
Traduction Française Indisponible
Theses & dissertations.
Theses and dissertations are extended scholarly essays that incorporate original research on a specific topic. They are usually written as part of the requirements for a graduate degree (e.g. MA or PhD).
Finding a York University thesis or dissertation Most doctoral dissertations and Master's theses completed at York University are available through the Libraries. Law dissertations are held in the Law Library; most others are held in Scott Library. Please note that the library does not normally hold copies of Major Research Papers (MRPs); for these, please check with the appropriate York University department or faculty.
For York dissertations and theses written from 1967 to 2012: Start by searching the Dissertations and Theses @ York University database. You can search by keyword, title, adviser or school. The full-text of most York theses and dissertations submitted between 1967 and 2012 can be downloaded for free.
This service is only available to registered York students and faculty. For York dissertations and theses written between 1967 and the present that were never microfilmed or have some form of embargo restricting access:
- Search the library catalogue . You can search by title, author, or keyword. When you find the entry, note the call number and location. A quick location guide is provided below.
For dissertations and theses written from 2013 to the present, search the library catalogue (NOT the classic catalogue) by title, author, or keyword.
Finding theses from other universities
- Proquest Digital Dissertations and Theses This database contains citations and abstracts of doctoral dissertations and some masters theses from colleges and universities in North America and Europe. Citations are available from 1861 to the present. Abstracts are available for dissertations from 1980 to the present and for masters theses from 1988 to the present. From 1997, sometimes earlier, the full-text of some dissertations and theses may be downloaded for free in PDF format. Please note that this service is only available to registered York students and faculty.
- Theses Canada Portal The Theses Canada Portal provides free access to the full text electronic versions of Canadian theses and dissertations that were published from the beginning of 1998 to the present.
- Index to theses (Great Britain and Ireland) An index to theses accepted in the Universities of Great Britain and Ireland. Covers 1716 – present.
- EThOS (Great Britain) Launched in 2008, the Electronic Theses Online System (EThOS) offers free access to full text versions of British theses. New theses are digitized and added to the database in response to requests from researchers.
Many other periodical indexes and databases include references to dissertations.
Note : Theses and dissertations not available in the Libraries or online can be requested through the Resource Sharing Department.
Doctoral Dissertation
Doctoral general requirements, types of dissertations.
Doctoral dissertations shall be on a topic approved by the student’s supervisor and supervisory committee, and shall include submission and approval of a dissertation proposal, including appropriate ethics review and approval, in accordance with Faculty and program requirements and procedures. Dissertations must embody the results of original research and must be successfully defended at an oral examination.
The doctoral dissertation must embody original work conducted while in program, and must constitute a significant contribution to knowledge. It should contain evidence of critical understanding of the relevant literature. The material embodied in the dissertation should merit publication.
By submitting a thesis or dissertation, a student is making the representation that it is entirely his or her own work and that it has been done while he or she was a graduate student at York University.
If such is not the case, then the student must indicate in a signed, written statement what part of the thesis or dissertation is solely his or her own or co-authored. If co-authored, the candidate must provide an account of its provenance. The supervisor must produce her or his own corroborative written statement.
If a thesis or dissertation is the result of collaborative work, then the nature of the collaboration and the extent of the candidate’s contribution must be described in a written statement signed by the candidate and approved in writing by the candidate’s supervisor. Where there has been collaboration with others in the collection or preparation of data, materials, or documentation included in the thesis or dissertation, then appropriate acknowledgment must be made in the thesis or dissertation.
If a thesis or dissertation—or any part thereof—has been published prior to submission of the dissertation, then the candidate must disclose this fact in a signed written statement, and the supervisor must approve in writing the inclusion of such work in the thesis or dissertation. In cases where one or more chapters of the thesis or dissertation have been previously published in a journal or book to which the author has assigned copyright, permission to include the chapter(s) in the thesis or dissertation must be obtained from the copyright holder(s). Please see the section on Copyright for more details.
A thesis or dissertation containing previously published material of which the candidate is the author and/or co-author should also contain a review of the literature that adequately explains the relationship to the literature of the work undertaken. In addition, it should contain a rationale for the study. These elements may form part of the body of the work – normally an introduction or opening chapter – that leads coherently into the publications. Furthermore, there should be a concluding chapter or section that discusses the body of the thesis or dissertation, including all previously published parts.
A false representation or failure to make a disclosure as outlined above is an academic offence and renders the thesis or dissertation ineligible for consideration of the relevant degree.
The general form and style of a dissertation may differ from program to program, but a dissertation should be a coherent work. This means that if a dissertation contains separate manuscripts, there needs also to be introductory and concluding chapters that explain how these separate manuscripts fit together into a unified body of research. If previously published materials are included, then it should be made clear what exactly is the student’s own work and what is the contribution of other researchers, as outlined above under Originality of a Dissertation.
All theses and dissertations must contain a written component. Theses and dissertations may, however, include other components in addition to the written component.
A complex electronic dissertation is a work with a high reliance on slides, film or videos, electronically interactive word/image-based text on CD-ROM or the internet. For complex electronic theses/dissertations, part of the work can be produced in traditional written form, but key elements of the work depend on direct experience with or interaction with a text whose physical form may be changed as a consequence of the interaction. Students producing a multimedia dissertation should consult with the Library and Archives Canada website for advice on formats supportable for preservation. However, a student may work in or submit work in an unsupported format as part of the oral exam as long as the work is readily accessible by the exam committee and the student submits a written component.
A multimodal dissertation is a work in which the key component is a performance or piece of art. For multimodal theses/dissertations, part of the work can be produced in traditional written form, but key elements of the work depend on direct experience by the exam committee with, for example, displayed artworks or theatrical productions.
For both electronic and multimodal theses/dissertations, students may wish to include supplementary files as part of their final submission (see Final Dissertation Submission below).
A thesis or dissertation should be written in English, but approval may be given to a written request from a student for a thesis or dissertation to be written in French or in the language of any Aboriginal/First Nations people in North America, subject to confirmation from the director of the graduate program concerned that relevant supervision and sufficient support for the completion of such written work can be provided.
For theses/dissertation written in English, either American or British spelling is acceptable provided that it is used consistently throughout.
Students preparing their dissertation should follow a single style guide appropriate to their discipline. The York University Libraries provides links to various style guides for various disciplines.
Dissertation Proposals
In accordance with program requirements and procedures, all students should prepare a thesis/dissertation proposal, normally in consultation with their supervisor in advance of commencing their proposed inquiry. Each program should have written guidelines and should communicate them to candidates, as and when appropriate.
At a minimum, the proposal should contain a brief statement in non-technical language on the purpose/goals of the thesis/dissertation research, its relationship to existing work in the area, through an abbreviated literature review, the research question(s), the proposed methodology(ies) with rationale, and the contribution which the researcher hopes to make to the advancement of knowledge in the field. In addition, the proposal includes a title, the name of the supervisor and the supervisory committee. The title should indicate as clearly as possible the area of research, but it is understood that this title may change. The recommended maximum length of a proposal is 3,500 words, but individual programs may require proposals of a greater length. Proposals must be reviewed and approved by a student’s thesis or dissertation committee.
Following approval of the proposal by the supervisory committee, students must submit one or more copies of the proposal to the graduate program director. After confirming that the relevant Faculty and internal program requirements have been satisfied, the program director is responsible for submitting the proposals to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies using the Form TD1: Dissertation Research Submission.
As indicated on Form TD1: Dissertation Research Submission, submission of the proposal to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, includes submission of the relevant research ethics forms and documentation. For more information, please refer to the Research Ethics section of this Handbook.
For a doctoral dissertation, the supervisory committee must review the student’s research proposal and recommend its approval not less than six months prior to the date set for the oral examination.
Please note that the deadlines outlined above are the Faculty’s minimum requirements, and individual graduate programs may have more specific requirements and timelines with respect to the development, review and approval of dissertation proposals. Students should consult their program for more details. Further, the Faculty deadlines outlined above may not provide the time necessary for ethics approval, if required. More information regarding research ethics is provided below.
Research Ethics
York University is committed to the highest standards of integrity in research. All projects involving the use of human subjects, animals, and biohazardous materials are subject to review by the appropriate University committee. York has formulated policies and procedures for the conduct of research involving all three of these areas.
As indicated on Form TD1: Thesis/Dissertation Research Submission , submission of the thesis/dissertation proposal to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies for approval must include the relevant research ethics forms and documentation.
All research involving human participants is governed by the Senate Policy for the Ethics Review Process for Research Involving Human Participants . The Senate Policy stipulates that all University-based research involving human participants, whether funded or non-funded, faculty or student, scholarly, commercial or consultative, is subject to an ethics review process. The Senate Policy for the Ethics Review Process for Research Involving Human Participants and corresponding review procedures adhere to the published guidelines of the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council, and the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council, known as the Tri-Council Policy Statement (TCPS).
Please note that in accordance with the TCPS and Senate policy, graduate students undertaking research with human participants may not begin that research until their proposal has received approval from the appropriate body . Further, prior to conducting research involving human participants, graduate students are required to complete the complete the TCPS tutorial .
Details regarding the ethics review procedures for thesis/dissertation research involving human participants is available on the Faculty of Graduate Studies research ethics web page.
Students conducting research with human participants may be required to submit the Form TD2: Human Participants Research Protocol (.pdf). Additional forms may be required.
Further details regarding the University policies and ethics review procedures for thesis/dissertation research involving animals and bio-hazardous materials is available on the Office of Research Ethics web page.
Ethics guidelines for other research situations are also available on the Office of Research Ethics web page, including:
- Invasive Procedures
- Health and Safety Checklist
- Surveys and Research in an Online Environment
- Research Conducted by External Researchers
- Research Conducted in Hospital Clinical Settings
- Research in Educational Settings
- Research Involving Minor Age Participants
- Research with People who are Homeless
Students hold copyright to their dissertations, regardless of the method of submission. Consequently, a student is free to publish his or her dissertation following a successful oral examination. Please note that if a dissertation includes any work which is copyrighted to another party, permission may be required to publish the dissertation.
After a successful oral examination the Library and Archives Canada Thesis Non-Exclusive License must be submitted to the Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies. The student must also accept the terms of the York University Copyright License as part of the electronic submission of their dissertation using the Electronic Thesis and Dissertation (ETD).
By signing these licenses, a student is confirming that his or her dissertation is his or her original work, that his or her dissertation does not infringe any rights of others, and that he or she has the right to make the grant conferred by those copyright licenses. In addition, the student is granting a Licence to York University to make copies including electronically formatted copies, and/or distribute worldwide all or part of the dissertation, subject to the conditions outlined.
If applicable, the student should submit copies of any required copyright permissions prior to the final dissertation submission to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies. The student should also retain copies of all copyright permission requests and approvals.
The following sections provide guidance and suggestions with respect to when and how to secure copyright permission. It is, however, the responsibility of the student to confirm that if there is copyrighted material in his or her dissertation, it either complies with the “fair dealing” provisions of the Canadian Copyright Act or documented permission has been obtained to use the copyrighted material. The Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies cannot offer legal advice as to whether or not copyright permission is required.
Limit of Copyright Protection : Copyright protection applies to original, literary, musical, dramatic or artistic works in a variety of forms, including written materials, computer software, and web-based formats regardless of whether the work in question is published or not and whether someone has made it available to the public or not. This protection expires 50 years after the death of the originator, regardless of who holds copyright at that time.
Public Domain : A work that is freely available to the public is not necessarily in the public domain. For a work to be in the public domain, the originator must have specifically waived copyright to the work, or copyright must have legally expired. Work that is in the public domain can be used by anyone without copyright being violated.
Fair Dealing : A student is allowed to use copyrighted material in his or her dissertation provided it falls under the Canadian Copyright Act's definition of "fair dealing". Information on York University’s Fair Dealing Guidelines can be reviewed at York University—Copyright .
While it is required academic practice to cite sources, proper citation does not remove the obligation to obtain documented permission to use copyrighted permission that is not covered under the “fair dealing” provisions of the Canadian Copyright Act. If a dissertation includes any of the following elements, the student should seek copyright permission. (Please note that this is not an exhaustive list. If you require additional information on York’s Copyright Policy or Fair Dealing Guidelines contact the Copyright Office at [email protected] ).
- Material or parts of material written by the dissertation author which have been previously published in a journal and to which the author has assigned copyright
- Material co-authored with another author(s) who share copyright
- Tables, figures, and all forms of images including photos, maps, graphs, drawings, logos etc. that have been obtained from a copyrighted source, including websites, newspapers, journals, books, brochures, professors' lecture notes, etc.
- Scripts and recordings of any performance
In cases where a student is not certain that his or her use of copyrighted material is covered under the "fair dealing" provisions of the Canadian Copyright Act, documented permission from the copyright holder(s) must be obtained in order to include the material in the dissertation. Since securing copyright permission may take some time, it is strongly recommended that students being this process sooner rather than later. Please note that the copyright holder must be aware of and agree to the terms of the York University Copyright License and Library and Archives Canada Thesis Non-Exclusive License.
If seeking permission from a journal, a good first step is to check the journal’s website, which may provide information with respect to copyright, including advance permission to journal authors who have signed over copyright, how to request permission, and uses that are specifically prohibited. There are also a number of websites that may be helpful in determining the copyright policies of particular journals/publishers, including Sherpa Romeo and EPrints . Some journals and publishers provide (on their website or on request) a policy statement granting copyright permission to the author of a dissertation who signed over copyright to the journal/publisher. In such cases, retain a copy of that policy statement as evidence of documented permission.
Alternatively, a student should contact the copyright holder. Sample text for a copyright permission request is included below. Although email proof of permission is acceptable, please note that an original, signed letter on the copyright holder’s letterhead is the best protection against accusations of copyright violation.
Students should provide copies of any required copyright permissions prior to submission of their final dissertation to the thesis coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies. Students should also retain copies of all copyright permission requests and approvals.
[Date] [Name] [Address] Re: Request for Permission to Use Copyrighted Material in a Dissertation Dear: I am a York University student preparing my dissertation for submission as part of the requirements of my master’s/doctoral degree in [program]. The title of my [dissertation] is: […] The reason I am writing is to ask permission to include the following material in my dissertation: [Provide standard reference information for the material, including figure/table number, if any, and page numbers. If appropriate, you can also briefly describe the manner/context in which the material will be used in dissertation.] The material will be fully cited in my dissertation. In the interest of facilitating research by others, my dissertation will be available on the internet for reference, study and/or copy. The electronic version of my dissertation will be accessible through the York University Libraries website and catalogue, and also through various web search engines. I will be granting Library and Archives Canada a non-exclusive license to reproduce, loan, distribute, or sell single copies of my thesis by any means and in any form or format. These rights will in no way restrict republication of the material in any other form by you or by others authorized by you. Could you please confirm in writing or by email that these arrangements meet with your approval. If you do not solely control the copyright in the material, please let me know as soon as possible. I would also appreciate any information you can provide about others to whom I should write to request permission. If you would like to confirm permission in writing, you can do so by signing and completing the information below and returning this signed and completed letter in the enclosed self-addressed stamped envelope by [date]. If you would like to confirm permission by email, my email address is […]. Sincerely,[Your Name and Signature] I, the undersigned, hereby represent and warrant that I have authority to grant the permission requested and do grant the permission. Signature: Name:
Students must include full citations for any copyrighted material used in their dissertation regardless of source, including photos, pictures, charts, graphs and tables.
Each citation must include the copyright symbol, name of the copyright holder (who may or may not be the author), and, if applicable, a statement that the use of the material or adaptation (in the case of adapted graphics) is by permission of the copyright holder.
In cases where use of copyrighted material is not covered under the "fair dealing" provisions of the Canadian Copyright Act and a student is unable to secure permission from the copyright holder (or there is a charge for obtaining permission), the material in question must be removed from the dissertation. In its place, the student should indicate that the material has been removed because of copyright restrictions.
Depending upon the nature of the material, the student may want to include additional information. In the case of a figure or image that has been removed, a description of the missing material and a full citation of source material and where it can be found (including, if possible, a link to an online source) would be helpful to those reading the dissertation. In the case of a chapter that was previously published in a journal, an abstract of the chapter content and link to the journal website where the article can be found could be provided.
