- Columbia University in the City of New York
- Office of Teaching, Learning, and Innovation
- University Policies
- Columbia Online
- Academic Calendar
- Resources and Technology
- Resources and Guides

Case Method Teaching and Learning
What is the case method? How can the case method be used to engage learners? What are some strategies for getting started? This guide helps instructors answer these questions by providing an overview of the case method while highlighting learner-centered and digitally-enhanced approaches to teaching with the case method. The guide also offers tips to instructors as they get started with the case method and additional references and resources.
On this page:
What is case method teaching.
- Case Method at Columbia
Why use the Case Method?
Case method teaching approaches, how do i get started.
- Additional Resources
The CTL is here to help!
For support with implementing a case method approach in your course, email [email protected] to schedule your 1-1 consultation .
Cite this resource: Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning (2019). Case Method Teaching and Learning. Columbia University. Retrieved from [today’s date] from https://ctl.columbia.edu/resources-and-technology/resources/case-method/
Case method 1 teaching is an active form of instruction that focuses on a case and involves students learning by doing 2 3 . Cases are real or invented stories 4 that include “an educational message” or recount events, problems, dilemmas, theoretical or conceptual issue that requires analysis and/or decision-making.
Case-based teaching simulates real world situations and asks students to actively grapple with complex problems 5 6 This method of instruction is used across disciplines to promote learning, and is common in law, business, medicine, among other fields. See Table 1 below for a few types of cases and the learning they promote.
Table 1: Types of cases and the learning they promote.
For a more complete list, see Case Types & Teaching Methods: A Classification Scheme from the National Center for Case Study Teaching in Science.
Back to Top
Case Method Teaching and Learning at Columbia
The case method is actively used in classrooms across Columbia, at the Morningside campus in the School of International and Public Affairs (SIPA), the School of Business, Arts and Sciences, among others, and at Columbia University Irving Medical campus.
Faculty Spotlight:
Professor Mary Ann Price on Using Case Study Method to Place Pre-Med Students in Real-Life Scenarios
Read more
Professor De Pinho on Using the Case Method in the Mailman Core
Case method teaching has been found to improve student learning, to increase students’ perception of learning gains, and to meet learning objectives 8 9 . Faculty have noted the instructional benefits of cases including greater student engagement in their learning 10 , deeper student understanding of concepts, stronger critical thinking skills, and an ability to make connections across content areas and view an issue from multiple perspectives 11 .
Through case-based learning, students are the ones asking questions about the case, doing the problem-solving, interacting with and learning from their peers, “unpacking” the case, analyzing the case, and summarizing the case. They learn how to work with limited information and ambiguity, think in professional or disciplinary ways, and ask themselves “what would I do if I were in this specific situation?”
The case method bridges theory to practice, and promotes the development of skills including: communication, active listening, critical thinking, decision-making, and metacognitive skills 12 , as students apply course content knowledge, reflect on what they know and their approach to analyzing, and make sense of a case.
Though the case method has historical roots as an instructor-centered approach that uses the Socratic dialogue and cold-calling, it is possible to take a more learner-centered approach in which students take on roles and tasks traditionally left to the instructor.
Cases are often used as “vehicles for classroom discussion” 13 . Students should be encouraged to take ownership of their learning from a case. Discussion-based approaches engage students in thinking and communicating about a case. Instructors can set up a case activity in which students are the ones doing the work of “asking questions, summarizing content, generating hypotheses, proposing theories, or offering critical analyses” 14 .
The role of the instructor is to share a case or ask students to share or create a case to use in class, set expectations, provide instructions, and assign students roles in the discussion. Student roles in a case discussion can include:
- discussion “starters” get the conversation started with a question or posing the questions that their peers came up with;
- facilitators listen actively, validate the contributions of peers, ask follow-up questions, draw connections, refocus the conversation as needed;
- recorders take-notes of the main points of the discussion, record on the board, upload to CourseWorks, or type and project on the screen; and
- discussion “wrappers” lead a summary of the main points of the discussion.
Prior to the case discussion, instructors can model case analysis and the types of questions students should ask, co-create discussion guidelines with students, and ask for students to submit discussion questions. During the discussion, the instructor can keep time, intervene as necessary (however the students should be doing the talking), and pause the discussion for a debrief and to ask students to reflect on what and how they learned from the case activity.
Note: case discussions can be enhanced using technology. Live discussions can occur via video-conferencing (e.g., using Zoom ) or asynchronous discussions can occur using the Discussions tool in CourseWorks (Canvas) .
Table 2 includes a few interactive case method approaches. Regardless of the approach selected, it is important to create a learning environment in which students feel comfortable participating in a case activity and learning from one another. See below for tips on supporting student in how to learn from a case in the “getting started” section and how to create a supportive learning environment in the Guide for Inclusive Teaching at Columbia .
Table 2. Strategies for Engaging Students in Case-Based Learning
Approaches to case teaching should be informed by course learning objectives, and can be adapted for small, large, hybrid, and online classes. Instructional technology can be used in various ways to deliver, facilitate, and assess the case method. For instance, an online module can be created in CourseWorks (Canvas) to structure the delivery of the case, allow students to work at their own pace, engage all learners, even those reluctant to speak up in class, and assess understanding of a case and student learning. Modules can include text, embedded media (e.g., using Panopto or Mediathread ) curated by the instructor, online discussion, and assessments. Students can be asked to read a case and/or watch a short video, respond to quiz questions and receive immediate feedback, post questions to a discussion, and share resources.
For more information about options for incorporating educational technology to your course, please contact your Learning Designer .
To ensure that students are learning from the case approach, ask them to pause and reflect on what and how they learned from the case. Time to reflect builds your students’ metacognition, and when these reflections are collected they provides you with insights about the effectiveness of your approach in promoting student learning.
Well designed case-based learning experiences: 1) motivate student involvement, 2) have students doing the work, 3) help students develop knowledge and skills, and 4) have students learning from each other.
Designing a case-based learning experience should center around the learning objectives for a course. The following points focus on intentional design.
Identify learning objectives, determine scope, and anticipate challenges.
- Why use the case method in your course? How will it promote student learning differently than other approaches?
- What are the learning objectives that need to be met by the case method? What knowledge should students apply and skills should they practice?
- What is the scope of the case? (a brief activity in a single class session to a semester-long case-based course; if new to case method, start small with a single case).
- What challenges do you anticipate (e.g., student preparation and prior experiences with case learning, discomfort with discussion, peer-to-peer learning, managing discussion) and how will you plan for these in your design?
- If you are asking students to use transferable skills for the case method (e.g., teamwork, digital literacy) make them explicit.
Determine how you will know if the learning objectives were met and develop a plan for evaluating the effectiveness of the case method to inform future case teaching.
- What assessments and criteria will you use to evaluate student work or participation in case discussion?
- How will you evaluate the effectiveness of the case method? What feedback will you collect from students?
- How might you leverage technology for assessment purposes? For example, could you quiz students about the case online before class, accept assignment submissions online, use audience response systems (e.g., PollEverywhere) for formative assessment during class?
Select an existing case, create your own, or encourage students to bring course-relevant cases, and prepare for its delivery
- Where will the case method fit into the course learning sequence?
- Is the case at the appropriate level of complexity? Is it inclusive, culturally relevant, and relatable to students?
- What materials and preparation will be needed to present the case to students? (e.g., readings, audiovisual materials, set up a module in CourseWorks).
Plan for the case discussion and an active role for students
- What will your role be in facilitating case-based learning? How will you model case analysis for your students? (e.g., present a short case and demo your approach and the process of case learning) (Davis, 2009).
- What discussion guidelines will you use that include your students’ input?
- How will you encourage students to ask and answer questions, summarize their work, take notes, and debrief the case?
- If students will be working in groups, how will groups form? What size will the groups be? What instructions will they be given? How will you ensure that everyone participates? What will they need to submit? Can technology be leveraged for any of these areas?
- Have you considered students of varied cognitive and physical abilities and how they might participate in the activities/discussions, including those that involve technology?
Student preparation and expectations
- How will you communicate about the case method approach to your students? When will you articulate the purpose of case-based learning and expectations of student engagement? What information about case-based learning and expectations will be included in the syllabus?
- What preparation and/or assignment(s) will students complete in order to learn from the case? (e.g., read the case prior to class, watch a case video prior to class, post to a CourseWorks discussion, submit a brief memo, complete a short writing assignment to check students’ understanding of a case, take on a specific role, prepare to present a critique during in-class discussion).
Andersen, E. and Schiano, B. (2014). Teaching with Cases: A Practical Guide . Harvard Business Press.
Bonney, K. M. (2015). Case Study Teaching Method Improves Student Performance and Perceptions of Learning Gains†. Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education , 16 (1), 21–28. https://doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v16i1.846
Davis, B.G. (2009). Chapter 24: Case Studies. In Tools for Teaching. Second Edition. Jossey-Bass.
Garvin, D.A. (2003). Making the Case: Professional Education for the world of practice. Harvard Magazine. September-October 2003, Volume 106, Number 1, 56-107.
Golich, V.L. (2000). The ABCs of Case Teaching. International Studies Perspectives. 1, 11-29.
Golich, V.L.; Boyer, M; Franko, P.; and Lamy, S. (2000). The ABCs of Case Teaching. Pew Case Studies in International Affairs. Institute for the Study of Diplomacy.
Heath, J. (2015). Teaching & Writing Cases: A Practical Guide. The Case Center, UK.
Herreid, C.F. (2011). Case Study Teaching. New Directions for Teaching and Learning. No. 128, Winder 2011, 31 – 40.
Herreid, C.F. (2007). Start with a Story: The Case Study Method of Teaching College Science . National Science Teachers Association. Available as an ebook through Columbia Libraries.
Herreid, C.F. (2006). “Clicker” Cases: Introducing Case Study Teaching Into Large Classrooms. Journal of College Science Teaching. Oct 2006, 36(2). https://search.proquest.com/docview/200323718?pq-origsite=gscholar
Krain, M. (2016). Putting the Learning in Case Learning? The Effects of Case-Based Approaches on Student Knowledge, Attitudes, and Engagement. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching. 27(2), 131-153.
Lundberg, K.O. (Ed.). (2011). Our Digital Future: Boardrooms and Newsrooms. Knight Case Studies Initiative.
Popil, I. (2011). Promotion of critical thinking by using case studies as teaching method. Nurse Education Today, 31(2), 204–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2010.06.002
Schiano, B. and Andersen, E. (2017). Teaching with Cases Online . Harvard Business Publishing.
Thistlethwaite, JE; Davies, D.; Ekeocha, S.; Kidd, J.M.; MacDougall, C.; Matthews, P.; Purkis, J.; Clay D. (2012). The effectiveness of case-based learning in health professional education: A BEME systematic review . Medical Teacher. 2012; 34(6): e421-44.
Yadav, A.; Lundeberg, M.; DeSchryver, M.; Dirkin, K.; Schiller, N.A.; Maier, K. and Herreid, C.F. (2007). Teaching Science with Case Studies: A National Survey of Faculty Perceptions of the Benefits and Challenges of Using Cases. Journal of College Science Teaching; Sept/Oct 2007; 37(1).
Weimer, M. (2013). Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key Changes to Practice. Second Edition. Jossey-Bass.
Additional resources
Teaching with Cases , Harvard Kennedy School of Government.
Features “what is a teaching case?” video that defines a teaching case, and provides documents to help students prepare for case learning, Common case teaching challenges and solutions, tips for teaching with cases.
Promoting excellence and innovation in case method teaching: Teaching by the Case Method , Christensen Center for Teaching & Learning. Harvard Business School.
National Center for Case Study Teaching in Science . University of Buffalo.
A collection of peer-reviewed STEM cases to teach scientific concepts and content, promote process skills and critical thinking. The Center welcomes case submissions. Case classification scheme of case types and teaching methods:
- Different types of cases: analysis case, dilemma/decision case, directed case, interrupted case, clicker case, a flipped case, a laboratory case.
- Different types of teaching methods: problem-based learning, discussion, debate, intimate debate, public hearing, trial, jigsaw, role-play.
Columbia Resources
Resources available to support your use of case method: The University hosts a number of case collections including: the Case Consortium (a collection of free cases in the fields of journalism, public policy, public health, and other disciplines that include teaching and learning resources; SIPA’s Picker Case Collection (audiovisual case studies on public sector innovation, filmed around the world and involving SIPA student teams in producing the cases); and Columbia Business School CaseWorks , which develops teaching cases and materials for use in Columbia Business School classrooms.
Center for Teaching and Learning
The Center for Teaching and Learning (CTL) offers a variety of programs and services for instructors at Columbia. The CTL can provide customized support as you plan to use the case method approach through implementation. Schedule a one-on-one consultation.
Office of the Provost
The Hybrid Learning Course Redesign grant program from the Office of the Provost provides support for faculty who are developing innovative and technology-enhanced pedagogy and learning strategies in the classroom. In addition to funding, faculty awardees receive support from CTL staff as they redesign, deliver, and evaluate their hybrid courses.
The Start Small! Mini-Grant provides support to faculty who are interested in experimenting with one new pedagogical strategy or tool. Faculty awardees receive funds and CTL support for a one-semester period.
Explore our teaching resources.
- Blended Learning
- Contemplative Pedagogy
- Inclusive Teaching Guide
- FAQ for Teaching Assistants
- Metacognition
CTL resources and technology for you.
- Overview of all CTL Resources and Technology
- The origins of this method can be traced to Harvard University where in 1870 the Law School began using cases to teach students how to think like lawyers using real court decisions. This was followed by the Business School in 1920 (Garvin, 2003). These professional schools recognized that lecture mode of instruction was insufficient to teach critical professional skills, and that active learning would better prepare learners for their professional lives. ↩
- Golich, V.L. (2000). The ABCs of Case Teaching. International Studies Perspectives. 1, 11-29. ↩
- Herreid, C.F. (2007). Start with a Story: The Case Study Method of Teaching College Science . National Science Teachers Association. Available as an ebook through Columbia Libraries. ↩
- Davis, B.G. (2009). Chapter 24: Case Studies. In Tools for Teaching. Second Edition. Jossey-Bass. ↩
- Andersen, E. and Schiano, B. (2014). Teaching with Cases: A Practical Guide . Harvard Business Press. ↩
- Lundberg, K.O. (Ed.). (2011). Our Digital Future: Boardrooms and Newsrooms. Knight Case Studies Initiative. ↩
- Heath, J. (2015). Teaching & Writing Cases: A Practical Guide. The Case Center, UK. ↩
- Bonney, K. M. (2015). Case Study Teaching Method Improves Student Performance and Perceptions of Learning Gains†. Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education , 16 (1), 21–28. https://doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v16i1.846 ↩
- Krain, M. (2016). Putting the Learning in Case Learning? The Effects of Case-Based Approaches on Student Knowledge, Attitudes, and Engagement. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching. 27(2), 131-153. ↩
- Thistlethwaite, JE; Davies, D.; Ekeocha, S.; Kidd, J.M.; MacDougall, C.; Matthews, P.; Purkis, J.; Clay D. (2012). The effectiveness of case-based learning in health professional education: A BEME systematic review . Medical Teacher. 2012; 34(6): e421-44. ↩
- Yadav, A.; Lundeberg, M.; DeSchryver, M.; Dirkin, K.; Schiller, N.A.; Maier, K. and Herreid, C.F. (2007). Teaching Science with Case Studies: A National Survey of Faculty Perceptions of the Benefits and Challenges of Using Cases. Journal of College Science Teaching; Sept/Oct 2007; 37(1). ↩
- Popil, I. (2011). Promotion of critical thinking by using case studies as teaching method. Nurse Education Today, 31(2), 204–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2010.06.002 ↩
- Weimer, M. (2013). Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key Changes to Practice. Second Edition. Jossey-Bass. ↩
- Herreid, C.F. (2006). “Clicker” Cases: Introducing Case Study Teaching Into Large Classrooms. Journal of College Science Teaching. Oct 2006, 36(2). https://search.proquest.com/docview/200323718?pq-origsite=gscholar ↩
This website uses cookies to identify users, improve the user experience and requires cookies to work. By continuing to use this website, you consent to Columbia University's use of cookies and similar technologies, in accordance with the Columbia University Website Cookie Notice .
Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
Center for Excellence in Teaching and Learning
- Case Based Learning
What is the case method?
In case-based learning, students learn to interact with and manipulate basic foundational knowledge by working with situations resembling specific real-world scenarios.
How does it work?
Case studies encourage students to use critical thinking skills to identify and narrow an issue, develop and evaluate alternatives, and offer a solution. In fact, Nkhoma (2016), who studied the value of developing case-based learning activities based on Bloom’s Taxonomy of thinking skills, suggests that this approach encourages deep learning through critical thinking:
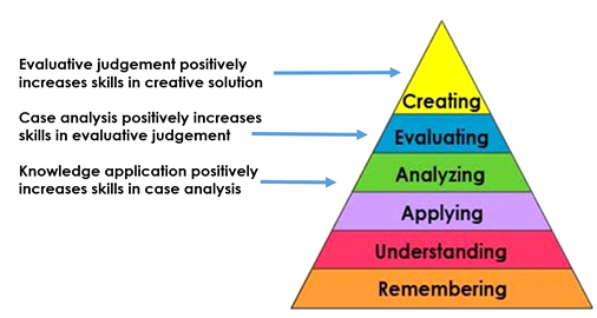
Sherfield (2004) confirms this, asserting that working through case studies can begin to build and expand these six critical thinking strategies:
- Emotional restraint
- Questioning
- Distinguishing fact from fiction
- Searching for ambiguity
What makes a good case?
Case-based learning can focus on anything from a one-sentence physics word problem to a textbook-sized nursing case or a semester-long case in a law course. Though we often assume that a case is a “problem,” Ellet (2007) suggests that most cases entail one of four types of situations:
- Evaluations
- What are the facts you know about the case?
- What are some logical assumptions you can make about the case?
- What are the problems involved in the case as you see it?
- What is the root problem (the main issue)?
- What do you estimate is the cause of the root problem?
- What are the reasons that the root problem exists?
- What is the solution to the problem?
- Are there any moral or ethical considerations to your solution?
- What are the real-world implications for this case?
- How might the lives of the people in the case study be changed because of your proposed solution?
- Where in your world (campus/town/country) might a problem like this occur?
- Where could someone get help with this problem?
- What personal advice would you give to the person or people concerned?
Adapted from Sherfield’s Case Studies for the First Year (2004)
Some faculty buy prepared cases from publishers, but many create their own based on their unique course needs. When introducing case-based learning to students, be sure to offer a series of guidelines or questions to prompt deep thinking. One option is to provide a scenario followed by questions; for example, questions designed for a first year experience problem might include these:
Before you begin, take a look at what others are doing with cases in your field. Pre-made case studies are available from various publishers, and you can find case-study templates online.
- Choose scenarios carefully
- Tell a story from beginning to end, including many details
- Create real-life characters and use quotes when possible
- Write clearly and concisely and format the writing simply
- Ask students to reflect on their learning—perhaps identifying connections between the lesson and specific course learning outcomes—after working a case
Additional Resources
- Barnes, Louis B. et al. Teaching and the Case Method , 3 rd (1994). Harvard, 1994.
- Campoy, Renee. Case Study Analysis in the Classroom: Becoming a Reflective Teacher . Sage Publications, 2005.
- Ellet, William. The Case Study Handbook . Harvard, 2007.
- Herreid, Clyde Freeman, ed. Start with a Story: The Case Study Method of Teaching College Science . NSTA, 2007.
- Herreid, Clyde Freeman, et al. Science Stories: Using Case Studies to Teach Critical Thinking . NSTA, 2012.
- Nkhoma, M., Lam, et al. Developing case-based learning activities based on the revised Bloom’s Taxonomy . Proceedings of Informing Science & IT Education Conference (In SITE) 2016, 85-93. 2016.
- Rolls, Geoff. Classic Case Studies in Psychology , 3 rd Hodder Education, Bookpoint, 2014.
- Sherfield, Robert M., et al. Case Studies for the First Year . Pearson, 2004.
- Shulman, Judith H., ed. Case Methods in Teacher Education . Teacher’s College, 1992.
Quick Links
- Developing Learning Objectives
- Creating Your Syllabus
- Active Learning
- Service Learning
- Critical Thinking and other Higher-Order Thinking Skills
- Group and Team Based Learning
- Integrating Technology in the Classroom
- Effective PowerPoint Design
- Hybrid and Hybrid Limited Course Design
- Online Course Design
Consult with our CETL Professionals
Consultation services are available to all UConn faculty at all campuses at no charge.
Search form
- About Faculty Development and Support
- Programs and Funding Opportunities
Consultations, Observations, and Services
- Strategic Resources & Digital Publications
- Canvas @ Yale Support
- Learning Environments @ Yale
- Teaching Workshops
- Teaching Consultations and Classroom Observations
- Teaching Programs
- Spring Teaching Forum
- Written and Oral Communication Workshops and Panels
- Writing Resources & Tutorials
- About the Graduate Writing Laboratory
- Writing and Public Speaking Consultations
- Writing Workshops and Panels
- Writing Peer-Review Groups
- Writing Retreats and All Writes
- Online Writing Resources for Graduate Students
- About Teaching Development for Graduate and Professional School Students
- Teaching Programs and Grants
- Teaching Forums
- Resources for Graduate Student Teachers
- About Undergraduate Writing and Tutoring
- Academic Strategies Program
- The Writing Center
- STEM Tutoring & Programs
- Humanities & Social Sciences
- Center for Language Study
- Online Course Catalog
- Antiracist Pedagogy
- NECQL 2019: NorthEast Consortium for Quantitative Literacy XXII Meeting
- STEMinar Series
- Teaching in Context: Troubling Times
- Helmsley Postdoctoral Teaching Scholars
- Pedagogical Partners
- Instructional Materials
- Evaluation & Research
- STEM Education Job Opportunities
- Yale Connect
- Online Education Legal Statements
You are here
Case-based learning.
Case-based learning (CBL) is an established approach used across disciplines where students apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios, promoting higher levels of cognition (see Bloom’s Taxonomy ). In CBL classrooms, students typically work in groups on case studies, stories involving one or more characters and/or scenarios. The cases present a disciplinary problem or problems for which students devise solutions under the guidance of the instructor. CBL has a strong history of successful implementation in medical, law, and business schools, and is increasingly used within undergraduate education, particularly within pre-professional majors and the sciences (Herreid, 1994). This method involves guided inquiry and is grounded in constructivism whereby students form new meanings by interacting with their knowledge and the environment (Lee, 2012).
There are a number of benefits to using CBL in the classroom. In a review of the literature, Williams (2005) describes how CBL: utilizes collaborative learning, facilitates the integration of learning, develops students’ intrinsic and extrinsic motivation to learn, encourages learner self-reflection and critical reflection, allows for scientific inquiry, integrates knowledge and practice, and supports the development of a variety of learning skills.
CBL has several defining characteristics, including versatility, storytelling power, and efficient self-guided learning. In a systematic analysis of 104 articles in health professions education, CBL was found to be utilized in courses with less than 50 to over 1000 students (Thistlethwaite et al., 2012). In these classrooms, group sizes ranged from 1 to 30, with most consisting of 2 to 15 students. Instructors varied in the proportion of time they implemented CBL in the classroom, ranging from one case spanning two hours of classroom time, to year-long case-based courses. These findings demonstrate that instructors use CBL in a variety of ways in their classrooms.
The stories that comprise the framework of case studies are also a key component to CBL’s effectiveness. Jonassen and Hernandez-Serrano (2002, p.66) describe how storytelling:
Is a method of negotiating and renegotiating meanings that allows us to enter into other’s realms of meaning through messages they utter in their stories,
Helps us find our place in a culture,
Allows us to explicate and to interpret, and
Facilitates the attainment of vicarious experience by helping us to distinguish the positive models to emulate from the negative model.
Neurochemically, listening to stories can activate oxytocin, a hormone that increases one’s sensitivity to social cues, resulting in more empathy, generosity, compassion and trustworthiness (Zak, 2013; Kosfeld et al., 2005). The stories within case studies serve as a means by which learners form new understandings through characters and/or scenarios.
CBL is often described in conjunction or in comparison with problem-based learning (PBL). While the lines are often confusingly blurred within the literature, in the most conservative of definitions, the features distinguishing the two approaches include that PBL involves open rather than guided inquiry, is less structured, and the instructor plays a more passive role. In PBL multiple solutions to the problem may exit, but the problem is often initially not well-defined. PBL also has a stronger emphasis on developing self-directed learning. The choice between implementing CBL versus PBL is highly dependent on the goals and context of the instruction. For example, in a comparison of PBL and CBL approaches during a curricular shift at two medical schools, students and faculty preferred CBL to PBL (Srinivasan et al., 2007). Students perceived CBL to be a more efficient process and more clinically applicable. However, in another context, PBL might be the favored approach.
In a review of the effectiveness of CBL in health profession education, Thistlethwaite et al. (2012), found several benefits:
Students enjoyed the method and thought it enhanced their learning,
Instructors liked how CBL engaged students in learning,
CBL seemed to facilitate small group learning, but the authors could not distinguish between whether it was the case itself or the small group learning that occurred as facilitated by the case.
Other studies have also reported on the effectiveness of CBL in achieving learning outcomes (Bonney, 2015; Breslin, 2008; Herreid, 2013; Krain, 2016). These findings suggest that CBL is a vehicle of engagement for instruction, and facilitates an environment whereby students can construct knowledge.
Science – Students are given a scenario to which they apply their basic science knowledge and problem-solving skills to help them solve the case. One example within the biological sciences is two brothers who have a family history of a genetic illness. They each have mutations within a particular sequence in their DNA. Students work through the case and draw conclusions about the biological impacts of these mutations using basic science. Sample cases: You are Not the Mother of Your Children ; Organic Chemisty and Your Cellphone: Organic Light-Emitting Diodes ; A Light on Physics: F-Number and Exposure Time
Medicine – Medical or pre-health students read about a patient presenting with specific symptoms. Students decide which questions are important to ask the patient in their medical history, how long they have experienced such symptoms, etc. The case unfolds and students use clinical reasoning, propose relevant tests, develop a differential diagnoses and a plan of treatment. Sample cases: The Case of the Crying Baby: Surgical vs. Medical Management ; The Plan: Ethics and Physician Assisted Suicide ; The Haemophilus Vaccine: A Victory for Immunologic Engineering
Public Health – A case study describes a pandemic of a deadly infectious disease. Students work through the case to identify Patient Zero, the person who was the first to spread the disease, and how that individual became infected. Sample cases: The Protective Parent ; The Elusive Tuberculosis Case: The CDC and Andrew Speaker ; Credible Voice: WHO-Beijing and the SARS Crisis
Law – A case study presents a legal dilemma for which students use problem solving to decide the best way to advise and defend a client. Students are presented information that changes during the case. Sample cases: Mortgage Crisis Call (abstract) ; The Case of the Unpaid Interns (abstract) ; Police-Community Dialogue (abstract)
Business – Students work on a case study that presents the history of a business success or failure. They apply business principles learned in the classroom and assess why the venture was successful or not. Sample cases: SELCO-Determining a path forward ; Project Masiluleke: Texting and Testing to Fight HIV/AIDS in South Africa ; Mayo Clinic: Design Thinking in Healthcare
Humanities - Students consider a case that presents a theater facing financial and management difficulties. They apply business and theater principles learned in the classroom to the case, working together to create solutions for the theater. Sample cases: David Geffen School of Drama
Recommendations
Finding and Writing Cases
Consider utilizing or adapting open access cases - The availability of open resources and databases containing cases that instructors can download makes this approach even more accessible in the classroom. Two examples of open databases are the Case Center on Public Leadership and Harvard Kennedy School (HKS) Case Program , which focus on government, leadership and public policy case studies.
- Consider writing original cases - In the event that an instructor is unable to find open access cases relevant to their course learning objectives, they may choose to write their own. See the following resources on case writing: Cooking with Betty Crocker: A Recipe for Case Writing ; The Way of Flesch: The Art of Writing Readable Cases ; Twixt Fact and Fiction: A Case Writer’s Dilemma ; And All That Jazz: An Essay Extolling the Virtues of Writing Case Teaching Notes .
Implementing Cases
Take baby steps if new to CBL - While entire courses and curricula may involve case-based learning, instructors who desire to implement on a smaller-scale can integrate a single case into their class, and increase the number of cases utilized over time as desired.
Use cases in classes that are small, medium or large - Cases can be scaled to any course size. In large classes with stadium seating, students can work with peers nearby, while in small classes with more flexible seating arrangements, teams can move their chairs closer together. CBL can introduce more noise (and energy) in the classroom to which an instructor often quickly becomes accustomed. Further, students can be asked to work on cases outside of class, and wrap up discussion during the next class meeting.
Encourage collaborative work - Cases present an opportunity for students to work together to solve cases which the historical literature supports as beneficial to student learning (Bruffee, 1993). Allow students to work in groups to answer case questions.
Form diverse teams as feasible - When students work within diverse teams they can be exposed to a variety of perspectives that can help them solve the case. Depending on the context of the course, priorities, and the background information gathered about the students enrolled in the class, instructors may choose to organize student groups to allow for diversity in factors such as current course grades, gender, race/ethnicity, personality, among other items.
Use stable teams as appropriate - If CBL is a large component of the course, a research-supported practice is to keep teams together long enough to go through the stages of group development: forming, storming, norming, performing and adjourning (Tuckman, 1965).
Walk around to guide groups - In CBL instructors serve as facilitators of student learning. Walking around allows the instructor to monitor student progress as well as identify and support any groups that may be struggling. Teaching assistants can also play a valuable role in supporting groups.
Interrupt strategically - Only every so often, for conversation in large group discussion of the case, especially when students appear confused on key concepts. An effective practice to help students meet case learning goals is to guide them as a whole group when the class is ready. This may include selecting a few student groups to present answers to discussion questions to the entire class, asking the class a question relevant to the case using polling software, and/or performing a mini-lesson on an area that appears to be confusing among students.
Assess student learning in multiple ways - Students can be assessed informally by asking groups to report back answers to various case questions. This practice also helps students stay on task, and keeps them accountable. Cases can also be included on exams using related scenarios where students are asked to apply their knowledge.
Barrows HS. (1996). Problem-based learning in medicine and beyond: a brief overview. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 68, 3-12.
Bonney KM. (2015). Case Study Teaching Method Improves Student Performance and Perceptions of Learning Gains. Journal of Microbiology and Biology Education, 16(1): 21-28.
Breslin M, Buchanan, R. (2008) On the Case Study Method of Research and Teaching in Design. Design Issues, 24(1), 36-40.
Bruffee KS. (1993). Collaborative learning: Higher education, interdependence, and authority of knowledge. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, MD.
Herreid CF. (2013). Start with a Story: The Case Study Method of Teaching College Science, edited by Clyde Freeman Herreid. Originally published in 2006 by the National Science Teachers Association (NSTA); reprinted by the National Center for Case Study Teaching in Science (NCCSTS) in 2013.
Herreid CH. (1994). Case studies in science: A novel method of science education. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 23(4), 221–229.
Jonassen DH and Hernandez-Serrano J. (2002). Case-based reasoning and instructional design: Using stories to support problem solving. Educational Technology, Research and Development, 50(2), 65-77.
Kosfeld M, Heinrichs M, Zak PJ, Fischbacher U, Fehr E. (2005). Oxytocin increases trust in humans. Nature, 435, 673-676.
Krain M. (2016) Putting the learning in case learning? The effects of case-based approaches on student knowledge, attitudes, and engagement. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching, 27(2), 131-153.
Lee V. (2012). What is Inquiry-Guided Learning? New Directions for Learning, 129:5-14.
Nkhoma M, Sriratanaviriyakul N. (2017). Using case method to enrich students’ learning outcomes. Active Learning in Higher Education, 18(1):37-50.
Srinivasan et al. (2007). Comparing problem-based learning with case-based learning: Effects of a major curricular shift at two institutions. Academic Medicine, 82(1): 74-82.
Thistlethwaite JE et al. (2012). The effectiveness of case-based learning in health professional education. A BEME systematic review: BEME Guide No. 23. Medical Teacher, 34, e421-e444.
Tuckman B. (1965). Development sequence in small groups. Psychological Bulletin, 63(6), 384-99.
Williams B. (2005). Case-based learning - a review of the literature: is there scope for this educational paradigm in prehospital education? Emerg Med, 22, 577-581.
Zak, PJ (2013). How Stories Change the Brain. Retrieved from: https://greatergood.berkeley.edu/article/item/how_stories_change_brain
YOU MAY BE INTERESTED IN

The Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning routinely supports members of the Yale community with individual instructional consultations and classroom observations.

Instructional Enhancement Fund
The Instructional Enhancement Fund (IEF) awards grants of up to $500 to support the timely integration of new learning activities into an existing undergraduate or graduate course. All Yale instructors of record, including tenured and tenure-track faculty, clinical instructional faculty, lecturers, lectors, and part-time acting instructors (PTAIs), are eligible to apply. Award decisions are typically provided within two weeks to help instructors implement ideas for the current semester.

Reserve a Room
The Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning partners with departments and groups on-campus throughout the year to share its space. Please review the reservation form and submit a request.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 10 min read
Case Study-Based Learning
Enhancing learning through immediate application.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

If you've ever tried to learn a new concept, you probably appreciate that "knowing" is different from "doing." When you have an opportunity to apply your knowledge, the lesson typically becomes much more real.
Adults often learn differently from children, and we have different motivations for learning. Typically, we learn new skills because we want to. We recognize the need to learn and grow, and we usually need – or want – to apply our newfound knowledge soon after we've learned it.
A popular theory of adult learning is andragogy (the art and science of leading man, or adults), as opposed to the better-known pedagogy (the art and science of leading children). Malcolm Knowles , a professor of adult education, was considered the father of andragogy, which is based on four key observations of adult learners:
- Adults learn best if they know why they're learning something.
- Adults often learn best through experience.
- Adults tend to view learning as an opportunity to solve problems.
- Adults learn best when the topic is relevant to them and immediately applicable.
This means that you'll get the best results with adults when they're fully involved in the learning experience. Give an adult an opportunity to practice and work with a new skill, and you have a solid foundation for high-quality learning that the person will likely retain over time.
So, how can you best use these adult learning principles in your training and development efforts? Case studies provide an excellent way of practicing and applying new concepts. As such, they're very useful tools in adult learning, and it's important to understand how to get the maximum value from them.
What Is a Case Study?
Case studies are a form of problem-based learning, where you present a situation that needs a resolution. A typical business case study is a detailed account, or story, of what happened in a particular company, industry, or project over a set period of time.
The learner is given details about the situation, often in a historical context. The key players are introduced. Objectives and challenges are outlined. This is followed by specific examples and data, which the learner then uses to analyze the situation, determine what happened, and make recommendations.
The depth of a case depends on the lesson being taught. A case study can be two pages, 20 pages, or more. A good case study makes the reader think critically about the information presented, and then develop a thorough assessment of the situation, leading to a well-thought-out solution or recommendation.
Why Use a Case Study?
Case studies are a great way to improve a learning experience, because they get the learner involved, and encourage immediate use of newly acquired skills.
They differ from lectures or assigned readings because they require participation and deliberate application of a broad range of skills. For example, if you study financial analysis through straightforward learning methods, you may have to calculate and understand a long list of financial ratios (don't worry if you don't know what these are). Likewise, you may be given a set of financial statements to complete a ratio analysis. But until you put the exercise into context, you may not really know why you're doing the analysis.
With a case study, however, you might explore whether a bank should provide financing to a borrower, or whether a company is about to make a good acquisition. Suddenly, the act of calculating ratios becomes secondary – it's more important to understand what the ratios tell you. This is how case studies can make the difference between knowing what to do, and knowing how, when, and why to do it.
Then, what really separates case studies from other practical forms of learning – like scenarios and simulations – is the ability to compare the learner's recommendations with what actually happened. When you know what really happened, it's much easier to evaluate the "correctness" of the answers given.
When to Use a Case Study
As you can see, case studies are powerful and effective training tools. They also work best with practical, applied training, so make sure you use them appropriately.
Remember these tips:
- Case studies tend to focus on why and how to apply a skill or concept, not on remembering facts and details. Use case studies when understanding the concept is more important than memorizing correct responses.
- Case studies are great team-building opportunities. When a team gets together to solve a case, they'll have to work through different opinions, methods, and perspectives.
- Use case studies to build problem-solving skills, particularly those that are valuable when applied, but are likely to be used infrequently. This helps people get practice with these skills that they might not otherwise get.
- Case studies can be used to evaluate past problem solving. People can be asked what they'd do in that situation, and think about what could have been done differently.
Ensuring Maximum Value From Case Studies
The first thing to remember is that you already need to have enough theoretical knowledge to handle the questions and challenges in the case study. Otherwise, it can be like trying to solve a puzzle with some of the pieces missing.
Here are some additional tips for how to approach a case study. Depending on the exact nature of the case, some tips will be more relevant than others.
- Read the case at least three times before you start any analysis. Case studies usually have lots of details, and it's easy to miss something in your first, or even second, reading.
- Once you're thoroughly familiar with the case, note the facts. Identify which are relevant to the tasks you've been assigned. In a good case study, there are often many more facts than you need for your analysis.
- If the case contains large amounts of data, analyze this data for relevant trends. For example, have sales dropped steadily, or was there an unexpected high or low point?
- If the case involves a description of a company's history, find the key events, and consider how they may have impacted the current situation.
- Consider using techniques like SWOT analysis and Porter's Five Forces Analysis to understand the organization's strategic position.
- Stay with the facts when you draw conclusions. These include facts given in the case as well as established facts about the environmental context. Don't rely on personal opinions when you put together your answers.
Writing a Case Study
You may have to write a case study yourself. These are complex documents that take a while to research and compile. The quality of the case study influences the quality of the analysis. Here are some tips if you want to write your own:
- Write your case study as a structured story. The goal is to capture an interesting situation or challenge and then bring it to life with words and information. You want the reader to feel a part of what's happening.
- Present information so that a "right" answer isn't obvious. The goal is to develop the learner's ability to analyze and assess, not necessarily to make the same decision as the people in the actual case.
- Do background research to fully understand what happened and why. You may need to talk to key stakeholders to get their perspectives as well.
- Determine the key challenge. What needs to be resolved? The case study should focus on one main question or issue.
- Define the context. Talk about significant events leading up to the situation. What organizational factors are important for understanding the problem and assessing what should be done? Include cultural factors where possible.
- Identify key decision makers and stakeholders. Describe their roles and perspectives, as well as their motivations and interests.
- Make sure that you provide the right data to allow people to reach appropriate conclusions.
- Make sure that you have permission to use any information you include.
A typical case study structure includes these elements:
- Executive summary. Define the objective, and state the key challenge.
- Opening paragraph. Capture the reader's interest.
- Scope. Describe the background, context, approach, and issues involved.
- Presentation of facts. Develop an objective picture of what's happening.
- Description of key issues. Present viewpoints, decisions, and interests of key parties.
Because case studies have proved to be such effective teaching tools, many are already written. Some excellent sources of free cases are The Times 100 , CasePlace.org , and Schroeder & Schroeder Inc . You can often search for cases by topic or industry. These cases are expertly prepared, based mostly on real situations, and used extensively in business schools to teach management concepts.
Case studies are a great way to improve learning and training. They provide learners with an opportunity to solve a problem by applying what they know.
There are no unpleasant consequences for getting it "wrong," and cases give learners a much better understanding of what they really know and what they need to practice.
Case studies can be used in many ways, as team-building tools, and for skill development. You can write your own case study, but a large number are already prepared. Given the enormous benefits of practical learning applications like this, case studies are definitely something to consider adding to your next training session.
Knowles, M. (1973). 'The Adult Learner: A Neglected Species [online].' Available here .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Infographic
Difficult Conversations: Common Mistakes Infographic
Infographic Transcript
Expert Interviews
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Team Management
Learn the key aspects of managing a team, from building and developing your team, to working with different types of teams, and troubleshooting common problems.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

