An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection


Problem solving through values: A challenge for thinking and capability development
- • This paper introduces the 4W framework of consistent problem solving through values.
- • The 4W suggests when, how and why the explication of values helps to solve a problem.
- • The 4W is significant to teach students to cope with problems having crucial consequences.
- • The paper considers challenges using such framework of thinking in different fields of education.
The paper aims to introduce the conceptual framework of problem solving through values. The framework consists of problem analysis, selection of value(s) as a background for the solution, the search for alternative ways of the solution, and the rationale for the solution. This framework reveals when, how, and why is important to think about values when solving problems. A consistent process fosters cohesive and creative value-based thinking during problem solving rather than teaching specific values. Therefore, the framework discloses the possibility for enabling the development of value-grounded problem solving capability.The application of this framework highlights the importance of responsibility for the chosen values that are the basis for the alternatives which determine actions. The 4W framework is meaningful for the people’s lives and their professional work. It is particularly important in the process of future professionals’ education. Critical issues concerning the development of problem solving through values are discussed when considering and examining options for the implementation of the 4W framework in educational institutions.
1. Introduction
The core competencies necessary for future professionals include problem solving based on complexity and collaborative approaches ( OECD, 2018 ). Currently, the emphasis is put on the development of technical, technological skills as well as system thinking and other cognitive abilities (e.g., Barber, 2018 ; Blanco, Schirmbeck, & Costa, 2018 ). Hence, education prepares learners with high qualifications yet lacking in moral values ( Nadda, 2017 ). Educational researchers (e.g., Barnett, 2007 ; Harland & Pickering, 2010 ) stress that such skills and abilities ( the how? ), as well as knowledge ( the what? ), are insufficient to educate a person for society and the world. The philosophy of education underlines both the epistemological and ontological dimensions of learning. Barnett (2007) points out that the ontological dimension has to be above the epistemological one. The ontological dimension encompasses the issues related to values that education should foster ( Harland & Pickering, 2010 ). In addition, values are closely related to the enablement of learners in educational environments ( Jucevičienė et al., 2010 ). For these reasons, ‘ the why ?’ based on values is required in the learning process. The question arises as to what values and how it makes sense to educate them. Value-based education seeks to address these issues and concentrates on values transfer due to their integration into the curriculum. Yazdani and Akbarilakeh (2017) discussed that value-based education could only convey factual knowledge of values and ethics. However, such education does not guarantee the internalization of values. Nevertheless, value-based education indicates problem solving as one of the possibilities to develop values.
Values guide and affect personal behavior encompassing the ethical aspects of solutions ( Roccas, Sagiv, & Navon, 2017 ; Schwartz, 1992 , 2012 ; Verplanken & Holland, 2002 ). Therefore, they represent the essential foundation for solving a problem. Growing evidence indicates the creative potential of values ( Dollinger, Burke, & Gump, 2007 ; Kasof, Chen, Himsel, & Greenberger, 2007 ; Lebedeva et al., 2019) and emphasizes their significance for problem solving. Meanwhile, research in problem solving pays little attention to values. Most of the problem solving models (e.g., Newell & Simon, 1972 ; Jonassen, 1997 ) utilize a rational economic approach. Principally, the research on the mechanisms of problem solving have been conducted under laboratory conditions performing simple tasks ( Csapó & Funke, 2017 ). Moreover, some of the decision-making models share the same steps as problem solving (c.f., Donovan, Guss, & Naslund, 2015 ). This explains why these terms are sometimes used interchangeably ( Huitt, 1992 ). Indeed, decision-making is a part of problem solving, which emerges while choosing between alternatives. Yet, values, moral, and ethical issues are more common in decision-making research (e.g., Keeney, 1994 ; Verplanken & Holland, 2002 ; Hall & Davis, 2007 ; Sheehan & Schmidt, 2015 ). Though, research by Shepherd, Patzelt, and Baron (2013) , Baron, Zhao, and Miao (2015) has affirmed that contemporary business decision makers rather often leave aside ethical issues and moral values. Thus, ‘ethical disengagement fallacy’ ( Sternberg, 2017, p.7 ) occurs as people think that ethics is more relevant to others. In the face of such disengagement, ethical issues lose their prominence.
The analysis of the literature revealed a wide field of problem solving research presenting a range of more theoretical insights rather empirical evidence. Despite this, to date, a comprehensive model that reveals how to solve problems emphasizing thinking about values is lacking. This underlines the relevance of the chosen topic, i.e. a challenge for thinking and for the development of capabilities addressing problems through values. To address this gap, the following issues need to be investigated: When, how, and why a problem solver should take into account values during problem solving? What challenges may occur for using such framework of thinking in different fields of education? Aiming this, the authors of the paper substantiated the conceptual framework of problem solving grounded in consistent thinking about values. The substantiation consists of several parts. First, different approaches to solving problems were examined. Second, searching to reveal the possibilities of values integration into problem solving, value-based approaches significant for problem solving were critically analyzed. Third, drawing on the effect of values when solving a problem and their creative potential, the authors of this paper claim that the identification of values and their choice for a solution need to be specified in the process of problem solving. As a synthesis of conclusions coming from the literature review and conceptual extensions regarding values, the authors of the paper created the coherent framework of problem solving through values (so called 4W).
The novelty of the 4W framework is exposed by several contributions. First, the clear design of overall problem solving process with attention on integrated thinking about values is used. Unlike in most models of problem solving, the first stage encompass the identification of a problem, an analysis of a context and the perspectives that influence the whole process, i.e. ‘What?’. The stage ‘What is the basis for a solution?’ focus on values identification and their choice. The stage ‘Ways how?’ encourages to create alternatives considering values. The stage ‘Why?’ represent justification of a chosen alternative according particular issues. Above-mentioned stages including specific steps are not found in any other model of problem solving. Second, even two key stages nurture thinking about values. The specificity of the 4W framework allows expecting its successful practical application. It may help to solve a problem more informed revealing when and how the explication of values helps to reach the desired value-based solution. The particular significance is that the 4W framework can be used to develop capabilities to solve problems through values. The challenges to use the 4W framework in education are discussed.
2. Methodology
To create the 4W framework, the integrative literature review was chosen. According to Snyder (2019) , this review is ‘useful when the purpose of the review is not to cover all articles ever published on the topic but rather to combine perspectives to create new theoretical models’ (p.334). The scope of this review focused on research disclosing problem solving process that paid attention on values. The following databases were used for relevant information search: EBSCO/Hostdatabases (ERIC, Education Source), Emerald, Google Scholar. The first step of this search was conducted using integrated keywords problem solving model , problem solving process, problem solving steps . These keywords were combined with the Boolean operator AND with the second keywords values approach, value-based . The inclusion criteria were used to identify research that: presents theoretical backgrounds and/or empirical evidences; performed within the last 5 years; within an educational context; availability of full text. The sources appropriate for this review was very limited in scope (N = 2).
We implemented the second search only with the same set of the integrated keywords. The inclusion criteria were the same except the date; this criterion was extended up to 10 years. This search presented 85 different sources. After reading the summaries, introductions and conclusions of the sources found, the sources that do not explicitly provide the process/models/steps of problem solving for teaching/learning purposes and eliminates values were excluded. Aiming to see a more accurate picture of the chosen topic, we selected secondary sources from these initial sources.
Several important issues were determined as well. First, most researchers ground their studies on existing problem solving models, however, not based on values. Second, some of them conducted empirical research in order to identify the process of studies participants’ problem solving. Therefore, we included sources without date restrictions trying to identify the principal sources that reveal the process/models/steps of problem solving. Third, decision-making is a part of problem solving process. Accordingly, we performed a search with the additional keywords decision-making AND values approach, value-based decision-making . We used such inclusion criteria: presents theoretical background and/or empirical evidence; no date restriction; within an educational context; availability of full text. These all searches resulted in a total of 16 (9 theoretical and 7 empirical) sources for inclusion. They were the main sources that contributed most fruitfully for the background. We used other sources for the justification the wholeness of the 4W framework. We present the principal results of the conducted literature review in the part ‘The background of the conceptual framework’.
3. The background of the conceptual framework
3.1. different approaches of how to solve a problem.
Researchers from different fields focus on problem solving. As a result, there still seems to be a lack of a conventional definition of problem solving. Regardless of some differences, there is an agreement that problem solving is a cognitive process and one of the meaningful and significant ways of learning ( Funke, 2014 ; Jonassen, 1997 ; Mayer & Wittrock, 2006 ). Differing in approaches to solving a problem, researchers ( Collins, Sibthorp, & Gookin, 2016 ; Jonassen, 1997 ; Litzinger et al., 2010 ; Mayer & Wittrock, 2006 ; O’Loughlin & McFadzean, 1999 ; ect.) present a variety of models that differ in the number of distinct steps. What is similar in these models is that they stress the procedural process of problem solving with the focus on the development of specific skills and competences.
For the sake of this paper, we have focused on those models of problem solving that clarify the process and draw attention to values, specifically, on Huitt (1992) , Basadur, Ellspermann, and Evans (1994) , and Morton (1997) . Integrating the creative approach to problem solving, Newell and Simon (1972) presents six phases: phase 1 - identifying the problem, phase 2 - understanding the problem, phase 3 - posing solutions, phase 4 - choosing solutions, phase 5 - implementing solutions, and phase 6 - final analysis. The weakness of this model is that these phases do not necessarily follow one another, and several can coincide. However, coping with simultaneously occurring phases could be a challenge, especially if these are, for instance, phases five and six. Certainly, it may be necessary to return to the previous phases for further analysis. According to Basadur et al. (1994) , problem solving consists of problem generation, problem formulation, problem solving, and solution implementation stages. Huitt (1992) distinguishes four stages in problem solving: input, processing, output, and review. Both Huitt (1992) and Basadur et al. (1994) four-stage models emphasize a sequential process of problem solving. Thus, problem solving includes four stages that are used in education. For example, problem-based learning employs such stages as introduction of the problem, problem analysis and learning issues, discovery and reporting, solution presentation and evaluation ( Chua, Tan, & Liu, 2016 ). Even PISA 2012 framework for problem solving composes four stages: exploring and understanding, representing and formulating, planning and executing, monitoring and reflecting ( OECD, 2013 ).
Drawing on various approaches to problem solving, it is possible to notice that although each stage is named differently, it is possible to reveal some general steps. These steps reflect the essential idea of problem solving: a search for the solution from the initial state to the desirable state. The identification of a problem and its contextual elements, the generation of alternatives to a problem solution, the evaluation of these alternatives according to specific criteria, the choice of an alternative for a solution, the implementation, and monitoring of the solution are the main proceeding steps in problem solving.
3.2. Value-based approaches relevant for problem solving
Huitt (1992) suggests that important values are among the criteria for the evaluation of alternatives and the effectiveness of a chosen solution. Basadur et al. (1994) point out to visible values in the problem formulation. Morton (1997) underlines that interests, investigation, prevention, and values of all types, which may influence the process, inspire every phase of problem solving. However, the aforementioned authors do not go deeper and do not seek to disclose the significance of values for problem solving.
Decision-making research shows more possibilities for problem solving and values integration. Sheehan and Schmidt (2015) model of ethical decision-making includes moral sensitivity, moral judgment, moral motivation, and moral action where values are presented in the component of moral motivation. Another useful approach concerned with values comes from decision-making in management. It is the concept of Value-Focused Thinking (VFT) proposed by Keeney (1994) . The author argues that the goals often are merely means of achieving results in traditional models of problem solving. Such models frequently do not help to identify logical links between the problem solving goals, values, and alternatives. Thus, according to Keeney (1994) , the decision-making starts with values as they are stated in the goals and objectives of decision-makers. VFT emphasizes the core values of decision-makers that are in a specific context as well as how to find a way to achieve them by using means-ends analysis. The weakness of VFT is its restriction to this means-ends analysis. According to Shin, Jonassen, and McGee (2003) , in searching for a solution, such analysis is weak as the problem solver focuses simply on removing inadequacies between the current state and the goal state. The strengths of this approach underline that values are included in the decision before alternatives are created. Besides, values help to find creative and meaningful alternatives and to assess them. Further, they include the forthcoming consequences of the decision. As VFT emphasizes the significant function of values and clarifies the possibilities of their integration into problem solving, we adapt this approach in the current paper.
3.3. The effect of values when solving a problem
In a broader sense, values provide a direction to a person’s life. Whereas the importance of values is relatively stable over time and across situations, Roccas et al. (2017) argue that values differ in their importance to a person. Verplanken and Holland (2002) investigated the relationship between values and choices or behavior. The research revealed that the activation of a value and the centrality of a value to the self, are the essential elements for value-guided behavior. The activation of values could happen in such cases: when values are the primary focus of attention; if the situation or the information a person is confronted with implies values; when the self is activated. The centrality of a particular value is ‘the degree to which an individual has incorporated this value as part of the self’ ( Verplanken & Holland, 2002, p.436 ). Thus, the perceived importance of values and attention to them determine value-guided behavior.
According to Argandoña (2003) , values can change due to external (changing values in the people around, in society, changes in situations, etc.) and internal (internalization by learning) factors affecting the person. The research by Hall and Davis (2007) indicates that the decision-makers’ applied value profile temporarily changed as they analyzed the issue from multiple perspectives and revealed the existence of a broader set of values. The study by Kirkman (2017) reveal that participants noticed the relevance of moral values to situations they encountered in various contexts.
Values are tightly related to personal integrity and identity and guide an individual’s perception, judgment, and behavior ( Halstead, 1996 ; Schwartz, 1992 ). Sheehan and Schmidt (2015) found that values influenced ethical decision-making of accounting study programme students when they uncovered their own values and grounded in them their individual codes of conduct for future jobs. Hence, the effect of values discloses by observing the problem solver’s decision-making. The latter observations could explain the abundance of ethics-laden research in decision-making rather than in problem solving.
Contemporary researchers emphasize the creative potential of values. Dollinger et al. (2007) , Kasof et al. (2007) , Lebedeva, Schwartz, Plucker, & Van De Vijver, 2019 present to some extent similar findings as they all used Schwartz Value Survey (respectively: Schwartz, 1992 ; ( Schwartz, 1994 ), Schwartz, 2012 ). These studies disclosed that such values as self-direction, stimulation and universalism foster creativity. Kasof et al. (2007) focused their research on identified motivation. Stressing that identified motivation is the only fully autonomous type of external motivation, authors define it as ‘the desire to commence an activity as a means to some end that one greatly values’ (p.106). While identified motivation toward specific values (italic in original) fosters the search for outcomes that express those specific values, this research demonstrated that it could also inhibit creative behavior. Thus, inhibition is necessary, especially in the case where reckless creativity could have painful consequences, for example, when an architect creates a beautiful staircase without a handrail. Consequently, creativity needs to be balanced.
Ultimately, values affect human beings’ lives as they express the motivational goals ( Schwartz, 1992 ). These motivational goals are the comprehensive criteria for a person’s choices when solving problems. Whereas some problem solving models only mention values as possible evaluation criteria, but they do not give any significant suggestions when and how the problem solver could think about the values coming to the understanding that his/her values direct the decision how to solve the problem. The authors of this paper claim that the identification of personal values and their choice for a solution need to be specified in the process of problem solving. This position is clearly reflected in humanistic philosophy and psychology ( Maslow, 2011 ; Rogers, 1995 ) that emphasize personal responsibility for discovering personal values through critical questioning, honest self-esteem, self-discovery, and open-mindedness in the constant pursuit of the truth in the path of individual life. However, fundamental (of humankind) and societal values should be taken into account. McLaughlin (1997) argues that a clear boundary between societal and personal values is difficult to set as they are intertwined due to their existence in complex cultural, social, and political contexts at a particular time. A person is related to time and context when choosing values. As a result, a person assumes existing values as implicit knowledge without as much as a consideration. This is particularly evident in the current consumer society.
Moreover, McLaughlin (1997) stresses that if a particular action should be tolerated and legitimated by society, it does not mean that this action is ultimately morally acceptable in all respects. Education has possibilities to reveal this. One such possibility is to turn to the capability approach ( Sen, 1990 ), which emphasizes what people are effectively able to do and to be. Capability, according to Sen (1990) , reflects a person’s freedom to choose between various ways of living, i.e., the focus is on the development of a person’s capability to choose the life he/she has a reason to value. According to Webster (2017) , ‘in order for people to value certain aspects of life, they need to appreciate the reasons and purposes – the whys – for certain valuing’ (italic in original; p.75). As values reflect and foster these whys, education should supplement the development of capability with attention to values ( Saito, 2003 ). In order to attain this possibility, a person has to be aware of and be able to understand two facets of values. Argandoña (2003) defines them as rationality and virtuality . Rationality refers to values as the ideal of conduct and involves the development of a person’s understanding of what values and why he/she should choose them when solving a problem. Virtuality approaches values as virtues and includes learning to enable a person to live according to his/her values. However, according to McLaughlin (1997) , some people may have specific values that are deep or self-evidently essential. These values are based on fundamental beliefs about the nature and purpose of the human being. Other values can be more or less superficial as they are based on giving priority to one or the other. Thus, virtuality highlights the depth of life harmonized to fundamentally rather than superficially laden values. These approaches inform the rationale for the framework of problem solving through values.
4. The 4W framework of problem solving through values
Similar to the above-presented stages of the problem solving processes, the introduced framework by the authors of this paper revisits them (see Fig. 1 ). The framework is titled 4W as its four stages respond to such questions: Analyzing the Problem: W hat ? → Choice of the value(s): W hat is the background for the solution? → Search for the alternative w ays of the solution: How ? → The rationale for problem solution: W hy is this alternative significant ? The stages of this framework cover seven steps that reveal the logical sequence of problem solving through values.

The 4 W framework: problem solving through values.
Though systematic problem solving models are criticized for being linear and inflexible (e.g., Treffinger & Isaksen, 2005 ), the authors of this paper assume a structural view of the problem solving process due to several reasons. First, the framework enables problem solvers to understand the thorough process of problem solving through values. Second, this framework reveals the depth of each stage and step. Third, problem solving through values encourages tackling problems that have crucial consequences. Only by understanding and mastering the coherence of how problems those require a value-based approach need to be addressed, a problem solver will be able to cope with them in the future. Finally, this framework aims at helping to recognize, to underline personal values, to solve problems through thinking about values, and to take responsibility for choices, even value-based. The feedback supports a direct interrelation between stages. It shapes a dynamic process of problem solving through values.
The first stage of problem solving through values - ‘ The analysis of the problem: What? ’- consists of three steps (see Fig. 1 ). The first step is ‘ Recognizing the problematic situation and naming the problem ’. This step is performed in the following sequence. First, the problem solver should perceive the problematic situation he/she faces in order to understand it. Dostál (2015) argues that the problematic situation has the potential to become the problem necessary to be addressed. Although each problem is limited by its context, not every problematic situation turns into a problem. This is related to the problem solver’s capability and the perception of reality: a person may not ‘see’ the problem if his/her capability to perceive it is not developed ( Dorst, 2006 ; Dostál, 2015 ). Second, after the problem solver recognizes the existence of the problematic situation, the problem solver has to identify the presence or absence of the problem itself, i.e. to name the problem. This is especially important in the case of the ill-structured problems since they cannot be directly visible to the problem solver ( Jonassen, 1997 ). Consequently, this step allows to determine whether the problem solver developed or has acquired the capability to perceive the problematic situation and the problem (naming the problem).
The second step is ‘ Analysing the context of the problem as a reason for its rise ’. At this step, the problem solver aims to analyse the context of the problem. The latter is one of the external issues, and it determines the solution ( Jonassen, 2011 ). However, if more attention is paid to the solution of the problem, it diverts attention from the context ( Fields, 2006 ). The problem solver has to take into account both the conveyed and implied contextual elements in the problematic situation ( Dostál, 2015 ). In other words, the problem solver has to examine it through his/her ‘contextual lenses’ ( Hester & MacG, 2017 , p.208). Thus, during this step the problem solver needs to identify the elements that shape the problem - reasons and circumstances that cause the problem, the factors that can be changed, and stakeholders that are involved in the problematic situation. Whereas the elements of the context mentioned above are within the problematic situation, the problem solver can control many of them. Such control can provide unique ways for a solution.
Although the problem solver tries to predict the undesirable results, some criteria remain underestimated. For that reason, it is necessary to highlight values underlying the various possible goals during the analysis ( Fields, 2006 ). According to Hester and MacG (2017) , values express one of the main features of the context and direct the attention of the problem solver to a given problematic situation. Hence, the problem solver should explore the value-based positions that emerge in the context of the problem.
The analysis of these contextual elements focus not only on a specific problematic situation but also on the problem that has emerged. This requires setting boundaries of attention for an in-depth understanding ( Fields, 2006 ; Hester & MacG, 2017 ). Such understanding influences several actions: (a) the recognition of inappropriate aspects of the problematic situation; (b) the emergence of paths in which identified aspects are expected to change. These actions ensure consistency and safeguard against distractions. Thus, the problem solver can now recognize and identify the factors that influence the problem although they are outside of the problematic situation. However, the problem solver possesses no control over them. With the help of such context analysis, the problem solver constructs a thorough understanding of the problem. Moreover, the problem solver becomes ready to look at the problem from different perspectives.
The third step is ‘ Perspectives emerging in the problem ’. Ims and Zsolnai (2009) argue that problem solving usually contains a ‘problematic search’. Such a search is a pragmatic activity as the problem itself induces it. Thus, the problem solver searches for a superficial solution. As a result, the focus is on control over the problem rather than a deeper understanding of the problem itself. The analysis of the problem, especially including value-based approaches, reveals the necessity to consider the problem from a variety of perspectives. Mitroff (2000) builds on Linstone (1989) ideas and claims that a sound foundation of both naming and solving any problem lays in such perspectives: the technical/scientific, the interpersonal/social, the existential, and the systemic (see Table 1 ).
The main characteristics of four perspectives for problem solving
Whereas all problems have significant aspects of each perspective, disregarding one or another may lead to the wrong way of solving the problem. While analysing all four perspectives is essential, this does not mean that they all are equally important. Therefore, it is necessary to justify why one or another perspective is more relevant and significant in a particular case. Such analysis, according to Linstone (1989) , ‘forces us to distinguish how we are looking from what we are looking at’ (p.312; italic in original). Hence, the problem solver broadens the understanding of various perspectives and develops the capability to see the bigger picture ( Hall & Davis, 2007 ).
The problem solver aims to identify and describe four perspectives that have emerged in the problem during this step. In order to identify perspectives, the problem solver search answers to the following questions. First, regarding the technical/scientific perspective: What technical/scientific reasons are brought out in the problem? How and to what extent do they influence a problem and its context? Second, regarding the interpersonal/social perspective: What is the impact of the problem on stakeholders? How does it influence their attitudes, living conditions, interests, needs? Third, regarding the existential perspective: How does the problem affect human feelings, experiences, perception, and/or discovery of meaning? Fourth, regarding the systemic perspective: What is the effect of the problem on the person → community → society → the world? Based on the analysis of this step, the problem solver obtains a comprehensive picture of the problem. The next stage is to choose the value(s) that will address the problem.
The second stage - ‘ The choice of value(s): What is the background for the solution?’ - includes the fourth and the fifth steps. The fourth step is ‘ The identification of value(s) as a base for the solution ’. During this step, the problem solver should activate his/her value(s) making it (them) explicit. In order to do this, the problem solver proceeds several sub-steps. First, the problem solver reflects taking into account the analysis done in previous steps. He/she raises up questions revealing values that lay in the background of this analysis: What values does this analyzed context allow me to notice? What values do different perspectives of the problem ‘offer’? Such questioning is important as values are deeply hidden ( Verplanken & Holland, 2002 ) and they form a bias, which restricts the development of the capability to see from various points of view ( Hall & Paradice, 2007 ). In the 4W framework, this bias is relatively eliminated due to the analysis of the context and exploration of the perspectives of a problem. As a result, the problem solver discovers distinct value-based positions and gets an opportunity to identify the ‘value uncaptured’ ( Yang, Evans, Vladimirova, & Rana, 2017, p.1796 ) within the problem analyzed. The problem solver observes that some values exist in the context (the second step) and the disclosed perspectives (the third step). Some of the identified values do not affect the current situation as they are not required, or their potential is not exploited. Thus, looking through various value-based lenses, the problem solver can identify and discover a congruence between the opportunities offered by the values in the problem’s context, disclosed perspectives and his/her value(s). Consequently, the problem solver decides what values he/she chooses as a basis for the desired solution. Since problems usually call for a list of values, it is important to find out their order of priority. Thus, the last sub-step requires the problem solver to choose between fundamentally and superficially laden values.
In some cases, the problem solver identifies that a set of values (more than one value) can lead to the desired solution. If a person chooses this multiple value-based position, two options emerge. The first option is concerned with the analysis of each value-based position separately (from the fifth to the seventh step). In the second option, a person has to uncover which of his/her chosen values are fundamentally laden and which are superficially chosen, considering the desired outcome in the current situation. Such clarification could act as a strategy where the path for the desired solution is possible going from superficially chosen value(s) to fundamentally laden one. When a basis for the solution is established, the problem solver formulates the goal for the desired solution.
The fifth step is ‘ The formulation of the goal for the solution ’. Problem solving highlights essential points that reveal the structure of a person’s goals; thus, a goal is the core element of problem solving ( Funke, 2014 ). Meantime, values reflect the motivational content of the goals ( Schwartz, 1992 ). The attention on the chosen value not only activates it, but also motivates the problem solver. The motivation directs the formulation of the goal. In such a way, values explicitly become a basis of the goal for the solution. Thus, this step involves the problem solver in formulating the goal for the solution as the desired outcome.
The way how to take into account value(s) when formulating the goal is the integration of value(s) chosen by the problem solver in the formulation of the goal ( Keeney, 1994 ). For this purpose the conjunction of a context for a solution (it is analyzed during the second step) and a direction of preference (the chosen value reveals it) serves for the formulation of the goal (that represents the desired solution). In other words, a value should be directly included into the formulation of the goal. The goal could lose value, if value is not included into the goal formulation and remains only in the context of the goal. Let’s take the actual example concerning COVID-19 situation. Naturally, many countries governments’ preference represents such value as human life (‘it is important of every individual’s life’). Thus, most likely the particular country government’s goal of solving the COVID situation could be to save the lifes of the country people. The named problem is a complex where the goal of its solution is also complex, although it sounds simple. However, if the goal as desired outcome is formulated without the chosen value, this value remains in the context and its meaning becomes tacit. In the case of above presented example - the goal could be formulated ‘to provide hospitals with the necessary equipment and facilities’. Such goal has the value ‘human’s life’ in the context, but eliminates the complexity of the problem that leads to a partial solution of the problem. Thus, this step from the problem solver requires caution when formulating the goal as the desired outcome. For this reason, maintaining value is very important when formulating the goal’s text. To avoid the loss of values and maintain their proposed direction, is necessary to take into account values again when creating alternatives.
