Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


Comparing the Effectiveness of Classroom and Online Learning: Teaching Research Methods

AbstrAct As public administration programs extend their online education offerings to reach more time-and place-bound students, and as accredited institutions become interested in documenting teaching and learning effectiveness, the degree to which online students are successful as compared to their classroom counterparts is of interest to teaching faculty and others charged with assessment. By comparing student performance measures and assessments of learning experience from both online and traditional sections of a required graduate public administration research methods course taught by the same instructor, this paper provides evidence that student performance as measured by grade is independent of the mode of instruction. Persistence in an online environment may be more challenging in research methods classes than in other public administration classes. Furthermore, participation may be less intimidating, and the quality and quantity of interaction may be increased in online classes.
Related Papers
Texas State PA Applied Research Projects
Purpose The purpose of this research is to describe the dimensions of innovative teaching in Master of Public Administration (MPA) programs. To separate itself from the learning styles of undergraduate education, graduate programs must take students into the next level of the cognitive domain because students entering public service careers need information and skills. This higher level of learning can be achieved by using appropriate innovative techniques. This research uses the literature to develop a conceptual framework that organizes dimensions of innovative teaching into the following categories: class activities, course projects, instructor characteristics, and environment. Method This research uses a survey, developed from the conceptual framework, to describe the extent to which MPA faculty use and value techniques identified by the literature. The survey was distributed to leadership from the top 170 MPA programs in the United States. These points of contact were used to distribute the survey to faculty members. Total of 217 faculty responded. Findings In general, faculty frequently used the innovative techniques that they considered important. Highly endorsed techniques included skill building, collaborative learning, and instructor characteristics such as encouragement and facilitation. Techniques with low endorsement included role play and Blended Learning Distance Education (BLDE). Respondents alluded to the possibility that not all techniques are applicable to all subjects. Additionally, respondents questioned the state of “innovation.”
Journal of Public Affairs Education
Claire Knox
Karina Moreno
This article presents key literature on team-based learning, a research-based teaching method derived from the cooperative learning paradigm. Team-based learning is presented as a means to teach public administration students, our future practitioners and policy makers, how to practice cultural competency as they address local community challenges. Team-based learning is a pedagogical tool that emphasizes diverse teams that are properly managed, individual and group preparedness and accountability, application of key course content, peer evaluations, and team development and interpersonal communication skills. This paper provides evidence of this instructional method’s effectiveness and of the link between team-based learning and cultural competency, presents stepby-step instructions on how to effectively implement team-based learning, provides numerous examples of in-class activities meant to develop and strengthen cultural competency skills in public affairs and administration curricula, and provides a number of key resources for public administration faculty interested in learning more about research-based teaching.
… OF PUBLIC AFFAIRS EDUCATION VOLUME 18 …
Heather Wyatt-Nichol
"This manuscript offers a firsthand account of obstacles I experienced as a working-class, first-generation college student and how my origins still affect my thoughts and actions as a professor of Public Administration. In this context, I consider larger issues of social class in admissions and the overall college experience, including proposing strategies to help students, especially those whose backgrounds are similar to mine, to maximize their odds of finishing their degrees. The manuscript ends by proposing that our field begin placing more emphasis on understanding social class inequalities."
Journal of Public Affairs
David Swindell
The growing capabilities of distance-education technologies, combined with potential cost and efficiency benefits, and the possibility to extend opportunities for higher education to wider, sometimes-isolated audiences, is creating a predictable move to offer increasing numbers of graduate public administration courses and even complete degrees, through various technological means. While these trends offer new and exciting opportunities to (1) reach students who in earlier times would not be able to engage in ...
Thomas Bryer
Abstract Collaborative governance is increasingly becoming a topic for scholarly research, practitioner skill development, and a component of graduate programs in public administration. This article documents a service learning project in a graduate level Masters in Public Administration class on cross-sector governance.
Goktug Morcol
This paper presents the results of a content analysis of the titles and descriptions of methods courses offered in 44 graduate programs in public policy at universities and colleges in the US, and compares the results to those of an earlier survey on the methodological preferences of policy professionals. The rationale for classifying methods courses as quantitative and qualitative and the results of the past research on methods courses are discussed.
Mitchell Rice
The topic of diversity in public administration tends to be approached as a necessary response to change.
Roy Heidelberg
Naim Kapucu
The development and use of the portfolio has become a critical feature of many Master of Public Administration (MPA) programs. The portfolio assignment has grown out of deepened appreciation of learning theory and the application of both performance measurement and management systems in MPA program curricula. The portfolio assignment as part of a capstone experience can contribute to the development of professional practitioners of public service. Based on review of the literature on the use of portfolios in professional degree programs and a case study of two MPA programs, this article seeks to deepen our understanding of the portfolio as an effective pedagogical tool and assessment strategy, and it offers conclusions about best practices in using portfolios.
RELATED PAPERS
works.bepress.com
Fatih Demiroz
Travis P Wagner
METE YILDIZ
Ignacio J . Martinez-Moyano
Mark Imperial
Eric Austin
Ralph A Gigliotti
Teaching Public Administration
Margaret Stout
Support Gooogl
Applied Research Project
sciepub.com SciEP
Maria J. D'Agostino , Nicole M Elias
Erik Johnston
Nadia Rubaii
Andrew Feenberg
METE YILDIZ , Cenay Babaoglu , Mehmet Akif Demircioglu
Tanya Joosten
International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education
Jesus Canelon
Adnan Boyaci
Tina Zappile , Cathleen O Erwin
Traci Temple
Online Learning
Majeda El-Banna
Margaret Partlo
The Internet and higher education
Steven Tello
Jennifer Taylor
The Internet and Higher Education
Journal of Interactive Online Learning
Carie S T King
Karen Brinkley
Dominique Daniel
Tahereh Ebrahimifar
Apeejay Journal of Management & Technology
Simple Sharma
Dr. Evangelia (Lia) Marinakou
Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks
Paula Bigatel
Sheri A Conklin
Sheri A Conklin , Beth Oyarzun , Daisyane Barreto
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

HOW TECHNOLOGY IMPACTS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT IN THE CLASSROOM
The integration of technology in classrooms has become increasingly prevalent, presenting both opportunities and challenges for educators. This study examines the impact of technology on student performance and behavior, particularly in seventh and eighth-grade classrooms. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift to online learning, raising concerns about learning loss and disparities in access to technology. Using a needs-based assessment survey, this research investigates teachers' perceptions of technology's effects on student engagement, academic achievement, and retention of curriculum content. The study explores the positive and negative implications of technology use, as well as non-technological strategies employed by teachers to support student learning. Findings reveal that while technology offers benefits such as student-centered education and immediate feedback, it also poses challenges such as distractions and decreased engagement. The study underscores the importance of understanding how technology impacts student learning and behavior and provides insights for developing effective intervention strategies. By considering the perspectives of educators, this research contributes to the ongoing dialogue on technology integration in education and informs evidence-based practices for promoting student success in technology-rich classrooms.
Degree Type
- Master of Science
- Educational Studies
Campus location
Advisor/supervisor/committee chair, advisor/supervisor/committee co-chair, additional committee member 2, usage metrics.
- Secondary education

A Comparison of Student Learning Outcomes: Online Education vs. Traditional Classroom Instruction
Despite the prevalence of online learning today, it is often viewed as a less favorable option when compared to the traditional, in-person educational experience. Criticisms of online learning come from various sectors, like employer groups, college faculty, and the general public, and generally includes a lack of perceived quality as well as rigor. Additionally, some students report feelings of social isolation in online learning (Protopsaltis & Baum, 2019).
In my experience as an online student as well as an online educator, online learning has been just the opposite. I have been teaching in a fully online master’s degree program for the last three years and have found it to be a rich and rewarding experience for students and faculty alike. As an instructor, I have felt more connected to and engaged with my online students when compared to in-person students. I have also found that students are actively engaged with course content and demonstrate evidence of higher-order thinking through their work. Students report high levels of satisfaction with their experiences in online learning as well as the program overall as indicated in their Student Evaluations of Teaching (SET) at the end of every course. I believe that intelligent course design, in addition to my engagement in professional development related to teaching and learning online, has greatly influenced my experience.
In an article by Wiley Education Services, authors identified the top six challenges facing US institutions of higher education, and include:
- Declining student enrollment
- Financial difficulties
- Fewer high school graduates
- Decreased state funding
- Lower world rankings
- Declining international student enrollments
Of the strategies that institutions are exploring to remedy these issues, online learning is reported to be a key focus for many universities (“Top Challenges Facing US Higher Education”, n.d.).
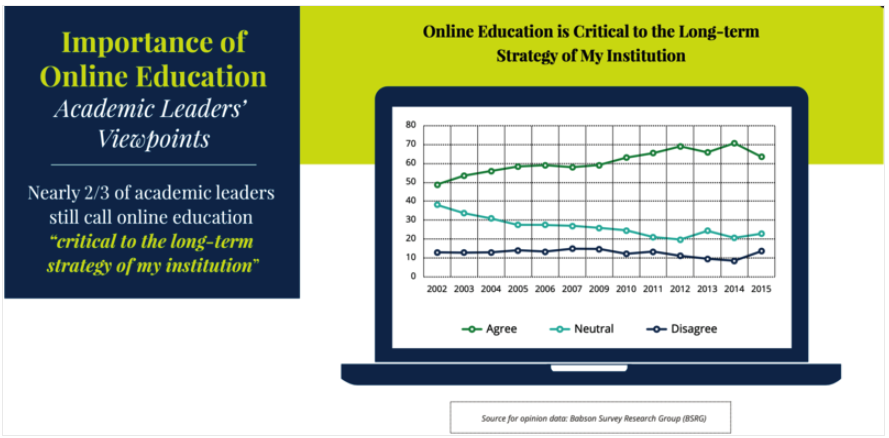
Babson Survey Research Group, 2016, [PDF file].
Some of the questions I would like to explore in further research include:
- What factors influence engagement and connection in distance education?
- Are the learning outcomes in online education any different than the outcomes achieved in a traditional classroom setting?
- How do course design and instructor training influence these factors?
- In what ways might educational technology tools enhance the overall experience for students and instructors alike?
In this literature review, I have chosen to focus on a comparison of student learning outcomes in online education versus the traditional classroom setting. My hope is that this research will unlock the answers to some of the additional questions posed above and provide additional direction for future research.
Online Learning Defined
According to Mayadas, Miller, and Sener (2015), online courses are defined by all course activity taking place online with no required in-person sessions or on-campus activity. It is important to note, however, that the Babson Survey Research Group, a prominent organization known for their surveys and research in online learning, defines online learning as a course in which 80-100% occurs online. While this distinction was made in an effort to provide consistency in surveys year over year, most institutions continue to define online learning as learning that occurs 100% online.
Blended or hybrid learning is defined by courses that mix face to face meetings, sessions, or activities with online work. The ratio of online to classroom activity is often determined by the label in which the course is given. For example, a blended classroom course would likely include more time spent in the classroom, with the remaining work occurring outside of the classroom with the assistance of technology. On the other hand, a blended online course would contain a greater percentage of work done online, with some required in-person sessions or meetings (Mayadas, Miller, & Sener, 2015).
A classroom course (also referred to as a traditional course) refers to course activity that is anchored to a regular meeting time.
Enrollment Trends in Online Education
There has been an upward trend in the number of postsecondary students enrolled in online courses in the U.S. since 2002. A report by the Babson Survey Research Group showed that in 2016, more than six million students were enrolled in at least one online course. This number accounted for 31.6% of all college students (Seaman, Allen, & Seaman, 2018). Approximately one in three students are enrolled in online courses with no in-person component. Of these students, 47% take classes in a fully online program. The remaining 53% take some, but not all courses online (Protopsaltis & Baum, 2019).
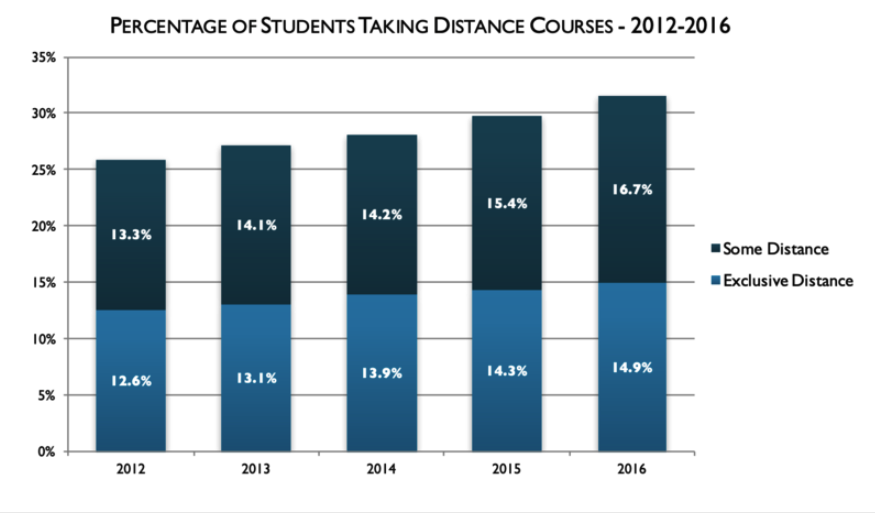
(Seaman et al., 2016, p. 11)
Perceptions of Online Education
In a 2016 report by the Babson Survey Research Group, surveys of faculty between 2002-2015 showed approval ratings regarding the value and legitimacy of online education ranged from 28-34 percent. While numbers have increased and decreased over the thirteen-year time frame, faculty approval was at 29 percent in 2015, just 1 percent higher than the approval ratings noted in 2002 – indicating that perceptions have remained relatively unchanged over the years (Allen, Seaman, Poulin, & Straut, 2016).
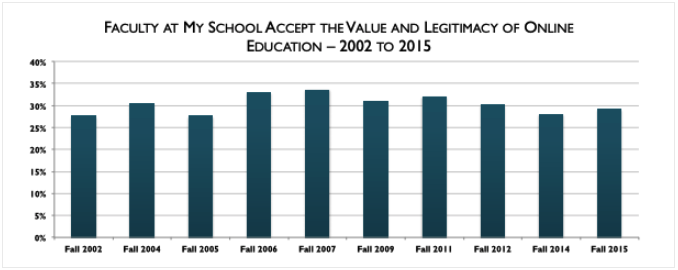
(Allen, I.E., Seaman, J., Poulin, R., Taylor Strout, T., 2016, p. 26)
In a separate survey of chief academic officers, perceptions of online learning appeared to align with that of faculty. In this survey, leaders were asked to rate their perceived quality of learning outcomes in online learning when compared to traditional in-person settings. While the percentage of leaders rating online learning as “inferior” or “somewhat inferior” to traditional face-to-face courses dropped from 43 percent to 23 percent between 2003 to 2012, the number rose again to 29 percent in 2015 (Allen, Seaman, Poulin, & Straut, 2016).
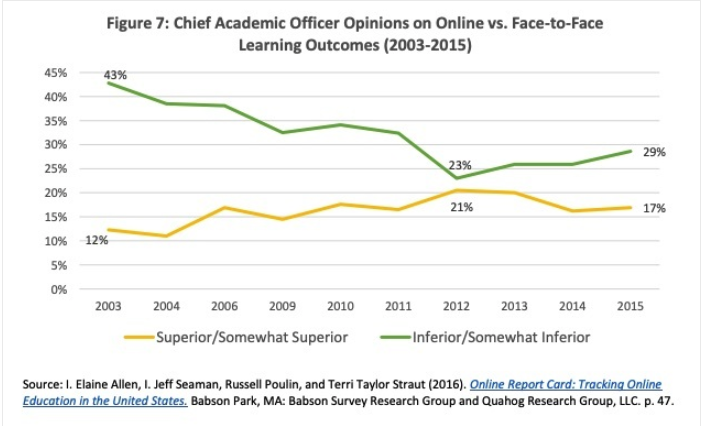
Faculty and academic leaders in higher education are not alone when it comes to perceptions of inferiority when compared to traditional classroom instruction. A 2013 Gallop poll assessing public perceptions showed that respondents rated online education as “worse” in five of the seven categories seen in the table below.

