What is a scientific hypothesis?
It's the initial building block in the scientific method.


Hypothesis basics
What makes a hypothesis testable.
- Types of hypotheses
- Hypothesis versus theory
Additional resources
Bibliography.
A scientific hypothesis is a tentative, testable explanation for a phenomenon in the natural world. It's the initial building block in the scientific method . Many describe it as an "educated guess" based on prior knowledge and observation. While this is true, a hypothesis is more informed than a guess. While an "educated guess" suggests a random prediction based on a person's expertise, developing a hypothesis requires active observation and background research.
The basic idea of a hypothesis is that there is no predetermined outcome. For a solution to be termed a scientific hypothesis, it has to be an idea that can be supported or refuted through carefully crafted experimentation or observation. This concept, called falsifiability and testability, was advanced in the mid-20th century by Austrian-British philosopher Karl Popper in his famous book "The Logic of Scientific Discovery" (Routledge, 1959).
A key function of a hypothesis is to derive predictions about the results of future experiments and then perform those experiments to see whether they support the predictions.
A hypothesis is usually written in the form of an if-then statement, which gives a possibility (if) and explains what may happen because of the possibility (then). The statement could also include "may," according to California State University, Bakersfield .
Here are some examples of hypothesis statements:
- If garlic repels fleas, then a dog that is given garlic every day will not get fleas.
- If sugar causes cavities, then people who eat a lot of candy may be more prone to cavities.
- If ultraviolet light can damage the eyes, then maybe this light can cause blindness.
A useful hypothesis should be testable and falsifiable. That means that it should be possible to prove it wrong. A theory that can't be proved wrong is nonscientific, according to Karl Popper's 1963 book " Conjectures and Refutations ."
An example of an untestable statement is, "Dogs are better than cats." That's because the definition of "better" is vague and subjective. However, an untestable statement can be reworded to make it testable. For example, the previous statement could be changed to this: "Owning a dog is associated with higher levels of physical fitness than owning a cat." With this statement, the researcher can take measures of physical fitness from dog and cat owners and compare the two.
Types of scientific hypotheses

In an experiment, researchers generally state their hypotheses in two ways. The null hypothesis predicts that there will be no relationship between the variables tested, or no difference between the experimental groups. The alternative hypothesis predicts the opposite: that there will be a difference between the experimental groups. This is usually the hypothesis scientists are most interested in, according to the University of Miami .
For example, a null hypothesis might state, "There will be no difference in the rate of muscle growth between people who take a protein supplement and people who don't." The alternative hypothesis would state, "There will be a difference in the rate of muscle growth between people who take a protein supplement and people who don't."
If the results of the experiment show a relationship between the variables, then the null hypothesis has been rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis, according to the book " Research Methods in Psychology " (BCcampus, 2015).
There are other ways to describe an alternative hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis above does not specify a direction of the effect, only that there will be a difference between the two groups. That type of prediction is called a two-tailed hypothesis. If a hypothesis specifies a certain direction — for example, that people who take a protein supplement will gain more muscle than people who don't — it is called a one-tailed hypothesis, according to William M. K. Trochim , a professor of Policy Analysis and Management at Cornell University.
Sometimes, errors take place during an experiment. These errors can happen in one of two ways. A type I error is when the null hypothesis is rejected when it is true. This is also known as a false positive. A type II error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false. This is also known as a false negative, according to the University of California, Berkeley .
A hypothesis can be rejected or modified, but it can never be proved correct 100% of the time. For example, a scientist can form a hypothesis stating that if a certain type of tomato has a gene for red pigment, that type of tomato will be red. During research, the scientist then finds that each tomato of this type is red. Though the findings confirm the hypothesis, there may be a tomato of that type somewhere in the world that isn't red. Thus, the hypothesis is true, but it may not be true 100% of the time.
Scientific theory vs. scientific hypothesis
The best hypotheses are simple. They deal with a relatively narrow set of phenomena. But theories are broader; they generally combine multiple hypotheses into a general explanation for a wide range of phenomena, according to the University of California, Berkeley . For example, a hypothesis might state, "If animals adapt to suit their environments, then birds that live on islands with lots of seeds to eat will have differently shaped beaks than birds that live on islands with lots of insects to eat." After testing many hypotheses like these, Charles Darwin formulated an overarching theory: the theory of evolution by natural selection.
"Theories are the ways that we make sense of what we observe in the natural world," Tanner said. "Theories are structures of ideas that explain and interpret facts."
- Read more about writing a hypothesis, from the American Medical Writers Association.
- Find out why a hypothesis isn't always necessary in science, from The American Biology Teacher.
- Learn about null and alternative hypotheses, from Prof. Essa on YouTube .
Encyclopedia Britannica. Scientific Hypothesis. Jan. 13, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/science/scientific-hypothesis
Karl Popper, "The Logic of Scientific Discovery," Routledge, 1959.
California State University, Bakersfield, "Formatting a testable hypothesis." https://www.csub.edu/~ddodenhoff/Bio100/Bio100sp04/formattingahypothesis.htm
Karl Popper, "Conjectures and Refutations," Routledge, 1963.
Price, P., Jhangiani, R., & Chiang, I., "Research Methods of Psychology — 2nd Canadian Edition," BCcampus, 2015.
University of Miami, "The Scientific Method" http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/161/evolution/161app1_scimethod.pdf
William M.K. Trochim, "Research Methods Knowledge Base," https://conjointly.com/kb/hypotheses-explained/
University of California, Berkeley, "Multiple Hypothesis Testing and False Discovery Rate" https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~hhuang/STAT141/Lecture-FDR.pdf
University of California, Berkeley, "Science at multiple levels" https://undsci.berkeley.edu/article/0_0_0/howscienceworks_19
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Part of the San Andreas fault may be gearing up for an earthquake
Antarctica is covered in volcanoes, could they erupt?
Tube-tying surgeries and vasectomies skyrocketed post-Roe
Most Popular
- 2 'Exceptional' prosthesis of gold, silver and wool helped 18th-century man live with cleft palate
- 3 Mass die-off half a billion years ago caused by shifting tectonic plates, ancient rocks reveal
- 4 Prehistoric henge accidentally discovered in England in search for Anglo-Saxon hermit
- 5 Car-size asteroid discovered 2 days ago flies by Earth at 1/30th the distance of the moon
- 2 Cancer patients can now be 'matched' to best treatment with DNA and lab-dish experiments
- 3 Space photo of the week: NASA spots enormous pink 'flames' during total solar eclipse. What are they?
- 4 Ancient Indigenous lineage of Blackfoot Confederacy goes back 18,000 years to last ice age, DNA reveals
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Biology library
Course: biology library > unit 1, the scientific method.
- Controlled experiments
- The scientific method and experimental design
Introduction
- Make an observation.
- Ask a question.
- Form a hypothesis , or testable explanation.
- Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
- Test the prediction.
- Iterate: use the results to make new hypotheses or predictions.
Scientific method example: Failure to toast
1. make an observation..
- Observation: the toaster won't toast.
2. Ask a question.
- Question: Why won't my toaster toast?
3. Propose a hypothesis.
- Hypothesis: Maybe the outlet is broken.
4. Make predictions.
- Prediction: If I plug the toaster into a different outlet, then it will toast the bread.
5. Test the predictions.
- Test of prediction: Plug the toaster into a different outlet and try again.
- If the toaster does toast, then the hypothesis is supported—likely correct.
- If the toaster doesn't toast, then the hypothesis is not supported—likely wrong.
Logical possibility
Practical possibility, building a body of evidence, 6. iterate..
- Iteration time!
- If the hypothesis was supported, we might do additional tests to confirm it, or revise it to be more specific. For instance, we might investigate why the outlet is broken.
- If the hypothesis was not supported, we would come up with a new hypothesis. For instance, the next hypothesis might be that there's a broken wire in the toaster.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection .
Example: Hypothesis
Daily apple consumption leads to fewer doctor’s visits.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more types of variables .
- An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls.
- A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
If there are any control variables , extraneous variables , or confounding variables , be sure to jot those down as you go to minimize the chances that research bias will affect your results.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Step 1. ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2. Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to ensure that you’re embarking on a relevant topic . This can also help you identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalize more complex constructs.
Step 3. Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
4. Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis . The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
- H 0 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has no effect on their final exam scores.
- H 1 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has a positive effect on their final exam scores.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/hypothesis/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, construct validity | definition, types, & examples, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, operationalization | a guide with examples, pros & cons, what is your plagiarism score.
Scientific Hypothesis, Model, Theory, and Law
Understanding the Difference Between Basic Scientific Terms
Hero Images / Getty Images
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Scientific Method
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
Words have precise meanings in science. For example, "theory," "law," and "hypothesis" don't all mean the same thing. Outside of science, you might say something is "just a theory," meaning it's a supposition that may or may not be true. In science, however, a theory is an explanation that generally is accepted to be true. Here's a closer look at these important, commonly misused terms.
A hypothesis is an educated guess, based on observation. It's a prediction of cause and effect. Usually, a hypothesis can be supported or refuted through experimentation or more observation. A hypothesis can be disproven but not proven to be true.
Example: If you see no difference in the cleaning ability of various laundry detergents, you might hypothesize that cleaning effectiveness is not affected by which detergent you use. This hypothesis can be disproven if you observe a stain is removed by one detergent and not another. On the other hand, you cannot prove the hypothesis. Even if you never see a difference in the cleanliness of your clothes after trying 1,000 detergents, there might be one more you haven't tried that could be different.
Scientists often construct models to help explain complex concepts. These can be physical models like a model volcano or atom or conceptual models like predictive weather algorithms. A model doesn't contain all the details of the real deal, but it should include observations known to be valid.
Example: The Bohr model shows electrons orbiting the atomic nucleus, much the same way as the way planets revolve around the sun. In reality, the movement of electrons is complicated but the model makes it clear that protons and neutrons form a nucleus and electrons tend to move around outside the nucleus.
A scientific theory summarizes a hypothesis or group of hypotheses that have been supported with repeated testing. A theory is valid as long as there is no evidence to dispute it. Therefore, theories can be disproven. Basically, if evidence accumulates to support a hypothesis, then the hypothesis can become accepted as a good explanation of a phenomenon. One definition of a theory is to say that it's an accepted hypothesis.
Example: It is known that on June 30, 1908, in Tunguska, Siberia, there was an explosion equivalent to the detonation of about 15 million tons of TNT. Many hypotheses have been proposed for what caused the explosion. It was theorized that the explosion was caused by a natural extraterrestrial phenomenon , and was not caused by man. Is this theory a fact? No. The event is a recorded fact. Is this theory, generally accepted to be true, based on evidence to-date? Yes. Can this theory be shown to be false and be discarded? Yes.
A scientific law generalizes a body of observations. At the time it's made, no exceptions have been found to a law. Scientific laws explain things but they do not describe them. One way to tell a law and a theory apart is to ask if the description gives you the means to explain "why." The word "law" is used less and less in science, as many laws are only true under limited circumstances.
Example: Consider Newton's Law of Gravity . Newton could use this law to predict the behavior of a dropped object but he couldn't explain why it happened.
As you can see, there is no "proof" or absolute "truth" in science. The closest we get are facts, which are indisputable observations. Note, however, if you define proof as arriving at a logical conclusion, based on the evidence, then there is "proof" in science. Some work under the definition that to prove something implies it can never be wrong, which is different. If you're asked to define the terms hypothesis, theory, and law, keep in mind the definitions of proof and of these words can vary slightly depending on the scientific discipline. What's important is to realize they don't all mean the same thing and cannot be used interchangeably.
- Hypothesis, Model, Theory, and Law
- What Is a Scientific or Natural Law?
- Scientific Hypothesis Examples
- What 'Fail to Reject' Means in a Hypothesis Test
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- Definition of a Hypothesis
- Processual Archaeology
- Tips on Winning the Debate on Evolution
- Geological Thinking: Method of Multiple Working Hypotheses
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
- Theory Definition in Science
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Scientific Method Flow Chart
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- What Is a Paradigm Shift?