The third stage - ‘ Search for the alternative ways for a solution: How? ’ - encompasses the sixth step, which is called ‘ Creation of value-based alternatives ’. Frequently problem solver invokes a traditional view of problem identification, generation of alternatives, and selection of criteria for evaluating findings. Keeney (1994) ; Ims and Zsolnai (2009) criticize this rational approach as it supports a search for a partial solution where an active search for alternatives is neglected. Moreover, a problematic situation, according to Perkins (2009) , can create the illusion of a fully framed problem with some apparent weighting and some variations of choices. In this case, essential and distinct alternatives to the solution frequently become unnoticeable. Therefore, Perkins (2009) suggest to replace the focus on the attempts to comprehend the problem itself. Thinking through the ‘value lenses’ offers such opportunities. The deep understanding of the problem leads to the search for the alternative ways of a solution.
Thus, the aim of this step is for the problem solver to reveal the possible alternative ways for searching a desired solution. Most people think they know how to create alternatives, but often without delving into the situation. First of all, the problem solver based on the reflection of (but not limited to) the analysis of the context and the perspectives of the problem generates a range of alternatives. Some of these alternatives represent anchored thinking as he/she accepts the assumptions implicit in generated alternatives and with too little focus on values.
The chosen value with the formulated goal indicates direction and encourages a broader and more creative search for a solution. Hence, the problem solver should consider some of the initial alternatives that could best support the achievement of the desired solution. Values are the principles for evaluating the desirability of any alternative or outcome ( Keeney, 1994 ). Thus, planned actions should reveal the desirable mode of conduct. After such consideration, he/she should draw up a plan setting out the actions required to implement each of considered alternatives.
Lastly, after a thorough examination of each considered alternative and a plan of its implementation, the problem solver chooses one of them. If the problem solver does not see an appropriate alternative, he/she develops new alternatives. However, the problem solver may notice (and usually does) that more than one alternative can help him/her to achieve the desired solution. In this case, he/she indicates which alternative is the main one and has to be implemented in the first place, and what other alternatives and in what sequence will contribute in searching for the desired solution.
The fourth stage - ‘ The rationale for the solution: Why ’ - leads to the seventh step: ‘ The justification of the chosen alternative ’. Keeney (1994) emphasizes the compatibility of alternatives in question with the values that guide the action. This underlines the importance of justifying the choices a person makes where the focus is on taking responsibility. According to Zsolnai (2008) , responsibility means a choice, i.e., the perceived responsibility essentially determines its choice. Responsible justification allows for discovering optimal balance when choosing between distinct value-based alternatives. It also refers to the alternative solution that best reflects responsibility in a particular value context, choice, and implementation.
At this stage, the problem solver revisits the chosen solution and revises it. The problem solver justifies his/her choice based on the following questions: Why did you choose this? Why is this alternative significant looking from the technical/scientific, the interpersonal/social, the existential, and the systemic perspectives? Could you take full responsibility for the implementation of this alternative? Why? How clearly do envisaged actions reflect the goal of the desired solution? Whatever interests and for what reasons do this alternative satisfies in principle? What else do you see in the chosen alternative?
As mentioned above, each person gives priority to one aspect or another. The problem solver has to provide solid arguments for the justification of the chosen alternative. The quality of arguments, according to Jonassen (2011) , should be judged based on the quality of the evidence supporting the chosen alternative and opposing arguments that can reject solutions. Besides, the pursuit of value-based goals reflects the interests of the individual or collective interests. Therefore, it becomes critical for the problem solver to justify the level of responsibility he/she takes in assessing the chosen alternative. Such a complex evaluation of the chosen alternative ensures the acceptance of an integral rather than unilateral solution, as ‘recognizing that, in the end, people benefit most when they act for the common good’ ( Sternberg, 2012, p.46 ).
5. Discussion
The constant emphasis on thinking about values as explicit reasoning in the 4W framework (especially from the choice of the value(s) to the rationale for problem solution) reflects the pursuit of virtues. Virtues form the features of the character that are related to the choice ( Argandoña, 2003 ; McLaughlin, 2005 ). Hence, the problem solver develops value-grounded problem solving capability as the virtuality instead of employing rationality for problem solving.
Argandoña (2003) suggests that, in order to make a sound valuation process of any action, extrinsic, transcendent, and intrinsic types of motives need to be considered. They cover the respective types of values. The 4W framework meets these requirements. An extrinsic motive as ‘attaining the anticipated or expected satisfaction’ ( Argandoña, 2003, p.17 ) is reflected in the formulation of the goal of the solution, the creation of alternatives and especially in the justification of the chosen alternative way when the problem solver revisits the external effect of his/her possible action. Transcendent motive as ‘generating certain effects in others’ ( Argandoña, 2003, p.17 ) is revealed within the analysis of the context, perspectives, and creating alternatives. When the learner considers the creation of alternatives and revisits the chosen alternative, he/she pays more attention to these motives. Two types of motives mentioned so far are closely related to an intrinsic motive that emphasizes learning development within the problem solver. These motives confirm that problem solving is, in fact, lifelong learning. In light of these findings, the 4W framework is concerned with some features of value internalization as it is ‘a psychological outcome of conscious mind reasoning about values’ ( Yazdani & Akbarilakeh, 2017, p.1 ).
The 4W framework is complicated enough in terms of learning. One issue is concerned with the educational environments ( Jucevičienė, 2008 ) required to enable the 4W framework. First, the learning paradigm, rather than direct instruction, lies at the foundation of such environments. Second, such educational environments include the following dimensions: (1) educational goal; (2) learning capacity of the learners; (3) educational content relevant to the educational goal: ways and means of communicating educational content as information presented in advance (they may be real, people among them, as well as virtual); (5) methods and means of developing educational content in the process of learners’ performance; (6) physical environment relevant to the educational goal and conditions of its implementation as well as different items in the environment; (7) individuals involved in the implementation of the educational goal.
Another issue is related to exercising this framework in practice. Despite being aware of the 4W framework, a person may still not want to practice problem solving through values, since most of the solutions are going to be complicated, or may even be painful. One idea worth looking into is to reveal the extent to which problem solving through values can become a habit of mind. Profound focus on personal values, context analysis, and highlighting various perspectives can involve changes in the problem solver’s habit of mind. The constant practice of problem solving through values could first become ‘the epistemic habit of mind’ ( Mezirow, 2009, p.93 ), which means a personal way of knowing things and how to use that knowledge. This echoes Kirkman (2017) findings. The developed capability to notice moral values in situations that students encountered changed some students’ habit of mind as ‘for having “ruined” things by making it impossible not to attend to values in such situations!’ (the feedback from one student; Kirkman, 2017, p.12 ). However, this is not enough, as only those problems that require a value-based approach are addressed. Inevitably, the problem solver eventually encounters the challenges of nurturing ‘the moral-ethical habit of mind’ ( Mezirow, 2009, p.93 ). In pursuance to develop such habits of mind, the curriculum should include the necessity of the practising of the 4W framework.
Thinking based on values when solving problems enables the problem solver to engage in thoughtful reflection in contrast to pragmatic and superficial thinking supported by the consumer society. Reflection begins from the first stage of the 4W framework. As personal values are the basis for the desired solution, the problem solver is also involved in self-reflection. The conscious and continuous reflection on himself/herself and the problematic situation reinforce each step of the 4W framework. Moreover, the fourth stage (‘The rationale for the solution: Why’) involves the problem solver in critical reflection as it concerned with justification of ‘the why , the reasons for and the consequences of what we do’ (italic, bold in original; Mezirow, 1990, p.8 ). Exercising the 4W framework in practice could foster reflective practice. Empirical evidence shows that reflective practice directly impacts knowledge, skills and may lead to changes in personal belief systems and world views ( Slade, Burnham, Catalana, & Waters, 2019 ). Thus, with the help of reflective practice it is possible to identify in more detail how and to what extent the 4W framework has been mastered, what knowledge gained, capabilities developed, how point of views changed, and what influence the change process.
Critical issues related to the development of problem solving through values need to be distinguished when considering and examining options for the implementation of the 4W framework at educational institutions. First, the question to what extent can the 4W framework be incorporated into various subjects needs to be answered. Researchers could focus on applying the 4W framework to specific subjects in the humanities and social sciences. The case is with STEM subjects. Though value issues of sustainable development and ecology are of great importance, in reality STEM teaching is often restricted to the development of knowledge and skills, leaving aside the thinking about values. The special task of the researchers is to help practitioners to apply the 4W framework in STEM subjects. Considering this, researchers could employ the concept of ‘dialogic space’ ( Wegerif, 2011, p.3 ) which places particular importance of dialogue in the process of education emphasizing both the voices of teachers and students, and materials. In addition, the dimensions of educational environments could be useful aligning the 4W framework with STEM subjects. As STEM teaching is more based on solving various special tasks and/or integrating problem-based learning, the 4W framework could be a meaningful tool through which content is mastered, skills are developed, knowledge is acquired by solving pre-prepared specific tasks. In this case, the 4W framework could act as a mean addressing values in STEM teaching.
Second is the question of how to enable the process of problem solving through values. In the current paper, the concept of enabling is understood as an integral component of the empowerment. Juceviciene et al. (2010) specify that at least two perspectives can be employed to explain empowerment : a) through the power of legitimacy (according to Freire, 1996 ); and b) through the perspective of conditions for the acquisition of the required knowledge, capabilities, and competence, i.e., enabling. In this paper the 4W framework does not entail the issue of legitimacy. This issue may occur, for example, when a teacher in economics is expected to provide students with subject knowledge only, rather than adding tasks that involve problem solving through values. Yet, the issue of legitimacy is often implicit. A widespread phenomenon exists that teaching is limited to certain periods that do not have enough time for problem solving through values. The issue of legitimacy as an organizational task that supports/or not the implementation of the 4W framework in any curriculum is a question that calls for further discussion.
Third (if not the first), the issue of an educator’s competence to apply such a framework needs to be addressed. In order for a teacher to be a successful enabler, he/she should have the necessary competence. This is related to the specific pedagogical knowledge and skills, which are highly dependent on the peculiarities of the subject being taught. Nowadays actualities are encouraging to pay attention to STEM subjects and their teacher training. For researchers and teacher training institutions, who will be interested in implementing the 4W framework in STEM subjects, it would be useful to draw attention to ‘a material-dialogic approach to pedagogy’ ( Hetherington & Wegerif, 2018, p.27 ). This approach creates the conditions for a deep learning of STEM subjects revealing additional opportunities for problem solving through values in teaching. Highlighting these opportunities is a task for further research.
In contrast to traditional problem solving models, the 4W framework is more concerned with educational purposes. The prescriptive approach to teaching ( Thorne, 1994 ) is applied to the 4W framework. This approach focuses on providing guidelines that enable students to make sound decisions by making explicit value judgements. The limitation is that the 4W framework is focused on thinking but not executing. It does not include the fifth stage, which would focus on the execution of the decision how to solve the problem. This stage may contain some deviation from the predefined process of the solution of the problem.
6. Conclusions
The current paper focuses on revealing the essence of the 4W framework, which is based on enabling the problem solver to draw attention to when, how, and why it is essential to think about values during the problem solving process from the perspective of it’s design. Accordingly, the 4W framework advocates the coherent approach when solving a problem by using a creative potential of values.
The 4W framework allows the problem solver to look through the lens of his/her values twice. The first time, while formulating the problem solving goal as the desired outcome. The second time is when the problem solver looks deeper into his/her values while exploring alternative ways to solve problems. The problem solver is encouraged to reason about, find, accept, reject, compare values, and become responsible for the consequences of the choices grounded on his/her values. Thus, the problem solver could benefit from the 4W framework especially when dealing with issues having crucial consequences.
An educational approach reveals that the 4W framework could enable the development of value-grounded problem solving capability. As problem solving encourages the development of higher-order thinking skills, the consistent inclusion of values enriches them.
The 4W framework requires the educational environments for its enablement. The enablement process of problem solving through values could be based on the perspective of conditions for the acquisition of the required knowledge and capability. Continuous practice of this framework not only encourages reflection, but can also contribute to the creation of the epistemic habit of mind. Applying the 4W framework to specific subjects in the humanities and social sciences might face less challenge than STEM ones. The issue of an educator’s competence to apply such a framework is highly important. The discussed issues present significant challenges for researchers and educators. Caring that the curriculum of different courses should foresee problem solving through values, both practicing and empirical research are necessary.
Declaration of interests
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Both authors have approved the final article.
- Argandoña A. Fostering values in organizations. Journal of Business Ethics. 2003; 45 (1–2):15–28. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1023/A:1024164210743.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Barber S. A truly “Transformative” MBA: Executive education for the fourth industrial revolution. Journal of Pedagogic Development. 2018; 8 (2):44–55. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barnett R. McGraw-Hill Education; UK): 2007. Will to learn: Being a student in an age of uncertainty. [ Google Scholar ]
- Baron R.A., Zhao H., Miao Q. Personal motives, moral disengagement, and unethical decisions by entrepreneurs: Cognitive mechanisms on the “slippery slope” Journal of Business Ethics. 2015; 128 (1):107–118. doi: 10.1007/s10551-014-2078-y. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Basadur M., Ellspermann S.J., Evans G.W. A new methodology for formulating ill-structured problems. Omega. 1994; 22 (6):627–645. doi: 10.1016/0305-0483(94)90053-1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blanco E., Schirmbeck F., Costa C. International Conference on Remote Engineering and Virtual Instrumentation . Springer; Cham: 2018. Vocational Education for the Industrial Revolution; pp. 649–658. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chua B.L., Tan O.S., Liu W.C. Journey into the problem-solving process: Cognitive functions in a PBL environment. Innovations in Education and Teaching International. 2016; 53 (2):191–202. doi: 10.1080/14703297.2014.961502. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Collins R.H., Sibthorp J., Gookin J. Developing ill-structured problem-solving skills through wilderness education. Journal of Experiential Education. 2016; 39 (2):179–195. doi: 10.1177/1053825916639611. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Csapó B., Funke J., editors. The nature of problem solving: Using research to inspire 21st century learning. OECD Publishing; 2017. The development and assessment of problem solving in 21st-century schools. (Chapter 1). [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dollinger S.J., Burke P.A., Gump N.W. Creativity and values. Creativity Research Journal. 2007; 19 (2-3):91–103. doi: 10.1080/10400410701395028. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Donovan S.J., Guss C.D., Naslund D. Improving dynamic decision making through training and self-reflection. Judgment and Decision Making. 2015; 10 (4):284–295. http://digitalcommons.unf.edu/apsy_facpub/2 [ Google Scholar ]
- Dorst K. Design problems and design paradoxes. Design Issues. 2006; 22 (3):4–17. doi: 10.1162/desi.2006.22.3.4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dostál J. Theory of problem solving. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2015; 174 :2798–2805. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.970. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fields A.M. Ill-structured problems and the reference consultation: The librarian’s role in developing student expertise. Reference Services Review. 2006; 34 (3):405–420. doi: 10.1108/00907320610701554. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Freire P. Continuum; New York: 1996. Pedagogy of the oppressed (revised) [ Google Scholar ]
- Funke J. Problem solving: What are the important questions?. Proceedings of the 36th Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society; Austin, TX: Cognitive Science Society; 2014. pp. 493–498. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hall D.J., Davis R.A. Engaging multiple perspectives: A value-based decision-making model. Decision Support Systems. 2007; 43 (4):1588–1604. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2006.03.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hall D.J., Paradice D. Investigating value-based decision bias and mediation: do you do as you think? Communications of the ACM. 2007; 50 (4):81–85. [ Google Scholar ]
- Halstead J.M. Values and values education in schools. In: Halstead J.M., Taylor M.J., editors. Values in education and education in values. The Falmer Press; London: 1996. pp. 3–14. [ Google Scholar ]
- Harland T., Pickering N. Routledge; 2010. Values in higher education teaching. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hester P.T., MacG K. Springer; New York: 2017. Systemic decision making: Fundamentals for addressing problems and messes. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hetherington L., Wegerif R. Developing a material-dialogic approach to pedagogy to guide science teacher education. Journal of Education for Teaching. 2018; 44 (1):27–43. doi: 10.1080/02607476.2018.1422611. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huitt W. Problem solving and decision making: Consideration of individual differences using the Myers-Briggs type indicator. Journal of Psychological Type. 1992; 24 (1):33–44. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ims K.J., Zsolnai L. The future international manager. Palgrave Macmillan; London: 2009. Holistic problem solving; pp. 116–129. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jonassen D. Supporting problem solving in PBL. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-based Learning. 2011; 5 (2):95–119. doi: 10.7771/1541-5015.1256. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jonassen D.H. Instructional design models for well-structured and III-structured problem-solving learning outcomes. Educational Technology Research and Development. 1997; 45 (1):65–94. doi: 10.1007/BF02299613. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jucevičienė P. Educational and learning environments as a factor for socioeducational empowering of innovation. Socialiniai mokslai. 2008; 1 :58–70. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jucevičienė P., Gudaitytė D., Karenauskaitė V., Lipinskienė D., Stanikūnienė B., Tautkevičienė G. Technologija; Kaunas: 2010. Universiteto edukacinė galia: Atsakas XXI amžiaus iššūkiams [The educational power of university: the response to the challenges of the 21st century] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kasof J., Chen C., Himsel A., Greenberger E. Values and creativity. Creativity Research Journal. 2007; 19 (2–3):105–122. doi: 10.1080/10400410701397164. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Keeney R.L. Creativity in decision making with value-focused thinking. MIT Sloan Management Review. 1994; 35 (4):33–41. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kirkman R. Problem-based learning in engineering ethics courses. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-based Learning. 2017; 11 (1) doi: 10.7771/1541-5015.1610. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lebedeva N., Schwartz S., Plucker J., Van De Vijver F. Domains of everyday creativity and personal values. Frontiers in Psychology. 2019; 9 :1–16. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02681. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Linstone H.A. Multiple perspectives: Concept, applications, and user guidelines. Systems Practice. 1989; 2 (3):307–331. [ Google Scholar ]
- Litzinger T.A., Meter P.V., Firetto C.M., Passmore L.J., Masters C.B., Turns S.R.…Zappe S.E. A cognitive study of problem solving in statics. Journal of Engineering Education. 2010; 99 (4):337–353. [ Google Scholar ]
- Maslow A.H. Vaga; Vilnius: 2011. Būties psichologija. [Psychology of Being] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mayer R., Wittrock M. Problem solving. In: Alexander P., Winne P., editors. Handbook of educational psychology. Psychology Press; New York, NY: 2006. pp. 287–303. [ Google Scholar ]
- McLaughlin T. The educative importance of ethos. British Journal of Educational Studies. 2005; 53 (3):306–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8527.2005.00297.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McLaughlin T.H. Technologija; Kaunas: 1997. Šiuolaikinė ugdymo filosofija: demokratiškumas, vertybės, įvairovė [Contemporary philosophy of education: democracy, values, diversity] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mezirow J. Jossey-Bass Publishers; San Francisco: 1990. Fostering critical reflection in adulthood; pp. 1–12. https://my.liberatedleaders.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/How-Critical-Reflection-triggers-Transformative-Learning-Mezirow.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Mezirow J. Contemporary theories of learning. Routledge; 2009. An overview on transformative learning; pp. 90–105. (Chapter 6) [ Google Scholar ]
- Mitroff I. Šviesa; Kaunas: 2000. Kaip neklysti šiais beprotiškais laikais: ar mokame spręsti esmines problemas. [How not to get lost in these crazy times: do we know how to solve essential problems] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morton L. Teaching creative problem solving: A paradigmatic approach. Cal. WL Rev. 1997; 34 :375. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nadda P. Need for value based education. International Education and Research Journal. 2017; 3 (2) http://ierj.in/journal/index.php/ierj/article/view/690/659 [ Google Scholar ]
- Newell A., Simon H.A. Prentice-Hall; Englewood Cliffs, NJ: 1972. Human problem solving. [ Google Scholar ]
- OECD . PISA, OECD Publishing; Paris: 2013. PISA 2012 assessment and analytical framework: Mathematics, reading, science, problem solving and financial literacy . https://www.oecd.org/pisa/pisaproducts/PISA%202012%20framework%20e-book_final.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- OECD . PISA, OECD Publishing; 2018. PISA 2015 results in focus . https://www.oecd.org/pisa/pisa-2015-results-in-focus.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- O’Loughlin A., McFadzean E. Toward a holistic theory of strategic problem solving. Team Performance Management: An International Journal. 1999; 5 (3):103–120. [ Google Scholar ]
- Perkins D.N. Decision making and its development. In: Callan E., Grotzer T., Kagan J., Nisbett R.E., Perkins D.N., Shulman L.S., editors. Education and a civil society: Teaching evidence-based decision making. American Academy of Arts and Sciences; Cambridge, MA: 2009. pp. 1–28. (Chapter 1) [ Google Scholar ]
- Roccas S., Sagiv L., Navon M. Values and behavior. Cham: Springer; 2017. Methodological issues in studying personal values; pp. 15–50. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rogers C.R. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt; Boston: 1995. On becoming a person: A therapist’s view of psychotherapy. [ Google Scholar ]
- Saito M. Amartya Sen’s capability approach to education: A critical exploration. Journal of Philosophy of Education. 2003; 37 (1):17–33. doi: 10.1111/1467-9752.3701002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwartz S.H. Universals in the content and structure of values: Theoretical advances and empirical tests in 20 countries. In: Zanna M.P., editor. Vol. 25. Academic Press; 1992. pp. 1–65. (Advances in experimental social psychology). [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwartz S.H. Are there universal aspects in the structure and contents of human values? Journal of social issues. 1994; 50 (4):19–45. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwartz S.H. An overview of the Schwartz theory of basic values. Online Readings in Psychology and Culture. 2012; 2 (1):1–20. doi: 10.9707/2307-0919.1116. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sen A. Development as capability expansion. The community development reader. 1990:41–58. http://www.masterhdfs.org/masterHDFS/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/Sen-development.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheehan N.T., Schmidt J.A. Preparing accounting students for ethical decision making: Developing individual codes of conduct based on personal values. Journal of Accounting Education. 2015; 33 (3):183–197. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccedu.2015.06.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shepherd D.A., Patzelt H., Baron R.A. “I care about nature, but…”: Disengaging values in assessing opportunities that cause harm. The Academy of Management Journal. 2013; 56 (5):1251–1273. doi: 10.5465/amj.2011.0776. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shin N., Jonassen D.H., McGee S. Predictors of well‐structured and ill‐structured problem solving in an astronomy simulation. Journal of Research in Science Teaching. 2003; 40 (1):6–33. doi: 10.1002/tea.10058. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Slade M.L., Burnham T.J., Catalana S.M., Waters T. The impact of reflective practice on teacher candidates’ learning. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning. 2019; 13 (2):15. doi: 10.20429/ijsotl.2019.130215. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Snyder H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research. 2019; 104 :333–339. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.039. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sternberg R. Teaching for ethical reasoning. International Journal of Educational Psychology. 2012; 1 (1):35–50. doi: 10.4471/ijep.2012.03. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sternberg R. Speculations on the role of successful intelligence in solving contemporary world problems. Journal of Intelligence. 2017; 6 (1):4. doi: 10.3390/jintelligence6010004. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thorne D.M. Environmental ethics in international business education: Descriptive and prescriptive dimensions. Journal of Teaching in International Business. 1994; 5 (1–2):109–122. doi: 10.1300/J066v05n01_08. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Treffinger D.J., Isaksen S.G. Creative problem solving: The history, development, and implications for gifted education and talent development. The Gifted Child Quarterly. 2005; 49 (4):342–353. doi: 10.1177/001698620504900407. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Verplanken B., Holland R.W. Motivated decision making: Effects of activation and self-centrality of values on choices and behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2002; 82 (3):434–447. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.82.3.434. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Webster R.S. Re-enchanting education and spiritual wellbeing. Routledge; 2017. Being spiritually educated; pp. 73–85. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wegerif R. Towards a dialogic theory of how children learn to think. Thinking Skills and Creativity. 2011; 6 (3):179–190. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2011.08.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang M., Evans S., Vladimirova D., Rana P. Value uncaptured perspective for sustainable business model innovation. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2017; 140 :1794–1804. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.07.102. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yazdani S., Akbarilakeh M. The model of value-based curriculum for medicine and surgery education in Iran. Journal of Minimally Invasive Surgical Sciences. 2017; 6 (3) doi: 10.5812/minsurgery.14053. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zsolnai L. Transaction Publishers; New Brunswick and London: 2008. Responsible decision making. [ Google Scholar ]
- Position paper
- Open access
- Published: 28 November 2019
Physics education research for 21 st century learning
- Lei Bao ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3348-4198 1 &
- Kathleen Koenig 2
Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Science Education Research volume 1 , Article number: 2 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
37k Accesses
69 Citations
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
Education goals have evolved to emphasize student acquisition of the knowledge and attributes necessary to successfully contribute to the workforce and global economy of the twenty-first Century. The new education standards emphasize higher end skills including reasoning, creativity, and open problem solving. Although there is substantial research evidence and consensus around identifying essential twenty-first Century skills, there is a lack of research that focuses on how the related subskills interact and develop over time. This paper provides a brief review of physics education research as a means for providing a context towards future work in promoting deep learning and fostering abilities in high-end reasoning. Through a synthesis of the literature around twenty-first Century skills and physics education, a set of concretely defined education and research goals are suggested for future research, along with how these may impact the next generation physics courses and how physics should be taught in the future.
Introduction
Education is the primary service offered by society to prepare its future generation workforce. The goals of education should therefore meet the demands of the changing world. The concept of learner-centered, active learning has broad, growing support in the research literature as an empirically validated teaching practice that best promotes learning for modern day students (Freeman et al., 2014 ). It stems out of the constructivist view of learning, which emphasizes that it is the learner who needs to actively construct knowledge and the teacher should assume the role of a facilitator rather than the source of knowledge. As implied by the constructivist view, learner-centered education usually emphasizes active-engagement and inquiry style teaching-learning methods, in which the learners can effectively construct their understanding under the guidance of instruction. The learner-centered education also requires educators and researchers to focus their efforts on the learners’ needs, not only to deliver effective teaching-learning approaches, but also to continuously align instructional practices to the education goals of the times. The goals of introductory college courses in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) disciplines have constantly evolved from some notion of weed-out courses that emphasize content drilling, to the current constructivist active-engagement type of learning that promotes interest in STEM careers and fosters high-end cognitive abilities.