SWOT Analysis

How to Build a Strong Culture in a Distributed Team
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Top tips for delegating.
Delegate work to your team members effectively with these top tips
Ten Dos and Don'ts of Change Conversations
Tips for tackling discussions about change
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Beyonder creativity.
Moving From the Ordinary to the Extraordinary
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches
- Nitin Nohria

Seven meta-skills that stick even if the cases fade from memory.
It’s been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment, bias recognition, judgement, collaboration, curiosity, and self-confidence.
During my decade as dean of Harvard Business School, I spent hundreds of hours talking with our alumni. To enliven these conversations, I relied on a favorite question: “What was the most important thing you learned from your time in our MBA program?”
- Nitin Nohria is the George F. Baker Jr. Professor at Harvard Business School and the former dean of HBS.
Partner Center
- Utility Menu
harvardchan_logo.png

Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health Case-Based Teaching & Learning Initiative
Teaching cases & active learning resources for public health education, teaching & learning with the case method.
2023. Case Compendium, University of California Berkeley Haas School of Business Center for Equity, Gender & Leadership . Visit website This resource, compiled by the Berkeley Haas Center for Equity, Gender & Leadership, is "a case compendium that includes: (a) case studies with diverse protagonists, and (b) case studies that build “equity fluency” by focusing on DEI-related issues and opportunities. The goal of the compendium is to support professors at Haas, and business schools globally, to identify cases they can use in their own classrooms, and ultimately contribute to advancing DEI in education and business."
Kane, N.M. , 2014. Benefits of Case-Based Teaching . Watch video Watch a demonstration of Prof. Nancy Kane teaching public health with the case method. (Part 3 of 3, 3 minutes)
Kane, N.M. , 2014. Case teaching demonstration: Should a health plan cover medical tourism? . Watch video Watch a demonstration of Prof. Nancy Kane teaching public health with the case method. (Part 2 of 3, 17 minutes)
Kane, N.M. , 2014. Case-based teaching at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health . Watch video Watch a demonstration of Prof. Nancy Kane teaching public health with the case method. (Part 1 of 3, 10 minutes)
2019. The Case Centre . Visit website A non-profit clearing house for materials on the case method, the Case Centre holds a large and diverse collection of cases, articles, book chapters and teaching materials, including the collections of leading business schools across the globe.
Austin, S.B. & Sonneville, K.R. , 2013. Closing the "know-do" gap: training public health professionals in eating disorders prevention via case-method teaching. International Journal of Eating Disorders , 46 (5) , pp. 533-537. Read online Abstract Expansion of our societies' capacity to prevent eating disorders will require strategic integration of the topic into the curricula of professional training programs. An ideal way to integrate new content into educational programs is through the case-method approach, a teaching method that is more effective than traditional teaching techniques. The Strategic Training Initiative for the Prevention of Eating Disorders has begun developing cases designed to be used in classroom settings to engage students in topical, high-impact issues in public health approaches to eating disorders prevention and screening. Dissemination of these cases will provide an opportunity for students in public health training programs to learn material in a meaningful context by actively applying skills as they are learning them, helping to bridge the "know-do" gap. The new curriculum is an important step toward realizing the goal that public health practitioners be fully equipped to address the challenge of eating disorders prevention. "Expansion of our societies' capacity to prevent eating disorders will require strategic integration of the topic into the curricula of professional training programs. An ideal way to integrate new content into educational programs is through the case-method approach, a teaching method that is more effective than traditional teaching techniques." Access full article with HarvardKey .
Ellet, W. , 2018. The Case Study Handbook, Revised Edition: A Student's Guide , Harvard Business School Publishing. Publisher's Version "If you're like many people, you may find interpreting and writing about cases mystifying and time-consuming. In The Case Study Handbook, Revised Edition , William Ellet presents a potent new approach for efficiently analyzing, discussing, and writing about cases."
Andersen, E. & Schiano, B. , 2014. Teaching with Cases: A Practical Guide , Harvard Business School Publishing. Publisher's Version "The class discussion inherent in case teaching is well known for stimulating the development of students' critical thinking skills, yet instructors often need guidance on managing that class discussion to maximize learning. Teaching with Cases focuses on practical advice for instructors that can be easily implemented. It covers how to plan a course, how to teach it, and how to evaluate it."
Honan, J. & Sternman Rule, C. , 2002. Case Method Instruction Versus Lecture-Based Instruction R. Reis, ed. Tomorrow's Professor . Read online "Faculty and discussion leaders who incorporate the case study method into their teaching offer various reasons for their enthusiasm for this type of pedagogy over more traditional, such as lecture-based, instructional methods and routes to learning." Exerpt from the book Using Cases in Higher Education: A Guide for Faculty and Administrators , by James P. Honan and Cheryl Sternman Rule.
Austin, J. , 1993. Teaching Notes: Communicating the Teacher's Wisdom , Harvard Business School Publishing. Publisher's Version "Provides guidance for the preparation of teaching notes. Sets forth the rationale for teaching notes, what they should contain and why, and how they can be prepared. Based on the experiences of Harvard Business School faculty."
Abell, D. , 1997. What makes a good case? . ECCHO–The Newsletter of the European Case Clearing House , 17 (1) , pp. 4-7. Read online "Case writing is both art and science. There are few, if any, specific prescriptions or recipes, but there are key ingredients that appear to distinguish excellent cases from the run-of-the-mill. This technical note lists ten ingredients to look for if you are teaching somebody else''s case - and to look out for if you are writing it yourself."
Herreid, C.F. , 2001. Don't! What not to do when teaching cases. Journal of College Science Teaching , 30 (5) , pp. 292. Read online "Be warned, I am about to unleash a baker’s dozen of 'don’ts' for aspiring case teachers willing to try running a classroom discussion armed with only a couple of pages of a story and a lot of chutzpah."
Garvin, D.A. , 2003. Making the case: Professional education for the world of practice . Harvard Magazine , 106 (1) , pp. 56-65. Read online A history and overview of the case-method in professional schools, which all “face the same difficult challenge: how to prepare students for the world of practice. Time in the classroom must somehow translate directly into real-world activity: how to diagnose, decide, and act."
- Writing a case (8)
- Writing a teaching note (4)
- Active learning (12)
- Active listening (1)
- Asking effective questions (5)
- Assessing learning (1)
- Engaging students (5)
- Leading discussion (10)
- Managing the classroom (4)
- Planning a course (1)
- Problem-based learning (1)
- Teaching & learning with the case method (14)
- Teaching inclusively (3)
Using Case Studies to Teach

Why Use Cases?
Many students are more inductive than deductive reasoners, which means that they learn better from examples than from logical development starting with basic principles. The use of case studies can therefore be a very effective classroom technique.
Case studies are have long been used in business schools, law schools, medical schools and the social sciences, but they can be used in any discipline when instructors want students to explore how what they have learned applies to real world situations. Cases come in many formats, from a simple “What would you do in this situation?” question to a detailed description of a situation with accompanying data to analyze. Whether to use a simple scenario-type case or a complex detailed one depends on your course objectives.
Most case assignments require students to answer an open-ended question or develop a solution to an open-ended problem with multiple potential solutions. Requirements can range from a one-paragraph answer to a fully developed group action plan, proposal or decision.
Common Case Elements
Most “full-blown” cases have these common elements:
- A decision-maker who is grappling with some question or problem that needs to be solved.
- A description of the problem’s context (a law, an industry, a family).
- Supporting data, which can range from data tables to links to URLs, quoted statements or testimony, supporting documents, images, video, or audio.
Case assignments can be done individually or in teams so that the students can brainstorm solutions and share the work load.
The following discussion of this topic incorporates material presented by Robb Dixon of the School of Management and Rob Schadt of the School of Public Health at CEIT workshops. Professor Dixon also provided some written comments that the discussion incorporates.
Advantages to the use of case studies in class
A major advantage of teaching with case studies is that the students are actively engaged in figuring out the principles by abstracting from the examples. This develops their skills in:
- Problem solving
- Analytical tools, quantitative and/or qualitative, depending on the case
- Decision making in complex situations
- Coping with ambiguities
Guidelines for using case studies in class
In the most straightforward application, the presentation of the case study establishes a framework for analysis. It is helpful if the statement of the case provides enough information for the students to figure out solutions and then to identify how to apply those solutions in other similar situations. Instructors may choose to use several cases so that students can identify both the similarities and differences among the cases.
Depending on the course objectives, the instructor may encourage students to follow a systematic approach to their analysis. For example:
- What is the issue?
- What is the goal of the analysis?
- What is the context of the problem?
- What key facts should be considered?
- What alternatives are available to the decision-maker?
- What would you recommend — and why?
An innovative approach to case analysis might be to have students role-play the part of the people involved in the case. This not only actively engages students, but forces them to really understand the perspectives of the case characters. Videos or even field trips showing the venue in which the case is situated can help students to visualize the situation that they need to analyze.
Accompanying Readings
Case studies can be especially effective if they are paired with a reading assignment that introduces or explains a concept or analytical method that applies to the case. The amount of emphasis placed on the use of the reading during the case discussion depends on the complexity of the concept or method. If it is straightforward, the focus of the discussion can be placed on the use of the analytical results. If the method is more complex, the instructor may need to walk students through its application and the interpretation of the results.
Leading the Case Discussion and Evaluating Performance
Decision cases are more interesting than descriptive ones. In order to start the discussion in class, the instructor can start with an easy, noncontroversial question that all the students should be able to answer readily. However, some of the best case discussions start by forcing the students to take a stand. Some instructors will ask a student to do a formal “open” of the case, outlining his or her entire analysis. Others may choose to guide discussion with questions that move students from problem identification to solutions. A skilled instructor steers questions and discussion to keep the class on track and moving at a reasonable pace.
In order to motivate the students to complete the assignment before class as well as to stimulate attentiveness during the class, the instructor should grade the participation—quantity and especially quality—during the discussion of the case. This might be a simple check, check-plus, check-minus or zero. The instructor should involve as many students as possible. In order to engage all the students, the instructor can divide them into groups, give each group several minutes to discuss how to answer a question related to the case, and then ask a randomly selected person in each group to present the group’s answer and reasoning. Random selection can be accomplished through rolling of dice, shuffled index cards, each with one student’s name, a spinning wheel, etc.
Tips on the Penn State U. website: http://tlt.its.psu.edu/suggestions/cases/
If you are interested in using this technique in a science course, there is a good website on use of case studies in the sciences at the University of Buffalo.
Dunne, D. and Brooks, K. (2004) Teaching with Cases (Halifax, NS: Society for Teaching and Learning in Higher Education), ISBN 0-7703-8924-4 (Can be ordered at http://www.bookstore.uwo.ca/ at a cost of $15.00)
- Our Mission
Making Learning Relevant With Case Studies
The open-ended problems presented in case studies give students work that feels connected to their lives.

To prepare students for jobs that haven’t been created yet, we need to teach them how to be great problem solvers so that they’ll be ready for anything. One way to do this is by teaching content and skills using real-world case studies, a learning model that’s focused on reflection during the problem-solving process. It’s similar to project-based learning, but PBL is more focused on students creating a product.
Case studies have been used for years by businesses, law and medical schools, physicians on rounds, and artists critiquing work. Like other forms of problem-based learning, case studies can be accessible for every age group, both in one subject and in interdisciplinary work.
You can get started with case studies by tackling relatable questions like these with your students:
- How can we limit food waste in the cafeteria?
- How can we get our school to recycle and compost waste? (Or, if you want to be more complex, how can our school reduce its carbon footprint?)
- How can we improve school attendance?
- How can we reduce the number of people who get sick at school during cold and flu season?
Addressing questions like these leads students to identify topics they need to learn more about. In researching the first question, for example, students may see that they need to research food chains and nutrition. Students often ask, reasonably, why they need to learn something, or when they’ll use their knowledge in the future. Learning is most successful for students when the content and skills they’re studying are relevant, and case studies offer one way to create that sense of relevance.
Teaching With Case Studies
Ultimately, a case study is simply an interesting problem with many correct answers. What does case study work look like in classrooms? Teachers generally start by having students read the case or watch a video that summarizes the case. Students then work in small groups or individually to solve the case study. Teachers set milestones defining what students should accomplish to help them manage their time.
During the case study learning process, student assessment of learning should be focused on reflection. Arthur L. Costa and Bena Kallick’s Learning and Leading With Habits of Mind gives several examples of what this reflection can look like in a classroom:
Journaling: At the end of each work period, have students write an entry summarizing what they worked on, what worked well, what didn’t, and why. Sentence starters and clear rubrics or guidelines will help students be successful. At the end of a case study project, as Costa and Kallick write, it’s helpful to have students “select significant learnings, envision how they could apply these learnings to future situations, and commit to an action plan to consciously modify their behaviors.”
Interviews: While working on a case study, students can interview each other about their progress and learning. Teachers can interview students individually or in small groups to assess their learning process and their progress.
Student discussion: Discussions can be unstructured—students can talk about what they worked on that day in a think-pair-share or as a full class—or structured, using Socratic seminars or fishbowl discussions. If your class is tackling a case study in small groups, create a second set of small groups with a representative from each of the case study groups so that the groups can share their learning.
4 Tips for Setting Up a Case Study
1. Identify a problem to investigate: This should be something accessible and relevant to students’ lives. The problem should also be challenging and complex enough to yield multiple solutions with many layers.
2. Give context: Think of this step as a movie preview or book summary. Hook the learners to help them understand just enough about the problem to want to learn more.
3. Have a clear rubric: Giving structure to your definition of quality group work and products will lead to stronger end products. You may be able to have your learners help build these definitions.
4. Provide structures for presenting solutions: The amount of scaffolding you build in depends on your students’ skill level and development. A case study product can be something like several pieces of evidence of students collaborating to solve the case study, and ultimately presenting their solution with a detailed slide deck or an essay—you can scaffold this by providing specified headings for the sections of the essay.
Problem-Based Teaching Resources
There are many high-quality, peer-reviewed resources that are open source and easily accessible online.
- The National Center for Case Study Teaching in Science at the University at Buffalo built an online collection of more than 800 cases that cover topics ranging from biochemistry to economics. There are resources for middle and high school students.
- Models of Excellence , a project maintained by EL Education and the Harvard Graduate School of Education, has examples of great problem- and project-based tasks—and corresponding exemplary student work—for grades pre-K to 12.
- The Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-Based Learning at Purdue University is an open-source journal that publishes examples of problem-based learning in K–12 and post-secondary classrooms.
- The Tech Edvocate has a list of websites and tools related to problem-based learning.
In their book Problems as Possibilities , Linda Torp and Sara Sage write that at the elementary school level, students particularly appreciate how they feel that they are taken seriously when solving case studies. At the middle school level, “researchers stress the importance of relating middle school curriculum to issues of student concern and interest.” And high schoolers, they write, find the case study method “beneficial in preparing them for their future.”