Intellectual Property
The Faculty of Graduate Studies recognizes the mission of the university to seek, preserve, and disseminate knowledge and to conduct research in a fair, open, and morally responsible manner.
In such regard, the Faculty of Graduate Studies believes that intellectual property rights are divided among several interests, and that the rights and obligations of various claimants should be specified, fairly regulated, and that disputes arising may be mediated. All parties (students and faculty) are expected to behave in an ethically appropriate manner beyond their immediate graduate student/supervisory relationship, to encompass intellectual property rights, dissemination of research data, and in making decisions on authorship and publication of joint research.
Because of the varied cultural aspects and practices that differ among the graduate programs, each program is responsible for enacting and enforcing this policy of appropriate ethical practices on intellectual property rights, in compliance with the Faculty Policy on Intellectual Property for Graduate Programs . Programs that choose not to enact their own specific policy are bound by the Faculty Policy on Intellectual Property for Graduate Programs .
Organization and Technical Requirements
Although the form, style, sections, etc. of main body (text) of the dissertation may differ from program to program, all theses/dissertations must include the following components in the following order.
The front matter of the dissertation must be numbered with lower case Roman numerals. The page number should be not be included on the title page, although the title page is considered page i. Numbering must be included starting with the abstract, as page ii, and continue until the end of the front matter, as follows:
The main body of the dissertation, starting with the introduction or chapter one, must be numbered with Arabic numerals, beginning with the number 1. Each chapter of the main body must begin on a separate page. Footnotes and/or endnotes are considered part of the main body of the dissertation.
The back matter of the dissertation includes references (or the bibliography), as well as any appendices, glossaries, indexes, where and as applicable. The back matter must be numbered with Arabic numerals, which should follow from the last page of the main body of the dissertation.
Each appendix must be assigned an alphabetical letter and title, (e.g., Appendix A: Title). Appendices are ordered in the same sequence as they are referred to in the body of the text; that is, the appendix first mentioned in the text is assigned the letter A, the second is B, etc. Materials in the appendices that are copied from other sources must meet the same requirements as the body of the paper, for example, copies or scans from books, maps, etc., must be clear and legible, and must maintain the same margins.
Technical Requirements
A sample title page is provided below. The title page should include the following information:
- Dissertation Title: The title should provide a concise and meaningful description of the thesis/dissertation. It is recommended that the title include keywords to make the dissertation more easily searchable. It is also recommended that formulas, Greek letters, symbols and abbreviations be avoided in the title, and that they be written out as words instead.
- Student Name: The name on the title page must be the one under which the student is registered at York University.
- All title pages must include the following statement: A Dissertation* submitted to the Faculty of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy* [*For a master’s thesis, replace “Dissertation” with “Thesis”, and indicate the master’s degree designation (e.g. Master of Arts, Master of Science, Master of Fine Arts) in place of “Doctor of Philosophy”]
- Program and Institution: Name of Program [e.g. English, Biology, Music], York University, Toronto, Ontario
- Date: The month and year that the Chair of the Examining Committee confirmed successful defence of the thesis/dissertation
- Copyright: The universal copyright symbol ©, followed by the student name (which must be the name under which the student is registered at York University) and year that the Chair of the Examining Committee confirmed successful defence of the dissertation.
The information on the title page may be centered, as long as all margins are at least 1 inch (25 mm). The font of the title page need not be the same as that used in the sample title page provided below.
Each dissertation must contain an abstract. The abstract is expected to give a succinct account of the dissertation so that a reader can decide whether to read the complete work.
For doctoral dissertations, the abstract cannot exceed 350 words. An abstract contains a statement of the problem, the procedure or methods used, the results and the conclusions.
The abstract should be inserted immediately following the Title Page, and should be numbered "ii".
An acknowledgements page may be included.
The Table of Contents, List of Tables and List of Figures, where applicable, should follow the abstract (or acknowledgements, if any). Curriculum vitae, list of student-authored publications, or conference presentations do not form part of the contents of the dissertation. A truncated version of the Table of Contents should not precede each chapter.
The document must be formatted using letter sized pages (8.5 x 11 inches).
The same font type (e.g. Arial or Times New Roman) should be used throughout the dissertation, particularly the main body.
The font size of the main body of the dissertation must be a minimum of 10 points, with smaller font sizes permitted for endnotes/footnotes, graphs, formulae, appendices, etc. A font size larger than 12 points is not recommended for the main body of the dissertation.
The line spacing must be at least one-and-a-half (1.5) spaces or double-spaced. Single spacing may be used for long quotations and foot/endnotes.
All margins must beat least 1 inch (25mm). Margins may be wider but not narrower than the stated requirements. For example, the first page of every chapter may have a top margin of 2.5 inches.
Running headers to put title, name, chapter, etc., on each page are not acceptable.
All page numbers should be in a consistent location, that is either centre bottom, centre top, right top corner, or right bottom corner. They must fall at the 1 inch (25 mm) margin. There should be no blank pages or large blank spaces within the dissertation.
Each diagram and table should be numbered. Page numbers should appear in the same position on the page as they appear elsewhere in the body of the text. Tables may be horizontal or vertical as long as the required margins are used. Diagrams must be generated by graphic software.
All images included in the thesis or dissertation should be of high quality and sufficient resolution.
- Sample Title Page (.pdf)
- Sample Table of Contents (.pdf)
- Sample List of Tables (.pdf)
Oral Examination
Doctoral dissertation exam committees.
A dissertation examining committee shall consist of at least five voting members, including the Chair, as follows:
- The Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies or her/his representative, who will be at arm’s length from the supervision of the dissertation, and who will serve as Chair of the examining committee;
- One external examiner, from outside York University, at arm’s length from the dissertation, recommended by the program director;
- one graduate faculty member at arm’s length from the dissertation, and normally from outside the program, recommended by the program director;
- two graduate faculty members from the supervisory committee, or one member from the supervisory committee and one graduate faculty member from the program.
These are minimum requirements with respect to the composition of and quorum for dissertation examining committees. Individual graduate programs may include one additional voting member on examining committees, in accordance with program requirements and procedures.
In exceptional circumstances, the Dean may approve a program director’s recommendation that a York University faculty member who is not a member of the graduate faculty serve as a member (but not the Chair) of an examining committee. Such recommendations are to be accompanied by a brief rationale and an up-to-date curriculum vitae, which may be attached to the Recommendation for Oral Examination Form .
In addition to the voting members, the thesis examining committee may include the following ex-officio members (non-voting, unless present as one of the voting members named above): Vice-President Academic & Provost, Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies or his/her representative, Graduate Program Director.
Only under rare, exceptional and compelling circumstances can an oral examination proceed in the absence of the external examiner, and only with the express permission of the Dean. In such circumstances, the following conditions must be met:
- the external’s absence must be unplanned and unavoidable (i.e. it must have been the initial intent that the external would be present);
- a written assessment of the dissertation must be received before the scheduled examination, including certification that the dissertation is examinable, and identification of any areas that need revision, or questioning and clarification at the oral exam. However, if the external examiner feels that the result of the examination depends upon the oral exam, then the external examiner shall be present or the oral exam will be postponed until the external examiner can be present or an alternative external examiner is appointed.
Prior to the establishment of a doctoral dissertation exam committee, the student’s supervisory committee must read the dissertation and agree that the version read is ready to proceed to oral examination.
Following agreement by the supervisory committee that the dissertation is ready to proceed to oral examination, recommendation for membership of a doctoral dissertation exam committee (as well as the date and location of the oral exam) is formally initiated by the graduate program director via submission of a Recommendation for Oral Examination Form .
Final approval of doctoral dissertation exam committee membership recommendations rests with the Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies.
The membership of each committee must be recommended by the appropriate graduate program director for approval and appointment by the Dean of Graduate Studies as soon as possible and no later than 20 business days before the date set for the oral examination.
Copies of the doctoral dissertation approved by the supervisory committee must be provided to the members of the examining committee no less than 20 business days before the date of the oral examination. (The oral exam may be held less than 20 business days from the time copies are sent to the examining committee provided all parties agree.)
External Examiners are expected to be established academics, normally members of a graduate Faculty at another university. Students may not initiate the invitation to external examiners; this is the responsibility of the program director and/or the supervisor.
Following approval by the Dean of the program’s external examiner recommendation, a formal letter of invitation will be written by the Dean to the external examiner, offering the examiner an honorarium and indicating how to claim expenses. Program directors must obtain prior approval from the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies of external examiners’ expenses above $350; therefore, external examiners should not be invited unless approval has been obtained.
The program assistant or the supervisor (not the student), should send the external examiner’s copy of the dissertation. The copy must be received by the external examiner at least 20 business days prior to the exam. It should be accompanied, at the minimum, by generic instructions and notification that the Dean’s official letter of invitation will follow (see below for generic instructions). For delivery to an Ontario university or home delivery, the minimum method used to send the dissertation should be by Express Post. The dissertation should be well packaged to protect it from damage. A follow-up e-mail or phone call should be made to the external examiner to ensure the dissertation was received.
The external examiner will be asked to submit written comments five business days in advance of the oral examination. These comments may be made available to the candidate after the oral, with the external examiner’s permission.
The following generic instructions should be used when sending a copy of the dissertation to the external examiner.
Enclosed is your copy of the dissertation for [student’s name] at whose oral examination you will serve as the external examiner.
As the external examiner, you are recognized as being an eminent person in the field of the dissertation, whose assessment will be treated as the standard by which the quality of the candidate’s work will be measured. As a voting member of the committee, you do not have a formal power of veto, but the exam committee must have substantial reasons for not accepting your recommendation, especially if the recommendation is negative.
Five business days before the date set for the oral defence, please send a written assessment of the dissertation to Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies. This written assessment may be sent by mail (Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies, 230 York Lanes, York University, 4700 Keele St, North York, Ontario, M3J 1P3), by FAX (416-736- 5592) or by e-mail to the appropriate Graduate Milestones Coordinator .
The written assessment report should:
- outline the strengths and weaknesses of the dissertation
- be more than a statement of errata and/or questions you would pose to the student
- contain an explicit statement indicating whether the dissertation is examinable
- be written with the understanding that should the dissertation be nominated for a Dissertation Prize, the report will form part of the nomination papers
- This report will be distributed to the program director and members of the Examining Committee before the examination.
- Where the Committee deems it advisable and if you agree, the report may be made available to the student at the end of the examination.
- If you have serious doubts about the examinability of this dissertation, please contact the Graduate Program Director «GPD name» (416-736-2100, ext. «GPD telephone») or the Dean at 416-736-5329 at least five business days before the date of the oral.
The formal invitation from the Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies will follow shortly. Thank you for your participation.
Scheduling of Doctoral Dissertation Oral Exams
In consultation with the student and the members of the exam committee, the graduate program director will recommend the date, time and location of an oral exam via submission of a Recommendation for Oral Examination Form .
Oral examinations for doctoral dissertations shall be held normally no less than 20 business days from the date on which copies of the completed dissertation approved by the supervisory committee are sent to each member of the examining committee. The oral exam may be held less than 20 business days from the time copies are sent to the examining committee provided all parties agree.
The student must be registered as active for the term in which the oral exam is scheduled to take place.
Number of Copies The number of copies of a dissertation required for an oral exam depends upon the number of members on the exam committee. A dissertation exam committee consists of at least five voting members, including the Chair. However, it is often the case that more than five copies of the dissertation are required for an oral exam. The dissertation supervisor or program director will inform the student how many copies of the dissertation are required for the exam.
Nature of Copies The student is responsible for ensuring that all members of the exam committee have an e-copy of the dissertation, unless prior approval has been received for the submission of a paper copy. (If paper copies are submitted for the oral exam, the pagination and formatting of each page of the paper copies and the e-copies must match.)
For a complex electronic dissertation, the student is responsible for ensuring that all members of the exam committee have an e-copy of the written component of the dissertation, unless prior approval has been received for the submission of a paper copy. (If paper copies are submitted for the oral exam, the pagination and formatting of each page of the paper copies and the e-copies must match.) For the remaining component of the work, it is the student’s responsibility to ensure that the work produced for the dissertation can be examined by the examining committee. Students producing a multimedia dissertation should consult with the Library and Archives Canada website for advice on formats supportable for preservation. However, a student may work in/submit work in an unsupported format as part of the oral exam as long as the work is readily accessible by the exam committee and the student submits a written component.
For a multimodal dissertation, the student is responsible for ensuring that all members of the exam committee have an e-copy of the written component of the dissertation, unless prior approval has been received for the submission of a paper copy. (If paper copies are submitted for the oral exam, the pagination and formatting of each page of the paper copies and the e-copies must match.) For the remaining component of the work, it is the student’s responsibility to make arrangements for the exam committee to view/engage in the non-written component.
Note: If an examining committee member requests a paper copy of the written component(s) of the dissertation, it is the graduate program's responsibility to make arrangements once an e-copy has been provided by the student.
Before an oral examination can be convened, a majority of the exam committee members must agree that the thesis is examinable. The graduate program director shall poll the members of the exam committee five business days before the scheduled date for the oral. If the student does not receive a majority vote, the members of the examining committee who do not agree that the thesis is examinable are required to give their reasons in writing to the student, the supervisor, and the Dean within five business days after the poll. In such cases, the oral shall be postponed for a period not to exceed 12 months. However, the student has the right to insist that the oral proceed as planned.
Members of the examining committee are normally expected to attend the oral examination in person, except where decanal permission for the use alternative technologies such as video- or teleconferencing has been granted. The rationale for this examination mode must be made by the program to the Dean. Normally, no more than one member of an examining committee should be linked to the examination process through alternative means. Only in exceptional circumstances would the supervisor, an internal York member, or the student be the off-site participant.
With the consent of the voting members of the examination committee, the program director and the student, the Dean may approve a recommendation that an oral examination be rescheduled due to exceptional circumstances.
The use of audio-visual (AV) equipment at oral exams is governed by the following principles:
- AV equipment may be used for oral exam presentations but the Faculty of Graduate Studies is not responsible for ordering supplies or equipment (e.g., overhead projectors).
- Audio-taping or videotaping of oral exams is not permitted.
The oral exam is a public academic event. Faculty members, graduate students and others may attend oral exams at the discretion of the Chair of the exam committee. They may, at the discretion of the Chair, participate in the questioning. Only members of the exam committee may be present for the evaluation and for the vote at the conclusion of an oral exam.
Graduate students have the right to choose to hold a thesis or dissertation defence in an electronically mediated, audio/visual, online format (via Zoom) or to defend in person. Consult with your supervisor, supervisory committee, and Graduate Program Assistant via email. GPAs can then convey this information to FGS.
If the external examiner is unable to participate in the defence medium chosen, then the defence must be cancelled and rescheduled when they are able to participate. Please contact the Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinators to convey this information by visiting our FGS Staff Directory .
Please note that the graduate regulation prohibiting audio-taping or videotaping oral exams remains in place for defences conducted online (see Use of Audio-Visual Equipment at Oral Exams for Master's students and doctoral students ).
Doctoral Dissertation Oral Exam Evaluation Guidelines and Reporting of Results
- Doctoral dissertations submitted by students in partial fulfillment of degree requirements must be successfully defended at oral examinations. The oral examination will centre on the dissertation.
- if the committee accepts the dissertation with no revisions; or,
- if the committee accepts the dissertation with specified revisions.
- Specified revisions could range from typographical errors or changes of a minor editorial nature, to specified insertions or deletions which do not radically modify the development/argument of the dissertation. The committee must specify such changes with precision. It is the responsibility of the supervisor to ensure that all such changes are made, and the Dean’s representative will confirm that this is the case. Specified revisions must be completed within six months of the date of the oral examination.
- In cases where there are no more than two votes for major revision or one vote for failure, then specified revisions are expected.
- A dissertation is referred for major revision if any of the following conditions exist:
- there are two votes for failure; or,
- there is one vote for failure plus a minimum of one vote for major revision; or,
- there are at least three votes for major revision.
- the committee will reconvene within twelve months to continue the oral examination; or,
- the revised dissertation will be circulated within twelve months to all members, who will inform the Dean’s representative whether they feel the stipulated requirements have been met.
- Detailed reasons for referring pending major revisions must be supplied in writing by the Chair to the Dean, the program director and the student concerned within 10 business days.
- After an adjournment and when the major revisions have been completed, the dissertation is failed if there are two or more votes for failure. A dissertation cannot be referred for major revisions more than once and no further adjournment is permitted. In the event of failure, detailed reasons must be supplied in writing by the Chair to the Dean, program director and student within 10 business days.