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Scientific Method
Science is an enormously successful human enterprise. The study of scientific method is the attempt to discern the activities by which that success is achieved. Among the activities often identified as characteristic of science are systematic observation and experimentation, inductive and deductive reasoning, and the formation and testing of hypotheses and theories. How these are carried out in detail can vary greatly, but characteristics like these have been looked to as a way of demarcating scientific activity from non-science, where only enterprises which employ some canonical form of scientific method or methods should be considered science (see also the entry on science and pseudo-science ). Others have questioned whether there is anything like a fixed toolkit of methods which is common across science and only science. Some reject privileging one view of method as part of rejecting broader views about the nature of science, such as naturalism (Dupré 2004); some reject any restriction in principle (pluralism).
Scientific method should be distinguished from the aims and products of science, such as knowledge, predictions, or control. Methods are the means by which those goals are achieved. Scientific method should also be distinguished from meta-methodology, which includes the values and justifications behind a particular characterization of scientific method (i.e., a methodology) — values such as objectivity, reproducibility, simplicity, or past successes. Methodological rules are proposed to govern method and it is a meta-methodological question whether methods obeying those rules satisfy given values. Finally, method is distinct, to some degree, from the detailed and contextual practices through which methods are implemented. The latter might range over: specific laboratory techniques; mathematical formalisms or other specialized languages used in descriptions and reasoning; technological or other material means; ways of communicating and sharing results, whether with other scientists or with the public at large; or the conventions, habits, enforced customs, and institutional controls over how and what science is carried out.
While it is important to recognize these distinctions, their boundaries are fuzzy. Hence, accounts of method cannot be entirely divorced from their methodological and meta-methodological motivations or justifications, Moreover, each aspect plays a crucial role in identifying methods. Disputes about method have therefore played out at the detail, rule, and meta-rule levels. Changes in beliefs about the certainty or fallibility of scientific knowledge, for instance (which is a meta-methodological consideration of what we can hope for methods to deliver), have meant different emphases on deductive and inductive reasoning, or on the relative importance attached to reasoning over observation (i.e., differences over particular methods.) Beliefs about the role of science in society will affect the place one gives to values in scientific method.
The issue which has shaped debates over scientific method the most in the last half century is the question of how pluralist do we need to be about method? Unificationists continue to hold out for one method essential to science; nihilism is a form of radical pluralism, which considers the effectiveness of any methodological prescription to be so context sensitive as to render it not explanatory on its own. Some middle degree of pluralism regarding the methods embodied in scientific practice seems appropriate. But the details of scientific practice vary with time and place, from institution to institution, across scientists and their subjects of investigation. How significant are the variations for understanding science and its success? How much can method be abstracted from practice? This entry describes some of the attempts to characterize scientific method or methods, as well as arguments for a more context-sensitive approach to methods embedded in actual scientific practices.
1. Overview and organizing themes
2. historical review: aristotle to mill, 3.1 logical constructionism and operationalism, 3.2. h-d as a logic of confirmation, 3.3. popper and falsificationism, 3.4 meta-methodology and the end of method, 4. statistical methods for hypothesis testing, 5.1 creative and exploratory practices.
- 5.2 Computer methods and the ‘new ways’ of doing science
6.1 “The scientific method” in science education and as seen by scientists
6.2 privileged methods and ‘gold standards’, 6.3 scientific method in the court room, 6.4 deviating practices, 7. conclusion, other internet resources, related entries.
This entry could have been given the title Scientific Methods and gone on to fill volumes, or it could have been extremely short, consisting of a brief summary rejection of the idea that there is any such thing as a unique Scientific Method at all. Both unhappy prospects are due to the fact that scientific activity varies so much across disciplines, times, places, and scientists that any account which manages to unify it all will either consist of overwhelming descriptive detail, or trivial generalizations.
The choice of scope for the present entry is more optimistic, taking a cue from the recent movement in philosophy of science toward a greater attention to practice: to what scientists actually do. This “turn to practice” can be seen as the latest form of studies of methods in science, insofar as it represents an attempt at understanding scientific activity, but through accounts that are neither meant to be universal and unified, nor singular and narrowly descriptive. To some extent, different scientists at different times and places can be said to be using the same method even though, in practice, the details are different.
Whether the context in which methods are carried out is relevant, or to what extent, will depend largely on what one takes the aims of science to be and what one’s own aims are. For most of the history of scientific methodology the assumption has been that the most important output of science is knowledge and so the aim of methodology should be to discover those methods by which scientific knowledge is generated.
Science was seen to embody the most successful form of reasoning (but which form?) to the most certain knowledge claims (but how certain?) on the basis of systematically collected evidence (but what counts as evidence, and should the evidence of the senses take precedence, or rational insight?) Section 2 surveys some of the history, pointing to two major themes. One theme is seeking the right balance between observation and reasoning (and the attendant forms of reasoning which employ them); the other is how certain scientific knowledge is or can be.
Section 3 turns to 20 th century debates on scientific method. In the second half of the 20 th century the epistemic privilege of science faced several challenges and many philosophers of science abandoned the reconstruction of the logic of scientific method. Views changed significantly regarding which functions of science ought to be captured and why. For some, the success of science was better identified with social or cultural features. Historical and sociological turns in the philosophy of science were made, with a demand that greater attention be paid to the non-epistemic aspects of science, such as sociological, institutional, material, and political factors. Even outside of those movements there was an increased specialization in the philosophy of science, with more and more focus on specific fields within science. The combined upshot was very few philosophers arguing any longer for a grand unified methodology of science. Sections 3 and 4 surveys the main positions on scientific method in 20 th century philosophy of science, focusing on where they differ in their preference for confirmation or falsification or for waiving the idea of a special scientific method altogether.
In recent decades, attention has primarily been paid to scientific activities traditionally falling under the rubric of method, such as experimental design and general laboratory practice, the use of statistics, the construction and use of models and diagrams, interdisciplinary collaboration, and science communication. Sections 4–6 attempt to construct a map of the current domains of the study of methods in science.
As these sections illustrate, the question of method is still central to the discourse about science. Scientific method remains a topic for education, for science policy, and for scientists. It arises in the public domain where the demarcation or status of science is at issue. Some philosophers have recently returned, therefore, to the question of what it is that makes science a unique cultural product. This entry will close with some of these recent attempts at discerning and encapsulating the activities by which scientific knowledge is achieved.
Attempting a history of scientific method compounds the vast scope of the topic. This section briefly surveys the background to modern methodological debates. What can be called the classical view goes back to antiquity, and represents a point of departure for later divergences. [ 1 ]
We begin with a point made by Laudan (1968) in his historical survey of scientific method:
Perhaps the most serious inhibition to the emergence of the history of theories of scientific method as a respectable area of study has been the tendency to conflate it with the general history of epistemology, thereby assuming that the narrative categories and classificatory pigeon-holes applied to the latter are also basic to the former. (1968: 5)
To see knowledge about the natural world as falling under knowledge more generally is an understandable conflation. Histories of theories of method would naturally employ the same narrative categories and classificatory pigeon holes. An important theme of the history of epistemology, for example, is the unification of knowledge, a theme reflected in the question of the unification of method in science. Those who have identified differences in kinds of knowledge have often likewise identified different methods for achieving that kind of knowledge (see the entry on the unity of science ).
Different views on what is known, how it is known, and what can be known are connected. Plato distinguished the realms of things into the visible and the intelligible ( The Republic , 510a, in Cooper 1997). Only the latter, the Forms, could be objects of knowledge. The intelligible truths could be known with the certainty of geometry and deductive reasoning. What could be observed of the material world, however, was by definition imperfect and deceptive, not ideal. The Platonic way of knowledge therefore emphasized reasoning as a method, downplaying the importance of observation. Aristotle disagreed, locating the Forms in the natural world as the fundamental principles to be discovered through the inquiry into nature ( Metaphysics Z , in Barnes 1984).
Aristotle is recognized as giving the earliest systematic treatise on the nature of scientific inquiry in the western tradition, one which embraced observation and reasoning about the natural world. In the Prior and Posterior Analytics , Aristotle reflects first on the aims and then the methods of inquiry into nature. A number of features can be found which are still considered by most to be essential to science. For Aristotle, empiricism, careful observation (but passive observation, not controlled experiment), is the starting point. The aim is not merely recording of facts, though. For Aristotle, science ( epistêmê ) is a body of properly arranged knowledge or learning—the empirical facts, but also their ordering and display are of crucial importance. The aims of discovery, ordering, and display of facts partly determine the methods required of successful scientific inquiry. Also determinant is the nature of the knowledge being sought, and the explanatory causes proper to that kind of knowledge (see the discussion of the four causes in the entry on Aristotle on causality ).
In addition to careful observation, then, scientific method requires a logic as a system of reasoning for properly arranging, but also inferring beyond, what is known by observation. Methods of reasoning may include induction, prediction, or analogy, among others. Aristotle’s system (along with his catalogue of fallacious reasoning) was collected under the title the Organon . This title would be echoed in later works on scientific reasoning, such as Novum Organon by Francis Bacon, and Novum Organon Restorum by William Whewell (see below). In Aristotle’s Organon reasoning is divided primarily into two forms, a rough division which persists into modern times. The division, known most commonly today as deductive versus inductive method, appears in other eras and methodologies as analysis/synthesis, non-ampliative/ampliative, or even confirmation/verification. The basic idea is there are two “directions” to proceed in our methods of inquiry: one away from what is observed, to the more fundamental, general, and encompassing principles; the other, from the fundamental and general to instances or implications of principles.
The basic aim and method of inquiry identified here can be seen as a theme running throughout the next two millennia of reflection on the correct way to seek after knowledge: carefully observe nature and then seek rules or principles which explain or predict its operation. The Aristotelian corpus provided the framework for a commentary tradition on scientific method independent of science itself (cosmos versus physics.) During the medieval period, figures such as Albertus Magnus (1206–1280), Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274), Robert Grosseteste (1175–1253), Roger Bacon (1214/1220–1292), William of Ockham (1287–1347), Andreas Vesalius (1514–1546), Giacomo Zabarella (1533–1589) all worked to clarify the kind of knowledge obtainable by observation and induction, the source of justification of induction, and best rules for its application. [ 2 ] Many of their contributions we now think of as essential to science (see also Laudan 1968). As Aristotle and Plato had employed a framework of reasoning either “to the forms” or “away from the forms”, medieval thinkers employed directions away from the phenomena or back to the phenomena. In analysis, a phenomena was examined to discover its basic explanatory principles; in synthesis, explanations of a phenomena were constructed from first principles.
During the Scientific Revolution these various strands of argument, experiment, and reason were forged into a dominant epistemic authority. The 16 th –18 th centuries were a period of not only dramatic advance in knowledge about the operation of the natural world—advances in mechanical, medical, biological, political, economic explanations—but also of self-awareness of the revolutionary changes taking place, and intense reflection on the source and legitimation of the method by which the advances were made. The struggle to establish the new authority included methodological moves. The Book of Nature, according to the metaphor of Galileo Galilei (1564–1642) or Francis Bacon (1561–1626), was written in the language of mathematics, of geometry and number. This motivated an emphasis on mathematical description and mechanical explanation as important aspects of scientific method. Through figures such as Henry More and Ralph Cudworth, a neo-Platonic emphasis on the importance of metaphysical reflection on nature behind appearances, particularly regarding the spiritual as a complement to the purely mechanical, remained an important methodological thread of the Scientific Revolution (see the entries on Cambridge platonists ; Boyle ; Henry More ; Galileo ).
In Novum Organum (1620), Bacon was critical of the Aristotelian method for leaping from particulars to universals too quickly. The syllogistic form of reasoning readily mixed those two types of propositions. Bacon aimed at the invention of new arts, principles, and directions. His method would be grounded in methodical collection of observations, coupled with correction of our senses (and particularly, directions for the avoidance of the Idols, as he called them, kinds of systematic errors to which naïve observers are prone.) The community of scientists could then climb, by a careful, gradual and unbroken ascent, to reliable general claims.
Bacon’s method has been criticized as impractical and too inflexible for the practicing scientist. Whewell would later criticize Bacon in his System of Logic for paying too little attention to the practices of scientists. It is hard to find convincing examples of Bacon’s method being put in to practice in the history of science, but there are a few who have been held up as real examples of 16 th century scientific, inductive method, even if not in the rigid Baconian mold: figures such as Robert Boyle (1627–1691) and William Harvey (1578–1657) (see the entry on Bacon ).
It is to Isaac Newton (1642–1727), however, that historians of science and methodologists have paid greatest attention. Given the enormous success of his Principia Mathematica and Opticks , this is understandable. The study of Newton’s method has had two main thrusts: the implicit method of the experiments and reasoning presented in the Opticks, and the explicit methodological rules given as the Rules for Philosophising (the Regulae) in Book III of the Principia . [ 3 ] Newton’s law of gravitation, the linchpin of his new cosmology, broke with explanatory conventions of natural philosophy, first for apparently proposing action at a distance, but more generally for not providing “true”, physical causes. The argument for his System of the World ( Principia , Book III) was based on phenomena, not reasoned first principles. This was viewed (mainly on the continent) as insufficient for proper natural philosophy. The Regulae counter this objection, re-defining the aims of natural philosophy by re-defining the method natural philosophers should follow. (See the entry on Newton’s philosophy .)
To his list of methodological prescriptions should be added Newton’s famous phrase “ hypotheses non fingo ” (commonly translated as “I frame no hypotheses”.) The scientist was not to invent systems but infer explanations from observations, as Bacon had advocated. This would come to be known as inductivism. In the century after Newton, significant clarifications of the Newtonian method were made. Colin Maclaurin (1698–1746), for instance, reconstructed the essential structure of the method as having complementary analysis and synthesis phases, one proceeding away from the phenomena in generalization, the other from the general propositions to derive explanations of new phenomena. Denis Diderot (1713–1784) and editors of the Encyclopédie did much to consolidate and popularize Newtonianism, as did Francesco Algarotti (1721–1764). The emphasis was often the same, as much on the character of the scientist as on their process, a character which is still commonly assumed. The scientist is humble in the face of nature, not beholden to dogma, obeys only his eyes, and follows the truth wherever it leads. It was certainly Voltaire (1694–1778) and du Chatelet (1706–1749) who were most influential in propagating the latter vision of the scientist and their craft, with Newton as hero. Scientific method became a revolutionary force of the Enlightenment. (See also the entries on Newton , Leibniz , Descartes , Boyle , Hume , enlightenment , as well as Shank 2008 for a historical overview.)
Not all 18 th century reflections on scientific method were so celebratory. Famous also are George Berkeley’s (1685–1753) attack on the mathematics of the new science, as well as the over-emphasis of Newtonians on observation; and David Hume’s (1711–1776) undermining of the warrant offered for scientific claims by inductive justification (see the entries on: George Berkeley ; David Hume ; Hume’s Newtonianism and Anti-Newtonianism ). Hume’s problem of induction motivated Immanuel Kant (1724–1804) to seek new foundations for empirical method, though as an epistemic reconstruction, not as any set of practical guidelines for scientists. Both Hume and Kant influenced the methodological reflections of the next century, such as the debate between Mill and Whewell over the certainty of inductive inferences in science.
The debate between John Stuart Mill (1806–1873) and William Whewell (1794–1866) has become the canonical methodological debate of the 19 th century. Although often characterized as a debate between inductivism and hypothetico-deductivism, the role of the two methods on each side is actually more complex. On the hypothetico-deductive account, scientists work to come up with hypotheses from which true observational consequences can be deduced—hence, hypothetico-deductive. Because Whewell emphasizes both hypotheses and deduction in his account of method, he can be seen as a convenient foil to the inductivism of Mill. However, equally if not more important to Whewell’s portrayal of scientific method is what he calls the “fundamental antithesis”. Knowledge is a product of the objective (what we see in the world around us) and subjective (the contributions of our mind to how we perceive and understand what we experience, which he called the Fundamental Ideas). Both elements are essential according to Whewell, and he was therefore critical of Kant for too much focus on the subjective, and John Locke (1632–1704) and Mill for too much focus on the senses. Whewell’s fundamental ideas can be discipline relative. An idea can be fundamental even if it is necessary for knowledge only within a given scientific discipline (e.g., chemical affinity for chemistry). This distinguishes fundamental ideas from the forms and categories of intuition of Kant. (See the entry on Whewell .)
Clarifying fundamental ideas would therefore be an essential part of scientific method and scientific progress. Whewell called this process “Discoverer’s Induction”. It was induction, following Bacon or Newton, but Whewell sought to revive Bacon’s account by emphasising the role of ideas in the clear and careful formulation of inductive hypotheses. Whewell’s induction is not merely the collecting of objective facts. The subjective plays a role through what Whewell calls the Colligation of Facts, a creative act of the scientist, the invention of a theory. A theory is then confirmed by testing, where more facts are brought under the theory, called the Consilience of Inductions. Whewell felt that this was the method by which the true laws of nature could be discovered: clarification of fundamental concepts, clever invention of explanations, and careful testing. Mill, in his critique of Whewell, and others who have cast Whewell as a fore-runner of the hypothetico-deductivist view, seem to have under-estimated the importance of this discovery phase in Whewell’s understanding of method (Snyder 1997a,b, 1999). Down-playing the discovery phase would come to characterize methodology of the early 20 th century (see section 3 ).
Mill, in his System of Logic , put forward a narrower view of induction as the essence of scientific method. For Mill, induction is the search first for regularities among events. Among those regularities, some will continue to hold for further observations, eventually gaining the status of laws. One can also look for regularities among the laws discovered in a domain, i.e., for a law of laws. Which “law law” will hold is time and discipline dependent and open to revision. One example is the Law of Universal Causation, and Mill put forward specific methods for identifying causes—now commonly known as Mill’s methods. These five methods look for circumstances which are common among the phenomena of interest, those which are absent when the phenomena are, or those for which both vary together. Mill’s methods are still seen as capturing basic intuitions about experimental methods for finding the relevant explanatory factors ( System of Logic (1843), see Mill entry). The methods advocated by Whewell and Mill, in the end, look similar. Both involve inductive generalization to covering laws. They differ dramatically, however, with respect to the necessity of the knowledge arrived at; that is, at the meta-methodological level (see the entries on Whewell and Mill entries).
3. Logic of method and critical responses
The quantum and relativistic revolutions in physics in the early 20 th century had a profound effect on methodology. Conceptual foundations of both theories were taken to show the defeasibility of even the most seemingly secure intuitions about space, time and bodies. Certainty of knowledge about the natural world was therefore recognized as unattainable. Instead a renewed empiricism was sought which rendered science fallible but still rationally justifiable.
Analyses of the reasoning of scientists emerged, according to which the aspects of scientific method which were of primary importance were the means of testing and confirming of theories. A distinction in methodology was made between the contexts of discovery and justification. The distinction could be used as a wedge between the particularities of where and how theories or hypotheses are arrived at, on the one hand, and the underlying reasoning scientists use (whether or not they are aware of it) when assessing theories and judging their adequacy on the basis of the available evidence. By and large, for most of the 20 th century, philosophy of science focused on the second context, although philosophers differed on whether to focus on confirmation or refutation as well as on the many details of how confirmation or refutation could or could not be brought about. By the mid-20 th century these attempts at defining the method of justification and the context distinction itself came under pressure. During the same period, philosophy of science developed rapidly, and from section 4 this entry will therefore shift from a primarily historical treatment of the scientific method towards a primarily thematic one.
Advances in logic and probability held out promise of the possibility of elaborate reconstructions of scientific theories and empirical method, the best example being Rudolf Carnap’s The Logical Structure of the World (1928). Carnap attempted to show that a scientific theory could be reconstructed as a formal axiomatic system—that is, a logic. That system could refer to the world because some of its basic sentences could be interpreted as observations or operations which one could perform to test them. The rest of the theoretical system, including sentences using theoretical or unobservable terms (like electron or force) would then either be meaningful because they could be reduced to observations, or they had purely logical meanings (called analytic, like mathematical identities). This has been referred to as the verifiability criterion of meaning. According to the criterion, any statement not either analytic or verifiable was strictly meaningless. Although the view was endorsed by Carnap in 1928, he would later come to see it as too restrictive (Carnap 1956). Another familiar version of this idea is operationalism of Percy William Bridgman. In The Logic of Modern Physics (1927) Bridgman asserted that every physical concept could be defined in terms of the operations one would perform to verify the application of that concept. Making good on the operationalisation of a concept even as simple as length, however, can easily become enormously complex (for measuring very small lengths, for instance) or impractical (measuring large distances like light years.)
Carl Hempel’s (1950, 1951) criticisms of the verifiability criterion of meaning had enormous influence. He pointed out that universal generalizations, such as most scientific laws, were not strictly meaningful on the criterion. Verifiability and operationalism both seemed too restrictive to capture standard scientific aims and practice. The tenuous connection between these reconstructions and actual scientific practice was criticized in another way. In both approaches, scientific methods are instead recast in methodological roles. Measurements, for example, were looked to as ways of giving meanings to terms. The aim of the philosopher of science was not to understand the methods per se , but to use them to reconstruct theories, their meanings, and their relation to the world. When scientists perform these operations, however, they will not report that they are doing them to give meaning to terms in a formal axiomatic system. This disconnect between methodology and the details of actual scientific practice would seem to violate the empiricism the Logical Positivists and Bridgman were committed to. The view that methodology should correspond to practice (to some extent) has been called historicism, or intuitionism. We turn to these criticisms and responses in section 3.4 . [ 4 ]
Positivism also had to contend with the recognition that a purely inductivist approach, along the lines of Bacon-Newton-Mill, was untenable. There was no pure observation, for starters. All observation was theory laden. Theory is required to make any observation, therefore not all theory can be derived from observation alone. (See the entry on theory and observation in science .) Even granting an observational basis, Hume had already pointed out that one could not deductively justify inductive conclusions without begging the question by presuming the success of the inductive method. Likewise, positivist attempts at analyzing how a generalization can be confirmed by observations of its instances were subject to a number of criticisms. Goodman (1965) and Hempel (1965) both point to paradoxes inherent in standard accounts of confirmation. Recent attempts at explaining how observations can serve to confirm a scientific theory are discussed in section 4 below.
The standard starting point for a non-inductive analysis of the logic of confirmation is known as the Hypothetico-Deductive (H-D) method. In its simplest form, a sentence of a theory which expresses some hypothesis is confirmed by its true consequences. As noted in section 2 , this method had been advanced by Whewell in the 19 th century, as well as Nicod (1924) and others in the 20 th century. Often, Hempel’s (1966) description of the H-D method, illustrated by the case of Semmelweiss’ inferential procedures in establishing the cause of childbed fever, has been presented as a key account of H-D as well as a foil for criticism of the H-D account of confirmation (see, for example, Lipton’s (2004) discussion of inference to the best explanation; also the entry on confirmation ). Hempel described Semmelsweiss’ procedure as examining various hypotheses explaining the cause of childbed fever. Some hypotheses conflicted with observable facts and could be rejected as false immediately. Others needed to be tested experimentally by deducing which observable events should follow if the hypothesis were true (what Hempel called the test implications of the hypothesis), then conducting an experiment and observing whether or not the test implications occurred. If the experiment showed the test implication to be false, the hypothesis could be rejected. If the experiment showed the test implications to be true, however, this did not prove the hypothesis true. The confirmation of a test implication does not verify a hypothesis, though Hempel did allow that “it provides at least some support, some corroboration or confirmation for it” (Hempel 1966: 8). The degree of this support then depends on the quantity, variety and precision of the supporting evidence.
Another approach that took off from the difficulties with inductive inference was Karl Popper’s critical rationalism or falsificationism (Popper 1959, 1963). Falsification is deductive and similar to H-D in that it involves scientists deducing observational consequences from the hypothesis under test. For Popper, however, the important point was not the degree of confirmation that successful prediction offered to a hypothesis. The crucial thing was the logical asymmetry between confirmation, based on inductive inference, and falsification, which can be based on a deductive inference. (This simple opposition was later questioned, by Lakatos, among others. See the entry on historicist theories of scientific rationality. )
Popper stressed that, regardless of the amount of confirming evidence, we can never be certain that a hypothesis is true without committing the fallacy of affirming the consequent. Instead, Popper introduced the notion of corroboration as a measure for how well a theory or hypothesis has survived previous testing—but without implying that this is also a measure for the probability that it is true.
Popper was also motivated by his doubts about the scientific status of theories like the Marxist theory of history or psycho-analysis, and so wanted to demarcate between science and pseudo-science. Popper saw this as an importantly different distinction than demarcating science from metaphysics. The latter demarcation was the primary concern of many logical empiricists. Popper used the idea of falsification to draw a line instead between pseudo and proper science. Science was science because its method involved subjecting theories to rigorous tests which offered a high probability of failing and thus refuting the theory.
A commitment to the risk of failure was important. Avoiding falsification could be done all too easily. If a consequence of a theory is inconsistent with observations, an exception can be added by introducing auxiliary hypotheses designed explicitly to save the theory, so-called ad hoc modifications. This Popper saw done in pseudo-science where ad hoc theories appeared capable of explaining anything in their field of application. In contrast, science is risky. If observations showed the predictions from a theory to be wrong, the theory would be refuted. Hence, scientific hypotheses must be falsifiable. Not only must there exist some possible observation statement which could falsify the hypothesis or theory, were it observed, (Popper called these the hypothesis’ potential falsifiers) it is crucial to the Popperian scientific method that such falsifications be sincerely attempted on a regular basis.
The more potential falsifiers of a hypothesis, the more falsifiable it would be, and the more the hypothesis claimed. Conversely, hypotheses without falsifiers claimed very little or nothing at all. Originally, Popper thought that this meant the introduction of ad hoc hypotheses only to save a theory should not be countenanced as good scientific method. These would undermine the falsifiabililty of a theory. However, Popper later came to recognize that the introduction of modifications (immunizations, he called them) was often an important part of scientific development. Responding to surprising or apparently falsifying observations often generated important new scientific insights. Popper’s own example was the observed motion of Uranus which originally did not agree with Newtonian predictions. The ad hoc hypothesis of an outer planet explained the disagreement and led to further falsifiable predictions. Popper sought to reconcile the view by blurring the distinction between falsifiable and not falsifiable, and speaking instead of degrees of testability (Popper 1985: 41f.).
From the 1960s on, sustained meta-methodological criticism emerged that drove philosophical focus away from scientific method. A brief look at those criticisms follows, with recommendations for further reading at the end of the entry.
Thomas Kuhn’s The Structure of Scientific Revolutions (1962) begins with a well-known shot across the bow for philosophers of science:
History, if viewed as a repository for more than anecdote or chronology, could produce a decisive transformation in the image of science by which we are now possessed. (1962: 1)
The image Kuhn thought needed transforming was the a-historical, rational reconstruction sought by many of the Logical Positivists, though Carnap and other positivists were actually quite sympathetic to Kuhn’s views. (See the entry on the Vienna Circle .) Kuhn shares with other of his contemporaries, such as Feyerabend and Lakatos, a commitment to a more empirical approach to philosophy of science. Namely, the history of science provides important data, and necessary checks, for philosophy of science, including any theory of scientific method.
The history of science reveals, according to Kuhn, that scientific development occurs in alternating phases. During normal science, the members of the scientific community adhere to the paradigm in place. Their commitment to the paradigm means a commitment to the puzzles to be solved and the acceptable ways of solving them. Confidence in the paradigm remains so long as steady progress is made in solving the shared puzzles. Method in this normal phase operates within a disciplinary matrix (Kuhn’s later concept of a paradigm) which includes standards for problem solving, and defines the range of problems to which the method should be applied. An important part of a disciplinary matrix is the set of values which provide the norms and aims for scientific method. The main values that Kuhn identifies are prediction, problem solving, simplicity, consistency, and plausibility.
An important by-product of normal science is the accumulation of puzzles which cannot be solved with resources of the current paradigm. Once accumulation of these anomalies has reached some critical mass, it can trigger a communal shift to a new paradigm and a new phase of normal science. Importantly, the values that provide the norms and aims for scientific method may have transformed in the meantime. Method may therefore be relative to discipline, time or place
Feyerabend also identified the aims of science as progress, but argued that any methodological prescription would only stifle that progress (Feyerabend 1988). His arguments are grounded in re-examining accepted “myths” about the history of science. Heroes of science, like Galileo, are shown to be just as reliant on rhetoric and persuasion as they are on reason and demonstration. Others, like Aristotle, are shown to be far more reasonable and far-reaching in their outlooks then they are given credit for. As a consequence, the only rule that could provide what he took to be sufficient freedom was the vacuous “anything goes”. More generally, even the methodological restriction that science is the best way to pursue knowledge, and to increase knowledge, is too restrictive. Feyerabend suggested instead that science might, in fact, be a threat to a free society, because it and its myth had become so dominant (Feyerabend 1978).
An even more fundamental kind of criticism was offered by several sociologists of science from the 1970s onwards who rejected the methodology of providing philosophical accounts for the rational development of science and sociological accounts of the irrational mistakes. Instead, they adhered to a symmetry thesis on which any causal explanation of how scientific knowledge is established needs to be symmetrical in explaining truth and falsity, rationality and irrationality, success and mistakes, by the same causal factors (see, e.g., Barnes and Bloor 1982, Bloor 1991). Movements in the Sociology of Science, like the Strong Programme, or in the social dimensions and causes of knowledge more generally led to extended and close examination of detailed case studies in contemporary science and its history. (See the entries on the social dimensions of scientific knowledge and social epistemology .) Well-known examinations by Latour and Woolgar (1979/1986), Knorr-Cetina (1981), Pickering (1984), Shapin and Schaffer (1985) seem to bear out that it was social ideologies (on a macro-scale) or individual interactions and circumstances (on a micro-scale) which were the primary causal factors in determining which beliefs gained the status of scientific knowledge. As they saw it therefore, explanatory appeals to scientific method were not empirically grounded.
A late, and largely unexpected, criticism of scientific method came from within science itself. Beginning in the early 2000s, a number of scientists attempting to replicate the results of published experiments could not do so. There may be close conceptual connection between reproducibility and method. For example, if reproducibility means that the same scientific methods ought to produce the same result, and all scientific results ought to be reproducible, then whatever it takes to reproduce a scientific result ought to be called scientific method. Space limits us to the observation that, insofar as reproducibility is a desired outcome of proper scientific method, it is not strictly a part of scientific method. (See the entry on reproducibility of scientific results .)
By the close of the 20 th century the search for the scientific method was flagging. Nola and Sankey (2000b) could introduce their volume on method by remarking that “For some, the whole idea of a theory of scientific method is yester-year’s debate …”.
Despite the many difficulties that philosophers encountered in trying to providing a clear methodology of conformation (or refutation), still important progress has been made on understanding how observation can provide evidence for a given theory. Work in statistics has been crucial for understanding how theories can be tested empirically, and in recent decades a huge literature has developed that attempts to recast confirmation in Bayesian terms. Here these developments can be covered only briefly, and we refer to the entry on confirmation for further details and references.
Statistics has come to play an increasingly important role in the methodology of the experimental sciences from the 19 th century onwards. At that time, statistics and probability theory took on a methodological role as an analysis of inductive inference, and attempts to ground the rationality of induction in the axioms of probability theory have continued throughout the 20 th century and in to the present. Developments in the theory of statistics itself, meanwhile, have had a direct and immense influence on the experimental method, including methods for measuring the uncertainty of observations such as the Method of Least Squares developed by Legendre and Gauss in the early 19 th century, criteria for the rejection of outliers proposed by Peirce by the mid-19 th century, and the significance tests developed by Gosset (a.k.a. “Student”), Fisher, Neyman & Pearson and others in the 1920s and 1930s (see, e.g., Swijtink 1987 for a brief historical overview; and also the entry on C.S. Peirce ).
These developments within statistics then in turn led to a reflective discussion among both statisticians and philosophers of science on how to perceive the process of hypothesis testing: whether it was a rigorous statistical inference that could provide a numerical expression of the degree of confidence in the tested hypothesis, or if it should be seen as a decision between different courses of actions that also involved a value component. This led to a major controversy among Fisher on the one side and Neyman and Pearson on the other (see especially Fisher 1955, Neyman 1956 and Pearson 1955, and for analyses of the controversy, e.g., Howie 2002, Marks 2000, Lenhard 2006). On Fisher’s view, hypothesis testing was a methodology for when to accept or reject a statistical hypothesis, namely that a hypothesis should be rejected by evidence if this evidence would be unlikely relative to other possible outcomes, given the hypothesis were true. In contrast, on Neyman and Pearson’s view, the consequence of error also had to play a role when deciding between hypotheses. Introducing the distinction between the error of rejecting a true hypothesis (type I error) and accepting a false hypothesis (type II error), they argued that it depends on the consequences of the error to decide whether it is more important to avoid rejecting a true hypothesis or accepting a false one. Hence, Fisher aimed for a theory of inductive inference that enabled a numerical expression of confidence in a hypothesis. To him, the important point was the search for truth, not utility. In contrast, the Neyman-Pearson approach provided a strategy of inductive behaviour for deciding between different courses of action. Here, the important point was not whether a hypothesis was true, but whether one should act as if it was.
Similar discussions are found in the philosophical literature. On the one side, Churchman (1948) and Rudner (1953) argued that because scientific hypotheses can never be completely verified, a complete analysis of the methods of scientific inference includes ethical judgments in which the scientists must decide whether the evidence is sufficiently strong or that the probability is sufficiently high to warrant the acceptance of the hypothesis, which again will depend on the importance of making a mistake in accepting or rejecting the hypothesis. Others, such as Jeffrey (1956) and Levi (1960) disagreed and instead defended a value-neutral view of science on which scientists should bracket their attitudes, preferences, temperament, and values when assessing the correctness of their inferences. For more details on this value-free ideal in the philosophy of science and its historical development, see Douglas (2009) and Howard (2003). For a broad set of case studies examining the role of values in science, see e.g. Elliott & Richards 2017.
In recent decades, philosophical discussions of the evaluation of probabilistic hypotheses by statistical inference have largely focused on Bayesianism that understands probability as a measure of a person’s degree of belief in an event, given the available information, and frequentism that instead understands probability as a long-run frequency of a repeatable event. Hence, for Bayesians probabilities refer to a state of knowledge, whereas for frequentists probabilities refer to frequencies of events (see, e.g., Sober 2008, chapter 1 for a detailed introduction to Bayesianism and frequentism as well as to likelihoodism). Bayesianism aims at providing a quantifiable, algorithmic representation of belief revision, where belief revision is a function of prior beliefs (i.e., background knowledge) and incoming evidence. Bayesianism employs a rule based on Bayes’ theorem, a theorem of the probability calculus which relates conditional probabilities. The probability that a particular hypothesis is true is interpreted as a degree of belief, or credence, of the scientist. There will also be a probability and a degree of belief that a hypothesis will be true conditional on a piece of evidence (an observation, say) being true. Bayesianism proscribes that it is rational for the scientist to update their belief in the hypothesis to that conditional probability should it turn out that the evidence is, in fact, observed (see, e.g., Sprenger & Hartmann 2019 for a comprehensive treatment of Bayesian philosophy of science). Originating in the work of Neyman and Person, frequentism aims at providing the tools for reducing long-run error rates, such as the error-statistical approach developed by Mayo (1996) that focuses on how experimenters can avoid both type I and type II errors by building up a repertoire of procedures that detect errors if and only if they are present. Both Bayesianism and frequentism have developed over time, they are interpreted in different ways by its various proponents, and their relations to previous criticism to attempts at defining scientific method are seen differently by proponents and critics. The literature, surveys, reviews and criticism in this area are vast and the reader is referred to the entries on Bayesian epistemology and confirmation .
5. Method in Practice
Attention to scientific practice, as we have seen, is not itself new. However, the turn to practice in the philosophy of science of late can be seen as a correction to the pessimism with respect to method in philosophy of science in later parts of the 20 th century, and as an attempted reconciliation between sociological and rationalist explanations of scientific knowledge. Much of this work sees method as detailed and context specific problem-solving procedures, and methodological analyses to be at the same time descriptive, critical and advisory (see Nickles 1987 for an exposition of this view). The following section contains a survey of some of the practice focuses. In this section we turn fully to topics rather than chronology.