Learning, Design, and Technology pp 2239–2242 Cite as
Case Studies in Learning Design and Instructional Technology: A Section Introduction
- Stephanie Moore 4 &
- Heather Leary 5
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 15 October 2023
27 Accesses
This short chapter is the section introduction for the section Case studies in Learning Design and Instructional technology in Learning, Design, and Technology: An International Compendium of Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy . It outlines and summarizes the organizing theme of learning design research and cases represented in the 20 chapters in this section with a discussion on newer design methods for research to clarify differences between design cases, design-based research, and case studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Boling, E. (2010). The need for design cases: Disseminating design knowledge. International Journal of Designs for Learning, 1 (1) https://scholarworks.iu.edu/journals/index.php/ijdl/article/view/919/978
Boling, E. (2020). The nature and use of precedent in designing. In J. K. McDonald & R. E. West (Eds.), Design for Learning: Principles, processes, and praxis . EdTech Books. Retrieved from https://edtechbooks.org/id/precedent
Google Scholar
Fishman, B. J., Penuel, W. R., Allen, A.-R., Cheng, B. H., & Sabelli, N. (2013). Design-based implementation research: An emerging model for transforming the relationship of research and practice. National Society for the Study of Education, 112 (2), 136–156.
Gray, C. M. (2020). Markers of quality in design precedent. International Journal of Designs for Learning, 11 (3), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.14434/ijdl.v11i3.31193
Article Google Scholar
Howard, C. D. (2011). Writing and rewriting the instructional design case: A view from two sides. International Journal of Designs for Learning, 2 (1), 41–56. Retrieved from https://scholarworks.iu.edu/journals/index.php/ijdl/article/view/1104/1315
Howard, C. D., Boling, E., Rowland, G., & Smith, K. M. (2012). Instructional design cases and why we need them. Educational Technology, 52 (3), 34–38.
McKenney, S., & Reeves, T. C. (2019). Conducting educational design research . Routledge.
Oxman, R. (1994). Precedents in Design: A Computational Model for the Organization of Precedent Knowledge. Design Studies , 15, 141–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-694X(94)90021-3
Penuel, W. R., Fishman, B. J., Cheng, B. H., & Sabelli, N. (2011). Organizing research and development at the intersection of learning, implementation, and design. Educational Researcher, 40 (7), 331–337.
Smith, K. (2010). Producing the rigorous design case. International Journal of Designs for Learning, 1 (1), 9–20. Retrieved from: https://scholarworks.iu.edu/journals/index.php/ijdl/article/view/917/980
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Organization, Information, and Learning Sciences, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM, USA
Stephanie Moore
Instructional Psychology and Technology, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT, USA
Heather Leary
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Stephanie Moore .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Learning Technologies, University of North Texas, Denton, TX, USA
J. Michael Spector
Instructional Design and Technology, Virginia Tech School of Education, Blacksburg, VA, USA
Barbara B. Lockee
Marcus D. Childress
Section Editor information
Stephanie L. Moore Ph.D.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Moore, S., Leary, H. (2023). Case Studies in Learning Design and Instructional Technology: A Section Introduction. In: Spector, J.M., Lockee, B.B., Childress, M.D. (eds) Learning, Design, and Technology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17461-7_143
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17461-7_143
Published : 15 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-17460-0
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-17461-7
eBook Packages : Education Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Education
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Res Methodol

The case study approach
Sarah crowe.
1 Division of Primary Care, The University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
Kathrin Cresswell
2 Centre for Population Health Sciences, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Ann Robertson
3 School of Health in Social Science, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Anthony Avery
Aziz sheikh.
The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in their real-life settings. The value of the case study approach is well recognised in the fields of business, law and policy, but somewhat less so in health services research. Based on our experiences of conducting several health-related case studies, we reflect on the different types of case study design, the specific research questions this approach can help answer, the data sources that tend to be used, and the particular advantages and disadvantages of employing this methodological approach. The paper concludes with key pointers to aid those designing and appraising proposals for conducting case study research, and a checklist to help readers assess the quality of case study reports.
Introduction
The case study approach is particularly useful to employ when there is a need to obtain an in-depth appreciation of an issue, event or phenomenon of interest, in its natural real-life context. Our aim in writing this piece is to provide insights into when to consider employing this approach and an overview of key methodological considerations in relation to the design, planning, analysis, interpretation and reporting of case studies.
The illustrative 'grand round', 'case report' and 'case series' have a long tradition in clinical practice and research. Presenting detailed critiques, typically of one or more patients, aims to provide insights into aspects of the clinical case and, in doing so, illustrate broader lessons that may be learnt. In research, the conceptually-related case study approach can be used, for example, to describe in detail a patient's episode of care, explore professional attitudes to and experiences of a new policy initiative or service development or more generally to 'investigate contemporary phenomena within its real-life context' [ 1 ]. Based on our experiences of conducting a range of case studies, we reflect on when to consider using this approach, discuss the key steps involved and illustrate, with examples, some of the practical challenges of attaining an in-depth understanding of a 'case' as an integrated whole. In keeping with previously published work, we acknowledge the importance of theory to underpin the design, selection, conduct and interpretation of case studies[ 2 ]. In so doing, we make passing reference to the different epistemological approaches used in case study research by key theoreticians and methodologists in this field of enquiry.
This paper is structured around the following main questions: What is a case study? What are case studies used for? How are case studies conducted? What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided? We draw in particular on four of our own recently published examples of case studies (see Tables Tables1, 1 , ,2, 2 , ,3 3 and and4) 4 ) and those of others to illustrate our discussion[ 3 - 7 ].
Example of a case study investigating the reasons for differences in recruitment rates of minority ethnic people in asthma research[ 3 ]
Example of a case study investigating the process of planning and implementing a service in Primary Care Organisations[ 4 ]
Example of a case study investigating the introduction of the electronic health records[ 5 ]
Example of a case study investigating the formal and informal ways students learn about patient safety[ 6 ]
What is a case study?
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table (Table5), 5 ), the central tenet being the need to explore an event or phenomenon in depth and in its natural context. It is for this reason sometimes referred to as a "naturalistic" design; this is in contrast to an "experimental" design (such as a randomised controlled trial) in which the investigator seeks to exert control over and manipulate the variable(s) of interest.
Definitions of a case study
Stake's work has been particularly influential in defining the case study approach to scientific enquiry. He has helpfully characterised three main types of case study: intrinsic , instrumental and collective [ 8 ]. An intrinsic case study is typically undertaken to learn about a unique phenomenon. The researcher should define the uniqueness of the phenomenon, which distinguishes it from all others. In contrast, the instrumental case study uses a particular case (some of which may be better than others) to gain a broader appreciation of an issue or phenomenon. The collective case study involves studying multiple cases simultaneously or sequentially in an attempt to generate a still broader appreciation of a particular issue.
These are however not necessarily mutually exclusive categories. In the first of our examples (Table (Table1), 1 ), we undertook an intrinsic case study to investigate the issue of recruitment of minority ethnic people into the specific context of asthma research studies, but it developed into a instrumental case study through seeking to understand the issue of recruitment of these marginalised populations more generally, generating a number of the findings that are potentially transferable to other disease contexts[ 3 ]. In contrast, the other three examples (see Tables Tables2, 2 , ,3 3 and and4) 4 ) employed collective case study designs to study the introduction of workforce reconfiguration in primary care, the implementation of electronic health records into hospitals, and to understand the ways in which healthcare students learn about patient safety considerations[ 4 - 6 ]. Although our study focusing on the introduction of General Practitioners with Specialist Interests (Table (Table2) 2 ) was explicitly collective in design (four contrasting primary care organisations were studied), is was also instrumental in that this particular professional group was studied as an exemplar of the more general phenomenon of workforce redesign[ 4 ].