- A dissertation is failed if there are a minimum of three votes for failure. In the event of failure, detailed reasons must be supplied in writing by the Chair to the Dean, program director and student within 10 business days.
The results of the oral exam, as determined by the exam committee in accordance with the evaluation guidelines described above, are reported to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Oral Examination Report Form . The form should be signed by the Chair of the exam committee and should include, where appropriate, details regarding any required revisions under “comments”.
In accordance with the evaluation guidelines described above, the Oral Examination Report Form requires that the committee reach one of the following four decisions: 1. Accepted with No Revision
2. Accepted Pending Specified Revisions The nature of the revisions should be agreed to by the exam committee and reported in detail on Oral Examination Report Form under “comments”. Specified revisions must be completed within six months of the date of the oral exam. Specified revisions must be completed within six months of the date of the oral exam. It is the responsibility of the supervisor to ensure that all of the specified revisions are made and the Chair will confirm that this is the case. Approval of specified revisions should be reported to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Revisions Approved Memorandum or via email to the appropriate Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
3. Referred Pending Major Revisions In cases involving a referred pending major revisions decisions, one of the following procedures, agreed upon by the committee before the examination is adjourned, must be used to finalize the oral results: a) the committee will reconvene within twelve months to continue the oral examination, or b) the revised dissertation will be circulated within twelve months to all members, who will inform the Chair whether they feel the stipulated requirements have been met.
Please note that a clear consensus must be reached by the committee as to the extent and nature of the revisions required. Detailed reasons for referring pending major revision must be supplied in writing by the Chair of the exam committee to the Dean, the program director and the candidate concerned within 10 business days.
Approval of major revisions should be reported to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Revisions Approved Memorandum or via email to the appropriate Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
4. Failed In the event of failure, detailed reasons must be supplied in writing by the Chair of the exam committee to the Dean, program director and candidate within 10 business days.
Exam Committee Roles and Responsibilities
Before an oral examination can be convened, a majority of the exam committee members must agree that the dissertation is examinable. The graduate program director shall poll the members of the exam committee five business days before the scheduled date for the oral. If the student does not receive a majority vote, the members of the examining committee who do not agree that the thesis is examinable are required to give their reasons in writing to the student, the supervisor, and the Dean within five business days after the poll. In such cases, the oral shall be postponed for a period not to exceed 12 months. However, the student has the right to insist that the oral proceed as planned.
For doctoral dissertations, the Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies or her/his representative, who will be at arm’s length from the supervision of the dissertation, will serve as Chair of the exam committee.
The Chair of the exam committee normally participates fully in the questioning of the candidate, the discussion and the vote.
In general, the role of the Chair of the exam committee is to ensure:
- that the process of oral exam is fair and orderly,
- that the student is truly being examined and challenged, and
- that high standards of scholarship are met.
Prior to the formal start of the oral exam, the Chair should:
- verify that all members of the exam committee are present. (If any member is not in attendance, the examination shall be postponed. Only under rare, exceptional and compelling circumstances can an oral examination proceed in the absence of the external examiner. Please see Role of the External Examiner below for more details.)
- verify that the members of the exam committee are agreed that the thesis/dissertation is “examinable”. (If the thesis/dissertation is found to be unexaminable at this time, the oral exam may be postponed for a period not to exceed 12 months. However, the student has the right to insist that the oral proceed as planned.)
- discuss with the members of the Committee the expected length of the examination, and the order in which the exam committee will question the student.
At the outset of and during the oral exam, the Chair should:
- clarify to both the exam committee and the student the procedures to be followed,
- determine the point at which further questioning will not produce additional useful information for the consideration of the exam committee, and
- monitor the procedures throughout the oral exam.
After the candidate and any observers have left the room, the Chair should:
- assess the committee’s opinion from the discussion, including whether the exam committee considers the work sufficiently outstanding to merit nomination for the Faculty of Graduate Studies Thesis/Dissertation Prize.
- If there is no consensus, the Chair should call for a vote to determine the outcome of the oral exam. The outcome of the vote shall be governed by the master’s thesis oral exam evaluation guidelines or doctoral dissertation oral exam evaluation guidelines, as appropriate.
- In cases of accepted pending specified revisions, the Chair should ensure the nature of the on the Oral Examination Report Form under “comments”. A clear consensus must be reached by the committee as to the extent of the revisions required.
- the revised dissertation will be circulated within twelve months to all members, who will inform the Chair whether they feel the stipulated requirements have been met.
After the exam committee has reached a decision, the Chair should:
- recall the candidate to convey the decision, including a description of any required revisions, as appropriate, and
- inform the program director if the thesis/dissertation has been nominated for the Faculty of Graduate Studies Dissertation Prize, where applicable.
If the thesis/dissertation was accepted with no revisions , the Chair should:
- ensure that a properly completed and signed Oral Examination Report Form, is returned to the thesis coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies.
If the dissertation was accepted pending specified revisions , the Chair should:
- ensure that a properly completed (including a clear description of the required revisions) and signed Oral Examination Report Form is returned to the thesis coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies. It is the responsibility of the supervisor to ensure that all of the specified revisions are made and the Chair will confirm that this is the case. Specified revisions must be completed within six months of the date of the oral exam.
- Approval of specified revisions should be reported to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Revisions Approved Memorandum or via email to the appropriate Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
In cases of referred pending major revisions , the Chair should:
- ensure that a properly completed (including a clear description of the required revisions) is returned to the thesis coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, and
- provide detailed reasons for the exam committee’s decision in writing to the Dean, program director and student within 10 business days of the oral exam.
When major revisions have been completed satisfactorily as decided by the exam committee, the Chair should:
- Report approval of the major revisions to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Revisions Approved Memorandum or via email to the appropriate Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator.
In cases of failure , the Chair should:
- ensure that a properly completed and signed Oral Examination Report Form is returned to the thesis coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, and
The exam committee members have the responsibility of ensuring that high standards of scholarship are met.
The “at arm’s length from the thesis/dissertation” committee member has a particular responsibility of ensuring that these high standards of scholarship are met from a perspective broader than that of the student’s own program. Such exam committee members who are appointed to the student’s program should be especially mindful of this responsibility.
Note: All doctoral dissertation exam committee must include an external examiner. The following description of external examiner roles and responsibilities also applies to those master’s programs that require an external or outside examiner on their exam committee.
External examiners are expected to be established academics, normally members of a graduate Faculty at another university. The assessment of the dissertation provided by the external examiner should be treated as the yardstick by which to measure the quality of the candidate’s work relative to standards at other universities. The external examiner is a voting member of the Committee and must have been at arm’s length from the dissertation. The external examiner does not have a formal power of veto, but the exam committee must have substantial reasons for not accepting an external examiner’s recommendation, especially if the recommendation is negative. The external examiner’s written comments will be provided to the other members of the exam committee prior to the oral exam and, where the exam committee deems advisable and the external examiner agrees, may be made available to the student at the end of the oral exam.
In addition to the voting members, the Vice-President Academic & Provost and Graduate Program Director may participate as ex-officio members (non-voting, unless present as one of the voting members) on doctoral dissertation exam committees.
As the oral examination is the culmination of a graduate student’s study and advances the mission of York University as a whole, the inclusion of these positions as ex-officio members of the dissertation exam committees recognizes and emphasizes the importance of the oral exam. Due to the nature of the workload of the incumbents in these positions, they are not expected to attend every oral exam. When they do attend in their capacity as ex-officio members, they are encouraged to be active participants, but they do not vote.
- For all doctoral dissertation oral exams and for those master’s programs that require an external or outside examiner, the written comments provided by the external examiner will be made available to the committee prior to the oral exam.
- At the oral exam, the student may be given the opportunity to present an oral summary of his or her work. If this procedure is followed, the Chair of the exam committee will inform the student and indicate the time available.
- Normally, the first round of questions will refer to general aspects of the work. Subsequent questions will deal with more detailed matters. For all doctoral dissertation oral exams and for those master’s programs that require an external or outside examiner, the external examiner will normally begin each round of questioning and will be followed by the other members of the committee in an order agreed upon before the exam.
- The Chair of the exam committee will ensure that each member of the exam committee has an equal opportunity to pose questions. After the formal rounds of questioning, general discussion and order of further questioning will be at the Chair’s discretion.
- The question period should normally run its natural course, with members of the exam committee indicating when they are satisfied. The Chair of the exam committee will, however use his/her discretion as to the appropriate closing point. For a master’s thesis, a general guideline for the length of the oral exam is approximately 10 to 20 minutes for presentation (if applicable) and 1.5 hours for questioning. For a doctoral dissertation, a general guideline for the length of the oral exam is 20 to 40 minutes for presentation (if applicable) and 2 hours for questioning.
- After the candidate and any observers have left the room, the exam committee will discuss the work and the oral defense of that work, the discussion beginning with the external examiner’s remarks.
- The Chair of the exam committee will then assess the committee’s opinion from the discussion.
- If there is no consensus, the Chair of the exam committee will call for a vote to determine the outcome of the oral exam. The outcome of the vote shall be governed by the master’s thesis oral exam evaluation guidelines and doctoral dissertation oral exam evaluation guidelines.
- In cases of accepted pending specified revisions , the nature of the revisions will be agreed to by the exam committee and reported in detail by the Chair in the “comments” section of the Oral Examination Report Form.
- In cases of major revision , the Chair of the exam committee will confirm which of the following two procedures, agreed upon by the committee before the exam is adjourned, will be used to finalize the oral results: a) the committee will reconvene within twelve months to continue the oral examination; or, b) the revised dissertation will be circulated within twelve months to all members, who will inform the Chair whether they feel the stipulated requirements have been met.
- After the exam committee has reached a decision, the candidate will be recalled and informed by the Chair of the outcome of the examination. Should revisions be required, their exact nature will be transmitted to the student by the Chair.
- The written comments of the external examiner will, with his or her permission, be provided to the student and program director.
- In cases of accepted pending specified revisions , it is the responsibility of the supervisor to ensure that all of the specified revisions are made and the Chair will confirm that this is the case. Specified revisions must be completed within six months of the date of the oral examination. Approval of specified revisions should be reported to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Revisions Approved Memorandum or via email to the appropriate Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
- In cases of referred pending major revisions or failure , the Chair will provide detailed reasons for the exam committee’s decision in writing to the Dean, program director and student within 10 business days of the oral exam. When major revisions have been completed satisfactorily as decided by the exam committee, the Chair should report approval of the major revisions to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, via the Revisions Approved Memorandum or via email to the appropriate Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
Final Submission
Following a successful oral exam (including confirmed approval of any specified revisions or major revisions), submission by the student of the final approved thesis/dissertation is a requirement for graduation and convocation.
The thesis or dissertation is submitted electronically using York University’s Electronic Thesis and Dissertation (ETD) platform. The thesis coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, will check that the thesis/dissertation meets the Faculty’s organizational and technical requirements, and has the right to refuse any unacceptable document until it is submitted in acceptable form.
Once the submission is approved and all requirements for graduation are met, the thesis/ dissertation will be transferred to YorkSpace, York University's institutional repository of research outputs, where it will be accessible to Library and Archives Canada as well as major search engines and other repositories.
The degree completion date is NOT based on the date of the oral examination; it is based on the date of submission to the Office of the Electronic Thesis & Dissertation Tool (ETD) and the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies, of the acceptable final approved copy. Students are responsible for active registration and all tuition fees until the final copy is submitted to and approved by the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies.
Submission deadlines with respect to convocation can be found under Important Dates .
An ETD record will be created for each student by the thesis coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies once all of the following have been received:
- Oral Examination Report (passed)
- Revisions Approved Memorandum, if applicable
- Library and Archives Canada Theses Non-Exclusive License form, signed and dated
- Copies of copyright permissions (if applicable)
Once an ETD record is opened, the student will receive an email with instructions on how to log in and complete their submission. Students should ensure that they have followed the organization and technical requirements for theses/dissertations prior to making a submission to the Office of the Dean, Graduate Studies through the ETD platform. If, after reading the Organization & Technical Requirements section of this handbook, students have any questions concerning formatting and preparation, they should direct these questions to the thesis coordinator. Instructions for the use of the ETD platform are available at Electronic Thesis and Dissertation (ETD) .
By signing the Library and Archives Canada (LAC) Theses Non-Exclusive License form, the student authorizes LAC to reproduce, publish, archive, preserve, conserve, communicate to the public, loan, distribute and sell the thesis/dissertation for commercial or non-commercial purposes. Further information about the Non-Exclusive License and the Library & Archives Canada thesis program is available on the Library and Archives Canada website.
The student must also accept the terms of the York University Copyright License as part of the electronic submission of their thesis/dissertation using the Electronic Thesis and Dissertation (ETD) application.
If required, students should provide copies of any needed copyright permissions prior to the final thesis/dissertation submission. Students should also retain copies of all copyright permission requests and approvals.
As a publicly funded institution, York University has an obligation to ensure that research produced by its graduate students is available for the benefit of the public, particularly by making successfully defended theses and dissertations available through York University Libraries and Library and Archives Canada. With that in mind, there is normally no restriction on the publication of and access to successfully defended theses and dissertations. However, in some exceptional instances it may be detrimental to the author or sponsor of the thesis/dissertation research to have the thesis/dissertation publicly available immediately following a successful defence. Valid reasons to delay publication/restrict access to a successfully defended thesis/dissertation may include:
- approved intellectual property contract between a research sponsor and the University that specifies a period of confidentiality;
- that public distribution of the thesis/dissertation would invalidate a patent application;
- that public distribution of the thesis/dissertation would invalidate a publication contract; and,
- that public distribution of the thesis/dissertation would pose a risk to the personal safety of the author.
Prior to submission of the final version of their thesis being accepted on the Electronic Thesis & Dissertation Tool (ETD), students may request to delay (or to extend a previously approved delay) publication of/restrict access to their thesis/dissertation for a maximum of three years. Requests for embargo must be made to the Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies, through the Request for a Delay of Publication (Embargo) on a Thesis or Dissertation form , prior to the submission of the final version of the thesis/dissertation. Requests will only be considered with the recommendation of the student’s supervisor and graduate program director. If approved, the body of the thesis/dissertation will be withheld from York University Libraries and Library and Archives Canada for the approved period. At the end of the approved period, the body of the thesis/dissertation will be released to York University Libraries and Library and Archives Canada via YorkSpace. To submit a request for an embargo/delay of publication, including extension requests, please do so using the Request for a Delay of Publication (Embargo) on a Thesis or Dissertation Form . Your request will be reviewed by the Faculty of Graduate Studies and a decision will be communicated to you by email. For more information on the Delay of Publication/Embargo Processes, please contact the Graduate Record & Enrolment Coordinator for your Faculty.
Students who wish to have personal copies of the thesis/dissertation bound must make their own arrangements.
How to Submit
Submitting your thesis/dissertation using York University's Electronic Theses and Dissertations (ETD) application is a quick and easy process.
The instructions below outline the step by step process of using the application. Please refer to the Thesis, Dissertation and Submission Guidelines below for details on the policies and process leading up to the point of final submission, including formatting and other requirements. To view the York University ETD collection, visit the Faculty of Graduate Studies section on YorkSpace .
You can access the ETD application from any computer with an internet connection. Recommended browsers include Google Chrome, Firefox, Safari or Opera.
Instructions for converting your thesis to a PDF file are available on the YorkSpace Resources Site .
An ETD record will be set up for you by a staff member in the Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies (FGS). FGS will need to receive the following before you will be able to access your record:
- Oral Examination Report (normally provided by the Dean’s representative on your Examining Committee as soon as possible following your defense);
- Revisions Approved Memorandum, if applicable (if your thesis/dissertation was approved with specified revisions). A blank form is usually provided to you by FGS prior to your defense. You will need to ensure it is completed and returned to FGS;
- Library and Archives Canada Theses Non–Exclusive License Form , signed and dated;
- Copies of copyright permissions, if applicable.
Once all of the above items have been received, you will receive an email from a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator letting you know that your ETD record has been created and inviting you to log in using your Passport York ID . Click on the link provided in the email to take you to etd.library.yorku.ca .
You’ll notice that there is a navigation bar across the top of the screen. You can click on any of the “tabs” to move back and forth through the process.
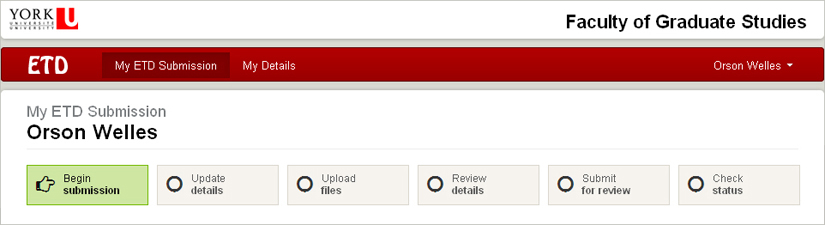
At the bottom right of each screen there are also arrows you can click on to move on to the next step (or move back).

