

Essay Writing Skills & Techniques
Many of our articles and guides frequently refer to essay writing, so to simplify this, we have collated our best essay writing skills and techniques into one section to assist students and teachers in learning the fundamentals of writing a wide variety of essays, learning the essential elements of all essays and even provide some activities and resource to help you along the way.
WHAT IS AN ESSAY?
Defining an essay is challenging as it crosses many genres and elements of writing. Still, in simple terms, an essay is a piece of writing allowing the author to state an argument, justify their position on a topic, express their emotions, and interpret information, facts and procedures.
The term essay comes from the Latin word ‘exagium’, meaning the presentation of a case or, as we may more commonly say “stating your case.” When writing a high-quality essay, it should be considered your definitive opportunity to have your say on something of meaning and purpose to you so make every word count by following our step-by-step guides below.
ESSAY WRITING SKILLS

How to Start an Essay with Strong Hooks and Leads

Top 5 Essay Writing Tips

How to write a perfect 5 Paragraph Essay

Essay Writing: A complete guide for students and teachers

The Writing Process

How to write a Conclusion

Top Research strategies for Students

Perfect Paragraph Writing: The Ultimate Guide

Teaching Proofreading and Editing Skills

Punctuation rules for students and teachers: A complete guide

Teaching Fact and Opinion

Point of view in literacy: A guide for students and teachers
Sentence Structure: A Complete Guide (With Examples & Tasks)

How to Summarize an Article

HOW TO WRITE A HYPOTHESIS
Guides for specific essay types.

How To Write a My Best Friend Essay

How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay

How to Write Excellent Expository Essays

How to write an Argumentative Essay

How to Write Perfect Persuasive Essays in 5 Simple Steps

How to Write a Novel Study: A Complete Guide for Students & Teachers

How to Write a Biography

How to Write a Book Review: The Ultimate Guide

How to Write an Excellent Explanation Text

How to Write a Recount Text (And Improve your Writing Skills)

How to write a text response

Narrative Writing: A Complete Guide for Teachers and Students

How to write excellent Procedural Texts

How to Write an Excellent Information Report

How to Write a Historical Recount Text

Personal Narrative Writing Guide
Teaching resources and lessons to support essay writing.

Top 25 Essay Topics for 2024

Glossary of literary terms

7 Evergreen Writing Activities for Elementary Students

The Author’s Purpose for students and teachers

The Ultimate Guide to Opinion Writing for Students and Teachers

Top 7 High School Writing Skills for Students and Teachers

5 Top Persuasive Writing Lesson Plans for Students and Teachers

Explanation Texts: Top 5 Writing tips for younger students

How to Write a Winning Debate Speech

23 Persuasive writing Topics for High School students
Don’t forget that we have loads of essay writing prompts and loads of essay resources and tools you can download today and use with your students.

15 Best Writing Strategies With Examples
When you’re a writer , you need to know the best strategies to get your reader’s attention and hold onto it.
The goal is to get them hooked on your content, so they’ll want to read more.
Only then can you cultivate a relationship that serves you both.
So, how do you do that (without actually hypnotizing them)?
You learn different writing strategies, applied to advantage by the pros, and work on making them your own.
The first question to answer is, “What is a writing strategy?”
What Are the Different Types of Writing Strategies?
1. start with a strong hook. , 2. give your opening paragraph a strong sense of direction. , 3. be authentic in every sentence. , 4. create a reader avatar. , 5. create an outline. , 6. have fun with it. , 7. start a dialogue with your reader. , 8. get time on your side. , 9. prioritize clarity. , 10. break it up with visuals. , 11. put your reader to the test., 12. dazzle them with surprising facts. , 13. add interesting quotes from authorities in the field. , 14. ask questions to get your readers thinking , 15. tell your reader a story. , which writing strategies will you use.
A strategy is a general plan — or set of plans — you make to achieve a goal.
So, a writing strategy involves tactics you use to ensure your writing meets the goals you’ve set for it.
Your number one goal is to capture and hold onto your reader’s interest. Your related goals will depend on the overall purpose of your writing:
- To sell something (and make money)
- To motivate your reader to do something
- To evoke an emotional response (pathos, anger, levity, etc.)
While the reason for your writing goal can vary, the goal itself does not. And the sooner you learn how to put the following 15 writing strategies into practice, the sooner your audience will grow.
15 Writing Strategies with Examples
No doubt, you’ve already become familiar with some of these time-tested examples of writing strategies. It’s what you don’t (yet) know that can hold you back and limit your influence.
That’s about to change.
Your first sentence should hook your reader and make them curious enough to read the second sentence, which should lead them irresistibly to the third, and so on.
That first sentence should grab hold of their interest and get them thinking, “I need to know what will come next.” Your entire opening hook doesn’t have to consist of one sentence, but a few sentences at most should suffice to get under your reader’s skin.
Strong hooks can include any of the following:
- Probing or rhetorical questions
- Anecdotes
- Bold claims
Example:
“Did you know every year the amount of garbage we toss into the ocean is three times the weight of fish caught?” (statistic)
Your first paragraph should clearly communicate the direction of your piece. And it should give the reader a reason to care about it. They should want to know more and feel compelled to see what you’ll reveal. Give them a reason to feel invested.
Otherwise, they might bookmark your page to “save it for later,” but we all know what that usually means. It’s the internet version of walking away.
“As a lifelong crabber (that is, one who catches crabs, not a chronic complainer), I can tell you that anyone who has patience and a great love for the river is qualified to join the ranks of crabbers. However, if you want your first crabbing experience to be a successful one, you must come prepared.”
– (Mary Zeigler, “How to Catch River Crabs” )
Come as you are. This is not a place to show off or pretend to be someone else. Try to trick your reader, and they’ll most likely leave and never return. So, ix-nay on the bait and switch. Put yourself in the reader’s shoes and give them what you know they would want.
Be genuine, and show that you care as much about their time as you do about yours.
“I haven’t wanted to call myself a functional alcoholic . For just a second, the word “functional” makes it easier to accept the word that comes after it.
“Then the reality hits: I’m not as functional as I’d like to think. And being an alcoholic means having to give up alcohol….”
Design an ideal reader based on what you know — including demographic info (married/single, age range, interests, culture, politics, geographical area). Then write as if addressing a respected friend.
Don’t assume your reader can’t figure stuff out, but don’t use ten-dollar words when one-dollar words will do. Write the way you would talk in a friendly conversation.
Ideal reader Alexis is a health-conscious socialite in her mid-twenties. Her interests include public relations, fashion, and social media (mainly Instagram). She reads to stay well-informed about things that matter to her. She’s visually oriented. Her dream is to work in New York as a successful public relations professional.
The easiest way to make sure you make all your points in a logical, easy-to-follow manner is to start with an outline, breaking down your work into smaller, more focused sections. Use your outline to plan your subheadings and brainstorm content ideas.
As you add content, you can connect each thought, making every sentence earn its place and respect its neighbors to ensure each thought flows effortlessly to the next.
I. Why soy candles are healthier than paraffin.
- All natural (no toxic chemicals)
- Supports U.S. soy farmers
- Cleaner, cooler burn with less soot
II. 5 Best Sources of Ethically-Made Soy Candles
III. 3 Candle-Making Charities That Support Women
If you’re not all that interested in what you’re writing, your reader will pick up on that. Boredom is contagious. The good news? The opposite is even more so. Find something to love about what you’re writing, and your reader will feel your excitement and lean in.
The more fun you have with the writing, the more your audience will enjoy reading it.
Examples:
- Include a fun, illustrative bit of dialogue.
- Paint a (word) picture your reader will want to be a part of.
- Lead with the thing that excites you (an interesting bit of news, etc.)
More Related Articles:
How To Write A Profitable, Life-Changing Self-Help Book
9 Of The Most Useful Thesauruses For Writers
11 Creative Writing Exercises To Awaken Your Inner Author
Remember that bit about seeing your reader as a respected friend? The more you see your article or blog post as a friendly conversation with your reader, the easier (and more fun) it will be to write, and the more invested you’ll feel in being as helpful as possible.
Imagine a friendly, animated dialogue with your ideal reader and write as you hear the words in your head.
Example:
“I’m glad you’re here. I have so many questions! First, I have to ask, how do you feel about zombie fiction? I have a theory, and you can tell me if I’m wrong.
“For starters, I’ll make the bold guess that if you’re reading this blog, you’re not into the gory, graphic zombie violence some shows glory in. In fact, I’m willing to bet you’re more of an I Zombie fan. Because you’re not an all-or-nothing thinker.
“Here’s where I’m going with this…”
It can only benefit you to address timely issues that matter to your reader. If you’re writing about a subject that’s dominating the headlines, put your own creative spin on it to make it stand out. What can you bring to the subject that few or no one else can?
Make the subject more personal to your reader, and your content will be timeless.
“It’s happened! The results of the 2020 election are finally in, and people around the world (not to mention over half the U.S. population) are celebrating, crying tears of relief, and dancing in the streets for joy.
“So, what comes next? Specifically, what comes next for you? ”
Know your message and express it with clarity, simplicity, and elegance. Every thought should be organic, and every sentence’s meaning should be unmistakable. Confuse your reader, and they’re far more likely to stop reading and move on.
Don’t make them work to decipher what you’re trying to say. It’s not their job.
Examples of strategies for writing with clarity:
- Know your message, and write with intention.
- Know your audience and speak their language.
- Define your (unfamiliar) terms.
- Use your punctuation wisely (especially commas).
- Use strong , active, and carefully-chosen verbs.
If all you’re giving your reader is a long succession of paragraphs with some subheads thrown in, consider adding some relevant visuals — images, graphs, infographics, tables, diagrams, etc. Give their brain a brief but meaningful eye-candy break.
By varying the delivery of helpful information, you hit “refresh” on their attention and keep them curious.
Examples of effective visuals:
- Infographics or diagrams to visually illustrate your points
- Images that set the mood and make your content more relatable
- Graphs and tables to show organized and relevant data.
Include an interesting quiz/test for your reader to take, with a result they can share. Give them a chance to test their knowledge while they learn something new. Quizzes that give them a result they can feel good about and make your content more memorable.
Challenge your reader with questions that make them think, and they’re more likely to respect and remember you.
Examples of quiz ideas:
“How compatible are you and your partner?”
“How much do you know about climate change?”
“What crystals are best for your personality?”
Throw in some juicy facts to make your readers think, “Wow! I didn’t know that.” Keep them short and easy to remember and make sure they add value to your whole piece. It should feel organic — not like it came out of nowhere.
Your reader shouldn’t have to wonder if they accidentally clicked on a different link.
- Surprising statistics about bullying to reconsider “zero-tolerance” policies.
- The truth about “German” chocolate cake in a post on a beloved family recipe.
- Daniel Radcliffe’s allergy to his Harry Potter glasses in a post on unusual allergies.
Quotes from well-known authorities can add credibility to your piece if it bolsters one of the points you’re making. Depending on your quote choice, It can also add a touch of humor or pathos to draw your reader in and encourage a stronger connection.
A short, powerful quote can make your work more memorable by association.
- Shocking or funny quotes from famous authors in a post on the creative process.
- Quotes from famous fictional sleuths in a post about cozy mysteries.
- Quotes from disgruntled politicians in a post about running for office.
Another way to make your reader feel more invested in what they’re reading is to ask them questions about something that matters to them.
Get them thinking about the answer, and they’ll be more likely to feel a need to answer it or find the answer in what you’ve written. And if your answer satisfies them, or if their own answer leads to other meaningful discoveries, they’re likely to come back for more.
- Questions about your reader’s writing process in a post on the same.
- Questions on your reader’s biggest fears in a post about anxiety
- Questions on favorite scents and related memories in a post about candles.
Everyone loves a good story . Introduce a compelling story early on in your post (or chapter), and your reader is much more likely to keep reading. Your story should closely relate to the rest of your content, so it can communicate useful information while it entertains your audience. Keep it short, relevant, and memorable.
- A brief fable that teaches a moral lesson
- A brief story from your past that illustrates a point you’re trying to make
- A short, funny story that leads to a surprising revelation
Now that you’re more familiar with the 15 best writing strategies, how will this change the way you write from now on? What strategies will you implement in your next project?
The best part about using these strategies is their potential for making the writing itself more enjoyable and fulfilling for you — as well as more engaging for your reader.
May your skill and influence grow as you put these strategies to work.

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Academic Skills
- Reading, writing and referencing
Writing a great essay
This resource covers key considerations when writing an essay.
While reading a student’s essay, markers will ask themselves questions such as:
- Does this essay directly address the set task?
- Does it present a strong, supported position?
- Does it use relevant sources appropriately?
- Is the expression clear, and the style appropriate?
- Is the essay organised coherently? Is there a clear introduction, body and conclusion?
You can use these questions to reflect on your own writing. Here are six top tips to help you address these criteria.
1. Analyse the question
Student essays are responses to specific questions. As an essay must address the question directly, your first step should be to analyse the question. Make sure you know exactly what is being asked of you.
Generally, essay questions contain three component parts:
- Content terms: Key concepts that are specific to the task
- Limiting terms: The scope that the topic focuses on
- Directive terms: What you need to do in relation to the content, e.g. discuss, analyse, define, compare, evaluate.
Look at the following essay question:
Discuss the importance of light in Gothic architecture.
- Content terms: Gothic architecture
- Limiting terms: the importance of light. If you discussed some other feature of Gothic architecture, for example spires or arches, you would be deviating from what is required. This essay question is limited to a discussion of light. Likewise, it asks you to write about the importance of light – not, for example, to discuss how light enters Gothic churches.
- Directive term: discuss. This term asks you to take a broad approach to the variety of ways in which light may be important for Gothic architecture. You should introduce and consider different ideas and opinions that you have met in academic literature on this topic, citing them appropriately .
For a more complex question, you can highlight the key words and break it down into a series of sub-questions to make sure you answer all parts of the task. Consider the following question (from Arts):
To what extent can the American Revolution be understood as a revolution ‘from below’? Why did working people become involved and with what aims in mind?
The key words here are American Revolution and revolution ‘from below’. This is a view that you would need to respond to in this essay. This response must focus on the aims and motivations of working people in the revolution, as stated in the second question.
2. Define your argument
As you plan and prepare to write the essay, you must consider what your argument is going to be. This means taking an informed position or point of view on the topic presented in the question, then defining and presenting a specific argument.
Consider these two argument statements:
The architectural use of light in Gothic cathedrals physically embodied the significance of light in medieval theology.
In the Gothic cathedral of Cologne, light served to accentuate the authority and ritual centrality of the priest.
Statements like these define an essay’s argument. They give coherence by providing an overarching theme and position towards which the entire essay is directed.
3. Use evidence, reasoning and scholarship
To convince your audience of your argument, you must use evidence and reasoning, which involves referring to and evaluating relevant scholarship.
- Evidence provides concrete information to support your claim. It typically consists of specific examples, facts, quotations, statistics and illustrations.
- Reasoning connects the evidence to your argument. Rather than citing evidence like a shopping list, you need to evaluate the evidence and show how it supports your argument.
- Scholarship is used to show how your argument relates to what has been written on the topic (citing specific works). Scholarship can be used as part of your evidence and reasoning to support your argument.
4. Organise a coherent essay
An essay has three basic components - introduction, body and conclusion.
The purpose of an introduction is to introduce your essay. It typically presents information in the following order:
- A general statement about the topic that provides context for your argument
- A thesis statement showing your argument. You can use explicit lead-ins, such as ‘This essay argues that...’
- A ‘road map’ of the essay, telling the reader how it is going to present and develop your argument.
Example introduction
"To what extent can the American Revolution be understood as a revolution ‘from below’? Why did working people become involved and with what aims in mind?"
Introduction*
Historians generally concentrate on the twenty-year period between 1763 and 1783 as the period which constitutes the American Revolution [This sentence sets the general context of the period] . However, when considering the involvement of working people, or people from below, in the revolution it is important to make a distinction between the pre-revolutionary period 1763-1774 and the revolutionary period 1774-1788, marked by the establishment of the continental Congress(1) [This sentence defines the key term from below and gives more context to the argument that follows] . This paper will argue that the nature and aims of the actions of working people are difficult to assess as it changed according to each phase [This is the thesis statement] . The pre-revolutionary period was characterised by opposition to Britain’s authority. During this period the aims and actions of the working people were more conservative as they responded to grievances related to taxes and scarce land, issues which directly affected them. However, examination of activities such as the organisation of crowd action and town meetings, pamphlet writing, formal communications to Britain of American grievances and physical action in the streets, demonstrates that their aims and actions became more revolutionary after 1775 [These sentences give the ‘road map’ or overview of the content of the essay] .
The body of the essay develops and elaborates your argument. It does this by presenting a reasoned case supported by evidence from relevant scholarship. Its shape corresponds to the overview that you provided in your introduction.
The body of your essay should be written in paragraphs. Each body paragraph should develop one main idea that supports your argument. To learn how to structure a paragraph, look at the page developing clarity and focus in academic writing .
Your conclusion should not offer any new material. Your evidence and argumentation should have been made clear to the reader in the body of the essay.
Use the conclusion to briefly restate the main argumentative position and provide a short summary of the themes discussed. In addition, also consider telling your reader:
- What the significance of your findings, or the implications of your conclusion, might be
- Whether there are other factors which need to be looked at, but which were outside the scope of the essay
- How your topic links to the wider context (‘bigger picture’) in your discipline.
Do not simply repeat yourself in this section. A conclusion which merely summarises is repetitive and reduces the impact of your paper.
Example conclusion
Conclusion*.
Although, to a large extent, the working class were mainly those in the forefront of crowd action and they also led the revolts against wealthy plantation farmers, the American Revolution was not a class struggle [This is a statement of the concluding position of the essay]. Working people participated because the issues directly affected them – the threat posed by powerful landowners and the tyranny Britain represented. Whereas the aims and actions of the working classes were more concerned with resistance to British rule during the pre-revolutionary period, they became more revolutionary in nature after 1775 when the tension with Britain escalated [These sentences restate the key argument]. With this shift, a change in ideas occurred. In terms of considering the Revolution as a whole range of activities such as organising riots, communicating to Britain, attendance at town hall meetings and pamphlet writing, a difficulty emerges in that all classes were involved. Therefore, it is impossible to assess the extent to which a single group such as working people contributed to the American Revolution [These sentences give final thoughts on the topic].
5. Write clearly
An essay that makes good, evidence-supported points will only receive a high grade if it is written clearly. Clarity is produced through careful revision and editing, which can turn a good essay into an excellent one.
When you edit your essay, try to view it with fresh eyes – almost as if someone else had written it.
Ask yourself the following questions:
Overall structure
- Have you clearly stated your argument in your introduction?
- Does the actual structure correspond to the ‘road map’ set out in your introduction?
- Have you clearly indicated how your main points support your argument?
- Have you clearly signposted the transitions between each of your main points for your reader?
- Does each paragraph introduce one main idea?
- Does every sentence in the paragraph support that main idea?
- Does each paragraph display relevant evidence and reasoning?
- Does each paragraph logically follow on from the one before it?
- Is each sentence grammatically complete?
- Is the spelling correct?
- Is the link between sentences clear to your readers?
- Have you avoided redundancy and repetition?
See more about editing on our editing your writing page.
6. Cite sources and evidence
Finally, check your citations to make sure that they are accurate and complete. Some faculties require you to use a specific citation style (e.g. APA) while others may allow you to choose a preferred one. Whatever style you use, you must follow its guidelines correctly and consistently. You can use Recite, the University of Melbourne style guide, to check your citations.
Further resources
- Germov, J. (2011). Get great marks for your essays, reports and presentations (3rd ed.). NSW: Allen and Unwin.
- Using English for Academic Purposes: A guide for students in Higher Education [online]. Retrieved January 2020 from http://www.uefap.com
- Williams, J.M. & Colomb, G. G. (2010) Style: Lessons in clarity and grace. 10th ed. New York: Longman.
* Example introduction and conclusion adapted from a student paper.

Looking for one-on-one advice?
Get tailored advice from an Academic Skills Adviser by booking an Individual appointment, or get quick feedback from one of our Academic Writing Mentors via email through our Writing advice service.
Go to Student appointments
- Enroll & Pay
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Degree Programs
Prewriting Strategies
Five useful strategies.
Pre-writing strategies use writing to generate and clarify ideas. While many writers have traditionally created outlines before beginning writing, there are several other effective prewriting activities. We often call these prewriting strategies “brainstorming techniques.” Five useful strategies are listing, clustering, freewriting, looping, and asking the six journalists' questions. These strategies help you with both your invention and organization of ideas, and they can aid you in developing topics for your writing.
Listing is a process of producing a lot of information within a short time by generating some broad ideas and then building on those associations for more detail with a bullet point list. Listing is particularly useful if your starting topic is very broad, and you need to narrow it down.
- Jot down all the possible terms that emerge from the general topic you are working on. This procedure works especially well if you work in a team. All team members can generate ideas, with one member acting as scribe. Do not worry about editing or throwing out what might not be a good idea. Simply write down as many possibilities as you can.
- Group the items that you have listed according to arrangements that make sense to you. Are things thematically related?
- Give each group a label. Now you have a narrower topic with possible points of development.
- Write a sentence about the label you have given the group of ideas. Now you have a topic sentence or possibly a thesis statement .

Clustering, also called mind mapping or idea mapping, is a strategy that allows you to explore the relationships between ideas.
- Put the subject in the center of a page. Circle or underline it.
- As you think of other ideas, write them on the page surrounding the central idea. Link the new ideas to the central circle with lines.
- As you think of ideas that relate to the new ideas, add to those in the same way.
The result will look like a web on your page. Locate clusters of interest to you, and use the terms you attached to the key ideas as departure points for your paper.
Clustering is especially useful in determining the relationship between ideas. You will be able to distinguish how the ideas fit together, especially where there is an abundance of ideas. Clustering your ideas lets you see them visually in a different way, so that you can more readily understand possible directions your paper may take.

Freewriting
Freewriting is a process of generating a lot of information by writing non-stop in full sentences for a predetermined amount of time. It allows you to focus on a specific topic but forces you to write so quickly that you are unable to edit any of your ideas.
- Freewrite on the assignment or general topic for five to ten minutes non-stop. Force yourself to continue writing even if nothing specific comes to mind (so you could end up writing “I don’t know what to write about” over and over until an idea pops into your head. This is okay; the important thing is that you do not stop writing). This freewriting will include many ideas; at this point, generating ideas is what is important, not the grammar or the spelling.
- After you have finished freewriting, look back over what you have written and highlight the most prominent and interesting ideas; then you can begin all over again, with a tighter focus (see looping). You will narrow your topic and, in the process, you will generate several relevant points about the topic.

Looping is a freewriting technique that allows you to focus your ideas continually while trying to discover a writing topic. After you freewrite for the first time, identify a key thought or idea in your writing, and begin to freewrite again, with that idea as your starting point. You will loop one 5-10 minute freewriting after another, so you have a sequence of freewritings, each more specific than the last. The same rules that apply to freewriting apply to looping: write quickly, do not edit, and do not stop.
Loop your freewriting as many times as necessary, circling another interesting topic, idea, phrase, or sentence each time. When you have finished four or five rounds of looping, you will begin to have specific information that indicates what you are thinking about a particular topic. You may even have the basis for a tentative thesis or an improved idea for an approach to your assignment when you have finished.

The Journalists' Questions
Journalists traditionally ask six questions when they are writing assignments that are broken down into five W's and one H: Who? , What? , Where? , When? , Why? , and How? You can use these questions to explore the topic you are writing about for an assignment. A key to using the journalists' questions is to make them flexible enough to account for the specific details of your topic. For instance, if your topic is the rise and fall of the Puget Sound tides and its effect on salmon spawning, you may have very little to say about Who if your focus does not account for human involvement. On the other hand, some topics may be heavy on the Who , especially if human involvement is a crucial part of the topic.
The journalists' questions are a powerful way to develop a great deal of information about a topic very quickly. Learning to ask the appropriate questions about a topic takes practice, however. At times during writing an assignment, you may wish to go back and ask the journalists' questions again to clarify important points that may be getting lost in your planning and drafting.
Possible generic questions you can ask using the six journalists' questions follow:
- Who? Who are the participants? Who is affected? Who are the primary actors? Who are the secondary actors?
- What? What is the topic? What is the significance of the topic? What is the basic problem? What are the issues related to that problem?
- Where? Where does the activity take place? Where does the problem or issue have its source? At what place is the cause or effect of the problem most visible?
- When? When is the issue most apparent? (in the past? present? future?) When did the issue or problem develop? What historical forces helped shape the problem or issue and at what point in time will the problem or issue culminate in a crisis? When is action needed to address the issue or problem?
- Why? Why did the issue or problem arise? Why is it (your topic) an issue or problem at all? Why did the issue or problem develop in the way that it did?
- How? How is the issue or problem significant? How can it be addressed? How does it affect the participants? How can the issue or problem be resolved?

Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 7 Techniques from Creative Writing You Can Use to Improve Your Essays

You wouldn’t have thought that essays have much in common with creative writing.
You should also read…
- How to Improve Your English Writing Skills
- How to Write Dazzlingly Brilliant Essays
Creative writing, by definition, involves being ‘creative’: making things up, letting your imagination run wild. Essays are about being factual and objective, communicating ideas and arguments in the clearest way possible and attempting to enhance the reader’s knowledge, rather than their imagination. But while the literary devices and colourful tales we associate with creative writing are indeed out of place in an essay, these two very different kinds of writing actually have a few similarities. Above all, they’re both meant to be read by other people, and that means that they need to sustain the reader’s interest. So, are there any writing techniques you can borrow from creative writing to help make your essays more interesting and original? Yes there are, and in this article, we’re going to show you how. Before we start, if you’re interested in attending a summer school to help develop these skills , click the link.
1. Think about your reader

With creative writing, as with any kind of writing, your reader is your most important consideration. You need to know and understand whom you’re writing for if you’re to do a good job of keeping them interested. Let’s think for a moment about the kind of person you’re writing for when you’re writing an essay and what you need to do to write specifically for them:
- Teachers or university lecturers – they’re going to be marking your essay, so it needs to answer the question effectively.
- They’ve set the question and they probably have a pretty good idea of how you’re going to answer it – so be original and unpredictable; catch them by surprise with an unusual approach or structure.
- They’re going to be reading many other responses to the same question – so they may well be bored by the time they get to yours. Keep them interested!
- They’re probably going to be pressed for time – so they won’t have time to reread badly written passages to try to understand what you’re getting at. Keep your writing easy to read, succinct and to the point.
What all these points boil down to is the importance of keeping your reader interested in what you have to say. Since creative writing is all about holding the reader’s interest, there must be some lessons to be learned from it and techniques that can be applied within the more limited style constraints of the academic essay. We’ll now turn to what these are.
2. Three-act structure

The three-act structure is a writing device used extensively in modern writing, including for film and television dramas. These ‘acts’ aren’t as distinct as acts in a play, as one follows seamlessly on from another and the audience wouldn’t consciously realise that one act had ended and another began. The structure refers to a plotline that looks something like this:
- Set-up – establishes the characters, how they relate to each other, and the world they inhabit. Within this first ‘act’, a dramatic occurrence called an ‘inciting incident’ takes place (typically around 19 minutes into a film) involving the principal character. They try to deal with it, but this results in another dramatic occurrence called a ‘turning point’. This sets the scene for the rest of the story.
- Confrontation – the turning point in the previous ‘act’ becomes the central problem, which the main character attempts to resolve – usually with plenty of adversity thrown their way that hampers their efforts. In a murder mystery, for example, this act would involve the detective trying to solve the murder. The central character – with the help of supporting characters – undergoes a journey and develops their knowledge, skills or character to a sufficient degree to be able to overcome the problem.
- Resolution – the climax of the story, in which the drama reaches a peak, the problem is overcome, and loose ends are tied up.
This structure sounds all very well for made-up stories, but what has it got to do with essay-writing? The key similarities here are:
- The central argument of your essay is the equivalent of the main character.
- The essay equivalent of the set-up and resolution are the introduction and conclusion.
- The inciting incident in an essay encourages you to get to the point early on in the essay.
- The equivalent of character development in the second act is developing your argument.
- The equivalent of the supporting characters is the evidence you refer to in your essay.
So, applying the three-act structure to an essay gives you something like this:
- Set-up – the introduction. This establishes what you’re talking about, setting the scene. The ‘inciting incident’ could be the introduction of evidence that contradicts a common theory, or the highlighting of a central disagreement in how something is interpreted.
- Confrontation – you discuss the different problems surrounding the topic you’re writing about. You develop the argument using various bits of evidence, moving towards an overall conclusion.
- Resolution – the conclusion. You summarise and resolve the argument with your own opinion, by coming down on one side or the other, having weighed up the evidence you’ve discussed. You could perhaps tie up loose ends by offering an alternative explanation for evidence that doesn’t sit with your conclusion.
Using this structure keeps you focused on the central point, and stops you from waffling, because everything you write is working towards resolving your argument. The use of the inciting incident in the first ‘act’ encourages you to get to the point early on in your essay, thereby keeping the reader interested. The principles of good plot-writing are centred around the connection between different events that show cause and effect, and this central tenet of the three-act structure has obvious parallels with the way in which essays work through presenting evidence in support of arguments.
3. An attention-grabbing opening

An oft-spouted piece of advice in creative writing is to use an attention-grabbing opening. One way of doing this is to start with a ‘flashback’, which could disrupt the chronology of events by transporting the reader directly back to the midst of the action, so that the story begins with maximum excitement. In a murder mystery, for instance, the writer might skip a slow build-up and instead use the murder itself to form the opening of the novel, with the rest of the story charting the efforts of the detective to uncover the perpetrator and perhaps telling the events prior to the murder in a series of flashbacks. The same principle can be applied to essays, though it’s easier to use in some subjects than others. To take an example, let’s say you were writing about how the First World War started. Rather than building up slowly with the various factors, an attention-grabbing opening could (briefly) describe the drama of the Battle of the Somme, perhaps citing some statistics about the number of men involved and killed, and quoting some war poetry about the horrors faced by the soldiers on the Front Line. Then, to introduce the purpose of the essay and launch into your argument about what started the war, a phrase such as, “It seems hard to imagine that all this began with…”. Alternatively, a rhetorical question: “But how did these tens of thousands of soldiers end up in the mud and horror of trench warfare? The story begins several years earlier, with…” It may not be the standard way of writing an essay, but you’ll certainly score points for originality and perhaps ruffle a few feathers.
4. Extended metaphors

Creative writing often makes use of extended metaphors. For example, when Shakespeare wrote the passage in Romeo and Juliet referring to “It is the East, and Juliet is the sun!” he was using an extended metaphor. With this in mind, it’s time to revisit a point we made in a previous article about writing more original essays , in which we argued that, rather than battling on with trying to explain a complex concept in a straightforward way, it might be easier to use an analogy to convey the meaning by drawing comparisons, which people find easier to understand. A metaphor is a kind of analogy, so the similarities with creative writing are strong here. In our previous article we used the example of radioactive decay. An analogy for this is the pressure with which water escapes from a hole in a bucket. It does so exponentially, just as radioactive substances decay exponentially. In both instances, the rate of a consumptive process depends on how much there is left of whatever is being depleted, which results in an exponential rate of decay. This concept is so much easier to explain using the analogy of water flowing from a hole in a bucket, as you give your reader something familiar to visualise in order to explain a concept with which they are unfamiliar.
5. Interesting details about setting and location

Another way of keeping your reader interested is to bring your essay to life with details about setting and location, just as creative writers do. Essays can become quite dry if you focus solely on the academic problems, but you can make them more interesting by peppering them with details. This may not work quite so well for a scientific essay, but it’s certainly relevant for some humanities subjects, in particular English literature, history and archaeology. For example, an essay about the Roman emperor Augustus could mention that he lived a famously modest lifestyle, quoting details from Roman writers and archaeological evidence that support this: Suetonius mentions his “low bed” (interesting because of what it says about accepted standards of Roman beds!) and coarse bread and cheese diet, and the relatively small and non-lavish remains of his house on the Palatine Hill in Rome back up the idea of his having lived a modest life. Incidental details like these can actually prove to be more significant than you initially realise, and you can use them to build your argument; in the case of Augustus, for example, his modest lifestyle is particularly important when seen in the context of Rome’s troubled history with kings. As he gradually acquired more power and became Rome’s first emperor, he had to avoid coming across as being too ‘regal’, and the little details we know about his way of life are significant in light of this. So, not only have you brought your essay to life, but you’ve raised an interesting point, too.
Few writers get it right first time . Once you’ve written a first draft, read through it and think about whether the order of your points is optimal and whether what you’ve written actually makes sense. It’s easy in the age of computers to chop and change – you can simply copy and paste part of your essay into another part where it might fit better, and then make minor changes to your wording so that it flows. After you’ve finished editing, have a final read through and check that you’re happy with the wording. Don’t forget to proofread to ensure that your spelling and grammar is impeccable!
7. And finally… record your ideas

Creative writers swear by having a notebook with them at all times, ready to jot down any ideas that suddenly spring to mind. You can adopt the same principle for your essay-writing, because you never know when the inspiration might strike. Have a think about your essay topic when you’re out and about; you’d be surprised what occurs to you when you’re away from your normal place of study. As you can see, there are more similarities between two apparently unrelated kinds of writing than you might have realised. It is, of course, possible to go too far with the creative writing idea when you’re essay-writing: literary devices aren’t always appropriate, and your essay still needs to retain objectivity and conform to the more formal conventions of academic writing. But there are certainly techniques to be borrowed from creative writing that will help your essays stand out from the crowd and give your teacher or lecturer a welcome break from the monotony of essay-marking.
See also our fabulous guide explaining more about ” What is Creative Writing ”.
Comments are closed.

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
A (Very) Simple Way to Improve Your Writing
- Mark Rennella

It’s called the “one-idea rule” — and any level of writer can use it.
The “one idea” rule is a simple concept that can help you sharpen your writing, persuade others by presenting your argument in a clear, concise, and engaging way. What exactly does the rule say?
- Every component of a successful piece of writing should express only one idea.
- In persuasive writing, your “one idea” is often the argument or belief you are presenting to the reader. Once you identify what that argument is, the “one-idea rule” can help you develop, revise, and connect the various components of your writing.
- For instance, let’s say you’re writing an essay. There are three components you will be working with throughout your piece: the title, the paragraphs, and the sentences.
- Each of these parts should be dedicated to just one idea. The ideas are not identical, of course, but they’re all related. If done correctly, the smaller ideas (in sentences) all build (in paragraphs) to support the main point (suggested in the title).
Where your work meets your life. See more from Ascend here .
Most advice about writing looks like a long laundry list of “do’s and don’ts.” These lists can be helpful from time to time, but they’re hard to remember … and, therefore, hard to depend on when you’re having trouble putting your thoughts to paper. During my time in academia, teaching composition at the undergraduate and graduate levels, I saw many people struggle with this.
- MR Mark Rennella is Associate Editor at HBP and has published two books, Entrepreneurs, Managers, and Leaders and The Boston Cosmopolitans .
Partner Center

Essay writing technique
Being able to write well is not only fundamental to passing your exams, it’s a vital life skill. Using good grammar and correct spelling are essential, so if you’re weak on these, try and brush up a little more! Make sure you understand how to use paragraphs correctly. No one wants to read one long stream of consciousness. So take a look at these essay writing technique tips.
General technique
Essays need to have a beginning, a middle and an end. The introduction should outline the problem, explain why it’s important, and briefly outline the main arguments. Don’t start with a dictionary definition – this is clichéd and boring. It should sum up the main arguments in the middle and finish with a conclusions that finally answers the essay question.
Good essay writing technique means having a well-ordered essay. Make sure you plan your essay. Make a bullet point list, table, or spider diagram with the main components of your answer and clearly order them. Poor structure is one of the main reasons students get marked down in essays. Order your thoughts logically and stick to your essay plan. You may want to use subtitles to help you organise your essay.
The main thing that the examiners are looking for is to see that you’ve understood the question. Demonstrate your keen conceptual awareness and understanding of the key issues. Do not be vague. Be specific and illustrate your work with appropriately referenced examples. Use figures or pictures or maps to illustrate your point. Demonstrate that you’ve done the wider reading.
Make sure you answer the question. If it’s a ‘compare and contrast’ kind of question, you’ll need to demonstrate both sides of the argument. If it’s a ‘define and explain’ kind of question, you’ll need to show that you have a deep understanding of the topic. If it has two parts, divide your essay into two parts to answer the question. Read widely around the topic before you even start and you’re halfway there.
In the conclusions, you need to sum up your arguments. Do not introduce anything new at this stage. Highlight the most important points and provide a final conclusion.
Remember to proof read your work! Critically read it through with a red pen. Have you repeated yourself? Be your worst critic and CUT savagely. Use everyone one of your alloted words to good effect. Cut the waffle and stick to justified (and referenced) statements. Keep your writing clear and simple.
Correct spelling and grammar is a must. Some general language tips:
- Avoid semicolons as they are difficult to use correctly and effectively.
- Paragraphs should follow a ‘theme’. They generally consist of more than one sentence.
- It comprises, but is composed of (it never comprises of).
- Avoid using the same word too frequently or twice in quick succession.
- Do not use clichés, metaphores or similes.
- Do not use abbreviations. Stick to formal English (don’t use don’t).
- Try to avoid using the first person. (“I”).
- Try to use the active voice rather than the passive voice where possible – it makes for more direct and interesting reading.
If you don’t understand English grammar, read Eats, shoots and leaves by Lynne Truss.
Finally, make sure you read carefully any feedback you are given on your essays. Your tutors will be keen to help you learn and progress.
Referencing and citations
At undergraduate level, more so than at A-Level, you will need to demonstrate evidence of further reading. Lectures are supposed to be a pointer and guide for your further reading. By reading, we mean published, peer-reviewed literature; Wikipedia does not count! Other websites (including this one) should not be cited in essays, but you can use them to further your understanding and get lists of peer-reviewed literature to read.
Make sure you understand the referencing style (copy the syle used in Elsevier journals as a good guide), and if you don’t understand, ask your lecturer and teacher. See the example paragraph below.
Example referencing style
Despite substantial evidence for multiple glaciations in Britain and Scandinavia during the Quaternary, the interaction between these ice masses in eastern England and in the North Sea remains unclear. There is extensive evidence of large Scandinavian and British ice sheets in the North Sea during each of the main glacial stages (Ehlers et al. 1984; Sejrup et al. 2005; Davies et al. 2011). Coalescence of the British-Irish Ice Sheet (BIIS) and Fennoscandian Ice Sheet (FIS) have been suggested during MIS 12, MIS 6 and the Devensian (MIS 5d-2) (Catt and Penny 1966; Catt and Digby 1988; Bowen 1999; Carr et al. 2006; Catt 2007; Davies et al. 2009; 2012), with Scandinavian ice reaching the coast of eastern England during MIS 6 and MIS 12. However, recent research in north Norfolk has challenged this argument, suggesting that the North Sea Drift tills, which were traditionally thought to comprise Scandinavian and Scottish tills, have purely a Scottish provenance, and may in fact be older than MIS 12 (Lee et al. 2002; 2004; 2012).
Bowen, D.Q., 1999. On the correlation and classification of Quaternary deposits and land-sea correlations, A Revised Correlation of Quaternary Deposits in the British Isles. Geological Society Special Report , Special Report 23. Geological Society of London, London, pp. 1-10.
Carr, S.J., Holmes, R., van der Meer, J.J.M. and Rose, J., 2006. The Last Glacial Maximum in the North Sea: Micromorphological evidence of extensive glaciation. Journal of Quaternary Science , 21(2): 131-153.
Catt, J.A., 2007. The Pleistocene glaciations of eastern Yorkshire: a review. Proceedings of the Yorkshire Geological Society , 56(3): 177-207.
Catt, J.A. and Digby, P.G.N., 1988. Boreholes in the Wolstonian Basement Till at Easington, Holderness, July 1985. Proceedings of the Yorkshire Geological Society , 47(1): 21-27.
Catt, J.A. and Penny, L.F., 1966. The Pleistocene deposits of Holderness, East Yorkshire. Proceedings of the Yorkshire Geological Society , 35: 375-420.
Davies, B.J., Roberts, D.H., Bridgland, D.R., Ó Cofaigh, C. and Riding, J.B., 2011. Provenance and depositional environments of Quaternary sedimentary formations of the western North Sea Basin. Journal of Quaternary Science , 26(1): 59-75.
Davies, B.J., Roberts, D.H., Bridgland, D.R., Ó Cofaigh, C., Riding, J.B., Demarchi, B., Penkman, K. and Pawley, S.M., 2012. Timing and depositional environments of a Middle Pleistocene glaciation of northeast England: New evidence from Warren House Gill, County Durham. Quaternary Science Reviews , 44: 180-212.
Davies, B.J., Roberts, D.H., Bridgland, D.R., Ó Cofaigh, C., Riding, J.B., Phillips, E.R. and Teasdale, D.A., 2009. Interlobate ice sheet dynamics during the Last Glacial Maximum at Whitburn Bay, County Durham, England. Boreas , 38: 555-575.
Ehlers, J., Meyer, K.-D. and Stephan, H.-J., 1984. The Pre-Weichselian glaciations of North-West Europe. Quaternary Science Reviews , 3(1): 1-40.
Lee, J.R., Busschers, F.S. and Sejrup, H.P., 2012. Pre-Weichselian Quaternary glaciations of the British Isles, The Netherlands, Norway and adjacent marine areas south of 68°N: implications for long-term ice sheet development in northern Europe. Quaternary Science Reviews , 44: 213-228.
Lee, J.R., Rose, J., Hamblin, R.J.O. and Moorlock, B.S.P., 2004. Dating the earliest lowland glaciation of eastern England: a pre-MIS 12 early Middle Pleistocene Happisburgh glaciation. Quaternary Science Reviews , 23(14-15): 1551-1566.
Lee, J.R., Rose, J., Riding, J.B., Moorlock, B.S.P. and Hamblin, R.J.O., 2002. Testing the case for a Middle Pleistocene Scandinavian glaciation in Eastern England: evidence for a Scottish ice source for tills within the Corton Formation of East Anglia, UK. Boreas , 31(4): 345-355.
Sejrup, H.P., Hjelstuen, B.O., Torbjorn Dahlgren, K.I., Haflidason, H., Kuijpers, A., Nygard, A., Praeg, D., Stoker, M.S. and Vorren, T.O., 2005. Pleistocene glacial history of the NW European continental margin. Marine and Petroleum Geology , 22(9-10): 1111-1129.
Related Articles
21 thoughts on “essay writing technique”.
nice!, thank you for the help 🙂
Where exactly did u actually pick up the points to post ““Essay Writing Technique”? Regards -Danielle
Hi Danielle, The post is based on years of experience reading, writing and marking essays!
Hi Bethan, I agree with you. It is really a great post and for that kind of writing absolutely need a great experience too.
thank you for help me I want these techniques I am learning to write essay
Thanks for this article this helps a lot.I admire you and your knowledge in writing.You make essay writing fun!
Is being so wonderful being with your work. It has really help me to do much meaningful WRITE UP today. Thanks alot, I quite Appreciate and Commend the time you took to put this together.
very nice..
Thanks for your “Essay writing technique” Even though i am a francophone this article is still usefull to me in other to write up a meaningfull and a nice essay Thanks a lot.
Thank you for any other informative blog. Where else could I get that kind of info written in such an ideal means? I have a undertaking that I’m just now working on, and I have been at the glance out for such info.
Essay writing technique is good article writing .
ary news tv live streaming
Good Luck Essay writing technique & Excellent Performance
Thank You Very Much
IAM comfortable with your articles
A lot of cool information is on this blog. I am very happy I see this page.
Thank you for a good essay writing technique. It was so helpful to me.
That’s a wonderful post i and I searched for this and I found your web post and thanks a lot I love to read.
Pingback: Unlock Your Full Potential: Exam Techniques to Boost Your Grades
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- Services for education institutions
- Academic subject areas
- Peer connection
- Evidence of Studiosity impact
- Case studies from our partners
- Research Hub
- The Tracey Bretag Integrity Prize
- The Studiosity Symposium
- Studiosity for English learners
- Video case studies
- Meet the online team
Academic Advisory Board
Meet the board.
- Social responsibility
- Meet the team
- Join the team

How to structure paragraphs using the PEEL method
Sophia Gardner
Sep 1, 2023
You may have heard of the acronym PEEL for essays, but what exactly does it mean? And how can it help you? We’re here to explain it all, plus give you some tips on how to nail your next essay.
There’s certainly an art to writing essays. If you haven’t written one for a while, or if you would like to hone your academic writing skills, the PEEL paragraph method is an easy way to get your point across in a clear and concise way, that is easily digestible to the reader.
So, what exactly is PEEL ?

The PEEL paragraph method is a technique used in writing to help structure paragraphs in a way that presents a single clear and focused argument, which links back to the essay topic or thesis statement.
It’s good practice to dedicate each paragraph to one aspect of your argument, and the PEEL structure simplifies this for you.
It allows you to create a paragraph that is easy and accessible for others to understand. Remember, when you’re writing something, it’s not just you who is reading it - you need to consider the reader and how they are going to be digesting this new information.
What does PEEL stand for?
P = Point: start your paragraph with a clear topic sentence that establishes what your paragraph is going to be about. Your point should support your essay argument or thesis statement.
E = Evidence/Example: here you should use a piece of evidence or an example that helps to reaffirm your initial point and develop the argument.
E = Explain: next you need to explain exactly how your evidence/example supports your point, giving further information to ensure that your reader understands its relevance.
L = Link: to finish the paragraph off, you need to link the point you’ve just made back to your essay question, topic, or thesis.
Download a free PEEL paragraph planner below. 👇

Studiosity English specialist Ellen, says says students often underestimate the importance of a well-structured paragraph.
PEEL in practice
Here’s an example of what you might include in a PEEL structured paragraph:
Topic: Should infants be given iPads? Thesis/argument: Infants should not be given iPads.
Point : Infants should not be given iPads, because studies show children under two can face developmental delays if they are exposed to too much screen time.
Evidence/Example: A recent paediatric study showed that infants who are exposed to too much screen time may experience delays in speech development.
Explanation: The reason infants are facing these delays is because screen time is replacing other key developmental activities.
Link: The evidence suggests that infants who have a lot of screen time experience negative consequences in their speech development, and therefore they should not be exposed to iPads at such a young age.
Once you’ve written your PEEL paragraph, do a checklist to ensure you have covered off all four elements of the PEEL structure. Your point should be a clear introduction to the argument you are making in this paragraph; your example or evidence should be strong and relevant (ask yourself, have you chosen the best example?); your explanation should be demonstrate why your evidence is important and how it conveys meaning; and your link should summarise the point you’ve just made and link back to the broader essay argument or topic.

