or imaginary... (read full apostrophe explanation with examples) Apostrophe is a figure of speech in which a speaker directly addresses someone (or something) that is not present or... (read more)
Assonance is a figure of speech in which the same vowel sound repeats within a group of words. An example of assonance is: "Who gave Newt and Scooter the blue tuna? It was too soon!" (read full assonance explanation with examples) Assonance is a figure of speech in which the same vowel sound repeats within a group of words. An example... (read more)
An asyndeton (sometimes called asyndetism) is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and", "or", and "but" that join other words or clauses in a sentence into relationships of equal importance—are omitted.... (read full asyndeton explanation with examples) An asyndeton (sometimes called asyndetism) is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and", "or", and "but"... (read more)
A ballad is a type of poem that tells a story and was traditionally set to music. English language ballads are typically composed of four-line stanzas that follow an ABCB rhyme scheme. (read full ballad explanation with examples) A ballad is a type of poem that tells a story and was traditionally set to music. English language ballads... (read more)
A ballade is a form of lyric poetry that originated in medieval France. Ballades follow a strict rhyme scheme ("ababbcbc"), and typically have three eight-line stanzas followed by a shorter four-line stanza called an envoi.... (read full ballade explanation with examples) A ballade is a form of lyric poetry that originated in medieval France. Ballades follow a strict rhyme scheme ("ababbcbc"),... (read more)
Bildungsroman is a genre of novel that shows a young protagonist's journey from childhood to adulthood (or immaturity to maturity), with a focus on the trials and misfortunes that affect the character's growth. (read full bildungsroman explanation with examples) Bildungsroman is a genre of novel that shows a young protagonist's journey from childhood to adulthood (or immaturity to maturity),... (read more)
Blank verse is the name given to poetry that lacks rhymes but does follow a specific meter—a meter that is almost always iambic pentameter. Blank verse was particularly popular in English poetry written between the... (read full blank verse explanation with examples) Blank verse is the name given to poetry that lacks rhymes but does follow a specific meter—a meter that is... (read more)
A cacophony is a combination of words that sound harsh or unpleasant together, usually because they pack a lot of percussive or "explosive" consonants (like T, P, or K) into relatively little space. For instance, the... (read full cacophony explanation with examples) A cacophony is a combination of words that sound harsh or unpleasant together, usually because they pack a lot of... (read more)
A caesura is a pause that occurs within a line of poetry, usually marked by some form of punctuation such as a period, comma, ellipsis, or dash. A caesura doesn't have to be placed in... (read full caesura explanation with examples) A caesura is a pause that occurs within a line of poetry, usually marked by some form of punctuation such... (read more)
Catharsis is the process of releasing strong or pent-up emotions through art. Aristotle coined the term catharsis—which comes from the Greek kathairein meaning "to cleanse or purge"—to describe the release of emotional tension that he... (read full catharsis explanation with examples) Catharsis is the process of releasing strong or pent-up emotions through art. Aristotle coined the term catharsis—which comes from the... (read more)
Characterization is the representation of the traits, motives, and psychology of a character in a narrative. Characterization may occur through direct description, in which the character's qualities are described by a narrator, another character, or... (read full characterization explanation with examples) Characterization is the representation of the traits, motives, and psychology of a character in a narrative. Characterization may occur through... (read more)
Chiasmus is a figure of speech in which the grammar of one phrase is inverted in the following phrase, such that two key concepts from the original phrase reappear in the second phrase in inverted... (read full chiasmus explanation with examples) Chiasmus is a figure of speech in which the grammar of one phrase is inverted in the following phrase, such... (read more)
The word cinquain can refer to two different things. Historically, it referred to any stanza of five lines written in any type of verse. More recently, cinquain has come to refer to particular types of... (read full cinquain explanation with examples) The word cinquain can refer to two different things. Historically, it referred to any stanza of five lines written in... (read more)
A cliché is a phrase that, due to overuse, is seen as lacking in substance or originality. For example, telling a heartbroken friend that there are "Plenty of fish in the sea" is such a... (read full cliché explanation with examples) A cliché is a phrase that, due to overuse, is seen as lacking in substance or originality. For example, telling... (read more)
Climax is a figure of speech in which successive words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are arranged in ascending order of importance, as in "Look! Up in the sky! It's a bird! It's a plane! It's... (read full climax (figure of speech) explanation with examples) Climax is a figure of speech in which successive words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are arranged in ascending order of... (read more)
The climax of a plot is the story's central turning point—the moment of peak tension or conflict—which all the preceding plot developments have been leading up to. In a traditional "good vs. evil" story (like many superhero movies)... (read full climax (plot) explanation with examples) The climax of a plot is the story's central turning point—the moment of peak tension or conflict—which all the preceding plot... (read more)
Colloquialism is the use of informal words or phrases in writing or speech. Colloquialisms are usually defined in geographical terms, meaning that they are often defined by their use within a dialect, a regionally-defined variant... (read full colloquialism explanation with examples) Colloquialism is the use of informal words or phrases in writing or speech. Colloquialisms are usually defined in geographical terms,... (read more)
Common meter is a specific type of meter that is often used in lyric poetry. Common meter has two key traits: it alternates between lines of eight syllables and lines of six syllables, and it... (read full common meter explanation with examples) Common meter is a specific type of meter that is often used in lyric poetry. Common meter has two key... (read more)
A conceit is a fanciful metaphor, especially a highly elaborate or extended metaphor in which an unlikely, far-fetched, or strained comparison is made between two things. A famous example comes from John Donne's poem, "A... (read full conceit explanation with examples) A conceit is a fanciful metaphor, especially a highly elaborate or extended metaphor in which an unlikely, far-fetched, or strained... (read more)
Connotation is the array of emotions and ideas suggested by a word in addition to its dictionary definition. Most words carry meanings, impressions, or associations apart from or beyond their literal meaning. For example, the... (read full connotation explanation with examples) Connotation is the array of emotions and ideas suggested by a word in addition to its dictionary definition. Most words... (read more)
Consonance is a figure of speech in which the same consonant sound repeats within a group of words. An example of consonance is: "Traffic figures, on July Fourth, to be tough." (read full consonance explanation with examples) Consonance is a figure of speech in which the same consonant sound repeats within a group of words. An example... (read more)
A couplet is a unit of two lines of poetry, especially lines that use the same or similar meter, form a rhyme, or are separated from other lines by a double line break. (read full couplet explanation with examples) A couplet is a unit of two lines of poetry, especially lines that use the same or similar meter, form... (read more)
A dactyl is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by two unstressed syllables. The word “poetry” itself is a great example of a dactyl, with the stressed syllable... (read full dactyl explanation with examples) A dactyl is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by two unstressed syllables.... (read more)
Denotation is the literal meaning, or "dictionary definition," of a word. Denotation is defined in contrast to connotation, which is the array of emotions and ideas suggested by a word in addition to its dictionary... (read full denotation explanation with examples) Denotation is the literal meaning, or "dictionary definition," of a word. Denotation is defined in contrast to connotation, which is... (read more)
The dénouement is the final section of a story's plot, in which loose ends are tied up, lingering questions are answered, and a sense of resolution is achieved. The shortest and most well known dénouement, it could be... (read full dénouement explanation with examples) The dénouement is the final section of a story's plot, in which loose ends are tied up, lingering questions are answered, and... (read more)
A deus ex machina is a plot device whereby an unsolvable conflict or point of tension is suddenly resolved by the unexpected appearance of an implausible character, object, action, ability, or event. For example, if... (read full deus ex machina explanation with examples) A deus ex machina is a plot device whereby an unsolvable conflict or point of tension is suddenly resolved by... (read more)
Diacope is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated with a small number of intervening words. The first line of Anna Karenina by Leo Tolstoy, "Happy families are all alike;... (read full diacope explanation with examples) Diacope is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated with a small number of intervening... (read more)
Dialogue is the exchange of spoken words between two or more characters in a book, play, or other written work. In prose writing, lines of dialogue are typically identified by the use of quotation marks... (read full dialogue explanation with examples) Dialogue is the exchange of spoken words between two or more characters in a book, play, or other written work.... (read more)
Diction is a writer's unique style of expression, especially his or her choice and arrangement of words. A writer's vocabulary, use of language to produce a specific tone or atmosphere, and ability to communicate clearly... (read full diction explanation with examples) Diction is a writer's unique style of expression, especially his or her choice and arrangement of words. A writer's vocabulary,... (read more)
Dramatic irony is a plot device often used in theater, literature, film, and television to highlight the difference between a character's understanding of a given situation, and that of the audience. More specifically, in dramatic... (read full dramatic irony explanation with examples) Dramatic irony is a plot device often used in theater, literature, film, and television to highlight the difference between a... (read more)
A dynamic character undergoes substantial internal changes as a result of one or more plot developments. The dynamic character's change can be extreme or subtle, as long as his or her development is important to... (read full dynamic character explanation with examples) A dynamic character undergoes substantial internal changes as a result of one or more plot developments. The dynamic character's change... (read more)
An elegy is a poem of serious reflection, especially one mourning the loss of someone who died. Elegies are defined by their subject matter, and don't have to follow any specific form in terms of... (read full elegy explanation with examples) An elegy is a poem of serious reflection, especially one mourning the loss of someone who died. Elegies are defined... (read more)
End rhyme refers to rhymes that occur in the final words of lines of poetry. For instance, these lines from Dorothy Parker's poem "Interview" use end rhyme: "The ladies men admire, I’ve heard, / Would shudder... (read full end rhyme explanation with examples) End rhyme refers to rhymes that occur in the final words of lines of poetry. For instance, these lines from... (read more)
An end-stopped line is a line of poetry in which a sentence or phrase comes to a conclusion at the end of the line. For example, the poet C.P. Cavafy uses end-stopped lines in his... (read full end-stopped line explanation with examples) An end-stopped line is a line of poetry in which a sentence or phrase comes to a conclusion at the... (read more)
Enjambment is the continuation of a sentence or clause across a line break. For example, the poet John Donne uses enjambment in his poem "The Good-Morrow" when he continues the opening sentence across the line... (read full enjambment explanation with examples) Enjambment is the continuation of a sentence or clause across a line break. For example, the poet John Donne uses... (read more)
An envoi is a brief concluding stanza at the end of a poem that can either summarize the preceding poem or serve as its dedication. The envoi tends to follow the same meter and rhyme... (read full envoi explanation with examples) An envoi is a brief concluding stanza at the end of a poem that can either summarize the preceding poem... (read more)
Epanalepsis is a figure of speech in which the beginning of a clause or sentence is repeated at the end of that same clause or sentence, with words intervening. The sentence "The king is dead,... (read full epanalepsis explanation with examples) Epanalepsis is a figure of speech in which the beginning of a clause or sentence is repeated at the end... (read more)
An epigram is a short and witty statement, usually written in verse, that conveys a single thought or observation. Epigrams typically end with a punchline or a satirical twist. (read full epigram explanation with examples) An epigram is a short and witty statement, usually written in verse, that conveys a single thought or observation. Epigrams... (read more)
An epigraph is a short quotation, phrase, or poem that is placed at the beginning of another piece of writing to encapsulate that work's main themes and to set the tone. For instance, the epigraph of Mary... (read full epigraph explanation with examples) An epigraph is a short quotation, phrase, or poem that is placed at the beginning of another piece of writing to... (read more)
Epistrophe is a figure of speech in which one or more words repeat at the end of successive phrases, clauses, or sentences. In his Gettysburg Address, Abraham Lincoln urged the American people to ensure that,... (read full epistrophe explanation with examples) Epistrophe is a figure of speech in which one or more words repeat at the end of successive phrases, clauses,... (read more)
Epizeuxis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated in immediate succession, with no intervening words. In the play Hamlet, when Hamlet responds to a question about what he's reading... (read full epizeuxis explanation with examples) Epizeuxis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated in immediate succession, with no intervening... (read more)