You will not lose data by moving back and forth.
You can stop and save your work at any point in the process, and resume your submission simply by logging back in. To save your work, click on the navigation arrow at the bottom right of your screen. The information you have entered will be stored until you log back in.
As long as the status of your ETD record is “Open”, you can continue to make edits, updates and changes. Only once you have clicked on “I accept and send for review” on the “Submit for Review” tab will your record be closed.
If for some reason you need to request that your submission be re-opened (for example if you notice a mistake or forgot to add something), please email a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator .
If you’d like more information or instructions for any of the fields you are being asked to fill out, just click on the question mark icon next to the field.
If you still have questions, you may wish to contact:
- A Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies;
- Your Graduate Program Assistant.
Step by Step Instructions
On the first screen you will find welcome text, along with the title of your thesis/dissertation and some other information from your student record (such as your degree name and program).
To begin entering your details, click on the title of your thesis/dissertation. Alternatively, you can click on the “Update Details” button on the bottom right, or on the “Update Details” tab in the navigation bar.
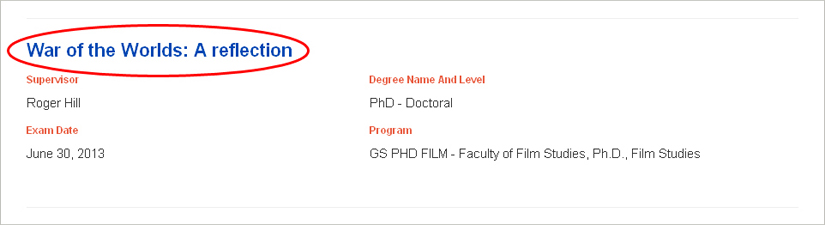
On the second screen, “Update Details”, you’ll notice that there are some fields already filled in, and others that you will need to complete.
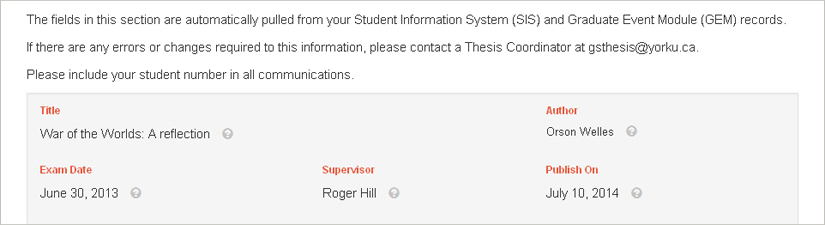
The fields that are already filled in are automatically pulled from your Student Information System (SIS) and Graduate Event Module (GEM) records. You cannot edit these fields yourself, so if you notice an error, please contact a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Faculty of Graduate Studies.
In the second section, you’ll find the following fields for you to complete:
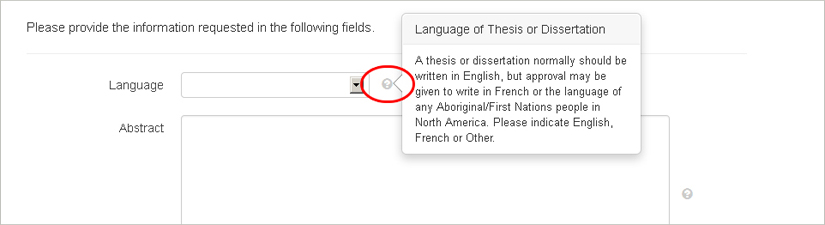
Language Click on the arrow to see the drop-down menu. You will be able to select English, French, or Other (a thesis or dissertation normally should be written in English, but approval may be given to write in French or the language of any Aboriginal/First Nations people in North America).
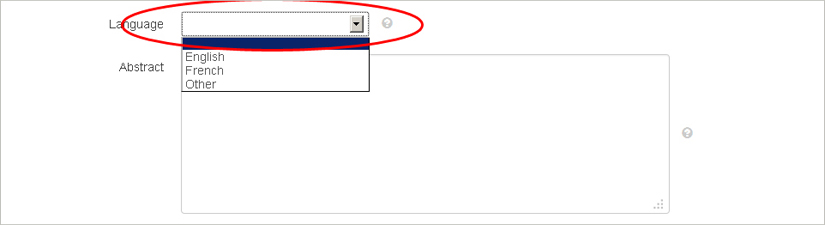
Abstract Copy and paste your abstract into this field (the abstract must be provided in English regardless of the language of your thesis or dissertation). Please note the maximum number of words allowed (Master’s thesis 150 words; doctoral dissertation 350 words).
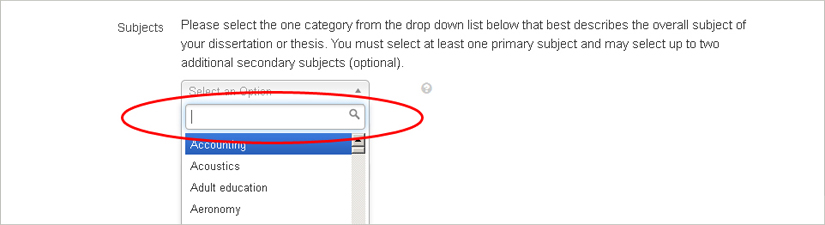
S ubjects Click on the arrow to see the drop-down menu. You must select at least one subject that best describes the overall subject of your thesis or dissertation. You have the option of selecting up to two additional secondary subjects from the other drop-down menu boxes.
Keywords Enter as many terms or search phrases as you like. Please use a comma to separate each keyword or string of keywords. Tip: the more terms you provide, the more likely it is that users will find your work in their searches.
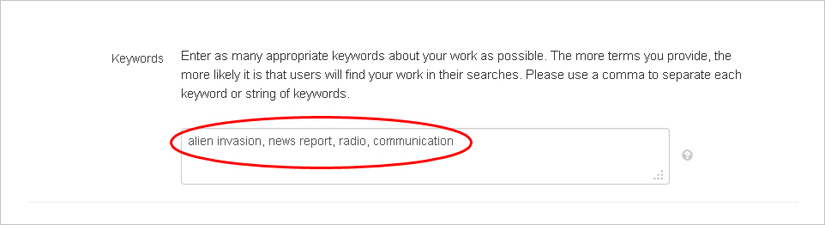
When you are finished updating your details, click “Save Details” on the bottom right to move to the next screen, or to save and return later to make further updates.
Uploading Files
Before uploading your files, you will need to save your thesis or dissertation as a PDF file (.pdf), which must be compatible with Adobe Acrobat version 5.0 or higher
This PDF document should contain the full body of your thesis/dissertation, including:
- title page;
- dedication (optional);
- acknowledgements (optional);
- table of contents;
- list of tables, figures and illustrations (if applicable);
- all chapters and written body of the thesis/dissertation;
- references or bibliography;
- all appendices.
You may upload only ONE PDF file.
Your document must be saved using the following naming convention:
Lastname_Firstname_MiddleInitial_yearofcopyright_PhDORMasters
Replace “Lastname” with your last name and “Firstname” with your first name. So, for example, if Jane Smith completed her PhD in 2014, she would save her documents as
Smith_Jane_E_2014_PhD.pdf
The “year of copyright” refers to the date that appears on the title page of your thesis/dissertation (this is the year you successfully defended).
To upload your file, simply click on the “upload primary file” button.