Keep your paragraphs clear, focused, and not too long. If you find your paragraphs are getting lengthy, take a look at how you could split them into multiple paragraphs, and ensure you’re creating a new paragraph for each new idea you introduce to the essay.
Finally, it’s important to always proofread your paragraph. Read it once, twice, and then read it again. Check your paragraph for spelling, grammar, language and sentence flow. A good way to do this is to read it aloud to yourself, and if it sounds clunky or unclear, consider rewriting it.
That’s it! We hope this helps explain the PEEL method and how it can help you with your next essay. 😊
You might also like: Proofreading vs editing: what's the difference? How to get easy marks in an exam 5 study hacks that actually work
Topics: English , Writing , Grammar
About Studiosity
Asking for feedback on your work is an essential part of learning. So when you want to better understand a concept or check you're on the right track, we're here for you.
Find out if you have free access through your institution here .
Recent Posts
Posts by topic.
- Students (85)
- Higher education (63)
- Student Experience (46)
- University (46)
- Education (41)
- online study (34)
- Learning (28)
- Tertiary education (28)
- Educators (27)
- Interview (24)
- Research (24)
- Parents (23)
- English (18)
- High School (18)
- Technology (17)
- students first (17)
- Writing (16)
- Podcast (14)
- Homework (13)
- Student stories (13)
- Assignment Help (12)
- Education policy (12)
- Formative feedback (12)
- Literacy (12)
- academic integrity (12)
- student wellbeing (12)
- Events (11)
- Academic Advisory Board (10)
- Studiosity (10)
- covid19 (10)
- international student (10)
- Australia (9)
- Health and Wellbeing (9)
- Learning trends (9)
- Student satisfaction (9)
- Teaching (9)
- Secondary education (8)
- Equality (7)
- Science (7)
- Student retention (7)
- UK students (7)
- staff wellbeing (7)
- UK Higher Education (6)
- academic services (6)
- online learning (6)
- CanHigherEd (5)
- Online Tutoring (5)
- Student support (5)
- Workload (5)
- belonging (5)
- CVs and cover letters (4)
- Internet (4)
- Mathematics (4)
- Partnerships (4)
- School holidays (4)
- Student performance (4)
- Widening Participation (4)
- #InthisTogether (3)
- Grammar (3)
- University of Exeter (3)
- student success (3)
- teaching & learning (3)
- Charity (2)
- Government (2)
- Mentors (2)
- Primary education (2)
- Subject Specialists (2)
- accessibility (2)
- community (2)
- diversity (2)
- plagiarism prevention (2)
- student stress (2)
- webinar (2)
- Biology (1)
- Careers (1)
- Chemistry (1)
- EU students (1)
- First years (1)
- Indigenous Strategy (1)
- Nutrition (1)
- Teacher (1)
- academic support (1)
- academic writing (1)
- business schools (1)
- choice of language (1)
- dyslexia (1)
- ethical AI (1)
- job help (1)
- library services (1)
- podcasts (1)
- reflection (1)
- university of west of england (1)
- July 2015 (12)
- March 2020 (11)
- June 2020 (10)
- July 2020 (8)
- September 2020 (8)
- March 2015 (7)
- April 2015 (7)
- October 2019 (7)
- April 2020 (7)
- May 2018 (6)
- April 2019 (6)
- May 2020 (6)
- September 2022 (6)
- June 2015 (5)
- August 2015 (5)
- December 2017 (5)
- March 2018 (5)
- February 2020 (5)
- March 2021 (5)
- June 2021 (5)
- July 2016 (4)
- March 2017 (4)
- October 2017 (4)
- February 2018 (4)
- August 2018 (4)
- May 2019 (4)
- July 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (4)
- March 2024 (4)
- February 2015 (3)
- May 2015 (3)
- September 2015 (3)
- December 2015 (3)
- January 2016 (3)
- April 2016 (3)
- October 2016 (3)
- December 2016 (3)
- April 2017 (3)
- September 2017 (3)
- April 2018 (3)
- October 2018 (3)
- March 2019 (3)
- January 2020 (3)
- October 2020 (3)
- November 2020 (3)
- June 2022 (3)
- October 2022 (3)
- November 2022 (3)
- August 2023 (3)
- November 2023 (3)
- March 2016 (2)
- May 2016 (2)
- August 2016 (2)
- July 2017 (2)
- January 2018 (2)
- November 2018 (2)
- December 2018 (2)
- February 2019 (2)
- June 2019 (2)
- September 2019 (2)
- January 2021 (2)
- February 2021 (2)
- April 2021 (2)
- August 2021 (2)
- September 2021 (2)
- December 2021 (2)
- August 2022 (2)
- February 2023 (2)
- March 2023 (2)
- May 2023 (2)
- December 2023 (2)
- April 2024 (2)
- October 2008 (1)
- August 2013 (1)
- October 2015 (1)
- February 2016 (1)
- June 2016 (1)
- September 2016 (1)
- November 2016 (1)
- January 2017 (1)
- May 2017 (1)
- June 2017 (1)
- August 2017 (1)
- November 2017 (1)
- June 2018 (1)
- September 2018 (1)
- January 2019 (1)
- November 2019 (1)
- December 2019 (1)
- August 2020 (1)
- December 2020 (1)
- May 2021 (1)
- February 2022 (1)
- March 2022 (1)
- July 2022 (1)
- December 2022 (1)
- January 2023 (1)
- June 2023 (1)
- July 2023 (1)
- September 2023 (1)
- October 2023 (1)
- February 2024 (1)
Studiosity is personalised study help, anytime, anywhere. We partner with institutions to extend their core academic skills support online with timely, after-hours help for all their students, at scale - regardless of their background, study mode or location.
Now you can subscribe to our educator newsletter, for insights and free downloads straight to your inbox:

ABN 41 114 279 668
Student zone, assignment calculator, calendars and organisers, study survival guides, free practice tests, student faqs, download our mobile app, student sign in, success stories.
Student Reviews & Testimonials
Specialist Sign In
Meet our specialists
Meet the team, media and research, student reviews.
Read more on Google

Studiosity acknowledges the Traditional Indigenous Custodians of country throughout Australia, and all lands where we work, and recognises their continuing connection to land, waters, and culture. We pay our respects to Elders past and present.
Contact • (02) 9906 2700 • FAQ • Privacy • Accessibility • Acceptable Use • Terms of Use Education Policies • Academic Integrity Policy

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7.1 Sentence Variety
Learning objectives.
- Identify ways to vary sentence structure.
- Write and revise sentence structure at the beginning of sentences.
- Write and revise sentence structure by connecting ideas.
Have you ever ordered a dish in a restaurant and been not happy with its taste, even though it contained most of your favorite ingredients? Just as a meal might lack the finishing touches needed to spice it up, so too might a paragraph contain all the basic components but still lack the stylistic finesse required to engage a reader. Sometimes writers have a tendency to reuse the same sentence pattern throughout their writing. Like any repetitive task, reading text that contains too many sentences with the same length and structure can become monotonous and boring. Experienced writers mix it up by using an assortment of sentence patterns, rhythms, and lengths.
In this chapter, you will follow a student named Naomi who has written a draft of an essay but needs to refine her writing. This section discusses how to introduce sentence variety into writing, how to open sentences using a variety of techniques, and how to use different types of sentence structure when connecting ideas. You can use these techniques when revising a paper to bring life and rhythm to your work. They will also make reading your work more enjoyable.
Incorporating Sentence Variety
Experienced writers incorporate sentence variety into their writing by varying sentence style and structure. Using a mixture of different sentence structures reduces repetition and adds emphasis to important points in the text. Read the following example:
During my time in office I have achieved several goals. I have helped increase funding for local schools. I have reduced crime rates in the neighborhood. I have encouraged young people to get involved in their community. My competitor argues that she is the better choice in the upcoming election. I argue that it is ridiculous to fix something that isn’t broken. If you reelect me this year, I promise to continue to serve this community.
In this extract from an election campaign, the writer uses short, simple sentences of a similar length and style. Writers often mistakenly believe that this technique makes the text more clear for the reader, but the result is a choppy, unsophisticated paragraph that does not grab the audience’s attention. Now read the revised paragraph with sentence variety:
During my time in office, I have helped increase funding for local schools, reduced crime rates in the neighborhood, and encouraged young people to get involved in their community. Why fix what isn’t broken? If you reelect me this year, I will continue to achieve great things for this community. Don’t take a chance on an unknown contender; vote for the proven success.
Notice how introducing a short rhetorical question among the longer sentences in the paragraph is an effective means of keeping the reader’s attention. In the revised version, the writer combines the choppy sentences at the beginning into one longer sentence, which adds rhythm and interest to the paragraph.
Effective writers often implement the “rule of three,” which is basically the thought that things that contain three elements are more memorable and more satisfying to readers than any other number. Try to use a series of three when providing examples, grouping adjectives, or generating a list.
Combine each set of simple sentences into a compound or a complex sentence. Write the combined sentence on your own sheet of paper.
- Heroin is an extremely addictive drug. Thousands of heroin addicts die each year.
- Shakespeare’s writing is still relevant today. He wrote about timeless themes. These themes include love, hate, jealousy, death, and destiny.
- Gay marriage is now legal in six states. Iowa, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine all permit same-sex marriage. Other states are likely to follow their example.
- Prewriting is a vital stage of the writing process. Prewriting helps you organize your ideas. Types of prewriting include outlining, brainstorming, and idea mapping.
- Mitch Bancroft is a famous writer. He also serves as a governor on the local school board. Mitch’s two children attend the school.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Using Sentence Variety at the Beginning of Sentences
Read the following sentences and consider what they all have in common:
John and Amanda will be analyzing this week’s financial report.
The car screeched to a halt just a few inches away from the young boy.
Students rarely come to the exam adequately prepared.
If you are having trouble figuring out why these sentences are similar, try underlining the subject in each. You will notice that the subject is positioned at the beginning of each sentence— John and Amanda , the car , students . Since the subject-verb-object pattern is the simplest sentence structure, many writers tend to overuse this technique, which can result in repetitive paragraphs with little sentence variety.
Naomi wrote an essay about the 2008 government bailout. Read this excerpt from Naomi’s essay:

This section examines several ways to introduce sentence variety at the beginning of sentences, using Naomi’s essay as an example.
Starting a Sentence with an Adverb
One technique you can use so as to avoid beginning a sentence with the subject is to use an adverb. An adverb is a word that describes a verb, adjective, or other adverb and often ends in – ly . Examples of adverbs include quickly , softly , quietly , angrily , and timidly . Read the following sentences:
She slowly turned the corner and peered into the murky basement.
Slowly, she turned the corner and peered into the murky basement.
In the second sentence, the adverb slowly is placed at the beginning of the sentence. If you read the two sentences aloud, you will notice that moving the adverb changes the rhythm of the sentence and slightly alters its meaning. The second sentence emphasizes how the subject moves—slowly—creating a buildup of tension. This technique is effective in fictional writing.
Note that an adverb used at the beginning of a sentence is usually followed by a comma. A comma indicates that the reader should pause briefly, which creates a useful rhetorical device. Read the following sentences aloud and consider the effect of pausing after the adverb:
Cautiously, he unlocked the kennel and waited for the dog’s reaction.
Solemnly, the policeman approached the mayor and placed him under arrest.
Suddenly, he slammed the door shut and sprinted across the street.
In an academic essay, moving an adverb to the beginning of a sentence serves to vary the rhythm of a paragraph and increase sentence variety.

Naomi has used two adverbs in her essay that could be moved to the beginning of their respective sentences. Notice how the following revised version creates a more varied paragraph:

Adverbs of time—adverbs that indicate when an action takes place—do not always require a comma when used at the beginning of a sentence. Adverbs of time include words such as yesterday , today , later , sometimes , often , and now .
On your own sheet of paper, rewrite the following sentences by moving the adverbs to the beginning.
- The red truck sped furiously past the camper van, blaring its horn.
- Jeff snatched at the bread hungrily, polishing off three slices in under a minute.
- Underage drinking typically results from peer pressure and lack of parental attention.
- The firefighters bravely tackled the blaze, but they were beaten back by flames.
- Mayor Johnson privately acknowledged that the budget was excessive and that further discussion was needed.
Starting a Sentence with a Prepositional Phrase
A prepositional phrase is a group of words that behaves as an adjective or an adverb, modifying a noun or a verb. Prepositional phrases contain a preposition (a word that specifies place, direction, or time) and an object of the preposition (a noun phrase or pronoun that follows the preposition).
Table 7.1 Common Prepositions
Read the following sentence:
The terrified child hid underneath the table .
In this sentence, the prepositional phrase is underneath the table. The preposition underneath relates to the object that follows the preposition— the table . Adjectives may be placed between the preposition and the object in a prepositional phrase.
The terrified child hid underneath the heavy wooden table .
Some prepositional phrases can be moved to the beginning of a sentence in order to create variety in a piece of writing. Look at the following revised sentence:
Underneath the heavy wooden table , the terrified child hid.
Notice that when the prepositional phrase is moved to the beginning of the sentence, the emphasis shifts from the subject—the terrified child—to the location in which the child is hiding. Words that are placed at the beginning or end of a sentence generally receive the greatest emphasis. Take a look at the following examples. The prepositional phrase is underlined in each:
The bandaged man waited in the doctor’s office .
In the doctor’s office , the bandaged man waited.
My train leaves the station at 6:45 a.m .
At 6:45 a.m. , my train leaves the station.
Teenagers exchange drugs and money under the railway bridge .
Under the railway bridge , teenagers exchange drugs and money.
Prepositional phrases are useful in any type of writing. Take another look at Naomi’s essay on the government bailout.

Now read the revised version.

The underlined words are all prepositional phrases. Notice how they add additional information to the text and provide a sense of flow to the essay, making it less choppy and more pleasurable to read.
Unmovable Prepositional Phrases
Not all prepositional phrases can be placed at the beginning of a sentence. Read the following sentence:
I would like a chocolate sundae without whipped cream .
In this sentence, without whipped cream is the prepositional phrase. Because it describes the chocolate sundae, it cannot be moved to the beginning of the sentence. “Without whipped cream I would like a chocolate sundae” does not make as much (if any) sense. To determine whether a prepositional phrase can be moved, we must determine the meaning of the sentence.
Overuse of Prepositional Phrases
Experienced writers often include more than one prepositional phrase in a sentence; however, it is important not to overload your writing. Using too many modifiers in a paragraph may create an unintentionally comical effect as the following example shows:
The treasure lay buried under the old oak tree, behind the crumbling fifteenth-century wall, near the schoolyard, where children played merrily during their lunch hour, unaware of the riches that remained hidden beneath their feet.
A sentence is not necessarily effective just because it is long and complex. If your sentence appears cluttered with prepositional phrases, divide it into two shorter sentences. The previous sentence is far more effective when written as two simpler sentences:
The treasure lay buried under the old oak tree, behind the crumbling fifteenth-century wall. In the nearby schoolyard, children played merrily during their lunch hour, unaware of the riches that remained hidden beneath their feet.
Writing at Work
The overuse of prepositional phrases often occurs when our thoughts are jumbled and we are unsure how concepts or ideas relate to one another. If you are preparing a report or a proposal, take the time to organize your thoughts in an outline before writing a rough draft. Read the draft aloud, either to yourself or to a colleague, and identify areas that are rambling or unclear. If you notice that a particular part of your report contains several sentences over twenty words, you should double check that particular section to make certain that it is coherent and does not contain unnecessary prepositional phrases. Reading aloud sometimes helps detect unclear and wordy sentences. You can also ask a colleague to paraphrase your main points to ensure that the meaning is clear.
Starting a Sentence by Inverting Subject and Verb
As we noted earlier, most writers follow the subject-verb-object sentence structure. In an inverted sentence , the order is reversed so that the subject follows the verb. Read the following sentence pairs:
- A truck was parked in the driveway.
- Parked in the driveway was a truck.
- A copy of the file is attached.
- Attached is a copy of the file.
Notice how the second sentence in each pair places more emphasis on the subject— a truck in the first example and the file in the second. This technique is useful for drawing the reader’s attention to your primary area of focus. We can apply this method to an academic essay. Take another look at Naomi’s paragraph.

To emphasize the subject in certain sentences, Naomi can invert the traditional sentence structure. Read her revised paragraph:

Notice that in the first underlined sentence, the subject ( some economists ) is placed after the verb ( argued ). In the second underlined sentence, the subject ( the government ) is placed after the verb ( expects ).
On your own sheet of paper, rewrite the following sentences as inverted sentences.
- Teresa will never attempt to run another marathon.
- A detailed job description is enclosed with this letter.
- Bathroom facilities are across the hall to the left of the water cooler.
- The well-dressed stranger stumbled through the doorway.
- My colleagues remain unconvinced about the proposed merger.
Connecting Ideas to Increase Sentence Variety
Reviewing and rewriting the beginning of sentences is a good way of introducing sentence variety into your writing. Another useful technique is to connect two sentences using a modifier, a relative clause, or an appositive. This section examines how to connect ideas across several sentences in order to increase sentence variety and improve writing.
Joining Ideas Using an – ing Modifier
Sometimes it is possible to combine two sentences by converting one of them into a modifier using the – ing verb form— singing , dancing , swimming . A modifier is a word or phrase that qualifies the meaning of another element in the sentence. Read the following example:
Original sentences: Steve checked the computer system. He discovered a virus.
Revised sentence: Checking the computer system, Steve discovered a virus.
To connect two sentences using an – ing modifier, add – ing to one of the verbs in the sentences ( checking ) and delete the subject ( Steve ). Use a comma to separate the modifier from the subject of the sentence. It is important to make sure that the main idea in your revised sentence is contained in the main clause, not in the modifier. In this example, the main idea is that Steve discovered a virus, not that he checked the computer system.
In the following example, an – ing modifier indicates that two actions are occurring at the same time:
Noticing the police car, she shifted gears and slowed down.
This means that she slowed down at the same time she noticed the police car.
Barking loudly, the dog ran across the driveway.
This means that the dog barked as it ran across the driveway.
You can add an – ing modifier to the beginning or the end of a sentence, depending on which fits best.
Beginning: Conducting a survey among her friends , Amanda found that few were happy in their jobs.
End: Maria filed the final report, meeting her deadline .
Dangling Modifiers
A common mistake when combining sentences using the – ing verb form is to misplace the modifier so that it is not logically connected to the rest of the sentence. This creates a dangling modifier . Look at the following example:
Jogging across the parking lot, my breath grew ragged and shallow.
In this sentence, jogging across the parking lot seems to modify my breath . Since breath cannot jog, the sentence should be rewritten so that the subject is placed immediately after the modifier or added to the dangling phrase.
Jogging across the parking lot, I felt my breath grow ragged and shallow.
For more information on dangling modifiers, see Chapter 2 “Writing Basics: What Makes a Good Sentence?” .
Joining Ideas Using an – ed Modifier
Some sentences can be combined using an – ed verb form— stopped , finished , played . To use this method, one of the sentences must contain a form of be as a helping verb in addition to the – ed verb form. Take a look at the following example:
Original sentences: The Jones family was delayed by a traffic jam. They arrived several hours after the party started.
Revised sentence: Delayed by a traffic jam, the Jones family arrived several hours after the party started.
In the original version, was acts as a helping verb —it has no meaning by itself, but it serves a grammatical function by placing the main verb ( delayed ) in the perfect tense.
To connect two sentences using an – ed modifier, drop the helping verb ( was ) and the subject ( the Jones family ) from the sentence with an – ed verb form. This forms a modifying phrase ( delayed by a traffic jam ) that can be added to the beginning or end of the other sentence according to which fits best. As with the – ing modifier, be careful to place the word that the phrase modifies immediately after the phrase in order to avoid a dangling modifier.
Using – ing or – ed modifiers can help streamline your writing by drawing obvious connections between two sentences. Take a look at how Naomi might use modifiers in her paragraph.

The revised version of the essay uses the – ing modifier opting to draw a connection between the government’s decision to bail out the banks and the result of that decision—the acquisition of the mortgage-backed securities.
Joining Ideas Using a Relative Clause
Another technique that writers use to combine sentences is to join them using a relative clause. A relative clause is a group of words that contains a subject and a verb and describes a noun. Relative clauses function as adjectives by answering questions such as which one? or what kind? Relative clauses begin with a relative pronoun, such as who , which , where , why , or when . Read the following examples:
Original sentences: The managing director is visiting the company next week. He lives in Seattle.
Revised sentence: The managing director, who lives in Seattle, is visiting the company next week.
To connect two sentences using a relative clause, substitute the subject of one of the sentences ( he ) for a relative pronoun ( who ). This gives you a relative clause ( who lives in Seattle ) that can be placed next to the noun it describes ( the managing director ). Make sure to keep the sentence you want to emphasize as the main clause. For example, reversing the main clause and subordinate clause in the preceding sentence emphasizes where the managing director lives, not the fact that he is visiting the company.
Revised sentence: The managing director, who is visiting the company next week, lives in Seattle.
Relative clauses are a useful way of providing additional, nonessential information in a sentence. Take a look at how Naomi might incorporate relative clauses into her essay.

Notice how the underlined relative clauses can be removed from Naomi’s essay without changing the meaning of the sentence.
To check the punctuation of relative clauses, assess whether or not the clause can be taken out of the sentence without changing its meaning. If the relative clause is not essential to the meaning of the sentence, it should be placed in commas. If the relative clause is essential to the meaning of the sentence, it does not require commas around it.
Joining Ideas Using an Appositive
An appositive is a word or group of words that describes or renames a noun or pronoun. Incorporating appositives into your writing is a useful way of combining sentences that are too short and choppy. Take a look at the following example:
Original sentences: Harland Sanders began serving food for hungry travelers in 1930. He is Colonel Sanders or “the Colonel.”
Revised sentence: Harland Sanders, “the Colonel,” began serving food for hungry travelers in 1930.
In the revised sentence, “the Colonel” is an appositive because it renames Harland Sanders. To combine two sentences using an appositive, drop the subject and verb from the sentence that renames the noun and turn it into a phrase. Note that in the previous example, the appositive is positioned immediately after the noun it describes. An appositive may be placed anywhere in a sentence, but it must come directly before or after the noun to which it refers:
Appositive after noun: Scott, a poorly trained athlete, was not expected to win the race.
Appositive before noun: A poorly trained athlete, Scott was not expected to win the race.
Unlike relative clauses, appositives are always punctuated by a comma or a set commas. Take a look at the way Naomi uses appositives to include additional facts in her essay.

On your own sheet of paper, rewrite the following sentence pairs as one sentence using the techniques you have learned in this section.
- Baby sharks are called pups. Pups can be born in one of three ways.
- The Pacific Ocean is the world’s largest ocean. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south.
- Michael Phelps won eight gold medals in the 2008 Olympics. He is a champion swimmer.
- Ashley introduced her colleague Dan to her husband, Jim. She speculated that the two of them would have a lot in common.
- Cacao is harvested by hand. It is then sold to chocolate-processing companies at the Coffee, Sugar, and Cocoa Exchange.
In addition to varying sentence structure, consider varying the types of sentences you are using in a report or other workplace document. Most sentences are declarative, but a carefully placed question, exclamation, or command can pique colleagues’ interest, even if the subject material is fairly dry. Imagine that you are writing a budget analysis. Beginning your report with a rhetorical question, such as “Where is our money going?” or “How can we increase sales?” encourages people to continue reading to find out the answers. Although they should be used sparingly in academic and professional writing, questions or commands are effective rhetorical devices.
Key Takeaways
- Sentence variety reduces repetition in a piece of writing and adds emphasis to important points in the text.
- Sentence variety can be introduced to the beginning of sentences by starting a sentence with an adverb, starting a sentence with a prepositional phrase, or by inverting the subject and verb.
- Combine ideas, using modifiers, relative clauses, or appositives, to achieve sentence variety.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


1.5: The Writing Process
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 53675

