Montaigne: Essays
53 pages • 1 hour read

Montaigne: Selected Essays
A modern alternative to SparkNotes and CliffsNotes, SuperSummary offers high-quality Study Guides with detailed chapter summaries and analysis of major themes, characters, and more.
Chapter Summaries & Analyses
Translator’s Preface-Book 1, Chapter 21
Book 1, Chapters 26, 28, 31, 39, and 50
Book 2, Chapters 6, 11, and 17
Book 2, Chapters 18, 28, and 30
Book 3, Chapters 2, 12, and 13
“Discourse on Voluntary Servitude”
Key Figures
Symbols & Motifs
Important Quotes
Essay Topics
Discussion Questions
Summary and Study Guide
Montaigne: Selected Essays comes from the pen of Michel de Montaigne , a 16th-century French jurist, advisor, and diplomat whose many adventures would make a compelling autobiography. Instead, Montaigne writes a series of short works that examine his innermost thoughts and feelings, attitudes and beliefs, preferences and daily habits. This would seem a dull topic, but Montaigne’s charm, wit, and wisdom shine through and make the mundane seem fascinating. His attitude is tolerant and open-minded for his era, and his ideas and insights remain relevant today. The essays have entertained and enlightened readers worldwide for over 400 years.
This edition of his book features eighteen of Montaigne’s 107 essays, along with a well-known and influential discourse by Montaigne’s dearest friend, Étienne de la Boétie . The essays were first published as three Books; those chosen for this edition are organized by Book. Most of the essays discuss several topics, but each contains a central theme.
Get access to this full Study Guide and much more!
- 7,500+ In-Depth Study Guides
- 4,900+ Quick-Read Plot Summaries
- Downloadable PDFs
In Book 1, the first essay, “By Differing Means We Attain the Same End,” describes two ways to win mercy after defeat in battle. The second essay, “Idleness,” explores the problem of a wandering mind. The third, “Through Philosophy We Learn How to Die,” suggests a proper attitude toward death. “The Power of the Imagination” shows how superstitions can kill, self-consciousness can defeat, and a doctor’s reassurance can cure.
“The Education of Children” lists Montaigne’s surprisingly modern ideas for how kids should be taught. In the process, we learn his prescription for how to help a young person grow into someone who will lead a worthwhile life.
“Friendship” explores the difference between ordinary companions and true friends. “The Cannibals” suggests that so-called “barbaric” tribes have lessons to teach Europeans. “Democritus and Heraclitus” finds common cause with famous pessimists.
The SuperSummary difference
- 8x more resources than SparkNotes and CliffsNotes combined
- Study Guides you won ' t find anywhere else
- 100+ new titles every month
In Book 2, “Practice” gives tips on how to prepare for death; “Cruelty” talks about how hard it is to be virtuous; “Being Presumptuous” attacks vanity and putting on airs; “Correcting” rails against lying. In “To Everything There Is a Season,” Montaigne scoffs at old men who try to stay young. “A Malformed Child” opines that everything, even the strange or deformed, is part of Nature’s plan.
Three selections come from Book 3: “Repenting”, on the folly of apologizing for who you really are; “Physiognomy,” on the wars and plagues that visit Montaigne’s neighborhood; and “Experience,” which touts the virtues of common sense over fancy ideals.
The final section is the essay “Discourse on Voluntary Servitude,” a call to arms against tyranny that influences revolutionaries and philosophers for centuries. It also affects Montaigne’s thinking, as it comes from the man Montaigne loved most in the world, Étienne de la Boétie.
Montaigne’s style is direct, lively, humorous, and sometimes bawdy and coarse. He wanders from topic to topic in the style of a lively conversation. Though he cites frequently the sayings of ancient philosophers, he also trusts his own judgment, and the gist of the essays is that we, too, should trust ourselves—that life isn’t so much a problem to be solved as an experience to be enjoyed for what it is.
The book’s original French is translated into English for modern Americans; it contains extensive footnotes, many of which provide historical background and serve as annotations well worth consulting.
Editor’s note: This guide refers to the 2012 Hackett Classics edition, translated by James B. Atkinson and Martin Sices.

Don't Miss Out!
Access Study Guide Now
Featured Collections
Elizabethan Era
View Collection
French Literature
Philosophy, Logic, & Ethics
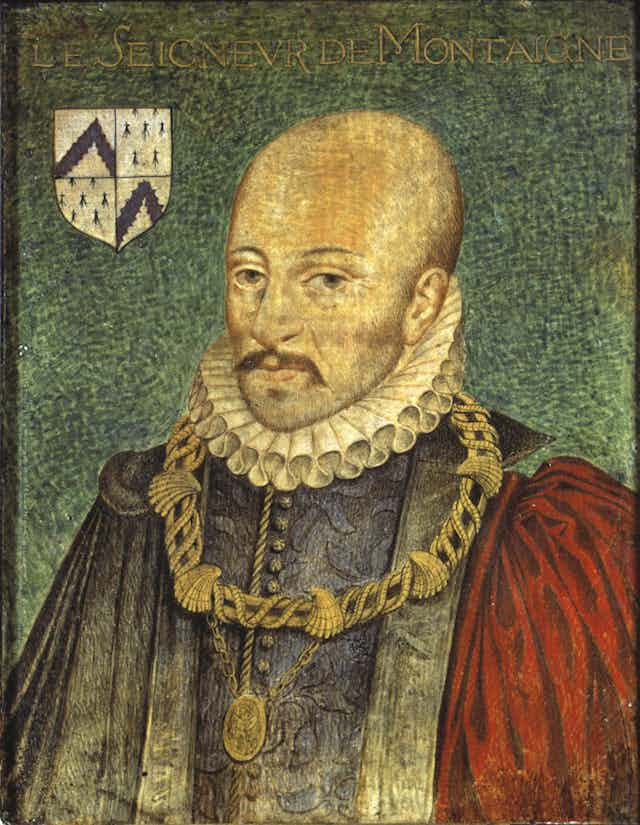

Guide to the classics: Michel de Montaigne’s Essays
Associate Professor in Philosophy, Deakin University
Disclosure statement
Matthew Sharpe is part of an ARC funded project on modern reinventions of the ancient idea of "philosophy as a way of life", in which Montaigne is a central figure.
Deakin University provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
When Michel de Montaigne retired to his family estate in 1572, aged 38, he tells us that he wanted to write his famous Essays as a distraction for his idle mind . He neither wanted nor expected people beyond his circle of friends to be too interested.
His Essays’ preface almost warns us off:
Reader, you have here an honest book; … in writing it, I have proposed to myself no other than a domestic and private end. I have had no consideration at all either to your service or to my glory … Thus, reader, I myself am the matter of my book: there’s no reason that you should employ your leisure upon so frivolous and vain a subject. Therefore farewell.
The ensuing, free-ranging essays, although steeped in classical poetry, history and philosophy, are unquestionably something new in the history of Western thought. They were almost scandalous for their day.
No one before Montaigne in the Western canon had thought to devote pages to subjects as diverse and seemingly insignificant as “Of Smells”, “Of the Custom of Wearing Clothes”, “Of Posting” (letters, that is), “Of Thumbs” or “Of Sleep” — let alone reflections on the unruliness of the male appendage , a subject which repeatedly concerned him.
French philosopher Jacques Rancière has recently argued that modernism began with the opening up of the mundane, private and ordinary to artistic treatment. Modern art no longer restricts its subject matters to classical myths, biblical tales, the battles and dealings of Princes and prelates.

If Rancière is right, it could be said that Montaigne’s 107 Essays, each between several hundred words and (in one case) several hundred pages, came close to inventing modernism in the late 16th century.
Montaigne frequently apologises for writing so much about himself. He is only a second rate politician and one-time Mayor of Bourdeaux, after all. With an almost Socratic irony , he tells us most about his own habits of writing in the essays titled “Of Presumption”, “Of Giving the Lie”, “Of Vanity”, and “Of Repentance”.
But the message of this latter essay is, quite simply, that non, je ne regrette rien , as a more recent French icon sang:
Were I to live my life over again, I should live it just as I have lived it; I neither complain of the past, nor do I fear the future; and if I am not much deceived, I am the same within that I am without … I have seen the grass, the blossom, and the fruit, and now see the withering; happily, however, because naturally.
Montaigne’s persistence in assembling his extraordinary dossier of stories, arguments, asides and observations on nearly everything under the sun (from how to parley with an enemy to whether women should be so demure in matters of sex , has been celebrated by admirers in nearly every generation.
Within a decade of his death, his Essays had left their mark on Bacon and Shakespeare. He was a hero to the enlighteners Montesquieu and Diderot. Voltaire celebrated Montaigne - a man educated only by his own reading, his father and his childhood tutors – as “the least methodical of all philosophers, but the wisest and most amiable”. Nietzsche claimed that the very existence of Montaigne’s Essays added to the joy of living in this world.

More recently, Sarah Bakewell’s charming engagement with Montaigne, How to Live or a Life of Montaigne in One Question and Twenty Attempts at an Answer (2010) made the best-sellers’ lists. Even today’s initiatives in teaching philosophy in schools can look back to Montaigne (and his “ On the Education of Children ”) as a patron saint or sage .
So what are these Essays, which Montaigne protested were indistinguishable from their author? (“ My book and I go hand in hand together ”).
It’s a good question.
Anyone who tries to read the Essays systematically soon finds themselves overwhelmed by the sheer wealth of examples, anecdotes, digressions and curios Montaigne assembles for our delectation, often without more than the hint of a reason why.
To open the book is to venture into a world in which fortune consistently defies expectations; our senses are as uncertain as our understanding is prone to error; opposites turn out very often to be conjoined (“ the most universal quality is diversity ”); even vice can lead to virtue. Many titles seem to have no direct relation to their contents. Nearly everything our author says in one place is qualified, if not overturned, elsewhere.
Without pretending to untangle all of the knots of this “ book with a wild and desultory plan ”, let me tug here on a couple of Montaigne’s threads to invite and assist new readers to find their own way.
Philosophy (and writing) as a way of life
Some scholars argued that Montaigne began writing his essays as a want-to-be Stoic , hardening himself against the horrors of the French civil and religious wars , and his grief at the loss of his best friend Étienne de La Boétie through dysentery.

Certainly, for Montaigne, as for ancient thinkers led by his favourites, Plutarch and the Roman Stoic Seneca, philosophy was not solely about constructing theoretical systems, writing books and articles. It was what one more recent admirer of Montaigne has called “ a way of life ”.
Montaigne has little time for forms of pedantry that value learning as a means to insulate scholars from the world, rather than opening out onto it. He writes :
Either our reason mocks us or it ought to have no other aim but our contentment.
We are great fools . ‘He has passed over his life in idleness,’ we say: ‘I have done nothing today.’ What? have you not lived? that is not only the fundamental, but the most illustrious of all your occupations.
One feature of the Essays is, accordingly, Montaigne’s fascination with the daily doings of men like Socrates and Cato the Younger ; two of those figures revered amongst the ancients as wise men or “ sages ”.
Their wisdom, he suggests , was chiefly evident in the lives they led (neither wrote a thing). In particular, it was proven by the nobility each showed in facing their deaths. Socrates consented serenely to taking hemlock, having been sentenced unjustly to death by the Athenians. Cato stabbed himself to death after having meditated upon Socrates’ example , in order not to cede to Julius Caesar’s coup d’état .

To achieve such “philosophic” constancy, Montaigne saw, requires a good deal more than book learning . Indeed, everything about our passions and, above all, our imagination , speaks against achieving that perfect tranquillity the classical thinkers saw as the highest philosophical goal.
We discharge our hopes and fears, very often, on the wrong objects, Montaigne notes , in an observation that anticipates the thinking of Freud and modern psychology. Always, these emotions dwell on things we cannot presently change. Sometimes, they inhibit our ability to see and deal in a supple way with the changing demands of life.
Philosophy, in this classical view, involves a retraining of our ways of thinking, seeing and being in the world. Montaigne’s earlier essay “ To philosophise is to learn how to die ” is perhaps the clearest exemplar of his indebtedness to this ancient idea of philosophy.
Yet there is a strong sense in which all of the Essays are a form of what one 20th century author has dubbed “ self-writing ”: an ethical exercise to “strengthen and enlighten” Montaigne’s own judgement, as much as that of we readers:
And though nobody should read me, have I wasted time in entertaining myself so many idle hours in so pleasing and useful thoughts? … I have no more made my book than my book has made me: it is a book consubstantial with the author, of a peculiar design, a parcel of my life …
As for the seeming disorder of the product, and Montaigne’s frequent claims that he is playing the fool , this is arguably one more feature of the Essays that reflects his Socratic irony. Montaigne wants to leave us with some work to do and scope to find our own paths through the labyrinth of his thoughts, or alternatively, to bobble about on their diverting surfaces .
A free-thinking sceptic
Yet Montaigne’s Essays, for all of their classicism and their idiosyncracies, are rightly numbered as one of the founding texts of modern thought . Their author keeps his own prerogatives, even as he bows deferentially before the altars of ancient heroes like Socrates, Cato, Alexander the Great or the Theban general Epaminondas .

There is a good deal of the Christian, Augustinian legacy in Montaigne’s makeup. And of all the philosophers, he most frequently echoes ancient sceptics like Pyrrho or Carneades who argued that we can know almost nothing with certainty. This is especially true concerning the “ultimate questions” the Catholics and Huguenots of Montaigne’s day were bloodily contesting.
Writing in a time of cruel sectarian violence , Montaigne is unconvinced by the ageless claim that having a dogmatic faith is necessary or especially effective in assisting people to love their neighbours :
Between ourselves, I have ever observed supercelestial opinions and subterranean manners to be of singular accord …
This scepticism applies as much to the pagan ideal of a perfected philosophical sage as it does to theological speculations.
Socrates’ constancy before death, Montaigne concludes, was simply too demanding for most people, almost superhuman . As for Cato’s proud suicide, Montaigne takes liberty to doubt whether it was as much the product of Stoic tranquility, as of a singular turn of mind that could take pleasure in such extreme virtue .
Indeed when it comes to his essays “ Of Moderation ” or “ Of Virtue ”, Montaigne quietly breaks the ancient mold. Instead of celebrating the feats of the world’s Catos or Alexanders, here he lists example after example of people moved by their sense of transcendent self-righteousness to acts of murderous or suicidal excess.
Even virtue can become vicious, these essays imply, unless we know how to moderate our own presumptions.
Of cannibals and cruelties
If there is one form of argument Montaigne uses most often, it is the sceptical argument drawing on the disagreement amongst even the wisest authorities.
If human beings could know if, say, the soul was immortal, with or without the body, or dissolved when we die … then the wisest people would all have come to the same conclusions by now, the argument goes. Yet even the “most knowing” authorities disagree about such things, Montaigne delights in showing us .
The existence of such “ an infinite confusion ” of opinions and customs ceases to be the problem, for Montaigne. It points the way to a new kind of solution, and could in fact enlighten us.
Documenting such manifold differences between customs and opinions is, for him, an education in humility :
Manners and opinions contrary to mine do not so much displease as instruct me; nor so much make me proud as they humble me.
His essay “ Of Cannibals ” for instance, presents all of the different aspects of American Indian culture, as known to Montaigne through travellers’ reports then filtering back into Europe. For the most part, he finds these “savages’” society ethically equal, if not far superior, to that of war-torn France’s — a perspective that Voltaire and Rousseau would echo nearly 200 years later.
We are horrified at the prospect of eating our ancestors. Yet Montaigne imagines that from the Indians’ perspective, Western practices of cremating our deceased, or burying their bodies to be devoured by the worms must seem every bit as callous.
And while we are at it, Montaigne adds that consuming people after they are dead seems a good deal less cruel and inhumane than torturing folk we don’t even know are guilty of any crime whilst they are still alive …
A gay and sociable wisdom

“So what is left then?”, the reader might ask, as Montaigne undermines one presumption after another, and piles up exceptions like they had become the only rule.
A very great deal , is the answer. With metaphysics, theology, and the feats of godlike sages all under a “ suspension of judgment ”, we become witnesses as we read the Essays to a key document in the modern revaluation and valorization of everyday life.
There is, for instance, Montaigne’s scandalously demotic habit of interlacing words, stories and actions from his neighbours, the local peasants (and peasant women) with examples from the greats of Christian and pagan history. As he writes :
I have known in my time a hundred artisans, a hundred labourers, wiser and more happy than the rectors of the university, and whom I had much rather have resembled.
By the end of the Essays, Montaigne has begun openly to suggest that, if tranquillity, constancy, bravery, and honour are the goals the wise hold up for us, they can all be seen in much greater abundance amongst the salt of the earth than amongst the rich and famous:
I propose a life ordinary and without lustre: ‘tis all one … To enter a breach, conduct an embassy, govern a people, are actions of renown; to … laugh, sell, pay, love, hate, and gently and justly converse with our own families and with ourselves … not to give our selves the lie, that is rarer, more difficult and less remarkable …
And so we arrive with these last Essays at a sentiment better known today from another philosopher, Friedrich Nietzsche, the author of A Gay Science (1882) .
Montaigne’s closing essays repeat the avowal that: “ I love a gay and civil wisdom … .” But in contrast to his later Germanic admirer, the music here is less Wagner or Beethoven than it is Mozart (as it were), and Montaigne’s spirit much less agonised than gently serene.
It was Voltaire, again, who said that life is a tragedy for those who feel, and a comedy for those who think. Montaigne adopts and admires the comic perspective . As he writes in “Of Experience”:
It is not of much use to go upon stilts , for, when upon stilts, we must still walk with our legs; and when seated upon the most elevated throne in the world, we are still perched on our own bums.
- Classic literature
- Michel de Montaigne

Project Offier - Diversity & Inclusion

Senior Lecturer - Earth System Science

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Deputy Social Media Producer

Associate Professor, Occupational Therapy

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top

François Quesnel, “Montaigne”, c. 1590, drawing reprinted with permission from the Montaigne Studies website
Michel de Montaigne
The question is not who will hit the ring, but who will make the best runs at it.
Given the huge breadth of his readings, Montaigne could have been ranked among the most erudite humanists of the XVI th century. But in the Essays , his aim is above all to exercise his own judgment properly. Readers who might want to convict him of ignorance would find nothing to hold against him, he said, for he was exerting his natural capacities, not borrowed ones. He thought that too much knowledge could prove a burden, preferring to exert his “natural judgment” to displaying his erudition.
3. A Philosophy of Free Judgment
4. montaigne’s scepticism, 5. montaigne and relativism, 6. montaigne’s legacy from charron to hobbes, 7. conclusion, translations in english, secondary sources, translations, related entries.
Montaigne (1533–1592) came from a rich bourgeois family that acquired nobility after his father fought in Italy in the army of King Francis I of France; he came back with the firm intention of bringing refined Italian culture to France. He decorated his Périgord castle in the style of an ancient Roman villa. He also decided that his son would not learn Latin in school. He arranged instead for a German preceptor and the household to speak to him exclusively in Latin at home. So the young Montaigne grew up speaking Latin and reading Vergil, Ovid, and Horace on his own. At the age of six, he was sent to board at the Collège de Guyenne in Bordeaux, which he later praised as the best humanist college in France, though he found fault with humanist colleges in general. Where Montaigne later studied law, or, indeed, whether he ever studied law at all is not clear. The only thing we know with certainty is that his father bought him an office in the Court of Périgueux. He then met Etienne de La Boëtie with whom he formed an intimate friendship and whose death some years later, in 1563, left him deeply distraught. Tired of active life, he retired at the age of only 37 to his father’s castle. In the same year, 1571, he was nominated Gentleman of King Charles IX’s Ordinary Chamber, and soon thereafter, also of Henri de Navarre’s Chamber. He received the decoration of the Order of Saint-Michel, a distinction all the more exceptional as Montaigne’s lineage was from recent nobility. On the title page of the first edition (1580) of the Essays , we read: “Essais de Messire Michel Seigneur de Montaigne, Chevalier de l’ordre du Roy, & Gentilhomme ordinaire de sa chambre.” Initially keen to show off his titles and, thus, his social standing, Montaigne had the honorifics removed in the second edition (1582).
Replicating Petrarca’s choice in De vita solitaria , Montaigne chose to dedicate himself to the Muses. In his library, which was quite large for the period, he had wisdom formulas carved on the wooden beams. They were drawn from, amongst others, Ecclesiastes , Sextus Empiricus, Lucretius, and other classical authors, whom he read intensively. To escape fits of melancholy, he began to commit his thoughts to paper. In 1580, he undertook a journey to Italy, whose main goal was to cure the pain of his kidney stones at thermal resorts. The journey is related in part by a secretary, in part by Montaigne himself, in a manuscript that was only discovered during the XVIII th century, given the title The Journal of the Journey to Italy , and forgotten soon after. While Montaigne was taking the baths near Pisa, he learnt of his election as Mayor of Bordeaux. He was first tempted to refuse out of modesty, but eventually accepted (he even received a letter from the King urging him to take the post) and was later re-elected. In his second term he came under criticism for having abandoned the town during the great plague in an attempt to protect himself and his family. His time in office was dimmed by the wars of religion between Catholics and Protestants. Several members of his family converted to Protestantism, but Montaigne himself remained a Catholic.
Montaigne wrote three books of Essays . (“Essay” was an original name for this kind of work; it became an appreciated genre soon after.) Three main editions are recognized: 1580 (at this stage, only the first two books were written), 1588, and 1595. The last edition, which could not be supervised by Montaigne himself, was edited from the manuscript by his adoptive daughter Marie de Gournay. Till the end of the XIX th century, the copy text for all new editions was that of 1595; Fortunat Strowski and shortly after him Pierre Villey dismissed it in favor of the “Bordeaux copy”, a text of the 1588 edition supplemented by manuscript additions. [ 1 ] Montaigne enriched his text continuously; he preferred to add for the sake of diversity, rather than to correct. [ 2 ] The unity of the work and the order of every single chapter remain problematic. We are unable to detect obvious links from one chapter to the next: in the first book, Montaigne jumps from “Idleness” (I,8) to “Liars” (I,9), then from “Prompt or slow speech” (I,10) to “Prognostications” (I,11). The random aspect of the work, acknowledged by the author himself, has been a challenge for commentators ever since. Part of the brilliance of the Essays lies in this very ability to elicit various forms of explanatory coherence whilst at the same time defying them. The work is so rich and flexible that it accommodates virtually any academic trend. Yet, it is also so resistant to interpretation that it reveals the limits of each interpretation.
Critical studies of the Essays have, until recently, been mainly of a literary nature. However, to consider Montaigne as a writer rather than as a philosopher can be a way of ignoring a disturbing thinker. Indeed, he shook some fundamental aspects of Western thought, such as the superiority we assign to man over animals, [ 3 ] to European civilization over “Barbarians”, [ 4 ] or to reason as an alleged universal standard. A tradition rooted in the 19th century tends to relegate his work to the status of literary impressionism or to the expression of a frivolous subjectivity. To do him justice, one needs to bear in mind the inseparable unity of thought and style in his work. Montaigne’s repeated revisions of his text, as modern editions show with the three letters A, B, C, standing for the three main editions, mirror the relationship between the activity of his thought and the Essays as a work in progress. The Essays display both the laboriousness and the delight of thinking.
In Montaigne we have a writer whose work is deeply infused by philosophical thought. One verse out of sixteen in Lucretius’ De natura rerum is quoted in the Essays . [ 5 ] If it is true, as Edmund Husserl said, that philosophy is a shared endeavor, Montaigne is perhaps the most exemplary of philosophers since his work extensively borrows and quotes from others. Montaigne managed to internalize a huge breadth of reading, so that his erudition does not appear as such. He created a most singular work, yet one that remains deeply rooted in the community of poets, historians, and philosophers. His decision to use only his own judgment in dealing with all sorts of matters, his resolutely distant attitude towards memory and knowledge, his warning that we should not mix God or transcendent principles with the human world, are some of the key elements that characterize Montaigne’s position. As a humanist, he considered that one has to assimilate the classics, but above all to display virtue, “according to the opinion of Plato, who says that steadfastness, faith, and sincerity are real philosophy, and the other sciences which aim at other things are only powder and rouge.” [ 6 ]
Montaigne rejects the theoretical or speculative way of philosophizing that prevailed under the Scholastics ever since the Middle Ages. According to him, science does not exist, but only a general belief in science. Petrarch had already criticized the Scholastics for worshiping Aristotle as their God. Siding with the humanists, Montaigne develops a sharp criticism of science “à la mode des Geométriens”, [ 7 ] the mos geometricus deemed to be the most rigorous. It is merely “a practice and business of science”, [ 8 ] he says, which is restricted to the University and essentially carried out between masters and their disciples. The main problem of this kind of science is that it makes us spend our time justifying as rational the beliefs we inherit, instead of calling into question their foundations; it makes us label fashionable opinions as truth, instead of gauging their strength. Whereas science should be a free inquiry, it consists only in gibberish discussions on how we should read Aristotle or Galen. [ 9 ] Critical judgment is systematically silenced. Montaigne demands a thought process that would not be tied down by any doctrinaire principle, a thought process that would lead to free enquiry.
If we trace back the birth of modern science, we find that Montaigne as a philosopher was ahead of his time. In 1543, Copernicus put the earth in motion, depriving man of his cosmological centrality. Yet he nevertheless changed little in the medieval conception of the world as a sphere. The Copernican world became an “open” world only with Thomas Digges (1576) although his sky was still situated in space, inhabited by gods and angels. [ 10 ] One has to wait for Giordano Bruno to find the first representative of the modern conception of an infinite universe (1584). But whether Bruno is a modern mind remains controversial (the planets are still animals, etc). Montaigne, on the contrary, is entirely free from the medieval conception of the spheres. He owes his cosmological freedom to his deep interest in ancient philosophers, to Lucretius in particular. In the longest chapter of the Essays , the “Apologie de Raymond Sebond”, Montaigne conjures up many opinions, regarding the nature of the cosmos, or the nature of the soul. He weighs the Epicureans’ opinion that several worlds exist, against that of the unicity of the world put forth by both Aristotle and Aquinas. He comes out in favor of the former, without ranking his own evaluation as a truth.
As a humanist, Montaigne conceived of philosophy as morals. In the chapter “On the education of children”, [ 11 ] education is identified with philosophy, this being understood as the formation of judgment and manners in everyday life: “for philosophy, which, as the molder of judgment and conduct, will be his principal lesson, has the privilege of being everywhere at home”. [ 12 ] Philosophy, which consists essentially in the use of judgment, is significant to the very ordinary, varied and “undulating” [ 13 ] process of life. In fact, under the guise of innocuous anecdotes, Montaigne achieved the humanist revolution in philosophy. He moved from a conception of philosophy conceived of as theoretical science, to a philosophy conceived of as the practice of free judgment. Lamenting that “philosophy, even with people of understanding, should be an empty and fantastic name, a thing of no use and no value”, [ 14 ] he asserted that philosophy should be the most cheerful activity. He practised philosophy by setting his judgment to trial, in order to become aware of its weaknesses, but also to get to know its strength. “Every movement reveals us”, [ 15 ] but our judgments do so the best. At the beginning of the past century, one of Montaigne’s greatest commentators, Pierre Villey, developed the idea that Montaigne truly became himself through writing. This idea remains more or less true, in spite of its obvious link with late romanticist psychology. The Essays remain an exceptional historical testimony of the progress of privacy and individualism, a blossoming of subjectivity, an attainment of personal maturity that will be copied, but maybe never matched since. It seems that Montaigne, who dedicated himself to freedom of the mind and peacefulness of the soul, did not have any other aim through writing than cultivating and educating himself. Since philosophy had failed to determine a secure path towards happiness, he committed each individual to do so in his own way. [ 16 ]
Montaigne wants to escape the stifling of thought by knowledge, a wide-spread phenomenon which he called “pedantism”, [ 17 ] an idea that he may have gleaned from the tarnishing of professors by the Commedia dell’arte . He praises one of the most famous professors of the day, Adrianus Turnebus, for having combined robust judgment with massive erudition. We have to moderate our thirst for knowledge, just as we do our appetite for pleasure. Siding here with Callicles against Plato, Montaigne asserts that a gentleman should not dedicate himself entirely to philosophy. [ 18 ] Practised with restraint, it proves useful, whereas in excess it leads to eccentricity and insociability. [ 19 ] Reflecting on the education of the children of the aristocracy (chapter I, 26, is dedicated to the countess Diane de Foix, who was then pregnant), Montaigne departs significantly from a traditional humanist education, the very one he himself received. Instead of focusing on the ways and means of making the teaching of Latin more effective, as pedagogues in the wake of Erasmus usually did, Montaigne stresses the need for action and playful activities. The child will conform early to social and political customs, but without servility. The use of judgment in every circumstance, as a warrant for practical intelligence and personal freedom, has to remain at the core of education. He transfers the major responsibility of education from the school to everyday life: “Wonderful brilliance may be gained for human judgment by getting to know men”. [ 20 ] The priority given to the formation of judgment and character strongly opposes the craving for a powerful memory during his time. He reserves for himself the freedom to pick up bits of knowledge here and there, displaying the “nonchalance” or unconcern intellectually, much in the same way that Castiglione’s courtier would use sprezzatura in social relationships. Although Montaigne presents this nonchalance as essential to his nature, his position is not innocent: it allows him to take on the voice now of a Stoic, and then of a Sceptic, now of an Epicurean and then of a Christian. Although his views are never fully original, they always bear his unmistakable mark. Montaigne’s thought, which is often rated as modern in so many aspects, remains deeply rooted in the classical tradition. Montaigne navigates easily through heaps of classical knowledge, proposing remarkable literary and philosophical innovations along the way.
Montaigne begins his project to know man by noticing that the same human behavior can have opposite effects, or that even opposite conducts can have the same effects: “by diverse means we arrive at the same end”. [ 21 ] Human life cannot be turned into an object of rational theory. Human conduct does not obey universal rules, but a great diversity of rules, among which the most accurate still fall short of the intended mark. “Human reason is a tincture infused in about equal strength in all our opinions and ways, whatever their form: infinite in substance, infinite in diversity” [ 22 ] says the chapter on custom. By focusing on anecdotal experience, Montaigne comes thus to write “the masterpiece of modern moral science”, according to the great commentator Hugo Friedrich. He gives up the moral ambition of telling how men should live, in order to arrive at a non-prejudiced mind for knowing man as he is. “Others form man, I tell of him”. [ 23 ] Man is ever since “without a definition”, as philosopher Marcel Conche commented. [ 24 ] In the chapter “Apologie de Raimond Sebond”, Montaigne draws from classical and Renaissance knowledge in order to remind us that, in some parts of the world, we find men that bear little resemblance to us. Our experience of man and things should not be perceived as limited by our present standards of judgment. It is a sort of madness when we settle limits for the possible and the impossible. [ 25 ]
Philosophy has failed to secure man a determined idea of his place in the world, or of his nature. Metaphysical or psychological opinions, indeed far too numerous, come as a burden more than as a help. Montaigne pursues his quest for knowledge through experience; the meaning of concepts is not set down by means of a definition, it is related to common language or to historical examples. One of the essential elements of experience is the ability to reflect on one’s actions and thoughts. Montaigne is engaging in a case-by-case gnôti seauton , “know thyself”: although truth in general is not truly an appropriate object for human faculties, we can reflect on our experience. What counts is not the fact that we eventually know the truth or not, but rather the way in which we seek it. “The question is not who will hit the ring, but who will make the best runs at it.” [ 26 ] The aim is to properly exercise our judgment.
Montaigne’s thinking baffles our most common categories. The vision of an ever-changing world that he developed threatens the being of all things. “We have no communication with being”. [ 27 ] We wrongly take that which appears for that which is, and we indulge in a dogmatic, deceptive language that is cut off from an ever-changing reality. We ought to be more careful with our use of language. Montaigne would prefer that children be taught other ways of speaking, more appropriate to the nature of human inquiry, such as “What does that mean ?”, “I do not understand it”, “This might be”, “Is it true?” [ 28 ] Montaigne himself is fond of “these formulas that soften the boldness of our propositions”: “perhaps”, “to some extent”, “they say”, “I think”, [ 29 ] and the like. Criticism on theory and dogmatism permeates for example his reflexion on politics. Because social order is too complicated to be mastered by individual reason, he deems conservatism as the wisest stance. [ 30 ] This policy is grounded on the general evaluation that change is usually more damaging than the conservation of social institutions. Nevertheless, there may be certain circumstances that advocate change as a better solution, as history sometimes showed. Reason being then unable to decide a priori , judgment must come into play and alternate its views to find the best option.
With Cornelius Agrippa, Henri Estienne or Francisco Sanchez, among others, Montaigne has largely contributed to the rebirth of scepticism during the XVI th century. His literary encounter with Sextus produced a decisive shock: around 1576, when Montaigne had his own personal medal coined, he had it engraved with his age, with “ Epecho ” , “I abstain” in Greek, and another Sceptic motto in French: “ Que sais-je ?”: what do I know ? At this period in his life, Montaigne is thought to have undergone a “sceptical crisis”, as Pierre Villey famously commented. In fact, this interpretation dates back to Pascal, for whom scepticism could only be a sort of momentary frenzy. [ 31 ] The “Apologie de Raimond Sebond”, the longest chapter of the Essays , bears the sign of intellectual despair that Montaigne manages to shake off elsewhere. But another interpretation of scepticism formulates it as a strategy used to confront “fideism”: because reason is unable to demonstrate religious dogmas, we must rely on spiritual revelation and faith. The paradigm of fideism, a word which Montaigne does not use, has been delivered by Richard Popkin in History of Scepticism [ 32 ] . Montaigne appears here as a founding father of the Counter Reformation, being the leader of the “Nouveaux Pyrrhoniens”, for whom scepticism is used as a means to an end, that is, to neutralize the grip that philosophy once had on religion.
Commentators now agree upon the fact that Montaigne largely transformed the type of scepticism he borrowed from Sextus. The two sides of the scale are never perfectly balanced, since reason always tips the scale in favor of the present at hand. This imbalance undermines the key mechanism of isosthenia , the equality of strength of two opposing arguments. Since the suspension of judgment cannot occur “casually”, as Sextus Empiricus would like it to, judgment must abstain from giving its assent. In fact, the sources of Montaigne’s scepticism are much wider: his child readings of Ovid’s Metamorphosis , which gave him a deep awareness of change, the in utramque partem academic debate which he practised at the Collège de Guyenne (a pro and contra discussion inherited from Aristotle and Cicero), and the humanist philosophy of action, dealing with the uncertainty of human affairs, shaped his mind early on. Through them, he learned repeatedly that rational appearances are deceptive. In most of the chapters of the Essays , Montaigne now and then reverses his judgment: these sudden shifts of perspective are designed to escape adherence, and to tackle the matter from another point of view. [ 33 ] The Essays mirror a discreet conduct of judgment, in keeping with the formula iudicio alternante , which we still find engraved today on the beams of the Périgord castle’s library. The aim is not to ruin arguments by opposing them, as it is the case in the Pyrrhonian “antilogy”, but rather to counterbalance a single opinion by taking into account other opinions. In order to work, each scale of judgment has to be laden. If we take morals, for example, Montaigne refers to varied moral authorities, one of them being custom and the other reason. Against every form of dogmatism, Montaigne returns moral life to its original diversity and inherent uneasiness. Through philosophy, he seeks full accordance with the diversity of life: “As for me, I love life and cultivate it as God has been pleased to grant it to us”. [ 34 ]
We find two readings of Montaigne as a Sceptic. The first one concentrates on the polemical, negative arguments drawn from Sextus Empiricus, at the end of the “Apology”. This hard-line scepticism draws the picture of man as “humiliated”. [ 35 ] Its aim is essentially to fight the pretensions of reason and to annihilate human knowledge. “Truth”, “being” and “justice” are equally dismissed as unattainable. Doubt foreshadows here Descartes’ Meditations , on the problem of the reality of the outside world. Dismissing the objective value of one’s representations, Montaigne would have created the long-lasting problem of “solipsism”. We notice, nevertheless, that he does not question the reality of things — except occasionally at the very end of the “Apology” — but the value of opinions and men. The second reading of his scepticism puts forth that Cicero’s probabilism is of far greater significance in shaping the sceptical content of the Essays . After the 1570s, Montaigne no longer read Sextus; additions show, however, that he took up a more and more extensive reading of Cicero’s philosophical writings. We assume that, in his early search for polemical arguments against rationalism during the 1570s, Montaigne borrowed much from Sextus, but as he got tired of the sceptical machinery, and understood scepticism rather as an ethics of judgment, he went back to Cicero. [ 36 ] The paramount importance of the Academica for XVI th century thought has been underlined by Charles B. Schmitt. [ 37 ] In the free enquiry, which Cicero engaged throughout the varied doctrines, the humanists found an ideal mirror of their own relationship with the Classics. “The Academy, of which I am a follower, gives me the opportunity to hold an opinion as if it were ours, as soon as it shows itself to be highly probable” [ 38 ] , wrote Cicero in the De Officiis . Reading Seneca, Montaigne will think as if he were a member of the Stoa; then changing for Lucretius, he will think as if he had become an Epicurean, and so on. Doctrines or opinions, beside historical stuff and personal experiences, make up the nourishment of judgment. Montaigne assimilates opinions, according to what appears to him as true, without taking it to be absolutely true. He insists on the dialogical nature of thought, referring to Socrates’ way of keeping the discussion going: “The leader of Plato’s dialogues, Socrates, is always asking questions and stirring up discussion, never concluding, never satisfying (…).” [ 39 ] Judgment has to determine the most convincing position, or at least to determine the strengths and weaknesses of each position. The simple dismissal of truth would be too dogmatic a position; but if absolute truth is lacking, we still have the possibility to balance opinions. We have resources enough, to evaluate the various authorities that we have to deal with in ordinary life.
The original failure of commentators was perhaps in labelling Montaigne’s thought as “sceptic” without reflecting on the proper meaning of the essay. Montaigne’s exercise of judgment is an exercise of “natural judgment”, which means that judgment does not need any principle or any rule as a presupposition. In this way, many aspects of Montaigne’s thinking can be considered as sceptical, although they were not used for the sake of scepticism. For example, when Montaigne sets down the exercise of doubt as a good start in education, he understands doubt as part of the process of the formation of judgment. This process should lead to wisdom, characterized as “always joyful”. [ 40 ] Montaigne’s scepticism is not a desperate one. On the contrary, it offers the reader a sort of jubilation which relies on the modest but effective pleasure in dismissing knowledge, thus making room for the exercise of one’s natural faculties.
Renaissance thinkers strongly felt the necessity to revise their discourse on man. But no one accentuated this necessity more than Montaigne: what he was looking for, when reading historians or travellers such as Lopez de Gomara’s History of Indies , was the utmost variety of beliefs and customs that would enrich his image of man. Neither the Hellenistic Sage, nor the Christian Saint, nor the Renaissance Scholar, are unquestioned models in the Essays . Instead, Montaigne is considering real men, who are the product of customs. “Here they live on human flesh; there it is an act of piety to kill one’s father at a certain age (…).” [ 41 ] The importance of custom plays a polemical part: alongside with scepticism, the strength of imagination (chapter I,21) or Fortune (chapters I,1, I,24, etc.), it contributes to the devaluation of reason and will. It is bound to destroy our spontaneous confidence that we do know the truth, and that we live according to justice. During the XVI th century, the jurists of the “French school of law” showed that the law is tied up with historical determinations. [ 42 ] In chapter I,23, “On custom”, Montaigne seems to extrapolate on this idea : our opinions and conducts being everywhere the product of custom, references to universal “reason”, “truth”, or “justice” are to be dismissed as illusions. Pierre Villey was the first to use the terms “relativity” and “relativism”, which proved to be useful tools when commenting on the fact that Montaigne acknowledges that no universal reason presides over the birth of our beliefs. [ 43 ] The notion of absolute truth, applied to human matters, vitiates the understanding and wreaks havoc in society. Upon further reflexion, contingent customs impact everything: “in short, to my way of thinking, there is nothing that custom will not or cannot do”. [ 44 ] Montaigne calls it “Circe’s drink”. [ 45 ] Custom is a sort of witch, whose spell, among other effects, casts moral illusion. “The laws of conscience, which we say are born from nature, are born of custom. Each man, holding in inward veneration the opinions and the behavior approved and accepted around him, cannot break loose from them without remorse, or apply himself to them without self-satisfaction.” [ 46 ] The power of custom, indeed, not only guides man in his behavior, but also persuades him of its legitimacy. What is crime for one person will appear normal to another. In the XVII th century, Blaise Pascal will use this argument when challenging the pretension of philosophers of knowing truth. One century later, David Hume will lay stress on the fact that the power of custom is all the stronger, specifically because we are not aware of it. What are we supposed to do, then, if our reason is so flexible that it “changes with two degrees of elevation towards the pole”, as Pascal puts it? [ 47 ] For the Jansenist thinker, only one alternative exists, faith in Jesus Christ. However, it is more complicated in the case of Montaigne. Getting to know all sorts of customs, through his readings or travels, he makes an exemplary effort to open his mind. “We are all huddled and concentrated in ourselves, and our vision is reduced to the length of our nose.” [ 48 ] Custom’s grip is so strong that it is dubious as to whether we are in a position to become aware of it and shake off its power.
Montaigne was hailed by Claude Lévi-Strauss as the progenitor of the human sciences, and the pioneer of cultural relativism. [ 49 ] However, Montaigne has not been willing to indulge entirely in relativism. Judgment is at first sight unable to stop the relativistic discourse, but it is not left without remedy when facing the power of custom. Exercise of thought is the first counterweight we can make use of, for example when criticizing an existing law. Customs are not almighty, since their authority can be reflected upon, evaluated or challenged by individual judgment. The comparative method can also be applied to the freeing of judgment: although lacking a universal standard, we can nevertheless stand back from particular customs, by the mere fact of comparing them. Montaigne thus compares heating or circulating means between people. In a more tragical way, he denounces the fanaticism and the cruelty displayed by Christians against one another, during the civil wars in France, through a comparison with cannibalism: “I think there is more barbarity in eating a man alive than in eating him dead, and in tearing by tortures and the rack a body still full of feeling (…).” [ 50 ] The meaning of the word “barbarity” is not merely relative to a culture or a point of view, since there are degrees of barbarity. Passing a judgment on cannibals, Montaigne also says: “So we may well call these people barbarians, in respect to the rules of reason, but not in respect to ourselves, who surpass them in every kind of barbarity (…).” [ 51 ] Judgment is still endowed with the possibility of postulating universal standards, such as “reason” or “nature”, which help when evaluating actions and behaviors. Although Montaigne maintains in the “Apologie” that true reason and true justice are only known by God, he asserts in other chapters that these standards are somehow accessible to man, since they allow judgment to consider customs as particular and contingent rules. [ 52 ] In order to criticize the changeable and the relative, we must suppose that our judgment is still able to “bring things back to truth and reason”. [ 53 ] Man is everywhere enslaved by custom, but this does not mean that we should accept the numbing of our mind. Montaigne elaborates a pedagogy, which rests on the practice of judgment itself. The task of the pupil is not to repeat what the master said, but, on a given subject of problem, to confront his judgment with the master’s one. Moreover, relativistic readings of the Essays are forced to ignore certain passages that carry a more rationalistic tone. “The violent detriment inflicted by custom” (I,23) is certainly not a praise of custom, but an invitation to escape it. In the same way that Circe’s potion has changed men into pigs, custom turns their intelligence into stupidity. In the toughest cases, Montaigne’s critical use of judgment aims at giving “a good whiplash to the ordinary stupidity of judgment.” [ 54 ] In many other places, Montaigne boasts of himself being able to resist vulgar opinion. Independence of thinking, alongside with clear-mindedness and good faith, are the first virtues a young gentleman should acquire.
Pierre Charron was Montaigne’s friend and official heir. In De la sagesse (1601 and 1604), he re-organized many of his master’s ideas, setting aside the most disturbing ones. His work is now usually dismissed as a dogmatic misrepresentation of Montaigne’s thought. Nevertheless, his book was given priority over the Essays themselves during the whole XVII th century, especially after Malebranche’s critics conspired to have the Essays included in the Roman Index of 1677. Montaigne’s historical influence must be reckoned through the lens of this mediation. Moreover, Charron’s reading is not simply faulty. According to him, wisdom relies on the readiness of judgment to revise itself towards a more favorable outcome: [ 55 ] this idea is one of the most remarkable readings of the Essays in the early history of their reception.
The critical conception of the essay was taken up by the English scientist and philosopher Francis Bacon, who considered his own Essays as “fragments of [his] conceits” and “dispersed meditations”, aiming to stimulate the reader’s appetite for thinking and knowledge rather than satisfying it with expositions of dogmas and methods. [ 56 ] Even in his more scientific works, such as The Advancement of Learning , Bacon’s writing was inconclusive. He posited that this open and fragmentary style was the best way to inspire further thought and examination: “Aphorisms, representing a knowledge broken, do invite men to inquire further”. [ 57 ] Bacon’s reflections allow us to appreciate the scientific value of Montaigne’s Essays, insofar as they are incomplete works, always calling for subsequent reflections by the author and the reader, thus inspiring and promoting the development of ideas and the advancement of research.
The influence Montaigne had on Descartes has been commented upon by many critics, at least from the XIX th century on, within the context of the birth of modern science. As a sceptic, calling into question the natural link between mind and things, Montaigne would have won his position in the modern philosophical landscape. The scepticism in the “Apologie” is, no doubt, a main source of “solipsism”, but Descartes cannot be called a disciple of Montaigne in the sense that he would have inherited a doctrine. Above all, he owes the Périgourdin gentleman a way of educating himself. Far from substituting Montaigne for his Jesuit schoolteachers, Descartes decided to teach himself from scratch, following the path indicated by Montaigne to achieve independence and firmness of judgment. The mindset that Descartes inherited from the Essays appears as something particularly obvious, in the two first parts of the Discours de la méthode . As the young Descartes left the Collège de La Flèche, he decided to travel, and to test his own value in action. “I employed the rest of my youth to travel, to see courts and armies, to meet people of varied humors and conditions, to collect varied experiences, to try myself in the meetings that fortune was offering me (…).” [ 58 ] Education, taken out of a school context, is presented as an essay of the self through experience. The world, as pedagogue, has been substituted for books and teachers. This new education allows Descartes to get rid of the prejudice of overrating his own customs, a widespread phenomenon that we now call ethnocentrism. Montaigne’s legacy becomes particularly conspicuous when Descartes draws the lesson from his travels, “having acknowledged that those who have very contrary feelings to ours are not barbarians or savages, but that many of them make use of reason as much or more so than we do”. And also : “It is good to know something of different people, in order to judge our own with more sanity, and not to think that everything that is against our customs and habits is ridiculous and against reason, as usually do those who have never seen anything.” [ 59 ] Like Montaigne, Descartes begins by philosophizing on life with no other device than the a discipline of judgment: “I was learning not to believe anything too firmly, of which I had been persuaded through example and custom.” [ 60 ] He departs nevertheless from Montaigne when he will equate with error opinions that are grounded on custom. [ 61 ] The latter would not have dared to speak of error: varied opinions, having more or less authority, are to be weighed upon the scale of judgment. It is thus not correct to interpret Montaigne’s philosophy as a “criticism of prejudice” from a Cartesian stance.
In recent years, critics have stressed the importance of the connection between Montaigne and Hobbes for the development of a modern vision of politics, rooted in a criticism of traditional doctrines of man and society. At the time when Shakespeare was writing his plays, the first English translation of Montaigne’s Essays by John Florio (1603) became a widely-read classic in England. As a former student of Magdalen Hall (Oxford) and Saint John’s College (Cambridge), and as a young tutor and secretary to aristocratic and wealthy families, Thomas Hobbes had many opportunities to read Montaigne in the libraries he frequented. In his capacity as tutor, he traveled widely in Europe and spent several sojourns in France, before the English Civil War forced him into exile in Paris (1641–1651). During this period, Hobbes moved in skeptical and libertine circles and met scholars such as Sorbière, Gassendi, and La Mothe Le Vayer, all influenced by a shared reference to Montaigne’s skepticism. Historical documents and comparative research confirm the relevance of Montaigne’s influence on Hobbes’s work, from Elements of Law to Leviathan . [ 62 ] The two authors share a philosophical conception of man as driven by desire and imagination, and relentlessly striving for self-conservation and power. Montaigne identified human life with movement and instability, and pointed to the power that our passions have to push us toward imaginary future accomplishments (honor, glory, science, reason, and so on). [ 63 ] In Leviathan , Hobbes builds on this position to assert, as a general inclination of all mankind, “a perpetual and restless desire of power after power, that ceases only in death”. [ 64 ] This shared anthropology shows the extent to which Montaigne and Hobbes refute the Scholastic and Renaissance anthropocentric idea of man as a rational being at the summit of creation. On the contrary, they underline his instinctive and passionate nature, which eventually leads to violence and conflict wherever the political community collapses. This negative anthropology is to be understood in the light of the historical experience of the civil wars upsetting both their countries. [ 65 ] The threat of political turmoil imbued both Montaigne and Hobbes’ lives. Whereas Hobbes quoted the ancient saying homo homini lupus , and described the human condition outside the civil state as a war “where every man is enemy to every man”, [ 66 ] Montaigne seemed to go further, “having learned by experience, from the cruelty of some Christians, that there is no beast in the world to be feared by man as man”. [ 67 ] In order to avoid the outburst of violence, they both recognize the necessity of laws and obedience, a necessity that does not rely on any ontological or moral foundation. The normative force of law results from its practical necessity, as it is the rational condition of life in society. [ 68 ] As Montaigne wrote: “Now laws remain in credit not because they are just, but because they are laws”. [ 69 ] Questioning the Aristotelian vision of politics as a natural goal for humanity, Montaigne and Hobbes pointed out the man-made nature of civil authority, as founded in the need to preserve life and peace, avoiding violence and war.
Montaigne cultivates his liberty by not adhering exclusively to any one idea, while at the same time exploring them all. In exercising his judgment on various topics, he trains himself to go off on fresh tracks, starting from something he read or experienced. For Montaigne this also means calling into question the convictions of his time, reflecting upon his beliefs and education, and cultivating his own personal thoughts. His language can be said to obey only one rule, that is, to be “an effect of judgment and sincerity,” [ 70 ] which is the very one that he demands from the pupil. His language bears an unmistakable tone but contradicts itself sometimes from one place to another, perhaps for the very reason that it follows so closely the movements of thought.
If being a philosopher means being insensitive to human frailties and to the evils or to the pleasures which befall us, then Montaigne is not a philosopher. If it means using a “jargon”, and being able to enter the world of scholars, then Montaigne is not one either. Yet, if being a philosopher is being able to judge properly in any circumstances of life, then the Essays are the exemplary testimony of an author who wanted to be a philosopher for good. Montaigne is putting his judgment to trial on whatever subject, in order not only to get to know its value, but also to form and strengthen it.
He manages thus to offer us a philosophy in accordance with life. As Nietzsche puts it, “that such a man has written, joy on earth has truly increased…If my task were to make this earth a home, I would attach myself to him.” Or, as Stefan Zweig said, in a context which was closer to the historical reality experienced by Montaigne himself : “Montaigne helps us answer this one question: ‘How to stay free? How to preserve our inborn clear-mindedness in front of all the threats and dangers of fanaticism, how to preserve the humanity of our hearts among the upsurge of bestiality?’”
- Essais , F. Strowski (ed.), Paris: Hachette, 1912, Phototypic reproduction of the “Exemplaire de Bordeaux”, showing Montaigne’s handwritten additions of 1588–1592.
- Essais , Pierre Villey (ed.), 3 volumes, Alcan, 1922–1923, revised by V.-L. Saulnier, 1965. Gives the 3 strata indications, probable dates of composition of the chapters, and many sources.
- Michel de Montaigne. Les Essais , J. Balsamo, C. Magnien-Simonin & M. Magnien (eds.) (with “Notes de lecture” and “Sentences peintes” edited by Alain Legros), Paris, “Pléiade”, Gallimard, 2007. The Essays are based on the 1595 published version.
- La Théologie naturelle de Raymond Sebond , traduicte nouvellement en François par Messire Michel, Seigneur de Montaigne, Chevalier de l’ordre du Roy et Gentilhomme ordinaire de sa chambre . Ed. by Dr Armaingaud, Paris: Conard, 1935.
- Le Journal de Voyage en Italie de Michel de Montaigne . Ed. by François Rigolot, Paris: PUF, 1992.
- Lettres . Ed. by Arthur Armaingaud, Paris, Conard, 1939 (vol. XI, in Œuvres complètes , pp. 159–266).
- The Essayes , tr. by John Florio. London: V. Sims, 1603.
- The Essays , tr. by Charles Cotton. 3 vol., London: T. Basset, M. Gilliflower and W. Hensman, 1685–1686.
- The Essays , tr. by E.J. Trechmann. 2 vol., Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1927.
- Michel de Montaigne. The Complete Works. Essays, Travel Journal, Letters, tr. by Donald M. Frame , Stanford: Stanford University Press, 1958, renewed 1971 & 1976.
- The Complete Essays , tr. by M.A. Screech, London/New York: Penguin, 1993.
- The Journal of Montaigne’s Travels , tr. by W.G. Watters, 3 vol., London: John Murray, 1903.
- The Diary of Montaigne’s Journey to Italy in 1580 and 1581 , tr. by E.J. Trechmann. London: Hogarth Press, 1929.
- Auerbach, Erich, 1946, “l’humaine condition” (on Montaigne) in Mimesis: The Representation of Reality in Western Literature, trans . Willard Trask. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2003 (originally pub. Bern: Francke).
- Burke, Peter, 1981, Montaigne , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Compayré, Gabriel, 1908, Montaigne and the Education of the Judgment, trans. J. E. Mansion, New York: Burt Franklin, 1971.
- Conche, Marcel, 1996, Montaigne et la philosophie , Paris: PUF.
- Desan, Philippe, 2017, Montaigne: A Life , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- ––– (ed.), 2007, Dictionnaire de Montaigne , Paris: Champion.
- ––– (ed.), 2016, The Oxford Handbook of Montaigne , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Ferrari, Emiliano, & Gontier, Thierry, 2016, L’Axe Montaigne-Hobbes: anthropologie et politique , Paris: Classiques Garnier.
- Frame, Donald M., 1984, Montaigne: A Biography , New York: Harcourt/ London: Hamish Hamilton, 1965/ San Francisco: North Point Press.
- Friedrich, Hugo, 1991, Montaigne , Bern: Francke, 1949; Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Fontana, Biancamaria, 2008, Montaigne’s Politics: Authority and Governance in the Essays , Geneva: Princeton University Press.
- Hoffmann, Georges, 1998, Montaigne’s Career , Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Horkheimer, Max, 1938, Montaigne und die Funktion der Skepsis , Frankfurt: Fischer, reprinted 1971.
- Imbach, Ruedi, 1983, “‘Et toutefois nostre outrecuidance veut faire passer la divinité par nostre estamine’, l’essai II,12 et la genèse de la pensée moderne. Construction d’une thèse explicative” in Paradigmes de théologie philosophique , O. Höffe et R. Imbach (eds.), Fribourg.
- Ulrich Langer, 2005, The Cambridge Companion to Montaigne , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Leake, R.E., 1981, Concordance des Essais de Montaigne , 2 vol., Genève: Droz.
- Paganini, Gianni, 2008, Skepsis. Le débat des modernes sur le scepticisme , Paris: Vrin.
- Popkin, Richard, 1960, The History of Scepticism from Erasmus to Descartes , Assen: Van Gorcum.
- –––, 1979, The History of Scepticism from Erasmus to Spinoza , Berkeley: University of California Press.
- –––, 2003, The History of Scepticism from Savonarola to Bayle , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Schmitt, Charles B., 1972, Cicero scepticus : A Study of the Influence of the Academica in the Renaissance , The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff.
- Screech, Michael, 1983, Montaigne & Melancholy — The Wisdom of the Essays , London: Duckworth.
- –––, 1998, Montaigne’s Annotated Copy of Lucretius, A transcription and study of the manuscript, notes and pen-marks , Geneva: Droz.
- Skinner, Quentin, 2002, Visions of Politics (Volume 3: Hobbes and Civil Science), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Starobinski, Jean, 2009, Montaigne in Motion , University of Chicago Press.
- Supple, James, 1984, Arms versus Letters, The Military and Literary Ideals in the Essays , Cambridge: Clarendon Press.
- Thompson, Douglas, 2018, Montaigne and the Tolerance of Politics , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Tournon, André, 1983, La glose et l’essai , Paris: H. Champion, reprinted 2001.
- Zweig, Stefan, 1960, Montaigne [written 1935–1941] Frankfurt: Fischer.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
Other Internet Resources
- The complete, searchable text of the Villey-Saulnier edition , from the ARFTL project at the University of Chicago (French)
- Montaigne Studies: An Interdisciplinary Forum , Philippe Desan, ed., (University of Chicago).
- Portrait Gallery , in Montaigne Studies: An Interdisciplinary Forum
- Montaigne’s Essays John Florio’s translation (first published 1603, Ben R. Schneider (ed.), Lawrence University, Wisconsin, from The World’s Classics, 1904, 1910, 1924), published at Renascence Editions, U. Oregon
- Essays of Michel De Montaigne , translated (1685–1686) by Charles Cotton, edited by William Carew Hazlitt, London: Reeves anbd Turner.
civic humanism | Descartes, René | -->humanism: in the Renaissance --> | liberty: positive and negative | relativism | Sextus Empiricus | skepticism | Stoicism
Copyright © 2019 by Marc Foglia < marc . foglia @ gmail . com > Emiliano Ferrari < ferrariemil @ gmail . com >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054