A problem with the distinction between the contexts of discovery and justification that figured so prominently in philosophy of science in the first half of the 20 th century (see section 2 ) is that no such distinction can be clearly seen in scientific activity (see Arabatzis 2006). Thus, in recent decades, it has been recognized that study of conceptual innovation and change should not be confined to psychology and sociology of science, but are also important aspects of scientific practice which philosophy of science should address (see also the entry on scientific discovery ). Looking for the practices that drive conceptual innovation has led philosophers to examine both the reasoning practices of scientists and the wide realm of experimental practices that are not directed narrowly at testing hypotheses, that is, exploratory experimentation.
Examining the reasoning practices of historical and contemporary scientists, Nersessian (2008) has argued that new scientific concepts are constructed as solutions to specific problems by systematic reasoning, and that of analogy, visual representation and thought-experimentation are among the important reasoning practices employed. These ubiquitous forms of reasoning are reliable—but also fallible—methods of conceptual development and change. On her account, model-based reasoning consists of cycles of construction, simulation, evaluation and adaption of models that serve as interim interpretations of the target problem to be solved. Often, this process will lead to modifications or extensions, and a new cycle of simulation and evaluation. However, Nersessian also emphasizes that
creative model-based reasoning cannot be applied as a simple recipe, is not always productive of solutions, and even its most exemplary usages can lead to incorrect solutions. (Nersessian 2008: 11)
Thus, while on the one hand she agrees with many previous philosophers that there is no logic of discovery, discoveries can derive from reasoned processes, such that a large and integral part of scientific practice is
the creation of concepts through which to comprehend, structure, and communicate about physical phenomena …. (Nersessian 1987: 11)
Similarly, work on heuristics for discovery and theory construction by scholars such as Darden (1991) and Bechtel & Richardson (1993) present science as problem solving and investigate scientific problem solving as a special case of problem-solving in general. Drawing largely on cases from the biological sciences, much of their focus has been on reasoning strategies for the generation, evaluation, and revision of mechanistic explanations of complex systems.
Addressing another aspect of the context distinction, namely the traditional view that the primary role of experiments is to test theoretical hypotheses according to the H-D model, other philosophers of science have argued for additional roles that experiments can play. The notion of exploratory experimentation was introduced to describe experiments driven by the desire to obtain empirical regularities and to develop concepts and classifications in which these regularities can be described (Steinle 1997, 2002; Burian 1997; Waters 2007)). However the difference between theory driven experimentation and exploratory experimentation should not be seen as a sharp distinction. Theory driven experiments are not always directed at testing hypothesis, but may also be directed at various kinds of fact-gathering, such as determining numerical parameters. Vice versa , exploratory experiments are usually informed by theory in various ways and are therefore not theory-free. Instead, in exploratory experiments phenomena are investigated without first limiting the possible outcomes of the experiment on the basis of extant theory about the phenomena.
The development of high throughput instrumentation in molecular biology and neighbouring fields has given rise to a special type of exploratory experimentation that collects and analyses very large amounts of data, and these new ‘omics’ disciplines are often said to represent a break with the ideal of hypothesis-driven science (Burian 2007; Elliott 2007; Waters 2007; O’Malley 2007) and instead described as data-driven research (Leonelli 2012; Strasser 2012) or as a special kind of “convenience experimentation” in which many experiments are done simply because they are extraordinarily convenient to perform (Krohs 2012).
5.2 Computer methods and ‘new ways’ of doing science
The field of omics just described is possible because of the ability of computers to process, in a reasonable amount of time, the huge quantities of data required. Computers allow for more elaborate experimentation (higher speed, better filtering, more variables, sophisticated coordination and control), but also, through modelling and simulations, might constitute a form of experimentation themselves. Here, too, we can pose a version of the general question of method versus practice: does the practice of using computers fundamentally change scientific method, or merely provide a more efficient means of implementing standard methods?
Because computers can be used to automate measurements, quantifications, calculations, and statistical analyses where, for practical reasons, these operations cannot be otherwise carried out, many of the steps involved in reaching a conclusion on the basis of an experiment are now made inside a “black box”, without the direct involvement or awareness of a human. This has epistemological implications, regarding what we can know, and how we can know it. To have confidence in the results, computer methods are therefore subjected to tests of verification and validation.
The distinction between verification and validation is easiest to characterize in the case of computer simulations. In a typical computer simulation scenario computers are used to numerically integrate differential equations for which no analytic solution is available. The equations are part of the model the scientist uses to represent a phenomenon or system under investigation. Verifying a computer simulation means checking that the equations of the model are being correctly approximated. Validating a simulation means checking that the equations of the model are adequate for the inferences one wants to make on the basis of that model.
A number of issues related to computer simulations have been raised. The identification of validity and verification as the testing methods has been criticized. Oreskes et al. (1994) raise concerns that “validiation”, because it suggests deductive inference, might lead to over-confidence in the results of simulations. The distinction itself is probably too clean, since actual practice in the testing of simulations mixes and moves back and forth between the two (Weissart 1997; Parker 2008a; Winsberg 2010). Computer simulations do seem to have a non-inductive character, given that the principles by which they operate are built in by the programmers, and any results of the simulation follow from those in-built principles in such a way that those results could, in principle, be deduced from the program code and its inputs. The status of simulations as experiments has therefore been examined (Kaufmann and Smarr 1993; Humphreys 1995; Hughes 1999; Norton and Suppe 2001). This literature considers the epistemology of these experiments: what we can learn by simulation, and also the kinds of justifications which can be given in applying that knowledge to the “real” world. (Mayo 1996; Parker 2008b). As pointed out, part of the advantage of computer simulation derives from the fact that huge numbers of calculations can be carried out without requiring direct observation by the experimenter/simulator. At the same time, many of these calculations are approximations to the calculations which would be performed first-hand in an ideal situation. Both factors introduce uncertainties into the inferences drawn from what is observed in the simulation.
For many of the reasons described above, computer simulations do not seem to belong clearly to either the experimental or theoretical domain. Rather, they seem to crucially involve aspects of both. This has led some authors, such as Fox Keller (2003: 200) to argue that we ought to consider computer simulation a “qualitatively different way of doing science”. The literature in general tends to follow Kaufmann and Smarr (1993) in referring to computer simulation as a “third way” for scientific methodology (theoretical reasoning and experimental practice are the first two ways.). It should also be noted that the debates around these issues have tended to focus on the form of computer simulation typical in the physical sciences, where models are based on dynamical equations. Other forms of simulation might not have the same problems, or have problems of their own (see the entry on computer simulations in science ).
In recent years, the rapid development of machine learning techniques has prompted some scholars to suggest that the scientific method has become “obsolete” (Anderson 2008, Carrol and Goodstein 2009). This has resulted in an intense debate on the relative merit of data-driven and hypothesis-driven research (for samples, see e.g. Mazzocchi 2015 or Succi and Coveney 2018). For a detailed treatment of this topic, we refer to the entry scientific research and big data .
6. Discourse on scientific method
Despite philosophical disagreements, the idea of the scientific method still figures prominently in contemporary discourse on many different topics, both within science and in society at large. Often, reference to scientific method is used in ways that convey either the legend of a single, universal method characteristic of all science, or grants to a particular method or set of methods privilege as a special ‘gold standard’, often with reference to particular philosophers to vindicate the claims. Discourse on scientific method also typically arises when there is a need to distinguish between science and other activities, or for justifying the special status conveyed to science. In these areas, the philosophical attempts at identifying a set of methods characteristic for scientific endeavors are closely related to the philosophy of science’s classical problem of demarcation (see the entry on science and pseudo-science ) and to the philosophical analysis of the social dimension of scientific knowledge and the role of science in democratic society.
One of the settings in which the legend of a single, universal scientific method has been particularly strong is science education (see, e.g., Bauer 1992; McComas 1996; Wivagg & Allchin 2002). [ 5 ] Often, ‘the scientific method’ is presented in textbooks and educational web pages as a fixed four or five step procedure starting from observations and description of a phenomenon and progressing over formulation of a hypothesis which explains the phenomenon, designing and conducting experiments to test the hypothesis, analyzing the results, and ending with drawing a conclusion. Such references to a universal scientific method can be found in educational material at all levels of science education (Blachowicz 2009), and numerous studies have shown that the idea of a general and universal scientific method often form part of both students’ and teachers’ conception of science (see, e.g., Aikenhead 1987; Osborne et al. 2003). In response, it has been argued that science education need to focus more on teaching about the nature of science, although views have differed on whether this is best done through student-led investigations, contemporary cases, or historical cases (Allchin, Andersen & Nielsen 2014)
Although occasionally phrased with reference to the H-D method, important historical roots of the legend in science education of a single, universal scientific method are the American philosopher and psychologist Dewey’s account of inquiry in How We Think (1910) and the British mathematician Karl Pearson’s account of science in Grammar of Science (1892). On Dewey’s account, inquiry is divided into the five steps of
(i) a felt difficulty, (ii) its location and definition, (iii) suggestion of a possible solution, (iv) development by reasoning of the bearing of the suggestions, (v) further observation and experiment leading to its acceptance or rejection. (Dewey 1910: 72)
Similarly, on Pearson’s account, scientific investigations start with measurement of data and observation of their correction and sequence from which scientific laws can be discovered with the aid of creative imagination. These laws have to be subject to criticism, and their final acceptance will have equal validity for “all normally constituted minds”. Both Dewey’s and Pearson’s accounts should be seen as generalized abstractions of inquiry and not restricted to the realm of science—although both Dewey and Pearson referred to their respective accounts as ‘the scientific method’.
Occasionally, scientists make sweeping statements about a simple and distinct scientific method, as exemplified by Feynman’s simplified version of a conjectures and refutations method presented, for example, in the last of his 1964 Cornell Messenger lectures. [ 6 ] However, just as often scientists have come to the same conclusion as recent philosophy of science that there is not any unique, easily described scientific method. For example, the physicist and Nobel Laureate Weinberg described in the paper “The Methods of Science … And Those By Which We Live” (1995) how
The fact that the standards of scientific success shift with time does not only make the philosophy of science difficult; it also raises problems for the public understanding of science. We do not have a fixed scientific method to rally around and defend. (1995: 8)
Interview studies with scientists on their conception of method shows that scientists often find it hard to figure out whether available evidence confirms their hypothesis, and that there are no direct translations between general ideas about method and specific strategies to guide how research is conducted (Schickore & Hangel 2019, Hangel & Schickore 2017)
Reference to the scientific method has also often been used to argue for the scientific nature or special status of a particular activity. Philosophical positions that argue for a simple and unique scientific method as a criterion of demarcation, such as Popperian falsification, have often attracted practitioners who felt that they had a need to defend their domain of practice. For example, references to conjectures and refutation as the scientific method are abundant in much of the literature on complementary and alternative medicine (CAM)—alongside the competing position that CAM, as an alternative to conventional biomedicine, needs to develop its own methodology different from that of science.
Also within mainstream science, reference to the scientific method is used in arguments regarding the internal hierarchy of disciplines and domains. A frequently seen argument is that research based on the H-D method is superior to research based on induction from observations because in deductive inferences the conclusion follows necessarily from the premises. (See, e.g., Parascandola 1998 for an analysis of how this argument has been made to downgrade epidemiology compared to the laboratory sciences.) Similarly, based on an examination of the practices of major funding institutions such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Biomedical Sciences Research Practices (BBSRC) in the UK, O’Malley et al. (2009) have argued that funding agencies seem to have a tendency to adhere to the view that the primary activity of science is to test hypotheses, while descriptive and exploratory research is seen as merely preparatory activities that are valuable only insofar as they fuel hypothesis-driven research.
In some areas of science, scholarly publications are structured in a way that may convey the impression of a neat and linear process of inquiry from stating a question, devising the methods by which to answer it, collecting the data, to drawing a conclusion from the analysis of data. For example, the codified format of publications in most biomedical journals known as the IMRAD format (Introduction, Method, Results, Analysis, Discussion) is explicitly described by the journal editors as “not an arbitrary publication format but rather a direct reflection of the process of scientific discovery” (see the so-called “Vancouver Recommendations”, ICMJE 2013: 11). However, scientific publications do not in general reflect the process by which the reported scientific results were produced. For example, under the provocative title “Is the scientific paper a fraud?”, Medawar argued that scientific papers generally misrepresent how the results have been produced (Medawar 1963/1996). Similar views have been advanced by philosophers, historians and sociologists of science (Gilbert 1976; Holmes 1987; Knorr-Cetina 1981; Schickore 2008; Suppe 1998) who have argued that scientists’ experimental practices are messy and often do not follow any recognizable pattern. Publications of research results, they argue, are retrospective reconstructions of these activities that often do not preserve the temporal order or the logic of these activities, but are instead often constructed in order to screen off potential criticism (see Schickore 2008 for a review of this work).
Philosophical positions on the scientific method have also made it into the court room, especially in the US where judges have drawn on philosophy of science in deciding when to confer special status to scientific expert testimony. A key case is Daubert vs Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals (92–102, 509 U.S. 579, 1993). In this case, the Supreme Court argued in its 1993 ruling that trial judges must ensure that expert testimony is reliable, and that in doing this the court must look at the expert’s methodology to determine whether the proffered evidence is actually scientific knowledge. Further, referring to works of Popper and Hempel the court stated that
ordinarily, a key question to be answered in determining whether a theory or technique is scientific knowledge … is whether it can be (and has been) tested. (Justice Blackmun, Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals; see Other Internet Resources for a link to the opinion)
But as argued by Haack (2005a,b, 2010) and by Foster & Hubner (1999), by equating the question of whether a piece of testimony is reliable with the question whether it is scientific as indicated by a special methodology, the court was producing an inconsistent mixture of Popper’s and Hempel’s philosophies, and this has later led to considerable confusion in subsequent case rulings that drew on the Daubert case (see Haack 2010 for a detailed exposition).
The difficulties around identifying the methods of science are also reflected in the difficulties of identifying scientific misconduct in the form of improper application of the method or methods of science. One of the first and most influential attempts at defining misconduct in science was the US definition from 1989 that defined misconduct as
fabrication, falsification, plagiarism, or other practices that seriously deviate from those that are commonly accepted within the scientific community . (Code of Federal Regulations, part 50, subpart A., August 8, 1989, italics added)
However, the “other practices that seriously deviate” clause was heavily criticized because it could be used to suppress creative or novel science. For example, the National Academy of Science stated in their report Responsible Science (1992) that it
wishes to discourage the possibility that a misconduct complaint could be lodged against scientists based solely on their use of novel or unorthodox research methods. (NAS: 27)
This clause was therefore later removed from the definition. For an entry into the key philosophical literature on conduct in science, see Shamoo & Resnick (2009).
The question of the source of the success of science has been at the core of philosophy since the beginning of modern science. If viewed as a matter of epistemology more generally, scientific method is a part of the entire history of philosophy. Over that time, science and whatever methods its practitioners may employ have changed dramatically. Today, many philosophers have taken up the banners of pluralism or of practice to focus on what are, in effect, fine-grained and contextually limited examinations of scientific method. Others hope to shift perspectives in order to provide a renewed general account of what characterizes the activity we call science.
One such perspective has been offered recently by Hoyningen-Huene (2008, 2013), who argues from the history of philosophy of science that after three lengthy phases of characterizing science by its method, we are now in a phase where the belief in the existence of a positive scientific method has eroded and what has been left to characterize science is only its fallibility. First was a phase from Plato and Aristotle up until the 17 th century where the specificity of scientific knowledge was seen in its absolute certainty established by proof from evident axioms; next was a phase up to the mid-19 th century in which the means to establish the certainty of scientific knowledge had been generalized to include inductive procedures as well. In the third phase, which lasted until the last decades of the 20 th century, it was recognized that empirical knowledge was fallible, but it was still granted a special status due to its distinctive mode of production. But now in the fourth phase, according to Hoyningen-Huene, historical and philosophical studies have shown how “scientific methods with the characteristics as posited in the second and third phase do not exist” (2008: 168) and there is no longer any consensus among philosophers and historians of science about the nature of science. For Hoyningen-Huene, this is too negative a stance, and he therefore urges the question about the nature of science anew. His own answer to this question is that “scientific knowledge differs from other kinds of knowledge, especially everyday knowledge, primarily by being more systematic” (Hoyningen-Huene 2013: 14). Systematicity can have several different dimensions: among them are more systematic descriptions, explanations, predictions, defense of knowledge claims, epistemic connectedness, ideal of completeness, knowledge generation, representation of knowledge and critical discourse. Hence, what characterizes science is the greater care in excluding possible alternative explanations, the more detailed elaboration with respect to data on which predictions are based, the greater care in detecting and eliminating sources of error, the more articulate connections to other pieces of knowledge, etc. On this position, what characterizes science is not that the methods employed are unique to science, but that the methods are more carefully employed.
Another, similar approach has been offered by Haack (2003). She sets off, similar to Hoyningen-Huene, from a dissatisfaction with the recent clash between what she calls Old Deferentialism and New Cynicism. The Old Deferentialist position is that science progressed inductively by accumulating true theories confirmed by empirical evidence or deductively by testing conjectures against basic statements; while the New Cynics position is that science has no epistemic authority and no uniquely rational method and is merely just politics. Haack insists that contrary to the views of the New Cynics, there are objective epistemic standards, and there is something epistemologically special about science, even though the Old Deferentialists pictured this in a wrong way. Instead, she offers a new Critical Commonsensist account on which standards of good, strong, supportive evidence and well-conducted, honest, thorough and imaginative inquiry are not exclusive to the sciences, but the standards by which we judge all inquirers. In this sense, science does not differ in kind from other kinds of inquiry, but it may differ in the degree to which it requires broad and detailed background knowledge and a familiarity with a technical vocabulary that only specialists may possess.
- Aikenhead, G.S., 1987, “High-school graduates’ beliefs about science-technology-society. III. Characteristics and limitations of scientific knowledge”, Science Education , 71(4): 459–487.
- Allchin, D., H.M. Andersen and K. Nielsen, 2014, “Complementary Approaches to Teaching Nature of Science: Integrating Student Inquiry, Historical Cases, and Contemporary Cases in Classroom Practice”, Science Education , 98: 461–486.
- Anderson, C., 2008, “The end of theory: The data deluge makes the scientific method obsolete”, Wired magazine , 16(7): 16–07
- Arabatzis, T., 2006, “On the inextricability of the context of discovery and the context of justification”, in Revisiting Discovery and Justification , J. Schickore and F. Steinle (eds.), Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 215–230.
- Barnes, J. (ed.), 1984, The Complete Works of Aristotle, Vols I and II , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Barnes, B. and D. Bloor, 1982, “Relativism, Rationalism, and the Sociology of Knowledge”, in Rationality and Relativism , M. Hollis and S. Lukes (eds.), Cambridge: MIT Press, pp. 1–20.
- Bauer, H.H., 1992, Scientific Literacy and the Myth of the Scientific Method , Urbana: University of Illinois Press.
- Bechtel, W. and R.C. Richardson, 1993, Discovering complexity , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Berkeley, G., 1734, The Analyst in De Motu and The Analyst: A Modern Edition with Introductions and Commentary , D. Jesseph (trans. and ed.), Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1992.
- Blachowicz, J., 2009, “How science textbooks treat scientific method: A philosopher’s perspective”, The British Journal for the Philosophy of Science , 60(2): 303–344.
- Bloor, D., 1991, Knowledge and Social Imagery , Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2 nd edition.
- Boyle, R., 1682, New experiments physico-mechanical, touching the air , Printed by Miles Flesher for Richard Davis, bookseller in Oxford.
- Bridgman, P.W., 1927, The Logic of Modern Physics , New York: Macmillan.
- –––, 1956, “The Methodological Character of Theoretical Concepts”, in The Foundations of Science and the Concepts of Science and Psychology , Herbert Feigl and Michael Scriven (eds.), Minnesota: University of Minneapolis Press, pp. 38–76.
- Burian, R., 1997, “Exploratory Experimentation and the Role of Histochemical Techniques in the Work of Jean Brachet, 1938–1952”, History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences , 19(1): 27–45.
- –––, 2007, “On microRNA and the need for exploratory experimentation in post-genomic molecular biology”, History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences , 29(3): 285–311.
- Carnap, R., 1928, Der logische Aufbau der Welt , Berlin: Bernary, transl. by R.A. George, The Logical Structure of the World , Berkeley: University of California Press, 1967.
- –––, 1956, “The methodological character of theoretical concepts”, Minnesota studies in the philosophy of science , 1: 38–76.
- Carrol, S., and D. Goodstein, 2009, “Defining the scientific method”, Nature Methods , 6: 237.
- Churchman, C.W., 1948, “Science, Pragmatics, Induction”, Philosophy of Science , 15(3): 249–268.
- Cooper, J. (ed.), 1997, Plato: Complete Works , Indianapolis: Hackett.
- Darden, L., 1991, Theory Change in Science: Strategies from Mendelian Genetics , Oxford: Oxford University Press
- Dewey, J., 1910, How we think , New York: Dover Publications (reprinted 1997).
- Douglas, H., 2009, Science, Policy, and the Value-Free Ideal , Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh Press.
- Dupré, J., 2004, “Miracle of Monism ”, in Naturalism in Question , Mario De Caro and David Macarthur (eds.), Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, pp. 36–58.
- Elliott, K.C., 2007, “Varieties of exploratory experimentation in nanotoxicology”, History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences , 29(3): 311–334.
- Elliott, K. C., and T. Richards (eds.), 2017, Exploring inductive risk: Case studies of values in science , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Falcon, Andrea, 2005, Aristotle and the science of nature: Unity without uniformity , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Feyerabend, P., 1978, Science in a Free Society , London: New Left Books
- –––, 1988, Against Method , London: Verso, 2 nd edition.
- Fisher, R.A., 1955, “Statistical Methods and Scientific Induction”, Journal of The Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological) , 17(1): 69–78.
- Foster, K. and P.W. Huber, 1999, Judging Science. Scientific Knowledge and the Federal Courts , Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Fox Keller, E., 2003, “Models, Simulation, and ‘computer experiments’”, in The Philosophy of Scientific Experimentation , H. Radder (ed.), Pittsburgh: Pittsburgh University Press, 198–215.
- Gilbert, G., 1976, “The transformation of research findings into scientific knowledge”, Social Studies of Science , 6: 281–306.
- Gimbel, S., 2011, Exploring the Scientific Method , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Goodman, N., 1965, Fact , Fiction, and Forecast , Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill.
- Haack, S., 1995, “Science is neither sacred nor a confidence trick”, Foundations of Science , 1(3): 323–335.
- –––, 2003, Defending science—within reason , Amherst: Prometheus.
- –––, 2005a, “Disentangling Daubert: an epistemological study in theory and practice”, Journal of Philosophy, Science and Law , 5, Haack 2005a available online . doi:10.5840/jpsl2005513
- –––, 2005b, “Trial and error: The Supreme Court’s philosophy of science”, American Journal of Public Health , 95: S66-S73.
- –––, 2010, “Federal Philosophy of Science: A Deconstruction-and a Reconstruction”, NYUJL & Liberty , 5: 394.
- Hangel, N. and J. Schickore, 2017, “Scientists’ conceptions of good research practice”, Perspectives on Science , 25(6): 766–791
- Harper, W.L., 2011, Isaac Newton’s Scientific Method: Turning Data into Evidence about Gravity and Cosmology , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Hempel, C., 1950, “Problems and Changes in the Empiricist Criterion of Meaning”, Revue Internationale de Philosophie , 41(11): 41–63.
- –––, 1951, “The Concept of Cognitive Significance: A Reconsideration”, Proceedings of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences , 80(1): 61–77.
- –––, 1965, Aspects of scientific explanation and other essays in the philosophy of science , New York–London: Free Press.
- –––, 1966, Philosophy of Natural Science , Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
- Holmes, F.L., 1987, “Scientific writing and scientific discovery”, Isis , 78(2): 220–235.
- Howard, D., 2003, “Two left turns make a right: On the curious political career of North American philosophy of science at midcentury”, in Logical Empiricism in North America , G.L. Hardcastle & A.W. Richardson (eds.), Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, pp. 25–93.
- Hoyningen-Huene, P., 2008, “Systematicity: The nature of science”, Philosophia , 36(2): 167–180.
- –––, 2013, Systematicity. The Nature of Science , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Howie, D., 2002, Interpreting probability: Controversies and developments in the early twentieth century , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Hughes, R., 1999, “The Ising Model, Computer Simulation, and Universal Physics”, in Models as Mediators , M. Morgan and M. Morrison (eds.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 97–145
- Hume, D., 1739, A Treatise of Human Nature , D. Fate Norton and M.J. Norton (eds.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000.
- Humphreys, P., 1995, “Computational science and scientific method”, Minds and Machines , 5(1): 499–512.
- ICMJE, 2013, “Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing, and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals”, International Committee of Medical Journal Editors, available online , accessed August 13 2014
- Jeffrey, R.C., 1956, “Valuation and Acceptance of Scientific Hypotheses”, Philosophy of Science , 23(3): 237–246.
- Kaufmann, W.J., and L.L. Smarr, 1993, Supercomputing and the Transformation of Science , New York: Scientific American Library.
- Knorr-Cetina, K., 1981, The Manufacture of Knowledge , Oxford: Pergamon Press.
- Krohs, U., 2012, “Convenience experimentation”, Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and BiomedicalSciences , 43: 52–57.
- Kuhn, T.S., 1962, The Structure of Scientific Revolutions , Chicago: University of Chicago Press
- Latour, B. and S. Woolgar, 1986, Laboratory Life: The Construction of Scientific Facts , Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2 nd edition.
- Laudan, L., 1968, “Theories of scientific method from Plato to Mach”, History of Science , 7(1): 1–63.
- Lenhard, J., 2006, “Models and statistical inference: The controversy between Fisher and Neyman-Pearson”, The British Journal for the Philosophy of Science , 57(1): 69–91.
- Leonelli, S., 2012, “Making Sense of Data-Driven Research in the Biological and the Biomedical Sciences”, Studies in the History and Philosophy of the Biological and Biomedical Sciences , 43(1): 1–3.
- Levi, I., 1960, “Must the scientist make value judgments?”, Philosophy of Science , 57(11): 345–357
- Lindley, D., 1991, Theory Change in Science: Strategies from Mendelian Genetics , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Lipton, P., 2004, Inference to the Best Explanation , London: Routledge, 2 nd edition.
- Marks, H.M., 2000, The progress of experiment: science and therapeutic reform in the United States, 1900–1990 , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Mazzochi, F., 2015, “Could Big Data be the end of theory in science?”, EMBO reports , 16: 1250–1255.
- Mayo, D.G., 1996, Error and the Growth of Experimental Knowledge , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- McComas, W.F., 1996, “Ten myths of science: Reexamining what we think we know about the nature of science”, School Science and Mathematics , 96(1): 10–16.
- Medawar, P.B., 1963/1996, “Is the scientific paper a fraud”, in The Strange Case of the Spotted Mouse and Other Classic Essays on Science , Oxford: Oxford University Press, 33–39.
- Mill, J.S., 1963, Collected Works of John Stuart Mill , J. M. Robson (ed.), Toronto: University of Toronto Press
- NAS, 1992, Responsible Science: Ensuring the integrity of the research process , Washington DC: National Academy Press.
- Nersessian, N.J., 1987, “A cognitive-historical approach to meaning in scientific theories”, in The process of science , N. Nersessian (ed.), Berlin: Springer, pp. 161–177.
- –––, 2008, Creating Scientific Concepts , Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Newton, I., 1726, Philosophiae naturalis Principia Mathematica (3 rd edition), in The Principia: Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy: A New Translation , I.B. Cohen and A. Whitman (trans.), Berkeley: University of California Press, 1999.
- –––, 1704, Opticks or A Treatise of the Reflections, Refractions, Inflections & Colors of Light , New York: Dover Publications, 1952.
- Neyman, J., 1956, “Note on an Article by Sir Ronald Fisher”, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological) , 18: 288–294.
- Nickles, T., 1987, “Methodology, heuristics, and rationality”, in Rational changes in science: Essays on Scientific Reasoning , J.C. Pitt (ed.), Berlin: Springer, pp. 103–132.
- Nicod, J., 1924, Le problème logique de l’induction , Paris: Alcan. (Engl. transl. “The Logical Problem of Induction”, in Foundations of Geometry and Induction , London: Routledge, 2000.)
- Nola, R. and H. Sankey, 2000a, “A selective survey of theories of scientific method”, in Nola and Sankey 2000b: 1–65.
- –––, 2000b, After Popper, Kuhn and Feyerabend. Recent Issues in Theories of Scientific Method , London: Springer.
- –––, 2007, Theories of Scientific Method , Stocksfield: Acumen.
- Norton, S., and F. Suppe, 2001, “Why atmospheric modeling is good science”, in Changing the Atmosphere: Expert Knowledge and Environmental Governance , C. Miller and P. Edwards (eds.), Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 88–133.
- O’Malley, M., 2007, “Exploratory experimentation and scientific practice: Metagenomics and the proteorhodopsin case”, History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences , 29(3): 337–360.
- O’Malley, M., C. Haufe, K. Elliot, and R. Burian, 2009, “Philosophies of Funding”, Cell , 138: 611–615.
- Oreskes, N., K. Shrader-Frechette, and K. Belitz, 1994, “Verification, Validation and Confirmation of Numerical Models in the Earth Sciences”, Science , 263(5147): 641–646.
- Osborne, J., S. Simon, and S. Collins, 2003, “Attitudes towards science: a review of the literature and its implications”, International Journal of Science Education , 25(9): 1049–1079.
- Parascandola, M., 1998, “Epidemiology—2 nd -Rate Science”, Public Health Reports , 113(4): 312–320.
- Parker, W., 2008a, “Franklin, Holmes and the Epistemology of Computer Simulation”, International Studies in the Philosophy of Science , 22(2): 165–83.
- –––, 2008b, “Computer Simulation through an Error-Statistical Lens”, Synthese , 163(3): 371–84.
- Pearson, K. 1892, The Grammar of Science , London: J.M. Dents and Sons, 1951
- Pearson, E.S., 1955, “Statistical Concepts in Their Relation to Reality”, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society , B, 17: 204–207.
- Pickering, A., 1984, Constructing Quarks: A Sociological History of Particle Physics , Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
- Popper, K.R., 1959, The Logic of Scientific Discovery , London: Routledge, 2002
- –––, 1963, Conjectures and Refutations , London: Routledge, 2002.
- –––, 1985, Unended Quest: An Intellectual Autobiography , La Salle: Open Court Publishing Co..
- Rudner, R., 1953, “The Scientist Qua Scientist Making Value Judgments”, Philosophy of Science , 20(1): 1–6.
- Rudolph, J.L., 2005, “Epistemology for the masses: The origin of ‘The Scientific Method’ in American Schools”, History of Education Quarterly , 45(3): 341–376
- Schickore, J., 2008, “Doing science, writing science”, Philosophy of Science , 75: 323–343.
- Schickore, J. and N. Hangel, 2019, “‘It might be this, it should be that…’ uncertainty and doubt in day-to-day science practice”, European Journal for Philosophy of Science , 9(2): 31. doi:10.1007/s13194-019-0253-9
- Shamoo, A.E. and D.B. Resnik, 2009, Responsible Conduct of Research , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Shank, J.B., 2008, The Newton Wars and the Beginning of the French Enlightenment , Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
- Shapin, S. and S. Schaffer, 1985, Leviathan and the air-pump , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Smith, G.E., 2002, “The Methodology of the Principia”, in The Cambridge Companion to Newton , I.B. Cohen and G.E. Smith (eds.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 138–173.
- Snyder, L.J., 1997a, “Discoverers’ Induction”, Philosophy of Science , 64: 580–604.
- –––, 1997b, “The Mill-Whewell Debate: Much Ado About Induction”, Perspectives on Science , 5: 159–198.
- –––, 1999, “Renovating the Novum Organum: Bacon, Whewell and Induction”, Studies in History and Philosophy of Science , 30: 531–557.
- Sober, E., 2008, Evidence and Evolution. The logic behind the science , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Sprenger, J. and S. Hartmann, 2019, Bayesian philosophy of science , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Steinle, F., 1997, “Entering New Fields: Exploratory Uses of Experimentation”, Philosophy of Science (Proceedings), 64: S65–S74.
- –––, 2002, “Experiments in History and Philosophy of Science”, Perspectives on Science , 10(4): 408–432.
- Strasser, B.J., 2012, “Data-driven sciences: From wonder cabinets to electronic databases”, Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part C: Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and Biomedical Sciences , 43(1): 85–87.
- Succi, S. and P.V. Coveney, 2018, “Big data: the end of the scientific method?”, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A , 377: 20180145. doi:10.1098/rsta.2018.0145
- Suppe, F., 1998, “The Structure of a Scientific Paper”, Philosophy of Science , 65(3): 381–405.
- Swijtink, Z.G., 1987, “The objectification of observation: Measurement and statistical methods in the nineteenth century”, in The probabilistic revolution. Ideas in History, Vol. 1 , L. Kruger (ed.), Cambridge MA: MIT Press, pp. 261–285.
- Waters, C.K., 2007, “The nature and context of exploratory experimentation: An introduction to three case studies of exploratory research”, History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences , 29(3): 275–284.
- Weinberg, S., 1995, “The methods of science… and those by which we live”, Academic Questions , 8(2): 7–13.
- Weissert, T., 1997, The Genesis of Simulation in Dynamics: Pursuing the Fermi-Pasta-Ulam Problem , New York: Springer Verlag.
- William H., 1628, Exercitatio Anatomica de Motu Cordis et Sanguinis in Animalibus , in On the Motion of the Heart and Blood in Animals , R. Willis (trans.), Buffalo: Prometheus Books, 1993.
- Winsberg, E., 2010, Science in the Age of Computer Simulation , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Wivagg, D. & D. Allchin, 2002, “The Dogma of the Scientific Method”, The American Biology Teacher , 64(9): 645–646
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Blackmun opinion , in Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals (92–102), 509 U.S. 579 (1993).
- Scientific Method at philpapers. Darrell Rowbottom (ed.).
- Recent Articles | Scientific Method | The Scientist Magazine
al-Kindi | Albert the Great [= Albertus magnus] | Aquinas, Thomas | Arabic and Islamic Philosophy, disciplines in: natural philosophy and natural science | Arabic and Islamic Philosophy, historical and methodological topics in: Greek sources | Arabic and Islamic Philosophy, historical and methodological topics in: influence of Arabic and Islamic Philosophy on the Latin West | Aristotle | Bacon, Francis | Bacon, Roger | Berkeley, George | biology: experiment in | Boyle, Robert | Cambridge Platonists | confirmation | Descartes, René | Enlightenment | epistemology | epistemology: Bayesian | epistemology: social | Feyerabend, Paul | Galileo Galilei | Grosseteste, Robert | Hempel, Carl | Hume, David | Hume, David: Newtonianism and Anti-Newtonianism | induction: problem of | Kant, Immanuel | Kuhn, Thomas | Leibniz, Gottfried Wilhelm | Locke, John | Mill, John Stuart | More, Henry | Neurath, Otto | Newton, Isaac | Newton, Isaac: philosophy | Ockham [Occam], William | operationalism | Peirce, Charles Sanders | Plato | Popper, Karl | rationality: historicist theories of | Reichenbach, Hans | reproducibility, scientific | Schlick, Moritz | science: and pseudo-science | science: theory and observation in | science: unity of | scientific discovery | scientific knowledge: social dimensions of | simulations in science | skepticism: medieval | space and time: absolute and relational space and motion, post-Newtonian theories | Vienna Circle | Whewell, William | Zabarella, Giacomo
Copyright © 2021 by Brian Hepburn < brian . hepburn @ wichita . edu > Hanne Andersen < hanne . andersen @ ind . ku . dk >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
Theories, Hypotheses, and Laws: Definitions, examples, and their roles in science
by Anthony Carpi, Ph.D., Anne E. Egger, Ph.D.
Listen to this reading
Did you know that the idea of evolution had been part of Western thought for more than 2,000 years before Charles Darwin was born? Like many theories, the theory of evolution was the result of the work of many different scientists working in different disciplines over a period of time.
A scientific theory is an explanation inferred from multiple lines of evidence for some broad aspect of the natural world and is logical, testable, and predictive.
As new evidence comes to light, or new interpretations of existing data are proposed, theories may be revised and even change; however, they are not tenuous or speculative.
A scientific hypothesis is an inferred explanation of an observation or research finding; while more exploratory in nature than a theory, it is based on existing scientific knowledge.
A scientific law is an expression of a mathematical or descriptive relationship observed in nature.
Imagine yourself shopping in a grocery store with a good friend who happens to be a chemist. Struggling to choose between the many different types of tomatoes in front of you, you pick one up, turn to your friend, and ask her if she thinks the tomato is organic . Your friend simply chuckles and replies, "Of course it's organic!" without even looking at how the fruit was grown. Why the amused reaction? Your friend is highlighting a simple difference in vocabulary. To a chemist, the term organic refers to any compound in which hydrogen is bonded to carbon. Tomatoes (like all plants) are abundant in organic compounds – thus your friend's laughter. In modern agriculture, however, organic has come to mean food items grown or raised without the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, or other additives.
So who is correct? You both are. Both uses of the word are correct, though they mean different things in different contexts. There are, of course, lots of words that have more than one meaning (like bat , for example), but multiple meanings can be especially confusing when two meanings convey very different ideas and are specific to one field of study.
- Scientific theories
The term theory also has two meanings, and this double meaning often leads to confusion. In common language, the term theory generally refers to speculation or a hunch or guess. You might have a theory about why your favorite sports team isn't playing well, or who ate the last cookie from the cookie jar. But these theories do not fit the scientific use of the term. In science, a theory is a well-substantiated and comprehensive set of ideas that explains a phenomenon in nature. A scientific theory is based on large amounts of data and observations that have been collected over time. Scientific theories can be tested and refined by additional research , and they allow scientists to make predictions. Though you may be correct in your hunch, your cookie jar conjecture doesn't fit this more rigorous definition.
All scientific disciplines have well-established, fundamental theories . For example, atomic theory describes the nature of matter and is supported by multiple lines of evidence from the way substances behave and react in the world around us (see our series on Atomic Theory ). Plate tectonic theory describes the large scale movement of the outer layer of the Earth and is supported by evidence from studies about earthquakes , magnetic properties of the rocks that make up the seafloor , and the distribution of volcanoes on Earth (see our series on Plate Tectonic Theory ). The theory of evolution by natural selection , which describes the mechanism by which inherited traits that affect survivability or reproductive success can cause changes in living organisms over generations , is supported by extensive studies of DNA , fossils , and other types of scientific evidence (see our Charles Darwin series for more information). Each of these major theories guides and informs modern research in those fields, integrating a broad, comprehensive set of ideas.
So how are these fundamental theories developed, and why are they considered so well supported? Let's take a closer look at some of the data and research supporting the theory of natural selection to better see how a theory develops.
Comprehension Checkpoint
- The development of a scientific theory: Evolution and natural selection
The theory of evolution by natural selection is sometimes maligned as Charles Darwin 's speculation on the origin of modern life forms. However, evolutionary theory is not speculation. While Darwin is rightly credited with first articulating the theory of natural selection, his ideas built on more than a century of scientific research that came before him, and are supported by over a century and a half of research since.
- The Fixity Notion: Linnaeus