- Edgar Perez, Jenell Rae, Jacob Skelton, Lisa Horvath, & Sara Behseta
- ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
The Writing Process
If you think that a blank sheet of paper or a blinking cursor on the computer screen is a scary sight, you are not alone. Many writers, students, and employees find that beginning to write can be intimidating. When faced with a blank page, however, experienced writers remind themselves that writing, like other everyday activities, is a process. Every process, from writing to cooking, bike riding, and learning to use a new cell phone, will get significantly easier with practice .
Just as you need a recipe, ingredients, and the proper tools to cook a delicious meal, you also need a plan , resources , and adequate time to create a well-written composition. In other words, writing is a process that requires following steps and using strategies to accomplish your goals.
Effective writing can be simply described as good ideas that are expressed well and arranged in the proper order. This chapter will give you the chance to work on all these important aspects of writing. In this chapter, we will be using the Proces s of writing an essay to illustrate the idea of of process writing.
Prewriting Home
Loosely defined, prewriting includes all the writing strategies employed before writing your first draft. Although many more prewriting strategies exist, the following section covers: using experience and observations, reading, freewriting, asking questions, listing, and clustering/idea mapping. Using the strategies in the following section can help you overcome the fear of the blank page and confidently begin the writing process.
C hoosing a Topic/Theme
In addition to understanding that writing is a process, writers also understand that choosing a good general topic for an assignment is an essential first step. Sometimes your instructor will give you an idea to begin an assignment, and other times your instructor will ask you to come up with a topic on your own. A good topic not only covers what an assignment will be about, but it also fits the assignment’s purpose and its audience . This textbook is theme-based, which means that each chapter has an underlying set of thematic readings.
In the next few sections, you will follow a writer named Romina as she explores and develops her essay’s topic and focus. You will also be planning one of your own. The first important step is for you to tell yourself why you are writing (to inform, to explain, or some other purpose) and for whom you are writing. Write your purpose and your audience on your own sheet of paper, and keep the paper close by as you read and complete exercises in this chapter and write the first draft.
- My purpose: ____________________________________________
- My audience: ___________________________________________
Prewriting Techniques: Brainstorming Home
Brainstorming refers to writing techniques used to:
- Generate topic ideas
- Transfer your abstract thoughts on a topic into more concrete ideas on paper (or digitally on a computer screen)
- Organize the ideas you have generated to discover a focus and develop a working thesis
Although brainstorming techniques can be helpful in all stages of the writing process, you will have to find the techniques that are most effective for your writing needs. The following general strategies can be used when initially deciding on a topic, or for narrowing the focus for a topic: Freewriting , Asking questions , Listing , and Clustering/Idea Mapping .
In the initial stage of the writing process, it is fine if you choose a general topic. Later you can use brainstorming strategies to narrow the focus of the topic.
Experience and Observations
When selecting a topic, you may want to consider something that interests you or something based on your own life and personal experiences. Even everyday observations can lead to interesting topics. After writers think about their experiences and observations, they often take notes on paper to better develop their thoughts. These notes help writers discover what they have to say about their topic.
Reading plays a vital role in all the stages of the writing process, but it first figures in the development of ideas and topics. Different kinds of documents can help you choose and develop a topic. For example, a magazine cover advertising the latest research on the threat of global warming may catch your eye in the supermarket. This subject may interest you, and you may consider global warming as a topic. Or maybe a novel’s courtroom drama sparks your curiosity of a particular lawsuit or legal controversy.
After you choose a topic, critical reading is essential to the development of a topic. While reading almost any document, you evaluate the author’s point of view by thinking about his main idea and his support. When you judge the author’s argument, you discover more about not only the author’s opinion but also your own. If this step already seems daunting, remember that even the best writers need to use prewriting strategies to generate ideas.
Prewriting strategies depend on your critical reading skills. Reading, prewriting and brainstorming exercises (and outlines and drafts later in the writing process) will further develop your topic and ideas. As you continue to follow the writing process, you will see how Romina uses critical reading skills to assess her own prewriting exercises.
Freewriting
Freewriting is an exercise in which you write freely about any topic for a set amount of time (usually five to seven minutes). During the time limit, you may jot down any thoughts that come to your mind. Try not to worry about grammar, spelling, or punctuation. Instead, write as quickly as you can without stopping. If you get stuck, just copy the same word or phrase over and over again until you come up with a new thought.
Writing often comes easier when you have a personal connection with the topic you have chosen. Remember, to generate ideas in your freewriting, you may also think about readings that you have enjoyed or that have challenged your thinking. Doing this may lead your thoughts in interesting directions.
Quickly recording your thoughts on paper will help you discover what you have to say about a topic. When writing quickly, try not to doubt or question your ideas. Allow yourself to write freely and unselfconsciously. Once you start writing with few limitations, you may find you have more to say than you first realized. Your flow of thoughts can lead you to discover even more ideas about the topic. Freewriting may even lead you to discover another topic that excites you even more.
Look at Romina’s example below. The instructor allowed the members of the class to choose their own topics, and Romina thought about her experiences as a communications major. She used this freewriting exercise to help her generate more concrete ideas from her own experience.
Freewriting Example
Last semester my favorite class was about mass media. We got to study radio and television. People say we watch too much television, and even though I try not to, I end up watching a few reality shows just to relax. Everyone has to relax! It’s too hard to relax when something like the news (my husband watches all the time) is on because it’s too scary now. Too much bad news, not enough good news. News. Newspapers I don’t read as much anymore. I can get the headlines on my homepage when I check my email. Email could be considered mass media too these days. I used to go to the video store a few times a week before I started school, but now the only way I know what movies are current is to listen for the Oscar nominations. We have cable but we can’t afford movie channels, so I sometimes look at older movies late at night. UGH. A few of them get played again and again until you’re sick of them. My husband thinks I’m crazy, but sometimes there are old black-and-whites on from the 1930s and ‘40s. I could never live my life in black-and-white. I like the home decorating shows and love how people use color on their walls. Makes rooms look so bright. When we buy a home, if we ever can, I’ll use lots of color. Some of those shows even show you how to do major renovations by yourself. Knock down walls and everything. Not for me–or my husband. I’m handier than he is. I wonder if they could make a reality show about us?
EXERCISE 1 Home
Freewrite about one event you have recently experienced. With this event in mind, write without stopping for five minutes. After you finish, read over what you wrote. Does anything stand out to you as a good general topic to write about? One of the following prompts may help you get started:
- A celebration
- The first day of a job or the first day of school
- The loss of a friend or relative
- Finding a place to live
Asking Questions
Who? What? Where? When? Why? How?
In everyday situations, you pose these kinds of questions to get more information. Who will be my partner for the project? When is the next meeting? Why is my car making that odd noise? When faced with a writing assignment, you might ask yourself, “How do I begin?”
You seek the answers to these questions to gain knowledge, to better understand your daily experiences, and to plan for the future. Asking these types of questions will also help you with the writing process. As you choose your topic, answering these questions can help you revisit the ideas you already have and generate new ways to think about your topic. You may also discover aspects of the topic that are unfamiliar to you and that you would like to learn more about. All these idea-gathering techniques will help you plan for future work on your assignment.
When Romina reread her freewriting notes, she found she had rambled and her thoughts were disjointed. She realized that the topic that interested her most was the one she started with, the media. She then decided to explore that topic by asking herself questions about it. Her purpose was to refine media into a topic she felt comfortable writing about. To see how asking questions can help you choose a topic, take a look at the following chart that Romina completed to record her questions and answers. She asked herself the questions that reporters and journalists use to gather information for their stories. The questions are often called the 5WH questions, after their initial letters.
Example of “Asking Questions”
Who? I use media. Students teachers, parents, employers and employees– almost everyone uses media.
What? The media can be a lot of things– television, radio, email (I think), newspapers, magazines, books.
Where? The media is almost everywhere now. It’s at home, at work, in cars, and even on cell phones.
When? The media has been around for a long time, but it seems a lot more important now.
Why? Hmm. This is a good question. I don’t know why there is mass media. Maybe we have it because we have the technology now. Or people live far away from their families and have to stay in touch.
How? Well, media is possible because of the technology inventions, but I don’t know how they all work.
EXERCISE 2 Home
Using the prompt you chose to practice freewriting in Exercise 1 , continue to explore the topic by answering the 5 WH questions, as Romina does in the above example.
Narrowing the focus
After rereading her essay assignment, Romina realized her general topic, mass media, is too broad for her class’s short paper requirement. Three pages are not enough to cover all the concerns in mass media today. Romina also realized that although her readers are other communications majors who are interested in the topic, they might want to read a paper about a particular issue in mass media.
The prewriting techniques of brainstorming by freewriting and asking questions helped Romina think more about her topic, but the following prewriting strategies can help her (and you) narrow the focus of the topic:
- Clustering/Idea Mapping
Narrowing the focus means breaking up the topic into subtopics, or more specific points. Generating lots of subtopics will help you eventually select the ones that fit the assignment and appeal to you and your audience.
Listing is a term often applied to describe any prewriting technique writers use to generate ideas on a topic, including freewriting and asking questions. You can make a list on your own or in a group with your classmates. Start with a blank sheet of paper (or a blank computer screen) and write your general topic across the top. Underneath your topic, make a list of more specific ideas. Think of your general topic as a broad category and the list items as things that fit in that category. Often you will find that one item can lead to the next, creating a flow of ideas that can help you narrow your focus to a more specific paper topic. The following is Romina’s brainstorming list:
From this list, Romina could narrow her focus to a particular technology under the broad category of “mass media.”
Idea Mapping
Idea mapping, sometimes called clustering or webbing, allows you to visualize your ideas on paper using circles, lines, and arrows. This technique is also known as clustering because ideas are broken down and clustered, or grouped together. Many writers like this method because the shapes show how the ideas relate or connect, and writers can find a focused topic from the connections mapped. Using idea mapping, you might discover interesting connections between topics that you had not thought of before.
To create an idea map:
- Start by writing your general topic in a circle in the center of a blank sheet of paper. Moving out from the main circle, write down as many concepts and terms ideas you can think of related to your general topic in blank areas of the page. Jot down your ideas quickly–do not overthink your responses. Try to fill the page.
- Once you’ve filled the page, circle the concepts and terms that are relevant to your topic. Use lines or arrows to categorize and connect closely related ideas. Add and cluster as many ideas as you can think of.
To continue brainstorming, Romina tried idea mapping. Review the following idea map that Romina created:
Notice Romina’s largest circle contains her general topic, mass media. Then, the general topic branches into two subtopics written in two smaller circles: television and radio. The subtopic television branches into even more specific topics: cable and DVDs. From there, Romina drew more circles and wrote more specific ideas: high definition and digital recording from cable and Blu-ray from DVDs. The radio topic led Romina to draw connections between music, downloads versus CDs, and, finally, piracy. From this idea map, Romina saw she could consider narrowing the focus of her mass media topic to the more specific topic of music piracy.
Topic Checklist: Developing a Good Topic
- Am I interested in this topic?
- Would my audience be interested?
- Do I have prior knowledge or experience with this topic? If so, would I be comfortable exploring this topic and sharing my experience?
- Do I want to learn more about this topic?
- Is this topic specific?
- Does it fit the length of the assignment
Prewriting strategies are a vital first step in the writing process. First, they help you choose a broad topic, and then they help you narrow the focus of the topic to a more specific idea. An effective topic ensures that you are ready for the next step: Developing a working thesis and planning the organization of your essay by creating an outline.
EXERCISE 3 Home
Return to the topic explored in Exercise 2 through the prewriting technique of answering questions (5 WH). Explore and narrow the topic further by practicing the prewriting techniques of Brainstorming (listing) and Idea Mapping. Allow yourself no more than five to seven minutes for each technique.
Collaboration: Share your results with a classmate or in small groups, and compare answers. Offer feedback to your classmate(s) on what you find interesting about his or her topic.
Key Takeaways
- All writers rely on steps and strategies to begin the writing process.
- The steps in the writing process are prewriting, outlining, writing a rough draft, revising, and editing.
- Writers often choose a general topic first and then narrow the focus to a more specific topic.
- Prewriting includes any brainstorming technique used to generate ideas, narrow the focus of abstract thoughts and ideas, and transfer them into written form.
- A good topic interests the writer, appeals to the audience, and fits the purpose of the writing project.
Purpose of an Outline
Once your topic has been chosen, your ideas have been generated through brainstorming techniques, and you’ve developed a working thesis, the next step in the prewriting stage is to create an outline. Sometimes called a “blueprint,” or “plan” for your paper, an outline helps writers organize their thoughts and categorize the main points they wish to make in an order that makes sense.
Creating an outline is an important step in the writing process!
The purpose of an outline is to help you organize your paper by checking to see if and how your ideas connect to each other, or whether you need to flesh out a point or two.
No matter the length of the paper, from a three-page weekly assignment to a 50-page senior thesis, outlines can help you see the overall picture.
Having an outline also helps prevent writers from “getting stuck” when writing the first draft of an essay.
A well-developed outline will show the essential elements of an essay:
- thesis of essay
- main idea of each body paragraph
- evidence/support offered in each paragraph to substantiate the main points
A well-developed outline breaks down the parts of your thesis in a clear, hierarchical manner. Writing an outline before beginning an essay helps the writer organize ideas generated through brainstorming and/or research. In short, a well-developed outline makes your paper easier to write.
The formatting of any outline is not arbitrary; the system of formatting and number/letter designations creates a visual hierarchy of the ideas, or points, being made in the essay.
Major points, in other words, should not be buried in subtopic levels.
Types of Outlines
Alphanumeric Outlines
This is the most common type of outline used and is usually instantly recognizable to most people. The formatting follows these characters, in this order:
Level 1: Roman Numerals (I, II, III, IV, V, etc.)
Level 2: Capitalized Letters (A, B, C, D, E, etc.)
Level 3: Arabic Numerals (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc.)
Level 4: Lowercase Letters (a, b, c, d, e, etc.)
Alphanumeric Example
I. (Main point) Lowering the speed limit to 55 mph on Interstate highways is a cost effective way to reduce pollution and greenhouse gases
A. (Supporting detail) Gas mileage significantly decreases at speeds over 55 mph
1. (Supporting detail for sub-point) Slowing down from 65 mph to 55 mph can increase MPG by as much as 15 percent
a. (Additional explanation/support for supporting detail) Each 5 mph driven over 60 mph is like paying an additional $0.21 per gallon for gas (at $3.00 per gallon).
If the outline needs to subdivide beyond these divisions, use Arabic numerals inside parentheses and then lowercase letters inside parentheses.
Decimal Outlines
The decimal outline follows the same levels of indentation when formatting to indicate the hierarchy of ideas/points as the alphanumeric outline. The added benefit of decimal notation, however, is that it clearly shows, through the decimal breakdown, how each progressive level relates to the larger whole.
Decimal Example
1. (Main point) Lowering the speed limit on all Interstate highways to 55 mph would create a significant, cost free reduction in air pollution
1.1 (Supporting detail) Gas consumption significantly increases at speeds over 55 mph
1.2 (Supporting detail for sub-point) Slowing down from 65 mph to 55 mph can increase your MPG by as much as 15 percent, and thereby eliminate 15 percent of carbon emissions
1.3 (Additional explanation/support for supporting detail) According to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), “as a rule of thumb, each 5 mph driven over 60 mph is like paying an additional $0.21 per gallon for gas (at $3.00 per gallon).”
Micro and Macro Outlines
The indentation/formatting of a micro (full sentence) or macro (topic) outline is essentially the same as alphanumeric/decimal outlines. The difference between micro and macro outlines lies in the specificity and depth of the content.
Micro outlines focus on the “micro,” the drilled-down specific details of the essay’s content. They are particularly useful when the topic you are discussing is complex in nature. When creating a micro outline, it can also be useful to insert the quotations you plan to include in the essay (with citations) and subsequent analyses of quotes. Taking this extra step helps ensure that you have enough support for your ideas, as well as reminding writers to actually analyze and discuss quotations, rather than simply inserting quotes and moving on. While time-consuming to create, micro outlines can be seen as basically creating the first rough draft of an essay.
Macro outlines, in contrast, focus on the “big picture” of an essay’s main points and support by using short phrases or keywords to indicate the focus and content at each level of the essay’s development. A macro outline is useful when writing about a variety of ideas and issues where the ordering of points is more flexible. Macro outlines are also especially helpful when writing timed essays, or essay exam questions–or any rhetorical situation where writers need to quickly get their ideas down in an organized essay format.
Micro/Full-Sentence Outline Example
I. (Main point) Lowering the speed limit on all Interstate highways to 55 mph would create a significant, cost free reduction in air pollution.
A. (Supporting detail) Gas consumption significantly increases at speeds over 55 mph.
(Supporting detail for sub-point) Slowing down from 65 mph to 55 mph can increase your car’s MPG by as much as 15 percent, and thereby eliminate 15 percent of carbon emissions.
a. (Additional explanation/support for supporting detail) According to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), “as a rule of thumb, each 5 mph driven over 60 mph is like paying an additional $0.21 per gallon for gas (at $3.00 per gallon)”.
Macro/Topic Outline Example
A. (Supporting detail) Increase of Consumption over 55 mph
1. (Supporting detail for sub-point) Consumption and carbon emissions
a. (Additional explanation/support for supporting detail) Amount of money saved
Creating an Outline
Identify your topic: Put the topic in your own words in with a single sentence or phrase to help you stay on topic.
Determine your main points. What are the main points you want to make to convince your audience? Refer back to the prewriting/brainstorming exercise of answering 5 WH questions: “why or how is the main topic important?” Using your brainstorming notes, you should be able to create a working thesis.
List your main points/ideas in a logical order. You can always change the order later as you evaluate your outline.
Create sub-points for each major idea. Typically, each time you have a new number or letter, there need to be at least two points (i.e. if you have an A, you need a B; if you have a 1, you need a 2; etc.). Though perhaps frustrating at first, it is indeed useful because it forces you to think hard about each point; if you can’t create two points, then reconsider including the first in your paper, as it may be extraneous information that may detract from your argument.
Evaluate: Review your organizational plan, your blueprint for your paper. Does each paragraph have a controlling idea/topic sentence? Is each point adequately supported? Look over what you have written. Does it make logical sense? Is each point suitably fleshed out? Is there anything included that is unnecessary?
EXERCISE 4 Home
1. Create a sentence outline from the following introductory paragraph in alphanumeric format:
The popularity of knitting is cyclical, rising and falling according to the prevailing opinion of women’s places in society. Though internationally a unisex hobby, knitting is pervasively thought of as a woman’s hobby in the United States. Knitting is currently enjoying a boost in popularity as traditionally minded women pick up the craft while women who enjoy subverting traditional gender roles have also picked up the needles to reclaim “the lost domestic arts” and give traditionally feminine crafts the proper respect. American men are also picking up the needles in greater numbers, with men’s knitting guilds and retreats nationwide. This rise in popularity has made the receiving of hand-knit items special, and many people enjoy receiving these long-lasting, painstakingly crafted items. For any knitters, the perfect gift starts by choosing the perfect yarn. Choosing the perfect yarn for a knitting project relies on the preferences of the person for whom the project is being made, the availability of the yarn, and the type of yarn recommended by the pattern.
What is the thesis? How is the topic introduced? Is there a hierarchy of supporting points?
2. Now create your own outline based on the topic you developed in Exercise 3 .
Sample of 3-Level Alphanumeric Outline
Drafting is the stage of the writing process in which you develop a complete first version of a piece of writing. Even professional writers admit that an empty page scares them because they feel they need to come up with something fresh and original every time they open a blank document on their computers. Because you have completed the first two steps in the writing process, you have already recovered from empty page syndrome. You have prewriting and planning already done, so you know what will go on that blank page: what you wrote in your outline.
Goals and Strategies for Drafting
Your objective at this stage of the writing process is to draft an essay with at least three body paragraphs, which means that the essay will contain a minimum of five paragraphs, including an introduction and a conclusion. A draft is a complete version of a piece of writing, but it is not the final version. The step in the writing process after drafting, as you may remember, is revising. During revising, you will have the opportunity to make changes to your first draft before you put the finishing touches on it during the editing and proofreading stage. A first draft gives you a working version that you can later improve.
If you are more comfortable starting on paper than on the computer, you can start on paper and then type it before you revise. You can also use a voice recorder to get yourself started, dictating a paragraph or two to get you thinking. In this lesson, Romina does all her work on the computer, but you may use pen and paper or the computer to write a rough draft.
Making the Writing Process Work for You
The following approaches, done alone or in combination with others, may improve your writing and help you move forward in the writing process:
- Begin writing with the part you know the most about: You can start with the third paragraph in your outline if ideas come easily to mind. You can start with the second paragraph or the first paragraph, too. Although paragraphs may vary in length, keep in mind that short paragraphs may contain insufficient support. Readers may also think the writing is abrupt. Long paragraphs may be wordy and may lose your reader’s interest. As a guideline, try to write paragraphs longer than one sentence but shorter than the length of an entire double-spaced page.
- Write one paragraph at a time and then stop: As long as you complete the assignment on time, you may choose how many paragraphs you complete in one sitting. Pace yourself. On the other hand, try not to procrastinate. Writers should always meet their deadlines.
- Take short breaks to refresh your mind: This tip might be most useful if you are writing a multi-page report or essay. Still, if you are antsy or cannot concentrate, take a break to let your mind rest. But do not let breaks extend too long. If you spend too much time away from your essay, you may have trouble starting again. You may forget key points or lose momentum. Try setting an alarm to limit your break, and when the time is up, return to your desk to write.
- Be reasonable with your goals: If you decide to take ten-minute breaks, try to stick to that goal. If you told yourself that you need more facts, then commit to finding them. Holding yourself to your own goals will create successful writing assignments.
- Keep your audience and purpose in mind as you write: These aspects of writing are just as important when you are writing a single paragraph for your essay as when you are considering the direction of the entire essay.
Of all of these considerations, keeping your purpose and your audience at the front of your mind is the most important key to writing success. If your purpose is to persuade, for example, you will present your facts and details in the most logical and convincing way you can. Your purpose will guide your mind as you compose your sentences. Your audience will guide word choice. Are you writing for experts, for a general audience, for other college students, or for people who know very little about your topic? Keep asking yourself what your readers, with their background and experience, need to be told in order to understand your ideas. How can you best express your ideas so they are totally clear and your communication is effective?
You may want to identify your purpose and audience on an index card that you clip to your paper (or keep next to your computer). On that card, you may want to write notes to yourself—perhaps about what that audience might not know or what it needs to know—so that you will be sure to address those issues when you write. It may be a good idea to also state exactly what you want to explain to that audience, or to inform them of, or to persuade them about.
Using the topic for the essay that you outlined in the second step of Exercise 4 , describe your purpose and your audience as specifically as you can. Use your own sheet of paper to record your responses. Then keep these responses near you during future stages of the writing process.
Purpose: ______________________________________________
Audience: _____________________________________________
Discovering the Basic Elements of a First Draft
If you have been using the information in the previous chapters step by step to help you develop an assignment, you already have both a formal topic outline and a formal sentence outline to direct your writing. Knowing what a first draft looks like will help you make the creative leap from the outline to the first draft
A first draft should include the following elements:
- An introduction that piques the audience’s interest, tells what the essay is about, and motivates readers to keep reading.
- A thesis statement that presents the main point, or controlling idea, of the entire piece of writing.
- A topic sentence in each paragraph that states the main idea of the paragraph and implies how that main idea connects to the thesis statement.
- Supporting sentences in each paragraph that develop or explain the topic sentence. These can be specific facts, examples, anecdotes, or other details that elaborate on the topic sentence.
- A conclusion that reinforces the thesis statement and leaves the audience with a feeling of completion.
The Bowtie Method
There are many ways to think about the writing process as a whole. One way to imagine your essay is to see it like a bowtie. In the figure below, you will find a visual representation of this metaphor. The left side of the bow is the introduction, which begins with a hook and ends with the thesis statement. In the center, you will find the body paragraphs, which grow with strength as the paper progresses, and each paragraph contains a supported topic sentence. On the right side, you will find the conclusion. Your conclusion should reword your thesis and then wrap up the paper with a summation, clinch, or challenge. In the end, your paper should present itself as a neat package, like a bowtie.
Figure of the “Bowtie Method”
Starting Your First Draft Home
Now we are finally ready to look over Romina’s shoulder as she begins to write her essay about digital technology and the confusing choices that consumers face. As she does, you should have in front of you your outline, with its thesis statement and topic sentences, and the notes you wrote earlier in this lesson on your purpose and audience. Reviewing these will put both you and Romina in the proper mind-set to start.
The following is Romina’s thesis statement:
E-book readers are changing the way people read.
Here are the notes that Romina wrote to herself to characterize her purpose and audience:
Everyone wants the newest and the best digital technology, but the choices are many, and the specifications are often confusing.
Purpose: My purpose is to inform readers about the wide variety of consumer digital technology available in stores and to explain why the specifications for these products, expressed in numbers that average consumers don’t understand, often cause bad or misinformed buying decisions.
Audience: My audience is my instructor and members of this class. Most of them are not heavy into technology except for the usual laptops, cell phones, and MP3 players, which are not topics I’m writing about. I’ll have to be as exact and precise as I can be when I explain possibly unfamiliar product specifications. At the same time, they’re more with it electronically than my grandparents’ VCR-flummoxed generation, so I won’t have to explain every last detail.
Romina chose to begin by writing a quick introduction based on her thesis statement. She knew that she would want to improve her introduction significantly when she revised. Right now, she just wanted to give herself a starting point. Remember that she could have started directly with any of the body paragraphs. You will learn more about writing attention-getting introductions and effective conclusions later in this chapter.
With her thesis statement and her purpose and audience notes in front of her, Romina then looked at her sentence outline. She chose to use that outline because it includes the topic sentences. The following is the portion of her outline for the first body paragraph. The Roman numeral I identifies the topic sentence for the paragraph, capital letters indicate supporting details, and Arabic numerals label sub-points.
I. Ebook readers are changing the way people read.
A. Ebook readers make books easy to access and to carry.
1. Books can be downloaded electronically.
2. Devices can store hundreds of books in memory.
B. The market expands as a variety of companies enter it.
1. Booksellers sell their own ebook readers.
2. Electronics and computer companies also sell ebook readers.
C. Current ebook readers have significant limitations.
1. The devices are owned by different brands and may not be compatible.
2. Few programs have been made to duplicate the way Americans borrow and read printed books.
Romina then began to expand the ideas in her outline into a paragraph. Notice how the outline helped her guarantee that all her sentences in the body of the paragraph develop the topic sentence.
Ebook readers are changing the way people read, or so ebook developers hope. The main selling point for these handheld devices, which are sort of the size of a paperback book, is that they make books easy to access and carry. Electronic versions of printed books can be downloaded online for a few bucks or directly from your cell phone. These devices can store hundreds of books in memory and, with text-to-speech features, can even read the texts. The market for ebooks and ebook readers keeps expanding as a lot of companies enter it. Online and traditional booksellers have been the first to market ebook readers to the public, but computer companies, especially the ones already involved in cell phone, online music, and notepad computer technology, will also enter the market. The problem for consumers, however, is which device to choose. Incompatibility is the norm. Ebooks can be read-only on the devices they were intended for. Furthermore, use is restricted by the same kind of DRM systems that restrict the copying of music and videos. So, book buyers are often unable to lend books to other readers, as they can with a read book. Few accommodations have been made to fit the other way Americans read: by borrowing books from libraries. What is a buyer to do?
If you write your first draft on the computer, consider creating a new file folder for each course with a set of sub-folders inside the course folders for each assignment you are given. Label the folders clearly with the course names, and label each assignment folder and word processing document with a title that you will easily recognize. The assignment name is a good choice for the document. Then use that sub-folder to store all the drafts you create. When you start each new draft, do not just write over the last one. Instead, save the draft with a new tag after the title—draft 1, draft 2, and so on—so that you will have a complete history of drafts in case your instructor wishes you to submit them. In your documents, observe any formatting requirements—for margins, headers, placement of page numbers, and other layout matters—that your instructor requires.
Study how Romina made the transition from her sentence outline to her first draft. First, copy her outline onto your own sheet of paper. Leave a few spaces between each part of the outline. Then copy sentences from Romina’s paragraph to align each sentence with its corresponding entry in her outline.
Continuing the First Draft
Romina continued writing her essay, moving to the second and third body paragraphs. She had supporting details but no numbered sub-points in her outline, so she had to consult her prewriting notes for specific information to include.
If you decide to take a break between finishing your first body paragraph and starting the next one, do not start writing immediately when you return to your work. Put yourself back in context and in the mood by rereading what you have already written. This is what Romina did. If she had stopped writing in the middle of writing the paragraph, she could have jotted down some quick notes to herself about what she would write next.
Preceding each body paragraph that Romina wrote is the appropriate section of her sentence outline. Notice how she expanded Roman numeral II from her outline into a first draft of the second body paragraph. As you read, ask yourself how closely she stayed on purpose and how well she paid attention to the needs of her audience.