Following the conceptually defined framework of twenty-first Century teaching and learning, this paper aims to provide contextualized operational definitions of the goals for twenty-first Century learning in physics (and STEM in general) as well as the rationale for the importance of these outcomes for current students. Aligning to the twenty-first Century learning goals, research in physics education is briefly reviewed to provide a context towards future work in promoting deep learning and fostering abilities in high-end reasoning in parallel. Through a synthesis of the literature around twenty-first Century skills and physics education, a set of concretely defined education and research goals are suggested for future research. These goals include: domain-specific research in physics learning; fostering scientific reasoning abilities that are transferable across the STEM disciplines; and dissemination of research-validated curriculum and approaches to teaching and learning. Although this review has a focus on physics education research (PER), it is beneficial to expand the perspective to view physics education in the broader context of STEM learning. Therefore, much of the discussion will blend PER with STEM education as a continuum body of work on teaching and learning.
Education goals for twenty-first century learning
Education goals have evolved to emphasize student acquisition of essential “21 st Century skills”, which define the knowledge and attributes necessary to successfully contribute to the workforce and global economy of the 21st Century (National Research Council, 2011 , 2012a ). In general, these standards seek to transition from emphasizing content-based drilling and memorization towards fostering higher-end skills including reasoning, creativity, and open problem solving (United States Chamber of Commerce, 2017 ). Initiatives on advancing twenty-first Century education focus on skills that converge on three broad clusters: cognitive, interpersonal, and intrapersonal, all of which include a rich set of sub-dimensions.
Within the cognitive domain, multiple competencies have been proposed, including deep learning, non-routine problem solving, systems thinking, critical thinking, computational and information literacy, reasoning and argumentation, and innovation (National Research Council, 2012b ; National Science and Technology Council, 2018 ). Interpersonal skills are those necessary for relating to others, including the ability to work creatively and collaboratively as well as communicate clearly. Intrapersonal skills, on the other hand, reside within the individual and include metacognitive thinking, adaptability, and self-management. These involve the ability to adjust one’s strategy or approach along with the ability to work towards important goals without significant distraction, both essential for sustained success in long-term problem solving and career development.
Although many descriptions exist for what qualifies as twenty-first Century skills, student abilities in scientific reasoning and critical thinking are the most commonly noted and widely studied. They are highly connected with the other cognitive skills of problem solving, decision making, and creative thinking (Bailin, 1996 ; Facione, 1990 ; Fisher, 2001 ; Lipman, 2003 ; Marzano et al., 1988 ), and have been important educational goals since the 1980s (Binkley et al., 2010 ; NCET, 1987 ). As a result, they play a foundational role in defining, assessing, and developing twenty-first Century skills.
The literature for critical thinking is extensive (Bangert-Drowns & Bankert, 1990 ; Facione, 1990 ; Glaser, 1941 ). Various definitions exist with common underlying principles. Broadly defined, critical thinking is the application of the cognitive skills and strategies that aim for and support evidence-based decision making. It is the thinking involved in solving problems, formulating inferences, calculating likelihoods, and making decisions (Halpern, 1999 ). It is the “reasonable reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do” (Ennis, 1993 ). Critical thinking is recognized as a way to understand and evaluate subject matter; producing reliable knowledge and improving thinking itself (Paul, 1990 ; Siegel, 1988 ).
The notion of scientific reasoning is often used to label the set of skills that support critical thinking, problem solving, and creativity in STEM. Broadly defined, scientific reasoning includes the thinking and reasoning skills involved in inquiry, experimentation, evidence evaluation, inference and argument that support the formation and modification of concepts and theories about the natural world; such as the ability to systematically explore a problem, formulate and test hypotheses, manipulate and isolate variables, and observe and evaluate consequences (Bao et al., 2009 ; Zimmerman, 2000 ). Critical thinking and scientific reasoning share many features, where both emphasize evidence-based decision making in multivariable causal conditions. Critical thinking can be promoted through the development of scientific reasoning, which includes student ability to reach a reliable conclusion after identifying a question, formulating hypotheses, gathering relevant data, and logically testing and evaluating the hypothesis. In this way, scientific reasoning can be viewed as a scientific domain instantiation of critical thinking in the context of STEM learning.
In STEM learning, cognitive aspects of the twenty-first Century skills aim to develop reasoning skills, critical thinking skills, and deep understanding, all of which allow students to develop well connected expert-like knowledge structures and engage in meaningful scientific inquiry and problem solving. Within physics education, a core component of STEM education, the learning of conceptual understanding and problem solving remains a current emphasis. However, the fast-changing work environment and technology-driven world require a new set of core knowledge, skills, and habits of mind to solve complex interdisciplinary problems, gather and evaluate evidence, and make sense of information from a variety of sources (Tanenbaum, 2016 ). The education goals in physics are transitioning towards ability fostering as well as extension and integration with other STEM disciplines. Although curriculum that supports these goals is limited, there are a number of attempts, particularly in developing active learning classrooms and inquiry-based laboratory activities, which have demonstrated success. Some of these are described later in this paper as they provide a foundation for future work in physics education.
Interpersonal skills, such as communication and collaboration, are also essential for twenty-first Century problem-solving tasks, which are often open-ended, complex, and team-based. As the world becomes more connected in a multitude of dimensions, tackling significant problems involving complex systems often goes beyond the individual and requires working with others who are increasingly from culturally diverse backgrounds. Due to the rise of communication technologies, being able to articulate thoughts and ideas in a variety of formats and contexts is crucial, as well as the ability to effectively listen or observe to decipher meaning. Interpersonal skills can be promoted by integrating group-learning experiences into the classroom setting, while providing students with the opportunity to engage in open-ended tasks with a team of peer learners who may propose more than one plausible solution. These experiences should be designed such that students must work collaboratively and responsibly in teams to develop creative solutions, which are later disseminated through informative presentations and clearly written scientific reports. Although educational settings in general have moved to providing students with more and more opportunities for collaborative learning, a lack of effective assessments for these important skills has been a limiting factor for producing informative research and widespread implementation. See Liu ( 2010 ) for an overview of measurement instruments reported in the research literature.
Intrapersonal skills are based on the individual and include the ability to manage one’s behavior and emotions to achieve goals. These are especially important for adapting in the fast-evolving collaborative modern work environment and for learning new tasks to solve increasingly challenging interdisciplinary problems, both of which require intellectual openness, work ethic, initiative, and metacognition, to name a few. These skills can be promoted using instruction which, for example, includes metacognitive learning strategies, provides opportunities to make choices and set goals for learning, and explicitly connects to everyday life events. However, like interpersonal skills, the availability of relevant assessments challenges advancement in this area. In this review, the vast amount of studies on interpersonal and intrapersonal skills will not be discussed in order to keep the main focus on the cognitive side of skills and reasoning.
The purpose behind discussing twenty-first Century skills is that this set of skills provides important guidance for establishing essential education goals for modern society and learners. However, although there is substantial research evidence and consensus around identifying necessary twenty-first Century skills, there is a lack of research that focuses on how the related subskills interact and develop over time (Reimers & Chung, 2016 ), with much of the existing research residing in academic literature that is focused on psychology rather than education systems (National Research Council, 2012a ). Therefore, a major and challenging task for discipline-based education researchers and educators is to operationally define discipline-specific goals that align with the twenty-first Century skills for each of the STEM fields. In the following sections, this paper will provide a limited vision of the research endeavors in physics education that can translate the past and current success into sustained impact for twenty-first Century teaching and learning.
Proposed education and research goals
Physics education research (PER) is often considered an early pioneer in discipline-based education research (National Research Council, 2012c ), with well-established, broad, and influential outcomes (e.g., Hake, 1998 ; Hsu, Brewe, Foster, & Harper, 2004 ; McDermott & Redish, 1999 ; Meltzer & Thornton, 2012 ). Through the integration of twenty-first Century skills with the PER literature, a set of broadly defined education and research goals is proposed for future PER work:
Discipline-specific deep learning: Cognitive and education research involving physics learning has established a rich literature on student learning behaviors along with a number of frameworks. Some of the popular frameworks include conceptual understanding and concept change, problem solving, knowledge structure, deep learning, and knowledge integration. Aligned with twenty-first Century skills, future research in physics learning should aim to integrate the multiple areas of existing work, such that they help students develop well integrated knowledge structures in order to achieve deep leaning in physics.
Fostering scientific reasoning for transfer across STEM disciplines: The broad literature in physics learning and scientific reasoning can provide a solid foundation to further develop effective physics education approaches, such as active engagement instruction and inquiry labs, specifically targeting scientific inquiry abilities and reasoning skills. Since scientific reasoning is a more domain-general cognitive ability, success in physics can also more readily inform research and education practices in other STEM fields.
Research, development, assessment, and dissemination of effective education approaches: Developing and maintaining a supportive infrastructure of education research and implementation has always been a challenge, not only in physics but in all STEM areas. The twenty-first Century education requires researchers and instructors across STEM to work together as an extended community in order to construct a sustainable integrated STEM education environment. Through this new infrastructure, effective team-based inquiry learning and meaningful assessment can be delivered to help students develop a comprehensive skills set including deep understanding and scientific reasoning, as well as communication and other non-cognitive abilities.
The suggested research will generate understanding and resources to support education practices that meet the requirements of the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS), which explicitly emphasize three areas of learning including disciplinary core ideas, crosscutting concepts, and practices (National Research Council, 2012b ). The first goal for promoting deep learning of disciplinary knowledge corresponds well to the NGSS emphasis on disciplinary core ideas, which play a central role in helping students develop well integrated knowledge structures to achieve deep understanding. The second goal on fostering transferable scientific reasoning skills supports the NGSS emphasis on crosscutting concepts and practices. Scientific reasoning skills are crosscutting cognitive abilities that are essential to the development of domain-general concepts and modeling strategies. In addition, the development of scientific reasoning requires inquiry-based learning and practices. Therefore, research on scientific reasoning can produce a valuable knowledge base on education means that are effective for developing crosscutting concepts and promoting meaningful practices in STEM. The third research goal addresses the challenge in the assessment of high-end skills and the dissemination of effective educational approaches, which supports all NGSS initiatives to ensure sustainable development and lasting impact. The following sections will discuss the research literature that provides the foundation for these three research goals and identify the specific challenges that will need to be addressed in future work.
Promoting deep learning in physics education
Physics education for the twenty-first Century aims to foster high-end reasoning skills and promote deep conceptual understanding. However, many traditional education systems place strong emphasis on only problem solving with the expectation that students obtain deep conceptual understanding through repetitive problem-solving practices, which often doesn’t occur (Alonso, 1992 ). This focus on problem solving has been shown to have limitations as a number of studies have revealed disconnections between learning conceptual understanding and problem-solving skills (Chiu, 2001 ; Chiu, Guo, & Treagust, 2007 ; Hoellwarth, Moelter, & Knight, 2005 ; Kim & Pak, 2002 ; Nakhleh, 1993 ; Nakhleh & Mitchell, 1993 ; Nurrenbern & Pickering, 1987 ; Stamovlasis, Tsaparlis, Kamilatos, Papaoikonomou, & Zarotiadou, 2005 ). In fact, drilling in problem solving may actually promote memorization of context-specific solutions with minimal generalization rather than transitioning students from novices to experts.
Towards conceptual understanding and learning, many models and definitions have been established to study and describe student conceptual knowledge states and development. For example, students coming into a physics classroom often hold deeply rooted, stable understandings that differ from expert conceptions. These are commonly referred to as misconceptions or alternative conceptions (Clement, 1982 ; Duit & Treagust, 2003 ; Dykstra Jr, Boyle, & Monarch, 1992 ; Halloun & Hestenes, 1985a , 1985b ). Such students’ conceptions are context dependent and exist as disconnected knowledge fragments, which are strongly situated within specific contexts (Bao & Redish, 2001 , 2006 ; Minstrell, 1992 ).
In modeling students’ knowledge structures, DiSessa’s proposed phenomenological primitives (p-prim) describe a learner’s implicit thinking, cued from specific contexts, as an underpinning cognitive construct for a learner’s expressed conception (DiSessa, 1993 ; Smith III, DiSessa, & Roschelle, 1994 ). Facets, on the other hand, map between the implicit p-prim and concrete statements of beliefs and are developed as discrete and independent units of thought, knowledge, or strategies used by individuals to address specific situations (Minstrell, 1992 ). Ontological categories, defined by Chi, describe student reasoning in the most general sense. Chi believed that these are distinct, stable, and constraining, and that a core reason behind novices’ difficulties in physics is that they think of physics within the category of matter instead of processes (Chi, 1992 ; Chi & Slotta, 1993 ; Chi, Slotta, & De Leeuw, 1994 ; Slotta, Chi, & Joram, 1995 ). More details on conceptual learning and problem solving are well summarized in the literature (Hsu et al., 2004 ; McDermott & Redish, 1999 ), from which a common theme emerges from the models and definitions. That is, learning is context dependent and students with poor conceptual understanding typically have locally connected knowledge structures with isolated conceptual constructs that are unable to establish similarities and contrasts between contexts.
Additionally, this idea of fragmentation is demonstrated through many studies on student problem solving in physics and other fields. It has been shown that a student’s knowledge organization is a key aspect for distinguishing experts from novices (Bagno, Eylon, & Ganiel, 2000 ; Chi, Feltovich, & Glaser, 1981 ; De Jong & Ferguson-Hesler, 1986 ; Eylon & Reif, 1984 ; Ferguson-Hesler & De Jong, 1990 ; Heller & Reif, 1984 ; Larkin, McDermott, Simon, & Simon, 1980 ; Smith, 1992 ; Veldhuis, 1990 ; Wexler, 1982 ). Expert’s knowledge is organized around core principles of physics, which are applied to guide problem solving and develop connections between different domains as well as new, unfamiliar situations (Brown, 1989 ; Perkins & Salomon, 1989 ; Salomon & Perkins, 1989 ). Novices, on the other hand, lack a well-organized knowledge structure and often solve problems by relying on surface features that are directly mapped to certain problem-solving outcomes through memorization (Chi, Bassok, Lewis, Reimann, & Glaser, 1989 ; Hardiman, Dufresne, & Mestre, 1989 ; Schoenfeld & Herrmann, 1982 ).
This lack of organization creates many difficulties in the comprehension of basic concepts and in solving complex problems. This leads to the common complaint that students’ knowledge of physics is reduced to formulas and vague labels of the concepts, which are unable to substantively contribute to meaningful reasoning processes. A novice’s fragmented knowledge structure severely limits the learner’s conceptual understanding. In essence, these students are able to memorize how to approach a problem given specific information but lack the understanding of the underlying concept of the approach, limiting their ability to apply this approach to a novel situation. In order to achieve expert-like understanding, a student’s knowledge structure must integrate all of the fragmented ideas around the core principle to form a coherent and fully connected conceptual framework.
Towards a more general theoretical consideration, students’ alternative conceptions and fragmentation in knowledge structures can be viewed through both the “naïve theory” framework (e.g., Posner, Strike, Hewson, & Gertzog, 1982 ; Vosniadou, Vamvakoussi, & Skopeliti, 2008 ) and the “knowledge in pieces” (DiSessa, 1993 ) perspective. The “naïve theory” framework considers students entering the classroom with stable and coherent ideas (naïve theories) about the natural world that differ from those presented by experts. In the “knowledge in pieces” perspective, student knowledge is constructed in real-time and incorporates context features with the p-prims to form the observed conceptual expressions. Although there exists an ongoing debate between these two views (Kalman & Lattery, 2018 ), it is more productive to focus on their instructional implications for promoting meaningful conceptual change in students’ knowledge structures.
In the process of learning, students may enter the classroom with a range of initial states depending on the population and content. For topics with well-established empirical experiences, students often have developed their own ideas and understanding, while on topics without prior exposure, students may create their initial understanding in real-time based on related prior knowledge and given contextual features (Bao & Redish, 2006 ). These initial states of understanding, regardless of their origin, are usually different from those of experts. Therefore, the main function of teaching and learning is to guide students to modify their initial understanding towards the experts’ views. Although students’ initial understanding may exist as a body of coherent ideas within limited contexts, as students start to change their knowledge structures throughout the learning process, they may evolve into a wide range of transitional states with varying levels of knowledge integration and coherence. The discussion in this brief review on students’ knowledge structures regarding fragmentation and integration are primarily focused on the transitional stages emerged through learning.
The corresponding instructional goal is then to help students more effectively develop an integrated knowledge structure so as to achieve a deep conceptual understanding. From an educator’s perspective, Bloom’s taxonomy of education objectives establishes a hierarchy of six levels of cognitive skills based on their specificity and complexity: Remember (lowest and most specific), Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, and Create (highest and most general and complex) (Anderson et al., 2001 ; Bloom, Engelhart, Furst, Hill, & Krathwohl, 1956 ). This hierarchy of skills exemplifies the transition of a learner’s cognitive development from a fragmented and contextually situated knowledge structure (novice with low level cognitive skills) to a well-integrated and globally networked expert-like structure (with high level cognitive skills).
As a student’s learning progresses from lower to higher cognitive levels, the student’s knowledge structure becomes more integrated and is easier to transfer across contexts (less context specific). For example, beginning stage students may only be able to memorize and perform limited applications of the features of certain contexts and their conditional variations, with which the students were specifically taught. This leads to the establishment of a locally connected knowledge construct. When a student’s learning progresses from the level of Remember to Understand, the student begins to develop connections among some of the fragmented pieces to form a more fully connected network linking a larger set of contexts, thus advancing into a higher level of understanding. These connections and the ability to transfer between different situations form the basis of deep conceptual understanding. This growth of connections leads to a more complete and integrated cognitive structure, which can be mapped to a higher level on Bloom’s taxonomy. This occurs when students are able to relate a larger number of different contextual and conditional aspects of a concept for analyzing and evaluating to a wider variety of problem situations.
Promoting the growth of connections would appear to aid in student learning. Exactly which teaching methods best facilitate this are dependent on the concepts and skills being learned and should be determined through research. However, it has been well recognized that traditional instruction often fails to help students obtain expert-like conceptual understanding, with many misconceptions still existing after instruction, indicating weak integration within a student’s knowledge structure (McKeachie, 1986 ).
Recognizing the failures of traditional teaching, various research-informed teaching methods have been developed to enhance student conceptual learning along with diagnostic tests, which aim to measure the existence of misconceptions. Most advances in teaching methods focus on the inclusion of inquiry-based interactive-engagement elements in lecture, recitations, and labs. In physics education, these methods were popularized after Hake’s landmark study demonstrated the effectiveness of interactive-engagement over traditional lectures (Hake, 1998 ). Some of these methods include the use of peer instruction (Mazur, 1997 ), personal response systems (e.g., Reay, Bao, Li, Warnakulasooriya, & Baugh, 2005 ), studio-style instruction (Beichner et al., 2007 ), and inquiry-based learning (Etkina & Van Heuvelen, 2001 ; Laws, 2004 ; McDermott, 1996 ; Thornton & Sokoloff, 1998 ). The key approach of these methods aims to improve student learning by carefully targeting deficits in student knowledge and actively encouraging students to explore and discuss. Rather than rote memorization, these approaches help promote generalization and deeper conceptual understanding by building connections between knowledge elements.
Based on the literature, including Bloom’s taxonomy and the new education standards that emphasize twenty-first Century skills, a common focus on teaching and learning can be identified. This focus emphasizes helping students develop connections among fragmented segments of their knowledge pieces and is aligned with the knowledge integration perspective, which focuses on helping students develop and refine their knowledge structure toward a more coherently organized and extensively connected network of ideas (Lee, Liu, & Linn, 2011 ; Linn, 2005 ; Nordine, Krajcik, & Fortus, 2011 ; Shen, Liu, & Chang, 2017 ). For meaningful learning to occur, new concepts must be integrated into a learner’s existing knowledge structure by linking the new knowledge to already understood concepts.
Forming an integrated knowledge structure is therefore essential to achieving deep learning, not only in physics but also in all STEM fields. However, defining what connections must occur at different stages of learning, as well as understanding the instructional methods necessary for effectively developing such connections within each STEM disciplinary context, are necessary for current and future research. Together these will provide the much needed foundational knowledge base to guide the development of the next generation of curriculum and classroom environment designed around twenty-first Century learning.
Developing scientific reasoning with inquiry labs
Scientific reasoning is part of the widely emphasized cognitive strand of twenty-first Century skills. Through development of scientific reasoning skills, students’ critical thinking, open-ended problem-solving abilities, and decision-making skills can be improved. In this way, targeting scientific reasoning as a curricular objective is aligned with the goals emphasized in twenty-first Century education. Also, there is a growing body of research on the importance of student development of scientific reasoning, which have been found to positively correlate with course achievement (Cavallo, Rozman, Blickenstaff, & Walker, 2003 ; Johnson & Lawson, 1998 ), improvement on concept tests (Coletta & Phillips, 2005 ; She & Liao, 2010 ), engagement in higher levels of problem solving (Cracolice, Deming, & Ehlert, 2008 ; Fabby & Koenig, 2013 ); and success on transfer (Ates & Cataloglu, 2007 ; Jensen & Lawson, 2011 ).
Unfortunately, research has shown that college students are lacking in scientific reasoning. Lawson ( 1992 ) found that ~ 50% of intro biology students are not capable of applying scientific reasoning in learning, including the ability to develop hypotheses, control variables, and design experiments; all necessary for meaningful scientific inquiry. Research has also found that traditional courses do not significantly develop these abilities, with pre-to-post-test gains of 1%–2%, while inquiry-based courses have gains around 7% (Koenig, Schen, & Bao, 2012 ; Koenig, Schen, Edwards, & Bao, 2012 ). Others found that undergraduates have difficulty developing evidence-based decisions and differentiating between and linking evidence with claims (Kuhn, 1992 ; Shaw, 1996 ; Zeineddin & Abd-El-Khalick, 2010 ). A large scale international study suggested that learning of physics content knowledge with traditional teaching practices does not improve students’ scientific reasoning skills (Bao et al., 2009 ).
Aligned to twenty-first Century learning, it is important to implement curriculum that is specifically designed for developing scientific reasoning abilities within current education settings. Although traditional lectures may continue for decades due to infrastructure constraints, a unique opportunity can be found in the lab curriculum, which may be more readily transformed to include hands-on minds-on group learning activities that are ideal for developing students’ abilities in scientific inquiry and reasoning.
For well over a century, the laboratory has held a distinctive role in student learning (Meltzer & Otero, 2015 ). However, many existing labs, which haven’t changed much since the late 1980s, have received criticism for their outdated cookbook style that lacks effectiveness in developing high-end skills. In addition, labs have been primarily used as a means for verifying the physical principles presented in lecture, and unfortunately, Hofstein and Lunetta ( 1982 ) found in an early review of the literature that research was unable to demonstrate the impact of the lab on student content learning.
About this same time, a shift towards a constructivist view of learning gained popularity and influenced lab curriculum development towards engaging students in the process of constructing knowledge through science inquiry. Curricula, such as Physics by Inquiry (McDermott, 1996 ), Real-Time Physics (Sokoloff, Thornton, & Laws, 2011 ), and Workshop Physics (Laws, 2004 ), were developed with a primary focus on engaging students in cognitive conflict to address misconceptions. Although these approaches have been shown to be highly successful in improving deep learning of physics concepts (McDermott & Redish, 1999 ), the emphasis on conceptual learning does not sufficiently impact the domain general scientific reasoning skills necessitated in the goals of twenty-first Century learning.
Reform in science education, both in terms of targeted content and skills, along with the emergence of knowledge regarding human cognition and learning (Bransford, Brown, & Cocking, 2000 ), have generated renewed interest in the potential of inquiry-based lab settings for skill development. In these types of hands-on minds-on learning, students apply the methods and procedures of science inquiry to investigate phenomena and construct scientific claims, solve problems, and communicate outcomes, which holds promise for developing both conceptual understanding and scientific reasoning skills in parallel (Trowbridge, Bybee, & Powell, 2000 ). In addition, the availability of technology to enhance inquiry-based learning has seen exponential growth, along with the emergence of more appropriate research methodologies to support research on student learning.
Although inquiry-based labs hold promise for developing students’ high-end reasoning, analytic, and scientific inquiry abilities, these educational endeavors have not become widespread, with many existing physics laboratory courses still viewed merely as a place to illustrate the physical principles from the lecture course (Meltzer & Otero, 2015 ). Developing scientific ideas from practical experiences, however, is a complex process. Students need sufficient time and opportunity for interaction and reflection on complex, investigative tasks. Blended learning, which merges lecture and lab (such as studio style courses), addresses this issue to some extent, but has experienced limited adoption, likely due to the demanding infrastructure resources, including dedicated technology-intensive classroom space, equipment and maintenance costs, and fully committed trained staff.
Therefore, there is an immediate need to transform the existing standalone lab courses, within the constraints of the existing education infrastructure, into more inquiry-based designs, with one of its primary goals dedicated to developing scientific reasoning skills. These labs should center on constructing knowledge, along with hands-on minds-on practical skills and scientific reasoning, to support modeling a problem, designing and implementing experiments, analyzing and interpreting data, drawing and evaluating conclusions, and effective communication. In particular, training on scientific reasoning needs to be explicitly addressed in the lab curriculum, which should contain components specifically targeting a set of operationally-defined scientific reasoning skills, such as ability to control variables or engage in multivariate causal reasoning. Although effective inquiry may also implicitly develop some aspects of scientific reasoning skills, such development is far less efficient and varies with context when the primary focus is on conceptual learning.
Several recent efforts to enhance the standalone lab course have shown promise in supporting education goals that better align with twenty-first Century learning. For example, the Investigative Science Learning Environment (ISLE) labs involve a series of tasks designed to help students develop the “habits of mind” of scientists and engineers (Etkina et al., 2006 ). The curriculum targets reasoning as well as the lab learning outcomes published by the American Association of Physics Teachers (Kozminski et al., 2014 ). Operationally, ISLE methods focus on scaffolding students’ developing conceptual understanding using inquiry learning without a heavy emphasis on cognitive conflict, making it more appropriate and effective for entry level students and K-12 teachers.
Likewise, Koenig, Wood, Bortner, and Bao ( 2019 ) have developed a lab curriculum that is intentionally designed around the twenty-first Century learning goals for developing cognitive, interpersonal, and intrapersonal abilities. In terms of the cognitive domain, the lab learning outcomes center on critical thinking and scientific reasoning but do so through operationally defined sub-skills, all of which are transferrable across STEM. These selected sub-skills are found in the research literature, and include the ability to control variables and engage in data analytics and causal reasoning. For each targeted sub-skill, a series of pre-lab and in-class activities provide students with repeated, deliberate practice within multiple hypothetical science-based scenarios followed by real inquiry-based lab contexts. This explicit instructional strategy has been shown to be essential for the development of scientific reasoning (Chen & Klahr, 1999 ). In addition, the Karplus Learning Cycle (Karplus, 1964 ) provides the foundation for the structure of the lab activities and involves cycles of exploration, concept introduction, and concept application. The curricular framework is such that as the course progresses, the students engage in increasingly complex tasks, which allow students the opportunity to learn gradually through a progression from simple to complex skills.