A box will open giving you the option to choose a file from your computer or a disk, USB key or other source.
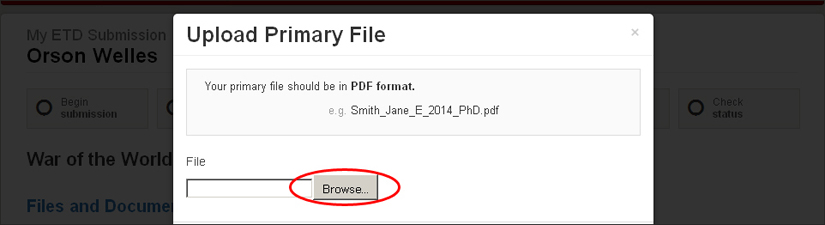
Once you have chosen the file, click on “upload.”
In addition to the PDF of your thesis or dissertation, you may have supplementary files to add. Supplementary files refer to items that are part of the approved, examined thesis/dissertation that cannot be included in the PDF, such as multi–media, sound, video or hypertext
A list of acceptable file formats includes:
- Documents: Portable Document Format (.pdf), Text (.txt), Hypertext Markup Language (.html, .htm), Open Document Format (.odt, .odp, .ods);
- Images: Portable Network Graphics format (.png), Tagged Image File format (.tif), JPEG (.jpg);
- Data: Comma–separated values (.csv) or other delimited text, Extensible Markup Language (.xml);
- Video: 8–10 bit uncompressed AVI (.avi);
- Audio: Free Lossless Audio Codec or WAVE (.flac or .wav).
If you wish to upload a type of file that you do not see on this list, please email Digital Initiatives @ York .
Keep in mind that a supplementary file is NOT an appendix. Regular appendices can be included in the PDF document of your thesis/dissertation.
To upload your file, simply click on the "upload supplementary files“ button.