Ethos, along with logos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Ethos is an argument that appeals to the audience by emphasizing the... (read full ethos explanation with examples) Ethos, along with logos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective... (read more)
Euphony is the combining of words that sound pleasant together or are easy to pronounce, usually because they contain lots of consonants with soft or muffled sounds (like L, M, N, and R) instead of consonants with harsh, percussive sounds (like... (read full euphony explanation with examples) Euphony is the combining of words that sound pleasant together or are easy to pronounce, usually because they contain lots of consonants with soft... (read more)
Exposition is the description or explanation of background information within a work of literature. Exposition can cover characters and their relationship to one another, the setting or time and place of events, as well as... (read full exposition explanation with examples) Exposition is the description or explanation of background information within a work of literature. Exposition can cover characters and their... (read more)
An extended metaphor is a metaphor that unfolds across multiple lines or even paragraphs of a text, making use of multiple interrelated metaphors within an overarching one. So while "life is a highway" is a... (read full extended metaphor explanation with examples) An extended metaphor is a metaphor that unfolds across multiple lines or even paragraphs of a text, making use of... (read more)
An external conflict is a problem, antagonism, or struggle that takes place between a character and an outside force. External conflict drives the action of a plot forward. (read full external conflict explanation with examples) An external conflict is a problem, antagonism, or struggle that takes place between a character and an outside force. External conflict... (read more)
The falling action of a story is the section of the plot following the climax, in which the tension stemming from the story's central conflict decreases and the story moves toward its conclusion. For instance, the traditional "good... (read full falling action explanation with examples) The falling action of a story is the section of the plot following the climax, in which the tension stemming from... (read more)
Figurative language is language that contains or uses figures of speech. When people use the term "figurative language," however, they often do so in a slightly narrower way. In this narrower definition, figurative language refers... (read full figurative language explanation with examples) Figurative language is language that contains or uses figures of speech. When people use the term "figurative language," however, they... (read more)
A figure of speech is a literary device in which language is used in an unusual—or "figured"—way in order to produce a stylistic effect. Figures of speech can be broken into two main groups: figures... (read full figure of speech explanation with examples) A figure of speech is a literary device in which language is used in an unusual—or "figured"—way in order to... (read more)
A character is said to be "flat" if it is one-dimensional or lacking in complexity. Typically, flat characters can be easily and accurately described using a single word (like "bully") or one short sentence (like "A naive... (read full flat character explanation with examples) A character is said to be "flat" if it is one-dimensional or lacking in complexity. Typically, flat characters can be easily... (read more)
Foreshadowing is a literary device in which authors hint at plot developments that don't actually occur until later in the story. Foreshadowing can be achieved directly or indirectly, by making explicit statements or leaving subtle... (read full foreshadowing explanation with examples) Foreshadowing is a literary device in which authors hint at plot developments that don't actually occur until later in the... (read more)
Formal verse is the name given to rhymed poetry that uses a strict meter (a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables). This two-line poem by Emily Dickinson is formal verse because it rhymes and... (read full formal verse explanation with examples) Formal verse is the name given to rhymed poetry that uses a strict meter (a regular pattern of stressed and... (read more)
Free verse is the name given to poetry that doesn’t use any strict meter or rhyme scheme. Because it has no set meter, poems written in free verse can have lines of any length, from... (read full free verse explanation with examples) Free verse is the name given to poetry that doesn’t use any strict meter or rhyme scheme. Because it has... (read more)
Hamartia is a literary term that refers to a tragic flaw or error that leads to a character's downfall. In the novel Frankenstein, Victor Frankenstein's arrogant conviction that he can usurp the roles of God... (read full hamartia explanation with examples) Hamartia is a literary term that refers to a tragic flaw or error that leads to a character's downfall. In... (read more)
Hubris refers to excessive pride or overconfidence, which drives a person to overstep limits in a way that leads to their downfall. In Greek mythology, the legend of Icarus involves an iconic case of hubris:... (read full hubris explanation with examples) Hubris refers to excessive pride or overconfidence, which drives a person to overstep limits in a way that leads to... (read more)
Hyperbole is a figure of speech in which a writer or speaker exaggerates for the sake of emphasis. Hyperbolic statements are usually quite obvious exaggerations intended to emphasize a point, rather than be taken literally.... (read full hyperbole explanation with examples) Hyperbole is a figure of speech in which a writer or speaker exaggerates for the sake of emphasis. Hyperbolic statements... (read more)
An iamb is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which one unstressed syllable is followed by a stressed syllable. The word "define" is an iamb, with the unstressed syllable of "de" followed by the... (read full iamb explanation with examples) An iamb is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which one unstressed syllable is followed by a stressed syllable.... (read more)
An idiom is a phrase that conveys a figurative meaning that is difficult or impossible to understand based solely on a literal interpretation of the words in the phrase. For example, saying that something is... (read full idiom explanation with examples) An idiom is a phrase that conveys a figurative meaning that is difficult or impossible to understand based solely on... (read more)
Imagery, in any sort of writing, refers to descriptive language that engages the human senses. For instance, the following lines from Robert Frost's poem "After Apple-Picking" contain imagery that engages the senses of touch, movement,... (read full imagery explanation with examples) Imagery, in any sort of writing, refers to descriptive language that engages the human senses. For instance, the following lines... (read more)
Internal rhyme is rhyme that occurs in the middle of lines of poetry, instead of at the ends of lines. A single line of poetry can contain internal rhyme (with multiple words in the same... (read full internal rhyme explanation with examples) Internal rhyme is rhyme that occurs in the middle of lines of poetry, instead of at the ends of lines.... (read more)
Irony is a literary device or event in which how things seem to be is in fact very different from how they actually are. If this seems like a loose definition, don't worry—it is. Irony is a... (read full irony explanation with examples) Irony is a literary device or event in which how things seem to be is in fact very different from how... (read more)
Juxtaposition occurs when an author places two things side by side as a way of highlighting their differences. Ideas, images, characters, and actions are all things that can be juxtaposed with one another. For example,... (read full juxtaposition explanation with examples) Juxtaposition occurs when an author places two things side by side as a way of highlighting their differences. Ideas, images,... (read more)
A kenning is a figure of speech in which two words are combined in order to form a poetic expression that refers to a person or a thing. For example, "whale-road" is a kenning for... (read full kenning explanation with examples) A kenning is a figure of speech in which two words are combined in order to form a poetic expression... (read more)
A line break is the termination of one line of poetry, and the beginning of a new line. (read full line break explanation with examples) A line break is the termination of one line of poetry, and the beginning of a new line. (read more)
Litotes is a figure of speech and a form of understatement in which a sentiment is expressed ironically by negating its contrary. For example, saying "It's not the best weather today" during a hurricane would... (read full litotes explanation with examples) Litotes is a figure of speech and a form of understatement in which a sentiment is expressed ironically by negating... (read more)
Logos, along with ethos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Logos is an argument that appeals to an audience's sense of logic... (read full logos explanation with examples) Logos, along with ethos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective... (read more)
A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two different things by saying that one thing is the other. The comparison in a metaphor can be stated explicitly, as in the sentence "Love is... (read full metaphor explanation with examples) A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two different things by saying that one thing is the other.... (read more)
Meter is a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables that defines the rhythm of some poetry. These stress patterns are defined in groupings, called feet, of two or three syllables. A pattern of unstressed-stressed,... (read full meter explanation with examples) Meter is a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables that defines the rhythm of some poetry. These stress patterns... (read more)
Metonymy is a type of figurative language in which an object or concept is referred to not by its own name, but instead by the name of something closely associated with it. For example, in... (read full metonymy explanation with examples) Metonymy is a type of figurative language in which an object or concept is referred to not by its own... (read more)
The mood of a piece of writing is its general atmosphere or emotional complexion—in short, the array of feelings the work evokes in the reader. Every aspect of a piece of writing can influence its mood, from the... (read full mood explanation with examples) The mood of a piece of writing is its general atmosphere or emotional complexion—in short, the array of feelings the work evokes... (read more)
A motif is an element or idea that recurs throughout a work of literature. Motifs, which are often collections of related symbols, help develop the central themes of a book or play. For example, one... (read full motif explanation with examples) A motif is an element or idea that recurs throughout a work of literature. Motifs, which are often collections of... (read more)
A narrative is an account of connected events. Two writers describing the same set of events might craft very different narratives, depending on how they use different narrative elements, such as tone or point of view. For... (read full narrative explanation with examples) A narrative is an account of connected events. Two writers describing the same set of events might craft very different narratives,... (read more)
Onomatopoeia is a figure of speech in which words evoke the actual sound of the thing they refer to or describe. The “boom” of a firework exploding, the “tick tock” of a clock, and the... (read full onomatopoeia explanation with examples) Onomatopoeia is a figure of speech in which words evoke the actual sound of the thing they refer to or... (read more)
An oxymoron is a figure of speech in which two contradictory terms or ideas are intentionally paired in order to make a point—particularly to reveal a deeper or hidden truth. The most recognizable oxymorons are... (read full oxymoron explanation with examples) An oxymoron is a figure of speech in which two contradictory terms or ideas are intentionally paired in order to... (read more)
A paradox is a figure of speech that seems to contradict itself, but which, upon further examination, contains some kernel of truth or reason. Oscar Wilde's famous declaration that "Life is much too important to be... (read full paradox explanation with examples) A paradox is a figure of speech that seems to contradict itself, but which, upon further examination, contains some kernel... (read more)
Parallelism is a figure of speech in which two or more elements of a sentence (or series of sentences) have the same grammatical structure. These "parallel" elements can be used to intensify the rhythm of... (read full parallelism explanation with examples) Parallelism is a figure of speech in which two or more elements of a sentence (or series of sentences) have... (read more)
Parataxis is a figure of speech in which words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are set next to each other so that each element is equally important. Parataxis usually involves simple sentences or phrases whose relationships... (read full parataxis explanation with examples) Parataxis is a figure of speech in which words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are set next to each other so... (read more)
A parody is a work that mimics the style of another work, artist, or genre in an exaggerated way, usually for comic effect. Parodies can take many forms, including fiction, poetry, film, visual art, and... (read full parody explanation with examples) A parody is a work that mimics the style of another work, artist, or genre in an exaggerated way, usually... (read more)
Pathetic fallacy occurs when a writer attributes human emotions to things that aren't human, such as objects, weather, or animals. It is often used to make the environment reflect the inner experience of a narrator... (read full pathetic fallacy explanation with examples) Pathetic fallacy occurs when a writer attributes human emotions to things that aren't human, such as objects, weather, or animals.... (read more)
Pathos, along with logos and ethos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Pathos is an argument that appeals to an audience's emotions. When a... (read full pathos explanation with examples) Pathos, along with logos and ethos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective... (read more)
Personification is a type of figurative language in which non-human things are described as having human attributes, as in the sentence, "The rain poured down on the wedding guests, indifferent to their plans." Describing the... (read full personification explanation with examples) Personification is a type of figurative language in which non-human things are described as having human attributes, as in the... (read more)