(Saad, L., Busteed, B., and Ogisi, M., 2013, October 15)
In general, Americans believed that online education provides both lower quality and less individualized instruction and less rigorous testing and grading when compared to the traditional classroom setting. In addition, respondents also thought that employers would perceive a degree from an online program less positively when compared to a degree obtained through traditional classroom instruction (Saad, Busteed, & Ogisi, 2013).
Student Perceptions of Online Learning
So what do students have to say about online learning? In Online College Students 2015: Comprehensive Data on Demands and Preferences, 1500 college students who were either enrolled or planning to enroll in a fully online undergraduate, graduate, or certificate program were surveyed. 78 percent of students believed the academic quality of their online learning experience to be better than or equal to their experiences with traditional classroom learning. Furthermore, 30 percent of online students polled said that they would likely not attend classes face to face if their program were not available online (Clienfelter & Aslanian, 2015). The following video describes some of the common reasons why students choose to attend college online.
How Online Learning Affects the Lives of Students ( Pearson North America, 2018, June 25)
In a 2015 study comparing student perceptions of online learning with face to face learning, researchers found that the majority of students surveyed expressed a preference for traditional face to face classes. A content analysis of the findings, however, brought attention to two key ideas: 1) student opinions of online learning may be based on “old typology of distance education” (Tichavsky, et al, 2015, p.6) as opposed to actual experience, and 2) a student’s inclination to choose one form over another is connected to issues of teaching presence and self-regulated learning (Tichavsky et al, 2015).
Student Learning Outcomes
Given the upward trend in student enrollment in online courses in postsecondary schools and the steady ratings of the low perceived value of online learning by stakeholder groups, it should be no surprise that there is a large body of literature comparing student learning outcomes in online classes to the traditional classroom environment.
While a majority of the studies reviewed found no significant difference in learning outcomes when comparing online to traditional courses (Cavanaugh & Jacquemin, 2015; Kemp & Grieve, 2014; Lyke & Frank 2012; Nichols, Shaffer, & Shockey, 2003; Stack, 2015; Summers, Waigandt, & Whittaker, 2005), there were a few outliers. In a 2019 report by Protopsaltis & Baum, authors confirmed that while learning is often found to be similar between the two mediums, students “with weak academic preparation and those from low-income and underrepresented backgrounds consistently underperform in fully-online environments” (Protopsaltis & Baum, 2019, n.p.). An important consideration, however, is that these findings are primarily based on students enrolled in online courses at the community college level – a demographic with a historically high rate of attrition compared to students attending four-year institutions (Ashby, Sadera, & McNary, 2011). Furthermore, students enrolled in online courses have been shown to have a 10 – 20 percent increase in attrition over their peers who are enrolled in traditional classroom instruction (Angelino, Williams, & Natvig, 2007). Therefore, attrition may be a key contributor to the lack of achievement seen in this subgroup of students enrolled in online education.
In contrast, there were a small number of studies that showed that online students tend to outperform those enrolled in traditional classroom instruction. One study, in particular, found a significant difference in test scores for students enrolled in an online, undergraduate business course. The confounding variable, in this case, was age. Researchers found a significant difference in performance in nontraditional age students over their traditional age counterparts. Authors concluded that older students may elect to take online classes for practical reasons related to outside work schedules, and this may, in turn, contribute to the learning that occurs overall (Slover & Mandernach, 2018).
In a meta-analysis and review of online learning spanning the years 1996 to 2008, authors from the US Department of Education found that students who took all or part of their classes online showed better learning outcomes than those students who took the same courses face-to-face. In these cases, it is important to note that there were many differences noted in the online and face-to-face versions, including the amount of time students spent engaged with course content. The authors concluded that the differences in learning outcomes may be attributed to learning design as opposed to the specific mode of delivery (Means, Toyoma, Murphy, Bakia, Jones, 2009).
Limitations and Opportunities
After examining the research comparing student learning outcomes in online education with the traditional classroom setting, there are many limitations that came to light, creating areas of opportunity for additional research. In many of the studies referenced, it is difficult to determine the pedagogical practices used in course design and delivery. Research shows the importance of student-student and student-teacher interaction in online learning, and the positive impact of these variables on student learning (Bernard, Borokhovski, Schmid, Tamim, & Abrami, 2014). Some researchers note that while many studies comparing online and traditional classroom learning exist, the methodologies and design issues make it challenging to explain the results conclusively (Mollenkopf, Vu, Crow, & Black, 2017). For example, some online courses may be structured in a variety of ways, i.e. self-paced, instructor-led and may be classified as synchronous or asynchronous (Moore, Dickson-Deane, Galyan, 2011)
Another gap in the literature is the failure to use a common language across studies to define the learning environment. This issue is explored extensively in a 2011 study by Moore, Dickson-Deane, and Galyan. Here, the authors examine the differences between e-learning, online learning, and distance learning in the literature, and how the terminology is often used interchangeably despite the variances in characteristics that define each. The authors also discuss the variability in the terms “course” versus “program”. This variability in the literature presents a challenge when attempting to compare one study of online learning to another (Moore, Dickson-Deane, & Galyan, 2011).
Finally, much of the literature in higher education focuses on undergraduate-level classes within the United States. Little research is available on outcomes in graduate-level classes as well as general information on student learning outcomes and perceptions of online learning outside of the U.S.
As we look to the future, there are additional questions to explore in the area of online learning. Overall, this research led to questions related to learning design when comparing the two modalities in higher education. Further research is needed to investigate the instructional strategies used to enhance student learning, especially in students with weaker academic preparation or from underrepresented backgrounds. Given the integral role that online learning is expected to play in the future of higher education in the United States, it may be even more critical to move beyond comparisons of online versus face to face. Instead, choosing to focus on sound pedagogical quality with consideration for the mode of delivery as a means for promoting positive learning outcomes.
Allen, I.E., Seaman, J., Poulin, R., & Straut, T. (2016). Online Report Card: Tracking Online Education in the United States [PDF file]. Babson Survey Research Group. http://onlinelearningsurvey.com/reports/onlinereportcard.pdf
Angelino, L. M., Williams, F. K., & Natvig, D. (2007). Strategies to engage online students and reduce attrition rates. The Journal of Educators Online , 4(2).
Ashby, J., Sadera, W.A., & McNary, S.W. (2011). Comparing student success between developmental math courses offered online, blended, and face-to-face. Journal of Interactive Online Learning , 10(3), 128-140.
Bernard, R.M., Borokhovski, E., Schmid, R.F., Tamim, R.M., & Abrami, P.C. (2014). A meta-analysis of blended learning and technology use in higher education: From the general to the applied. Journal of Computing in Higher Education , 26(1), 87-122.
Cavanaugh, J.K. & Jacquemin, S.J. (2015). A large sample comparison of grade based student learning outcomes in online vs. face-fo-face courses. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Network, 19(2).
Clinefelter, D. L., & Aslanian, C. B. (2015). Online college students 2015: Comprehensive data on demands and preferences. https://www.learninghouse.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/OnlineCollegeStudents2015.pdf
Golubovskaya, E.A., Tikhonova, E.V., & Mekeko, N.M. (2019). Measuring learning outcome and students’ satisfaction in ELT (e-learning against conventional learning). Paper presented the ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, 34-38. Doi: 10.1145/3337682.3337704
Kemp, N. & Grieve, R. (2014). Face-to-face or face-to-screen? Undergraduates’ opinions and test performance in classroom vs. online learning. Frontiers in Psychology , 5. Doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01278
Lyke, J., & Frank, M. (2012). Comparison of student learning outcomes in online and traditional classroom environments in a psychology course. (Cover story). Journal of Instructional Psychology , 39(3/4), 245-250.
Mayadas, F., Miller, G. & Senner, J. Definitions of E-Learning Courses and Programs Version 2.0. Online Learning Consortium. https://onlinelearningconsortium.org/updated-e-learning-definitions-2/
Means, B., Toyama, Y., Murphy, R., Bakia, M., & Jones, K. (2010). Evaluation of evidence-based practices in online learning: A meta-analysis and review of online learning studies. US Department of Education. https://www2.ed.gov/rschstat/eval/tech/evidence-based-practices/finalreport.pdf
Mollenkopf, D., Vu, P., Crow, S, & Black, C. (2017). Does online learning deliver? A comparison of student teacher outcomes from candidates in face to face and online program pathways. Online Journal of Distance Learning Administration. 20(1).
Moore, J.L., Dickson-Deane, C., & Galyan, K. (2011). E-Learning, online learning, and distance learning environments: Are they the same? The Internet and Higher Education . 14(2), 129-135.
Nichols, J., Shaffer, B., & Shockey, K. (2003). Changing the face of instruction: Is online or in-class more effective? College & Research Libraries , 64(5), 378–388. https://doi-org.proxy2.library.illinois.edu/10.5860/crl.64.5.378
Parsons-Pollard, N., Lacks, T.R., & Grant, P.H. (2008). A comparative assessment of student learning outcomes in large online and traditional campus based introduction to criminal justice courses. Criminal Justice Studies , 2, 225-239.
Pearson North America. (2018, June 25). How Online Learning Affects the Lives of Students . YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mPDMagf_oAE
Protopsaltis, S., & Baum, S. (2019). Does online education live up to its promise? A look at the evidence and implications for federal policy [PDF file]. http://mason.gmu.edu/~sprotops/OnlineEd.pdf
Saad, L., Busteed, B., & Ogisi, M. (October 15, 2013). In U.S., Online Education Rated Best for Value and Options. https://news.gallup.com/poll/165425/online-education-rated-best-value-options.aspx
Stack, S. (2015). Learning Outcomes in an Online vs Traditional Course. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning , 9(1).
Seaman, J.E., Allen, I.E., & Seaman, J. (2018). Grade Increase: Tracking Distance Education in the United States [PDF file]. Babson Survey Research Group. http://onlinelearningsurvey.com/reports/gradeincrease.pdf
Slover, E. & Mandernach, J. (2018). Beyond Online versus Face-to-Face Comparisons: The Interaction of Student Age and Mode of Instruction on Academic Achievement. Journal of Educators Online, 15(1) . https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1168945.pdf
Summers, J., Waigandt, A., & Whittaker, T. (2005). A Comparison of Student Achievement and Satisfaction in an Online Versus a Traditional Face-to-Face Statistics Class. Innovative Higher Education , 29(3), 233–250. https://doi-org.proxy2.library.illinois.edu/10.1007/s10755-005-1938-x
Tichavsky, L.P., Hunt, A., Driscoll, A., & Jicha, K. (2015). “It’s just nice having a real teacher”: Student perceptions of online versus face-to-face instruction. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning. 9(2).
Wiley Education Services. (n.d.). Top challenges facing U.S. higher education. https://edservices.wiley.com/top-higher-education-challenges/
July 17, 2020
Online Learning
college , distance education , distance learning , face to face , higher education , online learning , postsecondary , traditional learning , university , virtual learning
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
© 2024 — Powered by WordPress
Theme by Anders Noren — Up ↑
(Stanford users can avoid this Captcha by logging in.)
- Send to text email RefWorks RIS download printer
Comparative Study of Online Learning and Classroom Learning.
Best source.
- View/download PDF
All available sources
About this article.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Wiley - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Online and face‐to‐face learning: Evidence from students’ performance during the Covid‐19 pandemic
Carolyn chisadza.
1 Department of Economics, University of Pretoria, Hatfield South Africa
Matthew Clance
Thulani mthembu.
2 Department of Education Innovation, University of Pretoria, Hatfield South Africa
Nicky Nicholls
Eleni yitbarek.
This study investigates the factors that predict students' performance after transitioning from face‐to‐face to online learning as a result of the Covid‐19 pandemic. It uses students' responses from survey questions and the difference in the average assessment grades between pre‐lockdown and post‐lockdown at a South African university. We find that students' performance was positively associated with good wifi access, relative to using mobile internet data. We also observe lower academic performance for students who found transitioning to online difficult and who expressed a preference for self‐study (i.e. reading through class slides and notes) over assisted study (i.e. joining live lectures or watching recorded lectures). The findings suggest that improving digital infrastructure and reducing the cost of internet access may be necessary for mitigating the impact of the Covid‐19 pandemic on education outcomes.
1. INTRODUCTION
The Covid‐19 pandemic has been a wake‐up call to many countries regarding their capacity to cater for mass online education. This situation has been further complicated in developing countries, such as South Africa, who lack the digital infrastructure for the majority of the population. The extended lockdown in South Africa saw most of the universities with mainly in‐person teaching scrambling to source hardware (e.g. laptops, internet access), software (e.g. Microsoft packages, data analysis packages) and internet data for disadvantaged students in order for the semester to recommence. Not only has the pandemic revealed the already stark inequality within the tertiary student population, but it has also revealed that high internet data costs in South Africa may perpetuate this inequality, making online education relatively inaccessible for disadvantaged students. 1
The lockdown in South Africa made it possible to investigate the changes in second‐year students' performance in the Economics department at the University of Pretoria. In particular, we are interested in assessing what factors predict changes in students' performance after transitioning from face‐to‐face (F2F) to online learning. Our main objectives in answering this study question are to establish what study materials the students were able to access (i.e. slides, recordings, or live sessions) and how students got access to these materials (i.e. the infrastructure they used).
The benefits of education on economic development are well established in the literature (Gyimah‐Brempong, 2011 ), ranging from health awareness (Glick et al., 2009 ), improved technological innovations, to increased capacity development and employment opportunities for the youth (Anyanwu, 2013 ; Emediegwu, 2021 ). One of the ways in which inequality is perpetuated in South Africa, and Africa as a whole, is through access to education (Anyanwu, 2016 ; Coetzee, 2014 ; Tchamyou et al., 2019 ); therefore, understanding the obstacles that students face in transitioning to online learning can be helpful in ensuring more equal access to education.
Using students' responses from survey questions and the difference in the average grades between pre‐lockdown and post‐lockdown, our findings indicate that students' performance in the online setting was positively associated with better internet access. Accessing assisted study material, such as narrated slides or recordings of the online lectures, also helped students. We also find lower academic performance for students who reported finding transitioning to online difficult and for those who expressed a preference for self‐study (i.e. reading through class slides and notes) over assisted study (i.e. joining live lectures or watching recorded lectures). The average grades between pre‐lockdown and post‐lockdown were about two points and three points lower for those who reported transitioning to online teaching difficult and for those who indicated a preference for self‐study, respectively. The findings suggest that improving the quality of internet infrastructure and providing assisted learning can be beneficial in reducing the adverse effects of the Covid‐19 pandemic on learning outcomes.
Our study contributes to the literature by examining the changes in the online (post‐lockdown) performance of students and their F2F (pre‐lockdown) performance. This approach differs from previous studies that, in most cases, use between‐subject designs where one group of students following online learning is compared to a different group of students attending F2F lectures (Almatra et al., 2015 ; Brown & Liedholm, 2002 ). This approach has a limitation in that that there may be unobserved characteristics unique to students choosing online learning that differ from those choosing F2F lectures. Our approach avoids this issue because we use a within‐subject design: we compare the performance of the same students who followed F2F learning Before lockdown and moved to online learning during lockdown due to the Covid‐19 pandemic. Moreover, the study contributes to the limited literature that compares F2F and online learning in developing countries.
Several studies that have also compared the effectiveness of online learning and F2F classes encounter methodological weaknesses, such as small samples, not controlling for demographic characteristics, and substantial differences in course materials and assessments between online and F2F contexts. To address these shortcomings, our study is based on a relatively large sample of students and includes demographic characteristics such as age, gender and perceived family income classification. The lecturer and course materials also remained similar in the online and F2F contexts. A significant proportion of our students indicated that they never had online learning experience before. Less than 20% of the students in the sample had previous experience with online learning. This highlights the fact that online education is still relatively new to most students in our sample.
Given the global experience of the fourth industrial revolution (4IR), 2 with rapidly accelerating technological progress, South Africa needs to be prepared for the possibility of online learning becoming the new norm in the education system. To this end, policymakers may consider engaging with various organizations (schools, universities, colleges, private sector, and research facilities) To adopt interventions that may facilitate the transition to online learning, while at the same time ensuring fair access to education for all students across different income levels. 3
1.1. Related literature
Online learning is a form of distance education which mainly involves internet‐based education where courses are offered synchronously (i.e. live sessions online) and/or asynchronously (i.e. students access course materials online in their own time, which is associated with the more traditional distance education). On the other hand, traditional F2F learning is real time or synchronous learning. In a physical classroom, instructors engage with the students in real time, while in the online format instructors can offer real time lectures through learning management systems (e.g. Blackboard Collaborate), or record the lectures for the students to watch later. Purely online courses are offered entirely over the internet, while blended learning combines traditional F2F classes with learning over the internet, and learning supported by other technologies (Nguyen, 2015 ).
Moreover, designing online courses requires several considerations. For example, the quality of the learning environment, the ease of using the learning platform, the learning outcomes to be achieved, instructor support to assist and motivate students to engage with the course material, peer interaction, class participation, type of assessments (Paechter & Maier, 2010 ), not to mention training of the instructor in adopting and introducing new teaching methods online (Lundberg et al., 2008 ). In online learning, instructors are more facilitators of learning. On the other hand, traditional F2F classes are structured in such a way that the instructor delivers knowledge, is better able to gauge understanding and interest of students, can engage in class activities, and can provide immediate feedback on clarifying questions during the class. Additionally, the designing of traditional F2F courses can be less time consuming for instructors compared to online courses (Navarro, 2000 ).
Online learning is also particularly suited for nontraditional students who require flexibility due to work or family commitments that are not usually associated with the undergraduate student population (Arias et al., 2018 ). Initially the nontraditional student belonged to the older adult age group, but with blended learning becoming more commonplace in high schools, colleges and universities, online learning has begun to traverse a wider range of age groups. However, traditional F2F classes are still more beneficial for learners that are not so self‐sufficient and lack discipline in working through the class material in the required time frame (Arias et al., 2018 ).
For the purpose of this literature review, both pure online and blended learning are considered to be online learning because much of the evidence in the literature compares these two types against the traditional F2F learning. The debate in the literature surrounding online learning versus F2F teaching continues to be a contentious one. A review of the literature reveals mixed findings when comparing the efficacy of online learning on student performance in relation to the traditional F2F medium of instruction (Lundberg et al., 2008 ; Nguyen, 2015 ). A number of studies conducted Before the 2000s find what is known today in the empirical literature as the “No Significant Difference” phenomenon (Russell & International Distance Education Certificate Center (IDECC), 1999 ). The seminal work from Russell and IDECC ( 1999 ) involved over 350 comparative studies on online/distance learning versus F2F learning, dating back to 1928. The author finds no significant difference overall between online and traditional F2F classroom education outcomes. Subsequent studies that followed find similar “no significant difference” outcomes (Arbaugh, 2000 ; Fallah & Ubell, 2000 ; Freeman & Capper, 1999 ; Johnson et al., 2000 ; Neuhauser, 2002 ). While Bernard et al. ( 2004 ) also find that overall there is no significant difference in achievement between online education and F2F education, the study does find significant heterogeneity in student performance for different activities. The findings show that students in F2F classes outperform the students participating in synchronous online classes (i.e. classes that require online students to participate in live sessions at specific times). However, asynchronous online classes (i.e. students access class materials at their own time online) outperform F2F classes.
More recent studies find significant results for online learning outcomes in relation to F2F outcomes. On the one hand, Shachar and Yoram ( 2003 ) and Shachar and Neumann ( 2010 ) conduct a meta‐analysis of studies from 1990 to 2009 and find that in 70% of the cases, students taking courses by online education outperformed students in traditionally instructed courses (i.e. F2F lectures). In addition, Navarro and Shoemaker ( 2000 ) observe that learning outcomes for online learners are as effective as or better than outcomes for F2F learners, regardless of background characteristics. In a study on computer science students, Dutton et al. ( 2002 ) find online students perform significantly better compared to the students who take the same course on campus. A meta‐analysis conducted by the US Department of Education finds that students who took all or part of their course online performed better, on average, than those taking the same course through traditional F2F instructions. The report also finds that the effect sizes are larger for studies in which the online learning was collaborative or instructor‐driven than in those studies where online learners worked independently (Means et al., 2010 ).
On the other hand, evidence by Brown and Liedholm ( 2002 ) based on test scores from macroeconomics students in the United States suggest that F2F students tend to outperform online students. These findings are supported by Coates et al. ( 2004 ) who base their study on macroeconomics students in the United States, and Xu and Jaggars ( 2014 ) who find negative effects for online students using a data set of about 500,000 courses taken by over 40,000 students in Washington. Furthermore, Almatra et al. ( 2015 ) compare overall course grades between online and F2F students for a Telecommunications course and find that F2F students significantly outperform online learning students. In an experimental study where students are randomly assigned to attend live lectures versus watching the same lectures online, Figlio et al. ( 2013 ) observe some evidence that the traditional format has a positive effect compared to online format. Interestingly, Callister and Love ( 2016 ) specifically compare the learning outcomes of online versus F2F skills‐based courses and find that F2F learners earned better outcomes than online learners even when using the same technology. This study highlights that some of the inconsistencies that we find in the results comparing online to F2F learning might be influenced by the nature of the course: theory‐based courses might be less impacted by in‐person interaction than skills‐based courses.
The fact that the reviewed studies on the effects of F2F versus online learning on student performance have been mainly focused in developed countries indicates the dearth of similar studies being conducted in developing countries. This gap in the literature may also highlight a salient point: online learning is still relatively underexplored in developing countries. The lockdown in South Africa therefore provides us with an opportunity to contribute to the existing literature from a developing country context.
2. CONTEXT OF STUDY
South Africa went into national lockdown in March 2020 due to the Covid‐19 pandemic. Like most universities in the country, the first semester for undergraduate courses at the University of Pretoria had already been running since the start of the academic year in February. Before the pandemic, a number of F2F lectures and assessments had already been conducted in most courses. The nationwide lockdown forced the university, which was mainly in‐person teaching, to move to full online learning for the remainder of the semester. This forced shift from F2F teaching to online learning allows us to investigate the changes in students' performance.
Before lockdown, classes were conducted on campus. During lockdown, these live classes were moved to an online platform, Blackboard Collaborate, which could be accessed by all registered students on the university intranet (“ClickUP”). However, these live online lectures involve substantial internet data costs for students. To ensure access to course content for those students who were unable to attend the live online lectures due to poor internet connections or internet data costs, several options for accessing course content were made available. These options included prerecorded narrated slides (which required less usage of internet data), recordings of the live online lectures, PowerPoint slides with explanatory notes and standard PDF lecture slides.
At the same time, the university managed to procure and loan out laptops to a number of disadvantaged students, and negotiated with major mobile internet data providers in the country for students to have free access to study material through the university's “connect” website (also referred to as the zero‐rated website). However, this free access excluded some video content and live online lectures (see Table 1 ). The university also provided between 10 and 20 gigabytes of mobile internet data per month, depending on the network provider, sent to students' mobile phones to assist with internet data costs.
Sites available on zero‐rated website
Note : The table summarizes the sites that were available on the zero‐rated website and those that incurred data costs.
High data costs continue to be a contentious issue in Africa where average incomes are low. Gilbert ( 2019 ) reports that South Africa ranked 16th of the 45 countries researched in terms of the most expensive internet data in Africa, at US$6.81 per gigabyte, in comparison to other Southern African countries such as Mozambique (US$1.97), Zambia (US$2.70), and Lesotho (US$4.09). Internet data prices have also been called into question in South Africa after the Competition Commission published a report from its Data Services Market Inquiry calling the country's internet data pricing “excessive” (Gilbert, 2019 ).
3. EMPIRICAL APPROACH
We use a sample of 395 s‐year students taking a macroeconomics module in the Economics department to compare the effects of F2F and online learning on students' performance using a range of assessments. The module was an introduction to the application of theoretical economic concepts. The content was both theory‐based (developing economic growth models using concepts and equations) and skill‐based (application involving the collection of data from online data sources and analyzing the data using statistical software). Both individual and group assignments formed part of the assessments. Before the end of the semester, during lockdown in June 2020, we asked the students to complete a survey with questions related to the transition from F2F to online learning and the difficulties that they may have faced. For example, we asked the students: (i) how easy or difficult they found the transition from F2F to online lectures; (ii) what internet options were available to them and which they used the most to access the online prescribed work; (iii) what format of content they accessed and which they preferred the most (i.e. self‐study material in the form of PDF and PowerPoint slides with notes vs. assisted study with narrated slides and lecture recordings); (iv) what difficulties they faced accessing the live online lectures, to name a few. Figure 1 summarizes the key survey questions that we asked the students regarding their transition from F2F to online learning.