What are case studies used for?
According to Yin, case studies can be used to explain, describe or explore events or phenomena in the everyday contexts in which they occur[ 1 ]. These can, for example, help to understand and explain causal links and pathways resulting from a new policy initiative or service development (see Tables Tables2 2 and and3, 3 , for example)[ 1 ]. In contrast to experimental designs, which seek to test a specific hypothesis through deliberately manipulating the environment (like, for example, in a randomised controlled trial giving a new drug to randomly selected individuals and then comparing outcomes with controls),[ 9 ] the case study approach lends itself well to capturing information on more explanatory ' how ', 'what' and ' why ' questions, such as ' how is the intervention being implemented and received on the ground?'. The case study approach can offer additional insights into what gaps exist in its delivery or why one implementation strategy might be chosen over another. This in turn can help develop or refine theory, as shown in our study of the teaching of patient safety in undergraduate curricula (Table (Table4 4 )[ 6 , 10 ]. Key questions to consider when selecting the most appropriate study design are whether it is desirable or indeed possible to undertake a formal experimental investigation in which individuals and/or organisations are allocated to an intervention or control arm? Or whether the wish is to obtain a more naturalistic understanding of an issue? The former is ideally studied using a controlled experimental design, whereas the latter is more appropriately studied using a case study design.
Case studies may be approached in different ways depending on the epistemological standpoint of the researcher, that is, whether they take a critical (questioning one's own and others' assumptions), interpretivist (trying to understand individual and shared social meanings) or positivist approach (orientating towards the criteria of natural sciences, such as focusing on generalisability considerations) (Table (Table6). 6 ). Whilst such a schema can be conceptually helpful, it may be appropriate to draw on more than one approach in any case study, particularly in the context of conducting health services research. Doolin has, for example, noted that in the context of undertaking interpretative case studies, researchers can usefully draw on a critical, reflective perspective which seeks to take into account the wider social and political environment that has shaped the case[ 11 ].
Example of epistemological approaches that may be used in case study research
How are case studies conducted?
Here, we focus on the main stages of research activity when planning and undertaking a case study; the crucial stages are: defining the case; selecting the case(s); collecting and analysing the data; interpreting data; and reporting the findings.
Defining the case
Carefully formulated research question(s), informed by the existing literature and a prior appreciation of the theoretical issues and setting(s), are all important in appropriately and succinctly defining the case[ 8 , 12 ]. Crucially, each case should have a pre-defined boundary which clarifies the nature and time period covered by the case study (i.e. its scope, beginning and end), the relevant social group, organisation or geographical area of interest to the investigator, the types of evidence to be collected, and the priorities for data collection and analysis (see Table Table7 7 )[ 1 ]. A theory driven approach to defining the case may help generate knowledge that is potentially transferable to a range of clinical contexts and behaviours; using theory is also likely to result in a more informed appreciation of, for example, how and why interventions have succeeded or failed[ 13 ].
Example of a checklist for rating a case study proposal[ 8 ]
For example, in our evaluation of the introduction of electronic health records in English hospitals (Table (Table3), 3 ), we defined our cases as the NHS Trusts that were receiving the new technology[ 5 ]. Our focus was on how the technology was being implemented. However, if the primary research interest had been on the social and organisational dimensions of implementation, we might have defined our case differently as a grouping of healthcare professionals (e.g. doctors and/or nurses). The precise beginning and end of the case may however prove difficult to define. Pursuing this same example, when does the process of implementation and adoption of an electronic health record system really begin or end? Such judgements will inevitably be influenced by a range of factors, including the research question, theory of interest, the scope and richness of the gathered data and the resources available to the research team.
Selecting the case(s)
The decision on how to select the case(s) to study is a very important one that merits some reflection. In an intrinsic case study, the case is selected on its own merits[ 8 ]. The case is selected not because it is representative of other cases, but because of its uniqueness, which is of genuine interest to the researchers. This was, for example, the case in our study of the recruitment of minority ethnic participants into asthma research (Table (Table1) 1 ) as our earlier work had demonstrated the marginalisation of minority ethnic people with asthma, despite evidence of disproportionate asthma morbidity[ 14 , 15 ]. In another example of an intrinsic case study, Hellstrom et al.[ 16 ] studied an elderly married couple living with dementia to explore how dementia had impacted on their understanding of home, their everyday life and their relationships.
For an instrumental case study, selecting a "typical" case can work well[ 8 ]. In contrast to the intrinsic case study, the particular case which is chosen is of less importance than selecting a case that allows the researcher to investigate an issue or phenomenon. For example, in order to gain an understanding of doctors' responses to health policy initiatives, Som undertook an instrumental case study interviewing clinicians who had a range of responsibilities for clinical governance in one NHS acute hospital trust[ 17 ]. Sampling a "deviant" or "atypical" case may however prove even more informative, potentially enabling the researcher to identify causal processes, generate hypotheses and develop theory.
In collective or multiple case studies, a number of cases are carefully selected. This offers the advantage of allowing comparisons to be made across several cases and/or replication. Choosing a "typical" case may enable the findings to be generalised to theory (i.e. analytical generalisation) or to test theory by replicating the findings in a second or even a third case (i.e. replication logic)[ 1 ]. Yin suggests two or three literal replications (i.e. predicting similar results) if the theory is straightforward and five or more if the theory is more subtle. However, critics might argue that selecting 'cases' in this way is insufficiently reflexive and ill-suited to the complexities of contemporary healthcare organisations.
The selected case study site(s) should allow the research team access to the group of individuals, the organisation, the processes or whatever else constitutes the chosen unit of analysis for the study. Access is therefore a central consideration; the researcher needs to come to know the case study site(s) well and to work cooperatively with them. Selected cases need to be not only interesting but also hospitable to the inquiry [ 8 ] if they are to be informative and answer the research question(s). Case study sites may also be pre-selected for the researcher, with decisions being influenced by key stakeholders. For example, our selection of case study sites in the evaluation of the implementation and adoption of electronic health record systems (see Table Table3) 3 ) was heavily influenced by NHS Connecting for Health, the government agency that was responsible for overseeing the National Programme for Information Technology (NPfIT)[ 5 ]. This prominent stakeholder had already selected the NHS sites (through a competitive bidding process) to be early adopters of the electronic health record systems and had negotiated contracts that detailed the deployment timelines.
It is also important to consider in advance the likely burden and risks associated with participation for those who (or the site(s) which) comprise the case study. Of particular importance is the obligation for the researcher to think through the ethical implications of the study (e.g. the risk of inadvertently breaching anonymity or confidentiality) and to ensure that potential participants/participating sites are provided with sufficient information to make an informed choice about joining the study. The outcome of providing this information might be that the emotive burden associated with participation, or the organisational disruption associated with supporting the fieldwork, is considered so high that the individuals or sites decide against participation.
In our example of evaluating implementations of electronic health record systems, given the restricted number of early adopter sites available to us, we sought purposively to select a diverse range of implementation cases among those that were available[ 5 ]. We chose a mixture of teaching, non-teaching and Foundation Trust hospitals, and examples of each of the three electronic health record systems procured centrally by the NPfIT. At one recruited site, it quickly became apparent that access was problematic because of competing demands on that organisation. Recognising the importance of full access and co-operative working for generating rich data, the research team decided not to pursue work at that site and instead to focus on other recruited sites.
Collecting the data
In order to develop a thorough understanding of the case, the case study approach usually involves the collection of multiple sources of evidence, using a range of quantitative (e.g. questionnaires, audits and analysis of routinely collected healthcare data) and more commonly qualitative techniques (e.g. interviews, focus groups and observations). The use of multiple sources of data (data triangulation) has been advocated as a way of increasing the internal validity of a study (i.e. the extent to which the method is appropriate to answer the research question)[ 8 , 18 - 21 ]. An underlying assumption is that data collected in different ways should lead to similar conclusions, and approaching the same issue from different angles can help develop a holistic picture of the phenomenon (Table (Table2 2 )[ 4 ].
Brazier and colleagues used a mixed-methods case study approach to investigate the impact of a cancer care programme[ 22 ]. Here, quantitative measures were collected with questionnaires before, and five months after, the start of the intervention which did not yield any statistically significant results. Qualitative interviews with patients however helped provide an insight into potentially beneficial process-related aspects of the programme, such as greater, perceived patient involvement in care. The authors reported how this case study approach provided a number of contextual factors likely to influence the effectiveness of the intervention and which were not likely to have been obtained from quantitative methods alone.
In collective or multiple case studies, data collection needs to be flexible enough to allow a detailed description of each individual case to be developed (e.g. the nature of different cancer care programmes), before considering the emerging similarities and differences in cross-case comparisons (e.g. to explore why one programme is more effective than another). It is important that data sources from different cases are, where possible, broadly comparable for this purpose even though they may vary in nature and depth.
Analysing, interpreting and reporting case studies
Making sense and offering a coherent interpretation of the typically disparate sources of data (whether qualitative alone or together with quantitative) is far from straightforward. Repeated reviewing and sorting of the voluminous and detail-rich data are integral to the process of analysis. In collective case studies, it is helpful to analyse data relating to the individual component cases first, before making comparisons across cases. Attention needs to be paid to variations within each case and, where relevant, the relationship between different causes, effects and outcomes[ 23 ]. Data will need to be organised and coded to allow the key issues, both derived from the literature and emerging from the dataset, to be easily retrieved at a later stage. An initial coding frame can help capture these issues and can be applied systematically to the whole dataset with the aid of a qualitative data analysis software package.
The Framework approach is a practical approach, comprising of five stages (familiarisation; identifying a thematic framework; indexing; charting; mapping and interpretation) , to managing and analysing large datasets particularly if time is limited, as was the case in our study of recruitment of South Asians into asthma research (Table (Table1 1 )[ 3 , 24 ]. Theoretical frameworks may also play an important role in integrating different sources of data and examining emerging themes. For example, we drew on a socio-technical framework to help explain the connections between different elements - technology; people; and the organisational settings within which they worked - in our study of the introduction of electronic health record systems (Table (Table3 3 )[ 5 ]. Our study of patient safety in undergraduate curricula drew on an evaluation-based approach to design and analysis, which emphasised the importance of the academic, organisational and practice contexts through which students learn (Table (Table4 4 )[ 6 ].
Case study findings can have implications both for theory development and theory testing. They may establish, strengthen or weaken historical explanations of a case and, in certain circumstances, allow theoretical (as opposed to statistical) generalisation beyond the particular cases studied[ 12 ]. These theoretical lenses should not, however, constitute a strait-jacket and the cases should not be "forced to fit" the particular theoretical framework that is being employed.
When reporting findings, it is important to provide the reader with enough contextual information to understand the processes that were followed and how the conclusions were reached. In a collective case study, researchers may choose to present the findings from individual cases separately before amalgamating across cases. Care must be taken to ensure the anonymity of both case sites and individual participants (if agreed in advance) by allocating appropriate codes or withholding descriptors. In the example given in Table Table3, 3 , we decided against providing detailed information on the NHS sites and individual participants in order to avoid the risk of inadvertent disclosure of identities[ 5 , 25 ].
What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided?
The case study approach is, as with all research, not without its limitations. When investigating the formal and informal ways undergraduate students learn about patient safety (Table (Table4), 4 ), for example, we rapidly accumulated a large quantity of data. The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted on the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources. This highlights a more general point of the importance of avoiding the temptation to collect as much data as possible; adequate time also needs to be set aside for data analysis and interpretation of what are often highly complex datasets.
Case study research has sometimes been criticised for lacking scientific rigour and providing little basis for generalisation (i.e. producing findings that may be transferable to other settings)[ 1 ]. There are several ways to address these concerns, including: the use of theoretical sampling (i.e. drawing on a particular conceptual framework); respondent validation (i.e. participants checking emerging findings and the researcher's interpretation, and providing an opinion as to whether they feel these are accurate); and transparency throughout the research process (see Table Table8 8 )[ 8 , 18 - 21 , 23 , 26 ]. Transparency can be achieved by describing in detail the steps involved in case selection, data collection, the reasons for the particular methods chosen, and the researcher's background and level of involvement (i.e. being explicit about how the researcher has influenced data collection and interpretation). Seeking potential, alternative explanations, and being explicit about how interpretations and conclusions were reached, help readers to judge the trustworthiness of the case study report. Stake provides a critique checklist for a case study report (Table (Table9 9 )[ 8 ].
Potential pitfalls and mitigating actions when undertaking case study research
Stake's checklist for assessing the quality of a case study report[ 8 ]
Conclusions
The case study approach allows, amongst other things, critical events, interventions, policy developments and programme-based service reforms to be studied in detail in a real-life context. It should therefore be considered when an experimental design is either inappropriate to answer the research questions posed or impossible to undertake. Considering the frequency with which implementations of innovations are now taking place in healthcare settings and how well the case study approach lends itself to in-depth, complex health service research, we believe this approach should be more widely considered by researchers. Though inherently challenging, the research case study can, if carefully conceptualised and thoughtfully undertaken and reported, yield powerful insights into many important aspects of health and healthcare delivery.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AS conceived this article. SC, KC and AR wrote this paper with GH, AA and AS all commenting on various drafts. SC and AS are guarantors.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/11/100/prepub
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participants and colleagues who contributed to the individual case studies that we have drawn on. This work received no direct funding, but it has been informed by projects funded by Asthma UK, the NHS Service Delivery Organisation, NHS Connecting for Health Evaluation Programme, and Patient Safety Research Portfolio. We would also like to thank the expert reviewers for their insightful and constructive feedback. Our thanks are also due to Dr. Allison Worth who commented on an earlier draft of this manuscript.
- Yin RK. Case study research, design and method. 4. London: Sage Publications Ltd.; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Keen J, Packwood T. Qualitative research; case study evaluation. BMJ. 1995; 311 :444–446. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Halani L, Bhopal R, Netuveli G, Partridge M, Car J. et al. Facilitating the Recruitment of Minority Ethnic People into Research: Qualitative Case Study of South Asians and Asthma. PLoS Med. 2009; 6 (10):1–11. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pinnock H, Huby G, Powell A, Kielmann T, Price D, Williams S, The process of planning, development and implementation of a General Practitioner with a Special Interest service in Primary Care Organisations in England and Wales: a comparative prospective case study. Report for the National Co-ordinating Centre for NHS Service Delivery and Organisation R&D (NCCSDO) 2008. http://www.sdo.nihr.ac.uk/files/project/99-final-report.pdf
- Robertson A, Cresswell K, Takian A, Petrakaki D, Crowe S, Cornford T. et al. Prospective evaluation of the implementation and adoption of NHS Connecting for Health's national electronic health record in secondary care in England: interim findings. BMJ. 2010; 41 :c4564. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pearson P, Steven A, Howe A, Sheikh A, Ashcroft D, Smith P. the Patient Safety Education Study Group. Learning about patient safety: organisational context and culture in the education of healthcare professionals. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2010; 15 :4–10. doi: 10.1258/jhsrp.2009.009052. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Harten WH, Casparie TF, Fisscher OA. The evaluation of the introduction of a quality management system: a process-oriented case study in a large rehabilitation hospital. Health Policy. 2002; 60 (1):17–37. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8510(01)00187-7. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE. The art of case study research. London: Sage Publications Ltd.; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Smeeth L, Ashcroft R. Randomised controlled trials in primary care: scope and application. Br J Gen Pract. 2002; 52 (482):746–51. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King G, Keohane R, Verba S. Designing Social Inquiry. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doolin B. Information technology as disciplinary technology: being critical in interpretative research on information systems. Journal of Information Technology. 1998; 13 :301–311. doi: 10.1057/jit.1998.8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- George AL, Bennett A. Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Eccles M. the Improved Clinical Effectiveness through Behavioural Research Group (ICEBeRG) Designing theoretically-informed implementation interventions. Implementation Science. 2006; 1 :1–8. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-1-1. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Netuveli G, Hurwitz B, Levy M, Fletcher M, Barnes G, Durham SR, Sheikh A. Ethnic variations in UK asthma frequency, morbidity, and health-service use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2005; 365 (9456):312–7. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Panesar SS, Lasserson T, Netuveli G. Recruitment of ethnic minorities to asthma studies. Thorax. 2004; 59 (7):634. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hellström I, Nolan M, Lundh U. 'We do things together': A case study of 'couplehood' in dementia. Dementia. 2005; 4 :7–22. doi: 10.1177/1471301205049188. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Som CV. Nothing seems to have changed, nothing seems to be changing and perhaps nothing will change in the NHS: doctors' response to clinical governance. International Journal of Public Sector Management. 2005; 18 :463–477. doi: 10.1108/09513550510608903. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lincoln Y, Guba E. Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park: Sage Publications; 1985. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barbour RS. Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog? BMJ. 2001; 322 :1115–1117. doi: 10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1115. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mays N, Pope C. Qualitative research in health care: Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ. 2000; 320 :50–52. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7226.50. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mason J. Qualitative researching. London: Sage; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brazier A, Cooke K, Moravan V. Using Mixed Methods for Evaluating an Integrative Approach to Cancer Care: A Case Study. Integr Cancer Ther. 2008; 7 :5–17. doi: 10.1177/1534735407313395. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles MB, Huberman M. Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook. 2. CA: Sage Publications Inc.; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N. Analysing qualitative data. Qualitative research in health care. BMJ. 2000; 320 :114–116. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7227.114. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cresswell KM, Worth A, Sheikh A. Actor-Network Theory and its role in understanding the implementation of information technology developments in healthcare. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2010; 10 (1):67. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-10-67. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Malterud K. Qualitative research: standards, challenges, and guidelines. Lancet. 2001; 358 :483–488. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05627-6. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. Case study research: design and methods. 2. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. Enhancing the quality of case studies in health services research. Health Serv Res. 1999; 34 :1209–1224. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Green J, Thorogood N. Qualitative methods for health research. 2. Los Angeles: Sage; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Howcroft D, Trauth E. Handbook of Critical Information Systems Research, Theory and Application. Cheltenham, UK: Northampton, MA, USA: Edward Elgar; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blakie N. Approaches to Social Enquiry. Cambridge: Polity Press; 1993. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doolin B. Power and resistance in the implementation of a medical management information system. Info Systems J. 2004; 14 :343–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2575.2004.00176.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bloomfield BP, Best A. Management consultants: systems development, power and the translation of problems. Sociological Review. 1992; 40 :533–560. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shanks G, Parr A. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems. Naples; 2003. Positivist, single case study research in information systems: A critical analysis. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved April 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- Open access
- Published: 07 October 2022
Advances in e-learning in undergraduate clinical medicine: a systematic review
- T. Delungahawatta 1 ,
- S. S. Dunne 1 ,
- S. Hyde 1 ,
- L. Halpenny 1 ,
- D. McGrath 1 , 2 ,
- A. O’Regan 1 &
- C. P. Dunne 1 , 2
BMC Medical Education volume 22 , Article number: 711 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
4771 Accesses
10 Citations
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
E-learning is recognised as a useful educational tool and is becoming more common in undergraduate medical education. This review aims to examine the scope and impact of e-learning interventions on medical student learning in clinical medicine, in order to aid medical educators when implementing e-learning strategies in programme curricula.
A systematic review compliant with PRISMA guidelines that appraises study design, setting and population, context and type of evaluations. Specific search terms were used to locate articles across nine databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, ScienceDirect, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, ERIC, Academic Search Complete, CINAHL, Scopus and Google Scholar. Only studies evaluating e-learning interventions in undergraduate clinical medical education between January 1990 and August 2021 were selected. Of the 4,829 papers identified by the search, 42 studies met the inclusion criteria.
The 42 studies included varied in scope, cognitive domain, subject matter, design, quality and evaluation. The most popular approaches involved multimedia platforms (33%) and case-based approaches (26%), were interactive (83%), asynchronous (71%) and accessible from home (83%). Twelve studies (29%) evaluated usability, all of which reported positive feedback. Competence in use of technology, high motivation and an open attitude were key characteristics of successful students and preceptors.
Conclusions
Medical education is evolving consistently to accommodate rapid changes in therapies and procedures. In today’s technologically adept world, e-learning is an effective and convenient pedagogical approach for the teaching of undergraduate clinical medicine.
Peer Review reports
E-learning, a pedagogical approach supported by the principles of connectivism learning theory, involves the use of technology and electronic media in knowledge transfer [ 1 , 2 ]. Connectivism views knowledge as a fluid entity circulated through technology enabled networks that foster interactions between individuals, organizations, and societies at large [ 2 ]. Based on this conceptual framework, medical curricula can potentially benefit from enhanced communication and knowledge exchange using technology.
Common e-learning instructional designs in clinical medicine include “online and offline computer-based programmes, massive open online courses, virtual reality environments, virtual patients, mobile learning, digital game-based learning and psychomotor skills trainers”[ 1 ]. To maximize the potential for e-learning, it seems rational that the roles and needs of the e-learner, e-teacher and host institution should be defined and appreciated. According to the Association for Medical Education in Europe (AMEE), an e-learner is any individual taught in an online learning environment [ 1 ]. As the role of the e-learner is central to the learning process, effective e-learning strategies should consider potential learning challenges encountered by the e-learner. Employing skilled e-teachers and providing them with sufficient supports are also important considerations. Furthermore, institutional management of the content versus process elements of educational technology use should best align with the objectives of the program [ 1 ]. For example, if the intent is to provide student access to digital content, then managing sound or video files, podcasts, and online access to research papers, clinical protocols, or reference materials, should be prioritized. On the other hand, if the focus is on student participation in digital activities, then managing processes such as discussion boards and test-taking should take precedence. Accounting for the role of the e-learner, e-teacher, and host institution in this manner, can result in successful implementation of an e-learning system. In fact, e-learning has been shown to be at least as effective as, and can serve as an adjunct to, face-to-face teaching and learning methods [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
An institution may choose to employ educational technologies for the entirety of the course or provide a combination of online and in-class interactions, with the latter approach referred to as ‘blended learning’ [ 1 ]. Incorporation of e-learning into the curriculum allows for new avenues of interactive knowledge and skill transfer between teachers and students and amongst students. Interactions are not limited to face-to-face conversations but can involve text, audio, images, or video, thereby enriching the learning experience. Giving access to a greater breadth of learning resources further develops lifelong learning skills in students as they are required to independently evaluate and extract the pertinent information [ 1 ]. E-learning interventions can also be accessed at any time from almost any location, which facilitates a student-centred approach through self-directed and flexible learning [ 6 ]. As such, e-learning is an attractive instructional undergraduate health education approach [ 7 ].
To date, e-learning interventions in the sciences, particularly anatomy [ 8 ] and physiology [ 9 ], and postgraduate medical training [ 3 , 4 ] have been described. However, their use has not been reviewed systematically in the specific context of augmenting, enhancing or supporting student learning in undergraduate clinical medicine [ 10 ], or replacing face-to-face learning with online learning in the case of COVID-19 emergency remote teaching. In 2014, survey responses from senior medical students in Illinois, reported use of online collaborative authoring, multimedia, social-networking, and communication tools as point of opportunity study resources during clinical rotations [ 11 ]. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has necessitated stepping away from traditional classroom and bedside teaching, and development of more flexible course delivery. A recent survey by Barton et al. collected 1,626 responses from medical students across 41 medical schools in the United Kingdom during the COVID lockdown. Results of study resources accessed daily showed that 41.6% of students used information provided by university (PowerPoint lecture slides, personal notes), 29.6% accessed free websites and question banks, and 18.4% accessed paid websites and question banks [ 12 ]. The work therefore suggests a strong tendency for students to supplement university materials with online resources [ 12 , 13 ]. The popularity of online learning platforms seems to stem from an association with achieving higher exam scores [ 14 , 15 ], ability to self-monitor knowledge gaps [ 16 ], improved knowledge retention from repeat exposure [ 17 , 18 ], and to practice exam technique [ 16 ].
Medical school educators are, therefore, called to evaluate e-learning approaches and to consider incorporation of suitable strategies into current curricula to ensure equitable access and student success. Thus, we aimed to systematically review the scope and impact of e-learning interventions published regarding undergraduate clinical medicine, and to inform medical educators of the effectiveness and character of various online learning environments.
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines are used for the reporting of this systematic review [ 19 ]. The PRISMA checklist is included as Additional File 1 .
Search methods
The early 1990s marked the commercial availability of computer-based learning multimedia [ 20 ] as well as the emergence of online education programs [ 21 ]. Thus, medical subject headings (MeSH), key words and specific database headings were used to locate articles published between January 1990 and August 2021: ‘e-learning’ or ‘digital resources’ or ‘internet learning resources’ AND ‘medical education’ AND ‘undergraduate’ AND ‘techniques’ or ‘programmes’ or ‘interventions’. The search was piloted on PubMed and adapted subsequently for the databases. A total of nine databases were searched: MEDLINE/PubMed, ScienceDirect, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, ERIC, Academic Search Complete, CINAHL, Scopus, Google Scholar and grey literature. The bibliographies of each selected paper were searched manually for further studies. Websites of medical education organisations were searched for position statements and guidelines, including the Association for the Study of Medical Education, AMEE and the British Medical Journal.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Only studies in the English language that evaluated an e-learning intervention in subjects related to clinical medicine were selected. These included: family medicine, surgery, internal medicine, radiology, psychiatry, dermatology, paediatrics and obstetrics. Studies that did not involve undergraduate medical students, were based on pre-clinical sciences or were not focussed on an e-learning intervention were excluded. Studies that focussed on the use of internet for assessment and course administration only were not included. Additionally, studies that described interventions but not their evaluation were excluded. Of the 4,829 papers identified by the search, 42 studies were deemed eligible for inclusion in this review.
Data extraction and analysis
AMEE guidelines on e-learning interventions [ 1 ] were used to modify a previous data extraction tool that had been used in a systematic evaluation of effectiveness of medical education interventions [ 22 ]. This was subsequently piloted and refined by three of the authors until consensus was achieved to form the data extraction tool (see Additional File 2 ). With application of connectivism, individual elements of e-learning were identified to infer and appreciate their collective effects on the learning process. More specifically, data was extracted by examining two central questions: how and when to use e-learning in undergraduate clinical medical education. The primary outcomes relating to how to use e-learning were: instructional features that made the e-learning intervention effective; usability features; assessment of effectiveness and quality of the intervention. Primary outcomes relating to when were: the context, and the learner and preceptor characteristics. In addition to the outcomes measured, descriptive data was also extracted to summarise the studies including: the study design, setting and population; context and discipline; type of evaluations. All selected papers were filed in an Endnote library and the data extraction tool for each was stored in an Excel file, a summary of which is provided as Additional File 2 and Additional File 3 .
Guidelines for evaluating papers on medical education interventions from the Education Group for Guidelines on Evaluation were used as a framework to assign a global score for the strength of each paper [ 23 ]. Among these guidelines, significant value is placed on development of strong intervention rationale and intervention evaluation methods [ 23 ]. The impact of the evaluation was also measured using Kirkpatrick’s levels, a recognised system of understanding the effect of interventions [ 24 ]. The first level, reaction, is a measure of learner satisfaction with the intervention [ 24 ]. The second Kirkpatrick level, learning, is a measure of change in knowledge, skills, or experience. The third Kirkpatrick level of behaviour is a measure of behavioural change. The final level, results, is a measure of overall impact on the organization (i.e., improved quality of work, reduction in time wasted, better patient care).
Search results
A total of 4,829 papers were retrieved from database and manual searches, and this number was reduced to 42 after removal of duplicates and application of inclusion/exclusion criteria at set stages (see Fig. 1 for the PRISMA flow diagram). Two papers were retrieved from manual searches of bibliographies [ 25 , 26 ]. The main reasons for excluding studies were a lack of focus on undergraduate medical students (112 studies) or absence of an e-learning intervention (34 studies).
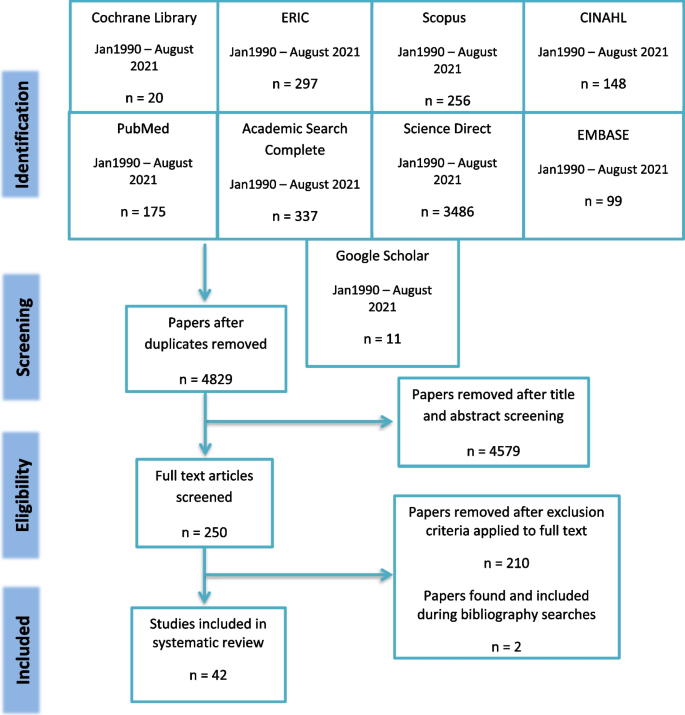
PRISMA flow diagram
Design of included studies
The year of publication ranged from 2003 to 2021, with most conducted within the past ten years (31 studies). Interventions were conducted in nine different countries, mainly the United States (13 studies) and Germany (9 studies). More than half of the studies were conducted in the European Union (21 studies). Several research designs were described, including 17 observational studies [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 ], 13 randomised control trials [ 26 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 ], three non-randomised control trials [ 55 , 56 , 57 ], eight qualitative studies [ 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 ], and one mixed methods study [ 66 ]. Thirteen of the total studies included data collection both pre- and post- intervention [ 25 , 27 , 31 , 34 , 36 , 38 , 39 , 45 , 48 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 61 ]. Six studies had follow-up data (collected weeks to months after intervention) [ 34 , 45 , 49 , 52 , 54 , 56 ] and twelve papers reported ethical approval [ 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 33 , 34 , 39 , 40 , 42 , 46 , 49 , 54 ]. Furthermore, eight studies described learning theories in the development or evaluation of medical curricula [ 29 , 30 , 33 , 49 , 51 , 52 , 56 , 58 ]. Of these studies, five referenced constructivism [ 29 , 49 , 51 , 52 , 58 ] three studies highlighted cognitivism [ 30 , 56 , 59 ], and one study evaluated behaviourist learning theory [ 33 ].
Study population
Students in the third year of medical school experiencing clinical exposure were the most commonly studied (sixteen studies), with fourteen studies involving multiple cohorts of students (see Additional File 3 ). Sample sizes ranged from 10 to 42,190 individuals. The most common disciplines investigated were interdisciplinary (13 studies), surgery (8 studies), radiology (7 studies), and dermatology (4 studies) (see Fig. 2 Intervention Discipline).
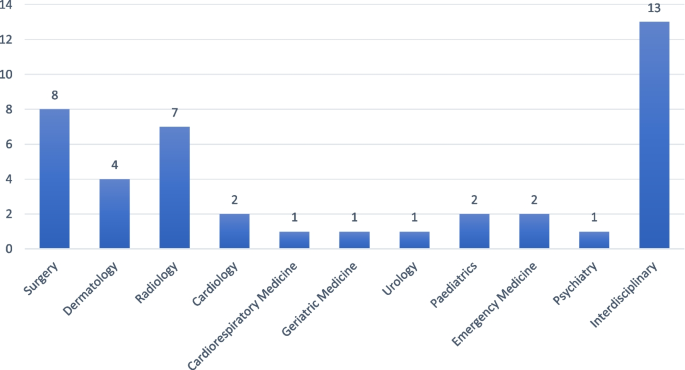
Intervention discipline
Intervention characteristics
Twelve types of intervention were described and the most commonly used were multimedia platforms (fourteen studies) and case-based learning (eleven studies), as per Additional File 2 and Fig. 3 . In terms of cognitive domain, 27 interventions were in the domain of knowledge [ 25 , 26 , 27 , 29 , 30 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 39 , 40 , 42 , 43 , 47 , 48 , 50 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 57 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 66 , 67 ]; eight were in the domain of skills [ 9 , 30 , 31 , 36 , 37 , 46 , 49 , 51 ] and seven in combined knowledge and skills [ 38 , 41 , 44 , 45 , 56 , 59 , 65 ]. The interventions ranged in duration from a single session to a complete academic year. Thirteen of the interventions were synchronous, where users log on at a given time [ 8 , 26 , 27 , 31 , 33 , 34 , 37 , 43 , 47 , 51 , 52 , 58 , 66 ], and the remaining 29 used an asynchronous platform (users logging on independently in their own time). Seven were accessible in a classroom setting only [ 26 , 27 , 36 , 47 , 52 , 58 , 66 ] while the others could be accessed from home (Fig. 4 ).
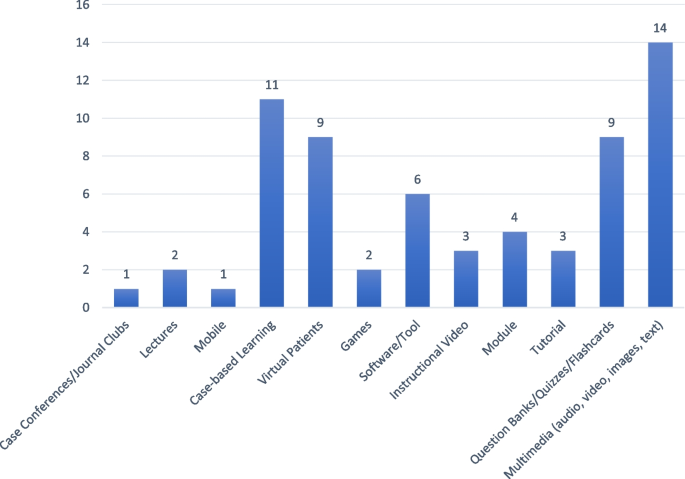
Intervention type
Reported roles for e-learning within the curriculum included a revision aid for examinations [ 58 ]; the flipped classroom concept [ 44 , 57 ], whereby lectures held after an e-lecture become an interactive session; to facilitate an online community where knowledge could be discussed/ shared [ 25 ]; and, enabling just-in-time learning through timely access to facts [ 30 , 31 , 37 ]. Seven (17%) of the 42 interventions were didactic in approach [ 27 , 30 , 37 , 55 , 57 , 63 , 65 ], while the others were interactive. Twelve studies described a collaborative approach, whereby students discussed cases and problems with one another and engaged in role-plays [ 25 , 26 , 36 , 38 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 46 , 52 , 59 , 61 , 66 ]. The context of e-learning in relation to the curriculum was not stated in ten of the studies but another thirteen studies used the terms “adjunct”, “complement”, “supplement”,”hybrid” and “blended” to illustrate the common theme of integrating e-learning with traditional learning [ 25 , 29 , 30 , 32 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 50 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 62 , 63 ]. Seven studies describe temporary replacement of traditional curricula with e-learning platforms in response to COVID-19 [ 33 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 61 , 62 , 64 ]. Eight studies described a pilot phase or the inclusion of students in the development of the intervention [ 33 , 37 , 44 , 45 , 48 , 49 , 53 , 66 ]. Nineteen of the interventions had a built-in assessment, with multiple choice questions being used in most cases, to evaluate whether an improvement in learning had taken place [ 25 , 27 , 31 , 34 , 37 , 39 , 43 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 54 , 55 , 59 , 66 ]. Justification for the chosen assessment strategy or a statement on its suitability was included in two studies [ 50 , 66 ]. Kourdioukova et al. reported an improvement in knowledge and skills with computer supported collaborative case-based approach as judged by in-built multiple-choice questions (MCQ), suggesting the importance of content-specific scripting [ 66 ]. Schneider et al. used a combination of MCQ and survey, and justified their use by demonstrating that learning improved with the intervention compared to the control [ 50 ]. Five of the interventions used end of module assessments as the marker of quality [ 26 , 29 , 53 , 56 , 57 ], with one stating that this was not a suitable mechanism due to its inability to assess the students’ ability to take a patient history or perform a clinical examination [ 53 ].
Intervention evaluation
Each study was given a global rating from 1–5 based on guideline criteria from the Education Group for Guidelines on Evaluation, including whether learning outcomes and curricular context were outlined and the power and rigor of the studies [ 23 ] (Additional File 2 ). Accordingly, eleven studies scored 4/5; two scored 3.5/5; twelve studies scored 3/5; twelve studies scored 2.5/5; and five scored 2/5 (σ = 0.138).
Intervention effectiveness and acceptability
Nine studies described an impact matching a Kirkpatrick level 1, where the student reaction to e-learning intervention was evaluated using student surveys or questionnaires [ 32 , 35 , 44 , 58 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 64 , 65 ]. All these studies report that most students were satisfied with the addition of an e-learning intervention. For instance, Orton et al. note that over 91% of survey responses either ‘strongly agreed’ or ‘agreed’ that use of computer-based virtual patients enabled learning [ 35 ].
Twenty-one (50%) of the 42 studies evaluated acceptability [ 26 , 30 , 32 , 33 , 36 , 37 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 44 , 48 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 63 , 65 , 66 , 68 ]. Of these, 17 reported that the intervention was acceptable. A neutral attitude was reported to a radiology e-learning intervention that involved peer collaboration and was found to be time consuming[ 66 ]. Attitude in another study was much more favourable in junior years than in senior years, with the authors commenting on the conflict between completing assignments and preparing for high stakes examinations [ 55 ]. Another study that focussed on acceptability, with positive outcomes, found that perceived utility and ease of use were the key factors [ 30 ]. Twelve (57%) of the 21 studies further evaluated usability [ 30 , 36 , 37 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 44 , 53 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 65 ], all with positive outcomes, but only one used a formal usability assessment tool [ 58 ]. In that study, Farrimond et al. found that a usable intervention should be: simple and intuitive to use and, from a learner perspective, interactive and enjoyable [ 58 ]. In the development of virtual lectures, ease of navigation, audio-visual quality and accessibility were the key usability features [ 57 ]. Wahlgren et al. concluded that as well as navigation, interactivity is a priority for e-learning development [ 53 ]. Regarding mobile learning, the display should be adaptable to varying screen sizes, termed ‘chunking’, and it should be suitable for a number of platforms [ 30 ].
Twenty-nine (69%) of the 42 studies described an impact matching a Kirkpatrick level 2, where evaluation of whether learning took place was assessed through post intervention scores [ 25 , 27 , 31 , 36 , 38 , 39 , 47 , 48 , 50 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 56 , 57 , 61 ], final exam results [ 26 , 29 , 45 , 66 ], direct observation [ 28 , 31 , 33 , 43 , 46 , 51 , 55 ] and student survey [ 25 , 26 , 30 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 45 , 48 , 49 , 53 , 54 , 56 , 65 , 66 ]. Among these studies, two studies had included both pre- and post- intervention evaluations but neither had a control group nor longer term follow-up [ 25 , 27 ]. One randomised control trial showed a statistically significant improvement in factual knowledge acquisition after participation in an online module as judged based on performance in end of year assessments, compared to a traditional teaching control group (84.8% ± 1.3 vs. 79.5% ± 1.4, p = 0.006, effect size 0.67) [ 26 ]. Likewise, Davis et al., found that the use of a procedural animation video on mobile device resulted in higher medical student scores on skills checklist (9.33 ± 2.65 vs. 4.52 ± 3.64, p < 0.001, effect size 1.5) [ 30 ]. Similarly, in Sijstermans et al., mean students’ self-evaluation of their skills using five-point Likert scale questionnaire, before and after two patient stimulations showed improvement (3.91 ± 0.28 vs 3.56 ± 0.34, P < 0.0001, effect size 1.12). Furthermore, in one study employing a problem-based e-learning approach, the number of first-class honours awarded were found to be significantly improved when compared to control group [ 29 ]. However, in another study using a problem-based e-learning intervention, no significant difference was found between control and intervention groups in subsequent examinations ( p = 0.11) [ 53 ]. In contrast, Al Zahrani et al. found that delivery of new e-learning platforms (Blackboard Collaborate, ZOOM) in response to COVID-19 was poorly accepted by students, whereby 59.2% did not feel adequately educated on learning outcomes, 30% felt no educational difference between e-learning and traditional curriculums, and 56.1% felt e-learning is insufficient as an educational tool for the health sciences [ 40 ].
Four studies demonstrated a change in student behaviour in line with Kirkpatrick level 3 [ 50 , 52 , 59 , 63 ]. In de Villiers et al., it was found that students were using podcasts to learn course content and the classroom teaching setting to strengthen their understanding, inadvertently accepting the flipped classroom approach [ 63 ]. In Sward et al., students who were assigned to a gaming intervention were more willing to engage in answer creating and answer generating as well as independent study of subject materials prior to session time [ 52 ]. Similarly, in Schneider et al., students in the computer case-based intervention group were found to invest more time into studying course subjects (38.5 min vs 15.9 min) which resulted in significantly higher test scores [ 50 ]. Finally, in Moriates et al., following the integration of value-based modules, students have reported increased awareness of patient needs and discussions with peers regarding value-based decision-making during clerkship [ 59 ].
Learner and preceptor characteristics
Learner characteristics identified to enable successful e-learning include: good digital skills, less resistance to change [ 32 ] and a willingness to collaborate with peers [ 66 ]. Preceptor characteristics were not described in most of the studies, but the role involved guiding students through their learning [ 33 , 46 , 61 , 66 ], selection of topics of broad interest to students [ 60 ], technical support [ 54 ], student evaluation[ 28 , 31 , 37 , 40 , 42 , 45 , 46 , 49 , 51 ], content development and management [ 32 , 41 , 42 , 46 , 54 , 62 ] and providing feedback and clear instruction on what is expected of the learners [ 28 , 37 , 40 , 42 , 51 , 54 , 60 ].
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in global university closures during periods of lockdown, necessitating educators to quickly adopt alternate pedagogical approaches. As a result, there has been a substantial increase in the use of e-learning, by which teaching and learning activities occur at a distance on online platforms [ 69 ].
In enabling a shift in the control of knowledge acquisition and distribution from the teacher to the student, e-learning facilitates the learning process. Learners filter the available information, develop new perspectives, log into networks to share their understanding, and repeat the cycle [ 2 ]. This view of learning as a fluid and dynamic process is the basis of the learning theory of connectivism and highlights the benefit of this instructional design in medical education – a field amenable to rapid changes in therapies and procedures. In fact, educational theorists have significantly influenced the development of medical curricula throughout history. Amongst the 25 higher impact studies (achieving a global score greater or equal to 3), only 7 studies (28%) were found to have described theoretical underpinnings [ 30 , 33 , 49 , 51 , 52 , 58 , 59 ]. Initially, the behaviourist perspective supported pedological practices [ 70 ]. Behaviourism described learning as largely deriving from responses to external stimuli and led to curricula aimed to influence behaviour through reward and positive and negative reinforcement. In one study reviewed, the lack of direct observation of non-verbal communication by instructors was seen as a significant learning challenge in the virtual environment [ 33 ]. A shift from behaviourism to cognitivism later ensued with the belief that the brain is much more than a ‘black box’ and learning rather involved mental processing and organization of knowledge, and memory functions [ 70 ]. With the recognition of individual differences in the learning process, online systems attempted to introduce interventions that suited multiple learning strategies. For example, learning from auditory narration with animation was found to be more effective than use of text with animation [ 71 ]. This review further highlighted the impact of repetition [ 30 ] and clinical reasoning [ 56 , 59 ] on the learning process. More recently, constructivist learning theory and the perception that learners incorporate new information into pre-existing knowledge schemas has greatly contributed to reformation of medical education [ 70 ]. Incorporating real world connections [ 29 , 49 , 58 ], building on motivations [ 52 ], application of feedback [ 51 ] and continuous reflection [ 49 ] has been noted in this review as important factors in knowledge handling and retention. Presently, e-learning interventions often utilize aspects of more than one theoretical perspective. For instance, problem-based learning interventions have emphasised the critical thinking processes of cognitivism and the self-direction of constructivism [ 29 ]. While primary studies have increased the reporting of underlying theory over time, there is still a significant lack of discussion – future work should reference theoretical principles to objectively frame and assess online education.
In addition to recognizing the needs of the e-learner, identifying required skills of e-teachers and developing content that appropriately supplement the curriculum are vital to ensuring successful implementation of an e-learning system [ 1 ]. Therefore, this study involved review of studies published between 1990 and 2021, assessing the effectiveness and character of various online learning environments in undergraduate clinical medical education. Specifically, these studies involved medical students pursuing medicine as a primary degree and those enrolled with prior degrees.
Intervention design
Critical appraisal of the collected studies using EGGE criteria, identified seventeen studies (40%) meeting a global rating of less than 3. The EGGE criteria encompass a standardized framework by which quality indicators can be recognized. Lower ratings of included studies suggests that conducting and reporting of e-learning interventions is largely lacking in methodological rigour and therefore limits transferability of study results. This finding is consistent with conclusions from a review by Kim et al., describing how most of the existing literature on e-learning interventions have little quantitative data, evaluate a limited range of outcomes and have significant gaps in study designs [ 72 ]. Additionally, only 13 (31%) randomized control trials (RCTs) were included in the review [ 26 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 ]. Amongst these studies, five reported pre and post test scores [ 45 , 48 , 52 , 53 , 54 ], three of which report long term follow up [ 45 , 52 , 54 ]. Interestingly, all the RCTs report no significant differences in knowledge mastery between control and intervention groups. However, in the immediate short term, e-learning interventions were associated with greater learner satisfaction. For example, in Lee et al., mobile learning with interactive multimedia had higher satisfaction scores compared with conventional Microsoft PowerPoint Show content, despite non-significant differences in knowledge gain [ 48 ]. Similarly, in the study by Wahlgren et al., the majority of students in the intervention group reported that the interactive computerised cases enabled better understanding of disease diagnosis and management, particularly referencing the user-friendliness and feedback [ 53 ]. Yet, knowledge gain as assessed by post-intervention examination scores did not show statistically significant differences between the two groups. Systematic reviews examining the effect of e-learning on nursing education have also demonstrated no differences between e-learning and traditional teaching modalities but report high satisfaction rates with the former [ 73 , 74 ]. While these studies suggest that e-learning is as effective as traditional educational methods, higher student satisfaction levels are indicative of more effective learning programs [ 75 ]. Therefore, the lack of longitudinal data may limit our ability to accurately evaluate the impact of e-learning technologies.
Many of the studies in this review used virtual patient and case-based pedagogical methods reflecting an educational trend towards more critical thinking [ 76 ]. Thirty-five of the interventions under review used an interactive approach, encouraging a style in which students collaborated and discussed ideas with their peers and tutors, the importance of which has been recognised [ 77 ]. Two studies of mobile learning identified wasted time for students as a concern that could be addressed by allowing immediate access to information that would soon be required [ 30 , 55 ]. This ‘just in time learning’, defined as a “brief educational experience targeting a specific need or clinical question” [ 78 ], can be facilitated through e-learning. Ten of the included studies concluded that an integrated approach works best, whereby educators do not seek to replace traditional methods but rather supplement them. This has previously been described as a ‘blended-learning’ style [ 77 ]. A recent study suggests that students thrive in blended- versus self-directed virtual reality environments due to face-to-face teacher support [ 79 ].
Despite variability in methodological design, several studies of e-learning across domains of education, politics, business, and military training have shown knowledge gains assessed by pre- versus post-intervention tests [ 80 ]. Similarly, subjects within the studies we have reviewed have reported e-learning interventions to be conducive to learning [ 32 , 35 , 36 , 44 , 58 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 64 , 65 ], have demonstrated improvements in learning [ 25 , 26 , 27 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 34 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 43 , 46 , 48 , 49 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 66 ] and modified learning strategies [ 50 , 52 , 63 ]. The specific features of e-learning strategies most likely to enhance the learning experience may include: peer-to-peer learning [ 52 ], making use of wasted time [ 30 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 81 ], feedback from clinicians and ongoing technical support [ 32 , 82 ], consolidation of information and skill through repetition [ 52 , 82 , 83 ], and convenience of online content access [ 25 , 30 , 40 , 41 , 42 ]. Usability of the intervention has specifically featured strongly in this review. Vital features of e-learning interventions facilitating its use may include: interactive software, active learning promotion (built-in quizzes following cases), asynchronous use, multimedia platforms (i.e., slideshows, videos, images), ease of use and adaptability [ 76 , 81 , 84 ]. Unsurprisingly, students are more engaged with educational material after the typical 9-to-5 work hours [ 25 , 35 ]. Whereas traditional learning opportunities may be restricted to these hours, the flexibility of being able to access online resources outside of this timeframe, may better facilitate achievement of learning objectives [ 25 , 35 ]. Additionally, the use of discussion boards [ 78 ] and games [ 77 ] may facilitate active learning and feedback to be sought and received in a timely manner. Furthermore, quality assurance is recognized as a critical factor, and if considered at the planning stage of an intervention and built into e-learning interventions, may lead to more favourable outcomes [ 23 ]. Engagement with students in this manner is in keeping with the AMEE recommended goals of e-learning [ 1 ]. Several studies also highlight how online learning might provide an encouraging environment for the development of knowledge and skills, relatively easily tailored to individual learning preferences and prior knowledge, and with the possibility of compensating for a lack of accessibility of patients or teachers [ 35 , 36 , 38 , 63 , 85 ]. Furthermore, the ability to access an extensive network of additional resources may allow students to take control of their learning and regulate the volume of information studied [ 36 ].
While our review found improved learning outcomes, other systematic reviews assessing the effectiveness of technology and electronic media in health education, report equivocal findings [ 77 , 86 ]. Proposed factors that may limit learning capacity include: hesitancy to adopt changes by students and teachers, poor technical or financial support, limited technological skills, and the lack of direct and personalized teacher communication [ 25 , 32 , 82 , 87 ]. For example, Davies et al. suggests that an open outlook on mobile device usage was required by students and clinicians, to limit non-use and acquire potential benefits [ 30 ]. In another study conducted by Alsoufi et al., online medical education programs implemented in Libya in response to COVID-19 were found to be negatively received by respondents [ 87 ]. Financial and technical barriers and the lack of hands-on bedside teaching were stated by respondents as limitations to acceptance of e-learning. The shift to online medical learning in the Philippines during the COVID-19 pandemic also identified lack of access to computers and the internet as a significant barrier [ 82 ]. Of course, with these later interventions, the rapid onset of the pandemic required development of e-learning platforms with relatively little training and preparation. As such, the logistics of e-learning curricula as it pertains to specific communities may not have been foreseen. Another reason for such discrepancies may be the underlying discipline in which the intervention is being evaluated [ 47 ]. For instance, the use of only e-learning materials when teaching new skills may not be sufficient, as the direct observation and guidance of an expert is valuable [ 88 ]. A blended-learning environment may be more appropriate in these circumstances [ 47 ]. Indeed, viewing e-learning as a complement rather than replacement of traditional approaches is already well accepted amongst students [ 80 ].
Learner, preceptor and institution characteristics
The twenty-first century learners are known to be avid consumers of various digital platforms. However, studies have shown an incongruence between their ability to use technology for entertainment and ability to use it for educational purposes [ 89 ]. Most students require guidance to synthesize information and create new understanding. In fact, students in middle school through undergraduate level studies have consistently demonstrated poor digital research skills [ 90 , 91 ]. Furthermore, students may require adjustment of learning practices to best engage with the presented e-learning platform. For example, use of PowerPoint presentations or handouts in replacement of in-class teaching can cause visual and auditory learners to require more time to comprehend the information [ 82 ]. Therefore, in addition to carrying an acceptant attitude and a willingness to collaborate with peers, the ability to engage with and extract relevant content from online resources, is a characteristic linked to success in e-learning [ 32 , 66 ].
Nevertheless, recognition of the need for continued mentoring and support in the online learning environment, requires appreciation of the role of the e-teacher. Preceptors’ roles involve development and delivery of the intervention and acting as a resource person for the duration of the module [ 68 ]. In our previous discussion of e-learning strategy effectiveness, two further roles of the e-teacher can be recognized. Firstly, the e-teacher is instrumental in providing timely feedback, one of the main features associated with improved e-learning outcomes [ 32 ]. E-teachers should actively monitor student activity and provide feedback or support where needed [ 92 ]. Secondly, success of e-learning is also strongly related to the motivation of the students and indirectly the motivation demonstrated by the e-teacher [ 30 , 92 ]. The ARCS motivational model highlights four components needed to create a highly motivational e-learning system: maintain student attention, content relevance, student confidence, student satisfaction [ 93 ]. If e-teachers can convey subject material through strategies which encompass use of interactive multimedia, humour, and inquiry for instance, they can satisfy the first component of attention [ 92 ]. Generating activities that best illustrate main ideas, tailoring to the learner knowledge level and providing positive feedback are examples of methods to instil content relevance, student confidence and student satisfaction, accordingly. In Gradl-Dietsch et al., combination of video-based learning, team-based learning and peer-teaching, along with practical skills teaching in point of care ultrasound, feedback from peer teachers, and positive instructor-learner interactions, collectively fulfil the components of the ARCS model [ 54 ]. In Sox et al., the use of a web-based module to teach oral case presentation skills satisfied student attention and content relevance [ 51 ]. However, poor adherence to module largely due to time constraints, can be suggestive of poor student satisfaction. As a result, student confidence and the quality of oral case presentations did not differ from controls (faculty-led feedback sessions). As suggested by the authors, a combination of web module with direct faculty feedback may better instil student confidence and satisfaction with module content, and thereby improve student performance [ 51 ]. Recent studies have shown that the digital literacy skills of most instructors are inadequate [ 90 , 91 ]. Therefore, institutions need to invest into the provision of training programs and supports to allow e-teachers to develop and strengthen competencies needed to sufficiently handle educational technologies [ 92 , 94 , 95 ]. For example, the use of offline tablet-based materials was shown to improve medical education in Zambia, but reported usage amongst healthcare workers was low [ 95 ]. Authors suggest that a lack of training in tablet use was the underlying reason. Taken together, while the role of the teacher has changed compared to traditional pedological approaches, their actions can still heavily influence student learning outcomes.
Limitations and future directions
In a field where technology is changing faster than studies can be completed and interventions are evolving rapidly, medical education research has become a challenging topic of debate. Research can “provide the evidence to prove—and improve—the quality and effectiveness of teaching” and therefore advise the restructuring of curricula to respond to advances in science and technology [ 96 ]. In this review, 29 studies received a global score of 3 or less out of 5, highlighting a lack of transparency and rigour in most of the studies. This justifies a need for a standardised approach for reporting medical education interventions. Pre- and post-intervention testing is informative, but follow-up months later would be an important measure of knowledge retention and therefore intervention effectiveness. Moreover, most of the studies in this review examined knowledge or skill development but few examined higher Kirkpatrick levels. The inclination towards focus on the lower levels of the Kirkpatrick model may stem from difficulty following students in the field to evaluate long-term results of the educational intervention on student behaviours (level three) and the organization at large (level four) [ 97 ]. Future work on the evaluation of associated changes in behaviour, professional practice or patient outcomes would be valuable. Other e-learning characteristics that can be evaluated in future work (Fig. 4 ) may include the capacity for adaptivity (to accommodate changing student needs and performance) and collaboration [ 98 ]. Including descriptions of curricula context can also facilitate the exploration of which e-learning strategies are best suited for specific medicine disciplines and socioeconomic settings. The use of internet resources by both students and patients alike, and the exponential growth in social media influence may also provide a platform for future e-learning interventions [ 99 ].