Plot is the sequence of interconnected events within the story of a play, novel, film, epic, or other narrative literary work. More than simply an account of what happened, plot reveals the cause-and-effect relationships between... (read full plot explanation with examples) Plot is the sequence of interconnected events within the story of a play, novel, film, epic, or other narrative literary... (read more)
Point of view refers to the perspective that the narrator holds in relation to the events of the story. The three primary points of view are first person, in which the narrator tells a story from... (read full point of view explanation with examples) Point of view refers to the perspective that the narrator holds in relation to the events of the story. The... (read more)
Polyptoton is a figure of speech that involves the repetition of words derived from the same root (such as "blood" and "bleed"). For instance, the question, "Who shall watch the watchmen?" is an example of... (read full polyptoton explanation with examples) Polyptoton is a figure of speech that involves the repetition of words derived from the same root (such as "blood"... (read more)
Polysyndeton is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and," "or," and "but" that join other words or clauses in a sentence into relationships of equal importance—are used several times in close... (read full polysyndeton explanation with examples) Polysyndeton is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and," "or," and "but" that join other words... (read more)
The protagonist of a story is its main character, who has the sympathy and support of the audience. This character tends to be involved in or affected by most of the choices or conflicts that... (read full protagonist explanation with examples) The protagonist of a story is its main character, who has the sympathy and support of the audience. This character... (read more)
A pun is a figure of speech that plays with words that have multiple meanings, or that plays with words that sound similar but mean different things. The comic novelist Douglas Adams uses both types... (read full pun explanation with examples) A pun is a figure of speech that plays with words that have multiple meanings, or that plays with words... (read more)
A quatrain is a four-line stanza of poetry. It can be a single four-line stanza, meaning that it is a stand-alone poem of four lines, or it can be a four-line stanza that makes up... (read full quatrain explanation with examples) A quatrain is a four-line stanza of poetry. It can be a single four-line stanza, meaning that it is a... (read more)
A red herring is a piece of information in a story that distracts readers from an important truth, or leads them to mistakenly expect a particular outcome. Most often, the term red herring is used to refer... (read full red herring explanation with examples) A red herring is a piece of information in a story that distracts readers from an important truth, or leads them... (read more)
In a poem or song, a refrain is a line or group of lines that regularly repeat, usually at the end of a stanza in a poem or at the end of a verse in... (read full refrain explanation with examples) In a poem or song, a refrain is a line or group of lines that regularly repeat, usually at the... (read more)
Repetition is a literary device in which a word or phrase is repeated two or more times. Repetition occurs in so many different forms that it is usually not thought of as a single figure... (read full repetition explanation with examples) Repetition is a literary device in which a word or phrase is repeated two or more times. Repetition occurs in... (read more)
A rhetorical question is a figure of speech in which a question is asked for a reason other than to get an answer—most commonly, it's asked to make a persuasive point. For example, if a... (read full rhetorical question explanation with examples) A rhetorical question is a figure of speech in which a question is asked for a reason other than to... (read more)
A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds in two or more words. Rhyming is particularly common in many types of poetry, especially at the ends of lines, and is a requirement in formal verse.... (read full rhyme explanation with examples) A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds in two or more words. Rhyming is particularly common in many types... (read more)
A rhyme scheme is the pattern according to which end rhymes (rhymes located at the end of lines) are repeated in works poetry. Rhyme schemes are described using letters of the alphabet, such that all... (read full rhyme scheme explanation with examples) A rhyme scheme is the pattern according to which end rhymes (rhymes located at the end of lines) are repeated... (read more)
The rising action of a story is the section of the plot leading up to the climax, in which the tension stemming from the story's central conflict grows through successive plot developments. For example, in the story of "Little... (read full rising action explanation with examples) The rising action of a story is the section of the plot leading up to the climax, in which the tension stemming... (read more)
A character is said to be "round" if they are lifelike or complex. Round characters typically have fully fleshed-out and multi-faceted personalities, backgrounds, desires, and motivations. Jay Gatsby in F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby... (read full round character explanation with examples) A character is said to be "round" if they are lifelike or complex. Round characters typically have fully fleshed-out and... (read more)
Satire is the use of humor, irony, sarcasm, or ridicule to criticize something or someone. Public figures, such as politicians, are often the subject of satire, but satirists can take aim at other targets as... (read full satire explanation with examples) Satire is the use of humor, irony, sarcasm, or ridicule to criticize something or someone. Public figures, such as politicians,... (read more)
A sestet is a six-line stanza of poetry. It can be any six-line stanza—one that is, itself, a whole poem, or one that makes up a part of a longer poem. Most commonly, the term... (read full sestet explanation with examples) A sestet is a six-line stanza of poetry. It can be any six-line stanza—one that is, itself, a whole poem,... (read more)
Setting is where and when a story or scene takes place. The where can be a real place like the city of New York, or it can be an imagined location, like Middle Earth in... (read full setting explanation with examples) Setting is where and when a story or scene takes place. The where can be a real place like the... (read more)
Sibilance is a figure of speech in which a hissing sound is created within a group of words through the repetition of "s" sounds. An example of sibilance is: "Sadly, Sam sold seven venomous serpents to Sally and... (read full sibilance explanation with examples) Sibilance is a figure of speech in which a hissing sound is created within a group of words through the repetition... (read more)
A simile is a figure of speech that directly compares two unlike things. To make the comparison, similes most often use the connecting words "like" or "as," but can also use other words that indicate... (read full simile explanation with examples) A simile is a figure of speech that directly compares two unlike things. To make the comparison, similes most often... (read more)
Traditionally, slant rhyme referred to a type of rhyme in which two words located at the end of a line of poetry themselves end in similar—but not identical—consonant sounds. For instance, the words "pact" and... (read full slant rhyme explanation with examples) Traditionally, slant rhyme referred to a type of rhyme in which two words located at the end of a line... (read more)
A soliloquy is a literary device, most often found in dramas, in which a character speaks to him or herself, relating his or her innermost thoughts and feelings as if thinking aloud. In some cases,... (read full soliloquy explanation with examples) A soliloquy is a literary device, most often found in dramas, in which a character speaks to him or herself,... (read more)
A sonnet is a type of fourteen-line poem. Traditionally, the fourteen lines of a sonnet consist of an octave (or two quatrains making up a stanza of 8 lines) and a sestet (a stanza of... (read full sonnet explanation with examples) A sonnet is a type of fourteen-line poem. Traditionally, the fourteen lines of a sonnet consist of an octave (or... (read more)
A spondee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which both syllables are stressed. The word "downtown" is a spondee, with the stressed syllable of "down" followed by another stressed syllable, “town”: Down-town. (read full spondee explanation with examples) A spondee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which both syllables are stressed. The word "downtown" is a... (read more)
A stanza is a group of lines form a smaller unit within a poem. A single stanza is usually set apart from other lines or stanza within a poem by a double line break or... (read full stanza explanation with examples) A stanza is a group of lines form a smaller unit within a poem. A single stanza is usually set... (read more)
A character is said to be "static" if they do not undergo any substantial internal changes as a result of the story's major plot developments. Antagonists are often static characters, but any character in a... (read full static character explanation with examples) A character is said to be "static" if they do not undergo any substantial internal changes as a result of... (read more)
Stream of consciousness is a style or technique of writing that tries to capture the natural flow of a character's extended thought process, often by incorporating sensory impressions, incomplete ideas, unusual syntax, and rough grammar. (read full stream of consciousness explanation with examples) Stream of consciousness is a style or technique of writing that tries to capture the natural flow of a character's... (read more)
A syllogism is a three-part logical argument, based on deductive reasoning, in which two premises are combined to arrive at a conclusion. So long as the premises of the syllogism are true and the syllogism... (read full syllogism explanation with examples) A syllogism is a three-part logical argument, based on deductive reasoning, in which two premises are combined to arrive at... (read more)
Symbolism is a literary device in which a writer uses one thing—usually a physical object or phenomenon—to represent something more abstract. A strong symbol usually shares a set of key characteristics with whatever it is... (read full symbolism explanation with examples) Symbolism is a literary device in which a writer uses one thing—usually a physical object or phenomenon—to represent something more... (read more)
Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which, most often, a part of something is used to refer to its whole. For example, "The captain commands one hundred sails" is a synecdoche that uses "sails"... (read full synecdoche explanation with examples) Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which, most often, a part of something is used to refer to its... (read more)
A theme is a universal idea, lesson, or message explored throughout a work of literature. One key characteristic of literary themes is their universality, which is to say that themes are ideas that not only... (read full theme explanation with examples) A theme is a universal idea, lesson, or message explored throughout a work of literature. One key characteristic of literary... (read more)
The tone of a piece of writing is its general character or attitude, which might be cheerful or depressive, sarcastic or sincere, comical or mournful, praising or critical, and so on. For instance, an editorial in a newspaper... (read full tone explanation with examples) The tone of a piece of writing is its general character or attitude, which might be cheerful or depressive, sarcastic or sincere, comical... (read more)
A tragic hero is a type of character in a tragedy, and is usually the protagonist. Tragic heroes typically have heroic traits that earn them the sympathy of the audience, but also have flaws or... (read full tragic hero explanation with examples) A tragic hero is a type of character in a tragedy, and is usually the protagonist. Tragic heroes typically have... (read more)
A trochee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by an unstressed syllable. The word "poet" is a trochee, with the stressed syllable of "po" followed by the... (read full trochee explanation with examples) A trochee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by an unstressed syllable.... (read more)
Understatement is a figure of speech in which something is expressed less strongly than would be expected, or in which something is presented as being smaller, worse, or lesser than it really is. Typically, understatement is... (read full understatement explanation with examples) Understatement is a figure of speech in which something is expressed less strongly than would be expected, or in which something... (read more)
Verbal irony occurs when the literal meaning of what someone says is different from—and often opposite to—what they actually mean. When there's a hurricane raging outside and someone remarks "what lovely weather we're having," this... (read full verbal irony explanation with examples) Verbal irony occurs when the literal meaning of what someone says is different from—and often opposite to—what they actually mean.... (read more)
A villanelle is a poem of nineteen lines, and which follows a strict form that consists of five tercets (three-line stanzas) followed by one quatrain (four-line stanza). Villanelles use a specific rhyme scheme of ABA... (read full villanelle explanation with examples) A villanelle is a poem of nineteen lines, and which follows a strict form that consists of five tercets (three-line... (read more)
A zeugma is a figure of speech in which one "governing" word or phrase modifies two distinct parts of a sentence. Often, the governing word will mean something different when applied to each part, as... (read full zeugma explanation with examples) A zeugma is a figure of speech in which one "governing" word or phrase modifies two distinct parts of a... (read more)

- PDF downloads of each of the 136 Lit Terms we cover
- PDF downloads of 1909 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,206 quotes across 1909 Lit Guides
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play

- Literary Terms
- Figures of Speech
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Use Figures of Speech
I. What are Figures of Speech?
A figure of speech is a word or phrase using figurative language—language that has other meaning than its normal definition. In other words, figures of speeches rely on implied or suggested meaning, rather than a dictionary definition. We express and develop them through hundreds of different rhetorical techniques, from specific types like metaphors and similes , to more general forms like sarcasm and slang.
Figures of speech make up a huge portion of the English language, making it more creative, more expressive, and just more interesting! Many have been around for hundreds of years—some even thousands—and more are added to our language essentially every day. This article will focus on a few key forms of figures of speech, but remember, the types are nearly endless!