As part of this same curriculum, students’ interpersonal skills are developed, in part, through teamwork, as students work in groups of 3 or 4 to address open-ended research questions, such as, What impacts the period of a pendulum? In addition, due to time constraints, students learn early on about the importance of working together in an efficient manor towards a common goal, with one set of written lab records per team submitted after each lab. Checkpoints built into all in-class activities involve Socratic dialogue between the instructor and students and promote oral communication. This use of directed questioning guides students in articulating their reasoning behind decisions and claims made, while supporting the development of scientific reasoning and conceptual understanding in parallel (Hake, 1992 ). Students’ intrapersonal skills, as well as communication skills, are promoted through the submission of individual lab reports. These reports require students to reflect upon their learning over each of four multi-week experiments and synthesize their ideas into evidence-based arguments, which support a claim. Due to the length of several weeks over which students collect data for each of these reports, the ability to organize the data and manage their time becomes essential.
Despite the growing emphasis on research and development of curriculum that targets twenty-first Century learning, converting a traditionally taught lab course into a meaningful inquiry-based learning environment is challenging in current reform efforts. Typically, the biggest challenge is a lack of resources; including faculty time to create or adapt inquiry-based materials for the local setting, training faculty and graduate student instructors who are likely unfamiliar with this approach, and the potential cost of new equipment. Koenig et al. ( 2019 ) addressed these potential implementation barriers by designing curriculum with these challenges in mind. That is, the curriculum was designed as a flexible set of modules that target specific sub-skills, with each module consisting of pre-lab (hypothetical) and in-lab (real) activities. Each module was designed around a curricular framework such that an adopting institution can use the materials as written, or can incorporate their existing equipment and experiments into the framework with minimal effort. Other non-traditional approaches have also been experimented with, such as the work by Sobhanzadeh, Kalman, and Thompson ( 2017 ), which targets typical misconceptions by using conceptual questions to engage students in making a prediction, designing and conducting a related experiment, and determining whether or not the results support the hypothesis.
Another challenge for inquiry labs is the assessment of skills-based learning outcomes. For assessment of scientific reasoning, a new instrument on inquiry in scientific thinking analytics and reasoning (iSTAR) has been developed, which can be easily implemented across large numbers of students as both a pre- and post-test to assess gains. iSTAR assesses reasoning skills necessary in the systematical conduct of scientific inquiry, which includes the ability to explore a problem, formulate and test hypotheses, manipulate and isolate variables, and observe and evaluate the consequences (see www.istarassessment.org ). The new instrument expands upon the commonly used classroom test of scientific reasoning (Lawson, 1978 , 2000 ), which has been identified with a number of validity weaknesses and a ceiling effect for college students (Bao, Xiao, Koenig, & Han, 2018 ).
Many education innovations need supporting infrastructures that can ensure adoption and lasting impact. However, making large-scale changes to current education settings can be risky, if not impossible. New education approaches, therefore, need to be designed to adapt to current environmental constraints. Since higher-end skills are a primary focus of twenty-first Century learning, which are most effectively developed in inquiry-based group settings, transforming current lecture and lab courses into this new format is critical. Although this transformation presents great challenges, promising solutions have already emerged from various research efforts. Perhaps the biggest challenge is for STEM educators and researchers to form an alliance to work together to re-engineer many details of the current education infrastructure in order to overcome the multitude of implementation obstacles.
This paper attempts to identify a few central ideas to provide a broad picture for future research and development in physics education, or STEM education in general, to promote twenty-first Century learning. Through a synthesis of the existing literature within the authors’ limited scope, a number of views surface.
Education is a service to prepare (not to select) the future workforce and should be designed as learner-centered, with the education goals and teaching-learning methods tailored to the needs and characteristics of the learners themselves. Given space constraints, the reader is referred to the meta-analysis conducted by Freeman et al. ( 2014 ), which provides strong support for learner-centered instruction. The changing world of the twenty-first Century informs the establishment of new education goals, which should be used to guide research and development of teaching and learning for present day students. Aligned to twenty-first Century learning, the new science standards have set the goals for STEM education to transition towards promoting deep learning of disciplinary knowledge, thereby building upon decades of research in PER, while fostering a wide range of general high-end cognitive and non-cognitive abilities that are transferable across all disciplines.
Following these education goals, more research is needed to operationally define and assess the desired high-end reasoning abilities. Building on a clear definition with effective assessments, a large number of empirical studies are needed to investigate how high-end abilities can be developed in parallel with deep learning of concepts, such that what is learned can be generalized to impact the development of curriculum and teaching methods which promote skills-based learning across all STEM fields. Specifically for PER, future research should emphasize knowledge integration to promote deep conceptual understanding in physics along with inquiry learning to foster scientific reasoning. Integration of physics learning in contexts that connect to other STEM disciplines is also an area for more research. Cross-cutting, interdisciplinary connections are becoming important features of the future generation physics curriculum and defines how physics should be taught collaboratively with other STEM courses.
This paper proposed meaningful areas for future research that are aligned with clearly defined education goals for twenty-first Century learning. Based on the existing literature, a number of challenges are noted for future directions of research, including the need for:
clear and operational definitions of goals to guide research and practice
concrete operational definitions of high-end abilities for which students are expected to develop
effective assessment methods and instruments to measure high-end abilities and other components of twenty-first Century learning
a knowledge base of the curriculum and teaching and learning environments that effectively support the development of advanced skills
integration of knowledge and ability development regarding within-discipline and cross-discipline learning in STEM
effective means to disseminate successful education practices
The list is by no means exhaustive, but these themes emerge above others. In addition, the high-end abilities discussed in this paper focus primarily on scientific reasoning, which is highly connected to other skills, such as critical thinking, systems thinking, multivariable modeling, computational thinking, design thinking, etc. These abilities are expected to develop in STEM learning, although some may be emphasized more within certain disciplines than others. Due to the limited scope of this paper, not all of these abilities were discussed in detail but should be considered an integral part of STEM learning.
Finally, a metacognitive position on education research is worth reflection. One important understanding is that the fundamental learning mechanism hasn’t changed, although the context in which learning occurs has evolved rapidly as a manifestation of the fast-forwarding technology world. Since learning is a process at the interface between a learner’s mind and the environment, the main focus of educators should always be on the learner’s interaction with the environment, not just the environment. In recent education developments, many new learning platforms have emerged at an exponential rate, such as the massive open online courses (MOOCs), STEM creative labs, and other online learning resources, to name a few. As attractive as these may be, it is risky to indiscriminately follow trends in education technology and commercially-incentivized initiatives before such interventions are shown to be effective by research. Trends come and go but educators foster students who have only a limited time to experience education. Therefore, delivering effective education is a high-stakes task and needs to be carefully and ethically planned and implemented. When game-changing opportunities emerge, one needs to not only consider the winners (and what they can win), but also the impact on all that is involved.
Based on a century of education research, consensus has settled on a fundamental mechanism of teaching and learning, which suggests that knowledge is developed within a learner through constructive processes and that team-based guided scientific inquiry is an effective method for promoting deep learning of content knowledge as well as developing high-end cognitive abilities, such as scientific reasoning. Emerging technology and methods should serve to facilitate (not to replace) such learning by providing more effective education settings and conveniently accessible resources. This is an important relationship that should survive many generations of technological and societal changes in the future to come. From a physicist’s point of view, a fundamental relation like this can be considered the “mechanics” of teaching and learning. Therefore, educators and researchers should hold on to these few fundamental principles without being distracted by the surfacing ripples of the world’s motion forward.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
American Association of Physics Teachers
Investigative Science Learning Environment
Inquiry in Scientific Thinking Analytics and Reasoning
Massive open online course
New Generation Science Standards
- Physics education research
Science Technology Engineering and Math
Alonso, M. (1992). Problem solving vs. conceptual understanding. American Journal of Physics , 60 (9), 777–778. https://doi.org/10.1119/1.17056 .
Article Google Scholar
Anderson, L. W., Krathwohl, D. R., Airasian, P. W., Cruikshank, K. A., Mayer, R. E., Pintrich, P. R., … Wittrock, M. C. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives, abridged edition . White Plains: Longman.
Ates, S., & Cataloglu, E. (2007). The effects of students’ reasoning abilities on conceptual understandings and problem-solving abilities in introductory mechanics. European Journal of Physics , 28 , 1161–1171.
Bagno, E., Eylon, B.-S., & Ganiel, U. (2000). From fragmented knowledge to a knowledge structure: Linking the domains of mechanics and electromagnetism. American Journal of Physics , 68 (S1), S16–S26.
Bailin, S. (1996). Critical thinking. In J. J. Chambliss (Ed.), Philosophy of education: An encyclopedia , (vol. 1671, pp. 119–123). Routledge.
Bangert-Drowns, R. L., & Bankert, E. (1990). Meta-analysis of effects of explicit instruction for critical thinking. Research report. ERIC Number: ED328614.
Google Scholar
Bao, L., Cai, T., Koenig, K., Fang, K., Han, J., Wang, J., … Wu, N. (2009). Learning and scientific reasoning. Science , 323 , 586–587. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1167740 .
Bao, L., & Redish, E. F. (2001). Concentration analysis: A quantitative assessment of student states. American Journal of Physics , 69 (S1), S45–S53.
Bao, L., & Redish, E. F. (2006). Model analysis: Representing and assessing the dynamics of student learning. Physical Review Special Topics-Physics Education Research , 2 (1), 010103.
Bao, L., Xiao, Y., Koenig, K., & Han, J. (2018). Validity evaluation of the Lawson classroom test of scientific reasoning. Physical Review Physics Education Research , 14 (2), 020106.
Beichner, R. J., Saul, J. M., Abbott, D. S., Morse, J. J., Deardorff, D., Allain, R. J., … Risley, J. S. (2007). The student-centered activities for large enrollment undergraduate programs (SCALE-UP) project. Research-Based Reform of University Physics , 1 (1), 2–39.
Binkley, M., Erstad, O., Herman, J., Raizen, S., Ripley, M., & Rumble, M. (2010). Draft White paper defining 21st century skills . Melbourne: ACTS.
Bloom, B. S., Engelhart, M. D., Furst, E. J., Hill, W. H., & Krathwohl, D. R. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: Handbook 1: Cognitive domain . New York: Longman.
Bransford, J. D., Brown, A. L., & Cocking, R. R. (2000). How people learn , (vol. 11). Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Brown, A. (1989). Analogical learning and transfer: What develops? In S. Vosniadu, & A. Ortony (Eds.), Similarity and analogical reasoning , (pp. 369–412). New York: Cambridge U.P.
Chapter Google Scholar
Cavallo, A. M. L., Rozman, M., Blickenstaff, J., & Walker, N. (2003). Learning, reasoning, motivation, and epistemological beliefs: Differing approaches in college science courses. Journal of College Science Teaching , 33 (3), 18–22.
Chen, Z., & Klahr, D. (1999). All other things being equal: Acquisition and transfer of the control of variables strategy. Child Development , 70 , 1098–1120.
Chi, M. T., Bassok, M., Lewis, M. W., Reimann, P., & Glaser, R. (1989). Self-explanations: How students study and use examples in learning to solve problems. Cognitive Science , 13 (2), 145–182.
Chi, M. T., Feltovich, P. J., & Glaser, R. (1981). Categorization and representation of physics problems by experts and novices. Cognitive Science , 5 (2), 121–152.
Chi, M. T., & Slotta, J. D. (1993). The ontological coherence of intuitive physics. Cognition and Instruction , 10 (2–3), 249–260.
Chi, M. T., Slotta, J. D., & De Leeuw, N. (1994). From things to processes: A theory of conceptual change for learning science concepts. Learning and Instruction , 4 (1), 27–43.
Chi, M. T. H. (1992). Conceptual change within and across ontological categories: Examples from learning and discovery in science. In R. N. Giere (Ed.), Cognitive models of science . Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Chiu, M. H. (2001). Algorithmic problem solving and conceptual understanding of chemistry by students at a local high school in Taiwan. Proceedings-National Science Council Republic of China Part D Mathematics Science and Technology Education , 11 (1), 20–38.
Chiu, M.-H., Guo, C. J., & Treagust, D. F. (2007). Assessing students’ conceptual understanding in science: An introduction about a national project in Taiwan. International Journal of Science Education , 29 (4), 379–390.
Clement, J. (1982). Students’ preconceptions in introductory mechanics. American Journal of Physics , 50 (1), 66–71.
Coletta, V. P., & Phillips, J. A. (2005). Interpreting FCI scores: Normalized gain, preinstruction scores, and scientific reasoning ability. American Journal of Physics , 73 (12), 1172–1182.
Cracolice, M. S., Deming, J. C., & Ehlert, B. (2008). Concept learning versus problem solving: A cognitive difference. Journal of Chemical Education , 85 (6), 873.
De Jong, T., & Ferguson-Hesler, M. G. M. (1986). Cognitive structure of good and poor problem solvers in physics. Journal of Educational Psychology , 78 , 279–288.
DiSessa, A. A. (1993). Toward an epistemology of physics. Cognition and Instruction , 10 (2–3), 105–225.
Duit, R., & Treagust, D. F. (2003). Conceptual change: A powerful framework for improving science teaching and learning. International Journal of Science Education , 25 (6), 671–688.
Dykstra Jr., D. I., Boyle, C. F., & Monarch, I. A. (1992). Studying conceptual change in learning physics. Science Education , 76 (6), 615–652.
Ennis, R. (1993). Critical thinking assessment. Theory Into Practice , 32 (3), 179–186.
Etkina, E., & Van Heuvelen, A. (2001). Investigative science learning environment: Using the processes of science and cognitive strategies to learn physics. In Proceedings of the 2001 physics education research conference , (pp. 17–21). Rochester.
Etkina, E., Van Heuvelen, A., White-Brahmia, S., Brookes, D. T., Gentile, M., Murthy, S., … Warren, A. (2006). Scientific abilities and their assessment. Physical Review Special Topics-Physics Education Research , 2 (2), 020103.
Eylon, B.-S., & Reif, F. (1984). Effects of knowledge organization on task performance. Cognition and Instruction , 1 (1), 5–44.
Fabby, C., & Koenig, K. (2013). Relationship of scientific reasoning to solving different physics problem types. In Proceedings of the 2013 Physics Education Research Conference, Portland, OR .
Facione, P. A. (1990). Critical thinking: A statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction – The Delphi report . Millbrae: California Academic Press.
Ferguson-Hesler, M. G. M., & De Jong, T. (1990). Studying physics texts: Differences in study processes between good and poor solvers. Cognition and Instruction , 7 (1), 41–54.
Fisher, A. (2001). Critical thinking: An introduction . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Freeman, S., Eddy, S. L., McDonough, M., Smith, M. K., Okoroafor, N., Jordt, H., & Wenderoth, M. P. (2014). Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 111 (23), 8410–8415.
Glaser, E. M. (1941). An experiment in the development of critical thinking . New York: Teachers College, Columbia University.
Hake, R. R. (1992). Socratic pedagogy in the introductory physics laboratory. The Physics Teacher , 30 , 546.
Hake, R. R. (1998). Interactive-engagement versus traditional methods: A six-thousand-student survey of mechanics test data for introductory physics courses. American Journal of Physics , 66 (1), 64–74.
Halloun, I. A., & Hestenes, D. (1985a). The initial knowledge state of college physics students. American Journal of Physics , 53 (11), 1043–1055.
Halloun, I. A., & Hestenes, D. (1985b). Common sense concepts about motion. American Journal of Physics , 53 (11), 1056–1065.
Halpern, D. F. (1999). Teaching for critical thinking: Helping college students develop the skills and dispositions of a critical thinker. New Directions for Teaching and Learning , 80 , 69–74. https://doi.org/10.1002/tl.8005 .
Hardiman, P. T., Dufresne, R., & Mestre, J. P. (1989). The relation between problem categorization and problem solving among experts and novices. Memory & Cognition , 17 (5), 627–638.
Heller, J. I., & Reif, F. (1984). Prescribing effective human problem-solving processes: Problem description in physics. Cognition and Instruction , 1 (2), 177–216.
Hoellwarth, C., Moelter, M. J., & Knight, R. D. (2005). A direct comparison of conceptual learning and problem solving ability in traditional and studio style classrooms. American Journal of Physics , 73 (5), 459–462.
Hofstein, A., & Lunetta, V. N. (1982). The role of the laboratory in science teaching: Neglected aspects of research. Review of Educational Research , 52 (2), 201–217.
Hsu, L., Brewe, E., Foster, T. M., & Harper, K. A. (2004). Resource letter RPS-1: Research in problem solving. American Journal of Physics , 72 (9), 1147–1156.
Jensen, J. L., & Lawson, A. (2011). Effects of collaborative group composition and inquiry instruction on reasoning gains and achievement in undergraduate biology. CBE - Life Sciences Education , 10 , 64–73.
Johnson, M. A., & Lawson, A. E. (1998). What are the relative effects of reasoning ability and prior knowledge on biology achievement in expository and inquiry classes? Journal of Research in Science Teaching , 35 (1), 89–103.
Kalman, C., & Lattery, M. (2018). Three active learning strategies to address mixed student epistemologies and promote conceptual change. Frontiers in ICT , 5 (19), 1–9.
Karplus, R. (1964). The science curriculum improvement study. Journal of College Science Teaching , 2 (4), 293–303.
Kim, E., & Pak, S.-J. (2002). Students do not overcome conceptual difficulties after solving 1000 traditional problems. American Journal of Physics , 70 (7), 759–765.
Koenig, K., Schen, M., & Bao, L. (2012). Explicitly targeting pre-service teacher scientific reasoning abilities and understanding of nature of science through an introductory science course. Science Educator , 21 (2), 1–9.
Koenig, K., Schen, M., Edwards, M., & Bao, L. (2012). Addressing STEM retention through a scientific thought and methods course. Journal of College Science Teaching , 41 , 23–29.
Koenig, K., Wood, K., Bortner, L., & Bao, L. (2019). Modifying traditional labs to target scientific reasoning. Journal of College Science Teaching , 48 (5), 28-35.
Kozminski, J., Beverly, N., Deardorff, D., Dietz, R., Eblen-Zayas, M., Hobbs, R., … Zwickl, B. (2014). AAPT recommendations for the undergraduate physics laboratory curriculum , (pp. 1–29). American Association of Physics Teachers Retrieved from https://www.aapt.org/Resources/upload/LabGuidlinesDocument_EBendorsed_nov10.pdf .
Kuhn, D. (1992). Thinking as argument. Harvard Educational Review , 62 (2), 155–178.
Larkin, J., McDermott, J., Simon, D. P., & Simon, H. A. (1980). Expert and novice performance in solving physics problems. Science , 208 (4450), 1335–1342.
Laws, P. W. (2004). Workshop physics activity guide, module 4: Electricity and magnetism. In Workshop physics activity guide . Wiley-VCH.
Lawson, A. E. (1978), The development and validation of a classroom test of formal reasoning, Journal of Research in Science Teaching , 15 (1), 11–24.
Lawson, A. E. (1992). The development of reasoning among college biology students - a review of research. Journal of College Science Teaching , 21 , 338–344.
Lawson, A. E. (2000). Classroom test of scientific reasoning: Multiple choice version, based on Lawson, A. E. 1978. Development and validation of the classroom test of formal reasoning. Journal of Research in Science Teaching , 15 (1), 11–24.
Lee, H. S., Liu, O. L., & Linn, M. C. (2011). Validating measurement of knowledge integration in science using multiple-choice and explanation items. Applied Measurement in Education , 24 (2), 115–136.
Linn, M. C. (2005). The knowledge integration perspective on learning and instruction. In R. K. Sawyer (Ed.), The Cambridge handbook of the learning sciences , (pp. 243–264). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511816833.016 .
Lipman, M. (2003). Thinking in education , (2nd ed., ). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Liu, X. (2010). Science and engineering education sources. Using and developing measurement instruments in science education: A Rasch modeling approach . Charlotte: IAP Information Age Publishing.
Marzano, R. J., Brandt, R. S., Hughes, C. S., Jones, B. F., Presseisen, B. Z., Rankin, S. C., et al. (1988). Dimensions of thinking, a framework for curriculum and instruction . Alexandria: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.
Mazur, E. (1997). Peer instruction: A user’s manual . Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
McDermott, L. C. (1996). Physics by Inquiry: An Introduction to the Physical Sciences . John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY.
McDermott, L. C., & Redish, E. F. (1999). Resource letter: PER-1: Physics education research. American Journal of Physics , 67 (9), 755–767.
McKeachie, W. J. (1986). Teaching and learning in the college classroom: A review of the research literature . Ann Arbor: National Center for Research to Improve Postsecondary Teaching and Learning.
Meltzer, D. E., & Otero, V. K. (2015). A brief history of physics education in the United States. American Journal of Physics , 83 (5), 447–458.
Meltzer, D. E., & Thornton, R. K. (2012). Resource letter ALIP-1: Active-learning instruction in physics. American Journal of Physics , 80 (6), 478–496.
Minstrell, J. (1992). Facets of students’ knowledge and relevant instruction. In R. Duit, F. Goldberg, & H. Niedderer (Eds.), Proceedings of the international workshop: Research in physics learning- theoretical issues and empirical studies , (pp. 110–128). The Institute for Science Education.
Nakhleh, M. B. (1993). Are our students conceptual thinkers or algorithmic problem solvers? Identifying conceptual students in general chemistry. Journal of Chemical Education , 70 (1), 52. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed070p52 .
Nakhleh, M. B., & Mitchell, R. C. (1993). Concept learning versus problem solving: There is a difference. Journal of Chemical Education , 70 (3), 190. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed070p190 .
National Research Council (2011). Assessing 21st century skills: Summary of a workshop . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/13215 .
Book Google Scholar
National Research Council (2012a). Education for life and work: Developing transferable knowledge and skills in the 21st century . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
National Research Council (2012b). A framework for K-12 science education: Practices, crosscutting concepts, and core ideas . Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
National Research Council (2012c). Discipline-based education research: Understanding and improving learning in undergraduate science and engineering . Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
National Science & Technology Council (2018). Charting a course for success: America’s strategy for STEM education . Washington, DC: Office of Science and Technology Policy.
NCET. (1987). Critical thinking as defined by the National Council for excellence in critical thinking, statement by Michael Scriven & Richard Paul, presented at the 8th annual conference on critical thinking and education reform. Retrieved December 4, 2018, from http://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/defining-critical-thinking/766 .
Nordine, J., Krajcik, J., & Fortus, D. (2011). Transforming energy instruction in middle school to support integrated understanding and future learning. Science Education , 95 (4), 670–699.
Nurrenbern, S. C., & Pickering, M. (1987). Concept learning versus problem solving: Is there a difference? Journal of Chemical Education , 64 (6), 508.
Paul, R. (1990). Critical thinking: What every person needs to survive in a rapidly changing world . Rohnert Park: Center for Critical Thinking and Moral Critique.
Perkins, D. N., & Salomon, G. (1989). Are cognitive skills context-bound? Educational Researcher , 18 (1), 16–25.
Posner, G., Strike, K., Hewson, P., & Gertzog, W. (1982). Accommodation of a scientific conception: Toward a theory of conceptual change. Science Education , 66 (2), 211–227.
Reay, N. W., Bao, L., Li, P., Warnakulasooriya, R., & Baugh, G. (2005). Toward the effective use of voting machines in physics lectures. American Journal of Physics , 73 (6), 554–558.
Reimers, F. M., & Chung, C. K. (Eds.) (2016). Teaching and learning for the twenty-first century: Educational goals, policies and curricula from six nations . Cambridge: Harvard Education Press.
Salomon, G., & Perkins, D. N. (1989). Rocky roads to transfer: Rethinking mechanism of a neglected phenomenon. Educational Psychologist , 24 (2), 113–142.
Schoenfeld, A. H., & Herrmann, D. J. (1982). Problem perception and knowledge structure in expert and novice mathematical problem solvers. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition , 8 (5), 484.
Shaw, V. F. (1996). The cognitive processes in informal reasoning. Thinking and Reasoning , 2 (1), 51–80.
She, H., & Liao, Y. (2010). Bridging scientific reasoning and conceptual change through adaptive web-based learning. Journal of Research in Science Teaching , 47 (1), 91–119.
Shen, J., Liu, O. L., & Chang, H.-Y. (2017). Assessing students’ deep conceptual understanding in physical sciences: An example on sinking and floating. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education , 15 (1), 57–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-015-9680-z .
Siegel, H. (1988). Educating reason: Rationality, critical thinking and education , (vol. 1). New York: Routledge.
Slotta, J. D., Chi, M. T., & Joram, E. (1995). Assessing students’ misclassifications of physics concepts: An ontological basis for conceptual change. Cognition and Instruction , 13 (3), 373–400.
Smith III, J. P., DiSessa, A. A., & Roschelle, J. (1994). Misconceptions reconceived: A constructivist analysis of knowledge in transition. The Journal of the Learning Sciences , 3 (2), 115–163.
Smith, M. U. (1992). Expertise and organization of knowledge: Unexpected differences among genetic counselors, faculty members and students on problem categorization tasks. Journal of Research in Science Teaching , 29 (2), 179–205.
Sobhanzadeh, M., Kalman, C. S., & Thompson, R. I. (2017). Labatorials in introductory physics courses. European Journal of Physics , 38 , 1–18.
Sokoloff, D. R., Thornton, R. K., & Laws, P. W. (2011). RealTime physics: Active learning laboratories . New York: Wiley.
Stamovlasis, D., Tsaparlis, G., Kamilatos, C., Papaoikonomou, D., & Zarotiadou, E. (2005). Conceptual understanding versus algorithmic problem solving: Further evidence from a national chemistry examination. Chemistry Education Research and Practice , 6 (2), 104–118.
Tanenbaum, C. (2016). STEM 2026: A vision for innovation in STEM education . Washington, DC: US Department of Education.
Thornton, R. K., & Sokoloff, D. R. (1998). Assessing student learning of Newton’s laws: The force and motion conceptual evaluation and the evaluation of active learning laboratory and lecture curricula. American Journal of Physics , 66 (4), 338–352.
Trowbridge, L. W., Bybee, R. W., & Powell, J. C. (2000). Teaching secondary school science: Strategies for developing scientific literacy . Upper Saddle River: Merrill-Prentice Hall.
United States Chamber of Commerce (2017). Bridging the soft skills gap: How the business and education sectors are partnering to prepare students for the 21 st century workforce . Washington DC: Center for Education and Workforce, U.S. Chamber of Commerce Foundation.
Veldhuis, G. H. (1990). The use of cluster analysis in categorization of physics problems. Science Education , 74 (1), 105–118.
Vosniadou, S., Vamvakoussi, X., & Skopeliti, I. (2008). The framework theory approach to the problem of conceptual change. In S. Vosniadou (Ed.), International handbook of research on conceptual change . New York: Routledge.