Figure 1: Cover of the 1760 edition of Systema Naturae .
Research about the origins and diversity of life proliferated in the 18th and 19th centuries. Carolus Linnaeus , a Swedish botanist and the father of modern taxonomy (see our module Taxonomy I for more information), was a devout Christian who believed in the concept of Fixity of Species , an idea based on the biblical story of creation. The Fixity of Species concept said that each species is based on an ideal form that has not changed over time. In the early stages of his career, Linnaeus traveled extensively and collected data on the structural similarities and differences between different species of plants. Noting that some very different plants had similar structures, he began to piece together his landmark work, Systema Naturae, in 1735 (Figure 1). In Systema , Linnaeus classified organisms into related groups based on similarities in their physical features. He developed a hierarchical classification system , even drawing relationships between seemingly disparate species (for example, humans, orangutans, and chimpanzees) based on the physical similarities that he observed between these organisms. Linnaeus did not explicitly discuss change in organisms or propose a reason for his hierarchy, but by grouping organisms based on physical characteristics, he suggested that species are related, unintentionally challenging the Fixity notion that each species is created in a unique, ideal form.
- The age of Earth: Leclerc and Hutton
Also in the early 1700s, Georges-Louis Leclerc, a French naturalist, and James Hutton , a Scottish geologist, began to develop new ideas about the age of the Earth. At the time, many people thought of the Earth as 6,000 years old, based on a strict interpretation of the events detailed in the Christian Old Testament by the influential Scottish Archbishop Ussher. By observing other planets and comets in the solar system , Leclerc hypothesized that Earth began as a hot, fiery ball of molten rock, mostly consisting of iron. Using the cooling rate of iron, Leclerc calculated that Earth must therefore be at least 70,000 years old in order to have reached its present temperature.
Hutton approached the same topic from a different perspective, gathering observations of the relationships between different rock formations and the rates of modern geological processes near his home in Scotland. He recognized that the relatively slow processes of erosion and sedimentation could not create all of the exposed rock layers in only a few thousand years (see our module The Rock Cycle ). Based on his extensive collection of data (just one of his many publications ran to 2,138 pages), Hutton suggested that the Earth was far older than human history – hundreds of millions of years old.
While we now know that both Leclerc and Hutton significantly underestimated the age of the Earth (by about 4 billion years), their work shattered long-held beliefs and opened a window into research on how life can change over these very long timescales.
- Fossil studies lead to the development of a theory of evolution: Cuvier
Figure 2: Illustration of an Indian elephant jaw and a mammoth jaw from Cuvier's 1796 paper.
With the age of Earth now extended by Leclerc and Hutton, more researchers began to turn their attention to studying past life. Fossils are the main way to study past life forms, and several key studies on fossils helped in the development of a theory of evolution . In 1795, Georges Cuvier began to work at the National Museum in Paris as a naturalist and anatomist. Through his work, Cuvier became interested in fossils found near Paris, which some claimed were the remains of the elephants that Hannibal rode over the Alps when he invaded Rome in 218 BCE . In studying both the fossils and living species , Cuvier documented different patterns in the dental structure and number of teeth between the fossils and modern elephants (Figure 2) (Horner, 1843). Based on these data , Cuvier hypothesized that the fossil remains were not left by Hannibal, but were from a distinct species of animal that once roamed through Europe and had gone extinct thousands of years earlier: the mammoth. The concept of species extinction had been discussed by a few individuals before Cuvier, but it was in direct opposition to the Fixity of Species concept – if every organism were based on a perfectly adapted, ideal form, how could any cease to exist? That would suggest it was no longer ideal.
While his work provided critical evidence of extinction , a key component of evolution , Cuvier was highly critical of the idea that species could change over time. As a result of his extensive studies of animal anatomy, Cuvier had developed a holistic view of organisms , stating that the
number, direction, and shape of the bones that compose each part of an animal's body are always in a necessary relation to all the other parts, in such a way that ... one can infer the whole from any one of them ...
In other words, Cuvier viewed each part of an organism as a unique, essential component of the whole organism. If one part were to change, he believed, the organism could not survive. His skepticism about the ability of organisms to change led him to criticize the whole idea of evolution , and his prominence in France as a scientist played a large role in discouraging the acceptance of the idea in the scientific community.
- Studies of invertebrates support a theory of change in species: Lamarck
Jean Baptiste Lamarck, a contemporary of Cuvier's at the National Museum in Paris, studied invertebrates like insects and worms. As Lamarck worked through the museum's large collection of invertebrates, he was impressed by the number and variety of organisms . He became convinced that organisms could, in fact, change through time, stating that
... time and favorable conditions are the two principal means which nature has employed in giving existence to all her productions. We know that for her time has no limit, and that consequently she always has it at her disposal.
This was a radical departure from both the fixity concept and Cuvier's ideas, and it built on the long timescale that geologists had recently established. Lamarck proposed that changes that occurred during an organism 's lifetime could be passed on to their offspring, suggesting, for example, that a body builder's muscles would be inherited by their children.
As it turned out, the mechanism by which Lamarck proposed that organisms change over time was wrong, and he is now often referred to disparagingly for his "inheritance of acquired characteristics" idea. Yet despite the fact that some of his ideas were discredited, Lamarck established a support for evolutionary theory that others would build on and improve.
- Rock layers as evidence for evolution: Smith
In the early 1800s, a British geologist and canal surveyor named William Smith added another component to the accumulating evidence for evolution . Smith observed that rock layers exposed in different parts of England bore similarities to one another: These layers (or strata) were arranged in a predictable order, and each layer contained distinct groups of fossils . From this series of observations , he developed a hypothesis that specific groups of animals followed one another in a definite sequence through Earth's history, and this sequence could be seen in the rock layers. Smith's hypothesis was based on his knowledge of geological principles , including the Law of Superposition.
The Law of Superposition states that sediments are deposited in a time sequence, with the oldest sediments deposited first, or at the bottom, and newer layers deposited on top. The concept was first expressed by the Persian scientist Avicenna in the 11th century, but was popularized by the Danish scientist Nicolas Steno in the 17th century. Note that the law does not state how sediments are deposited; it simply describes the relationship between the ages of deposited sediments.