Essays by Michel de Montaigne (Book Analysis)
Detailed summary, analysis and reading guide.
This practical and insightful reading guide offers a complete summary and analysis of the Essays, by Michel de Montaigne . It provides a thorough exploration of the essay’s plot, context and main themes, including – to list but a few – medicine, knowledge and manners. The clear and concise style makes for easy understanding, providing the perfect opportunity to improve your literary knowledge in no time.
This clear and detailed 50-page reading guide is structured as follows:
- Biography of Michel de Montaigne
- Presentation of the Essays
- Summary of the Essays
- The composition and structure of the Essays
- A self-portrait
- Montaigne’s writing
- A critical judgement
- Human relationships
- The search for wisdom
About the Essays
The Essays were first published in 1580 after ten years of writing. They deal with a huge variety of themes and subjects, including – but not limited to – medicine, knowledge, manners and reflections on life in general. In addressing such a wide range of questions, Montaigne hoped to discover the reality of the human condition. In the work, Montaigne paints himself as he truly is, so that his loved ones can find solace in his Essays after his death.
About Michel de Montaigne
Michel Eyquem de Montaigne, Lord of Montaigne, was a French writer, philosopher, politician and humanist during the Renaissance. He was born in 1533. He was a great traveler, particularly for his time – he journeyed through France, Switzerland, South Germany and Italy, to name but a few of the places he visited, and wrote about this time in his Journal de voyage en Italie .
Montaigne was also very involved in French politics; he even became the mayor of Bordeaux later on in his life. However, reading and writing were his passion and came before all other occupations, which is what led to his famous Essays . He had a major work on many Western writers, including Jean-Jacques Rousseau and – possibly – William Shakespeare.
Product details
- Share On Facebook
- Tweet This Product
- Pin This Product
- Mail This Product
Related guides

The Maids by Jean Genet (Book Analysis)

Phaedra by Jean Racine (Book Analysis)

A Bag of Marbles by Joseph Joffo (Book Analysis)

Father Goriot by Honoré de Balzac (Book Analysis)

The School for Wives by Molière (Book Analysis)

The Outsider by Albert Camus (Book Analysis)
Already subscribed ? Click here
Find the right plan for you
Brightsummaries standard.
- Ideal for casual readers
- More than 200 guides
- Download 5 guides per month
- Standard technical support
BrightSummaries Premium
- Ideal for serious readers
- Download 20 guides per month
- Premium technical support
Selections from the Essays of Montaigne
By michel de montaigne, selections from the essays of montaigne analysis.
These notes were contributed by members of the GradeSaver community. We are thankful for their contributions and encourage you to make your own.
Written by people who wish to remain anonymous
“Of Idleness”
Montaigne alludes to gender to particularize the repercussions of idleness: “as we see women that, without knowledge of man, do sometimes of themselves bring forth inanimate and formless lumps of flesh, but that to cause a natural and perfect generation they are to be husbanded with another kind of seed: even so it is with minds, which if not applied to some certain study that may fix and restrain them, run into a thousand extravagances, eternally roving here and there in the vague expanse of the imagination.” The ‘formless lumps’ are representative of the upshots of sedentariness that may subsidize overweightness in women. If the women were materially active, the lumps would not have established. The course of husbanding contributes pertinently to the curbing of idleness. Restrain is contributory in extenuating idleness for it condenses the rife overindulgences that arouse idle minds. Besides, an idle mind is susceptible to ‘vain phantasms.’
“Of Constancy”
Montaigne’s ideological message in “Of Constancy” is that constancy is not unqualifiedly ‘carved in stone.’ It is imperative to harness flexibility for constancy is subject to both controllable and irrepressible circumstances. Montaigne illustrates:
“The law of resolution and constancy does not imply that we ought not, as much as in us lies, to decline and secure ourselves from the mischiefs and inconveniences that threaten us; nor, consequently, that we shall not fear lest they should surprise us: on the contrary, all decent and honest ways and means of securing ourselves from harms, are not only permitted, but, moreover, commendable, and the business of constancy chiefly is, bravely to stand to, and stoutly to suffer those inconveniences which are not possibly to be avoided.”
Tenacity does not rationalize uncovering one to precarious circumstances that may culminate in threatening ends. Fear is an inherent reaction that should not be used to induce superfluous constancy. Existence cannot be emphatically narrowed down to the Constancy versus Inconstancy binary for there are voluminous factors that command individuals’ predisposition to constancy. Individual’s welfare should transcend constancy. Constancy can be defensible when it does not discommode one’s well-being. Subordinating one’s safety with the object perpetuating constancy is tantamount to self-crippling. Constancy should be applied in the conservation individuals and not jeopardizing them.
Update this section!
You can help us out by revising, improving and updating this section.
After you claim a section you’ll have 24 hours to send in a draft. An editor will review the submission and either publish your submission or provide feedback.

Selections from the Essays of Montaigne Questions and Answers
The Question and Answer section for Selections from the Essays of Montaigne is a great resource to ask questions, find answers, and discuss the novel.
Study Guide for Selections from the Essays of Montaigne
Selections from the Essays of Montaigne study guide contains a biography of author Michel De Montaigne, literature essays, a complete e-text, quiz questions, major themes, characters, and a full summary and analysis.
- About Selections from the Essays of Montaigne
- Selections from the Essays of Montaigne Summary
- Character List
Essays for Selections from the Essays of Montaigne
Essays of Montaigne literature essays are academic essays for citation. These papers were written primarily by students and provide critical analysis of selected essays written by Michel De Montaigne.
- Ontological Freedom in Montaigne’s Selections from the Essays
- In Sickness and In Health: Exploring the Paradox of Pain in Cervantes and Montaigne
- Preparations and Actions: Thought on Life and Death in Montaigne's Essays
- On Which Cannibal? The Clever Rhetoric of Montaigne's "On the Cannibals"
- Can Evil be Fought with Evil?: Analyzing the Works of Machiavelli, Erasmus, and Montaigne
Wikipedia Entries for Selections from the Essays of Montaigne
- Introduction
- Montaigne's influence on psychology
- Related writers and influence
ESSAYS OF MICHEL DE MONTAIGNE
Translated by charles cotton edited by william carew hazlitt.