III. Types of Figure of Speech
There are countless figures of speech in every language, and they fall into hundreds of categories. Here, though, is a short list of some of the most common types of figure of speech:
A. Metaphor
Many common figures of speech are metaphors. That is, they use words in a manner other than their literal meaning. However, metaphors use figurative language to make comparisons between unrelated things or ideas. The “peak of her career,” for example, is a metaphor, since a career is not a literal mountain with a peak , but the metaphor represents the idea of arriving at the highest point of one’s career.
An idiom is a common phrase with a figurative meaning. Idioms are different from other figures of speech in that their figurative meanings are mostly known within a particular language, culture, or group of people. In fact, the English language alone has about 25,000 idioms. Some examples include “it’s raining cats and dogs” when it is raining hard, or “break a leg” when wishing someone good luck.
This sentence uses an idiom to make it more interesting:
There’s a supermarket and a pharmacy in the mall, so if we go there, we can kill two birds with one stone.
The idiom is a common way of saying that two tasks can be completed in the same amount of time or same place.
A proverb is a short, commonplace saying that is universally understood in today’s language and used to express general truths. “Don’t cry over spilt milk” is a popular example. Most proverbs employ metaphors (e.g. the proverb about milk isn’t literally about milk).
This example uses a proverb to emphasize the situation:
I know you think you’re going to sell all of those cookies, but don’t count your chickens before they hatch!
Here, “don’t count your chickens before they hatch” means that you shouldn’t act like something has happened before it actually does.
A simile is a very common figure of speech that uses the words “like” and “as” to compare two things that are not related by definition. For example, “he is as tall as a mountain,” doesn’t mean he was actually 1,000 feet tall, it just means he was really tall.
This example uses a simile for comparison:
The internet is like a window to the world —you can learn about everything online!
The common phrase “window to the world” refers to a hypothetical window that lets you see the whole world from it. So, saying the internet is like a window to the world implies that it lets you see anything and everything.
E. Oxymoron
An oxymoron is when you use two words together that have contradictory meanings. Some common examples include s mall crowd, definitely possible, old news, little giant , and so on.
A metonym is a word or phrase that is used to represent something related to bigger meaning. For example, fleets are sometimes described as being “thirty sails strong,” meaning thirty (curiously, this metonym survives in some places, even when the ships in question are not sail-powered!) Similarly, the crew on board those ships may be described as “hands” rather than people.
Irony is when a word or phrase’s literal meaning is the opposite of its figurative meaning. Many times (but not always), irony is expressed with sarcasm (see Related Terms). For example, maybe you eat a really bad cookie, and then say “Wow, that was the best cookie I ever had”—of course, what you really mean is that it’s the worst cookie you ever had, but being ironic actually emphasizes just how bad it was!
IV. The Importance of Figures of Speech
In general, the purpose of a figure of speech is to lend texture and color to your writing. (This is itself a figure of speech, since figures of speech don’t actually change the colors or textures on the page!) For instance, metaphors allow you to add key details that make the writing more lively and relatable. Slang and verbal irony, on the other hand, make the writing seem much more informal and youthful (although they can have the opposite effect when misused!) Finally, other figures of speech, like idioms and proverbs, allows a writer to draw on a rich cultural tradition and express complex ideas in a short space.
V. Examples of Figures of Speech in Literature
“All the world’s a stage, and all the men and women merely players. They have their exits and their entrances, and one man in his time plays many parts.” (William Shakespeare, As You Like It)
This is one of the most famous metaphors ever crafted in the English language. Shakespeare uses his extended metaphor to persuade the audience of the similarities between the stage and real life. But rather than making his play seem more like life, he suggests that life is more like a play. His metaphor calls attention to the performative, creative, and fictional aspects of human life.
“Our words are b ut crumbs that fall down from the feast o f the mind.” (Khalil Gibran, Sand & Foam )
Gibran’s timeless metaphor succeeds for a number of reasons. For one thing, it is not a cliché – had Gibran said “words are just the tip of the iceberg ,” he would have been making roughly the same point, but in a much more clichéd way. But the feast of the mind is a highly original metaphor. In addition, it’s a successful double metaphor. The crumbs and the feast are two parts of the same image, but they work together rather than being “mixed” (see How to Use Figures of Speech ).
“If you chase two rabbits, you will lose them both.” (Russian Proverb)
Like many proverbs, this one draws on a simple metaphor of chasing rabbits. The rabbits can stand in for all sorts of objectives, from jobs to relationships, but the coded message is quite clear – focus your energy on a single objective, or you will likely fail. This literal statement, though, is quite dry and not terribly memorable, which shows the power of figures of speech.

VI. Examples of Figures of Speech in Pop Culture
The chorus to Sean Kingston’s Fire Burning contains a couple of figures of speech. First of all, there’s the word “shorty” used as a slang term (see Related Terms ) for a young woman. She may or may not be literally short, but the figure of speech applies either way (though it could easily be taken as belittling and derogatory). Second, Kingston sings the metaphor: “she’s fire, burning on the dance floor.” Hopefully this is a figure of speech and not a literal statement; otherwise, Kingston and everyone else in the club are in mortal danger!
“Oh, thanks! This is much better!” (Townspeople, South Park )
This is an example of irony. In the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina, South Park satirized the government’s response to the disaster by writing about a similar disaster in South Park. In a bumbling effort to rescue people from the floods, the authorities accidentally spill oil on the flood waters and set it on fire, making the situation far more dangerous. In response, they ironically “thank” the people responsible—their meaning is obviously the opposite of their words!
Years of talks between Washington and Havana resulted in Obama’s historic visit to Cuba on March 21st. (Patreon 2016)
This is a common form of metonym in foreign policy and news media. The capital city of a country is used as a metonym for the national government. The talks, of course, are not literally between these two cities, but between the leaders and government officials of the two countries (US and Cuba).
VII. Related Terms
Literal and figurative language.
Language is generally divided into two categories: literal, and figurative. Literal language relies on the real definition of words and phrases, or their literal meanings. Figurative language, on the other hand, relies on implied meanings, which can be understood differently depending on the location or who is using it. For example, “the sky is blue” relies on the literal definition of the word “blue,” while “I am feeling blue” relies on the figurative definition. All figures of speech rely on the use of figurative language for their meaning.
Sarcasm is mocking or bitter language that we use to express different meaning than what we say; often the exact opposite. When your intended meaning is the opposite of the literal meaning, that’s irony (another type of figure of speech), which includes common phrases like “Oh, great…” when you really mean something is bad.
Slang is language that uses atypical words and phrases to express specific meanings. It varies greatly by region, demographic, and language—for example, you would find different slang in the U.S. and in the U.K. even though they are both English speaking countries. Likewise, teenagers and the elderly will use different slang terms, as would Spanish and English. Many slang terms are figures of speech. For example, “bro” could be used to describe a friend rather than an actual brother; this would be using the word as a figure of speech.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
figure of speech
What is a figure of speech definition, usage, and literary examples, figure of speech definition.
Figures of speech (FIG-yurs of SPEEchuh) are words or phrases used in a non-literal sense for rhetorical effect. They are often constructed using literary devices such as metaphor , simile , alliteration , metonymy, synecdoche, and personification. Figures of speech allow writers to apply familiar ideas and imagery to less familiar concepts, and they are widespread in written and spoken language.
Figure of Speech Categories
Figures of speech fall into two broad categories: tropes and scheme. These are dozens of figures of speech that fall into each category, so the following are a select few examples.
These are figures of speech that play with syntax, sound, and words. They often achieve their effects by utilizing repetition of words, phrases, or sounds; omission of words or punctuation; unexpected changes in word order; or paired identical grammatical structures.
- Alliteration : Repeating consonant sounds in a series of words
- Diacope: Repeating words or phrases, interrupted by one or two other words
- Homonyms: Identical words that have different meanings
- Sibilance: Repeating hissing sounds
- Asyndeton: Omitting conjunctions between related series of clauses
- Brachylogia: Omitting conjunctions between individual words
- Ellipsis: Omitting words without losing context or understanding
- Syncope: Omitting word or phrase parts
Changes in Word Order
- Anastrophe: Rearranging the subject, object and verb order in a phrase
- Apposition: Two phrases, often separated by commas, where the second defines the first
- Parenthesis: A rhetorical, qualifying phrase inserted into a sentence or passage
- Spoonerism: Switching syllables between two words
Paired Grammatical Structures
- Antithesis : Juxtaposing ideas
- Isocolon: Consecutive phrases of identical length in words or syllables
- Parallelism: Similar grammatical structure between two or more clauses
- Tricolon: Three consecutive phrases of identical length in words or syllables
These are figures of speech that deviate in some way from the literal meanings of words. They tend to include association or comparison to shift readers’ perceptions from words’ true definitions to a layered figurative meaning. They can be broken into five categories: reference, word play/puns, substitutions, overstatement/understatement, and inversion.
- Allegory : A narrative that is an indirect metaphor for a broader, real-world concept
- Allusion : An intertextual reference to another creative work
- Metaphor : A direct comparison between two unrelated things
- Personification: Attributing human characteristics to non-human entities
Word Play/Puns
- Innuendo: A phrase or sentence with a hidden (often salacious) meaning
- Malapropism: Confusing a word with a similar sounding one
- Paraprosdokian : An unexpected ending to a phrase
- Pun : Word play that makes use of a word’s multiple meanings
Substitutions
- Dysphemism: Using a harsh word or phrase to replace a gentler one
- Euphemism : Using a more agreeable word or phrase to replace an offensive one
- Metonymy: Replacing a word or term with something associated with it
- Synecdoche: Referring to a whole by its part(s) or vice versa
Overstatement/Understatement
- Grandiloquence: Speech that is pompous or grandiose
- Hyperbole : An emphatic exaggeration
- Litotes : Emphasizing a statement by negating its opposite
- Satire: Criticism of society through humorous means
- Irony : Conveying the opposite of a word’s literal meaning
- Oxymoron : Using contradictory words together
- Paradox: Using contradictory ideas to make a point
- Synesthesia: Using sensory-specific words to describe a different sense
Most Common Figures of Speech
The following are some of the most common figures of speech that appear in literature and other written forms.
- Alliteration : This is a scheme that uses repetition of the same first consonant sound to create a musical effect. “Francine found France quite lovely” is an example of alliteration because of the repeating f sound in the words Francine , found , and France .
- Apostrophe: With apostrophe, a speaker directly addresses an inanimate object, an abstract concept, or a person who is either imaginary or not present. John Donne use apostrophe in his poem “ Holy Sonnet: Death, be not proud ,” wherein he speaks directly to a personified idea of death.
- Chiasmus: This is a scheme where the second half of an expression is balanced against the first half in a reversed order. “You should eat to live, not live to eat” is one example; it repeats the words eat and live but reverses the order the second time they occur.
- Euphemism: This literary device takes a mild or indirect word or expression and replaces something harsh, unpleasant, or offensive with it. Saying someone passed on is a euphemism for died ; powder my nose is a euphemism for go to the bathroom .
- Hyperbole: This is the use of exaggeration for emphasis or heightened effect. “If I don’t nap right now, I will die” is a hyperbolic statement; it conveys the experience of feeling tired, but readers understand the speaker won’t literally die.
- Irony: This literary device occurs when words are used to convey the opposite of their meaning or when a situation seems directly contrary to what is expected. Famously, Alanis Morissette’s song “Ironic” lists many situations she deems ironic when they aren’t ironic at all; thus, irony.
- Litotes: This figure of speech refers to a type of understatement. It is used to negate a statement in a way that actually affirms it. For example, saying “That’s no small chunk of change” indicates that the sum in question is, in fact, large.