Summary of survey data
Before the lockdown, the students had already attended several F2F classes and completed three assessments. We are therefore able to create a dependent variable that is comprised of the average grades of three assignments taken before lockdown and the average grades of three assignments taken after the start of the lockdown for each student. Specifically, we use the difference between the post‐ and pre‐lockdown average grades as the dependent variable. However, the number of student observations dropped to 275 due to some students missing one or more of the assessments. The lecturer, content and format of the assessments remain similar across the module. We estimate the following equation using ordinary least squares (OLS) with robust standard errors:
where Y i is the student's performance measured by the difference between the post and pre‐lockdown average grades. B represents the vector of determinants that measure the difficulty faced by students to transition from F2F to online learning. This vector includes access to the internet, study material preferred, quality of the online live lecture sessions and pre‐lockdown class attendance. X is the vector of student demographic controls such as race, gender and an indicator if the student's perceived family income is below average. The ε i is unobserved student characteristics.
4. ANALYSIS
4.1. descriptive statistics.
Table 2 gives an overview of the sample of students. We find that among the black students, a higher proportion of students reported finding the transition to online learning more difficult. On the other hand, more white students reported finding the transition moderately easy, as did the other races. According to Coetzee ( 2014 ), the quality of schools can vary significantly between higher income and lower‐income areas, with black South Africans far more likely to live in lower‐income areas with lower quality schools than white South Africans. As such, these differences in quality of education from secondary schooling can persist at tertiary level. Furthermore, persistent income inequality between races in South Africa likely means that many poorer black students might not be able to afford wifi connections or large internet data bundles which can make the transition difficult for black students compared to their white counterparts.
Descriptive statistics
Notes : The transition difficulty variable was ordered 1: Very Easy; 2: Moderately Easy; 3: Difficult; and 4: Impossible. Since we have few responses to the extremes, we combined Very Easy and Moderately as well as Difficult and Impossible to make the table easier to read. The table with a full breakdown is available upon request.
A higher proportion of students reported that wifi access made the transition to online learning moderately easy. However, relatively more students reported that mobile internet data and accessing the zero‐rated website made the transition difficult. Surprisingly, not many students made use of the zero‐rated website which was freely available. Figure 2 shows that students who reported difficulty transitioning to online learning did not perform as well in online learning versus F2F when compared to those that found it less difficult to transition.