A box will open giving you the option to choose a file from your computer or a disk, USB key or another source. You may upload as many files as necessary, but no single file can exceed 500 MB. If you have a file that exceeds this size, please contact a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator in the Faculty of Graduate Studies .
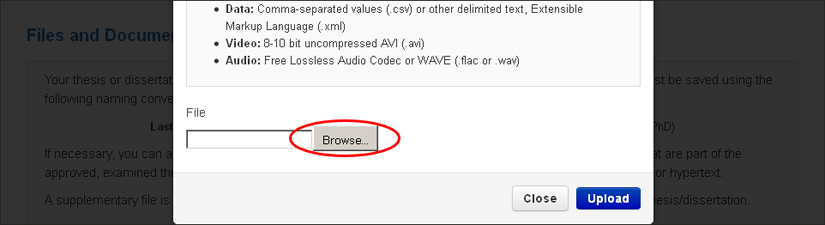
Once you have chosen the file, click on “upload.” To upload more than one file, simply click on the “upload supplementary files” button as many times as necessary.
When you have finished uploading all files, click “Review Details” on the bottom right to move to the next screen, or to save and return later to make further updates.
This is an opportunity for you to do a final confirmation that all of the details are accurate and your record is complete. Please make sure that all uploaded files are attached (they will be listed at the bottom of this screen).
As always, you can use the navigation bar at the top or arrows in the bottom right corner to go back and update any information.
When you are certain that all the information is correct and complete, click on “Submit for Review” at bottom right.
The final step in submitting your thesis or dissertation is agreeing to the York University Copyright License.
By clicking on “I Accept and Send for Review,” you are confirming that your thesis/dissertation is your original work, that your thesis/dissertation does not infringe on any rights of others and that you have the right to make the grant conferred by this copyright license. In addition, you are granting a license to York University to make copies, including electronically formatted copies, and/or distribute worldwide all or part of your thesis or dissertation, subject to the conditions outlined.
You retain copyright to your thesis/dissertation and may make it available on a personal website and pursue other sources of publication as well.
If you have questions or concerns about this license, please contact your supervisor or a Thesis Coordinator in the Faculty of Graduate Studies. You can then log back in to agree to the terms and make your submission once any queries you have are resolved.
Please carefully read this information and click on “I Accept and Send for Review” to send your thesis/dissertation to the Faculty of Graduate Studies.
Congratulations! You have completed your submission.
What Happens Next?
Once you send your thesis/dissertation for review, the status of your ETD record will change from “Open” to “Under Review” and you will not be able to make further changes. You will receive a confirmation email letting you know it is being reviewed.
If for some reason you realize you have made an error or forgotten to add something, you can email a Graduate Milestones and Progression Coordinator to request that your record be re–opened. Please remember to include your student ID number in all correspondence
After your submission has been reviewed by a Thesis Coordinator in FGS, you will receive an email notifying you of one of two outcomes:
- Your submission has been approved and will be deposited in YorkSpace upon conferral of your degree; or,
- Your submission has formatting or other errors and has been returned to you for modification.
If your submission is returned to you for modification, your ETD record will be reopened to enable you to make the required changes and resubmit. The required changes will be outlined in the email you receive from the Thesis Coordinator. If you are asked to make changes to your PDF thesis/dissertation document, simply replace the previously uploaded file with the updated one. Make sure you click on “I Accept and Send for Review” on the “Submit for Review” tab to resubmit your thesis/dissertation to FGS.
At any time you can log in to your ETD record to check on the status of your submission. Simply click on the “Check Status” tab in the navigation bar.
YorkSpace is York University’s Open Access Institutional Repository (IR). It is a platform that enables York community members to post, organize and preserve their research online in an institutional context. It showcases the scholarship of the York University community through the use of a special standards-based software platform that collects usage statistics and promotes visibility on the web.
Once your submission is approved by the Thesis Coordinator and all required forms received and fees paid, your thesis/dissertation will be deposited in YorkSpace at the time of conferral of your degree, according to the publication date listed on your ETD record (normally November 1, July 1 or March 1).
Once the thesis/dissertation is deposited in YorkSpace, it will be available for harvesting by Library and Archives Canada (LAC) Theses Portal , other Open Archives Initiative (OAI) metadata harvesters, and major search engines such as Google Scholar . You retain copyright to your thesis/dissertation and may make it available on a personal website and pursue other sources of publication as well.
Students who wish to have personal copies of their thesis/dissertation bound must make their own arrangements. Some options include:
- Wallaceburg Bookbinding
- Campus Photo and Printing, York Lanes
Please note that you may be required to make minor formatting adjustments to your document to prepare it for binding. For example, many binders will require that the top and left margins are at least 1.5 inches.
Graduate students who are members of CUPE 3903 (Unit 1) may submit reimbursement requests for thesis, dissertation or MRP production costs to the Office of the Dean, Faculty of Graduate Studies, using the Reimbursement of Thesis/Dissertation Production Costs Form .
- Theses Canada
- Theses and Dissertations in YorkSpace
Connect with FGS
Current students
- Studying at York
- Yorkshare VLE
- Library catalogue
- Semester dates
- Student home
- Manage your studies
- Programmes and modules
- Things to know this week
- Student news
- Student events
- New students' welcome
- Teaching hours
- Enrol or re-enrol
- Your student record
- Your timetable
- Change your plan
- Programme specifications
- Studying beyond your department
- Module catalogue
- University study spaces
- Student Visa holders
- Study skills
- Assessment and examination
- Academic progress issues
Support and advice
Health and wellbeing, work, volunteering and career planning, study and work abroad, accommodation, it and online services, student life in york, if things go wrong.
- Student Centre
History Dissertation - HIS00048H
« Back to module search
Department : History Module co-ordinator : Dr. Mark Roodhouse Credit value : 40 credits Credit level : H Academic year of delivery : 2024-25 See module specification for other years: 2021-22 2022-23 2023-24
Module summary
This module gives students the chance to work as active and independent scholars. Students design their own research project during the third year, research the primary materials needed, organise and reflect on the material they have gathered, plan the structure of their arguments and interpretations, draft a chapter and outline to submit for feedback, and then write and submit their 8,000-word dissertation. This work will spread across the whole academic year. Throughout they have the support of a member of academic staff as their dissertation advisor. Full details of tasks to be completed, and the relevant deadlines, are provided on the Dissertation VLE. This guidance also provides much advice and information to help and support students as they work on their dissertations.
Module will run
Module aims.
The aims of this module are:
- To enable students to undertake an independently chosen, designed and managed project;
- To provide the opportunity to work extensively with original historical material;
- To allow students to explore a chosen aspect of the past at length; and
- To engage with opinions and debates around a specific topic using original research.
Module learning outcomes
Students who complete this module successfully will:
- Have gained experience of designing and managing a large scale project to completion;
- Have gained experience of exploring and explaining a specific research topic at length;
- Have acquired skills and understanding from extended research into original material; and
- Have learned to situate their specific research results among the debates and views of others.
Module content
In semester two of year two, following a lecture outlining the dissertation module, students are encouraged to discuss ideas for the dissertation with academic staff. Students then submit a proposal in week 11, which will be used to allocate academic advisors for the start of year three. Students are undertaking an independently researched project and not a taught module. They will continue, however, to have support, advice, and feedback from their dissertation advisor as they work to produce their dissertation. They will have meetings and dissertation workshops with their advisor in semester one focused on bibliography, research questions and their project as a whole. In addition in semester one there are lectures on dissertation skills, sources and project design. In semester two, after submitting formative draft work, students will receive written feedback and a one-to-one tutorial with their advisor.
Special assessment rules
Additional assessment information.
Students have the opportunity to submit up to 2,500 words of draft dissertation work and a plan for completion in week 1 of semester two. The 8,000-word dissertation, written and presented according to our requirements and conventions (set out on the Dissertation VLE), is then to be submitted in week 1 of the assessment period for semester two.
Reassessment
Module feedback.
Students will receive detailed feedback on the draft work submitted at the start of semester two as well as timetabled sessions with their advisor. Throughout they are encouraged to consult with their advisor and other academic staff in student hours. For more information, see the Statement of Assessment .
Indicative reading
There are no key texts for this module.
- Student visa holders
- Develop your skills
- University card
- Student Hub
- Student Connect
- International students
- Student Buddying Scheme
- Faith and religion
- Equality and diversity
- Self-certification of illness
- Help and support
- In crisis now
- Tips for wellbeing
- Workshops and groups
- Exploring your options
- Finding jobs
- Get skills and experience
York Futures
- Campus accommodation
- Private sector accommodation
- Paying the University
- Tuition fees
- Managing your money
- Assistance funding
- Bursaries and scholarships
- Student loans
- Where do your fees go?
© University of York Legal statements | Privacy | Cookies | Accessibility