Future intervention design recommendations
Over the past twenty years and with the recent advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a substantial increase in the use of e-learning. This review found that e-learning interventions are positively perceived by students and associated with improvements in learning. Improved learning outcomes are closely correlated with interactive, asynchronous, easily accessible and usable interventions, and those involving students and preceptors with digital skills, high motivation and receptive attitudes. While further exploration of the strengths and weaknesses of e-learning technologies is warranted, use of online platforms is a creditable educational tool for undergraduate clinical medicine.
Abbreviations
Association for Medical Education in Europe
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Ellaway R, Masters K. AMEE Guide 32: e-Learning In Medical Education - Part 1: Learning. Teaching And Assessment Med Teach. 2008;30(5):455–73.
Google Scholar
Goldie JG. Connectivism: A Knowledge Learning Theory For The Digital Age? Med Teach. 2016;38(10):1064–9.
Article Google Scholar
Maertens H, Madani A, Landry T, Vermassen F, Van Herzeele I, Aggarwal R. Systematic Review Of E-Learning For Surgical Training. Br J Surg. 2016;103(11):1428–37.
Tarpada SP, Morris MT, Burton DA. E-Learning In Orthopedic Surgery Training: A Systematic Review. J Orthop. 2016;13(4):425–30.
Feng J-Y, Chang Y-T, Chang H-Y, Erdley WS, Lin C-H, Chang Y-J. Systematic Review of Effectiveness of Situated E-Learning on Medical and Nursing Education. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2013;10(3):174–83.
Price Kerfoot B, Masser BA, Hafler JP. Influence Of New Educational Technology On Problem-Based Learning At Harvard Medical School. Med Educ. 2005;39(4):380–7.
Guarino S, Leopardi E, Sorrenti S, De Antoni E, Catania A, Alagaratnam S. Internet-Based Versus Traditional Teaching And Learning Methods. Clin Teach. 2014;11(6):449–53.
Trelease RB. From Chalkboard, Slides, And Paper To E-Learning: How Computing Technologies Have Transformed Anatomical Sciences Education. Anat Sci Educ. 2016;9(6):583–602.
Felder E, Fauler M, Geiler S. Introducing E-Learning/Teaching In A Physiology Course For Medical Students: Acceptance By Students And Subjective Effect On Learning. Adv Physiol Educ. 2013;37(4):337–42.
Martin EA. Concise medical dictionary. 9th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2015.
Book Google Scholar
Han H, Nelson E, Wetter N. Medical students’ online learning technology needs. Clin Teach. 2014;11(1):15–9.
Barton J, Rallis KS, Corrigan AE, Hubbard E, Round A, Portone G, et al. Medical students’ pattern of self-directed learning prior to and during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic period and its implications for Free Open Access Meducation within the United Kingdom. J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2021;18:5.
O’Hanlon R, Laynor G. Responding to a new generation of proprietary study resources in medical education. J Med Libr Assoc. 2019;107(2):251–7.
Zhang J, Peterson RF, Ozolins IZ. Student approaches for learning in medicine: What does it tell us about the informal curriculum? BMC Med Educ. 2011;11(1):87.
Cooper AL, Elnicki DM. Resource utilisation patterns of third-year medical students. Clin Teach. 2011;8(1):43–7.
Wynter L, Burgess A, Kalman E, Heron JE, Bleasel J. Medical students: what educational resources are they using? BMC Med Educ. 2019;19(1):36.
Larsen DP, Butler AC, Roediger HL 3rd. Test-enhanced learning in medical education. Med Educ. 2008;42(10):959–66.
Augustin M. How to learn effectively in medical school: test yourself, learn actively, and repeat in intervals. Yale J Biol Med. 2014;87(2):207–12.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Reprint—Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Phys Ther. 2009;89(9):873–80.
Hammond M, editor Learning From Experience: Approaching The Research Of CD-ROM In Schools. WCCE; 1995.
Kentnor HE. Distance Education and the Evolution of Online Learning in the United States. Curric Teach. 2015;17:21–34.
Barry Issenberg S, McGaghie WC, Petrusa ER, Lee Gordon D, Scalese RJ. Features And Uses Of High-Fidelity Medical Simulations That Lead To Effective Learning: A BEME Systematic Review. Med Teach. 2005;27(1):10–28.
Evaluation. EGfGo. Guidelines for Evaluating Papers on Educational Interventions. Education Group for Guidelines on Evaluation ed: BMJ; 1999. p. 1265–7.
Kirkpatrick D, Kirkpatrick J. Transferring Learning to Behavior : Using the Four Levels to Improve Performance. Oakland, United States: Berrett-Koehler Publishers, Incorporated; 2005.
Bernardo V, Ramos MP, Plapler H, De Figueiredo LF, Nader HB, Ancao MS, et al. Web-Based Learning In Undergraduate Medical Education: Development And Assessment Of An Online Course On Experimental Surgery. Int J Med Inform. 2004;73(9–10):731–42.
Raupach T, Munscher C, Pukrop T, Anders S, Harendza S. Significant Increase In Factual Knowledge With Web-Assisted Problem-Based Learning As Part Of An Undergraduate Cardio-Respiratory Curriculum. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2010;15(3):349–56.
Casillas JM, Gremeaux V. Evaluation Of Medical Students’ Expectations For Multimedia Teaching Materials: Illustration By An Original Method Using The Evaluation Of A Web Site On Cardiovascular Rehabilitation. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2012;55(1):25–37.
Cevik AA, Shaban S, El Zubeir M, Abu-Zidan FM. The Role Of Emergency Medicine Clerkship E-Portfolio To Monitor The Learning Experience Of Students In Different Settings: A Prospective Cohort Study. Int J Emerg Med. 2018;11(1):24.
Corrigan M, Reardon M, Shields C, Redmond H. “SURGENT” – Student E-Learning For Reality: The Application Of Interactive Visual Images To Problem-Based Learning In Undergraduate Surgery. J Surg Educ. 2008;65(2):120–5.
Davies BS, Rafique J, Vincent TR, Fairclough J, Packer MH, Vincent R, et al. Mobile Medical Education (Momed) - How Mobile Information Resources Contribute To Learning For Undergraduate Clinical Students - A Mixed Methods Study. BMC Med Educ. 2012;12:1.
de Sena DP, Fabricio DD, Lopes MH, da Silva VD. Computer-Assisted Teaching Of Skin Flap Surgery: Validation Of A Mobile Platform Software For Medical Students. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(7):e65833.
Howlett D, Vincent T, Gainsborough N, Fairclough J, Taylor N, Cohen J, et al. Integration Of A Case-Based Online Module Into An Undergraduate Curriculum: What Is Involved And Is It Effective? E-Learn. 2009;6(4):372–84.
Khalil R, Mansour AE, Fadda WA, Almisnid K, Aldamegh M, Al-Nafeesah A, et al. The Sudden Transition To Synchronized Online Learning During The COVID-19 Pandemic In Saudi Arabia: A Qualitative Study Exploring Medical Students’ Perspectives. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20(1):285.
Ogura A, Hayashi N, Negishi T, Watanabe H. Effectiveness of an e-Learning Platform for Image Interpretation Education of Medical Staff and Students. J Digit Imaging. 2018;31(5):622–7.
Orton E, Mulhausen P. E-Learning Virtual Patients For Geriatric Education. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2008;28(3):73–88.
Sijstermans R, Jaspers MW, Bloemendaal PM, Schoonderwaldt EM. Training Inter-Physician Communication Using The Dynamic Patient Simulator. Int J Med Inform. 2007;76(5–6):336–43.
Tews M, Brennan K, Begaz T, Treat R. Medical Student Case Presentation Performance And Perception When Using Mobile Learning Technology In The Emergency Department. Med Educ Online. 2011;16. https://doi.org/10.3402/meo.v16i0.7327 .
Wunschel M, Leichtle U, Wulker N, Kluba T. Using A Web-Based Orthopaedic Clinic In The Curricular Teaching Of A German University Hospital: Analysis Of Learning Effect, Student Usage And Reception. Int J Med Inform. 2010;79(10):716–21.
Zayed MA, Lilo EA, Lee JT. Impact of an Interactive Vascular Surgery Web-Based Educational Curriculum on Surgical Trainee Knowledge and Interest. J Surg Educ. 2017;74(2):251–7.
Al Zahrani EM, Al Naam YA, AlRabeeah SM, Aldossary DN, Al-Jamea LH, Woodman A, et al. E- Learning experience of the medical profession’s college students during COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):443.
Dost S, Hossain A, Shehab M, Abdelwahed A, Al-Nusair L. Perceptions of medical students towards online teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic: a national cross-sectional survey of 2721 UK medical students. BMJ Open. 2020;10(11): e042378.
Coffey CS, MacDonald BV, Shahrvini B, Baxter SL, Lander L. Student Perspectives on Remote Medical Education in Clinical Core Clerkships During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Medical Science Educator. 2020;30(4):1577–84.
Diekhoff T, Kainberger F, Oleaga L, Dewey M, Zimmermann E. Effectiveness Of The Clinical Decision Support Tool ESR Eguide For Teaching Medical Students The Appropriate Selection Of Imaging Tests: Randomized Cross-Over Evaluation. Eur Radiol. 2020;30(10):5684–9.
Dombrowski T, Wrobel C, Dazert S, Volkenstein S. Flipped Classroom Frameworks Improve Efficacy In Undergraduate Practical Courses – A Quasi-Randomized Pilot Study In Otorhinolaryngology. BMC Med Educ. 2018;18(1):294.
Hari R, Kälin K, Harris M, Walter R, Serra A. Comparing Blended Learning With Faculty-Led Ultrasound Training: Protocol For A Randomised Controlled Trial (The SIGNATURE Trial). Praxis (Bern 1994). 2020;109(8):636–40.
Herrmann-Werner A, Weber H, Loda T, Keifenheim KE, Erschens R, Mölbert SC, et al. “But Dr Google Said…” - Training Medical Students How To Communicate With E-Patients. Med Teach. 2019;41(12):1434–40.
Jenkins S, Goel R, Morrell DS. Computer-Assisted Instruction Versus Traditional Lecture For Medical Student Teaching Of Dermatology Morphology: A Randomized Control Trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59(2):255–9.
Lee LA, Chao YP, Huang CG, Fang JT, Wang SL, Chuang CK, et al. Cognitive Style and Mobile E-Learning in Emergent Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Disorders for Millennial Undergraduate Medical Students: Randomized Controlled Trial. J Med Internet Res. 2018;20(2): e56.
Plackett R, Kassianos AP, Kambouri M, Kay N, Mylan S, Hopwood J, et al. Online Patient Simulation Training To Improve Clinical Reasoning: A Feasibility Randomised Controlled Trial. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20(1):245.
Schneider AT, Albers P, Muller-Mattheis V. E-Learning in Urology: Implementation of the Learning and Teaching Platform CASUS(R) - Do Virtual Patients Lead to Improved Learning Outcomes? A Randomized Study among Students. Urol Int. 2015;94(4):412–8.
Sox CM, Tenney-Soeiro R, Lewin LO, Ronan J, Brown M, King M, et al. Efficacy of a Web-Based Oral Case Presentation Instruction Module: Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Acad Pediatr. 2018;18(5):535–41.
Sward KARNP, Richardson SRNP, Kendrick JMD, Maloney CMDP. Use of a Web-Based Game to Teach Pediatric Content to Medical Students. Acad Pediatr. 2008;8(6):354–9.
Wahlgren CF, Edelbring S, Fors U, Hindbeck H, Stahle M. Evaluation Of An Interactive Case Simulation System In Dermatology And Venereology For Medical Students. BMC Med Educ. 2006;6:40.
Gradl-Dietsch G, Menon AK, Gürsel A, Götzenich A, Hatam N, Aljalloud A, et al. Basic Echocardiography For Undergraduate Students: A Comparison Of Different Peer-Teaching Approaches. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018;44(1):143–52.
Davis JS, Garcia GD, Wyckoff MM, Alsafran S, Graygo JM, Withum KF, et al. Use Of Mobile Learning Module Improves Skills In Chest Tube Insertion. J Surg Res. 2012;177(1):21–6.
Roesch A, Gruber H, Hawelka B, Hamm H, Arnold N, Popal H, et al. Computer Assisted Learning In Medicine: A Long-Term Evaluation Of The “Practical Training Programme Dermatology 2000.” Med Inform Internet Med. 2003;28(3):147–59.
Sendra-Portero F, Torales-Chaparro OE, Ruiz-Gomez MJ, Martinez-Morillo M. A Pilot Study To Evaluate The Use Of Virtual Lectures For Undergraduate Radiology Teaching. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82(5):888–93.
Farrimond H, Dornan TL, Cockcroft A, Rhodes LE. Development And Evaluation Of An E-Learning Package For Teaching Skin Examination. Action Research Br J Dermatol. 2006;155(3):592–9.
Moriates C, Valencia V, Stamets S, Joo J, MacClements J, Wilkerson L, et al. Using Interactive Learning Modules to Teach Value-Based Health Care to Health Professions Trainees Across the United States. Acad Med. 2019;94(9):1332–6.
Naeger DM, Straus CM, Phelps A, Courtier J, Webb EM. Student-Created Independent Learning Modules: An Easy High-Value Addition To Radiology Clerkships. Acad Radiol. 2014;21(7):879–87.
Smith E, Boscak A. A Virtual Emergency: Learning Lessons From Remote Medical Student Education During The COVID-19 Pandemic. Emerg Radiol. 2021;28(3):445–52.
Taurines R, Radtke F, Romanos M, König S. Using Real Patients In E-Learning: Case-Based Online Training In Child And Adolescent Psychiatry. GMS J Med Educ. 2020;37(7):Doc96-Doc.
De Villiers M, Walsh S. How Podcasts Influence Medical Students’ Learning – A Descriptive Qualitative Study. Afr J Health Prof Educ. 2015;7(1):130–3.
Wagner-Menghin M, Szenes V, Scharitzer M, Pokieser P. Designing Virtual Patient Based Self-Study Quizzes Covering Learning Goals In Clinical Diagnostic Sciences For Undergraduate Medical Students - The Radiology Example. GMS J Med. 2020;37(7):Doc91.
Nelson TM. Preparing for Practice: Strengthening Third-Year Medical Students’ Awareness of Point-of-Care Resources. Med Ref Serv Q. 2018;37(3):312–8.
Kourdioukova EV, Verstraete KL, Valcke M. The Quality And Impact Of Computer Supported Collaborative Learning (CSCL) In Radiology Case-Based Learning. Eur J Radiol. 2011;78(3):353–62.
Clark RC, Mayer RE. E-Learning and the Science of Instruction: Proven Guidelines for Consumers and Designers of Multimedia Learning. Hoboken: Center for Creative Leadership; 2016.
Gruner D, Pottie K, Archibald D, Allison J, Sabourin V, Belcaid I, et al. Introducing global health into the undergraduate medical school curriculum using an e-learning program: a mixed method pilot study. BMC Med Educ. 2015;15(1):142.
UNESCO. National education responses to COVID-19: summary report of UNESCO's online survey. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization.
Mann KV. Theoretical Perspectives In Medical Education: Past Experience And Future Possibilities. Med Ed. 2011;45(1):60–8.
Moreno R, Mayer RE. Cognitive Principles Of Multimedia Learning: The Role Of Modality And Contiguity. J Educ Psychol. 1999;91(2):358–68.
Kim S. The Future of e-Learning in Medical Education: Current Trend and Future Opportunity. J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2006;3:3.
Du S, Liu Z, Liu S, Yin H, Xu G, Zhang H, et al. Web-based distance learning for nurse education: a systematic review. Int Nurs Rev. 2013;60(2):167–77.
Lahti M, Hätönen H, Välimäki M. Impact of e-learning on nurses’ and student nurses knowledge, skills, and satisfaction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Nurs Stud. 2014;51(1):136–49.
Kirkpatrick DL. The Four Levels of Evaluation. In: Brown SM, Seidner CJ, editors. Evaluating Corporate Training: Models and Issues. Dordrecht: Springer, Netherlands; 1998. p. 95–112.
Chapter Google Scholar
Fuks A, Boudreau JD, Cassell EJ. Teaching Clinical Thinking To First-Year Medical Students. Med Teach. 2009;31(2):105–11.
Chumley-Jones HS, Dobbie A, Alford CL. Web-Based Learning: Sound Educational Method Or Hype? A Review Of The Evaluation Literature. Acad Med. 2002;77(10 Suppl):S86-93.
Kahn CE Jr, Ehlers KC, Wood BP. Radiologists’ Preferences for Just-in-Time Learning. J Digit Imaging. 2006;19(3):202–6.
Fairén M, Moyés J, Insa E. VR4Health: Personalized teaching and learning anatomy using VR. J Med Syst. 2020;44(5):94.
Ruiz JG, Mintzer MJ, Leipzig RM. The impact of E-learning in medical education. Acad Med. 2006;81(3):207–12.
Klímová B. Mobile Learning in Medical Education. J Med Syst. 2018;42(10):194.
Baticulon RE, Sy JJ, Alberto NRI, Baron MBC, Mabulay REC, Rizada LGT, et al. Barriers to Online Learning in the Time of COVID-19: A National Survey of Medical Students in the Philippines. Medical Science Educator. 2021;31(2):615–26.
Mehrpour SR, Aghamirsalim M, Motamedi SM, Ardeshir Larijani F, Sorbi R. A supplemental video teaching tool enhances splinting skills. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(2):649–54.
Larvin M. E-Learning In Surgical Education And Training. ANZ J Surg. 2009;79(3):133–7.
Lane J, Slavin S. Simulation in Medical Education: A Review. Simulation & Gaming - Simulat Gaming. 2001;32.
Bell DS, Fonarow GC, Hays RD, Mangione CM. elf-study from web-based and printed guideline materials. A randomized, controlled trial among resident physicians. Annals of internal medicine. 2000;132(12):938–46.
Alsoufi A, Alsuyihili A, Msherghi A, Elhadi A, Atiyah H, Ashini A, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on medical education: Medical students’ knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding electronic learning. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(11):e0242905.
Rogers DA, Regehr G, Yeh KA, Howdieshell TR. Computer-assisted Learning versus a Lecture and Feedback Seminar for Teaching a Basic Surgical Technical Skill. The American journal of surgery. 1998;175(6):508–10.
Guri RS. E-Teaching In Higher Education: An Essential Prerequisite For E-Learning. J New Approaches Educ Res. 2018;7(2):93–7.
Alexander B, Adams-Becker S, Cummins M, Hall-Giesinger C. Digital Literacy in Higher Education, Part II: An NMC Horizon Project Strategic Brief. . Austin, Texas; 2017.
Wineburg S, McGrew S, Breakstone J, Ortega T. Evaluating Information: The Cornerstone of Civic Online Reasoning. Stanford Digital Repository; 2016.
Yengin İ, Karahoca D, Karahoca A, Yücel A. Roles Of Teachers In E-Learning: How To Engage Students & How To Get Free E-Learning And The Future. Procedia Soc. 2010;2(2):5775–87.
Keller J, Suzuki K. Learner Motivation and E-learning Design: A Multinationally Validated Process. Learn Media Technol. 2004;29:229–39.
Howe DL, Heitner KL, Dozier A, Silas S. Health Professions Faculty Experiences Teaching Online During the COVID-19 Pandemic. ABNF J. 2021;32(1):6–11.
Barteit S, Neuhann F, Bärnighausen T, Bowa A, Lüders S, Malunga G, et al. Perspectives of Nonphysician Clinical Students and Medical Lecturers on Tablet-Based Health Care Practice Support for Medical Education in Zambia, Africa: Qualitative Study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019;7(1):e12637.
Easton G. Primary care education research-time to raise our game? Educ Prim Care. 2014;25(6):304–7.
Cahapay M. Kirkpatrick Model: Its Limitations As Used in Higher Education Evaluation. IJATE. 2021;8:135–44.
Byrnes KG, Kiely PA, Dunne CP, McDermott KW, Coffey JC. Communication, collaboration and contagion: “Virtualisation” of anatomy during COVID-19. Clin Anat. 2021;34(1):82–9.
Dunne S, Cummins NM, Hannigan A, Shannon, Dunne C, Cullen W. A method for the design and development of medical or health care information websites to optimize search engine results page rankings on Google. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2013;15(8):e2632.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
No funding received.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Medicine, University of Limerick, Limerick, Ireland
T. Delungahawatta, S. S. Dunne, S. Hyde, L. Halpenny, D. McGrath, A. O’Regan & C. P. Dunne
Centre for Interventions in Infection, Inflammation & Immunity (4I), University of Limerick, Limerick, Ireland
D. McGrath & C. P. Dunne
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
CPD, AOR, SH and DM conceived the study and its design. LH and AOR performed initial analysis. TD and SSD drafted and revised the manuscript. All authors co-wrote and approved the final manuscript.
A uthors’ information
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to C. P. Dunne .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, availability of data and material.
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:.
PRISMA Checklist.
Additional file 2:
Summary of Review Results.
Additional file 3:
Intervention Characteristics.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Delungahawatta, T., Dunne, S.S., Hyde, S. et al. Advances in e-learning in undergraduate clinical medicine: a systematic review. BMC Med Educ 22 , 711 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-022-03773-1
Download citation
Received : 26 February 2022
Accepted : 26 September 2022
Published : 07 October 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-022-03773-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Online learning
- Distance learning
- Medical education
- Medical students
- Clinical medicine
- Systematic review
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Teaching & Learning
- Education Excellence
- Professional development
- Case studies
- Teaching toolkits
- MicroCPD-UCL
- Assessment resources
- Student partnership
- Generative AI Hub
- Community Engaged Learning
- UCL Student Success