PREFACE THE LETTERS OF MONTAIGNE I. — To Monsieur de MONTAIGNE II. — To Monseigneur, Monseigneur de MONTAIGNE. III. — To Monsieur, Monsieur de LANSAC, IV. — To Monsieur, Monsieur de MESMES, Lord of Roissy and Malassize, Privy V. — To Monsieur, Monsieur de L’HOSPITAL, Chancellor of France VI. — To Monsieur, Monsieur de Folx, Privy Councillor, to the Signory of Venice. VII. — To Mademoiselle de MONTAIGNE, my Wife. VIII. — To Monsieur DUPUY, IX. — To the Jurats of Bordeaux. X. — To the same. XI. — To the same. XII. — XIII. — To Mademoiselle PAULMIER. XIV. — To the KING, HENRY IV. XV. — To the same. XVI. — To the Governor of Guienne. BOOK THE FIRST — CHAPTER I — THAT MEN BY VARIOUS WAYS ARRIVE AT THE SAME END. CHAPTER II — OF SORROW CHAPTER III — THAT OUR AFFECTIONS CARRY THEMSELVES BEYOND US CHAPTER IV — THAT THE SOUL EXPENDS ITS PASSIONS UPON FALSE OBJECTS CHAPTER V — WHETHER THE GOVERNOR HIMSELF GO OUT TO PARLEY CHAPTER VI — THAT THE HOUR OF PARLEY DANGEROUS CHAPTER VII — THAT THE INTENTION IS JUDGE OF OUR ACTIONS CHAPTER VIII — OF IDLENESS CHAPTER IX — OF LIARS CHAPTER X — OF QUICK OR SLOW SPEECH CHAPTER XI — OF PROGNOSTICATIONS CHAPTER XII — OF CONSTANCY CHAPTER XIII — THE CEREMONY OF THE INTERVIEW OF PRINCES CHAPTER XIV — THAT MEN ARE JUSTLY PUNISHED FOR BEING OBSTINATE CHAPTER XV — OF THE PUNISHMENT OF COWARDICE CHAPTER XVI — A PROCEEDING OF SOME AMBASSADORS CHAPTER XVII — OF FEAR CHAPTER XVIII — NOT TO JUDGE OF OUR HAPPINESS TILL AFTER DEATH. CHAPTER XIX — THAT TO STUDY PHILOSOPY IS TO LEARN TO DIE CHAPTER XX — OF THE FORCE OF IMAGINATION CHAPTER XXI — THAT THE PROFIT OF ONE MAN IS THE DAMAGE OF ANOTHER CHAPTER XXII — OF CUSTOM; WE SHOULD NOT EASILY CHANGE A LAW RECEIVED CHAPTER XXIII — VARIOUS EVENTS FROM THE SAME COUNSEL CHAPTER XXIV — OF PEDANTRY CHAPTER XXV — OF THE EDUCATION OF CHILDREN CHAPTER XXVI — FOLLY TO MEASURE TRUTH AND ERROR BY OUR OWN CAPACITY CHAPTER XXVII — OF FRIENDSHIP CHAPTER XXVIII — NINE AND TWENTY SONNETS OF ESTIENNE DE LA BOITIE CHAPTER XXIX — OF MODERATION CHAPTER XXX — OF CANNIBALS CHAPTER XXXI — THAT A MAN IS SOBERLY TO JUDGE OF THE DIVINE ORDINANCES CHAPTER XXXII — WE ARE TO AVOID PLEASURES, EVEN AT THE EXPENSE OF LIFE CHAPTER XXXIII — FORTUNE IS OFTEN OBSERVED TO ACT BY THE RULE OF REASON CHAPTER XXXIV — OF ONE DEFECT IN OUR GOVERNMENT CHAPTER XXXV — OF THE CUSTOM OF WEARING CLOTHES CHAPTER XXXVI — OF CATO THE YOUNGER CHAPTER XXXVII — THAT WE LAUGH AND CRY FOR THE SAME THING CHAPTER XXXVIII — OF SOLITUDE CHAPTER XXXIX — A CONSIDERATION UPON CICERO CHAPTER XL — RELISH FOR GOOD AND EVIL DEPENDS UPON OUR OPINION CHAPTER XLI — NOT TO COMMUNICATE A MAN’S HONOUR CHAPTER XLII — OF THE INEQUALITY AMOUNGST US. CHAPTER XLIII — OF SUMPTUARY LAWS CHAPTER XLIV — OF SLEEP CHAPTER XLV — OF THE BATTLE OF DREUX CHAPTER XLVI — OF NAMES CHAPTER XLVII — OF THE UNCERTAINTY OF OUR JUDGMENT CHAPTER XLVIII — OF WAR HORSES, OR DESTRIERS CHAPTER XLIX — OF ANCIENT CUSTOMS CHAPTER L — OF DEMOCRITUS AND HERACLITUS CHAPTER LI — OF THE VANITY OF WORDS CHAPTER LII — OF THE PARSIMONY OF THE ANCIENTS CHAPTER LIII — OF A SAYING OF CAESAR CHAPTER LIV — OF VAIN SUBTLETIES CHAPTER LV — OF SMELLS CHAPTER LVI — OF PRAYERS CHAPTER LVII — OF AGE BOOK THE SECOND — CHAPTER I — OF THE INCONSTANCY OF OUR ACTIONS CHAPTER II — OF DRUNKENNESS CHAPTER III — A CUSTOM OF THE ISLE OF CEA CHAPTER IV — TO-MORROW’S A NEW DAY CHAPTER V — OF CONSCIENCE CHAPTER VI — USE MAKES PERFECT CHAPTER VII — OF RECOMPENSES OF HONOUR CHAPTER VIII — OF THE AFFECTION OF FATHERS TO THEIR CHILDREN CHAPTER IX — OF THE ARMS OF THE PARTHIANS CHAPTER X — OF BOOKS CHAPTER XI — OF CRUELTY CHAPTER XII — APOLOGY FOR RAIMOND SEBOND CHAPTER XIII — OF JUDGING OF THE DEATH OF ANOTHER CHAPTER XIV — THAT OUR MIND HINDERS ITSELF CHAPTER XV — THAT OUR DESIRES ARE AUGMENTED BY DIFFICULTY CHAPTER XVI — OF GLORY CHAPTER XVII — OF PRESUMPTION CHAPTER XVIII — OF GIVING THE LIE CHAPTER XIX — OF LIBERTY OF CONSCIENCE CHAPTER XX — THAT WE TASTE NOTHING PURE CHAPTER XXI — AGAINST IDLENESS CHAPTER XXII — OF POSTING CHAPTER XXIII — OF ILL MEANS EMPLOYED TO A GOOD END CHAPTER XXIV — OF THE ROMAN GRANDEUR CHAPTER XXV — NOT TO COUNTERFEIT BEING SICK CHAPTER XXVI — OF THUMBS CHAPTER XXVII — COWARDICE THE MOTHER OF CRUELTY CHAPTER XXVIII — ALL THINGS HAVE THEIR SEASON CHAPTER XXIX — OF VIRTUE CHAPTER XXX — OF A MONSTROUS CHILD CHAPTER XXXI — OF ANGER CHAPTER XXXII — DEFENCE OF SENECA AND PLUTARCH CHAPTER XXXIII — THE STORY OF SPURINA CHAPTER XXXIV — OBSERVATION ON A WAR ACCORDING TO JULIUS CAESAR CHAPTER XXXV — OF THREE GOOD WOMEN CHAPTER XXXVI — OF THE MOST EXCELLENT MEN CHAPTER XXXVII — OF THE RESEMBLANCE OF CHILDREN TO THEIR FATHERS BOOK THE THIRD — CHAPTER I — OF PROFIT AND HONESTY CHAPTER II — OF REPENTANCE CHAPTER III — OF THREE COMMERCES CHAPTER IV — OF DIVERSION CHAPTER V — UPON SOME VERSES OF VIRGIL CHAPTER VI — OF COACHES CHAPTER VII — OF THE INCONVENIENCE OF GREATNESS CHAPTER VIII — OF THE ART OF CONFERENCE CHAPTER IX — OF VANITY CHAPTER X — OF MANAGING THE WILL CHAPTER XI — OF CRIPPLES CHAPTER XII — OF PHYSIOGNOMY CHAPTER XIII — OF EXPERIENCE APOLOGY PROJECT GUTENBERG EDITOR’S BOOKMARKS
The present publication is intended to supply a recognised deficiency in our literature—a library edition of the Essays of Montaigne. This great French writer deserves to be regarded as a classic, not only in the land of his birth, but in all countries and in all literatures. His Essays, which are at once the most celebrated and the most permanent of his productions, form a magazine out of which such minds as those of Bacon and Shakespeare did not disdain to help themselves; and, indeed, as Hallam observes, the Frenchman’s literary importance largely results from the share which his mind had in influencing other minds, coeval and subsequent. But, at the same time, estimating the value and rank of the essayist, we are not to leave out of the account the drawbacks and the circumstances of the period: the imperfect state of education, the comparative scarcity of books, and the limited opportunities of intellectual intercourse. Montaigne freely borrowed of others, and he has found men willing to borrow of him as freely. We need not wonder at the reputation which he with seeming facility achieved. He was, without being aware of it, the leader of a new school in letters and morals. His book was different from all others which were at that date in the world. It diverted the ancient currents of thought into new channels. It told its readers, with unexampled frankness, what its writer’s opinion was about men and things, and threw what must have been a strange kind of new light on many matters but darkly understood. Above all, the essayist uncased himself, and made his intellectual and physical organism public property. He took the world into his confidence on all subjects. His essays were a sort of literary anatomy, where we get a diagnosis of the writer’s mind, made by himself at different levels and under a large variety of operating influences.
Of all egotists, Montaigne, if not the greatest, was the most fascinating, because, perhaps, he was the least affected and most truthful. What he did, and what he had professed to do, was to dissect his mind, and show us, as best he could, how it was made, and what relation it bore to external objects. He investigated his mental structure as a schoolboy pulls his watch to pieces, to examine the mechanism of the works; and the result, accompanied by illustrations abounding with originality and force, he delivered to his fellow-men in a book.
Eloquence, rhetorical effect, poetry, were alike remote from his design. He did not write from necessity, scarcely perhaps for fame. But he desired to leave France, nay, and the world, something to be remembered by, something which should tell what kind of a man he was—what he felt, thought, suffered—and he succeeded immeasurably, I apprehend, beyond his expectations.
It was reasonable enough that Montaigne should expect for his work a certain share of celebrity in Gascony, and even, as time went on, throughout France; but it is scarcely probable that he foresaw how his renown was to become world-wide; how he was to occupy an almost unique position as a man of letters and a moralist; how the Essays would be read, in all the principal languages of Europe, by millions of intelligent human beings, who never heard of Perigord or the League, and who are in doubt, if they are questioned, whether the author lived in the sixteenth or the eighteenth century. This is true fame. A man of genius belongs to no period and no country. He speaks the language of nature, which is always everywhere the same.
The text of these volumes is taken from the first edition of Cotton’s version, printed in 3 vols. 8vo, 1685-6, and republished in 1693, 1700, 1711, 1738, and 1743, in the same number of volumes and the same size. In the earliest impression the errors of the press are corrected merely as far as page 240 of the first volume, and all the editions follow one another. That of 1685-6 was the only one which the translator lived to see. He died in 1687, leaving behind him an interesting and little-known collection of poems, which appeared posthumously, 8vo, 1689.
It was considered imperative to correct Cotton’s translation by a careful collation with the ‘variorum’ edition of the original, Paris, 1854, 4 vols. 8vo or 12mo, and parallel passages from Florin’s earlier undertaking have occasionally been inserted at the foot of the page. A Life of the Author and all his recovered Letters, sixteen in number, have also been given; but, as regards the correspondence, it can scarcely be doubted that it is in a purely fragmentary state. To do more than furnish a sketch of the leading incidents in Montaigne’s life seemed, in the presence of Bayle St. John’s charming and able biography, an attempt as difficult as it was useless.
The besetting sin of both Montaigne’s translators seems to have been a propensity for reducing his language and phraseology to the language and phraseology of the age and country to which they belonged, and, moreover, inserting paragraphs and words, not here and there only, but constantly and habitually, from an evident desire and view to elucidate or strengthen their author’s meaning. The result has generally been unfortunate; and I have, in the case of all these interpolations on Cotton’s part, felt bound, where I did not cancel them, to throw them down into the notes, not thinking it right that Montaigne should be allowed any longer to stand sponsor for what he never wrote; and reluctant, on the other hand, to suppress the intruding matter entirely, where it appeared to possess a value of its own.
Nor is redundancy or paraphrase the only form of transgression in Cotton, for there are places in his author which he thought proper to omit, and it is hardly necessary to say that the restoration of all such matter to the text was considered essential to its integrity and completeness.
My warmest thanks are due to my father, Mr Registrar Hazlitt, the author of the well-known and excellent edition of Montaigne published in 1842, for the important assistance which he has rendered to me in verifying and retranslating the quotations, which were in a most corrupt state, and of which Cotton’s English versions were singularly loose and inexact, and for the zeal with which he has co-operated with me in collating the English text, line for line and word for word, with the best French edition.
By the favour of Mr F. W. Cosens, I have had by me, while at work on this subject, the copy of Cotgrave’s Dictionary, folio, 1650, which belonged to Cotton. It has his autograph and copious MSS. notes, nor is it too much to presume that it is the very book employed by him in his translation.
KENSINGTON, November 1877.
THE LIFE OF MONTAIGNE
[This is translated freely from that prefixed to the ‘variorum’ Paris edition, 1854, 4 vols. 8vo. This biography is the more desirable that it contains all really interesting and important matter in the journal of the Tour in Germany and Italy, which, as it was merely written under Montaigne’s dictation, is in the third person, is scarcely worth publication, as a whole, in an English dress.]
The author of the Essays was born, as he informs us himself, between eleven and twelve o’clock in the day, the last of February 1533, at the chateau of St. Michel de Montaigne. His father, Pierre Eyquem, esquire, was successively first Jurat of the town of Bordeaux (1530), Under-Mayor 1536, Jurat for the second time in 1540, Procureur in 1546, and at length Mayor from 1553 to 1556. He was a man of austere probity, who had “a particular regard for honour and for propriety in his person and attire . . . a mighty good faith in his speech, and a conscience and a religious feeling inclining to superstition, rather than to the other extreme."[Essays, ii. 2.] Pierre Eyquem bestowed great care on the education of his children, especially on the practical side of it. To associate closely his son Michel with the people, and attach him to those who stand in need of assistance, he caused him to be held at the font by persons of meanest position; subsequently he put him out to nurse with a poor villager, and then, at a later period, made him accustom himself to the most common sort of living, taking care, nevertheless, to cultivate his mind, and superintend its development without the exercise of undue rigour or constraint. Michel, who gives us the minutest account of his earliest years, charmingly narrates how they used to awake him by the sound of some agreeable music, and how he learned Latin, without suffering the rod or shedding a tear, before beginning French, thanks to the German teacher whom his father had placed near him, and who never addressed him except in the language of Virgil and Cicero. The study of Greek took precedence. At six years of age young Montaigne went to the College of Guienne at Bordeaux, where he had as preceptors the most eminent scholars of the sixteenth century, Nicolas Grouchy, Guerente, Muret, and Buchanan. At thirteen he had passed through all the classes, and as he was destined for the law he left school to study that science. He was then about fourteen, but these early years of his life are involved in obscurity. The next information that we have is that in 1554 he received the appointment of councillor in the Parliament of Bordeaux; in 1559 he was at Bar-le-Duc with the court of Francis II, and in the year following he was present at Rouen to witness the declaration of the majority of Charles IX. We do not know in what manner he was engaged on these occasions.
Between 1556 and 1563 an important incident occurred in the life of Montaigne, in the commencement of his romantic friendship with Etienne de la Boetie, whom he had met, as he tells us, by pure chance at some festive celebration in the town. From their very first interview the two found themselves drawn irresistibly close to one another, and during six years this alliance was foremost in the heart of Montaigne, as it was afterwards in his memory, when death had severed it.
Although he blames severely in his own book [Essays, i. 27.] those who, contrary to the opinion of Aristotle, marry before five-and-thirty, Montaigne did not wait for the period fixed by the philosopher of Stagyra, but in 1566, in his thirty-third year, he espoused Francoise de Chassaigne, daughter of a councillor in the Parliament of Bordeaux. The history of his early married life vies in obscurity with that of his youth. His biographers are not agreed among themselves; and in the same degree that he lays open to our view all that concerns his secret thoughts, the innermost mechanism of his mind, he observes too much reticence in respect to his public functions and conduct, and his social relations. The title of Gentleman in Ordinary to the King, which he assumes, in a preface, and which Henry II. gives him in a letter, which we print a little farther on; what he says as to the commotions of courts, where he passed a portion of his life; the Instructions which he wrote under the dictation of Catherine de Medici for King Charles IX., and his noble correspondence with Henry IV., leave no doubt, however, as to the part which he played in the transactions of those times, and we find an unanswerable proof of the esteem in which he was held by the most exalted personages, in a letter which was addressed to him by Charles at the time he was admitted to the Order of St. Michael, which was, as he informs us himself, the highest honour of the French noblesse.
According to Lacroix du Maine, Montaigne, upon the death of his eldest brother, resigned his post of Councillor, in order to adopt the military profession, while, if we might credit the President Bouhier, he never discharged any functions connected with arms. However, several passages in the Essays seem to indicate that he not only took service, but that he was actually in numerous campaigns with the Catholic armies. Let us add, that on his monument he is represented in a coat of mail, with his casque and gauntlets on his right side, and a lion at his feet, all which signifies, in the language of funeral emblems, that the departed has been engaged in some important military transactions.
However it may be as to these conjectures, our author, having arrived at his thirty-eighth year, resolved to dedicate to study and contemplation the remaining term of his life; and on his birthday, the last of February 1571, he caused a philosophical inscription, in Latin, to be placed upon one of the walls of his chateau, where it is still to be seen, and of which the translation is to this effect:—“In the year of Christ . . . in his thirty-eighth year, on the eve of the Calends of March, his birthday, Michel Montaigne, already weary of court employments and public honours, withdrew himself entirely into the converse of the learned virgins where he intends to spend the remaining moiety of the to allotted to him in tranquil seclusion.”
At the time to which we have come, Montaigne was unknown to the world of letters, except as a translator and editor. In 1569 he had published a translation of the “Natural Theology” of Raymond de Sebonde, which he had solely undertaken to please his father. In 1571 he had caused to be printed at Paris certain ‘opuscucla’ of Etienne de la Boetie; and these two efforts, inspired in one case by filial duty, and in the other by friendship, prove that affectionate motives overruled with him mere personal ambition as a literary man. We may suppose that he began to compose the Essays at the very outset of his retirement from public engagements; for as, according to his own account, observes the President Bouhier, he cared neither for the chase, nor building, nor gardening, nor agricultural pursuits, and was exclusively occupied with reading and reflection, he devoted himself with satisfaction to the task of setting down his thoughts just as they occurred to him. Those thoughts became a book, and the first part of that book, which was to confer immortality on the writer, appeared at Bordeaux in 1580. Montaigne was then fifty-seven; he had suffered for some years past from renal colic and gravel; and it was with the necessity of distraction from his pain, and the hope of deriving relief from the waters, that he undertook at this time a great journey. As the account which he has left of his travels in Germany and Italy comprises some highly interesting particulars of his life and personal history, it seems worth while to furnish a sketch or analysis of it.
“The Journey, of which we proceed to describe the course simply,” says the editor of the Itinerary, “had, from Beaumont-sur-Oise to Plombieres, in Lorraine, nothing sufficiently interesting to detain us . . . we must go as far, as Basle, of which we have a description, acquainting us with its physical and political condition at that period, as well as with the character of its baths. The passage of Montaigne through Switzerland is not without interest, as we see there how our philosophical traveller accommodated himself everywhere to the ways of the country. The hotels, the provisions, the Swiss cookery, everything, was agreeable to him; it appears, indeed, as if he preferred to the French manners and tastes those of the places he was visiting, and of which the simplicity and freedom (or frankness) accorded more with his own mode of life and thinking. In the towns where he stayed, Montaigne took care to see the Protestant divines, to make himself conversant with all their dogmas. He even had disputations with them occasionally.
“Having left Switzerland he went to Isne, an imperial then on to Augsburg and Munich. He afterwards proceeded to the Tyrol, where he was agreeably surprised, after the warnings which he had received, at the very slight inconveniences which he suffered, which gave him occasion to remark that he had all his life distrusted the statements of others respecting foreign countries, each person’s tastes being according to the notions of his native place; and that he had consequently set very little on what he was told beforehand.
“Upon his arrival at Botzen, Montaigne wrote to Francois Hottmann, to say that he had been so pleased with his visit to Germany that he quitted it with great regret, although it was to go into Italy. He then passed through Brunsol, Trent, where he put up at the Rose; thence going to Rovera; and here he first lamented the scarcity of crawfish, but made up for the loss by partaking of truffles cooked in oil and vinegar; oranges, citrons, and olives, in all of which he delighted.”
After passing a restless night, when he bethought himself in the morning that there was some new town or district to be seen, he rose, we are told, with alacrity and pleasure.
His secretary, to whom he dictated his Journal, assures us that he never saw him take so much interest in surrounding scenes and persons, and believes that the complete change helped to mitigate his sufferings in concentrating his attention on other points. When there was a complaint made that he had led his party out of the beaten route, and then returned very near the spot from which they started, his answer was that he had no settled course, and that he merely proposed to himself to pay visits to places which he had not seen, and so long as they could not convict him of traversing the same path twice, or revisiting a point already seen, he could perceive no harm in his plan. As to Rome, he cared less to go there, inasmuch as everybody went there; and he said that he never had a lacquey who could not tell him all about Florence or Ferrara. He also would say that he seemed to himself like those who are reading some pleasant story or some fine book, of which they fear to come to the end: he felt so much pleasure in travelling that he dreaded the moment of arrival at the place where they were to stop for the night.
We see that Montaigne travelled, just as he wrote, completely at his ease, and without the least constraint, turning, just as he fancied, from the common or ordinary roads taken by tourists. The good inns, the soft beds, the fine views, attracted his notice at every point, and in his observations on men and things he confines himself chiefly to the practical side. The consideration of his health was constantly before him, and it was in consequence of this that, while at Venice, which disappointed him, he took occasion to note, for the benefit of readers, that he had an attack of colic, and that he evacuated two large stones after supper. On quitting Venice, he went in succession to Ferrara, Rovigo, Padua, Bologna (where he had a stomach-ache), Florence, &c.; and everywhere, before alighting, he made it a rule to send some of his servants to ascertain where the best accommodation was to be had. He pronounced the Florentine women the finest in the world, but had not an equally good opinion of the food, which was less plentiful than in Germany, and not so well served. He lets us understand that in Italy they send up dishes without dressing, but in Germany they were much better seasoned, and served with a variety of sauces and gravies. He remarked further, that the glasses were singularly small and the wines insipid.
After dining with the Grand-Duke of Florence, Montaigne passed rapidly over the intermediate country, which had no fascination for him, and arrived at Rome on the last day of November, entering by the Porta del Popolo, and putting up at Bear. But he afterwards hired, at twenty crowns a month, fine furnished rooms in the house of a Spaniard, who included in these terms the use of the kitchen fire. What most annoyed him in the Eternal City was the number of Frenchmen he met, who all saluted him in his native tongue; but otherwise he was very comfortable, and his stay extended to five months. A mind like his, full of grand classical reflections, could not fail to be profoundly impressed in the presence of the ruins at Rome, and he has enshrined in a magnificent passage of the Journal the feelings of the moment: “He said,” writes his secretary, “that at Rome one saw nothing but the sky under which she had been built, and the outline of her site: that the knowledge we had of her was abstract, contemplative, not palpable to the actual senses: that those who said they beheld at least the ruins of Rome, went too far, for the ruins of so gigantic a structure must have commanded greater reverence-it was nothing but her sepulchre. The world, jealous of her, prolonged empire, had in the first place broken to pieces that admirable body, and then, when they perceived that the remains attracted worship and awe, had buried the very wreck itself.—[Compare a passage in one of Horace Walpole’s letters to Richard West, 22 March 1740 (Cunningham’s edit. i. 41), where Walpole, speaking of Rome, describes her very ruins as ruined.]—As to those small fragments which were still to be seen on the surface, notwithstanding the assaults of time and all other attacks, again and again repeated, they had been favoured by fortune to be some slight evidence of that infinite grandeur which nothing could entirely extingish. But it was likely that these disfigured remains were the least entitled to attention, and that the enemies of that immortal renown, in their fury, had addressed themselves in the first instance to the destruction of what was most beautiful and worthiest of preservation; and that the buildings of this bastard Rome, raised upon the ancient productions, although they might excite the admiration of the present age, reminded him of the crows’ and sparrows’ nests built in the walls and arches of the old churches, destroyed by the Huguenots. Again, he was apprehensive, seeing the space which this grave occupied, that the whole might not have been recovered, and that the burial itself had been buried. And, moreover, to see a wretched heap of rubbish, as pieces of tile and pottery, grow (as it had ages since) to a height equal to that of Mount Gurson,—[In Perigord.]—and thrice the width of it, appeared to show a conspiracy of destiny against the glory and pre-eminence of that city, affording at the same time a novel and extraordinary proof of its departed greatness. He (Montaigne) observed that it was difficult to believe considering the limited area taken up by any of her seven hills and particularly the two most favoured ones, the Capitoline and the Palatine, that so many buildings stood on the site. Judging only from what is left of the Temple of Concord, along the ‘Forum Romanum’, of which the fall seems quite recent, like that of some huge mountain split into horrible crags, it does not look as if more than two such edifices could have found room on the Capitoline, on which there were at one period from five-and-twenty to thirty temples, besides private dwellings. But, in point of fact, there is scarcely any probability of the views which we take of the city being correct, its plan and form having changed infinitely; for instance, the ‘Velabrum’, which on account of its depressed level, received the sewage of the city, and had a lake, has been raised by artificial accumulation to a height with the other hills, and Mount Savello has, in truth, grown simply out of the ruins of the theatre of Marcellus. He believed that an ancient Roman would not recognise the place again. It often happened that in digging down into earth the workmen came upon the crown of some lofty column, which, though thus buried, was still standing upright. The people there have no recourse to other foundations than the vaults and arches of the old houses, upon which, as on slabs of rock, they raise their modern palaces. It is easy to see that several of the ancient streets are thirty feet below those at present in use.”
Sceptical as Montaigne shows himself in his books, yet during his sojourn at Rome he manifested a great regard for religion. He solicited the honour of being admitted to kiss the feet of the Holy Father, Gregory XIII.; and the Pontiff exhorted him always to continue in the devotion which he had hitherto exhibited to the Church and the service of the Most Christian King.
“After this, one sees,” says the editor of the Journal, “Montaigne employing all his time in making excursions bout the neighbourhood on horseback or on foot, in visits, in observations of every kind. The churches, the stations, the processions even, the sermons; then the palaces, the vineyards, the gardens, the public amusements, as the Carnival, &c.—nothing was overlooked. He saw a Jewish child circumcised, and wrote down a most minute account of the operation. He met at San Sisto a Muscovite ambassador, the second who had come to Rome since the pontificate of Paul III. This minister had despatches from his court for Venice, addressed to the ‘Grand Governor of the Signory’. The court of Muscovy had at that time such limited relations with the other powers of Europe, and it was so imperfect in its information, that it thought Venice to be a dependency of the Holy See.”
Of all the particulars with which he has furnished us during his stay at Rome, the following passage in reference to the Essays is not the least singular: “The Master of the Sacred Palace returned him his Essays, castigated in accordance with the views of the learned monks. ‘He had only been able to form a judgment of them,’ said he, ‘through a certain French monk, not understanding French himself’”—we leave Montaigne himself to tell the story—“and he received so complacently my excuses and explanations on each of the passages which had been animadverted upon by the French monk, that he concluded by leaving me at liberty to revise the text agreeably to the dictates of my own conscience. I begged him, on the contrary, to abide by the opinion of the person who had criticised me, confessing, among other matters, as, for example, in my use of the word fortune, in quoting historical poets, in my apology for Julian, in my animadversion on the theory that he who prayed ought to be exempt from vicious inclinations for the time being; item, in my estimate of cruelty, as something beyond simple death; item, in my view that a child ought to be brought up to do everything, and so on; that these were my opinions, which I did not think wrong; as to other things, I said that the corrector understood not my meaning. The Master, who is a clever man, made many excuses for me, and gave me to suppose that he did not concur in the suggested improvements; and pleaded very ingeniously for me in my presence against another (also an Italian) who opposed my sentiments.”
Such is what passed between Montaigne and these two personages at that time; but when the Essayist was leaving, and went to bid them farewell, they used very different language to him. “They prayed me,” says he, “to pay no attention to the censure passed on my book, in which other French persons had apprised them that there were many foolish things; adding, that they honoured my affectionate intention towards the Church, and my capacity; and had so high an opinion of my candour and conscientiousness that they should leave it to me to make such alterations as were proper in the book, when I reprinted it; among other things, the word fortune. To excuse themselves for what they had said against my book, they instanced works of our time by cardinals and other divines of excellent repute which had been blamed for similar faults, which in no way affected reputation of the author, or of the publication as a whole; they requested me to lend the Church the support of my eloquence (this was their fair speech), and to make longer stay in the place, where I should be free from all further intrusion on their part. It seemed to me that we parted very good friends.”
Before quitting Rome, Montaigne received his diploma of citizenship, by which he was greatly flattered; and after a visit to Tivoli he set out for Loretto, stopping at Ancona, Fano, and Urbino. He arrived at the beginning of May 1581, at Bagno della Villa, where he established himself, order to try the waters. There, we find in the Journal, of his own accord the Essayist lived in the strictest conformity with the regime, and henceforth we only hear of diet, the effect which the waters had by degrees upon system, of the manner in which he took them; in a word, he does not omit an item of the circumstances connected with his daily routine, his habit of body, his baths, and the rest. It was no longer the journal of a traveller which he kept, but the diary of an invalid,—[“I am reading Montaigne’s Travels, which have lately been found; there is little in them but the baths and medicines he took, and what he had everywhere for dinner.”—H. Walpole to Sir Horace Mann, June 8, 1774.]—attentive to the minutest details of the cure which he was endeavouring to accomplish: a sort of memorandum book, in which he was noting down everything that he felt and did, for the benefit of his medical man at home, who would have the care of his health on his return, and the attendance on his subsequent infirmities. Montaigne gives it as his reason and justification for enlarging to this extent here, that he had omitted, to his regret, to do so in his visits to other baths, which might have saved him the trouble of writing at such great length now; but it is perhaps a better reason in our eyes, that what he wrote he wrote for his own use.
We find in these accounts, however, many touches which are valuable as illustrating the manners of the place. The greater part of the entries in the Journal, giving the account of these waters, and of the travels, down to Montaigne’s arrival at the first French town on his homeward route, are in Italian, because he wished to exercise himself in that language.
The minute and constant watchfulness of Montaigne over his health and over himself might lead one to suspect that excessive fear of death which degenerates into cowardice. But was it not rather the fear of the operation for the stone, at that time really formidable? Or perhaps he was of the same way of thinking with the Greek poet, of whom Cicero reports this saying: “I do not desire to die; but the thought of being dead is indifferent to me.” Let us hear, however, what he says himself on this point very frankly: “It would be too weak and unmanly on my part if, certain as I am of always finding myself in the position of having to succumb in that way,—[To the stone or gravel.]—and death coming nearer and nearer to me, I did not make some effort, before the time came, to bear the trial with fortitude. For reason prescribes that we should joyfully accept what it may please God to send us. Therefore the only remedy, the only rule, and the sole doctrine for avoiding the evils by which mankind is surrounded, whatever they are, is to resolve to bear them so far as our nature permits, or to put an end to them courageously and promptly.”
He was still at the waters of La Villa, when, on the 7th September 1581, he learned by letter that he had been elected Mayor of Bordeaux on the 1st August preceding. This intelligence made him hasten his departure; and from Lucca he proceeded to Rome. He again made some stay in that city, and he there received the letter of the jurats of Bordeaux, notifying to him officially his election to the Mayoralty, and inviting him to return as speedily as possible. He left for France, accompanied by young D’Estissac and several other gentlemen, who escorted him a considerable distance; but none went back to France with him, not even his travelling companion. He passed by Padua, Milan, Mont Cenis, and Chambery; thence he went on to Lyons, and lost no time in repairing to his chateau, after an absence of seventeen months and eight days.
We have just seen that, during his absence in Italy, the author of the Essays was elected mayor of Bordeaux. “The gentlemen of Bordeaux,” says he, “elected me Mayor of their town while I was at a distance from France, and far from the thought of such a thing. I excused myself; but they gave to understand that I was wrong in so doing, it being also the command of the king that I should stand.” This the letter which Henry III. wrote to him on the occasion:
MONSIEUR, DE MONTAIGNE,—Inasmuch as I hold in great esteem your fidelity and zealous devotion to my service, it has been a pleasure to me to learn that you have been chosen mayor of my town of Bordeaux. I have had the agreeable duty of confirming the selection, and I did so the more willingly, seeing that it was made during your distant absence; wherefore it is my desire, and I require and command you expressly that you proceed without delay to enter on the duties to which you have received so legitimate a call. And so you will act in a manner very agreeable to me, while the contrary will displease me greatly. Praying God, M. de Montaigne, to have you in his holy keeping.
“Written at Paris, the 25th day of November 1581.
“A Monsieur de MONTAIGNE, Knight of my Order, Gentleman in Ordinary of my Chamber, being at present in Rome.”
Montaigne, in his new employment, the most important in the province, obeyed the axiom, that a man may not refuse a duty, though it absorb his time and attention, and even involve the sacrifice of his blood. Placed between two extreme parties, ever on the point of getting to blows, he showed himself in practice what he is in his book, the friend of a middle and temperate policy. Tolerant by character and on principle, he belonged, like all the great minds of the sixteenth century, to that political sect which sought to improve, without destroying, institutions; and we may say of him, what he himself said of La Boetie, “that he had that maxim indelibly impressed on his mind, to obey and submit himself religiously to the laws under which he was born. Affectionately attached to the repose of his country, an enemy to changes and innovations, he would have preferred to employ what means he had towards their discouragement and suppression, than in promoting their success.” Such was the platform of his administration.
He applied himself, in an especial manner, to the maintenance of peace between the two religious factions which at that time divided the town of Bordeaux; and at the end of his two first years of office, his grateful fellow-citizens conferred on him (in 1583) the mayoralty for two years more, a distinction which had been enjoyed, as he tells us, only twice before. On the expiration of his official career, after four years’ duration, he could say fairly enough of himself that he left behind him neither hatred nor cause of offence.
In the midst of the cares of government, Montaigne found time to revise and enlarge his Essays, which, since their appearance in 1580, were continually receiving augmentation in the form of additional chapters or papers. Two more editions were printed in 1582 and 1587; and during this time the author, while making alterations in the original text, had composed part of the Third Book. He went to Paris to make arrangements for the publication of his enlarged labours, and a fourth impression in 1588 was the result. He remained in the capital some time on this occasion, and it was now that he met for the first time Mademoiselle de Gournay. Gifted with an active and inquiring spirit, and, above all, possessing a sound and healthy tone of mind, Mademoiselle de Gournay had been carried from her childhood with that tide which set in with sixteenth century towards controversy, learning, and knowledge. She learnt Latin without a master; and when, the age of eighteen, she accidentally became possessor of a copy of the Essays, she was transported with delight and admiration.
She quitted the chateau of Gournay, to come and see him. We cannot do better, in connection with this journey of sympathy, than to repeat the words of Pasquier: “That young lady, allied to several great and noble families of Paris, proposed to herself no other marriage than with her honour, enriched with the knowledge gained from good books, and, beyond all others, from the essays of M. de Montaigne, who making in the year 1588 a lengthened stay in the town of Paris, she went there for the purpose of forming his personal acquaintance; and her mother, Madame de Gournay, and herself took him back with them to their chateau, where, at two or three different times, he spent three months altogether, most welcome of visitors.” It was from this moment that Mademoiselle de Gournay dated her adoption as Montaigne’s daughter, a circumstance which has tended to confer immortality upon her in a far greater measure than her own literary productions.
Montaigne, on leaving Paris, stayed a short time at Blois, to attend the meeting of the States-General. We do not know what part he took in that assembly: but it is known that he was commissioned, about this period, to negotiate between Henry of Navarre (afterwards Henry IV.) and the Duke of Guise. His political life is almost a blank; but De Thou assures us that Montaigne enjoyed the confidence of the principal persons of his time. De Thou, who calls him a frank man without constraint, tells us that, walking with him and Pasquier in the court at the Castle of Blois, he heard him pronounce some very remarkable opinions on contemporary events, and he adds that Montaigne had foreseen that the troubles in France could not end without witnessing the death of either the King of Navarre or of the Duke of Guise. He had made himself so completely master of the views of these two princes, that he told De Thou that the King of Navarre would have been prepared to embrace Catholicism, if he had not been afraid of being abandoned by his party, and that the Duke of Guise, on his part, had no particular repugnance to the Confession of Augsburg, for which the Cardinal of Lorraine, his uncle, had inspired him with a liking, if it had not been for the peril involved in quitting the Romish communion. It would have been easy for Montaigne to play, as we call it, a great part in politics, and create for himself a lofty position but his motto was, ‘Otio et Libertati’; and he returned quietly home to compose a chapter for his next edition on inconveniences of Greatness.
The author of the Essays was now fifty-five. The malady which tormented him grew only worse and worse with years; and yet he occupied himself continually with reading, meditating, and composition. He employed the years 1589, 1590, and 1591 in making fresh additions to his book; and even in the approaches of old age he might fairly anticipate many happy hours, when he was attacked by quinsy, depriving him of the power utterance. Pasquier, who has left us some details his last hours, narrates that he remained three days in full possession of his faculties, but unable to speak, so that, in order to make known his desires, he was obliged to resort to writing; and as he felt his end drawing near, he begged his wife to summon certain of the gentlemen who lived in the neighbourhood to bid them a last farewell. When they had arrived, he caused mass to be celebrated in apartment; and just as the priest was elevating the host, Montaigne fell forward with his arms extended in front of him, on the bed, and so expired. He was in his sixtieth year. It was the 13th September 1592.
Montaigne was buried near his own house; but a few years after his decease, his remains were removed to the church of a Commandery of St. Antoine at Bordeaux, where they still continue. His monument was restored in 1803 by a descendant. It was seen about 1858 by an English traveller (Mr. St. John).’—[“Montaigne the Essayist,” by Bayle St. John, 1858, 2 vols. 8vo, is one of most delightful books of the kind.]— and was then in good preservation.
In 1595 Mademoiselle de Gournay published a new edition of Montaigne’s Essays, and the first with the latest emendations of the author, from a copy presented to her by his widow, and which has not been recovered, although it is known to have been in existence some years after the date of the impression, made on its authority.
Coldly as Montaigne’s literary productions appear to have been received by the generation immediately succeeding his own age, his genius grew into just appreciation in the seventeenth century, when such great spirits arose as La Bruyere, Moliere, La Fontaine, Madame de Sevigne. “O,” exclaimed the Chatelaine des Rochers, “what capital company he is, the dear man! he is my old friend; and just for the reason that he is so, he always seems new. My God! how full is that book of sense!” Balzac said that he had carried human reason as far and as high as it could go, both in politics and in morals. On the other hand, Malebranche and the writers of Port Royal were against him; some reprehended the licentiousness of his writings; others their impiety, materialism, epicureanism. Even Pascal, who had carefully read the Essays, and gained no small profit by them, did not spare his reproaches. But Montaigne has outlived detraction. As time has gone on, his admirers and borrowers have increased in number, and his Jansenism, which recommended him to the eighteenth century, may not be his least recommendation in the nineteenth. Here we have certainly, on the whole, a first-class man, and one proof of his masterly genius seems to be, that his merits and his beauties are sufficient to induce us to leave out of consideration blemishes and faults which would have been fatal to an inferior writer.
I.——To Monsieur de MONTAIGNE
[This account of the death of La Boetie begins imperfectly. It first appeared in a little volume of Miscellanies in 1571. See Hazlitt, ubi sup. p. 630.]—As to his last words, doubtless, if any man can give good account of them, it is I, both because, during the whole of his sickness he conversed as fully with me as with any one, and also because, in consequence of the singular and brotherly friendship which we had entertained for each other, I was perfectly acquainted with the intentions, opinions, and wishes which he had formed in the course of his life, as much so, certainly, as one man can possibly be with those of another man; and because I knew them to be elevated, virtuous, full of steady resolution, and (after all said) admirable. I well foresaw that, if his illness permitted him to express himself, he would allow nothing to fall from him, in such an extremity, that was not replete with good example. I consequently took every care in my power to treasure what was said. True it is, Monseigneur, as my memory is not only in itself very short, but in this case affected by the trouble which I have undergone, through so heavy and important a loss, that I have forgotten a number of things which I should wish to have had known; but those which I recollect shall be related to you as exactly as lies in my power. For to represent in full measure his noble career suddenly arrested, to paint to you his indomitable courage, in a body worn out and prostrated by pain and the assaults of death, I confess, would demand a far better ability than mine: because, although, when in former years he discoursed on serious and important matters, he handled them in such a manner that it was difficult to reproduce exactly what he said, yet his ideas and his words at the last seemed to rival each other in serving him. For I am sure that I never knew him give birth to such fine conceptions, or display so much eloquence, as in the time of his sickness. If, Monseigneur, you blame me for introducing his more ordinary observations, please to know that I do so advisedly; for since they proceeded from him at a season of such great trouble, they indicate the perfect tranquillity of his mind and thoughts to the last.
On Monday, the 9th day of August 1563, on my return from the Court, I sent an invitation to him to come and dine with me. He returned word that he was obliged, but, being indisposed, he would thank me to do him the pleasure of spending an hour with him before he started for Medoc. Shortly after my dinner I went to him. He had laid himself down on the bed with his clothes on, and he was already, I perceived, much changed. He complained of diarrhoea, accompanied by the gripes, and said that he had it about him ever since he played with M. d’Escars with nothing but his doublet on, and that with him a cold often brought on such attacks. I advised him to go as he had proposed, but to stay for the night at Germignac, which is only about two leagues from the town. I gave him this advice, because some houses, near to that where he was ping, were visited by the plague, about which he was nervous since his return from Perigord and the Agenois, here it had been raging; and, besides, horse exercise was, from my own experience, beneficial under similar circumstances. He set out, accordingly, with his wife and M. Bouillhonnas, his uncle.
Early on the following morning, however, I had intelligence from Madame de la Boetie, that in the night he had fresh and violent attack of dysentery. She had called in physician and apothecary, and prayed me to lose no time coming, which (after dinner) I did. He was delighted to see me; and when I was going away, under promise to turn the following day, he begged me more importunately and affectionately than he was wont to do, to give him as such of my company as possible. I was a little affected; yet was about to leave, when Madame de la Boetie, as if she foresaw something about to happen, implored me with tears to stay the night. When I consented, he seemed to grow more cheerful. I returned home the next day, and on the Thursday I paid him another visit. He had become worse; and his loss of blood from the dysentery, which reduced his strength very much, was largely on the increase. I quitted his side on Friday, but on Saturday I went to him, and found him very weak. He then gave me to understand that his complaint was infectious, and, moreover, disagreeable and depressing; and that he, knowing thoroughly my constitution, desired that I should content myself with coming to see him now and then. On the contrary, after that I never left his side.
It was only on the Sunday that he began to converse with me on any subject beyond the immediate one of his illness, and what the ancient doctors thought of it: we had not touched on public affairs, for I found at the very outset that he had a dislike to them.
But, on the Sunday, he had a fainting fit; and when he came to himself, he told me that everything seemed to him confused, as if in a mist and in disorder, and that, nevertheless, this visitation was not unpleasing to him. “Death,” I replied, “has no worse sensation, my brother.” “None so bad,” was his answer. He had had no regular sleep since the beginning of his illness; and as he became worse and worse, he began to turn his attention to questions which men commonly occupy themselves with in the last extremity, despairing now of getting better, and intimating as much to me. On that day, as he appeared in tolerably good spirits, I took occasion to say to him that, in consideration of the singular love I bore him, it would become me to take care that his affairs, which he had conducted with such rare prudence in his life, should not be neglected at present; and that I should regret it if, from want of proper counsel, he should leave anything unsettled, not only on account of the loss to his family, but also to his good name.
He thanked me for my kindness; and after a little reflection, as if he was resolving certain doubts in his own mind, he desired me to summon his uncle and his wife by themselves, in order that he might acquaint them with his testamentary dispositions. I told him that this would shock them. “No, no,” he answered, “I will cheer them by making out my case to be better than it is.” And then he inquired, whether we were not all much taken by surprise at his having fainted? I replied, that it was of no importance, being incidental to the complaint from which he suffered. “True, my brother,” said he; “it would be unimportant, even though it should lead to what you most dread.” “For you,” I rejoined, “it might be a happy thing; but I should be the loser, who would thereby be deprived of so great, so wise, and so steadfast a friend, a friend whose place I should never see supplied.” “It is very likely you may not,” was his answer; “and be sure that one thing which makes me somewhat anxious to recover, and to delay my journey to that place, whither I am already half-way gone, is the thought of the loss both you and that poor man and woman there (referring to his uncle and wife) must sustain; for I love them with my whole heart, and I feel certain that they will find it very hard to lose me. I should also regret it on account of such as have, in my lifetime, valued me, and whose conversation I should like to have enjoyed a little longer; and I beseech you, my brother, if I leave the world, to carry to them for me an assurance of the esteem I entertained for them to the last moment of my existence. My birth was, moreover, scarcely to so little purpose but that, had I lived, I might have done some service to the public; but, however this may be, I am prepared to submit to the will of God, when it shall please Him to call me, being confident of enjoying the tranquillity which you have foretold for me. As for you, my friend, I feel sure that you are so wise, that you will control your emotions, and submit to His divine ordinance regarding me; and I beg of you to see that that good man and woman do not mourn for my departure unnecessarily.”
He proceeded to inquire how they behaved at present. “Very well,” said I, “considering the circumstances.” “Ah!” he replied, “that is, so long as they do not abandon all hope of me; but when that shall be the case, you will have a hard task to support them.” It was owing to his strong regard for his wife and uncle that he studiously disguised from them his own conviction as to the certainty of his end, and he prayed me to do the same. When they were near him he assumed an appearance of gaiety, and flattered them with hopes. I then went to call them. They came, wearing as composed an air as possible; and when we four were together, he addressed us, with an untroubled countenance, as follows: “Uncle and wife, rest assured that no new attack of my disease, or fresh doubt that I have as to my recovery, has led me to take this step of communicating to you my intentions, for, thank God, I feel very well and hopeful; but taught by observation and experience the instability of all human things, and even of the life to which we are so much attached, and which is, nevertheless, a mere bubble; and knowing, moreover, that my state of health brings me more within the danger of death, I have thought proper to settle my worldly affairs, having the benefit of your advice.” Then addressing himself more particularly to his uncle, “Good uncle,” said he, “if I were to rehearse all the obligations under which I lie to you, I am sure that I never should make an end. Let me only say that, wherever I have been, and with whomsoever I have conversed, I have represented you as doing for me all that a father could do for a son; both in the care with which you tended my education, and in the zeal with which you pushed me forward into public life, so that my whole existence is a testimony of your good offices towards me. In short, I am indebted for all that I have to you, who have been to me as a parent; and therefore I have no right to part with anything, unless it be with your approval.”
There was a general silence hereupon, and his uncle was prevented from replying by tears and sobs. At last he said that whatever he thought for the best would be agreeable to him; and as he intended to make him his heir, he was at liberty to dispose of what would be his.
Then he turned to his wife. “My image,” said he (for so he often called her, there being some sort of relationship between them), “since I have been united to you by marriage, which is one of the most weighty and sacred ties imposed on us by God, for the purpose of maintaining human society, I have continued to love, cherish, and value you; and I know that you have returned my affection, for which I have no sufficient acknowledgment. I beg you to accept such portion of my estate as I bequeath to you, and be satisfied with it, though it is very inadequate to your desert.”
Afterwards he turned to me. “My brother,” he began, “for whom I have so entire a love, and whom I selected out of so large a number, thinking to revive with you that virtuous and sincere friendship which, owing to the degeneracy of the age, has grown to be almost unknown to us, and now exists only in certain vestiges of antiquity, I beg of you, as a mark of my affection to you, to accept my library: a slender offering, but given with a cordial will, and suitable to you, seeing that you are fond of learning. It will be a memorial of your old companion.”
Then he addressed all three of us. He blessed God that in his extremity he had the happiness to be surrounded by those whom he held dearest in the world, and he looked upon it as a fine spectacle, where four persons were together, so unanimous in their feelings, and loving each other for each other’s sake. He commended us one to the other; and proceeded thus: “My worldly matters being arranged, I must now think of the welfare of my soul. I am a Christian; I am a Catholic. I have lived one, and I shall die one. Send for a priest; for I wish to conform to this last Christian obligation.” He now concluded his discourse, which he had conducted with such a firm face and with so distinct an utterance, that whereas, when I first entered his room, he was feeble, inarticulate in his speech, his pulse low and feverish, and his features pallid, now, by a sort of miracle, he appeared to have rallied, and his pulse was so strong that for the sake of comparison, I asked him to feel mine.
I felt my heart so oppressed at this moment, that I had not the power to make him any answer; but in the course of two or three hours, solicitous to keep up his courage, and, likewise, out of the tenderness which I had had all my life for his honour and fame, wishing a larger number of witnesses to his admirable fortitude, I said to him, how much I was ashamed to think that I lacked courage to listen to what he, so great a sufferer, had the courage to deliver; that down to the present time I had scarcely conceived that God granted us such command over human infirmities, and had found a difficulty in crediting the examples I had read in histories; but that with such evidence of the thing before my eyes, I gave praise to God that it had shown itself in one so excessively dear to me, and who loved me so entirely, and that his example would help me to act in a similar manner when my turn came. Interrupting me, he begged that it might happen so, and that the conversation which had passed between us might not be mere words, but might be impressed deeply on our minds, to be put in exercise at the first occasion; and that this was the real object and aim of all philosophy.
He then took my hand, and continued: “Brother, friend, there are many acts of my life, I think, which have cost me as much difficulty as this one is likely to do; and, after all, I have been long prepared for it, and have my lesson by heart. Have I not lived long enough? I am just upon thirty-three. By the grace of God, my days so far have known nothing but health and happiness; but in the ordinary course of our unstable human affairs, this could not have lasted much longer; it would have become time for me to enter on graver avocations, and I should thus have involved myself in numberless vexations, and, among them, the troubles of old age, from which I shall now be exempt. Moreover, it is probable that hitherto my life has been spent more simply, and with less of evil, than if God had spared me, and I had survived to feel the thirst for riches and worldly prosperity. I am sure, for my part, that I now go to God and the place of the blessed.” He seemed to detect in my expression some inquietude at his words; and he exclaimed, “What, my brother, would you make me entertain apprehensions? Had I any, whom would it become so much as yourself to remove them?”
The notary, who had been summoned to draw up his will, came in the evening, and when he had the documents prepared, I inquired of La Boetie if he would sign them. “Sign them,” cried he; “I will do so with my own hand; but I could desire more time, for I feel exceedingly timid and weak, and in a manner exhausted.” But when I was going to change the conversation, he suddenly rallied, said he had but a short time to live, and asked if the notary wrote rapidly, for he should dictate without making any pause. The notary was called, and he dictated his will there and then with such speed that the man could scarcely keep up with him; and when he had done, he asked me to read it out, saying to me, “What a good thing it is to look after what are called our riches.” ‘Sunt haec, quoe hominibus vocantur bona’. As soon as the will was signed, the chamber being full, he asked me if it would hurt him to talk. I answered, that it would not, if he did not speak too loud. He then summoned Mademoiselle de Saint Quentin, his niece, to him, and addressed her thus: “Dear niece, since my earliest acquaintance with thee, I have observed the marks of, great natural goodness in thee; but the services which thou rendered to me, with so much affectionate diligence, in my present and last necessity, inspire me with high hopes of thee; and I am under great obligations to thee, and give thee most affectionate thanks. Let me relieve my conscience by counselling thee to be, in the first place, devout, to God: for this doubtless is our first duty, failing which all others can be of little advantage or grace, but which, duly observed, carries with it necessarily all other virtues. After God, thou shouldest love thy father and mother—thy mother, my sister, whom I regard as one of the best and most intelligent of women, and by whom I beg of thee to let thy own life be regulated. Allow not thyself to be led away by pleasures; shun, like the plague, the foolish familiarities thou seest between some men and women; harmless enough at first, but which by insidious degrees corrupt the heart, and thence lead it to negligence, and then into the vile slough of vice. Credit me, the greatest safeguard to female chastity is sobriety of demeanour. I beseech and direct that thou often call to mind the friendship which was betwixt us; but I do not wish thee to mourn for me too much—an injunction which, so far as it is in my power, I lay on all my friends, since it might seem that by doing so they felt a jealousy of that blessed condition in which I am about to be placed by death. I assure thee, my dear, that if I had the option now of continuing in life or of completing the voyage on which I have set out, I should find it very hard to choose. Adieu, dear niece.”
Mademoiselle d’Arsat, his stepdaughter, was next called. He said to her: “Daughter, you stand in no great need of advice from me, insomuch as you have a mother, whom I have ever found most sagacious, and entirely in conformity with my own opinions and wishes, and whom I have never found faulty; with such a preceptress, you cannot fail to be properly instructed. Do not account it singular that I, with no tie of blood to you, am interested in you; for, being the child of one who is so closely allied to me, I am necessarily concerned in what concerns you; and consequently the affairs of your brother, M. d’Arsat, have ever been watched by me with as much care as my own; nor perhaps will it be to your disadvantage that you were my step-daughter. You enjoy sufficient store of wealth and beauty; you are a lady of good family; it only remains for you to add to these possessions the cultivation of your mind, in which I exhort you not to fail. I do not think necessary to warn you against vice, a thing so odious in women, for I would not even suppose that you could harbour any inclination for it—nay, I believe that you hold the very name in abhorrence. Dear daughter, farewell.”
All in the room were weeping and lamenting; but he held without interruption the thread of his discourse, which was pretty long. But when he had done, he directed us all to leave the room, except the women attendants, whom he styled his garrison. But first, calling to him my brother, M. de Beauregard, he said to him: “M. de Beauregard, you have my best thanks for all the care you have taken of me. I have now a thing which I am very anxious indeed to mention to you, and with your permission I will do so.” As my brother gave him encouragement to proceed, he added: “I assure you that I never knew any man who engaged in the reformation of our Church with greater sincerity, earnestness, and single-heartedness than yourself. I consider that you were led to it by observing the vicious character of our prelates, which no doubt much requires setting in order, and by imperfections which time has brought into our Church. It is not my desire at present discourage you from this course, for I would have no one act in opposition to his conscience; but I wish, having regard to the good repute acquired by your family from its enduring concord—a family than which none can be dearer to me; a family, thank God! no member of which has ever been guilty of dishonour —in regard, further, to the will of your good father to whom you owe so much, and of your, uncle, I wish you to avoid extreme means; avoid harshness and violence: be reconciled with your relatives; do not act apart, but unite. You perceive what disasters our quarrels have brought upon this kingdom, and I anticipate still worse mischiefs; and in your goodness and wisdom, beware of involving your family in such broils; let it continue to enjoy its former reputation and happiness. M. de Beauregard, take what I say in good part, and as a proof of the friendship I feel for you. I postponed till now any communication with you on the subject, and perhaps the condition in which you see me address you, may cause my advice and opinion to carry greater authority.” My brother expressed his thanks to him cordially.
On the Monday morning he had become so ill that he quite despaired of himself; and he said to me very pitifully: “Brother, do not you feel pain for all the pain I am suffering? Do you not perceive now that the help you give me has no other effect than that of lengthening my suffering?”
Shortly afterwards he fainted, and we all thought him gone; but by the application of vinegar and wine he rallied. But he soon sank, and when he heard us in lamentation, he murmured, “O God! who is it that teases me so? Why did you break the agreeable repose I was enjoying? I beg of you to leave me.” And then, when he caught the sound of my voice, he continued: “And art thou, my brother, likewise unwilling to see me at peace? O, how thou robbest me of my repose!” After a while, he seemed to gain more strength, and called for wine, which he relished, and declared it to be the finest drink possible. I, in order to change the current of his thoughts, put in, “Surely not; water is the best.” “Ah, yes,” he returned, “doubtless so;—(Greek phrase)—.” He had now become, icy-cold at his extremities, even to his face; a deathly perspiration was upon him, and his pulse was scarcely perceptible.
This morning he confessed, but the priest had omitted to bring with him the necessary apparatus for celebrating Mass. On the Tuesday, however, M. de la Boetie summoned him to aid him, as he said, in discharging the last office of a Christian. After the conclusion of Mass, he took the sacrament; when the priest was about to depart, he said to him: “Spiritual father, I implore you humbly, as well as those over whom you are set, to pray to the Almighty on my behalf; that, if it be decreed in heaven that I am now to end my life, He will take compassion on my soul, and pardon me my sins, which are manifold, it not being possible for so weak and poor a creature as I to obey completely the will of such a Master; or, if He think fit to keep me longer here, that it may please Him to release my present extreme anguish, and to direct my footsteps in the right path, that I may become a better man than I have been.” He paused to recover breath a little; priest was about to go away, he called him back and proceeded: “I desire to say, besides, in your hearing this: I declare that I was christened and I have lived, and that so I wish to die, in the faith which Moses preached in Egypt; which afterwards the Patriarchs accepted and professed in Judaea; and which, in the course of time, has been transmitted to France and to us.” He seemed desirous of adding something more, but he ended with a request to his uncle and me to send up prayers for him; “for those are,” he said, “the best duties that Christians can fulfil one for another.” In the course of talking, his shoulder was uncovered, and although a man-servant stood near him, he asked his uncle to re-adjust the clothes. Then, turning his eyes towards me, he said, “Ingenui est, cui multum debeas, ei plurimum velle debere.”
M. de Belot called in the afternoon to see him, and M. de la Boetie, taking his hand, said to him: “I was on the point of discharging my debt, but my kind creditor has given me a little further time.” A little while after, appearing to wake out of a sort of reverie, he uttered words which he had employed once or twice before in the course of his sickness: “Ah well, ah well, whenever the hour comes, I await it with pleasure and fortitude.” And then, as they were holding his mouth open by force to give him a draught, he observed to M. de Belot: “An vivere tanti est?”
As the evening approached, he began perceptibly to sink; and while I supped, he sent for me to come, being no more than the shadow of a man, or, as he put it himself, ‘non homo, sed species hominis’; and he said to me with the utmost difficulty: “My brother, my friend, please God I may realise the imaginations I have just enjoyed.” Afterwards, having waited for some time while he remained silent, and by painful efforts was drawing long sighs (for his tongue at this point began to refuse its functions), I said, “What are they?” “Grand, grand!” he replied. “I have never yet failed,” returned I, “to have the honour of hearing your conceptions and imaginations communicated to me; will you not now still let me enjoy them?” “I would indeed,” he answered; “but, my brother, I am not able to do so; they are admirable, infinite, and unspeakable.” We stopped short there, for he could not go on. A little before, indeed, he had shown a desire to speak to his wife, and had told her, with as gay a countenance as he could contrive to assume, that he had a story to tell her. And it seemed as if he was making an attempt to gain utterance; but, his strength failing him, he begged a little wine to resuscitate it. It was of no avail, for he fainted away suddenly, and was for some time insensible. Having become so near a neighbour to death, and hearing the sobs of Mademoiselle de la Boetie, he called her, and said to her thus: “My own likeness, you grieve yourself beforehand; will you not have pity on me? take courage. Assuredly, it costs me more than half the pain I endure, to see you suffer; and reasonably so, because the evils which we ourselves feel we do not actually ourselves suffer, but it certain sentient faculties which God plants in us, that feel them: whereas what we feel on account of others, we feel by consequence of a certain reasoning process which goes on within our minds. But I am going away” —That he said because his strength was failing him; and fearing that he had frightened his wife, he resumed, observing: “I am going to sleep. Good night, my wife; go thy way.” This was the last farewell he took of her.
After she had left, “My brother,” said he to me, “keep near me, if you please;” and then feeling the advance of death more pressing and more acute, or else the effect of some warm draught which they had made him swallow, his voice grew stronger and clearer, and he turned quite with violence in his bed, so that all began again to entertain the hope which we had lost only upon witnessing his extreme prostration.
At this stage he proceeded, among other things, to pray me again and again, in a most affectionate manner, to give him a place; so that I was apprehensive that his reason might be impaired, particularly when, on my pointing out to him that he was doing himself harm, and that these were not of the words of a rational man, he did not yield at first, but redoubled his outcry, saying, “My brother, my brother! dost thou then refuse me a place?” insomuch that he constrained me to demonstrate to him that, as he breathed and spoke, and had his physical being, therefore he had his place. “Yes, yes,” he responded, “I have; but it is not that which I need; and, besides, when all is said, I have no longer any existence.” “God,” I replied, “will grant you a better one soon.” “Would it were now, my brother,” was his answer. “It is now three days since I have been eager to take my departure.”
Being in this extremity, he frequently called me, merely to satisfy him that I was at his side. At length, he composed himself a little to rest, which strengthened our hopes; so much so, indeed, that I left the room, and went to rejoice thereupon with Mademoiselle de la Boetie. But, an hour or so afterwards, he called me by name once or twice, and then with a long sigh expired at three o’clock on Wednesday morning, the 18th August 1563, having lived thirty-two years, nine months, and seventeen days.
II.——To Monseigneur, Monseigneur de MONTAIGNE.
[This letter is prefixed to Montaigne’s translation of the “Natural Theology” of Raymond de Sebonde, printed at Paris in 1569.]
In pursuance of the instructions which you gave me last year in your house at Montaigne, Monseigneur, I have put into a French dress, with my own hand, Raymond de Sebonde, that great Spanish theologian and philosopher; and I have divested him, so far as I could, of that rough bearing and barbaric appearance which you saw him wear at first; that, in my opinion, he is now qualified to present himself in the best company. It is perfectly possible that some fastidious persons will detect in the book some trace of Gascon parentage; but it will be so much the more to their discredit, that they allowed the task to devolve on one who is quite a novice in these things. It is only right, Monseigneur, that the work should come before the world under your auspices, since whatever emendations and polish it may have received, are owing to you. Still I see well that, if you think proper to balance accounts with the author, you will find yourself much his debtor; for against his excellent and religious discourses, his lofty and, so to speak, divine conceptions, you will find that you will have to set nothing but words and phraseology; a sort of merchandise so ordinary and commonplace, that whoever has the most of it, peradventure is the worst off.
Monseigneur, I pray God to grant you a very long and happy life. From Paris, this 18th of June 1568. Your most humble and most obedient son,
MICHEL DE MONTAIGNE
III.——To Monsieur, Monsieur de LANSAC,
—[This letter appears to belong to 1570.]—Knight of the King’s Order, Privy Councillor, Sub-controller of his Finance, and Captain of the Cent Gardes of his Household.
MONSIEUR,—I send you the OEconomics of Xenophon, put into French by the late M. de la Boetie,—[Printed at Paris, 8vo, 1571, and reissued, with the addition of some notes, in 1572, with a fresh title-page.]—a present which appears to me to be appropriate, as well because it is the work of a gentleman of mark,—[Meaning Xenophon.]—a man illustrious in war and peace, as because it has taken its second shape from a personage whom I know to have been held by you in affectionate regard during his life. This will be an inducement to you to continue to cherish towards his memory, your good opinion and goodwill. And to be bold with you, Monsieur, do not fear to increase these sentiments somewhat; for, as you had knowledge of his high qualities only in his public capacity, it rests with me to assure you how many endowments he possessed beyond your personal experience of him. He did me the honour, while he lived, and I count it amongst the most fortunate circumstances in my own career, to have with me a friendship so close and so intricately knit, that no movement, impulse, thought, of his mind was kept from me, and if I have not formed a right judgment of him, I must suppose it to be from my own want of scope. Indeed, without exaggeration, he was so nearly a prodigy, that I am afraid of not being credited when I speak of him, even though I should keep much within the mark of my own actual knowledge. And for this time, Monsieur, I shall content myself with praying you, for the honour and respect we owe to truth, to testify and believe that our Guienne never beheld his peer among the men of his vocation. Under the hope, therefore, that you will pay him his just due, and in order to refresh him in your memory, I present you this book, which will answer for me that, were it not for the insufficiency of my power, I would offer you as willingly something of my own, as an acknowledgment of the obligations I owe to you, and of the ancient favour and friendship which you have borne towards the members of our house. But, Monsieur, in default of better coin, I offer you in payment the assurance of my desire to do you humble service.
Monsieur, I pray God to have you in His keeping. Your obedient servant, MICHEL DE MONTAIGNE.
IV.——To Monsieur, Monsieur de MESMES, Lord of Roissy and Malassize, Privy
Councillor to the King.
MONSIEUR,—It is one of the most conspicuous follies committed by men, to employ the strength of their understanding in overturning and destroying those opinions which are commonly received among us, and which afford us satisfaction and content; for while everything beneath heaven employs the ways and means placed at its disposal by nature for the advancement and commodity of its being, these, in order to appear of a more sprightly and enlightened wit, not accepting anything which has not been tried and balanced a thousand times with the most subtle reasoning, sacrifice their peace of mind to doubt, uneasiness, and feverish excitement. It is not without reason that childhood and simplicity have been recommended by holy writ itself. For my part, I prefer to be quiet rather than clever: give me content, even if I am not to be so wide in my range. This is the reason, Monsieur, why, although persons of an ingenious turn laugh at our care as to what will happen after our own time, for instance, to our souls, which, lodged elsewhere, will lose all consciousness of what goes on here below, yet I consider it to be a great consolation for the frailty and brevity of life, to reflect that we have the power of prolonging it by reputation and fame; and I embrace very readily this pleasant and favourable notion original with our being, without inquiring too critically how or why it is. Insomuch that having loved, beyond everything, the late M. de la Boetie, the greatest man, in my judgment, of our age, I should think myself very negligent of my duty if I failed, to the utmost of my power, to prevent such a name as his, and a memory so richly meriting remembrance, from falling into oblivion; and if I did not use my best endeavour to keep them fresh. I believe that he feels something of what I do on his behalf, and that my services touch and rejoice him. In fact, he lives in my heart so vividly and so wholly, that I am loath to believe him committed to the dull ground, or altogether cast off from communication with us. Therefore, Monsieur, since every new light I can shed on him and his name, is so much added to his second period of existence, and, moreover, since his name is ennobled and honoured by the place which receives it, it falls to me not only to extend it as widely as I can, but to confide it to the keeping of persons of honour and virtue; among whom you hold such a rank, that, to afford you the opportunity of receiving this new guest, and giving him good entertainment, I decided on presenting to you this little work, not for any profit you are likely to derive from it, being well aware that you do not need to have Plutarch and his companions interpreted to you—but it is possible that Madame de Roissy, reading in it the order of her household management and of your happy accord painted to the life, will be pleased to see how her own natural inclination has not only reached but surpassed the theories of the wisest philosophers, regarding the duties and laws of the wedded state. And, at all events, it will be always an honour to me, to be able to do anything which shall be for the pleasure of you and yours, on account of the obligation under which I lie to serve you.
Monsieur, I pray God to grant you a long and happy life. From Montaigne, this 30th April 1570. Your humble servant, MICHEL DE MONTAIGNE.
V.——To Monsieur, Monsieur de L’HOSPITAL, Chancellor of France
MONSEIGNEUR,—I am of the opinion that persons such as you, to whom fortune and reason have committed the charge of public affairs, are not more inquisitive in any point than in ascertaining the character of those in office under you; for no society is so poorly furnished, but that, if a proper distribution of authority be used, it has persons sufficient for the discharge of all official duties; and when this is the case, nothing is wanting to make a State perfect in its constitution. Now, in proportion as this is so much to be desired, so it is the more difficult of accomplishment, since you cannot have eyes to embrace a multitude so large and so widely extended, nor to see to the bottom of hearts, in order that you may discover intentions and consciences, matters principally to be considered; so that there has never been any commonwealth so well organised, in which we might not detect often enough defect in such a department or such a choice; and in those systems, where ignorance and malice, favouritism, intrigue, and violence govern, if any selection happens to be made on the ground of merit and regularity, we may doubtless thank Fortune, which, in its capricious movements, has for once taken the path of reason.
This consideration, Monseigneur, often consoled me, when I beheld M. Etienne de la Boetie, one of the fittest men for high office in France, pass his whole life without employment and notice, by his domestic hearth, to the singular detriment of the public; for, so far as he was concerned, I may assure you, Monseigneur, that he was so rich in those treasures which defy fortune, that never was man more satisfied or content. I know, indeed, that he was raised to the dignities connected with his neighbourhood—dignities accounted considerable; and I know also, that no one ever acquitted himself better of them; and when he died at the age of thirty-two, he enjoyed a reputation in that way beyond all who had preceded him.
But for all that, it is no reason that a man should be left a common soldier, who deserves to become a captain; nor to assign mean functions to those who are perfectly equal to the highest. In truth, his powers were badly economised and too sparingly employed; insomuch that, over and above his actual work, there was abundant capacity lying idle which might have been called into service, both to the public advantage and his own private glory.
Therefore, Monseigneur, since he was so indifferent to his own fame (for virtue and ambition, unfortunately, seldom lodge together), and since he lived in an age when others were too dull or too jealous to witness to his character, I have it marvellously at heart that his memory, at all events, to which I owe the good offices of a friend, should enjoy the recompense of his brave life; and that it should survive in the good report of men of honour and virtue. On this account, sir, I have been desirous to bring to light, and present to you, such few Latin verses as he left behind. Different from the builder, who places the most attractive, portion of his house towards the street, and to the draper, who displays in his window his best goods, that which was most precious in my friend, the juice and marrow of his genius, departed with him, and there have remained to us but the bark and the leaves.
The exactly regulated movements of his mind, his piety, his virtue, his justice, his vivacity, the solidity and soundness of his judgment, the loftiness of his ideas, raised so far above the common level, his learning, the grace which accompanied his most ordinary actions, the tender affection he had for his miserable country, and his supreme and sworn detestation of all vice, but principally of that villainous traffic which disguises itself under the honourable name of justice, should certainly impress all well-disposed persons with a singular love towards him, and an extraordinary regret for his loss. But, sir, I am unable to do justice to all these qualities; and of the fruit of his own studies it had not entered into his mind to leave any proof to posterity; all that remains, is the little which, as a pastime, he did at intervals.
However this may be, I beg you, sir, to receive it kindly; and as our judgment of great things is many times formed from lesser things, and as even the recreations of illustrious men carry with them, to intelligent observers, some honourable traits of their origin, I would have you form from this, some knowledge of him, and hence lovingly cherish his name and his memory. In this, sir, you will only reciprocate the high opinion which he had of your virtue, and realise what he infinitely desired in his lifetime; for there was no one in the world in whose acquaintance and friendship he would have been so happy to see himself established, as in your own. But if any man is offended by the freedom which I use with the belongings of another, I can tell him that nothing which has been written or been laid down, even in the schools of philosophy, respecting the sacred duties and rights of friendship, could give an adequate idea of the relations which subsisted between this personage and myself.
Moreover, sir, this slender gift, to make two throws of one stone at the same time, may likewise serve, if you please, to testify the honour and respect which I entertain for your ability and high qualities; for as to those gifts which are adventitious and accidental, it is not to my taste to take them into account.
Sir, I pray God to grant you a very happy and a very long life. From Montaigne, this 30th of April 1570.—Your humble and obedient servant,
MICHEL DE MONTAIGNE.
VI.——To Monsieur, Monsieur de Folx, Privy Councillor, and Ambassador of His Majesty to the Signory of Venice.
—[ printed before the ‘vers francois’ of etienne de la boetie, 8vo, paris, 1572.].
SIR,—Being on the point of commending to you and to posterity the memory of the late Etienne de la Boetie, as well for his extreme virtue as for the singular affection which he bore to me, it struck me as an indiscretion very serious in its results, and meriting some coercion from our laws, the practice which often prevails of robbing virtue of glory, its faithful associate, in order to confer it, in accordance with our private interests and without discrimination, on the first comer; seeing that our two principal guiding reins are reward and punishment, which only touch us properly, and as men, through the medium of honour and dishonour, forasmuch as these penetrate the mind, and come home to our most intimate feelings: just where animals themselves are susceptible, more or less, to all other kinds of recompense and corporal chastisement. Moreover, it is well to notice that the custom of praising virtue, even in those who are no longer with us, impalpable as it is to them, serves as a stimulant to the living to imitate their example; just as capital sentences are carried out by the law, more for the sake of warning to others, than in relation to those who suffer. Now, commendation and its opposite being analogous as regards effects, we cannot easily deny the fact, that although the law prohibits one man from slandering the reputation of another, it does not prevent us from bestowing reputation without cause. This pernicious licence in respect to the distribution of praise, has formerly been confined in its area of operations; and it may be the reason why poetry once lost favour with the more judicious. However this may be, it cannot be concealed that the vice of falsehood is one very unbecoming in gentleman, let it assume what guise it will.
As for that personage of whom I am speaking to you, sir he leads me far away indeed from this kind of language; for the danger in his case is not, lest I should lend him anything, but that I might take something from him; and it is his ill-fortune that, while he has supplied me, so far as ever a man could, with just and obvious opportunities for commendation, I find myself unable and unqualified to render it to him —I, who am his debtor for so many vivid communications, and who alone have it in my power to answer for a million of accomplishments, perfections, and virtues, latent (thanks to his unkind stars) in so noble a soul. For the nature of things having (I know not how) permitted that truth, fair and acceptable—as it may be of itself, is only embraced where there are arts of persuasion, to insinuate it into our minds, I see myself so wanting, both in authority to support my simple testimony, and in the eloquence requisite for lending it value and weight, that I was on the eve of relinquishing the task, having nothing of his which would enable me to exhibit to the world a proof of his genius and knowledge.
In truth, sir, having been overtaken by his fate in the flower of his age, and in the full enjoyment of the most vigorous health, it had been his design to publish some day works which would have demonstrated to posterity what sort of a man he was; and, peradventure, he was indifferent enough to fame, having formed such a plan in his head, to proceed no further in it. But I have come to the conclusion, that it was far more excusable in him to bury with him all his rare endowments, than it would be on my part to bury also with me the knowledge of them which I had acquired from him; and, therefore, having collected with care all the remains which I found scattered here and there among his papers, I intend to distribute them so as to recommend his memory to as many persons as possible, selecting the most suitable and worthy of my acquaintance, and those whose testimony might do him greatest honour: such as you, sir, who may very possibly have had some knowledge of him during his life, but assuredly too slight to discover the perfect extent of his worth. Posterity may credit me, if it chooses, when I swear upon my conscience, that I knew and saw him to be such as, all things considered, I could neither desire nor imagine a genius surpassing his.
I beg you very humbly, sir, not only to take his name under your general protection, but also these ten or twelve French stanzas, which lay themselves, as of necessity, under shadow of your patronage. For I will not disguise from you, that their publication was deferred, upon the appearance of his other writings, under the pretext (as it was alleged yonder at Paris) that they were too crude to come to light. You will judge, sir, how much truth there is in this; and since it is thought that hereabout nothing can be produced in our own dialect but what is barbarous and unpolished, it falls to you, who, besides your rank as the first house in Guienne, indeed down from your ancestors, possess every other sort of qualification, to establish, not merely by your example, but by your authoritative testimony, that such is not always the case: the more so that, though ‘tis more natural with the Gascons to act than talk, yet sometimes they employ the tongue more than the arm, and wit in place of valour.
For my own part; sir, it is not in my way to judge of such matters; but I have heard persons who are supposed to understand them, say that these stanzas are not only worthy to be presented in the market-place, but, independently of that, as regards beauty and wealth of invention, they are full of marrow and matter as any compositions of the kind, which have appeared in our language. Naturally each workman feels himself more strong in some special part his art, and those are to be regarded as most fortunate, who lay hands on the noblest, for all the parts essential to the construction of any whole are not equally precious. We find elsewhere, perhaps, greater delicacy phrase, greater softness and harmony of language; but imaginative grace, and in the store of pointed wit, I do not think he has been surpassed; and we should take the account that he made these things neither his occupation nor his study, and that he scarcely took a pen in his hand more than once a year, as is shown by the very slender quantity of his remains. For you see here, sir, green wood and dry, without any sort of selection, all that has come into my possession; insomuch that there are among the rest efforts even of his boyhood. In point of fact, he seems to have written them merely to show that he was capable of dealing with all subjects: for otherwise, thousands of times, in the course of ordinary conversation, I have heard things drop from him infinitely more worthy of being admired, infinitely more worthy of being preserved.
Such, sir, is what justice and affection, forming in this instance a rare conjunction, oblige me to say of this great and good man; and if I have at all offended by the freedom which I have taken in addressing myself to you on such a subject at such a length, be pleased to recollect that the principal result of greatness and eminence is to lay one open to importunate appeals on behalf of the rest of the world. Herewith, after desiring you to accept my affectionate devotion to your service, I beseech God to vouchsafe you, sir, a fortunate and prolonged life. From Montaigne, this 1st of September 1570.—Your obedient servant,
VII.——To Mademoiselle de MONTAIGNE, my Wife.
—[Printed as a preface to the “Consolation of Plutarch to his Wife,” published by Montaigne, with several other tracts by La Boetie, about 1571.]
MY WIFE,—You understand well that it is not proper for a man of the world, according to the rules of this our time, to continue to court and caress you; for they say that a sensible person may take a wife indeed, but that to espouse her is to act like a fool. Let them talk; I adhere for my part the custom of the good old days; I also wear my hair as it used to be then; and, in truth, novelty costs this poor country up to the present moment so dear (and I do not know whether we have reached the highest pitch yet), that everywhere and in everything I renounce the fashion. Let us live, my wife, you and I, in the old French method. Now, you may recollect that the late M. de la Boetie, my brother and inseparable companion, gave me, on his death-bed, all his books and papers, which have remained ever since the most precious part of my effects. I do not wish to keep them niggardly to myself alone, nor do I deserve to have the exclusive use of them; so that I have resolved to communicate them to my friends; and because I have none, I believe, more particularly intimate you, I send you the Consolatory Letter written by Plutarch to his Wife, translated by him into French; regretting much that fortune has made it so suitable a present you, and that, having had but one child, and that a daughter, long looked for, after four years of your married life it was your lot to lose her in the second year of her age. But I leave to Plutarch the duty of comforting you, acquainting you with your duty herein, begging you to put your faith in him for my sake; for he will reveal to you my own ideas, and will express the matter far better than I should myself. Hereupon, my wife, I commend myself very heartily to your good will, and pray God to have you in His keeping. From Paris, this 10th September 1570.—Your good husband,