Transition from F2F to online learning.
Notes : This graph shows the students' responses to the question “How easy did you find the transition from face‐to‐face lectures to online lectures?” in relation to the outcome variable for performance
In Figure 3 , the kernel density shows that students who had access to wifi performed better than those who used mobile internet data or the zero‐rated data.

Access to online learning.
Notes : This graph shows the students' responses to the question “What do you currently use the most to access most of your prescribed work?” in relation to the outcome variable for performance
The regression results are reported in Table 3 . We find that the change in students' performance from F2F to online is negatively associated with the difficulty they faced in transitioning from F2F to online learning. According to student survey responses, factors contributing to difficulty in transitioning included poor internet access, high internet data costs and lack of equipment such as laptops or tablets to access the study materials on the university website. Students who had access to wifi (i.e. fixed wireless broadband, Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) or optic fiber) performed significantly better, with on average 4.5 points higher grade, in relation to students that had to use mobile internet data (i.e. personal mobile internet data, wifi at home using mobile internet data, or hotspot using mobile internet data) or the zero‐rated website to access the study materials. The insignificant results for the zero‐rated website are surprising given that the website was freely available and did not incur any internet data costs. However, most students in this sample complained that the internet connection on the zero‐rated website was slow, especially in uploading assignments. They also complained about being disconnected when they were in the middle of an assessment. This may have discouraged some students from making use of the zero‐rated website.
Results: Predictors for student performance using the difference on average assessment grades between pre‐ and post‐lockdown
Coefficients reported. Robust standard errors in parentheses.
∗∗∗ p < .01.
Students who expressed a preference for self‐study approaches (i.e. reading PDF slides or PowerPoint slides with explanatory notes) did not perform as well, on average, as students who preferred assisted study (i.e. listening to recorded narrated slides or lecture recordings). This result is in line with Means et al. ( 2010 ), where student performance was better for online learning that was collaborative or instructor‐driven than in cases where online learners worked independently. Interestingly, we also observe that the performance of students who often attended in‐person classes before the lockdown decreased. Perhaps these students found the F2F lectures particularly helpful in mastering the course material. From the survey responses, we find that a significant proportion of the students (about 70%) preferred F2F to online lectures. This preference for F2F lectures may also be linked to the factors contributing to the difficulty some students faced in transitioning to online learning.
We find that the performance of low‐income students decreased post‐lockdown, which highlights another potential challenge to transitioning to online learning. The picture and sound quality of the live online lectures also contributed to lower performance. Although this result is not statistically significant, it is worth noting as the implications are linked to the quality of infrastructure currently available for students to access online learning. We find no significant effects of race on changes in students' performance, though males appeared to struggle more with the shift to online teaching than females.
For the robustness check in Table 4 , we consider the average grades of the three assignments taken after the start of the lockdown as a dependent variable (i.e. the post‐lockdown average grades for each student). We then include the pre‐lockdown average grades as an explanatory variable. The findings and overall conclusions in Table 4 are consistent with the previous results.
Robustness check: Predictors for student performance using the average assessment grades for post‐lockdown
As a further robustness check in Table 5 , we create a panel for each student across the six assignment grades so we can control for individual heterogeneity. We create a post‐lockdown binary variable that takes the value of 1 for the lockdown period and 0 otherwise. We interact the post‐lockdown dummy variable with a measure for transition difficulty and internet access. The internet access variable is an indicator variable for mobile internet data, wifi, or zero‐rated access to class materials. The variable wifi is a binary variable taking the value of 1 if the student has access to wifi and 0 otherwise. The zero‐rated variable is a binary variable taking the value of 1 if the student used the university's free portal access and 0 otherwise. We also include assignment and student fixed effects. The results in Table 5 remain consistent with our previous findings that students who had wifi access performed significantly better than their peers.
Interaction model
Notes : Coefficients reported. Robust standard errors in parentheses. The dependent variable is the assessment grades for each student on each assignment. The number of observations include the pre‐post number of assessments multiplied by the number of students.
6. CONCLUSION
The Covid‐19 pandemic left many education institutions with no option but to transition to online learning. The University of Pretoria was no exception. We examine the effect of transitioning to online learning on the academic performance of second‐year economic students. We use assessment results from F2F lectures before lockdown, and online lectures post lockdown for the same group of students, together with responses from survey questions. We find that the main contributor to lower academic performance in the online setting was poor internet access, which made transitioning to online learning more difficult. In addition, opting to self‐study (read notes instead of joining online classes and/or watching recordings) did not help the students in their performance.
The implications of the results highlight the need for improved quality of internet infrastructure with affordable internet data pricing. Despite the university's best efforts not to leave any student behind with the zero‐rated website and free monthly internet data, the inequality dynamics in the country are such that invariably some students were negatively affected by this transition, not because the student was struggling academically, but because of inaccessibility of internet (wifi). While the zero‐rated website is a good collaborative initiative between universities and network providers, the infrastructure is not sufficient to accommodate mass students accessing it simultaneously.
This study's findings may highlight some shortcomings in the academic sector that need to be addressed by both the public and private sectors. There is potential for an increase in the digital divide gap resulting from the inequitable distribution of digital infrastructure. This may lead to reinforcement of current inequalities in accessing higher education in the long term. To prepare the country for online learning, some considerations might need to be made to make internet data tariffs more affordable and internet accessible to all. We hope that this study's findings will provide a platform (or will at least start the conversation for taking remedial action) for policy engagements in this regard.
We are aware of some limitations presented by our study. The sample we have at hand makes it difficult to extrapolate our findings to either all students at the University of Pretoria or other higher education students in South Africa. Despite this limitation, our findings highlight the negative effect of the digital divide on students' educational outcomes in the country. The transition to online learning and the high internet data costs in South Africa can also have adverse learning outcomes for low‐income students. With higher education institutions, such as the University of Pretoria, integrating online teaching to overcome the effect of the Covid‐19 pandemic, access to stable internet is vital for students' academic success.
It is also important to note that the data we have at hand does not allow us to isolate wifi's causal effect on students' performance post‐lockdown due to two main reasons. First, wifi access is not randomly assigned; for instance, there is a high chance that students with better‐off family backgrounds might have better access to wifi and other supplementary infrastructure than their poor counterparts. Second, due to the university's data access policy and consent, we could not merge the data at hand with the student's previous year's performance. Therefore, future research might involve examining the importance of these elements to document the causal impact of access to wifi on students' educational outcomes in the country.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors acknowledge the helpful comments received from the editor, the anonymous reviewers, and Elizabeth Asiedu.
Chisadza, C. , Clance, M. , Mthembu, T. , Nicholls, N. , & Yitbarek, E. (2021). Online and face‐to‐face learning: Evidence from students’ performance during the Covid‐19 pandemic . Afr Dev Rev , 33 , S114–S125. 10.1111/afdr.12520 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
1 https://mybroadband.co.za/news/cellular/309693-mobile-data-prices-south-africa-vs-the-world.html .
2 The 4IR is currently characterized by increased use of new technologies, such as advanced wireless technologies, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, robotics, among others. This era has also facilitated the use of different online learning platforms ( https://www.brookings.edu/research/the-fourth-industrialrevolution-and-digitization-will-transform-africa-into-a-global-powerhouse/ ).
3 Note that we control for income, but it is plausible to assume other unobservable factors such as parental preference and parenting style might also affect access to the internet of students.
- Almatra, O. , Johri, A. , Nagappan, K. , & Modanlu, A. (2015). An empirical study of face‐to‐face and distance learning sections of a core telecommunication course (Conference Proceedings Paper No. 12944). 122nd ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition, Seattle, Washington State.
- Anyanwu, J. C. (2013). Characteristics and macroeconomic determinants of youth employment in Africa . African Development Review , 25 ( 2 ), 107–129. [ Google Scholar ]
- Anyanwu, J. C. (2016). Accounting for gender equality in secondary school enrolment in Africa: Accounting for gender equality in secondary school enrolment . African Development Review , 28 ( 2 ), 170–191. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arbaugh, J. (2000). Virtual classroom versus physical classroom: An exploratory study of class discussion patterns and student learning in an asynchronous internet‐based MBA course . Journal of Management Education , 24 ( 2 ), 213–233. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arias, J. J. , Swinton, J. , & Anderson, K. (2018). On‐line vs. face‐to‐face: A comparison of student outcomes with random assignment . e‐Journal of Business Education and Scholarship of Teaching, , 12 ( 2 ), 1–23. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bernard, R. M. , Abrami, P. C. , Lou, Y. , Borokhovski, E. , Wade, A. , Wozney, L. , Wallet, P. A. , Fiset, M. , & Huang, B. (2004). How does distance education compare with classroom instruction? A meta‐analysis of the empirical literature . Review of Educational Research , 74 ( 3 ), 379–439. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown, B. , & Liedholm, C. (2002). Can web courses replace the classroom in principles of microeconomics? American Economic Review , 92 ( 2 ), 444–448. [ Google Scholar ]
- Callister, R. R. , & Love, M. S. (2016). A comparison of learning outcomes in skills‐based courses: Online versus face‐to‐face formats . Decision Sciences Journal of Innovative Education , 14 ( 2 ), 243–256. [ Google Scholar ]
- Coates, D. , Humphreys, B. R. , Kane, J. , & Vachris, M. A. (2004). “No significant distance” between face‐to‐face and online instruction: Evidence from principles of economics . Economics of Education Review , 23 ( 5 ), 533–546. [ Google Scholar ]
- Coetzee, M. (2014). School quality and the performance of disadvantaged learners in South Africa (Working Paper No. 22). University of Stellenbosch Economics Department, Stellenbosch
- Dutton, J. , Dutton, M. , & Perry, J. (2002). How do online students differ from lecture students? Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks , 6 ( 1 ), 1–20. [ Google Scholar ]
- Emediegwu, L. (2021). Does educational investment enhance capacity development for Nigerian youths? An autoregressive distributed lag approach . African Development Review , 32 ( S1 ), S45–S53. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fallah, M. H. , & Ubell, R. (2000). Blind scores in a graduate test. Conventional compared with web‐based outcomes . ALN Magazine , 4 ( 2 ). [ Google Scholar ]
- Figlio, D. , Rush, M. , & Yin, L. (2013). Is it live or is it internet? Experimental estimates of the effects of online instruction on student learning . Journal of Labor Economics , 31 ( 4 ), 763–784. [ Google Scholar ]
- Freeman, M. A. , & Capper, J. M. (1999). Exploiting the web for education: An anonymous asynchronous role simulation . Australasian Journal of Educational Technology , 15 ( 1 ), 95–116. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gilbert, P. (2019). The most expensive data prices in Africa . Connecting Africa. https://www.connectingafrica.com/author.asp?section_id=761%26doc_id=756372
- Glick, P. , Randriamamonjy, J. , & Sahn, D. (2009). Determinants of HIV knowledge and condom use among women in Madagascar: An analysis using matched household and community data . African Development Review , 21 ( 1 ), 147–179. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gyimah‐Brempong, K. (2011). Education and economic development in Africa . African Development Review , 23 ( 2 ), 219–236. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson, S. , Aragon, S. , Shaik, N. , & Palma‐Rivas, N. (2000). Comparative analysis of learner satisfaction and learning outcomes in online and face‐to‐face learning environments . Journal of Interactive Learning Research , 11 ( 1 ), 29–49. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lundberg, J. , Merino, D. , & Dahmani, M. (2008). Do online students perform better than face‐to‐face students? Reflections and a short review of some empirical findings . Revista de Universidad y Sociedad del Conocimiento , 5 ( 1 ), 35–44. [ Google Scholar ]
- Means, B. , Toyama, Y. , Murphy, R. , Bakia, M. , & Jones, K. (2010). Evaluation of evidence‐based practices in online learning: A meta‐analysis and review of online learning studies (Report No. ed‐04‐co‐0040 task 0006). U.S. Department of Education, Office of Planning, Evaluation, and Policy Development, Washington DC.
- Navarro, P. (2000). Economics in the cyber‐classroom . Journal of Economic Perspectives , 14 ( 2 ), 119–132. [ Google Scholar ]
- Navarro, P. , & Shoemaker, J. (2000). Performance and perceptions of distance learners in cyberspace . American Journal of Distance Education , 14 ( 2 ), 15–35. [ Google Scholar ]
- Neuhauser, C. (2002). Learning style and effectiveness of online and face‐to‐face instruction . American Journal of Distance Education , 16 ( 2 ), 99–113. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nguyen, T. (2015). The effectiveness of online learning: Beyond no significant difference and future horizons . MERLOT Journal of Online Teaching and Learning , 11 ( 2 ), 309–319. [ Google Scholar ]
- Paechter, M. , & Maier, B. (2010). Online or face‐to‐face? Students' experiences and preferences in e‐learning . Internet and Higher Education , 13 ( 4 ), 292–297. [ Google Scholar ]
- Russell, T. L. , & International Distance Education Certificate Center (IDECC) (1999). The no significant difference phenomenon: A comparative research annotated bibliography on technology for distance education: As reported in 355 research reports, summaries and papers . North Carolina State University. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shachar, M. , & Neumann, Y. (2010). Twenty years of research on the academic performance differences between traditional and distance learning: Summative meta‐analysis and trend examination . MERLOT Journal of Online Learning and Teaching , 6 ( 2 ), 318–334. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shachar, M. , & Yoram, N. (2003). Differences between traditional and distance education academic performances: A meta‐analytic approach . International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning , 4 ( 2 ), 1–20. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tchamyou, V. S. , Asongu, S. , & Odhiambo, N. (2019). The role of ICT in modulating the effect of education and lifelong learning on income inequality and economic growth in Africa . African Development Review , 31 ( 3 ), 261–274. [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu, D. , & Jaggars, S. S. (2014). Performance gaps between online and face‐to‐face courses: Differences across types of students and academic subject areas . The Journal of Higher Education , 85 ( 5 ), 633–659. [ Google Scholar ]