Teaching difficult and sensitive topics in higher education: some starting points
Helen Knowler, Associate Professor (Teaching), the Eugenics Legacy Education Project, offers thoughtful advice on how to help your students constructively tackle difficult or sensitive topics.
12 April 2024
MediaCentral Widget Placeholder https://mediacentral.ucl.ac.uk/Player/Cd00GDie
Watch the video on MediaCentral . Download the transcript [docx] .
What are difficult and/or sensitive topics?
Defining and agreeing what constitutes a difficult and/or sensitive topic can be hard to agree on because what is ‘difficult’ for some, is not for others. A key aspect for success in the classroom is dependent on some careful thinking and planning as well as challenging some ‘taken for granted’ aspects of our practices. Generally, difficult topics are characterised by engagement with curriculum content that can make learners feel discomfort, where disagreement becomes a feature of the classroom space, perhaps in ways it was not in previous modules or sessions. So, talking to colleagues about the ways you define and understand ‘difficulty’ can be a really valuable first step in understanding how best to teach these areas.
Why do we need to think about this?
Higher education classrooms are diverse and dynamic and, while this can bring many benefits for learners, it can pose tensions and dilemmas for educators introducing difficult topics within a short space of time (such as one module session). We cannot always do justice to the complexity of the topic. Conversely, working with colleagues to introduce or revise teaching to incorporate direct engagement with difficult topics can be creative and drive innovation – because we need to think about issues such as inclusive learning, culturally relevant teaching, authentic assessment and preparing students to work in institutions where difficult topics and conversations may be the norm. Teaching difficult topics offers enormous potential to teach critical thinking skills, using evidence and reasoning to agree on productive solutions and to think about wider concepts around social justice and equity.
What can we do?
There are three key strategies important when thinking about and planning for teaching topics that could be described as difficult or sensitive.
Prepare your students
Firstly, it is helpful to think about the ways that students encounter potentially difficult or sensitive topics across a module or a programme. It is useful to think about the timing of the introduction of difficult content from the perspective of students. The research shows that introducing content too early or too late restricts opportunities to prepare students to learn about difficult content and for us to ensure we have laid the groundwork in terms of skills and understanding.
For example, we might want to teach students to understand the legacy of eugenics at UCL and ask them to present their research on the topic. If this topic is introduced in a way that leaves students unprepared to do the task, to understand the rationale behind including this work, and not understanding why this is relevant to learning outcomes, we are more likely to encounter a lack of engagement or strong emotions related to wanting to question the inclusion of such content.
Explain your approach
Linked to mapping, offering and explicit educational rationale and justification is critical. In my experience, when colleagues offer a short overview of their teaching approach, explain the inclusion of content and their choices for learning strategies, students understand the decision-making around the inclusion of difficult content, and can see the connections between teaching philosophies and practical approaches.
This doesn’t have to be a huge piece of work – I have seen examples of this done well as part of module introductions on Moodle or as part of introductory sessions with students where tutors have explored, with students, the use of approaches and their intended aims. This is important if we want our sessions to be productive and engaging for students and it also enables us to work with students before difficult topics appear.
Alignment pedagogies
The final tool that I see used by educators relates to alignment. Reflecting on times when I have seen things ‘go wrong’ in teaching session, I have worked with colleagues to explore and identify places in their work where there is a small misalignment in their teaching. This is usually almost imperceptible, but its impact can be significant for students.
For example, we might be wanting to teach an area that is sensitive, and our goal is to support students to understand many perspectives and to think about empathy, and develop their critical thinking skills. So, these are lofty aims for one session and when we add a pedagogic approach that is not quite aligned, we might find that students do not engage. So here, we’d want to think about reducing the content and aims of the session, and choosing a pedagogic approach that offers students time and space to think about the complexity. We would want the students to understand and experience that the goal is NOT to decide for or against, or offer simplistic solutions to complex issues.
Find out more
Access a range of resources relating to the Eugenics Legacy Education project , including recordings of many of our sessions.
More MicroCPD-UCL
Funnelback feed: https://cms-feed.ucl.ac.uk/s/search.json?collection=drupal-teaching-lear... Double click the feed URL above to edit