Wexler, P. (1982). Structure, text, and subject: A critical sociology of school knowledge. In M. W. Apple (Ed.), Cultural and economic reproduction in education: Essays on class, ideology and the state . London: Routledge & Regan Paul.
Zeineddin, A., & Abd-El-Khalick, F. (2010). Scientific reasoning and epistemological commitments: Coordination of theory and evidence among college science students. Journal of Research in Science Teaching , 47 (9), 1064–1093.
Zimmerman, C. (2000). The development of scientific reasoning skills. Developmental Review , 20 (1), 99–149.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The research is supported in part by NSF Awards DUE-1431908 and DUE-1712238. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this paper are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
The research is supported in part by NSF Awards DUE-1431908 and DUE-1712238.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, 43210, USA
University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, 45221, USA
Kathleen Koenig
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
LB developed the concept, wrote a significant portion of the review and position, and synthesized the paper. KK wrote and edited a significant portion of the paper. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lei Bao .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Bao, L., Koenig, K. Physics education research for 21 st century learning. Discip Interdscip Sci Educ Res 1 , 2 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43031-019-0007-8
Download citation
Received : 17 April 2019
Accepted : 13 June 2019
Published : 28 November 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s43031-019-0007-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Twenty-first century learning
- STEM education
- Scientific reasoning
- Deep learning
Developing real life problem-solving skills through situational design: a pilot study
- Development Article
- Published: 09 July 2019
- Volume 67 , pages 1529–1545, ( 2019 )
Cite this article
- Lin Zhong ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2875-3461 1 &
- Xinhao Xu 2
1506 Accesses
11 Citations
Explore all metrics
Current problem-solving research has advanced our understanding of the problem-solving process but has provided little advice on how to teach problem-solving skills. In addition, literature reveals that individual difference is an essential issue in problem-solving skills instruction but has been rarely addressed in current research. Building upon information-processing theory, this article proposes an instructional design model, namely the situational design model, which serves as an approach to accommodate individual difference in problem-solving skills instruction. This design model was further examined with a pilot study in an introductory technology course and results showed a significant difference in students’ academic performance and problem-solving skills, especially the non-recurrent skills. The proposed situational design model contributes to research and practice by providing a novel lens to explore problem-solving skills and assisting in the design of instruction that aims to develop student’s expertise in solving real world problems.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
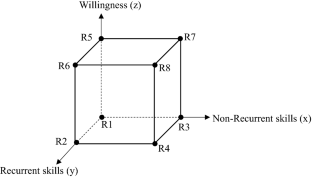
Angeli, C. (2013). Examining the effects of field dependence–independence on learners’ problem-solving performance and interaction with a computer modeling tool: Implications for the design of joint cognitive systems. Computers & Education, 62, 221–230.
Article Google Scholar
Bulu, S. T., & Pedersen, S. (2012). Supporting problem-solving performance in a hypermedia learning environment: The role of students’ prior knowledge and metacognitive skills. Computers in Human Behavior, 28 (4), 1162–1169.
Cronbach, L. J., & Snow, R. E. (1977). Aptitudes and instructional methods . New York: Irvington.
Google Scholar
Delahaye, B. L., & Smith, H. E. (1995). The validity of the learning preference assessment. Adult Education Quarterly, 45, 159–173.
Eseryel, D., Ge, X., Ifenthaler, D., & Law, V. (2011). Dynamic modeling as a cognitive regulation scaffold for developing complex problem-solving skills in an educational massively multiplayer online game environment. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 45 (3), 265–286.
Frensch, P. A., & Funke, J. (1995). Definitions, traditions, and a general framework for understanding complex problem solving. In P. A. Frensch & J. Funke (Eds.), Complex problem solving: The European perspective (pp. 3–26). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Ge, X. (2013). Designing learning technologies to support self-regulation during ill-structured problem-solving processes. In R. Azevedo & V. Aleven (Eds.), International Handbook of Metacognition and Learning Technologies (pp. 213–228). Berlin: Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Ge, X., & Land, S. M. (2004). A conceptual framework for scaffolding ill-structured problem-solving processes using question prompts and peer interactions. Educational Technology Research and Development, 52 (2), 5–22.
Ge, X., Law, V., & Huang, K. (2016). Detangling the interrelationships between self-regulation and ill-structured problem solving in problem-based learning. The Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-Based Learning, 10 (2), 11. https://doi.org/10.7771/1541-5015.1622 .
Guglielmino, L. M. (1978). Development of the self-directed learning readiness scale. (Doctoral dissertation, University of Georgia, 1977). Dissertation. Abstracts International, 38 , 6467.
Hanover Research. (2016). McGraw - hill education 2016 workforce readiness survey . Retrieved from https://www.fastcompany.com/3059940/these-are-the-biggest-skills-that-new-graduates-lack .
Hersey, P., Blanchard, K. H., & Johnson, D. E. (2012). Management of organizational behavior: Leading human resources (10th ed.). Upper Saddle, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Jeotee, K. (2012). Reasoning skills, problem solving ability and academic ability: Implications for study programme and career choice in the context of higher education in Thailand (Doctoral dissertation, Durham University).
Jonassen, D. H. (2007). Learning to solve complex, scientific problems . Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Jonassen, D. H., & Grabowski, B. (2012). Handbook of individual differences, learning, and instruction . New York: Routledge.
Kalyuga, S., & Sweller, J. (2004). Measuring knowledge to optimize cognitive load factors during instruction. Journal of Educational Psychology, 96 (3), 558–568.
Kalyuga, S., & Sweller, J. (2005). Rapid dynamic assessment of expertise to improve the efficiency of adaptive e-learning. Educational Technology Research and Development, 53 (3), 83–93.
Kim, M. K. (2012). Theoretically grounded guidelines for assessing learning progress: Cognitive changes in ill-structured complex problem-solving contexts. Educational Technology Research and Development, 60 (4), 601–622.
Kim, M. C., & Hannafin, M. J. (2011). Scaffolding problem solving in technology-enhanced learning environments (TELEs): Bridging research and theory with practice. Computers & Education, 56 (2), 403–417.
Klegeris, K., Bahniwal, M., & Hurren, H. (2013). Improvement in generic problem-solving abilities of students by use of tutor-less problem-based learning in a large classroom setting. CBE Life Sciences Education, 12, 70–73.
Lee, C. B. (2010). The interactions between problem solving and conceptual change: System dynamic modeling as a platform for learning. Computers & Education, 55 (3), 1145–1158.
Matemba, C. K., Awinja, J., & Otieno, K. O. (2014). Relationship between problem solving approaches and academic performance: A case of Kakamega municipality, Kenya. International Journal of Human Resource Studies, 4 (4), 10.
McCormick, N. J., Clark, L. M., & Raines, J. M. (2015). Engaging students in critical thinking and problem solving: A brief review of the literature. Journal of Studies in Education , 5 (4), 100–113.
Muna, K., Sanjaya, R. E., Syahmani, & Bakti, I. (2017). Metacognitive skills and students’ motivation toward chemical equilibrium problem solving ability: A correlational study on students of XI IPA SMAN 2 Banjarmasin. In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 1911, No. 1, p. 020008). AIP Publishing.
Newell, A., & Rosenbloom, P. (1981). Mechanisms of skill acquisition and the law of practice. In J. R. Anderson (Ed.), Cognitive skills and their acquisition (pp. 1–55). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Nokes, T. J., Schunn, C. D., & Chi, M. T. H. (2010). Problem solving and human expertise. In International encyclopedia of education (pp. 265–272). Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-044894-7.00486-3 .
Raes, A., Schellens, T., Wever, B. D., & Vanderhoven, E. (2012). Scaffolding information problem solving in web-based collaborative inquiry learning. Computers & Education, 59 (1), 82–94.
Renkl, A., & Atkinson, R. K. (2007). Cognitive skill acquisition: Ordering instructional events in example-based learning. In F. E. Ritter, J. Nerb, E. Lehtinen, & T. O’Shea (Eds.), In order to learn: How ordering effect in machine learning illuminate human learning and vice versa . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Robertson, I. S. (2016). Problem solving: Perspectives from cognition and neuroscience (2nd ed.). Hove: Psychology Press.
Book Google Scholar
Salden, R., Aleve, V., Schwonke, R., & Renkl, A. (2010). The expertise reversal effect and worked examples in tutored problem solving. Instructional Science, 38, 289–307.
Säljö, R., & Wyndhamn, J. (1990). Problem-solving, academic performance and situated reasoning. A study of joint cognitive activity in the formal setting. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 60 (3), 245–254.
Shute, V., Wang, L., Greiff, S., Zhao, W., & Moore, G. (2016). Measuring problem solving skills via stealth assessment in an engaging video game. Computers in Human Behavior, 63, 106–117.
Van Merriënboer, J. J. G. (1997). Training complex cognitive skills . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Educational Technology Publications.
Van Merriënboer, J. J. G. (2013). Perspectives on problem solving and instruction. Computers & Education, 64 (1), 153–160.
Van Merriënboer, J. J. G. (2016). How people learn. In N. Rushby & D. W. Surry (Eds.), The Wiley handbook of learning technology (pp. 15–34). West Sussex: Wiley.
Van Merriënboer, J. J. G., & Bruin, A. B. H. (2013). Research paradigms and perspectives on learning. In J. M. Spector, et al. (Eds.), Handbook of research on educational communications and technology (pp. 21–29). New York: Springer.
Van Merriënboer, J. J. G., Clark, R. E., & Croock, M. B. M. (2002). Blueprints for complex learning: The 4C/ID-model. Educational Technology Research and Development, 50 (2), 39–64.
Yu, K., Fan, S., & Lin, K. (2014). Enhancing students’ problem-solving skills through context-based learning. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 13, 1377–1401.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Workforce Education and Development, Southern Illinois University Carbondale, 475 Clocktower Drive #4605, Carbondale, IL, 62901, USA
School of Information Science & Learning Technologies, University of Missouri Columbia, 221H Townsend Hall, Columbia, MO, 65211, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lin Zhong .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Learning readiness survey
For each of the following questions and statements, please rate yourself for each item. Mark the number that best reflects your situation.
Situational design of lesson 4
Learning goal Improve information visualization skills by demonstrating effective interactive image editing skills for specific purposes by using Thinglink.
Recurrent skills
Basic understanding of information visualization by using images;
Basic understanding of interactive images;
Basic image editing skills.
Non-recurrent skills
Decision-making skills to determine the purpose of the image;
Monitoring skills to ensure task completion;
Comparing and evaluation skills to ensure the quality of the newly created image;
Procedural learning activities Create interactive images by using Thinglink.
HP—create at least three interactive images by using Thinglink.
LP—create one interactive image by using Thinglink.
Supportive learning activities Consider the purpose of the images.
HS—pick up a purpose (educational, commercial, personal) and improve the image quality to achieve that purpose.
LS—consider how to create images for educational purpose.
Relationship activities
HR-interaction with students is mainly two-way communication. For example, relationship activities can focus on reviewing whether the image achieves the chosen purpose or not, checking the quality of the images, providing guidance for further improvement, keeping check emotional level, reducing the fear of making mistakes, and avoiding overwhelming.
LR-interaction with students is mainly one-way communication. For example, relationship activities can focus on clarifying task requirements, checking task completion, making sure all the given tasks are completed and providing step-by-step assistance when necessary.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Zhong, L., Xu, X. Developing real life problem-solving skills through situational design: a pilot study. Education Tech Research Dev 67 , 1529–1545 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-019-09691-2
Download citation
Published : 09 July 2019
Issue Date : December 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-019-09691-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Problem-solving skills
- Individual differences
- Learning readiness
- Situational design
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
fa51e2b1dc8cca8f7467da564e77b5ea
- Make a Gift
- Join Our Email List
- Problem Solving in STEM
Solving problems is a key component of many science, math, and engineering classes. If a goal of a class is for students to emerge with the ability to solve new kinds of problems or to use new problem-solving techniques, then students need numerous opportunities to develop the skills necessary to approach and answer different types of problems. Problem solving during section or class allows students to develop their confidence in these skills under your guidance, better preparing them to succeed on their homework and exams. This page offers advice about strategies for facilitating problem solving during class.
How do I decide which problems to cover in section or class?
In-class problem solving should reinforce the major concepts from the class and provide the opportunity for theoretical concepts to become more concrete. If students have a problem set for homework, then in-class problem solving should prepare students for the types of problems that they will see on their homework. You may wish to include some simpler problems both in the interest of time and to help students gain confidence, but it is ideal if the complexity of at least some of the in-class problems mirrors the level of difficulty of the homework. You may also want to ask your students ahead of time which skills or concepts they find confusing, and include some problems that are directly targeted to their concerns.
You have given your students a problem to solve in class. What are some strategies to work through it?
- Try to give your students a chance to grapple with the problems as much as possible. Offering them the chance to do the problem themselves allows them to learn from their mistakes in the presence of your expertise as their teacher. (If time is limited, they may not be able to get all the way through multi-step problems, in which case it can help to prioritize giving them a chance to tackle the most challenging steps.)
- When you do want to teach by solving the problem yourself at the board, talk through the logic of how you choose to apply certain approaches to solve certain problems. This way you can externalize the type of thinking you hope your students internalize when they solve similar problems themselves.
- Start by setting up the problem on the board (e.g you might write down key variables and equations; draw a figure illustrating the question). Ask students to start solving the problem, either independently or in small groups. As they are working on the problem, walk around to hear what they are saying and see what they are writing down. If several students seem stuck, it might be a good to collect the whole class again to clarify any confusion. After students have made progress, bring the everyone back together and have students guide you as to what to write on the board.
- It can help to first ask students to work on the problem by themselves for a minute, and then get into small groups to work on the problem collaboratively.
- If you have ample board space, have students work in small groups at the board while solving the problem. That way you can monitor their progress by standing back and watching what they put up on the board.
- If you have several problems you would like to have the students practice, but not enough time for everyone to do all of them, you can assign different groups of students to work on different – but related - problems.
When do you want students to work in groups to solve problems?
- Don’t ask students to work in groups for straightforward problems that most students could solve independently in a short amount of time.
- Do have students work in groups for thought-provoking problems, where students will benefit from meaningful collaboration.
- Even in cases where you plan to have students work in groups, it can be useful to give students some time to work on their own before collaborating with others. This ensures that every student engages with the problem and is ready to contribute to a discussion.
What are some benefits of having students work in groups?
- Students bring different strengths, different knowledge, and different ideas for how to solve a problem; collaboration can help students work through problems that are more challenging than they might be able to tackle on their own.
- In working in a group, students might consider multiple ways to approach a problem, thus enriching their repertoire of strategies.
- Students who think they understand the material will gain a deeper understanding by explaining concepts to their peers.
What are some strategies for helping students to form groups?
- Instruct students to work with the person (or people) sitting next to them.
- Count off. (e.g. 1, 2, 3, 4; all the 1’s find each other and form a group, etc)
- Hand out playing cards; students need to find the person with the same number card. (There are many variants to this. For example, you can print pictures of images that go together [rain and umbrella]; each person gets a card and needs to find their partner[s].)
- Based on what you know about the students, assign groups in advance. List the groups on the board.
- Note: Always have students take the time to introduce themselves to each other in a new group.
What should you do while your students are working on problems?
- Walk around and talk to students. Observing their work gives you a sense of what people understand and what they are struggling with. Answer students’ questions, and ask them questions that lead in a productive direction if they are stuck.
- If you discover that many people have the same question—or that someone has a misunderstanding that others might have—you might stop everyone and discuss a key idea with the entire class.
After students work on a problem during class, what are strategies to have them share their answers and their thinking?
- Ask for volunteers to share answers. Depending on the nature of the problem, student might provide answers verbally or by writing on the board. As a variant, for questions where a variety of answers are relevant, ask for at least three volunteers before anyone shares their ideas.
- Use online polling software for students to respond to a multiple-choice question anonymously.
- If students are working in groups, assign reporters ahead of time. For example, the person with the next birthday could be responsible for sharing their group’s work with the class.
- Cold call. To reduce student anxiety about cold calling, it can help to identify students who seem to have the correct answer as you were walking around the class and checking in on their progress solving the assigned problem. You may even want to warn the student ahead of time: "This is a great answer! Do you mind if I call on you when we come back together as a class?"
- Have students write an answer on a notecard that they turn in to you. If your goal is to understand whether students in general solved a problem correctly, the notecards could be submitted anonymously; if you wish to assess individual students’ work, you would want to ask students to put their names on their notecard.
- Use a jigsaw strategy, where you rearrange groups such that each new group is comprised of people who came from different initial groups and had solved different problems. Students now are responsible for teaching the other students in their new group how to solve their problem.
- Have a representative from each group explain their problem to the class.
- Have a representative from each group draw or write the answer on the board.
What happens if a student gives a wrong answer?
- Ask for their reasoning so that you can understand where they went wrong.
- Ask if anyone else has other ideas. You can also ask this sometimes when an answer is right.
- Cultivate an environment where it’s okay to be wrong. Emphasize that you are all learning together, and that you learn through making mistakes.
- Do make sure that you clarify what the correct answer is before moving on.
- Once the correct answer is given, go through some answer-checking techniques that can distinguish between correct and incorrect answers. This can help prepare students to verify their future work.
How can you make your classroom inclusive?
- The goal is that everyone is thinking, talking, and sharing their ideas, and that everyone feels valued and respected. Use a variety of teaching strategies (independent work and group work; allow students to talk to each other before they talk to the class). Create an environment where it is normal to struggle and make mistakes.
- See Kimberly Tanner’s article on strategies to promoste student engagement and cultivate classroom equity.
A few final notes…
- Make sure that you have worked all of the problems and also thought about alternative approaches to solving them.
- Board work matters. You should have a plan beforehand of what you will write on the board, where, when, what needs to be added, and what can be erased when. If students are going to write their answers on the board, you need to also have a plan for making sure that everyone gets to the correct answer. Students will copy what is on the board and use it as their notes for later study, so correct and logical information must be written there.
For more information...
Tipsheet: Problem Solving in STEM Sections
Tanner, K. D. (2013). Structure matters: twenty-one teaching strategies to promote student engagement and cultivate classroom equity . CBE-Life Sciences Education, 12(3), 322-331.
- Designing Your Course
- A Teaching Timeline: From Pre-Term Planning to the Final Exam
- The First Day of Class
- Group Agreements
- Classroom Debate
- Flipped Classrooms
- Leading Discussions
- Polling & Clickers
- Teaching with Cases
- Engaged Scholarship
- Devices in the Classroom
- Beyond the Classroom
- On Professionalism
- Getting Feedback
- Equitable & Inclusive Teaching
- Advising and Mentoring
- Teaching and Your Career
- Teaching Remotely
- Tools and Platforms
- The Science of Learning
- Bok Publications
- Other Resources Around Campus
Problem-solving skill development through STEM learning approaches
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
How to improve your problem solving skills and build effective problem solving strategies

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
Effective problem solving is all about using the right process and following a plan tailored to the issue at hand. Recognizing your team or organization has an issue isn’t enough to come up with effective problem solving strategies.
To truly understand a problem and develop appropriate solutions, you will want to follow a solid process, follow the necessary problem solving steps, and bring all of your problem solving skills to the table.
We’ll first guide you through the seven step problem solving process you and your team can use to effectively solve complex business challenges. We’ll also look at what problem solving strategies you can employ with your team when looking for a way to approach the process. We’ll then discuss the problem solving skills you need to be more effective at solving problems, complete with an activity from the SessionLab library you can use to develop that skill in your team.
Let’s get to it!
What is a problem solving process?
- What are the problem solving steps I need to follow?
Problem solving strategies
What skills do i need to be an effective problem solver, how can i improve my problem solving skills.
Solving problems is like baking a cake. You can go straight into the kitchen without a recipe or the right ingredients and do your best, but the end result is unlikely to be very tasty!
Using a process to bake a cake allows you to use the best ingredients without waste, collect the right tools, account for allergies, decide whether it is a birthday or wedding cake, and then bake efficiently and on time. The result is a better cake that is fit for purpose, tastes better and has created less mess in the kitchen. Also, it should have chocolate sprinkles. Having a step by step process to solve organizational problems allows you to go through each stage methodically and ensure you are trying to solve the right problems and select the most appropriate, effective solutions.
What are the problem solving steps I need to follow?
All problem solving processes go through a number of steps in order to move from identifying a problem to resolving it.
Depending on your problem solving model and who you ask, there can be anything between four and nine problem solving steps you should follow in order to find the right solution. Whatever framework you and your group use, there are some key items that should be addressed in order to have an effective process.
We’ve looked at problem solving processes from sources such as the American Society for Quality and their four step approach , and Mediate ‘s six step process. By reflecting on those and our own problem solving processes, we’ve come up with a sequence of seven problem solving steps we feel best covers everything you need in order to effectively solve problems.
1. Problem identification
The first stage of any problem solving process is to identify the problem or problems you might want to solve. Effective problem solving strategies always begin by allowing a group scope to articulate what they believe the problem to be and then coming to some consensus over which problem they approach first. Problem solving activities used at this stage often have a focus on creating frank, open discussion so that potential problems can be brought to the surface.
2. Problem analysis
Though this step is not a million miles from problem identification, problem analysis deserves to be considered separately. It can often be an overlooked part of the process and is instrumental when it comes to developing effective solutions.
The process of problem analysis means ensuring that the problem you are seeking to solve is the right problem . As part of this stage, you may look deeper and try to find the root cause of a specific problem at a team or organizational level.
Remember that problem solving strategies should not only be focused on putting out fires in the short term but developing long term solutions that deal with the root cause of organizational challenges.
Whatever your approach, analyzing a problem is crucial in being able to select an appropriate solution and the problem solving skills deployed in this stage are beneficial for the rest of the process and ensuring the solutions you create are fit for purpose.
3. Solution generation
Once your group has nailed down the particulars of the problem you wish to solve, you want to encourage a free flow of ideas connecting to solving that problem. This can take the form of problem solving games that encourage creative thinking or problem solving activities designed to produce working prototypes of possible solutions.
The key to ensuring the success of this stage of the problem solving process is to encourage quick, creative thinking and create an open space where all ideas are considered. The best solutions can come from unlikely places and by using problem solving techniques that celebrate invention, you might come up with solution gold.
4. Solution development
No solution is likely to be perfect right out of the gate. It’s important to discuss and develop the solutions your group has come up with over the course of following the previous problem solving steps in order to arrive at the best possible solution. Problem solving games used in this stage involve lots of critical thinking, measuring potential effort and impact, and looking at possible solutions analytically.
During this stage, you will often ask your team to iterate and improve upon your frontrunning solutions and develop them further. Remember that problem solving strategies always benefit from a multitude of voices and opinions, and not to let ego get involved when it comes to choosing which solutions to develop and take further.
Finding the best solution is the goal of all problem solving workshops and here is the place to ensure that your solution is well thought out, sufficiently robust and fit for purpose.
5. Decision making
Nearly there! Once your group has reached consensus and selected a solution that applies to the problem at hand you have some decisions to make. You will want to work on allocating ownership of the project, figure out who will do what, how the success of the solution will be measured and decide the next course of action.
The decision making stage is a part of the problem solving process that can get missed or taken as for granted. Fail to properly allocate roles and plan out how a solution will actually be implemented and it less likely to be successful in solving the problem.
Have clear accountabilities, actions, timeframes, and follow-ups. Make these decisions and set clear next-steps in the problem solving workshop so that everyone is aligned and you can move forward effectively as a group.
Ensuring that you plan for the roll-out of a solution is one of the most important problem solving steps. Without adequate planning or oversight, it can prove impossible to measure success or iterate further if the problem was not solved.
6. Solution implementation
This is what we were waiting for! All problem solving strategies have the end goal of implementing a solution and solving a problem in mind.
Remember that in order for any solution to be successful, you need to help your group through all of the previous problem solving steps thoughtfully. Only then can you ensure that you are solving the right problem but also that you have developed the correct solution and can then successfully implement and measure the impact of that solution.
Project management and communication skills are key here – your solution may need to adjust when out in the wild or you might discover new challenges along the way.
7. Solution evaluation
So you and your team developed a great solution to a problem and have a gut feeling its been solved. Work done, right? Wrong. All problem solving strategies benefit from evaluation, consideration, and feedback. You might find that the solution does not work for everyone, might create new problems, or is potentially so successful that you will want to roll it out to larger teams or as part of other initiatives.
None of that is possible without taking the time to evaluate the success of the solution you developed in your problem solving model and adjust if necessary.
Remember that the problem solving process is often iterative and it can be common to not solve complex issues on the first try. Even when this is the case, you and your team will have generated learning that will be important for future problem solving workshops or in other parts of the organization.
It’s worth underlining how important record keeping is throughout the problem solving process. If a solution didn’t work, you need to have the data and records to see why that was the case. If you go back to the drawing board, notes from the previous workshop can help save time. Data and insight is invaluable at every stage of the problem solving process and this one is no different.
Problem solving workshops made easy
Problem solving strategies are methods of approaching and facilitating the process of problem-solving with a set of techniques , actions, and processes. Different strategies are more effective if you are trying to solve broad problems such as achieving higher growth versus more focused problems like, how do we improve our customer onboarding process?
Broadly, the problem solving steps outlined above should be included in any problem solving strategy though choosing where to focus your time and what approaches should be taken is where they begin to differ. You might find that some strategies ask for the problem identification to be done prior to the session or that everything happens in the course of a one day workshop.
The key similarity is that all good problem solving strategies are structured and designed. Four hours of open discussion is never going to be as productive as a four-hour workshop designed to lead a group through a problem solving process.
Good problem solving strategies are tailored to the team, organization and problem you will be attempting to solve. Here are some example problem solving strategies you can learn from or use to get started.

Use a workshop to lead a team through a group process
Often, the first step to solving problems or organizational challenges is bringing a group together effectively. Most teams have the tools, knowledge, and expertise necessary to solve their challenges – they just need some guidance in how to use leverage those skills and a structure and format that allows people to focus their energies.
Facilitated workshops are one of the most effective ways of solving problems of any scale. By designing and planning your workshop carefully, you can tailor the approach and scope to best fit the needs of your team and organization.
Problem solving workshop
- Creating a bespoke, tailored process
- Tackling problems of any size
- Building in-house workshop ability and encouraging their use
Workshops are an effective strategy for solving problems. By using tried and test facilitation techniques and methods, you can design and deliver a workshop that is perfectly suited to the unique variables of your organization. You may only have the capacity for a half-day workshop and so need a problem solving process to match.
By using our session planner tool and importing methods from our library of 700+ facilitation techniques, you can create the right problem solving workshop for your team. It might be that you want to encourage creative thinking or look at things from a new angle to unblock your groups approach to problem solving. By tailoring your workshop design to the purpose, you can help ensure great results.
One of the main benefits of a workshop is the structured approach to problem solving. Not only does this mean that the workshop itself will be successful, but many of the methods and techniques will help your team improve their working processes outside of the workshop.