- < Previous
Home > THESES > 631
Traditional classroom versus distance learning approaches in providing eduactaion for students at the College of Applied Science and Technology at RIT
Ryan Griske
This thesis discusses the current controversial issue of traditional classroom vs. distance learning approaches in higher education institutions using a case study in the College of Applied Science and Technology at RIT. The most important question addressed in the thesis is, "Are distance learning methods effective for addressing university-level learning goals?" (Kathleen Davey, 1999, p. 45). There are currently many disputes between educational researchers on this issue. The first four chapters cover details of the proposal stage as previously approved by the Thesis Committee. Chapter One briefly introduces this issue and several important terms used throughout the thesis (e.g., distance learning, traditional classroom, and self-directing learning). Chapter Two presents an in-depth review and analysis of educational and psychological theories and research literature. Chapters Three and Four present principal research questions explored in addressing this issue, as well as ways that relevant data was obtained and analyzed using an action research methodology. The next three chapters discuss the data collection and analysis stage. Chapter Five presents data secured from surveyed RIT administrators' interviews and questionnaire responses. Chapter Six describes data collected and analyzed based on observations in both the traditional classroom and distance learning sections of the surveyed course. Chapters Seven and Eight provide the results of data collection and analysis activities completed for instructors and students in the same two sections. These chapters include operational definitions, visual graphs, tables, and analytical interpretations of the data collected. The last three chapters present conclusions based on the data and analyses previously documented. Chapter Nine discusses gaps between instructors' teaching styles and students' learning styles for the surveyed course. Chapter Ten compares RIT's university learning goals with the viewpoints and performance of instructors and students in both the traditional classroom and distance learning sections, and recommends ways to alleviate the performance discrepancies detected. Chapter Eleven presents serendipitous findings and limitations of the study. The general answer to the most important question addressed in the thesis is that current RIT distance learning methods are not as effective as needed to fully comply with university-level learning goals. However, Chapter Ten concludes that both traditional classroom and distance learning methods can be much more successful in meeting these goals if RIT implements the recommendations presented in this chapter and explores other ways to enhance both environments of the education system.
Library of Congress Subject Headings
Rochester Institute of Technology. College of Applied Science and Technology--Curricula--Evaluation; Distance education--New York (State)--Rochester--Evaluation; Technical education--New York (State)--Rochester--Evaluation; Telecommunication in education-
Publication Date
Document type, department, program, or center.
Information Sciences and Technologies (GCCIS)
Perry, Ronald
Advisor/Committee Member
Doubleday, Nancy
Note: imported from RIT’s Digital Media Library running on DSpace to RIT Scholar Works. Physical copy available through RIT's The Wallace Library at: LC5806.N7 G74 2000
Recommended Citation
Griske, Ryan, "Traditional classroom versus distance learning approaches in providing eduactaion for students at the College of Applied Science and Technology at RIT" (2000). Thesis. Rochester Institute of Technology. Accessed from https://repository.rit.edu/theses/631
RIT – Main Campus
Since January 06, 2014
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Colleges and Departments
- Student Scholarship
- Faculty & Staff Scholarship
- RIT Open Access Journals
- RIT Open Access Books
- RIT Conferences
Author Corner
- RIT Open Access Publishing
- RIT Libraries
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
Rating Content
The 7 biggest differences between online learning vs classroom learning.

Table of contents
Share this article.
Online learning vs classroom learning is two popular options for acquiring knowledge and skills.
While both have their advantages and disadvantages, each approach offers a unique learning experience.
As technology continues to advance, online learning has become an increasingly popular alternative to traditional classroom learning.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the seven biggest differences between online learning vs classroom learning, including factors such as flexibility, cost, interaction, and more.
Whether you're a student or a teacher, understanding the differences between these two approaches can help you choose the best learning method for your needs.
So what are we waiting for? Let’s dive into all that you need to know about online learning vs classroom learning.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Online Learning

Let’s have a look at some of the advantages and disadvantages of online learning.
Advantages of Online Learning:
1. flexibility.
It allows learners to study at their own pace and on their schedule, making it an ideal option for those with busy lifestyles or other commitments.
2. Cost-Effective
Online courses are often less expensive than traditional classroom-based courses, making education more accessible to a wider range of learners.
3. Accessibility
It is available to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of geographic location or physical disabilities.
4. Personalized Learning
Online courses often offer personalized learning experiences, allowing learners to focus on their areas of interest or weaknesses.
Disadvantages of Online Learning
1. limited interaction.
It lacks the face-to-face interaction and socialization opportunities of traditional classroom learning, which may be a disadvantage for some learners.

2. Technical Issues
Technical difficulties such as internet connectivity issues, software glitches, or hardware malfunctions can disrupt the learning experience.
3. Self-Motivation
It requires a high degree of self-discipline and self-motivation, which may be challenging for some learners who require more structured learning environments.
4. Lack Of Feedback
It may offer limited feedback opportunities from instructors or peers, which can make it difficult for learners to gauge their progress and receive constructive criticism.
Now that we have discussed the advantages and disadvantages of online learning, let’s move on to those of classroom learning.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Classroom Learning

Advantages of Classroom Learning:
1. face-to-face interaction.
Classroom learning allows learners to engage in face-to-face interaction with their peers and instructors, facilitating collaboration and the exchange of ideas.
2. Structured Learning Environment
It provides a structured learning environment that may be beneficial for learners who require a more hands-on, guided approach to learning.
3. Immediate Feedback
It offers immediate feedback opportunities from instructors and peers, enabling learners to gauge their progress and receive constructive criticism.
4. Enhanced Socialization
It offers socialization opportunities that may help learners develop important social skills and networks.
Disadvantages of Classroom Learning:
1. limited flexibility.
Classroom learning may be less flexible than online learning, requiring learners to attend classes at specific times and locations.
2. Higher Cost
It may be more expensive than online learning due to costs associated with facilities, materials, and travel.
3. Distractions
It may be subject to distractions such as noise, disruptions, or interruptions, which can disrupt the learning experience.
4. Limited Customization
It may offer limited customization options, making it difficult for learners to focus on their specific areas of interest or weaknesses.
Online Learning Vs Classroom Learning

Let’s have a look at the top 7 differences between online learning vs classroom learning.
1. Learning Environment
The learning environment is one of the most significant differences between online learning and classroom learning.
Classroom learning takes place in a physical classroom, where students are present in-person with their teachers and peers.
The classroom provides a structured environment, which helps students stay on task, focus on their work, and receive immediate feedback from the teacher.
In contrast, online learning takes place in a virtual classroom, where students connect to a course via their computer or mobile device.
Online learners can access their course materials and assignments from anywhere, and at any time, making it a more flexible and convenient option.
2. Interaction
Another significant difference between online and classroom learning is the level of interaction between students and instructors .
In a classroom setting, students have the opportunity to interact with their peers and instructors face-to-face, which can help build strong relationships and a sense of community.
Classroom learning also allows for immediate feedback from the instructor, which can be very beneficial to students.
Online learning, on the other hand, relies on virtual communication, which can be less personal and less engaging than face-to-face interaction.
3. Schedule
One of the major benefits of online learning is the flexibility it offers.
Online courses are self-paced, which means that students can study when it's most convenient for them.
This makes it easier for students to balance their studies with work, family, and other commitments.
In contrast, classroom learning follows a set schedule, with specific times and locations for classes. This can be a challenge for students who have busy schedules or who live far from the school or university.
4. Teaching Methodology
Classroom learning and online learning differ in their teaching methodology. In a classroom setting, teachers use lectures, discussions, and group work to deliver the course material.
This can be very effective for students who learn best through social interaction and discussion. In contrast, online learning is more self-directed, with students responsible for reading the course materials and completing assignments on their own.
This can be beneficial for students who are more self-motivated or who prefer to work at their own pace.
Cost is another major difference between online and classroom learning.
Online courses are often less expensive than classroom courses, as there are fewer costs associated with facilities, materials, and travel.
This makes online learning a more accessible option for many students.
In contrast, classroom learning can be quite expensive, as students must pay for tuition, textbooks, transportation, and other expenses.
6. Technology
Technology plays a critical role in online learning, as students must have access to a computer and internet connection to participate in the course.
Online courses often incorporate a variety of technology tools, such as videos, podcasts, interactive quizzes, and online discussion forums.
In contrast, classroom learning may also use technology, but to a lesser extent.
7. Learning Style
Finally, online and classroom learning may be better suited to different learning styles.
Classroom learning may be more beneficial for students who learn best through social interaction and discussion, while online learning may be more effective for students who prefer self-directed learning and need to work at their own pace.
Ultimately, the best approach to learning will depend on each student's unique learning style, preferences, and circumstances.
Learn With Oreed
Experience enhanced learning capabilities in your workplace with Oreed's all-in-one platform.
- Gain a 360-degree understanding of your employees and better gauge their training needs.
- Oreed offers tailor-made training and courses to fit your organization's specific needs.
- You can measure the effectiveness of your training/courses with the platform's impact assessment feature.
So what are you waiting for? Book a demo with Oreed today to find out more.
Promote lifelong learning through Oreed by experiencing the most powerful all-in-one training and development intelligent platform that streamlines all your organization's learning, training, and development activities in one place.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, online learning vs classroom learning has its advantages and disadvantages.
While online learning offers flexibility and convenience, classroom learning provides face-to-face interaction and a structured learning environment.
Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on individual preferences and learning styles.
It is important to carefully consider the differences between online learning and classroom learning and choose the approach that best fits your needs and goals.
As technology continues to advance, the line between these two learning modes will likely continue to blur, creating even more options for learners in the future.
1. What is collaborative online learning?
Collaborative online learning is an approach to education that emphasizes collaborative group work and online communication tools to facilitate learning .
It involves students working together in virtual environments to complete learning activities and achieve shared learning goals.
Collaborative online learning allows students to engage in collaborative projects and activities regardless of their physical location, creating a sense of community and encouraging participation and engagement.
This approach can be implemented in various learning contexts, from traditional classroom settings to fully online courses, and is aimed at fostering critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and teamwork skills.
2. What are some interesting facts about online learning?
Here are some interesting facts about online learning:
- Online courses are often more affordable than traditional in-person courses.
- It allows for greater flexibility and convenience, allowing students to learn at their own pace and on their schedule.
- Another fact about online learning is that online courses can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making education more accessible to a wider audience.
- It is just as effective, and in some cases more effective, than traditional in-person learning.
- It often offers a wide range of multimedia content, including videos, animations, and interactive simulations, which can enhance the learning experience.
Subscribe to our weekly email newsletter
Stay updated with the latest e-learning news and receive all the essential updates regarding the Oreed platform.
Please fix the following errors:
keep reading
![online learning vs classroom learning thesis Learning Experience Platform Market Size [2024]](https://oreed.org/cdn/1619638329_6089b83993722/1658391437_62d90b8d45216/1658391471_62d90baf0898f/1702465413_65798f85e1464/1702465413_65798f85e1078.jpeg)
Learning Experience Platform Market Size [2024]
Explore our in-depth analysis of the learning experience platform market size, trends, and forecasts for 2024. Dive into our expert LXP market insights.
![online learning vs classroom learning thesis What is a Learning Experience Platform [2024 Full Guide]](https://oreed.org/cdn/1619638329_6089b83993722/1658391437_62d90b8d45216/1658391471_62d90baf0898f/1702464014_65798a0ecf990/1702464014_65798a0ecf60a.jpeg)
What is a Learning Experience Platform [2024 Full Guide]
Learning Experience Platforms (LXPs) have revolutionized the field of learning and development, providing learners with innovative and personalized learning experiences.

AI In Recruitment
AI in recruitment enhances efficiency without replacing human recruiters. Discover Oreed for advanced employee development.
Supporting your growth every step of the way
Our support superheroes are a click away to help you get the most out of oreed.com, so you can focus on working without limits.
Support anytime, anywhere
Welcome to your new training intelligent platform
unlock your organization's potential and prepare to become a global leader of the future
MINI REVIEW article
The impact of virtual reality on student engagement in the classroom–a critical review of the literature.