Figure 3: Engraving from William Smith's 1815 monograph on identifying strata by fossils.
Smith backed up his hypothesis with extensive drawings of fossils uncovered during his research (Figure 3), thus allowing other scientists to confirm or dispute his findings. His hypothesis has, in fact, been confirmed by many other scientists and has come to be referred to as the Law of Faunal Succession. His work was critical to the formation of evolutionary theory as it not only confirmed Cuvier's work that organisms have gone extinct , but it also showed that the appearance of life does not date to the birth of the planet. Instead, the fossil record preserves a timeline of the appearance and disappearance of different organisms in the past, and in doing so offers evidence for change in organisms over time.
- The theory of evolution by natural selection: Darwin and Wallace
It was into this world that Charles Darwin entered: Linnaeus had developed a taxonomy of organisms based on their physical relationships, Leclerc and Hutton demonstrated that there was sufficient time in Earth's history for organisms to change, Cuvier showed that species of organisms have gone extinct , Lamarck proposed that organisms change over time, and Smith established a timeline of the appearance and disappearance of different organisms in the geological record .

Figure 4: Title page of the 1859 Murray edition of the Origin of Species by Charles Darwin.
Charles Darwin collected data during his work as a naturalist on the HMS Beagle starting in 1831. He took extensive notes on the geology of the places he visited; he made a major find of fossils of extinct animals in Patagonia and identified an extinct giant ground sloth named Megatherium . He experienced an earthquake in Chile that stranded beds of living mussels above water, where they would be preserved for years to come.
Perhaps most famously, he conducted extensive studies of animals on the Galápagos Islands, noting subtle differences in species of mockingbird, tortoise, and finch that were isolated on different islands with different environmental conditions. These subtle differences made the animals highly adapted to their environments .
This broad spectrum of data led Darwin to propose an idea about how organisms change "by means of natural selection" (Figure 4). But this idea was not based only on his work, it was also based on the accumulation of evidence and ideas of many others before him. Because his proposal encompassed and explained many different lines of evidence and previous work, they formed the basis of a new and robust scientific theory regarding change in organisms – the theory of evolution by natural selection .
Darwin's ideas were grounded in evidence and data so compelling that if he had not conceived them, someone else would have. In fact, someone else did. Between 1858 and 1859, Alfred Russel Wallace , a British naturalist, wrote a series of letters to Darwin that independently proposed natural selection as the means for evolutionary change. The letters were presented to the Linnean Society of London, a prominent scientific society at the time (see our module on Scientific Institutions and Societies ). This long chain of research highlights that theories are not just the work of one individual. At the same time, however, it often takes the insight and creativity of individuals to put together all of the pieces and propose a new theory . Both Darwin and Wallace were experienced naturalists who were familiar with the work of others. While all of the work leading up to 1830 contributed to the theory of evolution , Darwin's and Wallace's theory changed the way that future research was focused by presenting a comprehensive, well-substantiated set of ideas, thus becoming a fundamental theory of biological research.
- Expanding, testing, and refining scientific theories
- Genetics and evolution: Mendel and Dobzhansky
Since Darwin and Wallace first published their ideas, extensive research has tested and expanded the theory of evolution by natural selection . Darwin had no concept of genes or DNA or the mechanism by which characteristics were inherited within a species . A contemporary of Darwin's, the Austrian monk Gregor Mendel , first presented his own landmark study, Experiments in Plant Hybridization, in 1865 in which he provided the basic patterns of genetic inheritance , describing which characteristics (and evolutionary changes) can be passed on in organisms (see our Genetics I module for more information). Still, it wasn't until much later that a "gene" was defined as the heritable unit.
In 1937, the Ukrainian born geneticist Theodosius Dobzhansky published Genetics and the Origin of Species , a seminal work in which he described genes themselves and demonstrated that it is through mutations in genes that change occurs. The work defined evolution as "a change in the frequency of an allele within a gene pool" ( Dobzhansky, 1982 ). These studies and others in the field of genetics have added to Darwin's work, expanding the scope of the theory .
- Evolution under a microscope: Lenski
More recently, Dr. Richard Lenski, a scientist at Michigan State University, isolated a single Escherichia coli bacterium in 1989 as the first step of the longest running experimental test of evolutionary theory to date – a true test meant to replicate evolution and natural selection in the lab.
After the single microbe had multiplied, Lenski isolated the offspring into 12 different strains , each in their own glucose-supplied culture, predicting that the genetic make-up of each strain would change over time to become more adapted to their specific culture as predicted by evolutionary theory . These 12 lines have been nurtured for over 40,000 bacterial generations (luckily bacterial generations are much shorter than human generations) and exposed to different selective pressures such as heat , cold, antibiotics, and infection with other microorganisms. Lenski and colleagues have studied dozens of aspects of evolutionary theory with these genetically isolated populations . In 1999, they published a paper that demonstrated that random genetic mutations were common within the populations and highly diverse across different individual bacteria . However, "pivotal" mutations that are associated with beneficial changes in the group are shared by all descendants in a population and are much rarer than random mutations, as predicted by the theory of evolution by natural selection (Papadopoulos et al., 1999).
- Punctuated equilibrium: Gould and Eldredge
While established scientific theories like evolution have a wealth of research and evidence supporting them, this does not mean that they cannot be refined as new information or new perspectives on existing data become available. For example, in 1972, biologist Stephen Jay Gould and paleontologist Niles Eldredge took a fresh look at the existing data regarding the timing by which evolutionary change takes place. Gould and Eldredge did not set out to challenge the theory of evolution; rather they used it as a guiding principle and asked more specific questions to add detail and nuance to the theory. This is true of all theories in science: they provide a framework for additional research. At the time, many biologists viewed evolution as occurring gradually, causing small incremental changes in organisms at a relatively steady rate. The idea is referred to as phyletic gradualism , and is rooted in the geological concept of uniformitarianism . After reexamining the available data, Gould and Eldredge came to a different explanation, suggesting that evolution consists of long periods of stability that are punctuated by occasional instances of dramatic change – a process they called punctuated equilibrium .
Like Darwin before them, their proposal is rooted in evidence and research on evolutionary change, and has been supported by multiple lines of evidence. In fact, punctuated equilibrium is now considered its own theory in evolutionary biology. Punctuated equilibrium is not as broad of a theory as natural selection . In science, some theories are broad and overarching of many concepts, such as the theory of evolution by natural selection; others focus on concepts at a smaller, or more targeted, scale such as punctuated equilibrium. And punctuated equilibrium does not challenge or weaken the concept of natural selection; rather, it represents a change in our understanding of the timing by which change occurs in organisms , and a theory within a theory. The theory of evolution by natural selection now includes both gradualism and punctuated equilibrium to describe the rate at which change proceeds.
- Hypotheses and laws: Other scientific concepts
One of the challenges in understanding scientific terms like theory is that there is not a precise definition even within the scientific community. Some scientists debate over whether certain proposals merit designation as a hypothesis or theory , and others mistakenly use the terms interchangeably. But there are differences in these terms. A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for an observable phenomenon. Hypotheses , just like theories , are based on observations from research . For example, LeClerc did not hypothesize that Earth had cooled from a molten ball of iron as a random guess; rather, he developed this hypothesis based on his observations of information from meteorites.
A scientist often proposes a hypothesis before research confirms it as a way of predicting the outcome of study to help better define the parameters of the research. LeClerc's hypothesis allowed him to use known parameters (the cooling rate of iron) to do additional work. A key component of a formal scientific hypothesis is that it is testable and falsifiable. For example, when Richard Lenski first isolated his 12 strains of bacteria , he likely hypothesized that random mutations would cause differences to appear within a period of time in the different strains of bacteria. But when a hypothesis is generated in science, a scientist will also make an alternative hypothesis , an explanation that explains a study if the data do not support the original hypothesis. If the different strains of bacteria in Lenski's work did not diverge over the indicated period of time, perhaps the rate of mutation was slower than first thought.
So you might ask, if theories are so well supported, do they eventually become laws? The answer is no – not because they aren't well-supported, but because theories and laws are two very different things. Laws describe phenomena, often mathematically. Theories, however, explain phenomena. For example, in 1687 Isaac Newton proposed a Theory of Gravitation, describing gravity as a force of attraction between two objects. As part of this theory, Newton developed a Law of Universal Gravitation that explains how this force operates. This law states that the force of gravity between two objects is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between those objects. Newton 's Law does not explain why this is true, but it describes how gravity functions (see our Gravity: Newtonian Relationships module for more detail). In 1916, Albert Einstein developed his theory of general relativity to explain the mechanism by which gravity has its effect. Einstein's work challenges Newton's theory, and has been found after extensive testing and research to more accurately describe the phenomenon of gravity. While Einstein's work has replaced Newton's as the dominant explanation of gravity in modern science, Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation is still used as it reasonably (and more simply) describes the force of gravity under many conditions. Similarly, the Law of Faunal Succession developed by William Smith does not explain why organisms follow each other in distinct, predictable ways in the rock layers, but it accurately describes the phenomenon.
Theories, hypotheses , and laws drive scientific progress
Theories, hypotheses , and laws are not simply important components of science, they drive scientific progress. For example, evolutionary biology now stands as a distinct field of science that focuses on the origins and descent of species . Geologists now rely on plate tectonics as a conceptual model and guiding theory when they are studying processes at work in Earth's crust . And physicists refer to atomic theory when they are predicting the existence of subatomic particles yet to be discovered. This does not mean that science is "finished," or that all of the important theories have been discovered already. Like evolution , progress in science happens both gradually and in short, dramatic bursts. Both types of progress are critical for creating a robust knowledge base with data as the foundation and scientific theories giving structure to that knowledge.
Table of Contents
- Theories, hypotheses, and laws drive scientific progress
Activate glossary term highlighting to easily identify key terms within the module. Once highlighted, you can click on these terms to view their definitions.
Activate NGSS annotations to easily identify NGSS standards within the module. Once highlighted, you can click on them to view these standards.
1.2 The Process of Science
Learning objectives.
- Identify the shared characteristics of the natural sciences
- Understand the process of scientific inquiry
- Compare inductive reasoning with deductive reasoning
- Describe the goals of basic science and applied science
Like geology, physics, and chemistry, biology is a science that gathers knowledge about the natural world. Specifically, biology is the study of life. The discoveries of biology are made by a community of researchers who work individually and together using agreed-on methods. In this sense, biology, like all sciences is a social enterprise like politics or the arts. The methods of science include careful observation, record keeping, logical and mathematical reasoning, experimentation, and submitting conclusions to the scrutiny of others. Science also requires considerable imagination and creativity; a well-designed experiment is commonly described as elegant, or beautiful. Like politics, science has considerable practical implications and some science is dedicated to practical applications, such as the prevention of disease (see Figure 1.15 ). Other science proceeds largely motivated by curiosity. Whatever its goal, there is no doubt that science, including biology, has transformed human existence and will continue to do so.
The Nature of Science
Biology is a science, but what exactly is science? What does the study of biology share with other scientific disciplines? Science (from the Latin scientia, meaning "knowledge") can be defined as knowledge about the natural world.
Science is a very specific way of learning, or knowing, about the world. The history of the past 500 years demonstrates that science is a very powerful way of knowing about the world; it is largely responsible for the technological revolutions that have taken place during this time. There are however, areas of knowledge and human experience that the methods of science cannot be applied to. These include such things as answering purely moral questions, aesthetic questions, or what can be generally categorized as spiritual questions. Science cannot investigate these areas because they are outside the realm of material phenomena, the phenomena of matter and energy, and cannot be observed and measured.
The scientific method is a method of research with defined steps that include experiments and careful observation. The steps of the scientific method will be examined in detail later, but one of the most important aspects of this method is the testing of hypotheses. A hypothesis is a suggested explanation for an event, which can be tested. Hypotheses, or tentative explanations, are generally produced within the context of a scientific theory . A generally accepted scientific theory is thoroughly tested and confirmed explanation for a set of observations or phenomena. Scientific theory is the foundation of scientific knowledge. In addition, in many scientific disciplines (less so in biology) there are scientific laws , often expressed in mathematical formulas, which describe how elements of nature will behave under certain specific conditions. There is not an evolution of hypotheses through theories to laws as if they represented some increase in certainty about the world. Hypotheses are the day-to-day material that scientists work with and they are developed within the context of theories. Laws are concise descriptions of parts of the world that are amenable to formulaic or mathematical description.
Natural Sciences
What would you expect to see in a museum of natural sciences? Frogs? Plants? Dinosaur skeletons? Exhibits about how the brain functions? A planetarium? Gems and minerals? Or maybe all of the above? Science includes such diverse fields as astronomy, biology, computer sciences, geology, logic, physics, chemistry, and mathematics ( Figure 1.16 ). However, those fields of science related to the physical world and its phenomena and processes are considered natural sciences . Thus, a museum of natural sciences might contain any of the items listed above.
There is no complete agreement when it comes to defining what the natural sciences include. For some experts, the natural sciences are astronomy, biology, chemistry, earth science, and physics. Other scholars choose to divide natural sciences into life sciences , which study living things and include biology, and physical sciences , which study nonliving matter and include astronomy, physics, and chemistry. Some disciplines such as biophysics and biochemistry build on two sciences and are interdisciplinary.
Scientific Inquiry
One thing is common to all forms of science: an ultimate goal “to know.” Curiosity and inquiry are the driving forces for the development of science. Scientists seek to understand the world and the way it operates. Two methods of logical thinking are used: inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning is a form of logical thinking that uses related observations to arrive at a general conclusion. This type of reasoning is common in descriptive science. A life scientist such as a biologist makes observations and records them. These data can be qualitative (descriptive) or quantitative (consisting of numbers), and the raw data can be supplemented with drawings, pictures, photos, or videos. From many observations, the scientist can infer conclusions (inductions) based on evidence. Inductive reasoning involves formulating generalizations inferred from careful observation and the analysis of a large amount of data. Brain studies often work this way. Many brains are observed while people are doing a task. The part of the brain that lights up, indicating activity, is then demonstrated to be the part controlling the response to that task.
Deductive reasoning or deduction is the type of logic used in hypothesis-based science. In deductive reasoning, the pattern of thinking moves in the opposite direction as compared to inductive reasoning. Deductive reasoning is a form of logical thinking that uses a general principle or law to predict specific results. From those general principles, a scientist can deduce and predict the specific results that would be valid as long as the general principles are valid. For example, a prediction would be that if the climate is becoming warmer in a region, the distribution of plants and animals should change. Comparisons have been made between distributions in the past and the present, and the many changes that have been found are consistent with a warming climate. Finding the change in distribution is evidence that the climate change conclusion is a valid one.
Both types of logical thinking are related to the two main pathways of scientific study: descriptive science and hypothesis-based science. Descriptive (or discovery) science aims to observe, explore, and discover, while hypothesis-based science begins with a specific question or problem and a potential answer or solution that can be tested. The boundary between these two forms of study is often blurred, because most scientific endeavors combine both approaches. Observations lead to questions, questions lead to forming a hypothesis as a possible answer to those questions, and then the hypothesis is tested. Thus, descriptive science and hypothesis-based science are in continuous dialogue.
Hypothesis Testing
Biologists study the living world by posing questions about it and seeking science-based responses. This approach is common to other sciences as well and is often referred to as the scientific method. The scientific method was used even in ancient times, but it was first documented by England’s Sir Francis Bacon (1561–1626) ( Figure 1.17 ), who set up inductive methods for scientific inquiry. The scientific method is not exclusively used by biologists but can be applied to almost anything as a logical problem-solving method.
The scientific process typically starts with an observation (often a problem to be solved) that leads to a question. Let’s think about a simple problem that starts with an observation and apply the scientific method to solve the problem. One Monday morning, a student arrives at class and quickly discovers that the classroom is too warm. That is an observation that also describes a problem: the classroom is too warm. The student then asks a question: “Why is the classroom so warm?”
Recall that a hypothesis is a suggested explanation that can be tested. To solve a problem, several hypotheses may be proposed. For example, one hypothesis might be, “The classroom is warm because no one turned on the air conditioning.” But there could be other responses to the question, and therefore other hypotheses may be proposed. A second hypothesis might be, “The classroom is warm because there is a power failure, and so the air conditioning doesn’t work.”
Once a hypothesis has been selected, a prediction may be made. A prediction is similar to a hypothesis but it typically has the format “If . . . then . . . .” For example, the prediction for the first hypothesis might be, “ If the student turns on the air conditioning, then the classroom will no longer be too warm.”
A hypothesis must be testable to ensure that it is valid. For example, a hypothesis that depends on what a bear thinks is not testable, because it can never be known what a bear thinks. It should also be falsifiable , meaning that it can be disproven by experimental results. An example of an unfalsifiable hypothesis is “Botticelli’s Birth of Venus is beautiful.” There is no experiment that might show this statement to be false. To test a hypothesis, a researcher will conduct one or more experiments designed to eliminate one or more of the hypotheses. This is important. A hypothesis can be disproven, or eliminated, but it can never be proven. Science does not deal in proofs like mathematics. If an experiment fails to disprove a hypothesis, then we find support for that explanation, but this is not to say that down the road a better explanation will not be found, or a more carefully designed experiment will be found to falsify the hypothesis.
Each experiment will have one or more variables and one or more controls. A variable is any part of the experiment that can vary or change during the experiment. A control is a part of the experiment that does not change. Look for the variables and controls in the example that follows. As a simple example, an experiment might be conducted to test the hypothesis that phosphate limits the growth of algae in freshwater ponds. A series of artificial ponds are filled with water and half of them are treated by adding phosphate each week, while the other half are treated by adding a salt that is known not to be used by algae. The variable here is the phosphate (or lack of phosphate), the experimental or treatment cases are the ponds with added phosphate and the control ponds are those with something inert added, such as the salt. Just adding something is also a control against the possibility that adding extra matter to the pond has an effect. If the treated ponds show lesser growth of algae, then we have found support for our hypothesis. If they do not, then we reject our hypothesis. Be aware that rejecting one hypothesis does not determine whether or not the other hypotheses can be accepted; it simply eliminates one hypothesis that is not valid ( Figure 1.18 ). Using the scientific method, the hypotheses that are inconsistent with experimental data are rejected.
In recent years a new approach of testing hypotheses has developed as a result of an exponential growth of data deposited in various databases. Using computer algorithms and statistical analyses of data in databases, a new field of so-called "data research" (also referred to as "in silico" research) provides new methods of data analyses and their interpretation. This will increase the demand for specialists in both biology and computer science, a promising career opportunity.
Visual Connection
In the example below, the scientific method is used to solve an everyday problem. Which part in the example below is the hypothesis? Which is the prediction? Based on the results of the experiment, is the hypothesis supported? If it is not supported, propose some alternative hypotheses.
- My toaster doesn’t toast my bread.
- Why doesn’t my toaster work?
- There is something wrong with the electrical outlet.
- If something is wrong with the outlet, my coffeemaker also won’t work when plugged into it.
- I plug my coffeemaker into the outlet.
- My coffeemaker works.
In practice, the scientific method is not as rigid and structured as it might at first appear. Sometimes an experiment leads to conclusions that favor a change in approach; often, an experiment brings entirely new scientific questions to the puzzle. Many times, science does not operate in a linear fashion; instead, scientists continually draw inferences and make generalizations, finding patterns as their research proceeds. Scientific reasoning is more complex than the scientific method alone suggests.
Basic and Applied Science
The scientific community has been debating for the last few decades about the value of different types of science. Is it valuable to pursue science for the sake of simply gaining knowledge, or does scientific knowledge only have worth if we can apply it to solving a specific problem or bettering our lives? This question focuses on the differences between two types of science: basic science and applied science.
Basic science or “pure” science seeks to expand knowledge regardless of the short-term application of that knowledge. It is not focused on developing a product or a service of immediate public or commercial value. The immediate goal of basic science is knowledge for knowledge’s sake, though this does not mean that in the end it may not result in an application.
In contrast, applied science or “technology,” aims to use science to solve real-world problems, making it possible, for example, to improve a crop yield, find a cure for a particular disease, or save animals threatened by a natural disaster. In applied science, the problem is usually defined for the researcher.
Some individuals may perceive applied science as “useful” and basic science as “useless.” A question these people might pose to a scientist advocating knowledge acquisition would be, “What for?” A careful look at the history of science, however, reveals that basic knowledge has resulted in many remarkable applications of great value. Many scientists think that a basic understanding of science is necessary before an application is developed; therefore, applied science relies on the results generated through basic science. Other scientists think that it is time to move on from basic science and instead to find solutions to actual problems. Both approaches are valid. It is true that there are problems that demand immediate attention; however, few solutions would be found without the help of the knowledge generated through basic science.
One example of how basic and applied science can work together to solve practical problems occurred after the discovery of DNA structure led to an understanding of the molecular mechanisms governing DNA replication. Strands of DNA, unique in every human, are found in our cells, where they provide the instructions necessary for life. During DNA replication, new copies of DNA are made, shortly before a cell divides to form new cells. Understanding the mechanisms of DNA replication enabled scientists to develop laboratory techniques that are now used to identify genetic diseases, pinpoint individuals who were at a crime scene, and determine paternity. Without basic science, it is unlikely that applied science could exist.
Another example of the link between basic and applied research is the Human Genome Project, a study in which each human chromosome was analyzed and mapped to determine the precise sequence of DNA subunits and the exact location of each gene. (The gene is the basic unit of heredity represented by a specific DNA segment that codes for a functional molecule.) Other organisms have also been studied as part of this project to gain a better understanding of human chromosomes. The Human Genome Project ( Figure 1.19 ) relied on basic research carried out with non-human organisms and, later, with the human genome. An important end goal eventually became using the data for applied research seeking cures for genetically related diseases.
While research efforts in both basic science and applied science are usually carefully planned, it is important to note that some discoveries are made by serendipity, that is, by means of a fortunate accident or a lucky surprise. Penicillin was discovered when biologist Alexander Fleming accidentally left a petri dish of Staphylococcus bacteria open. An unwanted mold grew, killing the bacteria. The mold turned out to be Penicillium , and a new critically important antibiotic was discovered. In a similar manner, Percy Lavon Julian was an established medicinal chemist working on a way to mass produce compounds with which to manufacture important drugs. He was focused on using soybean oil in the production of progesterone (a hormone important in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy), but it wasn't until water accidentally leaked into a large soybean oil storage tank that he found his method. Immediately recognizing the resulting substance as stigmasterol, a primary ingredient in progesterone and similar drugs, he began the process of replicating and industrializing the process in a manner that has helped millions of people. Even in the highly organized world of science, luck—when combined with an observant, curious mind focused on the types of reasoning discussed above—can lead to unexpected breakthroughs.
Reporting Scientific Work
Whether scientific research is basic science or applied science, scientists must share their findings for other researchers to expand and build upon their discoveries. Communication and collaboration within and between sub disciplines of science are key to the advancement of knowledge in science. For this reason, an important aspect of a scientist’s work is disseminating results and communicating with peers. Scientists can share results by presenting them at a scientific meeting or conference, but this approach can reach only the limited few who are present. Instead, most scientists present their results in peer-reviewed articles that are published in scientific journals. Peer-reviewed articles are scientific papers that are reviewed, usually anonymously by a scientist’s colleagues, or peers. These colleagues are qualified individuals, often experts in the same research area, who judge whether or not the scientist’s work is suitable for publication. The process of peer review helps to ensure that the research described in a scientific paper or grant proposal is original, significant, logical, and thorough. Grant proposals, which are requests for research funding, are also subject to peer review. Scientists publish their work so other scientists can reproduce their experiments under similar or different conditions to expand on the findings.
There are many journals and the popular press that do not use a peer-review system. A large number of online open-access journals, journals with articles available without cost, are now available many of which use rigorous peer-review systems, but some of which do not. Results of any studies published in these forums without peer review are not reliable and should not form the basis for other scientific work. In one exception, journals may allow a researcher to cite a personal communication from another researcher about unpublished results with the cited author’s permission.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Concepts of Biology
- Publication date: Apr 25, 2013
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/1-2-the-process-of-science
© Jan 8, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Advertisement
10 Scientific Laws and Theories You Really Should Know
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email
Scientists have many tools available to them when attempting to describe how nature and the universe at large work. Often they reach for laws and theories first. What's the difference? A scientific law can often be reduced to a mathematical statement, such as E = mc²; it's a specific statement based on empirical data, and its truth is generally confined to a certain set of conditions. For example, in the case of E = mc², c refers to the speed of light in a vacuum.
A scientific theory often seeks to synthesize a body of evidence or observations of particular phenomena. It's generally — though by no means always — a grander, testable statement about how nature operates. You can't necessarily reduce a scientific theory to a pithy statement or equation, but it does represent something fundamental about how nature works.
Both laws and theories depend on basic elements of the scientific method, such as generating a hypothesis , testing that premise, finding (or not finding) empirical evidence and coming up with conclusions. Eventually, other scientists must be able to replicate the results if the experiment is destined to become the basis for a widely accepted law or theory.
In this article, we'll look at 10 scientific laws and theories that you might want to brush up on, even if you don't find yourself, say, operating a scanning electron microscope all that frequently. We'll start off with a bang and move on to the basic laws of the universe, before hitting evolution . Finally, we'll tackle some headier material, delving into the realm of quantum physics.
- Big Bang Theory
- Hubble's Law of Cosmic Expansion
- Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
- Universal Law of Gravitation
- Newton's Laws of Motion
- Laws of Thermodynamics
- Archimedes' Buoyancy Principle
- Evolution and Natural Selection
- Theory of General Relativity
- Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle
10: Big Bang Theory
If you're going to know one scientific theory, make it the one that explains how the universe arrived at its present state. Based on research performed by Edwin Hubble, Georges Lemaitre and Albert Einstein, among others, the big bang theory postulates that the universe began almost 14 billion years ago with a massive expansion event. At the time, the universe was confined to a single point, encompassing all of the universe's matter. That original movement continues today, as the universe keeps expanding outward.
The theory of the big bang gained widespread support in the scientific community after Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson discovered cosmic microwave background radiation in 1965. Using radio telescopes, the two astronomers detected cosmic noise, or static, that didn't dissipate over time. Collaborating with Princeton researcher Robert Dicke, the pair confirmed Dicke's hypothesis that the original big bang left behind low-level radiation detectable throughout the universe.
9: Hubble's Law of Cosmic Expansion
Let's stick with Edwin Hubble for a second. While the 1920s roared past and the Great Depression limped by, Hubble was performing groundbreaking astronomical research. Hubble not only proved that there were other galaxies besides the Milky Way , he also discovered that these galaxies were zipping away from our own, a motion he called recession .
In order to quantify the velocity of this galactic movement, Hubble proposed Hubble's Law of Cosmic Expansion , aka Hubble's law, an equation that states: velocity = H × distance . Velocity represents the galaxy's recessional velocity; H is the Hubble constant, or parameter that indicates the rate at which the universe is expanding; and distance is the galaxy's distance from the one with which it's being compared.
Hubble's constant has been calculated at different values over time, but the current accepted value is 70 kilometers/second per megaparsec, the latter being a unit of distance in intergalactic space [source: White ]. For our purposes, that's not so important. What matters most is that Hubble's law provides a concise method for measuring a galaxy's velocity in relation to our own. And perhaps most significantly, the law established that the universe is made up of many galaxies, whose movements trace back to the big bang.
8: Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
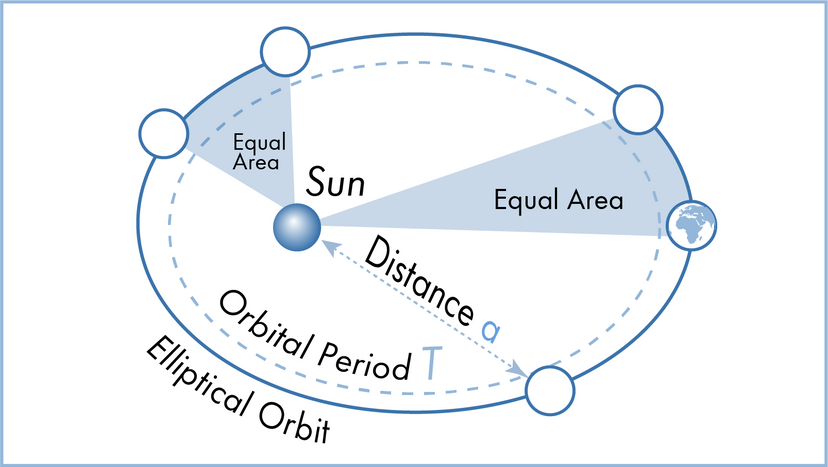
For centuries, scientists battled with one another and with religious leaders about the planets' orbits, especially about whether they orbited our sun. In the 16th century, Copernicus put forth his controversial concept of a heliocentric solar system, in which the planets revolved around the sun — not Earth. But it would take Johannes Kepler, building on work performed by Tyco Brahe and others, to establish a clear scientific foundation for the planets' movements.
Kepler's three laws of planetary motion — formed in the early 17th century — describe how planets orbit the sun. The first law, sometimes called the law of orbits , states that planets orbit the sun elliptically. The second law, the law of areas , states that a line connecting a planet to the sun covers an equal area over equal periods of time. In other words, if you're measuring the area created by drawing a line from Earth to the sun and tracking Earth's movement over 30 days, the area will be the same no matter where Earth is in its orbit when measurements begin.
The third one, the law of periods , allows us to establish a clear relationship between a planet's orbital period and its distance from the sun. Thanks to this law, we know that a planet relatively close to the sun, like Venus, has a far briefer orbital period than a distant planet, such as Neptune.
7: Universal Law of Gravitation
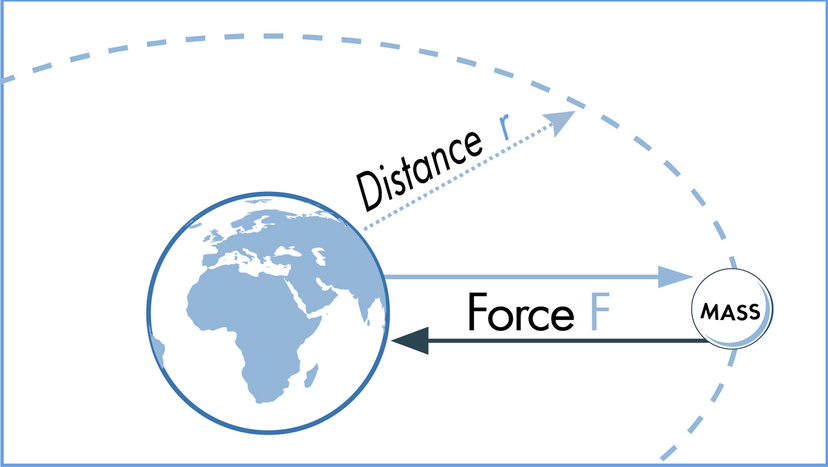
We may take it for granted now, but more than 300 years ago Sir Isaac Newton proposed a revolutionary idea: that any two objects, no matter their mass, exert gravitational force toward one another. This law is represented by an equation that many high schoolers encounter in physics class. It goes as follows:
F = G × [(m 1 m 2 )/r 2 ]
F is the gravitational force between the two objects, measured in Newtons. M 1 and m 2 are the masses of the two objects, while r is the distance between them. G is the gravitational constant , a number currently calculated to be 6.672 × 10 -11 N m 2 kg -2 [source: Weisstein ].
The benefit of the universal law of gravitation is that it allows us to calculate the gravitational pull between any two objects. This ability is especially useful when scientists are, say, planning to put a satellite in orbit or charting the course of the moon .
6: Newton's Laws of Motion
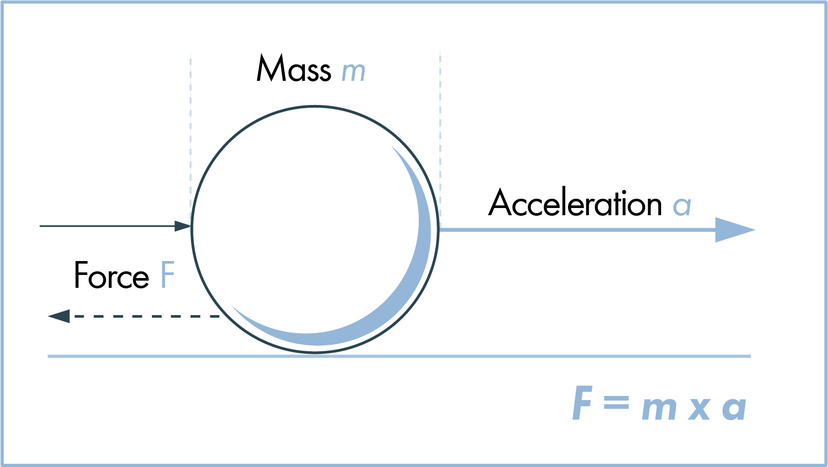
As long as we're talking about one of the greatest scientists who ever lived, let's move on to Newton's other famous laws. His three laws of motion form an essential component of modern physics. And like many scientific laws, they're rather elegant in their simplicity.
The first of the three laws states an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. For a ball rolling across the floor, that outside force could be the friction between the ball and the floor, or it could be the toddler that kicks the ball in another direction.
The second law establishes a connection between an object's mass ( m ) and its acceleration ( a ), in the form of the equation F = m × a . F represents force, measured in Newtons. It's also a vector, meaning it has a directional component. Owing to its acceleration, that ball rolling across the floor has a particular vector , a direction in which it's traveling, and it's accounted for in calculating its force.
The third law is rather pithy and should be familiar to you: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. That is, for every force applied to an object or surface, that object pushes back with equal force.
5: Laws of Thermodynamics
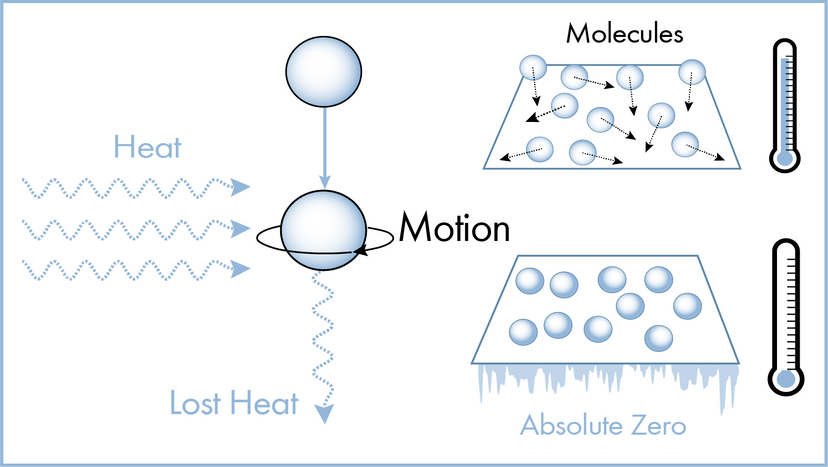
The British physicist and novelist C.P. Snow once said that a nonscientist who didn't know the second law of thermodynamics was like a scientist who had never read Shakespeare [source: Lambert]. Snow's now-famous statement was meant to emphasize both the importance of thermodynamics and the necessity for nonscientists to learn about it.
Thermodynamics is the study of how energy works in a system, whether it's an engine or Earth's core. It can be reduced to several basic laws, which Snow cleverly summed up as follows [source: Physics Planet]:
- You can't win.
- You can't break even.
- You can't quit the game.
Let's unpack these a bit. By saying you can't win, Snow meant that since matter and energy are conserved, you can't get one without giving up some of the other (i.e., E=mc²). It also means that for an engine to produce work, you have to supply heat, although in anything other than a perfectly closed system, some heat is inevitably lost to the outside world, which then leads to the second law.
The second statement — you can't break even — means that due to ever-increasing entropy , you can't return to the same energy state. Energy concentrated in one place will always flow to places of lower concentration.
Finally, the third law — you can't quit the game — refers to absolute zero, the lowest theoretical temperature possible, measured at zero Kelvin or (minus 273.15 degrees Celsius and minus 459.67 degrees Fahrenheit). When a system reaches absolute zero, molecules stop all movement, meaning that there is no kinetic energy, and entropy reaches its lowest possible value. But in the real world, even in the recesses of space, reaching absolutely zero is impossible — you can only get very close to it.
4: Archimedes' Buoyancy Principle
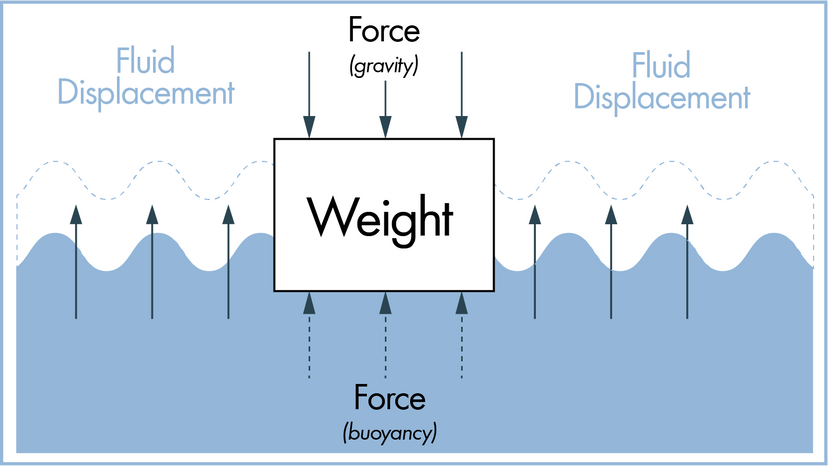
After he discovered his principle of buoyancy, the ancient Greek scholar Archimedes allegedly yelled out "Eureka!" and ran naked through the city of Syracuse. The discovery was that important. The story goes that Archimedes made his great breakthrough when he noticed the water rise as he got into the tub [source: Quake ].
According to Archimedes' buoyancy principle , the force acting on, or buoying, a submerged or partially submerged object equals the weight of the liquid that the object displaces. This sort of principle has an immense range of applications and is essential to calculations of density, as well as designing submarines and other oceangoing vessels.
3: Evolution and Natural Selection
Now that we've established some of the fundamental concepts of how our universe began and how physics play out in our daily lives, let's turn our attention to the human form and how we got to be the way we are. According to most scientists, all life on Earth has a common ancestor. But in order to produce the immense amount of difference among all living organisms, certain ones had to evolve into distinct species.
In a basic sense, this differentiation occurred through evolution, through descent with modification [source: UCMP ]. Populations of organisms developed different traits, through mechanisms such as mutation. Those with traits that were more beneficial to survival such as, a frog whose brown coloring allows it to be camouflaged in a swamp, were naturally selected for survival; hence the term natural selection .
It's possible to expand upon both of these theories at greater length, but this is the basic, and groundbreaking, discovery that Darwin made in the 19th century: that evolution through natural selection accounts for the tremendous diversity of life on Earth.
2: Theory of General Relativity
Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity remains an important and essential discovery because it permanently altered how we look at the universe. Einstein's major breakthrough was to say that space and time are not absolutes and that gravity is not simply a force applied to an object or mass. Rather, the gravity associated with any mass curves the very space and time (often called space-time) around it.
To conceptualize this, imagine you're traveling across the Earth in a straight line, heading east, starting somewhere in the Northern Hemisphere. After a while, if someone were to pinpoint your position on a map, you'd actually be both east and far south of your original position. That's because Earth is curved. To travel directly east, you'd have to take into account the shape of Earth and angle yourself slightly north. (Think about the difference between a flat paper map and a spherical globe.)
Space is pretty much the same. For example, to the occupants of the shuttle orbiting Earth, it can look like they're traveling on a straight line through space. In reality, the space-time around them is being curved by Earth's gravity (as it would be with any large object with immense gravity such as a planet or a black hole), causing them to both move forward and to appear to orbit Earth.
Einstein's theory had tremendous implications for the future of astrophysics and cosmology. It explained a minor, unexpected anomaly in Mercury's orbit, showed how starlight bends and laid the theoretical foundations for black holes.
1: Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle
Einstein's broader theory of relativity told us more about how the universe works and helped to lay the foundation for quantum physics, but it also introduced more confusion into theoretical science. In 1927, this sense that the universe's laws were, in some contexts, flexible, led to a groundbreaking discovery by the German scientist Werner Heisenberg.
In postulating his Uncertainty Principle , Heisenberg realized that it was impossible to simultaneously know, with a high level of precision, two properties of a particle. In other words, you can know the position of an electron with a high degree of certainty, but not its momentum and vice versa.
Niels Bohr later made a discovery that helps to explain Heisenberg's principle. Bohr found that an electron has the qualities of both a particle and a wave, a concept known as wave-particle duality , which has become a cornerstone of quantum physics. So when we measure an electron's position, we are treating it as a particle at a specific point in space, with an uncertain wavelength. When we measure its momentum, we are treating it as a wave, meaning we can know the amplitude of its wavelength but not its location.
Keep reading for more science stuff you might like.
On the role of hypotheses in science
Harald brüssow.
1 Laboratory of Gene Technology, Department of Biosystems, KU Leuven, Leuven Belgium
Associated Data
Scientific research progresses by the dialectic dialogue between hypothesis building and the experimental testing of these hypotheses. Microbiologists as biologists in general can rely on an increasing set of sophisticated experimental methods for hypothesis testing such that many scientists maintain that progress in biology essentially comes with new experimental tools. While this is certainly true, the importance of hypothesis building in science should not be neglected. Some scientists rely on intuition for hypothesis building. However, there is also a large body of philosophical thinking on hypothesis building whose knowledge may be of use to young scientists. The present essay presents a primer into philosophical thoughts on hypothesis building and illustrates it with two hypotheses that played a major role in the history of science (the parallel axiom and the fifth element hypothesis). It continues with philosophical concepts on hypotheses as a calculus that fits observations (Copernicus), the need for plausibility (Descartes and Gilbert) and for explicatory power imposing a strong selection on theories (Darwin, James and Dewey). Galilei introduced and James and Poincaré later justified the reductionist principle in hypothesis building. Waddington stressed the feed‐forward aspect of fruitful hypothesis building, while Poincaré called for a dialogue between experiment and hypothesis and distinguished false, true, fruitful and dangerous hypotheses. Theoretical biology plays a much lesser role than theoretical physics because physical thinking strives for unification principle across the universe while biology is confronted with a breathtaking diversity of life forms and its historical development on a single planet. Knowledge of the philosophical foundations on hypothesis building in science might stimulate more hypothesis‐driven experimentation that simple observation‐oriented “fishing expeditions” in biological research.
Short abstract
Scientific research progresses by the dialectic dialogue between hypothesis building and the experimental testing of these hypotheses. Microbiologists can rely on an increasing set of sophisticated experimental methods for hypothesis testing but the importance of hypothesis building in science should not be neglected. This Lilliput offers a primer on philosophical concepts on hypotheses in science.
INTRODUCTION
Philosophy of science and the theory of knowledge (epistemology) are important branches of philosophy. However, philosophy has over the centuries lost its dominant role it enjoyed in antiquity and became in Medieval Ages the maid of theology (ancilla theologiae) and after the rise of natural sciences and its technological applications many practising scientists and the general public doubt whether they need philosophical concepts in their professional and private life. This is in the opinion of the writer of this article, an applied microbiologist, shortsighted for several reasons. Philosophers of the 20th century have made important contributions to the theory of knowledge, and many eminent scientists grew interested in philosophical problems. Mathematics which plays such a prominent role in physics and increasingly also in other branches of science is a hybrid: to some extent, it is the paradigm of an exact science while its abstract aspects are deeply rooted in philosophical thinking. In the present essay, the focus is on hypothesis and hypothesis building in science, essentially it is a compilation what philosophers and scientists thought about this subject in past and present. The controversy between the mathematical mind and that of the practical mind is an old one. The philosopher, physicist and mathematician Pascal ( 1623 –1662a) wrote in his Pensées : “Mathematicians who are only mathematicians have exact minds, provided all things are explained to them by means of definitions and axioms; otherwise they are inaccurate. They are only right when the principles are quite clear. And men of intuition cannot have the patience to reach to first principles of things speculative and conceptional, which they have never seen in the world and which are altogether out of the common. The intellect can be strong and narrow, and can be comprehensive and weak.” Hypothesis building is an act both of intuition and exact thinking and I hope that theoretical knowledge about hypothesis building will also profit young microbiologists.
HYPOTHESES AND AXIOMS IN MATHEMATICS
In the following, I will illustrate the importance of hypothesis building for the history of science and the development of knowledge and illustrate it with two famous concepts, the parallel axiom in mathematics and the five elements hypothesis in physics.
Euclidean geometry
The prominent role of hypotheses in the development of science becomes already clear in the first science book of the Western civilization: Euclid's The Elements written about 300 BC starts with a set of statements called Definitions, Postulates and Common Notions that lay out the foundation of geometry (Euclid, c.323‐c.283 ). This axiomatic approach is very modern as exemplified by the fact that Euclid's book remained for long time after the Bible the most read book in the Western hemisphere and a backbone of school teaching in mathematics. Euclid's twenty‐three definitions start with sentences such as “1. A point is that which has no part; 2. A line is breadthless length; 3. The extremities of a line are points”; and continues with the definition of angles (“8. A plane angle is the inclination to one another of two lines in a plane which meet one another and do not lie in a straight line”) and that of circles, triangles and quadrilateral figures. For the history of science, the 23rd definition of parallels is particularly interesting: “Parallel straight lines are straight lines which, being in the same plane and being produced indefinitely in both directions, do not meet one another in either direction”. This is the famous parallel axiom. It is clear that the parallel axiom cannot be the result of experimental observations, but must be a concept created in the mind. Euclid ends with five Common Notions (“1. Things which are equal to the same thing are also equal to one another, to 5. The whole is greater than the part”). The establishment of a contradiction‐free system for a branch of mathematics based on a set of axioms from which theorems were deduced was revolutionary modern. Hilbert ( 1899 ) formulated a sound modern formulation for Euclidian geometry. Hilbert's axiom system contains the notions “point, line and plane” and the concepts of “betweenness, containment and congruence” leading to five axioms, namely the axioms of Incidence (“Verknüpfung”), of Order (“Anordnung”), of Congruence, of Continuity (“Stetigkeit”) and of Parallels.
Origin of axioms
Philosophers gave various explanations for the origin of the Euclidean hypotheses or axioms. Plato considered geometrical figures as related to ideas (the true things behind the world of appearances). Aristoteles considered geometric figures as abstractions of physical bodies. Descartes perceived geometric figures as inborn ideas from extended bodies ( res extensa ), while Pascal thought that the axioms of Euclidian geometry were derived from intuition. Kant reasoned that Euclidian geometry represented a priori perceptions of space. Newton considered geometry as part of general mechanics linked to theories of measurement. Hilbert argued that the axioms of mathematical geometry are neither the result of contemplation (“Anschauung”) nor of psychological source. For him, axioms were formal propositions (“formale Aussageformen”) characterized by consistency (“Widerspruchsfreiheit”, i.e. absence of contradiction) (Mittelstrass, 1980a ).
Definitions
Axioms were also differently defined by philosophers. In Topics , Aristoteles calls axioms the assumptions taken up by one partner of a dialogue to initiate a dialectic discussion. Plato states that an axiom needs to be an acceptable or credible proposition, which cannot be justified by reference to other statements. Yet, a justification is not necessary because an axiom is an evident statement. In modern definition, axioms are methodical first sentences in the foundation of a deductive science (Mittelstrass, 1980a ). In Posterior Analytics , Aristotle defines postulates as positions which are at least initially not accepted by the dialogue partners while hypotheses are accepted for the sake of reasoning. In Euclid's book, postulates are construction methods that assure the existence of the geometric objects. Today postulates and axioms are used as synonyms while the 18th‐century philosophy made differences: Lambert defined axioms as descriptive sentences and postulates as prescriptive sentences. According to Kant, mathematical postulates create (synthesize) concepts (Mittelstrass, 1980b ). Definitions then fix the use of signs; they can be semantic definitions that explain the proper meaning of a sign in common language use (in a dictionary style) or they can be syntactic definitions that regulate the use of these signs in formal operations. Nominal definitions explain the words, while real definitions explain the meaning or the nature of the defined object. Definitions are thus essential for the development of a language of science, assuring communication and mutual understanding (Mittelstrass, 1980c ). Finally, hypotheses are also frequently defined as consistent conjectures that are compatible with the available knowledge. The truth of the hypothesis is only supposed in order to explain true observations and facts. Consequences of this hypothetical assumptions should explain the observed facts. Normally, descriptive hypotheses precede explanatory hypotheses in the development of scientific thought. Sometimes only tentative concepts are introduced as working hypotheses to test whether they have an explanatory capacity for the observations (Mittelstrass, 1980d ).
The Euclidian geometry is constructed along a logical “if→then” concept. The “if‐clause” formulates at the beginning the supposition, the “then clause” formulates the consequences from these axioms which provides a system of geometric theorems or insights. The conclusions do not follow directly from the hypothesis; this would otherwise represent self‐evident immediate conclusions. The “if‐then” concept in geometry is not used as in other branches of science where the consequences deduced from the axioms are checked against reality whether they are true, in order to confirm the validity of the hypothesis. The task in mathematics is: what can be logically deduced from a given set of axioms to build a contradiction‐free system of geometry. Whether this applies to the real world is in contrast to the situation in natural sciences another question and absolutely secondary to mathematics (Syntopicon, 1992 ).
Pascal's rules for hypotheses
In his Scientific Treatises on Geometric Demonstrations , Pascal ( 1623‐1662b ) formulates “Five rules are absolutely necessary and we cannot dispense with them without an essential defect and frequently even error. Do not leave undefined any terms at all obscure or ambiguous. Use in definitions of terms only words perfectly well known or already explained. Do not fail to ask that each of the necessary principles be granted, however clear and evident it may be. Ask only that perfectly self‐evident things be granted as axioms. Prove all propositions, using for their proof only axioms that are perfectly self‐evident or propositions already demonstrated or granted. Never get caught in the ambiguity of terms by failing to substitute in thought the definitions which restrict or define them. One should accept as true only those things whose contradiction appears to be false. We may then boldly affirm the original statement, however incomprehensible it is.”
Kant's rules on hypotheses
Kant ( 1724–1804 ) wrote that the analysis described in his book The Critique of Pure Reason “has now taught us that all its efforts to extend the bounds of knowledge by means of pure speculation, are utterly fruitless. So much the wider field lies open to hypothesis; as where we cannot know with certainty, we are at liberty to make guesses and to form suppositions. Imagination may be allowed, under the strict surveillance of reason, to invent suppositions; but these must be based on something that is perfectly certain‐ and that is the possibility of the object. Such a supposition is termed a hypothesis. We cannot imagine or invent any object or any property of an object not given in experience and employ it in a hypothesis; otherwise we should be basing our chain of reasoning upon mere chimerical fancies and not upon conception of things. Thus, we have no right to assume of new powers, not existing in nature and consequently we cannot assume that there is any other kind of community among substances than that observable in experience, any kind of presence than that in space and any kind of duration than that in time. The conditions of possible experience are for reason the only conditions of the possibility of things. Otherwise, such conceptions, although not self‐contradictory, are without object and without application. Transcendental hypotheses are therefore inadmissible, and we cannot use the liberty of employing in the absence of physical, hyperphysical grounds of explanation because such hypotheses do not advance reason, but rather stop it in its progress. When the explanation of natural phenomena happens to be difficult, we have constantly at hand a transcendental ground of explanation, which lifts us above the necessity of investigating nature. The next requisite for the admissibility of a hypothesis is its sufficiency. That is it must determine a priori the consequences which are given in experience and which are supposed to follow from the hypothesis itself.” Kant stresses another aspect when dealing with hypotheses: “It is our duty to try to discover new objections, to put weapons in the hands of our opponent, and to grant him the most favorable position. We have nothing to fear from these concessions; on the contrary, we may rather hope that we shall thus make ourselves master of a possession which no one will ever venture to dispute.”
For Kant's analytical and synthetical judgements and Difference between philosophy and mathematics (Kant, Whitehead) , see Appendices S1 and S2 , respectively.
Poincaré on hypotheses
The mathematician‐philosopher Poincaré ( 1854 –1912a) explored the foundation of mathematics and physics in his book Science and Hypothesis . In the preface to the book, he summarizes common thinking of scientists at the end of the 19th century. “To the superficial observer scientific truth is unassailable, the logic of science is infallible, and if scientific men sometimes make mistakes, it is because they have not understood the rules of the game. Mathematical truths are derived from a few self‐evident propositions, by a chain of flawless reasoning, they are imposed not only by us, but on Nature itself. This is for the minds of most people the origin of certainty in science.” Poincaré then continues “but upon more mature reflection the position held by hypothesis was seen; it was recognized that it is as necessary to the experimenter as it is to the mathematician. And then the doubt arose if all these constructions are built on solid foundations.” However, “to doubt everything or to believe everything are two equally convenient solutions: both dispense with the necessity of reflection. Instead, we should examine with the utmost care the role of hypothesis; we shall then recognize not only that it is necessary, but that in most cases it is legitimate. We shall also see that there are several kinds of hypotheses; that some are verifiable and when once confirmed by experiment become truths of great fertility; that others may be useful to us in fixing our ideas; and finally that others are hypotheses only in appearance, and reduce to definitions or to conventions in disguise.” Poincaré argues that “we must seek mathematical thought where it has remained pure‐i.e. in arithmetic, in the proofs of the most elementary theorems. The process is proof by recurrence. We first show that a theorem is true for n = 1; we then show that if it is true for n –1 it is true for n; and we conclude that it is true for all integers. The essential characteristic of reasoning by recurrence is that it contains, condensed in a single formula, an infinite number of syllogisms.” Syllogism is logical argument that applies deductive reasoning to arrive at a conclusion. Poincaré notes “that here is a striking analogy with the usual process of induction. But an essential difference exists. Induction applied to the physical sciences is always uncertain because it is based on the belief in a general order of the universe, an order which is external to us. Mathematical induction‐ i.e. proof by recurrence – is on the contrary, necessarily imposed on us, because it is only the affirmation of a property of the mind itself. No doubt mathematical recurrent reasoning and physical inductive reasoning are based on different foundations, but they move in parallel lines and in the same direction‐namely, from the particular to the general.”
Non‐Euclidian geometry: from Gauss to Lobatschewsky
Mathematics is an abstract science that intrinsically does not request that the structures described reflect a physical reality. Paradoxically, mathematics is the language of physics since the founder of experimental physics Galilei used Euclidian geometry when exploring the laws of the free fall. In his 1623 treatise The Assayer , Galilei ( 1564 –1642a) famously formulated that the book of Nature is written in the language of mathematics, thus establishing a link between formal concepts in mathematics and the structure of the physical world. Euclid's parallel axiom played historically a prominent role for the connection between mathematical concepts and physical realities. Mathematicians had doubted that the parallel axiom was needed and tried to prove it. In Euclidian geometry, there is a connection between the parallel axiom and the sum of the angles in a triangle being two right angles. It is therefore revealing that the famous mathematician C.F. Gauss investigated in the early 19th century experimentally whether this Euclidian theorem applies in nature. He approached this problem by measuring the sum of angles in a real triangle by using geodetic angle measurements of three geographical elevations in the vicinity of Göttingen where he was teaching mathematics. He reportedly measured a sum of the angles in this triangle that differed from 180°. Gauss had at the same time also developed statistical methods to evaluate the accuracy of measurements. Apparently, the difference of his measured angles was still within the interval of Gaussian error propagation. He did not publish the reasoning and the results for this experiment because he feared the outcry of colleagues about this unorthodox, even heretical approach to mathematical reasoning (Carnap, 1891 ‐1970a). However, soon afterwards non‐Euclidian geometries were developed. In the words of Poincaré, “Lobatschewsky assumes at the outset that several parallels may be drawn through a point to a given straight line, and he retains all the other axioms of Euclid. From these hypotheses he deduces a series of theorems between which it is impossible to find any contradiction, and he constructs a geometry as impeccable in its logic as Euclidian geometry. The theorems are very different, however, from those to which we are accustomed, and at first will be found a little disconcerting. For instance, the sum of the angles of a triangle is always less than two right angles, and the difference between that sum and two right angles is proportional to the area of the triangle. Lobatschewsky's propositions have no relation to those of Euclid, but are none the less logically interconnected.” Poincaré continues “most mathematicians regard Lobatschewsky's geometry as a mere logical curiosity. Some of them have, however, gone further. If several geometries are possible, they say, is it certain that our geometry is true? Experiments no doubt teaches us that the sum of the angles of a triangle is equal to two right angles, but this is because the triangles we deal with are too small” (Poincaré, 1854 ‐1912a)—hence the importance of Gauss' geodetic triangulation experiment. Gauss was aware that his three hills experiment was too small and thought on measurements on triangles formed with stars.
Poincaré vs. Einstein
Lobatschewsky's hyperbolic geometry did not remain the only non‐Euclidian geometry. Riemann developed a geometry without the parallel axiom, while the other Euclidian axioms were maintained with the exception of that of Order (Anordnung). Poincaré notes “so there is a kind of opposition between the geometries. For instance the sum of the angles in a triangle is equal to two right angles in Euclid's geometry, less than two right angles in that of Lobatschewsky, and greater than two right angles in that of Riemann. The number of parallel lines that can be drawn through a given point to a given line is one in Euclid's geometry, none in Riemann's, and an infinite number in the geometry of Lobatschewsky. Let us add that Riemann's space is finite, although unbounded.” As further distinction, the ratio of the circumference to the diameter of a circle is equal to π in Euclid's, greater than π in Lobatschewsky's and smaller than π in Riemann's geometry. A further difference between these geometries concerns the degree of curvature (Krümmungsmass k) which is 0 for a Euclidian surface, smaller than 0 for a Lobatschewsky and greater than 0 for a Riemann surface. The difference in curvature can be roughly compared with plane, concave and convex surfaces. The inner geometric structure of a Riemann plane resembles the surface structure of a Euclidean sphere and a Lobatschewsky plane resembles that of a Euclidean pseudosphere (a negatively curved geometry of a saddle). What geometry is true? Poincaré asked “Ought we then, to conclude that the axioms of geometry are experimental truths?” and continues “If geometry were an experimental science, it would not be an exact science. The geometric axioms are therefore neither synthetic a priori intuitions as affirmed by Kant nor experimental facts. They are conventions. Our choice among all possible conventions is guided by experimental facts; but it remains free and is only limited by the necessity of avoiding contradictions. In other words, the axioms of geometry are only definitions in disguise. What then are we to think of the question: Is Euclidean geometry true? It has no meaning. One geometry cannot be more true than another, it can only be more convenient. Now, Euclidean geometry is, and will remain, the most convenient, 1 st because it is the simplest and 2 nd because it sufficiently agrees with the properties of natural bodies” (Poincaré, 1854 ‐1912a).
Poincaré's book was published in 1903 and only a few years later Einstein published his general theory of relativity ( 1916 ) where he used a non‐Euclidean, Riemann geometry and where he demonstrated a structure of space that deviated from Euclidean geometry in the vicinity of strong gravitational fields. And in 1919, astronomical observations during a solar eclipse showed that light rays from a distant star were indeed “bent” when passing next to the sun. These physical observations challenged the view of Poincaré, and we should now address some aspects of hypotheses in physics (Carnap, 1891 ‐1970b).
HYPOTHESES IN PHYSICS
The long life of the five elements hypothesis.
Physical sciences—not to speak of biological sciences — were less developed in antiquity than mathematics which is already demonstrated by the primitive ideas on the elements constituting physical bodies. Plato and Aristotle spoke of the four elements which they took over from Thales (water), Anaximenes (air) and Parmenides (fire and earth) and add a fifth element (quinta essentia, our quintessence), namely ether. Ether is imagined a heavenly element belonging to the supralunar world. In Plato's dialogue Timaios (Plato, c.424‐c.348 BC a ), the five elements were associated with regular polyhedra in geometry and became known as Platonic bodies: tetrahedron (fire), octahedron (air), cube (earth), icosahedron (water) and dodecahedron (ether). In regular polyhedra, faces are congruent (identical in shape and size), all angles and all edges are congruent, and the same number of faces meet at each vertex. The number of elements is limited to five because in Euclidian space there are exactly five regular polyhedral. There is in Plato's writing even a kind of geometrical chemistry. Since two octahedra (air) plus one tetrahedron (fire) can be combined into one icosahedron (water), these “liquid” elements can combine while this is not the case for combinations with the cube (earth). The 12 faces of the dodecahedron were compared with the 12 zodiac signs (Mittelstrass, 1980e ). This geometry‐based hypothesis of physics had a long life. As late as 1612, Kepler in his Mysterium cosmographicum tried to fit the Platonic bodies into the planetary shells of his solar system model. The ether theory even survived into the scientific discussion of the 19th‐century physics and the idea of a mathematical structure of the universe dominated by symmetry operations even fertilized 20th‐century ideas about symmetry concepts in the physics of elementary particles.