VIII.——To Monsieur DUPUY,
—[This is probably the Claude Dupuy, born at Paris in 1545, and one of the fourteen judges sent into Guienne after the treaty of Fleix in 1580. It was perhaps under these circumstances that Montaigne addressed to him the present letter.]—the King’s Councillor in his Court and Parliament of Paris.
MONSIEUR,—The business of the Sieur de Verres, a prisoner, who is extremely well known to me, deserves, in the arrival at a decision, the exercise of the clemency natural to you, if, in the public interest, you can fairly call it into play. He has done a thing not only excusable, according to the military laws of this age, but necessary and (as we are of opinion) commendable. He committed the act, without doubt, unwillingly and under pressure; there is no other passage of his life which is open to reproach. I beseech you, sir, to lend the matter your attentive consideration; you will find the character of it as I represent it to you. He is persecuted on this crime, in a way which is far worse than the offence itself. If it is likely to be of use to him, I desire to inform you that he is a man brought up in my house, related to several respectable families, and a person who, having led an honourable life, is my particular friend. By saving him you lay me under an extreme obligation. I beg you very humbly to regard him as recommended by me, and, after kissing your hands, I pray God, sir, to grant you a long and happy life. From Castera, this 23d of April 1580. Your affectionate servant, MONTAIGNE.
IX.——To the Jurats of Bordeaux.
—[Published from the original among the archives of the town of Bordeaux, M. Gustave Brunet in the Bulletin du Bibliophile, July 1839.]
GENTLEMEN,—I trust that the journey of Monsieur de Cursol will be of advantage to the town. Having in hand a case so just and so favourable, you did all in your power to put the business in good trim; and matters being so well situated, I beg you to excuse my absence for some little time longer, and I will abridge my stay so far as the pressure of my affairs permits. I hope that the delay will be short; however, you will keep me, if you please, in your good grace, and will command me, if the occasion shall arise, in employing me in the public service and in yours. Monsieur de Cursol has also written to me and apprised me of his journey. I humbly commend myself to you, and pray God, gentlemen, to grant you long and happy life. From Montaigne, this 21st of May 1582. Your humble brother and servant, MONTAIGNE.
X.——To the same.
—[the original is among the archives of toulouse.].
GENTLEMEN,—I have taken my fair share of the satisfaction which you announce to me as feeling at the good despatch of your business, as reported to you by your deputies, and I regard it as a favourable sign that you have made such an auspicious commencement of the year. I hope to join you at the earliest convenient opportunity. I recommend myself very humbly to your gracious consideration, and pray God to grant you, gentlemen, a happy and long life. From Montaigne, this 8th February 1585. Your humble brother and servant, MONTAIGNE.
XI.——To the same.
GENTLEMEN,—I have here received news of you from M. le Marechal. I will not spare either my life or anything else for your service, and will leave it to your judgment whether the assistance I might be able to render by my presence at the forthcoming election, would be worth the risk I should run by going into the town, seeing the bad state it is in, —[This refers to the plague then raging, and which carried off 14,000 persons at Bordeaux.]—particularly for people coming away from so fine an air as this is where I am. I will draw as near to you on Wednesday as I can, that is, to Feuillas, if the malady has not reached that place, where, as I write to M. de la Molte, I shall be very pleased to have the honour of seeing one of you to take your directions, and relieve myself of the credentials which M. le Marechal will give me for you all: commending myself hereupon humbly to your good grace, and praying God to grant you, gentlemen, long and happy life. At Libourne, this 30th of July 1585. Your humble servant and brother, MONTAIGNE.
—[“According to Dr. Payen, this letter belongs to 1588. Its authenticity has been called in question; but wrongly, in our opinion. See ‘Documents inedits’, 1847, p. 12.”—Note in ‘Essais’, ed. Paris, 1854, iv. 381. It does not appear to whom the letter was addressed.]
MONSEIGNEUR,—You have heard of our baggage being taken from us under our eyes in the forest of Villebois: then, after a good deal of discussion and delay, of the capture being pronounced illegal by the Prince. We dared not, however, proceed on our way, from an uncertainty as to the safety of our persons, which should have been clearly expressed on our passports. The League has done this, M. de Barrant and M. de la Rochefocault; the storm has burst on me, who had my money in my box. I have recovered none of it, and most of my papers and cash—[The French word is hardes, which St. John renders things. But compare Chambers’s “Domestic Annals of Scotland,” 2d ed. i. 48.]—remain in their possession. I have not seen the Prince. Fifty were lost . . . as for the Count of Thorigny, he lost some ver plate and a few articles of clothing. He diverged from his route to pay a visit to the mourning ladies at Montresor, where are the remains of his two brothers and his grandmother, and came to us again in this town, whence we shall resume our journey shortly. The journey to Normandy is postponed. The King has despatched MM. De Bellieure and de la Guiche to M. de Guise to summon him to court; we shall be there on Thursday.
From Orleans, this 16th of February, in the morning [1588-9?].—Your very humble servant, MONTAIGNE.
XIII.——To Mademoiselle PAULMIER.
—[This letter, at the time of the publication of the variorum edition of 1854, appears to have been in private hands. See vol. iv. p. 382.]
MADEMOISELLE,—My friends know that, from the first moment of our acquaintance, I have destined a copy of my book for you; for I feel that you have done it much honour. The courtesy of M. Paulmier would deprive me of the pleasure of giving it to you now, for he has obliged me since a great deal beyond the worth of my book. You will accept it then, if you please, as having been yours before I owed it to you, and will confer on me the favour of loving it, whether for its own sake or for mine; and I will keep my debt to M. Paulmier undischarged, that I may requite him, if I have at some other time the means of serving him.
XIV.——To the KING, HENRY IV.
—[The original is in the French national library, in the Dupuy collection. It was first discovered by M. Achille Jubinal, who printed it with a facsimile of the entire autograph, in 1850. St. John gives the date wrongly as the 1st January 1590.]
SIRE, It is to be above the weight and crowd of your great and important affairs, to know, as you do, how to lend yourself, and attend to small matters in their turn, according to the duty of your royal dignity, which exposes you at all times to every description and degree of person and employment. Yet, that your Majesty should have deigned to consider my letter, and direct a reply to be made to it, I prefer to owe, less to your strong understanding, than to your kindness of heart. I have always looked forward to your enjoyment of your present fortune, and you may recollect that, even when I had to make confession of itto my cure, I viewed your successes with satisfaction: now, with the greater propriety and freedom, I embrace them affectionately. They serve you where you are as positive matters of fact; but they serve us here no less by the fame which they diffuse: the echo carries as much weight as the blow. We should not be able to derive from the justice of your cause such powerful arguments for the maintenance and reduction of your subjects, as we do from the reports of the success of your undertaking; and then I have to assure your Majesty, that the recent changes to your advantage, which you observe hereabouts, the prosperous issue of your proceedings at Dieppe, have opportunely seconded the honest zeal and marvellous prudence of M. the Marshal de Matignon, from whom I flatter myself that you do not receive day by day accounts of such good and signal services without remembering my assurances and expectations. I look to the next summer, not only for fruits which we may eat, but for those to grow out of our common tranquillity, and that it will pass over our heads with the same even tenor of happiness, dissipating, like its predecessors, all the fine promises with which your adversaries sustain the spirits of their followers. The popular inclinations resemble a tidal wave; if the current once commences in your favour, it will go on of its own force to the end. I could have desired much that the private gain of the soldiers of your army, and the necessity for satisfying them, had not deprived you, especially in this principal town, of the glorious credit of treating your mutinous subjects, in the midst of victory, with greater clemency than their own protectors, and that, as distinguished from a passing and usurped repute, you could have shown them to be really your own, by the exercise of a protection truly paternal and royal. In the conduct of such affairs as you have in hand, men are obliged to have recourse to unusual expedients. It is always seen that they are surmounted by their magnitude and difficulty; it not being found easy to complete the conquest by arms and force, the end has been accomplished by clemency and generosity, excellent lures to draw men particularly towards the just and legitimate side. If there is to be severity and punishment, let it be deferred till success has been assured. A great conqueror of past times boasts that he gave his enemies as great an inducement to love him, as his friends. And here we feel already some effect of the favourable impression produced upon our rebellious towns by the contrast between their rude treatment, and that of those which are loyal to you. Desiring your Majesty a happiness more tangible and less hazardous, and that you may be beloved rather than feared by your people, and believing that your welfare and theirs are of necessity knit together, I rejoice to think that the progress which you make is one towards more practicable conditions of peace, as well as towards victory!
Sire, your letter of the last of November came to my hand only just now, when the time which it pleased you to name for meeting you at Tours had already passed. I take it as a singular favour that you should have deigned to desire a visit from so useless a person, but one who is wholly yours, and more so even by affection than from duty. You have acted very commendably in adapting yourself, in the matter of external forms, to your new fortunes; but the preservation of your old affability and frankness in private intercourse is entitled to an equal share of praise. You have condescended to take thought for my age, no less than for the desire which I have to see you, where you may be at rest from these laborious agitations. Will not that be soon at Paris, Sire? and may nothing prevent me from presenting myself there!—Your very humble and very obedient servant and subject, MONTAIGNE.
From Montaigne, this 18th of January 1590.
XV.——To the same.
—[ This letter is also in the national collection, among the Dupuy papers. It was first printed in the “Journal de l’Instruction Publique,” 4th November 1846.]
SIRE,—The letter which it pleased your majesty to write to me on the 20th of July, was not delivered to me till this morning, and found me laid up with a very violent tertian ague, a complaint very common in this part of the country during the last month. Sire, I consider myself greatly honoured by the receipt of your commands, and I have not omitted to communicate to M. the Marshal de Matignon three times most emphatically my intention and obligation to proceed to him, and even so far as to indicate the route by which I proposed to join him secretly, if he thought proper. Having received no answer, I consider that he has weighed the difficulty and risk of the journey to me. Sire, your Majesty dill do me the favour to believe, if you please, that I shall never complain of the expense on occasions where I should not hesitate to devote my life. I have never derived any substantial benefit whatever from the bounty of kings, which I have neither sought nor merited; nor have I had any recompense for the services which I have performed for them: whereof your majesty is in part aware. What I have done for your predecessors I shall do still more readily for you. I am as rich, Sire, as I desire to be. When I shall have exhausted my purse in attendance on your Majesty at Paris, I will take the liberty to tell you, and then, if you should regard me as worthy of being retained any longer in your suite, you will find me more modest in my claims upon you than the humblest of your officers.
Sire, I pray God for your prosperity and health. Your very humble and very obedient servant and subject, MONTAIGNE.
From Montaigne, this 2d of September 1590.
XVI.——To the Governor of Guienne.
MONSEIGNEUR,—I have received this morning your letter, which I have communicated to M. de Gourgues, and we have dined together at the house of M.[the mayor] of Bourdeaux. As to the inconvenience of transporting the money named in your memorandum, you see how difficult a thing it is to provide for; but you may be sure that we shall keep as close a watch over it as possible. I used every exertion to discover the man of whom you spoke. He has not been here; and M. de Bordeaux has shown me a letter in which he mentions that he could not come to see the Director of Bordeaux, as he intended, having been informed that you mistrust him. The letter is of the day before yesterday. If I could have found him, I might perhaps have pursued the gentler course, being uncertain of your views; but I entreat you nevertheless to feel no manner of doubt that I refuse to carry out any wishes of yours, and that, where your commands are concerned, I know no distinction of person or matter. I hope that you have in Guienne many as well affected to you as I am. They report that the Nantes galleys are advancing towards Brouage. M. the Marshal de Biron has not yet left. Those who were charged to convey the message to M. d’Usee say that they cannot find him; and I believe that, if he has been here, he is so no longer. We keep a vigilant eye on our gates and guards, and we look after them a little more attentively in your absence, which makes me apprehensive, not merely on account of the preservation of the town, but likewise for your oven sake, knowing that the enemies of the king feel how necessary you are to his service, and how ill we should prosper without you. I am afraid that, in the part where you are, you will be overtaken by so many affairs requiring your attention on every side, that it will take you a long time and involve great difficulty before you have disposed of everything. If there is any important news, I will despatch an express at once, and you may conclude that nothing is stirring if you do not hear from me: at the same time begging you to bear in mind that movements of this kind are wont to be so sudden and unexpected that, if they occur, they will grasp me by the throat, before they say a word. I will do what I can to collect news, and for this purpose I will make a point of visiting and seeing men of every shade of opinion. Down to the present time nothing is stirring. M. de Londel has seen me this morning, and we have been arranging for some advances for the place, where I shall go to-morrow morning. Since I began this letter, I have learnt from Chartreux that two gentlemen, describing themselves as in the service of M. de Guise, and coming from Agen, have passed near Chartreux; but I was not able to ascertain which road they have taken. They are expecting you at Agen. The Sieur de Mauvesin came as far as Canteloup, and thence returned, having got some intelligence. I am in search of one Captain Rous, to whom . . . wrote, trying to draw him into his cause by all sorts of promises. The rumour of the two Nantes galleys ready to descend on Brouage is confirmed as certain; they carry two companies of foot. M. de Mercure is at Nantes. The Sieur de la Courbe said to M. the President Nesmond that M. d’Elbeuf is on this side of Angiers, and lodges with his father. He is drawing towards Lower Poictou with 4000 foot and 400 or 500 horse, having been reinforced by the troops of M. de Brissac and others, and M. de Mercure is to join him. The report goes also that M. du Maine is about to take the command of all the forces they have collected in Auvergne, and that he will cross Le Foret to advance on Rouergue and us, that is to say, on the King of Navarre, against whom all this is being directed. M. de Lansac is at Bourg, and has two war vessels, which remain in attendance on him. His functions are naval. I tell you what I learn, and mix up together the more or less probable hearsay of the town with actual matter of fact, that you may be in possession of everything. I beg you most humbly to return directly affairs may allow you to do so, and assure you that, meanwhile, we shall not spare our labour, or (if that were necessary) our life, to maintain the king’s authority throughout. Monseigneur, I kiss your hands very respectfully, and pray God to have you in His keeping. From Bordeaux, Wednesday night, 22d May (1590-91).—Your very humble servant,
I have seen no one from the king of Navarre; they say that M. de Biron has seen him.
—[Omitted by Cotton.]—
READER, thou hast here an honest book; it doth at the outset forewarn thee that, in contriving the same, I have proposed to myself no other than a domestic and private end: I have had no consideration at all either to thy service or to my glory. My powers are not capable of any such design. I have dedicated it to the particular commodity of my kinsfolk and friends, so that, having lost me (which they must do shortly), they may therein recover some traits of my conditions and humours, and by that means preserve more whole, and more life-like, the knowledge they had of me. Had my intention been to seek the world’s favour, I should surely have adorned myself with borrowed beauties: I desire therein to be viewed as I appear in mine own genuine, simple, and ordinary manner, without study and artifice: for it is myself I paint. My defects are therein to be read to the life, and any imperfections and my natural form, so far as public reverence hath permitted me. If I had lived among those nations, which (they say) yet dwell under the sweet liberty of nature’s primitive laws, I assure thee I would most willingly have painted myself quite fully and quite naked. Thus, reader, myself am the matter of my book: there’s no reason thou shouldst employ thy leisure about so frivolous and vain a subject. Therefore farewell.
From Montaigne, the 12th June 1580—[So in the edition of 1595; the edition of 1588 has 12th June 1588]
From Montaigne, the 1st March 1580.
Translated by Charles Cotton
Edited by william carew hazlitt, chapter i——that men by various ways arrive at the same end..
The most usual way of appeasing the indignation of such as we have any way offended, when we see them in possession of the power of revenge, and find that we absolutely lie at their mercy, is by submission, to move them to commiseration and pity; and yet bravery, constancy, and resolution, however quite contrary means, have sometimes served to produce the same effect.—[Florio’s version begins thus: “The most vsuall waie to appease those minds wee have offended, when revenge lies in their hands, and that we stand at their mercie, is by submission to move them to commiseration and pity: Nevertheless, courage, constancie, and resolution (means altogether opposite) have sometimes wrought the same effect.”—] [The spelling is Florio’s D.W.]
Edward, Prince of Wales [Edward, the Black Prince. D.W.] (the same who so long governed our Guienne, a personage whose condition and fortune have in them a great deal of the most notable and most considerable parts of grandeur), having been highly incensed by the Limousins, and taking their city by assault, was not, either by the cries of the people, or the prayers and tears of the women and children, abandoned to slaughter and prostrate at his feet for mercy, to be stayed from prosecuting his revenge; till, penetrating further into the town, he at last took notice of three French gentlemen,—[These were Jean de Villemure, Hugh de la Roche, and Roger de Beaufort.—Froissart, i. c. 289. {The city was Limoges. D.W.}]—who with incredible bravery alone sustained the power of his victorious army. Then it was that consideration and respect unto so remarkable a valour first stopped the torrent of his fury, and that his clemency, beginning with these three cavaliers, was afterwards extended to all the remaining inhabitants of the city.
Scanderbeg, Prince of Epirus, pursuing one of his soldiers with purpose to kill him, the soldier, having in vain tried by all the ways of humility and supplication to appease him, resolved, as his last refuge, to face about and await him sword in hand: which behaviour of his gave a sudden stop to his captain’s fury, who, for seeing him assume so notable a resolution, received him into grace; an example, however, that might suffer another interpretation with such as have not read of the prodigious force and valour of that prince.
The Emperor Conrad III. having besieged Guelph, Duke of Bavaria,—[In 1140, in Weinsberg, Upper Bavaria.]—would not be prevailed upon, what mean and unmanly satisfactions soever were tendered to him, to condescend to milder conditions than that the ladies and gentlewomen only who were in the town with the duke might go out without violation of their honour, on foot, and with so much only as they could carry about them. Whereupon they, out of magnanimity of heart, presently contrived to carry out, upon their shoulders, their husbands and children, and the duke himself; a sight at which the emperor was so pleased, that, ravished with the generosity of the action, he wept for joy, and immediately extinguishing in his heart the mortal and capital hatred he had conceived against this duke, he from that time forward treated him and his with all humanity. The one and the other of these two ways would with great facility work upon my nature; for I have a marvellous propensity to mercy and mildness, and to such a degree that I fancy of the two I should sooner surrender my anger to compassion than to esteem. And yet pity is reputed a vice amongst the Stoics, who will that we succour the afflicted, but not that we should be so affected with their sufferings as to suffer with them. I conceived these examples not ill suited to the question in hand, and the rather because therein we observe these great souls assaulted and tried by these two several ways, to resist the one without relenting, and to be shook and subjected by the other. It may be true that to suffer a man’s heart to be totally subdued by compassion may be imputed to facility, effeminacy, and over-tenderness; whence it comes to pass that the weaker natures, as of women, children, and the common sort of people, are the most subject to it but after having resisted and disdained the power of groans and tears, to yield to the sole reverence of the sacred image of Valour, this can be no other than the effect of a strong and inflexible soul enamoured of and honouring masculine and obstinate courage. Nevertheless, astonishment and admiration may, in less generous minds, beget a like effect: witness the people of Thebes, who, having put two of their generals upon trial for their lives for having continued in arms beyond the precise term of their commission, very hardly pardoned Pelopidas, who, bowing under the weight of so dangerous an accusation, made no manner of defence for himself, nor produced other arguments than prayers and supplications; whereas, on the contrary, Epaminondas, falling to recount magniloquently the exploits he had performed in their service, and, after a haughty and arrogant manner reproaching them with ingratitude and injustice, they had not the heart to proceed any further in his trial, but broke up the court and departed, the whole assembly highly commending the high courage of this personage.—[Plutarch, How far a Man may praise Himself, c. 5.]
Dionysius the elder, after having, by a tedious siege and through exceeding great difficulties, taken the city of Reggio, and in it the governor Phyton, a very gallant man, who had made so obstinate a defence, was resolved to make him a tragical example of his revenge: in order whereunto he first told him, “That he had the day before caused his son and all his kindred to be drowned.” To which Phyton returned no other answer but this: “That they were then by one day happier than he.” After which, causing him to be stripped, and delivering him into the hands of the tormentors, he was by them not only dragged through the streets of the town, and most ignominiously and cruelly whipped, but moreover vilified with most bitter and contumelious language: yet still he maintained his courage entire all the way, with a strong voice and undaunted countenance proclaiming the honourable and glorious cause of his death; namely, for that he would not deliver up his country into the hands of a tyrant; at the same time denouncing against him a speedy chastisement from the offended gods. At which Dionysius, reading in his soldiers’ looks, that instead of being incensed at the haughty language of this conquered enemy, to the contempt of their captain and his triumph, they were not only struck with admiration of so rare a virtue, but moreover inclined to mutiny, and were even ready to rescue the prisoner out of the hangman’s hands, he caused the torturing to cease, and afterwards privately caused him to be thrown into the sea.—[Diod. Sic., xiv. 29.]
Man (in good earnest) is a marvellous vain, fickle, and unstable subject, and on whom it is very hard to form any certain and uniform judgment. For Pompey could pardon the whole city of the Mamertines, though furiously incensed against it, upon the single account of the virtue and magnanimity of one citizen, Zeno,—[Plutarch calls him Stheno, and also Sthemnus and Sthenis]—who took the fault of the public wholly upon himself; neither entreated other favour, but alone to undergo the punishment for all: and yet Sylla’s host, having in the city of Perugia —[Plutarch says Preneste, a town of Latium.]—manifested the same virtue, obtained nothing by it, either for himself or his fellow-citizens.
And, directly contrary to my first examples, the bravest of all men, and who was reputed so gracious to all those he overcame, Alexander, having, after many great difficulties, forced the city of Gaza, and, entering, found Betis, who commanded there, and of whose valour in the time of this siege he had most marvellous manifest proof, alone, forsaken by all his soldiers, his armour hacked and hewed to pieces, covered all over with blood and wounds, and yet still fighting in the crowd of a number of Macedonians, who were laying on him on all sides, he said to him, nettled at so dear-bought a victory (for, in addition to the other damage, he had two wounds newly received in his own person), “Thou shalt not die, Betis, as thou dost intend; be sure thou shall suffer all the torments that can be inflicted on a captive.” To which menace the other returning no other answer, but only a fierce and disdainful look; “What,” says Alexander, observing his haughty and obstinate silence, “is he too stiff to bend a knee! Is he too proud to utter one suppliant word! Truly, I will conquer this silence; and if I cannot force a word from his mouth, I will, at least, extract a groan from his heart.” And thereupon converting his anger into fury, presently commanded his heels to be bored through, causing him, alive, to be dragged, mangled, and dismembered at a cart’s tail.—[Quintus Curtius, iv. 6. This act of cruelty has been doubted, notwithstanding the statement of Curtius.]—Was it that the height of courage was so natural and familiar to this conqueror, that because he could not admire, he respected it the less? Or was it that he conceived valour to be a virtue so peculiar to himself, that his pride could not, without envy, endure it in another? Or was it that the natural impetuosity of his fury was incapable of opposition? Certainly, had it been capable of moderation, it is to be believed that in the sack and desolation of Thebes, to see so many valiant men, lost and totally destitute of any further defence, cruelly massacred before his eyes, would have appeased it: where there were above six thousand put to the sword, of whom not one was seen to fly, or heard to cry out for quarter; but, on the contrary, every one running here and there to seek out and to provoke the victorious enemy to help them to an honourable end. Not one was seen who, however weakened with wounds, did not in his last gasp yet endeavour to revenge himself, and with all the arms of a brave despair, to sweeten his own death in the death of an enemy. Yet did their valour create no pity, and the length of one day was not enough to satiate the thirst of the conqueror’s revenge, but the slaughter continued to the last drop of blood that was capable of being shed, and stopped not till it met with none but unarmed persons, old men, women, and children, of them to carry away to the number of thirty thousand slaves.
CHAPTER II——OF SORROW
No man living is more free from this passion than I, who yet neither like it in myself nor admire it in others, and yet generally the world, as a settled thing, is pleased to grace it with a particular esteem, clothing therewith wisdom, virtue, and conscience. Foolish and sordid guise! —[“No man is more free from this passion than I, for I neither love nor regard it: albeit the world hath undertaken, as it were upon covenant, to grace it with a particular favour. Therewith they adorne age, vertue, and conscience. Oh foolish and base ornament!” Florio, 1613, p. 3] —The Italians have more fitly baptized by this name—[La tristezza]— malignity; for ‘tis a quality always hurtful, always idle and vain; and as being cowardly, mean, and base, it is by the Stoics expressly and particularly forbidden to their sages.
But the story—[Herodotus, iii. 14.]—says that Psammenitus, King of Egypt, being defeated and taken prisoner by Cambyses, King of Persia, seeing his own daughter pass by him as prisoner, and in a wretched habit, with a bucket to draw water, though his friends about him were so concerned as to break out into tears and lamentations, yet he himself remained unmoved, without uttering a word, his eyes fixed upon the ground; and seeing, moreover, his son immediately after led to execution, still maintained the same countenance; till spying at last one of his domestic and familiar friends dragged away amongst the captives, he fell to tearing his hair and beating his breast, with all the other extravagances of extreme sorrow.
A story that may very fitly be coupled with another of the same kind, of recent date, of a prince of our own nation, who being at Trent, and having news there brought him of the death of his elder brother, a brother on whom depended the whole support and honour of his house, and soon after of that of a younger brother, the second hope of his family, and having withstood these two assaults with an exemplary resolution; one of his servants happening a few days after to die, he suffered his constancy to be overcome by this last accident; and, parting with his courage, so abandoned himself to sorrow and mourning, that some thence were forward to conclude that he was only touched to the quick by this last stroke of fortune; but, in truth, it was, that being before brimful of grief, the least addition overflowed the bounds of all patience. Which, I think, might also be said of the former example, did not the story proceed to tell us that Cambyses asking Psammenitus, “Why, not being moved at the calamity of his son and daughter, he should with so great impatience bear the misfortune of his friend?” “It is,” answered he, “because only this last affliction was to be manifested by tears, the two first far exceeding all manner of expression.”
And, peradventure, something like this might be working in the fancy of the ancient painter,—[Cicero, De Orator., c. 22 ; Pliny, xxxv. 10.]— who having, in the sacrifice of Iphigenia, to represent the sorrow of the assistants proportionably to the several degrees of interest every one had in the death of this fair innocent virgin, and having, in the other figures, laid out the utmost power of his art, when he came to that of her father, he drew him with a veil over his face, meaning thereby that no kind of countenance was capable of expressing such a degree of sorrow. Which is also the reason why the poets feign the miserable mother, Niobe, having first lost seven sons, and then afterwards as many daughters (overwhelmed with her losses), to have been at last transformed into a rock—
thereby to express that melancholic, dumb, and deaf stupefaction, which benumbs all our faculties, when oppressed with accidents greater than we are able to bear. And, indeed, the violence and impression of an excessive grief must of necessity astonish the soul, and wholly deprive her of her ordinary functions: as it happens to every one of us, who, upon any sudden alarm of very ill news, find ourselves surprised, stupefied, and in a manner deprived of all power of motion, so that the soul, beginning to vent itself in tears and lamentations, seems to free and disengage itself from the sudden oppression, and to have obtained some room to work itself out at greater liberty.
In the war that Ferdinand made upon the widow of King John of Hungary, about Buda, a man-at-arms was particularly taken notice of by every one for his singular gallant behaviour in a certain encounter; and, unknown, highly commended, and lamented, being left dead upon the place: but by none so much as by Raisciac, a German lord, who was infinitely enamoured of so rare a valour. The body being brought off, and the count, with the common curiosity coming to view it, the armour was no sooner taken off but he immediately knew him to be his own son, a thing that added a second blow to the compassion of all the beholders; only he, without uttering a word, or turning away his eyes from the woeful object, stood fixedly contemplating the body of his son, till the vehemency of sorrow having overcome his vital spirits, made him sink down stone-dead to the ground.
say the Innamoratos, when they would represent an ‘insupportable passion.
Neither is it in the height and greatest fury of the fit that we are in a condition to pour out our complaints or our amorous persuasions, the soul being at that time over-burdened, and labouring with profound thoughts; and the body dejected and languishing with desire; and thence it is that sometimes proceed those accidental impotencies that so unseasonably surprise the lover, and that frigidity which by the force of an immoderate ardour seizes him even in the very lap of fruition. —[The edition of 1588 has here, “An accident not unknown to myself.”]— For all passions that suffer themselves to be relished and digested are but moderate:
A surprise of unexpected joy does likewise often produce the same effect:
Besides the examples of the Roman lady, who died for joy to see her son safe returned from the defeat of Cannae; and of Sophocles and of Dionysius the Tyrant,—[Pliny, vii. 53. Diodorus Siculus, however (xv. c. 20), tells us that Dionysius “was so overjoyed at the news that he made a great sacrifice upon it to the gods, prepared sumptuous feasts, to which he invited all his friends, and therein drank so excessively that it threw him into a very bad distemper.”]—who died of joy; and of Thalna, who died in Corsica, reading news of the honours the Roman Senate had decreed in his favour, we have, moreover, one in our time, of Pope Leo X., who upon news of the taking of Milan, a thing he had so ardently desired, was rapt with so sudden an excess of joy that he immediately fell into a fever and died.—[Guicciardini, Storia d’Italia, vol. xiv.]—And for a more notable testimony of the imbecility of human nature, it is recorded by the ancients—[Pliny, ‘ut supra’]—that Diodorus the dialectician died upon the spot, out of an extreme passion of shame, for not having been able in his own school, and in the presence of a great auditory, to disengage himself from a nice argument that was propounded to him. I, for my part, am very little subject to these violent passions; I am naturally of a stubborn apprehension, which also, by reasoning, I every day harden and fortify.
CHAPTER III——THAT OUR AFFECTIONS CARRY THEMSELVES BEYOND US.
Such as accuse mankind of the folly of gaping after future things, and advise us to make our benefit of those which are present, and to set up our rest upon them, as having no grasp upon that which is to come, even less than that which we have upon what is past, have hit upon the most universal of human errors, if that may be called an error to which nature herself has disposed us, in order to the continuation of her own work, prepossessing us, amongst several others, with this deceiving imagination, as being more jealous of our action than afraid of our knowledge.
We are never present with, but always beyond ourselves: fear, desire, hope, still push us on towards the future, depriving us, in the meantime, of the sense and consideration of that which is to amuse us with the thought of what shall be, even when we shall be no more.[1]—
We find this great precept often repeated in Plato, “Do thine own work, and know thyself.” Of which two parts, both the one and the other generally, comprehend our whole duty, and do each of them in like manner involve the other; for who will do his own work aright will find that his first lesson is to know what he is, and that which is proper to himself; and who rightly understands himself will never mistake another man’s work for his own, but will love and improve himself above all other things, will refuse superfluous employments, and reject all unprofitable thoughts and propositions. As folly, on the one side, though it should enjoy all it desire, would notwithstanding never be content, so, on the other, wisdom, acquiescing in the present, is never dissatisfied with itself. —[Cicero, Tusc. Quae., 57, v. 18.]—Epicurus dispenses his sages from all foresight and care of the future.
Amongst those laws that relate to the dead, I look upon that to be very sound by which the actions of princes are to be examined after their decease.—[Diodorus Siculus, i. 6.]— They are equals with, if not masters of the laws, and, therefore, what justice could not inflict upon their persons, ‘tis but reason should be executed upon their reputations and the estates of their successors—things that we often value above life itself. ‘Tis a custom of singular advantage to those countries where it is in use, and by all good princes to be desired, who have reason to take it ill, that the memories of the wicked should be used with the same reverence and respect with their own. We owe subjection and obedience to all our kings, whether good or bad, alike, for that has respect unto their office; but as to esteem and affection, these are only due to their virtue. Let us grant to political government to endure them with patience, however unworthy; to conceal their vices; and to assist them with our recommendation in their indifferent actions, whilst their authority stands in need of our support. But, the relation of prince and subject being once at an end, there is no reason we should deny the expression of our real opinions to our own liberty and common justice, and especially to interdict to good subjects the glory of having reverently and faithfully served a prince, whose imperfections were to them so well known; this were to deprive posterity of a useful example. And such as, out of respect to some private obligation, unjustly espouse and vindicate the memory of a faulty prince, do private right at the expense of public justice. Livy does very truly say,—[xxxv. 48.]— “That the language of men bred up in courts is always full of vain ostentation and false testimony, every one indifferently magnifying his own master, and stretching his commendation to the utmost extent of virtue and sovereign grandeur.” Some may condemn the freedom of those two soldiers who so roundly answered Nero to his beard; the one being asked by him why he bore him ill-will? “I loved thee,” answered he, “whilst thou wert worthy of it, but since thou art become a parricide, an incendiary, a player, and a coachman, I hate thee as thou dost deserve.” And the other, why he should attempt to kill him? “Because,” said he, “I could think of no other remedy against thy perpetual mischiefs.” —[Tacitus, Annal., xv. 67.]—But the public and universal testimonies that were given of him after his death (and so will be to all posterity, both of him and all other wicked princes like him), of his tyrannies and abominable deportment, who, of a sound judgment, can reprove them?
I am scandalised, that in so sacred a government as that of the Lacedaemonians there should be mixed so hypocritical a ceremony at the interment of their kings; where all their confederates and neighbours, and all sorts and degrees of men and women, as well as their slaves, cut and slashed their foreheads in token of sorrow, repeating in their cries and lamentations that that king (let him have been as wicked as the devil) was the best that ever they had;—[Herodotus, vi. 68.]—by this means attributing to his quality the praise that only belongs to merit, and that of right is due to supreme desert, though lodged in the lowest and most inferior subject.
Aristotle, who will still have a hand in everything, makes a ‘quaere’ upon the saying of Solon, that none can be said to be happy until he is dead: “whether, then, he who has lived and died according to his heart’s desire, if he have left an ill repute behind him, and that his posterity be miserable, can be said to be happy?” Whilst we have life and motion, we convey ourselves by fancy and preoccupation, whither and to what we please; but once out of being, we have no more any manner of communication with that which is, and it had therefore been better said by Solon that man is never happy, because never so, till he is no more.
Bertrand de Guesclin, dying at the siege of the Castle of Rancon, near unto Puy, in Auvergne, the besieged were afterwards, upon surrender, enjoined to lay down the keys of the place upon the corpse of the dead general. Bartolommeo d’Alviano, the Venetian General, happening to die in the service of the Republic in Brescia, and his corpse being to be carried through the territory of Verona, an enemy’s country, most of the army were inclined to demand safe-conduct from the Veronese; but Theodoro Trivulzio opposed the motion, rather choosing to make his way by force of arms, and to run the hazard of a battle, saying it was by no means fit that he who in his life was never afraid of his enemies should seem to apprehend them when he was dead. In truth, in affairs of the same nature, by the Greek laws, he who made suit to an enemy for a body to give it burial renounced his victory, and had no more right to erect a trophy, and he to whom such suit was made was reputed victor. By this means it was that Nicias lost the advantage he had visibly obtained over the Corinthians, and that Agesilaus, on the contrary, assured that which he had before very doubtfully gained over the Boeotians.—[Plutarch, Life of Nicias, c. ii.; Life of Agesilaus, c. vi.]
These things might appear strange, had it not been a general practice in all ages not only to extend the concern of ourselves beyond this life, but, moreover, to fancy that the favour of Heaven does not only very often accompany us to the grave, but has also, even after life, a concern for our ashes. Of which there are so many ancient examples (to say nothing of those of our own observation), that it is not necessary I should longer insist upon it. Edward I., King of England, having in the long wars betwixt him and Robert, King of Scotland, had experience of how great importance his own immediate presence was to the success of his affairs, having ever been victorious in whatever he undertook in his own person, when he came to die, bound his son in a solemn oath that, so soon as he should be dead he should boil his body till the flesh parted from the bones, and bury the flesh, reserving the bones to carry continually with him in his army, so often as he should be obliged to go against the Scots, as if destiny had inevitably attached victory, even to his remains. John Zisca, the same who, to vindication of Wicliffe’s heresies, troubled the Bohemian state, left order that they should flay him after his death, and of his skin make a drum to carry in the war against his enemies, fancying it would contribute to the continuation of the successes he had always obtained in the wars against them. In like manner certain of the Indians, in their battles with the Spaniards, carried with them the bones of one of their captains, in consideration of the victories they had formerly obtained under his conduct. And other people of the same New World carry about with them, in their wars, the relics of valiant men who have died in battle, to incite their courage and advance their fortune. Of which examples the first reserve nothing for the tomb but the reputation they have acquired by their former achievements, but these attribute to them a certain present and active power.
The proceeding of Captain Bayard is of a better composition, who finding himself wounded to death with an harquebuss shot, and being importuned to retire out of the fight, made answer that he would not begin at the last gasp to turn his back to the enemy, and accordingly still fought on, till feeling himself too faint and no longer able to sit on his horse, he commanded his steward to set him down at the foot of a tree, but so that he might die with his face towards the enemy, which he did.
I must yet add another example, equally remarkable for the present consideration with any of the former. The Emperor Maximilian, great-grandfather to the now King Philip,—[Philip II. of Spain.]—was a prince endowed throughout with great and extraordinary qualities, and amongst the rest with a singular beauty of person, but had withal a humour very contrary to that of other princes, who for the despatch of their most important affairs convert their close-stool into a chair of State, which was, that he would never permit any of his bedchamber, how familiar soever, to see him in that posture, and would steal aside to make water as religiously as a virgin, shy to discover to his physician or any other whomsoever those parts that we are accustomed to conceal. I myself, who have so impudent a way of talking, am, nevertheless, naturally so modest this way, that unless at the importunity of necessity or pleasure, I scarcely ever communicate to the sight of any either those parts or actions that custom orders us to conceal, wherein I suffer more constraint than I conceive is very well becoming a man, especially of my profession. But he nourished this modest humour to such a degree of superstition as to give express orders in his last will that they should put him on drawers so soon as he should be dead; to which, methinks, he would have done well to have added that he should be blindfolded, too, that put them on. The charge that Cyrus left with his children, that neither they, nor any other, should either see or touch his body after the soul was departed from it,—[Xenophon, Cyropedia, viii. 7.]—I attribute to some superstitious devotion of his; for both his historian and himself, amongst their great qualities, marked the whole course of their lives with a singular respect and reverence to religion.
I was by no means pleased with a story, told me by a man of very great quality of a relation of mine, and one who had given a very good account of himself both in peace and war, that, coming to die in a very old age, of excessive pain of the stone, he spent the last hours of his life in an extraordinary solicitude about ordering the honour and ceremony of his funeral, pressing all the men of condition who came to see him to engage their word to attend him to his grave: importuning this very prince, who came to visit him at his last gasp, with a most earnest supplication that he would order his family to be there, and presenting before him several reasons and examples to prove that it was a respect due to a man of his condition; and seemed to die content, having obtained this promise, and appointed the method and order of his funeral parade. I have seldom heard of so persistent a vanity.
Another, though contrary curiosity (of which singularity, also, I do not want domestic example), seems to be somewhat akin to this, that a man shall cudgel his brains at the last moments of his life to contrive his obsequies to so particular and unusual a parsimony as of one servant with a lantern, I see this humour commended, and the appointment of Marcus. Emilius Lepidus, who forbade his heirs to bestow upon his hearse even the common ceremonies in use upon such occasions. Is it yet temperance and frugality to avoid expense and pleasure of which the use and knowledge are imperceptible to us? See, here, an easy and cheap reformation. If instruction were at all necessary in this case, I should be of opinion that in this, as in all other actions of life, each person should regulate the matter according to his fortune; and the philosopher Lycon prudently ordered his friends to dispose of his body where they should think most fit, and as to his funeral, to order it neither too superfluous nor too mean. For my part, I should wholly refer the ordering of this ceremony to custom, and shall, when the time comes, accordingly leave it to their discretion to whose lot it shall fall to do me that last office. “Totus hic locus est contemnendus in nobis, non negligendus in nostris;”—[“The place of our sepulture is to be contemned by us, but not to be neglected by our friends.”—Cicero, Tusc. i. 45.]— and it was a holy saying of a saint, “Curatio funeris, conditio sepultura: pompa exequiarum, magis sunt vivorum solatia, quam subsidia mortuorum.”—[“The care of death, the place of sepulture, the pomps of obsequies, are rather consolations to the living than succours to the dead.” August. De Civit. Dei, i. 12.]—Which made Socrates answer Crito, who, at death, asked him how he would be buried: “How you will,” said he. “If I were to concern myself beyond the present about this affair, I should be most tempted, as the greatest satisfaction of this kind, to imitate those who in their lifetime entertain themselves with the ceremony and honours of their own obsequies beforehand, and are pleased with beholding their own dead countenance in marble. Happy are they who can gratify their senses by insensibility, and live by their death!”
I am ready to conceive an implacable hatred against all popular domination, though I think it the most natural and equitable of all, so oft as I call to mind the inhuman injustice of the people of Athens, who, without remission, or once vouchsafing to hear what they had to say for themselves, put to death their brave captains newly returned triumphant from a naval victory they had obtained over the Lacedaemonians near the Arginusian Isles, the most bloody and obstinate engagement that ever the Greeks fought at sea; because (after the victory) they followed up the blow and pursued the advantages presented to them by the rule of war, rather than stay to gather up and bury their dead. And the execution is yet rendered more odious by the behaviour of Diomedon, who, being one of the condemned, and a man of most eminent virtue, political and military, after having heard the sentence, advancing to speak, no audience till then having been allowed, instead of laying before them his own cause, or the impiety of so cruel a sentence, only expressed a solicitude for his judges’ preservation, beseeching the gods to convert this sentence to their good, and praying that, for neglecting to fulfil the vows which he and his companions had made (with which he also acquainted them) in acknowledgment of so glorious a success, they might not draw down the indignation of the gods upon them; and so without more words went courageously to his death.
Fortune, a few years after, punished them in the same kind; for Chabrias, captain-general of their naval forces, having got the better of Pollis, Admiral of Sparta, at the Isle of Naxos, totally lost the fruits of his victory, one of very great importance to their affairs, in order not to incur the danger of this example, and so that he should not lose a few bodies of his dead friends that were floating in the sea, gave opportunity to a world of living enemies to sail away in safety, who afterwards made them pay dear for this unseasonable superstition:—
This other restores the sense of repose to a body without a soul:
As nature demonstrates to us that several dead things retain yet an occult relation to life; wine changes its flavour and complexion in cellars, according to the changes and seasons of the vine from whence it came; and the flesh of—venison alters its condition in the powdering-tub, and its taste according to the laws of the living flesh of its kind, as it is said.
CHAPTER IV——THAT THE SOUL EXPENDS ITS PASSIONS UPON FALSE OBJECTS, WHERE THE TRUE ARE WANTING
A gentleman of my country, marvellously tormented with the gout, being importuned by his physicians totally to abstain from all manner of salt meats, was wont pleasantly to reply, that in the extremity of his fits he must needs have something to quarrel with, and that railing at and cursing, one while the Bologna sausages, and another the dried tongues and the hams, was some mitigation to his pain. But, in good earnest, as the arm when it is advanced to strike, if it miss the blow, and goes by the wind, it pains us; and as also, that, to make a pleasant prospect, the sight should not be lost and dilated in vague air, but have some bound and object to limit and circumscribe it at a reasonable distance.
So it seems that the soul, being transported and discomposed, turns its violence upon itself, if not supplied with something to oppose it, and therefore always requires an object at which to aim, and whereon to act. Plutarch says of those who are delighted with little dogs and monkeys, that the amorous part that is in us, for want of a legitimate object, rather than lie idle, does after that manner forge and create one false and frivolous. And we see that the soul, in its passions, inclines rather to deceive itself, by creating a false and fantastical a subject, even contrary to its own belief, than not to have something to work upon. After this manner brute beasts direct their fury to fall upon the stone or weapon that has hurt them, and with their teeth a even execute revenge upon themselves for the injury they have received from another:
What causes of the misadventures that befall us do we not invent? what is it that we do not lay the fault to, right or wrong, that we may have something to quarrel with? It is not those beautiful tresses you tear, nor is it the white bosom that in your anger you so unmercifully beat, that with an unlucky bullet have slain your beloved brother; quarrel with something else. Livy, speaking of the Roman army in Spain, says that for the loss of the two brothers, their great captains:
‘Tis a common practice. And the philosopher Bion said pleasantly of the king, who by handsful pulled his hair off his head for sorrow, “Does this man think that baldness is a remedy for grief?”—[Cicero, Tusc. Quest., iii. 26.]—Who has not seen peevish gamesters chew and swallow the cards, and swallow the dice, in revenge for the loss of their money? Xerxes whipped the sea, and wrote a challenge to Mount Athos; Cyrus employed a whole army several days at work, to revenge himself of the river Gyndas, for the fright it had put him into in passing over it; and Caligula demolished a very beautiful palace for the pleasure his mother had once enjoyed there.
I remember there was a story current, when I was a boy, that one of our neighbouring kings—[Probably Alfonso XI. of Castile]—having received a blow from the hand of God, swore he would be revenged, and in order to it, made proclamation that for ten years to come no one should pray to Him, or so much as mention Him throughout his dominions, or, so far as his authority went, believe in Him; by which they meant to paint not so much the folly as the vainglory of the nation of which this tale was told. They are vices that always go together, but in truth such actions as these have in them still more of presumption than want of wit. Augustus Caesar, having been tossed with a tempest at sea, fell to defying Neptune, and in the pomp of the Circensian games, to be revenged, deposed his statue from the place it had amongst the other deities. Wherein he was still less excusable than the former, and less than he was afterwards when, having lost a battle under Quintilius Varus in Germany, in rage and despair he went running his head against the wall, crying out, “O Varus! give me back my legions!” for these exceed all folly, forasmuch as impiety is joined therewith, invading God Himself, or at least Fortune, as if she had ears that were subject to our batteries; like the Thracians, who when it thunders or lightens, fall to shooting against heaven with Titanian vengeance, as if by flights of arrows they intended to bring God to reason. Though the ancient poet in Plutarch tells us—
But we can never enough decry the disorderly sallies of our minds.
CHAPTER V——WHETHER THE GOVERNOR OF A PLACE BESIEGED OUGHT HIMSELF TO GO OUT TO PARLEY
Quintus Marcius, the Roman legate in the war against Perseus, King of Macedon, to gain time wherein to reinforce his army, set on foot some overtures of accommodation, with which the king being lulled asleep, concluded a truce for some days, by this means giving his enemy opportunity and leisure to recruit his forces, which was afterwards the occasion of the king’s final ruin. Yet the elder senators, mindful of their forefathers’ manners, condemned this proceeding as degenerating from their ancient practice, which, they said, was to fight by valour, and not by artifice, surprises, and night-encounters; neither by pretended flight nor unexpected rallies to overcome their enemies; never making war till having first proclaimed it, and very often assigned both the hour and place of battle. Out of this generous principle it was that they delivered up to Pyrrhus his treacherous physician, and to the Etrurians their disloyal schoolmaster. This was, indeed, a procedure truly Roman, and nothing allied to the Grecian subtlety, nor to the Punic cunning, where it was reputed a victory of less glory to overcome by force than by fraud. Deceit may serve for a need, but he only confesses himself overcome who knows he is neither subdued by policy nor misadventure, but by dint of valour, man to man, in a fair and just war. It very well appears, by the discourse of these good old senators, that this fine sentence was not yet received amongst them.
The Achaians, says Polybius, abhorred all manner of double-dealing in war, not reputing it a victory unless where the courage of the enemy was fairly subdued:
“Eam vir sanctus et sapiens sciet veram esse victoriam, quae, salva fide et integra dignitate, parabitur.”—[“An honest and prudent man will acknowledge that only to be a true victory which shall be obtained saving his own good faith and dignity.”—Florus, i. 12.]—Says another:
In the kingdom of Ternate, amongst those nations which we so broadly call barbarians, they have a custom never to commence war, till it be first proclaimed; adding withal an ample declaration of what means they have to do it with, with what and how many men, what ammunitions, and what, both offensive and defensive, arms; but also, that being done, if their enemies do not yield and come to an agreement, they conceive it lawful to employ without reproach in their wars any means which may help them to conquer.
The ancient Florentines were so far from seeking to obtain any advantage over their enemies by surprise, that they always gave them a month’s warning before they drew their army into the field, by the continual tolling of a bell they called Martinella.—[After St. Martin.]
For what concerns ourselves, who are not so scrupulous in this affair, and who attribute the honour of the war to him who has the profit of it, and who after Lysander say, “Where the lion’s skin is too short, we must eke it out with a bit from that of a fox”; the most usual occasions of surprise are derived from this practice, and we hold that there are no moments wherein a chief ought to be more circumspect, and to have his eye so much at watch, as those of parleys and treaties of accommodation; and it is, therefore, become a general rule amongst the martial men of these latter times, that a governor of a place never ought, in a time of siege, to go out to parley. It was for this that in our fathers’ days the Seigneurs de Montmord and de l’Assigni, defending Mousson against the Count of Nassau, were so highly censured. But yet, as to this, it would be excusable in that governor who, going out, should, notwithstanding, do it in such manner that the safety and advantage should be on his side; as Count Guido di Rangone did at Reggio (if we are to believe Du Bellay, for Guicciardini says it was he himself) when the Seigneur de l’Escut approached to parley, who stepped so little away from his fort, that a disorder happening in the interim of parley, not only Monsieur de l’Escut and his party who were advanced with him, found themselves by much the weaker, insomuch that Alessandro Trivulcio was there slain, but he himself follow the Count, and, relying upon his honour, to secure himself from the danger of the shot within the walls of the town.
Eumenes, being shut up in the city of Nora by Antigonus, and by him importuned to come out to speak with him, as he sent him word it was fit he should to a greater man than himself, and one who had now an advantage over him, returned this noble answer. “Tell him,” said he, “that I shall never think any man greater than myself whilst I have my sword in my hand,” and would not consent to come out to him till first, according to his own demand, Antigonus had delivered him his own nephew Ptolomeus in hostage.
And yet some have done very well in going out in person to parley, on the word of the assailant: witness Henry de Vaux, a cavalier of Champagne, who being besieged by the English in the Castle of Commercy, and Bartholomew de Brunes, who commanded at the Leaguer, having so sapped the greatest part of the castle without, that nothing remained but setting fire to the props to bury the besieged under the ruins, he requested the said Henry to come out to speak with him for his own good, which he did with three more in company; and, his ruin being made apparent to him, he conceived himself singularly obliged to his enemy, to whose discretion he and his garrison surrendered themselves; and fire being presently applied to the mine, the props no sooner began to fail, but the castle was immediately blown up from its foundations, no one stone being left upon another.
I could, and do, with great facility, rely upon the faith of another; but I should very unwillingly do it in such a case, as it should thereby be judged that it was rather an effect of my despair and want of courage than voluntarily and out of confidence and security in the faith of him with whom I had to do.
CHAPTER VI——THAT THE HOUR OF PARLEY DANGEROUS
I saw, notwithstanding, lately at Mussidan, a place not far from my house, that those who were driven out thence by our army, and others of their party, highly complained of treachery, for that during a treaty of accommodation, and in the very interim that their deputies were treating, they were surprised and cut to pieces: a thing that, peradventure, in another age, might have had some colour of foul play; but, as I have just said, the practice of arms in these days is quite another thing, and there is now no confidence in an enemy excusable till the treaty is finally sealed; and even then the conqueror has enough to do to keep his word: so hazardous a thing it is to entrust the observation of the faith a man has engaged to a town that surrenders upon easy and favourable conditions, to the licence of a victorious army, and to give the soldier free entrance into it in the heat of blood.
Lucius AEmilius Regillus, the Roman praetor, having lost his time in attempting to take the city of Phocaea by force, by reason of the singular valour wherewith the inhabitants defended themselves, conditioned, at last, to receive them as friends to the people of Rome, and to enter the town, as into a confederate city, without any manner of hostility, of which he gave them all assurance; but having, for the greater pomp, brought his whole army in with him, it was no more in his power, with all the endeavour he could use, to restrain his people: so that, avarice and revenge trampling under foot both his authority and all military discipline, he there saw a considerable part of the city sacked and ruined before his face.
Cleomenes was wont to say, “that what mischief soever a man could do his enemy in time of war was above justice, and nothing accountable to it in the sight of gods and men.” And so, having concluded a truce with those of Argos for seven days, the third night after he fell upon them when they were all buried in sleep, and put them to the sword, alleging that there had no nights been mentioned in the truce; but the gods punished this subtle perfidy.
In a time of parley also; and while the citizens were relying upon their safety warrant, the city of Casilinum was taken by surprise, and that even in the age of the justest captains and the most perfect Roman military discipline; for it is not said that it is not lawful for us, in time and place, to make advantage of our enemies’ want of understanding, as well as their want of courage.
And, doubtless, war has naturally many privileges that appear reasonable even to the prejudice of reason. And therefore here the rule fails, “Neminem id agere ut ex alte rius praedetur inscitia.”—[“No one should preys upon another’s folly.”—Cicero, De Offic., iii. 17.]—But I am astonished at the great liberty allowed by Xenophon in such cases, and that both by precept and by the example of several exploits of his complete emperor; an author of very great authority, I confess, in those affairs, as being in his own person both a great captain and a philosopher of the first form of Socrates’ disciples; and yet I cannot consent to such a measure of licence as he dispenses in all things and places.
Monsieur d’Aubigny, besieging Capua, and after having directed a furious battery against it, Signor Fabricio Colonna, governor of the town, having from a bastion begun to parley, and his soldiers in the meantime being a little more remiss in their guard, our people entered the place at unawares, and put them all to the sword. And of later memory, at Yvoy, Signor Juliano Romero having played that part of a novice to go out to parley with the Constable, at his return found his place taken. But, that we might not scape scot-free, the Marquess of Pescara having laid siege to Genoa, where Duke Ottaviano Fregosa commanded under our protection, and the articles betwixt them being so far advanced that it was looked upon as a done thing, and upon the point to be concluded, the Spaniards in the meantime having slipped in, made use of this treachery as an absolute victory. And since, at Ligny, in Barrois, where the Count de Brienne commanded, the emperor having in his own person beleaguered that place, and Bertheville, the said Count’s lieutenant, going out to parley, whilst he was capitulating the town was taken.
But the philosopher Chrysippus was of another opinion, wherein I also concur; for he was used to say that those who run a race ought to employ all the force they have in what they are about, and to run as fast as they can; but that it is by no means fair in them to lay any hand upon their adversary to stop him, nor to set a leg before him to throw him down. And yet more generous was the answer of that great Alexander to Polypercon who was persuading him to take the advantage of the night’s obscurity to fall upon Darius. “By no means,” said be; “it is not for such a man as I am to steal a victory, ‘Malo me fortunae poeniteat, quam victoria pudeat.’”—[“I had rather complain of ill-fortune than be ashamed of victory.” Quint. Curt, iv. 13]—
CHAPTER VII——THAT THE INTENTION IS JUDGE OF OUR ACTIONS
‘Tis a saying, “That death discharges us of all our obligations.” I know some who have taken it in another sense. Henry VII., King of England, articled with Don Philip, son to Maximilian the emperor, or (to place him more honourably) father to the Emperor Charles V., that the said Philip should deliver up the Duke of Suffolk of the White Rose, his enemy, who was fled into the Low Countries, into his hands; which Philip accordingly did, but upon condition, nevertheless, that Henry should attempt nothing against the life of the said Duke; but coming to die, the king in his last will commanded his son to put him to death immediately after his decease. And lately, in the tragedy that the Duke of Alva presented to us in the persons of the Counts Horn and Egmont at Brussels, —[Decapitated 4th June 1568]—there were very remarkable passages, and one amongst the rest, that Count Egmont (upon the security of whose word and faith Count Horn had come and surrendered himself to the Duke of Alva) earnestly entreated that he might first mount the scaffold, to the end that death might disengage him from the obligation he had passed to the other. In which case, methinks, death did not acquit the former of his promise, and that the second was discharged from it without dying. We cannot be bound beyond what we are able to perform, by reason that effect and performance are not at all in our power, and that, indeed, we are masters of nothing but the will, in which, by necessity, all the rules and whole duty of mankind are founded and established: therefore Count Egmont, conceiving his soul and will indebted to his promise, although he had not the power to make it good, had doubtless been absolved of his duty, even though he had outlived the other; but the King of England wilfully and premeditately breaking his faith, was no more to be excused for deferring the execution of his infidelity till after his death than the mason in Herodotus, who having inviolably, during the time of his life, kept the secret of the treasure of the King of Egypt, his master, at his death discovered it to his children.—[Herod., ii. 121.]
I have taken notice of several in my time, who, convicted by their consciences of unjustly detaining the goods of another, have endeavoured to make amends by their will, and after their decease; but they had as good do nothing, as either in taking so much time in so pressing an affair, or in going about to remedy a wrong with so little dissatisfaction or injury to themselves. They owe, over and above, something of their own; and by how much their payment is more strict and incommodious to themselves, by so much is their restitution more just meritorious. Penitency requires penalty; but they yet do worse than these, who reserve the animosity against their neighbour to the last gasp, having concealed it during their life; wherein they manifest little regard of their own honour, irritating the party offended in their memory; and less to their the power, even out of to make their malice die with them, but extending the life of their hatred even beyond their own. Unjust judges, who defer judgment to a time wherein they can have no knowledge of the cause! For my part, I shall take care, if I can, that my death discover nothing that my life has not first and openly declared.
CHAPTER VIII——OF IDLENESS
As we see some grounds that have long lain idle and untilled, when grown rich and fertile by rest, to abound with and spend their virtue in the product of innumerable sorts of weeds and wild herbs that are unprofitable, and that to make them perform their true office, we are to cultivate and prepare them for such seeds as are proper for our service; and as we see women that, without knowledge of man, do sometimes of themselves bring forth inanimate and formless lumps of flesh, but that to cause a natural and perfect generation they are to be husbanded with another kind of seed: even so it is with minds, which if not applied to some certain study that may fix and restrain them, run into a thousand extravagances, eternally roving here and there in the vague expanse of the imagination—
—in which wild agitation there is no folly, nor idle fancy they do not light upon:—
The soul that has no established aim loses itself, for, as it is said—
When I lately retired to my own house, with a resolution, as much as possibly I could, to avoid all manner of concern in affairs, and to spend in privacy and repose the little remainder of time I have to live, I fancied I could not more oblige my mind than to suffer it at full leisure to entertain and divert itself, which I now hoped it might henceforth do, as being by time become more settled and mature; but I find—
that, quite contrary, it is like a horse that has broke from his rider, who voluntarily runs into a much more violent career than any horseman would put him to, and creates me so many chimaeras and fantastic monsters, one upon another, without order or design, that, the better at leisure to contemplate their strangeness and absurdity, I have begun to commit them to writing, hoping in time to make it ashamed of itself.
CHAPTER IX——OF LIARS
There is not a man living whom it would so little become to speak from memory as myself, for I have scarcely any at all, and do not think that the world has another so marvellously treacherous as mine. My other faculties are all sufficiently ordinary and mean; but in this I think myself very rare and singular, and deserving to be thought famous. Besides the natural inconvenience I suffer by it (for, certes, the necessary use of memory considered, Plato had reason when he called it a great and powerful goddess), in my country, when they would say a man has no sense, they say, such an one has no memory; and when I complain of the defect of mine, they do not believe me, and reprove me, as though I accused myself for a fool: not discerning the difference betwixt memory and understanding, which is to make matters still worse for me. But they do me wrong; for experience, rather, daily shows us, on the contrary, that a strong memory is commonly coupled with infirm judgment. They do, me, moreover (who am so perfect in nothing as in friendship), a great wrong in this, that they make the same words which accuse my infirmity, represent me for an ungrateful person; they bring my affections into question upon the account of my memory, and from a natural imperfection, make out a defect of conscience. “He has forgot,” says one, “this request, or that promise; he no more remembers his friends; he has forgot to say or do, or conceal such and such a thing, for my sake.” And, truly, I am apt enough to forget many things, but to neglect anything my friend has given me in charge, I never do it. And it should be enough, methinks, that I feel the misery and inconvenience of it, without branding me with malice, a vice so contrary to my humour.