- Metaphor : A form of trope, metaphors make an implicit comparison between two unrelated things. “Love is a battlefield” is metaphoric, as it implies the experience of being in love is the same as being on a battlefield.
- Onomatopoeia : Words that are onomatopoeic evoke the sounds of the thing they are referring to. Hiss , crash , and tick tock are all examples because they sound like what they are describing—the sound of a snake, thunder, and a clock, respectively.
- Oxymoron: This literary device consists of contradictory words paired together. Although the words initially appear to negate each other, they make sense when joined. Deafening silence is an oxymoronic pair; the adjective deafening means “a volume so high that nothing can be heard over it,” and the noun silence means “without sound.” These words are incongruous, but together they mean an overbearing, noticeable absence of sound.
- Personification: When greater qualities of animation are given to a non-human or inanimate object, that is personification. In T.S. Eliot’s “The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock,” fog is described as “The yellow fog that rubs its back upon the window-panes/The yellow smoke that rubs its muzzle on the window-panes.” Here, Eliot is personifying the fog by giving it the attributes of a cat.
- Pun : This is a humorous play on words, often using homonyms, homographs, or homophones. For example, “I’ve been to the dentist many times, so I know the drill” is a pun; it plays with the double meaning of the word drill as a tool of the dentistry trade and as a concept of something being routine.
- Simile : Related to metaphors, similes are explicit comparisons made using the words like or as . “Lucille’s dress was as red as a fire truck” makes an explicit comparison between the color of the dress and the color of a fire truck. This allows the reader to properly visualize what Lucille is wearing.
- Synecdoche: This is a figure of speech wherein a part of something stands in for the whole thing. “All hands on deck” is a synecdoche because hands stands in for the whole crew of a ship.”
Figure of Speech and Figurative Language
People often use the terms figurative language and figure of speech interchangeably; however, they are not the same. Instead, figurative language is a broad category that contains figures of speech, as well as imagery and sound devices .
Imagery adds additional aesthetic resonance to texts through the evocation of sensory details. Sound devices enhance the text through sonic means. These elements, in conjunction with figures of speech, give a deeper meaning to the language a writer uses in their work.
Why Figures of Speech Are Used
These literary devices emphasize, embellish, or clarify written or spoken language. They allow an audience to understand ideas through implied or suggested meaning, thus giving the language a more surprising, creative, and playful effect. Some figures of speech enhance imagery, while others allow writers to employ rich cultural traditions to express their ideas. Even further, other figures of speech allow writers to experiment with structure and sound to create specific effects. No matter which type is used, the expressive quality of figures of speech helps keep audiences engaged.
Examples of Figures of Speech in Literature
1. Hafizah Geter, “ Testimony ”
Geter begins her poem :
Mr. President,
After they shot me they tackled my sister.
the sound of her knees hitting the sidewalk
made my stomach ache. It was a bad pain.
The poem is a dramatic monologue spoken by Tamir Rice, a 12-year old black child who was killed by police officers who mistook his toy gun for a real one. This poem uses apostrophe as the speaker, Tamir, talks directly to “Mr. President” (then president Barack Obama).
2. William Shakespeare, Macbeth
In Act III, Scene iii., of this play, before King Duncan’s murder is discovered, Lennox and Macbeth converse:
LENNOX: The night has been unruly: where we lay,
Our chimneys were blown down: and, as they say,
Lamentings heard i’the air; strange screams of death,
And prophesying with accents terrible
Of fire combustion and confused events
New hatch’d to the woeful time: the obscure bird
Clamour’d the livelong night: some say, the earth
Was feverous and did shake.
MACBETH: ‘Twas a rough night.
LENNOX: My young remembrance cannot parallel
A fellow to it.
Pathetic fallacy is a type of trope. It occurs when human feelings and attributes are ascribed to nature. This figure of speech is used throughout this Shakespearean tragedy. In this particular scene, Lennox describes how terrible and strange the weather was on the evening of the murder. The way the wind and earth seem to embody the horror of King Duncan’s death is pathetic fallacy.
3. Karl Marx, Das Kapital
In Part I (“Commodities and Money”) of Marx’s treatise on economics, philosophy, history, and political science, he claims:
In the pre-capitalist stages of society, commerce rules industry. In capitalist society, industry rules commerce.
These two sentences are an example of chiasmus. Here, “commerce” first rules “industry,” and then “industry” rules “commerce.” By reversing the order of these words/concepts, Marx employs chiasmus.
4. Toni Morrison, Sula
The last line of Morrison’s novel is considered by some to be one of the best lines in fiction and nonfiction. The sentence describes protagonist Nel’s grief at the death of her childhood friend Sula:
It was a fine cry—loud and long—but it had no bottom and it had no top, just circles and circles of sorrow.
This sentence is rich in alliteration: “loud and long” contain L sounds at the beginning, as well as the repetition of c and s sounds with cry , circles , circles , and sorrow . The latter is also an example of sibilance.
5. Oscar Wilde, The Importance of Being Earnest
In Wilde’s play, the main characters John Worthing and Algernon Moncrieff pose as men named Ernest, only for Jack to learn that his given name really is Ernest. He delivers the final line of the play:
On the contrary, Aunt Augusta, I’ve now realized for the first time in my life the vital importance of being Earnest.
Jack/Ernest’s declaration is a homographic pun. It means both that he understands the importance of being Ernest (his real name), as well as the importance of being earnest (sincere).
6. Aimee Nezhukumatathil, “ On Listening to Your Teacher Take Attendance ”
In this poem, Nezhukumatathil describes the experience of one’s name being mispronounced by a teacher taking attendance:
everyone turns around to check out
your face, no need to flush red and warm.
Just picture all the eyes as if your classroom
is one big scallop with its dozens of icy blues
and you will remember that winter your family
took you to the China see and you sank
your face in it to gaze at baby clams and sea stars
She uses a simile, “Just picture all the eyes as if your classroom/is one big scallop with its dozens of icy blues,” to explicitly compare the staring kids to the dozens of eyes that a sea scallop has.
Further Resources on Figure of Speech
Thought Catalog has a wonderful list of figures of speech used by Homer Simpson in The Simpsons.
Jamcampus published a great list of twenty examples of metaphors in popular songs.
This is an entertaining round up of oxymorons .
SuperSummary's library of resources and content , such as " A Beginner's Guide to Literary Analysis " and " How to Write a Summary ."
Related Terms
- Figurative language

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.19: Figures of Speech
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 37340

- Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
Figure of Speech
Definition of figure of speech.
A figure of speech is a word or phrase that is used in a non-literal way to create an effect. This effect may be rhetorical as in the deliberate arrangement of words to achieve something poetic, or imagery as in the use of language to suggest a visual picture or make an idea more vivid. Overall, figures of speech function as literary devices because of their expressive use of language. Words are used in other ways than their literal meanings or typical manner of application.
For example, Margaret Atwood utilizes figures of speech in her poem “ you fit into me ” as a means of achieving poetic meaning and creating a vivid picture for the reader.
you fit into me like a hook into an eye a fish hook an open eye
The simile in the first two lines sets forth a comparison between the way “you” fits into the poet like a hook and eye closure for perhaps a garment. This is an example of rhetorical effect in that the wording carefully achieves the idea of two things meant to connect to each other. In the second two lines, the wording is clarified by adding “fish” to “hook” and “open” to “eye,” which calls forth an unpleasant and even violent image. The poet’s descriptions of hooks and eyes are not meant literally in the poem. Yet the use of figurative language allows the poet to express two very different meanings and images that enhance the interpretation of the poem through contrast .
Types of Figures of Speech
The term figure of speech covers a wide range of literary devices, techniques, and other forms of figurative language, a few of which include:
Personification
Understatement.
- Alliteration
- Onomatopoeia
- Circumlocution
Common Examples of Figures of Speech Used in Conversation
Many people use figures of speech in conversation as a way of clarifying or emphasizing what they mean. Here are some common examples of conversational figures of speech:
Hyperbole is a figure of speech that utilizes extreme exaggeration to emphasize a certain quality or feature.
- I have a million things to do.
- This suitcase weighs a ton.
- This room is an ice-box.
- I’ll die if he doesn’t ask me on a date.
- I’m too poor to pay attention.
Understatement is a figure of speech that invokes less emotion than would be expected in reaction to something. This downplaying of reaction is a surprise for the reader and generally has the effect of showing irony .
- I heard she has cancer, but it’s not a big deal.
- Joe got his dream job, so that’s not too bad.
- Sue won the lottery, so she’s a bit excited.
- That condemned house just needs a coat of paint.
- The hurricane brought a couple of rain showers with it.
A paradox is a figure of speech that appears to be self-contradictory but actually reveals something truthful.
- You have to spend money to save it.
- What I’ve learned is that I know nothing.
- You have to be cruel to be kind.
- Things get worse before they get better.
- The only rule is to ignore all rules.
A pun is a figure of speech that contains a “ play ” on words, such as using words that mean one thing to mean something else or words that sound alike in as a means of changing meaning.
- A sleeping bull is called a bull-dozer.
- Baseball players eat on home plates.
- Polar bears vote at the North Poll.
- Fish are smart because they travel in schools.
- One bear told another that life without them would be grizzly.
An oxymoron is a figure of speech that connects two opposing ideas, usually in two-word phrases, to create a contradictory effect.
- open secret
- Alone together
- controlled chaos
- pretty ugly
Common Examples of Figure of Speech in Writing
Writers also use figures of speech in their work as a means of description or developing meaning. Here are some common examples of figures of speech used in writing:
Simile is a figure of speech in which two dissimilar things are compared to each other using the terms “like” or “as.”
- She’s as pretty as a picture.
- I’m pleased as punch.
- He’s strong like an ox.
- You are sly like a fox.
- I’m happy as a clam.
A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two different things without the use of the terms “like” or “as.”
- He is a fish out of water.
- She is a star in the sky.
- My grandchildren are the flowers of my garden.
- That story is music to my ears.
- Your words are a broken record.
Euphemism is a figure of speech that refers to figurative language designed to replace words or phrases that would otherwise be considered harsh, impolite, or unpleasant.
- Last night , Joe’s grandfather passed away (died).
- She was starting to feel over the hill (old).
- Young adults are curious about the birds and bees (sex).
- I need to powder my nose (go to the bathroom).
- Our company has decided to let you go (fire you).
Personification is a figure of speech that attributes human characteristics to something that is not human.
- I heard the wind whistling.
- The water danced across my window.
- My dog is telling me to start dinner.
- The moon is smiling at me.
- Her alarm hummed in the background.
Writing Figure of Speech
As a literary device, figures of speech enhance the meaning of written and spoken words. In oral communication, figures of speech can clarify, enhance description, and create interesting use of language. In writing, when figures of speech are used effectively, these devices enhance the writer’s ability for description and expression so that readers have a better understanding of what is being conveyed.
It’s important that writers construct effective figures of speech so that the meaning is not lost for the reader. In other words, simple rearrangement or juxtaposition of words is not effective in the way that deliberate wording and phrasing are. For example, the hyperbole “I could eat a horse” is effective in showing great hunger by using figurative language. If a writer tried the hyperbole “I could eat a barn made of licorice,” the figurative language is ineffective and the meaning would be lost for most readers.
Here are some ways that writers benefit from incorporating figures of speech into their work:
Figure of Speech as Artistic Use of Language
Effective use of figures of speech is one of the greatest demonstrations of artistic use of language. Being able to create poetic meaning, comparisons, and expressions with these literary devices is how writers form art with words.