- Subject Guides

10 Top Tips for a Tip Top Undergraduate Dissertation: a Practical Guide
Manage your time effectively
Specify a clear research question
Understand your research methodology
Construct a comprehensive search strategy
Engage critically with the literature
Leave no stone unturned in your search for resources
Think carefully about how to structure your argument
Write with an analytical style
Make the most of Word
Seek help when you need it
As you start to move towards writing your dissertation, think carefully about how to structure your argument. Dissertations usually follow a fairly set structure, but be sure to check whether your department expects you to use specific sections.

Using literature throughout your dissertation

We've explored already the importance of literature in your dissertation, but remember that it's not confined just to a literature review section. You'll also need to use literature in your methods section to justify your approach, and likely later in your discussion and conclusion to add some context to your findings.
The structure of your dissertation will depend very much on the expectations set by your department. The following gives an example structure for empirical research:
Introduction - where you set out the aims and objectives of your dissertation, and where you might explain why you have chosen your specific topic.
Literature review - where you present a critical overview of the extent and content of the current literature which informs your topic.
Methodology - where you present your chosen approach to your research, drawing on research methods literature to justify your choices.
Findings/results - where you present your data from your research, at this stage without any commentary or analysis.
Discussion - where you analyse the results of your research and draw parallels with the earlier analysis in your literature review. You might decide to present your discussion thematically.
Conclusion/recommendations - where you summarise your research and the extent to which you’ve met the aims and objectives of your introduction.
Appendices (where appropriate)
Headings and sub-headings

We’ve said already that the dissertation is much longer than a normal essay, and the sections listed above will give you a sense of that. It’s perfectly acceptable (and often encouraged) to use headings for each section in a dissertation, as this helps to break up the text and to make it clear for the reader how everything fits together. You can use sub-headings too, but try not to include too much subdivision; it can get a bit confusing, especially if you’re numbering your headings.
As well as maintaining the overall structure, remember that each individual section should have a structure and logic of its own. You might like to think of each section as a mini-essay; each should make it clear what is included in that section, and conclude that content in some way before moving on to the next section.
First out of the gates

Many people find the introduction and conclusion sections the most difficult to write. The introduction should concisely explain what you’re trying to achieve in the dissertation, including any limitations which you’re deliberately imposing on the topic to keep it within scope of your word count. Although the introduction comes first in your actual dissertation, you don’t have to start there in your writing. You might find it easier to write a brief, draft introduction, then come back to expand on it when you have written more of the rest of the dissertation; you’ll then have a better understanding of what you’ve written as a whole.
The University of Manchester's Academic Phrasebank has some useful advise about how to write your introduction .
Finish with a bang

At the other end of the process is your conclusion, which should be a summary of what you have found or achieved in the dissertation. How far have you been able to achieve the aims and objectives which you set out in your introduction? How overall have you answered your central research question(s)? You shouldn’t introduce any new material in your conclusion, as that might undermine your research so far and confuse the reader. You may choose to provide some recommendations, either for practical implications of your research or for further research to take place. Try to avoid the latter unless you have something specific to recommend; noting that ‘more research is needed’ doesn’t necessarily add anything, and is overused in dissertations (to say the least!). You will almost certainly write your conclusion last, but don’t forget about it until the end; why not keep notes as you go of useful points to include when it comes to writing the conclusion?
The Academic Phrasebank has some good tips of what you should aim to cover in your conclusion .
References and appendices

Your references and any appendices are not usually included in the word count of your dissertation (although in-text citations are included). The reference list would usually just include those items which you have directly cited in the dissertation and not other items which you have read for background information, but your department will give you specific guidance on this. Remember to follow the format and presentation of the referencing style chosen by your department. Examples in all styles are available on the University’s Guide to Referencing Styles . As with your conclusion, why not write the reference list as you go? It’s most definitely not a fun job to have to write at the end! Explore tip 9 for some advice on using reference management software.
You won't necessarily need to include appendices, but they might be a good place to note any supplementary information about the dissertation. For example, if you’ve undertaken interviews you could include a copy of the consent form and interview questions as appendices. Remember, however, that you shouldn’t attempt to hide in the appendices anything which belongs in the main body of the dissertation.
More advice
Our Skills Guide on writing structure gives further guidance. Although it’s written for smaller essays, you will find some useful tips about what to include for specific sections of your dissertation.
- << Previous: 6
- Next: 8 >>
- Last Updated: Mar 18, 2024 2:01 PM
- URL: https://subjectguides.york.ac.uk/dissertation
Welcome to White Rose eTheses Online
White rose etheses online.
Welcome to White Rose eTheses Online, a shared repository of electronic theses from the University of Leeds, the University of Sheffield and the University of York.

Student from the University of Leeds, Sheffield or York? Need to upload your thesis? Start by creating an account , or login to your account
If you are unsure if this is the right place for you, check the FAQs .
Recent additions for Leeds , Sheffield , York or all recent additions .
What is White Rose eTheses Online?
This repository gives access to theses awarded by the Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York. The available repository content can be accessed for free, without the need to log on or create an account, as per the instructions of the depositing author. We also make the content available through aggregator sites via harvesting mechanisms.
- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Dissertations & Theses: Guide to Research
Finding UB Dissertations and Theses
Dissertations & theses: guide to research: finding ub dissertations and theses.
- Identifying Dissertations and Theses
- Obtaining Dissertations and Theses
- Information for UB Theses Authors
To borrow a UB dissertation or thesis from our collection, do an author or title search in the UB Libraries Catalog to get a library location and call number.
By Department To find or browse dissertations or theses by department conduct a keyword search in the Library Catalog , search by department name You may also choose to include the year to limit your search.
Example Search:
Dissertation (in any field)
American Studies (in any field)
Thesis (in any field)
Media Study (in any field)
Dissertations & Theses @ SUNY Buffalo - this database provides title, author, and subject access to University at Buffalo dissertations submitted to ProQuest's Dissertations & Theses database. You can search by department as well.
- << Previous: Identifying Dissertations and Theses
- Next: Obtaining Dissertations and Theses >>
- Research Guides
- CUNY Graduate Center's Mina Rees Library
Dissertations and Theses
- Find CUNY Dissertations
- About the Dissertation Office
- Graduation Dates
- Deposit Procedure
- Format Requirements
- Survey of Earned Doctorates (SED)
- Master's Exit Survey
- Citation Styles
- Digital Dissertations
Graduate Center Dissertations
- Graduate Center Dissertations and Theses in Academic Works, 2014-present As of 2014, all Graduate Center dissertations, theses, and capstone projects are posted to CUNY Academic Works. Some are immediately available to read and download, and some become available after an embargo period set by the author.
- ProQuest Dissertation Express For anyone without a current GC network userid/pwd, search for CUNY or non-CUNY dissertations here. Order copies in print or PDF formats.
Graduate Center Master's Theses
- Master's Theses in CUNY Academic Works : As of 2014, all Graduate Center master's theses appear in the CUNY Academic Works repository. Many are open access, but some are embargoed and will not become available until a future date.
- Bound copies of CUNY master's theses and capstone projects are shelved on the library's 2nd floor
Bound Dissertation Colors by Program
Graduate Center print dissertations are shelved by year, alphabetically by author. To facilitate browsing by program, bindings were color coded by program (see chart below). In November 2015 the library ceased archiving print dissertations.
Microfilm copies of PhD dissertations from all the programs above are housed in the GC Library.
*Note that print dissertations from some programs are held at libraries located on other CUNY campuses: Business (Baruch), Criminal Justice (John Jay), Engineering (City College).
- << Previous: Find Dissertations
- Next: Alumni >>
- Last Updated: Apr 1, 2024 1:08 PM
- URL: https://libguides.gc.cuny.edu/dissertations
Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Resources Everyone Should Know
- Background & Reference
- Article Searching Using Databases
- Bibliographic Tools
- Conference Proceedings etc.
- Dissertations & Theses
- Professional Organizations, News & Jobs
Dissertations & Theses as Research Sources
Repositories of dissertations and theses submitted by PhD and masters students are good places to survey pre-publication research. Dissertations are usually very narrowly-focused thorough and in-depth explorations of a topic. Dissertations and theses are also excellent bibliography-mining territory. Because submitters of Masters and PhD theses and dissertations are required to conduct a comprehensive survey of the existing literature relevant to their question, these documents often contain useful literature reviews and contain meticulously compiled bibliographies.
Searching Dissertations & Theses
Dissertations and theses in Electrical and Electronic Engineering can be searched across institutions using ProQuest Dissertations and Theses.
- Dissertations & Theses Global This link opens in a new window Dissertations and Theses Global contains indexes, dissertations and some theses. Full-text is available for many dissertations and theses, including those from NYU.
Dissertations & Theses in Institutional Repositories
Many academic institutions host their own repositories of faculty and student research. In addition to dissertations and theses, institutional repositories often contain technical reports , datasets , conference papers and other files associated with conference presentations . The following is a list of some of the more robust institutional Computer Science repositories.
Hundreds of PhD theses and other technical reports from Cambridge University’s Computer Laboratory. The repository contains current documents and extends back to the 1970s.
- Carnegie Mellon Research Showcase Carnegie Mellon’s institutional repository contains conference proceedings, working papers and technical reports, and theses in four separate collections relevant to Electrical and Electronic Engineering. The two main relevant collections are: the “Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering” and the “Robotics Institute” Of the two the “Robotics Institute” is more current.
Over 300 documents related to Electrical Engineering, including Columbia dissertations, articles, datasets, and technical reports.
- << Previous: Conference Proceedings etc.
- Next: Professional Organizations, News & Jobs >>
- Last Updated: Mar 13, 2024 4:18 PM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/electricaleng
CUNY Academic Works
Home > Dissertations, Theses & Capstones Projects by Program
Dissertations, Theses, and Capstone Projects by Program
All Graduate Center dissertations, theses, and capstone projects since 2014 are posted to Academic Works. Some are immediately available to read and download, and some become available after an embargo period set by the author. In addition, all pre-2014 dissertations and doctoral capstone projects have been digitized and are available to the CUNY community via our Retrospective Dissertations, 1965-2013 database (CUNY Login required). (Pre-2014 master’s theses have not yet been digitized and are only available in print.)
Dissertations, theses, and capstone projects are listed by program below. To browse by year, go to the top-level Dissertations, Theses, and Capstone Projects page.
Are you an alum? Do you want to make your dissertation or capstone project freely available to the public by adding it to CUNY Academic Works? Contact the GC Dissertation Office at [email protected].
Browse the Dissertations, Theses, and Capstone Projects by Program Collections:
Anthropology Dissertations
Art History Dissertations
Audiology Capstone Projects
Biochemistry Dissertations
Biography and Memoir Master’s Theses
Biology Dissertations
Business Dissertations
Chemistry Dissertations
Classics Dissertations
Classics Master's Theses
Cognitive Neuroscience Master's Theses
Comparative Literature Dissertations
Comparative Literature Master's Theses
Computer Science Dissertations
Criminal Justice Dissertations
Data Analysis & Visualization Master’s Theses and Capstone Projects
Digital Dissertations and Capstone Projects
Digital Humanities Master’s Theses and Capstone Projects
Earth and Environmental Sciences Dissertations
Economics Dissertations
Educational Psychology Dissertations
Engineering Dissertations
English Dissertations
French Dissertations
History Dissertations
International Migration Studies Master's Capstone Projects
Latin American, Iberian and Latino Cultures Dissertations
Liberal Studies Master's Theses and Capstones
Linguistics Dissertations
Linguistics Master's Theses
Mathematics Dissertations
Middle Eastern Studies Master's Theses
Music Dissertations
Nanoscience Master’s Theses
Nursing Dissertations
Philosophy Dissertations
Physical Therapy Capstone Projects
Physics Dissertations
Political Science Dissertations
Political Science Master's Theses
Psychology Dissertations
Public Health Dissertations
Social Welfare Dissertations
Sociology Dissertations
Speech-Language-Hearing Sciences Dissertations
Theatre and Performance Dissertations
Urban Education Dissertations
Women's and Gender Studies Master's Theses
- Colleges, Schools, Centers
- Disciplines
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
Author Corner
- The Graduate Center
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
Department of Music Columbia University in the City of New York
Jessie cox defends dissertation.