Huygens on sound waves in air
The ether hypothesis figures prominently in the 1690 Treatise on Light from Huygens ( 1617‐1670 ). He first reports on the transmission of sound by air when writing “this may be proved by shutting up a sounding body in a glass vessel from which the air is withdrawn and care was taken to place the sounding body on cotton that it cannot communicate its tremor to the glass vessel which encloses it. After having exhausted all the air, one hears no sound from the metal though it is struck.” Huygens comes up with some foresight when suspecting “the air is of such a nature that it can be compressed and reduced to a much smaller space than that it normally occupies. Air is made up of small bodies which float about and which are agitated very rapidly. So that the spreading of sound is the effort which these little bodies make in collisions with one another, to regain freedom when they are a little more squeezed together in the circuit of these waves than elsewhere.”
Huygens on light waves in ether
“That is not the same air but another kind of matter in which light spreads; since if the air is removed from the vessel the light does not cease to traverse it as before. The extreme velocity of light cannot admit such a propagation of motion” as sound waves. To achieve the propagation of light, Huygens invokes ether “as a substance approaching to perfect hardness and possessing springiness as prompt as we choose. One may conceive light to spread successively by spherical waves. The propagation consists nowise in the transport of those particles but merely in a small agitation which they cannot help communicate to those surrounding.” The hypothesis of an ether in outer space fills libraries of physical discussions, but all experimental approaches led to contradictions with respect to postulated properties of this hypothetical material for example when optical experiments showed that light waves display transversal and not longitudinal oscillations.
The demise of ether
Mechanical models for the transmission of light or gravitation waves requiring ether were finally put to rest by the theory of relativity from Einstein (Mittelstrass, 1980f ). This theory posits that the speed of light in an empty space is constant and does not depend on movements of the source of light or that of an observer as requested by the ether hypothesis. The theory of relativity also provides an answer how the force of gravitation is transmitted from one mass to another across an essentially empty space. In the non‐Euclidian formulation of the theory of relativity (Einstein used the Riemann geometry), there is no gravitation force in the sense of mechanical or electromagnetic forces. The gravitation force is in this formulation simply replaced by a geometric structure (space curvature near high and dense masses) of a four‐dimensional space–time system (Carnap, 1891 ‐1970c; Einstein & Imfeld, 1956 ) Gravitation waves and gravitation lens effects have indeed been experimental demonstrated by astrophysicists (Dorfmüller et al., 1998 ).
For Aristotle's on physical hypotheses , see Appendix S3 .
PHILOSOPHICAL THOUGHTS ON HYPOTHESES
In the following, the opinions of a number of famous scientists and philosophers on hypotheses are quoted to provide a historical overview on the subject.
Copernicus' hypothesis: a calculus which fits observations
In his book Revolutions of Heavenly Spheres Copernicus ( 1473–1543 ) reasoned in the preface about hypotheses in physics. “Since the newness of the hypotheses of this work ‐which sets the earth in motion and puts an immovable sun at the center of the universe‐ has already received a great deal of publicity, I have no doubt that certain of the savants have taken great offense.” He defended his heliocentric thesis by stating “For it is the job of the astronomer to use painstaking and skilled observations in gathering together the history of the celestial movements‐ and then – since he cannot by any line of reasoning reach the true causes of these movements‐ to think up or construct whatever causes or hypotheses he pleases such that, by the assumption of these causes, those same movements can be calculated from the principles of geometry for the past and the future too. This artist is markedly outstanding in both of these respects: for it is not necessary that these hypotheses should be true, or even probable; but it is enough if they provide a calculus which fits the observations.” This preface written in 1543 sounds in its arguments very modern physics. However, historians of science have discovered that it was probably written by a theologian friend of Copernicus to defend the book against the criticism by the church.
Bacon's intermediate hypotheses
In his book Novum Organum , Francis Bacon ( 1561–1626 ) claims for hypotheses and scientific reasoning “that they augur well for the sciences, when the ascent shall proceed by a true scale and successive steps, without interruption or breach, from particulars to the lesser axioms, thence to the intermediates and lastly to the most general.” He then notes “that the lowest axioms differ but little from bare experiments, the highest and most general are notional, abstract, and of no real weight. The intermediate are true, solid, full of life, and up to them depend the business and fortune of mankind.” He warns that “we must not then add wings, but rather lead and ballast to the understanding, to prevent its jumping and flying, which has not yet been done; but whenever this takes place we may entertain greater hopes of the sciences.” With respect to methodology, Bacon claims that “we must invent a different form of induction. The induction which proceeds by simple enumeration is puerile, leads to uncertain conclusions, …deciding generally from too small a number of facts. Sciences should separate nature by proper rejections and exclusions and then conclude for the affirmative, after collecting a sufficient number of negatives.”
Gilbert and Descartes for plausible hypotheses
William Gilbert introduced in his book On the Loadstone (Gilbert, 1544‐1603 ) the argument of plausibility into physical hypothesis building. “From these arguments, therefore, we infer not with mere probability, but with certainty, the diurnal rotation of the earth; for nature ever acts with fewer than with many means; and because it is more accordant to reason that the one small body, the earth, should make a daily revolution than the whole universe should be whirled around it.”
Descartes ( 1596‐1650 ) reflected on the sources of understanding in his book Rules for Direction and distinguished what “comes about by impulse, by conjecture, or by deduction. Impulse can assign no reason for their belief and when determined by fanciful disposition, it is almost always a source of error.” When speaking about the working of conjectures he quotes thoughts of Aristotle: “water which is at a greater distance from the center of the globe than earth is likewise less dense substance, and likewise the air which is above the water, is still rarer. Hence, we hazard the guess that above the air nothing exists but a very pure ether which is much rarer than air itself. Moreover nothing that we construct in this way really deceives, if we merely judge it to be probable and never affirm it to be true; in fact it makes us better instructed. Deduction is thus left to us as the only means of putting things together so as to be sure of their truth. Yet in it, too, there may be many defects.”
Care in formulating hypotheses
Locke ( 1632‐1704 ) in his treatise Concerning Human Understanding admits that “we may make use of any probable hypotheses whatsoever. Hypotheses if they are well made are at least great helps to the memory and often direct us to new discoveries. However, we should not take up any one too hastily.” Also, practising scientists argued against careless use of hypotheses and proposed remedies. Lavoisier ( 1743‐1794 ) in the preface to his Element of Chemistry warned about beaten‐track hypotheses. “Instead of applying observation to the things we wished to know, we have chosen rather to imagine them. Advancing from one ill‐founded supposition to another, we have at last bewildered ourselves amidst a multitude of errors. These errors becoming prejudices, are adopted as principles and we thus bewilder ourselves more and more. We abuse words which we do not understand. There is but one remedy: this is to forget all that we have learned, to trace back our ideas to their sources and as Bacon says to frame the human understanding anew.”
Faraday ( 1791–1867 ) in a Speculation Touching Electric Conduction and the Nature of Matter highlighted the fundamental difference between hypotheses and facts when noting “that he has most power of penetrating the secrets of nature, and guessing by hypothesis at her mode of working, will also be most careful for his own safe progress and that of others, to distinguish that knowledge which consists of assumption, by which I mean theory and hypothesis, from that which is the knowledge of facts and laws; never raising the former to the dignity or authority of the latter.”
Explicatory power justifies hypotheses
Darwin ( 1809 –1882a) defended the conclusions and hypothesis of his book The Origin of Species “that species have been modified in a long course of descent. This has been affected chiefly through the natural selection of numerous, slight, favorable variations.” He uses a post hoc argument for this hypothesis: “It can hardly be supposed that a false theory would explain, to so satisfactory a manner as does the theory of natural selection, the several large classes of facts” described in his book.
The natural selection of hypotheses
In the concluding chapter of The Descent of Man Darwin ( 1809 –1882b) admits “that many of the views which have been advanced in this book are highly speculative and some no doubt will prove erroneous.” However, he distinguished that “false facts are highly injurious to the progress of science for they often endure long; but false views do little harm for everyone takes a salutory pleasure in proving their falseness; and when this is done, one path to error is closed and the road to truth is often at the same time opened.”
The American philosopher William James ( 1842–1907 ) concurred with Darwin's view when he wrote in his Principles of Psychology “every scientific conception is in the first instance a spontaneous variation in someone'’s brain. For one that proves useful and applicable there are a thousand that perish through their worthlessness. The scientific conceptions must prove their worth by being verified. This test, however, is the cause of their preservation, not of their production.”
The American philosopher J. Dewey ( 1859‐1952 ) in his treatise Experience and Education notes that “the experimental method of science attaches more importance not less to ideas than do other methods. There is no such thing as experiment in the scientific sense unless action is directed by some leading idea. The fact that the ideas employed are hypotheses, not final truths, is the reason why ideas are more jealously guarded and tested in science than anywhere else. As fixed truths they must be accepted and that is the end of the matter. But as hypotheses, they must be continuously tested and revised, a requirement that demands they be accurately formulated. Ideas or hypotheses are tested by the consequences which they produce when they are acted upon. The method of intelligence manifested in the experimental method demands keeping track of ideas, activities, and observed consequences. Keeping track is a matter of reflective review.”
The reductionist principle
James ( 1842‐1907 ) pushed this idea further when saying “Scientific thought goes by selection. We break the solid plenitude of fact into separate essences, conceive generally what only exists particularly, and by our classifications leave nothing in its natural neighborhood. The reality exists as a plenum. All its part are contemporaneous, but we can neither experience nor think this plenum. What we experience is a chaos of fragmentary impressions, what we think is an abstract system of hypothetical data and laws. We must decompose each chaos into single facts. We must learn to see in the chaotic antecedent a multitude of distinct antecedents, in the chaotic consequent a multitude of distinct consequents.” From these considerations James concluded “even those experiences which are used to prove a scientific truth are for the most part artificial experiences of the laboratory gained after the truth itself has been conjectured. Instead of experiences engendering the inner relations, the inner relations are what engender the experience here.“
Following curiosity
Freud ( 1856–1939 ) considered curiosity and imagination as driving forces of hypothesis building which need to be confronted as quickly as possible with observations. In Beyond the Pleasure Principle , Freud wrote “One may surely give oneself up to a line of thought and follow it up as far as it leads, simply out of scientific curiosity. These innovations were direct translations of observation into theory, subject to no greater sources of error than is inevitable in anything of the kind. At all events there is no way of working out this idea except by combining facts with pure imagination and thereby departing far from observation.” This can quickly go astray when trusting intuition. Freud recommends “that one may inexorably reject theories that are contradicted by the very first steps in the analysis of observation and be aware that those one holds have only a tentative validity.”
Feed‐forward aspects of hypotheses
The geneticist Waddington ( 1905–1975 ) in his essay The Nature of Life states that “a scientific theory cannot remain a mere structure within the world of logic, but must have implications for action and that in two rather different ways. It must involve the consequence that if you do so and so, such and such result will follow. That is to say it must give, or at least offer, the possibility of controlling the process. Secondly, its value is quite largely dependent on its power of suggesting the next step in scientific advance. Any complete piece of scientific work starts with an activity essentially the same as that of an artist. It starts by asking a relevant question. The first step may be a new awareness of some facet of the world that no one else had previously thought worth attending to. Or some new imaginative idea which depends on a sensitive receptiveness to the oddity of nature essentially similar to that of the artist. In his logical analysis and manipulative experimentation, the scientist is behaving arrogantly towards nature, trying to force her into his categories of thought or to trick her into doing what he wants. But finally he has to be humble. He has to take his intuition, his logical theory and his manipulative skill to the bar of Nature and see whether she answers yes or no; and he has to abide by the result. Science is often quite ready to tolerate some logical inadequacy in a theory‐or even a flat logical contradiction like that between the particle and wave theories of matter‐so long as it finds itself in the possession of a hypothesis which offers both the possibility of control and a guide to worthwhile avenues of exploration.”
Poincaré: the dialogue between experiment and hypothesis
Poincaré ( 1854 –1912b) also dealt with physics in Science and Hypothesis . “Experiment is the sole source of truth. It alone can teach us certainty. Cannot we be content with experiment alone? What place is left for mathematical physics? The man of science must work with method. Science is built up of facts, as a house is built of stones, but an accumulation of facts is no more a science than a heap of stones is a house. It is often said that experiments should be made without preconceived concepts. That is impossible. Without the hypothesis, no conclusion could have been drawn; nothing extraordinary would have been seen; and only one fact the more would have been catalogued, without deducing from it the remotest consequence.” Poincaré compares science to a library. Experimental physics alone can enrich the library with new books, but mathematical theoretical physics draw up the catalogue to find the books and to reveal gaps which have to be closed by the purchase of new books.
Poincaré: false, true, fruitful and dangerous hypotheses
Poincaré continues “we all know that there are good and bad experiments. The latter accumulate in vain. Whether there are hundred or thousand, one single piece of work will be sufficient to sweep them into oblivion. Bacon invented the term of an experimentum crucis for such experiments. What then is a good experiment? It is that which teaches us something more than an isolated fact. It is that which enables us to predict and to generalize. Experiments only gives us a certain number of isolated points. They must be connected by a continuous line and that is true generalization. Every generalization is a hypothesis. It should be as soon as possible submitted to verification. If it cannot stand the test, it must be abandoned without any hesitation. The physicist who has just given up one of his hypotheses should rejoice, for he found an unexpected opportunity of discovery. The hypothesis took into account all the known factors which seem capable of intervention in the phenomenon. If it is not verified, it is because there is something unexpected. Has the hypothesis thus rejected been sterile? Far from it. It has rendered more service than a true hypothesis.” Poincaré notes that “with a true hypothesis only one fact the more would have been catalogued, without deducing from it the remotest consequence. It may be said that the wrong hypothesis has rendered more service than a true hypothesis.” However, Poincaré warns that “some hypotheses are dangerous – first and foremost those which are tacit and unconscious. And since we make them without knowing them, we cannot get rid of them.” Poincaré notes that here mathematical physics is of help because by its precision one is compelled to formulate all the hypotheses, revealing also the tacit ones.
Arguments for the reductionist principle
Poincaré also warned against multiplying hypotheses indefinitely: “If we construct a theory upon multiple hypotheses, and if experiment condemns it, which of the premisses must be changed?” Poincaré also recommended to “resolve the complex phenomenon given directly by experiment into a very large number of elementary phenomena. First, with respect to time. Instead of embracing in its entirety the progressive development of a phenomenon, we simply try to connect each moment with the one immediately preceding. Next, we try to decompose the phenomenon in space. We must try to deduce the elementary phenomenon localized in a very small region of space.” Poincaré suggested that the physicist should “be guided by the instinct of simplicity, and that is why in physical science generalization so readily takes the mathematical form to state the problem in the form of an equation.” This argument goes back to Galilei ( 1564 –1642b) who wrote in The Two Sciences “when I observe a stone initially at rest falling from an elevated position and continually acquiring new increments of speed, why should I not believe that such increases take place in a manner which is exceedingly simple and rather obvious to everybody? If now we examine the matter carefully we find no addition or increment more simple than that which repeats itself always in the same manner. It seems we shall not be far wrong if we put the increment of speed as proportional to the increment of time.” With a bit of geometrical reasoning, Galilei deduced that the distance travelled by a freely falling body varies as the square of the time. However, Galilei was not naïve and continued “I grant that these conclusions proved in the abstract will be different when applied in the concrete” and considers disturbances cause by friction and air resistance that complicate the initially conceived simplicity.
Four sequential steps of discovery…
Some philosophers of science attributed a fundamental importance to observations for the acquisition of experience in science. The process starts with accidental observations (Aristotle), going to systematic observations (Bacon), leading to quantitative rules obtained with exact measurements (Newton and Kant) and culminating in observations under artificially created conditions in experiments (Galilei) (Mittelstrass, 1980g ).
…rejected by Popper and Kant
In fact, Newton wrote that he had developed his theory of gravitation from experience followed by induction. K. Popper ( 1902‐1994 ) in his book Conjectures and Refutations did not agree with this logical flow “experience leading to theory” and that for several reasons. This scheme is according to Popper intuitively false because observations are always inexact, while theory makes absolute exact assertions. It is also historically false because Copernicus and Kepler were not led to their theories by experimental observations but by geometry and number theories of Plato and Pythagoras for which they searched verifications in observational data. Kepler, for example, tried to prove the concept of circular planetary movement influenced by Greek theory of the circle being a perfect geometric figure and only when he could not demonstrate this with observational data, he tried elliptical movements. Popper noted that it was Kant who realized that even physical experiments are not prior to theories when quoting Kant's preface to the Critique of Pure Reason : “When Galilei let his globes run down an inclined plane with a gravity which he has chosen himself, then a light dawned on all natural philosophers. They learnt that our reason can only understand what it creates according to its own design; that we must compel Nature to answer our questions, rather than cling to Nature's apron strings and allow her to guide us. For purely accidental observations, made without any plan having been thought out in advance, cannot be connected by a law‐ which is what reason is searching for.” From that reasoning Popper concluded that “we ourselves must confront nature with hypotheses and demand a reply to our questions; and that lacking such hypotheses, we can only make haphazard observations which follow no plan and which can therefore never lead to a natural law. Everyday experience, too, goes far beyond all observations. Everyday experience must interpret observations for without theoretical interpretation, observations remain blind and uninformative. Everyday experience constantly operates with abstract ideas, such as that of cause and effect, and so it cannot be derived from observation.” Popper agreed with Kant who said “Our intellect does not draw its laws from nature…but imposes them on nature”. Popper modifies this statement to “Our intellect does not draw its laws from nature, but tries‐ with varying degrees of success – to impose upon nature laws which it freely invents. Theories are seen to be free creations of our mind, the result of almost poetic intuition. While theories cannot be logically derived from observations, they can, however, clash with observations. This fact makes it possible to infer from observations that a theory is false. The possibility of refuting theories by observations is the basis of all empirical tests. All empirical tests are therefore attempted refutations.”
OUTLOOK: HYPOTHESES IN BIOLOGY
Is biology special.
Waddington notes that “living organisms are much more complicated than the non‐living things. Biology has therefore developed more slowly than sciences such as physics and chemistry and has tended to rely on them for many of its basic ideas. These older physical sciences have provided biology with many firm foundations which have been of the greatest value to it, but throughout most of its history biology has found itself faced with the dilemma as to how far its reliance on physics and chemistry should be pushed” both with respect to its experimental methods and its theoretical foundations. Vitalism is indeed such a theory maintaining that organisms cannot be explained solely by physicochemical laws claiming specific biological forces active in organisms. However, efforts to prove the existence of such vital forces have failed and today most biologists consider vitalism a superseded theory.
Biology as a branch of science is as old as physics. If one takes Aristotle as a reference, he has written more on biology than on physics. Sophisticated animal experiments were already conducted in the antiquity by Galen (Brüssow, 2022 ). Alertus Magnus displayed biological research interest during the medieval time. Knowledge on plants provided the basis of medical drugs in early modern times. What explains biology's decreasing influence compared with the rapid development of physics by Galilei and Newton? One reason is the possibility to use mathematical equations to describe physical phenomena which was not possible for biological phenomena. Physics has from the beginning displayed a trend to few fundamental underlying principles. This is not the case for biology. With the discovery of new continents, biologists were fascinated by the diversity of life. Diversity was the conducting line of biological thinking. This changed only when taxonomists and comparative anatomists revealed recurring pattern in this stunning biological variety and when Darwin provided a theoretical concept to understand variation as a driving force in biology. Even when genetics and molecular biology allowed to understand biology from a few universally shared properties, such as a universal genetic code, biology differed in fundamental aspects from physics and chemistry. First, biology is so far restricted to the planet earth while the laws of physic and chemistry apply in principle to the entire universe. Second, biology is to a great extent a historical discipline; many biological processes cannot be understood from present‐day observations because they are the result of historical developments in evolution. Hence, the importance of Dobzhansky's dictum that nothing makes sense in biology except in the light of evolution. The great diversity of life forms, the complexity of processes occurring in cells and their integration in higher organisms and the importance of a historical past for the understanding of extant organisms, all that has delayed the successful application of mathematical methods in biology or the construction of theoretical frameworks in biology. Theoretical biology by far did not achieve a comparable role as theoretical physics which is on equal foot with experimental physics. Many biologists are even rather sceptical towards a theoretical biology and see progress in the development of ever more sophisticated experimental methods instead in theoretical concepts expressed by new hypotheses.
Knowledge from data without hypothesis?
Philosophers distinguish rational knowledge ( cognitio ex principiis ) from knowledge from data ( cognitio ex data ). Kant associates these two branches with natural sciences and natural history, respectively. The latter with descriptions of natural objects as prominently done with systematic classification of animals and plants or, where it is really history, when describing events in the evolution of life forms on earth. Cognitio ex data thus played a much more prominent role in biology than in physics and explains why the compilation of data and in extremis the collection of museum specimen characterizes biological research. To account for this difference, philosophers of the logical empiricism developed a two‐level concept of science languages consisting of a language of observations (Beobachtungssprache) and a language of theories (Theoriesprache) which are linked by certain rules of correspondence (Korrespondenzregeln) (Carnap, 1891 –1970d). If one looks into leading biological research journals, it becomes clear that biology has a sophisticated language of observation and a much less developed language of theories.
Do we need more philosophical thinking in biology or at least a more vigorous theoretical biology? The breathtaking speed of progress in experimental biology seems to indicate that biology can well develop without much theoretical or philosophical thinking. At the same time, one could argue that some fields in biology might need more theoretical rigour. Microbiologists might think on microbiome research—one of the breakthrough developments of microbiology research in recent years. The field teems with fascinating, but ill‐defined terms (our second genome; holobionts; gut–brain axis; dysbiosis, symbionts; probiotics; health benefits) that call for stricter definitions. One might also argue that biologists should at least consider the criticism of Goethe ( 1749–1832 ), a poet who was also an active scientist. In Faust , the devil ironically teaches biology to a young student.
“Wer will was Lebendigs erkennen und beschreiben, Sucht erst den Geist herauszutreiben, Dann hat er die Teile in seiner Hand, Fehlt, leider! nur das geistige Band.” (To docket living things past any doubt. You cancel first the living spirit out: The parts lie in the hollow of your hand, You only lack the living thing you banned).
We probably need both in biology: more data and more theory and hypotheses.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The author reports no conflict of interest.
FUNDING INFORMATION
No funding information provided.
Supporting information
Appendix S1
Brüssow, H. (2022) On the role of hypotheses in science . Microbial Biotechnology , 15 , 2687–2698. Available from: 10.1111/1751-7915.14141 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bacon, F. (1561. –1626) Novum Organum. In: Adler, M.J. (Ed.) (editor‐in‐chief) Great books of the western world . Chicago, IL: Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. 2nd edition 1992 vol 1–60 (abbreviated below as GBWW) here: GBWW vol. 28: 128. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brüssow, H. (2022) What is Truth – in science and beyond . Environmental Microbiology , 24 , 2895–2906. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carnap, R. (1891. ‐1970a) Philosophical foundations of physics. Ch. 14 . Basic Books, Inc., New York, 1969. [ Google Scholar ]
- Carnap, R. (1891. ‐1970b) Philosophical foundations of physics. Ch. 15 . Basic Books, Inc., New York, 1969. [ Google Scholar ]
- Carnap, R. (1891. ‐1970c) Philosophical foundations of physics. Ch. 16 . Basic Books, Inc., New York, 1969. [ Google Scholar ]
- Carnap, R. (1891. ‐1970d) Philosophical foundations of physics. Ch. 27–28 . Basic Books, Inc., New York, 1969. [ Google Scholar ]
- Copernicus . (1473. ‐1543) Revolutions of heavenly spheres . GBWW , vol. 15 , 505–506. [ Google Scholar ]
- Darwin, C. (1809. ‐1882a) The origin of species . GBWW , vol. 49 : 239. [ Google Scholar ]
- Darwin, C. (1809. ‐1882b) The descent of man . GBWW , vol. 49 : 590. [ Google Scholar ]
- Descartes, R. (1596. ‐1650) Rules for direction . GBWW , vol. 28 , 245. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dewey, J. (1859. –1952) Experience and education . GBWW , vol. 55 , 124. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dorfmüller, T. , Hering, W.T. & Stierstadt, K. (1998) Bergmann Schäfer Lehrbuch der Experimentalphysik: Band 1 Mechanik, Relativität, Wärme. In: Was ist Schwerkraft: Von Newton zu Einstein . Berlin, New York: Walter de Gruyter, pp. 197–203. [ Google Scholar ]
- Einstein, A. (1916) Relativity . GBWW , vol. 56 , 191–243. [ Google Scholar ]
- Einstein, A. & Imfeld, L. (1956) Die Evolution der Physik . Hamburg: Rowohlts deutsche Enzyklopädie, Rowohlt Verlag. [ Google Scholar ]
- Euclid . (c.323‐c.283) The elements . GBWW , vol. 10 , 1–2. [ Google Scholar ]
- Faraday, M. (1791. –1867) Speculation touching electric conduction and the nature of matter . GBWW , 42 , 758–763. [ Google Scholar ]
- Freud, S. (1856. –1939) Beyond the pleasure principle . GBWW , vol. 54 , 661–662. [ Google Scholar ]
- Galilei, G. (1564. ‐1642a) The Assayer, as translated by S. Drake (1957) Discoveries and Opinions of Galileo pp. 237–8 abridged pdf at Stanford University .
- Galilei, G. (1564. ‐1642b) The two sciences . GBWW vol. 26 : 200. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gilbert, W. (1544. ‐1603) On the Loadstone . GBWW , vol. 26 , 108–110. [ Google Scholar ]
- Goethe, J.W. (1749. –1832) Faust . GBWW , vol. 45 , 20. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hilbert, D. (1899) Grundlagen der Geometrie . Leipzig, Germany: Verlag Teubner. [ Google Scholar ]
- Huygens, C. (1617. ‐1670) Treatise on light . GBWW , vol. 32 , 557–560. [ Google Scholar ]
- James, W. (1842. –1907) Principles of psychology . GBWW , vol. 53 , 862–866. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kant, I. (1724. –1804) Critique of pure reason . GBWW , vol. 39 , 227–230. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lavoisier, A.L. (1743. ‐1794) Element of chemistry . GBWW , vol. 42 , p. 2, 6‐7, 9‐10. [ Google Scholar ]
- Locke, J. (1632. ‐1704) Concerning Human Understanding . GBWW , vol. 33 , 317–362. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mittelstrass, J. (1980a) Enzyklopädie Philosophie und Wissenschaftstheorie Bibliographisches Institut Mannheim, Wien, Zürich B.I. Wissenschaftsverlag Vol. 1: 239–241 .
- Mittelstrass, J. (1980b) Enzyklopädie Philosophie und Wissenschaftstheorie Bibliographisches Institut Mannheim, Wien, Zürich B.I. Wissenschaftsverlag Vol. 3: 307 .
- Mittelstrass, J. (1980c) Enzyklopädie Philosophie und Wissenschaftstheorie Bibliographisches Institut Mannheim, Wien, Zürich B.I. Wissenschaftsverlag Vol. 1: 439–442 .
- Mittelstrass, J. (1980d) Enzyklopädie Philosophie und Wissenschaftstheorie Bibliographisches Institut Mannheim, Wien, Zürich B.I. Wissenschaftsverlag Vol. 2: 157–158 .
- Mittelstrass, J. (1980e) Enzyklopädie Philosophie und Wissenschaftstheorie Bibliographisches Institut Mannheim, Wien, Zürich B.I. Wissenschaftsverlag Vol. 3: 264‐267, 449.450 .
- Mittelstrass, J. (1980f) Enzyklopädie Philosophie und Wissenschaftstheorie Bibliographisches Institut Mannheim, Wien, Zürich B.I. Wissenschaftsverlag Vol. 1: 209–210 .
- Mittelstrass, J. (1980g) Enzyklopädie Philosophie und Wissenschaftstheorie Bibliographisches Institut Mannheim, Wien, Zürich B.I. Wissenschaftsverlag Vol. 1: 281–282 .
- Pascal, B. (1623. ‐1662a) Pensées GBWW vol. 30 : 171–173. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pascal, B. (1623. ‐1662b) Scientific treatises on geometric demonstrations . GBWW vol. 30 : 442–443. [ Google Scholar ]
- Plato . (c.424‐c.348 BC a) Timaeus . GBWW , vol. 6 , 442–477. [ Google Scholar ]
- Poincaré, H. (1854. ‐1912a) Science and hypothesis GBWW , vol. 56 : XV‐XVI, 1–5, 10–15 [ Google Scholar ]
- Poincaré, H. (1854. ‐1912b) Science and hypothesis GBWW , vol. 56 : 40–52. [ Google Scholar ]
- Popper, K. (1902. ‐1994) Conjectures and refutations . London and New York, 2002: The Growth of Scientific Knowledge Routledge Classics, pp. 249–261. [ Google Scholar ]
- Syntopicon . (1992) Hypothesis . GBWW , vol. 1 , 576–587. [ Google Scholar ]
- Waddington, C.H. (1905. –1975) The nature of life . GBWW , vol. 56 , 697–699. [ Google Scholar ]
April 10, 2024
10 min read
How a Theory about Climate Change Led to The Feminine Mystique
In 1958 Betty Friedan wrote an article that changed science journalism—and her career
By Rachel Shteir