Digital cameras have almost totally replaced film cameras in amateur photographers’ gadget bags. My father took hundreds of slides when his children were growing up, but he had more and more trouble getting them developed. So, he decided to go modern. But, what kind of camera should he buy? The small compact digital cameras could slip right in his pocket, but if he tried to print a photograph larger than an 8 x 10, the quality would be poor. When he investigated buying a single lens reflex camera, or SLR, he discovered that they were as versatile as his old film camera, also an SLR, but they were big and bulky. Then he discovered yet a third type, which combined the smaller size of the compact digital cameras with the zoom lenses available for SLRs. His first thought was to buy one of those, but then he realized he had a lot of decisions to make. How many megapixels should the camera be? Five? Ten? What is the advantage of each? Then came the size of the zoom lens. He knew that 3x was too small, but what about 25x? Could he hold a lens that long without causing camera shake? He read many photography magazines and buying guides, and he still wasn’t sure he was right.
Romina then began her third and final body paragraph using Roman numeral III from her outline.

Nothing is more confusing to me than choosing among televisions. It confuses lots of people who want a new high-definition digital television (HDTV) with a large screen to watch sports and DVDs on. You could listen to the guys in the electronics stores, but word has it they know little more than you do. They want to sell you what they have in stock, not what best fits your needs. You face decisions you never had to make with the old, bulky picture-tube televisions. Screen resolution means the number of horizontal scan lines the screen can show. This resolution is often 1080p, or full HD, or 768p. The trouble is that if you have a smaller screen, 32 inches or 37 inches, you won’t be able to tell the difference with the naked eye. The 1080p televisions cost more, though, so those are what the salespeople want you to buy. They get bigger commissions. The other important decision you face as you walk around the sales floor is whether to get a plasma screen or an LCD screen. Now here the salespeople may finally give you decent info. Plasma flat-panel television screens can be much larger in diameter than their LCD rivals. Plasma screens show decent lacks and can be viewed at a wider angle than current LCD screens. But be careful and tell the salesperson you have budget constraints. Large flat- panel plasma screens are much more expensive than flat-screen LCD models. Don’t buy more television than you need.
Reread body paragraphs two and three of the essay that Romina is writing. Then answer the questions on your own sheet of paper.
- In body paragraph two, Romina decided to develop her paragraph as a nonfiction narrative. Do you agree with her decision? Explain. How else could she have chosen to develop the paragraph? Why is that better?
- Compare the writing styles of paragraphs two and three. What evidence do you have that Romina was getting tired or running out of steam? What advice would you give her? Why?
- Choose one of these two body paragraphs. Write a version of your own that you think better fits Romina’s audience and purpose.
Writing a Title
A writer’s best choice for a title is one that alludes to the main point of the entire essay. Like the headline in a newspaper or the big, bold title in a magazine, an essay’s title gives the audience a first peek at the content. If readers like the title, they are likely to keep reading.
Following her outline carefully, Romina crafted each paragraph of her essay. Moving step by step in the writing process, Romina finished the draft and even included a brief concluding paragraph which you will read later. She then decided, as the final touch for her writing session, to add an engaging title.
Thesis Statement:
Working Title:
Digital Technology: The Newest and the Best at What Price?
- Make the writing process work for you. Use any and all of the strategies that help you move forward in the writing process.
- Always be aware of your purpose for writing and the needs of your audience. Cater to those needs in every sensible way.
- Remember to include all the key structural parts of an essay: a thesis statement that is part of your introductory paragraph, three or more body paragraphs as described in your outline, and a concluding paragraph. Then add an engaging title to draw in readers.
- Write paragraphs of an appropriate length for your writing assignment. Paragraphs in college-level writing can be a page long, as long as they cover the main topics in your outline.
- Use your topic outline or your sentence outline to guide the development of your paragraphs and the elaboration of your ideas. Each main idea, indicated by a Roman numeral in your outline, becomes the topic of a new paragraph. Develop it with the supporting details and the sub-points of those details that you included in your outline.
- Generally speaking, write your introduction and conclusion last, after you have fleshed out the body paragraphs.
Drafting Body Paragraphs Home
If your thesis gives the reader a roadmap to your essay, then body paragraphs should closely follow that map. The reader should be able to predict what follows your introductory paragraph by simply reading the thesis statement. The body paragraphs present the evidence you have gathered to confirm your thesis. Before you begin to support your thesis in the body, you must find information from a variety of sources that support and give credit to what you are trying to prove.
Select Primary Support for Your Thesis
Without primary support, your argument is not likely to be convincing.
Primary support can be described as the major points you choose to expand on your thesis. It is the most important information you select to argue for your point of view. Each point you choose will be incorporated into the topic sentence for each body paragraph you write. Your primary supporting points are further supported by supporting details within the paragraphs.
Remember that a worthy argument is backed by examples. In order to construct a valid argument, good writers conduct lots of background research and take careful notes.
They also talk to people knowledgeable about a topic in order to understand its implications before writing about it. For guidance on incorporating research into your paragraphs, see the section “Using Sources.”
Identify the Characteristics of Good Primary Support
In order to fulfill the requirements of good primary support, the information you choose must meet the following standards:
- Be relevant to the thesis: Primary support is considered strong when it relates directly to the thesis. Primary support should show, explain, or prove your main argument without delving into irrelevant details. When faced with lots of information that could be used to prove your thesis, you may think you need to include it all in your body paragraphs. But effective writers resist the temptation to lose focus. Choose your supporting points wisely by making sure they directly connect to your thesis.
- Be specific: The main points you make about your thesis and the examples you use to expand on those points need to be more specific than the thesis. Use specific examples to provide the evidence and to build upon your general ideas. These types of examples give your reader something narrow to focus on, and if used properly, they leave little doubt about your claim. General examples, while they convey the necessary information, are not nearly as compelling or useful in writing because they are too obvious and typical.
- Be detailed: Remember that your thesis, while specific, should not be very detailed. The body paragraphs are where you develop the discussion that a thorough essay requires. Using detailed support shows readers that you have considered all the facts and chosen only the most precise details to enhance your point of view.
Pre-write to Identify Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
Recall that when you pre-write you essentially make a list of examples or reasons why you support your stance. Stemming from each point, you further provide details to support those reasons. After prewriting, you are then able to look back at the information and choose the most compelling pieces you will use in your body paragraphs.
Select the Most Effective Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
As you developed a working thesis through prewriting techniques, you may have generated a lot of information, which may be edited out later. Remember that your primary support must be relevant to your thesis. Remind yourself of your main argument, and delete any ideas that do not directly relate to it. Omitting unrelated ideas ensures that you will use only the most convincing information in your body paragraphs. Choose at least three of only the most compelling points. These will serve as the topic sentences for your body paragraphs.
When you support your thesis, you are revealing evidence. Evidence includes anything that can help support your stance. The following are the kinds of evidence you will encounter as you conduct your research:
- Facts: Facts are the best kind of evidence to use because they often cannot be disputed. They can support your stance by providing background information on or a solid foundation for your point of view. However, some facts may still need explanation. For example, the sentence “The most populated state in the United States is California” is a pure fact, but it may require some explanation to make it relevant to your specific argument.
- Judgments: Judgments are conclusions drawn from the given facts. Judgments are more credible than opinions because they are founded upon careful reasoning and examination of a topic.
- Testimony: Testimony consists of direct quotations from either an eyewitness or an expert witness. An eyewitness is someone who has direct experience with a subject; he adds authenticity to an argument based on facts. An expert witness is a person who has extensive experience with a topic. This person studies the facts and provides commentary based on either facts or judgments, or both. An expert witness adds authority and credibility to an argument.
- Personal observation: Personal observation is similar to testimony, but personal observation consists of your testimony. It reflects what you know to be true because you have experiences and have formed either opinions or judgments about them. For instance, if you are one of five children and your thesis states that being part of a large family is beneficial to a child’s social development, you could use your own experience to support your thesis.
You can consult a vast pool of resources to gather support for your stance. Citing relevant information from reliable sources ensures that your reader will take you seriously and consider your assertions. Use any of the following sources for your essay: newspapers or news organization websites, magazines, encyclopedias, and scholarly journals, which are periodicals that address topics in a specialized field. When using sources, you are responsible for properly documenting the borrowed information properly. Refer to the section “ Using Sources” for more information.
Choose Supporting Topic Sentences
Each body paragraph contains a topic sentence that states one aspect of your thesis and then expands upon it. Like the thesis statement, each topic sentence should be specific and supported by concrete details, facts, or explanations.
Each body paragraph should comprise the following elements: topic sentence + supporting details (examples, reasons, or arguments)
As you read in Writing Paragraphs , topic sentences indicate the location and main points of the basic arguments of your essay. These sentences are vital to writing your body paragraphs because they always refer back to and support your thesis statement. Topic sentences are linked to the ideas you have introduced in your thesis, thus reminding readers what your essay is about. A paragraph without a clearly identified topic sentence may be unclear and scattered, just like an essay without a thesis statement.
Unless your professor instructs otherwise, you should include at least three body paragraphs in your essay. A five-paragraph essay, including the introduction and conclusion, is commonly the standard for exams and essay assignments because it is meant to help students create fully developed essays; however, writers should maintain flexibility and not expect all essays to conform to that model. The emphasis is on creating an essay that provides enough support to tell a story, create an image or idea, or inform or persuade the audience.
Consider the following example of a thesis statement:
Author J.D. Salinger relied primarily on his personal life and belief system as the foundation for the themes in the majority of his works.
The following topic sentence is a primary supporting point for the thesis. The topic sentence states exactly what the controlling idea of the paragraph is .
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from post-traumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced themes in many of his works.
The following paragraph contains supporting detail sentences for the primary support sentence (the topic sentence), which is underlined.
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from post-traumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced the themes in many of his works. He did not hide his mental anguish over the horrors of war and once told his daughter, “You never really get the smell of burning flesh out of your nose, no matter how long you live.” His short story “A Perfect Day for Bananafish” details a day in the life of a WWII veteran who was recently released form an army hospital for psychiatric problems. The man acts questionably with a little girl he meets on the beach before he returns to his hotel room and commits suicide. Another short Story, “For Esme – with Love and Squalor,” is narrated by a traumatized soldier who sparks an unusual relationship with a young girl he meets before he departs to partake in D-Day. Finally, in Salinger’s only novel, the Catcher in The Rye, he continues with the theme of posttraumatic stress, though not directly related to war. From a rest home for the mentally ill, sixteen-year-old Holden Caulfield narrates the story of his nervous breakdown following the death of his younger brother.
Draft Supporting Detail Sentences for Each Primary Support Sentence
After deciding which primary support points you will use as your topic sentences, you must add details to clarify and demonstrate each of those points. These supporting details provide examples, facts, or evidence that support the topic sentence. The writer drafts possible supporting detail sentences for each primary support sentence based on the thesis statement:
Thesis: Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
I. Dogs can scare cyclists.
A. Cyclists are forced to zigzag on the roads.
B. School children panic and turn wildly on their bikes.
C. People walking at night freeze in fear.
II. Loose dogs are traffic hazards.
A. Dogs in the street make people swerve their cars.
B. To avoid dogs, drivers run into other cars or pedestrians.
C. Children coaxing dogs across city streets create danger.
III. Unleashed dogs damage gardens.
A. They step on flowers and vegetables.
B. They destroy hedges by urinating on them.
C. They mess up lawns by digging holes.
You have the option of writing your topic sentences in one of three ways. You can state it at the beginning of the body paragraph, or at the end of the paragraph, or you do not have to write it at all. This is called an implied topic sentence . An implied topic sentence lets readers form the main idea for themselves. For beginning writers, it is best to not use implied topic sentences because it makes it harder to focus your writing. Your instructor may also want to clearly identify the sentences that support your thesis.
- Your body paragraphs should closely follow the path set forth by your thesis statement.
- Strong body paragraphs contain evidence that supports your thesis.
- Primary support comprises the most important points you use to support your thesis. Strong primary support is specific, detailed, and relevant to the thesis.
- Prewriting helps you determine your most compelling primary support.
- Evidence includes facts, judgments, testimony, and personal observation.
- Reliable sources may include newspapers, magazines, academic journals, books, encyclopedias, and firsthand testimony.
- A topic sentence presents one point of your thesis statement while the information in the rest of the paragraph supports that point.
- A body paragraph comprises a topic sentence plus supporting details.
Print out the first draft of your essay and use a highlighter to mark your topic sentences in the body paragraphs. Make sure they are clearly stated and accurately present your paragraphs, as well as accurately reflect your thesis. If your topic sentence contains information that does not exist in the rest of the paragraph, rewrite it to more accurately match the rest of the paragraph.
EXERCISE 9 Home
Choose one of the following working thesis statements. On a separate sheet of paper, write for at least five minutes using one of the prewriting techniques you learned in Chapter 2, “Pre-Writing Techniques.”
- Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
- Students cheat for many different reasons.
- Drug use among teens and young adults is a problem.
- The most important change that should occur at my college or university is _______________________________________________
EXERCISE 10 Home
Refer to the previous Exercise 9 and select three of your most compelling reasons to support the thesis statement. Remember that the points you choose must be specific and relevant to the thesis. The statements you choose will be your primary support points, and you will later incorporate them into the topic sentences for the body paragraphs.
Collaboration : Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
EXERCISE 11 Home
In the previous Exercise 10 , you chose three of your most convincing points to support the thesis statement you selected from the list. Take each point and incorporate it into a topic sentence for each body paragraph.

EXERCISE 12
Using the three topic sentences you composed for the thesis statement in Exercise 11 , draft at least three supporting details for each point.