Figure of Speech as Entertainment for Reader
Effective figures of speech often elevate the entertainment value of a literary work for the reader. Many figures of speech invoke humor or provide a sense of irony in ways that literal expressions do not. This can create a greater sense of engagement for the reader when it comes to a literary work.
Figure of Speech as Memorable Experience for Reader
By using effective figures of speech to enhance description and meaning, writers make their works more memorable for readers as an experience. Writers can often share a difficult truth or convey a particular concept through figurative language so that the reader has a greater understanding of the material and one that lasts in memory.
Examples of Figure of Speech in Literature
Works of literature feature innumerable figures of speech that are used as literary devices. These figures of speech add meaning to literature and showcase the power and beauty of figurative language. Here are some examples of figures of speech in well-known literary works:
Example 1: The Great Gatsby (F. Scott Fitzgerald)
In his blue gardens men and girls came and went like moths among the whisperings and the champagne and the stars.
Fitzgerald makes use of simile here as a figure of speech to compare Gatsby’s party guests to moths. The imagery used by Fitzgerald is one of delicacy and beauty, and creates an ephemeral atmosphere . However, the likening of Gatsby’s guests to moths also reinforces the idea that they are only attracted to the sensation of the parties and that they will depart without having made any true impact or connection. This simile, as a figure of speech, underscores the themes of superficiality and transience in the novel .
Example 2: One Hundred Years of Solitude (Gabriel Garcia Marquez)
Both described at the same time how it was always March there and always Monday, and then they understood that José Arcadio Buendía was not as crazy as the family said, but that he was the only one who had enough lucidity to sense the truth of the fact that time also stumbled and had accidents and could therefore splinter and leave an eternalized fragment in a room.
In this passage, Garcia Marquez utilizes personification as a figure of speech. Time is personified as an entity that “stumbled” and “had accidents.” This is an effective use of figurative language in that this personification of time indicates a level of human frailty that is rarely associated with something so measured. In addition, this is effective in the novel as a figure of speech because time has a great deal of influence on the plot and characters of the story. Personified in this way, the meaning of time in the novel is enhanced to the point that it is a character in and of itself.
Example 3: Fahrenheit 451 (Ray Bradbury)
A book is a loaded gun in the house next door…Who knows who might be the target of the well-read man?
In this passage, Bradbury utilizes metaphor as a figure of speech to compare a book to a loaded gun. This is an effective literary device for this novel because, in the story, books are considered weapons of free thought and possession of them is illegal. Of course, Bradbury is only stating that a book is a loaded gun as a means of figurative, not literal meaning. This metaphor is particularly powerful because the comparison is so unlikely; books are generally not considered to be dangerous weapons. However, the comparison does have a level of logic in the context of the story in which the pursuit of knowledge is weaponized and criminalized.
Related posts:
- Speech: “Is this a dagger which I see before me
Post navigation

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Figures of Speech: Types, Usage & Examples [Download PDF]
- Updated on
- Nov 6, 2023

All of us use different figures of speech in our everyday lives, no matter which language we speak. Being familiar with different types of figures of speech can not only increase your vocabulary in a particular language but also help you in your career. This is especially true for those who want to pursue a career in translation, poetry or writing. Also, having a solid idea of the different figures of speech can come in handy for a wide range of exams, including both language proficiency exams for studying abroad , and different competitive exams for work or study.
Want to familiarise yourself with this? Take a look at this blog for detailed information on the popular types of figures of speech.
This Blog Includes:
What are figures of speech, importance of figures of speech, 1. personification, 2. metaphor, 4. alliteration, 5. onomatopoeia, 6. hyperbole, 7. euphemism, 9. anaphora, 10. apostrophe, 12. paradox, 13. oxymoron, 14. assonance, 15. metonymy, classifying of figures of speech, download figures of speech pdf, 15 most common examples of figures of speech, writing figures of speech, examples in english literature, how to ace figures of speech.
Check out our essay on peer pressure
It is an integral part of any language, which is used extensively not only in our day-to-day speech but also in written texts and oral literature . These are words or phrases used in a distinctive way to produce a rhetorical effect.
To say it in very simple terms, it is a phrase whose actual meaning is different from its literal meaning.
Figures of Speech are developed and expressed through a variety of different rhetorical techniques. All of us use different figures of speech in our daily conversations, both deliberately and subconsciously.
It enhances your writing and content. For example, metaphors add important details that make the writing more relatable to the readers. Idioms help to express complex ideas in a short space. It makes the content presentable and more enjoyable to the writers. Most of the time, you may use these words as a sarcastic response or just to demonstrate your command of the language.
Must Read: Best Novels for Students
15. Types of Figures of Speech with Example
There is a wide range of different types of figures of speech that are used in our daily communication. Let us take a look at some of the most popular ones that are used extensively:
Personification attributes human nature or human qualities to abstract or inanimate objects.
For example , we often use phrases like the howling wind, dancing leaves, time flies etc. Some examples of personification in a sentence are:
- The opportunity knocked at his door
- The plants in her house silently begged to be watered
- Lightning danced across the sky
- The wind howled in the night.
A metaphor is used to imply a comparison between two things that have something in common but are in general different from each other.
Some examples of the usage of metaphors in a sentence are as follows:
- It is raining cats and dogs
- He is the star of our class
- Life is a highway.
- Her eyes were diamonds.
A simile is a figure of speech that compares two things that are different from each other but have similar qualities. These are generally formed through the usage of the words ‘as’ or ‘like’.
Some examples of similes in a sentence include:
- He is as brave as a lion
- Her expression was as cold as ice
- Swim like a fish
- As light as a feather
Alliteration is a sentence that consists of a series of words that have the same consonant sound at the beginning.
Some popular examples of alliteration in a sentence include:
- She sells sea shells on the seashore
- A good cook could cook as many cookies as a good cook who could cook cookies
- All Adam ate in August was apples and almonds
- Barry bought a book to bring to the backyard barbecue
This is a figure of speech that is used to express a sound. To be more precise, it involves the use of words that imitate the sounds associated with the action or object referred to i.e. hiss, clap etc.
Some examples of onomatopoeia include:
- The buzzing bee flew over my head
- The stone hit the water with a splash
- The boulder hit the ground with a flump .
- Leaves rustle in the wind and are whipped into the air.
A hyperbole is a figure of speech that consists of an exaggeration. It is the usage of exaggerated terms in order to emphasize or heighten the effect of something.
Some examples of using hyperboles in a sentence include:
- I have told you a million times to not touch my stuff!
- She has got a pea-sized brain
- I’m so hungry I could eat a horse.
- She’s as old as the hills.
Euphemism is the usage of a mild word in substitution of something that is more explicit or harsh when referring to something unfavourable or unpleasant. Some examples of its usage include:
- This mall has good facilities for differently-abled people
- He passed away in his sleep
- Passed away” instead of “died”
- “Let go” instead of “fired”
Irony or sarcasm is a figure of speech in which the usage of words conveys the opposite of their literal meaning. These are often used in a humorous manner. Some examples of irony include:
- Your hands are as clean as mud
- The dinner you served was as hot as ice
- Coming home to a big mess and saying, “it’s great to be back”
- Telling a rude customer to “have a nice day”
It is a repetition of a word or phrase at the start of several sentences of clauses.
Some of the examples of anaphora are as follows:
- Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.: “I Have a Dream” Speech
- Charles Dickens: A Tale of Two Cities
- “Be bold. Be brief. Be gone.”
- “Get busy living or get busy dying.”
It addresses a subject that is not present in the work. In this case, the object is absent or inanimate.
Here are some examples of apostrophes.
- Twinkle, twinkle, little star, How I wonder what you are
- Welcome, O life!
- Alarm clock, please don’t fail me.
- Seven, you are my lucky number!
Puns are among the most frequently used figures of speech in daily conversation. They may be great conversation starters since they make you sound clever and occasionally even humorous.
Here are a few instances of puns in speech:
- Denial is a river in Egypt (referring to The Nile using the word Denial).
- Her cat is near the computer to keep an eye on the mouse.
- No matter how much you push the envelope, it will still be stationery.
- Everyone thinks my runny nose is funny, but it’s snot.
These figures of speech, like ironies, emphasize something by discussing the exact opposite of it. A paradox, on the other hand, differs from irony in that it does not make the contrast as evident.
Let’s examine two instances of paradoxical figures of speech:
- “Some of my biggest triumphs have also been failures,” (According to US actress Pearl Bailey)
- “War is good. Slavery is freedom. “Ignorance is power,” (As said by English author George Orwell)
- Save money by spending it
- If I know one thing, it’s that I know nothing
This figure of speech, which should not be confused with ironies and paradoxes, links two opposing ideas at once. This indicates that two opposing concepts are utilized inside a single sentence to create levity in an oxymoron figure of speech. For instance ,
- This is another fine mess you have got us into
- Suddenly the room filled with a deafening silence
- The comedian was seriously funny
- You are clearly confused by the situation you have found yourself in
Internal vowels in nearby words that are the same or comparable in sound. Here are a few examples of assonance in speech:
- How now, brown cow?
- The light of the fire is a sight
- Go slow over the road
- Try as I might, the kite did not fly
Metonymy is a figure of speech when one term or phrase is used in place of another with which it is closely related. It is also a rhetorical technique used to describe something indirectly by making references to objects around it.
Here are a few instances of Metonym:
- “That stuffed suit with the briefcase is a poor excuse for a salesman,” the manager said angrily.
- The pen is mightier than the sword”
- I’m a Silicon Valley guy. I just think people from Silicon Valley can do anything.
- Most of the successful people in Hollywood are failures as human beings.
How to Use a Figure of Speech?
Figures of speeches do not convey the literal meaning, hence, it is very important to know how to use the figure of speech. The most significant way of doing this is by making sure that the figure of speech that you are using implies, or gives out the desired effect and feeling.
There are different ways and points you can remember to easily do this. Some of them are as follows.
Figures of speech can be categorized into categories that are based on their functions when they are used in sentences. The main categories from these are as follows:
- Those figures of speech show phonetic resemblances and represent sounds. Similes, personification, metaphors, metonymy, euphemism, and synecdoche are the figures of speech used for this purpose.
- Those figures of speech that show a relationship or resemblance. This kind of speech is used to create a similar effect by using similar-sounding words
- Those figures of speech that show emphasis or unimportance. This kind of speech provides emphasis showing the level of importance or unimportance. Hyperbole, oxymoron, antithesis, and irony are the figures of speech used for this purpose.
50 Figures of Speech Examples
- When dissolving like soap in water. (Smile)
- John is a goat. (Metaphor)
- A rain starts or thinner, then look at the joy in the soil, the birds told me that you are going to distant lands. That beautiful sound of the mountain has travelled all around. (Personification)
- The wave of the sea did not go as far as my heart. (Hyperbole)
- Can you hear the clicks coming from the roof? (Onomatopoeia)
- The monkey ate the beans in his hand. (Onomatopoeia)
- I could not sleep through my mother’s snort during the night. (Onomatopoeia)
- The flowing waters of the waterfall took all my troubles. (Onomatopoeia)
- The food in the cauldron was boiling and scalding. (Onomatopoeia)
- I don’t want to hear the buzz of the fly standing by my ear. (Onomatopoeia)
- He suddenly exploded when he threw the ball into the thorns. (Onomatopoeia)
- I lubricated the creaking door hinges beautifully. (Onomatopoeia)
- Daredevil: someone who takes unnecessary risks
- Cheapskate: someone who hates to spend money
- Joined at the hip: to be exceptionally close to someone
- Elbow grease: hard physical effort
- Oddball: a weirdo or a strange person
- Down-To-Earth: sensible and realistic
- Go-Getter: a person who is active, energetic, and has the initiative to pursue the things they want.