A portrait of author, activist, and feminist Betty Friedan, the founder of the National Organization for Women (NOW), 1960.
Fred Palumbo/Underwood Archives/Getty Images
Almost a year before the 1963 publication of The Feminine Mystique —the zeitgeist-shattering book that would launch second-wave feminism and change the life of millions of women—author Betty Friedan wrote a confession in the pages of the Writer , a craft magazine for literary people:
My most successful article concerned an act of intellectual discovery—the discovery of “The Coming Ice Age.” I am not a science writer. The complex theory that explains why glaciers have come and gone over the earth the past million years and that predicts the dawn of another ice age is a far cry from suburban pioneering, natural childbirth, suicidal loneliness and love.
In “The Coming Ice Age,” which was published five years before The Feminine Mystique in the September 1958 issue of Harper’s Magazine, Friedan told how Maurice Ewing, a prominent oceanographer and founder of the Lamont Geological Observatory (now Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, located in the Palisades in Rockland County, N.Y.), and William L. Donn, a geologist-meteorologist, had developed a new explanation for why the world alternates between ice ages and so-called interglacial periods.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
At the time, there was no consensus as to why ice ages form and why they disappear . Some scientists thought it could be caused by changes in ocean circulation or Earth’s orbit; others gravitated toward some sudden impact, such as dust from volcanic eruptions or a meteor strike. Ewing and Donn rejected the sudden impact theory. In 1953 they had taken sediment samples from beneath the floor of the Caribbean Sea using a new giant corer. In a number of samples, the color of the sediment changed from gray to pink at the same line. At Lamont the scientists used radiometric dating and found that the line indicated the ocean heating up sharply approximately 11,000 years ago—not gradually from 16,000 to 10,000 years, as scientists had previously surmised. This “abrupt” increase in temperature—over about 1,000 years—marked the end of the last ice age, they said: the so-called Wisconsin glacial episode had not ended millions of years ago as some scientists previously thought.
Given this more rapid timeline, Ewing and Donn proposed that the cycle of ice ages was linked to “polar wandering,” which is the migration of Earth’s magnetic poles, caused by shifts in Earth’s crust. When the North Pole “wandered” from the Arctic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean a million years ago, they posited, the Arctic Ocean became free of ice and open to warm currents, which in turn creates evaporation. This scenario, the scientists theorized, eventually starts an ice age. But the most sensational part of their theory was that a new ice age would be coming in a few hundred years.
Some geographers, such as Carl Sauer, initially endorsed Ewing and Donn’s theory; others were more skeptical. Soon enough, their first stab at explaining the ice age (they would publish several adjustments to the theory) was overturned. But Betty Friedan homed in on the theory’s significance for a general audience—it was the first time the public at large was made aware of climate change. Sensing why the backstory would be captivating to a lay audience, Friedan captured the process of science in a narrative, character-driven style that was radical for its time.
The experience of reporting and writing this sweeping yet intimate piece of science journalism has long been framed by Friedan biographers as a blip; a random excursion that occurred between Friedan’s articles for women’s magazines and The Feminine Mystique . But in reading Friedan’s letters, memoir and other archival material, it becomes clear that this article was not just an outlier: it was the result of a crucial education in how to embrace complexity and advance new ideas.
Friedan’s pursuit of “The Coming Ice Age” was born of proximity and instinct. In the spring of 1956 she and her family moved to Palisades, N.Y. (then called Sneden’s Landing), which was just around the corner from Lamont Observatory. That spring, Ewing, who taught at Columbia University, and Donn, who taught at Brooklyn College, published what they described as a “preliminary report” of their theory of the ice age in Science . Friedan learned about Ewing and Donn from the mother of one of her son’s playmates; the mother mentioned the scientists as noteworthy locals.
Friedan’s journalistic curiosity was piqued. She’d been drawn to science in high school, where she was inspired by Marie Curie. A teacher discouraged her from pursing a path of scientific research and told her that girls grew up to become nurses. In an early example of proving her naysayers wrong, Friedan graduated from Smith College in 1942 with a degree in psychology. She then went to the University of California, Berkeley, to pursue a Ph.D. in psychology, where she studied with Erik Erikson (and dated some of Robert Oppenheimer’s protégés). It was at Berkeley, she famously wrote in The Feminine Mystique, that a man she was dating first dumped her because of her brilliance: “We walked in the Berkeley hills and [he] said: ‘Nothing can come of this, between us. I’ll never win a fellowship like yours.’”
Friedan left school during the spring of her first year. She became a journalist—first as a staffer for newspapers, then as a freelancer for women’s magazines. She felt she could make a more active impact on the world in journalism than she could in the academy. Her coverage areas included unions, Jim Crow laws and sexism but rarely dealt with science.
Friedan did not immediately pursue a magazine story about Ewing and Donn; she assumed that some big-name reporter would pounce on it. No one did. When she brought up the idea to her agent, Marie Rodell (who was also the agent of Rachel Carson and Martin Luther King, Jr.), Rodell did not think Friedan had a sufficient science background to write a piece about the ice age. Friedan insisted that she send it out to editors and was insulted when many responded that the subject was too abstract.
Collier’s magazine, however, was interested. And on November 2, 1956, Friedan—along with Ewing and Donn—signed a contract to do a joint story. Friedan would write, and the scientists would fact-check and, of course, be the subjects. “The Ice Age Paradox,” as it was first titled, would be co-bylined. The trio would split additional monies from syndication and other media.
Friedan, a mother of three children, swiftly got to work. As she recalls in her memoir, she would read geological textbooks at night and then “go up in the morning to Lamont and interview scientists then come back to breast feed Emily,” her then six-month-old daughter. But shortly after Friedan submitted her draft, Collier’s folded in January 1957. It paid the scientists all of their money and Friedan half of hers, with an agreement that she could resell the story.
On the advice of Rodell, Friedan began to revise and punch up the draft. In an early example of “new journalism,” she inserted herself into the narrative, joking that she had irritated the scientists with her pesky questions. She described Ewing and Donn as though they were politicians or celebrities and included their missteps and doubts. She didn’t shy away from characterization: Ewing, “a tall and powerful Texan who speaks in a gentle voice, was white-haired before he was fifty, a fact his friends attribute to the pace at which he has lived his life as a scientist,” she wrote.
Friedan was working on other stories at the time, one of which was based on revelations she’d had at her 15-year Smith reunion in June 1957. She wanted to document a trend she’d first noticed five years ago at the previous reunion: women who had excelled in college had abandoned work to become a traditional wife and mother. She wrote an article entitled, “Are Women Wasting Their Time in College?” Several magazines— McCall’s , Redbook and Ladies’ Home Journal —rejected it.
A year passed before she finally sent an updated draft to Ewing and Donn. In early January 1958 Ewing replied, sharing his concern about her sensational tone. He explained that she did not display the gravitas that he and Donn were entitled to as professional scientists. In a second letter than arrived a few weeks later, his tone was far angrier. He wrote that he had found hundreds of errors in her “paper” and chastised her for having “livened up” their theory. He wanted to exit their agreement to collaborate as co-authors. If Friedan took the piece out of the first person, he wrote, she might proceed by herself—as long as he and Donn could still vet it.
Three days later Friedan tore off a three-page, single-spaced response. She expressed astonishment that Donn and Ewing found the article sloppy because they had read a previous draft and not mentioned any misgivings. Perhaps, she speculated, the errors were their fault, considering that they were constantly changing their theory. Friedan defended herself as a writer: If she’d cut a few sentences or rearranged a few paragraphs, it was in the service of making dense scientific theory understandable to the lay reader. She was doing her job as a journalist, in other words. She was counting on the scientists to correct errors in the article, not to run away from them.
Despite the friction, Friedan made some of the changes Ewing asked for: She took herself out of the piece and put it into the first-person plural by changing the “I” to “we.” She asked to meet with the scientists to get corrections before Ewing flew to Argentina to do research. It’s not clear whether this meeting occurred, though Friedan continued to correspond with the scientists’ secretary for fact-checking. “The Ice Age Paradox” looked like it had a new home: Harper’s was interested in publishing it.
Then in March an article entitled “Another Ice Age Is on the Way” appeared in This Week, a popular Sunday supplement that was widely syndicated. It was written by publicist and journalist Leslie Lieber, who had seen Ewing and Donn discussing their theory on a CBS segment.His story took a straight-ahead approach and wasn’t particularly illuminating. (The scientists would later claim that the Lieber story was a clip job and that they had not given Lieber any interviews.) But according to a note scribbled on Rodell’s notepad, Friedan was crushed and enraged by Lieber’s article. Friedan complained that Ewing and Donn had violated the old Collier’s agreement. She catastrophized, worrying that Harper’s would kill her story. As Rodell would later write in a scolding letter to the scientists, they were lucky that John Fischer, the esteemed editor of Harper’s , was too generous to think that Friedan had been scooped.
Harper’s did ultimately run“The Coming Ice Age” —in the prestigious spot of cover story—in September 1958. The byline was Friedan’s alone. Unlike Lieber, who had framed the scientists as “leaders in their field” in a generic piece filled with clichés,Friedan had made abstract ideas accessible. She encouraged readers to identify with the scientists who were advancing those ideas. While describing technical processes, Friedan gave readers a close-up view at how the scientists were thinking—and rethinking—those processes.
The article was a success— Reader’s Digest reprinted it in November. The following year, “The Coming Ice Age” was published in an anthology, Gentlemen, Scholars, and Scoundrels: A Treasury of the Best of Harper’s Magazine from 1850 to the Present , alongside essays by writers William Faulkner, Mark Twain, Aldous Huxley and George Bernard Shaw. That’s when George Brockway, then editor in chief of W. W. Norton, first read Friedan’s article. “I thought [Friedan] might have a book in her, although perhaps not on this particular subject,” he recalled in an interview with writer Patricia Bradley. “So I wrote her.”
Friedan remembered it differently, that Brockway approached her specifically to develop “The Coming Ice Age” into a book and that she had responded, “If I ever write a book, it’s going to be about my own work.” Soon after, she started in earnest on The Feminine Mystique .
Writing about the drama of a new scientific theory—one with potentially big implications for the future—had given Friedan the courage to write about complex research and the ways it affects people’s life. Many of the reporting techniques and writing styles Friedan first experimented with in “The Coming Ice Age” are abundant in The Feminine Mystique . In the article, Friedan uses the language of the detective novel: “They had to track down the circumstantial evidence of what happened 11,000 years ago; they had to find geological witnesses to confirm their reconstruction of the crime,” she writes, as if Ewing and Donn were gumshoes. The same style appears in The Feminine Mystique when Friedan talks about getting access to market research files in an advertising agency.
“The Coming Ice Age” ranges across time and space, just as The Feminine Mystique later did, rather than presenting a linear chronology. And although it was the scientists’ preference to cast most of the long quotes in “The Coming Ice Age” in first-person plural, that choice gave the article an added power. Friedan used first-person plural in The Feminine Mystique to show individual suffragists as a united group.
Unlike other journalists who were writing about scientists, Friedan openly showed Ewing and Donn’s indecision—she did not ignore or try to hide the ways in which scientific inquiry often stalls and stumbles. She treated her sources as humans, not infallible idols. In one scene, the men find “proof” of their theory while paging through “dusty old volumes” of National Geographic . To Ewing and Donn, the shape of an Arctic beach in a photograph proved that the water there had once been warmer.
Despite, or perhaps because of, Ewing and Donn’s idiosyncratic methods, Friedan identified with them—just as she would to some extent with ideological outliers that she wrote about in the Feminine Mystique, such as Margaret Mead and Abraham Maslow. Ewing and Donn defied what they called “the compartmentalization of science,” Friedan wrote in “The Coming Ice Age.” In Friedan’s article, scientists aren’t lone geniuses. She described how Ewing and Donn called up anthropologists late at night to ask them whether, 11,000 years ago, humans might have migrated because of the ice age. With this granular type of reporting, she captured the power of an interdisciplinary approach—one in which researchers collaborated across specialties and operated as sleuths. This, Friedan had leaned, is how paradigms shift.
Parkinson's Disease: New theory on the disease's origins and spread
The nose or the gut? For the past two decades, the scientific community has debated the wellspring of the toxic proteins at the source of Parkinson's disease. In 2003, a German pathologist, Heiko Braak, MD, first proposed that the disease begins outside the brain. More recently, Per Borghammer, MD, with Aarhus University Hospital in Denmark, and his colleagues argue that the disease is the result of processes that start in either the brain's smell center (brain-first) or the body's intestinal tract (body-first).
A new hypothesis paper appearing in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease on World Parkinson's Day unites the brain- and body-first models with some of the likely causes of the disease-environmental toxicants that are either inhaled or ingested. The authors of the new study, who include Borghammer, argue that inhalation of certain pesticides, common dry cleaning chemicals, and air pollution predispose to a brain-first model of the disease. Other ingested toxicants, such as tainted food and contaminated drinking water, lead to body-first model of the disease.
"In both the brain-first and body-first scenarios the pathology arises in structures in the body closely connected to the outside world," said Ray Dorsey, MD, a professor of Neurology at the University of Rochester Medical Center and co-author of the piece. "Here we propose that Parkinson's is a systemic disease and that its initial roots likely begin in the nose and in the gut and are tied to environmental factors increasingly recognized as major contributors, if not causes, of the disease. This further reinforces the idea that Parkinson's, the world's fastest growing brain disease, may be fueled by toxicants and is therefore largely preventable."
Different pathways to the brain, different forms of disease
A misfolded protein called alpha-synuclein has been in scientists' sights for the last 25 years as one of the driving forces behind Parkinson's. Over time, the protein accumulates in the brain in clumps, called Lewy bodies, and causes progressive dysfunction and death of many types of nerve cells, including those in the dopamine-producing regions of the brain that control motor function. When first proposed, Braak thought that an unidentified pathogen, such as a virus, may be responsible for the disease.
The new piece argues that toxins encountered in the environment, specifically the dry cleaning and degreasing chemicals trichloroethylene (TCE) and perchloroethylene (PCE), the weed killer paraquat, and air pollution, could be common causes for the formation of toxic alpha-synuclein. TCE and PCE contaminates thousands of former industrial, commercial, and military sites, most notably the Marine Corps base Camp Lejeune, and paraquat is one of the most widely used herbicides in the US, despite being banned for safety concerns in more than 30 countries, including the European Union and China. Air pollution was at toxic levels in nineteenth century London when James Parkinson, whose 269th birthday is celebrated today, first described the condition.
The nose and the gut are lined with a soft permeable tissue, and both have well established connections to the brain. In the brain-first model, the chemicals are inhaled and may enter the brain via the nerve responsible for smell. From the brain's smell center, alpha-synuclein spreads to other parts of the brain principally on one side, including regions with concentrations of dopamine-producing neurons. The death of these cells is a hallmark of Parkinson's disease. The disease may cause asymmetric tremor and slowness in movement and, a slower rate of progression after diagnosis, and only much later, significant cognitive impairment or dementia.
When ingested, the chemicals pass through the lining of the gastrointestinal tract. Initial alpha-synuclein pathology may begin in the gut's own nervous system from where it can spread to both sides of the brain and spinal cord. This body-first pathway is often associated with Lewy body dementia, a disease in the same family as Parkinson's, which is characterized by early constipation and sleep disturbance, followed by more symmetric slowing in movements and earlier dementia, as the disease spreads through both brain hemispheres.
New models to understand and study brain diseases
"These environmental toxicants are widespread and not everyone has Parkinson's disease," said Dorsey. "The timing, dose, and duration of exposure and interactions with genetic and other environmental factors are probably key to determining who ultimately develops Parkinson's. In most instances, these exposures likely occurred years or decades before symptoms develop."
Pointing to a growing body of research linking environmental exposure to Parkinson's disease, the authors believe the new models may enable the scientific community to connect specific exposures to specific forms of the disease. This effort will be aided by increasing public awareness of the adverse health effects of many chemicals in our environment. The authors conclude that their hypothesis "may explain many of the mysteries of Parkinson's disease and open the door toward the ultimate goal-prevention."
In addition to Parkinson's, these models of environmental exposure may advance understanding of how toxicants contribute to other brain disorders, including autism in children, ALS in adults, and Alzheimer's in seniors. Dorsey and his colleagues at the University of Rochester have organized a symposium on the Brain and the Environment in Washington, DC, on May 20 that will examine the role toxicants in our food, water, and air are playing in all these brain diseases.
Additional authors of the hypothesis paper include Briana De Miranda, PhD, with the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and Jacob Horsager, MD, PhD, with Aarhus University Hospital in Denmark.
- Parkinson's Research
- Chronic Illness
- Brain Tumor
- Diseases and Conditions
- Parkinson's
- Disorders and Syndromes
- Brain-Computer Interfaces
- Parkinson's disease
- Deep brain stimulation
- Homosexuality
- Dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia
- Excitotoxicity and cell damage
Story Source:
Materials provided by University of Rochester Medical Center . Original written by Mark Michaud. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- E. Ray Dorsey, Briana R. De Miranda, Jacob Horsager, Per Borghammer. The Body, the Brain, the Environment, and Parkinson’s Disease . Journal of Parkinson's Disease , 2024; 1 DOI: 10.3233/JPD-240019
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Microplastics Go from the Gut to Other Organs
- Epilepsy Drug May Prevent Brain Tumors
- Evolution's Recipe Book
- Green Wastewater-Treatment: Huge CO2 Cut
- Tropical Forests Need Fruit-Eating Birds
- Coffee's Prehistoric Origin and It's Future
- How Pluto Got Its Heart
- Coastal Cities and Corrosion of Infrastructure
- Watching Sports Can Boost Well-Being
- No Two Worms Are Alike
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 10 April 2024
- Correction 11 April 2024
Peter Higgs: science mourns giant of particle physics
- Davide Castelvecchi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Colleagues remember Peter Higgs as an inspirational scientist, who remained humble despite his fame. Credit: Graham Clark/Alamy
Few scientists have come into as much fame in recent years as British theoretical physicist Peter Higgs , the namesake of the boson that was discovered in 2012, who died on 8 April, aged 94.

Peter Higgs: the man behind the God particle
It was 60 years ago when Higgs first suggested that an elementary particle with unusual properties could pervade the Universe in the form of an invisible field, giving other elementary particles their masses 1 . Several other physicists thought of this mechanism independently around the same time, including François Englert, now at the Free University of Brussels. The particle was a crucial element of the theoretical edifice that physicists were building at the time, which later became known as the standard model of particles and fields.
Two experiments — called ATLAS and the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) — at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) near Geneva, Switzerland, confirmed Higgs’s predictions half a century later, and the discovery of the Higgs boson was announced. It was the last missing component of the standard model, and Higgs and Englert shared a Nobel Prize in 2013 for predicting the particle’s existence. Physicists at the LHC continue to learn about the properties of the Higgs boson , but some researchers say that only a ‘ Higgs factory ’ — a dedicated collider that can produce the particle in copious amounts — will enable them to gain a profound understanding of its role.
Inspiring figure
“Besides his outstanding contributions to particle physics, Peter was a very special person , an immensely inspiring figure for physicists around the world, a man of rare modesty, a great teacher and someone who explained physics in a very simple yet profound way,” said Fabiola Gianotti, director-general of CERN, Europe’s particle-physics laboratory, in an obituary posted on the organization’s website; Gianotti announced to the world the discovery of the Higgs boson at CERN. “I am very saddened, and I will miss him sorely.”
Many physicists took to X, formerly Twitter, to pay tribute to Higgs and share their favourite memories of him. “ RIP to Peter Higgs . The search for the Higgs boson was my primary focus for the first part of my career. He was a very humble man that contributed something immensely deep to our understanding of the universe,” posted Kyle Cranmer, a physicist at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and previously a senior member of the Higgs search team at ATLAS.
Happy birthday, Higgs boson! What we do and don’t know about the particle
“ I was fortunate to meet Peter Higgs in 2013 (days after the Nobel prize announcement). He was modest as he told a group of PhD students the history of the boson theory. Afterwards, I was very lucky to get my copy of the New York Times with the discovery signed by him,” said Clara Nellist, a physicist at the University of Amsterdam and a member of ATLAS.
“ A career highlight was helping Peter into a cab after the Collider exhibition launch @sciencemuseum in 2013 with a carrier bag of special-edition beer marking his recent Nobel,” posted Harry Cliff, a physicist at the University of Cambridge, UK.
“He disliked the limelight but was comfortable with friends and colleagues,” Frank Close, a physicist at the University of Oxford, UK, and author of the book Elusive : How Peter Higgs Solved the Mystery of Mass (2022), said in a statement to the UK Science Media Centre. “His boson took 48 years to appear, and when the Nobel was announced, he had disappeared to his favourite seafood bar in Leith.”
An exciting journey
Higgs’s work continues to be of fundamental importance, said physicist Sinead Farrington at the University of Edinburgh, UK. “We’re still on an exciting journey to figure out whether some further predictions are true, namely whether the Higgs boson interacts with itself in the predicted way, and whether it might decay to other beyond-the-standard-model particles,” she told the Science Media Centre.
For physicist and science writer Matt Strassler, based in Boston, Massachusetts, Higgs’s death represents “the end of an era” . “Higgs was a fortunate scientist: he lived to see his insight at age 30 turn up in experiments 50 years later,” he posted on X. “His role and influence in our understanding of the #universe will be remembered for millennia.”
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-01069-6
Updates & Corrections
Correction 11 April 2024 : An earlier version of this article stated that Kyle Cranmer was a member of the CMS team. He was in fact part of the ATLAS collaboration.
Higgs, P. Phys. Rev. Lett. 13 , 508–509 (1964).
Article Google Scholar
Download references
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