Drafting Introductory and Concluding Paragraphs
Picture your introduction as a storefront window: You have a certain amount of space to attract your customers (readers) to your goods (subject) and bring them inside your store (discussion). Once you have enticed them with something intriguing, you then point them in a specific direction and try to make the sale (convince them to accept your thesis). Your introduction is an invitation to your readers to consider what you have to say and then to follow your train of thought as you expand upon your thesis statement.
Writing an Introduction
An introduction serves the following purposes:
- Establishes your voice and tone, or your attitude, toward the subject
- Introduces the general topic of the essay
- States the thesis that will be supported in the body paragraphs
First impressions are crucial and can leave lasting effects in your reader’s mind, which is why the introduction is so important to your essay. If your introductory paragraph is dull or disjointed, your reader probably will not have much interest in continuing with the essay.
Attracting Interest in Your Introductory Paragraph
Your introduction should begin with an engaging statement devised to provoke your readers’ interest. In the next few sentences, introduce them to your topic by stating general facts or ideas about the subject. As you move deeper into your introduction, you gradually narrow the focus, moving closer to your thesis. Moving smoothly and logically from your introductory remarks to your thesis statement can be achieved using a funnel technique, as illustrated in the diagram “Funnel Technique.”
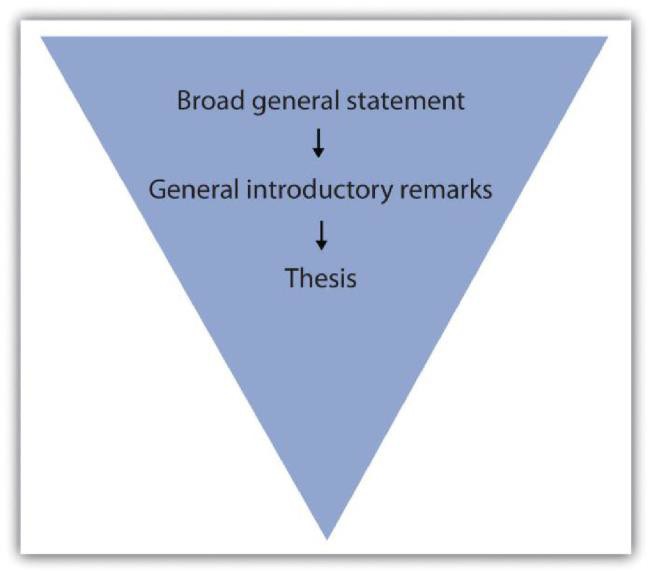
Immediately capturing your readers’ interest increases the chances of having them read what you are about to discuss. You can garner curiosity for your essay in a number of ways. Try to get your readers personally involved by doing any of the following:
- Appealing to their emotions
- Using logic
- Beginning with a provocative question or opinion
- Opening with a startling statistic or surprising fact
- Raising a question or series of questions
- Presenting an explanation or rationalization for your essay
- Opening with a relevant quotation or incident
- Opening with a striking image
- Including a personal anecdote
Remember that your diction, or word choice, while always important, is most crucial in your introductory paragraph. Boring diction could extinguish any desire a person might have to read through your discussion. Choose words that create images or express action.
Earlier in this chapter we followed Romina as she moved through the writing process. In this section, Romina writes her introduction and conclusion for the same essay. Romina incorporates some of the introductory elements into her introductory paragraph, which she previously outlined. Her thesis statement is underlined.
Play Atari on a General Electric brand television set? Maybe watch Dynasty? Or read old newspaper articles on microfiche at the library? Twenty-five years ago, the average college student did not have many options when it came to entertainment in the form of technology. Fast forward to the twenty-first century, and the digital age has revolutionized the way people entertain themselves. In today’s rapidly evolving world of digital technology, consumers are bombarded with endless options for how they do most everything, from buying and reading books to taking and developing photographs. In a society that is obsessed with digital means of entertainment, it is easy for the average person to become baffled. Everyone wants the newest and best digital technology, but the choices are many and the specifications are often confusing.
Writing a Conclusion
It is not unusual to want to rush when you approach your conclusion, and even experienced writers may fade. But what good writers remember is that it is vital to put just as much attention into the conclusion as in the rest of the essay. After all, a hasty ending can undermine an otherwise strong essay.
A conclusion that does not correspond to the rest of your essay, has loose ends, or is unorganized can unsettle your readers and raise doubts about the entire essay.
However, if you have worked hard to write the introduction and body, your conclusion can often be the most logical part to compose.
The Anatomy of a Strong Conclusion
Keep in mind that the ideas in your conclusion must conform to the rest of your essay. In order to tie these components together, restate your thesis at the beginning of your conclusion. This helps you assemble, in an orderly fashion, all the information you have explained in the body. Repeating your thesis reminds your readers of the major arguments you have been trying to prove and also indicates that your essay is drawing to a close. A strong conclusion also reviews your main points and emphasizes the importance of the topic.
The construction of the conclusion is similar to the introduction, in which you make general introductory statements and then present your thesis. The difference is that in the conclusion you first paraphrase, or state in different words, your thesis and then follow up with general concluding remarks. These sentences should progressively broaden the focus of your thesis and maneuver your readers out of the essay.
Many writers like to end their essays with a final emphatic statement. This strong closing statement will cause your readers to continue thinking about the implications of your essay; it will make your conclusion, and thus your essay, more memorable. Another powerful technique is to challenge your readers to make a change in either their thoughts or their actions. Challenging your readers to see the subject through new eyes is a powerful way to ease yourself and your readers out of the essay.
When closing your essay, do not expressly state that you are drawing to a close. Relying on statements such as in conclusion , it is clear that , as you can see , or in summation is unnecessary and can be considered trite.
It is wise to avoid doing any of the following in your conclusion:
- Introducing new material : Introducing new material in your conclusion has an unsettling effect on your reader. When you raise new points, you make your reader want more information, which you could not possibly provide in the limited space of your final paragraph.
- Contradicting your thesis: Contradicting or changing your thesis statement causes your readers to think that you do not actually have a conviction about your topic. After all, you have spent several paragraphs adhering to a specific point of view.
- Changing your thesis: When you change sides or open up your point of view in the conclusion, your reader becomes less inclined to believe your original argument.
- Using apologies or disclaimers: By apologizing for your opinion or stating that you know it is tough to digest, you are in fact admitting that even you know what you have discussed is irrelevant or unconvincing. You do not want your readers to feel this way. Effective writers stand by their thesis statement and do not stray from it.
Romina incorporates some of these pointers into her conclusion. She has paraphrased her thesis statement in the first sentence, which is underlined.
In a society fixated on the latest and smartest digital technology, a consumer can easily become confused by the countless options and specifications. The ever-changing state of digital technology challenges consumer with its updates and add-ons and expanding markets and incompatible formats and restrictions – a fact that is complicated by salesmen who want to sell them anything. In a world that is increasingly driven by instant gratification, it’s easy for people to buy the first thing they see. The solution for many people should be to avoid buying on impulse. Consumers should think about what they really need, not what is advertised.
Make sure your essay is balanced by not having an excessively long or short introduction or conclusion. Check that they match each other in length as closely as possible, and try to mirror the formula you used in each. Parallelism strengthens the message of your essay.
EXERCISE 14 Home
On a separate sheet of a paper, restate your thesis from an earlier exercise in this section and then make some general concluding remarks. Next, compose a final emphatic statement. Finally, incorporate what you have written into a strong conclusion paragraph for your essay.
Revising and Editing Home
Revising and editing are the two tasks you undertake to significantly improve your essay. Both are very important elements of the writing process. You may think that a completed first draft means little improvement is needed. However, even experienced writers need to improve their drafts and rely on peers during revising and editing. You may know that athletes miss catches, fumble balls, or overshoot goals. Dancers forget steps, turn too slowly, or miss beats. For both athletes and dancers, the more they practice, the stronger their performance will become. Web designers seek better images, a more clever design, or a more appealing background for their web pages. Writing has the same capacity to profit from improvement and revision.
Understanding the Purpose of Revising and Editing
Revising and editing allow you to examine two important aspects of your writing separately, so that you can give each task your undivided attention.
- When you revise , you take a second look at your ideas. You might add, cut, move, or change information in order to make your ideas clearer, more accurate, more interesting, or more convincing.
- When you edit , you take a second look at how you expressed your ideas. You add or change words. You fix any problems in grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure. You improve your writing style. You make your essay into a polished, mature piece of writing, the end product of your best efforts.
Here are some strategies that writers have developed to look at their first drafts from a fresh perspective. Try them over the course of this semester; then keep using the ones that bring results.
- Take a break. You are proud of what you wrote, but you might be too close to it to make changes. Set aside your writing for a few hours or even a day until you can look at it objectively.
- Ask someone you trust for feedback and constructive criticism.
- Use the resources that your college provides. Find out where your school’s writing lab is located and ask about the assistance they provide online and in person.
- Pretend you are one of your readers. Are you satisfied or dissatisfied? Why?
Many people hear the words critic , critical , and criticism and pick up only negative vibes that provoke feelings that make them blush, grumble, or shout. However, as a writer and a thinker, you need to learn to be critical of yourself in a positive way and have high expectations for your work. You also need to train your eye and trust your ability to fix what needs fixing. For this, you need to teach yourself where to look.
When you reread your writing to find revisions to make, look for each type of problem in a separate sweep. Read it straight through once to locate any problems with unity.
Read it straight through a second time to find problems with coherence. You may follow this same practice during many stages of the writing process.
Completing a Peer Review
After working so closely with a piece of writing, writers often need to step back and ask for a more objective reader. What writers most need is feedback from readers who can respond only to the words on the page. When they are ready, writers show their drafts to someone they respect and who can give an honest response about its strengths and weaknesses.
You, too, can ask a peer to read your draft when it is ready. After evaluating the feedback and assessing what is most helpful, the reader’s feedback will help you when you revise your draft. This process is called peer review . You can work with a partner in your class and identify specific ways to strengthen each other’s essays. Although you may be uncomfortable sharing your writing at first, remember that each writer is working toward the same goal: a final draft that fits the audience and the purpose. Maintaining a positive attitude when providing feedback will put you and your partner at ease. The box that follows provides a useful framework for the peer review session.
<Embed Peer Review Form Here>
EXERCISE 15
Exchange essays with a classmate and complete a peer review of each other’s draft in progress. Remember to give positive feedback and to be courteous and polite in your responses. Focus on providing one positive comment and one question for more information to the author.
Using Feedback
Using Feedback Objectively
The purpose of peer feedback is to receive constructive criticism of your essay. Your peer reviewer is your first real audience, and you have the opportunity to learn what confuses and delights a reader so that you can improve your work before sharing the final draft with a wider audience (or your intended audience). It may not be necessary to incorporate every recommendation your peer reviewer makes. However, if you start to observe a pattern in the responses you receive from peer reviewers, you might want to take that feedback into consideration in future assignments. For example, if you read consistent comments about a need for more research, then you may want to consider including more research in future assignments.
Using Feedback from Multiple Sources
You might get feedback from more than one reader as you share different stages of your revised draft. In this situation, you may receive feedback from readers who do not understand the assignment or who lack your involvement with and enthusiasm for it.
You need to evaluate the responses you receive according to two important criteria:
- Determine if the feedback supports the purpose of the assignment.
- Determine if the suggested revisions are appropriate to the audience.
Then, using these standards, accept or reject revision feedback.
EXERCISE 16
Work with two partners. Go back Exercise 14 in this lesson and compare your responses to Romina’s paragraph, with your partners’ response. Recall Romina’s purpose for writing and her audience. Then, working individually, list where you agree and where you disagree about revision needs.
Creating Unity and Coherence
Following your outline closely offers you a reasonable guarantee that your writing will stay on purpose and not drift away from the controlling idea. However, when writers are rushed, are tired, or cannot find the right words, their writing may become less than they want it to be. Their writing may no longer be clear and concise, and they may be adding information that is not needed to develop the main idea.
When a piece of writing has unity, all the ideas in each paragraph and in the entire essay clearly belong and are arranged in an order that makes logical sense. When the writing has coherence, the ideas flow smoothly. The wording clearly indicates how one idea leads to another within a paragraph and from paragraph to paragraph.
Reading your writing aloud will often help you find problems with unity and coherence. Listen for the clarity and flow of your ideas. Identify places where you find yourself confused, and write a note to yourself about possible fixes.
Creating Unity
Sometimes writers get caught up in the moment and cannot resist a good digression. Even though you might enjoy such detours when you chat with friends, unplanned digressions usually harm a piece of writing.
Romina stayed close to her outline when she drafted the three body paragraphs of her essay she tentatively titled “Digital Technology: The Newest and the Best at What Price?” But a recent shopping trip for an HDTV upset her enough that she digressed from the main topic of her third paragraph and included comments about the sales staff at the electronics store she visited. When she revised her essay, she deleted the off- topic sentences that affected the unity of the paragraph. Read the following paragraph twice, the first time without Romina’s changes, and the second time with them.
Nothing is more confusing to me than choosing among televisions. It confuses lots of people who want a new high-definition digital television (HDTV) with a large screen to watch sports and DVDs on. You could listen to the guys in the electronics store, but word has it they know little more than you do. They want to sell you what they have in stock, not what best fits your needs. You face decisions you never had to make with the old, bulky picture-tube televisions. Screen resolution means the number of horizontal scan lines the screen can show. This resolution is often 1080p, or full HD, or 768p. The trouble is that if you have a smaller screen, 32 inches or 37 inches, you won’t be able to tell the difference with the naked eye. The 1080p televisions cost more, though, so those are what the salespeople want you to buy. They get bigger commissions. The other important decision you face as you walk around the sales floor is whether to get a plasma screen or an LCD screen. Now here the salespeople may finally give you decent info. Plasma flat-panel television screens can be much larger in diameter than their LCD rivals. Plasma screens show decent lacks and can be viewed at a wider angle than current LCD screens. But be careful and tell the salesperson you have budget constraints . Large flat-panel plasma screens are much more expensive than flat-screen LCD models. Don’t let someone make you buy more television than you need!
EXERCISE 17
1) Answer the following two questions about Romina’s paragraph:
- Do you agree with Mariah’s decision to make the deletions she made? Did she cut too much, too little, or just enough? Explain.
- Is the explanation of what screen resolution means a digression? Or is it audience friendly and essential to understanding the paragraph? Explain.
2) Now start to revise the first draft of the essay you wrote at the end of Writing Your Own First Draft . Reread it to find any statements that affect the unity of your writing. Decide how best to revise.
Creating Coherence
Careful writers use transitions to clarify how the ideas in their sentences and paragraphs are related. These words and phrases help the writing flow smoothly. Adding transitions is not the only way to improve coherence, but they are often useful and give a mature feel to your essays. The Table of Common Transitional Words and Phrases groups many common transitions according to their purpose.
After Romina revised for unity, she next examined her paragraph about televisions to check for coherence. She looked for places where she needed to add a transition or perhaps reword the text to make the flow of ideas clear. In the version that follows, she has already deleted the sentences that were off topic.
Many writers make their revisions on a printed copy and then transfer them to the version on-screen. They conventionally use a small arrow called a caret (^) to show where to insert an addition or correction.
^ Finally, Nothing is more confusing to me than choosing among televisions. It confuses lots of people who want a new high-definition digital television (HD television) with a large screen to watch sports and DVDs on. ^ There’s good reason for this confusion: You face a decision you never had to make with the old, bulky picture-tube televisions. ^ The first big decision is the screen resolution you want. Screen resolution means the number of horizontal scan lines the screen can show. This resolution is often 1080p, or full HD, or 768p. The trouble is that if you have a smaller screen, 32 inches or 37 inches diagonal, you won’t be able to tell the difference with the naked eye. The ^ second other important decision you face as you walk around the sales floor is whether to get a plasma screen or an LCD screen. ^ Along with the choice of display type, a further decision buyers face is screen size and features. Plasma flat-panel television screens can be much larger in diameter than their LCD rivals. Plasma screens show truer blacks and can be viewed at a wider angle than current LCD screens. ^ However, Large flat-panel plasma screens are much more expensive than flat-screen LCD models. Don’t buy more television than you need!
EXERCISE 18
1) Answer the following questions about Romina’s revised paragraph.
- Do you agree with the transitions and other changes that Romina made to her paragraph? Which would you keep and which were unnecessary? Explain.
- What transition words or phrases did Romina add to her paragraph? Why did she choose each one?
- What effect does adding additional sentences have on the coherence of the paragraph? Explain. When you read both versions aloud, which version has a more logical flow of ideas? Explain.
2) Now return to the first draft of the essay you wrote in Starting Your First Draft and revise it for coherence. Add transition words and phrases where they are needed, and make any other changes that are needed to improve the flow and connection between ideas.
Being Clear and Concise
Some writers are very methodical and painstaking when they write a first draft. Other writers unleash a lot of words in order to get out all that they feel they need to say. Do either of these composing styles match your style? Or is your composing style somewhere in between? No matter which description best fits you, the first draft of almost every piece of writing, no matter its author, can be made clearer and more concise. If you have a tendency to write too much, you will need to look for unnecessary words. If you have a tendency to be vague or imprecise in your wording, you will need to find specific words to replace any overly general language.
Identifying Wordiness
Sometimes writers use too many words when fewer words will appeal more to their audience and better fit their purpose. Here are some common examples of wordiness to look for in your draft. Eliminating wordiness helps all readers, because it makes your ideas clear, direct, and straightforward.
- Sentences that begin with There is or There are .
Wordy: There are two major experiments that the Biology Department sponsors.
Revised: The Biology Department sponsors two major experiments.
- Sentences with unnecessary modifiers.
Wordy: Two extremely famous and well-known consumer advocates spoke eloquently in favor of the proposed important legislation.
Revised: Two well-known consumer advocates spoke in favor of the proposed legislation.
- Sentences with deadwood phrases that add little to the meaning. Be judicious when you use phrases such as in terms of , with a mind to , on the subject of , as to whether or not , more or less , as far as…is concerned , and similar expressions. You can usually find a more straightforward way to state your point.
Wordy: As a world leader in the field of green technology, the company plans to focus its efforts in the area of geothermal energy.
A report as to whether or not to use geysers as an energy source is in the process of preparation.
Revised: As a world leader in green technology, the company plans to focus on geothermal energy. A report about using geysers as an energy source is in preparation.
- Sentences in the passive voice or with forms of the verb to be . Sentences with passive-voice verbs often create confusion, because the subject of the sentence does not perform an action. Sentences are clearer when the subject of the sentence performs the action and is followed by a strong verb. Use strong active-voice verbs in place of forms of to be , which can lead to wordiness. Avoid passive voice when you can.
Wordy: It might perhaps be said that using a GPS device is something that is a benefit to drivers who have a poor sense of direction.
Revised: Using a GPS device benefits drivers who have a poor sense of direction.
- Sentences with constructions that can be shortened.
Wordy: The ebook reader, which is a recent invention, may become as commonplace as the cell phone. My over-sixty uncle bought an ebook reader, and his wife bought an ebook reader, too.
Revised: The ebook reader, a recent invention, may become as commonplace as the cell phone. My over-sixty uncle and his wife both bought ebook readers.
EXERCISE 19
Now return once more to the first draft of the essay you have been revising. Check it for unnecessary words. Try making your sentences as concise as they can be.
Choosing Specific, Appropriate Words
Most college essays should be written in formal English, suitable for an academic situation. Follow these principles to be sure that your word choice is appropriate.
- Avoid slang: Find alternatives to bummer , kewl , and rad .
- Avoid language that is overly casual: Write about “men and women” rather than “girls and guys” unless you are trying to create a specific effect. A formal tone calls for formal language.
- Avoid contractions: Use do not in place of don’t , I am in place of I’m , have not in place of haven’t , and so on. Contractions are considered casual speech.
- Avoid clichés: Overused expressions such as green with envy , face the music , better late than never , and similar expressions are empty of meaning and may not appeal to your audience.
- Be careful when you use words that sound alike but have different meanings: Some examples are allusion/illusion, complement/compliment, council/counsel, concurrent/consecutive, founder/flounder, and historic/historical. When in doubt, check a dictionary.
- Choose words with the connotations you want: Choosing a word for its connotations is as important in formal essay writing as it is in all kinds of writing. Compare the positive connotations of the word proud and the negative connotations of arrogant and conceited .
- Use specific words rather than overly general words: Find synonyms for thing , people , nice , good , bad , interesting , and other vague words. Or use specific details to make your exact meaning clear.
Now read the revisions Romina made to make her third paragraph clearer and more concise. She has already incorporated the changes she made to improve unity and coherence.
Finally, nothing ^ confuses buyers more than purchasing is more confusing to me than choosing among televisions. It confuses lots of people who want a new high-definition digital television (HDTV), with a large screen to watch sports and DVDs on. ^and with There’s a good reason. for this confusion. You face decisions you never had to make with the old, bulky picture-tube televisions. The first big decision is ^ involves screen resolution, you want . ^ which Screen resolution means the number of horizontal scan lines the screen can show. This resolution is often 1080p, or full HD, or ^ as 720p. The trouble is that ^ on if you have a smaller screen, 32-inch or 37-inch diagonal, ^ screen, viewers will not you won’t be able to tell the difference ^ between them with the naked eye. The other important decision you face as you walk around the sales floor is whether to get a plasma screen or an LCD screen. Along with the choice of display type, a further decision buyers face is screen size and features. Plasma flat-panel television screens can be much larger in diameter than their LCD rivals. Plasma screens show truer ^ deeper blacks and can be viewed at a wider angle than current LCD screens. However, large flat-panel plasma screens are much more expensive than flat-screen LCD models. ^ Only after buyers are totally certain they know what they want should they open their wallets. Don’t buy more television than you need!
EXERCISE 20
1. Answer the following questions about Romina’s revised paragraph:
a. Read the unrevised and the revised paragraphs aloud. Explain in your own words how changes in word choice have affected Romina’s writing.
b. Do you agree with the changes that Romina made to her paragraph? Which changes would you keep and which were unnecessary? Explain. What other changes would you have made?
c. What effect does removing contractions and the pronoun you have on the tone of the paragraph? How would you characterize the tone now? Why?
2. Now return once more to your essay in progress. Read carefully for problems with word choice. Be sure that your draft is written in formal language and that your word choice is specific and appropriate.
Editing Your Draft
If you have been incorporating each set of revisions as Romina has, you have produced multiple drafts of your writing. So far, all your changes have been content changes.
Perhaps with the help of peer feedback, you have made sure that you sufficiently supported your ideas. You have checked for problems with unity and coherence. You have examined your essay for word choice, revising to cut unnecessary words and to replace weak wording with specific and appropriate wording.
The next step after revising the content is editing . When you edit, you examine the surface features of your text. You examine your spelling, grammar, usage, and punctuation. You also make sure you use the proper format when creating your finished assignment.
Editing often takes time. Budgeting time into the writing process allows you to complete additional edits after revising. Editing and proofreading your writing helps you create a finished work that represents your best efforts. Here are a few more tips to remember about your readers:
- Readers do not notice correct spelling, but they do notice misspellings. Readers look past your sentences to get to your ideas—unless the sentences are awkward, poorly constructed, and frustrating to read.
- Readers notice when every sentence has the same rhythm as every other sentence, with no variety.
- Readers do not cheer when you use there, their, and they’re correctly; but they notice when you do not.
- Readers will notice the care with which you handled your assignment and your attention to detail in the delivery of an error-free document.
Unit 12 offers a useful review of grammar, mechanics, and usage. Use it to help you eliminate major errors in your writing and refine your understanding of the conventions of language. Do not hesitate to ask for help, too, from peer tutors in your academic department or in the college’s Writing Center. In the meantime, use the following checklists to help you edit your writing.
Checklists for Editing Your Writing
- Are some sentences actually sentence fragments?
- Are some sentences run-on sentences? How can I correct them?
- Do some sentences need conjunctions between independent clauses?
- Does every verb agree with its subject?
- Is every verb in the correct tense?
- Are tense forms, especially for irregular verbs, written correctly?
- Have I used subject, object, and possessive personal pronouns correctly?
- Have I used who and whom correctly?
- Is the antecedent of every pronoun clear?
- Do all personal pronouns agree with their antecedents?
- Have I used the correct comparative and superlative forms of adjectives and adverbs?
- Is it clear which word a participial phrase modifies, or is it a dangling modifier?
Sentence Structure
- Are all my sentences simple sentences, or do I vary my sentence structure?
- Have I chosen the best coordinating or subordinating conjunctions to join clauses?
- Have I created long, overpacked sentences that should be shortened for clarity?
- Do I see any mistakes in parallel structure?
Punctuation
- Does every sentence end with the correct end punctuation?
- Can I justify the use of every exclamation point?
- Have I used apostrophes correctly to write all singular and plural possessive forms?
- Have I used quotation marks correctly?
Mechanics and Usage
- Can I find any spelling errors? How can I correct them?
- Have I used capital letters where they are needed?
- Have I written abbreviations, when allowed, correctly?
- Can I find any errors in the use of commonly confused words, such as to/too/two?
Be careful about relying too much on spelling checkers and grammar checkers. A spelling checker cannot recognize that you meant to write principle but wrote principal instead. A grammar checker often queries constructions that are perfectly correct. The program does not understand your meaning; it makes its check against a general set of formulas that might not apply in each instance. If you use a grammar checker, accept the suggestions that make sense, but consider why the suggestions came up.
Proofreading requires patience; it is very easy to read past a mistake. Set your paper aside for at least a few hours, if not a day or more, so your mind will rest. Some professional proofreaders read a text backward so they can concentrate on spelling and punctuation. Another helpful technique is to slowly read a paper aloud, paying attention to every word, letter, and punctuation mark. If you need additional proofreading help, ask a reliable friend, a classmate, or a peer tutor to make a final pass on your paper to look for anything you missed.
Remember to use proper format when creating your finished assignment. Sometimes an instructor, a department, or a college will require students to follow specific instructions on titles, margins, page numbers, or the location of the writer’s name.
These requirements may be more detailed and rigid for research projects and term papers, which often observe the Modern Language Association (MLA) style guide, especially when citations of sources are included. To ensure the format is correct and follows any specific instructions, make a final check before you submit an assignment.
EXERCISE 21
With the help of the checklist, edit and proofread your essay.
- Revising and editing are the stages of the writing process in which you improve your work before producing a final draft.
- During revising, you add, cut, move, or change information in order to improve content.
- During editing, you take a second look at the words and sentences you used to express your ideas and fix any problems in grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure.
- Unity in writing means that all the ideas in each paragraph and in the entire essay clearly belong together and are arranged in an order that makes logical sense.
- Coherence in writing means that the writer’s wording clearly indicates how one idea leads to another within a paragraph and between paragraphs.
- Transitional words and phrases effectively make writing more coherent. Writing should be clear and concise, with no unnecessary words.
- Effective formal writing uses specific, appropriate words and avoids slang, contractions, clichés, and overly general words.
- Peer reviews, done properly, can give writers objective feedback about their writing. It is the writer’s responsibility to evaluate the results of peer reviews and incorporate only useful feedback.
- Remember to budget time for careful editing and proofreading. Use all available resources, including editing checklists, peer editing, and your institution’s writing lab, to improve your editing skills.
EXERCISE 22
Write a thesis statement and a formal sentence outline for an essay about the writing process. Include separate paragraphs for prewriting, drafting, and revising and editing. Your audience will be a general audience of educated adults who are unfamiliar with how writing is taught at the community college level. Your purpose is to explain the stages of the writing process so that readers will understand its benefits.
EXERCISE 23
Group activity: Working in a peer-review group of four, go to the section on Drafting and reread the draft of the first two body paragraphs of Romina’s essay, “Digital Technology: The Newest and the Best at What Price?” Review those two paragraphs using the same level of inspection given to the essay’s third paragraph in the section Revising and Editing . Suggest and agree on changes to improve unity and coherence, eliminate unneeded words, and refine word choice. Your purpose is to help Romina produce two effective paragraphs for a formal college-level essay about her topic.
Sample Student Paper with Outline
The following paper and outline by Pere Ellis, entitled “Aquaponics: A Viable Solution to World Hunger,” clearly breaks down the argument presented in his thesis, providing specific examples in the sub-points and further developing and expanding the sub- points.
The Process Essay
The purpose of the process essay.
The purpose of a process essay is to explain how to do something (directional) or how something works (informative). In either case, the formula for a process essay remains the same. The process is articulated into clear, definitive steps.
Almost everything we do involves following a step-by-step process. From learning to ride a bike as a child to starting a new job as an adult, we initially needed instructions to effectively execute the task. Likewise, we have likely had to instruct others, so we know how important good directions are—and how frustrating it is when they are poorly put together.
EXERCISE 24 Home
On a separate sheet of paper, make a bulleted list of all the steps that you feel are required to clearly illustrate three of the following four processes (note that the first three are directional and the fourth is informative).
- Tying a shoelace
- Parallel parking
- Planning a successful first date
- How a historical event occurred (pick one you know well!)
The Structure of a Process Essay
The process essay opens with a discussion of the process and a thesis statement that states the goal of the process. The organization of a process essay typically follows chronological order. The steps of the process are conveyed in the order in which they usually occur, and so your body paragraphs will be constructed based on these steps. If a particular step is complicated and needs a lot of explaining, then it will likely take up a paragraph on its own. But if a series of simple steps is easy to understand, then the steps can be grouped into a single paragraph.
The time transition phrases covered in the Narration section are also helpful for organizing process analysis essays (see Table of Transition Words and Phrases for Expressing Time ) . Words such as first , second , third , next , and finally are cues to orient readers and organize the content of the essay.
Finally, it’s a good idea to always have someone else read your process analysis to make sure it makes sense. Once we get too close to a subject, it is difficult to determine how clearly an idea is coming across. Having a peer read over your analysis will serve as a good way to troubleshoot any confusing spots.
EXERCISE 25 Home
Choose two of the lists you created in Exercise 24 and start writing out the processes in paragraph form. Try to construct paragraphs based on the complexity of each step. For complicated steps, dedicate an entire paragraph. If less complicated steps fall in succession, group them into a single paragraph.
Writing a Process Essay
Choose a topic that is interesting, is relatively complex, and can be explained in a series of steps. As with other rhetorical writing modes, it is best to choose a process that you know well so that you can more easily describe the finer details about each step in the process. Your thesis statement should come at the end of your introduction, and it should state the final outcome of the process you are describing.
Body paragraphs are composed of the steps in the process. Each step should be expressed using strong details and clear examples. If you are writing a directional essay, you should provide every detail necessary for your reader to complete the process. If you are writing an instructional essay, your body paragraphs should explain the process and how it works, although you should not expect your reader to be actually performing the process. Use time transition phrases to help organize steps in the process and to orient readers. The conclusion should thoroughly describe the result of the process described in the body paragraphs. See the student paper, “Keep Them in Stitches,” on Canvas or your LMS, or read the sample professional essay below to read an example of a process analysis essay.
EXERCISE 26
Choose one of the expanded lists from Exercise 25. Construct a full process essay from the work you have already done. That means adding an engaging introduction, a clear thesis, time transition phrases, body paragraphs, and a solid conclusion.
Online Process Essay Alternatives:
Stanley Fish, an American literary theorist, public intellectual, and professor of humanities and law, tells us why “ Getting Coffee Is Hard to Do .”
- About Our Blog
- Essay Writing Service
30 Writing Techniques from Literature for Your Texts to Blossom
- by Lesley V.
- January 23, 2023 December 7, 2023
Whether you’re a creative content writer, a sales copywriter, a blogger, or a student, it would be helpful to know various writing techniques and understand how they work.
For web content creators, it’s an instrument of audience engagement and persuasion. When used right, writing tricks can turn ordinary texts into masterpieces your target readers will remember.
For students, it’s an instrument to craft A-worthy essays and other college papers.
In today’s blog post, we’ll reveal the list of writing techniques that come from literary works. These literary devices fit web content and academic papers, either: So, don’t hesitate to use them in your texts whenever relevant to surprise readers and make your writings stand out.
What Are Writing Techniques?
Writing techniques are tools authors use to create a specific effect on their texts. They serve to convey meanings, express ideas, and highlight core themes.
Writing techniques come from different niches: Some are literary devices peculiar to fiction works or creative non-fiction, and others are more salesy and, therefore, intrinsic to marketing texts aimed at persuading online users and making them act.
Different writing methods serve different purposes. Thus, literary devices allow writers to hint at broader themes and meanings. Some work on an intellectual level, while others are more about emotions; some operate at a sentence level, while others influence a whole writing piece.
The most famous literary device is a metaphor.
30 Writing Techniques from Literature to Try in Content
Types of writing techniques in literature are many, and, sure thing, you won’t use all writing methods in one content piece. (Though some of them work great in tandem!)
Most of them are figurative language, and your readers won’t identify each technique by name. (Though they can “feel” some literary devices’ presence when noticing an unusual narrative structure you use in texts.)
Below are 30 writing techniques from literature to consider for your creative or academic works, with these writing techniques examples for you to understand how they work in texts.
So, here we go!
- Asyndeton and polysyndeton
- Cliffhanger
- Colloquialism
- In Medias Res
- Juxtaposition
- Onomatopoeia
- Anadiplosis
- Personification
- The Rule of Three
1 — Asyndeton and Polysyndeton
Two simple yet powerful methods of writing to create rhythm in your sentences and paragraphs:
- Asyndeton is about leaving out conjunctions when writing direct statements.
- Polysyndeton is about using extra conjunctions (frequently) to create a stylistic effect.
Both are common for political speeches or when the author wants to focus the reader’s attention on a particular scene.
2 — Anastrophe
Anastrophe is a figure of speech where an author reverses the traditional sentence structure. If you are a Star Wars fan, you will understand it best: Yoda’s talking is a prime example of using apostrophes.
- “Ready are you? What know you of ready? For eight hundred years have I trained Jedi. My own counsel will I keep on who is to be trained.”
- “Patience you must have my young Padawan.”
- “Powerful you have become, the dark side I sense in you.”
Writers also use this literary device in their works:
- “Never have I found the limits of the photographic potential. Every horizon, upon being reached, reveals another beckoning in the distance.” — Eugene Smith
- “Deep into that darkness peering, long I stood there wondering, fearing.” — Edgar Allan Poe
3 — Chiasmus
As well as anastrophe, chiasmus is about a reversal sentence structure to create an artistic effect. But here you invert (crisscross) two or more parallel clauses for your message to sound more convincing.
Chiasmus is among the best friends of political speechwriters. Let’s take John F. Kennedy’s statements as an example:
- “Mankind must put an end to war or war will put an end to mankind.”
- “Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country.”
4 — Cliffhanger
Movie fans, are you here? A cliffhanger is a plot device when an author ends an episode, a chapter, or a scene in some unexpected or shocking way to hook the audience so they would keep reading or watching.
As a rule, cliffhanger endings are of two types:
- A protagonist faces a dangerous or life-threatening situation.
- A shocking revelation appears, unexpected, and able to change the whole course of the narrative.
In plain English, cliffhangers are scene endings that leave the audience with more questions than answers.
- Professor Dumbledore’s death in the Harry Potter series
- Darth Vader’s “Luke, I’m your father!” in Star Wars
- Jon Snow’s assassination in Game of Thrones
5 — Colloquialism
Colloquialism is the use of casual language in writing, including slang or dialects to provide context to characters or settings and make your texts sound more authentic.
This literary device is intrinsic to dialogues or monologues when a writer wants to demonstrate a character’s origins or background. You can use colloquialisms in blog articles, creative writing assets, or social media posts, either — given your brand voice and your target audience allow.
- “Hey Sue, what’d you get up to last night? This science test is gonna suck.”
- “Thing is, as ye git aulder, this character-deficiency gig becomes mair sapping. Thir wis a time ah used tae say tae aw the teachers, bosses, dole punters, poll-tax guys, magistrates, when they telt me ah was deficient: ‘Hi, cool it, gadge, ah’m jist me, jist intae a different sort ay gig fae youse but, ken?'”
6 — Contrast
This one is among the most popular writing tricks, emphasizing the differences between two statements, people, places, or things. Contrast is a surefire way to grab readers’ attention and explain something by comparing it to other items and highlighting their differences.
Contrast attracts attention to your words, adds drama, and makes sales copies more enchanting and persuasive. It’s a powerful technique to use in business writing .
This literary device is also among the writing techniques for essays: Students write compare-and-contrast papers where they analyze the similarities and differences between two subjects of the same category: historical figures, literary works, research methods, etc.
7 — Hypophora
Hypophora is a writing trick when an author or a character asks a question and answers it immediately. Perfect to use in web writing and explaining some concepts to the audience; in fiction, hypophora helps when a character needs to reason something aloud.
8 — Imagery
“Show, don’t tell.” As a writer, you’ve heard this expression thousands of times, haven’t you? It’s the perfect one to explain the nature of the imagery in texts, no matter if you write a novel, a blog post, or a business newsletter.
Imagery is about using figurative language in writing to evoke a sensory experience in the reader. It’s about highly descriptive adjectives, sensory words, power verbs, and other language tricks playing with readers’ senses and helping them “see, hear, smell, and taste” your text.
In other words, imagery is about directing a mental movie in your reader’s mind.
9 — In Medias Res
“In medias res” means “in the middle of things” in Latin. It’s the practice of beginning a narrative with a conflict or crucial situation, skipping a prologue, an introduction, etc. You launch straight into a scene to hook readers, and then extend and explain everything through flashbacks, dialogues, and other writing techniques.
- “ Many years later, as he faced the firing squad, Colonel Aureliano Buendía was to remember that distant afternoon when his father took him to discover ice.” — The opening line of One Hundred Years of Solitude by Gabriel García Márquez
In marketing writing and journalism, such a tactic is known as an “ inverted pyramid ,” when you present the information in descending order of importance: The most fundamental info appears at the top of a story, and non-essential details come in the following paragraphs.
Speaking of writing techniques for essays, In Media Res reflects in thesis statements a student places in introductions: core thoughts they will develop throughout the paper.
10 — Isocolon
Isocolon is a writing trick of crafting two or more words (phrases) using a similar structure, rhythm, and length. Perfect to use for slogans and catchy hooks throughout the content:
Thanks to the balanced rhythm, writings with isocolon look and sound memorable.
- Eat Healthily. Think Better. — Britannia
- Food, folks, and fun. — McDonald’s
- But in a larger sense, we cannot dedicate, we cannot consecrate, we cannot hallow this ground. — Abraham Lincoln
- I came, I saw, I conquered. (Veni, Vidi, Vici)
11 — Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition reminds contrast as it places two or more dissimilar things (concepts, themes, characters) side by side to highlight their differences that way. Other related methods of writing are oxymorons and paradoxes (see below).
- “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness.” — A Tale of Two Cities , Charles Dickens
12 — Oxymoron
While a juxtaposition is a figurative language contrasting two story elements, an oxymoron is about using two contradictory words to describe something.
Examples:
Sweet sorrow; bittersweet; sad smile; old news; joyful sadness; negative income; and so on
13 — Paradox
A paradox is a writing trick of using seemingly illogical yet true premises to encourage the audience to think outside the box. It’s a statement with contradictory ideas.
The primary example is George Orwell’s 1984 with its slogans, “War is Peace, Freedom is Slavery, Ignorance is Strength.” Contradictory, these statements have become the accepted truth in this novel’s context.
Other examples of paradox:
- “I must be cruel to be kind.” — Hamlet
- “ Life is much too important to be taken seriously.” — Oscar Wilde
Using paradoxes in your writing, you can add conflict, challenge your readers and keep them in suspense, point out some inconsistencies, or add a touch of humor.
14 — Litotes
Litotes is a literary device to affirm something positive by making a double negative. Thus, writers express certain sentiments by saying that the opposite is not the case.
- “You won’t be sorry.” (read: You’ll be happy)
- “You’re not wrong.” (read: You’re right)
- “Not bad.” (read: Good)
- “He’s not as young as he used to be.” (read: He’s old)
15 — Metaphors
A metaphor is among the most popular and widely-used writing techniques, and it’s about poetically comparing one thing to another. A writer takes a characteristic of something unknown and compares it to something known for readers to understand the meaning.
- “The sun in the west was a drop of burning gold that slid near and nearer the sill of the world.” — Lord of the Flies , William Golding
- “Her mouth was a fountain of delight.” — The Storm , Kate Chopin
As defined by Grammarly ,
A metaphor is a figure of speech that describes an object or action in a way that isn’t literally true but helps explain an idea or make a comparison.
Other literary devices to write about comparisons are similes and analogies. More on them below.
16 — Similes
Unlike metaphors, similes compare two things directly, using the words “like” or “as.” This literary device is not about specifying that two things are the same but only that they are alike .
Examples:
- “The ships were golden and huge as leviathans , their rails carved from ivory and horn. They were towed by grinning dolphins or else crewed by fifty black-haired nereids, faces silver as moonlight .” — Circe by Madeline Miller
- “Life is like a box of chocolates.” — Forrest Gump
17 — Analogies
An analogy serves a similar purpose to a simile and a metaphor: to show how two things are alike. However, the point here is not only to show but also to explain this comparison. So, analogies are a more complex writing technique than a metaphor.
- Finding that lost dog will be like finding a needle in a haystack.
- She’s as blind as a bat.
- “My mom always said life was like a box of chocolates. You never know what you’re gonna get.” — Forrest Gump (Without the second sentence here, the saying is a simile; with it, it becomes an analogy.)
18 — Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is about describing sounds. All those “buzz,” “snap,” “clap,” “moo,” “meow,” “tick-tock,” “ding-dong,” etc. are great examples of using this literary device in texts.
19 — Repetition
This writing method is exactly what it is: repetition of words or phrases to create a particular atmosphere or communicate a specific context to readers.
For example, in Stephen King’s The Shining, Jack Torrance types one phrase on his typewriter again and again: “All work and no play makes Jack a dull boy.” With such an obsessive repetition, the author demonstrates Jack’s unraveling mind.
Types of repetitions are many: epizeuxis, epistrophe, anaphora, anadiplosis, and polyptoton.
More on them below.
20 — Epizeuxis
Epizeuxis is a figurative language trick to repeat simple words or phrases to emphasize the message and get the attention of the readers. Often, there are no other words in between.
- “Never give in — never , never , never , never , in nothing great or small, large or petty, never give in except to convictions of honor and good sense.” — Winston Churchill
- “Holy , holy , holy is the Lord of hosts; the whole earth is full of his glory!” — Isaiah 6:3
21 — Epistrophe
Epistrophe is a repetition of words or phrases at the end of sentences.
- “When I was a child , I spoke as a child , I understood as a child , I thought as a child .” — 1 Corinthians 13:11
- “What lies behind us and what lies before us are tiny compared to what lies within us .” — Ralph Waldo Emerson
22 — Anaphora
Anaphora is a repetition of words or phrases at the beginning of clauses or sentences. It’s among the methods of writing most often used in poetry and speeches to provoke an emotional response from the audience.
- Stay safe. Stay well. Stay happy.
- You’re damned if you do and you’re damned if you don’t.
- “Mad world! Mad kings! Mad composition!” — William Shakespeare, King John , II
- Martin Luther King’s 1963 “I Have A Dream” speech where he repeated this expression at the beginning of each new paragraph.
23 — Anadiplosis
Anadiplosis is the repetition of words or phrases at the beginning AND end of a sentence. This writing trick creates a flow and makes paragraphs sound original and memorable.
- “Fear leads to anger . Anger leads to hate . Hate leads to suffering.”
- Yoda, Star Wars (Yes, again!)
- “The frog was a prince / The prince was a brick / The brick was an egg / The egg was a bird.” Genesis, Supper’s Ready
24 — Polyptoton
Polyptoton is a repetition of the root word in sentences and paragraphs. For example, a writer uses words like “strength” and “strong” instead of repeating the same word again and again.
- “To be ignorant of one’s ignorance is the malady of the ignorant.” — A. Bronson Alcott
- “Absolute power corrupts absolutely .” — Lord Acton
- “Not as a call to battle, though embattled we are.” — John F. Kennedy
25 — Personification
Personification is a writing technique of using human traits to describe non-human things but in figurative language only.
- “The land, released from its cycle of drudgery, seemed to be breathing a sigh of relief. And as the land relaxed, so did we.” — Wilding: The Return of Nature to a British Farm by Isabelle Tree. (The land relaxes and breathes; it’s human traits.)
- “The light danced on the surface of the water.”
26 — Symbolism
Symbolism is about representing abstract concepts and ideas through objects or non-humans. Thus, we all know that a dove represents peace while a raven might represent death. In Fitzgerald’s The Great Gatsby, Doctor T.J. Eckleburg symbolizes God judging the Jazz Age.
Other examples of symbolism include an apple as a temptation, red roses as love, a rainbow as hope, etc.
Metonymy and motif are two other literary devices sharing the same meaning as symbolism but with slight differences. (See below)
27 — Metonymy
Metonymy is about a single object representing entire institutions. The word comes from the Greek metōnymía, meaning “a change of name.”
- “The Crown” = monarchy
- “Washington” = “the U.S. government”
- “Hollywood” = the world of cinematography
- “Silicon Valley” = tech and innovative
A motif is about writing techniques in literature: It can be a symbol, an image, or a concept — anything helping to develop your narrative’s theme.
In other words, it’s a narrative element with symbolic significance.
For example, in the Harry Potter series, the motifs are a scar (destiny) and muggles vs. purebloods (racism and tolerance). In Lord of the Flies by W. Golding, motifs are fire (technology and civilization) and religion (moral truth).
In Leo Tolstoy’s Anna Karenina , a train is a motif to symbolize transition, violence, and destruction.
29 — Tautology
A tautology is about repeating oneself, expressing the same idea with different words or phrases within a sentence or a paragraph. While it often means revising your writing and removing redundancy, sometimes tautology works as a poetic emphasis.
Examples of poor use of tautology: frozen ice, added bonus, me personally, come together to unite.
Examples of good use:
30 — The Rule of Three
The rule of three is a popular writing trick among content creators: It’s the idea that groups of three words, phrases, or ideas are more engaging, effective, and memorable.
The Three Musketeers, The Three Little Pigs, “Faster, Higher, Stronger,” the Three Wise Men, “Lights, Camera, Action,” the Three Blind Mice, and tons of other examples like these ones.
Given the human brain reacts to three best, everything you need to persuade readers and make them remember your writing is to put your message in a sequence of three.
Trios create a sense of poetry and rhythm, make content more compelling to read, and add stress to your statement.
Other examples:
- In title: 37 Tips for Writing Outreach Emails That Get Opened, Read, and Clicked
- Father, Son, and Holy Spirit
- “Homes have been lost; jobs shed; businesses shuttered.” — Barack Obama’s 2008 Inaugural Speech
- Sex, Drugs & Rock-n-Roll
- Ready, Set, Go
Final Thoughts
So, here they go, the top 30 writing techniques from literature to use in your texts for more engaging and persuasive content. They work for various content types: Whether you craft blog articles, marketing texts, poetry, short stories, or novels — these literary devices help your texts blossom.
And if you’re a student looking for writing techniques for essays and wondering which of the above are okay to use in academic works, feel free to ask our writers for assistance . We are here to answer all your questions and provide professional writing services whenever you need them.
4 thoughts on “30 Writing Techniques from Literature for Your Texts to Blossom”
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Yes OK. I put it 5.
Very nice post. I can’t even imagine how much time it took to gether all this information and examples and structure it to look so compelling. Kudos to you, and thank you!
Hello, it’s a good article concerning media print! I think the techniques will look and sound engaging in newspapers or magazines’ articles. Thanks for sharing!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Use AI to Enhance Your College Essays and Thesis