- 1 Faculty of Education, Silpakorn University, Nakhon Pathom, Thailand
- 2 Melbourne Graduate School of Education, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
- 3 Graduate Department, Xi’an Physical Education University, Xi’an, China
- 4 College of Commerce and Tourism, Hunan Vocational College for Nationalities, Yueyang, China
- 5 Graduate Department, Sehan University, Yeongam County, Republic of Korea
Objective: The purpose of this review is to identify the impact of virtual reality (VR) technology on student engagement, specifically cognitive engagement, behavioral engagement, and affective engagement.
Methods: A comprehensive search of databases such as Google, Scopus, and Elsevier was conducted to identify English-language articles related to VR and classroom engagement for the period from 2014 to 2023. After systematic screening, 33 articles were finally reviewed.
Results: The use of VR in the classroom is expected to improve student engagement and learning outcomes, and is particularly effective for students with learning disabilities. However, introducing VR into middle school education poses several challenges, including difficulties in the education system to keep up with VR developments, increased demands on students’ digital literacy, and insufficient proficiency of teachers in using VR.
Conclusion: To effectively utilize VR to increase student engagement, we advocate for educational policymakers to provide training and technical support to teachers to ensure that they can fully master and integrate VR to increase student engagement and instructional effectiveness.
Introduction
In recent years, virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a transformative technology in education, providing new avenues for immersive and interactive learning experiences ( Pottle, 2019 ). At its core, VR offers a departure from the tangible, allowing users to delve into an environment transcending conventional reality ( Brooks, 1999 ; Jeong et al., 2019 ). VR’s essence is captured in three pillars: presence, interactivity, and immersion ( Lee et al., 2017 ). Presence grants users access to previously unreachable 3D landscapes, facilitating a unique, experiential insight ( Poux et al., 2020 ). Interactivity kindles user curiosity, enabling dynamic engagements within the virtual milieu ( Steuer et al. 1995 ; Huvila, 2013 ; Song et al., 2023 ). Immersion pushes the boundaries of conventional experiences, reviving or manifesting phenomena outside the realm of everyday life ( Sanchez-Vives and Slater, 2005 ; Poux et al., 2020 ).
The introduction of VR in education might increase student engagement, which is closely related to the cognitive, behavioral, and affective dimensions of the engagement model ( Wang and Degol, 2014 ). Cognitive engagement underscores the depth of students’ attention, comprehension, and retention ( Wang and Degol, 2014 ). Behavioral engagement is observable, characterized by consistent attendance and active classroom participation ( Wang and Degol, 2014 ). Affective engagement delves into the emotional realm, encompassing motivation, passion, and learning efficacy ( Wang and Degol, 2014 ).
Existing literature emphasizes the importance of virtual reality technology in promoting full student engagement in cognitive, behavioral, and affective dimensions, and states that the application of virtual reality technology in education has become a trend ( Mystakidis et al., 2021 ). Some literature shows that higher education institutions are increasingly adopting VR, with adoption rates as high as 46% at US universities and 96% at United Kingdom universities ( United Kingdom Authority, 2019 ; Agbo et al., 2021 ). In addition, the establishment of dedicated VR laboratories at leading universities such as Harvard University and Colorado State University underscores the commitment to using VR for educational innovation and advancement ( Reid, 1987 ; Leidner and Jarvenpaa, 1995 ). This literature shows that the widespread use of VR in education has attracted the attention of a growing number of researchers and educators, with a particular interest in the impact of VR in the classroom in terms of students’ cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement.
It is worth noting that although existing literature begins to discuss the impact of VR on student engagement, there are still shortcomings in determining the impact of VR on various dimensions of student engagement, which may limit our overall understanding of the topic. Therefore, further discussion is needed to more specifically identify the impact of VR on the various dimensions of student engagement to gain a more comprehensive and concrete understanding. To accomplish this, this review is guided by the following three questions: (1) What are the positive impacts of VR in education? (2) What are the challenges of VR in education? (3) What interventions can address these challenges? With this in mind, the article will first discuss the positive impact of VR on students’ cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement to help readers understand its potential in education. It will then discuss the challenges facing VR to make constructive recommendations to address the problems in education.
Searching strategy
In our methods, we used critical review. According to Grant and Booth (2009) “an effective critical review presents, analyses and synthesizes material from diverse sources”(p.93). Critical perspectives were used to assess the potential of VR in reforming educational practices and improving teaching and learning outcomes. The purpose of this article was to collect literature on the impact of VR on student engagement. Therefore, this article summarizes the previous studies as follows. First, information was obtained from Google, Scopus, and Elsevier databases: “virtual reality,” “cognitive engagement,” “affective engagement,” “behavioral engagement” and “learning outcomes.” The search was limited to articles published between January 2014 and December 2023 in English. The first search used all combinations of the above keywords and, after an initial review, produced 97 potentially relevant articles (Google: 92, Scopus: 3, Elsevier: 2).
In the second phase, secondary terms such as “affect,” “challenge,” and “education” were added, reducing the number of studies to 63 (Google:60, Scopus:1, Elsevier:2). Of these, 34 did not meet the criteria and were excluded. They were excluded because their target audience was teachers and did not discuss the impact of VR on student engagement from the student’s perspective. In the final stage, another 53 articles were excluded because they were repetitive and their purpose was to discuss either technology or engagement, or both. Finally, their full texts were reviewed to determine if their work fits the focus of this article 20 articles (Google: 17, Scopus: 1, Elsevier: 2) qualified for final review, covered a sample on the impact of VR on student engagement, and were included in the analysis.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
To ensure the quality of the literature, we selected only peer-reviewed journal articles published in English in the last decade. The main purpose of this article was to review the impact of VR on student engagement. Therefore, we selected only review articles on the impact of VR on student engagement in educational settings. Articles that were not written in English did not discuss the impact on engagement from a student perspective, and were published beyond the previously established time and language were excluded. In addition, a selection of articles was identified and assessed by manually searching the references of articles related to the topic, of which 13 met the eligibility criteria. Therefore, 13 additional articles were added to the 20 identified. In total, 33 articles that met these eligibility criteria were included and reviewed here. Full-text versions of the articles were obtained, with each article being reviewed and confirmed as appropriate by the authors. Finally, to maximize transparency and traceability, we list the rationale and relevant evidence for all articles included (see Table 1 ). The process of article selection followed the Preferred Reporting of Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Statement ( Moher et al., 2009 ; see Figure 1 ). Figure 1 illustrates the process of article selection.
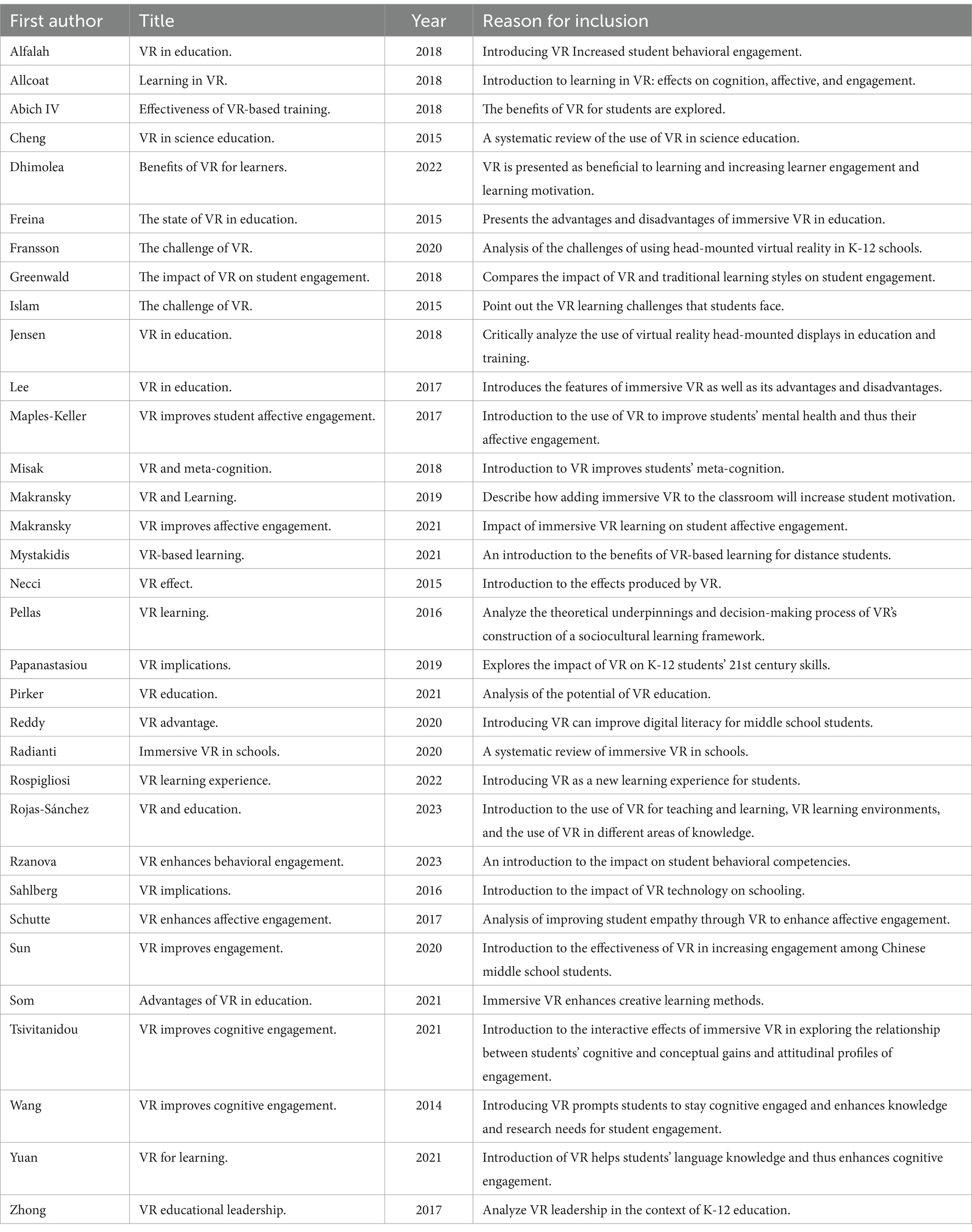
Table 1 . Publications reviewed in full text with reasons for inclusion or exclusion.
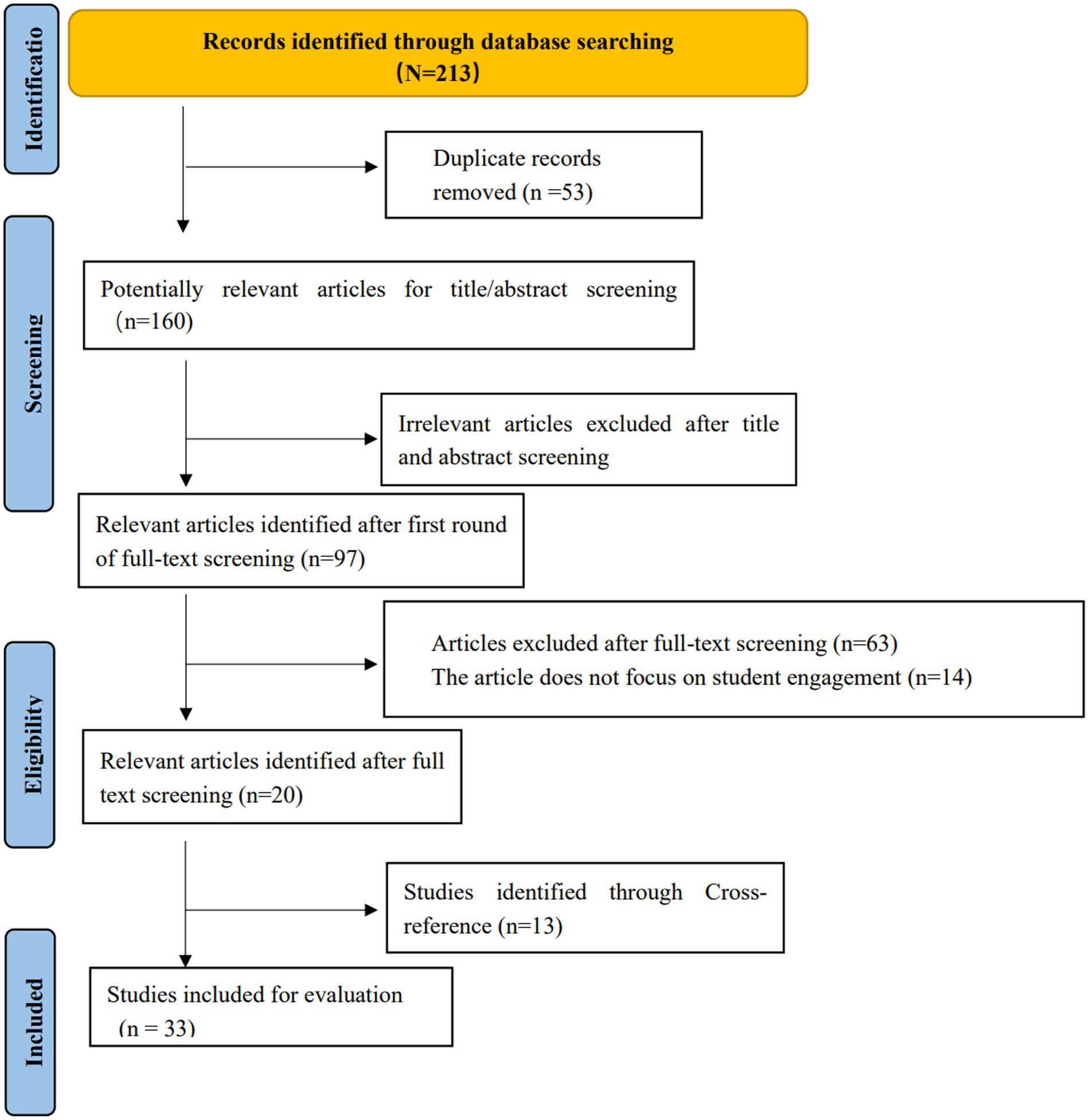
Figure 1 . PRISMA flow diagram for article selection.
The review found that the number of publications increased each year from 2014 to 2023, indicating the continued interest of researchers in exploring the impact of VR on student engagement. When reviewing the impact of VR on student engagement, Wang and Degol’s (2014) article had the most citations at 450, suggesting that the article had a strong impact in the area of student use of VR in the classroom. The majority of articles had only 10 or fewer citations, which may have indicated that these articles were relatively new or had less impact in the field. It was worth noting that more recently published articles, such as Rzanova et al. (2023) , did not have enough time to accumulate citations, so their impact on the field may not have been fully reflected in current citations.
To summarize, the differences in the number of citations for these articles highlighted their different levels of influence in the area of VR’s impact on student engagement. However, there were some limitations to the review methods. For example, some articles might not have fully reflected their impact on the field in the current citations due to their short time frames, which might have resulted in less comprehensive findings. Furthermore, the literature included was small, and in the future consideration would be given to expanding the search of literature and databases, such as PubMed and Web of Science databases, as well as expanding the search with keywords, such as “students’ attitudes toward VR.” In addition, the inclusion and exclusion criteria might have limited the generalizability of the results of the review, and therefore more caution was needed when generalizing the results of the review.
The positive impact of VR on education
This section will discuss the impact of VR on students’ cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement participation. It is important in the field of education. Radianti et al. (2020) noted that student engagement in educational settings was critical to learning outcomes and classroom climate. Yuan and Wang (2021) further noted that the combined effects of cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement could directly impact student learning outcomes and classroom contextual experiences. Therefore, a deeper understanding of the impact of VR on these three dimensions of engagement can provide valuable insights into educational practices and help educators better optimize classroom environments and teaching methods.
First, Papanastasiou et al. (2019) noted that VR immersive learning experiences promoted students’ cognitive engagement and aided in understanding complex and abstract knowledge. That is, through immersive learning, students can understand and remember what they have learned in greater depth and increase cognitive engagement. Pellas (2016) also found that VR encouraged students to learn through self-directed inquiry and move away from traditional teacher-centered instruction. Pellas (2016) further explained that, through VR scenario reenactments and simulations, students could engage in real-world unavailable learning experiences such as exploring historical sites and visiting distant planets. This means that such learning experiences enable students to explore knowledge in deeper and more varied ways, thus increasing cognitive engagement. Similarly, Maples-Keller et al. (2017) showed that VR was beneficial in engaging different types of students in learning, particularly for at-risk students, including those with learning difficulties, anxiety disorders, and other mental illnesses. VR provided personalized and adaptive learning environments that helped students improve cognitive engagement and achievement ( Maples-Keller et al., 2017 ). In summary, VR facilitates understanding of complex knowledge and promotes cognitive engagement for different types of students through immersive learning experiences and self-directed inquiry learning.
Secondly, Pirker and Dengel (2021) demonstrated that VR could promote student behavioral engagement. They discussed the potential of immersive VR in education through an in-depth analysis of 64 articles. They showed that “learning tasks in 3-D VLEs can foster intrinsic motivation for and engagement with the learning content” (p.77). Sun and Peng (2020) also suggested that by combining classical educational concepts with VR, such as Confucianism’s promotion of teaching for fun, students were better able to engage in learning activities. For example, Rzanova et al. (2023) found that the use of VR in the teaching of poetry to create the scenarios depicted in the verses enabled students to actively participate in classroom activities. Similarly, Freina and Ott (2015) also found that by simulating real school escape scenarios in VR, students could take on different roles to perform escape drills, and this sense of behavioral engagement can help students better master escape techniques and enhance safety awareness. These articles seem to echo that VR helps to enhance student behavioral engagement.
It is worth noting that there is debate about whether VR has a positive impact on student behavioral engagement. Proponents noted that students’ hands-on experience and exploration in virtual environments stimulated interest and behavioral engagement ( Wong et al., 2010 ; Allcoat and Von Mühlenen, 2018 ). This view suggests that VR provides an immersive learning experience that enhances students’ motivation and promotes deeper engagement in classroom activities. However, contrary findings exist, suggesting that the use of VR may have some negative effects. For example, students might have become addicted to the virtual world and neglected their real-life tasks and responsibilities, thus affecting their behavior in the classroom ( Cheng et al., 2015 ; Greenwald et al., 2018 ; Makransky et al., 2019 ). In addition, some other scholars noted that there might have been a gap between learning experiences in virtual environments and real-world learning experiences, which might have affected students’ ability to acquire and apply knowledge ( Makransky and Petersen, 2021 ). These conflicting results remind us that these complexities and diversities need to be taken into account when evaluating the role of VR technology in improving student engagement in the classroom.