However, I derive these comforts from my infirmity: first, that it is an evil from which principally I have found reason to correct a worse, that would easily enough have grown upon me, namely, ambition; the defect being intolerable in those who take upon them public affairs. That, like examples in the progress of nature demonstrate to us, she has fortified me in my other faculties proportionably as she has left me unfurnished in this; I should otherwise have been apt implicitly to have reposed my mind and judgment upon the bare report of other men, without ever setting them to work upon their own force, had the inventions and opinions of others been ever been present with me by the benefit of memory. That by this means I am not so talkative, for the magazine of the memory is ever better furnished with matter than that of the invention. Had mine been faithful to me, I had ere this deafened all my friends with my babble, the subjects themselves arousing and stirring up the little faculty I have of handling and employing them, heating and distending my discourse, which were a pity: as I have observed in several of my intimate friends, who, as their memories supply them with an entire and full view of things, begin their narrative so far back, and crowd it with so many impertinent circumstances, that though the story be good in itself, they make a shift to spoil it; and if otherwise, you are either to curse the strength of their memory or the weakness of their judgment: and it is a hard thing to close up a discourse, and to cut it short, when you have once started; there is nothing wherein the force of a horse is so much seen as in a round and sudden stop. I see even those who are pertinent enough, who would, but cannot stop short in their career; for whilst they are seeking out a handsome period to conclude with, they go on at random, straggling about upon impertinent trivialities, as men staggering upon weak legs. But, above all, old men who retain the memory of things past, and forget how often they have told them, are dangerous company; and I have known stories from the mouth of a man of very great quality, otherwise very pleasant in themselves, become very wearisome by being repeated a hundred times over and over again to the same people.
Secondly, that, by this means, I the less remember the injuries I have received; insomuch that, as the ancient said,—[Cicero, Pro Ligar. c. 12.]—I should have a register of injuries, or a prompter, as Darius, who, that he might not forget the offence he had received from those of Athens, so oft as he sat down to dinner, ordered one of his pages three times to repeat in his ear, “Sir, remember the Athenians”;—[Herod., v. 105.]—and then, again, the places which I revisit, and the books I read over again, still smile upon me with a fresh novelty.
It is not without good reason said “that he who has not a good memory should never take upon him the trade of lying.” I know very well that the grammarians—[Nigidius, Aulus Gellius, xi. ii; Nonius, v. 80.]— distinguish betwixt an untruth and a lie, and say that to tell an untruth is to tell a thing that is false, but that we ourselves believe to be true; and that the definition of the word to lie in Latin, from which our French is taken, is to tell a thing which we know in our conscience to be untrue; and it is of this last sort of liars only that I now speak. Now, these do either wholly contrive and invent the untruths they utter, or so alter and disguise a true story that it ends in a lie. When they disguise and often alter the same story, according to their own fancy, ‘tis very hard for them, at one time or another, to escape being trapped, by reason that the real truth of the thing, having first taken possession of the memory, and being there lodged impressed by the medium of knowledge and science, it will be difficult that it should not represent itself to the imagination, and shoulder out falsehood, which cannot there have so sure and settled footing as the other; and the circumstances of the first true knowledge evermore running in their minds, will be apt to make them forget those that are illegitimate, and only, forged by their own fancy. In what they, wholly invent, forasmuch as there is no contrary impression to jostle their invention there seems to be less danger of tripping; and yet even this by reason it is a vain body and without any hold, is very apt to escape the memory, if it be not well assured. Of which I had very pleasant experience, at the expense of such as profess only to form and accommodate their speech to the affair they have in hand, or to humour of the great folks to whom they are speaking; for the circumstances to which these men stick not to enslave their faith and conscience being subject to several changes, their language must vary accordingly: whence it happens that of the same thing they tell one man that it is this, and another that it is that, giving it several colours; which men, if they once come to confer notes, and find out the cheat, what becomes of this fine art? To which may be added, that they must of necessity very often ridiculously trap themselves; for what memory can be sufficient to retain so many different shapes as they have forged upon one and the same subject? I have known many in my time very ambitious of the repute of this fine wit; but they do not see that if they have the reputation of it, the effect can no longer be.
In plain truth, lying is an accursed vice. We are not men, nor have other tie upon one another, but by our word. If we did but discover the horror and gravity of it, we should pursue it with fire and sword, and more justly than other crimes. I see that parents commonly, and with indiscretion enough, correct their children for little innocent faults, and torment them for wanton tricks, that have neither impression nor consequence; whereas, in my opinion, lying only, and, which is of something a lower form, obstinacy, are the faults which are to be severely whipped out of them, both in their infancy and in their progress, otherwise they grow up and increase with them; and after a tongue has once got the knack of lying, ‘tis not to be imagined how impossible it is to reclaim it whence it comes to pass that we see some, who are otherwise very honest men, so subject and enslaved to this vice. I have an honest lad to my tailor, whom I never knew guilty of one truth, no, not when it had been to his advantage. If falsehood had, like truth, but one face only, we should be upon better terms; for we should then take for certain the contrary to what the liar says: but the reverse of truth has a hundred thousand forms, and a field indefinite, without bound or limit. The Pythagoreans make good to be certain and finite, and evil, infinite and uncertain. There are a thousand ways to miss the white, there is only one to hit it. For my own part, I have this vice in so great horror, that I am not sure I could prevail with my conscience to secure myself from the most manifest and extreme danger by an impudent and solemn lie. An ancient father says “that a dog we know is better company than a man whose language we do not understand.”
And how much less sociable is false speaking than silence?
King Francis I. vaunted that he had by this means nonplussed Francesco Taverna, ambassador of Francesco Sforza, Duke of Milan, a man very famous for his science in talking in those days. This gentleman had been sent to excuse his master to his Majesty about a thing of very great consequence, which was this: the King, still to maintain some intelligence with Italy, out of which he had lately been driven, and particularly with the duchy of Milan, had thought it convenient to have a gentleman on his behalf to be with that Duke: an ambassador in effect, but in outward appearance a private person who pretended to reside there upon his own particular affairs; for the Duke, much more depending upon the Emperor, especially at a time when he was in a treaty of marriage with his niece, daughter to the King of Denmark, who is now dowager of Lorraine, could not manifest any practice and conference with us without his great interest. For this commission one Merveille, a Milanese gentleman, and an equerry to the King, being thought very fit, was accordingly despatched thither with private credentials, and instructions as ambassador, and with other letters of recommendation to the Duke about his own private concerns, the better to mask and colour the business; and was so long in that court, that the Emperor at last had some inkling of his real employment there; which was the occasion of what followed after, as we suppose; which was, that under pretence of some murder, his trial was in two days despatched, and his head in the night struck off in prison. Messire Francesco being come, and prepared with a long counterfeit history of the affair (for the King had applied himself to all the princes of Christendom, as well as to the Duke himself, to demand satisfaction), had his audience at the morning council; where, after he had for the support of his cause laid open several plausible justifications of the fact, that his master had never looked upon this Merveille for other than a private gentleman and his own subject, who was there only in order to his own business, neither had he ever lived under any other aspect; absolutely disowning that he had ever heard he was one of the King’s household or that his Majesty so much as knew him, so far was he from taking him for an ambassador: the King, in his turn, pressing him with several objections and demands, and challenging him on all sides, tripped him up at last by asking, why, then, the execution was performed by night, and as it were by stealth? At which the poor confounded ambassador, the more handsomely to disengage himself, made answer, that the Duke would have been very loth, out of respect to his Majesty, that such an execution should have been performed by day. Any one may guess if he was not well rated when he came home, for having so grossly tripped in the presence of a prince of so delicate a nostril as King Francis.
Pope Julius II. having sent an ambassador to the King of England to animate him against King Francis, the ambassador having had his audience, and the King, before he would give an answer, insisting upon the difficulties he should find in setting on foot so great a preparation as would be necessary to attack so potent a King, and urging some reasons to that effect, the ambassador very unseasonably replied that he had also himself considered the same difficulties, and had represented them to the Pope. From which saying of his, so directly opposite to the thing propounded and the business he came about, which was immediately to incite him to war, the King of England first derived the argument (which he afterward found to be true), that this ambassador, in his own mind, was on the side of the French; of which having advertised his master, his estate at his return home was confiscated, and he himself very narrowly escaped the losing of his head.—[Erasmi Op. (1703), iv. col. 684.]
CHAPTER X——OF QUICK OR SLOW SPEECH
So we see in the gift of eloquence, wherein some have such a facility and promptness, and that which we call a present wit so easy, that they are ever ready upon all occasions, and never to be surprised; and others more heavy and slow, never venture to utter anything but what they have long premeditated, and taken great care and pains to fit and prepare.
Now, as we teach young ladies those sports and exercises which are most proper to set out the grace and beauty of those parts wherein their chiefest ornament and perfection lie, so it should be in these two advantages of eloquence, to which the lawyers and preachers of our age seem principally to pretend. If I were worthy to advise, the slow speaker, methinks, should be more proper for the pulpit, and the other for the bar: and that because the employment of the first does naturally allow him all the leisure he can desire to prepare himself, and besides, his career is performed in an even and unintermitted line, without stop or interruption; whereas the pleader’s business and interest compels him to enter the lists upon all occasions, and the unexpected objections and replies of his adverse party jostle him out of his course, and put him, upon the instant, to pump for new and extempore answers and defences. Yet, at the interview betwixt Pope Clement and King Francis at Marseilles, it happened, quite contrary, that Monsieur Poyet, a man bred up all his life at the bar, and in the highest repute for eloquence, having the charge of making the harangue to the Pope committed to him, and having so long meditated on it beforehand, as, so they said, to have brought it ready made along with him from Paris; the very day it was to have been pronounced, the Pope, fearing something might be said that might give offence to the other princes’ ambassadors who were there attending on him, sent to acquaint the King with the argument which he conceived most suiting to the time and place, but, by chance, quite another thing to that Monsieur de Poyet had taken so much pains about: so that the fine speech he had prepared was of no use, and he was upon the instant to contrive another; which finding himself unable to do, Cardinal du Bellay was constrained to perform that office. The pleader’s part is, doubtless, much harder than that of the preacher; and yet, in my opinion, we see more passable lawyers than preachers, at all events in France. It should seem that the nature of wit is to have its operation prompt and sudden, and that of judgment to have it more deliberate and more slow. But he who remains totally silent, for want of leisure to prepare himself to speak well, and he also whom leisure does noways benefit to better speaking, are equally unhappy.
‘Tis said of Severus Cassius that he spoke best extempore, that he stood more obliged to fortune than to his own diligence; that it was an advantage to him to be interrupted in speaking, and that his adversaries were afraid to nettle him, lest his anger should redouble his eloquence. I know, experimentally, the disposition of nature so impatient of tedious and elaborate premeditation, that if it do not go frankly and gaily to work, it can perform nothing to purpose. We say of some compositions that they stink of oil and of the lamp, by reason of a certain rough harshness that laborious handling imprints upon those where it has been employed. But besides this, the solicitude of doing well, and a certain striving and contending of a mind too far strained and overbent upon its undertaking, breaks and hinders itself like water, that by force of its own pressing violence and abundance, cannot find a ready issue through the neck of a bottle or a narrow sluice. In this condition of nature, of which I am now speaking, there is this also, that it would not be disordered and stimulated with such passions as the fury of Cassius (for such a motion would be too violent and rude); it would not be jostled, but solicited; it would be roused and heated by unexpected, sudden, and accidental occasions. If it be left to itself, it flags and languishes; agitation only gives it grace and vigour. I am always worst in my own possession, and when wholly at my own disposition: accident has more title to anything that comes from me than I; occasion, company, and even the very rising and falling of my own voice, extract more from my fancy than I can find, when I sound and employ it by myself. By which means, the things I say are better than those I write, if either were to be preferred, where neither is worth anything. This, also, befalls me, that I do not find myself where I seek myself, and I light upon things more by chance than by any inquisition of my own judgment. I perhaps sometimes hit upon something when I write, that seems quaint and sprightly to me, though it will appear dull and heavy to another.—But let us leave these fine compliments; every one talks thus of himself according to his talent. But when I come to speak, I am already so lost that I know not what I was about to say, and in such cases a stranger often finds it out before me. If I should make erasure so often as this inconvenience befalls me, I should make clean work; occasion will, at some other time, lay it as visible to me as the light, and make me wonder what I should stick at.
CHAPTER XI——OF PROGNOSTICATIONS
For what concerns oracles, it is certain that a good while before the coming of Jesus Christ they had begun to lose their credit; for we see that Cicero troubled to find out the cause of their decay, and he has these words:
But as to the other prognostics, calculated from the anatomy of beasts at sacrifices (to which purpose Plato does, in part, attribute the natural constitution of the intestines of the beasts themselves), the scraping of poultry, the flight of birds—
claps of thunder, the overflowing of rivers—
—and others of the like nature, upon which antiquity founded most of their public and private enterprises, our religion has totally abolished them. And although there yet remain amongst us some practices of divination from the stars, from spirits, from the shapes and complexions of men, from dreams and the like (a notable example of the wild curiosity of our nature to grasp at and anticipate future things, as if we had not enough to do to digest the present)—
yet are they of much less authority now than heretofore. Which makes so much more remarkable the example of Francesco, Marquis of Saluzzo, who being lieutenant to King Francis I. in his ultramontane army, infinitely favoured and esteemed in our court, and obliged to the king’s bounty for the marquisate itself, which had been forfeited by his brother; and as to the rest, having no manner of provocation given him to do it, and even his own affection opposing any such disloyalty, suffered himself to be so terrified, as it was confidently reported, with the fine prognostics that were spread abroad everywhere in favour of the Emperor Charles V., and to our disadvantage (especially in Italy, where these foolish prophecies were so far believed, that at Rome great sums of money were ventured out upon return of greater, when the prognostics came to pass, so certain they made themselves of our ruin), that, having often bewailed, to those of his acquaintance who were most intimate with him, the mischiefs that he saw would inevitably fall upon the Crown of France and the friends he had in that court, he revolted and turned to the other side; to his own misfortune, nevertheless, what constellation soever governed at that time. But he carried himself in this affair like a man agitated by divers passions; for having both towns and forces in his hands, the enemy’s army under Antonio de Leyva close by him, and we not at all suspecting his design, it had been in his power to have done more than he did; for we lost no men by this infidelity of his, nor any town, but Fossano only, and that after a long siege and a brave defence.—(1536)
And those who take this sentence in a contrary sense interpret it amiss:
Much more wisely Pacuvius—
The so celebrated art of divination amongst the Tuscans took its beginning thus: A labourer striking deep with his cutter into the earth, saw the demigod Tages ascend, with an infantine aspect, but endued with a mature and senile wisdom. Upon the rumour of which, all the people ran to see the sight, by whom his words and science, containing the principles and means to attain to this art, were recorded, and kept for many ages.—[Cicero, De Devina, ii. 23]—A birth suitable to its progress; I, for my part, should sooner regulate my affairs by the chance of a die than by such idle and vain dreams. And, indeed, in all republics, a good share of the government has ever been referred to chance. Plato, in the civil regimen that he models according to his own fancy, leaves to it the decision of several things of very great importance, and will, amongst other things, that marriages should be appointed by lot; attributing so great importance to this accidental choice as to ordain that the children begotten in such wedlock be brought up in the country, and those begotten in any other be thrust out as spurious and base; yet so, that if any of those exiles, notwithstanding, should, peradventure, in growing up give any good hope of himself, he might be recalled, as, also, that such as had been retained, should be exiled, in case they gave little expectation of themselves in their early growth.
I see some who are mightily given to study and comment upon their almanacs, and produce them to us as an authority when anything has fallen out pat; and, for that matter, it is hardly possible but that these alleged authorities sometimes stumble upon a truth amongst an infinite number of lies.
I think never the better of them for some such accidental hit. There would be more certainty in it if there were a rule and a truth of always lying. Besides, nobody records their flimflams and false prognostics, forasmuch as they are infinite and common; but if they chop upon one truth, that carries a mighty report, as being rare, incredible, and prodigious. So Diogenes, surnamed the Atheist, answered him in Samothrace, who, showing him in the temple the several offerings and stories in painting of those who had escaped shipwreck, said to him, “Look, you who think the gods have no care of human things, what do you say to so many persons preserved from death by their especial favour?” “Why, I say,” answered he, “that their pictures are not here who were cast away, who are by much the greater number.”—[Cicero, De Natura Deor., i. 37.]
Cicero observes that of all the philosophers who have acknowledged a deity, Xenophanes the Colophonian only has endeavoured to eradicate all manner of divination—[Cicero, De Divin., i. 3.]—; which makes it the less a wonder if we have now and then seen some of our princes, sometimes to their own cost, rely too much upon these vanities. I had given anything with my own eyes to see those two great marvels, the book of Joachim the Calabrian abbot, which foretold all the future Popes, their names and qualities; and that of the Emperor Leo, which prophesied all the emperors and patriarchs of Greece. This I have been an eyewitness of, that in public confusions, men astonished at their fortune, have abandoned their own reason, superstitiously to seek out in the stars the ancient causes and menaces of the present mishaps, and in my time have been so strangely successful in it, as to make me believe that this being an amusement of sharp and volatile wits, those who have been versed in this knack of unfolding and untying riddles, are capable, in any sort of writing, to find out what they desire. But above all, that which gives them the greatest room to play in, is the obscure, ambiguous, and fantastic gibberish of the prophetic canting, where their authors deliver nothing of clear sense, but shroud all in riddle, to the end that posterity may interpret and apply it according to its own fancy.
Socrates demon might, perhaps, be no other but a certain impulsion of the will, which obtruded itself upon him without the advice or consent of his judgment; and in a soul so enlightened as his was, and so prepared by a continual exercise of wisdom-and virtue, ‘tis to be supposed those inclinations of his, though sudden and undigested, were very important and worthy to be followed. Every one finds in himself some image of such agitations, of a prompt, vehement, and fortuitous opinion; and I may well allow them some authority, who attribute so little to our prudence, and who also myself have had some, weak in reason, but violent in persuasion and dissuasion, which were most frequent with Socrates,—[Plato, in his account of Theages the Pythagorean]—by which I have suffered myself to be carried away so fortunately, and so much to my own advantage, that they might have been judged to have had something in them of a divine inspiration.
CHAPTER XII——OF CONSTANCY
The law of resolution and constancy does not imply that we ought not, as much as in us lies, to decline and secure ourselves from the mischiefs and inconveniences that threaten us; nor, consequently, that we shall not fear lest they should surprise us: on the contrary, all decent and honest ways and means of securing ourselves from harms, are not only permitted, but, moreover, commendable, and the business of constancy chiefly is, bravely to stand to, and stoutly to suffer those inconveniences which are not possibly to be avoided. So that there is no supple motion of body, nor any movement in the handling of arms, how irregular or ungraceful soever, that we need condemn, if they serve to protect us from the blow that is made against us.
Several very warlike nations have made use of a retreating and flying way of fight as a thing of singular advantage, and, by so doing, have made their backs more dangerous to their enemies than their faces. Of which kind of fighting the Turks still retain something in their practice of arms; and Socrates, in Plato, laughs at Laches, who had defined fortitude to be a standing firm in the ranks against the enemy. “What!” says he, “would it, then, be a reputed cowardice to overcome them by giving ground?” urging, at the same time, the authority of Homer, who commends in AEneas the science of flight. And whereas Laches, considering better of it, admits the practice as to the Scythians, and, in general, all cavalry whatever, he again attacks him with the example of the Lacedaemonian foot—a nation of all other the most obstinate in maintaining their ground—who, in the battle of Plataea, not being able to break into the Persian phalanx, bethought themselves to disperse and retire, that by the enemy supposing they fled, they might break and disunite that vast body of men in the pursuit, and by that stratagem obtained the victory.
As for the Scythians, ‘tis said of them, that when Darius went his expedition to subdue them, he sent, by a herald, highly to reproach their king, that he always retired before him and declined a battle; to which Idanthyrses,—[Herod., iv. 127.]—for that was his name, returned answer, that it was not for fear of him, or of any man living, that he did so, but that it was the way of marching in practice with his nation, who had neither tilled fields, cities, nor houses to defend, or to fear the enemy should make any advantage of but that if he had such a stomach to fight, let him but come to view their ancient places of sepulture, and there he should have his fill.
Nevertheless, as to cannon-shot, when a body of men are drawn up in the face of a train of artillery, as the occasion of war often requires, it is unhandsome to quit their post to avoid the danger, forasmuch as by reason of its violence and swiftness we account it inevitable; and many a one, by ducking, stepping aside, and such other motions of fear, has been, at all events, sufficiently laughed at by his companions. And yet, in the expedition that the Emperor Charles V. made against us into Provence, the Marquis de Guast going to reconnoitre the city of Arles, and advancing out of the cover of a windmill, under favour of which he had made his approach, was perceived by the Seigneurs de Bonneval and the Seneschal of Agenois, who were walking upon the ‘theatre aux ayenes’; who having shown him to the Sieur de Villiers, commissary of the artillery, he pointed a culverin so admirably well, and levelled it so exactly right against him, that had not the Marquis, seeing fire given to it, slipped aside, it was certainly concluded the shot had taken him full in the body. And, in like manner, some years before, Lorenzo de’ Medici, Duke of Urbino, and father to the queen-mother—[Catherine de’ Medici, mother of Henry III.]—laying siege to Mondolfo, a place in the territories of the Vicariat in Italy, seeing the cannoneer give fire to a piece that pointed directly against him, it was well for him that he ducked, for otherwise the shot, that only razed the top of his head, had doubtless hit him full in the breast. To say truth, I do not think that these evasions are performed upon the account of judgment; for how can any man living judge of high or low aim on so sudden an occasion? And it is much more easy to believe that fortune favoured their apprehension, and that it might be as well at another time to make them face the danger, as to seek to avoid it. For my own part, I confess I cannot forbear starting when the rattle of a harquebuse thunders in my ears on a sudden, and in a place where I am not to expect it, which I have also observed in others, braver fellows than I.
Neither do the Stoics pretend that the soul of their philosopher need be proof against the first visions and fantasies that surprise him; but, as to a natural subjection, consent that he should tremble at the terrible noise of thunder, or the sudden clatter of some falling ruin, and be affrighted even to paleness and convulsion; and so in other passions, provided his judgment remain sound and entire, and that the seat of his reason suffer no concussion nor alteration, and that he yield no consent to his fright and discomposure. To him who is not a philosopher, a fright is the same thing in the first part of it, but quite another thing in the second; for the impression of passions does not remain superficially in him, but penetrates farther, even to the very seat of reason, infecting and corrupting it, so that he judges according to his fear, and conforms his behaviour to it. In this verse you may see the true state of the wise Stoic learnedly and plainly expressed:—
The Peripatetic sage does not exempt himself totally from perturbations of mind, but he moderates them.
CHAPTER XIII——THE CEREMONY OF THE INTERVIEW OF PRINCES
There is no subject so frivolous that does not merit a place in this rhapsody. According to our common rule of civility, it would be a notable affront to an equal, and much more to a superior, to fail being at home when he has given you notice he will come to visit you. Nay, Queen Margaret of Navarre further adds, that it would be a rudeness in a gentleman to go out, as we so often do, to meet any that is coming to see him, let him be of what high condition soever; and that it is more respectful and more civil to stay at home to receive him, if only upon the account of missing him by the way, and that it is enough to receive him at the door, and to wait upon him. For my part, who as much as I can endeavour to reduce the ceremonies of my house, I very often forget both the one and the other of these vain offices. If, peradventure, some one may take offence at this, I can’t help it; it is much better to offend him once than myself every day, for it would be a perpetual slavery. To what end do we avoid the servile attendance of courts, if we bring the same trouble home to our own private houses? It is also a common rule in all assemblies, that those of less quality are to be first upon the place, by reason that it is more due to the better sort to make others wait and expect them.
Nevertheless, at the interview betwixt Pope Clement and King Francis at Marseilles,—[in 1533.]—the King, after he had taken order for the necessary preparations for his reception and entertainment, withdrew out of the town, and gave the Pope two or three days’ respite for his entry, and to repose and refresh himself, before he came to him. And in like manner, at the assignation of the Pope and the Emperor,—[Charles V. in 1532.] at Bologna, the Emperor gave the Pope opportunity to come thither first, and came himself after; for which the reason given was this, that at all the interviews of such princes, the greater ought to be first at the appointed place, especially before the other in whose territories the interview is appointed to be, intimating thereby a kind of deference to the other, it appearing proper for the less to seek out and to apply themselves to the greater, and not the greater to them.
Not every country only, but every city and every society has its particular forms of civility. There was care enough to this taken in my education, and I have lived in good company enough to know the formalities of our own nation, and am able to give lessons in it. I love to follow them, but not to be so servilely tied to their observation that my whole life should be enslaved to ceremonies, of which there are some so troublesome that, provided a man omits them out of discretion, and not for want of breeding, it will be every whit as handsome. I have seen some people rude, by being overcivil and troublesome in their courtesy.
Still, these excesses excepted, the knowledge of courtesy and good manners is a very necessary study. It is, like grace and beauty, that which begets liking and an inclination to love one another at the first sight, and in the very beginning of acquaintance; and, consequently, that which first opens the door and intromits us to instruct ourselves by the example of others, and to give examples ourselves, if we have any worth taking notice of and communicating.
CHAPTER XIV——THAT MEN ARE JUSTLY PUNISHED FOR BEING OBSTINATE IN THE DEFENCE OF A FORT THAT IS NOT IN REASON TO BE DEFENDED
Valour has its bounds as well as other virtues, which, once transgressed, the next step is into the territories of vice; so that by having too large a proportion of this heroic virtue, unless a man be very perfect in its limits, which upon the confines are very hard to discern, he may very easily unawares run into temerity, obstinacy, and folly. From this consideration it is that we have derived the custom, in times of war, to punish, even with death, those who are obstinate to defend a place that by the rules of war is not tenable; otherwise men would be so confident upon the hope of impunity, that not a henroost but would resist and seek to stop an army.
The Constable Monsieur de Montmorenci, having at the siege of Pavia been ordered to pass the Ticino, and to take up his quarters in the Faubourg St. Antonio, being hindered by a tower at the end of the bridge, which was so obstinate as to endure a battery, hanged every man he found within it for their labour. And again, accompanying the Dauphin in his expedition beyond the Alps, and taking the Castle of Villano by assault, and all within it being put to the sword by the fury of the soldiers, the governor and his ensign only excepted, he caused them both to be trussed up for the same reason; as also did the Captain Martin du Bellay, then governor of Turin, with the governor of San Buono, in the same country, all his people having been cut to pieces at the taking of the place.
But forasmuch as the strength or weakness of a fortress is always measured by the estimate and counterpoise of the forces that attack it —for a man might reasonably enough despise two culverins, that would be a madman to abide a battery of thirty pieces of cannon—where also the greatness of the prince who is master of the field, his reputation, and the respect that is due unto him, are also put into the balance, there is danger that the balance be pressed too much in that direction. And it may happen that a man is possessed with so great an opinion of himself and his power, that thinking it unreasonable any place should dare to shut its gates against him, he puts all to the sword where he meets with any opposition, whilst his fortune continues; as is plain in the fierce and arrogant forms of summoning towns and denouncing war, savouring so much of barbarian pride and insolence, in use amongst the Oriental princes, and which their successors to this day do yet retain and practise. And in that part of the world where the Portuguese subdued the Indians, they found some states where it was a universal and inviolable law amongst them that every enemy overcome by the king in person, or by his lieutenant, was out of composition.
So above all both of ransom and mercy a man should take heed, if he can, of falling into the hands of a judge who is an enemy and victorious.
CHAPTER XV——OF THE PUNISHMENT OF COWARDICE
I once heard of a prince, and a great captain, having a narration given him as he sat at table of the proceeding against Monsieur de Vervins, who was sentenced to death for having surrendered Boulogne to the English, —[To Henry VIII. in 1544]—openly maintaining that a soldier could not justly be put to death for want of courage. And, in truth, ‘tis reason that a man should make a great difference betwixt faults that merely proceed from infirmity, and those that are visibly the effects of treachery and malice: for, in the last, we act against the rules of reason that nature has imprinted in us; whereas, in the former, it seems as if we might produce the same nature, who left us in such a state of imperfection and weakness of courage, for our justification. Insomuch that many have thought we are not fairly questionable for anything but what we commit against our conscience; and it is partly upon this rule that those ground their opinion who disapprove of capital or sanguinary punishments inflicted upon heretics and misbelievers; and theirs also who advocate or a judge is not accountable for having from mere ignorance failed in his administration.
But as to cowardice, it is certain that the most usual way of chastising it is by ignominy and and it is supposed that this practice brought into use by the legislator Charondas; and that, before his time, the laws of Greece punished those with death who fled from a battle; whereas he ordained only that they be for three days exposed in the public dressed in woman’s attire, hoping yet for some service from them, having awakened their courage by this open shame:
It appears also that the Roman laws did anciently punish those with death who had run away; for Ammianus Marcellinus says that the Emperor Julian commanded ten of his soldiers, who had turned their backs in an encounter against the Parthians, to be first degraded, and afterward put to death, according, says he, to the ancient laws,—[Ammianus Marcellinus, xxiv. 4; xxv. i.]—and yet elsewhere for the like offence he only condemned others to remain amongst the prisoners under the baggage ensign. The severe punishment the people of Rome inflicted upon those who fled from the battle of Cannae, and those who ran away with Aeneius Fulvius at his defeat, did not extend to death. And yet, methinks, ‘tis to be feared, lest disgrace should make such delinquents desperate, and not only faint friends, but enemies.
Of late memory,—[In 1523]—the Seigneur de Frauget, lieutenant to the Mareschal de Chatillon’s company, having by the Mareschal de Chabannes been put in government of Fuentarabia in the place of Monsieur de Lude, and having surrendered it to the Spaniard, he was for that condemned to be degraded from all nobility, and both himself and his posterity declared ignoble, taxable, and for ever incapable of bearing arms, which severe sentence was afterwards accordingly executed at Lyons.—[In 1536] —And, since that, all the gentlemen who were in Guise when the Count of Nassau entered into it, underwent the same punishment, as several others have done since for the like offence. Notwithstanding, in case of such a manifest ignorance or cowardice as exceeds all ordinary example, ‘tis but reason to take it for a sufficient proof of treachery and malice, and for such to be punished.
CHAPTER XVI——A PROCEEDING OF SOME AMBASSADORS
I observe in my travels this custom, ever to learn something from the information of those with whom I confer (which is the best school of all others), and to put my company upon those subjects they are the best able to speak of:—
For it often falls out that, on the contrary, every one will rather choose to be prating of another man’s province than his own, thinking it so much new reputation acquired; witness the jeer Archidamus put upon Pertander, “that he had quitted the glory of being an excellent physician to gain the repute of a very bad poet.—[Plutarch, Apoth. of the Lacedaemonians, ‘in voce’ Archidamus.]—And do but observe how large and ample Caesar is to make us understand his inventions of building bridges and contriving engines of war,—[De Bello Gall., iv. 17.]—and how succinct and reserved in comparison, where he speaks of the offices of his profession, his own valour, and military conduct. His exploits sufficiently prove him a great captain, and that he knew well enough; but he would be thought an excellent engineer to boot; a quality something different, and not necessary to be expected in him. The elder Dionysius was a very great captain, as it befitted his fortune he should be; but he took very great pains to get a particular reputation by poetry, and yet he was never cut out for a poet. A man of the legal profession being not long since brought to see a study furnished with all sorts of books, both of his own and all other faculties, took no occasion at all to entertain himself with any of them, but fell very rudely and magisterially to descant upon a barricade placed on the winding stair before the study door, a thing that a hundred captains and common soldiers see every day without taking any notice or offence.
By this course a man shall never improve himself, nor arrive at any perfection in anything. He must, therefore, make it his business always to put the architect, the painter, the statuary, every mechanic artisan, upon discourse of their own capacities.
And, to this purpose, in reading histories, which is everybody’s subject, I use to consider what kind of men are the authors: if they be persons that profess nothing but mere letters, I, in and from them, principally observe and learn style and language; if physicians, I the rather incline to credit what they report of the temperature of the air, of the health and complexions of princes, of wounds and diseases; if lawyers, we are from them to take notice of the controversies of rights and wrongs, the establishment of laws and civil government, and the like; if divines, the affairs of the Church, ecclesiastical censures, marriages, and dispensations; if courtiers, manners and ceremonies; if soldiers, the things that properly belong to their trade, and, principally, the accounts of the actions and enterprises wherein they were personally engaged; if ambassadors, we are to observe negotiations, intelligences, and practices, and the manner how they are to be carried on.
And this is the reason why (which perhaps I should have lightly passed over in another) I dwelt upon and maturely considered one passage in the history written by Monsieur de Langey, a man of very great judgment in things of that nature: after having given a narrative of the fine oration Charles V. had made in the Consistory at Rome, and in the presence of the Bishop of Macon and Monsieur du Velly, our ambassadors there, wherein he had mixed several injurious expressions to the dishonour of our nation; and amongst the rest, “that if his captains and soldiers were not men of another kind of fidelity, resolution, and sufficiency in the knowledge of arms than those of the King, he would immediately go with a rope about his neck and sue to him for mercy” (and it should seem the Emperor had really this, or a very little better opinion of our military men, for he afterwards, twice or thrice in his life, said the very same thing); as also, that he challenged the King to fight him in his shirt with rapier and poignard in a boat. The said Sieur de Langey, pursuing his history, adds that the forenamed ambassadors, sending a despatch to the King of these things, concealed the greatest part, and particularly the last two passages. At which I could not but wonder that it should be in the power of an ambassador to dispense with anything which he ought to signify to his master, especially of so great importance as this, coming from the mouth of such a person, and spoken in so great an assembly; and I should rather conceive it had been the servant’s duty faithfully to have represented to him the whole thing as it passed, to the end that the liberty of selecting, disposing, judging, and concluding might have remained in him: for either to conceal or to disguise the truth for fear he should take it otherwise than he ought to do, and lest it should prompt him to some extravagant resolution, and, in the meantime, to leave him ignorant of his affairs, should seem, methinks, rather to belong to him who is to give the law than to him who is only to receive it; to him who is in supreme command, and not to him who ought to look upon himself as inferior, not only in authority, but also in prudence and good counsel. I, for my part, would not be so served in my little concerns.
We so willingly slip the collar of command upon any pretence whatever, and are so ready to usurp upon dominion, every one does so naturally aspire to liberty and power, that no utility whatever derived from the wit or valour of those he employs ought to be so dear to a superior as a downright and sincere obedience. To obey more upon the account of understanding than of subjection, is to corrupt the office of command —[Taken from Aulus Gellius, i. 13.]—; insomuch that P. Crassus, the same whom the Romans reputed five times happy, at the time when he was consul in Asia, having sent to a Greek engineer to cause the greater of two masts of ships that he had taken notice of at Athens to be brought to him, to be employed about some engine of battery he had a design to make; the other, presuming upon his own science and sufficiency in those affairs, thought fit to do otherwise than directed, and to bring the less, which, according to the rules of art, was really more proper for the use to which it was designed; but Crassus, though he gave ear to his reasons with great patience, would not, however, take them, how sound or convincing soever, for current pay, but caused him to be well whipped for his pains, valuing the interest of discipline much more than that of the work in hand.
Notwithstanding, we may on the other side consider that so precise and implicit an obedience as this is only due to positive and limited commands. The employment of ambassadors is never so confined, many things in their management of affairs being wholly referred to the absolute sovereignty of their own conduct; they do not simply execute, but also, to their own discretion and wisdom, form and model their master’s pleasure. I have, in my time, known men of command checked for having rather obeyed the express words of the king’s letters, than the necessity of the affairs they had in hand. Men of understanding do yet, to this day, condemn the custom of the kings of Persia to give their lieutenants and agents so little rein, that, upon the least arising difficulties, they must fain have recourse to their further commands; this delay, in so vast an extent of dominion, having often very much prejudiced their affairs; and Crassus, writing to a man whose profession it was best to understand those things, and pre-acquainting him to what use this mast was designed, did he not seem to consult his advice, and in a manner invite him to interpose his better judgment?
CHAPTER XVII——OF FEAR
I am not so good a naturalist (as they call it) as to discern by what secret springs fear has its motion in us; but, be this as it may, ‘tis a strange passion, and such a one that the physicians say there is no other whatever that sooner dethrones our judgment from its proper seat; which is so true, that I myself have seen very many become frantic through fear; and, even in those of the best settled temper it is most certain that it begets a terrible astonishment and confusion during the fit. I omit the vulgar sort, to whom it one while represents their great-grandsires risen out of their graves in their shrouds, another while werewolves, nightmares, and chimaeras; but even amongst soldiers, a sort of men over whom, of all others, it ought to have the least power, how often has it converted flocks of sheep into armed squadrons, reeds and bullrushes into pikes and lances, friends into enemies, and the French white cross into the red cross of Spain! When Monsieur de Bourbon took Rome,—[In 1527]—an ensign who was upon guard at Borgo San Pietro was seized with such a fright upon the first alarm, that he threw himself out at a breach with his colours upon his shoulder, and ran directly upon the enemy, thinking he had retreated toward the inward defences of the city, and with much ado, seeing Monsieur de Bourbon’s people, who thought it had been a sally upon them, draw up to receive him, at last came to himself, and saw his error; and then facing about, he retreated full speed through the same breach by which he had gone out, but not till he had first blindly advanced above three hundred paces into the open field. It did not, however, fall out so well with Captain Giulio’s ensign, at the time when St. Paul was taken from us by the Comte de Bures and Monsieur de Reu, for he, being so astonished with fear as to throw himself, colours and all, out of a porthole, was immediately, cut to pieces by the enemy; and in the same siege, it was a very memorable fear that so seized, contracted, and froze up the heart of a gentleman, that he sank down, stone-dead, in the breach, without any manner of wound or hurt at all. The like madness does sometimes push on a whole multitude; for in one of the encounters that Germanicus had with the Germans, two great parties were so amazed with fear that they ran two opposite ways, the one to the same place from which the other had fled.—[Tacit, Annal., i. 63.]—Sometimes it adds wings to the heels, as in the two first: sometimes it nails them to the ground, and fetters them from moving; as we read of the Emperor Theophilus, who, in a battle he lost against the Agarenes, was so astonished and stupefied that he had no power to fly—
—till such time as Manuel, one of the principal commanders of his army, having jogged and shaked him so as to rouse him out of his trance, said to him, “Sir, if you will not follow me, I will kill you; for it is better you should lose your life than, by being taken, lose your empire.” —[Zonaras, lib. iii.]—But fear does then manifest its utmost power when it throws us upon a valiant despair, having before deprived us of all sense both of duty and honour. In the first pitched battle the Romans lost against Hannibal, under the Consul Sempronius, a body of ten thousand foot, that had taken fright, seeing no other escape for their cowardice, went and threw themselves headlong upon the great battalion of the enemies, which with marvellous force and fury they charged through and through, and routed with a very great slaughter of the Carthaginians, thus purchasing an ignominious flight at the same price they might have gained a glorious victory.—[Livy, xxi. 56.]
The thing in the world I am most afraid of is fear, that passion alone, in the trouble of it, exceeding all other accidents. What affliction could be greater or more just than that of Pompey’s friends, who, in his ship, were spectators of that horrible murder? Yet so it was, that the fear of the Egyptian vessels they saw coming to board them, possessed them with so great alarm that it is observed they thought of nothing but calling upon the mariners to make haste, and by force of oars to escape away, till being arrived at Tyre, and delivered from fear, they had leisure to turn their thoughts to the loss of their captain, and to give vent to those tears and lamentations that the other more potent passion had till then suspended.
Such as have been well rubbed in some skirmish, may yet, all wounded and bloody as they are, be brought on again the next day to charge; but such as have once conceived a good sound fear of the enemy, will never be made so much as to look him in the face. Such as are in immediate fear of a losing their estates, of banishment, or of slavery, live in perpetual anguish, and lose all appetite and repose; whereas such as are actually poor, slaves, or exiles, ofttimes live as merrily as other folk. And the many people who, impatient of the perpetual alarms of fear, have hanged or drowned themselves, or dashed themselves to pieces, give us sufficiently to understand that fear is more importunate and insupportable than death itself.
The Greeks acknowledged another kind of fear, differing from any we have spoken of yet, that surprises us without any visible cause, by an impulse from heaven, so that whole nations and whole armies have been struck with it. Such a one was that which brought so wonderful a desolation upon Carthage, where nothing was to be heard but affrighted voices and outcries; where the inhabitants were seen to sally out of their houses as to an alarm, and there to charge, wound, and kill one another, as if they had been enemies come to surprise their city. All things were in disorder and fury till, with prayers and sacrifices, they had appeased their gods—[Diod. Sic., xv. 7]; and this is that they call panic terrors.—[Ibid. ; Plutarch on Isis and Osiris, c. 8.]
CHAPTER XVIII——THAT MEN ARE NOT TO JUDGE OF OUR HAPPINESS TILL AFTER DEATH.
The very children know the story of King Croesus to this purpose, who being taken prisoner by Cyrus, and by him condemned to die, as he was going to execution cried out, “O Solon, Solon!” which being presently reported to Cyrus, and he sending to inquire of him what it meant, Croesus gave him to understand that he now found the teaching Solon had formerly given him true to his cost; which was, “That men, however fortune may smile upon them, could never be said to be happy till they had been seen to pass over the last day of their lives,” by reason of the uncertainty and mutability of human things, which, upon very light and trivial occasions, are subject to be totally changed into a quite contrary condition. And so it was that Agesilaus made answer to one who was saying what a happy young man the King of Persia was, to come so young to so mighty a kingdom: “‘Tis true,” said he, “but neither was Priam unhappy at his years.”—[Plutarch, Apothegms of the Lacedaemonians.]—In a short time, kings of Macedon, successors to that mighty Alexander, became joiners and scriveners at Rome; a tyrant of Sicily, a pedant at Corinth; a conqueror of one-half of the world and general of so many armies, a miserable suppliant to the rascally officers of a king of Egypt: so much did the prolongation of five or six months of life cost the great Pompey; and, in our fathers’ days, Ludovico Sforza, the tenth Duke of Milan, whom all Italy had so long truckled under, was seen to die a wretched prisoner at Loches, but not till he had lived ten years in captivity,—[He was imprisoned by Louis XI. in an iron cage]— which was the worst part of his fortune. The fairest of all queens, —[Mary, Queen of Scots.]—widow to the greatest king in Europe, did she not come to die by the hand of an executioner? Unworthy and barbarous cruelty! And a thousand more examples there are of the same kind; for it seems that as storms and tempests have a malice against the proud and overtowering heights of our lofty buildings, there are also spirits above that are envious of the greatnesses here below:
And it should seem, also, that Fortune sometimes lies in wait to surprise the last hour of our lives, to show the power she has, in a moment, to overthrow what she was so many years in building, making us cry out with Laberius:
And, in this sense, this good advice of Solon may reasonably be taken; but he, being a philosopher (with which sort of men the favours and disgraces of Fortune stand for nothing, either to the making a man happy or unhappy, and with whom grandeurs and powers are accidents of a quality almost indifferent) I am apt to think that he had some further aim, and that his meaning was, that the very felicity of life itself, which depends upon the tranquillity and contentment of a well-descended spirit, and the resolution and assurance of a well-ordered soul, ought never to be attributed to any man till he has first been seen to play the last, and, doubtless, the hardest act of his part. There may be disguise and dissimulation in all the rest: where these fine philosophical discourses are only put on, and where accident, not touching us to the quick, gives us leisure to maintain the same gravity of aspect; but, in this last scene of death, there is no more counterfeiting: we must speak out plain, and discover what there is of good and clean in the bottom of the pot,
Wherefore, at this last, all the other actions of our life ought to be tried and sifted: ‘tis the master-day, ‘tis the day that is judge of all the rest, “‘tis the day,” says one of the ancients,—[Seneca, Ep., 102]— “that must be judge of all my foregoing years.” To death do I refer the assay of the fruit of all my studies: we shall then see whether my discourses came only from my mouth or from my heart. I have seen many by their death give a good or an ill repute to their whole life. Scipio, the father-in-law of Pompey, in dying, well removed the ill opinion that till then every one had conceived of him. Epaminondas being asked which of the three he had in greatest esteem, Chabrias, Iphicrates, or himself. “You must first see us die,” said he, “before that question can be resolved.”—[Plutarch, Apoth.]—And, in truth, he would infinitely wrong that man who would weigh him without the honour and grandeur of his end.
God has ordered all things as it has best pleased Him; but I have, in my time, seen three of the most execrable persons that ever I knew in all manner of abominable living, and the most infamous to boot, who all died a very regular death, and in all circumstances composed, even to perfection. There are brave and fortunate deaths: I have seen death cut the thread of the progress of a prodigious advancement, and in the height and flower of its increase, of a certain person,—[Montaigne doubtless refers to his friend Etienne de la Boetie, at whose death in 1563 he was present.]—with so glorious an end that, in my opinion, his ambitious and generous designs had nothing in them so high and great as their interruption. He arrived, without completing his course, at the place to which his ambition aimed, with greater glory than he could either have hoped or desired, anticipating by his fall the name and power to which he aspired in perfecting his career. In the judgment I make of another man’s life, I always observe how he carried himself at his death; and the principal concern I have for my own is that I may die well—that is, patiently and tranquilly.
CHAPTER XIX——THAT TO STUDY PHILOSOPY IS TO LEARN TO DIE
Cicero says—[Tusc., i. 31.]—“that to study philosophy is nothing but to prepare one’s self to die.” The reason of which is, because study and contemplation do in some sort withdraw from us our soul, and employ it separately from the body, which is a kind of apprenticeship and a resemblance of death; or, else, because all the wisdom and reasoning in the world do in the end conclude in this point, to teach us not to fear to die. And to say the truth, either our reason mocks us, or it ought to have no other aim but our contentment only, nor to endeavour anything but, in sum, to make us live well, and, as the Holy Scripture says, at our ease. All the opinions of the world agree in this, that pleasure is our end, though we make use of divers means to attain it: they would, otherwise, be rejected at the first motion; for who would give ear to him that should propose affliction and misery for his end? The controversies and disputes of the philosophical sects upon this point are merely verbal:
—there is more in them of opposition and obstinacy than is consistent with so sacred a profession; but whatsoever personage a man takes upon himself to perform, he ever mixes his own part with it.
Let the philosophers say what they will, the thing at which we all aim, even in virtue is pleasure. It amuses me to rattle in ears this word, which they so nauseate to and if it signify some supreme pleasure and contentment, it is more due to the assistance of virtue than to any other assistance whatever. This pleasure, for being more gay, more sinewy, more robust and more manly, is only the more seriously voluptuous, and we ought give it the name of pleasure, as that which is more favourable, gentle, and natural, and not that from which we have denominated it. The other and meaner pleasure, if it could deserve this fair name, it ought to be by way of competition, and not of privilege. I find it less exempt from traverses and inconveniences than virtue itself; and, besides that the enjoyment is more momentary, fluid, and frail, it has its watchings, fasts, and labours, its sweat and its blood; and, moreover, has particular to itself so many several sorts of sharp and wounding passions, and so dull a satiety attending it, as equal it to the severest penance. And we mistake if we think that these incommodities serve it for a spur and a seasoning to its sweetness (as in nature one contrary is quickened by another), or say, when we come to virtue, that like consequences and difficulties overwhelm and render it austere and inaccessible; whereas, much more aptly than in voluptuousness, they ennoble, sharpen, and heighten the perfect and divine pleasure they procure us. He renders himself unworthy of it who will counterpoise its cost with its fruit, and neither understands the blessing nor how to use it. Those who preach to us that the quest of it is craggy, difficult, and painful, but its fruition pleasant, what do they mean by that but to tell us that it is always unpleasing? For what human means will ever attain its enjoyment? The most perfect have been fain to content themselves to aspire unto it, and to approach it only, without ever possessing it. But they are deceived, seeing that of all the pleasures we know, the very pursuit is pleasant. The attempt ever relishes of the quality of the thing to which it is directed, for it is a good part of, and consubstantial with, the effect. The felicity and beatitude that glitters in Virtue, shines throughout all her appurtenances and avenues, even to the first entry and utmost limits.
Now, of all the benefits that virtue confers upon us, the contempt of death is one of the greatest, as the means that accommodates human life with a soft and easy tranquillity, and gives us a pure and pleasant taste of living, without which all other pleasure would be extinct. Which is the reason why all the rules centre and concur in this one article. And although they all in like manner, with common accord, teach us also to despise pain, poverty, and the other accidents to which human life is subject, it is not, nevertheless, with the same solicitude, as well by reason these accidents are not of so great necessity, the greater part of mankind passing over their whole lives without ever knowing what poverty is, and some without sorrow or sickness, as Xenophilus the musician, who lived a hundred and six years in a perfect and continual health; as also because, at the worst, death can, whenever we please, cut short and put an end to all other inconveniences. But as to death, it is inevitable:—
and, consequently, if it frights us, ‘tis a perpetual torment, for which there is no sort of consolation. There is no way by which it may not reach us. We may continually turn our heads this way and that, as in a suspected country:
Our courts of justice often send back condemned criminals to be executed upon the place where the crime was committed; but, carry them to fine houses by the way, prepare for them the best entertainment you can—
Do you think they can relish it? and that the fatal end of their journey being continually before their eyes, would not alter and deprave their palate from tasting these regalios?
The end of our race is death; ‘tis the necessary object of our aim, which, if it fright us, how is it possible to advance a step without a fit of ague? The remedy the vulgar use is not to think on’t; but from what brutish stupidity can they derive so gross a blindness? They must bridle the ass by the tail:
‘tis no wonder if he be often trapped in the pitfall. They affright people with the very mention of death, and many cross themselves, as it were the name of the devil. And because the making a man’s will is in reference to dying, not a man will be persuaded to take a pen in hand to that purpose, till the physician has passed sentence upon and totally given him over, and then betwixt and terror, God knows in how fit a condition of understanding he is to do it.
The Romans, by reason that this poor syllable death sounded so harshly to their ears and seemed so ominous, found out a way to soften and spin it out by a periphrasis, and instead of pronouncing such a one is dead, said, “Such a one has lived,” or “Such a one has ceased to live” —[Plutarch, Life of Cicero, c. 22:]—for, provided there was any mention of life in the case, though past, it carried yet some sound of consolation. And from them it is that we have borrowed our expression, “The late Monsieur such and such a one.”—[“feu Monsieur un tel.”] Peradventure, as the saying is, the term we have lived is worth our money. I was born betwixt eleven and twelve o’clock in the forenoon the last day of February 1533, according to our computation, beginning the year the 1st of January,—[This was in virtue of an ordinance of Charles IX. in 1563. Previously the year commenced at Easter, so that the 1st January 1563 became the first day of the year 1563.]—and it is now but just fifteen days since I was complete nine-and-thirty years old; I make account to live, at least, as many more. In the meantime, to trouble a man’s self with the thought of a thing so far off were folly. But what? Young and old die upon the same terms; no one departs out of life otherwise than if he had but just before entered into it; neither is any man so old and decrepit, who, having heard of Methuselah, does not think he has yet twenty good years to come. Fool that thou art! who has assured unto thee the term of life? Thou dependest upon physicians’ tales: rather consult effects and experience. According to the common course of things, ‘tis long since that thou hast lived by extraordinary favour; thou hast already outlived the ordinary term of life. And that it is so, reckon up thy acquaintance, how many more have died before they arrived at thy age than have attained unto it; and of those who have ennobled their lives by their renown, take but an account, and I dare lay a wager thou wilt find more who have died before than after five-and-thirty years of age. It is full both of reason and piety, too, to take example by the humanity of Jesus Christ Himself; now, He ended His life at three-and-thirty years. The greatest man, that was no more than a man, Alexander, died also at the same age. How many several ways has death to surprise us?
To omit fevers and pleurisies, who would ever have imagined that a duke of Brittany,—[Jean II. died 1305.]—should be pressed to death in a crowd as that duke was at the entry of Pope Clement, my neighbour, into Lyons?—[Montaigne speaks of him as if he had been a contemporary neighbour, perhaps because he was the Archbishop of Bordeaux. Bertrand le Got was Pope under the title of Clement V., 1305-14.]—Hast thou not seen one of our kings—[Henry II., killed in a tournament, July 10, 1559]—killed at a tilting, and did not one of his ancestors die by jostle of a hog?—[Philip, eldest son of Louis le Gros.]—AEschylus, threatened with the fall of a house, was to much purpose circumspect to avoid that danger, seeing that he was knocked on the head by a tortoise falling out of an eagle’s talons in the air. Another was choked with a grape-stone;—[Val. Max., ix. 12, ext. 2.]—an emperor killed with the scratch of a comb in combing his head. AEmilius Lepidus with a stumble at his own threshold,—[Pliny, Nat. Hist., vii. 33.]— and Aufidius with a jostle against the door as he entered the council-chamber. And betwixt the very thighs of women, Cornelius Gallus the proctor; Tigillinus, captain of the watch at Rome; Ludovico, son of Guido di Gonzaga, Marquis of Mantua; and (of worse example) Speusippus, a Platonic philosopher, and one of our Popes. The poor judge Bebius gave adjournment in a case for eight days; but he himself, meanwhile, was condemned by death, and his own stay of life expired. Whilst Caius Julius, the physician, was anointing the eyes of a patient, death closed his own; and, if I may bring in an example of my own blood, a brother of mine, Captain St. Martin, a young man, three-and-twenty years old, who had already given sufficient testimony of his valour, playing a match at tennis, received a blow of a ball a little above his right ear, which, as it gave no manner of sign of wound or contusion, he took no notice of it, nor so much as sat down to repose himself, but, nevertheless, died within five or six hours after of an apoplexy occasioned by that blow.
These so frequent and common examples passing every day before our eyes, how is it possible a man should disengage himself from the thought of death, or avoid fancying that it has us every moment by the throat? What matter is it, you will say, which way it comes to pass, provided a man does not terrify himself with the expectation? For my part, I am of this mind, and if a man could by any means avoid it, though by creeping under a calf’s skin, I am one that should not be ashamed of the shift; all I aim at is, to pass my time at my ease, and the recreations that will most contribute to it, I take hold of, as little glorious and exemplary as you will:
But ‘tis folly to think of doing anything that way. They go, they come, they gallop and dance, and not a word of death. All this is very fine; but withal, when it comes either to themselves, their wives, their children, or friends, surprising them at unawares and unprepared, then, what torment, what outcries, what madness and despair! Did you ever see anything so subdued, so changed, and so confounded? A man must, therefore, make more early provision for it; and this brutish negligence, could it possibly lodge in the brain of any man of sense (which I think utterly impossible), sells us its merchandise too dear. Were it an enemy that could be avoided, I would then advise to borrow arms even of cowardice itself; but seeing it is not, and that it will catch you as well flying and playing the poltroon, as standing to’t like an honest man:—
And seeing that no temper of arms is of proof to secure us:—
—let us learn bravely to stand our ground, and fight him. And to begin to deprive him of the greatest advantage he has over us, let us take a way quite contrary to the common course. Let us disarm him of his novelty and strangeness, let us converse and be familiar with him, and have nothing so frequent in our thoughts as death. Upon all occasions represent him to our imagination in his every shape; at the stumbling of a horse, at the falling of a tile, at the least prick with a pin, let us presently consider, and say to ourselves, “Well, and what if it had been death itself?” and, thereupon, let us encourage and fortify ourselves. Let us evermore, amidst our jollity and feasting, set the remembrance of our frail condition before our eyes, never suffering ourselves to be so far transported with our delights, but that we have some intervals of reflecting upon, and considering how many several ways this jollity of ours tends to death, and with how many dangers it threatens it. The Egyptians were wont to do after this manner, who in the height of their feasting and mirth, caused a dried skeleton of a man to be brought into the room to serve for a memento to their guests:
Where death waits for us is uncertain; let us look for him everywhere. The premeditation of death is the premeditation of liberty; he who has learned to die has unlearned to serve. There is nothing evil in life for him who rightly comprehends that the privation of life is no evil: to know, how to die delivers us from all subjection and constraint. Paulus Emilius answered him whom the miserable King of Macedon, his prisoner, sent to entreat him that he would not lead him in his triumph, “Let him make that request to himself.”—[ Plutarch, Life of Paulus Aemilius, c. 17; Cicero, Tusc., v. 40.]
In truth, in all things, if nature do not help a little, it is very hard for art and industry to perform anything to purpose. I am in my own nature not melancholic, but meditative; and there is nothing I have more continually entertained myself withal than imaginations of death, even in the most wanton time of my age:
In the company of ladies, and at games, some have perhaps thought me possessed with some jealousy, or the uncertainty of some hope, whilst I was entertaining myself with the remembrance of some one, surprised, a few days before, with a burning fever of which he died, returning from an entertainment like this, with his head full of idle fancies of love and jollity, as mine was then, and that, for aught I knew, the same-destiny was attending me.
Yet did not this thought wrinkle my forehead any more than any other. It is impossible but we must feel a sting in such imaginations as these, at first; but with often turning and returning them in one’s mind, they, at last, become so familiar as to be no trouble at all: otherwise, I, for my part, should be in a perpetual fright and frenzy; for never man was so distrustful of his life, never man so uncertain as to its duration. Neither health, which I have hitherto ever enjoyed very strong and vigorous, and very seldom interrupted, does prolong, nor sickness contract my hopes. Every minute, methinks, I am escaping, and it eternally runs in my mind, that what may be done to-morrow, may be done to-day. Hazards and dangers do, in truth, little or nothing hasten our end; and if we consider how many thousands more remain and hang over our heads, besides the accident that immediately threatens us, we shall find that the sound and the sick, those that are abroad at sea, and those that sit by the fire, those who are engaged in battle, and those who sit idle at home, are the one as near it as the other.
For anything I have to do before I die, the longest leisure would appear too short, were it but an hour’s business I had to do.
A friend of mine the other day turning over my tablets, found therein a memorandum of something I would have done after my decease, whereupon I told him, as it was really true, that though I was no more than a league’s distance only from my own house, and merry and well, yet when that thing came into my head, I made haste to write it down there, because I was not certain to live till I came home. As a man that am eternally brooding over my own thoughts, and confine them to my own particular concerns, I am at all hours as well prepared as I am ever like to be, and death, whenever he shall come, can bring nothing along with him I did not expect long before. We should always, as near as we can, be booted and spurred, and ready to go, and, above all things, take care, at that time, to have no business with any one but one’s self:—
for we shall there find work enough to do, without any need of addition. One man complains, more than of death, that he is thereby prevented of a glorious victory; another, that he must die before he has married his daughter, or educated his children; a third seems only troubled that he must lose the society of his wife; a fourth, the conversation of his son, as the principal comfort and concern of his being. For my part, I am, thanks be to God, at this instant in such a condition, that I am ready to dislodge, whenever it shall please Him, without regret for anything whatsoever. I disengage myself throughout from all worldly relations; my leave is soon taken of all but myself. Never did any one prepare to bid adieu to the world more absolutely and unreservedly, and to shake hands with all manner of interest in it, than I expect to do. The deadest deaths are the best:
And the builder,