We believe that workshops are one of the best tools you can use to improve the way your team works together. Start with a problem solving workshop and then see what team building, culture or design workshops can do for your organization!
Run a design sprint
Great for:
- aligning large, multi-discipline teams
- quickly designing and testing solutions
- tackling large, complex organizational challenges and breaking them down into smaller tasks
By using design thinking principles and methods, a design sprint is a great way of identifying, prioritizing and prototyping solutions to long term challenges that can help solve major organizational problems with quick action and measurable results.
Some familiarity with design thinking is useful, though not integral, and this strategy can really help a team align if there is some discussion around which problems should be approached first.
The stage-based structure of the design sprint is also very useful for teams new to design thinking. The inspiration phase, where you look to competitors that have solved your problem, and the rapid prototyping and testing phases are great for introducing new concepts that will benefit a team in all their future work.
It can be common for teams to look inward for solutions and so looking to the market for solutions you can iterate on can be very productive. Instilling an agile prototyping and testing mindset can also be great when helping teams move forwards – generating and testing solutions quickly can help save time in the long run and is also pretty exciting!
Break problems down into smaller issues
Organizational challenges and problems are often complicated and large scale in nature. Sometimes, trying to resolve such an issue in one swoop is simply unachievable or overwhelming. Try breaking down such problems into smaller issues that you can work on step by step. You may not be able to solve the problem of churning customers off the bat, but you can work with your team to identify smaller effort but high impact elements and work on those first.
This problem solving strategy can help a team generate momentum, prioritize and get some easy wins. It’s also a great strategy to employ with teams who are just beginning to learn how to approach the problem solving process. If you want some insight into a way to employ this strategy, we recommend looking at our design sprint template below!
Use guiding frameworks or try new methodologies
Some problems are best solved by introducing a major shift in perspective or by using new methodologies that encourage your team to think differently.
Props and tools such as Methodkit , which uses a card-based toolkit for facilitation, or Lego Serious Play can be great ways to engage your team and find an inclusive, democratic problem solving strategy. Remember that play and creativity are great tools for achieving change and whatever the challenge, engaging your participants can be very effective where other strategies may have failed.
LEGO Serious Play
- Improving core problem solving skills
- Thinking outside of the box
- Encouraging creative solutions
LEGO Serious Play is a problem solving methodology designed to get participants thinking differently by using 3D models and kinesthetic learning styles. By physically building LEGO models based on questions and exercises, participants are encouraged to think outside of the box and create their own responses.
Collaborate LEGO Serious Play exercises are also used to encourage communication and build problem solving skills in a group. By using this problem solving process, you can often help different kinds of learners and personality types contribute and unblock organizational problems with creative thinking.
Problem solving strategies like LEGO Serious Play are super effective at helping a team solve more skills-based problems such as communication between teams or a lack of creative thinking. Some problems are not suited to LEGO Serious Play and require a different problem solving strategy.
Card Decks and Method Kits
- New facilitators or non-facilitators
- Approaching difficult subjects with a simple, creative framework
- Engaging those with varied learning styles
Card decks and method kids are great tools for those new to facilitation or for whom facilitation is not the primary role. Card decks such as the emotional culture deck can be used for complete workshops and in many cases, can be used right out of the box. Methodkit has a variety of kits designed for scenarios ranging from personal development through to personas and global challenges so you can find the right deck for your particular needs.
Having an easy to use framework that encourages creativity or a new approach can take some of the friction or planning difficulties out of the workshop process and energize a team in any setting. Simplicity is the key with these methods. By ensuring everyone on your team can get involved and engage with the process as quickly as possible can really contribute to the success of your problem solving strategy.
Source external advice
Looking to peers, experts and external facilitators can be a great way of approaching the problem solving process. Your team may not have the necessary expertise, insights of experience to tackle some issues, or you might simply benefit from a fresh perspective. Some problems may require bringing together an entire team, and coaching managers or team members individually might be the right approach. Remember that not all problems are best resolved in the same manner.
If you’re a solo entrepreneur, peer groups, coaches and mentors can also be invaluable at not only solving specific business problems, but in providing a support network for resolving future challenges. One great approach is to join a Mastermind Group and link up with like-minded individuals and all grow together. Remember that however you approach the sourcing of external advice, do so thoughtfully, respectfully and honestly. Reciprocate where you can and prepare to be surprised by just how kind and helpful your peers can be!
Mastermind Group
- Solo entrepreneurs or small teams with low capacity
- Peer learning and gaining outside expertise
- Getting multiple external points of view quickly
Problem solving in large organizations with lots of skilled team members is one thing, but how about if you work for yourself or in a very small team without the capacity to get the most from a design sprint or LEGO Serious Play session?
A mastermind group – sometimes known as a peer advisory board – is where a group of people come together to support one another in their own goals, challenges, and businesses. Each participant comes to the group with their own purpose and the other members of the group will help them create solutions, brainstorm ideas, and support one another.
Mastermind groups are very effective in creating an energized, supportive atmosphere that can deliver meaningful results. Learning from peers from outside of your organization or industry can really help unlock new ways of thinking and drive growth. Access to the experience and skills of your peers can be invaluable in helping fill the gaps in your own ability, particularly in young companies.
A mastermind group is a great solution for solo entrepreneurs, small teams, or for organizations that feel that external expertise or fresh perspectives will be beneficial for them. It is worth noting that Mastermind groups are often only as good as the participants and what they can bring to the group. Participants need to be committed, engaged and understand how to work in this context.
Coaching and mentoring
- Focused learning and development
- Filling skills gaps
- Working on a range of challenges over time
Receiving advice from a business coach or building a mentor/mentee relationship can be an effective way of resolving certain challenges. The one-to-one format of most coaching and mentor relationships can really help solve the challenges those individuals are having and benefit the organization as a result.
A great mentor can be invaluable when it comes to spotting potential problems before they arise and coming to understand a mentee very well has a host of other business benefits. You might run an internal mentorship program to help develop your team’s problem solving skills and strategies or as part of a large learning and development program. External coaches can also be an important part of your problem solving strategy, filling skills gaps for your management team or helping with specific business issues.
Now we’ve explored the problem solving process and the steps you will want to go through in order to have an effective session, let’s look at the skills you and your team need to be more effective problem solvers.
Problem solving skills are highly sought after, whatever industry or team you work in. Organizations are keen to employ people who are able to approach problems thoughtfully and find strong, realistic solutions. Whether you are a facilitator , a team leader or a developer, being an effective problem solver is a skill you’ll want to develop.
Problem solving skills form a whole suite of techniques and approaches that an individual uses to not only identify problems but to discuss them productively before then developing appropriate solutions.
Here are some of the most important problem solving skills everyone from executives to junior staff members should learn. We’ve also included an activity or exercise from the SessionLab library that can help you and your team develop that skill.
If you’re running a workshop or training session to try and improve problem solving skills in your team, try using these methods to supercharge your process!
Active listening
Active listening is one of the most important skills anyone who works with people can possess. In short, active listening is a technique used to not only better understand what is being said by an individual, but also to be more aware of the underlying message the speaker is trying to convey. When it comes to problem solving, active listening is integral for understanding the position of every participant and to clarify the challenges, ideas and solutions they bring to the table.
Some active listening skills include:
- Paying complete attention to the speaker.
- Removing distractions.
- Avoid interruption.
- Taking the time to fully understand before preparing a rebuttal.
- Responding respectfully and appropriately.
- Demonstrate attentiveness and positivity with an open posture, making eye contact with the speaker, smiling and nodding if appropriate. Show that you are listening and encourage them to continue.
- Be aware of and respectful of feelings. Judge the situation and respond appropriately. You can disagree without being disrespectful.
- Observe body language.
- Paraphrase what was said in your own words, either mentally or verbally.
- Remain neutral.
- Reflect and take a moment before responding.
- Ask deeper questions based on what is said and clarify points where necessary.
Active Listening #hyperisland #skills #active listening #remote-friendly This activity supports participants to reflect on a question and generate their own solutions using simple principles of active listening and peer coaching. It’s an excellent introduction to active listening but can also be used with groups that are already familiar with it. Participants work in groups of three and take turns being: “the subject”, the listener, and the observer.
Analytical skills
All problem solving models require strong analytical skills, particularly during the beginning of the process and when it comes to analyzing how solutions have performed.
Analytical skills are primarily focused on performing an effective analysis by collecting, studying and parsing data related to a problem or opportunity.
It often involves spotting patterns, being able to see things from different perspectives and using observable facts and data to make suggestions or produce insight.
Analytical skills are also important at every stage of the problem solving process and by having these skills, you can ensure that any ideas or solutions you create or backed up analytically and have been sufficiently thought out.
Nine Whys #innovation #issue analysis #liberating structures With breathtaking simplicity, you can rapidly clarify for individuals and a group what is essentially important in their work. You can quickly reveal when a compelling purpose is missing in a gathering and avoid moving forward without clarity. When a group discovers an unambiguous shared purpose, more freedom and more responsibility are unleashed. You have laid the foundation for spreading and scaling innovations with fidelity.
Collaboration
Trying to solve problems on your own is difficult. Being able to collaborate effectively, with a free exchange of ideas, to delegate and be a productive member of a team is hugely important to all problem solving strategies.
Remember that whatever your role, collaboration is integral, and in a problem solving process, you are all working together to find the best solution for everyone.
Marshmallow challenge with debriefing #teamwork #team #leadership #collaboration In eighteen minutes, teams must build the tallest free-standing structure out of 20 sticks of spaghetti, one yard of tape, one yard of string, and one marshmallow. The marshmallow needs to be on top. The Marshmallow Challenge was developed by Tom Wujec, who has done the activity with hundreds of groups around the world. Visit the Marshmallow Challenge website for more information. This version has an extra debriefing question added with sample questions focusing on roles within the team.
Communication
Being an effective communicator means being empathetic, clear and succinct, asking the right questions, and demonstrating active listening skills throughout any discussion or meeting.
In a problem solving setting, you need to communicate well in order to progress through each stage of the process effectively. As a team leader, it may also fall to you to facilitate communication between parties who may not see eye to eye. Effective communication also means helping others to express themselves and be heard in a group.
Bus Trip #feedback #communication #appreciation #closing #thiagi #team This is one of my favourite feedback games. I use Bus Trip at the end of a training session or a meeting, and I use it all the time. The game creates a massive amount of energy with lots of smiles, laughs, and sometimes even a teardrop or two.
Creative problem solving skills can be some of the best tools in your arsenal. Thinking creatively, being able to generate lots of ideas and come up with out of the box solutions is useful at every step of the process.
The kinds of problems you will likely discuss in a problem solving workshop are often difficult to solve, and by approaching things in a fresh, creative manner, you can often create more innovative solutions.
Having practical creative skills is also a boon when it comes to problem solving. If you can help create quality design sketches and prototypes in record time, it can help bring a team to alignment more quickly or provide a base for further iteration.
The paper clip method #sharing #creativity #warm up #idea generation #brainstorming The power of brainstorming. A training for project leaders, creativity training, and to catalyse getting new solutions.
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is one of the fundamental problem solving skills you’ll want to develop when working on developing solutions. Critical thinking is the ability to analyze, rationalize and evaluate while being aware of personal bias, outlying factors and remaining open-minded.
Defining and analyzing problems without deploying critical thinking skills can mean you and your team go down the wrong path. Developing solutions to complex issues requires critical thinking too – ensuring your team considers all possibilities and rationally evaluating them.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Data analysis
Though it shares lots of space with general analytical skills, data analysis skills are something you want to cultivate in their own right in order to be an effective problem solver.
Being good at data analysis doesn’t just mean being able to find insights from data, but also selecting the appropriate data for a given issue, interpreting it effectively and knowing how to model and present that data. Depending on the problem at hand, it might also include a working knowledge of specific data analysis tools and procedures.
Having a solid grasp of data analysis techniques is useful if you’re leading a problem solving workshop but if you’re not an expert, don’t worry. Bring people into the group who has this skill set and help your team be more effective as a result.
Decision making
All problems need a solution and all solutions require that someone make the decision to implement them. Without strong decision making skills, teams can become bogged down in discussion and less effective as a result.
Making decisions is a key part of the problem solving process. It’s important to remember that decision making is not restricted to the leadership team. Every staff member makes decisions every day and developing these skills ensures that your team is able to solve problems at any scale. Remember that making decisions does not mean leaping to the first solution but weighing up the options and coming to an informed, well thought out solution to any given problem that works for the whole team.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
Dependability
Most complex organizational problems require multiple people to be involved in delivering the solution. Ensuring that the team and organization can depend on you to take the necessary actions and communicate where necessary is key to ensuring problems are solved effectively.
Being dependable also means working to deadlines and to brief. It is often a matter of creating trust in a team so that everyone can depend on one another to complete the agreed actions in the agreed time frame so that the team can move forward together. Being undependable can create problems of friction and can limit the effectiveness of your solutions so be sure to bear this in mind throughout a project.
Team Purpose & Culture #team #hyperisland #culture #remote-friendly This is an essential process designed to help teams define their purpose (why they exist) and their culture (how they work together to achieve that purpose). Defining these two things will help any team to be more focused and aligned. With support of tangible examples from other companies, the team members work as individuals and a group to codify the way they work together. The goal is a visual manifestation of both the purpose and culture that can be put up in the team’s work space.
Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence is an important skill for any successful team member, whether communicating internally or with clients or users. In the problem solving process, emotional intelligence means being attuned to how people are feeling and thinking, communicating effectively and being self-aware of what you bring to a room.
There are often differences of opinion when working through problem solving processes, and it can be easy to let things become impassioned or combative. Developing your emotional intelligence means being empathetic to your colleagues and managing your own emotions throughout the problem and solution process. Be kind, be thoughtful and put your points across care and attention.
Being emotionally intelligent is a skill for life and by deploying it at work, you can not only work efficiently but empathetically. Check out the emotional culture workshop template for more!
Facilitation
As we’ve clarified in our facilitation skills post, facilitation is the art of leading people through processes towards agreed-upon objectives in a manner that encourages participation, ownership, and creativity by all those involved. While facilitation is a set of interrelated skills in itself, the broad definition of facilitation can be invaluable when it comes to problem solving. Leading a team through a problem solving process is made more effective if you improve and utilize facilitation skills – whether you’re a manager, team leader or external stakeholder.
The Six Thinking Hats #creative thinking #meeting facilitation #problem solving #issue resolution #idea generation #conflict resolution The Six Thinking Hats are used by individuals and groups to separate out conflicting styles of thinking. They enable and encourage a group of people to think constructively together in exploring and implementing change, rather than using argument to fight over who is right and who is wrong.
Flexibility
Being flexible is a vital skill when it comes to problem solving. This does not mean immediately bowing to pressure or changing your opinion quickly: instead, being flexible is all about seeing things from new perspectives, receiving new information and factoring it into your thought process.
Flexibility is also important when it comes to rolling out solutions. It might be that other organizational projects have greater priority or require the same resources as your chosen solution. Being flexible means understanding needs and challenges across the team and being open to shifting or arranging your own schedule as necessary. Again, this does not mean immediately making way for other projects. It’s about articulating your own needs, understanding the needs of others and being able to come to a meaningful compromise.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
Working in any group can lead to unconscious elements of groupthink or situations in which you may not wish to be entirely honest. Disagreeing with the opinions of the executive team or wishing to save the feelings of a coworker can be tricky to navigate, but being honest is absolutely vital when to comes to developing effective solutions and ensuring your voice is heard.
Remember that being honest does not mean being brutally candid. You can deliver your honest feedback and opinions thoughtfully and without creating friction by using other skills such as emotional intelligence.
Explore your Values #hyperisland #skills #values #remote-friendly Your Values is an exercise for participants to explore what their most important values are. It’s done in an intuitive and rapid way to encourage participants to follow their intuitive feeling rather than over-thinking and finding the “correct” values. It is a good exercise to use to initiate reflection and dialogue around personal values.
Initiative
The problem solving process is multi-faceted and requires different approaches at certain points of the process. Taking initiative to bring problems to the attention of the team, collect data or lead the solution creating process is always valuable. You might even roadtest your own small scale solutions or brainstorm before a session. Taking initiative is particularly effective if you have good deal of knowledge in that area or have ownership of a particular project and want to get things kickstarted.
That said, be sure to remember to honor the process and work in service of the team. If you are asked to own one part of the problem solving process and you don’t complete that task because your initiative leads you to work on something else, that’s not an effective method of solving business challenges.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
Impartiality
A particularly useful problem solving skill for product owners or managers is the ability to remain impartial throughout much of the process. In practice, this means treating all points of view and ideas brought forward in a meeting equally and ensuring that your own areas of interest or ownership are not favored over others.
There may be a stage in the process where a decision maker has to weigh the cost and ROI of possible solutions against the company roadmap though even then, ensuring that the decision made is based on merit and not personal opinion.
Empathy map #frame insights #create #design #issue analysis An empathy map is a tool to help a design team to empathize with the people they are designing for. You can make an empathy map for a group of people or for a persona. To be used after doing personas when more insights are needed.
Being a good leader means getting a team aligned, energized and focused around a common goal. In the problem solving process, strong leadership helps ensure that the process is efficient, that any conflicts are resolved and that a team is managed in the direction of success.
It’s common for managers or executives to assume this role in a problem solving workshop, though it’s important that the leader maintains impartiality and does not bulldoze the group in a particular direction. Remember that good leadership means working in service of the purpose and team and ensuring the workshop is a safe space for employees of any level to contribute. Take a look at our leadership games and activities post for more exercises and methods to help improve leadership in your organization.
Leadership Pizza #leadership #team #remote-friendly This leadership development activity offers a self-assessment framework for people to first identify what skills, attributes and attitudes they find important for effective leadership, and then assess their own development and initiate goal setting.
In the context of problem solving, mediation is important in keeping a team engaged, happy and free of conflict. When leading or facilitating a problem solving workshop, you are likely to run into differences of opinion. Depending on the nature of the problem, certain issues may be brought up that are emotive in nature.
Being an effective mediator means helping those people on either side of such a divide are heard, listen to one another and encouraged to find common ground and a resolution. Mediating skills are useful for leaders and managers in many situations and the problem solving process is no different.
Conflict Responses #hyperisland #team #issue resolution A workshop for a team to reflect on past conflicts, and use them to generate guidelines for effective conflict handling. The workshop uses the Thomas-Killman model of conflict responses to frame a reflective discussion. Use it to open up a discussion around conflict with a team.
Planning
Solving organizational problems is much more effective when following a process or problem solving model. Planning skills are vital in order to structure, deliver and follow-through on a problem solving workshop and ensure your solutions are intelligently deployed.
Planning skills include the ability to organize tasks and a team, plan and design the process and take into account any potential challenges. Taking the time to plan carefully can save time and frustration later in the process and is valuable for ensuring a team is positioned for success.
3 Action Steps #hyperisland #action #remote-friendly This is a small-scale strategic planning session that helps groups and individuals to take action toward a desired change. It is often used at the end of a workshop or programme. The group discusses and agrees on a vision, then creates some action steps that will lead them towards that vision. The scope of the challenge is also defined, through discussion of the helpful and harmful factors influencing the group.
Prioritization
As organisations grow, the scale and variation of problems they face multiplies. Your team or is likely to face numerous challenges in different areas and so having the skills to analyze and prioritize becomes very important, particularly for those in leadership roles.
A thorough problem solving process is likely to deliver multiple solutions and you may have several different problems you wish to solve simultaneously. Prioritization is the ability to measure the importance, value, and effectiveness of those possible solutions and choose which to enact and in what order. The process of prioritization is integral in ensuring the biggest challenges are addressed with the most impactful solutions.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
Project management
Some problem solving skills are utilized in a workshop or ideation phases, while others come in useful when it comes to decision making. Overseeing an entire problem solving process and ensuring its success requires strong project management skills.
While project management incorporates many of the other skills listed here, it is important to note the distinction of considering all of the factors of a project and managing them successfully. Being able to negotiate with stakeholders, manage tasks, time and people, consider costs and ROI, and tie everything together is massively helpful when going through the problem solving process.
Record keeping
Working out meaningful solutions to organizational challenges is only one part of the process. Thoughtfully documenting and keeping records of each problem solving step for future consultation is important in ensuring efficiency and meaningful change.
For example, some problems may be lower priority than others but can be revisited in the future. If the team has ideated on solutions and found some are not up to the task, record those so you can rule them out and avoiding repeating work. Keeping records of the process also helps you improve and refine your problem solving model next time around!
Personal Kanban #gamestorming #action #agile #project planning Personal Kanban is a tool for organizing your work to be more efficient and productive. It is based on agile methods and principles.
Research skills
Conducting research to support both the identification of problems and the development of appropriate solutions is important for an effective process. Knowing where to go to collect research, how to conduct research efficiently, and identifying pieces of research are relevant are all things a good researcher can do well.
In larger groups, not everyone has to demonstrate this ability in order for a problem solving workshop to be effective. That said, having people with research skills involved in the process, particularly if they have existing area knowledge, can help ensure the solutions that are developed with data that supports their intention. Remember that being able to deliver the results of research efficiently and in a way the team can easily understand is also important. The best data in the world is only as effective as how it is delivered and interpreted.
Customer experience map #ideation #concepts #research #design #issue analysis #remote-friendly Customer experience mapping is a method of documenting and visualizing the experience a customer has as they use the product or service. It also maps out their responses to their experiences. To be used when there is a solution (even in a conceptual stage) that can be analyzed.
Risk management
Managing risk is an often overlooked part of the problem solving process. Solutions are often developed with the intention of reducing exposure to risk or solving issues that create risk but sometimes, great solutions are more experimental in nature and as such, deploying them needs to be carefully considered.
Managing risk means acknowledging that there may be risks associated with more out of the box solutions or trying new things, but that this must be measured against the possible benefits and other organizational factors.
Be informed, get the right data and stakeholders in the room and you can appropriately factor risk into your decision making process.
Decisions, Decisions… #communication #decision making #thiagi #action #issue analysis When it comes to decision-making, why are some of us more prone to take risks while others are risk-averse? One explanation might be the way the decision and options were presented. This exercise, based on Kahneman and Tversky’s classic study , illustrates how the framing effect influences our judgement and our ability to make decisions . The participants are divided into two groups. Both groups are presented with the same problem and two alternative programs for solving them. The two programs both have the same consequences but are presented differently. The debriefing discussion examines how the framing of the program impacted the participant’s decision.
Team-building
No single person is as good at problem solving as a team. Building an effective team and helping them come together around a common purpose is one of the most important problem solving skills, doubly so for leaders. By bringing a team together and helping them work efficiently, you pave the way for team ownership of a problem and the development of effective solutions.
In a problem solving workshop, it can be tempting to jump right into the deep end, though taking the time to break the ice, energize the team and align them with a game or exercise will pay off over the course of the day.
Remember that you will likely go through the problem solving process multiple times over an organization’s lifespan and building a strong team culture will make future problem solving more effective. It’s also great to work with people you know, trust and have fun with. Working on team building in and out of the problem solving process is a hallmark of successful teams that can work together to solve business problems.
9 Dimensions Team Building Activity #ice breaker #teambuilding #team #remote-friendly 9 Dimensions is a powerful activity designed to build relationships and trust among team members. There are 2 variations of this icebreaker. The first version is for teams who want to get to know each other better. The second version is for teams who want to explore how they are working together as a team.
Time management
The problem solving process is designed to lead a team from identifying a problem through to delivering a solution and evaluating its effectiveness. Without effective time management skills or timeboxing of tasks, it can be easy for a team to get bogged down or be inefficient.
By using a problem solving model and carefully designing your workshop, you can allocate time efficiently and trust that the process will deliver the results you need in a good timeframe.
Time management also comes into play when it comes to rolling out solutions, particularly those that are experimental in nature. Having a clear timeframe for implementing and evaluating solutions is vital for ensuring their success and being able to pivot if necessary.
Improving your skills at problem solving is often a career-long pursuit though there are methods you can use to make the learning process more efficient and to supercharge your problem solving skillset.
Remember that the skills you need to be a great problem solver have a large overlap with those skills you need to be effective in any role. Investing time and effort to develop your active listening or critical thinking skills is valuable in any context. Here are 7 ways to improve your problem solving skills.
Share best practices
Remember that your team is an excellent source of skills, wisdom, and techniques and that you should all take advantage of one another where possible. Best practices that one team has for solving problems, conducting research or making decisions should be shared across the organization. If you have in-house staff that have done active listening training or are data analysis pros, have them lead a training session.
Your team is one of your best resources. Create space and internal processes for the sharing of skills so that you can all grow together.
Ask for help and attend training
Once you’ve figured out you have a skills gap, the next step is to take action to fill that skills gap. That might be by asking your superior for training or coaching, or liaising with team members with that skill set. You might even attend specialized training for certain skills – active listening or critical thinking, for example, are business-critical skills that are regularly offered as part of a training scheme.
Whatever method you choose, remember that taking action of some description is necessary for growth. Whether that means practicing, getting help, attending training or doing some background reading, taking active steps to improve your skills is the way to go.
Learn a process
Problem solving can be complicated, particularly when attempting to solve large problems for the first time. Using a problem solving process helps give structure to your problem solving efforts and focus on creating outcomes, rather than worrying about the format.
Tools such as the seven-step problem solving process above are effective because not only do they feature steps that will help a team solve problems, they also develop skills along the way. Each step asks for people to engage with the process using different skills and in doing so, helps the team learn and grow together. Group processes of varying complexity and purpose can also be found in the SessionLab library of facilitation techniques . Using a tried and tested process and really help ease the learning curve for both those leading such a process, as well as those undergoing the purpose.
Effective teams make decisions about where they should and shouldn’t expend additional effort. By using a problem solving process, you can focus on the things that matter, rather than stumbling towards a solution haphazardly.
Create a feedback loop
Some skills gaps are more obvious than others. It’s possible that your perception of your active listening skills differs from those of your colleagues.
It’s valuable to create a system where team members can provide feedback in an ordered and friendly manner so they can all learn from one another. Only by identifying areas of improvement can you then work to improve them.
Remember that feedback systems require oversight and consideration so that they don’t turn into a place to complain about colleagues. Design the system intelligently so that you encourage the creation of learning opportunities, rather than encouraging people to list their pet peeves.
While practice might not make perfect, it does make the problem solving process easier. If you are having trouble with critical thinking, don’t shy away from doing it. Get involved where you can and stretch those muscles as regularly as possible.
Problem solving skills come more naturally to some than to others and that’s okay. Take opportunities to get involved and see where you can practice your skills in situations outside of a workshop context. Try collaborating in other circumstances at work or conduct data analysis on your own projects. You can often develop those skills you need for problem solving simply by doing them. Get involved!