Separation Anxiety Dog
An unconventional approach to separation anxiety.
Expand your tools by learning different nuances of the SA training protocol
"An Unconventional Approach to Separation Anxiety"
Are you familiar with the CSAT approach to separation anxiety cases? If you are, and have been implementing it with your own separation anxiety clients I'm sure that you have found that this approach has a high rate of success, and I hope that you are feeling great about helping so many dogs and their families to successfully overcome this challenge. This approach is wonderful, and I personally implement it all the time and have lots of success doing so.
During my journey as a Certified Separation Anxiety Trainer I have realized more and more how all dogs benefit from a balance between predictability and flexibility. How beneficial is each of these parts of the puzzle, and in which amount will depend on each dog, and finding the right combination of both will ultimately set the dog (and us) up for success.
For the dogs who benefit from predictability over flexibility, the conventional training protocol can prove to be challenging, and it can lead to inconsistencies in the progress. Dogs who count steps, who learn that getting up makes the guardian come back earlier and earlier, or for the ones who just have a hard time grasping not knowing exactly when the guardian will return, an unconventional and more predictable protocol can make all the difference!
During this 90-min webinar we will discuss a specific case study where we successfully implemented an unconventional approach to separation anxiety within the same frame of the desensitization protocol that you are already familiar with. And where increasing predictability, among other things (always considering an integrative approach) was a game changer that got us from a 3-min absence where we had been stuck for over a year to a current 45-min absence duration.
If you would like to expand your knowledge about how to implement different nuances of the classic separation anxiety training model depending on what is more beneficial for each dog, this webinar is for you!
It is recommended to be familiar with the CSAT separation anxiety desensitization protocol before taking this webinar.
This webinar was live on Wednesday, June the 22nd at 2pm EST, and included a 60-min lecture plus 30-min of Q&A. You can now watch it ON DEMAND.

ACCESS ON DEMAND
Access now and have access to the recording for one year
What is included?
60-min lecture (recording)
30-min Q&A (recording)
One year access to the webinar recording
1.5 CEUs for CCPDT, 1.5 CEUs for IAABC and KPA

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case method 1 teaching is an active form of instruction that focuses on a case and involves students learning by doing 2 3. Cases are real or invented stories 4 that include "an educational message" or recount events, problems, dilemmas, theoretical or conceptual issue that requires analysis and/or decision-making.
INTRODUCTION. The case study teaching method is a highly adaptable style of teaching that involves problem-based learning and promotes the development of analytical skills ().By presenting content in the format of a narrative accompanied by questions and activities that promote group discussion and solving of complex problems, case studies facilitate development of the higher levels of Bloom ...
Case-based learning can focus on anything from a one-sentence physics word problem to a textbook-sized nursing case or a semester-long case in a law course. Though we often assume that a case is a "problem," Ellet (2007) suggests that most cases entail one of four types of situations: Problems. Decisions. Evaluations.
Case-Based Learning. Case-based learning (CBL) is an established approach used across disciplines where students apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios, promoting higher levels of cognition (see Bloom's Taxonomy ). In CBL classrooms, students typically work in groups on case studies, stories involving one or more characters and/or ...
Case studies are a form of problem-based learning, where you present a situation that needs a resolution. A typical business case study is a detailed account, or story, of what happened in a particular company, industry, or project over a set period of time. The learner is given details about the situation, often in a historical context.
It's been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students.
The case study approach aligns with constructivist theory, and is anchored in the tradition of active and experiential learning, supporting students to develop critical thinking and decision-making skills alongside subject specific content (Auster & Wylie, Citation 2006; Cox, Citation 2014; Kim et al., Citation 2006).
In The Case Study Handbook, Revised Edition, William Ellet presents a potent new approach for efficiently analyzing, discussing, and writing about cases." Andersen, E. & Schiano, B. , 2014. Teaching with Cases: A Practical Guide , Harvard Business School Publishing.
2.1.2 Case Method in Learning. This is a method of learning in which the student is able to move beyond theoretical knowledge by using the content and facts of the case study to make assessments. The case study approach develops the competence of students and is a central tenant to learning in the classroom.
The Case Method in Teaching and Learning. The case method has been considered a successful pedagogy via the problem-solving approach [4]. Through case studies, a type of context-dependent knowledge is produced that enables the student to develop their situational analytic skills. Case study pedagogy applies and incorporates theory to practical
Advantages to the use of case studies in class. A major advantage of teaching with case studies is that the students are actively engaged in figuring out the principles by abstracting from the examples. This develops their skills in: Problem solving. Analytical tools, quantitative and/or qualitative, depending on the case.
These study findings add to the existing body of knowledge that places case study based teaching as a tested method that promotes perception learning where students' senses are engaged as a result of the real-life and authentic clinical scenarios (Malesela, 2009), resulting in deeper learning and achievement of long-lasting knowledge (Fiscus ...
1. Identify a problem to investigate: This should be something accessible and relevant to students' lives. The problem should also be challenging and complex enough to yield multiple solutions with many layers. 2. Give context: Think of this step as a movie preview or book summary.
Case study-based learning is a proven strategy for a professional to integrate their knowledge and skills to an actual problem or scenario that they may encounter . This type of learning is effective in multiple disciplines of study and provides opportunity for networking, collaboration, and/or self-assessment with regard to honing, refreshing ...
An example of this approach to case studies is reflected in Walker's (Chap. 99, "Parent Learning Through Complementary Online Social Collaboration: A Case Study of Parentopia") piece. Walker's chapter covers an eight-year span of the design, revision, implementation, and scaling up of an online platform to support parents called ...
occur later in their professional practice. Using the case study approach is one way to add meaning and relevance to the learning process. Case studies bring actual examples to the classroom, which can be significant because theory and reality do not always align, and reality itself is not always quite as it is imagined to be (Shenker, 2010).
The case study approach is particularly useful to employ when there is a need to obtain an in-depth appreciation of an issue, event or phenomenon of interest, in its natural real-life context. ... "A case study is both the process of learning about the case and the product of our learning" (p.237) Yin[1,27,28]
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
The still developing student brain plays a significant part in the success of an. experiential learning approach. As our knowledge of the brain and its functions grow. through imaging and testing ...
This first course treats the machine learning method as a black box. Using this abstraction, you will focus on understanding tasks of interest, matching these tasks to machine learning tools, and assessing the quality of the output. In subsequent courses, you will delve into the components of this black box by examining models and algorithms.
Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory. The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
This case study investigated the learners' brain dominance by employing the s uitable pedagogical. strategies to ensure a high level o f transfer of learning. As to realise the objective, the ...
E-learning is recognised as a useful educational tool and is becoming more common in undergraduate medical education. This review aims to examine the scope and impact of e-learning interventions on medical student learning in clinical medicine, in order to aid medical educators when implementing e-learning strategies in programme curricula. A systematic review compliant with PRISMA guidelines ...
In my experience, when colleagues offer a short overview of their teaching approach, explain the inclusion of content and their choices for learning strategies, students understand the decision-making around the inclusion of difficult content, and can see the connections between teaching philosophies and practical approaches.
Using a hermeneutic phenomenological approach to data analysis, case study findings revealed that embodied explorations of poetry immersed participants socially and imaginatively whilst pushing them beyond their additional language comfort zone. ... , A. The School Drama Experience: A Case Study of Learning in and through the Art of Drama ...
On this 90-min webinar we will discuss a specific case study where an unconventional, more predictable approach to separation anxiety as a nuance of the conventional SA desensitization protocol was highly successful, and a game changer. ... Expand your tools by learning different nuances of the SA training protocol. Buy now $29.95. CASE STUDY ...
Shrinking cities suffer from a decreased level of resident activities. As a result, areas with low levels of resident activities may become breeding grounds for social issues. To ease and prevent social issues, it is important to deploy physical space optimisation strategies to effectively guide the distribution of resident activities in shrinking cities. To support the development of such ...