- Break a leg: good luck
- Cutting corners: Doing something poorly in order to save time or money
- Hang in there: Don’t give up
- Pull yourself together: Calm down
- So far so good: Things are going well so far
- A busybody: always wants to know about other people’s private lives
- Forty winks: a short nap
- Barrel of laugh: someone who is very funny
- Old as the hills: some who is very old
- Red tape; Official or bureaucratic tasks
- To be yellow; To be cowardly
- To see red; To be very angry
- Blackout; Faint
- Black and blue; Describe something that is badly bruised
- Golden opportunity; The perfect chance
- Have the blues; Be sad or depressed
- Black sheep; A person who is a disgrace to a family or group
- That’s a storm in a teacup, stop fussing about it, you can do it.
- The air hostess greeted the passengers with a sunny smile.
- They have the intention to flood the market with their new mobile phones.
- If someone has a clean bill of health, they apply to many profession
- My grandmother’s old, but she’s as fit as a fiddle.
- If you a few days of rest and medication, you’ll be as fit as a fiddle.
- I’m sorry I can’t make it. I’m feeling a bit under the weather today.
- If someone looks or feels like ill or tired, they look dead warmed up.
- Oh dear! You look like death warmed up, I think the doctor will prescribe you a lot of medicine. You shouldn’t be working all night when you’re so ill, you look like death warmed up.
- My mum’s not worried about the operation. She’s been under the knife several times.
- Stacy went under the knife last week.
Must Read: Poetic Devices
Given below are some of the common examples to explain the figures of speech:

Let’s learn more about figures of speech and their examples below.
In writing, when figures of speech are used effectively, these devices enhance the writer’s ability for description and expression so that readers have a better understanding of what is being conveyed. Here are some ways that writers benefit from incorporating it into their work:
- Figure of Speech as Artistic Use of Language : Effective use of figures of speech is one of the greatest demonstrations of artistic use of language. Being able to create poetic meaning, comparisons, and expressions with these literary devices are how writers form art with words.
- Figure of Speech as Entertainment for Reader: Effective figures of speech often elevate the entertainment value of a literary work for the reader. Many invoke humour or provide a sense of irony in ways that literal expressions do not. This can create a greater sense of engagement for the reader when it comes to a literary work.
- Figure of Speech as Memorable Experience for Reader: By using it effectively to enhance description and meaning, writers make their works more memorable for readers as an experience. Writers can often share a difficult truth or convey a particular concept through figurative language so that the reader has a greater understanding of the material and one that lasts in memory.
Numerous figures of speech that are used as literary devices may be seen in works of literature. These add meaning to literature and showcase the power and beauty of figurative language. Here are some examples in well-known literary works:
- The Great Gatsby (F. Scott Fitzgerald)
In his blue gardens men and girls came and went like moths among the whisperings and the champagne and the stars.
Fitzgerald makes use of simile here as a figure of speech to compare Gatsby’s party guests to moths. The imagery used by Fitzgerald is one of delicacy and beauty and creates an ephemeral atmosphere. However, the likening of Gatsby’s guests to moths also reinforces the idea that they are only attracted to the sensation of the parties and that they will depart without having made any true impact or connection. This simile underscores the themes of superficiality and transience in the novel.
- One Hundred Years of Solitude (Gabriel Garcia Marquez)
Both described at the same time how it was always March there and always Monday, and then they understood that José Arcadio Buendía was not as crazy as the family said, but that he was the only one who had enough lucidity to sense the truth of the fact that time also stumbled and had accidents and could therefore splinter and leave an eternalized fragment in a room.
In this passage, Garcia Marquez utilizes personification as a figure of speech. Time is personified as an entity that “stumbled” and “had accidents.” This is an effective use of figurative language in that this personification of time indicates a level of human frailty that is rarely associated with something so measured. In addition, this is effective in the novel because time has a great deal of influence on the plot and characters of the story. Personified in this way, the meaning of time in the novel is enhanced to the point that it is a character in and of itself.
- Fahrenheit 451 (Ray Bradbury)
A book is a loaded gun in the house next door…Who knows who might be the target of the well-read man?
In this passage, Bradbury utilizes metaphor as a figure of speech to compare a book to a loaded gun. This is an effective literary device for this novel because, in the story, books are considered weapons of free thought and possession of them is illegal. Of course, Bradbury is only stating that a book is a loaded gun as a means of figurative, not the literal meaning. This metaphor is particularly powerful because the comparison is so unlikely; books are generally not considered to be dangerous weapons. However, the comparison does have a level of logic in the context of the story in which the pursuit of knowledge is weaponized and criminalized.
Also Read: History of English Literature
Wondering what the hard and fast rule is to ace this section? The only thing that will help you is practice. We have curated a list of the best books that will help you ace it like a pro:
Test Yourself and Complete this Exercise on Figures of Speech
Related Posts
Some common figures of speech are alliteration, anaphora, antimetabole, antithesis, apostrophe, assonance, hyperbole, irony, metonymy, onomatopoeia, paradox, personification, pun, simile, synecdoche, and understatement.
Simile. Browse more Topics under Vocabulary. Metaphor. Personification. Hyperbole. Onomatopeia.
A figure of speech is a word or phrase that possesses a separate meaning from its literal definition. It can be a metaphor or simile designed to make a comparison. It can be the repetition of alliteration or the exaggeration of hyperbole to provide a dramatic effect
” Life is a highway” is an example of a metaphor.
“Life is like a box of chocolates” is an example of a simile.
Hope you found this blog on some popular figures of speech interesting and informative. Being familiar with these figures of speech can help you tremendously in preparing for various competitive exams. Need help in your preparation for IELTS , TOEFL or GMAT ? Leverage Live offers live interactive classes and doubt-clarification sessions by top certified experts who can help you ace your test with flying colours. Reach out to us today !Call us immediately at 1800 57 2000 for a free 30-minute counselling session.
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
14 comments
Wow this is amazing for better knowledge
Thanks for reading. You can also check: English Speech Topics for Students Speech on Right to Education Speech on Tourism in India Speech on Importance of Social Media
Thanks for reading. You can also check: English Speech Topics for Students Speech on Right to Education Speech on Tourism in India Speech on Importance of Social Media For more call us at 1800 57 2000!
Thanks for reading. Also, read: English Speech Topics for Students Speech on Child Labour Speech on Indian Culture Speech on Right to Education
This is so educational to an English teacher and very helpful for lesson preparation and presentation. I need more
Hi Ruth! Thank you for the comment, here are some more blogs for you to enjoy- https://leverageedu.com/blog/one-word-substitution/ https://leverageedu.com/blog/examples-of-simile/ https://leverageedu.com/blog/antonyms/
Tell us in the comments if these are helpful!
Figure of speech are a word or a phrase used in a distinctive way to produce a rhetorical effect
Excellent presentation
Hi, Ashit! Thank you for giving our blog a read! Here we are referring few other topics to read: Generation Gap Speech How to Write a Speech on Discipline? Parts of Speech
Hi Joy, It’s a delight to know that you have found our blog interesting and excellent. Thanks for the positive feedback. We highly appreciate it. Here are some more interesting reads that we would like to suggest to you: https://leverageedu.com/blog/english-speech-topics/ https://leverageedu.com/blog/asl-topics/ https://leverageedu.com/blog/speech-writing/ https://leverageedu.com/blog/public-speaking/

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
6 Figures of speech in English Literature with examples pdf
Table of Contents
Figures of Speech
What are figures of speech? What are 6 figures of speech in literature pdf?
The Figures of speech are explained in detail with pdf. You can learn all figures of speech with examples and definitions.
We have laid stress upon the qualities of simplicity in writing, because they are of the first importance and are the very aspects in which untrained writers are most likely to fail.
They feel that in order to write well they must employ unusual and high surrounding words. But we must remember that words are only to be used for the sake of sense.
Keeping in mind that the only real use of words is for the expression of thought, we wish you now to consider how the thought may be expressed with special clearness, force and beauty.
What are called Figures of Rhetoric or Figures of Speech?
An important means of doing this is by the use of what are called Figures of Rhetoric or Figures of Speech. A figure of rhetoric is a form of expression that departs in some way from direct, literal statement.
This may be in the choice or application of single words so as to make them mean more than in ordinary use. Aristotle said that Homer was the only poet who had found out “living words”.
This was because of Homer’s use of daring metaphors, such as, ‘An arrow impatient to be on the wing’, and ‘A weapon thirsting to drink the blood of an enemy.
Often the figure goes beyond any mere choice or arrangement of words, into the very structure and essence of thought. Such a figure may be a well-chosen comparison called in rhetoric a simile.
Thus we may say in direct, literal statement. The ship was helpless in the heavy sea. This is the plain, bare fact. But can we not picture that in some way, so as to make it more impressive?
Suppose we use a comparison and say: The ship was tossed like a chip on the waves. Now has not the cold, literal statement come to life? Do you not see the great ship flung about as a plaything by the wild waters? Such a figure appeals to the imagination, and thus renders the expression of the thought more vivid and interesting.
Observe that the thought is there; otherwise the figure would be empty and bombastic. There is some fault with a figure of speech which cannot be translated at will into clear, plain, literal statement. That fault is, that the figure has not a clear thought behind it. Keeping this in mind, you may trust an intelligent common sense to tell you when figure of speech is, or is not appropriate.
Language is figurative when the words used are not to be understood in their simple and literal signification, but in one suggested by the imagination of the speaker, and therefore appealing to the imagination of the hearer. Figures serve not merely to embellish language, but often to give it a point and force that it could not otherwise have.
Figurative and ordinary language may both be accurate and true to nature, but whereas one is bare presentation of the truth, the other is the truth aglow with colour, beauty and life. The purpose of speaking in figurative language is to give increased power and effect to what is said. Recapitulating the whole discussion.
When words are deflected from their normal use or invested with a special significance for the sake of increased effect, a departure is made from the plain ordinary mode of speaking, and this departure is termed a figure of speech. Thus, if instead of saying “It is wonderful” we say “How wonderful” or “He fights like a tiger instead of “He fights with great ferocity, “or” I shall leave your roof for “I shall leave your house”, we use language that is figurative. In the first case, the exclamatory form makes the words much more expressive. In the second case, the comparison with a tiger immediately calls up in the mind a vivid picture of this ferocious beast, and the words acquire a greater force than by the mere statement of an abstract quality. Abstract terms blur the lines of a picture because they are difficult to visualize. In the third instance, the mention of the roof brings more effectively home to us the protection implied by living in the same house.
From where figures of Speech is deviated?
“A Figure of Speech is a deviation from the plain and ordinary mode of writing, with a view to greater effect”. (Bain). By figures of speech we mean stylistic devices adopted by an author or a speaker with the object of giving clarity, tone, force or colour to his writing, or speech. In order to secure emphasis, vividness, beauty, or some other special effects, the ordinary arrangement or application of words is often found inadequate. In such cases, we intentionally adopt some special way of expressing our ideas: and these special ways of expression are called “Figures of Speech”. For instance, the phrase “as slowly as a snail” is much more vivid than the mere adverb “slowly”.