The Department warmly congratulates Jessie Cox, who successfully defended his DMA dissertation in Music Composition, titled "Listening with the Unknown: Unforming the World with Slave Ears" on March 29, 2024. Jessie's dissertation was advised by Professor George Lewis , and his committee included Professors Seth Cluett , Georg Haas , Brent Hayes Edwards , and Charles Uzor .
Congratulations, Jessie!
Search form
info This is a space for the teal alert bar.
notifications This is a space for the yellow alert bar.

SCoE: Ed.D. Library Resources
- Finding Articles
- Accessing E-Books
- Discovering Online Resources
- Locating Videos, Statistics, and More
- Dissertation Research
- Sample Dissertations on Organizational Innovation
- Understanding Research This link opens in a new window
- Using Citations This link opens in a new window
Finding Disserations
Use the two databases below to search for disserations on your topic:
Content: Global student dissertations and literature reviews.
Purpose: Use for foundational research, to locate test instruments and data, and more.
Special Features: Search by advisor (chair), degree, degree level, or department. Includes a read-aloud feature
The ProQuest Dissertations & Theses database (PQDT) is the world's most comprehensive collection of dissertations and theses. It is the database of record for graduate research, with over 2.3 million dissertations and theses included from around the world.
Content: National University & NCU student dissertations and literature reviews.
Special Features: Search by advisor (chair), degree, degree level, or department. Includes a read-aloud feature.
- << Previous: Locating Videos, Statistics, and More
- Next: Sample Dissertations on Organizational Innovation >>
- Last Updated: Mar 29, 2024 10:55 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/edd

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Consulting a thesis/dissertation in the Library. Our physical theses and dissertations are kept in a secure store. To consult them you will need to request access via Borthwick Institute for Archives by emailing borthwick-institute @york.ac.uk with the details of the thesis and a preferred appointment date. Note: theses and dissertations can ...
Submitting Your YorkU Thesis or Dissertation The Faculty of Graduate Studies manages the submissions process for Theses and Dissertations. Learn more about the process by visiting their pages: Electronic Theses and Dissertations Collection As of September 2013, York University Electronic Theses and Dissertations are hosted in the YorkSpace repository. Frequently Asked Questions Found a typo […]
Types of thesis. There are two main types of thesis. A monograph or traditional thesis: a unified, single author document comprising a number of chapters with an introduction and conclusion.; A journal-style thesis: a document that incorporates one or more chapters that are in a format suitable for publication in a peer-reviewed title alongside a supporting commentary.
Theses and dissertations are extended scholarly essays that incorporate original research on a specific topic. They are usually written as part of the requirements for a graduate degree (e.g. MA or PhD). Finding a York University thesis or dissertation Most doctoral dissertations and Master's theses completed at York University are available through the Libraries. Law […]
Submitting your thesis/dissertation using York University's Electronic Theses and Dissertations (ETD) application is a quick and easy process. The instructions below outline the step by step process of using the application. Please refer to the Thesis, Dissertation and Submission Guidelines below for details on the policies and process leading ...
There are lots of other sources of help across your department and the University, including: Your department might provide timetabled classes to support the Dissertation module. You should attend these to get an overview of the process and specific support for the research and writing of your dissertation.
Remember that, as well as the guidance in these tips, there are lots of books in the University Library about writing dissertations. Many of these are focused on specific subjects or sections of the dissertation, such as the literature review. Search YorSearch to see what is available to suit your topic, or try the following examples. Note that ...
A dissertation is usually a long-term project, often across a full academic year, to produce a long-form piece of writing; think of it a little like an extended, structured essay. You might carry out your own original research, or base your dissertation on existing research literature (we'll explore more about the differences later).
History Dissertation - HIS00048H « Back to module search. Department: History; Module co-ordinator: Dr. Mark Roodhouse; Credit value: 40 credits; Credit level: H; Academic year of delivery: 2024-25 . See module specification for other years: 2021-22 2022-23 2023-24 Module summary
The University of Manchester's Academic Phrasebank has some useful advise about how to write your introduction. Finish with a bang At the other end of the process is your conclusion, which should be a summary of what you have found or achieved in the dissertation.
Welcome to White Rose eTheses Online, a shared repository of electronic theses from the University of Leeds, the University of Sheffield and the University of York. Please note: the teams that support the repositories will be out of the office for the Easter break. The closure periods differ between the three sites, and some services will be ...
Based in Chicago, the Center for Research Libraries was founded in 1948 by a consortium of Midwestern universities seeking to pool lesser-used resources. The collection holds over 800,000 dissertations from 90+ universities in Germany (66%), Netherlands (2%), France (16%), Switzerland, Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and the UK; also from Latin America, South America, and Africa.
NYU Dissertations Online. All dissertations completed at NYU are indexed in the online database Dissertations and Theses Global. Users who wish to access NYU dissertations, especially dissertations completed since 1997, would be best served by searching this database. Many (but not all) dissertations will be available in full-text.
To borrow a UB dissertation or thesis from our collection, do an author or title search in the UB Libraries Catalog to get a library location and call number. By Department ... University at Buffalo Libraries 433 Capen Hall Buffalo, NY 14260-1625 716-645-2965. Contact Us; Directions;
Political Power at the City University of New York: A Case Study of Meritocracy vs. Democracy - Open Admissions and the Imposition of Tuition, 1969-1976, Douglas A. Medina PDF Integration of Field- and Space-Based Observations Toward Assessing Drivers of Biogeochemical Variability Across Vulnerable Coastal Ecosystems , Alana B. Menendez
Current CUNY students, faculty and staff can log in with their CUNYfirst credentials to access GC dissertations and capstones from 1965-2013. (Pre-2014 master's theses are available only in print). ... Dissertations & Theses @ City University of New York Graduate Center This link opens in a new window. This link opens in a new window;
Dissertations and theses are also excellent bibliography-mining territory. Because submitters of Masters and PhD theses and dissertations are required to conduct a comprehensive survey of the existing literature relevant to their question, these documents often contain useful literature reviews and contain meticulously compiled bibliographies.
In addition, all pre-2014 dissertations and doctoral capstone projects have been digitized and are available to the CUNY community via our Retrospective Dissertations, 1965-2013 database (CUNY Login required). (Pre-2014 master's theses have not yet been digitized and are only available in print.)
While key, completing a thesis is the least important aspect of your Ph.D., writes María P. Ángel, and you should also focus on three other areas. In the first quarter of my Ph.D., I enrolled in indoor cycling classes at the university gym. One evening, the instructor delivered a motivational phrase that, though meant to encourage us to break out in a sweat, has shaped my Ph.D. journey to ...
Jessie Cox Defends Dissertation. The Department warmly congratulates Jessie Cox, who successfully defended his DMA dissertation in Music Composition, titled "Listening with the Unknown: Unforming the World with Slave Ears" on March 29, 2024. Jessie's dissertation was advised by Professor George Lewis, and his committee included Professors Seth ...
The ProQuest Dissertations & Theses database (PQDT) is the world's most comprehensive collection of dissertations and theses. It is the database of record for graduate research, with over 2.3 million dissertations and theses included from around the world. Content: National University & NCU student dissertations and literature reviews.