With the integration of AI, the academic trends are gradually starting to leverage the AI tools to enhance the quality and efficiency of their work. From grammar correction to content generation, these digital assistants AI-powered tools have revolutionized the writing process by providing language editing, paraphrasing, and structural guidance to students navigating the complexities of scholarly writing.
Amidst this technological revolution, Paperpal stands out as the go-to academic writing assistant—equipped with intuitive interface and comprehensive suite of advanced features like language suggestions to built-in templates, tailored specifically for academic writing. Paperpal streamlines the writing process, enabling students to produce high-quality, consistent, and academically sound documents with ease.
Table of Contents
Language suggestions and consistency check (edit), paraphrase and contextual synonyms (rewrite), built-in academic writing prompts (templates).
- Why should students use Paperpal to enhance their essays and thesis?
How to Use Paperpal to Improve Your Essays and Thesis?
Paperpal’s Language and Consistency Check feature is invaluable for maintaining uniformity and professionalism in your academic writing, whether it involves tables, figures, equation labels, word forms, data formats, or variations between US and UK English. By using advanced NLP algorithms, Paperpal streamlines the proofreading process, sparing researchers from manual effort and ensuring consistent styling throughout the document. This feature swiftly detects errors, preserving coherence and professionalism in your essays and thesis writing for research.
Here’s a a step-by-step guide to enhance your essay and thesis writing for research with Paperpal:
- Sign up or log in to Paperpal and open a new or existing document.
- Go to the Edit section on the right sidebar and choose the first tab for Language or the second tab for Consistency .
- Paperpal will generate suggestions and reviews for improvement based on the provided content, helping you refine your writing effortlessly.
This feature enables users to enhance the clarity and academic tone of their writing by offering alternative word choices. By utilizing Paperpal’s paraphrasing tool, students can maintain the originality of their writing while enhancing its readability and effectiveness.
Here’s how to use it:
- Sign up or log in to your Paperpal account. Open a new document or access an existing one.
- Navigate to the Rewrite section on the right-hand pane and choose Paraphrase or Synonyms based on your needs.
- Select the content you wish to paraphrase, then click on Generate to allow Paperpal to produce an improved version of the provided information.
Similarly, for synonyms, select a specific word for which you want alternatives. Paperpal will generate suggestions that closely match the given context and adhere to academic writing norms.
Paperpal’s Templates feature includes built-in academic writing prompts, offering students a starting point for their writing tasks. These prompts cover various academic genres such as academic journals, essays, and theses writing for research, providing students with structured guidelines to follow. By leveraging these templates, students can streamline their writing process and ensure that their documents adhere to academic standards.
Here’s how to access this feature:
- Sign up or log in to your Paperpal account and open a new document or access an existing one.
- Navigate to the right sidebar and select Templates . From the list of options, choose the built-in prompts that best suit your requirements.
Why should students use Paperpal to enhance their essays and thesis?
In academic writing, precision, clarity, and adherence to norms are crucial. Paperpal stands out in this category, with a range of advanced capabilities designed exclusively for scholarly writing. Here’s why students should use Paperpal to improve their essays and theses:
Writing Quality: With advanced grammar and vocabulary correction, precise rephrase suggestions, adherence to academic writing conventions, meticulous consistency checks, and invaluable writing tips, Paperpal ensures that your academic work reflects the highest standard of clarity and professionalism.
Consistency and Accuracy: Ensures consistency throughout the document. Paperpal identifies spelling errors, verb tense issues, and offers rephrasing options. This feature acts as a virtual writing assistant, helping students produce error-free and polished documents.
No Prompt Writing: Paperpal’s in-built academic writing prompts embedded with templates eliminates the need to write lengthy prompts to get academically aligned results. Students can use this time organize their thoughts and ideas more effectively.
Consistent Learning: Paperpal’s suggestions come with in-depth reasoning that allows students to learn their mistakes and not repeat them. Instead of bulk correcting all errors in a go, Paperpal empowers students to achieve academic writing perfection over time.
Paperpal has helped 750,000 students and researchers ace their essays, thesis, research papers, and more. Before submitting your essay, thesis, or an any other academic work, give Paperpal a try !
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What are Journal Guidelines on Using Generative AI Tools
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- Webinar: How to Use Generative AI Tools Ethically in Your Academic Writing
AI + Human Expertise – A Paradigm Shift In Safeguarding Research Integrity
What is hedging in academic writing , you may also like, how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid..., how to write an essay introduction (with examples)....
To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- Backchannel
- Newsletters
- WIRED Insider
- WIRED Consulting
Amanda Hoover
Students Are Likely Writing Millions of Papers With AI
Students have submitted more than 22 million papers that may have used generative AI in the past year, new data released by plagiarism detection company Turnitin shows.
A year ago, Turnitin rolled out an AI writing detection tool that was trained on its trove of papers written by students as well as other AI-generated texts. Since then, more than 200 million papers have been reviewed by the detector, predominantly written by high school and college students. Turnitin found that 11 percent may contain AI-written language in 20 percent of its content, with 3 percent of the total papers reviewed getting flagged for having 80 percent or more AI writing. (Turnitin is owned by Advance, which also owns Condé Nast, publisher of WIRED.) Turnitin says its detector has a false positive rate of less than 1 percent when analyzing full documents.
ChatGPT’s launch was met with knee-jerk fears that the English class essay would die . The chatbot can synthesize information and distill it near-instantly—but that doesn’t mean it always gets it right. Generative AI has been known to hallucinate , creating its own facts and citing academic references that don’t actually exist. Generative AI chatbots have also been caught spitting out biased text on gender and race . Despite those flaws, students have used chatbots for research, organizing ideas, and as a ghostwriter . Traces of chatbots have even been found in peer-reviewed, published academic writing .
Teachers understandably want to hold students accountable for using generative AI without permission or disclosure. But that requires a reliable way to prove AI was used in a given assignment. Instructors have tried at times to find their own solutions to detecting AI in writing, using messy, untested methods to enforce rules , and distressing students. Further complicating the issue, some teachers are even using generative AI in their grading processes.
Detecting the use of gen AI is tricky. It’s not as easy as flagging plagiarism, because generated text is still original text. Plus, there’s nuance to how students use gen AI; some may ask chatbots to write their papers for them in large chunks or in full, while others may use the tools as an aid or a brainstorm partner.
Students also aren't tempted by only ChatGPT and similar large language models. So-called word spinners are another type of AI software that rewrites text, and may make it less obvious to a teacher that work was plagiarized or generated by AI. Turnitin’s AI detector has also been updated to detect word spinners, says Annie Chechitelli, the company’s chief product officer. It can also flag work that was rewritten by services like spell checker Grammarly, which now has its own generative AI tool . As familiar software increasingly adds generative AI components, what students can and can’t use becomes more muddled.
Detection tools themselves have a risk of bias. English language learners may be more likely to set them off; a 2023 study found a 61.3 percent false positive rate when evaluating Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) exams with seven different AI detectors. The study did not examine Turnitin’s version. The company says it has trained its detector on writing from English language learners as well as native English speakers. A study published in October found that Turnitin was among the most accurate of 16 AI language detectors in a test that had the tool examine undergraduate papers and AI-generated papers.
Charlie Wood

Eric Ravenscraft

Caitlin Kelly
Schools that use Turnitin had access to the AI detection software for a free pilot period, which ended at the start of this year. Chechitelli says a majority of the service’s clients have opted to purchase the AI detection. But the risks of false positives and bias against English learners have led some universities to ditch the tools for now. Montclair State University in New Jersey announced in November that it would pause use of Turnitin’s AI detector. Vanderbilt University and Northwestern University did the same last summer.
“This is hard. I understand why people want a tool,” says Emily Isaacs, executive director of the Office of Faculty Excellence at Montclair State. But Isaacs says the university is concerned about potentially biased results from AI detectors, as well as the fact that the tools can’t provide confirmation the way they can with plagiarism. Plus, Montclair State doesn’t want to put a blanket ban on AI, which will have some place in academia. With time and more trust in the tools, the policies could change. “It’s not a forever decision, it’s a now decision,” Isaacs says.
Chechitelli says the Turnitin tool shouldn’t be the only consideration in passing or failing a student. Instead, it’s a chance for teachers to start conversations with students that touch on all of the nuance in using generative AI. “People don’t really know where that line should be,” she says.
You Might Also Like …
In your inbox: The best and weirdest stories from WIRED’s archive
Jeffrey Epstein’s island visitors exposed by data broker
8 Google employees invented modern AI. Here’s the inside story
The crypto fraud kingpin who almost got away
It's shadow time! How to view the solar eclipse, online and in person

Steven Levy

Will Knight

Lauren Goode

Matt Burgess
Benj Edwards, Ars Technica
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
Published on September 4, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays.
Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and descriptive essays are about exercising creativity and writing in an interesting way. At university level, argumentative essays are the most common type.
In high school and college, you will also often have to write textual analysis essays, which test your skills in close reading and interpretation.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Argumentative essays, expository essays, narrative essays, descriptive essays, textual analysis essays, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about types of essays.
An argumentative essay presents an extended, evidence-based argument. It requires a strong thesis statement —a clearly defined stance on your topic. Your aim is to convince the reader of your thesis using evidence (such as quotations ) and analysis.
Argumentative essays test your ability to research and present your own position on a topic. This is the most common type of essay at college level—most papers you write will involve some kind of argumentation.
The essay is divided into an introduction, body, and conclusion:
- The introduction provides your topic and thesis statement
- The body presents your evidence and arguments
- The conclusion summarizes your argument and emphasizes its importance
The example below is a paragraph from the body of an argumentative essay about the effects of the internet on education. Mouse over it to learn more.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An expository essay provides a clear, focused explanation of a topic. It doesn’t require an original argument, just a balanced and well-organized view of the topic.
Expository essays test your familiarity with a topic and your ability to organize and convey information. They are commonly assigned at high school or in exam questions at college level.
The introduction of an expository essay states your topic and provides some general background, the body presents the details, and the conclusion summarizes the information presented.
A typical body paragraph from an expository essay about the invention of the printing press is shown below. Mouse over it to learn more.
The invention of the printing press in 1440 changed this situation dramatically. Johannes Gutenberg, who had worked as a goldsmith, used his knowledge of metals in the design of the press. He made his type from an alloy of lead, tin, and antimony, whose durability allowed for the reliable production of high-quality books. This new technology allowed texts to be reproduced and disseminated on a much larger scale than was previously possible. The Gutenberg Bible appeared in the 1450s, and a large number of printing presses sprang up across the continent in the following decades. Gutenberg’s invention rapidly transformed cultural production in Europe; among other things, it would lead to the Protestant Reformation.
A narrative essay is one that tells a story. This is usually a story about a personal experience you had, but it may also be an imaginative exploration of something you have not experienced.
Narrative essays test your ability to build up a narrative in an engaging, well-structured way. They are much more personal and creative than other kinds of academic writing . Writing a personal statement for an application requires the same skills as a narrative essay.
A narrative essay isn’t strictly divided into introduction, body, and conclusion, but it should still begin by setting up the narrative and finish by expressing the point of the story—what you learned from your experience, or why it made an impression on you.
Mouse over the example below, a short narrative essay responding to the prompt “Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself,” to explore its structure.
Since elementary school, I have always favored subjects like science and math over the humanities. My instinct was always to think of these subjects as more solid and serious than classes like English. If there was no right answer, I thought, why bother? But recently I had an experience that taught me my academic interests are more flexible than I had thought: I took my first philosophy class.
Before I entered the classroom, I was skeptical. I waited outside with the other students and wondered what exactly philosophy would involve—I really had no idea. I imagined something pretty abstract: long, stilted conversations pondering the meaning of life. But what I got was something quite different.
A young man in jeans, Mr. Jones—“but you can call me Rob”—was far from the white-haired, buttoned-up old man I had half-expected. And rather than pulling us into pedantic arguments about obscure philosophical points, Rob engaged us on our level. To talk free will, we looked at our own choices. To talk ethics, we looked at dilemmas we had faced ourselves. By the end of class, I’d discovered that questions with no right answer can turn out to be the most interesting ones.
The experience has taught me to look at things a little more “philosophically”—and not just because it was a philosophy class! I learned that if I let go of my preconceptions, I can actually get a lot out of subjects I was previously dismissive of. The class taught me—in more ways than one—to look at things with an open mind.
A descriptive essay provides a detailed sensory description of something. Like narrative essays, they allow you to be more creative than most academic writing, but they are more tightly focused than narrative essays. You might describe a specific place or object, rather than telling a whole story.
Descriptive essays test your ability to use language creatively, making striking word choices to convey a memorable picture of what you’re describing.
A descriptive essay can be quite loosely structured, though it should usually begin by introducing the object of your description and end by drawing an overall picture of it. The important thing is to use careful word choices and figurative language to create an original description of your object.
Mouse over the example below, a response to the prompt “Describe a place you love to spend time in,” to learn more about descriptive essays.
On Sunday afternoons I like to spend my time in the garden behind my house. The garden is narrow but long, a corridor of green extending from the back of the house, and I sit on a lawn chair at the far end to read and relax. I am in my small peaceful paradise: the shade of the tree, the feel of the grass on my feet, the gentle activity of the fish in the pond beside me.
My cat crosses the garden nimbly and leaps onto the fence to survey it from above. From his perch he can watch over his little kingdom and keep an eye on the neighbours. He does this until the barking of next door’s dog scares him from his post and he bolts for the cat flap to govern from the safety of the kitchen.
With that, I am left alone with the fish, whose whole world is the pond by my feet. The fish explore the pond every day as if for the first time, prodding and inspecting every stone. I sometimes feel the same about sitting here in the garden; I know the place better than anyone, but whenever I return I still feel compelled to pay attention to all its details and novelties—a new bird perched in the tree, the growth of the grass, and the movement of the insects it shelters…
Sitting out in the garden, I feel serene. I feel at home. And yet I always feel there is more to discover. The bounds of my garden may be small, but there is a whole world contained within it, and it is one I will never get tired of inhabiting.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Though every essay type tests your writing skills, some essays also test your ability to read carefully and critically. In a textual analysis essay, you don’t just present information on a topic, but closely analyze a text to explain how it achieves certain effects.
Rhetorical analysis
A rhetorical analysis looks at a persuasive text (e.g. a speech, an essay, a political cartoon) in terms of the rhetorical devices it uses, and evaluates their effectiveness.
The goal is not to state whether you agree with the author’s argument but to look at how they have constructed it.
The introduction of a rhetorical analysis presents the text, some background information, and your thesis statement; the body comprises the analysis itself; and the conclusion wraps up your analysis of the text, emphasizing its relevance to broader concerns.
The example below is from a rhetorical analysis of Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech . Mouse over it to learn more.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
Literary analysis
A literary analysis essay presents a close reading of a work of literature—e.g. a poem or novel—to explore the choices made by the author and how they help to convey the text’s theme. It is not simply a book report or a review, but an in-depth interpretation of the text.
Literary analysis looks at things like setting, characters, themes, and figurative language. The goal is to closely analyze what the author conveys and how.
The introduction of a literary analysis essay presents the text and background, and provides your thesis statement; the body consists of close readings of the text with quotations and analysis in support of your argument; and the conclusion emphasizes what your approach tells us about the text.
Mouse over the example below, the introduction to a literary analysis essay on Frankenstein , to learn more.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
At high school and in composition classes at university, you’ll often be told to write a specific type of essay , but you might also just be given prompts.
Look for keywords in these prompts that suggest a certain approach: The word “explain” suggests you should write an expository essay , while the word “describe” implies a descriptive essay . An argumentative essay might be prompted with the word “assess” or “argue.”
The vast majority of essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Almost all academic writing involves building up an argument, though other types of essay might be assigned in composition classes.
Essays can present arguments about all kinds of different topics. For example:
- In a literary analysis essay, you might make an argument for a specific interpretation of a text
- In a history essay, you might present an argument for the importance of a particular event
- In a politics essay, you might argue for the validity of a certain political theory
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-types/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write an expository essay, how to write an essay outline | guidelines & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
100 Creative Writing Prompts for Middle & High School – 2024
April 15, 2024