Finally, scholars such as Wu et al. (2013) , Schutte and Stilinović (2017) , and Yuen et al. (2011) found that VR helped to promote student affective engagement. For example, Schutte and Stilinović (2017) found that contexts provided by VR for children with emotional impairments or disabilities taught them skills in communicating with people and managing their emotions, thus fostering empathy. This implies that VR may stimulate affective engagement. Wu et al. (2013) and Yuen et al. (2011) also found that VR provided opportunities for affective interaction, enabling students to interact with characters in the virtual environment. In language learning, for example, practicing through conversations with virtual characters could help students improve their oral expression ( Dhimolea et al., 2022 ). This means that affective interactions may increase students’ affective engagement with the learning content. Similarly, Misak (2018) noted that VR allowed students to role-play in virtual literature and experience the affective portrayed in the story. In other words, affective experiences may deepen students’ understanding of literary works and increase affective engagement. This literature seems to reflect that VR can promote student affective engagement.
In general, VR positively impacts students’ cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement. In terms of cognitive engagement, VR can facilitate students’ cognitive engagement with learning materials and better understanding of abstract and complex knowledge by creating immersive situations. In terms of behavioral engagement, VR stimulates active student engagement and action through interactive learning. Although there is debate about whether VR has a positive impact on student behavioral engagement, literature has demonstrated the positive impact of VR on student behavioral engagement. In terms of affective engagement, VR promotes students’ emotional engagement by triggering affective resonance through affective experience and affective interaction. This full engagement helps students improve their learning and develop empathy.
The following section discusses the challenges faced when introducing VR in education. Through understanding these challenges, we can better understand the problems in the education system and make some constructive suggestions to help address them.
The challenge of VR in education
Despite the positive impact of VR on students’ cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement, there are still two challenges to introducing VR into middle education, namely the difficulty of the educational system in keeping up with VR developments and the lack of teacher proficiency in VR use ( Islam et al., 2015 ; Zhong, 2017 ; Abich et al., 2021 ). For example, Islam et al. (2015) observed that the pace of technological advancement, including VR, outpaced the ability of the education system to adapt. This phenomenon is due to the slow reform of the education system, which takes time for the acceptance and adoption of emerging technologies ( Islam et al., 2015 ). To this end, the education sector may take longer to standardize the syllabus, resulting in students not having immediate access to VR ( Zhong, 2017 ). In other words, students may not have the opportunity to experience VR in the classroom until the education department completes the standardization process. Sahlberg (2016) further stated that while reform and standardization in the education sector took time, once VR and the education system evolved in tandem, students benefited from an education that matched the VR of the day.
Other scholars observed that VR education faced several challenges in developing digital literacy in students ( Aviram and Eshet-Alkalai, 2006 ; Sahlberg, 2016 ). According to Reddy et al. (2020) , “digital literacy is a set of skills required by 21st Century individuals to use digital tools to support the achievement of goals in their life situations” (p. 66). Digital literacy encompasses the assessment of digital technologies, critical thinking, and the ability to create and express oneself digitally ( Reddy et al., 2020 ). For example, Tsivitanidou et al. (2021) and Necci et al. (2015) emphasized the need for students to identify the differences between the results of simulation experiments and real experiments and to assess the reliability and accuracy of simulation experiments. In other words, students need to judge the plausibility of the results of simulation experiments and interpret and evaluate those results in real-world situations.
Similarly, Farmer and Farmer (2023) found that digital literacy required students to master VR painting and sculpting tools to create art. This involved learning to select appropriate colors and textures and creating three-dimensional effects with VR tools ( Skulmowski et al., 2021 ). Meanwhile, Andone et al. (2018) further noted that students also needed to learn to share and present their work to others in virtual reality. This observation seems to reflect the high demand for students’ creativity, technical skills, and expressive abilities when introducing VR into education. In sum, while the development of VR education benefits students’ learning in conjunction with VR, there are challenges to students’ digital literacy and the technological adaptability of the education system.
In addition, teachers’ lack of proficiency in the use of VR is another major challenge in introducing VR into middle education. For example, Abich et al. (2021) found that teachers might lack proficiency in the operation and application of VR, which might result in teachers not being able to fully utilize VR to supplement instruction. Jensen and Konradsen (2018) claimed that “for HMDs to become a relevant tool for instructors they must have the ability to produce and edit their content” (p.1525). This means that teachers need to spend time familiarizing themselves with HMDs and related software to create, edit, and customize content to meet their specific instructional needs. Similarly, Fransson et al. (2020) discussed the challenges of teachers operating VR equipment and software. They interviewed 28 teachers to understand teachers’ challenges with implementing helmet display VR in educational settings. Fransson et al. (2020) indicated that there might be a technological threshold and learning curve for teachers in controlling and operating VR devices, which might affect the effective use of VR for teaching and learning.
While teachers may lack familiarity with VR, there are solutions to this challenge. For example, Alfalah (2018) noted that proper training and support could help teachers make the most of VR to supplement instruction. That is, teacher training can provide teachers with the technical knowledge and operational skills they need to familiarize themselves with how VR equipment and software work. To this end, Alfalah (2018) found the impact of providing teachers with VR training in schools. They used a quantitative approach by distributing a questionnaire online to 30 IT teachers. Alfalah (2018) indicated that “technology training may be maximized for the integration of VR technology” (P.2634). This finding seems to reflect that proper teacher training and support can be effective in helping teachers overcome the operational and application of VR technology’s difficulties.
In sum, prior literature has shown that introducing VR into middle school education faces several challenges. First, the rapid development of technology makes the educational system keep up with VR, resulting in a disconnect between the educational curriculum and VR. Second, there may be a lack of proficiency in students’ digital literacy and teachers’ handling and application of VR. However, these challenges are not insurmountable. With proper training and support, teachers can make full use of VR to supplement their teaching and learning to realize the potential of VR in education. It is worth noting that through the literature we have found that in practice, due to the rapid development of technology and the limitations of the educational system, achieving a complete balance may take some time and effort. Therefore, considering how to address the gap between the speed of VR development and the education system to better integrate and apply VR in education makes sense.
This article describes the impact of VR on student cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement and the challenges posed by VR education. The literature review finds that using VR in the classroom can positively impact student engagement and learning outcomes. An interesting finding is that VR can be a promising tool for providing education to students with learning disabilities. For example, the previous literature review section describes how for students with learning difficulties, anxiety disorders, and other mental illnesses, VR can provide personalized and adaptive learning environments that can help students improve cognitive engagement and academic performance. And, for children with emotional disorders or disabilities, VR provides contexts that can teach them skills for communicating with others and managing their emotions, thereby developing empathy and stimulating affective engagement.
However, the potential problems with incorporating VR in middle education are the difficulty of the education system in keeping up with VR developments, the higher demands of student digital literacy, and the lack of teacher proficiency in the use of VR. These challenges require educational policymakers to provide training and technical support to teachers to ensure that they can fully master and integrate VR to improve student engagement and teaching effectiveness.
Author contributions
XL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZNY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZY: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the General Topics of China’s Hunan Province Social Science Achievement Evaluation Committee Fund [Grant no. XSP2023JYC123].
Acknowledgments
We are deeply appreciative of the editors and reviewers of this journal for their unwavering dedication and contributions that have shaped the publication of this article. Their constructive feedback and invaluable insights were instrumental in bringing this piece to fruition. We extend our heartfelt thanks to the readers with a keen interest in virtual reality technology. It is our sincere hope that this article will inspire enriched discussions within the academic community about the potential and nuances of using virtual reality in educational contexts.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abich, J., Parker, J., Murphy, J. S., and Eudy, M. (2021). A review of the evidence for training effectiveness with virtual reality technology. Virtual Reality 25, 919–933. doi: 10.1007/s10055-020-00498-8
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Agbo, F. J., Sanusi, I. T., Oyelere, S. S., and Suhonen, J. (2021). Application of virtual reality in computer science education: a systemic review based on bibliometric and content analysis methods. Educ. Sci. 11, 1–23. doi: 10.3390/educsci11030142
Alfalah, S. F. (2018). Perceptions toward adopting virtual reality as a teaching aid in information technology. Educ. Inf. Technol. 23, 2633–2653. doi: 10.1007/s10639-018-9734-2
Allcoat, D., and Von Mühlenen, A. (2018). Learning in virtual reality: effects on performance, emotion, and engagement. Res. Learn. Technol. 26, 1–13. doi: 10.25304/rlt.v26.2140
Andone, D., Vert, S., Frydenberg, M., and Vasiu, R. (2018). Open virtual reality project to improve students’ skills. In 2018 IEEE 18th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT) , 6–10. doi: 10.1109/ICALT.2018.00008
Aviram, A., and Eshet-Alkalai, Y. (2006). Towards a theory of digital literacy: three scenarios for the next steps. Eur. J. Open Distance E Learn 9, 1–11.
Google Scholar
Brooks, F. P. (1999). What's real about virtual reality? Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE). Comput. Graph. Appl. 19, 16–27. doi: 10.1109/38.799723
Cheng, M.-T., Chen, J.-H., Chu, S.-J., and Chen, S.-Y. (2015). The use of serious games in science education: a review of selected empirical research from 2002 to 2013. J. Comput. Educ. 2, 353–375. doi: 10.1007/s40692-015-0039-9
Dhimolea, T. K., Kaplan-Rakowski, R., and Lin, L. (2022). A systematic review of research on high-immersion virtual reality for language learning. TechTrends 66, 810–824. doi: 10.1007/s11528-022-00717-w
Fransson, G., Holmberg, J., and Westelius, C. (2020). The challenges of using head mounted virtual reality in K-12 schools from a teacher perspective. Educ. Inf. Technol. 25, 3383–3404. doi: 10.1007/s10639-020-10119-1
Freina, L., and Ott, M. (2015). A literature review on immersive virtual reality in education: state of the art and perspectives. Int. Sci. Conf. E Learn. Softw. Educ. 1, 10–1007. doi: 10.12753/2066-026x-15-020
Grant, M. J., and Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf. Libr. J. 26, 91–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Greenwald, S. W., Corning, W., Funk, M., and Maes, P. (2018). Comparing learning in virtual reality with learning on a 2D screen using electrostatics activities. J. Comput. Sci. 24, 220–245. doi: 10.3217/jucs-024-02-0220
Huvila, I. (2013). Sorting out the metaverse and how the metaverse is sorting us out . London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Islam, N., Beer, M., and Slack, F. (2015). E-learning challenges faced by academics in higher education. J. Educ. Train. Stud. 3, 102–112. doi: 10.11114/jets.v3i5.947
Jensen, L., and Konradsen, F. (2018). A review of the use of virtual reality head-mounted displays in education and training. Educ. Inf. Technol. 23, 1515–1529. doi: 10.1007/s10639-017-9676-0
Jeong, K., Kim, J., Kim, M., Lee, J., and Kim, C. (2019). Asymmetric interface: user interface of asymmetric virtual reality for new presence and experience. Symmetry 12, 1–25. doi: 10.3390/sym12010053
Lee, J., Kim, M., and Kim, J. (2017). A study on immersion and VR sickness in walking interaction for immersive virtual reality applications. Symmetry 9, 1–17. doi: 10.3390/sym9050078
Leidner, D. E., and Jarvenpaa, S. L. (1995). The use of information technology to enhance management school education: a theoretical view. Manag. Inf. Serv. Q. 19, 265–291. doi: 10.2307/249596
Makransky, G., and Petersen, G. B. (2021). The cognitive-affective model of immersive learning: a theoretical research-based model of learning in immersive virtual reality. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 33, 937–958. doi: 10.1007/s10648-020-09586-2
Makransky, G., Terkildsen, T. S., and Mayer, R. E. (2019). Adding immersive virtual reality to a science lab simulation causes more presence but less learning. Learn. Instr. 60, 225–236. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2017.12.007
Maples-Keller, J. L., Bunnell, B. E., Kim, S.-J., and Rothbaum, B. O. (2017). The use of virtual reality technology in the treatment of anxiety and other psychiatric disorders. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 25, 103–113. doi: 10.1097/HRP.0000000000000138