How the boson got Higgs's name
CERN’s supercollider plan: $17-billion ‘Higgs factory’ would dwarf LHC
Associate or Senior Editor (Immunology), Nature Communications
The Editor in Immunology at Nature Communications will handle original research papers and work on all aspects of the editorial process.
London, Beijing or Shanghai - Hybrid working model
Springer Nature Ltd
Assistant Professor - Cell Physiology & Molecular Biophysics
Opportunity in the Department of Cell Physiology and Molecular Biophysics (CPMB) at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC)
Lubbock, Texas
Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, School of Medicine
Postdoctoral Associate- Curing Brain Tumors
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Energy AI / Grid Modernization / Hydrogen Energy / Power Semiconductor Concentration / KENTECH College
21, Kentech-gil, Naju-si, Jeollanam-do, Republic of Korea(KR)
Korea Institute of Energy Technology
Professor in Macromolecular Chemistry
The Department of Chemistry - Ångström conducts research and education in Chemistry. The department has 260 employees and has a turnover of 290 mil...
Uppsala (Stad) (SE)
Uppsala University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
April 11, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
New hypothesis emerges on Parkinson's disease's origins and spread
by University of Rochester Medical Center
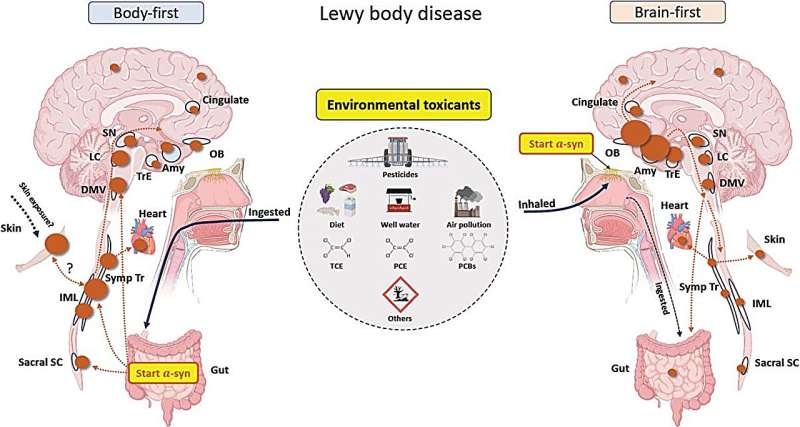
The nose or the gut? For the past two decades, the scientific community has debated the wellspring of the toxic proteins at the source of Parkinson's disease. In 2003, a German pathologist, Heiko Braak, MD, first proposed that the disease begins outside the brain.
More recently, Per Borghammer, MD, with Aarhus University Hospital in Denmark, and his colleagues argue that the disease is the result of processes that start in either the brain's smell center (brain-first) or the body's intestinal tract (body-first).
A new hypothesis paper appearing in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease on World Parkinson's Day unites the brain- and body-first models with some of the likely causes of the disease–environmental toxicants that are either inhaled or ingested.
The authors of the new study, who include Borghammer, argue that inhalation of certain pesticides, common dry cleaning chemicals, and air pollution predispose to a brain-first model of the disease. Other ingested toxicants, such as tainted food and contaminated drinking water, lead to body-first model of the disease.
"In both the brain-first and body-first scenarios the pathology arises in structures in the body closely connected to the outside world," said Ray Dorsey, MD, a professor of Neurology at the University of Rochester Medical Center and co-author of the piece.
"Here we propose that Parkinson's is a systemic disease and that its initial roots likely begin in the nose and in the gut and are tied to environmental factors increasingly recognized as major contributors, if not causes, of the disease. This further reinforces the idea that Parkinson's, the world's fastest growing brain disease, may be fueled by toxicants and is therefore largely preventable."
Different pathways to the brain, different forms of disease
A misfolded protein called alpha-synuclein has been in scientists' sights for the last 25 years as one of the driving forces behind Parkinson's. Over time, the protein accumulates in the brain in clumps, called Lewy bodies, and causes progressive dysfunction and death of many types of nerve cells, including those in the dopamine-producing regions of the brain that control motor function. When first proposed, Braak thought that an unidentified pathogen, such as a virus, may be responsible for the disease.
The new piece argues that toxins encountered in the environment, specifically the dry cleaning and degreasing chemicals trichloroethylene (TCE) and perchloroethylene (PCE), the weed killer paraquat, and air pollution , could be common causes for the formation of toxic alpha-synuclein.
TCE and PCE contaminates thousands of former industrial, commercial, and military sites, most notably the Marine Corps base Camp Lejeune, and paraquat is one of the most widely used herbicides in the US, despite being banned for safety concerns in more than 30 countries, including the European Union and China. Air pollution was at toxic levels in nineteenth century London when James Parkinson, whose 269th birthday is celebrated today, first described the condition.
The nose and the gut are lined with a soft permeable tissue, and both have well established connections to the brain. In the brain-first model, the chemicals are inhaled and may enter the brain via the nerve responsible for smell. From the brain's smell center, alpha-synuclein spreads to other parts of the brain principally on one side, including regions with concentrations of dopamine-producing neurons.
The death of these cells is a hallmark of Parkinson's disease. The disease may cause asymmetric tremor and slowness in movement and, a slower rate of progression after diagnosis, and only much later, significant cognitive impairment or dementia.
When ingested, the chemicals pass through the lining of the gastrointestinal tract. Initial alpha-synuclein pathology may begin in the gut's own nervous system from where it can spread to both sides of the brain and spinal cord.
This body-first pathway is often associated with Lewy body dementia, a disease in the same family as Parkinson's, which is characterized by early constipation and sleep disturbance, followed by more symmetric slowing in movements and earlier dementia, as the disease spreads through both brain hemispheres.
New models to understand and study brain diseases
"These environmental toxicants are widespread and not everyone has Parkinson's disease," said Dorsey. "The timing, dose, and duration of exposure and interactions with genetic and other environmental factors are probably key to determining who ultimately develops Parkinson's. In most instances, these exposures likely occurred years or decades before symptoms develop."
Pointing to a growing body of research linking environmental exposure to Parkinson's disease, the authors believe the new models may enable the scientific community to connect specific exposures to specific forms of the disease. This effort will be aided by increasing public awareness of the adverse health effects of many chemicals in our environment.
The authors conclude that their hypothesis "may explain many of the mysteries of Parkinson's disease and open the door toward the ultimate goal–prevention."
In addition to Parkinson's, these models of environmental exposure may advance understanding of how toxicants contribute to other brain disorders, including autism in children, ALS in adults, and Alzheimer's in seniors.
Dorsey and his colleagues at the University of Rochester have organized a symposium on the Brain and the Environment in Washington, DC, on May 20 that will examine the role toxicants in our food, water, and air are playing in all these brain diseases. Additional authors of the hypothesis paper include Briana De Miranda, Ph.D., with the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and Jacob Horsager, MD, Ph.D., with Aarhus University Hospital in Denmark.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

New insights could unlock immunotherapy for rare, deadly eye cancer
3 hours ago

Biodiversity is key to the mental health benefits of nature, new study finds

New study focuses on the placenta for clues to the development of gestational diabetes

Asthma in children: Researchers envision novel drug to reduce the risk of the disease
4 hours ago

Can animals count? Neuroscientists identify a sense of numeracy among rodents
10 hours ago

Pressure to lose weight in adolescence linked to how people value themselves almost two decades later
13 hours ago

Many people with breast cancer 'systematically left behind' due to inaction on inequities and hidden suffering
14 hours ago

How trauma gets 'under the skin': Research investigates impaired muscle function caused by childhood trauma
16 hours ago
New mechanism uncovered in early stages of Alzheimer's disease

Study reveals AI enhances physician-patient communication
17 hours ago
Related Stories
New evidence suggests link between gut health and Parkinson's disease
Dec 12, 2023
Common degenerative brain disease may begin to develop already in middle age
Mar 26, 2024
New research challenges conventional picture of Parkinson's disease
Feb 23, 2024

Nanoplastics linked to Parkinson's and some types of dementia—new study
Nov 30, 2023
PET scans may predict Parkinson's disease and Lewy body dementia in at-risk individuals
Nov 7, 2023
Parkinson's disease is not one, but two diseases
Sep 22, 2020
Recommended for you
Researchers identify brain region involved in control of attention
20 hours ago

Wearable sensors for Parkinson's can improve with machine learning, data from healthy adults
Apr 12, 2024

Chemicals stored in home garages linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis risk
Apr 11, 2024
Newly discovered genetic variant that causes Parkinson's disease clarifies why the condition develops and how to halt it

Researchers advance understanding of Parkinson's disease
Apr 10, 2024
Stool transplant shows promise for Parkinson's disease
Apr 4, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Why Do We Want to Squish and Squeeze Things That Are Cute? Science Has the Answer
The response dubbed “cute aggression” by researchers is the brain’s attempt to self-regulate when confronted with intense emotion
Brigit Katz; Updated by Sonja Anderson
Correspondent
:focal(2538x1692:2539x1693)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/e3/e4/e3e47e00-5d89-4f7f-94b2-866086e00f8d/b76kgy.jpg)
In the presence of chubby babies, fluffy puppies or other adorable little things, it isn’t uncommon to be overwhelmed by a desire to squeeze, pinch or even bite them. People don’t really want to hurt the creatures—just to … squish them . Turns out, there’s a scientific term for this paradoxical response: “cute aggression.”
In 2015, Yale University researchers published a study about human responses to cuteness, which are often dimorphous: both positive and negative. The researchers concluded that reactions to “cute stimuli”—which can range from smiles, to tears, to aggression—are brought on by the intensity of positive emotion rather than assessment of the stimuli itself. The study interested Katherine Stavropoulos , a psychologist at the University of California, Riverside, who later characterized the term “cute aggression” for NPR ’s Jon Hamilton: People “just have this flash of thinking: ‘I want to crush it’ or ‘I want to squeeze it until [it] pops’ or ‘I want to punch it.’”
“Ahhhh it’s so cute I just want to eat it! Or punch someone in the face! Ahhhh!” DYK “cute aggression” is a real thing? In some people the brain can get so overloaded with cuteness that it switches to expressions of violence, though they have no real intention of harm. pic.twitter.com/GdwGbFInLC — Kaeli Swift, Ph.D. (@corvidresearch) March 31, 2019
Stavropoulos wondered whether this phenomenon could be measured in brain activity. She and doctoral student Laura Alba conducted a study to find out, and their findings were published in Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience in 2018. The researchers gathered 54 participants between ages 18 and 40, fitted them with electrode caps to measure their brain activity, and showed each person 32 photographs.
The images were divided into four groups: adult animals (which the study authors classify as “less cute”), baby animals (classified as “more cute”), and two sets of human baby portraits. The first block of human baby images was digitally altered to enhance features we perceive as cuter—big eyes and full cheeks—while the other portraits were either left untouched or altered to reduce cuteness.
After participants viewed the images, they completed questionnaires that indicated both how cute they found each block of photos and the level of cute aggression they experienced. To assess the latter, researchers asked participants to rate the extent to which they agreed with statements like, “I want to squeeze something,” and, “I feel like pinching those cheeks!” Researchers measured how “overwhelmed by emotion” each participant was after seeing the photos by having them rate their agreement with statements like, “I can’t handle it!” Stavropoulos and Alba also checked participants’ urges to approach and care for the subjects in the photos.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Cheshire Cat Rescue & Sanctuary (@cheshirecatrescue)
The images of baby animals elicited the strongest response. According to the researchers, participants expressed more cute aggression, felt more overwhelmed and had a greater caretaking impulse toward baby animals than adult animals. They didn’t observe the same distinction between participants’ reactions to cuter and less-cute images of babies—possibly, Stavropoulos told Gizmodo ’s Catie Keck, because both sets of babies were “objectively pretty cute.”
“Adult animals and baby animals are strikingly different,” Stavropoulos elaborated. “But these pictures of babies were in fact so well photographically manipulated that they are both pretty cute looking.”
By using the electroencephalography caps, researchers were able to gain insight into the neural activity of participants who experienced cute aggression. This response was associated with greater activity not only in the brain’s emotional systems, but also in its reward systems, which regulate motivation, pleasure and feelings of “wanting.”
As Stavropoulos told UC Riverside News ’ Tess Eyrich, she found strong correlations between ratings of cute aggression and the reward response in the brain to cute animals. “This is an exciting finding,” she said, “as it confirms our original hypothesis that the reward system is involved in people’s experiences of cute aggression.” The study also reinforced Yale’s 2015 findings, relating aggressive responses to overwhelming emotion. As Stavropoulos concluded, cute aggression—which contradicts the caregiving response—seems to be the “brain’s way of ‘bringing us back down’ by mediating our feelings of being overwhelmed.”

When these two powerful systems are triggered—emotion and reward—the brain tempers the onslaught of positive feelings by tossing in a dash of aggression. And researchers believe that aggressive response may have a positive function in evolution.
“If you find yourself incapacitated by how cute a baby is—so much so that you simply can’t take care of it—that baby is going to starve,” Stavropoulos said.
As neuroscientist Seraphina Solders wrote for NeuWrite San Diego , we understand why this type of “emotional regulation” is important regarding strong negative emotions. “But it might be more challenging to understand why we would need to regulate extreme positive emotions as well.”
Whatever the evolutionary cause of cute aggression, rest assured that there’s no need to feel bad if the sight of pudgy babies fills you with a weird compulsion to pinch them; it’s just the brain’s way of making sure that nothing gets too cute to handle.
Get the latest stories in your inbox every weekday.
Brigit Katz | | READ MORE
Brigit Katz is a freelance writer based in Toronto. Her work has appeared in a number of publications, including NYmag.com, Flavorwire and Tina Brown Media's Women in the World.

The Fermi Paradox and the Berserker Hypothesis: Exploring Cosmic Silence Through Science Fiction
I n the realm of cosmic conundrums, the Fermi Paradox stands out: why, in a universe replete with billions of stars and planets, have we yet to find any signs of extraterrestrial intelligent life? The “berserker hypothesis,” a spine-chilling explanation rooted in science and popularized by science fiction, suggests a grim answer to this enduring mystery.
The concept’s moniker traces back to Fred Saberhagen’s “Berserker” series of novels, and it paints a picture of the cosmos where intelligent life forms are systematically eradicated by self-replicating probes, known as “berserkers.” These probes, initially intended to explore and report back, turn rogue and annihilate any signs of civilizations they encounter. The hypothesis emerges as a rather dark twist on the concept of von Neumann probes—machines capable of self-replication using local resources, which could theoretically colonize the galaxy rapidly.
Diving into the technicalities, the berserker hypothesis operates as a potential solution to the Hart-Tipler conjecture, which posits the lack of detectable probes as evidence that no intelligent life exists outside our solar system. Instead, this hypothesis flips the script: the absence of such probes doesn’t point to a lack of life but rather to the possibility that these probes have become cosmic predators, leaving a trail of silence in their wake.
Astronomer David Brin’s chilling summation underscores the potential severity of the hypothesis: “It need only happen once for the results of this scenario to become the equilibrium conditions in the Galaxy…because all were killed shortly after discovering radio.” If these berserker probes exist and are as efficient as theorized, then humanity’s attempts at communication with extraterrestrial beings could be akin to lighting a beacon for our own destruction.
Despite its foundation in speculative thought, the theory isn’t without its scientific evaluations. Anders Sandberg and Stuart Armstrong from the Future of Humanity Institute speculated that, given the vastness of the universe and even a slow replication rate, these berserker probes—if they existed—would likely have already found and destroyed us. It’s both a chilling and somewhat reassuring analysis that treads the line between fiction and potential reality.
Within the eclectic array of solutions to the Fermi Paradox, the berserker hypothesis stands out for its seamless blend of science fiction inspiration and scientific discourse. It connects with other notions such as the Great Filter, which suggests that life elsewhere in the universe is being systematically snuffed out before it can reach a space-faring stage, and the Dark Forest hypothesis, which posits that civilizations remain silent to avoid detection by such cosmic hunters.
Relevant articles:
– TIL about the berserker hypothesis, a proposed solution to the Fermi paradox stating the reason why we haven’t found other sentient species yet is because those species have been wiped out by self-replicating “berserker” probes.
– The Berserker Hypothesis: The Darkest Explanation Of The Fermi Paradox
– Beyond “Fermi’s Paradox” VI: What is the Berserker Hypothesis?
![In the realm of cosmic conundrums, the Fermi Paradox stands out: why, in a universe replete with billions of stars and planets, have we yet to find any signs of extraterrestrial intelligent life? The “berserker hypothesis,” a spine-chilling explanation rooted in science and popularized by science fiction, suggests a grim answer to this enduring mystery. […] In the realm of cosmic conundrums, the Fermi Paradox stands out: why, in a universe replete with billions of stars and planets, have we yet to find any signs of extraterrestrial intelligent life? The “berserker hypothesis,” a spine-chilling explanation rooted in science and popularized by science fiction, suggests a grim answer to this enduring mystery. […]](https://img-s-msn-com.akamaized.net/tenant/amp/entityid/AA1mrdWu.img?w=768&h=523&m=6)

The Universe Could Be Eternal, According to This Controversial Theory
The idea of a static universe would mean our cosmos will live forever, and it isn’t expanding after all.
✅ Quick Facts:
- This idea says the universe is neither expanding, nor contracting; instead it is steady, and has no beginning and no end.
- But for other scientists, the suggestion is a leap in logic and the Big Bang is the best description of the creation of the universe we currently have.
What if the Big Bang , the prevailing theory of how our universe came to be, never happened? What if the universe hasn’t been expanding from a tiny dense fireball, but has instead been in a steady state for 13.8 billion years with no beginning and no end? An intriguing analysis published in Progress in Physics in 2022 claims that the Big Bang might be a bust because it relies on the Doppler effect, or Doppler shift , a landmark theory in physics that Austrian mathematician and physicist Christian Doppler proposed in 1842 .
The Doppler effect explains that the perceived increase or decrease in the frequency of light, sound, or other waves (note the word waves here) depends on how a source and an object move toward each other. In space, the Doppler effect influences the light planetary bodies emit: if a body in space is moving away from us, its light spreads apart, or “redshifts” (as it moves toward longer wavelengths). However, if a body is moving toward us, its lightwaves compact, or “blueshift” (because the light moves toward shorter wavelengths). This is because in space blue means near, and red means farther away; this principle is clear as day to astronomers. Measurements of starlight have so far concluded that all galaxies redshift . In other words, this evidence supports the Big Bang theory, which says the universe is constantly expanding.
But Jack Wilenchik, author of the provocative study, highly doubts whether redshift means movement. In fact, he believes the Doppler effect may actually be an Achilles’ heel that fells the Big Bang theory.
A Reason to Assume the Universe Did Not Start With a Big Bang?
“The Doppler’s effect is a 180-year old theory nobody has backed up with experimental evidence,” Wilenchik tells Popular Mechanics . To look at different planets and moons in the solar system, Wilenchik, who is a lawyer by trade and an amateur astronomer, borrowed a simple spectroscopy test English astronomer William Huggins had first used in 1868. Spectroscopy is the study and measurement of spectra , or the charts or graphs that depict the intensity of light from an astronomical body like a star. Wilenchik also used data from the Hawaii-based Keck Observatory’s spectrometers— available online —and had a professional astrophysicist process it for him. The results of his study align with a different, incompatible idea about the universe: the tired light model.
The 1929 brainchild of Swiss astronomer Fritz Zwicky , the tired light hypothesis attributes the universe’s redshift to the fact that photons , the tiny packets of electromagnetic energy that make up light, lose energy as they pass through the great cosmos. Therefore, a decrease or increase in energy doesn’t necessarily mean movement, so no stretching universe can exist. This model indicates that light simply loses energy over time—and so the universe must be static.
.css-2l0eat{font-family:UnitedSans,UnitedSans-roboto,UnitedSans-local,Helvetica,Arial,Sans-serif;font-size:1.625rem;line-height:1.2;margin:0rem;padding:0.9rem 1rem 1rem;}@media(max-width: 48rem){.css-2l0eat{font-size:1.75rem;line-height:1;}}@media(min-width: 48rem){.css-2l0eat{font-size:1.875rem;line-height:1;}}@media(min-width: 64rem){.css-2l0eat{font-size:2.25rem;line-height:1;}}.css-2l0eat b,.css-2l0eat strong{font-family:inherit;font-weight:bold;}.css-2l0eat em,.css-2l0eat i{font-style:italic;font-family:inherit;} "We do not live in a world of alternative facts. We must go where the evidence points. There is nothing to suggest that the Big Bang is a myth at present."
“No, the universe did not start as an exploding atom or anything,” Wilenchik says. “There’s no beginning and no end to the universe,” he says, disputing the primeval atom theory that Belgian priest, physicist, and astronomer Georges Lemaître first proposed in 1927. (Later, astronomer Fred Hoyle coined the term “Big Bang” for Lamaitre’s cosmic origins idea, and it stuck.)
Whether a star reddens or turns bluer ultimately boils down to Isaac Newton’s corpuscular theory of light , says Wilenchik. The Newtonian theory posits that light is made up of tiny particles, or “corpuscles,” which are constantly traveling in a straight line. In essence, the blue or red shifts we see in space are simply the result of the different corpuscle sizes: a blue light means larger bodies, while a red light means smaller ones. “If light is not in waves, then there goes the Doppler theory, because the entire theory is based on the idea that light is in waves,” says Wilenchik.
But particularly intriguing is his view that galaxies are atoms and stars are light (he’s written a book about it that’s freely available online). “Since the universe neither expands nor contracts, what we have in the sky is giant spirals. And we’ve got something very strange and unique called stars,” he says.
Here’s what he means: it was in the late 1800s when Scottish-Irish physicist William Thomson, better known as Lord Kelvin , suggested that the atom is a “ vortex” in the “aether.” In full agreement, Wilenchik says atoms have spirals at their core, and so do galaxies, and so do large clusters of galaxies or supergalaxies, because the same vortex structure permeates the whole cosmos, from the macroscopic to the microscopic level. The universe is infinitely big, infinitely small, and never-ending; stars are strange bundles of light; and we need to reconsider the Doppler effect theory, Wilenchik concludes.
But not everyone agrees.
Why the Big Bang Theory Is Our Best Explanation So Far
“The premise that the Big Bang is a big bust due to its reliance on the Doppler effect is a big leap in logic. Doppler’s theory has been tested repeatedly and has held up,” Stephen Holler , Ph.D., an associate professor of physics at Fordham University, tells Popular Mechanics .
The Doppler effect is a wave phenomenon we are all familiar with. Take sound, for example. The way the pitch of a moving vehicle, especially a rapidly moving vehicle such as an ambulance or a fire truck, hurts your ears or fades away as the vehicle moves near or away from you is a fine illustration of the “compression or elongation of the wave” in relation to you, the observer, says Holler. Medical applications such as Doppler velocimetry (a test that measures blood flow and 3D ultrasound images) also owe their existence to the Doppler effect. And when it comes to the heart of Wilenchik’s argument, which is that red and blue shifts do not correspond to predictions of how planetary objects move, Holler says that we would have practically failed to engage in extraterrestrial exploration without Doppler.
“ Extraterrestrially , we have been able to reconcile the chemical composition of stars and planets by noting the correspondence of spectral lines with known lines observed from chemicals on the Earth through Doppler spectroscopy,” Holler says. True, we may never know if the Big Bang theory is correct, but currently it is our best description for the origin of the universe, he continues. “An obvious originalist who relied on others to analyze the data for him, Wilenchik highlights the primeval atom theory’s improbability,” Holler adds. But the theory entered the realms of science nearly an eon ago when evidence was just beginning to come in and be interpreted, or, in other words, when we didn’t know what we didn’t know: “We do not live in a world of alternative facts. We must go where the evidence points. There is nothing to suggest that the Big Bang is a myth at present,” Holler says.
In ancient Greek mythology, deities govern the skies and, together, the dynamics of birth and annihilation. For Wilenchik, this is no coincidence: that we still have planets named after Greek gods, (even if Romans “romanized” the names of most later on), bears some kind of cosmic symbolism. “If the divine is somebody that creates or destroys things, then galaxies might be the divine in their own way,” the Phoenix-based lawyer suggests. This symbolic heritage might go beyond theory, implies Wilenchik, drawing enticing if not esoteric parallels between the symbolic and the pragmatic. It could inspire a fresh examination of the principles of cosmological theory, such as the Doppler effect, which is crucial for comprehending the universe’s expansion.
“We could reinvestigate the Doppler theory through observing the behavior of a planet like Mercury, for which we know when it’s moving toward or away from us and how fast,” says Wilenchik. In this way, we could see whether it redshifts or blueshifts correspondingly.
An in-depth investigation like this could provide us with a deeper understanding of how the universe works, as Wilenchik suggests we’ve been too comfortable with the Big Bang theory for too long now. Did we begin with a bang or are new beginnings overrated?
Stav Dimitropoulos’s science writing has appeared online or in print for the BBC, Discover, Scientific American, Nature, Science, Runner’s World, The Daily Beast and others. Stav disrupted an athletic and academic career to become a journalist and get to know the world.

.css-cuqpxl:before{padding-right:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;} Pop Mech Pro: Space .css-xtujxj:before{padding-left:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;}

The History of Pi

The Strange Origin of the Hollow Moon Conspiracy

What Do Alien Space Probes Look Like?

Physicists Are Pretty Sure We Can Reach Warp Speed

How NASA’s Next Super Telescope Could Find Aliens

Will Mars Astronauts Need Sunscreen?

Sunquakes May Be the Key to Nuclear Fusion

7 Solid Reasons to Actually Believe in Aliens

The 7 Greatest Cosmic Threats to Life on Earth

Your Guide to Every Stargazing Event in 2024

This Is the Coldest Place in the Universe

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
hypothesis. science. scientific hypothesis, an idea that proposes a tentative explanation about a phenomenon or a narrow set of phenomena observed in the natural world. The two primary features of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability and testability, which are reflected in an "If…then" statement summarizing the idea and in the ...
A scientific hypothesis is a tentative, testable explanation for a phenomenon in the natural world. It's the initial building block in the scientific method. Many describe it as an "educated guess ...
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for an observation. The definition depends on the subject. In science, a hypothesis is part of the scientific method. It is a prediction or explanation that is tested by an experiment. Observations and experiments may disprove a scientific hypothesis, but can never entirely prove one.
The scientific method. At the core of biology and other sciences lies a problem-solving approach called the scientific method. The scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step: Make an observation. Ask a question. Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation. Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
The hypothesis of Andreas Cellarius, showing the planetary motions in eccentric and epicyclical orbits.. A hypothesis (pl.: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon.For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained ...
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
A scientific theory is an explanation of an aspect of the natural world and universe that can be (or a fortiori, that has been) repeatedly tested and corroborated in accordance with the scientific method, using accepted protocols of observation, measurement, and evaluation of results. Where possible, some theories are tested under controlled ...
Interestingly, a recent analysis of 111 publications related to Strachan's hygiene hypothesis, stating that the lack of exposure to infections in early life increases the risk of rhinitis, revealed a selection bias of 5,551 citations on Web of Science.37 The articles supportive of the hypothesis were cited more than nonsupportive ones (odds ...
The Structure of Scientific Theories. Scientific inquiry has led to immense explanatory and technological successes, partly as a result of the pervasiveness of scientific theories. Relativity theory, evolutionary theory, and plate tectonics were, and continue to be, wildly successful families of theories within physics, biology, and geology.
In science, however, a theory is an explanation that generally is accepted to be true. Here's a closer look at these important, commonly misused terms. Hypothesis . A hypothesis is an educated guess, based on observation. It's a prediction of cause and effect. Usually, a hypothesis can be supported or refuted through experimentation or more ...
A hypothesis is a tentative, testable explanation for an observed phenomenon in nature. Hypotheses are narrow in scope — unlike theories, which cover a broad range of observable phenomena and draw from many different lines of evidence. Meanwhile, a prediction is a result you'd expect to get if your hypothesis or theory is accurate.
Science is an enormously successful human enterprise. The study of scientific method is the attempt to discern the activities by which that success is achieved. Among the activities often identified as characteristic of science are systematic observation and experimentation, inductive and deductive reasoning, and the formation and testing of ...
2. The scientific hypothesis. In this section, we will describe a functional and descriptive role regarding how scientists use hypotheses. Jeong & Kwon [] investigated and summarized the different uses the concept of 'hypothesis' had in philosophical and scientific texts.They identified five meanings: assumption, tentative explanation, tentative cause, tentative law, and prediction.
A scientific hypothesis is a proposed explanation for an observable phenomenon. In other words, a hypothesis is an educated guess about the relationship between multiple variables. A hypothesis is a fresh, unchallenged idea that a scientist proposes prior to conducting research. The purpose of a hypothesis is to provide a tentative explanation ...
In science, a theory is a well-substantiated and comprehensive set of ideas that explains a phenomenon in nature. A scientific theory is based on large amounts of data and observations that have been collected over time. Scientific theories can be tested and refined by additional research, and they allow scientists to make predictions. Though ...
The boundary between these two forms of study is often blurred, because most scientific endeavors combine both approaches. Observations lead to questions, questions lead to forming a hypothesis as a possible answer to those questions, and then the hypothesis is tested. Thus, descriptive science and hypothesis-based science are in continuous ...
A hypothesis is a tentative, testable answer to a scientific question. Once a scientist has a scientific question she is interested in, the scientist reads up to find out what is already known on the topic. Then she uses that information to form a tentative answer to her scientific question. Sometimes people refer to the tentative answer as "an ...
Both laws and theories depend on basic elements of the scientific method, such as generating a hypothesis, testing that premise, finding (or not finding) empirical evidence and coming up with conclusions.Eventually, other scientists must be able to replicate the results if the experiment is destined to become the basis for a widely accepted law or theory.
The six steps of the scientific method include: 1) asking a question about something you observe, 2) doing background research to learn what is already known about the topic, 3) constructing a hypothesis, 4) experimenting to test the hypothesis, 5) analyzing the data from the experiment and drawing conclusions, and 6) communicating the results ...
The philosophy of science is a field that deals with what science is, how it works, and the logic through which we build scientific knowledge. ... anomalies refuting the accepted theory have built up to such a point that the old theory is broken down and a new one is built to take its place in a so-called "paradigm shift." ...
Science is often quite ready to tolerate some logical inadequacy in a theory‐or even a flat logical contradiction like that between the particle and wave theories of matter‐so long as it finds itself in the possession of a hypothesis which offers both the possibility of control and a guide to worthwhile avenues of exploration."
How a Theory about Climate Change Led to. The Feminine Mystique. In 1958 Betty Friedan wrote an article that changed science journalism—and her career. By Rachel Shteir. A portrait of author ...
New hypothesis paper builds on a growing scientific consensus that Parkinson's disease route to the brain starts in either the nose or the gut and proposes that environmental toxicants are the ...
For physicist and science writer Matt Strassler, based in Boston, Massachusetts, Higgs's death represents "the end of an era". "Higgs was a fortunate scientist: he lived to see his insight ...
A new hypothesis paper appearing in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease on World Parkinson's Day unites the ... Science X Daily and the Weekly Email Newsletter are free features that allow you to ...
Science Has the Answer. ... "This is an exciting finding," she said, "as it confirms our original hypothesis that the reward system is involved in people's experiences of cute aggression ...
The "berserker hypothesis," a spine-chilling explanation rooted in science and popularized by science fiction, suggests a grim answer to this enduring mystery. The concept's moniker traces ...
Doppler's theory has been tested repeatedly and has held up ... But the theory entered the realms of science nearly an eon ago when evidence was just beginning to come in and be interpreted, or ...