Some high school students dream of writing for a living, perhaps pursuing an English major in college, or even attending a creative writing MFA program later on. For other students, creative writing can be useful for school assignments, in English and other subjects, and also for preparing their Common App essays . In a less goal-oriented sense, daily freewriting in a journal can be a healthy life practice for many high schoolers. Not sure where to start? Continue reading for 100 creative writing prompts for middle school and high school students. These middle/high school writing prompts offer inspiration for getting started with writing in a number of genres and styles.
Click here to view the 35 Best Colleges for Creative Writing .
What are Creative Writing Prompts?
Similar to how an academic essay prompt provides a jumping-off point for forming and organizing an argument, creative writing prompts are points of initiation for writing a story, poem, or creative essay. Prompts can be useful for writers of all ages, helping many to get past writer’s block and just start (often one of the most difficult parts of a writing process).
Writing prompts come in a variety of forms. Sometimes they are phrases used to begin sentences. Other times they are questions, more like academic essay prompts Writing prompts can also involve objects such as photographs, or activities such as walking. Below, you will find high school writing prompts that use memories, objects, senses (smell/taste/touch), abstract ideas , and even songs as jumping-off points for creative writing. These prompts can be used to write in a variety of forms, from short stories to creative essays, to poems.
How to use Creative Writing Prompts
Before we get started with the list, are a few tips when using creative writing prompts:
Experiment with different formats : Prose is great, but there’s no need to limit yourself to full sentences, at least at first. A piece of creative writing can begin with a poem, or a dialogue, or even a list. You can always bring it back to prose later if needed.
Interpret the prompt broadly : The point of a creative writing prompt is not to answer it “correctly” or “precisely.” You might begin with the prompt, but then your ideas could take you in a completely different direction. The words in the prompt also don’t need to open your poem or essay, but could appear somewhere in the middle.
Switch up/pile up the prompts : Try using two or three prompts and combine them, or weave between them. Perhaps choose a main prompt, and a different “sub-prompt.” For example, your main prompt might be “write about being in transit from one place to another,” and within that prompt, you might use the prompt to “describe a physical sensation,” and/or one the dialogue prompts. This could be a fun way to find complexity as you write.
Creative Writing Prompts for Middle School & High School Students (Continued)
Write first, edit later : While you’re first getting started with a prompt, leave the typos and bad grammar. Obsessing over details can take away from your flow of thoughts. You will inevitably make many fixes when you go back through to edit.
Write consistently : It often becomes easier to write when it’s a practice , rather than a once-in-a-while kind of activity. For some, it’s useful to write daily. Others find time to write every few days, or every weekend. Sometimes, a word-count goal can help (100 words a day, 2,000 words a month, etc.). If you set a goal, make sure it’s realistic. Start small and build from there, rather than starting with an unachievable goal and quickly giving up.
100 Creative Writing Prompts for Middle School & High School Teens
Here are some prompts for getting started with your creative writing. These are organized by method, rather than genre, so they can inspire writing in a variety of forms. Pick and choose the ones that work best for you, and enjoy!
Prompts using memories
- Begin each sentence or group of sentences with the phrase, “I remember…”
- Describe a family ritual.
- Choose an event in your life, and write about it from the perspective of someone else who was there.
- Pick a pathway you take on a regular basis (to school, or to a friend’s house). Describe five landmarks that you remember from this pathway.
- Write about your house or apartment using a memory from each room.
- Write an imaginary history of the previous people who lived in your house or apartment.
- Write about an ancestor based on stories you’ve heard from relatives.
- What’s your earliest memory?
- Who was your first friend?
- Write a letter to someone you haven’t seen since childhood.
- Write about yourself now from the perspective of yourself twenty, or eighty, years from now.
- Write about the best month of the year.
- Write about the worst day of the year.
- Rant about something that has always annoyed you.
- Write about the hottest or coldest day you can remember.
- Visualize a fleeting moment in your life and as though it’s a photograph, and time yourself 5 minutes to write every detail you can remember about the scene.
- Draw out a timeline of your life so far. Then choose three years to write about, as though you were writing for a history book.
- Write about a historical event in the first person, as though you remember it.
- Write about a memory of being in transit from one place to another.
Objects and photographs as creative writing prompts
- Describe the first object you see in the room. What importance does it have in your life? What memories do you have with this object? What might it symbolize?
- Pick up an object, and spend some time holding it/examining it. Write about how it looks, feels, and smells. Write about the material that it’s made from.
- Choose a favorite family photograph. What could someone know just by looking at the photograph? What’s secretly happening in the photograph?
- Choose a photograph and tell the story of this photograph from the perspective of someone or something in it.
- Write about a color by describing three objects that are that color.
- Tell the story of a piece of trash.
- Tell the story of a pair of shoes.
- Tell the story of your oldest piece of clothing.
Senses and observations as creative writing prompts
- Describe a sound you hear in the room or outside. Choose the first sound you notice. What are its qualities? It’s rhythms? What other sounds does it remind you of?
- Describe a physical sensation you feel right now, in as much detail as possible.
- Listen to a conversation and write down a phrase that you hear someone say. Start a free-write with this phrase.
- Write about a food by describing its qualities, but don’t say what it is.
- Describe a flavor (salty, sweet, bitter, etc.) to someone who has never tasted it before.
- Narrate your day through tastes you tasted.
- Narrate your day through sounds you heard.
- Narrate your day through physical sensations you felt.
- Describe in detail the physical process of doing an action you consider simple or mundane, like walking or lying down or chopping vegetables.
- Write about the sensation of doing an action you consider physically demanding or tiring, like running or lifting heavy boxes.
- Describe something that gives you goosebumps.
- Write a story that involves drinking a cold glass of water on a hot day.
- Write a story that involves entering a warm house from a cold snowy day.
- Describe someone’s facial features in as much detail as possible.
Songs, books, and other art
- Choose a song quote, write it down, and free-write from there.
- Choose a song, and write a story in which that song is playing in the car.
- Choose a song, and write to the rhythm of that song.
- Choose a character from a book, and describe an event in your life from the perspective of that character.
- Go to a library and write down 10 book titles that catch your eye. Free-write for 5 minutes beginning with each one.
- Go to a library and open to random book pages, and write down 5 sentences that catch your attention. Use those sentences as prompts and free-write for 5-minutes with each.
- Choose a piece of abstract artwork. Jot down 10 words that come to mind from the painting or drawing, and free-write for 2 minutes based on each word.
- Find a picture of a dramatic Renaissance painting online. Tell a story about what’s going on in the painting that has nothing to do with what the artist intended.
- Write about your day in five acts, like a Shakespearean play. If your day were a play, what would be the introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution?
- Narrate a complicated book or film plot using only short sentences.
- Read a short poem. Then write a poem that could be a “sister” or “cousin” of that poem.
Abstract ideas as creative writing prompts
- Write about an experience that demonstrates an abstract idea, such as “love” or “home” or “freedom” or “loss” without ever using the word itself.
- Write a list of ways to say “hello” without actually saying “hello.”
- Write a list of ways to say “I love you” without actually saying “I love you.”
- Do you believe in ghosts? Describe a ghost.
- Invent a mode of time travel.
- Glass half-full/half-empty: Write about an event or situation with a positive outlook. Then write about it with a miserable outlook.
- Free-write beginning with “my religion is…” (what comes next can have as much or as little to do with organized religion as you’d like).
- Free-write beginning with “my gender is…” (what comes next can have as much or as little to do with common ideas of gender as you’d like).
- Write about a person or character that is “good” and one that is “evil.” Then write about the “evil” in the good character and the “good” in the evil character.
- Write like you’re telling a secret.
- Describe a moment of beauty you witnessed. What makes something beautiful?
Prompts for playing with narrative and character
- Begin writing with the phrase, “It all started when…”
- Tell a story from the middle of the most dramatic part.
- Write a story that begins with the ending.
- Begin a story but give it 5 possible endings.
- Write a list of ways to dramatically quit a terrible job.
- Write about a character breaking a social rule or ritual (i.e., walking backwards, sitting on the floor of a restaurant, wearing a ballgown to the grocery store). What are the ramifications?
- You are sent to the principal’s office. Justify your bad behavior.
- Re-write a well-known fairytale but set it in your school.
- Write your own version of the TV show trope where someone gets stuck in an elevator with a stranger, or a secret love interest, or a nemesis.
- Imagine a day where you said everything you were thinking, and write about it.
- Write about a scenario in which you have too much of a good thing.
- Write about a scenario in which money can buy happiness.
- Invent a bank or museum heist.
- Invent a superhero, including an origin story.
- Write using the form of the scientific method (question, hypothesis, test, analyze data conclusion).
- Write using the form of a recipe.
Middle School & High School Creative writing prompts for playing with fact vs. fiction
- Write something you know for sure is true, and then, “but maybe it isn’t.” Then explain why that thing may not be true.
- Write a statement and contradict that statement. Then do it again.
- Draft an email with an outlandish excuse as to why you didn’t do your homework or why you need an extension.
- Write about your morning routine, and make it sound extravagant/luxurious (even if it isn’t).
- You’ve just won an award for doing a very mundane and simple task. Write your acceptance speech.
- Write about a non-athletic event as though it were a sports game.
- Write about the most complicated way to complete a simple task.
- Write a brief history of your life, and exaggerate everything.
- Write about your day, but lie about some things.
- Tell the story of your birth.
- Choose a historical event and write an alternative outcome.
- Write about a day in the life of a famous person in history.
- Read an instructional manual, and change three instructions to include some kind of magical or otherwise impossible element.
Prompts for starting with dialogue
- Write a texting conversation between two friends who haven’t spoken in years.
- Write a texting conversation between two friends who speak every day and know each other better than anyone.
- Watch two people on the street having a conversation, and imagine the conversation they’re having. Write it down.
- Write an overheard conversation behind a closed door that you shouldn’t be listening to.
- Write a conversation between two characters arguing about contradicting memories of what happened.
- You have a difficult decision to make. Write a conversation about it with yourself.
- Write a conversation with a total lack of communication.
- Write a job interview gone badly.
Final Thoughts – Creative Writing Prompts for Middle School & High School
Hopefully you have found several of these creative writing prompts helpful. Remember that when writing creatively, especially on your own, you can mix, match, and change prompts. For more on writing for high school students, check out the following articles:
- College Application Essay Topics to Avoid
- 160 Good Argumentative Essay Topics
- 150 Good Persuasive Speech Topics
- Good Transition Words for Essays
- High School Success

Sarah Mininsohn
With a BA from Wesleyan University and an MFA from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Sarah is a writer, educator, and artist. She served as a graduate instructor at the University of Illinois, a tutor at St Peter’s School in Philadelphia, and an academic writing tutor and thesis mentor at Wesleyan’s Writing Workshop.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
I am a... Student Student Parent Counselor Educator Other First Name Last Name Email Address Zip Code Area of Interest Business Computer Science Engineering Fine/Performing Arts Humanities Mathematics STEM Pre-Med Psychology Social Studies/Sciences Submit

Styles of Writing Texts That Should Be Used In Content Marketing

Writing good content is just half the job done, so to make it stand out, you need to focus on other critical things too. This is why choosing the right text style in content marketing is important.
Marketers use different types of content to increase brand awareness and sales. They do SEO writing, video content, copywriting, social media, and emails. Any content marketing message must resonate with the target audience. It must create an urge in them to take action and buy, subscribe, or click a link. The writing style is important for marketing success. It ensures the marketer uses the right voice tone and writes relevant content. The right style creates an emotional impact and builds trust.
Understanding your audience: Tailoring your writing style
In content marketing, one audience is different from another. Each audience displays differing behavior and characteristics. The marketer must focus on tailoring their message to each audience. In this section, we will explore the importance of understanding your target audience. We will discuss how it should influence the writing style you use in your efforts.
Understanding your target audience is important in branding. It makes tailoring their marketing message easier. Web Tribunal reports that targeted marketing records a 5.3 times success rate. 37% of social media customers buy products that contain targeted messages. The report says 76% of marketers fail to use maximum customized marketing.
When you understand your target market, you design a storytelling strategy for them. You understand which platforms to find them online. It is easier to know what products they use and the alternatives you can suggest. You focus all your marketing efforts and money on areas that will increase ROI. It is one of the best ways to generate leads most cost-effectively. When you are writing content marketing messages, it is important to communicate with your product designer, who can help to find the best fonts. For that, your Mac should have a high quality web camera, make sure light is on and therefore have a good meeting.
Before writing your message, do an audience analysis first. It helps you understand what message should go in your content. You develop unique narrative techniques for the audience. It is the best way to develop a writing tone, the right information, and structure.
The power of storytelling: Incorporating narrative techniques
Narrative techniques can make your material more engaging. Your audience remembers your brand and messages more. Here, we will discuss the art of storytelling. We will discuss how it can be applied to different forms of content.
Building the art of storytelling in product marketing is simple. Move away from listing features and narrate your product’s impact on users. You create an emotional connection with your audience. It improves engagement between customers and your brand. Storytelling is a strategy that increases conversions and revenue growth.
Go-Globe reports that storytelling enhances product value by up to 2,700%. It can convince customers to pay higher for a product. 55% of audiences consider buying if the story behind the product is appealing. 45% of Facebook users like a brand page if they find its story on the platform good.
Storytelling is vital. However, you must decide the type of style to use in different types of content. Marketers use content like blog posts, social media posts, and case studies. In marketing, the art of storytelling can be applied to achieve different goals.
- Capture audience attention: Tailoring audience-specific content helps capture attention.
- Creating memories: Studies show audiences remember relevant stories 22 times more.
- Triggering action: Stories should be engaging, motivating, and inspiring to trigger action.
- Create desire: Telling about how your products have solved needs creates a desire to buy.
Finding your voice: Developing a consistent writing style
A consistent writing style can help establish your brand and build trust with your audience. In this section, we’ll explore how to find and develop your unique voice as a content marketer. Brands hire teams of marketers, each with a unique writing style. Nevertheless, you should adopt a unique tone for the entire company.
Develop a guide for your writing style: Let there be a guide for marketers to follow. It helps in developing standardized messages in your company. The guide should include the type of tone and voice to use. Restrict the terminologies to use, fonts, spacing, and content length. The content length should be based on content type.
Develop a voice and tone for your brand: Voice does not change, and it defines brand personality. The tone can change based on the marketing content you are creating. Voice can be defined as knowledgeable, confident, quality-oriented, and so on.
Develop engaging content: Your content should resonate with your audience. It should make them feel comfortable and well-considered. Use a language style that is familiar to the audience. It might help if you use an editor or hire an experienced content writer.
Customize your content for individuals and not crowds: Your content should communicate to individuals but not to crowds. Understand the needs of the individual and suggest the solution your product offers. Let the person feel the message was crafted just for them.
Storytelling in content marketing can help build trust and loyalty. Develop your brand’s consistent writing style to achieve success in marketing. When writing to an audience, write to an individual instead of a crowd. Develop narrative techniques that help in brand promotion.
Was this news helpful?

Also Popular on Sellbery
Product marketers drive sales and stay relevant by understanding market trends, crafting compelling messages, and collaborating with sales teams.
Learn how loyalty programs work, explore different types, discover tips for maximizing rewards, and consider potential drawbacks to make informed decisions.
Discover how software transforms higher education, leveraging AI, BYOD, cloud computing, and VR/AR for more accessible, personalized learning.
Discover essential strategies to enhance your business's growth and success. Learn from expert insights on improving customer engagement, increasing revenue, and optimizing operations for a thriving business.
Discover the power of social media for e-commerce. Learn how to build an ideal strategy, boost sales, and elevate brand visibility. Find out the secrets to mastering social media from scratch.
Discover the essential tools and techniques for effective project management, from planning and organization to communication and problem-solving. Learn how to drive success in your projects and achieve better outcomes with these expert insights.
Understand international tax laws to navigate global business complexities, ensuring compliance and optimizing fiscal strategies for significant savings.
Explore the top 6 myths surrounding small business loans and understand the truths behind them. Learn about the simplicity of obtaining loans, the role of credit scores, and the viability of startup loans. Find out why online lenders are a viable option and how banks can offer benefits. Make informed decisions to foster the growth of your business.
Discover proven strategies for optimizing business communication. Improve efficiency and effectiveness with these expert tips for seamless communication within your organization.
PIM (Product Information Management) is an eCommerce solution that collects, manages, enriches, and distributes your product data. Here's how to integrate it to your business.

- Multichannel Product Listing
- Product Information Management
- Order Management
- Inventory Management
- Online Brands
- eCommerce Gurus
- Marketplace Sellers
- Dropshipper sellers
- WooCommerce
- Facebook shop
- Instagram market
- Shopify to Amazon
- Shopify to eBay
- Shopify to Etsy
- WooCommerce to eBay
- WooCommerce to Etsy
- Etsy to eBay
- Help Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
oConsideration of counterarguments (what Sandel might say in response to this section of your argument) Each argument you will make in an essay will be different, but this strategy will often be a useful first step in figuring out the path of your argument. Strategy #2: Use subheadings, even if you remove themlater.
Table of contents. Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
Come up with a thesis. Create an essay outline. Write the introduction. Write the main body, organized into paragraphs. Write the conclusion. Evaluate the overall organization. Revise the content of each paragraph. Proofread your essay or use a Grammar Checker for language errors. Use a plagiarism checker.
The basic steps for how to write an essay are: Generate ideas and pick a type of essay to write. Outline your essay paragraph by paragraph. Write a rough first draft without worrying about details like word choice or grammar. Edit your rough draft, and revise and fix the details. Review your essay for typos, mistakes, and any other problems.
Essay Writing Skills & Techniques. By Shane Mac Donnchaidh September 7, 2021March 5, 2024 March 5, 2024. Many of our articles and guides frequently refer to essay writing, so to simplify this, we have collated our best essay writing skills and techniques into one section to assist students and teachers in learning the fundamentals of writing a ...
An essay is a written composition that presents and supports a particular idea, argument, or point of view. It's a way to express your thoughts, share information, and persuade others to see things from your perspective. Essays come in various forms, such as argumentative, persuasive, expository, and descriptive, each serving a unique purpose.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Examples of strategies for writing with clarity: Know your message, and write with intention. Know your audience and speak their language. Define your (unfamiliar) terms. Use your punctuation wisely (especially commas). Use strong, active, and carefully-chosen verbs. 10. Break it up with visuals.
How to Write Better: 6 Techniques to Improve Your Writing. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Sep 10, 2021 • 7 min read. As a writer, it's easy to get stuck in your own ways. However, adopting new techniques in your writing can help you develop your creative style. As a writer, it's easy to get stuck in your own ways.
2. Define your argument. As you plan and prepare to write the essay, you must consider what your argument is going to be. This means taking an informed position or point of view on the topic presented in the question, then defining and presenting a specific argument. Consider these two argument statements:
While many writers have traditionally created outlines before beginning writing, there are several other effective prewriting activities. We often call these prewriting strategies "brainstorming techniques.". Five useful strategies are listing, clustering, freewriting, looping, and asking the six journalists' questions.
The principles of good plot-writing are centred around the connection between different events that show cause and effect, and this central tenet of the three-act structure has obvious parallels with the way in which essays work through presenting evidence in support of arguments. 3. An attention-grabbing opening.
1 Choose wording carefully. Word choice—the words and phrases you decide to use—is crucial in persuasive writing as a way to build a personal relationship with the reader. You want to always pick the best possible words and phrases in each instance to convince the reader that your opinion is right. Persuasive writing often uses strong ...
In persuasive writing, your "one idea" is often the argument or belief you are presenting to the reader. Once you identify what that argument is, the "one-idea rule" can help you develop ...
Good essay writing technique means having a well-ordered essay. Make sure you plan your essay. Make a bullet point list, table, or spider diagram with the main components of your answer and clearly order them. Poor structure is one of the main reasons students get marked down in essays. Order your thoughts logically and stick to your essay plan.
The PEEL paragraph method is a technique used in writing to help structure paragraphs in a way that presents a single clear and focused argument, which links back to the essay topic or thesis statement. It's good practice to dedicate each paragraph to one aspect of your argument, and the PEEL structure simplifies this for you.
Types of writing techniques. There are four different types of writing techniques in business: 1. Descriptive writing style. Descriptive writing immerses the reader into a story by creating a vivid picture of characters, settings and events in their mind. Writers who use a descriptive writing style often use literary tools like similes and ...
The second sentence emphasizes how the subject moves—slowly—creating a buildup of tension. This technique is effective in fictional writing. Note that an adverb used at the beginning of a sentence is usually followed by a comma. A comma indicates that the reader should pause briefly, which creates a useful rhetorical device.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
Key Takeaways. All writers rely on steps and strategies to begin the writing process. The steps in the writing process are prewriting, outlining, writing a rough draft, revising, and editing. Writers often choose a general topic first and then narrow the focus to a more specific topic.
Speaking of writing techniques for essays, In Media Res reflects in thesis statements a student places in introductions: core thoughts they will develop throughout the paper. 10 — Isocolon. Isocolon is a writing trick of crafting two or more words (phrases) using a similar structure, rhythm, and length. Perfect to use for slogans and catchy ...
Here's a a step-by-step guide to enhance your essay and thesis writing for research with Paperpal: Sign up or log in to Paperpal and open a new or existing document. Go to the Edit section on the right sidebar and choose the first tab for Language or the second tab for Consistency . Paperpal will generate suggestions and reviews for ...
Meanwhile, while fewer faculty members used AI, the percentage grew to 22% of faculty members in the fall of 2023, up from 9% in spring 2023. Teachers are turning to AI tools and platforms ...
Since then, more than 200 million papers have been reviewed by the detector, predominantly written by high school and college students. Turnitin found that 11 percent may contain AI-written ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
Some high school students dream of writing for a living, perhaps pursuing an English major in college, or even attending a creative writing MFA program later on. For other students, creative writing can be useful for school assignments, in English and other subjects, and also for preparing their Common App essays.In a less goal-oriented sense, daily freewriting in a journal can be a healthy ...
Step 1: Before Writing a Poem Analysis, Read the Poem. A thorough comprehension of each layer is necessary for a competent analysis of poetry. The best approach to be sure of this is to read the main stanza two or more times before beginning to classify its elements and draw conclusions.
1207 Words5 Pages. 'The Universal Soldier' by Buffy Sainte-Marie (link) is a passionate anti-war song that utilises a plethora of writing techniques to help illustrate the question: who's really responsible for war? This song was originally released in 1963, right at the heart of the Vietnam War. This is an important detail, because it ...
They do SEO writing, video content, copywriting, social media, and emails. Any content marketing message must resonate with the target audience. It must create an urge in them to take action and buy, subscribe, or click a link. The writing style is important for marketing success. It ensures the marketer uses the right voice tone and writes ...