Misak, J. (2018). A (virtual) bridge not too far: teaching narrative sense of place with virtual reality. Comput. Compos. 50, 39–52. doi: 10.1016/j.compcom.2018.07.007
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., and Altman, D. G.PRISMA Group* (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 151, 264–269. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
Mystakidis, S., Berki, E., and Valtanen, J. P. (2021). Deep and meaningful e-learning with social virtual reality environments in higher education: a systematic literature review. Appl. Sci. 11, 1–25. doi: 10.3390/app11052412
Necci, A., Cozzani, V., Spadoni, G., and Khan, F. (2015). Assessment of domino effect: state of the art and research needs. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 143, 3–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2015.05.017
Papanastasiou, G., Drigas, A., Skianis, C., Lytras, M., and Papanastasiou, E. (2019). Virtual and augmented reality effects on K-12, higher, and tertiary education students’twenty-first-century skills. Virtual Reality 23, 425–436. doi: 10.1007/s10055-018-0363-2
Pellas, N. (2016). “Unraveling a progressive inquiry script in persistent virtual worlds: theoretical foundations and decision processes for constructing a socio-cultural learning framework” in Web design and development: Concepts, methodologies, tools, and applications (Pennsylvania, US: IGI Global), 610–647.
Pirker, J., and Dengel, A. (2021). The potential of 360 virtual reality videos and real VR for education—a literature review. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 41, 76–89. doi: 10.1109/MCG.2021.3067999
Pottle, J. (2019). Virtual reality and the transformation of medical education. Future Healthcare J. 6, 181–185. doi: 10.7861/fhj.2019-0036
Poux, F., Valembois, Q., Mattes, C., Kobbelt, L., and Billen, R. (2020). Initial user-centered design of a virtual reality heritage system: applications for digital tourism. Remote Sens. 12, 1–25. doi: 10.3390/rs12162583
Radianti, J., Majchrzak, T. A., Fromm, J., and Wohlgenannt, I. (2020). A systematic review of immersive virtual reality applications for higher education: design elements, lessons learned, and research agenda. Comput. Educ. 147, 103778–103729. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103778
Reddy, P., Sharma, B., and Chaudhary, K. (2020). Digital literacy: a review of literature. Int. J. Technoethics (IJT) 11, 65–94. doi: 10.4018/IJT.20200701.oa1
Reid, J. M. (1987). The learning style preferences of English as a second language (ESL) students. Teach. Engl. Speakers Other Lang. Q. 21, 87–111. doi: 10.2307/3586356
Rzanova, S., Yushchik, E., Markova, S., and Sergeeva, A. (2023). Impact of virtual reality technologies in the context of the case method on engineering students’ competencies. Educ. Inf. Technol. 7, 1–19. doi: 10.56028/aetr.7.1.7.2023
Sahlberg, P. (2016). The global educational reform movement and its impact on schooling. In: K. Mundy, A. Green, B. Lingard, and A. Verger The Handbook of Global Education Policy . Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons, 128–144.
Sanchez-Vives, M. V., and Slater, M. (2005). From presence to consciousness through virtual reality. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6, 332–339. doi: 10.1038/nrn1651
Schutte, N. S., and Stilinović, E. J. (2017). Facilitating empathy through virtual reality. Motiv. Emot. 41, 708–712. doi: 10.1007/s11031-017-9641-7
Skulmowski, A., Nebel, S., Remmele, M., and Rey, G. D. (2021). Is a preference for realism really naive after all? A cognitive model of learning with realistic visualizations. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 34, 1–27. doi: 10.1007/s10648-021-09638-1
Song, C., Shin, S. Y., and Shin, K. S. (2023). Optimizing foreign language learning in virtual reality: a comprehensive theoretical framework based on constructivism and cognitive load theory. Appl. Sci. 13, 1–31. doi: 10.3390/app132312557
Steuer, J., Biocca, F., and Levy, M. R. (1995). Communication in the age of virtual reality , New York: Routledge
Sun, S. Y., and Peng, L. H. (2020). Study of the virtual reality education and digitalization in China. J. Physics 1456, 012042–012047. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1456/1/012042
Tsivitanidou, O. E., Georgiou, Y., and Ioannou, A. (2021). A learning experience in inquiry-based physics with immersive virtual reality: student perceptions and an interaction effect between conceptual gains and attitudinal profiles. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 30, 841–861. doi: 10.1007/s10956-021-09924-1
United Kingdom Authority. (2019). VR and AR attract education sector interest . Available at: https://www.ukauthority.com/articles/vr-and-ar-attract-education-sector-interest/ .
Wang, M. T., and Degol, J. (2014). Staying engaged: knowledge and research need in student engagement. Child Dev. Perspect. 8, 137–143. doi: 10.1111/cdep.12073
Wong, B. M., Etchells, E. E., Kuper, A., Levinson, W., and Shojania, K. G. (2010). Teaching quality improvement and patient safety to trainees: a systematic review. Acad. Med. 85, 1425–1439. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181e2d0c6
Wu, H.-K., Lee, S. W.-Y., Chang, H.-Y., and Liang, J.-C. (2013). Current status, opportunities and challenges of augmented reality in education. Comput. Educ. 62, 41–49. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2012.10.024
Yuan, H., and Wang, Z. (2021). A review of research on technology enhancing Chinese learning . 2021 international conference on internet, education and information technology (IEIT), pp. 462–467.
Yuen, S. C.-Y., Yaoyuneyong, G., and Johnson, E. (2011). Augmented reality: an overview and five directions for augmented reality (AR) in education. J. Educ. Technol. Dev. Exchange 4, 119–140. doi: 10.18785/jetde.0401.10
Zhong, L. (2017). Indicators of digital leadership in the context of K-12 education. J. Educ. Technol. Dev. Exchange 10, 27–40. doi: 10.18785/jetde.1001.03
Keywords: virtual reality technology, cognitive engagement, affective engagement, behavioral engagement, learning outcomes
Citation: Lin XP, Li BB, Yao ZN, Yang Z and Zhang M (2024) The impact of virtual reality on student engagement in the classroom–a critical review of the literature. Front. Psychol . 15:1360574. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1360574
Received: 23 December 2023; Accepted: 22 March 2024; Published: 10 April 2024.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2024 Lin, Li, Yao, Yang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhi Yang, [email protected] ; Mingshu Zhang, [email protected]
† These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Conclusion. This study compares the effectiveness of online and classroom learning, attempt ing to go beyond grades and to include a logical assessment of interaction, effective. ness in achieving learning objectives, and student persistence.
found that female students were more receptive to online learning than male students (Selwyn, 2007). Motivation and self-regulation also played a role in successful online learning. Online students, as compared to traditional F2F students, were more predisposed to self-study, self-discipline, and time-management (Tratnik et al., 2019). According to
THE DESIGN OF ONLINE LEARNING ENVIRONMENTS. A Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences of Georgetown University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Arts in Communication, Culture, and Technology. By. Daniel John Davis, B.A.
For example, a study of learning outcomes (exam scores) in online vs. traditional classes in microeconomics determined that students in the online class scored higher on the final exam than the traditional class (68.1% vs. 61.6%).
understand student perceptions of classroom learning and Online learning. This is followed by research methodology which includes the design of the survey instrument. The results of the survey are then discussed. Finally, conclusions are drawn. KEY WORDS: Traditional Learning, Online Learning, Students Perception & Preferences. INTRODUCTION:
ONLINE VS. CLASSROOM LEARNING ENVIRONMENT The impact of learning environments in relation to learning outcomes has constantly been explored by researchers of education. For example, Ramsden and Entwistle (1981) empirically identiied a relationship between approaches to learning and perceived characteristics of the academic environment. Haertela ...
Online students a re more confident in their ability to learn the. material required on their ow n. Given the nature of the online. course vs. the in the classroom experience the instructor came ...
Table 1 Performance E-Learning vs. Classroom . The classroom learners improved t heir performance from 51.5% in the pre-course test to 60.5% in the . assessments. In comparison, ...
The spread of online learning has grown exponentially at every academic level and in many. countries in our COVID-19 world. Due to the relatively new nature of such widespread use of. online learning, little analysis or studies have been conducted on whether student performance.
The integration of technology in classrooms has become increasingly prevalent, presenting both opportunities and challenges for educators. This study examines the impact of technology on student performance and behavior, particularly in seventh and eighth-grade classrooms. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift to online learning, raising concerns about learning loss and disparities in ...
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily shifted the teaching and learning mode in most tertiary institutions in Ghana from the classroom to online. Accordingly, this present study aimed to compare ...
Introduction. There has been an international explosion of online learning and products in recent years, including the online delivery of Vocational Education and Training (VET) programs (Brennan et al., 2001).Online VET changes the relationship between educators and learners, interaction with the learning content, and among learners themselves, and contributes to alleviating time and space ...
A Comparison of Student Learning Outcomes: Online Education vs. Traditional Classroom Instruction. Despite the prevalence of online learning today, it is often viewed as a less favorable option when compared to the traditional, in-person educational experience. Criticisms of online learning come from various sectors, like employer groups ...
Abstract. Online learning has become the need of a time. It is important to compare the effectiveness of classroom and online learning: teaching research methods that face to face interaction, online interactions are important components of learning and teaching in blended learning environment. Online courses help to reach more time and place ...
As for effectiveness of teacher-student interaction, 39.5% of the students would choose direct communication in the classroom, 15.8% would prefer to interact with their teachers online, 44.7% see no difference and consider, that way of communication has no significant impact on teacher-student interaction (Figure 2). There is no difference 44.7%.
On the other hand, traditional F2F learning is real time or synchronous learning. In a physical classroom, instructors engage with the students in real time, while in the online format instructors can offer real time lectures through learning management systems (e.g. Blackboard Collaborate), or record the lectures for the students to watch ...
Results showed that the performance of university students has been better via this method than traditional learning. Classroom activity was shown to positively affect overall student performance. Moreover, the adaptation of technology positively affected the validity of using online learning and student performance.
The option for full-time e-learning was also extended to students in Grades 9-12. Given this exceptional delivery model of education, effects of online versus in-person learning should be examined closely. In this study, we were interested in understanding whether learning fully online or in-person impacted students' perceptions of mattering.
A: Online learning can be as good or even better than in-person classroom learning. Research has shown that students in online learning performed better than those receiving face-to-face instruction, but it has to be done right. The best online learning combines elements where students go at their own pace, on their own time, and are set up to ...
During the COVID-19 pandemic, transformation from face-to-face classrooms to online classrooms took place in higher education. This study aims to evaluate the impact of teaching and learning of this change on students' and teachers' perspectives. The study also investigated the various impact factors that hindered online teaching and learning during the COVID-19 lockdown period.
This thesis discusses the current controversial issue of traditional classroom vs. distance learning approaches in higher education institutions using a case study in the College of Applied Science and Technology at RIT. The most important question addressed in the thesis is, "Are distance learning methods effective for addressing university-level learning goals?" (Kathleen Davey, 1999, p. 45 ...
returns-on-investment for online education. (In fact, she finds that students personally pay more for online education relative to face-to-face education.) Although the online approach offers freedom, it requires more discipline from both students and educators. Students must make the effort to complete the material within the required time frame.
It allows learners to study at their own pace and on their schedule, making it an ideal option for those with busy lifestyles or other commitments. 2. Cost-Effective. Online courses are often less expensive than traditional classroom-based courses, making education more accessible to a wider range of learners. 3.
The article discusses challenges of effective learning in classroom and online environments from the student perspective. The aim of the study is to analyse university students' perception of ...
Four years on from the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic, schools worldwide continue to transform the way teaching and learning is delivered both in and outside of their classrooms.. Indeed, the shift to remote learning following the lockdowns of 2020 and 2021 provided some crucial lessons for educators, leaders, students, parents, and policymakers - namely, what works and what doesn't ...
Introduction. In recent years, virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a transformative technology in education, providing new avenues for immersive and interactive learning experiences (Pottle, 2019).At its core, VR offers a departure from the tangible, allowing users to delve into an environment transcending conventional reality (Brooks, 1999; Jeong et al., 2019).
Online collaborative learning. Online learning is when student s receive instruction online with some aspect of student. discretion over time, place, path, pace, or online or face -to- fac e (Horn ...