A man must design nothing that will require so much time to the finishing, or, at least, with no such passionate desire to see it brought to perfection. We are born to action:
I would always have a man to be doing, and, as much as in him lies, to extend and spin out the offices of life; and then let death take me planting my cabbages, indifferent to him, and still less of my gardens not being finished. I saw one die, who, at his last gasp, complained of nothing so much as that destiny was about to cut the thread of a chronicle he was then compiling, when he was gone no farther than the fifteenth or sixteenth of our kings:
We are to discharge ourselves from these vulgar and hurtful humours. To this purpose it was that men first appointed the places of sepulture adjoining the churches, and in the most frequented places of the city, to accustom, says Lycurgus, the common people, women, and children, that they should not be startled at the sight of a corpse, and to the end, that the continual spectacle of bones, graves, and funeral obsequies should put us in mind of our frail condition:
And as the Egyptians after their feasts were wont to present the company with a great image of death, by one that cried out to them, “Drink and be merry, for such shalt thou be when thou art dead”; so it is my custom to have death not only in my imagination, but continually in my mouth. Neither is there anything of which I am so inquisitive, and delight to inform myself, as the manner of men’s deaths, their words, looks, and bearing; nor any places in history I am so intent upon; and it is manifest enough, by my crowding in examples of this kind, that I have a particular fancy for that subject. If I were a writer of books, I would compile a register, with a comment, of the various deaths of men: he who should teach men to die would at the same time teach them to live. Dicarchus made one, to which he gave that title; but it was designed for another and less profitable end.
Peradventure, some one may object, that the pain and terror of dying so infinitely exceed all manner of imagination, that the best fencer will be quite out of his play when it comes to the push. Let them say what they will: to premeditate is doubtless a very great advantage; and besides, is it nothing to go so far, at least, without disturbance or alteration? Moreover, Nature herself assists and encourages us: if the death be sudden and violent, we have not leisure to fear; if otherwise, I perceive that as I engage further in my disease, I naturally enter into a certain loathing and disdain of life. I find I have much more ado to digest this resolution of dying, when I am well in health, than when languishing of a fever; and by how much I have less to do with the commodities of life, by reason that I begin to lose the use and pleasure of them, by so much I look upon death with less terror. Which makes me hope, that the further I remove from the first, and the nearer I approach to the latter, I shall the more easily exchange the one for the other. And, as I have experienced in other occurrences, that, as Caesar says, things often appear greater to us at distance than near at hand, I have found, that being well, I have had maladies in much greater horror than when really afflicted with them. The vigour wherein I now am, the cheerfulness and delight wherein I now live, make the contrary estate appear in so great a disproportion to my present condition, that, by imagination, I magnify those inconveniences by one-half, and apprehend them to be much more troublesome, than I find them really to be, when they lie the most heavy upon me; I hope to find death the same.
Let us but observe in the ordinary changes and declinations we daily suffer, how nature deprives us of the light and sense of our bodily decay. What remains to an old man of the vigour of his youth and better days?
Caesar, to an old weather-beaten soldier of his guards, who came to ask him leave that he might kill himself, taking notice of his withered body and decrepit motion, pleasantly answered, “Thou fanciest, then, that thou art yet alive.”—[Seneca, Ep., 77.]—Should a man fall into this condition on the sudden, I do not think humanity capable of enduring such a change: but nature, leading us by the hand, an easy and, as it were, an insensible pace, step by step conducts us to that miserable state, and by that means makes it familiar to us, so that we are insensible of the stroke when our youth dies in us, though it be really a harder death than the final dissolution of a languishing body, than the death of old age; forasmuch as the fall is not so great from an uneasy being to none at all, as it is from a sprightly and flourishing being to one that is troublesome and painful. The body, bent and bowed, has less force to support a burden; and it is the same with the soul, and therefore it is, that we are to raise her up firm and erect against the power of this adversary. For, as it is impossible she should ever be at rest, whilst she stands in fear of it; so, if she once can assure herself, she may boast (which is a thing as it were surpassing human condition) that it is impossible that disquiet, anxiety, or fear, or any other disturbance, should inhabit or have any place in her:
She is then become sovereign of all her lusts and passions, mistress of necessity, shame, poverty, and all the other injuries of fortune. Let us, therefore, as many of us as can, get this advantage; ‘tis the true and sovereign liberty here on earth, that fortifies us wherewithal to defy violence and injustice, and to contemn prisons and chains:
Our very religion itself has no surer human foundation than the contempt of life. Not only the argument of reason invites us to it—for why should we fear to lose a thing, which being lost, cannot be lamented? —but, also, seeing we are threatened by so many sorts of death, is it not infinitely worse eternally to fear them all, than once to undergo one of them? And what matters it, when it shall happen, since it is inevitable? To him that told Socrates, “The thirty tyrants have sentenced thee to death”; “And nature them,” said he.—[Socrates was not condemned to death by the thirty tyrants, but by the Athenians.-Diogenes Laertius, ii.35.]— What a ridiculous thing it is to trouble ourselves about taking the only step that is to deliver us from all trouble! As our birth brought us the birth of all things, so in our death is the death of all things included. And therefore to lament that we shall not be alive a hundred years hence, is the same folly as to be sorry we were not alive a hundred years ago. Death is the beginning of another life. So did we weep, and so much it cost us to enter into this, and so did we put off our former veil in entering into it. Nothing can be a grievance that is but once. Is it reasonable so long to fear a thing that will so soon be despatched? Long life, and short, are by death made all one; for there is no long, nor short, to things that are no more. Aristotle tells us that there are certain little beasts upon the banks of the river Hypanis, that never live above a day: they which die at eight of the clock in the morning, die in their youth, and those that die at five in the evening, in their decrepitude: which of us would not laugh to see this moment of continuance put into the consideration of weal or woe? The most and the least, of ours, in comparison with eternity, or yet with the duration of mountains, rivers, stars, trees, and even of some animals, is no less ridiculous.—[ Seneca, Consol. ad Marciam, c. 20.]
But nature compels us to it. “Go out of this world,” says she, “as you entered into it; the same pass you made from death to life, without passion or fear, the same, after the same manner, repeat from life to death. Your death is a part of the order of the universe, ‘tis a part of the life of the world.
“Shall I exchange for you this beautiful contexture of things? ‘Tis the condition of your creation; death is a part of you, and whilst you endeavour to evade it, you evade yourselves. This very being of yours that you now enjoy is equally divided betwixt life and death. The day of your birth is one day’s advance towards the grave:
“All the whole time you live, you purloin from life and live at the expense of life itself. The perpetual work of your life is but to lay the foundation of death. You are in death, whilst you are in life, because you still are after death, when you are no more alive; or, if you had rather have it so, you are dead after life, but dying all the while you live; and death handles the dying much more rudely than the dead, and more sensibly and essentially. If you have made your profit of life, you have had enough of it; go your way satisfied.
“If you have not known how to make the best use of it, if it was unprofitable to you, what need you care to lose it, to what end would you desire longer to keep it?
“Life in itself is neither good nor evil; it is the scene of good or evil as you make it.’ And, if you have lived a day, you have seen all: one day is equal and like to all other days. There is no other light, no other shade; this very sun, this moon, these very stars, this very order and disposition of things, is the same your ancestors enjoyed, and that shall also entertain your posterity:
“And, come the worst that can come, the distribution and variety of all the acts of my comedy are performed in a year. If you have observed the revolution of my four seasons, they comprehend the infancy, the youth, the virility, and the old age of the world: the year has played his part, and knows no other art but to begin again; it will always be the same thing:
“I am not prepared to create for you any new recreations:
“Give place to others, as others have given place to you. Equality is the soul of equity. Who can complain of being comprehended in the same destiny, wherein all are involved? Besides, live as long as you can, you shall by that nothing shorten the space you are to be dead; ‘tis all to no purpose; you shall be every whit as long in the condition you so much fear, as if you had died at nurse:
“And yet I will place you in such a condition as you shall have no reason to be displeased.
“Nor shall you so much as wish for the life you are so concerned about:
“Death is less to be feared than nothing, if there could be anything less than nothing.
“Neither can it any way concern you, whether you are living or dead: living, by reason that you are still in being; dead, because you are no more. Moreover, no one dies before his hour: the time you leave behind was no more yours than that was lapsed and gone before you came into the world; nor does it any more concern you.
Wherever your life ends, it is all there. The utility of living consists not in the length of days, but in the use of time; a man may have lived long, and yet lived but a little. Make use of time while it is present with you. It depends upon your will, and not upon the number of days, to have a sufficient length of life. Is it possible you can imagine never to arrive at the place towards which you are continually going? and yet there is no journey but hath its end. And, if company will make it more pleasant or more easy to you, does not all the world go the self-same way?
“Does not all the world dance the same brawl that you do? Is there anything that does not grow old, as well as you? A thousand men, a thousand animals, a thousand other creatures, die at the same moment that you die:
“To what end should you endeavour to draw back, if there be no possibility to evade it? you have seen examples enough of those who have been well pleased to die, as thereby delivered from heavy miseries; but have you ever found any who have been dissatisfied with dying? It must, therefore, needs be very foolish to condemn a thing you have neither experimented in your own person, nor by that of any other. Why dost thou complain of me and of destiny? Do we do thee any wrong? Is it for thee to govern us, or for us to govern thee? Though, peradventure, thy age may not be accomplished, yet thy life is: a man of low stature is as much a man as a giant; neither men nor their lives are measured by the ell. Chiron refused to be immortal, when he was acquainted with the conditions under which he was to enjoy it, by the god of time itself and its duration, his father Saturn. Do but seriously consider how much more insupportable and painful an immortal life would be to man than what I have already given him. If you had not death, you would eternally curse me for having deprived you of it; I have mixed a little bitterness with it, to the end, that seeing of what convenience it is, you might not too greedily and indiscreetly seek and embrace it: and that you might be so established in this moderation, as neither to nauseate life, nor have any antipathy for dying, which I have decreed you shall once do, I have tempered the one and the other betwixt pleasure and pain. It was I that taught Thales, the most eminent of your sages, that to live and to die were indifferent; which made him, very wisely, answer him, ‘Why then he did not die?’ ‘Because,’ said he, ‘it is indifferent.’—[Diogenes Laertius, i. 35.]—Water, earth, air, and fire, and the other parts of this creation of mine, are no more instruments of thy life than they are of thy death. Why dost thou fear thy last day? it contributes no more to thy dissolution, than every one of the rest: the last step is not the cause of lassitude: it does not confess it. Every day travels towards death; the last only arrives at it.” These are the good lessons our mother Nature teaches.
I have often considered with myself whence it should proceed, that in war the image of death, whether we look upon it in ourselves or in others, should, without comparison, appear less dreadful than at home in our own houses (for if it were not so, it would be an army of doctors and whining milksops), and that being still in all places the same, there should be, notwithstanding, much more assurance in peasants and the meaner sort of people, than in others of better quality. I believe, in truth, that it is those terrible ceremonies and preparations wherewith we set it out, that more terrify us than the thing itself; a new, quite contrary way of living; the cries of mothers, wives, and children; the visits of astounded and afflicted friends; the attendance of pale and blubbering servants; a dark room, set round with burning tapers; our beds environed with physicians and divines; in sum, nothing but ghostliness and horror round about us; we seem dead and buried already. Children are afraid even of those they are best acquainted with, when disguised in a visor; and so ‘tis with us; the visor must be removed as well from things as from persons, that being taken away, we shall find nothing underneath but the very same death that a mean servant or a poor chambermaid died a day or two ago, without any manner of apprehension. Happy is the death that deprives us of leisure for preparing such ceremonials.
CHAPTER XX——OF THE FORCE OF IMAGINATION
I am one of those who are most sensible of the power of imagination: every one is jostled by it, but some are overthrown by it. It has a very piercing impression upon me; and I make it my business to avoid, wanting force to resist it. I could live by the sole help of healthful and jolly company: the very sight of another’s pain materially pains me, and I often usurp the sensations of another person. A perpetual cough in another tickles my lungs and throat. I more unwillingly visit the sick in whom by love and duty I am interested, than those I care not for, to whom I less look. I take possession of the disease I am concerned at, and take it to myself. I do not at all wonder that fancy should give fevers and sometimes kill such as allow it too much scope, and are too willing to entertain it. Simon Thomas was a great physician of his time: I remember, that happening one day at Toulouse to meet him at a rich old fellow’s house, who was troubled with weak lungs, and discoursing with the patient about the method of his cure, he told him, that one thing which would be very conducive to it, was to give me such occasion to be pleased with his company, that I might come often to see him, by which means, and by fixing his eyes upon the freshness of my complexion, and his imagination upon the sprightliness and vigour that glowed in my youth, and possessing all his senses with the flourishing age wherein I then was, his habit of body might, peradventure, be amended; but he forgot to say that mine, at the same time, might be made worse. Gallus Vibius so much bent his mind to find out the essence and motions of madness, that, in the end, he himself went out of his wits, and to such a degree, that he could never after recover his judgment, and might brag that he was become a fool by too much wisdom. Some there are who through fear anticipate the hangman; and there was the man, whose eyes being unbound to have his pardon read to him, was found stark dead upon the scaffold, by the stroke of imagination. We start, tremble, turn pale, and blush, as we are variously moved by imagination; and, being a-bed, feel our bodies agitated with its power to that degree, as even sometimes to expiring. And boiling youth, when fast asleep, grows so warm with fancy, as in a dream to satisfy amorous desires:—
Although it be no new thing to see horns grown in a night on the forehead of one that had none when he went to bed, notwithstanding, what befell Cippus, King of Italy, is memorable; who having one day been a very delighted spectator of a bullfight, and having all the night dreamed that he had horns on his head, did, by the force of imagination, really cause them to grow there. Passion gave to the son of Croesus the voice which nature had denied him. And Antiochus fell into a fever, inflamed with the beauty of Stratonice, too deeply imprinted in his soul. Pliny pretends to have seen Lucius Cossitius, who from a woman was turned into a man upon her very wedding-day. Pontanus and others report the like metamorphosis to have happened in these latter days in Italy. And, through the vehement desire of him and his mother:
Myself passing by Vitry le Francois, saw a man the Bishop of Soissons had, in confirmation, called Germain, whom all the inhabitants of the place had known to be a girl till two-and-twenty years of age, called Mary. He was, at the time of my being there, very full of beard, old, and not married. He told us, that by straining himself in a leap his male organs came out; and the girls of that place have, to this day, a song, wherein they advise one another not to take too great strides, for fear of being turned into men, as Mary Germain was. It is no wonder if this sort of accident frequently happen; for if imagination have any power in such things, it is so continually and vigorously bent upon this subject, that to the end it may not so often relapse into the same thought and violence of desire, it were better, once for all, to give these young wenches the things they long for.
Some attribute the scars of King Dagobert and of St. Francis to the force of imagination. It is said, that by it bodies will sometimes be removed from their places; and Celsus tells us of a priest whose soul would be ravished into such an ecstasy that the body would, for a long time, remain without sense or respiration. St. Augustine makes mention of another, who, upon the hearing of any lamentable or doleful cries, would presently fall into a swoon, and be so far out of himself, that it was in vain to call, bawl in his ears, pinch or burn him, till he voluntarily came to himself; and then he would say, that he had heard voices as it were afar off, and did feel when they pinched and burned him; and, to prove that this was no obstinate dissimulation in defiance of his sense of feeling, it was manifest, that all the while he had neither pulse nor breathing.
‘Tis very probable, that visions, enchantments, and all extraordinary effects of that nature, derive their credit principally from the power of imagination, working and making its chiefest impression upon vulgar and more easy souls, whose belief is so strangely imposed upon, as to think they see what they do not see.
I am not satisfied whether those pleasant ligatures—[Les nouements d’aiguillettes, as they were called, knots tied by some one, at a wedding, on a strip of leather, cotton, or silk, and which, especially when passed through the wedding-ring, were supposed to have the magical effect of preventing a consummation of the marriage until they were untied. See Louandre, La Sorcellerie, 1853, p. 73. The same superstition and appliance existed in England.]—with which this age of ours is so occupied, that there is almost no other talk, are not mere voluntary impressions of apprehension and fear; for I know, by experience, in the case of a particular friend of mine, one for whom I can be as responsible as for myself, and a man that cannot possibly fall under any manner of suspicion of insufficiency, and as little of being enchanted, who having heard a companion of his make a relation of an unusual frigidity that surprised him at a very unseasonable time; being afterwards himself engaged upon the same account, the horror of the former story on a sudden so strangely possessed his imagination, that he ran the same fortune the other had done; and from that time forward, the scurvy remembrance of his disaster running in his mind and tyrannising over him, he was subject to relapse into the same misfortune. He found some remedy, however, for this fancy in another fancy, by himself frankly confessing and declaring beforehand to the party with whom he was to have to do, this subjection of his, by which means, the agitation of his soul was, in some sort, appeased; and knowing that, now, some such misbehaviour was expected from him, the restraint upon his faculties grew less. And afterwards, at such times as he was in no such apprehension, when setting about the act (his thoughts being then disengaged and free, and his body in its true and natural estate) he was at leisure to cause the part to be handled and communicated to the knowledge of the other party, he was totally freed from that vexatious infirmity. After a man has once done a woman right, he is never after in danger of misbehaving himself with that person, unless upon the account of some excusable weakness. Neither is this disaster to be feared, but in adventures, where the soul is overextended with desire or respect, and, especially, where the opportunity is of an unforeseen and pressing nature; in those cases, there is no means for a man to defend himself from such a surprise, as shall put him altogether out of sorts. I have known some, who have secured themselves from this mischance, by coming half sated elsewhere, purposely to abate the ardour of the fury, and others, who, being grown old, find themselves less impotent by being less able; and one, who found an advantage in being assured by a friend of his, that he had a counter-charm of enchantments that would secure him from this disgrace. The story itself is not, much amiss, and therefore you shall have it.
A Count of a very great family, and with whom I was very intimate, being married to a fair lady, who had formerly been courted by one who was at the wedding, all his friends were in very great fear; but especially an old lady his kinswoman, who had the ordering of the solemnity, and in whose house it was kept, suspecting his rival would offer foul play by these sorceries. Which fear she communicated to me. I bade her rely upon me: I had, by chance, about me a certain flat plate of gold, whereon were graven some celestial figures, supposed good against sunstroke or pains in the head, being applied to the suture: where, that it might the better remain firm, it was sewed to a ribbon to be tied under the chin; a foppery cousin-german to this of which I am speaking. Jaques Pelletier, who lived in my house, had presented this to me for a singular rarity. I had a fancy to make some use of this knack, and therefore privately told the Count, that he might possibly run the same fortune other bridegrooms had sometimes done, especially some one being in the house, who, no doubt, would be glad to do him such a courtesy: but let him boldly go to bed. For I would do him the office of a friend, and, if need were, would not spare a miracle it was in my power to do, provided he would engage to me, upon his honour, to keep it to himself; and only, when they came to bring him his caudle,—[A custom in France to bring the bridegroom a caudle in the middle of the night on his wedding-night]— if matters had not gone well with him, to give me such a sign, and leave the rest to me. Now he had had his ears so battered, and his mind so prepossessed with the eternal tattle of this business, that when he came to’t, he did really find himself tied with the trouble of his imagination, and, accordingly, at the time appointed, gave me the sign. Whereupon, I whispered him in the ear, that he should rise, under pretence of putting us out of the room, and after a jesting manner pull my nightgown from my shoulders—we were of much about the same height— throw it over his own, and there keep it till he had performed what I had appointed him to do, which was, that when we were all gone out of the chamber, he should withdraw to make water, should three times repeat such and such words, and as often do such and such actions; that at every of the three times, he should tie the ribbon I put into his hand about his middle, and be sure to place the medal that was fastened to it, the figures in such a posture, exactly upon his reins, which being done, and having the last of the three times so well girt and fast tied the ribbon that it could neither untie nor slip from its place, let him confidently return to his business, and withal not forget to spread my gown upon the bed, so that it might be sure to cover them both. These ape’s tricks are the main of the effect, our fancy being so far seduced as to believe that such strange means must, of necessity, proceed from some abstruse science: their very inanity gives them weight and reverence. And, certain it is, that my figures approved themselves more venereal than solar, more active than prohibitive. ‘Twas a sudden whimsey, mixed with a little curiosity, that made me do a thing so contrary to my nature; for I am an enemy to all subtle and counterfeit actions, and abominate all manner of trickery, though it be for sport, and to an advantage; for though the action may not be vicious in itself, its mode is vicious.
Amasis, King of Egypt, having married Laodice, a very beautiful Greek virgin, though noted for his abilities elsewhere, found himself quite another man with his wife, and could by no means enjoy her; at which he was so enraged, that he threatened to kill her, suspecting her to be a witch. As ‘tis usual in things that consist in fancy, she put him upon devotion, and having accordingly made his vows to Venus, he found himself divinely restored the very first night after his oblations and sacrifices. Now women are to blame to entertain us with that disdainful, coy, and angry countenance, which extinguishes our vigour, as it kindles our desire; which made the daughter-in-law of Pythagoras—[Theano, the lady in question was the wife, not the daughter-in-law of Pythagoras.]— say, “That the woman who goes to bed to a man, must put off her modesty with her petticoat, and put it on again with the same.” The soul of the assailant, being disturbed with many several alarms, readily loses the power of performance; and whoever the imagination has once put this trick upon, and confounded with the shame of it (and she never does it but at the first acquaintance, by reason men are then more ardent and eager, and also, at this first account a man gives of himself, he is much more timorous of miscarrying), having made an ill beginning, he enters into such fever and despite at the accident, as are apt to remain and continue with him upon following occasions.
Married people, having all their time before them, ought never to compel or so much as to offer at the feat, if they do not find themselves quite ready: and it is less unseemly to fail of handselling the nuptial sheets, when a man perceives himself full of agitation and trembling, and to await another opportunity at more private and more composed leisure, than to make himself perpetually miserable, for having misbehaved himself and been baffled at the first assault. Till possession be taken, a man that knows himself subject to this infirmity, should leisurely and by degrees make several little trials and light offers, without obstinately attempting at once, to Force an absolute conquest over his own mutinous and indisposed faculties. Such as know their members to be naturally obedient, need take no other care but only to counterplot their fantasies.
The indocile liberty of this member is very remarkable, so importunately unruly in its tumidity and impatience, when we do not require it, and so unseasonably disobedient, when we stand most in need of it: so imperiously contesting in authority with the will, and with so much haughty obstinacy denying all solicitation, both of hand and mind. And yet, though his rebellion is so universally complained of, and that proof is thence deduced to condemn him, if he had, nevertheless, feed me to plead his cause, I should peradventure, bring the rest of his fellow-members into suspicion of complotting this mischief against him, out of pure envy at the importance and pleasure especial to his employment; and to have, by confederacy, armed the whole world against him, by malevolently charging him alone, with their common offence. For let any one consider, whether there is any one part of our bodies that does not often refuse to perform its office at the precept of the will, and that does not often exercise its function in defiance of her command. They have every one of them passions of their own, that rouse and awaken, stupefy and benumb them, without our leave or consent. How often do the involuntary motions of the countenance discover our inward thoughts, and betray our most private secrets to the bystanders. The same cause that animates this member, does also, without our knowledge, animate the lungs, pulse, and heart, the sight of a pleasing object imperceptibly diffusing a flame through all our parts, with a feverish motion. Is there nothing but these veins and muscles that swell and flag without the consent, not only of the will, but even of our knowledge also? We do not command our hairs to stand on end, nor our skin to shiver either with fear or desire; the hands often convey themselves to parts to which we do not direct them; the tongue will be interdict, and the voice congealed, when we know not how to help it. When we have nothing to eat, and would willingly forbid it, the appetite does not, for all that, forbear to stir up the parts that are subject to it, no more nor less than the other appetite we were speaking of, and in like manner, as unseasonably leaves us, when it thinks fit. The vessels that serve to discharge the belly have their own proper dilatations and compressions, without and beyond our concurrence, as well as those which are destined to purge the reins; and that which, to justify the prerogative of the will, St. Augustine urges, of having seen a man who could command his rear to discharge as often together as he pleased, Vives, his commentator, yet further fortifies with another example in his time,—of one that could break wind in tune; but these cases do not suppose any more pure obedience in that part; for is anything commonly more tumultuary or indiscreet? To which let me add, that I myself knew one so rude and ungoverned, as for forty years together made his master vent with one continued and unintermitted outbursting, and ‘tis like will do so till he die of it. And I could heartily wish, that I only knew by reading, how often a man’s belly, by the denial of one single puff, brings him to the very door of an exceeding painful death; and that the emperor,—[The Emperor Claudius, who, however, according to Suetonius (Vita, c. 32), only intended to authorise this singular privilege by an edict.]—who gave liberty to let fly in all places, had, at the same time, given us power to do it. But for our will, in whose behalf we prefer this accusation, with how much greater probability may we reproach herself with mutiny and sedition, for her irregularity and disobedience? Does she always will what we would have her to do? Does she not often will what we forbid her to will, and that to our manifest prejudice? Does she suffer herself, more than any of the rest, to be governed and directed by the results of our reason? To conclude, I should move, in the behalf of the gentleman, my client, it might be considered, that in this fact, his cause being inseparably and indistinctly conjoined with an accessory, yet he only is called in question, and that by arguments and accusations, which cannot be charged upon the other; whose business, indeed, it is sometimes inopportunely to invite, but never to refuse, and invite, moreover, after a tacit and quiet manner; and therefore is the malice and injustice of his accusers most manifestly apparent. But be it how it will, protesting against the proceedings of the advocates and judges, nature will, in the meantime, proceed after her own way, who had done but well, had she endowed this member with some particular privilege; the author of the sole immortal work of mortals; a divine work, according to Socrates; and love, the desire of immortality, and himself an immortal demon.
Some one, perhaps, by such an effect of imagination may have had the good luck to leave behind him here, the scrofula, which his companion who has come after, has carried with him into Spain. And ‘tis for this reason you may see why men in such cases require a mind prepared for the thing that is to be done. Why do the physicians possess, before hand, their patients’ credulity with so many false promises of cure, if not to the end, that the effect of imagination may supply the imposture of their decoctions? They know very well, that a great master of their trade has given it under his hand, that he has known some with whom the very sight of physic would work. All which conceits come now into my head, by the remembrance of a story was told me by a domestic apothecary of my father’s, a blunt Swiss, a nation not much addicted to vanity and lying, of a merchant he had long known at Toulouse, who being a valetudinary, and much afflicted with the stone, had often occasion to take clysters, of which he caused several sorts to be prescribed him by the physicians, acccording to the accidents of his disease; which, being brought him, and none of the usual forms, as feeling if it were not too hot, and the like, being omitted, he lay down, the syringe advanced, and all ceremonies performed, injection alone excepted; after which, the apothecary being gone, and the patient accommodated as if he had really received a clyster, he found the same operation and effect that those do who have taken one indeed; and if at any time the physician did not find the operation sufficient, he would usually give him two or three more doses, after the same manner. And the fellow swore, that to save charges (for he paid as if he had really taken them) this sick man’s wife, having sometimes made trial of warm water only, the effect discovered the cheat, and finding these would do no good, was fain to return to the old way.
A woman fancying she had swallowed a pin in a piece of bread, cried and lamented as though she had an intolerable pain in her throat, where she thought she felt it stick; but an ingenious fellow that was brought to her, seeing no outward tumour nor alteration, supposing it to be only a conceit taken at some crust of bread that had hurt her as it went down, caused her to vomit, and, unseen, threw a crooked pin into the basin, which the woman no sooner saw, but believing she had cast it up, she presently found herself eased of her pain. I myself knew a gentleman, who having treated a large company at his house, three or four days after bragged in jest (for there was no such thing), that he had made them eat of a baked cat; at which, a young gentlewoman, who had been at the feast, took such a horror, that falling into a violent vomiting and fever, there was no possible means to save her. Even brute beasts are subject to the force of imagination as well as we; witness dogs, who die of grief for the loss of their masters; and bark and tremble and start in their sleep; so horses will kick and whinny in their sleep.
Now all this may be attributed to the close affinity and relation betwixt the soul and the body intercommunicating their fortunes; but ‘tis quite another thing when the imagination works not only upon one’s own particular body, but upon that of others also. And as an infected body communicates its malady to those that approach or live near it, as we see in the plague, the smallpox, and sore eyes, that run through whole families and cities:—
—so the imagination, being vehemently agitated, darts out infection capable of offending the foreign object. The ancients had an opinion of certain women of Scythia, that being animated and enraged against any one, they killed him only with their looks. Tortoises and ostriches hatch their eggs with only looking on them, which infers that their eyes have in them some ejaculative virtue. And the eyes of witches are said to be assailant and hurtful:—
Magicians are no very good authority with me. But we experimentally see that women impart the marks of their fancy to the children they carry in the womb; witness her that was brought to bed of a Moor; and there was presented to Charles the Emperor and King of Bohemia, a girl from about Pisa, all over rough and covered with hair, whom her mother said to be so conceived by reason of a picture of St. John the Baptist, that hung within the curtains of her bed.
It is the same with beasts; witness Jacob’s sheep, and the hares and partridges that the snow turns white upon the mountains. There was at my house, a little while ago, a cat seen watching a bird upon the top of a tree: these, for some time, mutually fixing their eyes one upon another, the bird at last let herself fall dead into the cat’s claws, either dazzled by the force of its own imagination, or drawn by some attractive power of the cat. Such as are addicted to the pleasures of the field, have, I make no question, heard the story of the falconer, who having earnestly fixed his eyes upon a kite in the air; laid a wager that he would bring her down with the sole power of his sight, and did so, as it was said; for the tales I borrow I charge upon the consciences of those from whom I have them. The discourses are my own, and found themselves upon the proofs of reason, not of experience; to which every one has liberty to add his own examples; and who has none, let him not forbear, the number and varieties of accidents considered, to believe that there are plenty of them; if I do not apply them well, let some other do it for me. And, also, in the subject of which I treat, our manners and motions, testimonies and instances; how fabulous soever, provided they are possible, serve as well as the true; whether they have really happened or no, at Rome or Paris, to John or Peter, ‘tis still within the verge of human capacity, which serves me to good use. I see, and make my advantage of it, as well in shadow as in substance; and amongst the various readings thereof in history, I cull out the most rare and memorable to fit my own turn. There are authors whose only end and design it is to give an account of things that have happened; mine, if I could arrive unto it, should be to deliver of what may happen. There is a just liberty allowed in the schools, of supposing similitudes, when they have none at hand. I do not, however, make any use of that privilege, and as to that matter, in superstitious religion, surpass all historical authority. In the examples which I here bring in, of what I have heard, read, done, or said, I have forbidden myself to dare to alter even the most light and indifferent circumstances; my conscience does not falsify one tittle; what my ignorance may do, I cannot say.
And this it is that makes me sometimes doubt in my own mind, whether a divine, or a philosopher, and such men of exact and tender prudence and conscience, are fit to write history: for how can they stake their reputation upon a popular faith? how be responsible for the opinions of men they do not know? and with what assurance deliver their conjectures for current pay? Of actions performed before their own eyes, wherein several persons were actors, they would be unwilling to give evidence upon oath before a judge; and there is no man, so familiarly known to them, for whose intentions they would become absolute caution. For my part, I think it less hazardous to write of things past, than present, by how much the writer is only to give an account of things every one knows he must of necessity borrow upon trust.
I am solicited to write the affairs of my own time by some, who fancy I look upon them with an eye less blinded with passion than another, and have a clearer insight into them by reason of the free access fortune has given me to the heads of various factions; but they do not consider, that to purchase the glory of Sallust, I would not give myself the trouble, sworn enemy as I am to obligation, assiduity, or perseverance: that there is nothing so contrary to my style, as a continued narrative, I so often interrupt and cut myself short in my writing for want of breath; I have neither composition nor explanation worth anything, and am ignorant, beyond a child, of the phrases and even the very words proper to express the most common things; and for that reason it is, that I have undertaken to say only what I can say, and have accommodated my subject to my strength. Should I take one to be my guide, peradventure I should not be able to keep pace with him; and in the freedom of my liberty might deliver judgments, which upon better thoughts, and according to reason, would be illegitimate and punishable. Plutarch would say of what he has delivered to us, that it is the work of others: that his examples are all and everywhere exactly true: that they are useful to posterity, and are presented with a lustre that will light us the way to virtue, is his own work. It is not of so dangerous consequence, as in a medicinal drug, whether an old story be so or so.
CHAPTER XXI——THAT THE PROFIT OF ONE MAN IS THE DAMAGE OF ANOTHER
Demades the Athenian—[Seneca, De Beneficiis, vi. 38, whence nearly the whole of this chapter is taken.]—condemned one of his city, whose trade it was to sell the necessaries for funeral ceremonies, upon pretence that he demanded unreasonable profit, and that that profit could not accrue to him, but by the death of a great number of people. A judgment that appears to be ill grounded, forasmuch as no profit whatever can possibly be made but at the expense of another, and that by the same rule he should condemn all gain of what kind soever. The merchant only thrives by the debauchery of youth, the husband man by the dearness of grain, the architect by the ruin of buildings, lawyers and officers of justice by the suits and contentions of men: nay, even the honour and office of divines are derived from our death and vices. A physician takes no pleasure in the health even of his friends, says the ancient Greek comic writer, nor a soldier in the peace of his country, and so of the rest. And, which is yet worse, let every one but dive into his own bosom, and he will find his private wishes spring and his secret hopes grow up at another’s expense. Upon which consideration it comes into my head, that nature does not in this swerve from her general polity; for physicians hold, that the birth, nourishment, and increase of every thing is the dissolution and corruption of another:
CHAPTER XXII——OF CUSTOM, AND THAT WE SHOULD NOT EASILY CHANGE A LAW RECEIVED
He seems to me to have had a right and true apprehension of the power of custom, who first invented the story of a country-woman who, having accustomed herself to play with and carry a young calf in her arms, and daily continuing to do so as it grew up, obtained this by custom, that, when grown to be a great ox, she was still able to bear it. For, in truth, custom is a violent and treacherous schoolmistress. She, by little and little, slily and unperceived, slips in the foot of her authority, but having by this gentle and humble beginning, with the benefit of time, fixed and established it, she then unmasks a furious and tyrannic countenance, against which we have no more the courage or the power so much as to lift up our eyes. We see her, at every turn, forcing and violating the rules of nature:
I refer to her Plato’s cave in his Republic, and the physicians, who so often submit the reasons of their art to her authority; as the story of that king, who by custom brought his stomach to that pass, as to live by poison, and the maid that Albertus reports to have lived upon spiders. In that new world of the Indies, there were found great nations, and in very differing climates, who were of the same diet, made provision of them, and fed them for their tables; as also, they did grasshoppers, mice, lizards, and bats; and in a time of scarcity of such delicacies, a toad was sold for six crowns, all which they cook, and dish up with several sauces. There were also others found, to whom our diet, and the flesh we eat, were venomous and mortal:
These strange examples will not appear so strange if we consider what we have ordinary experience of, how much custom stupefies our senses. We need not go to what is reported of the people about the cataracts of the Nile; and what philosophers believe of the music of the spheres, that the bodies of those circles being solid and smooth, and coming to touch and rub upon one another, cannot fail of creating a marvellous harmony, the changes and cadences of which cause the revolutions and dances of the stars; but that the hearing sense of all creatures here below, being universally, like that of the Egyptians, deafened, and stupefied with the continual noise, cannot, how great soever, perceive it—[This passage is taken from Cicero, “Dream of Scipio”; see his De Republica, vi. II. The Egyptians were said to be stunned by the noise of the Cataracts.]— Smiths, millers, pewterers, forgemen, and armourers could never be able to live in the perpetual noise of their own trades, did it strike their ears with the same violence that it does ours.
My perfumed doublet gratifies my own scent at first; but after I have worn it three days together, ‘tis only pleasing to the bystanders. This is yet more strange, that custom, notwithstanding long intermissions and intervals, should yet have the power to unite and establish the effect of its impressions upon our senses, as is manifest in such as live near unto steeples and the frequent noise of the bells. I myself lie at home in a tower, where every morning and evening a very great bell rings out the Ave Maria: the noise shakes my very tower, and at first seemed insupportable to me; but I am so used to it, that I hear it without any manner of offence, and often without awaking at it.
Plato—[Diogenes Laertius, iii. 38. But he whom Plato censured was not a boy playing at nuts, but a man throwing dice.]—reprehending a boy for playing at nuts, “Thou reprovest me,” says the boy, “for a very little thing.” “Custom,” replied Plato, “is no little thing.” I find that our greatest vices derive their first propensity from our most tender infancy, and that our principal education depends upon the nurse. Mothers are mightily pleased to see a child writhe off the neck of a chicken, or to please itself with hurting a dog or a cat; and such wise fathers there are in the world, who look upon it as a notable mark of a martial spirit, when they hear a son miscall, or see him domineer over a poor peasant, or a lackey, that dares not reply, nor turn again; and a great sign of wit, when they see him cheat and overreach his playfellow by some malicious treachery and deceit. Yet these are the true seeds and roots of cruelty, tyranny, and treason; they bud and put out there, and afterwards shoot up vigorously, and grow to prodigious bulk, cultivated by custom. And it is a very dangerous mistake to excuse these vile inclinations upon the tenderness of their age, and the triviality of the subject: first, it is nature that speaks, whose declaration is then more sincere, and inward thoughts more undisguised, as it is more weak and young; secondly, the deformity of cozenage does not consist nor depend upon the difference betwixt crowns and pins; but I rather hold it more just to conclude thus: why should he not cozen in crowns since he does it in pins, than as they do, who say they only play for pins, they would not do it if it were for money? Children should carefully be instructed to abhor vices for their own contexture; and the natural deformity of those vices ought so to be represented to them, that they may not only avoid them in their actions, but especially so to abominate them in their hearts, that the very thought should be hateful to them, with what mask soever they may be disguised.
I know very well, for what concerns myself, that from having been brought up in my childhood to a plain and straightforward way of dealing, and from having had an aversion to all manner of juggling and foul play in my childish sports and recreations (and, indeed, it is to be noted, that the plays of children are not performed in play, but are to be judged in them as their most serious actions), there is no game so small wherein from my own bosom naturally, and without study or endeavour, I have not an extreme aversion from deceit. I shuffle and cut and make as much clatter with the cards, and keep as strict account for farthings, as it were for double pistoles; when winning or losing against my wife and daughter, ‘tis indifferent to me, as when I play in good earnest with others, for round sums. At all times, and in all places, my own eyes are sufficient to look to my fingers; I am not so narrowly watched by any other, neither is there any I have more respect to.
I saw the other day, at my own house, a little fellow, a native of Nantes, born without arms, who has so well taught his feet to perform the services his hands should have done him, that truly these have half forgotten their natural office; and, indeed, the fellow calls them his hands; with them he cuts anything, charges and discharges a pistol, threads a needle, sews, writes, puts off his hat, combs his head, plays at cards and dice, and all this with as much dexterity as any other could do who had more, and more proper limbs to assist him. The money I gave him—for he gains his living by shewing these feats—he took in his foot, as we do in our hand. I have seen another who, being yet a boy, flourished a two-handed sword, and, if I may so say, handled a halberd with the mere motions of his neck and shoulders for want of hands; tossed them into the air, and caught them again, darted a dagger, and cracked a whip as well as any coachman in France.
But the effects of custom are much more manifest in the strange impressions she imprints in our minds, where she meets with less resistance. What has she not the power to impose upon our judgments and beliefs? Is there any so fantastic opinion (omitting the gross impostures of religions, with which we see so many great nations, and so many understanding men, so strangely besotted; for this being beyond the reach of human reason, any error is more excusable in such as are not endued, through the divine bounty, with an extraordinary illumination from above), but, of other opinions, are there any so extravagant, that she has not planted and established for laws in those parts of the world upon which she has been pleased to exercise her power? And therefore that ancient exclamation was exceeding just:
I do believe, that no so absurd or ridiculous fancy can enter into human imagination, that does not meet with some example of public practice, and that, consequently, our reason does not ground and back up. There are people, amongst whom it is the fashion to turn their backs upon him they salute, and never look upon the man they intend to honour. There is a place, where, whenever the king spits, the greatest ladies of his court put out their hands to receive it; and another nation, where the most eminent persons about him stoop to take up his ordure in a linen cloth. Let us here steal room to insert a story.
A French gentleman was always wont to blow his nose with his fingers (a thing very much against our fashion), and he justifying himself for so doing, and he was a man famous for pleasant repartees, he asked me, what privilege this filthy excrement had, that we must carry about us a fine handkerchief to receive it, and, which was more, afterwards to lap it carefully up, and carry it all day about in our pockets, which, he said, could not but be much more nauseous and offensive, than to see it thrown away, as we did all other evacuations. I found that what he said was not altogether without reason, and by being frequently in his company, that slovenly action of his was at last grown familiar to me; which nevertheless we make a face at, when we hear it reported of another country. Miracles appear to be so, according to our ignorance of nature, and not according to the essence of nature the continually being accustomed to anything, blinds the eye of our judgment. Barbarians are no more a wonder to us, than we are to them; nor with any more reason, as every one would confess, if after having travelled over those remote examples, men could settle themselves to reflect upon, and rightly to confer them, with their own. Human reason is a tincture almost equally infused into all our opinions and manners, of what form soever they are; infinite in matter, infinite in diversity. But I return to my subject.
There are peoples, where, his wife and children excepted, no one speaks to the king but through a tube. In one and the same nation, the virgins discover those parts that modesty should persuade them to hide, and the married women carefully cover and conceal them. To which, this custom, in another place, has some relation, where chastity, but in marriage, is of no esteem, for unmarried women may prostitute themselves to as many as they please, and being got with child, may lawfully take physic, in the sight of every one, to destroy their fruit. And, in another place, if a tradesman marry, all of the same condition, who are invited to the wedding, lie with the bride before him; and the greater number of them there is, the greater is her honour, and the opinion of her ability and strength: if an officer marry, ‘tis the same, the same with a labourer, or one of mean condition; but then it belongs to the lord of the place to perform that office; and yet a severe loyalty during marriage is afterward strictly enjoined. There are places where brothels of young men are kept for the pleasure of women; where the wives go to war as well as the husbands, and not only share in the dangers of battle, but, moreover, in the honours of command. Others, where they wear rings not only through their noses, lips, cheeks, and on their toes, but also weighty gimmals of gold thrust through their paps and buttocks; where, in eating, they wipe their fingers upon their thighs, genitories, and the soles of their feet: where children are excluded, and brothers and nephews only inherit; and elsewhere, nephews only, saving in the succession of the prince: where, for the regulation of community in goods and estates, observed in the country, certain sovereign magistrates have committed to them the universal charge and overseeing of the agriculture, and distribution of the fruits, according to the necessity of every one where they lament the death of children, and feast at the decease of old men: where they lie ten or twelve in a bed, men and their wives together: where women, whose husbands come to violent ends, may marry again, and others not: where the condition of women is looked upon with such contempt, that they kill all the native females, and buy wives of their neighbours to supply their use; where husbands may repudiate their wives, without showing any cause, but wives cannot part from their husbands, for what cause soever; where husbands may sell their wives in case of sterility; where they boil the bodies of their dead, and afterward pound them to a pulp, which they mix with their wine, and drink it; where the most coveted sepulture is to be eaten by dogs, and elsewhere by birds; where they believe the souls of the blessed live in all manner of liberty, in delightful fields, furnished with all sorts of delicacies, and that it is these souls, repeating the words we utter, which we call Echo; where they fight in the water, and shoot their arrows with the most mortal aim, swimming; where, for a sign of subjection, they lift up their shoulders, and hang down their heads; where they put off their shoes when they enter the king’s palace; where the eunuchs, who take charge of the sacred women, have, moreover, their lips and noses cut off, that they may not be loved; where the priests put out their own eyes, to be better acquainted with their demons, and the better to receive their oracles; where every one makes to himself a deity of what he likes best; the hunter of a lion or a fox, the fisher of some fish; idols of every human action or passion; in which place, the sun, the moon, and the earth are the ‘principal deities, and the form of taking an oath is, to touch the earth, looking up to heaven; where both flesh and fish is eaten raw; where the greatest oath they take is, to swear by the name of some dead person of reputation, laying their hand upon his tomb; where the newyear’s gift the king sends every year to the princes, his vassals, is fire, which being brought, all the old fire is put out, and the neighbouring people are bound to fetch of the new, every one for themselves, upon pain of high treason; where, when the king, to betake himself wholly to devotion, retires from his administration (which often falls out), his next successor is obliged to do the same, and the right of the kingdom devolves to the third in succession: where they vary the form of government, according to the seeming necessity of affairs: depose the king when they think good, substituting certain elders to govern in his stead, and sometimes transferring it into the hands of the commonality: where men and women are both circumcised and also baptized: where the soldier, who in one or several engagements, has been so fortunate as to present seven of the enemies’ heads to the king, is made noble: where they live in that rare and unsociable opinion of the mortality of the soul: where the women are delivered without pain or fear: where the women wear copper leggings upon both legs, and if a louse bite them, are bound in magnanimity to bite them again, and dare not marry, till first they have made their king a tender of their virginity, if he please to accept it: where the ordinary way of salutation is by putting a finger down to the earth, and then pointing it up toward heaven: where men carry burdens upon their heads, and women on their shoulders; where the women make water standing, and the men squatting: where they send their blood in token of friendship, and offer incense to the men they would honour, like gods: where, not only to the fourth, but in any other remote degree, kindred are not permitted to marry: where the children are four years at nurse, and often twelve; in which place, also, it is accounted mortal to give the child suck the first day after it is born: where the correction of the male children is peculiarly designed to the fathers, and to the mothers of the girls; the punishment being to hang them by the heels in the smoke: where they circumcise the women: where they eat all sorts of herbs, without other scruple than of the badness of the smell: where all things are open the finest houses, furnished in the richest manner, without doors, windows, trunks, or chests to lock, a thief being there punished double what they are in other places: where they crack lice with their teeth like monkeys, and abhor to see them killed with one’s nails: where in all their lives they neither cut their hair nor pare their nails; and, in another place, pare those of the right hand only, letting the left grow for ornament and bravery: where they suffer the hair on the right side to grow as long as it will, and shave the other; and in the neighbouring provinces, some let their hair grow long before, and some behind, shaving close the rest: where parents let out their children, and husbands their wives, to their guests to hire: where a man may get his own mother with child, and fathers make use of their own daughters or sons, without scandal: where, at their solemn feasts, they interchangeably lend their children to one another, without any consideration of nearness of blood. In one place, men feed upon human flesh; in another, ‘tis reputed a pious office for a man to kill his father at a certain age; elsewhere, the fathers dispose of their children, whilst yet in their mothers’ wombs, some to be preserved and carefully brought up, and others to be abandoned or made away. Elsewhere the old husbands lend their wives to young men; and in another place they are in common without offence; in one place particularly, the women take it for a mark of honour to have as many gay fringed tassels at the bottom of their garment, as they have lain with several men. Moreover, has not custom made a republic of women separately by themselves? has it not put arms into their hands, and made them raise armies and fight battles? And does she not, by her own precept, instruct the most ignorant vulgar, and make them perfect in things which all the philosophy in the world could never beat into the heads of the wisest men? For we know entire nations, where death was not only despised, but entertained with the greatest triumph; where children of seven years old suffered themselves to be whipped to death, without changing countenance; where riches were in such contempt, that the meanest citizen would not have deigned to stoop to take up a purse of crowns. And we know regions, very fruitful in all manner of provisions, where, notwithstanding, the most ordinary diet, and that they are most pleased with, is only bread, cresses, and water. Did not custom, moreover, work that miracle in Chios that, in seven hundred years, it was never known that ever maid or wife committed any act to the prejudice of her honour?
To conclude; there is nothing, in my opinion, that she does not, or may not do; and therefore, with very good reason it is that Pindar calls her the ruler of the world. He that was seen to beat his father, and reproved for so doing, made answer, that it was the custom of their family; that, in like manner, his father had beaten his grandfather, his grandfather his great-grandfather, “And this,” says he, pointing to his son, “when he comes to my age, shall beat me.” And the father, whom the son dragged and hauled along the streets, commanded him to stop at a certain door, for he himself, he said, had dragged his father no farther, that being the utmost limit of the hereditary outrage the sons used to practise upon the fathers in their family. It is as much by custom as infirmity, says Aristotle, that women tear their hair, bite their nails, and eat coals and earth, and more by custom than nature that men abuse themselves with one another.
The laws of conscience, which we pretend to be derived from nature, proceed from custom; every one, having an inward veneration for the opinions and manners approved and received amongst his own people, cannot, without very great reluctance, depart from them, nor apply himself to them without applause. In times past, when those of Crete would curse any one, they prayed the gods to engage him in some ill custom. But the principal effect of its power is, so to seize and ensnare us, that it is hardly in us to disengage ourselves from its gripe, or so to come to ourselves, as to consider of and to weigh the things it enjoins. To say the truth, by reason that we suck it in with our milk, and that the face of the world presents itself in this posture to our first sight, it seems as if we were born upon condition to follow on this track; and the common fancies that we find in repute everywhere about us, and infused into our minds with the seed of our fathers, appear to be the most universal and genuine; from whence it comes to pass, that whatever is off the hinges of custom, is believed to be also off the hinges of reason; how unreasonably for the most part, God knows.
If, as we who study ourselves have learned to do, every one who hears a good sentence, would immediately consider how it does in any way touch his own private concern, every one would find, that it was not so much a good saying, as a severe lash to the ordinary stupidity of his own judgment: but men receive the precepts and admonitions of truth, as directed to the common sort, and never to themselves; and instead of applying them to their own manners, do only very ignorantly and unprofitably commit them to memory. But let us return to the empire of custom.
Such people as have been bred up to liberty, and subject to no other dominion but the authority of their own will, look upon all other form of government as monstrous and contrary to nature. Those who are inured to monarchy do the same; and what opportunity soever fortune presents them with to change, even then, when with the greatest difficulties they have disengaged themselves from one master, that was troublesome and grievous to them, they presently run, with the same difficulties, to create another; being unable to take into hatred subjection itself.
‘Tis by the mediation of custom, that every one is content with the place where he is planted by nature; and the Highlanders of Scotland no more pant after Touraine; than the Scythians after Thessaly. Darius asking certain Greeks what they would take to assume the custom of the Indians, of eating the dead bodies of their fathers (for that was their use, believing they could not give them a better nor more noble sepulture than to bury them in their own bodies), they made answer, that nothing in the world should hire them to do it; but having also tried to persuade the Indians to leave their custom, and, after the Greek manner, to burn the bodies of their fathers, they conceived a still greater horror at the motion.—[Herodotus, iii. 38.]—Every one does the same, for use veils from us the true aspect of things.
Taking upon me once to justify something in use amongst us, and that was received with absolute authority for a great many leagues round about us, and not content, as men commonly do, to establish it only by force of law and example, but inquiring still further into its origin, I found the foundation so weak, that I who made it my business to confirm others, was very near being dissatisfied myself. ‘Tis by this receipt that Plato —[Laws, viii. 6.]—undertakes to cure the unnatural and preposterous loves of his time, as one which he esteems of sovereign virtue, namely, that the public opinion condemns them; that the poets, and all other sorts of writers, relate horrible stories of them; a recipe, by virtue of which the most beautiful daughters no more allure their fathers’ lust; nor brothers, of the finest shape and fashion, their sisters’ desire; the very fables of Thyestes, OEdipus, and Macareus, having with the harmony of their song, infused this wholesome opinion and belief into the tender brains of children. Chastity is, in truth, a great and shining virtue, and of which the utility is sufficiently known; but to treat of it, and to set it off in its true value, according to nature, is as hard as ‘tis easy to do so according to custom, laws, and precepts. The fundamental and universal reasons are of very obscure and difficult research, and our masters either lightly pass them over, or not daring so much as to touch them, precipitate themselves into the liberty and protection of custom, there puffing themselves out and triumphing to their heart’s content: such as will not suffer themselves to be withdrawn from this original source, do yet commit a greater error, and subject themselves to wild opinions; witness Chrysippus,—[Sextus Empiricus, Pyyrhon. Hypotyp., i. 14.]—who, in so many of his writings, has strewed the little account he made of incestuous conjunctions, committed with how near relations soever.
Whoever would disengage himself from this violent prejudice of custom, would find several things received with absolute and undoubting opinion, that have no other support than the hoary head and rivelled face of ancient usage. But the mask taken off, and things being referred to the decision of truth and reason, he will find his judgment as it were altogether overthrown, and yet restored to a much more sure estate. For example, I shall ask him, what can be more strange than to see a people obliged to obey laws they never understood; bound in all their domestic affairs, as marriages, donations, wills, sales, and purchases, to rules they cannot possibly know, being neither written nor published in their own language, and of which they are of necessity to purchase both the interpretation and the use? Not according to the ingenious opinion of Isocrates,—[Discourse to Nicocles.]—who counselled his king to make the traffics and negotiations of his subjects, free, frank, and of profit to them, and their quarrels and disputes burdensome, and laden with heavy impositions and penalties; but, by a prodigious opinion, to make sale of reason itself, and to give to laws a course of merchandise. I think myself obliged to fortune that, as our historians report, it was a Gascon gentleman, a countryman of mine, who first opposed Charlemagne, when he attempted to impose upon us Latin and imperial laws.
What can be more savage, than to see a nation where, by lawful custom, the office of a judge is bought and sold, where judgments are paid for with ready money, and where justice may legitimately be denied to him that has not wherewithal to pay; a merchandise in so great repute, as in a government to create a fourth estate of wrangling lawyers, to add to the three ancient ones of the church, nobility, and people; which fourth estate, having the laws in their own hands, and sovereign power over men’s lives and fortunes, makes another body separate from nobility: whence it comes to pass, that there are double laws, those of honour and those of justice, in many things altogether opposite one to another; the nobles as rigorously condemning a lie taken, as the other do a lie revenged: by the law of arms, he shall be degraded from all nobility and honour who puts up with an affront; and by the civil law, he who vindicates his reputation by revenge incurs a capital punishment: he who applies himself to the law for reparation of an offence done to his honour, disgraces himself; and he who does not, is censured and punished by the law. Yet of these two so different things, both of them referring to one head, the one has the charge of peace, the other of war; those have the profit, these the honour; those the wisdom, these the virtue; those the word, these the action; those justice, these valour; those reason, these force; those the long robe, these the short;—divided betwixt them.
For what concerns indifferent things, as clothes, who is there seeking to bring them back to their true use, which is the body’s service and convenience, and upon which their original grace and fitness depend; for the most fantastic, in my opinion, that can be imagined, I will instance amongst others, our flat caps, that long tail of velvet that hangs down from our women’s heads, with its party-coloured trappings; and that vain and futile model of a member we cannot in modesty so much as name, which, nevertheless, we make show and parade of in public. These considerations, notwithstanding, will not prevail upon any understanding man to decline the common mode; but, on the contrary, methinks, all singular and particular fashions are rather marks of folly and vain affectation than of sound reason, and that a wise man, within, ought to withdraw and retire his soul from the crowd, and there keep it at liberty and in power to judge freely of things; but as to externals, absolutely to follow and conform himself to the fashion of the time. Public society has nothing to do with our thoughts, but the rest, as our actions, our labours, our fortunes, and our lives, we are to lend and abandon them to its service and to the common opinion, as did that good and great Socrates who refused to preserve his life by a disobedience to the magistrate, though a very wicked and unjust one for it is the rule of rules, the general law of laws, that every one observe those of the place wherein he lives.
And now to another point. It is a very great doubt, whether any so manifest benefit can accrue from the alteration of a law received, let it be what it will, as there is danger and inconvenience in altering it; forasmuch as government is a structure composed of divers parts and members joined and united together, with so strict connection, that it is impossible to stir so much as one brick or stone, but the whole body will be sensible of it. The legislator of the Thurians—[Charondas; Diod. Sic., xii. 24.]—ordained, that whosoever would go about either to abolish an old law, or to establish a new, should present himself with a halter about his neck to the people, to the end, that if the innovation he would introduce should not be approved by every one, he might immediately be hanged; and he of the Lacedaemonians employed his life to obtain from his citizens a faithful promise that none of his laws should be violated.—[Lycurgus; Plutarch, in Vita, c. 22.]—The Ephoros who so rudely cut the two strings that Phrynis had added to music never stood to examine whether that addition made better harmony, or that by its means the instrument was more full and complete; it was enough for him to condemn the invention, that it was a novelty, and an alteration of the old fashion. Which also is the meaning of the old rusty sword carried before the magistracy of Marseilles.
For my own part, I have a great aversion from a novelty, what face or what pretence soever it may carry along with it, and have reason, having been an eyewitness of the great evils it has produced. For those which for so many years have lain so heavy upon us, it is not wholly accountable; but one may say, with colour enough, that it has accidentally produced and begotten the mischiefs and ruin that have since happened, both without and against it; it, principally, we are to accuse for these disorders:
They who give the first shock to a state, are almost naturally the first overwhelmed in its ruin the fruits of public commotion are seldom enjoyed by him who was the first motor; he beats and disturbs the water for another’s net. The unity and contexture of this monarchy, of this grand edifice, having been ripped and torn in her old age, by this thing called innovation, has since laid open a rent, and given sufficient admittance to such injuries: the royal majesty with greater difficulty declines from the summit to the middle, then it falls and tumbles headlong from the middle to the bottom. But if the inventors do the greater mischief, the imitators are more vicious to follow examples of which they have felt and punished both the horror and the offence. And if there can be any degree of honour in ill-doing, these last must yield to the others the glory of contriving, and the courage of making the first attempt. All sorts of new disorders easily draw, from this primitive and ever-flowing fountain, examples and precedents to trouble and discompose our government: we read in our very laws, made for the remedy of this first evil, the beginning and pretences of all sorts of wicked enterprises; and that befalls us, which Thucydides said of the civil wars of his time, that, in favour of public vices, they gave them new and more plausible names for their excuse, sweetening and disguising their true titles; which must be done, forsooth, to reform our conscience and belief:
but the best pretence for innovation is of very dangerous consequence:
And freely to speak my thoughts, it argues a strange self-love and great presumption to be so fond of one’s own opinions, that a public peace must be overthrown to establish them, and to introduce so many inevitable mischiefs, and so dreadful a corruption of manners, as a civil war and the mutations of state consequent to it, always bring in their train, and to introduce them, in a thing of so high concern, into the bowels of one’s own country. Can there be worse husbandry than to set up so many certain and knowing vices against errors that are only contested and disputable? And are there any worse sorts of vices than those committed against a man’s own conscience, and the natural light of his own reason? The Senate, upon the dispute betwixt it and the people about the administration of their religion, was bold enough to return this evasion for current pay:
according to what the oracle answered to those of Delphos who, fearing to be invaded by the Persians in the Median war, inquired of Apollo, how they should dispose of the holy treasure of his temple; whether they should hide, or remove it to some other place? He returned them answer, that they should stir nothing from thence, and only take care of themselves, for he was sufficient to look to what belonged to him. —[Herodotus, viii. 36.].—
The Christian religion has all the marks of the utmost utility and justice: but none more manifest than the severe injunction it lays indifferently upon all to yield absolute obedience to the civil magistrate, and to maintain and defend the laws. Of which, what a wonderful example has the divine wisdom left us, that, to establish the salvation of mankind, and to conduct His glorious victory over death and sin, would do it after no other way, but at the mercy of our ordinary forms of justice subjecting the progress and issue of so high and so salutiferous an effect, to the blindness and injustice of our customs and observances; sacrificing the innocent blood of so many of His elect, and so long a loss of so many years, to the maturing of this inestimable fruit? There is a vast difference betwixt the case of one who follows the forms and laws of his country, and of another who will undertake to regulate and change them; of whom the first pleads simplicity, obedience, and example for his excuse, who, whatever he shall do, it cannot be imputed to malice; ‘tis at the worst but misfortune:
besides what Isocrates says, that defect is nearer allied to moderation than excess: the other is a much more ruffling gamester; for whosoever shall take upon him to choose and alter, usurps the authority of judging, and should look well about him, and make it his business to discern clearly the defect of what he would abolish, and the virtue of what he is about to introduce.
This so vulgar consideration is that which settled me in my station, and kept even my most extravagant and ungoverned youth under the rein, so as not to burden my shoulders with so great a weight, as to render myself responsible for a science of that importance, and in this to dare, what in my better and more mature judgment, I durst not do in the most easy and indifferent things I had been instructed in, and wherein the temerity of judging is of no consequence at all; it seeming to me very unjust to go about to subject public and established customs and institutions, to the weakness and instability of a private and particular fancy (for private reason has but a private jurisdiction), and to attempt that upon the divine, which no government will endure a man should do, upon the civil laws; with which, though human reason has much more commerce than with the other, yet are they sovereignly judged by their own proper judges, and the extreme sufficiency serves only to expound and set forth the law and custom received, and neither to wrest it, nor to introduce anything, of innovation. If, sometimes, the divine providence has gone beyond the rules to which it has necessarily bound and obliged us men, it is not to give us any dispensation to do the same; those are masterstrokes of the divine hand, which we are not to imitate, but to admire, and extraordinary examples, marks of express and particular purposes, of the nature of miracles, presented before us for manifestations of its almightiness, equally above both our rules and force, which it would be folly and impiety to attempt to represent and imitate; and that we ought not to follow, but to contemplate with the greatest reverence: acts of His personage, and not for us. Cotta very opportunely declares:
God knows, in the present quarrel of our civil war, where there are a hundred articles to dash out and to put in, great and very considerable, how many there are who can truly boast, they have exactly and perfectly weighed and understood the grounds and reasons of the one and the other party; ‘tis a number, if they make any number, that would be able to give us very little disturbance. But what becomes of all the rest, under what ensigns do they march, in what quarter do they lie? Theirs have the same effect with other weak and ill-applied medicines; they have only set the humours they would purge more violently in work, stirred and exasperated by the conflict, and left them still behind. The potion was too weak to purge, but strong enough to weaken us; so that it does not work, but we keep it still in our bodies, and reap nothing from the operation but intestine gripes and dolours.
So it is, nevertheless, that Fortune still reserving her authority in defiance of whatever we are able to do or say, sometimes presents us with a necessity so urgent, that ‘tis requisite the laws should a little yield and give way; and when one opposes the increase of an innovation that thus intrudes itself by violence, to keep a man’s self in so doing, in all places and in all things within bounds and rules against those who have the power, and to whom all things are lawful that may in any way serve to advance their design, who have no other law nor rule but what serves best to their own purpose, ‘tis a dangerous obligation and an intolerable inequality:
forasmuch as the ordinary discipline of a healthful state does not provide against these extraordinary accidents; it presupposes a body that supports itself in its principal members and offices, and a common consent to its obedience and observation. A legitimate proceeding is cold, heavy, and constrained, and not fit to make head against a headstrong and unbridled proceeding. ‘Tis known to be to this day cast in the dish of those two great men, Octavius and Cato, in the two civil wars of Sylla and Caesar, that they would rather suffer their country to undergo the last extremities, than relieve their fellow-citizens at the expense of its laws, or be guilty of any innovation; for in truth, in these last necessities, where there is no other remedy, it would, peradventure, be more discreetly done, to stoop and yield a little to receive the blow, than, by opposing without possibility of doing good, to give occasion to violence to trample all under foot; and better to make the laws do what they can, when they cannot do what they would. After this manner did he—[Agesilaus.]—who suspended them for four-and-twenty hours, and he who, for once shifted a day in the calendar, and that other—[Alexander the Great.]—who of the month of June made a second of May. The Lacedaemonians themselves, who were so religious observers of the laws of their country, being straitened by one of their own edicts, by which it was expressly forbidden to choose the same man twice to be admiral; and on the other side, their affairs necessarily requiring, that Lysander should again take upon him that command, they made one Aratus admiral; ‘tis true, but withal, Lysander went general of the navy; and, by the same subtlety, one of their ambassadors being sent to the Athenians to obtain the revocation of some decree, and Pericles remonstrating to him, that it was forbidden to take away the tablet wherein a law had once been engrossed, he advised him to turn it only, that being not forbidden; and Plutarch commends Philopoemen, that being born to command, he knew how to do it, not only according to the laws, but also to overrule even the laws themselves, when the public necessity so required.
CHAPTER XXIII——VARIOUS EVENTS FROM THE SAME COUNSEL
Jacques Amiot, grand almoner of France, one day related to me this story, much to the honour of a prince of ours (and ours he was upon several very good accounts, though originally of foreign extraction),—[The Duc de Guise, surnamed Le Balafre.]—that in the time of our first commotions, at the siege of Rouen,—[In 1562]—this prince, having been advertised by the queen-mother of a conspiracy against his life, and in her letters particular notice being given him of the person who was to execute the business (who was a gentleman of Anjou or of Maine, and who to this effect ordinarily frequented this prince’s house), discovered not a syllable of this intelligence to any one whatever; but going the next day to the St. Catherine’s Mount,—[An eminence outside Rouen overlooking the Seine. D.W.]—from which our battery played against the town (for it was during the time of the siege), and having in company with him the said lord almoner, and another bishop, he saw this gentleman, who had been denoted to him, and presently sent for him; to whom, being come before him, seeing him already pale and trembling with the conscience of his guilt, he thus said, “Monsieur,” such an one, “you guess what I have to say to you; your countenance discovers it; ‘tis in vain to disguise your practice, for I am so well informed of your business, that it will but make worse for you, to go about to conceal or deny it: you know very well such and such passages” (which were the most secret circumstances of his conspiracy), “and therefore be sure, as you tender your own life, to confess to me the whole truth of the design.” The poor man seeing himself thus trapped and convicted (for the whole business had been discovered to the queen by one of the accomplices), was in such a taking, he knew not what to do; but, folding his hands, to beg and sue for mercy, he threw himself at his prince’s feet, who taking him up, proceeded to say, “Come, sir; tell me, have I at any time done you offence? or have I, through private hatred or malice, offended any kinsman or friend of yours? It is not above three weeks that I have known you; what inducement, then, could move you to attempt my death?” To which the gentleman with a trembling voice replied, “That it was no particular grudge he had to his person, but the general interest and concern of his party, and that he had been put upon it by some who had persuaded him it would be a meritorious act, by any means, to extirpate so great and so powerful an enemy of their religion.” “Well,” said the prince, “I will now let you see, how much more charitable the religion is that I maintain, than that which you profess: yours has counselled you to kill me, without hearing me speak, and without ever having given you any cause of offence; and mine commands me to forgive you, convict as you are, by your own confession, of a design to kill me without reason.—[Imitated by Voltaire. See Nodier, Questions, p. 165.]—Get you gone; let me see you no more; and, if you are wise, choose henceforward honester men for your counsellors in your designs.”—[Dampmartin, La Fortune de la Coup, liv. ii., p. 139]
The Emperor Augustus,—[This story is taken from Seneca, De Clementia, i. 9.]—being in Gaul, had certain information of a conspiracy L. Cinna was contriving against him; he therefore resolved to make him an example; and, to that end, sent to summon his friends to meet the next morning in counsel. But the night between he passed in great unquietness of mind, considering that he was about to put to death a young man, of an illustrious family, and nephew to the great Pompey, and this made him break out into several passionate complainings. “What then,” said he, “is it possible that I am to live in perpetual anxiety and alarm, and suffer my would-be assassin, meantime, to walk abroad at liberty? Shall he go unpunished, after having conspired against my life, a life that I have hitherto defended in so many civil wars, in so many battles by land and by sea? And after having settled the universal peace of the whole world, shall this man be pardoned, who has conspired not only to murder, but to sacrifice me?”—for the conspiracy was to kill him at sacrifice. After which, remaining for some time silent, he began again, in louder tones, and exclaimed against himself, saying: “Why livest thou, if it be for the good of so many that thou shouldst die? must there be no end of thy revenges and cruelties? Is thy life of so great value, that so many mischiefs must be done to preserve it?” His wife Livia, seeing him in this perplexity: “Will you take a woman’s counsel?” said she. “Do as the physicians do, who, when the ordinary recipes will do no good, make trial of the contrary. By severity you have hitherto prevailed nothing; Lepidus has followed Salvidienus; Murena, Lepidus; Caepio, Murena; Egnatius, Caepio. Begin now, and try how sweetness and clemency will succeed. Cinna is convict; forgive him, he will never henceforth have the heart to hurt thee, and it will be an act to thy glory.” Augustus was well pleased that he had met with an advocate of his own humour; wherefore, having thanked his wife, and, in the morning, countermanded his friends he had before summoned to council, he commanded Cinna all alone to be brought to him; who being accordingly come, and a chair by his appointment set him, having ordered all the rest out of the room, he spake to him after this manner: “In the first place, Cinna, I demand of thee patient audience; do not interrupt me in what I am about to say, and I will afterwards give thee time and leisure to answer. Thou knowest, Cinna,—[This passage, borrowed from Seneca, has been paraphrased in verse by Corneille. See Nodier, Questions de la Literature llgale, 1828, pp. 7, 160. The monologue of Augustus in this chapter is also from Seneca. Ibid., 164.]—that having taken thee prisoner in the enemy’s camp, and thou an enemy, not only so become, but born so, I gave thee thy life, restored to thee all thy goods, and, finally, put thee in so good a posture, by my bounty, of living well and at thy ease, that the victorious envied the conquered. The sacerdotal office which thou madest suit to me for, I conferred upon thee, after having denied it to others, whose fathers have ever borne arms in my service. After so many obligations, thou hast undertaken to kill me.” At which Cinna crying out that he was very far from entertaining any so wicked a thought: “Thou dost not keep thy promise, Cinna,” continued Augustus, “that thou wouldst not interrupt me. Yes, thou hast undertaken to murder me in such a place, on such a day, in such and such company, and in such a manner.” At which words, seeing Cinna astounded and silent, not upon the account of his promise so to be, but interdict with the weight of his conscience: “Why,” proceeded Augustus, “to what end wouldst thou do it? Is it to be emperor? Believe me, the Republic is in very ill condition, if I am the only man betwixt thee and the empire. Thou art not able so much as to defend thy own house, and but t’other day was baffled in a suit, by the opposed interest of a mere manumitted slave. What, hast thou neither means nor power in any other thing, but only to undertake Caesar? I quit the throne, if there be no other than I to obstruct thy hopes. Canst thou believe that Paulus, that Fabius, that the Cossii and the Servilii, and so many noble Romans, not only so in title, but who by their virtue honour their nobility, would suffer or endure thee?” After this, and a great deal more that he said to him (for he was two long hours in speaking), “Now go, Cinna, go thy way: I give thee that life as traitor and parricide, which I before gave thee in the quality of an enemy. Let friendship from this time forward begin betwixt us, and let us show whether I have given, or thou hast received thy life with the better faith”; and so departed from him. Some time after, he preferred him to the consular dignity, complaining that he had not the confidence to demand it; had him ever after for his very great friend, and was, at last, made by him sole heir to all his estate. Now, from the time of this accident which befell Augustus in the fortieth year of his age, he never had any conspiracy or attempt against him, and so reaped the due reward of this his so generous clemency. But it did not so happen with our prince, his moderation and mercy not so securing him, but that he afterwards fell into the toils of the like treason,—[The Duc de Guise was assassinated in 1563 by Poltrot.]—so vain and futile a thing is human prudence; throughout all our projects, counsels and precautions, Fortune will still be mistress of events.
We repute physicians fortunate when they hit upon a lucky cure, as if there was no other art but theirs that could not stand upon its own legs, and whose foundations are too weak to support itself upon its own basis; as if no other art stood in need of Fortune’s hand to help it. For my part, I think of physic as much good or ill as any one would have me: for, thanks be to God, we have no traffic together. I am of a quite contrary humour to other men, for I always despise it; but when I am sick, instead of recanting, or entering into composition with it, I begin, moreover, to hate and fear it, telling them who importune me to take physic, that at all events they must give me time to recover my strength and health, that I may be the better able to support and encounter the violence and danger of their potions. I let nature work, supposing her to be sufficiently armed with teeth and claws to defend herself from the assaults of infirmity, and to uphold that contexture, the dissolution of which she flies and abhors. I am afraid, lest, instead of assisting her when close grappled and struggling with disease, I should assist her adversary, and burden her still more with work to do.
Now, I say, that not in physic only, but in other more certain arts, fortune has a very great part.
The poetic raptures, the flights of fancy, that ravish and transport the author out of himself, why should we not attribute them to his good fortune, since he himself confesses that they exceed his sufficiency and force, and acknowledges them to proceed from something else than himself, and that he has them no more in his power than the orators say they have those extraordinary motions and agitations that sometimes push them beyond their design. It is the same in painting, where touches shall sometimes slip from the hand of the painter, so surpassing both his conception and his art, as to beget his own admiration and astonishment. But Fortune does yet more evidently manifest the share she has in all things of this kind, by the graces and elegances we find in them, not only beyond the intention, but even without the knowledge of the workman: a competent reader often discovers in other men’s writings other perfections than the author himself either intended or perceived, a richer sense and more quaint expression.
As to military enterprises, every one sees how great a hand Fortune has in them. Even in our counsels and deliberations there must, certainly, be something of chance and good-luck mixed with human prudence; for all that our wisdom can do alone is no great matter; the more piercing, quick, and apprehensive it is, the weaker it finds itself, and is by so much more apt to mistrust itself. I am of Sylla’s opinion;—[“Who freed his great deeds from envy by ever attributing them to his good fortune, and finally by surnaming himself Faustus, the Lucky.”—Plutarch, How far a Man may praise Himself, c. 9.]—and when I closely examine the most glorious exploits of war, I perceive, methinks, that those who carry them on make use of counsel and debate only for custom’s sake, and leave the best part of the enterprise to Fortune, and relying upon her aid, transgress, at every turn, the bounds of military conduct and the rules of war. There happen, sometimes, fortuitous alacrities and strange furies in their deliberations, that for the most part prompt them to follow the worst grounded counsels, and swell their courage beyond the limits of reason. Whence it happened that several of the great captains of old, to justify those rash resolutions, have been fain to tell their soldiers that they were invited to such attempts by some inspiration, some sign and prognostic.
Wherefore, in this doubt and uncertainty, that the shortsightedness of human wisdom to see and choose the best (by reason of the difficulties that the various accidents and circumstances of things bring along with them) perplexes us withal, the surest way, in my opinion, did no other consideration invite us to it, is to pitch upon that wherein is the greatest appearance of honesty and justice; and not, being certain of the shortest, to keep the straightest and most direct way; as in the two examples I have just given, there is no question but it was more noble and generous in him who had received the offence, to pardon it, than to do otherwise. If the former—[The Duc de Guise.]—miscarried in it, he is not, nevertheless, to be blamed for his good intention; neither does any one know if he had proceeded otherwise, whether by that means he had avoided the end his destiny had appointed for him; and he had, moreover, lost the glory of so humane an act.
You will read in history, of many who have been in such apprehension, that the most part have taken the course to meet and anticipate conspiracies against them by punishment and revenge; but I find very few who have reaped any advantage by this proceeding; witness so many Roman emperors. Whoever finds himself in this danger, ought not to expect much either from his vigilance or power; for how hard a thing is it for a man to secure himself from an enemy, who lies concealed under the countenance of the most assiduous friend we have, and to discover and know the wills and inward thoughts of those who are in our personal service. ‘Tis to much purpose to have a guard of foreigners about one, and to be always fenced about with a pale of armed men; whosoever despises his own life, is always master of that of another man.—[Seneca, Ep., 4.]—And moreover, this continual suspicion, that makes a prince jealous of all the world, must of necessity be a strange torment to him. Therefore it was, that Dion, being advertised that Callippus watched all opportunities to take away his life, had never the heart to inquire more particularly into it, saying, that he had rather die than live in that misery, that he must continually stand upon his guard, not only against his enemies, but his friends also;—[Plutarch, Apothegms.]—which Alexander much more vividly and more roundly manifested in effect, when, having notice by a letter from Parmenio, that Philip, his most beloved physician, was by Darius’ money corrupted to poison him, at the same time he gave the letter to Philip to read, drank off the potion he had brought him. Was not this to express a resolution, that if his friends had a mind to despatch him out of the world, he was willing to give them opportunity to do it? This prince is, indeed, the sovereign pattern of hazardous actions; but I do not know whether there be another passage in his life wherein there is so much firm courage as in this, nor so illustrious an image of the beauty and greatness of his mind.
Those who preach to princes so circumspect and vigilant a jealousy and distrust, under colour of security, preach to them ruin and dishonour: nothing noble can be performed without danger. I know a person, naturally of a very great daring and enterprising courage, whose good fortune is continually marred by such persuasions, that he keep himself close surrounded by his friends, that he must not hearken to any reconciliation with his ancient enemies, that he must stand aloof, and not trust his person in hands stronger than his own, what promises or offers soever they may make him, or what advantages soever he may see before him. And I know another, who has unexpectedly advanced his fortunes by following a clear contrary advice.
Courage, the reputation and glory of which men seek with so greedy an appetite, presents itself, when need requires, as magnificently in cuerpo, as in full armour; in a closet, as in a camp; with arms pendant, as with arms raised.
This over-circumspect and wary prudence is a mortal enemy to all high and generous exploits. Scipio, to sound Syphax’s intention, leaving his army, abandoning Spain, not yet secure nor well settled in his new conquest, could pass over into Africa in two small ships, to commit himself, in an enemy’s country, to the power of a barbarian king, to a faith untried and unknown, without obligation, without hostage, under the sole security of the grandeur of his own courage, his good fortune, and the promise of his high hopes.—[ Livy, xxviii. 17.]
In a life of ambition and glory, it is necessary to hold a stiff rein upon suspicion: fear and distrust invite and draw on offence. The most mistrustful of our kings—[ Louis XI.]—established his affairs principally by voluntarily committing his life and liberty into his enemies’ hands, by that action manifesting that he had absolute confidence in them, to the end they might repose as great an assurance in him. Caesar only opposed the authority of his countenance and the haughty sharpness of his rebukes to his mutinous legions in arms against him:
But it is true, withal, that this undaunted assurance is not to be represented in its simple and entire form, but by such whom the apprehension of death, and the worst that can happen, does not terrify and affright; for to represent a pretended resolution with a pale and doubtful countenance and trembling limbs, for the service of an important reconciliation, will effect nothing to purpose. ‘Tis an excellent way to gain the heart and will of another, to submit and intrust one’s self to him, provided it appear to be freely done, and without the constraint of necessity, and in such a condition, that a man manifestly does it out of a pure and entire confidence in the party, at least, with a countenance clear from any cloud of suspicion. I saw, when I was a boy, a gentleman, who was governor of a great city, upon occasion of a popular commotion and fury, not knowing what other course to take, go out of a place of very great strength and security, and commit himself to the mercy of the seditious rabble, in hopes by that means to appease the tumult before it grew to a more formidable head; but it was ill for him that he did so, for he was there miserably slain. But I am not, nevertheless, of opinion, that he committed so great an error in going out, as men commonly reproach his memory withal, as he did in choosing a gentle and submissive way for the effecting his purpose, and in endeavouring to quiet this storm, rather by obeying than commanding, and by entreaty rather than remonstrance; and I am inclined to believe, that a gracious severity, with a soldierlike way of commanding, full of security and confidence, suitable to the quality of his person, and the dignity of his command, would have succeeded better with him; at least, he had perished with greater decency and, reputation. There is nothing so little to be expected or hoped for from this many-headed monster, in its fury, as humanity and good nature; it is much more capable of reverence and fear. I should also reproach him, that having taken a resolution (in my judgment rather brave than rash) to expose himself, weak and naked, in this tempestuous sea of enraged madmen, he ought to have stuck to his text, and not for an instant to have abandoned the high part he had undertaken; whereas, coming to discover his danger nearer hand, and his nose happening to bleed, he again changed that demiss and fawning countenance he had at first put on, into another of fear and amazement, filling his voice with entreaties and his eyes with tears, and, endeavouring so to withdraw and secure his person, that carriage more inflamed their fury, and soon brought the effects of it upon him.
It was upon a time intended that there should be a general muster of several troops in arms (and that is the most proper occasion of secret revenges, and there is no place where they can be executed with greater safety), and there were public and manifest appearances, that there was no safe coming for some, whose principal and necessary office it was to review them. Whereupon a consultation was held, and several counsels were proposed, as in a case that was very nice and of great difficulty; and moreover of grave consequence. Mine, amongst the rest, was, that they should by all means avoid giving any sign of suspicion, but that the officers who were most in danger should boldly go, and with cheerful and erect countenances ride boldly and confidently through the ranks, and that instead of sparing fire (which the counsels of the major part tended to) they should entreat the captains to command the soldiers to give round and full volleys in honour of the spectators, and not to spare their powder. This was accordingly done, and served so good use, as to please and gratify the suspected troops, and thenceforward to beget a mutual and wholesome confidence and intelligence amongst them.
I look upon Julius Caesar’s way of winning men to him as the best and finest that can be put in practice. First, he tried by clemency to make himself beloved even by his very enemies, contenting himself, in detected conspiracies, only publicly to declare, that he was pre-acquainted with them; which being done, he took a noble resolution to await without solicitude or fear, whatever might be the event, wholly resigning himself to the protection of the gods and fortune: for, questionless, in this state he was at the time when he was killed.
A stranger having publicly said, that he could teach Dionysius, the tyrant of Syracuse, an infallible way to find out and discover all the conspiracies his subjects could contrive against him, if he would give him a good sum of money for his pains, Dionysius hearing of it, caused the man to be brought to him, that he might learn an art so necessary to his preservation. The man made answer, that all the art he knew, was, that he should give him a talent, and afterwards boast that he had obtained a singular secret from him. Dionysius liked the invention, and accordingly caused six hundred crowns to be counted out to him. —[Plutarch, Apothegms.]—It was not likely he should give so great a sum to a person unknown, but upon the account of some extraordinary discovery, and the belief of this served to keep his enemies in awe. Princes, however, do wisely to publish the informations they receive of all the practices against their lives, to possess men with an opinion they have so good intelligence that nothing can be plotted against them, but they have present notice of it. The Duke of Athens did a great many foolish things in the establishment of his new tyranny over Florence: but this especially was most notable, that having received the first intimation of the conspiracies the people were hatching against him, from Matteo di Morozzo, one of the conspirators, he presently put him to death, to suppress that rumour, that it might not be thought any of the city disliked his government.
I remember I have formerly read a story—[In Appian’s Civil Wars, book iv..]—of some Roman of great quality who, flying the tyranny of the Triumvirate, had a thousand times by the subtlety of as many inventions escaped from falling into the hands of those that pursued him. It happened one day that a troop of horse, which was sent out to take him, passed close by a brake where he was squat, and missed very narrowly of spying him: but he considering, at this point, the pains and difficulties wherein he had so long continued to evade the strict and incessant searches that were every day made for him, the little pleasure he could hope for in such a kind of life, and how much better it was for him to die once for all, than to be perpetually at this pass, he started from his seat, called them back, showed them his form,—[as of a squatting hare.]—and voluntarily delivered himself up to their cruelty, by that means to free both himself and them from further trouble. To invite a man’s enemies to come and cut his throat, seems a resolution a little extravagant and odd; and yet I think he did better to take that course, than to live in continual feverish fear of an accident for which there was no cure. But seeing all the remedies a man can apply to such a disease, are full of unquietness and uncertainty, ‘tis better with a manly courage to prepare one’s self for the worst that can happen, and to extract some consolation from this, that we are not certain the thing we fear will ever come to pass.
CHAPTER XXIV——OF PEDANTRY
I was often, when a boy, wonderfully concerned to see, in the Italian farces, a pedant always brought in for the fool of the play, and that the title of Magister was in no greater reverence amongst us: for being delivered up to their tuition, what could I do less than be jealous of their honour and reputation? I sought indeed to excuse them by the natural incompatibility betwixt the vulgar sort and men of a finer thread, both in judgment and knowledge, forasmuch as they go a quite contrary way to one another: but in this, the thing I most stumbled at was, that the finest gentlemen were those who most despised them; witness our famous poet Du Bellay—
And ‘twas so in former times; for Plutarch says that Greek and Scholar were terms of reproach and contempt amongst the Romans. But since, with the better experience of age, I find they had very great reason so to do, and that—
But whence it should come to pass, that a mind enriched with the knowledge of so many things should not become more quick and sprightly, and that a gross and vulgar understanding should lodge within it, without correcting and improving itself, all the discourses and judgments of the greatest minds the world ever had, I am yet to seek. To admit so many foreign conceptions, so great, and so high fancies, it is necessary (as a young lady, one of the greatest princesses of the kingdom, said to me once, speaking of a certain person) that a man’s own brain must be crowded and squeezed together into a less compass, to make room for the others; I should be apt to conclude, that as plants are suffocated and drowned with too much nourishment, and lamps with too much oil, so with too much study and matter is the active part of the understanding which, being embarrassed, and confounded with a great diversity of things, loses the force and power to disengage itself, and by the pressure of this weight, is bowed, subjected, and doubled up. But it is quite otherwise; for our soul stretches and dilates itself proportionably as it fills; and in the examples of elder times, we see, quite contrary, men very proper for public business, great captains, and great statesmen very learned withal.
And, as to the philosophers, a sort of men remote from all public affairs, they have been sometimes also despised by the comic liberty of their times; their opinions and manners making them appear, to men of another sort, ridiculous. Would you make them judges of a lawsuit, of the actions of men? they are ready to take it upon them, and straight begin to examine if there be life, if there be motion, if man be any other than an ox;—[“If Montaigne has copied all this from Plato’s Theatetes, p.127, F. as it is plain by all which he has added immediately after, that he has taken it from that dialogue, he has grossly mistaken Plato’s sentiment, who says here no more than this, that the philosopher is so ignorant of what his neighbour does, that he scarce knows whether he is a man, or some other animal:—Coste.”]—what it is to do and to suffer? what animals law and justice are? Do they speak of the magistrates, or to him, ‘tis with a rude, irreverent, and indecent liberty. Do they hear their prince, or a king commended? they make no more of him, than of a shepherd, goatherd, or neatherd: a lazy Coridon, occupied in milking and shearing his herds and flocks, but more rudely and harshly than the herd or shepherd himself. Do you repute any man the greater for being lord of two thousand acres of land? they laugh at such a pitiful pittance, as laying claim themselves to the whole world for their possession. Do you boast of your nobility, as being descended from seven rich successive ancestors? they look upon you with an eye of contempt, as men who have not a right idea of the universal image of nature, and that do not consider how many predecessors every one of us has had, rich, poor, kings, slaves, Greeks, and barbarians; and though you were the fiftieth descendant from Hercules, they look upon it as a great vanity, so highly to value this, which is only a gift of fortune. And ‘twas so the vulgar sort contemned them, as men ignorant of the most elementary and ordinary things; as presumptuous and insolent.
But this Platonic picture is far different from that these pedants are presented by. Those were envied for raising themselves above the common sort, for despising the ordinary actions and offices of life, for having assumed a particular and inimitable way of living, and for using a certain method of high-flight and obsolete language, quite different from the ordinary way of speaking: but these are contemned as being as much below the usual form, as incapable of public employment, as leading a life and conforming themselves to the mean and vile manners of the vulgar:
For what concerns the philosophers, as I have said, if they were in science, they were yet much greater in action. And, as it is said of the geometrician of Syracuse,—[Archimedes.]—who having been disturbed from his contemplation, to put some of his skill in practice for the defence of his country, that he suddenly set on foot dreadful and prodigious engines, that wrought effects beyond all human expectation; himself, notwithstanding, disdaining all his handiwork, and thinking in this he had played the mere mechanic, and violated the dignity of his art, of which these performances of his he accounted but trivial experiments and playthings so they, whenever they have been put upon the proof of action, have been seen to fly to so high a pitch, as made it very well appear, their souls were marvellously elevated, and enriched by the knowledge of things. But some of them, seeing the reins of government in the hands of incapable men, have avoided all management of political affairs; and he who demanded of Crates, how long it was necessary to philosophise, received this answer: “Till our armies are no more commanded by fools.” —[Diogenes Laertius, vi. 92.]—Heraclitus resigned the royalty to his brother; and, to the Ephesians, who reproached him that he spent his time in playing with children before the temple: “Is it not better,” said he, “to do so, than to sit at the helm of affairs in your company?” Others having their imagination advanced above the world and fortune, have looked upon the tribunals of justice, and even the thrones of kings, as paltry and contemptible; insomuch, that Empedocles refused the royalty that the Agrigentines offered to him. Thales, once inveighing in discourse against the pains and care men put themselves to to become rich, was answered by one in the company, that he did like the fox, who found fault with what he could not obtain. Whereupon, he had a mind, for the jest’s sake, to show them to the contrary; and having, for this occasion, made a muster of all his wits, wholly to employ them in the service of profit and gain, he set a traffic on foot, which in one year brought him in so great riches, that the most experienced in that trade could hardly in their whole lives, with all their industry, have raked so much together.—[Diogenes Laertius, Life of Thales, i. 26; Cicero, De Divin., i. 49.]—That which Aristotle reports of some who called both him and Anaxagoras, and others of their profession, wise but not prudent, in not applying their study to more profitable things—though I do not well digest this verbal distinction—that will not, however, serve to excuse my pedants, for to see the low and necessitous fortune wherewith they are content, we have rather reason to pronounce that they are neither wise nor prudent.
But letting this first reason alone, I think it better to say, that this evil proceeds from their applying themselves the wrong way to the study of the sciences; and that, after the manner we are instructed, it is no wonder if neither the scholars nor the masters become, though more learned, ever the wiser, or more able. In plain truth, the cares and expense our parents are at in our education, point at nothing, but to furnish our heads with knowledge; but not a word of judgment and virtue. Cry out, of one that passes by, to the people: “O, what a learned man!” and of another, “O, what a good man!”—[Translated from Seneca, Ep., 88.]—they will not fail to turn their eyes, and address their respect to the former. There should then be a third crier, “O, the blockheads!” Men are apt presently to inquire, does such a one understand Greek or Latin? Is he a poet? or does he write in prose? But whether he be grown better or more discreet, which are qualities of principal concern, these are never thought of. We should rather examine, who is better learned, than who is more learned.
We only labour to stuff the memory, and leave the conscience and the understanding unfurnished and void. Like birds who fly abroad to forage for grain, and bring it home in the beak, without tasting it themselves, to feed their young; so our pedants go picking knowledge here and there, out of books, and hold it at the tongue’s end, only to spit it out and distribute it abroad. And here I cannot but smile to think how I have paid myself in showing the foppery of this kind of learning, who myself am so manifest an example; for, do I not the same thing throughout almost this whole composition? I go here and there, culling out of several books the sentences that best please me, not to keep them (for I have no memory to retain them in), but to transplant them into this; where, to say the truth, they are no more mine than in their first places. We are, I conceive, knowing only in present knowledge, and not at all in what is past, or more than is that which is to come. But the worst on’t is, their scholars and pupils are no better nourished by this kind of inspiration; and it makes no deeper impression upon them, but passes from hand to hand, only to make a show to be tolerable company, and to tell pretty stories, like a counterfeit coin in counters, of no other use or value, but to reckon with, or to set up at cards:
Nature, to shew that there is nothing barbarous where she has the sole conduct, oftentimes, in nations where art has the least to do, causes productions of wit, such as may rival the greatest effect of art whatever. In relation to what I am now speaking of, the Gascon proverb, derived from a cornpipe, is very quaint and subtle:
We can say, Cicero says thus; these were the manners of Plato; these are the very words of Aristotle: but what do we say ourselves? What do we judge? A parrot would say as much as that.
And this puts me in mind of that rich gentleman of Rome,—[Calvisius Sabinus. Seneca, Ep., 27.]—who had been solicitous, with very great expense, to procure men that were excellent in all sorts of science, whom he had always attending his person, to the end, that when amongst his friends any occasion fell out of speaking of any subject whatsoever, they might supply his place, and be ready to prompt him, one with a sentence of Seneca, another with a verse of Homer, and so forth, every one according to his talent; and he fancied this knowledge to be his own, because it was in the heads of those who lived upon his bounty; as they also do, whose learning consists in having noble libraries. I know one, who, when I question him what he knows, he presently calls for a book to shew me, and dares not venture to tell me so much, as that he has piles in his posteriors, till first he has consulted his dictionary, what piles and what posteriors are.
We take other men’s knowledge and opinions upon trust; which is an idle and superficial learning. We must make it our own. We are in this very like him, who having need of fire, went to a neighbour’s house to fetch it, and finding a very good one there, sat down to warm himself without remembering to carry any with him home.—[Plutarch, How a Man should Listen.]—What good does it do us to have the stomach full of meat, if it do not digest, if it be not incorporated with us, if it does not nourish and support us? Can we imagine that Lucullus, whom letters, without any manner of experience, made so great a captain, learned to be so after this perfunctory manner?—[Cicero, Acad., ii. I.]—We suffer ourselves to lean and rely so strongly upon the arm of another, that we destroy our own strength and vigour. Would I fortify myself against the fear of death, it must be at the expense of Seneca: would I extract consolation for myself or my friend, I borrow it from Cicero. I might have found it in myself, had I been trained to make use of my own reason. I do not like this relative and mendicant understanding; for though we could become learned by other men’s learning, a man can never be wise but by his own wisdom:
Whence Ennius:
Dionysius—[It was not Dionysius, but Diogenes the cynic. Diogenes Laertius, vi. 27.]—laughed at the grammarians, who set themselves to inquire into the miseries of Ulysses, and were ignorant of their own; at musicians, who were so exact in tuning their instruments, and never tuned their manners; at orators, who made it a study to declare what is justice, but never took care to do it. If the mind be not better disposed, if the judgment be no better settled, I had much rather my scholar had spent his time at tennis, for, at least, his body would by that means be in better exercise and breath. Do but observe him when he comes back from school, after fifteen or sixteen years that he has been there; there is nothing so unfit for employment; all you shall find he has got, is, that his Latin and Greek have only made him a greater coxcomb than when he went from home. He should bring back his soul replete with good literature, and he brings it only swelled and puffed up with vain and empty shreds and patches of learning; and has really nothing more in him than he had before.—[Plato’s Dialogues: Protagoras.]
These pedants of ours, as Plato says of the Sophists, their cousin-germans, are, of all men, they who most pretend to be useful to mankind, and who alone, of all men, not only do not better and improve that which is committed to them, as a carpenter or a mason would do, but make them much worse, and make us pay them for making them worse, to boot. If the rule which Protagoras proposed to his pupils were followed —either that they should give him his own demand, or make affidavit upon oath in the temple how much they valued the profit they had received under his tuition, and satisfy him accordingly—my pedagogues would find themselves sorely gravelled, if they were to be judged by the affidavits of my experience. My Perigordin patois very pleasantly calls these pretenders to learning, ‘lettre-ferits’, as a man should say, letter-marked—men on whom letters have been stamped by the blow of a mallet. And, in truth, for the most part, they appear to be deprived even of common sense; for you see the husbandman and the cobbler go simply and fairly about their business, speaking only of what they know and understand; whereas these fellows, to make parade and to get opinion, mustering this ridiculous knowledge of theirs, that floats on the superficies of the brain, are perpetually perplexing, and entangling themselves in their own nonsense. They speak fine words sometimes, ‘tis true, but let somebody that is wiser apply them. They are wonderfully well acquainted with Galen, but not at all with the disease of the patient; they have already deafened you with a long ribble-row of laws, but understand nothing of the case in hand; they have the theory of all things, let who will put it in practice.
I have sat by, when a friend of mine, in my own house, for sport-sake, has with one of these fellows counterfeited a jargon of Galimatias, patched up of phrases without head or tail, saving that he interlarded here and there some terms that had relation to their dispute, and held the coxcomb in play a whole afternoon together, who all the while thought he had answered pertinently and learnedly to all his objections; and yet this was a man of letters, and reputation, and a fine gentleman of the long robe:
Whosoever shall narrowly pry into and thoroughly sift this sort of people, wherewith the world is so pestered, will, as I have done, find, that for the most part, they neither understand others, nor themselves; and that their memories are full enough, but the judgment totally void and empty; some excepted, whose own nature has of itself formed them into better fashion. As I have observed, for example, in Adrian Turnebus, who having never made other profession than that of mere learning only, and in that, in my opinion, he was the greatest man that has been these thousand years, had nothing at all in him of the pedant, but the wearing of his gown, and a little exterior fashion, that could not be civilised to courtier ways, which in themselves are nothing. I hate our people, who can worse endure an ill-contrived robe than an ill-contrived mind, and take their measure by the leg a man makes, by his behaviour, and so much as the very fashion of his boots, what kind of man he is. For within there was not a more polished soul upon earth. I have often purposely put him upon arguments quite wide of his profession, wherein I found he had so clear an insight, so quick an apprehension, so solid a judgment, that a man would have thought he had never practised any other thing but arms, and been all his life employed in affairs of State. These are great and vigorous natures,
that can keep themselves upright in despite of a pedantic education. But it is not enough that our education does not spoil us; it must, moreover, alter us for the better.
Some of our Parliaments, when they are to admit officers, examine only their learning; to which some of the others also add the trial of understanding, by asking their judgment of some case in law; of these the latter, methinks, proceed with the better method; for although both are necessary, and that it is very requisite they should be defective in neither, yet, in truth, knowledge is not so absolutely necessary as judgment; the last may make shift without the other, but the other never without this. For as the Greek verse says—
Would to God that, for the good of our judicature, these societies were as well furnished with understanding and conscience as they are with knowledge.
We are not to tie learning to the soul, but to work and incorporate them together: not to tincture it only, but to give it a thorough and perfect dye; which, if it will not take colour, and meliorate its imperfect state, it were without question better to let it alone. ‘Tis a dangerous weapon, that will hinder and wound its master, if put into an awkward and unskilful hand:
And this, peradventure, is the reason why neither we nor theology require much learning in women; and that Francis, Duke of Brittany, son of John V., one talking with him about his marriage with Isabella the daughter of Scotland, and adding that she was homely bred, and without any manner of learning, made answer, that he liked her the better, and that a woman was wise enough, if she could distinguish her husband’s shirt from his doublet. So that it is no so great wonder, as they make of it, that our ancestors had letters in no greater esteem, and that even to this day they are but rarely met with in the principal councils of princes; and if the end and design of acquiring riches, which is the only thing we propose to ourselves, by the means of law, physic, pedantry, and even divinity itself, did not uphold and keep them in credit, you would, with doubt, see them in as pitiful a condition as ever. And what loss would this be, if they neither instruct us to think well nor to do well?
All other knowledge is hurtful to him who has not the science of goodness.
But the reason I glanced upon but now, may it not also hence proceed, that, our studies in France having almost no other aim but profit, except as to those who, by nature born to offices and employments rather of glory than gain, addict themselves to letters, if at all, only for so short a time (being taken from their studies before they can come to have any taste of them, to a profession that has nothing to do with books), there ordinarily remain no others to apply themselves wholly to learning, but people of mean condition, who in that only seek the means to live; and by such people, whose souls are, both by nature and by domestic education and example, of the basest alloy the fruits of knowledge are immaturely gathered and ill digested, and delivered to their recipients quite another thing. For it is not for knowledge to enlighten a soul that is dark of itself, nor to make a blind man see. Her business is not to find a man’s eyes, but to guide, govern, and direct them, provided he have sound feet and straight legs to go upon. Knowledge is an excellent drug, but no drug has virtue enough to preserve itself from corruption and decay, if the vessel be tainted and impure wherein it is put to keep. Such a one may have a sight clear enough who looks asquint, and consequently sees what is good, but does not follow it, and sees knowledge, but makes no use of it. Plato’s principal institution in his Republic is to fit his citizens with employments suitable to their nature. Nature can do all, and does all. Cripples are very unfit for exercises of the body, and lame souls for exercises of the mind. Degenerate and vulgar souls are unworthy of philosophy. If we see a shoemaker with his shoes out at the toes, we say, ‘tis no wonder; for, commonly, none go worse shod than they. In like manner, experience often presents us a physician worse physicked, a divine less reformed, and (constantly) a scholar of less sufficiency, than other people.
Old Aristo of Chios had reason to say that philosophers did their auditors harm, forasmuch as most of the souls of those that heard them were not capable of deriving benefit from instruction, which, if not applied to good, would certainly be applied to ill:
In that excellent institution that Xenophon attributes to the Persians, we find that they taught their children virtue, as other nations do letters. Plato tells us that the eldest son in their royal succession was thus brought up; after his birth he was delivered, not to women, but to eunuchs of the greatest authority about their kings for their virtue, whose charge it was to keep his body healthful and in good plight; and after he came to seven years of age, to teach him to ride and to go a-hunting. When he arrived at fourteen he was transferred into the hands of four, the wisest, the most just, the most temperate, and most valiant of the nation; of whom the first was to instruct him in religion, the second to be always upright and sincere, the third to conquer his appetites and desires, and the fourth to despise all danger.
It is a thing worthy of very great consideration, that in that excellent, and, in truth, for its perfection, prodigious form of civil regimen set down by Lycurgus, though so solicitous of the education of children, as a thing of the greatest concern, and even in the very seat of the Muses, he should make so little mention of learning; as if that generous youth, disdaining all other subjection but that of virtue, ought to be supplied, instead of tutors to read to them arts and sciences, with such masters as should only instruct them in valour, prudence, and justice; an example that Plato has followed in his laws. The manner of their discipline was to propound to them questions in judgment upon men and their actions; and if they commended or condemned this or that person or fact, they were to give a reason for so doing; by which means they at once sharpened their understanding, and learned what was right. Astyages, in Xenophon, asks Cyrus to give an account of his last lesson; and thus it was, “A great boy in our school, having a little short cassock, by force took a longer from another that was not so tall as he, and gave him his own in exchange: whereupon I, being appointed judge of the controversy, gave judgment, that I thought it best each should keep the coat he had, for that they both of them were better fitted with that of one another than with their own: upon which my master told me, I had done ill, in that I had only considered the fitness of the garments, whereas I ought to have considered the justice of the thing, which required that no one should have anything forcibly taken from him that is his own.” And Cyrus adds that he was whipped for his pains, as we are in our villages for forgetting the first aorist of———.
My pedant must make me a very learned oration, ‘in genere demonstrativo’, before he can persuade me that his school is like unto that. They knew how to go the readiest way to work; and seeing that science, when most rightly applied and best understood, can do no more but teach us prudence, moral honesty, and resolution, they thought fit, at first hand, to initiate their children with the knowledge of effects, and to instruct them, not by hearsay and rote, but by the experiment of action, in lively forming and moulding them; not only by words and precepts, but chiefly by works and examples; to the end it might not be a knowledge in the mind only, but its complexion and habit: not an acquisition, but a natural possession. One asking to this purpose, Agesilaus, what he thought most proper for boys to learn? “What they ought to do when they come to be men,” said he.—[Plutarch, Apothegms of the Lacedamonians. Rousseau adopts the expression in his Diswuys sur tes Lettres.]—It is no wonder, if such an institution produced so admirable effects.
They used to go, it is said, to the other cities of Greece, to inquire out rhetoricians, painters, and musicians; but to Lacedaemon for legislators, magistrates, and generals of armies; at Athens they learned to speak well: here to do well; there to disengage themselves from a sophistical argument, and to unravel the imposture of captious syllogisms; here to evade the baits and allurements of pleasure, and with a noble courage and resolution to conquer the menaces of fortune and death; those cudgelled their brains about words, these made it their business to inquire into things; there was an eternal babble of the tongue, here a continual exercise of the soul. And therefore it is nothing strange if, when Antipater demanded of them fifty children for hostages, they made answer, quite contrary to what we should do, that they would rather give him twice as many full-grown men, so much did they value the loss of their country’s education. When Agesilaus courted Xenophon to send his children to Sparta to be bred, “it is not,” said he, “there to learn logic or rhetoric, but to be instructed in the noblest of all sciences, namely, the science to obey and to command.”—[Plutarch, Life of Agesilaus, c. 7.]
It is very pleasant to see Socrates, after his manner, rallying Hippias, —[Plato’s Dialogues: Hippias Major.]—who recounts to him what a world of money he has got, especially in certain little villages of Sicily, by teaching school, and that he made never a penny at Sparta: “What a sottish and stupid people,” said Socrates, “are they, without sense or understanding, that make no account either of grammar or poetry, and only busy themselves in studying the genealogies and successions of their kings, the foundations, rises, and declensions of states, and such tales of a tub!” After which, having made Hippias from one step to another acknowledge the excellency of their form of public administration, and the felicity and virtue of their private life, he leaves him to guess at the conclusion he makes of the inutilities of his pedantic arts.
Examples have demonstrated to us that in military affairs, and all others of the like active nature, the study of sciences more softens and untempers the courages of men than it in any way fortifies and excites them. The most potent empire that at this day appears to be in the whole world is that of the Turks, a people equally inured to the estimation of arms and the contempt of letters. I find Rome was more valiant before she grew so learned. The most warlike nations at this time in being are the most rude and ignorant: the Scythians, the Parthians, Tamerlane, serve for sufficient proof of this. When the Goths overran Greece, the only thing that preserved all the libraries from the fire was, that some one possessed them with an opinion that they were to leave this kind of furniture entire to the enemy, as being most proper to divert them from the exercise of arms, and to fix them to a lazy and sedentary life. When our King Charles VIII., almost without striking a blow, saw himself possessed of the kingdom of Naples and a considerable part of Tuscany, the nobles about him attributed this unexpected facility of conquest to this, that the princes and nobles of Italy, more studied to render themselves ingenious and learned, than vigorous and warlike.
CHAPTER XXV——OF THE EDUCATION OF CHILDREN
To madame diane de foix, comtesse de gurson.
I never yet saw that father, but let his son be never so decrepit or deformed, would not, notwithstanding, own him: not, nevertheless, if he were not totally besotted, and blinded with his paternal affection, that he did not well enough discern his defects; but that with all defaults he was still his. Just so, I see better than any other, that all I write here are but the idle reveries of a man that has only nibbled upon the outward crust of sciences in his nonage, and only retained a general and formless image of them; who has got a little snatch of everything and nothing of the whole, ‘a la Francoise’. For I know, in general, that there is such a thing as physic, as jurisprudence: four parts in mathematics, and, roughly, what all these aim and point at; and, peradventure, I yet know farther, what sciences in general pretend unto, in order to the service of our life: but to dive farther than that, and to have cudgelled my brains in the study of Aristotle, the monarch of all modern learning, or particularly addicted myself to any one science, I have never done it; neither is there any one art of which I am able to draw the first lineaments and dead colour; insomuch that there is not a boy of the lowest form in a school, that may not pretend to be wiser than I, who am not able to examine him in his first lesson, which, if I am at any time forced upon, I am necessitated in my own defence, to ask him, unaptly enough, some universal questions, such as may serve to try his natural understanding; a lesson as strange and unknown to him, as his is to me.
I never seriously settled myself to the reading any book of solid learning but Plutarch and Seneca; and there, like the Danaides, I eternally fill, and it as constantly runs out; something of which drops upon this paper, but little or nothing stays with me. History is my particular game as to matter of reading, or else poetry, for which I have particular kindness and esteem: for, as Cleanthes said, as the voice, forced through the narrow passage of a trumpet, comes out more forcible and shrill: so, methinks, a sentence pressed within the harmony of verse darts out more briskly upon the understanding, and strikes my ear and apprehension with a smarter and more pleasing effect. As to the natural parts I have, of which this is the essay, I find them to bow under the burden; my fancy and judgment do but grope in the dark, tripping and stumbling in the way; and when I have gone as far as I can, I am in no degree satisfied; I discover still a new and greater extent of land before me, with a troubled and imperfect sight and wrapped up in clouds, that I am not able to penetrate. And taking upon me to write indifferently of whatever comes into my head, and therein making use of nothing but my own proper and natural means, if it befall me, as oft-times it does, accidentally to meet in any good author, the same heads and commonplaces upon which I have attempted to write (as I did but just now in Plutarch’s “Discourse of the Force of Imagination”), to see myself so weak and so forlorn, so heavy and so flat, in comparison of those better writers, I at once pity or despise myself. Yet do I please myself with this, that my opinions have often the honour and good fortune to jump with theirs, and that I go in the same path, though at a very great distance, and can say, “Ah, that is so.” I am farther satisfied to find that I have a quality, which every one is not blessed withal, which is, to discern the vast difference between them and me; and notwithstanding all that, suffer my own inventions, low and feeble as they are, to run on in their career, without mending or plastering up the defects that this comparison has laid open to my own view. And, in plain truth, a man had need of a good strong back to keep pace with these people. The indiscreet scribblers of our times, who, amongst their laborious nothings, insert whole sections and pages out of ancient authors, with a design, by that means, to illustrate their own writings, do quite contrary; for this infinite dissimilitude of ornaments renders the complexion of their own compositions so sallow and deformed, that they lose much more than they get.
The philosophers, Chrysippus and Epicurus, were in this of two quite contrary humours: the first not only in his books mixed passages and sayings of other authors, but entire pieces, and, in one, the whole Medea of Euripides; which gave Apollodorus occasion to say, that should a man pick out of his writings all that was none of his, he would leave him nothing but blank paper: whereas the latter, quite on the contrary, in three hundred volumes that he left behind him, has not so much as one quotation.—[Diogenes Laertius, Lives of Chyysippus, vii. 181, and Epicurus, x. 26.]
I happened the other day upon this piece of fortune; I was reading a French book, where after I had a long time run dreaming over a great many words, so dull, so insipid, so void of all wit or common sense, that indeed they were only French words: after a long and tedious travel, I came at last to meet with a piece that was lofty, rich, and elevated to the very clouds; of which, had I found either the declivity easy or the ascent gradual, there had been some excuse; but it was so perpendicular a precipice, and so wholly cut off from the rest of the work, that by the first six words, I found myself flying into the other world, and thence discovered the vale whence I came so deep and low, that I have never had since the heart to descend into it any more. If I should set out one of my discourses with such rich spoils as these, it would but too evidently manifest the imperfection of my own writing. To reprehend the fault in others that I am guilty of myself, appears to me no more unreasonable, than to condemn, as I often do, those of others in myself: they are to be everywhere reproved, and ought to have no sanctuary allowed them. I know very well how audaciously I myself, at every turn, attempt to equal myself to my thefts, and to make my style go hand in hand with them, not without a temerarious hope of deceiving the eyes of my reader from discerning the difference; but withal it is as much by the benefit of my application, that I hope to do it, as by that of my invention or any force of my own. Besides, I do not offer to contend with the whole body of these champions, nor hand to hand with anyone of them: ‘tis only by flights and little light attempts that I engage them; I do not grapple with them, but try their strength only, and never engage so far as I make a show to do. If I could hold them in play, I were a brave fellow; for I never attack them; but where they are most sinewy and strong. To cover a man’s self (as I have seen some do) with another man’s armour, so as not to discover so much as his fingers’ ends; to carry on a design (as it is not hard for a man that has anything of a scholar in him, in an ordinary subject to do) under old inventions patched up here and there with his own trumpery, and then to endeavour to conceal the theft, and to make it pass for his own, is first injustice and meanness of spirit in those who do it, who having nothing in them of their own fit to procure them a reputation, endeavour to do it by attempting to impose things upon the world in their own name, which they have no manner of title to; and next, a ridiculous folly to content themselves with acquiring the ignorant approbation of the vulgar by such a pitiful cheat, at the price at the same time of degrading themselves in the eyes of men of understanding, who turn up their noses at all this borrowed incrustation, yet whose praise alone is worth the having. For my own part, there is nothing I would not sooner do than that, neither have I said so much of others, but to get a better opportunity to explain myself. Nor in this do I glance at the composers of centos, who declare themselves for such; of which sort of writers I have in my time known many very ingenious, and particularly one under the name of Capilupus, besides the ancients. These are really men of wit, and that make it appear they are so, both by that and other ways of writing; as for example, Lipsius, in that learned and laborious contexture of his Politics.
But, be it how it will, and how inconsiderable soever these ineptitudes may be, I will say I never intended to conceal them, no more than my old bald grizzled likeness before them, where the painter has presented you not with a perfect face, but with mine. For these are my own particular opinions and fancies, and I deliver them as only what I myself believe, and not for what is to be believed by others. I have no other end in this writing, but only to discover myself, who, also shall, peradventure, be another thing to-morrow, if I chance to meet any new instruction to change me. I have no authority to be believed, neither do I desire it, being too conscious of my own inerudition to be able to instruct others.
Some one, then, having seen the preceding chapter, the other day told me at my house, that I should a little farther have extended my discourse on the education of children.—[“Which, how fit I am to do, let my friends flatter me if they please, I have in the meantime no such opinion of my own talent, as to promise myself any very good success from my endeavour.” This passage would appear to be an interpolation by Cotton. At all events, I do not find it in the original editions before me, or in Coste.]—
Now, madam, if I had any sufficiency in this subject, I could not possibly better employ it, than to present my best instructions to the little man that threatens you shortly with a happy birth (for you are too generous to begin otherwise than with a male); for, having had so great a hand in the treaty of your marriage, I have a certain particular right and interest in the greatness and prosperity of the issue that shall spring from it; beside that, your having had the best of my services so long in possession, sufficiently obliges me to desire the honour and advantage of all wherein you shall be concerned. But, in truth, all I understand as to that particular is only this, that the greatest and most important difficulty of human science is the education of children. For as in agriculture, the husbandry that is to precede planting, as also planting itself, is certain, plain, and well known; but after that which is planted comes to life, there is a great deal more to be done, more art to be used, more care to be taken, and much more difficulty to cultivate and bring it to perfection so it is with men; it is no hard matter to get children; but after they are born, then begins the trouble, solicitude, and care rightly to train, principle, and bring them up. The symptoms of their inclinations in that tender age are so obscure, and the promises so uncertain and fallacious, that it is very hard to establish any solid judgment or conjecture upon them. Look at Cimon, for example, and Themistocles, and a thousand others, who very much deceived the expectation men had of them. Cubs of bears and puppies readily discover their natural inclination; but men, so soon as ever they are grownup, applying themselves to certain habits, engaging themselves in certain opinions, and conforming themselves to particular laws and customs, easily alter, or at least disguise, their true and real disposition; and yet it is hard to force the propension of nature. Whence it comes to pass, that for not having chosen the right course, we often take very great pains, and consume a good part of our time in training up children to things, for which, by their natural constitution, they are totally unfit. In this difficulty, nevertheless, I am clearly of opinion, that they ought to be elemented in the best and most advantageous studies, without taking too much notice of, or being too superstitious in those light prognostics they give of themselves in their tender years, and to which Plato, in his Republic, gives, methinks, too much authority.
The Essays of Montaigne
First published in 1686; from the edition revised and edited in 1877 by William Carew Hazlitt
Table of Contents
- The Letters of Montaigne
- Chapter XXXIV. Means to carry on a war according to Julius Caesar.
- Chapter I. Of Profit and Honesty.
- Chapter II. Of Repentance.
- Chapter III. Of Three Commerces.
- Chapter IV. Of Diversion.
- Chapter V. Upon Some verses of Virgil.
- Chapter VI. Of Coaches.
- Chapter VII. Of the Inconvenience of Greatness.
- Chapter VIII. Of the Art of Conference.
- Chapter IX. Of Vanity.
- Chapter X. Of Managing the Will.
- Chapter XI. Of Cripples.
- Chapter XII. Of Physiognomy.
- Chapter XIII. Of Experience.
- ↑ Translator John Florio
- French essays
- Works originally in French
- Headers applying DefaultSort key
Navigation menu
We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!
Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
The complete works of Montaigne : essays, travel journal, letters
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
625 Previews
36 Favorites
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
PDF access not available for this item.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by station03.cebu on February 9, 2022
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
I Thought the Bragg Case Against Trump Was a Legal Embarrassment. Now I Think It’s a Historic Mistake.