Use expert exercises and methods
Learn from the best. Our library of 700+ facilitation techniques is full of activities and methods that help develop the skills you need to be an effective problem solver. Check out our templates to see how to approach problem solving and other organizational challenges in a structured and intelligent manner.
There is no single approach to improving problem solving skills, but by using the techniques employed by others you can learn from their example and develop processes that have seen proven results.
Try new ways of thinking and change your mindset
Using tried and tested exercises that you know well can help deliver results, but you do run the risk of missing out on the learning opportunities offered by new approaches. As with the problem solving process, changing your mindset can remove blockages and be used to develop your problem solving skills.
Most teams have members with mixed skill sets and specialties. Mix people from different teams and share skills and different points of view. Teach your customer support team how to use design thinking methods or help your developers with conflict resolution techniques. Try switching perspectives with facilitation techniques like Flip It! or by using new problem solving methodologies or models. Give design thinking, liberating structures or lego serious play a try if you want to try a new approach. You will find that framing problems in new ways and using existing skills in new contexts can be hugely useful for personal development and improving your skillset. It’s also a lot of fun to try new things. Give it a go!
Encountering business challenges and needing to find appropriate solutions is not unique to your organization. Lots of very smart people have developed methods, theories and approaches to help develop problem solving skills and create effective solutions. Learn from them!
Books like The Art of Thinking Clearly , Think Smarter, or Thinking Fast, Thinking Slow are great places to start, though it’s also worth looking at blogs related to organizations facing similar problems to yours, or browsing for success stories. Seeing how Dropbox massively increased growth and working backward can help you see the skills or approach you might be lacking to solve that same problem. Learning from others by reading their stories or approaches can be time-consuming but ultimately rewarding.
A tired, distracted mind is not in the best position to learn new skills. It can be tempted to burn the candle at both ends and develop problem solving skills outside of work. Absolutely use your time effectively and take opportunities for self-improvement, though remember that rest is hugely important and that without letting your brain rest, you cannot be at your most effective.
Creating distance between yourself and the problem you might be facing can also be useful. By letting an idea sit, you can find that a better one presents itself or you can develop it further. Take regular breaks when working and create a space for downtime. Remember that working smarter is preferable to working harder and that self-care is important for any effective learning or improvement process.
Want to design better group processes?
Over to you
Now we’ve explored some of the key problem solving skills and the problem solving steps necessary for an effective process, you’re ready to begin developing more effective solutions and leading problem solving workshops.
Need more inspiration? Check out our post on problem solving activities you can use when guiding a group towards a great solution in your next workshop or meeting. Have questions? Did you have a great problem solving technique you use with your team? Get in touch in the comments below. We’d love to chat!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

THE PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS OF GRADE 11 STUDENTS IN

Related Papers
Dissertation - Florida International University
Mark Osterman
With evidence that arts engagement and nonlinear thinking style both utilize insight, intuition, and emotion in the decision making process, the literature has driven an investigation of the relationship between levels of arts engagement and thinking style preference. This nonexperimental correlational study (N = 101) explored (a) the prevalence of linear, nonlinear, or balanced linear/nonlinear thinking style of professionals working in museums. (b) Whether thinking style has a relationship with (i) age; (ii) sex; (iii) academic major; (iv) occupation; (v) levels of arts engagement. Two theoretical frameworks underpinned this study: (a) new literacies and (b) cognitive styles. A Web-based self-report survey instrument was used to investigate the relation among the variables of interest. Existing literature was used to provide a foundation for the study and guide the research. Correlational, means, and hierarchical regression analysis were used to test the hypothesized model and examine the hypotheses. The means analyses at the descriptive level revealed that females, those in the 60 or older age group, Humanities majors, and those who worked in education demonstrated more balanced linear/nonlinear thinking styles. The correlations results indicated that there was a statistically significant relationship between thinking style and sex and thinking styles and academic major. The hierarchical regression results suggested that after controlling for select demographic variables, only being a Humanities major uniquely predicted significant variance in thinking style. The lack of significant findings of a relationship between thinking style and age did not correspond to existing research that supports a correlation. Additionally, a significant relationship between thinking style and levels of arts engagement was not found during correlational and hierarchical regression analysis. A limitation of this research study was that the Web-based self-report survey version of the Linear/Nonlinear Thinking Style Profile (LNTSP) instrument did not transfer well to online use because the participants had some problem understanding how to score their answers properly. This issue could be handled readily and recommendations are made to revise the Web-base self-report version of the survey for future research use.
“Human beings differ from one another and there is absolutely no reason to teach and assess all individual in the identical way”. - Dr. Howard Gardner Keeping this in mind, the Multiple Intelligence Theory has paved its way to the teaching process to treat individual differences seriously. The Multiple-Intelligence (MI) theory primarily listed seven intelligences which come and work together: verbal-linguistic, logical-mathematical, interpersonal, intrapersonal, visual-spatial, bodily-kinesthetic and musical/rhythmic. Eventually, he added the naturalist intelligence, the existential intelligence, and the so-called “pedagogical intelligence”. His theory became highly popular with K-12 educators around the world who seeks ways in reaching their students until trying a different approach. Because of these kinds of experiences, the idea of learning styles and multiple intelligences reverberate with many educators. As pointed out by Fliess (2009), Gardner developed the multiple intelligences on 1983 to help educators, psychologists and parenting experts better understand how children process and learn information. While in the excerpt written by Westerberg (2012), Gardner directly says that multiple intelligences are not a statement about learning styles. In addition, he emphasized that Gardner himself describe learning style as an “incoherent hypothesis”. However, either of the two is still learning theory until now. The use of MI and LS, based on most educational researchers, have many benefits in the field of teaching and learning process. On the other hand, McLeod (2010) explore the idea about learning styles regarding with “Kolb-Learning Style Theory”. He found out that both learning stages and cycle present by Kolb could be used by teachers to critically evaluate the learning provision typically available to students, and develop more appropriate learning opportunities. While Liston (2009)in her study about Different Learning styles in mathematics teaching, have found out that conceptions of mathematics open a window to students understanding of mathematics. Students’ view of mathematics affects the quality of the students understanding and learning outcomes. Teachers’ conceptions of mathematics are perhaps most important for the future of mathematics education, since it is these very conceptions that influence teachers’ approaches to teaching and bring about change in the mathematics classroom. In seeking for applicable learning opportunities, many teachers are challenged in their teaching stint. In spite of their cautious preparation in their lesson planning and the use of all sorts of learning aids, the dilemma of academic performance is still on the line, which is commonly the measure of classroom learning. As emphasized by Bruke& Dunn (2006), classroom teachers and educators are aware that each student learns differently. Through education classes and constant discussion, educators are aware that by identifying each student learning style, teaching to his or her learning style and implementing curriculum that compliments student learning can improve on-task behavior and increase content knowledge. The thought of identifying each student learning style may seem impossible and time consuming. However, with the right instrument, that is quick and effective, the process will be much more approachable. A pressure has been placed on teachers to increase students’ grades on academic achievement test. The researchers know that teaching to a students’ learning style will improve scores. The researchers tend to explore on how the multiple-intelligence and the learning styles affects the academic performance of the students specifically in Mathematics. The academic performance of school reflects the academic achievement of the learner’s as the purpose of the National Achievement Test imposed by the Department of Education. As lectured by Benito (2010), NAT, is a Philippine ‐made standardized test designed to determine pupils/students’ achievement level, strengths and weaknesses in five key curricular subject areas at the end of the school year. The result of the National Achievement Test is chosen as a basis of the school’s academic performance. The schools served as samples are the ones where the researchers are taking their field study. Table1 NAT results 2011-2014 (School Ranking in Mathematics) School 2011-2012 2012-2013 2013-2014 Rank MPS Rank MPS Rank MPS Justice Emilio Angeles Gancayco Memorial National High School 17th 59.13 30th 32.03 11th 53.52 LimayNational High School 13th 65.78 18th 46.8 22nd 42.45 Lamao National High School 14th 63.83 10th 61.88 17th 44.28 Mariveles National High School (Cabcaben) 18th 40.3 17th 48.22 15th 47. 24 As the preceding table shows, Limay National High School has shown a decline in the NAT ranking in the past three years when it regards to its performance in Mathematics. In fact, in the recent NAT results, it ranked lowest among the four schools. Because of this, the researchers chose Limay National High School, as the research local. In reality, majority of Math classes consist of a teacher-led lesson, directed at the whole class, followed by individual practice (e.g. board works, drills) and sometimes group-activity reinforcement. It is mainly because Mathematics deals solely with concepts and theories. As the course of classroom learning shifted its gears to progressive classroom, the monotony of classroom instruction in Mathematics is ceased. From the teacher-centered instruction, students’ diversity is also taken into consideration. Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory can greatly help teachers to revolutionize the classroom instruction. On the other hand, Loori (2005) tackles the differences of intelligence preferences according to gender. Males preferred learning activities involving logic and mathematical intelligences, whereas females preferred learning activities involving intrapersonal intelligence. The comparative study between the genders regarding with the differences of intelligences reflects that either male or female, multiple intelligences and learning styles should not incorporate in identical way. It is fair and functional if all individuals perform on its domain rather than be traditionally tested in general intelligence. This would bring the chances of every individual on its field of inclination, expertise and actual intelligence. In addition to the use of MI-based instruction and how it affects the preferred learning styles of students, Orog (2012) states that student with musical inclination are doing a well-coordinated skill level with that of tactile-kinesthetic group of learners, or the presence of both intelligences to the same group of students. This information only reveals that a musically inclined learner is almost have the same level of learning style with tactile-kinesthetic learners as the performance-based assessment, in accordance to Orogs’ study, affirms the correlation to each other. There are many ways to incorporate MI and learning style theory in the curriculum, and there is no set method by which to incorporate these theories. The proponents of this study have been entering the world of field study required in their profession for almost 3 years. It can be typically observed that some students, despite of attending and sitting inside the classroom, are still deprived of learning since, the gap of the teaching style and learning style was not narrowed down. Most of the teachers, specifically mathematics educators, do not incorporate the theories about multiple intelligences and learning styles in classroom instruction. Adding the fact, that it narrows the measurement of academic performance to test scores. Hence, students do not receive the learning they need to acquire, disrupting the utilization of their true potentials. This research may help the teachers to consider incorporating MI and learning styles in the field of instructing mathematics. The primary goal of this research is to help math teachers realize that they should know more about the two concepts, assess the students’ learning styles as soon as possible in order to help students develop their different intelligence factors in a way which is conducive to their individual learning styles. As a result, when these important aspects are understood and acted upon, teaching strategies will become more efficient and effective and learning becomes more enjoyable for students who find difficulties in the traditional classrooms. Consequently, the diversity of students, due to various learning styles and multiple intelligences, can be more appreciated and its implication with the students’ academic performance can be used as a guideline to improve the classroom instruction in Mathematics, as the researchers want to address. All in all, this research aims to initiate change, to the educational system, in order to produce globally-competitive, productive, and life-long learners with the inclusion of MI and LS in the teaching-learning process.
Christine Pacinello
The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of instructional strategies on teacher self-efficacy beliefs about teaching mathematics to more fully understand the relationship between the two groups, and two determine what factors, if any, improve mathematics teaching self- efficacy bThe findings revealed that respondents’ perceived ability to provide feedback and clarification, as well as accommodating individual student needs, were the two principal factors which explain the variance in teacher’s self- efficacy beliefs. These two factors themselves are influenced by the teachers’ understanding mathematical concepts. From the data gathered in this study, we can conclude although teachers may welcome student questions, they do not always feel confident in their ability to answer these questions sufficiently. The data also revealed that overall, teachers lack confidence in their performance in front of superiors, their ability to get students interested in mathematics, as well as their ability to increase student retention. The instructional practices of the respondents were more traditional, and teacher- centric; the data revealed that this was related to underlying beliefs about mathematics instruction as well as the respondents’ perceived understanding of mathematical concepts.
… International Seminar and the Fourth National …
Ratna Fillah
Nelviyanti Podilito
Fikrah Imayu
Igor' Kontorovich
Gie Llagoso
ABSTRACT Mathematics education experts elaborate that motivational, meta-cognitive, and behavioral processes are as important as cognitive processes of students’ mathematics learning. These processes embodied the students’ self-regulated learning. Hence, this study looked into the self-regulated learning strategies, multiple intelligences, and academic mathematics performance of high and low self-regulated learners. The respondents of the study were grade 10 students comprised of fifteen (15) high self-regulated and fifteen (15) low self-regulated learners of Bulak National High School, in the Cebu Province Division for school year 2016- 2017. A qualitative method was used to delve into the different self-regulated strategies of high and low self-regulated learners. A Pearson Correlation using SPSS 23.0 also unravel the significant correlation between high level of academic self-regulation and logical/ mathematical intelligence, as well as the academic mathematics performance. It was found out that students with high self-regulation utilized higher frequencies of self-regulation strategies compared to their low self-regulated peers. The learners’ high level of self- regulation has also significant relationship with logical/ mathematical intelligence, and high academic performance in mathematics. Thus, high self-regulated learners have used powerful self-regulated strategies in regulating their learning to attain high academic mathematics performance. These strategies involve Meta-cognitive (Self- Evaluation), Motivational (Goal Setting and Planning, Rehearsing and Memorizing, Organizing and Transforming), and Behavioral (Environmental and Structuring) processes of self-regulated learning. Key words: Self- regulated learning strategies, multiple intelligences, academic math performance, Self-regulation
nina sariana
Division of facilities and infrastructures at Trilogi University in Jakarta important role in the smooth implementation of the teaching. Services provided in a campus environment, among others, is to provide the needs of printers among office equipment, paper, pens folders, and so forth. Car lending services office for employees who want to perform office tasks, in addition to providing services to students in rental lockers or classrooms that will be used the meeting. Division advice and infrastructures receive complaints from students or Lecturer who feel uncomfortable because infocus less functioning well, ac not cold, leakage, breakage bench, damage to the table and so on. The services provided to the general public who want to hire in the atrium or auditorium that will be in use as a wedding or a seminar. In providing services to students, faculty, staff within the Trilogi University as well as people outside the campus still done manually, for example when receiving orders and leasing of office equipment lockers are still recorded on paper. Vehicle rental and atrium room or auditorium writing done on the board. By looking at these conditions, the author makes a concept of information system for the division of facilities and infrastructures by using Cardinalities Mapping Keywords : Cardinalities Mapping
RELATED PAPERS
viedelia debroglie
Serhat Ozgokceler
Libreriauniversitaria.it Edizioni
Center for Teaching and Learning Hostos CC
Peter Mulendema
Mathematical Thinking and Learning
Po-Hung Liu
MIJCRP Journal
Peter Rich , Emily K. Yoshikawa , Sam Browning , Timothy Shoop
FR FIANTIKA
ramsel eclarin
USHA CHANDAR
Emelyn Cudapas
jerald moneva
NIYOMAYIRA VINCENT
Celia Booyse , Joan Houston , Simangele P Tenza
ICLEHI 2015
Dondon B. Buensuceso
Marco Vieira
Journal of Educational Chronicle (JEC)
Quentin Maire , esther doecke
Erika Novotna
Heaven Martin
James Trinidad
Dharel Acut
Samuel Baah-Duodu
Keith Jones , Helia Jacinto
Angela Francisca B Veloso
Rainulfo Pagaran
Johari Surif
Asia Pacific Journal of Education, Arts and Sciences
Research and Statistics Center
Jamal Daoud
Julia Miller
Auli A Guilland
Isaac Pinamang
Conference on Learning and Teaching
Aini Akmar Mohd Kasim
Dr. Muhammad Akhtar Kang
Muhammad Lodhi
Studies in Higher Education
Denise Jackson
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Open access
- Published: 05 February 2018
The role of problem solving ability on innovative behavior and opportunity recognition in university students
- Ji Young Kim 1 ,
- Dae Soo Choi 1 ,
- Chang-Soo Sung 1 &
- Joo Y. Park 2
Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity volume 4 , Article number: 4 ( 2018 ) Cite this article
24k Accesses
28 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Universities engage in entrepreneurship education to increase social value creation, through students’ new opportunities recognition. However, there are not enough of empirical researches on whether the current entrepreneurship education can be differentiated from other curriculum to improve the opportunity recognition process. This study argues that it is very important for cognitive abilities to be manifested as behavior when students in university are new opportunities recognition. For this purpose, the relationship between problem solving ability, innovation behavior, and opportunity perception was verified empirically. This study was conducted on 203 students who took entrepreneurship education courses at Korean universities. The results of this study showed that problem solving ability positively influenced innovation behavior and opportunity perception. Innovation behavior was identified as a key parameter that partially mediated the relationship between problem solving ability and innovation behavior. The implication of this study is to prove the relationship between individual ‘s problem - solving ability considering the characteristics of education in Korea and the opportunity through innovative behavior and various learning strategies to help entrepreneurship education to design better courses for the future It has important implications for strategic pedagogy that can enhance behavioral elements in development.
It is the new opportunity recognition that all firms focus on for a new economic paradigm (Ancona and Caldwell, 1992 ). Recognizing high opportunities can significantly improve profit, growth, and / or competitive positioning. And this new opportunity leads to innovation. From a conceptual point of view, research is continuing on the question of ‘what is opportunity’ and ‘where is opportunity’ (Gartner and Carter, 2003 ; Venkataraman & Sarasvathy, 2001 ). Research on the discovery and realization of new opportunities is a very important research area that suggests how to discover and utilize creative opportunities that create new value and profit for pre-service workers, and is the ultimate goal of entrepreneurship education. (Kim et al., 2016 ). Particularly, there is a lot of debate about the relationship between opportunity perception and personal characteristics. Despite many arguments, however, research on individual characteristics and opportunity perceptions is still insufficient, and a unified opinion has not been created due to differences between cognitive and behavioral theories (Ko & Butler, 2003 ). In particular, there is much controversy over the relationship between opportunity recognition and personal traits, and research has been continuing to demonstrate that organizational learning in organizations can influence opportunity recognition (Shane & Venkataraman, 2000 ). In particular, learning enhances cognitive ability, which is an opportunity that leads to opportunity recognition through the manifestation of behavior (Lumpkin and Dess, 2004 ). Many studies have also demonstrated the difference in behavior that successful entrepreneurs see as contributing to their ability to recognize opportunities and create innovative business ideas (Dyer et al., 2008 ; Kim et al., 2017 ). For example, Alvarez and Barney ( 2005 ) argue for mountain climbing and mountain building to understand the implications of entrepreneurial behavior in relation to these theories. In other words, a new opportunity for entrepreneurs is not a passive case that is generally found and climbed by climbers such as mountains, but rather by the actions of entrepreneurs, creating competition for the market, creating another market, Is the same. Therefore, in order for a person’s cognitive ability to recognize a new opportunity, it must focus on manifesting an action that can realize an innovative idea. In this regard, Kanter ( 1988 ) proved the relationship between new opportunity recognition and those with innovative tendencies and regarded this new opportunity recognition as innovation activity through organizational education. Scott and Bruce ( 1994 ) have integrated a number of research flows into innovation pioneers to develop and test individual innovative behavioral models. In particular, they argued that individual problem-solving styles are very important to induce innovative behavior. Although there are a number of studies on problem solving ability, innovation behavior, and new opportunities, most of the opportunistic researches have been conducted in organizational units of companies. Is still insufficient. Furthermore, unified opinions were not created due to differences between cognitive theory and behavioral theory (Ko & Butler, 2003 ). It is also true that the effects of entrepreneurship education in university have not been studied empirically because they are mainly focused on promoting cognitive ability and applied to various kinds of teaching methods.
This study argues that it is very important for cognitive abilities to be manifested as behavior that. “Through” courses, In other words, it is very important to induce students to act through ‘learning through process’ learning through behavioral learning by providing students with some (virtual or real) business to start doing some of the actions of the entrepreneur. When students in university are new opportunity recognition. Especially, entrepreneurship education, which ultimately focuses on whether it is a new opportunity, is very important to induce behavior through behavior learning beyond the cognitive ability as the general education curriculum. Particularly, innovative behaviors that create and realize innovative ideas are very important for new opportunity recognition (Paine & Organ, 2000 ).In order to achieve this, various kinds of teaching methods are being pursued in the university, but studies on the effectiveness of behavioral learning have not been studied yet. In this study, we are based on team-based learning among various teaching methods for behavior learning that leads to innovative behaviors. Team learning instructional activity sequence designed by Michaelsen and Sweet ( 2008 ), the most well known team-based learning in entrepreneurship education as in class-primarily group work and outside class-primarily individual work. In this way, we demonstrate empirically the relationship between individual problem solving ability and opportunity through innovative behavior, and develop a variety of learning strategies that help entrepreneurship education to design better courses for the future. I would like to point out some implications for strategic pedagogy to increase the element.
The paper proceeds as follows: Initially we present the theory of innovative behavior with individual problem-solving ability, innovative behavior and opportunity recognition. We develop hypotheses to confirm its basic predictions in the student context. Finally, we link the findings with the wider social effect of entrepreneurship literature and highlight the theoretical contributions and practical implications.
Theoretical background
‘opportunity recognition’ as entrepreneurship education unit of analysis.
A commonly focused analysis in entrepreneurship research over the last 30 years has been the ‘opportunity’, most simply defined as any situation in which new products or services can be development of production (Casson, 1982 ; Shane & Venkataraman, 2000 ; Venkataraman, 1997 ). The definition of opportunity recognition is defined in many ways, but opportunity is defined as a perceived means of generating economic value (ie, profit) that has not been exploited previously and is not currently exploited by others. If opportunity is defined in this way, opportunity recognition can be defined as a cognitive process (or process) that concludes that an individual has identified an opportunity (Baron and Ensley, 2006 ). Kirzner ( 1997 ) pointed out that the distribution of information in society affects the discovery of entrepreneurial opportunities and that only a few individuals can identify and recognize specific opportunities in the market. The process of finding opportunities also depends on the individual’s ability and discovery (Stevenson & Gumpert, 1985 ). For example, people may miss opportunities due to a lack of cognitive ability to change external environments (Stevenson & Gumpert, 1985 ). Only those who recognize and value the existence of opportunity can benefit from new opportunities (Ardichvili et al., 2003a , b ; Shane & Venkataraman, 2000 ). Opportunity recognition is an early step in transforming value into a business concept that creates value and generates revenue and distinguishes it from the aggressive stages of detailed assessment and development of recognized opportunities and potential economic value. The focus of the new venture business is also an innovative opportunity to create new opportunities rather than merely expanding or repeating existing business models (Gaglio & Katz, 2001 ). As a result, universities need to make use of a variety of initiatives to educate students to recognize innovative opportunities. Therefore, entrepreneurship education aimed at a new opportunity recognition should be able to provide learning opportunities based on various theories of favorable conditions for new business creation and the types of traits required for new ventures (Garavan & O’Cinne’ide, 1994 ).
Based on these considerations, we also define opportunity recognition as the formation of beliefs that can be translated into actions in order to understand the signals of change (new information on new conditions) and respond to these changes.
Problem-solving ability and innovative behavior of education for students
Problem-solving abilities have been proven to be one of the key factors for success in organizations and personal careers (Anderson & Anderson 1995 ). Through decades of research data, organizations and schools have studied factors that affect improvement. Problem-solving abilities are defined in a number of prior studies, and problem-solving abilities in a volatile and sophisticated knowledge- and technology-based industry are an important ability to drive innovation and sustainable growth and development in the industry. Table 1 show the concept of problem solving ability defined in previous research.
There have been a number of previous studies, emphasis has been placed on the importance and meaning of rational problem-solving processes in order to improve problem-solving abilities, and research has focused on individual problem solving styles (Woodman et al., 1993 ; Scott & Bruce, 1994 ). According to the personal innovation behavior model of Scott and Bruce ( 1994 ), climate has shown individual innovative behavior as a result of individuals signaling the organization’s expectations of behavior and the potential consequences of action. Innovative organizations are, last but not least, equipment, facilities and time, including the direction of creativity and innovative change (Kanter, 1983 ; Siegel & Kaemmerer, 1978 ) Proper supply of such resources is important to innovation (Amabile, 1988 ; Van de Ven & Angle, 1989 ; Dubickis & Gaile-Sarkane, 2017 ). Based on a study of Koestler’s ( 1964 ) creative thinking, Jabri conceptualized a problem-solving style consisting of two independent thinking styles. He uses a structured problem-solving styles that is based on associative thinking, follows a set of rules, resolves reasonably logically, and uses an intuitive problem-solving ability that focuses on problem-solving, not tied to existing rules with multiple ideas. Intuitive problem solving styles tend to process information from different paradigms simultaneously. It is therefore more likely to create new problem solutions as possible (Isaksen, 1987 ; Kirton, 1976 ). However, style assessment is not desirable because the style of problem solving affects style differently depending on the individual problem-solving situations (Scott & Bruce, 1994 ). We are proposing a role for the University to encourage innovative behavior based on the individuality of our students in order to recognize new opportunities through education about Scott and Bruce’s innovative behavioral models and diverse entrepreneurship education approaches. And involvement of resources, such as entrepreneurship awareness programs, ultimately leads to the identification of individual characteristics and innovation. In addition, current Korean entrepreneurship education is mainly focused on cognitive learning to improve problem solving ability, and one aspect of cognitive learning plays an important role in learning process of new venture firms. This study has a more direct focus on behavior learning such as team-based learning.
Hypothesis development
Problem-solving ability and innovative behavior.
Problem solving is to discover knowledge and skills that reach the target country by interfering with a set of processes and goals where the solution is unknown, unfamiliar, or reaching a new state of goal (Jonassen, 2004 ; Inkinen, 2015 ). There are various approaches to solve this problem. To solve problems and improve problem solving with a successful solution experience, you should adopt the method that best suits your problem solution. You need to select the appropriate inputs for the solution elements and a flexible process structure. Problem solving ability has been recognized as a key element of innovative behavior in responding to rapid changes with the ability to find various alternatives and predict outcomes from these alternatives to maximize positive results, minimize negative consequences, and select solutions to problems (Barron & Harrington, 1981 ; Jabri, 1991 ; Kirton, 1976 ). We pose the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1: Individual problem-solving ability has an effect on the innovative behavior of students.