In order to make it more emphatic, an unfeeling, merciless man can be described as having “a heart of stone”. Instead of saying “She is very lovely”, we may say, “She is lovely as a rose” in order to secure greater vividness,
Such figures are intended to impress an idea on the understanding more strikingly or to touch the feelings more effectively. At the same time, they often add beauty; but in ordinary prose they should not be introduced merely for ornament. The ornamental use should be left to poets. Students should remember that over-decoration smacks of bad taste and, therefore, it is best to refrain from using too many similes and metaphors. “Whenever writing is tortured and twisted in order that a striking effect may be produced, it ceases to be agreeable; it smells of the lamp and like paint and powder when too evident, repels rather than attracts”. However, a simile or metaphor or an antithesis, if judiciously used, enhances the beauty of writing. Figurative language is intentional departure from normal, regular language to gain strength and freshness of expression, to create a picture quality and a poetic effect.
Figures of speech may be divided into six classes accordingly as they are based on
(1) Resemblance
(2) Contrast
(3) Association
(4) Construction
(5) Indirectness of Speech
FIGURES BASED ON RESEMBLANCE
These are by far the most numerous and important. The resemblance is generally between things widely different in nature, and is usually of such a character as to require the play of imagination to detect it. In a figure which assists the understanding by illuminating an idea as by a sudden flash of light, it will be invariably found that the word or words used figuratively deal with the commoner and more familiar perceptions or thoughts. In the use of figures of resemblance, the mind draws upon the simple and concrete in thought and speech to define, elucidate or illustrate the abstract and less known.
What are 6 Figures of Speech?
The chief figures of resemblance are:
When two unlike objects are compared and the comparison is introduced by the words as, as–so, like, we have a simile as:
My faith is as firm as a rock.
(2) Metaphor
It is an informal or implied simile in which the words “like’ ‘as’ are avoided. For example, “He is like a Giant. (Simile) “and “He is a Giant. (metaphor)”.
(3) Personification
Personification consists in attributing life and mind to inanimate things. ‘The mountains sing together, the hills rejoice and clap hands.
(4) Apostrophe
An apostrophe is a figure of speech by which some person (generally absent or dead) or some abstract idea personified is addressed. It consists in addressing something absent, as if present.
(5) Hyperbole
Hyperbole (Greek = overshooting) is a figure of speech in which the bounds of strict veracity are over-shot not for the sake of deceit but on account of emotion and for the sake of emphasis or humour.
(6) Euphemism
The prefix eu — is the Greek adverb = well, favourably. When something bad, shocking or ugly is glossed over from motives of delicacy or politeness, we have euphemism (literally, ‘speaking well’).
Vision, Allegory, Parable and Fable also come under the category of figures of resemblance.
Related Posts

8 Tips on Writing an Effective Essay in English
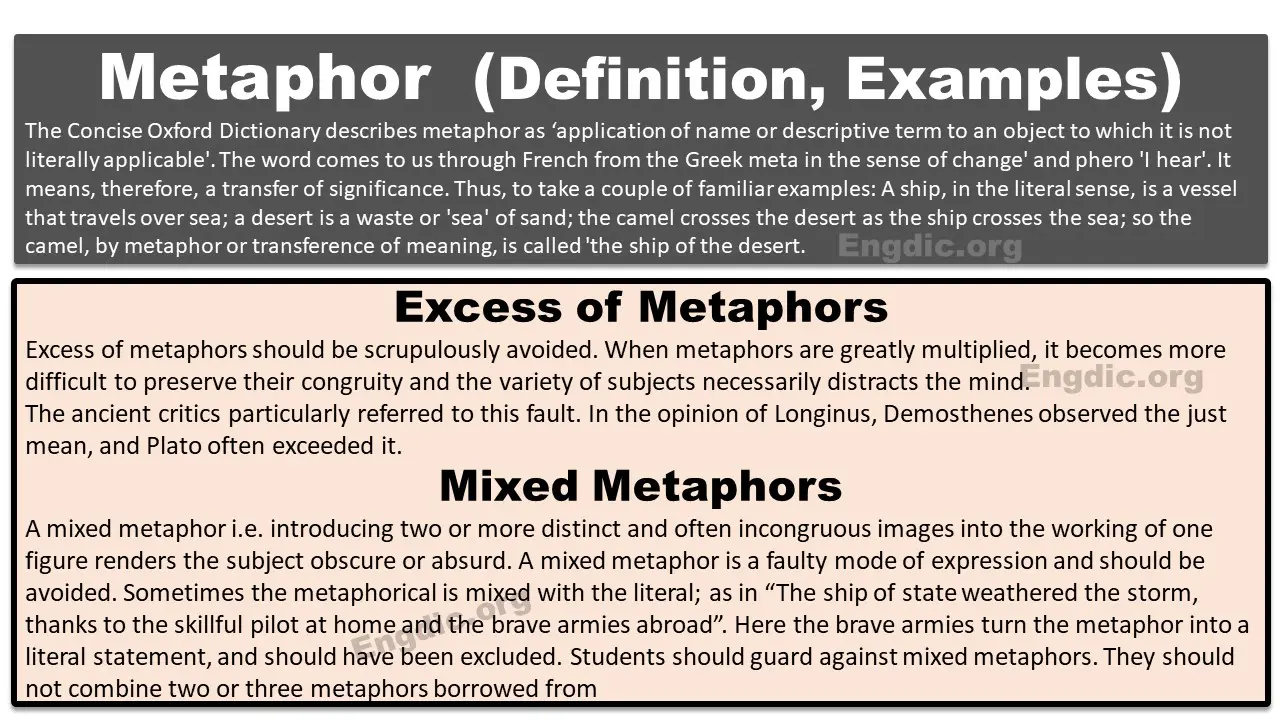
Metaphor in English literature with examples PDF

Examples of Hyperbole in English grammar

Essay Idioms: Idioms for Argumentative Essay

Simile and its types with examples PDF – Simile in Literature

Apostrophe in English with examples PDF
About the author.
Hi, I'm USMI, engdic.org's Author & Lifestyle Linguist. My decade-long journey in language and lifestyle curation fuels my passion for weaving words into everyday life. Join me in exploring the dynamic interplay between English and our diverse lifestyles. Dive into my latest insights, where language enriches every aspect of living.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Figures of Speech or Literary devices refer to the use of language in ways that are unusual or unique. These expressions are different from the way we ordinarily use language. Example: A: Ordinary Usage: I fell asleep at 10:00 pm. B: Special/Unusual: Sleep visited me at 10:00 pm. 'B' therefore contains a figure of speech.
TYPES OF FIGURES OF SPEECH The figures of speech list is over a hundred but some commonly used types are given along with examples. 1. SIMILE In simile two unlike things are explicitly compared. For example, "She is like a fairy". A simile is introduced by words such as like, so, as etc. 2. METAPHOR It is an informal or implied simile in ...
A figure of speech is a literary device in which language is used in an unusual—or "figured"—way in order to produce a stylistic effect. Figures of speech can be broken into two main groups: figures of speech that play with the ordinary meaning of words (such as metaphor, simile, and hyperbole ), and figures of speech that play with the ...
Download Free PDF. View PDF. Running head: 100 LITERARY DEVICES AND FIGURES OF SPEECH 1 100 Literary Devices and Figures of Speech Edward R. Raupp Gori State Teaching University 2020 Author Note Edward R. Raupp is Professor and Director of the Center for Foreign Languages at Gori State Teaching University.
Anaphora: [uh-naf-er-uh] Figure of repetition that occurs when the first word or set of words in one sentence, clause, or phrase is/are repeated at or very near the beginning of successive sentences, clauses, or phrases; repetition of the initial word(s) over successive phrases or clauses. Let us not wallow in the valley of despair.
PDF | On Apr 14, 2021, Ahmed T. Hussein published Literary Figures of Speech | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate ... In literature, apostrophe is a figure of speech ...
Literary Devices & Terms. Literary devices and terms are the techniques and elements—from figures of speech to narrative devices to poetic meters—that writers use to create narrative literature, poetry, speeches, or any other form of writing. All.
A figure of speech involving an inversion of a language's ordinary order of . words; for example, saying "smart you are" to mean "you are smart". In English, with its settled natural word order, departure from the expected word order emphasizes the displaced word or phrase: "beautiful" is emphasized in the City .
A figure of speech is a departure from the usual form of expression for the purpose of making the meaning clearer, more forceful, or more beautiful. Figures of speech are highly effective, for they add vividness, vigor, and beauty to our utterances. Though figures are the ornaments of speech, they should not be used unless they are natural and ...
A figure of speech is a word or phrase using figurative language—language that has other meaning than its normal definition. In other words, figures of speeches rely on implied or suggested meaning, rather than a dictionary definition. We express and develop them through hundreds of different rhetorical techniques, from specific types like ...
Most Common Figures of Speech. The following are some of the most common figures of speech that appear in literature and other written forms. Alliteration: This is a scheme that uses repetition of the same first consonant sound to create a musical effect."Francine found France quite lovely" is an example of alliteration because of the repeating f sound in the words Francine, found, and France.
City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative. Table of contents. No headers. This page titled 4.19: Figures of Speech is shared under a CC BY-NC license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap ( ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative) . Back to top. 4.18: Types of Imagery.
A figure of speech is a word or phrase possessing a figurative meaning that is different from its literal definition. Metaphor, simile, and irony are all examples of figures of speech. Figure ...
figure of speech, any intentional deviation from literal statement or common usage that emphasizes, clarifies, or embellishes both written and spoken language.Forming an integral part of language, figures of speech are found in oral literatures as well as in polished poetry and prose and in everyday speech. Greeting-card rhymes, advertising slogans, newspaper headlines, the captions of ...
A figure of speech is a word or phrase that is used in a non-literal way to create an effect. This effect may be rhetorical as in the deliberate arrangement of words to achieve something poetic, or imagery as in the use of language to suggest a visual picture or make an idea more vivid. Overall, figures of speech function as literary devices ...
This study aims at analysing the role of figur e of speech and its meaning in literary works. The use of. figure of speech in literary works is not only to create layers of meaning but also sense ...
Refrain/ (Repetition)- a word, phrase, line, or group of lines that is repeated, for effect, several times in a poem. Rhyme- the repetition of vowel sounds in accented syllables and all succeeding syllables. Internal- rhyme that occurs within a line of poetry or within consecutive lines. End Rhyme- rhyme that occurs at the ends of lines.
Types of Figures of Speech with Examples, Exercises, PDF, Different Types, in Poetry, About Life, rhetoric, Class 8, 9, Poetry. ... Examples in English Literature. Numerous figures of speech that are used as literary devices may be seen in works of literature. These add meaning to literature and showcase the power and beauty of figurative language.
Some figures of speech, like metaphor, simile, and metonymy, are found in everyday language. Others, like antithesis, circumlocution, and puns take more practice to implement in writing. Below are some common figures of speech with examples, so you can recognize them and use them in your writing. Give your writing extra polish.
PDF | Poetry, a form of literature, displays varieties of language use through figures of speech, the rhetorical devices. ... A History of English Literature is a comprehensive survey, in ...
Figurative Language Worksheet 3 - This file is actually four worksheets. Contains over 20 figures of speech from classic poems and stories and asks students to identifying the examples of figurative language and explain their answers. SITE NAVIGATION. Reading Worksheets Figurative Language Genre Language. from classic poems.
Figurative language is intentional departure from normal, regular language to gain strength and freshness of expression, to create a picture quality and a poetic effect. Figures of speech may be divided into six classes accordingly as they are based on. (1) Resemblance. (2) Contrast. (3) Association. (4) Construction. (5) Indirectness of Speech.
Figures of Speech.pdf - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.