By Jed Handelsman Shugerman
Mr. Shugerman is a law professor at Boston University.
About a year ago, when Alvin Bragg, the Manhattan district attorney, indicted former President Donald Trump, I was critical of the case and called it an embarrassment. I thought an array of legal problems would and should lead to long delays in federal courts.
After listening to Monday’s opening statement by prosecutors, I still think the Manhattan D.A. has made a historic mistake. Their vague allegation about “a criminal scheme to corrupt the 2016 presidential election” has me more concerned than ever about their unprecedented use of state law and their persistent avoidance of specifying an election crime or a valid theory of fraud.
To recap: Mr. Trump is accused in the case of falsifying business records. Those are misdemeanor charges. To elevate it to a criminal case, Mr. Bragg and his team have pointed to potential violations of federal election law and state tax fraud. They also cite state election law, but state statutory definitions of “public office” seem to limit those statutes to state and local races.
Both the misdemeanor and felony charges require that the defendant made the false record with “intent to defraud.” A year ago, I wondered how entirely internal business records (the daily ledger, pay stubs and invoices) could be the basis of any fraud if they are not shared with anyone outside the business. I suggested that the real fraud was Mr. Trump’s filing an (allegedly) false report to the Federal Election Commission, and only federal prosecutors had jurisdiction over that filing.
A recent conversation with Jeffrey Cohen, a friend, Boston College law professor and former prosecutor, made me think that the case could turn out to be more legitimate than I had originally thought. The reason has to do with those allegedly falsified business records: Most of them were entered in early 2017, generally before Mr. Trump filed his Federal Election Commission report that summer. Mr. Trump may have foreseen an investigation into his campaign, leading to its financial records. Mr. Trump may have falsely recorded these internal records before the F.E.C. filing as consciously part of the same fraud: to create a consistent paper trail and to hide intent to violate federal election laws, or defraud the F.E.C.
In short: It’s not the crime; it’s the cover-up.
Looking at the case in this way might address concerns about state jurisdiction. In this scenario, Mr. Trump arguably intended to deceive state investigators, too. State investigators could find these inconsistencies and alert federal agencies. Prosecutors could argue that New York State agencies have an interest in detecting conspiracies to defraud federal entities; they might also have a plausible answer to significant questions about whether New York State has jurisdiction or whether this stretch of a state business filing law is pre-empted by federal law.
However, this explanation is a novel interpretation with many significant legal problems. And none of the Manhattan D.A.’s filings or today’s opening statement even hint at this approach.
Instead of a theory of defrauding state regulators, Mr. Bragg has adopted a weak theory of “election interference,” and Justice Juan Merchan described the case , in his summary of it during jury selection, as an allegation of falsifying business records “to conceal an agreement with others to unlawfully influence the 2016 election.”
As a reality check, it is legal for a candidate to pay for a nondisclosure agreement. Hush money is unseemly, but it is legal. The election law scholar Richard Hasen rightly observed , “Calling it election interference actually cheapens the term and undermines the deadly serious charges in the real election interference cases.”
In Monday’s opening argument, the prosecutor Matthew Colangelo still evaded specifics about what was illegal about influencing an election, but then he claimed , “It was election fraud, pure and simple.” None of the relevant state or federal statutes refer to filing violations as fraud. Calling it “election fraud” is a legal and strategic mistake, exaggerating the case and setting up the jury with high expectations that the prosecutors cannot meet.
The most accurate description of this criminal case is a federal campaign finance filing violation. Without a federal violation (which the state election statute is tethered to), Mr. Bragg cannot upgrade the misdemeanor counts into felonies. Moreover, it is unclear how this case would even fulfill the misdemeanor requirement of “intent to defraud” without the federal crime.
In stretching jurisdiction and trying a federal crime in state court, the Manhattan D.A. is now pushing untested legal interpretations and applications. I see three red flags raising concerns about selective prosecution upon appeal.
First, I could find no previous case of any state prosecutor relying on the Federal Election Campaign Act either as a direct crime or a predicate crime. Whether state prosecutors have avoided doing so as a matter of law, norms or lack of expertise, this novel attempt is a sign of overreach.
Second, Mr. Trump’s lawyers argued that the New York statute requires that the predicate (underlying) crime must also be a New York crime, not a crime in another jurisdiction. The Manhattan D.A. responded with judicial precedents only about other criminal statutes, not the statute in this case. In the end, they could not cite a single judicial interpretation of this particular statute supporting their use of the statute (a plea deal and a single jury instruction do not count).
Third, no New York precedent has allowed an interpretation of defrauding the general public. Legal experts have noted that such a broad “election interference” theory is unprecedented, and a conviction based on it may not survive a state appeal.
Mr. Trump’s legal team also undercut itself for its decisions in the past year: His lawyers essentially put all of their eggs in the meritless basket of seeking to move the trial to federal court, instead of seeking a federal injunction to stop the trial entirely. If they had raised the issues of selective or vindictive prosecution and a mix of jurisdictional, pre-emption and constitutional claims, they could have delayed the trial past Election Day, even if they lost at each federal stage.
Another reason a federal crime has wound up in state court is that President Biden’s Justice Department bent over backward not to reopen this valid case or appoint a special counsel. Mr. Trump has tried to blame Mr. Biden for this prosecution as the real “election interference.” The Biden administration’s extra restraint belies this allegation and deserves more credit.
Eight years after the alleged crime itself, it is reasonable to ask if this is more about Manhattan politics than New York law. This case should serve as a cautionary tale about broader prosecutorial abuses in America — and promote bipartisan reforms of our partisan prosecutorial system.
Nevertheless, prosecutors should have some latitude to develop their case during trial, and maybe they will be more careful and precise about the underlying crime, fraud and the jurisdictional questions. Mr. Trump has received sufficient notice of the charges, and he can raise his arguments on appeal. One important principle of “ our Federalism ,” in the Supreme Court’s terms, is abstention , that federal courts should generally allow state trials to proceed first and wait to hear challenges later.
This case is still an embarrassment of prosecutorial ethics and apparent selective prosecution. Nevertheless, each side should have its day in court. If convicted, Mr. Trump can fight many other days — and perhaps win — in appellate courts. But if Monday’s opening is a preview of exaggerated allegations, imprecise legal theories and persistently unaddressed problems, the prosecutors might not win a conviction at all.
Jed Handelsman Shugerman (@jedshug) is a law professor at Boston University.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Get unlimited access to SuperSummaryfor only $0.70/week. Thanks for exploring this SuperSummary Study Guide of "Montaigne: Essays" by Michel de Montaigne. A modern alternative to SparkNotes and CliffsNotes, SuperSummary offers high-quality Study Guides with detailed chapter summaries and analysis of major themes, characters, and more.
The Essays (French: Essais, pronounced) of Michel de Montaigne are contained in three books and 107 chapters of varying length. They were originally written in Middle French and published in the Kingdom of France.Montaigne's stated design in writing, publishing and revising the Essays over the period from approximately 1570 to 1592 was to record "some traits of my character and of my humours."
Summary. Last Updated September 5, 2023. Michel Eyquem de Montaigne was a skeptical philosopher and perhaps the most influential writer of the French Renaissance. His Essays are difficult—maybe ...
Montaigne saw his age as one of dissimulation, corruption, violence, and hypocrisy, and it is therefore not surprising that the point of departure of the Essays is situated in negativity: the negativity of Montaigne's recognition of the rule of appearances and of the loss of connection with the truth of being. Montaigne's much-discussed skepticism results from that initial negativity, as ...
Montaigne anticipated much of modern thought, and was profoundly shaped by the classics. His Essays, so personal yet so urbane, continue to challenge and charm readers.
The question is not who will hit the ring, but who will make the best runs at it. Given the huge breadth of his readings, Montaigne could have been ranked among the most erudite humanists of the XVI th century. But in the Essays, his aim is above all to exercise his own judgment properly.Readers who might want to convict him of ignorance would find nothing to hold against him, he said, for he ...
According to Montaigne, they are fake and manipulative. The essays are actually his observations and thoughts on the Renaissance world. The essays are organized in a chronological way. Montaigne did not really approve the oratory of sixteenth century. For him, rhetoric and oratory were the two methods used by the government to aggravate the ...
This practical and insightful reading guide offers a complete summary and analysis of the Essays, by Michel de Montaigne. It provides a thorough exploration of the essay's plot, context and main themes, including - to list but a few - medicine, knowledge and manners. The clear and concise style makes for easy understanding, providing the ...
Essays, Book I Michel de Montaigne 1. We reach the same end by different means To the reader [A] This is a book written in good faith, reader. It warns you from the start that my only goal here is a private family one. I have not been concerned to serve you or my reputation: my powers are inadequate for that. I have dedicated this book to the ...
Selections from the Essays of Montaigne study guide contains a biography of author Michel De Montaigne, literature essays, a complete e-text, quiz questions, major themes, characters, and a full summary and analysis. Essays of Montaigne literature essays are academic essays for citation. These papers were written primarily by students and ...
Michel de Montaigne (1533-1592) Michel de Montaigne, the sixteenth century French essayist, is one of the most renowned literary and philosophical figures of the late Renaissance. The one book he wrote, Les Essais de Michel de Montaigne, is not a traditional work of philosophy. Having begun work on it around 1572, he published the first edition ...
THE LIFE OF MONTAIGNE [This is translated freely from that prefixed to the 'variorum' Paris edition, 1854, 4 vols. 8vo. This biography is the more desirable that it contains all really interesting and important matter in the journal of the Tour in Germany and Italy, which, as it was merely written under Montaigne's dictation, is in the third person, is scarcely worth publication, as a ...
Essays, work by the French writer and philosopher Michel de Montaigne (1533-92) that established a new literary form, the essay. The first two volumes of the Essais ( Essays) were published in 1580; a third volume was published in 1588, along with enlarged editions of the first two. In his Essays, Montaigne wrote one of the most captivating ...
That the soul discharges her passions upon false objects, where the true are wanting. Chapter V. Whether the governor of a place besieged ought himself to go out to parley. Chapter VI. That the hour of parley is dangerous. Chapter VII. That the intention is judge of our actions. Chapter VIII. Of idleness.
Essays, Book II Michel de Montaigne Glossary braverie: Courage, usually thought of as swaggering courage. colic: This is used to translate colique on page 44 and in essay 37; the OED defines it as 'Acute episodic abdominal pain, especially one arising from the twisting, spasm, or obstruction of a hollow organ'; but as essay 37 proceeds it
Also included in this complete edition of his works are Montaigne's letters and his travel journal, fascinating records of the experiences and contemplations that would shape and infuse his essays. Montaigne speaks to us always in a personal voice in which his virtues of tolerance, moderation, and understanding are dazzlingly manifest. (from ...
Summary. In Montaigne's final essay he expounds upon the results of his long search for self knowledge via life experience. He uses disease, health, medicine and doctors as prime arenas for demonstration of what he has learned from living. On physicians: to be a "right" physician, one must have experienced every illness, accident or mishap one ...
Now I Think It's a Historic Mistake. Mr. Shugerman is a law professor at Boston University. About a year ago, when Alvin Bragg, the Manhattan district attorney, indicted former President Donald ...