Innovative behavior and opportunity recognition
Innovation involves introducing ideas from outside the organization, through creative processes, and linking these ideas to products or processes. Many scholars studying innovation recognize that designing ideas is only one step in the innovation process (Kanter, 1988 ). Innovation is changing at the organizational or individual level. Kanter, Scott and Bruce defined personal innovation. In other words, an innovation act starts with recognition of a problem, adoption of a new idea, or creation of a solution, and an individual with an innovative tendency wants to create a realistically realizable group with the sympathy of such an idea. Innovative individuals create prototypes for innovations that enable ideas to be realized specifically with goods or services and become productive use and social day merchandising. According to previous studies, opportunity perception can be seen as an individual’s corporate strategy that focuses on the perception and exploitation of individuals about potential business ideas and opportunities and finds resources to create innovative outcomes (Manev et al., 2005 ). New Venture Ideas (NVI) are imaginary combinations of product/service offerings; potential markets or users, and means of bringing these offerings into existence (Davidsson, 2015 ). From the viewpoint of a potential entrepreneur like a university student, entrepreneurship starts with an idea. This process continues with a range of practices including attractiveness and feasibility of an idea, gathering information to minimize value-related uncertainty and possibility and perhaps the main idea’s conformity ratio in terms of newly discovered needs (Hayton & Cholakova, 2012 ). Earlier we proposed that the program as a whole increases the students’ innovative behavior and that innovative performance is the new venture ideas. Since it is logical to assume that the relationship between innovative behavior and opportunity recognition. We pose the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 2: Innovative behavior will be a more potent inducer of opportunity recognition.
Problem-solving ability and opportunity recognition
Among the many factors influencing opportunity perception, the problems that arise in the fourth industry, the knowledge-based industry of the twenty-first century, are unpredictable and unstructured; they cannot be solved with existing solutions and require creative problem-solving skills. In order to determine how to solve problem situations that are different from the current situation and have unknown results, problems are solved through the process of adjusting previous experience, knowledge, and intuition (Charles & Lester, 1982 ). Experience, knowledge, and intuition are applied simultaneously to a single problem, not individually or collectively, and the intellectual and creative results that can be quickly and effectively solved in problem solving are seen as problem solving abilities (Ardichvili et al., 2003a , b ). Empirical studies of problem-solving abilities and opportunity perceptions have provided strong evidence that there is a positive relationship between theoretical integrative processes and corporate opportunity recognition (Ucbasaran et al., 2009 ). Therefore, we hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 3: Problem solving ability has an effect on the opportunity recognition.
The respondents for this study were randomly selected from three universities in Korea. Most of the respondents in this study were Korean university students who experienced team-based learning during behavioral learning through entrepreneurship education. Since then, we have been guided by two main criteria when choosing these universities. First, students who take entrepreneurship courses are critical to their innovation behavior. This led us to realize that innovative behavior is an important factor in an individual’s survival and growth. The second is that the parallel process of theoretical and behavioral learning is highly satisfied. A pilot study was conducted to verify the reliability and validity of the research measurements with 28 students at a university. The results of the pilot study showed high clarity and reliability (Cronbach ‘s alphas were all above 0.70) of the research measurements. The sample of the pilot study was not incorporated in the present study.
This study was conducted in a four - year undergraduate course (various majors) that took entrepreneurship courses in Korea university programs. Students in this course have a mix of students who have previously experienced entrepreneurship and those who have not. During the course, students were taught the theoretical lessons for 8 weeks and the team for the 8 weeks. The questionnaire was administered during the last week of the course.
The data were analyzed from 203 participants, out of a total of 209, of which 7 were not appropriate. Of the 203 participants, 27% were female and 73% were male and the grade distribution was 3% for freshmen, 12% for grade 2, 26% for grade 2, and 59% for grade 2. The main distribution is 26% in social science, 16% in business and economics, 39% in engineering, 11% in music and athletics and 7% in others (see Table 2 ).
Measurement
The structure of the model was measured by questionnaires (problem-solving ability, innovation behavior and opportunity recognition questionnaire) consisting of the scale taken from questionnaires verified in previous studies. Tool selection was performed on two criteria. First, the selected tool should measure the same structure (ie, the original measured structure had to be conceptually identical to the way the structure was defined in this study model). Secondly, the psychometric qualities of the instrument for the student had to be high.
Assessment of the factors was carried out through principal component analyses (varimax rotation with eigenvalues of 1.0 or above) of the scales connected to the same level of the model to confirm the uniqueness of the scales with respect to each other. This was supplemented by the computation of the internal consistency reliability of the scales (Cronbach’s α). These analyses were executed using the individual participants’ responses (Nunnally & Bernstein, 1994 ).
Problem- solving ability was measured on a 7-point Likert-scale (1 = ‘completely disagree’; 7 = ‘completely agree’). Jabri ( 1991 ) used a measurement tool to measure individual problem solving ability.
Innovative behavior was measured on a 7-point Likert-scale (1 = ‘completely disagree’; 7 = ‘completely agree’). In order to measure innovation behavior, we modified the questionnaire items to fit the intention of this study among the questionnaire items used by Scott and Bruce ( 1994 ) and Kim and Rho ( 2010 ).
Opportunity recognition was measured on a 7-point Likert-scale (1 = ‘completely disagree’; 7 = ‘completely agree’). In order to measure opportunity recognition, we modified the questionnaire items to fit the intention of this study among the questionnaire items used by Kim and Rho ( 2010 ).
Methods of analysis
The first two parts of the analysis were primarily based on (multiple) regression analyses. The last part of the analysis was informed through the path analyses. The adequacy of the models was assessed by AMOS 18(Arbuckle & Wothke, 2003 ). Models were all tested with standardized coefficients obtained from the Principal Component Analysis. To ascertain the model fit, we analyzed the comparative fit index (CFI), the normed fit index (NFI), the Root Mean Square Err of Approximation (RMSEA), the standardized root mean square residual (SRMR) and the chi-square test statistic.
Reliability and validity are essential psychometrics to be reported. The first step to evaluate those aspects was to use the Cronbach’s alpha and the composite reliability to test reliability of the proposed scales. The usual threshold level is 0.7 for newly developed measures (Fornell and Larcker, 1981 ). Values range from 0.69 to 0.79 in the case of Cronbach’s alpha, and from 0.85 to 0.92 in the case of composite reliability (see Table 3 ). Therefore, these scales may be considered as reliable. Next, we estimated the research model, displayed in Fig. 1 , using structural equation modeling (SEM) and AMOS 18 (Arbuckle & Wothke, 2003 ). Our analysis revealed an adequate measurement model with high factor loadings for all the items on the expected factors and communalities of each item exceeding 0.50. We discuss three fit indices that are generally considered as important (Hu & Bentler, 1998 ). First, the CFI-value represents the overall difference between observed and predicted correlations. A value of 0.04 which is situated well below the cut-off value of 0.08, suggests that the hypothesized model resembles the actual correlations. Secondly, Bentler’s CFI (comparative fit index) greater than 0.90 and 0.95 which is above the cut-off of 0.90 (Schumacker & Lomax, 1996 ). Thirdly, NFI greater greater than 0.90 and 0.95 which is above the cut-off of 0.90 (Schumacker & Lomax, 1996 ). Fourthly, the standardized root mean square residual (SRMR) value of 0.0392 which is situated well below the cut-off value of 0.05(Hu & Bentler, 1998 ), and the chi-square value of 3581.622 which is situated well below the cut-off value of 0.0005. Finally, the RMSEA (root mean square error of approximation) equals 0.04 with a 90% confidence interval between 0.03 and 0.05.
Analysis of mediation effect
The value and confidence interval are situated over but below the cut-off value of 0.1 which suggests not a great but a good fit. Factor analysis was verified by factor analysis using principal component analysis and only factors with an eigenvalue of 1 or more by orthogonal rotation method were selected. Factor loading was considered to be significant at 0.5 or more (Hair et al., 2006a , b ). As a result of the analysis, cumulative explanation for 72.4% of the total variance. Confirmatory factor analysis thus supported the differentiation of the three components Also we tested the confirmatory validity of the construct by testing whether the structural linkage of each square is greater than the mean variance extraction (AVE) of each structure. The AVE ranged from 0.52 to 0.53, reaching the recommended level of .50 for both Fornell and Larcker ( 1981 ). Therefore, all constructs showed sufficient convergent validity (see Table 3 ).
As shown in Table 4 , the AVE value of each variable has a higher value than that of other factors. Therefore, the discriminant validity of the proposed model can be judged as appropriate.
Means, standard deviations, and correlations among the study variables are shown in Table 5 .
The mean scores for the conceptual model were as follows for problem-solving ability (MD. 5.20, SD.1.08), innovative behavior (MD.5.20, SD.1.03), and opportunity recognition (MD. 5.14, SD. 1.06) conditions. The means of problem-solving ability, innovative behavior, and opportunity recognition were high. Furthermore, those variables correlated positively with each other.
Figure 1 showed that all paths and their significance levels are presented in Table 6 . The path between the latent variables problem-solving ability and innovative behavior was significant (p, 0.001), consistent with Hypotheses 1. In addition, there was innovative behavior and opportunity recognition (p, 0.01), this result provide empirical support for Hypothesis 2.
H3 proposed that Problem-solving ability is positively related to opportunity recognition. The results of the correlation analysis: The coefficient of problem solving and opportunity perception weakened from .717 to .444, but it is still partly mediated because it is still significant (C. R = 7.604 ***). This supports H3 (see Table 6 ).
In order to verify the significance of the indirect effect, the bootstrapping must be performed in AMOS, and the actual significance test should be identified using two-tailed significance. As a result, the significance of indirect effect is 0.04 ( p < 0.05), which is statistically significant (see Table 7 ).
Discussion and conclusion
We have tried to demonstrate the effects of behavior and its significance by differentiating from the general curriculum emphasizing cognitive effects as a model of problem solving ability emerging as innovative behavior through opportunity of university entrepreneurship education.. This supports the premise that entrepreneurship education can improve opportunities or processes through behavioral learning. The results of this study support the role of entrepreneurship education in creating opportunities for innovative behavior and problem solving abilities. Entrepreneurship education should provide different types of learning for new opportunities and focus on what is manifested in behavior.
In addition, based on previous research, we propose whether the following contents are well followed and whether it is effective. First, the emergence of innovative behavior in problem-solving abilities increases as the cognitive diversity of students with diverse majors and diverse backgrounds increases. Second, the more entrepreneurial learning experiences, the greater the chance of new opportunities. Third, it is necessary to investigate students’ problem solving style and problem-solving ability first, and then a teaching strategy based on this combination of systematic and effective theory and practice is needed. Of course, as demonstrated by many studies, it may be easier to enhance the effectiveness of opportunity recognition through cognitive learning. This is because it emphasizes the achievement of knowledge and understanding with acquiring skills and competence. This process, however, is not enough for entrepreneurship education. However, we do not support full team-based behavioral learning in the class designed by Michaelsen and Sweet ( 2008 ). As with the results of this study, problem solving ability is positively related to opportunity perception directly. As previously demonstrated in previous studies, problem solving ability can be enhanced by cognitive learning (Anderson et al., 2001 ; Charles & Lester, 1982 ).
Therefore, it has been demonstrated that it is more efficient to balance a certain level of cognitive learning and behavior learning in consideration of the level of students in a course. Also this study satisfies the need for empirical research by Lumpkin and Lichtenstein ( 2005 ) and Robinson et al. ( 2016 ) and others. This will help to improve understanding of how entrepreneurship training is linked to various learning models and their effectiveness and to design better courses for the future. Finally, this study sought to provide an awareness of entrepreneurship education as the best curriculum for solutions that evolved into innovative behaviors that create new values and ultimately represent new opportunities. This study shows that it can positively influence the social effect of creating new value, that is, not only the cognitive effect of general pedagogy, but also the innovation behavior. By providing this awareness, we have laid the groundwork for empirical research on entrepreneurship education in order to create more opportunities for prospective students in education through education and to expand their capabilities.
Limitation and future research
Indeed, the concepts presented here and the limitations of this study have important implications that can fruitfully be addressed in future research. First, we selected a sample of college students taking entrepreneurship training. However, since it is not the whole of Korean university students, it is difficult to extend the research results to all college students in Korea. Second, there is no precedent research on the role of innovation behavior as intermedia in college students. Therefore, we were forced to proceed as an exploratory study.
The ability to recognize opportunities can provide significant benefits that can remain firm and competitive in an ever-changing environment. Future research should therefore expand these insights and try to empirically test more ways in which entrepreneurship pedagogy teaches how learning methods can be integrated into venture creation and growth processes to help new process opportunities. By providing this study, we will help entrepreneurship education in the university to create more opportunities and expand the capacity of prospective members.
Alvarez, S. A., & Barney, J. B. (2005). How do entrepreneurs organize firms under conditions of uncertainty? Journal of Management, 31 (5), 776–793.
Article Google Scholar
Amabile, T. M. (1988). A model of creativity and innovation in organizations. Research in Organizational Behavior, 10 (1), 123–167.
Google Scholar
Ancona, D. G., & Caldwell, D. F. (1992). Demography and design: Predictors of new product team performance. Organization Science, 3 (3), 321–341.
Anderson, P. M., & Anderson, P. M. (1995). Analysis of faulted power systems (Vol. 445). New York: IEEE press.
Anderson, L. W., Krathwohl, D. R., Airasian, P., Cruikshank, K., Mayer, R., Pintrich, P., & Wittrock, M. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy . New York: Longman Publishing.
Arbuckle, J. L., & Wothke, W. (2003). AMOS 5 user’s guide . Chicago: Smallwaters.
Ardichvili, A., Cardozo, R., & Ray, S. (2003a). A theory of entrepreneurial opportunity identification and development. Journal of Business Venturing, 18 (1), 105–123.
Ardichvili, A., Cardozo, R., & Ray, S. (2003b). A theory of entrepreneurial opportunity identification and development. Journal of Business Venturing, 18 (1), 105–123.
Baron, R. A., & Ensley, M. D. (2006). Opportunity recognition as the detection of meaningful patterns: Evidence from comparisons of novice and experienced entrepreneurs. Management Science, 52 (9), 1331–1344.
Barron, F., & Harrington, D. M. (1981). Creativity, intelligence, and personality. Annual review of psychology, 32 (1), 439–476.
Casson, M. (1982). The entrepreneur: An economic theory . Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield.
Charles, R., & Lester, F. (1982). Teaching problem solving: What, why & how . Palo Alto: Dale Seymour Publications.
Davidsson, P. (2015). Entrepreneurial opportunities and the entrepreneurship nexus: A re-conceptualization. Journal of Business Venturing, 30 (5), 674–695.
Dubickis, M., & Gaile-Sarkane, E. (2017). Transfer of know-how based on learning outcomes for development of open innovation. Journal of Open Innovation : Technology, market, and complexity , 3 (1), 4.
Dyer, J. H., Gregersen, H. B., & Christensen, C. (2008). Entrepreneur behaviors, opportunity recognition, and the origins of innovative ventures. Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, 2 (4), 317–338.
D'zurilla, T. J., & Nezu, A. M. (1990). Development and preliminary evaluation of the social problem-solving inventory. Psychological Assessment: A Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 2 (2), 156.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research , 39–50.
Gaglio, C. M., & Katz, J. A. (2001). The psychological basis of opportunity identification: Entrepreneurial alertness. Small Business Economics, 16 (2), 95–111.
Garavan, T. N., & O’Cinneide, B. (1994). Entrepreneurship education and training programmes: A review and evaluation-part 1. Journal of European Industrial Training, 18 (8), 3–12.
Gartner, W. B., & Carter, N. M. (2003). Entrepreneurial behavior and firm organizing processes. In Handbook of entrepreneurship research (pp. 195–221). New Mexico: Springer US.
Hair, E., Halle, T., Terry-Humen, E., Lavelle, B., & Calkins, J. (2006a). Children's school readiness in the ECLS-K: Predictions to academic, health, and social outcomes in first grade. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 21 (4), 431–454.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., & Tatham, R. L. (2006b). Multivariate Data Analysis (6th ed.). Upper Saddle River: Pearson Education, Inc..
Hayton, J. C., & Cholakova, M. (2012). The role of affect in the creation and intentional pursuit of entrepreneurial ideas. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 36 (1), 41–68.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1998). Fit indices in covariance structure modeling: Sensitivity to underparameterized model misspecification. Psychological Methods, 3 (4), 424.
Inkinen, T. (2015). Reflections on the innovative city: Examining three innovative locations in a knowledge bases framework. Journal of Open Innovation : Technolodgy, market. Complexity, 1 (1), 8.
Isaksen, S. G. (1987). Frontiers of creativity research: Beyond the basics. Bearly Ltd.
Jabri, M. M. (1991). The development of conceptually independent subscales in the measurement of modes of problem solving. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 51 (4), 975–983.
Jonassen, D. H. (2004). Learning to solve problems: An instructional design guide (Vol. 6). Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.
Kanter, R. M. (1983). The change masters: Binnovation and entrepreneturship in the American corporation. Touchstone Book.
Kanter, R. M. (1988). Three tiers for innovation research. Communication Research, 15 (5), 509–523.
Kim, H. C., Song, C. H., & An, B. R. (2016). A study on effects of personal characteristics on start-up opportunity and entrepreneurial intention of start-up. Korean Management Consulting review, 16 (3), 75–87.
Kim, S. A., Ryoo, H. Y., & Ahn, H. J. (2017). Student customized creative education model based on open innovation. Journal of Open Innovation : Technology, Market, and Complexity , 3 (1), 6.
Kim, T. H., & Roh, J. H. (2010). A Study of the Impact of Public Service Motivation on Innovative Behavior of Organizational Members. Korean Journal of Public Administration, 48(3).
Kirton, M. (1976). Adaptors and innovators: A description and measure. Journal of Applied Psychology, 61 (5), 622.
Kirzner, I. M. (1997). Entrepreneurial discovery and the competitive market process: An Austrian approach. Journal of Economic Literature, 35 (1), 60–85.
Ko, S., & Butler, J. E. (2003). Alertness, bisociative thinking ability, and discovery of entrepreneurial opportunities in Asian hi-tech firms.
Koestler, A. (1964). The act of creation: A study of the conscious and unconscious processes of humor, scientific discovery and art.
Lumpkin, G. T., & Dess, G. G. (2004). E-Business Strategies and Internet Business Models: How the Internet Adds Value. Organizational Dynamics, 33 (2), 161–173.
Lumpkin, G. T., & Lichtenstein, B. B. (2005). The role of organizational learning in the opportunity-recognition process. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 29 (4), 451–472.
Manev, I. M., Gyoshev, B. S., & Manolova, T. S. (2005). The role of human and social capital and entrepreneurial orientation for small business performance in a transitional economy. International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation Management, 5 (3–4), 298–318.
Michaelsen, L. K., & Sweet, M. (2008). The essential elements of team-based learning. New directions for teaching and learning, 2008 (116), 7–27.
Nunnally, J. C., & Bernstein, I. H. (1994). Validity. Psychometric theory, 99–132.
Paine, J. B., & Organ, D. W. (2000). The cultural matrix of organizational citizenship behavior: Some preliminary conceptual and empirical observations. Human Resource Management Review, 10 (1), 45–59.
Robinson, S., Neergaard, H., Tanggaard, L., & Krueger, N. F. (2016). New horizons in entrepreneurship education: from teacher-led to student-centered learning. Education+ Training, 58(7/8), 661–683.
Schumacker, R. E., & Lomax, R. G. (1996). A beginner's guide to structural equation modeling . Mahwah: Laurence Erlbaum Google Scholar.
Scott, S. G., & Bruce, R. A. (1994). Determinants of innovative behavior: A path model of individual innovation in the workplace. Academy of Management Journal, 37 (3), 580–607.
Shane, S. A. (2003). A general theory of entrepreneurship: The individual-opportunity nexus . Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Book Google Scholar
Shane, S., & Venkataraman, S. (2000). The promise of entrepreneurship as a field of research. Academy of Management Review, 25 (1), 217–226.
Siegel, S. M., & Kaemmerer, W. F. (1978). Measuring the perceived support for innovation in organizations. Journal of Applied Psychology, 63 (5), 553–562.
Spivack, G., Platt, J. J., & Shure, M. B. (1976). The problem-solving approach to adjustment . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Stevenson, H., & Gumpert, D. (1985). The heart of entrepreneurship.
Stevenson, H. H. & J. C. Jarillo (1990). 'A paradigm of entrepreneurship: Entrepreneurial management', Strategic Management Journal, 11, pp. 17–27.
Ucbasaran, D., Westhead, P., & Wright, M. (2009). The extent and nature of opportunity identification by experienced entrepreneurs. Journal of Business Venturing, 24 (2), 99–115.
Van de Ven, A. H., & Angle, H. L. (1989). Suggestions for managing the innovation journey (No. 9). Strategic Management Research Center, University of Minnesota.
Venkataraman, S. (1997). The distinctive domain of entrepreneurship research. Advances in entrepreneurship, firm emergence and growth, 3 (1), 119–138.
Venkataraman, S., & Sarasvathy, S. D. (2001). Strategy and entrepreneurship: Outlines of an untold story.
Warner, M. (2002). Publics and counterpublics. Public Culture, 14 (1), 49–90.
Woodman, R. W., Sawyer, J. E., & Griffin, R. W. (1993). Toward a theory of organizational creativity. Academy of Management Review, 18 (2), 293–321.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Dept. of Technology Entrepreneurship (Graduate School), Dongguk University, 904 Chungmurogwn, Toegye-ro 36Gil, Jung-gu, Seoul, 100-272, South Korea
Ji Young Kim, Dae Soo Choi & Chang-Soo Sung
Yonsei School of Business, Yonsei University, 50 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul, 120-749, South Korea
Joo Y. Park
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Joo Y. Park .
Ethics declarations
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kim, J.Y., Choi, D.S., Sung, CS. et al. The role of problem solving ability on innovative behavior and opportunity recognition in university students. J. open innov. 4 , 4 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40852-018-0085-4
Download citation
Received : 12 September 2017
Accepted : 22 January 2018
Published : 05 February 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40852-018-0085-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Problem-solving ability
- Innovative behavior
- Opportunity recognition
- Entrepreneurship education

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Also, Totan (2011) examined the effect of the problem-solving skills training program on the 6th class primary school students' social-emotional learning skills. Similarly, relational studies on problem-solving skills are also included in the literature. Uysal (2007) conducted a study on the relationship between secondary school students ...
PDF | Problem solving is often challenging for students because they do not understand the problem-solving process (PSP). ... problem-solving skills (Barak & Mesika, 2007; Hong, Hwang & Tai, 2012; ...
Problem-solving skills are essential for adaptation to society, and game-based learning has emerged as the best method of improving such skills; for instance, Han (2015) found that learning through interactive sessions helps students learn more and improves their problem-solving cognitive abilities. Game-based learning, by
This is particularly true for real world problem-solving competency, which has been recognized as one of the 21 st century skills (Sarathy, 2018;World Economic Forum, 2016).
Among the most frequently discussed learning skills are critical thinking skills. Critical thinking skills are believed to have an essential role in interpreting, analyzing, evaluating, concluding ...
Behare (2009) in his study of problem solving skills in mathematics learning investigated cognitive skills in solving mathematical problems of learner at the terminal stage of elementary education. It revealed that those who can verbalize the process of solution are better at solving problems. Mohanty (2009) studied the effect of cognitive and ...
In this study, we conducted a comprehensive review of recent articles exploring the influence of student roles on the development of collaborative problem-solving skills. We specifically assessed whether student roles could effectively promote collaborative problem-solving and whether different role types have different effects.
Balancing disciplinary knowledge and practical reasoning in problem solving is needed for meaningful learning. In STEM problem solving, science subject matter with associated practices often appears distant to learners due to its abstract nature. Consequently, learners experience difficulties making meaningful connections between science and their daily experiences. Applying Dewey's idea of ...
For instance, students viewed as self-regulated learners should be cognitively engaged in learning or problem-solving, while cognitive engagement is explicitly defined by some ... (1985). Cognitive engagement variations among students of different ability level and sex in a computer problem solving game 1. Sex Roles, 13(3-4), 241-251 ...
Abstract. The paper aims to introduce the conceptual framework of problem solving through values. The framework consists of problem analysis, selection of value (s) as a background for the solution, the search for alternative ways of the solution, and the rationale for the solution. This framework reveals when, how, and why is important to ...
Physics education for the twenty-first Century aims to foster high-end reasoning skills and promote deep conceptual understanding. However, many traditional education systems place strong emphasis on only problem solving with the expectation that students obtain deep conceptual understanding through repetitive problem-solving practices, which often doesn't occur (Alonso, 1992).
Current problem-solving research has advanced our understanding of the problem-solving process but has provided little advice on how to teach problem-solving skills. In addition, literature reveals that individual difference is an essential issue in problem-solving skills instruction but has been rarely addressed in current research. Building upon information-processing theory, this article ...
Problem Solving in STEM. Solving problems is a key component of many science, math, and engineering classes. If a goal of a class is for students to emerge with the ability to solve new kinds of problems or to use new problem-solving techniques, then students need numerous opportunities to develop the skills necessary to approach and answer ...
This research to practice full paper presents problem solving skill development through STEM learning approaches. There is a rapid growing interest in STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) education. One reason for this ever growing interest is to develop the skills in pupils, which are required by the industry 4.0 (Artificial intelligence, big data, Internet of things) in an ...
The problem solving ability is a personal capability to identify the existing condition and relate it to knowledge owned by students. The steps in problem solving according to Polya are problem ...
key words as a problem solving method for word problems does not help students. develop a conceptual understanding. Jitendra and Star (2011), explain that the keyword. method does not allow students to focus on the meaning and structure of the problem. which prevents them from fully understanding what they are reading.
Employers also value problem-solving skills, which are described as the ability to identify key issues and develop practical solutions to contextually sited problems. Self-confidence is noted as a key enabler of efficiency and productivity and thus is highly valued by employers. The skills identified are not domain specific (e.g. self ...
6. Solution implementation. This is what we were waiting for! All problem solving strategies have the end goal of implementing a solution and solving a problem in mind. Remember that in order for any solution to be successful, you need to help your group through all of the previous problem solving steps thoughtfully.
The ability to use your own initiative to think for yourself to be creative and pro-active. To resolve problems to think logically and laterally to use ingenuity to overcome difficulties. fStatement of the Problem This study aims is to determine the problem solving skills of grade students. 1.
There have been a number of previous studies, emphasis has been placed on the importance and meaning of rational problem-solving processes in order to improve problem-solving abilities, and research has focused on individual problem solving styles (Woodman et al., 1993; Scott & Bruce, 1994).According to the personal innovation behavior model of Scott and Bruce (), climate has shown individual ...
conceptual understanding, problem solving, categorizing, and reasoning. In a similar vein, Slavin (1989) reported on a best-evidence synthesis of 60 studies across both elementary and ... skills required to manage disagreements among group members. These skills need to be explicitly negotiated (older students) or taught (younger children) and ...
For problem 1 and 2 To determine the Grade 11 students' level of problem skills the following formulae were used: Problem Solving Ability = Number of correct answers x 100% Number of questions. Problem Solving skills level of the Grade 11 students was classified as follows: Level Satisfactory Good Poor.
Definitions and Examples. Jennifer Herrity. Updated July 31, 2023. When employers talk about problem-solving skills, they are often referring to the ability to handle difficult or unexpected situations in the workplace as well as complex business challenges. Organizations rely on people who can assess both kinds of situations and calmly ...